User login
Real-world efficacy and safety of apremilast in patients with psoriatic arthritis
Key clinical point: This real-world study confirms sustained improvements in signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) with apremilast along with a tolerable safety profile.
Major finding: Overall, 43.5% of patients who received apremilast within 30 days of participating in the study and completed ≥150 days of treatment achieved PsA Response Criteria. In detail, 26.8% and 41.8% of patients with 68-tender joint count >0 and 66-swollen joint count >0 at baseline, respectively, achieved complete joint count resolution at month 6. No new adverse events were reported.
Study details: Findings are from the prospective, observational APOLO study including 107 patients with active PsA, of which 106 patients received ≥1 dose of apremilast.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Celgene. Some of the authors declared receiving research grants and consultancy and speaker fees from Celgene and other sources.
Source: Vlam KD et al. Adv Ther. 2022 (Jan 3). Doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-02016-x.
Key clinical point: This real-world study confirms sustained improvements in signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) with apremilast along with a tolerable safety profile.
Major finding: Overall, 43.5% of patients who received apremilast within 30 days of participating in the study and completed ≥150 days of treatment achieved PsA Response Criteria. In detail, 26.8% and 41.8% of patients with 68-tender joint count >0 and 66-swollen joint count >0 at baseline, respectively, achieved complete joint count resolution at month 6. No new adverse events were reported.
Study details: Findings are from the prospective, observational APOLO study including 107 patients with active PsA, of which 106 patients received ≥1 dose of apremilast.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Celgene. Some of the authors declared receiving research grants and consultancy and speaker fees from Celgene and other sources.
Source: Vlam KD et al. Adv Ther. 2022 (Jan 3). Doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-02016-x.
Key clinical point: This real-world study confirms sustained improvements in signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) with apremilast along with a tolerable safety profile.
Major finding: Overall, 43.5% of patients who received apremilast within 30 days of participating in the study and completed ≥150 days of treatment achieved PsA Response Criteria. In detail, 26.8% and 41.8% of patients with 68-tender joint count >0 and 66-swollen joint count >0 at baseline, respectively, achieved complete joint count resolution at month 6. No new adverse events were reported.
Study details: Findings are from the prospective, observational APOLO study including 107 patients with active PsA, of which 106 patients received ≥1 dose of apremilast.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Celgene. Some of the authors declared receiving research grants and consultancy and speaker fees from Celgene and other sources.
Source: Vlam KD et al. Adv Ther. 2022 (Jan 3). Doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-02016-x.
Younger age at psoriasis diagnosis or severe disease tied to delayed transition from psoriasis to PsA
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriasis were more likely to have a delayed onset of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) if they were diagnosed with psoriasis at a younger age or suffered from severe psoriasis.
Major finding: The median time from psoriasis diagnosis to the incidence of PsA was 35.5 months with age at psoriasis onset (odds ratio [OR] per 10-year decrease 1.63; 95% CI 1.26-2.11) and its severity (OR for severe vs. mild 3.65; 95% CI 1.18-11.32) being associated with having a psoriasis diagnosis >1 year prior to incident PsA.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective nested case-control study including 158 patients with incident PsA, of which 41% had concurrent psoriasis and 59% patients had onset of psoriasis before PsA.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the Rochester Epidemiology Project supported by National Institute on Aging, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, and others. The authors declared serving as consultants or receiving grants, consulting fees, honoraria, and research support from several sources.
Source: Karmacharya P et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021;151949 (Dec 31). Doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.12.013.
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriasis were more likely to have a delayed onset of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) if they were diagnosed with psoriasis at a younger age or suffered from severe psoriasis.
Major finding: The median time from psoriasis diagnosis to the incidence of PsA was 35.5 months with age at psoriasis onset (odds ratio [OR] per 10-year decrease 1.63; 95% CI 1.26-2.11) and its severity (OR for severe vs. mild 3.65; 95% CI 1.18-11.32) being associated with having a psoriasis diagnosis >1 year prior to incident PsA.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective nested case-control study including 158 patients with incident PsA, of which 41% had concurrent psoriasis and 59% patients had onset of psoriasis before PsA.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the Rochester Epidemiology Project supported by National Institute on Aging, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, and others. The authors declared serving as consultants or receiving grants, consulting fees, honoraria, and research support from several sources.
Source: Karmacharya P et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021;151949 (Dec 31). Doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.12.013.
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriasis were more likely to have a delayed onset of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) if they were diagnosed with psoriasis at a younger age or suffered from severe psoriasis.
Major finding: The median time from psoriasis diagnosis to the incidence of PsA was 35.5 months with age at psoriasis onset (odds ratio [OR] per 10-year decrease 1.63; 95% CI 1.26-2.11) and its severity (OR for severe vs. mild 3.65; 95% CI 1.18-11.32) being associated with having a psoriasis diagnosis >1 year prior to incident PsA.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective nested case-control study including 158 patients with incident PsA, of which 41% had concurrent psoriasis and 59% patients had onset of psoriasis before PsA.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the Rochester Epidemiology Project supported by National Institute on Aging, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, and others. The authors declared serving as consultants or receiving grants, consulting fees, honoraria, and research support from several sources.
Source: Karmacharya P et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021;151949 (Dec 31). Doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.12.013.
Dactylitis indicates a more severe disease phenotype in early PsA
Key clinical point: Presence of dactylitis independently confirmed more severe disease burden with higher swollen joint counts (SJC), C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, ultrasound-detected synovitis, and bone erosion in disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)-naive patients with early psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: Dactylitic vs. nondactylitic PsA was associated with a higher SJC (P < .001) and CRP level (P = .006) and a higher prevalence of ultrasound synovitis (P < .001) and bone erosions (P < .001). After excluding dactylitic digits, SJC was greater (P = .002) and ultrasound-detected synovitis (P < .001) and erosions (P = .008) were more prevalent in dactylitic vs. nondactylitic PsA.
Study details: This study included 177 DMARD-naive patients with early PsA who were stratified by the presence or absence of dactylitis at baseline.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Biomedical Research Centre. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Dubash S et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021 (Dec 10). Doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220964.
Key clinical point: Presence of dactylitis independently confirmed more severe disease burden with higher swollen joint counts (SJC), C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, ultrasound-detected synovitis, and bone erosion in disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)-naive patients with early psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: Dactylitic vs. nondactylitic PsA was associated with a higher SJC (P < .001) and CRP level (P = .006) and a higher prevalence of ultrasound synovitis (P < .001) and bone erosions (P < .001). After excluding dactylitic digits, SJC was greater (P = .002) and ultrasound-detected synovitis (P < .001) and erosions (P = .008) were more prevalent in dactylitic vs. nondactylitic PsA.
Study details: This study included 177 DMARD-naive patients with early PsA who were stratified by the presence or absence of dactylitis at baseline.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Biomedical Research Centre. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Dubash S et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021 (Dec 10). Doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220964.
Key clinical point: Presence of dactylitis independently confirmed more severe disease burden with higher swollen joint counts (SJC), C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, ultrasound-detected synovitis, and bone erosion in disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)-naive patients with early psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: Dactylitic vs. nondactylitic PsA was associated with a higher SJC (P < .001) and CRP level (P = .006) and a higher prevalence of ultrasound synovitis (P < .001) and bone erosions (P < .001). After excluding dactylitic digits, SJC was greater (P = .002) and ultrasound-detected synovitis (P < .001) and erosions (P = .008) were more prevalent in dactylitic vs. nondactylitic PsA.
Study details: This study included 177 DMARD-naive patients with early PsA who were stratified by the presence or absence of dactylitis at baseline.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Biomedical Research Centre. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Dubash S et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021 (Dec 10). Doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220964.
Risankizumab shows promise in PsA patients with inadequate response to csDMARDs
Key clinical point: Risankizumab effectively reduced clinical manifestations of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients with inadequate response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD) with no new adverse events (AE).
Major finding: At week 24, at least a 20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score was achieved by a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab vs. placebo (57.3% vs. 33.5%; P < .001). Treatment-emergent AEs were mild/moderate and reported at similar frequencies in risankizumab (40.4%) and placebo (38.7%) groups.
Study details: Findings are from a double-blind, phase 3 KEEPsAKE 1 study including 964 patients with active PsA and inadequate response to ≥1 csDMARDs who were randomly assigned to receive 150 mg risankizumab or placebo at weeks 0, 4, and 16.
Disclosures: This study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared serving as speaker, consultant, investigator, or receiving honoraria, fees, and grants from several sources. Five authors declared being employees or shareholders of AbbVie.
Source: Kristensen LE et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;81:225-231 (Dec 15). Doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221019.
Key clinical point: Risankizumab effectively reduced clinical manifestations of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients with inadequate response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD) with no new adverse events (AE).
Major finding: At week 24, at least a 20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score was achieved by a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab vs. placebo (57.3% vs. 33.5%; P < .001). Treatment-emergent AEs were mild/moderate and reported at similar frequencies in risankizumab (40.4%) and placebo (38.7%) groups.
Study details: Findings are from a double-blind, phase 3 KEEPsAKE 1 study including 964 patients with active PsA and inadequate response to ≥1 csDMARDs who were randomly assigned to receive 150 mg risankizumab or placebo at weeks 0, 4, and 16.
Disclosures: This study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared serving as speaker, consultant, investigator, or receiving honoraria, fees, and grants from several sources. Five authors declared being employees or shareholders of AbbVie.
Source: Kristensen LE et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;81:225-231 (Dec 15). Doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221019.
Key clinical point: Risankizumab effectively reduced clinical manifestations of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients with inadequate response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD) with no new adverse events (AE).
Major finding: At week 24, at least a 20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score was achieved by a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab vs. placebo (57.3% vs. 33.5%; P < .001). Treatment-emergent AEs were mild/moderate and reported at similar frequencies in risankizumab (40.4%) and placebo (38.7%) groups.
Study details: Findings are from a double-blind, phase 3 KEEPsAKE 1 study including 964 patients with active PsA and inadequate response to ≥1 csDMARDs who were randomly assigned to receive 150 mg risankizumab or placebo at weeks 0, 4, and 16.
Disclosures: This study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared serving as speaker, consultant, investigator, or receiving honoraria, fees, and grants from several sources. Five authors declared being employees or shareholders of AbbVie.
Source: Kristensen LE et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;81:225-231 (Dec 15). Doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221019.
Psoriatic arthritis management should target both clinical and biochemical inflammation
Key clinical point: In patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), clinical inflammation monitored by swollen joint counts (SJC) and biochemical inflammation monitored by C-reactive protein (CRP) level, have a direct effect on structural progression.
Major finding: Progression was significantly higher in patients with active vs. inactive time-averaged SJC (odds ratio [OR] 1.24; P = .016) and time-averaged CRP (OR 6.08; P = .036). Progression was greatest in presence of both clinical and biochemical inflammation and lowest in absence of both (P = .05).
Study details: Findings are secondary analysis of patient data from the IMPACT 2 trial, including 145 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared serving as associate editor or receiving grants and honoraria from several sources.
Source: Borst C et al. RMD Open. 2021;7:e002038 (Dec 8). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-002038.
Key clinical point: In patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), clinical inflammation monitored by swollen joint counts (SJC) and biochemical inflammation monitored by C-reactive protein (CRP) level, have a direct effect on structural progression.
Major finding: Progression was significantly higher in patients with active vs. inactive time-averaged SJC (odds ratio [OR] 1.24; P = .016) and time-averaged CRP (OR 6.08; P = .036). Progression was greatest in presence of both clinical and biochemical inflammation and lowest in absence of both (P = .05).
Study details: Findings are secondary analysis of patient data from the IMPACT 2 trial, including 145 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared serving as associate editor or receiving grants and honoraria from several sources.
Source: Borst C et al. RMD Open. 2021;7:e002038 (Dec 8). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-002038.
Key clinical point: In patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), clinical inflammation monitored by swollen joint counts (SJC) and biochemical inflammation monitored by C-reactive protein (CRP) level, have a direct effect on structural progression.
Major finding: Progression was significantly higher in patients with active vs. inactive time-averaged SJC (odds ratio [OR] 1.24; P = .016) and time-averaged CRP (OR 6.08; P = .036). Progression was greatest in presence of both clinical and biochemical inflammation and lowest in absence of both (P = .05).
Study details: Findings are secondary analysis of patient data from the IMPACT 2 trial, including 145 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared serving as associate editor or receiving grants and honoraria from several sources.
Source: Borst C et al. RMD Open. 2021;7:e002038 (Dec 8). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-002038.
PsA: Upadacitinib shows similar benefits as monotherapy or in combination with nbDMARDs
Key clinical point: Upadacitinib showed similar efficacy and a consistent safety profile as monotherapy or in combination with nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (nbDMARDs) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: At week 12, ≥20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving 15 mg upadacitinib or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy (15 mg: 33.7%; 95% CI, 24.4%-43.1%; 30 mg: 45.7%; 95% CI, 36.9%-54.5%) or combination therapy (15 mg: 34.0%; 95% CI, 27.9%-40.1%; 30 mg: 39.6%; 95% CI, 33.7%-45.5%). Adverse events were generally similar with monotherapy and combination therapy.
Study details: This is a pooled analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2, including 1,916 patients with active PsA with an inadequate response to ≥1 nbDMARD/bDMARD who were randomly assigned to placebo, 15 mg upadacitinib, or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy or in combination with ≤2 nbDMARDs for 24 weeks.
Disclosures: This work was supported by AbbVie. Six authors reported being employees and stockholders of AbbVie. The other authors reported ties with several sources including AbbVie.
Source: Nash P et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;keab905 (Dec 3). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab905.
Key clinical point: Upadacitinib showed similar efficacy and a consistent safety profile as monotherapy or in combination with nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (nbDMARDs) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: At week 12, ≥20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving 15 mg upadacitinib or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy (15 mg: 33.7%; 95% CI, 24.4%-43.1%; 30 mg: 45.7%; 95% CI, 36.9%-54.5%) or combination therapy (15 mg: 34.0%; 95% CI, 27.9%-40.1%; 30 mg: 39.6%; 95% CI, 33.7%-45.5%). Adverse events were generally similar with monotherapy and combination therapy.
Study details: This is a pooled analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2, including 1,916 patients with active PsA with an inadequate response to ≥1 nbDMARD/bDMARD who were randomly assigned to placebo, 15 mg upadacitinib, or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy or in combination with ≤2 nbDMARDs for 24 weeks.
Disclosures: This work was supported by AbbVie. Six authors reported being employees and stockholders of AbbVie. The other authors reported ties with several sources including AbbVie.
Source: Nash P et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;keab905 (Dec 3). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab905.
Key clinical point: Upadacitinib showed similar efficacy and a consistent safety profile as monotherapy or in combination with nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (nbDMARDs) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: At week 12, ≥20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving 15 mg upadacitinib or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy (15 mg: 33.7%; 95% CI, 24.4%-43.1%; 30 mg: 45.7%; 95% CI, 36.9%-54.5%) or combination therapy (15 mg: 34.0%; 95% CI, 27.9%-40.1%; 30 mg: 39.6%; 95% CI, 33.7%-45.5%). Adverse events were generally similar with monotherapy and combination therapy.
Study details: This is a pooled analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2, including 1,916 patients with active PsA with an inadequate response to ≥1 nbDMARD/bDMARD who were randomly assigned to placebo, 15 mg upadacitinib, or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy or in combination with ≤2 nbDMARDs for 24 weeks.
Disclosures: This work was supported by AbbVie. Six authors reported being employees and stockholders of AbbVie. The other authors reported ties with several sources including AbbVie.
Source: Nash P et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;keab905 (Dec 3). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab905.
Discontinuing TNF inhibitors may not be required in PsA patients receiving BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine
Key clinical point: Continuation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapy throughout the vaccination period was safe and did not hamper the immune response elicited by BNT162b2 (BioNTech-Pfizer) mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: There was no change in Clinical Disease Activity Index in patients with PsA before and after vaccination (P = .92). After 2 doses of BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, all patients with PsA showed a positive immune response with mean anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody level not significantly different from matched controls (P = .08).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective study including 40 patients with PsA on TNF inhibitor therapy matched with 40 healthy controls; both groups received 2 shots of the BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Venerito V et al. RMD Open. 2022;8:e001847 (Jan 5). Doi: 10.1136/ rmdopen-2021-001847.
Key clinical point: Continuation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapy throughout the vaccination period was safe and did not hamper the immune response elicited by BNT162b2 (BioNTech-Pfizer) mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: There was no change in Clinical Disease Activity Index in patients with PsA before and after vaccination (P = .92). After 2 doses of BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, all patients with PsA showed a positive immune response with mean anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody level not significantly different from matched controls (P = .08).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective study including 40 patients with PsA on TNF inhibitor therapy matched with 40 healthy controls; both groups received 2 shots of the BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Venerito V et al. RMD Open. 2022;8:e001847 (Jan 5). Doi: 10.1136/ rmdopen-2021-001847.
Key clinical point: Continuation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapy throughout the vaccination period was safe and did not hamper the immune response elicited by BNT162b2 (BioNTech-Pfizer) mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: There was no change in Clinical Disease Activity Index in patients with PsA before and after vaccination (P = .92). After 2 doses of BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, all patients with PsA showed a positive immune response with mean anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody level not significantly different from matched controls (P = .08).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective study including 40 patients with PsA on TNF inhibitor therapy matched with 40 healthy controls; both groups received 2 shots of the BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Venerito V et al. RMD Open. 2022;8:e001847 (Jan 5). Doi: 10.1136/ rmdopen-2021-001847.
Decades of research fail to resolve disparities in gastrointestinal cancer care
Men and White people receive better treatment for gastroesophageal cancer than women, Blacks, and Latinos despite years of studies highlighting disparities in care, researchers say.
The problem is complex because it stems from both biological and socioeconomic factors, but some signs of improvement are beginning to show, said Nathaniel R. Evans III, MD, a professor of surgery at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.
“Repeatedly, we see that, although we know how patients should be treated, there are oftentimes subsets of patients who don’t receive that same level of care,” said Dr. Evans in a general session talk at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium.
Black patients with esophageal cancer are 38% more likely to die from the condition than White patients, he said, citing a 2013 study (Ann Surg Oncol. 2013 doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2807-3). For Latino patients, mortality is 20% higher than for White patients.
The difference can mostly be explained by the rate of esophagectomy, which is 52% lower for Black patients and 29% lower for Latino patients, compared with White patients, the study found.
Besides race and gender, insurance status also influences who gets surgery, Dr. Evans said, citing data from the National Cancer Database. Black patients are less likely to get surgery and more likely to die at all stages and histologies, he said. They wait longer for treatment and are more likely to receive no treatment at all.
Women also suffer from disparities, said Anna Dorothea Wagner, MD, head of the gastrointestinal cancer clinic at Lausanne University Hospital in Lausanne (Switzerland), who spoke at the symposium with Dr Evans.
Seventy-five percent of men with esophageal and gastric adenocarcinoma get curative treatments, compared with only 60% of women, Dr. Wagner said, citing a 2020 study on which she is an author. Women are more likely to get palliative care. As a result, only 30% of women survive the condition for 5 years or more compared to 34% of men, she said. “At the moment we don’t know whether this is due to either patient preferences or cognitive or bias of physicians.”
Disparities in treatment outcomes because of biological differences
For women, some disparities also arise out of clear biological differences, Dr. Wagner said. Sex hormone signaling affects cancer susceptibility, and sex-biased gene expression signatures have been detected in multiple cancer types.
Women with poorly differentiated and signet-cell pathology are less likely to survive their cancer than men with the same histology, she said.
Many studies have shown that chemotherapy is more toxic to women than men without being more efficacious, she added. This suggests that the optimal doses might be different for women and men.
Responding to a question from the audience, Dr. Wagner said more research is needed on transgender patients to understand how these factors affect them.
Dr. Evans attributed the racial and ethnic disparities to some combination of differential histology, stage at diagnosis, access to care, socioeconomics, and inherent bias.
“The problem is not new,” Dr. Evans said. He described studies that found disparities in the 1970s. “But the good news is that things do seem to be getting better.”
Between 2000 and 2011, the number of esophagectomies being performed at high-volume hospitals increased, he said. The overall mortality after esophagectomy has consequently decreased over this time, and the gap in this rate between White and Black people has closed, he said. “Specialization and centralization clearly improve outcomes for certain surgical procedures.”
To address the problem everyone should acknowledge the disparities, particularly in the access to surgery. “I think one of the best tools we have to try to address the disparity is education, both for patients and providers,” Dr. Evans said.
Care teams must become more diverse and culturally competent to combat longstanding distrust and improve communication, he said.
In December, ASCO announced an “action plan” to address equity, diversity and inclusion in cancer care. The organization promised to improve clinical trial eligibility, and train researchers about inherent bias in order to make the trials more representative of the cancer population.
It vowed to increase participation of underrepresented groups in its professional development programs and leadership roles, and educate its members about equity. And, it resolved to provide resources to providers so they could advocate for better quality of care, especially in rural and disadvantaged settings.
Dr. Wagner disclosed relationships with Alligator Bioscience, BMS, Dragonfly Therapeutics, Lilly, Merck KGaA, MSD Oncology, Servier/Pfizer, and Abbvie. Dr. Evans disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation and Intuitive Surgical.
This article was updated 1/28/22.
Men and White people receive better treatment for gastroesophageal cancer than women, Blacks, and Latinos despite years of studies highlighting disparities in care, researchers say.
The problem is complex because it stems from both biological and socioeconomic factors, but some signs of improvement are beginning to show, said Nathaniel R. Evans III, MD, a professor of surgery at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.
“Repeatedly, we see that, although we know how patients should be treated, there are oftentimes subsets of patients who don’t receive that same level of care,” said Dr. Evans in a general session talk at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium.
Black patients with esophageal cancer are 38% more likely to die from the condition than White patients, he said, citing a 2013 study (Ann Surg Oncol. 2013 doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2807-3). For Latino patients, mortality is 20% higher than for White patients.
The difference can mostly be explained by the rate of esophagectomy, which is 52% lower for Black patients and 29% lower for Latino patients, compared with White patients, the study found.
Besides race and gender, insurance status also influences who gets surgery, Dr. Evans said, citing data from the National Cancer Database. Black patients are less likely to get surgery and more likely to die at all stages and histologies, he said. They wait longer for treatment and are more likely to receive no treatment at all.
Women also suffer from disparities, said Anna Dorothea Wagner, MD, head of the gastrointestinal cancer clinic at Lausanne University Hospital in Lausanne (Switzerland), who spoke at the symposium with Dr Evans.
Seventy-five percent of men with esophageal and gastric adenocarcinoma get curative treatments, compared with only 60% of women, Dr. Wagner said, citing a 2020 study on which she is an author. Women are more likely to get palliative care. As a result, only 30% of women survive the condition for 5 years or more compared to 34% of men, she said. “At the moment we don’t know whether this is due to either patient preferences or cognitive or bias of physicians.”
Disparities in treatment outcomes because of biological differences
For women, some disparities also arise out of clear biological differences, Dr. Wagner said. Sex hormone signaling affects cancer susceptibility, and sex-biased gene expression signatures have been detected in multiple cancer types.
Women with poorly differentiated and signet-cell pathology are less likely to survive their cancer than men with the same histology, she said.
Many studies have shown that chemotherapy is more toxic to women than men without being more efficacious, she added. This suggests that the optimal doses might be different for women and men.
Responding to a question from the audience, Dr. Wagner said more research is needed on transgender patients to understand how these factors affect them.
Dr. Evans attributed the racial and ethnic disparities to some combination of differential histology, stage at diagnosis, access to care, socioeconomics, and inherent bias.
“The problem is not new,” Dr. Evans said. He described studies that found disparities in the 1970s. “But the good news is that things do seem to be getting better.”
Between 2000 and 2011, the number of esophagectomies being performed at high-volume hospitals increased, he said. The overall mortality after esophagectomy has consequently decreased over this time, and the gap in this rate between White and Black people has closed, he said. “Specialization and centralization clearly improve outcomes for certain surgical procedures.”
To address the problem everyone should acknowledge the disparities, particularly in the access to surgery. “I think one of the best tools we have to try to address the disparity is education, both for patients and providers,” Dr. Evans said.
Care teams must become more diverse and culturally competent to combat longstanding distrust and improve communication, he said.
In December, ASCO announced an “action plan” to address equity, diversity and inclusion in cancer care. The organization promised to improve clinical trial eligibility, and train researchers about inherent bias in order to make the trials more representative of the cancer population.
It vowed to increase participation of underrepresented groups in its professional development programs and leadership roles, and educate its members about equity. And, it resolved to provide resources to providers so they could advocate for better quality of care, especially in rural and disadvantaged settings.
Dr. Wagner disclosed relationships with Alligator Bioscience, BMS, Dragonfly Therapeutics, Lilly, Merck KGaA, MSD Oncology, Servier/Pfizer, and Abbvie. Dr. Evans disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation and Intuitive Surgical.
This article was updated 1/28/22.
Men and White people receive better treatment for gastroesophageal cancer than women, Blacks, and Latinos despite years of studies highlighting disparities in care, researchers say.
The problem is complex because it stems from both biological and socioeconomic factors, but some signs of improvement are beginning to show, said Nathaniel R. Evans III, MD, a professor of surgery at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.
“Repeatedly, we see that, although we know how patients should be treated, there are oftentimes subsets of patients who don’t receive that same level of care,” said Dr. Evans in a general session talk at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium.
Black patients with esophageal cancer are 38% more likely to die from the condition than White patients, he said, citing a 2013 study (Ann Surg Oncol. 2013 doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2807-3). For Latino patients, mortality is 20% higher than for White patients.
The difference can mostly be explained by the rate of esophagectomy, which is 52% lower for Black patients and 29% lower for Latino patients, compared with White patients, the study found.
Besides race and gender, insurance status also influences who gets surgery, Dr. Evans said, citing data from the National Cancer Database. Black patients are less likely to get surgery and more likely to die at all stages and histologies, he said. They wait longer for treatment and are more likely to receive no treatment at all.
Women also suffer from disparities, said Anna Dorothea Wagner, MD, head of the gastrointestinal cancer clinic at Lausanne University Hospital in Lausanne (Switzerland), who spoke at the symposium with Dr Evans.
Seventy-five percent of men with esophageal and gastric adenocarcinoma get curative treatments, compared with only 60% of women, Dr. Wagner said, citing a 2020 study on which she is an author. Women are more likely to get palliative care. As a result, only 30% of women survive the condition for 5 years or more compared to 34% of men, she said. “At the moment we don’t know whether this is due to either patient preferences or cognitive or bias of physicians.”
Disparities in treatment outcomes because of biological differences
For women, some disparities also arise out of clear biological differences, Dr. Wagner said. Sex hormone signaling affects cancer susceptibility, and sex-biased gene expression signatures have been detected in multiple cancer types.
Women with poorly differentiated and signet-cell pathology are less likely to survive their cancer than men with the same histology, she said.
Many studies have shown that chemotherapy is more toxic to women than men without being more efficacious, she added. This suggests that the optimal doses might be different for women and men.
Responding to a question from the audience, Dr. Wagner said more research is needed on transgender patients to understand how these factors affect them.
Dr. Evans attributed the racial and ethnic disparities to some combination of differential histology, stage at diagnosis, access to care, socioeconomics, and inherent bias.
“The problem is not new,” Dr. Evans said. He described studies that found disparities in the 1970s. “But the good news is that things do seem to be getting better.”
Between 2000 and 2011, the number of esophagectomies being performed at high-volume hospitals increased, he said. The overall mortality after esophagectomy has consequently decreased over this time, and the gap in this rate between White and Black people has closed, he said. “Specialization and centralization clearly improve outcomes for certain surgical procedures.”
To address the problem everyone should acknowledge the disparities, particularly in the access to surgery. “I think one of the best tools we have to try to address the disparity is education, both for patients and providers,” Dr. Evans said.
Care teams must become more diverse and culturally competent to combat longstanding distrust and improve communication, he said.
In December, ASCO announced an “action plan” to address equity, diversity and inclusion in cancer care. The organization promised to improve clinical trial eligibility, and train researchers about inherent bias in order to make the trials more representative of the cancer population.
It vowed to increase participation of underrepresented groups in its professional development programs and leadership roles, and educate its members about equity. And, it resolved to provide resources to providers so they could advocate for better quality of care, especially in rural and disadvantaged settings.
Dr. Wagner disclosed relationships with Alligator Bioscience, BMS, Dragonfly Therapeutics, Lilly, Merck KGaA, MSD Oncology, Servier/Pfizer, and Abbvie. Dr. Evans disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation and Intuitive Surgical.
This article was updated 1/28/22.
FROM GI CANCERS SYMPOSIUM 2022
Can immunotherapy replace surgery for stomach cancer?
GERCOR NEONIPIGA was a phase 2 study with no comparator group and only 32 patients, but even so, after a 6-cycle course of nivolumab and ipilimumab, there was no sign of tumor in 17 of the 29 patients (59%) who had surgery specimens evaluable by pathology.
Indeed, two patients refused surgery after their preop endoscopic biopsies came back clear with no tumor cells. Surgery was called off in a third patient who developed metastases beforehand.
After a median of 12 months follow-up, there’s was no recurrence or progression in 30 patients (94%). The remaining two included the metastatic patient and one who died 3 days after surgery from cardiovascular complications.
If the findings pan out with additional research, the approach could be a boon for people who respond. “Avoiding surgery is a dream for these patients,” said lead investigator Thierry Andre, MD, a medical oncology professor at Sorbonne University, Paris, when he presented the findings at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium.
The trial “raises the question whether surgery can be delayed or avoided in some patients with localized” disease. Given the findings, “it seems possible not for all but probably for half, maybe more.” As in the two subjects who opted out of surgery, preop endoscopic biopsies could be used to identify complete responders with active surveillance afterwards, he said.
The study included 16 patients with gastric cancer and 16 with esophagogastric adenocarcinoma. They were mismatch repair deficient, which Dr. Andre said predicts response to immunotherapy.
At baseline, 22 had stage T3 disease and four had stage T2 disease, and stage was not evaluable by echo-endoscopy in 6. Nodal status was unknown, but the patients had no metastases at baseline.
They underwent six nivolumab 240-mg infusions and two ipilimumab 1–mg/kg infusions over 12 weeks, followed by R0 resections a median of 5 weeks after the last nivolumab injection.
Surgical specimens from 17 patients (59%) showed a complete pathological response to neoadjuvant immunotherapy (Becker tumor regression grade (TRG) 1a, ypT0N0). TRG was 1b – less than 10% residual tumor in tumor bed in four patients. TRG was 2 in two patients with 10%-50% of residual tumor remaining, and six had a TRG of 3 with more than half of the tumor remaining after immunotherapy.
Based on tumor response, 25 patients had nine additional nivolumab infusions after surgery with 480 mg infused monthly.
Dr. Andre explained that people want to avoid surgery because of the substantial morbidity that was shown in the study, plus 54% of patients had complications, including anastomotic leaks, pancreatitis, pneumonia, and other problems.
There were no new safety signals with neoadjuvant therapy; 25% of patients had grade 3 or 4 events.
The study was conducted in 10 centers in France. About three-quarters of the subjects were men and the median age was 65 years.
Bristol Meyers Squibb supplied the nivolumab and ipilimumab and partially funded the work. Many of the investigators had ties to the company, including Dr. Andre, who is a consultant for BMS and reported payments from the company.
GERCOR NEONIPIGA was a phase 2 study with no comparator group and only 32 patients, but even so, after a 6-cycle course of nivolumab and ipilimumab, there was no sign of tumor in 17 of the 29 patients (59%) who had surgery specimens evaluable by pathology.
Indeed, two patients refused surgery after their preop endoscopic biopsies came back clear with no tumor cells. Surgery was called off in a third patient who developed metastases beforehand.
After a median of 12 months follow-up, there’s was no recurrence or progression in 30 patients (94%). The remaining two included the metastatic patient and one who died 3 days after surgery from cardiovascular complications.
If the findings pan out with additional research, the approach could be a boon for people who respond. “Avoiding surgery is a dream for these patients,” said lead investigator Thierry Andre, MD, a medical oncology professor at Sorbonne University, Paris, when he presented the findings at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium.
The trial “raises the question whether surgery can be delayed or avoided in some patients with localized” disease. Given the findings, “it seems possible not for all but probably for half, maybe more.” As in the two subjects who opted out of surgery, preop endoscopic biopsies could be used to identify complete responders with active surveillance afterwards, he said.
The study included 16 patients with gastric cancer and 16 with esophagogastric adenocarcinoma. They were mismatch repair deficient, which Dr. Andre said predicts response to immunotherapy.
At baseline, 22 had stage T3 disease and four had stage T2 disease, and stage was not evaluable by echo-endoscopy in 6. Nodal status was unknown, but the patients had no metastases at baseline.
They underwent six nivolumab 240-mg infusions and two ipilimumab 1–mg/kg infusions over 12 weeks, followed by R0 resections a median of 5 weeks after the last nivolumab injection.
Surgical specimens from 17 patients (59%) showed a complete pathological response to neoadjuvant immunotherapy (Becker tumor regression grade (TRG) 1a, ypT0N0). TRG was 1b – less than 10% residual tumor in tumor bed in four patients. TRG was 2 in two patients with 10%-50% of residual tumor remaining, and six had a TRG of 3 with more than half of the tumor remaining after immunotherapy.
Based on tumor response, 25 patients had nine additional nivolumab infusions after surgery with 480 mg infused monthly.
Dr. Andre explained that people want to avoid surgery because of the substantial morbidity that was shown in the study, plus 54% of patients had complications, including anastomotic leaks, pancreatitis, pneumonia, and other problems.
There were no new safety signals with neoadjuvant therapy; 25% of patients had grade 3 or 4 events.
The study was conducted in 10 centers in France. About three-quarters of the subjects were men and the median age was 65 years.
Bristol Meyers Squibb supplied the nivolumab and ipilimumab and partially funded the work. Many of the investigators had ties to the company, including Dr. Andre, who is a consultant for BMS and reported payments from the company.
GERCOR NEONIPIGA was a phase 2 study with no comparator group and only 32 patients, but even so, after a 6-cycle course of nivolumab and ipilimumab, there was no sign of tumor in 17 of the 29 patients (59%) who had surgery specimens evaluable by pathology.
Indeed, two patients refused surgery after their preop endoscopic biopsies came back clear with no tumor cells. Surgery was called off in a third patient who developed metastases beforehand.
After a median of 12 months follow-up, there’s was no recurrence or progression in 30 patients (94%). The remaining two included the metastatic patient and one who died 3 days after surgery from cardiovascular complications.
If the findings pan out with additional research, the approach could be a boon for people who respond. “Avoiding surgery is a dream for these patients,” said lead investigator Thierry Andre, MD, a medical oncology professor at Sorbonne University, Paris, when he presented the findings at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium.
The trial “raises the question whether surgery can be delayed or avoided in some patients with localized” disease. Given the findings, “it seems possible not for all but probably for half, maybe more.” As in the two subjects who opted out of surgery, preop endoscopic biopsies could be used to identify complete responders with active surveillance afterwards, he said.
The study included 16 patients with gastric cancer and 16 with esophagogastric adenocarcinoma. They were mismatch repair deficient, which Dr. Andre said predicts response to immunotherapy.
At baseline, 22 had stage T3 disease and four had stage T2 disease, and stage was not evaluable by echo-endoscopy in 6. Nodal status was unknown, but the patients had no metastases at baseline.
They underwent six nivolumab 240-mg infusions and two ipilimumab 1–mg/kg infusions over 12 weeks, followed by R0 resections a median of 5 weeks after the last nivolumab injection.
Surgical specimens from 17 patients (59%) showed a complete pathological response to neoadjuvant immunotherapy (Becker tumor regression grade (TRG) 1a, ypT0N0). TRG was 1b – less than 10% residual tumor in tumor bed in four patients. TRG was 2 in two patients with 10%-50% of residual tumor remaining, and six had a TRG of 3 with more than half of the tumor remaining after immunotherapy.
Based on tumor response, 25 patients had nine additional nivolumab infusions after surgery with 480 mg infused monthly.
Dr. Andre explained that people want to avoid surgery because of the substantial morbidity that was shown in the study, plus 54% of patients had complications, including anastomotic leaks, pancreatitis, pneumonia, and other problems.
There were no new safety signals with neoadjuvant therapy; 25% of patients had grade 3 or 4 events.
The study was conducted in 10 centers in France. About three-quarters of the subjects were men and the median age was 65 years.
Bristol Meyers Squibb supplied the nivolumab and ipilimumab and partially funded the work. Many of the investigators had ties to the company, including Dr. Andre, who is a consultant for BMS and reported payments from the company.
FROM GI CANCERS SYMPOSIUM 2022
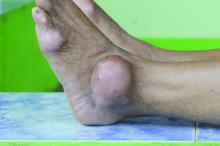
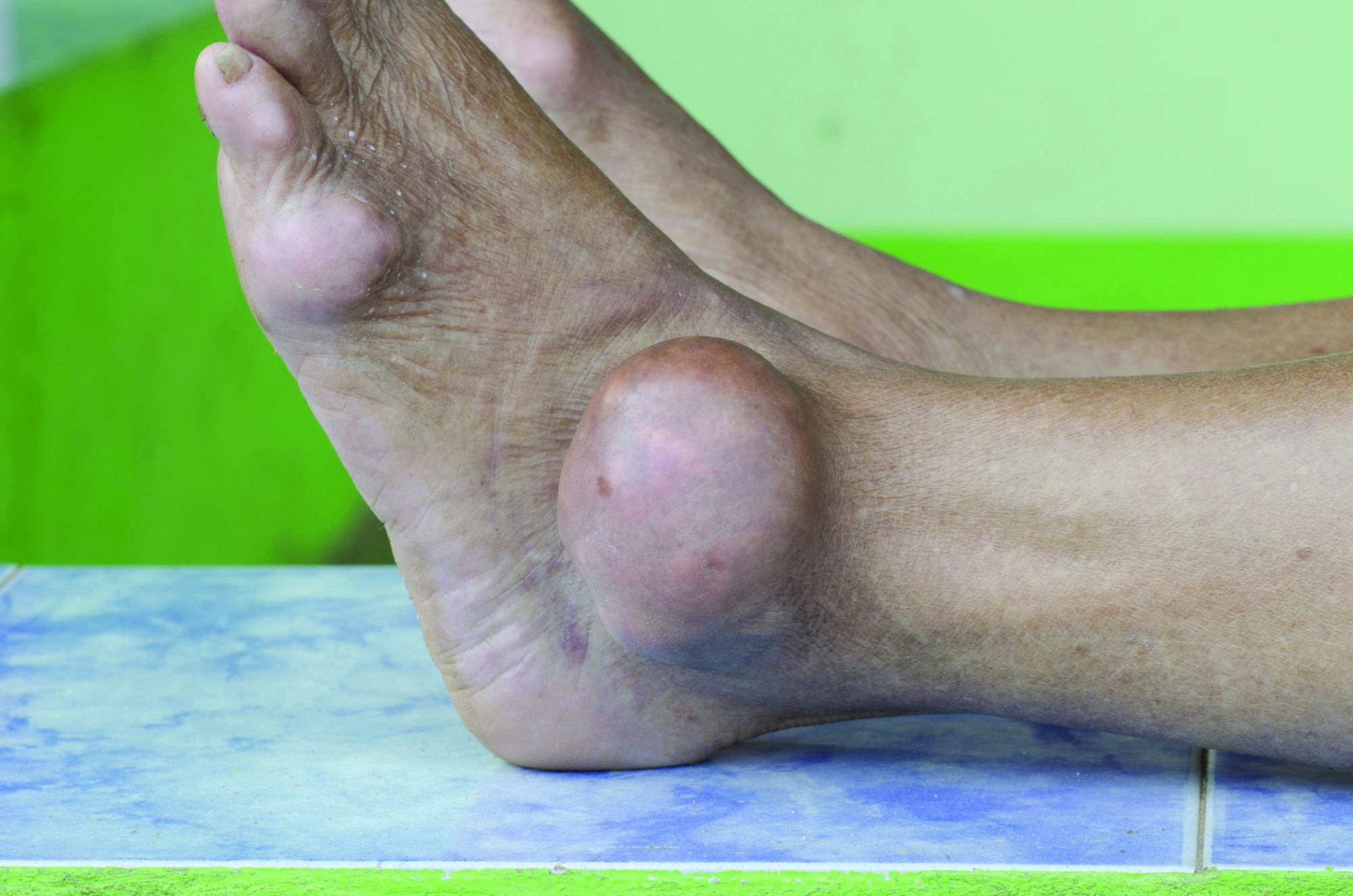
Allopurinol found safe in patients with concomitant gout, CKD
Allopurinol treatment is not associated with increased mortality in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease even at 5 years after starting treatment, a study has found.
Around one in five patients with gout also have chronic kidney disease, and previous research suggests that hyperuricemia is itself a contributor to renal disease, which is why there has been interest in the use of serum urate–lowering medication in patients with both conditions.
Since the publication of two earlier randomized controlled trials suggested a twofold increase in mortality among patients with renal disease who were treated with allopurinol in an attempt to slow progression, there has been wariness about the drug in patients with compromised renal function.
In a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, Jie Wei, PhD, of Xiangya Hospital at Central South University in Changsha, China, and coauthors report the results of their retrospective, population-based study of 5,277 adults aged 40 and older with gout and moderate to severe chronic kidney disease who were initiated on allopurinol and 5,277 matched individuals not on allopurinol.
At 5 years after the patients started allopurinol, the study found that mortality was a statistically significant 15% lower (hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.93) among those on allopurinol, compared with those not taking the drug. The rate was 4.9 deaths per 100 person-years among those on allopurinol, compared with 5.8 among those not taking it.
The researchers also created two simulated randomized clinical trials from the data for initiators of allopurinol, replicating each initiator twice. The first trial assigned patient replicates either to achieving a target serum urate level of less than 0.36 mmol/L within a year or not achieving it. The second assigned patient replicates to either an allopurinol dose-escalation group or no dose escalation.
For the target serum urate level study, 1,484 achieved the target, and this was associated with a 13% lower hazard ratio for mortality that just missed statistical significance (HR, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-1.01).
In the dose-escalation study, there were 773 participants who increased their dose of allopurinol in the first year after initiation – from a median of 100 mg/day to a median final dose of 300 mg/day – and 2,923 who didn’t. Those who escalated their dose had a nonsignificant 12% lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.73-1.07), compared with those who didn’t.
The authors suggest that this could be the result of confounding, as patients who achieved target serum urate levels may have been of better health generally than those who didn’t, which could also have contributed to lower mortality.
Coauthor of the study Yuqing Zhang, DSc, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said there had previously been a theory that allopurinol could protect against progression of renal disease. However, the two randomized, controlled trials in patients with chronic kidney disease but not gout published in 2020 suggested that allopurinol was instead associated with a doubling of mortality in this group.
“This study really shows convincing evidence that among gout patients with renal disease, allopurinol does not increase mortality,” Dr. Zhang told this news organization. He suggested the reason that the earlier studies had found higher mortality among patients on allopurinol was because those patients did not have gout. Given that gout can increase mortality, treating it effectively with allopurinol may therefore reduce mortality even in patients with concurrent chronic kidney disease.
Commenting on the study, Angelo Gaffo, MD, from the Birmingham VA Medical Center and the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that, while there had been data suggesting increased mortality, the findings from this “very well-done” study were reassuring and even suggested a possible decrease in mortality associated with allopurinol.
“I wouldn’t scream it out loud because it needs confirmation, but it’s something also that we have a sense that could be true,” he said.
Dr. Gaffo noted that patients treated with allopurinol tended to be those with fewer comorbidities. “Patients who have a lot of comorbidities probably are less likely to have their dose of allopurinol started or increased because of some concerns that practitioners may have about putting them on another medicine or increasing the dose of that medicine,” he said.
He also stressed that the findings still need replication in other large database studies, given that a prospective, randomized clinical trial addressing such a question would be difficult to conduct.
The study was supported by the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Two authors reported consulting fees from the pharmaceutical sector unrelated to the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Allopurinol treatment is not associated with increased mortality in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease even at 5 years after starting treatment, a study has found.
Around one in five patients with gout also have chronic kidney disease, and previous research suggests that hyperuricemia is itself a contributor to renal disease, which is why there has been interest in the use of serum urate–lowering medication in patients with both conditions.
Since the publication of two earlier randomized controlled trials suggested a twofold increase in mortality among patients with renal disease who were treated with allopurinol in an attempt to slow progression, there has been wariness about the drug in patients with compromised renal function.
In a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, Jie Wei, PhD, of Xiangya Hospital at Central South University in Changsha, China, and coauthors report the results of their retrospective, population-based study of 5,277 adults aged 40 and older with gout and moderate to severe chronic kidney disease who were initiated on allopurinol and 5,277 matched individuals not on allopurinol.
At 5 years after the patients started allopurinol, the study found that mortality was a statistically significant 15% lower (hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.93) among those on allopurinol, compared with those not taking the drug. The rate was 4.9 deaths per 100 person-years among those on allopurinol, compared with 5.8 among those not taking it.
The researchers also created two simulated randomized clinical trials from the data for initiators of allopurinol, replicating each initiator twice. The first trial assigned patient replicates either to achieving a target serum urate level of less than 0.36 mmol/L within a year or not achieving it. The second assigned patient replicates to either an allopurinol dose-escalation group or no dose escalation.
For the target serum urate level study, 1,484 achieved the target, and this was associated with a 13% lower hazard ratio for mortality that just missed statistical significance (HR, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-1.01).
In the dose-escalation study, there were 773 participants who increased their dose of allopurinol in the first year after initiation – from a median of 100 mg/day to a median final dose of 300 mg/day – and 2,923 who didn’t. Those who escalated their dose had a nonsignificant 12% lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.73-1.07), compared with those who didn’t.
The authors suggest that this could be the result of confounding, as patients who achieved target serum urate levels may have been of better health generally than those who didn’t, which could also have contributed to lower mortality.
Coauthor of the study Yuqing Zhang, DSc, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said there had previously been a theory that allopurinol could protect against progression of renal disease. However, the two randomized, controlled trials in patients with chronic kidney disease but not gout published in 2020 suggested that allopurinol was instead associated with a doubling of mortality in this group.
“This study really shows convincing evidence that among gout patients with renal disease, allopurinol does not increase mortality,” Dr. Zhang told this news organization. He suggested the reason that the earlier studies had found higher mortality among patients on allopurinol was because those patients did not have gout. Given that gout can increase mortality, treating it effectively with allopurinol may therefore reduce mortality even in patients with concurrent chronic kidney disease.
Commenting on the study, Angelo Gaffo, MD, from the Birmingham VA Medical Center and the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that, while there had been data suggesting increased mortality, the findings from this “very well-done” study were reassuring and even suggested a possible decrease in mortality associated with allopurinol.
“I wouldn’t scream it out loud because it needs confirmation, but it’s something also that we have a sense that could be true,” he said.
Dr. Gaffo noted that patients treated with allopurinol tended to be those with fewer comorbidities. “Patients who have a lot of comorbidities probably are less likely to have their dose of allopurinol started or increased because of some concerns that practitioners may have about putting them on another medicine or increasing the dose of that medicine,” he said.
He also stressed that the findings still need replication in other large database studies, given that a prospective, randomized clinical trial addressing such a question would be difficult to conduct.
The study was supported by the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Two authors reported consulting fees from the pharmaceutical sector unrelated to the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Allopurinol treatment is not associated with increased mortality in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease even at 5 years after starting treatment, a study has found.
Around one in five patients with gout also have chronic kidney disease, and previous research suggests that hyperuricemia is itself a contributor to renal disease, which is why there has been interest in the use of serum urate–lowering medication in patients with both conditions.
Since the publication of two earlier randomized controlled trials suggested a twofold increase in mortality among patients with renal disease who were treated with allopurinol in an attempt to slow progression, there has been wariness about the drug in patients with compromised renal function.
In a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, Jie Wei, PhD, of Xiangya Hospital at Central South University in Changsha, China, and coauthors report the results of their retrospective, population-based study of 5,277 adults aged 40 and older with gout and moderate to severe chronic kidney disease who were initiated on allopurinol and 5,277 matched individuals not on allopurinol.
At 5 years after the patients started allopurinol, the study found that mortality was a statistically significant 15% lower (hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.93) among those on allopurinol, compared with those not taking the drug. The rate was 4.9 deaths per 100 person-years among those on allopurinol, compared with 5.8 among those not taking it.
The researchers also created two simulated randomized clinical trials from the data for initiators of allopurinol, replicating each initiator twice. The first trial assigned patient replicates either to achieving a target serum urate level of less than 0.36 mmol/L within a year or not achieving it. The second assigned patient replicates to either an allopurinol dose-escalation group or no dose escalation.
For the target serum urate level study, 1,484 achieved the target, and this was associated with a 13% lower hazard ratio for mortality that just missed statistical significance (HR, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-1.01).
In the dose-escalation study, there were 773 participants who increased their dose of allopurinol in the first year after initiation – from a median of 100 mg/day to a median final dose of 300 mg/day – and 2,923 who didn’t. Those who escalated their dose had a nonsignificant 12% lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.73-1.07), compared with those who didn’t.
The authors suggest that this could be the result of confounding, as patients who achieved target serum urate levels may have been of better health generally than those who didn’t, which could also have contributed to lower mortality.
Coauthor of the study Yuqing Zhang, DSc, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said there had previously been a theory that allopurinol could protect against progression of renal disease. However, the two randomized, controlled trials in patients with chronic kidney disease but not gout published in 2020 suggested that allopurinol was instead associated with a doubling of mortality in this group.
“This study really shows convincing evidence that among gout patients with renal disease, allopurinol does not increase mortality,” Dr. Zhang told this news organization. He suggested the reason that the earlier studies had found higher mortality among patients on allopurinol was because those patients did not have gout. Given that gout can increase mortality, treating it effectively with allopurinol may therefore reduce mortality even in patients with concurrent chronic kidney disease.
Commenting on the study, Angelo Gaffo, MD, from the Birmingham VA Medical Center and the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that, while there had been data suggesting increased mortality, the findings from this “very well-done” study were reassuring and even suggested a possible decrease in mortality associated with allopurinol.
“I wouldn’t scream it out loud because it needs confirmation, but it’s something also that we have a sense that could be true,” he said.
Dr. Gaffo noted that patients treated with allopurinol tended to be those with fewer comorbidities. “Patients who have a lot of comorbidities probably are less likely to have their dose of allopurinol started or increased because of some concerns that practitioners may have about putting them on another medicine or increasing the dose of that medicine,” he said.
He also stressed that the findings still need replication in other large database studies, given that a prospective, randomized clinical trial addressing such a question would be difficult to conduct.
The study was supported by the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Two authors reported consulting fees from the pharmaceutical sector unrelated to the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE