User login
Dyspnea and mild edema
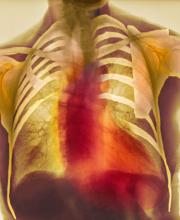
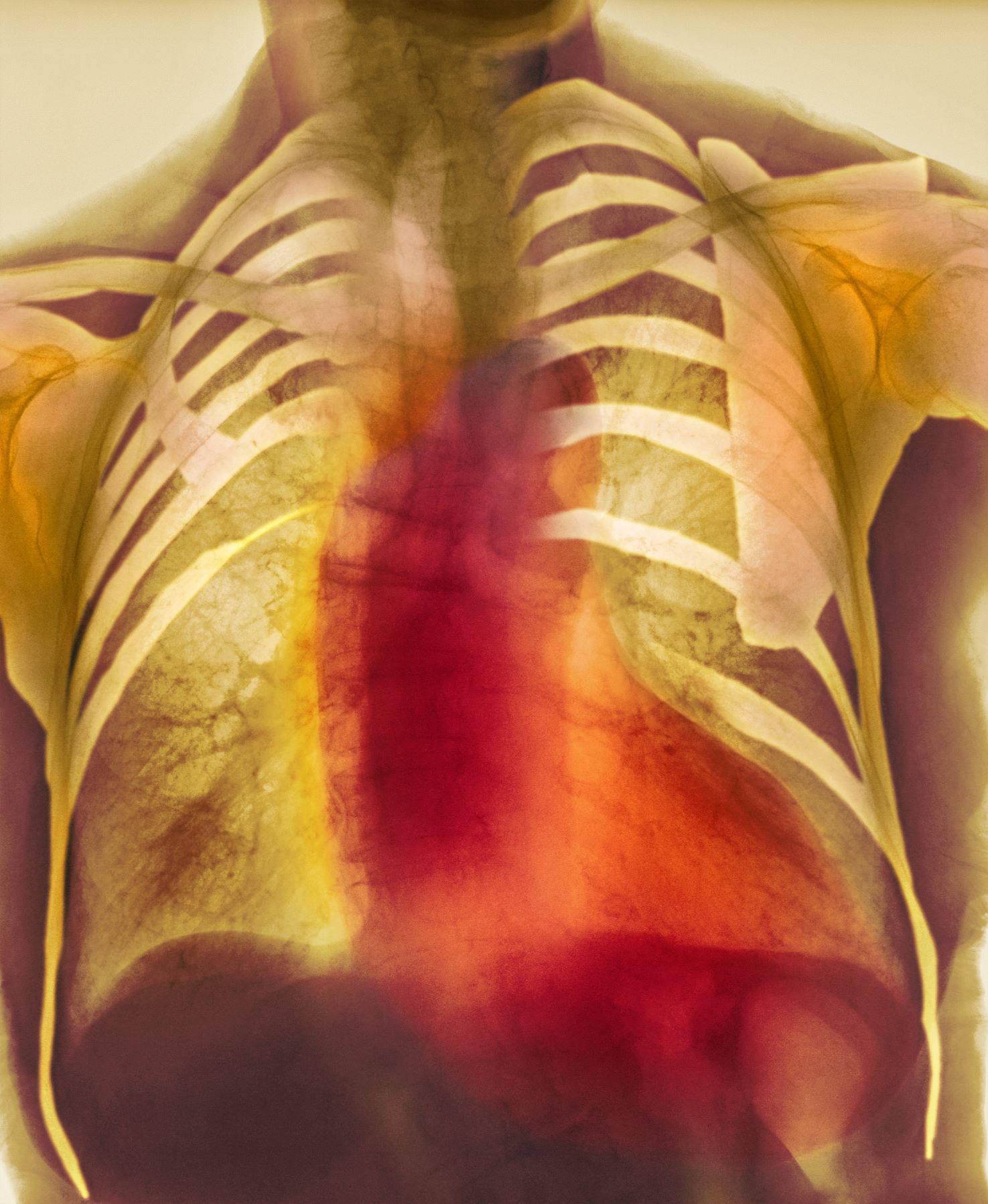
As seen in red on the radiogram, the patient's heart is grossly enlarged, indicating cardiomegaly. Cardiomegaly often is first diagnosed on chest imaging, with diagnosis based on a cardiothoracic ratio of < 0.5. It is not a disease but rather a manifestation of an underlying cause. Patients may have few or no cardiomegaly-related symptoms or have symptoms typical of cardiac dysfunction, like this patient's dyspnea and edema. Conditions that impair normal circulation and that are associated with cardiomegaly development include hypertension, obesity, heart valve disorders, thyroid dysfunction, and anemia. In this patient, cardiomegaly probably has been triggered by uncontrolled hypertension and ongoing obesity. This patient's bloodwork also indicates prediabetes and incipient type 2 diabetes (T2D) (the diagnostic criteria for which are A1c ≥ 6.5% and fasting plasma glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL).
As many as 42% of adults in the United States meet criteria for obesity and are at risk for obesity-related conditions, including cardiomegaly. Guidelines for management of patients with obesity have been published by The Obesity Society and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, and management of obesity is a necessary part of comprehensive care of patients with T2D as well. For most patients, a BMI ≥ 30 diagnoses obesity; this patient has class 1 obesity, based on a BMI of 30 to 34.9. The patient also has complications of obesity, including stage 2 hypertension and prediabetes. As such, lifestyle management plus medical therapy is the recommended approach to weight loss, with a goal of losing 5% to 10% or more of baseline body weight.
The Obesity Society states that all patients with obesity should be offered effective, evidence-based interventions. Medical management of obesity includes use of pharmacologic interventions with proven benefit in weight loss, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs; eg, semaglutide) or dual gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)/GLP-1 RAs (eg, tirzepatide). Semaglutide and tirzepatide are likely to have cardiovascular benefits for patients with obesity as well. Other medications approved for management of obesity include liraglutide, orlistat, phentermine HCl (with or without topiramate), and naltrexone plus bupropion. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommendations for management of obesity in patients with T2D give preference to semaglutide 2.4 mg/wk and tirzepatide at weekly doses of 5, 10, or 15 mg, depending on patient factors.
As important for this patient is to get control of hypertension. Studies have shown that lowering blood pressure improves left ventricular hypertrophy, a common source of cardiomegaly. Hypertension guidelines from the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association recommend a blood pressure goal < 130/80 mm Hg for most adults, which is consistent with the current recommendation from the ADA. Management of hypertension should first incorporate a low-sodium, healthy diet (such as the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension [DASH] diet), physical activity, and weight loss; however, many patients (especially with stage 2 hypertension) require pharmacologic therapy as well. Single-pill combination therapies of drugs from different classes (eg, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor plus calcium channel blocker) are preferred for patients with stage 2 hypertension to improve efficacy and enhance adherence.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
As seen in red on the radiogram, the patient's heart is grossly enlarged, indicating cardiomegaly. Cardiomegaly often is first diagnosed on chest imaging, with diagnosis based on a cardiothoracic ratio of < 0.5. It is not a disease but rather a manifestation of an underlying cause. Patients may have few or no cardiomegaly-related symptoms or have symptoms typical of cardiac dysfunction, like this patient's dyspnea and edema. Conditions that impair normal circulation and that are associated with cardiomegaly development include hypertension, obesity, heart valve disorders, thyroid dysfunction, and anemia. In this patient, cardiomegaly probably has been triggered by uncontrolled hypertension and ongoing obesity. This patient's bloodwork also indicates prediabetes and incipient type 2 diabetes (T2D) (the diagnostic criteria for which are A1c ≥ 6.5% and fasting plasma glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL).
As many as 42% of adults in the United States meet criteria for obesity and are at risk for obesity-related conditions, including cardiomegaly. Guidelines for management of patients with obesity have been published by The Obesity Society and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, and management of obesity is a necessary part of comprehensive care of patients with T2D as well. For most patients, a BMI ≥ 30 diagnoses obesity; this patient has class 1 obesity, based on a BMI of 30 to 34.9. The patient also has complications of obesity, including stage 2 hypertension and prediabetes. As such, lifestyle management plus medical therapy is the recommended approach to weight loss, with a goal of losing 5% to 10% or more of baseline body weight.
The Obesity Society states that all patients with obesity should be offered effective, evidence-based interventions. Medical management of obesity includes use of pharmacologic interventions with proven benefit in weight loss, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs; eg, semaglutide) or dual gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)/GLP-1 RAs (eg, tirzepatide). Semaglutide and tirzepatide are likely to have cardiovascular benefits for patients with obesity as well. Other medications approved for management of obesity include liraglutide, orlistat, phentermine HCl (with or without topiramate), and naltrexone plus bupropion. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommendations for management of obesity in patients with T2D give preference to semaglutide 2.4 mg/wk and tirzepatide at weekly doses of 5, 10, or 15 mg, depending on patient factors.
As important for this patient is to get control of hypertension. Studies have shown that lowering blood pressure improves left ventricular hypertrophy, a common source of cardiomegaly. Hypertension guidelines from the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association recommend a blood pressure goal < 130/80 mm Hg for most adults, which is consistent with the current recommendation from the ADA. Management of hypertension should first incorporate a low-sodium, healthy diet (such as the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension [DASH] diet), physical activity, and weight loss; however, many patients (especially with stage 2 hypertension) require pharmacologic therapy as well. Single-pill combination therapies of drugs from different classes (eg, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor plus calcium channel blocker) are preferred for patients with stage 2 hypertension to improve efficacy and enhance adherence.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
As seen in red on the radiogram, the patient's heart is grossly enlarged, indicating cardiomegaly. Cardiomegaly often is first diagnosed on chest imaging, with diagnosis based on a cardiothoracic ratio of < 0.5. It is not a disease but rather a manifestation of an underlying cause. Patients may have few or no cardiomegaly-related symptoms or have symptoms typical of cardiac dysfunction, like this patient's dyspnea and edema. Conditions that impair normal circulation and that are associated with cardiomegaly development include hypertension, obesity, heart valve disorders, thyroid dysfunction, and anemia. In this patient, cardiomegaly probably has been triggered by uncontrolled hypertension and ongoing obesity. This patient's bloodwork also indicates prediabetes and incipient type 2 diabetes (T2D) (the diagnostic criteria for which are A1c ≥ 6.5% and fasting plasma glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL).
As many as 42% of adults in the United States meet criteria for obesity and are at risk for obesity-related conditions, including cardiomegaly. Guidelines for management of patients with obesity have been published by The Obesity Society and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, and management of obesity is a necessary part of comprehensive care of patients with T2D as well. For most patients, a BMI ≥ 30 diagnoses obesity; this patient has class 1 obesity, based on a BMI of 30 to 34.9. The patient also has complications of obesity, including stage 2 hypertension and prediabetes. As such, lifestyle management plus medical therapy is the recommended approach to weight loss, with a goal of losing 5% to 10% or more of baseline body weight.
The Obesity Society states that all patients with obesity should be offered effective, evidence-based interventions. Medical management of obesity includes use of pharmacologic interventions with proven benefit in weight loss, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs; eg, semaglutide) or dual gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)/GLP-1 RAs (eg, tirzepatide). Semaglutide and tirzepatide are likely to have cardiovascular benefits for patients with obesity as well. Other medications approved for management of obesity include liraglutide, orlistat, phentermine HCl (with or without topiramate), and naltrexone plus bupropion. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommendations for management of obesity in patients with T2D give preference to semaglutide 2.4 mg/wk and tirzepatide at weekly doses of 5, 10, or 15 mg, depending on patient factors.
As important for this patient is to get control of hypertension. Studies have shown that lowering blood pressure improves left ventricular hypertrophy, a common source of cardiomegaly. Hypertension guidelines from the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association recommend a blood pressure goal < 130/80 mm Hg for most adults, which is consistent with the current recommendation from the ADA. Management of hypertension should first incorporate a low-sodium, healthy diet (such as the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension [DASH] diet), physical activity, and weight loss; however, many patients (especially with stage 2 hypertension) require pharmacologic therapy as well. Single-pill combination therapies of drugs from different classes (eg, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor plus calcium channel blocker) are preferred for patients with stage 2 hypertension to improve efficacy and enhance adherence.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 55-year-old patient with obesity presents with dyspnea and mild edema. The patient is 5 ft 9 in, weighs 210 lb (BMI 31), and received an obesity diagnosis 1 year ago with a weight of 220 lb (BMI 32.5) but notes having lived with a BMI ≥ 30 for at least 5 years. Since being diagnosed with obesity, the patient has participated in regular counseling with a clinical nutrition specialist and exercise therapy, reports satisfaction with these, and is happy to have lost 10 lb. The patient presents today for follow-up physical exam and lab workup, with a complaint of increasing dyspnea that has limited participation in exercise therapy over the past 2 months.
On physical exam, the patient appears pale, with shortness of breath and mild edema in the ankles. The heart rhythm is fluttery and the heart rate is elevated at 90 beats/min. Blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg. Lab results show A1c 6.6% and fasting glucose of 115 mg/dL. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is 101 mg/dL. Thyroid and hematologic findings are within normal parameters. The patient is sent for chest radiography, shown above (colorized).
Premenstrual Disorders and Perinatal Depression: A Two-Way Street
Premenstrual disorders (PMDs) and perinatal depression (PND) appear to have a bidirectional association, a Swedish national registry-based analysis found.
In women with PND, 2.9% had PMDs before pregnancy vs 0.6% in a matched cohort of unaffected women, according to an international team led by Quian Yang, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Environmental Medicine at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden. Their study appears in PLoS Medicine.
“Preconception and maternity care providers should be aware of the risk of developing perinatal depression among women with a history of PMDs,” Dr. Yang said in an interview. “Healthcare providers may inform women with perinatal depression about the potential risk of PMDs when menstruation returns after childbirth.” She recommended screening as part of routine perinatal care to identify and treat the condition at an early stage. Counseling and medication may help prevent adverse consequences.
In other findings, the correlation with PMDs held for both prenatal and postnatal depression, regardless of any history of psychiatric disorders and also in full-sister comparisons, the authors noted, with a stronger correlation in the absence of psychiatric disorders (P for interaction <.001).
“Interestingly, we noted a stronger association between PMDs and subsequent PND than the association in the other direction, Dr. Yang said. And although many experience PMD symptom onset in adolescence, symptom worsening has been reported with increasing age and parity. “It is possible that women with milder premenstrual symptoms experienced worse symptoms after pregnancy and are therefore first diagnosed with PMD after pregnancy,” the authors hypothesized.
Both PMDs and PND share depressive symptomatology and onset coinciding with hormonal fluctuations, particularly estrogen and progesterone, suggesting a shared etiology, Dr. Yang explained. “It’s plausible that an abnormal response to natural hormone fluctuations predisposes women to both PMDs and PND. However, the underlying mechanism is complex, and future research is needed to reveal the underlying etiology.”
Affecting a majority of women of reproductive age to some degree, PMDs in certain women can cause significant functional impairment and, when severe, have been linked to increased risks of accidents and suicidal behavior. The psychological symptoms of the more serious form, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, for example, are associated with a 50%-78% lifetime risk for psychiatric disorders, including major depressive, dysthymic, seasonal affective, and generalized anxiety disorders, as well as suicidality.
Mood disorders are common in pregnancy and the postpartum period.
The Swedish Study
In 1.8 million singleton pregnancies in Sweden during 2001-2018, the investigators identified 84,949 women with PND and 849,482 unaffected women and individually matched them 10:1 by age and calendar year. Incident PND and PMDs were identified through clinical diagnoses or prescribed medications, and adjustment was made for such demographics as country of birth, educational level, region of residency, and cohabitation status.
In an initial matched-cohort case-control study with a mean follow-up of 6.9 years, PMDs were associated with a nearly five times higher risk of subsequent PND (odds ratio, 4.76; 95% CI, 4.52-5.01; P <.001).
In another matched cohort with a mean follow-up of 7.0 years, there were 4227 newly diagnosed PMDs in women with PND (incidence rate [IR], 7.6/1000 person-years) and 21,326 among controls (IR, 3.8/1000). Compared with matched controls, women with PND were at almost twice the risk of subsequent PMDs (hazard ratio, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.74-1.88; P <.001).
Commenting on the study but not involved in it, Bernard L. Harlow, PhD, a professor of epidemiology at Boston University School of Public Health in Massachusetts who specializes in epidemiologic studies of female reproductive disorders, said he was not surprised at these findings, which clearly support the need for PMD screening in mothers-to-be. “Anything that is easy to measure and noninvasive that will minimize the risk of postpartum depression should be part of the standard of care during the prenatal period.” As to safety: If treatment is indicated, he added, “studies have shown that the risk to the mother and child is much greater if the mother’s mood disorder is not controlled than any risk to the baby due to depression treatment.” But though PMDs may be predictive of PND, there are still barriers to actual PND care. A 2023 analysis reported that 65% of mothers-to-be who screened positive for metal health comorbidities were not referred for treatment.
Dr. Yang and colleagues acknowledged that their findings may not be generalizable to mild forms of these disorders since the data were based on clinical diagnoses and prescriptions.
The study was supported by the Chinese Scholarship Council, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Icelandic Research Fund. The authors and Dr. Harlow had no relevant competing interests to disclose.
Premenstrual disorders (PMDs) and perinatal depression (PND) appear to have a bidirectional association, a Swedish national registry-based analysis found.
In women with PND, 2.9% had PMDs before pregnancy vs 0.6% in a matched cohort of unaffected women, according to an international team led by Quian Yang, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Environmental Medicine at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden. Their study appears in PLoS Medicine.
“Preconception and maternity care providers should be aware of the risk of developing perinatal depression among women with a history of PMDs,” Dr. Yang said in an interview. “Healthcare providers may inform women with perinatal depression about the potential risk of PMDs when menstruation returns after childbirth.” She recommended screening as part of routine perinatal care to identify and treat the condition at an early stage. Counseling and medication may help prevent adverse consequences.
In other findings, the correlation with PMDs held for both prenatal and postnatal depression, regardless of any history of psychiatric disorders and also in full-sister comparisons, the authors noted, with a stronger correlation in the absence of psychiatric disorders (P for interaction <.001).
“Interestingly, we noted a stronger association between PMDs and subsequent PND than the association in the other direction, Dr. Yang said. And although many experience PMD symptom onset in adolescence, symptom worsening has been reported with increasing age and parity. “It is possible that women with milder premenstrual symptoms experienced worse symptoms after pregnancy and are therefore first diagnosed with PMD after pregnancy,” the authors hypothesized.
Both PMDs and PND share depressive symptomatology and onset coinciding with hormonal fluctuations, particularly estrogen and progesterone, suggesting a shared etiology, Dr. Yang explained. “It’s plausible that an abnormal response to natural hormone fluctuations predisposes women to both PMDs and PND. However, the underlying mechanism is complex, and future research is needed to reveal the underlying etiology.”
Affecting a majority of women of reproductive age to some degree, PMDs in certain women can cause significant functional impairment and, when severe, have been linked to increased risks of accidents and suicidal behavior. The psychological symptoms of the more serious form, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, for example, are associated with a 50%-78% lifetime risk for psychiatric disorders, including major depressive, dysthymic, seasonal affective, and generalized anxiety disorders, as well as suicidality.
Mood disorders are common in pregnancy and the postpartum period.
The Swedish Study
In 1.8 million singleton pregnancies in Sweden during 2001-2018, the investigators identified 84,949 women with PND and 849,482 unaffected women and individually matched them 10:1 by age and calendar year. Incident PND and PMDs were identified through clinical diagnoses or prescribed medications, and adjustment was made for such demographics as country of birth, educational level, region of residency, and cohabitation status.
In an initial matched-cohort case-control study with a mean follow-up of 6.9 years, PMDs were associated with a nearly five times higher risk of subsequent PND (odds ratio, 4.76; 95% CI, 4.52-5.01; P <.001).
In another matched cohort with a mean follow-up of 7.0 years, there were 4227 newly diagnosed PMDs in women with PND (incidence rate [IR], 7.6/1000 person-years) and 21,326 among controls (IR, 3.8/1000). Compared with matched controls, women with PND were at almost twice the risk of subsequent PMDs (hazard ratio, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.74-1.88; P <.001).
Commenting on the study but not involved in it, Bernard L. Harlow, PhD, a professor of epidemiology at Boston University School of Public Health in Massachusetts who specializes in epidemiologic studies of female reproductive disorders, said he was not surprised at these findings, which clearly support the need for PMD screening in mothers-to-be. “Anything that is easy to measure and noninvasive that will minimize the risk of postpartum depression should be part of the standard of care during the prenatal period.” As to safety: If treatment is indicated, he added, “studies have shown that the risk to the mother and child is much greater if the mother’s mood disorder is not controlled than any risk to the baby due to depression treatment.” But though PMDs may be predictive of PND, there are still barriers to actual PND care. A 2023 analysis reported that 65% of mothers-to-be who screened positive for metal health comorbidities were not referred for treatment.
Dr. Yang and colleagues acknowledged that their findings may not be generalizable to mild forms of these disorders since the data were based on clinical diagnoses and prescriptions.
The study was supported by the Chinese Scholarship Council, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Icelandic Research Fund. The authors and Dr. Harlow had no relevant competing interests to disclose.
Premenstrual disorders (PMDs) and perinatal depression (PND) appear to have a bidirectional association, a Swedish national registry-based analysis found.
In women with PND, 2.9% had PMDs before pregnancy vs 0.6% in a matched cohort of unaffected women, according to an international team led by Quian Yang, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Environmental Medicine at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden. Their study appears in PLoS Medicine.
“Preconception and maternity care providers should be aware of the risk of developing perinatal depression among women with a history of PMDs,” Dr. Yang said in an interview. “Healthcare providers may inform women with perinatal depression about the potential risk of PMDs when menstruation returns after childbirth.” She recommended screening as part of routine perinatal care to identify and treat the condition at an early stage. Counseling and medication may help prevent adverse consequences.
In other findings, the correlation with PMDs held for both prenatal and postnatal depression, regardless of any history of psychiatric disorders and also in full-sister comparisons, the authors noted, with a stronger correlation in the absence of psychiatric disorders (P for interaction <.001).
“Interestingly, we noted a stronger association between PMDs and subsequent PND than the association in the other direction, Dr. Yang said. And although many experience PMD symptom onset in adolescence, symptom worsening has been reported with increasing age and parity. “It is possible that women with milder premenstrual symptoms experienced worse symptoms after pregnancy and are therefore first diagnosed with PMD after pregnancy,” the authors hypothesized.
Both PMDs and PND share depressive symptomatology and onset coinciding with hormonal fluctuations, particularly estrogen and progesterone, suggesting a shared etiology, Dr. Yang explained. “It’s plausible that an abnormal response to natural hormone fluctuations predisposes women to both PMDs and PND. However, the underlying mechanism is complex, and future research is needed to reveal the underlying etiology.”
Affecting a majority of women of reproductive age to some degree, PMDs in certain women can cause significant functional impairment and, when severe, have been linked to increased risks of accidents and suicidal behavior. The psychological symptoms of the more serious form, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, for example, are associated with a 50%-78% lifetime risk for psychiatric disorders, including major depressive, dysthymic, seasonal affective, and generalized anxiety disorders, as well as suicidality.
Mood disorders are common in pregnancy and the postpartum period.
The Swedish Study
In 1.8 million singleton pregnancies in Sweden during 2001-2018, the investigators identified 84,949 women with PND and 849,482 unaffected women and individually matched them 10:1 by age and calendar year. Incident PND and PMDs were identified through clinical diagnoses or prescribed medications, and adjustment was made for such demographics as country of birth, educational level, region of residency, and cohabitation status.
In an initial matched-cohort case-control study with a mean follow-up of 6.9 years, PMDs were associated with a nearly five times higher risk of subsequent PND (odds ratio, 4.76; 95% CI, 4.52-5.01; P <.001).
In another matched cohort with a mean follow-up of 7.0 years, there were 4227 newly diagnosed PMDs in women with PND (incidence rate [IR], 7.6/1000 person-years) and 21,326 among controls (IR, 3.8/1000). Compared with matched controls, women with PND were at almost twice the risk of subsequent PMDs (hazard ratio, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.74-1.88; P <.001).
Commenting on the study but not involved in it, Bernard L. Harlow, PhD, a professor of epidemiology at Boston University School of Public Health in Massachusetts who specializes in epidemiologic studies of female reproductive disorders, said he was not surprised at these findings, which clearly support the need for PMD screening in mothers-to-be. “Anything that is easy to measure and noninvasive that will minimize the risk of postpartum depression should be part of the standard of care during the prenatal period.” As to safety: If treatment is indicated, he added, “studies have shown that the risk to the mother and child is much greater if the mother’s mood disorder is not controlled than any risk to the baby due to depression treatment.” But though PMDs may be predictive of PND, there are still barriers to actual PND care. A 2023 analysis reported that 65% of mothers-to-be who screened positive for metal health comorbidities were not referred for treatment.
Dr. Yang and colleagues acknowledged that their findings may not be generalizable to mild forms of these disorders since the data were based on clinical diagnoses and prescriptions.
The study was supported by the Chinese Scholarship Council, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Icelandic Research Fund. The authors and Dr. Harlow had no relevant competing interests to disclose.
FROM PLOS MEDICINE
Abecma Approved for Earlier Lines in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma
The approval expands the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy’s indications to earlier lines of treatment after exposure to these other main therapy classes, Bristol Myers Squibb said in a press release.
Approval was based on the KarMMa-3 trial, in which 254 patients were randomly assigned to ide-cel and 132 to investigators’ choice of standard regimens, consisting of combinations of daratumumab, dexamethasone, and other agents.
After a median follow-up of 15.9 months, median progression-free survival was three times higher in the ide-cel arm: 13.3 months with the CAR T-cell therapy vs 4.4 months with standard treatment. Overall, 39% of patients on ide-cel had a complete response vs 5% on standard regimens.
The approval includes a new recommended dose range of 300-510 x 106 CAR-positive T cells.
Ide-cel carries a boxed warning for cytokine release syndrome, neurologic toxicities, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome, prolonged cytopenia, and secondary hematologic cancers.
In trials, cytokine release syndrome occurred in 89% (310 of 349) of patients in the KarMMa-3 and KarMMa studies, which included grade 3 syndrome in 7% (23 of 349) and fatal cases in 0.9% (3 of 349) of patients.
A one-time treatment is over $500,000, according to drugs.com.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The approval expands the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy’s indications to earlier lines of treatment after exposure to these other main therapy classes, Bristol Myers Squibb said in a press release.
Approval was based on the KarMMa-3 trial, in which 254 patients were randomly assigned to ide-cel and 132 to investigators’ choice of standard regimens, consisting of combinations of daratumumab, dexamethasone, and other agents.
After a median follow-up of 15.9 months, median progression-free survival was three times higher in the ide-cel arm: 13.3 months with the CAR T-cell therapy vs 4.4 months with standard treatment. Overall, 39% of patients on ide-cel had a complete response vs 5% on standard regimens.
The approval includes a new recommended dose range of 300-510 x 106 CAR-positive T cells.
Ide-cel carries a boxed warning for cytokine release syndrome, neurologic toxicities, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome, prolonged cytopenia, and secondary hematologic cancers.
In trials, cytokine release syndrome occurred in 89% (310 of 349) of patients in the KarMMa-3 and KarMMa studies, which included grade 3 syndrome in 7% (23 of 349) and fatal cases in 0.9% (3 of 349) of patients.
A one-time treatment is over $500,000, according to drugs.com.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The approval expands the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy’s indications to earlier lines of treatment after exposure to these other main therapy classes, Bristol Myers Squibb said in a press release.
Approval was based on the KarMMa-3 trial, in which 254 patients were randomly assigned to ide-cel and 132 to investigators’ choice of standard regimens, consisting of combinations of daratumumab, dexamethasone, and other agents.
After a median follow-up of 15.9 months, median progression-free survival was three times higher in the ide-cel arm: 13.3 months with the CAR T-cell therapy vs 4.4 months with standard treatment. Overall, 39% of patients on ide-cel had a complete response vs 5% on standard regimens.
The approval includes a new recommended dose range of 300-510 x 106 CAR-positive T cells.
Ide-cel carries a boxed warning for cytokine release syndrome, neurologic toxicities, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome, prolonged cytopenia, and secondary hematologic cancers.
In trials, cytokine release syndrome occurred in 89% (310 of 349) of patients in the KarMMa-3 and KarMMa studies, which included grade 3 syndrome in 7% (23 of 349) and fatal cases in 0.9% (3 of 349) of patients.
A one-time treatment is over $500,000, according to drugs.com.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Quality Measure Improves Follow-Up for CRC Screening
the developers said.
As part of their work, the researchers conducted a retrospective study of 20,581 adults aged 50-75 years from 38 health systems that showed that fewer than half (48%) had a follow-up colonoscopy within 180 days of an initial abnormal SBT for CRC.
“The low follow-up rates to an abnormal SBT were initially surprising,” first author Elizabeth L. Ciemins, PhD, MPH, MA, Research and Analytics, American Medical Group Association (AMGA), Alexandria, Virginia, told this news organization.
“However, once we interviewed clinicians and learned that this was not a measure they were tracking, along with their own incorrect assumptions of a much higher follow-up rate, the low rates made sense. As is commonly said, ‘you can’t change what you don’t measure,’” she said.
The CRC screening completion measure the researchers propose “builds on and addresses an important shortcoming in an existing measure and will help ensure complete screening for CRC,” they noted in their JAMA Network Open paper.
The key elements of the follow-up measure are the date and result of a SBT and the date of the follow-up colonoscopy — if it occurred, Dr. Ciemins explained.
“Currently, health systems are not consistently tracking this measure, but they have the data elements to do so, especially if they are doing colonoscopies in-house,” she said.
Field testing showed that use of this new measure is “feasible, valid, and reliable,” the authors said. Dr. Ciemins believed this CRC screening completion measure could be widely implemented.
“Three AMGA member health systems feasibility tested the data elements and found that they could reliably abstract the required elements from electronic health records (EHRs),” she told this news organization.
The researchers are currently testing the measure among 20 AMGA member health systems, that are submitting quarterly data on a version of the specified measure.
“Advancing this measure as a quality performance measure could significantly increase the early detection of CRC, thereby improving health and ultimately saving lives,” the authors concluded in their paper.
The Right Direction, But Questions Remain
The coauthors of a linked commentary said this research highlights the “suboptimal” rates of a timely follow-up colonoscopy after positive SBT results. They applauded the authors for “focusing attention on a meaningful approach to measuring high-quality CRC screening and providing guidance for standardized measurement.”
However, several questions arise from this study, “including whether 6 months is the ideal interval for colonoscopy completion after a positive SBT result, where this measure fits in the context of existing CRC screening measures, and how to implement it in practice,” Jennifer K. Maratt, MD, with Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, and coauthors wrote.
“This measure alone does not address all the gaps in the screening process, nor does it address barriers to colonoscopy completion, but it points us in the right direction for measuring the success of screening programs,” Dr. Maratt and her colleagues added.
The study was supported by a grant from the AARP. The authors and editorial writers had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
the developers said.
As part of their work, the researchers conducted a retrospective study of 20,581 adults aged 50-75 years from 38 health systems that showed that fewer than half (48%) had a follow-up colonoscopy within 180 days of an initial abnormal SBT for CRC.
“The low follow-up rates to an abnormal SBT were initially surprising,” first author Elizabeth L. Ciemins, PhD, MPH, MA, Research and Analytics, American Medical Group Association (AMGA), Alexandria, Virginia, told this news organization.
“However, once we interviewed clinicians and learned that this was not a measure they were tracking, along with their own incorrect assumptions of a much higher follow-up rate, the low rates made sense. As is commonly said, ‘you can’t change what you don’t measure,’” she said.
The CRC screening completion measure the researchers propose “builds on and addresses an important shortcoming in an existing measure and will help ensure complete screening for CRC,” they noted in their JAMA Network Open paper.
The key elements of the follow-up measure are the date and result of a SBT and the date of the follow-up colonoscopy — if it occurred, Dr. Ciemins explained.
“Currently, health systems are not consistently tracking this measure, but they have the data elements to do so, especially if they are doing colonoscopies in-house,” she said.
Field testing showed that use of this new measure is “feasible, valid, and reliable,” the authors said. Dr. Ciemins believed this CRC screening completion measure could be widely implemented.
“Three AMGA member health systems feasibility tested the data elements and found that they could reliably abstract the required elements from electronic health records (EHRs),” she told this news organization.
The researchers are currently testing the measure among 20 AMGA member health systems, that are submitting quarterly data on a version of the specified measure.
“Advancing this measure as a quality performance measure could significantly increase the early detection of CRC, thereby improving health and ultimately saving lives,” the authors concluded in their paper.
The Right Direction, But Questions Remain
The coauthors of a linked commentary said this research highlights the “suboptimal” rates of a timely follow-up colonoscopy after positive SBT results. They applauded the authors for “focusing attention on a meaningful approach to measuring high-quality CRC screening and providing guidance for standardized measurement.”
However, several questions arise from this study, “including whether 6 months is the ideal interval for colonoscopy completion after a positive SBT result, where this measure fits in the context of existing CRC screening measures, and how to implement it in practice,” Jennifer K. Maratt, MD, with Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, and coauthors wrote.
“This measure alone does not address all the gaps in the screening process, nor does it address barriers to colonoscopy completion, but it points us in the right direction for measuring the success of screening programs,” Dr. Maratt and her colleagues added.
The study was supported by a grant from the AARP. The authors and editorial writers had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
the developers said.
As part of their work, the researchers conducted a retrospective study of 20,581 adults aged 50-75 years from 38 health systems that showed that fewer than half (48%) had a follow-up colonoscopy within 180 days of an initial abnormal SBT for CRC.
“The low follow-up rates to an abnormal SBT were initially surprising,” first author Elizabeth L. Ciemins, PhD, MPH, MA, Research and Analytics, American Medical Group Association (AMGA), Alexandria, Virginia, told this news organization.
“However, once we interviewed clinicians and learned that this was not a measure they were tracking, along with their own incorrect assumptions of a much higher follow-up rate, the low rates made sense. As is commonly said, ‘you can’t change what you don’t measure,’” she said.
The CRC screening completion measure the researchers propose “builds on and addresses an important shortcoming in an existing measure and will help ensure complete screening for CRC,” they noted in their JAMA Network Open paper.
The key elements of the follow-up measure are the date and result of a SBT and the date of the follow-up colonoscopy — if it occurred, Dr. Ciemins explained.
“Currently, health systems are not consistently tracking this measure, but they have the data elements to do so, especially if they are doing colonoscopies in-house,” she said.
Field testing showed that use of this new measure is “feasible, valid, and reliable,” the authors said. Dr. Ciemins believed this CRC screening completion measure could be widely implemented.
“Three AMGA member health systems feasibility tested the data elements and found that they could reliably abstract the required elements from electronic health records (EHRs),” she told this news organization.
The researchers are currently testing the measure among 20 AMGA member health systems, that are submitting quarterly data on a version of the specified measure.
“Advancing this measure as a quality performance measure could significantly increase the early detection of CRC, thereby improving health and ultimately saving lives,” the authors concluded in their paper.
The Right Direction, But Questions Remain
The coauthors of a linked commentary said this research highlights the “suboptimal” rates of a timely follow-up colonoscopy after positive SBT results. They applauded the authors for “focusing attention on a meaningful approach to measuring high-quality CRC screening and providing guidance for standardized measurement.”
However, several questions arise from this study, “including whether 6 months is the ideal interval for colonoscopy completion after a positive SBT result, where this measure fits in the context of existing CRC screening measures, and how to implement it in practice,” Jennifer K. Maratt, MD, with Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, and coauthors wrote.
“This measure alone does not address all the gaps in the screening process, nor does it address barriers to colonoscopy completion, but it points us in the right direction for measuring the success of screening programs,” Dr. Maratt and her colleagues added.
The study was supported by a grant from the AARP. The authors and editorial writers had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Eliminating H pylori Lowers CRC Incidence, Mortality Risk
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- H pylori is a known cause of peptic ulcers and stomach cancer and has been classified as a group I carcinogen by the World Health Organization›s International Agency for Research on Cancer.
- Studies showed that H pylori increases the risk for gastric cancer and may increase the risk for CRC, but evidence supporting the CRC connection remains inconsistent.
- To investigate a possible H pylori-CRC link, investigators reviewed CRC incidence and mortality in a nationwide cohort of 812,736 veterans tested for H pylori at Veterans Health Administration facilities; of the 205,178 (25.2%) who tested positive for H pylori, 134,417 (34%) were treated.
- Patients were followed from their first H pylori test, and researchers tracked subsequent CRC diagnoses as well as CRC-related and non-CRC–related deaths.
TAKEAWAY:
- H pylori infection was associated with an 18% higher risk for CRC (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.18) and a 12% higher risk for CRC mortality (aHR, 1.12).
- Untreated patients had a 23% higher risk for CRC (aHR, 1.23) and a 40% higher risk for CRC mortality (aHR, 1.40) than treated individuals.
- Over the 15-year follow-up, receiving treatment for H pylori infection vs no treatment was associated with a lower risk of developing and dying from CRC (absolute risk reduction, 0.23%-0.35%). For context, among individuals receiving a screening colonoscopy, the invasive test was associated with a 0.84%-1.22% absolute risk reduction in CRC incidence and a 0.15-0.30% absolute risk reduction in CRC mortality.
- Excluding patients diagnosed with CRC within a year of H pylori testing did not change the associations in the study.
IN PRACTICE:
“We would like to highlight the potentially exciting clinical implications of these findings,” the authors of an accompanying editorial wrote. “Although the mechanistic connection between H pylori and colorectal cancer is not fully resolved,” the finding that eliminating H pylori “could reduce both gastric and colorectal cancers is incredibly potent and should be considered in clinical care for individuals at high risk for GI [gastrointestinal] cancers.”
SOURCE:
The work, led by Shailja C. Shah, MD, of the University of California San Diego, was published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, alongside the accompanying editorial by Julia Butt, PhD, of the German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany, and Meira Epplein, PhD, of Duke University in Durham, North Carolina.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited to US veterans, which means generalizability to other populations needed to be confirmed. There may have been differences in CRC risk factors between treated and untreated patients.
DISCLOSURES:
The work was funded by the Veterans Health Administration, the National Cancer Institute, and others. Investigators reported ties to numerous companies, including AstraZeneca, Novartis, Guardant Health, and Medscape Medical News, publisher of this article. The editorialists had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- H pylori is a known cause of peptic ulcers and stomach cancer and has been classified as a group I carcinogen by the World Health Organization›s International Agency for Research on Cancer.
- Studies showed that H pylori increases the risk for gastric cancer and may increase the risk for CRC, but evidence supporting the CRC connection remains inconsistent.
- To investigate a possible H pylori-CRC link, investigators reviewed CRC incidence and mortality in a nationwide cohort of 812,736 veterans tested for H pylori at Veterans Health Administration facilities; of the 205,178 (25.2%) who tested positive for H pylori, 134,417 (34%) were treated.
- Patients were followed from their first H pylori test, and researchers tracked subsequent CRC diagnoses as well as CRC-related and non-CRC–related deaths.
TAKEAWAY:
- H pylori infection was associated with an 18% higher risk for CRC (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.18) and a 12% higher risk for CRC mortality (aHR, 1.12).
- Untreated patients had a 23% higher risk for CRC (aHR, 1.23) and a 40% higher risk for CRC mortality (aHR, 1.40) than treated individuals.
- Over the 15-year follow-up, receiving treatment for H pylori infection vs no treatment was associated with a lower risk of developing and dying from CRC (absolute risk reduction, 0.23%-0.35%). For context, among individuals receiving a screening colonoscopy, the invasive test was associated with a 0.84%-1.22% absolute risk reduction in CRC incidence and a 0.15-0.30% absolute risk reduction in CRC mortality.
- Excluding patients diagnosed with CRC within a year of H pylori testing did not change the associations in the study.
IN PRACTICE:
“We would like to highlight the potentially exciting clinical implications of these findings,” the authors of an accompanying editorial wrote. “Although the mechanistic connection between H pylori and colorectal cancer is not fully resolved,” the finding that eliminating H pylori “could reduce both gastric and colorectal cancers is incredibly potent and should be considered in clinical care for individuals at high risk for GI [gastrointestinal] cancers.”
SOURCE:
The work, led by Shailja C. Shah, MD, of the University of California San Diego, was published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, alongside the accompanying editorial by Julia Butt, PhD, of the German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany, and Meira Epplein, PhD, of Duke University in Durham, North Carolina.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited to US veterans, which means generalizability to other populations needed to be confirmed. There may have been differences in CRC risk factors between treated and untreated patients.
DISCLOSURES:
The work was funded by the Veterans Health Administration, the National Cancer Institute, and others. Investigators reported ties to numerous companies, including AstraZeneca, Novartis, Guardant Health, and Medscape Medical News, publisher of this article. The editorialists had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- H pylori is a known cause of peptic ulcers and stomach cancer and has been classified as a group I carcinogen by the World Health Organization›s International Agency for Research on Cancer.
- Studies showed that H pylori increases the risk for gastric cancer and may increase the risk for CRC, but evidence supporting the CRC connection remains inconsistent.
- To investigate a possible H pylori-CRC link, investigators reviewed CRC incidence and mortality in a nationwide cohort of 812,736 veterans tested for H pylori at Veterans Health Administration facilities; of the 205,178 (25.2%) who tested positive for H pylori, 134,417 (34%) were treated.
- Patients were followed from their first H pylori test, and researchers tracked subsequent CRC diagnoses as well as CRC-related and non-CRC–related deaths.
TAKEAWAY:
- H pylori infection was associated with an 18% higher risk for CRC (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.18) and a 12% higher risk for CRC mortality (aHR, 1.12).
- Untreated patients had a 23% higher risk for CRC (aHR, 1.23) and a 40% higher risk for CRC mortality (aHR, 1.40) than treated individuals.
- Over the 15-year follow-up, receiving treatment for H pylori infection vs no treatment was associated with a lower risk of developing and dying from CRC (absolute risk reduction, 0.23%-0.35%). For context, among individuals receiving a screening colonoscopy, the invasive test was associated with a 0.84%-1.22% absolute risk reduction in CRC incidence and a 0.15-0.30% absolute risk reduction in CRC mortality.
- Excluding patients diagnosed with CRC within a year of H pylori testing did not change the associations in the study.
IN PRACTICE:
“We would like to highlight the potentially exciting clinical implications of these findings,” the authors of an accompanying editorial wrote. “Although the mechanistic connection between H pylori and colorectal cancer is not fully resolved,” the finding that eliminating H pylori “could reduce both gastric and colorectal cancers is incredibly potent and should be considered in clinical care for individuals at high risk for GI [gastrointestinal] cancers.”
SOURCE:
The work, led by Shailja C. Shah, MD, of the University of California San Diego, was published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, alongside the accompanying editorial by Julia Butt, PhD, of the German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany, and Meira Epplein, PhD, of Duke University in Durham, North Carolina.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited to US veterans, which means generalizability to other populations needed to be confirmed. There may have been differences in CRC risk factors between treated and untreated patients.
DISCLOSURES:
The work was funded by the Veterans Health Administration, the National Cancer Institute, and others. Investigators reported ties to numerous companies, including AstraZeneca, Novartis, Guardant Health, and Medscape Medical News, publisher of this article. The editorialists had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Congress Directly Provides $10 Million for Arthritis Research for First Time
Congress provided $10 million to fund arthritis research in the recently passed federal fiscal year 2024 budget.
The new arthritis program is part of the Department of Defense’s (DOD’s) Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs (CDMRP), which provides dedicated funding to study certain diseases and health conditions.
This is the first stand-alone research program for arthritis of the CDMRP, though the organization had previously funded arthritis-related research through their other programs, including chronic pain management, joint warfighter medical, peer-reviewed orthopedic, peer-reviewed medical, and tick-borne disease programs.
It is not yet known what specific aspects of arthritis this funding will go toward. The standard process for new programs involves speaking with researchers, clinicians, and individuals with these targeted health conditions to better understand research gaps and narrow focus, Akua Roach, PhD, the program manager for this new CDMRP arthritis research program, told this news organization.
“We’re not going to be able to solve every question,” she said, though the allocated $10 million is “a great number to do a lot of great work.”
While the CDMRP is under the DOD, research funding can go to studying patient populations outside of military personnel or veterans, she added.
“I think that is perhaps a common misconception that if you are getting funding from the DOD, that you have to have a DOD population, and that is not true,” she said.
Another misconception is that CDMRP funding only goes to military treatment facilities. In fact, on average, 92% of CDMRP funding goes to academia, industry, and other nonmilitary recipients, noted CDMRP Director Colonel Sarah Goldman.
“Anyone around the world can apply for funding,” she told this news organization. “We want to fund the best research.”
Because the funding is provided under the defense bill, there will be discussions around the military relevance of research, she added, which not only includes service members but also their families.
CDMRP anticipates that funding opportunities through this new arthritis research program will be available by July or August 2024.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Congress provided $10 million to fund arthritis research in the recently passed federal fiscal year 2024 budget.
The new arthritis program is part of the Department of Defense’s (DOD’s) Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs (CDMRP), which provides dedicated funding to study certain diseases and health conditions.
This is the first stand-alone research program for arthritis of the CDMRP, though the organization had previously funded arthritis-related research through their other programs, including chronic pain management, joint warfighter medical, peer-reviewed orthopedic, peer-reviewed medical, and tick-borne disease programs.
It is not yet known what specific aspects of arthritis this funding will go toward. The standard process for new programs involves speaking with researchers, clinicians, and individuals with these targeted health conditions to better understand research gaps and narrow focus, Akua Roach, PhD, the program manager for this new CDMRP arthritis research program, told this news organization.
“We’re not going to be able to solve every question,” she said, though the allocated $10 million is “a great number to do a lot of great work.”
While the CDMRP is under the DOD, research funding can go to studying patient populations outside of military personnel or veterans, she added.
“I think that is perhaps a common misconception that if you are getting funding from the DOD, that you have to have a DOD population, and that is not true,” she said.
Another misconception is that CDMRP funding only goes to military treatment facilities. In fact, on average, 92% of CDMRP funding goes to academia, industry, and other nonmilitary recipients, noted CDMRP Director Colonel Sarah Goldman.
“Anyone around the world can apply for funding,” she told this news organization. “We want to fund the best research.”
Because the funding is provided under the defense bill, there will be discussions around the military relevance of research, she added, which not only includes service members but also their families.
CDMRP anticipates that funding opportunities through this new arthritis research program will be available by July or August 2024.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Congress provided $10 million to fund arthritis research in the recently passed federal fiscal year 2024 budget.
The new arthritis program is part of the Department of Defense’s (DOD’s) Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs (CDMRP), which provides dedicated funding to study certain diseases and health conditions.
This is the first stand-alone research program for arthritis of the CDMRP, though the organization had previously funded arthritis-related research through their other programs, including chronic pain management, joint warfighter medical, peer-reviewed orthopedic, peer-reviewed medical, and tick-borne disease programs.
It is not yet known what specific aspects of arthritis this funding will go toward. The standard process for new programs involves speaking with researchers, clinicians, and individuals with these targeted health conditions to better understand research gaps and narrow focus, Akua Roach, PhD, the program manager for this new CDMRP arthritis research program, told this news organization.
“We’re not going to be able to solve every question,” she said, though the allocated $10 million is “a great number to do a lot of great work.”
While the CDMRP is under the DOD, research funding can go to studying patient populations outside of military personnel or veterans, she added.
“I think that is perhaps a common misconception that if you are getting funding from the DOD, that you have to have a DOD population, and that is not true,” she said.
Another misconception is that CDMRP funding only goes to military treatment facilities. In fact, on average, 92% of CDMRP funding goes to academia, industry, and other nonmilitary recipients, noted CDMRP Director Colonel Sarah Goldman.
“Anyone around the world can apply for funding,” she told this news organization. “We want to fund the best research.”
Because the funding is provided under the defense bill, there will be discussions around the military relevance of research, she added, which not only includes service members but also their families.
CDMRP anticipates that funding opportunities through this new arthritis research program will be available by July or August 2024.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Analysis Finds Low Malignancy Rate in Pediatric Longitudinal Melanonychia
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- LM — a pigmented band in the nail plate caused by increased melanin deposition — occurs in children and adults, resulting from melanocytic activation or proliferation in response to infection, systemic disease, medication, trauma, and other factors.
- Clinical features of LM in children mimic red-flag signs of subungual melanoma in adults although rarely is subungual melanoma.
- A biopsy can confirm the diagnosis, but other considerations include the scar, cost and stress of a procedure, and possibly pain or deformity.
- The researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of clinical and dermoscopic features in 1391 pediatric patients with LM (diagnosed at a mean age of 5-13 years) from 24 studies published between 1996 and 2023.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of 731 lesions in which a diagnosis was provided, benign nail matrix nevus accounted for 86% of cases.
- Only eight cases of subungual melanoma in situ were diagnosed, with no cases of invasive melanoma identified.
- Most lesions occurred on the fingernails (76%), particularly in the first digits (45%), and the most frequent clinical features included dark-colored bands (70%), multicolored bands (48%), broad bandwidth (41%), and pseudo-Hutchinson sign (41%).
- During a median follow-up of 1-5.5 years, 30% of lesions continued to evolve with changes in width or color, while 23% remained stable and 20% underwent spontaneous regression.
IN PRACTICE:
“In the pivotal clinical decision of whether to biopsy a child with longitudinal melanonychia, perhaps with features that would require a prompt biopsy in an adult, this study provides data to support the option of clinical monitoring,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The meta-analysis, led by Serena Yun-Chen Tsai, MD, in the Department of Dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Most studies were conducted in Asia, and data stratified by skin type were limited. Inconsistent reporting and missing critical features could affect data quality. Also, certain features displayed high heterogeneity.
DISCLOSURES:
This meta-analysis was supported by the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance Career Bridge Research Grant. One co-author disclosed relationships with UpToDate (author, reviewer), Skin Analytics (consultant), and DermTech (research materials).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- LM — a pigmented band in the nail plate caused by increased melanin deposition — occurs in children and adults, resulting from melanocytic activation or proliferation in response to infection, systemic disease, medication, trauma, and other factors.
- Clinical features of LM in children mimic red-flag signs of subungual melanoma in adults although rarely is subungual melanoma.
- A biopsy can confirm the diagnosis, but other considerations include the scar, cost and stress of a procedure, and possibly pain or deformity.
- The researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of clinical and dermoscopic features in 1391 pediatric patients with LM (diagnosed at a mean age of 5-13 years) from 24 studies published between 1996 and 2023.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of 731 lesions in which a diagnosis was provided, benign nail matrix nevus accounted for 86% of cases.
- Only eight cases of subungual melanoma in situ were diagnosed, with no cases of invasive melanoma identified.
- Most lesions occurred on the fingernails (76%), particularly in the first digits (45%), and the most frequent clinical features included dark-colored bands (70%), multicolored bands (48%), broad bandwidth (41%), and pseudo-Hutchinson sign (41%).
- During a median follow-up of 1-5.5 years, 30% of lesions continued to evolve with changes in width or color, while 23% remained stable and 20% underwent spontaneous regression.
IN PRACTICE:
“In the pivotal clinical decision of whether to biopsy a child with longitudinal melanonychia, perhaps with features that would require a prompt biopsy in an adult, this study provides data to support the option of clinical monitoring,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The meta-analysis, led by Serena Yun-Chen Tsai, MD, in the Department of Dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Most studies were conducted in Asia, and data stratified by skin type were limited. Inconsistent reporting and missing critical features could affect data quality. Also, certain features displayed high heterogeneity.
DISCLOSURES:
This meta-analysis was supported by the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance Career Bridge Research Grant. One co-author disclosed relationships with UpToDate (author, reviewer), Skin Analytics (consultant), and DermTech (research materials).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- LM — a pigmented band in the nail plate caused by increased melanin deposition — occurs in children and adults, resulting from melanocytic activation or proliferation in response to infection, systemic disease, medication, trauma, and other factors.
- Clinical features of LM in children mimic red-flag signs of subungual melanoma in adults although rarely is subungual melanoma.
- A biopsy can confirm the diagnosis, but other considerations include the scar, cost and stress of a procedure, and possibly pain or deformity.
- The researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of clinical and dermoscopic features in 1391 pediatric patients with LM (diagnosed at a mean age of 5-13 years) from 24 studies published between 1996 and 2023.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of 731 lesions in which a diagnosis was provided, benign nail matrix nevus accounted for 86% of cases.
- Only eight cases of subungual melanoma in situ were diagnosed, with no cases of invasive melanoma identified.
- Most lesions occurred on the fingernails (76%), particularly in the first digits (45%), and the most frequent clinical features included dark-colored bands (70%), multicolored bands (48%), broad bandwidth (41%), and pseudo-Hutchinson sign (41%).
- During a median follow-up of 1-5.5 years, 30% of lesions continued to evolve with changes in width or color, while 23% remained stable and 20% underwent spontaneous regression.
IN PRACTICE:
“In the pivotal clinical decision of whether to biopsy a child with longitudinal melanonychia, perhaps with features that would require a prompt biopsy in an adult, this study provides data to support the option of clinical monitoring,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The meta-analysis, led by Serena Yun-Chen Tsai, MD, in the Department of Dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Most studies were conducted in Asia, and data stratified by skin type were limited. Inconsistent reporting and missing critical features could affect data quality. Also, certain features displayed high heterogeneity.
DISCLOSURES:
This meta-analysis was supported by the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance Career Bridge Research Grant. One co-author disclosed relationships with UpToDate (author, reviewer), Skin Analytics (consultant), and DermTech (research materials).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Trials in Prostate Cancer: Could Your Patient Benefit?
Metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer
Adults with this diagnosis may be interested in a randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study examining whether an experimental poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor called saruparib can further delay disease progression when added to a next-generation hormonal agent such as abiraterone (Zytiga), darolutamide (Nubeqa), or enzalutamide (Xtandi).
One group of participants will take daily oral doses of saruparib plus physician’s choice of a next-generation hormonal agent until disease progression or another reason for stopping therapy. The other group will add a placebo to a next-generation hormonal agent.
Sites in Rhode Island, Arkansas, California, Michigan, Australia, Canada, Japan, Taiwan, Thailand, the United Kingdom, and South Korea began seeking the trial’s 1800 participants in November 2023. Research centers in 31 other US states and 18 other countries are gearing up. The primary endpoint is radiographic progression-free survival. Overall survival and quality of life (QoL) are secondary endpoints. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
This news organization asked Marc Garnick, MD, professor of medicine, Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, for his take on the trial. “The study is interesting since it is adding to the evaluations of continued intensification for first-line therapy and will help further elucidate the role of PARP inhibition regardless of homologous repair status,” Dr. Garnick said. “Plus, saruparib is supposedly more selective on PARP1, which in-and-of-itself is of potential benefit.”
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
People with this type of cancer who have progressed on a next-generation hormonal agent may be eligible for a randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial testing an investigational oral treatment called MK-5684 to see if it increases survival more effectively than switching to an alternative next-generation hormonal agent.
MK-5684 is designed to inhibit the CYP11A1 enzyme, thereby disrupting the androgen-receptor signaling pathway.
One group will take twice-daily tablets of MK-5684 plus hormone replacement therapy, oral dexamethasone, and oral fludrocortisone acetate (Florinef), with rescue hydrocortisone as needed. The other participants will take daily tablets of a next-generation hormonal agent: Either enzalutamide or abiraterone. Patients assigned to abiraterone will also be given prednisone tablets.
US-based sites in nine states and Puerto Rico started looking for the trial’s 1500 participants in December 2023 in partnership with study centers in Australia, Israel, South Korea, and Taiwan. The primary endpoints are radiographic progression-free survival and overall survival. QoL will not be tracked. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
Patients in this situation who have progressed on taxane-based chemotherapy as well as a next-generation hormonal agent have the option to enroll in another phase 3 MK-5684 study.
Like the trial described above, all patients will remain on their respective therapy until disease progression. In this trial, one group will take twice-daily tablets of MK-5684 without hormone replacement therapy but the same mix of oral dexamethasone and fludrocortisone. Rescue hydrocortisone will also be available. The second group will be assigned either enzalutamide or abiraterone plus prednisone.
Sites in Puerto Rico, Colorado, Nevada, and Virginia, and five other countries outside the United States, opened their doors to the first of 1200 patients in December 2023. The primary endpoints are radiographic progression-free survival and overall survival, analyzed separately for patients with and without an androgen receptor ligand-binding domain mutation. QoL will not be measured. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
High-risk prostate cancer
People with this diagnosis can join a randomized, open-label, phase 3 National Cancer Institute study to test whether stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is as effective as conventional external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) at preventing metastasis.
SBRT delivers radiation to tumors with higher precision than EBRT. The advantage of SBRT is the ability to deliver fewer doses over a shorter duration with less collateral damage to surrounding tissues.
In the trial, half of participants will undergo five treatments of SBRT over 2 weeks, while the other half will receive 20-45 treatments of EBRT over 4-9 weeks. Study sites in 14 US states began recruiting the trial’s 1209 participants in November 2023. Metastasis-free survival over 15 years is the primary endpoint, overall survival is a secondary endpoint, and QoL measures, apart from fatigue, will not be tracked. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
Dr. Garnick viewed this study as “problematic because patient accrual ends in 2036 with a readout in 2041.” He added, “What its relevance will be at that time is unlikely to provide practice changes, since in that interval there will undoubtedly be multiple advances in place.”
Newly diagnosed favorable intermediate risk prostate cancer
People with this type of cancer are eligible for an open-label, phase 4 real-world study of a radioactive diagnostic agent called piflufolastat F 18 (Pylarify) that targets prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–positive lesions. Piflufolastat is designed to enhance detection of metastases during PSMA-targeted PET.
Participants will receive a single injection of piflufolastat followed 1-2 hours later by a single whole-body PET-CT or PET-MRI scan. A study site at the Hoag Cancer Center in Irvine, California, welcomed the first of the trial’s 274 participants in February 2024. Sites in Tower Urology, Los Angeles, and the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, are gearing up. Detection rate is the primary endpoint. Overall survival and QoL are not measured. More details at clinicaltrials.gov
Stages I-IV prostate cancer without bone metastases. People 60 years or older with this type of prostate cancer who are just starting androgen deprivation therapy are eligible for a phase 3, placebo-controlled trial investigating whether high-dose vitamin D can prevent or reduce androgen-deprivation therapy-induced bone loss.
For 1 year, participants will take tablets of high-dose vitamin D or a placebo and then undergo dual x-ray absorptiometry. The Ochsner Medical Center in Jefferson, Louisiana, started recruiting 366 trial participants in December 2023. Reduction in bone mineral density loss in the hip and spine over 1 year is the primary objective. QoL is a secondary objective, and overall survival will not be measured. More details at clinicaltrials.gov
Dr. Garnick expressed some concerns with the trial design so far, including that “the dose of vitamin D is not delineated nor is the target vitamin D level.”
All trial information is from the National Institutes of Health’s National Library of Medicine (online at clinicaltrials.gov). Dr. Garnick did not report conflicts with any of the trials.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer
Adults with this diagnosis may be interested in a randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study examining whether an experimental poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor called saruparib can further delay disease progression when added to a next-generation hormonal agent such as abiraterone (Zytiga), darolutamide (Nubeqa), or enzalutamide (Xtandi).
One group of participants will take daily oral doses of saruparib plus physician’s choice of a next-generation hormonal agent until disease progression or another reason for stopping therapy. The other group will add a placebo to a next-generation hormonal agent.
Sites in Rhode Island, Arkansas, California, Michigan, Australia, Canada, Japan, Taiwan, Thailand, the United Kingdom, and South Korea began seeking the trial’s 1800 participants in November 2023. Research centers in 31 other US states and 18 other countries are gearing up. The primary endpoint is radiographic progression-free survival. Overall survival and quality of life (QoL) are secondary endpoints. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
This news organization asked Marc Garnick, MD, professor of medicine, Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, for his take on the trial. “The study is interesting since it is adding to the evaluations of continued intensification for first-line therapy and will help further elucidate the role of PARP inhibition regardless of homologous repair status,” Dr. Garnick said. “Plus, saruparib is supposedly more selective on PARP1, which in-and-of-itself is of potential benefit.”
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
People with this type of cancer who have progressed on a next-generation hormonal agent may be eligible for a randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial testing an investigational oral treatment called MK-5684 to see if it increases survival more effectively than switching to an alternative next-generation hormonal agent.
MK-5684 is designed to inhibit the CYP11A1 enzyme, thereby disrupting the androgen-receptor signaling pathway.
One group will take twice-daily tablets of MK-5684 plus hormone replacement therapy, oral dexamethasone, and oral fludrocortisone acetate (Florinef), with rescue hydrocortisone as needed. The other participants will take daily tablets of a next-generation hormonal agent: Either enzalutamide or abiraterone. Patients assigned to abiraterone will also be given prednisone tablets.
US-based sites in nine states and Puerto Rico started looking for the trial’s 1500 participants in December 2023 in partnership with study centers in Australia, Israel, South Korea, and Taiwan. The primary endpoints are radiographic progression-free survival and overall survival. QoL will not be tracked. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
Patients in this situation who have progressed on taxane-based chemotherapy as well as a next-generation hormonal agent have the option to enroll in another phase 3 MK-5684 study.
Like the trial described above, all patients will remain on their respective therapy until disease progression. In this trial, one group will take twice-daily tablets of MK-5684 without hormone replacement therapy but the same mix of oral dexamethasone and fludrocortisone. Rescue hydrocortisone will also be available. The second group will be assigned either enzalutamide or abiraterone plus prednisone.
Sites in Puerto Rico, Colorado, Nevada, and Virginia, and five other countries outside the United States, opened their doors to the first of 1200 patients in December 2023. The primary endpoints are radiographic progression-free survival and overall survival, analyzed separately for patients with and without an androgen receptor ligand-binding domain mutation. QoL will not be measured. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
High-risk prostate cancer
People with this diagnosis can join a randomized, open-label, phase 3 National Cancer Institute study to test whether stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is as effective as conventional external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) at preventing metastasis.
SBRT delivers radiation to tumors with higher precision than EBRT. The advantage of SBRT is the ability to deliver fewer doses over a shorter duration with less collateral damage to surrounding tissues.
In the trial, half of participants will undergo five treatments of SBRT over 2 weeks, while the other half will receive 20-45 treatments of EBRT over 4-9 weeks. Study sites in 14 US states began recruiting the trial’s 1209 participants in November 2023. Metastasis-free survival over 15 years is the primary endpoint, overall survival is a secondary endpoint, and QoL measures, apart from fatigue, will not be tracked. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
Dr. Garnick viewed this study as “problematic because patient accrual ends in 2036 with a readout in 2041.” He added, “What its relevance will be at that time is unlikely to provide practice changes, since in that interval there will undoubtedly be multiple advances in place.”
Newly diagnosed favorable intermediate risk prostate cancer
People with this type of cancer are eligible for an open-label, phase 4 real-world study of a radioactive diagnostic agent called piflufolastat F 18 (Pylarify) that targets prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–positive lesions. Piflufolastat is designed to enhance detection of metastases during PSMA-targeted PET.
Participants will receive a single injection of piflufolastat followed 1-2 hours later by a single whole-body PET-CT or PET-MRI scan. A study site at the Hoag Cancer Center in Irvine, California, welcomed the first of the trial’s 274 participants in February 2024. Sites in Tower Urology, Los Angeles, and the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, are gearing up. Detection rate is the primary endpoint. Overall survival and QoL are not measured. More details at clinicaltrials.gov
Stages I-IV prostate cancer without bone metastases. People 60 years or older with this type of prostate cancer who are just starting androgen deprivation therapy are eligible for a phase 3, placebo-controlled trial investigating whether high-dose vitamin D can prevent or reduce androgen-deprivation therapy-induced bone loss.
For 1 year, participants will take tablets of high-dose vitamin D or a placebo and then undergo dual x-ray absorptiometry. The Ochsner Medical Center in Jefferson, Louisiana, started recruiting 366 trial participants in December 2023. Reduction in bone mineral density loss in the hip and spine over 1 year is the primary objective. QoL is a secondary objective, and overall survival will not be measured. More details at clinicaltrials.gov
Dr. Garnick expressed some concerns with the trial design so far, including that “the dose of vitamin D is not delineated nor is the target vitamin D level.”
All trial information is from the National Institutes of Health’s National Library of Medicine (online at clinicaltrials.gov). Dr. Garnick did not report conflicts with any of the trials.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer
Adults with this diagnosis may be interested in a randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study examining whether an experimental poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor called saruparib can further delay disease progression when added to a next-generation hormonal agent such as abiraterone (Zytiga), darolutamide (Nubeqa), or enzalutamide (Xtandi).
One group of participants will take daily oral doses of saruparib plus physician’s choice of a next-generation hormonal agent until disease progression or another reason for stopping therapy. The other group will add a placebo to a next-generation hormonal agent.
Sites in Rhode Island, Arkansas, California, Michigan, Australia, Canada, Japan, Taiwan, Thailand, the United Kingdom, and South Korea began seeking the trial’s 1800 participants in November 2023. Research centers in 31 other US states and 18 other countries are gearing up. The primary endpoint is radiographic progression-free survival. Overall survival and quality of life (QoL) are secondary endpoints. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
This news organization asked Marc Garnick, MD, professor of medicine, Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, for his take on the trial. “The study is interesting since it is adding to the evaluations of continued intensification for first-line therapy and will help further elucidate the role of PARP inhibition regardless of homologous repair status,” Dr. Garnick said. “Plus, saruparib is supposedly more selective on PARP1, which in-and-of-itself is of potential benefit.”
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
People with this type of cancer who have progressed on a next-generation hormonal agent may be eligible for a randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial testing an investigational oral treatment called MK-5684 to see if it increases survival more effectively than switching to an alternative next-generation hormonal agent.
MK-5684 is designed to inhibit the CYP11A1 enzyme, thereby disrupting the androgen-receptor signaling pathway.
One group will take twice-daily tablets of MK-5684 plus hormone replacement therapy, oral dexamethasone, and oral fludrocortisone acetate (Florinef), with rescue hydrocortisone as needed. The other participants will take daily tablets of a next-generation hormonal agent: Either enzalutamide or abiraterone. Patients assigned to abiraterone will also be given prednisone tablets.
US-based sites in nine states and Puerto Rico started looking for the trial’s 1500 participants in December 2023 in partnership with study centers in Australia, Israel, South Korea, and Taiwan. The primary endpoints are radiographic progression-free survival and overall survival. QoL will not be tracked. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
Patients in this situation who have progressed on taxane-based chemotherapy as well as a next-generation hormonal agent have the option to enroll in another phase 3 MK-5684 study.
Like the trial described above, all patients will remain on their respective therapy until disease progression. In this trial, one group will take twice-daily tablets of MK-5684 without hormone replacement therapy but the same mix of oral dexamethasone and fludrocortisone. Rescue hydrocortisone will also be available. The second group will be assigned either enzalutamide or abiraterone plus prednisone.
Sites in Puerto Rico, Colorado, Nevada, and Virginia, and five other countries outside the United States, opened their doors to the first of 1200 patients in December 2023. The primary endpoints are radiographic progression-free survival and overall survival, analyzed separately for patients with and without an androgen receptor ligand-binding domain mutation. QoL will not be measured. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
High-risk prostate cancer
People with this diagnosis can join a randomized, open-label, phase 3 National Cancer Institute study to test whether stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is as effective as conventional external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) at preventing metastasis.
SBRT delivers radiation to tumors with higher precision than EBRT. The advantage of SBRT is the ability to deliver fewer doses over a shorter duration with less collateral damage to surrounding tissues.
In the trial, half of participants will undergo five treatments of SBRT over 2 weeks, while the other half will receive 20-45 treatments of EBRT over 4-9 weeks. Study sites in 14 US states began recruiting the trial’s 1209 participants in November 2023. Metastasis-free survival over 15 years is the primary endpoint, overall survival is a secondary endpoint, and QoL measures, apart from fatigue, will not be tracked. More details at clinicaltrials.gov.
Dr. Garnick viewed this study as “problematic because patient accrual ends in 2036 with a readout in 2041.” He added, “What its relevance will be at that time is unlikely to provide practice changes, since in that interval there will undoubtedly be multiple advances in place.”
Newly diagnosed favorable intermediate risk prostate cancer
People with this type of cancer are eligible for an open-label, phase 4 real-world study of a radioactive diagnostic agent called piflufolastat F 18 (Pylarify) that targets prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–positive lesions. Piflufolastat is designed to enhance detection of metastases during PSMA-targeted PET.
Participants will receive a single injection of piflufolastat followed 1-2 hours later by a single whole-body PET-CT or PET-MRI scan. A study site at the Hoag Cancer Center in Irvine, California, welcomed the first of the trial’s 274 participants in February 2024. Sites in Tower Urology, Los Angeles, and the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, are gearing up. Detection rate is the primary endpoint. Overall survival and QoL are not measured. More details at clinicaltrials.gov
Stages I-IV prostate cancer without bone metastases. People 60 years or older with this type of prostate cancer who are just starting androgen deprivation therapy are eligible for a phase 3, placebo-controlled trial investigating whether high-dose vitamin D can prevent or reduce androgen-deprivation therapy-induced bone loss.
For 1 year, participants will take tablets of high-dose vitamin D or a placebo and then undergo dual x-ray absorptiometry. The Ochsner Medical Center in Jefferson, Louisiana, started recruiting 366 trial participants in December 2023. Reduction in bone mineral density loss in the hip and spine over 1 year is the primary objective. QoL is a secondary objective, and overall survival will not be measured. More details at clinicaltrials.gov
Dr. Garnick expressed some concerns with the trial design so far, including that “the dose of vitamin D is not delineated nor is the target vitamin D level.”
All trial information is from the National Institutes of Health’s National Library of Medicine (online at clinicaltrials.gov). Dr. Garnick did not report conflicts with any of the trials.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tooth Enamel Disorder Is a Feature of Kindler EB
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- KEB or Kindler syndrome, a genetic skin-blistering disease associated with pathogenic variants in FERMT1, is the rarest type of EB. Early detection and preventive measures can minimize complications, such as gum disease and other oral health issues, that have been reported in patients with KEB.
- Amelogenesis imperfecta is a group of rare genetic developmental conditions characterized by tooth enamel defects and can be associated with hypersensitivity and eruption disturbances in teeth, as well as periodontal conditions.
- Researchers conducted a longitudinal study on 36 patients with KEB (age, 2 weeks to 70 years; 42% female) from two clinics in Germany and Chile from 2003 to 2023, with follow-up times of 1-24 years.
- The primary outcomes were presence of orofacial features, including amelogenesis imperfecta, intraoral wounds, and periodontal disease, and oral squamous cell carcinoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- All 11 patients with information on enamel structure in their records had pitted enamel anomalies (pitted amelogenesis imperfecta), with variable severity.
- Of patients whose enamel could not be analyzed, three had all teeth crowned in their 20s, suggesting enamel defects, and two had all teeth extracted in their teens or 20s, indicating severe periodontal disease.
- The most common orofacial features were periodontal disease (27 of 36 patients), intraoral lesions (16 of 22 patients), angular cheilitis (24 of 33 patients), and cheilitis (22 of 34 patients), gingival overgrowth (17 of 26 patients), microstomia (14 of 25 patients), and vestibular obliteration (8 of 16 patients).
- Oral squamous cell carcinoma was diagnosed at the site of chronic lip lesions in two patients, with lethal outcomes.
IN PRACTICE:
These findings highlight the extent and severity of oral manifestations in KEB, the authors concluded, adding that “oral care is mandatory” in patients with KEB.
SOURCE:
This report, led by Susanne Krämer, DDS, MSc, of Medical Faculty and Medical Center, University of Freiburg, Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany, was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the retrospective nature of the study could limit its generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose any source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- KEB or Kindler syndrome, a genetic skin-blistering disease associated with pathogenic variants in FERMT1, is the rarest type of EB. Early detection and preventive measures can minimize complications, such as gum disease and other oral health issues, that have been reported in patients with KEB.
- Amelogenesis imperfecta is a group of rare genetic developmental conditions characterized by tooth enamel defects and can be associated with hypersensitivity and eruption disturbances in teeth, as well as periodontal conditions.
- Researchers conducted a longitudinal study on 36 patients with KEB (age, 2 weeks to 70 years; 42% female) from two clinics in Germany and Chile from 2003 to 2023, with follow-up times of 1-24 years.
- The primary outcomes were presence of orofacial features, including amelogenesis imperfecta, intraoral wounds, and periodontal disease, and oral squamous cell carcinoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- All 11 patients with information on enamel structure in their records had pitted enamel anomalies (pitted amelogenesis imperfecta), with variable severity.
- Of patients whose enamel could not be analyzed, three had all teeth crowned in their 20s, suggesting enamel defects, and two had all teeth extracted in their teens or 20s, indicating severe periodontal disease.
- The most common orofacial features were periodontal disease (27 of 36 patients), intraoral lesions (16 of 22 patients), angular cheilitis (24 of 33 patients), and cheilitis (22 of 34 patients), gingival overgrowth (17 of 26 patients), microstomia (14 of 25 patients), and vestibular obliteration (8 of 16 patients).
- Oral squamous cell carcinoma was diagnosed at the site of chronic lip lesions in two patients, with lethal outcomes.
IN PRACTICE:
These findings highlight the extent and severity of oral manifestations in KEB, the authors concluded, adding that “oral care is mandatory” in patients with KEB.
SOURCE:
This report, led by Susanne Krämer, DDS, MSc, of Medical Faculty and Medical Center, University of Freiburg, Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany, was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the retrospective nature of the study could limit its generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose any source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- KEB or Kindler syndrome, a genetic skin-blistering disease associated with pathogenic variants in FERMT1, is the rarest type of EB. Early detection and preventive measures can minimize complications, such as gum disease and other oral health issues, that have been reported in patients with KEB.
- Amelogenesis imperfecta is a group of rare genetic developmental conditions characterized by tooth enamel defects and can be associated with hypersensitivity and eruption disturbances in teeth, as well as periodontal conditions.
- Researchers conducted a longitudinal study on 36 patients with KEB (age, 2 weeks to 70 years; 42% female) from two clinics in Germany and Chile from 2003 to 2023, with follow-up times of 1-24 years.
- The primary outcomes were presence of orofacial features, including amelogenesis imperfecta, intraoral wounds, and periodontal disease, and oral squamous cell carcinoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- All 11 patients with information on enamel structure in their records had pitted enamel anomalies (pitted amelogenesis imperfecta), with variable severity.
- Of patients whose enamel could not be analyzed, three had all teeth crowned in their 20s, suggesting enamel defects, and two had all teeth extracted in their teens or 20s, indicating severe periodontal disease.
- The most common orofacial features were periodontal disease (27 of 36 patients), intraoral lesions (16 of 22 patients), angular cheilitis (24 of 33 patients), and cheilitis (22 of 34 patients), gingival overgrowth (17 of 26 patients), microstomia (14 of 25 patients), and vestibular obliteration (8 of 16 patients).
- Oral squamous cell carcinoma was diagnosed at the site of chronic lip lesions in two patients, with lethal outcomes.
IN PRACTICE:
These findings highlight the extent and severity of oral manifestations in KEB, the authors concluded, adding that “oral care is mandatory” in patients with KEB.
SOURCE:
This report, led by Susanne Krämer, DDS, MSc, of Medical Faculty and Medical Center, University of Freiburg, Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany, was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the retrospective nature of the study could limit its generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose any source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.