User login
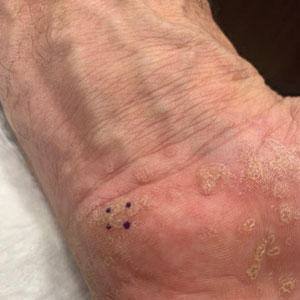
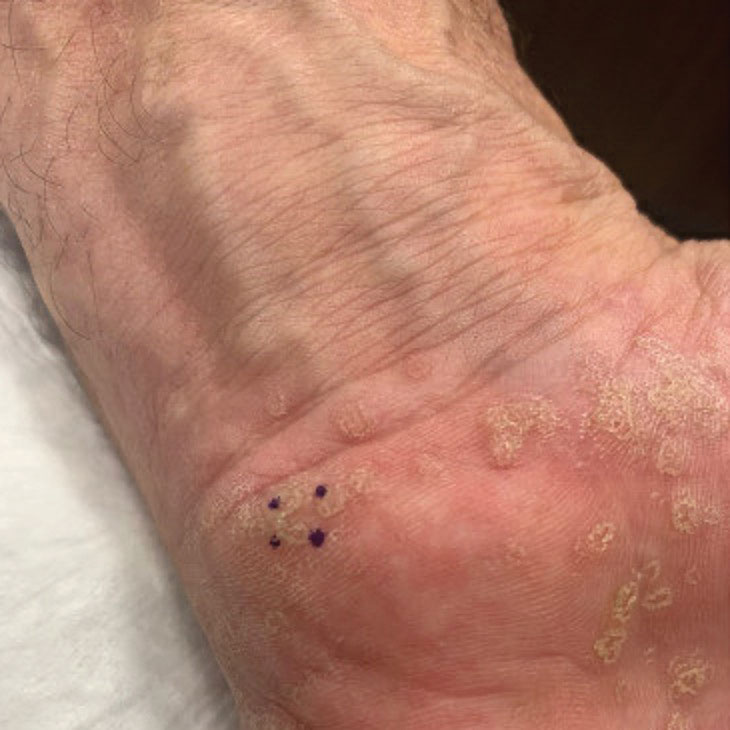
Symmetric Palmoplantar Papules With a Keratotic Border
The Diagnosis: Porokeratosis Plantaris Palmaris et Disseminata
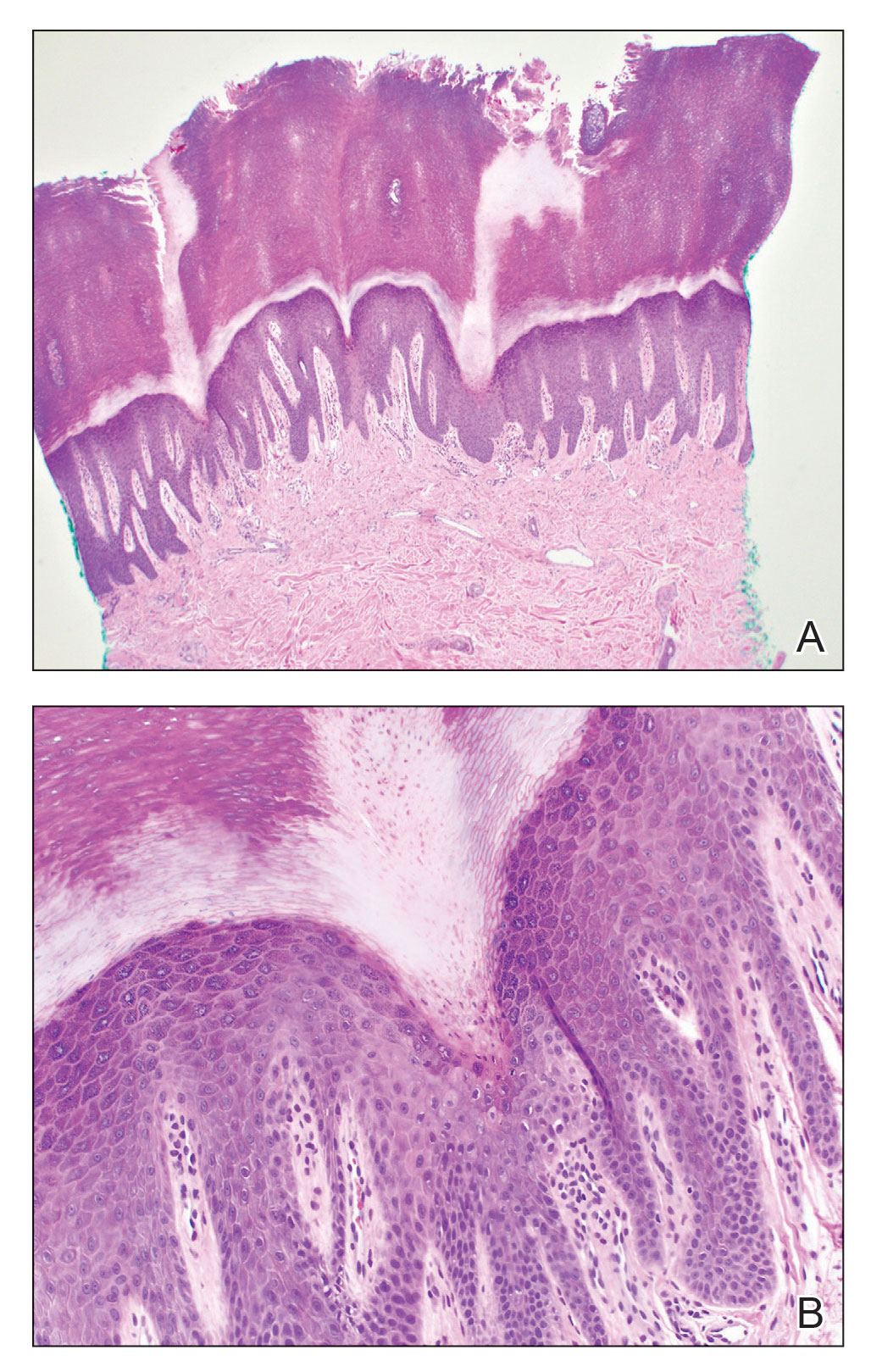
A 3-mm punch biopsy of the right upper arm showed incipient cornoid lamellae formation, pigment incontinence, and sparse dermal lymphocytic inflammation (Figure), suggestive of porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata (PPPD). The dermatopathologist recommended a second biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and to confirm that the lesions on the palms and soles also were suggestive of porokeratosis. A second 4-mm punch biopsy of the left palm was consistent with PPPD.
The risks of PPPD as a precancerous entity along with the benefits and side effects of the various management options were discussed with our patient. We recommended that he start low-dose isotretinoin (20 mg/d) due to the large body surface area affected, making focal and field treatments likely insufficient. However, our patient opted not to treat and did not return for follow-up.
Subtypes of porokeratosis, including disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis (DSAP) and PPPD, are conditions that disrupt the normal maturation of keratin and present clinically with symmetric, crusted, annular papules.1 The signature but nonspecific histopathologic feature shared among the subtypes is the presence of a cornoid lamellae.2 Several triggers of porokeratosis have been proposed, including trauma and exposure to UV and ionizing radiation.2,3 The clinical variants of porokeratosis are important conditions to diagnose correctly because they portend a risk for Bowen disease and invasive squamous cell carcinoma and may indicate the presence of an underlying hematologic and/or solid organ malignancy.4 Management of porokeratosis is difficult, as treatments have shown limited efficacy and variable recurrence rates. Treatment options include focal, field, and systemic options, such as 5-fluorouracil, topical compound of cholesterol and lovastatin, isotretinoin, and acitretin.1,2
Porokeratoses may arise from gene mutations in the mevalonate pathway,5 which is essential for the production of cholesterol.6 Topical cholesterol alone has not been shown to improve porokeratosis, but the combination topical therapy of cholesterol and lovastatin is promising. It is theorized to deliver benefit by both providing the essential end product of the pathway and simultaneously reducing the number of potentially toxic intermediates.6
Porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata (also known as porokeratosis plantaris) is unique among the subtypes of porokeratosis in that its annular, red-pink, papular rash with scaling and a keratotic border tends to start distally, involving the palms and soles, and progresses proximally to the trunk with smaller lesions.1,7 This centripetal progression can take years, as was seen in our patient.1 The disease is uncommon, with a dearth of published reports on PPPD.2 However, case reports have shown that PPPD is strongly linked to family history and may have an autosomal-dominant inheritance pattern. Penetrance is greater in men than in women, as PPPD is twice as common in men.8 Most cases of PPPD have been diagnosed in patients in their 20s and 30s, but Hartman et al9 reported a case wherein a patient was diagnosed with PPPD after 65 years of age, similar to our patient.
Although the lesions in DSAP can appear similar to those in PPPD, DSAP is more common among the family of porokeratotic conditions, affecting women twice as often as men, with a sporadic pattern of inheritance.2 These same features are present in some other types of porokeratosis but not PPPD. Furthermore, DSAP progresses proximally to distally but often with truncal sparing.2
Akin to PPPD, pityriasis rubra pilaris (PRP) often presents with palmoplantar keratoderma.10 There are at least 6 types of PRP with varying degrees of similarity to PPPD. However, in many cases PRP is associated with a background of diffuse erythema on the body with islands of spared skin. In addition, cases of PRP have been linked to extracutaneous findings such as ectropion and joint pain.11
Darier disease, especially the acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf variant, is more common in men and involves younger populations, as in PPPD.11 However, the crusted lesions seen in Darier disease frequently involve the skin folds. These intertriginous lesions may coalesce, mimicking warts in appearance, and are at risk for secondary infection. Nail findings in Darier disease also are distinct and include longitudinal white or red stripes running along the nail bed, in addition to V-shaped nicks at the nail tips.
Psoriasis can occur anywhere on the body and is associated with silver scaling atop a salmon-colored dermatitis.12 It results from aberrant proliferation of keratinocytes. Some distinguishing features of psoriasis include a disease course that waxes and wanes as well as pitting of the nails.
Although PPPD typically affects young adults, we presented a case of PPPD in an older man. Porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata in older adults may represent a delayed diagnosis, imply a broader range for the age of onset, or suggest its manifestation secondary to radiation treatment or another phenomenon. For example, our patient received 35 radiotherapy cycles for tongue cancer more than 5 years prior to the onset of PPPD.
- Irisawa R, Yamazaki M, Yamamoto T, et al. A case of porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:5.
- Vargas-Mora P, Morgado-Carrasco D, Fusta-Novell X. Porokeratosis: a review of its pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2020;111:545-560.
- James AJ, Clarke LE, Elenitsas R, et al. Segmental porokeratosis after radiation therapy for follicular lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(2 suppl):S49-S50.
- Schena D, Papagrigoraki A, Frigo A, et al. Eruptive disseminated porokeratosis associated with internal malignancies: a case report. Cutis. 2010;85:156-159.
- Zhang Z, Li C, Wu F, et al. Genomic variations of the mevalonate pathway in porokeratosis. Elife. 2015;4:E06322. doi:10.7554/eLife.06322
- Atzmony L, Lim YH, Hamilton C, et al. Topical cholesterol/lovastatin for the treatment of porokeratosis: a pathogenesis-directed therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:123-131. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.08.043
- Guss SB, Osbourn RA, Lutzner MA. Porokeratosis plantaris, palmaris, et disseminata. a third type of porokeratosis. Arch Dermatol. 1971;104:366-373.
- Kanitakis J. Porokeratoses: an update of clinical, aetiopathogenic and therapeutic features. Eur J Dermatol. 2014;24:533-544.
- Hartman R, Mandal R, Sanchez M, et al. Porokeratosis plantaris, palmaris, et disseminata. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:22.
- Suryawanshi H, Dhobley A, Sharma A, et al. Darier disease: a rare genodermatosis. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2017;21:321. doi:10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_170_16
- Eastham AB. Pityriasis rubra pilaris. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:404. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.5030
- Nair PA, Badri T. Psoriasis. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated April 6, 2022. Accessed March 13, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448194/
The Diagnosis: Porokeratosis Plantaris Palmaris et Disseminata
A 3-mm punch biopsy of the right upper arm showed incipient cornoid lamellae formation, pigment incontinence, and sparse dermal lymphocytic inflammation (Figure), suggestive of porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata (PPPD). The dermatopathologist recommended a second biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and to confirm that the lesions on the palms and soles also were suggestive of porokeratosis. A second 4-mm punch biopsy of the left palm was consistent with PPPD.

The risks of PPPD as a precancerous entity along with the benefits and side effects of the various management options were discussed with our patient. We recommended that he start low-dose isotretinoin (20 mg/d) due to the large body surface area affected, making focal and field treatments likely insufficient. However, our patient opted not to treat and did not return for follow-up.
Subtypes of porokeratosis, including disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis (DSAP) and PPPD, are conditions that disrupt the normal maturation of keratin and present clinically with symmetric, crusted, annular papules.1 The signature but nonspecific histopathologic feature shared among the subtypes is the presence of a cornoid lamellae.2 Several triggers of porokeratosis have been proposed, including trauma and exposure to UV and ionizing radiation.2,3 The clinical variants of porokeratosis are important conditions to diagnose correctly because they portend a risk for Bowen disease and invasive squamous cell carcinoma and may indicate the presence of an underlying hematologic and/or solid organ malignancy.4 Management of porokeratosis is difficult, as treatments have shown limited efficacy and variable recurrence rates. Treatment options include focal, field, and systemic options, such as 5-fluorouracil, topical compound of cholesterol and lovastatin, isotretinoin, and acitretin.1,2
Porokeratoses may arise from gene mutations in the mevalonate pathway,5 which is essential for the production of cholesterol.6 Topical cholesterol alone has not been shown to improve porokeratosis, but the combination topical therapy of cholesterol and lovastatin is promising. It is theorized to deliver benefit by both providing the essential end product of the pathway and simultaneously reducing the number of potentially toxic intermediates.6
Porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata (also known as porokeratosis plantaris) is unique among the subtypes of porokeratosis in that its annular, red-pink, papular rash with scaling and a keratotic border tends to start distally, involving the palms and soles, and progresses proximally to the trunk with smaller lesions.1,7 This centripetal progression can take years, as was seen in our patient.1 The disease is uncommon, with a dearth of published reports on PPPD.2 However, case reports have shown that PPPD is strongly linked to family history and may have an autosomal-dominant inheritance pattern. Penetrance is greater in men than in women, as PPPD is twice as common in men.8 Most cases of PPPD have been diagnosed in patients in their 20s and 30s, but Hartman et al9 reported a case wherein a patient was diagnosed with PPPD after 65 years of age, similar to our patient.
Although the lesions in DSAP can appear similar to those in PPPD, DSAP is more common among the family of porokeratotic conditions, affecting women twice as often as men, with a sporadic pattern of inheritance.2 These same features are present in some other types of porokeratosis but not PPPD. Furthermore, DSAP progresses proximally to distally but often with truncal sparing.2
Akin to PPPD, pityriasis rubra pilaris (PRP) often presents with palmoplantar keratoderma.10 There are at least 6 types of PRP with varying degrees of similarity to PPPD. However, in many cases PRP is associated with a background of diffuse erythema on the body with islands of spared skin. In addition, cases of PRP have been linked to extracutaneous findings such as ectropion and joint pain.11
Darier disease, especially the acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf variant, is more common in men and involves younger populations, as in PPPD.11 However, the crusted lesions seen in Darier disease frequently involve the skin folds. These intertriginous lesions may coalesce, mimicking warts in appearance, and are at risk for secondary infection. Nail findings in Darier disease also are distinct and include longitudinal white or red stripes running along the nail bed, in addition to V-shaped nicks at the nail tips.
Psoriasis can occur anywhere on the body and is associated with silver scaling atop a salmon-colored dermatitis.12 It results from aberrant proliferation of keratinocytes. Some distinguishing features of psoriasis include a disease course that waxes and wanes as well as pitting of the nails.
Although PPPD typically affects young adults, we presented a case of PPPD in an older man. Porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata in older adults may represent a delayed diagnosis, imply a broader range for the age of onset, or suggest its manifestation secondary to radiation treatment or another phenomenon. For example, our patient received 35 radiotherapy cycles for tongue cancer more than 5 years prior to the onset of PPPD.
The Diagnosis: Porokeratosis Plantaris Palmaris et Disseminata
A 3-mm punch biopsy of the right upper arm showed incipient cornoid lamellae formation, pigment incontinence, and sparse dermal lymphocytic inflammation (Figure), suggestive of porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata (PPPD). The dermatopathologist recommended a second biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and to confirm that the lesions on the palms and soles also were suggestive of porokeratosis. A second 4-mm punch biopsy of the left palm was consistent with PPPD.

The risks of PPPD as a precancerous entity along with the benefits and side effects of the various management options were discussed with our patient. We recommended that he start low-dose isotretinoin (20 mg/d) due to the large body surface area affected, making focal and field treatments likely insufficient. However, our patient opted not to treat and did not return for follow-up.
Subtypes of porokeratosis, including disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis (DSAP) and PPPD, are conditions that disrupt the normal maturation of keratin and present clinically with symmetric, crusted, annular papules.1 The signature but nonspecific histopathologic feature shared among the subtypes is the presence of a cornoid lamellae.2 Several triggers of porokeratosis have been proposed, including trauma and exposure to UV and ionizing radiation.2,3 The clinical variants of porokeratosis are important conditions to diagnose correctly because they portend a risk for Bowen disease and invasive squamous cell carcinoma and may indicate the presence of an underlying hematologic and/or solid organ malignancy.4 Management of porokeratosis is difficult, as treatments have shown limited efficacy and variable recurrence rates. Treatment options include focal, field, and systemic options, such as 5-fluorouracil, topical compound of cholesterol and lovastatin, isotretinoin, and acitretin.1,2
Porokeratoses may arise from gene mutations in the mevalonate pathway,5 which is essential for the production of cholesterol.6 Topical cholesterol alone has not been shown to improve porokeratosis, but the combination topical therapy of cholesterol and lovastatin is promising. It is theorized to deliver benefit by both providing the essential end product of the pathway and simultaneously reducing the number of potentially toxic intermediates.6
Porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata (also known as porokeratosis plantaris) is unique among the subtypes of porokeratosis in that its annular, red-pink, papular rash with scaling and a keratotic border tends to start distally, involving the palms and soles, and progresses proximally to the trunk with smaller lesions.1,7 This centripetal progression can take years, as was seen in our patient.1 The disease is uncommon, with a dearth of published reports on PPPD.2 However, case reports have shown that PPPD is strongly linked to family history and may have an autosomal-dominant inheritance pattern. Penetrance is greater in men than in women, as PPPD is twice as common in men.8 Most cases of PPPD have been diagnosed in patients in their 20s and 30s, but Hartman et al9 reported a case wherein a patient was diagnosed with PPPD after 65 years of age, similar to our patient.
Although the lesions in DSAP can appear similar to those in PPPD, DSAP is more common among the family of porokeratotic conditions, affecting women twice as often as men, with a sporadic pattern of inheritance.2 These same features are present in some other types of porokeratosis but not PPPD. Furthermore, DSAP progresses proximally to distally but often with truncal sparing.2
Akin to PPPD, pityriasis rubra pilaris (PRP) often presents with palmoplantar keratoderma.10 There are at least 6 types of PRP with varying degrees of similarity to PPPD. However, in many cases PRP is associated with a background of diffuse erythema on the body with islands of spared skin. In addition, cases of PRP have been linked to extracutaneous findings such as ectropion and joint pain.11
Darier disease, especially the acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf variant, is more common in men and involves younger populations, as in PPPD.11 However, the crusted lesions seen in Darier disease frequently involve the skin folds. These intertriginous lesions may coalesce, mimicking warts in appearance, and are at risk for secondary infection. Nail findings in Darier disease also are distinct and include longitudinal white or red stripes running along the nail bed, in addition to V-shaped nicks at the nail tips.
Psoriasis can occur anywhere on the body and is associated with silver scaling atop a salmon-colored dermatitis.12 It results from aberrant proliferation of keratinocytes. Some distinguishing features of psoriasis include a disease course that waxes and wanes as well as pitting of the nails.
Although PPPD typically affects young adults, we presented a case of PPPD in an older man. Porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata in older adults may represent a delayed diagnosis, imply a broader range for the age of onset, or suggest its manifestation secondary to radiation treatment or another phenomenon. For example, our patient received 35 radiotherapy cycles for tongue cancer more than 5 years prior to the onset of PPPD.
- Irisawa R, Yamazaki M, Yamamoto T, et al. A case of porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:5.
- Vargas-Mora P, Morgado-Carrasco D, Fusta-Novell X. Porokeratosis: a review of its pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2020;111:545-560.
- James AJ, Clarke LE, Elenitsas R, et al. Segmental porokeratosis after radiation therapy for follicular lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(2 suppl):S49-S50.
- Schena D, Papagrigoraki A, Frigo A, et al. Eruptive disseminated porokeratosis associated with internal malignancies: a case report. Cutis. 2010;85:156-159.
- Zhang Z, Li C, Wu F, et al. Genomic variations of the mevalonate pathway in porokeratosis. Elife. 2015;4:E06322. doi:10.7554/eLife.06322
- Atzmony L, Lim YH, Hamilton C, et al. Topical cholesterol/lovastatin for the treatment of porokeratosis: a pathogenesis-directed therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:123-131. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.08.043
- Guss SB, Osbourn RA, Lutzner MA. Porokeratosis plantaris, palmaris, et disseminata. a third type of porokeratosis. Arch Dermatol. 1971;104:366-373.
- Kanitakis J. Porokeratoses: an update of clinical, aetiopathogenic and therapeutic features. Eur J Dermatol. 2014;24:533-544.
- Hartman R, Mandal R, Sanchez M, et al. Porokeratosis plantaris, palmaris, et disseminata. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:22.
- Suryawanshi H, Dhobley A, Sharma A, et al. Darier disease: a rare genodermatosis. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2017;21:321. doi:10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_170_16
- Eastham AB. Pityriasis rubra pilaris. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:404. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.5030
- Nair PA, Badri T. Psoriasis. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated April 6, 2022. Accessed March 13, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448194/
- Irisawa R, Yamazaki M, Yamamoto T, et al. A case of porokeratosis plantaris palmaris et disseminata and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:5.
- Vargas-Mora P, Morgado-Carrasco D, Fusta-Novell X. Porokeratosis: a review of its pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2020;111:545-560.
- James AJ, Clarke LE, Elenitsas R, et al. Segmental porokeratosis after radiation therapy for follicular lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(2 suppl):S49-S50.
- Schena D, Papagrigoraki A, Frigo A, et al. Eruptive disseminated porokeratosis associated with internal malignancies: a case report. Cutis. 2010;85:156-159.
- Zhang Z, Li C, Wu F, et al. Genomic variations of the mevalonate pathway in porokeratosis. Elife. 2015;4:E06322. doi:10.7554/eLife.06322
- Atzmony L, Lim YH, Hamilton C, et al. Topical cholesterol/lovastatin for the treatment of porokeratosis: a pathogenesis-directed therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:123-131. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.08.043
- Guss SB, Osbourn RA, Lutzner MA. Porokeratosis plantaris, palmaris, et disseminata. a third type of porokeratosis. Arch Dermatol. 1971;104:366-373.
- Kanitakis J. Porokeratoses: an update of clinical, aetiopathogenic and therapeutic features. Eur J Dermatol. 2014;24:533-544.
- Hartman R, Mandal R, Sanchez M, et al. Porokeratosis plantaris, palmaris, et disseminata. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:22.
- Suryawanshi H, Dhobley A, Sharma A, et al. Darier disease: a rare genodermatosis. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2017;21:321. doi:10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_170_16
- Eastham AB. Pityriasis rubra pilaris. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:404. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.5030
- Nair PA, Badri T. Psoriasis. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated April 6, 2022. Accessed March 13, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448194/
A 67-year-old man presented to our office with a rash on the hands, feet, and periungual skin that began with wartlike growths many years prior and recently had started to involve the proximal arms and legs up to the thighs as well as the trunk. He had a medical history of essential hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. He had an 18-year smoking history and had quit more than 25 years prior, with tongue cancer diagnosed more than 5 years prior that was treated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. The lesions occasionally were itchy but not painful. He also reported that his nails frequently split down the middle. He denied any oral lesions and was not using any treatments for the rash. He had no history of skin cancer or other skin conditions. His family history was unclear. Physical examination revealed annular red-pink scaling with a keratotic border on the soles of the feet, palms, and periungual skin. There also were small hyperpigmented papules on the arms, legs, thighs, and trunk over a background of dry and discolored skin, as well as dystrophy of all nails.
Negative expectations of COVID shots may amplify side effects
It fits the psychosomatic role of “nocebo effects,” the researchers say – when “psychological characteristics including anxiety, depression, and the tendency to amplify benign bodily sensations” cause participants to report more bad effects than others.
In August 2021, researchers in Hamburg, Germany, followed 1,678 adults getting a second shot of Pfizer or Moderna mRNA-based vaccines. Participants reported symptoms in a diary, starting 2 weeks ahead of the vaccinations and going 7 days afterward.
Some participants said they weren’t expecting much benefit. Researchers said these people were more likely to “catastrophize instead of normalize benign bodily sensations.” People who’d had a bad experience with their first shot were more likely to say they felt aches, pains, and other side effects from the second.
The research was published in JAMA Network Open.
“Clinician-patient interactions and public vaccine campaigns may both benefit from these insights by optimizing and contextualizing information provided about COVID-19 vaccines,” the researchers said. “Unfavorable nocebo-related adverse effects could then be prevented, and overall vaccine acceptance could be improved.”
More than half of participants, 52.1%, expected bad effects to happen from the shot. Another 7.6% said they would be hospitalized from those bad effects, and 10.6% said the effects would last in the long term.
The Washington Times reported that “substantial numbers of patients reported adverse effects after vaccination,” but people with positive expectations reported them as minor. “Those who scored higher for anxiety, depression, and other psychosocial factors were more likely to flag these issues as severe.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
It fits the psychosomatic role of “nocebo effects,” the researchers say – when “psychological characteristics including anxiety, depression, and the tendency to amplify benign bodily sensations” cause participants to report more bad effects than others.
In August 2021, researchers in Hamburg, Germany, followed 1,678 adults getting a second shot of Pfizer or Moderna mRNA-based vaccines. Participants reported symptoms in a diary, starting 2 weeks ahead of the vaccinations and going 7 days afterward.
Some participants said they weren’t expecting much benefit. Researchers said these people were more likely to “catastrophize instead of normalize benign bodily sensations.” People who’d had a bad experience with their first shot were more likely to say they felt aches, pains, and other side effects from the second.
The research was published in JAMA Network Open.
“Clinician-patient interactions and public vaccine campaigns may both benefit from these insights by optimizing and contextualizing information provided about COVID-19 vaccines,” the researchers said. “Unfavorable nocebo-related adverse effects could then be prevented, and overall vaccine acceptance could be improved.”
More than half of participants, 52.1%, expected bad effects to happen from the shot. Another 7.6% said they would be hospitalized from those bad effects, and 10.6% said the effects would last in the long term.
The Washington Times reported that “substantial numbers of patients reported adverse effects after vaccination,” but people with positive expectations reported them as minor. “Those who scored higher for anxiety, depression, and other psychosocial factors were more likely to flag these issues as severe.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
It fits the psychosomatic role of “nocebo effects,” the researchers say – when “psychological characteristics including anxiety, depression, and the tendency to amplify benign bodily sensations” cause participants to report more bad effects than others.
In August 2021, researchers in Hamburg, Germany, followed 1,678 adults getting a second shot of Pfizer or Moderna mRNA-based vaccines. Participants reported symptoms in a diary, starting 2 weeks ahead of the vaccinations and going 7 days afterward.
Some participants said they weren’t expecting much benefit. Researchers said these people were more likely to “catastrophize instead of normalize benign bodily sensations.” People who’d had a bad experience with their first shot were more likely to say they felt aches, pains, and other side effects from the second.
The research was published in JAMA Network Open.
“Clinician-patient interactions and public vaccine campaigns may both benefit from these insights by optimizing and contextualizing information provided about COVID-19 vaccines,” the researchers said. “Unfavorable nocebo-related adverse effects could then be prevented, and overall vaccine acceptance could be improved.”
More than half of participants, 52.1%, expected bad effects to happen from the shot. Another 7.6% said they would be hospitalized from those bad effects, and 10.6% said the effects would last in the long term.
The Washington Times reported that “substantial numbers of patients reported adverse effects after vaccination,” but people with positive expectations reported them as minor. “Those who scored higher for anxiety, depression, and other psychosocial factors were more likely to flag these issues as severe.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Advanced Breast Cancer Pathophysiology
The end of the telemedicine era?
I started taking care of Jim, a 68-year-old man with metastatic renal cell carcinoma back in the fall of 2018. Jim lived far from our clinic in the rural western Sierra Mountains and had a hard time getting to Santa Monica, but needed ongoing pain and symptom management, as well as follow-up visits with oncology and discussions with our teams about preparing for the end of life.
Luckily for Jim, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services had relaxed the rules around telehealth because of the public health emergency, and we were easily able to provide telemedicine visits throughout the pandemic ensuring that Jim retained access to the care team that had managed his cancer for several years at that point. This would not have been possible without the use of telemedicine – at least not without great effort and expense by Jim to make frequent trips to our Santa Monica clinic.
So, you can imagine my apprehension when I received an email the other day from our billing department, informing billing providers like myself that “telehealth visits are still covered through the end of the year.” While this initially seemed like reassuring news, it immediately begged the question – what happens at the end of the year? What will care look like for patients like Jim who live at a significant distance from their providers?
The end of the COVID-19 public health emergency on May 11 has prompted states to reevaluate the future of telehealth for Medicaid and Medicare recipients. Most states plan to make some telehealth services permanent, particularly in rural areas. While other telehealth services have been extended through Dec. 31, 2024, under the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023.
But still, We can now see very ill patients in their own homes without imposing an undue burden on them to come in for yet another office visit. Prior to the public health emergency, our embedded palliative care program would see patients only when they were in the oncology clinic so as to not burden them with having to travel to yet another clinic. This made our palliative providers less efficient since patients were being seen by multiple providers in the same space, which led to some time spent waiting around. It also frequently tied up our clinic exam rooms for long periods of time, delaying care for patients sitting in the waiting room.
Telehealth changed that virtually overnight. With the widespread availability of smartphones and tablets, patients could stay at home and speak more comfortably in their own surroundings – especially about the difficult topics we tend to dig into in palliative care – such as fears, suffering, grief, loss, legacy, regret, trauma, gratitude, dying – without the impersonal, aseptic environment of a clinic. We could visit with their family/caregivers, kids, and their pets. We could tour their living space and see how they were managing from a functional standpoint. We could get to know aspects of our patients’ lives that we’d never have seen in the clinic that could help us understand their goals and values better and help care for them more fully.
The benefit to the institution was also measurable. We could see our patients faster – the time from referral to consult dropped dramatically because patients could be scheduled for next-day virtual visits instead of having to wait for them to come back to an oncology visit. We could do quick symptom-focused visits that prior to telehealth would have been conducted by phone without the ability to perform at the very least an observational physical exam of the patient, which is important when prescribing medications to medically frail populations.
If telemedicine goes, how will it affect outpatient palliative care?
If that goes away, I do not know what will happen to outpatient palliative care. I can tell you we will be much less efficient in terms of when we see patients. There will probably be a higher clinic burden to patients, as well as higher financial toxicity to patients (Parking in the structure attached to my office building is $22 per day). And, what about the uncaptured costs associated with transportation for those whose illness prevents them from driving themselves? This can range from Uber costs to the time cost for a patient’s family member to take off work and arrange for childcare in order to drive the patient to a clinic for a visit.
In February, I received emails from the Drug Enforcement Agency suggesting that they, too, may roll back providers’ ability to prescribe controlled substances to patients who are mainly receiving telehealth services. While I understand and fully support the need to curb inappropriate overprescribing of controlled medications, I am concerned about the unintended consequences to cancer patients who live at a remote distance from their oncologists and palliative care providers. I remain hopeful that DEA will consider a carveout exception for those patients who have cancer, are receiving palliative care services, or are deemed to be at the end of life, much like the chronic opioid guidelines developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have done.
Telemedicine in essential care
Back to Jim. Using telehealth and electronic prescribing, our oncology and palliative care programs were able to keep Jim comfortable and at home through the end of his life. He did not have to travel 3 hours each way to get care. He did not have to spend money on parking and gas, and his daughter did not have to take days off work and arrange for a babysitter in order to drive him to our clinic. We partnered with a local pharmacy that was willing to special order medications for Jim when his pain became worse and he required a long-acting opioid. We partnered with a local home health company that kept a close eye on Jim and let us know when he seemed to be declining further, prompting discussions about transitioning to hospice.
I’m proud of the fact that our group helped Jim stay in comfortable surroundings and out of the clinic and hospital over the last 6 months of his life, but that would never have happened without the safe and thoughtful use of telehealth by our team.
Ironically, because of a public health emergency, we were able to provide efficient and high-quality palliative care at the right time, to the right person, in the right place, satisfying CMS goals to provide better care for patients and whole populations at lower costs.
Ms. D’Ambruoso is a hospice and palliative care nurse practitioner for UCLA Health Cancer Care, Santa Monica, Calif.
I started taking care of Jim, a 68-year-old man with metastatic renal cell carcinoma back in the fall of 2018. Jim lived far from our clinic in the rural western Sierra Mountains and had a hard time getting to Santa Monica, but needed ongoing pain and symptom management, as well as follow-up visits with oncology and discussions with our teams about preparing for the end of life.
Luckily for Jim, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services had relaxed the rules around telehealth because of the public health emergency, and we were easily able to provide telemedicine visits throughout the pandemic ensuring that Jim retained access to the care team that had managed his cancer for several years at that point. This would not have been possible without the use of telemedicine – at least not without great effort and expense by Jim to make frequent trips to our Santa Monica clinic.
So, you can imagine my apprehension when I received an email the other day from our billing department, informing billing providers like myself that “telehealth visits are still covered through the end of the year.” While this initially seemed like reassuring news, it immediately begged the question – what happens at the end of the year? What will care look like for patients like Jim who live at a significant distance from their providers?
The end of the COVID-19 public health emergency on May 11 has prompted states to reevaluate the future of telehealth for Medicaid and Medicare recipients. Most states plan to make some telehealth services permanent, particularly in rural areas. While other telehealth services have been extended through Dec. 31, 2024, under the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023.
But still, We can now see very ill patients in their own homes without imposing an undue burden on them to come in for yet another office visit. Prior to the public health emergency, our embedded palliative care program would see patients only when they were in the oncology clinic so as to not burden them with having to travel to yet another clinic. This made our palliative providers less efficient since patients were being seen by multiple providers in the same space, which led to some time spent waiting around. It also frequently tied up our clinic exam rooms for long periods of time, delaying care for patients sitting in the waiting room.
Telehealth changed that virtually overnight. With the widespread availability of smartphones and tablets, patients could stay at home and speak more comfortably in their own surroundings – especially about the difficult topics we tend to dig into in palliative care – such as fears, suffering, grief, loss, legacy, regret, trauma, gratitude, dying – without the impersonal, aseptic environment of a clinic. We could visit with their family/caregivers, kids, and their pets. We could tour their living space and see how they were managing from a functional standpoint. We could get to know aspects of our patients’ lives that we’d never have seen in the clinic that could help us understand their goals and values better and help care for them more fully.
The benefit to the institution was also measurable. We could see our patients faster – the time from referral to consult dropped dramatically because patients could be scheduled for next-day virtual visits instead of having to wait for them to come back to an oncology visit. We could do quick symptom-focused visits that prior to telehealth would have been conducted by phone without the ability to perform at the very least an observational physical exam of the patient, which is important when prescribing medications to medically frail populations.
If telemedicine goes, how will it affect outpatient palliative care?
If that goes away, I do not know what will happen to outpatient palliative care. I can tell you we will be much less efficient in terms of when we see patients. There will probably be a higher clinic burden to patients, as well as higher financial toxicity to patients (Parking in the structure attached to my office building is $22 per day). And, what about the uncaptured costs associated with transportation for those whose illness prevents them from driving themselves? This can range from Uber costs to the time cost for a patient’s family member to take off work and arrange for childcare in order to drive the patient to a clinic for a visit.
In February, I received emails from the Drug Enforcement Agency suggesting that they, too, may roll back providers’ ability to prescribe controlled substances to patients who are mainly receiving telehealth services. While I understand and fully support the need to curb inappropriate overprescribing of controlled medications, I am concerned about the unintended consequences to cancer patients who live at a remote distance from their oncologists and palliative care providers. I remain hopeful that DEA will consider a carveout exception for those patients who have cancer, are receiving palliative care services, or are deemed to be at the end of life, much like the chronic opioid guidelines developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have done.
Telemedicine in essential care
Back to Jim. Using telehealth and electronic prescribing, our oncology and palliative care programs were able to keep Jim comfortable and at home through the end of his life. He did not have to travel 3 hours each way to get care. He did not have to spend money on parking and gas, and his daughter did not have to take days off work and arrange for a babysitter in order to drive him to our clinic. We partnered with a local pharmacy that was willing to special order medications for Jim when his pain became worse and he required a long-acting opioid. We partnered with a local home health company that kept a close eye on Jim and let us know when he seemed to be declining further, prompting discussions about transitioning to hospice.
I’m proud of the fact that our group helped Jim stay in comfortable surroundings and out of the clinic and hospital over the last 6 months of his life, but that would never have happened without the safe and thoughtful use of telehealth by our team.
Ironically, because of a public health emergency, we were able to provide efficient and high-quality palliative care at the right time, to the right person, in the right place, satisfying CMS goals to provide better care for patients and whole populations at lower costs.
Ms. D’Ambruoso is a hospice and palliative care nurse practitioner for UCLA Health Cancer Care, Santa Monica, Calif.
I started taking care of Jim, a 68-year-old man with metastatic renal cell carcinoma back in the fall of 2018. Jim lived far from our clinic in the rural western Sierra Mountains and had a hard time getting to Santa Monica, but needed ongoing pain and symptom management, as well as follow-up visits with oncology and discussions with our teams about preparing for the end of life.
Luckily for Jim, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services had relaxed the rules around telehealth because of the public health emergency, and we were easily able to provide telemedicine visits throughout the pandemic ensuring that Jim retained access to the care team that had managed his cancer for several years at that point. This would not have been possible without the use of telemedicine – at least not without great effort and expense by Jim to make frequent trips to our Santa Monica clinic.
So, you can imagine my apprehension when I received an email the other day from our billing department, informing billing providers like myself that “telehealth visits are still covered through the end of the year.” While this initially seemed like reassuring news, it immediately begged the question – what happens at the end of the year? What will care look like for patients like Jim who live at a significant distance from their providers?
The end of the COVID-19 public health emergency on May 11 has prompted states to reevaluate the future of telehealth for Medicaid and Medicare recipients. Most states plan to make some telehealth services permanent, particularly in rural areas. While other telehealth services have been extended through Dec. 31, 2024, under the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023.
But still, We can now see very ill patients in their own homes without imposing an undue burden on them to come in for yet another office visit. Prior to the public health emergency, our embedded palliative care program would see patients only when they were in the oncology clinic so as to not burden them with having to travel to yet another clinic. This made our palliative providers less efficient since patients were being seen by multiple providers in the same space, which led to some time spent waiting around. It also frequently tied up our clinic exam rooms for long periods of time, delaying care for patients sitting in the waiting room.
Telehealth changed that virtually overnight. With the widespread availability of smartphones and tablets, patients could stay at home and speak more comfortably in their own surroundings – especially about the difficult topics we tend to dig into in palliative care – such as fears, suffering, grief, loss, legacy, regret, trauma, gratitude, dying – without the impersonal, aseptic environment of a clinic. We could visit with their family/caregivers, kids, and their pets. We could tour their living space and see how they were managing from a functional standpoint. We could get to know aspects of our patients’ lives that we’d never have seen in the clinic that could help us understand their goals and values better and help care for them more fully.
The benefit to the institution was also measurable. We could see our patients faster – the time from referral to consult dropped dramatically because patients could be scheduled for next-day virtual visits instead of having to wait for them to come back to an oncology visit. We could do quick symptom-focused visits that prior to telehealth would have been conducted by phone without the ability to perform at the very least an observational physical exam of the patient, which is important when prescribing medications to medically frail populations.
If telemedicine goes, how will it affect outpatient palliative care?
If that goes away, I do not know what will happen to outpatient palliative care. I can tell you we will be much less efficient in terms of when we see patients. There will probably be a higher clinic burden to patients, as well as higher financial toxicity to patients (Parking in the structure attached to my office building is $22 per day). And, what about the uncaptured costs associated with transportation for those whose illness prevents them from driving themselves? This can range from Uber costs to the time cost for a patient’s family member to take off work and arrange for childcare in order to drive the patient to a clinic for a visit.
In February, I received emails from the Drug Enforcement Agency suggesting that they, too, may roll back providers’ ability to prescribe controlled substances to patients who are mainly receiving telehealth services. While I understand and fully support the need to curb inappropriate overprescribing of controlled medications, I am concerned about the unintended consequences to cancer patients who live at a remote distance from their oncologists and palliative care providers. I remain hopeful that DEA will consider a carveout exception for those patients who have cancer, are receiving palliative care services, or are deemed to be at the end of life, much like the chronic opioid guidelines developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have done.
Telemedicine in essential care
Back to Jim. Using telehealth and electronic prescribing, our oncology and palliative care programs were able to keep Jim comfortable and at home through the end of his life. He did not have to travel 3 hours each way to get care. He did not have to spend money on parking and gas, and his daughter did not have to take days off work and arrange for a babysitter in order to drive him to our clinic. We partnered with a local pharmacy that was willing to special order medications for Jim when his pain became worse and he required a long-acting opioid. We partnered with a local home health company that kept a close eye on Jim and let us know when he seemed to be declining further, prompting discussions about transitioning to hospice.
I’m proud of the fact that our group helped Jim stay in comfortable surroundings and out of the clinic and hospital over the last 6 months of his life, but that would never have happened without the safe and thoughtful use of telehealth by our team.
Ironically, because of a public health emergency, we were able to provide efficient and high-quality palliative care at the right time, to the right person, in the right place, satisfying CMS goals to provide better care for patients and whole populations at lower costs.
Ms. D’Ambruoso is a hospice and palliative care nurse practitioner for UCLA Health Cancer Care, Santa Monica, Calif.
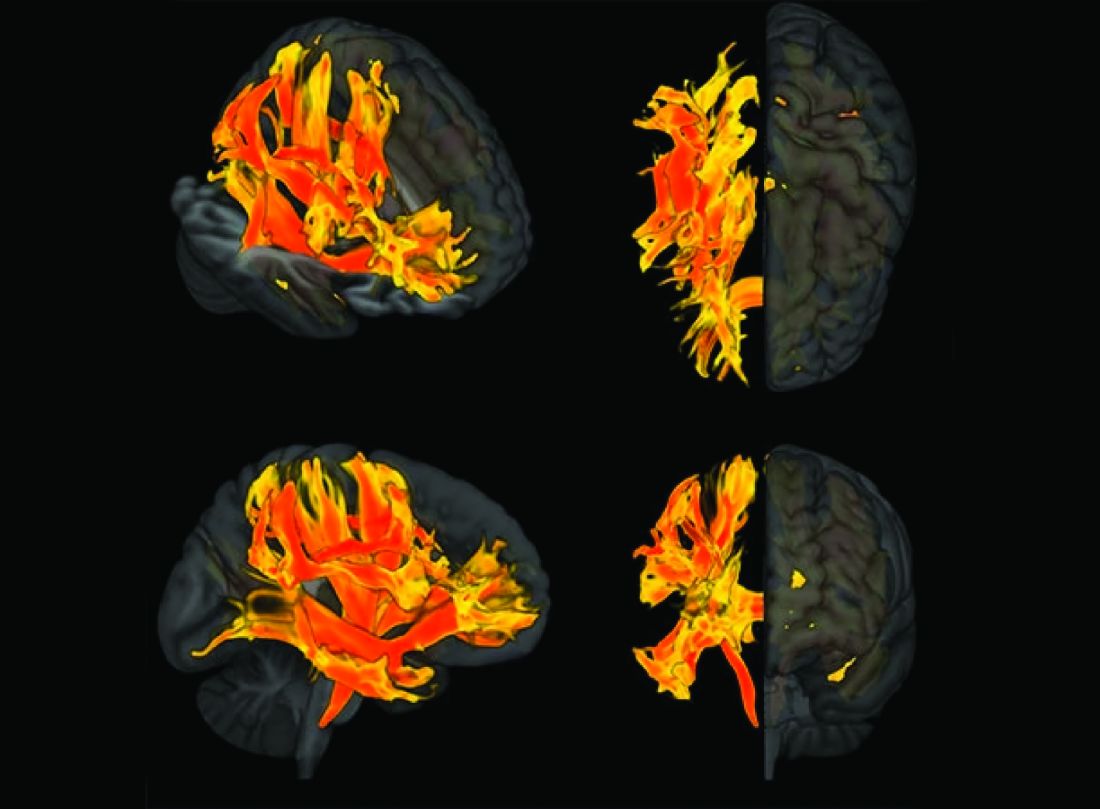
Specific brain damage links hypertension to cognitive impairment
Researchers have identified specific regions of the brain that appear to be damaged by high blood pressure. The finding may explain the link between hypertension and cognitive impairment.
They used genetic information from genome-wide association studies (GWASs) and MRI scans of the brain to study the relationship between hypertension, changes in brain structures, and cognitive impairment. Using Mendelian randomization techniques, they identified nine brain structures related to cognitive impairment that are affected by blood pressure.
“We knew before that raised blood pressure was related to changes in the brain, but our research has narrowed down the changes to those that appear to be potentially causally related to cognitive impairment,” senior author Tomasz Guzik, professor of cardiovascular medicine, at the University of Edinburgh and of the Jagiellonian University, Krakow, Poland, told this news organization.
“Our study confirms a potentially causal relationship between raised blood pressure and cognitive impairment, emphasizing the importance of preventing and treating hypertension,” Prof. Guzik noted.
“But it also identifies the brain culprits of this relationship,” he added.
In the future, it may be possible to assess these nine brain structures in people with high blood pressure to identify those at increased risk of developing cognitive impairment, he said. “These patients may need more intensive care for their blood pressure. We can also investigate these brain structures for potential signaling pathways and molecular changes to see if we can find new targets for treatment to prevent cognitive impairment.”
For this report, the investigators married together different research datasets to identify brain structures potentially responsible for the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function, using results from previous GWASs and observational data from 39,000 people in the UK Biobank registry for whom brain MRI data were available.
First, they mapped brain structures potentially influenced by blood pressure in midlife using MRI scans from people in the UK Biobank registry. Then they examined the relationship between blood pressure and cognitive function in the UK Biobank registry. Next, of the brain structures affected by blood pressure, they identified those that are causally linked to cognitive impairment.
This was possible thanks to genetic markers coding for increased blood pressure, brain structure imaging phenotypes, and those coding for cognitive impairment that could be used in Mendelian randomization studies.
“We looked at 3935 brain magnetic resonance imaging–derived phenotypes in the brain and cognitive function defined by fluid intelligence score to identify genetically predicted causal relationships,” Prof. Guzik said.
They identified 200 brain structures that were causally affected by systolic blood pressure. Of these, nine were also causally related to cognitive impairment. The results were validated in a second prospective cohort of patients with hypertension.
“Some of these structures, including putamen and the white matter regions spanning between the anterior corona radiata, anterior thalamic radiation, and anterior limb of the internal capsule, may represent the target brain regions at which systolic blood pressure acts on cognitive function,” the authors comment.
In an accompanying editorial, Ernesto Schiffrin, MD, and James Engert, PhD, McGill University, Montreal, say that further mechanistic studies of the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function are required to determine precise causal pathways and the roles of relevant brain regions.
“Eventually, biomarkers could be developed to inform antihypertensive trials. Whether clinical trials targeting the specific brain structures will be feasible or if specific antihypertensives could be found that target specific structures remains to be demonstrated,” they write.
“Thus, these new studies could lead to an understanding of the signaling pathways that explain how these structures relate vascular damage to cognitive impairment in hypertension, and contribute to the development of novel interventions to more successfully address the scourge of cognitive decline and dementia in the future,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the European Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, and the Italian Ministry of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers have identified specific regions of the brain that appear to be damaged by high blood pressure. The finding may explain the link between hypertension and cognitive impairment.
They used genetic information from genome-wide association studies (GWASs) and MRI scans of the brain to study the relationship between hypertension, changes in brain structures, and cognitive impairment. Using Mendelian randomization techniques, they identified nine brain structures related to cognitive impairment that are affected by blood pressure.
“We knew before that raised blood pressure was related to changes in the brain, but our research has narrowed down the changes to those that appear to be potentially causally related to cognitive impairment,” senior author Tomasz Guzik, professor of cardiovascular medicine, at the University of Edinburgh and of the Jagiellonian University, Krakow, Poland, told this news organization.
“Our study confirms a potentially causal relationship between raised blood pressure and cognitive impairment, emphasizing the importance of preventing and treating hypertension,” Prof. Guzik noted.
“But it also identifies the brain culprits of this relationship,” he added.
In the future, it may be possible to assess these nine brain structures in people with high blood pressure to identify those at increased risk of developing cognitive impairment, he said. “These patients may need more intensive care for their blood pressure. We can also investigate these brain structures for potential signaling pathways and molecular changes to see if we can find new targets for treatment to prevent cognitive impairment.”
For this report, the investigators married together different research datasets to identify brain structures potentially responsible for the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function, using results from previous GWASs and observational data from 39,000 people in the UK Biobank registry for whom brain MRI data were available.
First, they mapped brain structures potentially influenced by blood pressure in midlife using MRI scans from people in the UK Biobank registry. Then they examined the relationship between blood pressure and cognitive function in the UK Biobank registry. Next, of the brain structures affected by blood pressure, they identified those that are causally linked to cognitive impairment.
This was possible thanks to genetic markers coding for increased blood pressure, brain structure imaging phenotypes, and those coding for cognitive impairment that could be used in Mendelian randomization studies.
“We looked at 3935 brain magnetic resonance imaging–derived phenotypes in the brain and cognitive function defined by fluid intelligence score to identify genetically predicted causal relationships,” Prof. Guzik said.
They identified 200 brain structures that were causally affected by systolic blood pressure. Of these, nine were also causally related to cognitive impairment. The results were validated in a second prospective cohort of patients with hypertension.
“Some of these structures, including putamen and the white matter regions spanning between the anterior corona radiata, anterior thalamic radiation, and anterior limb of the internal capsule, may represent the target brain regions at which systolic blood pressure acts on cognitive function,” the authors comment.
In an accompanying editorial, Ernesto Schiffrin, MD, and James Engert, PhD, McGill University, Montreal, say that further mechanistic studies of the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function are required to determine precise causal pathways and the roles of relevant brain regions.
“Eventually, biomarkers could be developed to inform antihypertensive trials. Whether clinical trials targeting the specific brain structures will be feasible or if specific antihypertensives could be found that target specific structures remains to be demonstrated,” they write.
“Thus, these new studies could lead to an understanding of the signaling pathways that explain how these structures relate vascular damage to cognitive impairment in hypertension, and contribute to the development of novel interventions to more successfully address the scourge of cognitive decline and dementia in the future,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the European Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, and the Italian Ministry of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers have identified specific regions of the brain that appear to be damaged by high blood pressure. The finding may explain the link between hypertension and cognitive impairment.
They used genetic information from genome-wide association studies (GWASs) and MRI scans of the brain to study the relationship between hypertension, changes in brain structures, and cognitive impairment. Using Mendelian randomization techniques, they identified nine brain structures related to cognitive impairment that are affected by blood pressure.
“We knew before that raised blood pressure was related to changes in the brain, but our research has narrowed down the changes to those that appear to be potentially causally related to cognitive impairment,” senior author Tomasz Guzik, professor of cardiovascular medicine, at the University of Edinburgh and of the Jagiellonian University, Krakow, Poland, told this news organization.
“Our study confirms a potentially causal relationship between raised blood pressure and cognitive impairment, emphasizing the importance of preventing and treating hypertension,” Prof. Guzik noted.
“But it also identifies the brain culprits of this relationship,” he added.
In the future, it may be possible to assess these nine brain structures in people with high blood pressure to identify those at increased risk of developing cognitive impairment, he said. “These patients may need more intensive care for their blood pressure. We can also investigate these brain structures for potential signaling pathways and molecular changes to see if we can find new targets for treatment to prevent cognitive impairment.”
For this report, the investigators married together different research datasets to identify brain structures potentially responsible for the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function, using results from previous GWASs and observational data from 39,000 people in the UK Biobank registry for whom brain MRI data were available.
First, they mapped brain structures potentially influenced by blood pressure in midlife using MRI scans from people in the UK Biobank registry. Then they examined the relationship between blood pressure and cognitive function in the UK Biobank registry. Next, of the brain structures affected by blood pressure, they identified those that are causally linked to cognitive impairment.
This was possible thanks to genetic markers coding for increased blood pressure, brain structure imaging phenotypes, and those coding for cognitive impairment that could be used in Mendelian randomization studies.
“We looked at 3935 brain magnetic resonance imaging–derived phenotypes in the brain and cognitive function defined by fluid intelligence score to identify genetically predicted causal relationships,” Prof. Guzik said.
They identified 200 brain structures that were causally affected by systolic blood pressure. Of these, nine were also causally related to cognitive impairment. The results were validated in a second prospective cohort of patients with hypertension.
“Some of these structures, including putamen and the white matter regions spanning between the anterior corona radiata, anterior thalamic radiation, and anterior limb of the internal capsule, may represent the target brain regions at which systolic blood pressure acts on cognitive function,” the authors comment.
In an accompanying editorial, Ernesto Schiffrin, MD, and James Engert, PhD, McGill University, Montreal, say that further mechanistic studies of the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function are required to determine precise causal pathways and the roles of relevant brain regions.
“Eventually, biomarkers could be developed to inform antihypertensive trials. Whether clinical trials targeting the specific brain structures will be feasible or if specific antihypertensives could be found that target specific structures remains to be demonstrated,” they write.
“Thus, these new studies could lead to an understanding of the signaling pathways that explain how these structures relate vascular damage to cognitive impairment in hypertension, and contribute to the development of novel interventions to more successfully address the scourge of cognitive decline and dementia in the future,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the European Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, and the Italian Ministry of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cesarean deliveries drop in women at low risk
Although clinically indicated cesarean deliveries may improve outcomes for mothers and infants, “when not clinically indicated, cesarean delivery is a major surgical intervention that increases risk for adverse outcomes,” wrote Anna M. Frappaolo of Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, and colleagues.
The Healthy People 2030 campaign includes the reduction of cesarean deliveries, but trends in these procedures, especially with regard to diagnoses of labor arrest, have not been well studied, the researchers said.
In an analysis published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed delivery hospitalizations using data from the National Inpatient Sample from 2000 to 2019.
Births deemed low risk for cesarean delivery were identified by using criteria of the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine and additional criteria, and joinpoint regression analysis was used to estimate changes.
The researchers examined overall trends in cesarean deliveries as well as trends for three specific diagnoses: nonreassuring fetal status, labor arrest, and obstructed labor.
The final analysis included 40,517,867 deliveries; of these, 4,885,716 (12.1%) were cesarean deliveries.
Overall, cesarean deliveries in patients deemed at low risk increased from 9.7% in 2000 to 13.9% in 2009, then plateaued and decreased from 13.0% in 2012 to 11.1% in 2019. The average annual percentage change (AAPC) for cesarean delivery was 6.4% for the years from 2000 to 2005, 1.2% from 2005 to 2009, and −2.2% from 2009 to 2019.
Cesarean delivery for nonreassuring fetal status increased over the entire study period, from 3.4% in 2000 to 5.1% in 2019. By contrast, overall cesarean delivery for labor arrest increased from 3.6% in 2000 to a high of 4.8% in 2009, then decreased to 2.7% in 2019. Cesarean deliveries with a diagnosis of obstructed labor decreased from 0.9% in 2008 to 0.3% in 2019.
More specifically, cesarean deliveries for labor arrest in the active phase, latent phase, and second stage of labor increased from 1.5% to 2.1%, 1.1% to 1.5%, and 0.9% to 1.3%, respectively, from 2000 to 2009, and decreased from 2.1% to 1.7% for the active phase, from 1.5% to 1.2% for the latent phase, and from 1.2% to 0.9% for the second stage between 2010 and 2019.
Patients with increased odds of cesarean delivery were older (aged 35-39 years vs. 25-29 years, adjusted odds ratio 1.27), delivered in a hospital in the South vs. the Northeast of the United States (aOR 1.11), and were more likely to be non-Hispanic Black vs. non-Hispanic White (OR 1.23).
Notably, changes in nomenclature and interpretation of intrapartum electronic fetal heart monitoring occurred during the study period, with recommendations for the adoption of a three-tiered system for fetal heart rate patterns in 2008. “It is possible that current evidence and nomenclature related to intrapartum FHR interpretation may result in identification of a larger number of fetuses deemed at indeterminate risk for abnormal acid-base status,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of administrative discharge data rather than clinical records, the exclusion of patients with chronic conditions associated with cesarean delivery, changes in billing codes during the study period, and the inability to account for the effect of health factors, maternal age, and use of assisted reproductive technology, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and 20-year study period, as well as the stratification of labor arrest by stage, and suggest uptake of newer recommendations, they said. “Future reductions in cesarean deliveries among patients at low risk for cesarean delivery may be dependent on improved assessment of intrapartum fetal status,” they concluded.
Consider populations and outcomes in cesarean risk assessment
The decreasing rates of cesarean deliveries in the current study can be seen as positive, but more research is needed to examine maternal and neonatal outcomes, and to consider other conditions that affect risk for cesarean delivery, Paolo Ivo Cavoretto, MD, and Massimo Candiani, MD, of IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, and Antonio Farina, MD, of the University of Bologna, Italy, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Notably, the study authors identified a population aged 15-39 years as low risk, and an increased risk for cesarean delivery within this range increased with age. “Maternal age remains a major risk factor associated with the risk of cesarean delivery, both from results of this study and those of previous analyses assessing its independence from other related risk factors,” the editorialists said.
The study findings also reflect the changes in standards for labor duration during the study period, they noted. The longer duration of labor may reduce cesarean delivery rates, but it is not without maternal and fetal-neonatal risks, they wrote.
“To be sure that the described trend of cesarean delivery rate reduction can be considered positive, there would be the theoretical need to analyze other maternal-fetal-neonatal outcomes (e.g., rates of operative deliveries, neonatal acidemia, intensive care unit use, maternal hemorrhage, pelvic floor trauma and dysfunction, and psychological distress),” the editorialists concluded.
More research needed to explore clinical decisions
“Reducing the cesarean delivery rate is a top priority, but evidence is lacking on an optimal rate that improves maternal and neonatal outcomes,” Iris Krishna, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“Hospital quality and safety committees have been working to decrease cesarean deliveries amongst low-risk women, and identifying contemporary trends gives us insight on whether some of these efforts have translated to a lower cesarean delivery rate,” she said.
Dr. Krishna said she was not surprised by the higher cesarean section rate in the South. “The decision for cesarean delivery is multifaceted, and although this study was not able to assess clinical indications for cesarean delivery or maternal and fetal outcomes, we cannot ignore that social determinants of health contribute greatly to overall health outcomes,” she said. The trends in the current study further underscore the geographic disparities in access to health care present in the South, she added.
“This study notes that cesarean delivery for nonreassuring fetal status increased; however, nonreassuring fetal status as an indication for cesarean delivery can be subjective,” Dr. Krishna said. “Hospital quality and safety committees should consider reviewing the clinical scenarios that led to this decision to identify opportunities for improvement and further education,” she said.
“Defining contemporary trends in cesarean delivery for low-risk patients has merit, but the study findings should be interpreted with caution,” said Dr. Krishna, who is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News advisory board. More research is needed to define an optimal cesarean section rate that promotes positive maternal and fetal outcomes, and to determine whether identifying an optimal rate should be based on patient risk profiles, she said.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Ms. Frappaolo had no financial conflicts to disclose; nor did the editorial authors or Dr. Krishna.
Although clinically indicated cesarean deliveries may improve outcomes for mothers and infants, “when not clinically indicated, cesarean delivery is a major surgical intervention that increases risk for adverse outcomes,” wrote Anna M. Frappaolo of Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, and colleagues.
The Healthy People 2030 campaign includes the reduction of cesarean deliveries, but trends in these procedures, especially with regard to diagnoses of labor arrest, have not been well studied, the researchers said.
In an analysis published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed delivery hospitalizations using data from the National Inpatient Sample from 2000 to 2019.
Births deemed low risk for cesarean delivery were identified by using criteria of the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine and additional criteria, and joinpoint regression analysis was used to estimate changes.
The researchers examined overall trends in cesarean deliveries as well as trends for three specific diagnoses: nonreassuring fetal status, labor arrest, and obstructed labor.
The final analysis included 40,517,867 deliveries; of these, 4,885,716 (12.1%) were cesarean deliveries.
Overall, cesarean deliveries in patients deemed at low risk increased from 9.7% in 2000 to 13.9% in 2009, then plateaued and decreased from 13.0% in 2012 to 11.1% in 2019. The average annual percentage change (AAPC) for cesarean delivery was 6.4% for the years from 2000 to 2005, 1.2% from 2005 to 2009, and −2.2% from 2009 to 2019.
Cesarean delivery for nonreassuring fetal status increased over the entire study period, from 3.4% in 2000 to 5.1% in 2019. By contrast, overall cesarean delivery for labor arrest increased from 3.6% in 2000 to a high of 4.8% in 2009, then decreased to 2.7% in 2019. Cesarean deliveries with a diagnosis of obstructed labor decreased from 0.9% in 2008 to 0.3% in 2019.
More specifically, cesarean deliveries for labor arrest in the active phase, latent phase, and second stage of labor increased from 1.5% to 2.1%, 1.1% to 1.5%, and 0.9% to 1.3%, respectively, from 2000 to 2009, and decreased from 2.1% to 1.7% for the active phase, from 1.5% to 1.2% for the latent phase, and from 1.2% to 0.9% for the second stage between 2010 and 2019.
Patients with increased odds of cesarean delivery were older (aged 35-39 years vs. 25-29 years, adjusted odds ratio 1.27), delivered in a hospital in the South vs. the Northeast of the United States (aOR 1.11), and were more likely to be non-Hispanic Black vs. non-Hispanic White (OR 1.23).
Notably, changes in nomenclature and interpretation of intrapartum electronic fetal heart monitoring occurred during the study period, with recommendations for the adoption of a three-tiered system for fetal heart rate patterns in 2008. “It is possible that current evidence and nomenclature related to intrapartum FHR interpretation may result in identification of a larger number of fetuses deemed at indeterminate risk for abnormal acid-base status,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of administrative discharge data rather than clinical records, the exclusion of patients with chronic conditions associated with cesarean delivery, changes in billing codes during the study period, and the inability to account for the effect of health factors, maternal age, and use of assisted reproductive technology, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and 20-year study period, as well as the stratification of labor arrest by stage, and suggest uptake of newer recommendations, they said. “Future reductions in cesarean deliveries among patients at low risk for cesarean delivery may be dependent on improved assessment of intrapartum fetal status,” they concluded.
Consider populations and outcomes in cesarean risk assessment
The decreasing rates of cesarean deliveries in the current study can be seen as positive, but more research is needed to examine maternal and neonatal outcomes, and to consider other conditions that affect risk for cesarean delivery, Paolo Ivo Cavoretto, MD, and Massimo Candiani, MD, of IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, and Antonio Farina, MD, of the University of Bologna, Italy, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Notably, the study authors identified a population aged 15-39 years as low risk, and an increased risk for cesarean delivery within this range increased with age. “Maternal age remains a major risk factor associated with the risk of cesarean delivery, both from results of this study and those of previous analyses assessing its independence from other related risk factors,” the editorialists said.
The study findings also reflect the changes in standards for labor duration during the study period, they noted. The longer duration of labor may reduce cesarean delivery rates, but it is not without maternal and fetal-neonatal risks, they wrote.
“To be sure that the described trend of cesarean delivery rate reduction can be considered positive, there would be the theoretical need to analyze other maternal-fetal-neonatal outcomes (e.g., rates of operative deliveries, neonatal acidemia, intensive care unit use, maternal hemorrhage, pelvic floor trauma and dysfunction, and psychological distress),” the editorialists concluded.
More research needed to explore clinical decisions
“Reducing the cesarean delivery rate is a top priority, but evidence is lacking on an optimal rate that improves maternal and neonatal outcomes,” Iris Krishna, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“Hospital quality and safety committees have been working to decrease cesarean deliveries amongst low-risk women, and identifying contemporary trends gives us insight on whether some of these efforts have translated to a lower cesarean delivery rate,” she said.
Dr. Krishna said she was not surprised by the higher cesarean section rate in the South. “The decision for cesarean delivery is multifaceted, and although this study was not able to assess clinical indications for cesarean delivery or maternal and fetal outcomes, we cannot ignore that social determinants of health contribute greatly to overall health outcomes,” she said. The trends in the current study further underscore the geographic disparities in access to health care present in the South, she added.
“This study notes that cesarean delivery for nonreassuring fetal status increased; however, nonreassuring fetal status as an indication for cesarean delivery can be subjective,” Dr. Krishna said. “Hospital quality and safety committees should consider reviewing the clinical scenarios that led to this decision to identify opportunities for improvement and further education,” she said.
“Defining contemporary trends in cesarean delivery for low-risk patients has merit, but the study findings should be interpreted with caution,” said Dr. Krishna, who is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News advisory board. More research is needed to define an optimal cesarean section rate that promotes positive maternal and fetal outcomes, and to determine whether identifying an optimal rate should be based on patient risk profiles, she said.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Ms. Frappaolo had no financial conflicts to disclose; nor did the editorial authors or Dr. Krishna.
Although clinically indicated cesarean deliveries may improve outcomes for mothers and infants, “when not clinically indicated, cesarean delivery is a major surgical intervention that increases risk for adverse outcomes,” wrote Anna M. Frappaolo of Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, and colleagues.
The Healthy People 2030 campaign includes the reduction of cesarean deliveries, but trends in these procedures, especially with regard to diagnoses of labor arrest, have not been well studied, the researchers said.
In an analysis published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed delivery hospitalizations using data from the National Inpatient Sample from 2000 to 2019.
Births deemed low risk for cesarean delivery were identified by using criteria of the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine and additional criteria, and joinpoint regression analysis was used to estimate changes.
The researchers examined overall trends in cesarean deliveries as well as trends for three specific diagnoses: nonreassuring fetal status, labor arrest, and obstructed labor.
The final analysis included 40,517,867 deliveries; of these, 4,885,716 (12.1%) were cesarean deliveries.
Overall, cesarean deliveries in patients deemed at low risk increased from 9.7% in 2000 to 13.9% in 2009, then plateaued and decreased from 13.0% in 2012 to 11.1% in 2019. The average annual percentage change (AAPC) for cesarean delivery was 6.4% for the years from 2000 to 2005, 1.2% from 2005 to 2009, and −2.2% from 2009 to 2019.
Cesarean delivery for nonreassuring fetal status increased over the entire study period, from 3.4% in 2000 to 5.1% in 2019. By contrast, overall cesarean delivery for labor arrest increased from 3.6% in 2000 to a high of 4.8% in 2009, then decreased to 2.7% in 2019. Cesarean deliveries with a diagnosis of obstructed labor decreased from 0.9% in 2008 to 0.3% in 2019.
More specifically, cesarean deliveries for labor arrest in the active phase, latent phase, and second stage of labor increased from 1.5% to 2.1%, 1.1% to 1.5%, and 0.9% to 1.3%, respectively, from 2000 to 2009, and decreased from 2.1% to 1.7% for the active phase, from 1.5% to 1.2% for the latent phase, and from 1.2% to 0.9% for the second stage between 2010 and 2019.
Patients with increased odds of cesarean delivery were older (aged 35-39 years vs. 25-29 years, adjusted odds ratio 1.27), delivered in a hospital in the South vs. the Northeast of the United States (aOR 1.11), and were more likely to be non-Hispanic Black vs. non-Hispanic White (OR 1.23).
Notably, changes in nomenclature and interpretation of intrapartum electronic fetal heart monitoring occurred during the study period, with recommendations for the adoption of a three-tiered system for fetal heart rate patterns in 2008. “It is possible that current evidence and nomenclature related to intrapartum FHR interpretation may result in identification of a larger number of fetuses deemed at indeterminate risk for abnormal acid-base status,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of administrative discharge data rather than clinical records, the exclusion of patients with chronic conditions associated with cesarean delivery, changes in billing codes during the study period, and the inability to account for the effect of health factors, maternal age, and use of assisted reproductive technology, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and 20-year study period, as well as the stratification of labor arrest by stage, and suggest uptake of newer recommendations, they said. “Future reductions in cesarean deliveries among patients at low risk for cesarean delivery may be dependent on improved assessment of intrapartum fetal status,” they concluded.
Consider populations and outcomes in cesarean risk assessment
The decreasing rates of cesarean deliveries in the current study can be seen as positive, but more research is needed to examine maternal and neonatal outcomes, and to consider other conditions that affect risk for cesarean delivery, Paolo Ivo Cavoretto, MD, and Massimo Candiani, MD, of IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, and Antonio Farina, MD, of the University of Bologna, Italy, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Notably, the study authors identified a population aged 15-39 years as low risk, and an increased risk for cesarean delivery within this range increased with age. “Maternal age remains a major risk factor associated with the risk of cesarean delivery, both from results of this study and those of previous analyses assessing its independence from other related risk factors,” the editorialists said.
The study findings also reflect the changes in standards for labor duration during the study period, they noted. The longer duration of labor may reduce cesarean delivery rates, but it is not without maternal and fetal-neonatal risks, they wrote.
“To be sure that the described trend of cesarean delivery rate reduction can be considered positive, there would be the theoretical need to analyze other maternal-fetal-neonatal outcomes (e.g., rates of operative deliveries, neonatal acidemia, intensive care unit use, maternal hemorrhage, pelvic floor trauma and dysfunction, and psychological distress),” the editorialists concluded.
More research needed to explore clinical decisions
“Reducing the cesarean delivery rate is a top priority, but evidence is lacking on an optimal rate that improves maternal and neonatal outcomes,” Iris Krishna, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“Hospital quality and safety committees have been working to decrease cesarean deliveries amongst low-risk women, and identifying contemporary trends gives us insight on whether some of these efforts have translated to a lower cesarean delivery rate,” she said.
Dr. Krishna said she was not surprised by the higher cesarean section rate in the South. “The decision for cesarean delivery is multifaceted, and although this study was not able to assess clinical indications for cesarean delivery or maternal and fetal outcomes, we cannot ignore that social determinants of health contribute greatly to overall health outcomes,” she said. The trends in the current study further underscore the geographic disparities in access to health care present in the South, she added.
“This study notes that cesarean delivery for nonreassuring fetal status increased; however, nonreassuring fetal status as an indication for cesarean delivery can be subjective,” Dr. Krishna said. “Hospital quality and safety committees should consider reviewing the clinical scenarios that led to this decision to identify opportunities for improvement and further education,” she said.
“Defining contemporary trends in cesarean delivery for low-risk patients has merit, but the study findings should be interpreted with caution,” said Dr. Krishna, who is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News advisory board. More research is needed to define an optimal cesarean section rate that promotes positive maternal and fetal outcomes, and to determine whether identifying an optimal rate should be based on patient risk profiles, she said.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Ms. Frappaolo had no financial conflicts to disclose; nor did the editorial authors or Dr. Krishna.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
AHA, ACC push supervised exercise training for HFpEF
A statement released by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology advocates use of supervised exercise training in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), as well as coverage for these services by third-party payers.
The authors hope to boost the stature of supervised exercise training (SET) in HFpEF among practitioners and show Medicare and insurers that it deserves reimbursement. Currently, they noted, clinicians tend to recognize exercise as therapy more in HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). And Medicare covers exercise training within broader cardiac rehabilitation programs for patients with HFrEF but not HFpEF.
Yet exercise has been broadly effective in HFpEF clinical trials, as outlined in the document. And there are good mechanistic reasons to believe that patients with the disorder can gain as much or more from SET than those with HFrEF.
“The signals for improvement from exercise training, in symptoms and objective measures of exercise capacity, are considerably larger for HFpEF than for HFrEF,” Dalane W. Kitzman, MD, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in an interview.
So, it’s a bit of a paradox that clinicians don’t prescribe it as often in HFpEF, probably because of the lack of reimbursement but also from less “awareness” and understanding of the disease itself, he proposed.
Dr. Kitzman is senior author on the statement sponsored by the AHA and the ACC. It was published in the societies’ flagship journals Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. The statement was also endorsed by the Heart Failure Society of America, the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation, and the American Association of Heart Failure Nurses.
Carefully chosen words
The statement makes its case in HFpEF specifically for SET rather than cardiac rehabilitation, the latter typically a comprehensive program that goes beyond exercise, Dr. Kitzman noted. And SET is closer to the exercise interventions used in the supportive HFpEF trials.
“Also, Medicare in recent years has approved something called ‘supervised exercise training’ for other disorders, such as peripheral artery disease.” So, the document specifies SET “to be fully aligned with the evidence base,” he said, as well as “align it with a type of treatment that Medicare has a precedent for approving for other disorders.”
Data and physiologic basis
Core features of the AHA/ACC statement is its review of HFpEF exercise physiology, survey of randomized trials supporting SET in the disease, and characterization of exercise as an especially suitable pleiotropic therapy.
Increasingly, “HFpEF is now accepted as a systemic disorder that affects and impacts all organs,” Dr. Kitzman observed. “With a systemic multiorgan disorder, it would make sense that a broad treatment like exercise might be just the right thing. We think that’s the reason that its benefits are really quite large in magnitude.”
The document notes that exercise seems “potentially well suited for the treatment of both the cardiac and, in particular, the extracardiac abnormalities that contribute to exercise intolerance in HFpEF.”
Its effects in the disorder are “anti-inflammatory, rheological, lipid lowering, antihypertensive, positive inotropic, positive lusitropic, negative chronotropic, vasodilation, diuretic, weight-reducing, hypoglycemic, hypnotic, and antidepressive,” the statement notes. It achieves them via multiple pathways involving the heart, lungs, vasculature and, notably, the skeletal muscles.
“It’s been widely overlooked that at least 50% of low exercise capacity and symptoms in HFpEF are due to skeletal muscle dysfunction,” said Dr. Kitzman, an authority on exercise physiology in heart failure.
“But we’ve spent about 95% of our attention trying to modify and understand the cardiac component.” Skeletal muscles, he said, “are not an innocent bystander. They’re part of the problem. And that’s why we should really spend more time focusing on them.”
Dr. Kitzman disclosed receiving consulting fees from Bayer, Medtronic, Corvia Medical, Boehringer Ingelheim, Keyto, Rivus, NovoNordisk, AstraZeneca, and Pfizer; holding stock in Gilead; and receiving grants to his institution from Bayer, Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, Rivus, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A statement released by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology advocates use of supervised exercise training in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), as well as coverage for these services by third-party payers.
The authors hope to boost the stature of supervised exercise training (SET) in HFpEF among practitioners and show Medicare and insurers that it deserves reimbursement. Currently, they noted, clinicians tend to recognize exercise as therapy more in HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). And Medicare covers exercise training within broader cardiac rehabilitation programs for patients with HFrEF but not HFpEF.
Yet exercise has been broadly effective in HFpEF clinical trials, as outlined in the document. And there are good mechanistic reasons to believe that patients with the disorder can gain as much or more from SET than those with HFrEF.
“The signals for improvement from exercise training, in symptoms and objective measures of exercise capacity, are considerably larger for HFpEF than for HFrEF,” Dalane W. Kitzman, MD, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in an interview.
So, it’s a bit of a paradox that clinicians don’t prescribe it as often in HFpEF, probably because of the lack of reimbursement but also from less “awareness” and understanding of the disease itself, he proposed.
Dr. Kitzman is senior author on the statement sponsored by the AHA and the ACC. It was published in the societies’ flagship journals Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. The statement was also endorsed by the Heart Failure Society of America, the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation, and the American Association of Heart Failure Nurses.
Carefully chosen words
The statement makes its case in HFpEF specifically for SET rather than cardiac rehabilitation, the latter typically a comprehensive program that goes beyond exercise, Dr. Kitzman noted. And SET is closer to the exercise interventions used in the supportive HFpEF trials.
“Also, Medicare in recent years has approved something called ‘supervised exercise training’ for other disorders, such as peripheral artery disease.” So, the document specifies SET “to be fully aligned with the evidence base,” he said, as well as “align it with a type of treatment that Medicare has a precedent for approving for other disorders.”
Data and physiologic basis
Core features of the AHA/ACC statement is its review of HFpEF exercise physiology, survey of randomized trials supporting SET in the disease, and characterization of exercise as an especially suitable pleiotropic therapy.
Increasingly, “HFpEF is now accepted as a systemic disorder that affects and impacts all organs,” Dr. Kitzman observed. “With a systemic multiorgan disorder, it would make sense that a broad treatment like exercise might be just the right thing. We think that’s the reason that its benefits are really quite large in magnitude.”
The document notes that exercise seems “potentially well suited for the treatment of both the cardiac and, in particular, the extracardiac abnormalities that contribute to exercise intolerance in HFpEF.”
Its effects in the disorder are “anti-inflammatory, rheological, lipid lowering, antihypertensive, positive inotropic, positive lusitropic, negative chronotropic, vasodilation, diuretic, weight-reducing, hypoglycemic, hypnotic, and antidepressive,” the statement notes. It achieves them via multiple pathways involving the heart, lungs, vasculature and, notably, the skeletal muscles.
“It’s been widely overlooked that at least 50% of low exercise capacity and symptoms in HFpEF are due to skeletal muscle dysfunction,” said Dr. Kitzman, an authority on exercise physiology in heart failure.
“But we’ve spent about 95% of our attention trying to modify and understand the cardiac component.” Skeletal muscles, he said, “are not an innocent bystander. They’re part of the problem. And that’s why we should really spend more time focusing on them.”
Dr. Kitzman disclosed receiving consulting fees from Bayer, Medtronic, Corvia Medical, Boehringer Ingelheim, Keyto, Rivus, NovoNordisk, AstraZeneca, and Pfizer; holding stock in Gilead; and receiving grants to his institution from Bayer, Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, Rivus, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A statement released by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology advocates use of supervised exercise training in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), as well as coverage for these services by third-party payers.
The authors hope to boost the stature of supervised exercise training (SET) in HFpEF among practitioners and show Medicare and insurers that it deserves reimbursement. Currently, they noted, clinicians tend to recognize exercise as therapy more in HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). And Medicare covers exercise training within broader cardiac rehabilitation programs for patients with HFrEF but not HFpEF.
Yet exercise has been broadly effective in HFpEF clinical trials, as outlined in the document. And there are good mechanistic reasons to believe that patients with the disorder can gain as much or more from SET than those with HFrEF.
“The signals for improvement from exercise training, in symptoms and objective measures of exercise capacity, are considerably larger for HFpEF than for HFrEF,” Dalane W. Kitzman, MD, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in an interview.
So, it’s a bit of a paradox that clinicians don’t prescribe it as often in HFpEF, probably because of the lack of reimbursement but also from less “awareness” and understanding of the disease itself, he proposed.
Dr. Kitzman is senior author on the statement sponsored by the AHA and the ACC. It was published in the societies’ flagship journals Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. The statement was also endorsed by the Heart Failure Society of America, the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation, and the American Association of Heart Failure Nurses.
Carefully chosen words
The statement makes its case in HFpEF specifically for SET rather than cardiac rehabilitation, the latter typically a comprehensive program that goes beyond exercise, Dr. Kitzman noted. And SET is closer to the exercise interventions used in the supportive HFpEF trials.
“Also, Medicare in recent years has approved something called ‘supervised exercise training’ for other disorders, such as peripheral artery disease.” So, the document specifies SET “to be fully aligned with the evidence base,” he said, as well as “align it with a type of treatment that Medicare has a precedent for approving for other disorders.”
Data and physiologic basis
Core features of the AHA/ACC statement is its review of HFpEF exercise physiology, survey of randomized trials supporting SET in the disease, and characterization of exercise as an especially suitable pleiotropic therapy.
Increasingly, “HFpEF is now accepted as a systemic disorder that affects and impacts all organs,” Dr. Kitzman observed. “With a systemic multiorgan disorder, it would make sense that a broad treatment like exercise might be just the right thing. We think that’s the reason that its benefits are really quite large in magnitude.”
The document notes that exercise seems “potentially well suited for the treatment of both the cardiac and, in particular, the extracardiac abnormalities that contribute to exercise intolerance in HFpEF.”
Its effects in the disorder are “anti-inflammatory, rheological, lipid lowering, antihypertensive, positive inotropic, positive lusitropic, negative chronotropic, vasodilation, diuretic, weight-reducing, hypoglycemic, hypnotic, and antidepressive,” the statement notes. It achieves them via multiple pathways involving the heart, lungs, vasculature and, notably, the skeletal muscles.
“It’s been widely overlooked that at least 50% of low exercise capacity and symptoms in HFpEF are due to skeletal muscle dysfunction,” said Dr. Kitzman, an authority on exercise physiology in heart failure.
“But we’ve spent about 95% of our attention trying to modify and understand the cardiac component.” Skeletal muscles, he said, “are not an innocent bystander. They’re part of the problem. And that’s why we should really spend more time focusing on them.”
Dr. Kitzman disclosed receiving consulting fees from Bayer, Medtronic, Corvia Medical, Boehringer Ingelheim, Keyto, Rivus, NovoNordisk, AstraZeneca, and Pfizer; holding stock in Gilead; and receiving grants to his institution from Bayer, Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, Rivus, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Music at bedtime may aid depression-related insomnia
PARIS –
The Music to Improve Sleep Quality in Adults With Depression and Insomnia (MUSTAFI) trial randomly assigned more than 110 outpatients with depression to either a music intervention or a waiting list. Sleep quality and quality of life significantly improved after listening to music for half an hour at bedtime for 4 weeks.
“This is a low-cost, safe intervention that has no side effects and may easily be implemented in psychiatry” along with existing treatments, lead researcher Helle Nystrup Lund, PhD, unit for depression, Aalborg (Denmark) University Hospital, said in an interview.
The findings were presented at the European Psychiatric Association 2023 Congress, and recently published in the Nordic Journal of Psychiatry.
Difficult to resolve
The researchers noted that insomnia is common in patients with depression and is “difficult to resolve.”
They noted that, while music is commonly used as a sleep aid and a growing evidence base suggests it has positive effects, there have been few investigations into the effectiveness of music for patients with depression-related insomnia.
To fill this research gap, 112 outpatients with depression and comorbid insomnia who were receiving care at a single center were randomly assigned to either an intervention group or a wait list control group.
Participants in the intervention group listened to music for a minimum of 30 minutes at bedtime for 4 weeks. The music was delivered via the MusicStar app, which is available as a free download from the Apple and Android (Google Play) app stores. The app was developed by Dr. Lund and Lars Rye Bertelsen, a PhD student and music therapist at Aalborg University Hospital.
The app is designed as a multicolored star, with each arm of the star linking to a playlist lasting between 30 minutes and 1 hour. Each color of the star indicates a different tempo of music.
Blue playlists, Dr. Lund explained, offer the quietest music, green is more lively, and red is the most dynamic. Gray playlists linked to project-related soundtracks, such as summer rain.
Dr. Lund said organizing the playlists by stimuli and color code, instead of genre, allows users to regulate their level of arousal and makes the music choice intuitive and easy.
She said that the genres of music include New Age, folk, pop, classical, and film soundtracks, “but no hard rock.”
“There’s actually a quite large selection of music available, because studies show that individual choice is important, as are personal preferences,” she said, adding that the endless choices offered by streaming services can cause confusion.
“So we made curated playlists and designed them with well-known pieces, but also with newly composed music not associated with anything,” Dr. Lund said.
Participants were assessed using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, and two World Health Organization well-being questionnaires (WHO-5, WHOQOL-BREF), as well as actigraphy.
Results showed that, at 4 weeks, participants in the intervention group experienced significant improvements in sleep quality in comparison with control persons. The effect size for the PSQI was –2.1, and for quality of life on the WHO-5, the effect size was 8.4.
A subanalysis revealed that the length of nocturnal sleep in the intervention group increased by an average of 18 minutes during the study from a baseline of approximately 5 hours per night, said Dr. Lund.
However, there were no changes in actigraphy measurements and no significant improvements in HAMD-17 scores.
Dr. Lund said that, on the basis of these positive findings, music intervention as a sleep aid is now offered at Aalborg University Hospital to patients with depression-related insomnia.
Clinically meaningful?
Commenting on the findings, Gerald J. Haeffel, PhD, department of psychology, University of Notre Dame, South Bend, Ind., said that overall, the study showed there was a change in sleep-quality and quality of life scores of “about 10% in each.”
“This, on the surface, would seem to be a meaningful change,” although it is less clear whether it is “clinically meaningful.” Perhaps it is, “but it would be nice to have more information.”
It would be useful, he said, to “show the means for each group pre- to postintervention, along with standard deviations,” he added.
Dr. Haeffel added that on the basis of current results, it isn’t possible to determine whether individuals’ control over music choice is important.
“We have no idea if ‘choice’ or length of playlist had any causal role in the results. One would need to run a study with the same playlist, but in one group people have to listen to whatever song comes on versus another condition in which they get to choose a song off the same list,” he said.
He noted that his group conducted a study in which highly popular music that was chosen by individual participants was found to have a positive effect. Even so, he said, “we could not determine if it was ‘choice’ or ‘popularity’ that caused the positive effects of music.”
In addition, he said, the reason music has a positive effect on insomnia remains unclear.
“It is not because it helped with depression, and it’s not because it’s actually changing objective sleep parameters. It could be that it improves mood right before bed or helps distract people right before bed. At the same time, it could also just be a placebo effect,” said Dr. Haeffel.
In addition, he said, it’s important to note that the music intervention had no comparator, so “maybe just doing something different or getting to talk with researchers created the effect and has nothing to do with music.”
Overall, he believes that there are “not enough data” to use the sleep intervention that was employed in the current study “as primary intervention, but future work could show its usefulness as a supplement.”
Dr. Lund and Mr. Bertelsen reported ownership and sales of the MusicStar app. Dr. Haeffel reported no relevant financial relationships.
PARIS –
The Music to Improve Sleep Quality in Adults With Depression and Insomnia (MUSTAFI) trial randomly assigned more than 110 outpatients with depression to either a music intervention or a waiting list. Sleep quality and quality of life significantly improved after listening to music for half an hour at bedtime for 4 weeks.
“This is a low-cost, safe intervention that has no side effects and may easily be implemented in psychiatry” along with existing treatments, lead researcher Helle Nystrup Lund, PhD, unit for depression, Aalborg (Denmark) University Hospital, said in an interview.
The findings were presented at the European Psychiatric Association 2023 Congress, and recently published in the Nordic Journal of Psychiatry.
Difficult to resolve
The researchers noted that insomnia is common in patients with depression and is “difficult to resolve.”
They noted that, while music is commonly used as a sleep aid and a growing evidence base suggests it has positive effects, there have been few investigations into the effectiveness of music for patients with depression-related insomnia.
To fill this research gap, 112 outpatients with depression and comorbid insomnia who were receiving care at a single center were randomly assigned to either an intervention group or a wait list control group.
Participants in the intervention group listened to music for a minimum of 30 minutes at bedtime for 4 weeks. The music was delivered via the MusicStar app, which is available as a free download from the Apple and Android (Google Play) app stores. The app was developed by Dr. Lund and Lars Rye Bertelsen, a PhD student and music therapist at Aalborg University Hospital.
The app is designed as a multicolored star, with each arm of the star linking to a playlist lasting between 30 minutes and 1 hour. Each color of the star indicates a different tempo of music.
Blue playlists, Dr. Lund explained, offer the quietest music, green is more lively, and red is the most dynamic. Gray playlists linked to project-related soundtracks, such as summer rain.
Dr. Lund said organizing the playlists by stimuli and color code, instead of genre, allows users to regulate their level of arousal and makes the music choice intuitive and easy.
She said that the genres of music include New Age, folk, pop, classical, and film soundtracks, “but no hard rock.”
“There’s actually a quite large selection of music available, because studies show that individual choice is important, as are personal preferences,” she said, adding that the endless choices offered by streaming services can cause confusion.
“So we made curated playlists and designed them with well-known pieces, but also with newly composed music not associated with anything,” Dr. Lund said.
Participants were assessed using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, and two World Health Organization well-being questionnaires (WHO-5, WHOQOL-BREF), as well as actigraphy.
Results showed that, at 4 weeks, participants in the intervention group experienced significant improvements in sleep quality in comparison with control persons. The effect size for the PSQI was –2.1, and for quality of life on the WHO-5, the effect size was 8.4.
A subanalysis revealed that the length of nocturnal sleep in the intervention group increased by an average of 18 minutes during the study from a baseline of approximately 5 hours per night, said Dr. Lund.
However, there were no changes in actigraphy measurements and no significant improvements in HAMD-17 scores.
Dr. Lund said that, on the basis of these positive findings, music intervention as a sleep aid is now offered at Aalborg University Hospital to patients with depression-related insomnia.
Clinically meaningful?
Commenting on the findings, Gerald J. Haeffel, PhD, department of psychology, University of Notre Dame, South Bend, Ind., said that overall, the study showed there was a change in sleep-quality and quality of life scores of “about 10% in each.”
“This, on the surface, would seem to be a meaningful change,” although it is less clear whether it is “clinically meaningful.” Perhaps it is, “but it would be nice to have more information.”
It would be useful, he said, to “show the means for each group pre- to postintervention, along with standard deviations,” he added.
Dr. Haeffel added that on the basis of current results, it isn’t possible to determine whether individuals’ control over music choice is important.
“We have no idea if ‘choice’ or length of playlist had any causal role in the results. One would need to run a study with the same playlist, but in one group people have to listen to whatever song comes on versus another condition in which they get to choose a song off the same list,” he said.
He noted that his group conducted a study in which highly popular music that was chosen by individual participants was found to have a positive effect. Even so, he said, “we could not determine if it was ‘choice’ or ‘popularity’ that caused the positive effects of music.”
In addition, he said, the reason music has a positive effect on insomnia remains unclear.
“It is not because it helped with depression, and it’s not because it’s actually changing objective sleep parameters. It could be that it improves mood right before bed or helps distract people right before bed. At the same time, it could also just be a placebo effect,” said Dr. Haeffel.
In addition, he said, it’s important to note that the music intervention had no comparator, so “maybe just doing something different or getting to talk with researchers created the effect and has nothing to do with music.”
Overall, he believes that there are “not enough data” to use the sleep intervention that was employed in the current study “as primary intervention, but future work could show its usefulness as a supplement.”
Dr. Lund and Mr. Bertelsen reported ownership and sales of the MusicStar app. Dr. Haeffel reported no relevant financial relationships.
PARIS –
The Music to Improve Sleep Quality in Adults With Depression and Insomnia (MUSTAFI) trial randomly assigned more than 110 outpatients with depression to either a music intervention or a waiting list. Sleep quality and quality of life significantly improved after listening to music for half an hour at bedtime for 4 weeks.
“This is a low-cost, safe intervention that has no side effects and may easily be implemented in psychiatry” along with existing treatments, lead researcher Helle Nystrup Lund, PhD, unit for depression, Aalborg (Denmark) University Hospital, said in an interview.
The findings were presented at the European Psychiatric Association 2023 Congress, and recently published in the Nordic Journal of Psychiatry.
Difficult to resolve
The researchers noted that insomnia is common in patients with depression and is “difficult to resolve.”
They noted that, while music is commonly used as a sleep aid and a growing evidence base suggests it has positive effects, there have been few investigations into the effectiveness of music for patients with depression-related insomnia.
To fill this research gap, 112 outpatients with depression and comorbid insomnia who were receiving care at a single center were randomly assigned to either an intervention group or a wait list control group.
Participants in the intervention group listened to music for a minimum of 30 minutes at bedtime for 4 weeks. The music was delivered via the MusicStar app, which is available as a free download from the Apple and Android (Google Play) app stores. The app was developed by Dr. Lund and Lars Rye Bertelsen, a PhD student and music therapist at Aalborg University Hospital.
The app is designed as a multicolored star, with each arm of the star linking to a playlist lasting between 30 minutes and 1 hour. Each color of the star indicates a different tempo of music.
Blue playlists, Dr. Lund explained, offer the quietest music, green is more lively, and red is the most dynamic. Gray playlists linked to project-related soundtracks, such as summer rain.
Dr. Lund said organizing the playlists by stimuli and color code, instead of genre, allows users to regulate their level of arousal and makes the music choice intuitive and easy.
She said that the genres of music include New Age, folk, pop, classical, and film soundtracks, “but no hard rock.”
“There’s actually a quite large selection of music available, because studies show that individual choice is important, as are personal preferences,” she said, adding that the endless choices offered by streaming services can cause confusion.
“So we made curated playlists and designed them with well-known pieces, but also with newly composed music not associated with anything,” Dr. Lund said.
Participants were assessed using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, and two World Health Organization well-being questionnaires (WHO-5, WHOQOL-BREF), as well as actigraphy.
Results showed that, at 4 weeks, participants in the intervention group experienced significant improvements in sleep quality in comparison with control persons. The effect size for the PSQI was –2.1, and for quality of life on the WHO-5, the effect size was 8.4.
A subanalysis revealed that the length of nocturnal sleep in the intervention group increased by an average of 18 minutes during the study from a baseline of approximately 5 hours per night, said Dr. Lund.
However, there were no changes in actigraphy measurements and no significant improvements in HAMD-17 scores.
Dr. Lund said that, on the basis of these positive findings, music intervention as a sleep aid is now offered at Aalborg University Hospital to patients with depression-related insomnia.
Clinically meaningful?
Commenting on the findings, Gerald J. Haeffel, PhD, department of psychology, University of Notre Dame, South Bend, Ind., said that overall, the study showed there was a change in sleep-quality and quality of life scores of “about 10% in each.”
“This, on the surface, would seem to be a meaningful change,” although it is less clear whether it is “clinically meaningful.” Perhaps it is, “but it would be nice to have more information.”
It would be useful, he said, to “show the means for each group pre- to postintervention, along with standard deviations,” he added.
Dr. Haeffel added that on the basis of current results, it isn’t possible to determine whether individuals’ control over music choice is important.
“We have no idea if ‘choice’ or length of playlist had any causal role in the results. One would need to run a study with the same playlist, but in one group people have to listen to whatever song comes on versus another condition in which they get to choose a song off the same list,” he said.
He noted that his group conducted a study in which highly popular music that was chosen by individual participants was found to have a positive effect. Even so, he said, “we could not determine if it was ‘choice’ or ‘popularity’ that caused the positive effects of music.”
In addition, he said, the reason music has a positive effect on insomnia remains unclear.
“It is not because it helped with depression, and it’s not because it’s actually changing objective sleep parameters. It could be that it improves mood right before bed or helps distract people right before bed. At the same time, it could also just be a placebo effect,” said Dr. Haeffel.
In addition, he said, it’s important to note that the music intervention had no comparator, so “maybe just doing something different or getting to talk with researchers created the effect and has nothing to do with music.”
Overall, he believes that there are “not enough data” to use the sleep intervention that was employed in the current study “as primary intervention, but future work could show its usefulness as a supplement.”
Dr. Lund and Mr. Bertelsen reported ownership and sales of the MusicStar app. Dr. Haeffel reported no relevant financial relationships.
AT EPA 2023
Cancer risk elevated after stroke in younger people
In young people, stroke might be the first manifestation of an underlying cancer, according to the investigators, led by Jamie Verhoeven, MD, PhD, with the department of neurology, Radboud University Medical Centre, Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
The new study can be viewed as a “stepping stone for future studies investigating the usefulness of screening for cancer after stroke,” the researchers say.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Currently, the diagnostic workup for young people with stroke includes searching for rare clotting disorders, although screening for cancer is not regularly performed.
Some research suggests that stroke and cancer are linked, but the literature is limited. In prior studies among people of all ages, cancer incidence after stroke has been variable – from 1% to 5% at 1 year and from 11% to 30% after 10 years.
To the team’s knowledge, only two studies have described the incidence of cancer after stroke among younger patients. One put the risk at 0.5% for people aged 18-50 years in the first year after stroke; the other described a cumulative risk of 17.3% in the 10 years after stroke for patients aged 18-55 years.
Using Dutch data, Dr. Verhoeven and colleagues identified 27,616 young stroke patients (age, 15-49 years; median age, 45 years) and 362,782 older stroke patients (median age, 76 years).
The cumulative incidence of any new cancer at 10 years was 3.7% among the younger stroke patients and 8.5% among the older stroke patients.
The incidence of a new cancer after stroke among younger patients was higher among women than men, while the opposite was true for older stroke patients.
Compared with the general population, younger stroke patients had a more than 2.5-fold greater likelihood of being diagnosed with a new cancer in the first year after ischemic stroke (standardized incidence ratio, 2.6). The risk was highest for lung cancer (SIR, 6.9), followed by hematologic cancers (SIR, 5.2).
Compared with the general population, younger stroke patients had nearly a 5.5-fold greater likelihood of being diagnosed with a new cancer in the first year after intracerebral hemorrhage (SIR, 5.4), and the risk was highest for hematologic cancers (SIR, 14.2).
In younger patients, the cumulative incidence of any cancer decreased over the years but remained significantly higher for 8 years following a stroke.
For patients aged 50 years or older, the 1-year risk for any new cancer after either ischemic stroke or intracerebral hemorrhage was 1.2 times higher, compared with the general population.
“We typically think of occult cancer as being a cause of stroke in an older population, given that the incidence of cancer increases over time [but] what this study shows is that we probably do need to consider occult cancer as an underlying cause of stroke even in a younger population,” said Laura Gioia, MD, stroke neurologist at the University of Montreal, who was not involved in the research.
Dr. Verhoeven and colleagues conclude that their finding supports the hypothesis of a causal link between cancer and stroke. Given the timing between stroke and cancer diagnosis, cancer may have been present when the stroke occurred and possibly played a role in causing it, the authors note. However, conclusions on causal mechanisms cannot be drawn from the current study.
The question of whether young stroke patients should be screened for cancer is a tough one, Dr. Gioia noted. “Cancer represents a small percentage of causes of stroke. That means you would have to screen a lot of people with a benefit that is still uncertain for the moment,” Dr. Gioia said in an interview.
“I think we need to keep cancer in mind as a cause of stroke in our young patients, and that should probably guide our history-taking with the patient and consider imaging when it’s appropriate and when we think that there could be an underlying occult cancer,” Dr. Gioia suggested.
The study was funded in part through unrestricted funding by Stryker, Medtronic, and Cerenovus. Dr. Verhoeven and Dr. Gioia have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In young people, stroke might be the first manifestation of an underlying cancer, according to the investigators, led by Jamie Verhoeven, MD, PhD, with the department of neurology, Radboud University Medical Centre, Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
The new study can be viewed as a “stepping stone for future studies investigating the usefulness of screening for cancer after stroke,” the researchers say.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Currently, the diagnostic workup for young people with stroke includes searching for rare clotting disorders, although screening for cancer is not regularly performed.
Some research suggests that stroke and cancer are linked, but the literature is limited. In prior studies among people of all ages, cancer incidence after stroke has been variable – from 1% to 5% at 1 year and from 11% to 30% after 10 years.
To the team’s knowledge, only two studies have described the incidence of cancer after stroke among younger patients. One put the risk at 0.5% for people aged 18-50 years in the first year after stroke; the other described a cumulative risk of 17.3% in the 10 years after stroke for patients aged 18-55 years.
Using Dutch data, Dr. Verhoeven and colleagues identified 27,616 young stroke patients (age, 15-49 years; median age, 45 years) and 362,782 older stroke patients (median age, 76 years).
The cumulative incidence of any new cancer at 10 years was 3.7% among the younger stroke patients and 8.5% among the older stroke patients.
The incidence of a new cancer after stroke among younger patients was higher among women than men, while the opposite was true for older stroke patients.
Compared with the general population, younger stroke patients had a more than 2.5-fold greater likelihood of being diagnosed with a new cancer in the first year after ischemic stroke (standardized incidence ratio, 2.6). The risk was highest for lung cancer (SIR, 6.9), followed by hematologic cancers (SIR, 5.2).
Compared with the general population, younger stroke patients had nearly a 5.5-fold greater likelihood of being diagnosed with a new cancer in the first year after intracerebral hemorrhage (SIR, 5.4), and the risk was highest for hematologic cancers (SIR, 14.2).
In younger patients, the cumulative incidence of any cancer decreased over the years but remained significantly higher for 8 years following a stroke.
For patients aged 50 years or older, the 1-year risk for any new cancer after either ischemic stroke or intracerebral hemorrhage was 1.2 times higher, compared with the general population.
“We typically think of occult cancer as being a cause of stroke in an older population, given that the incidence of cancer increases over time [but] what this study shows is that we probably do need to consider occult cancer as an underlying cause of stroke even in a younger population,” said Laura Gioia, MD, stroke neurologist at the University of Montreal, who was not involved in the research.
Dr. Verhoeven and colleagues conclude that their finding supports the hypothesis of a causal link between cancer and stroke. Given the timing between stroke and cancer diagnosis, cancer may have been present when the stroke occurred and possibly played a role in causing it, the authors note. However, conclusions on causal mechanisms cannot be drawn from the current study.
The question of whether young stroke patients should be screened for cancer is a tough one, Dr. Gioia noted. “Cancer represents a small percentage of causes of stroke. That means you would have to screen a lot of people with a benefit that is still uncertain for the moment,” Dr. Gioia said in an interview.
“I think we need to keep cancer in mind as a cause of stroke in our young patients, and that should probably guide our history-taking with the patient and consider imaging when it’s appropriate and when we think that there could be an underlying occult cancer,” Dr. Gioia suggested.
The study was funded in part through unrestricted funding by Stryker, Medtronic, and Cerenovus. Dr. Verhoeven and Dr. Gioia have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In young people, stroke might be the first manifestation of an underlying cancer, according to the investigators, led by Jamie Verhoeven, MD, PhD, with the department of neurology, Radboud University Medical Centre, Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
The new study can be viewed as a “stepping stone for future studies investigating the usefulness of screening for cancer after stroke,” the researchers say.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Currently, the diagnostic workup for young people with stroke includes searching for rare clotting disorders, although screening for cancer is not regularly performed.
Some research suggests that stroke and cancer are linked, but the literature is limited. In prior studies among people of all ages, cancer incidence after stroke has been variable – from 1% to 5% at 1 year and from 11% to 30% after 10 years.
To the team’s knowledge, only two studies have described the incidence of cancer after stroke among younger patients. One put the risk at 0.5% for people aged 18-50 years in the first year after stroke; the other described a cumulative risk of 17.3% in the 10 years after stroke for patients aged 18-55 years.
Using Dutch data, Dr. Verhoeven and colleagues identified 27,616 young stroke patients (age, 15-49 years; median age, 45 years) and 362,782 older stroke patients (median age, 76 years).
The cumulative incidence of any new cancer at 10 years was 3.7% among the younger stroke patients and 8.5% among the older stroke patients.
The incidence of a new cancer after stroke among younger patients was higher among women than men, while the opposite was true for older stroke patients.
Compared with the general population, younger stroke patients had a more than 2.5-fold greater likelihood of being diagnosed with a new cancer in the first year after ischemic stroke (standardized incidence ratio, 2.6). The risk was highest for lung cancer (SIR, 6.9), followed by hematologic cancers (SIR, 5.2).
Compared with the general population, younger stroke patients had nearly a 5.5-fold greater likelihood of being diagnosed with a new cancer in the first year after intracerebral hemorrhage (SIR, 5.4), and the risk was highest for hematologic cancers (SIR, 14.2).
In younger patients, the cumulative incidence of any cancer decreased over the years but remained significantly higher for 8 years following a stroke.
For patients aged 50 years or older, the 1-year risk for any new cancer after either ischemic stroke or intracerebral hemorrhage was 1.2 times higher, compared with the general population.
“We typically think of occult cancer as being a cause of stroke in an older population, given that the incidence of cancer increases over time [but] what this study shows is that we probably do need to consider occult cancer as an underlying cause of stroke even in a younger population,” said Laura Gioia, MD, stroke neurologist at the University of Montreal, who was not involved in the research.
Dr. Verhoeven and colleagues conclude that their finding supports the hypothesis of a causal link between cancer and stroke. Given the timing between stroke and cancer diagnosis, cancer may have been present when the stroke occurred and possibly played a role in causing it, the authors note. However, conclusions on causal mechanisms cannot be drawn from the current study.
The question of whether young stroke patients should be screened for cancer is a tough one, Dr. Gioia noted. “Cancer represents a small percentage of causes of stroke. That means you would have to screen a lot of people with a benefit that is still uncertain for the moment,” Dr. Gioia said in an interview.
“I think we need to keep cancer in mind as a cause of stroke in our young patients, and that should probably guide our history-taking with the patient and consider imaging when it’s appropriate and when we think that there could be an underlying occult cancer,” Dr. Gioia suggested.
The study was funded in part through unrestricted funding by Stryker, Medtronic, and Cerenovus. Dr. Verhoeven and Dr. Gioia have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
SGLT2 inhibitors: Real-world data show benefits outweigh risks
Starting therapy with an SGLT2 inhibitor versus a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist was associated with more lower limb amputations, nonvertebral fractures, and genital infections, but these risks need to be balanced against cardiovascular and renoprotective benefits, according to the researchers.
The analysis showed that there would be 2.1 more lower limb amputations, 2.5 more nonvertebral fractures, and 41 more genital infections per 1,000 patients per year among those receiving SGLT2 inhibitors versus an equal number of patients receiving GLP-1 agonists, lead author Edouard Fu, PhD, explained to this news organization in an email.
“On the other hand, we know from the evidence from randomized controlled trials that taking an SGLT2 inhibitor compared with placebo lowers the risk of developing kidney failure,” said Dr. Fu, who is a research fellow in the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“For instance,” he continued, “in the DAPA-CKD clinical trial, dapagliflozin versus placebo led to 29 fewer events per 1,000 patients per year of the composite outcome (50% decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR], kidney failure, cardiovascular or kidney death).”
In the CREDENCE trial, canagliflozin versus placebo led to 18 fewer events per 1,000 person-years for the composite outcome of doubling of serum creatinine, kidney failure, and cardiovascular or kidney death.
And in the EMPA-KIDNEY study, empagliflozin versus placebo led to 21 fewer events per 1,000 person-years for the composite outcome of progression of kidney disease or cardiovascular death.
“Thus, benefits would still outweigh the risks,” Dr. Fu emphasized.
‘Quantifies absolute rate of events among routine care patients’
“The importance of our paper,” he summarized, “is that it quantifies the absolute rate of events among routine care patients and may be used to inform shared decision-making.”
The analysis also found that the risks of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), hypovolemia, hypoglycemia, and severe urinary tract infection (UTI) were similar with SGLT2 inhibitors versus GLP-1 agonists, but the risk of developing acute kidney injury (AKI) was lower with an SGLT2 inhibitor.
“Our study can help inform patient-physician decision-making regarding risks and benefits before prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors in this population” of patients with CKD and diabetes treated in clinical practice, the researchers conclude, “but needs to be interpreted in light of its limitations, including residual confounding, short follow-up time, and the use of diagnosis codes to identify patients with CKD.”
The study was recently published in the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.
Slow uptake, safety concerns
SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended as first-line therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes and CKD who have an eGFR equal to or greater than 20 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and thus are at high risk for cardiovascular disease and kidney disease progression, Dr. Fu and colleagues write.
However, studies report that as few as 6% of patients with CKD and type 2 diabetes are currently prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors in the United States.
This slow uptake of SGLT2 inhibitors among patients with CKD may be partly due to concerns about DKA, fractures, amputations, and urogenital infections observed in clinical trials.
However, such trials are generally underpowered to assess rare adverse events, use monitoring protocols to lower the risk of adverse events, and include a highly selected patient population, and so safety in routine clinical practice is often unclear.
To examine this, the researchers identified health insurance claims data from 96,128 individuals (from Optum, IBM MarketScan, and Medicare databases) who were 18 years or older (65 years or older for Medicare) and had type 2 diabetes and at least one inpatient or two outpatient diagnostic codes for stage 3 or 4 CKD.
Of these patients, 32,192 had a newly filled prescription for an SGLT2 inhibitor (empagliflozin, dapagliflozin, canagliflozin, or ertugliflozin) and 63,936 had a newly filled prescription for a GLP-1 agonist (liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, exenatide, albiglutide, or lixisenatide) between April 2013, when the first SGLT2 inhibitor was available in the United States, and 2021.
The researchers matched 28,847 individuals who were initiated on an SGLT2 inhibitor with an equal number who were initiated on a GLP-1 agonist, based on propensity scores, adjusting for more than 120 baseline characteristics.
Safety outcomes were based on previously identified potential safety signals.
Patients who were initiated on an SGLT2 inhibitor had 1.30-fold, 2.13-fold, and 3.08-fold higher risks of having a nonvertebral fracture, a lower limb amputation, and a genital infection, respectively, compared with patients who were initiated on a GLP-1 agonist, after a mean on-treatment time of 7.5 months,
Risks of DKA, hypovolemia, hypoglycemia, and severe UTI were similar in both groups.
Patients initiated on an SGLT2 inhibitor versus a GLP-1 agonist had a lower risk of AKI (hazard ratio, 0.93) equivalent to 6.75 fewer cases of AKI per 1,000 patients per year.
Patients had higher risks for lower limb amputation, genital infections, and nonvertebral fractures with SGLT2 inhibitors versus GLP-1 agonists across most of the prespecified subgroups by age, sex, cardiovascular disease, heart failure, and use of metformin, insulin, or sulfonylurea, but with wider confidence intervals.
Dr. Fu was supported by a Rubicon grant from the Dutch Research Council and has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Starting therapy with an SGLT2 inhibitor versus a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist was associated with more lower limb amputations, nonvertebral fractures, and genital infections, but these risks need to be balanced against cardiovascular and renoprotective benefits, according to the researchers.
The analysis showed that there would be 2.1 more lower limb amputations, 2.5 more nonvertebral fractures, and 41 more genital infections per 1,000 patients per year among those receiving SGLT2 inhibitors versus an equal number of patients receiving GLP-1 agonists, lead author Edouard Fu, PhD, explained to this news organization in an email.
“On the other hand, we know from the evidence from randomized controlled trials that taking an SGLT2 inhibitor compared with placebo lowers the risk of developing kidney failure,” said Dr. Fu, who is a research fellow in the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“For instance,” he continued, “in the DAPA-CKD clinical trial, dapagliflozin versus placebo led to 29 fewer events per 1,000 patients per year of the composite outcome (50% decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR], kidney failure, cardiovascular or kidney death).”
In the CREDENCE trial, canagliflozin versus placebo led to 18 fewer events per 1,000 person-years for the composite outcome of doubling of serum creatinine, kidney failure, and cardiovascular or kidney death.
And in the EMPA-KIDNEY study, empagliflozin versus placebo led to 21 fewer events per 1,000 person-years for the composite outcome of progression of kidney disease or cardiovascular death.
“Thus, benefits would still outweigh the risks,” Dr. Fu emphasized.
‘Quantifies absolute rate of events among routine care patients’
“The importance of our paper,” he summarized, “is that it quantifies the absolute rate of events among routine care patients and may be used to inform shared decision-making.”
The analysis also found that the risks of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), hypovolemia, hypoglycemia, and severe urinary tract infection (UTI) were similar with SGLT2 inhibitors versus GLP-1 agonists, but the risk of developing acute kidney injury (AKI) was lower with an SGLT2 inhibitor.
“Our study can help inform patient-physician decision-making regarding risks and benefits before prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors in this population” of patients with CKD and diabetes treated in clinical practice, the researchers conclude, “but needs to be interpreted in light of its limitations, including residual confounding, short follow-up time, and the use of diagnosis codes to identify patients with CKD.”
The study was recently published in the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.
Slow uptake, safety concerns
SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended as first-line therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes and CKD who have an eGFR equal to or greater than 20 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and thus are at high risk for cardiovascular disease and kidney disease progression, Dr. Fu and colleagues write.
However, studies report that as few as 6% of patients with CKD and type 2 diabetes are currently prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors in the United States.
This slow uptake of SGLT2 inhibitors among patients with CKD may be partly due to concerns about DKA, fractures, amputations, and urogenital infections observed in clinical trials.
However, such trials are generally underpowered to assess rare adverse events, use monitoring protocols to lower the risk of adverse events, and include a highly selected patient population, and so safety in routine clinical practice is often unclear.
To examine this, the researchers identified health insurance claims data from 96,128 individuals (from Optum, IBM MarketScan, and Medicare databases) who were 18 years or older (65 years or older for Medicare) and had type 2 diabetes and at least one inpatient or two outpatient diagnostic codes for stage 3 or 4 CKD.
Of these patients, 32,192 had a newly filled prescription for an SGLT2 inhibitor (empagliflozin, dapagliflozin, canagliflozin, or ertugliflozin) and 63,936 had a newly filled prescription for a GLP-1 agonist (liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, exenatide, albiglutide, or lixisenatide) between April 2013, when the first SGLT2 inhibitor was available in the United States, and 2021.
The researchers matched 28,847 individuals who were initiated on an SGLT2 inhibitor with an equal number who were initiated on a GLP-1 agonist, based on propensity scores, adjusting for more than 120 baseline characteristics.
Safety outcomes were based on previously identified potential safety signals.
Patients who were initiated on an SGLT2 inhibitor had 1.30-fold, 2.13-fold, and 3.08-fold higher risks of having a nonvertebral fracture, a lower limb amputation, and a genital infection, respectively, compared with patients who were initiated on a GLP-1 agonist, after a mean on-treatment time of 7.5 months,
Risks of DKA, hypovolemia, hypoglycemia, and severe UTI were similar in both groups.
Patients initiated on an SGLT2 inhibitor versus a GLP-1 agonist had a lower risk of AKI (hazard ratio, 0.93) equivalent to 6.75 fewer cases of AKI per 1,000 patients per year.
Patients had higher risks for lower limb amputation, genital infections, and nonvertebral fractures with SGLT2 inhibitors versus GLP-1 agonists across most of the prespecified subgroups by age, sex, cardiovascular disease, heart failure, and use of metformin, insulin, or sulfonylurea, but with wider confidence intervals.
Dr. Fu was supported by a Rubicon grant from the Dutch Research Council and has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Starting therapy with an SGLT2 inhibitor versus a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist was associated with more lower limb amputations, nonvertebral fractures, and genital infections, but these risks need to be balanced against cardiovascular and renoprotective benefits, according to the researchers.
The analysis showed that there would be 2.1 more lower limb amputations, 2.5 more nonvertebral fractures, and 41 more genital infections per 1,000 patients per year among those receiving SGLT2 inhibitors versus an equal number of patients receiving GLP-1 agonists, lead author Edouard Fu, PhD, explained to this news organization in an email.
“On the other hand, we know from the evidence from randomized controlled trials that taking an SGLT2 inhibitor compared with placebo lowers the risk of developing kidney failure,” said Dr. Fu, who is a research fellow in the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“For instance,” he continued, “in the DAPA-CKD clinical trial, dapagliflozin versus placebo led to 29 fewer events per 1,000 patients per year of the composite outcome (50% decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR], kidney failure, cardiovascular or kidney death).”
In the CREDENCE trial, canagliflozin versus placebo led to 18 fewer events per 1,000 person-years for the composite outcome of doubling of serum creatinine, kidney failure, and cardiovascular or kidney death.
And in the EMPA-KIDNEY study, empagliflozin versus placebo led to 21 fewer events per 1,000 person-years for the composite outcome of progression of kidney disease or cardiovascular death.
“Thus, benefits would still outweigh the risks,” Dr. Fu emphasized.
‘Quantifies absolute rate of events among routine care patients’
“The importance of our paper,” he summarized, “is that it quantifies the absolute rate of events among routine care patients and may be used to inform shared decision-making.”
The analysis also found that the risks of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), hypovolemia, hypoglycemia, and severe urinary tract infection (UTI) were similar with SGLT2 inhibitors versus GLP-1 agonists, but the risk of developing acute kidney injury (AKI) was lower with an SGLT2 inhibitor.
“Our study can help inform patient-physician decision-making regarding risks and benefits before prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors in this population” of patients with CKD and diabetes treated in clinical practice, the researchers conclude, “but needs to be interpreted in light of its limitations, including residual confounding, short follow-up time, and the use of diagnosis codes to identify patients with CKD.”
The study was recently published in the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.
Slow uptake, safety concerns
SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended as first-line therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes and CKD who have an eGFR equal to or greater than 20 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and thus are at high risk for cardiovascular disease and kidney disease progression, Dr. Fu and colleagues write.
However, studies report that as few as 6% of patients with CKD and type 2 diabetes are currently prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors in the United States.
This slow uptake of SGLT2 inhibitors among patients with CKD may be partly due to concerns about DKA, fractures, amputations, and urogenital infections observed in clinical trials.
However, such trials are generally underpowered to assess rare adverse events, use monitoring protocols to lower the risk of adverse events, and include a highly selected patient population, and so safety in routine clinical practice is often unclear.
To examine this, the researchers identified health insurance claims data from 96,128 individuals (from Optum, IBM MarketScan, and Medicare databases) who were 18 years or older (65 years or older for Medicare) and had type 2 diabetes and at least one inpatient or two outpatient diagnostic codes for stage 3 or 4 CKD.
Of these patients, 32,192 had a newly filled prescription for an SGLT2 inhibitor (empagliflozin, dapagliflozin, canagliflozin, or ertugliflozin) and 63,936 had a newly filled prescription for a GLP-1 agonist (liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, exenatide, albiglutide, or lixisenatide) between April 2013, when the first SGLT2 inhibitor was available in the United States, and 2021.
The researchers matched 28,847 individuals who were initiated on an SGLT2 inhibitor with an equal number who were initiated on a GLP-1 agonist, based on propensity scores, adjusting for more than 120 baseline characteristics.
Safety outcomes were based on previously identified potential safety signals.
Patients who were initiated on an SGLT2 inhibitor had 1.30-fold, 2.13-fold, and 3.08-fold higher risks of having a nonvertebral fracture, a lower limb amputation, and a genital infection, respectively, compared with patients who were initiated on a GLP-1 agonist, after a mean on-treatment time of 7.5 months,
Risks of DKA, hypovolemia, hypoglycemia, and severe UTI were similar in both groups.
Patients initiated on an SGLT2 inhibitor versus a GLP-1 agonist had a lower risk of AKI (hazard ratio, 0.93) equivalent to 6.75 fewer cases of AKI per 1,000 patients per year.
Patients had higher risks for lower limb amputation, genital infections, and nonvertebral fractures with SGLT2 inhibitors versus GLP-1 agonists across most of the prespecified subgroups by age, sex, cardiovascular disease, heart failure, and use of metformin, insulin, or sulfonylurea, but with wider confidence intervals.
Dr. Fu was supported by a Rubicon grant from the Dutch Research Council and has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.