User login
Emergency angiography for cardiac arrest without ST elevation?
Patients successfully resuscitated after an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest who did not have ST-segment elevation on their electrocardiogram did not benefit from emergency coronary angiography in a new randomized clinical trial.
In the EMERGE trial, a strategy of emergency coronary angiography was not found to be better than a strategy of delayed coronary angiography with respect to the 180-day survival rate with no or minimal neurologic sequelae.
The authors note that, although the study was underpowered, the results are consistent with previously published studies and do not support routine emergency coronary angiography in survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest without ST elevation.
But senior author, Christian Spaulding, MD, PhD, European Hospital Georges Pompidou, Paris, believes some such patients may still benefit from emergency angiography.
“Most patients who have been resuscitated after out of hospital cardiac arrest will have neurological damage, which will be the primary cause of death,” Dr. Spaulding told this news organization. “It will not make any difference to these patients if they have a coronary lesion treated. So, going forward, I think we need to look for patients who are likely not to have a high degree of neurological damage and who could still benefit from early angiography.”
The EMERGE study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
In patients who have suffered an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with no obvious noncardiac cause such as trauma, it is believed that the cardiac arrest is caused by coronary occlusions, and emergency angiography may be able to improve survival in these patients, Dr. Spaulding explained.
In about one-third of such patients, the ECG before hospitalization shows ST elevation, and in this group, there is a high probability (around 70%-80%) that there is going to be a coronary occlusion, so these patients are usually taken directly to emergency angiography.
But, in the other two-thirds of patients, there is no ST elevation on the ECG, and in these patients the chances of finding a coronary occlusion are lower (around 25%-35%).
The EMERGE trial was conducted in this latter group without ST elevation.
For the study, which was conducted in 22 French centers, 279 such patients (mean age, 64 years) were randomized to either emergency or delayed (48-96 hours) coronary angiography. The mean time delay between randomization and coronary angiography was 0.6 hours in the emergency group and 55.1 hours in the delayed group.
The primary outcome was the 180-day survival rate with minimal neurological damage, defined as Cerebral Performance Category of 2 or less. This occurred in 34.1% of the emergency angiography group and 30.7% of the delayed angiography group (hazard ratio, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.65-1.15; P = .32).
There was also no difference in the overall survival rate at 180 days (36.2% vs. 33.3%; HR, 0.86; P = .31) and in secondary outcomes between the two groups.
Dr. Spaulding noted that three other randomized trials in a similar patient population have all shown similar results, with no difference in survival found between patients who have emergency coronary angiography as soon as they are admitted to hospital and those in whom angiography was not performed until a couple of days later.
However, several registry studies in a total of more than 6,000 patients have suggested a benefit of immediate angiography in these patients. “So, there is some disconnect here,” he said.
Dr. Spaulding believes the reason for this disconnect may be that the registry studies may have included patients with less neurological damage so more likely to survive and to benefit from having coronary lesions treated promptly.
“Paramedics sometimes make a judgment on which patients may have minimal neurological damage, and this may affect the choice of hospital a patient is taken to, and then the emergency department doctor may again assess whether a patient should go for immediate angiography or not. So, patients in these registry studies who received emergency angiography were likely already preselected to some extent,” he suggested.
In contrast, the randomized trials have accepted all patients, so there were probably more with neurological damage. “In our trial, almost 70% of patients were in asystole. These are the ones who [are] the most likely to have neurological damage,” he pointed out.
“Because there was such a striking difference in the registry studies, I think there is a group of patients [who] will benefit from immediate emergency coronary angiography, but we have to work out how to select these patients,” he commented.
Dr. Spaulding noted that a recent registry study published in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions used a score known as MIRACLE2, (which takes into account various factors including age of patient and type of rhythm on ECG) and the degree of cardiogenic shock on arrival at hospital as measured by the SCAI shock score to define a potential cohort of patients at low risk for neurologic injury who benefit most from immediate coronary angiography.
“In my practice at present, I would advise the emergency team that a young patient who had had resuscitation started quickly, had been defibrillated early, and got to hospital quickly should go for an immediate coronary angiogram. It can’t do any harm, and there may be a benefit in such patients,” Dr. Spaulding added.The EMERGE study was supported in part by Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris and the French Ministry of Health, through the national Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique. Dr. Spaulding reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients successfully resuscitated after an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest who did not have ST-segment elevation on their electrocardiogram did not benefit from emergency coronary angiography in a new randomized clinical trial.
In the EMERGE trial, a strategy of emergency coronary angiography was not found to be better than a strategy of delayed coronary angiography with respect to the 180-day survival rate with no or minimal neurologic sequelae.
The authors note that, although the study was underpowered, the results are consistent with previously published studies and do not support routine emergency coronary angiography in survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest without ST elevation.
But senior author, Christian Spaulding, MD, PhD, European Hospital Georges Pompidou, Paris, believes some such patients may still benefit from emergency angiography.
“Most patients who have been resuscitated after out of hospital cardiac arrest will have neurological damage, which will be the primary cause of death,” Dr. Spaulding told this news organization. “It will not make any difference to these patients if they have a coronary lesion treated. So, going forward, I think we need to look for patients who are likely not to have a high degree of neurological damage and who could still benefit from early angiography.”
The EMERGE study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
In patients who have suffered an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with no obvious noncardiac cause such as trauma, it is believed that the cardiac arrest is caused by coronary occlusions, and emergency angiography may be able to improve survival in these patients, Dr. Spaulding explained.
In about one-third of such patients, the ECG before hospitalization shows ST elevation, and in this group, there is a high probability (around 70%-80%) that there is going to be a coronary occlusion, so these patients are usually taken directly to emergency angiography.
But, in the other two-thirds of patients, there is no ST elevation on the ECG, and in these patients the chances of finding a coronary occlusion are lower (around 25%-35%).
The EMERGE trial was conducted in this latter group without ST elevation.
For the study, which was conducted in 22 French centers, 279 such patients (mean age, 64 years) were randomized to either emergency or delayed (48-96 hours) coronary angiography. The mean time delay between randomization and coronary angiography was 0.6 hours in the emergency group and 55.1 hours in the delayed group.
The primary outcome was the 180-day survival rate with minimal neurological damage, defined as Cerebral Performance Category of 2 or less. This occurred in 34.1% of the emergency angiography group and 30.7% of the delayed angiography group (hazard ratio, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.65-1.15; P = .32).
There was also no difference in the overall survival rate at 180 days (36.2% vs. 33.3%; HR, 0.86; P = .31) and in secondary outcomes between the two groups.
Dr. Spaulding noted that three other randomized trials in a similar patient population have all shown similar results, with no difference in survival found between patients who have emergency coronary angiography as soon as they are admitted to hospital and those in whom angiography was not performed until a couple of days later.
However, several registry studies in a total of more than 6,000 patients have suggested a benefit of immediate angiography in these patients. “So, there is some disconnect here,” he said.
Dr. Spaulding believes the reason for this disconnect may be that the registry studies may have included patients with less neurological damage so more likely to survive and to benefit from having coronary lesions treated promptly.
“Paramedics sometimes make a judgment on which patients may have minimal neurological damage, and this may affect the choice of hospital a patient is taken to, and then the emergency department doctor may again assess whether a patient should go for immediate angiography or not. So, patients in these registry studies who received emergency angiography were likely already preselected to some extent,” he suggested.
In contrast, the randomized trials have accepted all patients, so there were probably more with neurological damage. “In our trial, almost 70% of patients were in asystole. These are the ones who [are] the most likely to have neurological damage,” he pointed out.
“Because there was such a striking difference in the registry studies, I think there is a group of patients [who] will benefit from immediate emergency coronary angiography, but we have to work out how to select these patients,” he commented.
Dr. Spaulding noted that a recent registry study published in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions used a score known as MIRACLE2, (which takes into account various factors including age of patient and type of rhythm on ECG) and the degree of cardiogenic shock on arrival at hospital as measured by the SCAI shock score to define a potential cohort of patients at low risk for neurologic injury who benefit most from immediate coronary angiography.
“In my practice at present, I would advise the emergency team that a young patient who had had resuscitation started quickly, had been defibrillated early, and got to hospital quickly should go for an immediate coronary angiogram. It can’t do any harm, and there may be a benefit in such patients,” Dr. Spaulding added.The EMERGE study was supported in part by Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris and the French Ministry of Health, through the national Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique. Dr. Spaulding reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients successfully resuscitated after an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest who did not have ST-segment elevation on their electrocardiogram did not benefit from emergency coronary angiography in a new randomized clinical trial.
In the EMERGE trial, a strategy of emergency coronary angiography was not found to be better than a strategy of delayed coronary angiography with respect to the 180-day survival rate with no or minimal neurologic sequelae.
The authors note that, although the study was underpowered, the results are consistent with previously published studies and do not support routine emergency coronary angiography in survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest without ST elevation.
But senior author, Christian Spaulding, MD, PhD, European Hospital Georges Pompidou, Paris, believes some such patients may still benefit from emergency angiography.
“Most patients who have been resuscitated after out of hospital cardiac arrest will have neurological damage, which will be the primary cause of death,” Dr. Spaulding told this news organization. “It will not make any difference to these patients if they have a coronary lesion treated. So, going forward, I think we need to look for patients who are likely not to have a high degree of neurological damage and who could still benefit from early angiography.”
The EMERGE study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
In patients who have suffered an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with no obvious noncardiac cause such as trauma, it is believed that the cardiac arrest is caused by coronary occlusions, and emergency angiography may be able to improve survival in these patients, Dr. Spaulding explained.
In about one-third of such patients, the ECG before hospitalization shows ST elevation, and in this group, there is a high probability (around 70%-80%) that there is going to be a coronary occlusion, so these patients are usually taken directly to emergency angiography.
But, in the other two-thirds of patients, there is no ST elevation on the ECG, and in these patients the chances of finding a coronary occlusion are lower (around 25%-35%).
The EMERGE trial was conducted in this latter group without ST elevation.
For the study, which was conducted in 22 French centers, 279 such patients (mean age, 64 years) were randomized to either emergency or delayed (48-96 hours) coronary angiography. The mean time delay between randomization and coronary angiography was 0.6 hours in the emergency group and 55.1 hours in the delayed group.
The primary outcome was the 180-day survival rate with minimal neurological damage, defined as Cerebral Performance Category of 2 or less. This occurred in 34.1% of the emergency angiography group and 30.7% of the delayed angiography group (hazard ratio, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.65-1.15; P = .32).
There was also no difference in the overall survival rate at 180 days (36.2% vs. 33.3%; HR, 0.86; P = .31) and in secondary outcomes between the two groups.
Dr. Spaulding noted that three other randomized trials in a similar patient population have all shown similar results, with no difference in survival found between patients who have emergency coronary angiography as soon as they are admitted to hospital and those in whom angiography was not performed until a couple of days later.
However, several registry studies in a total of more than 6,000 patients have suggested a benefit of immediate angiography in these patients. “So, there is some disconnect here,” he said.
Dr. Spaulding believes the reason for this disconnect may be that the registry studies may have included patients with less neurological damage so more likely to survive and to benefit from having coronary lesions treated promptly.
“Paramedics sometimes make a judgment on which patients may have minimal neurological damage, and this may affect the choice of hospital a patient is taken to, and then the emergency department doctor may again assess whether a patient should go for immediate angiography or not. So, patients in these registry studies who received emergency angiography were likely already preselected to some extent,” he suggested.
In contrast, the randomized trials have accepted all patients, so there were probably more with neurological damage. “In our trial, almost 70% of patients were in asystole. These are the ones who [are] the most likely to have neurological damage,” he pointed out.
“Because there was such a striking difference in the registry studies, I think there is a group of patients [who] will benefit from immediate emergency coronary angiography, but we have to work out how to select these patients,” he commented.
Dr. Spaulding noted that a recent registry study published in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions used a score known as MIRACLE2, (which takes into account various factors including age of patient and type of rhythm on ECG) and the degree of cardiogenic shock on arrival at hospital as measured by the SCAI shock score to define a potential cohort of patients at low risk for neurologic injury who benefit most from immediate coronary angiography.
“In my practice at present, I would advise the emergency team that a young patient who had had resuscitation started quickly, had been defibrillated early, and got to hospital quickly should go for an immediate coronary angiogram. It can’t do any harm, and there may be a benefit in such patients,” Dr. Spaulding added.The EMERGE study was supported in part by Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris and the French Ministry of Health, through the national Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique. Dr. Spaulding reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe COVID-19 and blood cancer: Plasma therapy may help
, new research shows.
The study demonstrated that “plasma from convalescent or vaccinated individuals shortens the time to improvement in hematological and solid cancer patients with severe COVID-19” and “prolongs overall survival,” said study coauthor Maike Janssen, MD, of the department of internal medicine at Heidelberg (Germany) University Hospital.
Dr. Janssen presented the study findings at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association held in Vienna.
Although people with COVID-19 do not appear to benefit from treatment with convalescent plasma, some data indicate that certain patients who cannot mount a strong immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection may benefit.
In this recent multicenter study, 134 patients with confirmed COVID-19 whose oxygen saturation was 94% or lower were randomly assigned to undergo treatment with convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma (n = 68) or to receive standard of care (n = 66). Patients fell into four clinical groups: those with a hematologic malignancy or who had undergone active cancer therapy for any cancer within the past 24 months; those with chronic immunosuppression; those between the ages of 50 and 75 with lymphopenia and/or elevated D-dimer levels; and those older than 75 years.
The convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma was administered in two bags (238-337 mL plasma each) from different donors on days 1 and 2. Only plasma from donors with high levels of neutralizing activity (titers above 1:80) were included. The primary endpoint was time to improvement by 2 points on a 7-point scale or discharge from the hospital. The secondary endpoint was improvement in overall survival.
The authors found that overall, patients in the plasma group demonstrated a shorter time to improvement – median of 12.5 days, vs. 18 days – but the difference was not significant (P = .29).
However, for the subgroup of 56 patients with hematologic/solid cancers, the time to improvement was significantly shorter: 13 days vs. 31 days (hazard ratio [HR], 2.5; P = .003).
Similarly, plasma therapy did not improve overall survival in the study population overall – there were 12 deaths in the plasma group over 80 days, vs. 15 in the control group (P = .80). Patients in the hematologic/solid cancer subgroup who received plasma therapy did demonstrate significantly better overall survival (HR, 0.28; P = .042).
No similar significant differences in time to improvement or overall survival were observed in the other three groups. “We found that plasma did not improve outcomes in immune-competent patients with other risk factors and/or older age,” Dr. Janssen said.
Although study enrollment ended when the Omicron variant began surging, Dr. Janssen noted that plasma from Omicron patients may also be of benefit to those with hematologic cancers.
“We have treated some patients in individual cases using plasma from Omicron patients who were already vaccinated or with breakthrough infections, and we did see benefits in those cases,” she noted.
The study was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany. Dr. Janssen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
The study demonstrated that “plasma from convalescent or vaccinated individuals shortens the time to improvement in hematological and solid cancer patients with severe COVID-19” and “prolongs overall survival,” said study coauthor Maike Janssen, MD, of the department of internal medicine at Heidelberg (Germany) University Hospital.
Dr. Janssen presented the study findings at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association held in Vienna.
Although people with COVID-19 do not appear to benefit from treatment with convalescent plasma, some data indicate that certain patients who cannot mount a strong immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection may benefit.
In this recent multicenter study, 134 patients with confirmed COVID-19 whose oxygen saturation was 94% or lower were randomly assigned to undergo treatment with convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma (n = 68) or to receive standard of care (n = 66). Patients fell into four clinical groups: those with a hematologic malignancy or who had undergone active cancer therapy for any cancer within the past 24 months; those with chronic immunosuppression; those between the ages of 50 and 75 with lymphopenia and/or elevated D-dimer levels; and those older than 75 years.
The convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma was administered in two bags (238-337 mL plasma each) from different donors on days 1 and 2. Only plasma from donors with high levels of neutralizing activity (titers above 1:80) were included. The primary endpoint was time to improvement by 2 points on a 7-point scale or discharge from the hospital. The secondary endpoint was improvement in overall survival.
The authors found that overall, patients in the plasma group demonstrated a shorter time to improvement – median of 12.5 days, vs. 18 days – but the difference was not significant (P = .29).
However, for the subgroup of 56 patients with hematologic/solid cancers, the time to improvement was significantly shorter: 13 days vs. 31 days (hazard ratio [HR], 2.5; P = .003).
Similarly, plasma therapy did not improve overall survival in the study population overall – there were 12 deaths in the plasma group over 80 days, vs. 15 in the control group (P = .80). Patients in the hematologic/solid cancer subgroup who received plasma therapy did demonstrate significantly better overall survival (HR, 0.28; P = .042).
No similar significant differences in time to improvement or overall survival were observed in the other three groups. “We found that plasma did not improve outcomes in immune-competent patients with other risk factors and/or older age,” Dr. Janssen said.
Although study enrollment ended when the Omicron variant began surging, Dr. Janssen noted that plasma from Omicron patients may also be of benefit to those with hematologic cancers.
“We have treated some patients in individual cases using plasma from Omicron patients who were already vaccinated or with breakthrough infections, and we did see benefits in those cases,” she noted.
The study was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany. Dr. Janssen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
The study demonstrated that “plasma from convalescent or vaccinated individuals shortens the time to improvement in hematological and solid cancer patients with severe COVID-19” and “prolongs overall survival,” said study coauthor Maike Janssen, MD, of the department of internal medicine at Heidelberg (Germany) University Hospital.
Dr. Janssen presented the study findings at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association held in Vienna.
Although people with COVID-19 do not appear to benefit from treatment with convalescent plasma, some data indicate that certain patients who cannot mount a strong immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection may benefit.
In this recent multicenter study, 134 patients with confirmed COVID-19 whose oxygen saturation was 94% or lower were randomly assigned to undergo treatment with convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma (n = 68) or to receive standard of care (n = 66). Patients fell into four clinical groups: those with a hematologic malignancy or who had undergone active cancer therapy for any cancer within the past 24 months; those with chronic immunosuppression; those between the ages of 50 and 75 with lymphopenia and/or elevated D-dimer levels; and those older than 75 years.
The convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma was administered in two bags (238-337 mL plasma each) from different donors on days 1 and 2. Only plasma from donors with high levels of neutralizing activity (titers above 1:80) were included. The primary endpoint was time to improvement by 2 points on a 7-point scale or discharge from the hospital. The secondary endpoint was improvement in overall survival.
The authors found that overall, patients in the plasma group demonstrated a shorter time to improvement – median of 12.5 days, vs. 18 days – but the difference was not significant (P = .29).
However, for the subgroup of 56 patients with hematologic/solid cancers, the time to improvement was significantly shorter: 13 days vs. 31 days (hazard ratio [HR], 2.5; P = .003).
Similarly, plasma therapy did not improve overall survival in the study population overall – there were 12 deaths in the plasma group over 80 days, vs. 15 in the control group (P = .80). Patients in the hematologic/solid cancer subgroup who received plasma therapy did demonstrate significantly better overall survival (HR, 0.28; P = .042).
No similar significant differences in time to improvement or overall survival were observed in the other three groups. “We found that plasma did not improve outcomes in immune-competent patients with other risk factors and/or older age,” Dr. Janssen said.
Although study enrollment ended when the Omicron variant began surging, Dr. Janssen noted that plasma from Omicron patients may also be of benefit to those with hematologic cancers.
“We have treated some patients in individual cases using plasma from Omicron patients who were already vaccinated or with breakthrough infections, and we did see benefits in those cases,” she noted.
The study was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany. Dr. Janssen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EHA 2022
My time as an AGA editorial fellow for Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
On the top left of my desktop is an electronic sticky note entitled, “Apply in Future.” This was where the AGA editorial fellowship was listed when I first started GI fellowship. My interest in the behind-the-scenes of scientific publishing developed early. I wanted to learn not only about the decision-making by the editorial board but also other aspects that impact the process from submission to publication. While waiting for my opportunity to apply, I became a reviewer for several journals and then an associate editor of ACG Case Reports Journal, which gave me some insight.
I applied to the editorial fellowship as a second-year fellow, to start as a third-year fellow. I figured this would give me several chances to apply again if I was not selected! I started off by talking to my program director to ensure that I would have enough time, given other responsibilities. The application consisted of a cover letter, where I expressed why I was interested, particularly focusing on my passion for research and my experience with scientific publishing, a letter of recommendation, and a CV. I was ecstatic when I was selected for the AGA editorial fellowship for Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology (CGH), whose editorial board’s mission best aligned with my interests.
Dr. Jonathan Buscaglia was the editorial fellows’ mentor for CGH – he met with us and provided an outline of the year. For the first 6 months, I was a reviewer for submitted manuscripts within my topic of interest – pancreaticobiliary diseases and advanced endoscopy and technology. Dr. Buscaglia gave me feedback on my reviews to improve my critical assessment of study designs and interpreted results. After 6 months as a reviewer, I took on the role of an associate editor. I selected reviewers, evaluated the reviews, and made the decision to accept or reject a manuscript. I presented my assigned manuscript at the weekly board of editors meeting, which was one of the biggest learning experiences. Leading researchers from all over the world gathered at a virtual table and discussed whether each study would have clinical impact on the medical community. Each editor contributed a unique perspective that facilitated a robust and thoughtful discussion of each manuscript brought to the table. I was in awe each week.
What I have learned so far during my year as an AGA editorial fellow with CGH has shaped my approach to personal research and will continue to do so as I develop my research career. It has greatly improved my assessment of the literature and I hope to continue to be involved in the critical review process, especially as a reviewer in my early career, and eventually, a part of an editorial board for a journal that truly impacts clinical medicine, such as Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Dr. Trieu is a gastroenterology and hepatology fellow at Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill. She has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
On the top left of my desktop is an electronic sticky note entitled, “Apply in Future.” This was where the AGA editorial fellowship was listed when I first started GI fellowship. My interest in the behind-the-scenes of scientific publishing developed early. I wanted to learn not only about the decision-making by the editorial board but also other aspects that impact the process from submission to publication. While waiting for my opportunity to apply, I became a reviewer for several journals and then an associate editor of ACG Case Reports Journal, which gave me some insight.
I applied to the editorial fellowship as a second-year fellow, to start as a third-year fellow. I figured this would give me several chances to apply again if I was not selected! I started off by talking to my program director to ensure that I would have enough time, given other responsibilities. The application consisted of a cover letter, where I expressed why I was interested, particularly focusing on my passion for research and my experience with scientific publishing, a letter of recommendation, and a CV. I was ecstatic when I was selected for the AGA editorial fellowship for Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology (CGH), whose editorial board’s mission best aligned with my interests.
Dr. Jonathan Buscaglia was the editorial fellows’ mentor for CGH – he met with us and provided an outline of the year. For the first 6 months, I was a reviewer for submitted manuscripts within my topic of interest – pancreaticobiliary diseases and advanced endoscopy and technology. Dr. Buscaglia gave me feedback on my reviews to improve my critical assessment of study designs and interpreted results. After 6 months as a reviewer, I took on the role of an associate editor. I selected reviewers, evaluated the reviews, and made the decision to accept or reject a manuscript. I presented my assigned manuscript at the weekly board of editors meeting, which was one of the biggest learning experiences. Leading researchers from all over the world gathered at a virtual table and discussed whether each study would have clinical impact on the medical community. Each editor contributed a unique perspective that facilitated a robust and thoughtful discussion of each manuscript brought to the table. I was in awe each week.
What I have learned so far during my year as an AGA editorial fellow with CGH has shaped my approach to personal research and will continue to do so as I develop my research career. It has greatly improved my assessment of the literature and I hope to continue to be involved in the critical review process, especially as a reviewer in my early career, and eventually, a part of an editorial board for a journal that truly impacts clinical medicine, such as Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Dr. Trieu is a gastroenterology and hepatology fellow at Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill. She has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
On the top left of my desktop is an electronic sticky note entitled, “Apply in Future.” This was where the AGA editorial fellowship was listed when I first started GI fellowship. My interest in the behind-the-scenes of scientific publishing developed early. I wanted to learn not only about the decision-making by the editorial board but also other aspects that impact the process from submission to publication. While waiting for my opportunity to apply, I became a reviewer for several journals and then an associate editor of ACG Case Reports Journal, which gave me some insight.
I applied to the editorial fellowship as a second-year fellow, to start as a third-year fellow. I figured this would give me several chances to apply again if I was not selected! I started off by talking to my program director to ensure that I would have enough time, given other responsibilities. The application consisted of a cover letter, where I expressed why I was interested, particularly focusing on my passion for research and my experience with scientific publishing, a letter of recommendation, and a CV. I was ecstatic when I was selected for the AGA editorial fellowship for Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology (CGH), whose editorial board’s mission best aligned with my interests.
Dr. Jonathan Buscaglia was the editorial fellows’ mentor for CGH – he met with us and provided an outline of the year. For the first 6 months, I was a reviewer for submitted manuscripts within my topic of interest – pancreaticobiliary diseases and advanced endoscopy and technology. Dr. Buscaglia gave me feedback on my reviews to improve my critical assessment of study designs and interpreted results. After 6 months as a reviewer, I took on the role of an associate editor. I selected reviewers, evaluated the reviews, and made the decision to accept or reject a manuscript. I presented my assigned manuscript at the weekly board of editors meeting, which was one of the biggest learning experiences. Leading researchers from all over the world gathered at a virtual table and discussed whether each study would have clinical impact on the medical community. Each editor contributed a unique perspective that facilitated a robust and thoughtful discussion of each manuscript brought to the table. I was in awe each week.
What I have learned so far during my year as an AGA editorial fellow with CGH has shaped my approach to personal research and will continue to do so as I develop my research career. It has greatly improved my assessment of the literature and I hope to continue to be involved in the critical review process, especially as a reviewer in my early career, and eventually, a part of an editorial board for a journal that truly impacts clinical medicine, such as Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Dr. Trieu is a gastroenterology and hepatology fellow at Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill. She has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
New guideline for in-hospital care of diabetes says use CGMs
Goal-directed glycemic management – which may include new technologies for glucose monitoring – for non–critically ill hospitalized patients who have diabetes or newly recognized hyperglycemia can improve outcomes, according to a new practice guideline from the Endocrine Society.
Even though roughly 35% of hospitalized patients have diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia, there is “wide variability in glycemic management in clinical practice,” writing panel chair Mary Korytkowski, MD, from the University of Pittsburgh, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society. “These patients get admitted to every patient service in the hospital, meaning that every clinical service will encounter this group of patients, and their glycemic management can have a major effect on their outcomes. Both short term and long term.”
This guideline provides strategies “to achieve previously recommended glycemic goals while also reducing the risk for hypoglycemia, and this includes inpatient use of insulin pump therapy or continuous glucose monitoring [CGM] devices, among others,” she said.
It also includes “recommendations for preoperative glycemic goals as well as when the use of correctional insulin – well known as sliding scale insulin – may be appropriate” and when it is not.
The document, which replaces a 2012 guideline, was published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
A multidisciplinary panel developed the document over the last 3 years to answer 10 clinical practice questions related to management of non–critically ill hospitalized patients with diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia.
Use of CGM devices in hospital
The first recommendation is: “In adults with insulin-treated diabetes hospitalized for noncritical illness who are at high risk of hypoglycemia, we suggest the use of real-time [CGM] with confirmatory bedside point-of-care blood glucose monitoring for adjustments in insulin dosing rather than point-of-care blood glucose rather than testing alone in hospital settings where resources and training are available.” (Conditional recommendation. Low certainty of evidence).
“We were actually very careful in terms of looking at the data” for use of CGMs, Dr. Korytkowski said in an interview.
Although CGMs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the outpatient setting, and that’s becoming the standard of care there, they are not yet approved for in-hospital use.
However, the FDA granted an emergency allowance for use of CGMs in hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic.
That was “when everyone was scrambling for what to do,” Dr. Korytkowski noted. “There was a shortage of personal protective equipment and a real interest in trying to limit the amount of exposure of healthcare personnel in some of these really critically ill patients for whom intravenous insulin therapy was used to control their glucose level.”
On March 1, the FDA granted Breakthrough Devices Designation for Dexcom CGM use in the hospital setting.
The new guideline suggests CGM be used to detect trends in glycemic management, with insulin dosing decisions made with point-of-care glucose measure (the standard of care).
To implement CGM for glycemic management in hospitals, Dr. Korytkowski said, would require “extensive staff and nursing education to have people with expertise available to provide support to nursing personnel who are both placing these devices, changing these devices, looking at trends, and then knowing when to remove them for certain procedures such as MRI or radiologic procedures.”
“We know that not all hospitals may be readily available to use these devices,” she said. “It is an area of active research. But the use of these devices during the pandemic, in both critical care and non–critical care setting has really provided us with a lot of information that was used to formulate this suggestion in the guideline.”
The document addresses the following areas: CGM, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump therapy, inpatient diabetes education, prespecified preoperative glycemic targets, use of neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin for glucocorticoid or enteral nutrition-associated hyperglycemia, noninsulin therapies, preoperative carbohydrate-containing oral fluids, carbohydrate counting for prandial (mealtime) insulin dosing, and correctional and scheduled (basal or basal bolus) insulin therapies.
Nine key recommendations
Dr. Korytkowski identified nine key recommendations:
- CGM systems can help guide glycemic management with reduced risk for hypoglycemia.
- Patients experiencing glucocorticoid- or enteral nutrition–associated hyperglycemia require scheduled insulin therapy to address anticipated glucose excursions.
- Selected patients using insulin pump therapy prior to a hospital admission can continue to use these devices in the hospital if they have the mental and physical capacity to do so with knowledgeable hospital personnel.
- Diabetes self-management education provided to hospitalized patients can promote improved glycemic control following discharge with reductions in the risk for hospital readmission. “We know that is recommended for patients in the outpatient setting but often they do not get this,” she said. “We were able to observe that this can also impact long-term outcomes “
- Patients with diabetes scheduled for elective surgery may have improved postoperative outcomes when preoperative hemoglobin A1c is 8% or less and preoperative blood glucose is less than 180 mg/dL. “This recommendation answers the question: ‘Where should glycemic goals be for people who are undergoing surgery?’ ”
- Providing preoperative carbohydrate-containing beverages to patients with known diabetes is not recommended.
- Patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or well-managed diabetes on noninsulin therapy may be treated with correctional insulin alone as initial therapy at hospital admission.
- Some noninsulin diabetes therapies can be used in combination with correction insulin for patients with type 2 diabetes who have mild hyperglycemia.
- Correctional insulin – “otherwise known as sliding-scale insulin” – can be used as initial therapy for patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or type 2 diabetes treated with noninsulin therapy prior to hospital admission.
- Scheduled insulin therapy is preferred for patients experiencing persistent blood glucose values greater than 180 mg/dL and is recommended for patients using insulin therapy prior to admission.
The guideline writers’ hopes
“We hope that this guideline will resolve debates” about appropriate preoperative glycemic management and when sliding-scale insulin can be used and should not be used, said Dr. Korytkowski.
The authors also hope that “it will stimulate research funding for this very important aspect of diabetes care, and that hospitals will recognize the importance of having access to knowledgeable diabetes care and education specialists who can provide staff education regarding inpatient glycemic management, provide oversight for patients using insulin pump therapy or CGM devices, and empower hospital nurses to provide diabetes [self-management] education prior to patient discharge.”
Claire Pegg, the patient representative on the panel, hopes “that this guideline serves as the beginning of a conversation that will allow inpatient caregivers to provide individualized care to patients – some of whom may be self-sufficient with their glycemic management and others who need additional assistance.”
Development of the guideline was funded by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Korytkowski has reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Goal-directed glycemic management – which may include new technologies for glucose monitoring – for non–critically ill hospitalized patients who have diabetes or newly recognized hyperglycemia can improve outcomes, according to a new practice guideline from the Endocrine Society.
Even though roughly 35% of hospitalized patients have diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia, there is “wide variability in glycemic management in clinical practice,” writing panel chair Mary Korytkowski, MD, from the University of Pittsburgh, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society. “These patients get admitted to every patient service in the hospital, meaning that every clinical service will encounter this group of patients, and their glycemic management can have a major effect on their outcomes. Both short term and long term.”
This guideline provides strategies “to achieve previously recommended glycemic goals while also reducing the risk for hypoglycemia, and this includes inpatient use of insulin pump therapy or continuous glucose monitoring [CGM] devices, among others,” she said.
It also includes “recommendations for preoperative glycemic goals as well as when the use of correctional insulin – well known as sliding scale insulin – may be appropriate” and when it is not.
The document, which replaces a 2012 guideline, was published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
A multidisciplinary panel developed the document over the last 3 years to answer 10 clinical practice questions related to management of non–critically ill hospitalized patients with diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia.
Use of CGM devices in hospital
The first recommendation is: “In adults with insulin-treated diabetes hospitalized for noncritical illness who are at high risk of hypoglycemia, we suggest the use of real-time [CGM] with confirmatory bedside point-of-care blood glucose monitoring for adjustments in insulin dosing rather than point-of-care blood glucose rather than testing alone in hospital settings where resources and training are available.” (Conditional recommendation. Low certainty of evidence).
“We were actually very careful in terms of looking at the data” for use of CGMs, Dr. Korytkowski said in an interview.
Although CGMs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the outpatient setting, and that’s becoming the standard of care there, they are not yet approved for in-hospital use.
However, the FDA granted an emergency allowance for use of CGMs in hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic.
That was “when everyone was scrambling for what to do,” Dr. Korytkowski noted. “There was a shortage of personal protective equipment and a real interest in trying to limit the amount of exposure of healthcare personnel in some of these really critically ill patients for whom intravenous insulin therapy was used to control their glucose level.”
On March 1, the FDA granted Breakthrough Devices Designation for Dexcom CGM use in the hospital setting.
The new guideline suggests CGM be used to detect trends in glycemic management, with insulin dosing decisions made with point-of-care glucose measure (the standard of care).
To implement CGM for glycemic management in hospitals, Dr. Korytkowski said, would require “extensive staff and nursing education to have people with expertise available to provide support to nursing personnel who are both placing these devices, changing these devices, looking at trends, and then knowing when to remove them for certain procedures such as MRI or radiologic procedures.”
“We know that not all hospitals may be readily available to use these devices,” she said. “It is an area of active research. But the use of these devices during the pandemic, in both critical care and non–critical care setting has really provided us with a lot of information that was used to formulate this suggestion in the guideline.”
The document addresses the following areas: CGM, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump therapy, inpatient diabetes education, prespecified preoperative glycemic targets, use of neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin for glucocorticoid or enteral nutrition-associated hyperglycemia, noninsulin therapies, preoperative carbohydrate-containing oral fluids, carbohydrate counting for prandial (mealtime) insulin dosing, and correctional and scheduled (basal or basal bolus) insulin therapies.
Nine key recommendations
Dr. Korytkowski identified nine key recommendations:
- CGM systems can help guide glycemic management with reduced risk for hypoglycemia.
- Patients experiencing glucocorticoid- or enteral nutrition–associated hyperglycemia require scheduled insulin therapy to address anticipated glucose excursions.
- Selected patients using insulin pump therapy prior to a hospital admission can continue to use these devices in the hospital if they have the mental and physical capacity to do so with knowledgeable hospital personnel.
- Diabetes self-management education provided to hospitalized patients can promote improved glycemic control following discharge with reductions in the risk for hospital readmission. “We know that is recommended for patients in the outpatient setting but often they do not get this,” she said. “We were able to observe that this can also impact long-term outcomes “
- Patients with diabetes scheduled for elective surgery may have improved postoperative outcomes when preoperative hemoglobin A1c is 8% or less and preoperative blood glucose is less than 180 mg/dL. “This recommendation answers the question: ‘Where should glycemic goals be for people who are undergoing surgery?’ ”
- Providing preoperative carbohydrate-containing beverages to patients with known diabetes is not recommended.
- Patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or well-managed diabetes on noninsulin therapy may be treated with correctional insulin alone as initial therapy at hospital admission.
- Some noninsulin diabetes therapies can be used in combination with correction insulin for patients with type 2 diabetes who have mild hyperglycemia.
- Correctional insulin – “otherwise known as sliding-scale insulin” – can be used as initial therapy for patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or type 2 diabetes treated with noninsulin therapy prior to hospital admission.
- Scheduled insulin therapy is preferred for patients experiencing persistent blood glucose values greater than 180 mg/dL and is recommended for patients using insulin therapy prior to admission.
The guideline writers’ hopes
“We hope that this guideline will resolve debates” about appropriate preoperative glycemic management and when sliding-scale insulin can be used and should not be used, said Dr. Korytkowski.
The authors also hope that “it will stimulate research funding for this very important aspect of diabetes care, and that hospitals will recognize the importance of having access to knowledgeable diabetes care and education specialists who can provide staff education regarding inpatient glycemic management, provide oversight for patients using insulin pump therapy or CGM devices, and empower hospital nurses to provide diabetes [self-management] education prior to patient discharge.”
Claire Pegg, the patient representative on the panel, hopes “that this guideline serves as the beginning of a conversation that will allow inpatient caregivers to provide individualized care to patients – some of whom may be self-sufficient with their glycemic management and others who need additional assistance.”
Development of the guideline was funded by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Korytkowski has reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Goal-directed glycemic management – which may include new technologies for glucose monitoring – for non–critically ill hospitalized patients who have diabetes or newly recognized hyperglycemia can improve outcomes, according to a new practice guideline from the Endocrine Society.
Even though roughly 35% of hospitalized patients have diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia, there is “wide variability in glycemic management in clinical practice,” writing panel chair Mary Korytkowski, MD, from the University of Pittsburgh, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society. “These patients get admitted to every patient service in the hospital, meaning that every clinical service will encounter this group of patients, and their glycemic management can have a major effect on their outcomes. Both short term and long term.”
This guideline provides strategies “to achieve previously recommended glycemic goals while also reducing the risk for hypoglycemia, and this includes inpatient use of insulin pump therapy or continuous glucose monitoring [CGM] devices, among others,” she said.
It also includes “recommendations for preoperative glycemic goals as well as when the use of correctional insulin – well known as sliding scale insulin – may be appropriate” and when it is not.
The document, which replaces a 2012 guideline, was published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
A multidisciplinary panel developed the document over the last 3 years to answer 10 clinical practice questions related to management of non–critically ill hospitalized patients with diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia.
Use of CGM devices in hospital
The first recommendation is: “In adults with insulin-treated diabetes hospitalized for noncritical illness who are at high risk of hypoglycemia, we suggest the use of real-time [CGM] with confirmatory bedside point-of-care blood glucose monitoring for adjustments in insulin dosing rather than point-of-care blood glucose rather than testing alone in hospital settings where resources and training are available.” (Conditional recommendation. Low certainty of evidence).
“We were actually very careful in terms of looking at the data” for use of CGMs, Dr. Korytkowski said in an interview.
Although CGMs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the outpatient setting, and that’s becoming the standard of care there, they are not yet approved for in-hospital use.
However, the FDA granted an emergency allowance for use of CGMs in hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic.
That was “when everyone was scrambling for what to do,” Dr. Korytkowski noted. “There was a shortage of personal protective equipment and a real interest in trying to limit the amount of exposure of healthcare personnel in some of these really critically ill patients for whom intravenous insulin therapy was used to control their glucose level.”
On March 1, the FDA granted Breakthrough Devices Designation for Dexcom CGM use in the hospital setting.
The new guideline suggests CGM be used to detect trends in glycemic management, with insulin dosing decisions made with point-of-care glucose measure (the standard of care).
To implement CGM for glycemic management in hospitals, Dr. Korytkowski said, would require “extensive staff and nursing education to have people with expertise available to provide support to nursing personnel who are both placing these devices, changing these devices, looking at trends, and then knowing when to remove them for certain procedures such as MRI or radiologic procedures.”
“We know that not all hospitals may be readily available to use these devices,” she said. “It is an area of active research. But the use of these devices during the pandemic, in both critical care and non–critical care setting has really provided us with a lot of information that was used to formulate this suggestion in the guideline.”
The document addresses the following areas: CGM, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump therapy, inpatient diabetes education, prespecified preoperative glycemic targets, use of neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin for glucocorticoid or enteral nutrition-associated hyperglycemia, noninsulin therapies, preoperative carbohydrate-containing oral fluids, carbohydrate counting for prandial (mealtime) insulin dosing, and correctional and scheduled (basal or basal bolus) insulin therapies.
Nine key recommendations
Dr. Korytkowski identified nine key recommendations:
- CGM systems can help guide glycemic management with reduced risk for hypoglycemia.
- Patients experiencing glucocorticoid- or enteral nutrition–associated hyperglycemia require scheduled insulin therapy to address anticipated glucose excursions.
- Selected patients using insulin pump therapy prior to a hospital admission can continue to use these devices in the hospital if they have the mental and physical capacity to do so with knowledgeable hospital personnel.
- Diabetes self-management education provided to hospitalized patients can promote improved glycemic control following discharge with reductions in the risk for hospital readmission. “We know that is recommended for patients in the outpatient setting but often they do not get this,” she said. “We were able to observe that this can also impact long-term outcomes “
- Patients with diabetes scheduled for elective surgery may have improved postoperative outcomes when preoperative hemoglobin A1c is 8% or less and preoperative blood glucose is less than 180 mg/dL. “This recommendation answers the question: ‘Where should glycemic goals be for people who are undergoing surgery?’ ”
- Providing preoperative carbohydrate-containing beverages to patients with known diabetes is not recommended.
- Patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or well-managed diabetes on noninsulin therapy may be treated with correctional insulin alone as initial therapy at hospital admission.
- Some noninsulin diabetes therapies can be used in combination with correction insulin for patients with type 2 diabetes who have mild hyperglycemia.
- Correctional insulin – “otherwise known as sliding-scale insulin” – can be used as initial therapy for patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or type 2 diabetes treated with noninsulin therapy prior to hospital admission.
- Scheduled insulin therapy is preferred for patients experiencing persistent blood glucose values greater than 180 mg/dL and is recommended for patients using insulin therapy prior to admission.
The guideline writers’ hopes
“We hope that this guideline will resolve debates” about appropriate preoperative glycemic management and when sliding-scale insulin can be used and should not be used, said Dr. Korytkowski.
The authors also hope that “it will stimulate research funding for this very important aspect of diabetes care, and that hospitals will recognize the importance of having access to knowledgeable diabetes care and education specialists who can provide staff education regarding inpatient glycemic management, provide oversight for patients using insulin pump therapy or CGM devices, and empower hospital nurses to provide diabetes [self-management] education prior to patient discharge.”
Claire Pegg, the patient representative on the panel, hopes “that this guideline serves as the beginning of a conversation that will allow inpatient caregivers to provide individualized care to patients – some of whom may be self-sufficient with their glycemic management and others who need additional assistance.”
Development of the guideline was funded by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Korytkowski has reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ENDO 2022
Self-injury and suicide ‘all too common’ in type 1 diabetes
Depression, self-harm, and suicide among people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes are “underappreciated” among health care practitioners, according to Katharine Barnard-Kelly, PhD, who founded the Reducing Suicide Rates Among Individuals With Diabetes (RESCUE) advocacy group in 2021.
“We have the most advanced technology to achieve glycemic control, but the mental burden remains underappreciated,” she said at a symposium with other speakers from RESCUE during the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Notably, suicide and self-harm are “all too common” among young adults with type 1 diabetes who are receiving insulin, said Dr. Barnard-Kelly, a psychologist and visiting professor at Southern Health NHS Foundation Trust, Southampton, United Kingdom. And insulin under- or overdosing is the most common method of self-harm.
However, “with a multipronged approach to awareness, education, and identification, we have the opportunity to intervene on the link between suicide and diabetes,” she said, noting that the aim is to “raise awareness and arm [doctors and others] with messages that can ultimately save a young person’s life if adopted in clinical practice and through mental health screenings.”
The rationale behind the RESCUE initiative is also described in a brief report published in Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.
Six key messages
RESCUE now has “approximately 30 members across academia, clinical practice, industry, advocacy, government, regulatory bodies [including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration], and people with diabetes from several countries,” Dr. Barnard-Kelly told this news organization.
She identified six key messages from the symposium:
- “Suicide prevalence is considerably higher among people with diabetes than the general population.
- Talking about suicide does not increase an individual’s risk of suicide.
- Current screening tools for depression and suicide are not sufficiently sensitive to be effective among people with diabetes.
- Identification of suicidal acts among people with diabetes is extremely difficult.
- For every suicide, the World Health Organization reports there are 20 suicide attempts.
- Health care providers often underestimate the prevalence of suicidality among their patient population and feel ill-equipped to initiate conversations with their patients about suicide.”
Dr. Barnard-Kelly also presented some sobering statistics that highlight the need for increased awareness.
A study reported that, of 160 cases of insulin overdose, 90% were suicides.
Adolescents and young adults with type 2 diabetes are 61% more likely to report suicidal thoughts than those without diabetes.
The risk of depression is two- to three-times higher in people with diabetes. According to another study, 7% of deaths in individuals with type 1 diabetes are estimated to be from suicide.
Survey about screening for depression, suicide risk in diabetes
During the symposium, Daniel R. Chernavvsky, MD, reported results from a small online survey of health care professionals who treat patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, which identified their concerns about screening for depression and assessing suicide risk in patients with diabetes.
Respondents were mainly from the United States (103) but were also from the United Kingdom (18), Slovenia, and the Netherlands (5), said Dr. Chernavvsky, who is senior director of medical affairs at Dexcom, Charlottesville, Va.
They included 59 doctors, 21 nurses,17 diabetes educators, 15 psychologists, seven dieticians, four social workers, and six “other” health care professionals, with a mean age of 46 (range, 25-72 years old) who had been working on average 14 years (range, 0.5-45 years).
Close to three-quarters (72%) reported that at least one of their patients had attempted suicide. The most common self-harm behaviors in their patients were insulin omission or a too large insulin bolus, and less often, binge eating.
Almost all respondents (95%) believed that routine visits to the diabetes clinic were appropriate times to discuss depression, self-injury, and suicidal ideation – at every visit (42% of respondents) or some visits (52%).
Only 30% were comfortable asking patients about self-harm or suicide.
Psychologists and social workers were very comfortable, but others were less comfortable or not comfortable at all.
Many respondents expressed concerns such as, “What do I do?” “Would I make the problem worse?” “Would I give the patient the idea?” Some reported they had “limited resources” or it “feels invasive.”
They identified a need for “a better understanding of what [they could] do to support and care for patients,” and “more knowledge about how to deal with [patients’] answers” to screening questionnaires.
Screening for psychological morbidities in diabetes
Guidelines from the ADA and the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes recommend routine screening of patients with diabetes for psychological morbidities, including depression, said Shideh Majidi, MD.
Depression is associated with higher A1c, noted Dr. Majidi, who is associate director, childhood and adolescent diabetes program at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, D.C.
She identified the following topics that need to be addressed when considering implementing a program for depression screening and suicide risk assessment in a diabetes clinic:
- Conducting screening: Which screening questionnaire will you use? Who will do it? Where? How often?
- Scoring screening questionnaires: Who will do it?
- Depression screening discussion: Who will do it? How will the person be notified of the score?
- Suicide risk assessment: Who will conduct it? What is the process to get someone to the emergency department?
- Resources/referral: Who will initiate and follow-up?
Next steps
The RESCUE advocacy group is preparing educational and support materials for health care professionals who treat patients with diabetes, as well as other materials for patients themselves.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Depression, self-harm, and suicide among people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes are “underappreciated” among health care practitioners, according to Katharine Barnard-Kelly, PhD, who founded the Reducing Suicide Rates Among Individuals With Diabetes (RESCUE) advocacy group in 2021.
“We have the most advanced technology to achieve glycemic control, but the mental burden remains underappreciated,” she said at a symposium with other speakers from RESCUE during the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Notably, suicide and self-harm are “all too common” among young adults with type 1 diabetes who are receiving insulin, said Dr. Barnard-Kelly, a psychologist and visiting professor at Southern Health NHS Foundation Trust, Southampton, United Kingdom. And insulin under- or overdosing is the most common method of self-harm.
However, “with a multipronged approach to awareness, education, and identification, we have the opportunity to intervene on the link between suicide and diabetes,” she said, noting that the aim is to “raise awareness and arm [doctors and others] with messages that can ultimately save a young person’s life if adopted in clinical practice and through mental health screenings.”
The rationale behind the RESCUE initiative is also described in a brief report published in Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.
Six key messages
RESCUE now has “approximately 30 members across academia, clinical practice, industry, advocacy, government, regulatory bodies [including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration], and people with diabetes from several countries,” Dr. Barnard-Kelly told this news organization.
She identified six key messages from the symposium:
- “Suicide prevalence is considerably higher among people with diabetes than the general population.
- Talking about suicide does not increase an individual’s risk of suicide.
- Current screening tools for depression and suicide are not sufficiently sensitive to be effective among people with diabetes.
- Identification of suicidal acts among people with diabetes is extremely difficult.
- For every suicide, the World Health Organization reports there are 20 suicide attempts.
- Health care providers often underestimate the prevalence of suicidality among their patient population and feel ill-equipped to initiate conversations with their patients about suicide.”
Dr. Barnard-Kelly also presented some sobering statistics that highlight the need for increased awareness.
A study reported that, of 160 cases of insulin overdose, 90% were suicides.
Adolescents and young adults with type 2 diabetes are 61% more likely to report suicidal thoughts than those without diabetes.
The risk of depression is two- to three-times higher in people with diabetes. According to another study, 7% of deaths in individuals with type 1 diabetes are estimated to be from suicide.
Survey about screening for depression, suicide risk in diabetes
During the symposium, Daniel R. Chernavvsky, MD, reported results from a small online survey of health care professionals who treat patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, which identified their concerns about screening for depression and assessing suicide risk in patients with diabetes.
Respondents were mainly from the United States (103) but were also from the United Kingdom (18), Slovenia, and the Netherlands (5), said Dr. Chernavvsky, who is senior director of medical affairs at Dexcom, Charlottesville, Va.
They included 59 doctors, 21 nurses,17 diabetes educators, 15 psychologists, seven dieticians, four social workers, and six “other” health care professionals, with a mean age of 46 (range, 25-72 years old) who had been working on average 14 years (range, 0.5-45 years).
Close to three-quarters (72%) reported that at least one of their patients had attempted suicide. The most common self-harm behaviors in their patients were insulin omission or a too large insulin bolus, and less often, binge eating.
Almost all respondents (95%) believed that routine visits to the diabetes clinic were appropriate times to discuss depression, self-injury, and suicidal ideation – at every visit (42% of respondents) or some visits (52%).
Only 30% were comfortable asking patients about self-harm or suicide.
Psychologists and social workers were very comfortable, but others were less comfortable or not comfortable at all.
Many respondents expressed concerns such as, “What do I do?” “Would I make the problem worse?” “Would I give the patient the idea?” Some reported they had “limited resources” or it “feels invasive.”
They identified a need for “a better understanding of what [they could] do to support and care for patients,” and “more knowledge about how to deal with [patients’] answers” to screening questionnaires.
Screening for psychological morbidities in diabetes
Guidelines from the ADA and the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes recommend routine screening of patients with diabetes for psychological morbidities, including depression, said Shideh Majidi, MD.
Depression is associated with higher A1c, noted Dr. Majidi, who is associate director, childhood and adolescent diabetes program at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, D.C.
She identified the following topics that need to be addressed when considering implementing a program for depression screening and suicide risk assessment in a diabetes clinic:
- Conducting screening: Which screening questionnaire will you use? Who will do it? Where? How often?
- Scoring screening questionnaires: Who will do it?
- Depression screening discussion: Who will do it? How will the person be notified of the score?
- Suicide risk assessment: Who will conduct it? What is the process to get someone to the emergency department?
- Resources/referral: Who will initiate and follow-up?
Next steps
The RESCUE advocacy group is preparing educational and support materials for health care professionals who treat patients with diabetes, as well as other materials for patients themselves.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Depression, self-harm, and suicide among people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes are “underappreciated” among health care practitioners, according to Katharine Barnard-Kelly, PhD, who founded the Reducing Suicide Rates Among Individuals With Diabetes (RESCUE) advocacy group in 2021.
“We have the most advanced technology to achieve glycemic control, but the mental burden remains underappreciated,” she said at a symposium with other speakers from RESCUE during the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Notably, suicide and self-harm are “all too common” among young adults with type 1 diabetes who are receiving insulin, said Dr. Barnard-Kelly, a psychologist and visiting professor at Southern Health NHS Foundation Trust, Southampton, United Kingdom. And insulin under- or overdosing is the most common method of self-harm.
However, “with a multipronged approach to awareness, education, and identification, we have the opportunity to intervene on the link between suicide and diabetes,” she said, noting that the aim is to “raise awareness and arm [doctors and others] with messages that can ultimately save a young person’s life if adopted in clinical practice and through mental health screenings.”
The rationale behind the RESCUE initiative is also described in a brief report published in Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.
Six key messages
RESCUE now has “approximately 30 members across academia, clinical practice, industry, advocacy, government, regulatory bodies [including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration], and people with diabetes from several countries,” Dr. Barnard-Kelly told this news organization.
She identified six key messages from the symposium:
- “Suicide prevalence is considerably higher among people with diabetes than the general population.
- Talking about suicide does not increase an individual’s risk of suicide.
- Current screening tools for depression and suicide are not sufficiently sensitive to be effective among people with diabetes.
- Identification of suicidal acts among people with diabetes is extremely difficult.
- For every suicide, the World Health Organization reports there are 20 suicide attempts.
- Health care providers often underestimate the prevalence of suicidality among their patient population and feel ill-equipped to initiate conversations with their patients about suicide.”
Dr. Barnard-Kelly also presented some sobering statistics that highlight the need for increased awareness.
A study reported that, of 160 cases of insulin overdose, 90% were suicides.
Adolescents and young adults with type 2 diabetes are 61% more likely to report suicidal thoughts than those without diabetes.
The risk of depression is two- to three-times higher in people with diabetes. According to another study, 7% of deaths in individuals with type 1 diabetes are estimated to be from suicide.
Survey about screening for depression, suicide risk in diabetes
During the symposium, Daniel R. Chernavvsky, MD, reported results from a small online survey of health care professionals who treat patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, which identified their concerns about screening for depression and assessing suicide risk in patients with diabetes.
Respondents were mainly from the United States (103) but were also from the United Kingdom (18), Slovenia, and the Netherlands (5), said Dr. Chernavvsky, who is senior director of medical affairs at Dexcom, Charlottesville, Va.
They included 59 doctors, 21 nurses,17 diabetes educators, 15 psychologists, seven dieticians, four social workers, and six “other” health care professionals, with a mean age of 46 (range, 25-72 years old) who had been working on average 14 years (range, 0.5-45 years).
Close to three-quarters (72%) reported that at least one of their patients had attempted suicide. The most common self-harm behaviors in their patients were insulin omission or a too large insulin bolus, and less often, binge eating.
Almost all respondents (95%) believed that routine visits to the diabetes clinic were appropriate times to discuss depression, self-injury, and suicidal ideation – at every visit (42% of respondents) or some visits (52%).
Only 30% were comfortable asking patients about self-harm or suicide.
Psychologists and social workers were very comfortable, but others were less comfortable or not comfortable at all.
Many respondents expressed concerns such as, “What do I do?” “Would I make the problem worse?” “Would I give the patient the idea?” Some reported they had “limited resources” or it “feels invasive.”
They identified a need for “a better understanding of what [they could] do to support and care for patients,” and “more knowledge about how to deal with [patients’] answers” to screening questionnaires.
Screening for psychological morbidities in diabetes
Guidelines from the ADA and the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes recommend routine screening of patients with diabetes for psychological morbidities, including depression, said Shideh Majidi, MD.
Depression is associated with higher A1c, noted Dr. Majidi, who is associate director, childhood and adolescent diabetes program at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, D.C.
She identified the following topics that need to be addressed when considering implementing a program for depression screening and suicide risk assessment in a diabetes clinic:
- Conducting screening: Which screening questionnaire will you use? Who will do it? Where? How often?
- Scoring screening questionnaires: Who will do it?
- Depression screening discussion: Who will do it? How will the person be notified of the score?
- Suicide risk assessment: Who will conduct it? What is the process to get someone to the emergency department?
- Resources/referral: Who will initiate and follow-up?
Next steps
The RESCUE advocacy group is preparing educational and support materials for health care professionals who treat patients with diabetes, as well as other materials for patients themselves.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2022
2022 GOLD Report: Tips for diagnosing and evaluating COPD
For many years, COPD has remained one of the top four leading causes of death in the United States according to CDC data. Around the world, it is responsible for about 3 million deaths annually. It is estimated that 16 million Americans are now diagnosed with COPD. However, it is commonly agreed by experts that it is widely underdiagnosed and there may be millions more suffering from this disease.
The direct costs of COPD are around $49 billion a year in direct costs, with billions more in indirect costs. Around the globe, COPD is one of the top three causes of death, with 90% of deaths happening in low- and middle-income countries. The burden of COPD is expected to grow over time because of the aging population and continued exposure to COPD risk factors.
The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease report (or GOLD) is revised every year, translated into many languages, and used by health care workers globally. It was started in 1998, and its aim was to produce guidelines based on the best scientific evidence available that was nonbiased to be used for assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with COPD. The first report was issued in 2001. The method of producing the GOLD report was to do a search of PubMed for evidence-based, peer-reviewed studies. Those not captured by this method could be submitted for review. The science committee then meets twice a year and reviews each publication, eventually agreeing on a set of guidelines/updates.
2022 GOLD Report
For the 2022 GOLD report, 160 new references were added. Overall, the GOLD report is five chapters (more than 150 pages) giving in-depth guidance for the diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of patients with stable COPD, COPD exacerbations, and hospitalized patients.
The report suggests that COPD is being underdiagnosed.
Family physicians and internists will be seeing more and more cases as the population ages, and we need to do a better job of recognizing patients who have COPD. If possible, we should try to have spirometry available in our practices. Like any other disease, we know prevention works best so primary care physicians also need to be looking for risk factors, such as smoking history, and help patients try to reduce them if possible. Below is more explanation of the latest guidelines.
For most of us, when we learned about COPD as a disease, the terms “chronic bronchitis” and “emphysema” were emphasized. These words are no longer used as synonymous for COPD.
The disease is now described as involving chronic limitation in airflow that results from a combination of small airway disease and parenchymal destruction (emphysema). The rates of each vary from person to person and progress at different rates. Key factors that contribute to COPD disease burden include chronic inflammation, narrowing of small airways, loss of alveolar attachments, loss of elastic recoil, and mucociliary dysfunction, according to the 2022 GOLD report.
Respiratory symptoms may precede the onset of airflow limitation. COPD should be considered in any patient with dyspnea, chronic cough or sputum production, a history of recurrent lower respiratory tract infections, and risk factors for the disease.
The biggest risk factor for COPD is smoking. Other risk factors include occupational exposure, e-cigarette use, pollution, genetic factors, and comorbid conditions. Symptoms of the disease can include chest tightness, wheezing, and fatigue.
To make a diagnosis of COPD, spirometry is required, the latest GOLD report says. A postbronchodilator FEV1/FVC less than 0.70 confirms persistent airflow limitation and hence COPD. This value is used in clinical trials and forms the basis of what most treatment guidelines are derived from. It would be beneficial for any physician treating COPD patients to have easy access to spirometry. It provides the most reproducible and objective measurement of airflow limitation. Also, it was found that assessing the degree of reversibility of airflow limitation to decide therapeutic decisions is no longer recommended and thus, asking the patient to stop inhaled medications beforehand is unnecessary. To access the impact COPD has on a patient’s life beyond dyspnea, the guidelines recommend doing a disease-specific health questionnaire, such as the COPD Assessment Test (CAT).
Along with patient symptoms and history of exacerbations, spirometry is crucial for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic decisions in COPD patients, according to the GOLD guidance. The best predictor of frequent exacerbations, however, is a history of previous exacerbations. In cases where there is a discrepancy between airflow limitation and symptoms, additional testing should be considered. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) screening should be considered in younger patients (under 45 years) with perilobular emphysema, and those in areas of high AATD prevalence. Chest x-rays are not recommended in diagnosing COPD but can be helpful if other comorbidities are present. CT scan is not routinely recommended but should be used only for the detection of bronchiectasis, if the patient meets the criteria for lung cancer screening, if surgery is necessary, or if other diseases may need to be evaluated.
Pulse oximetry can be helpful in accessing degree of severity, respiratory failure, and right heart failure. Walking tests can be helpful for evaluating disability and mortality risk. Other tests that have been used but are not routinely recommended include plethysmography and diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide.
Composite scores can identify patients who are at increased risk of mortality. One such score is the BODE (Body mass, Obstruction, Dyspnea, and Exercise) method. Biomarkers are being investigated, but data are still not available to recommend their routine use.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at [email protected].
For many years, COPD has remained one of the top four leading causes of death in the United States according to CDC data. Around the world, it is responsible for about 3 million deaths annually. It is estimated that 16 million Americans are now diagnosed with COPD. However, it is commonly agreed by experts that it is widely underdiagnosed and there may be millions more suffering from this disease.
The direct costs of COPD are around $49 billion a year in direct costs, with billions more in indirect costs. Around the globe, COPD is one of the top three causes of death, with 90% of deaths happening in low- and middle-income countries. The burden of COPD is expected to grow over time because of the aging population and continued exposure to COPD risk factors.
The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease report (or GOLD) is revised every year, translated into many languages, and used by health care workers globally. It was started in 1998, and its aim was to produce guidelines based on the best scientific evidence available that was nonbiased to be used for assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with COPD. The first report was issued in 2001. The method of producing the GOLD report was to do a search of PubMed for evidence-based, peer-reviewed studies. Those not captured by this method could be submitted for review. The science committee then meets twice a year and reviews each publication, eventually agreeing on a set of guidelines/updates.
2022 GOLD Report
For the 2022 GOLD report, 160 new references were added. Overall, the GOLD report is five chapters (more than 150 pages) giving in-depth guidance for the diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of patients with stable COPD, COPD exacerbations, and hospitalized patients.
The report suggests that COPD is being underdiagnosed.
Family physicians and internists will be seeing more and more cases as the population ages, and we need to do a better job of recognizing patients who have COPD. If possible, we should try to have spirometry available in our practices. Like any other disease, we know prevention works best so primary care physicians also need to be looking for risk factors, such as smoking history, and help patients try to reduce them if possible. Below is more explanation of the latest guidelines.
For most of us, when we learned about COPD as a disease, the terms “chronic bronchitis” and “emphysema” were emphasized. These words are no longer used as synonymous for COPD.
The disease is now described as involving chronic limitation in airflow that results from a combination of small airway disease and parenchymal destruction (emphysema). The rates of each vary from person to person and progress at different rates. Key factors that contribute to COPD disease burden include chronic inflammation, narrowing of small airways, loss of alveolar attachments, loss of elastic recoil, and mucociliary dysfunction, according to the 2022 GOLD report.
Respiratory symptoms may precede the onset of airflow limitation. COPD should be considered in any patient with dyspnea, chronic cough or sputum production, a history of recurrent lower respiratory tract infections, and risk factors for the disease.
The biggest risk factor for COPD is smoking. Other risk factors include occupational exposure, e-cigarette use, pollution, genetic factors, and comorbid conditions. Symptoms of the disease can include chest tightness, wheezing, and fatigue.
To make a diagnosis of COPD, spirometry is required, the latest GOLD report says. A postbronchodilator FEV1/FVC less than 0.70 confirms persistent airflow limitation and hence COPD. This value is used in clinical trials and forms the basis of what most treatment guidelines are derived from. It would be beneficial for any physician treating COPD patients to have easy access to spirometry. It provides the most reproducible and objective measurement of airflow limitation. Also, it was found that assessing the degree of reversibility of airflow limitation to decide therapeutic decisions is no longer recommended and thus, asking the patient to stop inhaled medications beforehand is unnecessary. To access the impact COPD has on a patient’s life beyond dyspnea, the guidelines recommend doing a disease-specific health questionnaire, such as the COPD Assessment Test (CAT).
Along with patient symptoms and history of exacerbations, spirometry is crucial for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic decisions in COPD patients, according to the GOLD guidance. The best predictor of frequent exacerbations, however, is a history of previous exacerbations. In cases where there is a discrepancy between airflow limitation and symptoms, additional testing should be considered. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) screening should be considered in younger patients (under 45 years) with perilobular emphysema, and those in areas of high AATD prevalence. Chest x-rays are not recommended in diagnosing COPD but can be helpful if other comorbidities are present. CT scan is not routinely recommended but should be used only for the detection of bronchiectasis, if the patient meets the criteria for lung cancer screening, if surgery is necessary, or if other diseases may need to be evaluated.
Pulse oximetry can be helpful in accessing degree of severity, respiratory failure, and right heart failure. Walking tests can be helpful for evaluating disability and mortality risk. Other tests that have been used but are not routinely recommended include plethysmography and diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide.
Composite scores can identify patients who are at increased risk of mortality. One such score is the BODE (Body mass, Obstruction, Dyspnea, and Exercise) method. Biomarkers are being investigated, but data are still not available to recommend their routine use.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at [email protected].
For many years, COPD has remained one of the top four leading causes of death in the United States according to CDC data. Around the world, it is responsible for about 3 million deaths annually. It is estimated that 16 million Americans are now diagnosed with COPD. However, it is commonly agreed by experts that it is widely underdiagnosed and there may be millions more suffering from this disease.
The direct costs of COPD are around $49 billion a year in direct costs, with billions more in indirect costs. Around the globe, COPD is one of the top three causes of death, with 90% of deaths happening in low- and middle-income countries. The burden of COPD is expected to grow over time because of the aging population and continued exposure to COPD risk factors.
The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease report (or GOLD) is revised every year, translated into many languages, and used by health care workers globally. It was started in 1998, and its aim was to produce guidelines based on the best scientific evidence available that was nonbiased to be used for assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with COPD. The first report was issued in 2001. The method of producing the GOLD report was to do a search of PubMed for evidence-based, peer-reviewed studies. Those not captured by this method could be submitted for review. The science committee then meets twice a year and reviews each publication, eventually agreeing on a set of guidelines/updates.
2022 GOLD Report
For the 2022 GOLD report, 160 new references were added. Overall, the GOLD report is five chapters (more than 150 pages) giving in-depth guidance for the diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of patients with stable COPD, COPD exacerbations, and hospitalized patients.
The report suggests that COPD is being underdiagnosed.
Family physicians and internists will be seeing more and more cases as the population ages, and we need to do a better job of recognizing patients who have COPD. If possible, we should try to have spirometry available in our practices. Like any other disease, we know prevention works best so primary care physicians also need to be looking for risk factors, such as smoking history, and help patients try to reduce them if possible. Below is more explanation of the latest guidelines.
For most of us, when we learned about COPD as a disease, the terms “chronic bronchitis” and “emphysema” were emphasized. These words are no longer used as synonymous for COPD.
The disease is now described as involving chronic limitation in airflow that results from a combination of small airway disease and parenchymal destruction (emphysema). The rates of each vary from person to person and progress at different rates. Key factors that contribute to COPD disease burden include chronic inflammation, narrowing of small airways, loss of alveolar attachments, loss of elastic recoil, and mucociliary dysfunction, according to the 2022 GOLD report.
Respiratory symptoms may precede the onset of airflow limitation. COPD should be considered in any patient with dyspnea, chronic cough or sputum production, a history of recurrent lower respiratory tract infections, and risk factors for the disease.
The biggest risk factor for COPD is smoking. Other risk factors include occupational exposure, e-cigarette use, pollution, genetic factors, and comorbid conditions. Symptoms of the disease can include chest tightness, wheezing, and fatigue.
To make a diagnosis of COPD, spirometry is required, the latest GOLD report says. A postbronchodilator FEV1/FVC less than 0.70 confirms persistent airflow limitation and hence COPD. This value is used in clinical trials and forms the basis of what most treatment guidelines are derived from. It would be beneficial for any physician treating COPD patients to have easy access to spirometry. It provides the most reproducible and objective measurement of airflow limitation. Also, it was found that assessing the degree of reversibility of airflow limitation to decide therapeutic decisions is no longer recommended and thus, asking the patient to stop inhaled medications beforehand is unnecessary. To access the impact COPD has on a patient’s life beyond dyspnea, the guidelines recommend doing a disease-specific health questionnaire, such as the COPD Assessment Test (CAT).
Along with patient symptoms and history of exacerbations, spirometry is crucial for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic decisions in COPD patients, according to the GOLD guidance. The best predictor of frequent exacerbations, however, is a history of previous exacerbations. In cases where there is a discrepancy between airflow limitation and symptoms, additional testing should be considered. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) screening should be considered in younger patients (under 45 years) with perilobular emphysema, and those in areas of high AATD prevalence. Chest x-rays are not recommended in diagnosing COPD but can be helpful if other comorbidities are present. CT scan is not routinely recommended but should be used only for the detection of bronchiectasis, if the patient meets the criteria for lung cancer screening, if surgery is necessary, or if other diseases may need to be evaluated.
Pulse oximetry can be helpful in accessing degree of severity, respiratory failure, and right heart failure. Walking tests can be helpful for evaluating disability and mortality risk. Other tests that have been used but are not routinely recommended include plethysmography and diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide.
Composite scores can identify patients who are at increased risk of mortality. One such score is the BODE (Body mass, Obstruction, Dyspnea, and Exercise) method. Biomarkers are being investigated, but data are still not available to recommend their routine use.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at [email protected].
62-year-old woman • dysuria • dyspareunia • urinary incontinence • Dx?
THE CASE
A 62-year-old postmenopausal woman presented to the clinic as a new patient for her annual physical examination. She reported a 9-year history of symptoms including dysuria, post-void dribbling, dyspareunia, and urinary incontinence on review of systems. Her physical examination revealed an anterior vaginal wall bulge (FIGURE). Results of a urinalysis were negative. The patient was referred to Urology for further evaluation.
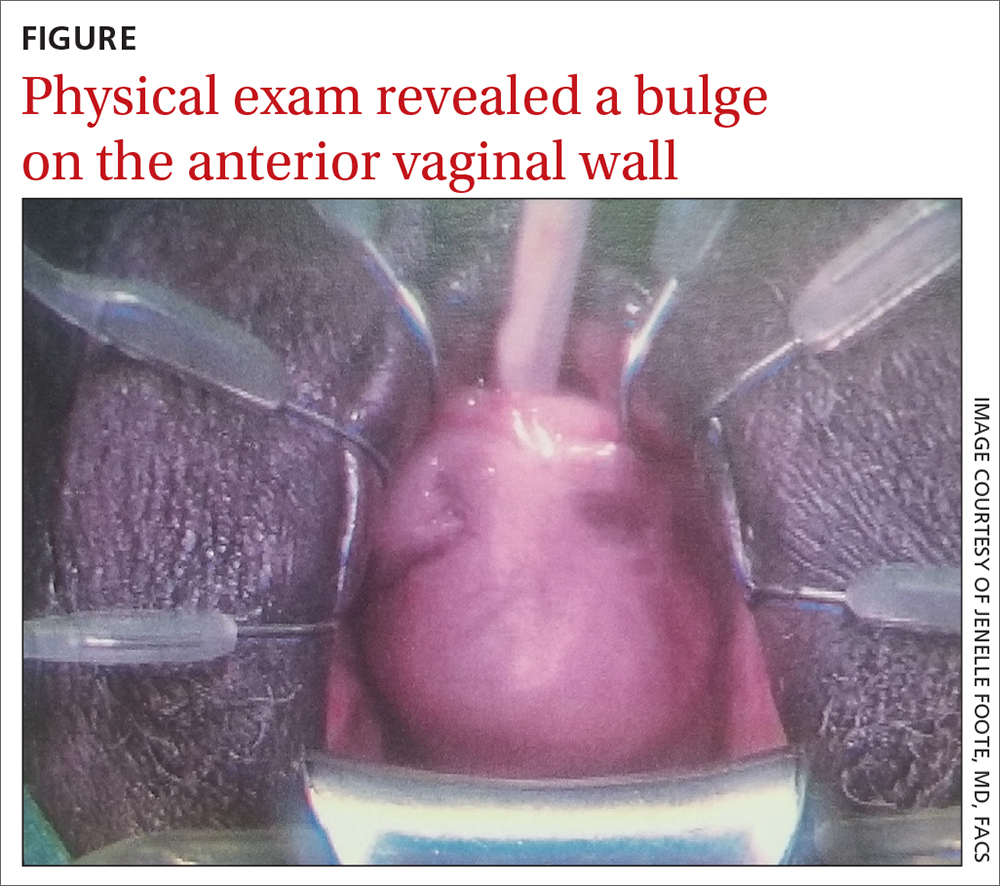
THE DIAGNOSIS
A pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan revealed a large periurethral diverticulum with a horseshoe shape.
DISCUSSION
Women are more likely than men to develop urethral diverticulum, and it can manifest at any age, usually in the third through seventh decade.4,5 It was once thought to be more common in Black women, although the literature does not support this.6 Black women are 3 times more likely to be operated on than White women to treat urethral diverticula.7
Unknown origin. Most cases of urethral diverticulum are acquired; the etiology is uncertain.8,9 The assumption is that urethral diverticulum occurs as a result of repeated infection of the periurethral glands with subsequent obstruction, abscess formation, and chronic inflammation.1,2,4 Childbirth trauma, iatrogenic causes, and urethral instrumentation have also been implicated.3,4 In rare cases of congenital urethral diverticula, the diverticula are thought to be remnants of Gartner duct cysts, and yet, incidence in the pediatric population is low.8
Diagnosis is confirmed through physical exam and imaging
The urethral diverticulum manifests anteriorly and palpation of the anterior vaginal wall may reveal a painful mass.10 A split-speculum is used for careful inspection and palpation of the anterior vaginal wall.9 If the diverticulum is found to be firm on palpation, or there is bloody urethral drainage, malignancy (although rare) must be ruled out.4,5 Refer such patients to a urologist or urogynecologist.
Radiologic imaging (eg, ultrasound,
Continue to: Nonspecific symptoms may lead to misdiagnosis
Nonspecific symptoms may lead to misdiagnosis. The symptoms associated with urethral diverticulum are diverse and linked to several differential diagnoses (TABLE).3,4,12 The most common signs and symptoms are pelvic pain, urethral mass, dyspareunia, dysuria, urinary incontinence, and post-void dribbling—all of which are considered nonspecific.3,10,11 These nonspecific symptoms (or even an absence of symptoms), along with a physician’s lack of familiarity with urethral diverticulum, can result in a misdiagnosis or even a delayed diagnosis (up to 5.2 years).3,10

Managing symptoms vs preventing recurrence
Conservative management with antibiotics, anticholinergics, and/or observation is acceptable for patients with mild symptoms and those who are pregnant or who have a current infection or serious comorbidities that preclude surgery.3,9 Complete excision of the urethral diverticulum with reconstruction is considered the most effective surgical management for symptom relief and recurrence prevention.3,4,11,14
Our patient underwent a successful transvaginal suburethral diverticulectomy.
THE TAKEAWAY
The diagnosis of female urethral diverticulum is often delayed or misdiagnosed because symptoms are diverse and nonspecific. One should have a high degree of suspicion for urethral diverticulum in patients with dysuria, dyspareunia, pelvic pain, urinary incontinence, and irritative voiding symptoms who are not responding to conservative management. Ultrasound is an appropriate first-line imaging modality. However, a pelvic MRI is the most sensitive and specific in diagnosing urethral diverticulum.12
CORRESPONDENCE
Folashade Omole, MD, FAAFP, 720 Westview Drive, Atlanta, GA 30310; [email protected]
1. Billow M, James R, Resnick K, et al. An unusual presentation of a urethral diverticulum as a vaginal wall mass: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2013;7:171. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-7-171
2. El-Nashar SA, Bacon MM, Kim-Fine S, et al. Incidence of female urethral diverticulum: a population-based analysis and literature review. Int Urogynecol J. 2014;25:73-79. doi: 10.1007/s00192-013-2155-2
3. Cameron AP. Urethral diverticulum in the female: a meta-analysis of modern series. Minerva Ginecol. 2016;68:186-210.
4. Greiman AK, Rolef J, Rovner ES. Urethral diverticulum: a systematic review. Arab J Urol. 2019;17:49-57. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2019.1589748
5. Allen D, Mishra V, Pepper W, et al. A single-center experience of symptomatic male urethral diverticula. Urology. 2007;70:650-653. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2007.06.1111
6. O’Connor E, Iatropoulou D, Hashimoto S, et al. Urethral diverticulum carcinoma in females—a case series and review of the English and Japanese literature. Transl Androl Urol. 2018;7:703-729. doi: 10.21037/tau.2018.07.08
7. Burrows LJ, Howden NL, Meyn L, et al. Surgical procedures for urethral diverticula in women in the United States, 1979-1997. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2005;16:158-161. doi: 10.1007/s00192-004-1145-9
8. Riyach O, Ahsaini M, Tazi MF, et al. Female urethral diverticulum: cases report and literature. Ann Surg Innov Res. 2014;8:1. doi: 10.1186/1750-1164-8-1
9. Antosh DD, Gutman RE. Diagnosis and management of female urethral diverticulum. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2011;17:264-271. doi: 10.1097/SPV.0b013e318234a242
10. Romanzi LJ, Groutz A, Blaivas JG. Urethral diverticulum in women: diverse presentations resulting in diagnostic delay and mismanagement. J Urol. 2000;164:428-433.
11. Reeves FA, Inman RD, Chapple CR. Management of symptomatic urethral diverticula in women: a single-centre experience. Eur Urol. 2014;66:164-172. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.02.041
12. Dwarkasing RS, Dinkelaar W, Hop WCJ, et al. MRI evaluation of urethral diverticula and differential diagnosis in symptomatic women. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197:676-682. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.6144
13. Porten S, Kielb S. Diagnosis of female diverticula using magnetic resonance imaging. Adv Urol. 2008;2008:213516. doi: 10.1155/2008/213516
14. Ockrim JL, Allen DJ, Shah PJ, et al. A tertiary experience of urethral diverticulectomy: diagnosis, imaging and surgical outcomes. BJU Int. 2009;103:1550-1554. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08348.x
THE CASE
A 62-year-old postmenopausal woman presented to the clinic as a new patient for her annual physical examination. She reported a 9-year history of symptoms including dysuria, post-void dribbling, dyspareunia, and urinary incontinence on review of systems. Her physical examination revealed an anterior vaginal wall bulge (FIGURE). Results of a urinalysis were negative. The patient was referred to Urology for further evaluation.

THE DIAGNOSIS
A pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan revealed a large periurethral diverticulum with a horseshoe shape.
DISCUSSION
Women are more likely than men to develop urethral diverticulum, and it can manifest at any age, usually in the third through seventh decade.4,5 It was once thought to be more common in Black women, although the literature does not support this.6 Black women are 3 times more likely to be operated on than White women to treat urethral diverticula.7
Unknown origin. Most cases of urethral diverticulum are acquired; the etiology is uncertain.8,9 The assumption is that urethral diverticulum occurs as a result of repeated infection of the periurethral glands with subsequent obstruction, abscess formation, and chronic inflammation.1,2,4 Childbirth trauma, iatrogenic causes, and urethral instrumentation have also been implicated.3,4 In rare cases of congenital urethral diverticula, the diverticula are thought to be remnants of Gartner duct cysts, and yet, incidence in the pediatric population is low.8
Diagnosis is confirmed through physical exam and imaging
The urethral diverticulum manifests anteriorly and palpation of the anterior vaginal wall may reveal a painful mass.10 A split-speculum is used for careful inspection and palpation of the anterior vaginal wall.9 If the diverticulum is found to be firm on palpation, or there is bloody urethral drainage, malignancy (although rare) must be ruled out.4,5 Refer such patients to a urologist or urogynecologist.
Radiologic imaging (eg, ultrasound,
Continue to: Nonspecific symptoms may lead to misdiagnosis
Nonspecific symptoms may lead to misdiagnosis. The symptoms associated with urethral diverticulum are diverse and linked to several differential diagnoses (TABLE).3,4,12 The most common signs and symptoms are pelvic pain, urethral mass, dyspareunia, dysuria, urinary incontinence, and post-void dribbling—all of which are considered nonspecific.3,10,11 These nonspecific symptoms (or even an absence of symptoms), along with a physician’s lack of familiarity with urethral diverticulum, can result in a misdiagnosis or even a delayed diagnosis (up to 5.2 years).3,10

Managing symptoms vs preventing recurrence
Conservative management with antibiotics, anticholinergics, and/or observation is acceptable for patients with mild symptoms and those who are pregnant or who have a current infection or serious comorbidities that preclude surgery.3,9 Complete excision of the urethral diverticulum with reconstruction is considered the most effective surgical management for symptom relief and recurrence prevention.3,4,11,14
Our patient underwent a successful transvaginal suburethral diverticulectomy.
THE TAKEAWAY
The diagnosis of female urethral diverticulum is often delayed or misdiagnosed because symptoms are diverse and nonspecific. One should have a high degree of suspicion for urethral diverticulum in patients with dysuria, dyspareunia, pelvic pain, urinary incontinence, and irritative voiding symptoms who are not responding to conservative management. Ultrasound is an appropriate first-line imaging modality. However, a pelvic MRI is the most sensitive and specific in diagnosing urethral diverticulum.12
CORRESPONDENCE
Folashade Omole, MD, FAAFP, 720 Westview Drive, Atlanta, GA 30310; [email protected]
THE CASE
A 62-year-old postmenopausal woman presented to the clinic as a new patient for her annual physical examination. She reported a 9-year history of symptoms including dysuria, post-void dribbling, dyspareunia, and urinary incontinence on review of systems. Her physical examination revealed an anterior vaginal wall bulge (FIGURE). Results of a urinalysis were negative. The patient was referred to Urology for further evaluation.

THE DIAGNOSIS
A pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan revealed a large periurethral diverticulum with a horseshoe shape.
DISCUSSION
Women are more likely than men to develop urethral diverticulum, and it can manifest at any age, usually in the third through seventh decade.4,5 It was once thought to be more common in Black women, although the literature does not support this.6 Black women are 3 times more likely to be operated on than White women to treat urethral diverticula.7
Unknown origin. Most cases of urethral diverticulum are acquired; the etiology is uncertain.8,9 The assumption is that urethral diverticulum occurs as a result of repeated infection of the periurethral glands with subsequent obstruction, abscess formation, and chronic inflammation.1,2,4 Childbirth trauma, iatrogenic causes, and urethral instrumentation have also been implicated.3,4 In rare cases of congenital urethral diverticula, the diverticula are thought to be remnants of Gartner duct cysts, and yet, incidence in the pediatric population is low.8
Diagnosis is confirmed through physical exam and imaging
The urethral diverticulum manifests anteriorly and palpation of the anterior vaginal wall may reveal a painful mass.10 A split-speculum is used for careful inspection and palpation of the anterior vaginal wall.9 If the diverticulum is found to be firm on palpation, or there is bloody urethral drainage, malignancy (although rare) must be ruled out.4,5 Refer such patients to a urologist or urogynecologist.
Radiologic imaging (eg, ultrasound,
Continue to: Nonspecific symptoms may lead to misdiagnosis
Nonspecific symptoms may lead to misdiagnosis. The symptoms associated with urethral diverticulum are diverse and linked to several differential diagnoses (TABLE).3,4,12 The most common signs and symptoms are pelvic pain, urethral mass, dyspareunia, dysuria, urinary incontinence, and post-void dribbling—all of which are considered nonspecific.3,10,11 These nonspecific symptoms (or even an absence of symptoms), along with a physician’s lack of familiarity with urethral diverticulum, can result in a misdiagnosis or even a delayed diagnosis (up to 5.2 years).3,10

Managing symptoms vs preventing recurrence
Conservative management with antibiotics, anticholinergics, and/or observation is acceptable for patients with mild symptoms and those who are pregnant or who have a current infection or serious comorbidities that preclude surgery.3,9 Complete excision of the urethral diverticulum with reconstruction is considered the most effective surgical management for symptom relief and recurrence prevention.3,4,11,14
Our patient underwent a successful transvaginal suburethral diverticulectomy.
THE TAKEAWAY
The diagnosis of female urethral diverticulum is often delayed or misdiagnosed because symptoms are diverse and nonspecific. One should have a high degree of suspicion for urethral diverticulum in patients with dysuria, dyspareunia, pelvic pain, urinary incontinence, and irritative voiding symptoms who are not responding to conservative management. Ultrasound is an appropriate first-line imaging modality. However, a pelvic MRI is the most sensitive and specific in diagnosing urethral diverticulum.12
CORRESPONDENCE
Folashade Omole, MD, FAAFP, 720 Westview Drive, Atlanta, GA 30310; [email protected]
1. Billow M, James R, Resnick K, et al. An unusual presentation of a urethral diverticulum as a vaginal wall mass: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2013;7:171. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-7-171
2. El-Nashar SA, Bacon MM, Kim-Fine S, et al. Incidence of female urethral diverticulum: a population-based analysis and literature review. Int Urogynecol J. 2014;25:73-79. doi: 10.1007/s00192-013-2155-2
3. Cameron AP. Urethral diverticulum in the female: a meta-analysis of modern series. Minerva Ginecol. 2016;68:186-210.
4. Greiman AK, Rolef J, Rovner ES. Urethral diverticulum: a systematic review. Arab J Urol. 2019;17:49-57. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2019.1589748
5. Allen D, Mishra V, Pepper W, et al. A single-center experience of symptomatic male urethral diverticula. Urology. 2007;70:650-653. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2007.06.1111
6. O’Connor E, Iatropoulou D, Hashimoto S, et al. Urethral diverticulum carcinoma in females—a case series and review of the English and Japanese literature. Transl Androl Urol. 2018;7:703-729. doi: 10.21037/tau.2018.07.08
7. Burrows LJ, Howden NL, Meyn L, et al. Surgical procedures for urethral diverticula in women in the United States, 1979-1997. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2005;16:158-161. doi: 10.1007/s00192-004-1145-9
8. Riyach O, Ahsaini M, Tazi MF, et al. Female urethral diverticulum: cases report and literature. Ann Surg Innov Res. 2014;8:1. doi: 10.1186/1750-1164-8-1
9. Antosh DD, Gutman RE. Diagnosis and management of female urethral diverticulum. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2011;17:264-271. doi: 10.1097/SPV.0b013e318234a242
10. Romanzi LJ, Groutz A, Blaivas JG. Urethral diverticulum in women: diverse presentations resulting in diagnostic delay and mismanagement. J Urol. 2000;164:428-433.
11. Reeves FA, Inman RD, Chapple CR. Management of symptomatic urethral diverticula in women: a single-centre experience. Eur Urol. 2014;66:164-172. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.02.041
12. Dwarkasing RS, Dinkelaar W, Hop WCJ, et al. MRI evaluation of urethral diverticula and differential diagnosis in symptomatic women. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197:676-682. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.6144
13. Porten S, Kielb S. Diagnosis of female diverticula using magnetic resonance imaging. Adv Urol. 2008;2008:213516. doi: 10.1155/2008/213516
14. Ockrim JL, Allen DJ, Shah PJ, et al. A tertiary experience of urethral diverticulectomy: diagnosis, imaging and surgical outcomes. BJU Int. 2009;103:1550-1554. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08348.x
1. Billow M, James R, Resnick K, et al. An unusual presentation of a urethral diverticulum as a vaginal wall mass: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2013;7:171. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-7-171
2. El-Nashar SA, Bacon MM, Kim-Fine S, et al. Incidence of female urethral diverticulum: a population-based analysis and literature review. Int Urogynecol J. 2014;25:73-79. doi: 10.1007/s00192-013-2155-2
3. Cameron AP. Urethral diverticulum in the female: a meta-analysis of modern series. Minerva Ginecol. 2016;68:186-210.
4. Greiman AK, Rolef J, Rovner ES. Urethral diverticulum: a systematic review. Arab J Urol. 2019;17:49-57. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2019.1589748
5. Allen D, Mishra V, Pepper W, et al. A single-center experience of symptomatic male urethral diverticula. Urology. 2007;70:650-653. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2007.06.1111
6. O’Connor E, Iatropoulou D, Hashimoto S, et al. Urethral diverticulum carcinoma in females—a case series and review of the English and Japanese literature. Transl Androl Urol. 2018;7:703-729. doi: 10.21037/tau.2018.07.08
7. Burrows LJ, Howden NL, Meyn L, et al. Surgical procedures for urethral diverticula in women in the United States, 1979-1997. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2005;16:158-161. doi: 10.1007/s00192-004-1145-9
8. Riyach O, Ahsaini M, Tazi MF, et al. Female urethral diverticulum: cases report and literature. Ann Surg Innov Res. 2014;8:1. doi: 10.1186/1750-1164-8-1
9. Antosh DD, Gutman RE. Diagnosis and management of female urethral diverticulum. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2011;17:264-271. doi: 10.1097/SPV.0b013e318234a242
10. Romanzi LJ, Groutz A, Blaivas JG. Urethral diverticulum in women: diverse presentations resulting in diagnostic delay and mismanagement. J Urol. 2000;164:428-433.
11. Reeves FA, Inman RD, Chapple CR. Management of symptomatic urethral diverticula in women: a single-centre experience. Eur Urol. 2014;66:164-172. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.02.041
12. Dwarkasing RS, Dinkelaar W, Hop WCJ, et al. MRI evaluation of urethral diverticula and differential diagnosis in symptomatic women. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197:676-682. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.6144
13. Porten S, Kielb S. Diagnosis of female diverticula using magnetic resonance imaging. Adv Urol. 2008;2008:213516. doi: 10.1155/2008/213516
14. Ockrim JL, Allen DJ, Shah PJ, et al. A tertiary experience of urethral diverticulectomy: diagnosis, imaging and surgical outcomes. BJU Int. 2009;103:1550-1554. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08348.x
Coalescing skin-colored papules
AN 8-YEAR-OLD BOY was evaluated by his family physician for a widespread rash that had first appeared on his arms 4 months earlier. Physical examination revealed 1- to 2-mm hypopigmented, smooth, and dome-shaped papules in clusters and linear arrays on the child’s back, shoulders, and extensor surfaces of both arms (FIGURE). There was no tenderness to palpation of the affected areas, but the patient complained of pruritus. Otherwise, he was in good health.
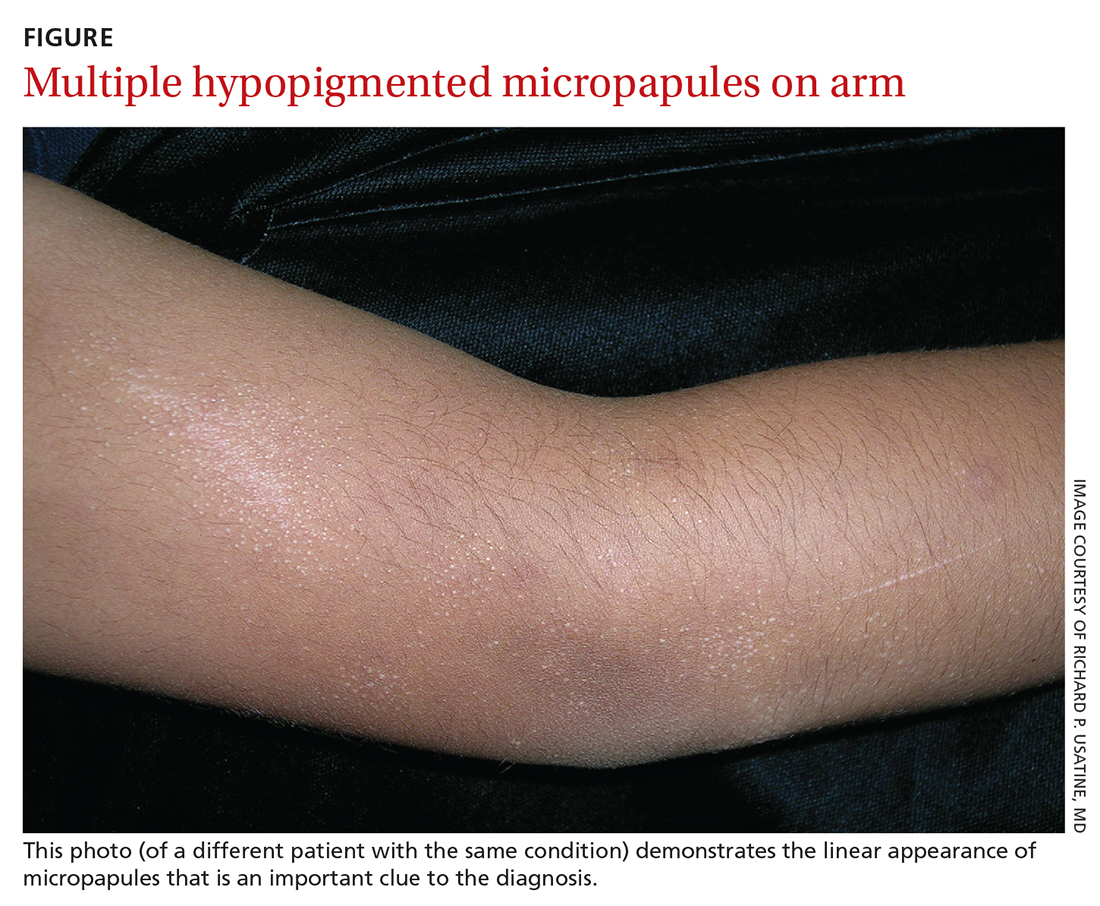
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Lichen nitidus
This clinical manifestation of multiple, hypopigmented, pinhead-sized papules is most consistent with the diagnosis of lichen nitidus.
A rare and chronic inflammatory skin condition, lichen nitidus is characterized by numerous small, skin-colored papules that are often arranged in clusters on the upper extremities, the genitalia, and the anterior trunk.1 The papules are less likely to occur on the face, lower extremities, palms, and soles. Oral mucosal and nail involvement are rare. The condition is usually asymptomatic but can sometimes be associated with pruritus.
Lichen nitidus occurs more frequently in children or young adults and has a female predominance.1 It does not exhibit a predilection of any race.2 The etiology and pathogenesis of lichen nitidus remain unclear. Genetic factors have been proposed as a potential cause; it has also been reported to be associated with Down syndrome.3
Making the Dx with dermoscopy, skin biopsy
Dermoscopy is a useful technique for diagnosing lichen nitidus. Dermoscopic features of lichen nitidus include white, well-demarcated circular areas with a brown shadow.4 Skin biopsy provides a definitive diagnosis. Lichen nitidus has a distinct histopathologic “ball and claw” appearance of rete ridges clutching a lymphohistiocytic infiltrate.1
Consider these common conditions in the differential
The differential diagnosis includes lichen spinulosus, papular eczema, lichen planus, keratosis pilaris, and verruca plana (flat warts).
Continue to: Lichen spinulosus
Lichen spinulosus lesions are similar in appearance to lichen nitidus but are grouped in patches on the neck, arms, abdomen, and buttocks.1 The Koebner phenomenon is not typically present. Lichen spinulosus lesions consist of follicular papules that may exhibit a central keratotic plug.
Papular eczema lesions lack the uniform and discrete appearance observed in lichen nitidus. Pruritus is also more likely to be present in papular eczema.
Lichen planus lesions are typically violaceous, flat, and larger in size than lichen nitidus (measuring 1 mm to 1 cm), and have characteristic Wickham striae. Oral involvement is also more suggestive of lichen planus.
Keratosis pilaris is distinguished by its much more common occurrence and perifollicular erythema.
Verruca plana, in contrast to lichen nitidus, are typically pink, flat-topped lesions. They are also larger in size (2 mm to 5 mm).
Continue to: Topical treatment can help manage the condition
Topical treatment can help manage the condition
Most patients experience spontaneous resolution of lesions within several years; treatment is primarily for symptomatic or cosmetic purposes. When pruritus is present, topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines may help (eg, hydrocortisone 2.5% cream and oral hydroxyzine). Topical calcineurin inhibitors, such as pimecrolimus cream, have also been reported as an effective therapy in children with lichen nitidus.1 In patients with generalized lichen nitidus who have not responded to topical corticosteroids, phototherapy can be used.5 There are no randomized controlled trials to assess the effectiveness of different types of treatments.
In this case, the patient was advised to start using an over-the-counter topical steroid, such as 1% hydrocortisone cream, to help control pruritus. He was scheduled for a follow-up appointment in 3 months.
1. Shiohara T, Mizukawa Y. Lichen planus and lichenoid dermatoses. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP, eds. Dermatology. 2nd ed. Elsevier Inc;2008:167-170.
2. Lapins NA, Willoughby C, Helwig EB. Lichen nitidus. A study of forty-three cases. Cutis. 1978;21:634-637.
3. Botelho LFF, de Magalhães JPJ, Ogawa MM, et al. Generalized Lichen nitidus associated with Down’s syndrome: case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:466-468. doi: 10.1590/s0365-05962012000300018
4. Malakar S, Save S, Mehta P. Brown shadow in lichen nitidus: a dermoscopic marker! Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:479-480. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_338_17
5. Synakiewicz J, Polańska A, Bowszyc-Dmochowska M, et al. Generalized lichen nitidus: a case report and review of the literature. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2016;33:488-490. doi: 10.5114/ada.2016.63890
AN 8-YEAR-OLD BOY was evaluated by his family physician for a widespread rash that had first appeared on his arms 4 months earlier. Physical examination revealed 1- to 2-mm hypopigmented, smooth, and dome-shaped papules in clusters and linear arrays on the child’s back, shoulders, and extensor surfaces of both arms (FIGURE). There was no tenderness to palpation of the affected areas, but the patient complained of pruritus. Otherwise, he was in good health.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Lichen nitidus
This clinical manifestation of multiple, hypopigmented, pinhead-sized papules is most consistent with the diagnosis of lichen nitidus.
A rare and chronic inflammatory skin condition, lichen nitidus is characterized by numerous small, skin-colored papules that are often arranged in clusters on the upper extremities, the genitalia, and the anterior trunk.1 The papules are less likely to occur on the face, lower extremities, palms, and soles. Oral mucosal and nail involvement are rare. The condition is usually asymptomatic but can sometimes be associated with pruritus.
Lichen nitidus occurs more frequently in children or young adults and has a female predominance.1 It does not exhibit a predilection of any race.2 The etiology and pathogenesis of lichen nitidus remain unclear. Genetic factors have been proposed as a potential cause; it has also been reported to be associated with Down syndrome.3
Making the Dx with dermoscopy, skin biopsy
Dermoscopy is a useful technique for diagnosing lichen nitidus. Dermoscopic features of lichen nitidus include white, well-demarcated circular areas with a brown shadow.4 Skin biopsy provides a definitive diagnosis. Lichen nitidus has a distinct histopathologic “ball and claw” appearance of rete ridges clutching a lymphohistiocytic infiltrate.1
Consider these common conditions in the differential
The differential diagnosis includes lichen spinulosus, papular eczema, lichen planus, keratosis pilaris, and verruca plana (flat warts).
Continue to: Lichen spinulosus
Lichen spinulosus lesions are similar in appearance to lichen nitidus but are grouped in patches on the neck, arms, abdomen, and buttocks.1 The Koebner phenomenon is not typically present. Lichen spinulosus lesions consist of follicular papules that may exhibit a central keratotic plug.
Papular eczema lesions lack the uniform and discrete appearance observed in lichen nitidus. Pruritus is also more likely to be present in papular eczema.
Lichen planus lesions are typically violaceous, flat, and larger in size than lichen nitidus (measuring 1 mm to 1 cm), and have characteristic Wickham striae. Oral involvement is also more suggestive of lichen planus.
Keratosis pilaris is distinguished by its much more common occurrence and perifollicular erythema.
Verruca plana, in contrast to lichen nitidus, are typically pink, flat-topped lesions. They are also larger in size (2 mm to 5 mm).
Continue to: Topical treatment can help manage the condition
Topical treatment can help manage the condition
Most patients experience spontaneous resolution of lesions within several years; treatment is primarily for symptomatic or cosmetic purposes. When pruritus is present, topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines may help (eg, hydrocortisone 2.5% cream and oral hydroxyzine). Topical calcineurin inhibitors, such as pimecrolimus cream, have also been reported as an effective therapy in children with lichen nitidus.1 In patients with generalized lichen nitidus who have not responded to topical corticosteroids, phototherapy can be used.5 There are no randomized controlled trials to assess the effectiveness of different types of treatments.
In this case, the patient was advised to start using an over-the-counter topical steroid, such as 1% hydrocortisone cream, to help control pruritus. He was scheduled for a follow-up appointment in 3 months.
AN 8-YEAR-OLD BOY was evaluated by his family physician for a widespread rash that had first appeared on his arms 4 months earlier. Physical examination revealed 1- to 2-mm hypopigmented, smooth, and dome-shaped papules in clusters and linear arrays on the child’s back, shoulders, and extensor surfaces of both arms (FIGURE). There was no tenderness to palpation of the affected areas, but the patient complained of pruritus. Otherwise, he was in good health.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Lichen nitidus
This clinical manifestation of multiple, hypopigmented, pinhead-sized papules is most consistent with the diagnosis of lichen nitidus.
A rare and chronic inflammatory skin condition, lichen nitidus is characterized by numerous small, skin-colored papules that are often arranged in clusters on the upper extremities, the genitalia, and the anterior trunk.1 The papules are less likely to occur on the face, lower extremities, palms, and soles. Oral mucosal and nail involvement are rare. The condition is usually asymptomatic but can sometimes be associated with pruritus.
Lichen nitidus occurs more frequently in children or young adults and has a female predominance.1 It does not exhibit a predilection of any race.2 The etiology and pathogenesis of lichen nitidus remain unclear. Genetic factors have been proposed as a potential cause; it has also been reported to be associated with Down syndrome.3
Making the Dx with dermoscopy, skin biopsy
Dermoscopy is a useful technique for diagnosing lichen nitidus. Dermoscopic features of lichen nitidus include white, well-demarcated circular areas with a brown shadow.4 Skin biopsy provides a definitive diagnosis. Lichen nitidus has a distinct histopathologic “ball and claw” appearance of rete ridges clutching a lymphohistiocytic infiltrate.1
Consider these common conditions in the differential
The differential diagnosis includes lichen spinulosus, papular eczema, lichen planus, keratosis pilaris, and verruca plana (flat warts).
Continue to: Lichen spinulosus
Lichen spinulosus lesions are similar in appearance to lichen nitidus but are grouped in patches on the neck, arms, abdomen, and buttocks.1 The Koebner phenomenon is not typically present. Lichen spinulosus lesions consist of follicular papules that may exhibit a central keratotic plug.
Papular eczema lesions lack the uniform and discrete appearance observed in lichen nitidus. Pruritus is also more likely to be present in papular eczema.
Lichen planus lesions are typically violaceous, flat, and larger in size than lichen nitidus (measuring 1 mm to 1 cm), and have characteristic Wickham striae. Oral involvement is also more suggestive of lichen planus.
Keratosis pilaris is distinguished by its much more common occurrence and perifollicular erythema.
Verruca plana, in contrast to lichen nitidus, are typically pink, flat-topped lesions. They are also larger in size (2 mm to 5 mm).
Continue to: Topical treatment can help manage the condition
Topical treatment can help manage the condition
Most patients experience spontaneous resolution of lesions within several years; treatment is primarily for symptomatic or cosmetic purposes. When pruritus is present, topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines may help (eg, hydrocortisone 2.5% cream and oral hydroxyzine). Topical calcineurin inhibitors, such as pimecrolimus cream, have also been reported as an effective therapy in children with lichen nitidus.1 In patients with generalized lichen nitidus who have not responded to topical corticosteroids, phototherapy can be used.5 There are no randomized controlled trials to assess the effectiveness of different types of treatments.
In this case, the patient was advised to start using an over-the-counter topical steroid, such as 1% hydrocortisone cream, to help control pruritus. He was scheduled for a follow-up appointment in 3 months.
1. Shiohara T, Mizukawa Y. Lichen planus and lichenoid dermatoses. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP, eds. Dermatology. 2nd ed. Elsevier Inc;2008:167-170.
2. Lapins NA, Willoughby C, Helwig EB. Lichen nitidus. A study of forty-three cases. Cutis. 1978;21:634-637.
3. Botelho LFF, de Magalhães JPJ, Ogawa MM, et al. Generalized Lichen nitidus associated with Down’s syndrome: case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:466-468. doi: 10.1590/s0365-05962012000300018
4. Malakar S, Save S, Mehta P. Brown shadow in lichen nitidus: a dermoscopic marker! Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:479-480. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_338_17
5. Synakiewicz J, Polańska A, Bowszyc-Dmochowska M, et al. Generalized lichen nitidus: a case report and review of the literature. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2016;33:488-490. doi: 10.5114/ada.2016.63890
1. Shiohara T, Mizukawa Y. Lichen planus and lichenoid dermatoses. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP, eds. Dermatology. 2nd ed. Elsevier Inc;2008:167-170.
2. Lapins NA, Willoughby C, Helwig EB. Lichen nitidus. A study of forty-three cases. Cutis. 1978;21:634-637.
3. Botelho LFF, de Magalhães JPJ, Ogawa MM, et al. Generalized Lichen nitidus associated with Down’s syndrome: case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:466-468. doi: 10.1590/s0365-05962012000300018
4. Malakar S, Save S, Mehta P. Brown shadow in lichen nitidus: a dermoscopic marker! Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:479-480. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_338_17
5. Synakiewicz J, Polańska A, Bowszyc-Dmochowska M, et al. Generalized lichen nitidus: a case report and review of the literature. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2016;33:488-490. doi: 10.5114/ada.2016.63890
New—and surprising—ways to approach migraine pain
Migraine headaches pose a challenge for many patients and their physicians, so new, effective approaches are always welcome. Sometimes new treatments come as total surprises. For example, who would have guessed that timolol eyedrops could be effective for acute migraine?1 Granted, the results (discussed in this issue's PURLs) are from a single randomized trial, but they look very promising.
This is not the only new and innovative treatment for migraine. Everyone knows about the heavily marketed calcium gene-related peptide antagonists, which include monoclonal antibodies and the so-called “gepants.” The monoclonal antibodies and atogepant are approved for migraine prevention, and they do a decent job (although at a high price). In randomized trials, these agents reduced migraine days per month by an average of about 1.5 to 2.5 days compared to placebo.2-5
Ubrogepant and rimegepant are approved for acute migraine treatment. In clinical trials, about 20% of patients taking ubrogepant or rimegepant were pain free at 2 hours post dose, compared to 12% to 14% taking placebo.6,7 Unfortunately, that means 80% of patients still have some pain at 2 hours. By comparison, zolmitriptan performs a bit better, with 34% of patients pain free at 2 hours.8 However, for those who can’t tolerate zolmitriptan, these newer options provide an alternative.
We also now have nonpharmacologic options. The caloric vestibular stimulation device is essentially a headset with ear probes that change temperature, alternating warm and cold. In a randomized controlled trial, it reduced monthly migraine days by 1.1 compared to placebo, from a baseline of 7.7 to 3.9 days.9 It can also be used to treat acute migraine. There is also a vagus nerve–stimulating device that reduced migraine headache severity by 20% on average in 32.2% of patients in 30 minutes. Sham treatment was as effective for 18.5% of patients, giving a number needed to treat of 6 compared to sham.10
And finally, there are complementary and alternative medicine options. Two recent randomized trials demonstrated that ≥ 2000 IU/d of vitamin D reduced monthly migraine days an average of 2 days, which is comparable to the effectiveness of the calcium gene-related peptide antagonists at a fraction of the cost.11,12 In another randomized trial, intranasal 1.5% peppermint oil was as effective as topical 4% lidocaine in providing substantial pain relief for acute migraine; about 42% of patients achieved significant relief with either treatment.13
While we may not have a perfect treatment for our patients with migraine headache, we certainly have many options to choose from.
1. Ge Y, Castelli G. Migraine relief in 20 minutes using eyedrops? J Fam Pract. 2022;71:222-223, 226.
2. Loder E, Renthal W. Calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibody treatments for migraine. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179:421-422. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.7536
3. Silberstein S, Diamond M, Hindiyeh NA, et al. Eptinezumab for the prevention of chronic migraine: efficacy and safety through 24 weeks of treatment in the phase 3 PROMISE-2 (Prevention of migraine via intravenous ALD403 safety and efficacy-2) study. J Headache Pain. 2020;21:120. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-01186-3
4. Ament M, Day K, Stauffer VL, et al. Effect of galcanezumab on severity and symptoms of migraine in phase 3 trials in patients with episodic or chronic migraine. J Headache Pain. 2021;22:6. doi: 10.1186/s10194-021-01215-9
5. Goadsby PJ, Dodick DW, Ailani J, et al. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of orally administered atogepant for the prevention of episodic migraine in adults: a double-blind, randomised phase 2b/3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:727-737. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30234-9
6. Lipton RB, Croop R, Stock EG, et al. Rimegepant, an oral calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist, for migraine. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:142-149. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1811090
7. Lipton RB, Dodick DW, Ailani J, et al. Effect of ubrogepant vs placebo on pain and the most bothersome associated symptom in the acute treatment of migraine: the ACHIEVE II randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019;322:1887-1898. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.16711
8. Bird S, Derry S, Moore R. Zolmitriptan for acute migraine attacks in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014:CD008616. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008616.pub2
9. Wilkinson D, Ade KK, Rogers LL, et al. Preventing episodic migraine with caloric vestibular stimulation: a randomized controlled trial. Headache. 2017;57:1065-1087. doi: 10.1111/head.13120
10. Grazzi L, Tassorelli C, de Tommaso M, et al; PRESTO Study Group. Practical and clinical utility of non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation (nVNS) for the acute treatment of migraine: a post hoc analysis of the randomized, sham-controlled, double-blind PRESTO trial. J Headache Pain. 2018;19:98. doi: 10.1186/s10194-018-0928-1
11. Gazerani P, Fuglsang R, Pedersen JG, et al. A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, parallel trial of vitamin D3 supplementation in adult patients with migraine. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019;35:715-723. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2018.1519503
12. Ghorbani Z, Togha M, Rafiee P, et al. Vitamin D3 might improve headache characteristics and protect against inflammation in migraine: a randomized clinical trial. Neurol Sci. 2020;41:1183-1192. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04220-8
13. Rafieian-Kopaei M, Hasanpour-Dehkordi A, Lorigooini Z, et al. Comparing the effect of intranasal lidocaine 4% with peppermint essential oil drop 1.5% on migraine attacks: a double-blind clinical trial. Int J Prev Med. 2019;10:121. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_530_17
Migraine headaches pose a challenge for many patients and their physicians, so new, effective approaches are always welcome. Sometimes new treatments come as total surprises. For example, who would have guessed that timolol eyedrops could be effective for acute migraine?1 Granted, the results (discussed in this issue's PURLs) are from a single randomized trial, but they look very promising.
This is not the only new and innovative treatment for migraine. Everyone knows about the heavily marketed calcium gene-related peptide antagonists, which include monoclonal antibodies and the so-called “gepants.” The monoclonal antibodies and atogepant are approved for migraine prevention, and they do a decent job (although at a high price). In randomized trials, these agents reduced migraine days per month by an average of about 1.5 to 2.5 days compared to placebo.2-5
Ubrogepant and rimegepant are approved for acute migraine treatment. In clinical trials, about 20% of patients taking ubrogepant or rimegepant were pain free at 2 hours post dose, compared to 12% to 14% taking placebo.6,7 Unfortunately, that means 80% of patients still have some pain at 2 hours. By comparison, zolmitriptan performs a bit better, with 34% of patients pain free at 2 hours.8 However, for those who can’t tolerate zolmitriptan, these newer options provide an alternative.
We also now have nonpharmacologic options. The caloric vestibular stimulation device is essentially a headset with ear probes that change temperature, alternating warm and cold. In a randomized controlled trial, it reduced monthly migraine days by 1.1 compared to placebo, from a baseline of 7.7 to 3.9 days.9 It can also be used to treat acute migraine. There is also a vagus nerve–stimulating device that reduced migraine headache severity by 20% on average in 32.2% of patients in 30 minutes. Sham treatment was as effective for 18.5% of patients, giving a number needed to treat of 6 compared to sham.10
And finally, there are complementary and alternative medicine options. Two recent randomized trials demonstrated that ≥ 2000 IU/d of vitamin D reduced monthly migraine days an average of 2 days, which is comparable to the effectiveness of the calcium gene-related peptide antagonists at a fraction of the cost.11,12 In another randomized trial, intranasal 1.5% peppermint oil was as effective as topical 4% lidocaine in providing substantial pain relief for acute migraine; about 42% of patients achieved significant relief with either treatment.13
While we may not have a perfect treatment for our patients with migraine headache, we certainly have many options to choose from.
Migraine headaches pose a challenge for many patients and their physicians, so new, effective approaches are always welcome. Sometimes new treatments come as total surprises. For example, who would have guessed that timolol eyedrops could be effective for acute migraine?1 Granted, the results (discussed in this issue's PURLs) are from a single randomized trial, but they look very promising.
This is not the only new and innovative treatment for migraine. Everyone knows about the heavily marketed calcium gene-related peptide antagonists, which include monoclonal antibodies and the so-called “gepants.” The monoclonal antibodies and atogepant are approved for migraine prevention, and they do a decent job (although at a high price). In randomized trials, these agents reduced migraine days per month by an average of about 1.5 to 2.5 days compared to placebo.2-5
Ubrogepant and rimegepant are approved for acute migraine treatment. In clinical trials, about 20% of patients taking ubrogepant or rimegepant were pain free at 2 hours post dose, compared to 12% to 14% taking placebo.6,7 Unfortunately, that means 80% of patients still have some pain at 2 hours. By comparison, zolmitriptan performs a bit better, with 34% of patients pain free at 2 hours.8 However, for those who can’t tolerate zolmitriptan, these newer options provide an alternative.
We also now have nonpharmacologic options. The caloric vestibular stimulation device is essentially a headset with ear probes that change temperature, alternating warm and cold. In a randomized controlled trial, it reduced monthly migraine days by 1.1 compared to placebo, from a baseline of 7.7 to 3.9 days.9 It can also be used to treat acute migraine. There is also a vagus nerve–stimulating device that reduced migraine headache severity by 20% on average in 32.2% of patients in 30 minutes. Sham treatment was as effective for 18.5% of patients, giving a number needed to treat of 6 compared to sham.10
And finally, there are complementary and alternative medicine options. Two recent randomized trials demonstrated that ≥ 2000 IU/d of vitamin D reduced monthly migraine days an average of 2 days, which is comparable to the effectiveness of the calcium gene-related peptide antagonists at a fraction of the cost.11,12 In another randomized trial, intranasal 1.5% peppermint oil was as effective as topical 4% lidocaine in providing substantial pain relief for acute migraine; about 42% of patients achieved significant relief with either treatment.13
While we may not have a perfect treatment for our patients with migraine headache, we certainly have many options to choose from.
1. Ge Y, Castelli G. Migraine relief in 20 minutes using eyedrops? J Fam Pract. 2022;71:222-223, 226.
2. Loder E, Renthal W. Calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibody treatments for migraine. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179:421-422. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.7536
3. Silberstein S, Diamond M, Hindiyeh NA, et al. Eptinezumab for the prevention of chronic migraine: efficacy and safety through 24 weeks of treatment in the phase 3 PROMISE-2 (Prevention of migraine via intravenous ALD403 safety and efficacy-2) study. J Headache Pain. 2020;21:120. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-01186-3
4. Ament M, Day K, Stauffer VL, et al. Effect of galcanezumab on severity and symptoms of migraine in phase 3 trials in patients with episodic or chronic migraine. J Headache Pain. 2021;22:6. doi: 10.1186/s10194-021-01215-9
5. Goadsby PJ, Dodick DW, Ailani J, et al. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of orally administered atogepant for the prevention of episodic migraine in adults: a double-blind, randomised phase 2b/3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:727-737. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30234-9
6. Lipton RB, Croop R, Stock EG, et al. Rimegepant, an oral calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist, for migraine. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:142-149. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1811090
7. Lipton RB, Dodick DW, Ailani J, et al. Effect of ubrogepant vs placebo on pain and the most bothersome associated symptom in the acute treatment of migraine: the ACHIEVE II randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019;322:1887-1898. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.16711
8. Bird S, Derry S, Moore R. Zolmitriptan for acute migraine attacks in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014:CD008616. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008616.pub2
9. Wilkinson D, Ade KK, Rogers LL, et al. Preventing episodic migraine with caloric vestibular stimulation: a randomized controlled trial. Headache. 2017;57:1065-1087. doi: 10.1111/head.13120
10. Grazzi L, Tassorelli C, de Tommaso M, et al; PRESTO Study Group. Practical and clinical utility of non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation (nVNS) for the acute treatment of migraine: a post hoc analysis of the randomized, sham-controlled, double-blind PRESTO trial. J Headache Pain. 2018;19:98. doi: 10.1186/s10194-018-0928-1
11. Gazerani P, Fuglsang R, Pedersen JG, et al. A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, parallel trial of vitamin D3 supplementation in adult patients with migraine. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019;35:715-723. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2018.1519503
12. Ghorbani Z, Togha M, Rafiee P, et al. Vitamin D3 might improve headache characteristics and protect against inflammation in migraine: a randomized clinical trial. Neurol Sci. 2020;41:1183-1192. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04220-8
13. Rafieian-Kopaei M, Hasanpour-Dehkordi A, Lorigooini Z, et al. Comparing the effect of intranasal lidocaine 4% with peppermint essential oil drop 1.5% on migraine attacks: a double-blind clinical trial. Int J Prev Med. 2019;10:121. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_530_17
1. Ge Y, Castelli G. Migraine relief in 20 minutes using eyedrops? J Fam Pract. 2022;71:222-223, 226.
2. Loder E, Renthal W. Calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibody treatments for migraine. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179:421-422. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.7536
3. Silberstein S, Diamond M, Hindiyeh NA, et al. Eptinezumab for the prevention of chronic migraine: efficacy and safety through 24 weeks of treatment in the phase 3 PROMISE-2 (Prevention of migraine via intravenous ALD403 safety and efficacy-2) study. J Headache Pain. 2020;21:120. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-01186-3
4. Ament M, Day K, Stauffer VL, et al. Effect of galcanezumab on severity and symptoms of migraine in phase 3 trials in patients with episodic or chronic migraine. J Headache Pain. 2021;22:6. doi: 10.1186/s10194-021-01215-9
5. Goadsby PJ, Dodick DW, Ailani J, et al. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of orally administered atogepant for the prevention of episodic migraine in adults: a double-blind, randomised phase 2b/3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:727-737. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30234-9
6. Lipton RB, Croop R, Stock EG, et al. Rimegepant, an oral calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist, for migraine. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:142-149. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1811090
7. Lipton RB, Dodick DW, Ailani J, et al. Effect of ubrogepant vs placebo on pain and the most bothersome associated symptom in the acute treatment of migraine: the ACHIEVE II randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019;322:1887-1898. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.16711
8. Bird S, Derry S, Moore R. Zolmitriptan for acute migraine attacks in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014:CD008616. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008616.pub2
9. Wilkinson D, Ade KK, Rogers LL, et al. Preventing episodic migraine with caloric vestibular stimulation: a randomized controlled trial. Headache. 2017;57:1065-1087. doi: 10.1111/head.13120
10. Grazzi L, Tassorelli C, de Tommaso M, et al; PRESTO Study Group. Practical and clinical utility of non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation (nVNS) for the acute treatment of migraine: a post hoc analysis of the randomized, sham-controlled, double-blind PRESTO trial. J Headache Pain. 2018;19:98. doi: 10.1186/s10194-018-0928-1
11. Gazerani P, Fuglsang R, Pedersen JG, et al. A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, parallel trial of vitamin D3 supplementation in adult patients with migraine. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019;35:715-723. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2018.1519503
12. Ghorbani Z, Togha M, Rafiee P, et al. Vitamin D3 might improve headache characteristics and protect against inflammation in migraine: a randomized clinical trial. Neurol Sci. 2020;41:1183-1192. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04220-8
13. Rafieian-Kopaei M, Hasanpour-Dehkordi A, Lorigooini Z, et al. Comparing the effect of intranasal lidocaine 4% with peppermint essential oil drop 1.5% on migraine attacks: a double-blind clinical trial. Int J Prev Med. 2019;10:121. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_530_17
How to better identify and manage women with elevated breast cancer risk
Breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women in the United States; it is estimated that there will be 287,850 new cases of breast cancer in the United States during 2022 with 43,250 deaths.1 Lives are extended and saved every day because of a robust arsenal of treatments and interventions available to those who have been given a diagnosis of breast cancer. And, of course, lives are also extended and saved when we identify women at risk and provide early interventions. But in busy offices where time is short and there are competing demands on our time, proper assessment of a woman’s risk of breast cancer does not always happen. As a result, women with a higher risk of breast cancer may not be getting appropriate management.2,3
Familiarizing yourself with several risk-assessment tools and knowing when genetic testing is needed can make a big difference. Knowing the timing of mammograms and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for women deemed to be at high risk is also key. The following review employs a case-based approach (with an accompanying ALGORITHM) to illustrate how best to identify women who are at heightened risk of breast cancer and maximize their care. We also discuss the chemoprophylaxis regimens that may be used for those at increased risk.
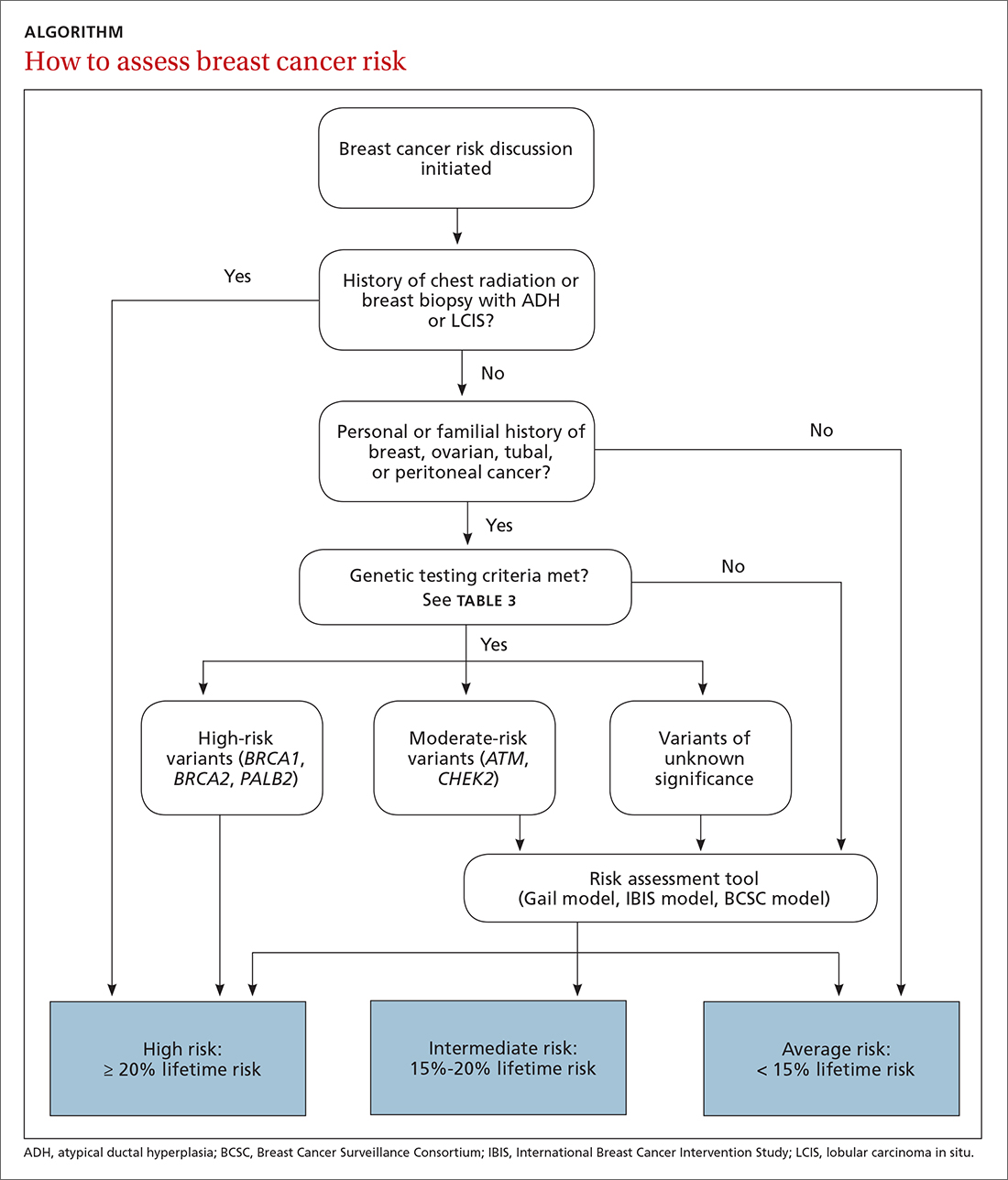
CASE
Rachel P, age 37, presents to establish care. She has an Ashkenazi Jewish background and wonders if she should start doing breast cancer screening before age 40. She has 2 children, ages 4 years and 2 years. Her maternal aunt had unilateral breast cancer at age 54, and her maternal grandmother died of ovarian cancer at age 65.
Risk assessment
The risk assessment process (see ALGORITHM) must start with either the clinician or the patient initiating the discussion about breast cancer risk. The clinician may initiate the discussion with a new patient or at an annual physical examination. The patient may start the discussion because they are experiencing new breast symptoms, have anxiety about developing breast cancer, or have a family member with a new cancer diagnosis.
Risk factors. There are single factors that convey enough risk to automatically designate the patient as high risk (see TABLE 14-9). These factors include having a history of chest radiation between the ages of 10 and 30, a history of breast biopsy with either lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) or atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH), past breast and/or ovarian cancer, and either a family or personal history of a high penetrant genetic variant for breast cancer.4-9
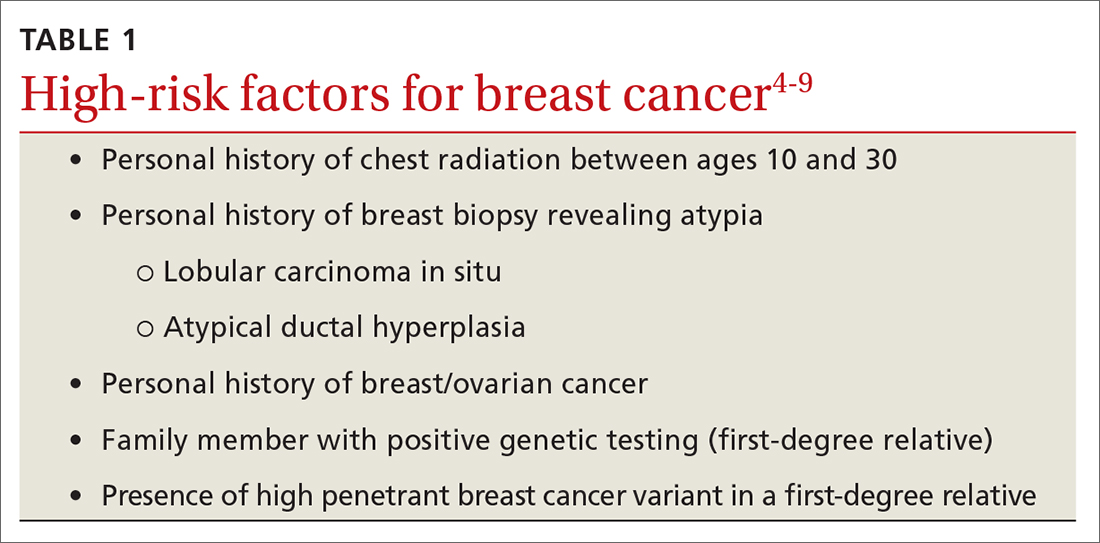
In women with previous chest radiation, breast cancer risk correlates with the total dose of radiation.5 For women with a personal history of breast cancer, the younger the age at diagnosis, the higher the risk of contralateral breast cancer.5 Precancerous changes such as ADH, LCIS, and ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) also confer moderate increases in risk. Women with these diagnoses will commonly have follow-up with specialists.
Risk assessment tools. There are several models available to assess a woman’s breast cancer risk (see TABLE 210-12). The Gail model (https://bcrisktool.cancer.gov/) is the oldest, quickest, and most widely known. However, the Gail model only accounts for first-degree relatives diagnosed with breast cancer, may underpredict risk in women with a more extensive family history, and has not been studied in women younger than 35. The International Breast Cancer Intervention Study (IBIS) Risk Evaluation Tool (https://ibis-risk-calculator.magview.com/), commonly referred to as the Tyrer-Cuzick model, incorporates second-degree relatives into the prediction model—although women may not know their full family history. Both the IBIS and the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) model (https://tools.bcsc-scc.org/BC5yearRisk/intro.htm) include breast density in the prediction algorithm. The choice of tool depends on clinician comfort and individual patient risk factors. There is no evidence that one model is better than another.10-12

Continue to: CASE
CASE
Ms. P’s clinician starts with an assessment using the Gail model. However, when the result comes back with average risk, the clinician decides to follow up with the Tyrer-Cuzick model in order to incorporate Ms. P’s multiple second-degree relatives with breast and ovarian cancer. (The BCSC model was not used because it only includes first-degree relatives.)
Genetic testing
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend genetic testing if a woman has a first- or second-degree relative with pancreatic cancer, metastatic prostate cancer, male breast cancer, breast cancer at age 45 or younger, 2 or more breast cancers in a single person, 2 or more people on the same side of the family with at least 1 diagnosed at age 50 or younger, or any relative with ovarian cancer (see TABLE 3).7 Before ordering genetic testing, it is useful to refer the patient to a genetic counselor for a thorough discussion of options.

Results of genetic testing may include high-risk variants, moderate-risk variants, and variants of unknown significance (VUS), or be negative for any variants. High-risk variants for breast cancer include BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, and cancer syndrome variants such as TP53, PTEN, STK11, and CDH1.5,6,9,13-15 These high-risk variants confer sufficient risk that women with these mutations are automatically categorized in the high-risk group. It is estimated that high-risk variants account for only 25% of the genetic risk for breast cancer.16
BRCA1/2 and PTEN mutations confer greater than 80% lifetime risk, while other high-risk variants such as TP53, CDH1, and STK11 confer risks between 25% and 40%. These variants are also associated with cancers of other organs, depending on the mutation.17
Moderate-risk variants—ATM and CHEK2—do not confer sufficient risk to elevate women into the high-risk group. However, they do qualify these intermediate-risk women to participate in a specialized management strategy.5,9,13,18
VUS are those for which the associated risk is unclear, but more research may be done to categorize the risk.9 The clinical management of women with VUS usually entails close monitoring.
In an effort to better characterize breast cancer risk using a combination of pathogenic variants found in broad multi-gene cancer predisposition panels, researchers have developed a method to combine risks in a “polygenic risk score” (PRS) that can be used to counsel women (see “What is a polygenic risk score for breast cancer?” on page 203).19-21PRS predicts an additional 18% of genetic risk in women of European descent.21
SIDEBAR
What is a polygenic risk score for breast cancer?
- A polygenic risk score (PRS) is a mathematical method to combine results from a variety of different single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs; ie, single base pair variants) into a prediction tool that can estimate a woman’s lifetime risk of breast cancer.
- A PRS may be most accurate in determining risk for women with intermediate pathogenic variants, such as ATM and CHEK2. 19,20
- PRS has not been studied in non-White women.21
Continue to: CASE
CASE
Using the assessment results, the clinician talks to Ms. P about her lifetime risk for breast cancer. The Gail model indicates her lifetime risk is 13.3%, just slightly higher than the average (12.5%), and her 5-year risk is 0.5% (average, 0.4%). The IBIS or Tyrer-Cuzick model, which takes into account her second-degree relatives with breast and ovarian cancer and her Ashkenazi ethnicity (which confers increased risk due to elevated risk of BRCA mutations), predicts her lifetime risk of breast cancer to be 20.4%. This categorizes Ms. P as high risk.
Enhanced screening recommendations for women at high risk
TABLE 48,13,22 summarizes screening recommendations for women deemed to be at high risk for breast cancer. The American Cancer Society (ACS), NCCN, and the American College of Radiology (ACR) recommend that women with at least a 20% lifetime risk have yearly magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and mammography (staggered so that the patient has 1 test every 6 months) starting 10 years before the age of onset for the youngest affected relative but not before age 30.8 For carriers of high-risk (as well as intermediate-risk) genes, NCCN recommends annual MRI screening starting at age 40.13BRCA1/2 screening includes annual MRI starting at age 25 and annual mammography every 6 months starting at age 30.22 Clinicians should counsel women with moderate risk factors (elevated breast density; personal history of ADH, LCIS, or DCIS) about the potential risks and benefits of enhanced screening and chemoprophylaxis.
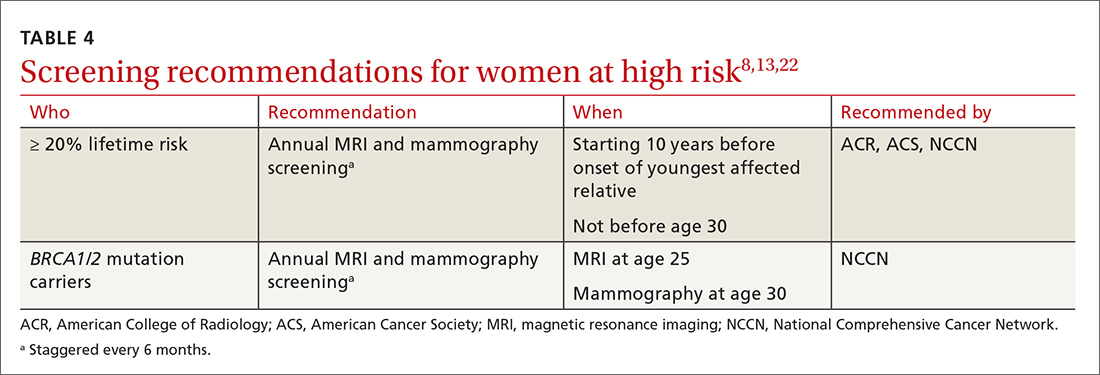
Risk-reduction strategies
Chemoprophylaxis
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that all women at increased risk for breast cancer consider chemoprophylaxis (B recommendation)23 based on convincing evidence that 5 years of treatment with either a synthetic estrogen reuptake modulator (SERM) or an aromatase inhibitor (AI) decreases the incidence of estrogen receptor positive breast cancers. (See TABLE 57,23,24 for absolute risk reduction.) There is no benefit for chemoprophylaxis in women at average risk (D recommendation).23 It is unclear whether chemoprophylaxis is indicated in women with moderate increased risk (ie, who do not meet the 20% lifetime risk criteria). Chemoprophylaxis may not be effective in women with BRCA1 mutations, as they often develop triple-negative breast cancers.
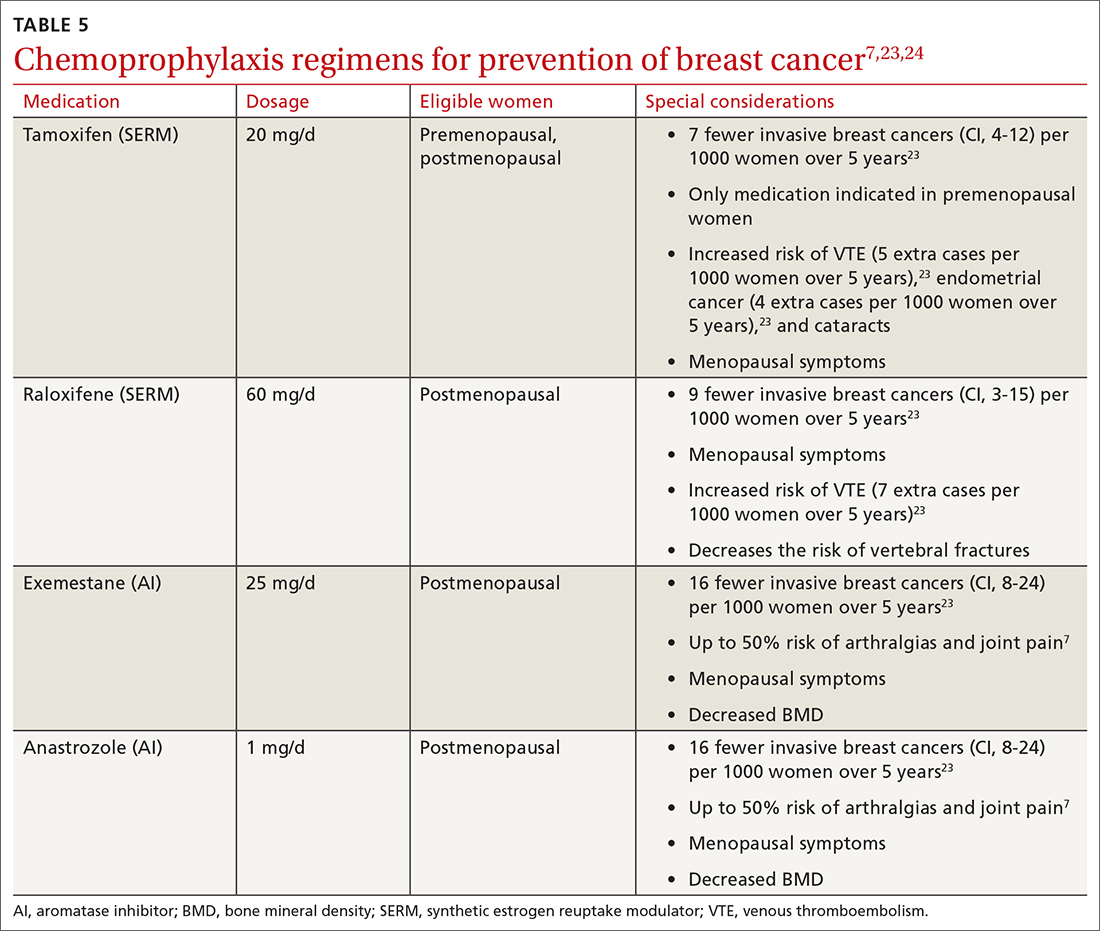
Accurate risk assessment and shared decision-making enable the clinician and patient to discuss the potential risks and benefits of chemoprophylaxis.7,24 The USPSTF did not find that any 1 risk prediction tool was better than another to identify women who should be counseled about chemoprophylaxis. Clinicians should counsel all women taking AIs about optimizing bone health with adequate calcium and vitamin D intake and routine bone density tests.
Surgical risk reduction
The NCCN guidelines state that risk-reducing bilateral mastectomy is reserved for individuals with high-risk gene variants and individuals with prior chest radiation between ages 10 and 30.25 NCCN also recommends discussing risk-reducing mastectomy with all women with BRCA mutations.22
Bilateral mastectomy is the most effective method to reduce breast cancer risk and should be discussed after age 25 in women with BRCA mutations and at least 8 years after chest radiation is completed.26 There is a reduction in breast cancer incidence of 90%.25 Breast imaging for screening (mammography or MRI) is not indicated after risk-reducing mastectomy. However, clinical breast examinations of the surgical site are important, because there is a small risk of developing breast cancer in that area.26
Risk-reducing oophorectomy is the standard of care for women with BRCA mutations to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer. It can also reduce the risk of breast cancer in women with BRCA mutations.27
Continue to: CASE
CASE
Based on her risk assessment results, family history, and genetic heritage, Ms. P qualifies for referral to a genetic counselor for discussion of BRCA testing. The clinician discusses adding annual MRI to Ms. P’s breast cancer screening regimen, based on ACS, NCCN, and ACR recommendations, due to her 20.4% lifetime risk. Discussion of whether and when to start chemoprophylaxis is typically based on breast cancer risk, projected benefit, and the potential impact of medication adverse effects. A high-risk woman is eligible for 5 years of chemoprophylaxis (tamoxifen if premenopausal) based on her lifetime risk. The clinician discusses timing with Ms. P, and even though she is finished with childbearing, she would like to wait until she is age 45, which is before the age at which her aunt was given a diagnosis of breast cancer.
Conclusion
Primary care clinicians are well positioned to identify women with an elevated risk of breast cancer and refer them for enhanced screening and chemoprophylaxis (see ALGORITHM). Shared decision-making with the inclusion of patient decision aids (https://decisionaid.ohri.ca/AZsearch.php?criteria=breast+cancer) about genetic testing, chemoprophylaxis, and prophylactic mastectomy or oophorectomy may help women at intermediate or high risk of breast cancer feel empowered to make decisions about their breast—and overall—health.
CORRESPONDENCE
Sarina Schrager, MD, MS, Professor, Department of Family Medicine and Community Health, University of Wisconsin, 1100 Delaplaine Court, Madison, WI 53715; [email protected]
1. National Cancer Institute. Cancer stat facts: female breast cancer. Accessed May 13, 2022. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html
2. Guerra CE, Sherman M, Armstrong K. Diffusion of breast cancer risk assessment in primary care. J Am Board Fam Med. 2009;22:272-279. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2009.03.080153
3. Hamilton JG, Abdiwahab E, Edwards HM, et al. Primary care providers’ cancer genetic testing-related knowledge, attitudes, and communication behaviors: a systematic review and research agenda. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:315-324. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3943-4
4. Eden KB, Ivlev I, Bensching KL, et al. Use of an online breast cancer risk assessment and patient decision aid in primary care practices. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2020;29:763-769. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2019.8143
5. Kleibl Z, Kristensen VN. Women at high risk of breast cancer: molecular characteristics, clinical presentation and management. Breast. 2016;28:136-44. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2016.05.006
6. Sciaraffa T, Guido B, Khan SA, et al. Breast cancer risk assessment and management programs: a practical guide. Breast J. 2020;26:1556-1564. doi: 10.1111/tbj.13967
7. Farkas A, Vanderberg R, Merriam S, et al. Breast cancer chemoprevention: a practical guide for the primary care provider. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2020;29:46-56. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2018.7643
8. McClintock AH, Golob AL, Laya MB. Breast cancer risk assessment: a step-wise approach for primary care providers on the front lines of shared decision making. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95:1268-1275. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.04.017
9. Catana A, Apostu AP, Antemie RG. Multi gene panel testing for hereditary breast cancer - is it ready to be used? Med Pharm Rep. 2019;92:220-225. doi: 10.15386/mpr-1083
10. Barke LD, Freivogel ME. Breast cancer risk assessment models and high-risk screening. Radiol Clin North Am. 2017;55:457-474. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2016.12.013
11. Amir E, Freedman OC, Seruga B, et al. Assessing women at high risk of breast cancer: a review of risk assessment models. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102:680-91. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djq088
12. Kim G, Bahl M. Assessing risk of breast cancer: a review of risk prediction models. J Breast Imaging. 2021;3:144-155. doi: 10.1093/jbi/wbab001
13. Narod SA. Which genes for hereditary breast cancer? N Engl J Med. 2021;384:471-473. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2035083
14. Couch FJ, Shimelis H, Hu C, et al. Associations between cancer predisposition testing panel genes and breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1190-1196. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0424
15. Obeid EI, Hall MJ, Daly MB. Multigene panel testing and breast cancer risk: is it time to scale down? JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1176-1177. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0342
16. Michailidou K, Lindström S, Dennis J, et al. Association analysis identifies 65 new breast cancer risk loci. Nature. 2017;551:92-94. doi: 10.1038/nature24284
17. Shiovitz S, Korde LA. Genetics of breast cancer: a topic in evolution. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:1291-1299. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv022
18. Hu C, Hart SN, Gnanaolivu R, et al. A population-based study of genes previously implicated in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:440-451. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2005936
19. Gao C, Polley EC, Hart SN, et al. Risk of breast cancer among carriers of pathogenic variants in breast cancer predisposition genes varies by polygenic risk score. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:2564-2573. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01992
20. Gallagher S, Hughes E, Wagner S, et al. Association of a polygenic risk score with breast cancer among women carriers of high- and moderate-risk breast cancer genes. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:e208501. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.8501
21. Yanes T, Young MA, Meiser B, et al. Clinical applications of polygenic breast cancer risk: a critical review and perspectives of an emerging field. Breast Cancer Res. 2020;22:21. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01260-3
22. Schrager S, Torell E, Ledford K, et al. Managing a woman with BRCA mutations? Shared decision-making is key. J Fam Pract. 2020;69:237-243
23. US Preventive Services Task Force; Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al. Medication use to reduce risk of breast cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2019;322:857-867. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.11885
24. Pruthi S, Heisey RE, Bevers TB. Chemoprevention for breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2015;22:3230-3235. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4715-9
25. Britt KL, Cuzick J, Phillips KA. Key steps for effective breast cancer prevention. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20:417-436. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0266-x
26. Jatoi I, Kemp Z. Risk-reducing mastectomy. JAMA. 2021;325:1781-1782. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.22414
27. Choi Y, Terry MB, Daly MB, et al. Association of risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy with breast cancer risk in women with BRCA1 and BRCA2 pathogenic variants. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7:585-592. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.7995
Breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women in the United States; it is estimated that there will be 287,850 new cases of breast cancer in the United States during 2022 with 43,250 deaths.1 Lives are extended and saved every day because of a robust arsenal of treatments and interventions available to those who have been given a diagnosis of breast cancer. And, of course, lives are also extended and saved when we identify women at risk and provide early interventions. But in busy offices where time is short and there are competing demands on our time, proper assessment of a woman’s risk of breast cancer does not always happen. As a result, women with a higher risk of breast cancer may not be getting appropriate management.2,3
Familiarizing yourself with several risk-assessment tools and knowing when genetic testing is needed can make a big difference. Knowing the timing of mammograms and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for women deemed to be at high risk is also key. The following review employs a case-based approach (with an accompanying ALGORITHM) to illustrate how best to identify women who are at heightened risk of breast cancer and maximize their care. We also discuss the chemoprophylaxis regimens that may be used for those at increased risk.

CASE
Rachel P, age 37, presents to establish care. She has an Ashkenazi Jewish background and wonders if she should start doing breast cancer screening before age 40. She has 2 children, ages 4 years and 2 years. Her maternal aunt had unilateral breast cancer at age 54, and her maternal grandmother died of ovarian cancer at age 65.
Risk assessment
The risk assessment process (see ALGORITHM) must start with either the clinician or the patient initiating the discussion about breast cancer risk. The clinician may initiate the discussion with a new patient or at an annual physical examination. The patient may start the discussion because they are experiencing new breast symptoms, have anxiety about developing breast cancer, or have a family member with a new cancer diagnosis.
Risk factors. There are single factors that convey enough risk to automatically designate the patient as high risk (see TABLE 14-9). These factors include having a history of chest radiation between the ages of 10 and 30, a history of breast biopsy with either lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) or atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH), past breast and/or ovarian cancer, and either a family or personal history of a high penetrant genetic variant for breast cancer.4-9

In women with previous chest radiation, breast cancer risk correlates with the total dose of radiation.5 For women with a personal history of breast cancer, the younger the age at diagnosis, the higher the risk of contralateral breast cancer.5 Precancerous changes such as ADH, LCIS, and ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) also confer moderate increases in risk. Women with these diagnoses will commonly have follow-up with specialists.
Risk assessment tools. There are several models available to assess a woman’s breast cancer risk (see TABLE 210-12). The Gail model (https://bcrisktool.cancer.gov/) is the oldest, quickest, and most widely known. However, the Gail model only accounts for first-degree relatives diagnosed with breast cancer, may underpredict risk in women with a more extensive family history, and has not been studied in women younger than 35. The International Breast Cancer Intervention Study (IBIS) Risk Evaluation Tool (https://ibis-risk-calculator.magview.com/), commonly referred to as the Tyrer-Cuzick model, incorporates second-degree relatives into the prediction model—although women may not know their full family history. Both the IBIS and the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) model (https://tools.bcsc-scc.org/BC5yearRisk/intro.htm) include breast density in the prediction algorithm. The choice of tool depends on clinician comfort and individual patient risk factors. There is no evidence that one model is better than another.10-12

Continue to: CASE
CASE
Ms. P’s clinician starts with an assessment using the Gail model. However, when the result comes back with average risk, the clinician decides to follow up with the Tyrer-Cuzick model in order to incorporate Ms. P’s multiple second-degree relatives with breast and ovarian cancer. (The BCSC model was not used because it only includes first-degree relatives.)
Genetic testing
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend genetic testing if a woman has a first- or second-degree relative with pancreatic cancer, metastatic prostate cancer, male breast cancer, breast cancer at age 45 or younger, 2 or more breast cancers in a single person, 2 or more people on the same side of the family with at least 1 diagnosed at age 50 or younger, or any relative with ovarian cancer (see TABLE 3).7 Before ordering genetic testing, it is useful to refer the patient to a genetic counselor for a thorough discussion of options.

Results of genetic testing may include high-risk variants, moderate-risk variants, and variants of unknown significance (VUS), or be negative for any variants. High-risk variants for breast cancer include BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, and cancer syndrome variants such as TP53, PTEN, STK11, and CDH1.5,6,9,13-15 These high-risk variants confer sufficient risk that women with these mutations are automatically categorized in the high-risk group. It is estimated that high-risk variants account for only 25% of the genetic risk for breast cancer.16
BRCA1/2 and PTEN mutations confer greater than 80% lifetime risk, while other high-risk variants such as TP53, CDH1, and STK11 confer risks between 25% and 40%. These variants are also associated with cancers of other organs, depending on the mutation.17
Moderate-risk variants—ATM and CHEK2—do not confer sufficient risk to elevate women into the high-risk group. However, they do qualify these intermediate-risk women to participate in a specialized management strategy.5,9,13,18
VUS are those for which the associated risk is unclear, but more research may be done to categorize the risk.9 The clinical management of women with VUS usually entails close monitoring.
In an effort to better characterize breast cancer risk using a combination of pathogenic variants found in broad multi-gene cancer predisposition panels, researchers have developed a method to combine risks in a “polygenic risk score” (PRS) that can be used to counsel women (see “What is a polygenic risk score for breast cancer?” on page 203).19-21PRS predicts an additional 18% of genetic risk in women of European descent.21
SIDEBAR
What is a polygenic risk score for breast cancer?
- A polygenic risk score (PRS) is a mathematical method to combine results from a variety of different single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs; ie, single base pair variants) into a prediction tool that can estimate a woman’s lifetime risk of breast cancer.
- A PRS may be most accurate in determining risk for women with intermediate pathogenic variants, such as ATM and CHEK2. 19,20
- PRS has not been studied in non-White women.21
Continue to: CASE
CASE
Using the assessment results, the clinician talks to Ms. P about her lifetime risk for breast cancer. The Gail model indicates her lifetime risk is 13.3%, just slightly higher than the average (12.5%), and her 5-year risk is 0.5% (average, 0.4%). The IBIS or Tyrer-Cuzick model, which takes into account her second-degree relatives with breast and ovarian cancer and her Ashkenazi ethnicity (which confers increased risk due to elevated risk of BRCA mutations), predicts her lifetime risk of breast cancer to be 20.4%. This categorizes Ms. P as high risk.
Enhanced screening recommendations for women at high risk
TABLE 48,13,22 summarizes screening recommendations for women deemed to be at high risk for breast cancer. The American Cancer Society (ACS), NCCN, and the American College of Radiology (ACR) recommend that women with at least a 20% lifetime risk have yearly magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and mammography (staggered so that the patient has 1 test every 6 months) starting 10 years before the age of onset for the youngest affected relative but not before age 30.8 For carriers of high-risk (as well as intermediate-risk) genes, NCCN recommends annual MRI screening starting at age 40.13BRCA1/2 screening includes annual MRI starting at age 25 and annual mammography every 6 months starting at age 30.22 Clinicians should counsel women with moderate risk factors (elevated breast density; personal history of ADH, LCIS, or DCIS) about the potential risks and benefits of enhanced screening and chemoprophylaxis.

Risk-reduction strategies
Chemoprophylaxis
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that all women at increased risk for breast cancer consider chemoprophylaxis (B recommendation)23 based on convincing evidence that 5 years of treatment with either a synthetic estrogen reuptake modulator (SERM) or an aromatase inhibitor (AI) decreases the incidence of estrogen receptor positive breast cancers. (See TABLE 57,23,24 for absolute risk reduction.) There is no benefit for chemoprophylaxis in women at average risk (D recommendation).23 It is unclear whether chemoprophylaxis is indicated in women with moderate increased risk (ie, who do not meet the 20% lifetime risk criteria). Chemoprophylaxis may not be effective in women with BRCA1 mutations, as they often develop triple-negative breast cancers.

Accurate risk assessment and shared decision-making enable the clinician and patient to discuss the potential risks and benefits of chemoprophylaxis.7,24 The USPSTF did not find that any 1 risk prediction tool was better than another to identify women who should be counseled about chemoprophylaxis. Clinicians should counsel all women taking AIs about optimizing bone health with adequate calcium and vitamin D intake and routine bone density tests.
Surgical risk reduction
The NCCN guidelines state that risk-reducing bilateral mastectomy is reserved for individuals with high-risk gene variants and individuals with prior chest radiation between ages 10 and 30.25 NCCN also recommends discussing risk-reducing mastectomy with all women with BRCA mutations.22
Bilateral mastectomy is the most effective method to reduce breast cancer risk and should be discussed after age 25 in women with BRCA mutations and at least 8 years after chest radiation is completed.26 There is a reduction in breast cancer incidence of 90%.25 Breast imaging for screening (mammography or MRI) is not indicated after risk-reducing mastectomy. However, clinical breast examinations of the surgical site are important, because there is a small risk of developing breast cancer in that area.26
Risk-reducing oophorectomy is the standard of care for women with BRCA mutations to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer. It can also reduce the risk of breast cancer in women with BRCA mutations.27
Continue to: CASE
CASE
Based on her risk assessment results, family history, and genetic heritage, Ms. P qualifies for referral to a genetic counselor for discussion of BRCA testing. The clinician discusses adding annual MRI to Ms. P’s breast cancer screening regimen, based on ACS, NCCN, and ACR recommendations, due to her 20.4% lifetime risk. Discussion of whether and when to start chemoprophylaxis is typically based on breast cancer risk, projected benefit, and the potential impact of medication adverse effects. A high-risk woman is eligible for 5 years of chemoprophylaxis (tamoxifen if premenopausal) based on her lifetime risk. The clinician discusses timing with Ms. P, and even though she is finished with childbearing, she would like to wait until she is age 45, which is before the age at which her aunt was given a diagnosis of breast cancer.
Conclusion
Primary care clinicians are well positioned to identify women with an elevated risk of breast cancer and refer them for enhanced screening and chemoprophylaxis (see ALGORITHM). Shared decision-making with the inclusion of patient decision aids (https://decisionaid.ohri.ca/AZsearch.php?criteria=breast+cancer) about genetic testing, chemoprophylaxis, and prophylactic mastectomy or oophorectomy may help women at intermediate or high risk of breast cancer feel empowered to make decisions about their breast—and overall—health.
CORRESPONDENCE
Sarina Schrager, MD, MS, Professor, Department of Family Medicine and Community Health, University of Wisconsin, 1100 Delaplaine Court, Madison, WI 53715; [email protected]
Breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women in the United States; it is estimated that there will be 287,850 new cases of breast cancer in the United States during 2022 with 43,250 deaths.1 Lives are extended and saved every day because of a robust arsenal of treatments and interventions available to those who have been given a diagnosis of breast cancer. And, of course, lives are also extended and saved when we identify women at risk and provide early interventions. But in busy offices where time is short and there are competing demands on our time, proper assessment of a woman’s risk of breast cancer does not always happen. As a result, women with a higher risk of breast cancer may not be getting appropriate management.2,3
Familiarizing yourself with several risk-assessment tools and knowing when genetic testing is needed can make a big difference. Knowing the timing of mammograms and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for women deemed to be at high risk is also key. The following review employs a case-based approach (with an accompanying ALGORITHM) to illustrate how best to identify women who are at heightened risk of breast cancer and maximize their care. We also discuss the chemoprophylaxis regimens that may be used for those at increased risk.

CASE
Rachel P, age 37, presents to establish care. She has an Ashkenazi Jewish background and wonders if she should start doing breast cancer screening before age 40. She has 2 children, ages 4 years and 2 years. Her maternal aunt had unilateral breast cancer at age 54, and her maternal grandmother died of ovarian cancer at age 65.
Risk assessment
The risk assessment process (see ALGORITHM) must start with either the clinician or the patient initiating the discussion about breast cancer risk. The clinician may initiate the discussion with a new patient or at an annual physical examination. The patient may start the discussion because they are experiencing new breast symptoms, have anxiety about developing breast cancer, or have a family member with a new cancer diagnosis.
Risk factors. There are single factors that convey enough risk to automatically designate the patient as high risk (see TABLE 14-9). These factors include having a history of chest radiation between the ages of 10 and 30, a history of breast biopsy with either lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) or atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH), past breast and/or ovarian cancer, and either a family or personal history of a high penetrant genetic variant for breast cancer.4-9

In women with previous chest radiation, breast cancer risk correlates with the total dose of radiation.5 For women with a personal history of breast cancer, the younger the age at diagnosis, the higher the risk of contralateral breast cancer.5 Precancerous changes such as ADH, LCIS, and ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) also confer moderate increases in risk. Women with these diagnoses will commonly have follow-up with specialists.
Risk assessment tools. There are several models available to assess a woman’s breast cancer risk (see TABLE 210-12). The Gail model (https://bcrisktool.cancer.gov/) is the oldest, quickest, and most widely known. However, the Gail model only accounts for first-degree relatives diagnosed with breast cancer, may underpredict risk in women with a more extensive family history, and has not been studied in women younger than 35. The International Breast Cancer Intervention Study (IBIS) Risk Evaluation Tool (https://ibis-risk-calculator.magview.com/), commonly referred to as the Tyrer-Cuzick model, incorporates second-degree relatives into the prediction model—although women may not know their full family history. Both the IBIS and the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) model (https://tools.bcsc-scc.org/BC5yearRisk/intro.htm) include breast density in the prediction algorithm. The choice of tool depends on clinician comfort and individual patient risk factors. There is no evidence that one model is better than another.10-12

Continue to: CASE
CASE
Ms. P’s clinician starts with an assessment using the Gail model. However, when the result comes back with average risk, the clinician decides to follow up with the Tyrer-Cuzick model in order to incorporate Ms. P’s multiple second-degree relatives with breast and ovarian cancer. (The BCSC model was not used because it only includes first-degree relatives.)
Genetic testing
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend genetic testing if a woman has a first- or second-degree relative with pancreatic cancer, metastatic prostate cancer, male breast cancer, breast cancer at age 45 or younger, 2 or more breast cancers in a single person, 2 or more people on the same side of the family with at least 1 diagnosed at age 50 or younger, or any relative with ovarian cancer (see TABLE 3).7 Before ordering genetic testing, it is useful to refer the patient to a genetic counselor for a thorough discussion of options.

Results of genetic testing may include high-risk variants, moderate-risk variants, and variants of unknown significance (VUS), or be negative for any variants. High-risk variants for breast cancer include BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, and cancer syndrome variants such as TP53, PTEN, STK11, and CDH1.5,6,9,13-15 These high-risk variants confer sufficient risk that women with these mutations are automatically categorized in the high-risk group. It is estimated that high-risk variants account for only 25% of the genetic risk for breast cancer.16
BRCA1/2 and PTEN mutations confer greater than 80% lifetime risk, while other high-risk variants such as TP53, CDH1, and STK11 confer risks between 25% and 40%. These variants are also associated with cancers of other organs, depending on the mutation.17
Moderate-risk variants—ATM and CHEK2—do not confer sufficient risk to elevate women into the high-risk group. However, they do qualify these intermediate-risk women to participate in a specialized management strategy.5,9,13,18
VUS are those for which the associated risk is unclear, but more research may be done to categorize the risk.9 The clinical management of women with VUS usually entails close monitoring.
In an effort to better characterize breast cancer risk using a combination of pathogenic variants found in broad multi-gene cancer predisposition panels, researchers have developed a method to combine risks in a “polygenic risk score” (PRS) that can be used to counsel women (see “What is a polygenic risk score for breast cancer?” on page 203).19-21PRS predicts an additional 18% of genetic risk in women of European descent.21
SIDEBAR
What is a polygenic risk score for breast cancer?
- A polygenic risk score (PRS) is a mathematical method to combine results from a variety of different single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs; ie, single base pair variants) into a prediction tool that can estimate a woman’s lifetime risk of breast cancer.
- A PRS may be most accurate in determining risk for women with intermediate pathogenic variants, such as ATM and CHEK2. 19,20
- PRS has not been studied in non-White women.21
Continue to: CASE
CASE
Using the assessment results, the clinician talks to Ms. P about her lifetime risk for breast cancer. The Gail model indicates her lifetime risk is 13.3%, just slightly higher than the average (12.5%), and her 5-year risk is 0.5% (average, 0.4%). The IBIS or Tyrer-Cuzick model, which takes into account her second-degree relatives with breast and ovarian cancer and her Ashkenazi ethnicity (which confers increased risk due to elevated risk of BRCA mutations), predicts her lifetime risk of breast cancer to be 20.4%. This categorizes Ms. P as high risk.
Enhanced screening recommendations for women at high risk
TABLE 48,13,22 summarizes screening recommendations for women deemed to be at high risk for breast cancer. The American Cancer Society (ACS), NCCN, and the American College of Radiology (ACR) recommend that women with at least a 20% lifetime risk have yearly magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and mammography (staggered so that the patient has 1 test every 6 months) starting 10 years before the age of onset for the youngest affected relative but not before age 30.8 For carriers of high-risk (as well as intermediate-risk) genes, NCCN recommends annual MRI screening starting at age 40.13BRCA1/2 screening includes annual MRI starting at age 25 and annual mammography every 6 months starting at age 30.22 Clinicians should counsel women with moderate risk factors (elevated breast density; personal history of ADH, LCIS, or DCIS) about the potential risks and benefits of enhanced screening and chemoprophylaxis.

Risk-reduction strategies
Chemoprophylaxis
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that all women at increased risk for breast cancer consider chemoprophylaxis (B recommendation)23 based on convincing evidence that 5 years of treatment with either a synthetic estrogen reuptake modulator (SERM) or an aromatase inhibitor (AI) decreases the incidence of estrogen receptor positive breast cancers. (See TABLE 57,23,24 for absolute risk reduction.) There is no benefit for chemoprophylaxis in women at average risk (D recommendation).23 It is unclear whether chemoprophylaxis is indicated in women with moderate increased risk (ie, who do not meet the 20% lifetime risk criteria). Chemoprophylaxis may not be effective in women with BRCA1 mutations, as they often develop triple-negative breast cancers.

Accurate risk assessment and shared decision-making enable the clinician and patient to discuss the potential risks and benefits of chemoprophylaxis.7,24 The USPSTF did not find that any 1 risk prediction tool was better than another to identify women who should be counseled about chemoprophylaxis. Clinicians should counsel all women taking AIs about optimizing bone health with adequate calcium and vitamin D intake and routine bone density tests.
Surgical risk reduction
The NCCN guidelines state that risk-reducing bilateral mastectomy is reserved for individuals with high-risk gene variants and individuals with prior chest radiation between ages 10 and 30.25 NCCN also recommends discussing risk-reducing mastectomy with all women with BRCA mutations.22
Bilateral mastectomy is the most effective method to reduce breast cancer risk and should be discussed after age 25 in women with BRCA mutations and at least 8 years after chest radiation is completed.26 There is a reduction in breast cancer incidence of 90%.25 Breast imaging for screening (mammography or MRI) is not indicated after risk-reducing mastectomy. However, clinical breast examinations of the surgical site are important, because there is a small risk of developing breast cancer in that area.26
Risk-reducing oophorectomy is the standard of care for women with BRCA mutations to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer. It can also reduce the risk of breast cancer in women with BRCA mutations.27
Continue to: CASE
CASE
Based on her risk assessment results, family history, and genetic heritage, Ms. P qualifies for referral to a genetic counselor for discussion of BRCA testing. The clinician discusses adding annual MRI to Ms. P’s breast cancer screening regimen, based on ACS, NCCN, and ACR recommendations, due to her 20.4% lifetime risk. Discussion of whether and when to start chemoprophylaxis is typically based on breast cancer risk, projected benefit, and the potential impact of medication adverse effects. A high-risk woman is eligible for 5 years of chemoprophylaxis (tamoxifen if premenopausal) based on her lifetime risk. The clinician discusses timing with Ms. P, and even though she is finished with childbearing, she would like to wait until she is age 45, which is before the age at which her aunt was given a diagnosis of breast cancer.
Conclusion
Primary care clinicians are well positioned to identify women with an elevated risk of breast cancer and refer them for enhanced screening and chemoprophylaxis (see ALGORITHM). Shared decision-making with the inclusion of patient decision aids (https://decisionaid.ohri.ca/AZsearch.php?criteria=breast+cancer) about genetic testing, chemoprophylaxis, and prophylactic mastectomy or oophorectomy may help women at intermediate or high risk of breast cancer feel empowered to make decisions about their breast—and overall—health.
CORRESPONDENCE
Sarina Schrager, MD, MS, Professor, Department of Family Medicine and Community Health, University of Wisconsin, 1100 Delaplaine Court, Madison, WI 53715; [email protected]
1. National Cancer Institute. Cancer stat facts: female breast cancer. Accessed May 13, 2022. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html
2. Guerra CE, Sherman M, Armstrong K. Diffusion of breast cancer risk assessment in primary care. J Am Board Fam Med. 2009;22:272-279. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2009.03.080153
3. Hamilton JG, Abdiwahab E, Edwards HM, et al. Primary care providers’ cancer genetic testing-related knowledge, attitudes, and communication behaviors: a systematic review and research agenda. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:315-324. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3943-4
4. Eden KB, Ivlev I, Bensching KL, et al. Use of an online breast cancer risk assessment and patient decision aid in primary care practices. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2020;29:763-769. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2019.8143
5. Kleibl Z, Kristensen VN. Women at high risk of breast cancer: molecular characteristics, clinical presentation and management. Breast. 2016;28:136-44. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2016.05.006
6. Sciaraffa T, Guido B, Khan SA, et al. Breast cancer risk assessment and management programs: a practical guide. Breast J. 2020;26:1556-1564. doi: 10.1111/tbj.13967
7. Farkas A, Vanderberg R, Merriam S, et al. Breast cancer chemoprevention: a practical guide for the primary care provider. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2020;29:46-56. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2018.7643
8. McClintock AH, Golob AL, Laya MB. Breast cancer risk assessment: a step-wise approach for primary care providers on the front lines of shared decision making. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95:1268-1275. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.04.017
9. Catana A, Apostu AP, Antemie RG. Multi gene panel testing for hereditary breast cancer - is it ready to be used? Med Pharm Rep. 2019;92:220-225. doi: 10.15386/mpr-1083
10. Barke LD, Freivogel ME. Breast cancer risk assessment models and high-risk screening. Radiol Clin North Am. 2017;55:457-474. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2016.12.013
11. Amir E, Freedman OC, Seruga B, et al. Assessing women at high risk of breast cancer: a review of risk assessment models. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102:680-91. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djq088
12. Kim G, Bahl M. Assessing risk of breast cancer: a review of risk prediction models. J Breast Imaging. 2021;3:144-155. doi: 10.1093/jbi/wbab001
13. Narod SA. Which genes for hereditary breast cancer? N Engl J Med. 2021;384:471-473. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2035083
14. Couch FJ, Shimelis H, Hu C, et al. Associations between cancer predisposition testing panel genes and breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1190-1196. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0424
15. Obeid EI, Hall MJ, Daly MB. Multigene panel testing and breast cancer risk: is it time to scale down? JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1176-1177. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0342
16. Michailidou K, Lindström S, Dennis J, et al. Association analysis identifies 65 new breast cancer risk loci. Nature. 2017;551:92-94. doi: 10.1038/nature24284
17. Shiovitz S, Korde LA. Genetics of breast cancer: a topic in evolution. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:1291-1299. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv022
18. Hu C, Hart SN, Gnanaolivu R, et al. A population-based study of genes previously implicated in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:440-451. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2005936
19. Gao C, Polley EC, Hart SN, et al. Risk of breast cancer among carriers of pathogenic variants in breast cancer predisposition genes varies by polygenic risk score. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:2564-2573. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01992
20. Gallagher S, Hughes E, Wagner S, et al. Association of a polygenic risk score with breast cancer among women carriers of high- and moderate-risk breast cancer genes. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:e208501. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.8501
21. Yanes T, Young MA, Meiser B, et al. Clinical applications of polygenic breast cancer risk: a critical review and perspectives of an emerging field. Breast Cancer Res. 2020;22:21. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01260-3
22. Schrager S, Torell E, Ledford K, et al. Managing a woman with BRCA mutations? Shared decision-making is key. J Fam Pract. 2020;69:237-243
23. US Preventive Services Task Force; Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al. Medication use to reduce risk of breast cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2019;322:857-867. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.11885
24. Pruthi S, Heisey RE, Bevers TB. Chemoprevention for breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2015;22:3230-3235. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4715-9
25. Britt KL, Cuzick J, Phillips KA. Key steps for effective breast cancer prevention. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20:417-436. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0266-x
26. Jatoi I, Kemp Z. Risk-reducing mastectomy. JAMA. 2021;325:1781-1782. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.22414
27. Choi Y, Terry MB, Daly MB, et al. Association of risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy with breast cancer risk in women with BRCA1 and BRCA2 pathogenic variants. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7:585-592. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.7995
1. National Cancer Institute. Cancer stat facts: female breast cancer. Accessed May 13, 2022. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html
2. Guerra CE, Sherman M, Armstrong K. Diffusion of breast cancer risk assessment in primary care. J Am Board Fam Med. 2009;22:272-279. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2009.03.080153
3. Hamilton JG, Abdiwahab E, Edwards HM, et al. Primary care providers’ cancer genetic testing-related knowledge, attitudes, and communication behaviors: a systematic review and research agenda. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:315-324. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3943-4
4. Eden KB, Ivlev I, Bensching KL, et al. Use of an online breast cancer risk assessment and patient decision aid in primary care practices. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2020;29:763-769. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2019.8143
5. Kleibl Z, Kristensen VN. Women at high risk of breast cancer: molecular characteristics, clinical presentation and management. Breast. 2016;28:136-44. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2016.05.006
6. Sciaraffa T, Guido B, Khan SA, et al. Breast cancer risk assessment and management programs: a practical guide. Breast J. 2020;26:1556-1564. doi: 10.1111/tbj.13967
7. Farkas A, Vanderberg R, Merriam S, et al. Breast cancer chemoprevention: a practical guide for the primary care provider. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2020;29:46-56. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2018.7643
8. McClintock AH, Golob AL, Laya MB. Breast cancer risk assessment: a step-wise approach for primary care providers on the front lines of shared decision making. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95:1268-1275. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.04.017
9. Catana A, Apostu AP, Antemie RG. Multi gene panel testing for hereditary breast cancer - is it ready to be used? Med Pharm Rep. 2019;92:220-225. doi: 10.15386/mpr-1083
10. Barke LD, Freivogel ME. Breast cancer risk assessment models and high-risk screening. Radiol Clin North Am. 2017;55:457-474. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2016.12.013
11. Amir E, Freedman OC, Seruga B, et al. Assessing women at high risk of breast cancer: a review of risk assessment models. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102:680-91. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djq088
12. Kim G, Bahl M. Assessing risk of breast cancer: a review of risk prediction models. J Breast Imaging. 2021;3:144-155. doi: 10.1093/jbi/wbab001
13. Narod SA. Which genes for hereditary breast cancer? N Engl J Med. 2021;384:471-473. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2035083
14. Couch FJ, Shimelis H, Hu C, et al. Associations between cancer predisposition testing panel genes and breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1190-1196. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0424
15. Obeid EI, Hall MJ, Daly MB. Multigene panel testing and breast cancer risk: is it time to scale down? JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1176-1177. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0342
16. Michailidou K, Lindström S, Dennis J, et al. Association analysis identifies 65 new breast cancer risk loci. Nature. 2017;551:92-94. doi: 10.1038/nature24284
17. Shiovitz S, Korde LA. Genetics of breast cancer: a topic in evolution. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:1291-1299. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv022
18. Hu C, Hart SN, Gnanaolivu R, et al. A population-based study of genes previously implicated in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:440-451. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2005936
19. Gao C, Polley EC, Hart SN, et al. Risk of breast cancer among carriers of pathogenic variants in breast cancer predisposition genes varies by polygenic risk score. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:2564-2573. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01992
20. Gallagher S, Hughes E, Wagner S, et al. Association of a polygenic risk score with breast cancer among women carriers of high- and moderate-risk breast cancer genes. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:e208501. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.8501
21. Yanes T, Young MA, Meiser B, et al. Clinical applications of polygenic breast cancer risk: a critical review and perspectives of an emerging field. Breast Cancer Res. 2020;22:21. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01260-3
22. Schrager S, Torell E, Ledford K, et al. Managing a woman with BRCA mutations? Shared decision-making is key. J Fam Pract. 2020;69:237-243
23. US Preventive Services Task Force; Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al. Medication use to reduce risk of breast cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2019;322:857-867. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.11885
24. Pruthi S, Heisey RE, Bevers TB. Chemoprevention for breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2015;22:3230-3235. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4715-9
25. Britt KL, Cuzick J, Phillips KA. Key steps for effective breast cancer prevention. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20:417-436. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0266-x
26. Jatoi I, Kemp Z. Risk-reducing mastectomy. JAMA. 2021;325:1781-1782. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.22414
27. Choi Y, Terry MB, Daly MB, et al. Association of risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy with breast cancer risk in women with BRCA1 and BRCA2 pathogenic variants. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7:585-592. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.7995
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Assess breast cancer risk in all women starting at age 35. C
› Perform enhanced screening in all women with a lifetime risk of breast cancer > 20%. A
› Discuss chemoprevention for all women at elevated risk for breast cancer. B
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series