User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
New DEA CME mandate affects 2 million prescribers
The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023 mandates that all Drug Enforcement Administration–registered physicians and health care providers complete a one-time, 8-hour CME training on managing and treating opioid and other substance abuse disorders. This requirement goes into effect on June 27, 2023. New DEA registrants must also comply. Veterinarians are exempt.
A DEA registration is required to prescribe any controlled substance. The DEA categorizes these as Schedule I-V, with V being the least likely to be abused (Table 1). For example, opioids like fentanyl, oxycodone, and morphine are Schedule II. Medications without abuse potential are not scheduled.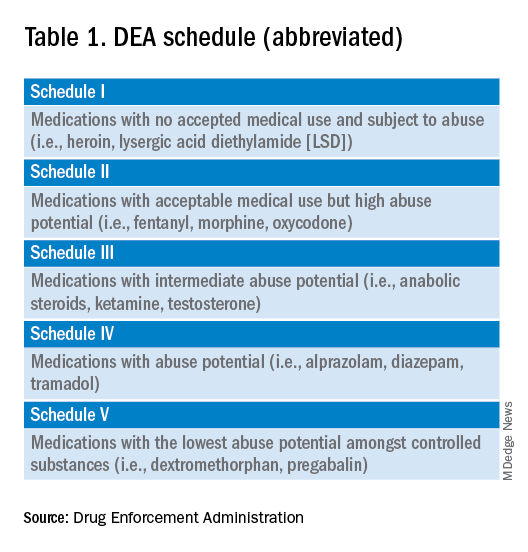
Will 16 million hours of opioid education save lives?
One should not underestimate the sweeping scope of this new federal requirement. DEA registrants include physicians and other health care providers such as nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and dentists. That is 8 hours per provider x 2 million providers: 16 million hours of CME!
Many states already require 1 or more hours of opioid training and pain management as part of their relicensure requirements (Table 2). To avoid redundancy, the DEA-mandated 8-hour training satisfies the various states’ requirements. 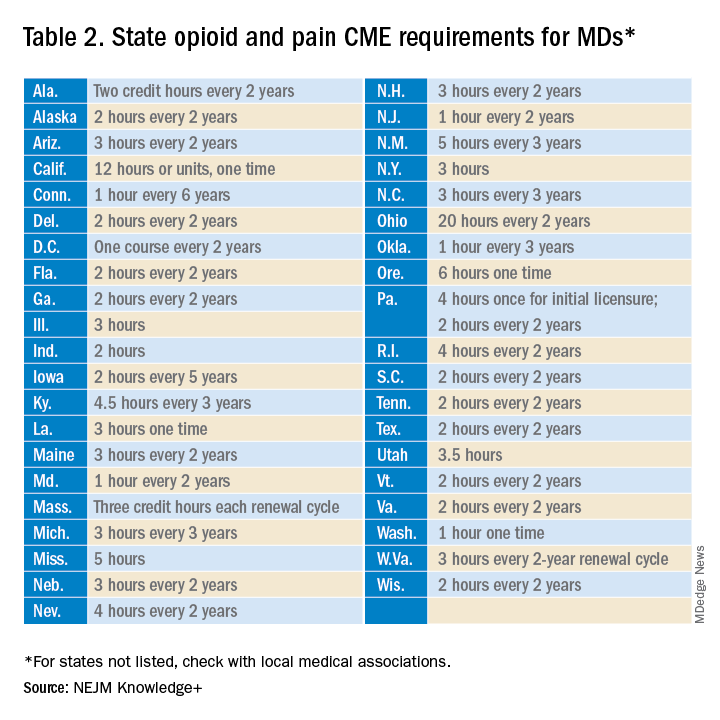
An uncompensated mandate
Physicians are no strangers to lifelong learning and most eagerly pursue educational opportunities. Though some physicians may have CME time and stipends allocated by their employers, many others, such as the approximately 50,000 locum tenens doctors, do not. However, as enthusiastic as these physicians may be about this new CME course, they will likely lose a day of seeing patients (and income) to comply with this new obligation.
Not just pain doctors
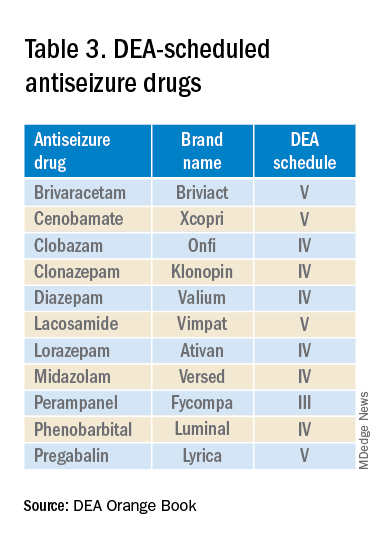
The mandate’s broad brush includes many health care providers who hold DEA certificates but do not prescribe opioids. For example, as a general neurologist and epileptologist, I do not treat patients with chronic pain and cannot remember the last time I wrote an opioid prescription. However, I frequently prescribe lacosamide, a Schedule V drug. A surprisingly large number of antiseizure drugs are Schedule III, IV, or V drugs (Table 3).
Real-world abuse?
How often scheduled antiseizure drugs are diverted or abused in an epilepsy population is unknown but appears to be infrequent. For example, perampanel abuse has not been reported despite its classification as a Schedule III drug. Anecdotally, in more than 40 years of clinical practice, I have never known a patient with epilepsy to abuse their antiseizure medications.
Take the course
Many organizations are happy to charge for the new 8-hour course. For example, the Tennessee Medical Association offers the training for $299 online or $400 in person. Materials from Elite Learning satisfy the 8-hour requirement for $80. However, NEJM Knowledge+ provides a complimentary 10-hour DEA-compliant course.
I recently completed the NEJM course. The information was thorough and took the whole 10 hours to finish. As excellent as it was, the content was only tangentially relevant to my clinical practice.
Conclusions
To obtain or renew a DEA certificate, neurologists, epilepsy specialists, and many other health care providers must comply with the new 8-hour CME opioid training mandate. Because the course requires 1 day to complete, health care providers would be prudent to obtain their CME well before their DEA certificate expires.
Though efforts to control the morbidity and mortality of the opioid epidemic are laudatory, perhaps the training should be more targeted to physicians who actually prescribe opioids rather than every DEA registrant. In the meantime, whether 16 million CME hours will save lives remains to be seen.
Dr. Wilner is professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported a conflict of interest with Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023 mandates that all Drug Enforcement Administration–registered physicians and health care providers complete a one-time, 8-hour CME training on managing and treating opioid and other substance abuse disorders. This requirement goes into effect on June 27, 2023. New DEA registrants must also comply. Veterinarians are exempt.
A DEA registration is required to prescribe any controlled substance. The DEA categorizes these as Schedule I-V, with V being the least likely to be abused (Table 1). For example, opioids like fentanyl, oxycodone, and morphine are Schedule II. Medications without abuse potential are not scheduled.
Will 16 million hours of opioid education save lives?
One should not underestimate the sweeping scope of this new federal requirement. DEA registrants include physicians and other health care providers such as nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and dentists. That is 8 hours per provider x 2 million providers: 16 million hours of CME!
Many states already require 1 or more hours of opioid training and pain management as part of their relicensure requirements (Table 2). To avoid redundancy, the DEA-mandated 8-hour training satisfies the various states’ requirements. 
An uncompensated mandate
Physicians are no strangers to lifelong learning and most eagerly pursue educational opportunities. Though some physicians may have CME time and stipends allocated by their employers, many others, such as the approximately 50,000 locum tenens doctors, do not. However, as enthusiastic as these physicians may be about this new CME course, they will likely lose a day of seeing patients (and income) to comply with this new obligation.
Not just pain doctors
The mandate’s broad brush includes many health care providers who hold DEA certificates but do not prescribe opioids. For example, as a general neurologist and epileptologist, I do not treat patients with chronic pain and cannot remember the last time I wrote an opioid prescription. However, I frequently prescribe lacosamide, a Schedule V drug. A surprisingly large number of antiseizure drugs are Schedule III, IV, or V drugs (Table 3).

Real-world abuse?
How often scheduled antiseizure drugs are diverted or abused in an epilepsy population is unknown but appears to be infrequent. For example, perampanel abuse has not been reported despite its classification as a Schedule III drug. Anecdotally, in more than 40 years of clinical practice, I have never known a patient with epilepsy to abuse their antiseizure medications.
Take the course
Many organizations are happy to charge for the new 8-hour course. For example, the Tennessee Medical Association offers the training for $299 online or $400 in person. Materials from Elite Learning satisfy the 8-hour requirement for $80. However, NEJM Knowledge+ provides a complimentary 10-hour DEA-compliant course.
I recently completed the NEJM course. The information was thorough and took the whole 10 hours to finish. As excellent as it was, the content was only tangentially relevant to my clinical practice.
Conclusions
To obtain or renew a DEA certificate, neurologists, epilepsy specialists, and many other health care providers must comply with the new 8-hour CME opioid training mandate. Because the course requires 1 day to complete, health care providers would be prudent to obtain their CME well before their DEA certificate expires.
Though efforts to control the morbidity and mortality of the opioid epidemic are laudatory, perhaps the training should be more targeted to physicians who actually prescribe opioids rather than every DEA registrant. In the meantime, whether 16 million CME hours will save lives remains to be seen.
Dr. Wilner is professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported a conflict of interest with Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023 mandates that all Drug Enforcement Administration–registered physicians and health care providers complete a one-time, 8-hour CME training on managing and treating opioid and other substance abuse disorders. This requirement goes into effect on June 27, 2023. New DEA registrants must also comply. Veterinarians are exempt.
A DEA registration is required to prescribe any controlled substance. The DEA categorizes these as Schedule I-V, with V being the least likely to be abused (Table 1). For example, opioids like fentanyl, oxycodone, and morphine are Schedule II. Medications without abuse potential are not scheduled.
Will 16 million hours of opioid education save lives?
One should not underestimate the sweeping scope of this new federal requirement. DEA registrants include physicians and other health care providers such as nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and dentists. That is 8 hours per provider x 2 million providers: 16 million hours of CME!
Many states already require 1 or more hours of opioid training and pain management as part of their relicensure requirements (Table 2). To avoid redundancy, the DEA-mandated 8-hour training satisfies the various states’ requirements. 
An uncompensated mandate
Physicians are no strangers to lifelong learning and most eagerly pursue educational opportunities. Though some physicians may have CME time and stipends allocated by their employers, many others, such as the approximately 50,000 locum tenens doctors, do not. However, as enthusiastic as these physicians may be about this new CME course, they will likely lose a day of seeing patients (and income) to comply with this new obligation.
Not just pain doctors
The mandate’s broad brush includes many health care providers who hold DEA certificates but do not prescribe opioids. For example, as a general neurologist and epileptologist, I do not treat patients with chronic pain and cannot remember the last time I wrote an opioid prescription. However, I frequently prescribe lacosamide, a Schedule V drug. A surprisingly large number of antiseizure drugs are Schedule III, IV, or V drugs (Table 3).

Real-world abuse?
How often scheduled antiseizure drugs are diverted or abused in an epilepsy population is unknown but appears to be infrequent. For example, perampanel abuse has not been reported despite its classification as a Schedule III drug. Anecdotally, in more than 40 years of clinical practice, I have never known a patient with epilepsy to abuse their antiseizure medications.
Take the course
Many organizations are happy to charge for the new 8-hour course. For example, the Tennessee Medical Association offers the training for $299 online or $400 in person. Materials from Elite Learning satisfy the 8-hour requirement for $80. However, NEJM Knowledge+ provides a complimentary 10-hour DEA-compliant course.
I recently completed the NEJM course. The information was thorough and took the whole 10 hours to finish. As excellent as it was, the content was only tangentially relevant to my clinical practice.
Conclusions
To obtain or renew a DEA certificate, neurologists, epilepsy specialists, and many other health care providers must comply with the new 8-hour CME opioid training mandate. Because the course requires 1 day to complete, health care providers would be prudent to obtain their CME well before their DEA certificate expires.
Though efforts to control the morbidity and mortality of the opioid epidemic are laudatory, perhaps the training should be more targeted to physicians who actually prescribe opioids rather than every DEA registrant. In the meantime, whether 16 million CME hours will save lives remains to be seen.
Dr. Wilner is professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported a conflict of interest with Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HPV rates skyrocket despite safe, effective vaccine
An epidemic of sexually transmitted HPV is now swirling around the United States and the United Kingdom, with some serious cases leading to oropharyngeal cancer, which can affect the back of the throat, tonsils, and tongue.
HPV is the leading cause (70%) of this oropharyngeal cancer, according to the CDC. It is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the nation, and around 3.6% of women and 10% of men report oral HPV specifically. But over the past decade, oropharyngeal cases have been steadily falling a little under 4% and 2%, respectively, according to the National Cancer Institute.
HPV is often undetectable and can clear up within a few months. But unfortunately for some, serious disease, such as throat cancer, can develop.
Studies show the HPV vaccine to be extremely effective in lowering sexually transmitted HPV cases. Yet, only 54.5% of young people aged 13-15 have taken the recommended two to three doses, according to the National Cancer Institute.
Why aren’t more young people taking the vaccine?
Low public awareness of the dangers of HPV may be behind young people’s poor vaccination rates, according to Teresa Lee, MD, of the Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia. “For example, while the link with head and neck cancers has been well-studied, the FDA labeling was not changed to reflect this as an indication until 2020,” she said.
Other reasons can include one’s socioeconomic background, poor health literacy, cultural or religious stigmas around vaccines, and lack of quality, low-cost health care, says Emmanuel Aguh, MD, a board-certified family medicine physician. “Some individuals and families are still resistant to vaccines and the noted lack of uptake.”
Doctors and other health care professionals should also be sure to tell patients of all ages about the risks of HPV infection and how well the vaccine works, Dr. Lee said. “Not everyone who is now eligible may have been offered the vaccine as a child, and the first time young adults may receive counseling on this subject may not be until they are entering a very busy period of their lives with many responsibilities – when it may be hard to fit in things like health maintenance.”
How safe is the HPV vaccine?
The Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have studied the HPV vaccine for years to find out how safe it is and how well it works, Dr. Aguh said. No major side effects have been reported, and the most common side effect is soreness where you get the shot (which is normal after most vaccines). Some dizziness and fainting in adolescents can also occur, so young people are usually asked to sit or lie down during the shot and for 15 minutes afterward, he said.
“Serious adverse events have not been reported at higher rates than expected following HPV vaccination, meaning there is no clear evidence they are related to the vaccine,” Dr. Lee said. “The vaccine is highly effective in decreasing rates of detectable infection with the high-risk HPV strains responsible for HPV-associated cancers.”
The HPV vaccine is largely recommended for people aged 9-26, and sometimes up to age 45, depending on the individual, Dr. Aguh said. If you are over 26, talk to your doctor about whether you should consider getting the vaccine.
“It is usually given in two doses for complete protection if taken before the 15th birthday,” Dr. Aguh said. “If taken afterward, or in those with a weak immune system, they might require three doses to be fully protected.”
The vaccine produces antibodies that can stop HPV from infecting cells and lowers your chances of catching an HPV-related cancer, such as throat cancer or cancer of the cervix, he said.
While the vaccine is not guaranteed to protect you from the more than 100 strains of HPV, it can protect you from HPV 16 and HPV 18 – two high-risk strains that cause around 70% of cervical cancers.
What is fueling the rise of HPV cases?
A misconception that oral sex is somehow a “safe and risk-free” alternative to anal or vaginal sex could be one reason, Dr. Aguh said.
“It is important to know that, with oral sex, you are exposed to many of the risks associated with vaginal intercourse, especially if you do not take any measures to protect yourself and/or your partner,” Dr. Aguh said. “[With oral sex] it is possible to end up contracting an infection like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and even HPV, leading to an increased risk of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancers.”
A lack of public awareness of what can cause throat cancer could also explain this phenomenon. The number of people you have oral sex with, along with the age you begin sexual activity, can greatly determine your risk of the disease, according to Dr. Lee. She echoes a report by Hisham Mehanna, PhD, in The Conversation.
“For oropharyngeal cancer, the main risk factor is the number of lifetime sexual partners, especially oral sex,” wrote Dr. Mehanna, a professor at the Institute of Cancer and Genomic Sciences at the University of Birmingham (England). “Those with six or more lifetime oral-sex partners are 8.5 times more likely to develop oropharyngeal cancer than those who do not practice oral sex.”
What are symptoms of oropharyngeal cancer?
Labored breathing or swallowing, a cough that won’t go away, and crackling or hoarseness of your voice could all be signs of throat cancer. Other symptoms include earaches, swelling of the head or neck, and enlarged lymph nodes, among others, Dr. Aguh said.
“The signs and symptoms of HPV-related throat cancers can be difficult to identify and recognize, as they can be vague and are also associated with other medical conditions. Sometimes, there are no signs at all, or they are not easily noticeable due to the location,” he said.
You should go see your doctor if you have any of these ailments for an extended period.
How to reduce your risk
In addition to having six or more oral-sex partners, smoking and drinking heavily could also raise your risk of throat cancer, said Dr. Lee. Proper dental health – like seeing your dentist regularly and practicing proper oral hygiene – can also shave your risk.
“[Good dental health] can help not just with head and neck cancer risk, but with many other inflammation-related diseases,” Dr. Lee said.
Using dental dams and condoms can also be a good method of protection, Dr. Aguh said. A dental dam is a stretchy sheet of latex, or polyurethane plastic, in the shape of a square that is made for blocking body fluid to lower your risk of contracting an STD via oral sex.
Keep in mind: Even with these protections, make sure you and your partner discuss each other’s sexual history, any prior or current STDs and their preferred protection from STDs, said Dr. Aguh.
If you or your partner is being treated for an STD, consider opting out of oral sex and consulting a doctor.
The HPV vaccine is another common method of protection. The shot is “approved for prevention of nine of the most high-risk strains of HPV,” or those that are most commonly linked to cancer, according to Dr. Lee. The vaccine “reduces the frequency of infection” with these viruses, which can ultimately lower the risk of cancers linked to HPV, including cervical, anal, and vulvar and vaginal cancers, she said.
“The best time to receive treatment for prevention of disease is prior to onset of sexual intercourse,” said Dr. Lee.
To get your HPV vaccine, head to your family doctor, school- or community-based health center, or state health department, suggests the CDC.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
An epidemic of sexually transmitted HPV is now swirling around the United States and the United Kingdom, with some serious cases leading to oropharyngeal cancer, which can affect the back of the throat, tonsils, and tongue.
HPV is the leading cause (70%) of this oropharyngeal cancer, according to the CDC. It is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the nation, and around 3.6% of women and 10% of men report oral HPV specifically. But over the past decade, oropharyngeal cases have been steadily falling a little under 4% and 2%, respectively, according to the National Cancer Institute.
HPV is often undetectable and can clear up within a few months. But unfortunately for some, serious disease, such as throat cancer, can develop.
Studies show the HPV vaccine to be extremely effective in lowering sexually transmitted HPV cases. Yet, only 54.5% of young people aged 13-15 have taken the recommended two to three doses, according to the National Cancer Institute.
Why aren’t more young people taking the vaccine?
Low public awareness of the dangers of HPV may be behind young people’s poor vaccination rates, according to Teresa Lee, MD, of the Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia. “For example, while the link with head and neck cancers has been well-studied, the FDA labeling was not changed to reflect this as an indication until 2020,” she said.
Other reasons can include one’s socioeconomic background, poor health literacy, cultural or religious stigmas around vaccines, and lack of quality, low-cost health care, says Emmanuel Aguh, MD, a board-certified family medicine physician. “Some individuals and families are still resistant to vaccines and the noted lack of uptake.”
Doctors and other health care professionals should also be sure to tell patients of all ages about the risks of HPV infection and how well the vaccine works, Dr. Lee said. “Not everyone who is now eligible may have been offered the vaccine as a child, and the first time young adults may receive counseling on this subject may not be until they are entering a very busy period of their lives with many responsibilities – when it may be hard to fit in things like health maintenance.”
How safe is the HPV vaccine?
The Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have studied the HPV vaccine for years to find out how safe it is and how well it works, Dr. Aguh said. No major side effects have been reported, and the most common side effect is soreness where you get the shot (which is normal after most vaccines). Some dizziness and fainting in adolescents can also occur, so young people are usually asked to sit or lie down during the shot and for 15 minutes afterward, he said.
“Serious adverse events have not been reported at higher rates than expected following HPV vaccination, meaning there is no clear evidence they are related to the vaccine,” Dr. Lee said. “The vaccine is highly effective in decreasing rates of detectable infection with the high-risk HPV strains responsible for HPV-associated cancers.”
The HPV vaccine is largely recommended for people aged 9-26, and sometimes up to age 45, depending on the individual, Dr. Aguh said. If you are over 26, talk to your doctor about whether you should consider getting the vaccine.
“It is usually given in two doses for complete protection if taken before the 15th birthday,” Dr. Aguh said. “If taken afterward, or in those with a weak immune system, they might require three doses to be fully protected.”
The vaccine produces antibodies that can stop HPV from infecting cells and lowers your chances of catching an HPV-related cancer, such as throat cancer or cancer of the cervix, he said.
While the vaccine is not guaranteed to protect you from the more than 100 strains of HPV, it can protect you from HPV 16 and HPV 18 – two high-risk strains that cause around 70% of cervical cancers.
What is fueling the rise of HPV cases?
A misconception that oral sex is somehow a “safe and risk-free” alternative to anal or vaginal sex could be one reason, Dr. Aguh said.
“It is important to know that, with oral sex, you are exposed to many of the risks associated with vaginal intercourse, especially if you do not take any measures to protect yourself and/or your partner,” Dr. Aguh said. “[With oral sex] it is possible to end up contracting an infection like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and even HPV, leading to an increased risk of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancers.”
A lack of public awareness of what can cause throat cancer could also explain this phenomenon. The number of people you have oral sex with, along with the age you begin sexual activity, can greatly determine your risk of the disease, according to Dr. Lee. She echoes a report by Hisham Mehanna, PhD, in The Conversation.
“For oropharyngeal cancer, the main risk factor is the number of lifetime sexual partners, especially oral sex,” wrote Dr. Mehanna, a professor at the Institute of Cancer and Genomic Sciences at the University of Birmingham (England). “Those with six or more lifetime oral-sex partners are 8.5 times more likely to develop oropharyngeal cancer than those who do not practice oral sex.”
What are symptoms of oropharyngeal cancer?
Labored breathing or swallowing, a cough that won’t go away, and crackling or hoarseness of your voice could all be signs of throat cancer. Other symptoms include earaches, swelling of the head or neck, and enlarged lymph nodes, among others, Dr. Aguh said.
“The signs and symptoms of HPV-related throat cancers can be difficult to identify and recognize, as they can be vague and are also associated with other medical conditions. Sometimes, there are no signs at all, or they are not easily noticeable due to the location,” he said.
You should go see your doctor if you have any of these ailments for an extended period.
How to reduce your risk
In addition to having six or more oral-sex partners, smoking and drinking heavily could also raise your risk of throat cancer, said Dr. Lee. Proper dental health – like seeing your dentist regularly and practicing proper oral hygiene – can also shave your risk.
“[Good dental health] can help not just with head and neck cancer risk, but with many other inflammation-related diseases,” Dr. Lee said.
Using dental dams and condoms can also be a good method of protection, Dr. Aguh said. A dental dam is a stretchy sheet of latex, or polyurethane plastic, in the shape of a square that is made for blocking body fluid to lower your risk of contracting an STD via oral sex.
Keep in mind: Even with these protections, make sure you and your partner discuss each other’s sexual history, any prior or current STDs and their preferred protection from STDs, said Dr. Aguh.
If you or your partner is being treated for an STD, consider opting out of oral sex and consulting a doctor.
The HPV vaccine is another common method of protection. The shot is “approved for prevention of nine of the most high-risk strains of HPV,” or those that are most commonly linked to cancer, according to Dr. Lee. The vaccine “reduces the frequency of infection” with these viruses, which can ultimately lower the risk of cancers linked to HPV, including cervical, anal, and vulvar and vaginal cancers, she said.
“The best time to receive treatment for prevention of disease is prior to onset of sexual intercourse,” said Dr. Lee.
To get your HPV vaccine, head to your family doctor, school- or community-based health center, or state health department, suggests the CDC.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
An epidemic of sexually transmitted HPV is now swirling around the United States and the United Kingdom, with some serious cases leading to oropharyngeal cancer, which can affect the back of the throat, tonsils, and tongue.
HPV is the leading cause (70%) of this oropharyngeal cancer, according to the CDC. It is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the nation, and around 3.6% of women and 10% of men report oral HPV specifically. But over the past decade, oropharyngeal cases have been steadily falling a little under 4% and 2%, respectively, according to the National Cancer Institute.
HPV is often undetectable and can clear up within a few months. But unfortunately for some, serious disease, such as throat cancer, can develop.
Studies show the HPV vaccine to be extremely effective in lowering sexually transmitted HPV cases. Yet, only 54.5% of young people aged 13-15 have taken the recommended two to three doses, according to the National Cancer Institute.
Why aren’t more young people taking the vaccine?
Low public awareness of the dangers of HPV may be behind young people’s poor vaccination rates, according to Teresa Lee, MD, of the Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia. “For example, while the link with head and neck cancers has been well-studied, the FDA labeling was not changed to reflect this as an indication until 2020,” she said.
Other reasons can include one’s socioeconomic background, poor health literacy, cultural or religious stigmas around vaccines, and lack of quality, low-cost health care, says Emmanuel Aguh, MD, a board-certified family medicine physician. “Some individuals and families are still resistant to vaccines and the noted lack of uptake.”
Doctors and other health care professionals should also be sure to tell patients of all ages about the risks of HPV infection and how well the vaccine works, Dr. Lee said. “Not everyone who is now eligible may have been offered the vaccine as a child, and the first time young adults may receive counseling on this subject may not be until they are entering a very busy period of their lives with many responsibilities – when it may be hard to fit in things like health maintenance.”
How safe is the HPV vaccine?
The Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have studied the HPV vaccine for years to find out how safe it is and how well it works, Dr. Aguh said. No major side effects have been reported, and the most common side effect is soreness where you get the shot (which is normal after most vaccines). Some dizziness and fainting in adolescents can also occur, so young people are usually asked to sit or lie down during the shot and for 15 minutes afterward, he said.
“Serious adverse events have not been reported at higher rates than expected following HPV vaccination, meaning there is no clear evidence they are related to the vaccine,” Dr. Lee said. “The vaccine is highly effective in decreasing rates of detectable infection with the high-risk HPV strains responsible for HPV-associated cancers.”
The HPV vaccine is largely recommended for people aged 9-26, and sometimes up to age 45, depending on the individual, Dr. Aguh said. If you are over 26, talk to your doctor about whether you should consider getting the vaccine.
“It is usually given in two doses for complete protection if taken before the 15th birthday,” Dr. Aguh said. “If taken afterward, or in those with a weak immune system, they might require three doses to be fully protected.”
The vaccine produces antibodies that can stop HPV from infecting cells and lowers your chances of catching an HPV-related cancer, such as throat cancer or cancer of the cervix, he said.
While the vaccine is not guaranteed to protect you from the more than 100 strains of HPV, it can protect you from HPV 16 and HPV 18 – two high-risk strains that cause around 70% of cervical cancers.
What is fueling the rise of HPV cases?
A misconception that oral sex is somehow a “safe and risk-free” alternative to anal or vaginal sex could be one reason, Dr. Aguh said.
“It is important to know that, with oral sex, you are exposed to many of the risks associated with vaginal intercourse, especially if you do not take any measures to protect yourself and/or your partner,” Dr. Aguh said. “[With oral sex] it is possible to end up contracting an infection like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and even HPV, leading to an increased risk of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancers.”
A lack of public awareness of what can cause throat cancer could also explain this phenomenon. The number of people you have oral sex with, along with the age you begin sexual activity, can greatly determine your risk of the disease, according to Dr. Lee. She echoes a report by Hisham Mehanna, PhD, in The Conversation.
“For oropharyngeal cancer, the main risk factor is the number of lifetime sexual partners, especially oral sex,” wrote Dr. Mehanna, a professor at the Institute of Cancer and Genomic Sciences at the University of Birmingham (England). “Those with six or more lifetime oral-sex partners are 8.5 times more likely to develop oropharyngeal cancer than those who do not practice oral sex.”
What are symptoms of oropharyngeal cancer?
Labored breathing or swallowing, a cough that won’t go away, and crackling or hoarseness of your voice could all be signs of throat cancer. Other symptoms include earaches, swelling of the head or neck, and enlarged lymph nodes, among others, Dr. Aguh said.
“The signs and symptoms of HPV-related throat cancers can be difficult to identify and recognize, as they can be vague and are also associated with other medical conditions. Sometimes, there are no signs at all, or they are not easily noticeable due to the location,” he said.
You should go see your doctor if you have any of these ailments for an extended period.
How to reduce your risk
In addition to having six or more oral-sex partners, smoking and drinking heavily could also raise your risk of throat cancer, said Dr. Lee. Proper dental health – like seeing your dentist regularly and practicing proper oral hygiene – can also shave your risk.
“[Good dental health] can help not just with head and neck cancer risk, but with many other inflammation-related diseases,” Dr. Lee said.
Using dental dams and condoms can also be a good method of protection, Dr. Aguh said. A dental dam is a stretchy sheet of latex, or polyurethane plastic, in the shape of a square that is made for blocking body fluid to lower your risk of contracting an STD via oral sex.
Keep in mind: Even with these protections, make sure you and your partner discuss each other’s sexual history, any prior or current STDs and their preferred protection from STDs, said Dr. Aguh.
If you or your partner is being treated for an STD, consider opting out of oral sex and consulting a doctor.
The HPV vaccine is another common method of protection. The shot is “approved for prevention of nine of the most high-risk strains of HPV,” or those that are most commonly linked to cancer, according to Dr. Lee. The vaccine “reduces the frequency of infection” with these viruses, which can ultimately lower the risk of cancers linked to HPV, including cervical, anal, and vulvar and vaginal cancers, she said.
“The best time to receive treatment for prevention of disease is prior to onset of sexual intercourse,” said Dr. Lee.
To get your HPV vaccine, head to your family doctor, school- or community-based health center, or state health department, suggests the CDC.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
Vaginal microbiota transfer may affect neurodevelopment in cesarean infants
Previous studies have shown that gut microbiota in infancy could affect neurodevelopment, and infants delivered by cesarean are not exposed to potentially helpful microbes acquired by infants during vaginal delivery, wrote Lepeng Zhou, MD, of Southern Medical University, Guangdong, China, and colleagues.
“Infants delivered by C-section start life with very different bacteria than those born vaginally,” corresponding author Jose Clemente, PhD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “Because this is the first time the newborn is exposed to microbes, we and others have hypothesized for some time that this ‘first encounter’ might be significant to shape the development of the baby,” he said.
“A few years ago, we demonstrated that it is possible to change the microbiome of C-section–delivered infants using an intervention that makes their microbiome more similar to that of a vaginally-delivered infant,” Dr. Clemente told this news organization. “In this study just published, we show that this procedure not only changes the microbiome of C-section infants, but it also modifies a health outcome (in this case, neurodevelopment). This is highly significant because it opens the way to reduce the risk that C-section infants have for certain conditions through a very simple microbial intervention,” he said.
‘Significantly higher’ ASQ-3 scores
In the current study, published in Cell Host & Microbe, the researchers examined the impact of vaginal microbiota transfer (VMT) on the neurodevelopment of cesarean-delivered infants. They randomized 35 women scheduled for cesarean delivery with a single infant to VMT and 41 to a control intervention of saline gauze for their infants immediately after delivery.
The primary outcome of infant neurodevelopment was assessed using the Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ-3) score at 6 months. The researchers also collected fecal samples and assessed safety outcomes for the infants at 3, 7, 30, and 42 days after birth. The final analysis comprised 32 infants in the VMT group and 36 in the control group. The mean age of the mothers was 32 years; the mean gestational age of the infants was 39 weeks, but the difference was significant and slightly less in the VMT group compared with the controls (38.38 weeks vs. 39.13 weeks, P = .007). A group of 33 vaginally-delivered infants (VD) underwent ASQ-3 testing to serve as a reference group.
At 6 months, ASQ-3 scores were significantly higher (10.09%, P = .014) with VMT compared with controls, and the difference remained significant after adjustment for multiple factors including gestational age.
ASQ-3 total scores at 6 months were not significantly different between the VMT group and the VD reference group (mean difference of 8.84 VMT to VD, P = .346); scores between these groups also were similar at 3 months (mean difference of –1.48 VMT to VD, P = .900) and no significant differences appeared in ASQ-3 subdomains between these groups at either time period.
An examination of gut metabolites in stool showed significant differences in fecal metabolites and metabolic function, signs of gut microbiota maturation, the researchers noted.
“Interestingly, all the genera and metabolites that exhibited positive correlations with neurodevelopmental scores were upregulated in the VMT group, whereas the only negative correlation of Klebsiella was downregulated, indicating that VMT may impact neurodevelopment through the modulation of specific gut microbial genera and metabolites,” the researchers wrote.
No serious adverse events occurred in either group during the study period. Nine adverse events were reported; 4 in the VMT group and 5 in the control group. The most common AEs were mild skin disorders, including papules, pustules, and erythema.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential for transfer not only of vaginal microbiota, but also vaginal metabolites, mycobiome, and virome, which blurs the potential mechanism of VMT, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the relatively short study period, small sample size, and cervical HPV screening within the past 5 years, not during pregnancy, they wrote.
However, the results suggest that VMT is safe, and may help improve the fecal microbiome in cesarean-delivered infants, and the long-term effects merit further studies in larger populations, they concluded.
Limitations and outlook
Dr. Clemente said in an interview that the researchers were “hopeful that the study would demonstrate a health benefit, as it does with some limitations.” The current study findings confirm some previous results showing that modification of the microbiomes of C-section infants is possible through a transfer of maternal vaginal microbes, he said.
“There is also an important aspect that was confirmed here: The lack of serious adverse events associated with the procedure, and the fact that transferring vaginal microbes did not increase the risk of adverse events compared to the control group or to vaginally-delivered infants. This is fundamental to establish that using rigorous exclusion criteria we can perform this procedure safely for infants and mothers,” he added.
“We are at very early stages yet to talk about clinical implications,” said Dr. Clemente. “This is one of the first studies to demonstrate a benefit to the transfer of microbes from mothers to infants, and as such it opens the way for future trials that confirm these findings. The clinical application is still in the future, but this is an important first step towards that goal.”
Interest in restoring gut microbiota to potentially benefit infants persists, but a recent study published in Frontiers and Cellular and Infection Microbiology contradicted the potential association between maternal vaginal microbiome and an infant’s gut microbiome based on an analysis of infant stool.
“There are many reasons why different studies might reach different conclusions: The experimental procedures, the analytical methods, the cohort under study,” Dr. Clemente said when asked to comment on the Frontiers study. “Further studies are needed to establish whether this procedure is equally effective under all conditions and whether health benefits are generalizable or specific to particular populations.”
Several research gaps remain, Dr. Clemente said. “First, neurodevelopment was measured through a questionnaire that captures various aspects such as communication, motor skills, or problem solving. While this is a standard way to establish that an infant is in the correct neurodevelopmental pathway, it is not a ‘hard’ measure of cellular or biochemical processes being impacted by the intervention. Some of our results suggest that there is a change in the metabolome of this infants, particularly an enrichment in GABA, a neurotransmitter, but the exact mechanisms by which the intervention is resulting in a health benefit still remains to be explored,” he said.
“We have an ongoing study here at Mount Sinai to test whether this microbial intervention can be effective in lowering the risk of developing food allergies in newborns who are at high risk, so that is another important future question: What other conditions could benefit from this approach,” said Dr. Clemente.
A third research goal, he added, is “determining what microbes precisely are responsible for the health benefits; this study uses a full microbial community to colonize infants. We show that this is effective and, importantly, that there were no significant adverse events in the treated infants,” he noted. “However, identifying what specific microbes are beneficial would further lower the risk of any potential side effects, while facilitating the development of drugs based on defined microbial consortia,” he said.
Safety and efficacy support further studies
“It is widely accepted that the gut microbiome of neonates varies based on mode of delivery,” Anna K. Knight, PhD, assistant professor of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“C-sections have been associated with increased risk of asthma and metabolic disease, and have been associated with differences in the development of the immune system,” said Dr. Knight, who was not involved in the study. “There have been small pilot studies examining the use of vaginal microbiome transplants to shift the gut microbiome of neonates born by C-section to be more like the gut microbiome of neonates born via vaginal delivery, but the safety and efficacy of this treatment has not been well established. This study examines both, while also evaluating potential changes in the metabolome and neurodevelopmental trajectories.”
The current study confirmed the impact of the neonatal gut microbe on neurodevelopmental outcomes during a sensitive period, said Dr. Knight. “The fact that these differences persisted at 6 months suggests that even if the microbiome composition between vaginally-delivered and preterm infants converged at 1-2 years old, there may be lasting impacts of mode of delivery,” she said.
“The results of this study suggest that vaginal microbiome transplant may be a safe and effective way to mitigate the negative impacts of C-section delivery on the neonatal gut microbiome, and may be protective for neurodevelopment,” she added.
Regarding the Frontiers in Medicine study, Dr. Knight noted that it examined a very different population, with Zhou and colleagues focusing on Chinese infants, while Dos Santos and colleagues focused on Canadian infants.
“There was also a substantial difference in sample size between the two studies, with Dos Santos and colleagues examining > 500 more infants,” she said. “Additionally, the two studies differed in the sequencing technology used, sample collection methods, and antibiotic exposure, which can all impact microbiome study results.”
Since the current study showed efficacy and safety of VMT in a small clinical trial, larger trials with more diverse participants are needed to further examine the impact of VMT, said Dr. Knight. “The risks of vaginal microbiome transplant in mothers with infections should also be considered, and the mechanisms by which the neonatal gut microbiome impacts neurodevelopment need further investigation,” she said.
The study was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, the Canadian Institute of Health Research, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Clinical Research Startup Program of Southern Medical University, China, and the Top Talent Program of Foshan Women and Children Hospital, China. The researchers and Dr. Knight had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Previous studies have shown that gut microbiota in infancy could affect neurodevelopment, and infants delivered by cesarean are not exposed to potentially helpful microbes acquired by infants during vaginal delivery, wrote Lepeng Zhou, MD, of Southern Medical University, Guangdong, China, and colleagues.
“Infants delivered by C-section start life with very different bacteria than those born vaginally,” corresponding author Jose Clemente, PhD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “Because this is the first time the newborn is exposed to microbes, we and others have hypothesized for some time that this ‘first encounter’ might be significant to shape the development of the baby,” he said.
“A few years ago, we demonstrated that it is possible to change the microbiome of C-section–delivered infants using an intervention that makes their microbiome more similar to that of a vaginally-delivered infant,” Dr. Clemente told this news organization. “In this study just published, we show that this procedure not only changes the microbiome of C-section infants, but it also modifies a health outcome (in this case, neurodevelopment). This is highly significant because it opens the way to reduce the risk that C-section infants have for certain conditions through a very simple microbial intervention,” he said.
‘Significantly higher’ ASQ-3 scores
In the current study, published in Cell Host & Microbe, the researchers examined the impact of vaginal microbiota transfer (VMT) on the neurodevelopment of cesarean-delivered infants. They randomized 35 women scheduled for cesarean delivery with a single infant to VMT and 41 to a control intervention of saline gauze for their infants immediately after delivery.
The primary outcome of infant neurodevelopment was assessed using the Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ-3) score at 6 months. The researchers also collected fecal samples and assessed safety outcomes for the infants at 3, 7, 30, and 42 days after birth. The final analysis comprised 32 infants in the VMT group and 36 in the control group. The mean age of the mothers was 32 years; the mean gestational age of the infants was 39 weeks, but the difference was significant and slightly less in the VMT group compared with the controls (38.38 weeks vs. 39.13 weeks, P = .007). A group of 33 vaginally-delivered infants (VD) underwent ASQ-3 testing to serve as a reference group.
At 6 months, ASQ-3 scores were significantly higher (10.09%, P = .014) with VMT compared with controls, and the difference remained significant after adjustment for multiple factors including gestational age.
ASQ-3 total scores at 6 months were not significantly different between the VMT group and the VD reference group (mean difference of 8.84 VMT to VD, P = .346); scores between these groups also were similar at 3 months (mean difference of –1.48 VMT to VD, P = .900) and no significant differences appeared in ASQ-3 subdomains between these groups at either time period.
An examination of gut metabolites in stool showed significant differences in fecal metabolites and metabolic function, signs of gut microbiota maturation, the researchers noted.
“Interestingly, all the genera and metabolites that exhibited positive correlations with neurodevelopmental scores were upregulated in the VMT group, whereas the only negative correlation of Klebsiella was downregulated, indicating that VMT may impact neurodevelopment through the modulation of specific gut microbial genera and metabolites,” the researchers wrote.
No serious adverse events occurred in either group during the study period. Nine adverse events were reported; 4 in the VMT group and 5 in the control group. The most common AEs were mild skin disorders, including papules, pustules, and erythema.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential for transfer not only of vaginal microbiota, but also vaginal metabolites, mycobiome, and virome, which blurs the potential mechanism of VMT, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the relatively short study period, small sample size, and cervical HPV screening within the past 5 years, not during pregnancy, they wrote.
However, the results suggest that VMT is safe, and may help improve the fecal microbiome in cesarean-delivered infants, and the long-term effects merit further studies in larger populations, they concluded.
Limitations and outlook
Dr. Clemente said in an interview that the researchers were “hopeful that the study would demonstrate a health benefit, as it does with some limitations.” The current study findings confirm some previous results showing that modification of the microbiomes of C-section infants is possible through a transfer of maternal vaginal microbes, he said.
“There is also an important aspect that was confirmed here: The lack of serious adverse events associated with the procedure, and the fact that transferring vaginal microbes did not increase the risk of adverse events compared to the control group or to vaginally-delivered infants. This is fundamental to establish that using rigorous exclusion criteria we can perform this procedure safely for infants and mothers,” he added.
“We are at very early stages yet to talk about clinical implications,” said Dr. Clemente. “This is one of the first studies to demonstrate a benefit to the transfer of microbes from mothers to infants, and as such it opens the way for future trials that confirm these findings. The clinical application is still in the future, but this is an important first step towards that goal.”
Interest in restoring gut microbiota to potentially benefit infants persists, but a recent study published in Frontiers and Cellular and Infection Microbiology contradicted the potential association between maternal vaginal microbiome and an infant’s gut microbiome based on an analysis of infant stool.
“There are many reasons why different studies might reach different conclusions: The experimental procedures, the analytical methods, the cohort under study,” Dr. Clemente said when asked to comment on the Frontiers study. “Further studies are needed to establish whether this procedure is equally effective under all conditions and whether health benefits are generalizable or specific to particular populations.”
Several research gaps remain, Dr. Clemente said. “First, neurodevelopment was measured through a questionnaire that captures various aspects such as communication, motor skills, or problem solving. While this is a standard way to establish that an infant is in the correct neurodevelopmental pathway, it is not a ‘hard’ measure of cellular or biochemical processes being impacted by the intervention. Some of our results suggest that there is a change in the metabolome of this infants, particularly an enrichment in GABA, a neurotransmitter, but the exact mechanisms by which the intervention is resulting in a health benefit still remains to be explored,” he said.
“We have an ongoing study here at Mount Sinai to test whether this microbial intervention can be effective in lowering the risk of developing food allergies in newborns who are at high risk, so that is another important future question: What other conditions could benefit from this approach,” said Dr. Clemente.
A third research goal, he added, is “determining what microbes precisely are responsible for the health benefits; this study uses a full microbial community to colonize infants. We show that this is effective and, importantly, that there were no significant adverse events in the treated infants,” he noted. “However, identifying what specific microbes are beneficial would further lower the risk of any potential side effects, while facilitating the development of drugs based on defined microbial consortia,” he said.
Safety and efficacy support further studies
“It is widely accepted that the gut microbiome of neonates varies based on mode of delivery,” Anna K. Knight, PhD, assistant professor of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“C-sections have been associated with increased risk of asthma and metabolic disease, and have been associated with differences in the development of the immune system,” said Dr. Knight, who was not involved in the study. “There have been small pilot studies examining the use of vaginal microbiome transplants to shift the gut microbiome of neonates born by C-section to be more like the gut microbiome of neonates born via vaginal delivery, but the safety and efficacy of this treatment has not been well established. This study examines both, while also evaluating potential changes in the metabolome and neurodevelopmental trajectories.”
The current study confirmed the impact of the neonatal gut microbe on neurodevelopmental outcomes during a sensitive period, said Dr. Knight. “The fact that these differences persisted at 6 months suggests that even if the microbiome composition between vaginally-delivered and preterm infants converged at 1-2 years old, there may be lasting impacts of mode of delivery,” she said.
“The results of this study suggest that vaginal microbiome transplant may be a safe and effective way to mitigate the negative impacts of C-section delivery on the neonatal gut microbiome, and may be protective for neurodevelopment,” she added.
Regarding the Frontiers in Medicine study, Dr. Knight noted that it examined a very different population, with Zhou and colleagues focusing on Chinese infants, while Dos Santos and colleagues focused on Canadian infants.
“There was also a substantial difference in sample size between the two studies, with Dos Santos and colleagues examining > 500 more infants,” she said. “Additionally, the two studies differed in the sequencing technology used, sample collection methods, and antibiotic exposure, which can all impact microbiome study results.”
Since the current study showed efficacy and safety of VMT in a small clinical trial, larger trials with more diverse participants are needed to further examine the impact of VMT, said Dr. Knight. “The risks of vaginal microbiome transplant in mothers with infections should also be considered, and the mechanisms by which the neonatal gut microbiome impacts neurodevelopment need further investigation,” she said.
The study was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, the Canadian Institute of Health Research, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Clinical Research Startup Program of Southern Medical University, China, and the Top Talent Program of Foshan Women and Children Hospital, China. The researchers and Dr. Knight had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Previous studies have shown that gut microbiota in infancy could affect neurodevelopment, and infants delivered by cesarean are not exposed to potentially helpful microbes acquired by infants during vaginal delivery, wrote Lepeng Zhou, MD, of Southern Medical University, Guangdong, China, and colleagues.
“Infants delivered by C-section start life with very different bacteria than those born vaginally,” corresponding author Jose Clemente, PhD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “Because this is the first time the newborn is exposed to microbes, we and others have hypothesized for some time that this ‘first encounter’ might be significant to shape the development of the baby,” he said.
“A few years ago, we demonstrated that it is possible to change the microbiome of C-section–delivered infants using an intervention that makes their microbiome more similar to that of a vaginally-delivered infant,” Dr. Clemente told this news organization. “In this study just published, we show that this procedure not only changes the microbiome of C-section infants, but it also modifies a health outcome (in this case, neurodevelopment). This is highly significant because it opens the way to reduce the risk that C-section infants have for certain conditions through a very simple microbial intervention,” he said.
‘Significantly higher’ ASQ-3 scores
In the current study, published in Cell Host & Microbe, the researchers examined the impact of vaginal microbiota transfer (VMT) on the neurodevelopment of cesarean-delivered infants. They randomized 35 women scheduled for cesarean delivery with a single infant to VMT and 41 to a control intervention of saline gauze for their infants immediately after delivery.
The primary outcome of infant neurodevelopment was assessed using the Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ-3) score at 6 months. The researchers also collected fecal samples and assessed safety outcomes for the infants at 3, 7, 30, and 42 days after birth. The final analysis comprised 32 infants in the VMT group and 36 in the control group. The mean age of the mothers was 32 years; the mean gestational age of the infants was 39 weeks, but the difference was significant and slightly less in the VMT group compared with the controls (38.38 weeks vs. 39.13 weeks, P = .007). A group of 33 vaginally-delivered infants (VD) underwent ASQ-3 testing to serve as a reference group.
At 6 months, ASQ-3 scores were significantly higher (10.09%, P = .014) with VMT compared with controls, and the difference remained significant after adjustment for multiple factors including gestational age.
ASQ-3 total scores at 6 months were not significantly different between the VMT group and the VD reference group (mean difference of 8.84 VMT to VD, P = .346); scores between these groups also were similar at 3 months (mean difference of –1.48 VMT to VD, P = .900) and no significant differences appeared in ASQ-3 subdomains between these groups at either time period.
An examination of gut metabolites in stool showed significant differences in fecal metabolites and metabolic function, signs of gut microbiota maturation, the researchers noted.
“Interestingly, all the genera and metabolites that exhibited positive correlations with neurodevelopmental scores were upregulated in the VMT group, whereas the only negative correlation of Klebsiella was downregulated, indicating that VMT may impact neurodevelopment through the modulation of specific gut microbial genera and metabolites,” the researchers wrote.
No serious adverse events occurred in either group during the study period. Nine adverse events were reported; 4 in the VMT group and 5 in the control group. The most common AEs were mild skin disorders, including papules, pustules, and erythema.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential for transfer not only of vaginal microbiota, but also vaginal metabolites, mycobiome, and virome, which blurs the potential mechanism of VMT, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the relatively short study period, small sample size, and cervical HPV screening within the past 5 years, not during pregnancy, they wrote.
However, the results suggest that VMT is safe, and may help improve the fecal microbiome in cesarean-delivered infants, and the long-term effects merit further studies in larger populations, they concluded.
Limitations and outlook
Dr. Clemente said in an interview that the researchers were “hopeful that the study would demonstrate a health benefit, as it does with some limitations.” The current study findings confirm some previous results showing that modification of the microbiomes of C-section infants is possible through a transfer of maternal vaginal microbes, he said.
“There is also an important aspect that was confirmed here: The lack of serious adverse events associated with the procedure, and the fact that transferring vaginal microbes did not increase the risk of adverse events compared to the control group or to vaginally-delivered infants. This is fundamental to establish that using rigorous exclusion criteria we can perform this procedure safely for infants and mothers,” he added.
“We are at very early stages yet to talk about clinical implications,” said Dr. Clemente. “This is one of the first studies to demonstrate a benefit to the transfer of microbes from mothers to infants, and as such it opens the way for future trials that confirm these findings. The clinical application is still in the future, but this is an important first step towards that goal.”
Interest in restoring gut microbiota to potentially benefit infants persists, but a recent study published in Frontiers and Cellular and Infection Microbiology contradicted the potential association between maternal vaginal microbiome and an infant’s gut microbiome based on an analysis of infant stool.
“There are many reasons why different studies might reach different conclusions: The experimental procedures, the analytical methods, the cohort under study,” Dr. Clemente said when asked to comment on the Frontiers study. “Further studies are needed to establish whether this procedure is equally effective under all conditions and whether health benefits are generalizable or specific to particular populations.”
Several research gaps remain, Dr. Clemente said. “First, neurodevelopment was measured through a questionnaire that captures various aspects such as communication, motor skills, or problem solving. While this is a standard way to establish that an infant is in the correct neurodevelopmental pathway, it is not a ‘hard’ measure of cellular or biochemical processes being impacted by the intervention. Some of our results suggest that there is a change in the metabolome of this infants, particularly an enrichment in GABA, a neurotransmitter, but the exact mechanisms by which the intervention is resulting in a health benefit still remains to be explored,” he said.
“We have an ongoing study here at Mount Sinai to test whether this microbial intervention can be effective in lowering the risk of developing food allergies in newborns who are at high risk, so that is another important future question: What other conditions could benefit from this approach,” said Dr. Clemente.
A third research goal, he added, is “determining what microbes precisely are responsible for the health benefits; this study uses a full microbial community to colonize infants. We show that this is effective and, importantly, that there were no significant adverse events in the treated infants,” he noted. “However, identifying what specific microbes are beneficial would further lower the risk of any potential side effects, while facilitating the development of drugs based on defined microbial consortia,” he said.
Safety and efficacy support further studies
“It is widely accepted that the gut microbiome of neonates varies based on mode of delivery,” Anna K. Knight, PhD, assistant professor of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“C-sections have been associated with increased risk of asthma and metabolic disease, and have been associated with differences in the development of the immune system,” said Dr. Knight, who was not involved in the study. “There have been small pilot studies examining the use of vaginal microbiome transplants to shift the gut microbiome of neonates born by C-section to be more like the gut microbiome of neonates born via vaginal delivery, but the safety and efficacy of this treatment has not been well established. This study examines both, while also evaluating potential changes in the metabolome and neurodevelopmental trajectories.”
The current study confirmed the impact of the neonatal gut microbe on neurodevelopmental outcomes during a sensitive period, said Dr. Knight. “The fact that these differences persisted at 6 months suggests that even if the microbiome composition between vaginally-delivered and preterm infants converged at 1-2 years old, there may be lasting impacts of mode of delivery,” she said.
“The results of this study suggest that vaginal microbiome transplant may be a safe and effective way to mitigate the negative impacts of C-section delivery on the neonatal gut microbiome, and may be protective for neurodevelopment,” she added.
Regarding the Frontiers in Medicine study, Dr. Knight noted that it examined a very different population, with Zhou and colleagues focusing on Chinese infants, while Dos Santos and colleagues focused on Canadian infants.
“There was also a substantial difference in sample size between the two studies, with Dos Santos and colleagues examining > 500 more infants,” she said. “Additionally, the two studies differed in the sequencing technology used, sample collection methods, and antibiotic exposure, which can all impact microbiome study results.”
Since the current study showed efficacy and safety of VMT in a small clinical trial, larger trials with more diverse participants are needed to further examine the impact of VMT, said Dr. Knight. “The risks of vaginal microbiome transplant in mothers with infections should also be considered, and the mechanisms by which the neonatal gut microbiome impacts neurodevelopment need further investigation,” she said.
The study was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, the Canadian Institute of Health Research, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Clinical Research Startup Program of Southern Medical University, China, and the Top Talent Program of Foshan Women and Children Hospital, China. The researchers and Dr. Knight had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM CELL HOST & MICROBE
Malpractice lawsuits over denied abortion care may be on the horizon
Some experts predict those providers could soon face a new legal threat: medical malpractice lawsuits alleging they harmed patients by failing to provide timely, necessary abortion care.
“We will absolutely see medical malpractice cases emerge,” said Diana Nordlund, an emergency physician in Grand Rapids, Mich., and former malpractice defense attorney, who chairs the Medical-Legal Committee of the American College of Emergency Physicians. When physicians decide not to provide treatments widely accepted as the standard of care because of these new laws, “that’s perceived as substandard care and there is increased civil liability.”
To some physicians and malpractice attorneys, the question is when – not if – a pregnant patient will die from lack of care and set the stage for a big-dollar wrongful death claim. Abortion rights supporters said such a case could pressure doctors and hospitals to provide appropriate abortion care, counterbalancing their fears of running afoul of state abortion bans, many of which call for criminal prosecution and revocation of medical licenses as punishment for violations.
“If we want to encourage proper care, there has to be some sort of counter-risk to physicians and hospitals for refusing to provide care that should be legal,” said Greer Donley, an associate professor at the University of Pittsburgh school of law who studies the impact of abortion bans. “But most rational people would be more afraid of going to jail.”
Some supporters of abortion bans said they would welcome malpractice lawsuits. Providers are refusing to use the exceptions in some state laws that allow them to perform abortions to save a patient’s life or health, they said.
“It could help achieve our goal if it clarifies that the law did not contradict standard medical practice,” said John Seago, president of Texas Right to Life, referring to the state’s abortion ban.
A new KFF poll found that 59% of ob.gyns. practicing in states with gestational limits on abortion, and 61% of those in states with bans, are somewhat or very concerned about their legal risk when making decisions about the necessity of an abortion.
Some attorneys are exploring lawsuits on behalf of women who they said have been harmed by a state abortion ban. An attorney for Mylissa Farmer, a Missouri woman who was refused an abortion at two hospitals in August after her water broke about 18 weeks into her pregnancy, said she may sue for malpractice. Missouri’s abortion ban, which took effect last year, makes an exception for medical emergencies.
The federal government recently found that the two hospitals violated a federal emergency care law in denying Ms. Farmer an abortion, which experts said could strengthen a malpractice claim. One of the hospitals, Freeman Health System in Joplin, Mo., did not respond to a request for comment. The other, the University of Kansas Health System in Kansas City, said the care provided “was reviewed by the hospital and found to be in accordance with hospital policy,” according to a spokesperson, Jill Chadwick.
Ms. Farmer “experienced permanent physical and emotional damage,” said Michelle Banker, one of her lawyers at the National Women’s Law Center, who added that Ms. Farmer and her attorneys are “considering all our legal options.”
News reports and medical studies show that some women with pregnancy complications have suffered serious health consequences when doctors and hospitals did not provide once-routine abortion care.
Last month, researchers released a study identifying dozens of cases in 14 states in which physicians said deficiencies in care due to abortion restrictions led to preventable complications and hospitalizations, with some patients nearly dying.
“The patients were sent home and told to come back when they had signs of infection,” said Daniel Grossman, an ob.gyn. at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the study. “Many developed serious infections. And it’s clear many of these cases were very emotionally traumatic.”
He said though the researchers did not track patient outcomes, the lack of timely abortion care in such cases could result in severe health harms including loss of fertility, stroke, or heart attack.
“It’s just a matter of time before there will be a death that comes to light,” Dr. Grossman said.
Still, considering the conflict for doctors between medical ethics and personal risk, some stakeholders said patients may be reluctant to sue doctors and juries may balk at finding them liable.
“It’s a terrible position that providers are being put into, and I don’t think juries will blame the doctor unless it’s a super clear case,” said Morgan Murphy, a malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Missouri.
She said her firm will not pursue malpractice cases based on abortion denials except in “pretty extreme” situations, such as when a patient dies. “Unless a mother is on her deathbed, it’s pretty hard to fault a provider who thinks if they provide treatment they’re going to be criminally liable or will lose their medical license.”
Another hurdle for malpractice cases is that state abortion bans could undermine the argument that abortion is the legal “standard of care,” meaning that it is a widely accepted and prescribed treatment for pregnancy complications such as miscarriage and for fatal fetal abnormalities.
“I absolutely see a breach of the standard of care in these cases,” said Maria A. Phillis, an ob.gyn. and former lawyer in Cleveland. “But if someone goes to trial in a malpractice case, it will come down to a battle of medical experts about whether it’s no longer the standard of care, and the jury would have to decide.”
An additional justification for physicians not to provide abortions is that medical liability insurers generally do not cover damages from criminal acts, which “puts the finger on the scales even more to not do anything,” Dr. Phillis said.
Stuart Grossman, a prominent malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Florida, said he would be eager to take an abortion-denial case in which the woman suffered serious health or emotional injuries.
Unlike other states with abortion bans, Florida does not cap damage amounts for pain and suffering in malpractice cases, making it more financially viable to sue there.
Mr. Grossman cited the case of Deborah Dorbert, a Florida woman who reportedly was denied an abortion despite being told by her physicians at 24 weeks of pregnancy that her fetus, with no kidneys and underdeveloped lungs, had a fatal condition called Potter syndrome.
Her doctors and the hospital refused to end the pregnancy even though the state’s abortion ban has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. Months later, her baby died in his parents’ arms shortly after birth.
“You can see how she’s been devastated mentally,” Mr. Grossman said. “She has a wrongful death case that I’d take in a minute.” He said the couple could file a malpractice suit for Ms. Dorbert’s physical and emotional damages and a separate malpractice and wrongful death suit for the couple’s suffering over the infant’s death.
Failing to counsel patients about their options and connect them with providers willing to terminate a pregnancy is also possible grounds for a malpractice suit, attorneys said. Katie Watson, an associate professor at Northwestern University, Chicago’s school of medicine who has studied state abortion bans, said counseling and referral are not prohibited under these laws and that physicians have an ethical obligation to offer those services.
“I think breaching the obligation for counseling would make a strong malpractice lawsuit,” she said.
Nancy Davis said she received no counseling or referral assistance last July after her doctors at Woman’s Hospital in Baton Rouge, La., told her 10 weeks into her pregnancy that her fetus would not survive because it was missing the top of its skull, a fatal condition called acrania. She said they recommended that she terminate the pregnancy and she agreed.
Ms. Davis said her doctors then told her a hospital executive had denied permission for the procedure because of Louisiana’s abortion ban, even though the law has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. A hospital spokesperson declined to comment.
Ms. Davis, who has three children, contacted Planned Parenthood of Greater New York, which arranged for child care and a flight to New York. She had an abortion performed there in September.
“The whole situation has been mentally and physically draining, and my family and I are receiving counseling,” Ms. Davis said. “I’m still very angry at the hospital and the doctors. I feel like I’m owed compensation for the trauma and the heartbreak.”
She sought the counsel of Benjamin Crump, a prominent attorney known for pursuing high-profile cases like wrongful death lawsuits on behalf of the families of Trayvon Martin and George Floyd.
But Mr. Crump said that after studying Ms. Davis’ legal options, he decided a judge would likely dismiss a malpractice suit and that Ms. Davis could end up paying the defendants’ legal fees and costs.
“The doctor’s lawyers will say, ‘You can’t expect my client to break the law and go to prison for up to 25 years,’ ” Mr. Crump said. “Unless you change the law, there is no option for her to receive compensation.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Some experts predict those providers could soon face a new legal threat: medical malpractice lawsuits alleging they harmed patients by failing to provide timely, necessary abortion care.
“We will absolutely see medical malpractice cases emerge,” said Diana Nordlund, an emergency physician in Grand Rapids, Mich., and former malpractice defense attorney, who chairs the Medical-Legal Committee of the American College of Emergency Physicians. When physicians decide not to provide treatments widely accepted as the standard of care because of these new laws, “that’s perceived as substandard care and there is increased civil liability.”
To some physicians and malpractice attorneys, the question is when – not if – a pregnant patient will die from lack of care and set the stage for a big-dollar wrongful death claim. Abortion rights supporters said such a case could pressure doctors and hospitals to provide appropriate abortion care, counterbalancing their fears of running afoul of state abortion bans, many of which call for criminal prosecution and revocation of medical licenses as punishment for violations.
“If we want to encourage proper care, there has to be some sort of counter-risk to physicians and hospitals for refusing to provide care that should be legal,” said Greer Donley, an associate professor at the University of Pittsburgh school of law who studies the impact of abortion bans. “But most rational people would be more afraid of going to jail.”
Some supporters of abortion bans said they would welcome malpractice lawsuits. Providers are refusing to use the exceptions in some state laws that allow them to perform abortions to save a patient’s life or health, they said.
“It could help achieve our goal if it clarifies that the law did not contradict standard medical practice,” said John Seago, president of Texas Right to Life, referring to the state’s abortion ban.
A new KFF poll found that 59% of ob.gyns. practicing in states with gestational limits on abortion, and 61% of those in states with bans, are somewhat or very concerned about their legal risk when making decisions about the necessity of an abortion.
Some attorneys are exploring lawsuits on behalf of women who they said have been harmed by a state abortion ban. An attorney for Mylissa Farmer, a Missouri woman who was refused an abortion at two hospitals in August after her water broke about 18 weeks into her pregnancy, said she may sue for malpractice. Missouri’s abortion ban, which took effect last year, makes an exception for medical emergencies.
The federal government recently found that the two hospitals violated a federal emergency care law in denying Ms. Farmer an abortion, which experts said could strengthen a malpractice claim. One of the hospitals, Freeman Health System in Joplin, Mo., did not respond to a request for comment. The other, the University of Kansas Health System in Kansas City, said the care provided “was reviewed by the hospital and found to be in accordance with hospital policy,” according to a spokesperson, Jill Chadwick.
Ms. Farmer “experienced permanent physical and emotional damage,” said Michelle Banker, one of her lawyers at the National Women’s Law Center, who added that Ms. Farmer and her attorneys are “considering all our legal options.”
News reports and medical studies show that some women with pregnancy complications have suffered serious health consequences when doctors and hospitals did not provide once-routine abortion care.
Last month, researchers released a study identifying dozens of cases in 14 states in which physicians said deficiencies in care due to abortion restrictions led to preventable complications and hospitalizations, with some patients nearly dying.
“The patients were sent home and told to come back when they had signs of infection,” said Daniel Grossman, an ob.gyn. at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the study. “Many developed serious infections. And it’s clear many of these cases were very emotionally traumatic.”
He said though the researchers did not track patient outcomes, the lack of timely abortion care in such cases could result in severe health harms including loss of fertility, stroke, or heart attack.
“It’s just a matter of time before there will be a death that comes to light,” Dr. Grossman said.
Still, considering the conflict for doctors between medical ethics and personal risk, some stakeholders said patients may be reluctant to sue doctors and juries may balk at finding them liable.
“It’s a terrible position that providers are being put into, and I don’t think juries will blame the doctor unless it’s a super clear case,” said Morgan Murphy, a malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Missouri.
She said her firm will not pursue malpractice cases based on abortion denials except in “pretty extreme” situations, such as when a patient dies. “Unless a mother is on her deathbed, it’s pretty hard to fault a provider who thinks if they provide treatment they’re going to be criminally liable or will lose their medical license.”
Another hurdle for malpractice cases is that state abortion bans could undermine the argument that abortion is the legal “standard of care,” meaning that it is a widely accepted and prescribed treatment for pregnancy complications such as miscarriage and for fatal fetal abnormalities.
“I absolutely see a breach of the standard of care in these cases,” said Maria A. Phillis, an ob.gyn. and former lawyer in Cleveland. “But if someone goes to trial in a malpractice case, it will come down to a battle of medical experts about whether it’s no longer the standard of care, and the jury would have to decide.”
An additional justification for physicians not to provide abortions is that medical liability insurers generally do not cover damages from criminal acts, which “puts the finger on the scales even more to not do anything,” Dr. Phillis said.
Stuart Grossman, a prominent malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Florida, said he would be eager to take an abortion-denial case in which the woman suffered serious health or emotional injuries.
Unlike other states with abortion bans, Florida does not cap damage amounts for pain and suffering in malpractice cases, making it more financially viable to sue there.
Mr. Grossman cited the case of Deborah Dorbert, a Florida woman who reportedly was denied an abortion despite being told by her physicians at 24 weeks of pregnancy that her fetus, with no kidneys and underdeveloped lungs, had a fatal condition called Potter syndrome.
Her doctors and the hospital refused to end the pregnancy even though the state’s abortion ban has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. Months later, her baby died in his parents’ arms shortly after birth.
“You can see how she’s been devastated mentally,” Mr. Grossman said. “She has a wrongful death case that I’d take in a minute.” He said the couple could file a malpractice suit for Ms. Dorbert’s physical and emotional damages and a separate malpractice and wrongful death suit for the couple’s suffering over the infant’s death.
Failing to counsel patients about their options and connect them with providers willing to terminate a pregnancy is also possible grounds for a malpractice suit, attorneys said. Katie Watson, an associate professor at Northwestern University, Chicago’s school of medicine who has studied state abortion bans, said counseling and referral are not prohibited under these laws and that physicians have an ethical obligation to offer those services.
“I think breaching the obligation for counseling would make a strong malpractice lawsuit,” she said.
Nancy Davis said she received no counseling or referral assistance last July after her doctors at Woman’s Hospital in Baton Rouge, La., told her 10 weeks into her pregnancy that her fetus would not survive because it was missing the top of its skull, a fatal condition called acrania. She said they recommended that she terminate the pregnancy and she agreed.
Ms. Davis said her doctors then told her a hospital executive had denied permission for the procedure because of Louisiana’s abortion ban, even though the law has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. A hospital spokesperson declined to comment.
Ms. Davis, who has three children, contacted Planned Parenthood of Greater New York, which arranged for child care and a flight to New York. She had an abortion performed there in September.
“The whole situation has been mentally and physically draining, and my family and I are receiving counseling,” Ms. Davis said. “I’m still very angry at the hospital and the doctors. I feel like I’m owed compensation for the trauma and the heartbreak.”
She sought the counsel of Benjamin Crump, a prominent attorney known for pursuing high-profile cases like wrongful death lawsuits on behalf of the families of Trayvon Martin and George Floyd.
But Mr. Crump said that after studying Ms. Davis’ legal options, he decided a judge would likely dismiss a malpractice suit and that Ms. Davis could end up paying the defendants’ legal fees and costs.
“The doctor’s lawyers will say, ‘You can’t expect my client to break the law and go to prison for up to 25 years,’ ” Mr. Crump said. “Unless you change the law, there is no option for her to receive compensation.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Some experts predict those providers could soon face a new legal threat: medical malpractice lawsuits alleging they harmed patients by failing to provide timely, necessary abortion care.
“We will absolutely see medical malpractice cases emerge,” said Diana Nordlund, an emergency physician in Grand Rapids, Mich., and former malpractice defense attorney, who chairs the Medical-Legal Committee of the American College of Emergency Physicians. When physicians decide not to provide treatments widely accepted as the standard of care because of these new laws, “that’s perceived as substandard care and there is increased civil liability.”
To some physicians and malpractice attorneys, the question is when – not if – a pregnant patient will die from lack of care and set the stage for a big-dollar wrongful death claim. Abortion rights supporters said such a case could pressure doctors and hospitals to provide appropriate abortion care, counterbalancing their fears of running afoul of state abortion bans, many of which call for criminal prosecution and revocation of medical licenses as punishment for violations.
“If we want to encourage proper care, there has to be some sort of counter-risk to physicians and hospitals for refusing to provide care that should be legal,” said Greer Donley, an associate professor at the University of Pittsburgh school of law who studies the impact of abortion bans. “But most rational people would be more afraid of going to jail.”
Some supporters of abortion bans said they would welcome malpractice lawsuits. Providers are refusing to use the exceptions in some state laws that allow them to perform abortions to save a patient’s life or health, they said.
“It could help achieve our goal if it clarifies that the law did not contradict standard medical practice,” said John Seago, president of Texas Right to Life, referring to the state’s abortion ban.
A new KFF poll found that 59% of ob.gyns. practicing in states with gestational limits on abortion, and 61% of those in states with bans, are somewhat or very concerned about their legal risk when making decisions about the necessity of an abortion.
Some attorneys are exploring lawsuits on behalf of women who they said have been harmed by a state abortion ban. An attorney for Mylissa Farmer, a Missouri woman who was refused an abortion at two hospitals in August after her water broke about 18 weeks into her pregnancy, said she may sue for malpractice. Missouri’s abortion ban, which took effect last year, makes an exception for medical emergencies.
The federal government recently found that the two hospitals violated a federal emergency care law in denying Ms. Farmer an abortion, which experts said could strengthen a malpractice claim. One of the hospitals, Freeman Health System in Joplin, Mo., did not respond to a request for comment. The other, the University of Kansas Health System in Kansas City, said the care provided “was reviewed by the hospital and found to be in accordance with hospital policy,” according to a spokesperson, Jill Chadwick.
Ms. Farmer “experienced permanent physical and emotional damage,” said Michelle Banker, one of her lawyers at the National Women’s Law Center, who added that Ms. Farmer and her attorneys are “considering all our legal options.”
News reports and medical studies show that some women with pregnancy complications have suffered serious health consequences when doctors and hospitals did not provide once-routine abortion care.
Last month, researchers released a study identifying dozens of cases in 14 states in which physicians said deficiencies in care due to abortion restrictions led to preventable complications and hospitalizations, with some patients nearly dying.
“The patients were sent home and told to come back when they had signs of infection,” said Daniel Grossman, an ob.gyn. at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the study. “Many developed serious infections. And it’s clear many of these cases were very emotionally traumatic.”
He said though the researchers did not track patient outcomes, the lack of timely abortion care in such cases could result in severe health harms including loss of fertility, stroke, or heart attack.
“It’s just a matter of time before there will be a death that comes to light,” Dr. Grossman said.
Still, considering the conflict for doctors between medical ethics and personal risk, some stakeholders said patients may be reluctant to sue doctors and juries may balk at finding them liable.
“It’s a terrible position that providers are being put into, and I don’t think juries will blame the doctor unless it’s a super clear case,” said Morgan Murphy, a malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Missouri.
She said her firm will not pursue malpractice cases based on abortion denials except in “pretty extreme” situations, such as when a patient dies. “Unless a mother is on her deathbed, it’s pretty hard to fault a provider who thinks if they provide treatment they’re going to be criminally liable or will lose their medical license.”
Another hurdle for malpractice cases is that state abortion bans could undermine the argument that abortion is the legal “standard of care,” meaning that it is a widely accepted and prescribed treatment for pregnancy complications such as miscarriage and for fatal fetal abnormalities.
“I absolutely see a breach of the standard of care in these cases,” said Maria A. Phillis, an ob.gyn. and former lawyer in Cleveland. “But if someone goes to trial in a malpractice case, it will come down to a battle of medical experts about whether it’s no longer the standard of care, and the jury would have to decide.”
An additional justification for physicians not to provide abortions is that medical liability insurers generally do not cover damages from criminal acts, which “puts the finger on the scales even more to not do anything,” Dr. Phillis said.
Stuart Grossman, a prominent malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Florida, said he would be eager to take an abortion-denial case in which the woman suffered serious health or emotional injuries.
Unlike other states with abortion bans, Florida does not cap damage amounts for pain and suffering in malpractice cases, making it more financially viable to sue there.
Mr. Grossman cited the case of Deborah Dorbert, a Florida woman who reportedly was denied an abortion despite being told by her physicians at 24 weeks of pregnancy that her fetus, with no kidneys and underdeveloped lungs, had a fatal condition called Potter syndrome.
Her doctors and the hospital refused to end the pregnancy even though the state’s abortion ban has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. Months later, her baby died in his parents’ arms shortly after birth.
“You can see how she’s been devastated mentally,” Mr. Grossman said. “She has a wrongful death case that I’d take in a minute.” He said the couple could file a malpractice suit for Ms. Dorbert’s physical and emotional damages and a separate malpractice and wrongful death suit for the couple’s suffering over the infant’s death.
Failing to counsel patients about their options and connect them with providers willing to terminate a pregnancy is also possible grounds for a malpractice suit, attorneys said. Katie Watson, an associate professor at Northwestern University, Chicago’s school of medicine who has studied state abortion bans, said counseling and referral are not prohibited under these laws and that physicians have an ethical obligation to offer those services.
“I think breaching the obligation for counseling would make a strong malpractice lawsuit,” she said.
Nancy Davis said she received no counseling or referral assistance last July after her doctors at Woman’s Hospital in Baton Rouge, La., told her 10 weeks into her pregnancy that her fetus would not survive because it was missing the top of its skull, a fatal condition called acrania. She said they recommended that she terminate the pregnancy and she agreed.
Ms. Davis said her doctors then told her a hospital executive had denied permission for the procedure because of Louisiana’s abortion ban, even though the law has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. A hospital spokesperson declined to comment.
Ms. Davis, who has three children, contacted Planned Parenthood of Greater New York, which arranged for child care and a flight to New York. She had an abortion performed there in September.
“The whole situation has been mentally and physically draining, and my family and I are receiving counseling,” Ms. Davis said. “I’m still very angry at the hospital and the doctors. I feel like I’m owed compensation for the trauma and the heartbreak.”
She sought the counsel of Benjamin Crump, a prominent attorney known for pursuing high-profile cases like wrongful death lawsuits on behalf of the families of Trayvon Martin and George Floyd.
But Mr. Crump said that after studying Ms. Davis’ legal options, he decided a judge would likely dismiss a malpractice suit and that Ms. Davis could end up paying the defendants’ legal fees and costs.
“The doctor’s lawyers will say, ‘You can’t expect my client to break the law and go to prison for up to 25 years,’ ” Mr. Crump said. “Unless you change the law, there is no option for her to receive compensation.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
New law allows international medical graduates to bypass U.S. residency
Pediatric nephrologist Bryan Carmody, MD, recalls working alongside an extremely experienced neonatologist during his residency. She had managed a neonatal intensive care unit in her home country of Lithuania, but because she wanted to practice in the United States, it took years of repeat training before she was eligible for a medical license.
“She was very accomplished, and she was wonderful to have as a coresident at the time,” Dr. Carmody said in an interview.
The neonatologist now practices at a U.S. academic medical center, but to obtain that position, she had to complete 3 years of pediatric residency and 3 years of fellowship in the United States, Dr. Carmody said.
Such training for international medical graduates (IMGs) is a routine part of obtaining a U.S. medical license, but
The American Medical Association took similar measures at its recent annual meeting, making it easier for IMGs to gain licensure. Because the pandemic and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine disrupted the process by which some IMGs had their licenses verified, the AMA is now encouraging state licensing boards and other credentialing institutions to accept certification from the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates as verification, rather than requiring documents directly from international medical schools.
When it comes to Tennessee’s new law, signed by Gov. Bill Lee in April, experienced IMGs who have received medical training abroad can skip U.S. residency requirements and obtain a temporary license to practice medicine in Tennessee if they meet certain qualifications.
The international doctors must demonstrate competency, as determined by the state medical board. In addition, they must have completed a 3-year postgraduate training program in the graduate’s licensing country or otherwise have practiced as a medical professional in which they performed the duties of a physician for at least 3 of the past 5 years outside the United States, according to the new law.
To be approved, IMGs must also have received an employment offer from a Tennessee health care provider that has a residency program accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
If physicians remain in good standing for 2 years, the board will grant them a full and unrestricted license to practice in Tennessee.
“The new legislation opens up a lot of doors for international medical graduates and is also a lifeline for a lot of underserved areas in Tennessee,” said Asim Ansari, MD, a Canadian who attended medical school in the Caribbean and is an advocate for IMGs.
Dr. Ansari is participating in a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, until he can apply for the sixth time to a residency program. “This could possibly be a model that other states may want to implement in a few years.”
What’s behind the law?
A predicted physician shortage in Tennessee drove the legislation, said Rep. Sabi “Doc” Kumar, MD, vice chair for the Tennessee House Health Committee and a cosponsor of the legislation. Legislators hope the law will mitigate that shortage and boost the number of physicians practicing in underserved areas of the state.
“Considering that one in four physicians in the U.S. are international medical gradates, it was important for us to be able to attract those physicians to Tennessee,” he said.
The Tennessee Board of Medical Examiners will develop administrative rules for the law, which may take up to a year, Rep. Kumar said. He expects the program to be available to IMGs beginning in mid-2024.
Upon completion of the program, IMGs will be able to practice general medicine in Tennessee, not a specialty. Requirements for specialty certification would have to be met through the specialties’ respective boards.
Dr. Carmody, who blogs about medical education, including the new legislation, said in an interview the law will greatly benefit experienced IMGs, who often are bypassed as residency candidates because they graduated years ago. Hospitals also win because they can fill positions that otherwise might sit vacant, he said.
Family physician Sahil Bawa, MD, an IMG from India who recently matched into his specialty, said the Tennessee legislation will help fellow IMGs find U.S. medical jobs.
“It’s very difficult for IMGs to get into residency in the U.S.,” he said. “I’ve seen people with medical degrees from other countries drive Uber or do odd jobs to sustain themselves here. I’ve known a few people who have left and gone back to their home country because they were not accepted into a residency.”
Who benefits most?
Dr. Bawa noted that the legislation would not have helped him, as he needed a visa to practice in the United States and the law does not include the sponsoring of visas. The legislation requires IMGs to show evidence of citizenship or evidence that they are legally entitled to live or work in the United States.
U.S. citizen IMGs who haven’t completed residency or who practiced in another country also are left out of the law, Dr. Carmody said.
“This law is designed to take the most accomplished cream of the crop international medical graduates with the most experience and the most sophisticated skill set and send them to Tennessee. I think that’s the intent,” he said. “But many international medical graduates are U.S. citizens who don’t have the opportunity to practice in countries other than United States or do residencies. A lot of these people are sitting on the sidelines, unable to secure residency positions. I’m sure they would be desperate for a program like this.”
Questions remain
“Just because the doctor can get a [temporary] license without the training doesn’t mean employers are going to be interested in sponsoring those doctors,” said Adam Cohen, an immigration attorney who practices in Memphis. “What is the inclination of these employers to hire these physicians who have undergone training outside the U.S.? And will there be skepticism on the part of employers about the competence of these doctors?”
“Hospital systems will be able to hire experienced practitioners for a very low cost,” Dr. Ansari said. “So now you have these additional bodies who can do the work of a physician, but you don’t have to pay them as much as a physician for 2 years. And because some are desperate to work, they will take lower pay as long as they have a pathway to full licensure in Tennessee. What are the protections for these physicians? Who will cover their insurance? Who will be responsible for them, the attendees? And will the attendees be willing to put their license on the line for them?”
In addition, Dr. Carmody questions what, if anything, will encourage IMGs to work in underserved areas in Tennessee after their 2 years are up and whether there will be any incentives to guide them. He wonders, too, whether the physicians will be stuck practicing in Tennessee following completion of the program.
“Will these physicians only be able to work in Tennessee?” he asked. “I think that’s probably going to be the case, because they’ll be licensed in Tennessee, but to go to another state, they would be missing the required residency training. So it might be these folks are stuck in Tennessee unless other states develop reciprocal arrangements.”
Other states would have to decide whether to recognize the Tennessee license acquired through this pathway, Rep. Kumar said.
He explained that the sponsoring sites would be responsible for providing work-hour restrictions and liability protections. There are currently no incentives in the legislation for IMGs to practice in rural, underserved areas, but the hospitals and communities there generally offer incentives when recruiting, Rep. Kumar said.
“The law definitely has the potential to be helpful,” Mr. Cohen said, “because there’s an ability to place providers in the state without having to go through the bottleneck of limited residency slots. If other states see a positive effect on Tennessee or are exploring ways to alleviate their own shortages, it’s possible [they] might follow suit.”
Rep. Kumar agreed that other states will be watching Tennessee to weigh the law’s success.
“I think the law will have to prove itself and show that Tennessee has benefited from it and that the results have been good,” he said. “We are providing a pioneering way for attracting medical graduates and making it easier for them to obtain a license. I would think other states would want to do that.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatric nephrologist Bryan Carmody, MD, recalls working alongside an extremely experienced neonatologist during his residency. She had managed a neonatal intensive care unit in her home country of Lithuania, but because she wanted to practice in the United States, it took years of repeat training before she was eligible for a medical license.
“She was very accomplished, and she was wonderful to have as a coresident at the time,” Dr. Carmody said in an interview.
The neonatologist now practices at a U.S. academic medical center, but to obtain that position, she had to complete 3 years of pediatric residency and 3 years of fellowship in the United States, Dr. Carmody said.
Such training for international medical graduates (IMGs) is a routine part of obtaining a U.S. medical license, but
The American Medical Association took similar measures at its recent annual meeting, making it easier for IMGs to gain licensure. Because the pandemic and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine disrupted the process by which some IMGs had their licenses verified, the AMA is now encouraging state licensing boards and other credentialing institutions to accept certification from the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates as verification, rather than requiring documents directly from international medical schools.
When it comes to Tennessee’s new law, signed by Gov. Bill Lee in April, experienced IMGs who have received medical training abroad can skip U.S. residency requirements and obtain a temporary license to practice medicine in Tennessee if they meet certain qualifications.
The international doctors must demonstrate competency, as determined by the state medical board. In addition, they must have completed a 3-year postgraduate training program in the graduate’s licensing country or otherwise have practiced as a medical professional in which they performed the duties of a physician for at least 3 of the past 5 years outside the United States, according to the new law.
To be approved, IMGs must also have received an employment offer from a Tennessee health care provider that has a residency program accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
If physicians remain in good standing for 2 years, the board will grant them a full and unrestricted license to practice in Tennessee.
“The new legislation opens up a lot of doors for international medical graduates and is also a lifeline for a lot of underserved areas in Tennessee,” said Asim Ansari, MD, a Canadian who attended medical school in the Caribbean and is an advocate for IMGs.
Dr. Ansari is participating in a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, until he can apply for the sixth time to a residency program. “This could possibly be a model that other states may want to implement in a few years.”
What’s behind the law?
A predicted physician shortage in Tennessee drove the legislation, said Rep. Sabi “Doc” Kumar, MD, vice chair for the Tennessee House Health Committee and a cosponsor of the legislation. Legislators hope the law will mitigate that shortage and boost the number of physicians practicing in underserved areas of the state.
“Considering that one in four physicians in the U.S. are international medical gradates, it was important for us to be able to attract those physicians to Tennessee,” he said.
The Tennessee Board of Medical Examiners will develop administrative rules for the law, which may take up to a year, Rep. Kumar said. He expects the program to be available to IMGs beginning in mid-2024.
Upon completion of the program, IMGs will be able to practice general medicine in Tennessee, not a specialty. Requirements for specialty certification would have to be met through the specialties’ respective boards.
Dr. Carmody, who blogs about medical education, including the new legislation, said in an interview the law will greatly benefit experienced IMGs, who often are bypassed as residency candidates because they graduated years ago. Hospitals also win because they can fill positions that otherwise might sit vacant, he said.
Family physician Sahil Bawa, MD, an IMG from India who recently matched into his specialty, said the Tennessee legislation will help fellow IMGs find U.S. medical jobs.
“It’s very difficult for IMGs to get into residency in the U.S.,” he said. “I’ve seen people with medical degrees from other countries drive Uber or do odd jobs to sustain themselves here. I’ve known a few people who have left and gone back to their home country because they were not accepted into a residency.”
Who benefits most?
Dr. Bawa noted that the legislation would not have helped him, as he needed a visa to practice in the United States and the law does not include the sponsoring of visas. The legislation requires IMGs to show evidence of citizenship or evidence that they are legally entitled to live or work in the United States.
U.S. citizen IMGs who haven’t completed residency or who practiced in another country also are left out of the law, Dr. Carmody said.
“This law is designed to take the most accomplished cream of the crop international medical graduates with the most experience and the most sophisticated skill set and send them to Tennessee. I think that’s the intent,” he said. “But many international medical graduates are U.S. citizens who don’t have the opportunity to practice in countries other than United States or do residencies. A lot of these people are sitting on the sidelines, unable to secure residency positions. I’m sure they would be desperate for a program like this.”
Questions remain
“Just because the doctor can get a [temporary] license without the training doesn’t mean employers are going to be interested in sponsoring those doctors,” said Adam Cohen, an immigration attorney who practices in Memphis. “What is the inclination of these employers to hire these physicians who have undergone training outside the U.S.? And will there be skepticism on the part of employers about the competence of these doctors?”
“Hospital systems will be able to hire experienced practitioners for a very low cost,” Dr. Ansari said. “So now you have these additional bodies who can do the work of a physician, but you don’t have to pay them as much as a physician for 2 years. And because some are desperate to work, they will take lower pay as long as they have a pathway to full licensure in Tennessee. What are the protections for these physicians? Who will cover their insurance? Who will be responsible for them, the attendees? And will the attendees be willing to put their license on the line for them?”
In addition, Dr. Carmody questions what, if anything, will encourage IMGs to work in underserved areas in Tennessee after their 2 years are up and whether there will be any incentives to guide them. He wonders, too, whether the physicians will be stuck practicing in Tennessee following completion of the program.
“Will these physicians only be able to work in Tennessee?” he asked. “I think that’s probably going to be the case, because they’ll be licensed in Tennessee, but to go to another state, they would be missing the required residency training. So it might be these folks are stuck in Tennessee unless other states develop reciprocal arrangements.”
Other states would have to decide whether to recognize the Tennessee license acquired through this pathway, Rep. Kumar said.
He explained that the sponsoring sites would be responsible for providing work-hour restrictions and liability protections. There are currently no incentives in the legislation for IMGs to practice in rural, underserved areas, but the hospitals and communities there generally offer incentives when recruiting, Rep. Kumar said.
“The law definitely has the potential to be helpful,” Mr. Cohen said, “because there’s an ability to place providers in the state without having to go through the bottleneck of limited residency slots. If other states see a positive effect on Tennessee or are exploring ways to alleviate their own shortages, it’s possible [they] might follow suit.”
Rep. Kumar agreed that other states will be watching Tennessee to weigh the law’s success.
“I think the law will have to prove itself and show that Tennessee has benefited from it and that the results have been good,” he said. “We are providing a pioneering way for attracting medical graduates and making it easier for them to obtain a license. I would think other states would want to do that.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatric nephrologist Bryan Carmody, MD, recalls working alongside an extremely experienced neonatologist during his residency. She had managed a neonatal intensive care unit in her home country of Lithuania, but because she wanted to practice in the United States, it took years of repeat training before she was eligible for a medical license.
“She was very accomplished, and she was wonderful to have as a coresident at the time,” Dr. Carmody said in an interview.
The neonatologist now practices at a U.S. academic medical center, but to obtain that position, she had to complete 3 years of pediatric residency and 3 years of fellowship in the United States, Dr. Carmody said.
Such training for international medical graduates (IMGs) is a routine part of obtaining a U.S. medical license, but
The American Medical Association took similar measures at its recent annual meeting, making it easier for IMGs to gain licensure. Because the pandemic and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine disrupted the process by which some IMGs had their licenses verified, the AMA is now encouraging state licensing boards and other credentialing institutions to accept certification from the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates as verification, rather than requiring documents directly from international medical schools.
When it comes to Tennessee’s new law, signed by Gov. Bill Lee in April, experienced IMGs who have received medical training abroad can skip U.S. residency requirements and obtain a temporary license to practice medicine in Tennessee if they meet certain qualifications.
The international doctors must demonstrate competency, as determined by the state medical board. In addition, they must have completed a 3-year postgraduate training program in the graduate’s licensing country or otherwise have practiced as a medical professional in which they performed the duties of a physician for at least 3 of the past 5 years outside the United States, according to the new law.
To be approved, IMGs must also have received an employment offer from a Tennessee health care provider that has a residency program accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
If physicians remain in good standing for 2 years, the board will grant them a full and unrestricted license to practice in Tennessee.
“The new legislation opens up a lot of doors for international medical graduates and is also a lifeline for a lot of underserved areas in Tennessee,” said Asim Ansari, MD, a Canadian who attended medical school in the Caribbean and is an advocate for IMGs.
Dr. Ansari is participating in a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, until he can apply for the sixth time to a residency program. “This could possibly be a model that other states may want to implement in a few years.”
What’s behind the law?
A predicted physician shortage in Tennessee drove the legislation, said Rep. Sabi “Doc” Kumar, MD, vice chair for the Tennessee House Health Committee and a cosponsor of the legislation. Legislators hope the law will mitigate that shortage and boost the number of physicians practicing in underserved areas of the state.
“Considering that one in four physicians in the U.S. are international medical gradates, it was important for us to be able to attract those physicians to Tennessee,” he said.
The Tennessee Board of Medical Examiners will develop administrative rules for the law, which may take up to a year, Rep. Kumar said. He expects the program to be available to IMGs beginning in mid-2024.
Upon completion of the program, IMGs will be able to practice general medicine in Tennessee, not a specialty. Requirements for specialty certification would have to be met through the specialties’ respective boards.
Dr. Carmody, who blogs about medical education, including the new legislation, said in an interview the law will greatly benefit experienced IMGs, who often are bypassed as residency candidates because they graduated years ago. Hospitals also win because they can fill positions that otherwise might sit vacant, he said.
Family physician Sahil Bawa, MD, an IMG from India who recently matched into his specialty, said the Tennessee legislation will help fellow IMGs find U.S. medical jobs.
“It’s very difficult for IMGs to get into residency in the U.S.,” he said. “I’ve seen people with medical degrees from other countries drive Uber or do odd jobs to sustain themselves here. I’ve known a few people who have left and gone back to their home country because they were not accepted into a residency.”
Who benefits most?
Dr. Bawa noted that the legislation would not have helped him, as he needed a visa to practice in the United States and the law does not include the sponsoring of visas. The legislation requires IMGs to show evidence of citizenship or evidence that they are legally entitled to live or work in the United States.
U.S. citizen IMGs who haven’t completed residency or who practiced in another country also are left out of the law, Dr. Carmody said.
“This law is designed to take the most accomplished cream of the crop international medical graduates with the most experience and the most sophisticated skill set and send them to Tennessee. I think that’s the intent,” he said. “But many international medical graduates are U.S. citizens who don’t have the opportunity to practice in countries other than United States or do residencies. A lot of these people are sitting on the sidelines, unable to secure residency positions. I’m sure they would be desperate for a program like this.”
Questions remain
“Just because the doctor can get a [temporary] license without the training doesn’t mean employers are going to be interested in sponsoring those doctors,” said Adam Cohen, an immigration attorney who practices in Memphis. “What is the inclination of these employers to hire these physicians who have undergone training outside the U.S.? And will there be skepticism on the part of employers about the competence of these doctors?”
“Hospital systems will be able to hire experienced practitioners for a very low cost,” Dr. Ansari said. “So now you have these additional bodies who can do the work of a physician, but you don’t have to pay them as much as a physician for 2 years. And because some are desperate to work, they will take lower pay as long as they have a pathway to full licensure in Tennessee. What are the protections for these physicians? Who will cover their insurance? Who will be responsible for them, the attendees? And will the attendees be willing to put their license on the line for them?”
In addition, Dr. Carmody questions what, if anything, will encourage IMGs to work in underserved areas in Tennessee after their 2 years are up and whether there will be any incentives to guide them. He wonders, too, whether the physicians will be stuck practicing in Tennessee following completion of the program.
“Will these physicians only be able to work in Tennessee?” he asked. “I think that’s probably going to be the case, because they’ll be licensed in Tennessee, but to go to another state, they would be missing the required residency training. So it might be these folks are stuck in Tennessee unless other states develop reciprocal arrangements.”
Other states would have to decide whether to recognize the Tennessee license acquired through this pathway, Rep. Kumar said.
He explained that the sponsoring sites would be responsible for providing work-hour restrictions and liability protections. There are currently no incentives in the legislation for IMGs to practice in rural, underserved areas, but the hospitals and communities there generally offer incentives when recruiting, Rep. Kumar said.
“The law definitely has the potential to be helpful,” Mr. Cohen said, “because there’s an ability to place providers in the state without having to go through the bottleneck of limited residency slots. If other states see a positive effect on Tennessee or are exploring ways to alleviate their own shortages, it’s possible [they] might follow suit.”
Rep. Kumar agreed that other states will be watching Tennessee to weigh the law’s success.
“I think the law will have to prove itself and show that Tennessee has benefited from it and that the results have been good,” he said. “We are providing a pioneering way for attracting medical graduates and making it easier for them to obtain a license. I would think other states would want to do that.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Imaging techniques will revolutionize cancer detection, expert predicts
PHOENIX –
In a lecture during a multispecialty roundup of cutting-edge energy-based device applications at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, Dr. Barton, a biomedical engineer who directs the BIO5 Institute at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said that while no current modality exists to enable physicians in dermatology and other specialties to view internal structures throughout the entire body with cellular resolution, refining existing technologies is a good way to start.
In 2011, renowned cancer researchers Douglas Hanahan, PhD, and Robert A. Weinberg, PhD, proposed six hallmarks of cancer, which include sustaining proliferative signaling, evading growth suppressors, resisting cell death, enabling replicative immortality, inducing angiogenesis, and activating invasion and metastasis. Each hallmark poses unique imaging challenges. For example, enabling replicative immortality “means that the cell nuclei change size and shape; they change their position,” said Dr. Barton, who is also professor of biomedical engineering and optical sciences at the university. “If we want to see that, we’re going to need an imaging modality that’s subcellular in resolution.”
Similarly, if clinicians want to view how proliferative signaling is changing, “that means being able to visualize the cell surface receptors; those are even smaller to actually visualize,” she said. “But we have technologies where we can target those receptors with fluorophores. And then we can look at large areas very quickly.” Meanwhile, the ability of cancer cells to resist cell death and evade growth suppressors often results in thickening of epithelium throughout the body. “So, if we can measure the thickness of the epithelium, we can see that there’s something wrong with that tissue,” she said.
As for cancer’s propensity for invasion and metastasis, “here, we’re looking at how the collagen structure [between the cells] has changed and whether there’s layer breakdown or not. Optical imaging can detect cancer. However, high resolution optical techniques can only image about 1 mm deep, so unless you’re looking at the skin or the eye, you’re going to have to develop an endoscope to be able to view these hallmarks.”
OCT images the tissue microstructure, generally in a resolution of 2-20 microns, at a depth of 1-2 mm, and it measures reflected light. When possible, Dr. Barton combines OCT with laser-induced fluorescence for enhanced accuracy of detection of cancer. Induced fluorescence senses molecular information with the natural fluorophores in the body or with targeted exogenous agents. Then there’s multiphoton microscopy, an advanced imaging technique that enables clinicians to view cellular and subcellular events within living tissue. Early models of this technology “took up entire benches” in physics labs, Dr. Barton said, but she and other investigators are designing smaller devices for use in clinics. “This is exciting, because not only do we [view] subcellular structure with this modality, but it can also be highly sensitive to collagen structure,” she said.
Ovarian cancer model
In a model of ovarian cancer, she and colleagues externalized the ovaries of a mouse, imaged the organs, put them back in, and reassessed them at 8 weeks. “This model develops cancer very quickly,” said Dr. Barton, who once worked for McDonnell Douglas on the Space Station program. At 8 weeks, using fluorescence and targeted agents with a tabletop multiphoton microscopy system, they observed that the proliferation signals of cancer had begun. “So, with an agent targeted to the folate receptor or to other receptors that are implicated in cancer development, we can see that ovaries and fallopian tubes are lighting up,” she said.
With proof of concept established with the mouse study, she and other researchers are drawing from technological advances to create tiny laser systems for use in the clinic to image a variety of structures in the human body. Optics advances include bulk optics and all-fiber designs where engineers can create an imaging probe that’s only 125 microns in diameter, “or maybe even as small as 70 microns in diameter,” she said. “We can do fabrications on the tips of endoscopes to redirect the light and focus it. We can also do 3-D printing and spiral scanning to create miniature devices to make new advances. That means that instead of just white light imaging of the colon or the lung like we have had in the past, we can start moving into smaller structures, such as the eustachian tube, the fallopian tube, the bile ducts, or making miniature devices for brain biopsies, lung biopsies, and maybe being able to get into bronchioles and arterioles.”
According to Dr. Barton, prior research has demonstrated that cerebral vasculature can be imaged with a catheter 400 microns in diameter, the spaces in the lungs can be imaged with a needle that is 310 microns in diameter, and the inner structures of the eustachian tube can be viewed with an endoscope 1 mm in diameter.
She and her colleagues are developing an OCT/fluorescence imaging falloposcope that is 0.8 mm in diameter, flexible, and steerable, as a tool for early detection of ovarian cancer in humans. “It’s now known that most ovarian cancer starts in the fallopian tubes,” Dr. Barton said. “It’s metastatic disease when those cells break off from the fallopian tubes and go to the ovaries. We wanted to create an imaging system where we created a fiber bundle that we could navigate with white light and with fluorescence so that we can see these early stages of cancer [and] how they fluoresce differently. We also wanted to have an OCT system so that we could image through the wall of the fallopian tube and look for that layer thickening and other precursors to ovarian cancer.”
To date, in vivo testing in healthy women has demonstrated that the miniature endoscope is able to reach the fallopian tubes through the natural orifice of the vagina and uterus. “That is pretty exciting,” she said. “The images may not be of the highest quality, but we are advancing.”
Dr. Barton reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
PHOENIX –
In a lecture during a multispecialty roundup of cutting-edge energy-based device applications at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, Dr. Barton, a biomedical engineer who directs the BIO5 Institute at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said that while no current modality exists to enable physicians in dermatology and other specialties to view internal structures throughout the entire body with cellular resolution, refining existing technologies is a good way to start.
In 2011, renowned cancer researchers Douglas Hanahan, PhD, and Robert A. Weinberg, PhD, proposed six hallmarks of cancer, which include sustaining proliferative signaling, evading growth suppressors, resisting cell death, enabling replicative immortality, inducing angiogenesis, and activating invasion and metastasis. Each hallmark poses unique imaging challenges. For example, enabling replicative immortality “means that the cell nuclei change size and shape; they change their position,” said Dr. Barton, who is also professor of biomedical engineering and optical sciences at the university. “If we want to see that, we’re going to need an imaging modality that’s subcellular in resolution.”
Similarly, if clinicians want to view how proliferative signaling is changing, “that means being able to visualize the cell surface receptors; those are even smaller to actually visualize,” she said. “But we have technologies where we can target those receptors with fluorophores. And then we can look at large areas very quickly.” Meanwhile, the ability of cancer cells to resist cell death and evade growth suppressors often results in thickening of epithelium throughout the body. “So, if we can measure the thickness of the epithelium, we can see that there’s something wrong with that tissue,” she said.
As for cancer’s propensity for invasion and metastasis, “here, we’re looking at how the collagen structure [between the cells] has changed and whether there’s layer breakdown or not. Optical imaging can detect cancer. However, high resolution optical techniques can only image about 1 mm deep, so unless you’re looking at the skin or the eye, you’re going to have to develop an endoscope to be able to view these hallmarks.”
OCT images the tissue microstructure, generally in a resolution of 2-20 microns, at a depth of 1-2 mm, and it measures reflected light. When possible, Dr. Barton combines OCT with laser-induced fluorescence for enhanced accuracy of detection of cancer. Induced fluorescence senses molecular information with the natural fluorophores in the body or with targeted exogenous agents. Then there’s multiphoton microscopy, an advanced imaging technique that enables clinicians to view cellular and subcellular events within living tissue. Early models of this technology “took up entire benches” in physics labs, Dr. Barton said, but she and other investigators are designing smaller devices for use in clinics. “This is exciting, because not only do we [view] subcellular structure with this modality, but it can also be highly sensitive to collagen structure,” she said.
Ovarian cancer model
In a model of ovarian cancer, she and colleagues externalized the ovaries of a mouse, imaged the organs, put them back in, and reassessed them at 8 weeks. “This model develops cancer very quickly,” said Dr. Barton, who once worked for McDonnell Douglas on the Space Station program. At 8 weeks, using fluorescence and targeted agents with a tabletop multiphoton microscopy system, they observed that the proliferation signals of cancer had begun. “So, with an agent targeted to the folate receptor or to other receptors that are implicated in cancer development, we can see that ovaries and fallopian tubes are lighting up,” she said.
With proof of concept established with the mouse study, she and other researchers are drawing from technological advances to create tiny laser systems for use in the clinic to image a variety of structures in the human body. Optics advances include bulk optics and all-fiber designs where engineers can create an imaging probe that’s only 125 microns in diameter, “or maybe even as small as 70 microns in diameter,” she said. “We can do fabrications on the tips of endoscopes to redirect the light and focus it. We can also do 3-D printing and spiral scanning to create miniature devices to make new advances. That means that instead of just white light imaging of the colon or the lung like we have had in the past, we can start moving into smaller structures, such as the eustachian tube, the fallopian tube, the bile ducts, or making miniature devices for brain biopsies, lung biopsies, and maybe being able to get into bronchioles and arterioles.”
According to Dr. Barton, prior research has demonstrated that cerebral vasculature can be imaged with a catheter 400 microns in diameter, the spaces in the lungs can be imaged with a needle that is 310 microns in diameter, and the inner structures of the eustachian tube can be viewed with an endoscope 1 mm in diameter.
She and her colleagues are developing an OCT/fluorescence imaging falloposcope that is 0.8 mm in diameter, flexible, and steerable, as a tool for early detection of ovarian cancer in humans. “It’s now known that most ovarian cancer starts in the fallopian tubes,” Dr. Barton said. “It’s metastatic disease when those cells break off from the fallopian tubes and go to the ovaries. We wanted to create an imaging system where we created a fiber bundle that we could navigate with white light and with fluorescence so that we can see these early stages of cancer [and] how they fluoresce differently. We also wanted to have an OCT system so that we could image through the wall of the fallopian tube and look for that layer thickening and other precursors to ovarian cancer.”
To date, in vivo testing in healthy women has demonstrated that the miniature endoscope is able to reach the fallopian tubes through the natural orifice of the vagina and uterus. “That is pretty exciting,” she said. “The images may not be of the highest quality, but we are advancing.”
Dr. Barton reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
PHOENIX –
In a lecture during a multispecialty roundup of cutting-edge energy-based device applications at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, Dr. Barton, a biomedical engineer who directs the BIO5 Institute at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said that while no current modality exists to enable physicians in dermatology and other specialties to view internal structures throughout the entire body with cellular resolution, refining existing technologies is a good way to start.
In 2011, renowned cancer researchers Douglas Hanahan, PhD, and Robert A. Weinberg, PhD, proposed six hallmarks of cancer, which include sustaining proliferative signaling, evading growth suppressors, resisting cell death, enabling replicative immortality, inducing angiogenesis, and activating invasion and metastasis. Each hallmark poses unique imaging challenges. For example, enabling replicative immortality “means that the cell nuclei change size and shape; they change their position,” said Dr. Barton, who is also professor of biomedical engineering and optical sciences at the university. “If we want to see that, we’re going to need an imaging modality that’s subcellular in resolution.”
Similarly, if clinicians want to view how proliferative signaling is changing, “that means being able to visualize the cell surface receptors; those are even smaller to actually visualize,” she said. “But we have technologies where we can target those receptors with fluorophores. And then we can look at large areas very quickly.” Meanwhile, the ability of cancer cells to resist cell death and evade growth suppressors often results in thickening of epithelium throughout the body. “So, if we can measure the thickness of the epithelium, we can see that there’s something wrong with that tissue,” she said.
As for cancer’s propensity for invasion and metastasis, “here, we’re looking at how the collagen structure [between the cells] has changed and whether there’s layer breakdown or not. Optical imaging can detect cancer. However, high resolution optical techniques can only image about 1 mm deep, so unless you’re looking at the skin or the eye, you’re going to have to develop an endoscope to be able to view these hallmarks.”
OCT images the tissue microstructure, generally in a resolution of 2-20 microns, at a depth of 1-2 mm, and it measures reflected light. When possible, Dr. Barton combines OCT with laser-induced fluorescence for enhanced accuracy of detection of cancer. Induced fluorescence senses molecular information with the natural fluorophores in the body or with targeted exogenous agents. Then there’s multiphoton microscopy, an advanced imaging technique that enables clinicians to view cellular and subcellular events within living tissue. Early models of this technology “took up entire benches” in physics labs, Dr. Barton said, but she and other investigators are designing smaller devices for use in clinics. “This is exciting, because not only do we [view] subcellular structure with this modality, but it can also be highly sensitive to collagen structure,” she said.
Ovarian cancer model
In a model of ovarian cancer, she and colleagues externalized the ovaries of a mouse, imaged the organs, put them back in, and reassessed them at 8 weeks. “This model develops cancer very quickly,” said Dr. Barton, who once worked for McDonnell Douglas on the Space Station program. At 8 weeks, using fluorescence and targeted agents with a tabletop multiphoton microscopy system, they observed that the proliferation signals of cancer had begun. “So, with an agent targeted to the folate receptor or to other receptors that are implicated in cancer development, we can see that ovaries and fallopian tubes are lighting up,” she said.
With proof of concept established with the mouse study, she and other researchers are drawing from technological advances to create tiny laser systems for use in the clinic to image a variety of structures in the human body. Optics advances include bulk optics and all-fiber designs where engineers can create an imaging probe that’s only 125 microns in diameter, “or maybe even as small as 70 microns in diameter,” she said. “We can do fabrications on the tips of endoscopes to redirect the light and focus it. We can also do 3-D printing and spiral scanning to create miniature devices to make new advances. That means that instead of just white light imaging of the colon or the lung like we have had in the past, we can start moving into smaller structures, such as the eustachian tube, the fallopian tube, the bile ducts, or making miniature devices for brain biopsies, lung biopsies, and maybe being able to get into bronchioles and arterioles.”
According to Dr. Barton, prior research has demonstrated that cerebral vasculature can be imaged with a catheter 400 microns in diameter, the spaces in the lungs can be imaged with a needle that is 310 microns in diameter, and the inner structures of the eustachian tube can be viewed with an endoscope 1 mm in diameter.
She and her colleagues are developing an OCT/fluorescence imaging falloposcope that is 0.8 mm in diameter, flexible, and steerable, as a tool for early detection of ovarian cancer in humans. “It’s now known that most ovarian cancer starts in the fallopian tubes,” Dr. Barton said. “It’s metastatic disease when those cells break off from the fallopian tubes and go to the ovaries. We wanted to create an imaging system where we created a fiber bundle that we could navigate with white light and with fluorescence so that we can see these early stages of cancer [and] how they fluoresce differently. We also wanted to have an OCT system so that we could image through the wall of the fallopian tube and look for that layer thickening and other precursors to ovarian cancer.”
To date, in vivo testing in healthy women has demonstrated that the miniature endoscope is able to reach the fallopian tubes through the natural orifice of the vagina and uterus. “That is pretty exciting,” she said. “The images may not be of the highest quality, but we are advancing.”
Dr. Barton reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
AT ASLMS 2023
Updates on pregnancy outcomes in transgender men
Despite increased societal gains, transgender individuals are still a medically and socially underserved group. The historic rise of antitransgender legislation and the overturning of Roe v. Wade, further compound existing health care disparities, particularly in the realm of contraception and pregnancy. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives are typically first-line providers when discussing family planning and fertility options for all patients assigned female at birth. Unfortunately,
Only individuals who are assigned female at birth and have a uterus are capable of pregnancy. This can include both cisgender women and nonbinary/transgender men. However, societal and medical institutions are struggling with this shift in perspective from a traditionally gendered role to a more inclusive one. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives can serve to bridge this gap between these patients and societal misconceptions surrounding transgender men who desire and experience pregnancy.
Providers need to remember that many transmasculine individuals will still retain their uterus and are therefore capable of getting pregnant. While testosterone causes amenorrhea, if patients are engaging in penile-vaginal intercourse, conception is still possible. If a patient does not desire pregnancy, all contraceptive options available for cisgender women, which also include combined oral contraceptives, should be offered.
For patients seeking to become pregnant, testosterone must be discontinued. Testosterone is teratogenic; it can cause abnormal urogenital development in the female fetus and should be avoided even prior to conception.1,2 The timing of testosterone discontinuation is debatable. There are no well-established guidelines dictating how early pregnancy can be attempted after cessation of testosterone, but typically if menses has resumed, the teratogenic effects of testosterone are less likely.
For amenorrheic patients on testosterone, menses will occur, on average, 3-6 months after testosterone is stopped. Of note, the longer that testosterone has been suspended, the greater the likelihood of achieving pregnancy.3 In a study by Light et al., 72% of patients conceived within 6 months of attempting pregnancy, 80% resumed menses within 6 months of stopping testosterone, and 20% of individuals conceived while they were amenorrheic from testosterone.4
Psychosocial support is an essential part of pregnancy care in transgender men. For some patients, pregnancy can worsen gender dysphoria, whereas others are empowered by the experience. Insurance companies may also deny obstetric care services to transgender males who have already changed their gender marker from female to male on insurance policies.
Whether transmasculine individuals are at higher risk for pregnancy complications is largely unknown, although emerging research in this field has yielded interesting results. While testosterone can cause vaginal atrophy, it does not seem to increase a patient’s risk of vaginal lacerations or their ability to have a successful vaginal delivery. For transgender men with significant discomfort around their genitalia, an elective cesarean section may be appropriate.5
More recently, Stroumsa et al. conducted an analysis of all deliveries at a Michigan institution from 2014 to 2018. Patients with male gender at the time of delivery or with the diagnostic code of gender dysphoria were identified as transgender.6 The primary outcome of this study was severe parental morbidity (such as amniotic fluid embolism, acute myocardial infarction, eclampsia, etc.), with secondary outcomes investigating rates of cesarean delivery and preterm birth.
During this time period, the researchers identified 256 transgender patients and 1.3 million cisgender patients in their Medicaid database and 1,651 transgender patients and 1.5 million cisgender patients in the commercial database who had experienced a delivery.6 Compared with cisgender patients, transgender patients in the Medicaid database were younger, less likely to be white, and more likely to have a chronic condition.6 Compared with cisgender patients in the commercial database, transgender patients experienced higher rates of anxiety and depression.6 Both transgender and cisgender patients had similar rates of severe parental morbidity. Ironically, rates of cesarean delivery were lower, compared with cisgender patients, in both the Medicaid and commercial databases, with no differences observed between rates of preterm birth.6
While more research is needed on pregnancy in transgender men, this analysis is not only one of the largest to date, but it also challenges many misconceptions providers have regarding pregnancy outcomes. Even though transmasculine patients may require additional medical interventions to achieve pregnancy, such as assisted reproductive technology, or increased psychosocial support during the process, these initial studies are reassuring. Based on current evidence, these patients are not at greater risk for perinatal complications than their cisgender counterparts.
Despite these encouraging findings, there are still several challenges faced by transgender men when it comes to getting pregnant. For instance, they may have difficulty accessing fertility services because of financial constraints or experience a lack of awareness or prejudice from providers; they might also be subject to discrimination or stigma within health care settings. As front-line providers for obstetrical care, we must lead the way towards improving the care for pregnant transmasculine individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Light A et al. Family planning and contraception use in transgender men. Contraception. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.06.006.
2. Krempasky C et al. Contraception across the transmasculine spectrum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.07.043.
3. Obedin-Maliver J, De Haan G. “Gynecologic care for transgender patients” in Ferrando C, ed., Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2019. 131-51.
4. Light AD et al. Transgender men who experienced pregnancy after female-to-male gender transitioning. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Dec. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000540.
5. Brandt JS et al. Transgender men, pregnancy, and the “new” advanced paternal age: A review of the literature. Maturitas. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.07.004.
6. Stroumsa D et al. Pregnancy outcomes in a U.S. cohort of transgender people. JAMA. 2023 Jun 6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.7688.
Despite increased societal gains, transgender individuals are still a medically and socially underserved group. The historic rise of antitransgender legislation and the overturning of Roe v. Wade, further compound existing health care disparities, particularly in the realm of contraception and pregnancy. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives are typically first-line providers when discussing family planning and fertility options for all patients assigned female at birth. Unfortunately,
Only individuals who are assigned female at birth and have a uterus are capable of pregnancy. This can include both cisgender women and nonbinary/transgender men. However, societal and medical institutions are struggling with this shift in perspective from a traditionally gendered role to a more inclusive one. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives can serve to bridge this gap between these patients and societal misconceptions surrounding transgender men who desire and experience pregnancy.
Providers need to remember that many transmasculine individuals will still retain their uterus and are therefore capable of getting pregnant. While testosterone causes amenorrhea, if patients are engaging in penile-vaginal intercourse, conception is still possible. If a patient does not desire pregnancy, all contraceptive options available for cisgender women, which also include combined oral contraceptives, should be offered.
For patients seeking to become pregnant, testosterone must be discontinued. Testosterone is teratogenic; it can cause abnormal urogenital development in the female fetus and should be avoided even prior to conception.1,2 The timing of testosterone discontinuation is debatable. There are no well-established guidelines dictating how early pregnancy can be attempted after cessation of testosterone, but typically if menses has resumed, the teratogenic effects of testosterone are less likely.
For amenorrheic patients on testosterone, menses will occur, on average, 3-6 months after testosterone is stopped. Of note, the longer that testosterone has been suspended, the greater the likelihood of achieving pregnancy.3 In a study by Light et al., 72% of patients conceived within 6 months of attempting pregnancy, 80% resumed menses within 6 months of stopping testosterone, and 20% of individuals conceived while they were amenorrheic from testosterone.4
Psychosocial support is an essential part of pregnancy care in transgender men. For some patients, pregnancy can worsen gender dysphoria, whereas others are empowered by the experience. Insurance companies may also deny obstetric care services to transgender males who have already changed their gender marker from female to male on insurance policies.
Whether transmasculine individuals are at higher risk for pregnancy complications is largely unknown, although emerging research in this field has yielded interesting results. While testosterone can cause vaginal atrophy, it does not seem to increase a patient’s risk of vaginal lacerations or their ability to have a successful vaginal delivery. For transgender men with significant discomfort around their genitalia, an elective cesarean section may be appropriate.5
More recently, Stroumsa et al. conducted an analysis of all deliveries at a Michigan institution from 2014 to 2018. Patients with male gender at the time of delivery or with the diagnostic code of gender dysphoria were identified as transgender.6 The primary outcome of this study was severe parental morbidity (such as amniotic fluid embolism, acute myocardial infarction, eclampsia, etc.), with secondary outcomes investigating rates of cesarean delivery and preterm birth.
During this time period, the researchers identified 256 transgender patients and 1.3 million cisgender patients in their Medicaid database and 1,651 transgender patients and 1.5 million cisgender patients in the commercial database who had experienced a delivery.6 Compared with cisgender patients, transgender patients in the Medicaid database were younger, less likely to be white, and more likely to have a chronic condition.6 Compared with cisgender patients in the commercial database, transgender patients experienced higher rates of anxiety and depression.6 Both transgender and cisgender patients had similar rates of severe parental morbidity. Ironically, rates of cesarean delivery were lower, compared with cisgender patients, in both the Medicaid and commercial databases, with no differences observed between rates of preterm birth.6
While more research is needed on pregnancy in transgender men, this analysis is not only one of the largest to date, but it also challenges many misconceptions providers have regarding pregnancy outcomes. Even though transmasculine patients may require additional medical interventions to achieve pregnancy, such as assisted reproductive technology, or increased psychosocial support during the process, these initial studies are reassuring. Based on current evidence, these patients are not at greater risk for perinatal complications than their cisgender counterparts.
Despite these encouraging findings, there are still several challenges faced by transgender men when it comes to getting pregnant. For instance, they may have difficulty accessing fertility services because of financial constraints or experience a lack of awareness or prejudice from providers; they might also be subject to discrimination or stigma within health care settings. As front-line providers for obstetrical care, we must lead the way towards improving the care for pregnant transmasculine individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Light A et al. Family planning and contraception use in transgender men. Contraception. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.06.006.
2. Krempasky C et al. Contraception across the transmasculine spectrum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.07.043.
3. Obedin-Maliver J, De Haan G. “Gynecologic care for transgender patients” in Ferrando C, ed., Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2019. 131-51.
4. Light AD et al. Transgender men who experienced pregnancy after female-to-male gender transitioning. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Dec. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000540.
5. Brandt JS et al. Transgender men, pregnancy, and the “new” advanced paternal age: A review of the literature. Maturitas. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.07.004.
6. Stroumsa D et al. Pregnancy outcomes in a U.S. cohort of transgender people. JAMA. 2023 Jun 6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.7688.
Despite increased societal gains, transgender individuals are still a medically and socially underserved group. The historic rise of antitransgender legislation and the overturning of Roe v. Wade, further compound existing health care disparities, particularly in the realm of contraception and pregnancy. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives are typically first-line providers when discussing family planning and fertility options for all patients assigned female at birth. Unfortunately,
Only individuals who are assigned female at birth and have a uterus are capable of pregnancy. This can include both cisgender women and nonbinary/transgender men. However, societal and medical institutions are struggling with this shift in perspective from a traditionally gendered role to a more inclusive one. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives can serve to bridge this gap between these patients and societal misconceptions surrounding transgender men who desire and experience pregnancy.
Providers need to remember that many transmasculine individuals will still retain their uterus and are therefore capable of getting pregnant. While testosterone causes amenorrhea, if patients are engaging in penile-vaginal intercourse, conception is still possible. If a patient does not desire pregnancy, all contraceptive options available for cisgender women, which also include combined oral contraceptives, should be offered.
For patients seeking to become pregnant, testosterone must be discontinued. Testosterone is teratogenic; it can cause abnormal urogenital development in the female fetus and should be avoided even prior to conception.1,2 The timing of testosterone discontinuation is debatable. There are no well-established guidelines dictating how early pregnancy can be attempted after cessation of testosterone, but typically if menses has resumed, the teratogenic effects of testosterone are less likely.
For amenorrheic patients on testosterone, menses will occur, on average, 3-6 months after testosterone is stopped. Of note, the longer that testosterone has been suspended, the greater the likelihood of achieving pregnancy.3 In a study by Light et al., 72% of patients conceived within 6 months of attempting pregnancy, 80% resumed menses within 6 months of stopping testosterone, and 20% of individuals conceived while they were amenorrheic from testosterone.4
Psychosocial support is an essential part of pregnancy care in transgender men. For some patients, pregnancy can worsen gender dysphoria, whereas others are empowered by the experience. Insurance companies may also deny obstetric care services to transgender males who have already changed their gender marker from female to male on insurance policies.
Whether transmasculine individuals are at higher risk for pregnancy complications is largely unknown, although emerging research in this field has yielded interesting results. While testosterone can cause vaginal atrophy, it does not seem to increase a patient’s risk of vaginal lacerations or their ability to have a successful vaginal delivery. For transgender men with significant discomfort around their genitalia, an elective cesarean section may be appropriate.5
More recently, Stroumsa et al. conducted an analysis of all deliveries at a Michigan institution from 2014 to 2018. Patients with male gender at the time of delivery or with the diagnostic code of gender dysphoria were identified as transgender.6 The primary outcome of this study was severe parental morbidity (such as amniotic fluid embolism, acute myocardial infarction, eclampsia, etc.), with secondary outcomes investigating rates of cesarean delivery and preterm birth.
During this time period, the researchers identified 256 transgender patients and 1.3 million cisgender patients in their Medicaid database and 1,651 transgender patients and 1.5 million cisgender patients in the commercial database who had experienced a delivery.6 Compared with cisgender patients, transgender patients in the Medicaid database were younger, less likely to be white, and more likely to have a chronic condition.6 Compared with cisgender patients in the commercial database, transgender patients experienced higher rates of anxiety and depression.6 Both transgender and cisgender patients had similar rates of severe parental morbidity. Ironically, rates of cesarean delivery were lower, compared with cisgender patients, in both the Medicaid and commercial databases, with no differences observed between rates of preterm birth.6
While more research is needed on pregnancy in transgender men, this analysis is not only one of the largest to date, but it also challenges many misconceptions providers have regarding pregnancy outcomes. Even though transmasculine patients may require additional medical interventions to achieve pregnancy, such as assisted reproductive technology, or increased psychosocial support during the process, these initial studies are reassuring. Based on current evidence, these patients are not at greater risk for perinatal complications than their cisgender counterparts.
Despite these encouraging findings, there are still several challenges faced by transgender men when it comes to getting pregnant. For instance, they may have difficulty accessing fertility services because of financial constraints or experience a lack of awareness or prejudice from providers; they might also be subject to discrimination or stigma within health care settings. As front-line providers for obstetrical care, we must lead the way towards improving the care for pregnant transmasculine individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Light A et al. Family planning and contraception use in transgender men. Contraception. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.06.006.
2. Krempasky C et al. Contraception across the transmasculine spectrum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.07.043.
3. Obedin-Maliver J, De Haan G. “Gynecologic care for transgender patients” in Ferrando C, ed., Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2019. 131-51.
4. Light AD et al. Transgender men who experienced pregnancy after female-to-male gender transitioning. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Dec. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000540.
5. Brandt JS et al. Transgender men, pregnancy, and the “new” advanced paternal age: A review of the literature. Maturitas. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.07.004.
6. Stroumsa D et al. Pregnancy outcomes in a U.S. cohort of transgender people. JAMA. 2023 Jun 6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.7688.
Multiprong strategy makes clinical trials less White
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASCO 2023
CBSM phone app eases anxiety, depression in cancer patients
CHICAGO – One-third of patients with cancer also experience anxiety or depression, and an estimated 70% of the 18 million patients with cancer and cancer survivors in the US experience emotional symptoms, including fear of recurrence.
Despite many having these symptoms, few patients with cancer have access to psycho-oncologic support.
A digital cognitive-behavioral stress management (CBSM) application may help to ease some of the burden, reported Allison Ramiller, MPH, of Blue Note Therapeutics in San Francisco, which developed the app version of the program.
In addition, patients assigned to the CBSM app were twice as likely as control persons to report that their symptoms were “much” or “very much” improved after using the app for 12 weeks, Ms. Ramiller reported at an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
However, the investigators did not report baseline characteristics of patients in each of the study arms, which might have helped to clarify the depth of the effects they saw.
The CBSM program was developed by Michael H. Antoni, PhD, and colleagues in the University of Miami Health System. It is based on cognitive-behavioral therapy but also includes stress management and relaxation techniques to help patients cope with cancer-specific stress.
“”It has been clinically validated and shown to benefit patients with cancer,” Ms. Ramiller said. “However, access is a problem,” she said.
“There aren’t enough qualified, trained providers for the need, and patients with cancer encounter barriers to in-person participation, including things like transportation or financial barriers. So to overcome this, we developed a digitized version of CBSM,” she explained.
Impressive and elegant
“Everything about [the study] I thought was very impressive, very elegant, very nicely done,” said invited discussant Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist at Baptist Memorial Health Care Corp in Memphis, Tenn.
“They showed efficacy, they showed safety – very nice – user friendliness – very good. Certainly they look like they’re trying to address a highly important, unmet need in a very elegant way. Certainly, they pointed out it needs longer follow-up to see sustainability. We need to see will this work in other settings. Will this be cost-effective? You’ve gotta believe it probably will be,” he said.
CBSM has previously been shown to help patients with cancer reduce stress, improve general and cancer-specific quality of life at various stages of treatment, reduce symptom burden, and improve coping skills, Ms. Ramiller said.
To see whether these benefits could be conveyed digitally rather than in face-to-face encounters, Ms. Ramiller and colleagues worked with Dr. Antoni to develop the CBSM app.
Patients using the app received therapeutic content over 10 sessions with audio, video, and interactive tools that mimicked the sessions they would have received during in-person interventions.
They then compared the app against the control educational app in the randomized, decentralized RESTORE study.
High-quality control
Ms. Ramiller said that the control app set “a high bar.”
“The control also offered 10 interactive self-guided sessions. Both treatment apps were professionally designed and visually similar in styling, and they were presented as digital therapeutic-specific for cancer patients. And they were also in a match condition, meaning they received the same attention from study staff and cadence of reminders, but importantly, only the intervention app was based on CBSM,” she explained.
A total of 449 patients with cancers of stage I–III who were undergoing active systemic treatment or were planning to undergo such treatment within 6 months were randomly assigned to the CBSM app or the control app.
The CBSM app was superior to the control app for the primary outcome of anxiety reduction over baseline, as measured at 4, 8 and 12 weeks by the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System Anxiety Scale (PROMIS-A) (beta = -.03; P = .019).
CBSM was also significantly better than the control app for the secondary endpoints of reducing symptoms of depression, as measured by the PROMIS-D scale (beta = -.02, P = .042), and also at increasing the percentage of patients who reported improvement in anxiety and depression symptoms on the Patient Global Impression of Change instrument (P < .001)
An extension study of the durability of the effects at 3 and 6 months is underway.
The investigators noted that the incremental cost of management of anxiety or depression is greater than $17,000 per patient per year.
“One of the big promises of a digital therapeutic like this is that it could potentially reduce costs,” Ms. Ramiller told the audience, but she acknowledged, “More work is really needed, however, to directly test the potential savings.”
The RESTORE study is funded by Blue Note Therapeutics. Dr. Osarogiagbon owns stock in Gilead, Lilly, and Pfizer, has received honoraria from Biodesix and Medscape, and has a consulting or advisory role for the American Cancer Society AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, LUNGevity, National Cancer Institute, and Triptych Health Partners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – One-third of patients with cancer also experience anxiety or depression, and an estimated 70% of the 18 million patients with cancer and cancer survivors in the US experience emotional symptoms, including fear of recurrence.
Despite many having these symptoms, few patients with cancer have access to psycho-oncologic support.
A digital cognitive-behavioral stress management (CBSM) application may help to ease some of the burden, reported Allison Ramiller, MPH, of Blue Note Therapeutics in San Francisco, which developed the app version of the program.
In addition, patients assigned to the CBSM app were twice as likely as control persons to report that their symptoms were “much” or “very much” improved after using the app for 12 weeks, Ms. Ramiller reported at an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
However, the investigators did not report baseline characteristics of patients in each of the study arms, which might have helped to clarify the depth of the effects they saw.
The CBSM program was developed by Michael H. Antoni, PhD, and colleagues in the University of Miami Health System. It is based on cognitive-behavioral therapy but also includes stress management and relaxation techniques to help patients cope with cancer-specific stress.
“”It has been clinically validated and shown to benefit patients with cancer,” Ms. Ramiller said. “However, access is a problem,” she said.
“There aren’t enough qualified, trained providers for the need, and patients with cancer encounter barriers to in-person participation, including things like transportation or financial barriers. So to overcome this, we developed a digitized version of CBSM,” she explained.
Impressive and elegant
“Everything about [the study] I thought was very impressive, very elegant, very nicely done,” said invited discussant Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist at Baptist Memorial Health Care Corp in Memphis, Tenn.
“They showed efficacy, they showed safety – very nice – user friendliness – very good. Certainly they look like they’re trying to address a highly important, unmet need in a very elegant way. Certainly, they pointed out it needs longer follow-up to see sustainability. We need to see will this work in other settings. Will this be cost-effective? You’ve gotta believe it probably will be,” he said.
CBSM has previously been shown to help patients with cancer reduce stress, improve general and cancer-specific quality of life at various stages of treatment, reduce symptom burden, and improve coping skills, Ms. Ramiller said.
To see whether these benefits could be conveyed digitally rather than in face-to-face encounters, Ms. Ramiller and colleagues worked with Dr. Antoni to develop the CBSM app.
Patients using the app received therapeutic content over 10 sessions with audio, video, and interactive tools that mimicked the sessions they would have received during in-person interventions.
They then compared the app against the control educational app in the randomized, decentralized RESTORE study.
High-quality control
Ms. Ramiller said that the control app set “a high bar.”
“The control also offered 10 interactive self-guided sessions. Both treatment apps were professionally designed and visually similar in styling, and they were presented as digital therapeutic-specific for cancer patients. And they were also in a match condition, meaning they received the same attention from study staff and cadence of reminders, but importantly, only the intervention app was based on CBSM,” she explained.
A total of 449 patients with cancers of stage I–III who were undergoing active systemic treatment or were planning to undergo such treatment within 6 months were randomly assigned to the CBSM app or the control app.
The CBSM app was superior to the control app for the primary outcome of anxiety reduction over baseline, as measured at 4, 8 and 12 weeks by the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System Anxiety Scale (PROMIS-A) (beta = -.03; P = .019).
CBSM was also significantly better than the control app for the secondary endpoints of reducing symptoms of depression, as measured by the PROMIS-D scale (beta = -.02, P = .042), and also at increasing the percentage of patients who reported improvement in anxiety and depression symptoms on the Patient Global Impression of Change instrument (P < .001)
An extension study of the durability of the effects at 3 and 6 months is underway.
The investigators noted that the incremental cost of management of anxiety or depression is greater than $17,000 per patient per year.
“One of the big promises of a digital therapeutic like this is that it could potentially reduce costs,” Ms. Ramiller told the audience, but she acknowledged, “More work is really needed, however, to directly test the potential savings.”
The RESTORE study is funded by Blue Note Therapeutics. Dr. Osarogiagbon owns stock in Gilead, Lilly, and Pfizer, has received honoraria from Biodesix and Medscape, and has a consulting or advisory role for the American Cancer Society AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, LUNGevity, National Cancer Institute, and Triptych Health Partners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – One-third of patients with cancer also experience anxiety or depression, and an estimated 70% of the 18 million patients with cancer and cancer survivors in the US experience emotional symptoms, including fear of recurrence.
Despite many having these symptoms, few patients with cancer have access to psycho-oncologic support.
A digital cognitive-behavioral stress management (CBSM) application may help to ease some of the burden, reported Allison Ramiller, MPH, of Blue Note Therapeutics in San Francisco, which developed the app version of the program.
In addition, patients assigned to the CBSM app were twice as likely as control persons to report that their symptoms were “much” or “very much” improved after using the app for 12 weeks, Ms. Ramiller reported at an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
However, the investigators did not report baseline characteristics of patients in each of the study arms, which might have helped to clarify the depth of the effects they saw.
The CBSM program was developed by Michael H. Antoni, PhD, and colleagues in the University of Miami Health System. It is based on cognitive-behavioral therapy but also includes stress management and relaxation techniques to help patients cope with cancer-specific stress.
“”It has been clinically validated and shown to benefit patients with cancer,” Ms. Ramiller said. “However, access is a problem,” she said.
“There aren’t enough qualified, trained providers for the need, and patients with cancer encounter barriers to in-person participation, including things like transportation or financial barriers. So to overcome this, we developed a digitized version of CBSM,” she explained.
Impressive and elegant
“Everything about [the study] I thought was very impressive, very elegant, very nicely done,” said invited discussant Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist at Baptist Memorial Health Care Corp in Memphis, Tenn.
“They showed efficacy, they showed safety – very nice – user friendliness – very good. Certainly they look like they’re trying to address a highly important, unmet need in a very elegant way. Certainly, they pointed out it needs longer follow-up to see sustainability. We need to see will this work in other settings. Will this be cost-effective? You’ve gotta believe it probably will be,” he said.
CBSM has previously been shown to help patients with cancer reduce stress, improve general and cancer-specific quality of life at various stages of treatment, reduce symptom burden, and improve coping skills, Ms. Ramiller said.
To see whether these benefits could be conveyed digitally rather than in face-to-face encounters, Ms. Ramiller and colleagues worked with Dr. Antoni to develop the CBSM app.
Patients using the app received therapeutic content over 10 sessions with audio, video, and interactive tools that mimicked the sessions they would have received during in-person interventions.
They then compared the app against the control educational app in the randomized, decentralized RESTORE study.
High-quality control
Ms. Ramiller said that the control app set “a high bar.”
“The control also offered 10 interactive self-guided sessions. Both treatment apps were professionally designed and visually similar in styling, and they were presented as digital therapeutic-specific for cancer patients. And they were also in a match condition, meaning they received the same attention from study staff and cadence of reminders, but importantly, only the intervention app was based on CBSM,” she explained.
A total of 449 patients with cancers of stage I–III who were undergoing active systemic treatment or were planning to undergo such treatment within 6 months were randomly assigned to the CBSM app or the control app.
The CBSM app was superior to the control app for the primary outcome of anxiety reduction over baseline, as measured at 4, 8 and 12 weeks by the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System Anxiety Scale (PROMIS-A) (beta = -.03; P = .019).
CBSM was also significantly better than the control app for the secondary endpoints of reducing symptoms of depression, as measured by the PROMIS-D scale (beta = -.02, P = .042), and also at increasing the percentage of patients who reported improvement in anxiety and depression symptoms on the Patient Global Impression of Change instrument (P < .001)
An extension study of the durability of the effects at 3 and 6 months is underway.
The investigators noted that the incremental cost of management of anxiety or depression is greater than $17,000 per patient per year.
“One of the big promises of a digital therapeutic like this is that it could potentially reduce costs,” Ms. Ramiller told the audience, but she acknowledged, “More work is really needed, however, to directly test the potential savings.”
The RESTORE study is funded by Blue Note Therapeutics. Dr. Osarogiagbon owns stock in Gilead, Lilly, and Pfizer, has received honoraria from Biodesix and Medscape, and has a consulting or advisory role for the American Cancer Society AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, LUNGevity, National Cancer Institute, and Triptych Health Partners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASCO 2023
Breast cancer family history linked to better BC survival
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators reviewed 28,649 Swedish women diagnosed with breast cancer from 1991 to 2019.
- Overall, 5,081 patients (17.7%) had at least one female first-degree relative previously diagnosed with breast cancer.
TAKEAWAYS:
- After adjusting for demographics, tumor characteristics, and treatments, a family history of breast cancer was associated with a lower risk of breast cancer–specific death in the full cohort (hazard ratio, 0.78) and in ER-negative women (HR, 0.57) within 5 years of diagnosis, after which point the association was no longer significant.
- The lower risk of death among women with a family history could mean that these women are more motivated and likely to get screened, potentially catching tumors earlier, and may be more likely to adhere to treatment recommendations.
- However, having a family history of early-onset breast cancer (before the age of 40) was associated with a higher risk of breast cancer–specific death (HR, 1.41).
IN PRACTICE:
Although the findings are reassuring for many women with breast cancer, “genetic testing of newly diagnosed patients with early-onset family history may provide useful information to aid treatment and future research,” the researchers concluded.
STUDY DETAILS:
The study was led by Yuqi Zhang, PhD, of the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, and published in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
- The main analysis did not include tumor characteristics only available within the last 20 years, including ERBB2 status.
- Relatively wide confidence intervals make the association between a family history of early-onset breast cancer and higher risk of breast cancer death somewhat uncertain.
DISCLOSURES:
- The work was funded by the Swedish Cancer Society and others.
- The investigators report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators reviewed 28,649 Swedish women diagnosed with breast cancer from 1991 to 2019.
- Overall, 5,081 patients (17.7%) had at least one female first-degree relative previously diagnosed with breast cancer.
TAKEAWAYS:
- After adjusting for demographics, tumor characteristics, and treatments, a family history of breast cancer was associated with a lower risk of breast cancer–specific death in the full cohort (hazard ratio, 0.78) and in ER-negative women (HR, 0.57) within 5 years of diagnosis, after which point the association was no longer significant.
- The lower risk of death among women with a family history could mean that these women are more motivated and likely to get screened, potentially catching tumors earlier, and may be more likely to adhere to treatment recommendations.
- However, having a family history of early-onset breast cancer (before the age of 40) was associated with a higher risk of breast cancer–specific death (HR, 1.41).
IN PRACTICE:
Although the findings are reassuring for many women with breast cancer, “genetic testing of newly diagnosed patients with early-onset family history may provide useful information to aid treatment and future research,” the researchers concluded.
STUDY DETAILS:
The study was led by Yuqi Zhang, PhD, of the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, and published in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
- The main analysis did not include tumor characteristics only available within the last 20 years, including ERBB2 status.
- Relatively wide confidence intervals make the association between a family history of early-onset breast cancer and higher risk of breast cancer death somewhat uncertain.
DISCLOSURES:
- The work was funded by the Swedish Cancer Society and others.
- The investigators report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators reviewed 28,649 Swedish women diagnosed with breast cancer from 1991 to 2019.
- Overall, 5,081 patients (17.7%) had at least one female first-degree relative previously diagnosed with breast cancer.
TAKEAWAYS:
- After adjusting for demographics, tumor characteristics, and treatments, a family history of breast cancer was associated with a lower risk of breast cancer–specific death in the full cohort (hazard ratio, 0.78) and in ER-negative women (HR, 0.57) within 5 years of diagnosis, after which point the association was no longer significant.
- The lower risk of death among women with a family history could mean that these women are more motivated and likely to get screened, potentially catching tumors earlier, and may be more likely to adhere to treatment recommendations.
- However, having a family history of early-onset breast cancer (before the age of 40) was associated with a higher risk of breast cancer–specific death (HR, 1.41).
IN PRACTICE:
Although the findings are reassuring for many women with breast cancer, “genetic testing of newly diagnosed patients with early-onset family history may provide useful information to aid treatment and future research,” the researchers concluded.
STUDY DETAILS:
The study was led by Yuqi Zhang, PhD, of the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, and published in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
- The main analysis did not include tumor characteristics only available within the last 20 years, including ERBB2 status.
- Relatively wide confidence intervals make the association between a family history of early-onset breast cancer and higher risk of breast cancer death somewhat uncertain.
DISCLOSURES:
- The work was funded by the Swedish Cancer Society and others.
- The investigators report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.



