User login
Low Follow-up of Abnormal Urine Proteinuria Dipstick Tests in Primary Care
Only 1 in 15 urine dipstick tests showing proteinuria in the primary care setting are followed up with albuminuria quantification testing, according to investigators.
These findings expose a broad gap in screening for chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is especially concerning since newer kidney-protecting agents are more effective when prescribed earlier in the disease course, reported lead author Yunwen Xu, PhD, of Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland, and colleagues.
“Evidence-based prescription of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1) agonists, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, and nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (nsMRAs) relies on the level of albuminuria,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Although urine albumin-creatinine ratio (ACR) is the most accurate method for quantifying albuminuria, dipstick urinalysis tests are inexpensive and are often used as an initial screening test, with guidelines recommending follow-up ACR testing if the protein dipstick test result is abnormal.”
Despite this guidance, real-world follow-up rates have been unknown, prompting the present study. Real-world data show a low follow-up rate. Dr. Xu and colleagues analyzed data from 1 million patients in 33 health systems who underwent urine dipstick testing in a primary care setting.
Across this population, 13% of patients had proteinuria, but only 6.7% underwent follow-up albuminuria quantification testing within the next year. ACR was the most common method (86%).
Likelihood of follow-up increased slightly with the level of proteinuria detected; however, absolute differences were marginal, with a 3+ result yielding a follow-up rate of just 8%, compared with 7.3% for a 2+ result and 6.3% for a 1+ result. When albuminuria quantification tests were conducted, 1+, 2+, and 3+ dipstick results were associated with albuminuria rates of 36.3%, 53.0%, and 64.9%, respectively.
Patients with diabetes had the highest follow-up rate, at 16.6%, vs 3.8% for those without diabetes.
Reasons for Low Follow-up Unclear
The dataset did not include information about reasons for ordering urinalyses, whether primary care providers knew about the abnormal dipstick tests, or awareness of guideline recommendations.
“I think they know it should be done,” said principal investigator Alexander R. Chang, MD, associate professor in the department of nephrology and population health sciences at Geisinger Health, Danville, Pennsylvania.
He suggested that real-time awareness issues, especially within electronic health record (EHR) systems, could explain the low follow-up rates. Blood test abnormalities are often flagged in red in EHRs, he said in an interview, but urine dipstick results typically remain in plain black and white.
“So, then it sort of requires that extra cognitive step to kind of look at that [result], and say, okay, that is pretty abnormal; I should do something about that,” he said.
Neil S. Skolnik, MD, a primary care physician at Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, was surprised by the findings. “If you get a urinalysis and there’s protein, normally you follow up,” Dr. Skolnik said in an interview. “I have a feeling that there’s something we’re not seeing here about what’s going on. It is hard to imagine that in only 1 out of 15 times that proteinuria is identified, is there any follow-up. I really don’t have a good explanation.”
Renee Marie Betancourt, MD, associate professor and vice chair of diversity, equity, and inclusion in the Department of Family Medicine and Community Health at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, said it is hard to draw conclusions from the available data, but agreed that low visibility of results could be partially to blame.
“The chart doesn’t tell me [a urine dipstick result] is abnormal,” Dr. Betancourt said in an interview. “The chart just reports it, agnostic of normal or abnormal.”
Beyond issues with visibility, Dr. Betancourt described how primary care physicians are often so flooded with other concerns that a positive dipstick test can become a low priority, particularly among patients with CKD, who typically have other health issues.
“I oftentimes spend the majority of my visit on the patient’s concerns, and sometimes, beyond their concerns, I have concerns, and [a urine dipstick result] might not make it to the top of the list,” she said.
EHR-Based Interventions Might Help Improve Follow-up
Dr. Chang suggested that improved visibility of dipstick results could help, or possibly EHR-integrated clinical decision tools.
Dr. Betancourt and colleagues at Penn Medicine are actively working on such a solution. Their EHR-based intervention is aimed at identifying and managing patients with CKD. The present design, slated for pilot testing at one or two primary care clinics beginning in January 2025, depends upon estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) to flag CKD patients, with ACR testing recommended yearly to predict disease progression.
Although urine dipstick findings are not currently a part of this software pathway, the findings from the present study might influence future strategy.
“I’m going to take this to our collaborators and ask about opportunities to ... encourage providers to be more active with dipsticks,” Dr. Betancourt said.
Newer Medications Are Effective, but Prescribing Challenges Remain
Ideally, CKD screening improvements will unlock a greater goal: prescribing kidney-protecting medications to patients who need them — as soon as they need them.
Here might lie the real knowledge gap among experienced primary care physicians, Dr. Chang suggested. “In the past, there wasn’t quite as much that you could do about having proteinuria,” he said. “But now we have lots more medications ... it’s not just tracking that they have a bad prognostic factor. [Proteinuria is] actually something that we can act upon.”
Who exactly should be prescribing these kidney-protecting medications, however, remains contested, as agents like GLP-1 agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors yield benefits across specialties, including nephrology, cardiology, and endocrinology.
“Everyone’s going to have to work together,” Dr. Chang said. “You can’t really put it all on the [primary care physician] to quarterback everything.”
And, regardless of who throws the ball, a touchdown is not guaranteed.
Dr. Betancourt called out the high cost of these newer drugs and described how some of her patients, already facing multiple health inequities, are left without.
“I have patients who cannot fill these medications because the copay is too high,” she said. “Just last week I received a message from a patient who stopped taking his SGLT2 inhibitor because the cost was too high ... it was over $300 per month.”
This study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. The authors’ conflicts of interests are available in the original paper. Dr. Skolnik and Dr. Betancourt reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Only 1 in 15 urine dipstick tests showing proteinuria in the primary care setting are followed up with albuminuria quantification testing, according to investigators.
These findings expose a broad gap in screening for chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is especially concerning since newer kidney-protecting agents are more effective when prescribed earlier in the disease course, reported lead author Yunwen Xu, PhD, of Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland, and colleagues.
“Evidence-based prescription of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1) agonists, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, and nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (nsMRAs) relies on the level of albuminuria,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Although urine albumin-creatinine ratio (ACR) is the most accurate method for quantifying albuminuria, dipstick urinalysis tests are inexpensive and are often used as an initial screening test, with guidelines recommending follow-up ACR testing if the protein dipstick test result is abnormal.”
Despite this guidance, real-world follow-up rates have been unknown, prompting the present study. Real-world data show a low follow-up rate. Dr. Xu and colleagues analyzed data from 1 million patients in 33 health systems who underwent urine dipstick testing in a primary care setting.
Across this population, 13% of patients had proteinuria, but only 6.7% underwent follow-up albuminuria quantification testing within the next year. ACR was the most common method (86%).
Likelihood of follow-up increased slightly with the level of proteinuria detected; however, absolute differences were marginal, with a 3+ result yielding a follow-up rate of just 8%, compared with 7.3% for a 2+ result and 6.3% for a 1+ result. When albuminuria quantification tests were conducted, 1+, 2+, and 3+ dipstick results were associated with albuminuria rates of 36.3%, 53.0%, and 64.9%, respectively.
Patients with diabetes had the highest follow-up rate, at 16.6%, vs 3.8% for those without diabetes.
Reasons for Low Follow-up Unclear
The dataset did not include information about reasons for ordering urinalyses, whether primary care providers knew about the abnormal dipstick tests, or awareness of guideline recommendations.
“I think they know it should be done,” said principal investigator Alexander R. Chang, MD, associate professor in the department of nephrology and population health sciences at Geisinger Health, Danville, Pennsylvania.
He suggested that real-time awareness issues, especially within electronic health record (EHR) systems, could explain the low follow-up rates. Blood test abnormalities are often flagged in red in EHRs, he said in an interview, but urine dipstick results typically remain in plain black and white.
“So, then it sort of requires that extra cognitive step to kind of look at that [result], and say, okay, that is pretty abnormal; I should do something about that,” he said.
Neil S. Skolnik, MD, a primary care physician at Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, was surprised by the findings. “If you get a urinalysis and there’s protein, normally you follow up,” Dr. Skolnik said in an interview. “I have a feeling that there’s something we’re not seeing here about what’s going on. It is hard to imagine that in only 1 out of 15 times that proteinuria is identified, is there any follow-up. I really don’t have a good explanation.”
Renee Marie Betancourt, MD, associate professor and vice chair of diversity, equity, and inclusion in the Department of Family Medicine and Community Health at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, said it is hard to draw conclusions from the available data, but agreed that low visibility of results could be partially to blame.
“The chart doesn’t tell me [a urine dipstick result] is abnormal,” Dr. Betancourt said in an interview. “The chart just reports it, agnostic of normal or abnormal.”
Beyond issues with visibility, Dr. Betancourt described how primary care physicians are often so flooded with other concerns that a positive dipstick test can become a low priority, particularly among patients with CKD, who typically have other health issues.
“I oftentimes spend the majority of my visit on the patient’s concerns, and sometimes, beyond their concerns, I have concerns, and [a urine dipstick result] might not make it to the top of the list,” she said.
EHR-Based Interventions Might Help Improve Follow-up
Dr. Chang suggested that improved visibility of dipstick results could help, or possibly EHR-integrated clinical decision tools.
Dr. Betancourt and colleagues at Penn Medicine are actively working on such a solution. Their EHR-based intervention is aimed at identifying and managing patients with CKD. The present design, slated for pilot testing at one or two primary care clinics beginning in January 2025, depends upon estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) to flag CKD patients, with ACR testing recommended yearly to predict disease progression.
Although urine dipstick findings are not currently a part of this software pathway, the findings from the present study might influence future strategy.
“I’m going to take this to our collaborators and ask about opportunities to ... encourage providers to be more active with dipsticks,” Dr. Betancourt said.
Newer Medications Are Effective, but Prescribing Challenges Remain
Ideally, CKD screening improvements will unlock a greater goal: prescribing kidney-protecting medications to patients who need them — as soon as they need them.
Here might lie the real knowledge gap among experienced primary care physicians, Dr. Chang suggested. “In the past, there wasn’t quite as much that you could do about having proteinuria,” he said. “But now we have lots more medications ... it’s not just tracking that they have a bad prognostic factor. [Proteinuria is] actually something that we can act upon.”
Who exactly should be prescribing these kidney-protecting medications, however, remains contested, as agents like GLP-1 agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors yield benefits across specialties, including nephrology, cardiology, and endocrinology.
“Everyone’s going to have to work together,” Dr. Chang said. “You can’t really put it all on the [primary care physician] to quarterback everything.”
And, regardless of who throws the ball, a touchdown is not guaranteed.
Dr. Betancourt called out the high cost of these newer drugs and described how some of her patients, already facing multiple health inequities, are left without.
“I have patients who cannot fill these medications because the copay is too high,” she said. “Just last week I received a message from a patient who stopped taking his SGLT2 inhibitor because the cost was too high ... it was over $300 per month.”
This study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. The authors’ conflicts of interests are available in the original paper. Dr. Skolnik and Dr. Betancourt reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Only 1 in 15 urine dipstick tests showing proteinuria in the primary care setting are followed up with albuminuria quantification testing, according to investigators.
These findings expose a broad gap in screening for chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is especially concerning since newer kidney-protecting agents are more effective when prescribed earlier in the disease course, reported lead author Yunwen Xu, PhD, of Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland, and colleagues.
“Evidence-based prescription of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1) agonists, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, and nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (nsMRAs) relies on the level of albuminuria,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Although urine albumin-creatinine ratio (ACR) is the most accurate method for quantifying albuminuria, dipstick urinalysis tests are inexpensive and are often used as an initial screening test, with guidelines recommending follow-up ACR testing if the protein dipstick test result is abnormal.”
Despite this guidance, real-world follow-up rates have been unknown, prompting the present study. Real-world data show a low follow-up rate. Dr. Xu and colleagues analyzed data from 1 million patients in 33 health systems who underwent urine dipstick testing in a primary care setting.
Across this population, 13% of patients had proteinuria, but only 6.7% underwent follow-up albuminuria quantification testing within the next year. ACR was the most common method (86%).
Likelihood of follow-up increased slightly with the level of proteinuria detected; however, absolute differences were marginal, with a 3+ result yielding a follow-up rate of just 8%, compared with 7.3% for a 2+ result and 6.3% for a 1+ result. When albuminuria quantification tests were conducted, 1+, 2+, and 3+ dipstick results were associated with albuminuria rates of 36.3%, 53.0%, and 64.9%, respectively.
Patients with diabetes had the highest follow-up rate, at 16.6%, vs 3.8% for those without diabetes.
Reasons for Low Follow-up Unclear
The dataset did not include information about reasons for ordering urinalyses, whether primary care providers knew about the abnormal dipstick tests, or awareness of guideline recommendations.
“I think they know it should be done,” said principal investigator Alexander R. Chang, MD, associate professor in the department of nephrology and population health sciences at Geisinger Health, Danville, Pennsylvania.
He suggested that real-time awareness issues, especially within electronic health record (EHR) systems, could explain the low follow-up rates. Blood test abnormalities are often flagged in red in EHRs, he said in an interview, but urine dipstick results typically remain in plain black and white.
“So, then it sort of requires that extra cognitive step to kind of look at that [result], and say, okay, that is pretty abnormal; I should do something about that,” he said.
Neil S. Skolnik, MD, a primary care physician at Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, was surprised by the findings. “If you get a urinalysis and there’s protein, normally you follow up,” Dr. Skolnik said in an interview. “I have a feeling that there’s something we’re not seeing here about what’s going on. It is hard to imagine that in only 1 out of 15 times that proteinuria is identified, is there any follow-up. I really don’t have a good explanation.”
Renee Marie Betancourt, MD, associate professor and vice chair of diversity, equity, and inclusion in the Department of Family Medicine and Community Health at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, said it is hard to draw conclusions from the available data, but agreed that low visibility of results could be partially to blame.
“The chart doesn’t tell me [a urine dipstick result] is abnormal,” Dr. Betancourt said in an interview. “The chart just reports it, agnostic of normal or abnormal.”
Beyond issues with visibility, Dr. Betancourt described how primary care physicians are often so flooded with other concerns that a positive dipstick test can become a low priority, particularly among patients with CKD, who typically have other health issues.
“I oftentimes spend the majority of my visit on the patient’s concerns, and sometimes, beyond their concerns, I have concerns, and [a urine dipstick result] might not make it to the top of the list,” she said.
EHR-Based Interventions Might Help Improve Follow-up
Dr. Chang suggested that improved visibility of dipstick results could help, or possibly EHR-integrated clinical decision tools.
Dr. Betancourt and colleagues at Penn Medicine are actively working on such a solution. Their EHR-based intervention is aimed at identifying and managing patients with CKD. The present design, slated for pilot testing at one or two primary care clinics beginning in January 2025, depends upon estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) to flag CKD patients, with ACR testing recommended yearly to predict disease progression.
Although urine dipstick findings are not currently a part of this software pathway, the findings from the present study might influence future strategy.
“I’m going to take this to our collaborators and ask about opportunities to ... encourage providers to be more active with dipsticks,” Dr. Betancourt said.
Newer Medications Are Effective, but Prescribing Challenges Remain
Ideally, CKD screening improvements will unlock a greater goal: prescribing kidney-protecting medications to patients who need them — as soon as they need them.
Here might lie the real knowledge gap among experienced primary care physicians, Dr. Chang suggested. “In the past, there wasn’t quite as much that you could do about having proteinuria,” he said. “But now we have lots more medications ... it’s not just tracking that they have a bad prognostic factor. [Proteinuria is] actually something that we can act upon.”
Who exactly should be prescribing these kidney-protecting medications, however, remains contested, as agents like GLP-1 agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors yield benefits across specialties, including nephrology, cardiology, and endocrinology.
“Everyone’s going to have to work together,” Dr. Chang said. “You can’t really put it all on the [primary care physician] to quarterback everything.”
And, regardless of who throws the ball, a touchdown is not guaranteed.
Dr. Betancourt called out the high cost of these newer drugs and described how some of her patients, already facing multiple health inequities, are left without.
“I have patients who cannot fill these medications because the copay is too high,” she said. “Just last week I received a message from a patient who stopped taking his SGLT2 inhibitor because the cost was too high ... it was over $300 per month.”
This study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. The authors’ conflicts of interests are available in the original paper. Dr. Skolnik and Dr. Betancourt reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Considerations for the Use of Biologics in Pregnancy
Biologics have revolutionized dermatologic treatment, offering substantial relief from chronic and debilitating skin conditions such as psoriasis,
Biologics for Cutaneous Conditions
Biologics—tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors; IL-17, IL-23, IL-12, and IL-36 inhibitors; and agents such as omalizumab and dupilumab—have shown remarkable efficacy in controlling severe or recalcitrant dermatologic conditions and typically are more effective than traditional systemic therapies.1 For instance, randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and real-world data have shown that patients with psoriasis can achieve considerable skin clearance with biologics, greatly enhancing QOL.2 Adalimumab and secukinumab, which have been approved for use in moderate to severe cases of hidradenitis suppurativa, reduce the frequency of painful nodules and abscesses, thereby decreasing pain and improving QOL. Dupilumab, an IL-4/13 receptor antagonist, has revolutionized the treatment of AD by drastically reducing itch and skin lesions and improving QOL.3 For chronic urticaria, the anti-IgE antibody omalizumab has effectively reduced the incidence of hives and itching, providing pronounced symptom relief when traditional antihistamines fail.4 Use of rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has led to remission in severe cases of pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid.5
Impact of Untreated Cutaneous Conditions in Pregnancy
When treating patients who are pregnant, dermatologists must consider the health of both the expectant mother and the developing fetus. This dual focus complicates decision-making, particularly with the use of biologics. Untreated cutaneous conditions can profoundly impact a pregnant patient’s health and QOL as well as lead to pregnancy complications affecting the fetus, such as preterm birth or low birth weight. In some studies, moderate to severe psoriasis has been associated with increased risk for complications during pregnancy, including preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction.6 Although specific data on hidradenitis suppurativa are lacking, the highly inflammatory nature of the condition suggests similar adverse effects on pregnancy.7 Atopic dermatitis can be exacerbated during pregnancy due to a shift in the immune system to become more allergic dominant.8 Generalized pustular psoriasis manifests with widespread pustules, fever, and systemic inflammation, posing serious risks to both the mother and the fetus if left untreated9; in such a life-threatening scenario, the use of potent treatments such as spesolimab, an IL-36 receptor antagonist, may be warranted. Therefore, managing these conditions effectively is crucial not only for the mother’s health but also for fetal well-being.
Which Biologics Can Dermatologists Safely Prescribe?
Despite the benefits, many dermatologists are hesitant to prescribe biologics to pregnant patients due to the lack of understanding and definitive safety data.10,11 Although there are no RCTs that involve pregnant patients, current evidence suggests that several biologics are not teratogenic and do not cause fetal malformations. Extensive postexposure data support the safety of TNF-α inhibitors during pregnancy.12 Research has shown that children exposed to these agents in utero have normal development, infection rates, and vaccination outcomes comparable to nonexposed children. For example, a systematic review and meta-analysis found no significant increase in the risk for major congenital malformations, spontaneous abortions, or preterm births among patients exposed to anti–TNF-α agents during pregnancy.2 The Organization of Teratology Information Specialists Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project has provided valuable real-world data indicating that the use of TNF-α inhibitors in pregnancy, particularly during the first trimester, does not substantially elevate the risk for adverse outcomes.13 These findings have been corroborated by several other registry studies and RCTs, providing a robust safety profile for these agents during pregnancy.14
Similarly, postexposure data on IL-17 and IL-12/23 inhibitors indicate a favorable safety profile, though the sample sizes are smaller than those for anti–TNF-α agents.12,14 Studies of drugs such as secukinumab (IL-17 inhibitor), guselkumab (IL-23 inhibitor), or ustekinumab (IL-12/23 inhibitor) have shown no association with teratogenic effects or increased risk for miscarriage.14 However, agents such as spesolimab (IL-36 inhibitor) are relatively new, and ongoing studies are expected to provide more comprehensive safety data.15 Similarly, omalizumab and dupilumab have not been associated with increased risk for fetal malformations or adverse pregnancy outcomes. Omalizumab, indicated for chronic urticaria, has a good safety profile in pregnancy, with no significant increase in adverse outcomes reported in studies and registries.16 Dupilumab, used for AD, has demonstrated safety in pregnancy, with ongoing studies continuing to monitor outcomes.17
Conversely, rituximab (an anti-CD20 antibody for autoimmune bullous diseases) has shown evidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including fetal harm.18 Its use generally is discouraged unless deemed absolutely necessary, and no safer alternatives are available. Rituximab can cross the placenta, especially in the second and third trimesters, and has been associated with B-cell depletion in the fetus, leading to potential immunosuppression and increased risk for infections.5
Although the data on the safety of biologics in pregnancy are largely reassuring, it is essential to recognize that potential risks have not been ruled out entirely. There are extensive safety data for anti–TNF-α inhibitors, which provides a level of confidence; although newer agents such as IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors have shown promising early results, further research is required to solidify their safety profiles during pregnancy.
Dermatologists must balance the risks and benefits of using biologics in pregnant patients. This decision-making process involves careful consideration of the severity of the mother’s condition, the potential risks to the fetus, and the availability of alternative treatments. For many severe dermatologic conditions, the benefits of biologics in controlling disease activity and improving QOL may outweigh the potential risks, especially when other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
Final Thoughts
The increasing use of biologics in dermatology has undoubtedly improved the management of severe skin conditions, substantially enhancing patients’ QOL. As more data become available and clinical guidelines evolve, health care providers will be better equipped to make informed decisions about the use of biologics, particularly in pregnant patients. Collaborative efforts between dermatologists, obstetricians, and researchers will help refine treatment guidelines and ensure that pregnant patients with severe dermatologic conditions receive the best possible care.
For now, although the current evidence supports the safety of many biologics during pregnancy,10,11 individualized care and informed decision-making remain paramount. Careful management and adherence to current guidelines make it possible to navigate the complexities of treating severe dermatologic conditions in pregnant patients, ensuring the best outcomes for both mother and child.
- Sehgal VN, Pandhi D, Khurana A. Biologics in dermatology: an integrated review. Indian J Dermatol. 2014; 59:425-441. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.139859
- Mahadevan U, Wolf DC, Dubinsky M, et al. Placental transfer of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:286-292. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2012.11.011
- Simpson EL, Bieber T, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Two phase 3 trials of dupilumab versus placebo in atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2335-2348.
- Saini SS, Bindslev-Jensen C, Maurer M, et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in patients with chronic idiopathic/spontaneous urticaria who remain symptomatic on H1 antihistamines: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:67-75. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.306
- Mariette X, Forger F, Abraham B, et al. Lack of placental transfer of certolizumab pegol during pregnancy: results from CRIB, a prospective, postmarketing, pharmacokinetic study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:228-233. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212196
- Yang Y-W, Chen C-S, Chen Y-H, et al. Psoriasis and pregnancy outcomes: a nationwide population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:71-77.
- Zouboulis CC, Del Marmol V, Mrowietz U, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: criteria for diagnosis, severity assessment, classification and disease evaluation. Dermatology. 2015;231:184-190.
- Balakirski G, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis and pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149:1185-1194. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.01.010
- Bachelez H, Choon S-E, Marrakchi S, et al. Inhibition of the interleukin-36 pathway for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:981-983.
- McMullan P, Yaghi M, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part I: pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.072
- Yaghi M, McMullan P, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part II: lactation. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.071
- Owczarek W, Walecka I, Lesiak A, et al. The use of biological drugs in psoriasis patients prior to pregnancy, during pregnancy and lactation: a review of current clinical guidelines. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2020;37:821-830. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.102089
- Organization of Teratology Information Services (OTIS) Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00116272. Updated October 6, 2023. Accessed August 29, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00116272
- Sanchez-Garcia V, Hernandez-Quiles R, de-Miguel-Balsa E, et al. Exposure to biologic therapy before and during pregnancy in patients with psoriasis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1971-1990. doi:10.1111/jdv.19238
- Silverberg JI, Boguniewicz M, Hanifin J, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis is efficacious regardless of age of disease onset: a post hoc analysis of two phase 3 clinical trials. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:2731-2746. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00822-x
- Levi-Schaffer F, Mankuta D. Omalizumab safety in pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145:481-483. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2019.11.018
- Thaci D, Simpson EL, Beck LA, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis inadequately controlled by topical treatments: a randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging phase 2b trial. Lancet. 2016;387:40-52.
- Chakravarty EF, Murray ER, Kelman A, et al. Pregnancy outcomes after maternal exposure to rituximab. Blood. 2011;117:1499-1506. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-07-295444
Biologics have revolutionized dermatologic treatment, offering substantial relief from chronic and debilitating skin conditions such as psoriasis,
Biologics for Cutaneous Conditions
Biologics—tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors; IL-17, IL-23, IL-12, and IL-36 inhibitors; and agents such as omalizumab and dupilumab—have shown remarkable efficacy in controlling severe or recalcitrant dermatologic conditions and typically are more effective than traditional systemic therapies.1 For instance, randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and real-world data have shown that patients with psoriasis can achieve considerable skin clearance with biologics, greatly enhancing QOL.2 Adalimumab and secukinumab, which have been approved for use in moderate to severe cases of hidradenitis suppurativa, reduce the frequency of painful nodules and abscesses, thereby decreasing pain and improving QOL. Dupilumab, an IL-4/13 receptor antagonist, has revolutionized the treatment of AD by drastically reducing itch and skin lesions and improving QOL.3 For chronic urticaria, the anti-IgE antibody omalizumab has effectively reduced the incidence of hives and itching, providing pronounced symptom relief when traditional antihistamines fail.4 Use of rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has led to remission in severe cases of pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid.5
Impact of Untreated Cutaneous Conditions in Pregnancy
When treating patients who are pregnant, dermatologists must consider the health of both the expectant mother and the developing fetus. This dual focus complicates decision-making, particularly with the use of biologics. Untreated cutaneous conditions can profoundly impact a pregnant patient’s health and QOL as well as lead to pregnancy complications affecting the fetus, such as preterm birth or low birth weight. In some studies, moderate to severe psoriasis has been associated with increased risk for complications during pregnancy, including preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction.6 Although specific data on hidradenitis suppurativa are lacking, the highly inflammatory nature of the condition suggests similar adverse effects on pregnancy.7 Atopic dermatitis can be exacerbated during pregnancy due to a shift in the immune system to become more allergic dominant.8 Generalized pustular psoriasis manifests with widespread pustules, fever, and systemic inflammation, posing serious risks to both the mother and the fetus if left untreated9; in such a life-threatening scenario, the use of potent treatments such as spesolimab, an IL-36 receptor antagonist, may be warranted. Therefore, managing these conditions effectively is crucial not only for the mother’s health but also for fetal well-being.
Which Biologics Can Dermatologists Safely Prescribe?
Despite the benefits, many dermatologists are hesitant to prescribe biologics to pregnant patients due to the lack of understanding and definitive safety data.10,11 Although there are no RCTs that involve pregnant patients, current evidence suggests that several biologics are not teratogenic and do not cause fetal malformations. Extensive postexposure data support the safety of TNF-α inhibitors during pregnancy.12 Research has shown that children exposed to these agents in utero have normal development, infection rates, and vaccination outcomes comparable to nonexposed children. For example, a systematic review and meta-analysis found no significant increase in the risk for major congenital malformations, spontaneous abortions, or preterm births among patients exposed to anti–TNF-α agents during pregnancy.2 The Organization of Teratology Information Specialists Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project has provided valuable real-world data indicating that the use of TNF-α inhibitors in pregnancy, particularly during the first trimester, does not substantially elevate the risk for adverse outcomes.13 These findings have been corroborated by several other registry studies and RCTs, providing a robust safety profile for these agents during pregnancy.14
Similarly, postexposure data on IL-17 and IL-12/23 inhibitors indicate a favorable safety profile, though the sample sizes are smaller than those for anti–TNF-α agents.12,14 Studies of drugs such as secukinumab (IL-17 inhibitor), guselkumab (IL-23 inhibitor), or ustekinumab (IL-12/23 inhibitor) have shown no association with teratogenic effects or increased risk for miscarriage.14 However, agents such as spesolimab (IL-36 inhibitor) are relatively new, and ongoing studies are expected to provide more comprehensive safety data.15 Similarly, omalizumab and dupilumab have not been associated with increased risk for fetal malformations or adverse pregnancy outcomes. Omalizumab, indicated for chronic urticaria, has a good safety profile in pregnancy, with no significant increase in adverse outcomes reported in studies and registries.16 Dupilumab, used for AD, has demonstrated safety in pregnancy, with ongoing studies continuing to monitor outcomes.17
Conversely, rituximab (an anti-CD20 antibody for autoimmune bullous diseases) has shown evidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including fetal harm.18 Its use generally is discouraged unless deemed absolutely necessary, and no safer alternatives are available. Rituximab can cross the placenta, especially in the second and third trimesters, and has been associated with B-cell depletion in the fetus, leading to potential immunosuppression and increased risk for infections.5
Although the data on the safety of biologics in pregnancy are largely reassuring, it is essential to recognize that potential risks have not been ruled out entirely. There are extensive safety data for anti–TNF-α inhibitors, which provides a level of confidence; although newer agents such as IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors have shown promising early results, further research is required to solidify their safety profiles during pregnancy.
Dermatologists must balance the risks and benefits of using biologics in pregnant patients. This decision-making process involves careful consideration of the severity of the mother’s condition, the potential risks to the fetus, and the availability of alternative treatments. For many severe dermatologic conditions, the benefits of biologics in controlling disease activity and improving QOL may outweigh the potential risks, especially when other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
Final Thoughts
The increasing use of biologics in dermatology has undoubtedly improved the management of severe skin conditions, substantially enhancing patients’ QOL. As more data become available and clinical guidelines evolve, health care providers will be better equipped to make informed decisions about the use of biologics, particularly in pregnant patients. Collaborative efforts between dermatologists, obstetricians, and researchers will help refine treatment guidelines and ensure that pregnant patients with severe dermatologic conditions receive the best possible care.
For now, although the current evidence supports the safety of many biologics during pregnancy,10,11 individualized care and informed decision-making remain paramount. Careful management and adherence to current guidelines make it possible to navigate the complexities of treating severe dermatologic conditions in pregnant patients, ensuring the best outcomes for both mother and child.
Biologics have revolutionized dermatologic treatment, offering substantial relief from chronic and debilitating skin conditions such as psoriasis,
Biologics for Cutaneous Conditions
Biologics—tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors; IL-17, IL-23, IL-12, and IL-36 inhibitors; and agents such as omalizumab and dupilumab—have shown remarkable efficacy in controlling severe or recalcitrant dermatologic conditions and typically are more effective than traditional systemic therapies.1 For instance, randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and real-world data have shown that patients with psoriasis can achieve considerable skin clearance with biologics, greatly enhancing QOL.2 Adalimumab and secukinumab, which have been approved for use in moderate to severe cases of hidradenitis suppurativa, reduce the frequency of painful nodules and abscesses, thereby decreasing pain and improving QOL. Dupilumab, an IL-4/13 receptor antagonist, has revolutionized the treatment of AD by drastically reducing itch and skin lesions and improving QOL.3 For chronic urticaria, the anti-IgE antibody omalizumab has effectively reduced the incidence of hives and itching, providing pronounced symptom relief when traditional antihistamines fail.4 Use of rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has led to remission in severe cases of pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid.5
Impact of Untreated Cutaneous Conditions in Pregnancy
When treating patients who are pregnant, dermatologists must consider the health of both the expectant mother and the developing fetus. This dual focus complicates decision-making, particularly with the use of biologics. Untreated cutaneous conditions can profoundly impact a pregnant patient’s health and QOL as well as lead to pregnancy complications affecting the fetus, such as preterm birth or low birth weight. In some studies, moderate to severe psoriasis has been associated with increased risk for complications during pregnancy, including preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction.6 Although specific data on hidradenitis suppurativa are lacking, the highly inflammatory nature of the condition suggests similar adverse effects on pregnancy.7 Atopic dermatitis can be exacerbated during pregnancy due to a shift in the immune system to become more allergic dominant.8 Generalized pustular psoriasis manifests with widespread pustules, fever, and systemic inflammation, posing serious risks to both the mother and the fetus if left untreated9; in such a life-threatening scenario, the use of potent treatments such as spesolimab, an IL-36 receptor antagonist, may be warranted. Therefore, managing these conditions effectively is crucial not only for the mother’s health but also for fetal well-being.
Which Biologics Can Dermatologists Safely Prescribe?
Despite the benefits, many dermatologists are hesitant to prescribe biologics to pregnant patients due to the lack of understanding and definitive safety data.10,11 Although there are no RCTs that involve pregnant patients, current evidence suggests that several biologics are not teratogenic and do not cause fetal malformations. Extensive postexposure data support the safety of TNF-α inhibitors during pregnancy.12 Research has shown that children exposed to these agents in utero have normal development, infection rates, and vaccination outcomes comparable to nonexposed children. For example, a systematic review and meta-analysis found no significant increase in the risk for major congenital malformations, spontaneous abortions, or preterm births among patients exposed to anti–TNF-α agents during pregnancy.2 The Organization of Teratology Information Specialists Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project has provided valuable real-world data indicating that the use of TNF-α inhibitors in pregnancy, particularly during the first trimester, does not substantially elevate the risk for adverse outcomes.13 These findings have been corroborated by several other registry studies and RCTs, providing a robust safety profile for these agents during pregnancy.14
Similarly, postexposure data on IL-17 and IL-12/23 inhibitors indicate a favorable safety profile, though the sample sizes are smaller than those for anti–TNF-α agents.12,14 Studies of drugs such as secukinumab (IL-17 inhibitor), guselkumab (IL-23 inhibitor), or ustekinumab (IL-12/23 inhibitor) have shown no association with teratogenic effects or increased risk for miscarriage.14 However, agents such as spesolimab (IL-36 inhibitor) are relatively new, and ongoing studies are expected to provide more comprehensive safety data.15 Similarly, omalizumab and dupilumab have not been associated with increased risk for fetal malformations or adverse pregnancy outcomes. Omalizumab, indicated for chronic urticaria, has a good safety profile in pregnancy, with no significant increase in adverse outcomes reported in studies and registries.16 Dupilumab, used for AD, has demonstrated safety in pregnancy, with ongoing studies continuing to monitor outcomes.17
Conversely, rituximab (an anti-CD20 antibody for autoimmune bullous diseases) has shown evidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including fetal harm.18 Its use generally is discouraged unless deemed absolutely necessary, and no safer alternatives are available. Rituximab can cross the placenta, especially in the second and third trimesters, and has been associated with B-cell depletion in the fetus, leading to potential immunosuppression and increased risk for infections.5
Although the data on the safety of biologics in pregnancy are largely reassuring, it is essential to recognize that potential risks have not been ruled out entirely. There are extensive safety data for anti–TNF-α inhibitors, which provides a level of confidence; although newer agents such as IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors have shown promising early results, further research is required to solidify their safety profiles during pregnancy.
Dermatologists must balance the risks and benefits of using biologics in pregnant patients. This decision-making process involves careful consideration of the severity of the mother’s condition, the potential risks to the fetus, and the availability of alternative treatments. For many severe dermatologic conditions, the benefits of biologics in controlling disease activity and improving QOL may outweigh the potential risks, especially when other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
Final Thoughts
The increasing use of biologics in dermatology has undoubtedly improved the management of severe skin conditions, substantially enhancing patients’ QOL. As more data become available and clinical guidelines evolve, health care providers will be better equipped to make informed decisions about the use of biologics, particularly in pregnant patients. Collaborative efforts between dermatologists, obstetricians, and researchers will help refine treatment guidelines and ensure that pregnant patients with severe dermatologic conditions receive the best possible care.
For now, although the current evidence supports the safety of many biologics during pregnancy,10,11 individualized care and informed decision-making remain paramount. Careful management and adherence to current guidelines make it possible to navigate the complexities of treating severe dermatologic conditions in pregnant patients, ensuring the best outcomes for both mother and child.
- Sehgal VN, Pandhi D, Khurana A. Biologics in dermatology: an integrated review. Indian J Dermatol. 2014; 59:425-441. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.139859
- Mahadevan U, Wolf DC, Dubinsky M, et al. Placental transfer of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:286-292. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2012.11.011
- Simpson EL, Bieber T, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Two phase 3 trials of dupilumab versus placebo in atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2335-2348.
- Saini SS, Bindslev-Jensen C, Maurer M, et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in patients with chronic idiopathic/spontaneous urticaria who remain symptomatic on H1 antihistamines: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:67-75. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.306
- Mariette X, Forger F, Abraham B, et al. Lack of placental transfer of certolizumab pegol during pregnancy: results from CRIB, a prospective, postmarketing, pharmacokinetic study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:228-233. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212196
- Yang Y-W, Chen C-S, Chen Y-H, et al. Psoriasis and pregnancy outcomes: a nationwide population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:71-77.
- Zouboulis CC, Del Marmol V, Mrowietz U, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: criteria for diagnosis, severity assessment, classification and disease evaluation. Dermatology. 2015;231:184-190.
- Balakirski G, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis and pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149:1185-1194. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.01.010
- Bachelez H, Choon S-E, Marrakchi S, et al. Inhibition of the interleukin-36 pathway for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:981-983.
- McMullan P, Yaghi M, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part I: pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.072
- Yaghi M, McMullan P, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part II: lactation. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.071
- Owczarek W, Walecka I, Lesiak A, et al. The use of biological drugs in psoriasis patients prior to pregnancy, during pregnancy and lactation: a review of current clinical guidelines. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2020;37:821-830. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.102089
- Organization of Teratology Information Services (OTIS) Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00116272. Updated October 6, 2023. Accessed August 29, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00116272
- Sanchez-Garcia V, Hernandez-Quiles R, de-Miguel-Balsa E, et al. Exposure to biologic therapy before and during pregnancy in patients with psoriasis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1971-1990. doi:10.1111/jdv.19238
- Silverberg JI, Boguniewicz M, Hanifin J, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis is efficacious regardless of age of disease onset: a post hoc analysis of two phase 3 clinical trials. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:2731-2746. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00822-x
- Levi-Schaffer F, Mankuta D. Omalizumab safety in pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145:481-483. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2019.11.018
- Thaci D, Simpson EL, Beck LA, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis inadequately controlled by topical treatments: a randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging phase 2b trial. Lancet. 2016;387:40-52.
- Chakravarty EF, Murray ER, Kelman A, et al. Pregnancy outcomes after maternal exposure to rituximab. Blood. 2011;117:1499-1506. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-07-295444
- Sehgal VN, Pandhi D, Khurana A. Biologics in dermatology: an integrated review. Indian J Dermatol. 2014; 59:425-441. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.139859
- Mahadevan U, Wolf DC, Dubinsky M, et al. Placental transfer of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:286-292. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2012.11.011
- Simpson EL, Bieber T, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Two phase 3 trials of dupilumab versus placebo in atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2335-2348.
- Saini SS, Bindslev-Jensen C, Maurer M, et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in patients with chronic idiopathic/spontaneous urticaria who remain symptomatic on H1 antihistamines: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:67-75. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.306
- Mariette X, Forger F, Abraham B, et al. Lack of placental transfer of certolizumab pegol during pregnancy: results from CRIB, a prospective, postmarketing, pharmacokinetic study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:228-233. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212196
- Yang Y-W, Chen C-S, Chen Y-H, et al. Psoriasis and pregnancy outcomes: a nationwide population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:71-77.
- Zouboulis CC, Del Marmol V, Mrowietz U, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: criteria for diagnosis, severity assessment, classification and disease evaluation. Dermatology. 2015;231:184-190.
- Balakirski G, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis and pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149:1185-1194. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.01.010
- Bachelez H, Choon S-E, Marrakchi S, et al. Inhibition of the interleukin-36 pathway for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:981-983.
- McMullan P, Yaghi M, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part I: pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.072
- Yaghi M, McMullan P, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part II: lactation. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.071
- Owczarek W, Walecka I, Lesiak A, et al. The use of biological drugs in psoriasis patients prior to pregnancy, during pregnancy and lactation: a review of current clinical guidelines. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2020;37:821-830. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.102089
- Organization of Teratology Information Services (OTIS) Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00116272. Updated October 6, 2023. Accessed August 29, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00116272
- Sanchez-Garcia V, Hernandez-Quiles R, de-Miguel-Balsa E, et al. Exposure to biologic therapy before and during pregnancy in patients with psoriasis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1971-1990. doi:10.1111/jdv.19238
- Silverberg JI, Boguniewicz M, Hanifin J, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis is efficacious regardless of age of disease onset: a post hoc analysis of two phase 3 clinical trials. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:2731-2746. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00822-x
- Levi-Schaffer F, Mankuta D. Omalizumab safety in pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145:481-483. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2019.11.018
- Thaci D, Simpson EL, Beck LA, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis inadequately controlled by topical treatments: a randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging phase 2b trial. Lancet. 2016;387:40-52.
- Chakravarty EF, Murray ER, Kelman A, et al. Pregnancy outcomes after maternal exposure to rituximab. Blood. 2011;117:1499-1506. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-07-295444
High Cadmium Level Associated With Cognitive Impairment Risk
TOPLINE:
High levels of urinary cadmium are associated with double the risk for global cognitive impairment in White adults, a new study shows. There was no such association between the heavy metal and cognitive function in Black adults.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators reviewed data on 2172 adults (mean age, 64 years; 61% White; 39% Black; 55% women) from the ongoing REGARDS population-based prospective cohort study in the United States who were free of cognitive impairment or stroke at baseline.
- Global cognitive impairment was assessed annually using the Six-Item Screener, and domain-based cognitive impairment was assessed every 2 years using the Enhanced Cognitive Battery.
- Blood and urine samples were collected from the participants at baseline, and levels of urinary cadmium were assessed using a urinary creatinine-correction method.
- Covariates included participants’ age, sex, smoking pack-years, alcohol consumption, and education level.
- Mean follow-up was 10 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Global cognitive impairment was observed in 195 cases and domain-based cognitive impairment in 53 cases.
- High levels of urinary cadmium were associated with double the risk of developing global cognitive impairment in White adults (odds ratio [OR], 2.07; 95% CI, 1.18-3.64).
- No association was observed between urinary cadmium and global cognitive impairment in the overall cohort or in Black adults.
- Median smoking pack-years — a significant source of cadmium exposure for the US population — was significantly higher in White participants than Black participants (P = .001 for the highest tertile of urinary cadmium concentration).
IN PRACTICE:
“These results need to be confirmed with studies that measure cadmium levels over time, include more people and follow people over a longer time, but there are many reasons to reduce exposure to cadmium, whether it’s through implementing policies and regulations for air pollution and drinking water or people changing their behaviors by stopping smoking or being around cigarette smoke,” lead author Liping Lu, MD, PhD, MS, Columbia University, New York City, said in a press release.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
Urinary cadmium levels were tested only at baseline, which may not have captured changes in exposure over time. A limited number of patients with cognitive impairment used the Enhanced Cognitive Battery. The study did not include occupational information, and the potential for residual confounding from smoking could not be completely excluded. The follow-up time may have been insufficient for observing a significant effect on cognition, and competing risks for mortality associated with cadmium exposure could also have affected the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was co-funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Several authors were partially supported by the NIH. Detailed disclosures are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
High levels of urinary cadmium are associated with double the risk for global cognitive impairment in White adults, a new study shows. There was no such association between the heavy metal and cognitive function in Black adults.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators reviewed data on 2172 adults (mean age, 64 years; 61% White; 39% Black; 55% women) from the ongoing REGARDS population-based prospective cohort study in the United States who were free of cognitive impairment or stroke at baseline.
- Global cognitive impairment was assessed annually using the Six-Item Screener, and domain-based cognitive impairment was assessed every 2 years using the Enhanced Cognitive Battery.
- Blood and urine samples were collected from the participants at baseline, and levels of urinary cadmium were assessed using a urinary creatinine-correction method.
- Covariates included participants’ age, sex, smoking pack-years, alcohol consumption, and education level.
- Mean follow-up was 10 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Global cognitive impairment was observed in 195 cases and domain-based cognitive impairment in 53 cases.
- High levels of urinary cadmium were associated with double the risk of developing global cognitive impairment in White adults (odds ratio [OR], 2.07; 95% CI, 1.18-3.64).
- No association was observed between urinary cadmium and global cognitive impairment in the overall cohort or in Black adults.
- Median smoking pack-years — a significant source of cadmium exposure for the US population — was significantly higher in White participants than Black participants (P = .001 for the highest tertile of urinary cadmium concentration).
IN PRACTICE:
“These results need to be confirmed with studies that measure cadmium levels over time, include more people and follow people over a longer time, but there are many reasons to reduce exposure to cadmium, whether it’s through implementing policies and regulations for air pollution and drinking water or people changing their behaviors by stopping smoking or being around cigarette smoke,” lead author Liping Lu, MD, PhD, MS, Columbia University, New York City, said in a press release.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
Urinary cadmium levels were tested only at baseline, which may not have captured changes in exposure over time. A limited number of patients with cognitive impairment used the Enhanced Cognitive Battery. The study did not include occupational information, and the potential for residual confounding from smoking could not be completely excluded. The follow-up time may have been insufficient for observing a significant effect on cognition, and competing risks for mortality associated with cadmium exposure could also have affected the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was co-funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Several authors were partially supported by the NIH. Detailed disclosures are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
High levels of urinary cadmium are associated with double the risk for global cognitive impairment in White adults, a new study shows. There was no such association between the heavy metal and cognitive function in Black adults.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators reviewed data on 2172 adults (mean age, 64 years; 61% White; 39% Black; 55% women) from the ongoing REGARDS population-based prospective cohort study in the United States who were free of cognitive impairment or stroke at baseline.
- Global cognitive impairment was assessed annually using the Six-Item Screener, and domain-based cognitive impairment was assessed every 2 years using the Enhanced Cognitive Battery.
- Blood and urine samples were collected from the participants at baseline, and levels of urinary cadmium were assessed using a urinary creatinine-correction method.
- Covariates included participants’ age, sex, smoking pack-years, alcohol consumption, and education level.
- Mean follow-up was 10 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Global cognitive impairment was observed in 195 cases and domain-based cognitive impairment in 53 cases.
- High levels of urinary cadmium were associated with double the risk of developing global cognitive impairment in White adults (odds ratio [OR], 2.07; 95% CI, 1.18-3.64).
- No association was observed between urinary cadmium and global cognitive impairment in the overall cohort or in Black adults.
- Median smoking pack-years — a significant source of cadmium exposure for the US population — was significantly higher in White participants than Black participants (P = .001 for the highest tertile of urinary cadmium concentration).
IN PRACTICE:
“These results need to be confirmed with studies that measure cadmium levels over time, include more people and follow people over a longer time, but there are many reasons to reduce exposure to cadmium, whether it’s through implementing policies and regulations for air pollution and drinking water or people changing their behaviors by stopping smoking or being around cigarette smoke,” lead author Liping Lu, MD, PhD, MS, Columbia University, New York City, said in a press release.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
Urinary cadmium levels were tested only at baseline, which may not have captured changes in exposure over time. A limited number of patients with cognitive impairment used the Enhanced Cognitive Battery. The study did not include occupational information, and the potential for residual confounding from smoking could not be completely excluded. The follow-up time may have been insufficient for observing a significant effect on cognition, and competing risks for mortality associated with cadmium exposure could also have affected the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was co-funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Several authors were partially supported by the NIH. Detailed disclosures are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hypothyroidism Treatment Does Not Affect Cognitive Decline in Menopausal Women
TOPLINE:
Women with hypothyroidism treated with levothyroxine show no significant cognitive decline across the menopausal transition compared with those without thyroid disease.
METHODOLOGY:
- Levothyroxine, the primary treatment for hypothyroidism, has been linked to perceived cognitive deficits, yet it is unclear whether this is due to the underlying condition being inadequately treated or other factors.
- Using data collected from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation, which encompasses five ethnic/racial groups from seven centers across the United States, researchers compared cognitive function over time between women with hypothyroidism treated with levothyroxine and those without thyroid disease.
- Participants underwent cognitive testing across three domains — processing speed, working memory, and episodic memory — which were assessed over a mean follow-up of 13 years.
- Further analyses assessed the impact of abnormal levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone on cognitive outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of 2033 women included, 227 (mean age, 49.8 years) had levothyroxine-treated hypothyroidism and 1806 (mean age, 50.0 years) did not have thyroid disease; the proportion of women with premenopausal or early perimenopausal status at baseline was higher in the hypothyroidism group (54.2% vs 49.8%; P = .010).
- At baseline, levothyroxine-treated women had higher scores for processing speed (mean score, 56.5 vs 54.4; P = .006) and working memory (mean score, 6.8 vs 6.4; P = .018) than those without thyroid disease; however, no difference in episodic memory was observed between the groups.
- Over the study period, there was no significant difference in cognitive decline between the groups.
- There was no significant effect of levothyroxine-treated hypothyroidism on working memory or episodic memory, although an annual decline in processing speed was observed (P < .001).
- Sensitivity analyses determined that abnormal levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone did not affect cognitive outcomes in women with hypothyroidism.
IN PRACTICE:
When cognitive decline is observed in these patients, the authors advised that “clinicians should resist anchoring on inadequate treatment of hypothyroidism as the cause of these symptoms and may investigate other disease processes (eg, iron deficiency, B12 deficiency, sleep apnea, celiac disease).”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Matthew D. Ettleson, Section of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, University of Chicago, was published online in Thyroid.
LIMITATIONS:
The cognitive assessments in the study were not designed to provide a thorough evaluation of all aspects of cognitive function. The study may not have been adequately powered to detect small effects of levothyroxine-treated hypothyroidism on cognitive outcomes. The higher levels of education attained by the study population may have acted as a protective factor against cognitive decline, potentially biasing the results.
DISCLOSURES:
The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), DHHS, through the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Nursing Research, and the NIH Office of Research on Women’s Health. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Women with hypothyroidism treated with levothyroxine show no significant cognitive decline across the menopausal transition compared with those without thyroid disease.
METHODOLOGY:
- Levothyroxine, the primary treatment for hypothyroidism, has been linked to perceived cognitive deficits, yet it is unclear whether this is due to the underlying condition being inadequately treated or other factors.
- Using data collected from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation, which encompasses five ethnic/racial groups from seven centers across the United States, researchers compared cognitive function over time between women with hypothyroidism treated with levothyroxine and those without thyroid disease.
- Participants underwent cognitive testing across three domains — processing speed, working memory, and episodic memory — which were assessed over a mean follow-up of 13 years.
- Further analyses assessed the impact of abnormal levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone on cognitive outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of 2033 women included, 227 (mean age, 49.8 years) had levothyroxine-treated hypothyroidism and 1806 (mean age, 50.0 years) did not have thyroid disease; the proportion of women with premenopausal or early perimenopausal status at baseline was higher in the hypothyroidism group (54.2% vs 49.8%; P = .010).
- At baseline, levothyroxine-treated women had higher scores for processing speed (mean score, 56.5 vs 54.4; P = .006) and working memory (mean score, 6.8 vs 6.4; P = .018) than those without thyroid disease; however, no difference in episodic memory was observed between the groups.
- Over the study period, there was no significant difference in cognitive decline between the groups.
- There was no significant effect of levothyroxine-treated hypothyroidism on working memory or episodic memory, although an annual decline in processing speed was observed (P < .001).
- Sensitivity analyses determined that abnormal levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone did not affect cognitive outcomes in women with hypothyroidism.
IN PRACTICE:
When cognitive decline is observed in these patients, the authors advised that “clinicians should resist anchoring on inadequate treatment of hypothyroidism as the cause of these symptoms and may investigate other disease processes (eg, iron deficiency, B12 deficiency, sleep apnea, celiac disease).”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Matthew D. Ettleson, Section of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, University of Chicago, was published online in Thyroid.
LIMITATIONS:
The cognitive assessments in the study were not designed to provide a thorough evaluation of all aspects of cognitive function. The study may not have been adequately powered to detect small effects of levothyroxine-treated hypothyroidism on cognitive outcomes. The higher levels of education attained by the study population may have acted as a protective factor against cognitive decline, potentially biasing the results.
DISCLOSURES:
The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), DHHS, through the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Nursing Research, and the NIH Office of Research on Women’s Health. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Women with hypothyroidism treated with levothyroxine show no significant cognitive decline across the menopausal transition compared with those without thyroid disease.
METHODOLOGY:
- Levothyroxine, the primary treatment for hypothyroidism, has been linked to perceived cognitive deficits, yet it is unclear whether this is due to the underlying condition being inadequately treated or other factors.
- Using data collected from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation, which encompasses five ethnic/racial groups from seven centers across the United States, researchers compared cognitive function over time between women with hypothyroidism treated with levothyroxine and those without thyroid disease.
- Participants underwent cognitive testing across three domains — processing speed, working memory, and episodic memory — which were assessed over a mean follow-up of 13 years.
- Further analyses assessed the impact of abnormal levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone on cognitive outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of 2033 women included, 227 (mean age, 49.8 years) had levothyroxine-treated hypothyroidism and 1806 (mean age, 50.0 years) did not have thyroid disease; the proportion of women with premenopausal or early perimenopausal status at baseline was higher in the hypothyroidism group (54.2% vs 49.8%; P = .010).
- At baseline, levothyroxine-treated women had higher scores for processing speed (mean score, 56.5 vs 54.4; P = .006) and working memory (mean score, 6.8 vs 6.4; P = .018) than those without thyroid disease; however, no difference in episodic memory was observed between the groups.
- Over the study period, there was no significant difference in cognitive decline between the groups.
- There was no significant effect of levothyroxine-treated hypothyroidism on working memory or episodic memory, although an annual decline in processing speed was observed (P < .001).
- Sensitivity analyses determined that abnormal levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone did not affect cognitive outcomes in women with hypothyroidism.
IN PRACTICE:
When cognitive decline is observed in these patients, the authors advised that “clinicians should resist anchoring on inadequate treatment of hypothyroidism as the cause of these symptoms and may investigate other disease processes (eg, iron deficiency, B12 deficiency, sleep apnea, celiac disease).”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Matthew D. Ettleson, Section of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, University of Chicago, was published online in Thyroid.
LIMITATIONS:
The cognitive assessments in the study were not designed to provide a thorough evaluation of all aspects of cognitive function. The study may not have been adequately powered to detect small effects of levothyroxine-treated hypothyroidism on cognitive outcomes. The higher levels of education attained by the study population may have acted as a protective factor against cognitive decline, potentially biasing the results.
DISCLOSURES:
The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), DHHS, through the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Nursing Research, and the NIH Office of Research on Women’s Health. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
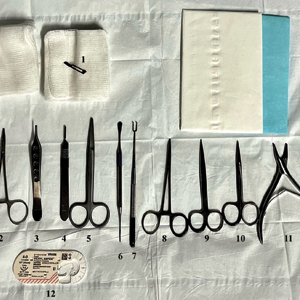
Nailing the Nail Biopsy: Surgical Instruments and Their Function in Nail Biopsy Procedures
Practice Gap
The term nail biopsy (NB) may refer to a punch, excisional, shave, or longitudinal biopsy of the nail matrix and/or nail bed.1 Nail surgeries, including NBs, are performed relatively infrequently. In a study using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017, only 1.01% of Mohs surgeons and 0.28% of general dermatologists in the United States performed NBs. Thirty-one states had no dermatologist-performed NBs, while 3 states had no nail biopsies performed by any physician, podiatrist, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant, indicating that there is a shortage of dermatology clinicians performing nail surgeries.2
Dermatologists may not be performing NBs due to unfamiliarity with nail unit anatomy and lack of formal NB training during residency.3 In a survey of 240 dermatology residents in the United States, 58% reported performing fewer than 10 nail procedures during residency, with 25% observing only.4 Of those surveyed, 1% had no exposure to nail procedures during 3 years of residency. Furthermore, when asked to assess their competency in nail surgery on a scale of not competent, competent, and very competent, approximately 30% responded that they were not competent.4 Without sufficient education on procedures involving the nail unit, residents may be reluctant to incorporate nail surgery into their clinical practice.
Due to their complexity, NBs require the use of several specialized surgical instruments that are not used for other dermatologic procedures, and residents and attending physicians who have limited nail training may be unfamiliar with these tools. To address this educational gap, we sought to create a guide that details the surgical instruments used for the nail matrix tangential excision (shave) biopsy technique—the most common technique used in our nail specialty clinic. This guide is intended for educational use by dermatologists who wish to incorporate NB as part of their practice.
Tools and Technique
As a major referral center, our New York City–based nail specialty clinic performs a large volume of NBs, many of them performed for clinically concerning longitudinal melanonychias for which a nail matrix shave biopsy most often is performed. We utilize a standardized tray consisting of 12 surgical instruments that are needed to successfully perform a NB from start to finish (Figure). In addition to standard surgical tray items, such as sutures and tissue scissors, additional specialized instruments are necessary for NB procedures, including a nail elevator, an English nail splitter, and skin hook.
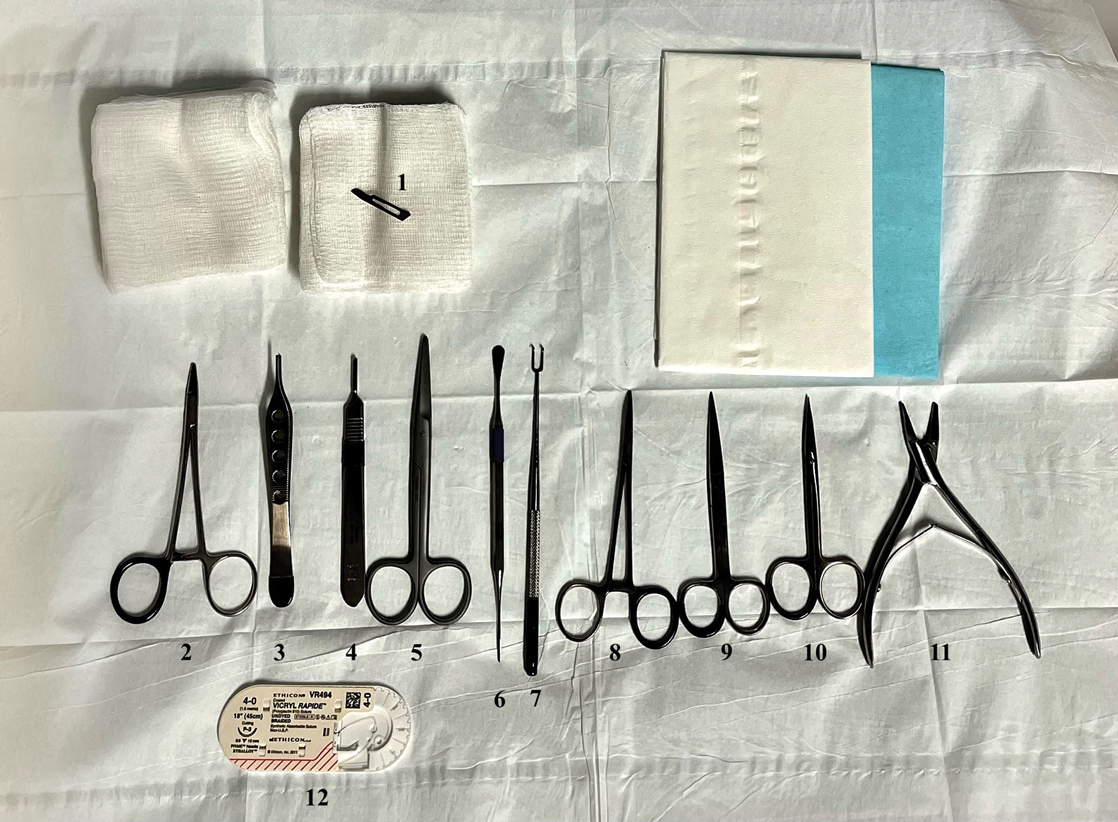
After the initial incisions are made at 45° angles to the proximal nail fold surrounding the longitudinal band, the nail elevator is used to separate the proximal nail plate from the underlying nail bed. The English nail splitter is used to create a transverse split separating the proximal from the distal nail plate, and the proximal nail plate then is retracted using a clamp. The skin hook is used to retract the proximal nail fold to expose the pigment in the nail matrix, which is biopsied using the #15 blade and sent for histopathology. The proximal nail fold and retracted nail plate then are put back in place, and absorbable sutures are used to repair the defect. In certain cases, a 3-mm punch biopsy may be used to sample the nail plate and/or the surrounding soft tissue.
Practice Implications
A guide to surgical tools used during NB procedures, including less commonly encountered tools such as a nail elevator and English nail splitter, helps to close the educational gap of NB procedures among dermatology trainees and attending physicians. In conjunction with practical training with cadavers and models, a guide to surgical tools can be reviewed by trainees before hands-on exposure to nail surgery in a clinical setting. By increasing awareness of the tools needed to complete the procedure from start to finish, dermatologists may feel more prepared and confident in their ability to perform NBs, ultimately allowing for more rapid diagnosis of nail malignancies.
- Grover C, Bansal S. Nail biopsy: a user’s manual. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:3-15. doi:10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_268_17
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273. doi:10.1016/j.det.2016.02.002
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.e4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
Practice Gap
The term nail biopsy (NB) may refer to a punch, excisional, shave, or longitudinal biopsy of the nail matrix and/or nail bed.1 Nail surgeries, including NBs, are performed relatively infrequently. In a study using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017, only 1.01% of Mohs surgeons and 0.28% of general dermatologists in the United States performed NBs. Thirty-one states had no dermatologist-performed NBs, while 3 states had no nail biopsies performed by any physician, podiatrist, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant, indicating that there is a shortage of dermatology clinicians performing nail surgeries.2
Dermatologists may not be performing NBs due to unfamiliarity with nail unit anatomy and lack of formal NB training during residency.3 In a survey of 240 dermatology residents in the United States, 58% reported performing fewer than 10 nail procedures during residency, with 25% observing only.4 Of those surveyed, 1% had no exposure to nail procedures during 3 years of residency. Furthermore, when asked to assess their competency in nail surgery on a scale of not competent, competent, and very competent, approximately 30% responded that they were not competent.4 Without sufficient education on procedures involving the nail unit, residents may be reluctant to incorporate nail surgery into their clinical practice.
Due to their complexity, NBs require the use of several specialized surgical instruments that are not used for other dermatologic procedures, and residents and attending physicians who have limited nail training may be unfamiliar with these tools. To address this educational gap, we sought to create a guide that details the surgical instruments used for the nail matrix tangential excision (shave) biopsy technique—the most common technique used in our nail specialty clinic. This guide is intended for educational use by dermatologists who wish to incorporate NB as part of their practice.
Tools and Technique
As a major referral center, our New York City–based nail specialty clinic performs a large volume of NBs, many of them performed for clinically concerning longitudinal melanonychias for which a nail matrix shave biopsy most often is performed. We utilize a standardized tray consisting of 12 surgical instruments that are needed to successfully perform a NB from start to finish (Figure). In addition to standard surgical tray items, such as sutures and tissue scissors, additional specialized instruments are necessary for NB procedures, including a nail elevator, an English nail splitter, and skin hook.

After the initial incisions are made at 45° angles to the proximal nail fold surrounding the longitudinal band, the nail elevator is used to separate the proximal nail plate from the underlying nail bed. The English nail splitter is used to create a transverse split separating the proximal from the distal nail plate, and the proximal nail plate then is retracted using a clamp. The skin hook is used to retract the proximal nail fold to expose the pigment in the nail matrix, which is biopsied using the #15 blade and sent for histopathology. The proximal nail fold and retracted nail plate then are put back in place, and absorbable sutures are used to repair the defect. In certain cases, a 3-mm punch biopsy may be used to sample the nail plate and/or the surrounding soft tissue.
Practice Implications
A guide to surgical tools used during NB procedures, including less commonly encountered tools such as a nail elevator and English nail splitter, helps to close the educational gap of NB procedures among dermatology trainees and attending physicians. In conjunction with practical training with cadavers and models, a guide to surgical tools can be reviewed by trainees before hands-on exposure to nail surgery in a clinical setting. By increasing awareness of the tools needed to complete the procedure from start to finish, dermatologists may feel more prepared and confident in their ability to perform NBs, ultimately allowing for more rapid diagnosis of nail malignancies.
Practice Gap
The term nail biopsy (NB) may refer to a punch, excisional, shave, or longitudinal biopsy of the nail matrix and/or nail bed.1 Nail surgeries, including NBs, are performed relatively infrequently. In a study using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017, only 1.01% of Mohs surgeons and 0.28% of general dermatologists in the United States performed NBs. Thirty-one states had no dermatologist-performed NBs, while 3 states had no nail biopsies performed by any physician, podiatrist, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant, indicating that there is a shortage of dermatology clinicians performing nail surgeries.2
Dermatologists may not be performing NBs due to unfamiliarity with nail unit anatomy and lack of formal NB training during residency.3 In a survey of 240 dermatology residents in the United States, 58% reported performing fewer than 10 nail procedures during residency, with 25% observing only.4 Of those surveyed, 1% had no exposure to nail procedures during 3 years of residency. Furthermore, when asked to assess their competency in nail surgery on a scale of not competent, competent, and very competent, approximately 30% responded that they were not competent.4 Without sufficient education on procedures involving the nail unit, residents may be reluctant to incorporate nail surgery into their clinical practice.
Due to their complexity, NBs require the use of several specialized surgical instruments that are not used for other dermatologic procedures, and residents and attending physicians who have limited nail training may be unfamiliar with these tools. To address this educational gap, we sought to create a guide that details the surgical instruments used for the nail matrix tangential excision (shave) biopsy technique—the most common technique used in our nail specialty clinic. This guide is intended for educational use by dermatologists who wish to incorporate NB as part of their practice.
Tools and Technique
As a major referral center, our New York City–based nail specialty clinic performs a large volume of NBs, many of them performed for clinically concerning longitudinal melanonychias for which a nail matrix shave biopsy most often is performed. We utilize a standardized tray consisting of 12 surgical instruments that are needed to successfully perform a NB from start to finish (Figure). In addition to standard surgical tray items, such as sutures and tissue scissors, additional specialized instruments are necessary for NB procedures, including a nail elevator, an English nail splitter, and skin hook.

After the initial incisions are made at 45° angles to the proximal nail fold surrounding the longitudinal band, the nail elevator is used to separate the proximal nail plate from the underlying nail bed. The English nail splitter is used to create a transverse split separating the proximal from the distal nail plate, and the proximal nail plate then is retracted using a clamp. The skin hook is used to retract the proximal nail fold to expose the pigment in the nail matrix, which is biopsied using the #15 blade and sent for histopathology. The proximal nail fold and retracted nail plate then are put back in place, and absorbable sutures are used to repair the defect. In certain cases, a 3-mm punch biopsy may be used to sample the nail plate and/or the surrounding soft tissue.
Practice Implications
A guide to surgical tools used during NB procedures, including less commonly encountered tools such as a nail elevator and English nail splitter, helps to close the educational gap of NB procedures among dermatology trainees and attending physicians. In conjunction with practical training with cadavers and models, a guide to surgical tools can be reviewed by trainees before hands-on exposure to nail surgery in a clinical setting. By increasing awareness of the tools needed to complete the procedure from start to finish, dermatologists may feel more prepared and confident in their ability to perform NBs, ultimately allowing for more rapid diagnosis of nail malignancies.
- Grover C, Bansal S. Nail biopsy: a user’s manual. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:3-15. doi:10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_268_17
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273. doi:10.1016/j.det.2016.02.002
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.e4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
- Grover C, Bansal S. Nail biopsy: a user’s manual. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:3-15. doi:10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_268_17
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273. doi:10.1016/j.det.2016.02.002
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.e4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
Women Are Entering Higher-Paid MD Specialties at Higher Rates
More women are enrolling into higher-paid physician specialty fields, especially surgery, but they still have a way to go before reaching parity with their male counterparts, an analysis found.
Rising Interest in Surgical Specialties
Among 490,188 students to “pipeline” specialties from 2008 to 2022 (47.4% women), the proportion of women entering higher-paid specialties grew from 32.7% to 40.8% (P = .003), powered by increased interest in surgical jobs, reported Karina Pereira-Lima, PhD, MSc, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, and colleagues in JAMA.
“It was exciting to see the proportion of women entering high-compensation surgical specialties jump from 28.8% in 2008 to 42.4% in 2022,” Dr. Pereira-Lima told this news organization. “At the same time, the proportion of women entering high-compensation nonsurgical specialties didn’t change much over time, and we even saw a decrease in female applicants to those fields.”
The researchers launched the analysis to better understand the career choices of medical students. “We’ve been seeing a national trend where more women are entering the medical profession, with women now making up more than half of medical school students. At the same time, most of the highest compensation specialties have traditionally been dominated by men,” Dr. Pereira-Lima said. “Tracking changes in the proportion of women entering these programs over time can give us insight into whether we’re making progress toward more equitable gender representation in these high-compensation specialties.”
Highest vs Lowest Compensated Specialties
The researchers analyzed 2008-2022 data from students and applicants to Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education–accredited residency programs in “pipeline” specialties, defined as those that lead to primary board certification.
Specialties defined as having the highest compensation, based on data from Doximity, were the surgical fields of neurosurgery, ophthalmology, orthopedic surgery, otorhinolaryngology, plastic surgery (integrated), surgery (general), thoracic surgery (integrated), urology, and vascular surgery (integrated) and the nonsurgical fields of anesthesiology, dermatology, nuclear medicine, radiation oncology, and radiology (diagnostic).
The lowest-compensated fields were all nonsurgical: Child neurology, emergency medicine, family medicine, internal medicine, internal medicine/pediatrics, medical genetics and genomics, neurology, nuclear medicine, obstetrics and gynecology, pathology, pediatrics, physical medicine and rehabilitation, and psychiatry.
The proportion of women entering lower-compensated specialties stayed steady from 2008 to 2022 (53.0% vs 53.3%, respectively; P = .44), as did the percentage entering nonsurgical specialties (37.6% vs 38.7%, respectively; P = .55).
Meanwhile, the proportion of women applicants to high-compensation nonsurgical specialties fell from 36.8% in 2009 to 34.3% in 2022 (P = .001), whereas the number grew in high-compensation surgical specialties from 28.1% in 2009 to 37.6% in 2022 (P < .001).
Implications for Future Representation
The findings suggest that “the issue of women’s underrepresentation isn’t just limited to surgical specialties,” Dr. Pereira-Lima said. “It’s affecting many of the highest-compensated specialties overall. Moving forward, it’ll be important to investigate what’s driving the increase in women entering these highly compensated surgical specialties and see if those same factors can be applied to other fields where women are still underrepresented.”
She added that it will take time for the dominance of women among medical students to translate into more representation in the physician workforce. Also, “studies show that female physicians have higher attrition rates than men. To achieve a more balanced gender representation in medicine, it’s crucial not just to have more women entering the profession, but to focus on addressing the barriers that hinder their career advancement.”
Shikha Jain, MD, University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, an oncologist who’s studied gender representation in medicine, told this news organization that the rise in women entering surgical fields may be due to an increased focus on gender disparity. “It’s nice to see that we’re actually seeing some movement there,” she said, especially in light of findings that female surgeons have better outcomes than male surgeons.
However, research has shown that women in surgical specialties aren’t as highly compensated as men, she said. “Bullying, harassment, micro- and macro-aggressions, and gaslighting are all huge problems that continue to persist in healthcare. They’re a huge part of the reason many women weren’t in these specialties. With the increase in women entering these fields, I hope we see a real concerted effort to address these challenges so we can continue to see these trends moving forward.”
Dr. Pereira-Lima is supported by the National Institutes of Health, and another author is supported by the National Institute of Mental Health. No author disclosures were reported. Dr. Jain had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More women are enrolling into higher-paid physician specialty fields, especially surgery, but they still have a way to go before reaching parity with their male counterparts, an analysis found.
Rising Interest in Surgical Specialties
Among 490,188 students to “pipeline” specialties from 2008 to 2022 (47.4% women), the proportion of women entering higher-paid specialties grew from 32.7% to 40.8% (P = .003), powered by increased interest in surgical jobs, reported Karina Pereira-Lima, PhD, MSc, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, and colleagues in JAMA.
“It was exciting to see the proportion of women entering high-compensation surgical specialties jump from 28.8% in 2008 to 42.4% in 2022,” Dr. Pereira-Lima told this news organization. “At the same time, the proportion of women entering high-compensation nonsurgical specialties didn’t change much over time, and we even saw a decrease in female applicants to those fields.”
The researchers launched the analysis to better understand the career choices of medical students. “We’ve been seeing a national trend where more women are entering the medical profession, with women now making up more than half of medical school students. At the same time, most of the highest compensation specialties have traditionally been dominated by men,” Dr. Pereira-Lima said. “Tracking changes in the proportion of women entering these programs over time can give us insight into whether we’re making progress toward more equitable gender representation in these high-compensation specialties.”
Highest vs Lowest Compensated Specialties
The researchers analyzed 2008-2022 data from students and applicants to Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education–accredited residency programs in “pipeline” specialties, defined as those that lead to primary board certification.
Specialties defined as having the highest compensation, based on data from Doximity, were the surgical fields of neurosurgery, ophthalmology, orthopedic surgery, otorhinolaryngology, plastic surgery (integrated), surgery (general), thoracic surgery (integrated), urology, and vascular surgery (integrated) and the nonsurgical fields of anesthesiology, dermatology, nuclear medicine, radiation oncology, and radiology (diagnostic).
The lowest-compensated fields were all nonsurgical: Child neurology, emergency medicine, family medicine, internal medicine, internal medicine/pediatrics, medical genetics and genomics, neurology, nuclear medicine, obstetrics and gynecology, pathology, pediatrics, physical medicine and rehabilitation, and psychiatry.
The proportion of women entering lower-compensated specialties stayed steady from 2008 to 2022 (53.0% vs 53.3%, respectively; P = .44), as did the percentage entering nonsurgical specialties (37.6% vs 38.7%, respectively; P = .55).
Meanwhile, the proportion of women applicants to high-compensation nonsurgical specialties fell from 36.8% in 2009 to 34.3% in 2022 (P = .001), whereas the number grew in high-compensation surgical specialties from 28.1% in 2009 to 37.6% in 2022 (P < .001).
Implications for Future Representation
The findings suggest that “the issue of women’s underrepresentation isn’t just limited to surgical specialties,” Dr. Pereira-Lima said. “It’s affecting many of the highest-compensated specialties overall. Moving forward, it’ll be important to investigate what’s driving the increase in women entering these highly compensated surgical specialties and see if those same factors can be applied to other fields where women are still underrepresented.”
She added that it will take time for the dominance of women among medical students to translate into more representation in the physician workforce. Also, “studies show that female physicians have higher attrition rates than men. To achieve a more balanced gender representation in medicine, it’s crucial not just to have more women entering the profession, but to focus on addressing the barriers that hinder their career advancement.”
Shikha Jain, MD, University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, an oncologist who’s studied gender representation in medicine, told this news organization that the rise in women entering surgical fields may be due to an increased focus on gender disparity. “It’s nice to see that we’re actually seeing some movement there,” she said, especially in light of findings that female surgeons have better outcomes than male surgeons.
However, research has shown that women in surgical specialties aren’t as highly compensated as men, she said. “Bullying, harassment, micro- and macro-aggressions, and gaslighting are all huge problems that continue to persist in healthcare. They’re a huge part of the reason many women weren’t in these specialties. With the increase in women entering these fields, I hope we see a real concerted effort to address these challenges so we can continue to see these trends moving forward.”
Dr. Pereira-Lima is supported by the National Institutes of Health, and another author is supported by the National Institute of Mental Health. No author disclosures were reported. Dr. Jain had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More women are enrolling into higher-paid physician specialty fields, especially surgery, but they still have a way to go before reaching parity with their male counterparts, an analysis found.
Rising Interest in Surgical Specialties
Among 490,188 students to “pipeline” specialties from 2008 to 2022 (47.4% women), the proportion of women entering higher-paid specialties grew from 32.7% to 40.8% (P = .003), powered by increased interest in surgical jobs, reported Karina Pereira-Lima, PhD, MSc, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, and colleagues in JAMA.
“It was exciting to see the proportion of women entering high-compensation surgical specialties jump from 28.8% in 2008 to 42.4% in 2022,” Dr. Pereira-Lima told this news organization. “At the same time, the proportion of women entering high-compensation nonsurgical specialties didn’t change much over time, and we even saw a decrease in female applicants to those fields.”
The researchers launched the analysis to better understand the career choices of medical students. “We’ve been seeing a national trend where more women are entering the medical profession, with women now making up more than half of medical school students. At the same time, most of the highest compensation specialties have traditionally been dominated by men,” Dr. Pereira-Lima said. “Tracking changes in the proportion of women entering these programs over time can give us insight into whether we’re making progress toward more equitable gender representation in these high-compensation specialties.”
Highest vs Lowest Compensated Specialties
The researchers analyzed 2008-2022 data from students and applicants to Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education–accredited residency programs in “pipeline” specialties, defined as those that lead to primary board certification.
Specialties defined as having the highest compensation, based on data from Doximity, were the surgical fields of neurosurgery, ophthalmology, orthopedic surgery, otorhinolaryngology, plastic surgery (integrated), surgery (general), thoracic surgery (integrated), urology, and vascular surgery (integrated) and the nonsurgical fields of anesthesiology, dermatology, nuclear medicine, radiation oncology, and radiology (diagnostic).
The lowest-compensated fields were all nonsurgical: Child neurology, emergency medicine, family medicine, internal medicine, internal medicine/pediatrics, medical genetics and genomics, neurology, nuclear medicine, obstetrics and gynecology, pathology, pediatrics, physical medicine and rehabilitation, and psychiatry.
The proportion of women entering lower-compensated specialties stayed steady from 2008 to 2022 (53.0% vs 53.3%, respectively; P = .44), as did the percentage entering nonsurgical specialties (37.6% vs 38.7%, respectively; P = .55).
Meanwhile, the proportion of women applicants to high-compensation nonsurgical specialties fell from 36.8% in 2009 to 34.3% in 2022 (P = .001), whereas the number grew in high-compensation surgical specialties from 28.1% in 2009 to 37.6% in 2022 (P < .001).
Implications for Future Representation
The findings suggest that “the issue of women’s underrepresentation isn’t just limited to surgical specialties,” Dr. Pereira-Lima said. “It’s affecting many of the highest-compensated specialties overall. Moving forward, it’ll be important to investigate what’s driving the increase in women entering these highly compensated surgical specialties and see if those same factors can be applied to other fields where women are still underrepresented.”
She added that it will take time for the dominance of women among medical students to translate into more representation in the physician workforce. Also, “studies show that female physicians have higher attrition rates than men. To achieve a more balanced gender representation in medicine, it’s crucial not just to have more women entering the profession, but to focus on addressing the barriers that hinder their career advancement.”
Shikha Jain, MD, University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, an oncologist who’s studied gender representation in medicine, told this news organization that the rise in women entering surgical fields may be due to an increased focus on gender disparity. “It’s nice to see that we’re actually seeing some movement there,” she said, especially in light of findings that female surgeons have better outcomes than male surgeons.
However, research has shown that women in surgical specialties aren’t as highly compensated as men, she said. “Bullying, harassment, micro- and macro-aggressions, and gaslighting are all huge problems that continue to persist in healthcare. They’re a huge part of the reason many women weren’t in these specialties. With the increase in women entering these fields, I hope we see a real concerted effort to address these challenges so we can continue to see these trends moving forward.”
Dr. Pereira-Lima is supported by the National Institutes of Health, and another author is supported by the National Institute of Mental Health. No author disclosures were reported. Dr. Jain had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treat-to-Target Outcomes With Tapinarof Cream 1% in Phase 3 Trials for Plaque Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 8 million adults in the United States and 2% of the global population.1,2 Psoriasis causes pain, itching, and disfigurement and is associated with a physical, psychological, and economic burden that substantially affects health-related quality of life.3-5
Setting treatment goals and treating to target are evidence-based approaches that have been successfully applied to several chronic diseases to improve patient outcomes, including diabetes, hypertension, and rheumatoid arthritis.6-9 Treat-to-target strategies generally set low disease activity (or remission) as an overall goal and seek to achieve this using available therapeutic options as necessary. Introduced following the availability of biologics and targeted systemic therapies, treat-to-target strategies generally provide guidance on expectations of treatment but not specific treatments, as personalized treatment decisions depend on an assessment of individual patients and consider clinical and demographic features as well as preferences for available therapeutic options. If targets are not achieved in the assigned time span, adjustments can be made to the treatment approach in close consultation with the patient. If the target is reached, follow-up visits can be scheduled to ensure improvement is maintained or to establish if more aggressive goals could be selected.
Treat-to-target strategies for the management of psoriasis developed by the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) Medical Board include reducing the extent of psoriasis to 1% or lower total body surface area (BSA) after 3 months of treatment.10 Treatment targets endorsed by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) in guidelines on the use of systemic therapies in psoriasis include achieving a 75% or greater reduction in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score within 3 to 4 months of treatment.11
In clinical practice, many patients do not achieve these treatment targets, and topical treatments alone generally are insufficient in achieving treatment goals for psoriasis.12,13 Moreover, conventional topical treatments (eg, topical corticosteroids) used by most patients with psoriasis regardless of disease severity are associated with adverse events that can limit their use. Most topical corticosteroids have US Food and Drug Administration label restrictions relating to sites of application, duration and extent of use, and frequency of administration.14,15
Tapinarof cream 1% (VTAMA [Dermavant Sciences, Inc]) is a first-in-class topical nonsteroidal aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults16 and is being studied for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in children 2 years and older as well as for atopic dermatitis in adults and children 2 years and older. In PSOARING 1 (ClinicalTrials .gov identifier NCT03956355) and PSOARING 2 (NCT03983980)—identical 12-week pivotal phase 3 trials—monotherapy with tapinarof cream 1% once daily (QD) demonstrated statistically significant efficacy vs vehicle cream and was well tolerated in adults with mild to severe plaque psoriasis (Supplementary Figure S1).17 Lebwohl et al17 reported that significantly higher PASI75 responses were observed at week 12 with tapinarof cream vs vehicle in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2 (36% and 48% vs 10% and 7%, respectively; both P<.0001). A significantly higher PASI90 response of 19% and 21% at week 12 also was observed with tapinarof cream vs 2% and 3% with vehicle in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2, respectively (P=.0005 and P<.0001).17
In PSOARING 3 (NCT04053387)—the long-term extension trial (Supplementary Figure S1)—efficacy continued to improve or was maintained beyond the two 12-week trials, with improvements in total BSA affected and PASI scores for up to 52 weeks.18 Tapinarof cream 1% QD demonstrated positive, rapid, and durable outcomes in PSOARING 3, including high rates of complete disease clearance (Physician Global Assessment [PGA] score=0 [clear])(40.9% [312/763]), durability of response on treatment with no evidence of tachyphylaxis, and a remittive effect of approximately 4 months when off therapy (defined as maintenance of a PGA score of 0 [clear] or 1 [almost clear] after first achieving a PGA score of 0).18
Herein, we report absolute treatment targets for patients with plaque psoriasis who received tapinarof cream 1% QD in the PSOARING trials that are at least as stringent as the corresponding NPF and EADV targets of achieving a total BSA affected of 1% or lower or a PASI75 response within 3 to 4 months, respectively.
METHODS
Study Design
The pooled efficacy analyses included all patients with a baseline PGA score of 2 or higher (mild or worse) before treatment with tapinarof cream 1% QD in the PSOARING trials. This included patients who received tapinarof cream 1% in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2 who may or may not have continued into PSOARING 3, as well as those who received the vehicle in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2 who enrolled in PSOARING 3 and had a PGA score of 2 or higher before receiving tapinarof cream 1%.
Trial Participants
Full methods, including inclusion and exclusion criteria, for the PSOARING trials have been previously reported.17,18 Patients were aged 18 to 75 years and had chronic plaque psoriasis that was stable for at least 6 months before randomization; 3% to 20% total BSA affected (excluding the scalp, palms, fingernails, toenails, and soles); and a PGA score of 2 (mild), 3 (moderate), or 4 (severe) at baseline.
The clinical trials were conducted in compliance with the guidelines for Good Clinical Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was obtained from local ethics committees or institutional review boards at each center. All patients provided written informed consent.
Trial Treatment
In PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2, patients were randomized (2:1) to receive tapinarof cream 1% or vehicle QD for 12 weeks. In PSOARING 3 (the long-term extension trial), patients received up to 40 weeks of open-label tapinarof, followed by 4 weeks of follow-up off treatment. Patients received intermittent or continuous treatment with tapinarof cream 1% in PSOARING 3 based on PGA score: those entering the trial with a PGA score of 1 or higher received tapinarof cream 1% until complete disease clearance was achieved (defined as a PGA score of 0 [clear]). Those entering PSOARING 3 with or achieving a PGA score of 0 (clear) discontinued treatment and were observed for the duration of maintenance of a PGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) while off therapy (the protocol-defined “duration of remittive effect”). If disease worsening (defined as a PGA score 2 or higher) occurred, tapinarof cream 1% was restarted and continued until a PGA score of 0 (clear) was achieved. This pattern of treatment, discontinuation on achieving a PGA score of 0 (clear), and retreatment on disease worsening continued until the end of the trial. As a result, patients in PSOARING 3 could receive tapinarof cream 1% continuously or intermittently for 40 weeks.
Outcome Measures and Statistical Analyses
The assessment of total BSA affected by plaque psoriasis is an estimate of the total extent of disease as a percentage of total skin area. In the PSOARING trials, the skin surface of one hand (palm and digits) was assumed to be approximately equivalent to 1% BSA. The total BSA affected by psoriasis was evaluated from 0% to 100%, with greater total BSA affected being an indication of more extensive disease. The BSA efficacy outcomes used in these analyses were based post hoc on the proportion of patients who achieved a 1% or lower or 0.5% or lower total BSA affected.
Psoriasis Area and Severity Index scores assess both the severity and extent of psoriasis. A PASI score lower than 5 often is considered indicative of mild psoriasis, a score of 5 to 10 indicates moderate disease, and a score higher than 10 indicates severe disease.19 The maximum PASI score is 72. The PASI efficacy outcomes used in these analyses were based post hoc on the proportion of patients who achieved an absolute total PASI score of 3 or lower, 2 or lower, and 1 or lower.
Efficacy analyses were based on pooled data for all patients in the PSOARING trials who had a PGA score of 2 to 4 (mild to severe) before treatment with tapinarof cream 1% in the intention-to-treat population using observed cases. Time-to-target analyses were based on Kaplan-Meier (KM) estimates using observed cases.
Safety analyses included the incidence and frequency of adverse events and were based on all patients who received tapinarof cream 1% in the PSOARING trials.
RESULTS
Baseline Patient Demographics and Disease Characteristics
The pooled efficacy analyses included 915 eligible patients (Table). At baseline, the mean (SD) age was 50.2 (13.25) years, 58.7% were male, the mean (SD) weight was 92.2 (23.67) kg, and the mean (SD) body mass index was 31.6 (7.53) kg/m2. The percentage of patients with a PGA score of 2 (mild), 3 (moderate), or 4 (severe) was 13.9%, 78.1%, and 8.0%, respectively. The mean (SD) PASI score was 8.7 (4.23) and mean (SD) total BSA affected was 7.8% (4.98).
Efficacy
Achievement of BSA-Affected Targets—
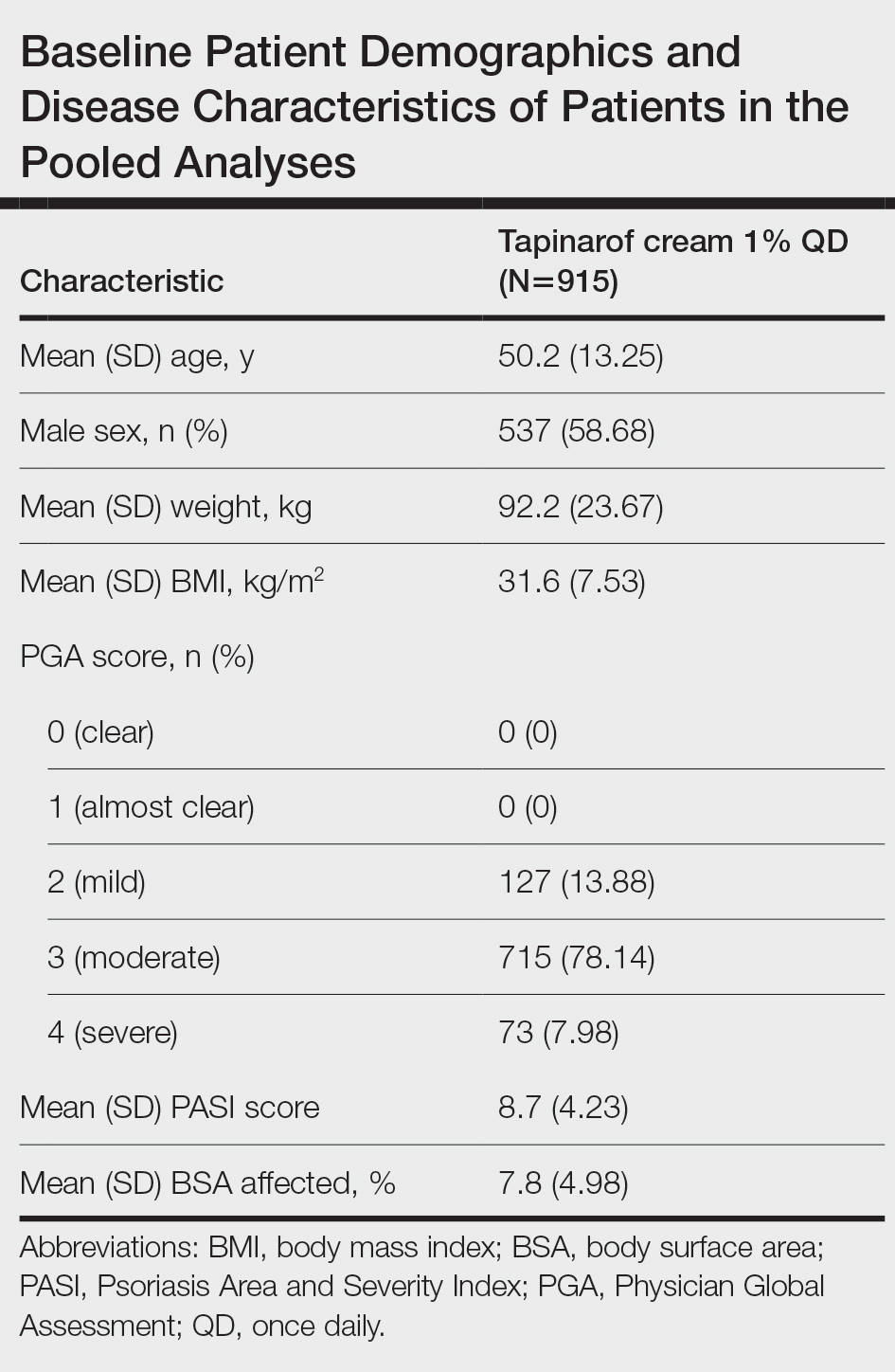
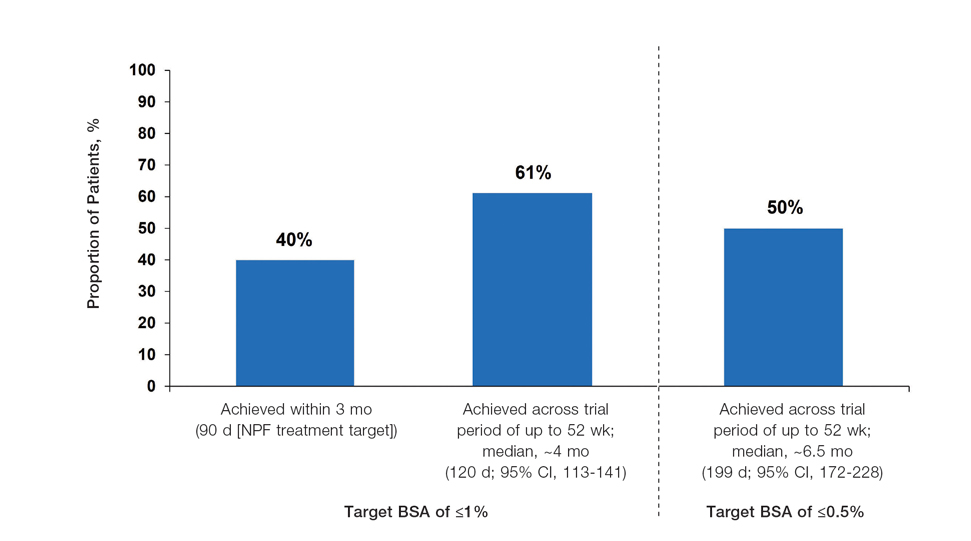
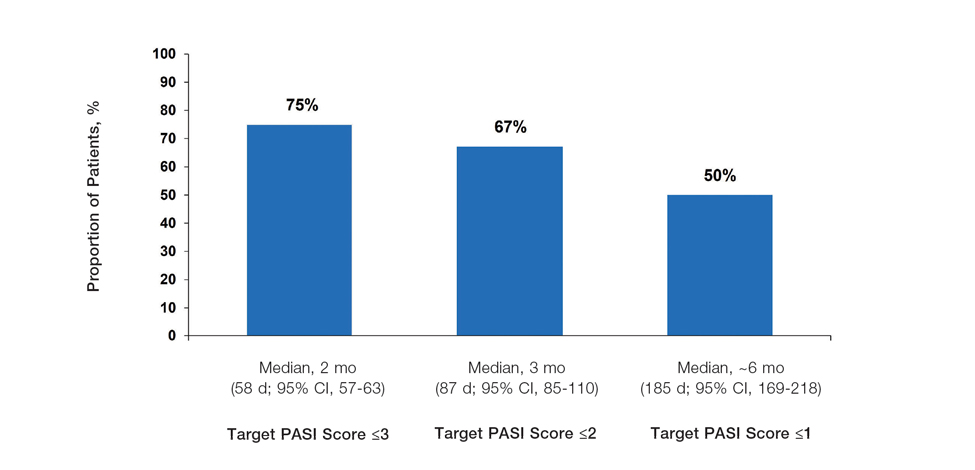
Achievement of Absolute PASI Targets—Across the total trial period (up to 52 weeks), an absolute total PASI score of 3 or lower was achieved by 75% of patients (686/915), with a median time to achieve this of 2 months (KM estimate: 58 days [95% CI, 57-63]); approximately 67% of patients (612/915) achieved a total PASI score of 2 or lower, with a median time to achieve of 3 months (KM estimate: 87 days [95% CI, 85-110])(Figure 2; Supplementary Figures S3a and S3b). A PASI score of 1 or lower was achieved by approximately 50% of patients (460/915), with a median time to achieve of approximately 6 months (KM estimate: 185 days [95% CI, 169-218])(Figure 2, Supplementary Figure S3c).
Illustrative Case—Case photography showing the clinical response in a 63-year-old man with moderate plaque psoriasis in PSOARING 2 is shown in Figure 3. After 12 weeks of treatment with tapinarof cream 1% QD, the patient achieved all primary and secondary efficacy end points. In addition to achieving the regulatory end point of a PGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) and a decrease from baseline of at least 2 points, achievement of 0% total BSA affected and a total PASI score of 0 at week 12 exceeded the NPF and EADV consensus treatment targets.10,11 Targets were achieved as early as week 4, with a total BSA affected of 0.5% or lower and a total PASI score of 1 or lower, illustrated by marked skin clearing and only faint residual erythema that completely resolved at week 12, with the absence of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Safety
Safety data for the PSOARING trials have been previously reported.17,18 The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were folliculitis, contact dermatitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and nasopharyngitis. Treatment-emergent adverse events generally were mild or moderate in severity and did not lead to trial discontinuation.17,18
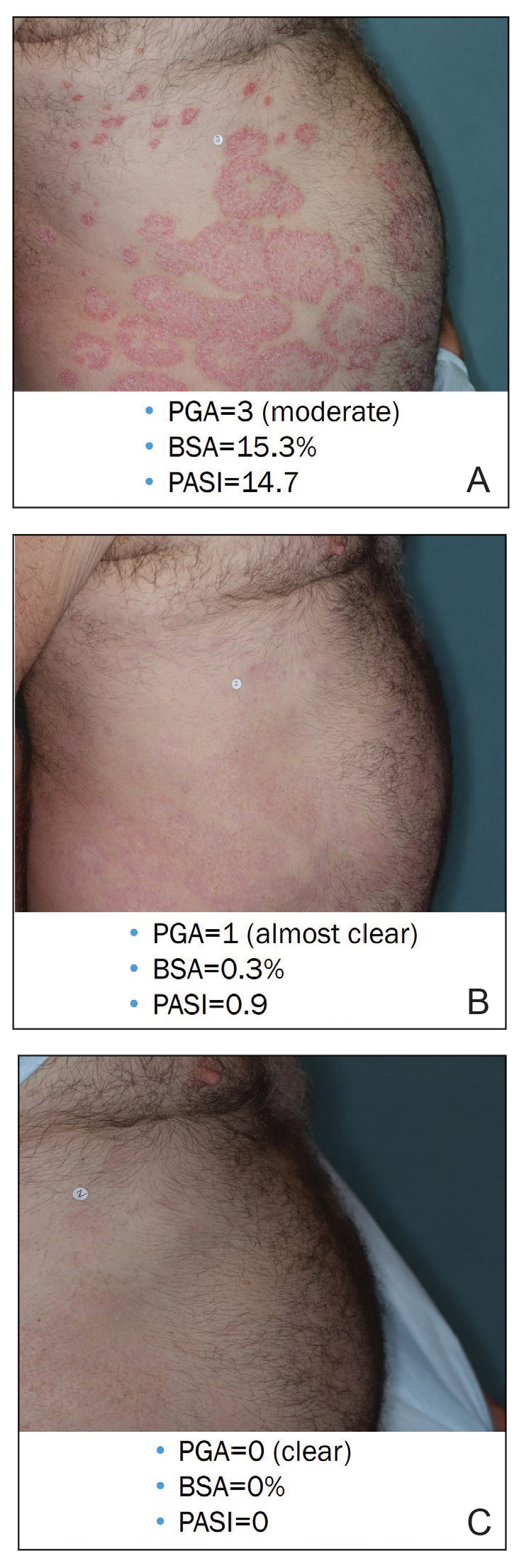
COMMENT
Treat-to-target management approaches aim to improve patient outcomes by striving to achieve optimal goals. The treat-to-target approach supports shared decision-making between clinicians and patients based on common expectations of what constitutes treatment success.
The findings of this analysis based on pooled data from a large cohort of patients demonstrate that a high proportion of patients can achieve or exceed recommended treatment targets with tapinarof cream 1% QD and maintain improvements long-term. The NPF-recommended treatment target of 1% or lower BSA affected within approximately 3 months (90 days) of treatment was achieved by 40% of tapinarof-treated patients. In addition, 1% or lower BSA affected at any time during the trials was achieved by 61% of patients (median, approximately 4 months). The analyses also indicated that PASI total scores of 3 or lower and 2 or lower were achieved by 75% and 67% of tapinarof-treated patients, respectively, within 2 to 3 months.
These findings support the previously reported efficacy of tapinarof cream, including high rates of complete disease clearance (40.9% [312/763]), durable response following treatment interruption, an off-therapy remittive effect of approximately 4 months, and good disease control on therapy with no evidence of tachyphylaxis.17,18
CONCLUSION
Taken together with previously reported tapinarof efficacy and safety results, our findings demonstrate that a high proportion of patients treated with tapinarof cream as monotherapy can achieve aggressive treatment targets set by both US and European guidelines developed for systemic and biologic therapies. Tapinarof cream 1% QD is an effective topical treatment option for patients with plaque psoriasis that has been approved without restrictions relating to severity or extent of disease treated, duration of use, or application sites, including application to sensitive and intertriginous skin.
Acknowledgments—Editorial and medical writing support under the guidance of the authors was provided by Melanie Govender, MSc (Med), ApotheCom (United Kingdom), and was funded by Dermavant Sciences, Inc, in accordance with Good Publication Practice (GPP) guidelines.
- Armstrong AW, Mehta MD, Schupp CW, et al. Psoriasis prevalence in adults in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:940-946.
- Parisi R, Iskandar IYK, Kontopantelis E, et al. National, regional, and worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis: systematic analysis and modelling study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1590.
- Pilon D, Teeple A, Zhdanava M, et al. The economic burden of psoriasis with high comorbidity among privately insured patients in the United States. J Med Econ. 2019;22:196-203.
- Singh S, Taylor C, Kornmehl H, et al. Psoriasis and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:425-440.e2.
- Feldman SR, Goffe B, Rice G, et al. The challenge of managing psoriasis: unmet medical needs and stakeholder perspectives. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2016;9:504-513.
- Ford JA, Solomon DH. Challenges in implementing treat-to-target strategies in rheumatology. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2019;45:101-112.
- Sitbon O, Galiè N. Treat-to-target strategies in pulmonary arterial hypertension: the importance of using multiple goals. Eur Respir Rev. 2010;19:272-278.
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JW, et al. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:631-637.
- Wangnoo SK, Sethi B, Sahay RK, et al. Treat-to-target trials in diabetes. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2014;18:166-174.
- Armstrong AW, Siegel MP, Bagel J, et al. From the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation: treatment targets for plaque psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:290-298.
- Pathirana D, Ormerod AD, Saiag P, et al. European S3-guidelines on the systemic treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23(Suppl 2):1-70.
- Strober BE, van der Walt JM, Armstrong AW, et al. Clinical goals and barriers to effective psoriasis care. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019; 9:5-18.
- Bagel J, Gold LS. Combining topical psoriasis treatment to enhance systemic and phototherapy: a review of the literature. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:1209-1222.
- Elmets CA, Korman NJ, Prater EF, et al. Joint AAD-NPF Guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapy and alternative medicine modalities for psoriasis severity measures. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:432-470.
- Stein Gold LF. Topical therapies for psoriasis: improving management strategies and patient adherence. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2016;35 (2 Suppl 2):S36-S44; quiz S45.
- VTAMA® (tapinarof) cream. Prescribing information. Dermavant Sciences; 2022. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215272s000lbl.pdf
- Lebwohl MG, Stein Gold L, Strober B, et al. Phase 3 trials of tapinarof cream for plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2219-2229 and supplementary appendix.
- Strober B, Stein Gold L, Bissonnette R, et al. One-year safety and efficacy of tapinarof cream for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: results from the PSOARING 3 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:800-806.
- Clinical Review Report: Guselkumab (Tremfya) [Internet]. Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2018. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534047/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK534047.pdf
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 8 million adults in the United States and 2% of the global population.1,2 Psoriasis causes pain, itching, and disfigurement and is associated with a physical, psychological, and economic burden that substantially affects health-related quality of life.3-5
Setting treatment goals and treating to target are evidence-based approaches that have been successfully applied to several chronic diseases to improve patient outcomes, including diabetes, hypertension, and rheumatoid arthritis.6-9 Treat-to-target strategies generally set low disease activity (or remission) as an overall goal and seek to achieve this using available therapeutic options as necessary. Introduced following the availability of biologics and targeted systemic therapies, treat-to-target strategies generally provide guidance on expectations of treatment but not specific treatments, as personalized treatment decisions depend on an assessment of individual patients and consider clinical and demographic features as well as preferences for available therapeutic options. If targets are not achieved in the assigned time span, adjustments can be made to the treatment approach in close consultation with the patient. If the target is reached, follow-up visits can be scheduled to ensure improvement is maintained or to establish if more aggressive goals could be selected.
Treat-to-target strategies for the management of psoriasis developed by the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) Medical Board include reducing the extent of psoriasis to 1% or lower total body surface area (BSA) after 3 months of treatment.10 Treatment targets endorsed by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) in guidelines on the use of systemic therapies in psoriasis include achieving a 75% or greater reduction in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score within 3 to 4 months of treatment.11
In clinical practice, many patients do not achieve these treatment targets, and topical treatments alone generally are insufficient in achieving treatment goals for psoriasis.12,13 Moreover, conventional topical treatments (eg, topical corticosteroids) used by most patients with psoriasis regardless of disease severity are associated with adverse events that can limit their use. Most topical corticosteroids have US Food and Drug Administration label restrictions relating to sites of application, duration and extent of use, and frequency of administration.14,15
Tapinarof cream 1% (VTAMA [Dermavant Sciences, Inc]) is a first-in-class topical nonsteroidal aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults16 and is being studied for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in children 2 years and older as well as for atopic dermatitis in adults and children 2 years and older. In PSOARING 1 (ClinicalTrials .gov identifier NCT03956355) and PSOARING 2 (NCT03983980)—identical 12-week pivotal phase 3 trials—monotherapy with tapinarof cream 1% once daily (QD) demonstrated statistically significant efficacy vs vehicle cream and was well tolerated in adults with mild to severe plaque psoriasis (Supplementary Figure S1).17 Lebwohl et al17 reported that significantly higher PASI75 responses were observed at week 12 with tapinarof cream vs vehicle in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2 (36% and 48% vs 10% and 7%, respectively; both P<.0001). A significantly higher PASI90 response of 19% and 21% at week 12 also was observed with tapinarof cream vs 2% and 3% with vehicle in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2, respectively (P=.0005 and P<.0001).17
In PSOARING 3 (NCT04053387)—the long-term extension trial (Supplementary Figure S1)—efficacy continued to improve or was maintained beyond the two 12-week trials, with improvements in total BSA affected and PASI scores for up to 52 weeks.18 Tapinarof cream 1% QD demonstrated positive, rapid, and durable outcomes in PSOARING 3, including high rates of complete disease clearance (Physician Global Assessment [PGA] score=0 [clear])(40.9% [312/763]), durability of response on treatment with no evidence of tachyphylaxis, and a remittive effect of approximately 4 months when off therapy (defined as maintenance of a PGA score of 0 [clear] or 1 [almost clear] after first achieving a PGA score of 0).18
Herein, we report absolute treatment targets for patients with plaque psoriasis who received tapinarof cream 1% QD in the PSOARING trials that are at least as stringent as the corresponding NPF and EADV targets of achieving a total BSA affected of 1% or lower or a PASI75 response within 3 to 4 months, respectively.
METHODS
Study Design
The pooled efficacy analyses included all patients with a baseline PGA score of 2 or higher (mild or worse) before treatment with tapinarof cream 1% QD in the PSOARING trials. This included patients who received tapinarof cream 1% in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2 who may or may not have continued into PSOARING 3, as well as those who received the vehicle in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2 who enrolled in PSOARING 3 and had a PGA score of 2 or higher before receiving tapinarof cream 1%.
Trial Participants
Full methods, including inclusion and exclusion criteria, for the PSOARING trials have been previously reported.17,18 Patients were aged 18 to 75 years and had chronic plaque psoriasis that was stable for at least 6 months before randomization; 3% to 20% total BSA affected (excluding the scalp, palms, fingernails, toenails, and soles); and a PGA score of 2 (mild), 3 (moderate), or 4 (severe) at baseline.
The clinical trials were conducted in compliance with the guidelines for Good Clinical Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was obtained from local ethics committees or institutional review boards at each center. All patients provided written informed consent.
Trial Treatment
In PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2, patients were randomized (2:1) to receive tapinarof cream 1% or vehicle QD for 12 weeks. In PSOARING 3 (the long-term extension trial), patients received up to 40 weeks of open-label tapinarof, followed by 4 weeks of follow-up off treatment. Patients received intermittent or continuous treatment with tapinarof cream 1% in PSOARING 3 based on PGA score: those entering the trial with a PGA score of 1 or higher received tapinarof cream 1% until complete disease clearance was achieved (defined as a PGA score of 0 [clear]). Those entering PSOARING 3 with or achieving a PGA score of 0 (clear) discontinued treatment and were observed for the duration of maintenance of a PGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) while off therapy (the protocol-defined “duration of remittive effect”). If disease worsening (defined as a PGA score 2 or higher) occurred, tapinarof cream 1% was restarted and continued until a PGA score of 0 (clear) was achieved. This pattern of treatment, discontinuation on achieving a PGA score of 0 (clear), and retreatment on disease worsening continued until the end of the trial. As a result, patients in PSOARING 3 could receive tapinarof cream 1% continuously or intermittently for 40 weeks.
Outcome Measures and Statistical Analyses
The assessment of total BSA affected by plaque psoriasis is an estimate of the total extent of disease as a percentage of total skin area. In the PSOARING trials, the skin surface of one hand (palm and digits) was assumed to be approximately equivalent to 1% BSA. The total BSA affected by psoriasis was evaluated from 0% to 100%, with greater total BSA affected being an indication of more extensive disease. The BSA efficacy outcomes used in these analyses were based post hoc on the proportion of patients who achieved a 1% or lower or 0.5% or lower total BSA affected.
Psoriasis Area and Severity Index scores assess both the severity and extent of psoriasis. A PASI score lower than 5 often is considered indicative of mild psoriasis, a score of 5 to 10 indicates moderate disease, and a score higher than 10 indicates severe disease.19 The maximum PASI score is 72. The PASI efficacy outcomes used in these analyses were based post hoc on the proportion of patients who achieved an absolute total PASI score of 3 or lower, 2 or lower, and 1 or lower.
Efficacy analyses were based on pooled data for all patients in the PSOARING trials who had a PGA score of 2 to 4 (mild to severe) before treatment with tapinarof cream 1% in the intention-to-treat population using observed cases. Time-to-target analyses were based on Kaplan-Meier (KM) estimates using observed cases.
Safety analyses included the incidence and frequency of adverse events and were based on all patients who received tapinarof cream 1% in the PSOARING trials.
RESULTS
Baseline Patient Demographics and Disease Characteristics
The pooled efficacy analyses included 915 eligible patients (Table). At baseline, the mean (SD) age was 50.2 (13.25) years, 58.7% were male, the mean (SD) weight was 92.2 (23.67) kg, and the mean (SD) body mass index was 31.6 (7.53) kg/m2. The percentage of patients with a PGA score of 2 (mild), 3 (moderate), or 4 (severe) was 13.9%, 78.1%, and 8.0%, respectively. The mean (SD) PASI score was 8.7 (4.23) and mean (SD) total BSA affected was 7.8% (4.98).
Efficacy
Achievement of BSA-Affected Targets—



Achievement of Absolute PASI Targets—Across the total trial period (up to 52 weeks), an absolute total PASI score of 3 or lower was achieved by 75% of patients (686/915), with a median time to achieve this of 2 months (KM estimate: 58 days [95% CI, 57-63]); approximately 67% of patients (612/915) achieved a total PASI score of 2 or lower, with a median time to achieve of 3 months (KM estimate: 87 days [95% CI, 85-110])(Figure 2; Supplementary Figures S3a and S3b). A PASI score of 1 or lower was achieved by approximately 50% of patients (460/915), with a median time to achieve of approximately 6 months (KM estimate: 185 days [95% CI, 169-218])(Figure 2, Supplementary Figure S3c).
Illustrative Case—Case photography showing the clinical response in a 63-year-old man with moderate plaque psoriasis in PSOARING 2 is shown in Figure 3. After 12 weeks of treatment with tapinarof cream 1% QD, the patient achieved all primary and secondary efficacy end points. In addition to achieving the regulatory end point of a PGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) and a decrease from baseline of at least 2 points, achievement of 0% total BSA affected and a total PASI score of 0 at week 12 exceeded the NPF and EADV consensus treatment targets.10,11 Targets were achieved as early as week 4, with a total BSA affected of 0.5% or lower and a total PASI score of 1 or lower, illustrated by marked skin clearing and only faint residual erythema that completely resolved at week 12, with the absence of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Safety
Safety data for the PSOARING trials have been previously reported.17,18 The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were folliculitis, contact dermatitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and nasopharyngitis. Treatment-emergent adverse events generally were mild or moderate in severity and did not lead to trial discontinuation.17,18

COMMENT
Treat-to-target management approaches aim to improve patient outcomes by striving to achieve optimal goals. The treat-to-target approach supports shared decision-making between clinicians and patients based on common expectations of what constitutes treatment success.
The findings of this analysis based on pooled data from a large cohort of patients demonstrate that a high proportion of patients can achieve or exceed recommended treatment targets with tapinarof cream 1% QD and maintain improvements long-term. The NPF-recommended treatment target of 1% or lower BSA affected within approximately 3 months (90 days) of treatment was achieved by 40% of tapinarof-treated patients. In addition, 1% or lower BSA affected at any time during the trials was achieved by 61% of patients (median, approximately 4 months). The analyses also indicated that PASI total scores of 3 or lower and 2 or lower were achieved by 75% and 67% of tapinarof-treated patients, respectively, within 2 to 3 months.
These findings support the previously reported efficacy of tapinarof cream, including high rates of complete disease clearance (40.9% [312/763]), durable response following treatment interruption, an off-therapy remittive effect of approximately 4 months, and good disease control on therapy with no evidence of tachyphylaxis.17,18
CONCLUSION
Taken together with previously reported tapinarof efficacy and safety results, our findings demonstrate that a high proportion of patients treated with tapinarof cream as monotherapy can achieve aggressive treatment targets set by both US and European guidelines developed for systemic and biologic therapies. Tapinarof cream 1% QD is an effective topical treatment option for patients with plaque psoriasis that has been approved without restrictions relating to severity or extent of disease treated, duration of use, or application sites, including application to sensitive and intertriginous skin.
Acknowledgments—Editorial and medical writing support under the guidance of the authors was provided by Melanie Govender, MSc (Med), ApotheCom (United Kingdom), and was funded by Dermavant Sciences, Inc, in accordance with Good Publication Practice (GPP) guidelines.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 8 million adults in the United States and 2% of the global population.1,2 Psoriasis causes pain, itching, and disfigurement and is associated with a physical, psychological, and economic burden that substantially affects health-related quality of life.3-5
Setting treatment goals and treating to target are evidence-based approaches that have been successfully applied to several chronic diseases to improve patient outcomes, including diabetes, hypertension, and rheumatoid arthritis.6-9 Treat-to-target strategies generally set low disease activity (or remission) as an overall goal and seek to achieve this using available therapeutic options as necessary. Introduced following the availability of biologics and targeted systemic therapies, treat-to-target strategies generally provide guidance on expectations of treatment but not specific treatments, as personalized treatment decisions depend on an assessment of individual patients and consider clinical and demographic features as well as preferences for available therapeutic options. If targets are not achieved in the assigned time span, adjustments can be made to the treatment approach in close consultation with the patient. If the target is reached, follow-up visits can be scheduled to ensure improvement is maintained or to establish if more aggressive goals could be selected.
Treat-to-target strategies for the management of psoriasis developed by the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) Medical Board include reducing the extent of psoriasis to 1% or lower total body surface area (BSA) after 3 months of treatment.10 Treatment targets endorsed by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) in guidelines on the use of systemic therapies in psoriasis include achieving a 75% or greater reduction in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score within 3 to 4 months of treatment.11
In clinical practice, many patients do not achieve these treatment targets, and topical treatments alone generally are insufficient in achieving treatment goals for psoriasis.12,13 Moreover, conventional topical treatments (eg, topical corticosteroids) used by most patients with psoriasis regardless of disease severity are associated with adverse events that can limit their use. Most topical corticosteroids have US Food and Drug Administration label restrictions relating to sites of application, duration and extent of use, and frequency of administration.14,15
Tapinarof cream 1% (VTAMA [Dermavant Sciences, Inc]) is a first-in-class topical nonsteroidal aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults16 and is being studied for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in children 2 years and older as well as for atopic dermatitis in adults and children 2 years and older. In PSOARING 1 (ClinicalTrials .gov identifier NCT03956355) and PSOARING 2 (NCT03983980)—identical 12-week pivotal phase 3 trials—monotherapy with tapinarof cream 1% once daily (QD) demonstrated statistically significant efficacy vs vehicle cream and was well tolerated in adults with mild to severe plaque psoriasis (Supplementary Figure S1).17 Lebwohl et al17 reported that significantly higher PASI75 responses were observed at week 12 with tapinarof cream vs vehicle in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2 (36% and 48% vs 10% and 7%, respectively; both P<.0001). A significantly higher PASI90 response of 19% and 21% at week 12 also was observed with tapinarof cream vs 2% and 3% with vehicle in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2, respectively (P=.0005 and P<.0001).17
In PSOARING 3 (NCT04053387)—the long-term extension trial (Supplementary Figure S1)—efficacy continued to improve or was maintained beyond the two 12-week trials, with improvements in total BSA affected and PASI scores for up to 52 weeks.18 Tapinarof cream 1% QD demonstrated positive, rapid, and durable outcomes in PSOARING 3, including high rates of complete disease clearance (Physician Global Assessment [PGA] score=0 [clear])(40.9% [312/763]), durability of response on treatment with no evidence of tachyphylaxis, and a remittive effect of approximately 4 months when off therapy (defined as maintenance of a PGA score of 0 [clear] or 1 [almost clear] after first achieving a PGA score of 0).18
Herein, we report absolute treatment targets for patients with plaque psoriasis who received tapinarof cream 1% QD in the PSOARING trials that are at least as stringent as the corresponding NPF and EADV targets of achieving a total BSA affected of 1% or lower or a PASI75 response within 3 to 4 months, respectively.
METHODS
Study Design
The pooled efficacy analyses included all patients with a baseline PGA score of 2 or higher (mild or worse) before treatment with tapinarof cream 1% QD in the PSOARING trials. This included patients who received tapinarof cream 1% in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2 who may or may not have continued into PSOARING 3, as well as those who received the vehicle in PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2 who enrolled in PSOARING 3 and had a PGA score of 2 or higher before receiving tapinarof cream 1%.
Trial Participants
Full methods, including inclusion and exclusion criteria, for the PSOARING trials have been previously reported.17,18 Patients were aged 18 to 75 years and had chronic plaque psoriasis that was stable for at least 6 months before randomization; 3% to 20% total BSA affected (excluding the scalp, palms, fingernails, toenails, and soles); and a PGA score of 2 (mild), 3 (moderate), or 4 (severe) at baseline.
The clinical trials were conducted in compliance with the guidelines for Good Clinical Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was obtained from local ethics committees or institutional review boards at each center. All patients provided written informed consent.
Trial Treatment
In PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2, patients were randomized (2:1) to receive tapinarof cream 1% or vehicle QD for 12 weeks. In PSOARING 3 (the long-term extension trial), patients received up to 40 weeks of open-label tapinarof, followed by 4 weeks of follow-up off treatment. Patients received intermittent or continuous treatment with tapinarof cream 1% in PSOARING 3 based on PGA score: those entering the trial with a PGA score of 1 or higher received tapinarof cream 1% until complete disease clearance was achieved (defined as a PGA score of 0 [clear]). Those entering PSOARING 3 with or achieving a PGA score of 0 (clear) discontinued treatment and were observed for the duration of maintenance of a PGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) while off therapy (the protocol-defined “duration of remittive effect”). If disease worsening (defined as a PGA score 2 or higher) occurred, tapinarof cream 1% was restarted and continued until a PGA score of 0 (clear) was achieved. This pattern of treatment, discontinuation on achieving a PGA score of 0 (clear), and retreatment on disease worsening continued until the end of the trial. As a result, patients in PSOARING 3 could receive tapinarof cream 1% continuously or intermittently for 40 weeks.
Outcome Measures and Statistical Analyses
The assessment of total BSA affected by plaque psoriasis is an estimate of the total extent of disease as a percentage of total skin area. In the PSOARING trials, the skin surface of one hand (palm and digits) was assumed to be approximately equivalent to 1% BSA. The total BSA affected by psoriasis was evaluated from 0% to 100%, with greater total BSA affected being an indication of more extensive disease. The BSA efficacy outcomes used in these analyses were based post hoc on the proportion of patients who achieved a 1% or lower or 0.5% or lower total BSA affected.
Psoriasis Area and Severity Index scores assess both the severity and extent of psoriasis. A PASI score lower than 5 often is considered indicative of mild psoriasis, a score of 5 to 10 indicates moderate disease, and a score higher than 10 indicates severe disease.19 The maximum PASI score is 72. The PASI efficacy outcomes used in these analyses were based post hoc on the proportion of patients who achieved an absolute total PASI score of 3 or lower, 2 or lower, and 1 or lower.
Efficacy analyses were based on pooled data for all patients in the PSOARING trials who had a PGA score of 2 to 4 (mild to severe) before treatment with tapinarof cream 1% in the intention-to-treat population using observed cases. Time-to-target analyses were based on Kaplan-Meier (KM) estimates using observed cases.
Safety analyses included the incidence and frequency of adverse events and were based on all patients who received tapinarof cream 1% in the PSOARING trials.
RESULTS
Baseline Patient Demographics and Disease Characteristics
The pooled efficacy analyses included 915 eligible patients (Table). At baseline, the mean (SD) age was 50.2 (13.25) years, 58.7% were male, the mean (SD) weight was 92.2 (23.67) kg, and the mean (SD) body mass index was 31.6 (7.53) kg/m2. The percentage of patients with a PGA score of 2 (mild), 3 (moderate), or 4 (severe) was 13.9%, 78.1%, and 8.0%, respectively. The mean (SD) PASI score was 8.7 (4.23) and mean (SD) total BSA affected was 7.8% (4.98).
Efficacy
Achievement of BSA-Affected Targets—



Achievement of Absolute PASI Targets—Across the total trial period (up to 52 weeks), an absolute total PASI score of 3 or lower was achieved by 75% of patients (686/915), with a median time to achieve this of 2 months (KM estimate: 58 days [95% CI, 57-63]); approximately 67% of patients (612/915) achieved a total PASI score of 2 or lower, with a median time to achieve of 3 months (KM estimate: 87 days [95% CI, 85-110])(Figure 2; Supplementary Figures S3a and S3b). A PASI score of 1 or lower was achieved by approximately 50% of patients (460/915), with a median time to achieve of approximately 6 months (KM estimate: 185 days [95% CI, 169-218])(Figure 2, Supplementary Figure S3c).
Illustrative Case—Case photography showing the clinical response in a 63-year-old man with moderate plaque psoriasis in PSOARING 2 is shown in Figure 3. After 12 weeks of treatment with tapinarof cream 1% QD, the patient achieved all primary and secondary efficacy end points. In addition to achieving the regulatory end point of a PGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) and a decrease from baseline of at least 2 points, achievement of 0% total BSA affected and a total PASI score of 0 at week 12 exceeded the NPF and EADV consensus treatment targets.10,11 Targets were achieved as early as week 4, with a total BSA affected of 0.5% or lower and a total PASI score of 1 or lower, illustrated by marked skin clearing and only faint residual erythema that completely resolved at week 12, with the absence of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Safety
Safety data for the PSOARING trials have been previously reported.17,18 The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were folliculitis, contact dermatitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and nasopharyngitis. Treatment-emergent adverse events generally were mild or moderate in severity and did not lead to trial discontinuation.17,18

COMMENT
Treat-to-target management approaches aim to improve patient outcomes by striving to achieve optimal goals. The treat-to-target approach supports shared decision-making between clinicians and patients based on common expectations of what constitutes treatment success.
The findings of this analysis based on pooled data from a large cohort of patients demonstrate that a high proportion of patients can achieve or exceed recommended treatment targets with tapinarof cream 1% QD and maintain improvements long-term. The NPF-recommended treatment target of 1% or lower BSA affected within approximately 3 months (90 days) of treatment was achieved by 40% of tapinarof-treated patients. In addition, 1% or lower BSA affected at any time during the trials was achieved by 61% of patients (median, approximately 4 months). The analyses also indicated that PASI total scores of 3 or lower and 2 or lower were achieved by 75% and 67% of tapinarof-treated patients, respectively, within 2 to 3 months.
These findings support the previously reported efficacy of tapinarof cream, including high rates of complete disease clearance (40.9% [312/763]), durable response following treatment interruption, an off-therapy remittive effect of approximately 4 months, and good disease control on therapy with no evidence of tachyphylaxis.17,18
CONCLUSION
Taken together with previously reported tapinarof efficacy and safety results, our findings demonstrate that a high proportion of patients treated with tapinarof cream as monotherapy can achieve aggressive treatment targets set by both US and European guidelines developed for systemic and biologic therapies. Tapinarof cream 1% QD is an effective topical treatment option for patients with plaque psoriasis that has been approved without restrictions relating to severity or extent of disease treated, duration of use, or application sites, including application to sensitive and intertriginous skin.
Acknowledgments—Editorial and medical writing support under the guidance of the authors was provided by Melanie Govender, MSc (Med), ApotheCom (United Kingdom), and was funded by Dermavant Sciences, Inc, in accordance with Good Publication Practice (GPP) guidelines.
- Armstrong AW, Mehta MD, Schupp CW, et al. Psoriasis prevalence in adults in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:940-946.
- Parisi R, Iskandar IYK, Kontopantelis E, et al. National, regional, and worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis: systematic analysis and modelling study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1590.
- Pilon D, Teeple A, Zhdanava M, et al. The economic burden of psoriasis with high comorbidity among privately insured patients in the United States. J Med Econ. 2019;22:196-203.
- Singh S, Taylor C, Kornmehl H, et al. Psoriasis and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:425-440.e2.
- Feldman SR, Goffe B, Rice G, et al. The challenge of managing psoriasis: unmet medical needs and stakeholder perspectives. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2016;9:504-513.
- Ford JA, Solomon DH. Challenges in implementing treat-to-target strategies in rheumatology. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2019;45:101-112.
- Sitbon O, Galiè N. Treat-to-target strategies in pulmonary arterial hypertension: the importance of using multiple goals. Eur Respir Rev. 2010;19:272-278.
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JW, et al. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:631-637.
- Wangnoo SK, Sethi B, Sahay RK, et al. Treat-to-target trials in diabetes. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2014;18:166-174.
- Armstrong AW, Siegel MP, Bagel J, et al. From the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation: treatment targets for plaque psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:290-298.
- Pathirana D, Ormerod AD, Saiag P, et al. European S3-guidelines on the systemic treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23(Suppl 2):1-70.
- Strober BE, van der Walt JM, Armstrong AW, et al. Clinical goals and barriers to effective psoriasis care. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019; 9:5-18.
- Bagel J, Gold LS. Combining topical psoriasis treatment to enhance systemic and phototherapy: a review of the literature. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:1209-1222.
- Elmets CA, Korman NJ, Prater EF, et al. Joint AAD-NPF Guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapy and alternative medicine modalities for psoriasis severity measures. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:432-470.
- Stein Gold LF. Topical therapies for psoriasis: improving management strategies and patient adherence. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2016;35 (2 Suppl 2):S36-S44; quiz S45.
- VTAMA® (tapinarof) cream. Prescribing information. Dermavant Sciences; 2022. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215272s000lbl.pdf
- Lebwohl MG, Stein Gold L, Strober B, et al. Phase 3 trials of tapinarof cream for plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2219-2229 and supplementary appendix.
- Strober B, Stein Gold L, Bissonnette R, et al. One-year safety and efficacy of tapinarof cream for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: results from the PSOARING 3 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:800-806.
- Clinical Review Report: Guselkumab (Tremfya) [Internet]. Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2018. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534047/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK534047.pdf
- Armstrong AW, Mehta MD, Schupp CW, et al. Psoriasis prevalence in adults in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:940-946.
- Parisi R, Iskandar IYK, Kontopantelis E, et al. National, regional, and worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis: systematic analysis and modelling study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1590.
- Pilon D, Teeple A, Zhdanava M, et al. The economic burden of psoriasis with high comorbidity among privately insured patients in the United States. J Med Econ. 2019;22:196-203.
- Singh S, Taylor C, Kornmehl H, et al. Psoriasis and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:425-440.e2.
- Feldman SR, Goffe B, Rice G, et al. The challenge of managing psoriasis: unmet medical needs and stakeholder perspectives. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2016;9:504-513.
- Ford JA, Solomon DH. Challenges in implementing treat-to-target strategies in rheumatology. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2019;45:101-112.
- Sitbon O, Galiè N. Treat-to-target strategies in pulmonary arterial hypertension: the importance of using multiple goals. Eur Respir Rev. 2010;19:272-278.
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JW, et al. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:631-637.
- Wangnoo SK, Sethi B, Sahay RK, et al. Treat-to-target trials in diabetes. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2014;18:166-174.
- Armstrong AW, Siegel MP, Bagel J, et al. From the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation: treatment targets for plaque psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:290-298.
- Pathirana D, Ormerod AD, Saiag P, et al. European S3-guidelines on the systemic treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23(Suppl 2):1-70.
- Strober BE, van der Walt JM, Armstrong AW, et al. Clinical goals and barriers to effective psoriasis care. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019; 9:5-18.
- Bagel J, Gold LS. Combining topical psoriasis treatment to enhance systemic and phototherapy: a review of the literature. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:1209-1222.
- Elmets CA, Korman NJ, Prater EF, et al. Joint AAD-NPF Guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapy and alternative medicine modalities for psoriasis severity measures. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:432-470.
- Stein Gold LF. Topical therapies for psoriasis: improving management strategies and patient adherence. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2016;35 (2 Suppl 2):S36-S44; quiz S45.
- VTAMA® (tapinarof) cream. Prescribing information. Dermavant Sciences; 2022. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215272s000lbl.pdf
- Lebwohl MG, Stein Gold L, Strober B, et al. Phase 3 trials of tapinarof cream for plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2219-2229 and supplementary appendix.
- Strober B, Stein Gold L, Bissonnette R, et al. One-year safety and efficacy of tapinarof cream for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: results from the PSOARING 3 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:800-806.
- Clinical Review Report: Guselkumab (Tremfya) [Internet]. Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2018. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534047/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK534047.pdf
Practice Points
- In clinical practice, many patients with psoriasis do not achieve treatment targets set forth by the National Psoriasis Foundation and the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, and topical treatments alone generally are insufficient in achieving treatment goals for psoriasis.
- Tapinarof cream 1% is a nonsteroidal aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults; it also is being studied for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in children 2 years and older.
- Tapinarof cream 1% is an effective topical treatment option for patients with plaque psoriasis of any severity, with no limitations on treatment duration, total extent of use, or application sites, including intertriginous skin and sensitive areas.
Hairless Scalp Lesion
The Diagnosis: Nevus Sebaceus of Jadassohn
The diagnosis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn was made clinically based on the lesion’s appearance and presence since birth as well as the absence of systemic symptoms. Clinically, nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn typically manifests as a well-demarcated, yellow- brown plaque often located on the scalp, as was seen in our patient. The lack of pruritus and pain further supported the diagnosis in our patient. No biopsy was performed, as the presentation was considered classic for this condition. Our patient opted to forgo surgery and will be routinely monitored for any changes, as nevus sebaceus has a potential risk, albeit low, for malignant transformation later in life. No changes have been observed since the initial presentation, and regular follow-ups are planned to monitor for future developments.
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn is a hamartomatous lesion involving the pilosebaceous follicle and adjacent adnexal structures.1-3 It most commonly forms on the scalp (59.3%) and is accompanied by partial or total alopecia. 3,4 It is seen less often on the face, periauricular area, or neck1,4; thorax or limbs5; and oral or genital mucosae.6 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn affects approximately 0.3% of newborns,1 usually as a solitary lesion that can form an extensive plaque. The male-to-female occurrence ratio has been reported as equal to slightly more predominant in females; all races and ethnicities are affected.1,5
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn follows 3 stages of clinical development: infantile, adolescent, and adulthood. It manifests at birth or shortly afterward as a smooth hairless patch or plaque that is yellowish and can be hyperpigmented in Black patients.5 It may have an oval or linear configuration, typically is asymptomatic, and often arises along the Blaschko lines when it occurs as multiple lesions (a rare manifestation).1 During puberty, hormonal changes cause accelerated growth, sebaceous gland maturation, and epidermal hyperplasia. 7 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn often is not identified until this stage, when its classic wartlike appearance has fully developed.1
Patients with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn have a 10% to 20% risk for tumor development in adulthood.2,7 Trichoblastoma and syringocystadenoma papilliferum are the most frequently described neoplasms.8 Basal cell carcinoma is the most common malignant secondary neoplasm with an occurrence rate of 0.8%.6,9 However, basal cell carcinoma and trichoblastoma may share histopathologic features, which may lead to misdiagnosis and a higher reported incidence of basal cell carcinoma in adults than is accurate.2
Early prophylactic surgical removal of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn has been recommended; however, surgical management is controversial because the risk for a benign secondary neoplasm remains relatively high while the risk for malignancy is much lower.2,7 Surgical excision remains an acceptable option once the patient is mature enough to tolerate the procedure.1 However, patient education regarding watchful waiting vs a surgical approach— and the risks of each—is critical to ensure shared decision-making and a management plan tailored to the individual.
The differential diagnosis includes hypertrophic lichen planus, Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type), epidermal nevus, and seborrheic keratosis. Hypertrophic lichen planus often occurs symmetrically on the dorsal feet and shins with thick, scaly, and extremely pruritic plaques. The lesions often persist for an average of 6 years and may lead to multiple keratoacanthomas or follicular base squamous cell carcinomas. Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type) manifests with acute, disseminated, visceral, and cutaneous lesions before 2 years of age. These lesions appear as 1- to 2-mm, pink, seborrheic papules, pustules, or vesicles on the scalp, flexural neck, axilla, perineum, and trunk; they often are associated with petechiae, purpura, scale, crust, erosion, impetiginization, and tender fissures. Epidermal nevus occurs within the first year of life and is a hamartoma of the epidermis and papillary dermis. It manifests as papillomatous pigmented linear lines along the Blaschko lines. Seborrheic keratosis manifests as well-demarcated, waxy/verrucous, brown papules with a “stuck on” appearance on hair-bearing skin sparing the mucosae. They are common benign lesions associated with sun exposure and often manifest in the fourth decade of life.10
- Baigrie D, Troxell T, Cook C. Nevus sebaceus. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed September 12, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482493/
- Terenzi V, Indrizzi E, Buonaccorsi S, et al. Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. J Craniofac Surg. 2006;17:1234-1239. doi:10.1097/01 .scs.0000221531.56529.cc
- Kelati A, Baybay H, Gallouj S, et al. Dermoscopic analysis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 13 cases. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;3:83-91. doi:10.1159/000460258
- Ugras N, Ozgun G, Adim SB, et al. Nevus sebaceous at unusual location: a rare presentation. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2012;55:419-420. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.101768
- Serpas de Lopez RM, Hernandez-Perez E. Jadassohn’s sebaceous nevus. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1985;11:68-72. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725 .1985.tb02893.x
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(2 pt 1):263-268. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(00)90136-1
- Santibanez-Gallerani A, Marshall D, Duarte AM, et al. Should nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn in children be excised? a study of 757 cases, and literature review. J Craniofac Surg. 2003;14:658-660. doi:10.1097/00001665-200309000-00010
- Chahboun F, Eljazouly M, Elomari M, et al. Trichoblastoma arising from the nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. Cureus. 2021;13:E15325. doi:10.7759/cureus.15325
- Cazzato G, Cimmino A, Colagrande A, et al. The multiple faces of nodular trichoblastoma: review of the literature with case presentation. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2021;8:265-270. doi:10.3390 /dermatopathology8030032
- Dandekar MN, Gandhi RK. Neoplastic dermatology. In: Alikhan A, Hocker TLH (eds). Review of Dermatology. Elsevier; 2016: 321-366.
The Diagnosis: Nevus Sebaceus of Jadassohn
The diagnosis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn was made clinically based on the lesion’s appearance and presence since birth as well as the absence of systemic symptoms. Clinically, nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn typically manifests as a well-demarcated, yellow- brown plaque often located on the scalp, as was seen in our patient. The lack of pruritus and pain further supported the diagnosis in our patient. No biopsy was performed, as the presentation was considered classic for this condition. Our patient opted to forgo surgery and will be routinely monitored for any changes, as nevus sebaceus has a potential risk, albeit low, for malignant transformation later in life. No changes have been observed since the initial presentation, and regular follow-ups are planned to monitor for future developments.
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn is a hamartomatous lesion involving the pilosebaceous follicle and adjacent adnexal structures.1-3 It most commonly forms on the scalp (59.3%) and is accompanied by partial or total alopecia. 3,4 It is seen less often on the face, periauricular area, or neck1,4; thorax or limbs5; and oral or genital mucosae.6 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn affects approximately 0.3% of newborns,1 usually as a solitary lesion that can form an extensive plaque. The male-to-female occurrence ratio has been reported as equal to slightly more predominant in females; all races and ethnicities are affected.1,5
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn follows 3 stages of clinical development: infantile, adolescent, and adulthood. It manifests at birth or shortly afterward as a smooth hairless patch or plaque that is yellowish and can be hyperpigmented in Black patients.5 It may have an oval or linear configuration, typically is asymptomatic, and often arises along the Blaschko lines when it occurs as multiple lesions (a rare manifestation).1 During puberty, hormonal changes cause accelerated growth, sebaceous gland maturation, and epidermal hyperplasia. 7 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn often is not identified until this stage, when its classic wartlike appearance has fully developed.1
Patients with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn have a 10% to 20% risk for tumor development in adulthood.2,7 Trichoblastoma and syringocystadenoma papilliferum are the most frequently described neoplasms.8 Basal cell carcinoma is the most common malignant secondary neoplasm with an occurrence rate of 0.8%.6,9 However, basal cell carcinoma and trichoblastoma may share histopathologic features, which may lead to misdiagnosis and a higher reported incidence of basal cell carcinoma in adults than is accurate.2
Early prophylactic surgical removal of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn has been recommended; however, surgical management is controversial because the risk for a benign secondary neoplasm remains relatively high while the risk for malignancy is much lower.2,7 Surgical excision remains an acceptable option once the patient is mature enough to tolerate the procedure.1 However, patient education regarding watchful waiting vs a surgical approach— and the risks of each—is critical to ensure shared decision-making and a management plan tailored to the individual.
The differential diagnosis includes hypertrophic lichen planus, Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type), epidermal nevus, and seborrheic keratosis. Hypertrophic lichen planus often occurs symmetrically on the dorsal feet and shins with thick, scaly, and extremely pruritic plaques. The lesions often persist for an average of 6 years and may lead to multiple keratoacanthomas or follicular base squamous cell carcinomas. Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type) manifests with acute, disseminated, visceral, and cutaneous lesions before 2 years of age. These lesions appear as 1- to 2-mm, pink, seborrheic papules, pustules, or vesicles on the scalp, flexural neck, axilla, perineum, and trunk; they often are associated with petechiae, purpura, scale, crust, erosion, impetiginization, and tender fissures. Epidermal nevus occurs within the first year of life and is a hamartoma of the epidermis and papillary dermis. It manifests as papillomatous pigmented linear lines along the Blaschko lines. Seborrheic keratosis manifests as well-demarcated, waxy/verrucous, brown papules with a “stuck on” appearance on hair-bearing skin sparing the mucosae. They are common benign lesions associated with sun exposure and often manifest in the fourth decade of life.10
The Diagnosis: Nevus Sebaceus of Jadassohn
The diagnosis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn was made clinically based on the lesion’s appearance and presence since birth as well as the absence of systemic symptoms. Clinically, nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn typically manifests as a well-demarcated, yellow- brown plaque often located on the scalp, as was seen in our patient. The lack of pruritus and pain further supported the diagnosis in our patient. No biopsy was performed, as the presentation was considered classic for this condition. Our patient opted to forgo surgery and will be routinely monitored for any changes, as nevus sebaceus has a potential risk, albeit low, for malignant transformation later in life. No changes have been observed since the initial presentation, and regular follow-ups are planned to monitor for future developments.
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn is a hamartomatous lesion involving the pilosebaceous follicle and adjacent adnexal structures.1-3 It most commonly forms on the scalp (59.3%) and is accompanied by partial or total alopecia. 3,4 It is seen less often on the face, periauricular area, or neck1,4; thorax or limbs5; and oral or genital mucosae.6 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn affects approximately 0.3% of newborns,1 usually as a solitary lesion that can form an extensive plaque. The male-to-female occurrence ratio has been reported as equal to slightly more predominant in females; all races and ethnicities are affected.1,5
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn follows 3 stages of clinical development: infantile, adolescent, and adulthood. It manifests at birth or shortly afterward as a smooth hairless patch or plaque that is yellowish and can be hyperpigmented in Black patients.5 It may have an oval or linear configuration, typically is asymptomatic, and often arises along the Blaschko lines when it occurs as multiple lesions (a rare manifestation).1 During puberty, hormonal changes cause accelerated growth, sebaceous gland maturation, and epidermal hyperplasia. 7 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn often is not identified until this stage, when its classic wartlike appearance has fully developed.1
Patients with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn have a 10% to 20% risk for tumor development in adulthood.2,7 Trichoblastoma and syringocystadenoma papilliferum are the most frequently described neoplasms.8 Basal cell carcinoma is the most common malignant secondary neoplasm with an occurrence rate of 0.8%.6,9 However, basal cell carcinoma and trichoblastoma may share histopathologic features, which may lead to misdiagnosis and a higher reported incidence of basal cell carcinoma in adults than is accurate.2
Early prophylactic surgical removal of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn has been recommended; however, surgical management is controversial because the risk for a benign secondary neoplasm remains relatively high while the risk for malignancy is much lower.2,7 Surgical excision remains an acceptable option once the patient is mature enough to tolerate the procedure.1 However, patient education regarding watchful waiting vs a surgical approach— and the risks of each—is critical to ensure shared decision-making and a management plan tailored to the individual.
The differential diagnosis includes hypertrophic lichen planus, Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type), epidermal nevus, and seborrheic keratosis. Hypertrophic lichen planus often occurs symmetrically on the dorsal feet and shins with thick, scaly, and extremely pruritic plaques. The lesions often persist for an average of 6 years and may lead to multiple keratoacanthomas or follicular base squamous cell carcinomas. Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type) manifests with acute, disseminated, visceral, and cutaneous lesions before 2 years of age. These lesions appear as 1- to 2-mm, pink, seborrheic papules, pustules, or vesicles on the scalp, flexural neck, axilla, perineum, and trunk; they often are associated with petechiae, purpura, scale, crust, erosion, impetiginization, and tender fissures. Epidermal nevus occurs within the first year of life and is a hamartoma of the epidermis and papillary dermis. It manifests as papillomatous pigmented linear lines along the Blaschko lines. Seborrheic keratosis manifests as well-demarcated, waxy/verrucous, brown papules with a “stuck on” appearance on hair-bearing skin sparing the mucosae. They are common benign lesions associated with sun exposure and often manifest in the fourth decade of life.10
- Baigrie D, Troxell T, Cook C. Nevus sebaceus. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed September 12, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482493/
- Terenzi V, Indrizzi E, Buonaccorsi S, et al. Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. J Craniofac Surg. 2006;17:1234-1239. doi:10.1097/01 .scs.0000221531.56529.cc
- Kelati A, Baybay H, Gallouj S, et al. Dermoscopic analysis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 13 cases. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;3:83-91. doi:10.1159/000460258
- Ugras N, Ozgun G, Adim SB, et al. Nevus sebaceous at unusual location: a rare presentation. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2012;55:419-420. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.101768
- Serpas de Lopez RM, Hernandez-Perez E. Jadassohn’s sebaceous nevus. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1985;11:68-72. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725 .1985.tb02893.x
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(2 pt 1):263-268. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(00)90136-1
- Santibanez-Gallerani A, Marshall D, Duarte AM, et al. Should nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn in children be excised? a study of 757 cases, and literature review. J Craniofac Surg. 2003;14:658-660. doi:10.1097/00001665-200309000-00010
- Chahboun F, Eljazouly M, Elomari M, et al. Trichoblastoma arising from the nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. Cureus. 2021;13:E15325. doi:10.7759/cureus.15325
- Cazzato G, Cimmino A, Colagrande A, et al. The multiple faces of nodular trichoblastoma: review of the literature with case presentation. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2021;8:265-270. doi:10.3390 /dermatopathology8030032
- Dandekar MN, Gandhi RK. Neoplastic dermatology. In: Alikhan A, Hocker TLH (eds). Review of Dermatology. Elsevier; 2016: 321-366.
- Baigrie D, Troxell T, Cook C. Nevus sebaceus. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed September 12, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482493/
- Terenzi V, Indrizzi E, Buonaccorsi S, et al. Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. J Craniofac Surg. 2006;17:1234-1239. doi:10.1097/01 .scs.0000221531.56529.cc
- Kelati A, Baybay H, Gallouj S, et al. Dermoscopic analysis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 13 cases. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;3:83-91. doi:10.1159/000460258
- Ugras N, Ozgun G, Adim SB, et al. Nevus sebaceous at unusual location: a rare presentation. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2012;55:419-420. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.101768
- Serpas de Lopez RM, Hernandez-Perez E. Jadassohn’s sebaceous nevus. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1985;11:68-72. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725 .1985.tb02893.x
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(2 pt 1):263-268. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(00)90136-1
- Santibanez-Gallerani A, Marshall D, Duarte AM, et al. Should nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn in children be excised? a study of 757 cases, and literature review. J Craniofac Surg. 2003;14:658-660. doi:10.1097/00001665-200309000-00010
- Chahboun F, Eljazouly M, Elomari M, et al. Trichoblastoma arising from the nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. Cureus. 2021;13:E15325. doi:10.7759/cureus.15325
- Cazzato G, Cimmino A, Colagrande A, et al. The multiple faces of nodular trichoblastoma: review of the literature with case presentation. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2021;8:265-270. doi:10.3390 /dermatopathology8030032
- Dandekar MN, Gandhi RK. Neoplastic dermatology. In: Alikhan A, Hocker TLH (eds). Review of Dermatology. Elsevier; 2016: 321-366.
A 23-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic with hair loss on the scalp of several years’ duration. The patient reported persistent pigmented bumps on the back of the scalp. He denied any pruritus or pain and had no systemic symptoms or comorbidities. Physical examination revealed a 1×1.5-cm, yellow-brown, hairless plaque on the left parietal scalp.
Which Medication Is Best? VA Genetic Tests May Have the Answer
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) now has a permanent pharmacogenomics service that provides genetic tests to give clinicians insight into the best medication options for their patients.
The tests, which have no extra cost, are available to all veterans, said pharmacist Jill S. Bates, PharmD, MS, executive director of the VA National Pharmacogenomics Program, who spoke in an interview and a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
Genetic testing is “a tool that can help optimize care that we provide for veterans,” she said. “Pharmacogenomics is additional information to help the clinician make a decision. We know that most veterans—greater than 90%—carry a variant in a pharmacogenomics gene that is actionable.”
The genetic tests can provide insight into the optimal medication for multiple conditions such as mental illness, gastrointestinal disorders, cancer, pain, and heart disease. According to a 2019 analysis of over 6 years of data, more than half of the VA patient population used medications whose efficacy may have been affected by detectable genetic variants.
For instance, Bates said tests can let clinicians know whether patients are susceptible to statin-associated muscle adverse effects if they take simvastatin, the cholesterol medication. An estimated 25.6% of the VA population has this variant.
Elsewhere on the cardiac front, an estimated 58.3% of the VA population has a genetic variant that increases sensitivity to the blood thinner warfarin.
Testing could help psychiatrists determine whether certain medications should not be prescribed—or should be prescribed at lower doses—in patients who’ve had adverse reactions to antidepressants, Bates said.
In cancer, Bates said, genetic testing can identify patients who have a genetic variant that boosts toxicity from fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy treatments, which include capecitabine, floxuridine, and fluorouracil. Meanwhile, an estimated 0.9% will have no reaction or limited reaction to capecitabine and fluorouracil, and 4.8% will have hypersensitivity to carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine.
Tests can also identify a genetic variant that can lead to poor metabolism of the chemotherapy drug irinotecan, which is used to treat colon cancer. “In those patients, you’d want to reduce the dose by 20%,” Bates said. In other cases, alternate drugs may be the best strategy to address genetic variations.
Prior to 2019, clinicians had to order pharmacogenomic tests outside of the VA system, according to Bates. That year, a donation from Sanford Health brought VA pharmacogenomics to 40 pilot sites. Since then, more than 88,000 tests have been performed.
The VA has now made its pharmacogenomic program permanent, Bates said. As of early September, testing was available at 139 VA sites and is coming soon to 4 more. It’s not available at another 23 sites that are scattered across the country.
A tool in the VA electronic health record now reminds clinicians about the availability of genetic testing and allows them to order tests. However, testing isn’t available for patients who have had liver transplants or certain bone marrow transplants.
The VA is working on developing decision-making tools to help clinicians determine when the tests are appropriate, Bates said. It typically takes 2 to 3 weeks to get results, she said, adding that external laboratories provide results. “We eventually would like to bring in all pharmacogenomics testing to be conducted within the VA enterprise.”
Bates reported that she had no disclosures.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) now has a permanent pharmacogenomics service that provides genetic tests to give clinicians insight into the best medication options for their patients.
The tests, which have no extra cost, are available to all veterans, said pharmacist Jill S. Bates, PharmD, MS, executive director of the VA National Pharmacogenomics Program, who spoke in an interview and a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
Genetic testing is “a tool that can help optimize care that we provide for veterans,” she said. “Pharmacogenomics is additional information to help the clinician make a decision. We know that most veterans—greater than 90%—carry a variant in a pharmacogenomics gene that is actionable.”
The genetic tests can provide insight into the optimal medication for multiple conditions such as mental illness, gastrointestinal disorders, cancer, pain, and heart disease. According to a 2019 analysis of over 6 years of data, more than half of the VA patient population used medications whose efficacy may have been affected by detectable genetic variants.
For instance, Bates said tests can let clinicians know whether patients are susceptible to statin-associated muscle adverse effects if they take simvastatin, the cholesterol medication. An estimated 25.6% of the VA population has this variant.
Elsewhere on the cardiac front, an estimated 58.3% of the VA population has a genetic variant that increases sensitivity to the blood thinner warfarin.
Testing could help psychiatrists determine whether certain medications should not be prescribed—or should be prescribed at lower doses—in patients who’ve had adverse reactions to antidepressants, Bates said.
In cancer, Bates said, genetic testing can identify patients who have a genetic variant that boosts toxicity from fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy treatments, which include capecitabine, floxuridine, and fluorouracil. Meanwhile, an estimated 0.9% will have no reaction or limited reaction to capecitabine and fluorouracil, and 4.8% will have hypersensitivity to carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine.
Tests can also identify a genetic variant that can lead to poor metabolism of the chemotherapy drug irinotecan, which is used to treat colon cancer. “In those patients, you’d want to reduce the dose by 20%,” Bates said. In other cases, alternate drugs may be the best strategy to address genetic variations.
Prior to 2019, clinicians had to order pharmacogenomic tests outside of the VA system, according to Bates. That year, a donation from Sanford Health brought VA pharmacogenomics to 40 pilot sites. Since then, more than 88,000 tests have been performed.
The VA has now made its pharmacogenomic program permanent, Bates said. As of early September, testing was available at 139 VA sites and is coming soon to 4 more. It’s not available at another 23 sites that are scattered across the country.
A tool in the VA electronic health record now reminds clinicians about the availability of genetic testing and allows them to order tests. However, testing isn’t available for patients who have had liver transplants or certain bone marrow transplants.
The VA is working on developing decision-making tools to help clinicians determine when the tests are appropriate, Bates said. It typically takes 2 to 3 weeks to get results, she said, adding that external laboratories provide results. “We eventually would like to bring in all pharmacogenomics testing to be conducted within the VA enterprise.”
Bates reported that she had no disclosures.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) now has a permanent pharmacogenomics service that provides genetic tests to give clinicians insight into the best medication options for their patients.
The tests, which have no extra cost, are available to all veterans, said pharmacist Jill S. Bates, PharmD, MS, executive director of the VA National Pharmacogenomics Program, who spoke in an interview and a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
Genetic testing is “a tool that can help optimize care that we provide for veterans,” she said. “Pharmacogenomics is additional information to help the clinician make a decision. We know that most veterans—greater than 90%—carry a variant in a pharmacogenomics gene that is actionable.”
The genetic tests can provide insight into the optimal medication for multiple conditions such as mental illness, gastrointestinal disorders, cancer, pain, and heart disease. According to a 2019 analysis of over 6 years of data, more than half of the VA patient population used medications whose efficacy may have been affected by detectable genetic variants.
For instance, Bates said tests can let clinicians know whether patients are susceptible to statin-associated muscle adverse effects if they take simvastatin, the cholesterol medication. An estimated 25.6% of the VA population has this variant.
Elsewhere on the cardiac front, an estimated 58.3% of the VA population has a genetic variant that increases sensitivity to the blood thinner warfarin.
Testing could help psychiatrists determine whether certain medications should not be prescribed—or should be prescribed at lower doses—in patients who’ve had adverse reactions to antidepressants, Bates said.
In cancer, Bates said, genetic testing can identify patients who have a genetic variant that boosts toxicity from fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy treatments, which include capecitabine, floxuridine, and fluorouracil. Meanwhile, an estimated 0.9% will have no reaction or limited reaction to capecitabine and fluorouracil, and 4.8% will have hypersensitivity to carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine.
Tests can also identify a genetic variant that can lead to poor metabolism of the chemotherapy drug irinotecan, which is used to treat colon cancer. “In those patients, you’d want to reduce the dose by 20%,” Bates said. In other cases, alternate drugs may be the best strategy to address genetic variations.
Prior to 2019, clinicians had to order pharmacogenomic tests outside of the VA system, according to Bates. That year, a donation from Sanford Health brought VA pharmacogenomics to 40 pilot sites. Since then, more than 88,000 tests have been performed.
The VA has now made its pharmacogenomic program permanent, Bates said. As of early September, testing was available at 139 VA sites and is coming soon to 4 more. It’s not available at another 23 sites that are scattered across the country.
A tool in the VA electronic health record now reminds clinicians about the availability of genetic testing and allows them to order tests. However, testing isn’t available for patients who have had liver transplants or certain bone marrow transplants.
The VA is working on developing decision-making tools to help clinicians determine when the tests are appropriate, Bates said. It typically takes 2 to 3 weeks to get results, she said, adding that external laboratories provide results. “We eventually would like to bring in all pharmacogenomics testing to be conducted within the VA enterprise.”
Bates reported that she had no disclosures.
FDA Approves Ustekinumab Biosimilar Otulfi
This is the fourth ustekinumab biosimilar approved in the United States. Like the reference product, ustekinumab-aauz is indicated for:
- Patients 6 years or older with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy
- Patients 6 years or older with active psoriatic arthritis
- Adult patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease
- Adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis
Ustekinumab-aauz, produced by a partnership between Fresenius Kabi and Formycon, has two formulations: subcutaneous injection (45 mg/0.5 mL or 90 mg/mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe) or intravenous infusion (130 mg/26 mL solution in a single-dose vial).
The biosimilar will launch in the United States “no later than February 22, 2025,” according to the press release, “in accordance with the patent settlement between Fresenius Kabi, Formycon, and Johnson & Johnson.”
Ustekinumab-aauz is Fresenius Kabi’s fourth biosimilar granted US approval, behind adalimumab-aacf (Idacio), tocilizumab-aazg (Tyenne), and pegfilgrastim-fpgk (Stimufend).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This is the fourth ustekinumab biosimilar approved in the United States. Like the reference product, ustekinumab-aauz is indicated for:
- Patients 6 years or older with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy
- Patients 6 years or older with active psoriatic arthritis
- Adult patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease
- Adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis
Ustekinumab-aauz, produced by a partnership between Fresenius Kabi and Formycon, has two formulations: subcutaneous injection (45 mg/0.5 mL or 90 mg/mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe) or intravenous infusion (130 mg/26 mL solution in a single-dose vial).
The biosimilar will launch in the United States “no later than February 22, 2025,” according to the press release, “in accordance with the patent settlement between Fresenius Kabi, Formycon, and Johnson & Johnson.”
Ustekinumab-aauz is Fresenius Kabi’s fourth biosimilar granted US approval, behind adalimumab-aacf (Idacio), tocilizumab-aazg (Tyenne), and pegfilgrastim-fpgk (Stimufend).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This is the fourth ustekinumab biosimilar approved in the United States. Like the reference product, ustekinumab-aauz is indicated for:
- Patients 6 years or older with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy
- Patients 6 years or older with active psoriatic arthritis
- Adult patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease
- Adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis
Ustekinumab-aauz, produced by a partnership between Fresenius Kabi and Formycon, has two formulations: subcutaneous injection (45 mg/0.5 mL or 90 mg/mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe) or intravenous infusion (130 mg/26 mL solution in a single-dose vial).
The biosimilar will launch in the United States “no later than February 22, 2025,” according to the press release, “in accordance with the patent settlement between Fresenius Kabi, Formycon, and Johnson & Johnson.”
Ustekinumab-aauz is Fresenius Kabi’s fourth biosimilar granted US approval, behind adalimumab-aacf (Idacio), tocilizumab-aazg (Tyenne), and pegfilgrastim-fpgk (Stimufend).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.