User login
Chemo-free induction in MCL keeps getting better
Lugano, Switzerland – It’s not the end of chemotherapy for young patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), but it’s a start.
For these patients, induction with a combination of ibrutinib and rituximab, followed by shorter cycles of chemoimmunotherapy, was associated in an early study with an objective response rate of 100%, including 90% complete responses (CR), reported Michael Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
“This is the first time for a chemo-free therapy – ibrutinib/rituximab – to achieve an overall response rate of 100%. This has an unprecedented efficacy in the frontline in young patients with mantle-cell lymphoma,” he said at the 14th International Congress on Malignant Lymphoma.
In patients with relapsed or refractory MCL, the combination of ibrutinib and rituximab has been associated with durable responses in 88% of patients. The success of the combination suggests that fit patients younger than age 65 years with newly diagnosed MCL might benefit from a chemotherapy-free induction regimen with ibrutinib and rituximab, followed by consolidation with a short but intense course of chemoimmunotherapy, Dr. Wang said.
He presented updated results from the phase II Window I study, first results of which were reported at the 2016 meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Frontline therapy is the most important therapy for mantle cell lymphoma, because mantle cell lymphoma cells are most vulnerable to frontline attack. If the frontline therapy is good enough, it could kill all the mantle cell lymphoma cells, therefore leaving no chance for secondary resistance, and thereby (resulting in) long-term survival. And it is really my belief that if we ideally optimized the frontline therapy, that would be a shortcut to a cure,” he said.
To test this idea, Dr. Wang and MD Anderson colleagues initiated a phase II trial at their institution with 50 patients age 65 years or under with newly diagnosed, CD20-positive and Cyclin D1-positive MCL.
A total of 50 patients age 65 years or younger (median age 54) with newly diagnosed, untreated MCL underwent induction with continuous daily ibrutinib 560 mg, plus rituximab 375 mg/m2 administered weekly for 4 weeks during cycle 1 and on day 1 of cycles 3-12. Consolidation consisted of rituximab plus hyper-CVAD (hyper-fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone), alternating every 28 days with rituximab plus high-dose methotrexate–cytarabine.
Patients who had complete responses to induction received four cycles of chemoimmunotherapy, while those who experienced disease progression and those who had partial responses received chemoimmunotherapy for two cycles beyond the point of complete remissions.
At the time of the presentation, all 50 patients were evaluable for the induction phase (part 2), and 47 were evaluable for both induction and consolidation (part 2) .Of the evaluable patients, the overall response rate (ORR) to chemotherapy-free induction therapy alone (Part 1 ) was 100% (50), with CR in 90% of patients and partial responses (PR) in 10%. Of the 47 patients evaluable for part 2 (chemoimmunotherapy), all had CRs, for an ORR of 100%.
Dr. Wang noted that one patient had a dramatic radiographic reduction in spleen size following just two cycles of chemotherapy-free induction, and two other patients had similar reductions after four and six cycles, respectively.
After a median follow-up of 15.9 months, neither the median duration of response, progression-free survival, nor overall survival have been reached. There have been no deaths and only one case of disease progression after one year of therapy.
The patients generally tolerated the regimen very well, Dr. Wang said. There were no cases of lymphocytosis, bleeding, or atrial fibrillation after 332 combined cycles.
Nonhematological adverse events were primarily grade 1 or 2. Grade 3 fatigue was reported in approximately 10% of patients. There were no grade 4 adverse events.
“This study may provide a window of opportunity to reduce the frontline therapies and reduce the long-term toxicities such as secondary malignancies.” Dr. Wang said.
He acknowledged that four cycles of intensive chemotherapy is still toxic and that further efforts to reduce these toxicities are needed. The investigators are currently planning the Window II study, in which a fraction of patients will be treated with no chemotherapy at all, he said.
The study was supported by Pharmacyclics and Janssen. Dr. Wang disclosed receiving research grants and honoraria and serving as a consultant for the companies.
Lugano, Switzerland – It’s not the end of chemotherapy for young patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), but it’s a start.
For these patients, induction with a combination of ibrutinib and rituximab, followed by shorter cycles of chemoimmunotherapy, was associated in an early study with an objective response rate of 100%, including 90% complete responses (CR), reported Michael Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
“This is the first time for a chemo-free therapy – ibrutinib/rituximab – to achieve an overall response rate of 100%. This has an unprecedented efficacy in the frontline in young patients with mantle-cell lymphoma,” he said at the 14th International Congress on Malignant Lymphoma.
In patients with relapsed or refractory MCL, the combination of ibrutinib and rituximab has been associated with durable responses in 88% of patients. The success of the combination suggests that fit patients younger than age 65 years with newly diagnosed MCL might benefit from a chemotherapy-free induction regimen with ibrutinib and rituximab, followed by consolidation with a short but intense course of chemoimmunotherapy, Dr. Wang said.
He presented updated results from the phase II Window I study, first results of which were reported at the 2016 meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Frontline therapy is the most important therapy for mantle cell lymphoma, because mantle cell lymphoma cells are most vulnerable to frontline attack. If the frontline therapy is good enough, it could kill all the mantle cell lymphoma cells, therefore leaving no chance for secondary resistance, and thereby (resulting in) long-term survival. And it is really my belief that if we ideally optimized the frontline therapy, that would be a shortcut to a cure,” he said.
To test this idea, Dr. Wang and MD Anderson colleagues initiated a phase II trial at their institution with 50 patients age 65 years or under with newly diagnosed, CD20-positive and Cyclin D1-positive MCL.
A total of 50 patients age 65 years or younger (median age 54) with newly diagnosed, untreated MCL underwent induction with continuous daily ibrutinib 560 mg, plus rituximab 375 mg/m2 administered weekly for 4 weeks during cycle 1 and on day 1 of cycles 3-12. Consolidation consisted of rituximab plus hyper-CVAD (hyper-fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone), alternating every 28 days with rituximab plus high-dose methotrexate–cytarabine.
Patients who had complete responses to induction received four cycles of chemoimmunotherapy, while those who experienced disease progression and those who had partial responses received chemoimmunotherapy for two cycles beyond the point of complete remissions.
At the time of the presentation, all 50 patients were evaluable for the induction phase (part 2), and 47 were evaluable for both induction and consolidation (part 2) .Of the evaluable patients, the overall response rate (ORR) to chemotherapy-free induction therapy alone (Part 1 ) was 100% (50), with CR in 90% of patients and partial responses (PR) in 10%. Of the 47 patients evaluable for part 2 (chemoimmunotherapy), all had CRs, for an ORR of 100%.
Dr. Wang noted that one patient had a dramatic radiographic reduction in spleen size following just two cycles of chemotherapy-free induction, and two other patients had similar reductions after four and six cycles, respectively.
After a median follow-up of 15.9 months, neither the median duration of response, progression-free survival, nor overall survival have been reached. There have been no deaths and only one case of disease progression after one year of therapy.
The patients generally tolerated the regimen very well, Dr. Wang said. There were no cases of lymphocytosis, bleeding, or atrial fibrillation after 332 combined cycles.
Nonhematological adverse events were primarily grade 1 or 2. Grade 3 fatigue was reported in approximately 10% of patients. There were no grade 4 adverse events.
“This study may provide a window of opportunity to reduce the frontline therapies and reduce the long-term toxicities such as secondary malignancies.” Dr. Wang said.
He acknowledged that four cycles of intensive chemotherapy is still toxic and that further efforts to reduce these toxicities are needed. The investigators are currently planning the Window II study, in which a fraction of patients will be treated with no chemotherapy at all, he said.
The study was supported by Pharmacyclics and Janssen. Dr. Wang disclosed receiving research grants and honoraria and serving as a consultant for the companies.
Lugano, Switzerland – It’s not the end of chemotherapy for young patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), but it’s a start.
For these patients, induction with a combination of ibrutinib and rituximab, followed by shorter cycles of chemoimmunotherapy, was associated in an early study with an objective response rate of 100%, including 90% complete responses (CR), reported Michael Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
“This is the first time for a chemo-free therapy – ibrutinib/rituximab – to achieve an overall response rate of 100%. This has an unprecedented efficacy in the frontline in young patients with mantle-cell lymphoma,” he said at the 14th International Congress on Malignant Lymphoma.
In patients with relapsed or refractory MCL, the combination of ibrutinib and rituximab has been associated with durable responses in 88% of patients. The success of the combination suggests that fit patients younger than age 65 years with newly diagnosed MCL might benefit from a chemotherapy-free induction regimen with ibrutinib and rituximab, followed by consolidation with a short but intense course of chemoimmunotherapy, Dr. Wang said.
He presented updated results from the phase II Window I study, first results of which were reported at the 2016 meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Frontline therapy is the most important therapy for mantle cell lymphoma, because mantle cell lymphoma cells are most vulnerable to frontline attack. If the frontline therapy is good enough, it could kill all the mantle cell lymphoma cells, therefore leaving no chance for secondary resistance, and thereby (resulting in) long-term survival. And it is really my belief that if we ideally optimized the frontline therapy, that would be a shortcut to a cure,” he said.
To test this idea, Dr. Wang and MD Anderson colleagues initiated a phase II trial at their institution with 50 patients age 65 years or under with newly diagnosed, CD20-positive and Cyclin D1-positive MCL.
A total of 50 patients age 65 years or younger (median age 54) with newly diagnosed, untreated MCL underwent induction with continuous daily ibrutinib 560 mg, plus rituximab 375 mg/m2 administered weekly for 4 weeks during cycle 1 and on day 1 of cycles 3-12. Consolidation consisted of rituximab plus hyper-CVAD (hyper-fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone), alternating every 28 days with rituximab plus high-dose methotrexate–cytarabine.
Patients who had complete responses to induction received four cycles of chemoimmunotherapy, while those who experienced disease progression and those who had partial responses received chemoimmunotherapy for two cycles beyond the point of complete remissions.
At the time of the presentation, all 50 patients were evaluable for the induction phase (part 2), and 47 were evaluable for both induction and consolidation (part 2) .Of the evaluable patients, the overall response rate (ORR) to chemotherapy-free induction therapy alone (Part 1 ) was 100% (50), with CR in 90% of patients and partial responses (PR) in 10%. Of the 47 patients evaluable for part 2 (chemoimmunotherapy), all had CRs, for an ORR of 100%.
Dr. Wang noted that one patient had a dramatic radiographic reduction in spleen size following just two cycles of chemotherapy-free induction, and two other patients had similar reductions after four and six cycles, respectively.
After a median follow-up of 15.9 months, neither the median duration of response, progression-free survival, nor overall survival have been reached. There have been no deaths and only one case of disease progression after one year of therapy.
The patients generally tolerated the regimen very well, Dr. Wang said. There were no cases of lymphocytosis, bleeding, or atrial fibrillation after 332 combined cycles.
Nonhematological adverse events were primarily grade 1 or 2. Grade 3 fatigue was reported in approximately 10% of patients. There were no grade 4 adverse events.
“This study may provide a window of opportunity to reduce the frontline therapies and reduce the long-term toxicities such as secondary malignancies.” Dr. Wang said.
He acknowledged that four cycles of intensive chemotherapy is still toxic and that further efforts to reduce these toxicities are needed. The investigators are currently planning the Window II study, in which a fraction of patients will be treated with no chemotherapy at all, he said.
The study was supported by Pharmacyclics and Janssen. Dr. Wang disclosed receiving research grants and honoraria and serving as a consultant for the companies.
AT14-ICML
Key clinical point: A chemotherapy-free induction regimen with ibrutinib and rituximab was associated with high response rates in patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: The overall response rate after induction was 100%, including 90% complete responses.
Data source: Update results from phase II investigator-initiated study in 50 patients aged 65 years and younger with MCL.
Disclosures: The study was supported by Pharmacyclics and Janssen. Dr. Wang disclosed receiving research grants and honoraria and serving as a consultant for the companies.
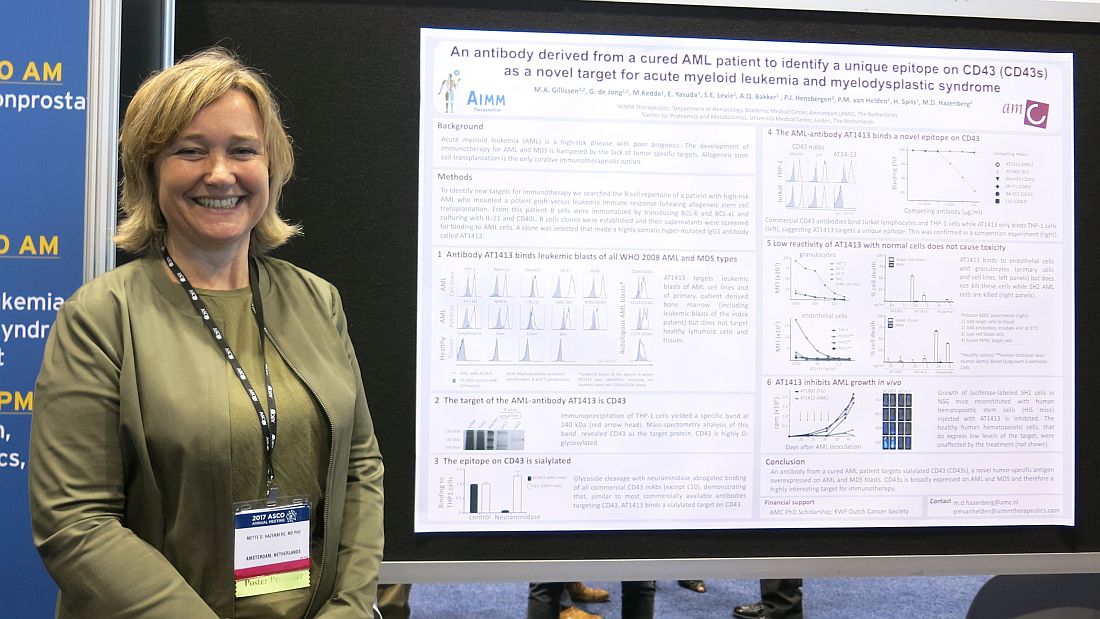
Antibody from AML survivor may prove therapeutic
CHICAGO – A therapeutic target and possibly a treatment for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome may lie in the immortalized B cells of a patient whose acute myeloid leukemia was cured after allogeneic stem cell transplantation.
A B cell clone isolated from this patient makes a hypermutated immunoglobulin G1 antibody that binds leukemic blasts of all World Health Organization 2008 AML and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) types, based on cells obtained from 60 AML or MDS patients, but does not target healthy cells and lymphoid tissue, Mette D. Hazenberg, MD, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“CD43 is broadly expressed on AML and MDS and, therefore, is a highly interesting target for immunotherapy,” said Dr. Hazenberg of AIMM Therapeutics and Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam.
The growth of luciferase-labeled AML cells expressing CD43s was inhibited in highly immunodeficient NOD scid-gamma mice that were reconstituted with human hematopoietic stem cells injected with AT1413. Healthy human hematopoietic cells, which express low levels of the target, were not affected by the treatment.
Next steps include further in vivo preclinical studies, according to Dr. Hazenberg.
AIMM Therapeutics is a biotech company comprising a joint venture between Immpact and the Academic Medical Center (AMC) at the University of Amsterdam. The study was supported by an AMC PhD scholarship and the KWF Dutch Cancer Society.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryjodales
CHICAGO – A therapeutic target and possibly a treatment for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome may lie in the immortalized B cells of a patient whose acute myeloid leukemia was cured after allogeneic stem cell transplantation.
A B cell clone isolated from this patient makes a hypermutated immunoglobulin G1 antibody that binds leukemic blasts of all World Health Organization 2008 AML and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) types, based on cells obtained from 60 AML or MDS patients, but does not target healthy cells and lymphoid tissue, Mette D. Hazenberg, MD, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“CD43 is broadly expressed on AML and MDS and, therefore, is a highly interesting target for immunotherapy,” said Dr. Hazenberg of AIMM Therapeutics and Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam.
The growth of luciferase-labeled AML cells expressing CD43s was inhibited in highly immunodeficient NOD scid-gamma mice that were reconstituted with human hematopoietic stem cells injected with AT1413. Healthy human hematopoietic cells, which express low levels of the target, were not affected by the treatment.
Next steps include further in vivo preclinical studies, according to Dr. Hazenberg.
AIMM Therapeutics is a biotech company comprising a joint venture between Immpact and the Academic Medical Center (AMC) at the University of Amsterdam. The study was supported by an AMC PhD scholarship and the KWF Dutch Cancer Society.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryjodales
CHICAGO – A therapeutic target and possibly a treatment for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome may lie in the immortalized B cells of a patient whose acute myeloid leukemia was cured after allogeneic stem cell transplantation.
A B cell clone isolated from this patient makes a hypermutated immunoglobulin G1 antibody that binds leukemic blasts of all World Health Organization 2008 AML and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) types, based on cells obtained from 60 AML or MDS patients, but does not target healthy cells and lymphoid tissue, Mette D. Hazenberg, MD, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“CD43 is broadly expressed on AML and MDS and, therefore, is a highly interesting target for immunotherapy,” said Dr. Hazenberg of AIMM Therapeutics and Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam.
The growth of luciferase-labeled AML cells expressing CD43s was inhibited in highly immunodeficient NOD scid-gamma mice that were reconstituted with human hematopoietic stem cells injected with AT1413. Healthy human hematopoietic cells, which express low levels of the target, were not affected by the treatment.
Next steps include further in vivo preclinical studies, according to Dr. Hazenberg.
AIMM Therapeutics is a biotech company comprising a joint venture between Immpact and the Academic Medical Center (AMC) at the University of Amsterdam. The study was supported by an AMC PhD scholarship and the KWF Dutch Cancer Society.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryjodales
AT ASCO 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The growth of luciferase-labeled SH2 cells was inhibited in highly immunodeficient NSG (NOD scid-gamma) mice that were reconstituted with human hematopoietic stem cells injected with AT1413.
Data source: Cellular studies and studies in severely immunodeficient mice.
Disclosures: Dr. Hazenberg is with AIMM Therapeutics and Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam. AIMM Therapeutics is a biotech company comprising a joint venture between Immpact and the Academic Medical Center (AMC) at the University of Amsterdam. The study was supported by an AMC PhD scholarship and the KWF Dutch Cancer Society.
ACIP approves new influenza vaccine recommendations
FROM AN ACIP MEETING
by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) after a lengthy debate over specifics regarding recommendations for pregnant women.
The proposed recommendation that sparked the debate would change the wording of the previous recommendation for pregnant women to receive a seasonal inactivated vaccine (IIV) to “any licensed, recommended, and age-appropriate, trivalent or quadrivalent IIV or RIV [recombinant influenza vaccine] may be used.”
“I think there’s a subtle, but important difference here between making what would appear to be an affirmative statement that RIV is safe in pregnant women, versus just staying silent on it, and saying ‘we’re not saying you shouldn’t use it, but we don’t have enough data to affirmatively say it is safe,’ ” said Cindy Pellegrini, senior vice president of Public Policy and Government Affairs at the March of Dimes Foundation.
In response, members of the committee pointed out that the responsibility of determining safety lies with the Food and Drug Administration, which has already licensed the Flublok trivalent vaccine with expectations that the quadrivalent vaccine soon will follow.
While Lisa Grohskopf, MD, MPH, medical officer of the influenza division of the CDC, did acknowledge that there were more data on the safety of inactivated influenza vaccines, she asserted to the committee that “the general overall safety profile of Flublok in comparison to inactivated vaccines is reassuring.”
“For example, one concern that arises is reactogenicity and inflammation. [In terms of] overall reactogenicity in the studies where Flublok and inactivated vaccines have been compared, rates of the adverse and systemic reactions were similar,” Dr. Grohskopf said.
A motion was made to change the wording of the recommendation; however, the motion was not passed, and the eventual vote on the approval was conducted.
The ACIP also voted unanimously to change the safe age limit noted in influenza guidelines for use of Afluria (IIV3) from 9 years and older to 5 years and older. A footnote saying that the ACIP recommends Afluria for children 9 years and older will be removed.
This change, which mirrors the licensing Afluria has with the FDA, was based on research conducted by Seqirus that showed fever levels were the same for Afluria trivalent and quadrivalent vaccines in children 5 to 9 years old, both of which were less than historical vaccine rates.
The approved recommendations will be sent to the director of the CDC and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Once reviewed and approved, the final recommendations will be published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. The committee members had no relevant financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
FROM AN ACIP MEETING
by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) after a lengthy debate over specifics regarding recommendations for pregnant women.
The proposed recommendation that sparked the debate would change the wording of the previous recommendation for pregnant women to receive a seasonal inactivated vaccine (IIV) to “any licensed, recommended, and age-appropriate, trivalent or quadrivalent IIV or RIV [recombinant influenza vaccine] may be used.”
“I think there’s a subtle, but important difference here between making what would appear to be an affirmative statement that RIV is safe in pregnant women, versus just staying silent on it, and saying ‘we’re not saying you shouldn’t use it, but we don’t have enough data to affirmatively say it is safe,’ ” said Cindy Pellegrini, senior vice president of Public Policy and Government Affairs at the March of Dimes Foundation.
In response, members of the committee pointed out that the responsibility of determining safety lies with the Food and Drug Administration, which has already licensed the Flublok trivalent vaccine with expectations that the quadrivalent vaccine soon will follow.
While Lisa Grohskopf, MD, MPH, medical officer of the influenza division of the CDC, did acknowledge that there were more data on the safety of inactivated influenza vaccines, she asserted to the committee that “the general overall safety profile of Flublok in comparison to inactivated vaccines is reassuring.”
“For example, one concern that arises is reactogenicity and inflammation. [In terms of] overall reactogenicity in the studies where Flublok and inactivated vaccines have been compared, rates of the adverse and systemic reactions were similar,” Dr. Grohskopf said.
A motion was made to change the wording of the recommendation; however, the motion was not passed, and the eventual vote on the approval was conducted.
The ACIP also voted unanimously to change the safe age limit noted in influenza guidelines for use of Afluria (IIV3) from 9 years and older to 5 years and older. A footnote saying that the ACIP recommends Afluria for children 9 years and older will be removed.
This change, which mirrors the licensing Afluria has with the FDA, was based on research conducted by Seqirus that showed fever levels were the same for Afluria trivalent and quadrivalent vaccines in children 5 to 9 years old, both of which were less than historical vaccine rates.
The approved recommendations will be sent to the director of the CDC and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Once reviewed and approved, the final recommendations will be published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. The committee members had no relevant financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
FROM AN ACIP MEETING
by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) after a lengthy debate over specifics regarding recommendations for pregnant women.
The proposed recommendation that sparked the debate would change the wording of the previous recommendation for pregnant women to receive a seasonal inactivated vaccine (IIV) to “any licensed, recommended, and age-appropriate, trivalent or quadrivalent IIV or RIV [recombinant influenza vaccine] may be used.”
“I think there’s a subtle, but important difference here between making what would appear to be an affirmative statement that RIV is safe in pregnant women, versus just staying silent on it, and saying ‘we’re not saying you shouldn’t use it, but we don’t have enough data to affirmatively say it is safe,’ ” said Cindy Pellegrini, senior vice president of Public Policy and Government Affairs at the March of Dimes Foundation.
In response, members of the committee pointed out that the responsibility of determining safety lies with the Food and Drug Administration, which has already licensed the Flublok trivalent vaccine with expectations that the quadrivalent vaccine soon will follow.
While Lisa Grohskopf, MD, MPH, medical officer of the influenza division of the CDC, did acknowledge that there were more data on the safety of inactivated influenza vaccines, she asserted to the committee that “the general overall safety profile of Flublok in comparison to inactivated vaccines is reassuring.”
“For example, one concern that arises is reactogenicity and inflammation. [In terms of] overall reactogenicity in the studies where Flublok and inactivated vaccines have been compared, rates of the adverse and systemic reactions were similar,” Dr. Grohskopf said.
A motion was made to change the wording of the recommendation; however, the motion was not passed, and the eventual vote on the approval was conducted.
The ACIP also voted unanimously to change the safe age limit noted in influenza guidelines for use of Afluria (IIV3) from 9 years and older to 5 years and older. A footnote saying that the ACIP recommends Afluria for children 9 years and older will be removed.
This change, which mirrors the licensing Afluria has with the FDA, was based on research conducted by Seqirus that showed fever levels were the same for Afluria trivalent and quadrivalent vaccines in children 5 to 9 years old, both of which were less than historical vaccine rates.
The approved recommendations will be sent to the director of the CDC and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Once reviewed and approved, the final recommendations will be published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. The committee members had no relevant financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
Novel ibuprofen formulation cuts GI side effects in patients with knee pain flares
LAS VEGAS – A novel lipid formulation of ibuprofen given at 1,200 mg/day proved noninferior to high-dose standard ibuprofen at 2,400 mg/day for management of episodic knee pain flares in a phase III randomized trial, and it accomplished this with significantly fewer gastrointestinal side effects, Sita M.A. Bierma-Zeinstra, MD, reported.
Episodic flares of knee pain are a disabling feature of knee osteoarthritis that can occur at all stages of the disease, including prior to clinical diagnosis. There is a need for a fast-acting analgesic designed for short-term use with minimal side effects to provide pain relief during these flares. This was the motivation for developing Flarin, a lipid formulation soft-gel capsule of ibuprofen that is effective at less-than-standard doses of the conventional NSAID, she explained at the World Congress on Osteoarthritis.
The primary outcome was change in the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain subscale after 5 days of treatment. The score dropped from a mean of 5.72 at baseline out of a possible maximum of 10 to 3.05 in the lipid ibuprofen group, from 5.6 to 3.26 in patients on standard ibuprofen at 1,200 mg/day, and from 5.61 to 2.82 in subjects on standard ibuprofen at 2,400 mg/day. Those between-group differences were not statistically significant, reported Dr. Bierma-Zeinstra, professor of osteoarthritis and related disorders at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam.
In contrast, the rate of gastrointestinal side effects was significantly different across the three treatment arms: 16.2% in the lipid ibuprofen group, 22.6% with conventional ibuprofen at 1,200 mg/day, and 28.3% with ibuprofen at 2,400 mg/day, she said at the congress, which was sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
The group on the investigational formulation of ibuprofen also showed a consistent trend for superior results on the WOMAC swelling, pain, stiffness, and function subscales after 5 days of treatment, although only the improvement in swelling achieved statistical significance, Dr. Bierma-Zeinstra continued.
Flarin is approved and marketed in the United Kingdom. Infirst Healthcare, the novel NSAID’s developer and the sponsor of the phase III randomized trial, is seeking to gain regulatory approval throughout Europe. The U.K. company also has an agreement with McNeil Consumer Pharmaceuticals to market its products in the United States, once approved.
Dr. Bierma-Zeinstra reported having received a research grant from Infirst.
LAS VEGAS – A novel lipid formulation of ibuprofen given at 1,200 mg/day proved noninferior to high-dose standard ibuprofen at 2,400 mg/day for management of episodic knee pain flares in a phase III randomized trial, and it accomplished this with significantly fewer gastrointestinal side effects, Sita M.A. Bierma-Zeinstra, MD, reported.
Episodic flares of knee pain are a disabling feature of knee osteoarthritis that can occur at all stages of the disease, including prior to clinical diagnosis. There is a need for a fast-acting analgesic designed for short-term use with minimal side effects to provide pain relief during these flares. This was the motivation for developing Flarin, a lipid formulation soft-gel capsule of ibuprofen that is effective at less-than-standard doses of the conventional NSAID, she explained at the World Congress on Osteoarthritis.
The primary outcome was change in the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain subscale after 5 days of treatment. The score dropped from a mean of 5.72 at baseline out of a possible maximum of 10 to 3.05 in the lipid ibuprofen group, from 5.6 to 3.26 in patients on standard ibuprofen at 1,200 mg/day, and from 5.61 to 2.82 in subjects on standard ibuprofen at 2,400 mg/day. Those between-group differences were not statistically significant, reported Dr. Bierma-Zeinstra, professor of osteoarthritis and related disorders at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam.
In contrast, the rate of gastrointestinal side effects was significantly different across the three treatment arms: 16.2% in the lipid ibuprofen group, 22.6% with conventional ibuprofen at 1,200 mg/day, and 28.3% with ibuprofen at 2,400 mg/day, she said at the congress, which was sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
The group on the investigational formulation of ibuprofen also showed a consistent trend for superior results on the WOMAC swelling, pain, stiffness, and function subscales after 5 days of treatment, although only the improvement in swelling achieved statistical significance, Dr. Bierma-Zeinstra continued.
Flarin is approved and marketed in the United Kingdom. Infirst Healthcare, the novel NSAID’s developer and the sponsor of the phase III randomized trial, is seeking to gain regulatory approval throughout Europe. The U.K. company also has an agreement with McNeil Consumer Pharmaceuticals to market its products in the United States, once approved.
Dr. Bierma-Zeinstra reported having received a research grant from Infirst.
LAS VEGAS – A novel lipid formulation of ibuprofen given at 1,200 mg/day proved noninferior to high-dose standard ibuprofen at 2,400 mg/day for management of episodic knee pain flares in a phase III randomized trial, and it accomplished this with significantly fewer gastrointestinal side effects, Sita M.A. Bierma-Zeinstra, MD, reported.
Episodic flares of knee pain are a disabling feature of knee osteoarthritis that can occur at all stages of the disease, including prior to clinical diagnosis. There is a need for a fast-acting analgesic designed for short-term use with minimal side effects to provide pain relief during these flares. This was the motivation for developing Flarin, a lipid formulation soft-gel capsule of ibuprofen that is effective at less-than-standard doses of the conventional NSAID, she explained at the World Congress on Osteoarthritis.
The primary outcome was change in the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain subscale after 5 days of treatment. The score dropped from a mean of 5.72 at baseline out of a possible maximum of 10 to 3.05 in the lipid ibuprofen group, from 5.6 to 3.26 in patients on standard ibuprofen at 1,200 mg/day, and from 5.61 to 2.82 in subjects on standard ibuprofen at 2,400 mg/day. Those between-group differences were not statistically significant, reported Dr. Bierma-Zeinstra, professor of osteoarthritis and related disorders at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam.
In contrast, the rate of gastrointestinal side effects was significantly different across the three treatment arms: 16.2% in the lipid ibuprofen group, 22.6% with conventional ibuprofen at 1,200 mg/day, and 28.3% with ibuprofen at 2,400 mg/day, she said at the congress, which was sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
The group on the investigational formulation of ibuprofen also showed a consistent trend for superior results on the WOMAC swelling, pain, stiffness, and function subscales after 5 days of treatment, although only the improvement in swelling achieved statistical significance, Dr. Bierma-Zeinstra continued.
Flarin is approved and marketed in the United Kingdom. Infirst Healthcare, the novel NSAID’s developer and the sponsor of the phase III randomized trial, is seeking to gain regulatory approval throughout Europe. The U.K. company also has an agreement with McNeil Consumer Pharmaceuticals to market its products in the United States, once approved.
Dr. Bierma-Zeinstra reported having received a research grant from Infirst.
AT OARSI 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The incidence of GI side effects in patients being treated for an episodic knee pain flare was 16.2% after 5 days of treatment with a novel lipid formulation of ibuprofen at 1,200 mg/day, significantly lower than in patients randomized to conventional ibuprofen soft-gel capsules at 1,200 or 2,400 mg/day.
Data source: This three-arm, multicenter, international randomized trial involved 462 patients experiencing a recent-onset episodic flare of knee pain.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having received a research grant from Infirst Healthcare, which funded the study.
Panel revises spondyloarthritis treat-to-target recommendations
MADRID – The newly revised recommendations from an unaffiliated, international expert panel on a treat-to-target approach for axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis has one conspicuous feature that the prior recommendations lacked: evidence.
The first treat-to-target recommendations for spondyloarthritis (SpA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) from 2013 were based entirely on expert opinion (Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Jan;73[1]:6-16), but in the new update 4 of the 11 recommendations now have an evidence base as well as a fifth recommendation for the part that pertains to PsA, Désirée van der Heijde, MD, said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
Among the evidence-based recommendations, the most striking was a new formulation for how to measure disease activity. The new recommendations call the ASDAS (Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score) the “preferred” disease activity measure for patients with axial SpA and cite both the DAPSA (Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis) as well as minimal disease activity as “considered to define the target” when treating PsA.
“This recommendation just made it,” squeaking onto the list with a 52% vote of approval from the task force members, said Dr. van der Heijde. “It had the longest discussion,” with a significant minority of panelists taking a different view.
ASDAS shook out as the preferred measure for axial SpA because of evidence linking a patient’s ASDAS with syndesmophyte formation. “The idea is that by targeting ASDAS you should have better outcomes,” she explained.
“Applying a treat-to-target approach in axial SpA is feasible but requires systematic collection of outcome parameters in daily practice,” such as ASDAS, said Dr. Dougados, professor of rheumatology at Cochin Hospital in Paris. Another piece currently lacking in the case for treat-to-target is demonstration of the clinical benefit from this approach in a trial, he added.
According to Dr. van der Heijde, the other four recommendations that now have evidence backup are:
- Define clinical remission or minimal disease as the absence of clinical and laboratory evidence of significant disease activity.
- An alternative treatment target for PsA may be low or minimal disease activity.
- Measure disease activity by clinical signs and symptoms and by acute phase reactants.
- Once a treatment target is reached it should be maintained.
The task force also outlined “an extensive research agenda” where evidence is needed, specifying close to 50 individual research topics. Among them Dr. van der Heijde particularly called out the role of the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), validation of PsA target outcomes, and better parsing of the differences using remission or low disease activity as the treatment target.
Dr. van der Heijde, Dr. Dougados, and Dr. Braun are all consultants for several drug companies.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
The evidence we now have is the difference between the new recommendations and the prior version. We have evidence from trials in patients with psoriatic arthritis using minimal disease activity as a target. And we have indirect evidence from observational studies in patients with SpA that suggest the higher the ASDAS, the more progression occurs. In addition, results reported at the EULAR 2017 Congress showed that reductions in the ASDAS appeared to correlate with the effect of a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor on reduced radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. But this is just an association; data from a randomized, prospective trial should be available next year.
The recommendations say to manage patients with axial SpA or psoriatic arthritis by treating them to a target. To do that a clinician needs a standardized assessment of a patient’s disease and to perform follow-up measurements to see if the target is met. The data Dr. Dougados cited from Paris document that assessments such as an ASDAS are rarely made. Getting an ASDAS means knowing either a patient’s C-reactive protein level or erythrocyte sedimentation rate. That requires blood work before a clinic visit, something patients often don’t want.
Will these recommendations change practice and make the ASDAS more widely used? That depends to some extent on whether any benefits or penalties linked to ASDAS use go into place.
Next year, we expect to see results from trials that are testing whether the treat-to-target approach produces better outcomes. Evidence like that will be important to further spur adoption.
Lianne S. Gensler, MD , is director of the ankylosing spondylitis clinic at the University of California, San Francisco. She has been a consultant to Novartis and Janssen and has received research support from AbbVie and UCB. Dr. Gensler was a member of the task force that issued the revised recommendations. She made these comments in an interview.
The evidence we now have is the difference between the new recommendations and the prior version. We have evidence from trials in patients with psoriatic arthritis using minimal disease activity as a target. And we have indirect evidence from observational studies in patients with SpA that suggest the higher the ASDAS, the more progression occurs. In addition, results reported at the EULAR 2017 Congress showed that reductions in the ASDAS appeared to correlate with the effect of a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor on reduced radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. But this is just an association; data from a randomized, prospective trial should be available next year.
The recommendations say to manage patients with axial SpA or psoriatic arthritis by treating them to a target. To do that a clinician needs a standardized assessment of a patient’s disease and to perform follow-up measurements to see if the target is met. The data Dr. Dougados cited from Paris document that assessments such as an ASDAS are rarely made. Getting an ASDAS means knowing either a patient’s C-reactive protein level or erythrocyte sedimentation rate. That requires blood work before a clinic visit, something patients often don’t want.
Will these recommendations change practice and make the ASDAS more widely used? That depends to some extent on whether any benefits or penalties linked to ASDAS use go into place.
Next year, we expect to see results from trials that are testing whether the treat-to-target approach produces better outcomes. Evidence like that will be important to further spur adoption.
Lianne S. Gensler, MD , is director of the ankylosing spondylitis clinic at the University of California, San Francisco. She has been a consultant to Novartis and Janssen and has received research support from AbbVie and UCB. Dr. Gensler was a member of the task force that issued the revised recommendations. She made these comments in an interview.
The evidence we now have is the difference between the new recommendations and the prior version. We have evidence from trials in patients with psoriatic arthritis using minimal disease activity as a target. And we have indirect evidence from observational studies in patients with SpA that suggest the higher the ASDAS, the more progression occurs. In addition, results reported at the EULAR 2017 Congress showed that reductions in the ASDAS appeared to correlate with the effect of a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor on reduced radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. But this is just an association; data from a randomized, prospective trial should be available next year.
The recommendations say to manage patients with axial SpA or psoriatic arthritis by treating them to a target. To do that a clinician needs a standardized assessment of a patient’s disease and to perform follow-up measurements to see if the target is met. The data Dr. Dougados cited from Paris document that assessments such as an ASDAS are rarely made. Getting an ASDAS means knowing either a patient’s C-reactive protein level or erythrocyte sedimentation rate. That requires blood work before a clinic visit, something patients often don’t want.
Will these recommendations change practice and make the ASDAS more widely used? That depends to some extent on whether any benefits or penalties linked to ASDAS use go into place.
Next year, we expect to see results from trials that are testing whether the treat-to-target approach produces better outcomes. Evidence like that will be important to further spur adoption.
Lianne S. Gensler, MD , is director of the ankylosing spondylitis clinic at the University of California, San Francisco. She has been a consultant to Novartis and Janssen and has received research support from AbbVie and UCB. Dr. Gensler was a member of the task force that issued the revised recommendations. She made these comments in an interview.
MADRID – The newly revised recommendations from an unaffiliated, international expert panel on a treat-to-target approach for axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis has one conspicuous feature that the prior recommendations lacked: evidence.
The first treat-to-target recommendations for spondyloarthritis (SpA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) from 2013 were based entirely on expert opinion (Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Jan;73[1]:6-16), but in the new update 4 of the 11 recommendations now have an evidence base as well as a fifth recommendation for the part that pertains to PsA, Désirée van der Heijde, MD, said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
Among the evidence-based recommendations, the most striking was a new formulation for how to measure disease activity. The new recommendations call the ASDAS (Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score) the “preferred” disease activity measure for patients with axial SpA and cite both the DAPSA (Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis) as well as minimal disease activity as “considered to define the target” when treating PsA.
“This recommendation just made it,” squeaking onto the list with a 52% vote of approval from the task force members, said Dr. van der Heijde. “It had the longest discussion,” with a significant minority of panelists taking a different view.
ASDAS shook out as the preferred measure for axial SpA because of evidence linking a patient’s ASDAS with syndesmophyte formation. “The idea is that by targeting ASDAS you should have better outcomes,” she explained.
“Applying a treat-to-target approach in axial SpA is feasible but requires systematic collection of outcome parameters in daily practice,” such as ASDAS, said Dr. Dougados, professor of rheumatology at Cochin Hospital in Paris. Another piece currently lacking in the case for treat-to-target is demonstration of the clinical benefit from this approach in a trial, he added.
According to Dr. van der Heijde, the other four recommendations that now have evidence backup are:
- Define clinical remission or minimal disease as the absence of clinical and laboratory evidence of significant disease activity.
- An alternative treatment target for PsA may be low or minimal disease activity.
- Measure disease activity by clinical signs and symptoms and by acute phase reactants.
- Once a treatment target is reached it should be maintained.
The task force also outlined “an extensive research agenda” where evidence is needed, specifying close to 50 individual research topics. Among them Dr. van der Heijde particularly called out the role of the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), validation of PsA target outcomes, and better parsing of the differences using remission or low disease activity as the treatment target.
Dr. van der Heijde, Dr. Dougados, and Dr. Braun are all consultants for several drug companies.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
MADRID – The newly revised recommendations from an unaffiliated, international expert panel on a treat-to-target approach for axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis has one conspicuous feature that the prior recommendations lacked: evidence.
The first treat-to-target recommendations for spondyloarthritis (SpA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) from 2013 were based entirely on expert opinion (Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Jan;73[1]:6-16), but in the new update 4 of the 11 recommendations now have an evidence base as well as a fifth recommendation for the part that pertains to PsA, Désirée van der Heijde, MD, said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
Among the evidence-based recommendations, the most striking was a new formulation for how to measure disease activity. The new recommendations call the ASDAS (Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score) the “preferred” disease activity measure for patients with axial SpA and cite both the DAPSA (Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis) as well as minimal disease activity as “considered to define the target” when treating PsA.
“This recommendation just made it,” squeaking onto the list with a 52% vote of approval from the task force members, said Dr. van der Heijde. “It had the longest discussion,” with a significant minority of panelists taking a different view.
ASDAS shook out as the preferred measure for axial SpA because of evidence linking a patient’s ASDAS with syndesmophyte formation. “The idea is that by targeting ASDAS you should have better outcomes,” she explained.
“Applying a treat-to-target approach in axial SpA is feasible but requires systematic collection of outcome parameters in daily practice,” such as ASDAS, said Dr. Dougados, professor of rheumatology at Cochin Hospital in Paris. Another piece currently lacking in the case for treat-to-target is demonstration of the clinical benefit from this approach in a trial, he added.
According to Dr. van der Heijde, the other four recommendations that now have evidence backup are:
- Define clinical remission or minimal disease as the absence of clinical and laboratory evidence of significant disease activity.
- An alternative treatment target for PsA may be low or minimal disease activity.
- Measure disease activity by clinical signs and symptoms and by acute phase reactants.
- Once a treatment target is reached it should be maintained.
The task force also outlined “an extensive research agenda” where evidence is needed, specifying close to 50 individual research topics. Among them Dr. van der Heijde particularly called out the role of the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), validation of PsA target outcomes, and better parsing of the differences using remission or low disease activity as the treatment target.
Dr. van der Heijde, Dr. Dougados, and Dr. Braun are all consultants for several drug companies.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE EULAR 2017 CONGRESS
Chemo-free triplet produces ‘favorable’ results in advanced disease
LUGANO, SWITZERLAND—A chemotherapy-free combination regimen has demonstrated “favorable” safety and efficacy in patients with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to researchers.
They found that treatment with ublituximab, umbralisib, and ibrutinib produced responses in patients with CLL/SLL, marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), follicular lymphoma (FL), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Many of these patients are still receiving the combination, some of them beyond 1 year, said Lorretta Nastoupil, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas.
She presented results with the treatment at the 14th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (ICML).
The research was sponsored by TG Therapeutics, the company developing ublituximab (TG-1101) and umbralisib (TGR-1202).
Patients and treatment
Dr Nastoupil presented data on 38 patients—20 with CLL/SLL, and 18 with NHL. Three of the CLL/SLL patients were treatment-naïve. The rest had relapsed/refractory disease.
All NHL patients had relapsed/refractory disease—6 with DLBCL, 6 with FL, 4 with MCL, and 2 with MZL.
For the entire cohort, the median age was 65 (range, 32-85), and most patients (n=29) were male. They had received a median of 3 prior treatment regimens (range, 0-6).
In this trial, the patients received:
- Ublituximab at 900 mg
- Ibrutinib at 420 mg (CLL/SLL) or 560 mg (NHL)
- Umbralisib at 400 mg, 600 mg, or 800 mg.
Eighty-one percent of patients have been on study for more than 6 months. The median time on study is 11.1 months (range, 0.4 to 30+ months).
Safety
There was 1 dose-limiting toxicity in the CLL cohort (umbralisib at 400 mg)—reactivated varicella zoster. And 2 patients discontinued treatment due to an adverse event (AE)—1 due to sepsis and 1 due to pneumonia.
Neutropenia (18%) and pneumonia (11%) were the only grade 3/4 AEs that occurred in more than 10% of patients. Other grade 3/4 AEs included thrombocytopenia (8%), diarrhea (3%), dizziness (3%), pyrexia (3%), rash (3%), anemia (3%), dyspnea (3%), and stomatitis (3%).
The most common AEs of any grade were diarrhea (47%), fatigue (47%), dizziness (37%), insomnia (34%), nausea (34%), neutropenia (32%), cough (32%), and infusion-related reactions (32%).
Efficacy
Thirty-six patients were evaluable for efficacy—19 with CLL/SLL and 17 with NHL patients. Two patients discontinued treatment before the first efficacy assessment—1 due to pneumonia and 1 at investigator discretion.
For the entire cohort, the overall response rate (ORR) was 83%.
In the CLL/SLL cohort, the ORR was 100% (19/19), and the complete response (CR) rate was 32% (n=6). However, 4 of the 6 CRs are pending bone marrow confirmation.
Dr Nastoupil noted that 8 of the CLL patients had a 17p and/or 11q deletion, and 3 had previously received treatment with a BTK and/or PI3Kδ inhibitor.
One patient who was refractory to both idelalisib and ibrutinib achieved a CR with the triplet regimen, and this response has been ongoing for more than 1.5 years.
Among patients with NHL, the ORR was 100% in patients with MZL (2/2) and MCL (4/4). The ORR was 80% (4/5) in FL patients, and 17% (1/6) in DLBCL patients.
The CR rate was 50% in patients with MZL (1/2) and MCL (2/4) and 20% in patients with FL (1/5).
Dr Nastoupil pointed out that the FL patients were heavily pretreated. Two of them had received an autologous stem cell transplant, 1 was refractory to prior ibrutinib treatment, and 1 had received 5 prior lines of rituximab-based therapy.
She also noted that the DLBCL patients had a median of 4 prior therapies, and 4 of these patients had non-GCB DLBCL, including the only patient who responded to the triplet.
“[T]he combination of ublituximab, umbralisib, and ibrutinib in advanced CLL and NHL demonstrated a favorable toxicity profile as well as favorable efficacy,” Dr Nastoupil said in closing.
“[This] suggests umbralisib may be safely combined with other targeted agents to overcome mechanisms of resistance.” ![]()
LUGANO, SWITZERLAND—A chemotherapy-free combination regimen has demonstrated “favorable” safety and efficacy in patients with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to researchers.
They found that treatment with ublituximab, umbralisib, and ibrutinib produced responses in patients with CLL/SLL, marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), follicular lymphoma (FL), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Many of these patients are still receiving the combination, some of them beyond 1 year, said Lorretta Nastoupil, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas.
She presented results with the treatment at the 14th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (ICML).
The research was sponsored by TG Therapeutics, the company developing ublituximab (TG-1101) and umbralisib (TGR-1202).
Patients and treatment
Dr Nastoupil presented data on 38 patients—20 with CLL/SLL, and 18 with NHL. Three of the CLL/SLL patients were treatment-naïve. The rest had relapsed/refractory disease.
All NHL patients had relapsed/refractory disease—6 with DLBCL, 6 with FL, 4 with MCL, and 2 with MZL.
For the entire cohort, the median age was 65 (range, 32-85), and most patients (n=29) were male. They had received a median of 3 prior treatment regimens (range, 0-6).
In this trial, the patients received:
- Ublituximab at 900 mg
- Ibrutinib at 420 mg (CLL/SLL) or 560 mg (NHL)
- Umbralisib at 400 mg, 600 mg, or 800 mg.
Eighty-one percent of patients have been on study for more than 6 months. The median time on study is 11.1 months (range, 0.4 to 30+ months).
Safety
There was 1 dose-limiting toxicity in the CLL cohort (umbralisib at 400 mg)—reactivated varicella zoster. And 2 patients discontinued treatment due to an adverse event (AE)—1 due to sepsis and 1 due to pneumonia.
Neutropenia (18%) and pneumonia (11%) were the only grade 3/4 AEs that occurred in more than 10% of patients. Other grade 3/4 AEs included thrombocytopenia (8%), diarrhea (3%), dizziness (3%), pyrexia (3%), rash (3%), anemia (3%), dyspnea (3%), and stomatitis (3%).
The most common AEs of any grade were diarrhea (47%), fatigue (47%), dizziness (37%), insomnia (34%), nausea (34%), neutropenia (32%), cough (32%), and infusion-related reactions (32%).
Efficacy
Thirty-six patients were evaluable for efficacy—19 with CLL/SLL and 17 with NHL patients. Two patients discontinued treatment before the first efficacy assessment—1 due to pneumonia and 1 at investigator discretion.
For the entire cohort, the overall response rate (ORR) was 83%.
In the CLL/SLL cohort, the ORR was 100% (19/19), and the complete response (CR) rate was 32% (n=6). However, 4 of the 6 CRs are pending bone marrow confirmation.
Dr Nastoupil noted that 8 of the CLL patients had a 17p and/or 11q deletion, and 3 had previously received treatment with a BTK and/or PI3Kδ inhibitor.
One patient who was refractory to both idelalisib and ibrutinib achieved a CR with the triplet regimen, and this response has been ongoing for more than 1.5 years.
Among patients with NHL, the ORR was 100% in patients with MZL (2/2) and MCL (4/4). The ORR was 80% (4/5) in FL patients, and 17% (1/6) in DLBCL patients.
The CR rate was 50% in patients with MZL (1/2) and MCL (2/4) and 20% in patients with FL (1/5).
Dr Nastoupil pointed out that the FL patients were heavily pretreated. Two of them had received an autologous stem cell transplant, 1 was refractory to prior ibrutinib treatment, and 1 had received 5 prior lines of rituximab-based therapy.
She also noted that the DLBCL patients had a median of 4 prior therapies, and 4 of these patients had non-GCB DLBCL, including the only patient who responded to the triplet.
“[T]he combination of ublituximab, umbralisib, and ibrutinib in advanced CLL and NHL demonstrated a favorable toxicity profile as well as favorable efficacy,” Dr Nastoupil said in closing.
“[This] suggests umbralisib may be safely combined with other targeted agents to overcome mechanisms of resistance.” ![]()
LUGANO, SWITZERLAND—A chemotherapy-free combination regimen has demonstrated “favorable” safety and efficacy in patients with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to researchers.
They found that treatment with ublituximab, umbralisib, and ibrutinib produced responses in patients with CLL/SLL, marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), follicular lymphoma (FL), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Many of these patients are still receiving the combination, some of them beyond 1 year, said Lorretta Nastoupil, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas.
She presented results with the treatment at the 14th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (ICML).
The research was sponsored by TG Therapeutics, the company developing ublituximab (TG-1101) and umbralisib (TGR-1202).
Patients and treatment
Dr Nastoupil presented data on 38 patients—20 with CLL/SLL, and 18 with NHL. Three of the CLL/SLL patients were treatment-naïve. The rest had relapsed/refractory disease.
All NHL patients had relapsed/refractory disease—6 with DLBCL, 6 with FL, 4 with MCL, and 2 with MZL.
For the entire cohort, the median age was 65 (range, 32-85), and most patients (n=29) were male. They had received a median of 3 prior treatment regimens (range, 0-6).
In this trial, the patients received:
- Ublituximab at 900 mg
- Ibrutinib at 420 mg (CLL/SLL) or 560 mg (NHL)
- Umbralisib at 400 mg, 600 mg, or 800 mg.
Eighty-one percent of patients have been on study for more than 6 months. The median time on study is 11.1 months (range, 0.4 to 30+ months).
Safety
There was 1 dose-limiting toxicity in the CLL cohort (umbralisib at 400 mg)—reactivated varicella zoster. And 2 patients discontinued treatment due to an adverse event (AE)—1 due to sepsis and 1 due to pneumonia.
Neutropenia (18%) and pneumonia (11%) were the only grade 3/4 AEs that occurred in more than 10% of patients. Other grade 3/4 AEs included thrombocytopenia (8%), diarrhea (3%), dizziness (3%), pyrexia (3%), rash (3%), anemia (3%), dyspnea (3%), and stomatitis (3%).
The most common AEs of any grade were diarrhea (47%), fatigue (47%), dizziness (37%), insomnia (34%), nausea (34%), neutropenia (32%), cough (32%), and infusion-related reactions (32%).
Efficacy
Thirty-six patients were evaluable for efficacy—19 with CLL/SLL and 17 with NHL patients. Two patients discontinued treatment before the first efficacy assessment—1 due to pneumonia and 1 at investigator discretion.
For the entire cohort, the overall response rate (ORR) was 83%.
In the CLL/SLL cohort, the ORR was 100% (19/19), and the complete response (CR) rate was 32% (n=6). However, 4 of the 6 CRs are pending bone marrow confirmation.
Dr Nastoupil noted that 8 of the CLL patients had a 17p and/or 11q deletion, and 3 had previously received treatment with a BTK and/or PI3Kδ inhibitor.
One patient who was refractory to both idelalisib and ibrutinib achieved a CR with the triplet regimen, and this response has been ongoing for more than 1.5 years.
Among patients with NHL, the ORR was 100% in patients with MZL (2/2) and MCL (4/4). The ORR was 80% (4/5) in FL patients, and 17% (1/6) in DLBCL patients.
The CR rate was 50% in patients with MZL (1/2) and MCL (2/4) and 20% in patients with FL (1/5).
Dr Nastoupil pointed out that the FL patients were heavily pretreated. Two of them had received an autologous stem cell transplant, 1 was refractory to prior ibrutinib treatment, and 1 had received 5 prior lines of rituximab-based therapy.
She also noted that the DLBCL patients had a median of 4 prior therapies, and 4 of these patients had non-GCB DLBCL, including the only patient who responded to the triplet.
“[T]he combination of ublituximab, umbralisib, and ibrutinib in advanced CLL and NHL demonstrated a favorable toxicity profile as well as favorable efficacy,” Dr Nastoupil said in closing.
“[This] suggests umbralisib may be safely combined with other targeted agents to overcome mechanisms of resistance.” ![]()
Senate health care proposal already facing uphill battle
Senate Republican leaders are facing pushback from almost every side on their Affordable Care Act repeal/replace proposal – so much so that the current plan is unlikely to gain enough support to pass.
“For a variety of reasons, we are not ready to vote for this bill, but we are open to negotiation and obtaining more information before it is brought to the floor,” Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.), Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas), Sen. Ron Johnson (R-Wis.), and Sen. Mike Lee (R-Utah) said in a joint statement issued June 22, the day the plan was published. “There are provisions in this draft that represent an improvement to our current health care system, but it does not appear this draft as written will accomplish the most important promise that we made to Americans to repeal Obamacare and lower their health care costs.”
Like the House-passed American Health Care Act (H.R. 1628), the proposed BCRA would reduce Medicaid spending and would address rising premiums in the individual health insurance marketplace; however, BCRA would take a slightly different path to the same destination.
Like the House bill, BCRA also targets funding for Planned Parenthood, although because of Senate procedural rules, it is a more indirect funding ban.
A key difference between BCRA and the House bill is how insurance premium support is calculated. The AHCA would base tax credits on age, providing a lesser benefit for older, but pre–Medicare-age adults. In contrast, BCRA would base tax credits on income while limiting eligibility to households at 350% of the federal poverty line. Further, credits would cover only 58% of the actuarial value of health insurance under BCRA.
The draft Senate plan would not allow states to request a waiver from the ACA’s so-called community waiver provisions – the portion of the law that requires health insurance premiums to be the same regardless of age or preexisting condition; the House-passed AHCA would allow those waivers.
Medicaid expansion would be rolled back under the Senate plan, but at a slower pace than the AHCA would require – by 2023 under BCRA vs. 2020 under AHCA.
The BCRA would establish a per capita funding mechanism for Medicaid going forward, which would base funding on historic Medicaid expenditures and uses an economic index to track inflation and adjust payments accordingly.
To address the needs of people with greater health care needs, the Senate proposal would provide $57 billion over the first 4 years, then another $57 billion over the next 8. The funds would be available for programs such as premium support or high-risk pools to help individuals who are expected to be high users of health care. States would be required to match funds starting in 2022.
Experts were quick to weigh in on the Senate plan.
The BCRA needs to do three things, according to Grace-Marie Turner, president of the Galen Institute: Provide a safety net for those covered through the ACA so that they do not lose coverage in the transition, modernize Medicaid, and give states more authority and options to reform their own health insurance markets.
“We have learned that the federal government is not able to regulate something as local as health insurance,” Ms. Turner said. “They cannot create policies and legislation that works for people in downtown Manhattan and rural Montana and southern New Mexico and the panhandle of Florida. There are too many different populations. The states need to do that, and this bill also would give the states more authority to begin to oversee their health insurance markets but with new funding to provide extra help for the people who have difficulty buying progress.”
She said it could be much better if the Senate did not use the reconciliation process, “but within the confines of that, both the House and Senate bills do the same thing.”
Ms. Turner also stressed that there are more reforms coming later, as the Senate and House address other portions of ACA repeal/replacement.
“I hope that [senators] would see moving this forward as beneficial so that then they can move additional pieces of legislation, hopefully, with 60 votes to go through the regular process, to have additional follow-up bills. This is not the end of the story. This is just rescuing us from Obamacare,” she said. “Then we need to go forward and think about what do we need to do to make our health sector work better in the future by putting doctors and patients, rather than government, in charge of choices.”
Doctors, however, did not agree.
“This bill significantly decreases patients’ ability to access high-quality health care, and affordable coverage for millions of Americans will be in jeopardy if the legislation is passed,” Boyd Buser, MD, a doctor of osteopathy and president of the American Osteopathic Association, said in a statement.
He noted that the Medicaid cuts will have a “devastating impact, especially in areas of our country hardest hit by the ongoing opioid epidemic. ... The Senate bill should have prioritized prevention and care coordination, two measures proven to reduce overall health costs by eliminating waste and addressing health problems at the most treatable stage. Decreasing the number of Americans with coverage as it intends does will not lower costs.”
A vote on the proposal could come as early as June 29 before the Senate breaks for the 4th of July recess.
Republican lawmakers and the Trump administration have vowed to address the ACA in other ways as well, by reviewing and possibly changing all relevant regulations, then using the regular legislative process, which would need 60 votes, to address issues that cannot be handled by the budget reconciliation process.
Senate Republican leaders are facing pushback from almost every side on their Affordable Care Act repeal/replace proposal – so much so that the current plan is unlikely to gain enough support to pass.
“For a variety of reasons, we are not ready to vote for this bill, but we are open to negotiation and obtaining more information before it is brought to the floor,” Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.), Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas), Sen. Ron Johnson (R-Wis.), and Sen. Mike Lee (R-Utah) said in a joint statement issued June 22, the day the plan was published. “There are provisions in this draft that represent an improvement to our current health care system, but it does not appear this draft as written will accomplish the most important promise that we made to Americans to repeal Obamacare and lower their health care costs.”
Like the House-passed American Health Care Act (H.R. 1628), the proposed BCRA would reduce Medicaid spending and would address rising premiums in the individual health insurance marketplace; however, BCRA would take a slightly different path to the same destination.
Like the House bill, BCRA also targets funding for Planned Parenthood, although because of Senate procedural rules, it is a more indirect funding ban.
A key difference between BCRA and the House bill is how insurance premium support is calculated. The AHCA would base tax credits on age, providing a lesser benefit for older, but pre–Medicare-age adults. In contrast, BCRA would base tax credits on income while limiting eligibility to households at 350% of the federal poverty line. Further, credits would cover only 58% of the actuarial value of health insurance under BCRA.
The draft Senate plan would not allow states to request a waiver from the ACA’s so-called community waiver provisions – the portion of the law that requires health insurance premiums to be the same regardless of age or preexisting condition; the House-passed AHCA would allow those waivers.
Medicaid expansion would be rolled back under the Senate plan, but at a slower pace than the AHCA would require – by 2023 under BCRA vs. 2020 under AHCA.
The BCRA would establish a per capita funding mechanism for Medicaid going forward, which would base funding on historic Medicaid expenditures and uses an economic index to track inflation and adjust payments accordingly.
To address the needs of people with greater health care needs, the Senate proposal would provide $57 billion over the first 4 years, then another $57 billion over the next 8. The funds would be available for programs such as premium support or high-risk pools to help individuals who are expected to be high users of health care. States would be required to match funds starting in 2022.
Experts were quick to weigh in on the Senate plan.
The BCRA needs to do three things, according to Grace-Marie Turner, president of the Galen Institute: Provide a safety net for those covered through the ACA so that they do not lose coverage in the transition, modernize Medicaid, and give states more authority and options to reform their own health insurance markets.
“We have learned that the federal government is not able to regulate something as local as health insurance,” Ms. Turner said. “They cannot create policies and legislation that works for people in downtown Manhattan and rural Montana and southern New Mexico and the panhandle of Florida. There are too many different populations. The states need to do that, and this bill also would give the states more authority to begin to oversee their health insurance markets but with new funding to provide extra help for the people who have difficulty buying progress.”
She said it could be much better if the Senate did not use the reconciliation process, “but within the confines of that, both the House and Senate bills do the same thing.”
Ms. Turner also stressed that there are more reforms coming later, as the Senate and House address other portions of ACA repeal/replacement.
“I hope that [senators] would see moving this forward as beneficial so that then they can move additional pieces of legislation, hopefully, with 60 votes to go through the regular process, to have additional follow-up bills. This is not the end of the story. This is just rescuing us from Obamacare,” she said. “Then we need to go forward and think about what do we need to do to make our health sector work better in the future by putting doctors and patients, rather than government, in charge of choices.”
Doctors, however, did not agree.
“This bill significantly decreases patients’ ability to access high-quality health care, and affordable coverage for millions of Americans will be in jeopardy if the legislation is passed,” Boyd Buser, MD, a doctor of osteopathy and president of the American Osteopathic Association, said in a statement.
He noted that the Medicaid cuts will have a “devastating impact, especially in areas of our country hardest hit by the ongoing opioid epidemic. ... The Senate bill should have prioritized prevention and care coordination, two measures proven to reduce overall health costs by eliminating waste and addressing health problems at the most treatable stage. Decreasing the number of Americans with coverage as it intends does will not lower costs.”
A vote on the proposal could come as early as June 29 before the Senate breaks for the 4th of July recess.
Republican lawmakers and the Trump administration have vowed to address the ACA in other ways as well, by reviewing and possibly changing all relevant regulations, then using the regular legislative process, which would need 60 votes, to address issues that cannot be handled by the budget reconciliation process.
Senate Republican leaders are facing pushback from almost every side on their Affordable Care Act repeal/replace proposal – so much so that the current plan is unlikely to gain enough support to pass.
“For a variety of reasons, we are not ready to vote for this bill, but we are open to negotiation and obtaining more information before it is brought to the floor,” Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.), Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas), Sen. Ron Johnson (R-Wis.), and Sen. Mike Lee (R-Utah) said in a joint statement issued June 22, the day the plan was published. “There are provisions in this draft that represent an improvement to our current health care system, but it does not appear this draft as written will accomplish the most important promise that we made to Americans to repeal Obamacare and lower their health care costs.”
Like the House-passed American Health Care Act (H.R. 1628), the proposed BCRA would reduce Medicaid spending and would address rising premiums in the individual health insurance marketplace; however, BCRA would take a slightly different path to the same destination.
Like the House bill, BCRA also targets funding for Planned Parenthood, although because of Senate procedural rules, it is a more indirect funding ban.
A key difference between BCRA and the House bill is how insurance premium support is calculated. The AHCA would base tax credits on age, providing a lesser benefit for older, but pre–Medicare-age adults. In contrast, BCRA would base tax credits on income while limiting eligibility to households at 350% of the federal poverty line. Further, credits would cover only 58% of the actuarial value of health insurance under BCRA.
The draft Senate plan would not allow states to request a waiver from the ACA’s so-called community waiver provisions – the portion of the law that requires health insurance premiums to be the same regardless of age or preexisting condition; the House-passed AHCA would allow those waivers.
Medicaid expansion would be rolled back under the Senate plan, but at a slower pace than the AHCA would require – by 2023 under BCRA vs. 2020 under AHCA.
The BCRA would establish a per capita funding mechanism for Medicaid going forward, which would base funding on historic Medicaid expenditures and uses an economic index to track inflation and adjust payments accordingly.
To address the needs of people with greater health care needs, the Senate proposal would provide $57 billion over the first 4 years, then another $57 billion over the next 8. The funds would be available for programs such as premium support or high-risk pools to help individuals who are expected to be high users of health care. States would be required to match funds starting in 2022.
Experts were quick to weigh in on the Senate plan.
The BCRA needs to do three things, according to Grace-Marie Turner, president of the Galen Institute: Provide a safety net for those covered through the ACA so that they do not lose coverage in the transition, modernize Medicaid, and give states more authority and options to reform their own health insurance markets.
“We have learned that the federal government is not able to regulate something as local as health insurance,” Ms. Turner said. “They cannot create policies and legislation that works for people in downtown Manhattan and rural Montana and southern New Mexico and the panhandle of Florida. There are too many different populations. The states need to do that, and this bill also would give the states more authority to begin to oversee their health insurance markets but with new funding to provide extra help for the people who have difficulty buying progress.”
She said it could be much better if the Senate did not use the reconciliation process, “but within the confines of that, both the House and Senate bills do the same thing.”
Ms. Turner also stressed that there are more reforms coming later, as the Senate and House address other portions of ACA repeal/replacement.
“I hope that [senators] would see moving this forward as beneficial so that then they can move additional pieces of legislation, hopefully, with 60 votes to go through the regular process, to have additional follow-up bills. This is not the end of the story. This is just rescuing us from Obamacare,” she said. “Then we need to go forward and think about what do we need to do to make our health sector work better in the future by putting doctors and patients, rather than government, in charge of choices.”
Doctors, however, did not agree.
“This bill significantly decreases patients’ ability to access high-quality health care, and affordable coverage for millions of Americans will be in jeopardy if the legislation is passed,” Boyd Buser, MD, a doctor of osteopathy and president of the American Osteopathic Association, said in a statement.
He noted that the Medicaid cuts will have a “devastating impact, especially in areas of our country hardest hit by the ongoing opioid epidemic. ... The Senate bill should have prioritized prevention and care coordination, two measures proven to reduce overall health costs by eliminating waste and addressing health problems at the most treatable stage. Decreasing the number of Americans with coverage as it intends does will not lower costs.”
A vote on the proposal could come as early as June 29 before the Senate breaks for the 4th of July recess.
Republican lawmakers and the Trump administration have vowed to address the ACA in other ways as well, by reviewing and possibly changing all relevant regulations, then using the regular legislative process, which would need 60 votes, to address issues that cannot be handled by the budget reconciliation process.
FDA approves rituximab + hyaluronidase human for FL, DLBCL, and CLL
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rituximab plus hyaluronidase human for adult patients with follicular lymphoma (FL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
The combination product, to be marketed as Rituxan Hycela, is administered subcutaneously, shortening administration time to 5 to 7 minutes as compared with the several hours needed for intravenous infusion, the FDA said in a statement.
Approval was based on noninferior rituximab trough concentrations for the subcutaneously administered combination, compared with intravenous rituximab, and comparable efficacy and safety results as shown in multiple randomized clinical trials.
The most common adverse events seen with the combination in patients with FL included infections, neutropenia, nausea, constipation, cough, and fatigue. In patients with DLBCL, the most common adverse events were infections, neutropenia, alopecia, nausea, and anemia; in CLL patients, infections, neutropenia, nausea, thrombocytopenia, pyrexia, vomiting, and injection site erythema occurred most commonly.
The combination is indicated for the following previously approved indications for rituximab:
- Relapsed or refractory FL as a single agent.
- Previously untreated FL in combination with first line chemotherapy and, in patients achieving a complete or partial response to rituximab in combination with chemotherapy, as single-agent maintenance therapy.
- Nonprogressing (including stable disease) FL as a single agent after first-line cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone chemotherapy.
- Previously untreated DLBCL in combination with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone or other anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens.
- Previously untreated and previously treated CLL in combination with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide.
The recommended doses are 1,400 mg rituximab and 23,400 units hyaluronidase human for FL and DLBCL and 1,600 mg rituximab and 26,800 units hyaluronidase human for CLL. The combination treatment should be initiated only after patients have received at least one full dose of a rituximab product by intravenous infusion, according to the prescribing information.
Rituxan Hycela is marketed by Genentech.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rituximab plus hyaluronidase human for adult patients with follicular lymphoma (FL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
The combination product, to be marketed as Rituxan Hycela, is administered subcutaneously, shortening administration time to 5 to 7 minutes as compared with the several hours needed for intravenous infusion, the FDA said in a statement.
Approval was based on noninferior rituximab trough concentrations for the subcutaneously administered combination, compared with intravenous rituximab, and comparable efficacy and safety results as shown in multiple randomized clinical trials.
The most common adverse events seen with the combination in patients with FL included infections, neutropenia, nausea, constipation, cough, and fatigue. In patients with DLBCL, the most common adverse events were infections, neutropenia, alopecia, nausea, and anemia; in CLL patients, infections, neutropenia, nausea, thrombocytopenia, pyrexia, vomiting, and injection site erythema occurred most commonly.
The combination is indicated for the following previously approved indications for rituximab:
- Relapsed or refractory FL as a single agent.
- Previously untreated FL in combination with first line chemotherapy and, in patients achieving a complete or partial response to rituximab in combination with chemotherapy, as single-agent maintenance therapy.
- Nonprogressing (including stable disease) FL as a single agent after first-line cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone chemotherapy.
- Previously untreated DLBCL in combination with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone or other anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens.
- Previously untreated and previously treated CLL in combination with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide.
The recommended doses are 1,400 mg rituximab and 23,400 units hyaluronidase human for FL and DLBCL and 1,600 mg rituximab and 26,800 units hyaluronidase human for CLL. The combination treatment should be initiated only after patients have received at least one full dose of a rituximab product by intravenous infusion, according to the prescribing information.
Rituxan Hycela is marketed by Genentech.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rituximab plus hyaluronidase human for adult patients with follicular lymphoma (FL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
The combination product, to be marketed as Rituxan Hycela, is administered subcutaneously, shortening administration time to 5 to 7 minutes as compared with the several hours needed for intravenous infusion, the FDA said in a statement.
Approval was based on noninferior rituximab trough concentrations for the subcutaneously administered combination, compared with intravenous rituximab, and comparable efficacy and safety results as shown in multiple randomized clinical trials.
The most common adverse events seen with the combination in patients with FL included infections, neutropenia, nausea, constipation, cough, and fatigue. In patients with DLBCL, the most common adverse events were infections, neutropenia, alopecia, nausea, and anemia; in CLL patients, infections, neutropenia, nausea, thrombocytopenia, pyrexia, vomiting, and injection site erythema occurred most commonly.
The combination is indicated for the following previously approved indications for rituximab:
- Relapsed or refractory FL as a single agent.
- Previously untreated FL in combination with first line chemotherapy and, in patients achieving a complete or partial response to rituximab in combination with chemotherapy, as single-agent maintenance therapy.
- Nonprogressing (including stable disease) FL as a single agent after first-line cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone chemotherapy.
- Previously untreated DLBCL in combination with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone or other anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens.
- Previously untreated and previously treated CLL in combination with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide.
The recommended doses are 1,400 mg rituximab and 23,400 units hyaluronidase human for FL and DLBCL and 1,600 mg rituximab and 26,800 units hyaluronidase human for CLL. The combination treatment should be initiated only after patients have received at least one full dose of a rituximab product by intravenous infusion, according to the prescribing information.
Rituxan Hycela is marketed by Genentech.
ACOG recommends women start mammography between ages 40 and 50 years
Woman at average risk for breast cancer should be offered their first screening mammogram at age 40, with initiation of screening beginning no later than age 50, according to new recommendations from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
ACOG suggested a screening interval of 1-2 years based on patient values and preferences.
Screening should continue until at least age 75 years. Past that age, continuation should be considered in terms of the patient’s overall health and expected lifespan, according to the Practice Bulletin.
That’s a welcome approach, according to Ritu Salani, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at the Ohio State University, Columbus. “I do believe the ACOG guidelines have the most flexibility and are probably the most comprehensive for average-risk patients,” said Dr. Salani, MD, who was not involved in the drafting of the guidelines.
The recommendations are based in part on a review of existing recommendations from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, the American Cancer Society, and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
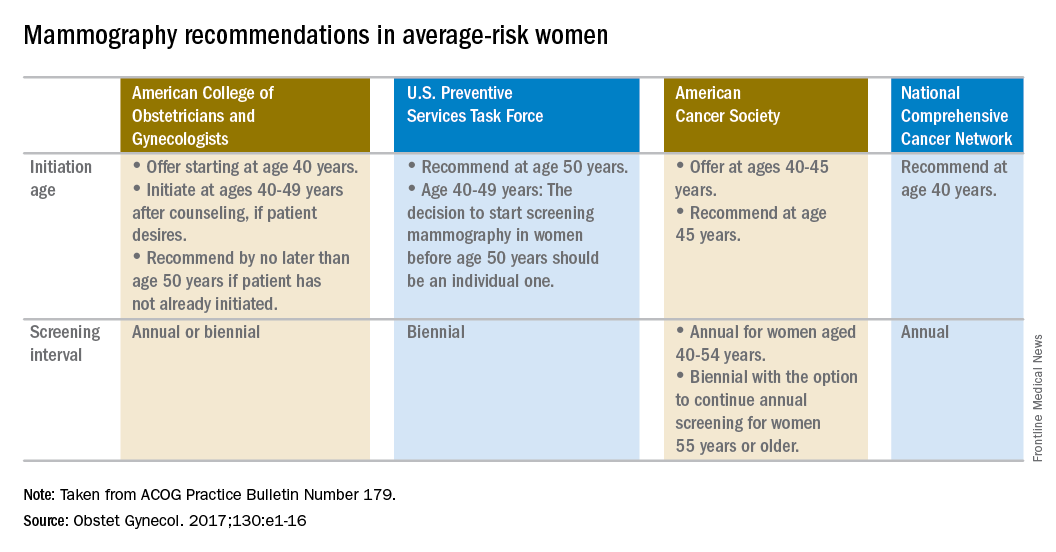
“For patients anxious about developing cancer, maybe every year would be appropriate. When you talk to patients, you have a sense of what would be beneficial for them,” said Dr. Salani, who applauded the flexibility built into the new ACOG guidelines, which says the screening interval can be annual or biennial. “It caters to shared decision-making, and that’s a nice way to frame it.”
The ACOG guidelines recommend against breast self examination because this practice carries the risk of false positives and lacks supporting evidence of benefit. But, ACOG encourages “breast self-awareness,” which means being “attuned to noticing a change or potential problem with her breasts” but without the routine examination.
Women who are asymptomatic and at average risk can be offered clinical breast examination as a screening tool, but clinicians should explain the “uncertainty of additional benefits and the possibility of adverse consequences of clinical breast examination beyond screening mammography.” If performed, ACOG recommends intervals of 1-3 years for women aged 25-39 years and annually for women aged 40 years and over.
The recommendations apply to average-risk women. To help determine risk, the Practice Bulletin also lays out a series of breast cancer risk factors that should be considered, including family history of cancer, known germline mutations, prior biopsy findings, early menarche, late menopause, breast density, and a range of lifestyle and other factors.
Woman at average risk for breast cancer should be offered their first screening mammogram at age 40, with initiation of screening beginning no later than age 50, according to new recommendations from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
ACOG suggested a screening interval of 1-2 years based on patient values and preferences.
Screening should continue until at least age 75 years. Past that age, continuation should be considered in terms of the patient’s overall health and expected lifespan, according to the Practice Bulletin.
That’s a welcome approach, according to Ritu Salani, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at the Ohio State University, Columbus. “I do believe the ACOG guidelines have the most flexibility and are probably the most comprehensive for average-risk patients,” said Dr. Salani, MD, who was not involved in the drafting of the guidelines.
The recommendations are based in part on a review of existing recommendations from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, the American Cancer Society, and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.

“For patients anxious about developing cancer, maybe every year would be appropriate. When you talk to patients, you have a sense of what would be beneficial for them,” said Dr. Salani, who applauded the flexibility built into the new ACOG guidelines, which says the screening interval can be annual or biennial. “It caters to shared decision-making, and that’s a nice way to frame it.”
The ACOG guidelines recommend against breast self examination because this practice carries the risk of false positives and lacks supporting evidence of benefit. But, ACOG encourages “breast self-awareness,” which means being “attuned to noticing a change or potential problem with her breasts” but without the routine examination.
Women who are asymptomatic and at average risk can be offered clinical breast examination as a screening tool, but clinicians should explain the “uncertainty of additional benefits and the possibility of adverse consequences of clinical breast examination beyond screening mammography.” If performed, ACOG recommends intervals of 1-3 years for women aged 25-39 years and annually for women aged 40 years and over.
The recommendations apply to average-risk women. To help determine risk, the Practice Bulletin also lays out a series of breast cancer risk factors that should be considered, including family history of cancer, known germline mutations, prior biopsy findings, early menarche, late menopause, breast density, and a range of lifestyle and other factors.
Woman at average risk for breast cancer should be offered their first screening mammogram at age 40, with initiation of screening beginning no later than age 50, according to new recommendations from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
ACOG suggested a screening interval of 1-2 years based on patient values and preferences.
Screening should continue until at least age 75 years. Past that age, continuation should be considered in terms of the patient’s overall health and expected lifespan, according to the Practice Bulletin.
That’s a welcome approach, according to Ritu Salani, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at the Ohio State University, Columbus. “I do believe the ACOG guidelines have the most flexibility and are probably the most comprehensive for average-risk patients,” said Dr. Salani, MD, who was not involved in the drafting of the guidelines.
The recommendations are based in part on a review of existing recommendations from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, the American Cancer Society, and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.

“For patients anxious about developing cancer, maybe every year would be appropriate. When you talk to patients, you have a sense of what would be beneficial for them,” said Dr. Salani, who applauded the flexibility built into the new ACOG guidelines, which says the screening interval can be annual or biennial. “It caters to shared decision-making, and that’s a nice way to frame it.”
The ACOG guidelines recommend against breast self examination because this practice carries the risk of false positives and lacks supporting evidence of benefit. But, ACOG encourages “breast self-awareness,” which means being “attuned to noticing a change or potential problem with her breasts” but without the routine examination.
Women who are asymptomatic and at average risk can be offered clinical breast examination as a screening tool, but clinicians should explain the “uncertainty of additional benefits and the possibility of adverse consequences of clinical breast examination beyond screening mammography.” If performed, ACOG recommends intervals of 1-3 years for women aged 25-39 years and annually for women aged 40 years and over.
The recommendations apply to average-risk women. To help determine risk, the Practice Bulletin also lays out a series of breast cancer risk factors that should be considered, including family history of cancer, known germline mutations, prior biopsy findings, early menarche, late menopause, breast density, and a range of lifestyle and other factors.
Lenalidomide consolidation linked to extended overall survival in non-del(11q) CLL
CHICAGO – Lenalidomide consolidation therapy was associated with an extended survival plateau for patients with non-del(11q) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), based on results from the phase 2 CALGB 10404 trial.
This unique survival plateau indicates future studies should continue to examine the role of lenalidomide, compared with fludarabine plus rituximab therapy, as well as the incorporation of lenalidomide into other novel treatment regimens, Amy Ruppert, MAS, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
All patients received 6 months of FR or FCR therapy, then patients underwent full staging. At 10 months, patients who had been randomized to the FR + lenalidomide group received lenalidomide 5 mg on days 1-21 of the first 28 day cycle and lenalidomide 10 mg on days 1-21 of the subsequent 5 cycles. At 18 months, patients in the FR+L group underwent full staging, and all patients underwent full staging at 24 months.
Based on pretreatment central interphase cytogenetic screening, patients who had del(11q22.3) in at least 20% of their cells were excluded from the primary analysis of 2-year progression-free survival.
Median progression-free survival was significantly shorter with FR, compared with FR+L (P = .03) and FCR (P less than .01), at 43 months (95% CI, 33-50), 66 months (95% CI, 45-not reached), and 78 months (95% CI, 58-not reached), respectively.
Median overall survival has not been reached for any arm of the study. While overall survival was similar across all arms at 1, 2, and 3 years of follow-up, there was a plateau in overall survival with no events seen beyond 41 months in the FR+L arm. Events continued to occur in the FR and FCR arms, reported Ms. Ruppert of the Comprehensive Cancer Center at Ohio State University, Columbus. At 48 months, the hazard ratio for overall survival in FR+L vs. FR was 0.27 (95% CI, 0.10-0.70; P = .01).
Ms. Ruppert had no financial disclosures. The study is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and Celgene.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryjodales
CHICAGO – Lenalidomide consolidation therapy was associated with an extended survival plateau for patients with non-del(11q) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), based on results from the phase 2 CALGB 10404 trial.
This unique survival plateau indicates future studies should continue to examine the role of lenalidomide, compared with fludarabine plus rituximab therapy, as well as the incorporation of lenalidomide into other novel treatment regimens, Amy Ruppert, MAS, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
All patients received 6 months of FR or FCR therapy, then patients underwent full staging. At 10 months, patients who had been randomized to the FR + lenalidomide group received lenalidomide 5 mg on days 1-21 of the first 28 day cycle and lenalidomide 10 mg on days 1-21 of the subsequent 5 cycles. At 18 months, patients in the FR+L group underwent full staging, and all patients underwent full staging at 24 months.
Based on pretreatment central interphase cytogenetic screening, patients who had del(11q22.3) in at least 20% of their cells were excluded from the primary analysis of 2-year progression-free survival.
Median progression-free survival was significantly shorter with FR, compared with FR+L (P = .03) and FCR (P less than .01), at 43 months (95% CI, 33-50), 66 months (95% CI, 45-not reached), and 78 months (95% CI, 58-not reached), respectively.
Median overall survival has not been reached for any arm of the study. While overall survival was similar across all arms at 1, 2, and 3 years of follow-up, there was a plateau in overall survival with no events seen beyond 41 months in the FR+L arm. Events continued to occur in the FR and FCR arms, reported Ms. Ruppert of the Comprehensive Cancer Center at Ohio State University, Columbus. At 48 months, the hazard ratio for overall survival in FR+L vs. FR was 0.27 (95% CI, 0.10-0.70; P = .01).
Ms. Ruppert had no financial disclosures. The study is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and Celgene.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryjodales
CHICAGO – Lenalidomide consolidation therapy was associated with an extended survival plateau for patients with non-del(11q) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), based on results from the phase 2 CALGB 10404 trial.
This unique survival plateau indicates future studies should continue to examine the role of lenalidomide, compared with fludarabine plus rituximab therapy, as well as the incorporation of lenalidomide into other novel treatment regimens, Amy Ruppert, MAS, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
All patients received 6 months of FR or FCR therapy, then patients underwent full staging. At 10 months, patients who had been randomized to the FR + lenalidomide group received lenalidomide 5 mg on days 1-21 of the first 28 day cycle and lenalidomide 10 mg on days 1-21 of the subsequent 5 cycles. At 18 months, patients in the FR+L group underwent full staging, and all patients underwent full staging at 24 months.
Based on pretreatment central interphase cytogenetic screening, patients who had del(11q22.3) in at least 20% of their cells were excluded from the primary analysis of 2-year progression-free survival.
Median progression-free survival was significantly shorter with FR, compared with FR+L (P = .03) and FCR (P less than .01), at 43 months (95% CI, 33-50), 66 months (95% CI, 45-not reached), and 78 months (95% CI, 58-not reached), respectively.
Median overall survival has not been reached for any arm of the study. While overall survival was similar across all arms at 1, 2, and 3 years of follow-up, there was a plateau in overall survival with no events seen beyond 41 months in the FR+L arm. Events continued to occur in the FR and FCR arms, reported Ms. Ruppert of the Comprehensive Cancer Center at Ohio State University, Columbus. At 48 months, the hazard ratio for overall survival in FR+L vs. FR was 0.27 (95% CI, 0.10-0.70; P = .01).
Ms. Ruppert had no financial disclosures. The study is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and Celgene.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryjodales
AT ASCO 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: At 48 months, the hazard ratio for overall survival in FR+L vs. FR was 0.27 (95% CI, 0.10-0.70; P = .01).
Data source: Results from 342 patients in the phase 2 CALGB 10404 trial.
Disclosures: Ms. Ruppert had no financial disclosures. The study is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and Celgene.