User login
Atopic dermatitis may be a risk factor for GBS colonization in pregnancy
suggest.
“The rate of GBS colonization among pregnant females with a history of AD has not been previously reported, but AD could be a risk factor for maternal carriage of GBS,” corresponding author David J. Margolis, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published as a letter to the editor online in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology. “GBS reporting in a large administrative database represents a unique opportunity to conduct a population-based evaluation of GBS carriage with AD. Understanding this association could expand our understanding of microbial changes associated with AD,” they noted.
To determine if an association between GBS and AD in pregnant women exists, the researchers performed a cross-sectional study using a random sample from an Optum administrative database of pregnant women who had vaginal deliveries between May of 2007 and September 2021. The primary outcome of interest was the presence of GBS based on American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists–recommended codes for GBS during 36 0/7 to 37 6/7 weeks of pregnancy. They used descriptive statistics to summarize categorical and continuous variables as proportions and means, and logistic regression to examine the association between AD and GBS status.
The cohort included 566,467 pregnant women with an average age of 38.8 years. Of these, 2.9% had a diagnosis of AD or a history of AD, and 24.9% had diagnoses of asthma, seasonal allergies, or both. Women with AD had an increased odds ratio of asthma (OR, 2.55), seasonal allergies (OR, 3.39), or both (OR, 5.35), compared with those without AD.
GBS was reported in 20.6% of the cohort. The median time of follow-up for those with and without GBS was 494 days and 468 days, respectively (P = .134). Among the women with AD, 24.1% had GBS, compared with 20.51% of the women without AD (P <.0001), which translated into an OR of 1.23 (95% confidence interval, 1.18-1.27).
Among the women with GBS, the OR of asthma was 1.08 (95% CI, 1.06-1.10) and was 1.07 (95% CI, 1.05-1.09) among those with seasonal allergies. When adjusted for potential confounders, these findings did not change substantively.
“It is not apparent why pregnant females with AD are more likely to specifically carry GBS,” the authors wrote. “However, several studies have shown that individuals with AD are more likely to carry [Staphylococcus] aureus and that individuals with AD might be deficient in host defenses against S. aureus and other pathogens,” they added.
“Individuals with AD frequently receive antibiotics as part of their AD treatment and this might alter their resident microbiome. Carriage rates may be enhanced by the inhibition of an important barrier protein called filaggrin (FLG) and FLG loss of function genetic variation is known to decrease barrier proteins thought to inhibit the colonization of S. aureus and other pathogens,” the researchers wrote.
They acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including its reliance on an administrative database that does not contain information on past disease.
Asked to comment on the results, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the study, characterized AD as “the poster child for cutaneous dysbiosis – an altered petri dish, so to speak, [that] facilitates survival of the few, leading to decreased microbial diversity that can both enable potential pathogen invasion and immune dysregulation.”
Though it’s not surprising that pregnant AD patients have dysbiosis, the focus on GBS, “which can be a bad actor in the perinatal period, is an interesting connection,” he said. “Will this change practices? Pregnant women should be screened for GBS regardless, but maybe more attention or counseling can be offered to AD patients about the importance of screening. Would decolonization regimens be employed early in pregnancy? This study can’t answer that but certainly raises good questions.”
Dr. Margolis disclosed that he is or recently has been a consultant for Pfizer, Leo, and Sanofi with respect to studies of atopic dermatitis and served on an advisory board for the National Eczema Association. Another author disclosed receiving grants from companies related to work with AD; other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant disclosures.
suggest.
“The rate of GBS colonization among pregnant females with a history of AD has not been previously reported, but AD could be a risk factor for maternal carriage of GBS,” corresponding author David J. Margolis, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published as a letter to the editor online in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology. “GBS reporting in a large administrative database represents a unique opportunity to conduct a population-based evaluation of GBS carriage with AD. Understanding this association could expand our understanding of microbial changes associated with AD,” they noted.
To determine if an association between GBS and AD in pregnant women exists, the researchers performed a cross-sectional study using a random sample from an Optum administrative database of pregnant women who had vaginal deliveries between May of 2007 and September 2021. The primary outcome of interest was the presence of GBS based on American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists–recommended codes for GBS during 36 0/7 to 37 6/7 weeks of pregnancy. They used descriptive statistics to summarize categorical and continuous variables as proportions and means, and logistic regression to examine the association between AD and GBS status.
The cohort included 566,467 pregnant women with an average age of 38.8 years. Of these, 2.9% had a diagnosis of AD or a history of AD, and 24.9% had diagnoses of asthma, seasonal allergies, or both. Women with AD had an increased odds ratio of asthma (OR, 2.55), seasonal allergies (OR, 3.39), or both (OR, 5.35), compared with those without AD.
GBS was reported in 20.6% of the cohort. The median time of follow-up for those with and without GBS was 494 days and 468 days, respectively (P = .134). Among the women with AD, 24.1% had GBS, compared with 20.51% of the women without AD (P <.0001), which translated into an OR of 1.23 (95% confidence interval, 1.18-1.27).
Among the women with GBS, the OR of asthma was 1.08 (95% CI, 1.06-1.10) and was 1.07 (95% CI, 1.05-1.09) among those with seasonal allergies. When adjusted for potential confounders, these findings did not change substantively.
“It is not apparent why pregnant females with AD are more likely to specifically carry GBS,” the authors wrote. “However, several studies have shown that individuals with AD are more likely to carry [Staphylococcus] aureus and that individuals with AD might be deficient in host defenses against S. aureus and other pathogens,” they added.
“Individuals with AD frequently receive antibiotics as part of their AD treatment and this might alter their resident microbiome. Carriage rates may be enhanced by the inhibition of an important barrier protein called filaggrin (FLG) and FLG loss of function genetic variation is known to decrease barrier proteins thought to inhibit the colonization of S. aureus and other pathogens,” the researchers wrote.
They acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including its reliance on an administrative database that does not contain information on past disease.
Asked to comment on the results, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the study, characterized AD as “the poster child for cutaneous dysbiosis – an altered petri dish, so to speak, [that] facilitates survival of the few, leading to decreased microbial diversity that can both enable potential pathogen invasion and immune dysregulation.”
Though it’s not surprising that pregnant AD patients have dysbiosis, the focus on GBS, “which can be a bad actor in the perinatal period, is an interesting connection,” he said. “Will this change practices? Pregnant women should be screened for GBS regardless, but maybe more attention or counseling can be offered to AD patients about the importance of screening. Would decolonization regimens be employed early in pregnancy? This study can’t answer that but certainly raises good questions.”
Dr. Margolis disclosed that he is or recently has been a consultant for Pfizer, Leo, and Sanofi with respect to studies of atopic dermatitis and served on an advisory board for the National Eczema Association. Another author disclosed receiving grants from companies related to work with AD; other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant disclosures.
suggest.
“The rate of GBS colonization among pregnant females with a history of AD has not been previously reported, but AD could be a risk factor for maternal carriage of GBS,” corresponding author David J. Margolis, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published as a letter to the editor online in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology. “GBS reporting in a large administrative database represents a unique opportunity to conduct a population-based evaluation of GBS carriage with AD. Understanding this association could expand our understanding of microbial changes associated with AD,” they noted.
To determine if an association between GBS and AD in pregnant women exists, the researchers performed a cross-sectional study using a random sample from an Optum administrative database of pregnant women who had vaginal deliveries between May of 2007 and September 2021. The primary outcome of interest was the presence of GBS based on American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists–recommended codes for GBS during 36 0/7 to 37 6/7 weeks of pregnancy. They used descriptive statistics to summarize categorical and continuous variables as proportions and means, and logistic regression to examine the association between AD and GBS status.
The cohort included 566,467 pregnant women with an average age of 38.8 years. Of these, 2.9% had a diagnosis of AD or a history of AD, and 24.9% had diagnoses of asthma, seasonal allergies, or both. Women with AD had an increased odds ratio of asthma (OR, 2.55), seasonal allergies (OR, 3.39), or both (OR, 5.35), compared with those without AD.
GBS was reported in 20.6% of the cohort. The median time of follow-up for those with and without GBS was 494 days and 468 days, respectively (P = .134). Among the women with AD, 24.1% had GBS, compared with 20.51% of the women without AD (P <.0001), which translated into an OR of 1.23 (95% confidence interval, 1.18-1.27).
Among the women with GBS, the OR of asthma was 1.08 (95% CI, 1.06-1.10) and was 1.07 (95% CI, 1.05-1.09) among those with seasonal allergies. When adjusted for potential confounders, these findings did not change substantively.
“It is not apparent why pregnant females with AD are more likely to specifically carry GBS,” the authors wrote. “However, several studies have shown that individuals with AD are more likely to carry [Staphylococcus] aureus and that individuals with AD might be deficient in host defenses against S. aureus and other pathogens,” they added.
“Individuals with AD frequently receive antibiotics as part of their AD treatment and this might alter their resident microbiome. Carriage rates may be enhanced by the inhibition of an important barrier protein called filaggrin (FLG) and FLG loss of function genetic variation is known to decrease barrier proteins thought to inhibit the colonization of S. aureus and other pathogens,” the researchers wrote.
They acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including its reliance on an administrative database that does not contain information on past disease.
Asked to comment on the results, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the study, characterized AD as “the poster child for cutaneous dysbiosis – an altered petri dish, so to speak, [that] facilitates survival of the few, leading to decreased microbial diversity that can both enable potential pathogen invasion and immune dysregulation.”
Though it’s not surprising that pregnant AD patients have dysbiosis, the focus on GBS, “which can be a bad actor in the perinatal period, is an interesting connection,” he said. “Will this change practices? Pregnant women should be screened for GBS regardless, but maybe more attention or counseling can be offered to AD patients about the importance of screening. Would decolonization regimens be employed early in pregnancy? This study can’t answer that but certainly raises good questions.”
Dr. Margolis disclosed that he is or recently has been a consultant for Pfizer, Leo, and Sanofi with respect to studies of atopic dermatitis and served on an advisory board for the National Eczema Association. Another author disclosed receiving grants from companies related to work with AD; other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY
What’s New in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma?
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most diagnosed non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), accounting for up to one-third of cases. For many decades, R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) has been the standard first-line treatment approach for eligible patients in the first-line setting, resulting in long-term remissions in about two-thirds of patients. However, as our understanding of the biologic heterogeneity of this disease has advanced with the ability to perform more sophisticated molecular testing at diagnosis, researchers have been able to identify high-risk patient subtypes with suboptimal outcomes. While survival outcomes among low-risk patient subgroups are favorable with first-line immunochemotherapy, the majority of high-risk patients will experience relapse and often succumb to their disease.
Given the poor outcomes among patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) DLBCL, there has been a massive research effort over the last decade to improve survival in this setting. Many experts agree that the approval of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy was the first major victory in this uphill battle. First approved in October of 2017, axicabtagene ciloleucel was the first of the 3 currently available commercial CAR T-cell therapy constructs to be approved in the third-line setting for DLBCL. Compared to historical controls, CAR T-cell therapy is associated with significant improvement in patient survival with complete response (CR) rates of 40%-50% compared to <20% with standard salvage immunochemotherapy.
Following approval in the third-line setting, these agents were quickly expedited to second-line therapy with pivotal trials demonstrating superiority with CAR T-cell therapy in the second line compared to salvage immunochemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant. In 2022 the ZUMA-7 study reported a 24-month event-free survival (EFS) of 41% with axicabtagene ciloleucel compared to 16% with standard of care, and the TRANSFORM study documented a median EFS not yet reached with lisocabtagene ciloleucel compared to 2.3 months with standard of care. Despite these drastic improvements in patient outcomes, more than half of patients will still fail CAR T-cell therapy and require further systemic therapy.
Thankfully, this year has seen even more advancement in the treatment landscape of R/R DLBCL with two new commercially approved agents in yet another novel therapeutic category: bispecific antibodies. The following is a description of the newest data leading to the latest approvals by the US Food and Drug Administration.
Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are an off-the-shelf product that activate endogenous immune cells by cotargeting both tumor antigens as well as host T cells or natural killer cells. Several different experimental agents with varying constructs are under active observation in a wide variety of both hematologic and solid malignancies. Specifically within the realm of B-cell NHL, however, this class of agents is extremely promising and possibly represents the next significant milestone in the treatment of lymphoma.
The toxicity profile of these agents has been reliably predictable in most early phase clinical studies and is related predominantly to T-cell overactivation. The most commonly reported adverse events consist of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) as well as neutropenia, anemia, and hypophosphatemia. While neurologic toxicity has been reported, the incidence is low, and the mechanism is thought to be different than that reported with CAR T-cell therapy given that BsAbs are not likely to cross the blood–brain barrier.
Epcoritamab is a subcutaneously administered bispecific antibody that targets CD3 and CD20 in a 1:1 ratio and activates T cells to destroy CD20-expressing malignant cells. The recent EPCORE NHL-1 clinical trial investigated epcoritamab monotherapy in R/R mature B-cell lymphomas. This agent is administered with a step-up dosing strategy seen consistently across the BsAb drug class. Patients receive a first priming dose of 0.16 mg on cycle 1 day 1, followed by an intermediate dose of 0.8 mg on cycle 1 day 8, followed by the first full dose of 48 mg on cycle 1 day 15. Subsequent doses are administered once weekly for cycles 1-3 followed by every 2 weeks for cycles 4-9, and every 4 weeks starting with cycle 10.
The study enrolled 157 patients globally with median age of 64 and 3 median prior lines of antilymphoma therapy. Nearly 40% of patients had received at least 4 prior lines of therapy, and 83% of patients were refractory to last systemic therapy. Thirty-nine percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy; 75% of these patients developed progressive disease within 6 months of CAR T-cell therapy.
Among patients treated in the study, the results were as follows:
CR rate 39% with an overall response rate (ORR) of 63%
Duration of response 12 months; duration of objective response not reached in patients with CR
Duration of CR 12 months
Median PFS 4.4 months; median OS not reached
Time to CR of 2.7 months
Toxicity profile was notable for the following:
Any grade CRS in 50%, grade ≥3 in 2.5%
Most CRS occurs with first full dose on cycle 1 day 15 with median time to onset of 20 hours and median time to resolution of 48 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 22%, grade ≥3 in 15%, febrile neutropenia in 2.5%
Any grade anemia in 18%, grade ≥3 in 10%
Injection site reaction, any grade, in 20%
Any grade neurotoxicity in 6%, grade ≥3 in 1 patient (0.6%)
Epcoritamab was granted accelerated approval on May 19, 2023, for use in patients with R/R DLBCL who have received at least 2 prior lines of systemic therapy.
Glofitamab is the more recently approved BsAb for DLBCL. This agent is distinguished by its 2:1 binding configuration that confers bivalency for the CD20 binding site. Glofitamab is delivered intravenously and requires pretreatment with obinutuzumab 1000 mg 7 days before the first dose. With a similar step-up dosing strategy, patients receive a priming dose of 2.5mg on cycle 1 day 8, an intermediate dose of 10mg on cycle 1 day 15, and a first full dose of 30mg on cycle 2 day 1. Subsequent treatments are administered every 21 days for up to 12 cycles.
The open-label phase 1-2 clinical trial of glofitamab monotherapy enrolled 155 patients with a median age of 66 and 3 median prior lines of therapy. Thirty-three percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy, and 86% were refractory to last line of therapy with 30% refractory to CAR T-cell therapy.
Results were as follows:
CR rate of 39%, ORR 52%
Median duration of CR not reached, median duration of objective response 18.4 months
Median PFS 4.9 months, median OS not reached
Toxicity profile demonstrated the following:
Any grade CRS 66%, grade ≥ 2 in 18%
Median time to onset 13.5 hours from cycle 1 day 8, median duration 30.5 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 38%, grade ≥ 3 in 27%
Grade ≥ 2 neurologic event in 15%
Glofitamab received accelerated approval from the FDA on June 15, 2023, with an identical indication to epcoritamab.
The introduction of BsAbs in DLBCL has highlighted some important issues. Will BsAbs supplant CAR T-cell therapy in DLBCL? Experts can be found on both sides of this debate. BsAbs circumvent the logistics surrounding the production of CAR T-cell therapy products and can, for the large part, be administered in the outpatient setting. However, CAR T-cell therapy has significantly longer follow-up times, which speaks to the curative potential of these agents even in the third-line setting. BsAbs, some may argue, seem to carry a more favorable toxicity profile with the CRS mitigation strategies. However, we still have much to learn about the downstream side effects with prolonged T-cell activation and the potential for T-cell exhaustion.
Finally, with the continued development of new agents in this arena, the art of sequencing therapies will become ever more important. What is the efficacy of CAR T-cell therapy after BsAb exposure? Can BsAbs be used as bridging therapy to a curative option with CAR T-cell therapy? With longer-term follow-up in several years, will we see late relapses after CR with BsAbs? Ongoing clinical trials investigating combination strategies and CAR T-cell therapy consolidation with BsAbs will hopefully eventually clarify some of these questions.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most diagnosed non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), accounting for up to one-third of cases. For many decades, R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) has been the standard first-line treatment approach for eligible patients in the first-line setting, resulting in long-term remissions in about two-thirds of patients. However, as our understanding of the biologic heterogeneity of this disease has advanced with the ability to perform more sophisticated molecular testing at diagnosis, researchers have been able to identify high-risk patient subtypes with suboptimal outcomes. While survival outcomes among low-risk patient subgroups are favorable with first-line immunochemotherapy, the majority of high-risk patients will experience relapse and often succumb to their disease.
Given the poor outcomes among patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) DLBCL, there has been a massive research effort over the last decade to improve survival in this setting. Many experts agree that the approval of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy was the first major victory in this uphill battle. First approved in October of 2017, axicabtagene ciloleucel was the first of the 3 currently available commercial CAR T-cell therapy constructs to be approved in the third-line setting for DLBCL. Compared to historical controls, CAR T-cell therapy is associated with significant improvement in patient survival with complete response (CR) rates of 40%-50% compared to <20% with standard salvage immunochemotherapy.
Following approval in the third-line setting, these agents were quickly expedited to second-line therapy with pivotal trials demonstrating superiority with CAR T-cell therapy in the second line compared to salvage immunochemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant. In 2022 the ZUMA-7 study reported a 24-month event-free survival (EFS) of 41% with axicabtagene ciloleucel compared to 16% with standard of care, and the TRANSFORM study documented a median EFS not yet reached with lisocabtagene ciloleucel compared to 2.3 months with standard of care. Despite these drastic improvements in patient outcomes, more than half of patients will still fail CAR T-cell therapy and require further systemic therapy.
Thankfully, this year has seen even more advancement in the treatment landscape of R/R DLBCL with two new commercially approved agents in yet another novel therapeutic category: bispecific antibodies. The following is a description of the newest data leading to the latest approvals by the US Food and Drug Administration.
Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are an off-the-shelf product that activate endogenous immune cells by cotargeting both tumor antigens as well as host T cells or natural killer cells. Several different experimental agents with varying constructs are under active observation in a wide variety of both hematologic and solid malignancies. Specifically within the realm of B-cell NHL, however, this class of agents is extremely promising and possibly represents the next significant milestone in the treatment of lymphoma.
The toxicity profile of these agents has been reliably predictable in most early phase clinical studies and is related predominantly to T-cell overactivation. The most commonly reported adverse events consist of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) as well as neutropenia, anemia, and hypophosphatemia. While neurologic toxicity has been reported, the incidence is low, and the mechanism is thought to be different than that reported with CAR T-cell therapy given that BsAbs are not likely to cross the blood–brain barrier.
Epcoritamab is a subcutaneously administered bispecific antibody that targets CD3 and CD20 in a 1:1 ratio and activates T cells to destroy CD20-expressing malignant cells. The recent EPCORE NHL-1 clinical trial investigated epcoritamab monotherapy in R/R mature B-cell lymphomas. This agent is administered with a step-up dosing strategy seen consistently across the BsAb drug class. Patients receive a first priming dose of 0.16 mg on cycle 1 day 1, followed by an intermediate dose of 0.8 mg on cycle 1 day 8, followed by the first full dose of 48 mg on cycle 1 day 15. Subsequent doses are administered once weekly for cycles 1-3 followed by every 2 weeks for cycles 4-9, and every 4 weeks starting with cycle 10.
The study enrolled 157 patients globally with median age of 64 and 3 median prior lines of antilymphoma therapy. Nearly 40% of patients had received at least 4 prior lines of therapy, and 83% of patients were refractory to last systemic therapy. Thirty-nine percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy; 75% of these patients developed progressive disease within 6 months of CAR T-cell therapy.
Among patients treated in the study, the results were as follows:
CR rate 39% with an overall response rate (ORR) of 63%
Duration of response 12 months; duration of objective response not reached in patients with CR
Duration of CR 12 months
Median PFS 4.4 months; median OS not reached
Time to CR of 2.7 months
Toxicity profile was notable for the following:
Any grade CRS in 50%, grade ≥3 in 2.5%
Most CRS occurs with first full dose on cycle 1 day 15 with median time to onset of 20 hours and median time to resolution of 48 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 22%, grade ≥3 in 15%, febrile neutropenia in 2.5%
Any grade anemia in 18%, grade ≥3 in 10%
Injection site reaction, any grade, in 20%
Any grade neurotoxicity in 6%, grade ≥3 in 1 patient (0.6%)
Epcoritamab was granted accelerated approval on May 19, 2023, for use in patients with R/R DLBCL who have received at least 2 prior lines of systemic therapy.
Glofitamab is the more recently approved BsAb for DLBCL. This agent is distinguished by its 2:1 binding configuration that confers bivalency for the CD20 binding site. Glofitamab is delivered intravenously and requires pretreatment with obinutuzumab 1000 mg 7 days before the first dose. With a similar step-up dosing strategy, patients receive a priming dose of 2.5mg on cycle 1 day 8, an intermediate dose of 10mg on cycle 1 day 15, and a first full dose of 30mg on cycle 2 day 1. Subsequent treatments are administered every 21 days for up to 12 cycles.
The open-label phase 1-2 clinical trial of glofitamab monotherapy enrolled 155 patients with a median age of 66 and 3 median prior lines of therapy. Thirty-three percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy, and 86% were refractory to last line of therapy with 30% refractory to CAR T-cell therapy.
Results were as follows:
CR rate of 39%, ORR 52%
Median duration of CR not reached, median duration of objective response 18.4 months
Median PFS 4.9 months, median OS not reached
Toxicity profile demonstrated the following:
Any grade CRS 66%, grade ≥ 2 in 18%
Median time to onset 13.5 hours from cycle 1 day 8, median duration 30.5 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 38%, grade ≥ 3 in 27%
Grade ≥ 2 neurologic event in 15%
Glofitamab received accelerated approval from the FDA on June 15, 2023, with an identical indication to epcoritamab.
The introduction of BsAbs in DLBCL has highlighted some important issues. Will BsAbs supplant CAR T-cell therapy in DLBCL? Experts can be found on both sides of this debate. BsAbs circumvent the logistics surrounding the production of CAR T-cell therapy products and can, for the large part, be administered in the outpatient setting. However, CAR T-cell therapy has significantly longer follow-up times, which speaks to the curative potential of these agents even in the third-line setting. BsAbs, some may argue, seem to carry a more favorable toxicity profile with the CRS mitigation strategies. However, we still have much to learn about the downstream side effects with prolonged T-cell activation and the potential for T-cell exhaustion.
Finally, with the continued development of new agents in this arena, the art of sequencing therapies will become ever more important. What is the efficacy of CAR T-cell therapy after BsAb exposure? Can BsAbs be used as bridging therapy to a curative option with CAR T-cell therapy? With longer-term follow-up in several years, will we see late relapses after CR with BsAbs? Ongoing clinical trials investigating combination strategies and CAR T-cell therapy consolidation with BsAbs will hopefully eventually clarify some of these questions.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most diagnosed non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), accounting for up to one-third of cases. For many decades, R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) has been the standard first-line treatment approach for eligible patients in the first-line setting, resulting in long-term remissions in about two-thirds of patients. However, as our understanding of the biologic heterogeneity of this disease has advanced with the ability to perform more sophisticated molecular testing at diagnosis, researchers have been able to identify high-risk patient subtypes with suboptimal outcomes. While survival outcomes among low-risk patient subgroups are favorable with first-line immunochemotherapy, the majority of high-risk patients will experience relapse and often succumb to their disease.
Given the poor outcomes among patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) DLBCL, there has been a massive research effort over the last decade to improve survival in this setting. Many experts agree that the approval of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy was the first major victory in this uphill battle. First approved in October of 2017, axicabtagene ciloleucel was the first of the 3 currently available commercial CAR T-cell therapy constructs to be approved in the third-line setting for DLBCL. Compared to historical controls, CAR T-cell therapy is associated with significant improvement in patient survival with complete response (CR) rates of 40%-50% compared to <20% with standard salvage immunochemotherapy.
Following approval in the third-line setting, these agents were quickly expedited to second-line therapy with pivotal trials demonstrating superiority with CAR T-cell therapy in the second line compared to salvage immunochemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant. In 2022 the ZUMA-7 study reported a 24-month event-free survival (EFS) of 41% with axicabtagene ciloleucel compared to 16% with standard of care, and the TRANSFORM study documented a median EFS not yet reached with lisocabtagene ciloleucel compared to 2.3 months with standard of care. Despite these drastic improvements in patient outcomes, more than half of patients will still fail CAR T-cell therapy and require further systemic therapy.
Thankfully, this year has seen even more advancement in the treatment landscape of R/R DLBCL with two new commercially approved agents in yet another novel therapeutic category: bispecific antibodies. The following is a description of the newest data leading to the latest approvals by the US Food and Drug Administration.
Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are an off-the-shelf product that activate endogenous immune cells by cotargeting both tumor antigens as well as host T cells or natural killer cells. Several different experimental agents with varying constructs are under active observation in a wide variety of both hematologic and solid malignancies. Specifically within the realm of B-cell NHL, however, this class of agents is extremely promising and possibly represents the next significant milestone in the treatment of lymphoma.
The toxicity profile of these agents has been reliably predictable in most early phase clinical studies and is related predominantly to T-cell overactivation. The most commonly reported adverse events consist of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) as well as neutropenia, anemia, and hypophosphatemia. While neurologic toxicity has been reported, the incidence is low, and the mechanism is thought to be different than that reported with CAR T-cell therapy given that BsAbs are not likely to cross the blood–brain barrier.
Epcoritamab is a subcutaneously administered bispecific antibody that targets CD3 and CD20 in a 1:1 ratio and activates T cells to destroy CD20-expressing malignant cells. The recent EPCORE NHL-1 clinical trial investigated epcoritamab monotherapy in R/R mature B-cell lymphomas. This agent is administered with a step-up dosing strategy seen consistently across the BsAb drug class. Patients receive a first priming dose of 0.16 mg on cycle 1 day 1, followed by an intermediate dose of 0.8 mg on cycle 1 day 8, followed by the first full dose of 48 mg on cycle 1 day 15. Subsequent doses are administered once weekly for cycles 1-3 followed by every 2 weeks for cycles 4-9, and every 4 weeks starting with cycle 10.
The study enrolled 157 patients globally with median age of 64 and 3 median prior lines of antilymphoma therapy. Nearly 40% of patients had received at least 4 prior lines of therapy, and 83% of patients were refractory to last systemic therapy. Thirty-nine percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy; 75% of these patients developed progressive disease within 6 months of CAR T-cell therapy.
Among patients treated in the study, the results were as follows:
CR rate 39% with an overall response rate (ORR) of 63%
Duration of response 12 months; duration of objective response not reached in patients with CR
Duration of CR 12 months
Median PFS 4.4 months; median OS not reached
Time to CR of 2.7 months
Toxicity profile was notable for the following:
Any grade CRS in 50%, grade ≥3 in 2.5%
Most CRS occurs with first full dose on cycle 1 day 15 with median time to onset of 20 hours and median time to resolution of 48 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 22%, grade ≥3 in 15%, febrile neutropenia in 2.5%
Any grade anemia in 18%, grade ≥3 in 10%
Injection site reaction, any grade, in 20%
Any grade neurotoxicity in 6%, grade ≥3 in 1 patient (0.6%)
Epcoritamab was granted accelerated approval on May 19, 2023, for use in patients with R/R DLBCL who have received at least 2 prior lines of systemic therapy.
Glofitamab is the more recently approved BsAb for DLBCL. This agent is distinguished by its 2:1 binding configuration that confers bivalency for the CD20 binding site. Glofitamab is delivered intravenously and requires pretreatment with obinutuzumab 1000 mg 7 days before the first dose. With a similar step-up dosing strategy, patients receive a priming dose of 2.5mg on cycle 1 day 8, an intermediate dose of 10mg on cycle 1 day 15, and a first full dose of 30mg on cycle 2 day 1. Subsequent treatments are administered every 21 days for up to 12 cycles.
The open-label phase 1-2 clinical trial of glofitamab monotherapy enrolled 155 patients with a median age of 66 and 3 median prior lines of therapy. Thirty-three percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy, and 86% were refractory to last line of therapy with 30% refractory to CAR T-cell therapy.
Results were as follows:
CR rate of 39%, ORR 52%
Median duration of CR not reached, median duration of objective response 18.4 months
Median PFS 4.9 months, median OS not reached
Toxicity profile demonstrated the following:
Any grade CRS 66%, grade ≥ 2 in 18%
Median time to onset 13.5 hours from cycle 1 day 8, median duration 30.5 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 38%, grade ≥ 3 in 27%
Grade ≥ 2 neurologic event in 15%
Glofitamab received accelerated approval from the FDA on June 15, 2023, with an identical indication to epcoritamab.
The introduction of BsAbs in DLBCL has highlighted some important issues. Will BsAbs supplant CAR T-cell therapy in DLBCL? Experts can be found on both sides of this debate. BsAbs circumvent the logistics surrounding the production of CAR T-cell therapy products and can, for the large part, be administered in the outpatient setting. However, CAR T-cell therapy has significantly longer follow-up times, which speaks to the curative potential of these agents even in the third-line setting. BsAbs, some may argue, seem to carry a more favorable toxicity profile with the CRS mitigation strategies. However, we still have much to learn about the downstream side effects with prolonged T-cell activation and the potential for T-cell exhaustion.
Finally, with the continued development of new agents in this arena, the art of sequencing therapies will become ever more important. What is the efficacy of CAR T-cell therapy after BsAb exposure? Can BsAbs be used as bridging therapy to a curative option with CAR T-cell therapy? With longer-term follow-up in several years, will we see late relapses after CR with BsAbs? Ongoing clinical trials investigating combination strategies and CAR T-cell therapy consolidation with BsAbs will hopefully eventually clarify some of these questions.
Post-SCT, better survival in children with healthy gut diversity
“To the best of our knowledge, we present the first evidence of an association between pretransplantation lower gut microbiota diversity and poorer outcome in children undergoing allo-HSCT,” the authors report, in research published in the journal Blood. “Our findings underscore the importance of pre-transplant gut microbiota diversity and compositional structure in influencing allo-HSCT-related clinical outcomes in the pediatric setting.”
While allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) can be potentially curative of hematologic malignancies, the stem cell transplantation process can wreak havoc on gut microbiota, because of factors including the conditioning regimen, antibiotic exposure, and dietary changes.
Specifically, the process can cause a substantial decrease in necessary alpha diversity and a potential expansion of possibly pathogenic bacteria.
While poor gut microbiota diversity has been linked to higher mortality in adult patients receiving allo-HSCT, research on the effects in pediatric patients is lacking.
“The gut microbiota of children differs from adults’ one, and this accounts for the need for specific pediatric studies on the gut microbiota-to–allo-HSCT relationship,” the authors write.
For the multicenter study, first author Riccardo Masetti, MD, PhD, of the department of pediatric oncology and hematology at the University of Bologna, Italy, and colleagues analyzed the gut microbiota diversity of 90 pediatric allo-HSCT recipients at four centers in Italy and one in Poland, stratifying the patients into groups of higher and lower diversity pretransplantation and again at the time of neutrophil engraftment.
Overall, gut microbiota diversity significantly declined from before allo-HSCT to afterward, at the time of neutrophil engraftment (P < .0001), with lower diversity observed in patients 3 years of age or younger.
With a median follow-up of 52 months, compared with the lower diversity group, those with higher diversity prior to transplantation had a significantly higher probability of overall survival (hazard ratio, 0.26; P = .011), after adjustment for age, graft source, donor type, intensity of conditioning regimen, center, and type of disease, with estimated overall survival at 52 months after allo-HSCT of 88.9% for the higher diversity group and 62.7% for the lower diversity group.
The cumulative incidence of grade II-IV acute GvHD was significantly lower for the higher diversity group versus lower diversity (20.0 versus 44.4, respectively; P = .017), as were the incidence rates of grade III-IV acute GvHD (2.2 versus 20.0; P = .007).
There were, however, no significant differences between the low and high diversity gut microbiota groups in relapse-free survival (P = .091).
The higher diversity group notably had higher relative abundances of potentially health-related bacterial families, including Ruminococcaceae and Oscillospiraceae, while the lower diversity group showed an overabundance of Enterococcaceae and Enterobacteriaceae.
Of note, the results differ from those observed in adults, among whom gut microbiota diversity before as well as after transplantation has been significantly associated with transplant outcomes, whereas with children, the association was limited to diversity prior to transplant.
In general, children have significantly lower diversity of gut microbiota than adults, with varying functional properties, and microbiota that is more easily modified by environmental factors, with larger changes occurring upon exposure to external stressors, the authors explain.
“Considering these different ecological properties compared to adults, we hypothesize that allo-HSCT–induced dysbiosis in the pediatric setting may imply loss of age-related gut microbiota signatures, including alpha diversity, with high interpatient variability,” they say.
Characteristics that were associated with higher or lower gut microbiota diversity prior to allo-HSCT included the treating center, suggesting that the geographical region may affect the diversity and the type of antibiotic exposure prior to the transplant.
Limitations included that “we didn’t assess other pretransplant characteristics such as the type of chemotherapy received, or the lifestyle, and this should be addressed in future studies on larger cohorts,” Dr. Masetti said in an interview.
While lengthy delays in screening of samples are barriers in the use of the gut microbiome as a tool in clinical practice, he noted that clinicians can take key measures to improve the microbiota.
“[Preventive measures] include the avoidance of unnecessary antibiotic treatment, which has a detrimental effect on the microbiota,” he said. “Moreover, some dietary changes may promote microbiota health.”
In addition, key measures can be taken during the allo-HSCT to preserve the microbiota, he added.
“In our center, we use enteral nutrition with a nasogastric tube rather than parenteral nutrition, which helps the microbiota to recover faster,” Dr. Masetti explained. “Moreover, other interventional measures such as fecal microbiota transplantation or the use of probiotics are under testing.”
“In particular, our data emphasize the importance of an overall healthy network, rather than the abundance of specific families or genera, in preventing complications and unfavorable outcomes.”
Commenting on the study, Robert Jenq, MD, an assistant professor in the departments of genomic medicine and stem cell transplantation and cellular therapy at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, noted that with the growing evidence of the effects of poor gut microbiota diversity on clinical outcomes, multiple early-phase clinical trials are being conducted to test various strategies to prevent or treat gut injury.
“I’m not aware of any one approach that has shown enough promise to warrant being tested in multicenter studies yet, but it’s still a bit early,” Dr. Jenq said.“In the meantime, discontinuing or de-escalating antibiotics when medically safe, and encouraging patients to eat as much as they’re able to is a reasonable recommendation.”
Dr. Jenq added that, with most of the data on the issue being retrospective, a causative role has not been established, and “the finding of an association between the gut microbiota composition and survival, while interesting and provocative, does not provide evidence that intervening on the gut microbiota will lead to a clinical benefit.”
“I’m hopeful that randomized clinical trials will eventually demonstrate that we can protect or restore the gut microbiota, and this will lead to substantial clinical benefits, but this remains to be seen,” he said.
The authors had no disclosures to report. Dr. Jenq is an advisor for Seres Therapeutics, Prolacta Biosciences, and MaaT Pharma.
“To the best of our knowledge, we present the first evidence of an association between pretransplantation lower gut microbiota diversity and poorer outcome in children undergoing allo-HSCT,” the authors report, in research published in the journal Blood. “Our findings underscore the importance of pre-transplant gut microbiota diversity and compositional structure in influencing allo-HSCT-related clinical outcomes in the pediatric setting.”
While allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) can be potentially curative of hematologic malignancies, the stem cell transplantation process can wreak havoc on gut microbiota, because of factors including the conditioning regimen, antibiotic exposure, and dietary changes.
Specifically, the process can cause a substantial decrease in necessary alpha diversity and a potential expansion of possibly pathogenic bacteria.
While poor gut microbiota diversity has been linked to higher mortality in adult patients receiving allo-HSCT, research on the effects in pediatric patients is lacking.
“The gut microbiota of children differs from adults’ one, and this accounts for the need for specific pediatric studies on the gut microbiota-to–allo-HSCT relationship,” the authors write.
For the multicenter study, first author Riccardo Masetti, MD, PhD, of the department of pediatric oncology and hematology at the University of Bologna, Italy, and colleagues analyzed the gut microbiota diversity of 90 pediatric allo-HSCT recipients at four centers in Italy and one in Poland, stratifying the patients into groups of higher and lower diversity pretransplantation and again at the time of neutrophil engraftment.
Overall, gut microbiota diversity significantly declined from before allo-HSCT to afterward, at the time of neutrophil engraftment (P < .0001), with lower diversity observed in patients 3 years of age or younger.
With a median follow-up of 52 months, compared with the lower diversity group, those with higher diversity prior to transplantation had a significantly higher probability of overall survival (hazard ratio, 0.26; P = .011), after adjustment for age, graft source, donor type, intensity of conditioning regimen, center, and type of disease, with estimated overall survival at 52 months after allo-HSCT of 88.9% for the higher diversity group and 62.7% for the lower diversity group.
The cumulative incidence of grade II-IV acute GvHD was significantly lower for the higher diversity group versus lower diversity (20.0 versus 44.4, respectively; P = .017), as were the incidence rates of grade III-IV acute GvHD (2.2 versus 20.0; P = .007).
There were, however, no significant differences between the low and high diversity gut microbiota groups in relapse-free survival (P = .091).
The higher diversity group notably had higher relative abundances of potentially health-related bacterial families, including Ruminococcaceae and Oscillospiraceae, while the lower diversity group showed an overabundance of Enterococcaceae and Enterobacteriaceae.
Of note, the results differ from those observed in adults, among whom gut microbiota diversity before as well as after transplantation has been significantly associated with transplant outcomes, whereas with children, the association was limited to diversity prior to transplant.
In general, children have significantly lower diversity of gut microbiota than adults, with varying functional properties, and microbiota that is more easily modified by environmental factors, with larger changes occurring upon exposure to external stressors, the authors explain.
“Considering these different ecological properties compared to adults, we hypothesize that allo-HSCT–induced dysbiosis in the pediatric setting may imply loss of age-related gut microbiota signatures, including alpha diversity, with high interpatient variability,” they say.
Characteristics that were associated with higher or lower gut microbiota diversity prior to allo-HSCT included the treating center, suggesting that the geographical region may affect the diversity and the type of antibiotic exposure prior to the transplant.
Limitations included that “we didn’t assess other pretransplant characteristics such as the type of chemotherapy received, or the lifestyle, and this should be addressed in future studies on larger cohorts,” Dr. Masetti said in an interview.
While lengthy delays in screening of samples are barriers in the use of the gut microbiome as a tool in clinical practice, he noted that clinicians can take key measures to improve the microbiota.
“[Preventive measures] include the avoidance of unnecessary antibiotic treatment, which has a detrimental effect on the microbiota,” he said. “Moreover, some dietary changes may promote microbiota health.”
In addition, key measures can be taken during the allo-HSCT to preserve the microbiota, he added.
“In our center, we use enteral nutrition with a nasogastric tube rather than parenteral nutrition, which helps the microbiota to recover faster,” Dr. Masetti explained. “Moreover, other interventional measures such as fecal microbiota transplantation or the use of probiotics are under testing.”
“In particular, our data emphasize the importance of an overall healthy network, rather than the abundance of specific families or genera, in preventing complications and unfavorable outcomes.”
Commenting on the study, Robert Jenq, MD, an assistant professor in the departments of genomic medicine and stem cell transplantation and cellular therapy at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, noted that with the growing evidence of the effects of poor gut microbiota diversity on clinical outcomes, multiple early-phase clinical trials are being conducted to test various strategies to prevent or treat gut injury.
“I’m not aware of any one approach that has shown enough promise to warrant being tested in multicenter studies yet, but it’s still a bit early,” Dr. Jenq said.“In the meantime, discontinuing or de-escalating antibiotics when medically safe, and encouraging patients to eat as much as they’re able to is a reasonable recommendation.”
Dr. Jenq added that, with most of the data on the issue being retrospective, a causative role has not been established, and “the finding of an association between the gut microbiota composition and survival, while interesting and provocative, does not provide evidence that intervening on the gut microbiota will lead to a clinical benefit.”
“I’m hopeful that randomized clinical trials will eventually demonstrate that we can protect or restore the gut microbiota, and this will lead to substantial clinical benefits, but this remains to be seen,” he said.
The authors had no disclosures to report. Dr. Jenq is an advisor for Seres Therapeutics, Prolacta Biosciences, and MaaT Pharma.
“To the best of our knowledge, we present the first evidence of an association between pretransplantation lower gut microbiota diversity and poorer outcome in children undergoing allo-HSCT,” the authors report, in research published in the journal Blood. “Our findings underscore the importance of pre-transplant gut microbiota diversity and compositional structure in influencing allo-HSCT-related clinical outcomes in the pediatric setting.”
While allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) can be potentially curative of hematologic malignancies, the stem cell transplantation process can wreak havoc on gut microbiota, because of factors including the conditioning regimen, antibiotic exposure, and dietary changes.
Specifically, the process can cause a substantial decrease in necessary alpha diversity and a potential expansion of possibly pathogenic bacteria.
While poor gut microbiota diversity has been linked to higher mortality in adult patients receiving allo-HSCT, research on the effects in pediatric patients is lacking.
“The gut microbiota of children differs from adults’ one, and this accounts for the need for specific pediatric studies on the gut microbiota-to–allo-HSCT relationship,” the authors write.
For the multicenter study, first author Riccardo Masetti, MD, PhD, of the department of pediatric oncology and hematology at the University of Bologna, Italy, and colleagues analyzed the gut microbiota diversity of 90 pediatric allo-HSCT recipients at four centers in Italy and one in Poland, stratifying the patients into groups of higher and lower diversity pretransplantation and again at the time of neutrophil engraftment.
Overall, gut microbiota diversity significantly declined from before allo-HSCT to afterward, at the time of neutrophil engraftment (P < .0001), with lower diversity observed in patients 3 years of age or younger.
With a median follow-up of 52 months, compared with the lower diversity group, those with higher diversity prior to transplantation had a significantly higher probability of overall survival (hazard ratio, 0.26; P = .011), after adjustment for age, graft source, donor type, intensity of conditioning regimen, center, and type of disease, with estimated overall survival at 52 months after allo-HSCT of 88.9% for the higher diversity group and 62.7% for the lower diversity group.
The cumulative incidence of grade II-IV acute GvHD was significantly lower for the higher diversity group versus lower diversity (20.0 versus 44.4, respectively; P = .017), as were the incidence rates of grade III-IV acute GvHD (2.2 versus 20.0; P = .007).
There were, however, no significant differences between the low and high diversity gut microbiota groups in relapse-free survival (P = .091).
The higher diversity group notably had higher relative abundances of potentially health-related bacterial families, including Ruminococcaceae and Oscillospiraceae, while the lower diversity group showed an overabundance of Enterococcaceae and Enterobacteriaceae.
Of note, the results differ from those observed in adults, among whom gut microbiota diversity before as well as after transplantation has been significantly associated with transplant outcomes, whereas with children, the association was limited to diversity prior to transplant.
In general, children have significantly lower diversity of gut microbiota than adults, with varying functional properties, and microbiota that is more easily modified by environmental factors, with larger changes occurring upon exposure to external stressors, the authors explain.
“Considering these different ecological properties compared to adults, we hypothesize that allo-HSCT–induced dysbiosis in the pediatric setting may imply loss of age-related gut microbiota signatures, including alpha diversity, with high interpatient variability,” they say.
Characteristics that were associated with higher or lower gut microbiota diversity prior to allo-HSCT included the treating center, suggesting that the geographical region may affect the diversity and the type of antibiotic exposure prior to the transplant.
Limitations included that “we didn’t assess other pretransplant characteristics such as the type of chemotherapy received, or the lifestyle, and this should be addressed in future studies on larger cohorts,” Dr. Masetti said in an interview.
While lengthy delays in screening of samples are barriers in the use of the gut microbiome as a tool in clinical practice, he noted that clinicians can take key measures to improve the microbiota.
“[Preventive measures] include the avoidance of unnecessary antibiotic treatment, which has a detrimental effect on the microbiota,” he said. “Moreover, some dietary changes may promote microbiota health.”
In addition, key measures can be taken during the allo-HSCT to preserve the microbiota, he added.
“In our center, we use enteral nutrition with a nasogastric tube rather than parenteral nutrition, which helps the microbiota to recover faster,” Dr. Masetti explained. “Moreover, other interventional measures such as fecal microbiota transplantation or the use of probiotics are under testing.”
“In particular, our data emphasize the importance of an overall healthy network, rather than the abundance of specific families or genera, in preventing complications and unfavorable outcomes.”
Commenting on the study, Robert Jenq, MD, an assistant professor in the departments of genomic medicine and stem cell transplantation and cellular therapy at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, noted that with the growing evidence of the effects of poor gut microbiota diversity on clinical outcomes, multiple early-phase clinical trials are being conducted to test various strategies to prevent or treat gut injury.
“I’m not aware of any one approach that has shown enough promise to warrant being tested in multicenter studies yet, but it’s still a bit early,” Dr. Jenq said.“In the meantime, discontinuing or de-escalating antibiotics when medically safe, and encouraging patients to eat as much as they’re able to is a reasonable recommendation.”
Dr. Jenq added that, with most of the data on the issue being retrospective, a causative role has not been established, and “the finding of an association between the gut microbiota composition and survival, while interesting and provocative, does not provide evidence that intervening on the gut microbiota will lead to a clinical benefit.”
“I’m hopeful that randomized clinical trials will eventually demonstrate that we can protect or restore the gut microbiota, and this will lead to substantial clinical benefits, but this remains to be seen,” he said.
The authors had no disclosures to report. Dr. Jenq is an advisor for Seres Therapeutics, Prolacta Biosciences, and MaaT Pharma.
FROM BLOOD
New recommendation expands antiretroviral guidance for HIV
.
“With these new options we could potentially extend pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to a wider population,” says James Stevermer, MD, a member of the task force and a professor of family and community medicine at the University of Missouri–Columbia.
The guidance, published in JAMA, updates the group’s previous recommendation from 2019 to take into account the new options that have become available since the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approvals that included a long-acting injectable form.
In the original report, daily oral tenofovir disoproxil fumarate with emtricitabine was the only approved medication available and the task force recommended it. Since then, two new regimens have been approved: daily oral tenofovir alafenamide with emtricitabine and the long-acting injectable cabotegravir.
The task force is backing all three options and is recommending that clinicians use whichever formulation is most appropriate for their patients at risk for HIV infection.
Task force in primary and preventive care
The USPSTF is a volunteer group of experts in primary and preventive care who make recommendations on the best preventative interventions clinicians should take on everything from cancer screening, to preventive aspirin use, to behavioral counseling. The group is convened and supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Recommendations from this group are particularly helpful for clinicians who may not see HIV as their area of expertise, says Carolyn Chu, MD, chief medical officer of the American Academy of HIV Medicine. “Hopefully, this will catch the eye of people who are not tracking all of the HIV updates,” she says.
A person’s risk for infection is mostly based on their behavior, Dr. Stevermer says. Those who use injectable drugs, particularly if they share needles, those who use condoms inconsistently and do not know their partner’s HIV status, and those who have recently had bacterial sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea and syphilis are all at higher risk.
The efficacy of each of the three options is close enough to equal that it doesn’t usually matter which is prescribed, according to the task force. However, daily oral tenofovir alafenamide with emtricitabine is not approved for use by people engaging in receptive vaginal sex. For most people, the best medication option is the one they are most likely able to integrate into their routine. Cabotegravir, for example, which requires injections every 2 months, is an easier method for some people, particularly those who don’t think they could successfully take a daily pill.
Reducing risk
“The evidence is very clear that being able to adhere to taking the medication daily was very closely associated with the effectiveness of PrEP,” Dr. Stevermer says. “So, everything that we can do to make sure that the person who wants to prevent HIV is getting their PrEP as it is supposed to be taken makes it that much more effective.”
Expanding access to antiretrovirals among at-risk groups is an important part of the Ending the HIV Epidemic in the United States initiative that aims to reduce new HIV cases by 90% by 2030.
But an editorial published alongside the recommendation in JAMA notes that uptake of PrEP has been disproportionately low among populations most heavily affected by HIV.
In 2021, 78% of White people expected to benefit from PrEP received it, compared with just 11% of Black people and 21% of Hispanic people, despite both of those populations having a higher incidence of HIV than Whites. PrEP use is also substantially lower among cisgender and transgender women, youth, and people who inject drugs.
“We have an intervention that can markedly reduce people’s risk of getting HIV and so we want to make sure we get this out to all those populations at increased risk,” Dr. Stevermer says.
Having multiple options when it comes to PrEP is a big part of expanding access to the treatment for underserved groups, Dr. Chu says. “Even though oral tenofovir disoproxil fumarate with emtricitabine has been out for a while, we know it’s not getting to everyone, and there may be clinical circumstances that means it’s not the right option,” she says. “Making sure we are supporting choices so people can make the decision for themselves is important.”
But doctors also need to be willing to have an open conversation with their patients and bring up the topic of PrEP in a way that doesn’t feel judgmental or stigmatizing, Dr. Chu says.
It is also important not to make assumptions about who would want to talk about medication, she adds. “How can we change the narrative around PrEP?” she asks. “The evidence is there, these medications are effective and safe; weave PrEP into your preventive care portfolio to at least start the conversation.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
.
“With these new options we could potentially extend pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to a wider population,” says James Stevermer, MD, a member of the task force and a professor of family and community medicine at the University of Missouri–Columbia.
The guidance, published in JAMA, updates the group’s previous recommendation from 2019 to take into account the new options that have become available since the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approvals that included a long-acting injectable form.
In the original report, daily oral tenofovir disoproxil fumarate with emtricitabine was the only approved medication available and the task force recommended it. Since then, two new regimens have been approved: daily oral tenofovir alafenamide with emtricitabine and the long-acting injectable cabotegravir.
The task force is backing all three options and is recommending that clinicians use whichever formulation is most appropriate for their patients at risk for HIV infection.
Task force in primary and preventive care
The USPSTF is a volunteer group of experts in primary and preventive care who make recommendations on the best preventative interventions clinicians should take on everything from cancer screening, to preventive aspirin use, to behavioral counseling. The group is convened and supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Recommendations from this group are particularly helpful for clinicians who may not see HIV as their area of expertise, says Carolyn Chu, MD, chief medical officer of the American Academy of HIV Medicine. “Hopefully, this will catch the eye of people who are not tracking all of the HIV updates,” she says.
A person’s risk for infection is mostly based on their behavior, Dr. Stevermer says. Those who use injectable drugs, particularly if they share needles, those who use condoms inconsistently and do not know their partner’s HIV status, and those who have recently had bacterial sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea and syphilis are all at higher risk.
The efficacy of each of the three options is close enough to equal that it doesn’t usually matter which is prescribed, according to the task force. However, daily oral tenofovir alafenamide with emtricitabine is not approved for use by people engaging in receptive vaginal sex. For most people, the best medication option is the one they are most likely able to integrate into their routine. Cabotegravir, for example, which requires injections every 2 months, is an easier method for some people, particularly those who don’t think they could successfully take a daily pill.
Reducing risk
“The evidence is very clear that being able to adhere to taking the medication daily was very closely associated with the effectiveness of PrEP,” Dr. Stevermer says. “So, everything that we can do to make sure that the person who wants to prevent HIV is getting their PrEP as it is supposed to be taken makes it that much more effective.”
Expanding access to antiretrovirals among at-risk groups is an important part of the Ending the HIV Epidemic in the United States initiative that aims to reduce new HIV cases by 90% by 2030.
But an editorial published alongside the recommendation in JAMA notes that uptake of PrEP has been disproportionately low among populations most heavily affected by HIV.
In 2021, 78% of White people expected to benefit from PrEP received it, compared with just 11% of Black people and 21% of Hispanic people, despite both of those populations having a higher incidence of HIV than Whites. PrEP use is also substantially lower among cisgender and transgender women, youth, and people who inject drugs.
“We have an intervention that can markedly reduce people’s risk of getting HIV and so we want to make sure we get this out to all those populations at increased risk,” Dr. Stevermer says.
Having multiple options when it comes to PrEP is a big part of expanding access to the treatment for underserved groups, Dr. Chu says. “Even though oral tenofovir disoproxil fumarate with emtricitabine has been out for a while, we know it’s not getting to everyone, and there may be clinical circumstances that means it’s not the right option,” she says. “Making sure we are supporting choices so people can make the decision for themselves is important.”
But doctors also need to be willing to have an open conversation with their patients and bring up the topic of PrEP in a way that doesn’t feel judgmental or stigmatizing, Dr. Chu says.
It is also important not to make assumptions about who would want to talk about medication, she adds. “How can we change the narrative around PrEP?” she asks. “The evidence is there, these medications are effective and safe; weave PrEP into your preventive care portfolio to at least start the conversation.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
.
“With these new options we could potentially extend pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to a wider population,” says James Stevermer, MD, a member of the task force and a professor of family and community medicine at the University of Missouri–Columbia.
The guidance, published in JAMA, updates the group’s previous recommendation from 2019 to take into account the new options that have become available since the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approvals that included a long-acting injectable form.
In the original report, daily oral tenofovir disoproxil fumarate with emtricitabine was the only approved medication available and the task force recommended it. Since then, two new regimens have been approved: daily oral tenofovir alafenamide with emtricitabine and the long-acting injectable cabotegravir.
The task force is backing all three options and is recommending that clinicians use whichever formulation is most appropriate for their patients at risk for HIV infection.
Task force in primary and preventive care
The USPSTF is a volunteer group of experts in primary and preventive care who make recommendations on the best preventative interventions clinicians should take on everything from cancer screening, to preventive aspirin use, to behavioral counseling. The group is convened and supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Recommendations from this group are particularly helpful for clinicians who may not see HIV as their area of expertise, says Carolyn Chu, MD, chief medical officer of the American Academy of HIV Medicine. “Hopefully, this will catch the eye of people who are not tracking all of the HIV updates,” she says.
A person’s risk for infection is mostly based on their behavior, Dr. Stevermer says. Those who use injectable drugs, particularly if they share needles, those who use condoms inconsistently and do not know their partner’s HIV status, and those who have recently had bacterial sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea and syphilis are all at higher risk.
The efficacy of each of the three options is close enough to equal that it doesn’t usually matter which is prescribed, according to the task force. However, daily oral tenofovir alafenamide with emtricitabine is not approved for use by people engaging in receptive vaginal sex. For most people, the best medication option is the one they are most likely able to integrate into their routine. Cabotegravir, for example, which requires injections every 2 months, is an easier method for some people, particularly those who don’t think they could successfully take a daily pill.
Reducing risk
“The evidence is very clear that being able to adhere to taking the medication daily was very closely associated with the effectiveness of PrEP,” Dr. Stevermer says. “So, everything that we can do to make sure that the person who wants to prevent HIV is getting their PrEP as it is supposed to be taken makes it that much more effective.”
Expanding access to antiretrovirals among at-risk groups is an important part of the Ending the HIV Epidemic in the United States initiative that aims to reduce new HIV cases by 90% by 2030.
But an editorial published alongside the recommendation in JAMA notes that uptake of PrEP has been disproportionately low among populations most heavily affected by HIV.
In 2021, 78% of White people expected to benefit from PrEP received it, compared with just 11% of Black people and 21% of Hispanic people, despite both of those populations having a higher incidence of HIV than Whites. PrEP use is also substantially lower among cisgender and transgender women, youth, and people who inject drugs.
“We have an intervention that can markedly reduce people’s risk of getting HIV and so we want to make sure we get this out to all those populations at increased risk,” Dr. Stevermer says.
Having multiple options when it comes to PrEP is a big part of expanding access to the treatment for underserved groups, Dr. Chu says. “Even though oral tenofovir disoproxil fumarate with emtricitabine has been out for a while, we know it’s not getting to everyone, and there may be clinical circumstances that means it’s not the right option,” she says. “Making sure we are supporting choices so people can make the decision for themselves is important.”
But doctors also need to be willing to have an open conversation with their patients and bring up the topic of PrEP in a way that doesn’t feel judgmental or stigmatizing, Dr. Chu says.
It is also important not to make assumptions about who would want to talk about medication, she adds. “How can we change the narrative around PrEP?” she asks. “The evidence is there, these medications are effective and safe; weave PrEP into your preventive care portfolio to at least start the conversation.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Mohs found to confer survival benefit in localized Merkel cell carcinoma
results from a national retrospective cohort study suggest.
The study found that, in patients with pathologically confirmed, localized T1/T2 MCC, “treatment with MMS was associated with an approximately 40% reduction in hazard of death compared with WLE,” reported John A. Carucci, MD, PhD, and colleagues in the department of dermatology at NYU Langone Health, New York. The results provide “preliminary data suggesting that treatment of localized, early-stage MCC with MMS may result in the most optimal patient survival outcomes for this aggressive form of skin cancer,” they added. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
“Although data for keratinocytic nonmelanoma skin cancers have been definitive in demonstrating the advantage of peripheral and deep en face margin assessment over conventional WLE or NME [narrow-margin excision], the data for MCC, likely because of the disease’s rarity and limitations of available data sets, have been mixed,” they wrote.
Results from national studies published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute and the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found no difference in survival among patients with localized MCC treated with WLE versus MMS. “However, these studies did not have confirmed pathologic node status, a substantial limitation considering that clinically node-negative cases of localized MCC have sentinel lymph node positivity rates ranging from 25% to 40%,” the authors noted.
To evaluate the association of the surgical excision modality and patient survival for pathologically confirmed localized T1/T2 MCC, Dr. Carucci and coauthors examined a cohort of 2,313 patients from the National Cancer Database with T1/T2 MCC diagnosed between Jan. 1, 2004, and Dec. 31, 2018, with pathologically confirmed, negative regional lymph nodes and treated with surgery. Their mean age was 71 years and 57.9% were male. Of the 2,313 patients, 1,452 underwent WLE, 104 underwent MMS, and 757 underwent NME.
The unadjusted analysis revealed that, compared with WLE, excision with MMS had the best unadjusted mean survival rates: 87.4% versus 86.1%, respectively, at 3 years, 84.5% versus 76.9% at 5 years, and 81.8% versus 60.9% at 10 years. Patients treated with NME had similar mean survival rates as those treated with WLE: 84.8% at 3 years, 78.3% at 5 years, and 60.8% at 10 years.
Multivariable survival analysis demonstrated that treatment with MMS was associated with significantly improved survival, compared with WLE (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.36-0.97; P = .04).
“These data suggest that MMS may provide a survival benefit in the treatment of localized MCC, although further prospective work studying this issue is required,” the authors concluded. “Future directions may also focus on elucidating the benefit of adjuvant radiotherapy in localized cases treated with MMS.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fewer numbers of patients receiving MMS surgery, lack of randomization, and potential for selection bias.
In an interview, Travis W. Blalock, MD, director of dermatologic surgery, Mohs micrographic surgery, and cutaneous oncology at Emory University, Atlanta, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the field of MCC “has undergone rapid and robust transformation over the past 20 years. These changes encompass advancements in diagnosing the condition, identifying linked viruses, and developing systemic treatments.”
The study findings “imply that comprehensive assessment of histologic margins might offer advantages beyond minimizing scars, minimizing functional impact, and reducing the likelihood of local recurrence,” he said.
“It’s beyond doubt,” he added, that the study “furnishes us with yet another set of real-world insights that will undoubtedly influence patient outcomes. These insights serve to bring clarity to the ways in which we can deliver precisely targeted surgical treatment with durable outcomes for localized MCC.”
Patricia M. Richey, MD, director of Mohs surgery at Boston University, who was also asked to comment on the study, added that, because of the nature of the National Cancer Database, “the authors of this study were unfortunately unable to report disease-specific survival or immunosuppression status. That being said, the preliminary data presented are convincing and should result in us further exploring this topic, as well as readdressing and questioning related issues such as whether or not adjuvant radiotherapy is truly beneficial in cases with histologic clearance via Mohs.”
Dr. Carucci reported receiving grant funding from Regeneron for investigator-initiated basic research. No other author disclosures were reported. Neither Dr. Blalock nor Dr. Richey had relevant disclosures.
results from a national retrospective cohort study suggest.
The study found that, in patients with pathologically confirmed, localized T1/T2 MCC, “treatment with MMS was associated with an approximately 40% reduction in hazard of death compared with WLE,” reported John A. Carucci, MD, PhD, and colleagues in the department of dermatology at NYU Langone Health, New York. The results provide “preliminary data suggesting that treatment of localized, early-stage MCC with MMS may result in the most optimal patient survival outcomes for this aggressive form of skin cancer,” they added. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
“Although data for keratinocytic nonmelanoma skin cancers have been definitive in demonstrating the advantage of peripheral and deep en face margin assessment over conventional WLE or NME [narrow-margin excision], the data for MCC, likely because of the disease’s rarity and limitations of available data sets, have been mixed,” they wrote.
Results from national studies published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute and the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found no difference in survival among patients with localized MCC treated with WLE versus MMS. “However, these studies did not have confirmed pathologic node status, a substantial limitation considering that clinically node-negative cases of localized MCC have sentinel lymph node positivity rates ranging from 25% to 40%,” the authors noted.
To evaluate the association of the surgical excision modality and patient survival for pathologically confirmed localized T1/T2 MCC, Dr. Carucci and coauthors examined a cohort of 2,313 patients from the National Cancer Database with T1/T2 MCC diagnosed between Jan. 1, 2004, and Dec. 31, 2018, with pathologically confirmed, negative regional lymph nodes and treated with surgery. Their mean age was 71 years and 57.9% were male. Of the 2,313 patients, 1,452 underwent WLE, 104 underwent MMS, and 757 underwent NME.
The unadjusted analysis revealed that, compared with WLE, excision with MMS had the best unadjusted mean survival rates: 87.4% versus 86.1%, respectively, at 3 years, 84.5% versus 76.9% at 5 years, and 81.8% versus 60.9% at 10 years. Patients treated with NME had similar mean survival rates as those treated with WLE: 84.8% at 3 years, 78.3% at 5 years, and 60.8% at 10 years.
Multivariable survival analysis demonstrated that treatment with MMS was associated with significantly improved survival, compared with WLE (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.36-0.97; P = .04).
“These data suggest that MMS may provide a survival benefit in the treatment of localized MCC, although further prospective work studying this issue is required,” the authors concluded. “Future directions may also focus on elucidating the benefit of adjuvant radiotherapy in localized cases treated with MMS.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fewer numbers of patients receiving MMS surgery, lack of randomization, and potential for selection bias.
In an interview, Travis W. Blalock, MD, director of dermatologic surgery, Mohs micrographic surgery, and cutaneous oncology at Emory University, Atlanta, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the field of MCC “has undergone rapid and robust transformation over the past 20 years. These changes encompass advancements in diagnosing the condition, identifying linked viruses, and developing systemic treatments.”
The study findings “imply that comprehensive assessment of histologic margins might offer advantages beyond minimizing scars, minimizing functional impact, and reducing the likelihood of local recurrence,” he said.
“It’s beyond doubt,” he added, that the study “furnishes us with yet another set of real-world insights that will undoubtedly influence patient outcomes. These insights serve to bring clarity to the ways in which we can deliver precisely targeted surgical treatment with durable outcomes for localized MCC.”
Patricia M. Richey, MD, director of Mohs surgery at Boston University, who was also asked to comment on the study, added that, because of the nature of the National Cancer Database, “the authors of this study were unfortunately unable to report disease-specific survival or immunosuppression status. That being said, the preliminary data presented are convincing and should result in us further exploring this topic, as well as readdressing and questioning related issues such as whether or not adjuvant radiotherapy is truly beneficial in cases with histologic clearance via Mohs.”
Dr. Carucci reported receiving grant funding from Regeneron for investigator-initiated basic research. No other author disclosures were reported. Neither Dr. Blalock nor Dr. Richey had relevant disclosures.
results from a national retrospective cohort study suggest.
The study found that, in patients with pathologically confirmed, localized T1/T2 MCC, “treatment with MMS was associated with an approximately 40% reduction in hazard of death compared with WLE,” reported John A. Carucci, MD, PhD, and colleagues in the department of dermatology at NYU Langone Health, New York. The results provide “preliminary data suggesting that treatment of localized, early-stage MCC with MMS may result in the most optimal patient survival outcomes for this aggressive form of skin cancer,” they added. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
“Although data for keratinocytic nonmelanoma skin cancers have been definitive in demonstrating the advantage of peripheral and deep en face margin assessment over conventional WLE or NME [narrow-margin excision], the data for MCC, likely because of the disease’s rarity and limitations of available data sets, have been mixed,” they wrote.
Results from national studies published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute and the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found no difference in survival among patients with localized MCC treated with WLE versus MMS. “However, these studies did not have confirmed pathologic node status, a substantial limitation considering that clinically node-negative cases of localized MCC have sentinel lymph node positivity rates ranging from 25% to 40%,” the authors noted.
To evaluate the association of the surgical excision modality and patient survival for pathologically confirmed localized T1/T2 MCC, Dr. Carucci and coauthors examined a cohort of 2,313 patients from the National Cancer Database with T1/T2 MCC diagnosed between Jan. 1, 2004, and Dec. 31, 2018, with pathologically confirmed, negative regional lymph nodes and treated with surgery. Their mean age was 71 years and 57.9% were male. Of the 2,313 patients, 1,452 underwent WLE, 104 underwent MMS, and 757 underwent NME.
The unadjusted analysis revealed that, compared with WLE, excision with MMS had the best unadjusted mean survival rates: 87.4% versus 86.1%, respectively, at 3 years, 84.5% versus 76.9% at 5 years, and 81.8% versus 60.9% at 10 years. Patients treated with NME had similar mean survival rates as those treated with WLE: 84.8% at 3 years, 78.3% at 5 years, and 60.8% at 10 years.
Multivariable survival analysis demonstrated that treatment with MMS was associated with significantly improved survival, compared with WLE (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.36-0.97; P = .04).
“These data suggest that MMS may provide a survival benefit in the treatment of localized MCC, although further prospective work studying this issue is required,” the authors concluded. “Future directions may also focus on elucidating the benefit of adjuvant radiotherapy in localized cases treated with MMS.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fewer numbers of patients receiving MMS surgery, lack of randomization, and potential for selection bias.
In an interview, Travis W. Blalock, MD, director of dermatologic surgery, Mohs micrographic surgery, and cutaneous oncology at Emory University, Atlanta, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the field of MCC “has undergone rapid and robust transformation over the past 20 years. These changes encompass advancements in diagnosing the condition, identifying linked viruses, and developing systemic treatments.”
The study findings “imply that comprehensive assessment of histologic margins might offer advantages beyond minimizing scars, minimizing functional impact, and reducing the likelihood of local recurrence,” he said.
“It’s beyond doubt,” he added, that the study “furnishes us with yet another set of real-world insights that will undoubtedly influence patient outcomes. These insights serve to bring clarity to the ways in which we can deliver precisely targeted surgical treatment with durable outcomes for localized MCC.”
Patricia M. Richey, MD, director of Mohs surgery at Boston University, who was also asked to comment on the study, added that, because of the nature of the National Cancer Database, “the authors of this study were unfortunately unable to report disease-specific survival or immunosuppression status. That being said, the preliminary data presented are convincing and should result in us further exploring this topic, as well as readdressing and questioning related issues such as whether or not adjuvant radiotherapy is truly beneficial in cases with histologic clearance via Mohs.”
Dr. Carucci reported receiving grant funding from Regeneron for investigator-initiated basic research. No other author disclosures were reported. Neither Dr. Blalock nor Dr. Richey had relevant disclosures.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Human frailty is a cash cow
Doctor, if you are caring for patients with diabetes, I sure hope you know more about it than I do. The longer I live, it seems, the less I understand.
In a free society, people can do what they want, and that’s great except when it isn’t. That’s why societies develop ethics and even public laws if ethics are not strong enough to protect us from ourselves and others.
Sugar, sugar
When I was growing up in small-town Alabama during the Depression and World War II, we called it sugar diabetes. Eat too much sugar, you got fat; your blood sugar went up, and you spilled sugar into your urine. Diabetes was fairly rare, and so was obesity. Doctors treated it by limiting the intake of sugar (and various sweet foods), along with attempting weight loss. If that didn’t do the trick, insulin injections.
From then until now, note these trends.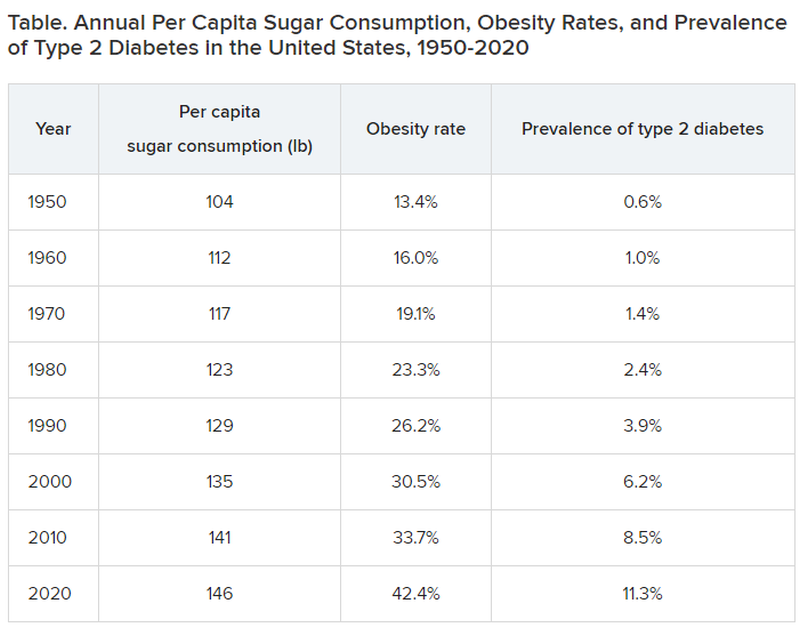
Type 2 diabetes was diagnosed even more infrequently before 1950:
- 1920: 0.2% of the population
- 1930: 0.3% of the population
- 1940: 0.4% of the population
In 2020, although 11.3% of the population was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, the unknown undiagnosed proportion could be much higher.
Notice a correlation between sugar consumption and prevalence of diabetes? Of course, correlation is not causation, but at the same time, it sure as hell is not negation. Such concordance can be considered hypothesis generating. It may not be true causation, but it’s a good bet when 89% of people with diabetes have overweight or obesity.
What did the entire medical, public health, government, agriculture, nursing, food manufacturing, marketing, advertising, restaurant, and education constituencies do about this as it was happening? They observed, documented, gave lip service, and wrung their hands in public a bit. I do not believe that this is an organized active conspiracy; it would take too many players cooperating over too long a period of time. But it certainly may be a passive conspiracy, and primary care physicians and their patients are trapped.
The proper daily practice of medicine consists of one patient, one physician, one moment, and one decision. Let it be a shared decision, informed by the best evidence and taking cost into consideration. That encounter represents an opportunity, a responsibility, and a conundrum.
Individual health is subsumed under the collective health of the public. As such, a patient’s health is out of the control of both physician and patient; instead, patients are the beneficiaries or victims of the “marketplace.” Humans are frail and easily taken advantage of by the brilliant and highly motivated strategic planning and execution of Big Agriculture, Big Food, Big Pharma, Big Marketing, and Big Money-Driven Medicine and generally failed by Big Government, Big Public Health, Big Education, Big Psychology, and Big Religion.
Rethinking diabetes
Consider diabetes as one of many examples. What a terrific deal for capitalism. then it discovers (invents) long-term, very expensive, compelling treatments to slim us down, with no end in sight, and still without ever understanding the true nature of diabetes.
Gary Taubes’s great new book, “Rethinking Diabetes: What Science Reveals About Diet, Insulin, and Successful Treatments,” is being published by Alfred A. Knopf in early 2024.
It is 404 pages of (dense) text, with 401 numbered references and footnotes, a bibliography of 790 references, alphabetically arranged for easy cross-checking, and a 25-page index.
Remember Mr. Taubes’s earlier definitive historical treatises: “Good Calories, Bad Calories” (2007), “Why We Get Fat” (2010), “The Case Against Sugar” (2016), and “The Case for Keto” (2020)?
This new book is more like “Good Calories, Bad Calories”: long, dense, detailed, definitive, and of great historical reference value, including original research information from other countries in other languages. The author told me that the many early research reference sources were available only in German and that his use of generative artificial intelligence as an assistant researcher was of great value.
Nonphysician author Mr. Taubes uses his deep understanding of science and history to inform his long-honed talents of impartial investigative journalism as he attempts to understand and then explain why after all these years, the medical scientific community still does not have a sound consensus about the essence of diabetes, diet, insulin, and proper prevention and treatment at a level that is actually effective – amazing and so sad.
To signal these evolved and evolving conflicts, the book includes the following chapters:
- “Rise of the Carbohydrate-Rich and Very-Low-Carbohydrate Diets”
- “The Fear of Fat and High-Fat Diets”
- “Insulin and The End of Carbohydrate Restriction and Low Blood Sugar”
Yes, it is difficult. Imagine the bookend segments: “The Nature of Medical Knowledge” and “The Conflicts of Evidence-Based Medicine.” There is also a detailed discussion of good versus bad science spanning three long chapters.
If all that reads like a greatly confused mess to you then you’re beginning to understand. If you are a fan of an unbiased explication of the evolution of understanding the ins and outs of scientific history in richly documented detail, this is a book for you. It’s not a quick nor easy read. And don’t expect to discover whether the newest wonder drugs for weight loss and control of diabetes will be the long-term solution for people with obesity and diabetes worldwide.
Obesity and overweight are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes. About 90% of patients with diabetes have either overweight or obesity. Thus, the complications of these two conditions, which largely overlap, include atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; myocardial infarction; stroke; hypertension; metabolic syndrome; lower-extremity gangrene; chronic kidney disease; retinopathy; glaucoma; cataracts; disabling osteoarthritis; breast, endometrial, colon, and other cancers; fatty liver; sleep apnea; and peripheral neuropathy. These diseases create a major lucrative business for a wide swathe of medical and surgical specialties, plus hospital, clinic, device, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
In summary, we’ve just been through 40 years of failure to recognize the sugar-elephant in the room and intervene with serious preventive efforts. Forty years of fleshing out both the populace and the American medical-industrial complex (AMIC). Talk about a sweet spot. The only successful long-term treatment of obesity (and with it, diabetes) is prevention. Don’t emphasize losing weight. Focus on preventing excessive weight gain, right now, for the population, beginning with yourselves. Otherwise, we continue openly to perpetuate a terrific deal for the AMIC, a travesty for everyone else. Time for some industrial grade penance and a course correction.
Meanwhile, here we are living out Big Pharma’s dream of a big populace, produced by the agriculture and food industries, enjoyed by capitalism after failures of education, medicine, and public health: a seemingly endless supply of people living with big complications who are ready for big (expensive, new) medications to fix the world’s big health problems.
Dr. Lundberg is editor in chief, Cancer Commons. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctor, if you are caring for patients with diabetes, I sure hope you know more about it than I do. The longer I live, it seems, the less I understand.
In a free society, people can do what they want, and that’s great except when it isn’t. That’s why societies develop ethics and even public laws if ethics are not strong enough to protect us from ourselves and others.
Sugar, sugar
When I was growing up in small-town Alabama during the Depression and World War II, we called it sugar diabetes. Eat too much sugar, you got fat; your blood sugar went up, and you spilled sugar into your urine. Diabetes was fairly rare, and so was obesity. Doctors treated it by limiting the intake of sugar (and various sweet foods), along with attempting weight loss. If that didn’t do the trick, insulin injections.
From then until now, note these trends.
Type 2 diabetes was diagnosed even more infrequently before 1950:
- 1920: 0.2% of the population
- 1930: 0.3% of the population
- 1940: 0.4% of the population
In 2020, although 11.3% of the population was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, the unknown undiagnosed proportion could be much higher.
Notice a correlation between sugar consumption and prevalence of diabetes? Of course, correlation is not causation, but at the same time, it sure as hell is not negation. Such concordance can be considered hypothesis generating. It may not be true causation, but it’s a good bet when 89% of people with diabetes have overweight or obesity.
What did the entire medical, public health, government, agriculture, nursing, food manufacturing, marketing, advertising, restaurant, and education constituencies do about this as it was happening? They observed, documented, gave lip service, and wrung their hands in public a bit. I do not believe that this is an organized active conspiracy; it would take too many players cooperating over too long a period of time. But it certainly may be a passive conspiracy, and primary care physicians and their patients are trapped.
The proper daily practice of medicine consists of one patient, one physician, one moment, and one decision. Let it be a shared decision, informed by the best evidence and taking cost into consideration. That encounter represents an opportunity, a responsibility, and a conundrum.
Individual health is subsumed under the collective health of the public. As such, a patient’s health is out of the control of both physician and patient; instead, patients are the beneficiaries or victims of the “marketplace.” Humans are frail and easily taken advantage of by the brilliant and highly motivated strategic planning and execution of Big Agriculture, Big Food, Big Pharma, Big Marketing, and Big Money-Driven Medicine and generally failed by Big Government, Big Public Health, Big Education, Big Psychology, and Big Religion.
Rethinking diabetes
Consider diabetes as one of many examples. What a terrific deal for capitalism. then it discovers (invents) long-term, very expensive, compelling treatments to slim us down, with no end in sight, and still without ever understanding the true nature of diabetes.
Gary Taubes’s great new book, “Rethinking Diabetes: What Science Reveals About Diet, Insulin, and Successful Treatments,” is being published by Alfred A. Knopf in early 2024.
It is 404 pages of (dense) text, with 401 numbered references and footnotes, a bibliography of 790 references, alphabetically arranged for easy cross-checking, and a 25-page index.
Remember Mr. Taubes’s earlier definitive historical treatises: “Good Calories, Bad Calories” (2007), “Why We Get Fat” (2010), “The Case Against Sugar” (2016), and “The Case for Keto” (2020)?
This new book is more like “Good Calories, Bad Calories”: long, dense, detailed, definitive, and of great historical reference value, including original research information from other countries in other languages. The author told me that the many early research reference sources were available only in German and that his use of generative artificial intelligence as an assistant researcher was of great value.
Nonphysician author Mr. Taubes uses his deep understanding of science and history to inform his long-honed talents of impartial investigative journalism as he attempts to understand and then explain why after all these years, the medical scientific community still does not have a sound consensus about the essence of diabetes, diet, insulin, and proper prevention and treatment at a level that is actually effective – amazing and so sad.
To signal these evolved and evolving conflicts, the book includes the following chapters:
- “Rise of the Carbohydrate-Rich and Very-Low-Carbohydrate Diets”
- “The Fear of Fat and High-Fat Diets”
- “Insulin and The End of Carbohydrate Restriction and Low Blood Sugar”
Yes, it is difficult. Imagine the bookend segments: “The Nature of Medical Knowledge” and “The Conflicts of Evidence-Based Medicine.” There is also a detailed discussion of good versus bad science spanning three long chapters.
If all that reads like a greatly confused mess to you then you’re beginning to understand. If you are a fan of an unbiased explication of the evolution of understanding the ins and outs of scientific history in richly documented detail, this is a book for you. It’s not a quick nor easy read. And don’t expect to discover whether the newest wonder drugs for weight loss and control of diabetes will be the long-term solution for people with obesity and diabetes worldwide.
Obesity and overweight are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes. About 90% of patients with diabetes have either overweight or obesity. Thus, the complications of these two conditions, which largely overlap, include atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; myocardial infarction; stroke; hypertension; metabolic syndrome; lower-extremity gangrene; chronic kidney disease; retinopathy; glaucoma; cataracts; disabling osteoarthritis; breast, endometrial, colon, and other cancers; fatty liver; sleep apnea; and peripheral neuropathy. These diseases create a major lucrative business for a wide swathe of medical and surgical specialties, plus hospital, clinic, device, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
In summary, we’ve just been through 40 years of failure to recognize the sugar-elephant in the room and intervene with serious preventive efforts. Forty years of fleshing out both the populace and the American medical-industrial complex (AMIC). Talk about a sweet spot. The only successful long-term treatment of obesity (and with it, diabetes) is prevention. Don’t emphasize losing weight. Focus on preventing excessive weight gain, right now, for the population, beginning with yourselves. Otherwise, we continue openly to perpetuate a terrific deal for the AMIC, a travesty for everyone else. Time for some industrial grade penance and a course correction.
Meanwhile, here we are living out Big Pharma’s dream of a big populace, produced by the agriculture and food industries, enjoyed by capitalism after failures of education, medicine, and public health: a seemingly endless supply of people living with big complications who are ready for big (expensive, new) medications to fix the world’s big health problems.
Dr. Lundberg is editor in chief, Cancer Commons. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctor, if you are caring for patients with diabetes, I sure hope you know more about it than I do. The longer I live, it seems, the less I understand.
In a free society, people can do what they want, and that’s great except when it isn’t. That’s why societies develop ethics and even public laws if ethics are not strong enough to protect us from ourselves and others.
Sugar, sugar
When I was growing up in small-town Alabama during the Depression and World War II, we called it sugar diabetes. Eat too much sugar, you got fat; your blood sugar went up, and you spilled sugar into your urine. Diabetes was fairly rare, and so was obesity. Doctors treated it by limiting the intake of sugar (and various sweet foods), along with attempting weight loss. If that didn’t do the trick, insulin injections.
From then until now, note these trends.
Type 2 diabetes was diagnosed even more infrequently before 1950:
- 1920: 0.2% of the population
- 1930: 0.3% of the population
- 1940: 0.4% of the population
In 2020, although 11.3% of the population was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, the unknown undiagnosed proportion could be much higher.
Notice a correlation between sugar consumption and prevalence of diabetes? Of course, correlation is not causation, but at the same time, it sure as hell is not negation. Such concordance can be considered hypothesis generating. It may not be true causation, but it’s a good bet when 89% of people with diabetes have overweight or obesity.
What did the entire medical, public health, government, agriculture, nursing, food manufacturing, marketing, advertising, restaurant, and education constituencies do about this as it was happening? They observed, documented, gave lip service, and wrung their hands in public a bit. I do not believe that this is an organized active conspiracy; it would take too many players cooperating over too long a period of time. But it certainly may be a passive conspiracy, and primary care physicians and their patients are trapped.
The proper daily practice of medicine consists of one patient, one physician, one moment, and one decision. Let it be a shared decision, informed by the best evidence and taking cost into consideration. That encounter represents an opportunity, a responsibility, and a conundrum.
Individual health is subsumed under the collective health of the public. As such, a patient’s health is out of the control of both physician and patient; instead, patients are the beneficiaries or victims of the “marketplace.” Humans are frail and easily taken advantage of by the brilliant and highly motivated strategic planning and execution of Big Agriculture, Big Food, Big Pharma, Big Marketing, and Big Money-Driven Medicine and generally failed by Big Government, Big Public Health, Big Education, Big Psychology, and Big Religion.
Rethinking diabetes
Consider diabetes as one of many examples. What a terrific deal for capitalism. then it discovers (invents) long-term, very expensive, compelling treatments to slim us down, with no end in sight, and still without ever understanding the true nature of diabetes.
Gary Taubes’s great new book, “Rethinking Diabetes: What Science Reveals About Diet, Insulin, and Successful Treatments,” is being published by Alfred A. Knopf in early 2024.
It is 404 pages of (dense) text, with 401 numbered references and footnotes, a bibliography of 790 references, alphabetically arranged for easy cross-checking, and a 25-page index.
Remember Mr. Taubes’s earlier definitive historical treatises: “Good Calories, Bad Calories” (2007), “Why We Get Fat” (2010), “The Case Against Sugar” (2016), and “The Case for Keto” (2020)?
This new book is more like “Good Calories, Bad Calories”: long, dense, detailed, definitive, and of great historical reference value, including original research information from other countries in other languages. The author told me that the many early research reference sources were available only in German and that his use of generative artificial intelligence as an assistant researcher was of great value.
Nonphysician author Mr. Taubes uses his deep understanding of science and history to inform his long-honed talents of impartial investigative journalism as he attempts to understand and then explain why after all these years, the medical scientific community still does not have a sound consensus about the essence of diabetes, diet, insulin, and proper prevention and treatment at a level that is actually effective – amazing and so sad.
To signal these evolved and evolving conflicts, the book includes the following chapters:
- “Rise of the Carbohydrate-Rich and Very-Low-Carbohydrate Diets”
- “The Fear of Fat and High-Fat Diets”
- “Insulin and The End of Carbohydrate Restriction and Low Blood Sugar”
Yes, it is difficult. Imagine the bookend segments: “The Nature of Medical Knowledge” and “The Conflicts of Evidence-Based Medicine.” There is also a detailed discussion of good versus bad science spanning three long chapters.
If all that reads like a greatly confused mess to you then you’re beginning to understand. If you are a fan of an unbiased explication of the evolution of understanding the ins and outs of scientific history in richly documented detail, this is a book for you. It’s not a quick nor easy read. And don’t expect to discover whether the newest wonder drugs for weight loss and control of diabetes will be the long-term solution for people with obesity and diabetes worldwide.
Obesity and overweight are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes. About 90% of patients with diabetes have either overweight or obesity. Thus, the complications of these two conditions, which largely overlap, include atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; myocardial infarction; stroke; hypertension; metabolic syndrome; lower-extremity gangrene; chronic kidney disease; retinopathy; glaucoma; cataracts; disabling osteoarthritis; breast, endometrial, colon, and other cancers; fatty liver; sleep apnea; and peripheral neuropathy. These diseases create a major lucrative business for a wide swathe of medical and surgical specialties, plus hospital, clinic, device, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
In summary, we’ve just been through 40 years of failure to recognize the sugar-elephant in the room and intervene with serious preventive efforts. Forty years of fleshing out both the populace and the American medical-industrial complex (AMIC). Talk about a sweet spot. The only successful long-term treatment of obesity (and with it, diabetes) is prevention. Don’t emphasize losing weight. Focus on preventing excessive weight gain, right now, for the population, beginning with yourselves. Otherwise, we continue openly to perpetuate a terrific deal for the AMIC, a travesty for everyone else. Time for some industrial grade penance and a course correction.
Meanwhile, here we are living out Big Pharma’s dream of a big populace, produced by the agriculture and food industries, enjoyed by capitalism after failures of education, medicine, and public health: a seemingly endless supply of people living with big complications who are ready for big (expensive, new) medications to fix the world’s big health problems.
Dr. Lundberg is editor in chief, Cancer Commons. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Commentary: Newer Drugs for AD Plus Dupilumab and Other Issues, September 2023
Amlitelimab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the OX40 ligand (Weidinger et al). It is predicted to have broad potential therapeutic application for multiple immune diseases, including atopic dermatitis. I'm not looking for that. I've been spoiled by drugs that have narrow therapeutic application (like IL-23 blockade and IL-4/IL-13 blockade) that target a specific disease very effectively with very little in the way of side effects.
The OX40 ligand/receptor interaction may be too important. When I Google "OX40 deficiency," the first thing that pops up is a combined T- and B-cell immunodeficiency associated with possible aggressive, childhood-onset, disseminated, cutaneous, and systemic Kaposi sarcoma. That doesn't mean that such a horrible outcome will come with the level of pharmacologic OX40 blockade that we would try to achieve in our patients. Clinical trials don't show horrible adverse events — so far. I'm in no hurry to find out in my patients whether real-life efficacy in large numbers of people treated for long periods of time matches up with the short-term safety profiles seen in relatively small clinical trial populations.
It might be nice to give patients upadacitinib only as needed, for example for a flare of their atopic dermatitis, then cut down the dose or stop altogether until the next flare. The study by Guttman-Yassky and colleagues found that atopic dermatitis came back quickly when upadacitinib was stopped. However, their study looked at patients with chronically bad atopic dermatitis. If we have a patient who tends to flare only intermittently, it may be that we could use upadacitinib or other systemic treatments on an intermittent basis. I know when it came to my son's mild atopic dermatitis, intermittent use of a little triamcinolone ointment was all that was needed. Yes, I know that's a "reactive," roller-coaster approach. Yes, I know that a "proactive" keep-the-disease-away approach sounds better. But I'm realistic when it comes to patients' adherence behaviors. I think there's a lot to be said for minimizing drug exposure and just using treatments as needed. Guttman-Yassky's work makes me believe that a lot of patients will need continuous treatment to keep their severe disease under control. I'm not convinced that everyone will need continuous treatment to be happy with their treatment.
O'Connor and colleagues found that emollient bathing is associated with later development of atopic dermatitis. They defined emollient bathing as baths with oil or emulsifier-based additives. This study illustrates the importance of randomization in a controlled trial. Because their study was not randomized, we don't know whether the emollient bathing caused atopic dermatitis or whether families that had more dry skin or more family history of atopic dermatitis were more likely to use emollient bathing.
When dupilumab was first approved, I prescribed it to my patients to take every 2 weeks as recommended on the label. I'm not so sure how many patients actually used it that way. I suspect that a lot of them took the medicine less often than recommended, especially when they were doing well. This report by Sánchez-García and colleagues suggests that patients who are doing very well on dupilumab may be able to take the drug less often. That's probably not news to my patients who are already taking the drug less often than I told them to.
I think less frequent dosing may become even more common over time, particularly for drugs that may have more safety risks than dupilumab. Many patients with atopic dermatitis probably don't need to be taking drugs all the time. Patients who tend to have flare-ups but who do very well for a long period of time between flares may only need drugs intermittently. It will be interesting to see if our patients can use oral treatments for atopic dermatitis that way.
Siegfried and colleagues assessed how well dupilumab worked in children with atopic dermatitis in different areas of the body: head and neck, trunk, upper extremities, lower extremities. Dupilumab worked well in all these areas, as expected.
Xu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of studies of dupilumab for atopic dermatitis and concluded, not shockingly, that dupilumab is safe and effective for atopic dermatitis. Okay, I believe that. They further concluded: "More long-term, high-quality, controlled studies in different regions are needed for further verification." I don't think so. I think the evidence is clear already.
Studies that measure the levels of things are generally not particularly helpful. The study by García-Reyes and colleagues studied the levels of serum thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) in patients with atopic dermatitis. TSLP levels were higher in patients with atopic dermatitis compared with patients without atopic dermatitis. This basically tells us nothing about the role of TSLP in atopic dermatitis. The elevated levels could be causing atopic dermatitis or they could be the body's response to having atopic dermatitis.
To tell whether something is causal we have to look at either genetic studies or studies with specific inhibitors. A specific inhibitor study was done by atopic dermatitis expert Eric Simpson and colleagues.1 This was a randomized, placebo-controlled study in which an anti-TSLP antibody was given to patients with atopic dermatitis. Both the anti-TSLP antibody and placebo groups were permitted to use topical steroids. While the anti-TSLP antibody–treated patients did better than placebo-treated patients, the difference did not achieve statistical significance, probably, I believe, because the placebo-treated patients used more topical steroids. When you want to assess whether a drug for atopic dermatitis is better than placebo, you must be careful about how much topical steroid you let patients in the study use!
Additional Reference
- Simpson EL, Parnes JR, She D, et al. Tezepelumab, an anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: A randomized phase 2a clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(4):1013-1021. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.059
Amlitelimab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the OX40 ligand (Weidinger et al). It is predicted to have broad potential therapeutic application for multiple immune diseases, including atopic dermatitis. I'm not looking for that. I've been spoiled by drugs that have narrow therapeutic application (like IL-23 blockade and IL-4/IL-13 blockade) that target a specific disease very effectively with very little in the way of side effects.
The OX40 ligand/receptor interaction may be too important. When I Google "OX40 deficiency," the first thing that pops up is a combined T- and B-cell immunodeficiency associated with possible aggressive, childhood-onset, disseminated, cutaneous, and systemic Kaposi sarcoma. That doesn't mean that such a horrible outcome will come with the level of pharmacologic OX40 blockade that we would try to achieve in our patients. Clinical trials don't show horrible adverse events — so far. I'm in no hurry to find out in my patients whether real-life efficacy in large numbers of people treated for long periods of time matches up with the short-term safety profiles seen in relatively small clinical trial populations.
It might be nice to give patients upadacitinib only as needed, for example for a flare of their atopic dermatitis, then cut down the dose or stop altogether until the next flare. The study by Guttman-Yassky and colleagues found that atopic dermatitis came back quickly when upadacitinib was stopped. However, their study looked at patients with chronically bad atopic dermatitis. If we have a patient who tends to flare only intermittently, it may be that we could use upadacitinib or other systemic treatments on an intermittent basis. I know when it came to my son's mild atopic dermatitis, intermittent use of a little triamcinolone ointment was all that was needed. Yes, I know that's a "reactive," roller-coaster approach. Yes, I know that a "proactive" keep-the-disease-away approach sounds better. But I'm realistic when it comes to patients' adherence behaviors. I think there's a lot to be said for minimizing drug exposure and just using treatments as needed. Guttman-Yassky's work makes me believe that a lot of patients will need continuous treatment to keep their severe disease under control. I'm not convinced that everyone will need continuous treatment to be happy with their treatment.
O'Connor and colleagues found that emollient bathing is associated with later development of atopic dermatitis. They defined emollient bathing as baths with oil or emulsifier-based additives. This study illustrates the importance of randomization in a controlled trial. Because their study was not randomized, we don't know whether the emollient bathing caused atopic dermatitis or whether families that had more dry skin or more family history of atopic dermatitis were more likely to use emollient bathing.
When dupilumab was first approved, I prescribed it to my patients to take every 2 weeks as recommended on the label. I'm not so sure how many patients actually used it that way. I suspect that a lot of them took the medicine less often than recommended, especially when they were doing well. This report by Sánchez-García and colleagues suggests that patients who are doing very well on dupilumab may be able to take the drug less often. That's probably not news to my patients who are already taking the drug less often than I told them to.
I think less frequent dosing may become even more common over time, particularly for drugs that may have more safety risks than dupilumab. Many patients with atopic dermatitis probably don't need to be taking drugs all the time. Patients who tend to have flare-ups but who do very well for a long period of time between flares may only need drugs intermittently. It will be interesting to see if our patients can use oral treatments for atopic dermatitis that way.
Siegfried and colleagues assessed how well dupilumab worked in children with atopic dermatitis in different areas of the body: head and neck, trunk, upper extremities, lower extremities. Dupilumab worked well in all these areas, as expected.
Xu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of studies of dupilumab for atopic dermatitis and concluded, not shockingly, that dupilumab is safe and effective for atopic dermatitis. Okay, I believe that. They further concluded: "More long-term, high-quality, controlled studies in different regions are needed for further verification." I don't think so. I think the evidence is clear already.
Studies that measure the levels of things are generally not particularly helpful. The study by García-Reyes and colleagues studied the levels of serum thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) in patients with atopic dermatitis. TSLP levels were higher in patients with atopic dermatitis compared with patients without atopic dermatitis. This basically tells us nothing about the role of TSLP in atopic dermatitis. The elevated levels could be causing atopic dermatitis or they could be the body's response to having atopic dermatitis.
To tell whether something is causal we have to look at either genetic studies or studies with specific inhibitors. A specific inhibitor study was done by atopic dermatitis expert Eric Simpson and colleagues.1 This was a randomized, placebo-controlled study in which an anti-TSLP antibody was given to patients with atopic dermatitis. Both the anti-TSLP antibody and placebo groups were permitted to use topical steroids. While the anti-TSLP antibody–treated patients did better than placebo-treated patients, the difference did not achieve statistical significance, probably, I believe, because the placebo-treated patients used more topical steroids. When you want to assess whether a drug for atopic dermatitis is better than placebo, you must be careful about how much topical steroid you let patients in the study use!
Additional Reference
- Simpson EL, Parnes JR, She D, et al. Tezepelumab, an anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: A randomized phase 2a clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(4):1013-1021. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.059
Amlitelimab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the OX40 ligand (Weidinger et al). It is predicted to have broad potential therapeutic application for multiple immune diseases, including atopic dermatitis. I'm not looking for that. I've been spoiled by drugs that have narrow therapeutic application (like IL-23 blockade and IL-4/IL-13 blockade) that target a specific disease very effectively with very little in the way of side effects.
The OX40 ligand/receptor interaction may be too important. When I Google "OX40 deficiency," the first thing that pops up is a combined T- and B-cell immunodeficiency associated with possible aggressive, childhood-onset, disseminated, cutaneous, and systemic Kaposi sarcoma. That doesn't mean that such a horrible outcome will come with the level of pharmacologic OX40 blockade that we would try to achieve in our patients. Clinical trials don't show horrible adverse events — so far. I'm in no hurry to find out in my patients whether real-life efficacy in large numbers of people treated for long periods of time matches up with the short-term safety profiles seen in relatively small clinical trial populations.
It might be nice to give patients upadacitinib only as needed, for example for a flare of their atopic dermatitis, then cut down the dose or stop altogether until the next flare. The study by Guttman-Yassky and colleagues found that atopic dermatitis came back quickly when upadacitinib was stopped. However, their study looked at patients with chronically bad atopic dermatitis. If we have a patient who tends to flare only intermittently, it may be that we could use upadacitinib or other systemic treatments on an intermittent basis. I know when it came to my son's mild atopic dermatitis, intermittent use of a little triamcinolone ointment was all that was needed. Yes, I know that's a "reactive," roller-coaster approach. Yes, I know that a "proactive" keep-the-disease-away approach sounds better. But I'm realistic when it comes to patients' adherence behaviors. I think there's a lot to be said for minimizing drug exposure and just using treatments as needed. Guttman-Yassky's work makes me believe that a lot of patients will need continuous treatment to keep their severe disease under control. I'm not convinced that everyone will need continuous treatment to be happy with their treatment.
O'Connor and colleagues found that emollient bathing is associated with later development of atopic dermatitis. They defined emollient bathing as baths with oil or emulsifier-based additives. This study illustrates the importance of randomization in a controlled trial. Because their study was not randomized, we don't know whether the emollient bathing caused atopic dermatitis or whether families that had more dry skin or more family history of atopic dermatitis were more likely to use emollient bathing.
When dupilumab was first approved, I prescribed it to my patients to take every 2 weeks as recommended on the label. I'm not so sure how many patients actually used it that way. I suspect that a lot of them took the medicine less often than recommended, especially when they were doing well. This report by Sánchez-García and colleagues suggests that patients who are doing very well on dupilumab may be able to take the drug less often. That's probably not news to my patients who are already taking the drug less often than I told them to.
I think less frequent dosing may become even more common over time, particularly for drugs that may have more safety risks than dupilumab. Many patients with atopic dermatitis probably don't need to be taking drugs all the time. Patients who tend to have flare-ups but who do very well for a long period of time between flares may only need drugs intermittently. It will be interesting to see if our patients can use oral treatments for atopic dermatitis that way.
Siegfried and colleagues assessed how well dupilumab worked in children with atopic dermatitis in different areas of the body: head and neck, trunk, upper extremities, lower extremities. Dupilumab worked well in all these areas, as expected.
Xu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of studies of dupilumab for atopic dermatitis and concluded, not shockingly, that dupilumab is safe and effective for atopic dermatitis. Okay, I believe that. They further concluded: "More long-term, high-quality, controlled studies in different regions are needed for further verification." I don't think so. I think the evidence is clear already.
Studies that measure the levels of things are generally not particularly helpful. The study by García-Reyes and colleagues studied the levels of serum thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) in patients with atopic dermatitis. TSLP levels were higher in patients with atopic dermatitis compared with patients without atopic dermatitis. This basically tells us nothing about the role of TSLP in atopic dermatitis. The elevated levels could be causing atopic dermatitis or they could be the body's response to having atopic dermatitis.
To tell whether something is causal we have to look at either genetic studies or studies with specific inhibitors. A specific inhibitor study was done by atopic dermatitis expert Eric Simpson and colleagues.1 This was a randomized, placebo-controlled study in which an anti-TSLP antibody was given to patients with atopic dermatitis. Both the anti-TSLP antibody and placebo groups were permitted to use topical steroids. While the anti-TSLP antibody–treated patients did better than placebo-treated patients, the difference did not achieve statistical significance, probably, I believe, because the placebo-treated patients used more topical steroids. When you want to assess whether a drug for atopic dermatitis is better than placebo, you must be careful about how much topical steroid you let patients in the study use!
Additional Reference
- Simpson EL, Parnes JR, She D, et al. Tezepelumab, an anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: A randomized phase 2a clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(4):1013-1021. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.059
First guidelines developed for childhood eosinophilic GI disorders beyond eosinophilic esophagitis
The limited scope and depth of existing literature on childhood eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) beyond eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) spurred an international group of researchers and clinicians to develop the first clinical practice guidelines for diagnosing and treating these rare conditions.
They were developed jointly by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition and the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition.
Non-EoE EGIDs are rare chronic inflammatory disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, estimated at less than 200,000 cases annually in the United States, with unknown long-term consequences, Glenn Furuta, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado at Denver and section head of gastroenterology at Children’s Hospital Colorado, both in Aurora, said in an interview
“There are many unmet needs. Research has been limited and has not progressed at the pace we want it to,” added Dr. Furuta, who is corresponding author of the guidelines.
The guidelines were published online in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition, by lead author Alexandra Papadopoulou, MD, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, first department of pediatrics, University of Athens, and Children’s Hospital Agia Sofia, also in Athens, and colleagues.
With these, we provide guidance for clinicians to better understand the conditions and also how to diagnose and initiate care for patients with these rare diseases, said Dr. Furuta.
Difficult-to-diagnose conditions
Guideline development involved a working group of 26 pediatric gastroenterologists, adult gastroenterologists, allergists/immunologists, and pathologists from 16 countries across five continents. The consensus document includes 34 statements based on available evidence and 41 recommendations based on expert opinion and best clinical practices. In cases where the supporting evidence was weak but agreement was strong, the authors issued conditional recommendations.
The guidelines subdivide the non-EoE EGIDs according to inflammation location: eosinophilic gastritis, eosinophilic duodenitis (EoD), eosinophilic colitis, and eosinophilic enteritis. The latter can be further subdivided into EoD, eosinophilic jejunitis, and eosinophilic ileitis.
Non-EoE EGIDs are hard to diagnose because symptoms are relatively nonspecific and may include abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and bloody stools, all of which could have any number of underlying causes, Dr. Furuta said.
If you are treating a patient who is not getting better with such symptoms as persisting infections, acid-related problems, significant bleeding leading to anemia, intestinal perforation or obstruction, or low serum protein leading to swelling, then you should think that something else is going on that requires more of an evaluation, Dr. Furuta noted.
Patients with personal or family histories of eosinophilic or allergic disease should raise greater suspicion, Dr. Furuta said. “The next step requires an endoscopy and biopsy.”
Awareness of non-EoE EGIDs has been higher among pediatric gastroenterologists than among those treating adult disease because pediatric gastroenterologists have always obtained biopsies of the intestinal tract, Dr. Furuta noted.
The guidelines recommend that diagnosis of non-EoE EGIDs in children and adolescents must include signs or symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction, dense eosinophilic infiltrates found in mucosal or full-thickness biopsies above organ-specific threshold values included in the document, and absence of other diseases associated with GI mucosal eosinophilic inflammation.
Individualized treatment
The authors noted that the strength of recommendations varies with the often-modest availability of randomized controlled trial data on treatment efficacy.
For example, they recommended that systemic steroids be considered to induce remission but only conditionally recommend topical steroids. They conditionally recommend consideration of empiric elimination diets and conditionally recommend against using food allergy testing to guide diet.
The choice of treatment should be individualized on the basis of the affected GI segment, severity of the disease, patient characteristics, and family resources and capabilities, the authors wrote.
“We’ve provided guidance on how to care for patients based on the consensus of experts who have the necessary experience and knowledge base,” Dr. Furuta said. “Our ability to say: ‘Here are the established treatments,’ is lacking, though. We need research studies to verify that our recommended approaches are indeed correct.”
The authors conditionally recommended that treatment goals include achieving symptom resolution, improving gross endoscopic and histologic abnormalities, promoting normal childhood growth and development, and preventing disease complications.
No pediatric study has determined the natural history of non-EoE EGIDs, and no study of maintenance therapy has been conducted, the authors noted.
For this reason, they conditionally recommended that the clinical decision to continue therapy should be discussed with patients and their parents/caregivers, and those discussions include the benefits and risk of long-term treatment, its cost, and its impact on health-related quality of life.
A starting point for patient management
In a comment, Vincent Mukkada, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati and an attending physician in gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center, observed that, though improved awareness among pediatric gastroenterologists may account for some of the increase in GI eosinophil disease, the incidence is also likely growing.
“We’re looking for them much more,” said Dr. Mukkada.
“But I also think they’re increasing, just like all other atopic diseases. We’re not sure why,” he added.
“The hope is that these guidelines will allow nonsubspecialized gastroenterologists and allergists feel comfortable to at least start on the journey of managing these patients. And, for pediatricians who learn that their patient has received a non-EoE EGID diagnosis, they can go to the summary figures in this one document and very quickly get an overview of the disease and its course,” Dr. Mukkada said.
Guideline development was funded by the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. The authors and Dr. Mukkada reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The limited scope and depth of existing literature on childhood eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) beyond eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) spurred an international group of researchers and clinicians to develop the first clinical practice guidelines for diagnosing and treating these rare conditions.
They were developed jointly by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition and the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition.
Non-EoE EGIDs are rare chronic inflammatory disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, estimated at less than 200,000 cases annually in the United States, with unknown long-term consequences, Glenn Furuta, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado at Denver and section head of gastroenterology at Children’s Hospital Colorado, both in Aurora, said in an interview
“There are many unmet needs. Research has been limited and has not progressed at the pace we want it to,” added Dr. Furuta, who is corresponding author of the guidelines.
The guidelines were published online in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition, by lead author Alexandra Papadopoulou, MD, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, first department of pediatrics, University of Athens, and Children’s Hospital Agia Sofia, also in Athens, and colleagues.
With these, we provide guidance for clinicians to better understand the conditions and also how to diagnose and initiate care for patients with these rare diseases, said Dr. Furuta.
Difficult-to-diagnose conditions
Guideline development involved a working group of 26 pediatric gastroenterologists, adult gastroenterologists, allergists/immunologists, and pathologists from 16 countries across five continents. The consensus document includes 34 statements based on available evidence and 41 recommendations based on expert opinion and best clinical practices. In cases where the supporting evidence was weak but agreement was strong, the authors issued conditional recommendations.
The guidelines subdivide the non-EoE EGIDs according to inflammation location: eosinophilic gastritis, eosinophilic duodenitis (EoD), eosinophilic colitis, and eosinophilic enteritis. The latter can be further subdivided into EoD, eosinophilic jejunitis, and eosinophilic ileitis.
Non-EoE EGIDs are hard to diagnose because symptoms are relatively nonspecific and may include abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and bloody stools, all of which could have any number of underlying causes, Dr. Furuta said.
If you are treating a patient who is not getting better with such symptoms as persisting infections, acid-related problems, significant bleeding leading to anemia, intestinal perforation or obstruction, or low serum protein leading to swelling, then you should think that something else is going on that requires more of an evaluation, Dr. Furuta noted.
Patients with personal or family histories of eosinophilic or allergic disease should raise greater suspicion, Dr. Furuta said. “The next step requires an endoscopy and biopsy.”
Awareness of non-EoE EGIDs has been higher among pediatric gastroenterologists than among those treating adult disease because pediatric gastroenterologists have always obtained biopsies of the intestinal tract, Dr. Furuta noted.
The guidelines recommend that diagnosis of non-EoE EGIDs in children and adolescents must include signs or symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction, dense eosinophilic infiltrates found in mucosal or full-thickness biopsies above organ-specific threshold values included in the document, and absence of other diseases associated with GI mucosal eosinophilic inflammation.
Individualized treatment
The authors noted that the strength of recommendations varies with the often-modest availability of randomized controlled trial data on treatment efficacy.
For example, they recommended that systemic steroids be considered to induce remission but only conditionally recommend topical steroids. They conditionally recommend consideration of empiric elimination diets and conditionally recommend against using food allergy testing to guide diet.
The choice of treatment should be individualized on the basis of the affected GI segment, severity of the disease, patient characteristics, and family resources and capabilities, the authors wrote.
“We’ve provided guidance on how to care for patients based on the consensus of experts who have the necessary experience and knowledge base,” Dr. Furuta said. “Our ability to say: ‘Here are the established treatments,’ is lacking, though. We need research studies to verify that our recommended approaches are indeed correct.”
The authors conditionally recommended that treatment goals include achieving symptom resolution, improving gross endoscopic and histologic abnormalities, promoting normal childhood growth and development, and preventing disease complications.
No pediatric study has determined the natural history of non-EoE EGIDs, and no study of maintenance therapy has been conducted, the authors noted.
For this reason, they conditionally recommended that the clinical decision to continue therapy should be discussed with patients and their parents/caregivers, and those discussions include the benefits and risk of long-term treatment, its cost, and its impact on health-related quality of life.
A starting point for patient management
In a comment, Vincent Mukkada, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati and an attending physician in gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center, observed that, though improved awareness among pediatric gastroenterologists may account for some of the increase in GI eosinophil disease, the incidence is also likely growing.
“We’re looking for them much more,” said Dr. Mukkada.
“But I also think they’re increasing, just like all other atopic diseases. We’re not sure why,” he added.
“The hope is that these guidelines will allow nonsubspecialized gastroenterologists and allergists feel comfortable to at least start on the journey of managing these patients. And, for pediatricians who learn that their patient has received a non-EoE EGID diagnosis, they can go to the summary figures in this one document and very quickly get an overview of the disease and its course,” Dr. Mukkada said.
Guideline development was funded by the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. The authors and Dr. Mukkada reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The limited scope and depth of existing literature on childhood eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) beyond eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) spurred an international group of researchers and clinicians to develop the first clinical practice guidelines for diagnosing and treating these rare conditions.
They were developed jointly by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition and the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition.
Non-EoE EGIDs are rare chronic inflammatory disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, estimated at less than 200,000 cases annually in the United States, with unknown long-term consequences, Glenn Furuta, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado at Denver and section head of gastroenterology at Children’s Hospital Colorado, both in Aurora, said in an interview
“There are many unmet needs. Research has been limited and has not progressed at the pace we want it to,” added Dr. Furuta, who is corresponding author of the guidelines.
The guidelines were published online in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition, by lead author Alexandra Papadopoulou, MD, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, first department of pediatrics, University of Athens, and Children’s Hospital Agia Sofia, also in Athens, and colleagues.
With these, we provide guidance for clinicians to better understand the conditions and also how to diagnose and initiate care for patients with these rare diseases, said Dr. Furuta.
Difficult-to-diagnose conditions
Guideline development involved a working group of 26 pediatric gastroenterologists, adult gastroenterologists, allergists/immunologists, and pathologists from 16 countries across five continents. The consensus document includes 34 statements based on available evidence and 41 recommendations based on expert opinion and best clinical practices. In cases where the supporting evidence was weak but agreement was strong, the authors issued conditional recommendations.
The guidelines subdivide the non-EoE EGIDs according to inflammation location: eosinophilic gastritis, eosinophilic duodenitis (EoD), eosinophilic colitis, and eosinophilic enteritis. The latter can be further subdivided into EoD, eosinophilic jejunitis, and eosinophilic ileitis.
Non-EoE EGIDs are hard to diagnose because symptoms are relatively nonspecific and may include abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and bloody stools, all of which could have any number of underlying causes, Dr. Furuta said.
If you are treating a patient who is not getting better with such symptoms as persisting infections, acid-related problems, significant bleeding leading to anemia, intestinal perforation or obstruction, or low serum protein leading to swelling, then you should think that something else is going on that requires more of an evaluation, Dr. Furuta noted.
Patients with personal or family histories of eosinophilic or allergic disease should raise greater suspicion, Dr. Furuta said. “The next step requires an endoscopy and biopsy.”
Awareness of non-EoE EGIDs has been higher among pediatric gastroenterologists than among those treating adult disease because pediatric gastroenterologists have always obtained biopsies of the intestinal tract, Dr. Furuta noted.
The guidelines recommend that diagnosis of non-EoE EGIDs in children and adolescents must include signs or symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction, dense eosinophilic infiltrates found in mucosal or full-thickness biopsies above organ-specific threshold values included in the document, and absence of other diseases associated with GI mucosal eosinophilic inflammation.
Individualized treatment
The authors noted that the strength of recommendations varies with the often-modest availability of randomized controlled trial data on treatment efficacy.
For example, they recommended that systemic steroids be considered to induce remission but only conditionally recommend topical steroids. They conditionally recommend consideration of empiric elimination diets and conditionally recommend against using food allergy testing to guide diet.
The choice of treatment should be individualized on the basis of the affected GI segment, severity of the disease, patient characteristics, and family resources and capabilities, the authors wrote.
“We’ve provided guidance on how to care for patients based on the consensus of experts who have the necessary experience and knowledge base,” Dr. Furuta said. “Our ability to say: ‘Here are the established treatments,’ is lacking, though. We need research studies to verify that our recommended approaches are indeed correct.”
The authors conditionally recommended that treatment goals include achieving symptom resolution, improving gross endoscopic and histologic abnormalities, promoting normal childhood growth and development, and preventing disease complications.
No pediatric study has determined the natural history of non-EoE EGIDs, and no study of maintenance therapy has been conducted, the authors noted.
For this reason, they conditionally recommended that the clinical decision to continue therapy should be discussed with patients and their parents/caregivers, and those discussions include the benefits and risk of long-term treatment, its cost, and its impact on health-related quality of life.
A starting point for patient management
In a comment, Vincent Mukkada, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati and an attending physician in gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center, observed that, though improved awareness among pediatric gastroenterologists may account for some of the increase in GI eosinophil disease, the incidence is also likely growing.
“We’re looking for them much more,” said Dr. Mukkada.
“But I also think they’re increasing, just like all other atopic diseases. We’re not sure why,” he added.
“The hope is that these guidelines will allow nonsubspecialized gastroenterologists and allergists feel comfortable to at least start on the journey of managing these patients. And, for pediatricians who learn that their patient has received a non-EoE EGID diagnosis, they can go to the summary figures in this one document and very quickly get an overview of the disease and its course,” Dr. Mukkada said.
Guideline development was funded by the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. The authors and Dr. Mukkada reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY & NUTRITION
Kidney stones on the rise: Where are the specialists?
While increasing the number of nephrologists who specialize in kidney stones is necessary, nonspecialists need to play a larger role in recognizing and preventing kidney stones.
Primary care and emergency department physicians can be the front lines of counseling patients who do not have underlying genetic causes of kidney stones on how to prevent a recurrence, according to Irina Jaeger, MD, a urologist at University Hospitals and an assistant professor of urology at Case Western Reserve University, both in Cleveland.
“A lot of this care can be implemented by our primary care physicians, such as counseling on decreasing sodium in the diet and increasing fluid intake, which benefits so many different health conditions as well as stones,” said Gregory E. Tasian, MD, MSCE, an attending pediatric urologist at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “If we can think about this holistically, we can really make strides.”
Focus on prevention
Taking a holistic approach, Dr. Tasian added, will require rethinking how health teams approach patient care and manage kidney stones.
“We think of stones as episodic events that are painful, and then pass,” he said. “But it’s really a disorder of mineral metabolism.”
Understanding these episodes as a chronic disease can also explain why nephrolithiasis often goes hand in hand with higher instances of heart attack and stroke, hypertension, and bone breaks, he added.
Simple measures such as staying hydrated and consuming citrate in the form of lemon water or lemonade can help patients prevent recurring kidney stones, Dr. Jaeger said.
But patients who have had a stone also need to see a specialist to rule out any underlying causes. Kidney stones are routinely viewed as episodic events that don’t pose much of a health threat, but between 30% and 50% of people diagnosed with stones will experience a recurrence within 5 years. Educating patients on how they can prevent future episodes is a crucial part of care.
“Even if they are passing the stones on their own without surgery, they should really be evaluated by a urologist or a nephrologist,” Dr. Jaeger said.
David S. Goldfarb, MD, clinical director of the division of nephrology at NYU Langone Health, New York, said that access to nephrologists who specialize in kidney stones is a critical piece of prevention. While urologists can treat stones, nephrologists get to the bottom of why the stones occurred in the first place and help patients prevent further stones from forming.
“The majority of urologists in the U.S. don’t do much in regard to prevention,” he said. “There needs to be more nephrologists.”
Kidney stones now appear to be increasingly common in patient populations that previously did not have the condition.
A study published in 2016 in the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology found that the annual incidence of kidney stones increased 16% from 1997 to 2012, with the biggest increase seen among teenagers. Stones were 52% more common among girls and women than among men, but the condition is also becoming more common in men starting at age 25. Meanwhile, Black Americans of all ages saw greater rates of kidney stone development than their White counterparts.
Fewer residents are choosing to specialize in nephrology, with a decrease in the choice of fellowship of 50% from 2009 to 2019, according to a 2023 report by the American Society of Nephrology.
A 2019 survey of nearly 4,200 residents found that only 60% of nephrology fellowship positions were filled in 2018, and the majority of those residents reported a lack of interest in the kidney as being the most critical factor in not selecting the specialty. Others reported lack of exposure to nephrology overall.
Diagnosing the root cause
Getting to the root cause of how further kidney stones can be prevented usually requires a nephrologist, according to Dr. Jaeger.
“As a urologist, 90% of what we do is surgery,” she said.
Although urologists are trained in analyzing 24-hour urine tests, which can reveal risks that can be addressed by preventive changes, many urologists tap a specialized nephrologist, who may analyze the samples with a keener eye.
“When individuals pass a stone, fewer than 10% seek care with a specialist after that and that’s a missed opportunity to prevent future stones,” Dr. Tasian said.
Not all nephrologists specialize in stones, but they may be better equipped to recognize when a patient needs to see someone who does. Failing to involve a nephrologist who specializes in kidney stones can have grave consequences for patient health.
Dr. Goldfarb is currently caring for a patient with a kidney transplant that had begun to lose function. Clinicians who originally cared for the patient took a kidney biopsy, which showed fragments of calcium oxalate, a common type of kidney stone, in her native kidneys.
After receiving a kidney transplant, her health began to decline again and a second biopsy found that the new kidney was forming the same type of stones. Her nephrologist knew this meant she likely had a genetic disorder and referred her to Dr. Goldfarb, who specializes in underlying genetic causes of kidney stones. A genetic test revealed that the patient had primary hyperoxaluria.
“She would have been treated completely differently if that had been recognized as the cause of her original kidney disease,” Dr. Goldfarb said. “Now her kidney transplant is getting kidney stones and I’m working with her to prevent that.”
Under Dr. Goldfarb, the patient will have access to a new experimental drug, called nedosiran, currently in clinical trials. It is specifically for primary hyperoxaluria.
“The kidney doctor that made the diagnosis correctly and referred her to me isn’t a kidney stone specialist; he is a general nephrologist who has taken an interest in the topic of kidney stones, recognizing there is sometimes some nuance and specialty of issues related to this,” Dr. Goldfarb said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
While increasing the number of nephrologists who specialize in kidney stones is necessary, nonspecialists need to play a larger role in recognizing and preventing kidney stones.
Primary care and emergency department physicians can be the front lines of counseling patients who do not have underlying genetic causes of kidney stones on how to prevent a recurrence, according to Irina Jaeger, MD, a urologist at University Hospitals and an assistant professor of urology at Case Western Reserve University, both in Cleveland.
“A lot of this care can be implemented by our primary care physicians, such as counseling on decreasing sodium in the diet and increasing fluid intake, which benefits so many different health conditions as well as stones,” said Gregory E. Tasian, MD, MSCE, an attending pediatric urologist at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “If we can think about this holistically, we can really make strides.”
Focus on prevention
Taking a holistic approach, Dr. Tasian added, will require rethinking how health teams approach patient care and manage kidney stones.
“We think of stones as episodic events that are painful, and then pass,” he said. “But it’s really a disorder of mineral metabolism.”
Understanding these episodes as a chronic disease can also explain why nephrolithiasis often goes hand in hand with higher instances of heart attack and stroke, hypertension, and bone breaks, he added.
Simple measures such as staying hydrated and consuming citrate in the form of lemon water or lemonade can help patients prevent recurring kidney stones, Dr. Jaeger said.
But patients who have had a stone also need to see a specialist to rule out any underlying causes. Kidney stones are routinely viewed as episodic events that don’t pose much of a health threat, but between 30% and 50% of people diagnosed with stones will experience a recurrence within 5 years. Educating patients on how they can prevent future episodes is a crucial part of care.
“Even if they are passing the stones on their own without surgery, they should really be evaluated by a urologist or a nephrologist,” Dr. Jaeger said.
David S. Goldfarb, MD, clinical director of the division of nephrology at NYU Langone Health, New York, said that access to nephrologists who specialize in kidney stones is a critical piece of prevention. While urologists can treat stones, nephrologists get to the bottom of why the stones occurred in the first place and help patients prevent further stones from forming.
“The majority of urologists in the U.S. don’t do much in regard to prevention,” he said. “There needs to be more nephrologists.”
Kidney stones now appear to be increasingly common in patient populations that previously did not have the condition.
A study published in 2016 in the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology found that the annual incidence of kidney stones increased 16% from 1997 to 2012, with the biggest increase seen among teenagers. Stones were 52% more common among girls and women than among men, but the condition is also becoming more common in men starting at age 25. Meanwhile, Black Americans of all ages saw greater rates of kidney stone development than their White counterparts.
Fewer residents are choosing to specialize in nephrology, with a decrease in the choice of fellowship of 50% from 2009 to 2019, according to a 2023 report by the American Society of Nephrology.
A 2019 survey of nearly 4,200 residents found that only 60% of nephrology fellowship positions were filled in 2018, and the majority of those residents reported a lack of interest in the kidney as being the most critical factor in not selecting the specialty. Others reported lack of exposure to nephrology overall.
Diagnosing the root cause
Getting to the root cause of how further kidney stones can be prevented usually requires a nephrologist, according to Dr. Jaeger.
“As a urologist, 90% of what we do is surgery,” she said.
Although urologists are trained in analyzing 24-hour urine tests, which can reveal risks that can be addressed by preventive changes, many urologists tap a specialized nephrologist, who may analyze the samples with a keener eye.
“When individuals pass a stone, fewer than 10% seek care with a specialist after that and that’s a missed opportunity to prevent future stones,” Dr. Tasian said.
Not all nephrologists specialize in stones, but they may be better equipped to recognize when a patient needs to see someone who does. Failing to involve a nephrologist who specializes in kidney stones can have grave consequences for patient health.
Dr. Goldfarb is currently caring for a patient with a kidney transplant that had begun to lose function. Clinicians who originally cared for the patient took a kidney biopsy, which showed fragments of calcium oxalate, a common type of kidney stone, in her native kidneys.
After receiving a kidney transplant, her health began to decline again and a second biopsy found that the new kidney was forming the same type of stones. Her nephrologist knew this meant she likely had a genetic disorder and referred her to Dr. Goldfarb, who specializes in underlying genetic causes of kidney stones. A genetic test revealed that the patient had primary hyperoxaluria.
“She would have been treated completely differently if that had been recognized as the cause of her original kidney disease,” Dr. Goldfarb said. “Now her kidney transplant is getting kidney stones and I’m working with her to prevent that.”
Under Dr. Goldfarb, the patient will have access to a new experimental drug, called nedosiran, currently in clinical trials. It is specifically for primary hyperoxaluria.
“The kidney doctor that made the diagnosis correctly and referred her to me isn’t a kidney stone specialist; he is a general nephrologist who has taken an interest in the topic of kidney stones, recognizing there is sometimes some nuance and specialty of issues related to this,” Dr. Goldfarb said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
While increasing the number of nephrologists who specialize in kidney stones is necessary, nonspecialists need to play a larger role in recognizing and preventing kidney stones.
Primary care and emergency department physicians can be the front lines of counseling patients who do not have underlying genetic causes of kidney stones on how to prevent a recurrence, according to Irina Jaeger, MD, a urologist at University Hospitals and an assistant professor of urology at Case Western Reserve University, both in Cleveland.
“A lot of this care can be implemented by our primary care physicians, such as counseling on decreasing sodium in the diet and increasing fluid intake, which benefits so many different health conditions as well as stones,” said Gregory E. Tasian, MD, MSCE, an attending pediatric urologist at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “If we can think about this holistically, we can really make strides.”
Focus on prevention
Taking a holistic approach, Dr. Tasian added, will require rethinking how health teams approach patient care and manage kidney stones.
“We think of stones as episodic events that are painful, and then pass,” he said. “But it’s really a disorder of mineral metabolism.”
Understanding these episodes as a chronic disease can also explain why nephrolithiasis often goes hand in hand with higher instances of heart attack and stroke, hypertension, and bone breaks, he added.
Simple measures such as staying hydrated and consuming citrate in the form of lemon water or lemonade can help patients prevent recurring kidney stones, Dr. Jaeger said.
But patients who have had a stone also need to see a specialist to rule out any underlying causes. Kidney stones are routinely viewed as episodic events that don’t pose much of a health threat, but between 30% and 50% of people diagnosed with stones will experience a recurrence within 5 years. Educating patients on how they can prevent future episodes is a crucial part of care.
“Even if they are passing the stones on their own without surgery, they should really be evaluated by a urologist or a nephrologist,” Dr. Jaeger said.
David S. Goldfarb, MD, clinical director of the division of nephrology at NYU Langone Health, New York, said that access to nephrologists who specialize in kidney stones is a critical piece of prevention. While urologists can treat stones, nephrologists get to the bottom of why the stones occurred in the first place and help patients prevent further stones from forming.
“The majority of urologists in the U.S. don’t do much in regard to prevention,” he said. “There needs to be more nephrologists.”
Kidney stones now appear to be increasingly common in patient populations that previously did not have the condition.
A study published in 2016 in the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology found that the annual incidence of kidney stones increased 16% from 1997 to 2012, with the biggest increase seen among teenagers. Stones were 52% more common among girls and women than among men, but the condition is also becoming more common in men starting at age 25. Meanwhile, Black Americans of all ages saw greater rates of kidney stone development than their White counterparts.
Fewer residents are choosing to specialize in nephrology, with a decrease in the choice of fellowship of 50% from 2009 to 2019, according to a 2023 report by the American Society of Nephrology.
A 2019 survey of nearly 4,200 residents found that only 60% of nephrology fellowship positions were filled in 2018, and the majority of those residents reported a lack of interest in the kidney as being the most critical factor in not selecting the specialty. Others reported lack of exposure to nephrology overall.
Diagnosing the root cause
Getting to the root cause of how further kidney stones can be prevented usually requires a nephrologist, according to Dr. Jaeger.
“As a urologist, 90% of what we do is surgery,” she said.
Although urologists are trained in analyzing 24-hour urine tests, which can reveal risks that can be addressed by preventive changes, many urologists tap a specialized nephrologist, who may analyze the samples with a keener eye.
“When individuals pass a stone, fewer than 10% seek care with a specialist after that and that’s a missed opportunity to prevent future stones,” Dr. Tasian said.
Not all nephrologists specialize in stones, but they may be better equipped to recognize when a patient needs to see someone who does. Failing to involve a nephrologist who specializes in kidney stones can have grave consequences for patient health.
Dr. Goldfarb is currently caring for a patient with a kidney transplant that had begun to lose function. Clinicians who originally cared for the patient took a kidney biopsy, which showed fragments of calcium oxalate, a common type of kidney stone, in her native kidneys.
After receiving a kidney transplant, her health began to decline again and a second biopsy found that the new kidney was forming the same type of stones. Her nephrologist knew this meant she likely had a genetic disorder and referred her to Dr. Goldfarb, who specializes in underlying genetic causes of kidney stones. A genetic test revealed that the patient had primary hyperoxaluria.
“She would have been treated completely differently if that had been recognized as the cause of her original kidney disease,” Dr. Goldfarb said. “Now her kidney transplant is getting kidney stones and I’m working with her to prevent that.”
Under Dr. Goldfarb, the patient will have access to a new experimental drug, called nedosiran, currently in clinical trials. It is specifically for primary hyperoxaluria.
“The kidney doctor that made the diagnosis correctly and referred her to me isn’t a kidney stone specialist; he is a general nephrologist who has taken an interest in the topic of kidney stones, recognizing there is sometimes some nuance and specialty of issues related to this,” Dr. Goldfarb said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID leads to greater health risks, research finds
That is the finding of a new study from Washington University in St. Louis. The school distributed a press release about the study, which was published in the journal Nature Medicine.
“Some estimates show more than 90% of the U.S. population has been infected with COVID-19,” Ziyad Al-Aly, chief of research and development at Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System and clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, told the St. Louis Post–Dispatch. “Doctors need to realize that their patients could be at risk of these conditions, be it heart disease or lung problems or brain problems – they’re at risk.”
The researchers compared the health records for 138,000 patients who had been infected with those of 6 million who had not. They followed 80 health conditions associated with long COVID for 2 years. They used unnamed records from the VA.
“There was really nothing at all looking at what happens to people at two years after the infection,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “So we decided to take a look.”
Patients who hadn’t been hospitalized within 30 days of infection had a higher risk of death 6 months after recovery, and a higher risk of hospitalization within 18 months. They had higher risk of diabetes, fatigue, joint pain, and other problems compared with people who had not been infected.
“In the nonhospitalized group, risks remained elevated for several problems, for several organ systems,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “For the people who were hospitalized, the risk was ubiquitous across all organ systems. It really spans the gamut with respect to the organ systems that are affected.”
People who had been hospitalized had a 65% greater risk of illnesses after 2 years. Nonhospitalized patients had just a 35% greater risk.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
That is the finding of a new study from Washington University in St. Louis. The school distributed a press release about the study, which was published in the journal Nature Medicine.
“Some estimates show more than 90% of the U.S. population has been infected with COVID-19,” Ziyad Al-Aly, chief of research and development at Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System and clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, told the St. Louis Post–Dispatch. “Doctors need to realize that their patients could be at risk of these conditions, be it heart disease or lung problems or brain problems – they’re at risk.”
The researchers compared the health records for 138,000 patients who had been infected with those of 6 million who had not. They followed 80 health conditions associated with long COVID for 2 years. They used unnamed records from the VA.
“There was really nothing at all looking at what happens to people at two years after the infection,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “So we decided to take a look.”
Patients who hadn’t been hospitalized within 30 days of infection had a higher risk of death 6 months after recovery, and a higher risk of hospitalization within 18 months. They had higher risk of diabetes, fatigue, joint pain, and other problems compared with people who had not been infected.
“In the nonhospitalized group, risks remained elevated for several problems, for several organ systems,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “For the people who were hospitalized, the risk was ubiquitous across all organ systems. It really spans the gamut with respect to the organ systems that are affected.”
People who had been hospitalized had a 65% greater risk of illnesses after 2 years. Nonhospitalized patients had just a 35% greater risk.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
That is the finding of a new study from Washington University in St. Louis. The school distributed a press release about the study, which was published in the journal Nature Medicine.
“Some estimates show more than 90% of the U.S. population has been infected with COVID-19,” Ziyad Al-Aly, chief of research and development at Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System and clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, told the St. Louis Post–Dispatch. “Doctors need to realize that their patients could be at risk of these conditions, be it heart disease or lung problems or brain problems – they’re at risk.”
The researchers compared the health records for 138,000 patients who had been infected with those of 6 million who had not. They followed 80 health conditions associated with long COVID for 2 years. They used unnamed records from the VA.
“There was really nothing at all looking at what happens to people at two years after the infection,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “So we decided to take a look.”
Patients who hadn’t been hospitalized within 30 days of infection had a higher risk of death 6 months after recovery, and a higher risk of hospitalization within 18 months. They had higher risk of diabetes, fatigue, joint pain, and other problems compared with people who had not been infected.
“In the nonhospitalized group, risks remained elevated for several problems, for several organ systems,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “For the people who were hospitalized, the risk was ubiquitous across all organ systems. It really spans the gamut with respect to the organ systems that are affected.”
People who had been hospitalized had a 65% greater risk of illnesses after 2 years. Nonhospitalized patients had just a 35% greater risk.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE

