User login
‘Never worry alone:’ Expand your child mental health comfort zone using supports
That mantra echoed through my postgraduate medical training, and is shared with patients to encourage reaching out for help. But providers are often in the exam room alone with patients whom they are, legitimately, very worried about.
Dr. Rettew’s column last month detailed the systems that are changing (slowly!) to better facilitate interface between mental health and primary care. There are increasingly supports available at a clinic level, and also a state level. Regardless of where your practice is in the process of integration, . This moment in time seems like a great opportunity to review a few favorites.
Who you gonna call?
Child Psychiatry Access Programs, sometimes called Psychiatry Access Lines, are almost everywhere!1 If you haven’t called one yet, click on your state and call! You will have immediate access to mental health resources that are curated and available in your state, child psychiatry expertise, and a way to connect families in need with targeted treatments. A long-term side effect of CPAP utilization may include improved system coordination on behalf of kids.
What about screening?
The AAP has an excellent mental health minute on screening.2 Pediatricians screen thoughtfully for psychosocial and medical concerns. Primary and secondary screenings for mental health are becoming ubiquitous in practices as a first step toward diagnosis and treatment. Primary, or initial, screening can catch concerns in your patient population. These include common tools like the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ, ages 2-17), or the Pediatric Symptom Checklist (PSC-14, ages 4-17). Subscale scores help point care toward the right direction.
Once we know there is a mental health problem through screening or interview, secondary mental health screening and rating scales help find a specific diagnosis. Some basics include the PHQ-A for depression (ages 11-17), the GAD-7 for general anxiety (ages 11+), the SCARED for specific anxiety (ages 8-18), and the Vanderbilt (ages 6+) or SNAP-IV (ages 5+) parent/teacher scales for ADHD/ODD/CD/anxiety/depressive symptoms. The CY-BOCS symptom checklist (ages 6-17) is excellent to determine the extent of OCD symptoms. The asQ (ages 10+) and Columbia (C-SSRS, ages 11+) are must-use screeners to help prevent suicide. Screeners and rating scales are found on many CPAP websites, such as New York’s.3 A site full of these can seem overwhelming, but once you get comfortable with a few favorites, expanding your repertoire little by little makes providing care a lot easier!
Treating to target?
When you are fairly certain of the diagnosis, you can feel more confident to treat. Diagnoses can be tools; find the best fit one, and in a few years with more information, a different tool might be a better fit.
Some favorite treatment resources include the CPAP guidebook from your state (for example, Washington’s4 and Virginia’s5), and the AACAP parent medication guides.6 They detail evidence-based treatments including medications, and can help us professionals and high health care–literacy families. The medication tracking form found at the back of each guide is especially key. Another great book is the DSM 5 Pocket Guide for Child and Adolescent Mental Health.7 Some screeners can be repeated to see if treatment is working, as the AIMS model suggests “treat to target”8 specific symptoms until they improve.
How to provide help with few resources?
There is knowing what your patient needs, like a specific therapy, and then there is the challenge of connecting the patient with help. Getting a family started on a first step of treatment while they are on a waiting list can be transformative. One example is treatment for oppositional defiant disorder (ODD); parents can start with the first step, “special time,”9 even before a therapist is available. Or, if a family is struggling with OCD, they can start an Exposure Therapy with Response Prevention (ERP) workbook10 or look at the iocdf.org website before seeing a specialized therapist. We all know how unsatisfactory a wait-list is as a treatment plan; it is so empowering to start the family with first steps.
What about connections for us providers?
Leveraging your own relationship with patients who have mental health challenges can be powerful, and staying connected with others is vital to maintaining your own emotional well-being. Having a therapist, being active in your medical chapters, gardening, and connecting your practice to local mental health providers and schools can be rejuvenating. Improving the systems around us prevents burnout and keeps us connected.
And finally ...
So, join the movement to help our fields work better together; walk out of that exam room and listen to your worry about your patients and the systems that support them. Reach out for help, toward child psychiatry access lines, the AAP, AACAP, and other collective agents of change. Share what is making your lives and your patients’ lives easier so we can amplify these together. Let’s worry together, and make things better.
Dr. Margaret Spottswood is a child psychiatrist practicing in an integrated care clinic at the Community Health Centers of Burlington, Vt., a Federally Qualified Health Center. She is also the medical director of the Vermont Child Psychiatry Access Program and a clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. National Network of Child Psychiatry Access Programs. Child Psychiatry Access Programs in the United States. https://www.nncpap.orgmap. 2023 Mar 14.
2. American Academy of Pediatrics. Screening Tools: Pediatric Mental Health Minute Series. https://www.aap.org/en/patient-care/mental-health-minute/screening-tools.
3. New York ProjectTEACH. Child Clinical Rating Scales. https://projectteachny.org/child-rating-scales.
4. Hilt H, Barclay R. Seattle Children’s Primary Care Principles for Child Mental Health. https://www.seattlechildrens.org/globalassets/documents/healthcare-professionals/pal/wa/wa-pal-care-guide.pdf.
5. Virginia Mental Health Access Program. VMAP Guidebook. https://vmap.org/guidebook.
6. American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. Parents’ Medication Guides. https://www.aacap.org/AACAP/Families_and_Youth/Family_Resources/Parents_Medication_Guides.aspx.
7. Hilt RJ, Nussbaum AM. DSM-5 Pocket Guide to Child and Adolescent Mental Health. Arlington, Va.: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2015.
8. Advanced Integration Mental Health Solutions. Measurement-Based Treatment to Target. https://aims.uw.edu/resource-library/measurement-based-treatment-target.
9. Vermont Child Psychiatry Access Program. Caregiver Guide: Special Time With Children. https://www.chcb.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Special-Time-with-Children-for-Caregivers.pdf.
10. Reuter T. Standing Up to OCD Workbook for Kids. New York: Simon and Schuster, 2019.
That mantra echoed through my postgraduate medical training, and is shared with patients to encourage reaching out for help. But providers are often in the exam room alone with patients whom they are, legitimately, very worried about.
Dr. Rettew’s column last month detailed the systems that are changing (slowly!) to better facilitate interface between mental health and primary care. There are increasingly supports available at a clinic level, and also a state level. Regardless of where your practice is in the process of integration, . This moment in time seems like a great opportunity to review a few favorites.
Who you gonna call?
Child Psychiatry Access Programs, sometimes called Psychiatry Access Lines, are almost everywhere!1 If you haven’t called one yet, click on your state and call! You will have immediate access to mental health resources that are curated and available in your state, child psychiatry expertise, and a way to connect families in need with targeted treatments. A long-term side effect of CPAP utilization may include improved system coordination on behalf of kids.
What about screening?
The AAP has an excellent mental health minute on screening.2 Pediatricians screen thoughtfully for psychosocial and medical concerns. Primary and secondary screenings for mental health are becoming ubiquitous in practices as a first step toward diagnosis and treatment. Primary, or initial, screening can catch concerns in your patient population. These include common tools like the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ, ages 2-17), or the Pediatric Symptom Checklist (PSC-14, ages 4-17). Subscale scores help point care toward the right direction.
Once we know there is a mental health problem through screening or interview, secondary mental health screening and rating scales help find a specific diagnosis. Some basics include the PHQ-A for depression (ages 11-17), the GAD-7 for general anxiety (ages 11+), the SCARED for specific anxiety (ages 8-18), and the Vanderbilt (ages 6+) or SNAP-IV (ages 5+) parent/teacher scales for ADHD/ODD/CD/anxiety/depressive symptoms. The CY-BOCS symptom checklist (ages 6-17) is excellent to determine the extent of OCD symptoms. The asQ (ages 10+) and Columbia (C-SSRS, ages 11+) are must-use screeners to help prevent suicide. Screeners and rating scales are found on many CPAP websites, such as New York’s.3 A site full of these can seem overwhelming, but once you get comfortable with a few favorites, expanding your repertoire little by little makes providing care a lot easier!
Treating to target?
When you are fairly certain of the diagnosis, you can feel more confident to treat. Diagnoses can be tools; find the best fit one, and in a few years with more information, a different tool might be a better fit.
Some favorite treatment resources include the CPAP guidebook from your state (for example, Washington’s4 and Virginia’s5), and the AACAP parent medication guides.6 They detail evidence-based treatments including medications, and can help us professionals and high health care–literacy families. The medication tracking form found at the back of each guide is especially key. Another great book is the DSM 5 Pocket Guide for Child and Adolescent Mental Health.7 Some screeners can be repeated to see if treatment is working, as the AIMS model suggests “treat to target”8 specific symptoms until they improve.
How to provide help with few resources?
There is knowing what your patient needs, like a specific therapy, and then there is the challenge of connecting the patient with help. Getting a family started on a first step of treatment while they are on a waiting list can be transformative. One example is treatment for oppositional defiant disorder (ODD); parents can start with the first step, “special time,”9 even before a therapist is available. Or, if a family is struggling with OCD, they can start an Exposure Therapy with Response Prevention (ERP) workbook10 or look at the iocdf.org website before seeing a specialized therapist. We all know how unsatisfactory a wait-list is as a treatment plan; it is so empowering to start the family with first steps.
What about connections for us providers?
Leveraging your own relationship with patients who have mental health challenges can be powerful, and staying connected with others is vital to maintaining your own emotional well-being. Having a therapist, being active in your medical chapters, gardening, and connecting your practice to local mental health providers and schools can be rejuvenating. Improving the systems around us prevents burnout and keeps us connected.
And finally ...
So, join the movement to help our fields work better together; walk out of that exam room and listen to your worry about your patients and the systems that support them. Reach out for help, toward child psychiatry access lines, the AAP, AACAP, and other collective agents of change. Share what is making your lives and your patients’ lives easier so we can amplify these together. Let’s worry together, and make things better.
Dr. Margaret Spottswood is a child psychiatrist practicing in an integrated care clinic at the Community Health Centers of Burlington, Vt., a Federally Qualified Health Center. She is also the medical director of the Vermont Child Psychiatry Access Program and a clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. National Network of Child Psychiatry Access Programs. Child Psychiatry Access Programs in the United States. https://www.nncpap.orgmap. 2023 Mar 14.
2. American Academy of Pediatrics. Screening Tools: Pediatric Mental Health Minute Series. https://www.aap.org/en/patient-care/mental-health-minute/screening-tools.
3. New York ProjectTEACH. Child Clinical Rating Scales. https://projectteachny.org/child-rating-scales.
4. Hilt H, Barclay R. Seattle Children’s Primary Care Principles for Child Mental Health. https://www.seattlechildrens.org/globalassets/documents/healthcare-professionals/pal/wa/wa-pal-care-guide.pdf.
5. Virginia Mental Health Access Program. VMAP Guidebook. https://vmap.org/guidebook.
6. American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. Parents’ Medication Guides. https://www.aacap.org/AACAP/Families_and_Youth/Family_Resources/Parents_Medication_Guides.aspx.
7. Hilt RJ, Nussbaum AM. DSM-5 Pocket Guide to Child and Adolescent Mental Health. Arlington, Va.: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2015.
8. Advanced Integration Mental Health Solutions. Measurement-Based Treatment to Target. https://aims.uw.edu/resource-library/measurement-based-treatment-target.
9. Vermont Child Psychiatry Access Program. Caregiver Guide: Special Time With Children. https://www.chcb.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Special-Time-with-Children-for-Caregivers.pdf.
10. Reuter T. Standing Up to OCD Workbook for Kids. New York: Simon and Schuster, 2019.
That mantra echoed through my postgraduate medical training, and is shared with patients to encourage reaching out for help. But providers are often in the exam room alone with patients whom they are, legitimately, very worried about.
Dr. Rettew’s column last month detailed the systems that are changing (slowly!) to better facilitate interface between mental health and primary care. There are increasingly supports available at a clinic level, and also a state level. Regardless of where your practice is in the process of integration, . This moment in time seems like a great opportunity to review a few favorites.
Who you gonna call?
Child Psychiatry Access Programs, sometimes called Psychiatry Access Lines, are almost everywhere!1 If you haven’t called one yet, click on your state and call! You will have immediate access to mental health resources that are curated and available in your state, child psychiatry expertise, and a way to connect families in need with targeted treatments. A long-term side effect of CPAP utilization may include improved system coordination on behalf of kids.
What about screening?
The AAP has an excellent mental health minute on screening.2 Pediatricians screen thoughtfully for psychosocial and medical concerns. Primary and secondary screenings for mental health are becoming ubiquitous in practices as a first step toward diagnosis and treatment. Primary, or initial, screening can catch concerns in your patient population. These include common tools like the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ, ages 2-17), or the Pediatric Symptom Checklist (PSC-14, ages 4-17). Subscale scores help point care toward the right direction.
Once we know there is a mental health problem through screening or interview, secondary mental health screening and rating scales help find a specific diagnosis. Some basics include the PHQ-A for depression (ages 11-17), the GAD-7 for general anxiety (ages 11+), the SCARED for specific anxiety (ages 8-18), and the Vanderbilt (ages 6+) or SNAP-IV (ages 5+) parent/teacher scales for ADHD/ODD/CD/anxiety/depressive symptoms. The CY-BOCS symptom checklist (ages 6-17) is excellent to determine the extent of OCD symptoms. The asQ (ages 10+) and Columbia (C-SSRS, ages 11+) are must-use screeners to help prevent suicide. Screeners and rating scales are found on many CPAP websites, such as New York’s.3 A site full of these can seem overwhelming, but once you get comfortable with a few favorites, expanding your repertoire little by little makes providing care a lot easier!
Treating to target?
When you are fairly certain of the diagnosis, you can feel more confident to treat. Diagnoses can be tools; find the best fit one, and in a few years with more information, a different tool might be a better fit.
Some favorite treatment resources include the CPAP guidebook from your state (for example, Washington’s4 and Virginia’s5), and the AACAP parent medication guides.6 They detail evidence-based treatments including medications, and can help us professionals and high health care–literacy families. The medication tracking form found at the back of each guide is especially key. Another great book is the DSM 5 Pocket Guide for Child and Adolescent Mental Health.7 Some screeners can be repeated to see if treatment is working, as the AIMS model suggests “treat to target”8 specific symptoms until they improve.
How to provide help with few resources?
There is knowing what your patient needs, like a specific therapy, and then there is the challenge of connecting the patient with help. Getting a family started on a first step of treatment while they are on a waiting list can be transformative. One example is treatment for oppositional defiant disorder (ODD); parents can start with the first step, “special time,”9 even before a therapist is available. Or, if a family is struggling with OCD, they can start an Exposure Therapy with Response Prevention (ERP) workbook10 or look at the iocdf.org website before seeing a specialized therapist. We all know how unsatisfactory a wait-list is as a treatment plan; it is so empowering to start the family with first steps.
What about connections for us providers?
Leveraging your own relationship with patients who have mental health challenges can be powerful, and staying connected with others is vital to maintaining your own emotional well-being. Having a therapist, being active in your medical chapters, gardening, and connecting your practice to local mental health providers and schools can be rejuvenating. Improving the systems around us prevents burnout and keeps us connected.
And finally ...
So, join the movement to help our fields work better together; walk out of that exam room and listen to your worry about your patients and the systems that support them. Reach out for help, toward child psychiatry access lines, the AAP, AACAP, and other collective agents of change. Share what is making your lives and your patients’ lives easier so we can amplify these together. Let’s worry together, and make things better.
Dr. Margaret Spottswood is a child psychiatrist practicing in an integrated care clinic at the Community Health Centers of Burlington, Vt., a Federally Qualified Health Center. She is also the medical director of the Vermont Child Psychiatry Access Program and a clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. National Network of Child Psychiatry Access Programs. Child Psychiatry Access Programs in the United States. https://www.nncpap.orgmap. 2023 Mar 14.
2. American Academy of Pediatrics. Screening Tools: Pediatric Mental Health Minute Series. https://www.aap.org/en/patient-care/mental-health-minute/screening-tools.
3. New York ProjectTEACH. Child Clinical Rating Scales. https://projectteachny.org/child-rating-scales.
4. Hilt H, Barclay R. Seattle Children’s Primary Care Principles for Child Mental Health. https://www.seattlechildrens.org/globalassets/documents/healthcare-professionals/pal/wa/wa-pal-care-guide.pdf.
5. Virginia Mental Health Access Program. VMAP Guidebook. https://vmap.org/guidebook.
6. American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. Parents’ Medication Guides. https://www.aacap.org/AACAP/Families_and_Youth/Family_Resources/Parents_Medication_Guides.aspx.
7. Hilt RJ, Nussbaum AM. DSM-5 Pocket Guide to Child and Adolescent Mental Health. Arlington, Va.: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2015.
8. Advanced Integration Mental Health Solutions. Measurement-Based Treatment to Target. https://aims.uw.edu/resource-library/measurement-based-treatment-target.
9. Vermont Child Psychiatry Access Program. Caregiver Guide: Special Time With Children. https://www.chcb.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Special-Time-with-Children-for-Caregivers.pdf.
10. Reuter T. Standing Up to OCD Workbook for Kids. New York: Simon and Schuster, 2019.
How has cannabis legalization affected pregnant mothers?
A population-based study shows that the rate of cannabis-related acute care use during pregnancy increased from 11 per 100,000 pregnancies before legalization to 20 per 100,000 pregnancies afterward: an increase of 82%. Absolute increases were small, however.
“Our findings are consistent with studies highlighting that cannabis use during pregnancy has been increasing in North America, and this study suggests that cannabis legalization might contribute to and accelerate such trends,” study author Daniel Myran, MD, MPH, a public health and preventive medicine physician at the University of Ottawa in Ontario, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Risks for newborns
In a 2019 study, 7% of U.S. women reported using cannabis during pregnancy during 2016-2017, which was double the rate of 3.4% for 2002-2003.
Dr. Myran and colleagues hypothesized that legalizing nonmedical cannabis has affected the drug’s use during pregnancy in Ontario. “We also hypothesized that hospital care for cannabis use would be associated with adverse neonatal outcomes, even after adjusting for other important risk factors that may differ between people with and without cannabis use,” he said.
The researchers’ repeated cross-sectional analysis evaluated changes in the number of pregnant people who received acute care from January 2015 to July 2021 among all patients who were eligible for Ontario’s public health coverage. The final study cohort included 691,242 pregnant patients, of whom 533 had at least one pregnancy with cannabis-related acute care visits. These mothers had a mean age of 24 years vs. 30 for their counterparts with no such visits.
Using segmented regression, the researchers compared changes in the quarterly rate of pregnant people with acute care related to cannabis use (the primary outcome) with those of acute care for mental health conditions or for noncannabis substance use (the control conditions).
“Severe morning sickness was a major risk factor for care in the emergency department or hospital for cannabis use,” said Dr. Myran. “Prior work has found that people who use cannabis during pregnancy often state that it was used to manage challenging symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness.”
Most acute care events (72.2%) were emergency department visits. The most common reasons for acute care were harmful cannabis use (57.6%), followed by cannabis dependence or withdrawal (21.5%), and acute cannabis intoxication (12.8%).
Compared with pregnancies without acute care, those with acute care related to cannabis had higher rates of adverse neonatal outcomes such as birth before 37 weeks’ gestational age (16.9% vs. 7.2%), birth weight at or below the bottom fifth percentile after adjustment for gestational age (12.1% vs. 4.4%), and neonatal intensive care unit admission in the first 28 days of life (31.5% vs. 13%).
An adjusted analysis found that patients younger than 35 years and those living in rural settings or the lowest-income neighborhoods had higher odds of acute cannabis-related care during pregnancy. Patients who received acute care for any substance use or schizophrenia before pregnancy or who accessed outpatient mental health services before pregnancy had higher risk for cannabis-related acute care during pregnancy. Mothers receiving acute care for cannabis also had higher risk for acute care for hyperemesis gravidarum during pregnancy (30.9%).
The rate of acute care for other types of substance use such as alcohol and opioids did not change after cannabis legalization, and acute care for mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression during pregnancy declined by 14%, Dr. Myran noted.
“Physicians who care for pregnant people should consider increasing screening for cannabis use during pregnancy,” said Dr. Myran. “In addition, repeated nonstigmatizing screening and counseling may be indicated for higher-risk groups identified in the study, including pregnancies with severe morning sickness.”
The U.S. perspective
Commenting on the study, M. Camille Hoffman, MD, MSc, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Colorado in Aurora, said that the findings likely indicate that legalization has made cannabis users less reluctant to come forward for urgent care. “They cannot really claim that this is equivalent to more use, just that more people are willing to present,” she said. Dr. Hoffman was not involved in the study.
The Canadian results do not align perfectly with what is seen in the United States. “It does suggest that there may be more cannabinoid hyperemesis being coded as hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a pregnancy-specific condition vs. a cannabis-dependence-related one,” said Dr. Hoffman.
Literature in the United States often includes tobacco use as a covariate, she added. “This study does not appear to do that,” she said. “Rather, it uses any substance use. Because of this, it is difficult to really know the contribution of cannabis to the adverse pregnancy outcomes vs. the combination of tobacco and cannabis.”
Finally, she pointed out, the proportion of those presenting for acute care for substance use in the 2 years before conception was 22% for acute care visits for cannabis vs 1% for no acute care visits. “This suggests to me that this was a highly vulnerable group before the legalization of cannabis as well. The overall absolute difference is nine in total per 100,000 – hardly enough to draw any real conclusions. Again, maybe those nine were simply more willing to come forth with concerns with cannabis being legal.”
There is no known safe level of cannabis consumption, and its use by pregnant women has been linked to later neurodevelopmental issues in their offspring. A 2022 U.S. study suggested that cannabis exposure in the womb may leave children later in life at risk for autism, psychiatric disorders, and problematic substance abuse, particularly as they enter peak periods of vulnerability in late adolescence.
As to the impact of legalization in certain U.S. states, a 2022 study found that women perceived legalization to mean greater access to cannabis, increased acceptance of use, and greater trust in cannabis retailers. In line with Dr. Hoffman’s view, this study suggested that legalization made pregnant women more willing to discuss cannabis use during pregnancy honestly with their care providers.
In the United States, prenatal cannabis use is still included in definitions of child abuse or neglect and can lead to termination of parental rights, even in states with full legalization.
“These findings highlight the need for ongoing monitoring of markers of cannabis use during pregnancy after legalization,” said Dr. Myran. He also called for effective policies in regions with legal cannabis, such as increased warning labels on cannabis products.
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Ottawa site of ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Myran reports a speaker fee from McMaster University. Dr. Hoffman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A population-based study shows that the rate of cannabis-related acute care use during pregnancy increased from 11 per 100,000 pregnancies before legalization to 20 per 100,000 pregnancies afterward: an increase of 82%. Absolute increases were small, however.
“Our findings are consistent with studies highlighting that cannabis use during pregnancy has been increasing in North America, and this study suggests that cannabis legalization might contribute to and accelerate such trends,” study author Daniel Myran, MD, MPH, a public health and preventive medicine physician at the University of Ottawa in Ontario, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Risks for newborns
In a 2019 study, 7% of U.S. women reported using cannabis during pregnancy during 2016-2017, which was double the rate of 3.4% for 2002-2003.
Dr. Myran and colleagues hypothesized that legalizing nonmedical cannabis has affected the drug’s use during pregnancy in Ontario. “We also hypothesized that hospital care for cannabis use would be associated with adverse neonatal outcomes, even after adjusting for other important risk factors that may differ between people with and without cannabis use,” he said.
The researchers’ repeated cross-sectional analysis evaluated changes in the number of pregnant people who received acute care from January 2015 to July 2021 among all patients who were eligible for Ontario’s public health coverage. The final study cohort included 691,242 pregnant patients, of whom 533 had at least one pregnancy with cannabis-related acute care visits. These mothers had a mean age of 24 years vs. 30 for their counterparts with no such visits.
Using segmented regression, the researchers compared changes in the quarterly rate of pregnant people with acute care related to cannabis use (the primary outcome) with those of acute care for mental health conditions or for noncannabis substance use (the control conditions).
“Severe morning sickness was a major risk factor for care in the emergency department or hospital for cannabis use,” said Dr. Myran. “Prior work has found that people who use cannabis during pregnancy often state that it was used to manage challenging symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness.”
Most acute care events (72.2%) were emergency department visits. The most common reasons for acute care were harmful cannabis use (57.6%), followed by cannabis dependence or withdrawal (21.5%), and acute cannabis intoxication (12.8%).
Compared with pregnancies without acute care, those with acute care related to cannabis had higher rates of adverse neonatal outcomes such as birth before 37 weeks’ gestational age (16.9% vs. 7.2%), birth weight at or below the bottom fifth percentile after adjustment for gestational age (12.1% vs. 4.4%), and neonatal intensive care unit admission in the first 28 days of life (31.5% vs. 13%).
An adjusted analysis found that patients younger than 35 years and those living in rural settings or the lowest-income neighborhoods had higher odds of acute cannabis-related care during pregnancy. Patients who received acute care for any substance use or schizophrenia before pregnancy or who accessed outpatient mental health services before pregnancy had higher risk for cannabis-related acute care during pregnancy. Mothers receiving acute care for cannabis also had higher risk for acute care for hyperemesis gravidarum during pregnancy (30.9%).
The rate of acute care for other types of substance use such as alcohol and opioids did not change after cannabis legalization, and acute care for mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression during pregnancy declined by 14%, Dr. Myran noted.
“Physicians who care for pregnant people should consider increasing screening for cannabis use during pregnancy,” said Dr. Myran. “In addition, repeated nonstigmatizing screening and counseling may be indicated for higher-risk groups identified in the study, including pregnancies with severe morning sickness.”
The U.S. perspective
Commenting on the study, M. Camille Hoffman, MD, MSc, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Colorado in Aurora, said that the findings likely indicate that legalization has made cannabis users less reluctant to come forward for urgent care. “They cannot really claim that this is equivalent to more use, just that more people are willing to present,” she said. Dr. Hoffman was not involved in the study.
The Canadian results do not align perfectly with what is seen in the United States. “It does suggest that there may be more cannabinoid hyperemesis being coded as hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a pregnancy-specific condition vs. a cannabis-dependence-related one,” said Dr. Hoffman.
Literature in the United States often includes tobacco use as a covariate, she added. “This study does not appear to do that,” she said. “Rather, it uses any substance use. Because of this, it is difficult to really know the contribution of cannabis to the adverse pregnancy outcomes vs. the combination of tobacco and cannabis.”
Finally, she pointed out, the proportion of those presenting for acute care for substance use in the 2 years before conception was 22% for acute care visits for cannabis vs 1% for no acute care visits. “This suggests to me that this was a highly vulnerable group before the legalization of cannabis as well. The overall absolute difference is nine in total per 100,000 – hardly enough to draw any real conclusions. Again, maybe those nine were simply more willing to come forth with concerns with cannabis being legal.”
There is no known safe level of cannabis consumption, and its use by pregnant women has been linked to later neurodevelopmental issues in their offspring. A 2022 U.S. study suggested that cannabis exposure in the womb may leave children later in life at risk for autism, psychiatric disorders, and problematic substance abuse, particularly as they enter peak periods of vulnerability in late adolescence.
As to the impact of legalization in certain U.S. states, a 2022 study found that women perceived legalization to mean greater access to cannabis, increased acceptance of use, and greater trust in cannabis retailers. In line with Dr. Hoffman’s view, this study suggested that legalization made pregnant women more willing to discuss cannabis use during pregnancy honestly with their care providers.
In the United States, prenatal cannabis use is still included in definitions of child abuse or neglect and can lead to termination of parental rights, even in states with full legalization.
“These findings highlight the need for ongoing monitoring of markers of cannabis use during pregnancy after legalization,” said Dr. Myran. He also called for effective policies in regions with legal cannabis, such as increased warning labels on cannabis products.
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Ottawa site of ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Myran reports a speaker fee from McMaster University. Dr. Hoffman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A population-based study shows that the rate of cannabis-related acute care use during pregnancy increased from 11 per 100,000 pregnancies before legalization to 20 per 100,000 pregnancies afterward: an increase of 82%. Absolute increases were small, however.
“Our findings are consistent with studies highlighting that cannabis use during pregnancy has been increasing in North America, and this study suggests that cannabis legalization might contribute to and accelerate such trends,” study author Daniel Myran, MD, MPH, a public health and preventive medicine physician at the University of Ottawa in Ontario, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Risks for newborns
In a 2019 study, 7% of U.S. women reported using cannabis during pregnancy during 2016-2017, which was double the rate of 3.4% for 2002-2003.
Dr. Myran and colleagues hypothesized that legalizing nonmedical cannabis has affected the drug’s use during pregnancy in Ontario. “We also hypothesized that hospital care for cannabis use would be associated with adverse neonatal outcomes, even after adjusting for other important risk factors that may differ between people with and without cannabis use,” he said.
The researchers’ repeated cross-sectional analysis evaluated changes in the number of pregnant people who received acute care from January 2015 to July 2021 among all patients who were eligible for Ontario’s public health coverage. The final study cohort included 691,242 pregnant patients, of whom 533 had at least one pregnancy with cannabis-related acute care visits. These mothers had a mean age of 24 years vs. 30 for their counterparts with no such visits.
Using segmented regression, the researchers compared changes in the quarterly rate of pregnant people with acute care related to cannabis use (the primary outcome) with those of acute care for mental health conditions or for noncannabis substance use (the control conditions).
“Severe morning sickness was a major risk factor for care in the emergency department or hospital for cannabis use,” said Dr. Myran. “Prior work has found that people who use cannabis during pregnancy often state that it was used to manage challenging symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness.”
Most acute care events (72.2%) were emergency department visits. The most common reasons for acute care were harmful cannabis use (57.6%), followed by cannabis dependence or withdrawal (21.5%), and acute cannabis intoxication (12.8%).
Compared with pregnancies without acute care, those with acute care related to cannabis had higher rates of adverse neonatal outcomes such as birth before 37 weeks’ gestational age (16.9% vs. 7.2%), birth weight at or below the bottom fifth percentile after adjustment for gestational age (12.1% vs. 4.4%), and neonatal intensive care unit admission in the first 28 days of life (31.5% vs. 13%).
An adjusted analysis found that patients younger than 35 years and those living in rural settings or the lowest-income neighborhoods had higher odds of acute cannabis-related care during pregnancy. Patients who received acute care for any substance use or schizophrenia before pregnancy or who accessed outpatient mental health services before pregnancy had higher risk for cannabis-related acute care during pregnancy. Mothers receiving acute care for cannabis also had higher risk for acute care for hyperemesis gravidarum during pregnancy (30.9%).
The rate of acute care for other types of substance use such as alcohol and opioids did not change after cannabis legalization, and acute care for mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression during pregnancy declined by 14%, Dr. Myran noted.
“Physicians who care for pregnant people should consider increasing screening for cannabis use during pregnancy,” said Dr. Myran. “In addition, repeated nonstigmatizing screening and counseling may be indicated for higher-risk groups identified in the study, including pregnancies with severe morning sickness.”
The U.S. perspective
Commenting on the study, M. Camille Hoffman, MD, MSc, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Colorado in Aurora, said that the findings likely indicate that legalization has made cannabis users less reluctant to come forward for urgent care. “They cannot really claim that this is equivalent to more use, just that more people are willing to present,” she said. Dr. Hoffman was not involved in the study.
The Canadian results do not align perfectly with what is seen in the United States. “It does suggest that there may be more cannabinoid hyperemesis being coded as hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a pregnancy-specific condition vs. a cannabis-dependence-related one,” said Dr. Hoffman.
Literature in the United States often includes tobacco use as a covariate, she added. “This study does not appear to do that,” she said. “Rather, it uses any substance use. Because of this, it is difficult to really know the contribution of cannabis to the adverse pregnancy outcomes vs. the combination of tobacco and cannabis.”
Finally, she pointed out, the proportion of those presenting for acute care for substance use in the 2 years before conception was 22% for acute care visits for cannabis vs 1% for no acute care visits. “This suggests to me that this was a highly vulnerable group before the legalization of cannabis as well. The overall absolute difference is nine in total per 100,000 – hardly enough to draw any real conclusions. Again, maybe those nine were simply more willing to come forth with concerns with cannabis being legal.”
There is no known safe level of cannabis consumption, and its use by pregnant women has been linked to later neurodevelopmental issues in their offspring. A 2022 U.S. study suggested that cannabis exposure in the womb may leave children later in life at risk for autism, psychiatric disorders, and problematic substance abuse, particularly as they enter peak periods of vulnerability in late adolescence.
As to the impact of legalization in certain U.S. states, a 2022 study found that women perceived legalization to mean greater access to cannabis, increased acceptance of use, and greater trust in cannabis retailers. In line with Dr. Hoffman’s view, this study suggested that legalization made pregnant women more willing to discuss cannabis use during pregnancy honestly with their care providers.
In the United States, prenatal cannabis use is still included in definitions of child abuse or neglect and can lead to termination of parental rights, even in states with full legalization.
“These findings highlight the need for ongoing monitoring of markers of cannabis use during pregnancy after legalization,” said Dr. Myran. He also called for effective policies in regions with legal cannabis, such as increased warning labels on cannabis products.
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Ottawa site of ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Myran reports a speaker fee from McMaster University. Dr. Hoffman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CMAJ
Transplant centers often skip the top spot on the kidney waitlist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
The idea of rationing medical care is anathema to most doctors. Sure, we acknowledge that the realities of health care costs and insurance companies might limit our options, but there is always a sense that when something is truly, truly needed, we can get it done.
Except in one very particular situation, a situation where rationing of care is the norm. That situation? Organ transplantation.
There is no way around this: More patients need organ transplants than there are organs available to transplant. It is cold, hard arithmetic. No amount of negotiating with an insurance company or engaging in prior authorization can change that.
As a kidney doctor, this issue is close to my heart. There are around 100,000 people on the kidney transplant waiting list in the U.S., with 3,000 new patients being added per month. There are only 25,000 kidney transplants per year. And each year, around 5,000 people die while waiting for a transplant.
A world of scarcity, like the world of kidney transplant, is ripe for bias at best and abuse at worst. It is in part for that reason that the Kidney Allocation System exists. It answers the cold, hard arithmetic of transplant scarcity with the cold, hard arithmetic of a computer algorithm, ranking individuals on the waitlist on a variety of factors to ensure that those who will benefit most from a transplant get it first.
This area is a bit complex but I’ll try to break it down into what you need to know. There are 56 organ procurement organizations (OPOs) in the United States. These are nonprofits with the responsibility to recover organs from deceased donors in their area.
Each of those OPOs maintains a ranked list of those waiting for a kidney transplant. Depending on the OPO, the list may range from a couple hundred people to a couple thousand, but one thing is the same, no matter what: If you are at the top of the list, you should be the next to get a transplant.
Most OPOs have multiple transplant centers in them, and each center is going to prioritize its own patients. If a Yale patient is No. 1 on the list and a kidney offer comes in, it would be a good idea for us to accept, because if we reject the offer, the organ may go to a competing center whose patients is ranked No. 2.
But 11 OPOs around the country are served by only one center. This gives that center huge flexibility to determine who gets what kidney, because if they refuse an offer for whoever is at the top of their list, they can still give the kidney to the second person on their list, or third, or 30th, theoretically.
But in practice, does this phenomenon, known colloquially as “list diving,” actually happen? This manuscript from Sumit Mohan and colleagues suggests that it does, and at rates that are, frankly, eye-popping.
The Columbia team used data from the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients to conduct the analysis. The database tracks all aspects of the transplant process, from listing to ranking to, eventually, the transplant itself. With that data, they could determine how often, across these 11 OPOs, the No. 1 person on the list did not get the available kidney.
The answer? Out of 4,668 transplants conducted from 2015 to 2019, the transplant centers skipped their highest-ranked person 3,169 times – 68% of the time.
This graph shows the distribution of where on the list these kidneys went. You can see some centers diving down 100 or 200 places.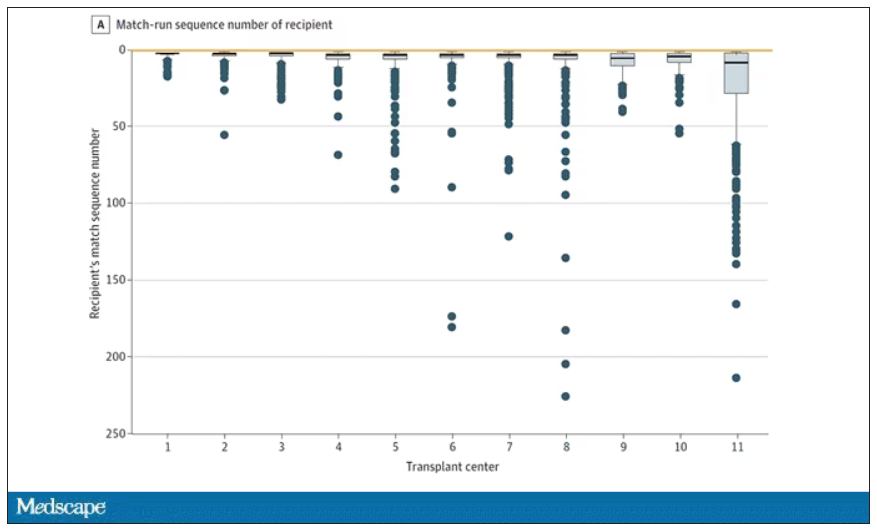
Transplant centers have lists of different lengths, so this graph shows you how far down on the percentage scale the centers dived. You can see centers skipping right to the bottom of their list in some cases.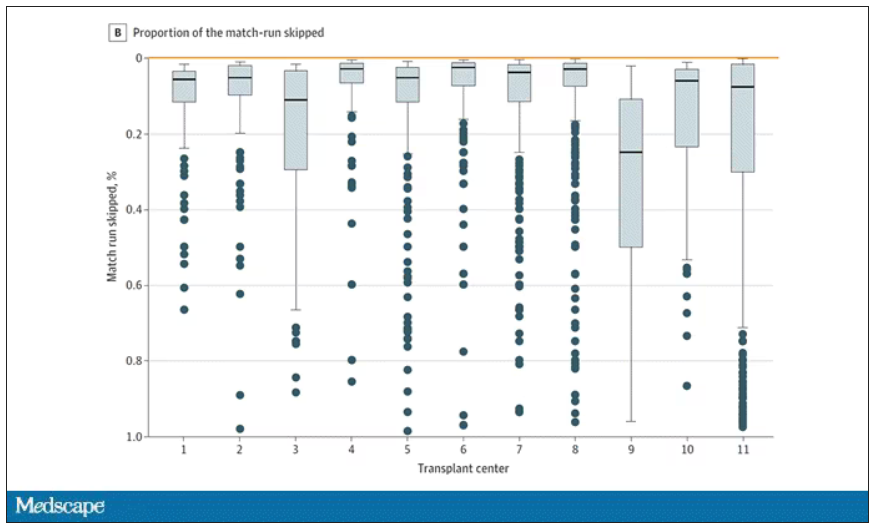
Now, I should make it clear that transplant centers do have legitimate discretion here. Transplant centers may pass up a less-than-perfect kidney for their No. 1 spot, knowing that that individual will get more offers soon, in favor of someone further down the list who will not see an offer for a while. It’s gaming the system a bit, but not, you know, for evil. And the data support this. Top-ranked people who got skipped had received a lower-quality kidney offer than those who did not get skipped. But I will also note that those who were skipped were less likely to be White, less likely to be Hispanic, and more likely to be male. That should raise your eyebrows.
Interestingly, this practice may not be limited to those cases where the OPO has only one transplant center. Conducting the same analysis across all 231 kidney transplant centers in the U.S., the authors found that the top candidate was skipped 76% of the time.
So, what’s going on here? I’m sure that some of this list-skipping is for legitimate medical reasons. And it should be pointed out that recipients have a right to refuse an offer as well – and might be more picky if they know they are at the top of the list. But patient preference was listed as the reason for list diving in only about 14% of cases. The vast majority (65%) of reasons given were based on donor quality. The problem is that donor quality can be quite subjective. And remember, these organs were transplanted eventually so they couldn’t have been that bad.
Putting the data together, though, I can’t shake the sense that centers are using the list more for guidance than as a real mechanism to ensure an equitable allocation system. With all the flexibility that centers have to bypass individuals on the list, the list loses its meaning and its power.
I spoke to one transplant nephrologist who suggested that these data should prompt an investigation by the United Network for Organ Sharing, the body that governs all these OPOs. That may be a necessary step.
I hope there comes a day when this issue is moot, when growing kidneys in the lab – or regenerating one’s own kidneys – is a possibility. But that day is not yet here and we must deal with the scarcity we have. In this world, we need the list to prevent abuse. But the list only works if the list is followed.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Conn. He reported having no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
The idea of rationing medical care is anathema to most doctors. Sure, we acknowledge that the realities of health care costs and insurance companies might limit our options, but there is always a sense that when something is truly, truly needed, we can get it done.
Except in one very particular situation, a situation where rationing of care is the norm. That situation? Organ transplantation.
There is no way around this: More patients need organ transplants than there are organs available to transplant. It is cold, hard arithmetic. No amount of negotiating with an insurance company or engaging in prior authorization can change that.
As a kidney doctor, this issue is close to my heart. There are around 100,000 people on the kidney transplant waiting list in the U.S., with 3,000 new patients being added per month. There are only 25,000 kidney transplants per year. And each year, around 5,000 people die while waiting for a transplant.
A world of scarcity, like the world of kidney transplant, is ripe for bias at best and abuse at worst. It is in part for that reason that the Kidney Allocation System exists. It answers the cold, hard arithmetic of transplant scarcity with the cold, hard arithmetic of a computer algorithm, ranking individuals on the waitlist on a variety of factors to ensure that those who will benefit most from a transplant get it first.
This area is a bit complex but I’ll try to break it down into what you need to know. There are 56 organ procurement organizations (OPOs) in the United States. These are nonprofits with the responsibility to recover organs from deceased donors in their area.
Each of those OPOs maintains a ranked list of those waiting for a kidney transplant. Depending on the OPO, the list may range from a couple hundred people to a couple thousand, but one thing is the same, no matter what: If you are at the top of the list, you should be the next to get a transplant.
Most OPOs have multiple transplant centers in them, and each center is going to prioritize its own patients. If a Yale patient is No. 1 on the list and a kidney offer comes in, it would be a good idea for us to accept, because if we reject the offer, the organ may go to a competing center whose patients is ranked No. 2.
But 11 OPOs around the country are served by only one center. This gives that center huge flexibility to determine who gets what kidney, because if they refuse an offer for whoever is at the top of their list, they can still give the kidney to the second person on their list, or third, or 30th, theoretically.
But in practice, does this phenomenon, known colloquially as “list diving,” actually happen? This manuscript from Sumit Mohan and colleagues suggests that it does, and at rates that are, frankly, eye-popping.
The Columbia team used data from the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients to conduct the analysis. The database tracks all aspects of the transplant process, from listing to ranking to, eventually, the transplant itself. With that data, they could determine how often, across these 11 OPOs, the No. 1 person on the list did not get the available kidney.
The answer? Out of 4,668 transplants conducted from 2015 to 2019, the transplant centers skipped their highest-ranked person 3,169 times – 68% of the time.
This graph shows the distribution of where on the list these kidneys went. You can see some centers diving down 100 or 200 places.
Transplant centers have lists of different lengths, so this graph shows you how far down on the percentage scale the centers dived. You can see centers skipping right to the bottom of their list in some cases.
Now, I should make it clear that transplant centers do have legitimate discretion here. Transplant centers may pass up a less-than-perfect kidney for their No. 1 spot, knowing that that individual will get more offers soon, in favor of someone further down the list who will not see an offer for a while. It’s gaming the system a bit, but not, you know, for evil. And the data support this. Top-ranked people who got skipped had received a lower-quality kidney offer than those who did not get skipped. But I will also note that those who were skipped were less likely to be White, less likely to be Hispanic, and more likely to be male. That should raise your eyebrows.
Interestingly, this practice may not be limited to those cases where the OPO has only one transplant center. Conducting the same analysis across all 231 kidney transplant centers in the U.S., the authors found that the top candidate was skipped 76% of the time.
So, what’s going on here? I’m sure that some of this list-skipping is for legitimate medical reasons. And it should be pointed out that recipients have a right to refuse an offer as well – and might be more picky if they know they are at the top of the list. But patient preference was listed as the reason for list diving in only about 14% of cases. The vast majority (65%) of reasons given were based on donor quality. The problem is that donor quality can be quite subjective. And remember, these organs were transplanted eventually so they couldn’t have been that bad.
Putting the data together, though, I can’t shake the sense that centers are using the list more for guidance than as a real mechanism to ensure an equitable allocation system. With all the flexibility that centers have to bypass individuals on the list, the list loses its meaning and its power.
I spoke to one transplant nephrologist who suggested that these data should prompt an investigation by the United Network for Organ Sharing, the body that governs all these OPOs. That may be a necessary step.
I hope there comes a day when this issue is moot, when growing kidneys in the lab – or regenerating one’s own kidneys – is a possibility. But that day is not yet here and we must deal with the scarcity we have. In this world, we need the list to prevent abuse. But the list only works if the list is followed.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Conn. He reported having no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
The idea of rationing medical care is anathema to most doctors. Sure, we acknowledge that the realities of health care costs and insurance companies might limit our options, but there is always a sense that when something is truly, truly needed, we can get it done.
Except in one very particular situation, a situation where rationing of care is the norm. That situation? Organ transplantation.
There is no way around this: More patients need organ transplants than there are organs available to transplant. It is cold, hard arithmetic. No amount of negotiating with an insurance company or engaging in prior authorization can change that.
As a kidney doctor, this issue is close to my heart. There are around 100,000 people on the kidney transplant waiting list in the U.S., with 3,000 new patients being added per month. There are only 25,000 kidney transplants per year. And each year, around 5,000 people die while waiting for a transplant.
A world of scarcity, like the world of kidney transplant, is ripe for bias at best and abuse at worst. It is in part for that reason that the Kidney Allocation System exists. It answers the cold, hard arithmetic of transplant scarcity with the cold, hard arithmetic of a computer algorithm, ranking individuals on the waitlist on a variety of factors to ensure that those who will benefit most from a transplant get it first.
This area is a bit complex but I’ll try to break it down into what you need to know. There are 56 organ procurement organizations (OPOs) in the United States. These are nonprofits with the responsibility to recover organs from deceased donors in their area.
Each of those OPOs maintains a ranked list of those waiting for a kidney transplant. Depending on the OPO, the list may range from a couple hundred people to a couple thousand, but one thing is the same, no matter what: If you are at the top of the list, you should be the next to get a transplant.
Most OPOs have multiple transplant centers in them, and each center is going to prioritize its own patients. If a Yale patient is No. 1 on the list and a kidney offer comes in, it would be a good idea for us to accept, because if we reject the offer, the organ may go to a competing center whose patients is ranked No. 2.
But 11 OPOs around the country are served by only one center. This gives that center huge flexibility to determine who gets what kidney, because if they refuse an offer for whoever is at the top of their list, they can still give the kidney to the second person on their list, or third, or 30th, theoretically.
But in practice, does this phenomenon, known colloquially as “list diving,” actually happen? This manuscript from Sumit Mohan and colleagues suggests that it does, and at rates that are, frankly, eye-popping.
The Columbia team used data from the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients to conduct the analysis. The database tracks all aspects of the transplant process, from listing to ranking to, eventually, the transplant itself. With that data, they could determine how often, across these 11 OPOs, the No. 1 person on the list did not get the available kidney.
The answer? Out of 4,668 transplants conducted from 2015 to 2019, the transplant centers skipped their highest-ranked person 3,169 times – 68% of the time.
This graph shows the distribution of where on the list these kidneys went. You can see some centers diving down 100 or 200 places.
Transplant centers have lists of different lengths, so this graph shows you how far down on the percentage scale the centers dived. You can see centers skipping right to the bottom of their list in some cases.
Now, I should make it clear that transplant centers do have legitimate discretion here. Transplant centers may pass up a less-than-perfect kidney for their No. 1 spot, knowing that that individual will get more offers soon, in favor of someone further down the list who will not see an offer for a while. It’s gaming the system a bit, but not, you know, for evil. And the data support this. Top-ranked people who got skipped had received a lower-quality kidney offer than those who did not get skipped. But I will also note that those who were skipped were less likely to be White, less likely to be Hispanic, and more likely to be male. That should raise your eyebrows.
Interestingly, this practice may not be limited to those cases where the OPO has only one transplant center. Conducting the same analysis across all 231 kidney transplant centers in the U.S., the authors found that the top candidate was skipped 76% of the time.
So, what’s going on here? I’m sure that some of this list-skipping is for legitimate medical reasons. And it should be pointed out that recipients have a right to refuse an offer as well – and might be more picky if they know they are at the top of the list. But patient preference was listed as the reason for list diving in only about 14% of cases. The vast majority (65%) of reasons given were based on donor quality. The problem is that donor quality can be quite subjective. And remember, these organs were transplanted eventually so they couldn’t have been that bad.
Putting the data together, though, I can’t shake the sense that centers are using the list more for guidance than as a real mechanism to ensure an equitable allocation system. With all the flexibility that centers have to bypass individuals on the list, the list loses its meaning and its power.
I spoke to one transplant nephrologist who suggested that these data should prompt an investigation by the United Network for Organ Sharing, the body that governs all these OPOs. That may be a necessary step.
I hope there comes a day when this issue is moot, when growing kidneys in the lab – or regenerating one’s own kidneys – is a possibility. But that day is not yet here and we must deal with the scarcity we have. In this world, we need the list to prevent abuse. But the list only works if the list is followed.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Conn. He reported having no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How can we make medical training less ‘toxic’?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical adviser for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Joining me to discuss ways to address and reform the toxic culture associated with medical training is Dr. Amy Faith Ho, senior vice president of clinical informatics and analytics at Integrative Emergency Services in Dallas. Also joining us is Dr. Júlia Loyola Ferreira, a pediatric surgeon originally from Brazil, now practicing at Montreal Children’s and focused on advocacy for gender equity and patient-centered care.
Welcome to both of you. Thanks so much for joining me.
Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH: Thanks so much for having us, Rob.
Dr. Glatter: Amy, I noticed a tweet recently where you talked about how your career choice was affected by the toxic environment in medical school, affecting your choice of residency. Can you elaborate on that?
Dr. Ho: In this instance, what we’re talking about is gender, but it can be directed toward any number of other groups as well.
What you’re alluding to is a tweet by Stanford Surgery Group showing the next residency class, and what was really stunning about this residency class was that it was almost all females. And this was something that took off on social media.
When I saw this, I was really brought back to one of my personal experiences that I chose to share, which was basically that, as a medical student, I really wanted to be a surgeon. I’m an emergency medicine doctor now, so you know that didn’t happen.
The story that I was sharing was that when I was a third-year medical student rotating on surgery, we had a male attending who was very well known at that school at the time who basically would take the female medical students, and instead of clinic, he would round us up. He would have us sit around him in the workplace room while everyone else was seeing patients, and he would have you look at news clippings of himself. He would tell you stories about himself, like he was holding court for the ladies.
It was this very weird culture where my takeaway as a med student was like, “Wow, this is kind of abusive patriarchy that is supported,” because everyone knew about it and was complicit. Even though I really liked surgery, this was just one instance and one example of where you see this culture that really resonates into the rest of life that I didn’t really want to be a part of.
I went into emergency medicine and loved it. It’s also highly procedural, and I was very happy with where I was. What was really interesting about this tweet to me, though, is that it really took off and garnered hundreds of thousands of views on a very niche topic, because what was most revealing is that everyone has a story like this.
It is not just surgery. It is definitely not just one specialty and it is not just one school. It is an endemic problem in medicine. Not only does it change the lives of young women, but it also says so much about the complicity and the culture that we have in medicine that many people were upset about just the same way I was.
Medical training experience in other countries vs. the United States
Dr. Glatter: Júlia, I want to hear about your experience in medical school, surgery, and then fellowship training and up to the present, if possible.
Júlia Loyola Ferreira, MD: In Brazil, as in many countries now, women have made up the majority of the medical students since 2010. It’s a more female-friendly environment when you’re going through medical school, and I was lucky enough to do rotations in areas of surgery where people were friendly to women.
I lived in this tiny bubble that also gave me the privilege of not facing some things that I can imagine that people in Brazil in different areas and smaller towns face. In Brazil, people try to not talk about this gender agenda. This is something that’s being talked about outside Brazil. But in Brazil, we are years back. People are not really engaging on this conversation. I thought it was going to be hard for me as a woman, because Brazil has around 20% female surgeons.
I knew it was going to be challenging, but I had no idea how bad it was. When I started and things started happening, the list was big. I have an example of everything that is written about – microaggression, implicit bias, discrimination, harassment.
Every time I would try to speak about it and talk to someone, I would be strongly gaslighted. It was the whole training, the whole 5 years. People would say, “Oh, I don’t think it was like that. I think you were overreacting.” People would come with all these different answers for what I was experiencing, and that was frustrating. That was even harder because I had to cope with everything that was happening and I had no one to turn to. I had no mentors.
When I looked up to women who were in surgery, they would be tougher on us young surgeons than the men and they would tell us that we should not complain because in their time it was even harder. Now, it’s getting better and we are supposed to accept whatever comes.
That was at least a little bit of what I experienced in my training. It was only after I finished and started to do research about it that I really encountered a field of people who would echo what I was trying to say to many people in different hospitals that I attended to.
That was the key for me to get out of that situation of being gaslighted and of not being able to really talk about it. Suddenly, I started to publish things about Brazil that nobody was even writing or studying. That gave me a large amount of responsibility, but also motivation to keep going and to see the change.
Valuing women in medicine
Dr. Glatter: This is a very important point that you’re raising about the environment of women being hard on other women. We know that men can be very difficult on and also judgmental toward their trainees.
Amy, how would you respond to that? Was your experience similar in emergency medicine training?
Dr. Ho: I actually don’t feel like it was. I think what Júlia is alluding to is this “mean girls” idea, of “I went through it and thus you have to go through it.” I think you do see this in many specialties. One of the classic ones we hear about, and I don’t want to speak to it too much because it’s not my specialty, is ob.gyn., where it is a very female-dominant surgery group. There’s almost a hazing level that you hear about in some of the more malignant workplaces.
I think that you speak to two really important things. Number one is the numbers game. As you were saying, Brazil actually has many women. That’s awesome. That’s actually different from the United States, especially for the historic, existing workplace and less so for the medical students and for residents. I think step one is having minorities like women just present and there.
Step two is actually including and valuing them. While I think it’s really easy to move away from the women discussion, because there are women when you look around in medicine, it doesn’t mean that women are actually being heard, that they’re actually being accepted, or that their viewpoints are being listened to. A big part of it is normalizing not only seeing women in medicine but also normalizing the narrative of women in medicine.
It’s not just about motherhood; it’s about things like normalizing talking about advancement, academic promotions, pay, culture, being called things like “too reactive,” “anxious,” or “too assertive.” These are all classic things that we hear about when we talk about women.
That’s why we’re looking to not only conversations like this, but also structured ways for women to discuss being women in medicine. There are many women in medicine groups in emergency medicine, including: Females Working in Emergency Medicine (FemInEM); the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) and Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM) women’s groups, which are American Association of Women Emergency Physicians (AAWEP) and Academy for Women in Academic Emergency Medicine (AWAEM), respectively; and the American Medical Women’s Association (AMWA), which is the American Medical Association’s offshoot.
All of these groups are geared toward normalizing women in medicine, normalizing the narrative of women in medicine, and then working on mentoring and educating so that we can advance our initiatives.
Gender balance is not gender equity
Dr. Glatter: Amy, you bring up a very critical point that mentoring is sort of the antidote to gender-based discrimination. Júlia had written a paper back in November of 2022 that was published in the Journal of Surgical Research talking exactly about this and how important it is to develop mentoring. Part of her research showed that about 20% of medical students who took the survey, about 1,000 people, had mentors, which was very disturbing.
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Mentorship is one of the ways of changing the reality about gender-based discrimination. Amy’s comment was very strong and we need to really keep saying it, which is that gender balance is not gender equity.
The idea of having more women is not the same as women being recognized as equals, as able as men, and as valued as men. To change this very long culture of male domination, we need support, and this support comes from mentorship.
Although I didn’t have one, I feel that since I started being a mentor for some students, it changed not only them but myself. It gave me strength to keep going, studying, publishing, and going further with this discussion. I feel like the relationship was as good for them as it is for me. That’s how things change.
Diversity, equity, and inclusion training
Dr. Glatter: We’re talking about the reality of gender equity in terms of the ability to have equal respect, recognition, opportunities, and access. That’s really an important point to realize, and for our audience, to understand that gender equity is not gender balance.
Amy, I want to talk about medical school curriculums. Are there advances that you’re aware of being made at certain schools, programs, even in residencies, to enforce these things and make it a priority?
Dr. Ho: We’re really lucky that, as a culture in the United States, medical training is certainly very geared toward diversity. Some of that is certainly unofficial. Some of that just means when they’re looking at a medical school class or looking at rank lists for residency, that they’re cognizant of the different backgrounds that people have. That’s still a step. That is a step, that we’re at least acknowledging it.
There are multiple medical schools and residencies that have more formal unconscious-bias training or diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) training, both of which are excellent not only for us in the workplace but also for our patients. Almost all of us will see patients of highly diverse backgrounds. I think the biggest push is looking toward the criteria that we use for selecting trainees and students into our programs. Historically, it’s been MCAT, GPA, and so on.
We’ve really started to ask the question of, are these sorts of “objective criteria” actually biased in institutional ways? They talk about this all the time where GPAs will bias against students from underrepresented minorities (URM). I think all medical students and residencies have really acknowledged that. Although there are still test cutoffs, we are putting an inquisitive eye to what those mean, why they exist, and what are the other things that we should consider. This is all very heartening from what I’m seeing in medical training.
Dr. Glatter: There’s no formal rating system for DEI curriculums right now, like ranking of this school, or this program has more advanced recognition in terms of DEI?
Dr. Ho: No, but on the flip side, the U.S. News & World Report was classically one of the major rankings for medical schools. What we saw fairly recently was that very high-tier schools like Harvard and University of Chicago pulled out of that ranking because that ranking did not acknowledge the value of diversity. That was an incredible stance for medical schools to take, to say, “Hey, you are not evaluating an important criterion of ours.”
Dr. Glatter: That’s a great point. Júlia, where are we now in Brazil in terms of awareness of DEI and curriculum in schools and training programs?
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Our reality is not as good as in the U.S., unfortunately. I don’t see much discussion on residency programs or medical schools at the moment. I see many students bringing it out and trying to make their schools engage in that discussion. This is something that is coming from the bottom up and not from the top down. I think it can lead to change as well. It is a step and it’s a beginning. Institutions should take the responsibility of doing this from the beginning. This is something where Brazil is still years behind you guys.
Dr. Glatter: It’s unfortunate, but certainly it’s important to hear that. What about in Canada and certainly your institution, McGill, where you just completed a master’s degree?
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Canada is very much like the U.S. This is something that is really happening and it’s happening fast. I see, at least at McGill, a large amount of DEI inclusion and everything on this discussion. They have institutional courses for us to do as students, and we are all obliged to do many courses, which I think is really educating, especially for people with different cultures and backgrounds.
Dr. Glatter: Amy, where do you think we are in emergency medicine to look at the other side of it? Comparing surgery with emergency medicine, do you think we’re well advanced in terms of DEI, inclusion criteria, respect, and dignity, or are we really far off?
Dr. Ho: I may be biased, but I think emergency medicine is one of the best in terms of this, and I think there are a couple of reasons for it. One is that we are an inherently team-based organization. The attending, the residents, and the students all work in line with one another. There’s less of a hierarchy.
The same is true for our nurses, pharmacists, techs, and EMS. We all work together as a team. Because of that fairly flat structure, it’s really easy for us to value one another as individuals with our diverse backgrounds. In a way, that’s harder for specialties that are more hierarchical, and I think surgery is certainly one of the most hierarchical.
The second reason why emergency medicine is fairly well off in this is that we’re, by nature, a safety-net specialty. We see patients of all-comers, all walks, all backgrounds. I think we both recognize the value of physician-patient concordance. When we share characteristics with our patients, we recognize that value immediately at the bedside.
It exposes us to so much diversity. I see a refugee one day and the next patient is someone who is incarcerated. The next patient after that is an important businessman in society. That diversity and whiplash in the type of patients that we see back-to-back helps us see the playing field in a really flat, diverse way. Because of that, I think our culture is much better, as is our understanding of the value and importance of diversity not only for our programs, but also for our patients.
Do female doctors have better patient outcomes?
Dr. Glatter: Specialties working together in the emergency department is so important. Building that team and that togetherness is so critical. Júlia, would you agree?
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Definitely. Something Amy said that is beautiful is that you recognize yourself in these patients. In surgery, we are taught to try to be away from the patients and not to put ourselves in the same position. We are taught to be less engaging, and this is not good. The good thing is when we really have patient-centered care, when we listen to them, and when we are involved with them.
I saw a publication showing that female and male surgeons treating similar patients had the same surgical outcomes. Women are as good as men technically to do surgery and have the same surgical outcomes. However, there is research showing that surgical teams with greater representation of women have improved surgical outcomes because of patient-centered care and the way women conduct bedside attention to patients. And they have better patient experience measures afterward. That is not only from the women who are treating the patients, but the whole environment. Women end up bringing men [into the conversation] and this better improves patient-centered care, and that makes the whole team a better team attending patients. Definitely, we are in the moment of patient experience and satisfaction, and increasing women is a way of achieving better patient satisfaction and experience.
Dr. Ho: There’s much to be said about having female clinicians available for patients. It doesn’t have to be just for female patients, although again, concordance between physicians and patients is certainly beneficial. Besides outcomes benefit, there’s even just a communication benefit. The way that women and men communicate is inherently different. The way women and men experience certain things is also inherently different.
A classic example of this is women who are experiencing a heart attack may not actually have chest pain but present with nausea. As a female who’s sensitive to this, when I see a woman throwing up, I am very attuned to something actually being wrong, knowing that they may not present with classic pain for a syndrome, but actually may be presenting with nausea instead. It doesn’t have to be a woman who takes that knowledge and turns it into something at the bedside. It certainly doesn’t have to, but it is just a natural, easy thing to step into as a female.
While I’m really careful to not step into this “women are better than men” or “men are better than women” argument, there’s something to be said about how the availability of female clinicians for all patients, not just female patients, can have benefit. Again, it’s shown in studies with cardiovascular outcomes and cardiologists, it’s certainly shown in ob.gyn., particularly for underrepresented minorities as well for maternal outcomes of Black mothers. It’s certainly shown again in patient satisfaction, which is concordance.
There is a profound level of research already on this that goes beyond just the idea of stacking the bench and putting more women in there. That’s not the value. We’re not just here to check off the box. We’re here to actually lend some value to our patients and, again, to one another as well.
Dr. Glatter: Absolutely. These are excellent points. The point you make about patient presentation is so vital. The fact that women have nausea sometimes in ACS presentations, the research never was really attentive to this. It was biased. The symptoms that women may have that are not “typical” for ACS weren’t included in patient presentations. Educating everyone about, overall, the types of presentations that we can recognize is vital and important.
Dr. Ho: Yes. It’s worth saying that, when you look at how medicine and research developed, classically, who were the research participants? They were often White men. They were college students who, historically, because women were not allowed to go to college, were men.
I say that not to fault the institution, because that was the culture of our history, but to just say it is okay to question things. It is okay to realize that someone’s presenting outside of the box and that maybe we actually need to reframe what even created the walls of the box in the first place.
Dr. Glatter: Thank you again for joining us. I truly appreciate your insight and expertise.
Dr. Glatter is assistant professor of emergency medicine, department of emergency medicine, Hofstra/Northwell, New York. Dr. Ho is senior vice president of clinical informatics & analytics, department of emergency medicine, Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas. Dr. Loyola Ferreira is a master of science candidate, department of experimental surgery, McGill University, Montreal. They reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical adviser for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Joining me to discuss ways to address and reform the toxic culture associated with medical training is Dr. Amy Faith Ho, senior vice president of clinical informatics and analytics at Integrative Emergency Services in Dallas. Also joining us is Dr. Júlia Loyola Ferreira, a pediatric surgeon originally from Brazil, now practicing at Montreal Children’s and focused on advocacy for gender equity and patient-centered care.
Welcome to both of you. Thanks so much for joining me.
Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH: Thanks so much for having us, Rob.
Dr. Glatter: Amy, I noticed a tweet recently where you talked about how your career choice was affected by the toxic environment in medical school, affecting your choice of residency. Can you elaborate on that?
Dr. Ho: In this instance, what we’re talking about is gender, but it can be directed toward any number of other groups as well.
What you’re alluding to is a tweet by Stanford Surgery Group showing the next residency class, and what was really stunning about this residency class was that it was almost all females. And this was something that took off on social media.
When I saw this, I was really brought back to one of my personal experiences that I chose to share, which was basically that, as a medical student, I really wanted to be a surgeon. I’m an emergency medicine doctor now, so you know that didn’t happen.
The story that I was sharing was that when I was a third-year medical student rotating on surgery, we had a male attending who was very well known at that school at the time who basically would take the female medical students, and instead of clinic, he would round us up. He would have us sit around him in the workplace room while everyone else was seeing patients, and he would have you look at news clippings of himself. He would tell you stories about himself, like he was holding court for the ladies.
It was this very weird culture where my takeaway as a med student was like, “Wow, this is kind of abusive patriarchy that is supported,” because everyone knew about it and was complicit. Even though I really liked surgery, this was just one instance and one example of where you see this culture that really resonates into the rest of life that I didn’t really want to be a part of.
I went into emergency medicine and loved it. It’s also highly procedural, and I was very happy with where I was. What was really interesting about this tweet to me, though, is that it really took off and garnered hundreds of thousands of views on a very niche topic, because what was most revealing is that everyone has a story like this.
It is not just surgery. It is definitely not just one specialty and it is not just one school. It is an endemic problem in medicine. Not only does it change the lives of young women, but it also says so much about the complicity and the culture that we have in medicine that many people were upset about just the same way I was.
Medical training experience in other countries vs. the United States
Dr. Glatter: Júlia, I want to hear about your experience in medical school, surgery, and then fellowship training and up to the present, if possible.
Júlia Loyola Ferreira, MD: In Brazil, as in many countries now, women have made up the majority of the medical students since 2010. It’s a more female-friendly environment when you’re going through medical school, and I was lucky enough to do rotations in areas of surgery where people were friendly to women.
I lived in this tiny bubble that also gave me the privilege of not facing some things that I can imagine that people in Brazil in different areas and smaller towns face. In Brazil, people try to not talk about this gender agenda. This is something that’s being talked about outside Brazil. But in Brazil, we are years back. People are not really engaging on this conversation. I thought it was going to be hard for me as a woman, because Brazil has around 20% female surgeons.
I knew it was going to be challenging, but I had no idea how bad it was. When I started and things started happening, the list was big. I have an example of everything that is written about – microaggression, implicit bias, discrimination, harassment.
Every time I would try to speak about it and talk to someone, I would be strongly gaslighted. It was the whole training, the whole 5 years. People would say, “Oh, I don’t think it was like that. I think you were overreacting.” People would come with all these different answers for what I was experiencing, and that was frustrating. That was even harder because I had to cope with everything that was happening and I had no one to turn to. I had no mentors.
When I looked up to women who were in surgery, they would be tougher on us young surgeons than the men and they would tell us that we should not complain because in their time it was even harder. Now, it’s getting better and we are supposed to accept whatever comes.
That was at least a little bit of what I experienced in my training. It was only after I finished and started to do research about it that I really encountered a field of people who would echo what I was trying to say to many people in different hospitals that I attended to.
That was the key for me to get out of that situation of being gaslighted and of not being able to really talk about it. Suddenly, I started to publish things about Brazil that nobody was even writing or studying. That gave me a large amount of responsibility, but also motivation to keep going and to see the change.
Valuing women in medicine
Dr. Glatter: This is a very important point that you’re raising about the environment of women being hard on other women. We know that men can be very difficult on and also judgmental toward their trainees.
Amy, how would you respond to that? Was your experience similar in emergency medicine training?
Dr. Ho: I actually don’t feel like it was. I think what Júlia is alluding to is this “mean girls” idea, of “I went through it and thus you have to go through it.” I think you do see this in many specialties. One of the classic ones we hear about, and I don’t want to speak to it too much because it’s not my specialty, is ob.gyn., where it is a very female-dominant surgery group. There’s almost a hazing level that you hear about in some of the more malignant workplaces.
I think that you speak to two really important things. Number one is the numbers game. As you were saying, Brazil actually has many women. That’s awesome. That’s actually different from the United States, especially for the historic, existing workplace and less so for the medical students and for residents. I think step one is having minorities like women just present and there.
Step two is actually including and valuing them. While I think it’s really easy to move away from the women discussion, because there are women when you look around in medicine, it doesn’t mean that women are actually being heard, that they’re actually being accepted, or that their viewpoints are being listened to. A big part of it is normalizing not only seeing women in medicine but also normalizing the narrative of women in medicine.
It’s not just about motherhood; it’s about things like normalizing talking about advancement, academic promotions, pay, culture, being called things like “too reactive,” “anxious,” or “too assertive.” These are all classic things that we hear about when we talk about women.
That’s why we’re looking to not only conversations like this, but also structured ways for women to discuss being women in medicine. There are many women in medicine groups in emergency medicine, including: Females Working in Emergency Medicine (FemInEM); the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) and Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM) women’s groups, which are American Association of Women Emergency Physicians (AAWEP) and Academy for Women in Academic Emergency Medicine (AWAEM), respectively; and the American Medical Women’s Association (AMWA), which is the American Medical Association’s offshoot.
All of these groups are geared toward normalizing women in medicine, normalizing the narrative of women in medicine, and then working on mentoring and educating so that we can advance our initiatives.
Gender balance is not gender equity
Dr. Glatter: Amy, you bring up a very critical point that mentoring is sort of the antidote to gender-based discrimination. Júlia had written a paper back in November of 2022 that was published in the Journal of Surgical Research talking exactly about this and how important it is to develop mentoring. Part of her research showed that about 20% of medical students who took the survey, about 1,000 people, had mentors, which was very disturbing.
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Mentorship is one of the ways of changing the reality about gender-based discrimination. Amy’s comment was very strong and we need to really keep saying it, which is that gender balance is not gender equity.
The idea of having more women is not the same as women being recognized as equals, as able as men, and as valued as men. To change this very long culture of male domination, we need support, and this support comes from mentorship.
Although I didn’t have one, I feel that since I started being a mentor for some students, it changed not only them but myself. It gave me strength to keep going, studying, publishing, and going further with this discussion. I feel like the relationship was as good for them as it is for me. That’s how things change.
Diversity, equity, and inclusion training
Dr. Glatter: We’re talking about the reality of gender equity in terms of the ability to have equal respect, recognition, opportunities, and access. That’s really an important point to realize, and for our audience, to understand that gender equity is not gender balance.
Amy, I want to talk about medical school curriculums. Are there advances that you’re aware of being made at certain schools, programs, even in residencies, to enforce these things and make it a priority?
Dr. Ho: We’re really lucky that, as a culture in the United States, medical training is certainly very geared toward diversity. Some of that is certainly unofficial. Some of that just means when they’re looking at a medical school class or looking at rank lists for residency, that they’re cognizant of the different backgrounds that people have. That’s still a step. That is a step, that we’re at least acknowledging it.
There are multiple medical schools and residencies that have more formal unconscious-bias training or diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) training, both of which are excellent not only for us in the workplace but also for our patients. Almost all of us will see patients of highly diverse backgrounds. I think the biggest push is looking toward the criteria that we use for selecting trainees and students into our programs. Historically, it’s been MCAT, GPA, and so on.
We’ve really started to ask the question of, are these sorts of “objective criteria” actually biased in institutional ways? They talk about this all the time where GPAs will bias against students from underrepresented minorities (URM). I think all medical students and residencies have really acknowledged that. Although there are still test cutoffs, we are putting an inquisitive eye to what those mean, why they exist, and what are the other things that we should consider. This is all very heartening from what I’m seeing in medical training.
Dr. Glatter: There’s no formal rating system for DEI curriculums right now, like ranking of this school, or this program has more advanced recognition in terms of DEI?
Dr. Ho: No, but on the flip side, the U.S. News & World Report was classically one of the major rankings for medical schools. What we saw fairly recently was that very high-tier schools like Harvard and University of Chicago pulled out of that ranking because that ranking did not acknowledge the value of diversity. That was an incredible stance for medical schools to take, to say, “Hey, you are not evaluating an important criterion of ours.”
Dr. Glatter: That’s a great point. Júlia, where are we now in Brazil in terms of awareness of DEI and curriculum in schools and training programs?
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Our reality is not as good as in the U.S., unfortunately. I don’t see much discussion on residency programs or medical schools at the moment. I see many students bringing it out and trying to make their schools engage in that discussion. This is something that is coming from the bottom up and not from the top down. I think it can lead to change as well. It is a step and it’s a beginning. Institutions should take the responsibility of doing this from the beginning. This is something where Brazil is still years behind you guys.
Dr. Glatter: It’s unfortunate, but certainly it’s important to hear that. What about in Canada and certainly your institution, McGill, where you just completed a master’s degree?
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Canada is very much like the U.S. This is something that is really happening and it’s happening fast. I see, at least at McGill, a large amount of DEI inclusion and everything on this discussion. They have institutional courses for us to do as students, and we are all obliged to do many courses, which I think is really educating, especially for people with different cultures and backgrounds.
Dr. Glatter: Amy, where do you think we are in emergency medicine to look at the other side of it? Comparing surgery with emergency medicine, do you think we’re well advanced in terms of DEI, inclusion criteria, respect, and dignity, or are we really far off?
Dr. Ho: I may be biased, but I think emergency medicine is one of the best in terms of this, and I think there are a couple of reasons for it. One is that we are an inherently team-based organization. The attending, the residents, and the students all work in line with one another. There’s less of a hierarchy.
The same is true for our nurses, pharmacists, techs, and EMS. We all work together as a team. Because of that fairly flat structure, it’s really easy for us to value one another as individuals with our diverse backgrounds. In a way, that’s harder for specialties that are more hierarchical, and I think surgery is certainly one of the most hierarchical.
The second reason why emergency medicine is fairly well off in this is that we’re, by nature, a safety-net specialty. We see patients of all-comers, all walks, all backgrounds. I think we both recognize the value of physician-patient concordance. When we share characteristics with our patients, we recognize that value immediately at the bedside.
It exposes us to so much diversity. I see a refugee one day and the next patient is someone who is incarcerated. The next patient after that is an important businessman in society. That diversity and whiplash in the type of patients that we see back-to-back helps us see the playing field in a really flat, diverse way. Because of that, I think our culture is much better, as is our understanding of the value and importance of diversity not only for our programs, but also for our patients.
Do female doctors have better patient outcomes?
Dr. Glatter: Specialties working together in the emergency department is so important. Building that team and that togetherness is so critical. Júlia, would you agree?
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Definitely. Something Amy said that is beautiful is that you recognize yourself in these patients. In surgery, we are taught to try to be away from the patients and not to put ourselves in the same position. We are taught to be less engaging, and this is not good. The good thing is when we really have patient-centered care, when we listen to them, and when we are involved with them.
I saw a publication showing that female and male surgeons treating similar patients had the same surgical outcomes. Women are as good as men technically to do surgery and have the same surgical outcomes. However, there is research showing that surgical teams with greater representation of women have improved surgical outcomes because of patient-centered care and the way women conduct bedside attention to patients. And they have better patient experience measures afterward. That is not only from the women who are treating the patients, but the whole environment. Women end up bringing men [into the conversation] and this better improves patient-centered care, and that makes the whole team a better team attending patients. Definitely, we are in the moment of patient experience and satisfaction, and increasing women is a way of achieving better patient satisfaction and experience.
Dr. Ho: There’s much to be said about having female clinicians available for patients. It doesn’t have to be just for female patients, although again, concordance between physicians and patients is certainly beneficial. Besides outcomes benefit, there’s even just a communication benefit. The way that women and men communicate is inherently different. The way women and men experience certain things is also inherently different.
A classic example of this is women who are experiencing a heart attack may not actually have chest pain but present with nausea. As a female who’s sensitive to this, when I see a woman throwing up, I am very attuned to something actually being wrong, knowing that they may not present with classic pain for a syndrome, but actually may be presenting with nausea instead. It doesn’t have to be a woman who takes that knowledge and turns it into something at the bedside. It certainly doesn’t have to, but it is just a natural, easy thing to step into as a female.
While I’m really careful to not step into this “women are better than men” or “men are better than women” argument, there’s something to be said about how the availability of female clinicians for all patients, not just female patients, can have benefit. Again, it’s shown in studies with cardiovascular outcomes and cardiologists, it’s certainly shown in ob.gyn., particularly for underrepresented minorities as well for maternal outcomes of Black mothers. It’s certainly shown again in patient satisfaction, which is concordance.
There is a profound level of research already on this that goes beyond just the idea of stacking the bench and putting more women in there. That’s not the value. We’re not just here to check off the box. We’re here to actually lend some value to our patients and, again, to one another as well.
Dr. Glatter: Absolutely. These are excellent points. The point you make about patient presentation is so vital. The fact that women have nausea sometimes in ACS presentations, the research never was really attentive to this. It was biased. The symptoms that women may have that are not “typical” for ACS weren’t included in patient presentations. Educating everyone about, overall, the types of presentations that we can recognize is vital and important.
Dr. Ho: Yes. It’s worth saying that, when you look at how medicine and research developed, classically, who were the research participants? They were often White men. They were college students who, historically, because women were not allowed to go to college, were men.
I say that not to fault the institution, because that was the culture of our history, but to just say it is okay to question things. It is okay to realize that someone’s presenting outside of the box and that maybe we actually need to reframe what even created the walls of the box in the first place.
Dr. Glatter: Thank you again for joining us. I truly appreciate your insight and expertise.
Dr. Glatter is assistant professor of emergency medicine, department of emergency medicine, Hofstra/Northwell, New York. Dr. Ho is senior vice president of clinical informatics & analytics, department of emergency medicine, Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas. Dr. Loyola Ferreira is a master of science candidate, department of experimental surgery, McGill University, Montreal. They reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical adviser for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Joining me to discuss ways to address and reform the toxic culture associated with medical training is Dr. Amy Faith Ho, senior vice president of clinical informatics and analytics at Integrative Emergency Services in Dallas. Also joining us is Dr. Júlia Loyola Ferreira, a pediatric surgeon originally from Brazil, now practicing at Montreal Children’s and focused on advocacy for gender equity and patient-centered care.
Welcome to both of you. Thanks so much for joining me.
Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH: Thanks so much for having us, Rob.
Dr. Glatter: Amy, I noticed a tweet recently where you talked about how your career choice was affected by the toxic environment in medical school, affecting your choice of residency. Can you elaborate on that?
Dr. Ho: In this instance, what we’re talking about is gender, but it can be directed toward any number of other groups as well.
What you’re alluding to is a tweet by Stanford Surgery Group showing the next residency class, and what was really stunning about this residency class was that it was almost all females. And this was something that took off on social media.
When I saw this, I was really brought back to one of my personal experiences that I chose to share, which was basically that, as a medical student, I really wanted to be a surgeon. I’m an emergency medicine doctor now, so you know that didn’t happen.
The story that I was sharing was that when I was a third-year medical student rotating on surgery, we had a male attending who was very well known at that school at the time who basically would take the female medical students, and instead of clinic, he would round us up. He would have us sit around him in the workplace room while everyone else was seeing patients, and he would have you look at news clippings of himself. He would tell you stories about himself, like he was holding court for the ladies.
It was this very weird culture where my takeaway as a med student was like, “Wow, this is kind of abusive patriarchy that is supported,” because everyone knew about it and was complicit. Even though I really liked surgery, this was just one instance and one example of where you see this culture that really resonates into the rest of life that I didn’t really want to be a part of.
I went into emergency medicine and loved it. It’s also highly procedural, and I was very happy with where I was. What was really interesting about this tweet to me, though, is that it really took off and garnered hundreds of thousands of views on a very niche topic, because what was most revealing is that everyone has a story like this.
It is not just surgery. It is definitely not just one specialty and it is not just one school. It is an endemic problem in medicine. Not only does it change the lives of young women, but it also says so much about the complicity and the culture that we have in medicine that many people were upset about just the same way I was.
Medical training experience in other countries vs. the United States
Dr. Glatter: Júlia, I want to hear about your experience in medical school, surgery, and then fellowship training and up to the present, if possible.
Júlia Loyola Ferreira, MD: In Brazil, as in many countries now, women have made up the majority of the medical students since 2010. It’s a more female-friendly environment when you’re going through medical school, and I was lucky enough to do rotations in areas of surgery where people were friendly to women.
I lived in this tiny bubble that also gave me the privilege of not facing some things that I can imagine that people in Brazil in different areas and smaller towns face. In Brazil, people try to not talk about this gender agenda. This is something that’s being talked about outside Brazil. But in Brazil, we are years back. People are not really engaging on this conversation. I thought it was going to be hard for me as a woman, because Brazil has around 20% female surgeons.
I knew it was going to be challenging, but I had no idea how bad it was. When I started and things started happening, the list was big. I have an example of everything that is written about – microaggression, implicit bias, discrimination, harassment.
Every time I would try to speak about it and talk to someone, I would be strongly gaslighted. It was the whole training, the whole 5 years. People would say, “Oh, I don’t think it was like that. I think you were overreacting.” People would come with all these different answers for what I was experiencing, and that was frustrating. That was even harder because I had to cope with everything that was happening and I had no one to turn to. I had no mentors.
When I looked up to women who were in surgery, they would be tougher on us young surgeons than the men and they would tell us that we should not complain because in their time it was even harder. Now, it’s getting better and we are supposed to accept whatever comes.
That was at least a little bit of what I experienced in my training. It was only after I finished and started to do research about it that I really encountered a field of people who would echo what I was trying to say to many people in different hospitals that I attended to.
That was the key for me to get out of that situation of being gaslighted and of not being able to really talk about it. Suddenly, I started to publish things about Brazil that nobody was even writing or studying. That gave me a large amount of responsibility, but also motivation to keep going and to see the change.
Valuing women in medicine
Dr. Glatter: This is a very important point that you’re raising about the environment of women being hard on other women. We know that men can be very difficult on and also judgmental toward their trainees.
Amy, how would you respond to that? Was your experience similar in emergency medicine training?
Dr. Ho: I actually don’t feel like it was. I think what Júlia is alluding to is this “mean girls” idea, of “I went through it and thus you have to go through it.” I think you do see this in many specialties. One of the classic ones we hear about, and I don’t want to speak to it too much because it’s not my specialty, is ob.gyn., where it is a very female-dominant surgery group. There’s almost a hazing level that you hear about in some of the more malignant workplaces.
I think that you speak to two really important things. Number one is the numbers game. As you were saying, Brazil actually has many women. That’s awesome. That’s actually different from the United States, especially for the historic, existing workplace and less so for the medical students and for residents. I think step one is having minorities like women just present and there.
Step two is actually including and valuing them. While I think it’s really easy to move away from the women discussion, because there are women when you look around in medicine, it doesn’t mean that women are actually being heard, that they’re actually being accepted, or that their viewpoints are being listened to. A big part of it is normalizing not only seeing women in medicine but also normalizing the narrative of women in medicine.
It’s not just about motherhood; it’s about things like normalizing talking about advancement, academic promotions, pay, culture, being called things like “too reactive,” “anxious,” or “too assertive.” These are all classic things that we hear about when we talk about women.
That’s why we’re looking to not only conversations like this, but also structured ways for women to discuss being women in medicine. There are many women in medicine groups in emergency medicine, including: Females Working in Emergency Medicine (FemInEM); the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) and Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM) women’s groups, which are American Association of Women Emergency Physicians (AAWEP) and Academy for Women in Academic Emergency Medicine (AWAEM), respectively; and the American Medical Women’s Association (AMWA), which is the American Medical Association’s offshoot.
All of these groups are geared toward normalizing women in medicine, normalizing the narrative of women in medicine, and then working on mentoring and educating so that we can advance our initiatives.
Gender balance is not gender equity
Dr. Glatter: Amy, you bring up a very critical point that mentoring is sort of the antidote to gender-based discrimination. Júlia had written a paper back in November of 2022 that was published in the Journal of Surgical Research talking exactly about this and how important it is to develop mentoring. Part of her research showed that about 20% of medical students who took the survey, about 1,000 people, had mentors, which was very disturbing.
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Mentorship is one of the ways of changing the reality about gender-based discrimination. Amy’s comment was very strong and we need to really keep saying it, which is that gender balance is not gender equity.
The idea of having more women is not the same as women being recognized as equals, as able as men, and as valued as men. To change this very long culture of male domination, we need support, and this support comes from mentorship.
Although I didn’t have one, I feel that since I started being a mentor for some students, it changed not only them but myself. It gave me strength to keep going, studying, publishing, and going further with this discussion. I feel like the relationship was as good for them as it is for me. That’s how things change.
Diversity, equity, and inclusion training
Dr. Glatter: We’re talking about the reality of gender equity in terms of the ability to have equal respect, recognition, opportunities, and access. That’s really an important point to realize, and for our audience, to understand that gender equity is not gender balance.
Amy, I want to talk about medical school curriculums. Are there advances that you’re aware of being made at certain schools, programs, even in residencies, to enforce these things and make it a priority?
Dr. Ho: We’re really lucky that, as a culture in the United States, medical training is certainly very geared toward diversity. Some of that is certainly unofficial. Some of that just means when they’re looking at a medical school class or looking at rank lists for residency, that they’re cognizant of the different backgrounds that people have. That’s still a step. That is a step, that we’re at least acknowledging it.
There are multiple medical schools and residencies that have more formal unconscious-bias training or diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) training, both of which are excellent not only for us in the workplace but also for our patients. Almost all of us will see patients of highly diverse backgrounds. I think the biggest push is looking toward the criteria that we use for selecting trainees and students into our programs. Historically, it’s been MCAT, GPA, and so on.
We’ve really started to ask the question of, are these sorts of “objective criteria” actually biased in institutional ways? They talk about this all the time where GPAs will bias against students from underrepresented minorities (URM). I think all medical students and residencies have really acknowledged that. Although there are still test cutoffs, we are putting an inquisitive eye to what those mean, why they exist, and what are the other things that we should consider. This is all very heartening from what I’m seeing in medical training.
Dr. Glatter: There’s no formal rating system for DEI curriculums right now, like ranking of this school, or this program has more advanced recognition in terms of DEI?
Dr. Ho: No, but on the flip side, the U.S. News & World Report was classically one of the major rankings for medical schools. What we saw fairly recently was that very high-tier schools like Harvard and University of Chicago pulled out of that ranking because that ranking did not acknowledge the value of diversity. That was an incredible stance for medical schools to take, to say, “Hey, you are not evaluating an important criterion of ours.”
Dr. Glatter: That’s a great point. Júlia, where are we now in Brazil in terms of awareness of DEI and curriculum in schools and training programs?
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Our reality is not as good as in the U.S., unfortunately. I don’t see much discussion on residency programs or medical schools at the moment. I see many students bringing it out and trying to make their schools engage in that discussion. This is something that is coming from the bottom up and not from the top down. I think it can lead to change as well. It is a step and it’s a beginning. Institutions should take the responsibility of doing this from the beginning. This is something where Brazil is still years behind you guys.
Dr. Glatter: It’s unfortunate, but certainly it’s important to hear that. What about in Canada and certainly your institution, McGill, where you just completed a master’s degree?
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Canada is very much like the U.S. This is something that is really happening and it’s happening fast. I see, at least at McGill, a large amount of DEI inclusion and everything on this discussion. They have institutional courses for us to do as students, and we are all obliged to do many courses, which I think is really educating, especially for people with different cultures and backgrounds.
Dr. Glatter: Amy, where do you think we are in emergency medicine to look at the other side of it? Comparing surgery with emergency medicine, do you think we’re well advanced in terms of DEI, inclusion criteria, respect, and dignity, or are we really far off?
Dr. Ho: I may be biased, but I think emergency medicine is one of the best in terms of this, and I think there are a couple of reasons for it. One is that we are an inherently team-based organization. The attending, the residents, and the students all work in line with one another. There’s less of a hierarchy.
The same is true for our nurses, pharmacists, techs, and EMS. We all work together as a team. Because of that fairly flat structure, it’s really easy for us to value one another as individuals with our diverse backgrounds. In a way, that’s harder for specialties that are more hierarchical, and I think surgery is certainly one of the most hierarchical.
The second reason why emergency medicine is fairly well off in this is that we’re, by nature, a safety-net specialty. We see patients of all-comers, all walks, all backgrounds. I think we both recognize the value of physician-patient concordance. When we share characteristics with our patients, we recognize that value immediately at the bedside.
It exposes us to so much diversity. I see a refugee one day and the next patient is someone who is incarcerated. The next patient after that is an important businessman in society. That diversity and whiplash in the type of patients that we see back-to-back helps us see the playing field in a really flat, diverse way. Because of that, I think our culture is much better, as is our understanding of the value and importance of diversity not only for our programs, but also for our patients.
Do female doctors have better patient outcomes?
Dr. Glatter: Specialties working together in the emergency department is so important. Building that team and that togetherness is so critical. Júlia, would you agree?
Dr. Loyola Ferreira: Definitely. Something Amy said that is beautiful is that you recognize yourself in these patients. In surgery, we are taught to try to be away from the patients and not to put ourselves in the same position. We are taught to be less engaging, and this is not good. The good thing is when we really have patient-centered care, when we listen to them, and when we are involved with them.
I saw a publication showing that female and male surgeons treating similar patients had the same surgical outcomes. Women are as good as men technically to do surgery and have the same surgical outcomes. However, there is research showing that surgical teams with greater representation of women have improved surgical outcomes because of patient-centered care and the way women conduct bedside attention to patients. And they have better patient experience measures afterward. That is not only from the women who are treating the patients, but the whole environment. Women end up bringing men [into the conversation] and this better improves patient-centered care, and that makes the whole team a better team attending patients. Definitely, we are in the moment of patient experience and satisfaction, and increasing women is a way of achieving better patient satisfaction and experience.
Dr. Ho: There’s much to be said about having female clinicians available for patients. It doesn’t have to be just for female patients, although again, concordance between physicians and patients is certainly beneficial. Besides outcomes benefit, there’s even just a communication benefit. The way that women and men communicate is inherently different. The way women and men experience certain things is also inherently different.
A classic example of this is women who are experiencing a heart attack may not actually have chest pain but present with nausea. As a female who’s sensitive to this, when I see a woman throwing up, I am very attuned to something actually being wrong, knowing that they may not present with classic pain for a syndrome, but actually may be presenting with nausea instead. It doesn’t have to be a woman who takes that knowledge and turns it into something at the bedside. It certainly doesn’t have to, but it is just a natural, easy thing to step into as a female.
While I’m really careful to not step into this “women are better than men” or “men are better than women” argument, there’s something to be said about how the availability of female clinicians for all patients, not just female patients, can have benefit. Again, it’s shown in studies with cardiovascular outcomes and cardiologists, it’s certainly shown in ob.gyn., particularly for underrepresented minorities as well for maternal outcomes of Black mothers. It’s certainly shown again in patient satisfaction, which is concordance.
There is a profound level of research already on this that goes beyond just the idea of stacking the bench and putting more women in there. That’s not the value. We’re not just here to check off the box. We’re here to actually lend some value to our patients and, again, to one another as well.
Dr. Glatter: Absolutely. These are excellent points. The point you make about patient presentation is so vital. The fact that women have nausea sometimes in ACS presentations, the research never was really attentive to this. It was biased. The symptoms that women may have that are not “typical” for ACS weren’t included in patient presentations. Educating everyone about, overall, the types of presentations that we can recognize is vital and important.
Dr. Ho: Yes. It’s worth saying that, when you look at how medicine and research developed, classically, who were the research participants? They were often White men. They were college students who, historically, because women were not allowed to go to college, were men.
I say that not to fault the institution, because that was the culture of our history, but to just say it is okay to question things. It is okay to realize that someone’s presenting outside of the box and that maybe we actually need to reframe what even created the walls of the box in the first place.
Dr. Glatter: Thank you again for joining us. I truly appreciate your insight and expertise.
Dr. Glatter is assistant professor of emergency medicine, department of emergency medicine, Hofstra/Northwell, New York. Dr. Ho is senior vice president of clinical informatics & analytics, department of emergency medicine, Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas. Dr. Loyola Ferreira is a master of science candidate, department of experimental surgery, McGill University, Montreal. They reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Acute diffuse rash on trunk
This patient’s diffusely erythematous and scaly rash, in association with recent antibiotic use, was a classic presentation of a drug eruption. Drug eruptions are adverse cutaneous reactions to various medications; they frequently involve antibiotics and anti-epileptics. They can manifest in a multitude of ways with different morphologies. Medication history and timing to onset of symptoms are paramount in making the diagnosis.
Classic reactions include those that are morbilliform (erythematous macules and papules), lichenoid (violaceous and hyperpigmented papules), exfoliative/erythrodermic, and/or urticarial.1 Petechiae and palpable purpura may also manifest.1 Severe reactions, while less common, must always be considered, given their significant morbidity and mortality. These include2:
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis with diffuse erythema and areas of denuded, necrotic epidermis,
- Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, and
- Acute, generalized, exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) consisting of confluent, nonfollicular pustules.
A general principle in the management of drug eruptions is the discontinuation of the offending drug (if known) as soon as possible. If the agent is not known, it is important to discontinue all drugs that are not deemed as essential, particularly medications that are often associated with reactions, such as antibiotics and anti-epileptics. Additionally, evaluation of the oral mucosa, eyes, and genitourinary tract is helpful to diagnose Stevens-Johnson syndrome, if indicated by symptoms or history.
Wound care with cleansing and covering of denuded skin with emollients and wet dressings should be performed. Infections are common complications in these patients due to the increased inflammation, fissuring, and excoriations that accompany the rash, with sepsis from staphylococcal bacteria being the most concerning complication of infection. Additionally, the compromised skin barrier may lead to heat loss and hypothermia, a compensatory hypermetabolism with hyperthermia, and electrolyte imbalances from insensible water losses.2
Most mild eruptions can be treated with topical corticosteroids and antihistamines. However, in severe eruptions, systemic corticosteroids, or referral for immunosuppressive and anticytokine therapies, also should be considered.1
This patient was treated with both a short course of systemic corticosteroids (prednisone 40 mg/d for 5 days, then tapered over 15 days) and topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% ointment bid) for symptomatic care. He also was started on an antihistamine (cetirizine 10 mg bid) for itching. Doxycycline and Augmentin were added to his allergy list. At a 1-week follow up, the patient had near resolution of his rash.
Images courtesy of Jose L. Cortez, MD. Text courtesy of Jose L. Cortez, MD, Department of Dermatology, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Riedl MA, Casillas AM. Adverse drug reactions: types and treatment options. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68:1781-1790.
2. Zhang J, Lei Z, Xu C, et al. Current perspectives on severe drug eruption. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021;61:282-298. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08859-0

This patient’s diffusely erythematous and scaly rash, in association with recent antibiotic use, was a classic presentation of a drug eruption. Drug eruptions are adverse cutaneous reactions to various medications; they frequently involve antibiotics and anti-epileptics. They can manifest in a multitude of ways with different morphologies. Medication history and timing to onset of symptoms are paramount in making the diagnosis.
Classic reactions include those that are morbilliform (erythematous macules and papules), lichenoid (violaceous and hyperpigmented papules), exfoliative/erythrodermic, and/or urticarial.1 Petechiae and palpable purpura may also manifest.1 Severe reactions, while less common, must always be considered, given their significant morbidity and mortality. These include2:
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis with diffuse erythema and areas of denuded, necrotic epidermis,
- Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, and
- Acute, generalized, exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) consisting of confluent, nonfollicular pustules.
A general principle in the management of drug eruptions is the discontinuation of the offending drug (if known) as soon as possible. If the agent is not known, it is important to discontinue all drugs that are not deemed as essential, particularly medications that are often associated with reactions, such as antibiotics and anti-epileptics. Additionally, evaluation of the oral mucosa, eyes, and genitourinary tract is helpful to diagnose Stevens-Johnson syndrome, if indicated by symptoms or history.
Wound care with cleansing and covering of denuded skin with emollients and wet dressings should be performed. Infections are common complications in these patients due to the increased inflammation, fissuring, and excoriations that accompany the rash, with sepsis from staphylococcal bacteria being the most concerning complication of infection. Additionally, the compromised skin barrier may lead to heat loss and hypothermia, a compensatory hypermetabolism with hyperthermia, and electrolyte imbalances from insensible water losses.2
Most mild eruptions can be treated with topical corticosteroids and antihistamines. However, in severe eruptions, systemic corticosteroids, or referral for immunosuppressive and anticytokine therapies, also should be considered.1
This patient was treated with both a short course of systemic corticosteroids (prednisone 40 mg/d for 5 days, then tapered over 15 days) and topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% ointment bid) for symptomatic care. He also was started on an antihistamine (cetirizine 10 mg bid) for itching. Doxycycline and Augmentin were added to his allergy list. At a 1-week follow up, the patient had near resolution of his rash.
Images courtesy of Jose L. Cortez, MD. Text courtesy of Jose L. Cortez, MD, Department of Dermatology, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.

This patient’s diffusely erythematous and scaly rash, in association with recent antibiotic use, was a classic presentation of a drug eruption. Drug eruptions are adverse cutaneous reactions to various medications; they frequently involve antibiotics and anti-epileptics. They can manifest in a multitude of ways with different morphologies. Medication history and timing to onset of symptoms are paramount in making the diagnosis.
Classic reactions include those that are morbilliform (erythematous macules and papules), lichenoid (violaceous and hyperpigmented papules), exfoliative/erythrodermic, and/or urticarial.1 Petechiae and palpable purpura may also manifest.1 Severe reactions, while less common, must always be considered, given their significant morbidity and mortality. These include2:
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis with diffuse erythema and areas of denuded, necrotic epidermis,
- Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, and
- Acute, generalized, exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) consisting of confluent, nonfollicular pustules.
A general principle in the management of drug eruptions is the discontinuation of the offending drug (if known) as soon as possible. If the agent is not known, it is important to discontinue all drugs that are not deemed as essential, particularly medications that are often associated with reactions, such as antibiotics and anti-epileptics. Additionally, evaluation of the oral mucosa, eyes, and genitourinary tract is helpful to diagnose Stevens-Johnson syndrome, if indicated by symptoms or history.
Wound care with cleansing and covering of denuded skin with emollients and wet dressings should be performed. Infections are common complications in these patients due to the increased inflammation, fissuring, and excoriations that accompany the rash, with sepsis from staphylococcal bacteria being the most concerning complication of infection. Additionally, the compromised skin barrier may lead to heat loss and hypothermia, a compensatory hypermetabolism with hyperthermia, and electrolyte imbalances from insensible water losses.2
Most mild eruptions can be treated with topical corticosteroids and antihistamines. However, in severe eruptions, systemic corticosteroids, or referral for immunosuppressive and anticytokine therapies, also should be considered.1
This patient was treated with both a short course of systemic corticosteroids (prednisone 40 mg/d for 5 days, then tapered over 15 days) and topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% ointment bid) for symptomatic care. He also was started on an antihistamine (cetirizine 10 mg bid) for itching. Doxycycline and Augmentin were added to his allergy list. At a 1-week follow up, the patient had near resolution of his rash.
Images courtesy of Jose L. Cortez, MD. Text courtesy of Jose L. Cortez, MD, Department of Dermatology, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Riedl MA, Casillas AM. Adverse drug reactions: types and treatment options. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68:1781-1790.
2. Zhang J, Lei Z, Xu C, et al. Current perspectives on severe drug eruption. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021;61:282-298. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08859-0
1. Riedl MA, Casillas AM. Adverse drug reactions: types and treatment options. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68:1781-1790.
2. Zhang J, Lei Z, Xu C, et al. Current perspectives on severe drug eruption. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021;61:282-298. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08859-0
Cell activity in psoriasis may predict disease severity and provide clues to comorbidities
The activity and clustering of certain cell types may distinguish mild and severe forms of psoriasis, with severe disease altering the cellular and metabolic composition of distal unaffected skin sites, according to a new analysis using single-cell transcriptomic technology.
On the surface, psoriasis severity is identified based on the visible lesions, Rochelle L. Castillo, MD, of the division of rheumatology and the NYU Psoriatic Arthritis Center, NYU Langone Health, New York, and colleagues wrote in their study, published in Science Immunology. Although cellular and molecular features of inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis have been characterized, activity at the tissue level and its systemic impact has not been explored.
“Our initial goal was to find measurable molecular signals that could tell us who is more likely to develop severe psoriasis, as well as who is at higher risk of developing related disorders that often accompany psoriasis, such as arthritis and cardiovascular disease,” study co–senior investigator Jose Scher, MD, director of the Psoriatic Arthritis Center and the Judith and Stewart Colton Center for Autoimmunity at NYU Langone Health, said in a press release accompanying the publication of the findings. “Having found signals with potential systemic consequences, we are now working to understand how skin inflammation can lead to widespread disease affecting other organs,”
In the study, the researchers used spatial transcriptomics, a technique that positions tissue sections onto genetic arrays to determine gene expression by cell type and histological location, helping to create a broad image-based map of where certain cell types are located in tissues and with what other cells they are communicating. They characterized the cell activity of skin samples from 11 men and women with mild to severe psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis, and three healthy adults who did not have psoriasis. They defined the cellular composition of 25 healthy skin biopsies and matched skin biopsies from psoriatic lesional and nonlesional skin, and identified 17 distinct clusters of cells, which they grouped into epidermal, dermis, pilosebaceous, and adipose categories.
The researchers found that cell activity associated with inflammation, as shown by clusters of fibroblasts and dermal macrophages, was more common in the upper layers of the skin in samples from patients with more severe psoriasis, compared with healthy control samples.
They also examined patterns of immune activity at the cellular level and found significant patterns around the upper follicle, around the perifollicular dermis, and within the hair follicle, where immune cells were enriched in healthy skin. Other cells enriched in these upper layer areas in healthy skin included dendritic cells, innate lymphoid cells, T helper cells, T cytotoxic cells, and myeloid cells.
Clusters of fibroblasts and macrophages, which are associated with inflammation, were clustered in psoriatic lesional skin, which also showed more inflammation at the dermal and suprabasal epidermal levels. B lymphocytes also were more prevalent in lesional skin.
The researchers then analyzed the skin samples according to disease severity; mild psoriasis was defined as a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score less than 12; moderate to severe disease was defined as a PASI score of 12 or higher. The macrophage, fibroblast, and lymphatic endothelium–associated clusters distinguished mild and moderate to severe endotypes.
The pathology of moderate to severe psoriasis in lesional and nonlesional skin showed the extensive effects of psoriasis-related inflammation. Although nonlesional mild disease was clustered with healthy skin, in cases of moderate to severe disease, nonlesional and lesional groups were clustered together. This effect was segregated according to disease severity, independent of the presence of joint disease, and “was particularly evident in distal, nonlesional samples,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also found evidence of increased gene activity in more than three dozen molecular pathways associated with metabolism and lipid levels in areas of lesional and nonlesional skin, Dr. Scher said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and the limits of spatial transcriptomics technology resolution, the researchers wrote. “As this technology evolves, platforms with higher density, and by extension, resolution, of spatially barcoded beads will provide more granularity about cellular microenvironments in healthy and diseased states.”
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Psoriasis Foundation, the NYU Colton Center for Autoimmunity, the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis, the Beatrice Snyder Foundation, The Riley Family Foundation, the Rheumatology Research Foundation, and the NY Stem Cell Foundation. Dr. Castillo had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Scher has served as a consultant for Janssen, Abbvie, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, UCB, and Bristol-Myers Squibb, and has received research funding from Janssen and Pfizer.
The activity and clustering of certain cell types may distinguish mild and severe forms of psoriasis, with severe disease altering the cellular and metabolic composition of distal unaffected skin sites, according to a new analysis using single-cell transcriptomic technology.
On the surface, psoriasis severity is identified based on the visible lesions, Rochelle L. Castillo, MD, of the division of rheumatology and the NYU Psoriatic Arthritis Center, NYU Langone Health, New York, and colleagues wrote in their study, published in Science Immunology. Although cellular and molecular features of inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis have been characterized, activity at the tissue level and its systemic impact has not been explored.
“Our initial goal was to find measurable molecular signals that could tell us who is more likely to develop severe psoriasis, as well as who is at higher risk of developing related disorders that often accompany psoriasis, such as arthritis and cardiovascular disease,” study co–senior investigator Jose Scher, MD, director of the Psoriatic Arthritis Center and the Judith and Stewart Colton Center for Autoimmunity at NYU Langone Health, said in a press release accompanying the publication of the findings. “Having found signals with potential systemic consequences, we are now working to understand how skin inflammation can lead to widespread disease affecting other organs,”
In the study, the researchers used spatial transcriptomics, a technique that positions tissue sections onto genetic arrays to determine gene expression by cell type and histological location, helping to create a broad image-based map of where certain cell types are located in tissues and with what other cells they are communicating. They characterized the cell activity of skin samples from 11 men and women with mild to severe psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis, and three healthy adults who did not have psoriasis. They defined the cellular composition of 25 healthy skin biopsies and matched skin biopsies from psoriatic lesional and nonlesional skin, and identified 17 distinct clusters of cells, which they grouped into epidermal, dermis, pilosebaceous, and adipose categories.
The researchers found that cell activity associated with inflammation, as shown by clusters of fibroblasts and dermal macrophages, was more common in the upper layers of the skin in samples from patients with more severe psoriasis, compared with healthy control samples.
They also examined patterns of immune activity at the cellular level and found significant patterns around the upper follicle, around the perifollicular dermis, and within the hair follicle, where immune cells were enriched in healthy skin. Other cells enriched in these upper layer areas in healthy skin included dendritic cells, innate lymphoid cells, T helper cells, T cytotoxic cells, and myeloid cells.
Clusters of fibroblasts and macrophages, which are associated with inflammation, were clustered in psoriatic lesional skin, which also showed more inflammation at the dermal and suprabasal epidermal levels. B lymphocytes also were more prevalent in lesional skin.
The researchers then analyzed the skin samples according to disease severity; mild psoriasis was defined as a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score less than 12; moderate to severe disease was defined as a PASI score of 12 or higher. The macrophage, fibroblast, and lymphatic endothelium–associated clusters distinguished mild and moderate to severe endotypes.
The pathology of moderate to severe psoriasis in lesional and nonlesional skin showed the extensive effects of psoriasis-related inflammation. Although nonlesional mild disease was clustered with healthy skin, in cases of moderate to severe disease, nonlesional and lesional groups were clustered together. This effect was segregated according to disease severity, independent of the presence of joint disease, and “was particularly evident in distal, nonlesional samples,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also found evidence of increased gene activity in more than three dozen molecular pathways associated with metabolism and lipid levels in areas of lesional and nonlesional skin, Dr. Scher said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and the limits of spatial transcriptomics technology resolution, the researchers wrote. “As this technology evolves, platforms with higher density, and by extension, resolution, of spatially barcoded beads will provide more granularity about cellular microenvironments in healthy and diseased states.”
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Psoriasis Foundation, the NYU Colton Center for Autoimmunity, the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis, the Beatrice Snyder Foundation, The Riley Family Foundation, the Rheumatology Research Foundation, and the NY Stem Cell Foundation. Dr. Castillo had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Scher has served as a consultant for Janssen, Abbvie, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, UCB, and Bristol-Myers Squibb, and has received research funding from Janssen and Pfizer.
The activity and clustering of certain cell types may distinguish mild and severe forms of psoriasis, with severe disease altering the cellular and metabolic composition of distal unaffected skin sites, according to a new analysis using single-cell transcriptomic technology.
On the surface, psoriasis severity is identified based on the visible lesions, Rochelle L. Castillo, MD, of the division of rheumatology and the NYU Psoriatic Arthritis Center, NYU Langone Health, New York, and colleagues wrote in their study, published in Science Immunology. Although cellular and molecular features of inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis have been characterized, activity at the tissue level and its systemic impact has not been explored.
“Our initial goal was to find measurable molecular signals that could tell us who is more likely to develop severe psoriasis, as well as who is at higher risk of developing related disorders that often accompany psoriasis, such as arthritis and cardiovascular disease,” study co–senior investigator Jose Scher, MD, director of the Psoriatic Arthritis Center and the Judith and Stewart Colton Center for Autoimmunity at NYU Langone Health, said in a press release accompanying the publication of the findings. “Having found signals with potential systemic consequences, we are now working to understand how skin inflammation can lead to widespread disease affecting other organs,”
In the study, the researchers used spatial transcriptomics, a technique that positions tissue sections onto genetic arrays to determine gene expression by cell type and histological location, helping to create a broad image-based map of where certain cell types are located in tissues and with what other cells they are communicating. They characterized the cell activity of skin samples from 11 men and women with mild to severe psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis, and three healthy adults who did not have psoriasis. They defined the cellular composition of 25 healthy skin biopsies and matched skin biopsies from psoriatic lesional and nonlesional skin, and identified 17 distinct clusters of cells, which they grouped into epidermal, dermis, pilosebaceous, and adipose categories.
The researchers found that cell activity associated with inflammation, as shown by clusters of fibroblasts and dermal macrophages, was more common in the upper layers of the skin in samples from patients with more severe psoriasis, compared with healthy control samples.
They also examined patterns of immune activity at the cellular level and found significant patterns around the upper follicle, around the perifollicular dermis, and within the hair follicle, where immune cells were enriched in healthy skin. Other cells enriched in these upper layer areas in healthy skin included dendritic cells, innate lymphoid cells, T helper cells, T cytotoxic cells, and myeloid cells.
Clusters of fibroblasts and macrophages, which are associated with inflammation, were clustered in psoriatic lesional skin, which also showed more inflammation at the dermal and suprabasal epidermal levels. B lymphocytes also were more prevalent in lesional skin.
The researchers then analyzed the skin samples according to disease severity; mild psoriasis was defined as a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score less than 12; moderate to severe disease was defined as a PASI score of 12 or higher. The macrophage, fibroblast, and lymphatic endothelium–associated clusters distinguished mild and moderate to severe endotypes.
The pathology of moderate to severe psoriasis in lesional and nonlesional skin showed the extensive effects of psoriasis-related inflammation. Although nonlesional mild disease was clustered with healthy skin, in cases of moderate to severe disease, nonlesional and lesional groups were clustered together. This effect was segregated according to disease severity, independent of the presence of joint disease, and “was particularly evident in distal, nonlesional samples,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also found evidence of increased gene activity in more than three dozen molecular pathways associated with metabolism and lipid levels in areas of lesional and nonlesional skin, Dr. Scher said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and the limits of spatial transcriptomics technology resolution, the researchers wrote. “As this technology evolves, platforms with higher density, and by extension, resolution, of spatially barcoded beads will provide more granularity about cellular microenvironments in healthy and diseased states.”
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Psoriasis Foundation, the NYU Colton Center for Autoimmunity, the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis, the Beatrice Snyder Foundation, The Riley Family Foundation, the Rheumatology Research Foundation, and the NY Stem Cell Foundation. Dr. Castillo had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Scher has served as a consultant for Janssen, Abbvie, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, UCB, and Bristol-Myers Squibb, and has received research funding from Janssen and Pfizer.
FROM SCIENCE IMMUNOLOGY
Does weight loss surgery up the risk for bone fractures?
Currently, the two most common types of weight loss surgery performed include sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). Sleeve gastrectomy involves removing a large portion of the stomach so that its capacity is significantly decreased (to about 20%), reducing the ability to consume large quantities of food. Also, the procedure leads to marked reductions in ghrelin (an appetite-stimulating hormone), and some studies have reported increases in glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY), hormones that induce satiety. Gastric bypass involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting the small intestine so that it bypasses much of the stomach and also the upper portion of the small intestine. This reduces the amount of food that can be consumed at any time, increases levels of GLP-1 and PYY, and reduces absorption of nutrients with resultant weight loss. Less common bariatric surgeries include gastric banding and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS). Gastric banding involves placing a ring in the upper portion of the stomach, and the size of the pouch created can be altered by injecting more or less saline through a port inserted under the skin. BPD-DS includes sleeve gastrectomy, resection of a large section of the small intestine, and diversion of the pancreatic and biliary duct to a point below the junction of the ends of the resected gut.
Weight loss surgery is currently recommended for people who have a body mass index greater than or equal to 35 regardless of obesity-related complication and may be considered for those with a BMI greater than or equal to 30. BMI is calculated by dividing the weight (in kilograms) by the height (in meters). In children and adolescents, weight loss surgery should be considered in those with a BMI greater than 120% of the 95th percentile and with a major comorbidity or in those with a BMI greater than 140% of the 95th percentile.
What impact does weight loss surgery have on bone?
Multiple studies in both adults and teenagers have demonstrated that sleeve gastrectomy, RYGB, and BPD-DS (but not gastric banding) are associated with a decrease in bone density, impaired bone structure, and reduced strength estimates over time (Beavers et al; Gagnon, Schafer; Misra, Bredella). The relative risk for fracture after RYGB and BPD-DS is reported to be 1.2-2.3 (that is, 20%-130% more than normal), whereas fracture risk after sleeve gastrectomy is still under study with some conflicting results. Fracture risk starts to increase 2-3 years after surgery and peaks at 5-plus years after surgery. Most of the data for fractures come from studies in adults. With the rising use of weight loss surgery, particularly sleeve gastrectomy, in teenagers, studies are needed to determine fracture risk in this younger age group, who also seem to experience marked reductions in bone density, altered bone structure, and reduced bone strength after bariatric surgery.
What contributes to impaired bone health after weight loss surgery?
The deleterious effect of weight loss surgery on bone appears to be caused by various factors, including the massive and rapid weight loss that occurs after surgery, because body weight has a mechanical loading effect on bone and otherwise promotes bone formation. Weight loss results in mechanical unloading and thus a decrease in bone density. Further, when weight loss occurs, there is loss of both muscle and fat mass, and the reduction in muscle mass is deleterious to bone.
Other possible causes of bone density reduction include reduced absorption of certain nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D critical for bone mineralization, and alterations in certain hormones that impact bone health. These include increases in parathyroid hormone, which increases bone loss when secreted in excess; increases in PYY (a hormone that reduces bone formation); decreases in ghrelin (a hormone that typically increases bone formation), particularly after sleeve gastrectomy; and decreases in estrone (a kind of estrogen that like other estrogens prevents bone loss). Further, age and gender may modify the bone consequences of surgery as outcomes in postmenopausal women appear to be worse than in younger women and men.
Preventing bone density loss
Given the many benefits of weight loss surgery, what can we do to prevent this decrease in bone density after surgery? It’s important for people undergoing weight loss surgery to be cognizant of this potentially negative outcome and to take appropriate precautions to mitigate this concern.
We should monitor bone density after surgery with the help of dual energy x-ray absorptiometry, starting a few years after surgery, particularly in those who are at greatest risk for fracture, so that we can be proactive about addressing any severe bone loss that warrants pharmacologic intervention.
More general recommendations include optimizing intake of calcium (1,200-1,500 mg/d), vitamin D (2,000-3,000 IUs/d), and protein (60-75 g/d) via diet and/or as supplements and engaging in weight-bearing physical activity because this exerts mechanical loading effects on the skeleton leading to increased bone formation and also increases muscle mass over time, which is beneficial to bone. A progressive resistance training program has been demonstrated to have beneficial effects on bone, and measures should be taken to reduce the risk for falls, which increases after certain kinds of weight loss surgery, such as gastric bypass.
Meeting with a dietitian can help determine any other nutrients that need to be optimized.
Though many hormonal changes after surgery have been linked to reductions in bone density, there are still no recommended hormonal therapies at this time, and more work is required to determine whether specific pharmacologic therapies might help improve bone outcomes after surgery.
Dr. Misra is chief of the division of pediatric endocrinology, Mass General for Children; associate director, Harvard Catalyst Translation and Clinical Research Center; director, Pediatric Endocrine-Sports Endocrine-Neuroendocrine Lab, Mass General Hospital; and professor, department of pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Currently, the two most common types of weight loss surgery performed include sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). Sleeve gastrectomy involves removing a large portion of the stomach so that its capacity is significantly decreased (to about 20%), reducing the ability to consume large quantities of food. Also, the procedure leads to marked reductions in ghrelin (an appetite-stimulating hormone), and some studies have reported increases in glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY), hormones that induce satiety. Gastric bypass involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting the small intestine so that it bypasses much of the stomach and also the upper portion of the small intestine. This reduces the amount of food that can be consumed at any time, increases levels of GLP-1 and PYY, and reduces absorption of nutrients with resultant weight loss. Less common bariatric surgeries include gastric banding and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS). Gastric banding involves placing a ring in the upper portion of the stomach, and the size of the pouch created can be altered by injecting more or less saline through a port inserted under the skin. BPD-DS includes sleeve gastrectomy, resection of a large section of the small intestine, and diversion of the pancreatic and biliary duct to a point below the junction of the ends of the resected gut.
Weight loss surgery is currently recommended for people who have a body mass index greater than or equal to 35 regardless of obesity-related complication and may be considered for those with a BMI greater than or equal to 30. BMI is calculated by dividing the weight (in kilograms) by the height (in meters). In children and adolescents, weight loss surgery should be considered in those with a BMI greater than 120% of the 95th percentile and with a major comorbidity or in those with a BMI greater than 140% of the 95th percentile.
What impact does weight loss surgery have on bone?
Multiple studies in both adults and teenagers have demonstrated that sleeve gastrectomy, RYGB, and BPD-DS (but not gastric banding) are associated with a decrease in bone density, impaired bone structure, and reduced strength estimates over time (Beavers et al; Gagnon, Schafer; Misra, Bredella). The relative risk for fracture after RYGB and BPD-DS is reported to be 1.2-2.3 (that is, 20%-130% more than normal), whereas fracture risk after sleeve gastrectomy is still under study with some conflicting results. Fracture risk starts to increase 2-3 years after surgery and peaks at 5-plus years after surgery. Most of the data for fractures come from studies in adults. With the rising use of weight loss surgery, particularly sleeve gastrectomy, in teenagers, studies are needed to determine fracture risk in this younger age group, who also seem to experience marked reductions in bone density, altered bone structure, and reduced bone strength after bariatric surgery.
What contributes to impaired bone health after weight loss surgery?
The deleterious effect of weight loss surgery on bone appears to be caused by various factors, including the massive and rapid weight loss that occurs after surgery, because body weight has a mechanical loading effect on bone and otherwise promotes bone formation. Weight loss results in mechanical unloading and thus a decrease in bone density. Further, when weight loss occurs, there is loss of both muscle and fat mass, and the reduction in muscle mass is deleterious to bone.
Other possible causes of bone density reduction include reduced absorption of certain nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D critical for bone mineralization, and alterations in certain hormones that impact bone health. These include increases in parathyroid hormone, which increases bone loss when secreted in excess; increases in PYY (a hormone that reduces bone formation); decreases in ghrelin (a hormone that typically increases bone formation), particularly after sleeve gastrectomy; and decreases in estrone (a kind of estrogen that like other estrogens prevents bone loss). Further, age and gender may modify the bone consequences of surgery as outcomes in postmenopausal women appear to be worse than in younger women and men.
Preventing bone density loss
Given the many benefits of weight loss surgery, what can we do to prevent this decrease in bone density after surgery? It’s important for people undergoing weight loss surgery to be cognizant of this potentially negative outcome and to take appropriate precautions to mitigate this concern.
We should monitor bone density after surgery with the help of dual energy x-ray absorptiometry, starting a few years after surgery, particularly in those who are at greatest risk for fracture, so that we can be proactive about addressing any severe bone loss that warrants pharmacologic intervention.
More general recommendations include optimizing intake of calcium (1,200-1,500 mg/d), vitamin D (2,000-3,000 IUs/d), and protein (60-75 g/d) via diet and/or as supplements and engaging in weight-bearing physical activity because this exerts mechanical loading effects on the skeleton leading to increased bone formation and also increases muscle mass over time, which is beneficial to bone. A progressive resistance training program has been demonstrated to have beneficial effects on bone, and measures should be taken to reduce the risk for falls, which increases after certain kinds of weight loss surgery, such as gastric bypass.
Meeting with a dietitian can help determine any other nutrients that need to be optimized.
Though many hormonal changes after surgery have been linked to reductions in bone density, there are still no recommended hormonal therapies at this time, and more work is required to determine whether specific pharmacologic therapies might help improve bone outcomes after surgery.
Dr. Misra is chief of the division of pediatric endocrinology, Mass General for Children; associate director, Harvard Catalyst Translation and Clinical Research Center; director, Pediatric Endocrine-Sports Endocrine-Neuroendocrine Lab, Mass General Hospital; and professor, department of pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Currently, the two most common types of weight loss surgery performed include sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). Sleeve gastrectomy involves removing a large portion of the stomach so that its capacity is significantly decreased (to about 20%), reducing the ability to consume large quantities of food. Also, the procedure leads to marked reductions in ghrelin (an appetite-stimulating hormone), and some studies have reported increases in glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY), hormones that induce satiety. Gastric bypass involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting the small intestine so that it bypasses much of the stomach and also the upper portion of the small intestine. This reduces the amount of food that can be consumed at any time, increases levels of GLP-1 and PYY, and reduces absorption of nutrients with resultant weight loss. Less common bariatric surgeries include gastric banding and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS). Gastric banding involves placing a ring in the upper portion of the stomach, and the size of the pouch created can be altered by injecting more or less saline through a port inserted under the skin. BPD-DS includes sleeve gastrectomy, resection of a large section of the small intestine, and diversion of the pancreatic and biliary duct to a point below the junction of the ends of the resected gut.
Weight loss surgery is currently recommended for people who have a body mass index greater than or equal to 35 regardless of obesity-related complication and may be considered for those with a BMI greater than or equal to 30. BMI is calculated by dividing the weight (in kilograms) by the height (in meters). In children and adolescents, weight loss surgery should be considered in those with a BMI greater than 120% of the 95th percentile and with a major comorbidity or in those with a BMI greater than 140% of the 95th percentile.
What impact does weight loss surgery have on bone?
Multiple studies in both adults and teenagers have demonstrated that sleeve gastrectomy, RYGB, and BPD-DS (but not gastric banding) are associated with a decrease in bone density, impaired bone structure, and reduced strength estimates over time (Beavers et al; Gagnon, Schafer; Misra, Bredella). The relative risk for fracture after RYGB and BPD-DS is reported to be 1.2-2.3 (that is, 20%-130% more than normal), whereas fracture risk after sleeve gastrectomy is still under study with some conflicting results. Fracture risk starts to increase 2-3 years after surgery and peaks at 5-plus years after surgery. Most of the data for fractures come from studies in adults. With the rising use of weight loss surgery, particularly sleeve gastrectomy, in teenagers, studies are needed to determine fracture risk in this younger age group, who also seem to experience marked reductions in bone density, altered bone structure, and reduced bone strength after bariatric surgery.
What contributes to impaired bone health after weight loss surgery?
The deleterious effect of weight loss surgery on bone appears to be caused by various factors, including the massive and rapid weight loss that occurs after surgery, because body weight has a mechanical loading effect on bone and otherwise promotes bone formation. Weight loss results in mechanical unloading and thus a decrease in bone density. Further, when weight loss occurs, there is loss of both muscle and fat mass, and the reduction in muscle mass is deleterious to bone.
Other possible causes of bone density reduction include reduced absorption of certain nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D critical for bone mineralization, and alterations in certain hormones that impact bone health. These include increases in parathyroid hormone, which increases bone loss when secreted in excess; increases in PYY (a hormone that reduces bone formation); decreases in ghrelin (a hormone that typically increases bone formation), particularly after sleeve gastrectomy; and decreases in estrone (a kind of estrogen that like other estrogens prevents bone loss). Further, age and gender may modify the bone consequences of surgery as outcomes in postmenopausal women appear to be worse than in younger women and men.
Preventing bone density loss
Given the many benefits of weight loss surgery, what can we do to prevent this decrease in bone density after surgery? It’s important for people undergoing weight loss surgery to be cognizant of this potentially negative outcome and to take appropriate precautions to mitigate this concern.
We should monitor bone density after surgery with the help of dual energy x-ray absorptiometry, starting a few years after surgery, particularly in those who are at greatest risk for fracture, so that we can be proactive about addressing any severe bone loss that warrants pharmacologic intervention.
More general recommendations include optimizing intake of calcium (1,200-1,500 mg/d), vitamin D (2,000-3,000 IUs/d), and protein (60-75 g/d) via diet and/or as supplements and engaging in weight-bearing physical activity because this exerts mechanical loading effects on the skeleton leading to increased bone formation and also increases muscle mass over time, which is beneficial to bone. A progressive resistance training program has been demonstrated to have beneficial effects on bone, and measures should be taken to reduce the risk for falls, which increases after certain kinds of weight loss surgery, such as gastric bypass.
Meeting with a dietitian can help determine any other nutrients that need to be optimized.
Though many hormonal changes after surgery have been linked to reductions in bone density, there are still no recommended hormonal therapies at this time, and more work is required to determine whether specific pharmacologic therapies might help improve bone outcomes after surgery.
Dr. Misra is chief of the division of pediatric endocrinology, Mass General for Children; associate director, Harvard Catalyst Translation and Clinical Research Center; director, Pediatric Endocrine-Sports Endocrine-Neuroendocrine Lab, Mass General Hospital; and professor, department of pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Menopause and long COVID: What women should know
British researchers have noted that women at midlife who have long COVID seem to get specific, and severe, symptoms, including brain fog, fatigue, new-onset dizziness, and difficulty sleeping through the night.
Doctors also think it’s possible that long COVID worsens the symptoms of perimenopause and menopause. Lower levels of estrogen and testosterone appear to be the reason.
“A long COVID theory is that there is a temporary disruption to physiological ovarian steroid hormone production, which could [worsen] symptoms of perimenopause and menopause,” said JoAnn V. Pinkerton, MD, professor of obstetrics at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and executive director of the North American Menopause Society.
Long COVID symptoms and menopause symptoms can also be very hard to tell apart.
Another U.K. study cautions that because of this kind of symptom overlap, women at midlife may be misdiagnosed. Research from the North American Menopause Society shows that many women may have trouble recovering from long COVID unless their hormone deficiency is treated.
What are the symptoms of long COVID?
There are over 200 symptoms that have been associated with long COVID, according to the American Medical Association. Some common symptoms are currently defined as the following: feeling extremely tired, feeling depleted after exertion, cognitive issues such as brain fog, heart beating over 100 times a minute, and a loss of sense of smell and taste.
Long COVID symptoms begin a few weeks to a few months after a COVID infection. They can last an indefinite amount of time, but “the hope is that long COVID will not be lifelong,” said Clare Flannery, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor in the departments of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive sciences and internal medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
What are the symptoms of menopause?
Some symptoms of menopause include vaginal infections, irregular bleeding, urinary problems, and sexual problems.
Women in their middle years have other symptoms that can be the same as perimenopause/menopause symptoms.
“Common symptoms of perimenopause and menopause which may also be symptoms ascribed to long COVID include hot flashes, night sweats, disrupted sleep, low mood, depression or anxiety, decreased concentration, memory problems, joint and muscle pains, and headaches,” Dr. Pinkerton said.
Can long COVID actually bring on menopause?
In short: Possibly.
A new study from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology/Patient-Led Research Collaborative/University of California, San Francisco, found that long COVID can cause disruptions to a woman’s menstrual cycle, ovaries, fertility, and menopause itself.
This could be caused by chronic inflammation caused by long COVID on hormones as well. This kind of inflammatory response could explain irregularities in a woman’s menstrual cycle, according to the Newson Health Research and Education study. For instance, “when the body has inflammation, ovulation can happen,” Dr. Flannery said.
The mechanism for how long COVID could spur menopause can also involve a woman’s ovaries.
“Since the theory is that COVID affects the ovary with declines in ovarian reserve and ovarian function, it makes sense that long COVID could bring on symptoms of perimenopause or menopause more acutely or more severely and lengthen the symptoms of the perimenopause and menopausal transition,” Dr. Pinkerton said.
How can hormone replacement therapy benefit women dealing with long COVID during menopause?
Estradiol, the strongest estrogen hormone in a woman’s body, has already been shown to have a positive effect against COVID.
“Estradiol therapy treats symptoms more aggressively in the setting of long COVID,” said Dr. Flannery.
Estradiol is also a form of hormone therapy for menopause symptoms.
“Estradiol has been shown to help hot flashes, night sweats, and sleep and improve mood during perimenopause,” said Dr. Pinkerton. “So it’s likely that perimenopausal or menopausal women with long COVID would see improvements both due to the action of estradiol on the ovary seen during COVID and the improvements in symptoms.”
Estrogen-based hormone therapy has been linked to an increased risk for endometrial, breast, and ovarian cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. This means you should carefully consider how comfortable you are with those additional risks before starting this kind of therapy.
“Which of your symptoms are the most difficult to manage? You may see if you can navigate one to three of them. What are you willing to do for your symptoms? If a woman is willing to favor her sleep for the next 6 months to a year, she may be willing to change how she perceives her risk for cancer,” Dr. Flannery said. “What risk is a woman willing to take? I think if someone has a very low concern about a risk of cancer, and she’s suffering a disrupted life, then taking estradiol in a 1- to 2-year trial period could be critical to help.”
What else can help ease long COVID during menopause?
Getting the COVID vaccine, as well as getting a booster, could help. Not only will this help prevent people from being reinfected with COVID, which can worsen symptoms, but a new Swedish study says there is no evidence that it will cause postmenopausal problems like irregular bleeding.
“Weak and inconsistent associations were observed between SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and healthcare contacts for bleeding in women who are postmenopausal, and even less evidence was recorded of an association for menstrual disturbance or bleeding in women who were premenopausal,” said study coauthor Rickard Ljung, MD, PhD, MPH, professor and acting head of the pharmacoepidemiology and analysis department in the division of use and information of the Swedish Medical Products Agency in Uppsala.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
British researchers have noted that women at midlife who have long COVID seem to get specific, and severe, symptoms, including brain fog, fatigue, new-onset dizziness, and difficulty sleeping through the night.
Doctors also think it’s possible that long COVID worsens the symptoms of perimenopause and menopause. Lower levels of estrogen and testosterone appear to be the reason.
“A long COVID theory is that there is a temporary disruption to physiological ovarian steroid hormone production, which could [worsen] symptoms of perimenopause and menopause,” said JoAnn V. Pinkerton, MD, professor of obstetrics at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and executive director of the North American Menopause Society.
Long COVID symptoms and menopause symptoms can also be very hard to tell apart.
Another U.K. study cautions that because of this kind of symptom overlap, women at midlife may be misdiagnosed. Research from the North American Menopause Society shows that many women may have trouble recovering from long COVID unless their hormone deficiency is treated.
What are the symptoms of long COVID?
There are over 200 symptoms that have been associated with long COVID, according to the American Medical Association. Some common symptoms are currently defined as the following: feeling extremely tired, feeling depleted after exertion, cognitive issues such as brain fog, heart beating over 100 times a minute, and a loss of sense of smell and taste.
Long COVID symptoms begin a few weeks to a few months after a COVID infection. They can last an indefinite amount of time, but “the hope is that long COVID will not be lifelong,” said Clare Flannery, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor in the departments of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive sciences and internal medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
What are the symptoms of menopause?
Some symptoms of menopause include vaginal infections, irregular bleeding, urinary problems, and sexual problems.
Women in their middle years have other symptoms that can be the same as perimenopause/menopause symptoms.
“Common symptoms of perimenopause and menopause which may also be symptoms ascribed to long COVID include hot flashes, night sweats, disrupted sleep, low mood, depression or anxiety, decreased concentration, memory problems, joint and muscle pains, and headaches,” Dr. Pinkerton said.
Can long COVID actually bring on menopause?
In short: Possibly.
A new study from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology/Patient-Led Research Collaborative/University of California, San Francisco, found that long COVID can cause disruptions to a woman’s menstrual cycle, ovaries, fertility, and menopause itself.
This could be caused by chronic inflammation caused by long COVID on hormones as well. This kind of inflammatory response could explain irregularities in a woman’s menstrual cycle, according to the Newson Health Research and Education study. For instance, “when the body has inflammation, ovulation can happen,” Dr. Flannery said.
The mechanism for how long COVID could spur menopause can also involve a woman’s ovaries.
“Since the theory is that COVID affects the ovary with declines in ovarian reserve and ovarian function, it makes sense that long COVID could bring on symptoms of perimenopause or menopause more acutely or more severely and lengthen the symptoms of the perimenopause and menopausal transition,” Dr. Pinkerton said.
How can hormone replacement therapy benefit women dealing with long COVID during menopause?
Estradiol, the strongest estrogen hormone in a woman’s body, has already been shown to have a positive effect against COVID.
“Estradiol therapy treats symptoms more aggressively in the setting of long COVID,” said Dr. Flannery.
Estradiol is also a form of hormone therapy for menopause symptoms.
“Estradiol has been shown to help hot flashes, night sweats, and sleep and improve mood during perimenopause,” said Dr. Pinkerton. “So it’s likely that perimenopausal or menopausal women with long COVID would see improvements both due to the action of estradiol on the ovary seen during COVID and the improvements in symptoms.”
Estrogen-based hormone therapy has been linked to an increased risk for endometrial, breast, and ovarian cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. This means you should carefully consider how comfortable you are with those additional risks before starting this kind of therapy.
“Which of your symptoms are the most difficult to manage? You may see if you can navigate one to three of them. What are you willing to do for your symptoms? If a woman is willing to favor her sleep for the next 6 months to a year, she may be willing to change how she perceives her risk for cancer,” Dr. Flannery said. “What risk is a woman willing to take? I think if someone has a very low concern about a risk of cancer, and she’s suffering a disrupted life, then taking estradiol in a 1- to 2-year trial period could be critical to help.”
What else can help ease long COVID during menopause?
Getting the COVID vaccine, as well as getting a booster, could help. Not only will this help prevent people from being reinfected with COVID, which can worsen symptoms, but a new Swedish study says there is no evidence that it will cause postmenopausal problems like irregular bleeding.
“Weak and inconsistent associations were observed between SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and healthcare contacts for bleeding in women who are postmenopausal, and even less evidence was recorded of an association for menstrual disturbance or bleeding in women who were premenopausal,” said study coauthor Rickard Ljung, MD, PhD, MPH, professor and acting head of the pharmacoepidemiology and analysis department in the division of use and information of the Swedish Medical Products Agency in Uppsala.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
British researchers have noted that women at midlife who have long COVID seem to get specific, and severe, symptoms, including brain fog, fatigue, new-onset dizziness, and difficulty sleeping through the night.
Doctors also think it’s possible that long COVID worsens the symptoms of perimenopause and menopause. Lower levels of estrogen and testosterone appear to be the reason.
“A long COVID theory is that there is a temporary disruption to physiological ovarian steroid hormone production, which could [worsen] symptoms of perimenopause and menopause,” said JoAnn V. Pinkerton, MD, professor of obstetrics at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and executive director of the North American Menopause Society.
Long COVID symptoms and menopause symptoms can also be very hard to tell apart.
Another U.K. study cautions that because of this kind of symptom overlap, women at midlife may be misdiagnosed. Research from the North American Menopause Society shows that many women may have trouble recovering from long COVID unless their hormone deficiency is treated.
What are the symptoms of long COVID?
There are over 200 symptoms that have been associated with long COVID, according to the American Medical Association. Some common symptoms are currently defined as the following: feeling extremely tired, feeling depleted after exertion, cognitive issues such as brain fog, heart beating over 100 times a minute, and a loss of sense of smell and taste.
Long COVID symptoms begin a few weeks to a few months after a COVID infection. They can last an indefinite amount of time, but “the hope is that long COVID will not be lifelong,” said Clare Flannery, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor in the departments of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive sciences and internal medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
What are the symptoms of menopause?
Some symptoms of menopause include vaginal infections, irregular bleeding, urinary problems, and sexual problems.
Women in their middle years have other symptoms that can be the same as perimenopause/menopause symptoms.
“Common symptoms of perimenopause and menopause which may also be symptoms ascribed to long COVID include hot flashes, night sweats, disrupted sleep, low mood, depression or anxiety, decreased concentration, memory problems, joint and muscle pains, and headaches,” Dr. Pinkerton said.
Can long COVID actually bring on menopause?
In short: Possibly.
A new study from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology/Patient-Led Research Collaborative/University of California, San Francisco, found that long COVID can cause disruptions to a woman’s menstrual cycle, ovaries, fertility, and menopause itself.
This could be caused by chronic inflammation caused by long COVID on hormones as well. This kind of inflammatory response could explain irregularities in a woman’s menstrual cycle, according to the Newson Health Research and Education study. For instance, “when the body has inflammation, ovulation can happen,” Dr. Flannery said.
The mechanism for how long COVID could spur menopause can also involve a woman’s ovaries.
“Since the theory is that COVID affects the ovary with declines in ovarian reserve and ovarian function, it makes sense that long COVID could bring on symptoms of perimenopause or menopause more acutely or more severely and lengthen the symptoms of the perimenopause and menopausal transition,” Dr. Pinkerton said.
How can hormone replacement therapy benefit women dealing with long COVID during menopause?
Estradiol, the strongest estrogen hormone in a woman’s body, has already been shown to have a positive effect against COVID.
“Estradiol therapy treats symptoms more aggressively in the setting of long COVID,” said Dr. Flannery.
Estradiol is also a form of hormone therapy for menopause symptoms.
“Estradiol has been shown to help hot flashes, night sweats, and sleep and improve mood during perimenopause,” said Dr. Pinkerton. “So it’s likely that perimenopausal or menopausal women with long COVID would see improvements both due to the action of estradiol on the ovary seen during COVID and the improvements in symptoms.”
Estrogen-based hormone therapy has been linked to an increased risk for endometrial, breast, and ovarian cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. This means you should carefully consider how comfortable you are with those additional risks before starting this kind of therapy.
“Which of your symptoms are the most difficult to manage? You may see if you can navigate one to three of them. What are you willing to do for your symptoms? If a woman is willing to favor her sleep for the next 6 months to a year, she may be willing to change how she perceives her risk for cancer,” Dr. Flannery said. “What risk is a woman willing to take? I think if someone has a very low concern about a risk of cancer, and she’s suffering a disrupted life, then taking estradiol in a 1- to 2-year trial period could be critical to help.”
What else can help ease long COVID during menopause?
Getting the COVID vaccine, as well as getting a booster, could help. Not only will this help prevent people from being reinfected with COVID, which can worsen symptoms, but a new Swedish study says there is no evidence that it will cause postmenopausal problems like irregular bleeding.
“Weak and inconsistent associations were observed between SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and healthcare contacts for bleeding in women who are postmenopausal, and even less evidence was recorded of an association for menstrual disturbance or bleeding in women who were premenopausal,” said study coauthor Rickard Ljung, MD, PhD, MPH, professor and acting head of the pharmacoepidemiology and analysis department in the division of use and information of the Swedish Medical Products Agency in Uppsala.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID vaccines safe for young children, study finds
TOPLINE:
COVID-19 vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech are safe for children under age 5 years, according to findings from a study funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data came from the Vaccine Safety Datalink, which gathers information from eight health systems in the United States.
- Analyzed data from 135,005 doses given to children age 4 and younger who received the Pfizer-BioNTech , and 112,006 doses given to children aged 5 and younger who received the Moderna version.
- Assessed for 23 safety outcomes, including myocarditis, pericarditis, and seizures.
TAKEAWAY:
- One case of hemorrhagic stroke and one case of pulmonary embolism occurred after vaccination but these were linked to preexisting congenital abnormalities.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results can provide reassurance to clinicians, parents, and policymakers alike.”
STUDY DETAILS:
The study was led by Kristin Goddard, MPH, a researcher at the Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center in Oakland, Calif., and was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers reported low statistical power for early analysis, especially for rare outcomes. In addition, fewer than 25% of children in the database had received a vaccine at the time of analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
A coauthor reported receiving funding from Janssen Vaccines and Prevention for a study unrelated to COVID-19 vaccines. Another coauthor reported receiving grants from Pfizer in 2019 for clinical trials for coronavirus vaccines, and from Merck, GSK, and Sanofi Pasteur for unrelated research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
COVID-19 vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech are safe for children under age 5 years, according to findings from a study funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data came from the Vaccine Safety Datalink, which gathers information from eight health systems in the United States.
- Analyzed data from 135,005 doses given to children age 4 and younger who received the Pfizer-BioNTech , and 112,006 doses given to children aged 5 and younger who received the Moderna version.
- Assessed for 23 safety outcomes, including myocarditis, pericarditis, and seizures.
TAKEAWAY:
- One case of hemorrhagic stroke and one case of pulmonary embolism occurred after vaccination but these were linked to preexisting congenital abnormalities.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results can provide reassurance to clinicians, parents, and policymakers alike.”
STUDY DETAILS:
The study was led by Kristin Goddard, MPH, a researcher at the Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center in Oakland, Calif., and was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers reported low statistical power for early analysis, especially for rare outcomes. In addition, fewer than 25% of children in the database had received a vaccine at the time of analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
A coauthor reported receiving funding from Janssen Vaccines and Prevention for a study unrelated to COVID-19 vaccines. Another coauthor reported receiving grants from Pfizer in 2019 for clinical trials for coronavirus vaccines, and from Merck, GSK, and Sanofi Pasteur for unrelated research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
COVID-19 vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech are safe for children under age 5 years, according to findings from a study funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data came from the Vaccine Safety Datalink, which gathers information from eight health systems in the United States.
- Analyzed data from 135,005 doses given to children age 4 and younger who received the Pfizer-BioNTech , and 112,006 doses given to children aged 5 and younger who received the Moderna version.
- Assessed for 23 safety outcomes, including myocarditis, pericarditis, and seizures.
TAKEAWAY:
- One case of hemorrhagic stroke and one case of pulmonary embolism occurred after vaccination but these were linked to preexisting congenital abnormalities.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results can provide reassurance to clinicians, parents, and policymakers alike.”
STUDY DETAILS:
The study was led by Kristin Goddard, MPH, a researcher at the Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center in Oakland, Calif., and was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers reported low statistical power for early analysis, especially for rare outcomes. In addition, fewer than 25% of children in the database had received a vaccine at the time of analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
A coauthor reported receiving funding from Janssen Vaccines and Prevention for a study unrelated to COVID-19 vaccines. Another coauthor reported receiving grants from Pfizer in 2019 for clinical trials for coronavirus vaccines, and from Merck, GSK, and Sanofi Pasteur for unrelated research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Review may help clinicians treat adolescents with depression
Depression is common among Canadian adolescents and often goes unnoticed. Many family physicians report feeling unprepared to identify and manage depression in these patients.
“Depression is an increasingly common but treatable condition among adolescents,” the authors wrote. “Primary care physicians and pediatricians are well positioned to support the assessment and first-line management of depression in this group, helping patients to regain their health and function.”
The article was published in CMAJ.
Distinct presentation
More than 40% of cases of depression begin during childhood. Onset at this life stage is associated with worse severity of depression in adulthood and worse social, occupational, and physical health outcomes.
Depression is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Family history of depression is associated with a three- to fivefold increased risk of depression among older children. Genetic loci are known to be associated with depression, but exposure to parental depression, adverse childhood experiences, and family conflict are also linked to greater risk. Bullying and stigma are associated with greater risk among lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth.
Compared with adults, adolescents with depression are more likely to be irritable and to have a labile mood, rather than a low mood. Social withdrawal is also more common among adolescents than among adults. Unusual features, such as hypersomnia and increased appetite, may also be present. Anxiety, somatic symptoms, psychomotor agitation, and hallucinations are more common in adolescents than in younger persons with depression. It is vital to assess risk of suicidality and self-injury as well as support systems, and validated scales such as the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale can be useful.
There is no consensus as to whether universal screening for depression is beneficial among adolescents. “Screening in this age group may be a reasonable approach, however, when implemented together with adequate systems that ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate follow-up,” wrote the authors.
Management of depression in adolescents should begin with psychoeducation and may include lifestyle modification, psychotherapy, and medication. “Importantly, a suicide risk assessment must be done to ensure appropriateness of an outpatient management plan and facilitate safety planning,” the authors wrote.
Lifestyle interventions may target physical activity, diet, and sleep, since unhealthy patterns in all three are associated with heightened symptoms of depression in this population. Regular moderate to vigorous physical activity, and perhaps physical activity of short duration, can improve mood in adolescents. Reduced consumption of sugar-sweetened drinks, processed foods, and meats, along with greater consumption of fruits and legumes, has been shown to reduce depressive symptoms in randomized, controlled trials with adults.
Among psychotherapeutic approaches, cognitive-behavioral therapy has shown the most evidence of efficacy among adolescents with depression, though it is less effective for those with more severe symptoms, poor coping skills, and nonsuicidal self-injury. Some evidence supports interpersonal therapy, which focuses on relationships and social functioning. The involvement of caregivers may improve the response, compared with psychotherapy that only includes the adolescent.
The authors recommend antidepressant medications in more severe cases or when psychotherapy is ineffective or impossible. Guidelines generally support trials with at least two SSRIs before switching to another drug class, since efficacy data for them are sparser, and other drugs have worse side effect profiles.
About 2% of adolescents with depression experience an increase in suicidal ideation and behavior after exposure to antidepressants, usually within the first weeks of initiation, so this potential risk should be discussed with patients and caregivers.
Clinicians feel unprepared
Commenting on the review, Pierre-Paul Tellier, MD, an associate professor of family medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said that clinicians frequently report that they do not feel confident in their ability to manage and diagnose adolescent depression. “We did two systematic reviews to look at the continuing professional development of family physicians in adolescent health, and it turned out that there’s really a very large lack. When we looked at residents and the training that they were getting in adolescent medicine, it was very similar, so they felt unprepared to deal with issues around mental health.”
Medication can be effective, but it can be seen as “an easy way out,” Dr. Tellier added. “It’s not necessarily an ideal plan. What we need to do is to change the person’s way of thinking, the person’s way of responding to a variety of things which will occur throughout their lives. People will have other transition periods in their lives. It’s best if they learn a variety of techniques to deal with depression.”
These techniques include exercise, relaxation methods [which reduce anxiety], and wellness training. Through such techniques, patients “learn a healthier way of living with themselves and who they are, and then this is a lifelong way of learning,” said Dr. Tellier. “If I give you a pill, what I’m teaching is, yes, you can feel better. But you’re not dealing with the problem, you’re just dealing with the symptoms.”
He frequently refers his patients to YouTube videos that outline and explain various strategies. A favorite is a deep breathing exercise presented by Jeremy Howick.
The authors and Dr. Tellier disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Depression is common among Canadian adolescents and often goes unnoticed. Many family physicians report feeling unprepared to identify and manage depression in these patients.
“Depression is an increasingly common but treatable condition among adolescents,” the authors wrote. “Primary care physicians and pediatricians are well positioned to support the assessment and first-line management of depression in this group, helping patients to regain their health and function.”
The article was published in CMAJ.
Distinct presentation
More than 40% of cases of depression begin during childhood. Onset at this life stage is associated with worse severity of depression in adulthood and worse social, occupational, and physical health outcomes.
Depression is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Family history of depression is associated with a three- to fivefold increased risk of depression among older children. Genetic loci are known to be associated with depression, but exposure to parental depression, adverse childhood experiences, and family conflict are also linked to greater risk. Bullying and stigma are associated with greater risk among lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth.
Compared with adults, adolescents with depression are more likely to be irritable and to have a labile mood, rather than a low mood. Social withdrawal is also more common among adolescents than among adults. Unusual features, such as hypersomnia and increased appetite, may also be present. Anxiety, somatic symptoms, psychomotor agitation, and hallucinations are more common in adolescents than in younger persons with depression. It is vital to assess risk of suicidality and self-injury as well as support systems, and validated scales such as the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale can be useful.
There is no consensus as to whether universal screening for depression is beneficial among adolescents. “Screening in this age group may be a reasonable approach, however, when implemented together with adequate systems that ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate follow-up,” wrote the authors.
Management of depression in adolescents should begin with psychoeducation and may include lifestyle modification, psychotherapy, and medication. “Importantly, a suicide risk assessment must be done to ensure appropriateness of an outpatient management plan and facilitate safety planning,” the authors wrote.
Lifestyle interventions may target physical activity, diet, and sleep, since unhealthy patterns in all three are associated with heightened symptoms of depression in this population. Regular moderate to vigorous physical activity, and perhaps physical activity of short duration, can improve mood in adolescents. Reduced consumption of sugar-sweetened drinks, processed foods, and meats, along with greater consumption of fruits and legumes, has been shown to reduce depressive symptoms in randomized, controlled trials with adults.
Among psychotherapeutic approaches, cognitive-behavioral therapy has shown the most evidence of efficacy among adolescents with depression, though it is less effective for those with more severe symptoms, poor coping skills, and nonsuicidal self-injury. Some evidence supports interpersonal therapy, which focuses on relationships and social functioning. The involvement of caregivers may improve the response, compared with psychotherapy that only includes the adolescent.
The authors recommend antidepressant medications in more severe cases or when psychotherapy is ineffective or impossible. Guidelines generally support trials with at least two SSRIs before switching to another drug class, since efficacy data for them are sparser, and other drugs have worse side effect profiles.
About 2% of adolescents with depression experience an increase in suicidal ideation and behavior after exposure to antidepressants, usually within the first weeks of initiation, so this potential risk should be discussed with patients and caregivers.
Clinicians feel unprepared
Commenting on the review, Pierre-Paul Tellier, MD, an associate professor of family medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said that clinicians frequently report that they do not feel confident in their ability to manage and diagnose adolescent depression. “We did two systematic reviews to look at the continuing professional development of family physicians in adolescent health, and it turned out that there’s really a very large lack. When we looked at residents and the training that they were getting in adolescent medicine, it was very similar, so they felt unprepared to deal with issues around mental health.”
Medication can be effective, but it can be seen as “an easy way out,” Dr. Tellier added. “It’s not necessarily an ideal plan. What we need to do is to change the person’s way of thinking, the person’s way of responding to a variety of things which will occur throughout their lives. People will have other transition periods in their lives. It’s best if they learn a variety of techniques to deal with depression.”
These techniques include exercise, relaxation methods [which reduce anxiety], and wellness training. Through such techniques, patients “learn a healthier way of living with themselves and who they are, and then this is a lifelong way of learning,” said Dr. Tellier. “If I give you a pill, what I’m teaching is, yes, you can feel better. But you’re not dealing with the problem, you’re just dealing with the symptoms.”
He frequently refers his patients to YouTube videos that outline and explain various strategies. A favorite is a deep breathing exercise presented by Jeremy Howick.
The authors and Dr. Tellier disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Depression is common among Canadian adolescents and often goes unnoticed. Many family physicians report feeling unprepared to identify and manage depression in these patients.
“Depression is an increasingly common but treatable condition among adolescents,” the authors wrote. “Primary care physicians and pediatricians are well positioned to support the assessment and first-line management of depression in this group, helping patients to regain their health and function.”
The article was published in CMAJ.
Distinct presentation
More than 40% of cases of depression begin during childhood. Onset at this life stage is associated with worse severity of depression in adulthood and worse social, occupational, and physical health outcomes.
Depression is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Family history of depression is associated with a three- to fivefold increased risk of depression among older children. Genetic loci are known to be associated with depression, but exposure to parental depression, adverse childhood experiences, and family conflict are also linked to greater risk. Bullying and stigma are associated with greater risk among lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth.
Compared with adults, adolescents with depression are more likely to be irritable and to have a labile mood, rather than a low mood. Social withdrawal is also more common among adolescents than among adults. Unusual features, such as hypersomnia and increased appetite, may also be present. Anxiety, somatic symptoms, psychomotor agitation, and hallucinations are more common in adolescents than in younger persons with depression. It is vital to assess risk of suicidality and self-injury as well as support systems, and validated scales such as the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale can be useful.
There is no consensus as to whether universal screening for depression is beneficial among adolescents. “Screening in this age group may be a reasonable approach, however, when implemented together with adequate systems that ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate follow-up,” wrote the authors.
Management of depression in adolescents should begin with psychoeducation and may include lifestyle modification, psychotherapy, and medication. “Importantly, a suicide risk assessment must be done to ensure appropriateness of an outpatient management plan and facilitate safety planning,” the authors wrote.
Lifestyle interventions may target physical activity, diet, and sleep, since unhealthy patterns in all three are associated with heightened symptoms of depression in this population. Regular moderate to vigorous physical activity, and perhaps physical activity of short duration, can improve mood in adolescents. Reduced consumption of sugar-sweetened drinks, processed foods, and meats, along with greater consumption of fruits and legumes, has been shown to reduce depressive symptoms in randomized, controlled trials with adults.
Among psychotherapeutic approaches, cognitive-behavioral therapy has shown the most evidence of efficacy among adolescents with depression, though it is less effective for those with more severe symptoms, poor coping skills, and nonsuicidal self-injury. Some evidence supports interpersonal therapy, which focuses on relationships and social functioning. The involvement of caregivers may improve the response, compared with psychotherapy that only includes the adolescent.
The authors recommend antidepressant medications in more severe cases or when psychotherapy is ineffective or impossible. Guidelines generally support trials with at least two SSRIs before switching to another drug class, since efficacy data for them are sparser, and other drugs have worse side effect profiles.
About 2% of adolescents with depression experience an increase in suicidal ideation and behavior after exposure to antidepressants, usually within the first weeks of initiation, so this potential risk should be discussed with patients and caregivers.
Clinicians feel unprepared
Commenting on the review, Pierre-Paul Tellier, MD, an associate professor of family medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said that clinicians frequently report that they do not feel confident in their ability to manage and diagnose adolescent depression. “We did two systematic reviews to look at the continuing professional development of family physicians in adolescent health, and it turned out that there’s really a very large lack. When we looked at residents and the training that they were getting in adolescent medicine, it was very similar, so they felt unprepared to deal with issues around mental health.”
Medication can be effective, but it can be seen as “an easy way out,” Dr. Tellier added. “It’s not necessarily an ideal plan. What we need to do is to change the person’s way of thinking, the person’s way of responding to a variety of things which will occur throughout their lives. People will have other transition periods in their lives. It’s best if they learn a variety of techniques to deal with depression.”
These techniques include exercise, relaxation methods [which reduce anxiety], and wellness training. Through such techniques, patients “learn a healthier way of living with themselves and who they are, and then this is a lifelong way of learning,” said Dr. Tellier. “If I give you a pill, what I’m teaching is, yes, you can feel better. But you’re not dealing with the problem, you’re just dealing with the symptoms.”
He frequently refers his patients to YouTube videos that outline and explain various strategies. A favorite is a deep breathing exercise presented by Jeremy Howick.
The authors and Dr. Tellier disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CMAJ