User login
Erenumab Treatment Interruption May Worsen Episodic or Chronic Migraine Symptoms
Key clinical point: In patients with episodic migraine (EM) or chronic migraine (CM), erenumab treatment interruption was associated with increased monthly migraine days (MMD) and worsening of migraine disability; these effects ameliorated on treatment restart.
Major finding: After erenumab treatment interruption for 3 months, the number of monthly migraine days (MMD) increased from 6.1 to 10.9 days for patients with EM and from 11.4 to 16.8 days for patients with CM; the modified Migraine Disability Assessment scores (mMIDAS) also worsened during this period. Both MMD and mMIDAS scores improved upon restarting treatment.
Study details: This interim analysis of the 24-month, multicentric, non-interventional observational study included 172 patients with CM or EM who received erenumab and underwent treatment interruptions on average 11.2 months after initiation, with interruptions lasting for a mean duration of 4 months.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG. Four authors declared being full-time employees of Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG, and others declared having ties with various sources, including Novartis.
Source: Gantenbein AR, Bonvin C, Kamm CP, et al. Implications of therapy interruption on monthly migraine days and modified migraine disability assessment in patients treated with erenumab for chronic and episodic migraine: SQUARE study interim results. J Neurol. 2024 (Jun 13). Doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12470-6 Source
Key clinical point: In patients with episodic migraine (EM) or chronic migraine (CM), erenumab treatment interruption was associated with increased monthly migraine days (MMD) and worsening of migraine disability; these effects ameliorated on treatment restart.
Major finding: After erenumab treatment interruption for 3 months, the number of monthly migraine days (MMD) increased from 6.1 to 10.9 days for patients with EM and from 11.4 to 16.8 days for patients with CM; the modified Migraine Disability Assessment scores (mMIDAS) also worsened during this period. Both MMD and mMIDAS scores improved upon restarting treatment.
Study details: This interim analysis of the 24-month, multicentric, non-interventional observational study included 172 patients with CM or EM who received erenumab and underwent treatment interruptions on average 11.2 months after initiation, with interruptions lasting for a mean duration of 4 months.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG. Four authors declared being full-time employees of Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG, and others declared having ties with various sources, including Novartis.
Source: Gantenbein AR, Bonvin C, Kamm CP, et al. Implications of therapy interruption on monthly migraine days and modified migraine disability assessment in patients treated with erenumab for chronic and episodic migraine: SQUARE study interim results. J Neurol. 2024 (Jun 13). Doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12470-6 Source
Key clinical point: In patients with episodic migraine (EM) or chronic migraine (CM), erenumab treatment interruption was associated with increased monthly migraine days (MMD) and worsening of migraine disability; these effects ameliorated on treatment restart.
Major finding: After erenumab treatment interruption for 3 months, the number of monthly migraine days (MMD) increased from 6.1 to 10.9 days for patients with EM and from 11.4 to 16.8 days for patients with CM; the modified Migraine Disability Assessment scores (mMIDAS) also worsened during this period. Both MMD and mMIDAS scores improved upon restarting treatment.
Study details: This interim analysis of the 24-month, multicentric, non-interventional observational study included 172 patients with CM or EM who received erenumab and underwent treatment interruptions on average 11.2 months after initiation, with interruptions lasting for a mean duration of 4 months.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG. Four authors declared being full-time employees of Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG, and others declared having ties with various sources, including Novartis.
Source: Gantenbein AR, Bonvin C, Kamm CP, et al. Implications of therapy interruption on monthly migraine days and modified migraine disability assessment in patients treated with erenumab for chronic and episodic migraine: SQUARE study interim results. J Neurol. 2024 (Jun 13). Doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12470-6 Source
Patients With Migraine Have Higher Risk for Retinal Vascular Occlusion
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine, migraine with aura (MA), or migraine without aura (MO) faced a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion.
Major findings: Compared with control individuals without migraine, those with migraine (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.69; 95% CI 1.57-1.83), MA (aHR 1.77; 95% CI 1.58-1.98), or MO (aHR 1.92; 95% CI 1.64-2.25; P < .001 for all) had a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion. The risk was, however, reduced in the migraine population that received nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aHR 0.19; 95% CI 0.16-0.22), propranolol (aHR 0.73; 95% CI 0.62-0.86), or flunarizine (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.76-0.93; P < .001 for all).
Study details: This population-based retrospective cohort study included 628,760 patients with migraine and 628,760 control individuals without migraine.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial Center, China Medical University Hospital, and National Science and Technology Council. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ho K-Y, Lin C-D, Hsu T-J, et al. Increased risks of retinal vascular occlusion in patients with migraine and the protective effects of migraine treatment: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2024;14:15429 (Jul 4). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66363-9 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine, migraine with aura (MA), or migraine without aura (MO) faced a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion.
Major findings: Compared with control individuals without migraine, those with migraine (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.69; 95% CI 1.57-1.83), MA (aHR 1.77; 95% CI 1.58-1.98), or MO (aHR 1.92; 95% CI 1.64-2.25; P < .001 for all) had a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion. The risk was, however, reduced in the migraine population that received nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aHR 0.19; 95% CI 0.16-0.22), propranolol (aHR 0.73; 95% CI 0.62-0.86), or flunarizine (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.76-0.93; P < .001 for all).
Study details: This population-based retrospective cohort study included 628,760 patients with migraine and 628,760 control individuals without migraine.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial Center, China Medical University Hospital, and National Science and Technology Council. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ho K-Y, Lin C-D, Hsu T-J, et al. Increased risks of retinal vascular occlusion in patients with migraine and the protective effects of migraine treatment: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2024;14:15429 (Jul 4). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66363-9 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine, migraine with aura (MA), or migraine without aura (MO) faced a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion.
Major findings: Compared with control individuals without migraine, those with migraine (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.69; 95% CI 1.57-1.83), MA (aHR 1.77; 95% CI 1.58-1.98), or MO (aHR 1.92; 95% CI 1.64-2.25; P < .001 for all) had a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion. The risk was, however, reduced in the migraine population that received nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aHR 0.19; 95% CI 0.16-0.22), propranolol (aHR 0.73; 95% CI 0.62-0.86), or flunarizine (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.76-0.93; P < .001 for all).
Study details: This population-based retrospective cohort study included 628,760 patients with migraine and 628,760 control individuals without migraine.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial Center, China Medical University Hospital, and National Science and Technology Council. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ho K-Y, Lin C-D, Hsu T-J, et al. Increased risks of retinal vascular occlusion in patients with migraine and the protective effects of migraine treatment: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2024;14:15429 (Jul 4). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66363-9 Source
Atogepant Effective in Chronic Migraine, Irrespective of Acute Medication Overuse
Key clinical point: Atogepant was effective in reducing monthly migraine days (MMD), monthly headache days (MHD), and acute medication use days in patients with chronic migraine (CM), irrespective of acute medication overuse.
Major findings: Patients with acute medication overuse receiving 30 mg or 60 mg atogepant vs placebo had a significantly greater reduction in MMD (least squares mean difference [LSMD] −2.7 and −1.9, respectively), MHD (LSMD −2.8 and −2.1, respectively), and monthly acute medication use days (LSMD −2.8 and −2.6, respectively). Similar reductions were observed in patients without acute medication overuse.
Study details: This subgroup analysis of the PROGRESS trial included 755 patients with CM with or without acute medication overuse who were randomly assigned to receive atogepant (30 mg or 60 mg) or placebo.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie. Six authors declared being employees or stockholders of AbbVie. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Goadsby PJ, Friedman DI, Holle-Lee D, et al. Efficacy of atogepant in chronic migraine with and without acute medication overuse in the randomized, double-blind, phase 3 PROGRESS trial. Neurology. 2024;103(2):e209584 (July 23). Doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209584 Source
Key clinical point: Atogepant was effective in reducing monthly migraine days (MMD), monthly headache days (MHD), and acute medication use days in patients with chronic migraine (CM), irrespective of acute medication overuse.
Major findings: Patients with acute medication overuse receiving 30 mg or 60 mg atogepant vs placebo had a significantly greater reduction in MMD (least squares mean difference [LSMD] −2.7 and −1.9, respectively), MHD (LSMD −2.8 and −2.1, respectively), and monthly acute medication use days (LSMD −2.8 and −2.6, respectively). Similar reductions were observed in patients without acute medication overuse.
Study details: This subgroup analysis of the PROGRESS trial included 755 patients with CM with or without acute medication overuse who were randomly assigned to receive atogepant (30 mg or 60 mg) or placebo.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie. Six authors declared being employees or stockholders of AbbVie. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Goadsby PJ, Friedman DI, Holle-Lee D, et al. Efficacy of atogepant in chronic migraine with and without acute medication overuse in the randomized, double-blind, phase 3 PROGRESS trial. Neurology. 2024;103(2):e209584 (July 23). Doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209584 Source
Key clinical point: Atogepant was effective in reducing monthly migraine days (MMD), monthly headache days (MHD), and acute medication use days in patients with chronic migraine (CM), irrespective of acute medication overuse.
Major findings: Patients with acute medication overuse receiving 30 mg or 60 mg atogepant vs placebo had a significantly greater reduction in MMD (least squares mean difference [LSMD] −2.7 and −1.9, respectively), MHD (LSMD −2.8 and −2.1, respectively), and monthly acute medication use days (LSMD −2.8 and −2.6, respectively). Similar reductions were observed in patients without acute medication overuse.
Study details: This subgroup analysis of the PROGRESS trial included 755 patients with CM with or without acute medication overuse who were randomly assigned to receive atogepant (30 mg or 60 mg) or placebo.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie. Six authors declared being employees or stockholders of AbbVie. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Goadsby PJ, Friedman DI, Holle-Lee D, et al. Efficacy of atogepant in chronic migraine with and without acute medication overuse in the randomized, double-blind, phase 3 PROGRESS trial. Neurology. 2024;103(2):e209584 (July 23). Doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209584 Source
Cyclosporine for Recalcitrant Bullous Pemphigoid Induced by Nivolumab Therapy for Malignant Melanoma
To the Editor:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized the treatment of advanced-stage melanoma, with remarkably improved progression-free survival.1 Anti–programmed death receptor 1 (anti–PD-1) therapies, such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab, are a class of checkpoint inhibitors that have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for unresectable metastatic melanoma. Anti–PD-1 agents block the interaction of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) found on tumor cells with the PD-1 receptor on T cells, facilitating a positive immune response.2
Although these therapies have demonstrated notable antitumor efficacy, they also give rise to numerous immune-related adverse events (irAEs). As many as 70% of patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors experience some type of organ system irAE, of which 30% to 40% are cutaneous.3-6 Dermatologic adverse events are the most common irAEs, specifically spongiotic dermatitis, lichenoid dermatitis, pruritus, and vitiligo.7 Bullous pemphigoid (BP), an autoimmune bullous skin disorder caused by autoantibodies to basement membrane zone antigens, is a rare but potentially serious cutaneous irAE.8 Systemic corticosteroids commonly are used to treat immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP; other options include tetracyclines for maintenance therapy and rituximab for corticosteroid-refractory BP associated with anti-PD-1.9 We present a case of recalcitrant BP secondary to nivolumab therapy in a patient with metastatic melanoma who had near-complete resolution of BP following 2 months of cyclosporine.
A 41-year-old man presented with a generalized papular skin eruption of 1 month’s duration. He had a history of stage IIIC malignant melanoma of the lower right leg with positive sentinel lymph node biopsy. The largest lymph node deposit was 0.03 mm without extracapsular extension. Whole-body positron emission tomography–computed tomography showed no evidence of distant disease. The patient was treated with wide local excision with clear surgical margins plus 12 cycles of nivolumab, which was discontinued due to colitis. Four months after the final cycle of nivolumab, the patient developed widespread erythematous papules with hemorrhagic yellow crusting and no mucosal involvement. He was referred to dermatology by his primary oncologist for further evaluation.
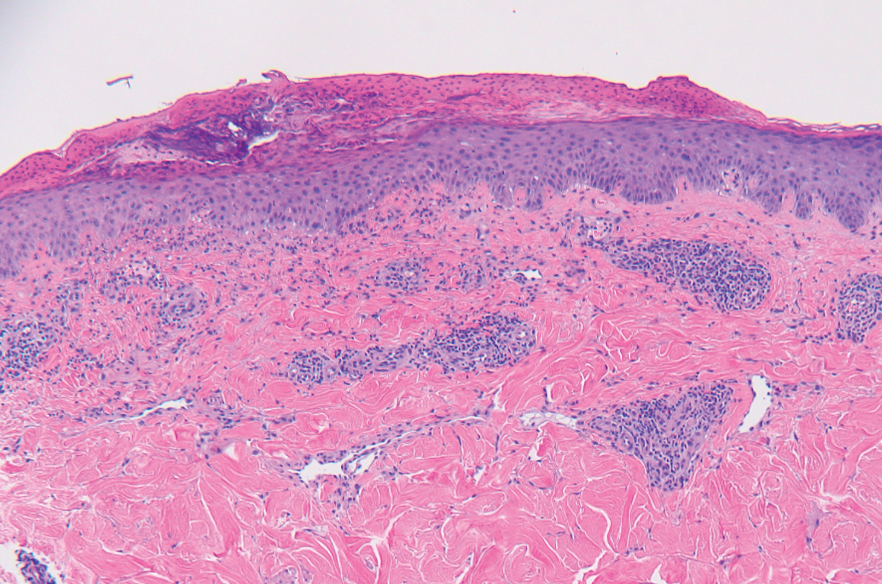
A punch biopsy from the abdomen showed parakeratosis with leukocytoclasis and a superficial dermal infiltrate of neutrophils and eosinophils (Figure 1). Direct immunofluorescence revealed linear basement membrane deposits of IgG and C3, consistent with subepidermal blistering disease. Indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated trace IgG and IgG4 antibodies localized to the epidermal roof of salt-split skin and was negative for IgA antibodies. An enzyme-linked immunoassay was positive for BP antigen 2 (BP180) antibodies (98.4 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]) and negative for BP antigen 1 (BP230) antibodies (4.3 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]). Overall, these findings were consistent with a diagnosis of BP.
The patient was treated with prednisone 60 mg daily with initial response; however, there was disease recurrence with tapering. Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and nicotinamide 500 mg twice daily were added as steroid-sparing agents, as prednisone was discontinued due to mood changes. Three months after the prednisone taper, the patient continued to develop new blisters. He completed treatment with doxycycline and nicotinamide. Rituximab 375 mg weekly was then initiated for 4 weeks.
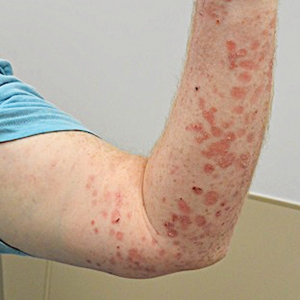
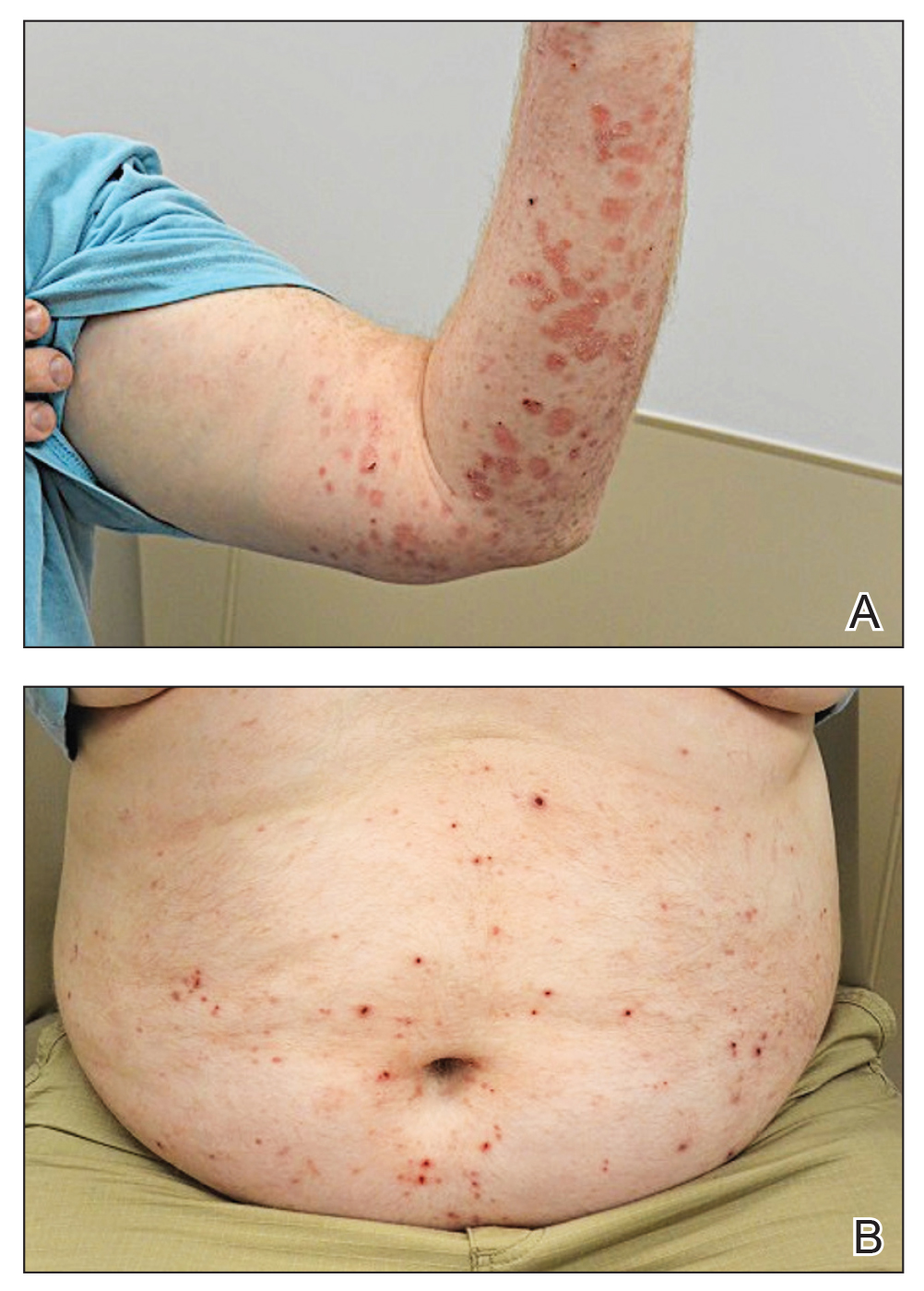
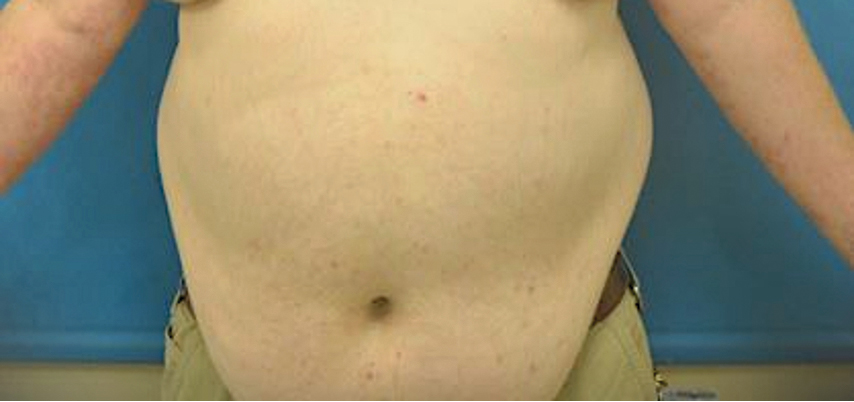
At 2-week follow-up after completing the rituximab course, the patient reported worsening symptoms and presented with new bullae on the abdomen and upper extremities (Figure 2). Because of the recent history of mood changes while taking prednisone, a trial of cyclosporine 100 mg twice daily (1.37 mg/kg/d) was initiated, with notable improvement within 2 weeks of treatment. After 2 months of cyclosporine, approximately 90% of the rash had resolved with a few tense bullae remaining on the left frontal scalp but no new flares (Figure 3). One month after treatment ended, the patient remained clear of lesions without relapse.
Programmed death receptor 1 inhibitors have shown dramatic efficacy for a growing number of solid and hematologic malignancies, especially malignant melanoma. However, their use is accompanied by nonspecific activation of the immune system, resulting in a variety of adverse events, many manifesting on the skin. Several cases of BP in patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors have been reported.9 Cutaneous irAEs usually manifest within 3 weeks of initiation of PD-1 inhibitor therapy; however, the onset of BP typically occurs later at approximately 21 weeks.4,9 Our patient developed cutaneous manifestations 4 months after cessation of nivolumab.
Bullous pemphigoid classically manifests with pruritus and tense bullae. Notably, our patient’s clinical presentation included a widespread eruption of papules without bullae, which was similar to a review by Tsiogka et al,9 which reported that one-third of patients first present with a nonspecific cutaneous eruption. Bullous pemphigoid induced by anti–PD-1 may manifest differently than traditional BP, illuminating the importance of a thorough diagnostic workup.
Although the pathogenesis of immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP has not been fully elucidated, it is hypothesized to be caused by increased T cell cytotoxic activity leading to tumor lysis and release of numerous autoantigens. These autoantigens cause priming of abnormal T cells that can lead to further tissue damage in peripheral tissue and to generation of aberrant B cells and subsequent autoantibodies such as BP180 in germinal centers.4,10,11
Cyclosporine is a calcineurin inhibitor that reduces synthesis of IL-2, resulting in reduced cell activation.12 Therefore, cyclosporine may alleviate BP in patients who are being treated, or were previously treated, with an immune checkpoint inhibitor by suppressing T cell–mediated immune reaction and may be a rapid alternative for patients who cannot tolerate systemic steroids.
Treatment options for mild to moderate cases of BP include topical corticosteroids and antihistamines, while severe cases may require high-dose systemic corticosteroids. In recalcitrant cases, rituximab infusion with or without intravenous immunoglobulin often is utilized.8,13 The use of cyclosporine for various bullous disorders, including pemphigus vulgaris and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, has been described.14 In recent years there has been a shift away from the use of cyclosporine for these conditions following the introduction of rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen on B lymphocytes. We utilized cyclosporine in our patient after he experienced worsening symptoms 1 month after completing treatment with rituximab.
Improvement from rituximab therapy may be delayed because it can take months to deplete CD20+ B lymphocytes from circulation, which may necessitate additional immunosuppressants or re-treatment with rituximab.15,16 In these instances, cyclosporine may be beneficial as a low-cost alternative in patients who are unable to tolerate systemic steroids, with a relatively good safety profile. The dosage of cyclosporine prescribed to the patient was chosen based on Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation management guidelines for psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies, which recommends an initial dosage of 1 to 3 mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses.17
As immunotherapy for treating various cancers gains popularity, the frequency of dermatologic irAEs will increase. Therefore, dermatologists must be aware of the array of cutaneous manifestations, such as BP, and potential treatment options. When first-line and second-line therapies are contraindicated or do not provide notable improvement, cyclosporine may be an effective alternative for immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP.
- Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:23-34. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1504030
- Alsaab HO, Sau S, Alzhrani R, et al. PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint signaling inhibition for cancer immunotherapy: mechanism, combinations, and clinical outcome. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:561. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00561
- Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; . Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5:95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
- Geisler AN, Phillips GS, Barrios DM, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related dermatologic adverse events. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1255-1268. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.132
- Villadolid J, Amin A. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice: update on management of immune-related toxicities. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4:560-575. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2015.06.06
- Kumar V, Chaudhary N, Garg M, et al. Current diagnosis and management of immune related adverse events (irAEs) induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:49. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00049
- Belum VR, Benhuri B, Postow MA, et al. Characterisation and management of dermatologic adverse events to agents targeting the PD-1 receptor. Eur J Cancer. 2016;60:12-25. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.02.010
- Schauer F, Rafei-Shamsabadi D, Mai S, et al. Hemidesmosomal reactivity and treatment recommendations in immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced bullous pemphigoid—a retrospective, monocentric study. Front Immunol. 2022;13:953546. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.953546
- Tsiogka A, Bauer JW, Patsatsi A. Bullous pemphigoid associated with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 and anti-programmed cell death ligand 1 therapy: a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00377. doi:10.2340/00015555-3740
- Lopez AT, Khanna T, Antonov N, et al. A review of bullous pemphigoid associated with PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:664-669. doi:10.1111/ijd.13984
- Yang H, Yao Z, Zhou X, et al. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors: insights into immunological dysregulation. Clin Immunol. 2020;213:108377. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108377
- Russell G, Graveley R, Seid J, et al. Mechanisms of action of cyclosporine and effects on connective tissues. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1992;21(6 suppl 3):16-22. doi:10.1016/0049-0172(92)90009-3
- Ahmed AR, Shetty S, Kaveri S, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant bullous pemphigoid (BP) with a novel protocol: a retrospective study with a 6-year follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:700-708.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.11.030
- Amor KT, Ryan C, Menter A. The use of cyclosporine in dermatology: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:925-946. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.02.063
- Schmidt E, Hunzelmann N, Zillikens D, et al. Rituximab in refractory autoimmune bullous diseases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:503-508. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2006.02151.x
- Kasperkiewicz M, Shimanovich I, Ludwig RJ, et al. Rituximab for treatment-refractory pemphigus and pemphigoid: a case series of 17 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:552-558.
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
To the Editor:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized the treatment of advanced-stage melanoma, with remarkably improved progression-free survival.1 Anti–programmed death receptor 1 (anti–PD-1) therapies, such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab, are a class of checkpoint inhibitors that have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for unresectable metastatic melanoma. Anti–PD-1 agents block the interaction of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) found on tumor cells with the PD-1 receptor on T cells, facilitating a positive immune response.2
Although these therapies have demonstrated notable antitumor efficacy, they also give rise to numerous immune-related adverse events (irAEs). As many as 70% of patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors experience some type of organ system irAE, of which 30% to 40% are cutaneous.3-6 Dermatologic adverse events are the most common irAEs, specifically spongiotic dermatitis, lichenoid dermatitis, pruritus, and vitiligo.7 Bullous pemphigoid (BP), an autoimmune bullous skin disorder caused by autoantibodies to basement membrane zone antigens, is a rare but potentially serious cutaneous irAE.8 Systemic corticosteroids commonly are used to treat immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP; other options include tetracyclines for maintenance therapy and rituximab for corticosteroid-refractory BP associated with anti-PD-1.9 We present a case of recalcitrant BP secondary to nivolumab therapy in a patient with metastatic melanoma who had near-complete resolution of BP following 2 months of cyclosporine.
A 41-year-old man presented with a generalized papular skin eruption of 1 month’s duration. He had a history of stage IIIC malignant melanoma of the lower right leg with positive sentinel lymph node biopsy. The largest lymph node deposit was 0.03 mm without extracapsular extension. Whole-body positron emission tomography–computed tomography showed no evidence of distant disease. The patient was treated with wide local excision with clear surgical margins plus 12 cycles of nivolumab, which was discontinued due to colitis. Four months after the final cycle of nivolumab, the patient developed widespread erythematous papules with hemorrhagic yellow crusting and no mucosal involvement. He was referred to dermatology by his primary oncologist for further evaluation.
A punch biopsy from the abdomen showed parakeratosis with leukocytoclasis and a superficial dermal infiltrate of neutrophils and eosinophils (Figure 1). Direct immunofluorescence revealed linear basement membrane deposits of IgG and C3, consistent with subepidermal blistering disease. Indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated trace IgG and IgG4 antibodies localized to the epidermal roof of salt-split skin and was negative for IgA antibodies. An enzyme-linked immunoassay was positive for BP antigen 2 (BP180) antibodies (98.4 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]) and negative for BP antigen 1 (BP230) antibodies (4.3 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]). Overall, these findings were consistent with a diagnosis of BP.
The patient was treated with prednisone 60 mg daily with initial response; however, there was disease recurrence with tapering. Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and nicotinamide 500 mg twice daily were added as steroid-sparing agents, as prednisone was discontinued due to mood changes. Three months after the prednisone taper, the patient continued to develop new blisters. He completed treatment with doxycycline and nicotinamide. Rituximab 375 mg weekly was then initiated for 4 weeks.
At 2-week follow-up after completing the rituximab course, the patient reported worsening symptoms and presented with new bullae on the abdomen and upper extremities (Figure 2). Because of the recent history of mood changes while taking prednisone, a trial of cyclosporine 100 mg twice daily (1.37 mg/kg/d) was initiated, with notable improvement within 2 weeks of treatment. After 2 months of cyclosporine, approximately 90% of the rash had resolved with a few tense bullae remaining on the left frontal scalp but no new flares (Figure 3). One month after treatment ended, the patient remained clear of lesions without relapse.
Programmed death receptor 1 inhibitors have shown dramatic efficacy for a growing number of solid and hematologic malignancies, especially malignant melanoma. However, their use is accompanied by nonspecific activation of the immune system, resulting in a variety of adverse events, many manifesting on the skin. Several cases of BP in patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors have been reported.9 Cutaneous irAEs usually manifest within 3 weeks of initiation of PD-1 inhibitor therapy; however, the onset of BP typically occurs later at approximately 21 weeks.4,9 Our patient developed cutaneous manifestations 4 months after cessation of nivolumab.



Bullous pemphigoid classically manifests with pruritus and tense bullae. Notably, our patient’s clinical presentation included a widespread eruption of papules without bullae, which was similar to a review by Tsiogka et al,9 which reported that one-third of patients first present with a nonspecific cutaneous eruption. Bullous pemphigoid induced by anti–PD-1 may manifest differently than traditional BP, illuminating the importance of a thorough diagnostic workup.
Although the pathogenesis of immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP has not been fully elucidated, it is hypothesized to be caused by increased T cell cytotoxic activity leading to tumor lysis and release of numerous autoantigens. These autoantigens cause priming of abnormal T cells that can lead to further tissue damage in peripheral tissue and to generation of aberrant B cells and subsequent autoantibodies such as BP180 in germinal centers.4,10,11
Cyclosporine is a calcineurin inhibitor that reduces synthesis of IL-2, resulting in reduced cell activation.12 Therefore, cyclosporine may alleviate BP in patients who are being treated, or were previously treated, with an immune checkpoint inhibitor by suppressing T cell–mediated immune reaction and may be a rapid alternative for patients who cannot tolerate systemic steroids.
Treatment options for mild to moderate cases of BP include topical corticosteroids and antihistamines, while severe cases may require high-dose systemic corticosteroids. In recalcitrant cases, rituximab infusion with or without intravenous immunoglobulin often is utilized.8,13 The use of cyclosporine for various bullous disorders, including pemphigus vulgaris and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, has been described.14 In recent years there has been a shift away from the use of cyclosporine for these conditions following the introduction of rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen on B lymphocytes. We utilized cyclosporine in our patient after he experienced worsening symptoms 1 month after completing treatment with rituximab.
Improvement from rituximab therapy may be delayed because it can take months to deplete CD20+ B lymphocytes from circulation, which may necessitate additional immunosuppressants or re-treatment with rituximab.15,16 In these instances, cyclosporine may be beneficial as a low-cost alternative in patients who are unable to tolerate systemic steroids, with a relatively good safety profile. The dosage of cyclosporine prescribed to the patient was chosen based on Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation management guidelines for psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies, which recommends an initial dosage of 1 to 3 mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses.17
As immunotherapy for treating various cancers gains popularity, the frequency of dermatologic irAEs will increase. Therefore, dermatologists must be aware of the array of cutaneous manifestations, such as BP, and potential treatment options. When first-line and second-line therapies are contraindicated or do not provide notable improvement, cyclosporine may be an effective alternative for immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP.
To the Editor:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized the treatment of advanced-stage melanoma, with remarkably improved progression-free survival.1 Anti–programmed death receptor 1 (anti–PD-1) therapies, such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab, are a class of checkpoint inhibitors that have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for unresectable metastatic melanoma. Anti–PD-1 agents block the interaction of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) found on tumor cells with the PD-1 receptor on T cells, facilitating a positive immune response.2
Although these therapies have demonstrated notable antitumor efficacy, they also give rise to numerous immune-related adverse events (irAEs). As many as 70% of patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors experience some type of organ system irAE, of which 30% to 40% are cutaneous.3-6 Dermatologic adverse events are the most common irAEs, specifically spongiotic dermatitis, lichenoid dermatitis, pruritus, and vitiligo.7 Bullous pemphigoid (BP), an autoimmune bullous skin disorder caused by autoantibodies to basement membrane zone antigens, is a rare but potentially serious cutaneous irAE.8 Systemic corticosteroids commonly are used to treat immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP; other options include tetracyclines for maintenance therapy and rituximab for corticosteroid-refractory BP associated with anti-PD-1.9 We present a case of recalcitrant BP secondary to nivolumab therapy in a patient with metastatic melanoma who had near-complete resolution of BP following 2 months of cyclosporine.
A 41-year-old man presented with a generalized papular skin eruption of 1 month’s duration. He had a history of stage IIIC malignant melanoma of the lower right leg with positive sentinel lymph node biopsy. The largest lymph node deposit was 0.03 mm without extracapsular extension. Whole-body positron emission tomography–computed tomography showed no evidence of distant disease. The patient was treated with wide local excision with clear surgical margins plus 12 cycles of nivolumab, which was discontinued due to colitis. Four months after the final cycle of nivolumab, the patient developed widespread erythematous papules with hemorrhagic yellow crusting and no mucosal involvement. He was referred to dermatology by his primary oncologist for further evaluation.
A punch biopsy from the abdomen showed parakeratosis with leukocytoclasis and a superficial dermal infiltrate of neutrophils and eosinophils (Figure 1). Direct immunofluorescence revealed linear basement membrane deposits of IgG and C3, consistent with subepidermal blistering disease. Indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated trace IgG and IgG4 antibodies localized to the epidermal roof of salt-split skin and was negative for IgA antibodies. An enzyme-linked immunoassay was positive for BP antigen 2 (BP180) antibodies (98.4 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]) and negative for BP antigen 1 (BP230) antibodies (4.3 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]). Overall, these findings were consistent with a diagnosis of BP.
The patient was treated with prednisone 60 mg daily with initial response; however, there was disease recurrence with tapering. Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and nicotinamide 500 mg twice daily were added as steroid-sparing agents, as prednisone was discontinued due to mood changes. Three months after the prednisone taper, the patient continued to develop new blisters. He completed treatment with doxycycline and nicotinamide. Rituximab 375 mg weekly was then initiated for 4 weeks.
At 2-week follow-up after completing the rituximab course, the patient reported worsening symptoms and presented with new bullae on the abdomen and upper extremities (Figure 2). Because of the recent history of mood changes while taking prednisone, a trial of cyclosporine 100 mg twice daily (1.37 mg/kg/d) was initiated, with notable improvement within 2 weeks of treatment. After 2 months of cyclosporine, approximately 90% of the rash had resolved with a few tense bullae remaining on the left frontal scalp but no new flares (Figure 3). One month after treatment ended, the patient remained clear of lesions without relapse.
Programmed death receptor 1 inhibitors have shown dramatic efficacy for a growing number of solid and hematologic malignancies, especially malignant melanoma. However, their use is accompanied by nonspecific activation of the immune system, resulting in a variety of adverse events, many manifesting on the skin. Several cases of BP in patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors have been reported.9 Cutaneous irAEs usually manifest within 3 weeks of initiation of PD-1 inhibitor therapy; however, the onset of BP typically occurs later at approximately 21 weeks.4,9 Our patient developed cutaneous manifestations 4 months after cessation of nivolumab.



Bullous pemphigoid classically manifests with pruritus and tense bullae. Notably, our patient’s clinical presentation included a widespread eruption of papules without bullae, which was similar to a review by Tsiogka et al,9 which reported that one-third of patients first present with a nonspecific cutaneous eruption. Bullous pemphigoid induced by anti–PD-1 may manifest differently than traditional BP, illuminating the importance of a thorough diagnostic workup.
Although the pathogenesis of immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP has not been fully elucidated, it is hypothesized to be caused by increased T cell cytotoxic activity leading to tumor lysis and release of numerous autoantigens. These autoantigens cause priming of abnormal T cells that can lead to further tissue damage in peripheral tissue and to generation of aberrant B cells and subsequent autoantibodies such as BP180 in germinal centers.4,10,11
Cyclosporine is a calcineurin inhibitor that reduces synthesis of IL-2, resulting in reduced cell activation.12 Therefore, cyclosporine may alleviate BP in patients who are being treated, or were previously treated, with an immune checkpoint inhibitor by suppressing T cell–mediated immune reaction and may be a rapid alternative for patients who cannot tolerate systemic steroids.
Treatment options for mild to moderate cases of BP include topical corticosteroids and antihistamines, while severe cases may require high-dose systemic corticosteroids. In recalcitrant cases, rituximab infusion with or without intravenous immunoglobulin often is utilized.8,13 The use of cyclosporine for various bullous disorders, including pemphigus vulgaris and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, has been described.14 In recent years there has been a shift away from the use of cyclosporine for these conditions following the introduction of rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen on B lymphocytes. We utilized cyclosporine in our patient after he experienced worsening symptoms 1 month after completing treatment with rituximab.
Improvement from rituximab therapy may be delayed because it can take months to deplete CD20+ B lymphocytes from circulation, which may necessitate additional immunosuppressants or re-treatment with rituximab.15,16 In these instances, cyclosporine may be beneficial as a low-cost alternative in patients who are unable to tolerate systemic steroids, with a relatively good safety profile. The dosage of cyclosporine prescribed to the patient was chosen based on Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation management guidelines for psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies, which recommends an initial dosage of 1 to 3 mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses.17
As immunotherapy for treating various cancers gains popularity, the frequency of dermatologic irAEs will increase. Therefore, dermatologists must be aware of the array of cutaneous manifestations, such as BP, and potential treatment options. When first-line and second-line therapies are contraindicated or do not provide notable improvement, cyclosporine may be an effective alternative for immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP.
- Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:23-34. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1504030
- Alsaab HO, Sau S, Alzhrani R, et al. PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint signaling inhibition for cancer immunotherapy: mechanism, combinations, and clinical outcome. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:561. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00561
- Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; . Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5:95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
- Geisler AN, Phillips GS, Barrios DM, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related dermatologic adverse events. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1255-1268. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.132
- Villadolid J, Amin A. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice: update on management of immune-related toxicities. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4:560-575. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2015.06.06
- Kumar V, Chaudhary N, Garg M, et al. Current diagnosis and management of immune related adverse events (irAEs) induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:49. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00049
- Belum VR, Benhuri B, Postow MA, et al. Characterisation and management of dermatologic adverse events to agents targeting the PD-1 receptor. Eur J Cancer. 2016;60:12-25. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.02.010
- Schauer F, Rafei-Shamsabadi D, Mai S, et al. Hemidesmosomal reactivity and treatment recommendations in immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced bullous pemphigoid—a retrospective, monocentric study. Front Immunol. 2022;13:953546. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.953546
- Tsiogka A, Bauer JW, Patsatsi A. Bullous pemphigoid associated with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 and anti-programmed cell death ligand 1 therapy: a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00377. doi:10.2340/00015555-3740
- Lopez AT, Khanna T, Antonov N, et al. A review of bullous pemphigoid associated with PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:664-669. doi:10.1111/ijd.13984
- Yang H, Yao Z, Zhou X, et al. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors: insights into immunological dysregulation. Clin Immunol. 2020;213:108377. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108377
- Russell G, Graveley R, Seid J, et al. Mechanisms of action of cyclosporine and effects on connective tissues. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1992;21(6 suppl 3):16-22. doi:10.1016/0049-0172(92)90009-3
- Ahmed AR, Shetty S, Kaveri S, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant bullous pemphigoid (BP) with a novel protocol: a retrospective study with a 6-year follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:700-708.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.11.030
- Amor KT, Ryan C, Menter A. The use of cyclosporine in dermatology: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:925-946. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.02.063
- Schmidt E, Hunzelmann N, Zillikens D, et al. Rituximab in refractory autoimmune bullous diseases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:503-508. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2006.02151.x
- Kasperkiewicz M, Shimanovich I, Ludwig RJ, et al. Rituximab for treatment-refractory pemphigus and pemphigoid: a case series of 17 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:552-558.
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
- Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:23-34. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1504030
- Alsaab HO, Sau S, Alzhrani R, et al. PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint signaling inhibition for cancer immunotherapy: mechanism, combinations, and clinical outcome. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:561. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00561
- Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; . Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5:95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
- Geisler AN, Phillips GS, Barrios DM, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related dermatologic adverse events. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1255-1268. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.132
- Villadolid J, Amin A. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice: update on management of immune-related toxicities. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4:560-575. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2015.06.06
- Kumar V, Chaudhary N, Garg M, et al. Current diagnosis and management of immune related adverse events (irAEs) induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:49. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00049
- Belum VR, Benhuri B, Postow MA, et al. Characterisation and management of dermatologic adverse events to agents targeting the PD-1 receptor. Eur J Cancer. 2016;60:12-25. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.02.010
- Schauer F, Rafei-Shamsabadi D, Mai S, et al. Hemidesmosomal reactivity and treatment recommendations in immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced bullous pemphigoid—a retrospective, monocentric study. Front Immunol. 2022;13:953546. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.953546
- Tsiogka A, Bauer JW, Patsatsi A. Bullous pemphigoid associated with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 and anti-programmed cell death ligand 1 therapy: a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00377. doi:10.2340/00015555-3740
- Lopez AT, Khanna T, Antonov N, et al. A review of bullous pemphigoid associated with PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:664-669. doi:10.1111/ijd.13984
- Yang H, Yao Z, Zhou X, et al. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors: insights into immunological dysregulation. Clin Immunol. 2020;213:108377. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108377
- Russell G, Graveley R, Seid J, et al. Mechanisms of action of cyclosporine and effects on connective tissues. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1992;21(6 suppl 3):16-22. doi:10.1016/0049-0172(92)90009-3
- Ahmed AR, Shetty S, Kaveri S, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant bullous pemphigoid (BP) with a novel protocol: a retrospective study with a 6-year follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:700-708.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.11.030
- Amor KT, Ryan C, Menter A. The use of cyclosporine in dermatology: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:925-946. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.02.063
- Schmidt E, Hunzelmann N, Zillikens D, et al. Rituximab in refractory autoimmune bullous diseases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:503-508. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2006.02151.x
- Kasperkiewicz M, Shimanovich I, Ludwig RJ, et al. Rituximab for treatment-refractory pemphigus and pemphigoid: a case series of 17 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:552-558.
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
Practice Points
- Bullous pemphigoid is a rare dermatologic immune-related adverse event that can occur secondary to anti–programmed death receptor 1 therapy.
- For cases of immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced bullous pemphigoid that are recalcitrant to corticosteroids and rituximab, cyclosporine might be an effective alternative.
Circulating Tumor DNA Hints at BC Recurrence Risk
CHICAGO — Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) can predict relapse risk in some cases of early, high-risk breast cancer, but it’s too soon to use it to guide adjuvant therapy decisions, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
Detectable ctDNA is “highly prognostic of worse outcomes, particularly in patients who [remain] persistently positive,” but the correlation isn’t perfect, said lead investigator Sherene Loi, MMBS, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
Although less likely, relapses also occurred in the study among women without ctDNA elevation. Conversely, there were women with elevated ctDNA who did not relapse, she said. The study was a subanalysis of the monarchE trial of adjuvant abemaciclib, a CDK 4/6 inhibitor.
Eventually, “we would like to use” ctDNA to guide adjuvant treatment decisions, but the research isn’t there yet, Dr. Loi said. It’s possible, for instance, that persistently detectable ctDNA indicates early treatment failure and the need for treatment intensification. Future research should tackle the issue.
Study discussant Francois-Clement Bidard, MD, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at Institut Curie, Paris, agreed that ctDNA isn’t ready for primetime in adjuvant early, high-risk breast cancer.
“There is no clinical evidence to suggest that there is clinical utility in this setting. There are several trials that are ongoing,” he said, but for now “you shouldn’t,” for example, “use ctDNA to de-escalate adjuvant CDK4/6 [inhibitors]. It could be in the future that we could have data on this, but at the moment, [the] clear clinical message [is] no way.”
At 5-year follow-up, the monarchE trial found a 7.6% invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) improvement when abemaciclib was added to the first 2 years of endocrine therapy in women with HR+, HER2-, node positive, high-risk early breast cancer. The combination is now a standard adjuvant option for the disease.
The ctDNA study focused on a subset of 910 subjects with adequate ctDNA testing to run the analysis. The study population was also selected to be enriched for overall IDFS events (27% versus 18% across the trial’s 5,637 subjects). An IDFS event was defined as a local, regional, contralateral or distant invasive recurrence; a new primary tumor; or death from any cause.
Testing was performed using the Signatera ctDNA assay. Baseline samples were taken after completion of adjuvant chemotherapy, then again at 3, 6, or 24 months.
Overall, ctDNA detection was infrequent. Just 8% of patients were positive at baseline and 17% were positive at any point during the trial. Even so, ctDNA detection at any point was adversely prognostic.
Patients who were ctDNA positive at baseline were more likely to experience an IDFS event, compared with those who were ctDNA negative at baseline (80% at 4 years follow-up versus 23%).
Similarly, those who remained positive or became positive during testing were more likely to experience an IDFS event compared with those who became negative or remained negative throughout testing.
For instance, all 34 patients who were positive at baseline and remained positive had an IDFS event by year 4, versus just 40% who started positive but then cleared their ctDNA.
Among women who were negative at baseline and remained negative, 13% had an IDFS event versus 89% who started negative but then turned positive. Subjects who turned positive also had the shortest time to an IDFS event, a median of 7 months.
Among women who recurred, those who were ctDNA negative tended to have local, regional, or contralateral recurrences, while ctDNA positive patients tended to have distant recurrences.
The finding “really highlights that ctDNA antedates the metastatic clinical relapse. What the ctDNA is telling you is that the metastatic process has been completed, and metastases are about to grow,” Dr. Bidard said.
The work was funded by Eli Lilly, maker of abemaciclib, with collaboration from Natera, maker of the Signatera assay. Dr. Loi is an adviser and researcher for Lilly, among other industry ties. Dr. Bidard is a speaker and consultant for Lilly, among other ties.
CHICAGO — Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) can predict relapse risk in some cases of early, high-risk breast cancer, but it’s too soon to use it to guide adjuvant therapy decisions, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
Detectable ctDNA is “highly prognostic of worse outcomes, particularly in patients who [remain] persistently positive,” but the correlation isn’t perfect, said lead investigator Sherene Loi, MMBS, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
Although less likely, relapses also occurred in the study among women without ctDNA elevation. Conversely, there were women with elevated ctDNA who did not relapse, she said. The study was a subanalysis of the monarchE trial of adjuvant abemaciclib, a CDK 4/6 inhibitor.
Eventually, “we would like to use” ctDNA to guide adjuvant treatment decisions, but the research isn’t there yet, Dr. Loi said. It’s possible, for instance, that persistently detectable ctDNA indicates early treatment failure and the need for treatment intensification. Future research should tackle the issue.
Study discussant Francois-Clement Bidard, MD, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at Institut Curie, Paris, agreed that ctDNA isn’t ready for primetime in adjuvant early, high-risk breast cancer.
“There is no clinical evidence to suggest that there is clinical utility in this setting. There are several trials that are ongoing,” he said, but for now “you shouldn’t,” for example, “use ctDNA to de-escalate adjuvant CDK4/6 [inhibitors]. It could be in the future that we could have data on this, but at the moment, [the] clear clinical message [is] no way.”
At 5-year follow-up, the monarchE trial found a 7.6% invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) improvement when abemaciclib was added to the first 2 years of endocrine therapy in women with HR+, HER2-, node positive, high-risk early breast cancer. The combination is now a standard adjuvant option for the disease.
The ctDNA study focused on a subset of 910 subjects with adequate ctDNA testing to run the analysis. The study population was also selected to be enriched for overall IDFS events (27% versus 18% across the trial’s 5,637 subjects). An IDFS event was defined as a local, regional, contralateral or distant invasive recurrence; a new primary tumor; or death from any cause.
Testing was performed using the Signatera ctDNA assay. Baseline samples were taken after completion of adjuvant chemotherapy, then again at 3, 6, or 24 months.
Overall, ctDNA detection was infrequent. Just 8% of patients were positive at baseline and 17% were positive at any point during the trial. Even so, ctDNA detection at any point was adversely prognostic.
Patients who were ctDNA positive at baseline were more likely to experience an IDFS event, compared with those who were ctDNA negative at baseline (80% at 4 years follow-up versus 23%).
Similarly, those who remained positive or became positive during testing were more likely to experience an IDFS event compared with those who became negative or remained negative throughout testing.
For instance, all 34 patients who were positive at baseline and remained positive had an IDFS event by year 4, versus just 40% who started positive but then cleared their ctDNA.
Among women who were negative at baseline and remained negative, 13% had an IDFS event versus 89% who started negative but then turned positive. Subjects who turned positive also had the shortest time to an IDFS event, a median of 7 months.
Among women who recurred, those who were ctDNA negative tended to have local, regional, or contralateral recurrences, while ctDNA positive patients tended to have distant recurrences.
The finding “really highlights that ctDNA antedates the metastatic clinical relapse. What the ctDNA is telling you is that the metastatic process has been completed, and metastases are about to grow,” Dr. Bidard said.
The work was funded by Eli Lilly, maker of abemaciclib, with collaboration from Natera, maker of the Signatera assay. Dr. Loi is an adviser and researcher for Lilly, among other industry ties. Dr. Bidard is a speaker and consultant for Lilly, among other ties.
CHICAGO — Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) can predict relapse risk in some cases of early, high-risk breast cancer, but it’s too soon to use it to guide adjuvant therapy decisions, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
Detectable ctDNA is “highly prognostic of worse outcomes, particularly in patients who [remain] persistently positive,” but the correlation isn’t perfect, said lead investigator Sherene Loi, MMBS, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
Although less likely, relapses also occurred in the study among women without ctDNA elevation. Conversely, there were women with elevated ctDNA who did not relapse, she said. The study was a subanalysis of the monarchE trial of adjuvant abemaciclib, a CDK 4/6 inhibitor.
Eventually, “we would like to use” ctDNA to guide adjuvant treatment decisions, but the research isn’t there yet, Dr. Loi said. It’s possible, for instance, that persistently detectable ctDNA indicates early treatment failure and the need for treatment intensification. Future research should tackle the issue.
Study discussant Francois-Clement Bidard, MD, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at Institut Curie, Paris, agreed that ctDNA isn’t ready for primetime in adjuvant early, high-risk breast cancer.
“There is no clinical evidence to suggest that there is clinical utility in this setting. There are several trials that are ongoing,” he said, but for now “you shouldn’t,” for example, “use ctDNA to de-escalate adjuvant CDK4/6 [inhibitors]. It could be in the future that we could have data on this, but at the moment, [the] clear clinical message [is] no way.”
At 5-year follow-up, the monarchE trial found a 7.6% invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) improvement when abemaciclib was added to the first 2 years of endocrine therapy in women with HR+, HER2-, node positive, high-risk early breast cancer. The combination is now a standard adjuvant option for the disease.
The ctDNA study focused on a subset of 910 subjects with adequate ctDNA testing to run the analysis. The study population was also selected to be enriched for overall IDFS events (27% versus 18% across the trial’s 5,637 subjects). An IDFS event was defined as a local, regional, contralateral or distant invasive recurrence; a new primary tumor; or death from any cause.
Testing was performed using the Signatera ctDNA assay. Baseline samples were taken after completion of adjuvant chemotherapy, then again at 3, 6, or 24 months.
Overall, ctDNA detection was infrequent. Just 8% of patients were positive at baseline and 17% were positive at any point during the trial. Even so, ctDNA detection at any point was adversely prognostic.
Patients who were ctDNA positive at baseline were more likely to experience an IDFS event, compared with those who were ctDNA negative at baseline (80% at 4 years follow-up versus 23%).
Similarly, those who remained positive or became positive during testing were more likely to experience an IDFS event compared with those who became negative or remained negative throughout testing.
For instance, all 34 patients who were positive at baseline and remained positive had an IDFS event by year 4, versus just 40% who started positive but then cleared their ctDNA.
Among women who were negative at baseline and remained negative, 13% had an IDFS event versus 89% who started negative but then turned positive. Subjects who turned positive also had the shortest time to an IDFS event, a median of 7 months.
Among women who recurred, those who were ctDNA negative tended to have local, regional, or contralateral recurrences, while ctDNA positive patients tended to have distant recurrences.
The finding “really highlights that ctDNA antedates the metastatic clinical relapse. What the ctDNA is telling you is that the metastatic process has been completed, and metastases are about to grow,” Dr. Bidard said.
The work was funded by Eli Lilly, maker of abemaciclib, with collaboration from Natera, maker of the Signatera assay. Dr. Loi is an adviser and researcher for Lilly, among other industry ties. Dr. Bidard is a speaker and consultant for Lilly, among other ties.
FROM ASCO 2024
Study Finds Varying Skin Cancer Rates Based on Sexual Orientation
Addressing dynamics of each SM subgroup will require increasingly tailored prevention, screening, and research efforts, the study authors said.
“We identified specific subgroups within the sexual minority community who are at higher risk for skin cancer, specifically White gay males and Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black SM men and women — particularly individuals who identify as bisexual,” senior author Matthew Mansh, MD, said in an interview. He is an assistant professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Using data of adults in the US general population from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System from January 2014 to December 2021, investigators included more than 1.5 million respondents. The proportions of SM women and men (who self-identified as bisexual, lesbian, gay, “something else,” or other) were 2.6% and 2.0%, respectively.
Lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher among SM men than among heterosexual men (7.4% vs 6.8%; adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.16). In analyses stratified by racial and ethnic group, AORs for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM men vs their heterosexual counterparts were 2.18 and 3.81, respectively. The corresponding figures for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM women were 2.33 and 2.46, respectively.
When investigators combined all minority respondents along gender lines, lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher in bisexual men (aOR, 3.94), bisexual women (aOR, 1.51), and women identifying as something else or other (aOR, 2.70) than in their heterosexual peers.
“I wasn’t expecting that Hispanic or non-Hispanic Black SMs would be at higher risk for skin cancer,” Dr. Mansh said. Even if these groups have more behavioral risk factors for UV radiation (UVR) exposure, he explained, UVR exposure is less strongly linked with skin cancer in darker skin than in lighter skin. Reasons for the counterintuitive finding could include different screening habits among SM people of different racial and ethnic groups, he said, and analyzing such factors will require further research.
Although some effect sizes were modest, the authors wrote, their findings may have important implications for population-based research and public health efforts aimed at early skin cancer detection and prevention. Presently, the United States lacks established guidelines for skin cancer screening. In a 2023 statement published in JAMA, the US Preventive Services Task Force said that there is insufficient evidence to determine the benefit-harm balance of skin cancer screening in asymptomatic people.
“So there has been a lot of recent talk and a need to identify which subset groups of patients might be higher risk for skin cancer and might benefit from more screening,” Dr. Mansh said in an interview. “Understanding more about the high-risk demographic and clinical features that predispose someone to skin cancer helps identify these high-risk populations that could be used to develop better screening guidelines.”
Identifying groups at a higher risk for skin cancer also allows experts to design more targeted counseling or public health interventions focused on these groups, Dr. Mansh added. Absent screening guidelines, experts emphasize changing modifiable risk factors such as UVR exposure, smoking, and alcohol use. “And we know that the message that might change behaviors in a cisgender heterosexual man might be different than in a gay White male or a Hispanic bisexual male.”
A 2017 review showed that interventions to reduce behaviors involving UVR exposure, such as indoor tanning, among young cisgender women focused largely on aging and appearance-based concerns. A 2019 study showed that messages focused on avoiding skin cancer may help motivate SM men to reduce tanning behaviors.
Furthermore, said Dr. Mansh, all electronic health record products available in the United States must provide data fields for sexual orientation. “I don’t believe many dermatologists, depending on the setting, collect that information routinely. Integrating sexual orientation and/or gender identity data into patient intake forms so that it can be integrated into the electronic health record is probably very helpful, not only for your clinical practice but also for future research studies.”
Asked to comment on the results, Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, MPH, who was not involved with the study, said that its impact on clinical practice will be challenging to ascertain. She is chief of dermatology with the VA Boston Healthcare System, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, and director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, all in Boston, Massachusetts.
“The study found significant adjusted odds ratios,” Dr. Hartman explained, “but for some of the different populations, the overall lifetime rate of skin cancer is still quite low.” For example, 1.0% for SM non-Hispanic Black men or a difference of 2.1% vs 1.8% in SM Hispanic women. “Thus, I am not sure specific screening recommendations are warranted, although some populations, such as Hispanic sexual minority males, seemed to have a much higher risk (3.8-fold on adjusted analysis) that warrants further investigation.”
For now, she advised assessing patients’ risks for skin cancer based on well-established risk factors such as sun exposure/indoor tanning, skin phototype, immunosuppression, and age.
Dr. Mansh reported no relevant conflicts or funding sources for the study. Dr. Hartman reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Addressing dynamics of each SM subgroup will require increasingly tailored prevention, screening, and research efforts, the study authors said.
“We identified specific subgroups within the sexual minority community who are at higher risk for skin cancer, specifically White gay males and Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black SM men and women — particularly individuals who identify as bisexual,” senior author Matthew Mansh, MD, said in an interview. He is an assistant professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Using data of adults in the US general population from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System from January 2014 to December 2021, investigators included more than 1.5 million respondents. The proportions of SM women and men (who self-identified as bisexual, lesbian, gay, “something else,” or other) were 2.6% and 2.0%, respectively.
Lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher among SM men than among heterosexual men (7.4% vs 6.8%; adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.16). In analyses stratified by racial and ethnic group, AORs for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM men vs their heterosexual counterparts were 2.18 and 3.81, respectively. The corresponding figures for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM women were 2.33 and 2.46, respectively.
When investigators combined all minority respondents along gender lines, lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher in bisexual men (aOR, 3.94), bisexual women (aOR, 1.51), and women identifying as something else or other (aOR, 2.70) than in their heterosexual peers.
“I wasn’t expecting that Hispanic or non-Hispanic Black SMs would be at higher risk for skin cancer,” Dr. Mansh said. Even if these groups have more behavioral risk factors for UV radiation (UVR) exposure, he explained, UVR exposure is less strongly linked with skin cancer in darker skin than in lighter skin. Reasons for the counterintuitive finding could include different screening habits among SM people of different racial and ethnic groups, he said, and analyzing such factors will require further research.
Although some effect sizes were modest, the authors wrote, their findings may have important implications for population-based research and public health efforts aimed at early skin cancer detection and prevention. Presently, the United States lacks established guidelines for skin cancer screening. In a 2023 statement published in JAMA, the US Preventive Services Task Force said that there is insufficient evidence to determine the benefit-harm balance of skin cancer screening in asymptomatic people.
“So there has been a lot of recent talk and a need to identify which subset groups of patients might be higher risk for skin cancer and might benefit from more screening,” Dr. Mansh said in an interview. “Understanding more about the high-risk demographic and clinical features that predispose someone to skin cancer helps identify these high-risk populations that could be used to develop better screening guidelines.”
Identifying groups at a higher risk for skin cancer also allows experts to design more targeted counseling or public health interventions focused on these groups, Dr. Mansh added. Absent screening guidelines, experts emphasize changing modifiable risk factors such as UVR exposure, smoking, and alcohol use. “And we know that the message that might change behaviors in a cisgender heterosexual man might be different than in a gay White male or a Hispanic bisexual male.”
A 2017 review showed that interventions to reduce behaviors involving UVR exposure, such as indoor tanning, among young cisgender women focused largely on aging and appearance-based concerns. A 2019 study showed that messages focused on avoiding skin cancer may help motivate SM men to reduce tanning behaviors.
Furthermore, said Dr. Mansh, all electronic health record products available in the United States must provide data fields for sexual orientation. “I don’t believe many dermatologists, depending on the setting, collect that information routinely. Integrating sexual orientation and/or gender identity data into patient intake forms so that it can be integrated into the electronic health record is probably very helpful, not only for your clinical practice but also for future research studies.”
Asked to comment on the results, Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, MPH, who was not involved with the study, said that its impact on clinical practice will be challenging to ascertain. She is chief of dermatology with the VA Boston Healthcare System, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, and director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, all in Boston, Massachusetts.
“The study found significant adjusted odds ratios,” Dr. Hartman explained, “but for some of the different populations, the overall lifetime rate of skin cancer is still quite low.” For example, 1.0% for SM non-Hispanic Black men or a difference of 2.1% vs 1.8% in SM Hispanic women. “Thus, I am not sure specific screening recommendations are warranted, although some populations, such as Hispanic sexual minority males, seemed to have a much higher risk (3.8-fold on adjusted analysis) that warrants further investigation.”
For now, she advised assessing patients’ risks for skin cancer based on well-established risk factors such as sun exposure/indoor tanning, skin phototype, immunosuppression, and age.
Dr. Mansh reported no relevant conflicts or funding sources for the study. Dr. Hartman reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Addressing dynamics of each SM subgroup will require increasingly tailored prevention, screening, and research efforts, the study authors said.
“We identified specific subgroups within the sexual minority community who are at higher risk for skin cancer, specifically White gay males and Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black SM men and women — particularly individuals who identify as bisexual,” senior author Matthew Mansh, MD, said in an interview. He is an assistant professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Using data of adults in the US general population from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System from January 2014 to December 2021, investigators included more than 1.5 million respondents. The proportions of SM women and men (who self-identified as bisexual, lesbian, gay, “something else,” or other) were 2.6% and 2.0%, respectively.
Lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher among SM men than among heterosexual men (7.4% vs 6.8%; adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.16). In analyses stratified by racial and ethnic group, AORs for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM men vs their heterosexual counterparts were 2.18 and 3.81, respectively. The corresponding figures for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM women were 2.33 and 2.46, respectively.
When investigators combined all minority respondents along gender lines, lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher in bisexual men (aOR, 3.94), bisexual women (aOR, 1.51), and women identifying as something else or other (aOR, 2.70) than in their heterosexual peers.
“I wasn’t expecting that Hispanic or non-Hispanic Black SMs would be at higher risk for skin cancer,” Dr. Mansh said. Even if these groups have more behavioral risk factors for UV radiation (UVR) exposure, he explained, UVR exposure is less strongly linked with skin cancer in darker skin than in lighter skin. Reasons for the counterintuitive finding could include different screening habits among SM people of different racial and ethnic groups, he said, and analyzing such factors will require further research.
Although some effect sizes were modest, the authors wrote, their findings may have important implications for population-based research and public health efforts aimed at early skin cancer detection and prevention. Presently, the United States lacks established guidelines for skin cancer screening. In a 2023 statement published in JAMA, the US Preventive Services Task Force said that there is insufficient evidence to determine the benefit-harm balance of skin cancer screening in asymptomatic people.
“So there has been a lot of recent talk and a need to identify which subset groups of patients might be higher risk for skin cancer and might benefit from more screening,” Dr. Mansh said in an interview. “Understanding more about the high-risk demographic and clinical features that predispose someone to skin cancer helps identify these high-risk populations that could be used to develop better screening guidelines.”
Identifying groups at a higher risk for skin cancer also allows experts to design more targeted counseling or public health interventions focused on these groups, Dr. Mansh added. Absent screening guidelines, experts emphasize changing modifiable risk factors such as UVR exposure, smoking, and alcohol use. “And we know that the message that might change behaviors in a cisgender heterosexual man might be different than in a gay White male or a Hispanic bisexual male.”
A 2017 review showed that interventions to reduce behaviors involving UVR exposure, such as indoor tanning, among young cisgender women focused largely on aging and appearance-based concerns. A 2019 study showed that messages focused on avoiding skin cancer may help motivate SM men to reduce tanning behaviors.
Furthermore, said Dr. Mansh, all electronic health record products available in the United States must provide data fields for sexual orientation. “I don’t believe many dermatologists, depending on the setting, collect that information routinely. Integrating sexual orientation and/or gender identity data into patient intake forms so that it can be integrated into the electronic health record is probably very helpful, not only for your clinical practice but also for future research studies.”
Asked to comment on the results, Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, MPH, who was not involved with the study, said that its impact on clinical practice will be challenging to ascertain. She is chief of dermatology with the VA Boston Healthcare System, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, and director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, all in Boston, Massachusetts.
“The study found significant adjusted odds ratios,” Dr. Hartman explained, “but for some of the different populations, the overall lifetime rate of skin cancer is still quite low.” For example, 1.0% for SM non-Hispanic Black men or a difference of 2.1% vs 1.8% in SM Hispanic women. “Thus, I am not sure specific screening recommendations are warranted, although some populations, such as Hispanic sexual minority males, seemed to have a much higher risk (3.8-fold on adjusted analysis) that warrants further investigation.”
For now, she advised assessing patients’ risks for skin cancer based on well-established risk factors such as sun exposure/indoor tanning, skin phototype, immunosuppression, and age.
Dr. Mansh reported no relevant conflicts or funding sources for the study. Dr. Hartman reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
The Disturbing Sexual Trend With Real Health Consequences
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: I have an interesting topic for you — kind of shocking, actually. Some of you may have read a story earlier this year in The New York Times about the alarming rise among young people of choking or strangulation during sex. I spoke recently with Dr. Debby Herbenick about this concerning and violent trend. Dr. Herbenick is a well-known sexuality researcher and professor at the Indiana University School of Public Health. Welcome, Dr. Herbenick. Can you tell us about your research into this new trend?
Debby Herbenick, PhD: This is some of the most important research that I’ve done. I’ve been studying sexual behaviors and trends for about 14 years in terms of nationally representative studies that we do. Over time, we noticed a trend of increasing prevalence of rough sex practices.
Now, there’s always been a lot of sexual diversity in the world throughout history. But . The increase is mostly seen in teenagers and young adults.
We’ve done US nationally representative surveys as well as college campus representative surveys. We find that consistently across four campus representative surveys that 64% of women report having ever been choked during sex, and around 1 in 3 women (aged 18-24 years) throughout the whole country report having been choked during their most recent sexual activity with another person. They call it choking, but because it involves usually one hand — sometimes two hands or a forearm or an object, like a belt or a cord to tie around the neck — it is technically strangulation, because it’s external pressure to the neck to reduce or stop airflow or blood flow.
Dr. Rubin: These numbers are staggering, right? Everyone listening now is taking care of someone who has been strangled as a form of sexual pleasure. What does this mean from a safety perspective? And as doctors who are working these patients up for migraines and other health problems, what is the research showing?
Dr. Herbenick: We certainly are seeing people report recurrent headaches and ringing in the ears. There are things we’ve just barely scratched the surface on. Those of us working in this space believe that for anybody coming in for an unexplained stroke (for example, under age 50), you might consider some imaging to see if they have a dissection. We are hearing about people who, when you really probe to find out whether they’ve had pressure on the neck, they report that indeed that they have. So, we have to be thinking about neurologic symptoms. We know that they’re experiencing these at a pretty high rate.
For people who are engaging in these practices, they should know about the health risks, but we find that most don’t. They may have heard that if it’s really intense high pressure, that in rare cases people can die, but most have never heard of anything in between. So, they’re not necessarily connecting their voice hoarseness, or the recurrent headaches or the sensitivity to light they are having, to an experience of being choked. We need to be paying attention to neurologic symptoms.
Most physicians I speak with at conferences say that where they feel like they can step into this conversation is through anticipatory guidance and letting their patients know that they may have heard about this trend, and a lot of people are talking about the health consequences, and I want to share some information with you — not coming at it from a place of shame or judgment, but providing some information so that [patients] actually get some medical facts about this that could be lifesaving.
Dr. Rubin: I see such a big gap in my medical training. I was taught to say, “Hey, do you smoke, do you drink, do you do drugs? Do you have sex? Men, women, or both?”And that’s it. And then maybe use birth control, and don’t get an STD, thinking about herpes, syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia. We weren’t really trained to talk to patients about what kind of sex they are having, or how to talk to patients in a way that is open-minded but also safety-conscious and how the concept of safe sex is more than wear a condom and use birth control.
This idea of rough sex practices and how to talk to teenagers — maybe our pediatricians should be talking about this. Where do we start in terms of how to bring up these conversations and with what level of detail?
Dr. Herbenick: We find that some young people are already being asked about some of the effects that might be showing on their bodies. It might be that their provider notices some bruising, or marks on their bodies from other types of rough sex practices like hitting and spanking. So that could be an entry point there. Choking is far more prevalent than slapping, so if you’re seeing some marks on the body, then it’s also a good time to ask about other practices they might be engaging in, especially higher risk ones like choking or strangulation. It’s offering some information and even saying, “Look, I’m not here to shame or judge you. I just want you to have some information about this” and giving them an opportunity to ask questions, too.
We have found that almost nobody talks with their nurse or doctor, even if they have symptoms after being choked or strangled during sex. Just 1% of women with choking-related symptoms, 7% of men, and far fewer trans and nonbinary young people report talking with a nurse or doctor, mostly because they say it doesn’t seem like a big deal. The symptoms got better quickly. Sometimes they’re afraid of being shamed for their sexual behavior, and that’s why they say they don’t talk with somebody.
They need some type of open-door anticipatory guidance as a way forward. Not everyone is comfortable directly asking whether a patient is engaging in this, but at least letting people know that you’ve heard of this behavior and providing some medical facts can give us a step forward with creating these conversations.
Dr. Rubin: Can you tell us where is this research going in terms of next steps? Other things that you’re looking at? And what are you excited about?
Dr. Herbenick: I’m excited about some work I did with a collaborator and colleague of mine, Dr. Keisuke Kawata, that he led a couple of years ago. He’s a neuroscientist. We were looking at potential cumulative effects on the brain. Now we’re taking some of that research into its next steps. We’re also doing more focused studies on other health consequences and hopefully finding out how we can test different educational messages and get people to learn more fact-based information about this, and then see if that is effective in prevention.
Dr. Rubin: It sounds like a public health campaign is really needed about how to get the word out there about the health consequences of these activities. We’re asking people often enough. In my clinic, I try to keep it open-ended — tell me what sex looks like. What does it look like, and what do you want it to look like? Because I see a lot of people with problems, but if they don’t bring it to me, I don’t necessarily bring it up to them. Until I heard your lecture, and I thought, oh my gosh, I’m not even asking the right questions. Are you hopeful that there will be more public health messaging out there?
Dr. Herbenick: I am. Years ago, when the child and adolescent choking game became a thing, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued reports about it and warnings to parents. And this is a far, far higher prevalence than that ever was. So, I would love to see organizations like the CDC and medical groups getting involved and educating their members and making statements. This is really impacting a huge generation of girls and women, because when it happens during sex between women and men, the choking is mostly happening to the girls and women. It’s also prevalent among sexual minority individuals. But we are talking about this whole generation of young women and what’s happening to their bodies and their brain health. We really need to step into this conversation.
Dr. Rubin: Very few of us are sexual medicine–trained physicians, and very few of us feel confident and comfortable talking about sexual health issues. But people are getting hurt. People are having real consequences of these behaviors because of our lack of education, knowledge, and even discussion around it. So thank you for doing this research, because had you not done this research, we wouldn’t have found out that 64% of people are engaging in these types of activities. That is not rare.
Dr. Rubin is an assistant clinical professor, Department of Urology, at Georgetown University, Washington. She reported conflicts of interest with Sprout, Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GSK, and Endo.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: I have an interesting topic for you — kind of shocking, actually. Some of you may have read a story earlier this year in The New York Times about the alarming rise among young people of choking or strangulation during sex. I spoke recently with Dr. Debby Herbenick about this concerning and violent trend. Dr. Herbenick is a well-known sexuality researcher and professor at the Indiana University School of Public Health. Welcome, Dr. Herbenick. Can you tell us about your research into this new trend?
Debby Herbenick, PhD: This is some of the most important research that I’ve done. I’ve been studying sexual behaviors and trends for about 14 years in terms of nationally representative studies that we do. Over time, we noticed a trend of increasing prevalence of rough sex practices.
Now, there’s always been a lot of sexual diversity in the world throughout history. But . The increase is mostly seen in teenagers and young adults.
We’ve done US nationally representative surveys as well as college campus representative surveys. We find that consistently across four campus representative surveys that 64% of women report having ever been choked during sex, and around 1 in 3 women (aged 18-24 years) throughout the whole country report having been choked during their most recent sexual activity with another person. They call it choking, but because it involves usually one hand — sometimes two hands or a forearm or an object, like a belt or a cord to tie around the neck — it is technically strangulation, because it’s external pressure to the neck to reduce or stop airflow or blood flow.
Dr. Rubin: These numbers are staggering, right? Everyone listening now is taking care of someone who has been strangled as a form of sexual pleasure. What does this mean from a safety perspective? And as doctors who are working these patients up for migraines and other health problems, what is the research showing?
Dr. Herbenick: We certainly are seeing people report recurrent headaches and ringing in the ears. There are things we’ve just barely scratched the surface on. Those of us working in this space believe that for anybody coming in for an unexplained stroke (for example, under age 50), you might consider some imaging to see if they have a dissection. We are hearing about people who, when you really probe to find out whether they’ve had pressure on the neck, they report that indeed that they have. So, we have to be thinking about neurologic symptoms. We know that they’re experiencing these at a pretty high rate.
For people who are engaging in these practices, they should know about the health risks, but we find that most don’t. They may have heard that if it’s really intense high pressure, that in rare cases people can die, but most have never heard of anything in between. So, they’re not necessarily connecting their voice hoarseness, or the recurrent headaches or the sensitivity to light they are having, to an experience of being choked. We need to be paying attention to neurologic symptoms.
Most physicians I speak with at conferences say that where they feel like they can step into this conversation is through anticipatory guidance and letting their patients know that they may have heard about this trend, and a lot of people are talking about the health consequences, and I want to share some information with you — not coming at it from a place of shame or judgment, but providing some information so that [patients] actually get some medical facts about this that could be lifesaving.
Dr. Rubin: I see such a big gap in my medical training. I was taught to say, “Hey, do you smoke, do you drink, do you do drugs? Do you have sex? Men, women, or both?”And that’s it. And then maybe use birth control, and don’t get an STD, thinking about herpes, syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia. We weren’t really trained to talk to patients about what kind of sex they are having, or how to talk to patients in a way that is open-minded but also safety-conscious and how the concept of safe sex is more than wear a condom and use birth control.
This idea of rough sex practices and how to talk to teenagers — maybe our pediatricians should be talking about this. Where do we start in terms of how to bring up these conversations and with what level of detail?
Dr. Herbenick: We find that some young people are already being asked about some of the effects that might be showing on their bodies. It might be that their provider notices some bruising, or marks on their bodies from other types of rough sex practices like hitting and spanking. So that could be an entry point there. Choking is far more prevalent than slapping, so if you’re seeing some marks on the body, then it’s also a good time to ask about other practices they might be engaging in, especially higher risk ones like choking or strangulation. It’s offering some information and even saying, “Look, I’m not here to shame or judge you. I just want you to have some information about this” and giving them an opportunity to ask questions, too.
We have found that almost nobody talks with their nurse or doctor, even if they have symptoms after being choked or strangled during sex. Just 1% of women with choking-related symptoms, 7% of men, and far fewer trans and nonbinary young people report talking with a nurse or doctor, mostly because they say it doesn’t seem like a big deal. The symptoms got better quickly. Sometimes they’re afraid of being shamed for their sexual behavior, and that’s why they say they don’t talk with somebody.
They need some type of open-door anticipatory guidance as a way forward. Not everyone is comfortable directly asking whether a patient is engaging in this, but at least letting people know that you’ve heard of this behavior and providing some medical facts can give us a step forward with creating these conversations.
Dr. Rubin: Can you tell us where is this research going in terms of next steps? Other things that you’re looking at? And what are you excited about?
Dr. Herbenick: I’m excited about some work I did with a collaborator and colleague of mine, Dr. Keisuke Kawata, that he led a couple of years ago. He’s a neuroscientist. We were looking at potential cumulative effects on the brain. Now we’re taking some of that research into its next steps. We’re also doing more focused studies on other health consequences and hopefully finding out how we can test different educational messages and get people to learn more fact-based information about this, and then see if that is effective in prevention.
Dr. Rubin: It sounds like a public health campaign is really needed about how to get the word out there about the health consequences of these activities. We’re asking people often enough. In my clinic, I try to keep it open-ended — tell me what sex looks like. What does it look like, and what do you want it to look like? Because I see a lot of people with problems, but if they don’t bring it to me, I don’t necessarily bring it up to them. Until I heard your lecture, and I thought, oh my gosh, I’m not even asking the right questions. Are you hopeful that there will be more public health messaging out there?
Dr. Herbenick: I am. Years ago, when the child and adolescent choking game became a thing, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued reports about it and warnings to parents. And this is a far, far higher prevalence than that ever was. So, I would love to see organizations like the CDC and medical groups getting involved and educating their members and making statements. This is really impacting a huge generation of girls and women, because when it happens during sex between women and men, the choking is mostly happening to the girls and women. It’s also prevalent among sexual minority individuals. But we are talking about this whole generation of young women and what’s happening to their bodies and their brain health. We really need to step into this conversation.
Dr. Rubin: Very few of us are sexual medicine–trained physicians, and very few of us feel confident and comfortable talking about sexual health issues. But people are getting hurt. People are having real consequences of these behaviors because of our lack of education, knowledge, and even discussion around it. So thank you for doing this research, because had you not done this research, we wouldn’t have found out that 64% of people are engaging in these types of activities. That is not rare.
Dr. Rubin is an assistant clinical professor, Department of Urology, at Georgetown University, Washington. She reported conflicts of interest with Sprout, Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GSK, and Endo.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: I have an interesting topic for you — kind of shocking, actually. Some of you may have read a story earlier this year in The New York Times about the alarming rise among young people of choking or strangulation during sex. I spoke recently with Dr. Debby Herbenick about this concerning and violent trend. Dr. Herbenick is a well-known sexuality researcher and professor at the Indiana University School of Public Health. Welcome, Dr. Herbenick. Can you tell us about your research into this new trend?
Debby Herbenick, PhD: This is some of the most important research that I’ve done. I’ve been studying sexual behaviors and trends for about 14 years in terms of nationally representative studies that we do. Over time, we noticed a trend of increasing prevalence of rough sex practices.
Now, there’s always been a lot of sexual diversity in the world throughout history. But . The increase is mostly seen in teenagers and young adults.
We’ve done US nationally representative surveys as well as college campus representative surveys. We find that consistently across four campus representative surveys that 64% of women report having ever been choked during sex, and around 1 in 3 women (aged 18-24 years) throughout the whole country report having been choked during their most recent sexual activity with another person. They call it choking, but because it involves usually one hand — sometimes two hands or a forearm or an object, like a belt or a cord to tie around the neck — it is technically strangulation, because it’s external pressure to the neck to reduce or stop airflow or blood flow.
Dr. Rubin: These numbers are staggering, right? Everyone listening now is taking care of someone who has been strangled as a form of sexual pleasure. What does this mean from a safety perspective? And as doctors who are working these patients up for migraines and other health problems, what is the research showing?
Dr. Herbenick: We certainly are seeing people report recurrent headaches and ringing in the ears. There are things we’ve just barely scratched the surface on. Those of us working in this space believe that for anybody coming in for an unexplained stroke (for example, under age 50), you might consider some imaging to see if they have a dissection. We are hearing about people who, when you really probe to find out whether they’ve had pressure on the neck, they report that indeed that they have. So, we have to be thinking about neurologic symptoms. We know that they’re experiencing these at a pretty high rate.
For people who are engaging in these practices, they should know about the health risks, but we find that most don’t. They may have heard that if it’s really intense high pressure, that in rare cases people can die, but most have never heard of anything in between. So, they’re not necessarily connecting their voice hoarseness, or the recurrent headaches or the sensitivity to light they are having, to an experience of being choked. We need to be paying attention to neurologic symptoms.
Most physicians I speak with at conferences say that where they feel like they can step into this conversation is through anticipatory guidance and letting their patients know that they may have heard about this trend, and a lot of people are talking about the health consequences, and I want to share some information with you — not coming at it from a place of shame or judgment, but providing some information so that [patients] actually get some medical facts about this that could be lifesaving.
Dr. Rubin: I see such a big gap in my medical training. I was taught to say, “Hey, do you smoke, do you drink, do you do drugs? Do you have sex? Men, women, or both?”And that’s it. And then maybe use birth control, and don’t get an STD, thinking about herpes, syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia. We weren’t really trained to talk to patients about what kind of sex they are having, or how to talk to patients in a way that is open-minded but also safety-conscious and how the concept of safe sex is more than wear a condom and use birth control.
This idea of rough sex practices and how to talk to teenagers — maybe our pediatricians should be talking about this. Where do we start in terms of how to bring up these conversations and with what level of detail?
Dr. Herbenick: We find that some young people are already being asked about some of the effects that might be showing on their bodies. It might be that their provider notices some bruising, or marks on their bodies from other types of rough sex practices like hitting and spanking. So that could be an entry point there. Choking is far more prevalent than slapping, so if you’re seeing some marks on the body, then it’s also a good time to ask about other practices they might be engaging in, especially higher risk ones like choking or strangulation. It’s offering some information and even saying, “Look, I’m not here to shame or judge you. I just want you to have some information about this” and giving them an opportunity to ask questions, too.
We have found that almost nobody talks with their nurse or doctor, even if they have symptoms after being choked or strangled during sex. Just 1% of women with choking-related symptoms, 7% of men, and far fewer trans and nonbinary young people report talking with a nurse or doctor, mostly because they say it doesn’t seem like a big deal. The symptoms got better quickly. Sometimes they’re afraid of being shamed for their sexual behavior, and that’s why they say they don’t talk with somebody.
They need some type of open-door anticipatory guidance as a way forward. Not everyone is comfortable directly asking whether a patient is engaging in this, but at least letting people know that you’ve heard of this behavior and providing some medical facts can give us a step forward with creating these conversations.
Dr. Rubin: Can you tell us where is this research going in terms of next steps? Other things that you’re looking at? And what are you excited about?
Dr. Herbenick: I’m excited about some work I did with a collaborator and colleague of mine, Dr. Keisuke Kawata, that he led a couple of years ago. He’s a neuroscientist. We were looking at potential cumulative effects on the brain. Now we’re taking some of that research into its next steps. We’re also doing more focused studies on other health consequences and hopefully finding out how we can test different educational messages and get people to learn more fact-based information about this, and then see if that is effective in prevention.
Dr. Rubin: It sounds like a public health campaign is really needed about how to get the word out there about the health consequences of these activities. We’re asking people often enough. In my clinic, I try to keep it open-ended — tell me what sex looks like. What does it look like, and what do you want it to look like? Because I see a lot of people with problems, but if they don’t bring it to me, I don’t necessarily bring it up to them. Until I heard your lecture, and I thought, oh my gosh, I’m not even asking the right questions. Are you hopeful that there will be more public health messaging out there?
Dr. Herbenick: I am. Years ago, when the child and adolescent choking game became a thing, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued reports about it and warnings to parents. And this is a far, far higher prevalence than that ever was. So, I would love to see organizations like the CDC and medical groups getting involved and educating their members and making statements. This is really impacting a huge generation of girls and women, because when it happens during sex between women and men, the choking is mostly happening to the girls and women. It’s also prevalent among sexual minority individuals. But we are talking about this whole generation of young women and what’s happening to their bodies and their brain health. We really need to step into this conversation.
Dr. Rubin: Very few of us are sexual medicine–trained physicians, and very few of us feel confident and comfortable talking about sexual health issues. But people are getting hurt. People are having real consequences of these behaviors because of our lack of education, knowledge, and even discussion around it. So thank you for doing this research, because had you not done this research, we wouldn’t have found out that 64% of people are engaging in these types of activities. That is not rare.
Dr. Rubin is an assistant clinical professor, Department of Urology, at Georgetown University, Washington. She reported conflicts of interest with Sprout, Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GSK, and Endo.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How to Get Patients Over a Weight Loss Plateau
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
On today’s edition of Beyond BMI, I’ll be discussing weight plateaus. This is something that our patients are very familiar with. Sometimes, they’re happy with their weight when they plateau; sometimes, they’re not. A weight plateau is simply a state of equilibrium.
There’s a common adage that the last 5 pounds are the hardest. When people decrease their calorie intake and increase their activity — as we instruct our patients to do to lose weight — the body starts to fight back because it believes this is a famine state. Our bodies feel that we are running around the jungle looking for food to help us survive a perceived famine state.
The body does a few things to help us keep weight on, and this is what leads to the frustration of not being able to lose those last 5 pounds. The first thing that happens in this process, which is called metabolic adaptation, is that when someone loses weight, the body naturally increases appetite signals from the brain, so the person becomes hungrier. Satiety signals from the stomach also decrease, so they feel more hungry and less full. And finally, stable fat cells form to allow the person to seek out more food without losing weight. This eventually leads the patient to regain weight, or they may plateau at a weight they’re not happy with.
I’m sure you’ve seen many studies looking at weight plateaus and the amount of weight loss people are able to achieve with diet, exercise, and behavior change alone vs the same lifestyle modifications plus medication. Studies show that patients who are taking anti-obesity medications achieve far more weight loss than do those who are not taking medications. The reason is related to the different mechanisms of action of the anti-obesity medications. Patients taking these medications are able to tolerate a lower caloric intake for a longer period of time, thus they’re able to burn more fat cells and lose more weight. Some medications perform this by decreasing appetite signals, so patients can continue to eat a small number of calories. Some medications affect the stability of fat cells. Some medications also increase satiety signals, so patients can move beyond that degree of metabolic adaptation and get beyond their previous plateau.
What can we do for patients who are frustrated with their weight plateau? I recommend taking a dive into their daily routine. Find out how many calories they are eating. Find out how much exercise they are doing and see whether there’s any room to reorganize the day or change their meals to create a caloric deficit. Are they eating things that are not filling enough, so they can’t get to the next meal without having a snack in between? We are looking at the quality of the meals as well and making sure there’s an adequate amount of protein and fiber in their meals to help with those increased appetite signals. We should also make sure these patients are getting adequate fluid intake.
These are all strategies that can help our patients try to get beyond their weight plateaus.
If the patient meets criteria for anti-obesity medication, which means a body mass index (BMI) of 27-29 with a weight-related comorbidity or BMI ≥ 30 with or without a comorbidity, you may want to consider anti-obesity medication to help that patient get beyond the plateau.
Plateaus will occur as a natural process because of the appetite signaling and hormonal changes that occur when patients lose weight from any modality. It’s important that we work with our patients to determine whether their weight plateau is due to metabolic adaptation. If they aren’t meeting their goals and they have weight-related comorbidities, we can use other available modalities to help those patients continue to lose weight. Of course, whenever we are prescribing a medication, we need to make sure that it is safe for the patient and the patient is on board with the potential side effects and risks. And we should always make sure our patients know we are their advocates in their weight journey.
Holly Lofton, clinical associate professor of surgery and medicine, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
On today’s edition of Beyond BMI, I’ll be discussing weight plateaus. This is something that our patients are very familiar with. Sometimes, they’re happy with their weight when they plateau; sometimes, they’re not. A weight plateau is simply a state of equilibrium.
There’s a common adage that the last 5 pounds are the hardest. When people decrease their calorie intake and increase their activity — as we instruct our patients to do to lose weight — the body starts to fight back because it believes this is a famine state. Our bodies feel that we are running around the jungle looking for food to help us survive a perceived famine state.
The body does a few things to help us keep weight on, and this is what leads to the frustration of not being able to lose those last 5 pounds. The first thing that happens in this process, which is called metabolic adaptation, is that when someone loses weight, the body naturally increases appetite signals from the brain, so the person becomes hungrier. Satiety signals from the stomach also decrease, so they feel more hungry and less full. And finally, stable fat cells form to allow the person to seek out more food without losing weight. This eventually leads the patient to regain weight, or they may plateau at a weight they’re not happy with.
I’m sure you’ve seen many studies looking at weight plateaus and the amount of weight loss people are able to achieve with diet, exercise, and behavior change alone vs the same lifestyle modifications plus medication. Studies show that patients who are taking anti-obesity medications achieve far more weight loss than do those who are not taking medications. The reason is related to the different mechanisms of action of the anti-obesity medications. Patients taking these medications are able to tolerate a lower caloric intake for a longer period of time, thus they’re able to burn more fat cells and lose more weight. Some medications perform this by decreasing appetite signals, so patients can continue to eat a small number of calories. Some medications affect the stability of fat cells. Some medications also increase satiety signals, so patients can move beyond that degree of metabolic adaptation and get beyond their previous plateau.
What can we do for patients who are frustrated with their weight plateau? I recommend taking a dive into their daily routine. Find out how many calories they are eating. Find out how much exercise they are doing and see whether there’s any room to reorganize the day or change their meals to create a caloric deficit. Are they eating things that are not filling enough, so they can’t get to the next meal without having a snack in between? We are looking at the quality of the meals as well and making sure there’s an adequate amount of protein and fiber in their meals to help with those increased appetite signals. We should also make sure these patients are getting adequate fluid intake.
These are all strategies that can help our patients try to get beyond their weight plateaus.
If the patient meets criteria for anti-obesity medication, which means a body mass index (BMI) of 27-29 with a weight-related comorbidity or BMI ≥ 30 with or without a comorbidity, you may want to consider anti-obesity medication to help that patient get beyond the plateau.
Plateaus will occur as a natural process because of the appetite signaling and hormonal changes that occur when patients lose weight from any modality. It’s important that we work with our patients to determine whether their weight plateau is due to metabolic adaptation. If they aren’t meeting their goals and they have weight-related comorbidities, we can use other available modalities to help those patients continue to lose weight. Of course, whenever we are prescribing a medication, we need to make sure that it is safe for the patient and the patient is on board with the potential side effects and risks. And we should always make sure our patients know we are their advocates in their weight journey.
Holly Lofton, clinical associate professor of surgery and medicine, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
On today’s edition of Beyond BMI, I’ll be discussing weight plateaus. This is something that our patients are very familiar with. Sometimes, they’re happy with their weight when they plateau; sometimes, they’re not. A weight plateau is simply a state of equilibrium.
There’s a common adage that the last 5 pounds are the hardest. When people decrease their calorie intake and increase their activity — as we instruct our patients to do to lose weight — the body starts to fight back because it believes this is a famine state. Our bodies feel that we are running around the jungle looking for food to help us survive a perceived famine state.
The body does a few things to help us keep weight on, and this is what leads to the frustration of not being able to lose those last 5 pounds. The first thing that happens in this process, which is called metabolic adaptation, is that when someone loses weight, the body naturally increases appetite signals from the brain, so the person becomes hungrier. Satiety signals from the stomach also decrease, so they feel more hungry and less full. And finally, stable fat cells form to allow the person to seek out more food without losing weight. This eventually leads the patient to regain weight, or they may plateau at a weight they’re not happy with.
I’m sure you’ve seen many studies looking at weight plateaus and the amount of weight loss people are able to achieve with diet, exercise, and behavior change alone vs the same lifestyle modifications plus medication. Studies show that patients who are taking anti-obesity medications achieve far more weight loss than do those who are not taking medications. The reason is related to the different mechanisms of action of the anti-obesity medications. Patients taking these medications are able to tolerate a lower caloric intake for a longer period of time, thus they’re able to burn more fat cells and lose more weight. Some medications perform this by decreasing appetite signals, so patients can continue to eat a small number of calories. Some medications affect the stability of fat cells. Some medications also increase satiety signals, so patients can move beyond that degree of metabolic adaptation and get beyond their previous plateau.
What can we do for patients who are frustrated with their weight plateau? I recommend taking a dive into their daily routine. Find out how many calories they are eating. Find out how much exercise they are doing and see whether there’s any room to reorganize the day or change their meals to create a caloric deficit. Are they eating things that are not filling enough, so they can’t get to the next meal without having a snack in between? We are looking at the quality of the meals as well and making sure there’s an adequate amount of protein and fiber in their meals to help with those increased appetite signals. We should also make sure these patients are getting adequate fluid intake.
These are all strategies that can help our patients try to get beyond their weight plateaus.
If the patient meets criteria for anti-obesity medication, which means a body mass index (BMI) of 27-29 with a weight-related comorbidity or BMI ≥ 30 with or without a comorbidity, you may want to consider anti-obesity medication to help that patient get beyond the plateau.
Plateaus will occur as a natural process because of the appetite signaling and hormonal changes that occur when patients lose weight from any modality. It’s important that we work with our patients to determine whether their weight plateau is due to metabolic adaptation. If they aren’t meeting their goals and they have weight-related comorbidities, we can use other available modalities to help those patients continue to lose weight. Of course, whenever we are prescribing a medication, we need to make sure that it is safe for the patient and the patient is on board with the potential side effects and risks. And we should always make sure our patients know we are their advocates in their weight journey.
Holly Lofton, clinical associate professor of surgery and medicine, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Irregular Sleep Patterns Increase Type 2 Diabetes Risk
Irregular sleep duration was associated with a higher risk for diabetes in middle-aged to older adults in a new UK Biobank study.
The analysis of more than 84,000 participants with 7-day accelerometry data suggested that individuals with the most irregular sleep duration patterns had a 34% higher risk for diabetes compared with their peers who had more consistent sleep patterns.
“It’s recommended to have 7-9 hours of nightly sleep, but what is not considered much in policy guidelines or at the clinical level is how regularly that’s needed,” Sina Kianersi, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, said in an interview. “What our study added is that it’s not just the duration but keeping it consistent. Patients can reduce their risk of diabetes by maintaining their 7-9 hours of sleep, not just for 1 night but throughout life.”
The study was published online in Diabetes Care.
Modifiable Lifestyle Factor
Researchers analyzed data from 84,421 UK Biobank participants who were free of diabetes when they provided accelerometer data in 2013-2015 and who were followed for a median of 7.5 years (622,080 person-years).
Participants had an average age of 62 years, 57% were women, 97% were White individuals, and 50% were employed in non–shift work jobs.
Sleep duration variability was quantified by the within-person standard deviation (SD) of 7-night accelerometer-measured sleep duration.
Participants with higher sleep duration SD were younger and more likely to be women, shift workers, or current smokers; those who reported definite “evening” chronotype (natural preference of the body to sleep at a certain time); those having lower socioeconomic status, higher body mass index, and shorter mean sleep duration; and were less likely to be White individuals.
In addition, a family history of diabetes and of depression was more prevalent among these participants.
A total of 2058 incident diabetes cases occurred during follow-up.
After adjustment for age, sex, and race, compared with a sleep duration SD ≤ 30 minutes, the hazard ratio (HR) was 1.15 for 31-45 minutes, 1.28 for 46-60 minutes, 1.54 for 61-90 minutes, and 1.59 for ≥ 91 minutes.
After the initial adjustment, individuals with a sleep duration SD of > 60 vs ≤ 60 minutes had a 34% higher diabetes risk. However, further adjustment for lifestyle, comorbidities, environmental factors, and adiposity attenuated the association — ie, the HR comparing sleep duration SD of > 60 vs ≤ 60 minutes was 1.11.
Furthermore, researchers found that the association between sleep duration and diabetes was stronger among individuals with lower diabetes polygenic risk score.
“One possible explanation for this finding is that the impact of sleep irregularity on diabetes risk may be less noticeable in individuals with a high genetic predisposition, where genetic factors dominate,” Dr. Kianersi said. “However, it is important to note that these sleep-gene interaction effects were not consistently observed across different measures and gene-related variables. This is something that remains to be further studied.”
Nevertheless, he added, “I want to emphasize that the association between irregular sleep duration and increased diabetes risk was evident across all levels of diabetes polygenic risk scores.”
The association also was stronger with longer sleep duration. The authors suggested that longer sleep duration “might reduce daylight exposure, which could, in turn, give rise to circadian disruption.”
Overall, Dr. Kianersi said, “Our study identified a modifiable lifestyle factor that can help lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.”
The study had several limitations. There was a time lag of a median of 5 years between sleep duration measurements and covariate assessments, which might bias lifestyle behaviors that may vary over time. In addition, a single 7-day sleep duration measurement may not capture long-term sleep patterns. A constrained random sampling approach was used to select participants, raising the potential of selection bias.
Regular Sleep Routine Best
Ana Krieger, MD, MPH, director of the Center for Sleep Medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City, commented on the study for this news organization. “This is a very interesting study, as it adds to the literature,” she said. “Previous research studies have shown metabolic abnormalities with variations in sleep time and duration.”
“This particular study evaluated a large sample of patients in the UK which were mostly White middle-aged and may not be representative of the general population,” she noted. “A similar study in a Hispanic/Latino group failed to demonstrate any significant association between sleep timing variability and incidence of diabetes. It would be desirable to see if prospective studies are able to demonstrate a reduction in diabetes risk by implementing a more regular sleep routine.”
The importance of the body’s natural circadian rhythm in regulating and anchoring many physiological processes was highlighted by the 2017 Nobel Prize of Medicine, which was awarded to three researchers in circadian biology, she pointed out.
“Alterations in the circadian rhythm are known to affect mood regulation, gastrointestinal function, and alertness, among other factors,” she said. “Keeping a regular sleep routine will help to improve our circadian rhythm and better regulate many processes, including our metabolism and appetite-controlling hormones.”
Notably, a study published online in Diabetologia in a racially and economically diverse US population also found that adults with persistent suboptimal sleep durations (< 7 or > 9 hours nightly over a mean of 5 years) were more likely to develop incident diabetes. The strongest association was found among participants reporting extreme changes and higher variability in their sleep durations.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grant number R01HL155395) and the UKB project 85501. Dr. Kianersi was supported by the American Heart Association Postdoctoral Fellowship. Dr. Kianersi and Dr. Krieger reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Irregular sleep duration was associated with a higher risk for diabetes in middle-aged to older adults in a new UK Biobank study.
The analysis of more than 84,000 participants with 7-day accelerometry data suggested that individuals with the most irregular sleep duration patterns had a 34% higher risk for diabetes compared with their peers who had more consistent sleep patterns.
“It’s recommended to have 7-9 hours of nightly sleep, but what is not considered much in policy guidelines or at the clinical level is how regularly that’s needed,” Sina Kianersi, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, said in an interview. “What our study added is that it’s not just the duration but keeping it consistent. Patients can reduce their risk of diabetes by maintaining their 7-9 hours of sleep, not just for 1 night but throughout life.”
The study was published online in Diabetes Care.
Modifiable Lifestyle Factor
Researchers analyzed data from 84,421 UK Biobank participants who were free of diabetes when they provided accelerometer data in 2013-2015 and who were followed for a median of 7.5 years (622,080 person-years).
Participants had an average age of 62 years, 57% were women, 97% were White individuals, and 50% were employed in non–shift work jobs.
Sleep duration variability was quantified by the within-person standard deviation (SD) of 7-night accelerometer-measured sleep duration.
Participants with higher sleep duration SD were younger and more likely to be women, shift workers, or current smokers; those who reported definite “evening” chronotype (natural preference of the body to sleep at a certain time); those having lower socioeconomic status, higher body mass index, and shorter mean sleep duration; and were less likely to be White individuals.
In addition, a family history of diabetes and of depression was more prevalent among these participants.
A total of 2058 incident diabetes cases occurred during follow-up.
After adjustment for age, sex, and race, compared with a sleep duration SD ≤ 30 minutes, the hazard ratio (HR) was 1.15 for 31-45 minutes, 1.28 for 46-60 minutes, 1.54 for 61-90 minutes, and 1.59 for ≥ 91 minutes.
After the initial adjustment, individuals with a sleep duration SD of > 60 vs ≤ 60 minutes had a 34% higher diabetes risk. However, further adjustment for lifestyle, comorbidities, environmental factors, and adiposity attenuated the association — ie, the HR comparing sleep duration SD of > 60 vs ≤ 60 minutes was 1.11.
Furthermore, researchers found that the association between sleep duration and diabetes was stronger among individuals with lower diabetes polygenic risk score.
“One possible explanation for this finding is that the impact of sleep irregularity on diabetes risk may be less noticeable in individuals with a high genetic predisposition, where genetic factors dominate,” Dr. Kianersi said. “However, it is important to note that these sleep-gene interaction effects were not consistently observed across different measures and gene-related variables. This is something that remains to be further studied.”
Nevertheless, he added, “I want to emphasize that the association between irregular sleep duration and increased diabetes risk was evident across all levels of diabetes polygenic risk scores.”
The association also was stronger with longer sleep duration. The authors suggested that longer sleep duration “might reduce daylight exposure, which could, in turn, give rise to circadian disruption.”
Overall, Dr. Kianersi said, “Our study identified a modifiable lifestyle factor that can help lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.”
The study had several limitations. There was a time lag of a median of 5 years between sleep duration measurements and covariate assessments, which might bias lifestyle behaviors that may vary over time. In addition, a single 7-day sleep duration measurement may not capture long-term sleep patterns. A constrained random sampling approach was used to select participants, raising the potential of selection bias.
Regular Sleep Routine Best
Ana Krieger, MD, MPH, director of the Center for Sleep Medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City, commented on the study for this news organization. “This is a very interesting study, as it adds to the literature,” she said. “Previous research studies have shown metabolic abnormalities with variations in sleep time and duration.”
“This particular study evaluated a large sample of patients in the UK which were mostly White middle-aged and may not be representative of the general population,” she noted. “A similar study in a Hispanic/Latino group failed to demonstrate any significant association between sleep timing variability and incidence of diabetes. It would be desirable to see if prospective studies are able to demonstrate a reduction in diabetes risk by implementing a more regular sleep routine.”
The importance of the body’s natural circadian rhythm in regulating and anchoring many physiological processes was highlighted by the 2017 Nobel Prize of Medicine, which was awarded to three researchers in circadian biology, she pointed out.
“Alterations in the circadian rhythm are known to affect mood regulation, gastrointestinal function, and alertness, among other factors,” she said. “Keeping a regular sleep routine will help to improve our circadian rhythm and better regulate many processes, including our metabolism and appetite-controlling hormones.”
Notably, a study published online in Diabetologia in a racially and economically diverse US population also found that adults with persistent suboptimal sleep durations (< 7 or > 9 hours nightly over a mean of 5 years) were more likely to develop incident diabetes. The strongest association was found among participants reporting extreme changes and higher variability in their sleep durations.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grant number R01HL155395) and the UKB project 85501. Dr. Kianersi was supported by the American Heart Association Postdoctoral Fellowship. Dr. Kianersi and Dr. Krieger reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Irregular sleep duration was associated with a higher risk for diabetes in middle-aged to older adults in a new UK Biobank study.
The analysis of more than 84,000 participants with 7-day accelerometry data suggested that individuals with the most irregular sleep duration patterns had a 34% higher risk for diabetes compared with their peers who had more consistent sleep patterns.
“It’s recommended to have 7-9 hours of nightly sleep, but what is not considered much in policy guidelines or at the clinical level is how regularly that’s needed,” Sina Kianersi, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, said in an interview. “What our study added is that it’s not just the duration but keeping it consistent. Patients can reduce their risk of diabetes by maintaining their 7-9 hours of sleep, not just for 1 night but throughout life.”
The study was published online in Diabetes Care.
Modifiable Lifestyle Factor
Researchers analyzed data from 84,421 UK Biobank participants who were free of diabetes when they provided accelerometer data in 2013-2015 and who were followed for a median of 7.5 years (622,080 person-years).
Participants had an average age of 62 years, 57% were women, 97% were White individuals, and 50% were employed in non–shift work jobs.
Sleep duration variability was quantified by the within-person standard deviation (SD) of 7-night accelerometer-measured sleep duration.
Participants with higher sleep duration SD were younger and more likely to be women, shift workers, or current smokers; those who reported definite “evening” chronotype (natural preference of the body to sleep at a certain time); those having lower socioeconomic status, higher body mass index, and shorter mean sleep duration; and were less likely to be White individuals.
In addition, a family history of diabetes and of depression was more prevalent among these participants.
A total of 2058 incident diabetes cases occurred during follow-up.
After adjustment for age, sex, and race, compared with a sleep duration SD ≤ 30 minutes, the hazard ratio (HR) was 1.15 for 31-45 minutes, 1.28 for 46-60 minutes, 1.54 for 61-90 minutes, and 1.59 for ≥ 91 minutes.
After the initial adjustment, individuals with a sleep duration SD of > 60 vs ≤ 60 minutes had a 34% higher diabetes risk. However, further adjustment for lifestyle, comorbidities, environmental factors, and adiposity attenuated the association — ie, the HR comparing sleep duration SD of > 60 vs ≤ 60 minutes was 1.11.
Furthermore, researchers found that the association between sleep duration and diabetes was stronger among individuals with lower diabetes polygenic risk score.
“One possible explanation for this finding is that the impact of sleep irregularity on diabetes risk may be less noticeable in individuals with a high genetic predisposition, where genetic factors dominate,” Dr. Kianersi said. “However, it is important to note that these sleep-gene interaction effects were not consistently observed across different measures and gene-related variables. This is something that remains to be further studied.”
Nevertheless, he added, “I want to emphasize that the association between irregular sleep duration and increased diabetes risk was evident across all levels of diabetes polygenic risk scores.”
The association also was stronger with longer sleep duration. The authors suggested that longer sleep duration “might reduce daylight exposure, which could, in turn, give rise to circadian disruption.”
Overall, Dr. Kianersi said, “Our study identified a modifiable lifestyle factor that can help lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.”
The study had several limitations. There was a time lag of a median of 5 years between sleep duration measurements and covariate assessments, which might bias lifestyle behaviors that may vary over time. In addition, a single 7-day sleep duration measurement may not capture long-term sleep patterns. A constrained random sampling approach was used to select participants, raising the potential of selection bias.
Regular Sleep Routine Best
Ana Krieger, MD, MPH, director of the Center for Sleep Medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City, commented on the study for this news organization. “This is a very interesting study, as it adds to the literature,” she said. “Previous research studies have shown metabolic abnormalities with variations in sleep time and duration.”
“This particular study evaluated a large sample of patients in the UK which were mostly White middle-aged and may not be representative of the general population,” she noted. “A similar study in a Hispanic/Latino group failed to demonstrate any significant association between sleep timing variability and incidence of diabetes. It would be desirable to see if prospective studies are able to demonstrate a reduction in diabetes risk by implementing a more regular sleep routine.”
The importance of the body’s natural circadian rhythm in regulating and anchoring many physiological processes was highlighted by the 2017 Nobel Prize of Medicine, which was awarded to three researchers in circadian biology, she pointed out.
“Alterations in the circadian rhythm are known to affect mood regulation, gastrointestinal function, and alertness, among other factors,” she said. “Keeping a regular sleep routine will help to improve our circadian rhythm and better regulate many processes, including our metabolism and appetite-controlling hormones.”
Notably, a study published online in Diabetologia in a racially and economically diverse US population also found that adults with persistent suboptimal sleep durations (< 7 or > 9 hours nightly over a mean of 5 years) were more likely to develop incident diabetes. The strongest association was found among participants reporting extreme changes and higher variability in their sleep durations.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grant number R01HL155395) and the UKB project 85501. Dr. Kianersi was supported by the American Heart Association Postdoctoral Fellowship. Dr. Kianersi and Dr. Krieger reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETES CARE
‘Alarming’ Rise in Mental Health Hospital Admissions Involving Methamphetamine
new research showed. Investigators found that between 2008 and 2020, such admissions increased by more than 10-fold.
“Overall, our results show an alarming increase in mental health disorder–related hospitalizations with concurrent methamphetamine use from 2008 to 2020,” wrote the investigators, led by Diensn Xing, Department of Medicine, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, Shreveport.
“These results are especially concerning because these hospitalizations outpace hospitalizations for methamphetamine use alone or mental health disorders alone,” they added.
The study was published online in Nature Mental Health .
Action Needed
Mental illness and methamphetamine use are both growing health problems. The investigators pointed out that methamphetamine use can cause serious harm to an individual’s mental, emotional, and social well-being and can significantly alter the brain.
They added that long-term methamphetamine users can exhibit “extreme anxiety, confusion, troubled sleep, mood changes, and aggressive behavior.” In addition, use of the drug can cause psychotic side effects such as paranoia, hallucinations, delusions, and suicidality.
The investigators noted that, to date, no studies have examined the combined effects of both diseases or characterized national trends over more than 10 years.
The researchers analyzed US mental health–related trends in methamphetamine users from 2008 to 2020. In particular, they wanted to characterize which demographic and geographic groups might be affected by both of these diseases because people with mental illness and co-occurring methamphetamine use are an “intersectional group” that is “doubly vulnerable to suicide and overdose death due to the synergistic effects of methamphetamine and mental health disorders.”
The investigators evaluated US trends in mental health disorder–related hospital admissions (MHD-HAs) and compared them with mental health admissions that involved concurrent methamphetamine use (MHD-HA-MUs) between 2008 and 2020.
Using data from the largest US inpatient care database, which encompasses more than 7 million hospital stays annually, they examined close to 4 million weighted hospital admissions and found more than a 10-fold increase in MHD-HA-MUs, compared with a 1.4-fold increase in MHD-HAs.
MHD-HA-MUs increased significantly among men (13-fold), non-Hispanic Black patients (39-fold), and those aged 41-64 years (16-fold). In the southern United States, MHD-HA-MUs increased 24-fold, larger than in any other region in the United States.
“Overall, the data suggest that there are synergistic effects with methamphetamine use and mental health disorder, highlighting this patient group’s unique needs, requiring distinct action,” the researchers wrote.
They proposed several interventions, including public education about substance use disorders, mental illness, and the effects of stigma. They also suggested decreasing criminal penalties for those with substance use disorders and improving healthcare delivery for this patient population.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health and an award from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. The study authors declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research showed. Investigators found that between 2008 and 2020, such admissions increased by more than 10-fold.
“Overall, our results show an alarming increase in mental health disorder–related hospitalizations with concurrent methamphetamine use from 2008 to 2020,” wrote the investigators, led by Diensn Xing, Department of Medicine, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, Shreveport.
“These results are especially concerning because these hospitalizations outpace hospitalizations for methamphetamine use alone or mental health disorders alone,” they added.
The study was published online in Nature Mental Health .
Action Needed
Mental illness and methamphetamine use are both growing health problems. The investigators pointed out that methamphetamine use can cause serious harm to an individual’s mental, emotional, and social well-being and can significantly alter the brain.
They added that long-term methamphetamine users can exhibit “extreme anxiety, confusion, troubled sleep, mood changes, and aggressive behavior.” In addition, use of the drug can cause psychotic side effects such as paranoia, hallucinations, delusions, and suicidality.
The investigators noted that, to date, no studies have examined the combined effects of both diseases or characterized national trends over more than 10 years.
The researchers analyzed US mental health–related trends in methamphetamine users from 2008 to 2020. In particular, they wanted to characterize which demographic and geographic groups might be affected by both of these diseases because people with mental illness and co-occurring methamphetamine use are an “intersectional group” that is “doubly vulnerable to suicide and overdose death due to the synergistic effects of methamphetamine and mental health disorders.”
The investigators evaluated US trends in mental health disorder–related hospital admissions (MHD-HAs) and compared them with mental health admissions that involved concurrent methamphetamine use (MHD-HA-MUs) between 2008 and 2020.
Using data from the largest US inpatient care database, which encompasses more than 7 million hospital stays annually, they examined close to 4 million weighted hospital admissions and found more than a 10-fold increase in MHD-HA-MUs, compared with a 1.4-fold increase in MHD-HAs.
MHD-HA-MUs increased significantly among men (13-fold), non-Hispanic Black patients (39-fold), and those aged 41-64 years (16-fold). In the southern United States, MHD-HA-MUs increased 24-fold, larger than in any other region in the United States.
“Overall, the data suggest that there are synergistic effects with methamphetamine use and mental health disorder, highlighting this patient group’s unique needs, requiring distinct action,” the researchers wrote.
They proposed several interventions, including public education about substance use disorders, mental illness, and the effects of stigma. They also suggested decreasing criminal penalties for those with substance use disorders and improving healthcare delivery for this patient population.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health and an award from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. The study authors declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research showed. Investigators found that between 2008 and 2020, such admissions increased by more than 10-fold.
“Overall, our results show an alarming increase in mental health disorder–related hospitalizations with concurrent methamphetamine use from 2008 to 2020,” wrote the investigators, led by Diensn Xing, Department of Medicine, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, Shreveport.
“These results are especially concerning because these hospitalizations outpace hospitalizations for methamphetamine use alone or mental health disorders alone,” they added.
The study was published online in Nature Mental Health .
Action Needed
Mental illness and methamphetamine use are both growing health problems. The investigators pointed out that methamphetamine use can cause serious harm to an individual’s mental, emotional, and social well-being and can significantly alter the brain.
They added that long-term methamphetamine users can exhibit “extreme anxiety, confusion, troubled sleep, mood changes, and aggressive behavior.” In addition, use of the drug can cause psychotic side effects such as paranoia, hallucinations, delusions, and suicidality.
The investigators noted that, to date, no studies have examined the combined effects of both diseases or characterized national trends over more than 10 years.
The researchers analyzed US mental health–related trends in methamphetamine users from 2008 to 2020. In particular, they wanted to characterize which demographic and geographic groups might be affected by both of these diseases because people with mental illness and co-occurring methamphetamine use are an “intersectional group” that is “doubly vulnerable to suicide and overdose death due to the synergistic effects of methamphetamine and mental health disorders.”
The investigators evaluated US trends in mental health disorder–related hospital admissions (MHD-HAs) and compared them with mental health admissions that involved concurrent methamphetamine use (MHD-HA-MUs) between 2008 and 2020.
Using data from the largest US inpatient care database, which encompasses more than 7 million hospital stays annually, they examined close to 4 million weighted hospital admissions and found more than a 10-fold increase in MHD-HA-MUs, compared with a 1.4-fold increase in MHD-HAs.
MHD-HA-MUs increased significantly among men (13-fold), non-Hispanic Black patients (39-fold), and those aged 41-64 years (16-fold). In the southern United States, MHD-HA-MUs increased 24-fold, larger than in any other region in the United States.
“Overall, the data suggest that there are synergistic effects with methamphetamine use and mental health disorder, highlighting this patient group’s unique needs, requiring distinct action,” the researchers wrote.
They proposed several interventions, including public education about substance use disorders, mental illness, and the effects of stigma. They also suggested decreasing criminal penalties for those with substance use disorders and improving healthcare delivery for this patient population.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health and an award from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. The study authors declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE MENTAL HEALTH