User login
Visceral fat may help ID heart risk in obese youth
The amount of fat surrounding abdominal organs may help clinicians identify cardiovascular risk in young people with obesity, researchers have found.
Severely overweight children and young adults showed a subtle association between visceral fat and arterial stiffness independent of body mass index (BMI). The association was not present in those of healthy weight, possibly because their visceral fat stores are too small to have a detectable effect on cardiovascular health, according to the researchers, who reported their findings in the latest issue of Pediatric Obesity.
“Those kids with greater visceral fat had stiffer arteries, which can overtax and overstress the system and lead to unfortunate consequences in terms of cardiovascular health down the line,” senior author Joseph M. Kindler, PhD, an assistant professor of nutritional sciences at the University of Georgia, Athens, told this news organization.
The data came from cross-sectional measurements in 605 youth (67% female, 56% non-Black) aged 10-23 years at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. The sample included 236 individuals of healthy weight, 224 with obesity, and 145 with type 2 diabetes.
Visceral fat was assessed with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), a widely used test of bone mineral density screening to assess fracture risk. Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (PWV) was used to gauge arterial stiffness, a subclinical sign of cardiovascular disease.
Visceral fat was associated with PWV in all three groups of study subjects (P < .05), the researchers found, whereas the amount of subcutaneous fat was linked to arterial stiffness in obese youth and those with obesity but not those whose weight was considered healthy.
The amount of fat was associated with an additional 1.6% of the variability in arterial stiffness in youth with obesity after accounting for BMI. Subcutaneous fat, meanwhile, did not appear to affect PWV, the researchers found. “In youth with healthy weight, visceral fat, subcutaneous fat, BMI, and waist circumference were not significantly associated with PWV in any analyses,” they write.
The researchers cited a paucity of data on the relationship between visceral fat and cardiovascular disease in children with obesity. Although BMI is a reliable and readily available indicator of risk for disease, DXA “might give us a little more information,” Dr. Kindler, a nutritionist and bone biologist, said. As for clinical use to supplement BMI and waist circumference, he said, “maybe there’s room for visceral fat, but we do need a lot more science to back those decisions down the line.”
For example, what normal visceral fat accumulation during childhood looks like is unknown, he said.
Rigorous longitudinal studies are needed to establish cause and effect, but the new findings offer “a potential connection between visceral fat and cardiovascular disease risk in youth in a relatively large sample,” Wei Shen, MD, MPH, the associate director of the body composition unit at the New York Obesity Nutrition Research Center at Columbia University, New York, said.
Ideally, said Dr. Shen, who was not involved in the latest study, it would be “more credible to use the most accurate measure of visceral fat, the volumetric measurement of visceral fat using MRI” to establish a causal relationship with cardiovascular risk. However, MRI is more expensive and less accessible than DXA. To assess visceral fat in the clinic, “waist circumference may still be a good choice, as it is so convenient to use,” she added.
Dr. Kindler and his colleagues highlighted the need to examine the effect of excess visceral fat as well as intrahepatic fat on youth with type 2 diabetes, who experience cardiovascular complications independent of whether they are obese. In the new study, the positive association between visceral fat and arterial stiffness did not differ between youth with obesity and normal glucose control and those with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Funding came from the Endocrine Fellows Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, and the University of Georgia Obesity Initiative. Dr. Kindler and Dr. Shen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The amount of fat surrounding abdominal organs may help clinicians identify cardiovascular risk in young people with obesity, researchers have found.
Severely overweight children and young adults showed a subtle association between visceral fat and arterial stiffness independent of body mass index (BMI). The association was not present in those of healthy weight, possibly because their visceral fat stores are too small to have a detectable effect on cardiovascular health, according to the researchers, who reported their findings in the latest issue of Pediatric Obesity.
“Those kids with greater visceral fat had stiffer arteries, which can overtax and overstress the system and lead to unfortunate consequences in terms of cardiovascular health down the line,” senior author Joseph M. Kindler, PhD, an assistant professor of nutritional sciences at the University of Georgia, Athens, told this news organization.
The data came from cross-sectional measurements in 605 youth (67% female, 56% non-Black) aged 10-23 years at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. The sample included 236 individuals of healthy weight, 224 with obesity, and 145 with type 2 diabetes.
Visceral fat was assessed with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), a widely used test of bone mineral density screening to assess fracture risk. Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (PWV) was used to gauge arterial stiffness, a subclinical sign of cardiovascular disease.
Visceral fat was associated with PWV in all three groups of study subjects (P < .05), the researchers found, whereas the amount of subcutaneous fat was linked to arterial stiffness in obese youth and those with obesity but not those whose weight was considered healthy.
The amount of fat was associated with an additional 1.6% of the variability in arterial stiffness in youth with obesity after accounting for BMI. Subcutaneous fat, meanwhile, did not appear to affect PWV, the researchers found. “In youth with healthy weight, visceral fat, subcutaneous fat, BMI, and waist circumference were not significantly associated with PWV in any analyses,” they write.
The researchers cited a paucity of data on the relationship between visceral fat and cardiovascular disease in children with obesity. Although BMI is a reliable and readily available indicator of risk for disease, DXA “might give us a little more information,” Dr. Kindler, a nutritionist and bone biologist, said. As for clinical use to supplement BMI and waist circumference, he said, “maybe there’s room for visceral fat, but we do need a lot more science to back those decisions down the line.”
For example, what normal visceral fat accumulation during childhood looks like is unknown, he said.
Rigorous longitudinal studies are needed to establish cause and effect, but the new findings offer “a potential connection between visceral fat and cardiovascular disease risk in youth in a relatively large sample,” Wei Shen, MD, MPH, the associate director of the body composition unit at the New York Obesity Nutrition Research Center at Columbia University, New York, said.
Ideally, said Dr. Shen, who was not involved in the latest study, it would be “more credible to use the most accurate measure of visceral fat, the volumetric measurement of visceral fat using MRI” to establish a causal relationship with cardiovascular risk. However, MRI is more expensive and less accessible than DXA. To assess visceral fat in the clinic, “waist circumference may still be a good choice, as it is so convenient to use,” she added.
Dr. Kindler and his colleagues highlighted the need to examine the effect of excess visceral fat as well as intrahepatic fat on youth with type 2 diabetes, who experience cardiovascular complications independent of whether they are obese. In the new study, the positive association between visceral fat and arterial stiffness did not differ between youth with obesity and normal glucose control and those with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Funding came from the Endocrine Fellows Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, and the University of Georgia Obesity Initiative. Dr. Kindler and Dr. Shen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The amount of fat surrounding abdominal organs may help clinicians identify cardiovascular risk in young people with obesity, researchers have found.
Severely overweight children and young adults showed a subtle association between visceral fat and arterial stiffness independent of body mass index (BMI). The association was not present in those of healthy weight, possibly because their visceral fat stores are too small to have a detectable effect on cardiovascular health, according to the researchers, who reported their findings in the latest issue of Pediatric Obesity.
“Those kids with greater visceral fat had stiffer arteries, which can overtax and overstress the system and lead to unfortunate consequences in terms of cardiovascular health down the line,” senior author Joseph M. Kindler, PhD, an assistant professor of nutritional sciences at the University of Georgia, Athens, told this news organization.
The data came from cross-sectional measurements in 605 youth (67% female, 56% non-Black) aged 10-23 years at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. The sample included 236 individuals of healthy weight, 224 with obesity, and 145 with type 2 diabetes.
Visceral fat was assessed with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), a widely used test of bone mineral density screening to assess fracture risk. Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (PWV) was used to gauge arterial stiffness, a subclinical sign of cardiovascular disease.
Visceral fat was associated with PWV in all three groups of study subjects (P < .05), the researchers found, whereas the amount of subcutaneous fat was linked to arterial stiffness in obese youth and those with obesity but not those whose weight was considered healthy.
The amount of fat was associated with an additional 1.6% of the variability in arterial stiffness in youth with obesity after accounting for BMI. Subcutaneous fat, meanwhile, did not appear to affect PWV, the researchers found. “In youth with healthy weight, visceral fat, subcutaneous fat, BMI, and waist circumference were not significantly associated with PWV in any analyses,” they write.
The researchers cited a paucity of data on the relationship between visceral fat and cardiovascular disease in children with obesity. Although BMI is a reliable and readily available indicator of risk for disease, DXA “might give us a little more information,” Dr. Kindler, a nutritionist and bone biologist, said. As for clinical use to supplement BMI and waist circumference, he said, “maybe there’s room for visceral fat, but we do need a lot more science to back those decisions down the line.”
For example, what normal visceral fat accumulation during childhood looks like is unknown, he said.
Rigorous longitudinal studies are needed to establish cause and effect, but the new findings offer “a potential connection between visceral fat and cardiovascular disease risk in youth in a relatively large sample,” Wei Shen, MD, MPH, the associate director of the body composition unit at the New York Obesity Nutrition Research Center at Columbia University, New York, said.
Ideally, said Dr. Shen, who was not involved in the latest study, it would be “more credible to use the most accurate measure of visceral fat, the volumetric measurement of visceral fat using MRI” to establish a causal relationship with cardiovascular risk. However, MRI is more expensive and less accessible than DXA. To assess visceral fat in the clinic, “waist circumference may still be a good choice, as it is so convenient to use,” she added.
Dr. Kindler and his colleagues highlighted the need to examine the effect of excess visceral fat as well as intrahepatic fat on youth with type 2 diabetes, who experience cardiovascular complications independent of whether they are obese. In the new study, the positive association between visceral fat and arterial stiffness did not differ between youth with obesity and normal glucose control and those with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Funding came from the Endocrine Fellows Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, and the University of Georgia Obesity Initiative. Dr. Kindler and Dr. Shen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Bariatric surgery can lead to diabetes remission, cut cancer risk
Patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes who underwent bariatric surgery and had 10-year durable diabetes remission had a 60% lower risk of incident cancer than patients who had usual obesity care.
And women who had bariatric surgery had a 42% lower risk of having cancer during a median 21-year follow-up, compared with women who had usual obesity care.
These findings from 701 patients in the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study who had type 2 diabetes were recently published in Diabetes Care.
The results illustrate the “connection between glucose control and cancer prevention” and suggest that “among patients with type 2 diabetes, many cancer cases are preventable,” lead author Kajsa Sjöholm, PhD, associate professor of molecular medicine at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg (Sweden), said in a press release from the university.
“The global epidemic of both obesity and diabetes leads to an increased risk of cancer, as well as an increased risk of premature death,” added senior author Magdalena Taube, PhD, associate professor of molecular medicine in the same academy.
“It has been estimated that, over the next 10-15 years, obesity may cause more cancer cases than smoking in several countries,” she noted. Therefore, “strategies are needed to prevent this development, and our results can provide vital guidance for prevention of cancer in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes.”
Durable diabetes remission seems key
Two-thirds of the patients in the bariatric surgery group had vertical banded gastroplasty (65%), and the rest had adjustable or nonadjustable gastric banding (18%) or gastric bypass (17%).
Each type of bariatric surgery was associated with higher diabetes remission rates, compared with usual care, in a previous study by these researchers, Dr. Taube said in an interview.
“In our present study,” she added, “we observed a nonsignificant trend, where patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes in the highest weight loss tertile (average weight loss, –44.8 kg) had somewhat lower risk of cancer compared to the lowest tertile [average weight loss, –14.9 kg].”
This might suggest, Dr. Taube continued, that with respect to cancer risk, surgery techniques resulting in greater weight loss (for example, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy) should be recommended in patients with obesity and diabetes.
“However, it should also be noted that long-term diabetes remission seems imperative for cancer risk reduction,” she said, “and in a recent meta-analysis by McTigue et al., published in JAMA Surgery, it was shown that patients who had Roux-en-Y gastric bypass had greater weight loss, a slightly higher type 2 diabetes remission rate, less type 2 diabetes relapse, and better long-term glycemic control, compared with those who had sleeve gastrectomy.
“The observed cancer reduction in women with obesity and type 2 diabetes is in line with previous findings showing that cancer risk reduction following bariatric surgery in patients with obesity is more marked among women than men,” Dr. Taube noted. This may be because cancer rates are higher in women with diabetes than in men with diabetes, and common cancer types associated with obesity are female specific.
The main cancers in women were breast cancer, followed by endometrial and colorectal cancer. In men, the main cancers were colorectal, prostate, and urothelial/malignant skin cancer.
Study design and findings
It is well established that obesity is a risk factor for 13 types of cancer, and some of these cancers (liver, pancreatic, endometrial, colon and rectal, breast, and bladder) may be related to type 2 diabetes. And bariatric surgery has been shown to reduce cancer risk in patients with obesity.
However, it is not clear how bariatric surgery may affect cancer risk in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
To study this, the researchers examined data from 393 patients who underwent bariatric surgery and 308 patients who received usual obesity treatment, who were part of the SOS study.
The SOS study enrolled men with a body mass index of at least 34 kg/m2, and women with a BMI of at least 38 kg/m2 who were aged 37-60 years between 1987 and 2001.
The current study outcome – cancer incidence in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes – was not a prespecified outcome
The intervention groups were matched on 18 variables, including age, sex, serum insulin, alcohol, education, and smoking.
At baseline, the patients had a mean age of about 49 and 60% were women. They had a mean BMI of about 42 and a mean hemoglobin A1c of 7.8%.
On average, patients in the surgery group had lost 27.5 kg and 22.7 kg, and patients in the usual care group had lost 3.2 kg and 4.8 kg, at 2 years and 10 years, respectively.
During a median follow-up of 21 years, there were 74 incident cancers in the control group and 68 cancers in the bariatric surgery group.
The risk of cancer during follow-up was 37% lower in the surgery group than in the usual care group, after multivariable adjustment (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.63; 95% confidence interval, 0.44-0.89; P = .008).
A deeper dive showed that there were 86 incident cancers in women and 56 cancers in men. The risk of cancer was significantly lower in women who had bariatric surgery, compared with those who had usual care (aHR, 0.58; 95% CI 0.38-0.90, P = .016). However, the risk of cancer was not significantly lower in men who had bariatric surgery versus those who had usual care (aHR 0.79, 95% CI, 0.46-1.38; P = .413).
Diabetes remission at 10 years was associated with a 60% reduced cancer incidence (aHR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.22-0.74, P = .003).
The study was funded by the Swedish state (under an agreement between the Swedish government and the county councils), the Swedish Research Council, the Novo Nordisk Foundation, the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, and the Swedish Diabetes Foundation. One author received consulting fees from Johnson & Johnson. The other authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes who underwent bariatric surgery and had 10-year durable diabetes remission had a 60% lower risk of incident cancer than patients who had usual obesity care.
And women who had bariatric surgery had a 42% lower risk of having cancer during a median 21-year follow-up, compared with women who had usual obesity care.
These findings from 701 patients in the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study who had type 2 diabetes were recently published in Diabetes Care.
The results illustrate the “connection between glucose control and cancer prevention” and suggest that “among patients with type 2 diabetes, many cancer cases are preventable,” lead author Kajsa Sjöholm, PhD, associate professor of molecular medicine at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg (Sweden), said in a press release from the university.
“The global epidemic of both obesity and diabetes leads to an increased risk of cancer, as well as an increased risk of premature death,” added senior author Magdalena Taube, PhD, associate professor of molecular medicine in the same academy.
“It has been estimated that, over the next 10-15 years, obesity may cause more cancer cases than smoking in several countries,” she noted. Therefore, “strategies are needed to prevent this development, and our results can provide vital guidance for prevention of cancer in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes.”
Durable diabetes remission seems key
Two-thirds of the patients in the bariatric surgery group had vertical banded gastroplasty (65%), and the rest had adjustable or nonadjustable gastric banding (18%) or gastric bypass (17%).
Each type of bariatric surgery was associated with higher diabetes remission rates, compared with usual care, in a previous study by these researchers, Dr. Taube said in an interview.
“In our present study,” she added, “we observed a nonsignificant trend, where patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes in the highest weight loss tertile (average weight loss, –44.8 kg) had somewhat lower risk of cancer compared to the lowest tertile [average weight loss, –14.9 kg].”
This might suggest, Dr. Taube continued, that with respect to cancer risk, surgery techniques resulting in greater weight loss (for example, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy) should be recommended in patients with obesity and diabetes.
“However, it should also be noted that long-term diabetes remission seems imperative for cancer risk reduction,” she said, “and in a recent meta-analysis by McTigue et al., published in JAMA Surgery, it was shown that patients who had Roux-en-Y gastric bypass had greater weight loss, a slightly higher type 2 diabetes remission rate, less type 2 diabetes relapse, and better long-term glycemic control, compared with those who had sleeve gastrectomy.
“The observed cancer reduction in women with obesity and type 2 diabetes is in line with previous findings showing that cancer risk reduction following bariatric surgery in patients with obesity is more marked among women than men,” Dr. Taube noted. This may be because cancer rates are higher in women with diabetes than in men with diabetes, and common cancer types associated with obesity are female specific.
The main cancers in women were breast cancer, followed by endometrial and colorectal cancer. In men, the main cancers were colorectal, prostate, and urothelial/malignant skin cancer.
Study design and findings
It is well established that obesity is a risk factor for 13 types of cancer, and some of these cancers (liver, pancreatic, endometrial, colon and rectal, breast, and bladder) may be related to type 2 diabetes. And bariatric surgery has been shown to reduce cancer risk in patients with obesity.
However, it is not clear how bariatric surgery may affect cancer risk in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
To study this, the researchers examined data from 393 patients who underwent bariatric surgery and 308 patients who received usual obesity treatment, who were part of the SOS study.
The SOS study enrolled men with a body mass index of at least 34 kg/m2, and women with a BMI of at least 38 kg/m2 who were aged 37-60 years between 1987 and 2001.
The current study outcome – cancer incidence in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes – was not a prespecified outcome
The intervention groups were matched on 18 variables, including age, sex, serum insulin, alcohol, education, and smoking.
At baseline, the patients had a mean age of about 49 and 60% were women. They had a mean BMI of about 42 and a mean hemoglobin A1c of 7.8%.
On average, patients in the surgery group had lost 27.5 kg and 22.7 kg, and patients in the usual care group had lost 3.2 kg and 4.8 kg, at 2 years and 10 years, respectively.
During a median follow-up of 21 years, there were 74 incident cancers in the control group and 68 cancers in the bariatric surgery group.
The risk of cancer during follow-up was 37% lower in the surgery group than in the usual care group, after multivariable adjustment (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.63; 95% confidence interval, 0.44-0.89; P = .008).
A deeper dive showed that there were 86 incident cancers in women and 56 cancers in men. The risk of cancer was significantly lower in women who had bariatric surgery, compared with those who had usual care (aHR, 0.58; 95% CI 0.38-0.90, P = .016). However, the risk of cancer was not significantly lower in men who had bariatric surgery versus those who had usual care (aHR 0.79, 95% CI, 0.46-1.38; P = .413).
Diabetes remission at 10 years was associated with a 60% reduced cancer incidence (aHR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.22-0.74, P = .003).
The study was funded by the Swedish state (under an agreement between the Swedish government and the county councils), the Swedish Research Council, the Novo Nordisk Foundation, the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, and the Swedish Diabetes Foundation. One author received consulting fees from Johnson & Johnson. The other authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes who underwent bariatric surgery and had 10-year durable diabetes remission had a 60% lower risk of incident cancer than patients who had usual obesity care.
And women who had bariatric surgery had a 42% lower risk of having cancer during a median 21-year follow-up, compared with women who had usual obesity care.
These findings from 701 patients in the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study who had type 2 diabetes were recently published in Diabetes Care.
The results illustrate the “connection between glucose control and cancer prevention” and suggest that “among patients with type 2 diabetes, many cancer cases are preventable,” lead author Kajsa Sjöholm, PhD, associate professor of molecular medicine at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg (Sweden), said in a press release from the university.
“The global epidemic of both obesity and diabetes leads to an increased risk of cancer, as well as an increased risk of premature death,” added senior author Magdalena Taube, PhD, associate professor of molecular medicine in the same academy.
“It has been estimated that, over the next 10-15 years, obesity may cause more cancer cases than smoking in several countries,” she noted. Therefore, “strategies are needed to prevent this development, and our results can provide vital guidance for prevention of cancer in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes.”
Durable diabetes remission seems key
Two-thirds of the patients in the bariatric surgery group had vertical banded gastroplasty (65%), and the rest had adjustable or nonadjustable gastric banding (18%) or gastric bypass (17%).
Each type of bariatric surgery was associated with higher diabetes remission rates, compared with usual care, in a previous study by these researchers, Dr. Taube said in an interview.
“In our present study,” she added, “we observed a nonsignificant trend, where patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes in the highest weight loss tertile (average weight loss, –44.8 kg) had somewhat lower risk of cancer compared to the lowest tertile [average weight loss, –14.9 kg].”
This might suggest, Dr. Taube continued, that with respect to cancer risk, surgery techniques resulting in greater weight loss (for example, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy) should be recommended in patients with obesity and diabetes.
“However, it should also be noted that long-term diabetes remission seems imperative for cancer risk reduction,” she said, “and in a recent meta-analysis by McTigue et al., published in JAMA Surgery, it was shown that patients who had Roux-en-Y gastric bypass had greater weight loss, a slightly higher type 2 diabetes remission rate, less type 2 diabetes relapse, and better long-term glycemic control, compared with those who had sleeve gastrectomy.
“The observed cancer reduction in women with obesity and type 2 diabetes is in line with previous findings showing that cancer risk reduction following bariatric surgery in patients with obesity is more marked among women than men,” Dr. Taube noted. This may be because cancer rates are higher in women with diabetes than in men with diabetes, and common cancer types associated with obesity are female specific.
The main cancers in women were breast cancer, followed by endometrial and colorectal cancer. In men, the main cancers were colorectal, prostate, and urothelial/malignant skin cancer.
Study design and findings
It is well established that obesity is a risk factor for 13 types of cancer, and some of these cancers (liver, pancreatic, endometrial, colon and rectal, breast, and bladder) may be related to type 2 diabetes. And bariatric surgery has been shown to reduce cancer risk in patients with obesity.
However, it is not clear how bariatric surgery may affect cancer risk in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
To study this, the researchers examined data from 393 patients who underwent bariatric surgery and 308 patients who received usual obesity treatment, who were part of the SOS study.
The SOS study enrolled men with a body mass index of at least 34 kg/m2, and women with a BMI of at least 38 kg/m2 who were aged 37-60 years between 1987 and 2001.
The current study outcome – cancer incidence in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes – was not a prespecified outcome
The intervention groups were matched on 18 variables, including age, sex, serum insulin, alcohol, education, and smoking.
At baseline, the patients had a mean age of about 49 and 60% were women. They had a mean BMI of about 42 and a mean hemoglobin A1c of 7.8%.
On average, patients in the surgery group had lost 27.5 kg and 22.7 kg, and patients in the usual care group had lost 3.2 kg and 4.8 kg, at 2 years and 10 years, respectively.
During a median follow-up of 21 years, there were 74 incident cancers in the control group and 68 cancers in the bariatric surgery group.
The risk of cancer during follow-up was 37% lower in the surgery group than in the usual care group, after multivariable adjustment (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.63; 95% confidence interval, 0.44-0.89; P = .008).
A deeper dive showed that there were 86 incident cancers in women and 56 cancers in men. The risk of cancer was significantly lower in women who had bariatric surgery, compared with those who had usual care (aHR, 0.58; 95% CI 0.38-0.90, P = .016). However, the risk of cancer was not significantly lower in men who had bariatric surgery versus those who had usual care (aHR 0.79, 95% CI, 0.46-1.38; P = .413).
Diabetes remission at 10 years was associated with a 60% reduced cancer incidence (aHR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.22-0.74, P = .003).
The study was funded by the Swedish state (under an agreement between the Swedish government and the county councils), the Swedish Research Council, the Novo Nordisk Foundation, the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, and the Swedish Diabetes Foundation. One author received consulting fees from Johnson & Johnson. The other authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETES CARE
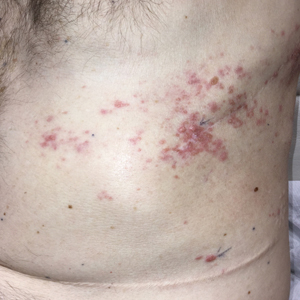
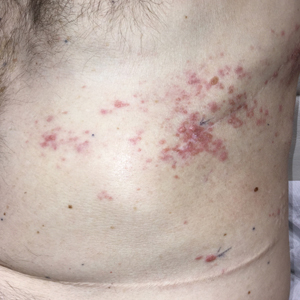
Zosteriform Eruption on the Chest and Abdomen
THE DIAGNOSIS:
Cutaneous Metastatic Mesothelioma
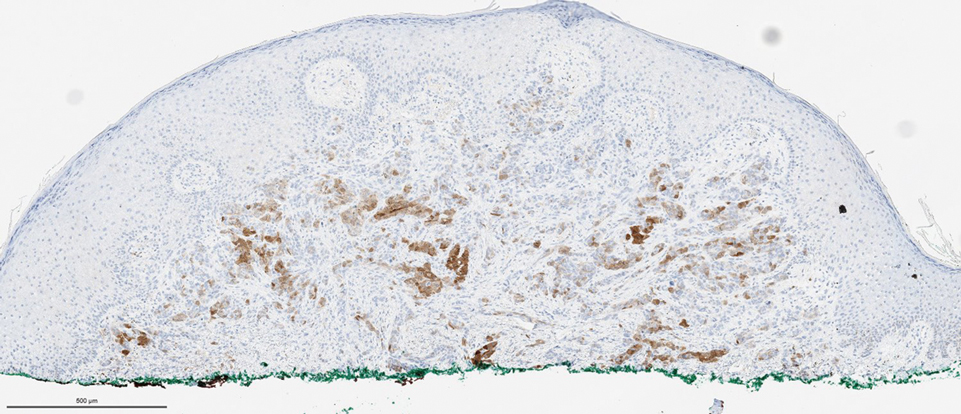
Biopsies of the larger erythematous papules revealed an infiltrate of atypical tumor cells with mitoses (Figure 1) that were immunoreactive for calretinin (Figure 2) and lacked nuclear BRCA1 associated protein-1, BAP1, expression (not shown). The patient’s prior mesothelioma was re-reviewed, and the cutaneous tumor cells were similar to the primary mesothelioma. A diagnosis of cutaneous metastatic mesothelioma (CMM) was made.
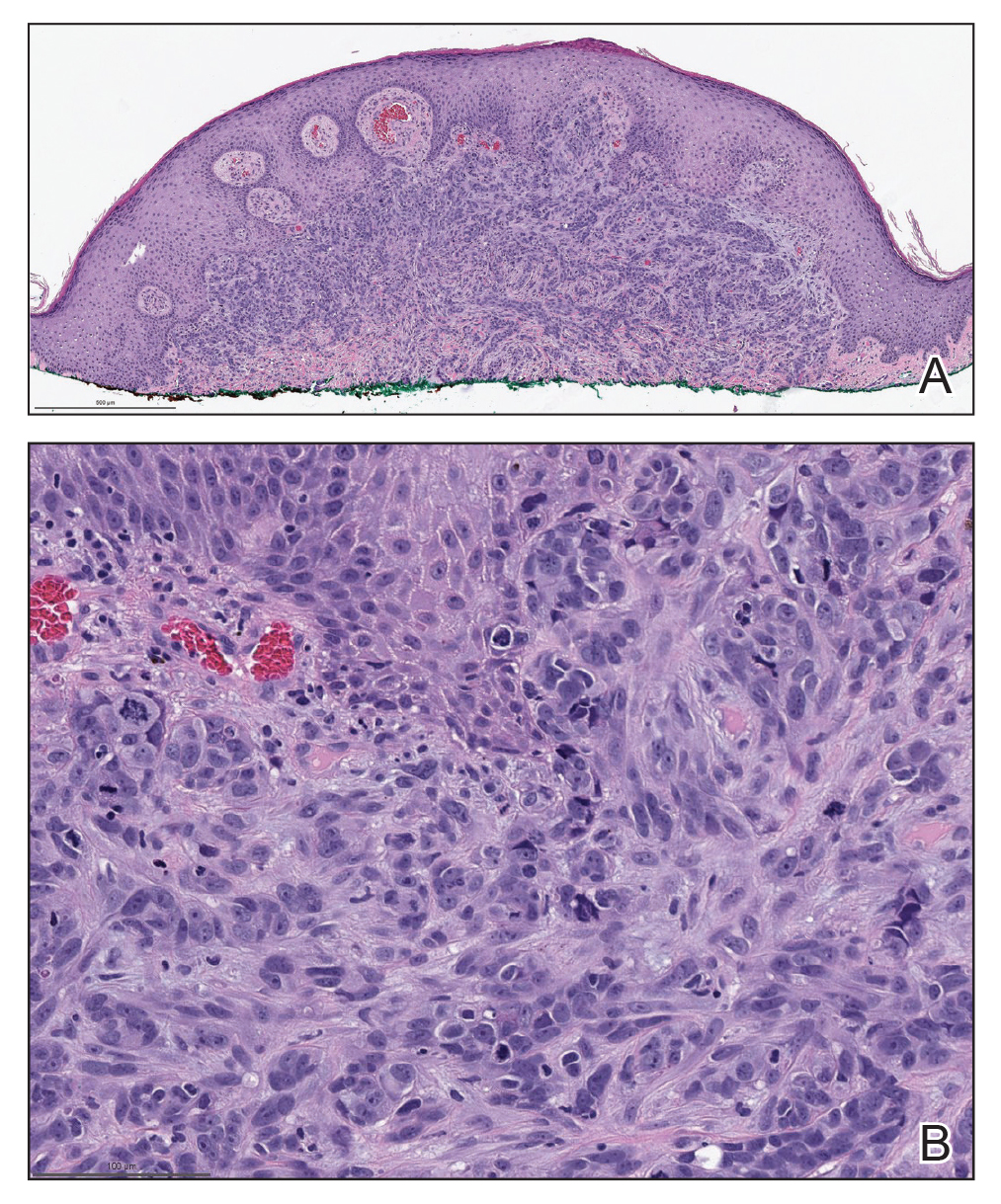
Mesothelioma is a rare neoplasm arising from the pleura, pericardium, peritoneum, and tunica vaginalis,1 with an estimated annual incidence of 2500 cases.2 The predominant risk factor for the development of pleural mesothelioma is asbestos exposure, which has been identified in up to 90% of cases. Mesothelioma can give rise to local and less frequently distant hematogenous metastases. Cutaneous involvement of mesothelioma is rare.3 More than 80% of CMM cases are attributed to seeding the skin at procedure sites or by direct infiltration of scars. Distant CMM is rare and typically presents as subcutaneous nodules.4 Few cases of inflammatory CMM have been published,1,4,5 with even fewer mimicking herpes zoster infection (HZI), as seen in our patient.
The most specific stain for mesothelioma is calretinin, which strongly and diffusely stains both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Other markers include Wilms tumor 1, cytokeratin 5/6, thrombomodulin, and HBME-1. Immunohistochemistry to detect the loss of BAP1 staining in the nucleus is important for differentiating between mesothelioma and mesothelial hyperplasia.3
Cutaneous metastases occur in 0.7% to 9% of patients with internal malignant disease. Most commonly, cutaneous metastases present as cutaneous nodules, though other reported inflammatory presentations include erysipeloides, generalized erythematous patches, telangiectasia, and zosteriform distributions.6 Zosteriform distributions are particularly rare and most commonly are due to breast carcinomas or lymphomas. The mechanism of zosteriform metastasis is unknown, but theories include tumoral spread along vessels, invasion of the thoracic perineural sheaths, localized spread of tumor cells from a surgical site, or a Koebner-like reaction at the site of an existing HZI. Regardless of primary tumor type or presentation, cutaneous metastasis is a poor prognostic sign, with survival rates varying based on primary tumor type.7
Other differential diagnoses include herpes zoster granulomatous dermatitis, radiation recall dermatitis, cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease, and zosteriform lichen planus, all of which have been reported after HZI.8-10 Herpes zoster granulomatous dermatitis typically presents weeks to years after acute HZI with erythematous to violaceous papules and plaques at the site of the prior HZI. A biopsy reveals interstitial granulomatous dermatitis and multinucleated giant cells.8 Radiation recall dermatitis is a cutaneous inflammatory reaction limited to regions of prior radiation exposure after the administration of a triggering medication. Radiation recall dermatitis can present days to many years after the completion of treatment.9 Although the eruption in our patient was at the site of prior radiation, the pathologic and clinical presentation was not consistent with radiation recall dermatitis. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease is a non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis that may present as either solitary or numerous papules, plaques, or nodules and has been reported to occur after HZI. Biopsy reveals a diffuse dermal histiocytic infiltration with plasma cells and lymphocytes. In contrast to metastatic disease, mitoses and nuclear atypia are rare in cutaneous RosaiDorfman disease.11 Lichen planus is an inflammatory disease of unknown etiology presenting as flat-topped, violaceous, pruritic papules12 that may present in a zosteriform pattern.13
Although it is uncommon, metastatic spread should be considered in patients with known malignancy presenting with zosteriform eruptions.2 Our patient remained on treatment with immunotherapy, as he was unable to undergo additional radiation and had failed multiple other lines of therapy. He died 3 months after presentation.
- Klebanov N, Reddy BY, Husain S, et al. Cutaneous presentation of mesothelioma with a sarcomatoid transformation. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:378-382.
- Patel SC, Dowell JE. Modern management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2016;7:63-72.
- Ward RE, Ali SA, Kuhar M. Epithelioid malignant mesothelioma metastatic to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:1057-1063.
- Prieto VG, Kenet BJ, Varghese M. Malignant mesothelioma metastatic to the skin, presenting as inflammatory carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:261-265.
- Gaudy-Marqueste C, Dales JP, Collet-Villette AM, et al. Cutaneous metastasis of pleural mesothelioma: two cases [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2003;130:455-459.
- Chiang A, Salomon N, Gaikwad R, et al. A case of cutaneous metastasis mimicking herpes zoster rash. IDCases. 2018;12:167-168.
- Thomaidou E, Armon G, Klapholz L, et al. Zosteriform cutaneous metastases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:734-736.
- Ferenczi K, Rosenberg AS, McCalmont TH, et al. Herpes zoster granulomatous dermatitis: histopathologic findings in a case series. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:739-745.
- Carrasco L, Pastor MA, Izquierdo MJ, et al. Drug eruption secondary to acyclovir with recall phenomenon in a dermatome previously affected by herpes zoster. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002;27:132-134.
- Malviya N, Marzuka A, Maamed-Tayeb M, et al. Cutaneous involvement of pre-existing Rosai-Dorfman disease via post-herpetic isotopic response. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:1211-1214.
- Fang S, Chen AJ. Facial cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: a case report and literature review. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9:1389-1392.
- Le Cleach L, Chosidow O. Clinical practice. lichen planus. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:723-732.
- Fink-Puches R, Hofmann-Wellenhof R, Smolle J. Zosteriform lichen planus. Dermatology. 1996;192:375-377.
THE DIAGNOSIS:
Cutaneous Metastatic Mesothelioma
Biopsies of the larger erythematous papules revealed an infiltrate of atypical tumor cells with mitoses (Figure 1) that were immunoreactive for calretinin (Figure 2) and lacked nuclear BRCA1 associated protein-1, BAP1, expression (not shown). The patient’s prior mesothelioma was re-reviewed, and the cutaneous tumor cells were similar to the primary mesothelioma. A diagnosis of cutaneous metastatic mesothelioma (CMM) was made.


Mesothelioma is a rare neoplasm arising from the pleura, pericardium, peritoneum, and tunica vaginalis,1 with an estimated annual incidence of 2500 cases.2 The predominant risk factor for the development of pleural mesothelioma is asbestos exposure, which has been identified in up to 90% of cases. Mesothelioma can give rise to local and less frequently distant hematogenous metastases. Cutaneous involvement of mesothelioma is rare.3 More than 80% of CMM cases are attributed to seeding the skin at procedure sites or by direct infiltration of scars. Distant CMM is rare and typically presents as subcutaneous nodules.4 Few cases of inflammatory CMM have been published,1,4,5 with even fewer mimicking herpes zoster infection (HZI), as seen in our patient.
The most specific stain for mesothelioma is calretinin, which strongly and diffusely stains both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Other markers include Wilms tumor 1, cytokeratin 5/6, thrombomodulin, and HBME-1. Immunohistochemistry to detect the loss of BAP1 staining in the nucleus is important for differentiating between mesothelioma and mesothelial hyperplasia.3
Cutaneous metastases occur in 0.7% to 9% of patients with internal malignant disease. Most commonly, cutaneous metastases present as cutaneous nodules, though other reported inflammatory presentations include erysipeloides, generalized erythematous patches, telangiectasia, and zosteriform distributions.6 Zosteriform distributions are particularly rare and most commonly are due to breast carcinomas or lymphomas. The mechanism of zosteriform metastasis is unknown, but theories include tumoral spread along vessels, invasion of the thoracic perineural sheaths, localized spread of tumor cells from a surgical site, or a Koebner-like reaction at the site of an existing HZI. Regardless of primary tumor type or presentation, cutaneous metastasis is a poor prognostic sign, with survival rates varying based on primary tumor type.7
Other differential diagnoses include herpes zoster granulomatous dermatitis, radiation recall dermatitis, cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease, and zosteriform lichen planus, all of which have been reported after HZI.8-10 Herpes zoster granulomatous dermatitis typically presents weeks to years after acute HZI with erythematous to violaceous papules and plaques at the site of the prior HZI. A biopsy reveals interstitial granulomatous dermatitis and multinucleated giant cells.8 Radiation recall dermatitis is a cutaneous inflammatory reaction limited to regions of prior radiation exposure after the administration of a triggering medication. Radiation recall dermatitis can present days to many years after the completion of treatment.9 Although the eruption in our patient was at the site of prior radiation, the pathologic and clinical presentation was not consistent with radiation recall dermatitis. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease is a non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis that may present as either solitary or numerous papules, plaques, or nodules and has been reported to occur after HZI. Biopsy reveals a diffuse dermal histiocytic infiltration with plasma cells and lymphocytes. In contrast to metastatic disease, mitoses and nuclear atypia are rare in cutaneous RosaiDorfman disease.11 Lichen planus is an inflammatory disease of unknown etiology presenting as flat-topped, violaceous, pruritic papules12 that may present in a zosteriform pattern.13
Although it is uncommon, metastatic spread should be considered in patients with known malignancy presenting with zosteriform eruptions.2 Our patient remained on treatment with immunotherapy, as he was unable to undergo additional radiation and had failed multiple other lines of therapy. He died 3 months after presentation.
THE DIAGNOSIS:
Cutaneous Metastatic Mesothelioma
Biopsies of the larger erythematous papules revealed an infiltrate of atypical tumor cells with mitoses (Figure 1) that were immunoreactive for calretinin (Figure 2) and lacked nuclear BRCA1 associated protein-1, BAP1, expression (not shown). The patient’s prior mesothelioma was re-reviewed, and the cutaneous tumor cells were similar to the primary mesothelioma. A diagnosis of cutaneous metastatic mesothelioma (CMM) was made.


Mesothelioma is a rare neoplasm arising from the pleura, pericardium, peritoneum, and tunica vaginalis,1 with an estimated annual incidence of 2500 cases.2 The predominant risk factor for the development of pleural mesothelioma is asbestos exposure, which has been identified in up to 90% of cases. Mesothelioma can give rise to local and less frequently distant hematogenous metastases. Cutaneous involvement of mesothelioma is rare.3 More than 80% of CMM cases are attributed to seeding the skin at procedure sites or by direct infiltration of scars. Distant CMM is rare and typically presents as subcutaneous nodules.4 Few cases of inflammatory CMM have been published,1,4,5 with even fewer mimicking herpes zoster infection (HZI), as seen in our patient.
The most specific stain for mesothelioma is calretinin, which strongly and diffusely stains both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Other markers include Wilms tumor 1, cytokeratin 5/6, thrombomodulin, and HBME-1. Immunohistochemistry to detect the loss of BAP1 staining in the nucleus is important for differentiating between mesothelioma and mesothelial hyperplasia.3
Cutaneous metastases occur in 0.7% to 9% of patients with internal malignant disease. Most commonly, cutaneous metastases present as cutaneous nodules, though other reported inflammatory presentations include erysipeloides, generalized erythematous patches, telangiectasia, and zosteriform distributions.6 Zosteriform distributions are particularly rare and most commonly are due to breast carcinomas or lymphomas. The mechanism of zosteriform metastasis is unknown, but theories include tumoral spread along vessels, invasion of the thoracic perineural sheaths, localized spread of tumor cells from a surgical site, or a Koebner-like reaction at the site of an existing HZI. Regardless of primary tumor type or presentation, cutaneous metastasis is a poor prognostic sign, with survival rates varying based on primary tumor type.7
Other differential diagnoses include herpes zoster granulomatous dermatitis, radiation recall dermatitis, cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease, and zosteriform lichen planus, all of which have been reported after HZI.8-10 Herpes zoster granulomatous dermatitis typically presents weeks to years after acute HZI with erythematous to violaceous papules and plaques at the site of the prior HZI. A biopsy reveals interstitial granulomatous dermatitis and multinucleated giant cells.8 Radiation recall dermatitis is a cutaneous inflammatory reaction limited to regions of prior radiation exposure after the administration of a triggering medication. Radiation recall dermatitis can present days to many years after the completion of treatment.9 Although the eruption in our patient was at the site of prior radiation, the pathologic and clinical presentation was not consistent with radiation recall dermatitis. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease is a non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis that may present as either solitary or numerous papules, plaques, or nodules and has been reported to occur after HZI. Biopsy reveals a diffuse dermal histiocytic infiltration with plasma cells and lymphocytes. In contrast to metastatic disease, mitoses and nuclear atypia are rare in cutaneous RosaiDorfman disease.11 Lichen planus is an inflammatory disease of unknown etiology presenting as flat-topped, violaceous, pruritic papules12 that may present in a zosteriform pattern.13
Although it is uncommon, metastatic spread should be considered in patients with known malignancy presenting with zosteriform eruptions.2 Our patient remained on treatment with immunotherapy, as he was unable to undergo additional radiation and had failed multiple other lines of therapy. He died 3 months after presentation.
- Klebanov N, Reddy BY, Husain S, et al. Cutaneous presentation of mesothelioma with a sarcomatoid transformation. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:378-382.
- Patel SC, Dowell JE. Modern management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2016;7:63-72.
- Ward RE, Ali SA, Kuhar M. Epithelioid malignant mesothelioma metastatic to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:1057-1063.
- Prieto VG, Kenet BJ, Varghese M. Malignant mesothelioma metastatic to the skin, presenting as inflammatory carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:261-265.
- Gaudy-Marqueste C, Dales JP, Collet-Villette AM, et al. Cutaneous metastasis of pleural mesothelioma: two cases [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2003;130:455-459.
- Chiang A, Salomon N, Gaikwad R, et al. A case of cutaneous metastasis mimicking herpes zoster rash. IDCases. 2018;12:167-168.
- Thomaidou E, Armon G, Klapholz L, et al. Zosteriform cutaneous metastases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:734-736.
- Ferenczi K, Rosenberg AS, McCalmont TH, et al. Herpes zoster granulomatous dermatitis: histopathologic findings in a case series. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:739-745.
- Carrasco L, Pastor MA, Izquierdo MJ, et al. Drug eruption secondary to acyclovir with recall phenomenon in a dermatome previously affected by herpes zoster. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002;27:132-134.
- Malviya N, Marzuka A, Maamed-Tayeb M, et al. Cutaneous involvement of pre-existing Rosai-Dorfman disease via post-herpetic isotopic response. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:1211-1214.
- Fang S, Chen AJ. Facial cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: a case report and literature review. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9:1389-1392.
- Le Cleach L, Chosidow O. Clinical practice. lichen planus. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:723-732.
- Fink-Puches R, Hofmann-Wellenhof R, Smolle J. Zosteriform lichen planus. Dermatology. 1996;192:375-377.
- Klebanov N, Reddy BY, Husain S, et al. Cutaneous presentation of mesothelioma with a sarcomatoid transformation. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:378-382.
- Patel SC, Dowell JE. Modern management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2016;7:63-72.
- Ward RE, Ali SA, Kuhar M. Epithelioid malignant mesothelioma metastatic to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:1057-1063.
- Prieto VG, Kenet BJ, Varghese M. Malignant mesothelioma metastatic to the skin, presenting as inflammatory carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:261-265.
- Gaudy-Marqueste C, Dales JP, Collet-Villette AM, et al. Cutaneous metastasis of pleural mesothelioma: two cases [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2003;130:455-459.
- Chiang A, Salomon N, Gaikwad R, et al. A case of cutaneous metastasis mimicking herpes zoster rash. IDCases. 2018;12:167-168.
- Thomaidou E, Armon G, Klapholz L, et al. Zosteriform cutaneous metastases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:734-736.
- Ferenczi K, Rosenberg AS, McCalmont TH, et al. Herpes zoster granulomatous dermatitis: histopathologic findings in a case series. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:739-745.
- Carrasco L, Pastor MA, Izquierdo MJ, et al. Drug eruption secondary to acyclovir with recall phenomenon in a dermatome previously affected by herpes zoster. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002;27:132-134.
- Malviya N, Marzuka A, Maamed-Tayeb M, et al. Cutaneous involvement of pre-existing Rosai-Dorfman disease via post-herpetic isotopic response. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:1211-1214.
- Fang S, Chen AJ. Facial cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: a case report and literature review. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9:1389-1392.
- Le Cleach L, Chosidow O. Clinical practice. lichen planus. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:723-732.
- Fink-Puches R, Hofmann-Wellenhof R, Smolle J. Zosteriform lichen planus. Dermatology. 1996;192:375-377.
A 50-year-old man presented with erythematous macules and papules with a dermatomal distribution on the left thoracic region with associated pain of 3 weeks’ duration. The lesions persisted after treatment for herpes zoster. His medical history was notable for mesothelioma that was diagnosed 6 years prior and was treated with ipilimumab and nivolumab following multiple lines of chemotherapy and investigational agents, left thoracotomy, extrapleural pneumonectomy, diaphragmatic reconstruction, and left chest radiation. His medical history also included Hodgkin lymphoma diagnosed 36 years prior that was treated with an appendectomy, splenectomy, systemic chemotherapy, and radiation. Three weeks prior to the current presentation, he was treated by oncology with valacyclovir 1 g 3 times daily for 7 days for presumed herpes zoster without improvement. Physical examination revealed the absence of vesicles, as well as firm, 1- to 6-mm, erythematous papules and plaques, including a few outside of the most affected dermatomes.
Axilla swelling after COVID booster puts focus on mammogram timing
This inflammation is caused by the enlargement of lymph nodes and can show up as an abnormal finding on mammograms and other types of chest scans, causing concern and even the need for additional imaging and follow up, wrote Constance D. Lehman, MD, PhD, and colleagues in an article published in Journal of the American College of Radiology.
Lymph node swelling is a normal immune system reaction to vaccination, and “COVID-19 vaccinations in the arm are a well-documented cause of inflammatory unilateral axillary adenopathy,” noted Dr. Lehman, in an interview. The side effect will occur on the side of the body where the patient received a vaccine, and it is not always noticeable to the woman experiencing it, she said.
“We’re finding that the patients’ bodies are responding to the booster in many ways that are similar to the initial COVID vaccines, with lymph node swelling, muscle aches and pains, headaches, and so on,” said Dr. Lehman, who is chief of breast imaging at the Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. There have been no real differences in reactions between the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines, she added.
Because axillary lymph node swelling can obscure mammogram results, staff of at least a few imaging centers, including Penn State Breast Center in Hershey, Pa., and Providence Women’s Imaging Center in Torrance, Calif., told this news organization that they are asking women to delay mammogram imaging either 6 weeks or 4-6 weeks after getting a COVID-19 booster.
Experts’ suggestions on mammograms, boosters timing
Other experts, including Jessica Leung, MD, acknowledged that vaccine-related reactive adenopathy is seen after the booster dose and provided recommendations for the timing of getting mammograms and the booster with this in mind.
“I would recommend getting the screening mammogram first, which can be followed immediately by vaccination, even on the same day,” said Jessica Leung, MD, a professor of diagnostic radiology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Tex.
“If this is not possible from the scheduling perspective, then the patient should consult her health care provider regarding whether it is okay to wait a bit after receiving the vaccine before getting her screening mammogram.”
The answer to that question will likely depend on the time interval since the prior mammogram and the patient’s personal risk factors for developing breast cancer. Dr. Leung noted. “This is all predicated on the assumption that the patient is asymptomatic. If she has any symptoms, for example a palpable breast lump, then she should seek medical attention regardless of timing of vaccination.”
The same holds true for boosters, she said.
She emphasized that careful consideration should be given before delaying the mammogram. “The medical community has a great deal more knowledge at this time than in the early days of COVID-19 vaccination, so we are often able to identify reactive adenopathy related to vaccination. If patients were to delay the mammogram, any reactive adenopathy may persist, on average, for 4-6 weeks.”
Debra Patt, MD, PhD, MBA, executive vice president at Texas Oncology, professor at the University of Texas at Austin, provided a specific example of when a patient should not delay the diagnostic imaging, which is “in the event that there is an abnormal mass in the breast that requires evaluation.”
Providers are now prepared to address these issues, she added.
Dr. Lehman’s nuanced recommendations
“It’s easy to get both a mammogram and booster, and just a matter of timing them – so that the reaction doesn’t interfere with the mammography results,” Dr. Lehman said.
But she emphasized that women should not be choosing between their mammograms or a booster. “We are now saying the same thing that we did with the initial vaccine,” said Dr. Lehman. “We don’t want patients delaying their mammograms, and we don’t want them delaying their boosters – both are critical to staying healthy.”
In her center, a model was developed to navigate vaccine-associated adenopathy. While this approach was developed for the primary vaccine series, the same applies for the booster, which is essentially a third dose of the same vaccine, explained Dr. Lehman.
When patients present for mammography, ultrasound, or MRI, the technologist will document their COVID-19 vaccination status (first or second dose or booster), the date it was given, and the location. Adding vaccination documentation to intake forms helps to support appropriate management of patients who undergo imaging after COVID-19 vaccination. Six weeks is used as the cutoff point for defining “recent” vaccination.
For patients who are getting a screening mammography or MRI, and who have no symptoms beyond unilateral axillary adenopathy on the same side of the body where they received the COVID-19 vaccination (given in the arm) within a 6-week period, the following is included in the screening mammography or screening MRI report: “In the specific setting of a patient with documented recent (within the past 6 weeks) COVID-19 vaccination in the ipsilateral arm, axillary adenopathy is a benign imaging finding. No further imaging is indicated at this time. If there is clinical concern that persists more than 6 weeks after the patient received the final vaccine dose, axillary ultrasound is recommended.”
The experts interviewed reported no conflicts of interest.
This inflammation is caused by the enlargement of lymph nodes and can show up as an abnormal finding on mammograms and other types of chest scans, causing concern and even the need for additional imaging and follow up, wrote Constance D. Lehman, MD, PhD, and colleagues in an article published in Journal of the American College of Radiology.
Lymph node swelling is a normal immune system reaction to vaccination, and “COVID-19 vaccinations in the arm are a well-documented cause of inflammatory unilateral axillary adenopathy,” noted Dr. Lehman, in an interview. The side effect will occur on the side of the body where the patient received a vaccine, and it is not always noticeable to the woman experiencing it, she said.
“We’re finding that the patients’ bodies are responding to the booster in many ways that are similar to the initial COVID vaccines, with lymph node swelling, muscle aches and pains, headaches, and so on,” said Dr. Lehman, who is chief of breast imaging at the Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. There have been no real differences in reactions between the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines, she added.
Because axillary lymph node swelling can obscure mammogram results, staff of at least a few imaging centers, including Penn State Breast Center in Hershey, Pa., and Providence Women’s Imaging Center in Torrance, Calif., told this news organization that they are asking women to delay mammogram imaging either 6 weeks or 4-6 weeks after getting a COVID-19 booster.
Experts’ suggestions on mammograms, boosters timing
Other experts, including Jessica Leung, MD, acknowledged that vaccine-related reactive adenopathy is seen after the booster dose and provided recommendations for the timing of getting mammograms and the booster with this in mind.
“I would recommend getting the screening mammogram first, which can be followed immediately by vaccination, even on the same day,” said Jessica Leung, MD, a professor of diagnostic radiology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Tex.
“If this is not possible from the scheduling perspective, then the patient should consult her health care provider regarding whether it is okay to wait a bit after receiving the vaccine before getting her screening mammogram.”
The answer to that question will likely depend on the time interval since the prior mammogram and the patient’s personal risk factors for developing breast cancer. Dr. Leung noted. “This is all predicated on the assumption that the patient is asymptomatic. If she has any symptoms, for example a palpable breast lump, then she should seek medical attention regardless of timing of vaccination.”
The same holds true for boosters, she said.
She emphasized that careful consideration should be given before delaying the mammogram. “The medical community has a great deal more knowledge at this time than in the early days of COVID-19 vaccination, so we are often able to identify reactive adenopathy related to vaccination. If patients were to delay the mammogram, any reactive adenopathy may persist, on average, for 4-6 weeks.”
Debra Patt, MD, PhD, MBA, executive vice president at Texas Oncology, professor at the University of Texas at Austin, provided a specific example of when a patient should not delay the diagnostic imaging, which is “in the event that there is an abnormal mass in the breast that requires evaluation.”
Providers are now prepared to address these issues, she added.
Dr. Lehman’s nuanced recommendations
“It’s easy to get both a mammogram and booster, and just a matter of timing them – so that the reaction doesn’t interfere with the mammography results,” Dr. Lehman said.
But she emphasized that women should not be choosing between their mammograms or a booster. “We are now saying the same thing that we did with the initial vaccine,” said Dr. Lehman. “We don’t want patients delaying their mammograms, and we don’t want them delaying their boosters – both are critical to staying healthy.”
In her center, a model was developed to navigate vaccine-associated adenopathy. While this approach was developed for the primary vaccine series, the same applies for the booster, which is essentially a third dose of the same vaccine, explained Dr. Lehman.
When patients present for mammography, ultrasound, or MRI, the technologist will document their COVID-19 vaccination status (first or second dose or booster), the date it was given, and the location. Adding vaccination documentation to intake forms helps to support appropriate management of patients who undergo imaging after COVID-19 vaccination. Six weeks is used as the cutoff point for defining “recent” vaccination.
For patients who are getting a screening mammography or MRI, and who have no symptoms beyond unilateral axillary adenopathy on the same side of the body where they received the COVID-19 vaccination (given in the arm) within a 6-week period, the following is included in the screening mammography or screening MRI report: “In the specific setting of a patient with documented recent (within the past 6 weeks) COVID-19 vaccination in the ipsilateral arm, axillary adenopathy is a benign imaging finding. No further imaging is indicated at this time. If there is clinical concern that persists more than 6 weeks after the patient received the final vaccine dose, axillary ultrasound is recommended.”
The experts interviewed reported no conflicts of interest.
This inflammation is caused by the enlargement of lymph nodes and can show up as an abnormal finding on mammograms and other types of chest scans, causing concern and even the need for additional imaging and follow up, wrote Constance D. Lehman, MD, PhD, and colleagues in an article published in Journal of the American College of Radiology.
Lymph node swelling is a normal immune system reaction to vaccination, and “COVID-19 vaccinations in the arm are a well-documented cause of inflammatory unilateral axillary adenopathy,” noted Dr. Lehman, in an interview. The side effect will occur on the side of the body where the patient received a vaccine, and it is not always noticeable to the woman experiencing it, she said.
“We’re finding that the patients’ bodies are responding to the booster in many ways that are similar to the initial COVID vaccines, with lymph node swelling, muscle aches and pains, headaches, and so on,” said Dr. Lehman, who is chief of breast imaging at the Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. There have been no real differences in reactions between the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines, she added.
Because axillary lymph node swelling can obscure mammogram results, staff of at least a few imaging centers, including Penn State Breast Center in Hershey, Pa., and Providence Women’s Imaging Center in Torrance, Calif., told this news organization that they are asking women to delay mammogram imaging either 6 weeks or 4-6 weeks after getting a COVID-19 booster.
Experts’ suggestions on mammograms, boosters timing
Other experts, including Jessica Leung, MD, acknowledged that vaccine-related reactive adenopathy is seen after the booster dose and provided recommendations for the timing of getting mammograms and the booster with this in mind.
“I would recommend getting the screening mammogram first, which can be followed immediately by vaccination, even on the same day,” said Jessica Leung, MD, a professor of diagnostic radiology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Tex.
“If this is not possible from the scheduling perspective, then the patient should consult her health care provider regarding whether it is okay to wait a bit after receiving the vaccine before getting her screening mammogram.”
The answer to that question will likely depend on the time interval since the prior mammogram and the patient’s personal risk factors for developing breast cancer. Dr. Leung noted. “This is all predicated on the assumption that the patient is asymptomatic. If she has any symptoms, for example a palpable breast lump, then she should seek medical attention regardless of timing of vaccination.”
The same holds true for boosters, she said.
She emphasized that careful consideration should be given before delaying the mammogram. “The medical community has a great deal more knowledge at this time than in the early days of COVID-19 vaccination, so we are often able to identify reactive adenopathy related to vaccination. If patients were to delay the mammogram, any reactive adenopathy may persist, on average, for 4-6 weeks.”
Debra Patt, MD, PhD, MBA, executive vice president at Texas Oncology, professor at the University of Texas at Austin, provided a specific example of when a patient should not delay the diagnostic imaging, which is “in the event that there is an abnormal mass in the breast that requires evaluation.”
Providers are now prepared to address these issues, she added.
Dr. Lehman’s nuanced recommendations
“It’s easy to get both a mammogram and booster, and just a matter of timing them – so that the reaction doesn’t interfere with the mammography results,” Dr. Lehman said.
But she emphasized that women should not be choosing between their mammograms or a booster. “We are now saying the same thing that we did with the initial vaccine,” said Dr. Lehman. “We don’t want patients delaying their mammograms, and we don’t want them delaying their boosters – both are critical to staying healthy.”
In her center, a model was developed to navigate vaccine-associated adenopathy. While this approach was developed for the primary vaccine series, the same applies for the booster, which is essentially a third dose of the same vaccine, explained Dr. Lehman.
When patients present for mammography, ultrasound, or MRI, the technologist will document their COVID-19 vaccination status (first or second dose or booster), the date it was given, and the location. Adding vaccination documentation to intake forms helps to support appropriate management of patients who undergo imaging after COVID-19 vaccination. Six weeks is used as the cutoff point for defining “recent” vaccination.
For patients who are getting a screening mammography or MRI, and who have no symptoms beyond unilateral axillary adenopathy on the same side of the body where they received the COVID-19 vaccination (given in the arm) within a 6-week period, the following is included in the screening mammography or screening MRI report: “In the specific setting of a patient with documented recent (within the past 6 weeks) COVID-19 vaccination in the ipsilateral arm, axillary adenopathy is a benign imaging finding. No further imaging is indicated at this time. If there is clinical concern that persists more than 6 weeks after the patient received the final vaccine dose, axillary ultrasound is recommended.”
The experts interviewed reported no conflicts of interest.
AAP updates guidance on HIV testing and prophylaxis in youth
Pediatricians should take a more proactive role in protecting children and adolescents from HIV infections, according to updated guidance from the American Academy of Pediatrics. The comprehensive new recommendations stress winning the trust and confidence of pediatric patients and reaffirm support for testing and treating adolescents without parental consent where state laws allow.
While the number of HIV-infected people in the United States remains high, most sexually active youth do not believe they are at risk and have never been tested, noted authors Katherine K. Hsu, MD, MPH, of the Massachusetts Department of Public Health and Boston University Medical Center, and Natella Yurievna Rakhmanina, MD, PhD, of Children’s National Hospital and George Washington University, both in Washington.
That is a knowledge gap that pediatricians are well situated to fill. “Pediatricians can play a key role in preventing and controlling HIV infection by promoting risk-reduction counseling and offering routine HIV testing and prophylaxis to adolescent and young adult (youth) patients,” they wrote on Dec. 20, 2021, in their study published in Pediatrics.
Key components of youth encounters, they stressed, is creating safe environments for obtaining an accurate sexual and reproductive health assessment and providing nonstigmatizing risk counseling.
According to Dr. Rakhmanina, major barriers to addressing preventive HIV counseling have included pediatricians’ lack of time, cultural differences, adolescents’ inaccurate responses, discomfort discussing sexual issues, and adolescents’ fear of parent or caregiver notification. Other concerns have been lack of adequate payment and insufficient training in how to talk to adolescents about sexual and reproductive issues.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at year end in 2018 an estimated 1,173,900 people age 13 or older were living with HIV infection in the United States, of whom 47,800 (4%) were adolescents and young adults 13-24 years of age.
These estimates include diagnosed and undiagnosed individuals. Between 2014 and 2018, new diagnoses of HIV infection accounted for 21% (7,817 of 37,515) of all new HIV diagnoses in the United States.
The new AAP clinical report updates policy statements from 2001 and again 2011 that encouraged HIV testing of all sexually active youth.
It reflects changes in epidemiology, advances in diagnostic testing with improved immunoassays, and updated recommendations for HIV testing and postexposure prophylaxis (PEP), as well as new guidance for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP).
A 2017 study found that the 2011 HIV testing guidelines was associated with only a slight increase in HIV screening and a shift toward testing younger people and away from testing on the basis of risk.
Against this backdrop of persistent HIV infection and to-date modest uptake of earlier guidance, the 2021 statement made 14 main recommendations to pediatricians. Among these:
- Foster open discussion of gender and sexual orientation and behavior, as well as reproductive health issues.
- Recognize the clinical presentation of the acute retroviral syndrome, which can present as syndromes resembling infectious mononucleosis and influenza.
- Consider including virologic testing in the diagnostic workup of sexually active youth.
- Consider routine HIV screening for all youth 15 years or older at least once and rescreening high-risk youth. Those at higher risk should be rescreened at least annually, and potentially as frequently as every 3-6 months.
- Youth at substantial risk should be routinely offered PrEP, while PEP with antiretroviral drugs is indicated after unsafe exposures such as unsafe sexual activity, unsafe needle use, or sexual violence. Survivors of sexual violence should have baseline HIV testing and sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening and treatment. They should also be offered mental health and other supportive counseling.
- Test youth who request HIV screening at any time even in the absence of reported risk factors. Although parent or guardian involvement is preferable, in most legal settings the adolescent’s consent should suffice for testing and treatment.
- For youth with a positive HIV test, facilitate and confirm prompt linkage to age-appropriate HIV specialty care.
Will the current report’s recommendations be met with greater uptake than previous iterations? Yes, according to Maria E. Trent, MD, MPH, chief of the division of adolescent/young adult medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, but a fundamental first step will be the establishment of honesty and confidentiality. “Pediatricians are essential stakeholders in HIV prevention and intervention efforts in the United States. Recent data, however, suggest that pediatricians often struggle to create the essential alone time with adolescents and young adults to conduct critical sexual health conversations that allow for adequate STI/HIV risk screening,” said Dr. Trent, who was not involved in the report. “Consistently creating that space will be the first task for ensuring adherence to these recommendations.”
Strategies to optimize risk screening for clinical decision support, such as confidential online previsit questionnaires that link to the electronic medical record, may facilitate discussions during the visit while maintaining clinician efficiency, she added.
Furthermore, while one-time general HIV screening during adolescence will be an easy goal, “integrating annual testing, biomedical intervention for PrEP/PEP, and ongoing follow-up and testing for those on biomedical intervention may present practical but not insurmountable challenges,” Dr. Trent said.
When pediatricians recognize that care is suboptimal in practice, ensuring that pediatricians have established linkages to adolescent-friendly services for free or low-cost HIV testing, PrEP/PEP, and HIV management will prevent gaps in care, Dr. Trent continued. “The most exciting development in health care is that telemedicine can now be used to work with young people, giving the practicing pediatrician more opportunities and flexibility to deliver and triage care.”
Will any of the guidelines such as an adolescent’s right to independent consent be considered unacceptable by parents? “While this part of the recommendations is not new, the thought that their adolescent can initiate and receive confidential care for HIV prevention or intervention without their knowledge or consent may initially be challenging to process,” Dr. Trent said. “Ultimately, what I’ve observed in practice is that parents are relieved and often proud of their young person for taking the initiative to engage in self-care to maintain their health and relieved to be involved as a critical support person.”
She added that pediatricians need to make their practice policies clear and have information available for parents on state laws related to confidential care. “They also need to carefully use the electronic health record to avoid errors in disclosures to proxies without patient consent.”
Dr. Rakhmanina agreed there will likely be greater adherence to this round of recommendations. “The culture of addressing sexual and reproductive health issues among adolescents in the U.S. is changing among pediatric providers, and we start seeing more champions of PrEP and HIV testing in our communities,” she said.
This study received no external funding. The authors had no financial relationships or potential conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Trent disclosed no competing interests relevant to her comments.
Pediatricians should take a more proactive role in protecting children and adolescents from HIV infections, according to updated guidance from the American Academy of Pediatrics. The comprehensive new recommendations stress winning the trust and confidence of pediatric patients and reaffirm support for testing and treating adolescents without parental consent where state laws allow.
While the number of HIV-infected people in the United States remains high, most sexually active youth do not believe they are at risk and have never been tested, noted authors Katherine K. Hsu, MD, MPH, of the Massachusetts Department of Public Health and Boston University Medical Center, and Natella Yurievna Rakhmanina, MD, PhD, of Children’s National Hospital and George Washington University, both in Washington.
That is a knowledge gap that pediatricians are well situated to fill. “Pediatricians can play a key role in preventing and controlling HIV infection by promoting risk-reduction counseling and offering routine HIV testing and prophylaxis to adolescent and young adult (youth) patients,” they wrote on Dec. 20, 2021, in their study published in Pediatrics.
Key components of youth encounters, they stressed, is creating safe environments for obtaining an accurate sexual and reproductive health assessment and providing nonstigmatizing risk counseling.
According to Dr. Rakhmanina, major barriers to addressing preventive HIV counseling have included pediatricians’ lack of time, cultural differences, adolescents’ inaccurate responses, discomfort discussing sexual issues, and adolescents’ fear of parent or caregiver notification. Other concerns have been lack of adequate payment and insufficient training in how to talk to adolescents about sexual and reproductive issues.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at year end in 2018 an estimated 1,173,900 people age 13 or older were living with HIV infection in the United States, of whom 47,800 (4%) were adolescents and young adults 13-24 years of age.
These estimates include diagnosed and undiagnosed individuals. Between 2014 and 2018, new diagnoses of HIV infection accounted for 21% (7,817 of 37,515) of all new HIV diagnoses in the United States.
The new AAP clinical report updates policy statements from 2001 and again 2011 that encouraged HIV testing of all sexually active youth.
It reflects changes in epidemiology, advances in diagnostic testing with improved immunoassays, and updated recommendations for HIV testing and postexposure prophylaxis (PEP), as well as new guidance for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP).
A 2017 study found that the 2011 HIV testing guidelines was associated with only a slight increase in HIV screening and a shift toward testing younger people and away from testing on the basis of risk.
Against this backdrop of persistent HIV infection and to-date modest uptake of earlier guidance, the 2021 statement made 14 main recommendations to pediatricians. Among these:
- Foster open discussion of gender and sexual orientation and behavior, as well as reproductive health issues.
- Recognize the clinical presentation of the acute retroviral syndrome, which can present as syndromes resembling infectious mononucleosis and influenza.
- Consider including virologic testing in the diagnostic workup of sexually active youth.
- Consider routine HIV screening for all youth 15 years or older at least once and rescreening high-risk youth. Those at higher risk should be rescreened at least annually, and potentially as frequently as every 3-6 months.
- Youth at substantial risk should be routinely offered PrEP, while PEP with antiretroviral drugs is indicated after unsafe exposures such as unsafe sexual activity, unsafe needle use, or sexual violence. Survivors of sexual violence should have baseline HIV testing and sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening and treatment. They should also be offered mental health and other supportive counseling.
- Test youth who request HIV screening at any time even in the absence of reported risk factors. Although parent or guardian involvement is preferable, in most legal settings the adolescent’s consent should suffice for testing and treatment.
- For youth with a positive HIV test, facilitate and confirm prompt linkage to age-appropriate HIV specialty care.
Will the current report’s recommendations be met with greater uptake than previous iterations? Yes, according to Maria E. Trent, MD, MPH, chief of the division of adolescent/young adult medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, but a fundamental first step will be the establishment of honesty and confidentiality. “Pediatricians are essential stakeholders in HIV prevention and intervention efforts in the United States. Recent data, however, suggest that pediatricians often struggle to create the essential alone time with adolescents and young adults to conduct critical sexual health conversations that allow for adequate STI/HIV risk screening,” said Dr. Trent, who was not involved in the report. “Consistently creating that space will be the first task for ensuring adherence to these recommendations.”
Strategies to optimize risk screening for clinical decision support, such as confidential online previsit questionnaires that link to the electronic medical record, may facilitate discussions during the visit while maintaining clinician efficiency, she added.
Furthermore, while one-time general HIV screening during adolescence will be an easy goal, “integrating annual testing, biomedical intervention for PrEP/PEP, and ongoing follow-up and testing for those on biomedical intervention may present practical but not insurmountable challenges,” Dr. Trent said.
When pediatricians recognize that care is suboptimal in practice, ensuring that pediatricians have established linkages to adolescent-friendly services for free or low-cost HIV testing, PrEP/PEP, and HIV management will prevent gaps in care, Dr. Trent continued. “The most exciting development in health care is that telemedicine can now be used to work with young people, giving the practicing pediatrician more opportunities and flexibility to deliver and triage care.”
Will any of the guidelines such as an adolescent’s right to independent consent be considered unacceptable by parents? “While this part of the recommendations is not new, the thought that their adolescent can initiate and receive confidential care for HIV prevention or intervention without their knowledge or consent may initially be challenging to process,” Dr. Trent said. “Ultimately, what I’ve observed in practice is that parents are relieved and often proud of their young person for taking the initiative to engage in self-care to maintain their health and relieved to be involved as a critical support person.”
She added that pediatricians need to make their practice policies clear and have information available for parents on state laws related to confidential care. “They also need to carefully use the electronic health record to avoid errors in disclosures to proxies without patient consent.”
Dr. Rakhmanina agreed there will likely be greater adherence to this round of recommendations. “The culture of addressing sexual and reproductive health issues among adolescents in the U.S. is changing among pediatric providers, and we start seeing more champions of PrEP and HIV testing in our communities,” she said.
This study received no external funding. The authors had no financial relationships or potential conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Trent disclosed no competing interests relevant to her comments.
Pediatricians should take a more proactive role in protecting children and adolescents from HIV infections, according to updated guidance from the American Academy of Pediatrics. The comprehensive new recommendations stress winning the trust and confidence of pediatric patients and reaffirm support for testing and treating adolescents without parental consent where state laws allow.
While the number of HIV-infected people in the United States remains high, most sexually active youth do not believe they are at risk and have never been tested, noted authors Katherine K. Hsu, MD, MPH, of the Massachusetts Department of Public Health and Boston University Medical Center, and Natella Yurievna Rakhmanina, MD, PhD, of Children’s National Hospital and George Washington University, both in Washington.
That is a knowledge gap that pediatricians are well situated to fill. “Pediatricians can play a key role in preventing and controlling HIV infection by promoting risk-reduction counseling and offering routine HIV testing and prophylaxis to adolescent and young adult (youth) patients,” they wrote on Dec. 20, 2021, in their study published in Pediatrics.
Key components of youth encounters, they stressed, is creating safe environments for obtaining an accurate sexual and reproductive health assessment and providing nonstigmatizing risk counseling.
According to Dr. Rakhmanina, major barriers to addressing preventive HIV counseling have included pediatricians’ lack of time, cultural differences, adolescents’ inaccurate responses, discomfort discussing sexual issues, and adolescents’ fear of parent or caregiver notification. Other concerns have been lack of adequate payment and insufficient training in how to talk to adolescents about sexual and reproductive issues.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at year end in 2018 an estimated 1,173,900 people age 13 or older were living with HIV infection in the United States, of whom 47,800 (4%) were adolescents and young adults 13-24 years of age.
These estimates include diagnosed and undiagnosed individuals. Between 2014 and 2018, new diagnoses of HIV infection accounted for 21% (7,817 of 37,515) of all new HIV diagnoses in the United States.
The new AAP clinical report updates policy statements from 2001 and again 2011 that encouraged HIV testing of all sexually active youth.
It reflects changes in epidemiology, advances in diagnostic testing with improved immunoassays, and updated recommendations for HIV testing and postexposure prophylaxis (PEP), as well as new guidance for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP).
A 2017 study found that the 2011 HIV testing guidelines was associated with only a slight increase in HIV screening and a shift toward testing younger people and away from testing on the basis of risk.
Against this backdrop of persistent HIV infection and to-date modest uptake of earlier guidance, the 2021 statement made 14 main recommendations to pediatricians. Among these:
- Foster open discussion of gender and sexual orientation and behavior, as well as reproductive health issues.
- Recognize the clinical presentation of the acute retroviral syndrome, which can present as syndromes resembling infectious mononucleosis and influenza.
- Consider including virologic testing in the diagnostic workup of sexually active youth.
- Consider routine HIV screening for all youth 15 years or older at least once and rescreening high-risk youth. Those at higher risk should be rescreened at least annually, and potentially as frequently as every 3-6 months.
- Youth at substantial risk should be routinely offered PrEP, while PEP with antiretroviral drugs is indicated after unsafe exposures such as unsafe sexual activity, unsafe needle use, or sexual violence. Survivors of sexual violence should have baseline HIV testing and sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening and treatment. They should also be offered mental health and other supportive counseling.
- Test youth who request HIV screening at any time even in the absence of reported risk factors. Although parent or guardian involvement is preferable, in most legal settings the adolescent’s consent should suffice for testing and treatment.
- For youth with a positive HIV test, facilitate and confirm prompt linkage to age-appropriate HIV specialty care.
Will the current report’s recommendations be met with greater uptake than previous iterations? Yes, according to Maria E. Trent, MD, MPH, chief of the division of adolescent/young adult medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, but a fundamental first step will be the establishment of honesty and confidentiality. “Pediatricians are essential stakeholders in HIV prevention and intervention efforts in the United States. Recent data, however, suggest that pediatricians often struggle to create the essential alone time with adolescents and young adults to conduct critical sexual health conversations that allow for adequate STI/HIV risk screening,” said Dr. Trent, who was not involved in the report. “Consistently creating that space will be the first task for ensuring adherence to these recommendations.”
Strategies to optimize risk screening for clinical decision support, such as confidential online previsit questionnaires that link to the electronic medical record, may facilitate discussions during the visit while maintaining clinician efficiency, she added.
Furthermore, while one-time general HIV screening during adolescence will be an easy goal, “integrating annual testing, biomedical intervention for PrEP/PEP, and ongoing follow-up and testing for those on biomedical intervention may present practical but not insurmountable challenges,” Dr. Trent said.
When pediatricians recognize that care is suboptimal in practice, ensuring that pediatricians have established linkages to adolescent-friendly services for free or low-cost HIV testing, PrEP/PEP, and HIV management will prevent gaps in care, Dr. Trent continued. “The most exciting development in health care is that telemedicine can now be used to work with young people, giving the practicing pediatrician more opportunities and flexibility to deliver and triage care.”
Will any of the guidelines such as an adolescent’s right to independent consent be considered unacceptable by parents? “While this part of the recommendations is not new, the thought that their adolescent can initiate and receive confidential care for HIV prevention or intervention without their knowledge or consent may initially be challenging to process,” Dr. Trent said. “Ultimately, what I’ve observed in practice is that parents are relieved and often proud of their young person for taking the initiative to engage in self-care to maintain their health and relieved to be involved as a critical support person.”
She added that pediatricians need to make their practice policies clear and have information available for parents on state laws related to confidential care. “They also need to carefully use the electronic health record to avoid errors in disclosures to proxies without patient consent.”
Dr. Rakhmanina agreed there will likely be greater adherence to this round of recommendations. “The culture of addressing sexual and reproductive health issues among adolescents in the U.S. is changing among pediatric providers, and we start seeing more champions of PrEP and HIV testing in our communities,” she said.
This study received no external funding. The authors had no financial relationships or potential conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Trent disclosed no competing interests relevant to her comments.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Coronary calcium better predictor of statin need than PCE
A feasibility study has found that coronary artery calcium scanning has the potential to better target patients who truly need statin therapy, reduce unnecessary statin prescriptions, and improve medication adherence than the current standard of using pooled cohort equations to determine atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk.
Researchers at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and Intermountain Healthcare, a network of 25 hospitals in Utah, reported that the rate of statin usage in patients evaluated with coronary artery calcium (CAC) was 25% lower than in those whose treatment decisions were based on pooled cohort equations (PCE). None of the patients were on statin therapy when they enrolled in the study, published online in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
“This study demonstrates that doing a large outcomes trial is feasible and has a reasonable likelihood of perhaps being a positive trial for the use of CAC,” lead author Joseph B. Muhlestein, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Muhlestein is codirector of cardiovascular research at Intermountain Healthcare and a professor at the University of Utah.
The findings address the 2018 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guideline that states PCE is the “single most robust tool for estimating 10-year risk in U.S. adults 40-75 years of age”. However, the guideline also bases statin determination on shared decision-making between the patient and physician, and recommends CAC for patients for whom a decision about statin treatment is uncertain and those at intermediate risk to fine-tune the need for statins.
The results also have spurred a larger randomized trial known as CorCal, which aims to enroll 5,500 patients and compare CAC and PCE, Dr. Muhlestein said. So far 3,000 patients have been enrolled.
Results of CAC vs. PCE
The feasibility study enrolled 601 patients randomized to CAC (302) or PCE (299), 504 of whom were included in the final analysis. In the CAC group, 35.9% went on statin therapy, compared with 47.9% of the PCE patients (P = .005). Participating physicians accepted the study-dictated recommendation to start a statin in 88.1% of patients in the CAC arm versus 75.0% in the PCE arm.
Dr. Muhlestein noted that the feasibility study did not evaluate key outcomes, such as stroke or heart attack, but they will be a key endpoint of the larger randomized trial. “We found in this feasibility study that the recommendations that come from the CAC arm, compared with the PCE arm are significantly different enough that there may be a different outcome,” he said.
“There were cases in which the PCE did not recommend a statin but the patient had a lot of coronary calcium, so we recommended the statin in that patient,” he said. “At the same time, there were also even more patients in which the PCE said they ought to take a statin but they had zero coronary calcium, so we didn’t recommend that they get a statin.”
Compared with PCE-based recommendations, CAC patients were taken off statins in 36% of cases and put on statins in 5.6% of cases. “We think that PCE gives statins to a lot of patients who don’t really need them,” Dr. Muhlestein said.
The feasibility study also found patients were more adherent to therapy if they had CAC than PCE – 63.3% versus 45.6% at a year (P = .03). “Patients and physicians are more likely to be concerned enough to begin preventative therapy when they know that they are not just at risk for the disease, but they actually have the disease; that’s what the CAC score tells them,” Dr. Muhlestein said.
He noted that, while observational evidence has embraced CAC, insurers have been hesitant to cover it. “That is one of the major motivations for us to do this study,” Dr. Muhlestein said. “CAC is not very expensive; it costs less than $100, which is about what it costs to get a lipid panel, but insurance won’t pay for it because we haven’t proved that CAC actually changes outcomes, and that’s a legitimate complaint. But, of course, there’s never been a randomized trial that proves that a PCE changes outcomes either.”
The findings validate the 2018 ACC/AHA guideline “and opens a way to broader use for CAC for statin assessment,” said Neil J. Stone, MD, chair of the ACC/AHA 2013 guideline-writing committee and vice chair of the 2018 committee. “The study confirms a large body of information that a deterministic approach, i.e., calcium score, outperforms a probabilistic approach on an individual patient level.” Dr. Stone is the Bonow Professor of Medicine at Northwestern University and medical director of the Vascular Center of the Bluhm Cardiovascular Institute of Northwestern Memorial Hospital, both in Chicago.
“I applaud the investigators for using this as a hypothesis-generating study and planning a larger, more definitive trial,” he said. “This study would encourage regulators and insurance companies to support the use of calcium scores as recommended by the 2018 guideline.”
Intermountain Healthcare is the sole source of funding for the CorCal feasibility study. Dr. Muhlestein and Dr. Stone have no relevant relationships to disclose.
A feasibility study has found that coronary artery calcium scanning has the potential to better target patients who truly need statin therapy, reduce unnecessary statin prescriptions, and improve medication adherence than the current standard of using pooled cohort equations to determine atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk.
Researchers at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and Intermountain Healthcare, a network of 25 hospitals in Utah, reported that the rate of statin usage in patients evaluated with coronary artery calcium (CAC) was 25% lower than in those whose treatment decisions were based on pooled cohort equations (PCE). None of the patients were on statin therapy when they enrolled in the study, published online in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
“This study demonstrates that doing a large outcomes trial is feasible and has a reasonable likelihood of perhaps being a positive trial for the use of CAC,” lead author Joseph B. Muhlestein, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Muhlestein is codirector of cardiovascular research at Intermountain Healthcare and a professor at the University of Utah.
The findings address the 2018 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guideline that states PCE is the “single most robust tool for estimating 10-year risk in U.S. adults 40-75 years of age”. However, the guideline also bases statin determination on shared decision-making between the patient and physician, and recommends CAC for patients for whom a decision about statin treatment is uncertain and those at intermediate risk to fine-tune the need for statins.
The results also have spurred a larger randomized trial known as CorCal, which aims to enroll 5,500 patients and compare CAC and PCE, Dr. Muhlestein said. So far 3,000 patients have been enrolled.
Results of CAC vs. PCE
The feasibility study enrolled 601 patients randomized to CAC (302) or PCE (299), 504 of whom were included in the final analysis. In the CAC group, 35.9% went on statin therapy, compared with 47.9% of the PCE patients (P = .005). Participating physicians accepted the study-dictated recommendation to start a statin in 88.1% of patients in the CAC arm versus 75.0% in the PCE arm.
Dr. Muhlestein noted that the feasibility study did not evaluate key outcomes, such as stroke or heart attack, but they will be a key endpoint of the larger randomized trial. “We found in this feasibility study that the recommendations that come from the CAC arm, compared with the PCE arm are significantly different enough that there may be a different outcome,” he said.
“There were cases in which the PCE did not recommend a statin but the patient had a lot of coronary calcium, so we recommended the statin in that patient,” he said. “At the same time, there were also even more patients in which the PCE said they ought to take a statin but they had zero coronary calcium, so we didn’t recommend that they get a statin.”
Compared with PCE-based recommendations, CAC patients were taken off statins in 36% of cases and put on statins in 5.6% of cases. “We think that PCE gives statins to a lot of patients who don’t really need them,” Dr. Muhlestein said.
The feasibility study also found patients were more adherent to therapy if they had CAC than PCE – 63.3% versus 45.6% at a year (P = .03). “Patients and physicians are more likely to be concerned enough to begin preventative therapy when they know that they are not just at risk for the disease, but they actually have the disease; that’s what the CAC score tells them,” Dr. Muhlestein said.
He noted that, while observational evidence has embraced CAC, insurers have been hesitant to cover it. “That is one of the major motivations for us to do this study,” Dr. Muhlestein said. “CAC is not very expensive; it costs less than $100, which is about what it costs to get a lipid panel, but insurance won’t pay for it because we haven’t proved that CAC actually changes outcomes, and that’s a legitimate complaint. But, of course, there’s never been a randomized trial that proves that a PCE changes outcomes either.”
The findings validate the 2018 ACC/AHA guideline “and opens a way to broader use for CAC for statin assessment,” said Neil J. Stone, MD, chair of the ACC/AHA 2013 guideline-writing committee and vice chair of the 2018 committee. “The study confirms a large body of information that a deterministic approach, i.e., calcium score, outperforms a probabilistic approach on an individual patient level.” Dr. Stone is the Bonow Professor of Medicine at Northwestern University and medical director of the Vascular Center of the Bluhm Cardiovascular Institute of Northwestern Memorial Hospital, both in Chicago.
“I applaud the investigators for using this as a hypothesis-generating study and planning a larger, more definitive trial,” he said. “This study would encourage regulators and insurance companies to support the use of calcium scores as recommended by the 2018 guideline.”
Intermountain Healthcare is the sole source of funding for the CorCal feasibility study. Dr. Muhlestein and Dr. Stone have no relevant relationships to disclose.
A feasibility study has found that coronary artery calcium scanning has the potential to better target patients who truly need statin therapy, reduce unnecessary statin prescriptions, and improve medication adherence than the current standard of using pooled cohort equations to determine atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk.
Researchers at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and Intermountain Healthcare, a network of 25 hospitals in Utah, reported that the rate of statin usage in patients evaluated with coronary artery calcium (CAC) was 25% lower than in those whose treatment decisions were based on pooled cohort equations (PCE). None of the patients were on statin therapy when they enrolled in the study, published online in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
“This study demonstrates that doing a large outcomes trial is feasible and has a reasonable likelihood of perhaps being a positive trial for the use of CAC,” lead author Joseph B. Muhlestein, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Muhlestein is codirector of cardiovascular research at Intermountain Healthcare and a professor at the University of Utah.
The findings address the 2018 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guideline that states PCE is the “single most robust tool for estimating 10-year risk in U.S. adults 40-75 years of age”. However, the guideline also bases statin determination on shared decision-making between the patient and physician, and recommends CAC for patients for whom a decision about statin treatment is uncertain and those at intermediate risk to fine-tune the need for statins.
The results also have spurred a larger randomized trial known as CorCal, which aims to enroll 5,500 patients and compare CAC and PCE, Dr. Muhlestein said. So far 3,000 patients have been enrolled.
Results of CAC vs. PCE
The feasibility study enrolled 601 patients randomized to CAC (302) or PCE (299), 504 of whom were included in the final analysis. In the CAC group, 35.9% went on statin therapy, compared with 47.9% of the PCE patients (P = .005). Participating physicians accepted the study-dictated recommendation to start a statin in 88.1% of patients in the CAC arm versus 75.0% in the PCE arm.
Dr. Muhlestein noted that the feasibility study did not evaluate key outcomes, such as stroke or heart attack, but they will be a key endpoint of the larger randomized trial. “We found in this feasibility study that the recommendations that come from the CAC arm, compared with the PCE arm are significantly different enough that there may be a different outcome,” he said.
“There were cases in which the PCE did not recommend a statin but the patient had a lot of coronary calcium, so we recommended the statin in that patient,” he said. “At the same time, there were also even more patients in which the PCE said they ought to take a statin but they had zero coronary calcium, so we didn’t recommend that they get a statin.”
Compared with PCE-based recommendations, CAC patients were taken off statins in 36% of cases and put on statins in 5.6% of cases. “We think that PCE gives statins to a lot of patients who don’t really need them,” Dr. Muhlestein said.
The feasibility study also found patients were more adherent to therapy if they had CAC than PCE – 63.3% versus 45.6% at a year (P = .03). “Patients and physicians are more likely to be concerned enough to begin preventative therapy when they know that they are not just at risk for the disease, but they actually have the disease; that’s what the CAC score tells them,” Dr. Muhlestein said.
He noted that, while observational evidence has embraced CAC, insurers have been hesitant to cover it. “That is one of the major motivations for us to do this study,” Dr. Muhlestein said. “CAC is not very expensive; it costs less than $100, which is about what it costs to get a lipid panel, but insurance won’t pay for it because we haven’t proved that CAC actually changes outcomes, and that’s a legitimate complaint. But, of course, there’s never been a randomized trial that proves that a PCE changes outcomes either.”
The findings validate the 2018 ACC/AHA guideline “and opens a way to broader use for CAC for statin assessment,” said Neil J. Stone, MD, chair of the ACC/AHA 2013 guideline-writing committee and vice chair of the 2018 committee. “The study confirms a large body of information that a deterministic approach, i.e., calcium score, outperforms a probabilistic approach on an individual patient level.” Dr. Stone is the Bonow Professor of Medicine at Northwestern University and medical director of the Vascular Center of the Bluhm Cardiovascular Institute of Northwestern Memorial Hospital, both in Chicago.
“I applaud the investigators for using this as a hypothesis-generating study and planning a larger, more definitive trial,” he said. “This study would encourage regulators and insurance companies to support the use of calcium scores as recommended by the 2018 guideline.”
Intermountain Healthcare is the sole source of funding for the CorCal feasibility study. Dr. Muhlestein and Dr. Stone have no relevant relationships to disclose.
FROM JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING
Voxelotor for sickle cell anemia now down to 4-year-olds
The indication had previously been for patients 12 years old and up, the FDA said in an announcement.
Voxelotor (Oxbryta) was originally approved for sickle cell disease in November 2019 and was described as the first drug that directly inhibits sickle hemoglobin polymerization, the root cause of the disease. It binds and stabilizes hemoglobin to prevent red blood cells from sickling and being destroyed.
Approval for the new indication of use in children down to age 4 was based on data from a phase 2 trial that involved 45 children aged 4-11 years; the results show that 36% had an increase in hemoglobin greater than 1 g/dL by week 24, the FDA said.
“Complications of [sickle cell disease] that can cause irreversible organ damage are known to begin in the first few years of life, which is why earlier intervention is critical,” commented Ted Love, MD, president and CEO of Global Blood Therapeutics, the manufacturer, in a press release.
The company is studying voxelotor in children as young as 9 months old.
The agent was granted an accelerated approval by the FDA, so continued approval depends on additional data to confirm that increases in hemoglobin have clinical benefit.
With the new approvals, voxelotor is now available in 500-mg tablets and the 300-mg tablets for oral suspension. Dosing for ages 12 years and up is 1,500 mg once daily. Dosing for children 4 to up to 12 years old is weight based.
The most common side effects are headache, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, rash, and fever.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The indication had previously been for patients 12 years old and up, the FDA said in an announcement.
Voxelotor (Oxbryta) was originally approved for sickle cell disease in November 2019 and was described as the first drug that directly inhibits sickle hemoglobin polymerization, the root cause of the disease. It binds and stabilizes hemoglobin to prevent red blood cells from sickling and being destroyed.
Approval for the new indication of use in children down to age 4 was based on data from a phase 2 trial that involved 45 children aged 4-11 years; the results show that 36% had an increase in hemoglobin greater than 1 g/dL by week 24, the FDA said.
“Complications of [sickle cell disease] that can cause irreversible organ damage are known to begin in the first few years of life, which is why earlier intervention is critical,” commented Ted Love, MD, president and CEO of Global Blood Therapeutics, the manufacturer, in a press release.
The company is studying voxelotor in children as young as 9 months old.
The agent was granted an accelerated approval by the FDA, so continued approval depends on additional data to confirm that increases in hemoglobin have clinical benefit.
With the new approvals, voxelotor is now available in 500-mg tablets and the 300-mg tablets for oral suspension. Dosing for ages 12 years and up is 1,500 mg once daily. Dosing for children 4 to up to 12 years old is weight based.
The most common side effects are headache, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, rash, and fever.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The indication had previously been for patients 12 years old and up, the FDA said in an announcement.
Voxelotor (Oxbryta) was originally approved for sickle cell disease in November 2019 and was described as the first drug that directly inhibits sickle hemoglobin polymerization, the root cause of the disease. It binds and stabilizes hemoglobin to prevent red blood cells from sickling and being destroyed.
Approval for the new indication of use in children down to age 4 was based on data from a phase 2 trial that involved 45 children aged 4-11 years; the results show that 36% had an increase in hemoglobin greater than 1 g/dL by week 24, the FDA said.
“Complications of [sickle cell disease] that can cause irreversible organ damage are known to begin in the first few years of life, which is why earlier intervention is critical,” commented Ted Love, MD, president and CEO of Global Blood Therapeutics, the manufacturer, in a press release.
The company is studying voxelotor in children as young as 9 months old.
The agent was granted an accelerated approval by the FDA, so continued approval depends on additional data to confirm that increases in hemoglobin have clinical benefit.
With the new approvals, voxelotor is now available in 500-mg tablets and the 300-mg tablets for oral suspension. Dosing for ages 12 years and up is 1,500 mg once daily. Dosing for children 4 to up to 12 years old is weight based.
The most common side effects are headache, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, rash, and fever.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Emergency docs cite ‘dire’ situation as COVID grows, nurses scarce
With emergency departments straining to keep up with the latest COVID surge, the American College of Emergency Physicians
The organization said that it is “very concerned that nursing shortages in emergency departments can complicate patient access to care and add to incredible levels of stress already on physician-led care teams,” according to a press release.
ACEP President Gillian Schmitz, MD, told this news organization, “The situation is dire in many emergency departments around the country. Emergency physicians are seeing more patients with fewer resources and less staff.
“Emergency physicians in the hardest hit communities are scrambling to locate available experts, exhausting federal support, and doing all they can to adapt to the demands of the current surge – everyone is being stretched to their limit.”
The Emergency Nurses Association (ENA) agrees with ACEP’s call for a team approach to stemming the shortage.
ENA President Ron Kraus, MSN, RN, said in an interview, “The pandemic has only amplified several long-standing issues impacting emergency nurses, such as workplace violence, a healthy work environment, and concerns about staffing shortages and the pipeline of new nurses. That said, we can’t lose focus on what’s most important in these challenging moments – ensuring every patient receives the high quality of care.”
The responsibility falls on the “collaborative effort” of the emergency department with emergency nurses playing a pivotal role, he said. But the stress, fatigue, and burnout driving nurses away from their jobs “should not be viewed as added inconvenience to anyone during a pandemic, but as a long-term threat to our health care system.”
ACEP’s press release stated that with fewer nurses available in the emergency department, team members are clocking extra hours, caring for more patients, and stretched to take on additional clinical and nonclinical duties.
“I am hearing from colleagues from Washington state to Michigan to New York that this is the worst they have seen since the beginning of the pandemic,” Dr. Schmitz said. “Everyone available is filling gaps as best they can, but the current path for many frontline workers is not sustainable,” she said in the release.
Meanwhile, ACEP is also tackling violence in the emergency department and has initiatives to protect the mental health of those working on the front lines, the release states.
“Emergency physicians will continue to do everything necessary to treat patients,” Dr. Schmitz said in the release, “but it will take a collaborative effort with legislators, policymakers and health system leaders to strengthen care teams, improve access and address capacity concerns with solutions that can save lives right now and in the months ahead.”
Dr. Schmitz stated that in Washington state, ICUs are at 97% to 100% capacity and less than 30 pediatric inpatient beds are available in the western part of the state.
“In Michigan and New York, several emergency departments are overflowing, and doctors are being called in to triage people in the waiting room because all of the emergency department beds are holding admissions. There are scenarios where entire hospitals are backing up into the emergency department and waiting room and we are physically running out of space and nursing staff.”
ACEP represents its 40,000 emergency physician members.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With emergency departments straining to keep up with the latest COVID surge, the American College of Emergency Physicians
The organization said that it is “very concerned that nursing shortages in emergency departments can complicate patient access to care and add to incredible levels of stress already on physician-led care teams,” according to a press release.
ACEP President Gillian Schmitz, MD, told this news organization, “The situation is dire in many emergency departments around the country. Emergency physicians are seeing more patients with fewer resources and less staff.
“Emergency physicians in the hardest hit communities are scrambling to locate available experts, exhausting federal support, and doing all they can to adapt to the demands of the current surge – everyone is being stretched to their limit.”
The Emergency Nurses Association (ENA) agrees with ACEP’s call for a team approach to stemming the shortage.
ENA President Ron Kraus, MSN, RN, said in an interview, “The pandemic has only amplified several long-standing issues impacting emergency nurses, such as workplace violence, a healthy work environment, and concerns about staffing shortages and the pipeline of new nurses. That said, we can’t lose focus on what’s most important in these challenging moments – ensuring every patient receives the high quality of care.”
The responsibility falls on the “collaborative effort” of the emergency department with emergency nurses playing a pivotal role, he said. But the stress, fatigue, and burnout driving nurses away from their jobs “should not be viewed as added inconvenience to anyone during a pandemic, but as a long-term threat to our health care system.”
ACEP’s press release stated that with fewer nurses available in the emergency department, team members are clocking extra hours, caring for more patients, and stretched to take on additional clinical and nonclinical duties.
“I am hearing from colleagues from Washington state to Michigan to New York that this is the worst they have seen since the beginning of the pandemic,” Dr. Schmitz said. “Everyone available is filling gaps as best they can, but the current path for many frontline workers is not sustainable,” she said in the release.
Meanwhile, ACEP is also tackling violence in the emergency department and has initiatives to protect the mental health of those working on the front lines, the release states.
“Emergency physicians will continue to do everything necessary to treat patients,” Dr. Schmitz said in the release, “but it will take a collaborative effort with legislators, policymakers and health system leaders to strengthen care teams, improve access and address capacity concerns with solutions that can save lives right now and in the months ahead.”
Dr. Schmitz stated that in Washington state, ICUs are at 97% to 100% capacity and less than 30 pediatric inpatient beds are available in the western part of the state.
“In Michigan and New York, several emergency departments are overflowing, and doctors are being called in to triage people in the waiting room because all of the emergency department beds are holding admissions. There are scenarios where entire hospitals are backing up into the emergency department and waiting room and we are physically running out of space and nursing staff.”
ACEP represents its 40,000 emergency physician members.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With emergency departments straining to keep up with the latest COVID surge, the American College of Emergency Physicians
The organization said that it is “very concerned that nursing shortages in emergency departments can complicate patient access to care and add to incredible levels of stress already on physician-led care teams,” according to a press release.
ACEP President Gillian Schmitz, MD, told this news organization, “The situation is dire in many emergency departments around the country. Emergency physicians are seeing more patients with fewer resources and less staff.
“Emergency physicians in the hardest hit communities are scrambling to locate available experts, exhausting federal support, and doing all they can to adapt to the demands of the current surge – everyone is being stretched to their limit.”
The Emergency Nurses Association (ENA) agrees with ACEP’s call for a team approach to stemming the shortage.
ENA President Ron Kraus, MSN, RN, said in an interview, “The pandemic has only amplified several long-standing issues impacting emergency nurses, such as workplace violence, a healthy work environment, and concerns about staffing shortages and the pipeline of new nurses. That said, we can’t lose focus on what’s most important in these challenging moments – ensuring every patient receives the high quality of care.”
The responsibility falls on the “collaborative effort” of the emergency department with emergency nurses playing a pivotal role, he said. But the stress, fatigue, and burnout driving nurses away from their jobs “should not be viewed as added inconvenience to anyone during a pandemic, but as a long-term threat to our health care system.”
ACEP’s press release stated that with fewer nurses available in the emergency department, team members are clocking extra hours, caring for more patients, and stretched to take on additional clinical and nonclinical duties.
“I am hearing from colleagues from Washington state to Michigan to New York that this is the worst they have seen since the beginning of the pandemic,” Dr. Schmitz said. “Everyone available is filling gaps as best they can, but the current path for many frontline workers is not sustainable,” she said in the release.
Meanwhile, ACEP is also tackling violence in the emergency department and has initiatives to protect the mental health of those working on the front lines, the release states.
“Emergency physicians will continue to do everything necessary to treat patients,” Dr. Schmitz said in the release, “but it will take a collaborative effort with legislators, policymakers and health system leaders to strengthen care teams, improve access and address capacity concerns with solutions that can save lives right now and in the months ahead.”
Dr. Schmitz stated that in Washington state, ICUs are at 97% to 100% capacity and less than 30 pediatric inpatient beds are available in the western part of the state.
“In Michigan and New York, several emergency departments are overflowing, and doctors are being called in to triage people in the waiting room because all of the emergency department beds are holding admissions. There are scenarios where entire hospitals are backing up into the emergency department and waiting room and we are physically running out of space and nursing staff.”
ACEP represents its 40,000 emergency physician members.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA agrees that mifepristone is safe enough to dispense by mail
The Food and Drug Administration has announced that women no longer will have to pick up the abortion pill mifepristone (Mifeprex) in person at certain certified sites and can get a prescription via an online consultation and delivery through the mail.
In April 2021, the FDA lifted the in-person dispensing requirement for mifepristone for the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic and in December the agency made that decision permanent.
As this news organization reported on April 12, 2021, acting commissioner of food and drugs, Janet Woodcock, MD, stated that the FDA would “permit the dispensing of mifepristone through the mail when done by or under the supervision of a certified prescriber; or through a mail-order pharmacy under the supervision of a certified prescriber.”
That decision came after suspension of the in-person dispensing requirement in response to COVID-19 safety concerns for patients as well as providers associated with in-person clinic visits.
Decision comes amid Supreme Court debate
The FDA decision comes as the Supreme Court nears a decision on whether to overturn its 1973 ruling on Roe v. Wade.
Additionally, the Supreme Court on returned a lawsuit over Texas’ ban on abortions after 6 weeks to a federal appeals court that has twice allowed the law to stay in effect, rather than to a district judge who wanted it blocked.
Alexis McGill Johnson, president and CEO, of the Planned Parenthood Federation of America, said in a statement, “Abortion is time sensitive, essential health care, and this decision will remove a sometimes insurmountable barrier for patients seeking an abortion. With abortion rights at risk like never before, the FDA’s decision is a long overdue step toward expanding people’s access to safe medication abortion.”
Georgeanne Usova, senior legislative counsel at the American Civil Liberties Union told CNBC News: “The FDA’s decision will come as a tremendous relief for countless abortion and miscarriage patients.”
Catherine D. Cansino, MD, MPH, associate clinical professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis, and member of the editorial advisory board for ObGyn News said in an interview: “I think that this change is a long time coming and speaks to the fact that science matters and medicine prevails over politics. We need to protect health rights first!”
Others expressed doubt or outrage.
Fidelma Rigby, MD, a professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology, division of maternal fetal medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond, said in an interview: “My concern is that what if there is an ectopic pregnancy? I’m not as enthusiastic as some of my partners would be about this announcement.”
“The FDA’s decision today places women at risk,” said Carol Tobias, president of the National Right to Life Committee. “These changes do not make this abortion process safer for women. What these changes do is make the process easier for the abortion industry.”
The antiabortion groups Charlotte Lozier Institute and the Susan B. Anthony List were among other organizations issuing statements against Dec. 16’s FDA ruling.
The FDA stated that mifepristone prescribers will still need to earn certification and training. Additionally, the agency said dispensing pharmacies will have to be certified.
The FDA said in updated guidance on its website that after conducting a review of the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy for mifepristone, it “determined that the data support modification of the REMS to reduce burden on patient access and the health care delivery system and to ensure the benefits of the product outweigh the risks.”
The modifications include:
- “Removing the requirement that mifepristone be dispensed only in certain health care settings, specifically clinics, medical offices, and hospitals (referred to as the ‘in-person dispensing requirement’).”
- Adding a requirement that pharmacies must be certified to dispense the drug.
The FDA said removing the in-person dispensing rule will allow delivery of mifepristone by mail via certified prescribers or pharmacies, in addition to in-person dispensing in clinics, medical offices, and hospitals.
In 2018, an expert National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine panel concluded that requiring that medication abortion be provided at only certain facilities, solely by a physician or in the physical presence of certain providers, did not improve safety or quality of care.
Mifepristone is used, together with misoprostol, to end an early pregnancy. The FDA first approved Mifeprex in 2000 for use through 10 weeks’ gestation. According to the FDA, mifepristone is approved in more than 60 other countries.
Many states bar mailing of abortion pills
However, according to the Guttmacher Institute, 19 U.S. states have laws that bar telehealth consultations or mailing of abortion pills.
Reuters reported that women in those states would not be able to make use of the rule change get the drug delivered to their home but could potentially travel to other states to obtain medication abortion.
“States such as California and New York that have sought to strengthen access to abortion may make the drug available to women from other states,” Reuters reported.
Jessica Arons, senior advocacy and policy counsel for reproductive freedom at the ACLU, told CBS News, “Medication abortion is one more lens through which we see that we are witnessing a tale of two countries. Half the states are protecting access to abortion and half are trying every single way they can to eliminate access to abortion care.”
Positive results when Canada lifted restrictions
As this news organization has reported, a study found positive results when Canada lifted restrictions on access to the abortion pills and a good safety profile for mifepristone.
A study in the New England Journal of Medicine found abortion rates remained stable and adverse events were rare after mifepristone prescribing restrictions were lifted in Canada.
Senior author Wendy V. Norman, MD, professor in the department of family practice at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, said in a statement, “Our study is a signal to other countries that restrictions are not necessary to ensure patient safety.”
Another recent study in JAMA Network Open (2021 Aug 24. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.22320) found that abortion via telehealth prescriptions may be just as safe and effective as in-person care.
The study investigators said that, “of the 110 women from whom researchers collected remote abortion outcome data, 95% had a complete abortion without additional medical interventions, such as aspiration or surgery, and none experienced adverse events. Researchers said this efficacy rate is similar to in-person visits.”
The Food and Drug Administration has announced that women no longer will have to pick up the abortion pill mifepristone (Mifeprex) in person at certain certified sites and can get a prescription via an online consultation and delivery through the mail.
In April 2021, the FDA lifted the in-person dispensing requirement for mifepristone for the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic and in December the agency made that decision permanent.
As this news organization reported on April 12, 2021, acting commissioner of food and drugs, Janet Woodcock, MD, stated that the FDA would “permit the dispensing of mifepristone through the mail when done by or under the supervision of a certified prescriber; or through a mail-order pharmacy under the supervision of a certified prescriber.”
That decision came after suspension of the in-person dispensing requirement in response to COVID-19 safety concerns for patients as well as providers associated with in-person clinic visits.
Decision comes amid Supreme Court debate
The FDA decision comes as the Supreme Court nears a decision on whether to overturn its 1973 ruling on Roe v. Wade.
Additionally, the Supreme Court on returned a lawsuit over Texas’ ban on abortions after 6 weeks to a federal appeals court that has twice allowed the law to stay in effect, rather than to a district judge who wanted it blocked.
Alexis McGill Johnson, president and CEO, of the Planned Parenthood Federation of America, said in a statement, “Abortion is time sensitive, essential health care, and this decision will remove a sometimes insurmountable barrier for patients seeking an abortion. With abortion rights at risk like never before, the FDA’s decision is a long overdue step toward expanding people’s access to safe medication abortion.”
Georgeanne Usova, senior legislative counsel at the American Civil Liberties Union told CNBC News: “The FDA’s decision will come as a tremendous relief for countless abortion and miscarriage patients.”
Catherine D. Cansino, MD, MPH, associate clinical professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis, and member of the editorial advisory board for ObGyn News said in an interview: “I think that this change is a long time coming and speaks to the fact that science matters and medicine prevails over politics. We need to protect health rights first!”
Others expressed doubt or outrage.
Fidelma Rigby, MD, a professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology, division of maternal fetal medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond, said in an interview: “My concern is that what if there is an ectopic pregnancy? I’m not as enthusiastic as some of my partners would be about this announcement.”
“The FDA’s decision today places women at risk,” said Carol Tobias, president of the National Right to Life Committee. “These changes do not make this abortion process safer for women. What these changes do is make the process easier for the abortion industry.”
The antiabortion groups Charlotte Lozier Institute and the Susan B. Anthony List were among other organizations issuing statements against Dec. 16’s FDA ruling.
The FDA stated that mifepristone prescribers will still need to earn certification and training. Additionally, the agency said dispensing pharmacies will have to be certified.
The FDA said in updated guidance on its website that after conducting a review of the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy for mifepristone, it “determined that the data support modification of the REMS to reduce burden on patient access and the health care delivery system and to ensure the benefits of the product outweigh the risks.”
The modifications include:
- “Removing the requirement that mifepristone be dispensed only in certain health care settings, specifically clinics, medical offices, and hospitals (referred to as the ‘in-person dispensing requirement’).”
- Adding a requirement that pharmacies must be certified to dispense the drug.
The FDA said removing the in-person dispensing rule will allow delivery of mifepristone by mail via certified prescribers or pharmacies, in addition to in-person dispensing in clinics, medical offices, and hospitals.
In 2018, an expert National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine panel concluded that requiring that medication abortion be provided at only certain facilities, solely by a physician or in the physical presence of certain providers, did not improve safety or quality of care.
Mifepristone is used, together with misoprostol, to end an early pregnancy. The FDA first approved Mifeprex in 2000 for use through 10 weeks’ gestation. According to the FDA, mifepristone is approved in more than 60 other countries.
Many states bar mailing of abortion pills
However, according to the Guttmacher Institute, 19 U.S. states have laws that bar telehealth consultations or mailing of abortion pills.
Reuters reported that women in those states would not be able to make use of the rule change get the drug delivered to their home but could potentially travel to other states to obtain medication abortion.
“States such as California and New York that have sought to strengthen access to abortion may make the drug available to women from other states,” Reuters reported.
Jessica Arons, senior advocacy and policy counsel for reproductive freedom at the ACLU, told CBS News, “Medication abortion is one more lens through which we see that we are witnessing a tale of two countries. Half the states are protecting access to abortion and half are trying every single way they can to eliminate access to abortion care.”
Positive results when Canada lifted restrictions
As this news organization has reported, a study found positive results when Canada lifted restrictions on access to the abortion pills and a good safety profile for mifepristone.
A study in the New England Journal of Medicine found abortion rates remained stable and adverse events were rare after mifepristone prescribing restrictions were lifted in Canada.
Senior author Wendy V. Norman, MD, professor in the department of family practice at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, said in a statement, “Our study is a signal to other countries that restrictions are not necessary to ensure patient safety.”
Another recent study in JAMA Network Open (2021 Aug 24. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.22320) found that abortion via telehealth prescriptions may be just as safe and effective as in-person care.
The study investigators said that, “of the 110 women from whom researchers collected remote abortion outcome data, 95% had a complete abortion without additional medical interventions, such as aspiration or surgery, and none experienced adverse events. Researchers said this efficacy rate is similar to in-person visits.”
The Food and Drug Administration has announced that women no longer will have to pick up the abortion pill mifepristone (Mifeprex) in person at certain certified sites and can get a prescription via an online consultation and delivery through the mail.
In April 2021, the FDA lifted the in-person dispensing requirement for mifepristone for the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic and in December the agency made that decision permanent.
As this news organization reported on April 12, 2021, acting commissioner of food and drugs, Janet Woodcock, MD, stated that the FDA would “permit the dispensing of mifepristone through the mail when done by or under the supervision of a certified prescriber; or through a mail-order pharmacy under the supervision of a certified prescriber.”
That decision came after suspension of the in-person dispensing requirement in response to COVID-19 safety concerns for patients as well as providers associated with in-person clinic visits.
Decision comes amid Supreme Court debate
The FDA decision comes as the Supreme Court nears a decision on whether to overturn its 1973 ruling on Roe v. Wade.
Additionally, the Supreme Court on returned a lawsuit over Texas’ ban on abortions after 6 weeks to a federal appeals court that has twice allowed the law to stay in effect, rather than to a district judge who wanted it blocked.
Alexis McGill Johnson, president and CEO, of the Planned Parenthood Federation of America, said in a statement, “Abortion is time sensitive, essential health care, and this decision will remove a sometimes insurmountable barrier for patients seeking an abortion. With abortion rights at risk like never before, the FDA’s decision is a long overdue step toward expanding people’s access to safe medication abortion.”
Georgeanne Usova, senior legislative counsel at the American Civil Liberties Union told CNBC News: “The FDA’s decision will come as a tremendous relief for countless abortion and miscarriage patients.”
Catherine D. Cansino, MD, MPH, associate clinical professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis, and member of the editorial advisory board for ObGyn News said in an interview: “I think that this change is a long time coming and speaks to the fact that science matters and medicine prevails over politics. We need to protect health rights first!”
Others expressed doubt or outrage.
Fidelma Rigby, MD, a professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology, division of maternal fetal medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond, said in an interview: “My concern is that what if there is an ectopic pregnancy? I’m not as enthusiastic as some of my partners would be about this announcement.”
“The FDA’s decision today places women at risk,” said Carol Tobias, president of the National Right to Life Committee. “These changes do not make this abortion process safer for women. What these changes do is make the process easier for the abortion industry.”
The antiabortion groups Charlotte Lozier Institute and the Susan B. Anthony List were among other organizations issuing statements against Dec. 16’s FDA ruling.
The FDA stated that mifepristone prescribers will still need to earn certification and training. Additionally, the agency said dispensing pharmacies will have to be certified.
The FDA said in updated guidance on its website that after conducting a review of the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy for mifepristone, it “determined that the data support modification of the REMS to reduce burden on patient access and the health care delivery system and to ensure the benefits of the product outweigh the risks.”
The modifications include:
- “Removing the requirement that mifepristone be dispensed only in certain health care settings, specifically clinics, medical offices, and hospitals (referred to as the ‘in-person dispensing requirement’).”
- Adding a requirement that pharmacies must be certified to dispense the drug.
The FDA said removing the in-person dispensing rule will allow delivery of mifepristone by mail via certified prescribers or pharmacies, in addition to in-person dispensing in clinics, medical offices, and hospitals.
In 2018, an expert National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine panel concluded that requiring that medication abortion be provided at only certain facilities, solely by a physician or in the physical presence of certain providers, did not improve safety or quality of care.
Mifepristone is used, together with misoprostol, to end an early pregnancy. The FDA first approved Mifeprex in 2000 for use through 10 weeks’ gestation. According to the FDA, mifepristone is approved in more than 60 other countries.
Many states bar mailing of abortion pills
However, according to the Guttmacher Institute, 19 U.S. states have laws that bar telehealth consultations or mailing of abortion pills.
Reuters reported that women in those states would not be able to make use of the rule change get the drug delivered to their home but could potentially travel to other states to obtain medication abortion.
“States such as California and New York that have sought to strengthen access to abortion may make the drug available to women from other states,” Reuters reported.
Jessica Arons, senior advocacy and policy counsel for reproductive freedom at the ACLU, told CBS News, “Medication abortion is one more lens through which we see that we are witnessing a tale of two countries. Half the states are protecting access to abortion and half are trying every single way they can to eliminate access to abortion care.”
Positive results when Canada lifted restrictions
As this news organization has reported, a study found positive results when Canada lifted restrictions on access to the abortion pills and a good safety profile for mifepristone.
A study in the New England Journal of Medicine found abortion rates remained stable and adverse events were rare after mifepristone prescribing restrictions were lifted in Canada.
Senior author Wendy V. Norman, MD, professor in the department of family practice at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, said in a statement, “Our study is a signal to other countries that restrictions are not necessary to ensure patient safety.”
Another recent study in JAMA Network Open (2021 Aug 24. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.22320) found that abortion via telehealth prescriptions may be just as safe and effective as in-person care.
The study investigators said that, “of the 110 women from whom researchers collected remote abortion outcome data, 95% had a complete abortion without additional medical interventions, such as aspiration or surgery, and none experienced adverse events. Researchers said this efficacy rate is similar to in-person visits.”
Who benefits most from device PFO closure after a stroke?
It has been well established that device closure has, on average, prevented stroke recurrence in people who’ve had patent foramen ovale–associated stroke, but a meta-analysis has drilled down into clinical trials to advance a potentially practice-changing principle: that, while device closure shows an overall benefit, not all patients derive a benefit and some may actually be harmed by the procedure.
What’s more, the researchers developed a scoring system that helps determine which patients are likely to benefit from device closure.
“What was unknown was how to treat individual patients because the decision to close the patent foramen ovale (PFO) is still preference sensitive because the risk of a recurrent stroke is low, and most of the strokes that recur are not terribly severe,” lead study author David M. Kent, MD, MS, said in an interview.
“On top of this,” he said, “it was still suspected that some of the PFOs, even in trials of well-selected patients, may not be causally related to stroke; the stroke may still have another occult cause, such as paroxysmal atrial fibrillation or aortic arch atheroma.” Dr. Kent is a professor of medicine at Tufts University in Boston and director of the Predictive Analytics and Comparative Effectiveness Center there.
The meta-analysis, conducted by the Systematic, Collaborative, PFO Closure Evaluation (SCOPE) consortium, analyzed data from six randomized clinical trials that compared device closure and medical therapy to medical therapy alone in 3,740 patients who had PFO-associated stroke from 2000 to 2017. It was published in JAMA.
Overall, the rate of recurrent ischemic stroke was less than half that in patients who had device closure, compared with those who were on medical therapy: 0.47% (n = 39 of 1,889) vs. 1.09% (n = 82 of 1,851).
The researchers also applied two tools designed to calculate the probability of recurrent stroke in individual patients: Risk of Paradoxical Embolism (RoPE), an index that assigns a score of 0-10 to stratify cryptogenic stroke patients with PFO by the likelihood that the stroke was associated with their PFO; and the PFO-Associated Stroke Causal Likelihood (PASCAL) classification system, which integrates the RoPE score with physiological and anatomical features – namely, the size of the PFO shunt and the presence of an atrial septal aneurysm.
“We came up with a way to more accurately identify those patients who are likely to get the most benefit from PFO closure based on mathematic modeling that estimates an individual’s probability that the PFO is causally related to the stroke,” Dr. Kent said.
Multivariate analysis determines risk
The study used a multivariate classification system that Dr. Kent had been developing to perform subgroup analyses of the clinical trials. It assigned patients to three different risk groups based on the likelihood that the PFO was causally related to their stroke: PASCAL categories of unlikely, possible, and probable.
The PASCAL unlikely group had a risk of stroke recurrence in the first 2 years of 3.4% (95% confidence interval, 1.1%-5.7%) if they were on medical therapy, and 4.1% (95% CI, 1.7%-6.4%) if they had device closure. In the PASCAL possible group, those risks were 3.6% (95% CI, 2.4%-4.9%) and 1.5% (95% CI, 0.7-2.3%), respectively. For the probable group, device closure represents “a near perfect therapy” with a 90% risk reduction, Dr. Kent said. “Moreover,” he said, “adverse events of device closure, such as atrial fibrillation, appear to be concentrated in those patients who fall into the unlikely classification, who appear to get no benefit.”
The ideal patient for device closure is age 60 years or younger and without vascular risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, a history of smoking, or a prior stroke, but has high-risk PFO features such as a large shunt or atrial septal aneurysm, Dr. Kent said.
“We think these findings should be practice changing now,” Dr. Kent said.
Faisal M. Merchant, MD, director of cardiac electrophysiology at Emory Healthcare in Atlanta, concurred with that statement. “This is in my mind probably as good as any data we’re going to get on this,” he said in an interview. “The results support what’s been a general gestalt in the clinical world, but [also] really provide an evidence base on how to make decisions.”
He noted that guidelines, including those of the American Academy of Neurology, recommend medical therapy or device closure to prevent recurrent stroke in people who’ve had PFO-associated ischemic stroke. “But they hedge a bit,” he said of the guidelines. “We haven’t had data that’s as robust as this. I think this really solidifies those recommendations.”
He also credited the “unique” study design to extract findings from clinical trials and apply them to personalized medicine. “Clinical trial results give you an average treatment effect of the patients included, but who are ones who really benefit? Who are the ones that don’t benefit? Who are the ones who are harmed?” Dr. Merchant said. “It’s rare that you can parse out this nicely between the people who both benefit and are less likely to be harmed and the people who don’t benefit and are more likely to be harmed.”
The study received funding from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Kent disclosed relationships with PCORI, W.L. Gore and the Canadian Stroke Consortium. Dr. Merchant has no relevant disclosures.
It has been well established that device closure has, on average, prevented stroke recurrence in people who’ve had patent foramen ovale–associated stroke, but a meta-analysis has drilled down into clinical trials to advance a potentially practice-changing principle: that, while device closure shows an overall benefit, not all patients derive a benefit and some may actually be harmed by the procedure.
What’s more, the researchers developed a scoring system that helps determine which patients are likely to benefit from device closure.
“What was unknown was how to treat individual patients because the decision to close the patent foramen ovale (PFO) is still preference sensitive because the risk of a recurrent stroke is low, and most of the strokes that recur are not terribly severe,” lead study author David M. Kent, MD, MS, said in an interview.
“On top of this,” he said, “it was still suspected that some of the PFOs, even in trials of well-selected patients, may not be causally related to stroke; the stroke may still have another occult cause, such as paroxysmal atrial fibrillation or aortic arch atheroma.” Dr. Kent is a professor of medicine at Tufts University in Boston and director of the Predictive Analytics and Comparative Effectiveness Center there.
The meta-analysis, conducted by the Systematic, Collaborative, PFO Closure Evaluation (SCOPE) consortium, analyzed data from six randomized clinical trials that compared device closure and medical therapy to medical therapy alone in 3,740 patients who had PFO-associated stroke from 2000 to 2017. It was published in JAMA.
Overall, the rate of recurrent ischemic stroke was less than half that in patients who had device closure, compared with those who were on medical therapy: 0.47% (n = 39 of 1,889) vs. 1.09% (n = 82 of 1,851).
The researchers also applied two tools designed to calculate the probability of recurrent stroke in individual patients: Risk of Paradoxical Embolism (RoPE), an index that assigns a score of 0-10 to stratify cryptogenic stroke patients with PFO by the likelihood that the stroke was associated with their PFO; and the PFO-Associated Stroke Causal Likelihood (PASCAL) classification system, which integrates the RoPE score with physiological and anatomical features – namely, the size of the PFO shunt and the presence of an atrial septal aneurysm.
“We came up with a way to more accurately identify those patients who are likely to get the most benefit from PFO closure based on mathematic modeling that estimates an individual’s probability that the PFO is causally related to the stroke,” Dr. Kent said.
Multivariate analysis determines risk
The study used a multivariate classification system that Dr. Kent had been developing to perform subgroup analyses of the clinical trials. It assigned patients to three different risk groups based on the likelihood that the PFO was causally related to their stroke: PASCAL categories of unlikely, possible, and probable.
The PASCAL unlikely group had a risk of stroke recurrence in the first 2 years of 3.4% (95% confidence interval, 1.1%-5.7%) if they were on medical therapy, and 4.1% (95% CI, 1.7%-6.4%) if they had device closure. In the PASCAL possible group, those risks were 3.6% (95% CI, 2.4%-4.9%) and 1.5% (95% CI, 0.7-2.3%), respectively. For the probable group, device closure represents “a near perfect therapy” with a 90% risk reduction, Dr. Kent said. “Moreover,” he said, “adverse events of device closure, such as atrial fibrillation, appear to be concentrated in those patients who fall into the unlikely classification, who appear to get no benefit.”
The ideal patient for device closure is age 60 years or younger and without vascular risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, a history of smoking, or a prior stroke, but has high-risk PFO features such as a large shunt or atrial septal aneurysm, Dr. Kent said.
“We think these findings should be practice changing now,” Dr. Kent said.
Faisal M. Merchant, MD, director of cardiac electrophysiology at Emory Healthcare in Atlanta, concurred with that statement. “This is in my mind probably as good as any data we’re going to get on this,” he said in an interview. “The results support what’s been a general gestalt in the clinical world, but [also] really provide an evidence base on how to make decisions.”
He noted that guidelines, including those of the American Academy of Neurology, recommend medical therapy or device closure to prevent recurrent stroke in people who’ve had PFO-associated ischemic stroke. “But they hedge a bit,” he said of the guidelines. “We haven’t had data that’s as robust as this. I think this really solidifies those recommendations.”
He also credited the “unique” study design to extract findings from clinical trials and apply them to personalized medicine. “Clinical trial results give you an average treatment effect of the patients included, but who are ones who really benefit? Who are the ones that don’t benefit? Who are the ones who are harmed?” Dr. Merchant said. “It’s rare that you can parse out this nicely between the people who both benefit and are less likely to be harmed and the people who don’t benefit and are more likely to be harmed.”
The study received funding from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Kent disclosed relationships with PCORI, W.L. Gore and the Canadian Stroke Consortium. Dr. Merchant has no relevant disclosures.
It has been well established that device closure has, on average, prevented stroke recurrence in people who’ve had patent foramen ovale–associated stroke, but a meta-analysis has drilled down into clinical trials to advance a potentially practice-changing principle: that, while device closure shows an overall benefit, not all patients derive a benefit and some may actually be harmed by the procedure.
What’s more, the researchers developed a scoring system that helps determine which patients are likely to benefit from device closure.
“What was unknown was how to treat individual patients because the decision to close the patent foramen ovale (PFO) is still preference sensitive because the risk of a recurrent stroke is low, and most of the strokes that recur are not terribly severe,” lead study author David M. Kent, MD, MS, said in an interview.
“On top of this,” he said, “it was still suspected that some of the PFOs, even in trials of well-selected patients, may not be causally related to stroke; the stroke may still have another occult cause, such as paroxysmal atrial fibrillation or aortic arch atheroma.” Dr. Kent is a professor of medicine at Tufts University in Boston and director of the Predictive Analytics and Comparative Effectiveness Center there.
The meta-analysis, conducted by the Systematic, Collaborative, PFO Closure Evaluation (SCOPE) consortium, analyzed data from six randomized clinical trials that compared device closure and medical therapy to medical therapy alone in 3,740 patients who had PFO-associated stroke from 2000 to 2017. It was published in JAMA.
Overall, the rate of recurrent ischemic stroke was less than half that in patients who had device closure, compared with those who were on medical therapy: 0.47% (n = 39 of 1,889) vs. 1.09% (n = 82 of 1,851).
The researchers also applied two tools designed to calculate the probability of recurrent stroke in individual patients: Risk of Paradoxical Embolism (RoPE), an index that assigns a score of 0-10 to stratify cryptogenic stroke patients with PFO by the likelihood that the stroke was associated with their PFO; and the PFO-Associated Stroke Causal Likelihood (PASCAL) classification system, which integrates the RoPE score with physiological and anatomical features – namely, the size of the PFO shunt and the presence of an atrial septal aneurysm.
“We came up with a way to more accurately identify those patients who are likely to get the most benefit from PFO closure based on mathematic modeling that estimates an individual’s probability that the PFO is causally related to the stroke,” Dr. Kent said.
Multivariate analysis determines risk
The study used a multivariate classification system that Dr. Kent had been developing to perform subgroup analyses of the clinical trials. It assigned patients to three different risk groups based on the likelihood that the PFO was causally related to their stroke: PASCAL categories of unlikely, possible, and probable.
The PASCAL unlikely group had a risk of stroke recurrence in the first 2 years of 3.4% (95% confidence interval, 1.1%-5.7%) if they were on medical therapy, and 4.1% (95% CI, 1.7%-6.4%) if they had device closure. In the PASCAL possible group, those risks were 3.6% (95% CI, 2.4%-4.9%) and 1.5% (95% CI, 0.7-2.3%), respectively. For the probable group, device closure represents “a near perfect therapy” with a 90% risk reduction, Dr. Kent said. “Moreover,” he said, “adverse events of device closure, such as atrial fibrillation, appear to be concentrated in those patients who fall into the unlikely classification, who appear to get no benefit.”
The ideal patient for device closure is age 60 years or younger and without vascular risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, a history of smoking, or a prior stroke, but has high-risk PFO features such as a large shunt or atrial septal aneurysm, Dr. Kent said.
“We think these findings should be practice changing now,” Dr. Kent said.
Faisal M. Merchant, MD, director of cardiac electrophysiology at Emory Healthcare in Atlanta, concurred with that statement. “This is in my mind probably as good as any data we’re going to get on this,” he said in an interview. “The results support what’s been a general gestalt in the clinical world, but [also] really provide an evidence base on how to make decisions.”
He noted that guidelines, including those of the American Academy of Neurology, recommend medical therapy or device closure to prevent recurrent stroke in people who’ve had PFO-associated ischemic stroke. “But they hedge a bit,” he said of the guidelines. “We haven’t had data that’s as robust as this. I think this really solidifies those recommendations.”
He also credited the “unique” study design to extract findings from clinical trials and apply them to personalized medicine. “Clinical trial results give you an average treatment effect of the patients included, but who are ones who really benefit? Who are the ones that don’t benefit? Who are the ones who are harmed?” Dr. Merchant said. “It’s rare that you can parse out this nicely between the people who both benefit and are less likely to be harmed and the people who don’t benefit and are more likely to be harmed.”
The study received funding from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Kent disclosed relationships with PCORI, W.L. Gore and the Canadian Stroke Consortium. Dr. Merchant has no relevant disclosures.
FROM JAMA