User login
Millennial Clinicians Face Pay Disparities by Specialty, Other Factors
Salaries for millennial physicians are slightly increasing, but clinicians still face pay disparities across location, practice type, and gender.
Medscape Medical News reviewed survey data from more than 1200 practicing doctors under age 40 across 29 specialties over a 4-month period starting in October 2023.
The average annual total compensation (including any bonuses) for young clinicians rose from $326,000 to $338,000, about 4%, between 2022 and 2023. Among millennials, primary care physicians saw a 5% increase. But a large pay gap exists between fields: Specialists under age 40 earned an average of $357,000 in 2023, compared with the average primary care clinician salary of $271,000.
“Procedures are reimbursed too high, while very little value is placed on primary care,” one survey respondent complained.
The type of practice plays a major part in compensation. Millennial doctors in office-based, single-specialty group practices earned an average of $358,000 per year, followed by those in office-based multispecialty group practices at 355,000 per year. Those in outpatient clinics earned $278,000 per year.
“I believe the practice situation is a huge portion of compensation,” said Tiffany Di Pietro, DO, a cardiologist and internal medicine physician in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. “Owning your own private practice is generally more lucrative (if you have good business sense), but it is also quite a bit more time-consuming, whereas employed physicians usually make less but have fewer concerns with staffing and overhead.”
Like in previous years, a gender pay gap equated to men outearning women. Female physicians under age 40 of any kind earned about $302,000 per year, 24% less than their male counterparts, on average.
Millennial doctors in the Midwest brought home the biggest earnings, with an average salary of $343,000 vs $332,000 on the West Coast.
Millennial physicians also reported higher levels of dissatisfaction. In the 2022 report, 46% said they were not paid fairly. That figure rose to 49%. Just 68% of millennial doctors would choose medicine again if they could do things over, down from 76% in the 2021 report.
“Doctors go through multiple years of school and then have to act like we are working at Dunkin’ Donuts — like we’re on an assembly line,” one survey respondent said. “We should not have to be paid per patient seen but valued for 8-9 years of training.”
Despite these complaints, close to 7 out of 10 millennial respondents said pay was not a major factor in what area of medicine they chose, with 29% saying it played no role at all in their decision.
Psychiatrists and anesthesiologists were the happiest with their earnings, with 61% of both specialties reporting that they felt fairly paid. They were followed by dermatologists and emergency medicine doctors, both of whom 60% reported fair earnings.
Many millennial doctors are finding ways to make money outside of their practice, with 18% securing other medical-related work, 15% doing medical moonlighting, and 5% taking on non–medical-related work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Salaries for millennial physicians are slightly increasing, but clinicians still face pay disparities across location, practice type, and gender.
Medscape Medical News reviewed survey data from more than 1200 practicing doctors under age 40 across 29 specialties over a 4-month period starting in October 2023.
The average annual total compensation (including any bonuses) for young clinicians rose from $326,000 to $338,000, about 4%, between 2022 and 2023. Among millennials, primary care physicians saw a 5% increase. But a large pay gap exists between fields: Specialists under age 40 earned an average of $357,000 in 2023, compared with the average primary care clinician salary of $271,000.
“Procedures are reimbursed too high, while very little value is placed on primary care,” one survey respondent complained.
The type of practice plays a major part in compensation. Millennial doctors in office-based, single-specialty group practices earned an average of $358,000 per year, followed by those in office-based multispecialty group practices at 355,000 per year. Those in outpatient clinics earned $278,000 per year.
“I believe the practice situation is a huge portion of compensation,” said Tiffany Di Pietro, DO, a cardiologist and internal medicine physician in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. “Owning your own private practice is generally more lucrative (if you have good business sense), but it is also quite a bit more time-consuming, whereas employed physicians usually make less but have fewer concerns with staffing and overhead.”
Like in previous years, a gender pay gap equated to men outearning women. Female physicians under age 40 of any kind earned about $302,000 per year, 24% less than their male counterparts, on average.
Millennial doctors in the Midwest brought home the biggest earnings, with an average salary of $343,000 vs $332,000 on the West Coast.
Millennial physicians also reported higher levels of dissatisfaction. In the 2022 report, 46% said they were not paid fairly. That figure rose to 49%. Just 68% of millennial doctors would choose medicine again if they could do things over, down from 76% in the 2021 report.
“Doctors go through multiple years of school and then have to act like we are working at Dunkin’ Donuts — like we’re on an assembly line,” one survey respondent said. “We should not have to be paid per patient seen but valued for 8-9 years of training.”
Despite these complaints, close to 7 out of 10 millennial respondents said pay was not a major factor in what area of medicine they chose, with 29% saying it played no role at all in their decision.
Psychiatrists and anesthesiologists were the happiest with their earnings, with 61% of both specialties reporting that they felt fairly paid. They were followed by dermatologists and emergency medicine doctors, both of whom 60% reported fair earnings.
Many millennial doctors are finding ways to make money outside of their practice, with 18% securing other medical-related work, 15% doing medical moonlighting, and 5% taking on non–medical-related work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Salaries for millennial physicians are slightly increasing, but clinicians still face pay disparities across location, practice type, and gender.
Medscape Medical News reviewed survey data from more than 1200 practicing doctors under age 40 across 29 specialties over a 4-month period starting in October 2023.
The average annual total compensation (including any bonuses) for young clinicians rose from $326,000 to $338,000, about 4%, between 2022 and 2023. Among millennials, primary care physicians saw a 5% increase. But a large pay gap exists between fields: Specialists under age 40 earned an average of $357,000 in 2023, compared with the average primary care clinician salary of $271,000.
“Procedures are reimbursed too high, while very little value is placed on primary care,” one survey respondent complained.
The type of practice plays a major part in compensation. Millennial doctors in office-based, single-specialty group practices earned an average of $358,000 per year, followed by those in office-based multispecialty group practices at 355,000 per year. Those in outpatient clinics earned $278,000 per year.
“I believe the practice situation is a huge portion of compensation,” said Tiffany Di Pietro, DO, a cardiologist and internal medicine physician in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. “Owning your own private practice is generally more lucrative (if you have good business sense), but it is also quite a bit more time-consuming, whereas employed physicians usually make less but have fewer concerns with staffing and overhead.”
Like in previous years, a gender pay gap equated to men outearning women. Female physicians under age 40 of any kind earned about $302,000 per year, 24% less than their male counterparts, on average.
Millennial doctors in the Midwest brought home the biggest earnings, with an average salary of $343,000 vs $332,000 on the West Coast.
Millennial physicians also reported higher levels of dissatisfaction. In the 2022 report, 46% said they were not paid fairly. That figure rose to 49%. Just 68% of millennial doctors would choose medicine again if they could do things over, down from 76% in the 2021 report.
“Doctors go through multiple years of school and then have to act like we are working at Dunkin’ Donuts — like we’re on an assembly line,” one survey respondent said. “We should not have to be paid per patient seen but valued for 8-9 years of training.”
Despite these complaints, close to 7 out of 10 millennial respondents said pay was not a major factor in what area of medicine they chose, with 29% saying it played no role at all in their decision.
Psychiatrists and anesthesiologists were the happiest with their earnings, with 61% of both specialties reporting that they felt fairly paid. They were followed by dermatologists and emergency medicine doctors, both of whom 60% reported fair earnings.
Many millennial doctors are finding ways to make money outside of their practice, with 18% securing other medical-related work, 15% doing medical moonlighting, and 5% taking on non–medical-related work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe Autoimmune Diseases Linked to Premature Ovarian Insufficiency
TOPLINE:
Women with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) have a 2.6 times higher prevalence of severe autoimmune diseases before diagnosis and a 2- to 3-fold increased risk for these diseases after diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based registry study including 3972 women diagnosed with spontaneous POI between 1988 and 2017.
- A total of 15,708 female population controls matched by age and municipality of residence were included for comparison.
- Autoimmune disease diagnoses were evaluated from childhood until the end of 2017 using the Hospital Discharge Registry.
- Women with a history of cancer or bilateral oophorectomy were excluded from the study.
TAKEAWAY:
- Women with POI had a 2.6 times higher prevalence of severe autoimmune diseases before diagnosis compared to controls (odds ratio [OR], 2.6; 95% CI, 2.2-3.1).
- The prevalence of specific autoimmune diseases such as polyglandular autoimmune diseases (OR, 25.8; 95% CI, 9.0-74.1) and Addison disease (OR, 22.9; 95% CI, 7.9-66.1) was significantly higher in women with POI.
- The standardized incidence ratios for being diagnosed with a severe autoimmune disease after POI diagnosis was 2.8 (95% CI, 2.3-3.4) during the first 3 years, decreasing to 1.3 (95% CI, 1.1-1.6) after 12 years.
- No significant difference was found in the prevalence of diabetes type 1 and ankylosing spondylitis between women with POI and the reference cohort.
IN PRACTICE:
“The study results strengthen the hypothesis that autoimmune mechanisms play an important role in the pathogenesis of POI. Future studies should focus on the immunological mechanism of POI from preventative and curative perspectives,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Susanna M. Savukoski, Oulu University Hospital in Finland. It was published online in Human Reproduction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included only autoimmune disorders diagnosed in specialized health care, which may underestimate the overall prevalence of autoimmune disorders in women with POI. Additionally, the study did not account for confounders such as body mass index and smoking, which are associated with the risk for autoimmune disease and POI.
DISCLOSURES:
Ms. Savukoski received grants from the Finnish Menopause Society, the Finnish Medical Foundation, and the Juho Vainio Foundation. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Women with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) have a 2.6 times higher prevalence of severe autoimmune diseases before diagnosis and a 2- to 3-fold increased risk for these diseases after diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based registry study including 3972 women diagnosed with spontaneous POI between 1988 and 2017.
- A total of 15,708 female population controls matched by age and municipality of residence were included for comparison.
- Autoimmune disease diagnoses were evaluated from childhood until the end of 2017 using the Hospital Discharge Registry.
- Women with a history of cancer or bilateral oophorectomy were excluded from the study.
TAKEAWAY:
- Women with POI had a 2.6 times higher prevalence of severe autoimmune diseases before diagnosis compared to controls (odds ratio [OR], 2.6; 95% CI, 2.2-3.1).
- The prevalence of specific autoimmune diseases such as polyglandular autoimmune diseases (OR, 25.8; 95% CI, 9.0-74.1) and Addison disease (OR, 22.9; 95% CI, 7.9-66.1) was significantly higher in women with POI.
- The standardized incidence ratios for being diagnosed with a severe autoimmune disease after POI diagnosis was 2.8 (95% CI, 2.3-3.4) during the first 3 years, decreasing to 1.3 (95% CI, 1.1-1.6) after 12 years.
- No significant difference was found in the prevalence of diabetes type 1 and ankylosing spondylitis between women with POI and the reference cohort.
IN PRACTICE:
“The study results strengthen the hypothesis that autoimmune mechanisms play an important role in the pathogenesis of POI. Future studies should focus on the immunological mechanism of POI from preventative and curative perspectives,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Susanna M. Savukoski, Oulu University Hospital in Finland. It was published online in Human Reproduction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included only autoimmune disorders diagnosed in specialized health care, which may underestimate the overall prevalence of autoimmune disorders in women with POI. Additionally, the study did not account for confounders such as body mass index and smoking, which are associated with the risk for autoimmune disease and POI.
DISCLOSURES:
Ms. Savukoski received grants from the Finnish Menopause Society, the Finnish Medical Foundation, and the Juho Vainio Foundation. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Women with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) have a 2.6 times higher prevalence of severe autoimmune diseases before diagnosis and a 2- to 3-fold increased risk for these diseases after diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based registry study including 3972 women diagnosed with spontaneous POI between 1988 and 2017.
- A total of 15,708 female population controls matched by age and municipality of residence were included for comparison.
- Autoimmune disease diagnoses were evaluated from childhood until the end of 2017 using the Hospital Discharge Registry.
- Women with a history of cancer or bilateral oophorectomy were excluded from the study.
TAKEAWAY:
- Women with POI had a 2.6 times higher prevalence of severe autoimmune diseases before diagnosis compared to controls (odds ratio [OR], 2.6; 95% CI, 2.2-3.1).
- The prevalence of specific autoimmune diseases such as polyglandular autoimmune diseases (OR, 25.8; 95% CI, 9.0-74.1) and Addison disease (OR, 22.9; 95% CI, 7.9-66.1) was significantly higher in women with POI.
- The standardized incidence ratios for being diagnosed with a severe autoimmune disease after POI diagnosis was 2.8 (95% CI, 2.3-3.4) during the first 3 years, decreasing to 1.3 (95% CI, 1.1-1.6) after 12 years.
- No significant difference was found in the prevalence of diabetes type 1 and ankylosing spondylitis between women with POI and the reference cohort.
IN PRACTICE:
“The study results strengthen the hypothesis that autoimmune mechanisms play an important role in the pathogenesis of POI. Future studies should focus on the immunological mechanism of POI from preventative and curative perspectives,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Susanna M. Savukoski, Oulu University Hospital in Finland. It was published online in Human Reproduction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included only autoimmune disorders diagnosed in specialized health care, which may underestimate the overall prevalence of autoimmune disorders in women with POI. Additionally, the study did not account for confounders such as body mass index and smoking, which are associated with the risk for autoimmune disease and POI.
DISCLOSURES:
Ms. Savukoski received grants from the Finnish Menopause Society, the Finnish Medical Foundation, and the Juho Vainio Foundation. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In Crohn’s Disease, Early Anti-TNF Levels May be Crucial
“The relationship between drug concentrations, immunogenicity and clinical response is likely to be multidirectional; as an observational study, we cannot definitively show the low drug levels are causative. However, our data are consistent with those from elsewhere and confirm the importance of achieving good drug levels to maximize the chances of success with anti-TNF therapy,” said Nicholas Kennedy, MBBS, PhD, a consultant gastroenterologist at Royal Devon University Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust, Exeter, United Kingdom, and coauthor of the study published in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology .
“We also showed that adequate dosing of thiopurines was needed to prevent immunogenicity, along the lines typically used to treat Crohn’s disease rather than the lower doses sometimes proposed,” he added.
The findings come from the Personalized Anti-TNF Therapy in Crohn’s Disease (PANTS) study conducted in the UK, which included 955 patients treated with infliximab and 655 treated with adalimumab between March 2014 and September 2017. The participants were 6 years or older, the median age was 32.5 years, and 51% were female.
The latest findings come from a 2-year extension of the original 1-year PANTS study, published in 2019, which found that low drug concentrations predicted anti-TNF treatment failure — a result likely attributable in part to immunogenicity, since low-drug concentrations predicted the presence of anti-drug antibodies, and anti-drug antibodies in turn predicted low drug concentrations, according to Miguel Regueiro, MD, AGAF, chief of the Digestive Diseases Institute and a professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio.
“This is one of the more important studies looking at the longitudinal care of patients with Crohn’s disease on infliximab and adalimumab,” said Dr. Regueiro, who was not involved with the study.
The extension study found that anti-drug antibodies and undetectable drug levels were associated with both treatment without an accompanying immunomodulator and carriage of the HLA-DQA1*05 genetic risk factor, though the latter was true only for treatment with infliximab.
Dr. Regueiro noted that the study demonstrates that “getting it right in induction is probably the most important part” of treating Crohn’s disease.
“Getting patients in remission early has probably a long-term prediction [of treatment success]. I do think that is practice changing. My practice has changed over the years, largely based on the initial PANTS study. I am measuring infliximab and adalimumab levels after induction, and I am using that number to decide if I dose intensify the drug, or if I’ve hit that sweet spot,” said Dr. Regueiro.
The study highlights a debate among clinicians, about whether higher drug levels are associated with remission because of the effects of higher doses, or because patients who respond have reduced leakiness in the gut, leading to greater retention of protein therapeutics.
“What the study clearly says is that the drug [level] after induction is important. It implies that there are higher remission rates early. The only thing that it didn’t really tell you is the total inflammatory burden in the body, and [if] lower inflammation equals higher drug level,” said Dr. Regueiro. He did note that the study found that obesity was a negative predictor of long-term remission, which could be attributable to the pro-inflammatory nature of adipose tissue, but he emphasized that the new study doesn’t prove causation.
The study also emphasizes the importance of the HLA-DQA1*05 genetic risk factor.
“I think it confirms that if you’re a carrier of that HLA-DQA1*05, especially with infliximab, if you’re not on an immunomodulator like a thiopurine, you have a very high likelihood of having very high antibodies against infliximab,” Dr. Regueiro said. “The long-term rates bear that out, meaning if you have one of those carriers and you’re not on a thiopurine, the likelihood of having 3-year success on infliximab — to a lesser degree, adalimumab — is very, very low.”
After exclusion of patients who had no initial response, among infliximab patients, the loss of response was 34.4% at 1 year (95% CI, 30.4-38.2%), 54.5% at 2 years (95% CI, 49.4-59%), and 60% at 3 years (95% CI, 54.1-65.2%). For adalimumab, the loss of response rates were 32.1% (95% CI, 26.7-37.1%), 47.2% (95% CI, 40.2-53.4%), and 68.4% (95% CI, 50.9-79.7%), respectively.
Drug concentrations were measured at week 14, and concentration ranges of 6.1-10 mg/L for infliximab and 10.1-12 mg/L for adalimumab were associated with remission at year 2 (infliximab odds ratio [OR], 2.2; 95% CI, 1.38-3.56. Adalimumab OR, 3.65; 95% CI, 1.83-8.67) and year 3 (infliximab OR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.16-3.11; adalimumab OR, 6.15; 95% CI, 2.5-23.19). A multivariate analysis found that each ten-fold increase in drug concentration at week 14 predicted lower odds of loss of response at year 2 or 3, both for infliximab (hazard ratio [HR], 0.45; 95% CI, 0.3-0.67) and adalimumab (HR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.22-0.7).
Among patients taking infliximab, loss of response at year 2 or 3 was associated with female sex (HR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.11-1.95) and obesity (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.08-2.42). After the researchers controlled for week 14 drug and antibody concentrations, as well as interaction between baseline immunomodulator and HLA-DQA1*05 risk variant, low thiopurine dose was associated with a higher risk of loss of response.
In the adalimumab group, there was an association between presence of the HLA-DQA1*05 risk variant and loss of response (HR, 1.95; 95% CI, 1.17-3.25).
Use of the anti-TNF drug without an immunomodulator was associated with development of anti-drug antibodies for infliximab (HR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.31-0.52) and adalimumab (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.24-0.75). Development of anti-drug antibodies was also associated with the presence of HLA-DQA1*05 for infliximab (HR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.13-1.88), but not adalimumab (HR, 1.6; 95% CI, 0.92-2.77). Use of an immunomodulator the day before or day of treatment with infliximab was associated with a delay in development of anti-drug antibodies and undetectable drug concentrations compared to only infliximab (HR, 2.87; 95% CI, 2.2-3.74) and to use of the immunomodulator following infliximab treatment (HR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.11-2.59).
“We suggest aiming to start thiopurines alongside infliximab; our data suggest that later introduction is less effective,” said Dr. Kennedy, who is currently chair of the British Society of Gastroenterology IBD Clinical Research Group.
Dr. Kennedy reported institutional grants or contracts, personal consulting fees, and personal payments or honoraria from a variety of pharmaceutical companies. See the original article for a complete list.
Dr. Regueiro reported that he has been on advisory boards and consulted for Abbvie, Janssen, UCB, Takeda, Pfizer, BMS, Organon, Amgen, Genentech, Gilead, Salix, Prometheus, Lilly, Celgene, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc. (BIPI), Celltrion, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“The relationship between drug concentrations, immunogenicity and clinical response is likely to be multidirectional; as an observational study, we cannot definitively show the low drug levels are causative. However, our data are consistent with those from elsewhere and confirm the importance of achieving good drug levels to maximize the chances of success with anti-TNF therapy,” said Nicholas Kennedy, MBBS, PhD, a consultant gastroenterologist at Royal Devon University Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust, Exeter, United Kingdom, and coauthor of the study published in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology .
“We also showed that adequate dosing of thiopurines was needed to prevent immunogenicity, along the lines typically used to treat Crohn’s disease rather than the lower doses sometimes proposed,” he added.
The findings come from the Personalized Anti-TNF Therapy in Crohn’s Disease (PANTS) study conducted in the UK, which included 955 patients treated with infliximab and 655 treated with adalimumab between March 2014 and September 2017. The participants were 6 years or older, the median age was 32.5 years, and 51% were female.
The latest findings come from a 2-year extension of the original 1-year PANTS study, published in 2019, which found that low drug concentrations predicted anti-TNF treatment failure — a result likely attributable in part to immunogenicity, since low-drug concentrations predicted the presence of anti-drug antibodies, and anti-drug antibodies in turn predicted low drug concentrations, according to Miguel Regueiro, MD, AGAF, chief of the Digestive Diseases Institute and a professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio.
“This is one of the more important studies looking at the longitudinal care of patients with Crohn’s disease on infliximab and adalimumab,” said Dr. Regueiro, who was not involved with the study.
The extension study found that anti-drug antibodies and undetectable drug levels were associated with both treatment without an accompanying immunomodulator and carriage of the HLA-DQA1*05 genetic risk factor, though the latter was true only for treatment with infliximab.
Dr. Regueiro noted that the study demonstrates that “getting it right in induction is probably the most important part” of treating Crohn’s disease.
“Getting patients in remission early has probably a long-term prediction [of treatment success]. I do think that is practice changing. My practice has changed over the years, largely based on the initial PANTS study. I am measuring infliximab and adalimumab levels after induction, and I am using that number to decide if I dose intensify the drug, or if I’ve hit that sweet spot,” said Dr. Regueiro.
The study highlights a debate among clinicians, about whether higher drug levels are associated with remission because of the effects of higher doses, or because patients who respond have reduced leakiness in the gut, leading to greater retention of protein therapeutics.
“What the study clearly says is that the drug [level] after induction is important. It implies that there are higher remission rates early. The only thing that it didn’t really tell you is the total inflammatory burden in the body, and [if] lower inflammation equals higher drug level,” said Dr. Regueiro. He did note that the study found that obesity was a negative predictor of long-term remission, which could be attributable to the pro-inflammatory nature of adipose tissue, but he emphasized that the new study doesn’t prove causation.
The study also emphasizes the importance of the HLA-DQA1*05 genetic risk factor.
“I think it confirms that if you’re a carrier of that HLA-DQA1*05, especially with infliximab, if you’re not on an immunomodulator like a thiopurine, you have a very high likelihood of having very high antibodies against infliximab,” Dr. Regueiro said. “The long-term rates bear that out, meaning if you have one of those carriers and you’re not on a thiopurine, the likelihood of having 3-year success on infliximab — to a lesser degree, adalimumab — is very, very low.”
After exclusion of patients who had no initial response, among infliximab patients, the loss of response was 34.4% at 1 year (95% CI, 30.4-38.2%), 54.5% at 2 years (95% CI, 49.4-59%), and 60% at 3 years (95% CI, 54.1-65.2%). For adalimumab, the loss of response rates were 32.1% (95% CI, 26.7-37.1%), 47.2% (95% CI, 40.2-53.4%), and 68.4% (95% CI, 50.9-79.7%), respectively.
Drug concentrations were measured at week 14, and concentration ranges of 6.1-10 mg/L for infliximab and 10.1-12 mg/L for adalimumab were associated with remission at year 2 (infliximab odds ratio [OR], 2.2; 95% CI, 1.38-3.56. Adalimumab OR, 3.65; 95% CI, 1.83-8.67) and year 3 (infliximab OR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.16-3.11; adalimumab OR, 6.15; 95% CI, 2.5-23.19). A multivariate analysis found that each ten-fold increase in drug concentration at week 14 predicted lower odds of loss of response at year 2 or 3, both for infliximab (hazard ratio [HR], 0.45; 95% CI, 0.3-0.67) and adalimumab (HR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.22-0.7).
Among patients taking infliximab, loss of response at year 2 or 3 was associated with female sex (HR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.11-1.95) and obesity (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.08-2.42). After the researchers controlled for week 14 drug and antibody concentrations, as well as interaction between baseline immunomodulator and HLA-DQA1*05 risk variant, low thiopurine dose was associated with a higher risk of loss of response.
In the adalimumab group, there was an association between presence of the HLA-DQA1*05 risk variant and loss of response (HR, 1.95; 95% CI, 1.17-3.25).
Use of the anti-TNF drug without an immunomodulator was associated with development of anti-drug antibodies for infliximab (HR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.31-0.52) and adalimumab (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.24-0.75). Development of anti-drug antibodies was also associated with the presence of HLA-DQA1*05 for infliximab (HR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.13-1.88), but not adalimumab (HR, 1.6; 95% CI, 0.92-2.77). Use of an immunomodulator the day before or day of treatment with infliximab was associated with a delay in development of anti-drug antibodies and undetectable drug concentrations compared to only infliximab (HR, 2.87; 95% CI, 2.2-3.74) and to use of the immunomodulator following infliximab treatment (HR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.11-2.59).
“We suggest aiming to start thiopurines alongside infliximab; our data suggest that later introduction is less effective,” said Dr. Kennedy, who is currently chair of the British Society of Gastroenterology IBD Clinical Research Group.
Dr. Kennedy reported institutional grants or contracts, personal consulting fees, and personal payments or honoraria from a variety of pharmaceutical companies. See the original article for a complete list.
Dr. Regueiro reported that he has been on advisory boards and consulted for Abbvie, Janssen, UCB, Takeda, Pfizer, BMS, Organon, Amgen, Genentech, Gilead, Salix, Prometheus, Lilly, Celgene, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc. (BIPI), Celltrion, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“The relationship between drug concentrations, immunogenicity and clinical response is likely to be multidirectional; as an observational study, we cannot definitively show the low drug levels are causative. However, our data are consistent with those from elsewhere and confirm the importance of achieving good drug levels to maximize the chances of success with anti-TNF therapy,” said Nicholas Kennedy, MBBS, PhD, a consultant gastroenterologist at Royal Devon University Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust, Exeter, United Kingdom, and coauthor of the study published in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology .
“We also showed that adequate dosing of thiopurines was needed to prevent immunogenicity, along the lines typically used to treat Crohn’s disease rather than the lower doses sometimes proposed,” he added.
The findings come from the Personalized Anti-TNF Therapy in Crohn’s Disease (PANTS) study conducted in the UK, which included 955 patients treated with infliximab and 655 treated with adalimumab between March 2014 and September 2017. The participants were 6 years or older, the median age was 32.5 years, and 51% were female.
The latest findings come from a 2-year extension of the original 1-year PANTS study, published in 2019, which found that low drug concentrations predicted anti-TNF treatment failure — a result likely attributable in part to immunogenicity, since low-drug concentrations predicted the presence of anti-drug antibodies, and anti-drug antibodies in turn predicted low drug concentrations, according to Miguel Regueiro, MD, AGAF, chief of the Digestive Diseases Institute and a professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio.
“This is one of the more important studies looking at the longitudinal care of patients with Crohn’s disease on infliximab and adalimumab,” said Dr. Regueiro, who was not involved with the study.
The extension study found that anti-drug antibodies and undetectable drug levels were associated with both treatment without an accompanying immunomodulator and carriage of the HLA-DQA1*05 genetic risk factor, though the latter was true only for treatment with infliximab.
Dr. Regueiro noted that the study demonstrates that “getting it right in induction is probably the most important part” of treating Crohn’s disease.
“Getting patients in remission early has probably a long-term prediction [of treatment success]. I do think that is practice changing. My practice has changed over the years, largely based on the initial PANTS study. I am measuring infliximab and adalimumab levels after induction, and I am using that number to decide if I dose intensify the drug, or if I’ve hit that sweet spot,” said Dr. Regueiro.
The study highlights a debate among clinicians, about whether higher drug levels are associated with remission because of the effects of higher doses, or because patients who respond have reduced leakiness in the gut, leading to greater retention of protein therapeutics.
“What the study clearly says is that the drug [level] after induction is important. It implies that there are higher remission rates early. The only thing that it didn’t really tell you is the total inflammatory burden in the body, and [if] lower inflammation equals higher drug level,” said Dr. Regueiro. He did note that the study found that obesity was a negative predictor of long-term remission, which could be attributable to the pro-inflammatory nature of adipose tissue, but he emphasized that the new study doesn’t prove causation.
The study also emphasizes the importance of the HLA-DQA1*05 genetic risk factor.
“I think it confirms that if you’re a carrier of that HLA-DQA1*05, especially with infliximab, if you’re not on an immunomodulator like a thiopurine, you have a very high likelihood of having very high antibodies against infliximab,” Dr. Regueiro said. “The long-term rates bear that out, meaning if you have one of those carriers and you’re not on a thiopurine, the likelihood of having 3-year success on infliximab — to a lesser degree, adalimumab — is very, very low.”
After exclusion of patients who had no initial response, among infliximab patients, the loss of response was 34.4% at 1 year (95% CI, 30.4-38.2%), 54.5% at 2 years (95% CI, 49.4-59%), and 60% at 3 years (95% CI, 54.1-65.2%). For adalimumab, the loss of response rates were 32.1% (95% CI, 26.7-37.1%), 47.2% (95% CI, 40.2-53.4%), and 68.4% (95% CI, 50.9-79.7%), respectively.
Drug concentrations were measured at week 14, and concentration ranges of 6.1-10 mg/L for infliximab and 10.1-12 mg/L for adalimumab were associated with remission at year 2 (infliximab odds ratio [OR], 2.2; 95% CI, 1.38-3.56. Adalimumab OR, 3.65; 95% CI, 1.83-8.67) and year 3 (infliximab OR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.16-3.11; adalimumab OR, 6.15; 95% CI, 2.5-23.19). A multivariate analysis found that each ten-fold increase in drug concentration at week 14 predicted lower odds of loss of response at year 2 or 3, both for infliximab (hazard ratio [HR], 0.45; 95% CI, 0.3-0.67) and adalimumab (HR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.22-0.7).
Among patients taking infliximab, loss of response at year 2 or 3 was associated with female sex (HR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.11-1.95) and obesity (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.08-2.42). After the researchers controlled for week 14 drug and antibody concentrations, as well as interaction between baseline immunomodulator and HLA-DQA1*05 risk variant, low thiopurine dose was associated with a higher risk of loss of response.
In the adalimumab group, there was an association between presence of the HLA-DQA1*05 risk variant and loss of response (HR, 1.95; 95% CI, 1.17-3.25).
Use of the anti-TNF drug without an immunomodulator was associated with development of anti-drug antibodies for infliximab (HR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.31-0.52) and adalimumab (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.24-0.75). Development of anti-drug antibodies was also associated with the presence of HLA-DQA1*05 for infliximab (HR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.13-1.88), but not adalimumab (HR, 1.6; 95% CI, 0.92-2.77). Use of an immunomodulator the day before or day of treatment with infliximab was associated with a delay in development of anti-drug antibodies and undetectable drug concentrations compared to only infliximab (HR, 2.87; 95% CI, 2.2-3.74) and to use of the immunomodulator following infliximab treatment (HR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.11-2.59).
“We suggest aiming to start thiopurines alongside infliximab; our data suggest that later introduction is less effective,” said Dr. Kennedy, who is currently chair of the British Society of Gastroenterology IBD Clinical Research Group.
Dr. Kennedy reported institutional grants or contracts, personal consulting fees, and personal payments or honoraria from a variety of pharmaceutical companies. See the original article for a complete list.
Dr. Regueiro reported that he has been on advisory boards and consulted for Abbvie, Janssen, UCB, Takeda, Pfizer, BMS, Organon, Amgen, Genentech, Gilead, Salix, Prometheus, Lilly, Celgene, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc. (BIPI), Celltrion, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How Experts Predicts This COVID and Flu Season Will Unfold
What’s the outlook for COVID-19 and flu this fall and winter? It’ll probably be a lot like last year, experts say.
“We currently expect this flu season to be comparable to last year’s season,” said Adrienne Keen, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Center for Forecasting and Outbreak Analytics. “We expect this year’s COVID-19 season peak to be similar to last year’s or lower.” The CDC is still analyzing COVID surveillance data from the summer and will update the forecast as more is learned.
For COVID, that means it won’t be as bad as the pandemic years, and for the flu, it’s a typical pre-pandemic season. But status quo does not mean great.
Between October 2023 and April 2024, as many as 75 million people got the flu in the United States, according to CDC estimates, resulting in up to 900,000 hospitalizations and between 17,000 and 100,000 deaths. In 2023, about 900,000 Americans were hospitalized with COVID and 75,000 died.
Getting vaccinated remains crucial, public health officials stressed.
Predicting COVID
Two key predictors of how bad an upcoming COVID season will be are the cycling of new variants and the population’s immunity (protection from an infectious disease that happens when a population is immune through vaccination or previous infection).
When new variants go up and immunity goes down, “we tend to see the increase in cases,” said Michael T. Osterholm, PhD, MPH, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy and a professor of public health at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. But if the number of variants goes down and immunity levels go up, the outlook is more favorable.
The new COVID variant called XEC has been found in at least 25 states. On September 27, the CDC added the variant to the COVID tracker. It now accounts for 6% of US cases. This was expected, as the variant has been circulating in Europe, said Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar and infectious disease expert at the Center for Health Security at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
“There will always be a new variant appearing, and one falling,” he said. “So the fact that this is happening is not surprising.”
Meanwhile, the summer COVID surge has provided postinfection immunity for some people. “What’s likely is, we are going to see substantial protection of the population for several months based on previous infection and in some cases vaccination,” Dr. Osterholm said. That means protection from serious illness, hospitalizations, and deaths (but not necessarily infection). That protection could last through the year or into early 2025.
The timing of 2024’s winter surge will likely be a bit later than 2023’s, said Andrew Pekosz, PhD, a professor and vice chair of molecular microbiology and immunology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, “peaking just after the Christmas/New Year holiday.”
During the 2023-2024 season, weekly COVID hospitalizations peaked the week of Dec. 30, said Justin Lessler, PhD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and a member of the COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub.
But variants are unpredictable. “There’s a chance that the XEC variant may take off and spread, or might not,” said Dr. Adalja. As of September 28, the Omicron variant KP.3.1.1 was leading, accounting for 58.7% of US cases, according to the CDC.
While Dr. Adalja agreed that 2024’s COVID season will probably be like 2023’s, “we have to be prepared for cases and hospitalizations going up,” he said, “but not to the point of a crisis.” A return to lockdowns and social distancing is unlikely.
Still, older adults and others at higher risk of getting very sick from COVID should consider masking during travel, said Rajendram Rajnarayanan, PhD, MSc, an associate professor at the New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University, Jonesboro.
Flu Forecasts
Predicting flu season this early is hard, said Jeffrey Shaman, PhD, a professor of environmental health sciences and professor of climate at Colombia University, New York.
“You can look at the CDC forecast and use it as a very loose guide right now,” said Dr. Shaman, who won the CDC’s first “Predict the Influenza Season Challenge” in 2014. “Until there is actually flu, it’s like trying to predict the landfall of a hurricane.” Flu activity remained low as of September 14 (the most current data available), according to the CDC.
When flu activity picks up, typically in mid-October or November, experts look at the dominant strain, exposure to similar strains in previous years, and how well-matched the current flu vaccine is to that dominant strain, Dr. Shaman said. Vaccine makers must make an educated guess months in advance regarding which strain to target, to allow time for production.
The vaccination rate plays a role, too, but that tends to remain constant, Dr. Shaman said. According to the CDC, less than half of adults age 18 and up got a flu vaccination last year.
Experts also consider flu patterns in the Southern Hemisphere, where 2024 flu activity has mostly involved two subtypes of influenza A — H1N1 and H3N2 — and some influenza B, the CDC found.
How Well Do This Year’s Vaccines and Viruses Match Up?
The FDA has authorized three updated COVID vaccines for this fall. Novavax targets the JN.1 strain of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Both mRNA vaccines, Moderna and Pfizer, target KP.2, a descendant of JN.1. All three target current predominant variants, and any one of them is recommended by the CDC.
The vaccines are a good “though not perfect match to virtually all the circulating variants of SARS-CoV-2,” said Dr. Pekosz.
Experts said that the shots will protect against the XEC variant.
“XEC and its sublineages are expected to be the dominant fall/winter variant group,” said Dr. Rajnarayanan.
This year’s flu vaccines, all trivalent (protecting against three viruses), will target the three strains expected to circulate — H1N1, H3N2, and influenza B (Victoria), according to the CDC.
People should still get vaccinated, Dr. Adalja said, and use home tests for flu and COVID and take antivirals promptly when needed. The goal should not be status quo but rather fewer COVID and flu hospitalizations and deaths.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
What’s the outlook for COVID-19 and flu this fall and winter? It’ll probably be a lot like last year, experts say.
“We currently expect this flu season to be comparable to last year’s season,” said Adrienne Keen, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Center for Forecasting and Outbreak Analytics. “We expect this year’s COVID-19 season peak to be similar to last year’s or lower.” The CDC is still analyzing COVID surveillance data from the summer and will update the forecast as more is learned.
For COVID, that means it won’t be as bad as the pandemic years, and for the flu, it’s a typical pre-pandemic season. But status quo does not mean great.
Between October 2023 and April 2024, as many as 75 million people got the flu in the United States, according to CDC estimates, resulting in up to 900,000 hospitalizations and between 17,000 and 100,000 deaths. In 2023, about 900,000 Americans were hospitalized with COVID and 75,000 died.
Getting vaccinated remains crucial, public health officials stressed.
Predicting COVID
Two key predictors of how bad an upcoming COVID season will be are the cycling of new variants and the population’s immunity (protection from an infectious disease that happens when a population is immune through vaccination or previous infection).
When new variants go up and immunity goes down, “we tend to see the increase in cases,” said Michael T. Osterholm, PhD, MPH, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy and a professor of public health at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. But if the number of variants goes down and immunity levels go up, the outlook is more favorable.
The new COVID variant called XEC has been found in at least 25 states. On September 27, the CDC added the variant to the COVID tracker. It now accounts for 6% of US cases. This was expected, as the variant has been circulating in Europe, said Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar and infectious disease expert at the Center for Health Security at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
“There will always be a new variant appearing, and one falling,” he said. “So the fact that this is happening is not surprising.”
Meanwhile, the summer COVID surge has provided postinfection immunity for some people. “What’s likely is, we are going to see substantial protection of the population for several months based on previous infection and in some cases vaccination,” Dr. Osterholm said. That means protection from serious illness, hospitalizations, and deaths (but not necessarily infection). That protection could last through the year or into early 2025.
The timing of 2024’s winter surge will likely be a bit later than 2023’s, said Andrew Pekosz, PhD, a professor and vice chair of molecular microbiology and immunology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, “peaking just after the Christmas/New Year holiday.”
During the 2023-2024 season, weekly COVID hospitalizations peaked the week of Dec. 30, said Justin Lessler, PhD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and a member of the COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub.
But variants are unpredictable. “There’s a chance that the XEC variant may take off and spread, or might not,” said Dr. Adalja. As of September 28, the Omicron variant KP.3.1.1 was leading, accounting for 58.7% of US cases, according to the CDC.
While Dr. Adalja agreed that 2024’s COVID season will probably be like 2023’s, “we have to be prepared for cases and hospitalizations going up,” he said, “but not to the point of a crisis.” A return to lockdowns and social distancing is unlikely.
Still, older adults and others at higher risk of getting very sick from COVID should consider masking during travel, said Rajendram Rajnarayanan, PhD, MSc, an associate professor at the New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University, Jonesboro.
Flu Forecasts
Predicting flu season this early is hard, said Jeffrey Shaman, PhD, a professor of environmental health sciences and professor of climate at Colombia University, New York.
“You can look at the CDC forecast and use it as a very loose guide right now,” said Dr. Shaman, who won the CDC’s first “Predict the Influenza Season Challenge” in 2014. “Until there is actually flu, it’s like trying to predict the landfall of a hurricane.” Flu activity remained low as of September 14 (the most current data available), according to the CDC.
When flu activity picks up, typically in mid-October or November, experts look at the dominant strain, exposure to similar strains in previous years, and how well-matched the current flu vaccine is to that dominant strain, Dr. Shaman said. Vaccine makers must make an educated guess months in advance regarding which strain to target, to allow time for production.
The vaccination rate plays a role, too, but that tends to remain constant, Dr. Shaman said. According to the CDC, less than half of adults age 18 and up got a flu vaccination last year.
Experts also consider flu patterns in the Southern Hemisphere, where 2024 flu activity has mostly involved two subtypes of influenza A — H1N1 and H3N2 — and some influenza B, the CDC found.
How Well Do This Year’s Vaccines and Viruses Match Up?
The FDA has authorized three updated COVID vaccines for this fall. Novavax targets the JN.1 strain of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Both mRNA vaccines, Moderna and Pfizer, target KP.2, a descendant of JN.1. All three target current predominant variants, and any one of them is recommended by the CDC.
The vaccines are a good “though not perfect match to virtually all the circulating variants of SARS-CoV-2,” said Dr. Pekosz.
Experts said that the shots will protect against the XEC variant.
“XEC and its sublineages are expected to be the dominant fall/winter variant group,” said Dr. Rajnarayanan.
This year’s flu vaccines, all trivalent (protecting against three viruses), will target the three strains expected to circulate — H1N1, H3N2, and influenza B (Victoria), according to the CDC.
People should still get vaccinated, Dr. Adalja said, and use home tests for flu and COVID and take antivirals promptly when needed. The goal should not be status quo but rather fewer COVID and flu hospitalizations and deaths.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
What’s the outlook for COVID-19 and flu this fall and winter? It’ll probably be a lot like last year, experts say.
“We currently expect this flu season to be comparable to last year’s season,” said Adrienne Keen, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Center for Forecasting and Outbreak Analytics. “We expect this year’s COVID-19 season peak to be similar to last year’s or lower.” The CDC is still analyzing COVID surveillance data from the summer and will update the forecast as more is learned.
For COVID, that means it won’t be as bad as the pandemic years, and for the flu, it’s a typical pre-pandemic season. But status quo does not mean great.
Between October 2023 and April 2024, as many as 75 million people got the flu in the United States, according to CDC estimates, resulting in up to 900,000 hospitalizations and between 17,000 and 100,000 deaths. In 2023, about 900,000 Americans were hospitalized with COVID and 75,000 died.
Getting vaccinated remains crucial, public health officials stressed.
Predicting COVID
Two key predictors of how bad an upcoming COVID season will be are the cycling of new variants and the population’s immunity (protection from an infectious disease that happens when a population is immune through vaccination or previous infection).
When new variants go up and immunity goes down, “we tend to see the increase in cases,” said Michael T. Osterholm, PhD, MPH, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy and a professor of public health at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. But if the number of variants goes down and immunity levels go up, the outlook is more favorable.
The new COVID variant called XEC has been found in at least 25 states. On September 27, the CDC added the variant to the COVID tracker. It now accounts for 6% of US cases. This was expected, as the variant has been circulating in Europe, said Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar and infectious disease expert at the Center for Health Security at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
“There will always be a new variant appearing, and one falling,” he said. “So the fact that this is happening is not surprising.”
Meanwhile, the summer COVID surge has provided postinfection immunity for some people. “What’s likely is, we are going to see substantial protection of the population for several months based on previous infection and in some cases vaccination,” Dr. Osterholm said. That means protection from serious illness, hospitalizations, and deaths (but not necessarily infection). That protection could last through the year or into early 2025.
The timing of 2024’s winter surge will likely be a bit later than 2023’s, said Andrew Pekosz, PhD, a professor and vice chair of molecular microbiology and immunology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, “peaking just after the Christmas/New Year holiday.”
During the 2023-2024 season, weekly COVID hospitalizations peaked the week of Dec. 30, said Justin Lessler, PhD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and a member of the COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub.
But variants are unpredictable. “There’s a chance that the XEC variant may take off and spread, or might not,” said Dr. Adalja. As of September 28, the Omicron variant KP.3.1.1 was leading, accounting for 58.7% of US cases, according to the CDC.
While Dr. Adalja agreed that 2024’s COVID season will probably be like 2023’s, “we have to be prepared for cases and hospitalizations going up,” he said, “but not to the point of a crisis.” A return to lockdowns and social distancing is unlikely.
Still, older adults and others at higher risk of getting very sick from COVID should consider masking during travel, said Rajendram Rajnarayanan, PhD, MSc, an associate professor at the New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University, Jonesboro.
Flu Forecasts
Predicting flu season this early is hard, said Jeffrey Shaman, PhD, a professor of environmental health sciences and professor of climate at Colombia University, New York.
“You can look at the CDC forecast and use it as a very loose guide right now,” said Dr. Shaman, who won the CDC’s first “Predict the Influenza Season Challenge” in 2014. “Until there is actually flu, it’s like trying to predict the landfall of a hurricane.” Flu activity remained low as of September 14 (the most current data available), according to the CDC.
When flu activity picks up, typically in mid-October or November, experts look at the dominant strain, exposure to similar strains in previous years, and how well-matched the current flu vaccine is to that dominant strain, Dr. Shaman said. Vaccine makers must make an educated guess months in advance regarding which strain to target, to allow time for production.
The vaccination rate plays a role, too, but that tends to remain constant, Dr. Shaman said. According to the CDC, less than half of adults age 18 and up got a flu vaccination last year.
Experts also consider flu patterns in the Southern Hemisphere, where 2024 flu activity has mostly involved two subtypes of influenza A — H1N1 and H3N2 — and some influenza B, the CDC found.
How Well Do This Year’s Vaccines and Viruses Match Up?
The FDA has authorized three updated COVID vaccines for this fall. Novavax targets the JN.1 strain of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Both mRNA vaccines, Moderna and Pfizer, target KP.2, a descendant of JN.1. All three target current predominant variants, and any one of them is recommended by the CDC.
The vaccines are a good “though not perfect match to virtually all the circulating variants of SARS-CoV-2,” said Dr. Pekosz.
Experts said that the shots will protect against the XEC variant.
“XEC and its sublineages are expected to be the dominant fall/winter variant group,” said Dr. Rajnarayanan.
This year’s flu vaccines, all trivalent (protecting against three viruses), will target the three strains expected to circulate — H1N1, H3N2, and influenza B (Victoria), according to the CDC.
People should still get vaccinated, Dr. Adalja said, and use home tests for flu and COVID and take antivirals promptly when needed. The goal should not be status quo but rather fewer COVID and flu hospitalizations and deaths.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Time to Revisit the Standard Treatment Approach in Children With MS?
COPENHAGEN — However, only few of these medications are licensed for pediatric use, indicating it may be time to reconsider the standard treatment approach for this patient population.
Treatments for pediatric-onset MS have mostly been used off-label until the recent approvals of fingolimod, dimethyl fumarate, and teriflunomide. Typically, children with MS start with moderately effective therapies, while more potent options are reserved for those who don’t respond.
However, recent research suggests this may not be the most effective treatment strategy for this patient population. Several studies suggesting impressive treatment responses to highly effective therapies (HETs) in children were presented at the 2024 ECTRIMS annual meeting.
In one study, initiating monoclonal antibody treatment during childhood was associated with reduced disability into early adulthood and beyond.
“Our findings are a strong argument for rethinking current treatment guidelines,” said study investigator Sifat Sharmin, PhD, The University of Melbourne, Australia.
“By allowing earlier access to highly effective treatments, we can significantly enhance the quality of life for children with MS and reduce the burden of long-term disability,” she added.
In another presentation, Yael Hacohen, MD, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London, England, noted that the use of these more effective monoclonal antibody therapies in children with MS has been associated with some improvements in Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores after 2 or 3 years of treatment.
Maybe this is a sign that “this is a population that can repair, in contrast to adult patients,” she wondered.
MS is primarily a disease of adults, but pediatric MS accounts for up to 5% of all cases. Children with MS tend to have much more active disease than adults, Dr. Hacohen explained. However, they also tend to recover from attacks more quickly with little disability, which sometimes causes diagnostic delays.
A pediatrician or family doctor will often dismiss pins and needles or blurred vision that only lasts a couple of days and won’t send the patient for an MRI, she said. But on MRI, pediatric patients with MS often have multiple lesions, even though they may have had very few symptoms. The EDSS may not change very much, but there can still be significant brain atrophy.
Over the past 20 years, there’s been an explosion of new disease-modifying treatments for MS, but these high-efficacy treatments, such as antibody therapies, are often not prescribed until the patient reaches the age of 18 years, both Dr. Sharmin and Dr. Hacohen pointed out.
“We need to get some of these medications approved for use in children,” Dr. Hacohen said.
Slowed Disability
In her presentation, Dr. Sharmin reported an observational study that included 282 patients younger than 18 years at MS onset identified from the French MS Registry, the Italian MS Register, and the Global MSBase Registry.
Of these, 110 (39%) had initiated therapy with ocrelizumab, rituximab, or natalizumab early in the disease course between ages 12 and 17 years and 172 (61%) had initiated treatment with one of these agents at ages 20-22 years.
The primary outcome was the difference in EDSS scores from baseline (at age 18 years) to ages 23-27 years between those who had started treatment with one of these agents early and those who had started late.
At the baseline of age 18 years, the median EDSS score was 1.5 in the early group and 1.3 in the late group. Median follow-up time was 10.8 years.
The data were adjusted for baseline differences in factors such as sex, age at symptom onset, time from onset to clinically definite MS, and the number of relapses (using inverse probability treatment weighting based on propensity scores).
Results showed that between ages 23 and 27 years, disability was a 0.57 step lower in the early group than in the late group. The mean absolute differences in EDSS from baseline were 0.40 in the early group and 0.95 in the late group. This benefit of early treatment persisted throughout the rest of the follow-up period.
The substantially lower risk of progressing to higher disability levels in the early treatment group was particularly evident in the moderate disability range, where further progression was reduced by up to 97%, Dr. Sharmin noted.
“Starting these highly effective therapies, before the onset of significant neurological impairments, appears crucial for preserving neurological function in children with relapsing-remitting MS over the long term,” she said.
These findings highlight the critical importance of early intervention in pediatric-onset MS, she concluded.
The researchers are planning further work to generate more evidence to support the proactive treatment of pediatric-onset MS, with a particular focus on assessing the long-term risks for immunosuppressive therapies in this population.
Ocrelizumab Experience in Children
Dr. Hacohen reported on a UK cohort of children with MS treated with ocrelizumab, with 66 patients having more than 12 months of follow-up. Of these, only four patients had relapses, and there was no evidence of disease activity in 94% patients.
“We’ve stopped doing relapse clinic because they really don’t relapse,” Dr. Hacohen reported.
“This has completely changed our practice in pediatric MS,” she said. Twice a year, patients come in to have pre-infusion bloods and clinical assessments and then return a month later for treatment.
“They only have to come to the hospital for 4 days a year, and the rest of the time, they can forget they have MS,” said Dr. Hacohen.
In terms of complications, one patient in the UK cohort developed enterovirus meningitis but recovered completely, and two patients had hypogammaglobulinemia and were changed to an extended interval or to a different agent.
Dr. Hacohen cautioned that hypogammaglobulinemia — a condition in which immunoglobulin levels are below normal — is “something that hypothetically we should maybe be more worried about in the pediatric population, particularly as these patients are more likely to be on anti-CD20 therapies for a much longer time.”
She said this complication tends to happen after about 4 or 5 years of treatment. “If we start seeing IgG levels dropping, we need to come up with a plan about extending the dosing interval. We need clinical trials to look at this.”
Dr. Hacohen also drew attention to the issue of vaccinations not being effective in patients on anti-CD20 antibody therapy, which could be a particular problem in children.
However, given that vaccinations do seem to be effective in patients taking natalizumab, pediatric patients with highly active disease could receive the drug for 3-6 months while receiving vaccines and then switched over to ocrelizumab, she said.
Giving natalizumab for such a short period is not believed to have a high risk of developing JCV antibodies, she added.
In another presentation, Brenda Banwell, MD, Johns Hopkins Children’s Center, Baltimore, reported new data from an early study (OPERETTA 1) with ocrelizumab in pediatric relapsing-remitting MS showing a safety profile similar to that observed in adults. The suggested dose is 300 mg for children under 35 kg and 600 mg for adults over 35 kg, administered every 24 weeks. These doses will be further investigated in the ongoing phase III OPERETTA 2 trial.
Dr. Sharmin received a postdoctoral fellowship from MS Australia. The OPERETTA studies were sponsored by F. Hoffmann-La Roche. Dr. Banwell served as a consultant to Roche. Dr. Hacohen reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COPENHAGEN — However, only few of these medications are licensed for pediatric use, indicating it may be time to reconsider the standard treatment approach for this patient population.
Treatments for pediatric-onset MS have mostly been used off-label until the recent approvals of fingolimod, dimethyl fumarate, and teriflunomide. Typically, children with MS start with moderately effective therapies, while more potent options are reserved for those who don’t respond.
However, recent research suggests this may not be the most effective treatment strategy for this patient population. Several studies suggesting impressive treatment responses to highly effective therapies (HETs) in children were presented at the 2024 ECTRIMS annual meeting.
In one study, initiating monoclonal antibody treatment during childhood was associated with reduced disability into early adulthood and beyond.
“Our findings are a strong argument for rethinking current treatment guidelines,” said study investigator Sifat Sharmin, PhD, The University of Melbourne, Australia.
“By allowing earlier access to highly effective treatments, we can significantly enhance the quality of life for children with MS and reduce the burden of long-term disability,” she added.
In another presentation, Yael Hacohen, MD, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London, England, noted that the use of these more effective monoclonal antibody therapies in children with MS has been associated with some improvements in Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores after 2 or 3 years of treatment.
Maybe this is a sign that “this is a population that can repair, in contrast to adult patients,” she wondered.
MS is primarily a disease of adults, but pediatric MS accounts for up to 5% of all cases. Children with MS tend to have much more active disease than adults, Dr. Hacohen explained. However, they also tend to recover from attacks more quickly with little disability, which sometimes causes diagnostic delays.
A pediatrician or family doctor will often dismiss pins and needles or blurred vision that only lasts a couple of days and won’t send the patient for an MRI, she said. But on MRI, pediatric patients with MS often have multiple lesions, even though they may have had very few symptoms. The EDSS may not change very much, but there can still be significant brain atrophy.
Over the past 20 years, there’s been an explosion of new disease-modifying treatments for MS, but these high-efficacy treatments, such as antibody therapies, are often not prescribed until the patient reaches the age of 18 years, both Dr. Sharmin and Dr. Hacohen pointed out.
“We need to get some of these medications approved for use in children,” Dr. Hacohen said.
Slowed Disability
In her presentation, Dr. Sharmin reported an observational study that included 282 patients younger than 18 years at MS onset identified from the French MS Registry, the Italian MS Register, and the Global MSBase Registry.
Of these, 110 (39%) had initiated therapy with ocrelizumab, rituximab, or natalizumab early in the disease course between ages 12 and 17 years and 172 (61%) had initiated treatment with one of these agents at ages 20-22 years.
The primary outcome was the difference in EDSS scores from baseline (at age 18 years) to ages 23-27 years between those who had started treatment with one of these agents early and those who had started late.
At the baseline of age 18 years, the median EDSS score was 1.5 in the early group and 1.3 in the late group. Median follow-up time was 10.8 years.
The data were adjusted for baseline differences in factors such as sex, age at symptom onset, time from onset to clinically definite MS, and the number of relapses (using inverse probability treatment weighting based on propensity scores).
Results showed that between ages 23 and 27 years, disability was a 0.57 step lower in the early group than in the late group. The mean absolute differences in EDSS from baseline were 0.40 in the early group and 0.95 in the late group. This benefit of early treatment persisted throughout the rest of the follow-up period.
The substantially lower risk of progressing to higher disability levels in the early treatment group was particularly evident in the moderate disability range, where further progression was reduced by up to 97%, Dr. Sharmin noted.
“Starting these highly effective therapies, before the onset of significant neurological impairments, appears crucial for preserving neurological function in children with relapsing-remitting MS over the long term,” she said.
These findings highlight the critical importance of early intervention in pediatric-onset MS, she concluded.
The researchers are planning further work to generate more evidence to support the proactive treatment of pediatric-onset MS, with a particular focus on assessing the long-term risks for immunosuppressive therapies in this population.
Ocrelizumab Experience in Children
Dr. Hacohen reported on a UK cohort of children with MS treated with ocrelizumab, with 66 patients having more than 12 months of follow-up. Of these, only four patients had relapses, and there was no evidence of disease activity in 94% patients.
“We’ve stopped doing relapse clinic because they really don’t relapse,” Dr. Hacohen reported.
“This has completely changed our practice in pediatric MS,” she said. Twice a year, patients come in to have pre-infusion bloods and clinical assessments and then return a month later for treatment.
“They only have to come to the hospital for 4 days a year, and the rest of the time, they can forget they have MS,” said Dr. Hacohen.
In terms of complications, one patient in the UK cohort developed enterovirus meningitis but recovered completely, and two patients had hypogammaglobulinemia and were changed to an extended interval or to a different agent.
Dr. Hacohen cautioned that hypogammaglobulinemia — a condition in which immunoglobulin levels are below normal — is “something that hypothetically we should maybe be more worried about in the pediatric population, particularly as these patients are more likely to be on anti-CD20 therapies for a much longer time.”
She said this complication tends to happen after about 4 or 5 years of treatment. “If we start seeing IgG levels dropping, we need to come up with a plan about extending the dosing interval. We need clinical trials to look at this.”
Dr. Hacohen also drew attention to the issue of vaccinations not being effective in patients on anti-CD20 antibody therapy, which could be a particular problem in children.
However, given that vaccinations do seem to be effective in patients taking natalizumab, pediatric patients with highly active disease could receive the drug for 3-6 months while receiving vaccines and then switched over to ocrelizumab, she said.
Giving natalizumab for such a short period is not believed to have a high risk of developing JCV antibodies, she added.
In another presentation, Brenda Banwell, MD, Johns Hopkins Children’s Center, Baltimore, reported new data from an early study (OPERETTA 1) with ocrelizumab in pediatric relapsing-remitting MS showing a safety profile similar to that observed in adults. The suggested dose is 300 mg for children under 35 kg and 600 mg for adults over 35 kg, administered every 24 weeks. These doses will be further investigated in the ongoing phase III OPERETTA 2 trial.
Dr. Sharmin received a postdoctoral fellowship from MS Australia. The OPERETTA studies were sponsored by F. Hoffmann-La Roche. Dr. Banwell served as a consultant to Roche. Dr. Hacohen reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COPENHAGEN — However, only few of these medications are licensed for pediatric use, indicating it may be time to reconsider the standard treatment approach for this patient population.
Treatments for pediatric-onset MS have mostly been used off-label until the recent approvals of fingolimod, dimethyl fumarate, and teriflunomide. Typically, children with MS start with moderately effective therapies, while more potent options are reserved for those who don’t respond.
However, recent research suggests this may not be the most effective treatment strategy for this patient population. Several studies suggesting impressive treatment responses to highly effective therapies (HETs) in children were presented at the 2024 ECTRIMS annual meeting.
In one study, initiating monoclonal antibody treatment during childhood was associated with reduced disability into early adulthood and beyond.
“Our findings are a strong argument for rethinking current treatment guidelines,” said study investigator Sifat Sharmin, PhD, The University of Melbourne, Australia.
“By allowing earlier access to highly effective treatments, we can significantly enhance the quality of life for children with MS and reduce the burden of long-term disability,” she added.
In another presentation, Yael Hacohen, MD, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London, England, noted that the use of these more effective monoclonal antibody therapies in children with MS has been associated with some improvements in Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores after 2 or 3 years of treatment.
Maybe this is a sign that “this is a population that can repair, in contrast to adult patients,” she wondered.
MS is primarily a disease of adults, but pediatric MS accounts for up to 5% of all cases. Children with MS tend to have much more active disease than adults, Dr. Hacohen explained. However, they also tend to recover from attacks more quickly with little disability, which sometimes causes diagnostic delays.
A pediatrician or family doctor will often dismiss pins and needles or blurred vision that only lasts a couple of days and won’t send the patient for an MRI, she said. But on MRI, pediatric patients with MS often have multiple lesions, even though they may have had very few symptoms. The EDSS may not change very much, but there can still be significant brain atrophy.
Over the past 20 years, there’s been an explosion of new disease-modifying treatments for MS, but these high-efficacy treatments, such as antibody therapies, are often not prescribed until the patient reaches the age of 18 years, both Dr. Sharmin and Dr. Hacohen pointed out.
“We need to get some of these medications approved for use in children,” Dr. Hacohen said.
Slowed Disability
In her presentation, Dr. Sharmin reported an observational study that included 282 patients younger than 18 years at MS onset identified from the French MS Registry, the Italian MS Register, and the Global MSBase Registry.
Of these, 110 (39%) had initiated therapy with ocrelizumab, rituximab, or natalizumab early in the disease course between ages 12 and 17 years and 172 (61%) had initiated treatment with one of these agents at ages 20-22 years.
The primary outcome was the difference in EDSS scores from baseline (at age 18 years) to ages 23-27 years between those who had started treatment with one of these agents early and those who had started late.
At the baseline of age 18 years, the median EDSS score was 1.5 in the early group and 1.3 in the late group. Median follow-up time was 10.8 years.
The data were adjusted for baseline differences in factors such as sex, age at symptom onset, time from onset to clinically definite MS, and the number of relapses (using inverse probability treatment weighting based on propensity scores).
Results showed that between ages 23 and 27 years, disability was a 0.57 step lower in the early group than in the late group. The mean absolute differences in EDSS from baseline were 0.40 in the early group and 0.95 in the late group. This benefit of early treatment persisted throughout the rest of the follow-up period.
The substantially lower risk of progressing to higher disability levels in the early treatment group was particularly evident in the moderate disability range, where further progression was reduced by up to 97%, Dr. Sharmin noted.
“Starting these highly effective therapies, before the onset of significant neurological impairments, appears crucial for preserving neurological function in children with relapsing-remitting MS over the long term,” she said.
These findings highlight the critical importance of early intervention in pediatric-onset MS, she concluded.
The researchers are planning further work to generate more evidence to support the proactive treatment of pediatric-onset MS, with a particular focus on assessing the long-term risks for immunosuppressive therapies in this population.
Ocrelizumab Experience in Children
Dr. Hacohen reported on a UK cohort of children with MS treated with ocrelizumab, with 66 patients having more than 12 months of follow-up. Of these, only four patients had relapses, and there was no evidence of disease activity in 94% patients.
“We’ve stopped doing relapse clinic because they really don’t relapse,” Dr. Hacohen reported.
“This has completely changed our practice in pediatric MS,” she said. Twice a year, patients come in to have pre-infusion bloods and clinical assessments and then return a month later for treatment.
“They only have to come to the hospital for 4 days a year, and the rest of the time, they can forget they have MS,” said Dr. Hacohen.
In terms of complications, one patient in the UK cohort developed enterovirus meningitis but recovered completely, and two patients had hypogammaglobulinemia and were changed to an extended interval or to a different agent.
Dr. Hacohen cautioned that hypogammaglobulinemia — a condition in which immunoglobulin levels are below normal — is “something that hypothetically we should maybe be more worried about in the pediatric population, particularly as these patients are more likely to be on anti-CD20 therapies for a much longer time.”
She said this complication tends to happen after about 4 or 5 years of treatment. “If we start seeing IgG levels dropping, we need to come up with a plan about extending the dosing interval. We need clinical trials to look at this.”
Dr. Hacohen also drew attention to the issue of vaccinations not being effective in patients on anti-CD20 antibody therapy, which could be a particular problem in children.
However, given that vaccinations do seem to be effective in patients taking natalizumab, pediatric patients with highly active disease could receive the drug for 3-6 months while receiving vaccines and then switched over to ocrelizumab, she said.
Giving natalizumab for such a short period is not believed to have a high risk of developing JCV antibodies, she added.
In another presentation, Brenda Banwell, MD, Johns Hopkins Children’s Center, Baltimore, reported new data from an early study (OPERETTA 1) with ocrelizumab in pediatric relapsing-remitting MS showing a safety profile similar to that observed in adults. The suggested dose is 300 mg for children under 35 kg and 600 mg for adults over 35 kg, administered every 24 weeks. These doses will be further investigated in the ongoing phase III OPERETTA 2 trial.
Dr. Sharmin received a postdoctoral fellowship from MS Australia. The OPERETTA studies were sponsored by F. Hoffmann-La Roche. Dr. Banwell served as a consultant to Roche. Dr. Hacohen reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECTRIMS 2024
‘Cancer Doesn’t Wait’: How Prior Authorization Harms Care
Fantine Giap, MD, sat across from a 21-year-old with a rare sarcoma at the base of her skull.
Despite the large tumor, nestled in a sensitive area, the Boston-based radiation oncologist could envision a bright future for her patient.
She and the other members of the patient’s care team had an impressive cancer-fighting arsenal at her fingertips. The team had recommended surgery, followed by proton therapy — a sophisticated tool able to deliver concentrated, razor-focused radiation to the once apple-sized growth, while sparing the fragile brain stem, optic nerve, and spinal cord.
Surgery went as planned. But as the days and weeks wore on and insurance prior authorization for the proton therapy never came, the tumor roared back, leading to more surgeries and more complications. Ultimately, the young woman needed a tracheostomy and a feeding tube.
By the time insurance said yes, more than 1 year from her initial visit, the future the team had envisioned seemed out of reach.
“Unfortunately for this patient, it went from a potentially curable situation to a likely not curable situation,” recalled Dr. Giap, a clinician at Massachusetts General Hospital and instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “I wanted to cry every day that she waited.’’
While a stark example, such insurance delays are not uncommon, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open.
Other studies have found that number to be even higher, with more than 86% of prior authorization requests ultimately approved with few changes.
‘’It gives you the idea that this entire process might be a little futile — that it’s just wasting people’s time,’’ said Fumiko Chino, MD, coauthor on the JAMA study and now an assistant professor in radiation oncology at MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. ‘’The problem is cancer doesn’t wait for bureaucracy.’’
Barriers at Every Step
As Dr. Chino and her study coauthors explained, advancements like intensity-modulated radiation therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery have allowed a new generation of specialists to treat previously untreatable cancers in ways that maximize tumor-killing power while minimizing collateral damage. But these tools require sophisticated planning, imaging, simulations and execution — all of which are subject to increased insurance scrutiny.
‘’We face barriers pretty much every step of the way for every patient,’’ said Dr. Chino.
To investigate how such barriers impact care, Dr. Chino and colleagues at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center — where she worked until July — looked at 206 cases in which payers denied prior authorization for radiation therapy from November 1, 2021 to December 8, 2022.
The team found that 62% were ultimately approved without any change to technique or dose, while 28% were authorized, but with lower doses or less sophisticated techniques. Four people, however, never got authorization at all — three abandoned treatment altogether, and one sought treatment at another institution.
Treatment delays ranged from 1 day to 49 days. Eighty-three patients died.
Would some of them have lived if it weren’t for prior authorization?
Dr. Chino cannot say for sure, but did note that certain cancers, like cervical cancer, can grow so quickly that every day of delayed treatment makes them harder to control.
Patients with metastatic or late-stage cancers are often denied more aggressive treatments by insurers who, in essence, “assume that they are going to die from their disease anyway,” Dr. Chino said.
She views this as tragically shortsighted.
‘’There’s actually a strong body of evidence to show that if you treat even metastatic stage IV diseases aggressively, you can prolong not just quality of life but also quantity,’’ she said.
In cases where the cancer is more localized and insurance mandates lower doses or cheaper techniques, the consequences can be equally heartbreaking.
‘’It’s like saying instead of taking an extra-strength Tylenol you can only have a baby aspirin,’’ she said. ‘’Their pain is less likely to be controlled, their disease is less likely to be controlled, and they are more likely to need retreatment.’’
Prior authorization delays can also significantly stress patients at the most vulnerable point of their lives.
In another recent study, Dr. Chino found that 69% of patients with cancer reported prior authorization-related delays in care, with one-third waiting a month or longer. One in five never got the care their doctors recommended, and 20% reported spending more than 11 hours on the phone haggling with their insurance companies.
Most patients rated the process as ‘’bad’’ or ‘’horrible,’’ and said it fueled anxiety.
Such delays can be hard on clinicians and the healthcare system too.
One 2022 study found that a typical academic radiation oncology practice spent about a half-million dollars per year seeking insurance preauthorization. Nationally, that number exceeds $40 million.
Then there is the burnout factor.
Dr. Giap, an early-career physician who specializes in rare, aggressive sarcomas, works at an institution that helped pioneer proton therapy. She says it pains her to tell a desperate patient, like the 21-year-old, who has traveled to her from out of state that they have to wait.
‘’Knowing that the majority of the cases are ultimately approved and that this wait is often unnecessary makes it even tougher,’’ she said.
Dr. Chino, a breast cancer specialist, has taken to warning patients before the alarming insurance letter arrives in the mail that their insurance may delay authorizing their care. But she tells patients that she will do everything she can to fight for them and develops a back-up plan to pivot to quickly, if needed.
‘’No one goes into medicine to spend their time talking to insurance companies,’’ said Dr. Chino.
The national trade group, America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP), did not return repeated requests for an interview for this story. But their official position, as stated on their website, is that “prior authorization is one of many tools health insurance providers use to promote safe, timely, evidence-based, affordable, and efficient care.”
Both Dr. Giap and Dr. Chino believe that prior authorization was developed with good intentions: to save healthcare costs and rein in treatments that don’t necessarily benefit patients.
But, in their specialty, the burden has proliferated to a point that Dr. Chino characterizes as ‘’unconscionable.’’
She believes that policy changes like the proposed Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act — which would require real-time decisions for procedures that are routinely approved — could go a long way in improving patient care.
Meanwhile, Dr. Giap said, more research and professional guidelines are necessary to bolster insurance company confidence in newer technologies, particularly for rare cancers.
Her patient ultimately got her proton therapy and is ‘’doing relatively well, all things considered.’’
But not all the stories end like this.
Dr. Chino will never forget a patient with a cancer growing so rapidly she could see it protruding through her chest wall. She called for an urgent PET scan to see where else in the body the cancer might be brewing and rushed the planning process for radiation therapy, both of which faced prior authorization barriers. That scan — which ultimately showed the cancer had spread — was delayed for months.*
If the team had had those imaging results upfront, she said, they would have recommended a completely different course of treatment.
And her patient might be alive today.
‘’Unfortunately,” Dr. Chino said, “the people with the very worst prior authorization stories aren’t here anymore to tell you about them.”
*Correction, 10/4/24: An earlier version of this article erroneously stated that Dr. Chino called for surgery for her patient. She actually called for a PET scan and an urgent radiation start.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fantine Giap, MD, sat across from a 21-year-old with a rare sarcoma at the base of her skull.
Despite the large tumor, nestled in a sensitive area, the Boston-based radiation oncologist could envision a bright future for her patient.
She and the other members of the patient’s care team had an impressive cancer-fighting arsenal at her fingertips. The team had recommended surgery, followed by proton therapy — a sophisticated tool able to deliver concentrated, razor-focused radiation to the once apple-sized growth, while sparing the fragile brain stem, optic nerve, and spinal cord.
Surgery went as planned. But as the days and weeks wore on and insurance prior authorization for the proton therapy never came, the tumor roared back, leading to more surgeries and more complications. Ultimately, the young woman needed a tracheostomy and a feeding tube.
By the time insurance said yes, more than 1 year from her initial visit, the future the team had envisioned seemed out of reach.
“Unfortunately for this patient, it went from a potentially curable situation to a likely not curable situation,” recalled Dr. Giap, a clinician at Massachusetts General Hospital and instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “I wanted to cry every day that she waited.’’
While a stark example, such insurance delays are not uncommon, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open.
Other studies have found that number to be even higher, with more than 86% of prior authorization requests ultimately approved with few changes.
‘’It gives you the idea that this entire process might be a little futile — that it’s just wasting people’s time,’’ said Fumiko Chino, MD, coauthor on the JAMA study and now an assistant professor in radiation oncology at MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. ‘’The problem is cancer doesn’t wait for bureaucracy.’’
Barriers at Every Step
As Dr. Chino and her study coauthors explained, advancements like intensity-modulated radiation therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery have allowed a new generation of specialists to treat previously untreatable cancers in ways that maximize tumor-killing power while minimizing collateral damage. But these tools require sophisticated planning, imaging, simulations and execution — all of which are subject to increased insurance scrutiny.
‘’We face barriers pretty much every step of the way for every patient,’’ said Dr. Chino.
To investigate how such barriers impact care, Dr. Chino and colleagues at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center — where she worked until July — looked at 206 cases in which payers denied prior authorization for radiation therapy from November 1, 2021 to December 8, 2022.
The team found that 62% were ultimately approved without any change to technique or dose, while 28% were authorized, but with lower doses or less sophisticated techniques. Four people, however, never got authorization at all — three abandoned treatment altogether, and one sought treatment at another institution.
Treatment delays ranged from 1 day to 49 days. Eighty-three patients died.
Would some of them have lived if it weren’t for prior authorization?
Dr. Chino cannot say for sure, but did note that certain cancers, like cervical cancer, can grow so quickly that every day of delayed treatment makes them harder to control.
Patients with metastatic or late-stage cancers are often denied more aggressive treatments by insurers who, in essence, “assume that they are going to die from their disease anyway,” Dr. Chino said.
She views this as tragically shortsighted.
‘’There’s actually a strong body of evidence to show that if you treat even metastatic stage IV diseases aggressively, you can prolong not just quality of life but also quantity,’’ she said.
In cases where the cancer is more localized and insurance mandates lower doses or cheaper techniques, the consequences can be equally heartbreaking.
‘’It’s like saying instead of taking an extra-strength Tylenol you can only have a baby aspirin,’’ she said. ‘’Their pain is less likely to be controlled, their disease is less likely to be controlled, and they are more likely to need retreatment.’’
Prior authorization delays can also significantly stress patients at the most vulnerable point of their lives.
In another recent study, Dr. Chino found that 69% of patients with cancer reported prior authorization-related delays in care, with one-third waiting a month or longer. One in five never got the care their doctors recommended, and 20% reported spending more than 11 hours on the phone haggling with their insurance companies.
Most patients rated the process as ‘’bad’’ or ‘’horrible,’’ and said it fueled anxiety.
Such delays can be hard on clinicians and the healthcare system too.
One 2022 study found that a typical academic radiation oncology practice spent about a half-million dollars per year seeking insurance preauthorization. Nationally, that number exceeds $40 million.
Then there is the burnout factor.
Dr. Giap, an early-career physician who specializes in rare, aggressive sarcomas, works at an institution that helped pioneer proton therapy. She says it pains her to tell a desperate patient, like the 21-year-old, who has traveled to her from out of state that they have to wait.
‘’Knowing that the majority of the cases are ultimately approved and that this wait is often unnecessary makes it even tougher,’’ she said.
Dr. Chino, a breast cancer specialist, has taken to warning patients before the alarming insurance letter arrives in the mail that their insurance may delay authorizing their care. But she tells patients that she will do everything she can to fight for them and develops a back-up plan to pivot to quickly, if needed.
‘’No one goes into medicine to spend their time talking to insurance companies,’’ said Dr. Chino.
The national trade group, America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP), did not return repeated requests for an interview for this story. But their official position, as stated on their website, is that “prior authorization is one of many tools health insurance providers use to promote safe, timely, evidence-based, affordable, and efficient care.”
Both Dr. Giap and Dr. Chino believe that prior authorization was developed with good intentions: to save healthcare costs and rein in treatments that don’t necessarily benefit patients.
But, in their specialty, the burden has proliferated to a point that Dr. Chino characterizes as ‘’unconscionable.’’
She believes that policy changes like the proposed Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act — which would require real-time decisions for procedures that are routinely approved — could go a long way in improving patient care.
Meanwhile, Dr. Giap said, more research and professional guidelines are necessary to bolster insurance company confidence in newer technologies, particularly for rare cancers.
Her patient ultimately got her proton therapy and is ‘’doing relatively well, all things considered.’’
But not all the stories end like this.
Dr. Chino will never forget a patient with a cancer growing so rapidly she could see it protruding through her chest wall. She called for an urgent PET scan to see where else in the body the cancer might be brewing and rushed the planning process for radiation therapy, both of which faced prior authorization barriers. That scan — which ultimately showed the cancer had spread — was delayed for months.*
If the team had had those imaging results upfront, she said, they would have recommended a completely different course of treatment.
And her patient might be alive today.
‘’Unfortunately,” Dr. Chino said, “the people with the very worst prior authorization stories aren’t here anymore to tell you about them.”
*Correction, 10/4/24: An earlier version of this article erroneously stated that Dr. Chino called for surgery for her patient. She actually called for a PET scan and an urgent radiation start.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fantine Giap, MD, sat across from a 21-year-old with a rare sarcoma at the base of her skull.
Despite the large tumor, nestled in a sensitive area, the Boston-based radiation oncologist could envision a bright future for her patient.
She and the other members of the patient’s care team had an impressive cancer-fighting arsenal at her fingertips. The team had recommended surgery, followed by proton therapy — a sophisticated tool able to deliver concentrated, razor-focused radiation to the once apple-sized growth, while sparing the fragile brain stem, optic nerve, and spinal cord.
Surgery went as planned. But as the days and weeks wore on and insurance prior authorization for the proton therapy never came, the tumor roared back, leading to more surgeries and more complications. Ultimately, the young woman needed a tracheostomy and a feeding tube.
By the time insurance said yes, more than 1 year from her initial visit, the future the team had envisioned seemed out of reach.
“Unfortunately for this patient, it went from a potentially curable situation to a likely not curable situation,” recalled Dr. Giap, a clinician at Massachusetts General Hospital and instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “I wanted to cry every day that she waited.’’
While a stark example, such insurance delays are not uncommon, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open.
Other studies have found that number to be even higher, with more than 86% of prior authorization requests ultimately approved with few changes.
‘’It gives you the idea that this entire process might be a little futile — that it’s just wasting people’s time,’’ said Fumiko Chino, MD, coauthor on the JAMA study and now an assistant professor in radiation oncology at MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. ‘’The problem is cancer doesn’t wait for bureaucracy.’’
Barriers at Every Step
As Dr. Chino and her study coauthors explained, advancements like intensity-modulated radiation therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery have allowed a new generation of specialists to treat previously untreatable cancers in ways that maximize tumor-killing power while minimizing collateral damage. But these tools require sophisticated planning, imaging, simulations and execution — all of which are subject to increased insurance scrutiny.
‘’We face barriers pretty much every step of the way for every patient,’’ said Dr. Chino.
To investigate how such barriers impact care, Dr. Chino and colleagues at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center — where she worked until July — looked at 206 cases in which payers denied prior authorization for radiation therapy from November 1, 2021 to December 8, 2022.
The team found that 62% were ultimately approved without any change to technique or dose, while 28% were authorized, but with lower doses or less sophisticated techniques. Four people, however, never got authorization at all — three abandoned treatment altogether, and one sought treatment at another institution.
Treatment delays ranged from 1 day to 49 days. Eighty-three patients died.
Would some of them have lived if it weren’t for prior authorization?
Dr. Chino cannot say for sure, but did note that certain cancers, like cervical cancer, can grow so quickly that every day of delayed treatment makes them harder to control.
Patients with metastatic or late-stage cancers are often denied more aggressive treatments by insurers who, in essence, “assume that they are going to die from their disease anyway,” Dr. Chino said.
She views this as tragically shortsighted.
‘’There’s actually a strong body of evidence to show that if you treat even metastatic stage IV diseases aggressively, you can prolong not just quality of life but also quantity,’’ she said.
In cases where the cancer is more localized and insurance mandates lower doses or cheaper techniques, the consequences can be equally heartbreaking.
‘’It’s like saying instead of taking an extra-strength Tylenol you can only have a baby aspirin,’’ she said. ‘’Their pain is less likely to be controlled, their disease is less likely to be controlled, and they are more likely to need retreatment.’’
Prior authorization delays can also significantly stress patients at the most vulnerable point of their lives.
In another recent study, Dr. Chino found that 69% of patients with cancer reported prior authorization-related delays in care, with one-third waiting a month or longer. One in five never got the care their doctors recommended, and 20% reported spending more than 11 hours on the phone haggling with their insurance companies.
Most patients rated the process as ‘’bad’’ or ‘’horrible,’’ and said it fueled anxiety.
Such delays can be hard on clinicians and the healthcare system too.
One 2022 study found that a typical academic radiation oncology practice spent about a half-million dollars per year seeking insurance preauthorization. Nationally, that number exceeds $40 million.
Then there is the burnout factor.
Dr. Giap, an early-career physician who specializes in rare, aggressive sarcomas, works at an institution that helped pioneer proton therapy. She says it pains her to tell a desperate patient, like the 21-year-old, who has traveled to her from out of state that they have to wait.
‘’Knowing that the majority of the cases are ultimately approved and that this wait is often unnecessary makes it even tougher,’’ she said.
Dr. Chino, a breast cancer specialist, has taken to warning patients before the alarming insurance letter arrives in the mail that their insurance may delay authorizing their care. But she tells patients that she will do everything she can to fight for them and develops a back-up plan to pivot to quickly, if needed.
‘’No one goes into medicine to spend their time talking to insurance companies,’’ said Dr. Chino.
The national trade group, America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP), did not return repeated requests for an interview for this story. But their official position, as stated on their website, is that “prior authorization is one of many tools health insurance providers use to promote safe, timely, evidence-based, affordable, and efficient care.”
Both Dr. Giap and Dr. Chino believe that prior authorization was developed with good intentions: to save healthcare costs and rein in treatments that don’t necessarily benefit patients.
But, in their specialty, the burden has proliferated to a point that Dr. Chino characterizes as ‘’unconscionable.’’
She believes that policy changes like the proposed Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act — which would require real-time decisions for procedures that are routinely approved — could go a long way in improving patient care.
Meanwhile, Dr. Giap said, more research and professional guidelines are necessary to bolster insurance company confidence in newer technologies, particularly for rare cancers.
Her patient ultimately got her proton therapy and is ‘’doing relatively well, all things considered.’’
But not all the stories end like this.
Dr. Chino will never forget a patient with a cancer growing so rapidly she could see it protruding through her chest wall. She called for an urgent PET scan to see where else in the body the cancer might be brewing and rushed the planning process for radiation therapy, both of which faced prior authorization barriers. That scan — which ultimately showed the cancer had spread — was delayed for months.*
If the team had had those imaging results upfront, she said, they would have recommended a completely different course of treatment.
And her patient might be alive today.
‘’Unfortunately,” Dr. Chino said, “the people with the very worst prior authorization stories aren’t here anymore to tell you about them.”
*Correction, 10/4/24: An earlier version of this article erroneously stated that Dr. Chino called for surgery for her patient. She actually called for a PET scan and an urgent radiation start.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Western Pygmy Rattlesnake Envenomation and Bite Management
There are 375 species of poisonous snakes, with approximately 20,000 deaths worldwide each year due to snakebites, mostly in Asia and Africa.1 The death rate in the United States is 14 to 20 cases per year. In the United States, a variety of rattlesnakes are poisonous. There are 2 genera of rattlesnakes: Sistrurus (3 species) and Crotalus (23 species). The pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Sistrurus miliarius species that is divided into 3 subspecies: the Carolina pigmy rattlesnake (S miliarius miliarius), the western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri), and the dusky pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius barbouri).2
The western pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Crotalidae family. The rattlesnakes in this family also are known as pit vipers. All pit vipers have common characteristics for identification: triangular head, fangs, elliptical pupils, and a heat-sensing pit between the eyes. The western pygmy rattlesnake is found in Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Kentucky, and Tennessee.1 It is small bodied (15–20 inches)3 and grayish-brown, with a brown dorsal stripe with black blotches on its back. It is found in glades, second-growth forests near rock ledges, and areas where powerlines cut through dense forest.3 Its venom is hemorrhagic, causing tissue damage, but does not contain neurotoxins.4 Bites from the western pygmy rattlesnake often do not lead to death, but the venom, which contains numerous proteins and enzymes, does cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration at the site of envenomation and possible loss of digit.5,6
We present a case of a man who was bitten on the right third digit by a western pygmy rattlesnake. We describe the clinical course and treatment.
Case Report
A 56-year-old right-handed man presented to the emergency department with a rapidly swelling, painful hand following a snakebite to the dorsal aspect of the right third digit (Figure 1). He was able to capture a photograph of the snake at the time of injury, which helped identify it as a western pygmy rattlesnake (Figure 2). He also photographed the hand immediately after the bite occurred (Figure 3). Vitals on presentation included an elevated blood pressure of 161/100 mm Hg; no fever (temperature, 36.4 °C); and normal pulse oximetry of 98%, pulse of 86 beats per minute, and respiratory rate of 16 breaths per minute.

After the snakebite, the patient’s family called the Missouri Poison Center immediately. The family identified the snake species and shared this information with the poison center. Poison control recommended calling the nearest hospitals to determine if antivenom was available and make notification of arrival.
The patient’s tetanus toxoid immunization was updated immediately upon arrival. The hand was marked to monitor swelling. Initial laboratory test results revealed the following values: sodium, 133 mmol/L (reference range, 136–145 mmol/L); potassium, 3.4 mmol/L (3.6–5.2 mmol/L); lactic acid, 2.4 mmol/L (0.5–2.2 mmol/L); creatine kinase, 425 U/L (55–170 U/L); platelet count, 68/µL (150,000–450,000/µL); fibrinogen, 169 mg/dL (185–410 mg/dL); and glucose, 121 mg/dL (74–106 mg/dL). The remainder of the complete blood cell count and metabolic panel was unremarkable. Radiographs of the hand did not show any fractures, dislocations, or foreign bodies. Missouri Poison Center was consulted. Given the patient’s severe pain, edema beyond 40 cm, and developing ecchymosis on the inner arm, the bite was graded as a 3 on the traditional snakebite severity scale. Poison control recommended 4 to 6 vials of antivenom over 60 minutes. Six vials of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom were given.
The patient’s complete blood cell count remained unremarkable throughout his admission. His metabolic panel returned to normal at 6 hours postadmission: sodium, 139 mmol/L; potassium, 4.0 mmol/L. His lactate and creatinine kinase were not rechecked. His fibrinogen was trending upward. Serial laboratory test results revealed fibrinogen levels of 153, 158, 161, 159, 173, and 216 mg/dL at 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36 hours, respectively. Other laboratory test results including prothrombin time (11.0 s) and international normalized ratio (0.98) remained within reference range (11–13 s and 0.80–1.39, respectively) during serial monitoring.
The patient was hospitalized for 40 hours while waiting for his fibrinogen level to normalize. The local skin necrosis worsened acutely in this 40-hour window (Figure 4). Intravenous antibiotics were not administered during the hospital stay. Before discharge, the patient was evaluated by the surgery service, who did not recommend debridement.
Following discharge, the patient consulted a wound care expert. The area of necrosis was unroofed and debrided in the outpatient setting (Figure 5). The patient was started on oral cefalexin 500 mg twice daily for 10 days and instructed to perform twice-daily dressing changes with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%. A hand surgeon was consulted for consideration of a reverse cross-finger flap, which was not recommended. Twice-daily dressing changes for the wound—consisting of application of silver sulfadiazine cream 1% directly to the wound followed by gauze, self-adhesive soft-rolled gauze, and elastic bandages—were performed for 2 weeks.
After 2 weeks, the wound was left open to the air and cleaned with soap and water as needed. At 6 weeks, the wound was completely healed via secondary intention, except for some minor remaining ulceration at the location of the fang entry point (Figure 6). The patient had no loss of finger function or sensation.
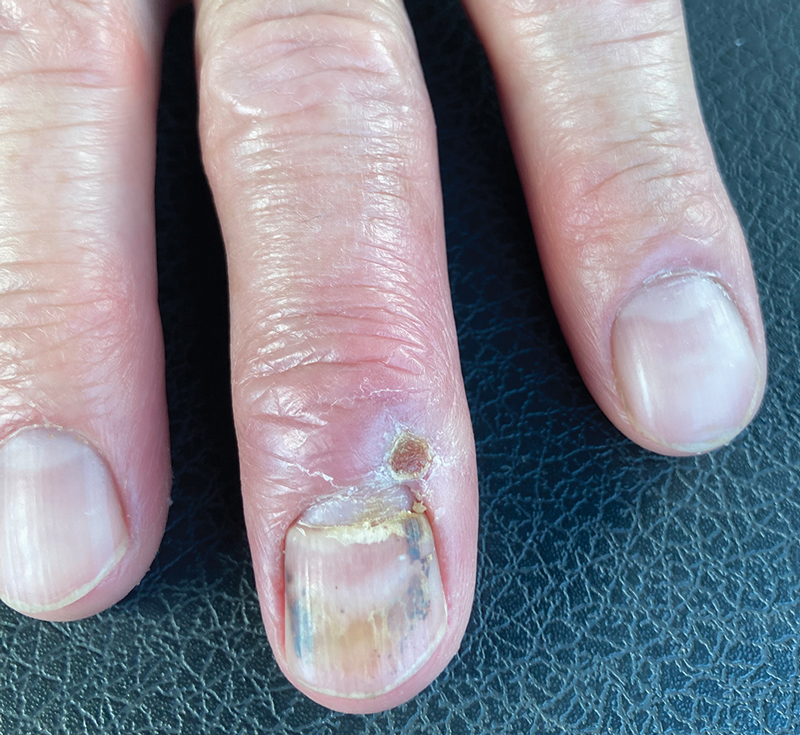
Surgical Management of Snakebites
The surgeon’s role in managing snakebites is controversial. Snakebites were once perceived as a surgical emergency due to symptoms mimicking compartment syndrome; however, snakebites rarely cause a true compartment syndrome.7 Prophylactic bite excision and fasciotomies are not recommended. Incision and suction of the fang marks may be beneficial if performed within 15 to 30 minutes from the time of the bite.8 With access to a surgeon in this short time period being nearly impossible, incision and suctioning of fang marks generally is not recommended.9 Retained snake fangs are a possibility, and the infection could spread to a nearby joint, causing septic arthritis,10 which would be an indication for surgical intervention. Bites to the finger often cause major swelling, and the benefits of dermotomy are documented.11 Generally, early administration of antivenom will decrease local tissue reaction and prevent additional tissue loss.12 In our patient, the decision to perform dermotomy was made when the area of necrosis had declared itself and the skin reached its elastic limit. Bozkurt et al13 described the neurovascular bundles within the digit as functioning as small compartments. When the skin of the digit reaches its elastic limit, pressure within the compartment may exceed the capillary closing pressure, and the integrity of small vessels and nerves may be compromised. Our case highlights the benefit of dermotomy as well as the functional and cosmetic results that can be achieved.
Wound Care for Snakebites
There is little published on the treatment of snakebites after patients are stabilized medically for hospital discharge. Venomous snakes inject toxins that predominantly consist of enzymes (eg, phospholipase A2, phosphodiesterase, hyaluronidase, peptidase, metalloproteinase) that cause tissue destruction through diverse mechanisms.14 The venom of western pygmy rattlesnakes is hemotoxic and can cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration,4 as was the case in our patient.
Silver sulfadiazine commonly is used to prevent infection in burn patients. Given the large surface area of exposed dermis after debridement and concern for infection, silver sulfadiazine was chosen in our patient for local wound care treatment. Silver sulfadiazine is a widely available and low-cost drug.15 Its antibacterial effects are due to the silver ions, which only act superficially and therefore limit systemic absorption.16 Application should be performed in a clean manner with minimal trauma to the tissue. This technique is best achieved by using sterile gloves and applying the medication manually. A 0.0625-inch layer should be applied to entirely cover the cleaned debrided area.17 When performing application with tongue blades or cotton swabs, it is important to never “double dip.” Patient education on proper administration is imperative to a successful outcome.
Final Thoughts
Our case demonstrates the safe use of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom for the treatment of western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri) envenomation. Early administration of antivenom following pit viper rattlesnake envenomations is important to mitigate systemic effects and the extent of soft tissue damage. There are few studies on local wound care treatment after rattlesnake envenomation. This case highlights the role of dermotomy and wound care with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%.
- Biggers B. Management of Missouri snake bites. Mo Med. 2017;114:254-257.
- Stamm R. Sistrurus miliarius pigmy rattlesnake. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Sistrurus_miliarius/
- Missouri Department of Conservation. Western pygmy rattlesnake. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/western-pygmy-rattlesnake
- AnimalSake. Facts about the pigmy rattlesnake that are sure to surprise you. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://animalsake.com/pygmy-rattlesnake
- King AM, Crim WS, Menke NB, et al. Pygmy rattlesnake envenomation treated with crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom. Toxicon. 2012;60:1287-1289.
- Juckett G, Hancox JG. Venomous snakebites in the United States: management review and update. Am Fam Physician. 2002;65:1367-1375.
- Toschlog EA, Bauer CR, Hall EL, et al. Surgical considerations in the management of pit viper snake envenomation. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217:726-735.
- Cribari C. Management of poisonous snakebite. American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma; 2004. https://www.hartcountyga.gov/documents/PoisonousSnakebiteTreatment.pdf
- Walker JP, Morrison RL. Current management of copperhead snakebite. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:470-474.
- Gelman D, Bates T, Nuelle JAV. Septic arthritis of the proximal interphalangeal joint after rattlesnake bite. J Hand Surg Am. 2022;47:484.e1-484.e4.
- Watt CH Jr. Treatment of poisonous snakebite with emphasis on digit dermotomy. South Med J. 1985;78:694-699.
- Corneille MG, Larson S, Stewart RM, et al. A large single-center experience with treatment of patients with crotalid envenomations: outcomes with and evolution of antivenin therapy. Am J Surg. 2006;192:848-852.
- Bozkurt M, Kulahci Y, Zor F, et al. The management of pit viper envenomation of the hand. Hand (NY). 2008;3:324-331.
- Aziz H, Rhee P, Pandit V, et al. The current concepts in management of animal (dog, cat, snake, scorpion) and human bite wounds. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78:641-648.
- Hummel RP, MacMillan BG, Altemeier WA. Topical and systemic antibacterial agents in the treatment of burns. Ann Surg. 1970;172:370-384.
- Modak SM, Sampath L, Fox CL. Combined topical use of silver sulfadiazine and antibiotics as a possible solution to bacterial resistance in burn wounds. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1988;9:359-363.
- Oaks RJ, Cindass R. Silver sulfadiazine. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated January 22, 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556054/
There are 375 species of poisonous snakes, with approximately 20,000 deaths worldwide each year due to snakebites, mostly in Asia and Africa.1 The death rate in the United States is 14 to 20 cases per year. In the United States, a variety of rattlesnakes are poisonous. There are 2 genera of rattlesnakes: Sistrurus (3 species) and Crotalus (23 species). The pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Sistrurus miliarius species that is divided into 3 subspecies: the Carolina pigmy rattlesnake (S miliarius miliarius), the western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri), and the dusky pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius barbouri).2
The western pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Crotalidae family. The rattlesnakes in this family also are known as pit vipers. All pit vipers have common characteristics for identification: triangular head, fangs, elliptical pupils, and a heat-sensing pit between the eyes. The western pygmy rattlesnake is found in Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Kentucky, and Tennessee.1 It is small bodied (15–20 inches)3 and grayish-brown, with a brown dorsal stripe with black blotches on its back. It is found in glades, second-growth forests near rock ledges, and areas where powerlines cut through dense forest.3 Its venom is hemorrhagic, causing tissue damage, but does not contain neurotoxins.4 Bites from the western pygmy rattlesnake often do not lead to death, but the venom, which contains numerous proteins and enzymes, does cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration at the site of envenomation and possible loss of digit.5,6
We present a case of a man who was bitten on the right third digit by a western pygmy rattlesnake. We describe the clinical course and treatment.
Case Report
A 56-year-old right-handed man presented to the emergency department with a rapidly swelling, painful hand following a snakebite to the dorsal aspect of the right third digit (Figure 1). He was able to capture a photograph of the snake at the time of injury, which helped identify it as a western pygmy rattlesnake (Figure 2). He also photographed the hand immediately after the bite occurred (Figure 3). Vitals on presentation included an elevated blood pressure of 161/100 mm Hg; no fever (temperature, 36.4 °C); and normal pulse oximetry of 98%, pulse of 86 beats per minute, and respiratory rate of 16 breaths per minute.



After the snakebite, the patient’s family called the Missouri Poison Center immediately. The family identified the snake species and shared this information with the poison center. Poison control recommended calling the nearest hospitals to determine if antivenom was available and make notification of arrival.
The patient’s tetanus toxoid immunization was updated immediately upon arrival. The hand was marked to monitor swelling. Initial laboratory test results revealed the following values: sodium, 133 mmol/L (reference range, 136–145 mmol/L); potassium, 3.4 mmol/L (3.6–5.2 mmol/L); lactic acid, 2.4 mmol/L (0.5–2.2 mmol/L); creatine kinase, 425 U/L (55–170 U/L); platelet count, 68/µL (150,000–450,000/µL); fibrinogen, 169 mg/dL (185–410 mg/dL); and glucose, 121 mg/dL (74–106 mg/dL). The remainder of the complete blood cell count and metabolic panel was unremarkable. Radiographs of the hand did not show any fractures, dislocations, or foreign bodies. Missouri Poison Center was consulted. Given the patient’s severe pain, edema beyond 40 cm, and developing ecchymosis on the inner arm, the bite was graded as a 3 on the traditional snakebite severity scale. Poison control recommended 4 to 6 vials of antivenom over 60 minutes. Six vials of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom were given.
The patient’s complete blood cell count remained unremarkable throughout his admission. His metabolic panel returned to normal at 6 hours postadmission: sodium, 139 mmol/L; potassium, 4.0 mmol/L. His lactate and creatinine kinase were not rechecked. His fibrinogen was trending upward. Serial laboratory test results revealed fibrinogen levels of 153, 158, 161, 159, 173, and 216 mg/dL at 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36 hours, respectively. Other laboratory test results including prothrombin time (11.0 s) and international normalized ratio (0.98) remained within reference range (11–13 s and 0.80–1.39, respectively) during serial monitoring.
The patient was hospitalized for 40 hours while waiting for his fibrinogen level to normalize. The local skin necrosis worsened acutely in this 40-hour window (Figure 4). Intravenous antibiotics were not administered during the hospital stay. Before discharge, the patient was evaluated by the surgery service, who did not recommend debridement.

Following discharge, the patient consulted a wound care expert. The area of necrosis was unroofed and debrided in the outpatient setting (Figure 5). The patient was started on oral cefalexin 500 mg twice daily for 10 days and instructed to perform twice-daily dressing changes with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%. A hand surgeon was consulted for consideration of a reverse cross-finger flap, which was not recommended. Twice-daily dressing changes for the wound—consisting of application of silver sulfadiazine cream 1% directly to the wound followed by gauze, self-adhesive soft-rolled gauze, and elastic bandages—were performed for 2 weeks.

After 2 weeks, the wound was left open to the air and cleaned with soap and water as needed. At 6 weeks, the wound was completely healed via secondary intention, except for some minor remaining ulceration at the location of the fang entry point (Figure 6). The patient had no loss of finger function or sensation.

Surgical Management of Snakebites
The surgeon’s role in managing snakebites is controversial. Snakebites were once perceived as a surgical emergency due to symptoms mimicking compartment syndrome; however, snakebites rarely cause a true compartment syndrome.7 Prophylactic bite excision and fasciotomies are not recommended. Incision and suction of the fang marks may be beneficial if performed within 15 to 30 minutes from the time of the bite.8 With access to a surgeon in this short time period being nearly impossible, incision and suctioning of fang marks generally is not recommended.9 Retained snake fangs are a possibility, and the infection could spread to a nearby joint, causing septic arthritis,10 which would be an indication for surgical intervention. Bites to the finger often cause major swelling, and the benefits of dermotomy are documented.11 Generally, early administration of antivenom will decrease local tissue reaction and prevent additional tissue loss.12 In our patient, the decision to perform dermotomy was made when the area of necrosis had declared itself and the skin reached its elastic limit. Bozkurt et al13 described the neurovascular bundles within the digit as functioning as small compartments. When the skin of the digit reaches its elastic limit, pressure within the compartment may exceed the capillary closing pressure, and the integrity of small vessels and nerves may be compromised. Our case highlights the benefit of dermotomy as well as the functional and cosmetic results that can be achieved.
Wound Care for Snakebites
There is little published on the treatment of snakebites after patients are stabilized medically for hospital discharge. Venomous snakes inject toxins that predominantly consist of enzymes (eg, phospholipase A2, phosphodiesterase, hyaluronidase, peptidase, metalloproteinase) that cause tissue destruction through diverse mechanisms.14 The venom of western pygmy rattlesnakes is hemotoxic and can cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration,4 as was the case in our patient.
Silver sulfadiazine commonly is used to prevent infection in burn patients. Given the large surface area of exposed dermis after debridement and concern for infection, silver sulfadiazine was chosen in our patient for local wound care treatment. Silver sulfadiazine is a widely available and low-cost drug.15 Its antibacterial effects are due to the silver ions, which only act superficially and therefore limit systemic absorption.16 Application should be performed in a clean manner with minimal trauma to the tissue. This technique is best achieved by using sterile gloves and applying the medication manually. A 0.0625-inch layer should be applied to entirely cover the cleaned debrided area.17 When performing application with tongue blades or cotton swabs, it is important to never “double dip.” Patient education on proper administration is imperative to a successful outcome.
Final Thoughts
Our case demonstrates the safe use of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom for the treatment of western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri) envenomation. Early administration of antivenom following pit viper rattlesnake envenomations is important to mitigate systemic effects and the extent of soft tissue damage. There are few studies on local wound care treatment after rattlesnake envenomation. This case highlights the role of dermotomy and wound care with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%.
There are 375 species of poisonous snakes, with approximately 20,000 deaths worldwide each year due to snakebites, mostly in Asia and Africa.1 The death rate in the United States is 14 to 20 cases per year. In the United States, a variety of rattlesnakes are poisonous. There are 2 genera of rattlesnakes: Sistrurus (3 species) and Crotalus (23 species). The pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Sistrurus miliarius species that is divided into 3 subspecies: the Carolina pigmy rattlesnake (S miliarius miliarius), the western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri), and the dusky pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius barbouri).2
The western pygmy rattlesnake belongs to the Crotalidae family. The rattlesnakes in this family also are known as pit vipers. All pit vipers have common characteristics for identification: triangular head, fangs, elliptical pupils, and a heat-sensing pit between the eyes. The western pygmy rattlesnake is found in Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Kentucky, and Tennessee.1 It is small bodied (15–20 inches)3 and grayish-brown, with a brown dorsal stripe with black blotches on its back. It is found in glades, second-growth forests near rock ledges, and areas where powerlines cut through dense forest.3 Its venom is hemorrhagic, causing tissue damage, but does not contain neurotoxins.4 Bites from the western pygmy rattlesnake often do not lead to death, but the venom, which contains numerous proteins and enzymes, does cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration at the site of envenomation and possible loss of digit.5,6
We present a case of a man who was bitten on the right third digit by a western pygmy rattlesnake. We describe the clinical course and treatment.
Case Report
A 56-year-old right-handed man presented to the emergency department with a rapidly swelling, painful hand following a snakebite to the dorsal aspect of the right third digit (Figure 1). He was able to capture a photograph of the snake at the time of injury, which helped identify it as a western pygmy rattlesnake (Figure 2). He also photographed the hand immediately after the bite occurred (Figure 3). Vitals on presentation included an elevated blood pressure of 161/100 mm Hg; no fever (temperature, 36.4 °C); and normal pulse oximetry of 98%, pulse of 86 beats per minute, and respiratory rate of 16 breaths per minute.



After the snakebite, the patient’s family called the Missouri Poison Center immediately. The family identified the snake species and shared this information with the poison center. Poison control recommended calling the nearest hospitals to determine if antivenom was available and make notification of arrival.
The patient’s tetanus toxoid immunization was updated immediately upon arrival. The hand was marked to monitor swelling. Initial laboratory test results revealed the following values: sodium, 133 mmol/L (reference range, 136–145 mmol/L); potassium, 3.4 mmol/L (3.6–5.2 mmol/L); lactic acid, 2.4 mmol/L (0.5–2.2 mmol/L); creatine kinase, 425 U/L (55–170 U/L); platelet count, 68/µL (150,000–450,000/µL); fibrinogen, 169 mg/dL (185–410 mg/dL); and glucose, 121 mg/dL (74–106 mg/dL). The remainder of the complete blood cell count and metabolic panel was unremarkable. Radiographs of the hand did not show any fractures, dislocations, or foreign bodies. Missouri Poison Center was consulted. Given the patient’s severe pain, edema beyond 40 cm, and developing ecchymosis on the inner arm, the bite was graded as a 3 on the traditional snakebite severity scale. Poison control recommended 4 to 6 vials of antivenom over 60 minutes. Six vials of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom were given.
The patient’s complete blood cell count remained unremarkable throughout his admission. His metabolic panel returned to normal at 6 hours postadmission: sodium, 139 mmol/L; potassium, 4.0 mmol/L. His lactate and creatinine kinase were not rechecked. His fibrinogen was trending upward. Serial laboratory test results revealed fibrinogen levels of 153, 158, 161, 159, 173, and 216 mg/dL at 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36 hours, respectively. Other laboratory test results including prothrombin time (11.0 s) and international normalized ratio (0.98) remained within reference range (11–13 s and 0.80–1.39, respectively) during serial monitoring.
The patient was hospitalized for 40 hours while waiting for his fibrinogen level to normalize. The local skin necrosis worsened acutely in this 40-hour window (Figure 4). Intravenous antibiotics were not administered during the hospital stay. Before discharge, the patient was evaluated by the surgery service, who did not recommend debridement.

Following discharge, the patient consulted a wound care expert. The area of necrosis was unroofed and debrided in the outpatient setting (Figure 5). The patient was started on oral cefalexin 500 mg twice daily for 10 days and instructed to perform twice-daily dressing changes with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%. A hand surgeon was consulted for consideration of a reverse cross-finger flap, which was not recommended. Twice-daily dressing changes for the wound—consisting of application of silver sulfadiazine cream 1% directly to the wound followed by gauze, self-adhesive soft-rolled gauze, and elastic bandages—were performed for 2 weeks.

After 2 weeks, the wound was left open to the air and cleaned with soap and water as needed. At 6 weeks, the wound was completely healed via secondary intention, except for some minor remaining ulceration at the location of the fang entry point (Figure 6). The patient had no loss of finger function or sensation.

Surgical Management of Snakebites
The surgeon’s role in managing snakebites is controversial. Snakebites were once perceived as a surgical emergency due to symptoms mimicking compartment syndrome; however, snakebites rarely cause a true compartment syndrome.7 Prophylactic bite excision and fasciotomies are not recommended. Incision and suction of the fang marks may be beneficial if performed within 15 to 30 minutes from the time of the bite.8 With access to a surgeon in this short time period being nearly impossible, incision and suctioning of fang marks generally is not recommended.9 Retained snake fangs are a possibility, and the infection could spread to a nearby joint, causing septic arthritis,10 which would be an indication for surgical intervention. Bites to the finger often cause major swelling, and the benefits of dermotomy are documented.11 Generally, early administration of antivenom will decrease local tissue reaction and prevent additional tissue loss.12 In our patient, the decision to perform dermotomy was made when the area of necrosis had declared itself and the skin reached its elastic limit. Bozkurt et al13 described the neurovascular bundles within the digit as functioning as small compartments. When the skin of the digit reaches its elastic limit, pressure within the compartment may exceed the capillary closing pressure, and the integrity of small vessels and nerves may be compromised. Our case highlights the benefit of dermotomy as well as the functional and cosmetic results that can be achieved.
Wound Care for Snakebites
There is little published on the treatment of snakebites after patients are stabilized medically for hospital discharge. Venomous snakes inject toxins that predominantly consist of enzymes (eg, phospholipase A2, phosphodiesterase, hyaluronidase, peptidase, metalloproteinase) that cause tissue destruction through diverse mechanisms.14 The venom of western pygmy rattlesnakes is hemotoxic and can cause necrotic hemorrhagic ulceration,4 as was the case in our patient.
Silver sulfadiazine commonly is used to prevent infection in burn patients. Given the large surface area of exposed dermis after debridement and concern for infection, silver sulfadiazine was chosen in our patient for local wound care treatment. Silver sulfadiazine is a widely available and low-cost drug.15 Its antibacterial effects are due to the silver ions, which only act superficially and therefore limit systemic absorption.16 Application should be performed in a clean manner with minimal trauma to the tissue. This technique is best achieved by using sterile gloves and applying the medication manually. A 0.0625-inch layer should be applied to entirely cover the cleaned debrided area.17 When performing application with tongue blades or cotton swabs, it is important to never “double dip.” Patient education on proper administration is imperative to a successful outcome.
Final Thoughts
Our case demonstrates the safe use of Crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom for the treatment of western pygmy rattlesnake (S miliarius streckeri) envenomation. Early administration of antivenom following pit viper rattlesnake envenomations is important to mitigate systemic effects and the extent of soft tissue damage. There are few studies on local wound care treatment after rattlesnake envenomation. This case highlights the role of dermotomy and wound care with silver sulfadiazine cream 1%.
- Biggers B. Management of Missouri snake bites. Mo Med. 2017;114:254-257.
- Stamm R. Sistrurus miliarius pigmy rattlesnake. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Sistrurus_miliarius/
- Missouri Department of Conservation. Western pygmy rattlesnake. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/western-pygmy-rattlesnake
- AnimalSake. Facts about the pigmy rattlesnake that are sure to surprise you. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://animalsake.com/pygmy-rattlesnake
- King AM, Crim WS, Menke NB, et al. Pygmy rattlesnake envenomation treated with crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom. Toxicon. 2012;60:1287-1289.
- Juckett G, Hancox JG. Venomous snakebites in the United States: management review and update. Am Fam Physician. 2002;65:1367-1375.
- Toschlog EA, Bauer CR, Hall EL, et al. Surgical considerations in the management of pit viper snake envenomation. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217:726-735.
- Cribari C. Management of poisonous snakebite. American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma; 2004. https://www.hartcountyga.gov/documents/PoisonousSnakebiteTreatment.pdf
- Walker JP, Morrison RL. Current management of copperhead snakebite. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:470-474.
- Gelman D, Bates T, Nuelle JAV. Septic arthritis of the proximal interphalangeal joint after rattlesnake bite. J Hand Surg Am. 2022;47:484.e1-484.e4.
- Watt CH Jr. Treatment of poisonous snakebite with emphasis on digit dermotomy. South Med J. 1985;78:694-699.
- Corneille MG, Larson S, Stewart RM, et al. A large single-center experience with treatment of patients with crotalid envenomations: outcomes with and evolution of antivenin therapy. Am J Surg. 2006;192:848-852.
- Bozkurt M, Kulahci Y, Zor F, et al. The management of pit viper envenomation of the hand. Hand (NY). 2008;3:324-331.
- Aziz H, Rhee P, Pandit V, et al. The current concepts in management of animal (dog, cat, snake, scorpion) and human bite wounds. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78:641-648.
- Hummel RP, MacMillan BG, Altemeier WA. Topical and systemic antibacterial agents in the treatment of burns. Ann Surg. 1970;172:370-384.
- Modak SM, Sampath L, Fox CL. Combined topical use of silver sulfadiazine and antibiotics as a possible solution to bacterial resistance in burn wounds. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1988;9:359-363.
- Oaks RJ, Cindass R. Silver sulfadiazine. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated January 22, 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556054/
- Biggers B. Management of Missouri snake bites. Mo Med. 2017;114:254-257.
- Stamm R. Sistrurus miliarius pigmy rattlesnake. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Sistrurus_miliarius/
- Missouri Department of Conservation. Western pygmy rattlesnake. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/western-pygmy-rattlesnake
- AnimalSake. Facts about the pigmy rattlesnake that are sure to surprise you. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://animalsake.com/pygmy-rattlesnake
- King AM, Crim WS, Menke NB, et al. Pygmy rattlesnake envenomation treated with crotalidae polyvalent immune fab antivenom. Toxicon. 2012;60:1287-1289.
- Juckett G, Hancox JG. Venomous snakebites in the United States: management review and update. Am Fam Physician. 2002;65:1367-1375.
- Toschlog EA, Bauer CR, Hall EL, et al. Surgical considerations in the management of pit viper snake envenomation. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217:726-735.
- Cribari C. Management of poisonous snakebite. American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma; 2004. https://www.hartcountyga.gov/documents/PoisonousSnakebiteTreatment.pdf
- Walker JP, Morrison RL. Current management of copperhead snakebite. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:470-474.
- Gelman D, Bates T, Nuelle JAV. Septic arthritis of the proximal interphalangeal joint after rattlesnake bite. J Hand Surg Am. 2022;47:484.e1-484.e4.
- Watt CH Jr. Treatment of poisonous snakebite with emphasis on digit dermotomy. South Med J. 1985;78:694-699.
- Corneille MG, Larson S, Stewart RM, et al. A large single-center experience with treatment of patients with crotalid envenomations: outcomes with and evolution of antivenin therapy. Am J Surg. 2006;192:848-852.
- Bozkurt M, Kulahci Y, Zor F, et al. The management of pit viper envenomation of the hand. Hand (NY). 2008;3:324-331.
- Aziz H, Rhee P, Pandit V, et al. The current concepts in management of animal (dog, cat, snake, scorpion) and human bite wounds. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78:641-648.
- Hummel RP, MacMillan BG, Altemeier WA. Topical and systemic antibacterial agents in the treatment of burns. Ann Surg. 1970;172:370-384.
- Modak SM, Sampath L, Fox CL. Combined topical use of silver sulfadiazine and antibiotics as a possible solution to bacterial resistance in burn wounds. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1988;9:359-363.
- Oaks RJ, Cindass R. Silver sulfadiazine. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated January 22, 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556054/
Practice Points
- Patients should seek medical attention immediately for western pygmy rattlesnake bites for early initiation of antivenom treatment.
- Contact the closest emergency department to confirm they are equipped to treat rattlesnake bites and notify them of a pending arrival.
- Consider dermotomy or local debridement of bites involving the digits.
- Monitor the wound in the days and weeks following the bite to ensure adequate healing.
Multiple Painless Whitish Papules on the Vulva and Perianal Region
THE DIAGNOSIS: Papular Acantholytic Dyskeratosis
Histopathology of the lesion in our patient revealed hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis of keratinocytes. The dermis showed variable chronic inflammatory cells. Corps ronds and grains in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis were identified. Hair follicles were not affected by acantholysis. Anti–desmoglein 1 and anti–desmoglein 3 serum antibodies were negative. Based on the combined clinical and histologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with papular acantholytic dyskeratosis (PAD) of the genitocrural area.
Although its typical histopathologic pattern mimics both Hailey-Hailey disease and Darier disease, PAD is a rare unique clinicopathologic entity recognized by dermatopathologists. It usually occurs in middle-aged women with no family history of similar conditions. The multiple localized, flesh-colored to whitish papules of PAD tend to coalesce into plaques in the anogenital and genitocrural regions. Plaques usually are asymptomatic but may be pruritic. Histopathologically, PAD will demonstrate hyperkeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis. Corps ronds and grains will be present in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis.1,2
The differential diagnosis for PAD includes pemphigus vegetans, Hailey-Hailey disease, Darier disease, and Grover disease. Patients usually develop pemphigus vegetans at an older age (typically 50–70 years).3 Histopathologically, it is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with an eosinophilic microabscess as well as acantholysis that involves the follicular epithelium (Figure 1),4 which were not seen in our patient. Direct immunofluorescence will show the intercellular pattern of the pemphigus group, and antidesmoglein antibodies can be detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.4,5
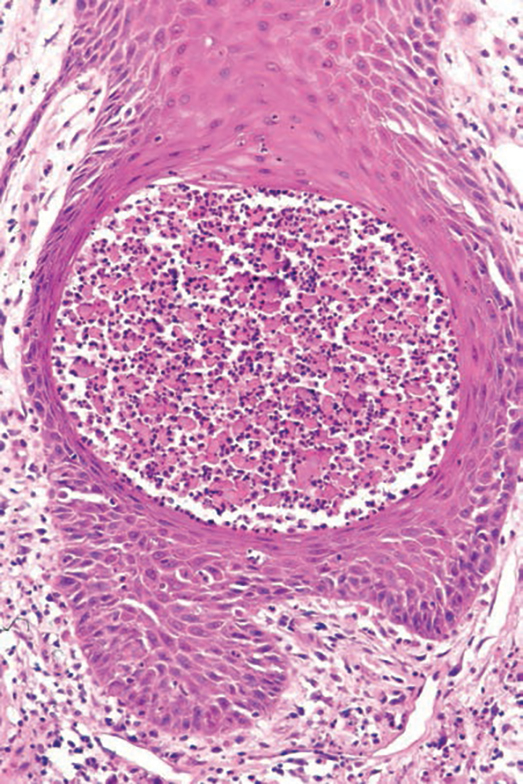
Hailey-Hailey disease (also known as benign familial pemphigus) typically manifests as itchy malodorous vesicles and erosions, especially in intertriginous areas. The most commonly affected sites are the groin, neck, under the breasts, and between the buttocks. In one study, two-thirds of affected patients reported a relevant family history.4 Histopathology will show minimal dyskeratosis and suprabasilar acantholysis with loss of intercellular bridges, classically described as resembling a dilapidated brick wall (Figure 2).4,5 There is no notable follicular involvement with acantholysis.4
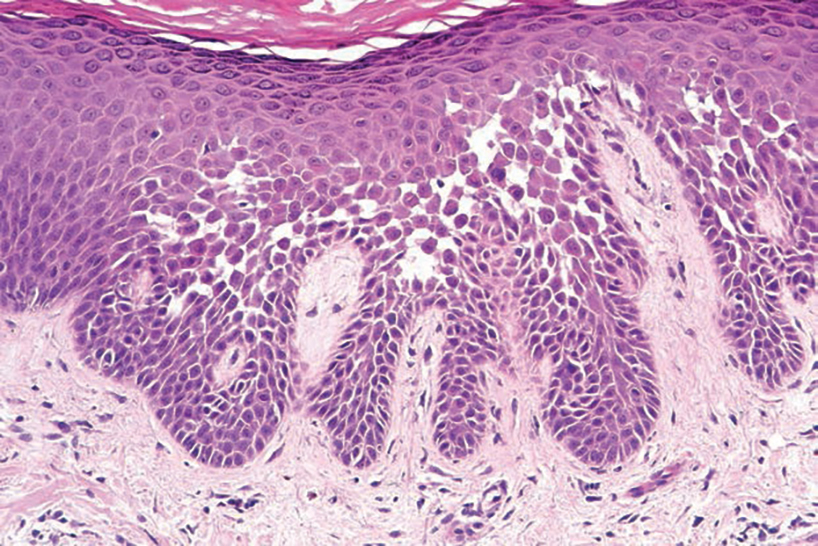
characteristic dilapidated brick wall appearance (H&E, original
magnification ×40).
Darier disease (also known as keratosis follicularis) typically is inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern.4 It is found on the seborrheic areas such as the scalp, forehead, nasolabial folds, and upper chest. Characteristic features include distal notching of the nails, mucosal lesions, and palmoplantar papules. Histopathology will reveal acantholysis, dyskeratosis, suprabasilar acantholysis, and corps ronds and grains.4 Acantholysis in Darier disease can be in discrete foci and/or widespread (Figure 3).4 Darier disease demonstrates more dyskeratosis than Hailey-Hailey disease.4,5

Grover disease (also referred to as transient acantholytic dermatosis) is observed predominantly in individuals who are middle-aged or older, though occurrence in children has been rarely reported.4 It affects the trunk, neck, and proximal limbs but spares the genital area. Histopathology may reveal acantholysis (similar to Hailey-Hailey disease or pemphigus vulgaris), dyskeratosis (resembling Darier disease), spongiosis, parakeratosis, and a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with eosinophils.4 A histologic clue to the diagnosis is small lesion size (1–3 mm). Usually, only 1 or 2 small discrete lesions that span a few rete ridges are noted (Figure 4).4 Grover disease can cause follicular or acrosyringeal involvement.4
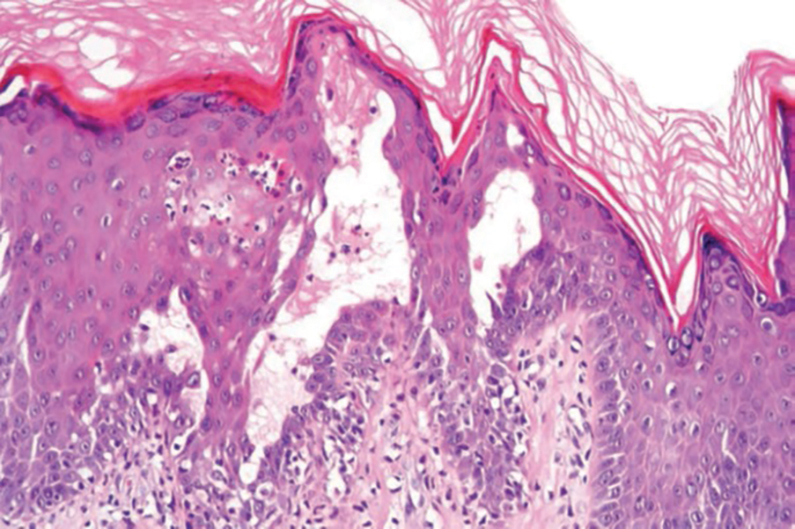
- Al-Muriesh M, Abdul-Fattah B, Wang X, et al. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the anogenital and genitocrural area: case series and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:749-758. doi:10.1111/cup.12736
- Harrell J, Nielson C, Beers P, et al. Eruption on the vulva and groin. JAAD Case Reports. 2019;6:6-8. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.11.003
- Messersmith L, Krauland K. Pemphigus vegetans. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 26, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545229
- Acantholytic disorders. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin: With Clinical Correlations. Elsevier/ Saunders; 2012:171-200.
- Mohr MR, Erdag G, Shada AL, et al. Two patients with Hailey- Hailey disease, multiple primary melanomas, and other cancers. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:211215. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.445
THE DIAGNOSIS: Papular Acantholytic Dyskeratosis
Histopathology of the lesion in our patient revealed hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis of keratinocytes. The dermis showed variable chronic inflammatory cells. Corps ronds and grains in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis were identified. Hair follicles were not affected by acantholysis. Anti–desmoglein 1 and anti–desmoglein 3 serum antibodies were negative. Based on the combined clinical and histologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with papular acantholytic dyskeratosis (PAD) of the genitocrural area.
Although its typical histopathologic pattern mimics both Hailey-Hailey disease and Darier disease, PAD is a rare unique clinicopathologic entity recognized by dermatopathologists. It usually occurs in middle-aged women with no family history of similar conditions. The multiple localized, flesh-colored to whitish papules of PAD tend to coalesce into plaques in the anogenital and genitocrural regions. Plaques usually are asymptomatic but may be pruritic. Histopathologically, PAD will demonstrate hyperkeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis. Corps ronds and grains will be present in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis.1,2
The differential diagnosis for PAD includes pemphigus vegetans, Hailey-Hailey disease, Darier disease, and Grover disease. Patients usually develop pemphigus vegetans at an older age (typically 50–70 years).3 Histopathologically, it is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with an eosinophilic microabscess as well as acantholysis that involves the follicular epithelium (Figure 1),4 which were not seen in our patient. Direct immunofluorescence will show the intercellular pattern of the pemphigus group, and antidesmoglein antibodies can be detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.4,5

Hailey-Hailey disease (also known as benign familial pemphigus) typically manifests as itchy malodorous vesicles and erosions, especially in intertriginous areas. The most commonly affected sites are the groin, neck, under the breasts, and between the buttocks. In one study, two-thirds of affected patients reported a relevant family history.4 Histopathology will show minimal dyskeratosis and suprabasilar acantholysis with loss of intercellular bridges, classically described as resembling a dilapidated brick wall (Figure 2).4,5 There is no notable follicular involvement with acantholysis.4

characteristic dilapidated brick wall appearance (H&E, original
magnification ×40).
Darier disease (also known as keratosis follicularis) typically is inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern.4 It is found on the seborrheic areas such as the scalp, forehead, nasolabial folds, and upper chest. Characteristic features include distal notching of the nails, mucosal lesions, and palmoplantar papules. Histopathology will reveal acantholysis, dyskeratosis, suprabasilar acantholysis, and corps ronds and grains.4 Acantholysis in Darier disease can be in discrete foci and/or widespread (Figure 3).4 Darier disease demonstrates more dyskeratosis than Hailey-Hailey disease.4,5

Grover disease (also referred to as transient acantholytic dermatosis) is observed predominantly in individuals who are middle-aged or older, though occurrence in children has been rarely reported.4 It affects the trunk, neck, and proximal limbs but spares the genital area. Histopathology may reveal acantholysis (similar to Hailey-Hailey disease or pemphigus vulgaris), dyskeratosis (resembling Darier disease), spongiosis, parakeratosis, and a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with eosinophils.4 A histologic clue to the diagnosis is small lesion size (1–3 mm). Usually, only 1 or 2 small discrete lesions that span a few rete ridges are noted (Figure 4).4 Grover disease can cause follicular or acrosyringeal involvement.4

THE DIAGNOSIS: Papular Acantholytic Dyskeratosis
Histopathology of the lesion in our patient revealed hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis of keratinocytes. The dermis showed variable chronic inflammatory cells. Corps ronds and grains in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis were identified. Hair follicles were not affected by acantholysis. Anti–desmoglein 1 and anti–desmoglein 3 serum antibodies were negative. Based on the combined clinical and histologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with papular acantholytic dyskeratosis (PAD) of the genitocrural area.
Although its typical histopathologic pattern mimics both Hailey-Hailey disease and Darier disease, PAD is a rare unique clinicopathologic entity recognized by dermatopathologists. It usually occurs in middle-aged women with no family history of similar conditions. The multiple localized, flesh-colored to whitish papules of PAD tend to coalesce into plaques in the anogenital and genitocrural regions. Plaques usually are asymptomatic but may be pruritic. Histopathologically, PAD will demonstrate hyperkeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis. Corps ronds and grains will be present in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis.1,2
The differential diagnosis for PAD includes pemphigus vegetans, Hailey-Hailey disease, Darier disease, and Grover disease. Patients usually develop pemphigus vegetans at an older age (typically 50–70 years).3 Histopathologically, it is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with an eosinophilic microabscess as well as acantholysis that involves the follicular epithelium (Figure 1),4 which were not seen in our patient. Direct immunofluorescence will show the intercellular pattern of the pemphigus group, and antidesmoglein antibodies can be detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.4,5

Hailey-Hailey disease (also known as benign familial pemphigus) typically manifests as itchy malodorous vesicles and erosions, especially in intertriginous areas. The most commonly affected sites are the groin, neck, under the breasts, and between the buttocks. In one study, two-thirds of affected patients reported a relevant family history.4 Histopathology will show minimal dyskeratosis and suprabasilar acantholysis with loss of intercellular bridges, classically described as resembling a dilapidated brick wall (Figure 2).4,5 There is no notable follicular involvement with acantholysis.4

characteristic dilapidated brick wall appearance (H&E, original
magnification ×40).
Darier disease (also known as keratosis follicularis) typically is inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern.4 It is found on the seborrheic areas such as the scalp, forehead, nasolabial folds, and upper chest. Characteristic features include distal notching of the nails, mucosal lesions, and palmoplantar papules. Histopathology will reveal acantholysis, dyskeratosis, suprabasilar acantholysis, and corps ronds and grains.4 Acantholysis in Darier disease can be in discrete foci and/or widespread (Figure 3).4 Darier disease demonstrates more dyskeratosis than Hailey-Hailey disease.4,5

Grover disease (also referred to as transient acantholytic dermatosis) is observed predominantly in individuals who are middle-aged or older, though occurrence in children has been rarely reported.4 It affects the trunk, neck, and proximal limbs but spares the genital area. Histopathology may reveal acantholysis (similar to Hailey-Hailey disease or pemphigus vulgaris), dyskeratosis (resembling Darier disease), spongiosis, parakeratosis, and a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with eosinophils.4 A histologic clue to the diagnosis is small lesion size (1–3 mm). Usually, only 1 or 2 small discrete lesions that span a few rete ridges are noted (Figure 4).4 Grover disease can cause follicular or acrosyringeal involvement.4

- Al-Muriesh M, Abdul-Fattah B, Wang X, et al. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the anogenital and genitocrural area: case series and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:749-758. doi:10.1111/cup.12736
- Harrell J, Nielson C, Beers P, et al. Eruption on the vulva and groin. JAAD Case Reports. 2019;6:6-8. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.11.003
- Messersmith L, Krauland K. Pemphigus vegetans. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 26, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545229
- Acantholytic disorders. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin: With Clinical Correlations. Elsevier/ Saunders; 2012:171-200.
- Mohr MR, Erdag G, Shada AL, et al. Two patients with Hailey- Hailey disease, multiple primary melanomas, and other cancers. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:211215. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.445
- Al-Muriesh M, Abdul-Fattah B, Wang X, et al. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the anogenital and genitocrural area: case series and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:749-758. doi:10.1111/cup.12736
- Harrell J, Nielson C, Beers P, et al. Eruption on the vulva and groin. JAAD Case Reports. 2019;6:6-8. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.11.003
- Messersmith L, Krauland K. Pemphigus vegetans. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 26, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545229
- Acantholytic disorders. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin: With Clinical Correlations. Elsevier/ Saunders; 2012:171-200.
- Mohr MR, Erdag G, Shada AL, et al. Two patients with Hailey- Hailey disease, multiple primary melanomas, and other cancers. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:211215. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.445
A 21-year-old woman presented with a chronic eruption in the anogenital region of 4 years’ duration. Clinical examination revealed numerous painless, mildly itchy, malodorous, whitish papules on an erythematous base that were distributed on the vulva and perianal region. There were no erosions, and no other areas were involved. Routine laboratory tests were within reference range. The patient had no sexual partner and no family history of similar lesions. A skin biopsy was performed.
Investigational Med for Tourette Syndrome Promising
PHILADELPHIA — , results of a new analysis suggest.
As previously reported, the first-in-class dopamine-1 (D1) receptor antagonist reduced the primary endpoint of tic severity scores by 30% compared with placebo among 149 patients in the 12-week, phase 2b D1AMOND trial.
What was unknown, however, is whether ecopipam would affect the comorbidities of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and depression that were present in two thirds of participants.
The two key findings in this post hoc analysis were “first, that patients with a nonmotor diagnosis like depression or ADHD did not do any worse in terms of tic efficacy; and second, we didn’t find any evidence that any of the nonmotor symptoms of Tourette’s got worse with ecopipam,” said study investigator Donald Gilbert, MD, professor of pediatrics and neurology at University of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Dr. Gilbert presented the results at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders (MDS) 2024.
No Worsening of ADHD Symptoms
Tourette syndrome affects approximately 1 in 160 children between 5 and 17 years of age in the United States, data from the Tourette Association of America show. Research has shown that 85% of patients with Tourette syndrome will have a co-occurring psychiatric condition.
Guidelines recommend Comprehensive Behavioral Intervention for Tics (CBIT) as first-line treatment for Tourette syndrome, but cost and access are barriers. The only currently approved medications to treat Tourette syndrome are antipsychotics that act on the D2 receptor, but their use is limited by the potential for weight gain, metabolic changes, drug-induced movement disorders, and risk for suicidality, said Dr. Gilbert.
The D1AMOND study randomly assigned patients aged 6-17 years with Tourette syndrome and a Yale Global Tic Severity Total Tic Scale score of at least 20 to receive a target steady-state dose of 2 mg/kg/d of oral ecopipam or placebo for a 4-week titration period, followed by an 8-week treatment phase before being tapered off the study drug.
Patients were allowed to remain on medications without D2-receptor blocking activity for anxiety, OCD, and ADHD if the dosage was stable for 4 weeks before screening and not specifically prescribed for tics.
A mixed model for repeated measures was used to assess changes in several scales administered at baseline and at weeks 4, 6, 8, and 12: the Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham Teacher and Parent Rating Scale (SNAP-IV); Pediatric Anxiety Rating Scale; Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale (CY-BOCS), and Children’s Depression Rating Scale–Revised (CDRS-R).
In patients with a co-occurring psychiatric condition, no significant differences were found over time between ecopipam and placebo in terms of SNAP-IV (-4.4; P = .45), Pediatric Anxiety Rating Scale (1.0; P = .62), CDRS-R (-3.2; P = .65), or CY-BOCS (-0.7; P = .76) scores.
For ADHD, the most frequent comorbidity, scores trended lower in the ecopipam group but were not significantly different from those in the placebo group. “We found no evidence that ecopipam worsened ADHD symptoms,” Dr. Gilbert said.
No Weight Gain
Suicidal ideation was reported during the dosing period in eight patients in the placebo group and none in the ecopipam group. One patient treated with ecopipam had multiple depressive episodes and dropped out of the study on day 79. Ecopipam was discontinued in another patient because of anxiety.
Notably, there was more weight gain in the placebo group than in the ecopipam group (2.4 kg vs 1.8 kg) by 12 weeks. No shifts from baseline were seen in blood glucose, A1c, total cholesterol, or triglycerides in either group.
The lack of weight gain with ecopipam is important, Dr. Gilbert stressed. “Medicines that block D2 so often cause weight gain, and a lot of our patients, unfortunately, can be heavier already,” he explained. “We don’t want to make that worse or put them at a long-term risk of type 2 diabetes.”
For patients with more severe disease, we really “do need something else besides D2-blockers in our tool kit,” he added.
Commenting on the study, Tanya Simuni, MD, co-moderator of the session and director of the Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center, Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said the aim of assessing D1-directed medications is to reduce the negative impact of traditional antipsychotics with a theoretical benefit on hyperkinetic movement.
But the most important thing that they’ve shown is that “there was no negative effect, no liability for the nonmotor manifestations of Tourette’s. That is important because Tourette’s is not a pure motor syndrome, and psychiatric manifestations in a lot of cases are associated with more disease-related quality of life impairment compared to the motor manifestations,” said Dr. Simuni.
That said, she noted, the “ideal drug would be the one that would have benefit for both motor and nonmotor domains.”
Multiple Agents in the Pipeline
“The neuropharmacology of Tourette syndrome has long remained stagnant, and most existing treatments often fail to balance efficacy with tolerability, underscoring the urgent need for newer therapeutics,” Christos Ganos, MD, professor of neurology, University of Toronto, said in a press release.
He noted that three studies have been published on ecopipam since 2014: an 8-week, open-label trial in adults with Tourette syndrome, a 4-week, placebo-controlled crossover trial in 38 children with Tourette syndrome, and the 12-week D1AMOND trial.
“These studies demonstrated clinically meaningful reductions in tics, without relevant safety concerns or changes in Tourette syndrome-typical neuropsychiatric measures, as also shown by the abstract highlighted here,” Dr. Ganos said.
“This emerging body of research provides a solid foundation for introducing ecopipam as a novel pharmacological agent to treat tics and may motivate further work, both on the pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy of tic disorders and their associations.”
A single-arm, phase 3 trial is currently underway at 58 centers in North America and Europe investigating the long-term safety and tolerability of ecopipam over 24 months in 150 children, adolescents, and adults with Tourette syndrome. The study is expected to be completed in 2027.
Several other new medications are also under investigation including the vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT2) inhibitors tetrabenazine, deutetrabenazine, and valbenazine; the PEDE10A inhibitor gemlapodect; the allopregnanolone antagonist sepranolone; and SCI-110, which combines dronabinol (the synthetic form of tetrahydrocannabinol) and the endocannabinoid palmitoylethanolamide.
The study was funded by Emalex Biosciences. Dr. Gilbert’s institution received research support from Emalex Biosciences and PTC Therapeutics. Dr. Gilbert has received publishing royalties from a healthcare-related publication; compensation for serving as a medical expert with Teladoc; Advanced Medical; and the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program, US Department of Health and Human Services. Simuni reports no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Ganos has received honoraria for educational activities from the Movement Disorder Society and academic research support from VolkswagenStiftung.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — , results of a new analysis suggest.
As previously reported, the first-in-class dopamine-1 (D1) receptor antagonist reduced the primary endpoint of tic severity scores by 30% compared with placebo among 149 patients in the 12-week, phase 2b D1AMOND trial.
What was unknown, however, is whether ecopipam would affect the comorbidities of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and depression that were present in two thirds of participants.
The two key findings in this post hoc analysis were “first, that patients with a nonmotor diagnosis like depression or ADHD did not do any worse in terms of tic efficacy; and second, we didn’t find any evidence that any of the nonmotor symptoms of Tourette’s got worse with ecopipam,” said study investigator Donald Gilbert, MD, professor of pediatrics and neurology at University of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Dr. Gilbert presented the results at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders (MDS) 2024.
No Worsening of ADHD Symptoms
Tourette syndrome affects approximately 1 in 160 children between 5 and 17 years of age in the United States, data from the Tourette Association of America show. Research has shown that 85% of patients with Tourette syndrome will have a co-occurring psychiatric condition.
Guidelines recommend Comprehensive Behavioral Intervention for Tics (CBIT) as first-line treatment for Tourette syndrome, but cost and access are barriers. The only currently approved medications to treat Tourette syndrome are antipsychotics that act on the D2 receptor, but their use is limited by the potential for weight gain, metabolic changes, drug-induced movement disorders, and risk for suicidality, said Dr. Gilbert.
The D1AMOND study randomly assigned patients aged 6-17 years with Tourette syndrome and a Yale Global Tic Severity Total Tic Scale score of at least 20 to receive a target steady-state dose of 2 mg/kg/d of oral ecopipam or placebo for a 4-week titration period, followed by an 8-week treatment phase before being tapered off the study drug.
Patients were allowed to remain on medications without D2-receptor blocking activity for anxiety, OCD, and ADHD if the dosage was stable for 4 weeks before screening and not specifically prescribed for tics.
A mixed model for repeated measures was used to assess changes in several scales administered at baseline and at weeks 4, 6, 8, and 12: the Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham Teacher and Parent Rating Scale (SNAP-IV); Pediatric Anxiety Rating Scale; Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale (CY-BOCS), and Children’s Depression Rating Scale–Revised (CDRS-R).
In patients with a co-occurring psychiatric condition, no significant differences were found over time between ecopipam and placebo in terms of SNAP-IV (-4.4; P = .45), Pediatric Anxiety Rating Scale (1.0; P = .62), CDRS-R (-3.2; P = .65), or CY-BOCS (-0.7; P = .76) scores.
For ADHD, the most frequent comorbidity, scores trended lower in the ecopipam group but were not significantly different from those in the placebo group. “We found no evidence that ecopipam worsened ADHD symptoms,” Dr. Gilbert said.
No Weight Gain
Suicidal ideation was reported during the dosing period in eight patients in the placebo group and none in the ecopipam group. One patient treated with ecopipam had multiple depressive episodes and dropped out of the study on day 79. Ecopipam was discontinued in another patient because of anxiety.
Notably, there was more weight gain in the placebo group than in the ecopipam group (2.4 kg vs 1.8 kg) by 12 weeks. No shifts from baseline were seen in blood glucose, A1c, total cholesterol, or triglycerides in either group.
The lack of weight gain with ecopipam is important, Dr. Gilbert stressed. “Medicines that block D2 so often cause weight gain, and a lot of our patients, unfortunately, can be heavier already,” he explained. “We don’t want to make that worse or put them at a long-term risk of type 2 diabetes.”
For patients with more severe disease, we really “do need something else besides D2-blockers in our tool kit,” he added.
Commenting on the study, Tanya Simuni, MD, co-moderator of the session and director of the Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center, Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said the aim of assessing D1-directed medications is to reduce the negative impact of traditional antipsychotics with a theoretical benefit on hyperkinetic movement.
But the most important thing that they’ve shown is that “there was no negative effect, no liability for the nonmotor manifestations of Tourette’s. That is important because Tourette’s is not a pure motor syndrome, and psychiatric manifestations in a lot of cases are associated with more disease-related quality of life impairment compared to the motor manifestations,” said Dr. Simuni.
That said, she noted, the “ideal drug would be the one that would have benefit for both motor and nonmotor domains.”
Multiple Agents in the Pipeline
“The neuropharmacology of Tourette syndrome has long remained stagnant, and most existing treatments often fail to balance efficacy with tolerability, underscoring the urgent need for newer therapeutics,” Christos Ganos, MD, professor of neurology, University of Toronto, said in a press release.
He noted that three studies have been published on ecopipam since 2014: an 8-week, open-label trial in adults with Tourette syndrome, a 4-week, placebo-controlled crossover trial in 38 children with Tourette syndrome, and the 12-week D1AMOND trial.
“These studies demonstrated clinically meaningful reductions in tics, without relevant safety concerns or changes in Tourette syndrome-typical neuropsychiatric measures, as also shown by the abstract highlighted here,” Dr. Ganos said.
“This emerging body of research provides a solid foundation for introducing ecopipam as a novel pharmacological agent to treat tics and may motivate further work, both on the pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy of tic disorders and their associations.”
A single-arm, phase 3 trial is currently underway at 58 centers in North America and Europe investigating the long-term safety and tolerability of ecopipam over 24 months in 150 children, adolescents, and adults with Tourette syndrome. The study is expected to be completed in 2027.
Several other new medications are also under investigation including the vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT2) inhibitors tetrabenazine, deutetrabenazine, and valbenazine; the PEDE10A inhibitor gemlapodect; the allopregnanolone antagonist sepranolone; and SCI-110, which combines dronabinol (the synthetic form of tetrahydrocannabinol) and the endocannabinoid palmitoylethanolamide.
The study was funded by Emalex Biosciences. Dr. Gilbert’s institution received research support from Emalex Biosciences and PTC Therapeutics. Dr. Gilbert has received publishing royalties from a healthcare-related publication; compensation for serving as a medical expert with Teladoc; Advanced Medical; and the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program, US Department of Health and Human Services. Simuni reports no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Ganos has received honoraria for educational activities from the Movement Disorder Society and academic research support from VolkswagenStiftung.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — , results of a new analysis suggest.
As previously reported, the first-in-class dopamine-1 (D1) receptor antagonist reduced the primary endpoint of tic severity scores by 30% compared with placebo among 149 patients in the 12-week, phase 2b D1AMOND trial.
What was unknown, however, is whether ecopipam would affect the comorbidities of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and depression that were present in two thirds of participants.
The two key findings in this post hoc analysis were “first, that patients with a nonmotor diagnosis like depression or ADHD did not do any worse in terms of tic efficacy; and second, we didn’t find any evidence that any of the nonmotor symptoms of Tourette’s got worse with ecopipam,” said study investigator Donald Gilbert, MD, professor of pediatrics and neurology at University of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Dr. Gilbert presented the results at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders (MDS) 2024.
No Worsening of ADHD Symptoms
Tourette syndrome affects approximately 1 in 160 children between 5 and 17 years of age in the United States, data from the Tourette Association of America show. Research has shown that 85% of patients with Tourette syndrome will have a co-occurring psychiatric condition.
Guidelines recommend Comprehensive Behavioral Intervention for Tics (CBIT) as first-line treatment for Tourette syndrome, but cost and access are barriers. The only currently approved medications to treat Tourette syndrome are antipsychotics that act on the D2 receptor, but their use is limited by the potential for weight gain, metabolic changes, drug-induced movement disorders, and risk for suicidality, said Dr. Gilbert.
The D1AMOND study randomly assigned patients aged 6-17 years with Tourette syndrome and a Yale Global Tic Severity Total Tic Scale score of at least 20 to receive a target steady-state dose of 2 mg/kg/d of oral ecopipam or placebo for a 4-week titration period, followed by an 8-week treatment phase before being tapered off the study drug.
Patients were allowed to remain on medications without D2-receptor blocking activity for anxiety, OCD, and ADHD if the dosage was stable for 4 weeks before screening and not specifically prescribed for tics.
A mixed model for repeated measures was used to assess changes in several scales administered at baseline and at weeks 4, 6, 8, and 12: the Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham Teacher and Parent Rating Scale (SNAP-IV); Pediatric Anxiety Rating Scale; Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale (CY-BOCS), and Children’s Depression Rating Scale–Revised (CDRS-R).
In patients with a co-occurring psychiatric condition, no significant differences were found over time between ecopipam and placebo in terms of SNAP-IV (-4.4; P = .45), Pediatric Anxiety Rating Scale (1.0; P = .62), CDRS-R (-3.2; P = .65), or CY-BOCS (-0.7; P = .76) scores.
For ADHD, the most frequent comorbidity, scores trended lower in the ecopipam group but were not significantly different from those in the placebo group. “We found no evidence that ecopipam worsened ADHD symptoms,” Dr. Gilbert said.
No Weight Gain
Suicidal ideation was reported during the dosing period in eight patients in the placebo group and none in the ecopipam group. One patient treated with ecopipam had multiple depressive episodes and dropped out of the study on day 79. Ecopipam was discontinued in another patient because of anxiety.
Notably, there was more weight gain in the placebo group than in the ecopipam group (2.4 kg vs 1.8 kg) by 12 weeks. No shifts from baseline were seen in blood glucose, A1c, total cholesterol, or triglycerides in either group.
The lack of weight gain with ecopipam is important, Dr. Gilbert stressed. “Medicines that block D2 so often cause weight gain, and a lot of our patients, unfortunately, can be heavier already,” he explained. “We don’t want to make that worse or put them at a long-term risk of type 2 diabetes.”
For patients with more severe disease, we really “do need something else besides D2-blockers in our tool kit,” he added.
Commenting on the study, Tanya Simuni, MD, co-moderator of the session and director of the Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center, Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said the aim of assessing D1-directed medications is to reduce the negative impact of traditional antipsychotics with a theoretical benefit on hyperkinetic movement.
But the most important thing that they’ve shown is that “there was no negative effect, no liability for the nonmotor manifestations of Tourette’s. That is important because Tourette’s is not a pure motor syndrome, and psychiatric manifestations in a lot of cases are associated with more disease-related quality of life impairment compared to the motor manifestations,” said Dr. Simuni.
That said, she noted, the “ideal drug would be the one that would have benefit for both motor and nonmotor domains.”
Multiple Agents in the Pipeline
“The neuropharmacology of Tourette syndrome has long remained stagnant, and most existing treatments often fail to balance efficacy with tolerability, underscoring the urgent need for newer therapeutics,” Christos Ganos, MD, professor of neurology, University of Toronto, said in a press release.
He noted that three studies have been published on ecopipam since 2014: an 8-week, open-label trial in adults with Tourette syndrome, a 4-week, placebo-controlled crossover trial in 38 children with Tourette syndrome, and the 12-week D1AMOND trial.
“These studies demonstrated clinically meaningful reductions in tics, without relevant safety concerns or changes in Tourette syndrome-typical neuropsychiatric measures, as also shown by the abstract highlighted here,” Dr. Ganos said.
“This emerging body of research provides a solid foundation for introducing ecopipam as a novel pharmacological agent to treat tics and may motivate further work, both on the pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy of tic disorders and their associations.”
A single-arm, phase 3 trial is currently underway at 58 centers in North America and Europe investigating the long-term safety and tolerability of ecopipam over 24 months in 150 children, adolescents, and adults with Tourette syndrome. The study is expected to be completed in 2027.
Several other new medications are also under investigation including the vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT2) inhibitors tetrabenazine, deutetrabenazine, and valbenazine; the PEDE10A inhibitor gemlapodect; the allopregnanolone antagonist sepranolone; and SCI-110, which combines dronabinol (the synthetic form of tetrahydrocannabinol) and the endocannabinoid palmitoylethanolamide.
The study was funded by Emalex Biosciences. Dr. Gilbert’s institution received research support from Emalex Biosciences and PTC Therapeutics. Dr. Gilbert has received publishing royalties from a healthcare-related publication; compensation for serving as a medical expert with Teladoc; Advanced Medical; and the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program, US Department of Health and Human Services. Simuni reports no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Ganos has received honoraria for educational activities from the Movement Disorder Society and academic research support from VolkswagenStiftung.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MDS 2024
New Guidelines Emphasize Liver Care in T2D, Obesity
MADRID — Individuals with type 2 diabetes and/or obesity plus one or more metabolic risk factors are at a higher risk for metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) with fibrosis and progression to more severe liver disease, stated new European guidelines that provide recommendations for diagnosis and management.
“The availability of improved treatment options underlines the need to identify at-risk individuals with MASLD early, as we now possess the tools to positively influence the course of the diseases, which is expected to prevent relevant clinical events,” stated the clinical practice guidelines, updated for the first time since 2016.
“Now we have guidelines that tell clinicians how to monitor the liver,” said Amalia Gastaldelli, PhD, research director at the Institute of Clinical Physiology of the National Research Council in Pisa, Italy, and a member of the panel that developed the guidelines.
Dr. Gastaldelli moderated a session focused on the guidelines at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). In an interview after the session, Dr. Gastaldelli, who leads a cardiometabolic risk research group, stressed the importance of the liver’s role in the body and the need for diabetes specialists to start paying more attention to this vital organ.
“It’s an important organ for monitoring because liver disease is silent, and the patient doesn’t feel unwell until disease is severe,” she said. “Diabetologists already monitor the eye, the heart, the kidney, and so on, but the liver is often neglected,” she said. A 2024 study found that the global pooled prevalence of MASLD among patients with type 2 diabetes was 65.33%.
Dr. Gastaldelli noted the importance of liver status in diabetes care. The liver makes triglycerides and very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, which are all major risk factors for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease (CVD), she said, as well as producing glucose, which in excess can lead to hyperglycemia.
The guidelines were jointly written by EASD, the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and the European Association for the Study of Obesity, and published in Diabetologia, The Journal of Hepatology, and Obesity Facts.
A Metabolic Condition
In the EASD meeting session, Dr. Gastaldelli discussed the reasons for, and implications of, shifting the name from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) to MASLD.
“The name change focuses on the fact that this is a metabolic disease, while NAFLD had no mention of this and was considered stigmatizing by patients, especially in relation to the words ‘fatty’ and ‘nonalcoholic,’” she said.
According to the guidelines, MASLD is defined as liver steatosis in the presence of one or more cardiometabolic risk factor(s) and the absence of excess alcohol intake.
MASLD has become the most common chronic liver disease and includes isolated steatosis, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH, previously NASH), MASH-related fibrosis, and cirrhosis.
In the overarching group of steatotic liver disease, a totally new intermediate category has been added: MASLD with moderate (increased) alcohol intake (MetALD), which represents MASLD in people who consume greater amounts of alcohol per week (140-350 g/week and 210-420 g/week for women and men, respectively).
The change in the nomenclature has been incremental and regional, Dr. Gastaldelli said. “The definition first changed from NAFLD to MAFLD, which recognizes the importance of metabolism in the pathophysiology of this disease but does not take into account alcohol intake. MAFLD is still used in Asia, Australasia, and North Africa, while Europe and the Americas have endorsed MASLD.”
Case-Finding and Diagnosis
Identifying MASLD cases in people at risk remains incidental, largely because it is a silent disease and is symptom-free until it becomes severe, said Dr. Gastaldelli.
The guideline recognizes that individuals with type 2 diabetes or obesity with additional metabolic risk factor(s) are at a higher risk for MASLD with fibrosis and progression to MASH.
Assessment strategies for severe liver fibrosis in MASLD include the use of noninvasive tests in people who have cardiometabolic risk factors, abnormal liver enzymes, and/or radiological signs of hepatic steatosis, particularly in the presence of type 2 diabetes or obesity or in the presence of one or more metabolic risk factors.
Dr. Gastaldelli noted that type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity, including abdominal obesity identified by large waist circumference, are the major risk factors and should be warning signs.
“We need to consider abdominal obesity too — we’ve published data in relatively lean people, body mass index < 25, with MASH but without diabetes. Most of the patients accumulated fat viscerally and in the liver and had hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia,” she said.
“The guidelines reflect this because the definition of MASLD includes steatosis plus at least one metabolic factor — waist circumference, for example, which is related to visceral fat, hyperlipidemia, or hyperglycemia. Of note, in both pharmacological and diet-induced weight loss, the decrease in liver fat was associated with the decrease in visceral fat.”
The noninvasive biomarker test, Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) may be used to assess the risk for liver fibrosis. The FIB-4 index is calculated using a patient’s age and results of three blood tests — aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and platelet count.
Advanced fibrosis (grade F3-F4) “is a major risk factor for severe outcomes,” said Dr. Gastaldelli. A FIB-4 test result below 1.3 indicates low risk for advanced liver fibrosis, 1.30-2.67 indicates intermediate risk, and above 2.67 indicates high risk.
“When fibrosis increases, then liver enzymes increase and the platelets decrease,” said Dr. Gastaldelli. “It is not a perfect tool, and we need to add in age because at a young age, it is prone to false negatives and when very old — false positives. It’s important to take a global view, especially if the patient has persistent high liver enzymes, but FIB-4 is low.”
“And if they have more than one metabolic risk factor, proceed with more tests, for example, transient elastography,” she advised. Imaging techniques such as transient elastography may rule out or rule in advanced fibrosis, which is predictive of liver-related outcomes.
“However, imaging techniques only diagnose steatosis and fibrosis, and right now, MASH can only be diagnosed with liver biopsy because we do not have any markers of liver inflammation and ballooning. In the future, noninvasive tests based on imaging and blood tests will be used to identify patients with MASH,” she added.
Management of MASLD — Lifestyle and Treatment
“Pharmacological treatments are designed for [patients] with MASH and fibrosis grade F2 or F3, but not MASLD,” Dr. Gastaldelli said. As such, lifestyle interventions are the mainstay of management — including weight loss, dietary changes, physical exercise, and low to no alcohol consumption. “Eating good-quality food and reducing calories are both important because the metabolism responds differently to different nutrients,” Dr. Gastaldelli said.
“In particular, the guidelines advise dietary management because some foods carry liver toxicity, for example, sugary foods with sucrose/fructose especially,” she said, adding that, “complex carbohydrates are less harmful than refined carbohydrates. Processed foods should be avoided if possible because they contain sugars, [as well as] saturated fats and hydrogenated fat, which is particularly bad for the liver. Olive oil is better than butter or margarine, which are rich in saturated fat, and fish and white meat are preferable.”
She added that a diet to help manage type 2 diabetes was not so dissimilar because sugar again needs to be reduced.
If a patient has severe obesity (and MASLD), data show that bariatric surgery is beneficial. “It not only helps weight loss, but it improves liver histology and has been shown to improve or resolve type 2 diabetes and reduce CVD risk. Importantly, regarding fibrosis, nutritional management after the bariatric surgery is the most important thing,” said Dr. Gastaldelli.
Optimal management of comorbidities — including the use of incretin-based therapies such as semaglutide or tirzepatide for type 2 diabetes or obesity, if indicated — is advised, according to the guidelines.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have been shown to have a beneficial effect on MASH, said Dr. Gastaldelli. “They have not shown effectiveness in the resolution of fibrosis, but this might take longer to manifest. However, if the medication is started early enough, it may prevent severe fibrosis. Significant weight loss, both with lifestyle and pharmacological treatment, should lead to an improvement in the liver too.”
There are currently no drugs available in Europe for the treatment of noncirrhotic MASH and severe fibrosis (stage ≥ 2). Resmetirom is the first approved MASH-targeted treatment in noncirrhotic MASH and significant liver fibrosis, with histological effectiveness on steatohepatitis and fibrosis, together with an acceptable safety and tolerability profile, but, for the moment, this agent is only available in United States.
Finally, turning to MASH-related cirrhosis, the guidelines advise adaptations of metabolic drugs, nutritional counseling, and surveillance for portal hypertension and hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as liver transplantation in decompensated cirrhosis.
After the session, this news organization spoke to Tushy Kailayanathan, MBBS BSc, medical director of the liver MRI company, Perspectum, who reviewed the limitations of the FIB-4 test. The FIB-4 test identifies those with advanced fibrosis in the liver, for example, patients with hepatitis C, she noted; however, “it performs worse in type 2 diabetic patients and in the elderly. There is little clinical guidance on the adjustment of FIB-4 thresholds needed for these high cardiometabolic risk groups. The priority patients are missed by FIB-4 because those individuals with early and active disease may not yet have progressed to advanced disease detected by FIB-4.”
These individuals are exactly those amenable to primary care prevention strategies, said Dr. Kailayanathan. Because of the nature of early and active liver disease in patients with high cardiometabolic risk, it would make sense to shift some diagnostic protocols into primary care.
“These individuals are exactly those amenable to primary care prevention strategies at annual diabetic review because they are likely to have modifiable cardiometabolic risk factors such as metabolic syndrome and would benefit from lifestyle and therapeutic intervention, including GLP-1 RAs and SGLT2is [sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors],” she said. “Case-finding and detection of early-stage MASLD is a priority in diabetics, and there is an unmet need for accurate biomarkers to measure liver fat and inflammation early.”
Dr. Gastaldelli has been on the advisory board or consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Fractyl, Pfizer, Merck-MSD, MetaDeq and a speaker for Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. Dr. Kailayanathan is medical director at Perspectum, a UK-based company involved in liver imaging technology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID — Individuals with type 2 diabetes and/or obesity plus one or more metabolic risk factors are at a higher risk for metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) with fibrosis and progression to more severe liver disease, stated new European guidelines that provide recommendations for diagnosis and management.
“The availability of improved treatment options underlines the need to identify at-risk individuals with MASLD early, as we now possess the tools to positively influence the course of the diseases, which is expected to prevent relevant clinical events,” stated the clinical practice guidelines, updated for the first time since 2016.
“Now we have guidelines that tell clinicians how to monitor the liver,” said Amalia Gastaldelli, PhD, research director at the Institute of Clinical Physiology of the National Research Council in Pisa, Italy, and a member of the panel that developed the guidelines.
Dr. Gastaldelli moderated a session focused on the guidelines at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). In an interview after the session, Dr. Gastaldelli, who leads a cardiometabolic risk research group, stressed the importance of the liver’s role in the body and the need for diabetes specialists to start paying more attention to this vital organ.
“It’s an important organ for monitoring because liver disease is silent, and the patient doesn’t feel unwell until disease is severe,” she said. “Diabetologists already monitor the eye, the heart, the kidney, and so on, but the liver is often neglected,” she said. A 2024 study found that the global pooled prevalence of MASLD among patients with type 2 diabetes was 65.33%.
Dr. Gastaldelli noted the importance of liver status in diabetes care. The liver makes triglycerides and very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, which are all major risk factors for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease (CVD), she said, as well as producing glucose, which in excess can lead to hyperglycemia.
The guidelines were jointly written by EASD, the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and the European Association for the Study of Obesity, and published in Diabetologia, The Journal of Hepatology, and Obesity Facts.
A Metabolic Condition
In the EASD meeting session, Dr. Gastaldelli discussed the reasons for, and implications of, shifting the name from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) to MASLD.
“The name change focuses on the fact that this is a metabolic disease, while NAFLD had no mention of this and was considered stigmatizing by patients, especially in relation to the words ‘fatty’ and ‘nonalcoholic,’” she said.
According to the guidelines, MASLD is defined as liver steatosis in the presence of one or more cardiometabolic risk factor(s) and the absence of excess alcohol intake.
MASLD has become the most common chronic liver disease and includes isolated steatosis, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH, previously NASH), MASH-related fibrosis, and cirrhosis.
In the overarching group of steatotic liver disease, a totally new intermediate category has been added: MASLD with moderate (increased) alcohol intake (MetALD), which represents MASLD in people who consume greater amounts of alcohol per week (140-350 g/week and 210-420 g/week for women and men, respectively).
The change in the nomenclature has been incremental and regional, Dr. Gastaldelli said. “The definition first changed from NAFLD to MAFLD, which recognizes the importance of metabolism in the pathophysiology of this disease but does not take into account alcohol intake. MAFLD is still used in Asia, Australasia, and North Africa, while Europe and the Americas have endorsed MASLD.”
Case-Finding and Diagnosis
Identifying MASLD cases in people at risk remains incidental, largely because it is a silent disease and is symptom-free until it becomes severe, said Dr. Gastaldelli.
The guideline recognizes that individuals with type 2 diabetes or obesity with additional metabolic risk factor(s) are at a higher risk for MASLD with fibrosis and progression to MASH.
Assessment strategies for severe liver fibrosis in MASLD include the use of noninvasive tests in people who have cardiometabolic risk factors, abnormal liver enzymes, and/or radiological signs of hepatic steatosis, particularly in the presence of type 2 diabetes or obesity or in the presence of one or more metabolic risk factors.
Dr. Gastaldelli noted that type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity, including abdominal obesity identified by large waist circumference, are the major risk factors and should be warning signs.
“We need to consider abdominal obesity too — we’ve published data in relatively lean people, body mass index < 25, with MASH but without diabetes. Most of the patients accumulated fat viscerally and in the liver and had hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia,” she said.
“The guidelines reflect this because the definition of MASLD includes steatosis plus at least one metabolic factor — waist circumference, for example, which is related to visceral fat, hyperlipidemia, or hyperglycemia. Of note, in both pharmacological and diet-induced weight loss, the decrease in liver fat was associated with the decrease in visceral fat.”
The noninvasive biomarker test, Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) may be used to assess the risk for liver fibrosis. The FIB-4 index is calculated using a patient’s age and results of three blood tests — aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and platelet count.
Advanced fibrosis (grade F3-F4) “is a major risk factor for severe outcomes,” said Dr. Gastaldelli. A FIB-4 test result below 1.3 indicates low risk for advanced liver fibrosis, 1.30-2.67 indicates intermediate risk, and above 2.67 indicates high risk.
“When fibrosis increases, then liver enzymes increase and the platelets decrease,” said Dr. Gastaldelli. “It is not a perfect tool, and we need to add in age because at a young age, it is prone to false negatives and when very old — false positives. It’s important to take a global view, especially if the patient has persistent high liver enzymes, but FIB-4 is low.”
“And if they have more than one metabolic risk factor, proceed with more tests, for example, transient elastography,” she advised. Imaging techniques such as transient elastography may rule out or rule in advanced fibrosis, which is predictive of liver-related outcomes.
“However, imaging techniques only diagnose steatosis and fibrosis, and right now, MASH can only be diagnosed with liver biopsy because we do not have any markers of liver inflammation and ballooning. In the future, noninvasive tests based on imaging and blood tests will be used to identify patients with MASH,” she added.
Management of MASLD — Lifestyle and Treatment
“Pharmacological treatments are designed for [patients] with MASH and fibrosis grade F2 or F3, but not MASLD,” Dr. Gastaldelli said. As such, lifestyle interventions are the mainstay of management — including weight loss, dietary changes, physical exercise, and low to no alcohol consumption. “Eating good-quality food and reducing calories are both important because the metabolism responds differently to different nutrients,” Dr. Gastaldelli said.
“In particular, the guidelines advise dietary management because some foods carry liver toxicity, for example, sugary foods with sucrose/fructose especially,” she said, adding that, “complex carbohydrates are less harmful than refined carbohydrates. Processed foods should be avoided if possible because they contain sugars, [as well as] saturated fats and hydrogenated fat, which is particularly bad for the liver. Olive oil is better than butter or margarine, which are rich in saturated fat, and fish and white meat are preferable.”
She added that a diet to help manage type 2 diabetes was not so dissimilar because sugar again needs to be reduced.
If a patient has severe obesity (and MASLD), data show that bariatric surgery is beneficial. “It not only helps weight loss, but it improves liver histology and has been shown to improve or resolve type 2 diabetes and reduce CVD risk. Importantly, regarding fibrosis, nutritional management after the bariatric surgery is the most important thing,” said Dr. Gastaldelli.
Optimal management of comorbidities — including the use of incretin-based therapies such as semaglutide or tirzepatide for type 2 diabetes or obesity, if indicated — is advised, according to the guidelines.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have been shown to have a beneficial effect on MASH, said Dr. Gastaldelli. “They have not shown effectiveness in the resolution of fibrosis, but this might take longer to manifest. However, if the medication is started early enough, it may prevent severe fibrosis. Significant weight loss, both with lifestyle and pharmacological treatment, should lead to an improvement in the liver too.”
There are currently no drugs available in Europe for the treatment of noncirrhotic MASH and severe fibrosis (stage ≥ 2). Resmetirom is the first approved MASH-targeted treatment in noncirrhotic MASH and significant liver fibrosis, with histological effectiveness on steatohepatitis and fibrosis, together with an acceptable safety and tolerability profile, but, for the moment, this agent is only available in United States.
Finally, turning to MASH-related cirrhosis, the guidelines advise adaptations of metabolic drugs, nutritional counseling, and surveillance for portal hypertension and hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as liver transplantation in decompensated cirrhosis.
After the session, this news organization spoke to Tushy Kailayanathan, MBBS BSc, medical director of the liver MRI company, Perspectum, who reviewed the limitations of the FIB-4 test. The FIB-4 test identifies those with advanced fibrosis in the liver, for example, patients with hepatitis C, she noted; however, “it performs worse in type 2 diabetic patients and in the elderly. There is little clinical guidance on the adjustment of FIB-4 thresholds needed for these high cardiometabolic risk groups. The priority patients are missed by FIB-4 because those individuals with early and active disease may not yet have progressed to advanced disease detected by FIB-4.”
These individuals are exactly those amenable to primary care prevention strategies, said Dr. Kailayanathan. Because of the nature of early and active liver disease in patients with high cardiometabolic risk, it would make sense to shift some diagnostic protocols into primary care.
“These individuals are exactly those amenable to primary care prevention strategies at annual diabetic review because they are likely to have modifiable cardiometabolic risk factors such as metabolic syndrome and would benefit from lifestyle and therapeutic intervention, including GLP-1 RAs and SGLT2is [sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors],” she said. “Case-finding and detection of early-stage MASLD is a priority in diabetics, and there is an unmet need for accurate biomarkers to measure liver fat and inflammation early.”
Dr. Gastaldelli has been on the advisory board or consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Fractyl, Pfizer, Merck-MSD, MetaDeq and a speaker for Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. Dr. Kailayanathan is medical director at Perspectum, a UK-based company involved in liver imaging technology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID — Individuals with type 2 diabetes and/or obesity plus one or more metabolic risk factors are at a higher risk for metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) with fibrosis and progression to more severe liver disease, stated new European guidelines that provide recommendations for diagnosis and management.
“The availability of improved treatment options underlines the need to identify at-risk individuals with MASLD early, as we now possess the tools to positively influence the course of the diseases, which is expected to prevent relevant clinical events,” stated the clinical practice guidelines, updated for the first time since 2016.
“Now we have guidelines that tell clinicians how to monitor the liver,” said Amalia Gastaldelli, PhD, research director at the Institute of Clinical Physiology of the National Research Council in Pisa, Italy, and a member of the panel that developed the guidelines.
Dr. Gastaldelli moderated a session focused on the guidelines at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). In an interview after the session, Dr. Gastaldelli, who leads a cardiometabolic risk research group, stressed the importance of the liver’s role in the body and the need for diabetes specialists to start paying more attention to this vital organ.
“It’s an important organ for monitoring because liver disease is silent, and the patient doesn’t feel unwell until disease is severe,” she said. “Diabetologists already monitor the eye, the heart, the kidney, and so on, but the liver is often neglected,” she said. A 2024 study found that the global pooled prevalence of MASLD among patients with type 2 diabetes was 65.33%.
Dr. Gastaldelli noted the importance of liver status in diabetes care. The liver makes triglycerides and very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, which are all major risk factors for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease (CVD), she said, as well as producing glucose, which in excess can lead to hyperglycemia.
The guidelines were jointly written by EASD, the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and the European Association for the Study of Obesity, and published in Diabetologia, The Journal of Hepatology, and Obesity Facts.
A Metabolic Condition
In the EASD meeting session, Dr. Gastaldelli discussed the reasons for, and implications of, shifting the name from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) to MASLD.
“The name change focuses on the fact that this is a metabolic disease, while NAFLD had no mention of this and was considered stigmatizing by patients, especially in relation to the words ‘fatty’ and ‘nonalcoholic,’” she said.
According to the guidelines, MASLD is defined as liver steatosis in the presence of one or more cardiometabolic risk factor(s) and the absence of excess alcohol intake.
MASLD has become the most common chronic liver disease and includes isolated steatosis, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH, previously NASH), MASH-related fibrosis, and cirrhosis.
In the overarching group of steatotic liver disease, a totally new intermediate category has been added: MASLD with moderate (increased) alcohol intake (MetALD), which represents MASLD in people who consume greater amounts of alcohol per week (140-350 g/week and 210-420 g/week for women and men, respectively).
The change in the nomenclature has been incremental and regional, Dr. Gastaldelli said. “The definition first changed from NAFLD to MAFLD, which recognizes the importance of metabolism in the pathophysiology of this disease but does not take into account alcohol intake. MAFLD is still used in Asia, Australasia, and North Africa, while Europe and the Americas have endorsed MASLD.”
Case-Finding and Diagnosis
Identifying MASLD cases in people at risk remains incidental, largely because it is a silent disease and is symptom-free until it becomes severe, said Dr. Gastaldelli.
The guideline recognizes that individuals with type 2 diabetes or obesity with additional metabolic risk factor(s) are at a higher risk for MASLD with fibrosis and progression to MASH.
Assessment strategies for severe liver fibrosis in MASLD include the use of noninvasive tests in people who have cardiometabolic risk factors, abnormal liver enzymes, and/or radiological signs of hepatic steatosis, particularly in the presence of type 2 diabetes or obesity or in the presence of one or more metabolic risk factors.
Dr. Gastaldelli noted that type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity, including abdominal obesity identified by large waist circumference, are the major risk factors and should be warning signs.
“We need to consider abdominal obesity too — we’ve published data in relatively lean people, body mass index < 25, with MASH but without diabetes. Most of the patients accumulated fat viscerally and in the liver and had hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia,” she said.
“The guidelines reflect this because the definition of MASLD includes steatosis plus at least one metabolic factor — waist circumference, for example, which is related to visceral fat, hyperlipidemia, or hyperglycemia. Of note, in both pharmacological and diet-induced weight loss, the decrease in liver fat was associated with the decrease in visceral fat.”
The noninvasive biomarker test, Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) may be used to assess the risk for liver fibrosis. The FIB-4 index is calculated using a patient’s age and results of three blood tests — aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and platelet count.
Advanced fibrosis (grade F3-F4) “is a major risk factor for severe outcomes,” said Dr. Gastaldelli. A FIB-4 test result below 1.3 indicates low risk for advanced liver fibrosis, 1.30-2.67 indicates intermediate risk, and above 2.67 indicates high risk.
“When fibrosis increases, then liver enzymes increase and the platelets decrease,” said Dr. Gastaldelli. “It is not a perfect tool, and we need to add in age because at a young age, it is prone to false negatives and when very old — false positives. It’s important to take a global view, especially if the patient has persistent high liver enzymes, but FIB-4 is low.”
“And if they have more than one metabolic risk factor, proceed with more tests, for example, transient elastography,” she advised. Imaging techniques such as transient elastography may rule out or rule in advanced fibrosis, which is predictive of liver-related outcomes.
“However, imaging techniques only diagnose steatosis and fibrosis, and right now, MASH can only be diagnosed with liver biopsy because we do not have any markers of liver inflammation and ballooning. In the future, noninvasive tests based on imaging and blood tests will be used to identify patients with MASH,” she added.
Management of MASLD — Lifestyle and Treatment
“Pharmacological treatments are designed for [patients] with MASH and fibrosis grade F2 or F3, but not MASLD,” Dr. Gastaldelli said. As such, lifestyle interventions are the mainstay of management — including weight loss, dietary changes, physical exercise, and low to no alcohol consumption. “Eating good-quality food and reducing calories are both important because the metabolism responds differently to different nutrients,” Dr. Gastaldelli said.
“In particular, the guidelines advise dietary management because some foods carry liver toxicity, for example, sugary foods with sucrose/fructose especially,” she said, adding that, “complex carbohydrates are less harmful than refined carbohydrates. Processed foods should be avoided if possible because they contain sugars, [as well as] saturated fats and hydrogenated fat, which is particularly bad for the liver. Olive oil is better than butter or margarine, which are rich in saturated fat, and fish and white meat are preferable.”
She added that a diet to help manage type 2 diabetes was not so dissimilar because sugar again needs to be reduced.
If a patient has severe obesity (and MASLD), data show that bariatric surgery is beneficial. “It not only helps weight loss, but it improves liver histology and has been shown to improve or resolve type 2 diabetes and reduce CVD risk. Importantly, regarding fibrosis, nutritional management after the bariatric surgery is the most important thing,” said Dr. Gastaldelli.
Optimal management of comorbidities — including the use of incretin-based therapies such as semaglutide or tirzepatide for type 2 diabetes or obesity, if indicated — is advised, according to the guidelines.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have been shown to have a beneficial effect on MASH, said Dr. Gastaldelli. “They have not shown effectiveness in the resolution of fibrosis, but this might take longer to manifest. However, if the medication is started early enough, it may prevent severe fibrosis. Significant weight loss, both with lifestyle and pharmacological treatment, should lead to an improvement in the liver too.”
There are currently no drugs available in Europe for the treatment of noncirrhotic MASH and severe fibrosis (stage ≥ 2). Resmetirom is the first approved MASH-targeted treatment in noncirrhotic MASH and significant liver fibrosis, with histological effectiveness on steatohepatitis and fibrosis, together with an acceptable safety and tolerability profile, but, for the moment, this agent is only available in United States.
Finally, turning to MASH-related cirrhosis, the guidelines advise adaptations of metabolic drugs, nutritional counseling, and surveillance for portal hypertension and hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as liver transplantation in decompensated cirrhosis.
After the session, this news organization spoke to Tushy Kailayanathan, MBBS BSc, medical director of the liver MRI company, Perspectum, who reviewed the limitations of the FIB-4 test. The FIB-4 test identifies those with advanced fibrosis in the liver, for example, patients with hepatitis C, she noted; however, “it performs worse in type 2 diabetic patients and in the elderly. There is little clinical guidance on the adjustment of FIB-4 thresholds needed for these high cardiometabolic risk groups. The priority patients are missed by FIB-4 because those individuals with early and active disease may not yet have progressed to advanced disease detected by FIB-4.”
These individuals are exactly those amenable to primary care prevention strategies, said Dr. Kailayanathan. Because of the nature of early and active liver disease in patients with high cardiometabolic risk, it would make sense to shift some diagnostic protocols into primary care.
“These individuals are exactly those amenable to primary care prevention strategies at annual diabetic review because they are likely to have modifiable cardiometabolic risk factors such as metabolic syndrome and would benefit from lifestyle and therapeutic intervention, including GLP-1 RAs and SGLT2is [sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors],” she said. “Case-finding and detection of early-stage MASLD is a priority in diabetics, and there is an unmet need for accurate biomarkers to measure liver fat and inflammation early.”
Dr. Gastaldelli has been on the advisory board or consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Fractyl, Pfizer, Merck-MSD, MetaDeq and a speaker for Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. Dr. Kailayanathan is medical director at Perspectum, a UK-based company involved in liver imaging technology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EASD 2024

