User login
Chronicling gastroenterology’s history
Each May, the gastroenterology community gathers for Digestive Disease Week® to be inspired, meet up with friends and colleagues from across the globe, and learn the latest in scientific advances to inform how we care for our patients in the clinic, on inpatient wards, and in our endoscopy suites. DDW® 2023, held in the Windy City of Chicago, does not disappoint. This year’s conference features a dizzying array of offerings, including 3,500 poster and ePoster presentations and 1,300 abstract lectures, as well as the perennially well-attended AGA Post-Graduate Course and other offerings.
This year’s AGA Presidential Plenary, hosted on May 8 by outgoing AGA President Dr. John M. Carethers, is not to be missed. The session will honor the 125-year history of the AGA and recognizes the barriers overcome in diversifying the practice of gastroenterology. You will learn about individuals such as Alexis St. Martin, MD; Basil Hirschowitz, MD, AGAF; Leonidas Berry, MD; Sadye Curry, MD; and, other barrier-breakers in GI who have been instrumental in shaping the modern practice of gastroenterology. I hope you will join me in attending.
In this month’s issue of GIHN, we introduce the winner of the 2023 AGA Shark Tank innovation competition, which was held during the 2023 AGA Tech Summit. We also report on a landmark phase 4, double-blind randomized trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine demonstrating the effectiveness of vedolizumab in inducing remission in chronic pouchitis, and a new AGA clinical practice update on the role of EUS-guided gallbladder drainage in acute cholecystitis.
The AGA Government Affairs Committee also updates us on their advocacy to reform prior authorization policies affecting GI practice, and explains how you can assist in these efforts. In our Member Spotlight, we introduce you to gastroenterologist Sharmila Anandasabapthy, MD, who shares her passion for global health and the one piece of career advice she’s glad she ignored.
Finally, GIHN Associate Editor Dr. Avi Ketwaroo presents our quarterly Perspectives column highlighting differing approaches to clinical management of pancreatic cystic lesions. We hope you enjoy all of the exciting content featured in this issue and look forward to seeing you in Chicago (or, virtually) for DDW.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Each May, the gastroenterology community gathers for Digestive Disease Week® to be inspired, meet up with friends and colleagues from across the globe, and learn the latest in scientific advances to inform how we care for our patients in the clinic, on inpatient wards, and in our endoscopy suites. DDW® 2023, held in the Windy City of Chicago, does not disappoint. This year’s conference features a dizzying array of offerings, including 3,500 poster and ePoster presentations and 1,300 abstract lectures, as well as the perennially well-attended AGA Post-Graduate Course and other offerings.
This year’s AGA Presidential Plenary, hosted on May 8 by outgoing AGA President Dr. John M. Carethers, is not to be missed. The session will honor the 125-year history of the AGA and recognizes the barriers overcome in diversifying the practice of gastroenterology. You will learn about individuals such as Alexis St. Martin, MD; Basil Hirschowitz, MD, AGAF; Leonidas Berry, MD; Sadye Curry, MD; and, other barrier-breakers in GI who have been instrumental in shaping the modern practice of gastroenterology. I hope you will join me in attending.
In this month’s issue of GIHN, we introduce the winner of the 2023 AGA Shark Tank innovation competition, which was held during the 2023 AGA Tech Summit. We also report on a landmark phase 4, double-blind randomized trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine demonstrating the effectiveness of vedolizumab in inducing remission in chronic pouchitis, and a new AGA clinical practice update on the role of EUS-guided gallbladder drainage in acute cholecystitis.
The AGA Government Affairs Committee also updates us on their advocacy to reform prior authorization policies affecting GI practice, and explains how you can assist in these efforts. In our Member Spotlight, we introduce you to gastroenterologist Sharmila Anandasabapthy, MD, who shares her passion for global health and the one piece of career advice she’s glad she ignored.
Finally, GIHN Associate Editor Dr. Avi Ketwaroo presents our quarterly Perspectives column highlighting differing approaches to clinical management of pancreatic cystic lesions. We hope you enjoy all of the exciting content featured in this issue and look forward to seeing you in Chicago (or, virtually) for DDW.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Each May, the gastroenterology community gathers for Digestive Disease Week® to be inspired, meet up with friends and colleagues from across the globe, and learn the latest in scientific advances to inform how we care for our patients in the clinic, on inpatient wards, and in our endoscopy suites. DDW® 2023, held in the Windy City of Chicago, does not disappoint. This year’s conference features a dizzying array of offerings, including 3,500 poster and ePoster presentations and 1,300 abstract lectures, as well as the perennially well-attended AGA Post-Graduate Course and other offerings.
This year’s AGA Presidential Plenary, hosted on May 8 by outgoing AGA President Dr. John M. Carethers, is not to be missed. The session will honor the 125-year history of the AGA and recognizes the barriers overcome in diversifying the practice of gastroenterology. You will learn about individuals such as Alexis St. Martin, MD; Basil Hirschowitz, MD, AGAF; Leonidas Berry, MD; Sadye Curry, MD; and, other barrier-breakers in GI who have been instrumental in shaping the modern practice of gastroenterology. I hope you will join me in attending.
In this month’s issue of GIHN, we introduce the winner of the 2023 AGA Shark Tank innovation competition, which was held during the 2023 AGA Tech Summit. We also report on a landmark phase 4, double-blind randomized trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine demonstrating the effectiveness of vedolizumab in inducing remission in chronic pouchitis, and a new AGA clinical practice update on the role of EUS-guided gallbladder drainage in acute cholecystitis.
The AGA Government Affairs Committee also updates us on their advocacy to reform prior authorization policies affecting GI practice, and explains how you can assist in these efforts. In our Member Spotlight, we introduce you to gastroenterologist Sharmila Anandasabapthy, MD, who shares her passion for global health and the one piece of career advice she’s glad she ignored.
Finally, GIHN Associate Editor Dr. Avi Ketwaroo presents our quarterly Perspectives column highlighting differing approaches to clinical management of pancreatic cystic lesions. We hope you enjoy all of the exciting content featured in this issue and look forward to seeing you in Chicago (or, virtually) for DDW.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Pancreas cysts – What’s the best approach?
Dear colleagues,
Pancreas cysts have become almost ubiquitous in this era of high-resolution cross-sectional imaging. They are a common GI consult with patients and providers worried about the potential risk of malignant transformation. Despite significant research over the past few decades, predicting the natural history of these cysts, especially the side-branch intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs), remains difficult. There have been a variety of expert recommendations and guidelines, but heterogeneity exists in management especially regarding timing of endoscopic ultrasound, imaging surveillance, and cessation of surveillance. Some centers will present these cysts at multidisciplinary conferences, while others will follow general or local algorithms. In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Lauren G. Khanna, assistant professor of medicine at NYU Langone Health, New York, and Dr. Santhi Vege, professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., present updated and differing approaches to managing these cysts. Which side of the debate are you on? We welcome your thoughts, questions and input– share with us on Twitter @AGA_GIHN
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and chief of endoscopy at West Haven (Conn.) VA Medical Center. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Continuing pancreas cyst surveillance indefinitely is reasonable
BY LAUREN G. KHANNA, MD, MS
Pancreas cysts remain a clinical challenge. The true incidence of pancreas cysts is unknown, but from MRI and autopsy series, may be up to 50%. Patients presenting with a pancreas cyst often have significant anxiety about their risk of pancreas cancer. We as a medical community initially did too; but over the past few decades as we have gathered more data, we have become more comfortable observing many pancreas cysts. Yet our recommendations for how, how often, and for how long to evaluate pancreas cysts are still very much under debate; there are multiple guidelines with discordant recommendations. In this article, I will discuss my approach to patients with a pancreas cyst.
At the first evaluation, I review available imaging to see if there are characteristic features to determine the type of pancreas cyst: IPMN (including main duct, branch duct, or mixed type), serous cystic neoplasm (SCA), mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN), solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (SPN), cystic neuroendocrine tumor (NET), or pseudocyst. I also review symptoms, including abdominal pain, weight loss, history of pancreatitis, and onset of diabetes, and check hemoglobin A1c and Ca19-9. I often recommend magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) if it has not already been obtained and is feasible (that is, if a patient does not have severe claustrophobia or a medical device incompatible with MRI). If a patient is not a candidate for treatment should a pancreatic malignancy be identified, because of age, comorbidities, or preference, I recommend no further evaluation.
Where cyst type remains unclear despite MRCP, and for cysts over 2 cm, I recommend endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) for fluid sampling to assist in determining cyst type and to rule out any other high-risk features. In accordance with international guidelines, if a patient has any concerning imaging features, including main pancreatic duct dilation >5 mm, solid component or mural nodule, or thickened or enhancing duct walls, regardless of cyst size, I recommend EUS to assess for and biopsy any solid component and to sample cyst fluid to examine for dysplasia. Given the lower sensitivity of CT for high-risk features, if MRCP is not feasible, for cysts 1-2 cm, I recommend EUS for better evaluation.
If a cyst is determined to be a cystic NET; main duct or mixed-type IPMN; MCN; or SPN; or a branch duct IPMN with mural nodule, high-grade dysplasia, or adenocarcinoma, and the patient is a surgical candidate, I refer the patient for surgical evaluation. If a cyst is determined to be an SCA, the malignant potential is minimal, and patients do not require follow-up. Patients with a pseudocyst are managed according to their clinical scenario.
Many patients have a proven or suspected branch duct IPMN, an indeterminate cyst, or multiple cysts. Cyst management during surveillance is then determined by the size of the largest cyst and stability of the cyst(s). Of note, patients with an IPMN also have been shown to have an elevated risk of concurrent pancreas adenocarcinoma, which I believe is one of the strongest arguments for heightened surveillance of the entire pancreas in pancreas cyst patients. EUS in particular can identify small or subtle lesions that are not detected by cross-sectional imaging.
If a patient has no prior imaging, in accordance with international and European guidelines, I recommend the first surveillance MRCP at a 6-month interval for cysts <2 cm, which may offer the opportunity to identify rapidly progressing cysts. If a patient has previous imaging available demonstrating stability, I recommend surveillance on an annual basis for cysts <2 cm. For patients with a cyst >2 cm, as above, I recommend EUS, and if there are no concerning features on imaging or EUS, I then recommend annual surveillance.
While the patient is under surveillance, if there is more than minimal cyst growth, a change in cyst appearance, or development of any imaging high-risk feature, pancreatitis, new onset or worsening diabetes, or elevation of Ca19-9, I recommend EUS for further evaluation and consideration of surgery based on EUS findings. If an asymptomatic cyst <2 cm remains stable for 5 years, I offer patients the option to extend imaging to every 2 years, if they are comfortable. In my experience, though, many patients prefer to continue annual imaging. The American Gastroenterological Association guidelines promote stopping surveillance after 5 years of stability, however there are studies demonstrating development of malignancy in cysts that were initially stable over the first 5 years of surveillance. Therefore, I discuss with patients that it is reasonable to continue cyst surveillance indefinitely, until they would no longer be interested in pursuing treatment of any kind if a malignant lesion were to be identified.
There are two special groups of pancreas cyst patients who warrant specific attention. Patients who are at elevated risk of pancreas adenocarcinoma because of an associated genetic mutation or a family history of pancreatic cancer already may be undergoing annual pancreas cancer screening with either MRCP, EUS, or alternating MRCP and EUS. When these high-risk patients also have pancreas cysts, I utilize whichever strategy would image their pancreas most frequently and do not extend beyond 1-year intervals. Another special group is patients who have undergone partial pancreatectomy for IPMN. As discussed above, given the elevated risk of concurrent pancreas adenocarcinoma in IPMN patients, I recommend indefinite continued surveillance of the remaining pancreas parenchyma in these patients.
Given the prevalence of pancreas cysts, it certainly would be convenient if guidelines were straightforward enough for primary care physicians to manage pancreas cyst surveillance, as they do for breast cancer screening. However, the complexities of pancreas cysts necessitate the expertise of gastroenterologists and pancreas surgeons, and a multidisciplinary team approach is best where possible.
Dr. Khanna is chief, advanced endoscopy, Tisch Hospital; director, NYU Advanced Endoscopy Fellowship; assistant professor of medicine, NYU Langone Health. Email: [email protected]. There are no relevant conflicts to disclose.
References
Tanaka M et al. Pancreatology. 2017 Sep-Oct;17(5):738-75.
Sahora K et al. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016 Feb;42(2):197-204.
Del Chiaro M et al. Gut. 2018 May;67(5):789-804
Vege SS et al. Gastroenterology. 2015 Apr;148(4):819-22
Petrone MC et al. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018 Jun 13;9(6):158
Pancreas cysts: More is not necessarily better!
BY SANTHI SWAROOP VEGE, MD
Pancreas cysts (PC) are very common, incidental findings on cross-sectional imaging, performed for non–pancreas-related symptoms. The important issues in management of patients with PC in my practice are the prevalence, natural history, frequency of occurrence of high-grade dysplasia (HGD) and/or pancreatic cancer (PDAC), concerning clinical symptoms and imaging findings, indications for EUS and fine-needle aspiration cytology, ideal method and frequency of surveillance, indications for surgery (up front and during follow-up), follow-up after surgery, stopping surveillance, costs, and unintentional harms of management. Good population-based evidence regarding many of the issues described above does not exist, and all information is from selected clinic, radiology, EUS, and surgical cohorts (very important when trying to assess the publications). Cohort studies should start with all PC undergoing surveillance and assess various outcomes, rather than looking backward from EUS or surgical cohorts.
The 2015 American Gastroenterological Association guidelines on asymptomatic neoplastic pancreas cysts, which I coauthored, recommend, consistent with principles of High Value Care (minimal unintentional harms and cost effectiveness), that two of three high-risk features (mural nodule, cyst size greater than 3 cm, and dilated pancreatic duct) be present for EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA). By the same token, they advise surgery for those with two of three high-risk features and or concerning features on EUS and cytology. Finally, they suggest stopping surveillance at 5 years if there are no significant changes. Rigorous GRADE methodology along with systematic review of all relevant questions (rather than cohorts of 500 or fewer patients) formed the basis of the guidelines. Those meta-analyses showed that risk of PDAC in mural nodules, cyst size >3 cm, and dilated pancreatic duct, while elevated, still is very low in absolute terms. Less than 20% of resections for highly selected, high-risk cysts showed PDAC. The guidelines were met with a lot of resistance from several societies and physician groups. The recommendations for stopping surveillance after 5 years and no surveillance for absent or low-grade dysplasia after surgery are hotly contested, and these areas need larger, long-term studies.
The whole area of cyst fluid molecular markers that would suggest mucinous type (KRAS and GNAS mutations) and, more importantly, the presence or imminent development of PDAC (next-generation sequencing or NGS) is an exciting field. One sincerely hopes that there will be a breakthrough in this area to achieve the holy grail. Cost effectiveness studies demonstrate the futility of existing guidelines and favor a less intensive approach. Guidelines are only a general framework, and management of individual patients in the clinic is entirely at the discretion of the treating physician. One should make every attempt to detect advanced lesions in PC, but such effort should not subject a large majority of patients to unintentional harms by overtreatment and add further to the burgeoning health care costs in the country.
PC are extremely common (10% of all abdominal imaging), increase with age, are seen in as many as 40%-50% of MRI examinations for nonpancreatic indications, and most (>50%) are IPMNs. Most of the debate centers around the concerns of PDAC and/or HGD associated with mucinous cysts (MCN, IPMN, side-branch, main duct, or mixed).
The various guidelines by multiple societies differ in some aspects, such as in selection of patients based on clinical, laboratory, and imaging findings for up-front surgery or surveillance, the frequency of surveillance based on the size of the cyst and the presence of other concerning cyst features (usually with MRCP), the indications for EUS (both initial and subsequent), importance of the magnitude of growth (most IPMNs slowly grow over a period of time), indications for surgery during surveillance and postsurgery surveillance, and the decision to stop surveillance at some point in time. The literature is replete with small case series reporting a proportion of cancers detected and often ignoring the harms of surgery. Incidence of and mortality caused by PDAC are very low (about 1% for both) in a large national cohort of VA pancreatic cyst patients with long-term follow-up and other studies.
Marcov modeling suggests that none of the guidelines would lead to cost-effective care with low mortality because of overtreatment of low-risk lesions, and a specificity of 67% or more for PDAC/HGB is required. AGA guidelines came close to it but with low sensitivity. Monte Carlo modeling suggests that less intensive strategies, compared with more intensive, result in a similar number of deaths at a much lower cost. While molecular markers in PC fluid are reported to increase the specificity of PDAC/HGD to greater than 70%, it should be observed that such validation was done in a small percentage of patients who had both those markers and resection.
The costs of expensive procedures like EUS, MRI, and surgery, the 3% complication rate with EUS-FNA (primarily acute pancreatitis), and the 1% mortality and approximately 20%-30% morbidity with surgery (bleeding, infection, fistula) and postpancreatectomy diabetes of approximately 30% in the long run need special attention.
In conclusion, one could say pancreas cysts are extremely frequent, most of the neoplastic cysts are mucinous (IPMN and MCN) and slowly growing over time without an associated cancer, and the greatest need at this time is to identify the small proportion of such cysts with PDAC and/or HGD. Until such time, judicious selection of patients for surveillance and reasonable intervals of such surveillance with selective use of EUS will help identify patients requiring resection. In our enthusiasm to detect every possible pancreatic cancer, we should not ignore the unintentional outcomes of surgery to a large majority of patients who would never develop PDAC and the astronomical costs associated with such practice.
Dr. Vege is professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic. He reported having no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
Vege SS et al. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:819-22.
Lobo JM et al. Surgery. 2020;168:601-9.
Lennon AM and Vege SS. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:1663-7.
Harris RP. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:787-9.
Dear colleagues,
Pancreas cysts have become almost ubiquitous in this era of high-resolution cross-sectional imaging. They are a common GI consult with patients and providers worried about the potential risk of malignant transformation. Despite significant research over the past few decades, predicting the natural history of these cysts, especially the side-branch intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs), remains difficult. There have been a variety of expert recommendations and guidelines, but heterogeneity exists in management especially regarding timing of endoscopic ultrasound, imaging surveillance, and cessation of surveillance. Some centers will present these cysts at multidisciplinary conferences, while others will follow general or local algorithms. In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Lauren G. Khanna, assistant professor of medicine at NYU Langone Health, New York, and Dr. Santhi Vege, professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., present updated and differing approaches to managing these cysts. Which side of the debate are you on? We welcome your thoughts, questions and input– share with us on Twitter @AGA_GIHN
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and chief of endoscopy at West Haven (Conn.) VA Medical Center. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Continuing pancreas cyst surveillance indefinitely is reasonable
BY LAUREN G. KHANNA, MD, MS
Pancreas cysts remain a clinical challenge. The true incidence of pancreas cysts is unknown, but from MRI and autopsy series, may be up to 50%. Patients presenting with a pancreas cyst often have significant anxiety about their risk of pancreas cancer. We as a medical community initially did too; but over the past few decades as we have gathered more data, we have become more comfortable observing many pancreas cysts. Yet our recommendations for how, how often, and for how long to evaluate pancreas cysts are still very much under debate; there are multiple guidelines with discordant recommendations. In this article, I will discuss my approach to patients with a pancreas cyst.
At the first evaluation, I review available imaging to see if there are characteristic features to determine the type of pancreas cyst: IPMN (including main duct, branch duct, or mixed type), serous cystic neoplasm (SCA), mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN), solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (SPN), cystic neuroendocrine tumor (NET), or pseudocyst. I also review symptoms, including abdominal pain, weight loss, history of pancreatitis, and onset of diabetes, and check hemoglobin A1c and Ca19-9. I often recommend magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) if it has not already been obtained and is feasible (that is, if a patient does not have severe claustrophobia or a medical device incompatible with MRI). If a patient is not a candidate for treatment should a pancreatic malignancy be identified, because of age, comorbidities, or preference, I recommend no further evaluation.
Where cyst type remains unclear despite MRCP, and for cysts over 2 cm, I recommend endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) for fluid sampling to assist in determining cyst type and to rule out any other high-risk features. In accordance with international guidelines, if a patient has any concerning imaging features, including main pancreatic duct dilation >5 mm, solid component or mural nodule, or thickened or enhancing duct walls, regardless of cyst size, I recommend EUS to assess for and biopsy any solid component and to sample cyst fluid to examine for dysplasia. Given the lower sensitivity of CT for high-risk features, if MRCP is not feasible, for cysts 1-2 cm, I recommend EUS for better evaluation.
If a cyst is determined to be a cystic NET; main duct or mixed-type IPMN; MCN; or SPN; or a branch duct IPMN with mural nodule, high-grade dysplasia, or adenocarcinoma, and the patient is a surgical candidate, I refer the patient for surgical evaluation. If a cyst is determined to be an SCA, the malignant potential is minimal, and patients do not require follow-up. Patients with a pseudocyst are managed according to their clinical scenario.
Many patients have a proven or suspected branch duct IPMN, an indeterminate cyst, or multiple cysts. Cyst management during surveillance is then determined by the size of the largest cyst and stability of the cyst(s). Of note, patients with an IPMN also have been shown to have an elevated risk of concurrent pancreas adenocarcinoma, which I believe is one of the strongest arguments for heightened surveillance of the entire pancreas in pancreas cyst patients. EUS in particular can identify small or subtle lesions that are not detected by cross-sectional imaging.
If a patient has no prior imaging, in accordance with international and European guidelines, I recommend the first surveillance MRCP at a 6-month interval for cysts <2 cm, which may offer the opportunity to identify rapidly progressing cysts. If a patient has previous imaging available demonstrating stability, I recommend surveillance on an annual basis for cysts <2 cm. For patients with a cyst >2 cm, as above, I recommend EUS, and if there are no concerning features on imaging or EUS, I then recommend annual surveillance.
While the patient is under surveillance, if there is more than minimal cyst growth, a change in cyst appearance, or development of any imaging high-risk feature, pancreatitis, new onset or worsening diabetes, or elevation of Ca19-9, I recommend EUS for further evaluation and consideration of surgery based on EUS findings. If an asymptomatic cyst <2 cm remains stable for 5 years, I offer patients the option to extend imaging to every 2 years, if they are comfortable. In my experience, though, many patients prefer to continue annual imaging. The American Gastroenterological Association guidelines promote stopping surveillance after 5 years of stability, however there are studies demonstrating development of malignancy in cysts that were initially stable over the first 5 years of surveillance. Therefore, I discuss with patients that it is reasonable to continue cyst surveillance indefinitely, until they would no longer be interested in pursuing treatment of any kind if a malignant lesion were to be identified.
There are two special groups of pancreas cyst patients who warrant specific attention. Patients who are at elevated risk of pancreas adenocarcinoma because of an associated genetic mutation or a family history of pancreatic cancer already may be undergoing annual pancreas cancer screening with either MRCP, EUS, or alternating MRCP and EUS. When these high-risk patients also have pancreas cysts, I utilize whichever strategy would image their pancreas most frequently and do not extend beyond 1-year intervals. Another special group is patients who have undergone partial pancreatectomy for IPMN. As discussed above, given the elevated risk of concurrent pancreas adenocarcinoma in IPMN patients, I recommend indefinite continued surveillance of the remaining pancreas parenchyma in these patients.
Given the prevalence of pancreas cysts, it certainly would be convenient if guidelines were straightforward enough for primary care physicians to manage pancreas cyst surveillance, as they do for breast cancer screening. However, the complexities of pancreas cysts necessitate the expertise of gastroenterologists and pancreas surgeons, and a multidisciplinary team approach is best where possible.
Dr. Khanna is chief, advanced endoscopy, Tisch Hospital; director, NYU Advanced Endoscopy Fellowship; assistant professor of medicine, NYU Langone Health. Email: [email protected]. There are no relevant conflicts to disclose.
References
Tanaka M et al. Pancreatology. 2017 Sep-Oct;17(5):738-75.
Sahora K et al. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016 Feb;42(2):197-204.
Del Chiaro M et al. Gut. 2018 May;67(5):789-804
Vege SS et al. Gastroenterology. 2015 Apr;148(4):819-22
Petrone MC et al. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018 Jun 13;9(6):158
Pancreas cysts: More is not necessarily better!
BY SANTHI SWAROOP VEGE, MD
Pancreas cysts (PC) are very common, incidental findings on cross-sectional imaging, performed for non–pancreas-related symptoms. The important issues in management of patients with PC in my practice are the prevalence, natural history, frequency of occurrence of high-grade dysplasia (HGD) and/or pancreatic cancer (PDAC), concerning clinical symptoms and imaging findings, indications for EUS and fine-needle aspiration cytology, ideal method and frequency of surveillance, indications for surgery (up front and during follow-up), follow-up after surgery, stopping surveillance, costs, and unintentional harms of management. Good population-based evidence regarding many of the issues described above does not exist, and all information is from selected clinic, radiology, EUS, and surgical cohorts (very important when trying to assess the publications). Cohort studies should start with all PC undergoing surveillance and assess various outcomes, rather than looking backward from EUS or surgical cohorts.
The 2015 American Gastroenterological Association guidelines on asymptomatic neoplastic pancreas cysts, which I coauthored, recommend, consistent with principles of High Value Care (minimal unintentional harms and cost effectiveness), that two of three high-risk features (mural nodule, cyst size greater than 3 cm, and dilated pancreatic duct) be present for EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA). By the same token, they advise surgery for those with two of three high-risk features and or concerning features on EUS and cytology. Finally, they suggest stopping surveillance at 5 years if there are no significant changes. Rigorous GRADE methodology along with systematic review of all relevant questions (rather than cohorts of 500 or fewer patients) formed the basis of the guidelines. Those meta-analyses showed that risk of PDAC in mural nodules, cyst size >3 cm, and dilated pancreatic duct, while elevated, still is very low in absolute terms. Less than 20% of resections for highly selected, high-risk cysts showed PDAC. The guidelines were met with a lot of resistance from several societies and physician groups. The recommendations for stopping surveillance after 5 years and no surveillance for absent or low-grade dysplasia after surgery are hotly contested, and these areas need larger, long-term studies.
The whole area of cyst fluid molecular markers that would suggest mucinous type (KRAS and GNAS mutations) and, more importantly, the presence or imminent development of PDAC (next-generation sequencing or NGS) is an exciting field. One sincerely hopes that there will be a breakthrough in this area to achieve the holy grail. Cost effectiveness studies demonstrate the futility of existing guidelines and favor a less intensive approach. Guidelines are only a general framework, and management of individual patients in the clinic is entirely at the discretion of the treating physician. One should make every attempt to detect advanced lesions in PC, but such effort should not subject a large majority of patients to unintentional harms by overtreatment and add further to the burgeoning health care costs in the country.
PC are extremely common (10% of all abdominal imaging), increase with age, are seen in as many as 40%-50% of MRI examinations for nonpancreatic indications, and most (>50%) are IPMNs. Most of the debate centers around the concerns of PDAC and/or HGD associated with mucinous cysts (MCN, IPMN, side-branch, main duct, or mixed).
The various guidelines by multiple societies differ in some aspects, such as in selection of patients based on clinical, laboratory, and imaging findings for up-front surgery or surveillance, the frequency of surveillance based on the size of the cyst and the presence of other concerning cyst features (usually with MRCP), the indications for EUS (both initial and subsequent), importance of the magnitude of growth (most IPMNs slowly grow over a period of time), indications for surgery during surveillance and postsurgery surveillance, and the decision to stop surveillance at some point in time. The literature is replete with small case series reporting a proportion of cancers detected and often ignoring the harms of surgery. Incidence of and mortality caused by PDAC are very low (about 1% for both) in a large national cohort of VA pancreatic cyst patients with long-term follow-up and other studies.
Marcov modeling suggests that none of the guidelines would lead to cost-effective care with low mortality because of overtreatment of low-risk lesions, and a specificity of 67% or more for PDAC/HGB is required. AGA guidelines came close to it but with low sensitivity. Monte Carlo modeling suggests that less intensive strategies, compared with more intensive, result in a similar number of deaths at a much lower cost. While molecular markers in PC fluid are reported to increase the specificity of PDAC/HGD to greater than 70%, it should be observed that such validation was done in a small percentage of patients who had both those markers and resection.
The costs of expensive procedures like EUS, MRI, and surgery, the 3% complication rate with EUS-FNA (primarily acute pancreatitis), and the 1% mortality and approximately 20%-30% morbidity with surgery (bleeding, infection, fistula) and postpancreatectomy diabetes of approximately 30% in the long run need special attention.
In conclusion, one could say pancreas cysts are extremely frequent, most of the neoplastic cysts are mucinous (IPMN and MCN) and slowly growing over time without an associated cancer, and the greatest need at this time is to identify the small proportion of such cysts with PDAC and/or HGD. Until such time, judicious selection of patients for surveillance and reasonable intervals of such surveillance with selective use of EUS will help identify patients requiring resection. In our enthusiasm to detect every possible pancreatic cancer, we should not ignore the unintentional outcomes of surgery to a large majority of patients who would never develop PDAC and the astronomical costs associated with such practice.
Dr. Vege is professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic. He reported having no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
Vege SS et al. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:819-22.
Lobo JM et al. Surgery. 2020;168:601-9.
Lennon AM and Vege SS. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:1663-7.
Harris RP. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:787-9.
Dear colleagues,
Pancreas cysts have become almost ubiquitous in this era of high-resolution cross-sectional imaging. They are a common GI consult with patients and providers worried about the potential risk of malignant transformation. Despite significant research over the past few decades, predicting the natural history of these cysts, especially the side-branch intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs), remains difficult. There have been a variety of expert recommendations and guidelines, but heterogeneity exists in management especially regarding timing of endoscopic ultrasound, imaging surveillance, and cessation of surveillance. Some centers will present these cysts at multidisciplinary conferences, while others will follow general or local algorithms. In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Lauren G. Khanna, assistant professor of medicine at NYU Langone Health, New York, and Dr. Santhi Vege, professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., present updated and differing approaches to managing these cysts. Which side of the debate are you on? We welcome your thoughts, questions and input– share with us on Twitter @AGA_GIHN
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and chief of endoscopy at West Haven (Conn.) VA Medical Center. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Continuing pancreas cyst surveillance indefinitely is reasonable
BY LAUREN G. KHANNA, MD, MS
Pancreas cysts remain a clinical challenge. The true incidence of pancreas cysts is unknown, but from MRI and autopsy series, may be up to 50%. Patients presenting with a pancreas cyst often have significant anxiety about their risk of pancreas cancer. We as a medical community initially did too; but over the past few decades as we have gathered more data, we have become more comfortable observing many pancreas cysts. Yet our recommendations for how, how often, and for how long to evaluate pancreas cysts are still very much under debate; there are multiple guidelines with discordant recommendations. In this article, I will discuss my approach to patients with a pancreas cyst.
At the first evaluation, I review available imaging to see if there are characteristic features to determine the type of pancreas cyst: IPMN (including main duct, branch duct, or mixed type), serous cystic neoplasm (SCA), mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN), solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (SPN), cystic neuroendocrine tumor (NET), or pseudocyst. I also review symptoms, including abdominal pain, weight loss, history of pancreatitis, and onset of diabetes, and check hemoglobin A1c and Ca19-9. I often recommend magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) if it has not already been obtained and is feasible (that is, if a patient does not have severe claustrophobia or a medical device incompatible with MRI). If a patient is not a candidate for treatment should a pancreatic malignancy be identified, because of age, comorbidities, or preference, I recommend no further evaluation.
Where cyst type remains unclear despite MRCP, and for cysts over 2 cm, I recommend endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) for fluid sampling to assist in determining cyst type and to rule out any other high-risk features. In accordance with international guidelines, if a patient has any concerning imaging features, including main pancreatic duct dilation >5 mm, solid component or mural nodule, or thickened or enhancing duct walls, regardless of cyst size, I recommend EUS to assess for and biopsy any solid component and to sample cyst fluid to examine for dysplasia. Given the lower sensitivity of CT for high-risk features, if MRCP is not feasible, for cysts 1-2 cm, I recommend EUS for better evaluation.
If a cyst is determined to be a cystic NET; main duct or mixed-type IPMN; MCN; or SPN; or a branch duct IPMN with mural nodule, high-grade dysplasia, or adenocarcinoma, and the patient is a surgical candidate, I refer the patient for surgical evaluation. If a cyst is determined to be an SCA, the malignant potential is minimal, and patients do not require follow-up. Patients with a pseudocyst are managed according to their clinical scenario.
Many patients have a proven or suspected branch duct IPMN, an indeterminate cyst, or multiple cysts. Cyst management during surveillance is then determined by the size of the largest cyst and stability of the cyst(s). Of note, patients with an IPMN also have been shown to have an elevated risk of concurrent pancreas adenocarcinoma, which I believe is one of the strongest arguments for heightened surveillance of the entire pancreas in pancreas cyst patients. EUS in particular can identify small or subtle lesions that are not detected by cross-sectional imaging.
If a patient has no prior imaging, in accordance with international and European guidelines, I recommend the first surveillance MRCP at a 6-month interval for cysts <2 cm, which may offer the opportunity to identify rapidly progressing cysts. If a patient has previous imaging available demonstrating stability, I recommend surveillance on an annual basis for cysts <2 cm. For patients with a cyst >2 cm, as above, I recommend EUS, and if there are no concerning features on imaging or EUS, I then recommend annual surveillance.
While the patient is under surveillance, if there is more than minimal cyst growth, a change in cyst appearance, or development of any imaging high-risk feature, pancreatitis, new onset or worsening diabetes, or elevation of Ca19-9, I recommend EUS for further evaluation and consideration of surgery based on EUS findings. If an asymptomatic cyst <2 cm remains stable for 5 years, I offer patients the option to extend imaging to every 2 years, if they are comfortable. In my experience, though, many patients prefer to continue annual imaging. The American Gastroenterological Association guidelines promote stopping surveillance after 5 years of stability, however there are studies demonstrating development of malignancy in cysts that were initially stable over the first 5 years of surveillance. Therefore, I discuss with patients that it is reasonable to continue cyst surveillance indefinitely, until they would no longer be interested in pursuing treatment of any kind if a malignant lesion were to be identified.
There are two special groups of pancreas cyst patients who warrant specific attention. Patients who are at elevated risk of pancreas adenocarcinoma because of an associated genetic mutation or a family history of pancreatic cancer already may be undergoing annual pancreas cancer screening with either MRCP, EUS, or alternating MRCP and EUS. When these high-risk patients also have pancreas cysts, I utilize whichever strategy would image their pancreas most frequently and do not extend beyond 1-year intervals. Another special group is patients who have undergone partial pancreatectomy for IPMN. As discussed above, given the elevated risk of concurrent pancreas adenocarcinoma in IPMN patients, I recommend indefinite continued surveillance of the remaining pancreas parenchyma in these patients.
Given the prevalence of pancreas cysts, it certainly would be convenient if guidelines were straightforward enough for primary care physicians to manage pancreas cyst surveillance, as they do for breast cancer screening. However, the complexities of pancreas cysts necessitate the expertise of gastroenterologists and pancreas surgeons, and a multidisciplinary team approach is best where possible.
Dr. Khanna is chief, advanced endoscopy, Tisch Hospital; director, NYU Advanced Endoscopy Fellowship; assistant professor of medicine, NYU Langone Health. Email: [email protected]. There are no relevant conflicts to disclose.
References
Tanaka M et al. Pancreatology. 2017 Sep-Oct;17(5):738-75.
Sahora K et al. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016 Feb;42(2):197-204.
Del Chiaro M et al. Gut. 2018 May;67(5):789-804
Vege SS et al. Gastroenterology. 2015 Apr;148(4):819-22
Petrone MC et al. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018 Jun 13;9(6):158
Pancreas cysts: More is not necessarily better!
BY SANTHI SWAROOP VEGE, MD
Pancreas cysts (PC) are very common, incidental findings on cross-sectional imaging, performed for non–pancreas-related symptoms. The important issues in management of patients with PC in my practice are the prevalence, natural history, frequency of occurrence of high-grade dysplasia (HGD) and/or pancreatic cancer (PDAC), concerning clinical symptoms and imaging findings, indications for EUS and fine-needle aspiration cytology, ideal method and frequency of surveillance, indications for surgery (up front and during follow-up), follow-up after surgery, stopping surveillance, costs, and unintentional harms of management. Good population-based evidence regarding many of the issues described above does not exist, and all information is from selected clinic, radiology, EUS, and surgical cohorts (very important when trying to assess the publications). Cohort studies should start with all PC undergoing surveillance and assess various outcomes, rather than looking backward from EUS or surgical cohorts.
The 2015 American Gastroenterological Association guidelines on asymptomatic neoplastic pancreas cysts, which I coauthored, recommend, consistent with principles of High Value Care (minimal unintentional harms and cost effectiveness), that two of three high-risk features (mural nodule, cyst size greater than 3 cm, and dilated pancreatic duct) be present for EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA). By the same token, they advise surgery for those with two of three high-risk features and or concerning features on EUS and cytology. Finally, they suggest stopping surveillance at 5 years if there are no significant changes. Rigorous GRADE methodology along with systematic review of all relevant questions (rather than cohorts of 500 or fewer patients) formed the basis of the guidelines. Those meta-analyses showed that risk of PDAC in mural nodules, cyst size >3 cm, and dilated pancreatic duct, while elevated, still is very low in absolute terms. Less than 20% of resections for highly selected, high-risk cysts showed PDAC. The guidelines were met with a lot of resistance from several societies and physician groups. The recommendations for stopping surveillance after 5 years and no surveillance for absent or low-grade dysplasia after surgery are hotly contested, and these areas need larger, long-term studies.
The whole area of cyst fluid molecular markers that would suggest mucinous type (KRAS and GNAS mutations) and, more importantly, the presence or imminent development of PDAC (next-generation sequencing or NGS) is an exciting field. One sincerely hopes that there will be a breakthrough in this area to achieve the holy grail. Cost effectiveness studies demonstrate the futility of existing guidelines and favor a less intensive approach. Guidelines are only a general framework, and management of individual patients in the clinic is entirely at the discretion of the treating physician. One should make every attempt to detect advanced lesions in PC, but such effort should not subject a large majority of patients to unintentional harms by overtreatment and add further to the burgeoning health care costs in the country.
PC are extremely common (10% of all abdominal imaging), increase with age, are seen in as many as 40%-50% of MRI examinations for nonpancreatic indications, and most (>50%) are IPMNs. Most of the debate centers around the concerns of PDAC and/or HGD associated with mucinous cysts (MCN, IPMN, side-branch, main duct, or mixed).
The various guidelines by multiple societies differ in some aspects, such as in selection of patients based on clinical, laboratory, and imaging findings for up-front surgery or surveillance, the frequency of surveillance based on the size of the cyst and the presence of other concerning cyst features (usually with MRCP), the indications for EUS (both initial and subsequent), importance of the magnitude of growth (most IPMNs slowly grow over a period of time), indications for surgery during surveillance and postsurgery surveillance, and the decision to stop surveillance at some point in time. The literature is replete with small case series reporting a proportion of cancers detected and often ignoring the harms of surgery. Incidence of and mortality caused by PDAC are very low (about 1% for both) in a large national cohort of VA pancreatic cyst patients with long-term follow-up and other studies.
Marcov modeling suggests that none of the guidelines would lead to cost-effective care with low mortality because of overtreatment of low-risk lesions, and a specificity of 67% or more for PDAC/HGB is required. AGA guidelines came close to it but with low sensitivity. Monte Carlo modeling suggests that less intensive strategies, compared with more intensive, result in a similar number of deaths at a much lower cost. While molecular markers in PC fluid are reported to increase the specificity of PDAC/HGD to greater than 70%, it should be observed that such validation was done in a small percentage of patients who had both those markers and resection.
The costs of expensive procedures like EUS, MRI, and surgery, the 3% complication rate with EUS-FNA (primarily acute pancreatitis), and the 1% mortality and approximately 20%-30% morbidity with surgery (bleeding, infection, fistula) and postpancreatectomy diabetes of approximately 30% in the long run need special attention.
In conclusion, one could say pancreas cysts are extremely frequent, most of the neoplastic cysts are mucinous (IPMN and MCN) and slowly growing over time without an associated cancer, and the greatest need at this time is to identify the small proportion of such cysts with PDAC and/or HGD. Until such time, judicious selection of patients for surveillance and reasonable intervals of such surveillance with selective use of EUS will help identify patients requiring resection. In our enthusiasm to detect every possible pancreatic cancer, we should not ignore the unintentional outcomes of surgery to a large majority of patients who would never develop PDAC and the astronomical costs associated with such practice.
Dr. Vege is professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic. He reported having no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
Vege SS et al. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:819-22.
Lobo JM et al. Surgery. 2020;168:601-9.
Lennon AM and Vege SS. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:1663-7.
Harris RP. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:787-9.
Spring reflections
Dear friends,
I celebrate my achievements (both personal and work related), try not to be too hard on myself with unaccomplished tasks, and plan goals for the upcoming year. Most importantly, it’s a time to be grateful for both opportunities and challenges. Thank you for your engagement with The New Gastroenterologist, and as you go through this issue, I hope you can find time for some spring reflections as well!
In this issue’s In Focus, Dr. Tanisha Ronnie, Dr. Lauren Bloomberg, and Dr. Mukund Venu break down the approach to a patient with dysphagia, a common and difficult encounter in GI practice. They emphasize the importance of a good clinical history as well as understanding the role of diagnostic testing. In our Short Clinical Review section, Dr. Noa Krugliak Cleveland and Dr. David Rubin review the rising role of intestinal ultrasound in inflammatory bowel disease, how to be trained, and how to incorporate it in clinical practice.
As early-career gastroenterologists, Dr. Samad Soudagar and Dr. Mohammad Bilal were tasked with establishing an advanced endoscopy practice, which may be overwhelming for many. They synthesized their experiences into 10 practical tips to build a successful practice. Our Post-fellowship Pathways article highlights Dr. Katie Hutchins’s journey from private practice to academic medicine; she provides insights into the life-changing decision and what she learned about herself to make that pivot.
In our Finance section, Dr. Kelly Hathorn and Dr. David Creighton reflect on navigating as new parents while both working full time in medicine; their article weighs the pros and cons of various childcare options in the post–COVID pandemic world.
In an additional contribution this issue, gastroenterology and hepatology fellowship program leaders at the University of Florida, Gainesville, describe their experience with virtual recruitment, including feedback from their candidates, especially as we enter another cycle of GI Match.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Jillian Schweitzer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact, because we would not be where we are without appreciating where we were: The first formalized gastroenterology fellowship curriculum was a joint publication by four major GI and hepatology societies in 1996 – just 27 years ago!
Yours truly,
Judy A Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Advanced Endoscopy Fellow
Division of gastroenterology & hepatology
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Dear friends,
I celebrate my achievements (both personal and work related), try not to be too hard on myself with unaccomplished tasks, and plan goals for the upcoming year. Most importantly, it’s a time to be grateful for both opportunities and challenges. Thank you for your engagement with The New Gastroenterologist, and as you go through this issue, I hope you can find time for some spring reflections as well!
In this issue’s In Focus, Dr. Tanisha Ronnie, Dr. Lauren Bloomberg, and Dr. Mukund Venu break down the approach to a patient with dysphagia, a common and difficult encounter in GI practice. They emphasize the importance of a good clinical history as well as understanding the role of diagnostic testing. In our Short Clinical Review section, Dr. Noa Krugliak Cleveland and Dr. David Rubin review the rising role of intestinal ultrasound in inflammatory bowel disease, how to be trained, and how to incorporate it in clinical practice.
As early-career gastroenterologists, Dr. Samad Soudagar and Dr. Mohammad Bilal were tasked with establishing an advanced endoscopy practice, which may be overwhelming for many. They synthesized their experiences into 10 practical tips to build a successful practice. Our Post-fellowship Pathways article highlights Dr. Katie Hutchins’s journey from private practice to academic medicine; she provides insights into the life-changing decision and what she learned about herself to make that pivot.
In our Finance section, Dr. Kelly Hathorn and Dr. David Creighton reflect on navigating as new parents while both working full time in medicine; their article weighs the pros and cons of various childcare options in the post–COVID pandemic world.
In an additional contribution this issue, gastroenterology and hepatology fellowship program leaders at the University of Florida, Gainesville, describe their experience with virtual recruitment, including feedback from their candidates, especially as we enter another cycle of GI Match.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Jillian Schweitzer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact, because we would not be where we are without appreciating where we were: The first formalized gastroenterology fellowship curriculum was a joint publication by four major GI and hepatology societies in 1996 – just 27 years ago!
Yours truly,
Judy A Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Advanced Endoscopy Fellow
Division of gastroenterology & hepatology
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Dear friends,
I celebrate my achievements (both personal and work related), try not to be too hard on myself with unaccomplished tasks, and plan goals for the upcoming year. Most importantly, it’s a time to be grateful for both opportunities and challenges. Thank you for your engagement with The New Gastroenterologist, and as you go through this issue, I hope you can find time for some spring reflections as well!
In this issue’s In Focus, Dr. Tanisha Ronnie, Dr. Lauren Bloomberg, and Dr. Mukund Venu break down the approach to a patient with dysphagia, a common and difficult encounter in GI practice. They emphasize the importance of a good clinical history as well as understanding the role of diagnostic testing. In our Short Clinical Review section, Dr. Noa Krugliak Cleveland and Dr. David Rubin review the rising role of intestinal ultrasound in inflammatory bowel disease, how to be trained, and how to incorporate it in clinical practice.
As early-career gastroenterologists, Dr. Samad Soudagar and Dr. Mohammad Bilal were tasked with establishing an advanced endoscopy practice, which may be overwhelming for many. They synthesized their experiences into 10 practical tips to build a successful practice. Our Post-fellowship Pathways article highlights Dr. Katie Hutchins’s journey from private practice to academic medicine; she provides insights into the life-changing decision and what she learned about herself to make that pivot.
In our Finance section, Dr. Kelly Hathorn and Dr. David Creighton reflect on navigating as new parents while both working full time in medicine; their article weighs the pros and cons of various childcare options in the post–COVID pandemic world.
In an additional contribution this issue, gastroenterology and hepatology fellowship program leaders at the University of Florida, Gainesville, describe their experience with virtual recruitment, including feedback from their candidates, especially as we enter another cycle of GI Match.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Jillian Schweitzer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact, because we would not be where we are without appreciating where we were: The first formalized gastroenterology fellowship curriculum was a joint publication by four major GI and hepatology societies in 1996 – just 27 years ago!
Yours truly,
Judy A Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Advanced Endoscopy Fellow
Division of gastroenterology & hepatology
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Taking a global leap into GI technology
Sharmila Anandasabapathy, MD, knew she wanted to focus on endoscopy when she first started her career.
While leading an endoscopy unit in New York City, Dr. Anandasabapathy began developing endoscopic and imaging technologies for underresourced and underserved areas. These technologies eventually made their way into global clinical trials.
“We’ve gone to clinical trial in over 2,000 patients worldwide. When I made that jump into global GI, I was able to make that jump into global health in general,” said Dr. Anandasabapathy.

As vice president for global programs at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Dr. Anandasabapathy currently focuses on clinical and translational research.
“We’re looking at the development of new, low-cost devices for early cancer detection in GI globally. I oversee our global programs across the whole college, so it’s GI, it’s surgery, it’s anesthesia, it’s obstetrics, it’s everything.”
In an interview, Dr. Anandasabapathy discussed what attracted her to gastroenterology and why she always takes the time to smile at her patients.
Q: Why did you choose GI?
A: There’s two questions in there: Why I chose GI and why I chose endoscopy.
I chose GI because when I was in my internal medicine training, they seemed like the happiest people in the hospital. They liked what they did. You could make a meaningful impact even at 3 a.m. if you were coming in for a variceal bleed. Everybody seemed happy with their choice of specialty. I was ready to be an oncologist, and I ended up becoming a gastroenterologist.
I chose endoscopy because it was where I wanted to be when I woke up in the morning. I was happy there. I love the procedures; I love the hand-eye coordination. I liked the fact that these were relatively shorter procedures, that it was technology based, and there was infinite growth.
Q: Was there a time when you really helped a patient by doing that endoscopy, preventing Barrett’s esophagus or even cancer?
A: I can think of several times where we had early cancers and it was a question between endoscopic treatment or surgery. It was always discussed with the surgeons. We made the decision within a multidisciplinary group and with the patient, but we usually went with the endoscopic options and the patients have done great. We’ve given them a greater quality of life, and I think that’s really rewarding.
Q: What gives you the most joy in your day-to-day practice?
A: My patients. I work with Barrett’s esophagus patients, and they tend to be well informed about the research and the science. I’m lucky to have a patient population that is really interested and willing to participate in that. I also like my students, my junior faculty. I like teaching and the global application of teaching.
Q: What fears did you have to push past to get to where you are in your career?
A: That I would never become an independent researcher and do it alone. I was able to, over time. The ability to transition from being independent to teaching others and making them independent is a wonderful one.
Early on when I was doing GI, I remember looking at my division, and there were about 58 gastroenterologists and only 2 women. I thought at the time, “Well, can I do it? Is this a field that is conducive with being a woman and having a family?” It turned out that it is. Today, I’m really gratified to see that there are more women in GI than there ever were before.
Q: Have you ever received advice that you’ve ignored?A: Yes. Early in my training in internal medicine, I was told that I smiled too much and that my personality was such that patients and others would think I was too glib. Medicine was a serious business, and you shouldn’t be smiling. That’s not my personality – I’m not Eeyore. I think it’s served me well to be positive, and it’s served me well with patients to be smiling. Especially when you’re dealing with patients who have precancer or dysplasia and are scared – they want reassurance and they want a level of confidence. I’m glad I ignored that advice.
Q: What would be your advice to medical students?
A: Think about where you want to be when you wake up in the morning. If it’s either in a GI practice or doing GI research or doing endoscopy, then you should absolutely do it.
Lightning round
Cat person or dog person
Dog
Favorite sport
Tennis
What song do you have to sing along with when you hear it?
Dancing Queen
Favorite music genre
1980s pop
Favorite movie, show, or book
Wuthering Heights
Dr. Anandasabapathy is on LinkedIn and on Twitter at @anandasabapathy , @bcmglobalhealth , and @bcm_gihep .
Sharmila Anandasabapathy, MD, knew she wanted to focus on endoscopy when she first started her career.
While leading an endoscopy unit in New York City, Dr. Anandasabapathy began developing endoscopic and imaging technologies for underresourced and underserved areas. These technologies eventually made their way into global clinical trials.
“We’ve gone to clinical trial in over 2,000 patients worldwide. When I made that jump into global GI, I was able to make that jump into global health in general,” said Dr. Anandasabapathy.

As vice president for global programs at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Dr. Anandasabapathy currently focuses on clinical and translational research.
“We’re looking at the development of new, low-cost devices for early cancer detection in GI globally. I oversee our global programs across the whole college, so it’s GI, it’s surgery, it’s anesthesia, it’s obstetrics, it’s everything.”
In an interview, Dr. Anandasabapathy discussed what attracted her to gastroenterology and why she always takes the time to smile at her patients.
Q: Why did you choose GI?
A: There’s two questions in there: Why I chose GI and why I chose endoscopy.
I chose GI because when I was in my internal medicine training, they seemed like the happiest people in the hospital. They liked what they did. You could make a meaningful impact even at 3 a.m. if you were coming in for a variceal bleed. Everybody seemed happy with their choice of specialty. I was ready to be an oncologist, and I ended up becoming a gastroenterologist.
I chose endoscopy because it was where I wanted to be when I woke up in the morning. I was happy there. I love the procedures; I love the hand-eye coordination. I liked the fact that these were relatively shorter procedures, that it was technology based, and there was infinite growth.
Q: Was there a time when you really helped a patient by doing that endoscopy, preventing Barrett’s esophagus or even cancer?
A: I can think of several times where we had early cancers and it was a question between endoscopic treatment or surgery. It was always discussed with the surgeons. We made the decision within a multidisciplinary group and with the patient, but we usually went with the endoscopic options and the patients have done great. We’ve given them a greater quality of life, and I think that’s really rewarding.
Q: What gives you the most joy in your day-to-day practice?
A: My patients. I work with Barrett’s esophagus patients, and they tend to be well informed about the research and the science. I’m lucky to have a patient population that is really interested and willing to participate in that. I also like my students, my junior faculty. I like teaching and the global application of teaching.
Q: What fears did you have to push past to get to where you are in your career?
A: That I would never become an independent researcher and do it alone. I was able to, over time. The ability to transition from being independent to teaching others and making them independent is a wonderful one.
Early on when I was doing GI, I remember looking at my division, and there were about 58 gastroenterologists and only 2 women. I thought at the time, “Well, can I do it? Is this a field that is conducive with being a woman and having a family?” It turned out that it is. Today, I’m really gratified to see that there are more women in GI than there ever were before.
Q: Have you ever received advice that you’ve ignored?A: Yes. Early in my training in internal medicine, I was told that I smiled too much and that my personality was such that patients and others would think I was too glib. Medicine was a serious business, and you shouldn’t be smiling. That’s not my personality – I’m not Eeyore. I think it’s served me well to be positive, and it’s served me well with patients to be smiling. Especially when you’re dealing with patients who have precancer or dysplasia and are scared – they want reassurance and they want a level of confidence. I’m glad I ignored that advice.
Q: What would be your advice to medical students?
A: Think about where you want to be when you wake up in the morning. If it’s either in a GI practice or doing GI research or doing endoscopy, then you should absolutely do it.
Lightning round
Cat person or dog person
Dog
Favorite sport
Tennis
What song do you have to sing along with when you hear it?
Dancing Queen
Favorite music genre
1980s pop
Favorite movie, show, or book
Wuthering Heights
Dr. Anandasabapathy is on LinkedIn and on Twitter at @anandasabapathy , @bcmglobalhealth , and @bcm_gihep .
Sharmila Anandasabapathy, MD, knew she wanted to focus on endoscopy when she first started her career.
While leading an endoscopy unit in New York City, Dr. Anandasabapathy began developing endoscopic and imaging technologies for underresourced and underserved areas. These technologies eventually made their way into global clinical trials.
“We’ve gone to clinical trial in over 2,000 patients worldwide. When I made that jump into global GI, I was able to make that jump into global health in general,” said Dr. Anandasabapathy.

As vice president for global programs at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Dr. Anandasabapathy currently focuses on clinical and translational research.
“We’re looking at the development of new, low-cost devices for early cancer detection in GI globally. I oversee our global programs across the whole college, so it’s GI, it’s surgery, it’s anesthesia, it’s obstetrics, it’s everything.”
In an interview, Dr. Anandasabapathy discussed what attracted her to gastroenterology and why she always takes the time to smile at her patients.
Q: Why did you choose GI?
A: There’s two questions in there: Why I chose GI and why I chose endoscopy.
I chose GI because when I was in my internal medicine training, they seemed like the happiest people in the hospital. They liked what they did. You could make a meaningful impact even at 3 a.m. if you were coming in for a variceal bleed. Everybody seemed happy with their choice of specialty. I was ready to be an oncologist, and I ended up becoming a gastroenterologist.
I chose endoscopy because it was where I wanted to be when I woke up in the morning. I was happy there. I love the procedures; I love the hand-eye coordination. I liked the fact that these were relatively shorter procedures, that it was technology based, and there was infinite growth.
Q: Was there a time when you really helped a patient by doing that endoscopy, preventing Barrett’s esophagus or even cancer?
A: I can think of several times where we had early cancers and it was a question between endoscopic treatment or surgery. It was always discussed with the surgeons. We made the decision within a multidisciplinary group and with the patient, but we usually went with the endoscopic options and the patients have done great. We’ve given them a greater quality of life, and I think that’s really rewarding.
Q: What gives you the most joy in your day-to-day practice?
A: My patients. I work with Barrett’s esophagus patients, and they tend to be well informed about the research and the science. I’m lucky to have a patient population that is really interested and willing to participate in that. I also like my students, my junior faculty. I like teaching and the global application of teaching.
Q: What fears did you have to push past to get to where you are in your career?
A: That I would never become an independent researcher and do it alone. I was able to, over time. The ability to transition from being independent to teaching others and making them independent is a wonderful one.
Early on when I was doing GI, I remember looking at my division, and there were about 58 gastroenterologists and only 2 women. I thought at the time, “Well, can I do it? Is this a field that is conducive with being a woman and having a family?” It turned out that it is. Today, I’m really gratified to see that there are more women in GI than there ever were before.
Q: Have you ever received advice that you’ve ignored?A: Yes. Early in my training in internal medicine, I was told that I smiled too much and that my personality was such that patients and others would think I was too glib. Medicine was a serious business, and you shouldn’t be smiling. That’s not my personality – I’m not Eeyore. I think it’s served me well to be positive, and it’s served me well with patients to be smiling. Especially when you’re dealing with patients who have precancer or dysplasia and are scared – they want reassurance and they want a level of confidence. I’m glad I ignored that advice.
Q: What would be your advice to medical students?
A: Think about where you want to be when you wake up in the morning. If it’s either in a GI practice or doing GI research or doing endoscopy, then you should absolutely do it.
Lightning round
Cat person or dog person
Dog
Favorite sport
Tennis
What song do you have to sing along with when you hear it?
Dancing Queen
Favorite music genre
1980s pop
Favorite movie, show, or book
Wuthering Heights
Dr. Anandasabapathy is on LinkedIn and on Twitter at @anandasabapathy , @bcmglobalhealth , and @bcm_gihep .
News & Perspectives from Ob.Gyn. News
MASTER CLASS
Prepare for endometriosis excision surgery with a multidisciplinary approach
Iris Kerin Orbuch, MD
Director, Advanced Gynecologic Laparoscopy Center, Los Angeles and New York City.
Series introduction
Charles Miller, MD
Professor, Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, North Chicago, Illinois.
As I gained more interest and expertise in the treatment of endometriosis, I became aware of several articles concluding that if a woman sought treatment for chronic pelvic pain with an internist, the diagnosis would be irritable bowel syndrome (IBS); with a urologist, it would be interstitial cystitis; and with a gynecologist, endometriosis. Moreover, there is an increased propensity for IBS and IC in patients with endometriosis. There also is an increased risk of small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), as noted by our guest author for this latest installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, Iris Orbuch, MD.
Like our guest author, I have also noted increased risk of pelvic floor myalgia. Dr. Orbuch clearly outlines why this occurs. In fact, we can now understand why many patients have multiple pelvic pain–inducing issues compounding their pain secondary to endometriosis and leading to remodeling of the central nervous system. Therefore, it certainly makes sense to follow Dr. Orbuch’s recommendation for a multidisciplinary pre- and postsurgical approach “to downregulate the pain generators.”
Dr. Orbuch is a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Los Angeles who specializes in the treatment of patients diagnosed with endometriosis. Dr. Orbuch serves on the Board of Directors of the Foundation of the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists and has served as the chair of the AAGL’s Special Interest Group on Endometriosis and Reproductive Surgery. She is the coauthor of the book “Beating Endo —How to Reclaim Your Life From Endometriosis” (New York: HarperCollins; 2019). The book is written for patients but addresses many issues discussed in this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/master-class
GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY CONSULT
The perils of CA-125 as a diagnostic tool in patients with adnexal masses
Katherine Tucker, MD
Assistant Professor of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
CA-125, or cancer antigen 125, is an epitope (antigen) on the transmembrane glycoprotein MUC16, or mucin 16. This protein is expressed on the surface of tissue derived from embryonic coelomic and Müllerian epithelium including the reproductive tract. CA-125 is also expressed in other tissue such as the pleura, lungs, pericardium, intestines, and kidneys. MUC16 plays an important role in tumor proliferation, invasiveness, and cell motility.1 In patients with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), CA-125 may be found on the surface of ovarian cancer cells. It is shed in the bloodstream and can be quantified using a serum test.
There are a number of CA-125 assays in commercial use, and although none have been deemed to be clinically superior, there can be some differences between assays. It is important, if possible, to use the same assay when following serial CA-125 values. Most frequently, this will mean getting the test through the same laboratory.
https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/gynecologic-oncology-consult
LATEST NEWS
Few women identify breast density as a breast cancer risk
Walter Alexander
A qualitative study of breast cancer screening–age women finds that few women identified breast density as a risk factor for breast cancer.
Most women did not feel confident they knew what actions could mitigate breast cancer risk, leading researchers to the conclusion that comprehensive education about breast cancer risks and prevention strategies is needed.
CDC recommends universal hepatitis B screening of adults
Adults should be tested for hepatitis B virus (HBV) at least once in their lifetime, according to updated guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This is the first update to HBV screening guidelines since 2008, the agency said.
“Risk-based testing alone has not identified most persons living with chronic HBV infection and is considered inefficient for providers to implement,” the authors write in the new guidance, published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “Universal screening of adults for HBV infection is cost-effective, compared with risk-based screening and averts liver disease and death. Although a curative treatment is not yet available, early diagnosis and treatment of chronic HBV infections reduces the risk for cirrhosis, liver cancer, nd death.”
An estimated 580,000 to 2.4 million individuals are living with HBV infection in the United States, and two-thirds may be unaware they are infected, the agency said.
The virus spreads through contact with blood, semen, and other body fluids of an infected person.
The guidance now recommends using the triple panel (HBsAg, anti-HBs, total anti-HBc) for initial screening.
“It can help identify persons who have an active HBV infection and could be linked to care; have [a] resolved infection and might be susceptible to reactivation (for example, immunosuppressed persons); are susceptible and need vaccination; or are vaccinated,” the authors write.
Ectopic pregnancy risk and levonorgestrel-releasing IUD
Diana Swift
Researchers report that use of any levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system was associated with a significantly increased risk of ectopic pregnancy, compared with other hormonal contraceptives, in a study published in JAMA.
A national health database analysis headed by Amani Meaidi, MD, PhD, of the Danish Cancer Society Research Center, Cancer Surveillance and Pharmacoepidemiology, in Copenhagen, compared the 13.5-mg with the 19.5-mg and 52-mg dosages of levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine systems (IUSs).
The hormone content in levonorgestrel-releasing IUSs must be high enough to maintain optimal contraceptive effect but sufficiently low to minimize progestin-related adverse events, Dr. Meaidi and colleagues noted; they advised using the middle dosage of 19.5 mg. All dosages are recommended for contraception, with the highest dosage also recommended for heavy menstrual bleeding.
“If 10,000 women using the hormonal IUD for 1 year were given the 19.5-mg hormonal IUD instead of the 13.5-mg hormonal IUD, around nine ectopic pregnancies would be avoided,” Dr. Meaidi said in an interview.
EPA seeks to limit ‘forever’ chemicals in U.S. drinking water
The Environmental Protection Agency is proposing a new rule that would greatly limit the concentration of endocrine-disrupting “forever” chemicals in drinking water.
The EPA on Tuesday announced the proposed National Primary Drinking Water Regulation (NPDWR) for six polyfluoroalkyl substances, more commonly known as PFAS, which are human-made chemicals used as oil and water repellents and coatings for common products including cookware, carpets, and textiles. Such substances are also widely used in cosmetics and food packaging.
The Endocrine Society, which represents more than 18,000 doctors who treat hormone disorders, says it fully supports the new EPA proposal. It explains that these substances, also known as endocrine-disrupting chemicals, “do not break down when they are released into the environment, and they continue to accumulate over time. They pose health dangers at incredibly low levels and have been linked to endocrine disorders such as cancer, thyroid disruption, and reproductive difficulties.”
https://www.mdedge.com /obgyn/latest-news
MASTER CLASS
Prepare for endometriosis excision surgery with a multidisciplinary approach
Iris Kerin Orbuch, MD
Director, Advanced Gynecologic Laparoscopy Center, Los Angeles and New York City.
Series introduction
Charles Miller, MD
Professor, Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, North Chicago, Illinois.
As I gained more interest and expertise in the treatment of endometriosis, I became aware of several articles concluding that if a woman sought treatment for chronic pelvic pain with an internist, the diagnosis would be irritable bowel syndrome (IBS); with a urologist, it would be interstitial cystitis; and with a gynecologist, endometriosis. Moreover, there is an increased propensity for IBS and IC in patients with endometriosis. There also is an increased risk of small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), as noted by our guest author for this latest installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, Iris Orbuch, MD.
Like our guest author, I have also noted increased risk of pelvic floor myalgia. Dr. Orbuch clearly outlines why this occurs. In fact, we can now understand why many patients have multiple pelvic pain–inducing issues compounding their pain secondary to endometriosis and leading to remodeling of the central nervous system. Therefore, it certainly makes sense to follow Dr. Orbuch’s recommendation for a multidisciplinary pre- and postsurgical approach “to downregulate the pain generators.”
Dr. Orbuch is a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Los Angeles who specializes in the treatment of patients diagnosed with endometriosis. Dr. Orbuch serves on the Board of Directors of the Foundation of the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists and has served as the chair of the AAGL’s Special Interest Group on Endometriosis and Reproductive Surgery. She is the coauthor of the book “Beating Endo —How to Reclaim Your Life From Endometriosis” (New York: HarperCollins; 2019). The book is written for patients but addresses many issues discussed in this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/master-class
GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY CONSULT
The perils of CA-125 as a diagnostic tool in patients with adnexal masses
Katherine Tucker, MD
Assistant Professor of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
CA-125, or cancer antigen 125, is an epitope (antigen) on the transmembrane glycoprotein MUC16, or mucin 16. This protein is expressed on the surface of tissue derived from embryonic coelomic and Müllerian epithelium including the reproductive tract. CA-125 is also expressed in other tissue such as the pleura, lungs, pericardium, intestines, and kidneys. MUC16 plays an important role in tumor proliferation, invasiveness, and cell motility.1 In patients with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), CA-125 may be found on the surface of ovarian cancer cells. It is shed in the bloodstream and can be quantified using a serum test.
There are a number of CA-125 assays in commercial use, and although none have been deemed to be clinically superior, there can be some differences between assays. It is important, if possible, to use the same assay when following serial CA-125 values. Most frequently, this will mean getting the test through the same laboratory.
https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/gynecologic-oncology-consult
LATEST NEWS
Few women identify breast density as a breast cancer risk
Walter Alexander
A qualitative study of breast cancer screening–age women finds that few women identified breast density as a risk factor for breast cancer.
Most women did not feel confident they knew what actions could mitigate breast cancer risk, leading researchers to the conclusion that comprehensive education about breast cancer risks and prevention strategies is needed.
CDC recommends universal hepatitis B screening of adults
Adults should be tested for hepatitis B virus (HBV) at least once in their lifetime, according to updated guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This is the first update to HBV screening guidelines since 2008, the agency said.
“Risk-based testing alone has not identified most persons living with chronic HBV infection and is considered inefficient for providers to implement,” the authors write in the new guidance, published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “Universal screening of adults for HBV infection is cost-effective, compared with risk-based screening and averts liver disease and death. Although a curative treatment is not yet available, early diagnosis and treatment of chronic HBV infections reduces the risk for cirrhosis, liver cancer, nd death.”
An estimated 580,000 to 2.4 million individuals are living with HBV infection in the United States, and two-thirds may be unaware they are infected, the agency said.
The virus spreads through contact with blood, semen, and other body fluids of an infected person.
The guidance now recommends using the triple panel (HBsAg, anti-HBs, total anti-HBc) for initial screening.
“It can help identify persons who have an active HBV infection and could be linked to care; have [a] resolved infection and might be susceptible to reactivation (for example, immunosuppressed persons); are susceptible and need vaccination; or are vaccinated,” the authors write.
Ectopic pregnancy risk and levonorgestrel-releasing IUD
Diana Swift
Researchers report that use of any levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system was associated with a significantly increased risk of ectopic pregnancy, compared with other hormonal contraceptives, in a study published in JAMA.
A national health database analysis headed by Amani Meaidi, MD, PhD, of the Danish Cancer Society Research Center, Cancer Surveillance and Pharmacoepidemiology, in Copenhagen, compared the 13.5-mg with the 19.5-mg and 52-mg dosages of levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine systems (IUSs).
The hormone content in levonorgestrel-releasing IUSs must be high enough to maintain optimal contraceptive effect but sufficiently low to minimize progestin-related adverse events, Dr. Meaidi and colleagues noted; they advised using the middle dosage of 19.5 mg. All dosages are recommended for contraception, with the highest dosage also recommended for heavy menstrual bleeding.
“If 10,000 women using the hormonal IUD for 1 year were given the 19.5-mg hormonal IUD instead of the 13.5-mg hormonal IUD, around nine ectopic pregnancies would be avoided,” Dr. Meaidi said in an interview.
EPA seeks to limit ‘forever’ chemicals in U.S. drinking water
The Environmental Protection Agency is proposing a new rule that would greatly limit the concentration of endocrine-disrupting “forever” chemicals in drinking water.
The EPA on Tuesday announced the proposed National Primary Drinking Water Regulation (NPDWR) for six polyfluoroalkyl substances, more commonly known as PFAS, which are human-made chemicals used as oil and water repellents and coatings for common products including cookware, carpets, and textiles. Such substances are also widely used in cosmetics and food packaging.
The Endocrine Society, which represents more than 18,000 doctors who treat hormone disorders, says it fully supports the new EPA proposal. It explains that these substances, also known as endocrine-disrupting chemicals, “do not break down when they are released into the environment, and they continue to accumulate over time. They pose health dangers at incredibly low levels and have been linked to endocrine disorders such as cancer, thyroid disruption, and reproductive difficulties.”
https://www.mdedge.com /obgyn/latest-news
MASTER CLASS
Prepare for endometriosis excision surgery with a multidisciplinary approach
Iris Kerin Orbuch, MD
Director, Advanced Gynecologic Laparoscopy Center, Los Angeles and New York City.
Series introduction
Charles Miller, MD
Professor, Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, North Chicago, Illinois.
As I gained more interest and expertise in the treatment of endometriosis, I became aware of several articles concluding that if a woman sought treatment for chronic pelvic pain with an internist, the diagnosis would be irritable bowel syndrome (IBS); with a urologist, it would be interstitial cystitis; and with a gynecologist, endometriosis. Moreover, there is an increased propensity for IBS and IC in patients with endometriosis. There also is an increased risk of small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), as noted by our guest author for this latest installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, Iris Orbuch, MD.
Like our guest author, I have also noted increased risk of pelvic floor myalgia. Dr. Orbuch clearly outlines why this occurs. In fact, we can now understand why many patients have multiple pelvic pain–inducing issues compounding their pain secondary to endometriosis and leading to remodeling of the central nervous system. Therefore, it certainly makes sense to follow Dr. Orbuch’s recommendation for a multidisciplinary pre- and postsurgical approach “to downregulate the pain generators.”
Dr. Orbuch is a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Los Angeles who specializes in the treatment of patients diagnosed with endometriosis. Dr. Orbuch serves on the Board of Directors of the Foundation of the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists and has served as the chair of the AAGL’s Special Interest Group on Endometriosis and Reproductive Surgery. She is the coauthor of the book “Beating Endo —How to Reclaim Your Life From Endometriosis” (New York: HarperCollins; 2019). The book is written for patients but addresses many issues discussed in this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/master-class
GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY CONSULT
The perils of CA-125 as a diagnostic tool in patients with adnexal masses
Katherine Tucker, MD
Assistant Professor of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
CA-125, or cancer antigen 125, is an epitope (antigen) on the transmembrane glycoprotein MUC16, or mucin 16. This protein is expressed on the surface of tissue derived from embryonic coelomic and Müllerian epithelium including the reproductive tract. CA-125 is also expressed in other tissue such as the pleura, lungs, pericardium, intestines, and kidneys. MUC16 plays an important role in tumor proliferation, invasiveness, and cell motility.1 In patients with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), CA-125 may be found on the surface of ovarian cancer cells. It is shed in the bloodstream and can be quantified using a serum test.
There are a number of CA-125 assays in commercial use, and although none have been deemed to be clinically superior, there can be some differences between assays. It is important, if possible, to use the same assay when following serial CA-125 values. Most frequently, this will mean getting the test through the same laboratory.
https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/gynecologic-oncology-consult
LATEST NEWS
Few women identify breast density as a breast cancer risk
Walter Alexander
A qualitative study of breast cancer screening–age women finds that few women identified breast density as a risk factor for breast cancer.
Most women did not feel confident they knew what actions could mitigate breast cancer risk, leading researchers to the conclusion that comprehensive education about breast cancer risks and prevention strategies is needed.
CDC recommends universal hepatitis B screening of adults
Adults should be tested for hepatitis B virus (HBV) at least once in their lifetime, according to updated guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This is the first update to HBV screening guidelines since 2008, the agency said.
“Risk-based testing alone has not identified most persons living with chronic HBV infection and is considered inefficient for providers to implement,” the authors write in the new guidance, published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “Universal screening of adults for HBV infection is cost-effective, compared with risk-based screening and averts liver disease and death. Although a curative treatment is not yet available, early diagnosis and treatment of chronic HBV infections reduces the risk for cirrhosis, liver cancer, nd death.”
An estimated 580,000 to 2.4 million individuals are living with HBV infection in the United States, and two-thirds may be unaware they are infected, the agency said.
The virus spreads through contact with blood, semen, and other body fluids of an infected person.
The guidance now recommends using the triple panel (HBsAg, anti-HBs, total anti-HBc) for initial screening.
“It can help identify persons who have an active HBV infection and could be linked to care; have [a] resolved infection and might be susceptible to reactivation (for example, immunosuppressed persons); are susceptible and need vaccination; or are vaccinated,” the authors write.
Ectopic pregnancy risk and levonorgestrel-releasing IUD
Diana Swift
Researchers report that use of any levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system was associated with a significantly increased risk of ectopic pregnancy, compared with other hormonal contraceptives, in a study published in JAMA.
A national health database analysis headed by Amani Meaidi, MD, PhD, of the Danish Cancer Society Research Center, Cancer Surveillance and Pharmacoepidemiology, in Copenhagen, compared the 13.5-mg with the 19.5-mg and 52-mg dosages of levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine systems (IUSs).
The hormone content in levonorgestrel-releasing IUSs must be high enough to maintain optimal contraceptive effect but sufficiently low to minimize progestin-related adverse events, Dr. Meaidi and colleagues noted; they advised using the middle dosage of 19.5 mg. All dosages are recommended for contraception, with the highest dosage also recommended for heavy menstrual bleeding.
“If 10,000 women using the hormonal IUD for 1 year were given the 19.5-mg hormonal IUD instead of the 13.5-mg hormonal IUD, around nine ectopic pregnancies would be avoided,” Dr. Meaidi said in an interview.
EPA seeks to limit ‘forever’ chemicals in U.S. drinking water
The Environmental Protection Agency is proposing a new rule that would greatly limit the concentration of endocrine-disrupting “forever” chemicals in drinking water.
The EPA on Tuesday announced the proposed National Primary Drinking Water Regulation (NPDWR) for six polyfluoroalkyl substances, more commonly known as PFAS, which are human-made chemicals used as oil and water repellents and coatings for common products including cookware, carpets, and textiles. Such substances are also widely used in cosmetics and food packaging.
The Endocrine Society, which represents more than 18,000 doctors who treat hormone disorders, says it fully supports the new EPA proposal. It explains that these substances, also known as endocrine-disrupting chemicals, “do not break down when they are released into the environment, and they continue to accumulate over time. They pose health dangers at incredibly low levels and have been linked to endocrine disorders such as cancer, thyroid disruption, and reproductive difficulties.”
https://www.mdedge.com /obgyn/latest-news
ObGyn’s steady progress toward going green in the OR—but gaps persist
Have you ever looked at the operating room (OR) trash bin at the end of a case and wondered if all that waste is necessary? Since I started my residency, not a day goes by that I have not asked myself this question.
In the mid-1990s, John Elkington introduced the concept of the triple bottom line—that is, people, planet, and profit—for implementation and measurement of sustainability in businesses.1 The health care sector is no exception when it comes to the bottom line! However, “people” remain the priority. What is our role, as ObGyns, in protecting the “planet” while keeping the “people” safe?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), climate change remains the single biggest health threat to humanity.2 The health care system is both the victim and the culprit. Studies suggest that the health care system, second to the food industry, is the biggest contributor to waste production in the United States. This sector generates more than 6,000 metric tons of waste each day and nearly 4 million tons (3.6 million metric tons) of solid waste each year.3 The health care system is responsible for an estimated 8% to 10% of total greenhouse gas emissions in the United States; the US health care system alone contributes to more than one-fourth of the global health care carbon footprint. If it were a country, the US health care system would rank 13th among all countries in emissions.4In turn, pollution produced by the health sector negatively impacts population health, further burdening the health care system. According to 2013 study data, the annual health damage caused by health care pollution was comparable to that of the deaths caused by preventable medical error.4
Aside from the environmental aspects, hospital waste disposal is expensive; reducing this cost is a potential area of interest for institutions.
As ObGyns, what is our role in reducing our waste generation and carbon footprint while keeping patients safe?
Defining health care waste, and disposal considerations
The WHO defines health care waste as including “the waste generated by health-care establishments, research facilities, and laboratories” as well as waste from scattered sources such as home dialysis and insulin injections.5 Despite representing a relatively small physical area of hospitals, labor and delivery units combined with ORs account for approximately 70% of all hospital waste.3 Operating room waste consists of disposable surgical supplies, personal protective equipment, drapes, plastic wrappers, sterile blue wraps, glass, cardboard, packaging material, medications, fluids, and other materials (FIGURE 1).

The WHO also notes that of all the waste generated by health care activities, about 85% is general, nonhazardous waste that is comparable to domestic waste.6 Hazardous waste is any material that poses a health risk, including potentially infectious materials, such as blood-soaked gauze, sharps, pharmaceuticals, or radioactive materials.6
Disposal of hazardous waste is expensiveand energy consuming as it is typically incinerated rather than disposed of in a landfill. This process produces substantial greenhouse gases, about 3 kg of carbon dioxide for every 1 kg of hazardous waste.7
Red bags are used for hazardous waste disposal, while clear bags are used for general waste. Operating rooms produce about two-thirds of the hospital red-bag waste.8 Waste segregation unfortunately is not accurate, and as much as 90% of OR general waste is improperly designated as hazardous waste.3 Drapes and uncontaminated, needleless syringes, for example, should be disposed of in clear bags, but often they are instead directed to the red-bag and sharps container (FIGURE 2).

Obstetrics and gynecology has an important role to play in accurate waste segregation given the specialty’s frequent interaction with bodily fluids. Clinicians and other staff need to recognize and appropriately separate hazardous waste from general waste. For instance, not all fabrics involved in a case should be disposed of in the red bin, only those saturated with blood or body fluids. Educating health care staff and placing instruction posters on the red trash bins potentially could aid in accurate waste segregation and reduce regulated waste while decreasing disposal costs.
Recycling in the OR
Recycling has become an established practice in many health care facilities and ORs. Studies suggest that introducing recycling programs in ORs not only reduces carbon footprints but also reduces costs.3 One study reported that US academic medical centers consume 2 million lb ($15 million) each year of recoverable medical supplies.9
Single-stream recycling, a system in which all recyclable material—including plastics, paper, metal, and glass—are placed in a single bin without segregation at the collection site, has gained in popularity. Recycling can be implemented both in ORs and in other perioperative areas where regular trash bins are located.
In a study done at Oxford University Hospitals in the United Kingdom, introducing recycling bins in every OR, as well as in recovery and staff rest areas, helped improve waste segregation such that approximately 22% of OR waste was recycled.10 Studies show that recycling programs not only decrease the health care carbon footprint but also have a considerable financial impact. Albert and colleagues demonstrated that introducing a single-stream recycling program to a 9-OR day (or ambulatory) surgery center could redirect more than 4 tons of waste each month and saved thousands of dollars.11
Despite continued improvement in recycling programs, the segregation process is still far from optimal. In a survey done at the Mayo Clinic by Azouz and colleagues, more than half of the staff reported being unclear about which OR items are recyclable and nearly half reported that lack of knowledge was the barrier to proper recycling.12 That study also showed that after implementation of a recycling education program, costs decreased 10% relative to the same time period in prior years.12
Blue wraps. One example of recycling optimization is blue wraps, the polypropylene (No. 5 plastic) material used for wrapping surgical instruments. Blue wraps account for approximately 19% of OR waste and 5% of all hospital waste.11 Blue wraps are not biodegradable and also are not widely recycled. In recent years, a resale market has emerged for blue wraps, as they can be used for production of other No. 5 plastic items.9 By reselling blue wraps, revenue can be generated by recycling a necessary packing material that would otherwise require payment for disposal.
Sterility considerations. While recycling in ORs may raise concern due to the absolute sterility required in procedural settings, technologic developments have been promising in advancing safe recycling to reduce carbon footprints and health care costs without compromising patients’ safety. Segregation of waste from recyclable packaging material prior to the case, as well as directing trash to the correct bin (regular vs red bin), is one example. Moreover, because about 80% of all OR waste is generated during the set up before the patient arrives in the OR, it is not contaminated and can be safely recycled.13
Continue to: Packaging material...
Packaging material
A substantial part of OR waste consists of packaging material; of all OR waste, 26% consists of plastics and 7%, paper and cartons.14 Increasing use of disposable or “single use” medical products in ORs, along with the intention to safeguard sterility, contributes significantly to the generation of medical waste in operating units. Containers, wraps and overwraps, cardboard, and plastic packaging are all composed of materials that when clean, can be recycled; however, these items often end up in the landfill (FIGURE 3).
Although the segregation of packaging material to recycling versus regular trash versus red bin is of paramount importance, packaging design plays a significant role as well. In 2018, Boston Scientific introduced a new packaging design for ureteral stents that reduced plastic use in packaging by 120,000 lb each year.15 Despite the advances in the medical packaging industry to increase sustainability while safeguarding sterility for medical devices, there is still room for innovation in this area.
Reducing overage by judicious selection of surgical devices, instruments, and supplies
Overage is the term used to describe surgical inventory that is opened and prepared for surgery but ultimately not used and therefore discarded. Design of surgical carts and instrument and supply selection requires direct input from ObGyns. Opening only the needed instruments while ensuring ready availability of potentially needed supplies can significantly reduce OR waste generation as well as decrease chemical pollution generated by instrument sterilization. Decreasing OR overage reduces overall costs as well (FIGURE 4).
In a pilot study at the University of Massachusetts, Albert and colleagues examined the sets of disposable items and instruments designated for common plastic and hand surgery procedures.11 They identified the supplies and instruments that are routinely opened and wasted, based on surgeons’ interview responses, and redesigned the sets. Fifteen items were removed from disposable plastic surgery packs and 7 items from hand surgery packs. The authors reported saving thousands of dollars per year with these changes alone, as well as reducing waste.11 This same concept easily could be implemented in obstetrics and gynecology. We must ask ourselves: Do we always need, for example, a complete dilation and curettage kit to place the uterine manipulator prior to a minimally invasive hysterectomy?
In another pilot study, Greenberg and colleagues investigated whether cesarean deliveries consistently could be performed in a safe manner with only 20 instruments in the surgical kit.16 Obstetricians rated the 20-instrument kit an 8.7 out of 10 for performing cesarean deliveries safely.16
In addition to instrument selection, surgeons have a role in other supply use and waste generation: for instance, opening multiple pairs of surgical gloves and surgical gowns in advance when most of them will not be used during the case. Furthermore, many ObGyn surgeons routinely change gloves or even gowns during gynecologic procedures when they go back and forth between the vaginal and abdominal fields. Is the perineum “dirty” after application of a surgical prep solution?
In an observational study, Shockley and colleagues investigated the type and quantity of bacteria found intraoperatively on the abdomen, vagina, surgical gloves, instrument tips, and uterus at distinct time points during total laparoscopic hysterectomy.17 They showed that in 98.9% of cultures, the overall bacterial concentrations did not exceed the threshold for infection. There was no bacterial growth from vaginal cultures, and the only samples with some bacterial growth belonged to the surgeon’s gloves after specimen extraction; about one-third of samples showed growth after specimen extraction, but only 1 sample had a bacterial load above the infectious threshold of 5,000 colony-forming units per mL. The authors therefore suggested that if a surgeon changes gloves, doing so after specimen extraction and before turning attention back to the abdomen for vaginal cuff closure may be most effective in reducing bacterial load.17
Surgical site infection contributes to medical cost and likely medical waste as well. For example, surgical site infection may require prolonged treatments, tests, and medical instruments. In severe cases with abscesses, treatment entails hospitalization with prolonged antibiotic therapy with or without procedures to drain the collections. Further research therefore is warranted to investigate safe and environmentally friendly practices.
Myriad products are introduced to the medical system each day, some of which replace conventional tools. For instance, low-density polyethylene, or LDPE, transfer sheet is advertised for lateral patient transfer from the OR table to the bed or stretcher. This No. 4–coded plastic, while recyclable, is routinely discarded as trash in ORs. One ergonomic study found that reusable slide boards are as effective for reducing friction and staff muscle activities and are noninferior to the plastic sheets.18
Steps to making an impact
Operating rooms and labor and delivery units are responsible for a large proportion of hospital waste, and therefore they are of paramount importance in reducing waste and carbon footprint at the individual and institutional level. Reduction of OR waste not only is environmentally conscious but also decreases cost. Steps as small as individual practices to as big as changing infrastructures can make an impact. For instance:
- redesigning surgical carts
- reformulating surgeon-specific supply lists
- raising awareness about surgical overage
- encouraging recycling through education and audit
- optimizing surgical waste segregation through educational posters.
These are all simple steps that could significantly reduce waste and carbon footprint.
Bottom line
Although waste reduction is the responsibility of all health care providers, as leaders in their workplace physicians can serve as role models by implementing “green” practices in procedural units. Raising awareness and using a team approach is critical to succeed in our endeavors to move toward an environmentally friendly future. ●
- Elkington J. Towards the sustainable corporation: win-winwin business strategies for sustainable development. Calif Manage Rev. 1994;36:90-100.
- Climate change and health. October 30, 2021. World Health Organization. Accessed October 10, 2022. https://www.who .int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/climate-change-and -health
- Kwakye G, Brat GA, Makary MA. Green surgical practices for health care. Arch Surg. 2011;146:131-136.
- Eckelman MJ, Sherman J. Environmental impacts of the US health care system and effects on public health. PloS One. 2016;11:e0157014.
- Pruss A, Giroult E, Rushbrook P. Safe management of wastes from health-care activities. World Health Organization; 1999.
- Health-care waste. February 8, 2018. World Health Organization. Accessed October 4, 2022. https://www.who. int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/health-care-waste2
- Southorn T, Norrish AR, Gardner K, et al. Reducing the carbon footprint of the operating theatre: a multicentre quality improvement report. J Perioper Pract. 2013;23:144-146.
- Greening the OR. Practice Greenhealth. Accessed October 24, 2022. https://practicegreenhealth.org/topics/greening -operating-room/greening-or
- Babu MA, Dalenberg AK, Goodsell G, et al. Greening the operating room: results of a scalable initiative to reduce waste and recover supply costs. Neurosurgery. 2019;85:432-437.
- Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust. Introducing recycling into the operating theatres. Mapping Greener Healthcare. Accessed October 14, 2022. https://map .sustainablehealthcare.org.uk/oxford-radcliffe-hospitals -nhs-trust/introducing-recycling-operating-theatres
- Albert MG, Rothkopf DM. Operating room waste reduction in plastic and hand surgery. Plast Surg. 2015;23:235-238.
- Azouz S, Boyll P, Swanson M, et al. Managing barriers to recycling in the operating room. Am J Surg. 2019;217:634-638.
- Wyssusek KH, Keys MT, van Zundert AAJ. Operating room greening initiatives—the old, the new, and the way forward: a narrative review. Waste Manag Res. 2019;37:3-19.
- Tieszen ME, Gruenberg JC. A quantitative, qualitative, and critical assessment of surgical waste: surgeons venture through the trash can. JAMA. 1992;267:2765-2768.
- Boston Scientific 2018 Performance Report. Boston Scientific. Accessed November 19, 2022. https://www.bostonscientific. com/content/dam/bostonscientific/corporate/citizenship /sustainability/Boston_Scientific_Performance _Report_2018.pdf
- Greenberg JA, Wylie B, Robinson JN. A pilot study to assess the adequacy of the Brigham 20 Kit for cesarean delivery. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2012;117:157-159.
- Shockley ME, Beran B, Nutting H, et al. Sterility of selected operative sites during total laparoscopic hysterectomy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24:990-997.
- Al-Qaisi SK, El Tannir A, Younan LA, et al. An ergonomic assessment of using laterally-tilting operating room tables and friction reducing devices for patient lateral transfers. Appl Ergon. 2020;87:103122.
Have you ever looked at the operating room (OR) trash bin at the end of a case and wondered if all that waste is necessary? Since I started my residency, not a day goes by that I have not asked myself this question.
In the mid-1990s, John Elkington introduced the concept of the triple bottom line—that is, people, planet, and profit—for implementation and measurement of sustainability in businesses.1 The health care sector is no exception when it comes to the bottom line! However, “people” remain the priority. What is our role, as ObGyns, in protecting the “planet” while keeping the “people” safe?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), climate change remains the single biggest health threat to humanity.2 The health care system is both the victim and the culprit. Studies suggest that the health care system, second to the food industry, is the biggest contributor to waste production in the United States. This sector generates more than 6,000 metric tons of waste each day and nearly 4 million tons (3.6 million metric tons) of solid waste each year.3 The health care system is responsible for an estimated 8% to 10% of total greenhouse gas emissions in the United States; the US health care system alone contributes to more than one-fourth of the global health care carbon footprint. If it were a country, the US health care system would rank 13th among all countries in emissions.4In turn, pollution produced by the health sector negatively impacts population health, further burdening the health care system. According to 2013 study data, the annual health damage caused by health care pollution was comparable to that of the deaths caused by preventable medical error.4
Aside from the environmental aspects, hospital waste disposal is expensive; reducing this cost is a potential area of interest for institutions.
As ObGyns, what is our role in reducing our waste generation and carbon footprint while keeping patients safe?
Defining health care waste, and disposal considerations
The WHO defines health care waste as including “the waste generated by health-care establishments, research facilities, and laboratories” as well as waste from scattered sources such as home dialysis and insulin injections.5 Despite representing a relatively small physical area of hospitals, labor and delivery units combined with ORs account for approximately 70% of all hospital waste.3 Operating room waste consists of disposable surgical supplies, personal protective equipment, drapes, plastic wrappers, sterile blue wraps, glass, cardboard, packaging material, medications, fluids, and other materials (FIGURE 1).

The WHO also notes that of all the waste generated by health care activities, about 85% is general, nonhazardous waste that is comparable to domestic waste.6 Hazardous waste is any material that poses a health risk, including potentially infectious materials, such as blood-soaked gauze, sharps, pharmaceuticals, or radioactive materials.6
Disposal of hazardous waste is expensiveand energy consuming as it is typically incinerated rather than disposed of in a landfill. This process produces substantial greenhouse gases, about 3 kg of carbon dioxide for every 1 kg of hazardous waste.7
Red bags are used for hazardous waste disposal, while clear bags are used for general waste. Operating rooms produce about two-thirds of the hospital red-bag waste.8 Waste segregation unfortunately is not accurate, and as much as 90% of OR general waste is improperly designated as hazardous waste.3 Drapes and uncontaminated, needleless syringes, for example, should be disposed of in clear bags, but often they are instead directed to the red-bag and sharps container (FIGURE 2).

Obstetrics and gynecology has an important role to play in accurate waste segregation given the specialty’s frequent interaction with bodily fluids. Clinicians and other staff need to recognize and appropriately separate hazardous waste from general waste. For instance, not all fabrics involved in a case should be disposed of in the red bin, only those saturated with blood or body fluids. Educating health care staff and placing instruction posters on the red trash bins potentially could aid in accurate waste segregation and reduce regulated waste while decreasing disposal costs.
Recycling in the OR
Recycling has become an established practice in many health care facilities and ORs. Studies suggest that introducing recycling programs in ORs not only reduces carbon footprints but also reduces costs.3 One study reported that US academic medical centers consume 2 million lb ($15 million) each year of recoverable medical supplies.9
Single-stream recycling, a system in which all recyclable material—including plastics, paper, metal, and glass—are placed in a single bin without segregation at the collection site, has gained in popularity. Recycling can be implemented both in ORs and in other perioperative areas where regular trash bins are located.
In a study done at Oxford University Hospitals in the United Kingdom, introducing recycling bins in every OR, as well as in recovery and staff rest areas, helped improve waste segregation such that approximately 22% of OR waste was recycled.10 Studies show that recycling programs not only decrease the health care carbon footprint but also have a considerable financial impact. Albert and colleagues demonstrated that introducing a single-stream recycling program to a 9-OR day (or ambulatory) surgery center could redirect more than 4 tons of waste each month and saved thousands of dollars.11
Despite continued improvement in recycling programs, the segregation process is still far from optimal. In a survey done at the Mayo Clinic by Azouz and colleagues, more than half of the staff reported being unclear about which OR items are recyclable and nearly half reported that lack of knowledge was the barrier to proper recycling.12 That study also showed that after implementation of a recycling education program, costs decreased 10% relative to the same time period in prior years.12
Blue wraps. One example of recycling optimization is blue wraps, the polypropylene (No. 5 plastic) material used for wrapping surgical instruments. Blue wraps account for approximately 19% of OR waste and 5% of all hospital waste.11 Blue wraps are not biodegradable and also are not widely recycled. In recent years, a resale market has emerged for blue wraps, as they can be used for production of other No. 5 plastic items.9 By reselling blue wraps, revenue can be generated by recycling a necessary packing material that would otherwise require payment for disposal.
Sterility considerations. While recycling in ORs may raise concern due to the absolute sterility required in procedural settings, technologic developments have been promising in advancing safe recycling to reduce carbon footprints and health care costs without compromising patients’ safety. Segregation of waste from recyclable packaging material prior to the case, as well as directing trash to the correct bin (regular vs red bin), is one example. Moreover, because about 80% of all OR waste is generated during the set up before the patient arrives in the OR, it is not contaminated and can be safely recycled.13
Continue to: Packaging material...
Packaging material
A substantial part of OR waste consists of packaging material; of all OR waste, 26% consists of plastics and 7%, paper and cartons.14 Increasing use of disposable or “single use” medical products in ORs, along with the intention to safeguard sterility, contributes significantly to the generation of medical waste in operating units. Containers, wraps and overwraps, cardboard, and plastic packaging are all composed of materials that when clean, can be recycled; however, these items often end up in the landfill (FIGURE 3).

Although the segregation of packaging material to recycling versus regular trash versus red bin is of paramount importance, packaging design plays a significant role as well. In 2018, Boston Scientific introduced a new packaging design for ureteral stents that reduced plastic use in packaging by 120,000 lb each year.15 Despite the advances in the medical packaging industry to increase sustainability while safeguarding sterility for medical devices, there is still room for innovation in this area.
Reducing overage by judicious selection of surgical devices, instruments, and supplies
Overage is the term used to describe surgical inventory that is opened and prepared for surgery but ultimately not used and therefore discarded. Design of surgical carts and instrument and supply selection requires direct input from ObGyns. Opening only the needed instruments while ensuring ready availability of potentially needed supplies can significantly reduce OR waste generation as well as decrease chemical pollution generated by instrument sterilization. Decreasing OR overage reduces overall costs as well (FIGURE 4).

In a pilot study at the University of Massachusetts, Albert and colleagues examined the sets of disposable items and instruments designated for common plastic and hand surgery procedures.11 They identified the supplies and instruments that are routinely opened and wasted, based on surgeons’ interview responses, and redesigned the sets. Fifteen items were removed from disposable plastic surgery packs and 7 items from hand surgery packs. The authors reported saving thousands of dollars per year with these changes alone, as well as reducing waste.11 This same concept easily could be implemented in obstetrics and gynecology. We must ask ourselves: Do we always need, for example, a complete dilation and curettage kit to place the uterine manipulator prior to a minimally invasive hysterectomy?
In another pilot study, Greenberg and colleagues investigated whether cesarean deliveries consistently could be performed in a safe manner with only 20 instruments in the surgical kit.16 Obstetricians rated the 20-instrument kit an 8.7 out of 10 for performing cesarean deliveries safely.16
In addition to instrument selection, surgeons have a role in other supply use and waste generation: for instance, opening multiple pairs of surgical gloves and surgical gowns in advance when most of them will not be used during the case. Furthermore, many ObGyn surgeons routinely change gloves or even gowns during gynecologic procedures when they go back and forth between the vaginal and abdominal fields. Is the perineum “dirty” after application of a surgical prep solution?
In an observational study, Shockley and colleagues investigated the type and quantity of bacteria found intraoperatively on the abdomen, vagina, surgical gloves, instrument tips, and uterus at distinct time points during total laparoscopic hysterectomy.17 They showed that in 98.9% of cultures, the overall bacterial concentrations did not exceed the threshold for infection. There was no bacterial growth from vaginal cultures, and the only samples with some bacterial growth belonged to the surgeon’s gloves after specimen extraction; about one-third of samples showed growth after specimen extraction, but only 1 sample had a bacterial load above the infectious threshold of 5,000 colony-forming units per mL. The authors therefore suggested that if a surgeon changes gloves, doing so after specimen extraction and before turning attention back to the abdomen for vaginal cuff closure may be most effective in reducing bacterial load.17
Surgical site infection contributes to medical cost and likely medical waste as well. For example, surgical site infection may require prolonged treatments, tests, and medical instruments. In severe cases with abscesses, treatment entails hospitalization with prolonged antibiotic therapy with or without procedures to drain the collections. Further research therefore is warranted to investigate safe and environmentally friendly practices.
Myriad products are introduced to the medical system each day, some of which replace conventional tools. For instance, low-density polyethylene, or LDPE, transfer sheet is advertised for lateral patient transfer from the OR table to the bed or stretcher. This No. 4–coded plastic, while recyclable, is routinely discarded as trash in ORs. One ergonomic study found that reusable slide boards are as effective for reducing friction and staff muscle activities and are noninferior to the plastic sheets.18
Steps to making an impact
Operating rooms and labor and delivery units are responsible for a large proportion of hospital waste, and therefore they are of paramount importance in reducing waste and carbon footprint at the individual and institutional level. Reduction of OR waste not only is environmentally conscious but also decreases cost. Steps as small as individual practices to as big as changing infrastructures can make an impact. For instance:
- redesigning surgical carts
- reformulating surgeon-specific supply lists
- raising awareness about surgical overage
- encouraging recycling through education and audit
- optimizing surgical waste segregation through educational posters.
These are all simple steps that could significantly reduce waste and carbon footprint.
Bottom line
Although waste reduction is the responsibility of all health care providers, as leaders in their workplace physicians can serve as role models by implementing “green” practices in procedural units. Raising awareness and using a team approach is critical to succeed in our endeavors to move toward an environmentally friendly future. ●
Have you ever looked at the operating room (OR) trash bin at the end of a case and wondered if all that waste is necessary? Since I started my residency, not a day goes by that I have not asked myself this question.
In the mid-1990s, John Elkington introduced the concept of the triple bottom line—that is, people, planet, and profit—for implementation and measurement of sustainability in businesses.1 The health care sector is no exception when it comes to the bottom line! However, “people” remain the priority. What is our role, as ObGyns, in protecting the “planet” while keeping the “people” safe?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), climate change remains the single biggest health threat to humanity.2 The health care system is both the victim and the culprit. Studies suggest that the health care system, second to the food industry, is the biggest contributor to waste production in the United States. This sector generates more than 6,000 metric tons of waste each day and nearly 4 million tons (3.6 million metric tons) of solid waste each year.3 The health care system is responsible for an estimated 8% to 10% of total greenhouse gas emissions in the United States; the US health care system alone contributes to more than one-fourth of the global health care carbon footprint. If it were a country, the US health care system would rank 13th among all countries in emissions.4In turn, pollution produced by the health sector negatively impacts population health, further burdening the health care system. According to 2013 study data, the annual health damage caused by health care pollution was comparable to that of the deaths caused by preventable medical error.4
Aside from the environmental aspects, hospital waste disposal is expensive; reducing this cost is a potential area of interest for institutions.
As ObGyns, what is our role in reducing our waste generation and carbon footprint while keeping patients safe?
Defining health care waste, and disposal considerations
The WHO defines health care waste as including “the waste generated by health-care establishments, research facilities, and laboratories” as well as waste from scattered sources such as home dialysis and insulin injections.5 Despite representing a relatively small physical area of hospitals, labor and delivery units combined with ORs account for approximately 70% of all hospital waste.3 Operating room waste consists of disposable surgical supplies, personal protective equipment, drapes, plastic wrappers, sterile blue wraps, glass, cardboard, packaging material, medications, fluids, and other materials (FIGURE 1).

The WHO also notes that of all the waste generated by health care activities, about 85% is general, nonhazardous waste that is comparable to domestic waste.6 Hazardous waste is any material that poses a health risk, including potentially infectious materials, such as blood-soaked gauze, sharps, pharmaceuticals, or radioactive materials.6
Disposal of hazardous waste is expensiveand energy consuming as it is typically incinerated rather than disposed of in a landfill. This process produces substantial greenhouse gases, about 3 kg of carbon dioxide for every 1 kg of hazardous waste.7
Red bags are used for hazardous waste disposal, while clear bags are used for general waste. Operating rooms produce about two-thirds of the hospital red-bag waste.8 Waste segregation unfortunately is not accurate, and as much as 90% of OR general waste is improperly designated as hazardous waste.3 Drapes and uncontaminated, needleless syringes, for example, should be disposed of in clear bags, but often they are instead directed to the red-bag and sharps container (FIGURE 2).

Obstetrics and gynecology has an important role to play in accurate waste segregation given the specialty’s frequent interaction with bodily fluids. Clinicians and other staff need to recognize and appropriately separate hazardous waste from general waste. For instance, not all fabrics involved in a case should be disposed of in the red bin, only those saturated with blood or body fluids. Educating health care staff and placing instruction posters on the red trash bins potentially could aid in accurate waste segregation and reduce regulated waste while decreasing disposal costs.
Recycling in the OR
Recycling has become an established practice in many health care facilities and ORs. Studies suggest that introducing recycling programs in ORs not only reduces carbon footprints but also reduces costs.3 One study reported that US academic medical centers consume 2 million lb ($15 million) each year of recoverable medical supplies.9
Single-stream recycling, a system in which all recyclable material—including plastics, paper, metal, and glass—are placed in a single bin without segregation at the collection site, has gained in popularity. Recycling can be implemented both in ORs and in other perioperative areas where regular trash bins are located.
In a study done at Oxford University Hospitals in the United Kingdom, introducing recycling bins in every OR, as well as in recovery and staff rest areas, helped improve waste segregation such that approximately 22% of OR waste was recycled.10 Studies show that recycling programs not only decrease the health care carbon footprint but also have a considerable financial impact. Albert and colleagues demonstrated that introducing a single-stream recycling program to a 9-OR day (or ambulatory) surgery center could redirect more than 4 tons of waste each month and saved thousands of dollars.11
Despite continued improvement in recycling programs, the segregation process is still far from optimal. In a survey done at the Mayo Clinic by Azouz and colleagues, more than half of the staff reported being unclear about which OR items are recyclable and nearly half reported that lack of knowledge was the barrier to proper recycling.12 That study also showed that after implementation of a recycling education program, costs decreased 10% relative to the same time period in prior years.12
Blue wraps. One example of recycling optimization is blue wraps, the polypropylene (No. 5 plastic) material used for wrapping surgical instruments. Blue wraps account for approximately 19% of OR waste and 5% of all hospital waste.11 Blue wraps are not biodegradable and also are not widely recycled. In recent years, a resale market has emerged for blue wraps, as they can be used for production of other No. 5 plastic items.9 By reselling blue wraps, revenue can be generated by recycling a necessary packing material that would otherwise require payment for disposal.
Sterility considerations. While recycling in ORs may raise concern due to the absolute sterility required in procedural settings, technologic developments have been promising in advancing safe recycling to reduce carbon footprints and health care costs without compromising patients’ safety. Segregation of waste from recyclable packaging material prior to the case, as well as directing trash to the correct bin (regular vs red bin), is one example. Moreover, because about 80% of all OR waste is generated during the set up before the patient arrives in the OR, it is not contaminated and can be safely recycled.13
Continue to: Packaging material...
Packaging material
A substantial part of OR waste consists of packaging material; of all OR waste, 26% consists of plastics and 7%, paper and cartons.14 Increasing use of disposable or “single use” medical products in ORs, along with the intention to safeguard sterility, contributes significantly to the generation of medical waste in operating units. Containers, wraps and overwraps, cardboard, and plastic packaging are all composed of materials that when clean, can be recycled; however, these items often end up in the landfill (FIGURE 3).

Although the segregation of packaging material to recycling versus regular trash versus red bin is of paramount importance, packaging design plays a significant role as well. In 2018, Boston Scientific introduced a new packaging design for ureteral stents that reduced plastic use in packaging by 120,000 lb each year.15 Despite the advances in the medical packaging industry to increase sustainability while safeguarding sterility for medical devices, there is still room for innovation in this area.
Reducing overage by judicious selection of surgical devices, instruments, and supplies
Overage is the term used to describe surgical inventory that is opened and prepared for surgery but ultimately not used and therefore discarded. Design of surgical carts and instrument and supply selection requires direct input from ObGyns. Opening only the needed instruments while ensuring ready availability of potentially needed supplies can significantly reduce OR waste generation as well as decrease chemical pollution generated by instrument sterilization. Decreasing OR overage reduces overall costs as well (FIGURE 4).

In a pilot study at the University of Massachusetts, Albert and colleagues examined the sets of disposable items and instruments designated for common plastic and hand surgery procedures.11 They identified the supplies and instruments that are routinely opened and wasted, based on surgeons’ interview responses, and redesigned the sets. Fifteen items were removed from disposable plastic surgery packs and 7 items from hand surgery packs. The authors reported saving thousands of dollars per year with these changes alone, as well as reducing waste.11 This same concept easily could be implemented in obstetrics and gynecology. We must ask ourselves: Do we always need, for example, a complete dilation and curettage kit to place the uterine manipulator prior to a minimally invasive hysterectomy?
In another pilot study, Greenberg and colleagues investigated whether cesarean deliveries consistently could be performed in a safe manner with only 20 instruments in the surgical kit.16 Obstetricians rated the 20-instrument kit an 8.7 out of 10 for performing cesarean deliveries safely.16
In addition to instrument selection, surgeons have a role in other supply use and waste generation: for instance, opening multiple pairs of surgical gloves and surgical gowns in advance when most of them will not be used during the case. Furthermore, many ObGyn surgeons routinely change gloves or even gowns during gynecologic procedures when they go back and forth between the vaginal and abdominal fields. Is the perineum “dirty” after application of a surgical prep solution?
In an observational study, Shockley and colleagues investigated the type and quantity of bacteria found intraoperatively on the abdomen, vagina, surgical gloves, instrument tips, and uterus at distinct time points during total laparoscopic hysterectomy.17 They showed that in 98.9% of cultures, the overall bacterial concentrations did not exceed the threshold for infection. There was no bacterial growth from vaginal cultures, and the only samples with some bacterial growth belonged to the surgeon’s gloves after specimen extraction; about one-third of samples showed growth after specimen extraction, but only 1 sample had a bacterial load above the infectious threshold of 5,000 colony-forming units per mL. The authors therefore suggested that if a surgeon changes gloves, doing so after specimen extraction and before turning attention back to the abdomen for vaginal cuff closure may be most effective in reducing bacterial load.17
Surgical site infection contributes to medical cost and likely medical waste as well. For example, surgical site infection may require prolonged treatments, tests, and medical instruments. In severe cases with abscesses, treatment entails hospitalization with prolonged antibiotic therapy with or without procedures to drain the collections. Further research therefore is warranted to investigate safe and environmentally friendly practices.
Myriad products are introduced to the medical system each day, some of which replace conventional tools. For instance, low-density polyethylene, or LDPE, transfer sheet is advertised for lateral patient transfer from the OR table to the bed or stretcher. This No. 4–coded plastic, while recyclable, is routinely discarded as trash in ORs. One ergonomic study found that reusable slide boards are as effective for reducing friction and staff muscle activities and are noninferior to the plastic sheets.18
Steps to making an impact
Operating rooms and labor and delivery units are responsible for a large proportion of hospital waste, and therefore they are of paramount importance in reducing waste and carbon footprint at the individual and institutional level. Reduction of OR waste not only is environmentally conscious but also decreases cost. Steps as small as individual practices to as big as changing infrastructures can make an impact. For instance:
- redesigning surgical carts
- reformulating surgeon-specific supply lists
- raising awareness about surgical overage
- encouraging recycling through education and audit
- optimizing surgical waste segregation through educational posters.
These are all simple steps that could significantly reduce waste and carbon footprint.
Bottom line
Although waste reduction is the responsibility of all health care providers, as leaders in their workplace physicians can serve as role models by implementing “green” practices in procedural units. Raising awareness and using a team approach is critical to succeed in our endeavors to move toward an environmentally friendly future. ●
- Elkington J. Towards the sustainable corporation: win-winwin business strategies for sustainable development. Calif Manage Rev. 1994;36:90-100.
- Climate change and health. October 30, 2021. World Health Organization. Accessed October 10, 2022. https://www.who .int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/climate-change-and -health
- Kwakye G, Brat GA, Makary MA. Green surgical practices for health care. Arch Surg. 2011;146:131-136.
- Eckelman MJ, Sherman J. Environmental impacts of the US health care system and effects on public health. PloS One. 2016;11:e0157014.
- Pruss A, Giroult E, Rushbrook P. Safe management of wastes from health-care activities. World Health Organization; 1999.
- Health-care waste. February 8, 2018. World Health Organization. Accessed October 4, 2022. https://www.who. int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/health-care-waste2
- Southorn T, Norrish AR, Gardner K, et al. Reducing the carbon footprint of the operating theatre: a multicentre quality improvement report. J Perioper Pract. 2013;23:144-146.
- Greening the OR. Practice Greenhealth. Accessed October 24, 2022. https://practicegreenhealth.org/topics/greening -operating-room/greening-or
- Babu MA, Dalenberg AK, Goodsell G, et al. Greening the operating room: results of a scalable initiative to reduce waste and recover supply costs. Neurosurgery. 2019;85:432-437.
- Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust. Introducing recycling into the operating theatres. Mapping Greener Healthcare. Accessed October 14, 2022. https://map .sustainablehealthcare.org.uk/oxford-radcliffe-hospitals -nhs-trust/introducing-recycling-operating-theatres
- Albert MG, Rothkopf DM. Operating room waste reduction in plastic and hand surgery. Plast Surg. 2015;23:235-238.
- Azouz S, Boyll P, Swanson M, et al. Managing barriers to recycling in the operating room. Am J Surg. 2019;217:634-638.
- Wyssusek KH, Keys MT, van Zundert AAJ. Operating room greening initiatives—the old, the new, and the way forward: a narrative review. Waste Manag Res. 2019;37:3-19.
- Tieszen ME, Gruenberg JC. A quantitative, qualitative, and critical assessment of surgical waste: surgeons venture through the trash can. JAMA. 1992;267:2765-2768.
- Boston Scientific 2018 Performance Report. Boston Scientific. Accessed November 19, 2022. https://www.bostonscientific. com/content/dam/bostonscientific/corporate/citizenship /sustainability/Boston_Scientific_Performance _Report_2018.pdf
- Greenberg JA, Wylie B, Robinson JN. A pilot study to assess the adequacy of the Brigham 20 Kit for cesarean delivery. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2012;117:157-159.
- Shockley ME, Beran B, Nutting H, et al. Sterility of selected operative sites during total laparoscopic hysterectomy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24:990-997.
- Al-Qaisi SK, El Tannir A, Younan LA, et al. An ergonomic assessment of using laterally-tilting operating room tables and friction reducing devices for patient lateral transfers. Appl Ergon. 2020;87:103122.
- Elkington J. Towards the sustainable corporation: win-winwin business strategies for sustainable development. Calif Manage Rev. 1994;36:90-100.
- Climate change and health. October 30, 2021. World Health Organization. Accessed October 10, 2022. https://www.who .int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/climate-change-and -health
- Kwakye G, Brat GA, Makary MA. Green surgical practices for health care. Arch Surg. 2011;146:131-136.
- Eckelman MJ, Sherman J. Environmental impacts of the US health care system and effects on public health. PloS One. 2016;11:e0157014.
- Pruss A, Giroult E, Rushbrook P. Safe management of wastes from health-care activities. World Health Organization; 1999.
- Health-care waste. February 8, 2018. World Health Organization. Accessed October 4, 2022. https://www.who. int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/health-care-waste2
- Southorn T, Norrish AR, Gardner K, et al. Reducing the carbon footprint of the operating theatre: a multicentre quality improvement report. J Perioper Pract. 2013;23:144-146.
- Greening the OR. Practice Greenhealth. Accessed October 24, 2022. https://practicegreenhealth.org/topics/greening -operating-room/greening-or
- Babu MA, Dalenberg AK, Goodsell G, et al. Greening the operating room: results of a scalable initiative to reduce waste and recover supply costs. Neurosurgery. 2019;85:432-437.
- Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust. Introducing recycling into the operating theatres. Mapping Greener Healthcare. Accessed October 14, 2022. https://map .sustainablehealthcare.org.uk/oxford-radcliffe-hospitals -nhs-trust/introducing-recycling-operating-theatres
- Albert MG, Rothkopf DM. Operating room waste reduction in plastic and hand surgery. Plast Surg. 2015;23:235-238.
- Azouz S, Boyll P, Swanson M, et al. Managing barriers to recycling in the operating room. Am J Surg. 2019;217:634-638.
- Wyssusek KH, Keys MT, van Zundert AAJ. Operating room greening initiatives—the old, the new, and the way forward: a narrative review. Waste Manag Res. 2019;37:3-19.
- Tieszen ME, Gruenberg JC. A quantitative, qualitative, and critical assessment of surgical waste: surgeons venture through the trash can. JAMA. 1992;267:2765-2768.
- Boston Scientific 2018 Performance Report. Boston Scientific. Accessed November 19, 2022. https://www.bostonscientific. com/content/dam/bostonscientific/corporate/citizenship /sustainability/Boston_Scientific_Performance _Report_2018.pdf
- Greenberg JA, Wylie B, Robinson JN. A pilot study to assess the adequacy of the Brigham 20 Kit for cesarean delivery. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2012;117:157-159.
- Shockley ME, Beran B, Nutting H, et al. Sterility of selected operative sites during total laparoscopic hysterectomy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24:990-997.
- Al-Qaisi SK, El Tannir A, Younan LA, et al. An ergonomic assessment of using laterally-tilting operating room tables and friction reducing devices for patient lateral transfers. Appl Ergon. 2020;87:103122.
Looking at diseases associated with RA, May 2023
Although rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is well understood to be associated with cigarette smoking as well as with a risk for interstitial lung disease (ILD), its association with airway diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and with allergic disorders such as atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis, is unknown. Kim and colleagues performed a cross-sectional study using information from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey by 334 respondents with RA and over 13,000 respondents without RA and analyzed the association of RA with asthma and asthma-related comorbidities. The prevalence of asthma was higher in respondents with RA (7.5% vs 2.8%; P < .001), but the prevalence of other allergic disorders and COPD wassimilar between groups. This finding in a small group of respondents is not striking and its importance is unclear compared with other nonallergic pulmonary disorders. Inferring a mechanistic connection to T-helper (Th) 1- vs Th2 immunity would thus be premature.
Baker and colleagues examined the risk for RA-associated ILD in patients taking different therapies for RA, a topic of great interest due to the frequency of this complication as well as uncertainty regarding its association with medications, including anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) agents and methotrexate. Using a claims database, they performed a retrospective study of patients with RA without existing ILD who were treated with a biologic (b) or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD; abatacept, adalimumab, rituximab, tocilizumab, and tofacitinib). In over 28,000 patients with RA, incidence ratios for ILD were > 1 for all bDMARD, while the incidence ratio for ILD with tofacitinib was 1.47. As the group of patients treated with tofacitinib was the smallest, the reliability of this result is uncertain and thus not strong enough to suggest a protective effect or preference for this medication in patients with known ILD. However, prospective studies looking at ILD in RA patients taking tofacitinib would be of interest.
Kristensen and colleagues also looked at risks associated with tofacitinib and anti-TNF agents, in particular cardiovascular disease, malignancy, and venous thromboembolism, using data from the open-label randomized ORAL Surveillance study, which looked at patients taking 5 mg or 10 mg tofacitinib twice daily, adalimumab, or etanercept. The 10 mg dose was reduced to 5 mg twice daily after it was found that rates of pulmonary embolism were higher in the group taking the higher dose. Age and smoking are also known to be risk factors for malignancy and cardiovascular disease in patients with RA, and these findings carried through in this analysis as well. Within the study, patients taking tofacitinib over age 65 who had ever smoked had a higher risk for cardiovascular events, myocardial infarction, malignancy, venous thromboembolism, and death compared with patients on anti-TNF therapy, while patients taking tofacitinib who were younger than 65 and had never smoked had a risk similar to those on anti-TNF therapy.The study confirms prior knowledge regarding the risks of tofacitinib in different patient populations, suggesting that caution should be used with this medication in older patients and those who smoke.
Although rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is well understood to be associated with cigarette smoking as well as with a risk for interstitial lung disease (ILD), its association with airway diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and with allergic disorders such as atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis, is unknown. Kim and colleagues performed a cross-sectional study using information from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey by 334 respondents with RA and over 13,000 respondents without RA and analyzed the association of RA with asthma and asthma-related comorbidities. The prevalence of asthma was higher in respondents with RA (7.5% vs 2.8%; P < .001), but the prevalence of other allergic disorders and COPD wassimilar between groups. This finding in a small group of respondents is not striking and its importance is unclear compared with other nonallergic pulmonary disorders. Inferring a mechanistic connection to T-helper (Th) 1- vs Th2 immunity would thus be premature.
Baker and colleagues examined the risk for RA-associated ILD in patients taking different therapies for RA, a topic of great interest due to the frequency of this complication as well as uncertainty regarding its association with medications, including anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) agents and methotrexate. Using a claims database, they performed a retrospective study of patients with RA without existing ILD who were treated with a biologic (b) or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD; abatacept, adalimumab, rituximab, tocilizumab, and tofacitinib). In over 28,000 patients with RA, incidence ratios for ILD were > 1 for all bDMARD, while the incidence ratio for ILD with tofacitinib was 1.47. As the group of patients treated with tofacitinib was the smallest, the reliability of this result is uncertain and thus not strong enough to suggest a protective effect or preference for this medication in patients with known ILD. However, prospective studies looking at ILD in RA patients taking tofacitinib would be of interest.
Kristensen and colleagues also looked at risks associated with tofacitinib and anti-TNF agents, in particular cardiovascular disease, malignancy, and venous thromboembolism, using data from the open-label randomized ORAL Surveillance study, which looked at patients taking 5 mg or 10 mg tofacitinib twice daily, adalimumab, or etanercept. The 10 mg dose was reduced to 5 mg twice daily after it was found that rates of pulmonary embolism were higher in the group taking the higher dose. Age and smoking are also known to be risk factors for malignancy and cardiovascular disease in patients with RA, and these findings carried through in this analysis as well. Within the study, patients taking tofacitinib over age 65 who had ever smoked had a higher risk for cardiovascular events, myocardial infarction, malignancy, venous thromboembolism, and death compared with patients on anti-TNF therapy, while patients taking tofacitinib who were younger than 65 and had never smoked had a risk similar to those on anti-TNF therapy.The study confirms prior knowledge regarding the risks of tofacitinib in different patient populations, suggesting that caution should be used with this medication in older patients and those who smoke.
Although rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is well understood to be associated with cigarette smoking as well as with a risk for interstitial lung disease (ILD), its association with airway diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and with allergic disorders such as atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis, is unknown. Kim and colleagues performed a cross-sectional study using information from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey by 334 respondents with RA and over 13,000 respondents without RA and analyzed the association of RA with asthma and asthma-related comorbidities. The prevalence of asthma was higher in respondents with RA (7.5% vs 2.8%; P < .001), but the prevalence of other allergic disorders and COPD wassimilar between groups. This finding in a small group of respondents is not striking and its importance is unclear compared with other nonallergic pulmonary disorders. Inferring a mechanistic connection to T-helper (Th) 1- vs Th2 immunity would thus be premature.
Baker and colleagues examined the risk for RA-associated ILD in patients taking different therapies for RA, a topic of great interest due to the frequency of this complication as well as uncertainty regarding its association with medications, including anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) agents and methotrexate. Using a claims database, they performed a retrospective study of patients with RA without existing ILD who were treated with a biologic (b) or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD; abatacept, adalimumab, rituximab, tocilizumab, and tofacitinib). In over 28,000 patients with RA, incidence ratios for ILD were > 1 for all bDMARD, while the incidence ratio for ILD with tofacitinib was 1.47. As the group of patients treated with tofacitinib was the smallest, the reliability of this result is uncertain and thus not strong enough to suggest a protective effect or preference for this medication in patients with known ILD. However, prospective studies looking at ILD in RA patients taking tofacitinib would be of interest.
Kristensen and colleagues also looked at risks associated with tofacitinib and anti-TNF agents, in particular cardiovascular disease, malignancy, and venous thromboembolism, using data from the open-label randomized ORAL Surveillance study, which looked at patients taking 5 mg or 10 mg tofacitinib twice daily, adalimumab, or etanercept. The 10 mg dose was reduced to 5 mg twice daily after it was found that rates of pulmonary embolism were higher in the group taking the higher dose. Age and smoking are also known to be risk factors for malignancy and cardiovascular disease in patients with RA, and these findings carried through in this analysis as well. Within the study, patients taking tofacitinib over age 65 who had ever smoked had a higher risk for cardiovascular events, myocardial infarction, malignancy, venous thromboembolism, and death compared with patients on anti-TNF therapy, while patients taking tofacitinib who were younger than 65 and had never smoked had a risk similar to those on anti-TNF therapy.The study confirms prior knowledge regarding the risks of tofacitinib in different patient populations, suggesting that caution should be used with this medication in older patients and those who smoke.
Bariatric surgery cuts risk for obesity-related cancers in half: Study
For years evidence has pointed to multiple health benefits associated with bariatric surgery, including improvements in diabetes, sleep apnea, and blood pressure. Now researchers are adding cutting cancer risk by more than half to the list.
compared with 8.9% of their peers who did not undergo such surgery.
“We did see a difference in breast cancer, colon cancer, liver cancer, and ovarian cancer incidence. ... with patients in the bariatric surgery group having lower incidence of these four types of cancers when compared to the nonsurgical control group,” said Vibhu Chittajallu, MD, lead author and a gastroenterology fellow at Case Western Reserve University and University Hospitals in Cleveland.
The obesity epidemic is “one of the most serious health challenges in the United States today,” Dr. Chittajallu added at an April 27 media briefing during which select research was previewed for the annual Digestive Disease Week®. Obesity has been associated with multiple serious illnesses, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
Obesity is also common. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that nearly 42% of American adults have obesity, and rates continue to rise.
Dr. Chittajallu and colleagues used billing codes in a national database to identify 55,789 patients with obesity who underwent bariatric surgery (sleeve gastrectomy, gastric bypass, or gastric band procedures) and a control group of the same size who did not have surgery.
Investigators controlled for risk factors that contribute to cancer development, including smoking history, alcohol use, heart disease, and hormone therapies.
Key findings
In 10 years of follow-up, 2,206 patients who underwent bariatric surgery developed an obesity-associated cancer, compared with 4,960 patients who did not have bariatric surgery.
The bariatric surgery group had lower numbers of new cases for six types of cancers (Table 1).
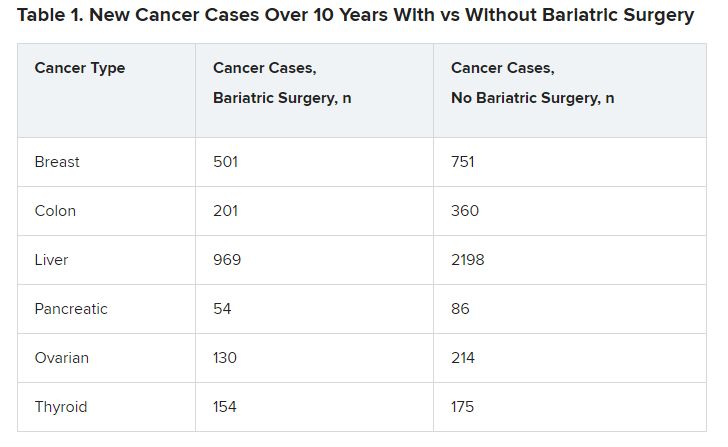
The differences were significant in four cancer types associated with obesity: breast cancer (P = .001), colon cancer (P < .01), liver cancer (P < .01), and ovarian cancer (P = .002).
The incidence of several other cancers, including renal carcinoma, and rectal and endometrial cancers, was not significantly different between the groups.
The mechanisms underlying excess cancer cases in patients with obesity are not completely understood, Dr. Chittajallu said. Bariatric surgery has been shown to decrease excess inflammation, elevate insulin, and moderate hormone levels.
‘Fascinating’ study but questions remain
The study is “fascinating,” said Loren Laine, MD, moderator of the media briefing. “Obesity is clearly associated with a number of different cancers, and that’s very important. So, it makes logical sense that if you lose weight, you will reduce that risk.”
Although investigators controlled for several known cancer risk factors, there are some they couldn’t control for because they were not included in the database, and there could be unknowns that also affected the results, noted Dr. Laine, who is professor of medicine (digestive diseases) and chief of digestive health at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
“You have to be circumspect when you look at retrospective observational studies,” he added.
It would be helpful to know when most cancers developed over the 10 years, Dr. Laine said. Dr. Chittajallu responded that the research team did not include cancers that developed in the first year after bariatric surgery to minimize incidental findings, but he did not provide a timeline for the cancers that developed.
Another unanswered question, Dr. Laine said, is whether a dose-response relationship exists. If future research shows that the more weight a person loses, the more likely they are to have a reduction in cancer risk, “that would be fascinating,” he said. Also, it would be interesting to know if endoscopic interventions and weight-loss medications decrease cancer risks in people with obesity.
More research is needed to understand how bariatric surgery affects cancer risk, Dr. Chittajallu said. “But the significant findings from this study suggest it’s an exciting avenue for further study.”
DDW 2023 will be held May 6-9 in Chicago and virtually.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Chittajallu and Dr. Laine have reported no relevant financial relationships.
The meeting is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For years evidence has pointed to multiple health benefits associated with bariatric surgery, including improvements in diabetes, sleep apnea, and blood pressure. Now researchers are adding cutting cancer risk by more than half to the list.
compared with 8.9% of their peers who did not undergo such surgery.
“We did see a difference in breast cancer, colon cancer, liver cancer, and ovarian cancer incidence. ... with patients in the bariatric surgery group having lower incidence of these four types of cancers when compared to the nonsurgical control group,” said Vibhu Chittajallu, MD, lead author and a gastroenterology fellow at Case Western Reserve University and University Hospitals in Cleveland.
The obesity epidemic is “one of the most serious health challenges in the United States today,” Dr. Chittajallu added at an April 27 media briefing during which select research was previewed for the annual Digestive Disease Week®. Obesity has been associated with multiple serious illnesses, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
Obesity is also common. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that nearly 42% of American adults have obesity, and rates continue to rise.
Dr. Chittajallu and colleagues used billing codes in a national database to identify 55,789 patients with obesity who underwent bariatric surgery (sleeve gastrectomy, gastric bypass, or gastric band procedures) and a control group of the same size who did not have surgery.
Investigators controlled for risk factors that contribute to cancer development, including smoking history, alcohol use, heart disease, and hormone therapies.
Key findings
In 10 years of follow-up, 2,206 patients who underwent bariatric surgery developed an obesity-associated cancer, compared with 4,960 patients who did not have bariatric surgery.
The bariatric surgery group had lower numbers of new cases for six types of cancers (Table 1).

The differences were significant in four cancer types associated with obesity: breast cancer (P = .001), colon cancer (P < .01), liver cancer (P < .01), and ovarian cancer (P = .002).
The incidence of several other cancers, including renal carcinoma, and rectal and endometrial cancers, was not significantly different between the groups.
The mechanisms underlying excess cancer cases in patients with obesity are not completely understood, Dr. Chittajallu said. Bariatric surgery has been shown to decrease excess inflammation, elevate insulin, and moderate hormone levels.
‘Fascinating’ study but questions remain
The study is “fascinating,” said Loren Laine, MD, moderator of the media briefing. “Obesity is clearly associated with a number of different cancers, and that’s very important. So, it makes logical sense that if you lose weight, you will reduce that risk.”
Although investigators controlled for several known cancer risk factors, there are some they couldn’t control for because they were not included in the database, and there could be unknowns that also affected the results, noted Dr. Laine, who is professor of medicine (digestive diseases) and chief of digestive health at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
“You have to be circumspect when you look at retrospective observational studies,” he added.
It would be helpful to know when most cancers developed over the 10 years, Dr. Laine said. Dr. Chittajallu responded that the research team did not include cancers that developed in the first year after bariatric surgery to minimize incidental findings, but he did not provide a timeline for the cancers that developed.
Another unanswered question, Dr. Laine said, is whether a dose-response relationship exists. If future research shows that the more weight a person loses, the more likely they are to have a reduction in cancer risk, “that would be fascinating,” he said. Also, it would be interesting to know if endoscopic interventions and weight-loss medications decrease cancer risks in people with obesity.
More research is needed to understand how bariatric surgery affects cancer risk, Dr. Chittajallu said. “But the significant findings from this study suggest it’s an exciting avenue for further study.”
DDW 2023 will be held May 6-9 in Chicago and virtually.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Chittajallu and Dr. Laine have reported no relevant financial relationships.
The meeting is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For years evidence has pointed to multiple health benefits associated with bariatric surgery, including improvements in diabetes, sleep apnea, and blood pressure. Now researchers are adding cutting cancer risk by more than half to the list.
compared with 8.9% of their peers who did not undergo such surgery.
“We did see a difference in breast cancer, colon cancer, liver cancer, and ovarian cancer incidence. ... with patients in the bariatric surgery group having lower incidence of these four types of cancers when compared to the nonsurgical control group,” said Vibhu Chittajallu, MD, lead author and a gastroenterology fellow at Case Western Reserve University and University Hospitals in Cleveland.
The obesity epidemic is “one of the most serious health challenges in the United States today,” Dr. Chittajallu added at an April 27 media briefing during which select research was previewed for the annual Digestive Disease Week®. Obesity has been associated with multiple serious illnesses, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
Obesity is also common. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that nearly 42% of American adults have obesity, and rates continue to rise.
Dr. Chittajallu and colleagues used billing codes in a national database to identify 55,789 patients with obesity who underwent bariatric surgery (sleeve gastrectomy, gastric bypass, or gastric band procedures) and a control group of the same size who did not have surgery.
Investigators controlled for risk factors that contribute to cancer development, including smoking history, alcohol use, heart disease, and hormone therapies.
Key findings
In 10 years of follow-up, 2,206 patients who underwent bariatric surgery developed an obesity-associated cancer, compared with 4,960 patients who did not have bariatric surgery.
The bariatric surgery group had lower numbers of new cases for six types of cancers (Table 1).

The differences were significant in four cancer types associated with obesity: breast cancer (P = .001), colon cancer (P < .01), liver cancer (P < .01), and ovarian cancer (P = .002).
The incidence of several other cancers, including renal carcinoma, and rectal and endometrial cancers, was not significantly different between the groups.
The mechanisms underlying excess cancer cases in patients with obesity are not completely understood, Dr. Chittajallu said. Bariatric surgery has been shown to decrease excess inflammation, elevate insulin, and moderate hormone levels.
‘Fascinating’ study but questions remain
The study is “fascinating,” said Loren Laine, MD, moderator of the media briefing. “Obesity is clearly associated with a number of different cancers, and that’s very important. So, it makes logical sense that if you lose weight, you will reduce that risk.”
Although investigators controlled for several known cancer risk factors, there are some they couldn’t control for because they were not included in the database, and there could be unknowns that also affected the results, noted Dr. Laine, who is professor of medicine (digestive diseases) and chief of digestive health at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
“You have to be circumspect when you look at retrospective observational studies,” he added.
It would be helpful to know when most cancers developed over the 10 years, Dr. Laine said. Dr. Chittajallu responded that the research team did not include cancers that developed in the first year after bariatric surgery to minimize incidental findings, but he did not provide a timeline for the cancers that developed.
Another unanswered question, Dr. Laine said, is whether a dose-response relationship exists. If future research shows that the more weight a person loses, the more likely they are to have a reduction in cancer risk, “that would be fascinating,” he said. Also, it would be interesting to know if endoscopic interventions and weight-loss medications decrease cancer risks in people with obesity.
More research is needed to understand how bariatric surgery affects cancer risk, Dr. Chittajallu said. “But the significant findings from this study suggest it’s an exciting avenue for further study.”
DDW 2023 will be held May 6-9 in Chicago and virtually.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Chittajallu and Dr. Laine have reported no relevant financial relationships.
The meeting is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT DDW 2023
Understanding clinic-reported IVF success rates
The field of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) continues to evolve from its first successful birth in 1978 in England, and then in 1981 in the United States. Over the last 6 years, the total number of cycles in the U.S. has increased by 44% to nearly 370,000.
SART membership consists of more than 350 clinics throughout the United States, representing 80% of ART clinics. Over 95% of ART cycles in 2021 in the United States were performed in SART-member clinics.
SART is an invaluable resource for both patients and physicians. Their website includes a “Predict My Success” calculator that allows patients and physicians to enter individualized data to calculate the chance of having a baby over one or more complete cycles of IVF. To help us understand the pregnancy outcome data from ART – cycles per clinic along with national results – I posed the questions below to Amy Sparks, PhD, HCLD, director of the IVF and Andrology Laboratories and the Center for Advanced Reproductive Care at University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City. Dr. Sparks is past president of SART and former chairperson of the SART Registry committee when the current Clinic Summary Report format was initially released.
Question: The Fertility Clinic Success Rate and Certification Act (FCSRCA) of 1992 mandated that all ART clinics report success rate data to the federal government, through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in a standardized manner. As ART is the only field in medicine to be required to annually report their patient outcomes, that is, all initiated cycles and live births, why do you believe this law was enacted and is limited to reproductive medicine?
Answer: The FCSRCA of 1992 was enacted in response to the lack of open and reliable pregnancy success rate information for patients seeking infertility care using assisted reproductive technologies. Success rates of 25%-50% were being advertised by independent clinics when, nationally, fewer than 15% of ART procedures led to live births. The Federal Trade Commission said such claims were deceptive and filed charges against five clinics, saying they misrepresented their success in helping women become pregnant. The government won one case by court order and the other four cases were settled out of court.
This field of medicine was in the spotlight as the majority of patients lacked insurance coverage for their ART cycles, and there was a strong desire to protect consumers paying out of pocket for relatively low success. Recognizing that the FTC’s mission is to ensure truth in advertising and not regulate medical care, Congress passed the FCSRCA, mandating that all centers providing ART services report all initiated cycles and their outcomes. The CDC was appointed as the agency responsible for collecting cycle data and reporting outcomes. Centers not reporting their cycles are listed as nonreporting centers.
This act also established standards for accreditation of embryology laboratories including personnel and traditional clinical laboratory management requirements. These standards serve as the foundation for embryology laboratory accrediting agencies.
Q: Why have live-birth rates on SART appeared to be focused on “per IVF cycle” as opposed to the CDC reporting of live births “per embryo transfer?”
A: An ART cycle “start” is defined as the initiation of ovarian stimulation with medication that may or may not include administration of exogenous gonadotropins, followed by oocyte retrieval and embryo transfer. Not every patient beginning a cycle will undergo an oocyte retrieval and not all patients who undergo oocyte retrieval have an embryo transfer. The live-birth rates (LBR) for each of these steps of progression in the ART process are available in the SART and CDC reports.
In 2016, SART recognized that practices were foregoing fresh embryo transfer after oocyte retrieval, opting to cryopreserve all embryos to either accommodate genetic testing of the embryos prior to transfer or to avoid embryo transfer to an unfavorable uterine environment. In response to changes in practice and in an effort to deemphasize live birth per transfer, thereby alleviating a potential motivator or pressure for practitioners to transfer multiple embryos, SART moved to a report that displays the cumulative live-birth rate per cycle start for oocyte retrieval. The cumulative live-birth rate per cycle start for oocyte retrieval is the chance of live birth from transfers of embryos derived from the oocyte retrieval and performed within 1 year of the oocyte retrieval.
This change in reporting further reduced the pressure to transfer multiple embryos and encouraged elective, single-embryo transfer. The outcome per transfer is no longer the report’s primary focus.
Q: The latest pregnancy outcomes statistics are from the year 2020 and are finalized by the CDC. Why does the SART website have this same year labeled “preliminary” outcomes?
A: Shortly after the 2016 SART report change, the CDC made similar changes to their report. The difference is that SART provides a “preliminary” report of outcomes within the year of the cycle start for oocyte retrieval. The cumulative outcome is not “finalized” until the following year as transfers may be performed as late as 12 months after the oocyte retrieval.
SART has opted to report both the “preliminary” or interim outcome and the “final” outcome a year later. The CDC has opted to limit their report to “final” outcomes. I’m happy to report that SART recently released the final report for 2021 cycles.
Q: Have national success rates in the United States continued to rise or have they plateaued?
A: It appears that success rates have plateaued; however, we find ourselves at another point where practice patterns and patients’ approach to using ART for family building have changed.
Recognizing the impact of maternal aging on reproductive potential, patients are opting to undergo multiple ART cycles to cryopreserve embryos for family building before they attempt to get pregnant. This family-building path reduces the value of measuring the LBR per cycle start as we may not know the outcome for many years. SART leaders are deliberating intently as to how to best represent this growing patient population in outcome reporting.
Q: Can you comment on the reduction of multiple gestations with the increasing use of single-embryo transfer?
A: The reduction in emphasis on live births per transfer, emphasis on singleton live-birth rates in both the SART and CDC reports, and American Society for Reproductive Medicine practice committee guidelines strongly supporting single embryo transfer have significantly reduced the rate of multiple gestations.
A decade ago, only a third of the transfers were single-embryo transfers and over 25% of live births resulted in a multiple birth. Today, the majority of embryo transfers are elective, single-embryo transfers, and the multiple birth rate has been reduced by nearly 80%. In 2020, 93% of live births from IVF were singletons.
Q: SART offers an online IVF calculator so both patients and physicians can plug in data for an approximate cumulative success rate for up to three IVF cycles. The calculator pools data from all U.S.-reporting IVF centers. Can you explain what an “IVF cycle” is and what patient information is required? Why do success rates increase over time?
A: Each “IVF cycle” is a cycle start for an oocyte retrieval and all transfers of embryos from that cycle within a year of the oocyte retrieval. If the first cycle and subsequent transfers do not lead to a live birth, patients still have a chance to achieve a live birth with a second or third cycle. The success rate increases over time as it reflects the chance of success for a population of patients, with some achieving a live birth after the first cycle and additional patients who achieve success following their third cycle.
Q: The SART IVF calculator can be used with no prior IVF cycles or following an unsuccessful cycle. Are there data to support an estimation of outcome following two or even more unsuccessful cycles?
A: The variables in the SART IVF calculator are based upon the cycle-specific data from patients seeking care at SART member clinics. The current predictor was built with data from cycles performed in 2015-2016. SART is adjusting the predictor and developing a calculator that will be routinely updated, accordingly.
Q: Only approximately 40% of states have some form of infertility coverage law in place; however the number of IVF cycles in the United States continues to increase on an annual basis. What do you think are the driving factors behind this?
A: Advocacy efforts to improve patients’ access to infertility care have included giving patients tools to encourage their employers to include infertility care in their health care benefits package. More recently, the “Great Resignation” has led to the “Great Recruitment” and employers are recognizing that the addition of infertility care to health care benefits is a powerful recruitment tool.
Dr. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
The field of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) continues to evolve from its first successful birth in 1978 in England, and then in 1981 in the United States. Over the last 6 years, the total number of cycles in the U.S. has increased by 44% to nearly 370,000.
SART membership consists of more than 350 clinics throughout the United States, representing 80% of ART clinics. Over 95% of ART cycles in 2021 in the United States were performed in SART-member clinics.
SART is an invaluable resource for both patients and physicians. Their website includes a “Predict My Success” calculator that allows patients and physicians to enter individualized data to calculate the chance of having a baby over one or more complete cycles of IVF. To help us understand the pregnancy outcome data from ART – cycles per clinic along with national results – I posed the questions below to Amy Sparks, PhD, HCLD, director of the IVF and Andrology Laboratories and the Center for Advanced Reproductive Care at University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City. Dr. Sparks is past president of SART and former chairperson of the SART Registry committee when the current Clinic Summary Report format was initially released.
Question: The Fertility Clinic Success Rate and Certification Act (FCSRCA) of 1992 mandated that all ART clinics report success rate data to the federal government, through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in a standardized manner. As ART is the only field in medicine to be required to annually report their patient outcomes, that is, all initiated cycles and live births, why do you believe this law was enacted and is limited to reproductive medicine?
Answer: The FCSRCA of 1992 was enacted in response to the lack of open and reliable pregnancy success rate information for patients seeking infertility care using assisted reproductive technologies. Success rates of 25%-50% were being advertised by independent clinics when, nationally, fewer than 15% of ART procedures led to live births. The Federal Trade Commission said such claims were deceptive and filed charges against five clinics, saying they misrepresented their success in helping women become pregnant. The government won one case by court order and the other four cases were settled out of court.
This field of medicine was in the spotlight as the majority of patients lacked insurance coverage for their ART cycles, and there was a strong desire to protect consumers paying out of pocket for relatively low success. Recognizing that the FTC’s mission is to ensure truth in advertising and not regulate medical care, Congress passed the FCSRCA, mandating that all centers providing ART services report all initiated cycles and their outcomes. The CDC was appointed as the agency responsible for collecting cycle data and reporting outcomes. Centers not reporting their cycles are listed as nonreporting centers.
This act also established standards for accreditation of embryology laboratories including personnel and traditional clinical laboratory management requirements. These standards serve as the foundation for embryology laboratory accrediting agencies.
Q: Why have live-birth rates on SART appeared to be focused on “per IVF cycle” as opposed to the CDC reporting of live births “per embryo transfer?”
A: An ART cycle “start” is defined as the initiation of ovarian stimulation with medication that may or may not include administration of exogenous gonadotropins, followed by oocyte retrieval and embryo transfer. Not every patient beginning a cycle will undergo an oocyte retrieval and not all patients who undergo oocyte retrieval have an embryo transfer. The live-birth rates (LBR) for each of these steps of progression in the ART process are available in the SART and CDC reports.
In 2016, SART recognized that practices were foregoing fresh embryo transfer after oocyte retrieval, opting to cryopreserve all embryos to either accommodate genetic testing of the embryos prior to transfer or to avoid embryo transfer to an unfavorable uterine environment. In response to changes in practice and in an effort to deemphasize live birth per transfer, thereby alleviating a potential motivator or pressure for practitioners to transfer multiple embryos, SART moved to a report that displays the cumulative live-birth rate per cycle start for oocyte retrieval. The cumulative live-birth rate per cycle start for oocyte retrieval is the chance of live birth from transfers of embryos derived from the oocyte retrieval and performed within 1 year of the oocyte retrieval.
This change in reporting further reduced the pressure to transfer multiple embryos and encouraged elective, single-embryo transfer. The outcome per transfer is no longer the report’s primary focus.
Q: The latest pregnancy outcomes statistics are from the year 2020 and are finalized by the CDC. Why does the SART website have this same year labeled “preliminary” outcomes?
A: Shortly after the 2016 SART report change, the CDC made similar changes to their report. The difference is that SART provides a “preliminary” report of outcomes within the year of the cycle start for oocyte retrieval. The cumulative outcome is not “finalized” until the following year as transfers may be performed as late as 12 months after the oocyte retrieval.
SART has opted to report both the “preliminary” or interim outcome and the “final” outcome a year later. The CDC has opted to limit their report to “final” outcomes. I’m happy to report that SART recently released the final report for 2021 cycles.
Q: Have national success rates in the United States continued to rise or have they plateaued?
A: It appears that success rates have plateaued; however, we find ourselves at another point where practice patterns and patients’ approach to using ART for family building have changed.
Recognizing the impact of maternal aging on reproductive potential, patients are opting to undergo multiple ART cycles to cryopreserve embryos for family building before they attempt to get pregnant. This family-building path reduces the value of measuring the LBR per cycle start as we may not know the outcome for many years. SART leaders are deliberating intently as to how to best represent this growing patient population in outcome reporting.
Q: Can you comment on the reduction of multiple gestations with the increasing use of single-embryo transfer?
A: The reduction in emphasis on live births per transfer, emphasis on singleton live-birth rates in both the SART and CDC reports, and American Society for Reproductive Medicine practice committee guidelines strongly supporting single embryo transfer have significantly reduced the rate of multiple gestations.
A decade ago, only a third of the transfers were single-embryo transfers and over 25% of live births resulted in a multiple birth. Today, the majority of embryo transfers are elective, single-embryo transfers, and the multiple birth rate has been reduced by nearly 80%. In 2020, 93% of live births from IVF were singletons.
Q: SART offers an online IVF calculator so both patients and physicians can plug in data for an approximate cumulative success rate for up to three IVF cycles. The calculator pools data from all U.S.-reporting IVF centers. Can you explain what an “IVF cycle” is and what patient information is required? Why do success rates increase over time?
A: Each “IVF cycle” is a cycle start for an oocyte retrieval and all transfers of embryos from that cycle within a year of the oocyte retrieval. If the first cycle and subsequent transfers do not lead to a live birth, patients still have a chance to achieve a live birth with a second or third cycle. The success rate increases over time as it reflects the chance of success for a population of patients, with some achieving a live birth after the first cycle and additional patients who achieve success following their third cycle.
Q: The SART IVF calculator can be used with no prior IVF cycles or following an unsuccessful cycle. Are there data to support an estimation of outcome following two or even more unsuccessful cycles?
A: The variables in the SART IVF calculator are based upon the cycle-specific data from patients seeking care at SART member clinics. The current predictor was built with data from cycles performed in 2015-2016. SART is adjusting the predictor and developing a calculator that will be routinely updated, accordingly.
Q: Only approximately 40% of states have some form of infertility coverage law in place; however the number of IVF cycles in the United States continues to increase on an annual basis. What do you think are the driving factors behind this?
A: Advocacy efforts to improve patients’ access to infertility care have included giving patients tools to encourage their employers to include infertility care in their health care benefits package. More recently, the “Great Resignation” has led to the “Great Recruitment” and employers are recognizing that the addition of infertility care to health care benefits is a powerful recruitment tool.
Dr. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
The field of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) continues to evolve from its first successful birth in 1978 in England, and then in 1981 in the United States. Over the last 6 years, the total number of cycles in the U.S. has increased by 44% to nearly 370,000.
SART membership consists of more than 350 clinics throughout the United States, representing 80% of ART clinics. Over 95% of ART cycles in 2021 in the United States were performed in SART-member clinics.
SART is an invaluable resource for both patients and physicians. Their website includes a “Predict My Success” calculator that allows patients and physicians to enter individualized data to calculate the chance of having a baby over one or more complete cycles of IVF. To help us understand the pregnancy outcome data from ART – cycles per clinic along with national results – I posed the questions below to Amy Sparks, PhD, HCLD, director of the IVF and Andrology Laboratories and the Center for Advanced Reproductive Care at University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City. Dr. Sparks is past president of SART and former chairperson of the SART Registry committee when the current Clinic Summary Report format was initially released.
Question: The Fertility Clinic Success Rate and Certification Act (FCSRCA) of 1992 mandated that all ART clinics report success rate data to the federal government, through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in a standardized manner. As ART is the only field in medicine to be required to annually report their patient outcomes, that is, all initiated cycles and live births, why do you believe this law was enacted and is limited to reproductive medicine?
Answer: The FCSRCA of 1992 was enacted in response to the lack of open and reliable pregnancy success rate information for patients seeking infertility care using assisted reproductive technologies. Success rates of 25%-50% were being advertised by independent clinics when, nationally, fewer than 15% of ART procedures led to live births. The Federal Trade Commission said such claims were deceptive and filed charges against five clinics, saying they misrepresented their success in helping women become pregnant. The government won one case by court order and the other four cases were settled out of court.
This field of medicine was in the spotlight as the majority of patients lacked insurance coverage for their ART cycles, and there was a strong desire to protect consumers paying out of pocket for relatively low success. Recognizing that the FTC’s mission is to ensure truth in advertising and not regulate medical care, Congress passed the FCSRCA, mandating that all centers providing ART services report all initiated cycles and their outcomes. The CDC was appointed as the agency responsible for collecting cycle data and reporting outcomes. Centers not reporting their cycles are listed as nonreporting centers.
This act also established standards for accreditation of embryology laboratories including personnel and traditional clinical laboratory management requirements. These standards serve as the foundation for embryology laboratory accrediting agencies.
Q: Why have live-birth rates on SART appeared to be focused on “per IVF cycle” as opposed to the CDC reporting of live births “per embryo transfer?”
A: An ART cycle “start” is defined as the initiation of ovarian stimulation with medication that may or may not include administration of exogenous gonadotropins, followed by oocyte retrieval and embryo transfer. Not every patient beginning a cycle will undergo an oocyte retrieval and not all patients who undergo oocyte retrieval have an embryo transfer. The live-birth rates (LBR) for each of these steps of progression in the ART process are available in the SART and CDC reports.
In 2016, SART recognized that practices were foregoing fresh embryo transfer after oocyte retrieval, opting to cryopreserve all embryos to either accommodate genetic testing of the embryos prior to transfer or to avoid embryo transfer to an unfavorable uterine environment. In response to changes in practice and in an effort to deemphasize live birth per transfer, thereby alleviating a potential motivator or pressure for practitioners to transfer multiple embryos, SART moved to a report that displays the cumulative live-birth rate per cycle start for oocyte retrieval. The cumulative live-birth rate per cycle start for oocyte retrieval is the chance of live birth from transfers of embryos derived from the oocyte retrieval and performed within 1 year of the oocyte retrieval.
This change in reporting further reduced the pressure to transfer multiple embryos and encouraged elective, single-embryo transfer. The outcome per transfer is no longer the report’s primary focus.
Q: The latest pregnancy outcomes statistics are from the year 2020 and are finalized by the CDC. Why does the SART website have this same year labeled “preliminary” outcomes?
A: Shortly after the 2016 SART report change, the CDC made similar changes to their report. The difference is that SART provides a “preliminary” report of outcomes within the year of the cycle start for oocyte retrieval. The cumulative outcome is not “finalized” until the following year as transfers may be performed as late as 12 months after the oocyte retrieval.
SART has opted to report both the “preliminary” or interim outcome and the “final” outcome a year later. The CDC has opted to limit their report to “final” outcomes. I’m happy to report that SART recently released the final report for 2021 cycles.
Q: Have national success rates in the United States continued to rise or have they plateaued?
A: It appears that success rates have plateaued; however, we find ourselves at another point where practice patterns and patients’ approach to using ART for family building have changed.
Recognizing the impact of maternal aging on reproductive potential, patients are opting to undergo multiple ART cycles to cryopreserve embryos for family building before they attempt to get pregnant. This family-building path reduces the value of measuring the LBR per cycle start as we may not know the outcome for many years. SART leaders are deliberating intently as to how to best represent this growing patient population in outcome reporting.
Q: Can you comment on the reduction of multiple gestations with the increasing use of single-embryo transfer?
A: The reduction in emphasis on live births per transfer, emphasis on singleton live-birth rates in both the SART and CDC reports, and American Society for Reproductive Medicine practice committee guidelines strongly supporting single embryo transfer have significantly reduced the rate of multiple gestations.
A decade ago, only a third of the transfers were single-embryo transfers and over 25% of live births resulted in a multiple birth. Today, the majority of embryo transfers are elective, single-embryo transfers, and the multiple birth rate has been reduced by nearly 80%. In 2020, 93% of live births from IVF were singletons.
Q: SART offers an online IVF calculator so both patients and physicians can plug in data for an approximate cumulative success rate for up to three IVF cycles. The calculator pools data from all U.S.-reporting IVF centers. Can you explain what an “IVF cycle” is and what patient information is required? Why do success rates increase over time?
A: Each “IVF cycle” is a cycle start for an oocyte retrieval and all transfers of embryos from that cycle within a year of the oocyte retrieval. If the first cycle and subsequent transfers do not lead to a live birth, patients still have a chance to achieve a live birth with a second or third cycle. The success rate increases over time as it reflects the chance of success for a population of patients, with some achieving a live birth after the first cycle and additional patients who achieve success following their third cycle.
Q: The SART IVF calculator can be used with no prior IVF cycles or following an unsuccessful cycle. Are there data to support an estimation of outcome following two or even more unsuccessful cycles?
A: The variables in the SART IVF calculator are based upon the cycle-specific data from patients seeking care at SART member clinics. The current predictor was built with data from cycles performed in 2015-2016. SART is adjusting the predictor and developing a calculator that will be routinely updated, accordingly.
Q: Only approximately 40% of states have some form of infertility coverage law in place; however the number of IVF cycles in the United States continues to increase on an annual basis. What do you think are the driving factors behind this?
A: Advocacy efforts to improve patients’ access to infertility care have included giving patients tools to encourage their employers to include infertility care in their health care benefits package. More recently, the “Great Resignation” has led to the “Great Recruitment” and employers are recognizing that the addition of infertility care to health care benefits is a powerful recruitment tool.
Dr. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
Gut microbiome may guide personalized heart failure therapy
Understanding more about the gut microbiome and how it may affect the development and treatment of heart failure could lead to a more personalized approach to managing the condition, a new review article suggests.
the authors note. “Interactions among the gut microbiome, diet, and medications offer potentially innovative modalities for management of patients with heart failure,” they add.
The review was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Over the past years we have gathered more understanding about how important the gut microbiome is in relation to how our bodies function overall and even though the cardiovascular system and the heart itself may appear to be quite distant from the gut, we know the gut microbiome affects the cardiovascular system and the physiology of heart failure,” lead author Petra Mamic, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University, told this news organization.
“We’ve also learnt that the microbiome is very personalized. It seems to be affected by a lot of intrinsic and as well as extrinsic factors. For cardiovascular diseases in particular, we always knew that diet and lifestyle were part of the environmental risk, and we now believe that the gut microbiome may be one of the factors that mediates that risk,” she said.
“Studies on the gut microbiome are difficult to do and we are right at the beginning of this type of research. But we have learned that the microbiome is altered or dysregulated in many diseases including many cardiovascular diseases, and many of the changes in the microbiome we see in different cardiovascular diseases seem to overlap,” she added.
Dr. Mamic explained that patients with heart failure have a microbiome that appears different and dysregulated, compared with the microbiome in healthy individuals.
“The difficulty is teasing out whether the microbiome changes are causing heart failure or if they are a consequence of the heart failure and all the medications and comorbidities associated with heart failure,” she commented.
Animal studies have shown that many microbial products, small molecules made by the microbiome, seem to affect how the heart recovers from injury, for example after a myocardial infarction, and how much the heart scars and hypertrophies after an injury, Dr. Mamic reported. These microbiome-derived small molecules can also affect blood pressure, which is dysregulated in heart failure.
Other products of the microbiome can be pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory, which can again affect the cardiovascular physiology and the heart, she noted.
High-fiber diet may be beneficial
One area of particular interest at present involves the role of short-chain fatty acids, which are a byproduct of microbes in the gut that digest fiber.
“These short chain fatty acids seem to have positive effects on the host physiology. They are anti-inflammatory; they lower blood pressure; and they seem to protect the heart from scarring and hypertrophy after injury. In heart failure, the gut microbes that make these short-chain fatty acids are significantly depleted,” Dr. Mamic explained.
They are an obvious focus of interest because these short-chain fatty acids are produced when gut bacteria break down dietary fiber, raising the possibility of beneficial effects from eating a high-fiber diet.
Another product of the gut microbiome of interest is trimethylamine N-oxide, formed when gut bacteria break down nutrients such as L-carnitine and phosphatidyl choline, nutrients abundant in foods of animal origin, especially red meat. This metabolite has proatherogenic and prothrombotic effects, and negatively affected cardiac remodeling in a mouse heart failure model, the review notes.
However, though it is too early to make specific dietary recommendations based on these findings, Dr. Mamic points out that a high-fiber diet is thought to be beneficial.
“Nutritional research is very hard to do and the data is limited, but as best as we can summarize things, we know that plant-based diets such as the Mediterranean and DASH diets seem to prevent some of the risk factors for the development of heart failure and seem to slow the progression of heart failure,” she added.
One of the major recommendations in these diets is a high intake of fiber, including whole foods, vegetables, fruits, legumes, and nuts, and less intake of processed food and red meat. “In general, I think everyone should eat like that, but I specifically recommend a plant-based diet with a high amount of fiber to my heart failure patients,” Dr. Mamic said.
Large variation in microbiome composition
The review also explores the idea of personalization of diet or specific treatments dependent on an individual’s gut microbiome composition.
Dr. Mamic explains: “When we look at the microbiome composition between individuals, it is very different. There is very little overlap between individuals, even in people who are related. It seems to be more to do with the environment – people who are living together are more likely to have similarities in their microbiome. We are still trying to understand what drives these differences.”
It is thought that these differences may affect the response to a specific diet or medication. Dr. Mamic gives the example of fiber. “Not all bacteria can digest the same types of fiber, so not everyone responds in the same way to a high-fiber diet. That’s probably because of differences in their microbiome.”
Another example is the response to the heart failure drug digoxin, which is metabolized by one particular strain of bacteria in the gut. The toxicity or effectiveness of digoxin seems to be influenced by levels of this bacterial strain, and this again can be influenced by diet, Dr. Mamic says.
Manipulating the microbiome as a therapeutic strategy
Microbiome-targeting therapies may also become part of future treatment strategies for many conditions, including heart failure, the review authors say.
Probiotics (foods and dietary supplements that contain live microbes) interact with the gut microbiota to alter host physiology beneficially. Certain probiotics may specifically modulate processes dysregulated in heart failure, as was suggested in a rodent heart failure model in which supplementation with Lactobacillus-containing and Bifidobacterium-containing probiotics resulted in markedly improved cardiac function, the authors report.
However, a randomized trial (GutHeart) of probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii in patients with heart failure found no improvement in cardiac function, compared with standard care.
Commenting on this, Dr. Mamic suggested that a more specific approach may be needed.
“Some of our preliminary data have shown people who have heart failure have severely depleted Bifidobacteria,” Dr. Mamic said. These bacteria are commercially available as a probiotic, and the researchers are planning a study to give patients with heart failure these specific probiotics. “We are trying to find practical ways forward and to be guided by the data. These people have very little Bifidobacteria, and we know that probiotics seem to be accepted best by the host where there is a specific need for them, so this seems like a sensible approach.”
Dr. Mamic does not recommend that heart failure patients take general probiotic products at present, but she tells her patients about the study she is doing. “Probiotics are quite different from each other. It is a very unregulated market. A general probiotic product may not contain the specific bacteria needed.”
Include microbiome data in biobanks
The review calls for more research on the subject and a more systematic approach to collecting data on the microbiome.
“At present for medical research, blood samples are collected, stored, and analyzed routinely. I think we should also be collecting stool samples in the same way to analyze the microbiome,” Dr. Mamic suggests.
“If we can combine that with data from blood tests on various metabolites/cytokines and look at how the microbiome changes over time or with medication, or with diet, and how the host responds including clinically relevant data, that would be really important. Given how quickly the field is growing I would think there would be biobanks including the microbiome in a few years’ time.”
“We need to gather this data. We would be looking for which bacteria are there, what their functionality is, how it changes over time, with diet or medication, and even whether we can use the microbiome data to predict who will respond to a specific drug.”
Dr. Mamic believes that in the future, analysis of the microbiome could be a routine part of deciding what people eat for good health and to characterize patients for personalized therapies.
“It is clear that the microbiome can influence health, and a dysregulated microbiome negatively affects the host, but there is lot of work to do. We need to learn a lot more about it, but we shouldn’t miss the opportunity to do this,” she concluded.
Dr. Mamic reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Understanding more about the gut microbiome and how it may affect the development and treatment of heart failure could lead to a more personalized approach to managing the condition, a new review article suggests.
the authors note. “Interactions among the gut microbiome, diet, and medications offer potentially innovative modalities for management of patients with heart failure,” they add.
The review was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Over the past years we have gathered more understanding about how important the gut microbiome is in relation to how our bodies function overall and even though the cardiovascular system and the heart itself may appear to be quite distant from the gut, we know the gut microbiome affects the cardiovascular system and the physiology of heart failure,” lead author Petra Mamic, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University, told this news organization.
“We’ve also learnt that the microbiome is very personalized. It seems to be affected by a lot of intrinsic and as well as extrinsic factors. For cardiovascular diseases in particular, we always knew that diet and lifestyle were part of the environmental risk, and we now believe that the gut microbiome may be one of the factors that mediates that risk,” she said.
“Studies on the gut microbiome are difficult to do and we are right at the beginning of this type of research. But we have learned that the microbiome is altered or dysregulated in many diseases including many cardiovascular diseases, and many of the changes in the microbiome we see in different cardiovascular diseases seem to overlap,” she added.
Dr. Mamic explained that patients with heart failure have a microbiome that appears different and dysregulated, compared with the microbiome in healthy individuals.
“The difficulty is teasing out whether the microbiome changes are causing heart failure or if they are a consequence of the heart failure and all the medications and comorbidities associated with heart failure,” she commented.
Animal studies have shown that many microbial products, small molecules made by the microbiome, seem to affect how the heart recovers from injury, for example after a myocardial infarction, and how much the heart scars and hypertrophies after an injury, Dr. Mamic reported. These microbiome-derived small molecules can also affect blood pressure, which is dysregulated in heart failure.
Other products of the microbiome can be pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory, which can again affect the cardiovascular physiology and the heart, she noted.
High-fiber diet may be beneficial
One area of particular interest at present involves the role of short-chain fatty acids, which are a byproduct of microbes in the gut that digest fiber.
“These short chain fatty acids seem to have positive effects on the host physiology. They are anti-inflammatory; they lower blood pressure; and they seem to protect the heart from scarring and hypertrophy after injury. In heart failure, the gut microbes that make these short-chain fatty acids are significantly depleted,” Dr. Mamic explained.
They are an obvious focus of interest because these short-chain fatty acids are produced when gut bacteria break down dietary fiber, raising the possibility of beneficial effects from eating a high-fiber diet.
Another product of the gut microbiome of interest is trimethylamine N-oxide, formed when gut bacteria break down nutrients such as L-carnitine and phosphatidyl choline, nutrients abundant in foods of animal origin, especially red meat. This metabolite has proatherogenic and prothrombotic effects, and negatively affected cardiac remodeling in a mouse heart failure model, the review notes.
However, though it is too early to make specific dietary recommendations based on these findings, Dr. Mamic points out that a high-fiber diet is thought to be beneficial.
“Nutritional research is very hard to do and the data is limited, but as best as we can summarize things, we know that plant-based diets such as the Mediterranean and DASH diets seem to prevent some of the risk factors for the development of heart failure and seem to slow the progression of heart failure,” she added.
One of the major recommendations in these diets is a high intake of fiber, including whole foods, vegetables, fruits, legumes, and nuts, and less intake of processed food and red meat. “In general, I think everyone should eat like that, but I specifically recommend a plant-based diet with a high amount of fiber to my heart failure patients,” Dr. Mamic said.
Large variation in microbiome composition
The review also explores the idea of personalization of diet or specific treatments dependent on an individual’s gut microbiome composition.
Dr. Mamic explains: “When we look at the microbiome composition between individuals, it is very different. There is very little overlap between individuals, even in people who are related. It seems to be more to do with the environment – people who are living together are more likely to have similarities in their microbiome. We are still trying to understand what drives these differences.”
It is thought that these differences may affect the response to a specific diet or medication. Dr. Mamic gives the example of fiber. “Not all bacteria can digest the same types of fiber, so not everyone responds in the same way to a high-fiber diet. That’s probably because of differences in their microbiome.”
Another example is the response to the heart failure drug digoxin, which is metabolized by one particular strain of bacteria in the gut. The toxicity or effectiveness of digoxin seems to be influenced by levels of this bacterial strain, and this again can be influenced by diet, Dr. Mamic says.
Manipulating the microbiome as a therapeutic strategy
Microbiome-targeting therapies may also become part of future treatment strategies for many conditions, including heart failure, the review authors say.
Probiotics (foods and dietary supplements that contain live microbes) interact with the gut microbiota to alter host physiology beneficially. Certain probiotics may specifically modulate processes dysregulated in heart failure, as was suggested in a rodent heart failure model in which supplementation with Lactobacillus-containing and Bifidobacterium-containing probiotics resulted in markedly improved cardiac function, the authors report.
However, a randomized trial (GutHeart) of probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii in patients with heart failure found no improvement in cardiac function, compared with standard care.
Commenting on this, Dr. Mamic suggested that a more specific approach may be needed.
“Some of our preliminary data have shown people who have heart failure have severely depleted Bifidobacteria,” Dr. Mamic said. These bacteria are commercially available as a probiotic, and the researchers are planning a study to give patients with heart failure these specific probiotics. “We are trying to find practical ways forward and to be guided by the data. These people have very little Bifidobacteria, and we know that probiotics seem to be accepted best by the host where there is a specific need for them, so this seems like a sensible approach.”
Dr. Mamic does not recommend that heart failure patients take general probiotic products at present, but she tells her patients about the study she is doing. “Probiotics are quite different from each other. It is a very unregulated market. A general probiotic product may not contain the specific bacteria needed.”
Include microbiome data in biobanks
The review calls for more research on the subject and a more systematic approach to collecting data on the microbiome.
“At present for medical research, blood samples are collected, stored, and analyzed routinely. I think we should also be collecting stool samples in the same way to analyze the microbiome,” Dr. Mamic suggests.
“If we can combine that with data from blood tests on various metabolites/cytokines and look at how the microbiome changes over time or with medication, or with diet, and how the host responds including clinically relevant data, that would be really important. Given how quickly the field is growing I would think there would be biobanks including the microbiome in a few years’ time.”
“We need to gather this data. We would be looking for which bacteria are there, what their functionality is, how it changes over time, with diet or medication, and even whether we can use the microbiome data to predict who will respond to a specific drug.”
Dr. Mamic believes that in the future, analysis of the microbiome could be a routine part of deciding what people eat for good health and to characterize patients for personalized therapies.
“It is clear that the microbiome can influence health, and a dysregulated microbiome negatively affects the host, but there is lot of work to do. We need to learn a lot more about it, but we shouldn’t miss the opportunity to do this,” she concluded.
Dr. Mamic reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Understanding more about the gut microbiome and how it may affect the development and treatment of heart failure could lead to a more personalized approach to managing the condition, a new review article suggests.
the authors note. “Interactions among the gut microbiome, diet, and medications offer potentially innovative modalities for management of patients with heart failure,” they add.
The review was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Over the past years we have gathered more understanding about how important the gut microbiome is in relation to how our bodies function overall and even though the cardiovascular system and the heart itself may appear to be quite distant from the gut, we know the gut microbiome affects the cardiovascular system and the physiology of heart failure,” lead author Petra Mamic, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University, told this news organization.
“We’ve also learnt that the microbiome is very personalized. It seems to be affected by a lot of intrinsic and as well as extrinsic factors. For cardiovascular diseases in particular, we always knew that diet and lifestyle were part of the environmental risk, and we now believe that the gut microbiome may be one of the factors that mediates that risk,” she said.
“Studies on the gut microbiome are difficult to do and we are right at the beginning of this type of research. But we have learned that the microbiome is altered or dysregulated in many diseases including many cardiovascular diseases, and many of the changes in the microbiome we see in different cardiovascular diseases seem to overlap,” she added.
Dr. Mamic explained that patients with heart failure have a microbiome that appears different and dysregulated, compared with the microbiome in healthy individuals.
“The difficulty is teasing out whether the microbiome changes are causing heart failure or if they are a consequence of the heart failure and all the medications and comorbidities associated with heart failure,” she commented.
Animal studies have shown that many microbial products, small molecules made by the microbiome, seem to affect how the heart recovers from injury, for example after a myocardial infarction, and how much the heart scars and hypertrophies after an injury, Dr. Mamic reported. These microbiome-derived small molecules can also affect blood pressure, which is dysregulated in heart failure.
Other products of the microbiome can be pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory, which can again affect the cardiovascular physiology and the heart, she noted.
High-fiber diet may be beneficial
One area of particular interest at present involves the role of short-chain fatty acids, which are a byproduct of microbes in the gut that digest fiber.
“These short chain fatty acids seem to have positive effects on the host physiology. They are anti-inflammatory; they lower blood pressure; and they seem to protect the heart from scarring and hypertrophy after injury. In heart failure, the gut microbes that make these short-chain fatty acids are significantly depleted,” Dr. Mamic explained.
They are an obvious focus of interest because these short-chain fatty acids are produced when gut bacteria break down dietary fiber, raising the possibility of beneficial effects from eating a high-fiber diet.
Another product of the gut microbiome of interest is trimethylamine N-oxide, formed when gut bacteria break down nutrients such as L-carnitine and phosphatidyl choline, nutrients abundant in foods of animal origin, especially red meat. This metabolite has proatherogenic and prothrombotic effects, and negatively affected cardiac remodeling in a mouse heart failure model, the review notes.
However, though it is too early to make specific dietary recommendations based on these findings, Dr. Mamic points out that a high-fiber diet is thought to be beneficial.
“Nutritional research is very hard to do and the data is limited, but as best as we can summarize things, we know that plant-based diets such as the Mediterranean and DASH diets seem to prevent some of the risk factors for the development of heart failure and seem to slow the progression of heart failure,” she added.
One of the major recommendations in these diets is a high intake of fiber, including whole foods, vegetables, fruits, legumes, and nuts, and less intake of processed food and red meat. “In general, I think everyone should eat like that, but I specifically recommend a plant-based diet with a high amount of fiber to my heart failure patients,” Dr. Mamic said.
Large variation in microbiome composition
The review also explores the idea of personalization of diet or specific treatments dependent on an individual’s gut microbiome composition.
Dr. Mamic explains: “When we look at the microbiome composition between individuals, it is very different. There is very little overlap between individuals, even in people who are related. It seems to be more to do with the environment – people who are living together are more likely to have similarities in their microbiome. We are still trying to understand what drives these differences.”
It is thought that these differences may affect the response to a specific diet or medication. Dr. Mamic gives the example of fiber. “Not all bacteria can digest the same types of fiber, so not everyone responds in the same way to a high-fiber diet. That’s probably because of differences in their microbiome.”
Another example is the response to the heart failure drug digoxin, which is metabolized by one particular strain of bacteria in the gut. The toxicity or effectiveness of digoxin seems to be influenced by levels of this bacterial strain, and this again can be influenced by diet, Dr. Mamic says.
Manipulating the microbiome as a therapeutic strategy
Microbiome-targeting therapies may also become part of future treatment strategies for many conditions, including heart failure, the review authors say.
Probiotics (foods and dietary supplements that contain live microbes) interact with the gut microbiota to alter host physiology beneficially. Certain probiotics may specifically modulate processes dysregulated in heart failure, as was suggested in a rodent heart failure model in which supplementation with Lactobacillus-containing and Bifidobacterium-containing probiotics resulted in markedly improved cardiac function, the authors report.
However, a randomized trial (GutHeart) of probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii in patients with heart failure found no improvement in cardiac function, compared with standard care.
Commenting on this, Dr. Mamic suggested that a more specific approach may be needed.
“Some of our preliminary data have shown people who have heart failure have severely depleted Bifidobacteria,” Dr. Mamic said. These bacteria are commercially available as a probiotic, and the researchers are planning a study to give patients with heart failure these specific probiotics. “We are trying to find practical ways forward and to be guided by the data. These people have very little Bifidobacteria, and we know that probiotics seem to be accepted best by the host where there is a specific need for them, so this seems like a sensible approach.”
Dr. Mamic does not recommend that heart failure patients take general probiotic products at present, but she tells her patients about the study she is doing. “Probiotics are quite different from each other. It is a very unregulated market. A general probiotic product may not contain the specific bacteria needed.”
Include microbiome data in biobanks
The review calls for more research on the subject and a more systematic approach to collecting data on the microbiome.
“At present for medical research, blood samples are collected, stored, and analyzed routinely. I think we should also be collecting stool samples in the same way to analyze the microbiome,” Dr. Mamic suggests.
“If we can combine that with data from blood tests on various metabolites/cytokines and look at how the microbiome changes over time or with medication, or with diet, and how the host responds including clinically relevant data, that would be really important. Given how quickly the field is growing I would think there would be biobanks including the microbiome in a few years’ time.”
“We need to gather this data. We would be looking for which bacteria are there, what their functionality is, how it changes over time, with diet or medication, and even whether we can use the microbiome data to predict who will respond to a specific drug.”
Dr. Mamic believes that in the future, analysis of the microbiome could be a routine part of deciding what people eat for good health and to characterize patients for personalized therapies.
“It is clear that the microbiome can influence health, and a dysregulated microbiome negatively affects the host, but there is lot of work to do. We need to learn a lot more about it, but we shouldn’t miss the opportunity to do this,” she concluded.
Dr. Mamic reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY