User login
TICOSPA: Efficacy of treat-to-target strategy suggested in axial spondyloarthritis
A treat-to-target strategy for managing patients with axial spondyloarthritis failed to meet its primary efficacy endpoint but still showed several suggestive indications of benefit compared with usual care in a multicenter, randomized study with 160 patients.
The treat-to-target management strategy tested aimed to get patients to an Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) of less than 2.1, as recommended for patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) by an international task force. Also notable about the study was its primary endpoint, at least a 30% improvement in the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society Health Index (ASAS HI), a measure of health-related quality-of-life that the study organizers selected in part because of its distinction from the treatment target.
“For the first time in rheumatology, we targeted inflammation to have an impact on another domain of the disease. Despite not reaching statistical significance, we see a difference between the groups,” Anna Moltó, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
After 12 months in the study, the 80 axSpA patients assigned to the treat-to-target regimen had a 47% rate of attainment of the primary endpoint, compared with 36% of the 80 patients assigned to usual care, an 11% absolute between-group difference with a P value that came close to but failed to achieve the conventional standard of statistical significance after adjustment for potential confounders (P = .09). Six secondary outcomes showed statistically significant improvements compared with the control patients, including the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), the ASAS 20, and ASAS 40. Five additional metrics showed nominal between-group improvements with the treat-to-target strategy that were not statistically significant, including various forms of the ASDAS.
One additional notable finding came from a cost-efficacy analysis run by Dr. Moltó and associates, which showed that the treat-to-target strategy was “dominant” over usual care by producing both better outcomes as well as a lower total cost, compared with control patients, even though twice as many patients on the treat-to-target strategy received a biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) compared with patients in the usual care group. The incremental cost utility ratio for treat-to-target was 19,430 euros (about $22,000) per quality-adjusted life-year gained, putting the strategy into the range of a “cost effective” approach, and the two treatment arms also had comparable safety, said Dr. Moltó, a rheumatologist at Cochin Hospital in Paris.
The 11% increase in treat-to-target patients achieving at least a 30% improvement in their ASAS HI score “is potentially clinically relevant” because the comparator arm in the study received “very active” usual care and was not by any measure a true placebo control group, noted Maxime Dougados, MD, a rheumatologist and professor or medicine at Cochin Hospital and senior investigator for the study. In general, in treatment studies of rheumatologic diseases a 10% or greater absolute increase in the incidence of a beneficial outcome is considered clinically meaningful when compared with an actively-treated control arm, he noted.
“Using the ASAS HI score was very ambitious for the study, and it’s a very relevant outcome,” said Sofia Ramiro, MD, a rheumatologist at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center who was not associated with the study and chaired the session where Dr. Moltó gave her report. “We have had treat-to-target trials that showed benefit when disease activity was the endpoint.” But when a study “targets treatment to [reducing] disease activity and then uses disease activity as the outcome measure you expect to see an effect, but it is circular reasoning and we are left with challenges in interpreting the results. Now we have a trial that is formally [neutral] but with a different, more ambitious endpoint. All the indications are for benefit from treat-to-target for both the primary endpoint and for all the other endpoints.”
“We were in a difficult situation when choosing the outcome. We didn’t know whether a 30% improvement in the ASAS HI was really relevant, but it seems to be,” said Désirée van der Heijde, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine at Leiden University Medical Center and a collaborator on Dr. Moltó’s study. “I’d choose ASAS HI again as a primary endpoint” for a treat-to-target study in patients with axSpA, she said, but added that a 30% improvement in this score as the response threshold may warrant reconsideration. Both Dr. van der Heijde and Dr. Dougados agreed that at least one additional study with a somewhat similar design is needed to better document and confirm a role for a treat-to-target strategy in axSpA patients.
The Tight Control in Spondyloarthritis (TICOSPA) study ran at 10 French centers and 4 centers each in Belgium and the Netherlands. The study enrolled adults with rheumatologist-diagnosed axSpA with an ASDAS score greater than 2.1 who had not yet received a bDMARD, had not yet maxed out on their dosage of NSAIDs, and had certain baseline immunologic and imaging findings available. The researchers randomized 160 patients to either treat-to-target or usual care management by the center they attended to prevent cross contamination of management strategies. The treat-to-target regimen involved office examinations and consultations every 4 weeks rather than every 3 months with usual care, and also required a predefined management strategy with treatment prompts based on the strategy sent to the treating clinicians via the EMR. The average age of the patients was 38 years, they had been diagnosed with axSpA for an average of just under 4 years, and their mean ASDAS score at entry was 3. During the 12 months of management, 56% of the patients in the treat-to-target arm initiated treatment with a bDMARD, compared with 28% among the controls. Use of NSAIDs was similar between the two study subgroups.
TICOSPA was sponsored by UCB. Dr. Moltó has been a consultant to and received research funding from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Dougados has had financial relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Merck, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. van der Heijde has had financial relationships with more than 20 companies including UCB. Dr. Ramiro had been a consultant to or received research funding from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, and Sanofi.
SOURCE: Moltó A et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79[suppl 1]:413.
A treat-to-target strategy for managing patients with axial spondyloarthritis failed to meet its primary efficacy endpoint but still showed several suggestive indications of benefit compared with usual care in a multicenter, randomized study with 160 patients.
The treat-to-target management strategy tested aimed to get patients to an Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) of less than 2.1, as recommended for patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) by an international task force. Also notable about the study was its primary endpoint, at least a 30% improvement in the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society Health Index (ASAS HI), a measure of health-related quality-of-life that the study organizers selected in part because of its distinction from the treatment target.
“For the first time in rheumatology, we targeted inflammation to have an impact on another domain of the disease. Despite not reaching statistical significance, we see a difference between the groups,” Anna Moltó, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
After 12 months in the study, the 80 axSpA patients assigned to the treat-to-target regimen had a 47% rate of attainment of the primary endpoint, compared with 36% of the 80 patients assigned to usual care, an 11% absolute between-group difference with a P value that came close to but failed to achieve the conventional standard of statistical significance after adjustment for potential confounders (P = .09). Six secondary outcomes showed statistically significant improvements compared with the control patients, including the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), the ASAS 20, and ASAS 40. Five additional metrics showed nominal between-group improvements with the treat-to-target strategy that were not statistically significant, including various forms of the ASDAS.
One additional notable finding came from a cost-efficacy analysis run by Dr. Moltó and associates, which showed that the treat-to-target strategy was “dominant” over usual care by producing both better outcomes as well as a lower total cost, compared with control patients, even though twice as many patients on the treat-to-target strategy received a biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) compared with patients in the usual care group. The incremental cost utility ratio for treat-to-target was 19,430 euros (about $22,000) per quality-adjusted life-year gained, putting the strategy into the range of a “cost effective” approach, and the two treatment arms also had comparable safety, said Dr. Moltó, a rheumatologist at Cochin Hospital in Paris.
The 11% increase in treat-to-target patients achieving at least a 30% improvement in their ASAS HI score “is potentially clinically relevant” because the comparator arm in the study received “very active” usual care and was not by any measure a true placebo control group, noted Maxime Dougados, MD, a rheumatologist and professor or medicine at Cochin Hospital and senior investigator for the study. In general, in treatment studies of rheumatologic diseases a 10% or greater absolute increase in the incidence of a beneficial outcome is considered clinically meaningful when compared with an actively-treated control arm, he noted.
“Using the ASAS HI score was very ambitious for the study, and it’s a very relevant outcome,” said Sofia Ramiro, MD, a rheumatologist at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center who was not associated with the study and chaired the session where Dr. Moltó gave her report. “We have had treat-to-target trials that showed benefit when disease activity was the endpoint.” But when a study “targets treatment to [reducing] disease activity and then uses disease activity as the outcome measure you expect to see an effect, but it is circular reasoning and we are left with challenges in interpreting the results. Now we have a trial that is formally [neutral] but with a different, more ambitious endpoint. All the indications are for benefit from treat-to-target for both the primary endpoint and for all the other endpoints.”
“We were in a difficult situation when choosing the outcome. We didn’t know whether a 30% improvement in the ASAS HI was really relevant, but it seems to be,” said Désirée van der Heijde, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine at Leiden University Medical Center and a collaborator on Dr. Moltó’s study. “I’d choose ASAS HI again as a primary endpoint” for a treat-to-target study in patients with axSpA, she said, but added that a 30% improvement in this score as the response threshold may warrant reconsideration. Both Dr. van der Heijde and Dr. Dougados agreed that at least one additional study with a somewhat similar design is needed to better document and confirm a role for a treat-to-target strategy in axSpA patients.
The Tight Control in Spondyloarthritis (TICOSPA) study ran at 10 French centers and 4 centers each in Belgium and the Netherlands. The study enrolled adults with rheumatologist-diagnosed axSpA with an ASDAS score greater than 2.1 who had not yet received a bDMARD, had not yet maxed out on their dosage of NSAIDs, and had certain baseline immunologic and imaging findings available. The researchers randomized 160 patients to either treat-to-target or usual care management by the center they attended to prevent cross contamination of management strategies. The treat-to-target regimen involved office examinations and consultations every 4 weeks rather than every 3 months with usual care, and also required a predefined management strategy with treatment prompts based on the strategy sent to the treating clinicians via the EMR. The average age of the patients was 38 years, they had been diagnosed with axSpA for an average of just under 4 years, and their mean ASDAS score at entry was 3. During the 12 months of management, 56% of the patients in the treat-to-target arm initiated treatment with a bDMARD, compared with 28% among the controls. Use of NSAIDs was similar between the two study subgroups.
TICOSPA was sponsored by UCB. Dr. Moltó has been a consultant to and received research funding from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Dougados has had financial relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Merck, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. van der Heijde has had financial relationships with more than 20 companies including UCB. Dr. Ramiro had been a consultant to or received research funding from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, and Sanofi.
SOURCE: Moltó A et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79[suppl 1]:413.
A treat-to-target strategy for managing patients with axial spondyloarthritis failed to meet its primary efficacy endpoint but still showed several suggestive indications of benefit compared with usual care in a multicenter, randomized study with 160 patients.
The treat-to-target management strategy tested aimed to get patients to an Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) of less than 2.1, as recommended for patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) by an international task force. Also notable about the study was its primary endpoint, at least a 30% improvement in the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society Health Index (ASAS HI), a measure of health-related quality-of-life that the study organizers selected in part because of its distinction from the treatment target.
“For the first time in rheumatology, we targeted inflammation to have an impact on another domain of the disease. Despite not reaching statistical significance, we see a difference between the groups,” Anna Moltó, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
After 12 months in the study, the 80 axSpA patients assigned to the treat-to-target regimen had a 47% rate of attainment of the primary endpoint, compared with 36% of the 80 patients assigned to usual care, an 11% absolute between-group difference with a P value that came close to but failed to achieve the conventional standard of statistical significance after adjustment for potential confounders (P = .09). Six secondary outcomes showed statistically significant improvements compared with the control patients, including the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), the ASAS 20, and ASAS 40. Five additional metrics showed nominal between-group improvements with the treat-to-target strategy that were not statistically significant, including various forms of the ASDAS.
One additional notable finding came from a cost-efficacy analysis run by Dr. Moltó and associates, which showed that the treat-to-target strategy was “dominant” over usual care by producing both better outcomes as well as a lower total cost, compared with control patients, even though twice as many patients on the treat-to-target strategy received a biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) compared with patients in the usual care group. The incremental cost utility ratio for treat-to-target was 19,430 euros (about $22,000) per quality-adjusted life-year gained, putting the strategy into the range of a “cost effective” approach, and the two treatment arms also had comparable safety, said Dr. Moltó, a rheumatologist at Cochin Hospital in Paris.
The 11% increase in treat-to-target patients achieving at least a 30% improvement in their ASAS HI score “is potentially clinically relevant” because the comparator arm in the study received “very active” usual care and was not by any measure a true placebo control group, noted Maxime Dougados, MD, a rheumatologist and professor or medicine at Cochin Hospital and senior investigator for the study. In general, in treatment studies of rheumatologic diseases a 10% or greater absolute increase in the incidence of a beneficial outcome is considered clinically meaningful when compared with an actively-treated control arm, he noted.
“Using the ASAS HI score was very ambitious for the study, and it’s a very relevant outcome,” said Sofia Ramiro, MD, a rheumatologist at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center who was not associated with the study and chaired the session where Dr. Moltó gave her report. “We have had treat-to-target trials that showed benefit when disease activity was the endpoint.” But when a study “targets treatment to [reducing] disease activity and then uses disease activity as the outcome measure you expect to see an effect, but it is circular reasoning and we are left with challenges in interpreting the results. Now we have a trial that is formally [neutral] but with a different, more ambitious endpoint. All the indications are for benefit from treat-to-target for both the primary endpoint and for all the other endpoints.”
“We were in a difficult situation when choosing the outcome. We didn’t know whether a 30% improvement in the ASAS HI was really relevant, but it seems to be,” said Désirée van der Heijde, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine at Leiden University Medical Center and a collaborator on Dr. Moltó’s study. “I’d choose ASAS HI again as a primary endpoint” for a treat-to-target study in patients with axSpA, she said, but added that a 30% improvement in this score as the response threshold may warrant reconsideration. Both Dr. van der Heijde and Dr. Dougados agreed that at least one additional study with a somewhat similar design is needed to better document and confirm a role for a treat-to-target strategy in axSpA patients.
The Tight Control in Spondyloarthritis (TICOSPA) study ran at 10 French centers and 4 centers each in Belgium and the Netherlands. The study enrolled adults with rheumatologist-diagnosed axSpA with an ASDAS score greater than 2.1 who had not yet received a bDMARD, had not yet maxed out on their dosage of NSAIDs, and had certain baseline immunologic and imaging findings available. The researchers randomized 160 patients to either treat-to-target or usual care management by the center they attended to prevent cross contamination of management strategies. The treat-to-target regimen involved office examinations and consultations every 4 weeks rather than every 3 months with usual care, and also required a predefined management strategy with treatment prompts based on the strategy sent to the treating clinicians via the EMR. The average age of the patients was 38 years, they had been diagnosed with axSpA for an average of just under 4 years, and their mean ASDAS score at entry was 3. During the 12 months of management, 56% of the patients in the treat-to-target arm initiated treatment with a bDMARD, compared with 28% among the controls. Use of NSAIDs was similar between the two study subgroups.
TICOSPA was sponsored by UCB. Dr. Moltó has been a consultant to and received research funding from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Dougados has had financial relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Merck, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. van der Heijde has had financial relationships with more than 20 companies including UCB. Dr. Ramiro had been a consultant to or received research funding from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, and Sanofi.
SOURCE: Moltó A et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79[suppl 1]:413.
REPORTING FROM THE EULAR 2020 E-CONGRESS
EBV may worsen immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced colitis
For patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced colitis, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection may increase risks of steroid-refractory disease and ulcers that contribute to colonic perforation, according to investigators.
Pending further research, routine monitoring of EBV status may be needed for patients undergoing checkpoint inhibitor therapy, reported lead author Matthew R. Pugh, FRCPath, of University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff, and colleagues.
“Few studies have investigated the role of viruses in the pathogenesis of immune-related colitis,” the investigators wrote. Their report is in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. While cytomegalovirus has been linked with worse disease, no studies to date have evaluated the role of EBV, they noted, despite theoretical concerns.
“A spectrum of EBV-positive lymphoproliferations shows a predilection for the GI tract, ranging from indolent lesions to aggressive lymphomas,” the investigators wrote. “One such proliferation, EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer (EBVMCU), is an indolent, ulcerating process associated with immunosuppression,” they added, referring to studies involving patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
To determine if EBV could be playing a similar role in cancer immunotherapy, the investigators retrospectively analyzed colon tissue samples from 16 patients who developed colitis after undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy between 2010 and 2018. Thirteen patients received an anti-CTLA-4 agent, three were treated with a PD-1 inhibitor, and four received both types of therapy. Most patients had advanced-stage melanoma (n = 14), while the remaining two patients had prostate and renal carcinoma, respectively. Ten samples were biopsies, whereas four specimens were collected from surgical repair of colon perforation.
EBV status was determined by chromogenic in situ hybridization for EBV-encoded small RNA, with positive samples further characterized by immunohistochemistry for CD3, CD15, CD20, CD30, CD138, MUM1, and PAX5. In addition, all samples were immunostained for cytomegalovirus, and PCR was used to assess B cell and T cell clonality.
The median time from induction of therapy to colitis onset was approximately 1 month (32.5 days), with symptoms typically lasting 3 weeks (22.5 days). Macroscopically, 10 patients had ulceration, and 6 displayed signs of hemorrhage.
EBVMCUs were found in four patients, of whom three had received anti-CTLA-4 therapy, one had received both anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 therapy, and all had undergone colonic resection. One case also tested positive for cytomegalovirus.
Immunostaining showed that EBVMCUs had underlying B cell and linear plasma cell infiltrates, with “a rim of small T lymphocytes at the base.” EBV-encoded small RNA expression was found in both plasma cells and small B cells.
The presence of EBVMCUs was significantly associated with more severe colitis.
All four EBV-positive patients had steroid-refractory colitis, compared with only two (12.5%) of the EBV-negative patients (P = .008), a difference that was echoed by the rate of colonic resection (100% vs. 12.5%; P .008). Furthermore, colon perforation occurred in all EBV-positive patients, versus none of the EBV-negative patients (P = .001).
For three EBV-positive patients, preresection biopsy samples were available, allowing for temporal analysis of EBV-encoded small RNA. Earlier samples had reduced or absent EBV-positive lymphoid cells, which offered some etiologic insight.
“The apparent absence or paucity of EBV-positive lymphoid cells in biopsies taken before resection suggests that EBVMCU is arising within preexisting immune-mediated inflammation rather than EBV driving the initial inflammatory insult,” the investigators wrote.
They suggested that EBVMCUs “likely contribute directly to colonic perforation,” since lesions are characterized by a form of localized tissue destruction that has been previously associated with colonic perforation in Crohn’s disease and intestinal perforation in rheumatoid arthritis.
Still, mechanisms of action remain unknown. “It is unclear why EBVMCUs should arise in the context of immune checkpoint regulator therapy, which, in contrast to conventional immunosuppressants, results in immune activation,” the investigators wrote. “It is possible that these patients may harbor residual immunosuppression resulting from their disease burden, advanced age, and prior immunosuppression.”
While more work is needed, Dr. Pugh and colleagues suggested that EBV testing may be valuable for some patients.
“The findings support the need for further studies investigating the role of EBV monitoring in immune checkpoint regulator therapy, which is not currently part of routine protocols.”
The study was funded by All Wales Lymphoma Panel. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Pugh et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Oct 11. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.09.031.
Immune checkpoint regulators (iCRs) have become common in the treatment for various cancers. Immune-related colitis (irColitis) is among the most common side effects of iCRs, as well as one of the most common etiologies of fatal toxicities from iCRs. However, much is still unknown on the pathophysiology behind irColitis or its complications. Pugh et al. performed detailed analyses of the potential role of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in irColitis. Rather than depend on serologies for EBV, the investigators utilized robust evaluation for colonic mucosal EBV with in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and polymerase chain reaction. Interestingly, in the EBV-positive patients with endoscopic biopsies performed prior to perforation, EBV RNA were minimal or absent on endoscopic biopsies. This finding suggests EBV may be related to the immunosuppression used to treat the colitis rather than the primary driver of irColitis. This observation could have important clinical implications in using steroids for irColitis; we may be increasing the risk of perforation related to EBV by using steroids or other immunosuppression. While we need to interpret these findings with caution given the small sample size and comparisons between endoscopic biopsies and surgical specimens for EBV, this study highlights the potential role of EBV in steroid-refractory irColitis. An additional clinical implication from this study is that endoscopic biopsies did not identify patients who would eventually develop colonic perforation. We therefore cannot assume a patient with negative colonic biopsies for EBV is truly negative. Better means for assessing EBV status and predicting complications are still needed.
Jason K. Hou, MD, is assistant professor of medicine and gastroenterology; director of the GI and hepatology fellowship program; and director of research and IBD at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. He is a staff physician in the department of gastroenterology, and medical director, IBD, at Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, Houston. He has no conflicts of interest.
Immune checkpoint regulators (iCRs) have become common in the treatment for various cancers. Immune-related colitis (irColitis) is among the most common side effects of iCRs, as well as one of the most common etiologies of fatal toxicities from iCRs. However, much is still unknown on the pathophysiology behind irColitis or its complications. Pugh et al. performed detailed analyses of the potential role of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in irColitis. Rather than depend on serologies for EBV, the investigators utilized robust evaluation for colonic mucosal EBV with in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and polymerase chain reaction. Interestingly, in the EBV-positive patients with endoscopic biopsies performed prior to perforation, EBV RNA were minimal or absent on endoscopic biopsies. This finding suggests EBV may be related to the immunosuppression used to treat the colitis rather than the primary driver of irColitis. This observation could have important clinical implications in using steroids for irColitis; we may be increasing the risk of perforation related to EBV by using steroids or other immunosuppression. While we need to interpret these findings with caution given the small sample size and comparisons between endoscopic biopsies and surgical specimens for EBV, this study highlights the potential role of EBV in steroid-refractory irColitis. An additional clinical implication from this study is that endoscopic biopsies did not identify patients who would eventually develop colonic perforation. We therefore cannot assume a patient with negative colonic biopsies for EBV is truly negative. Better means for assessing EBV status and predicting complications are still needed.
Jason K. Hou, MD, is assistant professor of medicine and gastroenterology; director of the GI and hepatology fellowship program; and director of research and IBD at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. He is a staff physician in the department of gastroenterology, and medical director, IBD, at Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, Houston. He has no conflicts of interest.
Immune checkpoint regulators (iCRs) have become common in the treatment for various cancers. Immune-related colitis (irColitis) is among the most common side effects of iCRs, as well as one of the most common etiologies of fatal toxicities from iCRs. However, much is still unknown on the pathophysiology behind irColitis or its complications. Pugh et al. performed detailed analyses of the potential role of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in irColitis. Rather than depend on serologies for EBV, the investigators utilized robust evaluation for colonic mucosal EBV with in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and polymerase chain reaction. Interestingly, in the EBV-positive patients with endoscopic biopsies performed prior to perforation, EBV RNA were minimal or absent on endoscopic biopsies. This finding suggests EBV may be related to the immunosuppression used to treat the colitis rather than the primary driver of irColitis. This observation could have important clinical implications in using steroids for irColitis; we may be increasing the risk of perforation related to EBV by using steroids or other immunosuppression. While we need to interpret these findings with caution given the small sample size and comparisons between endoscopic biopsies and surgical specimens for EBV, this study highlights the potential role of EBV in steroid-refractory irColitis. An additional clinical implication from this study is that endoscopic biopsies did not identify patients who would eventually develop colonic perforation. We therefore cannot assume a patient with negative colonic biopsies for EBV is truly negative. Better means for assessing EBV status and predicting complications are still needed.
Jason K. Hou, MD, is assistant professor of medicine and gastroenterology; director of the GI and hepatology fellowship program; and director of research and IBD at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. He is a staff physician in the department of gastroenterology, and medical director, IBD, at Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, Houston. He has no conflicts of interest.
For patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced colitis, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection may increase risks of steroid-refractory disease and ulcers that contribute to colonic perforation, according to investigators.
Pending further research, routine monitoring of EBV status may be needed for patients undergoing checkpoint inhibitor therapy, reported lead author Matthew R. Pugh, FRCPath, of University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff, and colleagues.
“Few studies have investigated the role of viruses in the pathogenesis of immune-related colitis,” the investigators wrote. Their report is in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. While cytomegalovirus has been linked with worse disease, no studies to date have evaluated the role of EBV, they noted, despite theoretical concerns.
“A spectrum of EBV-positive lymphoproliferations shows a predilection for the GI tract, ranging from indolent lesions to aggressive lymphomas,” the investigators wrote. “One such proliferation, EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer (EBVMCU), is an indolent, ulcerating process associated with immunosuppression,” they added, referring to studies involving patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
To determine if EBV could be playing a similar role in cancer immunotherapy, the investigators retrospectively analyzed colon tissue samples from 16 patients who developed colitis after undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy between 2010 and 2018. Thirteen patients received an anti-CTLA-4 agent, three were treated with a PD-1 inhibitor, and four received both types of therapy. Most patients had advanced-stage melanoma (n = 14), while the remaining two patients had prostate and renal carcinoma, respectively. Ten samples were biopsies, whereas four specimens were collected from surgical repair of colon perforation.
EBV status was determined by chromogenic in situ hybridization for EBV-encoded small RNA, with positive samples further characterized by immunohistochemistry for CD3, CD15, CD20, CD30, CD138, MUM1, and PAX5. In addition, all samples were immunostained for cytomegalovirus, and PCR was used to assess B cell and T cell clonality.
The median time from induction of therapy to colitis onset was approximately 1 month (32.5 days), with symptoms typically lasting 3 weeks (22.5 days). Macroscopically, 10 patients had ulceration, and 6 displayed signs of hemorrhage.
EBVMCUs were found in four patients, of whom three had received anti-CTLA-4 therapy, one had received both anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 therapy, and all had undergone colonic resection. One case also tested positive for cytomegalovirus.
Immunostaining showed that EBVMCUs had underlying B cell and linear plasma cell infiltrates, with “a rim of small T lymphocytes at the base.” EBV-encoded small RNA expression was found in both plasma cells and small B cells.
The presence of EBVMCUs was significantly associated with more severe colitis.
All four EBV-positive patients had steroid-refractory colitis, compared with only two (12.5%) of the EBV-negative patients (P = .008), a difference that was echoed by the rate of colonic resection (100% vs. 12.5%; P .008). Furthermore, colon perforation occurred in all EBV-positive patients, versus none of the EBV-negative patients (P = .001).
For three EBV-positive patients, preresection biopsy samples were available, allowing for temporal analysis of EBV-encoded small RNA. Earlier samples had reduced or absent EBV-positive lymphoid cells, which offered some etiologic insight.
“The apparent absence or paucity of EBV-positive lymphoid cells in biopsies taken before resection suggests that EBVMCU is arising within preexisting immune-mediated inflammation rather than EBV driving the initial inflammatory insult,” the investigators wrote.
They suggested that EBVMCUs “likely contribute directly to colonic perforation,” since lesions are characterized by a form of localized tissue destruction that has been previously associated with colonic perforation in Crohn’s disease and intestinal perforation in rheumatoid arthritis.
Still, mechanisms of action remain unknown. “It is unclear why EBVMCUs should arise in the context of immune checkpoint regulator therapy, which, in contrast to conventional immunosuppressants, results in immune activation,” the investigators wrote. “It is possible that these patients may harbor residual immunosuppression resulting from their disease burden, advanced age, and prior immunosuppression.”
While more work is needed, Dr. Pugh and colleagues suggested that EBV testing may be valuable for some patients.
“The findings support the need for further studies investigating the role of EBV monitoring in immune checkpoint regulator therapy, which is not currently part of routine protocols.”
The study was funded by All Wales Lymphoma Panel. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Pugh et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Oct 11. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.09.031.
For patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced colitis, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection may increase risks of steroid-refractory disease and ulcers that contribute to colonic perforation, according to investigators.
Pending further research, routine monitoring of EBV status may be needed for patients undergoing checkpoint inhibitor therapy, reported lead author Matthew R. Pugh, FRCPath, of University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff, and colleagues.
“Few studies have investigated the role of viruses in the pathogenesis of immune-related colitis,” the investigators wrote. Their report is in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. While cytomegalovirus has been linked with worse disease, no studies to date have evaluated the role of EBV, they noted, despite theoretical concerns.
“A spectrum of EBV-positive lymphoproliferations shows a predilection for the GI tract, ranging from indolent lesions to aggressive lymphomas,” the investigators wrote. “One such proliferation, EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer (EBVMCU), is an indolent, ulcerating process associated with immunosuppression,” they added, referring to studies involving patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
To determine if EBV could be playing a similar role in cancer immunotherapy, the investigators retrospectively analyzed colon tissue samples from 16 patients who developed colitis after undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy between 2010 and 2018. Thirteen patients received an anti-CTLA-4 agent, three were treated with a PD-1 inhibitor, and four received both types of therapy. Most patients had advanced-stage melanoma (n = 14), while the remaining two patients had prostate and renal carcinoma, respectively. Ten samples were biopsies, whereas four specimens were collected from surgical repair of colon perforation.
EBV status was determined by chromogenic in situ hybridization for EBV-encoded small RNA, with positive samples further characterized by immunohistochemistry for CD3, CD15, CD20, CD30, CD138, MUM1, and PAX5. In addition, all samples were immunostained for cytomegalovirus, and PCR was used to assess B cell and T cell clonality.
The median time from induction of therapy to colitis onset was approximately 1 month (32.5 days), with symptoms typically lasting 3 weeks (22.5 days). Macroscopically, 10 patients had ulceration, and 6 displayed signs of hemorrhage.
EBVMCUs were found in four patients, of whom three had received anti-CTLA-4 therapy, one had received both anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 therapy, and all had undergone colonic resection. One case also tested positive for cytomegalovirus.
Immunostaining showed that EBVMCUs had underlying B cell and linear plasma cell infiltrates, with “a rim of small T lymphocytes at the base.” EBV-encoded small RNA expression was found in both plasma cells and small B cells.
The presence of EBVMCUs was significantly associated with more severe colitis.
All four EBV-positive patients had steroid-refractory colitis, compared with only two (12.5%) of the EBV-negative patients (P = .008), a difference that was echoed by the rate of colonic resection (100% vs. 12.5%; P .008). Furthermore, colon perforation occurred in all EBV-positive patients, versus none of the EBV-negative patients (P = .001).
For three EBV-positive patients, preresection biopsy samples were available, allowing for temporal analysis of EBV-encoded small RNA. Earlier samples had reduced or absent EBV-positive lymphoid cells, which offered some etiologic insight.
“The apparent absence or paucity of EBV-positive lymphoid cells in biopsies taken before resection suggests that EBVMCU is arising within preexisting immune-mediated inflammation rather than EBV driving the initial inflammatory insult,” the investigators wrote.
They suggested that EBVMCUs “likely contribute directly to colonic perforation,” since lesions are characterized by a form of localized tissue destruction that has been previously associated with colonic perforation in Crohn’s disease and intestinal perforation in rheumatoid arthritis.
Still, mechanisms of action remain unknown. “It is unclear why EBVMCUs should arise in the context of immune checkpoint regulator therapy, which, in contrast to conventional immunosuppressants, results in immune activation,” the investigators wrote. “It is possible that these patients may harbor residual immunosuppression resulting from their disease burden, advanced age, and prior immunosuppression.”
While more work is needed, Dr. Pugh and colleagues suggested that EBV testing may be valuable for some patients.
“The findings support the need for further studies investigating the role of EBV monitoring in immune checkpoint regulator therapy, which is not currently part of routine protocols.”
The study was funded by All Wales Lymphoma Panel. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Pugh et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Oct 11. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.09.031.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Assessing Spinal Muscular Atrophy Across the Patient Journey

Click here to read.
Supplement Faculty
Perry Shieh, MD, PhD
Professor
Department of Neurology
David Geffen School
of Medicine at UCLA
Ronald Reagan UCLA
Medical Center
Los Angeles, CA
Sally Dunaway Young, PT, DPT
Physical Therapist
and Clinical Research
Evaluator/Manager
Stanford University School
of Medicine
Stanford, CA

Click here to read.
Supplement Faculty
Perry Shieh, MD, PhD
Professor
Department of Neurology
David Geffen School
of Medicine at UCLA
Ronald Reagan UCLA
Medical Center
Los Angeles, CA
Sally Dunaway Young, PT, DPT
Physical Therapist
and Clinical Research
Evaluator/Manager
Stanford University School
of Medicine
Stanford, CA

Click here to read.
Supplement Faculty
Perry Shieh, MD, PhD
Professor
Department of Neurology
David Geffen School
of Medicine at UCLA
Ronald Reagan UCLA
Medical Center
Los Angeles, CA
Sally Dunaway Young, PT, DPT
Physical Therapist
and Clinical Research
Evaluator/Manager
Stanford University School
of Medicine
Stanford, CA
Medical ethics in the time of COVID-19
It is clear that the coronavirus 2019 disease (COVID-19) pandemic is one of the most extraordinary epochs of our professional and personal lives. Besides the challenges to the techniques and technologies of care for this illness, we are seeing challenges to the fundamentals of health care, both to the systems whereby it is delivered, and to the ethical principles that guide that delivery. There is unprecedented relevance of certain ethical issues in the practice of medicine, many of which have previously been discussed in classrooms and textbooks, but now are at play in daily practice, particularly at the frontlines of the war against COVID-19.1 In this article, I highlight several ethical dilemmas that are salient to these unique times. Some of the most compelling issues can be sorted into 2 clearly overlapping domains: triage ethics and equity ethics.
Triage ethics
In the areas most greatly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, scarcity of treatment resources, such as ventilators, is a legitimate concern. French surgeon Dominique Jean Larry was the first to establish medical sorting protocols in the context of the battles of the Napoleonic wars, for which he used the French word triage, meaning “sorting.”2 He articulated 3 prognostic categories: 1) those who would die even with treatment, 2) those who would live without treatment, and 3) those who would die unless treated. Triage decisions arise in the context of insufficient resources, particularly space, staff, and supplies. Although usually identified with disasters, these decisions can arise in other contexts where personnel or technological resources are inadequate. Indeed, one of the first modern incarnations of triage ethics in American civilian life was in the early days of hemodialysis, when so-called “God committees” made complex decisions about which patients would be able to use this new, rare technology.3
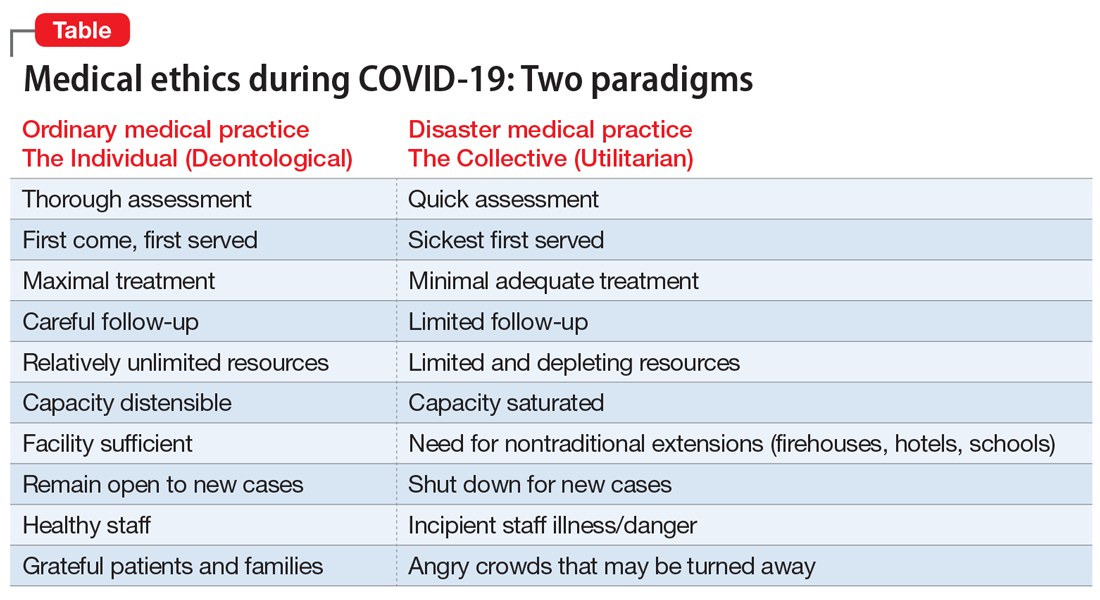
Two fundamental moral constructs undergird medical ethics: deontological and utilitarian. The former, in which most clinicians traffic in ordinary practice, is driven by principles or moral rules such as the sanctity of life, the rule of fairness, and the principle of autonomy.4 They apply primarily in the context of treating an individual patient. The utilitarian way of reasoning is not as familiar to clinicians. It is focused on the broader context, the common good, the health of the group. It asks to calculate “the greatest good for the greatest number” as a means of navigating ethical dilemmas.5 The utilitarian perspective is far more familiar to policymakers, health care administrators, and public health professionals. It tends to be anathema to clinicians. However, disasters such as the COVID-19 pandemic ask some clinicians, particularly inpatient physicians, to shift from their usual deontological perspective to a utilitarian one, because triage ethics fundamentally draw on utilitarian reasoning. This can be quite anguishing to clinicians who typically work with individual patients in settings of more adequate, if not abundant, resources. What may feel wrong in a deontological mode can be seen as ethically right in a utilitarian framework.
The Table compares and contrasts these 2 paradigms and how they manifest in the clinical trenches, in a protracted health care crisis with limited resources.
The COVID-19 crisis has produced an unprecedented and extended exposure of clinicians to triage situations in the face of limited resources such as ventilators, personnel, personal protective equipment, etc.6 Numerous possible approaches to deploying limited supplies are being considered. On what basis should such decisions be made? How can fairness be optimally manifest? Some possibilities include:
- first come, first served
- youngest first
- lottery
- short-term survivability
- long-term prognosis for quality of life
- value of a patient to the lives of others (eg, parents, health care workers, vaccine researchers).
One particularly interesting exploration of these questions was done in Maryland and reported in the “Maryland Framework for the Allocation of Scarce Life-sustaining Medical Resources in a Catastrophic Public Health Emergency.”7 This was the product of a multi-year consultation, ending in 2017, with several constituencies, including clinicians, politicians, hospital administrators, and members of the public brainstorming about approaches to allocating a hypothetical scarcity of ventilators. Interestingly, there was one broad consensus among these groups: a ventilator should not be withdrawn from a patient already using it to give to a “better” candidate who comes along later.
Some institutions have developed a method of making triage decisions that takes such decisions out of the hands of individual clinicians and instead assigns them to specialized “triage teams” made up of ethicists and clinicians experienced in critical care, to develop more distance from the emotions at the bedside. To minimize bias, such teams are often insulated from getting personal information about the patient, and receive only acute clinical information.8
Continue to: The pros and cons of these approaches...
The pros and cons of these approaches and the underlying ethical reasoning is beyond the scope of this overview. Policy documents from different states, regions, nations, and institutions have various approaches to making these choices. Presently, there is no coherent national or international agreement on triage ethics.9 It is important, however, that there be transparency in whatever approach an institution adopts for triage decisions.
Equity ethics
Though the equitable distribution of health care delivery has long been a concern, this problem has become magnified by the COVID-19 crisis. Race, sex, age, socioeconomic class, and type of illness have all been perennial sources of division between those who have better or worse access to health care and its outcomes. All of these distinctions have created differentials in rates of cases, hospitalizations, and deaths in the COVID-19 pandemic.10
The shifting of acute health care facilities to mostly COVID-19–related treatment, and postponing less critical and more “elective” care, creates a divide based on illness type. Many facilities have stopped taking admissions for other kinds of cases. This is particularly relevant to psychiatric units, many of which have had to decrease their bed capacities to make all rooms private, and limit their usual treatments offered to inpatients.11 Many long-term units, such as at state hospitals, are closing to new admissions. Many day hospitals and intensive outpatient programs remain closed, not even shifting to telehealth. In areas most affected by COVID-19, some institutions have closed psychiatric wards and reallocated psychiatrists to cover some of the medical units. So the availability of the more intensive, institutionally-based levels of care is significantly reduced, particularly for psychiatric patients.12 These patients already are a disadvantaged population in the distribution of health care resources, and the care of individuals with serious mental illness is more likely to be seen as “nonessential” in this time of suddenly scarcer institutional resources.
One of the cherished ethical values in health care is autonomy, and in a deontological triage environment, honoring patient autonomy is carefully and tenderly administered. However, in a utilitarian-driven triage environment, considerations of the common good can trump autonomy, even in subtle ways that create inequities. Clinicians have been advised to have more frank conversations with patients, particularly those with chronic illnesses, stepping up initiatives to make advanced directives during this crisis, explicitly reminding patients that there may not be enough ventilators for all who need one.13 Some have argued that such physician-initiated conversations can be inherently coercive, making these decisions not as autonomous as it may appear, similar to physicians suggesting medical euthanasia as an option.14 Interestingly, some jurisdictions that offer euthanasia have been suspending such services during the COVID-19 crisis.15 Some hospitals have even wrestled with the possibility that all COVID-19 admissions should be considered “do not resuscitate,” especially because cardiopulmonary resuscitation significantly elevates the risks of viral exposure for the treatment team.16,17 A more explicit example of how current standards protecting patient autonomy may be challenged is patients who are admitted involuntarily to a psychiatric unit. These are patients whose presumptively impaired autonomy is already being overridden by the involuntary nature of the admission. If a psychiatric unit requires admissions to be COVID-19–negative, and if patients refuse COVID-19 testing, should the testing be forced upon them to protect the entire milieu?
Many ethicists are highlighting the embedded equity bias known as “ableism” inherent in triage decisions—implicitly disfavoring resources for patients with COVID-19 who are already physically or intellectually disabled, chronically ill, aged, homeless, psychosocially low functioning, etc.18 Without explicit protections for individuals who are chronically disabled, triage decisions unguided by policy safeguards may reflexively favor the more “abled.” This bias towards the more abled is often inherent in how difficult it is to access health care. It can also be manifested in bedside triage decisions made in the moment by individual clinicians. Many disability rights advocates have been sounding this alarm during the COVID-19 crisis.19
Continue to: A special circumstance of equity...
A special circumstance of equity is arising during this ongoing pandemic—the possibility of treating health care workers as a privileged class. Unlike typical disasters, where health care workers come in afterwards, and therefore are in relatively less danger, pandemics create particularly high risks of danger for such individuals, with repeated exposure to the virus. They are both responders and potential victims. Should they have higher priority for ventilators, vaccines, funding, etc?6 This is a more robust degree of compensatory justice than merely giving appreciation. Giving health care workers such advantages may seem intuitively appealing, but perhaps professionalism and the self-obligation of duty mitigates such claims.20
A unique opportunity
The magnitude and pervasiveness of this pandemic crisis is unique in our lifetimes, as both professionals and as citizens. In the crucible of this extraordinary time, these and other medical ethics dilemmas burn hotter than ever before. Different societies and institutions may come up with different answers, based on their cultures and values. It is important, however, that the venerable ethos of medical ethics, which has evolved through the millennia, codified in oaths, codes, and scholarship, can be a compass at the bedside and in the meetings of legislatures, leaders, and policymakers. Perhaps we can emerge from this time with more clarity about how to balance the preciousness of individual rights with the needs of the common good.
Bottom Line
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has brought increased attention to triage ethics and equity ethics. There is no coherent national or international agreement on how to best deploy limited supplies such as ventilators and personal protective equipment. Although the equitable distribution of health care delivery has long been a concern, this problem has become magnified by COVID-19. Clinicians may be asked to view health care through the less familiar lens of the common good, as opposed to focusing strictly on an individual patient.
Related Resources
- Johns Hopkins Berman Institute of Bioethics. Coronavirus ethics and policy insights and resources. https://bioethics.jhu.edu/research-and-outreach/covid-19-bioethics-expert-insights/.
- Daugherty-Biddison L, Gwon H, Regenberg A, et al. Maryland framework for the allocation of scarce lifesustaining medical resources in a catastrophic public health emergency. www.law.umaryland.edu/media/SOL/pdfs/Programs/Health-Law/MHECN/ASR%20Framework_Final.pdf.
1. AMA Journal of Ethics. COVID-19 ethics resource center. https://journalofethics.ama-assn.org/COVID-19-ethics-resource-center. Updated May 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
2. Skandakalis PN, Lainas P, Zoras O, et al. “To afford the wounded speedy assistance”: Dominique Jean Larrey and Napoleon. World J Surg. 2006;30(8):1392-1399.
3. Ross W. God panels and the history of hemodialysis in America: a cautionary tale. Virtual Mentor. 2012;14(11):890-896.
4. Alexander L, Moore M. Deontological ethics. In: Zalta EN, ed. Stanford encyclopedia of philosophy. https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/ethics-deontological/. Revised October 17, 2016. Accessed May 26, 2020.
5. Driver J. The history of utilitarianism. In: Zalta EN, ed. Stanford encyclopedia of philosophy. https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/utilitarianism-history/. Revised September 22, 2014. Accessed May 26, 2020.
6. Emanuel EJ, Persad G, Upshur R, et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(21):2049-2055.
7. Daugherty-Biddison EL, Faden R, Gwon HW, et al. Too many patients…a framework to guide statewide allocation of scarce mechanical ventilation during disasters. Chest. 2019;155(4):848-854.
8. Dudzinski D, Campelia G, Brazg T. Pandemic resources including COVID-19 materials. Department of Bioethics and Humanities, University of Washington Medicine. http://depts.washington.edu/bhdept/ethics-medicine/bioethics-topics/detail/245. Published April 6, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
9. Antommaria AHM, Gibb TS, McGuire AL, et al; Task Force of the Association of Bioethics Program Directors. Ventilator triage policies during the COVID-19 pandemic at U.S. hospitals associated with members of the Association of Bioethics Program Directors [published online April 24, 2020]. Ann Intern Med. 2020;M20-1738. doi: 10.7326/M20-1738.
10. Cooney E. Who gets hospitalized for COVID-19? Report shows differences by race and sex. STAT. https://www.statnews.com/2020/04/09/hospitalized-COVID-19-patients-differences-by-race-and-sex/. Published April 9, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
11. Gessen M. Why psychiatric wards are uniquely vulnerable to the coronavirus. The New Yorker. https://www.newyorker.com/news/news-desk/why-psychiatric-wards-are-uniquely-vulnerable-to-the-coronavirus. Published April 21, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
12. American Psychiatric Association Ethics Committee. COVID-19 related opinions of the APA Ethics Committee. American Psychiatric Association. https://www.psychiatry.org/File%20Library/Psychiatrists/Practice/Ethics/APA-COVID-19-Ethics-Opinions.pdf. Published May 5, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
13. Wee M. Coronavirus and the misuse of ‘do not resuscitate’ orders. The Spectator. https://www.spectator.co.uk/article/coronavirus-and-the-misuse-of-do-not-resuscitate-orders. Published May 6, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
14. Prokopetz JZ, Lehmann LS. Redefining physicians’ role in assisted dying. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(20):97-99.
15. Yuill K, Boer T. What COVID-19 has revealed about euthanasia. spiked. https://www.spiked-online.com/2020/04/14/COVID-19-has-revealed-the-ugliness-of-euthanasia/. Published April 14, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
16. Plunkett AJ. COVID-19: hospitals should consider CoP carefully before deciding on DNR policy. PSQH. https://www.psqh.com/news/COVID-19-hospitals-should-consider-cop-carefully-before-deciding-on-dnr-policy/. Published March 26, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
17. Kramer DB, Lo B, Dickert NW. CPR in the COVID-19 era: an ethical framework [published online May 6, 2020]. N Engl J Med. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2010758.
18. Mykitiuk R, Lemmens T. Assessing the value of a life: COVID-19 triage orders mustn’t work against those with disabilities. CBC News. https://www.cbc.ca/news/opinion/opinion-disabled-COVID-19-triage-orders-1.5532137. Published April 19, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
19. Solomon MZ, Wynia MK, Gostin LO. COVID-19 crisis triage—optimizing health outcomes and disability rights [published online May 19, 2020]. N Engl J Med. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2008300.
20. Appel JM. Ethics consult: who’s first to get COVID-19 Vax? MD/JD bangs gavel. MedPage Today. https://www.medpagetoday.com/infectiousdisease/COVID19/86260. Published May 1, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
It is clear that the coronavirus 2019 disease (COVID-19) pandemic is one of the most extraordinary epochs of our professional and personal lives. Besides the challenges to the techniques and technologies of care for this illness, we are seeing challenges to the fundamentals of health care, both to the systems whereby it is delivered, and to the ethical principles that guide that delivery. There is unprecedented relevance of certain ethical issues in the practice of medicine, many of which have previously been discussed in classrooms and textbooks, but now are at play in daily practice, particularly at the frontlines of the war against COVID-19.1 In this article, I highlight several ethical dilemmas that are salient to these unique times. Some of the most compelling issues can be sorted into 2 clearly overlapping domains: triage ethics and equity ethics.
Triage ethics
In the areas most greatly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, scarcity of treatment resources, such as ventilators, is a legitimate concern. French surgeon Dominique Jean Larry was the first to establish medical sorting protocols in the context of the battles of the Napoleonic wars, for which he used the French word triage, meaning “sorting.”2 He articulated 3 prognostic categories: 1) those who would die even with treatment, 2) those who would live without treatment, and 3) those who would die unless treated. Triage decisions arise in the context of insufficient resources, particularly space, staff, and supplies. Although usually identified with disasters, these decisions can arise in other contexts where personnel or technological resources are inadequate. Indeed, one of the first modern incarnations of triage ethics in American civilian life was in the early days of hemodialysis, when so-called “God committees” made complex decisions about which patients would be able to use this new, rare technology.3
Two fundamental moral constructs undergird medical ethics: deontological and utilitarian. The former, in which most clinicians traffic in ordinary practice, is driven by principles or moral rules such as the sanctity of life, the rule of fairness, and the principle of autonomy.4 They apply primarily in the context of treating an individual patient. The utilitarian way of reasoning is not as familiar to clinicians. It is focused on the broader context, the common good, the health of the group. It asks to calculate “the greatest good for the greatest number” as a means of navigating ethical dilemmas.5 The utilitarian perspective is far more familiar to policymakers, health care administrators, and public health professionals. It tends to be anathema to clinicians. However, disasters such as the COVID-19 pandemic ask some clinicians, particularly inpatient physicians, to shift from their usual deontological perspective to a utilitarian one, because triage ethics fundamentally draw on utilitarian reasoning. This can be quite anguishing to clinicians who typically work with individual patients in settings of more adequate, if not abundant, resources. What may feel wrong in a deontological mode can be seen as ethically right in a utilitarian framework.
The Table compares and contrasts these 2 paradigms and how they manifest in the clinical trenches, in a protracted health care crisis with limited resources.
The COVID-19 crisis has produced an unprecedented and extended exposure of clinicians to triage situations in the face of limited resources such as ventilators, personnel, personal protective equipment, etc.6 Numerous possible approaches to deploying limited supplies are being considered. On what basis should such decisions be made? How can fairness be optimally manifest? Some possibilities include:
- first come, first served
- youngest first
- lottery
- short-term survivability
- long-term prognosis for quality of life
- value of a patient to the lives of others (eg, parents, health care workers, vaccine researchers).
One particularly interesting exploration of these questions was done in Maryland and reported in the “Maryland Framework for the Allocation of Scarce Life-sustaining Medical Resources in a Catastrophic Public Health Emergency.”7 This was the product of a multi-year consultation, ending in 2017, with several constituencies, including clinicians, politicians, hospital administrators, and members of the public brainstorming about approaches to allocating a hypothetical scarcity of ventilators. Interestingly, there was one broad consensus among these groups: a ventilator should not be withdrawn from a patient already using it to give to a “better” candidate who comes along later.
Some institutions have developed a method of making triage decisions that takes such decisions out of the hands of individual clinicians and instead assigns them to specialized “triage teams” made up of ethicists and clinicians experienced in critical care, to develop more distance from the emotions at the bedside. To minimize bias, such teams are often insulated from getting personal information about the patient, and receive only acute clinical information.8
Continue to: The pros and cons of these approaches...
The pros and cons of these approaches and the underlying ethical reasoning is beyond the scope of this overview. Policy documents from different states, regions, nations, and institutions have various approaches to making these choices. Presently, there is no coherent national or international agreement on triage ethics.9 It is important, however, that there be transparency in whatever approach an institution adopts for triage decisions.
Equity ethics
Though the equitable distribution of health care delivery has long been a concern, this problem has become magnified by the COVID-19 crisis. Race, sex, age, socioeconomic class, and type of illness have all been perennial sources of division between those who have better or worse access to health care and its outcomes. All of these distinctions have created differentials in rates of cases, hospitalizations, and deaths in the COVID-19 pandemic.10
The shifting of acute health care facilities to mostly COVID-19–related treatment, and postponing less critical and more “elective” care, creates a divide based on illness type. Many facilities have stopped taking admissions for other kinds of cases. This is particularly relevant to psychiatric units, many of which have had to decrease their bed capacities to make all rooms private, and limit their usual treatments offered to inpatients.11 Many long-term units, such as at state hospitals, are closing to new admissions. Many day hospitals and intensive outpatient programs remain closed, not even shifting to telehealth. In areas most affected by COVID-19, some institutions have closed psychiatric wards and reallocated psychiatrists to cover some of the medical units. So the availability of the more intensive, institutionally-based levels of care is significantly reduced, particularly for psychiatric patients.12 These patients already are a disadvantaged population in the distribution of health care resources, and the care of individuals with serious mental illness is more likely to be seen as “nonessential” in this time of suddenly scarcer institutional resources.
One of the cherished ethical values in health care is autonomy, and in a deontological triage environment, honoring patient autonomy is carefully and tenderly administered. However, in a utilitarian-driven triage environment, considerations of the common good can trump autonomy, even in subtle ways that create inequities. Clinicians have been advised to have more frank conversations with patients, particularly those with chronic illnesses, stepping up initiatives to make advanced directives during this crisis, explicitly reminding patients that there may not be enough ventilators for all who need one.13 Some have argued that such physician-initiated conversations can be inherently coercive, making these decisions not as autonomous as it may appear, similar to physicians suggesting medical euthanasia as an option.14 Interestingly, some jurisdictions that offer euthanasia have been suspending such services during the COVID-19 crisis.15 Some hospitals have even wrestled with the possibility that all COVID-19 admissions should be considered “do not resuscitate,” especially because cardiopulmonary resuscitation significantly elevates the risks of viral exposure for the treatment team.16,17 A more explicit example of how current standards protecting patient autonomy may be challenged is patients who are admitted involuntarily to a psychiatric unit. These are patients whose presumptively impaired autonomy is already being overridden by the involuntary nature of the admission. If a psychiatric unit requires admissions to be COVID-19–negative, and if patients refuse COVID-19 testing, should the testing be forced upon them to protect the entire milieu?
Many ethicists are highlighting the embedded equity bias known as “ableism” inherent in triage decisions—implicitly disfavoring resources for patients with COVID-19 who are already physically or intellectually disabled, chronically ill, aged, homeless, psychosocially low functioning, etc.18 Without explicit protections for individuals who are chronically disabled, triage decisions unguided by policy safeguards may reflexively favor the more “abled.” This bias towards the more abled is often inherent in how difficult it is to access health care. It can also be manifested in bedside triage decisions made in the moment by individual clinicians. Many disability rights advocates have been sounding this alarm during the COVID-19 crisis.19
Continue to: A special circumstance of equity...
A special circumstance of equity is arising during this ongoing pandemic—the possibility of treating health care workers as a privileged class. Unlike typical disasters, where health care workers come in afterwards, and therefore are in relatively less danger, pandemics create particularly high risks of danger for such individuals, with repeated exposure to the virus. They are both responders and potential victims. Should they have higher priority for ventilators, vaccines, funding, etc?6 This is a more robust degree of compensatory justice than merely giving appreciation. Giving health care workers such advantages may seem intuitively appealing, but perhaps professionalism and the self-obligation of duty mitigates such claims.20
A unique opportunity
The magnitude and pervasiveness of this pandemic crisis is unique in our lifetimes, as both professionals and as citizens. In the crucible of this extraordinary time, these and other medical ethics dilemmas burn hotter than ever before. Different societies and institutions may come up with different answers, based on their cultures and values. It is important, however, that the venerable ethos of medical ethics, which has evolved through the millennia, codified in oaths, codes, and scholarship, can be a compass at the bedside and in the meetings of legislatures, leaders, and policymakers. Perhaps we can emerge from this time with more clarity about how to balance the preciousness of individual rights with the needs of the common good.
Bottom Line
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has brought increased attention to triage ethics and equity ethics. There is no coherent national or international agreement on how to best deploy limited supplies such as ventilators and personal protective equipment. Although the equitable distribution of health care delivery has long been a concern, this problem has become magnified by COVID-19. Clinicians may be asked to view health care through the less familiar lens of the common good, as opposed to focusing strictly on an individual patient.
Related Resources
- Johns Hopkins Berman Institute of Bioethics. Coronavirus ethics and policy insights and resources. https://bioethics.jhu.edu/research-and-outreach/covid-19-bioethics-expert-insights/.
- Daugherty-Biddison L, Gwon H, Regenberg A, et al. Maryland framework for the allocation of scarce lifesustaining medical resources in a catastrophic public health emergency. www.law.umaryland.edu/media/SOL/pdfs/Programs/Health-Law/MHECN/ASR%20Framework_Final.pdf.
It is clear that the coronavirus 2019 disease (COVID-19) pandemic is one of the most extraordinary epochs of our professional and personal lives. Besides the challenges to the techniques and technologies of care for this illness, we are seeing challenges to the fundamentals of health care, both to the systems whereby it is delivered, and to the ethical principles that guide that delivery. There is unprecedented relevance of certain ethical issues in the practice of medicine, many of which have previously been discussed in classrooms and textbooks, but now are at play in daily practice, particularly at the frontlines of the war against COVID-19.1 In this article, I highlight several ethical dilemmas that are salient to these unique times. Some of the most compelling issues can be sorted into 2 clearly overlapping domains: triage ethics and equity ethics.
Triage ethics
In the areas most greatly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, scarcity of treatment resources, such as ventilators, is a legitimate concern. French surgeon Dominique Jean Larry was the first to establish medical sorting protocols in the context of the battles of the Napoleonic wars, for which he used the French word triage, meaning “sorting.”2 He articulated 3 prognostic categories: 1) those who would die even with treatment, 2) those who would live without treatment, and 3) those who would die unless treated. Triage decisions arise in the context of insufficient resources, particularly space, staff, and supplies. Although usually identified with disasters, these decisions can arise in other contexts where personnel or technological resources are inadequate. Indeed, one of the first modern incarnations of triage ethics in American civilian life was in the early days of hemodialysis, when so-called “God committees” made complex decisions about which patients would be able to use this new, rare technology.3
Two fundamental moral constructs undergird medical ethics: deontological and utilitarian. The former, in which most clinicians traffic in ordinary practice, is driven by principles or moral rules such as the sanctity of life, the rule of fairness, and the principle of autonomy.4 They apply primarily in the context of treating an individual patient. The utilitarian way of reasoning is not as familiar to clinicians. It is focused on the broader context, the common good, the health of the group. It asks to calculate “the greatest good for the greatest number” as a means of navigating ethical dilemmas.5 The utilitarian perspective is far more familiar to policymakers, health care administrators, and public health professionals. It tends to be anathema to clinicians. However, disasters such as the COVID-19 pandemic ask some clinicians, particularly inpatient physicians, to shift from their usual deontological perspective to a utilitarian one, because triage ethics fundamentally draw on utilitarian reasoning. This can be quite anguishing to clinicians who typically work with individual patients in settings of more adequate, if not abundant, resources. What may feel wrong in a deontological mode can be seen as ethically right in a utilitarian framework.
The Table compares and contrasts these 2 paradigms and how they manifest in the clinical trenches, in a protracted health care crisis with limited resources.
The COVID-19 crisis has produced an unprecedented and extended exposure of clinicians to triage situations in the face of limited resources such as ventilators, personnel, personal protective equipment, etc.6 Numerous possible approaches to deploying limited supplies are being considered. On what basis should such decisions be made? How can fairness be optimally manifest? Some possibilities include:
- first come, first served
- youngest first
- lottery
- short-term survivability
- long-term prognosis for quality of life
- value of a patient to the lives of others (eg, parents, health care workers, vaccine researchers).
One particularly interesting exploration of these questions was done in Maryland and reported in the “Maryland Framework for the Allocation of Scarce Life-sustaining Medical Resources in a Catastrophic Public Health Emergency.”7 This was the product of a multi-year consultation, ending in 2017, with several constituencies, including clinicians, politicians, hospital administrators, and members of the public brainstorming about approaches to allocating a hypothetical scarcity of ventilators. Interestingly, there was one broad consensus among these groups: a ventilator should not be withdrawn from a patient already using it to give to a “better” candidate who comes along later.
Some institutions have developed a method of making triage decisions that takes such decisions out of the hands of individual clinicians and instead assigns them to specialized “triage teams” made up of ethicists and clinicians experienced in critical care, to develop more distance from the emotions at the bedside. To minimize bias, such teams are often insulated from getting personal information about the patient, and receive only acute clinical information.8
Continue to: The pros and cons of these approaches...
The pros and cons of these approaches and the underlying ethical reasoning is beyond the scope of this overview. Policy documents from different states, regions, nations, and institutions have various approaches to making these choices. Presently, there is no coherent national or international agreement on triage ethics.9 It is important, however, that there be transparency in whatever approach an institution adopts for triage decisions.
Equity ethics
Though the equitable distribution of health care delivery has long been a concern, this problem has become magnified by the COVID-19 crisis. Race, sex, age, socioeconomic class, and type of illness have all been perennial sources of division between those who have better or worse access to health care and its outcomes. All of these distinctions have created differentials in rates of cases, hospitalizations, and deaths in the COVID-19 pandemic.10
The shifting of acute health care facilities to mostly COVID-19–related treatment, and postponing less critical and more “elective” care, creates a divide based on illness type. Many facilities have stopped taking admissions for other kinds of cases. This is particularly relevant to psychiatric units, many of which have had to decrease their bed capacities to make all rooms private, and limit their usual treatments offered to inpatients.11 Many long-term units, such as at state hospitals, are closing to new admissions. Many day hospitals and intensive outpatient programs remain closed, not even shifting to telehealth. In areas most affected by COVID-19, some institutions have closed psychiatric wards and reallocated psychiatrists to cover some of the medical units. So the availability of the more intensive, institutionally-based levels of care is significantly reduced, particularly for psychiatric patients.12 These patients already are a disadvantaged population in the distribution of health care resources, and the care of individuals with serious mental illness is more likely to be seen as “nonessential” in this time of suddenly scarcer institutional resources.
One of the cherished ethical values in health care is autonomy, and in a deontological triage environment, honoring patient autonomy is carefully and tenderly administered. However, in a utilitarian-driven triage environment, considerations of the common good can trump autonomy, even in subtle ways that create inequities. Clinicians have been advised to have more frank conversations with patients, particularly those with chronic illnesses, stepping up initiatives to make advanced directives during this crisis, explicitly reminding patients that there may not be enough ventilators for all who need one.13 Some have argued that such physician-initiated conversations can be inherently coercive, making these decisions not as autonomous as it may appear, similar to physicians suggesting medical euthanasia as an option.14 Interestingly, some jurisdictions that offer euthanasia have been suspending such services during the COVID-19 crisis.15 Some hospitals have even wrestled with the possibility that all COVID-19 admissions should be considered “do not resuscitate,” especially because cardiopulmonary resuscitation significantly elevates the risks of viral exposure for the treatment team.16,17 A more explicit example of how current standards protecting patient autonomy may be challenged is patients who are admitted involuntarily to a psychiatric unit. These are patients whose presumptively impaired autonomy is already being overridden by the involuntary nature of the admission. If a psychiatric unit requires admissions to be COVID-19–negative, and if patients refuse COVID-19 testing, should the testing be forced upon them to protect the entire milieu?
Many ethicists are highlighting the embedded equity bias known as “ableism” inherent in triage decisions—implicitly disfavoring resources for patients with COVID-19 who are already physically or intellectually disabled, chronically ill, aged, homeless, psychosocially low functioning, etc.18 Without explicit protections for individuals who are chronically disabled, triage decisions unguided by policy safeguards may reflexively favor the more “abled.” This bias towards the more abled is often inherent in how difficult it is to access health care. It can also be manifested in bedside triage decisions made in the moment by individual clinicians. Many disability rights advocates have been sounding this alarm during the COVID-19 crisis.19
Continue to: A special circumstance of equity...
A special circumstance of equity is arising during this ongoing pandemic—the possibility of treating health care workers as a privileged class. Unlike typical disasters, where health care workers come in afterwards, and therefore are in relatively less danger, pandemics create particularly high risks of danger for such individuals, with repeated exposure to the virus. They are both responders and potential victims. Should they have higher priority for ventilators, vaccines, funding, etc?6 This is a more robust degree of compensatory justice than merely giving appreciation. Giving health care workers such advantages may seem intuitively appealing, but perhaps professionalism and the self-obligation of duty mitigates such claims.20
A unique opportunity
The magnitude and pervasiveness of this pandemic crisis is unique in our lifetimes, as both professionals and as citizens. In the crucible of this extraordinary time, these and other medical ethics dilemmas burn hotter than ever before. Different societies and institutions may come up with different answers, based on their cultures and values. It is important, however, that the venerable ethos of medical ethics, which has evolved through the millennia, codified in oaths, codes, and scholarship, can be a compass at the bedside and in the meetings of legislatures, leaders, and policymakers. Perhaps we can emerge from this time with more clarity about how to balance the preciousness of individual rights with the needs of the common good.
Bottom Line
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has brought increased attention to triage ethics and equity ethics. There is no coherent national or international agreement on how to best deploy limited supplies such as ventilators and personal protective equipment. Although the equitable distribution of health care delivery has long been a concern, this problem has become magnified by COVID-19. Clinicians may be asked to view health care through the less familiar lens of the common good, as opposed to focusing strictly on an individual patient.
Related Resources
- Johns Hopkins Berman Institute of Bioethics. Coronavirus ethics and policy insights and resources. https://bioethics.jhu.edu/research-and-outreach/covid-19-bioethics-expert-insights/.
- Daugherty-Biddison L, Gwon H, Regenberg A, et al. Maryland framework for the allocation of scarce lifesustaining medical resources in a catastrophic public health emergency. www.law.umaryland.edu/media/SOL/pdfs/Programs/Health-Law/MHECN/ASR%20Framework_Final.pdf.
1. AMA Journal of Ethics. COVID-19 ethics resource center. https://journalofethics.ama-assn.org/COVID-19-ethics-resource-center. Updated May 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
2. Skandakalis PN, Lainas P, Zoras O, et al. “To afford the wounded speedy assistance”: Dominique Jean Larrey and Napoleon. World J Surg. 2006;30(8):1392-1399.
3. Ross W. God panels and the history of hemodialysis in America: a cautionary tale. Virtual Mentor. 2012;14(11):890-896.
4. Alexander L, Moore M. Deontological ethics. In: Zalta EN, ed. Stanford encyclopedia of philosophy. https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/ethics-deontological/. Revised October 17, 2016. Accessed May 26, 2020.
5. Driver J. The history of utilitarianism. In: Zalta EN, ed. Stanford encyclopedia of philosophy. https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/utilitarianism-history/. Revised September 22, 2014. Accessed May 26, 2020.
6. Emanuel EJ, Persad G, Upshur R, et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(21):2049-2055.
7. Daugherty-Biddison EL, Faden R, Gwon HW, et al. Too many patients…a framework to guide statewide allocation of scarce mechanical ventilation during disasters. Chest. 2019;155(4):848-854.
8. Dudzinski D, Campelia G, Brazg T. Pandemic resources including COVID-19 materials. Department of Bioethics and Humanities, University of Washington Medicine. http://depts.washington.edu/bhdept/ethics-medicine/bioethics-topics/detail/245. Published April 6, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
9. Antommaria AHM, Gibb TS, McGuire AL, et al; Task Force of the Association of Bioethics Program Directors. Ventilator triage policies during the COVID-19 pandemic at U.S. hospitals associated with members of the Association of Bioethics Program Directors [published online April 24, 2020]. Ann Intern Med. 2020;M20-1738. doi: 10.7326/M20-1738.
10. Cooney E. Who gets hospitalized for COVID-19? Report shows differences by race and sex. STAT. https://www.statnews.com/2020/04/09/hospitalized-COVID-19-patients-differences-by-race-and-sex/. Published April 9, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
11. Gessen M. Why psychiatric wards are uniquely vulnerable to the coronavirus. The New Yorker. https://www.newyorker.com/news/news-desk/why-psychiatric-wards-are-uniquely-vulnerable-to-the-coronavirus. Published April 21, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
12. American Psychiatric Association Ethics Committee. COVID-19 related opinions of the APA Ethics Committee. American Psychiatric Association. https://www.psychiatry.org/File%20Library/Psychiatrists/Practice/Ethics/APA-COVID-19-Ethics-Opinions.pdf. Published May 5, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
13. Wee M. Coronavirus and the misuse of ‘do not resuscitate’ orders. The Spectator. https://www.spectator.co.uk/article/coronavirus-and-the-misuse-of-do-not-resuscitate-orders. Published May 6, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
14. Prokopetz JZ, Lehmann LS. Redefining physicians’ role in assisted dying. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(20):97-99.
15. Yuill K, Boer T. What COVID-19 has revealed about euthanasia. spiked. https://www.spiked-online.com/2020/04/14/COVID-19-has-revealed-the-ugliness-of-euthanasia/. Published April 14, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
16. Plunkett AJ. COVID-19: hospitals should consider CoP carefully before deciding on DNR policy. PSQH. https://www.psqh.com/news/COVID-19-hospitals-should-consider-cop-carefully-before-deciding-on-dnr-policy/. Published March 26, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
17. Kramer DB, Lo B, Dickert NW. CPR in the COVID-19 era: an ethical framework [published online May 6, 2020]. N Engl J Med. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2010758.
18. Mykitiuk R, Lemmens T. Assessing the value of a life: COVID-19 triage orders mustn’t work against those with disabilities. CBC News. https://www.cbc.ca/news/opinion/opinion-disabled-COVID-19-triage-orders-1.5532137. Published April 19, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
19. Solomon MZ, Wynia MK, Gostin LO. COVID-19 crisis triage—optimizing health outcomes and disability rights [published online May 19, 2020]. N Engl J Med. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2008300.
20. Appel JM. Ethics consult: who’s first to get COVID-19 Vax? MD/JD bangs gavel. MedPage Today. https://www.medpagetoday.com/infectiousdisease/COVID19/86260. Published May 1, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
1. AMA Journal of Ethics. COVID-19 ethics resource center. https://journalofethics.ama-assn.org/COVID-19-ethics-resource-center. Updated May 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
2. Skandakalis PN, Lainas P, Zoras O, et al. “To afford the wounded speedy assistance”: Dominique Jean Larrey and Napoleon. World J Surg. 2006;30(8):1392-1399.
3. Ross W. God panels and the history of hemodialysis in America: a cautionary tale. Virtual Mentor. 2012;14(11):890-896.
4. Alexander L, Moore M. Deontological ethics. In: Zalta EN, ed. Stanford encyclopedia of philosophy. https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/ethics-deontological/. Revised October 17, 2016. Accessed May 26, 2020.
5. Driver J. The history of utilitarianism. In: Zalta EN, ed. Stanford encyclopedia of philosophy. https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/utilitarianism-history/. Revised September 22, 2014. Accessed May 26, 2020.
6. Emanuel EJ, Persad G, Upshur R, et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(21):2049-2055.
7. Daugherty-Biddison EL, Faden R, Gwon HW, et al. Too many patients…a framework to guide statewide allocation of scarce mechanical ventilation during disasters. Chest. 2019;155(4):848-854.
8. Dudzinski D, Campelia G, Brazg T. Pandemic resources including COVID-19 materials. Department of Bioethics and Humanities, University of Washington Medicine. http://depts.washington.edu/bhdept/ethics-medicine/bioethics-topics/detail/245. Published April 6, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
9. Antommaria AHM, Gibb TS, McGuire AL, et al; Task Force of the Association of Bioethics Program Directors. Ventilator triage policies during the COVID-19 pandemic at U.S. hospitals associated with members of the Association of Bioethics Program Directors [published online April 24, 2020]. Ann Intern Med. 2020;M20-1738. doi: 10.7326/M20-1738.
10. Cooney E. Who gets hospitalized for COVID-19? Report shows differences by race and sex. STAT. https://www.statnews.com/2020/04/09/hospitalized-COVID-19-patients-differences-by-race-and-sex/. Published April 9, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
11. Gessen M. Why psychiatric wards are uniquely vulnerable to the coronavirus. The New Yorker. https://www.newyorker.com/news/news-desk/why-psychiatric-wards-are-uniquely-vulnerable-to-the-coronavirus. Published April 21, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
12. American Psychiatric Association Ethics Committee. COVID-19 related opinions of the APA Ethics Committee. American Psychiatric Association. https://www.psychiatry.org/File%20Library/Psychiatrists/Practice/Ethics/APA-COVID-19-Ethics-Opinions.pdf. Published May 5, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
13. Wee M. Coronavirus and the misuse of ‘do not resuscitate’ orders. The Spectator. https://www.spectator.co.uk/article/coronavirus-and-the-misuse-of-do-not-resuscitate-orders. Published May 6, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
14. Prokopetz JZ, Lehmann LS. Redefining physicians’ role in assisted dying. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(20):97-99.
15. Yuill K, Boer T. What COVID-19 has revealed about euthanasia. spiked. https://www.spiked-online.com/2020/04/14/COVID-19-has-revealed-the-ugliness-of-euthanasia/. Published April 14, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
16. Plunkett AJ. COVID-19: hospitals should consider CoP carefully before deciding on DNR policy. PSQH. https://www.psqh.com/news/COVID-19-hospitals-should-consider-cop-carefully-before-deciding-on-dnr-policy/. Published March 26, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
17. Kramer DB, Lo B, Dickert NW. CPR in the COVID-19 era: an ethical framework [published online May 6, 2020]. N Engl J Med. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2010758.
18. Mykitiuk R, Lemmens T. Assessing the value of a life: COVID-19 triage orders mustn’t work against those with disabilities. CBC News. https://www.cbc.ca/news/opinion/opinion-disabled-COVID-19-triage-orders-1.5532137. Published April 19, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
19. Solomon MZ, Wynia MK, Gostin LO. COVID-19 crisis triage—optimizing health outcomes and disability rights [published online May 19, 2020]. N Engl J Med. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2008300.
20. Appel JM. Ethics consult: who’s first to get COVID-19 Vax? MD/JD bangs gavel. MedPage Today. https://www.medpagetoday.com/infectiousdisease/COVID19/86260. Published May 1, 2020. Accessed May 26, 2020.
COVID-19 guideline update: Wear N95 masks during endoscopy
Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are gastrointestinal symptoms that COVID-19 patients have had, and up to 30% have been reported to have liver symptoms. Because patients with these symptoms may require endoscopy, the American Gastroenterological Association has issued a rapid recommendation document that advises physicians and health care workers to use N95 masks, double gloves, and negative pressure rooms when performing GI procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The recommendations, published in Gastroenterology (2020. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.072), also cover non-COVID-19 patients and situations where N95 masks should be used, offer guidelines for triaging patients for endoscopy and timing of nonurgent procedures, and evaluate the latest evidence in the incidence of GI and liver manifestations of COVID-19. The guideline panel met in March.
The document includes seven recommendations for use of personal protective equipment by physicians and nurses performing GI procedures. The recommendations and the level of evidence supporting them fall under four categories:
1. Masks, comprising four recommendations: N95 masks for upper and lower GI procedures regardless of a patient’s COVID-19 status; no surgical masks only in confirmed COVID-19 patients or suspected cases; and reused N95 masks when fresh ones aren’t available instead of using a surgical mask only (very low to moderate level of evidence depending on the recommendation).
2. Double-gloving when performing any GI procedure regardless of the patient’s COVID-19 status (moderate quality evidence).
3. When available, a negative-pressure room should be used for any COVID-19 patient or suspect rather than a regular endoscopy room (very low certainty of evidence).
4. Continue to practice standard cleaning, endoscopic disinfection, and reprocessing protocols regardless of a patient’s COVID-19 status (good practice statement).
For decontamination, the panel noted that commonly used biocidal agents, such as hydrogen peroxide, alcohols, sodium hypochlorite, or benzalkonium chloride have proved effective for decontaminating of coronavirus.
For implementing the PPE recommendations, the panel stated that personnel still need to practice don and doff standard protocols, and that N95 masks should be fitted for each individual.
Other steps include banning personal belongings in the procedure area, minimizing the number of personnel in the room, avoiding change of personnel and keeping nonprocedural personnel out during the procedure, considering using nursing teams that follow the patient through preprocedure, procedure, and recovery, and considering having endoscopy teams remain together during the day to minimize exposure.
The triage recommendations stated that “trained medical personnel” should review all procedures and categorize them as time-sensitive or not time-sensitive, based on a framework the recommendation includes. In “an open-access endoscopy system” when there isn’t enough information to determine timing for the procedure, the recommendation provides a three-step approach: a phone consult with the referring physician, a telehealth visit with the patient, or a multidisciplinary team approach or virtual disease/tumor board.
“The proposed framework of separating procedures into time-sensitive and non–time-sensitive cases may be useful in determining which procedures if delayed may negatively impact on patient-important outcomes,” wrote Shahnaz Sultan, MD, AGAF, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and colleagues. The panel noted decision-making should focus on “patient-important outcomes.”
For nonurgent procedures, the panel arrived at a consensus that 8 weeks was an appropriate window for reassessment of deferred procedures, depending on the availability of resources and if the time sensitivity of the procedure changes.
The panel also attempted to determine the likelihood of GI and liver manifestations of COVID-19 by evaluating published cohort studies. They found that 2%-13.8% of patients had diarrhea, 1%-10.1% had nausea or vomiting, and one study reported 2% had abdominal pain (Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 May;115[5]766-73). What’s more, some studies have shown stool samples positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA even after respiratory samples were negative.
The evidence on liver manifestations isn’t as robust, but one study reported that 20%-30% of patients had liver injury upon diagnosis of COVID-19 (Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1518-9), and that severe hepatitis has been reported but liver failure seems rare (Lancet. 2020 Feb 15;395[10223]:507-13). “The pattern of liver injury appears to be predominantly hepatocellular, and the etiology remains uncertain but may represent a secondary effect of the systemic inflammatory response observed with COVID-19 disease, although direct viral infection and drug-induced liver injury cannot be excluded,” Dr. Sultan and colleagues noted.
There were no relevant author conflicts of interest. The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute funded the study.
SOURCE: Sultan S et al. Gastroenterology. 2020. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.072.
Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are gastrointestinal symptoms that COVID-19 patients have had, and up to 30% have been reported to have liver symptoms. Because patients with these symptoms may require endoscopy, the American Gastroenterological Association has issued a rapid recommendation document that advises physicians and health care workers to use N95 masks, double gloves, and negative pressure rooms when performing GI procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The recommendations, published in Gastroenterology (2020. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.072), also cover non-COVID-19 patients and situations where N95 masks should be used, offer guidelines for triaging patients for endoscopy and timing of nonurgent procedures, and evaluate the latest evidence in the incidence of GI and liver manifestations of COVID-19. The guideline panel met in March.
The document includes seven recommendations for use of personal protective equipment by physicians and nurses performing GI procedures. The recommendations and the level of evidence supporting them fall under four categories:
1. Masks, comprising four recommendations: N95 masks for upper and lower GI procedures regardless of a patient’s COVID-19 status; no surgical masks only in confirmed COVID-19 patients or suspected cases; and reused N95 masks when fresh ones aren’t available instead of using a surgical mask only (very low to moderate level of evidence depending on the recommendation).
2. Double-gloving when performing any GI procedure regardless of the patient’s COVID-19 status (moderate quality evidence).
3. When available, a negative-pressure room should be used for any COVID-19 patient or suspect rather than a regular endoscopy room (very low certainty of evidence).
4. Continue to practice standard cleaning, endoscopic disinfection, and reprocessing protocols regardless of a patient’s COVID-19 status (good practice statement).
For decontamination, the panel noted that commonly used biocidal agents, such as hydrogen peroxide, alcohols, sodium hypochlorite, or benzalkonium chloride have proved effective for decontaminating of coronavirus.
For implementing the PPE recommendations, the panel stated that personnel still need to practice don and doff standard protocols, and that N95 masks should be fitted for each individual.
Other steps include banning personal belongings in the procedure area, minimizing the number of personnel in the room, avoiding change of personnel and keeping nonprocedural personnel out during the procedure, considering using nursing teams that follow the patient through preprocedure, procedure, and recovery, and considering having endoscopy teams remain together during the day to minimize exposure.
The triage recommendations stated that “trained medical personnel” should review all procedures and categorize them as time-sensitive or not time-sensitive, based on a framework the recommendation includes. In “an open-access endoscopy system” when there isn’t enough information to determine timing for the procedure, the recommendation provides a three-step approach: a phone consult with the referring physician, a telehealth visit with the patient, or a multidisciplinary team approach or virtual disease/tumor board.
“The proposed framework of separating procedures into time-sensitive and non–time-sensitive cases may be useful in determining which procedures if delayed may negatively impact on patient-important outcomes,” wrote Shahnaz Sultan, MD, AGAF, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and colleagues. The panel noted decision-making should focus on “patient-important outcomes.”
For nonurgent procedures, the panel arrived at a consensus that 8 weeks was an appropriate window for reassessment of deferred procedures, depending on the availability of resources and if the time sensitivity of the procedure changes.
The panel also attempted to determine the likelihood of GI and liver manifestations of COVID-19 by evaluating published cohort studies. They found that 2%-13.8% of patients had diarrhea, 1%-10.1% had nausea or vomiting, and one study reported 2% had abdominal pain (Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 May;115[5]766-73). What’s more, some studies have shown stool samples positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA even after respiratory samples were negative.
The evidence on liver manifestations isn’t as robust, but one study reported that 20%-30% of patients had liver injury upon diagnosis of COVID-19 (Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1518-9), and that severe hepatitis has been reported but liver failure seems rare (Lancet. 2020 Feb 15;395[10223]:507-13). “The pattern of liver injury appears to be predominantly hepatocellular, and the etiology remains uncertain but may represent a secondary effect of the systemic inflammatory response observed with COVID-19 disease, although direct viral infection and drug-induced liver injury cannot be excluded,” Dr. Sultan and colleagues noted.
There were no relevant author conflicts of interest. The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute funded the study.
SOURCE: Sultan S et al. Gastroenterology. 2020. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.072.
Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are gastrointestinal symptoms that COVID-19 patients have had, and up to 30% have been reported to have liver symptoms. Because patients with these symptoms may require endoscopy, the American Gastroenterological Association has issued a rapid recommendation document that advises physicians and health care workers to use N95 masks, double gloves, and negative pressure rooms when performing GI procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The recommendations, published in Gastroenterology (2020. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.072), also cover non-COVID-19 patients and situations where N95 masks should be used, offer guidelines for triaging patients for endoscopy and timing of nonurgent procedures, and evaluate the latest evidence in the incidence of GI and liver manifestations of COVID-19. The guideline panel met in March.
The document includes seven recommendations for use of personal protective equipment by physicians and nurses performing GI procedures. The recommendations and the level of evidence supporting them fall under four categories:
1. Masks, comprising four recommendations: N95 masks for upper and lower GI procedures regardless of a patient’s COVID-19 status; no surgical masks only in confirmed COVID-19 patients or suspected cases; and reused N95 masks when fresh ones aren’t available instead of using a surgical mask only (very low to moderate level of evidence depending on the recommendation).
2. Double-gloving when performing any GI procedure regardless of the patient’s COVID-19 status (moderate quality evidence).
3. When available, a negative-pressure room should be used for any COVID-19 patient or suspect rather than a regular endoscopy room (very low certainty of evidence).
4. Continue to practice standard cleaning, endoscopic disinfection, and reprocessing protocols regardless of a patient’s COVID-19 status (good practice statement).
For decontamination, the panel noted that commonly used biocidal agents, such as hydrogen peroxide, alcohols, sodium hypochlorite, or benzalkonium chloride have proved effective for decontaminating of coronavirus.
For implementing the PPE recommendations, the panel stated that personnel still need to practice don and doff standard protocols, and that N95 masks should be fitted for each individual.
Other steps include banning personal belongings in the procedure area, minimizing the number of personnel in the room, avoiding change of personnel and keeping nonprocedural personnel out during the procedure, considering using nursing teams that follow the patient through preprocedure, procedure, and recovery, and considering having endoscopy teams remain together during the day to minimize exposure.
The triage recommendations stated that “trained medical personnel” should review all procedures and categorize them as time-sensitive or not time-sensitive, based on a framework the recommendation includes. In “an open-access endoscopy system” when there isn’t enough information to determine timing for the procedure, the recommendation provides a three-step approach: a phone consult with the referring physician, a telehealth visit with the patient, or a multidisciplinary team approach or virtual disease/tumor board.
“The proposed framework of separating procedures into time-sensitive and non–time-sensitive cases may be useful in determining which procedures if delayed may negatively impact on patient-important outcomes,” wrote Shahnaz Sultan, MD, AGAF, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and colleagues. The panel noted decision-making should focus on “patient-important outcomes.”
For nonurgent procedures, the panel arrived at a consensus that 8 weeks was an appropriate window for reassessment of deferred procedures, depending on the availability of resources and if the time sensitivity of the procedure changes.
The panel also attempted to determine the likelihood of GI and liver manifestations of COVID-19 by evaluating published cohort studies. They found that 2%-13.8% of patients had diarrhea, 1%-10.1% had nausea or vomiting, and one study reported 2% had abdominal pain (Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 May;115[5]766-73). What’s more, some studies have shown stool samples positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA even after respiratory samples were negative.
The evidence on liver manifestations isn’t as robust, but one study reported that 20%-30% of patients had liver injury upon diagnosis of COVID-19 (Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1518-9), and that severe hepatitis has been reported but liver failure seems rare (Lancet. 2020 Feb 15;395[10223]:507-13). “The pattern of liver injury appears to be predominantly hepatocellular, and the etiology remains uncertain but may represent a secondary effect of the systemic inflammatory response observed with COVID-19 disease, although direct viral infection and drug-induced liver injury cannot be excluded,” Dr. Sultan and colleagues noted.
There were no relevant author conflicts of interest. The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute funded the study.
SOURCE: Sultan S et al. Gastroenterology. 2020. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.072.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Upadacitinib looks effective for psoriatic arthritis
Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) improves joint and skin symptoms in patients with psoriatic arthritis for whom at least one other disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) didn’t work or wasn’t well tolerated, a pair of phase 3 trials suggests.
“In psoriatic arthritis patients, there’s still a high proportion of patients who do not respond to traditional, nonbiologic DMARDs, so there’s room for improvement,” said Marina Magrey, MD, from the MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, in Cleveland.
She and her colleagues evaluated the JAK inhibitor, already approved for rheumatoid arthritis in the United States, in the SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2 trials, which followed more than 2,300 patients with psoriatic arthritis for an average of 6-10 years.
No safety signals emerged for upadacitinib in either trial that weren’t already seen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, the investigators report, although a lower dose appeared to prompt fewer adverse events.
The research adds upadacitinib “to the armamentarium of medications we have against psoriatic arthritis,” said Dr. Magrey, who is a SELECT-PsA 1 investigator.
“The advantage of this medication is it’s available orally, so the convenience is there. It will enable both patients and physicians to choose from efficacious medications,” she told Medscape Medical News.
The team was “pleasantly surprised by the magnitude and rapidity of effect” of upadacitinib in study participants, said Philip Mease, MD, from the Swedish Medical Center and the University of Washington in Seattle, who is lead investigator for SELECT-PsA 2.
“It’s important to be able to understand if there’s adequate effectiveness in patients who’ve already been around the block several times with other treatments,” Dr. Mease told Medscape Medical News. “This trial demonstrated there was a high degree of effectiveness in each of the clinical domains” of psoriatic arthritis.
Results from both studies were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism 2020 Congress.
SELECT-PsA 1
In SELECT-PsA 1, upadacitinib was compared with adalimumab and placebo in 1705 patients who previously had an inadequate response or intolerance to at least one nonbiologic DMARD. Participants were randomized to receive upadacitinib – 15 mg or 30 mg once daily – adalimumab 40 mg every other week, or placebo.
The primary endpoint was an improvement of at least 20% (ACR20) at week 12.
Secondary endpoints included change in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI) score and change in patient assessment of pain on a numeric rating scale from baseline to week 12, achievement of ACR50 and ACR70 at week 12, and achievement of ACR20 at week 2.
Treatment-related adverse events were reported out to week 24 for patients who received at least one dose of upadacitinib.
Improvement in musculoskeletal symptoms, psoriasis, pain, physical function, and fatigue were seen by week 2 in both upadacitinib groups. At week 12, both doses of upadacitinib were noninferior to adalimumab for the achievement of ACR20 (P < .001), and the 30-mg dose was superior to adalimumab (P < .001).
More patients in the upadacitinib groups than in the placebo group met the stringent criteria for disease control, which included the achievement of minimal disease activity, ACR50, and ACR70.
The difference in effectiveness between the two doses of upadacitinib was small, but “there were relatively more adverse events,” such as infections, in the 30-mg group, Dr. Magrey reported, “so 15 mg seems like it will be the dose to go toward FDA approval.”
SELECT-PsA 2
SELECT-PsA 2 compared upadacitinib – 15 mg or 30 mg once daily – with placebo in 641 patients who previously had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more biologic DMARDs.
The primary endpoint was the achievement of ACR20 at week 12.
Among the many secondary endpoints were a 75% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75) at week 16, change in Self-Assessment of Psoriasis Symptoms (SAPS) score from baseline to week 16, the achievement of minimal disease activity at week 24, the achievement of ACR50 and ACR70 at week 12, and the achievement of ACR20 at week 2.
Adverse events were reported for patients who received at least one dose of upadacitinib.
At week 12, ACR20 was achieved by significantly more patients in the 15 mg and 30 mg upadacitinib groups than in the placebo group (56.9% vs. 63.8% vs. 24.1%; P < .0001), as was ACR50 (31.8% vs. 37.6% vs. 4.1%; P < .0001) and ACR70 (8.5% vs. 16.5% vs. 0.5%; P < .0001). In addition, all secondary endpoints were significantly better with upadacitinib than with placebo.
Rates of adverse events were similar in the 15 mg upadacitinib and placebo groups, but the rate was higher in the 30 mg upadacitinib group, including for herpes zoster.
“I was pleasantly surprised by the overall safety profile,” Dr. Mease said. “Yes, you need to pay attention to the potential for infection, but rates of serious infection were very low.”
“We didn’t see opportunistic infections occurring, and the overall adverse-events profile was one where we could be pretty reassuring with patients when introducing the medication and mechanism of action,” he added.
Upadacitinib appears to have significantly improved PASI scores in both trials, which is surprising, said Christopher Ritchlin, MD, from the University of Rochester Medical Center in New York.
“I think the data indicate that upadacitinib is a viable drug for treatment of psoriatic arthritis,” he told Medscape Medical News. “I don’t think it’s going to be tested in psoriasis, but for those with psoriatic arthritis and those whose burden of psoriasis is not particularly elevated, this drug looks like it might be very helpful to practicing physicians and their patients.”
Dr. Ritchlin added that he hopes future research will address whether upadacitinib is effective for axial disease in psoriatic arthritis, which wasn’t measured in these trials.
“I don’t see this as a weakness” of the current research, he said, but “having some spinal measures would be helpful. It’s something additional we’d like to know.”
Both trials were funded by AbbVie. Dr. Magrey reports financial relationships with Amgen, AbbVie, UCB Pharma, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Janssen. Dr. Mease reports financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Biogen, BMS, Celgene Corporation, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB, Genentech, and Janssen. Dr. Ritchlin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) improves joint and skin symptoms in patients with psoriatic arthritis for whom at least one other disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) didn’t work or wasn’t well tolerated, a pair of phase 3 trials suggests.
“In psoriatic arthritis patients, there’s still a high proportion of patients who do not respond to traditional, nonbiologic DMARDs, so there’s room for improvement,” said Marina Magrey, MD, from the MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, in Cleveland.
She and her colleagues evaluated the JAK inhibitor, already approved for rheumatoid arthritis in the United States, in the SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2 trials, which followed more than 2,300 patients with psoriatic arthritis for an average of 6-10 years.
No safety signals emerged for upadacitinib in either trial that weren’t already seen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, the investigators report, although a lower dose appeared to prompt fewer adverse events.
The research adds upadacitinib “to the armamentarium of medications we have against psoriatic arthritis,” said Dr. Magrey, who is a SELECT-PsA 1 investigator.
“The advantage of this medication is it’s available orally, so the convenience is there. It will enable both patients and physicians to choose from efficacious medications,” she told Medscape Medical News.
The team was “pleasantly surprised by the magnitude and rapidity of effect” of upadacitinib in study participants, said Philip Mease, MD, from the Swedish Medical Center and the University of Washington in Seattle, who is lead investigator for SELECT-PsA 2.
“It’s important to be able to understand if there’s adequate effectiveness in patients who’ve already been around the block several times with other treatments,” Dr. Mease told Medscape Medical News. “This trial demonstrated there was a high degree of effectiveness in each of the clinical domains” of psoriatic arthritis.
Results from both studies were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism 2020 Congress.
SELECT-PsA 1
In SELECT-PsA 1, upadacitinib was compared with adalimumab and placebo in 1705 patients who previously had an inadequate response or intolerance to at least one nonbiologic DMARD. Participants were randomized to receive upadacitinib – 15 mg or 30 mg once daily – adalimumab 40 mg every other week, or placebo.
The primary endpoint was an improvement of at least 20% (ACR20) at week 12.
Secondary endpoints included change in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI) score and change in patient assessment of pain on a numeric rating scale from baseline to week 12, achievement of ACR50 and ACR70 at week 12, and achievement of ACR20 at week 2.
Treatment-related adverse events were reported out to week 24 for patients who received at least one dose of upadacitinib.
Improvement in musculoskeletal symptoms, psoriasis, pain, physical function, and fatigue were seen by week 2 in both upadacitinib groups. At week 12, both doses of upadacitinib were noninferior to adalimumab for the achievement of ACR20 (P < .001), and the 30-mg dose was superior to adalimumab (P < .001).
More patients in the upadacitinib groups than in the placebo group met the stringent criteria for disease control, which included the achievement of minimal disease activity, ACR50, and ACR70.
The difference in effectiveness between the two doses of upadacitinib was small, but “there were relatively more adverse events,” such as infections, in the 30-mg group, Dr. Magrey reported, “so 15 mg seems like it will be the dose to go toward FDA approval.”
SELECT-PsA 2
SELECT-PsA 2 compared upadacitinib – 15 mg or 30 mg once daily – with placebo in 641 patients who previously had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more biologic DMARDs.
The primary endpoint was the achievement of ACR20 at week 12.
Among the many secondary endpoints were a 75% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75) at week 16, change in Self-Assessment of Psoriasis Symptoms (SAPS) score from baseline to week 16, the achievement of minimal disease activity at week 24, the achievement of ACR50 and ACR70 at week 12, and the achievement of ACR20 at week 2.
Adverse events were reported for patients who received at least one dose of upadacitinib.
At week 12, ACR20 was achieved by significantly more patients in the 15 mg and 30 mg upadacitinib groups than in the placebo group (56.9% vs. 63.8% vs. 24.1%; P < .0001), as was ACR50 (31.8% vs. 37.6% vs. 4.1%; P < .0001) and ACR70 (8.5% vs. 16.5% vs. 0.5%; P < .0001). In addition, all secondary endpoints were significantly better with upadacitinib than with placebo.
Rates of adverse events were similar in the 15 mg upadacitinib and placebo groups, but the rate was higher in the 30 mg upadacitinib group, including for herpes zoster.
“I was pleasantly surprised by the overall safety profile,” Dr. Mease said. “Yes, you need to pay attention to the potential for infection, but rates of serious infection were very low.”
“We didn’t see opportunistic infections occurring, and the overall adverse-events profile was one where we could be pretty reassuring with patients when introducing the medication and mechanism of action,” he added.
Upadacitinib appears to have significantly improved PASI scores in both trials, which is surprising, said Christopher Ritchlin, MD, from the University of Rochester Medical Center in New York.
“I think the data indicate that upadacitinib is a viable drug for treatment of psoriatic arthritis,” he told Medscape Medical News. “I don’t think it’s going to be tested in psoriasis, but for those with psoriatic arthritis and those whose burden of psoriasis is not particularly elevated, this drug looks like it might be very helpful to practicing physicians and their patients.”
Dr. Ritchlin added that he hopes future research will address whether upadacitinib is effective for axial disease in psoriatic arthritis, which wasn’t measured in these trials.
“I don’t see this as a weakness” of the current research, he said, but “having some spinal measures would be helpful. It’s something additional we’d like to know.”
Both trials were funded by AbbVie. Dr. Magrey reports financial relationships with Amgen, AbbVie, UCB Pharma, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Janssen. Dr. Mease reports financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Biogen, BMS, Celgene Corporation, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB, Genentech, and Janssen. Dr. Ritchlin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) improves joint and skin symptoms in patients with psoriatic arthritis for whom at least one other disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) didn’t work or wasn’t well tolerated, a pair of phase 3 trials suggests.
“In psoriatic arthritis patients, there’s still a high proportion of patients who do not respond to traditional, nonbiologic DMARDs, so there’s room for improvement,” said Marina Magrey, MD, from the MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, in Cleveland.
She and her colleagues evaluated the JAK inhibitor, already approved for rheumatoid arthritis in the United States, in the SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2 trials, which followed more than 2,300 patients with psoriatic arthritis for an average of 6-10 years.
No safety signals emerged for upadacitinib in either trial that weren’t already seen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, the investigators report, although a lower dose appeared to prompt fewer adverse events.
The research adds upadacitinib “to the armamentarium of medications we have against psoriatic arthritis,” said Dr. Magrey, who is a SELECT-PsA 1 investigator.
“The advantage of this medication is it’s available orally, so the convenience is there. It will enable both patients and physicians to choose from efficacious medications,” she told Medscape Medical News.
The team was “pleasantly surprised by the magnitude and rapidity of effect” of upadacitinib in study participants, said Philip Mease, MD, from the Swedish Medical Center and the University of Washington in Seattle, who is lead investigator for SELECT-PsA 2.
“It’s important to be able to understand if there’s adequate effectiveness in patients who’ve already been around the block several times with other treatments,” Dr. Mease told Medscape Medical News. “This trial demonstrated there was a high degree of effectiveness in each of the clinical domains” of psoriatic arthritis.
Results from both studies were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism 2020 Congress.
SELECT-PsA 1
In SELECT-PsA 1, upadacitinib was compared with adalimumab and placebo in 1705 patients who previously had an inadequate response or intolerance to at least one nonbiologic DMARD. Participants were randomized to receive upadacitinib – 15 mg or 30 mg once daily – adalimumab 40 mg every other week, or placebo.
The primary endpoint was an improvement of at least 20% (ACR20) at week 12.
Secondary endpoints included change in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI) score and change in patient assessment of pain on a numeric rating scale from baseline to week 12, achievement of ACR50 and ACR70 at week 12, and achievement of ACR20 at week 2.
Treatment-related adverse events were reported out to week 24 for patients who received at least one dose of upadacitinib.
Improvement in musculoskeletal symptoms, psoriasis, pain, physical function, and fatigue were seen by week 2 in both upadacitinib groups. At week 12, both doses of upadacitinib were noninferior to adalimumab for the achievement of ACR20 (P < .001), and the 30-mg dose was superior to adalimumab (P < .001).
More patients in the upadacitinib groups than in the placebo group met the stringent criteria for disease control, which included the achievement of minimal disease activity, ACR50, and ACR70.
The difference in effectiveness between the two doses of upadacitinib was small, but “there were relatively more adverse events,” such as infections, in the 30-mg group, Dr. Magrey reported, “so 15 mg seems like it will be the dose to go toward FDA approval.”
SELECT-PsA 2
SELECT-PsA 2 compared upadacitinib – 15 mg or 30 mg once daily – with placebo in 641 patients who previously had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more biologic DMARDs.
The primary endpoint was the achievement of ACR20 at week 12.
Among the many secondary endpoints were a 75% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75) at week 16, change in Self-Assessment of Psoriasis Symptoms (SAPS) score from baseline to week 16, the achievement of minimal disease activity at week 24, the achievement of ACR50 and ACR70 at week 12, and the achievement of ACR20 at week 2.
Adverse events were reported for patients who received at least one dose of upadacitinib.
At week 12, ACR20 was achieved by significantly more patients in the 15 mg and 30 mg upadacitinib groups than in the placebo group (56.9% vs. 63.8% vs. 24.1%; P < .0001), as was ACR50 (31.8% vs. 37.6% vs. 4.1%; P < .0001) and ACR70 (8.5% vs. 16.5% vs. 0.5%; P < .0001). In addition, all secondary endpoints were significantly better with upadacitinib than with placebo.
Rates of adverse events were similar in the 15 mg upadacitinib and placebo groups, but the rate was higher in the 30 mg upadacitinib group, including for herpes zoster.
“I was pleasantly surprised by the overall safety profile,” Dr. Mease said. “Yes, you need to pay attention to the potential for infection, but rates of serious infection were very low.”
“We didn’t see opportunistic infections occurring, and the overall adverse-events profile was one where we could be pretty reassuring with patients when introducing the medication and mechanism of action,” he added.
Upadacitinib appears to have significantly improved PASI scores in both trials, which is surprising, said Christopher Ritchlin, MD, from the University of Rochester Medical Center in New York.
“I think the data indicate that upadacitinib is a viable drug for treatment of psoriatic arthritis,” he told Medscape Medical News. “I don’t think it’s going to be tested in psoriasis, but for those with psoriatic arthritis and those whose burden of psoriasis is not particularly elevated, this drug looks like it might be very helpful to practicing physicians and their patients.”
Dr. Ritchlin added that he hopes future research will address whether upadacitinib is effective for axial disease in psoriatic arthritis, which wasn’t measured in these trials.
“I don’t see this as a weakness” of the current research, he said, but “having some spinal measures would be helpful. It’s something additional we’d like to know.”
Both trials were funded by AbbVie. Dr. Magrey reports financial relationships with Amgen, AbbVie, UCB Pharma, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Janssen. Dr. Mease reports financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Biogen, BMS, Celgene Corporation, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB, Genentech, and Janssen. Dr. Ritchlin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
JAK inhibitors go the distance in RA patients
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis remained on therapy longer with the relatively new JAK inhibitors than with TNF inhibitors, according to the large international JAK-pot study, offering encouraging signals about the efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors in these patients.
“We saw that efficacy with JAK inhibitors was at least as good as other current drugs on the market,” said investigator Kim Lauper, MD, from the University of Geneva in Switzerland and the University of Manchester in the United Kingdom.
“We don’t have datasets on JAK inhibitors over a long period of time, but we do have a lot of registers,” Dr. Lauper told Medscape Medical News.
“In general, we were really happy to see no big difference in effectiveness” for these disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for patients with RA, she said.
In many countries, JAK inhibitors have only recently been approved as a treatment for RA, Lauper explained. In the past several years, baricitinib, tofacitinib, and upadacitinib have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
For their study, Dr. Lauper and her colleagues analyzed data from registers in 19 countries.
When JAK inhibitors became available in each country, the team assessed effectiveness by comparing how long patients remained on JAK inhibitors or on long-available biologics. Dr. Lauper presented the findings at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress.
“In general, we know that drug retention is a measure of both effectiveness and safety,” she explained.
Of the 25,521 patients in the 19 registers, 6,063 started on a JAK inhibitor during the 3-year study period, 13,879 started on a TNF inhibitor, 2,348 started on abatacept, and 3,231 started on an interleukin-6 inhibitor.
Three-quarters of patients were women (average age, 55 years), and average time since the diagnosis of RA was 10 years.
At baseline, patients taking JAK inhibitors had higher levels of C-reactive protein and disease activity than patients taking a biologic. They had also been treated previously with more traditional and biologic DMARDs.
Ineffectiveness was the most common reason for discontinuing a drug, cited by 49% of patients, followed by adverse events, cited by 21%.
The rate of discontinuation was lower for JAK inhibitors than for TNF inhibitors, after adjustment. However, the discontinuation rate for JAK inhibitors, abatacept, and IL-6 inhibitors was comparable.
The observational nature of the study was a limitation, Dr. Lauper acknowledged, explaining that “we couldn’t adjust for confounding factors that were not measured.”
Notably, there were large variations in JAK inhibitor retention rates in the different countries, which surprised both Dr. Lauper and Loreto Carmona, MD, PhD, from the Musculoskeletal Health Institute in Madrid.
“It’s very interesting because there’s not much heterogeneity with abatacept and IL inhibitors,” said Dr. Carmona, who is chair of the EULAR abstract selection committee.
“It’s all over the spectrum with JAK inhibitors,” she told Medscape Medical News. But “what the research shows is that JAK inhibitors are maintained for longer, which means maybe the mix of efficacy, low toxicity, and adherence, on the whole, is better in JAK inhibitors.”
The study was funded by Pfizer. Dr. Lauper and Dr. Carmona have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis remained on therapy longer with the relatively new JAK inhibitors than with TNF inhibitors, according to the large international JAK-pot study, offering encouraging signals about the efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors in these patients.
“We saw that efficacy with JAK inhibitors was at least as good as other current drugs on the market,” said investigator Kim Lauper, MD, from the University of Geneva in Switzerland and the University of Manchester in the United Kingdom.
“We don’t have datasets on JAK inhibitors over a long period of time, but we do have a lot of registers,” Dr. Lauper told Medscape Medical News.
“In general, we were really happy to see no big difference in effectiveness” for these disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for patients with RA, she said.
In many countries, JAK inhibitors have only recently been approved as a treatment for RA, Lauper explained. In the past several years, baricitinib, tofacitinib, and upadacitinib have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
For their study, Dr. Lauper and her colleagues analyzed data from registers in 19 countries.
When JAK inhibitors became available in each country, the team assessed effectiveness by comparing how long patients remained on JAK inhibitors or on long-available biologics. Dr. Lauper presented the findings at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress.
“In general, we know that drug retention is a measure of both effectiveness and safety,” she explained.
Of the 25,521 patients in the 19 registers, 6,063 started on a JAK inhibitor during the 3-year study period, 13,879 started on a TNF inhibitor, 2,348 started on abatacept, and 3,231 started on an interleukin-6 inhibitor.
Three-quarters of patients were women (average age, 55 years), and average time since the diagnosis of RA was 10 years.
At baseline, patients taking JAK inhibitors had higher levels of C-reactive protein and disease activity than patients taking a biologic. They had also been treated previously with more traditional and biologic DMARDs.
Ineffectiveness was the most common reason for discontinuing a drug, cited by 49% of patients, followed by adverse events, cited by 21%.
The rate of discontinuation was lower for JAK inhibitors than for TNF inhibitors, after adjustment. However, the discontinuation rate for JAK inhibitors, abatacept, and IL-6 inhibitors was comparable.
The observational nature of the study was a limitation, Dr. Lauper acknowledged, explaining that “we couldn’t adjust for confounding factors that were not measured.”
Notably, there were large variations in JAK inhibitor retention rates in the different countries, which surprised both Dr. Lauper and Loreto Carmona, MD, PhD, from the Musculoskeletal Health Institute in Madrid.
“It’s very interesting because there’s not much heterogeneity with abatacept and IL inhibitors,” said Dr. Carmona, who is chair of the EULAR abstract selection committee.
“It’s all over the spectrum with JAK inhibitors,” she told Medscape Medical News. But “what the research shows is that JAK inhibitors are maintained for longer, which means maybe the mix of efficacy, low toxicity, and adherence, on the whole, is better in JAK inhibitors.”
The study was funded by Pfizer. Dr. Lauper and Dr. Carmona have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis remained on therapy longer with the relatively new JAK inhibitors than with TNF inhibitors, according to the large international JAK-pot study, offering encouraging signals about the efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors in these patients.
“We saw that efficacy with JAK inhibitors was at least as good as other current drugs on the market,” said investigator Kim Lauper, MD, from the University of Geneva in Switzerland and the University of Manchester in the United Kingdom.
“We don’t have datasets on JAK inhibitors over a long period of time, but we do have a lot of registers,” Dr. Lauper told Medscape Medical News.
“In general, we were really happy to see no big difference in effectiveness” for these disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for patients with RA, she said.
In many countries, JAK inhibitors have only recently been approved as a treatment for RA, Lauper explained. In the past several years, baricitinib, tofacitinib, and upadacitinib have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
For their study, Dr. Lauper and her colleagues analyzed data from registers in 19 countries.
When JAK inhibitors became available in each country, the team assessed effectiveness by comparing how long patients remained on JAK inhibitors or on long-available biologics. Dr. Lauper presented the findings at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress.
“In general, we know that drug retention is a measure of both effectiveness and safety,” she explained.
Of the 25,521 patients in the 19 registers, 6,063 started on a JAK inhibitor during the 3-year study period, 13,879 started on a TNF inhibitor, 2,348 started on abatacept, and 3,231 started on an interleukin-6 inhibitor.
Three-quarters of patients were women (average age, 55 years), and average time since the diagnosis of RA was 10 years.
At baseline, patients taking JAK inhibitors had higher levels of C-reactive protein and disease activity than patients taking a biologic. They had also been treated previously with more traditional and biologic DMARDs.
Ineffectiveness was the most common reason for discontinuing a drug, cited by 49% of patients, followed by adverse events, cited by 21%.
The rate of discontinuation was lower for JAK inhibitors than for TNF inhibitors, after adjustment. However, the discontinuation rate for JAK inhibitors, abatacept, and IL-6 inhibitors was comparable.
The observational nature of the study was a limitation, Dr. Lauper acknowledged, explaining that “we couldn’t adjust for confounding factors that were not measured.”
Notably, there were large variations in JAK inhibitor retention rates in the different countries, which surprised both Dr. Lauper and Loreto Carmona, MD, PhD, from the Musculoskeletal Health Institute in Madrid.
“It’s very interesting because there’s not much heterogeneity with abatacept and IL inhibitors,” said Dr. Carmona, who is chair of the EULAR abstract selection committee.
“It’s all over the spectrum with JAK inhibitors,” she told Medscape Medical News. But “what the research shows is that JAK inhibitors are maintained for longer, which means maybe the mix of efficacy, low toxicity, and adherence, on the whole, is better in JAK inhibitors.”
The study was funded by Pfizer. Dr. Lauper and Dr. Carmona have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid use up after TNF inhibitor for inflammatory arthritis
Opioid use does not decline after patients with inflammatory arthritis start TNF inhibitor therapy; in fact, average use appears to increase, results from a new study show.
“Starting a TNF inhibitor, you would think the pain would go down, and we were hoping the dose of opioids would go down with it,” said investigator Olafur Palsson, MD, from the University of Iceland in Reykjavik and Lund University in Sweden.
“But this research shows that the insertion of a TNF inhibitor has only a minor effect on that,” he told Medscape Medical News.
The findings are an “important reminder” to rheumatologists that they should broaden their consideration of other pain treatments and techniques for patients with inflammatory arthritis, Dr. Palsson said. “They should focus on trying other tactics to get patients’ pain and stiffness under control; there may be some underlying factors.”
The investigators compared opioid prescription rates in 940 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and undifferentiated arthritis with a control group of 4,700 matched subjects. Dr. Palsson presented the findings at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress.
The team assessed nationwide databases that capture all patients taking biologics for rheumatic diseases and more than 90% of all drug prescriptions. They found that patients with inflammatory arthritis in Iceland were more likely to have received at least one opioid prescription than control subjects (75% vs. 43%).
During the study period, average yearly opioid dose rose much more in the patient group than in the control group. And 2 years after the initiation of TNF inhibitors, the number of patients taking opioids was unchanged from baseline, at about 40%.
Overall, the patient group was prescribed nearly six times more opioids than the control group. The investigators used a bootstrapping analysis to obtain a reliable confidence interval.
“In a way, the data are extremely skewed,” Dr. Palsson explained. “Most patients were taking very low doses of opioids and a few were taking extremely high doses. It’s hard to do a statistical analysis.”
“With bootstrapping, you don’t detect small fluctuations in data,” he said, acknowledging this study limitation. Also, “prescription data don’t necessarily reflect consumption” of a drug. People prescribed high doses may not necessarily be consuming high doses.”
Additionally, the risk for addiction is low when opioids are used as intended, said John Isaacs, MBBS, PhD, from Newcastle University in Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom, who is chair of the EULAR scientific program committee.
To alleviate chronic pain, opioids “should, in any case, only be part of a comprehensive therapy program in which doctors, psychologists, and physiotherapists work together,” Dr. Isaacs said in a EULAR news release.
Dr. Palsson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Isaacs is a consultant or has received honoraria or grants from Pfizer, AbbVie, Amgen, Merck, Roche, and UCB.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid use does not decline after patients with inflammatory arthritis start TNF inhibitor therapy; in fact, average use appears to increase, results from a new study show.
“Starting a TNF inhibitor, you would think the pain would go down, and we were hoping the dose of opioids would go down with it,” said investigator Olafur Palsson, MD, from the University of Iceland in Reykjavik and Lund University in Sweden.
“But this research shows that the insertion of a TNF inhibitor has only a minor effect on that,” he told Medscape Medical News.
The findings are an “important reminder” to rheumatologists that they should broaden their consideration of other pain treatments and techniques for patients with inflammatory arthritis, Dr. Palsson said. “They should focus on trying other tactics to get patients’ pain and stiffness under control; there may be some underlying factors.”
The investigators compared opioid prescription rates in 940 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and undifferentiated arthritis with a control group of 4,700 matched subjects. Dr. Palsson presented the findings at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress.
The team assessed nationwide databases that capture all patients taking biologics for rheumatic diseases and more than 90% of all drug prescriptions. They found that patients with inflammatory arthritis in Iceland were more likely to have received at least one opioid prescription than control subjects (75% vs. 43%).
During the study period, average yearly opioid dose rose much more in the patient group than in the control group. And 2 years after the initiation of TNF inhibitors, the number of patients taking opioids was unchanged from baseline, at about 40%.
Overall, the patient group was prescribed nearly six times more opioids than the control group. The investigators used a bootstrapping analysis to obtain a reliable confidence interval.
“In a way, the data are extremely skewed,” Dr. Palsson explained. “Most patients were taking very low doses of opioids and a few were taking extremely high doses. It’s hard to do a statistical analysis.”
“With bootstrapping, you don’t detect small fluctuations in data,” he said, acknowledging this study limitation. Also, “prescription data don’t necessarily reflect consumption” of a drug. People prescribed high doses may not necessarily be consuming high doses.”
Additionally, the risk for addiction is low when opioids are used as intended, said John Isaacs, MBBS, PhD, from Newcastle University in Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom, who is chair of the EULAR scientific program committee.
To alleviate chronic pain, opioids “should, in any case, only be part of a comprehensive therapy program in which doctors, psychologists, and physiotherapists work together,” Dr. Isaacs said in a EULAR news release.
Dr. Palsson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Isaacs is a consultant or has received honoraria or grants from Pfizer, AbbVie, Amgen, Merck, Roche, and UCB.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid use does not decline after patients with inflammatory arthritis start TNF inhibitor therapy; in fact, average use appears to increase, results from a new study show.
“Starting a TNF inhibitor, you would think the pain would go down, and we were hoping the dose of opioids would go down with it,” said investigator Olafur Palsson, MD, from the University of Iceland in Reykjavik and Lund University in Sweden.
“But this research shows that the insertion of a TNF inhibitor has only a minor effect on that,” he told Medscape Medical News.
The findings are an “important reminder” to rheumatologists that they should broaden their consideration of other pain treatments and techniques for patients with inflammatory arthritis, Dr. Palsson said. “They should focus on trying other tactics to get patients’ pain and stiffness under control; there may be some underlying factors.”
The investigators compared opioid prescription rates in 940 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and undifferentiated arthritis with a control group of 4,700 matched subjects. Dr. Palsson presented the findings at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress.
The team assessed nationwide databases that capture all patients taking biologics for rheumatic diseases and more than 90% of all drug prescriptions. They found that patients with inflammatory arthritis in Iceland were more likely to have received at least one opioid prescription than control subjects (75% vs. 43%).
During the study period, average yearly opioid dose rose much more in the patient group than in the control group. And 2 years after the initiation of TNF inhibitors, the number of patients taking opioids was unchanged from baseline, at about 40%.
Overall, the patient group was prescribed nearly six times more opioids than the control group. The investigators used a bootstrapping analysis to obtain a reliable confidence interval.
“In a way, the data are extremely skewed,” Dr. Palsson explained. “Most patients were taking very low doses of opioids and a few were taking extremely high doses. It’s hard to do a statistical analysis.”
“With bootstrapping, you don’t detect small fluctuations in data,” he said, acknowledging this study limitation. Also, “prescription data don’t necessarily reflect consumption” of a drug. People prescribed high doses may not necessarily be consuming high doses.”
Additionally, the risk for addiction is low when opioids are used as intended, said John Isaacs, MBBS, PhD, from Newcastle University in Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom, who is chair of the EULAR scientific program committee.
To alleviate chronic pain, opioids “should, in any case, only be part of a comprehensive therapy program in which doctors, psychologists, and physiotherapists work together,” Dr. Isaacs said in a EULAR news release.
Dr. Palsson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Isaacs is a consultant or has received honoraria or grants from Pfizer, AbbVie, Amgen, Merck, Roche, and UCB.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TNF inhibitors cut odds of VTE in RA patients
The risk for venous thromboembolism is almost 50% lower in patients with RA taking TNF inhibitors than in those taking conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), according to data from the German RABBIT registry.
“Some rheumatologists have thought TNF inhibitors could increase the risk for venous thromboembolism events, but we don’t think this is true, based on our findings,” said investigator Anja Strangfeld, MD, PhD, from the German Rheumatism Research Center in Berlin.
The risk is more than one-third lower in RA patients treated with other newer biologics, such as abatacept, rituximab, sarilumab, and tocilizumab.
However, risk for a serious venous thromboembolism is twice as high in patients with C-reactive protein (CRP) levels above 5 mg/L and is nearly three times as high in patients 65 years and older.
For the study, Dr. Strangfeld and her colleagues followed about 11,000 patients for more than 10 years. The findings were presented at the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress.
“Patients with RA have a greater risk for venous thromboembolism compared with the general population, but we didn’t know the risk conveyed by different DMARD treatments,” Dr. Strangfeld told Medscape Medical News. “It is also evident that higher age and lower capacity for physical function increase the risk, which was not so surprising.”
Chronic inflammation in RA patients elevates the risk for deep vein and pulmonary thrombosis by two to three times, said John Isaacs, MBBS, PhD, from Newcastle University in Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom, who is chair of the EULAR scientific program committee.
Among the supporting studies Dr. Isaacs discussed during an online press conference was a Swedish trial of more than 46,000 RA patients, which had been presented earlier by Viktor Molander, a PhD candidate from the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm (abstract OP0034).
Mr. Molander’s team showed that one in 100 patients with high disease activity will develop venous thromboembolism within a year, which is twice the number of events seen among patients in remission.
Combined with the RABBIT data, both studies “show if you can control their disease in the right way, you’re not only helping rheumatoid arthritis patients feel better, but you could be prolonging their lives,” Dr. Isaacs said.
The prospective RABBIT study followed RA patients who began receiving a new DMARD after treatment failed with at least one conventional synthetic DMARD, such as methotrexate or leflunomide. At baseline, those taking TNF inhibitors or other biologics had higher CRP levels on average, as well as a higher rate of existing cardiovascular disease. They also received glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, more often.
The observational nature of the RABBIT study is a weakness, Dr. Strangfeld said, and it could not prove cause and effect. But the methodology had several strengths, including input on patient factors from participating rheumatologists at least every 6 months.
“We enrolled patients at the start of treatment and observed them, regardless of any treatment changes, for up to 10 years,” she added. “That’s a really long observation period.”
The RABBIT data can help shape treatment decisions, said Loreto Carmona, MD, PhD, from the Musculoskeletal Health Institute in Madrid, who is chair of the EULAR abstract selection committee.
For a woman with RA who smokes and takes oral contraceptives, for example, “if she has high levels of inflammation, I think it’s okay to use TNF inhibitors, where maybe in the past we wouldn’t have thought that,” she said.
“The TNF inhibitors are actually reducing the inflammation and, therefore, reducing the risk,” Dr. Carmona told Medscape Medical News. “It could be an effect of using the drugs on people with higher levels of inflammation. It’s an indirect protective effect.”
The study was funded by a joint unconditional grant from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Fresenius-Kabi, Hexal, Lilly, MSD, Mylan, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi-Aventis, and UCB. Dr. Strangfeld is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, BMS, Pfizer, Roche and Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Isaacs is a consultant or has received honoraria or grants from Pfizer, AbbVie, Amgen, Merck, Roche, and UCB. Dr. Carmona has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk for venous thromboembolism is almost 50% lower in patients with RA taking TNF inhibitors than in those taking conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), according to data from the German RABBIT registry.
“Some rheumatologists have thought TNF inhibitors could increase the risk for venous thromboembolism events, but we don’t think this is true, based on our findings,” said investigator Anja Strangfeld, MD, PhD, from the German Rheumatism Research Center in Berlin.
The risk is more than one-third lower in RA patients treated with other newer biologics, such as abatacept, rituximab, sarilumab, and tocilizumab.
However, risk for a serious venous thromboembolism is twice as high in patients with C-reactive protein (CRP) levels above 5 mg/L and is nearly three times as high in patients 65 years and older.
For the study, Dr. Strangfeld and her colleagues followed about 11,000 patients for more than 10 years. The findings were presented at the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress.
“Patients with RA have a greater risk for venous thromboembolism compared with the general population, but we didn’t know the risk conveyed by different DMARD treatments,” Dr. Strangfeld told Medscape Medical News. “It is also evident that higher age and lower capacity for physical function increase the risk, which was not so surprising.”
Chronic inflammation in RA patients elevates the risk for deep vein and pulmonary thrombosis by two to three times, said John Isaacs, MBBS, PhD, from Newcastle University in Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom, who is chair of the EULAR scientific program committee.
Among the supporting studies Dr. Isaacs discussed during an online press conference was a Swedish trial of more than 46,000 RA patients, which had been presented earlier by Viktor Molander, a PhD candidate from the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm (abstract OP0034).
Mr. Molander’s team showed that one in 100 patients with high disease activity will develop venous thromboembolism within a year, which is twice the number of events seen among patients in remission.
Combined with the RABBIT data, both studies “show if you can control their disease in the right way, you’re not only helping rheumatoid arthritis patients feel better, but you could be prolonging their lives,” Dr. Isaacs said.
The prospective RABBIT study followed RA patients who began receiving a new DMARD after treatment failed with at least one conventional synthetic DMARD, such as methotrexate or leflunomide. At baseline, those taking TNF inhibitors or other biologics had higher CRP levels on average, as well as a higher rate of existing cardiovascular disease. They also received glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, more often.
The observational nature of the RABBIT study is a weakness, Dr. Strangfeld said, and it could not prove cause and effect. But the methodology had several strengths, including input on patient factors from participating rheumatologists at least every 6 months.
“We enrolled patients at the start of treatment and observed them, regardless of any treatment changes, for up to 10 years,” she added. “That’s a really long observation period.”
The RABBIT data can help shape treatment decisions, said Loreto Carmona, MD, PhD, from the Musculoskeletal Health Institute in Madrid, who is chair of the EULAR abstract selection committee.
For a woman with RA who smokes and takes oral contraceptives, for example, “if she has high levels of inflammation, I think it’s okay to use TNF inhibitors, where maybe in the past we wouldn’t have thought that,” she said.
“The TNF inhibitors are actually reducing the inflammation and, therefore, reducing the risk,” Dr. Carmona told Medscape Medical News. “It could be an effect of using the drugs on people with higher levels of inflammation. It’s an indirect protective effect.”
The study was funded by a joint unconditional grant from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Fresenius-Kabi, Hexal, Lilly, MSD, Mylan, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi-Aventis, and UCB. Dr. Strangfeld is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, BMS, Pfizer, Roche and Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Isaacs is a consultant or has received honoraria or grants from Pfizer, AbbVie, Amgen, Merck, Roche, and UCB. Dr. Carmona has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk for venous thromboembolism is almost 50% lower in patients with RA taking TNF inhibitors than in those taking conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), according to data from the German RABBIT registry.
“Some rheumatologists have thought TNF inhibitors could increase the risk for venous thromboembolism events, but we don’t think this is true, based on our findings,” said investigator Anja Strangfeld, MD, PhD, from the German Rheumatism Research Center in Berlin.
The risk is more than one-third lower in RA patients treated with other newer biologics, such as abatacept, rituximab, sarilumab, and tocilizumab.
However, risk for a serious venous thromboembolism is twice as high in patients with C-reactive protein (CRP) levels above 5 mg/L and is nearly three times as high in patients 65 years and older.
For the study, Dr. Strangfeld and her colleagues followed about 11,000 patients for more than 10 years. The findings were presented at the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress.
“Patients with RA have a greater risk for venous thromboembolism compared with the general population, but we didn’t know the risk conveyed by different DMARD treatments,” Dr. Strangfeld told Medscape Medical News. “It is also evident that higher age and lower capacity for physical function increase the risk, which was not so surprising.”
Chronic inflammation in RA patients elevates the risk for deep vein and pulmonary thrombosis by two to three times, said John Isaacs, MBBS, PhD, from Newcastle University in Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom, who is chair of the EULAR scientific program committee.
Among the supporting studies Dr. Isaacs discussed during an online press conference was a Swedish trial of more than 46,000 RA patients, which had been presented earlier by Viktor Molander, a PhD candidate from the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm (abstract OP0034).
Mr. Molander’s team showed that one in 100 patients with high disease activity will develop venous thromboembolism within a year, which is twice the number of events seen among patients in remission.
Combined with the RABBIT data, both studies “show if you can control their disease in the right way, you’re not only helping rheumatoid arthritis patients feel better, but you could be prolonging their lives,” Dr. Isaacs said.
The prospective RABBIT study followed RA patients who began receiving a new DMARD after treatment failed with at least one conventional synthetic DMARD, such as methotrexate or leflunomide. At baseline, those taking TNF inhibitors or other biologics had higher CRP levels on average, as well as a higher rate of existing cardiovascular disease. They also received glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, more often.
The observational nature of the RABBIT study is a weakness, Dr. Strangfeld said, and it could not prove cause and effect. But the methodology had several strengths, including input on patient factors from participating rheumatologists at least every 6 months.
“We enrolled patients at the start of treatment and observed them, regardless of any treatment changes, for up to 10 years,” she added. “That’s a really long observation period.”
The RABBIT data can help shape treatment decisions, said Loreto Carmona, MD, PhD, from the Musculoskeletal Health Institute in Madrid, who is chair of the EULAR abstract selection committee.
For a woman with RA who smokes and takes oral contraceptives, for example, “if she has high levels of inflammation, I think it’s okay to use TNF inhibitors, where maybe in the past we wouldn’t have thought that,” she said.
“The TNF inhibitors are actually reducing the inflammation and, therefore, reducing the risk,” Dr. Carmona told Medscape Medical News. “It could be an effect of using the drugs on people with higher levels of inflammation. It’s an indirect protective effect.”
The study was funded by a joint unconditional grant from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Fresenius-Kabi, Hexal, Lilly, MSD, Mylan, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi-Aventis, and UCB. Dr. Strangfeld is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, BMS, Pfizer, Roche and Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Isaacs is a consultant or has received honoraria or grants from Pfizer, AbbVie, Amgen, Merck, Roche, and UCB. Dr. Carmona has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tandem transplantation, long-term maintenance may extend MM remission
Tandem autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) could extend progression-free survival (PFS) for some patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, based on long-term data from the phase 3 STaMINA trial.
While the intent-to-treat analysis showed no difference in 6-year PFS rate between single versus tandem HSCT, the as-treated analysis showed that patients who received two transplants had a 6-year PFS rate that was approximately 10% higher than those who received just one transplant, reported lead author Parameswaran Hari, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, who presented the findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
The STaMINA trial, also known as BMT CTN 0702, involved 758 patients who were randomized to receive one of three treatment regimens followed by 3 years of maintenance lenalidomide: tandem HSCT (auto/auto), single HSCT plus consolidation with lenalidomide/bortezomib/dexamethasone (auto/RVD), and single HSCT (auto/len).
“At the time, we intended the study to stop approximately 38 months from randomization, allowing for the time for transplant, and then 3 years of maintenance,” Dr. Hari said. However, as the results of lenalidomide maintenance in CALGB 00104 study were reported, they allowed for a follow-on protocol, which provided patients who are progression-free at the completion of the original STaMINA trial to go on to a second follow-on trial, which allowed lenalidomide maintenance on an indefinite basis, he added.
The present analysis looked at the long-term results of this follow-on trial, including the impact of discontinuing lenalidomide.
Aligning with the original study, the present intent-to-treat analysis showed no significant difference between treatment arms for 6-year PFS rate or overall survival. Respectively, PFS rates for auto/auto, auto/RVD, and auto/len were 43.9%, 39.7%, and 40.9% (P = .6).
But 32% of patients in the tandem group never underwent second HSCT, Dr. Hari noted, prompting the as-treated analysis. Although overall survival remained similar between groups, the 6-year PFS was significantly higher for patients who underwent tandem HSCT, at 49.4%, compared with 39.7% for auto/RVD and 38.6% for auto/len (P = .03).
Subgroup analysis showed the statistical benefit of tandem HSCT was driven by high-risk patients, who had a significantly better PFS after tandem transplant, compared with standard-risk patients, who showed no significant benefit.
Dr. Hari called the findings “provocative.”
“The tandem auto approach may still be relevant in high-risk multiple myeloma patients,” he said.
Dr. Hari and his colleagues also found that patients who stayed on maintenance lenalidomide after 38 months had a better 5-year PFS rate than those who discontinued maintenance therapy (79.5% vs. 61%; P = .0004). Subgroup analysis showed this benefit was statistically significant among patients with standard-risk disease (86.3% vs. 66%; P less than .001) but not among those in the high-risk subgroup (86.7% vs. 67.8%; P = .2).
However, Dr. Hari suggested that, based on the similarity of proportions between subgroups, the lack of significance in the high-risk subgroup was likely because of small sample size, suggesting the benefit of maintenance was actually shared across risk strata.
“Lenalidomide maintenance becomes a significant factor for preventing patients from progression,” Dr. Hari said, noting that the tandem transplant approach requires further study, and that he and his colleagues would soon publish minimal residual disease data.
He finished his presentation with a clear clinical recommendation. “Preplanned lenalidomide discontinuation at 3 years is not recommended based on inferior progression-free survival among those who stopped such therapy,” he said.
Invited discussant Joshua R. Richter, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said the findings encourage high-dose maintenance therapy, and for some, tandem HSCT.
“The STaMINA study presented today supports the notion that some patients with high-risk disease still may benefit and have further tumor burden reduction with the second transplant that leads to deeper remissions and hopefully abrogates diminished outcomes,” Dr. Richter said during a virtual presentation.
But improvements are needed to better identify such patients, Dr. Richter added. He highlighted a lack of standardization in risk modeling, with various factors currently employed, such as patient characteristics and genomic markers, among several others.
“Better definitions will allow us to cross compare and make true analyses about how to manage these patients,” Dr. Richter said. “Despite the improvements across the board that we’ve seen in myeloma patients, high-risk disease continues to represent a more complicated arena. And patients continue to suffer from worse outcomes, despite all of the other advances.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Amgen, Celgene, Novartis, and others. Dr. Richter disclosed affiliations with Takeda, Sanofi, Janssen, and others.
SOURCE: Hari et al. ASCO 2020. Abstract 8506.
Tandem autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) could extend progression-free survival (PFS) for some patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, based on long-term data from the phase 3 STaMINA trial.
While the intent-to-treat analysis showed no difference in 6-year PFS rate between single versus tandem HSCT, the as-treated analysis showed that patients who received two transplants had a 6-year PFS rate that was approximately 10% higher than those who received just one transplant, reported lead author Parameswaran Hari, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, who presented the findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
The STaMINA trial, also known as BMT CTN 0702, involved 758 patients who were randomized to receive one of three treatment regimens followed by 3 years of maintenance lenalidomide: tandem HSCT (auto/auto), single HSCT plus consolidation with lenalidomide/bortezomib/dexamethasone (auto/RVD), and single HSCT (auto/len).
“At the time, we intended the study to stop approximately 38 months from randomization, allowing for the time for transplant, and then 3 years of maintenance,” Dr. Hari said. However, as the results of lenalidomide maintenance in CALGB 00104 study were reported, they allowed for a follow-on protocol, which provided patients who are progression-free at the completion of the original STaMINA trial to go on to a second follow-on trial, which allowed lenalidomide maintenance on an indefinite basis, he added.
The present analysis looked at the long-term results of this follow-on trial, including the impact of discontinuing lenalidomide.
Aligning with the original study, the present intent-to-treat analysis showed no significant difference between treatment arms for 6-year PFS rate or overall survival. Respectively, PFS rates for auto/auto, auto/RVD, and auto/len were 43.9%, 39.7%, and 40.9% (P = .6).
But 32% of patients in the tandem group never underwent second HSCT, Dr. Hari noted, prompting the as-treated analysis. Although overall survival remained similar between groups, the 6-year PFS was significantly higher for patients who underwent tandem HSCT, at 49.4%, compared with 39.7% for auto/RVD and 38.6% for auto/len (P = .03).
Subgroup analysis showed the statistical benefit of tandem HSCT was driven by high-risk patients, who had a significantly better PFS after tandem transplant, compared with standard-risk patients, who showed no significant benefit.
Dr. Hari called the findings “provocative.”
“The tandem auto approach may still be relevant in high-risk multiple myeloma patients,” he said.
Dr. Hari and his colleagues also found that patients who stayed on maintenance lenalidomide after 38 months had a better 5-year PFS rate than those who discontinued maintenance therapy (79.5% vs. 61%; P = .0004). Subgroup analysis showed this benefit was statistically significant among patients with standard-risk disease (86.3% vs. 66%; P less than .001) but not among those in the high-risk subgroup (86.7% vs. 67.8%; P = .2).
However, Dr. Hari suggested that, based on the similarity of proportions between subgroups, the lack of significance in the high-risk subgroup was likely because of small sample size, suggesting the benefit of maintenance was actually shared across risk strata.
“Lenalidomide maintenance becomes a significant factor for preventing patients from progression,” Dr. Hari said, noting that the tandem transplant approach requires further study, and that he and his colleagues would soon publish minimal residual disease data.
He finished his presentation with a clear clinical recommendation. “Preplanned lenalidomide discontinuation at 3 years is not recommended based on inferior progression-free survival among those who stopped such therapy,” he said.
Invited discussant Joshua R. Richter, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said the findings encourage high-dose maintenance therapy, and for some, tandem HSCT.
“The STaMINA study presented today supports the notion that some patients with high-risk disease still may benefit and have further tumor burden reduction with the second transplant that leads to deeper remissions and hopefully abrogates diminished outcomes,” Dr. Richter said during a virtual presentation.
But improvements are needed to better identify such patients, Dr. Richter added. He highlighted a lack of standardization in risk modeling, with various factors currently employed, such as patient characteristics and genomic markers, among several others.
“Better definitions will allow us to cross compare and make true analyses about how to manage these patients,” Dr. Richter said. “Despite the improvements across the board that we’ve seen in myeloma patients, high-risk disease continues to represent a more complicated arena. And patients continue to suffer from worse outcomes, despite all of the other advances.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Amgen, Celgene, Novartis, and others. Dr. Richter disclosed affiliations with Takeda, Sanofi, Janssen, and others.
SOURCE: Hari et al. ASCO 2020. Abstract 8506.
Tandem autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) could extend progression-free survival (PFS) for some patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, based on long-term data from the phase 3 STaMINA trial.
While the intent-to-treat analysis showed no difference in 6-year PFS rate between single versus tandem HSCT, the as-treated analysis showed that patients who received two transplants had a 6-year PFS rate that was approximately 10% higher than those who received just one transplant, reported lead author Parameswaran Hari, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, who presented the findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
The STaMINA trial, also known as BMT CTN 0702, involved 758 patients who were randomized to receive one of three treatment regimens followed by 3 years of maintenance lenalidomide: tandem HSCT (auto/auto), single HSCT plus consolidation with lenalidomide/bortezomib/dexamethasone (auto/RVD), and single HSCT (auto/len).
“At the time, we intended the study to stop approximately 38 months from randomization, allowing for the time for transplant, and then 3 years of maintenance,” Dr. Hari said. However, as the results of lenalidomide maintenance in CALGB 00104 study were reported, they allowed for a follow-on protocol, which provided patients who are progression-free at the completion of the original STaMINA trial to go on to a second follow-on trial, which allowed lenalidomide maintenance on an indefinite basis, he added.
The present analysis looked at the long-term results of this follow-on trial, including the impact of discontinuing lenalidomide.
Aligning with the original study, the present intent-to-treat analysis showed no significant difference between treatment arms for 6-year PFS rate or overall survival. Respectively, PFS rates for auto/auto, auto/RVD, and auto/len were 43.9%, 39.7%, and 40.9% (P = .6).
But 32% of patients in the tandem group never underwent second HSCT, Dr. Hari noted, prompting the as-treated analysis. Although overall survival remained similar between groups, the 6-year PFS was significantly higher for patients who underwent tandem HSCT, at 49.4%, compared with 39.7% for auto/RVD and 38.6% for auto/len (P = .03).
Subgroup analysis showed the statistical benefit of tandem HSCT was driven by high-risk patients, who had a significantly better PFS after tandem transplant, compared with standard-risk patients, who showed no significant benefit.
Dr. Hari called the findings “provocative.”
“The tandem auto approach may still be relevant in high-risk multiple myeloma patients,” he said.
Dr. Hari and his colleagues also found that patients who stayed on maintenance lenalidomide after 38 months had a better 5-year PFS rate than those who discontinued maintenance therapy (79.5% vs. 61%; P = .0004). Subgroup analysis showed this benefit was statistically significant among patients with standard-risk disease (86.3% vs. 66%; P less than .001) but not among those in the high-risk subgroup (86.7% vs. 67.8%; P = .2).
However, Dr. Hari suggested that, based on the similarity of proportions between subgroups, the lack of significance in the high-risk subgroup was likely because of small sample size, suggesting the benefit of maintenance was actually shared across risk strata.
“Lenalidomide maintenance becomes a significant factor for preventing patients from progression,” Dr. Hari said, noting that the tandem transplant approach requires further study, and that he and his colleagues would soon publish minimal residual disease data.
He finished his presentation with a clear clinical recommendation. “Preplanned lenalidomide discontinuation at 3 years is not recommended based on inferior progression-free survival among those who stopped such therapy,” he said.
Invited discussant Joshua R. Richter, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said the findings encourage high-dose maintenance therapy, and for some, tandem HSCT.
“The STaMINA study presented today supports the notion that some patients with high-risk disease still may benefit and have further tumor burden reduction with the second transplant that leads to deeper remissions and hopefully abrogates diminished outcomes,” Dr. Richter said during a virtual presentation.
But improvements are needed to better identify such patients, Dr. Richter added. He highlighted a lack of standardization in risk modeling, with various factors currently employed, such as patient characteristics and genomic markers, among several others.
“Better definitions will allow us to cross compare and make true analyses about how to manage these patients,” Dr. Richter said. “Despite the improvements across the board that we’ve seen in myeloma patients, high-risk disease continues to represent a more complicated arena. And patients continue to suffer from worse outcomes, despite all of the other advances.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Amgen, Celgene, Novartis, and others. Dr. Richter disclosed affiliations with Takeda, Sanofi, Janssen, and others.
SOURCE: Hari et al. ASCO 2020. Abstract 8506.
FROM ASCO 2020