User login
Definitive diverticular hemorrhage: Diagnosis and management
Diverticular hemorrhage is the most common cause of colonic bleeding, accounting for 20%-65% of cases of severe lower intestinal bleeding in adults.1 Urgent colonoscopy after purging the colon of blood, clots, and stool is the most accurate method of diagnosing and guiding treatment of definitive diverticular hemorrhage.2-5 The diagnosis of definitive diverticular hemorrhage depends upon identification of some stigmata of recent hemorrhage (SRH) in a single diverticulum (TIC), which can include active arterial bleeding, oozing, non-bleeding visible vessel, adherent clot, or flat spot.2-4 Although other approaches, such as nuclear medicine scans and angiography of various types (CT, MRI, or standard angiography), for the early diagnosis of patients with severe hematochezia are utilized in many medical centers, only active bleeding can be detected by these techniques. However, as subsequently discussed, this SRH is documented in only 26% of definitive diverticular bleeds found on urgent colonoscopy, so diagnostic yields of these techniques will be low.2-5
The diagnosis of patients with severe hematochezia and diverticulosis, as well as triage of all of them to specific medical, endoscopic, radiologic, or surgical management, is facilitated by an urgent endoscopic approach.2-5 Patients who are diagnosed with definitive diverticular hemorrhage on colonoscopy represent about 30% of all true TIC bleeds when urgent colonoscopy is the management approach.2-5 That is because approximately 50% of all patients with colon diverticulosis and first presentation of severe hematochezia have incidental diverticulosis; they have colonic diverticulosis, but another site of bleeding is identified as the cause of hemorrhage in the gastrointestinal tract.2-4 Presumptive diverticular hemorrhage is diagnosed when colonic diverticulosis without TIC stigmata are found but no other GI bleeding source is found on colonoscopy, anoscopy, enteroscopy, or capsule endoscopy.2-5 In our experience with urgent colonoscopy, the presumptive diverticular bleed group accounts for about 70% of patients with documented diverticular hemorrhage (e.g., not including incidental diverticulosis bleeds but combining subgroups of patients with either definitive or presumptive TIC diagnoses as documented TIC hemorrhage).
Clinical presentation
Patients with diverticular hemorrhage present with severe, painless large volume hematochezia. Hematochezia may be self-limited and spontaneously resolve in 75%-80% of all patients but with high rebleeding rates up to 40%.5-7 Of all patients with diverticulosis, only about 3%-5% develop diverticular hemorrhage.8 Risk factors for diverticular hemorrhage include medications (e.g., nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – NSAIDs, antiplatelet drugs, and anticoagulants) and other clinical factors, such as older age, low-fiber diet, and chronic constipation.9,10 On urgent colonoscopy, more than 70% of diverticulosis in U.S. patients are located anatomically in the descending colon or more distally. In contrast, about 60% of definitive diverticular hemorrhage cases in our experience had diverticula with stigmata identified at or proximal to the splenic flexure.2,4,11
Pathophysiology
Colonic diverticula are herniations of mucosa and submucosa with colonic arteries that penetrate the muscular wall. Bleeding can occur when there is asymmetric rupture of the vasa recta at either the base of the diverticulum or the neck.4 Thinning of the mucosa on the luminal surface (such as that resulting from impacted fecaliths and stool) can cause injury to the site of the penetrating vessels, resulting in hemorrhage.12
Initial management
Patients with acute, severe hematochezia should be triaged to an inpatient setting with a monitored bed. Admission to an intensive care unit should be considered for patients with hemodynamic instability, persistent bleeding, and/or significant comorbidities. Patients with TIC hemorrhage often require resuscitation with crystalloids and packed red blood cell transfusions for hemoglobin less than 8 g/dl.4 Unlike upper GI hemorrhage, which has been extensively reported on, data regarding a more restrictive transfusion threshold, compared with a liberal transfusion threshold, in lower intestinal bleeding are very limited. Correction of underlying coagulopathies is recommended but should be individualized, particularly in those patients on antithrombotic agents or with underlying bleeding disorders.
Urgent diagnosis and hemostasis
Urgent colonoscopy within 24 hours is the most accurate way to make a diagnosis of definitive diverticular hemorrhage and to effectively and safely treat them.2-4,10,11 For patients with severe hematochezia, when the colonoscopy is either not available in a medical center or does not reveal the source of bleeding, nuclear scintigraphy or angiography (CT, MRI, or interventional radiology [IR]) are recommended. CT angiography may be particularly helpful to diagnose patients with hemodynamic instability who are suspected to have active TIC bleeding and are not able to complete a bowel preparation. However, these imaging techniques require active bleeding at the time of the study to be diagnostic. This SRH is also uncommon for definitive diverticular hemorrhage, so the diagnostic yield is usually quite low.2-5,10,11 An additional limitation of scintigraphy and CT or MRI angiography is that, if active bleeding is found, some other type of treatment, such as colonoscopy, IR angiography, or surgery, will be required for definitive hemostasis.
For urgent colonoscopy, adequate colon preparation with a large volume preparation (6-8 liters of polyethylene glycol-based solution) is recommended to clear stool, blood, and clots to allow endoscopic visualization and localization of the bleeding source. Use of a nasogastric tube should be considered if the patient is unable to drink enough prep.2-4,13 Additionally, administration of a prokinetic agent, such as Metoclopramide, may improve gastric emptying and tolerance of the prep. During colonoscopy, careful inspection of the colonic mucosa during insertion and withdrawal is important since lesions may bleed intermittently and SRH can be missed. An adult or pediatric colonoscope with a large working channel (at least 3.3 mm) is recommended to facilitate suctioning of blood clots and stool, as well as allow the passage of endoscopic hemostasis accessories. Targeted water-jet irrigation, an expert colonoscopist, a cap attachment, and adequate colon preparation are all predictors for improved diagnosis of definitive diverticular hemorrhage.4,14
SRH in definitive TIC bleeds all have a high risk of TIC rebleeding,2-4,10,11 including active bleeding, nonbleeding visible vessel, adherent clot, and a flat spot (See Figure).
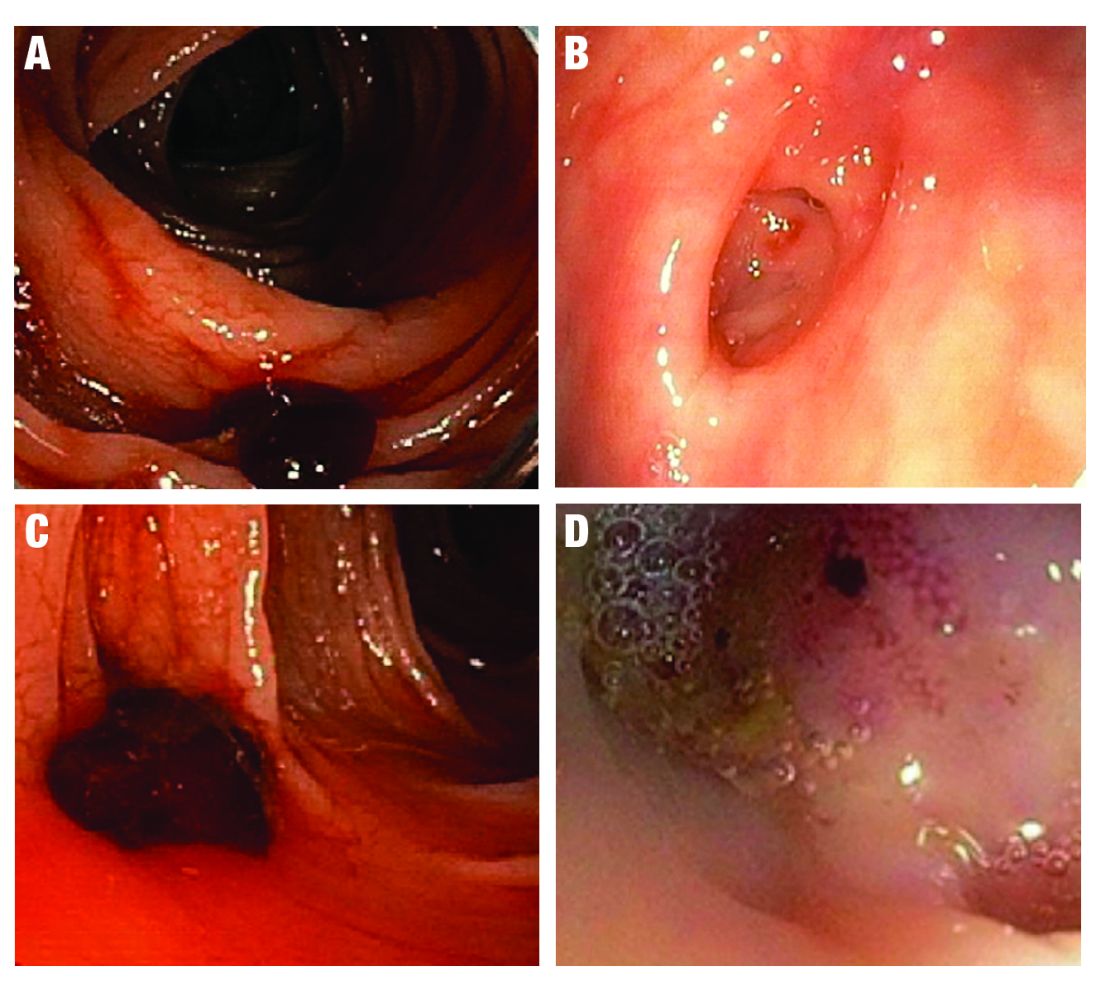
Based on CURE Hemostasis Group data of 118 definitive TIC bleeds, 26% had active bleeding, 24% had a nonbleeding visible vessel, 37% had an adherent clot, and 13% had a flat spot (with underlying arterial blood flow by Doppler probe monitoring).4 Approximately 50% of the SRH were found in the neck of the TIC and 50% at the base, with actively bleeding cases more often from the base. In CURE Doppler endoscopic probe studies, 90% of all stigmata had an underlying arterial blood flow detected with the Doppler probe.4,10 The Doppler probe is reported to be very useful for risk stratification and to confirm obliteration of the arterial blood flow underlying SRH for definitive hemostasis.4,10
Endoscopic treatment
Given high rates of rebleeding with medical management alone, definitive TIC hemorrhage can be effectively and safely treated with endoscopic therapies once SRH are localized.4,10 Endoscopic therapies that have been reported in the literature include electrocoagulation, hemoclip, band ligation, and over-the-scope clip. Four-quadrant injection of 1:20,000 epinephrine around the SRH can improve visualization of SRH and provide temporary control of bleeding, but it should be combined with other modalities because of risk of rebleeding with epinephrine alone.15 Results from studies reporting rates of both early rebleeding (occurring within 30 days) and late rebleeding (occurring after 30 days) are listed in the Table. 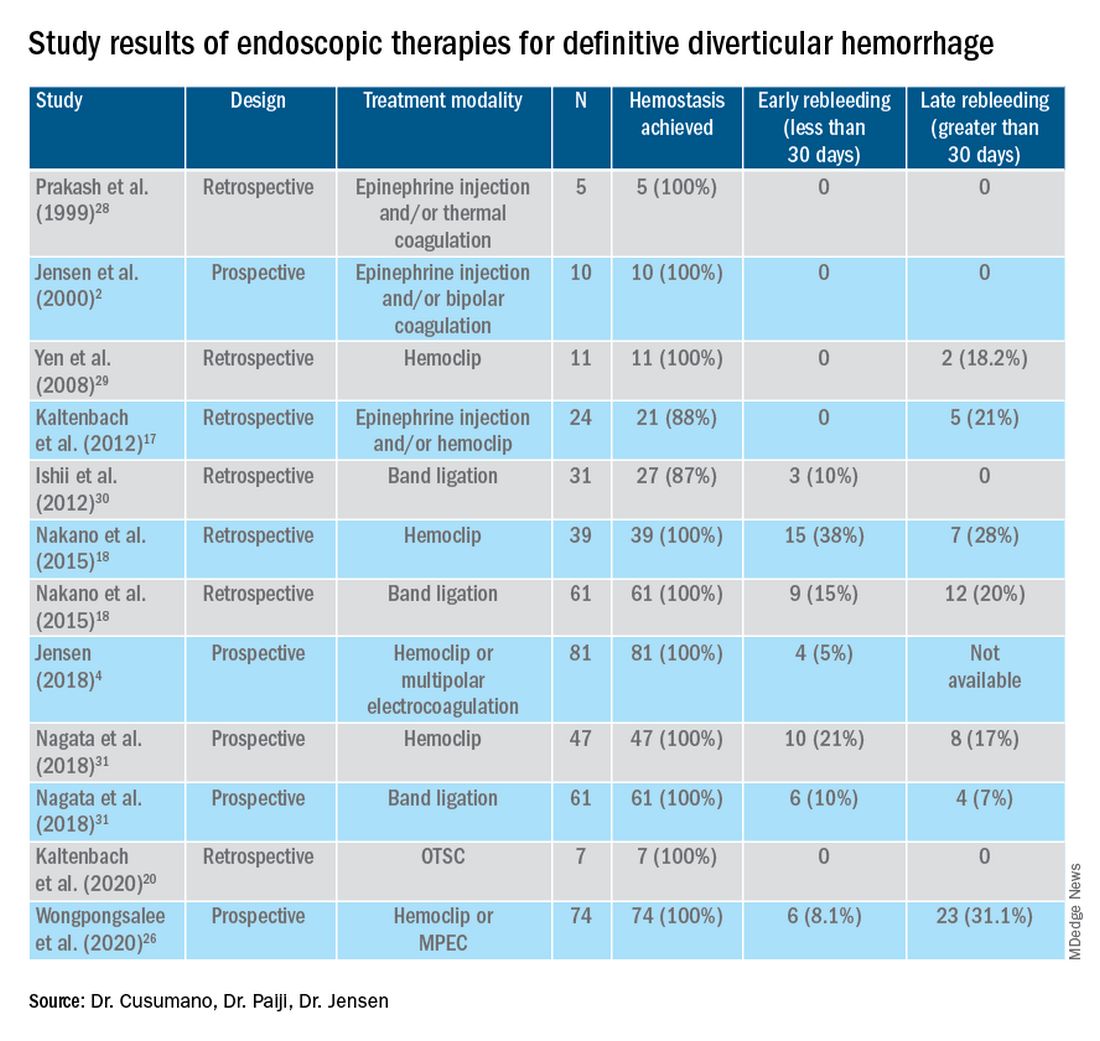
Multipolar electrocoagulation (MPEC), which utilizes a focal electric current to generate heat, can coaptively coagulate small TIC arteries.16 For SRH in the neck of TIC, MPEC is effective for coaptive coagulation at a power of 12-15 watts in 1-2 second pulses with moderate laterally applied tamponade pressure. MPEC should be avoided for treating SRH at the TIC base because of lack of muscularis propria and higher risk of perforation.
Hemoclip therapy has been reported to be safe and efficacious in treatment of definitive TIC hemorrhage, by causing mechanical hemostasis with occlusion of the bleeding artery.16 Hemoclips are recommended to treat stigmata in the base of TICs and should be targeted on either side of visible vessel in order to occlude the artery underneath it.4,10 With a cap on the tip of the colonoscope, suctioning can evert TICs, allowing more precise placement of hemoclip on SRH in the base of the TIC.17 Hemoclip retention rates vary with different models and can range from less than 7 days to more than 4 weeks. Hemoclips can also mark the site if early rebleeding occurs; then, reintervention (e.g., repeat endoscopy or angioembolization) is facilitated.
Another treatment is endoscopic band ligation, which provides mechanical hemostasis. Endoscopic band ligation has been reported to be efficacious for TIC hemorrhage.18 Suctioning the TIC with the SRH into the distal cap and deploying a band leads to obliteration of vessels and potentially necrosis and disappearance of banded TIC.16 This technique carries a risk of perforation because of the thin walls of TICs. This risk may be higher for right-sided colon lesions since an exvivo colon specimen study reported serosal entrapment and inclusion of muscularis propria postband ligation, both of which may result in ischemia of intestinal wall and delayed perforation.19
Over-the-scope clip (OTSC) has been reported in case series for treatment of definitive TIC hemorrhage. With a distal cap and large clip, suctioning can evert TICs and facilitate deployment over the SRH.20,21 OTSC can grasp an entire TIC with the SRH and obliterate the arterial blood flow with a single clip.20,21 No complications have been reported yet for treatment of TIC hemorrhage. However, the OTSC system is relatively expensive when compared with other modalities.
After endoscopic treatment is performed, four-quadrant spot tattooing is recommended adjacent to the TIC with the SRH. This step will facilitate localization and treatment in the case of TIC rebleeding.4,10
Outcomes following endoscopic treatment
Following endoscopic treatment, patients should be monitored for early and late rebleeding. In a pooled analysis of case series composed of 847 patients with TIC bleeding, among the 137 patients in which endoscopic hemostasis was initially achieved, early rebleeding occurred in 8% and late rebleeding occurred in 12% of patients.22 Risk factors for TIC rebleeding within 30 days were residual arterial blood flow following hemostasis and early reinitiation of antiplatelet agents.
Remote treatment of TIC hemorrhage distant from the SRH is a significant risk factor for early TIC rebleeding.4, 10 For example, using hemoclips to close the mouth of a TIC when active bleeding or an SRH is located in the TIC base often fails because arterial flow remains open in the base and the artery is larger there.4,10 This example highlights the importance of focal obliteration of arterial blood flow underlying SRH in order to achieve definitive hemostasis.4,10
Salvage treatments
For TIC hemorrhage that is not controlled by endoscopic therapy, transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) is recommended. If bleeding rate is high enough (at least 0.5 milliliters per minute) to be detected by angiography, TAE can serve as an effective method of diagnosis and immediate hemostasis.23 However, the most common major complication of embolization is intestinal ischemia. The incidence of intestinal ischemia has been reported as high as 10%, with highest risk with embolization of at least three vasa recta.24
Surgery is also recommended if TIC hemorrhage cannot be controlled with endoscopic therapy or TAE. Segmental colectomy is recommended if the bleeding site can be localized before surgery with colonoscopy or angiography resulting from significantly lower perioperative morbidity than subtotal colectomy.25 However, subtotal colectomy may be necessary if preoperative localization of bleeding is unsuccessful.
There are very few reports of short- or long-term results that compare endoscopy, TAE, and surgery for management of TIC bleeding. However, a recent retrospective study reported better outcomes with endoscopic treatment of definitive TIC bleeding.26 Patients who underwent endoscopic treatment had fewer RBC transfusions, shorter hospitalizations, and lower rates of postprocedure complications.
Management after cessation of hemorrhage
Medical management is important following an episode of TIC hemorrhage. A mainstay is daily fiber supplementation every morning and stool softener in the evening. Furthermore, patients are advised to drink an extra liter of fluids (not containing alcohol or caffeine) daily. By reducing colon transit time and increasing stool weight, these measures can help control constipation and prevent future complications of TIC disease.27
Patients with recurrent TIC hemorrhage should undergo evaluation for elective surgery, provided they are appropriate surgical candidates. If preoperative localization of bleeding site is successful, segmental colectomy is preferred. Segmental resection is associated with significantly decreased rebleeding rate, with lower rates of morbidity compared with subtotal colectomy.32
Chronic NSAIDs, aspirin, and antiplatelet drugs are risk factors for recurrent TIC hemorrhage, and avoiding these medications is recommended if possible.33,34 Although anticoagulants have shown to be associated with increased risk of all-cause gastrointestinal bleeding, these agents have not been shown to increase risk of recurrent TIC hemorrhage in recent large retrospective studies. Since antiplatelet and anticoagulation agents serve to reduce risk of thromboembolic events, the clinician who recommended these medications should be consulted after a TIC bleed to re-evaluate whether these medications can be discontinued or reduced in dose.
Conclusion
The most effective way to diagnose and treat definitive TIC hemorrhage is to perform an urgent colonoscopy within 24 hours to identify and treat TIC SRH. This procedure requires thoroughly cleansing the colon first, as well as an experienced colonoscopist who can identify and treat TIC SRH to obliterate arterial blood flow underneath SRH and achieve definitive TIC hemostasis. Other approaches to early diagnosis include nuclear medicine scintigraphy or angiography (CT, MRI, or IR). However, these techniques can only detect active bleeding which is documented in only 26% of colonoscopically diagnosed definitive TIC hemorrhages. So, the expected diagnostic yield of these tests will be low. When urgent colonoscopy fails to make a diagnosis or TIC bleeding continues, TAE and/or surgery are recommended. After definitive hemostasis of TIC hemorrhage and for long term management, control of constipation and discontinuation of chronic NSAIDs and antiplatelet drugs (if possible) are recommended to prevent recurrent TIC hemorrhage.
Dr. Cusumano and Dr. Paiji are fellow physicians in the Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases at University of California Los Angeles. Dr. Jensen is a professor of medicine in Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases and is with the CURE Digestive Diseases Research Center at the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, Calif. All authors declare that they have no competing interests or disclosures.
References
1. Longstreth GF. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92(3):419-24.
2. Jensen DM et al. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2000;342(2):78-82.
3. Jensen DM et al. Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2001;3(4):192-8.
4. Jensen DM. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113(11):1570-3.
5. Zuckerman GR et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 1999;49(2):228-38.
6. Stollman N et al. Lancet. 2004;363(9409):631-9.
7. McGuire HH et al. Ann Surg. 1994;220(5):653-6.
8. McGuire HH et al. Ann Surg. 1972;175(6):847-55.
9. Strate LL et al. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatol. 2008;6(9):1004-10.
10. Jensen DM et al. Gastrointestinal endoscopy. 2016;83(2):416-23.
11. Jensen DM et al. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1997;7(3):477-98.
12. Maykel JA et al. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2004;17(3):195-204.
13. Green BT et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100(11):2395-402.
14. Niikura R et al. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterol. 2015;49(3):e24-30.
15. Bloomfeld RS et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(8):2367-72.
16. Parsi MA,et al. VideoGIE. 2019;4(7):285-99.
17. Kaltenbach T et al. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatol. 2012;10(2):131-7.
18. Nakano K et al. Endosc Int Open. 2015;3(5):E529-33.
19. Barker KB et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2005;62(2):224-7.
20. Kaltenbach T et al. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2020;30(1):13-23.
21. Yamazaki K et al. VideoGIE. 2020;5(6):252-4.
22. Strate LL et al. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatol. 2010;8(4):333-43.
23. Evangelista et al. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2000;11(5):601-6.
24. Kodani M et al. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016;27(6):824-30.
25. Mohammed et al. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2018;31(4):243-50.
26. Wongpongsalee T et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2020;91(6):AB471-2.
27. Böhm SK. Viszeralmedizin. 2015;31(2):84-94.
28. Prakash C et al. Endoscopy. 1999;31(6):460-3.
29. Yen EF et al. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 2008;53(9):2480-5.
30. Ishii N et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2012;75(2):382-7.
31. Nagata N et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2018;88(5):841-53.e4.
32. Parkes BM et al. Am Surg. 1993;59(10):676-8.
33. Vajravelu RK et al. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(5):1416-27.
34. Oakland K et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(7):1276-84.e3.
35. Yamada A et al. Dis Colon Rectum. 2008;51(1):116-20.
36. Coleman CI et al. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66(1):53-63.
37. Holster IL et al. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(1):105-12.e15.
Diverticular hemorrhage is the most common cause of colonic bleeding, accounting for 20%-65% of cases of severe lower intestinal bleeding in adults.1 Urgent colonoscopy after purging the colon of blood, clots, and stool is the most accurate method of diagnosing and guiding treatment of definitive diverticular hemorrhage.2-5 The diagnosis of definitive diverticular hemorrhage depends upon identification of some stigmata of recent hemorrhage (SRH) in a single diverticulum (TIC), which can include active arterial bleeding, oozing, non-bleeding visible vessel, adherent clot, or flat spot.2-4 Although other approaches, such as nuclear medicine scans and angiography of various types (CT, MRI, or standard angiography), for the early diagnosis of patients with severe hematochezia are utilized in many medical centers, only active bleeding can be detected by these techniques. However, as subsequently discussed, this SRH is documented in only 26% of definitive diverticular bleeds found on urgent colonoscopy, so diagnostic yields of these techniques will be low.2-5
The diagnosis of patients with severe hematochezia and diverticulosis, as well as triage of all of them to specific medical, endoscopic, radiologic, or surgical management, is facilitated by an urgent endoscopic approach.2-5 Patients who are diagnosed with definitive diverticular hemorrhage on colonoscopy represent about 30% of all true TIC bleeds when urgent colonoscopy is the management approach.2-5 That is because approximately 50% of all patients with colon diverticulosis and first presentation of severe hematochezia have incidental diverticulosis; they have colonic diverticulosis, but another site of bleeding is identified as the cause of hemorrhage in the gastrointestinal tract.2-4 Presumptive diverticular hemorrhage is diagnosed when colonic diverticulosis without TIC stigmata are found but no other GI bleeding source is found on colonoscopy, anoscopy, enteroscopy, or capsule endoscopy.2-5 In our experience with urgent colonoscopy, the presumptive diverticular bleed group accounts for about 70% of patients with documented diverticular hemorrhage (e.g., not including incidental diverticulosis bleeds but combining subgroups of patients with either definitive or presumptive TIC diagnoses as documented TIC hemorrhage).
Clinical presentation
Patients with diverticular hemorrhage present with severe, painless large volume hematochezia. Hematochezia may be self-limited and spontaneously resolve in 75%-80% of all patients but with high rebleeding rates up to 40%.5-7 Of all patients with diverticulosis, only about 3%-5% develop diverticular hemorrhage.8 Risk factors for diverticular hemorrhage include medications (e.g., nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – NSAIDs, antiplatelet drugs, and anticoagulants) and other clinical factors, such as older age, low-fiber diet, and chronic constipation.9,10 On urgent colonoscopy, more than 70% of diverticulosis in U.S. patients are located anatomically in the descending colon or more distally. In contrast, about 60% of definitive diverticular hemorrhage cases in our experience had diverticula with stigmata identified at or proximal to the splenic flexure.2,4,11
Pathophysiology
Colonic diverticula are herniations of mucosa and submucosa with colonic arteries that penetrate the muscular wall. Bleeding can occur when there is asymmetric rupture of the vasa recta at either the base of the diverticulum or the neck.4 Thinning of the mucosa on the luminal surface (such as that resulting from impacted fecaliths and stool) can cause injury to the site of the penetrating vessels, resulting in hemorrhage.12
Initial management
Patients with acute, severe hematochezia should be triaged to an inpatient setting with a monitored bed. Admission to an intensive care unit should be considered for patients with hemodynamic instability, persistent bleeding, and/or significant comorbidities. Patients with TIC hemorrhage often require resuscitation with crystalloids and packed red blood cell transfusions for hemoglobin less than 8 g/dl.4 Unlike upper GI hemorrhage, which has been extensively reported on, data regarding a more restrictive transfusion threshold, compared with a liberal transfusion threshold, in lower intestinal bleeding are very limited. Correction of underlying coagulopathies is recommended but should be individualized, particularly in those patients on antithrombotic agents or with underlying bleeding disorders.
Urgent diagnosis and hemostasis
Urgent colonoscopy within 24 hours is the most accurate way to make a diagnosis of definitive diverticular hemorrhage and to effectively and safely treat them.2-4,10,11 For patients with severe hematochezia, when the colonoscopy is either not available in a medical center or does not reveal the source of bleeding, nuclear scintigraphy or angiography (CT, MRI, or interventional radiology [IR]) are recommended. CT angiography may be particularly helpful to diagnose patients with hemodynamic instability who are suspected to have active TIC bleeding and are not able to complete a bowel preparation. However, these imaging techniques require active bleeding at the time of the study to be diagnostic. This SRH is also uncommon for definitive diverticular hemorrhage, so the diagnostic yield is usually quite low.2-5,10,11 An additional limitation of scintigraphy and CT or MRI angiography is that, if active bleeding is found, some other type of treatment, such as colonoscopy, IR angiography, or surgery, will be required for definitive hemostasis.
For urgent colonoscopy, adequate colon preparation with a large volume preparation (6-8 liters of polyethylene glycol-based solution) is recommended to clear stool, blood, and clots to allow endoscopic visualization and localization of the bleeding source. Use of a nasogastric tube should be considered if the patient is unable to drink enough prep.2-4,13 Additionally, administration of a prokinetic agent, such as Metoclopramide, may improve gastric emptying and tolerance of the prep. During colonoscopy, careful inspection of the colonic mucosa during insertion and withdrawal is important since lesions may bleed intermittently and SRH can be missed. An adult or pediatric colonoscope with a large working channel (at least 3.3 mm) is recommended to facilitate suctioning of blood clots and stool, as well as allow the passage of endoscopic hemostasis accessories. Targeted water-jet irrigation, an expert colonoscopist, a cap attachment, and adequate colon preparation are all predictors for improved diagnosis of definitive diverticular hemorrhage.4,14
SRH in definitive TIC bleeds all have a high risk of TIC rebleeding,2-4,10,11 including active bleeding, nonbleeding visible vessel, adherent clot, and a flat spot (See Figure).

Based on CURE Hemostasis Group data of 118 definitive TIC bleeds, 26% had active bleeding, 24% had a nonbleeding visible vessel, 37% had an adherent clot, and 13% had a flat spot (with underlying arterial blood flow by Doppler probe monitoring).4 Approximately 50% of the SRH were found in the neck of the TIC and 50% at the base, with actively bleeding cases more often from the base. In CURE Doppler endoscopic probe studies, 90% of all stigmata had an underlying arterial blood flow detected with the Doppler probe.4,10 The Doppler probe is reported to be very useful for risk stratification and to confirm obliteration of the arterial blood flow underlying SRH for definitive hemostasis.4,10
Endoscopic treatment
Given high rates of rebleeding with medical management alone, definitive TIC hemorrhage can be effectively and safely treated with endoscopic therapies once SRH are localized.4,10 Endoscopic therapies that have been reported in the literature include electrocoagulation, hemoclip, band ligation, and over-the-scope clip. Four-quadrant injection of 1:20,000 epinephrine around the SRH can improve visualization of SRH and provide temporary control of bleeding, but it should be combined with other modalities because of risk of rebleeding with epinephrine alone.15 Results from studies reporting rates of both early rebleeding (occurring within 30 days) and late rebleeding (occurring after 30 days) are listed in the Table. 
Multipolar electrocoagulation (MPEC), which utilizes a focal electric current to generate heat, can coaptively coagulate small TIC arteries.16 For SRH in the neck of TIC, MPEC is effective for coaptive coagulation at a power of 12-15 watts in 1-2 second pulses with moderate laterally applied tamponade pressure. MPEC should be avoided for treating SRH at the TIC base because of lack of muscularis propria and higher risk of perforation.
Hemoclip therapy has been reported to be safe and efficacious in treatment of definitive TIC hemorrhage, by causing mechanical hemostasis with occlusion of the bleeding artery.16 Hemoclips are recommended to treat stigmata in the base of TICs and should be targeted on either side of visible vessel in order to occlude the artery underneath it.4,10 With a cap on the tip of the colonoscope, suctioning can evert TICs, allowing more precise placement of hemoclip on SRH in the base of the TIC.17 Hemoclip retention rates vary with different models and can range from less than 7 days to more than 4 weeks. Hemoclips can also mark the site if early rebleeding occurs; then, reintervention (e.g., repeat endoscopy or angioembolization) is facilitated.
Another treatment is endoscopic band ligation, which provides mechanical hemostasis. Endoscopic band ligation has been reported to be efficacious for TIC hemorrhage.18 Suctioning the TIC with the SRH into the distal cap and deploying a band leads to obliteration of vessels and potentially necrosis and disappearance of banded TIC.16 This technique carries a risk of perforation because of the thin walls of TICs. This risk may be higher for right-sided colon lesions since an exvivo colon specimen study reported serosal entrapment and inclusion of muscularis propria postband ligation, both of which may result in ischemia of intestinal wall and delayed perforation.19
Over-the-scope clip (OTSC) has been reported in case series for treatment of definitive TIC hemorrhage. With a distal cap and large clip, suctioning can evert TICs and facilitate deployment over the SRH.20,21 OTSC can grasp an entire TIC with the SRH and obliterate the arterial blood flow with a single clip.20,21 No complications have been reported yet for treatment of TIC hemorrhage. However, the OTSC system is relatively expensive when compared with other modalities.
After endoscopic treatment is performed, four-quadrant spot tattooing is recommended adjacent to the TIC with the SRH. This step will facilitate localization and treatment in the case of TIC rebleeding.4,10
Outcomes following endoscopic treatment
Following endoscopic treatment, patients should be monitored for early and late rebleeding. In a pooled analysis of case series composed of 847 patients with TIC bleeding, among the 137 patients in which endoscopic hemostasis was initially achieved, early rebleeding occurred in 8% and late rebleeding occurred in 12% of patients.22 Risk factors for TIC rebleeding within 30 days were residual arterial blood flow following hemostasis and early reinitiation of antiplatelet agents.
Remote treatment of TIC hemorrhage distant from the SRH is a significant risk factor for early TIC rebleeding.4, 10 For example, using hemoclips to close the mouth of a TIC when active bleeding or an SRH is located in the TIC base often fails because arterial flow remains open in the base and the artery is larger there.4,10 This example highlights the importance of focal obliteration of arterial blood flow underlying SRH in order to achieve definitive hemostasis.4,10
Salvage treatments
For TIC hemorrhage that is not controlled by endoscopic therapy, transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) is recommended. If bleeding rate is high enough (at least 0.5 milliliters per minute) to be detected by angiography, TAE can serve as an effective method of diagnosis and immediate hemostasis.23 However, the most common major complication of embolization is intestinal ischemia. The incidence of intestinal ischemia has been reported as high as 10%, with highest risk with embolization of at least three vasa recta.24
Surgery is also recommended if TIC hemorrhage cannot be controlled with endoscopic therapy or TAE. Segmental colectomy is recommended if the bleeding site can be localized before surgery with colonoscopy or angiography resulting from significantly lower perioperative morbidity than subtotal colectomy.25 However, subtotal colectomy may be necessary if preoperative localization of bleeding is unsuccessful.
There are very few reports of short- or long-term results that compare endoscopy, TAE, and surgery for management of TIC bleeding. However, a recent retrospective study reported better outcomes with endoscopic treatment of definitive TIC bleeding.26 Patients who underwent endoscopic treatment had fewer RBC transfusions, shorter hospitalizations, and lower rates of postprocedure complications.
Management after cessation of hemorrhage
Medical management is important following an episode of TIC hemorrhage. A mainstay is daily fiber supplementation every morning and stool softener in the evening. Furthermore, patients are advised to drink an extra liter of fluids (not containing alcohol or caffeine) daily. By reducing colon transit time and increasing stool weight, these measures can help control constipation and prevent future complications of TIC disease.27
Patients with recurrent TIC hemorrhage should undergo evaluation for elective surgery, provided they are appropriate surgical candidates. If preoperative localization of bleeding site is successful, segmental colectomy is preferred. Segmental resection is associated with significantly decreased rebleeding rate, with lower rates of morbidity compared with subtotal colectomy.32
Chronic NSAIDs, aspirin, and antiplatelet drugs are risk factors for recurrent TIC hemorrhage, and avoiding these medications is recommended if possible.33,34 Although anticoagulants have shown to be associated with increased risk of all-cause gastrointestinal bleeding, these agents have not been shown to increase risk of recurrent TIC hemorrhage in recent large retrospective studies. Since antiplatelet and anticoagulation agents serve to reduce risk of thromboembolic events, the clinician who recommended these medications should be consulted after a TIC bleed to re-evaluate whether these medications can be discontinued or reduced in dose.
Conclusion
The most effective way to diagnose and treat definitive TIC hemorrhage is to perform an urgent colonoscopy within 24 hours to identify and treat TIC SRH. This procedure requires thoroughly cleansing the colon first, as well as an experienced colonoscopist who can identify and treat TIC SRH to obliterate arterial blood flow underneath SRH and achieve definitive TIC hemostasis. Other approaches to early diagnosis include nuclear medicine scintigraphy or angiography (CT, MRI, or IR). However, these techniques can only detect active bleeding which is documented in only 26% of colonoscopically diagnosed definitive TIC hemorrhages. So, the expected diagnostic yield of these tests will be low. When urgent colonoscopy fails to make a diagnosis or TIC bleeding continues, TAE and/or surgery are recommended. After definitive hemostasis of TIC hemorrhage and for long term management, control of constipation and discontinuation of chronic NSAIDs and antiplatelet drugs (if possible) are recommended to prevent recurrent TIC hemorrhage.
Dr. Cusumano and Dr. Paiji are fellow physicians in the Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases at University of California Los Angeles. Dr. Jensen is a professor of medicine in Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases and is with the CURE Digestive Diseases Research Center at the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, Calif. All authors declare that they have no competing interests or disclosures.
References
1. Longstreth GF. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92(3):419-24.
2. Jensen DM et al. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2000;342(2):78-82.
3. Jensen DM et al. Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2001;3(4):192-8.
4. Jensen DM. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113(11):1570-3.
5. Zuckerman GR et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 1999;49(2):228-38.
6. Stollman N et al. Lancet. 2004;363(9409):631-9.
7. McGuire HH et al. Ann Surg. 1994;220(5):653-6.
8. McGuire HH et al. Ann Surg. 1972;175(6):847-55.
9. Strate LL et al. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatol. 2008;6(9):1004-10.
10. Jensen DM et al. Gastrointestinal endoscopy. 2016;83(2):416-23.
11. Jensen DM et al. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1997;7(3):477-98.
12. Maykel JA et al. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2004;17(3):195-204.
13. Green BT et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100(11):2395-402.
14. Niikura R et al. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterol. 2015;49(3):e24-30.
15. Bloomfeld RS et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(8):2367-72.
16. Parsi MA,et al. VideoGIE. 2019;4(7):285-99.
17. Kaltenbach T et al. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatol. 2012;10(2):131-7.
18. Nakano K et al. Endosc Int Open. 2015;3(5):E529-33.
19. Barker KB et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2005;62(2):224-7.
20. Kaltenbach T et al. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2020;30(1):13-23.
21. Yamazaki K et al. VideoGIE. 2020;5(6):252-4.
22. Strate LL et al. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatol. 2010;8(4):333-43.
23. Evangelista et al. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2000;11(5):601-6.
24. Kodani M et al. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016;27(6):824-30.
25. Mohammed et al. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2018;31(4):243-50.
26. Wongpongsalee T et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2020;91(6):AB471-2.
27. Böhm SK. Viszeralmedizin. 2015;31(2):84-94.
28. Prakash C et al. Endoscopy. 1999;31(6):460-3.
29. Yen EF et al. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 2008;53(9):2480-5.
30. Ishii N et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2012;75(2):382-7.
31. Nagata N et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2018;88(5):841-53.e4.
32. Parkes BM et al. Am Surg. 1993;59(10):676-8.
33. Vajravelu RK et al. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(5):1416-27.
34. Oakland K et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(7):1276-84.e3.
35. Yamada A et al. Dis Colon Rectum. 2008;51(1):116-20.
36. Coleman CI et al. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66(1):53-63.
37. Holster IL et al. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(1):105-12.e15.
Diverticular hemorrhage is the most common cause of colonic bleeding, accounting for 20%-65% of cases of severe lower intestinal bleeding in adults.1 Urgent colonoscopy after purging the colon of blood, clots, and stool is the most accurate method of diagnosing and guiding treatment of definitive diverticular hemorrhage.2-5 The diagnosis of definitive diverticular hemorrhage depends upon identification of some stigmata of recent hemorrhage (SRH) in a single diverticulum (TIC), which can include active arterial bleeding, oozing, non-bleeding visible vessel, adherent clot, or flat spot.2-4 Although other approaches, such as nuclear medicine scans and angiography of various types (CT, MRI, or standard angiography), for the early diagnosis of patients with severe hematochezia are utilized in many medical centers, only active bleeding can be detected by these techniques. However, as subsequently discussed, this SRH is documented in only 26% of definitive diverticular bleeds found on urgent colonoscopy, so diagnostic yields of these techniques will be low.2-5
The diagnosis of patients with severe hematochezia and diverticulosis, as well as triage of all of them to specific medical, endoscopic, radiologic, or surgical management, is facilitated by an urgent endoscopic approach.2-5 Patients who are diagnosed with definitive diverticular hemorrhage on colonoscopy represent about 30% of all true TIC bleeds when urgent colonoscopy is the management approach.2-5 That is because approximately 50% of all patients with colon diverticulosis and first presentation of severe hematochezia have incidental diverticulosis; they have colonic diverticulosis, but another site of bleeding is identified as the cause of hemorrhage in the gastrointestinal tract.2-4 Presumptive diverticular hemorrhage is diagnosed when colonic diverticulosis without TIC stigmata are found but no other GI bleeding source is found on colonoscopy, anoscopy, enteroscopy, or capsule endoscopy.2-5 In our experience with urgent colonoscopy, the presumptive diverticular bleed group accounts for about 70% of patients with documented diverticular hemorrhage (e.g., not including incidental diverticulosis bleeds but combining subgroups of patients with either definitive or presumptive TIC diagnoses as documented TIC hemorrhage).
Clinical presentation
Patients with diverticular hemorrhage present with severe, painless large volume hematochezia. Hematochezia may be self-limited and spontaneously resolve in 75%-80% of all patients but with high rebleeding rates up to 40%.5-7 Of all patients with diverticulosis, only about 3%-5% develop diverticular hemorrhage.8 Risk factors for diverticular hemorrhage include medications (e.g., nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – NSAIDs, antiplatelet drugs, and anticoagulants) and other clinical factors, such as older age, low-fiber diet, and chronic constipation.9,10 On urgent colonoscopy, more than 70% of diverticulosis in U.S. patients are located anatomically in the descending colon or more distally. In contrast, about 60% of definitive diverticular hemorrhage cases in our experience had diverticula with stigmata identified at or proximal to the splenic flexure.2,4,11
Pathophysiology
Colonic diverticula are herniations of mucosa and submucosa with colonic arteries that penetrate the muscular wall. Bleeding can occur when there is asymmetric rupture of the vasa recta at either the base of the diverticulum or the neck.4 Thinning of the mucosa on the luminal surface (such as that resulting from impacted fecaliths and stool) can cause injury to the site of the penetrating vessels, resulting in hemorrhage.12
Initial management
Patients with acute, severe hematochezia should be triaged to an inpatient setting with a monitored bed. Admission to an intensive care unit should be considered for patients with hemodynamic instability, persistent bleeding, and/or significant comorbidities. Patients with TIC hemorrhage often require resuscitation with crystalloids and packed red blood cell transfusions for hemoglobin less than 8 g/dl.4 Unlike upper GI hemorrhage, which has been extensively reported on, data regarding a more restrictive transfusion threshold, compared with a liberal transfusion threshold, in lower intestinal bleeding are very limited. Correction of underlying coagulopathies is recommended but should be individualized, particularly in those patients on antithrombotic agents or with underlying bleeding disorders.
Urgent diagnosis and hemostasis
Urgent colonoscopy within 24 hours is the most accurate way to make a diagnosis of definitive diverticular hemorrhage and to effectively and safely treat them.2-4,10,11 For patients with severe hematochezia, when the colonoscopy is either not available in a medical center or does not reveal the source of bleeding, nuclear scintigraphy or angiography (CT, MRI, or interventional radiology [IR]) are recommended. CT angiography may be particularly helpful to diagnose patients with hemodynamic instability who are suspected to have active TIC bleeding and are not able to complete a bowel preparation. However, these imaging techniques require active bleeding at the time of the study to be diagnostic. This SRH is also uncommon for definitive diverticular hemorrhage, so the diagnostic yield is usually quite low.2-5,10,11 An additional limitation of scintigraphy and CT or MRI angiography is that, if active bleeding is found, some other type of treatment, such as colonoscopy, IR angiography, or surgery, will be required for definitive hemostasis.
For urgent colonoscopy, adequate colon preparation with a large volume preparation (6-8 liters of polyethylene glycol-based solution) is recommended to clear stool, blood, and clots to allow endoscopic visualization and localization of the bleeding source. Use of a nasogastric tube should be considered if the patient is unable to drink enough prep.2-4,13 Additionally, administration of a prokinetic agent, such as Metoclopramide, may improve gastric emptying and tolerance of the prep. During colonoscopy, careful inspection of the colonic mucosa during insertion and withdrawal is important since lesions may bleed intermittently and SRH can be missed. An adult or pediatric colonoscope with a large working channel (at least 3.3 mm) is recommended to facilitate suctioning of blood clots and stool, as well as allow the passage of endoscopic hemostasis accessories. Targeted water-jet irrigation, an expert colonoscopist, a cap attachment, and adequate colon preparation are all predictors for improved diagnosis of definitive diverticular hemorrhage.4,14
SRH in definitive TIC bleeds all have a high risk of TIC rebleeding,2-4,10,11 including active bleeding, nonbleeding visible vessel, adherent clot, and a flat spot (See Figure).

Based on CURE Hemostasis Group data of 118 definitive TIC bleeds, 26% had active bleeding, 24% had a nonbleeding visible vessel, 37% had an adherent clot, and 13% had a flat spot (with underlying arterial blood flow by Doppler probe monitoring).4 Approximately 50% of the SRH were found in the neck of the TIC and 50% at the base, with actively bleeding cases more often from the base. In CURE Doppler endoscopic probe studies, 90% of all stigmata had an underlying arterial blood flow detected with the Doppler probe.4,10 The Doppler probe is reported to be very useful for risk stratification and to confirm obliteration of the arterial blood flow underlying SRH for definitive hemostasis.4,10
Endoscopic treatment
Given high rates of rebleeding with medical management alone, definitive TIC hemorrhage can be effectively and safely treated with endoscopic therapies once SRH are localized.4,10 Endoscopic therapies that have been reported in the literature include electrocoagulation, hemoclip, band ligation, and over-the-scope clip. Four-quadrant injection of 1:20,000 epinephrine around the SRH can improve visualization of SRH and provide temporary control of bleeding, but it should be combined with other modalities because of risk of rebleeding with epinephrine alone.15 Results from studies reporting rates of both early rebleeding (occurring within 30 days) and late rebleeding (occurring after 30 days) are listed in the Table. 
Multipolar electrocoagulation (MPEC), which utilizes a focal electric current to generate heat, can coaptively coagulate small TIC arteries.16 For SRH in the neck of TIC, MPEC is effective for coaptive coagulation at a power of 12-15 watts in 1-2 second pulses with moderate laterally applied tamponade pressure. MPEC should be avoided for treating SRH at the TIC base because of lack of muscularis propria and higher risk of perforation.
Hemoclip therapy has been reported to be safe and efficacious in treatment of definitive TIC hemorrhage, by causing mechanical hemostasis with occlusion of the bleeding artery.16 Hemoclips are recommended to treat stigmata in the base of TICs and should be targeted on either side of visible vessel in order to occlude the artery underneath it.4,10 With a cap on the tip of the colonoscope, suctioning can evert TICs, allowing more precise placement of hemoclip on SRH in the base of the TIC.17 Hemoclip retention rates vary with different models and can range from less than 7 days to more than 4 weeks. Hemoclips can also mark the site if early rebleeding occurs; then, reintervention (e.g., repeat endoscopy or angioembolization) is facilitated.
Another treatment is endoscopic band ligation, which provides mechanical hemostasis. Endoscopic band ligation has been reported to be efficacious for TIC hemorrhage.18 Suctioning the TIC with the SRH into the distal cap and deploying a band leads to obliteration of vessels and potentially necrosis and disappearance of banded TIC.16 This technique carries a risk of perforation because of the thin walls of TICs. This risk may be higher for right-sided colon lesions since an exvivo colon specimen study reported serosal entrapment and inclusion of muscularis propria postband ligation, both of which may result in ischemia of intestinal wall and delayed perforation.19
Over-the-scope clip (OTSC) has been reported in case series for treatment of definitive TIC hemorrhage. With a distal cap and large clip, suctioning can evert TICs and facilitate deployment over the SRH.20,21 OTSC can grasp an entire TIC with the SRH and obliterate the arterial blood flow with a single clip.20,21 No complications have been reported yet for treatment of TIC hemorrhage. However, the OTSC system is relatively expensive when compared with other modalities.
After endoscopic treatment is performed, four-quadrant spot tattooing is recommended adjacent to the TIC with the SRH. This step will facilitate localization and treatment in the case of TIC rebleeding.4,10
Outcomes following endoscopic treatment
Following endoscopic treatment, patients should be monitored for early and late rebleeding. In a pooled analysis of case series composed of 847 patients with TIC bleeding, among the 137 patients in which endoscopic hemostasis was initially achieved, early rebleeding occurred in 8% and late rebleeding occurred in 12% of patients.22 Risk factors for TIC rebleeding within 30 days were residual arterial blood flow following hemostasis and early reinitiation of antiplatelet agents.
Remote treatment of TIC hemorrhage distant from the SRH is a significant risk factor for early TIC rebleeding.4, 10 For example, using hemoclips to close the mouth of a TIC when active bleeding or an SRH is located in the TIC base often fails because arterial flow remains open in the base and the artery is larger there.4,10 This example highlights the importance of focal obliteration of arterial blood flow underlying SRH in order to achieve definitive hemostasis.4,10
Salvage treatments
For TIC hemorrhage that is not controlled by endoscopic therapy, transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) is recommended. If bleeding rate is high enough (at least 0.5 milliliters per minute) to be detected by angiography, TAE can serve as an effective method of diagnosis and immediate hemostasis.23 However, the most common major complication of embolization is intestinal ischemia. The incidence of intestinal ischemia has been reported as high as 10%, with highest risk with embolization of at least three vasa recta.24
Surgery is also recommended if TIC hemorrhage cannot be controlled with endoscopic therapy or TAE. Segmental colectomy is recommended if the bleeding site can be localized before surgery with colonoscopy or angiography resulting from significantly lower perioperative morbidity than subtotal colectomy.25 However, subtotal colectomy may be necessary if preoperative localization of bleeding is unsuccessful.
There are very few reports of short- or long-term results that compare endoscopy, TAE, and surgery for management of TIC bleeding. However, a recent retrospective study reported better outcomes with endoscopic treatment of definitive TIC bleeding.26 Patients who underwent endoscopic treatment had fewer RBC transfusions, shorter hospitalizations, and lower rates of postprocedure complications.
Management after cessation of hemorrhage
Medical management is important following an episode of TIC hemorrhage. A mainstay is daily fiber supplementation every morning and stool softener in the evening. Furthermore, patients are advised to drink an extra liter of fluids (not containing alcohol or caffeine) daily. By reducing colon transit time and increasing stool weight, these measures can help control constipation and prevent future complications of TIC disease.27
Patients with recurrent TIC hemorrhage should undergo evaluation for elective surgery, provided they are appropriate surgical candidates. If preoperative localization of bleeding site is successful, segmental colectomy is preferred. Segmental resection is associated with significantly decreased rebleeding rate, with lower rates of morbidity compared with subtotal colectomy.32
Chronic NSAIDs, aspirin, and antiplatelet drugs are risk factors for recurrent TIC hemorrhage, and avoiding these medications is recommended if possible.33,34 Although anticoagulants have shown to be associated with increased risk of all-cause gastrointestinal bleeding, these agents have not been shown to increase risk of recurrent TIC hemorrhage in recent large retrospective studies. Since antiplatelet and anticoagulation agents serve to reduce risk of thromboembolic events, the clinician who recommended these medications should be consulted after a TIC bleed to re-evaluate whether these medications can be discontinued or reduced in dose.
Conclusion
The most effective way to diagnose and treat definitive TIC hemorrhage is to perform an urgent colonoscopy within 24 hours to identify and treat TIC SRH. This procedure requires thoroughly cleansing the colon first, as well as an experienced colonoscopist who can identify and treat TIC SRH to obliterate arterial blood flow underneath SRH and achieve definitive TIC hemostasis. Other approaches to early diagnosis include nuclear medicine scintigraphy or angiography (CT, MRI, or IR). However, these techniques can only detect active bleeding which is documented in only 26% of colonoscopically diagnosed definitive TIC hemorrhages. So, the expected diagnostic yield of these tests will be low. When urgent colonoscopy fails to make a diagnosis or TIC bleeding continues, TAE and/or surgery are recommended. After definitive hemostasis of TIC hemorrhage and for long term management, control of constipation and discontinuation of chronic NSAIDs and antiplatelet drugs (if possible) are recommended to prevent recurrent TIC hemorrhage.
Dr. Cusumano and Dr. Paiji are fellow physicians in the Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases at University of California Los Angeles. Dr. Jensen is a professor of medicine in Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases and is with the CURE Digestive Diseases Research Center at the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, Calif. All authors declare that they have no competing interests or disclosures.
References
1. Longstreth GF. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92(3):419-24.
2. Jensen DM et al. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2000;342(2):78-82.
3. Jensen DM et al. Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2001;3(4):192-8.
4. Jensen DM. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113(11):1570-3.
5. Zuckerman GR et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 1999;49(2):228-38.
6. Stollman N et al. Lancet. 2004;363(9409):631-9.
7. McGuire HH et al. Ann Surg. 1994;220(5):653-6.
8. McGuire HH et al. Ann Surg. 1972;175(6):847-55.
9. Strate LL et al. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatol. 2008;6(9):1004-10.
10. Jensen DM et al. Gastrointestinal endoscopy. 2016;83(2):416-23.
11. Jensen DM et al. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1997;7(3):477-98.
12. Maykel JA et al. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2004;17(3):195-204.
13. Green BT et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100(11):2395-402.
14. Niikura R et al. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterol. 2015;49(3):e24-30.
15. Bloomfeld RS et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(8):2367-72.
16. Parsi MA,et al. VideoGIE. 2019;4(7):285-99.
17. Kaltenbach T et al. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatol. 2012;10(2):131-7.
18. Nakano K et al. Endosc Int Open. 2015;3(5):E529-33.
19. Barker KB et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2005;62(2):224-7.
20. Kaltenbach T et al. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2020;30(1):13-23.
21. Yamazaki K et al. VideoGIE. 2020;5(6):252-4.
22. Strate LL et al. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatol. 2010;8(4):333-43.
23. Evangelista et al. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2000;11(5):601-6.
24. Kodani M et al. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016;27(6):824-30.
25. Mohammed et al. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2018;31(4):243-50.
26. Wongpongsalee T et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2020;91(6):AB471-2.
27. Böhm SK. Viszeralmedizin. 2015;31(2):84-94.
28. Prakash C et al. Endoscopy. 1999;31(6):460-3.
29. Yen EF et al. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 2008;53(9):2480-5.
30. Ishii N et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2012;75(2):382-7.
31. Nagata N et al. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2018;88(5):841-53.e4.
32. Parkes BM et al. Am Surg. 1993;59(10):676-8.
33. Vajravelu RK et al. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(5):1416-27.
34. Oakland K et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(7):1276-84.e3.
35. Yamada A et al. Dis Colon Rectum. 2008;51(1):116-20.
36. Coleman CI et al. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66(1):53-63.
37. Holster IL et al. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(1):105-12.e15.
Emerging realities
Dear colleagues,
Welcome to the November edition of The New Gastroenterologist! Our fall newsletter features a particularly interesting compilation of articles. As the pandemic lingers on, we are forced to face the realities of coexisting with COVID-19 as the virus certainly seems to be here to stay.
To protect against ongoing risk of exposure, health care workers and other high-risk subsets of patients are now being offered booster shots. For our patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) on immune-modifying therapies, there has always been a question of vaccine efficacy. Dr. Freddy Caldera and Dr. Trevor Schell (University of Wisconsin-Madison) shed some much needed light on recommendations on the COVID-19 vaccine for IBD patients.
In April of 2021, a federal rule was implemented mandating that patients have immediate and free access to their electronic health information – which includes all documentation from their health care providers. Some physicians have been concerned about this practice, namely how patients will respond and whether this will increase the burden on clinicians. Clearly, this issue is multifaceted: Dr. Sachin Shah (University of Chicago) discusses the ethical implications from a clinical standpoint, while attorney Valerie Guttman Koch (University of Houston Law Center, MacLean Center for Clinical Medical Ethics, University of Chicago) shares a riveting legal perspective.
Colonic diverticular bleeding is the most common etiology of overt lower gastrointestinal bleeding and one of the most frequent consults we receive as gastroenterologists. However, even with the use of colonoscopy, obtaining a definitive diagnosis can often be difficult. Our “In Focus” feature for November, is an excellent piece written by Dr. Vivy Cusumano, Dr. Christopher Paiji, and Dr. Dennis Jensen (all with University of California, Los Angeles), detailing the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment.
Navigating pregnancy and parental leave during training is difficult. Drs. Joy Liu, Keith Summa, Ronak Patel, Erica Donnan, Amanda Guentner, and Leila Kia (all with Northwestern University) share their program’s experience, providing incredibly helpful and practical recommendations for both gastroenterology trainees and fellowship directors.
The Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists emerged against the backdrop of recent social and health care injustices. Dr. Kafayat Busari (Florida State University) and Dr. Alexandra Guillaume (Stony Brook University Hospital) discuss the critical importance and mission of this association and how it will help shape the field of gastroenterology in the years to come.
Medical pancreatology is a subspecialty that most gastroenterology fellows have little, if any, exposure to. In our post-fellowship pathways section, Dr. Sajan Nagpal (University of Chicago) details his own experiences in addition to discussing the important role of a medical pancreatologist within a gastroenterology division.
Lastly, our DHPA Private Practice Perspectives article, written by Dr. Sanjay Sandhir (Dayton [Ohio] Gastroenterology), discusses the importance of education and screening for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
If you have interest in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Ryan Farrell ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Stay well,
Vijaya L. Rao, MD
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of Chicago, Section of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition
Dear colleagues,
Welcome to the November edition of The New Gastroenterologist! Our fall newsletter features a particularly interesting compilation of articles. As the pandemic lingers on, we are forced to face the realities of coexisting with COVID-19 as the virus certainly seems to be here to stay.
To protect against ongoing risk of exposure, health care workers and other high-risk subsets of patients are now being offered booster shots. For our patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) on immune-modifying therapies, there has always been a question of vaccine efficacy. Dr. Freddy Caldera and Dr. Trevor Schell (University of Wisconsin-Madison) shed some much needed light on recommendations on the COVID-19 vaccine for IBD patients.
In April of 2021, a federal rule was implemented mandating that patients have immediate and free access to their electronic health information – which includes all documentation from their health care providers. Some physicians have been concerned about this practice, namely how patients will respond and whether this will increase the burden on clinicians. Clearly, this issue is multifaceted: Dr. Sachin Shah (University of Chicago) discusses the ethical implications from a clinical standpoint, while attorney Valerie Guttman Koch (University of Houston Law Center, MacLean Center for Clinical Medical Ethics, University of Chicago) shares a riveting legal perspective.
Colonic diverticular bleeding is the most common etiology of overt lower gastrointestinal bleeding and one of the most frequent consults we receive as gastroenterologists. However, even with the use of colonoscopy, obtaining a definitive diagnosis can often be difficult. Our “In Focus” feature for November, is an excellent piece written by Dr. Vivy Cusumano, Dr. Christopher Paiji, and Dr. Dennis Jensen (all with University of California, Los Angeles), detailing the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment.
Navigating pregnancy and parental leave during training is difficult. Drs. Joy Liu, Keith Summa, Ronak Patel, Erica Donnan, Amanda Guentner, and Leila Kia (all with Northwestern University) share their program’s experience, providing incredibly helpful and practical recommendations for both gastroenterology trainees and fellowship directors.
The Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists emerged against the backdrop of recent social and health care injustices. Dr. Kafayat Busari (Florida State University) and Dr. Alexandra Guillaume (Stony Brook University Hospital) discuss the critical importance and mission of this association and how it will help shape the field of gastroenterology in the years to come.
Medical pancreatology is a subspecialty that most gastroenterology fellows have little, if any, exposure to. In our post-fellowship pathways section, Dr. Sajan Nagpal (University of Chicago) details his own experiences in addition to discussing the important role of a medical pancreatologist within a gastroenterology division.
Lastly, our DHPA Private Practice Perspectives article, written by Dr. Sanjay Sandhir (Dayton [Ohio] Gastroenterology), discusses the importance of education and screening for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
If you have interest in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Ryan Farrell ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Stay well,
Vijaya L. Rao, MD
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of Chicago, Section of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition
Dear colleagues,
Welcome to the November edition of The New Gastroenterologist! Our fall newsletter features a particularly interesting compilation of articles. As the pandemic lingers on, we are forced to face the realities of coexisting with COVID-19 as the virus certainly seems to be here to stay.
To protect against ongoing risk of exposure, health care workers and other high-risk subsets of patients are now being offered booster shots. For our patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) on immune-modifying therapies, there has always been a question of vaccine efficacy. Dr. Freddy Caldera and Dr. Trevor Schell (University of Wisconsin-Madison) shed some much needed light on recommendations on the COVID-19 vaccine for IBD patients.
In April of 2021, a federal rule was implemented mandating that patients have immediate and free access to their electronic health information – which includes all documentation from their health care providers. Some physicians have been concerned about this practice, namely how patients will respond and whether this will increase the burden on clinicians. Clearly, this issue is multifaceted: Dr. Sachin Shah (University of Chicago) discusses the ethical implications from a clinical standpoint, while attorney Valerie Guttman Koch (University of Houston Law Center, MacLean Center for Clinical Medical Ethics, University of Chicago) shares a riveting legal perspective.
Colonic diverticular bleeding is the most common etiology of overt lower gastrointestinal bleeding and one of the most frequent consults we receive as gastroenterologists. However, even with the use of colonoscopy, obtaining a definitive diagnosis can often be difficult. Our “In Focus” feature for November, is an excellent piece written by Dr. Vivy Cusumano, Dr. Christopher Paiji, and Dr. Dennis Jensen (all with University of California, Los Angeles), detailing the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment.
Navigating pregnancy and parental leave during training is difficult. Drs. Joy Liu, Keith Summa, Ronak Patel, Erica Donnan, Amanda Guentner, and Leila Kia (all with Northwestern University) share their program’s experience, providing incredibly helpful and practical recommendations for both gastroenterology trainees and fellowship directors.
The Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists emerged against the backdrop of recent social and health care injustices. Dr. Kafayat Busari (Florida State University) and Dr. Alexandra Guillaume (Stony Brook University Hospital) discuss the critical importance and mission of this association and how it will help shape the field of gastroenterology in the years to come.
Medical pancreatology is a subspecialty that most gastroenterology fellows have little, if any, exposure to. In our post-fellowship pathways section, Dr. Sajan Nagpal (University of Chicago) details his own experiences in addition to discussing the important role of a medical pancreatologist within a gastroenterology division.
Lastly, our DHPA Private Practice Perspectives article, written by Dr. Sanjay Sandhir (Dayton [Ohio] Gastroenterology), discusses the importance of education and screening for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
If you have interest in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Ryan Farrell ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Stay well,
Vijaya L. Rao, MD
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of Chicago, Section of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition
FDA not recognizing efficacy of psychopharmacologic therapies
Many years ago, drug development in psychiatry turned to control of specific symptoms across disorders rather than within disorders, but regulatory agencies are still not yet on board, according to an expert psychopharmacologist outlining the ongoing evolution at the virtual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists, sponsored by Medscape Live.
If this reorientation is going to lead to the broad indications the newer drugs likely deserve, which is control of specific types of symptoms regardless of the diagnosis, “we have to move the [Food and Drug Administration] along,” said Stephen M. Stahl, MD, PhD, chairman of the Neuroscience Institute and an adjunct professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego.
On the side of drug development and clinical practice, the reorientation has already taken place. Dr. Stahl described numerous brain circuits known to produce symptoms when function is altered that are now treatment targets. This includes the ventral medial prefrontal cortex where deficient information processing leads to depression and the orbital frontal cortex where altered function leads to impulsivity.
“It is not like each part of the brain does a little bit of everything. Rather, each part of the brain has an assignment and duty and function,” Dr. Stahl explained. By addressing the disturbed signaling in brain circuits that lead to depression, impulsivity, agitation, or other symptoms, there is an opportunity for control, regardless of the psychiatric diagnosis with which the symptom is associated.
For example, Dr. Stahl predicted that pimavanserin, a highly selective 5-HT2A inverse agonist that is already approved for psychosis in Parkinson’s disease, is now likely to be approved for psychosis associated with other conditions on the basis of recent positive clinical studies in these other disorders.
Brexpiprazole, a serotonin-dopamine activity modulator already known to be useful for control of the agitation characteristic of schizophrenia, is now showing the same type of activity against agitation when it is associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Again, Dr. Stahl thinks this drug is on course for an indication across diseases once studies are conducted in each disease individually.
Another drug being evaluated for agitation, the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist dextromethorphan bupropion, is also being tested for treatment of symptoms across multiple disorders, he reported.
However, the FDA has so far taken the position that each drug must be tested separately for a given symptom in each disorder for which it is being considered despite the underlying premise that it is the symptom, not the disease, that is important.
Unlike physiological diseases where symptoms, like a fever or abdominal cramps, are the product of a disease, psychiatric symptoms are the disease and a fundamental target – regardless of the DSM-based diagnosis.
To some degree, the symptoms of psychiatric disorders have always been the focus of treatment, but a pivot toward developing therapies that will control a symptom regardless of the underlying diagnosis is an important conceptual change. It is being made possible by advances in the detail with which the neuropathology of these symptoms is understood .
“By my count, 79 symptoms are described in DSM-5, but they are spread across hundreds of syndromes because they are grouped together in different ways,” Dr. Stahl observed.
He noted that clinicians make a diagnosis on the basis symptom groupings, but their interventions are selected to address the manifestations of the disease, not the disease itself.
“If you are a real psychopharmacologist treating real patients, you are treating the specific symptoms of the specific patient,” according to Dr. Stahl.
So far, the FDA has not made this leap, insisting on trials in these categorical disorders rather than permitting trial designs that allow benefit to be demonstrated against a symptom regardless of the syndrome with which it is associated.
Of egregious examples, Dr. Stahl recounted a recent trial of a 5-HT2 antagonist that looked so promising against psychosis in Alzheimer’s disease that the trialists enrolled patients with psychosis regardless of type of dementia, such as vascular dementia and Lewy body disease. The efficacy was impressive.
“It worked so well that they stopped the trial, but the FDA declined to approve it,” Dr. Stahl recounted. Despite clear evidence of benefit, the regulators insisted that the investigators needed to show a significant benefit in each condition individually.
While the trial investigators acknowledged that there was not enough power in the trial to show a statistically significant benefit in each category, they argued that the overall benefit and the consistent response across categories required them to stop the trial for ethical reasons.
“That’s your problem, the FDA said to the investigators,” according to Dr. Stahl.
The failure of the FDA to recognize the efficacy of psychopharmacologic therapies across symptoms regardless of the associated disease is a failure to stay current with an important evolution in medicine, Dr. Stahl indicated.
“What we have come to understand is the neurobiology of any given symptom is likely to be the same across disorders,” he said.
Agency’s arbitrary decisions cited
“I completely agree with Dr. Stahl,” said Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience, University of Cincinnati.
In addition to the fact that symptoms are present across multiple categories, many patients manifest multiple symptoms at one time, Dr. Nasrallah pointed out. For neurodegenerative disorders associated with psychosis, depression, anxiety, aggression, and other symptoms, it is already well known that the heterogeneous symptoms “cannot be treated with a single drug,” he said. Rather different drugs targeting each symptom individually is essential for effective management.
Dr. Nasrallah, who chaired the Psychopharmacology Update meeting, has made this point many times in the past, including in his role as the editor of Current Psychiatry. In one editorial 10 years ago, he wrote that “it makes little sense for the FDA to mandate that a drug must work for a DSM diagnosis instead of specific symptoms.”
“The FDA must update its old policy, which has led to the widespread off-label use of psychiatric drugs, an artificial concept, simply because the FDA arbitrarily decided a long time ago that new drugs must be approved for a specific DSM diagnosis,” Dr. Nasrallah said.
Dr. Stahl reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including those that are involved in the development of drugs included in his talk. Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Many years ago, drug development in psychiatry turned to control of specific symptoms across disorders rather than within disorders, but regulatory agencies are still not yet on board, according to an expert psychopharmacologist outlining the ongoing evolution at the virtual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists, sponsored by Medscape Live.
If this reorientation is going to lead to the broad indications the newer drugs likely deserve, which is control of specific types of symptoms regardless of the diagnosis, “we have to move the [Food and Drug Administration] along,” said Stephen M. Stahl, MD, PhD, chairman of the Neuroscience Institute and an adjunct professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego.
On the side of drug development and clinical practice, the reorientation has already taken place. Dr. Stahl described numerous brain circuits known to produce symptoms when function is altered that are now treatment targets. This includes the ventral medial prefrontal cortex where deficient information processing leads to depression and the orbital frontal cortex where altered function leads to impulsivity.
“It is not like each part of the brain does a little bit of everything. Rather, each part of the brain has an assignment and duty and function,” Dr. Stahl explained. By addressing the disturbed signaling in brain circuits that lead to depression, impulsivity, agitation, or other symptoms, there is an opportunity for control, regardless of the psychiatric diagnosis with which the symptom is associated.
For example, Dr. Stahl predicted that pimavanserin, a highly selective 5-HT2A inverse agonist that is already approved for psychosis in Parkinson’s disease, is now likely to be approved for psychosis associated with other conditions on the basis of recent positive clinical studies in these other disorders.
Brexpiprazole, a serotonin-dopamine activity modulator already known to be useful for control of the agitation characteristic of schizophrenia, is now showing the same type of activity against agitation when it is associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Again, Dr. Stahl thinks this drug is on course for an indication across diseases once studies are conducted in each disease individually.
Another drug being evaluated for agitation, the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist dextromethorphan bupropion, is also being tested for treatment of symptoms across multiple disorders, he reported.
However, the FDA has so far taken the position that each drug must be tested separately for a given symptom in each disorder for which it is being considered despite the underlying premise that it is the symptom, not the disease, that is important.
Unlike physiological diseases where symptoms, like a fever or abdominal cramps, are the product of a disease, psychiatric symptoms are the disease and a fundamental target – regardless of the DSM-based diagnosis.
To some degree, the symptoms of psychiatric disorders have always been the focus of treatment, but a pivot toward developing therapies that will control a symptom regardless of the underlying diagnosis is an important conceptual change. It is being made possible by advances in the detail with which the neuropathology of these symptoms is understood .
“By my count, 79 symptoms are described in DSM-5, but they are spread across hundreds of syndromes because they are grouped together in different ways,” Dr. Stahl observed.
He noted that clinicians make a diagnosis on the basis symptom groupings, but their interventions are selected to address the manifestations of the disease, not the disease itself.
“If you are a real psychopharmacologist treating real patients, you are treating the specific symptoms of the specific patient,” according to Dr. Stahl.
So far, the FDA has not made this leap, insisting on trials in these categorical disorders rather than permitting trial designs that allow benefit to be demonstrated against a symptom regardless of the syndrome with which it is associated.
Of egregious examples, Dr. Stahl recounted a recent trial of a 5-HT2 antagonist that looked so promising against psychosis in Alzheimer’s disease that the trialists enrolled patients with psychosis regardless of type of dementia, such as vascular dementia and Lewy body disease. The efficacy was impressive.
“It worked so well that they stopped the trial, but the FDA declined to approve it,” Dr. Stahl recounted. Despite clear evidence of benefit, the regulators insisted that the investigators needed to show a significant benefit in each condition individually.
While the trial investigators acknowledged that there was not enough power in the trial to show a statistically significant benefit in each category, they argued that the overall benefit and the consistent response across categories required them to stop the trial for ethical reasons.
“That’s your problem, the FDA said to the investigators,” according to Dr. Stahl.
The failure of the FDA to recognize the efficacy of psychopharmacologic therapies across symptoms regardless of the associated disease is a failure to stay current with an important evolution in medicine, Dr. Stahl indicated.
“What we have come to understand is the neurobiology of any given symptom is likely to be the same across disorders,” he said.
Agency’s arbitrary decisions cited
“I completely agree with Dr. Stahl,” said Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience, University of Cincinnati.
In addition to the fact that symptoms are present across multiple categories, many patients manifest multiple symptoms at one time, Dr. Nasrallah pointed out. For neurodegenerative disorders associated with psychosis, depression, anxiety, aggression, and other symptoms, it is already well known that the heterogeneous symptoms “cannot be treated with a single drug,” he said. Rather different drugs targeting each symptom individually is essential for effective management.
Dr. Nasrallah, who chaired the Psychopharmacology Update meeting, has made this point many times in the past, including in his role as the editor of Current Psychiatry. In one editorial 10 years ago, he wrote that “it makes little sense for the FDA to mandate that a drug must work for a DSM diagnosis instead of specific symptoms.”
“The FDA must update its old policy, which has led to the widespread off-label use of psychiatric drugs, an artificial concept, simply because the FDA arbitrarily decided a long time ago that new drugs must be approved for a specific DSM diagnosis,” Dr. Nasrallah said.
Dr. Stahl reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including those that are involved in the development of drugs included in his talk. Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Many years ago, drug development in psychiatry turned to control of specific symptoms across disorders rather than within disorders, but regulatory agencies are still not yet on board, according to an expert psychopharmacologist outlining the ongoing evolution at the virtual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists, sponsored by Medscape Live.
If this reorientation is going to lead to the broad indications the newer drugs likely deserve, which is control of specific types of symptoms regardless of the diagnosis, “we have to move the [Food and Drug Administration] along,” said Stephen M. Stahl, MD, PhD, chairman of the Neuroscience Institute and an adjunct professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego.
On the side of drug development and clinical practice, the reorientation has already taken place. Dr. Stahl described numerous brain circuits known to produce symptoms when function is altered that are now treatment targets. This includes the ventral medial prefrontal cortex where deficient information processing leads to depression and the orbital frontal cortex where altered function leads to impulsivity.
“It is not like each part of the brain does a little bit of everything. Rather, each part of the brain has an assignment and duty and function,” Dr. Stahl explained. By addressing the disturbed signaling in brain circuits that lead to depression, impulsivity, agitation, or other symptoms, there is an opportunity for control, regardless of the psychiatric diagnosis with which the symptom is associated.
For example, Dr. Stahl predicted that pimavanserin, a highly selective 5-HT2A inverse agonist that is already approved for psychosis in Parkinson’s disease, is now likely to be approved for psychosis associated with other conditions on the basis of recent positive clinical studies in these other disorders.
Brexpiprazole, a serotonin-dopamine activity modulator already known to be useful for control of the agitation characteristic of schizophrenia, is now showing the same type of activity against agitation when it is associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Again, Dr. Stahl thinks this drug is on course for an indication across diseases once studies are conducted in each disease individually.
Another drug being evaluated for agitation, the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist dextromethorphan bupropion, is also being tested for treatment of symptoms across multiple disorders, he reported.
However, the FDA has so far taken the position that each drug must be tested separately for a given symptom in each disorder for which it is being considered despite the underlying premise that it is the symptom, not the disease, that is important.
Unlike physiological diseases where symptoms, like a fever or abdominal cramps, are the product of a disease, psychiatric symptoms are the disease and a fundamental target – regardless of the DSM-based diagnosis.
To some degree, the symptoms of psychiatric disorders have always been the focus of treatment, but a pivot toward developing therapies that will control a symptom regardless of the underlying diagnosis is an important conceptual change. It is being made possible by advances in the detail with which the neuropathology of these symptoms is understood .
“By my count, 79 symptoms are described in DSM-5, but they are spread across hundreds of syndromes because they are grouped together in different ways,” Dr. Stahl observed.
He noted that clinicians make a diagnosis on the basis symptom groupings, but their interventions are selected to address the manifestations of the disease, not the disease itself.
“If you are a real psychopharmacologist treating real patients, you are treating the specific symptoms of the specific patient,” according to Dr. Stahl.
So far, the FDA has not made this leap, insisting on trials in these categorical disorders rather than permitting trial designs that allow benefit to be demonstrated against a symptom regardless of the syndrome with which it is associated.
Of egregious examples, Dr. Stahl recounted a recent trial of a 5-HT2 antagonist that looked so promising against psychosis in Alzheimer’s disease that the trialists enrolled patients with psychosis regardless of type of dementia, such as vascular dementia and Lewy body disease. The efficacy was impressive.
“It worked so well that they stopped the trial, but the FDA declined to approve it,” Dr. Stahl recounted. Despite clear evidence of benefit, the regulators insisted that the investigators needed to show a significant benefit in each condition individually.
While the trial investigators acknowledged that there was not enough power in the trial to show a statistically significant benefit in each category, they argued that the overall benefit and the consistent response across categories required them to stop the trial for ethical reasons.
“That’s your problem, the FDA said to the investigators,” according to Dr. Stahl.
The failure of the FDA to recognize the efficacy of psychopharmacologic therapies across symptoms regardless of the associated disease is a failure to stay current with an important evolution in medicine, Dr. Stahl indicated.
“What we have come to understand is the neurobiology of any given symptom is likely to be the same across disorders,” he said.
Agency’s arbitrary decisions cited
“I completely agree with Dr. Stahl,” said Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience, University of Cincinnati.
In addition to the fact that symptoms are present across multiple categories, many patients manifest multiple symptoms at one time, Dr. Nasrallah pointed out. For neurodegenerative disorders associated with psychosis, depression, anxiety, aggression, and other symptoms, it is already well known that the heterogeneous symptoms “cannot be treated with a single drug,” he said. Rather different drugs targeting each symptom individually is essential for effective management.
Dr. Nasrallah, who chaired the Psychopharmacology Update meeting, has made this point many times in the past, including in his role as the editor of Current Psychiatry. In one editorial 10 years ago, he wrote that “it makes little sense for the FDA to mandate that a drug must work for a DSM diagnosis instead of specific symptoms.”
“The FDA must update its old policy, which has led to the widespread off-label use of psychiatric drugs, an artificial concept, simply because the FDA arbitrarily decided a long time ago that new drugs must be approved for a specific DSM diagnosis,” Dr. Nasrallah said.
Dr. Stahl reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including those that are involved in the development of drugs included in his talk. Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY UPDATE
HCV in pregnancy: One piece of a bigger problem
Mirroring the opioid crisis, maternal and newborn hepatitis C infections (HCV) more than doubled in the United States between 2009 and 2019, with disproportionate increases in people of White, American Indian, and Alaska Native race, especially those with less education, according to a cross-sectional study published in JAMA Health Forum. However, the level of risk within these populations was mitigated in counties with higher employment, reported Stephen W. Patrick, MD, of Vanderbilt University, in Nashville, Tenn., and coauthors.
“As we develop public health approaches to prevent HCV infections, connect to treatment, and monitor exposed infants, understanding these factors can be of critical importance to tailoring interventions,” Dr. Patrick said in an interview. “HCV is one more complication of the opioid crisis,” he added. “These data also enable us to step back a bit from HCV and look at the landscape of how the opioid crisis continues to grow in complexity and scope. Throughout the opioid crisis we have often failed to recognize and address the unique needs of pregnant people and infants.”
The study authors used data from the National Center for Health Statistics at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and from the Area Health Resource File to examine maternal-infant HCV infection among all U.S. births between 2009 and 2019. The researchers also examined community-level risk factors including rurality, employment, and access to medical care.
In counties reporting HCV, there were 39,380,122 people who had live births, of whom 138,343 (0.4%) were diagnosed with HCV. The overall rate of maternal HCV infection increased from 1.8 to 5.1 per 1,000 live births between 2009 and 2019.
Infection rates were highest in American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) and White people (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 7.94 and 7.37, respectively) compared with Black people. They were higher among individuals without a 4-year degree compared to those with higher education (aOR, 3.19).
Among these groups considered to be at higher risk for HCV infection, high employment rates somewhat mitigated the risk. Specifically, in counties in the 10th percentile of employment, the predicted probability of HCV increased from 0.16% to 1.37%, between 2009 and 2019, whereas in counties at the 90th percentile of employment, the predicted probability remained similar, at 0.36% in 2009 and 0.48% in 2019.
“With constrained national resources, understanding both individual and community-level factors associated with HCV infections in pregnant people could inform strategies to mitigate its spread, such as harm reduction efforts (e.g., syringe service programs), improving access to treatment for [opioid use disorder] or increasing the obstetrical workforce in high-risk communities, HCV testing strategies in pregnant people and people of childbearing age, and treatment with novel antiviral therapies,” wrote the authors.
In the time since the authors began the study, universal HCV screening for every pregnancy has been recommended by a number of groups, including the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM). However, Dr. Patrick says even though such recommendations are now adopted, it will be some time before they are fully operational, making knowledge of HCV risk factors important for obstetricians as well as pediatricians and family physicians. “We don’t know how if hospitals and clinicians have started universal screening for HCV and even when it is completely adopted, understanding individual and community-level factors associated with HCV in pregnant people is still of critical importance,” he explained. “In some of our previous work we have found that non-White HCV-exposed infants are less likely to be tested for HCV than are White infants, even after accounting for multiple individual and hospital-level factors. The pattern we are seeing in our research and in research in other groups is one of unequal treatment of pregnant people with substance use disorder in terms of being given evidence-based treatments, being tested for HCV, and even in child welfare outcomes like foster placement. It is important to know these issues are occurring, but we need specific equitable approaches to ensuring optimal outcomes for all families.
Jeffrey A. Kuller, MD, one of the authors of the SMFM’s new recommendations for universal HCV screening in pregnancy, agreed that until universal screening is widely adopted, awareness of maternal HCV risk factors is important, “to better determine who is at highest risk for hep C, barriers to care, and patients to better target.” This information also affects procedure at the time of delivery, added Dr. Kuller, professor of obstetrics and gynecology in the division of maternal-fetal medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. “We do not perform C-sections for the presence of hep C,” he told this publication. However, in labor, “we try to avoid internal fetal monitoring when possible, and early artificial rupture of membranes when possible, and avoid the use of routine episiotomy,” he said. “Hep C–positive patients should also be assessed for other sexually transmitted diseases including HIV, syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and hep B. “Although we do not typically treat hep C pharmacologically during pregnancy, we try to get the patient placed with a hepatologist for long-term management.”
The study has important implications for pediatric patients, added Audrey R. Lloyd, MD, a med-peds infectious disease fellow who is studying HCV in pregnancy at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. “In the setting of maternal HCV viremia, maternal-fetal transmission occurs in around 6% of exposed infants and around 10% if there is maternal HIV-HCV coinfection,” she said in an interview. “With the increasing rates of HCV in pregnant women described by Dr. Patrick et al., HCV infections among infants will also rise. Even when maternal HCV infection is documented, we often do not do a good job screening the infants for infection and linking them to treatment. This new data makes me worried we may see more complications of pediatric HCV infection in the future,” she added. She explained that safe and effective treatments for HCV infection are approved down to 3 years of age, but patients must first be diagnosed to receive treatment.
From whichever angle you approach it, tackling both the opioid epidemic and HCV infection in pregnancy will inevitably end up helping both parts of the mother-infant dyad, said Dr. Patrick. “Not too long ago I was caring for an opioid-exposed infant at the hospital where I practice who had transferred in from another center hours away. The mother had not been tested for HCV, so I tested the infant for HCV antibodies which were positive. Imagine that, determining a mother is HCV positive by testing the infant. There are so many layers of systems that should be fixed to make this not happen. And what are the chances the mother, after she found out, was able to access treatment for HCV? What about the infant being tested? The systems are just fragmented and we need to do better.”
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health. Neither Dr. Patrick, Dr. Kuller, nor Dr. Lloyd reported any conflicts of interest.
Mirroring the opioid crisis, maternal and newborn hepatitis C infections (HCV) more than doubled in the United States between 2009 and 2019, with disproportionate increases in people of White, American Indian, and Alaska Native race, especially those with less education, according to a cross-sectional study published in JAMA Health Forum. However, the level of risk within these populations was mitigated in counties with higher employment, reported Stephen W. Patrick, MD, of Vanderbilt University, in Nashville, Tenn., and coauthors.
“As we develop public health approaches to prevent HCV infections, connect to treatment, and monitor exposed infants, understanding these factors can be of critical importance to tailoring interventions,” Dr. Patrick said in an interview. “HCV is one more complication of the opioid crisis,” he added. “These data also enable us to step back a bit from HCV and look at the landscape of how the opioid crisis continues to grow in complexity and scope. Throughout the opioid crisis we have often failed to recognize and address the unique needs of pregnant people and infants.”
The study authors used data from the National Center for Health Statistics at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and from the Area Health Resource File to examine maternal-infant HCV infection among all U.S. births between 2009 and 2019. The researchers also examined community-level risk factors including rurality, employment, and access to medical care.
In counties reporting HCV, there were 39,380,122 people who had live births, of whom 138,343 (0.4%) were diagnosed with HCV. The overall rate of maternal HCV infection increased from 1.8 to 5.1 per 1,000 live births between 2009 and 2019.
Infection rates were highest in American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) and White people (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 7.94 and 7.37, respectively) compared with Black people. They were higher among individuals without a 4-year degree compared to those with higher education (aOR, 3.19).
Among these groups considered to be at higher risk for HCV infection, high employment rates somewhat mitigated the risk. Specifically, in counties in the 10th percentile of employment, the predicted probability of HCV increased from 0.16% to 1.37%, between 2009 and 2019, whereas in counties at the 90th percentile of employment, the predicted probability remained similar, at 0.36% in 2009 and 0.48% in 2019.
“With constrained national resources, understanding both individual and community-level factors associated with HCV infections in pregnant people could inform strategies to mitigate its spread, such as harm reduction efforts (e.g., syringe service programs), improving access to treatment for [opioid use disorder] or increasing the obstetrical workforce in high-risk communities, HCV testing strategies in pregnant people and people of childbearing age, and treatment with novel antiviral therapies,” wrote the authors.
In the time since the authors began the study, universal HCV screening for every pregnancy has been recommended by a number of groups, including the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM). However, Dr. Patrick says even though such recommendations are now adopted, it will be some time before they are fully operational, making knowledge of HCV risk factors important for obstetricians as well as pediatricians and family physicians. “We don’t know how if hospitals and clinicians have started universal screening for HCV and even when it is completely adopted, understanding individual and community-level factors associated with HCV in pregnant people is still of critical importance,” he explained. “In some of our previous work we have found that non-White HCV-exposed infants are less likely to be tested for HCV than are White infants, even after accounting for multiple individual and hospital-level factors. The pattern we are seeing in our research and in research in other groups is one of unequal treatment of pregnant people with substance use disorder in terms of being given evidence-based treatments, being tested for HCV, and even in child welfare outcomes like foster placement. It is important to know these issues are occurring, but we need specific equitable approaches to ensuring optimal outcomes for all families.
Jeffrey A. Kuller, MD, one of the authors of the SMFM’s new recommendations for universal HCV screening in pregnancy, agreed that until universal screening is widely adopted, awareness of maternal HCV risk factors is important, “to better determine who is at highest risk for hep C, barriers to care, and patients to better target.” This information also affects procedure at the time of delivery, added Dr. Kuller, professor of obstetrics and gynecology in the division of maternal-fetal medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. “We do not perform C-sections for the presence of hep C,” he told this publication. However, in labor, “we try to avoid internal fetal monitoring when possible, and early artificial rupture of membranes when possible, and avoid the use of routine episiotomy,” he said. “Hep C–positive patients should also be assessed for other sexually transmitted diseases including HIV, syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and hep B. “Although we do not typically treat hep C pharmacologically during pregnancy, we try to get the patient placed with a hepatologist for long-term management.”
The study has important implications for pediatric patients, added Audrey R. Lloyd, MD, a med-peds infectious disease fellow who is studying HCV in pregnancy at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. “In the setting of maternal HCV viremia, maternal-fetal transmission occurs in around 6% of exposed infants and around 10% if there is maternal HIV-HCV coinfection,” she said in an interview. “With the increasing rates of HCV in pregnant women described by Dr. Patrick et al., HCV infections among infants will also rise. Even when maternal HCV infection is documented, we often do not do a good job screening the infants for infection and linking them to treatment. This new data makes me worried we may see more complications of pediatric HCV infection in the future,” she added. She explained that safe and effective treatments for HCV infection are approved down to 3 years of age, but patients must first be diagnosed to receive treatment.
From whichever angle you approach it, tackling both the opioid epidemic and HCV infection in pregnancy will inevitably end up helping both parts of the mother-infant dyad, said Dr. Patrick. “Not too long ago I was caring for an opioid-exposed infant at the hospital where I practice who had transferred in from another center hours away. The mother had not been tested for HCV, so I tested the infant for HCV antibodies which were positive. Imagine that, determining a mother is HCV positive by testing the infant. There are so many layers of systems that should be fixed to make this not happen. And what are the chances the mother, after she found out, was able to access treatment for HCV? What about the infant being tested? The systems are just fragmented and we need to do better.”
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health. Neither Dr. Patrick, Dr. Kuller, nor Dr. Lloyd reported any conflicts of interest.
Mirroring the opioid crisis, maternal and newborn hepatitis C infections (HCV) more than doubled in the United States between 2009 and 2019, with disproportionate increases in people of White, American Indian, and Alaska Native race, especially those with less education, according to a cross-sectional study published in JAMA Health Forum. However, the level of risk within these populations was mitigated in counties with higher employment, reported Stephen W. Patrick, MD, of Vanderbilt University, in Nashville, Tenn., and coauthors.
“As we develop public health approaches to prevent HCV infections, connect to treatment, and monitor exposed infants, understanding these factors can be of critical importance to tailoring interventions,” Dr. Patrick said in an interview. “HCV is one more complication of the opioid crisis,” he added. “These data also enable us to step back a bit from HCV and look at the landscape of how the opioid crisis continues to grow in complexity and scope. Throughout the opioid crisis we have often failed to recognize and address the unique needs of pregnant people and infants.”
The study authors used data from the National Center for Health Statistics at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and from the Area Health Resource File to examine maternal-infant HCV infection among all U.S. births between 2009 and 2019. The researchers also examined community-level risk factors including rurality, employment, and access to medical care.
In counties reporting HCV, there were 39,380,122 people who had live births, of whom 138,343 (0.4%) were diagnosed with HCV. The overall rate of maternal HCV infection increased from 1.8 to 5.1 per 1,000 live births between 2009 and 2019.
Infection rates were highest in American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) and White people (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 7.94 and 7.37, respectively) compared with Black people. They were higher among individuals without a 4-year degree compared to those with higher education (aOR, 3.19).
Among these groups considered to be at higher risk for HCV infection, high employment rates somewhat mitigated the risk. Specifically, in counties in the 10th percentile of employment, the predicted probability of HCV increased from 0.16% to 1.37%, between 2009 and 2019, whereas in counties at the 90th percentile of employment, the predicted probability remained similar, at 0.36% in 2009 and 0.48% in 2019.
“With constrained national resources, understanding both individual and community-level factors associated with HCV infections in pregnant people could inform strategies to mitigate its spread, such as harm reduction efforts (e.g., syringe service programs), improving access to treatment for [opioid use disorder] or increasing the obstetrical workforce in high-risk communities, HCV testing strategies in pregnant people and people of childbearing age, and treatment with novel antiviral therapies,” wrote the authors.
In the time since the authors began the study, universal HCV screening for every pregnancy has been recommended by a number of groups, including the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM). However, Dr. Patrick says even though such recommendations are now adopted, it will be some time before they are fully operational, making knowledge of HCV risk factors important for obstetricians as well as pediatricians and family physicians. “We don’t know how if hospitals and clinicians have started universal screening for HCV and even when it is completely adopted, understanding individual and community-level factors associated with HCV in pregnant people is still of critical importance,” he explained. “In some of our previous work we have found that non-White HCV-exposed infants are less likely to be tested for HCV than are White infants, even after accounting for multiple individual and hospital-level factors. The pattern we are seeing in our research and in research in other groups is one of unequal treatment of pregnant people with substance use disorder in terms of being given evidence-based treatments, being tested for HCV, and even in child welfare outcomes like foster placement. It is important to know these issues are occurring, but we need specific equitable approaches to ensuring optimal outcomes for all families.
Jeffrey A. Kuller, MD, one of the authors of the SMFM’s new recommendations for universal HCV screening in pregnancy, agreed that until universal screening is widely adopted, awareness of maternal HCV risk factors is important, “to better determine who is at highest risk for hep C, barriers to care, and patients to better target.” This information also affects procedure at the time of delivery, added Dr. Kuller, professor of obstetrics and gynecology in the division of maternal-fetal medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. “We do not perform C-sections for the presence of hep C,” he told this publication. However, in labor, “we try to avoid internal fetal monitoring when possible, and early artificial rupture of membranes when possible, and avoid the use of routine episiotomy,” he said. “Hep C–positive patients should also be assessed for other sexually transmitted diseases including HIV, syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and hep B. “Although we do not typically treat hep C pharmacologically during pregnancy, we try to get the patient placed with a hepatologist for long-term management.”
The study has important implications for pediatric patients, added Audrey R. Lloyd, MD, a med-peds infectious disease fellow who is studying HCV in pregnancy at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. “In the setting of maternal HCV viremia, maternal-fetal transmission occurs in around 6% of exposed infants and around 10% if there is maternal HIV-HCV coinfection,” she said in an interview. “With the increasing rates of HCV in pregnant women described by Dr. Patrick et al., HCV infections among infants will also rise. Even when maternal HCV infection is documented, we often do not do a good job screening the infants for infection and linking them to treatment. This new data makes me worried we may see more complications of pediatric HCV infection in the future,” she added. She explained that safe and effective treatments for HCV infection are approved down to 3 years of age, but patients must first be diagnosed to receive treatment.
From whichever angle you approach it, tackling both the opioid epidemic and HCV infection in pregnancy will inevitably end up helping both parts of the mother-infant dyad, said Dr. Patrick. “Not too long ago I was caring for an opioid-exposed infant at the hospital where I practice who had transferred in from another center hours away. The mother had not been tested for HCV, so I tested the infant for HCV antibodies which were positive. Imagine that, determining a mother is HCV positive by testing the infant. There are so many layers of systems that should be fixed to make this not happen. And what are the chances the mother, after she found out, was able to access treatment for HCV? What about the infant being tested? The systems are just fragmented and we need to do better.”
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health. Neither Dr. Patrick, Dr. Kuller, nor Dr. Lloyd reported any conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA HEALTH FORUM
Droperidol/midazolam combo curbs agitation in ED patients
a study involving 86 adult patients at a single tertiary medical care center.
Patients with acute agitation present significant safety concerns in the emergency department, according to Jessica Javed, MD, of the University of Louisville (Ky.) and colleagues.
A combination of haloperidol and lorazepam has been widely used to curb agitation in these patients, but droperidol and midazolam could be more effective, owing to faster onset of action, Dr. Javed noted in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
Dr. Javed and colleagues conducted a prospective study to compare time to adequate sedation in agitated patients in the ED. In the trial, 43 patients received droperidol 5 mg plus midazolam 5 mg, and 43 patients received haloperidol plus lorazepam 2 mg. The average age of the patients in the droperidol/midazolam group was 34 years; the average age of the patients in the haloperidol/lorazepam group was 38 years. Baseline demographics, including height, weight, body mass index, and baseline Sedation Assessment Tool (SAT) scores, were similar between the groups.
The SAT score scale ranges from +3 (combative, violent, or out of control) to –3 (no response to stimulation); zero indicates being awake and calm/cooperative. The median baseline SAT score was 3 for both treatment groups.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients with adequate sedation (defined as SAT scores of ≤0) 10 min after treatment.
Significantly more patients in the droperidol/midazolam group met this outcome, compared with the patients in the haloperidol/lorazepam group (51.2% vs. 7%). Also, significantly more patients in the droperidol/midazolam group achieved adequate sedation at 5, 10, 15, and 30 min than in the haloperidol/lorazepam group.
Fewer patients in the haloperidol/lorazepam group required supplemental oxygen, compared with the droperidol/midazolam group (9.3% vs. 25.6%). However, none of the droperidol/midazolam patients required rescue sedation, compared with 16.3% of the haloperidol/lorazepam patients, Dr. Javed noted. None of the patients required endotracheal intubation or experienced extrapyramidal symptoms, she said.
The study was limited by the small sample size and inclusion of data from only a single center.
The results suggest that droperidol/midazolam is superior to intramuscular haloperidol/lorazepam for producing adequate sedation after 10 min in agitated patients, Dr. Javed concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a study involving 86 adult patients at a single tertiary medical care center.
Patients with acute agitation present significant safety concerns in the emergency department, according to Jessica Javed, MD, of the University of Louisville (Ky.) and colleagues.
A combination of haloperidol and lorazepam has been widely used to curb agitation in these patients, but droperidol and midazolam could be more effective, owing to faster onset of action, Dr. Javed noted in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
Dr. Javed and colleagues conducted a prospective study to compare time to adequate sedation in agitated patients in the ED. In the trial, 43 patients received droperidol 5 mg plus midazolam 5 mg, and 43 patients received haloperidol plus lorazepam 2 mg. The average age of the patients in the droperidol/midazolam group was 34 years; the average age of the patients in the haloperidol/lorazepam group was 38 years. Baseline demographics, including height, weight, body mass index, and baseline Sedation Assessment Tool (SAT) scores, were similar between the groups.
The SAT score scale ranges from +3 (combative, violent, or out of control) to –3 (no response to stimulation); zero indicates being awake and calm/cooperative. The median baseline SAT score was 3 for both treatment groups.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients with adequate sedation (defined as SAT scores of ≤0) 10 min after treatment.
Significantly more patients in the droperidol/midazolam group met this outcome, compared with the patients in the haloperidol/lorazepam group (51.2% vs. 7%). Also, significantly more patients in the droperidol/midazolam group achieved adequate sedation at 5, 10, 15, and 30 min than in the haloperidol/lorazepam group.
Fewer patients in the haloperidol/lorazepam group required supplemental oxygen, compared with the droperidol/midazolam group (9.3% vs. 25.6%). However, none of the droperidol/midazolam patients required rescue sedation, compared with 16.3% of the haloperidol/lorazepam patients, Dr. Javed noted. None of the patients required endotracheal intubation or experienced extrapyramidal symptoms, she said.
The study was limited by the small sample size and inclusion of data from only a single center.
The results suggest that droperidol/midazolam is superior to intramuscular haloperidol/lorazepam for producing adequate sedation after 10 min in agitated patients, Dr. Javed concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a study involving 86 adult patients at a single tertiary medical care center.
Patients with acute agitation present significant safety concerns in the emergency department, according to Jessica Javed, MD, of the University of Louisville (Ky.) and colleagues.
A combination of haloperidol and lorazepam has been widely used to curb agitation in these patients, but droperidol and midazolam could be more effective, owing to faster onset of action, Dr. Javed noted in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
Dr. Javed and colleagues conducted a prospective study to compare time to adequate sedation in agitated patients in the ED. In the trial, 43 patients received droperidol 5 mg plus midazolam 5 mg, and 43 patients received haloperidol plus lorazepam 2 mg. The average age of the patients in the droperidol/midazolam group was 34 years; the average age of the patients in the haloperidol/lorazepam group was 38 years. Baseline demographics, including height, weight, body mass index, and baseline Sedation Assessment Tool (SAT) scores, were similar between the groups.
The SAT score scale ranges from +3 (combative, violent, or out of control) to –3 (no response to stimulation); zero indicates being awake and calm/cooperative. The median baseline SAT score was 3 for both treatment groups.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients with adequate sedation (defined as SAT scores of ≤0) 10 min after treatment.
Significantly more patients in the droperidol/midazolam group met this outcome, compared with the patients in the haloperidol/lorazepam group (51.2% vs. 7%). Also, significantly more patients in the droperidol/midazolam group achieved adequate sedation at 5, 10, 15, and 30 min than in the haloperidol/lorazepam group.
Fewer patients in the haloperidol/lorazepam group required supplemental oxygen, compared with the droperidol/midazolam group (9.3% vs. 25.6%). However, none of the droperidol/midazolam patients required rescue sedation, compared with 16.3% of the haloperidol/lorazepam patients, Dr. Javed noted. None of the patients required endotracheal intubation or experienced extrapyramidal symptoms, she said.
The study was limited by the small sample size and inclusion of data from only a single center.
The results suggest that droperidol/midazolam is superior to intramuscular haloperidol/lorazepam for producing adequate sedation after 10 min in agitated patients, Dr. Javed concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: A look at the pace of vaccination
With children aged 5-11 years about to enter the battle-of-the-COVID-vaccine phase of the war on COVID, there are many questions. MDedge takes a look at one: How long will it take to get 5- to 11-year-olds vaccinated?
Previous experience may provide some guidance. The vaccine was approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for the closest group in age, 12- to 15-year-olds, on May 12, 2021, and according to data from the CDC.
(Use of the 5% figure acknowledges the uneven start after approval – the vaccine became available to different age groups at different times, even though it had been approved for all adults aged 18 years and older.)
The 16- to 17-year-olds, despite being a smaller group of less than 7.6 million individuals, took 120 days to go from 5% to 50% coverage. For those aged 18-24 years, the corresponding time was 132 days, while the 24- to 36-year-olds took longer than any other age group, 135 days, to reach the 50%-with-at-least-one-dose milestone. The time, in turn, decreased for each group as age increased, with those aged 75 and older taking just 41 days to get at least one dose in 50% of individuals, the CDC data show.
That trend also applies to full vaccination, for the most part. The oldest group, 75 and older, had the shortest time to 50% being fully vaccinated at 69 days, and the 25- to 39-year-olds had the longest time at 206 days, with the length rising as age decreased and dropping for groups younger than 25-39. Except for the 12- to 15-year-olds. It has been 160 days (as of Nov. 2) since the 5% mark was reached on May 17, but only 47.4% of the group is fully vaccinated, making it unlikely that the 50% mark will be reached earlier than the 169 days it took the 16- to 17-year-olds.
So where does that put the 5- to 11-year-olds?
The White House said on Nov. 1 that vaccinations could start the first week of November, pending approval from the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which meets on Nov. 2. “This is an important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator, said in a briefing. “As we await the CDC decision, we are not waiting on the operations and logistics. In fact, we’ve been preparing for weeks.”
Availability, of course, is not the only factor involved. In a survey conducted Oct. 14-24, the Kaiser Family Foundation found that only 27% of parents of children aged 5-11 years are planning to have them vaccinated against COVID-19 “right away” once the vaccine is available, and that 33% would “wait and see” how the vaccine works.
“Parents of 5-11 year-olds cite a range of concerns when it comes to vaccinating their children for COVID-19, with safety issues topping off the list,” and “two-thirds say they are concerned the vaccine may negatively impact their child’s fertility in the future,” Kaiser said.
With children aged 5-11 years about to enter the battle-of-the-COVID-vaccine phase of the war on COVID, there are many questions. MDedge takes a look at one: How long will it take to get 5- to 11-year-olds vaccinated?

Previous experience may provide some guidance. The vaccine was approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for the closest group in age, 12- to 15-year-olds, on May 12, 2021, and according to data from the CDC.
(Use of the 5% figure acknowledges the uneven start after approval – the vaccine became available to different age groups at different times, even though it had been approved for all adults aged 18 years and older.)
The 16- to 17-year-olds, despite being a smaller group of less than 7.6 million individuals, took 120 days to go from 5% to 50% coverage. For those aged 18-24 years, the corresponding time was 132 days, while the 24- to 36-year-olds took longer than any other age group, 135 days, to reach the 50%-with-at-least-one-dose milestone. The time, in turn, decreased for each group as age increased, with those aged 75 and older taking just 41 days to get at least one dose in 50% of individuals, the CDC data show.
That trend also applies to full vaccination, for the most part. The oldest group, 75 and older, had the shortest time to 50% being fully vaccinated at 69 days, and the 25- to 39-year-olds had the longest time at 206 days, with the length rising as age decreased and dropping for groups younger than 25-39. Except for the 12- to 15-year-olds. It has been 160 days (as of Nov. 2) since the 5% mark was reached on May 17, but only 47.4% of the group is fully vaccinated, making it unlikely that the 50% mark will be reached earlier than the 169 days it took the 16- to 17-year-olds.
So where does that put the 5- to 11-year-olds?
The White House said on Nov. 1 that vaccinations could start the first week of November, pending approval from the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which meets on Nov. 2. “This is an important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator, said in a briefing. “As we await the CDC decision, we are not waiting on the operations and logistics. In fact, we’ve been preparing for weeks.”
Availability, of course, is not the only factor involved. In a survey conducted Oct. 14-24, the Kaiser Family Foundation found that only 27% of parents of children aged 5-11 years are planning to have them vaccinated against COVID-19 “right away” once the vaccine is available, and that 33% would “wait and see” how the vaccine works.
“Parents of 5-11 year-olds cite a range of concerns when it comes to vaccinating their children for COVID-19, with safety issues topping off the list,” and “two-thirds say they are concerned the vaccine may negatively impact their child’s fertility in the future,” Kaiser said.
With children aged 5-11 years about to enter the battle-of-the-COVID-vaccine phase of the war on COVID, there are many questions. MDedge takes a look at one: How long will it take to get 5- to 11-year-olds vaccinated?

Previous experience may provide some guidance. The vaccine was approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for the closest group in age, 12- to 15-year-olds, on May 12, 2021, and according to data from the CDC.
(Use of the 5% figure acknowledges the uneven start after approval – the vaccine became available to different age groups at different times, even though it had been approved for all adults aged 18 years and older.)
The 16- to 17-year-olds, despite being a smaller group of less than 7.6 million individuals, took 120 days to go from 5% to 50% coverage. For those aged 18-24 years, the corresponding time was 132 days, while the 24- to 36-year-olds took longer than any other age group, 135 days, to reach the 50%-with-at-least-one-dose milestone. The time, in turn, decreased for each group as age increased, with those aged 75 and older taking just 41 days to get at least one dose in 50% of individuals, the CDC data show.
That trend also applies to full vaccination, for the most part. The oldest group, 75 and older, had the shortest time to 50% being fully vaccinated at 69 days, and the 25- to 39-year-olds had the longest time at 206 days, with the length rising as age decreased and dropping for groups younger than 25-39. Except for the 12- to 15-year-olds. It has been 160 days (as of Nov. 2) since the 5% mark was reached on May 17, but only 47.4% of the group is fully vaccinated, making it unlikely that the 50% mark will be reached earlier than the 169 days it took the 16- to 17-year-olds.
So where does that put the 5- to 11-year-olds?
The White House said on Nov. 1 that vaccinations could start the first week of November, pending approval from the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which meets on Nov. 2. “This is an important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator, said in a briefing. “As we await the CDC decision, we are not waiting on the operations and logistics. In fact, we’ve been preparing for weeks.”
Availability, of course, is not the only factor involved. In a survey conducted Oct. 14-24, the Kaiser Family Foundation found that only 27% of parents of children aged 5-11 years are planning to have them vaccinated against COVID-19 “right away” once the vaccine is available, and that 33% would “wait and see” how the vaccine works.
“Parents of 5-11 year-olds cite a range of concerns when it comes to vaccinating their children for COVID-19, with safety issues topping off the list,” and “two-thirds say they are concerned the vaccine may negatively impact their child’s fertility in the future,” Kaiser said.
Majority of justices seem receptive to bid to stop Texas abortion law
During over 3 hours of oral arguments on Nov. 1,
They seemed less certain about whether the federal government — which is also challenging the law — was within its rights to sue Texas.
Senate Bill 8, which went into effect September 1, allows any private citizen to file suit anywhere in the state against anyone who performs, induces, or “aids or abets” an abortion. If successful in court, the plaintiff is entitled to at least $10,000 and does not have to pay attorneys’ fees; rather, defendants are required to pay all legal costs.
In September, most justices denied an emergency request to stop the law but agreed to quickly hear the challenges in person.
At the Nov. 1 hearing, it appeared that a few justices who had let the law stand — notably conservatives Amy Coney Barrett and Brett Kavanaugh — were now agreeing that its challengers, in particular the abortion provider Whole Woman’s Health, might have a legal basis to move forward.
“I think it’s pretty likely the Court is going to do something that allows ‘someone’s’ suit against SB 8 to go ahead,” tweeted Raffi Melkonian, a Houston attorney, after the hearing. “I don’t know when they’re going to do that.”
The Supreme Court usually issues its opinions months after arguments. Since these two challenges — Whole Woman’s Health v. Jackson and US v. Texas — were heard on a faster schedule, there’s speculation that a decision could also come quickly.
“The court clearly is in a hurry,” wrote Florida State University law professor Mary Ziegler before the hearing in a post on court-tracking site SCOTUSblog. She said the court seems to be taking the abortion issue as seriously as most Americans, and that the justices could rule before it hears oral arguments on December 1 in a Mississippi case directly challenging Roe v. Wade.
In addition, data shows abortions have been severely curtailed in Texas since the law took effect — by as much as 50% according to researchers at the University of Texas at Austin. They reported that 2,164 abortions were provided in September 2021, compared with 4,313 in September 2020.
“The actual provisions in this law have prevented every woman in Texas from exercising a constitutional right as declared by this court,” said Justice Elena Kagan, clarifying that it was every woman who had not made a decision by 6 weeks.
“Usually, in these chilling effect cases, we’re kind of guessing,” she said. “Here, we’re not guessing. We know exactly what has happened as a result of this law. It has chilled everybody on the ground.”
Judge Edward Stone II, an attorney with the Texas Attorney General’s Office who argued for the state, denied Justice Kagan’s assertion.
Nineteen medical organizations, including the American Medical Association, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American College of Physicians, filed a friend of the court brief supporting both challenges, saying the Texas law allows legislators to interfere with the patient–doctor relationship and that it limits treatment options.
Texas argued that the only way to challenge the law at the federal level would be to be sued first.
Marc A. Hearron, a lawyer with the Center for Reproductive Rights who argued for Whole Woman’s Health, said that was untenable.
“What my friends on the other side are saying is that clinics should just violate the law,” and “subject themselves to the risk that they will be forced to close their doors,” said Mr. Hearron.
But even if providers decide to violate the law, “they may not find physicians, nurses, ultrasound technicians, staff members willing to work behind the desk, because this law targets all of them,” he said.
Plus, clinics run the risk of becoming permanent defendants because the law does not prohibit multiple suits, he said.
Whole Woman’s Health asked the justices to stop the law by preventing the state’s clerks from filing cases.
Federal standing not as clear
The U.S. Department of Justice sued Texas on September 9, saying the law negated the constitutional right to an abortion.
“The Act is clearly unconstitutional under longstanding Supreme Court precedent,” Attorney General Merrick Garland said at the time.
At the court, U.S. Solicitor General Elizabeth B. Prelogar called it a “brazen attack” on the supremacy of federal law and said it would open the door to other states mounting similar challenges.
Justice Kagan seemed to agree.
“The entire point of this law, its purpose, and its effect is to find the chink in the armor of Ex parte Young,” a 1908 law that “set out a basic principle of how our government is supposed to work and how people can seek review of unconstitutional state laws,” she said, decrying that “after all these many years, some geniuses came up with a way to evade the commands of that decision.”
Judge Stone waved off the concerns. “Nothing in this law even pretends that Texas courts could evade that because it can’t,” he said.
“Essentially, we would be inviting states, all 50 of them, with respect to their unpreferred constitutional rights, to try to nullify the law — that this Court has laid down as to the content of those rights,” said Justice Kagan.
Justice Kavanaugh also seemed concerned about that possibility.
“It could be free speech rights. It could be free exercise of religion rights. It could be Second Amendment rights if this position is accepted here,” he said, citing a brief submitted by the Firearms Policy Coalition that supported the Whole Woman’s Health challenge.
Justice Neil Gorsuch seemed dubious that the Texas law would undercut anybody’s right to challenge.
“Often constitutional rights, of course, can only be enforced in a defensive posture, when an individual is faced either with potential liability, punitive damages, but also, of course, civil fines — fines and even criminal sanction, including prison time,” he said.
Judge Stone argued that the U.S. government is “not a proper plaintiff” and did not have the right to sue Texas or any of its officials because none were involved in enforcing the law. If the federal government didn’t like the law, it should ask Congress to fix it, said Judge Stone.
After the hearing, Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton reiterated that position.
“The Biden Administration does not have the power to sue a state, such as Texas, just because it disagrees with a state law that protects the unborn,” he said in a statement.
A ruling on the challenges will not put an end to the litigation over SB 8.
“Even if the Supreme Court does rule that the abortion provider plaintiffs are allowed to sue, it is likely that there will still need to be more litigation in a federal trial court before SB 8 is actually determined to be unconstitutional and is blocked by a court order,” wrote Ian Millhiser, a Supreme Court scholar, after the hearing.
A federal judge in Austin did approve the Department of Justice’s request for a temporary halt to the law in October, but days later, the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals ruled it could go back into effect while the legal questions were being pondered in the courts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During over 3 hours of oral arguments on Nov. 1,
They seemed less certain about whether the federal government — which is also challenging the law — was within its rights to sue Texas.
Senate Bill 8, which went into effect September 1, allows any private citizen to file suit anywhere in the state against anyone who performs, induces, or “aids or abets” an abortion. If successful in court, the plaintiff is entitled to at least $10,000 and does not have to pay attorneys’ fees; rather, defendants are required to pay all legal costs.
In September, most justices denied an emergency request to stop the law but agreed to quickly hear the challenges in person.
At the Nov. 1 hearing, it appeared that a few justices who had let the law stand — notably conservatives Amy Coney Barrett and Brett Kavanaugh — were now agreeing that its challengers, in particular the abortion provider Whole Woman’s Health, might have a legal basis to move forward.
“I think it’s pretty likely the Court is going to do something that allows ‘someone’s’ suit against SB 8 to go ahead,” tweeted Raffi Melkonian, a Houston attorney, after the hearing. “I don’t know when they’re going to do that.”
The Supreme Court usually issues its opinions months after arguments. Since these two challenges — Whole Woman’s Health v. Jackson and US v. Texas — were heard on a faster schedule, there’s speculation that a decision could also come quickly.
“The court clearly is in a hurry,” wrote Florida State University law professor Mary Ziegler before the hearing in a post on court-tracking site SCOTUSblog. She said the court seems to be taking the abortion issue as seriously as most Americans, and that the justices could rule before it hears oral arguments on December 1 in a Mississippi case directly challenging Roe v. Wade.
In addition, data shows abortions have been severely curtailed in Texas since the law took effect — by as much as 50% according to researchers at the University of Texas at Austin. They reported that 2,164 abortions were provided in September 2021, compared with 4,313 in September 2020.
“The actual provisions in this law have prevented every woman in Texas from exercising a constitutional right as declared by this court,” said Justice Elena Kagan, clarifying that it was every woman who had not made a decision by 6 weeks.
“Usually, in these chilling effect cases, we’re kind of guessing,” she said. “Here, we’re not guessing. We know exactly what has happened as a result of this law. It has chilled everybody on the ground.”
Judge Edward Stone II, an attorney with the Texas Attorney General’s Office who argued for the state, denied Justice Kagan’s assertion.
Nineteen medical organizations, including the American Medical Association, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American College of Physicians, filed a friend of the court brief supporting both challenges, saying the Texas law allows legislators to interfere with the patient–doctor relationship and that it limits treatment options.
Texas argued that the only way to challenge the law at the federal level would be to be sued first.
Marc A. Hearron, a lawyer with the Center for Reproductive Rights who argued for Whole Woman’s Health, said that was untenable.
“What my friends on the other side are saying is that clinics should just violate the law,” and “subject themselves to the risk that they will be forced to close their doors,” said Mr. Hearron.
But even if providers decide to violate the law, “they may not find physicians, nurses, ultrasound technicians, staff members willing to work behind the desk, because this law targets all of them,” he said.
Plus, clinics run the risk of becoming permanent defendants because the law does not prohibit multiple suits, he said.
Whole Woman’s Health asked the justices to stop the law by preventing the state’s clerks from filing cases.
Federal standing not as clear
The U.S. Department of Justice sued Texas on September 9, saying the law negated the constitutional right to an abortion.
“The Act is clearly unconstitutional under longstanding Supreme Court precedent,” Attorney General Merrick Garland said at the time.
At the court, U.S. Solicitor General Elizabeth B. Prelogar called it a “brazen attack” on the supremacy of federal law and said it would open the door to other states mounting similar challenges.
Justice Kagan seemed to agree.
“The entire point of this law, its purpose, and its effect is to find the chink in the armor of Ex parte Young,” a 1908 law that “set out a basic principle of how our government is supposed to work and how people can seek review of unconstitutional state laws,” she said, decrying that “after all these many years, some geniuses came up with a way to evade the commands of that decision.”
Judge Stone waved off the concerns. “Nothing in this law even pretends that Texas courts could evade that because it can’t,” he said.
“Essentially, we would be inviting states, all 50 of them, with respect to their unpreferred constitutional rights, to try to nullify the law — that this Court has laid down as to the content of those rights,” said Justice Kagan.
Justice Kavanaugh also seemed concerned about that possibility.
“It could be free speech rights. It could be free exercise of religion rights. It could be Second Amendment rights if this position is accepted here,” he said, citing a brief submitted by the Firearms Policy Coalition that supported the Whole Woman’s Health challenge.
Justice Neil Gorsuch seemed dubious that the Texas law would undercut anybody’s right to challenge.
“Often constitutional rights, of course, can only be enforced in a defensive posture, when an individual is faced either with potential liability, punitive damages, but also, of course, civil fines — fines and even criminal sanction, including prison time,” he said.
Judge Stone argued that the U.S. government is “not a proper plaintiff” and did not have the right to sue Texas or any of its officials because none were involved in enforcing the law. If the federal government didn’t like the law, it should ask Congress to fix it, said Judge Stone.
After the hearing, Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton reiterated that position.
“The Biden Administration does not have the power to sue a state, such as Texas, just because it disagrees with a state law that protects the unborn,” he said in a statement.
A ruling on the challenges will not put an end to the litigation over SB 8.
“Even if the Supreme Court does rule that the abortion provider plaintiffs are allowed to sue, it is likely that there will still need to be more litigation in a federal trial court before SB 8 is actually determined to be unconstitutional and is blocked by a court order,” wrote Ian Millhiser, a Supreme Court scholar, after the hearing.
A federal judge in Austin did approve the Department of Justice’s request for a temporary halt to the law in October, but days later, the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals ruled it could go back into effect while the legal questions were being pondered in the courts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During over 3 hours of oral arguments on Nov. 1,
They seemed less certain about whether the federal government — which is also challenging the law — was within its rights to sue Texas.
Senate Bill 8, which went into effect September 1, allows any private citizen to file suit anywhere in the state against anyone who performs, induces, or “aids or abets” an abortion. If successful in court, the plaintiff is entitled to at least $10,000 and does not have to pay attorneys’ fees; rather, defendants are required to pay all legal costs.
In September, most justices denied an emergency request to stop the law but agreed to quickly hear the challenges in person.
At the Nov. 1 hearing, it appeared that a few justices who had let the law stand — notably conservatives Amy Coney Barrett and Brett Kavanaugh — were now agreeing that its challengers, in particular the abortion provider Whole Woman’s Health, might have a legal basis to move forward.
“I think it’s pretty likely the Court is going to do something that allows ‘someone’s’ suit against SB 8 to go ahead,” tweeted Raffi Melkonian, a Houston attorney, after the hearing. “I don’t know when they’re going to do that.”
The Supreme Court usually issues its opinions months after arguments. Since these two challenges — Whole Woman’s Health v. Jackson and US v. Texas — were heard on a faster schedule, there’s speculation that a decision could also come quickly.
“The court clearly is in a hurry,” wrote Florida State University law professor Mary Ziegler before the hearing in a post on court-tracking site SCOTUSblog. She said the court seems to be taking the abortion issue as seriously as most Americans, and that the justices could rule before it hears oral arguments on December 1 in a Mississippi case directly challenging Roe v. Wade.
In addition, data shows abortions have been severely curtailed in Texas since the law took effect — by as much as 50% according to researchers at the University of Texas at Austin. They reported that 2,164 abortions were provided in September 2021, compared with 4,313 in September 2020.
“The actual provisions in this law have prevented every woman in Texas from exercising a constitutional right as declared by this court,” said Justice Elena Kagan, clarifying that it was every woman who had not made a decision by 6 weeks.
“Usually, in these chilling effect cases, we’re kind of guessing,” she said. “Here, we’re not guessing. We know exactly what has happened as a result of this law. It has chilled everybody on the ground.”
Judge Edward Stone II, an attorney with the Texas Attorney General’s Office who argued for the state, denied Justice Kagan’s assertion.
Nineteen medical organizations, including the American Medical Association, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American College of Physicians, filed a friend of the court brief supporting both challenges, saying the Texas law allows legislators to interfere with the patient–doctor relationship and that it limits treatment options.
Texas argued that the only way to challenge the law at the federal level would be to be sued first.
Marc A. Hearron, a lawyer with the Center for Reproductive Rights who argued for Whole Woman’s Health, said that was untenable.
“What my friends on the other side are saying is that clinics should just violate the law,” and “subject themselves to the risk that they will be forced to close their doors,” said Mr. Hearron.
But even if providers decide to violate the law, “they may not find physicians, nurses, ultrasound technicians, staff members willing to work behind the desk, because this law targets all of them,” he said.
Plus, clinics run the risk of becoming permanent defendants because the law does not prohibit multiple suits, he said.
Whole Woman’s Health asked the justices to stop the law by preventing the state’s clerks from filing cases.
Federal standing not as clear
The U.S. Department of Justice sued Texas on September 9, saying the law negated the constitutional right to an abortion.
“The Act is clearly unconstitutional under longstanding Supreme Court precedent,” Attorney General Merrick Garland said at the time.
At the court, U.S. Solicitor General Elizabeth B. Prelogar called it a “brazen attack” on the supremacy of federal law and said it would open the door to other states mounting similar challenges.
Justice Kagan seemed to agree.
“The entire point of this law, its purpose, and its effect is to find the chink in the armor of Ex parte Young,” a 1908 law that “set out a basic principle of how our government is supposed to work and how people can seek review of unconstitutional state laws,” she said, decrying that “after all these many years, some geniuses came up with a way to evade the commands of that decision.”
Judge Stone waved off the concerns. “Nothing in this law even pretends that Texas courts could evade that because it can’t,” he said.
“Essentially, we would be inviting states, all 50 of them, with respect to their unpreferred constitutional rights, to try to nullify the law — that this Court has laid down as to the content of those rights,” said Justice Kagan.
Justice Kavanaugh also seemed concerned about that possibility.
“It could be free speech rights. It could be free exercise of religion rights. It could be Second Amendment rights if this position is accepted here,” he said, citing a brief submitted by the Firearms Policy Coalition that supported the Whole Woman’s Health challenge.
Justice Neil Gorsuch seemed dubious that the Texas law would undercut anybody’s right to challenge.
“Often constitutional rights, of course, can only be enforced in a defensive posture, when an individual is faced either with potential liability, punitive damages, but also, of course, civil fines — fines and even criminal sanction, including prison time,” he said.
Judge Stone argued that the U.S. government is “not a proper plaintiff” and did not have the right to sue Texas or any of its officials because none were involved in enforcing the law. If the federal government didn’t like the law, it should ask Congress to fix it, said Judge Stone.
After the hearing, Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton reiterated that position.
“The Biden Administration does not have the power to sue a state, such as Texas, just because it disagrees with a state law that protects the unborn,” he said in a statement.
A ruling on the challenges will not put an end to the litigation over SB 8.
“Even if the Supreme Court does rule that the abortion provider plaintiffs are allowed to sue, it is likely that there will still need to be more litigation in a federal trial court before SB 8 is actually determined to be unconstitutional and is blocked by a court order,” wrote Ian Millhiser, a Supreme Court scholar, after the hearing.
A federal judge in Austin did approve the Department of Justice’s request for a temporary halt to the law in October, but days later, the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals ruled it could go back into effect while the legal questions were being pondered in the courts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ASNC rejects new chest pain guideline it helped create
It was Oct. 28 when the two big North American cardiology societies issued a joint practice guideline on evaluating and managing chest pain that was endorsed by five other subspecialty groups. The next day, another group that had taken part in the document’s genesis explained why it wasn’t one of those five.
Although the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC) was “actively engaged at every stage of the guideline-writing and review process,” the society “could not endorse the guideline,” the society announced in a statement released to clinicians and the media. The most prominent cited reason: It doesn’t adequately “support the principle of Patient First Imaging.”
The guideline was published in Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, flagship journals of the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology, respectively.
The document notes at least two clinicians represented ASNC as peer reviewers, and another was on the writing committee, but the organization does not appear in the list of societies endorsing the document.
“We believe that the document fails to provide unbiased guidance to health care professionals on the optimal evaluation of patients with chest pain,” contends an editorial ASNC board members have scheduled for the Jan. 10 issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicine but is available now on an open-access preprint server.
“Despite the many important and helpful recommendations in the new guideline, there are several recommendations that we could not support,” it states.
“The ASNC board of directors reviewed the document twice during the endorsement process,” and the society “offered substantive comments after the first endorsement review, several of which were addressed,” Randall C. Thompson, MD, St. Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute and University of Missouri–Kansas City, said in an interview.
“However, some of the board’s concerns went unresolved. It was after the board’s second review, when the document had been declared finalized, that they voted not to endorse,” said Dr. Thompson, who is ASNC president.
“When we gather multiple organizations together to review and summarize the evidence, we work collaboratively to interpret the extensive catalog of peer-reviewed, published literature and create clinical practice recommendations,” Guideline Writing Committee Chair Martha Gulati, MD, University of Arizona, Phoenix, told this news organization in a prepared statement.
“The ASNC had a representative on the writing committee who is a coauthor on the paper and actively participated throughout the writing process the past 4 years,” she said. “The final guideline reflects the latest evidence-based recommendations for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain, as agreed by the seven endorsing organizations.”
The document does not clearly note that an ASNC representative was on the writing committee. However, ASNC confirmed that Renee Bullock-Palmer, MD, Deborah Heart and Lung Center, Browns Mills, N.J., is a fellow of the ASNC and had represented the group as one of the coauthors. Two “official reviewers” of the document, however, are listed as ASNC representatives.
Points of contention
“The decision about which test to order can be a nuanced one, and cardiac imaging tests tend to be complementary,” elaborates the editorial on the issue of patient-centered management.
Careful patient selection for different tests is important, “and physician and technical local expertise, availability, quality of equipment, and patient preference are extremely important factors to consider. There is not enough emphasis on this important point,” contend the authors. “This is an important limitation of the guideline.”
Other issues of concern include “lack of balance in the document’s presentation of the science on FFR-CT [fractional flow reserve assessment with computed tomography] and its inappropriately prominent endorsement,” the editorial states.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration–recognized “limitations and contraindications” to FFR-CT tend to be glossed over in the document, Dr. Thompson said. And most ASNC board members were “concerned with the prominent location of the recommendations for FFR-CT in various tables – especially since there was minimal-to-no discussion of the fact that it is currently provided by only one company, that it is not widely available nor covered routinely by health insurance carriers, and [that] the accuracy in the most relevant population is disputed.”
In other concerns, the document “inadequately discusses the benefit” of combining coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores with functional testing, which ASNC said it supports. For example, adding CAC scores to myocardial perfusion imaging improves its diagnostic accuracy and prognostic power.
Functional vs. anatomic testing?
Moreover, “it is no longer appropriate to bundle all types of stress testing together. All stress imaging tests have their unique advantages and limitations.” Yet, “the concept of the dichotomy of functional testing versus anatomic testing is a common theme in the guideline in many important patient groups,” the editorial states. That could overemphasize CT angiography and thus “blur distinction between different types of functional tests.”
Such concerns about “imbalance” in the portrayals of the two kinds of tests were “amplified by the problem of health insurance companies and radiologic benefits managers inappropriately substituting a test that was ordered by a physician with a different test,” Dr. Thompson elaborated. “There is the impression that some of them ‘cherry-pick’ certain guidelines and that this practice is harmful to patients.”
The ASNC currently does not plan its own corresponding guideline, he said. But the editorial says that “over the coming weeks and months ASNC will offer a series of webinars and other programs that address specific patient populations and dilemmas.” Also, “we will enhance our focus on programs to address quality and efficiency to support a patient-first approach to imaging.”
The five subspecialty groups that have endorsed the document are the American Society of Echocardiography, American College of Chest Physicians, Society for Academic Emergency Medicine, Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, and Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance.
Dr. Thompson has reported no relevant financial relationships. Statements of disclosure for the other editorial writers are listed in the publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It was Oct. 28 when the two big North American cardiology societies issued a joint practice guideline on evaluating and managing chest pain that was endorsed by five other subspecialty groups. The next day, another group that had taken part in the document’s genesis explained why it wasn’t one of those five.
Although the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC) was “actively engaged at every stage of the guideline-writing and review process,” the society “could not endorse the guideline,” the society announced in a statement released to clinicians and the media. The most prominent cited reason: It doesn’t adequately “support the principle of Patient First Imaging.”
The guideline was published in Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, flagship journals of the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology, respectively.
The document notes at least two clinicians represented ASNC as peer reviewers, and another was on the writing committee, but the organization does not appear in the list of societies endorsing the document.
“We believe that the document fails to provide unbiased guidance to health care professionals on the optimal evaluation of patients with chest pain,” contends an editorial ASNC board members have scheduled for the Jan. 10 issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicine but is available now on an open-access preprint server.
“Despite the many important and helpful recommendations in the new guideline, there are several recommendations that we could not support,” it states.
“The ASNC board of directors reviewed the document twice during the endorsement process,” and the society “offered substantive comments after the first endorsement review, several of which were addressed,” Randall C. Thompson, MD, St. Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute and University of Missouri–Kansas City, said in an interview.
“However, some of the board’s concerns went unresolved. It was after the board’s second review, when the document had been declared finalized, that they voted not to endorse,” said Dr. Thompson, who is ASNC president.
“When we gather multiple organizations together to review and summarize the evidence, we work collaboratively to interpret the extensive catalog of peer-reviewed, published literature and create clinical practice recommendations,” Guideline Writing Committee Chair Martha Gulati, MD, University of Arizona, Phoenix, told this news organization in a prepared statement.
“The ASNC had a representative on the writing committee who is a coauthor on the paper and actively participated throughout the writing process the past 4 years,” she said. “The final guideline reflects the latest evidence-based recommendations for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain, as agreed by the seven endorsing organizations.”
The document does not clearly note that an ASNC representative was on the writing committee. However, ASNC confirmed that Renee Bullock-Palmer, MD, Deborah Heart and Lung Center, Browns Mills, N.J., is a fellow of the ASNC and had represented the group as one of the coauthors. Two “official reviewers” of the document, however, are listed as ASNC representatives.
Points of contention
“The decision about which test to order can be a nuanced one, and cardiac imaging tests tend to be complementary,” elaborates the editorial on the issue of patient-centered management.
Careful patient selection for different tests is important, “and physician and technical local expertise, availability, quality of equipment, and patient preference are extremely important factors to consider. There is not enough emphasis on this important point,” contend the authors. “This is an important limitation of the guideline.”
Other issues of concern include “lack of balance in the document’s presentation of the science on FFR-CT [fractional flow reserve assessment with computed tomography] and its inappropriately prominent endorsement,” the editorial states.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration–recognized “limitations and contraindications” to FFR-CT tend to be glossed over in the document, Dr. Thompson said. And most ASNC board members were “concerned with the prominent location of the recommendations for FFR-CT in various tables – especially since there was minimal-to-no discussion of the fact that it is currently provided by only one company, that it is not widely available nor covered routinely by health insurance carriers, and [that] the accuracy in the most relevant population is disputed.”
In other concerns, the document “inadequately discusses the benefit” of combining coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores with functional testing, which ASNC said it supports. For example, adding CAC scores to myocardial perfusion imaging improves its diagnostic accuracy and prognostic power.
Functional vs. anatomic testing?
Moreover, “it is no longer appropriate to bundle all types of stress testing together. All stress imaging tests have their unique advantages and limitations.” Yet, “the concept of the dichotomy of functional testing versus anatomic testing is a common theme in the guideline in many important patient groups,” the editorial states. That could overemphasize CT angiography and thus “blur distinction between different types of functional tests.”
Such concerns about “imbalance” in the portrayals of the two kinds of tests were “amplified by the problem of health insurance companies and radiologic benefits managers inappropriately substituting a test that was ordered by a physician with a different test,” Dr. Thompson elaborated. “There is the impression that some of them ‘cherry-pick’ certain guidelines and that this practice is harmful to patients.”
The ASNC currently does not plan its own corresponding guideline, he said. But the editorial says that “over the coming weeks and months ASNC will offer a series of webinars and other programs that address specific patient populations and dilemmas.” Also, “we will enhance our focus on programs to address quality and efficiency to support a patient-first approach to imaging.”
The five subspecialty groups that have endorsed the document are the American Society of Echocardiography, American College of Chest Physicians, Society for Academic Emergency Medicine, Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, and Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance.
Dr. Thompson has reported no relevant financial relationships. Statements of disclosure for the other editorial writers are listed in the publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It was Oct. 28 when the two big North American cardiology societies issued a joint practice guideline on evaluating and managing chest pain that was endorsed by five other subspecialty groups. The next day, another group that had taken part in the document’s genesis explained why it wasn’t one of those five.
Although the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC) was “actively engaged at every stage of the guideline-writing and review process,” the society “could not endorse the guideline,” the society announced in a statement released to clinicians and the media. The most prominent cited reason: It doesn’t adequately “support the principle of Patient First Imaging.”
The guideline was published in Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, flagship journals of the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology, respectively.
The document notes at least two clinicians represented ASNC as peer reviewers, and another was on the writing committee, but the organization does not appear in the list of societies endorsing the document.
“We believe that the document fails to provide unbiased guidance to health care professionals on the optimal evaluation of patients with chest pain,” contends an editorial ASNC board members have scheduled for the Jan. 10 issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicine but is available now on an open-access preprint server.
“Despite the many important and helpful recommendations in the new guideline, there are several recommendations that we could not support,” it states.
“The ASNC board of directors reviewed the document twice during the endorsement process,” and the society “offered substantive comments after the first endorsement review, several of which were addressed,” Randall C. Thompson, MD, St. Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute and University of Missouri–Kansas City, said in an interview.
“However, some of the board’s concerns went unresolved. It was after the board’s second review, when the document had been declared finalized, that they voted not to endorse,” said Dr. Thompson, who is ASNC president.
“When we gather multiple organizations together to review and summarize the evidence, we work collaboratively to interpret the extensive catalog of peer-reviewed, published literature and create clinical practice recommendations,” Guideline Writing Committee Chair Martha Gulati, MD, University of Arizona, Phoenix, told this news organization in a prepared statement.
“The ASNC had a representative on the writing committee who is a coauthor on the paper and actively participated throughout the writing process the past 4 years,” she said. “The final guideline reflects the latest evidence-based recommendations for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain, as agreed by the seven endorsing organizations.”
The document does not clearly note that an ASNC representative was on the writing committee. However, ASNC confirmed that Renee Bullock-Palmer, MD, Deborah Heart and Lung Center, Browns Mills, N.J., is a fellow of the ASNC and had represented the group as one of the coauthors. Two “official reviewers” of the document, however, are listed as ASNC representatives.
Points of contention
“The decision about which test to order can be a nuanced one, and cardiac imaging tests tend to be complementary,” elaborates the editorial on the issue of patient-centered management.
Careful patient selection for different tests is important, “and physician and technical local expertise, availability, quality of equipment, and patient preference are extremely important factors to consider. There is not enough emphasis on this important point,” contend the authors. “This is an important limitation of the guideline.”
Other issues of concern include “lack of balance in the document’s presentation of the science on FFR-CT [fractional flow reserve assessment with computed tomography] and its inappropriately prominent endorsement,” the editorial states.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration–recognized “limitations and contraindications” to FFR-CT tend to be glossed over in the document, Dr. Thompson said. And most ASNC board members were “concerned with the prominent location of the recommendations for FFR-CT in various tables – especially since there was minimal-to-no discussion of the fact that it is currently provided by only one company, that it is not widely available nor covered routinely by health insurance carriers, and [that] the accuracy in the most relevant population is disputed.”
In other concerns, the document “inadequately discusses the benefit” of combining coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores with functional testing, which ASNC said it supports. For example, adding CAC scores to myocardial perfusion imaging improves its diagnostic accuracy and prognostic power.
Functional vs. anatomic testing?
Moreover, “it is no longer appropriate to bundle all types of stress testing together. All stress imaging tests have their unique advantages and limitations.” Yet, “the concept of the dichotomy of functional testing versus anatomic testing is a common theme in the guideline in many important patient groups,” the editorial states. That could overemphasize CT angiography and thus “blur distinction between different types of functional tests.”
Such concerns about “imbalance” in the portrayals of the two kinds of tests were “amplified by the problem of health insurance companies and radiologic benefits managers inappropriately substituting a test that was ordered by a physician with a different test,” Dr. Thompson elaborated. “There is the impression that some of them ‘cherry-pick’ certain guidelines and that this practice is harmful to patients.”
The ASNC currently does not plan its own corresponding guideline, he said. But the editorial says that “over the coming weeks and months ASNC will offer a series of webinars and other programs that address specific patient populations and dilemmas.” Also, “we will enhance our focus on programs to address quality and efficiency to support a patient-first approach to imaging.”
The five subspecialty groups that have endorsed the document are the American Society of Echocardiography, American College of Chest Physicians, Society for Academic Emergency Medicine, Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, and Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance.
Dr. Thompson has reported no relevant financial relationships. Statements of disclosure for the other editorial writers are listed in the publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 vaccines provide 5 times the protection of natural immunity, CDC study says
, according to a new study published recently in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The research team concluded that vaccination can provide a higher, stronger, and more consistent level of immunity against COVID-19 hospitalization than infection alone for at least six months.
“We now have additional evidence that reaffirms the importance of COVID-19 vaccines, even if you have had prior infection,” Rochelle Walensky, MD, director of the CDC, said in a statement.
“This study adds more to the body of knowledge demonstrating the protection of vaccines against severe disease from COVID-19,” she said. “The best way to stop COVID-19, including the emergence of variants, is with widespread COVID-19 vaccination and with disease prevention actions such as mask wearing, washing hands often, physical distancing and staying home when sick.”
Researchers looked at data from the VISION Network, which included more than 201,000 hospitalizations for COVID-like illness at 187 hospitals across nine states between Jan. 1 to Sept. 2. Among those, more than 94,000 had rapid testing for the coronavirus, and 7,300 had a lab-confirmed test for COVID-19.
The research team found that unvaccinated people with a prior infection within 3 to 6 months were about 5-1/2 times more likely to have laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 than those who were fully vaccinated within 3 to 6 months with the Pfizer or Moderna shots. They found similar results when looking at the months that the Delta variant was the dominant strain of the coronavirus.
Protection from the Moderna vaccine “appeared to be higher” than for the Pfizer vaccine, the study authors wrote. The boost in protection also “trended higher” among older adults, as compared to those under age 65.
Importantly, the research team noted, these estimates may change over time as immunity wanes. Future studies should consider infection-induced and vaccine-induced immunity as time passes during the pandemic, they wrote.
Additional research is also needed for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, they wrote. Those who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine are currently recommended to receive a booster shot at least two months after the first shot.
Overall, “all eligible persons should be vaccinated against COVID-19 as soon as possible, including unvaccinated persons previously infected,” the research team concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study published recently in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The research team concluded that vaccination can provide a higher, stronger, and more consistent level of immunity against COVID-19 hospitalization than infection alone for at least six months.
“We now have additional evidence that reaffirms the importance of COVID-19 vaccines, even if you have had prior infection,” Rochelle Walensky, MD, director of the CDC, said in a statement.
“This study adds more to the body of knowledge demonstrating the protection of vaccines against severe disease from COVID-19,” she said. “The best way to stop COVID-19, including the emergence of variants, is with widespread COVID-19 vaccination and with disease prevention actions such as mask wearing, washing hands often, physical distancing and staying home when sick.”
Researchers looked at data from the VISION Network, which included more than 201,000 hospitalizations for COVID-like illness at 187 hospitals across nine states between Jan. 1 to Sept. 2. Among those, more than 94,000 had rapid testing for the coronavirus, and 7,300 had a lab-confirmed test for COVID-19.
The research team found that unvaccinated people with a prior infection within 3 to 6 months were about 5-1/2 times more likely to have laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 than those who were fully vaccinated within 3 to 6 months with the Pfizer or Moderna shots. They found similar results when looking at the months that the Delta variant was the dominant strain of the coronavirus.
Protection from the Moderna vaccine “appeared to be higher” than for the Pfizer vaccine, the study authors wrote. The boost in protection also “trended higher” among older adults, as compared to those under age 65.
Importantly, the research team noted, these estimates may change over time as immunity wanes. Future studies should consider infection-induced and vaccine-induced immunity as time passes during the pandemic, they wrote.
Additional research is also needed for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, they wrote. Those who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine are currently recommended to receive a booster shot at least two months after the first shot.
Overall, “all eligible persons should be vaccinated against COVID-19 as soon as possible, including unvaccinated persons previously infected,” the research team concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study published recently in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The research team concluded that vaccination can provide a higher, stronger, and more consistent level of immunity against COVID-19 hospitalization than infection alone for at least six months.
“We now have additional evidence that reaffirms the importance of COVID-19 vaccines, even if you have had prior infection,” Rochelle Walensky, MD, director of the CDC, said in a statement.
“This study adds more to the body of knowledge demonstrating the protection of vaccines against severe disease from COVID-19,” she said. “The best way to stop COVID-19, including the emergence of variants, is with widespread COVID-19 vaccination and with disease prevention actions such as mask wearing, washing hands often, physical distancing and staying home when sick.”
Researchers looked at data from the VISION Network, which included more than 201,000 hospitalizations for COVID-like illness at 187 hospitals across nine states between Jan. 1 to Sept. 2. Among those, more than 94,000 had rapid testing for the coronavirus, and 7,300 had a lab-confirmed test for COVID-19.
The research team found that unvaccinated people with a prior infection within 3 to 6 months were about 5-1/2 times more likely to have laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 than those who were fully vaccinated within 3 to 6 months with the Pfizer or Moderna shots. They found similar results when looking at the months that the Delta variant was the dominant strain of the coronavirus.
Protection from the Moderna vaccine “appeared to be higher” than for the Pfizer vaccine, the study authors wrote. The boost in protection also “trended higher” among older adults, as compared to those under age 65.
Importantly, the research team noted, these estimates may change over time as immunity wanes. Future studies should consider infection-induced and vaccine-induced immunity as time passes during the pandemic, they wrote.
Additional research is also needed for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, they wrote. Those who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine are currently recommended to receive a booster shot at least two months after the first shot.
Overall, “all eligible persons should be vaccinated against COVID-19 as soon as possible, including unvaccinated persons previously infected,” the research team concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Patients given NSAIDs over antiemetics for headaches spend less time in the ED
based on data from approximately 7,000 patients.
Headache is the fourth-most common chief complaint in the ED, accounting for approximately 3% of all ED visits, said Philip Wang, a medical student at the Cleveland Clinic, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
A variety of pharmacotherapies are used to manage headache, which leads to a range of resource use, he said.
To understand the association between route of drug administration and length of ED stay, Mr. Wang and colleagues reviewed data from 7,233 visits by 6,715 patients at any of the 21 Cleveland Clinic Health System EDs in 2018 with headache as the primary discharge diagnosis. Patients admitted to the hospital were excluded; those treated with opioids, antiemetics, and/or NSAIDs were included. The average age of the study population was 31 years, 57% were White, and approximately half were Medicaid or Medicare patients.
Approximately 68% of patients received antiemetics, 66.8% received NSAIDs, and 9.8% received opioids. Approximately 42% of patients received parenteral-only treatment and 42% received oral-only treatment; 15% received mixed treatment. The average length of ED stay was 202 minutes.
In a multivariate analysis adjusted for sex, age, income, race, insurance status, ED type, and arrival time, treatment with oral drugs only was associated with an 11% reduction of length of stay, compared with treatment with parenteral medication only (P < .001). However, the length of stay for patients treated with mixed route of administration was 10% longer, compared with parenteral only (P < .001).
In terms of drug class (a secondary outcome), patients treated with opioids had a 10% increase in length of stay (P < .01) and those treated with antiemetics had a 14% increase in length of stay; however, patients treated with NSAIDs had a 7% decrease in length of stay.
The study findings were limited in part by the challenge of isolating patients presenting with a primary headache diagnosis, Mr. Wang noted in the presentation.
The challenge of controlling for all the potential factors impacting length of stay, which is “provider, resource, and situation dependent,” is an additional limitation, he said.
However, the results show that route of administration has a significant impact on length of ED stay in patients presenting with headache, he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
based on data from approximately 7,000 patients.
Headache is the fourth-most common chief complaint in the ED, accounting for approximately 3% of all ED visits, said Philip Wang, a medical student at the Cleveland Clinic, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
A variety of pharmacotherapies are used to manage headache, which leads to a range of resource use, he said.
To understand the association between route of drug administration and length of ED stay, Mr. Wang and colleagues reviewed data from 7,233 visits by 6,715 patients at any of the 21 Cleveland Clinic Health System EDs in 2018 with headache as the primary discharge diagnosis. Patients admitted to the hospital were excluded; those treated with opioids, antiemetics, and/or NSAIDs were included. The average age of the study population was 31 years, 57% were White, and approximately half were Medicaid or Medicare patients.
Approximately 68% of patients received antiemetics, 66.8% received NSAIDs, and 9.8% received opioids. Approximately 42% of patients received parenteral-only treatment and 42% received oral-only treatment; 15% received mixed treatment. The average length of ED stay was 202 minutes.
In a multivariate analysis adjusted for sex, age, income, race, insurance status, ED type, and arrival time, treatment with oral drugs only was associated with an 11% reduction of length of stay, compared with treatment with parenteral medication only (P < .001). However, the length of stay for patients treated with mixed route of administration was 10% longer, compared with parenteral only (P < .001).
In terms of drug class (a secondary outcome), patients treated with opioids had a 10% increase in length of stay (P < .01) and those treated with antiemetics had a 14% increase in length of stay; however, patients treated with NSAIDs had a 7% decrease in length of stay.
The study findings were limited in part by the challenge of isolating patients presenting with a primary headache diagnosis, Mr. Wang noted in the presentation.
The challenge of controlling for all the potential factors impacting length of stay, which is “provider, resource, and situation dependent,” is an additional limitation, he said.
However, the results show that route of administration has a significant impact on length of ED stay in patients presenting with headache, he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
based on data from approximately 7,000 patients.
Headache is the fourth-most common chief complaint in the ED, accounting for approximately 3% of all ED visits, said Philip Wang, a medical student at the Cleveland Clinic, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
A variety of pharmacotherapies are used to manage headache, which leads to a range of resource use, he said.
To understand the association between route of drug administration and length of ED stay, Mr. Wang and colleagues reviewed data from 7,233 visits by 6,715 patients at any of the 21 Cleveland Clinic Health System EDs in 2018 with headache as the primary discharge diagnosis. Patients admitted to the hospital were excluded; those treated with opioids, antiemetics, and/or NSAIDs were included. The average age of the study population was 31 years, 57% were White, and approximately half were Medicaid or Medicare patients.
Approximately 68% of patients received antiemetics, 66.8% received NSAIDs, and 9.8% received opioids. Approximately 42% of patients received parenteral-only treatment and 42% received oral-only treatment; 15% received mixed treatment. The average length of ED stay was 202 minutes.
In a multivariate analysis adjusted for sex, age, income, race, insurance status, ED type, and arrival time, treatment with oral drugs only was associated with an 11% reduction of length of stay, compared with treatment with parenteral medication only (P < .001). However, the length of stay for patients treated with mixed route of administration was 10% longer, compared with parenteral only (P < .001).
In terms of drug class (a secondary outcome), patients treated with opioids had a 10% increase in length of stay (P < .01) and those treated with antiemetics had a 14% increase in length of stay; however, patients treated with NSAIDs had a 7% decrease in length of stay.
The study findings were limited in part by the challenge of isolating patients presenting with a primary headache diagnosis, Mr. Wang noted in the presentation.
The challenge of controlling for all the potential factors impacting length of stay, which is “provider, resource, and situation dependent,” is an additional limitation, he said.
However, the results show that route of administration has a significant impact on length of ED stay in patients presenting with headache, he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.







