User login
Depression, sleep disorders linked to early mortality in breast cancer
Key clinical point: Comorbid depression, sleep disorders, or their combination is associated with early mortality in women with breast cancer.
Major finding: Depression (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.44; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.17-1.78) and sleep disorders (aHR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.02-1.84) were significantly associated with an increase in 5-year mortality. For the combination of depression and sleep disorders, aHR was 1.75 (95% CI: 1.17-2.60).
Study details: The data come from a retrospective cohort study of women diagnosed with breast cancer (2008-2012) in 1 of 200 general practices in the UK (n = 6,656; age, 18-80 years).
Disclosures: The study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Bach L et al. J Psychiatr Res. 2020 Nov 23. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.11.036.
Key clinical point: Comorbid depression, sleep disorders, or their combination is associated with early mortality in women with breast cancer.
Major finding: Depression (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.44; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.17-1.78) and sleep disorders (aHR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.02-1.84) were significantly associated with an increase in 5-year mortality. For the combination of depression and sleep disorders, aHR was 1.75 (95% CI: 1.17-2.60).
Study details: The data come from a retrospective cohort study of women diagnosed with breast cancer (2008-2012) in 1 of 200 general practices in the UK (n = 6,656; age, 18-80 years).
Disclosures: The study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Bach L et al. J Psychiatr Res. 2020 Nov 23. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.11.036.
Key clinical point: Comorbid depression, sleep disorders, or their combination is associated with early mortality in women with breast cancer.
Major finding: Depression (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.44; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.17-1.78) and sleep disorders (aHR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.02-1.84) were significantly associated with an increase in 5-year mortality. For the combination of depression and sleep disorders, aHR was 1.75 (95% CI: 1.17-2.60).
Study details: The data come from a retrospective cohort study of women diagnosed with breast cancer (2008-2012) in 1 of 200 general practices in the UK (n = 6,656; age, 18-80 years).
Disclosures: The study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Bach L et al. J Psychiatr Res. 2020 Nov 23. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.11.036.
Impact of BMI on overall survival in women with metastatic breast cancer
Key clinical point: Underweight appears as an independent negative prognostic factor for both overall survival (OS) and first-line progression-free survival (PFS) in women with metastatic breast cancer (MBC). In contrast, overweight and obesity are not associated with poorer outcomes.
Major finding: The median OS was 47.4 months (median follow-up, 48.6 months). Underweight (body mass index [BMI], less than 18.5 kg/m2) showed an independent association with worse OS (median OS, 33 months; hazard ratio [HR ], 1.14; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02-1.28) and first-line PFS (HR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.01-1.22). Overweight (BMI, 25.0-29.9 kg/m2) or obesity (BMI, 30.0 kg/m2 or higher) had no impact on OS.
Study details: This study evaluated the impact of BMI on survival outcomes among patients with metastatic breast cancer (n = 12,999) in the ESME-MBC cohort (median BMI, 24.9 kg/m2; 20% of women were obese and 5% underweight).
Disclosures: The ESME MBC database receives financial support from an industrial consortium (Roche, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, MSD, Eisai, and Daiichi Sankyo). Dr. K Saleh had no disclosures. Some of his coinvestigators reported ties with pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Saleh K et al. Breast. 2020 Dec 1. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2020.11.014.
Key clinical point: Underweight appears as an independent negative prognostic factor for both overall survival (OS) and first-line progression-free survival (PFS) in women with metastatic breast cancer (MBC). In contrast, overweight and obesity are not associated with poorer outcomes.
Major finding: The median OS was 47.4 months (median follow-up, 48.6 months). Underweight (body mass index [BMI], less than 18.5 kg/m2) showed an independent association with worse OS (median OS, 33 months; hazard ratio [HR ], 1.14; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02-1.28) and first-line PFS (HR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.01-1.22). Overweight (BMI, 25.0-29.9 kg/m2) or obesity (BMI, 30.0 kg/m2 or higher) had no impact on OS.
Study details: This study evaluated the impact of BMI on survival outcomes among patients with metastatic breast cancer (n = 12,999) in the ESME-MBC cohort (median BMI, 24.9 kg/m2; 20% of women were obese and 5% underweight).
Disclosures: The ESME MBC database receives financial support from an industrial consortium (Roche, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, MSD, Eisai, and Daiichi Sankyo). Dr. K Saleh had no disclosures. Some of his coinvestigators reported ties with pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Saleh K et al. Breast. 2020 Dec 1. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2020.11.014.
Key clinical point: Underweight appears as an independent negative prognostic factor for both overall survival (OS) and first-line progression-free survival (PFS) in women with metastatic breast cancer (MBC). In contrast, overweight and obesity are not associated with poorer outcomes.
Major finding: The median OS was 47.4 months (median follow-up, 48.6 months). Underweight (body mass index [BMI], less than 18.5 kg/m2) showed an independent association with worse OS (median OS, 33 months; hazard ratio [HR ], 1.14; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02-1.28) and first-line PFS (HR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.01-1.22). Overweight (BMI, 25.0-29.9 kg/m2) or obesity (BMI, 30.0 kg/m2 or higher) had no impact on OS.
Study details: This study evaluated the impact of BMI on survival outcomes among patients with metastatic breast cancer (n = 12,999) in the ESME-MBC cohort (median BMI, 24.9 kg/m2; 20% of women were obese and 5% underweight).
Disclosures: The ESME MBC database receives financial support from an industrial consortium (Roche, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, MSD, Eisai, and Daiichi Sankyo). Dr. K Saleh had no disclosures. Some of his coinvestigators reported ties with pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Saleh K et al. Breast. 2020 Dec 1. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2020.11.014.
Study supports clinical utility of CTC count for metastatic breast cancer
Key clinical point: Circulating tumor cell (CTC) count-driven first-line therapy (chemotherapy or endocrine therapy) is noninferior to clinician choice-driven first-line therapy for progression-free survival (PFS) in hormone receptor (HR)-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.
Major finding: The median PFS was 15.5 (95% confidence interval [CI], 12.7-17.3) months in the CTC-guided group and 13.9 (95% CI, 12.2-16.3) months in the clinician-driven choice group. The primary end point (PFS in the per-protocol population with a noninferiority margin of 1.25 for the 90% CI of the hazard ratio [HR]) was met with an HR of 0.94 (90% CI, 0.81-1.09). Overall survival was also noninferior with CTC guidance (HR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.71-1.16).
Study details: In this phase 3 STIC CTC trial, 755 women with HR-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive a CTC-driven first-line therapy (chemotherapy if 5 CTCs or more/7.5 mL; endocrine therapy if less than 5 CTCs/7.5 mL) or clinician choice-driven first-line therapy (chemotherapy or endocrine therapy) at 17 French centers.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Institut Curie, the French National Cancer Institute as part of the Programme de Soutien aux Techniques Innovantes Coûteuses 2011, and Menarini Silicon Biosystems. The lead author reported receiving grants and nonfinancial support from Menarini Silicon Biosystems during the conduct of the study.
Source: Bidard FC et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Nov 5. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.5660.
Key clinical point: Circulating tumor cell (CTC) count-driven first-line therapy (chemotherapy or endocrine therapy) is noninferior to clinician choice-driven first-line therapy for progression-free survival (PFS) in hormone receptor (HR)-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.
Major finding: The median PFS was 15.5 (95% confidence interval [CI], 12.7-17.3) months in the CTC-guided group and 13.9 (95% CI, 12.2-16.3) months in the clinician-driven choice group. The primary end point (PFS in the per-protocol population with a noninferiority margin of 1.25 for the 90% CI of the hazard ratio [HR]) was met with an HR of 0.94 (90% CI, 0.81-1.09). Overall survival was also noninferior with CTC guidance (HR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.71-1.16).
Study details: In this phase 3 STIC CTC trial, 755 women with HR-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive a CTC-driven first-line therapy (chemotherapy if 5 CTCs or more/7.5 mL; endocrine therapy if less than 5 CTCs/7.5 mL) or clinician choice-driven first-line therapy (chemotherapy or endocrine therapy) at 17 French centers.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Institut Curie, the French National Cancer Institute as part of the Programme de Soutien aux Techniques Innovantes Coûteuses 2011, and Menarini Silicon Biosystems. The lead author reported receiving grants and nonfinancial support from Menarini Silicon Biosystems during the conduct of the study.
Source: Bidard FC et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Nov 5. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.5660.
Key clinical point: Circulating tumor cell (CTC) count-driven first-line therapy (chemotherapy or endocrine therapy) is noninferior to clinician choice-driven first-line therapy for progression-free survival (PFS) in hormone receptor (HR)-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.
Major finding: The median PFS was 15.5 (95% confidence interval [CI], 12.7-17.3) months in the CTC-guided group and 13.9 (95% CI, 12.2-16.3) months in the clinician-driven choice group. The primary end point (PFS in the per-protocol population with a noninferiority margin of 1.25 for the 90% CI of the hazard ratio [HR]) was met with an HR of 0.94 (90% CI, 0.81-1.09). Overall survival was also noninferior with CTC guidance (HR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.71-1.16).
Study details: In this phase 3 STIC CTC trial, 755 women with HR-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive a CTC-driven first-line therapy (chemotherapy if 5 CTCs or more/7.5 mL; endocrine therapy if less than 5 CTCs/7.5 mL) or clinician choice-driven first-line therapy (chemotherapy or endocrine therapy) at 17 French centers.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Institut Curie, the French National Cancer Institute as part of the Programme de Soutien aux Techniques Innovantes Coûteuses 2011, and Menarini Silicon Biosystems. The lead author reported receiving grants and nonfinancial support from Menarini Silicon Biosystems during the conduct of the study.
Source: Bidard FC et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Nov 5. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.5660.
TNBC: Add-on ipatasertib fails to improve progression-free survival
Key clinical point: Addition of ipatasertib to paclitaxel does not improve progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-altered locally advanced unresectable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Major finding: The median PFS was 7.4 months with ipatasertib + paclitaxel vs 6.1 months with placebo + paclitaxel (hazard ratio, 1.02; P = .9237).
Study details: The data come from the Cohort A of phase 3 trial IPATunity130. 255 patients with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-altered TNBC were randomly assigned (2:1) to receive paclitaxel with either ipatasertib or placebo.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Hoffmann-La Roche. The presenting author Rebecca Dent declared relationships with AstraZeneca, Eisai, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
Source: Dent R et al. Abstract 4. SABCS 2020. 2020 Dec 10.
Key clinical point: Addition of ipatasertib to paclitaxel does not improve progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-altered locally advanced unresectable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Major finding: The median PFS was 7.4 months with ipatasertib + paclitaxel vs 6.1 months with placebo + paclitaxel (hazard ratio, 1.02; P = .9237).
Study details: The data come from the Cohort A of phase 3 trial IPATunity130. 255 patients with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-altered TNBC were randomly assigned (2:1) to receive paclitaxel with either ipatasertib or placebo.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Hoffmann-La Roche. The presenting author Rebecca Dent declared relationships with AstraZeneca, Eisai, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
Source: Dent R et al. Abstract 4. SABCS 2020. 2020 Dec 10.
Key clinical point: Addition of ipatasertib to paclitaxel does not improve progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-altered locally advanced unresectable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Major finding: The median PFS was 7.4 months with ipatasertib + paclitaxel vs 6.1 months with placebo + paclitaxel (hazard ratio, 1.02; P = .9237).
Study details: The data come from the Cohort A of phase 3 trial IPATunity130. 255 patients with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-altered TNBC were randomly assigned (2:1) to receive paclitaxel with either ipatasertib or placebo.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Hoffmann-La Roche. The presenting author Rebecca Dent declared relationships with AstraZeneca, Eisai, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
Source: Dent R et al. Abstract 4. SABCS 2020. 2020 Dec 10.
Sentinel node biopsy cuts surgery time over lymphadenectomy
Sentinel node biopsy shortens operative time by 13% and may play a role in reducing recovery time and length of hospital stay, reported David L. Tait, MD, of the Levine Cancer Institute, Charlotte, N.C., and colleagues.
In an effort to compare the immediate perioperative outcomes for narcotic usage and use of hospital resources for patients having sentinel node dissection, Dr. Tait and his colleagues conducted a retrospective study of 241 consecutive cases of minimally invasive surgery performed between Jan. 1, 2018, and Aug. 31, 2019, on endometrial cancer patients.
A total of 156 (65%) patients received nodal dissection, including 93 (60%) who received sentinel node biopsy and 63 (40%) who underwent a full lymphadenectomy in accordance with pathological criteria established at the time of surgery. The authors noted no differences between the sentinel group and the lymphadenectomy group in terms of age, body mass index, estimated blood loss, use of a preoperative enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) program, tobacco use, or ethanol use. They also found no difference in primary outcome of intravenous narcotics dispensed in surgery, recovery, or total dose.
Sentinel node biopsy offers several advantages
Dr. Tate and colleagues noted that a significantly shorter surgery time, by 27 minutes, on average, was not unexpected with the sentinel node biopsy technique. With lymphadenectomy, surgical procedure and recovery times were longer (214.2 minutes vs. 185.2 minutes and 157.6 minutes vs. 125.2 minutes, respectively) than sentinel biopsy, a difference the researchers could not explain given the similar use of narcotics between the two procedures. Lymphadenectomy also resulted in longer hospital stay than sentinel biopsy (23.5 hours vs. 15.5 hours), with same-day discharge significantly less frequent (16% vs. 50%).
The differences in operative time, recovery time, and hospital stay “are important with respect to improving the efficiency of the operating room, which has become even more important in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic,” the authors noted. They also found noteworthy that recovery and hospital stay are longer after full lymphadenectomy even though there was no difference in overall narcotic administration. Although this suggests surgeon and staff bias, other factors that were not accounted for in the study include distance from hospital, social situation, and functional status.
Change in practice patterns over time and the introduction of a universal ERAS program during the study period were noted as possible limitations. It was also noted that the study did not collect data on functional status or long-term outcome of patients.
The authors did note that using the sentinel node technique was advantageous because it was performed on all patients regardless of risk factors for extra uterine spread since the injection must be performed before hysterectomy. What makes this so beneficial is the potential it offers for detecting nodal metastasis in low-risk patients who may not have otherwise qualified for dissection, said Dr. Tait and colleagues.
In a separate interview, Justin Chura, MD, director of gynecologic oncology and robotic surgery at the Cancer Treatment Centers of America in Philadelphia, observed that “sentinel lymph node [SLN] mapping has been around since the late 1970s. It is most validated in melanoma and breast cancers but has also seen application for gynecological cancers including vulva, cervix, and endometrium. More than 5 years ago, the Society of Gynecologic Oncology issued a clinical practice statement regarding the role of sentinel lymph node mapping for endometrial cancer. An SLN algorithm has been part of [National Comprehensive Cancer Network] guidelines for a similar time frame. The technique faced a lot of skepticism and criticism in the breast cancer literature until randomized studies demonstrated that full axillary adenopathy did not confer a survival benefit. For endometrial cancer, it is unlikely that we will have as robust data, so we often look to retrospective studies such as the one presented by Tait et al.
“The study utilized a data set that was originally collected to assess the impact of an ERAS protocol. So, it is important to note that the data set was not collected with the intent of evaluating SLN mapping versus full lymphadenectomy. This explains why pathological data regarding lymph node yield and final surgicopathologic staging are absent,” he said.
Adoption of sentinel node biopsy is gaining popularity
“Overall, SLN mapping is safe (from a surgical standpoint) and may decrease perioperative morbidity,” Dr. Chura said. “The adoption of SLN mapping also appears to be increasing. Some gyn oncologists (including myself) are even performing SLN mapping on patients with endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia given the risk of malignancy being identified on final pathology.
“The current study provides more of a glimpse into the practice patterns of the authors’ institution where ‘full lymphadenectomy was very dependent upon the surgeon (P < .001)’ than it demonstrates one technique is better than the other. The ultimate question is how we define ‘better?’ Survival? Less morbidity? Improved accuracy of nodal metastasis? Shorter length of stay?” Dr. Chura said.Dr. Tait and colleagues as well as Dr. Chura had no conflicts of interest and no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Tate DL et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020 Dec 19. doi: 10.1016/jmig.2020.12.019.
Sentinel node biopsy shortens operative time by 13% and may play a role in reducing recovery time and length of hospital stay, reported David L. Tait, MD, of the Levine Cancer Institute, Charlotte, N.C., and colleagues.
In an effort to compare the immediate perioperative outcomes for narcotic usage and use of hospital resources for patients having sentinel node dissection, Dr. Tait and his colleagues conducted a retrospective study of 241 consecutive cases of minimally invasive surgery performed between Jan. 1, 2018, and Aug. 31, 2019, on endometrial cancer patients.
A total of 156 (65%) patients received nodal dissection, including 93 (60%) who received sentinel node biopsy and 63 (40%) who underwent a full lymphadenectomy in accordance with pathological criteria established at the time of surgery. The authors noted no differences between the sentinel group and the lymphadenectomy group in terms of age, body mass index, estimated blood loss, use of a preoperative enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) program, tobacco use, or ethanol use. They also found no difference in primary outcome of intravenous narcotics dispensed in surgery, recovery, or total dose.
Sentinel node biopsy offers several advantages
Dr. Tate and colleagues noted that a significantly shorter surgery time, by 27 minutes, on average, was not unexpected with the sentinel node biopsy technique. With lymphadenectomy, surgical procedure and recovery times were longer (214.2 minutes vs. 185.2 minutes and 157.6 minutes vs. 125.2 minutes, respectively) than sentinel biopsy, a difference the researchers could not explain given the similar use of narcotics between the two procedures. Lymphadenectomy also resulted in longer hospital stay than sentinel biopsy (23.5 hours vs. 15.5 hours), with same-day discharge significantly less frequent (16% vs. 50%).
The differences in operative time, recovery time, and hospital stay “are important with respect to improving the efficiency of the operating room, which has become even more important in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic,” the authors noted. They also found noteworthy that recovery and hospital stay are longer after full lymphadenectomy even though there was no difference in overall narcotic administration. Although this suggests surgeon and staff bias, other factors that were not accounted for in the study include distance from hospital, social situation, and functional status.
Change in practice patterns over time and the introduction of a universal ERAS program during the study period were noted as possible limitations. It was also noted that the study did not collect data on functional status or long-term outcome of patients.
The authors did note that using the sentinel node technique was advantageous because it was performed on all patients regardless of risk factors for extra uterine spread since the injection must be performed before hysterectomy. What makes this so beneficial is the potential it offers for detecting nodal metastasis in low-risk patients who may not have otherwise qualified for dissection, said Dr. Tait and colleagues.
In a separate interview, Justin Chura, MD, director of gynecologic oncology and robotic surgery at the Cancer Treatment Centers of America in Philadelphia, observed that “sentinel lymph node [SLN] mapping has been around since the late 1970s. It is most validated in melanoma and breast cancers but has also seen application for gynecological cancers including vulva, cervix, and endometrium. More than 5 years ago, the Society of Gynecologic Oncology issued a clinical practice statement regarding the role of sentinel lymph node mapping for endometrial cancer. An SLN algorithm has been part of [National Comprehensive Cancer Network] guidelines for a similar time frame. The technique faced a lot of skepticism and criticism in the breast cancer literature until randomized studies demonstrated that full axillary adenopathy did not confer a survival benefit. For endometrial cancer, it is unlikely that we will have as robust data, so we often look to retrospective studies such as the one presented by Tait et al.
“The study utilized a data set that was originally collected to assess the impact of an ERAS protocol. So, it is important to note that the data set was not collected with the intent of evaluating SLN mapping versus full lymphadenectomy. This explains why pathological data regarding lymph node yield and final surgicopathologic staging are absent,” he said.
Adoption of sentinel node biopsy is gaining popularity
“Overall, SLN mapping is safe (from a surgical standpoint) and may decrease perioperative morbidity,” Dr. Chura said. “The adoption of SLN mapping also appears to be increasing. Some gyn oncologists (including myself) are even performing SLN mapping on patients with endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia given the risk of malignancy being identified on final pathology.
“The current study provides more of a glimpse into the practice patterns of the authors’ institution where ‘full lymphadenectomy was very dependent upon the surgeon (P < .001)’ than it demonstrates one technique is better than the other. The ultimate question is how we define ‘better?’ Survival? Less morbidity? Improved accuracy of nodal metastasis? Shorter length of stay?” Dr. Chura said.Dr. Tait and colleagues as well as Dr. Chura had no conflicts of interest and no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Tate DL et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020 Dec 19. doi: 10.1016/jmig.2020.12.019.
Sentinel node biopsy shortens operative time by 13% and may play a role in reducing recovery time and length of hospital stay, reported David L. Tait, MD, of the Levine Cancer Institute, Charlotte, N.C., and colleagues.
In an effort to compare the immediate perioperative outcomes for narcotic usage and use of hospital resources for patients having sentinel node dissection, Dr. Tait and his colleagues conducted a retrospective study of 241 consecutive cases of minimally invasive surgery performed between Jan. 1, 2018, and Aug. 31, 2019, on endometrial cancer patients.
A total of 156 (65%) patients received nodal dissection, including 93 (60%) who received sentinel node biopsy and 63 (40%) who underwent a full lymphadenectomy in accordance with pathological criteria established at the time of surgery. The authors noted no differences between the sentinel group and the lymphadenectomy group in terms of age, body mass index, estimated blood loss, use of a preoperative enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) program, tobacco use, or ethanol use. They also found no difference in primary outcome of intravenous narcotics dispensed in surgery, recovery, or total dose.
Sentinel node biopsy offers several advantages
Dr. Tate and colleagues noted that a significantly shorter surgery time, by 27 minutes, on average, was not unexpected with the sentinel node biopsy technique. With lymphadenectomy, surgical procedure and recovery times were longer (214.2 minutes vs. 185.2 minutes and 157.6 minutes vs. 125.2 minutes, respectively) than sentinel biopsy, a difference the researchers could not explain given the similar use of narcotics between the two procedures. Lymphadenectomy also resulted in longer hospital stay than sentinel biopsy (23.5 hours vs. 15.5 hours), with same-day discharge significantly less frequent (16% vs. 50%).
The differences in operative time, recovery time, and hospital stay “are important with respect to improving the efficiency of the operating room, which has become even more important in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic,” the authors noted. They also found noteworthy that recovery and hospital stay are longer after full lymphadenectomy even though there was no difference in overall narcotic administration. Although this suggests surgeon and staff bias, other factors that were not accounted for in the study include distance from hospital, social situation, and functional status.
Change in practice patterns over time and the introduction of a universal ERAS program during the study period were noted as possible limitations. It was also noted that the study did not collect data on functional status or long-term outcome of patients.
The authors did note that using the sentinel node technique was advantageous because it was performed on all patients regardless of risk factors for extra uterine spread since the injection must be performed before hysterectomy. What makes this so beneficial is the potential it offers for detecting nodal metastasis in low-risk patients who may not have otherwise qualified for dissection, said Dr. Tait and colleagues.
In a separate interview, Justin Chura, MD, director of gynecologic oncology and robotic surgery at the Cancer Treatment Centers of America in Philadelphia, observed that “sentinel lymph node [SLN] mapping has been around since the late 1970s. It is most validated in melanoma and breast cancers but has also seen application for gynecological cancers including vulva, cervix, and endometrium. More than 5 years ago, the Society of Gynecologic Oncology issued a clinical practice statement regarding the role of sentinel lymph node mapping for endometrial cancer. An SLN algorithm has been part of [National Comprehensive Cancer Network] guidelines for a similar time frame. The technique faced a lot of skepticism and criticism in the breast cancer literature until randomized studies demonstrated that full axillary adenopathy did not confer a survival benefit. For endometrial cancer, it is unlikely that we will have as robust data, so we often look to retrospective studies such as the one presented by Tait et al.
“The study utilized a data set that was originally collected to assess the impact of an ERAS protocol. So, it is important to note that the data set was not collected with the intent of evaluating SLN mapping versus full lymphadenectomy. This explains why pathological data regarding lymph node yield and final surgicopathologic staging are absent,” he said.
Adoption of sentinel node biopsy is gaining popularity
“Overall, SLN mapping is safe (from a surgical standpoint) and may decrease perioperative morbidity,” Dr. Chura said. “The adoption of SLN mapping also appears to be increasing. Some gyn oncologists (including myself) are even performing SLN mapping on patients with endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia given the risk of malignancy being identified on final pathology.
“The current study provides more of a glimpse into the practice patterns of the authors’ institution where ‘full lymphadenectomy was very dependent upon the surgeon (P < .001)’ than it demonstrates one technique is better than the other. The ultimate question is how we define ‘better?’ Survival? Less morbidity? Improved accuracy of nodal metastasis? Shorter length of stay?” Dr. Chura said.Dr. Tait and colleagues as well as Dr. Chura had no conflicts of interest and no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Tate DL et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020 Dec 19. doi: 10.1016/jmig.2020.12.019.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF MINIMALLY INVASIVE GYNECOLOGY
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: RA Jan 2021
The availability of biologic DMARDs such as TNF-alpha inhibitors has expanded the therapies available to patient with RA. However, these agents have been associated with immunogenicity and the development of anti-drug antibodies that can in turn be associated with allergic reactions as well as secondary non-response to the medication. This observational study analyzes the potential relationship between the presence of anti-nuclear antibodies before and after administration of different TNF-alpha inhibitors (infliximab (IFX), adalimumab (ADA), and etanercept (ADA)) with the development of anti-drug antibodies, with the aim of predicting treatment failure. Interestingly, patients who were ANA negative (by immunofluorescence) prior to initiation of therapy did not develop antibodies to ADA or IFX (antibodies to ETN were not measured). How this is related to treatment efficacy is not clear; more patients who had anti-drug antibodies discontinued therapy within 52 weeks and were classified as non-responders to therapy, but whether there was a secondary non-response was not examined in this study. As many patients with RA are also ANA positive and have SSA antibodies, these findings could potentially greatly alter treatment algorithms if proven in longer-term randomized trials and should be examined in other biologic DMARDs as well.
The Leiden Early Arthritis Cohort (EAC) is an inception cohort that was established to study inflammatory arthritis early in the disease state, with a particular interest in RA. This cross-sectional study evaluates the frequency of intermetatarsal and submetatarsal bursitis (IMB and SMB) in early RA. The presence of these forefoot disorders on MRI was evaluated in 441 consecutive patients presenting to the EAC and in 193 healthy controls. IMB and SMB were found more frequently in RA than in other inflammatory arthritides or healthy controls, with a specificity of 70-97%. Sensitivity was higher for IMB than SMB. While the study was not designed to evaluate MRI of the forefoot as a predictive test for development of RA, these findings raise the possibility that this could be used as a diagnostic test in early arthritis and would be worthwhile studying prospectively.
Another question with regard to prediction of response of RA to therapy is that of the possibility of maintaining sustained DMARD-free remission (SDFR). Another study from the Leiden EAC examined 772 RA patients treated with synthetic and biologic DMARDs who had achieved clinical remission (DAS < 2.4) without synovitis. Taper and discontinuation of therapy was attempted, and patients were followed to evaluate whether absence of synovitis on exam was sustained on followup for at least 1 year. Of these patients, 149 achieved SDFR within 7 years of followup; 130 of these patients were seronegative for ACPA. Baseline DAS was similar between patients who did and did not achieve SDFR, but a better early DAS response (larger decrease between baseline and 4 months) was associated an increased chance of SDFR. As the study is observational without a control, it is hard to evaluate how SDFR may proceed in the natural course of the disease. Although the importance of treatment response at 4 months places a premium on early reduction of inflammation, achievement of SDFR in these patients may also be related to other baseline characteristics of the group, especially as ACPA-positive patients less frequently achieved SDFR.
The availability of biologic DMARDs such as TNF-alpha inhibitors has expanded the therapies available to patient with RA. However, these agents have been associated with immunogenicity and the development of anti-drug antibodies that can in turn be associated with allergic reactions as well as secondary non-response to the medication. This observational study analyzes the potential relationship between the presence of anti-nuclear antibodies before and after administration of different TNF-alpha inhibitors (infliximab (IFX), adalimumab (ADA), and etanercept (ADA)) with the development of anti-drug antibodies, with the aim of predicting treatment failure. Interestingly, patients who were ANA negative (by immunofluorescence) prior to initiation of therapy did not develop antibodies to ADA or IFX (antibodies to ETN were not measured). How this is related to treatment efficacy is not clear; more patients who had anti-drug antibodies discontinued therapy within 52 weeks and were classified as non-responders to therapy, but whether there was a secondary non-response was not examined in this study. As many patients with RA are also ANA positive and have SSA antibodies, these findings could potentially greatly alter treatment algorithms if proven in longer-term randomized trials and should be examined in other biologic DMARDs as well.
The Leiden Early Arthritis Cohort (EAC) is an inception cohort that was established to study inflammatory arthritis early in the disease state, with a particular interest in RA. This cross-sectional study evaluates the frequency of intermetatarsal and submetatarsal bursitis (IMB and SMB) in early RA. The presence of these forefoot disorders on MRI was evaluated in 441 consecutive patients presenting to the EAC and in 193 healthy controls. IMB and SMB were found more frequently in RA than in other inflammatory arthritides or healthy controls, with a specificity of 70-97%. Sensitivity was higher for IMB than SMB. While the study was not designed to evaluate MRI of the forefoot as a predictive test for development of RA, these findings raise the possibility that this could be used as a diagnostic test in early arthritis and would be worthwhile studying prospectively.
Another question with regard to prediction of response of RA to therapy is that of the possibility of maintaining sustained DMARD-free remission (SDFR). Another study from the Leiden EAC examined 772 RA patients treated with synthetic and biologic DMARDs who had achieved clinical remission (DAS < 2.4) without synovitis. Taper and discontinuation of therapy was attempted, and patients were followed to evaluate whether absence of synovitis on exam was sustained on followup for at least 1 year. Of these patients, 149 achieved SDFR within 7 years of followup; 130 of these patients were seronegative for ACPA. Baseline DAS was similar between patients who did and did not achieve SDFR, but a better early DAS response (larger decrease between baseline and 4 months) was associated an increased chance of SDFR. As the study is observational without a control, it is hard to evaluate how SDFR may proceed in the natural course of the disease. Although the importance of treatment response at 4 months places a premium on early reduction of inflammation, achievement of SDFR in these patients may also be related to other baseline characteristics of the group, especially as ACPA-positive patients less frequently achieved SDFR.
The availability of biologic DMARDs such as TNF-alpha inhibitors has expanded the therapies available to patient with RA. However, these agents have been associated with immunogenicity and the development of anti-drug antibodies that can in turn be associated with allergic reactions as well as secondary non-response to the medication. This observational study analyzes the potential relationship between the presence of anti-nuclear antibodies before and after administration of different TNF-alpha inhibitors (infliximab (IFX), adalimumab (ADA), and etanercept (ADA)) with the development of anti-drug antibodies, with the aim of predicting treatment failure. Interestingly, patients who were ANA negative (by immunofluorescence) prior to initiation of therapy did not develop antibodies to ADA or IFX (antibodies to ETN were not measured). How this is related to treatment efficacy is not clear; more patients who had anti-drug antibodies discontinued therapy within 52 weeks and were classified as non-responders to therapy, but whether there was a secondary non-response was not examined in this study. As many patients with RA are also ANA positive and have SSA antibodies, these findings could potentially greatly alter treatment algorithms if proven in longer-term randomized trials and should be examined in other biologic DMARDs as well.
The Leiden Early Arthritis Cohort (EAC) is an inception cohort that was established to study inflammatory arthritis early in the disease state, with a particular interest in RA. This cross-sectional study evaluates the frequency of intermetatarsal and submetatarsal bursitis (IMB and SMB) in early RA. The presence of these forefoot disorders on MRI was evaluated in 441 consecutive patients presenting to the EAC and in 193 healthy controls. IMB and SMB were found more frequently in RA than in other inflammatory arthritides or healthy controls, with a specificity of 70-97%. Sensitivity was higher for IMB than SMB. While the study was not designed to evaluate MRI of the forefoot as a predictive test for development of RA, these findings raise the possibility that this could be used as a diagnostic test in early arthritis and would be worthwhile studying prospectively.
Another question with regard to prediction of response of RA to therapy is that of the possibility of maintaining sustained DMARD-free remission (SDFR). Another study from the Leiden EAC examined 772 RA patients treated with synthetic and biologic DMARDs who had achieved clinical remission (DAS < 2.4) without synovitis. Taper and discontinuation of therapy was attempted, and patients were followed to evaluate whether absence of synovitis on exam was sustained on followup for at least 1 year. Of these patients, 149 achieved SDFR within 7 years of followup; 130 of these patients were seronegative for ACPA. Baseline DAS was similar between patients who did and did not achieve SDFR, but a better early DAS response (larger decrease between baseline and 4 months) was associated an increased chance of SDFR. As the study is observational without a control, it is hard to evaluate how SDFR may proceed in the natural course of the disease. Although the importance of treatment response at 4 months places a premium on early reduction of inflammation, achievement of SDFR in these patients may also be related to other baseline characteristics of the group, especially as ACPA-positive patients less frequently achieved SDFR.
Liquid Biopsies in a Veteran Patient Population With Advanced Prostate and Lung Non-Small Cell Carcinomas: A New Paradigm and Unique Challenge in Personalized Medicine
The advent of liquid biopsies targeting genetic mutations in solid tumors is a major milestone in the field of precision oncology.1 Conventional methods of obtaining tissue for molecular studies are limited by sample size and often do not represent the entire bulk of the tumor.2 This newer minimally invasive, revolutionary technique analyzes circulating cell-free DNA carrying tumor-specific alterations (circulating tumor DNA [ctDNA]) in peripheral blood and detects signature genomic alterations.1 Tp53 mutations have been reported in 25 to 40% of prostatic cancers and > 50% of non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC), being more common in late-stage and hormone refractory prostate cancers.3,4 Tp53 mutation has been found to be associated with poor prognosis and increased germline mutations.5
The veteran patient population has distinct demographic characteristics that make veterans more vulnerable to genetic mutations and malignancies, including risk of exposure to Agent Orange, smoking, substance abuse, and asbestos. This area is understudied and extremely sparse in the literature for frequency of genetic mutations, risk factors in solid malignancies occurring in the veteran patient population, and the clinical impact of these risk factors. We herein present a quality assurance study for the utility of liquid biopsies regarding the frequency of DNA damage repair (DDR) gene, Tp53, and androgen receptor (AR) mutations. The clinical impact in advanced lung and prostate cancers in the veteran patient population and frequency are the quality assurance observations that are the study endpoints.
Methods
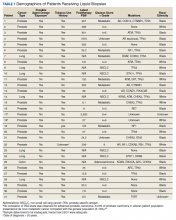
We reviewed for quality assurance documentation from the Foundation Medicine (www.foundationmedicine.com) cancer biomarker tests on liquid biopsies performed at the Corporal Michael J. Crescenz Veteran Affairs Medical Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania from May 2019 to April 15, 2020. All biopsies were performed on cancers with biochemical, imaging or tissue evidence of advanced tumor progression. The testing was performed on advanced solid malignancies, including NSCLC, prostate adenocarcinoma, and metastatic colon cancer. Statistical data for adequacy; cases with notable mutations; frequency; and type of mutations of AR, DDR, and Tp53 were noted. General and specific risk factors associated with the veteran patient population were studied and matched with the type of mutations (Table 1).
Results
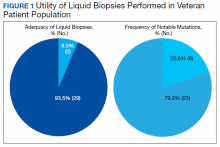
Thirty-one liquid biopsies were performed over this period—23 for prostate cancer, 7 for patients with lung cancer patients, and 1 for a patient with colon cancer. Of 31 cases, sensitivity/adequacy of liquid biopsy for genetic mutation was detected in 29 (93.5%) cases (Figure 1). Two inadequate biopsies (both from patients with prostate cancer) were excluded from the study, leaving 29 liquid biopsies with adequate ctDNA for analysis that were considered for further statistical purpose—21 prostate, 7 lung, and 1 colon cancer.
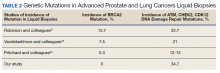
Multiple (common and different) genetic mutations were identified; however, our study subcategorized the mutations into the those that were related to prostate cancer, lung cancer, and some common mutations that occur in both cancers. Only the significant ones will be discussed in this review and equivocal result for AR is excluded from this study. Of the 21 prostate cancers, 4 (19.0%) had directed the targeted therapy to driver mutation (AR being most common in prostate cancer), while KRAS mutation, which was more common in lung cancer, was detected in 2/7 (28.6%) lung cancers. Mutations common to both cancer types were DDR gene mutations, which is a broad name for numerous genes including CDK12, ATM, and CHEK2.
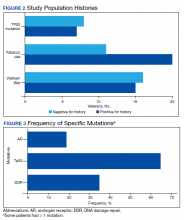
Of all cases irrespective of the cancer type, 23/29 (79.3%) showed notable mutations. DDR gene mutations were found in 6 of 21 (28.5%) patients with prostate cancer and 8 of 23 (34.7%) patients with advanced prostate and lung cancers, indicating poor outcome and possible resistance to the current therapy. Of 23 patients showing mutations irrespective of the cancer type, 15 (65.2%) harbored Tp53 mutations, which is much more frequent in veteran patient population when compared with the literature. Fifteen of the 31 (48.4%) total patients were Vietnam War-era veterans who were potentially exposed to Agent Orange and 20 (64.5%) patients who were not Vietnam War-era veterans had a history that included smoking (Figure 2).
Discussion
The veteran patient population is a unique cohort due to its distinct demographic characteristics with a high volume of cancer cases diagnosed each year. According to data from VA Central Cancer Registry (VACCR), the most frequently diagnosed cancers are prostate (29%) and lung (18%).6
Liquid biopsy is a novel, promising technology that uses ctDNA and circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood for detecting genetic alterations through next generation sequencing.7-9 The advent of this minimally invasive, revolutionary technology has been a breakthrough in the field of precision oncology for prognosis, to monitor treatment response or resistance to therapy and further personalize cancer therapy.9,10
Comprehensive genomic profiling by liquid biopsy has many advantages over the molecular studies performed on tissue biopsy. Due to the tumor heterogeneity, tissue samples may not represent the full profile of the tumor genomics of cancer, while liquid biopsy has full presentation of the disease.11,12 Many times, tissue biopsy may be limited by a sample size that precludes full genetic profiling in addition to higher total cost, potential technical issues during processing, and possible side effects of the biopsy procedure.7,13 Additionally, as the tumor progresses, new driver mutations other than the ones previously detected on the primary tissue may emerge, which can confer resistance to the existing therapy.7,13
Advanced prostatic and lung carcinomas with biochemical, distant organ, or bony progression harbor unique signature genetic mutations indicating poor prognosis, lack of response or resistance to the existing therapy, and high risk of relapse.14,15 Some of the unique characteristics of the veteran patient population include a more aged patient population multiple comorbidities, higher frequency of > 1 type of cancer, advanced cancer stage at presentation, and specific risks factors such as exposure to Agent Orange in veterans who served during the Vietnam War era.16,17 We studied the utility of liquid biopsy in cancer care, including type and incidence of genomic alterations associated with advanced prostate and lung cancers, in this unique patient population.
The amount of cell-free DNA (cfDNA), also known as ctDNA varies widely in cancer patients. Some of the factors associated with low concentration of cfDNA are disease stage, intervening therapy, proliferation rates, and tumor vascularization.18,19 In the peripheral blood, of the total cfDNA, fractions of cfDNA varies from 0.01 to 90%.18,19 All samples containing ≥ 20 ng cfDNA (20 - 100 ng) were subjected to the hybrid capture-based NGS FoundationACT assay.20 In our study, 2 specimens did not meet the minimum criteria of adequacy (20 ng cfDNA); however, the overall adequacy rate for the detection of mutation, irrespective of the cancer type was 29 of 31 (93.5%) with only 2 inadequate samples. This rate is higher than the rate reported in the literature, which is about 70%.20
Significant differences were encountered in the incidence of DNA damage repair genes including Tp53 mutations when compared with those in the general patient population (Table 2). According to recent National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, all prostate cancers should be screened for DDR gene mutations as these genes are common in aggressive prostate cancers and strongly associated with poor outcomes and shortened survival. Due to relatively high frequency of DDR gene mutations in advanced prostatic cancers, liquid biopsy in patients with these advanced stage prostate cancers may be a useful tool in clinical decision making and exploring targeted therapy.20
Mutations in BRCA2, ATM, CDK12, and CHEK2 (DDR gene family) are common. Incidence of ATM and CDK12 mutations in the literature is 3 to 6% of cases.21 Of 21 liquid biopsies of advanced prostate cancer patients, we found combined DDR gene mutation of ATM, CHEK2, and CDK12 genes in 6 (28.5%) cases, which is substantially higher than the 3 to 6% rate reported in the literature.21-24 Of the 23 patients who had notable mutations in our liquid biopsies, including both advanced prostate and lung cancer cases, 8 (34.7%) also showed mutation of the genes of DDR family. Our study did not show BRCA2 mutation, which is otherwise common in the literature.
We also evaluated the frequency of the most commonly occurring genetic mutations, Tp53 in advanced solid malignancies, especially advanced prostate and NSCLC. Previous studies have reported Tp53 mutation in association with risk factors (carcinogens) of cancer and have been a surrogate marker of poor survival or lack of response of therapy.25 Knowledge of Tp53 mutation is crucial for closer disease monitoring, preparing the patient for rapid progression, and encouraging the physician to prepare future lines of therapy.25-27 Although Tp53 mutation varies with histologic type and tissue of origin, Beltran and colleagues reported it in 30 to 40% of tumors, while Robles and colleagues reported about 40 to 42% incidence.25,27
Our study showed notable mutations in 23 of 29 adequate cases. Further, our study showed a high frequency of mutated Tp53 in 65.2% of combined advanced prostate and NSCLC cases. We then correlated cases of Vietnam War-era veterans with risk potential of Agent Orange exposure and Tp53 mutation. We found 7 of 15 Vietnam War-era veterans were positive for Tp53 mutations irrespective of the cancer type. The high incidence of Tp53 mutations in advanced prostate and lung carcinomas in the veteran patient population makes this tumor marker an aspiration not only as a surrogate of aggressive disease and tumor progression, but also as a key marker for targeted therapy in advanced prostate and lung cancers with loss of Tp53 function (Figure 3).
Mutations and amplifications in the AR gene are fundamental to progression of prostate cancer associated with advanced, hormone-refractory prostate cancer with the potential for targeted therapy with AR inhibitors. In our study, AR amplification was detected in 4 of 21 (19%) advanced prostate cancer cases, which is significantly lower than the 30 to 50% previously reported in the literature.28-32 Neither AR amplification or mutation was noted in advanced NSCLC in our study as previously reported in literature by Brennan and colleagues and Wang and colleagues.33-35 This is significant as it provides a pathway for future studies to focus on additional driver mutations for targeted therapies in advanced prostate carcinoma. To date, AR gene mutation does not play a role for personalized therapy in advanced NSCLC. Perhaps, a large cohort study with longitudinal analysis is needed for absolutely ruling out the possibility of personalized medicine in advanced lung cancer using this biomarker.
Conclusions
Liquid biopsy successfully provides precision-based oncology and information for decision making in this unique population of veterans. Difference in frequency of the genetic mutations in this cohort can provide future insight into disease progression, lack of response, and mechanism of resistance to the implemented therapy. Future studies focused on this veteran patient population are needed for developing targeted therapies and patient tailored oncologic therapy. ctDNA has a high potential for monitoring clinically relevant cancer-related genetic and epigenetic modifications for discovering more detailed information on the tumor characterization. Although larger cohort trial with longitudinal analyses are needed, high prevalence of DDR gene and Tp53 mutation in our study instills promising hope for therapeutic interventions in this unique cohort.
The minimally invasive liquid biopsy shows a great promise as both diagnostic and prognostic tool in the personalized clinical management of advanced prostate, and NSCLC in the veteran patient population with unique demographic characteristics. De novo metastatic prostate cancer is more common in veterans when compared with the general population, and therefore veterans may benefit by liquid biopsy. Differences in the frequency of genetic mutations (DDR, TP53, AR) in this cohort provides valuable information for disease progression, lack of response, mechanism of resistance to the implemented therapy and clinical decision making. Precision oncology can be further tailored for this cohort by focusing on DNA repair genes and Tp53 mutations for future targeted therapy.
1
9
16. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review the Health Effects in Vietnam Veterans of Exposure to Herbicides (Fourth Biennial Update). Veterans and Agent Orange: Update 2002. National Academies Press (US); 2003.
17. Eibner C, Krull H, Brown KM, et al. Current and projected characteristics and unique health care needs of the patient population served by the Department of Veterans Affairs. Rand Health Q. 2016;5(4):13. Published 2016 May 9.
18. Saarenheimo J, Eigeliene N, Andersen H, Tiirola M, Jekunen A. The value of liquid biopsies for guiding therapy decisions in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. 2019;9:129. Published 2019 Mar 5.doi:10.3389/fonc.2019.00129
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31. Antonarakis ES, Lu C, Luber B, et al. Clinical significance of androgen receptor splice variant-7 mRNA detection in circulating tumor cells of men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with first- and second-line abiraterone and enzalutamide. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(19):2149-2156. doi:10.1200/JCO.2016.70.1961
32

33. Jung A, Kirchner T. Liquid biopsy in tumor genetic diagnosis. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018;115(10):169-174. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2018.0169
34. Brennan S, Wang AR, Beyer H, et al. Androgen receptor as a potential target in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2017;77(Suppl13): abstract nr 4121. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2017-4121
35. Wang AR, Beyer H, Brennan S, et al. Androgen receptor drives differential gene expression in KRAS-mediated non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2018;78(Suppl 13): abstract nr 3946. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2018-3946
The advent of liquid biopsies targeting genetic mutations in solid tumors is a major milestone in the field of precision oncology.1 Conventional methods of obtaining tissue for molecular studies are limited by sample size and often do not represent the entire bulk of the tumor.2 This newer minimally invasive, revolutionary technique analyzes circulating cell-free DNA carrying tumor-specific alterations (circulating tumor DNA [ctDNA]) in peripheral blood and detects signature genomic alterations.1 Tp53 mutations have been reported in 25 to 40% of prostatic cancers and > 50% of non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC), being more common in late-stage and hormone refractory prostate cancers.3,4 Tp53 mutation has been found to be associated with poor prognosis and increased germline mutations.5
The veteran patient population has distinct demographic characteristics that make veterans more vulnerable to genetic mutations and malignancies, including risk of exposure to Agent Orange, smoking, substance abuse, and asbestos. This area is understudied and extremely sparse in the literature for frequency of genetic mutations, risk factors in solid malignancies occurring in the veteran patient population, and the clinical impact of these risk factors. We herein present a quality assurance study for the utility of liquid biopsies regarding the frequency of DNA damage repair (DDR) gene, Tp53, and androgen receptor (AR) mutations. The clinical impact in advanced lung and prostate cancers in the veteran patient population and frequency are the quality assurance observations that are the study endpoints.
Methods
We reviewed for quality assurance documentation from the Foundation Medicine (www.foundationmedicine.com) cancer biomarker tests on liquid biopsies performed at the Corporal Michael J. Crescenz Veteran Affairs Medical Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania from May 2019 to April 15, 2020. All biopsies were performed on cancers with biochemical, imaging or tissue evidence of advanced tumor progression. The testing was performed on advanced solid malignancies, including NSCLC, prostate adenocarcinoma, and metastatic colon cancer. Statistical data for adequacy; cases with notable mutations; frequency; and type of mutations of AR, DDR, and Tp53 were noted. General and specific risk factors associated with the veteran patient population were studied and matched with the type of mutations (Table 1).
Results
Thirty-one liquid biopsies were performed over this period—23 for prostate cancer, 7 for patients with lung cancer patients, and 1 for a patient with colon cancer. Of 31 cases, sensitivity/adequacy of liquid biopsy for genetic mutation was detected in 29 (93.5%) cases (Figure 1). Two inadequate biopsies (both from patients with prostate cancer) were excluded from the study, leaving 29 liquid biopsies with adequate ctDNA for analysis that were considered for further statistical purpose—21 prostate, 7 lung, and 1 colon cancer.
Multiple (common and different) genetic mutations were identified; however, our study subcategorized the mutations into the those that were related to prostate cancer, lung cancer, and some common mutations that occur in both cancers. Only the significant ones will be discussed in this review and equivocal result for AR is excluded from this study. Of the 21 prostate cancers, 4 (19.0%) had directed the targeted therapy to driver mutation (AR being most common in prostate cancer), while KRAS mutation, which was more common in lung cancer, was detected in 2/7 (28.6%) lung cancers. Mutations common to both cancer types were DDR gene mutations, which is a broad name for numerous genes including CDK12, ATM, and CHEK2.
Of all cases irrespective of the cancer type, 23/29 (79.3%) showed notable mutations. DDR gene mutations were found in 6 of 21 (28.5%) patients with prostate cancer and 8 of 23 (34.7%) patients with advanced prostate and lung cancers, indicating poor outcome and possible resistance to the current therapy. Of 23 patients showing mutations irrespective of the cancer type, 15 (65.2%) harbored Tp53 mutations, which is much more frequent in veteran patient population when compared with the literature. Fifteen of the 31 (48.4%) total patients were Vietnam War-era veterans who were potentially exposed to Agent Orange and 20 (64.5%) patients who were not Vietnam War-era veterans had a history that included smoking (Figure 2).
Discussion
The veteran patient population is a unique cohort due to its distinct demographic characteristics with a high volume of cancer cases diagnosed each year. According to data from VA Central Cancer Registry (VACCR), the most frequently diagnosed cancers are prostate (29%) and lung (18%).6
Liquid biopsy is a novel, promising technology that uses ctDNA and circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood for detecting genetic alterations through next generation sequencing.7-9 The advent of this minimally invasive, revolutionary technology has been a breakthrough in the field of precision oncology for prognosis, to monitor treatment response or resistance to therapy and further personalize cancer therapy.9,10
Comprehensive genomic profiling by liquid biopsy has many advantages over the molecular studies performed on tissue biopsy. Due to the tumor heterogeneity, tissue samples may not represent the full profile of the tumor genomics of cancer, while liquid biopsy has full presentation of the disease.11,12 Many times, tissue biopsy may be limited by a sample size that precludes full genetic profiling in addition to higher total cost, potential technical issues during processing, and possible side effects of the biopsy procedure.7,13 Additionally, as the tumor progresses, new driver mutations other than the ones previously detected on the primary tissue may emerge, which can confer resistance to the existing therapy.7,13
Advanced prostatic and lung carcinomas with biochemical, distant organ, or bony progression harbor unique signature genetic mutations indicating poor prognosis, lack of response or resistance to the existing therapy, and high risk of relapse.14,15 Some of the unique characteristics of the veteran patient population include a more aged patient population multiple comorbidities, higher frequency of > 1 type of cancer, advanced cancer stage at presentation, and specific risks factors such as exposure to Agent Orange in veterans who served during the Vietnam War era.16,17 We studied the utility of liquid biopsy in cancer care, including type and incidence of genomic alterations associated with advanced prostate and lung cancers, in this unique patient population.
The amount of cell-free DNA (cfDNA), also known as ctDNA varies widely in cancer patients. Some of the factors associated with low concentration of cfDNA are disease stage, intervening therapy, proliferation rates, and tumor vascularization.18,19 In the peripheral blood, of the total cfDNA, fractions of cfDNA varies from 0.01 to 90%.18,19 All samples containing ≥ 20 ng cfDNA (20 - 100 ng) were subjected to the hybrid capture-based NGS FoundationACT assay.20 In our study, 2 specimens did not meet the minimum criteria of adequacy (20 ng cfDNA); however, the overall adequacy rate for the detection of mutation, irrespective of the cancer type was 29 of 31 (93.5%) with only 2 inadequate samples. This rate is higher than the rate reported in the literature, which is about 70%.20
Significant differences were encountered in the incidence of DNA damage repair genes including Tp53 mutations when compared with those in the general patient population (Table 2). According to recent National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, all prostate cancers should be screened for DDR gene mutations as these genes are common in aggressive prostate cancers and strongly associated with poor outcomes and shortened survival. Due to relatively high frequency of DDR gene mutations in advanced prostatic cancers, liquid biopsy in patients with these advanced stage prostate cancers may be a useful tool in clinical decision making and exploring targeted therapy.20
Mutations in BRCA2, ATM, CDK12, and CHEK2 (DDR gene family) are common. Incidence of ATM and CDK12 mutations in the literature is 3 to 6% of cases.21 Of 21 liquid biopsies of advanced prostate cancer patients, we found combined DDR gene mutation of ATM, CHEK2, and CDK12 genes in 6 (28.5%) cases, which is substantially higher than the 3 to 6% rate reported in the literature.21-24 Of the 23 patients who had notable mutations in our liquid biopsies, including both advanced prostate and lung cancer cases, 8 (34.7%) also showed mutation of the genes of DDR family. Our study did not show BRCA2 mutation, which is otherwise common in the literature.
We also evaluated the frequency of the most commonly occurring genetic mutations, Tp53 in advanced solid malignancies, especially advanced prostate and NSCLC. Previous studies have reported Tp53 mutation in association with risk factors (carcinogens) of cancer and have been a surrogate marker of poor survival or lack of response of therapy.25 Knowledge of Tp53 mutation is crucial for closer disease monitoring, preparing the patient for rapid progression, and encouraging the physician to prepare future lines of therapy.25-27 Although Tp53 mutation varies with histologic type and tissue of origin, Beltran and colleagues reported it in 30 to 40% of tumors, while Robles and colleagues reported about 40 to 42% incidence.25,27
Our study showed notable mutations in 23 of 29 adequate cases. Further, our study showed a high frequency of mutated Tp53 in 65.2% of combined advanced prostate and NSCLC cases. We then correlated cases of Vietnam War-era veterans with risk potential of Agent Orange exposure and Tp53 mutation. We found 7 of 15 Vietnam War-era veterans were positive for Tp53 mutations irrespective of the cancer type. The high incidence of Tp53 mutations in advanced prostate and lung carcinomas in the veteran patient population makes this tumor marker an aspiration not only as a surrogate of aggressive disease and tumor progression, but also as a key marker for targeted therapy in advanced prostate and lung cancers with loss of Tp53 function (Figure 3).
Mutations and amplifications in the AR gene are fundamental to progression of prostate cancer associated with advanced, hormone-refractory prostate cancer with the potential for targeted therapy with AR inhibitors. In our study, AR amplification was detected in 4 of 21 (19%) advanced prostate cancer cases, which is significantly lower than the 30 to 50% previously reported in the literature.28-32 Neither AR amplification or mutation was noted in advanced NSCLC in our study as previously reported in literature by Brennan and colleagues and Wang and colleagues.33-35 This is significant as it provides a pathway for future studies to focus on additional driver mutations for targeted therapies in advanced prostate carcinoma. To date, AR gene mutation does not play a role for personalized therapy in advanced NSCLC. Perhaps, a large cohort study with longitudinal analysis is needed for absolutely ruling out the possibility of personalized medicine in advanced lung cancer using this biomarker.
Conclusions
Liquid biopsy successfully provides precision-based oncology and information for decision making in this unique population of veterans. Difference in frequency of the genetic mutations in this cohort can provide future insight into disease progression, lack of response, and mechanism of resistance to the implemented therapy. Future studies focused on this veteran patient population are needed for developing targeted therapies and patient tailored oncologic therapy. ctDNA has a high potential for monitoring clinically relevant cancer-related genetic and epigenetic modifications for discovering more detailed information on the tumor characterization. Although larger cohort trial with longitudinal analyses are needed, high prevalence of DDR gene and Tp53 mutation in our study instills promising hope for therapeutic interventions in this unique cohort.
The minimally invasive liquid biopsy shows a great promise as both diagnostic and prognostic tool in the personalized clinical management of advanced prostate, and NSCLC in the veteran patient population with unique demographic characteristics. De novo metastatic prostate cancer is more common in veterans when compared with the general population, and therefore veterans may benefit by liquid biopsy. Differences in the frequency of genetic mutations (DDR, TP53, AR) in this cohort provides valuable information for disease progression, lack of response, mechanism of resistance to the implemented therapy and clinical decision making. Precision oncology can be further tailored for this cohort by focusing on DNA repair genes and Tp53 mutations for future targeted therapy.
The advent of liquid biopsies targeting genetic mutations in solid tumors is a major milestone in the field of precision oncology.1 Conventional methods of obtaining tissue for molecular studies are limited by sample size and often do not represent the entire bulk of the tumor.2 This newer minimally invasive, revolutionary technique analyzes circulating cell-free DNA carrying tumor-specific alterations (circulating tumor DNA [ctDNA]) in peripheral blood and detects signature genomic alterations.1 Tp53 mutations have been reported in 25 to 40% of prostatic cancers and > 50% of non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC), being more common in late-stage and hormone refractory prostate cancers.3,4 Tp53 mutation has been found to be associated with poor prognosis and increased germline mutations.5
The veteran patient population has distinct demographic characteristics that make veterans more vulnerable to genetic mutations and malignancies, including risk of exposure to Agent Orange, smoking, substance abuse, and asbestos. This area is understudied and extremely sparse in the literature for frequency of genetic mutations, risk factors in solid malignancies occurring in the veteran patient population, and the clinical impact of these risk factors. We herein present a quality assurance study for the utility of liquid biopsies regarding the frequency of DNA damage repair (DDR) gene, Tp53, and androgen receptor (AR) mutations. The clinical impact in advanced lung and prostate cancers in the veteran patient population and frequency are the quality assurance observations that are the study endpoints.
Methods
We reviewed for quality assurance documentation from the Foundation Medicine (www.foundationmedicine.com) cancer biomarker tests on liquid biopsies performed at the Corporal Michael J. Crescenz Veteran Affairs Medical Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania from May 2019 to April 15, 2020. All biopsies were performed on cancers with biochemical, imaging or tissue evidence of advanced tumor progression. The testing was performed on advanced solid malignancies, including NSCLC, prostate adenocarcinoma, and metastatic colon cancer. Statistical data for adequacy; cases with notable mutations; frequency; and type of mutations of AR, DDR, and Tp53 were noted. General and specific risk factors associated with the veteran patient population were studied and matched with the type of mutations (Table 1).
Results
Thirty-one liquid biopsies were performed over this period—23 for prostate cancer, 7 for patients with lung cancer patients, and 1 for a patient with colon cancer. Of 31 cases, sensitivity/adequacy of liquid biopsy for genetic mutation was detected in 29 (93.5%) cases (Figure 1). Two inadequate biopsies (both from patients with prostate cancer) were excluded from the study, leaving 29 liquid biopsies with adequate ctDNA for analysis that were considered for further statistical purpose—21 prostate, 7 lung, and 1 colon cancer.
Multiple (common and different) genetic mutations were identified; however, our study subcategorized the mutations into the those that were related to prostate cancer, lung cancer, and some common mutations that occur in both cancers. Only the significant ones will be discussed in this review and equivocal result for AR is excluded from this study. Of the 21 prostate cancers, 4 (19.0%) had directed the targeted therapy to driver mutation (AR being most common in prostate cancer), while KRAS mutation, which was more common in lung cancer, was detected in 2/7 (28.6%) lung cancers. Mutations common to both cancer types were DDR gene mutations, which is a broad name for numerous genes including CDK12, ATM, and CHEK2.
Of all cases irrespective of the cancer type, 23/29 (79.3%) showed notable mutations. DDR gene mutations were found in 6 of 21 (28.5%) patients with prostate cancer and 8 of 23 (34.7%) patients with advanced prostate and lung cancers, indicating poor outcome and possible resistance to the current therapy. Of 23 patients showing mutations irrespective of the cancer type, 15 (65.2%) harbored Tp53 mutations, which is much more frequent in veteran patient population when compared with the literature. Fifteen of the 31 (48.4%) total patients were Vietnam War-era veterans who were potentially exposed to Agent Orange and 20 (64.5%) patients who were not Vietnam War-era veterans had a history that included smoking (Figure 2).
Discussion
The veteran patient population is a unique cohort due to its distinct demographic characteristics with a high volume of cancer cases diagnosed each year. According to data from VA Central Cancer Registry (VACCR), the most frequently diagnosed cancers are prostate (29%) and lung (18%).6
Liquid biopsy is a novel, promising technology that uses ctDNA and circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood for detecting genetic alterations through next generation sequencing.7-9 The advent of this minimally invasive, revolutionary technology has been a breakthrough in the field of precision oncology for prognosis, to monitor treatment response or resistance to therapy and further personalize cancer therapy.9,10
Comprehensive genomic profiling by liquid biopsy has many advantages over the molecular studies performed on tissue biopsy. Due to the tumor heterogeneity, tissue samples may not represent the full profile of the tumor genomics of cancer, while liquid biopsy has full presentation of the disease.11,12 Many times, tissue biopsy may be limited by a sample size that precludes full genetic profiling in addition to higher total cost, potential technical issues during processing, and possible side effects of the biopsy procedure.7,13 Additionally, as the tumor progresses, new driver mutations other than the ones previously detected on the primary tissue may emerge, which can confer resistance to the existing therapy.7,13
Advanced prostatic and lung carcinomas with biochemical, distant organ, or bony progression harbor unique signature genetic mutations indicating poor prognosis, lack of response or resistance to the existing therapy, and high risk of relapse.14,15 Some of the unique characteristics of the veteran patient population include a more aged patient population multiple comorbidities, higher frequency of > 1 type of cancer, advanced cancer stage at presentation, and specific risks factors such as exposure to Agent Orange in veterans who served during the Vietnam War era.16,17 We studied the utility of liquid biopsy in cancer care, including type and incidence of genomic alterations associated with advanced prostate and lung cancers, in this unique patient population.
The amount of cell-free DNA (cfDNA), also known as ctDNA varies widely in cancer patients. Some of the factors associated with low concentration of cfDNA are disease stage, intervening therapy, proliferation rates, and tumor vascularization.18,19 In the peripheral blood, of the total cfDNA, fractions of cfDNA varies from 0.01 to 90%.18,19 All samples containing ≥ 20 ng cfDNA (20 - 100 ng) were subjected to the hybrid capture-based NGS FoundationACT assay.20 In our study, 2 specimens did not meet the minimum criteria of adequacy (20 ng cfDNA); however, the overall adequacy rate for the detection of mutation, irrespective of the cancer type was 29 of 31 (93.5%) with only 2 inadequate samples. This rate is higher than the rate reported in the literature, which is about 70%.20
Significant differences were encountered in the incidence of DNA damage repair genes including Tp53 mutations when compared with those in the general patient population (Table 2). According to recent National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, all prostate cancers should be screened for DDR gene mutations as these genes are common in aggressive prostate cancers and strongly associated with poor outcomes and shortened survival. Due to relatively high frequency of DDR gene mutations in advanced prostatic cancers, liquid biopsy in patients with these advanced stage prostate cancers may be a useful tool in clinical decision making and exploring targeted therapy.20
Mutations in BRCA2, ATM, CDK12, and CHEK2 (DDR gene family) are common. Incidence of ATM and CDK12 mutations in the literature is 3 to 6% of cases.21 Of 21 liquid biopsies of advanced prostate cancer patients, we found combined DDR gene mutation of ATM, CHEK2, and CDK12 genes in 6 (28.5%) cases, which is substantially higher than the 3 to 6% rate reported in the literature.21-24 Of the 23 patients who had notable mutations in our liquid biopsies, including both advanced prostate and lung cancer cases, 8 (34.7%) also showed mutation of the genes of DDR family. Our study did not show BRCA2 mutation, which is otherwise common in the literature.
We also evaluated the frequency of the most commonly occurring genetic mutations, Tp53 in advanced solid malignancies, especially advanced prostate and NSCLC. Previous studies have reported Tp53 mutation in association with risk factors (carcinogens) of cancer and have been a surrogate marker of poor survival or lack of response of therapy.25 Knowledge of Tp53 mutation is crucial for closer disease monitoring, preparing the patient for rapid progression, and encouraging the physician to prepare future lines of therapy.25-27 Although Tp53 mutation varies with histologic type and tissue of origin, Beltran and colleagues reported it in 30 to 40% of tumors, while Robles and colleagues reported about 40 to 42% incidence.25,27
Our study showed notable mutations in 23 of 29 adequate cases. Further, our study showed a high frequency of mutated Tp53 in 65.2% of combined advanced prostate and NSCLC cases. We then correlated cases of Vietnam War-era veterans with risk potential of Agent Orange exposure and Tp53 mutation. We found 7 of 15 Vietnam War-era veterans were positive for Tp53 mutations irrespective of the cancer type. The high incidence of Tp53 mutations in advanced prostate and lung carcinomas in the veteran patient population makes this tumor marker an aspiration not only as a surrogate of aggressive disease and tumor progression, but also as a key marker for targeted therapy in advanced prostate and lung cancers with loss of Tp53 function (Figure 3).
Mutations and amplifications in the AR gene are fundamental to progression of prostate cancer associated with advanced, hormone-refractory prostate cancer with the potential for targeted therapy with AR inhibitors. In our study, AR amplification was detected in 4 of 21 (19%) advanced prostate cancer cases, which is significantly lower than the 30 to 50% previously reported in the literature.28-32 Neither AR amplification or mutation was noted in advanced NSCLC in our study as previously reported in literature by Brennan and colleagues and Wang and colleagues.33-35 This is significant as it provides a pathway for future studies to focus on additional driver mutations for targeted therapies in advanced prostate carcinoma. To date, AR gene mutation does not play a role for personalized therapy in advanced NSCLC. Perhaps, a large cohort study with longitudinal analysis is needed for absolutely ruling out the possibility of personalized medicine in advanced lung cancer using this biomarker.
Conclusions
Liquid biopsy successfully provides precision-based oncology and information for decision making in this unique population of veterans. Difference in frequency of the genetic mutations in this cohort can provide future insight into disease progression, lack of response, and mechanism of resistance to the implemented therapy. Future studies focused on this veteran patient population are needed for developing targeted therapies and patient tailored oncologic therapy. ctDNA has a high potential for monitoring clinically relevant cancer-related genetic and epigenetic modifications for discovering more detailed information on the tumor characterization. Although larger cohort trial with longitudinal analyses are needed, high prevalence of DDR gene and Tp53 mutation in our study instills promising hope for therapeutic interventions in this unique cohort.
The minimally invasive liquid biopsy shows a great promise as both diagnostic and prognostic tool in the personalized clinical management of advanced prostate, and NSCLC in the veteran patient population with unique demographic characteristics. De novo metastatic prostate cancer is more common in veterans when compared with the general population, and therefore veterans may benefit by liquid biopsy. Differences in the frequency of genetic mutations (DDR, TP53, AR) in this cohort provides valuable information for disease progression, lack of response, mechanism of resistance to the implemented therapy and clinical decision making. Precision oncology can be further tailored for this cohort by focusing on DNA repair genes and Tp53 mutations for future targeted therapy.
1
9
16. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review the Health Effects in Vietnam Veterans of Exposure to Herbicides (Fourth Biennial Update). Veterans and Agent Orange: Update 2002. National Academies Press (US); 2003.
17. Eibner C, Krull H, Brown KM, et al. Current and projected characteristics and unique health care needs of the patient population served by the Department of Veterans Affairs. Rand Health Q. 2016;5(4):13. Published 2016 May 9.
18. Saarenheimo J, Eigeliene N, Andersen H, Tiirola M, Jekunen A. The value of liquid biopsies for guiding therapy decisions in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. 2019;9:129. Published 2019 Mar 5.doi:10.3389/fonc.2019.00129
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31. Antonarakis ES, Lu C, Luber B, et al. Clinical significance of androgen receptor splice variant-7 mRNA detection in circulating tumor cells of men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with first- and second-line abiraterone and enzalutamide. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(19):2149-2156. doi:10.1200/JCO.2016.70.1961
32

33. Jung A, Kirchner T. Liquid biopsy in tumor genetic diagnosis. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018;115(10):169-174. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2018.0169
34. Brennan S, Wang AR, Beyer H, et al. Androgen receptor as a potential target in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2017;77(Suppl13): abstract nr 4121. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2017-4121
35. Wang AR, Beyer H, Brennan S, et al. Androgen receptor drives differential gene expression in KRAS-mediated non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2018;78(Suppl 13): abstract nr 3946. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2018-3946
1
9
16. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review the Health Effects in Vietnam Veterans of Exposure to Herbicides (Fourth Biennial Update). Veterans and Agent Orange: Update 2002. National Academies Press (US); 2003.
17. Eibner C, Krull H, Brown KM, et al. Current and projected characteristics and unique health care needs of the patient population served by the Department of Veterans Affairs. Rand Health Q. 2016;5(4):13. Published 2016 May 9.
18. Saarenheimo J, Eigeliene N, Andersen H, Tiirola M, Jekunen A. The value of liquid biopsies for guiding therapy decisions in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. 2019;9:129. Published 2019 Mar 5.doi:10.3389/fonc.2019.00129
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31. Antonarakis ES, Lu C, Luber B, et al. Clinical significance of androgen receptor splice variant-7 mRNA detection in circulating tumor cells of men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with first- and second-line abiraterone and enzalutamide. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(19):2149-2156. doi:10.1200/JCO.2016.70.1961
32

33. Jung A, Kirchner T. Liquid biopsy in tumor genetic diagnosis. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018;115(10):169-174. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2018.0169
34. Brennan S, Wang AR, Beyer H, et al. Androgen receptor as a potential target in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2017;77(Suppl13): abstract nr 4121. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2017-4121
35. Wang AR, Beyer H, Brennan S, et al. Androgen receptor drives differential gene expression in KRAS-mediated non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2018;78(Suppl 13): abstract nr 3946. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2018-3946
Sequential Targeted Treatment for a Geriatric Patient with Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Concurrent FLT3-TKD and IDH1 Mutations
Nearly 20,000 patients are diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in the US annually.1 Despite the use of aggressive chemotherapeutic agents, the prognosis remains poor, with a mean 5-year survival of 28.3%.2 Fortunately, with the refinement of next-generation sequencing (NGS) hematology panels and development of systemic targeted therapies, the treatment landscape for eligible patients has improved, both in frontline and relapsed or refractory (R/R) patients.
Specifically, investigations into alterations within the FMS-like tyrosine kinase (FLT3) and isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) genes have led to the discovery of a number of targeted treatments. Midostaurin is US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for use in combination with induction chemotherapy for patients with internal tandem duplication of the FLT3 (FLT3-ITD) gene or mutations within the tyrosine kinase domain (FLT3-TKD).3 Ivosidenib is indicated for frontline treatment for those who are poor candidates for induction chemotherapy, and R/R patients who have an R132H mutation in IDH1.4,5 Enasidenib is FDA-approved for R/R patients with R140Q, R172S, and R172K mutations in IDH2.6
The optimal treatment for patients with AML with ≥ 2 clinically actionable mutations has not been established. In this article we describe a geriatric patient who initially was diagnosed with AML with concurrent FLT3-TKD and IDH1 mutations and received targeted, sequential management. We detail changes in disease phenotype and mutational status by repeating an NGS hematology panel and cytogenetic studies after each stage of therapy. Lastly, we discuss the clonal evolution apparent within leukemic cells with use of ≥ 1 or more targeted agents.
Case Presentation
A 68-year-old man presented to the Emergency Department at The Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center in North Carolina with fatigue and light-headedness. Because of his symptoms and pancytopenia, a bone marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy were performed, which showed 57% myeloblasts, 12% promyelocytes/myelocytes, and 2% metamyelocytes in 20 to 30% cellular bone marrow. Flow cytometry confirmed a blast population consistent with AML. A LeukoVantage (Quest Diagnostics) hematologic NGS panel revealed the presence of FLT3-TKD, IDH1, RUNX1, BCOR-E1477, and SF3B1 mutations (Table). Initial fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) results showed a normal pattern of hybridization with no translocations. His disease was deemed to be intermediate-high risk because of the presence of FLT3-TKD and RUNX1 mutations, despite the normal cytogenetic profile and absence of additional clinical features.
Induction chemotherapy was started with idarubicin, 12 mg/m2, on days 1 to 3 and cytarabine, 200 mg/m2, on days 1 to 7. Because of the presence of a FLT3-TKD mutation, midostaurin was planned for days 8 to 21. After induction chemotherapy, a bone marrow biopsy on day 14 revealed an acellular marrow with no observed myeloblasts. A bone marrow biopsy conducted before initiating consolidation therapy, revealed 30% cellularity with morphologic remission. However, flow cytometry found 5% myeloblasts expressing CD34, CD117, CD13, CD38, and HLA-DR, consistent with measurable residual disease. He received 2 cycles of consolidation therapy with high-dose cytarabine combined with midostaurin. After the patient's second cycle of consolidation, he continued to experience transfusion-dependent cytopenias. Another bone marrow evaluation demonstrated 10% cellularity with nearly all cells appearing to be myeloblasts. A repeat LeukoVantage NGS panel demonstrated undetectable FLT3-TKD mutation and persistent IDH1-R123C mutation. FISH studies revealed a complex karyotype with monosomy of chromosomes 5 and 7 and trisomy of chromosome 8.
We discussed with the patient and his family the options available, which included initiating targeted therapy for his IDH1 mutation, administering hypomethylation therapy with or without venetoclax, or pursuing palliative measures. We collectively decided to pursue therapy with single-agent oral ivosidenib, 500 mg daily. After 1 month of treatment, our patient developed worsening fatigue. His white blood cell count had increased to > 43 k/cm2, raising concern for differentiation syndrome.
A review of the peripheral smear showed a wide-spectrum of maturing granulocytes, with a large percentage of blasts. Peripheral flow cytometry confirmed a blast population of 15%. After a short period of symptom improvement with steroids, the patient developed worsening confusion. Brain imaging identified 2 subdural hemorrhages. Because of a significant peripheral blast population and the development of these hemorrhages, palliative measures were pursued, and the patient was discharged to an inpatient hospice facility. A final NGS panel performed from peripheral blood detected mutations in IDH1, RUNX1, PTPN11, NRAS, BCOR-E1443, and SF3B1 genes.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of a patient who sequentially received targeted treatments directed against both FLT3 and IDH1 mutations. Initial management with midostaurin and cytarabine resulted in sustained remission of his FLT3-TKD mutation. However, despite receiving prompt standard of care with combination induction chemotherapy and targeted therapy, the patient experienced unfavorable clonal evolution based upon his molecular and cytogenetic testing. Addition of ivosidenib as a second targeting agent for his IDH1 mutation did not achieve a second remission.
Clonal evolution is a well-described phenomenon in hematology. Indolent conditions, such as clonal hematopoiesis of intermediate potential, or malignancies, such as myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative neoplasms, could transform into acute leukemia through the accumulation of driver mutations and/or cytogenetic abnormalities. Clonal evolution often is viewed as the culprit in patients with AML whose disease relapses after remission with initial chemotherapy.7-10 With the increasing availability of commercial NGS panels designed to assess mutations among patients experiencing hematologic malignancies, patterns of relapse, and, models of clonal evolution could be observed closely in patients with AML.
We were able to monitor molecular changes within our patient’s predominant clonal populations by repeating peripheral comprehensive NGS panels after lines of targeted therapies. The repeated sequencing revealed that clones with FLT3-TKD mutations responded to midostaurin with first-line chemotherapy whereas it was unclear whether clones with IDH1 mutation responded to ivosidenib. Development of complex cytogenetic findings along with the clonal expansion of BCOR mutation-harboring cells likely contributed to our patient’s acutely worsening condition. Several studies have found that the presence of a BCOR mutation in adults with AML leads to lower overall survival and relapse-free survival.11,12 As of now, there are no treatments specifically targeting BCOR mutations.
Although there are novel targeting agents with proven efficacy for both FLT3 and IDH1 mutations (Figure), it is difficult to determine which pathogenic mutation drives disease onset. No evidence suggests that these drugs could be administered in tandem. At the present time, interest is directed towards targeting all AML subclones simultaneously, which could reduce the likelihood of evolution among founder clones.7,10,13 In their comparison between molecular profiles and outcomes of patients with AML, Papaemmanuil and colleagues observed that > 80% of patients with AML harbor ≥ 2 driver mutations concurrently.14 Moreover, FLT3-ITD and IDH1 mutations tend to co-occur in approximately 9 to 27% of AML cases.15-18 Available targeted agents for AML are relatively new and hematologists’ familiarity with these drugs is continuing to grow. As the number of novel agents increases, investigations directed toward assessing the safety profile and efficacy of combining targeted agents will be beneficial for patients with AML with ≥ 1 driver mutation.
Conclusions
For our patient with AML, sequential targeted management of FLT3-TKD and IDH1 mutations was not beneficial. Higher-risk disease features, such as the development of a complex karyotype, likely contributed to our patient’s poor response to second-line ivosidenib. The sequential NGS malignant hematology panels allowed us to closely monitor changes to the molecular structure of our patient’s AML after each line of targeted therapy. Future investigations of combining targeted agents for patients with AML with concurrent actionable mutations would provide insight into outcomes of treating multiple clonal populations simultaneously.
1. De Kouchkovsky I, Abdul-Hay M. Acute myeloid leukemia: a comprehensive review and 2016 update. Blood Cancer J. 2016;6(7):e441. doi:10.1038/bcj.2016.50.
2. National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia — acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Accessed November 4, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html
3. Stone RM, Mandrekar SJ, Sanford BL, et al. Midostaurin plus chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia with a FLT3 mutation. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):454-464. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1614359.
4. DiNardo CD, Stein EM, de Botton S, et al. Durable remissions with ivosidenib in IDH1-mutated relapsed or refractory AML. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(25):2386-2398. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1716984.
5. Roboz, GJ, DiNardo, CD, Stein, EM, et al. Ivosidenib induces deep durable remissions in patients with newly diagnosed IDH1-mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2019;135(7), 463-471. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019002140
6. Stein EM, DiNardo CD, Pollyea DA, et al. Enasidenib in mutant IDH2 relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2017;130(6):722-731. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-04-779405.
7. Jan M, Majeti R. Clonal evolution of acute leukemia genomes. Oncogene. 2013;32(2):135-140. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.48.
8. Grove CS, Vassiliou GS. Acute myeloid leukaemia: a paradigm for the clonal evolution of cancer? Dis Model Mech. 2014;7(8):941-951. doi:10.1242/dmm.015974.
9. Anderson K, Lutz C, van Delft FW, et al. Genetic variegation of clonal architecture and propagating cells in leukaemia. Nature. 2011;469(7330):356-561. doi: 10.1038/nature09650.
10. Ding L, Ley TJ, Larson DE, et al. Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Nature. 2012;481(7382):506-510. doi:10.1038/nature10738.
11. Terada K, Yamaguchi H, Ueki T, et al. Usefulness of BCOR gene mutation as a prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia with intermediate cytogenetic prognosis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2018;57(8):401-408. doi:10.1002/gcc.22542.
12. Grossmann V, Tiacci E, Holmes AB, et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of BCOR in acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. Blood. 2011;118(23):6153-6163. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-07-365320.
13. Parkin B, Ouillette P, Li Y, et al. Clonal evolution and devolution after chemotherapy in adult acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 2013;121(2):369-377. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-04-427039.
14. Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Bullinger L, et al. Genomic classification and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(23):2209-2221. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1516192.
15. DiNardo CD, Ravandi F, Agresta S, et al. Characteristics, clinical outcome, and prognostic significance of IDH mutations in AML. Am J Hematol. 2015;90(8):732-736. doi:10.1002/ajh.24072.
16. Rakheja D, Konoplev S, Medeiros LJ, Chen W. IDH mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Hum Pathol. 2012;43 (10):1541-1551. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2012.05.003.
17. Lai C, Doucette K, Norsworthy K. Recent drug approvals for acute myeloid leukemia. J H Oncol. 2019;12(1):100. doi:10.1186/s13045-019-0774-x.
18. Boddu P, Takahashi K, Pemmaraju N, et al. Influence of IDH on FLT3-ITD status in newly diagnosed AML. Leukemia. 2017;31(11):2526-2529. doi:10.1038/leu.2017.244.
Nearly 20,000 patients are diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in the US annually.1 Despite the use of aggressive chemotherapeutic agents, the prognosis remains poor, with a mean 5-year survival of 28.3%.2 Fortunately, with the refinement of next-generation sequencing (NGS) hematology panels and development of systemic targeted therapies, the treatment landscape for eligible patients has improved, both in frontline and relapsed or refractory (R/R) patients.
Specifically, investigations into alterations within the FMS-like tyrosine kinase (FLT3) and isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) genes have led to the discovery of a number of targeted treatments. Midostaurin is US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for use in combination with induction chemotherapy for patients with internal tandem duplication of the FLT3 (FLT3-ITD) gene or mutations within the tyrosine kinase domain (FLT3-TKD).3 Ivosidenib is indicated for frontline treatment for those who are poor candidates for induction chemotherapy, and R/R patients who have an R132H mutation in IDH1.4,5 Enasidenib is FDA-approved for R/R patients with R140Q, R172S, and R172K mutations in IDH2.6
The optimal treatment for patients with AML with ≥ 2 clinically actionable mutations has not been established. In this article we describe a geriatric patient who initially was diagnosed with AML with concurrent FLT3-TKD and IDH1 mutations and received targeted, sequential management. We detail changes in disease phenotype and mutational status by repeating an NGS hematology panel and cytogenetic studies after each stage of therapy. Lastly, we discuss the clonal evolution apparent within leukemic cells with use of ≥ 1 or more targeted agents.
Case Presentation
A 68-year-old man presented to the Emergency Department at The Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center in North Carolina with fatigue and light-headedness. Because of his symptoms and pancytopenia, a bone marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy were performed, which showed 57% myeloblasts, 12% promyelocytes/myelocytes, and 2% metamyelocytes in 20 to 30% cellular bone marrow. Flow cytometry confirmed a blast population consistent with AML. A LeukoVantage (Quest Diagnostics) hematologic NGS panel revealed the presence of FLT3-TKD, IDH1, RUNX1, BCOR-E1477, and SF3B1 mutations (Table). Initial fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) results showed a normal pattern of hybridization with no translocations. His disease was deemed to be intermediate-high risk because of the presence of FLT3-TKD and RUNX1 mutations, despite the normal cytogenetic profile and absence of additional clinical features.
Induction chemotherapy was started with idarubicin, 12 mg/m2, on days 1 to 3 and cytarabine, 200 mg/m2, on days 1 to 7. Because of the presence of a FLT3-TKD mutation, midostaurin was planned for days 8 to 21. After induction chemotherapy, a bone marrow biopsy on day 14 revealed an acellular marrow with no observed myeloblasts. A bone marrow biopsy conducted before initiating consolidation therapy, revealed 30% cellularity with morphologic remission. However, flow cytometry found 5% myeloblasts expressing CD34, CD117, CD13, CD38, and HLA-DR, consistent with measurable residual disease. He received 2 cycles of consolidation therapy with high-dose cytarabine combined with midostaurin. After the patient's second cycle of consolidation, he continued to experience transfusion-dependent cytopenias. Another bone marrow evaluation demonstrated 10% cellularity with nearly all cells appearing to be myeloblasts. A repeat LeukoVantage NGS panel demonstrated undetectable FLT3-TKD mutation and persistent IDH1-R123C mutation. FISH studies revealed a complex karyotype with monosomy of chromosomes 5 and 7 and trisomy of chromosome 8.
We discussed with the patient and his family the options available, which included initiating targeted therapy for his IDH1 mutation, administering hypomethylation therapy with or without venetoclax, or pursuing palliative measures. We collectively decided to pursue therapy with single-agent oral ivosidenib, 500 mg daily. After 1 month of treatment, our patient developed worsening fatigue. His white blood cell count had increased to > 43 k/cm2, raising concern for differentiation syndrome.
A review of the peripheral smear showed a wide-spectrum of maturing granulocytes, with a large percentage of blasts. Peripheral flow cytometry confirmed a blast population of 15%. After a short period of symptom improvement with steroids, the patient developed worsening confusion. Brain imaging identified 2 subdural hemorrhages. Because of a significant peripheral blast population and the development of these hemorrhages, palliative measures were pursued, and the patient was discharged to an inpatient hospice facility. A final NGS panel performed from peripheral blood detected mutations in IDH1, RUNX1, PTPN11, NRAS, BCOR-E1443, and SF3B1 genes.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of a patient who sequentially received targeted treatments directed against both FLT3 and IDH1 mutations. Initial management with midostaurin and cytarabine resulted in sustained remission of his FLT3-TKD mutation. However, despite receiving prompt standard of care with combination induction chemotherapy and targeted therapy, the patient experienced unfavorable clonal evolution based upon his molecular and cytogenetic testing. Addition of ivosidenib as a second targeting agent for his IDH1 mutation did not achieve a second remission.
Clonal evolution is a well-described phenomenon in hematology. Indolent conditions, such as clonal hematopoiesis of intermediate potential, or malignancies, such as myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative neoplasms, could transform into acute leukemia through the accumulation of driver mutations and/or cytogenetic abnormalities. Clonal evolution often is viewed as the culprit in patients with AML whose disease relapses after remission with initial chemotherapy.7-10 With the increasing availability of commercial NGS panels designed to assess mutations among patients experiencing hematologic malignancies, patterns of relapse, and, models of clonal evolution could be observed closely in patients with AML.
We were able to monitor molecular changes within our patient’s predominant clonal populations by repeating peripheral comprehensive NGS panels after lines of targeted therapies. The repeated sequencing revealed that clones with FLT3-TKD mutations responded to midostaurin with first-line chemotherapy whereas it was unclear whether clones with IDH1 mutation responded to ivosidenib. Development of complex cytogenetic findings along with the clonal expansion of BCOR mutation-harboring cells likely contributed to our patient’s acutely worsening condition. Several studies have found that the presence of a BCOR mutation in adults with AML leads to lower overall survival and relapse-free survival.11,12 As of now, there are no treatments specifically targeting BCOR mutations.
Although there are novel targeting agents with proven efficacy for both FLT3 and IDH1 mutations (Figure), it is difficult to determine which pathogenic mutation drives disease onset. No evidence suggests that these drugs could be administered in tandem. At the present time, interest is directed towards targeting all AML subclones simultaneously, which could reduce the likelihood of evolution among founder clones.7,10,13 In their comparison between molecular profiles and outcomes of patients with AML, Papaemmanuil and colleagues observed that > 80% of patients with AML harbor ≥ 2 driver mutations concurrently.14 Moreover, FLT3-ITD and IDH1 mutations tend to co-occur in approximately 9 to 27% of AML cases.15-18 Available targeted agents for AML are relatively new and hematologists’ familiarity with these drugs is continuing to grow. As the number of novel agents increases, investigations directed toward assessing the safety profile and efficacy of combining targeted agents will be beneficial for patients with AML with ≥ 1 driver mutation.
Conclusions
For our patient with AML, sequential targeted management of FLT3-TKD and IDH1 mutations was not beneficial. Higher-risk disease features, such as the development of a complex karyotype, likely contributed to our patient’s poor response to second-line ivosidenib. The sequential NGS malignant hematology panels allowed us to closely monitor changes to the molecular structure of our patient’s AML after each line of targeted therapy. Future investigations of combining targeted agents for patients with AML with concurrent actionable mutations would provide insight into outcomes of treating multiple clonal populations simultaneously.
Nearly 20,000 patients are diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in the US annually.1 Despite the use of aggressive chemotherapeutic agents, the prognosis remains poor, with a mean 5-year survival of 28.3%.2 Fortunately, with the refinement of next-generation sequencing (NGS) hematology panels and development of systemic targeted therapies, the treatment landscape for eligible patients has improved, both in frontline and relapsed or refractory (R/R) patients.
Specifically, investigations into alterations within the FMS-like tyrosine kinase (FLT3) and isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) genes have led to the discovery of a number of targeted treatments. Midostaurin is US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for use in combination with induction chemotherapy for patients with internal tandem duplication of the FLT3 (FLT3-ITD) gene or mutations within the tyrosine kinase domain (FLT3-TKD).3 Ivosidenib is indicated for frontline treatment for those who are poor candidates for induction chemotherapy, and R/R patients who have an R132H mutation in IDH1.4,5 Enasidenib is FDA-approved for R/R patients with R140Q, R172S, and R172K mutations in IDH2.6
The optimal treatment for patients with AML with ≥ 2 clinically actionable mutations has not been established. In this article we describe a geriatric patient who initially was diagnosed with AML with concurrent FLT3-TKD and IDH1 mutations and received targeted, sequential management. We detail changes in disease phenotype and mutational status by repeating an NGS hematology panel and cytogenetic studies after each stage of therapy. Lastly, we discuss the clonal evolution apparent within leukemic cells with use of ≥ 1 or more targeted agents.
Case Presentation
A 68-year-old man presented to the Emergency Department at The Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center in North Carolina with fatigue and light-headedness. Because of his symptoms and pancytopenia, a bone marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy were performed, which showed 57% myeloblasts, 12% promyelocytes/myelocytes, and 2% metamyelocytes in 20 to 30% cellular bone marrow. Flow cytometry confirmed a blast population consistent with AML. A LeukoVantage (Quest Diagnostics) hematologic NGS panel revealed the presence of FLT3-TKD, IDH1, RUNX1, BCOR-E1477, and SF3B1 mutations (Table). Initial fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) results showed a normal pattern of hybridization with no translocations. His disease was deemed to be intermediate-high risk because of the presence of FLT3-TKD and RUNX1 mutations, despite the normal cytogenetic profile and absence of additional clinical features.
Induction chemotherapy was started with idarubicin, 12 mg/m2, on days 1 to 3 and cytarabine, 200 mg/m2, on days 1 to 7. Because of the presence of a FLT3-TKD mutation, midostaurin was planned for days 8 to 21. After induction chemotherapy, a bone marrow biopsy on day 14 revealed an acellular marrow with no observed myeloblasts. A bone marrow biopsy conducted before initiating consolidation therapy, revealed 30% cellularity with morphologic remission. However, flow cytometry found 5% myeloblasts expressing CD34, CD117, CD13, CD38, and HLA-DR, consistent with measurable residual disease. He received 2 cycles of consolidation therapy with high-dose cytarabine combined with midostaurin. After the patient's second cycle of consolidation, he continued to experience transfusion-dependent cytopenias. Another bone marrow evaluation demonstrated 10% cellularity with nearly all cells appearing to be myeloblasts. A repeat LeukoVantage NGS panel demonstrated undetectable FLT3-TKD mutation and persistent IDH1-R123C mutation. FISH studies revealed a complex karyotype with monosomy of chromosomes 5 and 7 and trisomy of chromosome 8.
We discussed with the patient and his family the options available, which included initiating targeted therapy for his IDH1 mutation, administering hypomethylation therapy with or without venetoclax, or pursuing palliative measures. We collectively decided to pursue therapy with single-agent oral ivosidenib, 500 mg daily. After 1 month of treatment, our patient developed worsening fatigue. His white blood cell count had increased to > 43 k/cm2, raising concern for differentiation syndrome.
A review of the peripheral smear showed a wide-spectrum of maturing granulocytes, with a large percentage of blasts. Peripheral flow cytometry confirmed a blast population of 15%. After a short period of symptom improvement with steroids, the patient developed worsening confusion. Brain imaging identified 2 subdural hemorrhages. Because of a significant peripheral blast population and the development of these hemorrhages, palliative measures were pursued, and the patient was discharged to an inpatient hospice facility. A final NGS panel performed from peripheral blood detected mutations in IDH1, RUNX1, PTPN11, NRAS, BCOR-E1443, and SF3B1 genes.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of a patient who sequentially received targeted treatments directed against both FLT3 and IDH1 mutations. Initial management with midostaurin and cytarabine resulted in sustained remission of his FLT3-TKD mutation. However, despite receiving prompt standard of care with combination induction chemotherapy and targeted therapy, the patient experienced unfavorable clonal evolution based upon his molecular and cytogenetic testing. Addition of ivosidenib as a second targeting agent for his IDH1 mutation did not achieve a second remission.
Clonal evolution is a well-described phenomenon in hematology. Indolent conditions, such as clonal hematopoiesis of intermediate potential, or malignancies, such as myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative neoplasms, could transform into acute leukemia through the accumulation of driver mutations and/or cytogenetic abnormalities. Clonal evolution often is viewed as the culprit in patients with AML whose disease relapses after remission with initial chemotherapy.7-10 With the increasing availability of commercial NGS panels designed to assess mutations among patients experiencing hematologic malignancies, patterns of relapse, and, models of clonal evolution could be observed closely in patients with AML.
We were able to monitor molecular changes within our patient’s predominant clonal populations by repeating peripheral comprehensive NGS panels after lines of targeted therapies. The repeated sequencing revealed that clones with FLT3-TKD mutations responded to midostaurin with first-line chemotherapy whereas it was unclear whether clones with IDH1 mutation responded to ivosidenib. Development of complex cytogenetic findings along with the clonal expansion of BCOR mutation-harboring cells likely contributed to our patient’s acutely worsening condition. Several studies have found that the presence of a BCOR mutation in adults with AML leads to lower overall survival and relapse-free survival.11,12 As of now, there are no treatments specifically targeting BCOR mutations.
Although there are novel targeting agents with proven efficacy for both FLT3 and IDH1 mutations (Figure), it is difficult to determine which pathogenic mutation drives disease onset. No evidence suggests that these drugs could be administered in tandem. At the present time, interest is directed towards targeting all AML subclones simultaneously, which could reduce the likelihood of evolution among founder clones.7,10,13 In their comparison between molecular profiles and outcomes of patients with AML, Papaemmanuil and colleagues observed that > 80% of patients with AML harbor ≥ 2 driver mutations concurrently.14 Moreover, FLT3-ITD and IDH1 mutations tend to co-occur in approximately 9 to 27% of AML cases.15-18 Available targeted agents for AML are relatively new and hematologists’ familiarity with these drugs is continuing to grow. As the number of novel agents increases, investigations directed toward assessing the safety profile and efficacy of combining targeted agents will be beneficial for patients with AML with ≥ 1 driver mutation.
Conclusions
For our patient with AML, sequential targeted management of FLT3-TKD and IDH1 mutations was not beneficial. Higher-risk disease features, such as the development of a complex karyotype, likely contributed to our patient’s poor response to second-line ivosidenib. The sequential NGS malignant hematology panels allowed us to closely monitor changes to the molecular structure of our patient’s AML after each line of targeted therapy. Future investigations of combining targeted agents for patients with AML with concurrent actionable mutations would provide insight into outcomes of treating multiple clonal populations simultaneously.
1. De Kouchkovsky I, Abdul-Hay M. Acute myeloid leukemia: a comprehensive review and 2016 update. Blood Cancer J. 2016;6(7):e441. doi:10.1038/bcj.2016.50.
2. National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia — acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Accessed November 4, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html
3. Stone RM, Mandrekar SJ, Sanford BL, et al. Midostaurin plus chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia with a FLT3 mutation. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):454-464. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1614359.
4. DiNardo CD, Stein EM, de Botton S, et al. Durable remissions with ivosidenib in IDH1-mutated relapsed or refractory AML. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(25):2386-2398. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1716984.
5. Roboz, GJ, DiNardo, CD, Stein, EM, et al. Ivosidenib induces deep durable remissions in patients with newly diagnosed IDH1-mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2019;135(7), 463-471. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019002140
6. Stein EM, DiNardo CD, Pollyea DA, et al. Enasidenib in mutant IDH2 relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2017;130(6):722-731. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-04-779405.
7. Jan M, Majeti R. Clonal evolution of acute leukemia genomes. Oncogene. 2013;32(2):135-140. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.48.
8. Grove CS, Vassiliou GS. Acute myeloid leukaemia: a paradigm for the clonal evolution of cancer? Dis Model Mech. 2014;7(8):941-951. doi:10.1242/dmm.015974.
9. Anderson K, Lutz C, van Delft FW, et al. Genetic variegation of clonal architecture and propagating cells in leukaemia. Nature. 2011;469(7330):356-561. doi: 10.1038/nature09650.
10. Ding L, Ley TJ, Larson DE, et al. Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Nature. 2012;481(7382):506-510. doi:10.1038/nature10738.
11. Terada K, Yamaguchi H, Ueki T, et al. Usefulness of BCOR gene mutation as a prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia with intermediate cytogenetic prognosis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2018;57(8):401-408. doi:10.1002/gcc.22542.
12. Grossmann V, Tiacci E, Holmes AB, et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of BCOR in acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. Blood. 2011;118(23):6153-6163. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-07-365320.
13. Parkin B, Ouillette P, Li Y, et al. Clonal evolution and devolution after chemotherapy in adult acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 2013;121(2):369-377. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-04-427039.
14. Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Bullinger L, et al. Genomic classification and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(23):2209-2221. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1516192.
15. DiNardo CD, Ravandi F, Agresta S, et al. Characteristics, clinical outcome, and prognostic significance of IDH mutations in AML. Am J Hematol. 2015;90(8):732-736. doi:10.1002/ajh.24072.
16. Rakheja D, Konoplev S, Medeiros LJ, Chen W. IDH mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Hum Pathol. 2012;43 (10):1541-1551. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2012.05.003.
17. Lai C, Doucette K, Norsworthy K. Recent drug approvals for acute myeloid leukemia. J H Oncol. 2019;12(1):100. doi:10.1186/s13045-019-0774-x.
18. Boddu P, Takahashi K, Pemmaraju N, et al. Influence of IDH on FLT3-ITD status in newly diagnosed AML. Leukemia. 2017;31(11):2526-2529. doi:10.1038/leu.2017.244.
1. De Kouchkovsky I, Abdul-Hay M. Acute myeloid leukemia: a comprehensive review and 2016 update. Blood Cancer J. 2016;6(7):e441. doi:10.1038/bcj.2016.50.
2. National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia — acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Accessed November 4, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html
3. Stone RM, Mandrekar SJ, Sanford BL, et al. Midostaurin plus chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia with a FLT3 mutation. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):454-464. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1614359.
4. DiNardo CD, Stein EM, de Botton S, et al. Durable remissions with ivosidenib in IDH1-mutated relapsed or refractory AML. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(25):2386-2398. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1716984.
5. Roboz, GJ, DiNardo, CD, Stein, EM, et al. Ivosidenib induces deep durable remissions in patients with newly diagnosed IDH1-mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2019;135(7), 463-471. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019002140
6. Stein EM, DiNardo CD, Pollyea DA, et al. Enasidenib in mutant IDH2 relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2017;130(6):722-731. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-04-779405.
7. Jan M, Majeti R. Clonal evolution of acute leukemia genomes. Oncogene. 2013;32(2):135-140. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.48.
8. Grove CS, Vassiliou GS. Acute myeloid leukaemia: a paradigm for the clonal evolution of cancer? Dis Model Mech. 2014;7(8):941-951. doi:10.1242/dmm.015974.
9. Anderson K, Lutz C, van Delft FW, et al. Genetic variegation of clonal architecture and propagating cells in leukaemia. Nature. 2011;469(7330):356-561. doi: 10.1038/nature09650.
10. Ding L, Ley TJ, Larson DE, et al. Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Nature. 2012;481(7382):506-510. doi:10.1038/nature10738.
11. Terada K, Yamaguchi H, Ueki T, et al. Usefulness of BCOR gene mutation as a prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia with intermediate cytogenetic prognosis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2018;57(8):401-408. doi:10.1002/gcc.22542.
12. Grossmann V, Tiacci E, Holmes AB, et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of BCOR in acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. Blood. 2011;118(23):6153-6163. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-07-365320.
13. Parkin B, Ouillette P, Li Y, et al. Clonal evolution and devolution after chemotherapy in adult acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 2013;121(2):369-377. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-04-427039.
14. Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Bullinger L, et al. Genomic classification and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(23):2209-2221. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1516192.
15. DiNardo CD, Ravandi F, Agresta S, et al. Characteristics, clinical outcome, and prognostic significance of IDH mutations in AML. Am J Hematol. 2015;90(8):732-736. doi:10.1002/ajh.24072.
16. Rakheja D, Konoplev S, Medeiros LJ, Chen W. IDH mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Hum Pathol. 2012;43 (10):1541-1551. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2012.05.003.
17. Lai C, Doucette K, Norsworthy K. Recent drug approvals for acute myeloid leukemia. J H Oncol. 2019;12(1):100. doi:10.1186/s13045-019-0774-x.
18. Boddu P, Takahashi K, Pemmaraju N, et al. Influence of IDH on FLT3-ITD status in newly diagnosed AML. Leukemia. 2017;31(11):2526-2529. doi:10.1038/leu.2017.244.
Long-Term Successful Treatment of Indolent Systemic Mastocytosis With Omalizumab
This case study suggests that omalizumab may help prevent anaphylaxis and reduce disease burden associated with systemic mastocytosis, but further studies and formal clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings.
Mastocytosis is a rare disease that causes allergic and anaphylactic symptoms due to chronic or episodic, excessive mast cell degranulation as well as mast cell infiltration of the skin or other organs.1 Mast cells aid in innate immunity by generation of a vasodilatory and inflammatory response and are significant contributors to allergic reactions. Cutaneous mastocytosis is defined by isolated skin involvement. Systemic mastocytosis (SM) is characterized by mast cell infiltration of extracutaneous organs, most often bone marrow.2
Background
SM is divided into distinct subtypes (Table 1). Nonadvanced SM subtypes include indolent SM and smoldering SM. These are the most common forms and tend to have more slowly progressing courses without evidence of organ tissue dysfunction, a myelodysplastic syndrome, or of a myeloproliferative disorder.3 Advanced SM is less common and is associated with organ tissue dysfunction. It also may be associated with myeloproliferative, myelodysplastic, or lymphoproliferative hematologic neoplasms, and subtypes include aggressive SM, SM with an associated hematologic neoplasm, and mast cell leukemia (Table 2).4
Treatment options approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for advanced SM include disease-altering medications, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (eg, imatinib), but the approved treatment options for nonadvanced SM are generally aimed at managing only symptoms (Table 3). Although not approved by the FDA for the treatment of SM, omalizumab may aid in the prevention of anaphylaxis, the reduction of disease burden, and the improvement in quality of life for patients with SM.5 Omalizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody against the Fc portion of immunoglobulin E (IgE). It is approved by the FDA for treatment of asthma as well as chronic idiopathic urticaria.6
Case Presentation
A 32-year-old female initially presented to Womack Army Medical Center at Fort Bragg, North Carolina, for evaluation due to recurrent episodes of anaphylaxis occurring 1 to 2 times per month as well as chronic skin rashes that progressed over the previous 5 years (Figure). She initially was diagnosed with idiopathic anaphylaxis and subsequently had multiple emergency department (ED) and clinic visits for vasovagal syncope, unexplained allergic reactions, dizziness, giddiness, and shortness of breath. More recently, she was diagnosed with idiopathic urticaria.
The patient reported at least 12 episodes in the previous year involving facial flushing that proceeded inferiorly, chest tightness, shortness of breath, labored breathing, crampy abdominal pain, and nausea without urticaria or significant pruritus. These bouts often were accompanied by mild facial angioedema, acute sinus pressure, vomiting, tachycardia, and lightheadedness. She reported experiencing brief losses of consciousness with at least 4 of these episodes. Home and ED blood pressure measurements revealed hypotension on several occasions with systolic readings in the 80s. She also developed nonpruritic freckles on her upper chest initially with subsequent increase in number and spread to involve her entire trunk, proximal extremities, and eventually distal extremities.
The patient had received intramuscular epinephrine several times, which led to rapid resolution of her symptoms. Intensive care unit admission for observation overnight was deemed necessary following one of her first episodes, but she did not require intubation or vasopressor support. Eventually, she began treating most episodes at home with diphenhydramine, ranitidine, and occasionally an epinephrine auto-injector, only presenting to the ED for severe dyspnea or loss of consciousness. Some episodes awoke her from sleeping but no triggers were identified (eg, foods, alcohol, supplements, medications, insect stings, latex exposure, exercise, strong emotions, or menstrual cycle).
Examination revealed hyperpigmented macules and papules scattered on the trunk and extremities, with a positive Darier sign. Punch biopsy of one of the macules revealed focal basal cell hyperpigmentation and sheets of benign-appearing mast cells in the superficial dermis, highlighted by CD117 immunohistochemical stain. A serum tryptase level was obtained and found to be significantly elevated (134 mcg/L). The patient was diagnosed with maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis (urticaria pigmentosa).
A bone marrow biopsy revealed multiple prominent infiltrates of monomorphic, spindled, CD117-positive, CD2-positive, and CD25-positive mast cells arranged interstitially and paratrabecularly, with associated reticulin fibrosis. Indolent SM was diagnosed according to the World Health Organization classification system with multifocal, dense aggregates of mast cells (> 25%) in the bone marrow and with persistently elevated serum tryptase levels (134, 134, 151, and 159 ng/mL) without laboratory evidence of an associated clonal myeloid disorder or findings consistent with infiltrating bone lesions on full body magnetic resonance imaging scan.4
Despite maximal antihistamine and antileukotriene therapy with ranitidine (150 mg twice daily), cetirizine (10 mg twice daily), montelukast (10 mg daily), and cromolyn sodium (200 mg daily), the patient continued to experience recurrent episodes of anaphylaxis requiring subcutaneous epinephrine and systemic corticosteroids. In May 2016, the patient began a trial of off-label therapy with omalizumab injections (300 mg subcutaneous every 4 weeks). She has continued on therapy for more than 4 years and experienced only 1 anaphylactic episode. She also has had significant improvement in cutaneous symptoms.
Discussion
Mast cell overactivation and degranulation in mastocytosis is largely driven by the IgE antibody, which plays a significant role in atopic conditions, immediate hypersensitivity reactions, and anaphylaxis, as well as in the immunologic response to parasitic infections. The severity of atopic disease seems to be associated with serum IgE levels in many patients.7 IgE binding to surface receptors on mast cells and eosinophils prompts the release of toxic mediators, incites inflammation, and induces allergic symptoms.8 Activation of mast cells is classically elicited by IgE binding to the high-affinity Fcε RI receptor, the expression of which correlates with IgE levels.9
The anti-IgE, recombinant, humanized immunoglobulin G monoclonal antibody, omalizumab, decreases mastocytic and eosinophilic symptoms by binding and inhibiting IgE. This diminishes free IgE levels, inhibits IgE binding to the Fcε RI receptor, and affects downregulation of this high-affinity receptor on mast cells and basophils.6 Omalizumab is currently FDA approved only for the treatment of moderate-to-severe, persistent, allergic asthma that is not controlled by inhaled corticosteroids in patients aged ≥ 6 years, and for chronic idiopathic urticaria not controlled by H1 antihistamine therapy in patients aged ≥ 12 years.10 However, it stands to reason that this therapy also should be effective in the treatment of other poorly controlled atopic conditions, especially mastocytosis, the symptoms of which are driven by excessive mast cell degranulation and tissue infiltration.
As early as 2007, preliminary data showed that treatment with omalizumab could decrease the frequency of episodes of anaphylaxis.11 A National Institutes of Health case report followed 2 patients, one for 5 months and the other for 24 months. Both patients experienced a decrease in frequency of anaphylaxis following initiation of omalizumab. In 2010, a second case report described the treatment of an Australian patient with recurrent idiopathic anaphylaxis also diagnosed with SM. After initiation of treatment with omalizumab, she, too, experienced decreased frequency of episodes of anaphylaxis over 14 months.12 A review of patients treated at the Mastocytosis Centre Odense University Hospital in Denmark was published in 2017. Of 13 patients with SM treated with omalizumab, 5 experienced what was considered a complete response to the medication, with 3 each experiencing major and partial responses.5 The median treatment time in these patients was 27 months. Each of these cases showed significant promise in the use of omalizumab to treat SM, informing the decision to attempt this treatment in our patient.
The potential positive effects of omalizumab in reducing symptom severity in patients with SM was further supported by a 2017 meta-analysis. This review included several individual case reports noting that omalizumab could decrease frequency of pulmonary and gastrointestinal manifestations of SM.13 A small randomized control trial of omalizumab for treatment of mild symptoms of SM found improvement in disease severity, although neither primary nor secondary endpoints reached statistical significance.14
This case demonstrates a substantial, long-term, clinical benefit and quality of life improvement with omalizumab therapy in a patient with indolent SM that was not adequately controlled by conventional therapies. This is evidenced by an impressive decline in the frequency of mastocytic anaphylactic episodes as well as diminished patient-endorsed cutaneous symptoms.
This case provides further evidence of the efficacy of this therapy in diminishing disease burden for patients with SM who are otherwise limited to treatments aimed at transient symptomatic relief without significant alteration of the underlying cause of symptoms. At the time this article was written, our patient had now 52 months of continuous treatment without any adverse reactions noted, suggesting the treatment's long-term efficacy. It also adds to a small but growing body of literature that supports the use of anti-IgE therapy as a treatment option for improved management of this distressing, life-altering illness. Even in the time that our patient has been receiving omalizumab for SM, another small case series of 2 patients has been published showing sustained treatment effect at 12 years of therapy.15 This adds further insight that omalizumab can offer long-term, safe treatment for this limiting condition.
Omalizumab therapy is not without risk, but for patients afflicted by unrestrained mastocytic disease, the benefits may outweigh the risks. The most common significant risk with this medication is anaphylaxis, occurring in 1 to 2 per 1,000 patients, usually within 2 hours of an injection.16 This may correlate to the underlying degree of atopy in patients receiving omalizumab, and the risk of anaphylaxis is relatively low compared with that of many other biologic medications.17 Additionally, early data from initial phases of clinical trials indicated a potentially elevated malignancy risk with omalizumab. However, subsequent pooled analysis of larger numbers of patients has decreased suspicion that a causal relationship exists.18
Conclusions
Omalizumab has proven value in the treatment of atopic conditions, such as asthma and idiopathic urticaria, for which it has been approved for use by the FDA. Its effectiveness in significantly decreasing free serum IgE levels, and inhibiting IgE activation of mast cells makes it a possible treatment option for patients with SM who are not sufficiently controlled with conventional therapy. The findings in this case suggest that omalizumab may be effective in the prevention of anaphylaxis and in the reduction of disease burden associated with SM. Further studies and formal clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings. Patients should be counseled appropriately concerning the risks, benefits, and off-label status of this treatment option.
1. Theoharides TC, Valent P, Akin C. Mast cells, mastocytosis, and related disorders. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(2):163-172. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1409760
2. Valent P, Sperr WR, Schwartz LB, Horny H-P. Diagnosis and classification of mast cell proliferative disorders: delineation from immunologic diseases and non-mast cell hematopoietic neoplasms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114(1):3-11. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2004.02.045
3. Valent P, Sotlar K, Sperr WR, et al. Refined diagnostic criteria and classification of mast cell leukemia (MCL) and myelomastocytic leukemia (MML): a consensus proposal. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(9):1691-1700. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdu047
4. Valent P, Akin C, Metcalfe DD. Mastocytosis: 2016 updated WHO classification and novel emerging treatment concepts. Blood. 2017;129(11):1420-1427. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-09-731893
5. Broesby-Olsen S, Vestergaard H, Mortz CG, et al. Omalizumab prevents anaphylaxis and improves symptoms in systemic mastocytosis: Efficacy and safety observations. 2018;73(1):230-238. doi:10.1111/all.13237
6. Kaplan AP, Giménez-Arnau AM, Saini SS.Mechanisms of action that contribute to efficacy of omalizumab in chronic spontaneous urticaria. Allergy. 2017;72(4):519-533. doi:10.1111/all.13083
7. Borish L, Chipps B, Deniz Y, Gujrathi S, Zheng B, Dolan C; TENOR Study Group. Total serum IgE levels in a large cohort of patients with severe or difficult-to-treat asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005;95(3):247-253. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61221-5
8. Corry DB, Kheradmand F. Induction and regulation of the IgE response. Nature. 1999;402(suppl 6760):18-23. doi:10.1038/35037014
9. MacGlashan D, McKenzie-White J, Chichester K, et al. In vitro regulation of FcRIα expression on human basophils by IgE antibody. Blood. 1998;91(5):1633-1643.
10. XOLAIR [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Revised 2019. Accessed November 11, 2020. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/103976s5234lbl.pdf
11. Carter MC, Robyn JA, Bressler PB, Walker JC, Shapiro GC, and Metcalfe DD. Omalizumab for the treatment of unprovoked anaphylaxis in patients with systemic mastocytosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119(6):1550-1551. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2007.03.032
12. Douglass JA, Carroll K, Voskamp A, Bourke P, Wei A, O’Hehir RE. Omalizumab is effective in treating systemic mastocytosis in a nonatopic patient. Allergy. 2010; 65(7):926-927. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02259.x
13. Le M, Miedzybrodzki B, Olynych T, Chapdelaine H, Ben-Shoshan M. Natural history and treatment of cutaneous and systemic mastocytosis. Postgrad Med. 2017;129(8):896-901. doi:10.1080/00325481.2017.1364124
14. Distler M, Maul J-T, Steiner T, et al. Efficacy of omalizumab in mastocytosis: allusive indication obtained from a prospective, double-blind, multicenter study (XOLMA Study) [published online ahead of print January 20, 2020]. Dermatology. doi:10.1159/000504842
15. Constantine G, Bressler P, Petroni D, Metcalfe D, Carter M. Twelve-year follow-up of omalizumab for anaphylaxis in 2 patients with systemic mastocytosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(4)1314-1316. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2018.07.041
16. Fanta CH. Asthma. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(10):1002-1014. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0804579
17. Baldo BA. Adverse events to monoclonal antibodies used for cancer therapy: focus on hypersensitivity responses. Oncoimmunology. 2013;2(10):e26333. doi:10.4161/onci.26333
18. Busse W, Buhl R, Fernandez Vidaurre C, et al. Omalizumab and the risk of malignancy: results from a pooled analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129(4):983-989.e6. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.01.033.
19. Castells M, Akin C. Mastocytosis (cutaneous and systemic): epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations. Accessed December 8, 2020. Updated June 12, 2018. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/mastocytosis-cutaneous-and-systemic-epidemiology-pathogenesis-and-clinical-manifestations
20. Czarny J, Lange M, Lugowska-Umer H, Nowicki R. Cutaneous mastocytosis treatment: strategies, limitations, and perspectives. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2018;35(6):541-545. doi:10.5114/ada.2018.77605
This case study suggests that omalizumab may help prevent anaphylaxis and reduce disease burden associated with systemic mastocytosis, but further studies and formal clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings.
This case study suggests that omalizumab may help prevent anaphylaxis and reduce disease burden associated with systemic mastocytosis, but further studies and formal clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings.
Mastocytosis is a rare disease that causes allergic and anaphylactic symptoms due to chronic or episodic, excessive mast cell degranulation as well as mast cell infiltration of the skin or other organs.1 Mast cells aid in innate immunity by generation of a vasodilatory and inflammatory response and are significant contributors to allergic reactions. Cutaneous mastocytosis is defined by isolated skin involvement. Systemic mastocytosis (SM) is characterized by mast cell infiltration of extracutaneous organs, most often bone marrow.2
Background
SM is divided into distinct subtypes (Table 1). Nonadvanced SM subtypes include indolent SM and smoldering SM. These are the most common forms and tend to have more slowly progressing courses without evidence of organ tissue dysfunction, a myelodysplastic syndrome, or of a myeloproliferative disorder.3 Advanced SM is less common and is associated with organ tissue dysfunction. It also may be associated with myeloproliferative, myelodysplastic, or lymphoproliferative hematologic neoplasms, and subtypes include aggressive SM, SM with an associated hematologic neoplasm, and mast cell leukemia (Table 2).4
Treatment options approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for advanced SM include disease-altering medications, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (eg, imatinib), but the approved treatment options for nonadvanced SM are generally aimed at managing only symptoms (Table 3). Although not approved by the FDA for the treatment of SM, omalizumab may aid in the prevention of anaphylaxis, the reduction of disease burden, and the improvement in quality of life for patients with SM.5 Omalizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody against the Fc portion of immunoglobulin E (IgE). It is approved by the FDA for treatment of asthma as well as chronic idiopathic urticaria.6
Case Presentation
A 32-year-old female initially presented to Womack Army Medical Center at Fort Bragg, North Carolina, for evaluation due to recurrent episodes of anaphylaxis occurring 1 to 2 times per month as well as chronic skin rashes that progressed over the previous 5 years (Figure). She initially was diagnosed with idiopathic anaphylaxis and subsequently had multiple emergency department (ED) and clinic visits for vasovagal syncope, unexplained allergic reactions, dizziness, giddiness, and shortness of breath. More recently, she was diagnosed with idiopathic urticaria.
The patient reported at least 12 episodes in the previous year involving facial flushing that proceeded inferiorly, chest tightness, shortness of breath, labored breathing, crampy abdominal pain, and nausea without urticaria or significant pruritus. These bouts often were accompanied by mild facial angioedema, acute sinus pressure, vomiting, tachycardia, and lightheadedness. She reported experiencing brief losses of consciousness with at least 4 of these episodes. Home and ED blood pressure measurements revealed hypotension on several occasions with systolic readings in the 80s. She also developed nonpruritic freckles on her upper chest initially with subsequent increase in number and spread to involve her entire trunk, proximal extremities, and eventually distal extremities.
The patient had received intramuscular epinephrine several times, which led to rapid resolution of her symptoms. Intensive care unit admission for observation overnight was deemed necessary following one of her first episodes, but she did not require intubation or vasopressor support. Eventually, she began treating most episodes at home with diphenhydramine, ranitidine, and occasionally an epinephrine auto-injector, only presenting to the ED for severe dyspnea or loss of consciousness. Some episodes awoke her from sleeping but no triggers were identified (eg, foods, alcohol, supplements, medications, insect stings, latex exposure, exercise, strong emotions, or menstrual cycle).
Examination revealed hyperpigmented macules and papules scattered on the trunk and extremities, with a positive Darier sign. Punch biopsy of one of the macules revealed focal basal cell hyperpigmentation and sheets of benign-appearing mast cells in the superficial dermis, highlighted by CD117 immunohistochemical stain. A serum tryptase level was obtained and found to be significantly elevated (134 mcg/L). The patient was diagnosed with maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis (urticaria pigmentosa).
A bone marrow biopsy revealed multiple prominent infiltrates of monomorphic, spindled, CD117-positive, CD2-positive, and CD25-positive mast cells arranged interstitially and paratrabecularly, with associated reticulin fibrosis. Indolent SM was diagnosed according to the World Health Organization classification system with multifocal, dense aggregates of mast cells (> 25%) in the bone marrow and with persistently elevated serum tryptase levels (134, 134, 151, and 159 ng/mL) without laboratory evidence of an associated clonal myeloid disorder or findings consistent with infiltrating bone lesions on full body magnetic resonance imaging scan.4
Despite maximal antihistamine and antileukotriene therapy with ranitidine (150 mg twice daily), cetirizine (10 mg twice daily), montelukast (10 mg daily), and cromolyn sodium (200 mg daily), the patient continued to experience recurrent episodes of anaphylaxis requiring subcutaneous epinephrine and systemic corticosteroids. In May 2016, the patient began a trial of off-label therapy with omalizumab injections (300 mg subcutaneous every 4 weeks). She has continued on therapy for more than 4 years and experienced only 1 anaphylactic episode. She also has had significant improvement in cutaneous symptoms.
Discussion
Mast cell overactivation and degranulation in mastocytosis is largely driven by the IgE antibody, which plays a significant role in atopic conditions, immediate hypersensitivity reactions, and anaphylaxis, as well as in the immunologic response to parasitic infections. The severity of atopic disease seems to be associated with serum IgE levels in many patients.7 IgE binding to surface receptors on mast cells and eosinophils prompts the release of toxic mediators, incites inflammation, and induces allergic symptoms.8 Activation of mast cells is classically elicited by IgE binding to the high-affinity Fcε RI receptor, the expression of which correlates with IgE levels.9
The anti-IgE, recombinant, humanized immunoglobulin G monoclonal antibody, omalizumab, decreases mastocytic and eosinophilic symptoms by binding and inhibiting IgE. This diminishes free IgE levels, inhibits IgE binding to the Fcε RI receptor, and affects downregulation of this high-affinity receptor on mast cells and basophils.6 Omalizumab is currently FDA approved only for the treatment of moderate-to-severe, persistent, allergic asthma that is not controlled by inhaled corticosteroids in patients aged ≥ 6 years, and for chronic idiopathic urticaria not controlled by H1 antihistamine therapy in patients aged ≥ 12 years.10 However, it stands to reason that this therapy also should be effective in the treatment of other poorly controlled atopic conditions, especially mastocytosis, the symptoms of which are driven by excessive mast cell degranulation and tissue infiltration.
As early as 2007, preliminary data showed that treatment with omalizumab could decrease the frequency of episodes of anaphylaxis.11 A National Institutes of Health case report followed 2 patients, one for 5 months and the other for 24 months. Both patients experienced a decrease in frequency of anaphylaxis following initiation of omalizumab. In 2010, a second case report described the treatment of an Australian patient with recurrent idiopathic anaphylaxis also diagnosed with SM. After initiation of treatment with omalizumab, she, too, experienced decreased frequency of episodes of anaphylaxis over 14 months.12 A review of patients treated at the Mastocytosis Centre Odense University Hospital in Denmark was published in 2017. Of 13 patients with SM treated with omalizumab, 5 experienced what was considered a complete response to the medication, with 3 each experiencing major and partial responses.5 The median treatment time in these patients was 27 months. Each of these cases showed significant promise in the use of omalizumab to treat SM, informing the decision to attempt this treatment in our patient.
The potential positive effects of omalizumab in reducing symptom severity in patients with SM was further supported by a 2017 meta-analysis. This review included several individual case reports noting that omalizumab could decrease frequency of pulmonary and gastrointestinal manifestations of SM.13 A small randomized control trial of omalizumab for treatment of mild symptoms of SM found improvement in disease severity, although neither primary nor secondary endpoints reached statistical significance.14
This case demonstrates a substantial, long-term, clinical benefit and quality of life improvement with omalizumab therapy in a patient with indolent SM that was not adequately controlled by conventional therapies. This is evidenced by an impressive decline in the frequency of mastocytic anaphylactic episodes as well as diminished patient-endorsed cutaneous symptoms.
This case provides further evidence of the efficacy of this therapy in diminishing disease burden for patients with SM who are otherwise limited to treatments aimed at transient symptomatic relief without significant alteration of the underlying cause of symptoms. At the time this article was written, our patient had now 52 months of continuous treatment without any adverse reactions noted, suggesting the treatment's long-term efficacy. It also adds to a small but growing body of literature that supports the use of anti-IgE therapy as a treatment option for improved management of this distressing, life-altering illness. Even in the time that our patient has been receiving omalizumab for SM, another small case series of 2 patients has been published showing sustained treatment effect at 12 years of therapy.15 This adds further insight that omalizumab can offer long-term, safe treatment for this limiting condition.
Omalizumab therapy is not without risk, but for patients afflicted by unrestrained mastocytic disease, the benefits may outweigh the risks. The most common significant risk with this medication is anaphylaxis, occurring in 1 to 2 per 1,000 patients, usually within 2 hours of an injection.16 This may correlate to the underlying degree of atopy in patients receiving omalizumab, and the risk of anaphylaxis is relatively low compared with that of many other biologic medications.17 Additionally, early data from initial phases of clinical trials indicated a potentially elevated malignancy risk with omalizumab. However, subsequent pooled analysis of larger numbers of patients has decreased suspicion that a causal relationship exists.18
Conclusions
Omalizumab has proven value in the treatment of atopic conditions, such as asthma and idiopathic urticaria, for which it has been approved for use by the FDA. Its effectiveness in significantly decreasing free serum IgE levels, and inhibiting IgE activation of mast cells makes it a possible treatment option for patients with SM who are not sufficiently controlled with conventional therapy. The findings in this case suggest that omalizumab may be effective in the prevention of anaphylaxis and in the reduction of disease burden associated with SM. Further studies and formal clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings. Patients should be counseled appropriately concerning the risks, benefits, and off-label status of this treatment option.
Mastocytosis is a rare disease that causes allergic and anaphylactic symptoms due to chronic or episodic, excessive mast cell degranulation as well as mast cell infiltration of the skin or other organs.1 Mast cells aid in innate immunity by generation of a vasodilatory and inflammatory response and are significant contributors to allergic reactions. Cutaneous mastocytosis is defined by isolated skin involvement. Systemic mastocytosis (SM) is characterized by mast cell infiltration of extracutaneous organs, most often bone marrow.2
Background
SM is divided into distinct subtypes (Table 1). Nonadvanced SM subtypes include indolent SM and smoldering SM. These are the most common forms and tend to have more slowly progressing courses without evidence of organ tissue dysfunction, a myelodysplastic syndrome, or of a myeloproliferative disorder.3 Advanced SM is less common and is associated with organ tissue dysfunction. It also may be associated with myeloproliferative, myelodysplastic, or lymphoproliferative hematologic neoplasms, and subtypes include aggressive SM, SM with an associated hematologic neoplasm, and mast cell leukemia (Table 2).4
Treatment options approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for advanced SM include disease-altering medications, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (eg, imatinib), but the approved treatment options for nonadvanced SM are generally aimed at managing only symptoms (Table 3). Although not approved by the FDA for the treatment of SM, omalizumab may aid in the prevention of anaphylaxis, the reduction of disease burden, and the improvement in quality of life for patients with SM.5 Omalizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody against the Fc portion of immunoglobulin E (IgE). It is approved by the FDA for treatment of asthma as well as chronic idiopathic urticaria.6
Case Presentation
A 32-year-old female initially presented to Womack Army Medical Center at Fort Bragg, North Carolina, for evaluation due to recurrent episodes of anaphylaxis occurring 1 to 2 times per month as well as chronic skin rashes that progressed over the previous 5 years (Figure). She initially was diagnosed with idiopathic anaphylaxis and subsequently had multiple emergency department (ED) and clinic visits for vasovagal syncope, unexplained allergic reactions, dizziness, giddiness, and shortness of breath. More recently, she was diagnosed with idiopathic urticaria.
The patient reported at least 12 episodes in the previous year involving facial flushing that proceeded inferiorly, chest tightness, shortness of breath, labored breathing, crampy abdominal pain, and nausea without urticaria or significant pruritus. These bouts often were accompanied by mild facial angioedema, acute sinus pressure, vomiting, tachycardia, and lightheadedness. She reported experiencing brief losses of consciousness with at least 4 of these episodes. Home and ED blood pressure measurements revealed hypotension on several occasions with systolic readings in the 80s. She also developed nonpruritic freckles on her upper chest initially with subsequent increase in number and spread to involve her entire trunk, proximal extremities, and eventually distal extremities.
The patient had received intramuscular epinephrine several times, which led to rapid resolution of her symptoms. Intensive care unit admission for observation overnight was deemed necessary following one of her first episodes, but she did not require intubation or vasopressor support. Eventually, she began treating most episodes at home with diphenhydramine, ranitidine, and occasionally an epinephrine auto-injector, only presenting to the ED for severe dyspnea or loss of consciousness. Some episodes awoke her from sleeping but no triggers were identified (eg, foods, alcohol, supplements, medications, insect stings, latex exposure, exercise, strong emotions, or menstrual cycle).
Examination revealed hyperpigmented macules and papules scattered on the trunk and extremities, with a positive Darier sign. Punch biopsy of one of the macules revealed focal basal cell hyperpigmentation and sheets of benign-appearing mast cells in the superficial dermis, highlighted by CD117 immunohistochemical stain. A serum tryptase level was obtained and found to be significantly elevated (134 mcg/L). The patient was diagnosed with maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis (urticaria pigmentosa).
A bone marrow biopsy revealed multiple prominent infiltrates of monomorphic, spindled, CD117-positive, CD2-positive, and CD25-positive mast cells arranged interstitially and paratrabecularly, with associated reticulin fibrosis. Indolent SM was diagnosed according to the World Health Organization classification system with multifocal, dense aggregates of mast cells (> 25%) in the bone marrow and with persistently elevated serum tryptase levels (134, 134, 151, and 159 ng/mL) without laboratory evidence of an associated clonal myeloid disorder or findings consistent with infiltrating bone lesions on full body magnetic resonance imaging scan.4
Despite maximal antihistamine and antileukotriene therapy with ranitidine (150 mg twice daily), cetirizine (10 mg twice daily), montelukast (10 mg daily), and cromolyn sodium (200 mg daily), the patient continued to experience recurrent episodes of anaphylaxis requiring subcutaneous epinephrine and systemic corticosteroids. In May 2016, the patient began a trial of off-label therapy with omalizumab injections (300 mg subcutaneous every 4 weeks). She has continued on therapy for more than 4 years and experienced only 1 anaphylactic episode. She also has had significant improvement in cutaneous symptoms.
Discussion
Mast cell overactivation and degranulation in mastocytosis is largely driven by the IgE antibody, which plays a significant role in atopic conditions, immediate hypersensitivity reactions, and anaphylaxis, as well as in the immunologic response to parasitic infections. The severity of atopic disease seems to be associated with serum IgE levels in many patients.7 IgE binding to surface receptors on mast cells and eosinophils prompts the release of toxic mediators, incites inflammation, and induces allergic symptoms.8 Activation of mast cells is classically elicited by IgE binding to the high-affinity Fcε RI receptor, the expression of which correlates with IgE levels.9
The anti-IgE, recombinant, humanized immunoglobulin G monoclonal antibody, omalizumab, decreases mastocytic and eosinophilic symptoms by binding and inhibiting IgE. This diminishes free IgE levels, inhibits IgE binding to the Fcε RI receptor, and affects downregulation of this high-affinity receptor on mast cells and basophils.6 Omalizumab is currently FDA approved only for the treatment of moderate-to-severe, persistent, allergic asthma that is not controlled by inhaled corticosteroids in patients aged ≥ 6 years, and for chronic idiopathic urticaria not controlled by H1 antihistamine therapy in patients aged ≥ 12 years.10 However, it stands to reason that this therapy also should be effective in the treatment of other poorly controlled atopic conditions, especially mastocytosis, the symptoms of which are driven by excessive mast cell degranulation and tissue infiltration.
As early as 2007, preliminary data showed that treatment with omalizumab could decrease the frequency of episodes of anaphylaxis.11 A National Institutes of Health case report followed 2 patients, one for 5 months and the other for 24 months. Both patients experienced a decrease in frequency of anaphylaxis following initiation of omalizumab. In 2010, a second case report described the treatment of an Australian patient with recurrent idiopathic anaphylaxis also diagnosed with SM. After initiation of treatment with omalizumab, she, too, experienced decreased frequency of episodes of anaphylaxis over 14 months.12 A review of patients treated at the Mastocytosis Centre Odense University Hospital in Denmark was published in 2017. Of 13 patients with SM treated with omalizumab, 5 experienced what was considered a complete response to the medication, with 3 each experiencing major and partial responses.5 The median treatment time in these patients was 27 months. Each of these cases showed significant promise in the use of omalizumab to treat SM, informing the decision to attempt this treatment in our patient.
The potential positive effects of omalizumab in reducing symptom severity in patients with SM was further supported by a 2017 meta-analysis. This review included several individual case reports noting that omalizumab could decrease frequency of pulmonary and gastrointestinal manifestations of SM.13 A small randomized control trial of omalizumab for treatment of mild symptoms of SM found improvement in disease severity, although neither primary nor secondary endpoints reached statistical significance.14
This case demonstrates a substantial, long-term, clinical benefit and quality of life improvement with omalizumab therapy in a patient with indolent SM that was not adequately controlled by conventional therapies. This is evidenced by an impressive decline in the frequency of mastocytic anaphylactic episodes as well as diminished patient-endorsed cutaneous symptoms.
This case provides further evidence of the efficacy of this therapy in diminishing disease burden for patients with SM who are otherwise limited to treatments aimed at transient symptomatic relief without significant alteration of the underlying cause of symptoms. At the time this article was written, our patient had now 52 months of continuous treatment without any adverse reactions noted, suggesting the treatment's long-term efficacy. It also adds to a small but growing body of literature that supports the use of anti-IgE therapy as a treatment option for improved management of this distressing, life-altering illness. Even in the time that our patient has been receiving omalizumab for SM, another small case series of 2 patients has been published showing sustained treatment effect at 12 years of therapy.15 This adds further insight that omalizumab can offer long-term, safe treatment for this limiting condition.
Omalizumab therapy is not without risk, but for patients afflicted by unrestrained mastocytic disease, the benefits may outweigh the risks. The most common significant risk with this medication is anaphylaxis, occurring in 1 to 2 per 1,000 patients, usually within 2 hours of an injection.16 This may correlate to the underlying degree of atopy in patients receiving omalizumab, and the risk of anaphylaxis is relatively low compared with that of many other biologic medications.17 Additionally, early data from initial phases of clinical trials indicated a potentially elevated malignancy risk with omalizumab. However, subsequent pooled analysis of larger numbers of patients has decreased suspicion that a causal relationship exists.18
Conclusions
Omalizumab has proven value in the treatment of atopic conditions, such as asthma and idiopathic urticaria, for which it has been approved for use by the FDA. Its effectiveness in significantly decreasing free serum IgE levels, and inhibiting IgE activation of mast cells makes it a possible treatment option for patients with SM who are not sufficiently controlled with conventional therapy. The findings in this case suggest that omalizumab may be effective in the prevention of anaphylaxis and in the reduction of disease burden associated with SM. Further studies and formal clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings. Patients should be counseled appropriately concerning the risks, benefits, and off-label status of this treatment option.
1. Theoharides TC, Valent P, Akin C. Mast cells, mastocytosis, and related disorders. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(2):163-172. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1409760
2. Valent P, Sperr WR, Schwartz LB, Horny H-P. Diagnosis and classification of mast cell proliferative disorders: delineation from immunologic diseases and non-mast cell hematopoietic neoplasms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114(1):3-11. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2004.02.045
3. Valent P, Sotlar K, Sperr WR, et al. Refined diagnostic criteria and classification of mast cell leukemia (MCL) and myelomastocytic leukemia (MML): a consensus proposal. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(9):1691-1700. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdu047
4. Valent P, Akin C, Metcalfe DD. Mastocytosis: 2016 updated WHO classification and novel emerging treatment concepts. Blood. 2017;129(11):1420-1427. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-09-731893
5. Broesby-Olsen S, Vestergaard H, Mortz CG, et al. Omalizumab prevents anaphylaxis and improves symptoms in systemic mastocytosis: Efficacy and safety observations. 2018;73(1):230-238. doi:10.1111/all.13237
6. Kaplan AP, Giménez-Arnau AM, Saini SS.Mechanisms of action that contribute to efficacy of omalizumab in chronic spontaneous urticaria. Allergy. 2017;72(4):519-533. doi:10.1111/all.13083
7. Borish L, Chipps B, Deniz Y, Gujrathi S, Zheng B, Dolan C; TENOR Study Group. Total serum IgE levels in a large cohort of patients with severe or difficult-to-treat asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005;95(3):247-253. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61221-5
8. Corry DB, Kheradmand F. Induction and regulation of the IgE response. Nature. 1999;402(suppl 6760):18-23. doi:10.1038/35037014
9. MacGlashan D, McKenzie-White J, Chichester K, et al. In vitro regulation of FcRIα expression on human basophils by IgE antibody. Blood. 1998;91(5):1633-1643.
10. XOLAIR [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Revised 2019. Accessed November 11, 2020. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/103976s5234lbl.pdf
11. Carter MC, Robyn JA, Bressler PB, Walker JC, Shapiro GC, and Metcalfe DD. Omalizumab for the treatment of unprovoked anaphylaxis in patients with systemic mastocytosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119(6):1550-1551. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2007.03.032
12. Douglass JA, Carroll K, Voskamp A, Bourke P, Wei A, O’Hehir RE. Omalizumab is effective in treating systemic mastocytosis in a nonatopic patient. Allergy. 2010; 65(7):926-927. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02259.x
13. Le M, Miedzybrodzki B, Olynych T, Chapdelaine H, Ben-Shoshan M. Natural history and treatment of cutaneous and systemic mastocytosis. Postgrad Med. 2017;129(8):896-901. doi:10.1080/00325481.2017.1364124
14. Distler M, Maul J-T, Steiner T, et al. Efficacy of omalizumab in mastocytosis: allusive indication obtained from a prospective, double-blind, multicenter study (XOLMA Study) [published online ahead of print January 20, 2020]. Dermatology. doi:10.1159/000504842
15. Constantine G, Bressler P, Petroni D, Metcalfe D, Carter M. Twelve-year follow-up of omalizumab for anaphylaxis in 2 patients with systemic mastocytosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(4)1314-1316. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2018.07.041
16. Fanta CH. Asthma. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(10):1002-1014. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0804579
17. Baldo BA. Adverse events to monoclonal antibodies used for cancer therapy: focus on hypersensitivity responses. Oncoimmunology. 2013;2(10):e26333. doi:10.4161/onci.26333
18. Busse W, Buhl R, Fernandez Vidaurre C, et al. Omalizumab and the risk of malignancy: results from a pooled analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129(4):983-989.e6. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.01.033.
19. Castells M, Akin C. Mastocytosis (cutaneous and systemic): epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations. Accessed December 8, 2020. Updated June 12, 2018. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/mastocytosis-cutaneous-and-systemic-epidemiology-pathogenesis-and-clinical-manifestations
20. Czarny J, Lange M, Lugowska-Umer H, Nowicki R. Cutaneous mastocytosis treatment: strategies, limitations, and perspectives. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2018;35(6):541-545. doi:10.5114/ada.2018.77605
1. Theoharides TC, Valent P, Akin C. Mast cells, mastocytosis, and related disorders. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(2):163-172. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1409760
2. Valent P, Sperr WR, Schwartz LB, Horny H-P. Diagnosis and classification of mast cell proliferative disorders: delineation from immunologic diseases and non-mast cell hematopoietic neoplasms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114(1):3-11. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2004.02.045
3. Valent P, Sotlar K, Sperr WR, et al. Refined diagnostic criteria and classification of mast cell leukemia (MCL) and myelomastocytic leukemia (MML): a consensus proposal. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(9):1691-1700. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdu047
4. Valent P, Akin C, Metcalfe DD. Mastocytosis: 2016 updated WHO classification and novel emerging treatment concepts. Blood. 2017;129(11):1420-1427. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-09-731893
5. Broesby-Olsen S, Vestergaard H, Mortz CG, et al. Omalizumab prevents anaphylaxis and improves symptoms in systemic mastocytosis: Efficacy and safety observations. 2018;73(1):230-238. doi:10.1111/all.13237
6. Kaplan AP, Giménez-Arnau AM, Saini SS.Mechanisms of action that contribute to efficacy of omalizumab in chronic spontaneous urticaria. Allergy. 2017;72(4):519-533. doi:10.1111/all.13083
7. Borish L, Chipps B, Deniz Y, Gujrathi S, Zheng B, Dolan C; TENOR Study Group. Total serum IgE levels in a large cohort of patients with severe or difficult-to-treat asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005;95(3):247-253. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61221-5
8. Corry DB, Kheradmand F. Induction and regulation of the IgE response. Nature. 1999;402(suppl 6760):18-23. doi:10.1038/35037014
9. MacGlashan D, McKenzie-White J, Chichester K, et al. In vitro regulation of FcRIα expression on human basophils by IgE antibody. Blood. 1998;91(5):1633-1643.
10. XOLAIR [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Revised 2019. Accessed November 11, 2020. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/103976s5234lbl.pdf
11. Carter MC, Robyn JA, Bressler PB, Walker JC, Shapiro GC, and Metcalfe DD. Omalizumab for the treatment of unprovoked anaphylaxis in patients with systemic mastocytosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119(6):1550-1551. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2007.03.032
12. Douglass JA, Carroll K, Voskamp A, Bourke P, Wei A, O’Hehir RE. Omalizumab is effective in treating systemic mastocytosis in a nonatopic patient. Allergy. 2010; 65(7):926-927. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02259.x
13. Le M, Miedzybrodzki B, Olynych T, Chapdelaine H, Ben-Shoshan M. Natural history and treatment of cutaneous and systemic mastocytosis. Postgrad Med. 2017;129(8):896-901. doi:10.1080/00325481.2017.1364124
14. Distler M, Maul J-T, Steiner T, et al. Efficacy of omalizumab in mastocytosis: allusive indication obtained from a prospective, double-blind, multicenter study (XOLMA Study) [published online ahead of print January 20, 2020]. Dermatology. doi:10.1159/000504842
15. Constantine G, Bressler P, Petroni D, Metcalfe D, Carter M. Twelve-year follow-up of omalizumab for anaphylaxis in 2 patients with systemic mastocytosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(4)1314-1316. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2018.07.041
16. Fanta CH. Asthma. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(10):1002-1014. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0804579
17. Baldo BA. Adverse events to monoclonal antibodies used for cancer therapy: focus on hypersensitivity responses. Oncoimmunology. 2013;2(10):e26333. doi:10.4161/onci.26333
18. Busse W, Buhl R, Fernandez Vidaurre C, et al. Omalizumab and the risk of malignancy: results from a pooled analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129(4):983-989.e6. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.01.033.
19. Castells M, Akin C. Mastocytosis (cutaneous and systemic): epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations. Accessed December 8, 2020. Updated June 12, 2018. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/mastocytosis-cutaneous-and-systemic-epidemiology-pathogenesis-and-clinical-manifestations
20. Czarny J, Lange M, Lugowska-Umer H, Nowicki R. Cutaneous mastocytosis treatment: strategies, limitations, and perspectives. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2018;35(6):541-545. doi:10.5114/ada.2018.77605
Retrospective Chart Review of Advanced Practice Pharmacist Prescribing of Controlled Substances for Pain Management at the Harry S. Truman Memorial Veterans’ Hospital
In the midst of an opioid overdose public health crisis, the US Department of Health and Human Services developed a 5-point strategy to combat this problem. One aspect of this strategy is improved pain management.1 There is high demand for pain management services with a limited number of health care professionals appropriately trained to deliver care.2 Pharmacists are integral members of the interdisciplinary pain team and meet this demand.
Background
For almost 50 years, pharmacists at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) have been functioning as advanced practice providers (APP).3 Clinical pharmacy specialists (CPS) provide comprehensive medication management (CMM) and have a scope of practice (SOP). The SOP serves as the collaborating agreement and outlines the clinical duties permitted in delivering patient care. In addition, the SOP may indicate specific practice areas and are standardized across VA (Table 1).4,5 Pharmacists apply for a SOP and must prove their competency in the practice area and provide documentation of their education, training, experience, knowledge, and skills.5,6 Residency and/or board certification are not required though helpful. A pharmacist’s SOP is reviewed and approved by the facility executive committee.5 Pharmacists with a SOP undergo professional practice evaluation twice a year. Prescribing controlled substances is permissible in the SOP if approved by the facility and allowed by the state of licensure. According to the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) as of February 10, 2020, 8 states (California, Washington, Idaho, Massachusetts, Montana, New Mexico, North Carolina, and Ohio) allow pharmacists to prescribe controlled substances.7
The VA developed the Pharmacists Achieve Results with Medications Documentation (PhARMD) tool that allows clinical pharmacists to document specific interventions made during clinical care and is included in their progress note. Data from fiscal year 2017 demonstrates that 136,041 pain management interventions were made by pharmacists across VA. The majority of these interventions were implemented by a CPS working autonomously as an APP.8
Several articles discuss the pharmacists role in the opioid crisis, although no outcomes data were provided. Chisholm-Burns and colleagues listed multiple potential ways that pharmacists can intervene, including managing pain in primary care clinic settings by using collaborative drug therapy agreements (CDTAs), using opioid exit plans and discharge planning in collaboration with other health care providers (HCPs), or making recommendations to the prescribers before writing prescriptions.9 Compton and colleagues similarly reviewed pharmacist roles in the opioid crisis. However, their focus was on dispensing pharmacists that provided education to patients about storage and disposal of opioids, identified opioid misuse, provided opioid overdose education and naloxone, and checked prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs).10 Missing from these articles was the role of the clinical pharmacist working as an APP delivering direct patient care and prescribing controlled substances.
Hammer and colleagues discussed the role of an oncology CPS with controlled substance prescriptive authority in pain management at an outpatient cancer center in Washington state.11 Under a CDTA, pharmacists could prescribe medications, including controlled substances if they obtain DEA registration. The pharmacist completed a comprehensive in-person assessment. The attending physician conducted a physical examination. Then the pharmacist presented the patient and proposed regimen to the interprofessional team to determine a final plan. Ultimately, the pharmacist wrote any controlled substance prescriptions. The patient followed up every 1 to 4 weeks by telephone with a nurse, and in-person assessments occurred at least every 6 months. No outcomes data were provided.11
Dole and colleagues reviewed the role of a pharmacist who had controlled substance prescriptive authority in a pain management clinic. The pharmacist provider saw up to 18 patients a day and then managed refill requests for 3 hours a day. The main outcome was change in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores. Findings showed that reductions in VAS pain scores were statistically significant (P < .01). The pharmacist processed about 150 refills with an unclear number of controlled substances requests a day based on a medication-refill protocol. This was felt to improve access to physicians for acute needs, improve consistency in refills, and capture patients in need of follow-up. Additionally, the clinic saved $455,238 after 1 year.12
Study Aims
A review of the literature indicated sparse data on the impact of a pharmacist on opioid tapering, opioid dose, and opioid risk mitigation when the pharmacist is prescribing controlled substances. The purpose of this retrospective review was to characterize the controlled substance prescribing practices by the pharmacy pain clinic. The aim was to examine the pharmacist impact on morphine milligram equivalent (MME) and compliance with opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Methods
This project was a retrospective, single-center, chart review. The project was reviewed and approved by the University of Missouri-Columbia Institutional Review Board used by the Harry S. Truman Memorial Veterans’ Hospital (HSTMVH) as a quality improvement project. The author applied for controlled substance registration through the DEA and was issued registration April 30, 2018. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy was contacted as required by Ohio Administrative Code. The author's updated SOP to allow controlled substance prescribing was approved July 23, 2018. The CPS functions as an APP within an interdisciplinary pain management team that includes physicians, occupational and physical therapists, complementary and integrative health, and a psychologist. The reason for Pharmacy Pain Consult is required and it is primarily submitted through the electronic health record. The consult is reviewed for appropriateness and once approved is scheduled by support staff. Once the patient is stabilized, the patient is discharged back to their primary care provider (PCP) or referring provider for continued care. Patients were considered stabilized when their patient-specific goals were met, which varied from use of the lowest effective opioid dose to taper to discontinuation of opioids with no further medication changes needed. The taper strategy for each patient was individualized. Patients were generally tapered on their existing opioid medication unless they were new to the VA and on nonformulary medications or experiencing a significant adverse reaction. Numerous references are available through VA to assist with opioid tapering.13,14 The CPS is able to refer patients to other services, including behavioral health for substance use disorder treatment and medication-assisted treatment if concerns were identified.
Initial data were collected from the Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 15 Corporate Data Warehouse by the VISN pharmacy analytics program manager. The original report included patients prescribed a Schedule II to V controlled substance by the author from July 1, 2018 to January 31, 2020. Chart review was conducted on each patient to obtain additional data. At the time of consult and discharge the following data were collected: opioid medication; MME; use of opioid risk mitigation strategies, such as urine drug screens (UDS), informed consent, opioid overdose education and naloxone distribution program (OEND), risk assessment via stratification tool for opioid risk mitigation (STORM), PDMP checks; and nonopioid medication number and classes.
Patients were included in the review if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance between July 1, 2018 and January 31, 2020. Patient were excluded if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance primarily as coverage for another prescriber. Patients prescribed only pregabalin, tramadol, or a benzodiazepine also were excluded.
The primary endpoint was change in MME from baseline to discharge from clinic. Secondary endpoints included change in opioid risk mitigation strategies and change in opioid medications prescribed from baseline to discharge.
Descriptive statistics were used to analyze parts of the data. A 2-sided t test was used to compare baseline and discharge MME. The Fisher exact test was used to compare nominal data of opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Calculation of MME was performed using the conversion factors provided by the Centers Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for opioid guideline.15 For buprenorphine, tapentadol, and levorphanol conversion ratios were obtained from other sources. The conversion ratios used, included 75:1 for oral morphine to transdermal buprenorphine, 1:3.3 for oral morphine to oral tapentadol, and 1:7.5 for oral levorphanol to oral morphine.16,17 The Revised Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) was used to write the manuscript.18
Results
Seventy-five patients were included in this review. The average age of patients was 66 years; and 12% were female (n = 9) (Table 2). The largest number of consults came from PCPs (44%, n = 33) and the pain clinic (43%, n = 32). Nearly half (48%) of the consultations were for opioid tapering (n = 36), followed by 37% for opioid optimization or monitoring (n = 28), and 19% for nonopioid optimization (n = 14). The most common primary diagnoses at consultation were for chronic low back pain (56%), chronic neck pain (20%), and osteoarthritis (16%).
The average MME at time of consult was 93 MME compared with 31 MME at discharge which was statisticially significant (P < .01) (Figure 1). The mean percent change in MME was 46%, including methadone and 42% excluding methadone. There was a 26% change in UDS, 28% change in informed consent, 85% change in PDMP, 194% change in naloxone, and 357% change in STORM reviews from baseline to discharge with all demonstrating statistical significance (P < .01) (Figure 2). At discharge, the most common opioid prescribed was morphine SA (short acting) (n = 10, 13%, 44 average MME) and oxycodone/acetaminophen (n = 10, 13%, 28 average MME) (Table 3).
The average number of days from consult to initial visit was 23 days (Table 4). Face-to-face was the primary means of initial visit with 92% (n = 69) of visits, but phone was the primary mode of follow-up with 73% of visits (n = 55). The average number of follow-up visits was 7, representing 176 average days of time in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Consultation to the behavioral health performance program was the most common referral (n = 13, 17%).
Five patients were new opioid starts in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Two patients were on tramadol at time of consult. Of the 5 new opioid starts, 3 patients received oxycodone/acetaminophen, 1 received buprenorphine patch, and 1 received hydrocodone/acetaminophen. The new opioid start average was 25 MME. All 5 patients had a UDS for opioid risk mitigation, 4 used consent and STORM reviews, and 2 patients had PDMP checks and naloxone.
Discussion
There was a statistically significant decrease of the mean MME between the time of consult and the time of discharge. There also were statistically significant changes in use of opioid risk mitigation strategies. Since methadone has a high MME, the mean reduction of MME was calculated with methadone (46%) and without methadone (42%). These data are consistent with other published studies examining opioid tapers in the VA population. Harden and colleagues calculated a 46% mean reduction in MME over 12 months for 72 veterans from opioid tapers implemented by PCPs, pain service, or pharmacist-run clinics.19
There is controversy about equianalgesic doses and no established universal equianalgesic conversion calculator or dose. Numerous equianalgesic opioid dose calculators are available, but for this analysis the CDC MME conversion factors were used (available at: https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/pdf/calculating_total_daily_dose-a.pdf). Previous literature compared existing calculators and found significant variances in calculated doses for methadone and fentanyl conversions.20 Additionally, there have been concerns expressed with the safety of the CDC opioid calculator specifically surrounding the conversions for methadone and tapentadol.21 In the end, I chose the CDC calculator because it is established, readily available, and consistent.
Pharmacists in pain management can address access issues.2,3,11,12 The average length of time from consult to initial visit was 23 days. Often patients may have seen a HCP who implemented a change at the time of consult and wanted the patient to be seen 1 month later. Many patients at the HSTMVH live far from the facility, making in-person visits difficult. A majority of the follow-up visits were conducted by telephone. Patients were offered all modalities available for follow-up, including telephone, in-person, or telemedicine, but patients most often picked telephone. Patients averaged 7 follow-up visits before discharge. This number of visits would have taken time from other health care team members who could have been addressing other veterans. Patients were seen in clinic for 176 days on average, which supports and follows recommendations for a slow, incremental taper.
The opioid medications prescribed changed over time in the clinic. Methadone prescriptions dropped from 20 to 6 at consult to discharge, and fentanyl prescriptions fell from 7 to 2, respectively. The CDC guideline suggests use of long-acting products with more predictable pharmacokinetics (eg, morphine SA or oxycodone SA) rather than fentanyl or methadone.15 Notably, the use of buprenorphine products with FDA approval for pain indications increased from consult to discharge. Many of the patients in this study had pulmonary comorbidities, placing them at higher risk for adverse outcomes. Buprenorphine is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist with a ceiling on respiratory depression so is potentially less risky in those with pulmonary comorbidities.
The biggest changes in opioid risk mitigation occurred in PDMP, OEND program, and STORM reviews. An 85% increase in PDMP reviews occurred with referral to the clinic. Missouri is the only state without a state-run PDMP. However, the St. Louis County PDMP was developed based on city or county participation and encompasses 85% of the population of Missouri and 94% of HCPs in Missouri as of August 29, 2019.22 Because there is no state-level PDMP, a review of the St. Louis County PDMP was not required during the review period. Nevertheless, the Pharmacy Pain Clinic uses the St. Louis County PDMP at the initial visit and regularly during care. VA policy requires a specific note title be used to document each check of the PDMP.23
There was a 194% increase in patients receiving naloxone with consultation to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Due to low coprescribing of naloxone for patients prescribed chronic opioid therapy, The author led an interdisciplinary team analysis of health care failure mode effects during the study period. This led to a process change with coprescribing of naloxone at refill in the primary care clinic.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 mandated that the VA review STORM on new start of opioids or patient identified as “very high-opioid prescription risk” category by an interdisciplinary opioid risk review team.24 Thus many of the patients referred to clinic didn’t require STORM reviews since they were not new opioid starts or identified as high risk. However, in the standard review of all new patients to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic, a STORM review is conducted and documented to assess the patient’s level of risk.
Only 5 patients were started on opioid medications during the study period. This is consistent with both CDC and the joint VA/US Department of Defense opioid prescribing guidelines that recommend against initiation of opioids for chronic nonmalignant pain.13,15 Two of the patients were prescribed tramadol for ineffective pain control at time of consult. Furthermore, 4 of the 5 patients were started on a short-acting opioid, which was supported by guidelines.13,15 One patient was initiated on buprenorphine patches due to comorbid chronic kidney disease. The VA does not limit the quantity of new opioid prescriptions, although some states and private insurance plans are implementing limitations. Guidelines also recommend against exceeding 90 MME due to risk. The average MME in this project at discharge was 25 MME. Use of opioid risk mitigation for the new opioid starts was reasonable. The reason for the missing PDMP report is unknown based on chart review and atypical according to clinic practice.
Recently, efforts to expand pharmacist training and positions in pain management at VA facilities have been undertaken. In 2016, there were just 11 American Society of Health-System Pharmacists-accredited pharmacy postgraduate year 2 pain and palliative care residency programs, which has expanded to 26 sites in 2020.2,3,25 In addition, the Clinical Pharmacy Practice Office and the VA Office of Rural Health have helped to hire 33 new pain management pharmacists.3
The role of pharmacists in prescribing controlled substances is limited mainly due to the small number of states that extend this authority.7 At the VA, a pharmacist can practice using any state of licensure. Therefore, a pharmacist working at a VA in a state that does not authorize controlled substance prescribing could obtain a license in a state that does permit it. However, the main barrier to obtaining other state licensures is the cost. At the time the author obtained controlled substance prescriptive authority, little direction was available on the process for advanced practice pharmacists at the VA. Since then, guidance has been developed to ease this process. Educational endeavors at VA have been implemented with the intent to increase the number of pharmacists with controlled substance prescriptive authority.
Barriers to pharmacists providing pain care extend beyond limited controlled substance prescriptive authority. Often pharmacists are still viewed in their traditional and operational role.9,10 Other health care team members and patients may not be aware or familiar with the training, knowledge, and skills of pharmacist's and their suitability as an APP.26,27 Most states permit pharmacists in establishing CDTA but not all. Additionally, some states recognize pharmacists as HCPs but many more do not. Furthermore, the Social Security Act does not include pharmacists as HCPs. This makes it challenging, though not impossible, for pharmacists to bill for their services.3
Strengths and Limitations
There were numerous strengths of the project. First, this addressed an unmet need in the literature with limited data discussing pharmacist prescribing controlled substances for pain management. There was 1 data reviewer who made the data collection process consistent. Since this retrospectively reviewed controlled substance prescribing in clinic, it captured real-world practice compared with that of experimental models. There were also several limitations in the project. The person collecting the data was also the person who conducted the clinic. The study was conducted retrospectively and based on documented information in the medical record. The population reviewed was primarily male and older, which fits the VA patient population but has less generalizability to other patient populations. This project was conducted at a single VA facility so may not be generalizable to other VA sites. It is unknown whether patients were again prescribed opioids if they left the VA for the community or another VA facility. The pain diagnoses or locations of pain were categorized to main groups and reliant on the referring provider. Another major weakness was the lack of comparison of pain scores or validated objective measure of function at baseline and at discharge. This consideration would be important for future work.
Conclusions
Pharmacists functioning as APP are key members of the pain management team. A review of a pharmacy-run pain clinic demonstrated statistically significant reduction in MME and improvement in opioid risk mitigation from consult to discharge. Patients enrolled in the pharmacy-managed clinic also had improvements in adherence to opioid risk mitigation strategies. Future attention should be focused on further expanding training and positions for pharmacists as APP in pain management.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Chris Sedgwick for his assistance with data capture.
1. US Department of Health and Human Services. Help and resources: national opioid crisis. Updated August 30, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.hhs.gov/opioids/about-the-epidemic/hhs-response/index.html
2. Atkinson TJ, Gulum AH, Forkum WG. The future of pain pharmacy: driven by need. Integr Pharm Res Pract. 2016;5:33-42. doi:10.2147/IPRP.S63824
3. Seckel E, Jorgenson T, McFarland S. Meeting the national need for expertise in pain management with clinical pharmacist advanced practice providers. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2019;45(5):387-392.doi:10.1016/j.jcjq.2019.01.002
4. McFarland MS, Groppi J, Ourth H, et al. Establishing a standardized clinical pharmacy practice model within the Veterans Health Administration: evolution of the credentialing and professional practice evaluation process. J Am Coll Clin Pharm. 2018;1(2):113-118. doi:10.1002/jac5.1022
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook. 1108.11. Clinical pharmacy services. Published July 1, 2015. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3120
6. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1100.19. Credentialing and priveleging. Published October 15, 2012. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=2910
7. US Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Agency. Mid-level practitioners authorization by state. Updated February 10, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drugreg/practioners/mlp_by_state.pdf
8. Groppi JA, Ourth H, Morreale AP, Hirsh JM, Wright S. Advancement of clinical pharmacy practice through intervention capture. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018;75(12):886-892. doi:10.2146/ajhp170186
9. Chisholm-Burns MA, Spivey CA, Sherwin E, Wheeler J, Hohmeier K. The opioid crisis: origins, trends, policies, and the roles of pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(7):424-435. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxy089
10. Compton WM, Jones CM, Stein JB, Wargo EM. Promising roles for pharmacists in addressing the U.S. opioid crisis. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2019;15(8):910-916. doi:10.1016/j.sapharm.2017.12.009
11. Hammer KJ, Segal EM, Alwan L, et al. Collaborative practice model for management of pain in patients with cancer. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1434-1441. doi:10.2146/ajhp150770
12. Dole EJ, Murawski MM, Adolphe AB, Aragon FD, Hochstadt B. Provision of pain management by a pharmacist with prescribing authority. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64(1):85-89. doi:10.2146/ajhp060056
13. US Department of Defense, US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for Opioid Therapy for Chronic Pain. Updated 2017. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/Pain/cot/VADoDOTCPG022717.pdf
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA, VHA, VA Academic Detailing Service. Veterans Health Administration. Opioid taper decision tool. Updated October 2016. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.pbm.va.gov/AcademicDetailingService/Documents/Pain_Opioid_Taper_Tool_IB_10_939_P96820.pdf
15. Dowell D, Haegerich TM, Chou R. CDC guideline for prescribing opioids for chronic pain - United States, 2016 [published correction appears in MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(11):295]. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(1):1-49. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6501e1
16. McPherson M. Demystifying opioid conversion calculations. Published 2009. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.ashp.org/-/media/store-files/p1985-frontmatter.ashx
17. Gudin J, Fudin J, Nalamachu S. Levorphanol use: past, present and future. Postgrad Med. 2016;128(1):46-53. doi:10.1080/00325481.2016.1128308
18. Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden P, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Qual Saf. 2016;25(12):986-992. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004411
19. Harden P, Ahmed S, Ang K, Wiedemer N. Clinical implications of tapering chronic opioids in a veteran population. Pain Med. 2015;16(10):1975-1981. doi:10.1111/pme.12812
20. Shaw K, Fudin J. Evaluation and comparison of online equianalgesic opioid dose conversion calculators. Practical Pain Manag. 2013;13(7):61-66. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.practicalpainmanagement.com/treatments/pharmacological/opioids/evaluation-comparison-online-equianalgesic-opioid-dose-conversion
21. Fudin J, Raouf M, Wegrzyn EL, Schatman ME. Safety concerns with the Centers for Disease Control opioid calculator. J Pain Res. 2017;11:1-4. Published 2017 Dec 18. doi:10.2147/JPR.S155444
22. Saint Louis County Public Health. St. Louis County Prescription Drug Monitoring Program. Participating jurisdictions. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://pdmp-stlcogis.hub.arcgis.com
23. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1306: querying state prescription drug monitoring programs. Updated October 21, 2019. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3283
24. Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016. 42 USC § 201 (2016).
25. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Residency directory. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://accreditation.ashp.org/directory/#/program/residency
26. Feehan M, Durante R, Ruble J, Munger MA. Qualitative interviews regarding pharmacist prescribing in the community setting. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1456-1461. doi:10.2146/ajhp150691
27. Giannitrapani KF, Glassman PA, Vang D, et al. Expanding the role of clinical pharmacists on interdisciplinary primary care teams for chronic pain and opioid management. BMC Fam Pract. 2018;19(1):107. doi:10.1186/s12875-018-0783-9
In the midst of an opioid overdose public health crisis, the US Department of Health and Human Services developed a 5-point strategy to combat this problem. One aspect of this strategy is improved pain management.1 There is high demand for pain management services with a limited number of health care professionals appropriately trained to deliver care.2 Pharmacists are integral members of the interdisciplinary pain team and meet this demand.
Background
For almost 50 years, pharmacists at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) have been functioning as advanced practice providers (APP).3 Clinical pharmacy specialists (CPS) provide comprehensive medication management (CMM) and have a scope of practice (SOP). The SOP serves as the collaborating agreement and outlines the clinical duties permitted in delivering patient care. In addition, the SOP may indicate specific practice areas and are standardized across VA (Table 1).4,5 Pharmacists apply for a SOP and must prove their competency in the practice area and provide documentation of their education, training, experience, knowledge, and skills.5,6 Residency and/or board certification are not required though helpful. A pharmacist’s SOP is reviewed and approved by the facility executive committee.5 Pharmacists with a SOP undergo professional practice evaluation twice a year. Prescribing controlled substances is permissible in the SOP if approved by the facility and allowed by the state of licensure. According to the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) as of February 10, 2020, 8 states (California, Washington, Idaho, Massachusetts, Montana, New Mexico, North Carolina, and Ohio) allow pharmacists to prescribe controlled substances.7
The VA developed the Pharmacists Achieve Results with Medications Documentation (PhARMD) tool that allows clinical pharmacists to document specific interventions made during clinical care and is included in their progress note. Data from fiscal year 2017 demonstrates that 136,041 pain management interventions were made by pharmacists across VA. The majority of these interventions were implemented by a CPS working autonomously as an APP.8
Several articles discuss the pharmacists role in the opioid crisis, although no outcomes data were provided. Chisholm-Burns and colleagues listed multiple potential ways that pharmacists can intervene, including managing pain in primary care clinic settings by using collaborative drug therapy agreements (CDTAs), using opioid exit plans and discharge planning in collaboration with other health care providers (HCPs), or making recommendations to the prescribers before writing prescriptions.9 Compton and colleagues similarly reviewed pharmacist roles in the opioid crisis. However, their focus was on dispensing pharmacists that provided education to patients about storage and disposal of opioids, identified opioid misuse, provided opioid overdose education and naloxone, and checked prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs).10 Missing from these articles was the role of the clinical pharmacist working as an APP delivering direct patient care and prescribing controlled substances.
Hammer and colleagues discussed the role of an oncology CPS with controlled substance prescriptive authority in pain management at an outpatient cancer center in Washington state.11 Under a CDTA, pharmacists could prescribe medications, including controlled substances if they obtain DEA registration. The pharmacist completed a comprehensive in-person assessment. The attending physician conducted a physical examination. Then the pharmacist presented the patient and proposed regimen to the interprofessional team to determine a final plan. Ultimately, the pharmacist wrote any controlled substance prescriptions. The patient followed up every 1 to 4 weeks by telephone with a nurse, and in-person assessments occurred at least every 6 months. No outcomes data were provided.11
Dole and colleagues reviewed the role of a pharmacist who had controlled substance prescriptive authority in a pain management clinic. The pharmacist provider saw up to 18 patients a day and then managed refill requests for 3 hours a day. The main outcome was change in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores. Findings showed that reductions in VAS pain scores were statistically significant (P < .01). The pharmacist processed about 150 refills with an unclear number of controlled substances requests a day based on a medication-refill protocol. This was felt to improve access to physicians for acute needs, improve consistency in refills, and capture patients in need of follow-up. Additionally, the clinic saved $455,238 after 1 year.12
Study Aims
A review of the literature indicated sparse data on the impact of a pharmacist on opioid tapering, opioid dose, and opioid risk mitigation when the pharmacist is prescribing controlled substances. The purpose of this retrospective review was to characterize the controlled substance prescribing practices by the pharmacy pain clinic. The aim was to examine the pharmacist impact on morphine milligram equivalent (MME) and compliance with opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Methods
This project was a retrospective, single-center, chart review. The project was reviewed and approved by the University of Missouri-Columbia Institutional Review Board used by the Harry S. Truman Memorial Veterans’ Hospital (HSTMVH) as a quality improvement project. The author applied for controlled substance registration through the DEA and was issued registration April 30, 2018. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy was contacted as required by Ohio Administrative Code. The author's updated SOP to allow controlled substance prescribing was approved July 23, 2018. The CPS functions as an APP within an interdisciplinary pain management team that includes physicians, occupational and physical therapists, complementary and integrative health, and a psychologist. The reason for Pharmacy Pain Consult is required and it is primarily submitted through the electronic health record. The consult is reviewed for appropriateness and once approved is scheduled by support staff. Once the patient is stabilized, the patient is discharged back to their primary care provider (PCP) or referring provider for continued care. Patients were considered stabilized when their patient-specific goals were met, which varied from use of the lowest effective opioid dose to taper to discontinuation of opioids with no further medication changes needed. The taper strategy for each patient was individualized. Patients were generally tapered on their existing opioid medication unless they were new to the VA and on nonformulary medications or experiencing a significant adverse reaction. Numerous references are available through VA to assist with opioid tapering.13,14 The CPS is able to refer patients to other services, including behavioral health for substance use disorder treatment and medication-assisted treatment if concerns were identified.
Initial data were collected from the Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 15 Corporate Data Warehouse by the VISN pharmacy analytics program manager. The original report included patients prescribed a Schedule II to V controlled substance by the author from July 1, 2018 to January 31, 2020. Chart review was conducted on each patient to obtain additional data. At the time of consult and discharge the following data were collected: opioid medication; MME; use of opioid risk mitigation strategies, such as urine drug screens (UDS), informed consent, opioid overdose education and naloxone distribution program (OEND), risk assessment via stratification tool for opioid risk mitigation (STORM), PDMP checks; and nonopioid medication number and classes.
Patients were included in the review if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance between July 1, 2018 and January 31, 2020. Patient were excluded if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance primarily as coverage for another prescriber. Patients prescribed only pregabalin, tramadol, or a benzodiazepine also were excluded.
The primary endpoint was change in MME from baseline to discharge from clinic. Secondary endpoints included change in opioid risk mitigation strategies and change in opioid medications prescribed from baseline to discharge.
Descriptive statistics were used to analyze parts of the data. A 2-sided t test was used to compare baseline and discharge MME. The Fisher exact test was used to compare nominal data of opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Calculation of MME was performed using the conversion factors provided by the Centers Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for opioid guideline.15 For buprenorphine, tapentadol, and levorphanol conversion ratios were obtained from other sources. The conversion ratios used, included 75:1 for oral morphine to transdermal buprenorphine, 1:3.3 for oral morphine to oral tapentadol, and 1:7.5 for oral levorphanol to oral morphine.16,17 The Revised Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) was used to write the manuscript.18
Results
Seventy-five patients were included in this review. The average age of patients was 66 years; and 12% were female (n = 9) (Table 2). The largest number of consults came from PCPs (44%, n = 33) and the pain clinic (43%, n = 32). Nearly half (48%) of the consultations were for opioid tapering (n = 36), followed by 37% for opioid optimization or monitoring (n = 28), and 19% for nonopioid optimization (n = 14). The most common primary diagnoses at consultation were for chronic low back pain (56%), chronic neck pain (20%), and osteoarthritis (16%).
The average MME at time of consult was 93 MME compared with 31 MME at discharge which was statisticially significant (P < .01) (Figure 1). The mean percent change in MME was 46%, including methadone and 42% excluding methadone. There was a 26% change in UDS, 28% change in informed consent, 85% change in PDMP, 194% change in naloxone, and 357% change in STORM reviews from baseline to discharge with all demonstrating statistical significance (P < .01) (Figure 2). At discharge, the most common opioid prescribed was morphine SA (short acting) (n = 10, 13%, 44 average MME) and oxycodone/acetaminophen (n = 10, 13%, 28 average MME) (Table 3).
The average number of days from consult to initial visit was 23 days (Table 4). Face-to-face was the primary means of initial visit with 92% (n = 69) of visits, but phone was the primary mode of follow-up with 73% of visits (n = 55). The average number of follow-up visits was 7, representing 176 average days of time in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Consultation to the behavioral health performance program was the most common referral (n = 13, 17%).
Five patients were new opioid starts in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Two patients were on tramadol at time of consult. Of the 5 new opioid starts, 3 patients received oxycodone/acetaminophen, 1 received buprenorphine patch, and 1 received hydrocodone/acetaminophen. The new opioid start average was 25 MME. All 5 patients had a UDS for opioid risk mitigation, 4 used consent and STORM reviews, and 2 patients had PDMP checks and naloxone.
Discussion
There was a statistically significant decrease of the mean MME between the time of consult and the time of discharge. There also were statistically significant changes in use of opioid risk mitigation strategies. Since methadone has a high MME, the mean reduction of MME was calculated with methadone (46%) and without methadone (42%). These data are consistent with other published studies examining opioid tapers in the VA population. Harden and colleagues calculated a 46% mean reduction in MME over 12 months for 72 veterans from opioid tapers implemented by PCPs, pain service, or pharmacist-run clinics.19
There is controversy about equianalgesic doses and no established universal equianalgesic conversion calculator or dose. Numerous equianalgesic opioid dose calculators are available, but for this analysis the CDC MME conversion factors were used (available at: https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/pdf/calculating_total_daily_dose-a.pdf). Previous literature compared existing calculators and found significant variances in calculated doses for methadone and fentanyl conversions.20 Additionally, there have been concerns expressed with the safety of the CDC opioid calculator specifically surrounding the conversions for methadone and tapentadol.21 In the end, I chose the CDC calculator because it is established, readily available, and consistent.
Pharmacists in pain management can address access issues.2,3,11,12 The average length of time from consult to initial visit was 23 days. Often patients may have seen a HCP who implemented a change at the time of consult and wanted the patient to be seen 1 month later. Many patients at the HSTMVH live far from the facility, making in-person visits difficult. A majority of the follow-up visits were conducted by telephone. Patients were offered all modalities available for follow-up, including telephone, in-person, or telemedicine, but patients most often picked telephone. Patients averaged 7 follow-up visits before discharge. This number of visits would have taken time from other health care team members who could have been addressing other veterans. Patients were seen in clinic for 176 days on average, which supports and follows recommendations for a slow, incremental taper.
The opioid medications prescribed changed over time in the clinic. Methadone prescriptions dropped from 20 to 6 at consult to discharge, and fentanyl prescriptions fell from 7 to 2, respectively. The CDC guideline suggests use of long-acting products with more predictable pharmacokinetics (eg, morphine SA or oxycodone SA) rather than fentanyl or methadone.15 Notably, the use of buprenorphine products with FDA approval for pain indications increased from consult to discharge. Many of the patients in this study had pulmonary comorbidities, placing them at higher risk for adverse outcomes. Buprenorphine is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist with a ceiling on respiratory depression so is potentially less risky in those with pulmonary comorbidities.
The biggest changes in opioid risk mitigation occurred in PDMP, OEND program, and STORM reviews. An 85% increase in PDMP reviews occurred with referral to the clinic. Missouri is the only state without a state-run PDMP. However, the St. Louis County PDMP was developed based on city or county participation and encompasses 85% of the population of Missouri and 94% of HCPs in Missouri as of August 29, 2019.22 Because there is no state-level PDMP, a review of the St. Louis County PDMP was not required during the review period. Nevertheless, the Pharmacy Pain Clinic uses the St. Louis County PDMP at the initial visit and regularly during care. VA policy requires a specific note title be used to document each check of the PDMP.23
There was a 194% increase in patients receiving naloxone with consultation to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Due to low coprescribing of naloxone for patients prescribed chronic opioid therapy, The author led an interdisciplinary team analysis of health care failure mode effects during the study period. This led to a process change with coprescribing of naloxone at refill in the primary care clinic.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 mandated that the VA review STORM on new start of opioids or patient identified as “very high-opioid prescription risk” category by an interdisciplinary opioid risk review team.24 Thus many of the patients referred to clinic didn’t require STORM reviews since they were not new opioid starts or identified as high risk. However, in the standard review of all new patients to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic, a STORM review is conducted and documented to assess the patient’s level of risk.
Only 5 patients were started on opioid medications during the study period. This is consistent with both CDC and the joint VA/US Department of Defense opioid prescribing guidelines that recommend against initiation of opioids for chronic nonmalignant pain.13,15 Two of the patients were prescribed tramadol for ineffective pain control at time of consult. Furthermore, 4 of the 5 patients were started on a short-acting opioid, which was supported by guidelines.13,15 One patient was initiated on buprenorphine patches due to comorbid chronic kidney disease. The VA does not limit the quantity of new opioid prescriptions, although some states and private insurance plans are implementing limitations. Guidelines also recommend against exceeding 90 MME due to risk. The average MME in this project at discharge was 25 MME. Use of opioid risk mitigation for the new opioid starts was reasonable. The reason for the missing PDMP report is unknown based on chart review and atypical according to clinic practice.
Recently, efforts to expand pharmacist training and positions in pain management at VA facilities have been undertaken. In 2016, there were just 11 American Society of Health-System Pharmacists-accredited pharmacy postgraduate year 2 pain and palliative care residency programs, which has expanded to 26 sites in 2020.2,3,25 In addition, the Clinical Pharmacy Practice Office and the VA Office of Rural Health have helped to hire 33 new pain management pharmacists.3
The role of pharmacists in prescribing controlled substances is limited mainly due to the small number of states that extend this authority.7 At the VA, a pharmacist can practice using any state of licensure. Therefore, a pharmacist working at a VA in a state that does not authorize controlled substance prescribing could obtain a license in a state that does permit it. However, the main barrier to obtaining other state licensures is the cost. At the time the author obtained controlled substance prescriptive authority, little direction was available on the process for advanced practice pharmacists at the VA. Since then, guidance has been developed to ease this process. Educational endeavors at VA have been implemented with the intent to increase the number of pharmacists with controlled substance prescriptive authority.
Barriers to pharmacists providing pain care extend beyond limited controlled substance prescriptive authority. Often pharmacists are still viewed in their traditional and operational role.9,10 Other health care team members and patients may not be aware or familiar with the training, knowledge, and skills of pharmacist's and their suitability as an APP.26,27 Most states permit pharmacists in establishing CDTA but not all. Additionally, some states recognize pharmacists as HCPs but many more do not. Furthermore, the Social Security Act does not include pharmacists as HCPs. This makes it challenging, though not impossible, for pharmacists to bill for their services.3
Strengths and Limitations
There were numerous strengths of the project. First, this addressed an unmet need in the literature with limited data discussing pharmacist prescribing controlled substances for pain management. There was 1 data reviewer who made the data collection process consistent. Since this retrospectively reviewed controlled substance prescribing in clinic, it captured real-world practice compared with that of experimental models. There were also several limitations in the project. The person collecting the data was also the person who conducted the clinic. The study was conducted retrospectively and based on documented information in the medical record. The population reviewed was primarily male and older, which fits the VA patient population but has less generalizability to other patient populations. This project was conducted at a single VA facility so may not be generalizable to other VA sites. It is unknown whether patients were again prescribed opioids if they left the VA for the community or another VA facility. The pain diagnoses or locations of pain were categorized to main groups and reliant on the referring provider. Another major weakness was the lack of comparison of pain scores or validated objective measure of function at baseline and at discharge. This consideration would be important for future work.
Conclusions
Pharmacists functioning as APP are key members of the pain management team. A review of a pharmacy-run pain clinic demonstrated statistically significant reduction in MME and improvement in opioid risk mitigation from consult to discharge. Patients enrolled in the pharmacy-managed clinic also had improvements in adherence to opioid risk mitigation strategies. Future attention should be focused on further expanding training and positions for pharmacists as APP in pain management.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Chris Sedgwick for his assistance with data capture.
In the midst of an opioid overdose public health crisis, the US Department of Health and Human Services developed a 5-point strategy to combat this problem. One aspect of this strategy is improved pain management.1 There is high demand for pain management services with a limited number of health care professionals appropriately trained to deliver care.2 Pharmacists are integral members of the interdisciplinary pain team and meet this demand.
Background
For almost 50 years, pharmacists at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) have been functioning as advanced practice providers (APP).3 Clinical pharmacy specialists (CPS) provide comprehensive medication management (CMM) and have a scope of practice (SOP). The SOP serves as the collaborating agreement and outlines the clinical duties permitted in delivering patient care. In addition, the SOP may indicate specific practice areas and are standardized across VA (Table 1).4,5 Pharmacists apply for a SOP and must prove their competency in the practice area and provide documentation of their education, training, experience, knowledge, and skills.5,6 Residency and/or board certification are not required though helpful. A pharmacist’s SOP is reviewed and approved by the facility executive committee.5 Pharmacists with a SOP undergo professional practice evaluation twice a year. Prescribing controlled substances is permissible in the SOP if approved by the facility and allowed by the state of licensure. According to the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) as of February 10, 2020, 8 states (California, Washington, Idaho, Massachusetts, Montana, New Mexico, North Carolina, and Ohio) allow pharmacists to prescribe controlled substances.7
The VA developed the Pharmacists Achieve Results with Medications Documentation (PhARMD) tool that allows clinical pharmacists to document specific interventions made during clinical care and is included in their progress note. Data from fiscal year 2017 demonstrates that 136,041 pain management interventions were made by pharmacists across VA. The majority of these interventions were implemented by a CPS working autonomously as an APP.8
Several articles discuss the pharmacists role in the opioid crisis, although no outcomes data were provided. Chisholm-Burns and colleagues listed multiple potential ways that pharmacists can intervene, including managing pain in primary care clinic settings by using collaborative drug therapy agreements (CDTAs), using opioid exit plans and discharge planning in collaboration with other health care providers (HCPs), or making recommendations to the prescribers before writing prescriptions.9 Compton and colleagues similarly reviewed pharmacist roles in the opioid crisis. However, their focus was on dispensing pharmacists that provided education to patients about storage and disposal of opioids, identified opioid misuse, provided opioid overdose education and naloxone, and checked prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs).10 Missing from these articles was the role of the clinical pharmacist working as an APP delivering direct patient care and prescribing controlled substances.
Hammer and colleagues discussed the role of an oncology CPS with controlled substance prescriptive authority in pain management at an outpatient cancer center in Washington state.11 Under a CDTA, pharmacists could prescribe medications, including controlled substances if they obtain DEA registration. The pharmacist completed a comprehensive in-person assessment. The attending physician conducted a physical examination. Then the pharmacist presented the patient and proposed regimen to the interprofessional team to determine a final plan. Ultimately, the pharmacist wrote any controlled substance prescriptions. The patient followed up every 1 to 4 weeks by telephone with a nurse, and in-person assessments occurred at least every 6 months. No outcomes data were provided.11
Dole and colleagues reviewed the role of a pharmacist who had controlled substance prescriptive authority in a pain management clinic. The pharmacist provider saw up to 18 patients a day and then managed refill requests for 3 hours a day. The main outcome was change in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores. Findings showed that reductions in VAS pain scores were statistically significant (P < .01). The pharmacist processed about 150 refills with an unclear number of controlled substances requests a day based on a medication-refill protocol. This was felt to improve access to physicians for acute needs, improve consistency in refills, and capture patients in need of follow-up. Additionally, the clinic saved $455,238 after 1 year.12
Study Aims
A review of the literature indicated sparse data on the impact of a pharmacist on opioid tapering, opioid dose, and opioid risk mitigation when the pharmacist is prescribing controlled substances. The purpose of this retrospective review was to characterize the controlled substance prescribing practices by the pharmacy pain clinic. The aim was to examine the pharmacist impact on morphine milligram equivalent (MME) and compliance with opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Methods
This project was a retrospective, single-center, chart review. The project was reviewed and approved by the University of Missouri-Columbia Institutional Review Board used by the Harry S. Truman Memorial Veterans’ Hospital (HSTMVH) as a quality improvement project. The author applied for controlled substance registration through the DEA and was issued registration April 30, 2018. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy was contacted as required by Ohio Administrative Code. The author's updated SOP to allow controlled substance prescribing was approved July 23, 2018. The CPS functions as an APP within an interdisciplinary pain management team that includes physicians, occupational and physical therapists, complementary and integrative health, and a psychologist. The reason for Pharmacy Pain Consult is required and it is primarily submitted through the electronic health record. The consult is reviewed for appropriateness and once approved is scheduled by support staff. Once the patient is stabilized, the patient is discharged back to their primary care provider (PCP) or referring provider for continued care. Patients were considered stabilized when their patient-specific goals were met, which varied from use of the lowest effective opioid dose to taper to discontinuation of opioids with no further medication changes needed. The taper strategy for each patient was individualized. Patients were generally tapered on their existing opioid medication unless they were new to the VA and on nonformulary medications or experiencing a significant adverse reaction. Numerous references are available through VA to assist with opioid tapering.13,14 The CPS is able to refer patients to other services, including behavioral health for substance use disorder treatment and medication-assisted treatment if concerns were identified.
Initial data were collected from the Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 15 Corporate Data Warehouse by the VISN pharmacy analytics program manager. The original report included patients prescribed a Schedule II to V controlled substance by the author from July 1, 2018 to January 31, 2020. Chart review was conducted on each patient to obtain additional data. At the time of consult and discharge the following data were collected: opioid medication; MME; use of opioid risk mitigation strategies, such as urine drug screens (UDS), informed consent, opioid overdose education and naloxone distribution program (OEND), risk assessment via stratification tool for opioid risk mitigation (STORM), PDMP checks; and nonopioid medication number and classes.
Patients were included in the review if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance between July 1, 2018 and January 31, 2020. Patient were excluded if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance primarily as coverage for another prescriber. Patients prescribed only pregabalin, tramadol, or a benzodiazepine also were excluded.
The primary endpoint was change in MME from baseline to discharge from clinic. Secondary endpoints included change in opioid risk mitigation strategies and change in opioid medications prescribed from baseline to discharge.
Descriptive statistics were used to analyze parts of the data. A 2-sided t test was used to compare baseline and discharge MME. The Fisher exact test was used to compare nominal data of opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Calculation of MME was performed using the conversion factors provided by the Centers Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for opioid guideline.15 For buprenorphine, tapentadol, and levorphanol conversion ratios were obtained from other sources. The conversion ratios used, included 75:1 for oral morphine to transdermal buprenorphine, 1:3.3 for oral morphine to oral tapentadol, and 1:7.5 for oral levorphanol to oral morphine.16,17 The Revised Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) was used to write the manuscript.18
Results
Seventy-five patients were included in this review. The average age of patients was 66 years; and 12% were female (n = 9) (Table 2). The largest number of consults came from PCPs (44%, n = 33) and the pain clinic (43%, n = 32). Nearly half (48%) of the consultations were for opioid tapering (n = 36), followed by 37% for opioid optimization or monitoring (n = 28), and 19% for nonopioid optimization (n = 14). The most common primary diagnoses at consultation were for chronic low back pain (56%), chronic neck pain (20%), and osteoarthritis (16%).
The average MME at time of consult was 93 MME compared with 31 MME at discharge which was statisticially significant (P < .01) (Figure 1). The mean percent change in MME was 46%, including methadone and 42% excluding methadone. There was a 26% change in UDS, 28% change in informed consent, 85% change in PDMP, 194% change in naloxone, and 357% change in STORM reviews from baseline to discharge with all demonstrating statistical significance (P < .01) (Figure 2). At discharge, the most common opioid prescribed was morphine SA (short acting) (n = 10, 13%, 44 average MME) and oxycodone/acetaminophen (n = 10, 13%, 28 average MME) (Table 3).
The average number of days from consult to initial visit was 23 days (Table 4). Face-to-face was the primary means of initial visit with 92% (n = 69) of visits, but phone was the primary mode of follow-up with 73% of visits (n = 55). The average number of follow-up visits was 7, representing 176 average days of time in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Consultation to the behavioral health performance program was the most common referral (n = 13, 17%).
Five patients were new opioid starts in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Two patients were on tramadol at time of consult. Of the 5 new opioid starts, 3 patients received oxycodone/acetaminophen, 1 received buprenorphine patch, and 1 received hydrocodone/acetaminophen. The new opioid start average was 25 MME. All 5 patients had a UDS for opioid risk mitigation, 4 used consent and STORM reviews, and 2 patients had PDMP checks and naloxone.
Discussion
There was a statistically significant decrease of the mean MME between the time of consult and the time of discharge. There also were statistically significant changes in use of opioid risk mitigation strategies. Since methadone has a high MME, the mean reduction of MME was calculated with methadone (46%) and without methadone (42%). These data are consistent with other published studies examining opioid tapers in the VA population. Harden and colleagues calculated a 46% mean reduction in MME over 12 months for 72 veterans from opioid tapers implemented by PCPs, pain service, or pharmacist-run clinics.19
There is controversy about equianalgesic doses and no established universal equianalgesic conversion calculator or dose. Numerous equianalgesic opioid dose calculators are available, but for this analysis the CDC MME conversion factors were used (available at: https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/pdf/calculating_total_daily_dose-a.pdf). Previous literature compared existing calculators and found significant variances in calculated doses for methadone and fentanyl conversions.20 Additionally, there have been concerns expressed with the safety of the CDC opioid calculator specifically surrounding the conversions for methadone and tapentadol.21 In the end, I chose the CDC calculator because it is established, readily available, and consistent.
Pharmacists in pain management can address access issues.2,3,11,12 The average length of time from consult to initial visit was 23 days. Often patients may have seen a HCP who implemented a change at the time of consult and wanted the patient to be seen 1 month later. Many patients at the HSTMVH live far from the facility, making in-person visits difficult. A majority of the follow-up visits were conducted by telephone. Patients were offered all modalities available for follow-up, including telephone, in-person, or telemedicine, but patients most often picked telephone. Patients averaged 7 follow-up visits before discharge. This number of visits would have taken time from other health care team members who could have been addressing other veterans. Patients were seen in clinic for 176 days on average, which supports and follows recommendations for a slow, incremental taper.
The opioid medications prescribed changed over time in the clinic. Methadone prescriptions dropped from 20 to 6 at consult to discharge, and fentanyl prescriptions fell from 7 to 2, respectively. The CDC guideline suggests use of long-acting products with more predictable pharmacokinetics (eg, morphine SA or oxycodone SA) rather than fentanyl or methadone.15 Notably, the use of buprenorphine products with FDA approval for pain indications increased from consult to discharge. Many of the patients in this study had pulmonary comorbidities, placing them at higher risk for adverse outcomes. Buprenorphine is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist with a ceiling on respiratory depression so is potentially less risky in those with pulmonary comorbidities.
The biggest changes in opioid risk mitigation occurred in PDMP, OEND program, and STORM reviews. An 85% increase in PDMP reviews occurred with referral to the clinic. Missouri is the only state without a state-run PDMP. However, the St. Louis County PDMP was developed based on city or county participation and encompasses 85% of the population of Missouri and 94% of HCPs in Missouri as of August 29, 2019.22 Because there is no state-level PDMP, a review of the St. Louis County PDMP was not required during the review period. Nevertheless, the Pharmacy Pain Clinic uses the St. Louis County PDMP at the initial visit and regularly during care. VA policy requires a specific note title be used to document each check of the PDMP.23
There was a 194% increase in patients receiving naloxone with consultation to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Due to low coprescribing of naloxone for patients prescribed chronic opioid therapy, The author led an interdisciplinary team analysis of health care failure mode effects during the study period. This led to a process change with coprescribing of naloxone at refill in the primary care clinic.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 mandated that the VA review STORM on new start of opioids or patient identified as “very high-opioid prescription risk” category by an interdisciplinary opioid risk review team.24 Thus many of the patients referred to clinic didn’t require STORM reviews since they were not new opioid starts or identified as high risk. However, in the standard review of all new patients to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic, a STORM review is conducted and documented to assess the patient’s level of risk.
Only 5 patients were started on opioid medications during the study period. This is consistent with both CDC and the joint VA/US Department of Defense opioid prescribing guidelines that recommend against initiation of opioids for chronic nonmalignant pain.13,15 Two of the patients were prescribed tramadol for ineffective pain control at time of consult. Furthermore, 4 of the 5 patients were started on a short-acting opioid, which was supported by guidelines.13,15 One patient was initiated on buprenorphine patches due to comorbid chronic kidney disease. The VA does not limit the quantity of new opioid prescriptions, although some states and private insurance plans are implementing limitations. Guidelines also recommend against exceeding 90 MME due to risk. The average MME in this project at discharge was 25 MME. Use of opioid risk mitigation for the new opioid starts was reasonable. The reason for the missing PDMP report is unknown based on chart review and atypical according to clinic practice.
Recently, efforts to expand pharmacist training and positions in pain management at VA facilities have been undertaken. In 2016, there were just 11 American Society of Health-System Pharmacists-accredited pharmacy postgraduate year 2 pain and palliative care residency programs, which has expanded to 26 sites in 2020.2,3,25 In addition, the Clinical Pharmacy Practice Office and the VA Office of Rural Health have helped to hire 33 new pain management pharmacists.3
The role of pharmacists in prescribing controlled substances is limited mainly due to the small number of states that extend this authority.7 At the VA, a pharmacist can practice using any state of licensure. Therefore, a pharmacist working at a VA in a state that does not authorize controlled substance prescribing could obtain a license in a state that does permit it. However, the main barrier to obtaining other state licensures is the cost. At the time the author obtained controlled substance prescriptive authority, little direction was available on the process for advanced practice pharmacists at the VA. Since then, guidance has been developed to ease this process. Educational endeavors at VA have been implemented with the intent to increase the number of pharmacists with controlled substance prescriptive authority.
Barriers to pharmacists providing pain care extend beyond limited controlled substance prescriptive authority. Often pharmacists are still viewed in their traditional and operational role.9,10 Other health care team members and patients may not be aware or familiar with the training, knowledge, and skills of pharmacist's and their suitability as an APP.26,27 Most states permit pharmacists in establishing CDTA but not all. Additionally, some states recognize pharmacists as HCPs but many more do not. Furthermore, the Social Security Act does not include pharmacists as HCPs. This makes it challenging, though not impossible, for pharmacists to bill for their services.3
Strengths and Limitations
There were numerous strengths of the project. First, this addressed an unmet need in the literature with limited data discussing pharmacist prescribing controlled substances for pain management. There was 1 data reviewer who made the data collection process consistent. Since this retrospectively reviewed controlled substance prescribing in clinic, it captured real-world practice compared with that of experimental models. There were also several limitations in the project. The person collecting the data was also the person who conducted the clinic. The study was conducted retrospectively and based on documented information in the medical record. The population reviewed was primarily male and older, which fits the VA patient population but has less generalizability to other patient populations. This project was conducted at a single VA facility so may not be generalizable to other VA sites. It is unknown whether patients were again prescribed opioids if they left the VA for the community or another VA facility. The pain diagnoses or locations of pain were categorized to main groups and reliant on the referring provider. Another major weakness was the lack of comparison of pain scores or validated objective measure of function at baseline and at discharge. This consideration would be important for future work.
Conclusions
Pharmacists functioning as APP are key members of the pain management team. A review of a pharmacy-run pain clinic demonstrated statistically significant reduction in MME and improvement in opioid risk mitigation from consult to discharge. Patients enrolled in the pharmacy-managed clinic also had improvements in adherence to opioid risk mitigation strategies. Future attention should be focused on further expanding training and positions for pharmacists as APP in pain management.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Chris Sedgwick for his assistance with data capture.
1. US Department of Health and Human Services. Help and resources: national opioid crisis. Updated August 30, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.hhs.gov/opioids/about-the-epidemic/hhs-response/index.html
2. Atkinson TJ, Gulum AH, Forkum WG. The future of pain pharmacy: driven by need. Integr Pharm Res Pract. 2016;5:33-42. doi:10.2147/IPRP.S63824
3. Seckel E, Jorgenson T, McFarland S. Meeting the national need for expertise in pain management with clinical pharmacist advanced practice providers. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2019;45(5):387-392.doi:10.1016/j.jcjq.2019.01.002
4. McFarland MS, Groppi J, Ourth H, et al. Establishing a standardized clinical pharmacy practice model within the Veterans Health Administration: evolution of the credentialing and professional practice evaluation process. J Am Coll Clin Pharm. 2018;1(2):113-118. doi:10.1002/jac5.1022
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook. 1108.11. Clinical pharmacy services. Published July 1, 2015. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3120
6. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1100.19. Credentialing and priveleging. Published October 15, 2012. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=2910
7. US Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Agency. Mid-level practitioners authorization by state. Updated February 10, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drugreg/practioners/mlp_by_state.pdf
8. Groppi JA, Ourth H, Morreale AP, Hirsh JM, Wright S. Advancement of clinical pharmacy practice through intervention capture. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018;75(12):886-892. doi:10.2146/ajhp170186
9. Chisholm-Burns MA, Spivey CA, Sherwin E, Wheeler J, Hohmeier K. The opioid crisis: origins, trends, policies, and the roles of pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(7):424-435. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxy089
10. Compton WM, Jones CM, Stein JB, Wargo EM. Promising roles for pharmacists in addressing the U.S. opioid crisis. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2019;15(8):910-916. doi:10.1016/j.sapharm.2017.12.009
11. Hammer KJ, Segal EM, Alwan L, et al. Collaborative practice model for management of pain in patients with cancer. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1434-1441. doi:10.2146/ajhp150770
12. Dole EJ, Murawski MM, Adolphe AB, Aragon FD, Hochstadt B. Provision of pain management by a pharmacist with prescribing authority. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64(1):85-89. doi:10.2146/ajhp060056
13. US Department of Defense, US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for Opioid Therapy for Chronic Pain. Updated 2017. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/Pain/cot/VADoDOTCPG022717.pdf
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA, VHA, VA Academic Detailing Service. Veterans Health Administration. Opioid taper decision tool. Updated October 2016. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.pbm.va.gov/AcademicDetailingService/Documents/Pain_Opioid_Taper_Tool_IB_10_939_P96820.pdf
15. Dowell D, Haegerich TM, Chou R. CDC guideline for prescribing opioids for chronic pain - United States, 2016 [published correction appears in MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(11):295]. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(1):1-49. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6501e1
16. McPherson M. Demystifying opioid conversion calculations. Published 2009. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.ashp.org/-/media/store-files/p1985-frontmatter.ashx
17. Gudin J, Fudin J, Nalamachu S. Levorphanol use: past, present and future. Postgrad Med. 2016;128(1):46-53. doi:10.1080/00325481.2016.1128308
18. Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden P, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Qual Saf. 2016;25(12):986-992. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004411
19. Harden P, Ahmed S, Ang K, Wiedemer N. Clinical implications of tapering chronic opioids in a veteran population. Pain Med. 2015;16(10):1975-1981. doi:10.1111/pme.12812
20. Shaw K, Fudin J. Evaluation and comparison of online equianalgesic opioid dose conversion calculators. Practical Pain Manag. 2013;13(7):61-66. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.practicalpainmanagement.com/treatments/pharmacological/opioids/evaluation-comparison-online-equianalgesic-opioid-dose-conversion
21. Fudin J, Raouf M, Wegrzyn EL, Schatman ME. Safety concerns with the Centers for Disease Control opioid calculator. J Pain Res. 2017;11:1-4. Published 2017 Dec 18. doi:10.2147/JPR.S155444
22. Saint Louis County Public Health. St. Louis County Prescription Drug Monitoring Program. Participating jurisdictions. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://pdmp-stlcogis.hub.arcgis.com
23. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1306: querying state prescription drug monitoring programs. Updated October 21, 2019. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3283
24. Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016. 42 USC § 201 (2016).
25. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Residency directory. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://accreditation.ashp.org/directory/#/program/residency
26. Feehan M, Durante R, Ruble J, Munger MA. Qualitative interviews regarding pharmacist prescribing in the community setting. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1456-1461. doi:10.2146/ajhp150691
27. Giannitrapani KF, Glassman PA, Vang D, et al. Expanding the role of clinical pharmacists on interdisciplinary primary care teams for chronic pain and opioid management. BMC Fam Pract. 2018;19(1):107. doi:10.1186/s12875-018-0783-9
1. US Department of Health and Human Services. Help and resources: national opioid crisis. Updated August 30, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.hhs.gov/opioids/about-the-epidemic/hhs-response/index.html
2. Atkinson TJ, Gulum AH, Forkum WG. The future of pain pharmacy: driven by need. Integr Pharm Res Pract. 2016;5:33-42. doi:10.2147/IPRP.S63824
3. Seckel E, Jorgenson T, McFarland S. Meeting the national need for expertise in pain management with clinical pharmacist advanced practice providers. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2019;45(5):387-392.doi:10.1016/j.jcjq.2019.01.002
4. McFarland MS, Groppi J, Ourth H, et al. Establishing a standardized clinical pharmacy practice model within the Veterans Health Administration: evolution of the credentialing and professional practice evaluation process. J Am Coll Clin Pharm. 2018;1(2):113-118. doi:10.1002/jac5.1022
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook. 1108.11. Clinical pharmacy services. Published July 1, 2015. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3120
6. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1100.19. Credentialing and priveleging. Published October 15, 2012. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=2910
7. US Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Agency. Mid-level practitioners authorization by state. Updated February 10, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drugreg/practioners/mlp_by_state.pdf
8. Groppi JA, Ourth H, Morreale AP, Hirsh JM, Wright S. Advancement of clinical pharmacy practice through intervention capture. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018;75(12):886-892. doi:10.2146/ajhp170186
9. Chisholm-Burns MA, Spivey CA, Sherwin E, Wheeler J, Hohmeier K. The opioid crisis: origins, trends, policies, and the roles of pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(7):424-435. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxy089
10. Compton WM, Jones CM, Stein JB, Wargo EM. Promising roles for pharmacists in addressing the U.S. opioid crisis. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2019;15(8):910-916. doi:10.1016/j.sapharm.2017.12.009
11. Hammer KJ, Segal EM, Alwan L, et al. Collaborative practice model for management of pain in patients with cancer. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1434-1441. doi:10.2146/ajhp150770
12. Dole EJ, Murawski MM, Adolphe AB, Aragon FD, Hochstadt B. Provision of pain management by a pharmacist with prescribing authority. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64(1):85-89. doi:10.2146/ajhp060056
13. US Department of Defense, US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for Opioid Therapy for Chronic Pain. Updated 2017. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/Pain/cot/VADoDOTCPG022717.pdf
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA, VHA, VA Academic Detailing Service. Veterans Health Administration. Opioid taper decision tool. Updated October 2016. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.pbm.va.gov/AcademicDetailingService/Documents/Pain_Opioid_Taper_Tool_IB_10_939_P96820.pdf
15. Dowell D, Haegerich TM, Chou R. CDC guideline for prescribing opioids for chronic pain - United States, 2016 [published correction appears in MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(11):295]. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(1):1-49. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6501e1
16. McPherson M. Demystifying opioid conversion calculations. Published 2009. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.ashp.org/-/media/store-files/p1985-frontmatter.ashx
17. Gudin J, Fudin J, Nalamachu S. Levorphanol use: past, present and future. Postgrad Med. 2016;128(1):46-53. doi:10.1080/00325481.2016.1128308
18. Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden P, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Qual Saf. 2016;25(12):986-992. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004411
19. Harden P, Ahmed S, Ang K, Wiedemer N. Clinical implications of tapering chronic opioids in a veteran population. Pain Med. 2015;16(10):1975-1981. doi:10.1111/pme.12812
20. Shaw K, Fudin J. Evaluation and comparison of online equianalgesic opioid dose conversion calculators. Practical Pain Manag. 2013;13(7):61-66. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.practicalpainmanagement.com/treatments/pharmacological/opioids/evaluation-comparison-online-equianalgesic-opioid-dose-conversion
21. Fudin J, Raouf M, Wegrzyn EL, Schatman ME. Safety concerns with the Centers for Disease Control opioid calculator. J Pain Res. 2017;11:1-4. Published 2017 Dec 18. doi:10.2147/JPR.S155444
22. Saint Louis County Public Health. St. Louis County Prescription Drug Monitoring Program. Participating jurisdictions. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://pdmp-stlcogis.hub.arcgis.com
23. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1306: querying state prescription drug monitoring programs. Updated October 21, 2019. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3283
24. Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016. 42 USC § 201 (2016).
25. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Residency directory. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://accreditation.ashp.org/directory/#/program/residency
26. Feehan M, Durante R, Ruble J, Munger MA. Qualitative interviews regarding pharmacist prescribing in the community setting. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1456-1461. doi:10.2146/ajhp150691
27. Giannitrapani KF, Glassman PA, Vang D, et al. Expanding the role of clinical pharmacists on interdisciplinary primary care teams for chronic pain and opioid management. BMC Fam Pract. 2018;19(1):107. doi:10.1186/s12875-018-0783-9