User login
What's your diagnosis?
Answer: Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome.
According to an American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline,1 for patients with recurrence of small bowel bleeding, endoscopic management could be considered depending on the patient’s clinical course and response to prior therapy. Consequently, injections of lauromacrogol with SBE (single-balloon enteroscopy) were given (Figure D). Lesions that ranged from 1 to 2 cm were injected with 1-2 mL lauromacrogol until the mucosa turned white. Three SBEs had been performed in a 5-month period. A total of 20 lesions were successfully treated with lauromacrogol. The treated hemangiomas became small, and the site healed 5 months after treatment (Figures E and F). The patient has been followed for 1 year, and he remains in good clinical condition with his latest hemoglobin level at 110 g/L. No further blood transfusion is needed.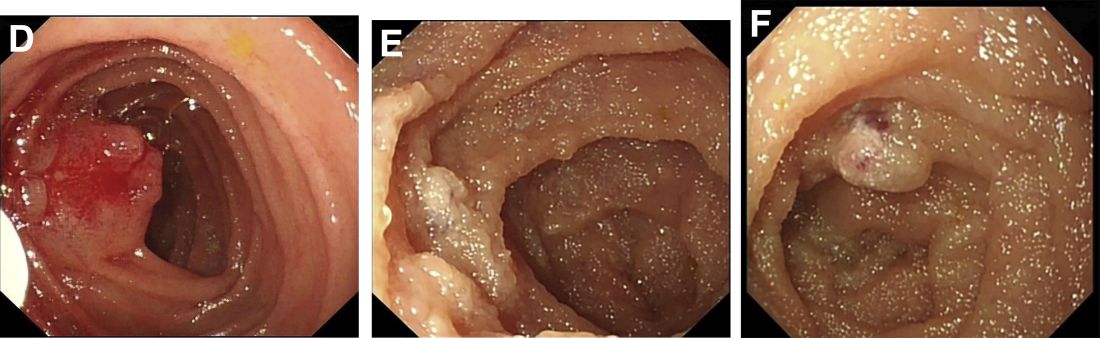
BRBNS is a rare disorder characterized by discrete venous malformations of varying size and appearance that are present on the skin and within the gastrointestinal tract.2With wider application of video capsule endoscopy (VCE) and the increase of image resolution, the detection rate and diagnostic accuracy of BRBNS are significantly improved. Treatment of BRBNS varies depending on the site, size, and number of lesions. Medication, surgery, and endoscopic therapy are currently clinically applied. The successful use of sirolimus was recently reported in the treatment of vascular lesions.3Sirolimus has potential adverse effects on renal function, bone marrow, and cholesterol metabolism, however. In consideration of the patient’s young age, we did not adopt this method. Surgical resection is more suitable for limited or life-threatening lesions. The lesions in this patient were mild and sporadic. Consequently, in this case, endoscopic injection of lauromacrogol was performed. This was the most complicated case of endoscopic treatment of BRBNS in our center and proved lauromacrogol injection was a feasible approach. According to a literature review, lauromacrogol has been used to treat vascular lesions for decades, but there is still no standard instruction for the dosage of lauromacrogol. We hope that our experience can be a reference for the endoscopic treatment of BRBNS.
References (add links)
1. Gerson LB et al. ACG clinical guideline: Diagnosis and management of small bowel bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol.
2. Felton SJ and Ferguson JE. Multiple cutaneous swellings associated with sudden collapse. JAMA.
3. Yuksekkaya H et al. Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome: Successful treatment with sirolimus. Pediatrics.
Answer: Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome.
According to an American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline,1 for patients with recurrence of small bowel bleeding, endoscopic management could be considered depending on the patient’s clinical course and response to prior therapy. Consequently, injections of lauromacrogol with SBE (single-balloon enteroscopy) were given (Figure D). Lesions that ranged from 1 to 2 cm were injected with 1-2 mL lauromacrogol until the mucosa turned white. Three SBEs had been performed in a 5-month period. A total of 20 lesions were successfully treated with lauromacrogol. The treated hemangiomas became small, and the site healed 5 months after treatment (Figures E and F). The patient has been followed for 1 year, and he remains in good clinical condition with his latest hemoglobin level at 110 g/L. No further blood transfusion is needed.
BRBNS is a rare disorder characterized by discrete venous malformations of varying size and appearance that are present on the skin and within the gastrointestinal tract.2With wider application of video capsule endoscopy (VCE) and the increase of image resolution, the detection rate and diagnostic accuracy of BRBNS are significantly improved. Treatment of BRBNS varies depending on the site, size, and number of lesions. Medication, surgery, and endoscopic therapy are currently clinically applied. The successful use of sirolimus was recently reported in the treatment of vascular lesions.3Sirolimus has potential adverse effects on renal function, bone marrow, and cholesterol metabolism, however. In consideration of the patient’s young age, we did not adopt this method. Surgical resection is more suitable for limited or life-threatening lesions. The lesions in this patient were mild and sporadic. Consequently, in this case, endoscopic injection of lauromacrogol was performed. This was the most complicated case of endoscopic treatment of BRBNS in our center and proved lauromacrogol injection was a feasible approach. According to a literature review, lauromacrogol has been used to treat vascular lesions for decades, but there is still no standard instruction for the dosage of lauromacrogol. We hope that our experience can be a reference for the endoscopic treatment of BRBNS.
References (add links)
1. Gerson LB et al. ACG clinical guideline: Diagnosis and management of small bowel bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol.
2. Felton SJ and Ferguson JE. Multiple cutaneous swellings associated with sudden collapse. JAMA.
3. Yuksekkaya H et al. Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome: Successful treatment with sirolimus. Pediatrics.
Answer: Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome.
According to an American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline,1 for patients with recurrence of small bowel bleeding, endoscopic management could be considered depending on the patient’s clinical course and response to prior therapy. Consequently, injections of lauromacrogol with SBE (single-balloon enteroscopy) were given (Figure D). Lesions that ranged from 1 to 2 cm were injected with 1-2 mL lauromacrogol until the mucosa turned white. Three SBEs had been performed in a 5-month period. A total of 20 lesions were successfully treated with lauromacrogol. The treated hemangiomas became small, and the site healed 5 months after treatment (Figures E and F). The patient has been followed for 1 year, and he remains in good clinical condition with his latest hemoglobin level at 110 g/L. No further blood transfusion is needed.
BRBNS is a rare disorder characterized by discrete venous malformations of varying size and appearance that are present on the skin and within the gastrointestinal tract.2With wider application of video capsule endoscopy (VCE) and the increase of image resolution, the detection rate and diagnostic accuracy of BRBNS are significantly improved. Treatment of BRBNS varies depending on the site, size, and number of lesions. Medication, surgery, and endoscopic therapy are currently clinically applied. The successful use of sirolimus was recently reported in the treatment of vascular lesions.3Sirolimus has potential adverse effects on renal function, bone marrow, and cholesterol metabolism, however. In consideration of the patient’s young age, we did not adopt this method. Surgical resection is more suitable for limited or life-threatening lesions. The lesions in this patient were mild and sporadic. Consequently, in this case, endoscopic injection of lauromacrogol was performed. This was the most complicated case of endoscopic treatment of BRBNS in our center and proved lauromacrogol injection was a feasible approach. According to a literature review, lauromacrogol has been used to treat vascular lesions for decades, but there is still no standard instruction for the dosage of lauromacrogol. We hope that our experience can be a reference for the endoscopic treatment of BRBNS.
References (add links)
1. Gerson LB et al. ACG clinical guideline: Diagnosis and management of small bowel bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol.
2. Felton SJ and Ferguson JE. Multiple cutaneous swellings associated with sudden collapse. JAMA.
3. Yuksekkaya H et al. Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome: Successful treatment with sirolimus. Pediatrics.
A 13-year-old boy presented with recurrent melena for 10 years accompanied with dizziness and fatigue. This patient had no history of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use, peptic ulcer, or chronic liver disease, and no family history of gastrointestinal bleeding. He was born with a right foot hemangioma that was resected when he was 2 years old. Additionally, he had received multiple blood transfusions for iron deficiency anemia since childhood. The body mass index was 16.5 kg/m2 and physical examination revealed active bowel sounds.
Laboratory examinations showed severe iron deficiency anemia (the lowest hemoglobin available was 36 g/L) and positive stool occult blood. Gastroscopy unveiled superficial gastritis and colonoscopy was normal. Second-look examinations showed the same results. No clinically important signs were observed on computed tomography scan. Given these results, small intestinal bleeding was considered. Therefore, a video capsule endoscopy (VCE) was carried out and revealed multifocal hemangioma-like purplish blue lesions in jejunum and ileum (Figure A). Then a single-balloon enteroscopy (SBE) was performed, which showed multifocal vascular lesions ranging between 1.0 and 2.0 cm in the jejunum and ileum (Figure B, C).
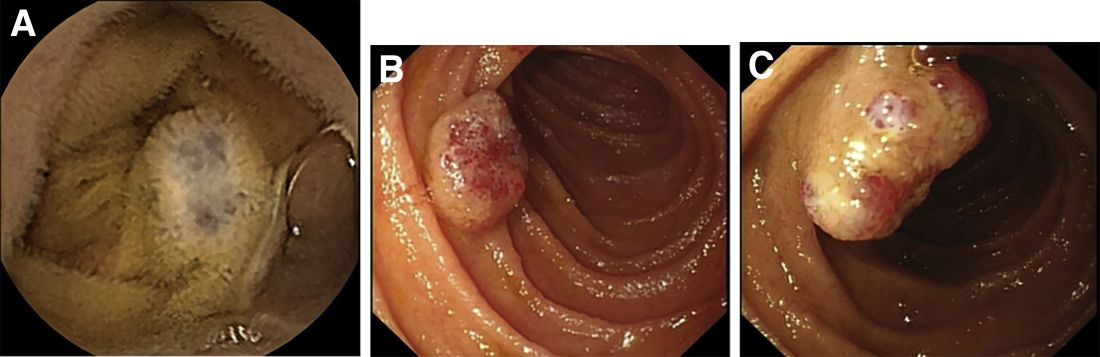
Based on these findings, what is your diagnosis? What is the next step in management for this patient?
Angioedema risk jumps when switching HF meds
New renin-angiotensin-system (RAS) inhibitor therapy using sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto) is no more likely to cause angioedema than starting out with an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB).
But the risk climbs when such patients start on an ACE inhibitor or ARB and then switch to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those prescribed the newer drug, the only available angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), in the first place.
Those findings and others from a large database analysis, by researchers at the Food and Drug Administration and Harvard Medical School, may clarify and help alleviate a residual safety concern about the ARNI – that it might promote angioedema – that persists after the drug’s major HF trials.
The angioedema risk increased the most right after the switch to the ARNI from one of the older RAS inhibitors. For example, the overall risk doubled for patients who started with an ARB then switched to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those who started on the newer drug. But it went up about 2.5 times during the first 14 days after the switch.
A similar pattern emerged for ACE inhibitors, but the increased angioedema risk reached significance only within 2 weeks of the switch from an ACE inhibitor to sacubitril-valsartan compared to starting on the latter.
The analysis, based on data from the FDA’s Sentinel adverse event reporting system, was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
A rare complication, but ...
Angioedema was rare overall in the study, with an unadjusted rate of about 6.75 per 1,000 person-years for users of ACE inhibitors, less than half that rate for ARB users, and only one-fifth that rate for sacubitril-valsartan recipients.
But even a rare complication can be a worry for drugs as widely used as RAS inhibitors. And it’s not unusual for patients cautiously started on an ACE inhibitor or ARB to be switched to sacubitril-valsartan, which is only recently a core guideline–recommended therapy for HF with reduced ejection fraction.
Such patients transitioning to the ARNI, the current study suggests, should probably be watched closely for signs of angioedema for 2 weeks but especially during the first few days. Indeed, the study’s event curves show most of the extra risk “popping up” right after the switch to sacubitril-valsartan, lead author Efe Eworuke, PhD, told this news organization.
The ARNI’s labeling, which states the drug should follow ACE inhibitors only after 36-hour washout period, “has done justice to this issue,” she said. But “whether clinicians are adhering to that, we can’t tell.”
Potentially, patients who miss the 36-hour washout between ACE inhibitors or ARBs and sacubitril-valsartan may account for the excess angioedema risk seen in the analysis, said Dr. Eworuke, with the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Silver Spring, Md.
But the analysis doesn’t nail down the window of excess risk to only 36 hours. It suggests that patients switching to the ARNI – even those pausing for 36 hours in between drugs – should probably be monitored “2 weeks or longer,” she said. “They could still have angioedema after the washout period.”
Indeed, the “timing of the switch may be critical,” according to an editorial accompanying the report. “Perhaps a longer initial exposure period of ACE inhibitor or ARB,” beyond 2 weeks, “should be considered before switching to an ARNI,” contended Robert L. Page II, PharmD, MSPH, University of Colorado Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Aurora.
Moreover, he wrote, the study suggests that “initiation of an ARNI de novo may be safer compared with trialing an ACE inhibitor or ARB then switching to an ARNI,” and “should be a consideration when beginning guideline-directed medical therapy for patients with HF.”
New RAS inhibition with ARNI ‘protective’
Compared with ARNI “new users” who had not received any RAS inhibitor in the prior 6 months, patients in the study who switched from an ACE inhibitor to ARNI (41,548 matched pairs) showed a hazard ratio (HR) for angioedema of 1.62 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.91-2.89), that is, only a “trend,” the report states.
But that trend became significant when the analysis considered only angioedema cases in the first 14 days after the drug switch: HR, 1.98 (95% CI, 1.11-3.53).
Those switching from an ARB to ARNI, compared with ARNI new users (37,893 matched pairs), showed a significant HR for angioedema of 2.03 (95% CI, 1.16-3.54). The effect was more pronounced when considering only angioedema arising in the first 2 weeks: HR, 2.45 (95% CI, 1.36-4.43).
Compared with new use of ACE inhibitors, new ARNI use (41,998 matched pairs) was “protective,” the report states, with an HR for angioedema of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.11-0.29). So was a switch from ACE inhibitors to the ARNI (69,639 matched pairs), with an HR of 0.31 (95% CI, 0.23-0.43).
But compared with starting with an ARB, ARNI new use (43,755 matched pairs) had a null effect on angioedema risk, HR, 0.59 (95% CI, 0.35-1.01); as did switching from an ARB to ARNI (49,137 matched pairs), HR, 0.85 (95% CI, 0.58-1.26).
The analysis has limitations, Dr. Eworuke acknowledged. The comparator groups probably differed in unknown ways given the limits of propensity matching, for example, and because the FDA’s Sentinel system data can reflect only cases that are reported, the study probably underestimates the true prevalence of angioedema.
For example, a patient may see a clinician for a milder case that resolves without a significant intervention, she noted. But “those types of angioedema would not have been captured by our study.”
Dr. Eworuke disclosed that her comments reflect her views and are not those of the Food and Drug Administration; she and the other authors, as well as editorialist Dr. Page, report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New renin-angiotensin-system (RAS) inhibitor therapy using sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto) is no more likely to cause angioedema than starting out with an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB).
But the risk climbs when such patients start on an ACE inhibitor or ARB and then switch to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those prescribed the newer drug, the only available angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), in the first place.
Those findings and others from a large database analysis, by researchers at the Food and Drug Administration and Harvard Medical School, may clarify and help alleviate a residual safety concern about the ARNI – that it might promote angioedema – that persists after the drug’s major HF trials.
The angioedema risk increased the most right after the switch to the ARNI from one of the older RAS inhibitors. For example, the overall risk doubled for patients who started with an ARB then switched to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those who started on the newer drug. But it went up about 2.5 times during the first 14 days after the switch.
A similar pattern emerged for ACE inhibitors, but the increased angioedema risk reached significance only within 2 weeks of the switch from an ACE inhibitor to sacubitril-valsartan compared to starting on the latter.
The analysis, based on data from the FDA’s Sentinel adverse event reporting system, was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
A rare complication, but ...
Angioedema was rare overall in the study, with an unadjusted rate of about 6.75 per 1,000 person-years for users of ACE inhibitors, less than half that rate for ARB users, and only one-fifth that rate for sacubitril-valsartan recipients.
But even a rare complication can be a worry for drugs as widely used as RAS inhibitors. And it’s not unusual for patients cautiously started on an ACE inhibitor or ARB to be switched to sacubitril-valsartan, which is only recently a core guideline–recommended therapy for HF with reduced ejection fraction.
Such patients transitioning to the ARNI, the current study suggests, should probably be watched closely for signs of angioedema for 2 weeks but especially during the first few days. Indeed, the study’s event curves show most of the extra risk “popping up” right after the switch to sacubitril-valsartan, lead author Efe Eworuke, PhD, told this news organization.
The ARNI’s labeling, which states the drug should follow ACE inhibitors only after 36-hour washout period, “has done justice to this issue,” she said. But “whether clinicians are adhering to that, we can’t tell.”
Potentially, patients who miss the 36-hour washout between ACE inhibitors or ARBs and sacubitril-valsartan may account for the excess angioedema risk seen in the analysis, said Dr. Eworuke, with the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Silver Spring, Md.
But the analysis doesn’t nail down the window of excess risk to only 36 hours. It suggests that patients switching to the ARNI – even those pausing for 36 hours in between drugs – should probably be monitored “2 weeks or longer,” she said. “They could still have angioedema after the washout period.”
Indeed, the “timing of the switch may be critical,” according to an editorial accompanying the report. “Perhaps a longer initial exposure period of ACE inhibitor or ARB,” beyond 2 weeks, “should be considered before switching to an ARNI,” contended Robert L. Page II, PharmD, MSPH, University of Colorado Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Aurora.
Moreover, he wrote, the study suggests that “initiation of an ARNI de novo may be safer compared with trialing an ACE inhibitor or ARB then switching to an ARNI,” and “should be a consideration when beginning guideline-directed medical therapy for patients with HF.”
New RAS inhibition with ARNI ‘protective’
Compared with ARNI “new users” who had not received any RAS inhibitor in the prior 6 months, patients in the study who switched from an ACE inhibitor to ARNI (41,548 matched pairs) showed a hazard ratio (HR) for angioedema of 1.62 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.91-2.89), that is, only a “trend,” the report states.
But that trend became significant when the analysis considered only angioedema cases in the first 14 days after the drug switch: HR, 1.98 (95% CI, 1.11-3.53).
Those switching from an ARB to ARNI, compared with ARNI new users (37,893 matched pairs), showed a significant HR for angioedema of 2.03 (95% CI, 1.16-3.54). The effect was more pronounced when considering only angioedema arising in the first 2 weeks: HR, 2.45 (95% CI, 1.36-4.43).
Compared with new use of ACE inhibitors, new ARNI use (41,998 matched pairs) was “protective,” the report states, with an HR for angioedema of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.11-0.29). So was a switch from ACE inhibitors to the ARNI (69,639 matched pairs), with an HR of 0.31 (95% CI, 0.23-0.43).
But compared with starting with an ARB, ARNI new use (43,755 matched pairs) had a null effect on angioedema risk, HR, 0.59 (95% CI, 0.35-1.01); as did switching from an ARB to ARNI (49,137 matched pairs), HR, 0.85 (95% CI, 0.58-1.26).
The analysis has limitations, Dr. Eworuke acknowledged. The comparator groups probably differed in unknown ways given the limits of propensity matching, for example, and because the FDA’s Sentinel system data can reflect only cases that are reported, the study probably underestimates the true prevalence of angioedema.
For example, a patient may see a clinician for a milder case that resolves without a significant intervention, she noted. But “those types of angioedema would not have been captured by our study.”
Dr. Eworuke disclosed that her comments reflect her views and are not those of the Food and Drug Administration; she and the other authors, as well as editorialist Dr. Page, report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New renin-angiotensin-system (RAS) inhibitor therapy using sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto) is no more likely to cause angioedema than starting out with an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB).
But the risk climbs when such patients start on an ACE inhibitor or ARB and then switch to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those prescribed the newer drug, the only available angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), in the first place.
Those findings and others from a large database analysis, by researchers at the Food and Drug Administration and Harvard Medical School, may clarify and help alleviate a residual safety concern about the ARNI – that it might promote angioedema – that persists after the drug’s major HF trials.
The angioedema risk increased the most right after the switch to the ARNI from one of the older RAS inhibitors. For example, the overall risk doubled for patients who started with an ARB then switched to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those who started on the newer drug. But it went up about 2.5 times during the first 14 days after the switch.
A similar pattern emerged for ACE inhibitors, but the increased angioedema risk reached significance only within 2 weeks of the switch from an ACE inhibitor to sacubitril-valsartan compared to starting on the latter.
The analysis, based on data from the FDA’s Sentinel adverse event reporting system, was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
A rare complication, but ...
Angioedema was rare overall in the study, with an unadjusted rate of about 6.75 per 1,000 person-years for users of ACE inhibitors, less than half that rate for ARB users, and only one-fifth that rate for sacubitril-valsartan recipients.
But even a rare complication can be a worry for drugs as widely used as RAS inhibitors. And it’s not unusual for patients cautiously started on an ACE inhibitor or ARB to be switched to sacubitril-valsartan, which is only recently a core guideline–recommended therapy for HF with reduced ejection fraction.
Such patients transitioning to the ARNI, the current study suggests, should probably be watched closely for signs of angioedema for 2 weeks but especially during the first few days. Indeed, the study’s event curves show most of the extra risk “popping up” right after the switch to sacubitril-valsartan, lead author Efe Eworuke, PhD, told this news organization.
The ARNI’s labeling, which states the drug should follow ACE inhibitors only after 36-hour washout period, “has done justice to this issue,” she said. But “whether clinicians are adhering to that, we can’t tell.”
Potentially, patients who miss the 36-hour washout between ACE inhibitors or ARBs and sacubitril-valsartan may account for the excess angioedema risk seen in the analysis, said Dr. Eworuke, with the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Silver Spring, Md.
But the analysis doesn’t nail down the window of excess risk to only 36 hours. It suggests that patients switching to the ARNI – even those pausing for 36 hours in between drugs – should probably be monitored “2 weeks or longer,” she said. “They could still have angioedema after the washout period.”
Indeed, the “timing of the switch may be critical,” according to an editorial accompanying the report. “Perhaps a longer initial exposure period of ACE inhibitor or ARB,” beyond 2 weeks, “should be considered before switching to an ARNI,” contended Robert L. Page II, PharmD, MSPH, University of Colorado Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Aurora.
Moreover, he wrote, the study suggests that “initiation of an ARNI de novo may be safer compared with trialing an ACE inhibitor or ARB then switching to an ARNI,” and “should be a consideration when beginning guideline-directed medical therapy for patients with HF.”
New RAS inhibition with ARNI ‘protective’
Compared with ARNI “new users” who had not received any RAS inhibitor in the prior 6 months, patients in the study who switched from an ACE inhibitor to ARNI (41,548 matched pairs) showed a hazard ratio (HR) for angioedema of 1.62 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.91-2.89), that is, only a “trend,” the report states.
But that trend became significant when the analysis considered only angioedema cases in the first 14 days after the drug switch: HR, 1.98 (95% CI, 1.11-3.53).
Those switching from an ARB to ARNI, compared with ARNI new users (37,893 matched pairs), showed a significant HR for angioedema of 2.03 (95% CI, 1.16-3.54). The effect was more pronounced when considering only angioedema arising in the first 2 weeks: HR, 2.45 (95% CI, 1.36-4.43).
Compared with new use of ACE inhibitors, new ARNI use (41,998 matched pairs) was “protective,” the report states, with an HR for angioedema of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.11-0.29). So was a switch from ACE inhibitors to the ARNI (69,639 matched pairs), with an HR of 0.31 (95% CI, 0.23-0.43).
But compared with starting with an ARB, ARNI new use (43,755 matched pairs) had a null effect on angioedema risk, HR, 0.59 (95% CI, 0.35-1.01); as did switching from an ARB to ARNI (49,137 matched pairs), HR, 0.85 (95% CI, 0.58-1.26).
The analysis has limitations, Dr. Eworuke acknowledged. The comparator groups probably differed in unknown ways given the limits of propensity matching, for example, and because the FDA’s Sentinel system data can reflect only cases that are reported, the study probably underestimates the true prevalence of angioedema.
For example, a patient may see a clinician for a milder case that resolves without a significant intervention, she noted. But “those types of angioedema would not have been captured by our study.”
Dr. Eworuke disclosed that her comments reflect her views and are not those of the Food and Drug Administration; she and the other authors, as well as editorialist Dr. Page, report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Disparities in breast cancer deaths, MRI screening persist
Despite improvements in access to health coverage under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), racial disparities in breast cancer mortality rates persist and the underuse of advanced breast imaging may be one culprit, experts say.
In a recent position statement, researchers highlighted the disproportionally high breast cancer mortality rates among Black women in Louisiana – a state that has one of the highest breast cancer mortality rates in the nation. In 2019, the breast cancer mortality rate among Black women in Louisiana was 29.3 per 100,000 women compared with the national rate of 19.4 per 100,000.
Although Louisiana has made strides in improving access to breast cancer screening in recent years, the use of advanced imaging – specifically breast MRI – remains underused in this high-risk population. A major barrier to wider use of breast MRI has been cost, and ACA expansion led to higher, not lower, out-of-pocket costs for this screening modality.
“Breast MRI is a powerful imaging tool for early detection and for screening women at high risk for breast cancer,” wrote the researchers, led by Brooke L. Morrell, MD, of Louisiana State University Health and Sciences Center, New Orleans.
However, greater access to health care has not necessarily translated to increased breast MRI screening or improved survival among Black women. Even years after the adoption of the ACA, “Black women in Louisiana continue to die of breast cancer at rates significantly greater than the national average,” the authors wrote.
The position statement was published in Cancer.
Breast MRI is known to provide the highest rate of breast cancer detection among commonly used imaging options, with a sensitivity ranging from 81% to 100%. That’s about twice as high as the sensitivity range for mammography after factoring in breast density.
“This is of particular importance when we consider the risk‐based screening of younger populations, in which dense breasts are more prevalent,” the authors explained.
For Black women in particular, studies show nearly a quarter (23%) who develop breast cancer are diagnosed under the age of 50, compared with 16% of White women. Black women are also more likely to develop more aggressive, premenopausal breast cancers, including triple-negative breast cancer, that are more easily detected on MRI.
“Adding supplemental screening breast MRI to annual mammography in higher risk women has been shown to detect up to 18 additional cancers out of 1,000 patients,” Dr. Morrell said. And “many of these cancers are detected much earlier than with mammography alone.”
Still, with ACA expansion, out-of-pocket costs for breast MRI actually increased. This increase likely occurred, in part, because the financial protections outlined in the ACA’s Women’s Preventive Services Guidelines covered mammograms but not breast MRI.
More specifically, under the ACA, Medicaid and most private health insurance plans are required to provide coverage for mammograms at no cost to the patient. The percentage of health plans providing zero cost sharing for mammograms increased under the ACA from 81.9% to 96.8%, but the corresponding rates of zero cost sharing for breast MRI screening went in the opposite direction – from 43.1% in 2009 to only 26.2% in 2017, a 2022 study found.
This study also highlighted geographic variations in zero cost sharing and out-of-pocket costs for screening breast MRI, with a higher financial burden observed for women living in the South. In addition, studies have demonstrated that race and socioeconomic factors, including education and income, play a role in the underuse of screening, including breast MRI.
These factors all likely contribute to screening breast MRI remaining inaccessible to many women, Dr. Morrell and colleagues said.
The authors also outlined three key action items that could help address barriers to MRI breast screening, which include reducing the high cost of breast MRI, lobbying to include breast MRI in ACA protections, and addressing knowledge gaps among patients and clinicians to better identify women who might benefit from breast MRI.
On the financial front, the team explained that a central driver for high costs is the scan time for breast MRI, which could be substantially reduced from 30 to 5 minutes, using an abbreviated protocol.
“Widespread use of low‐cost breast abbreviated MRI screening could remove the cost barrier of adding breast MRI screening to ACA coverage,” without compromising diagnostic accuracy, the authors noted.
Further efforts should focus on overcoming cultural barriers, including fear and mistrust of the health care system among Black women. Outreach efforts could include public campaigns or town hall and church gatherings that enlist patient navigators, advocates, or community members.
“Our visibility in the community builds trust and affords us the opportunity to share knowledge that may empower women to be their own health advocates,” the authors wrote.
In terms of the feasibility of revising ACA policies to improve breast MRI access and affordability, Dr. Morrell pointed to improvements made in colon cancer screening.
“Studies have demonstrated that after ACA policy changes lowering out-of-pocket cost for colonoscopies, screening colonoscopy rates significantly increased among men, predominantly in socioeconomically disadvantaged population,” she noted. “Similarly, we should investigate how to this can be applied to screening breast MRI.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite improvements in access to health coverage under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), racial disparities in breast cancer mortality rates persist and the underuse of advanced breast imaging may be one culprit, experts say.
In a recent position statement, researchers highlighted the disproportionally high breast cancer mortality rates among Black women in Louisiana – a state that has one of the highest breast cancer mortality rates in the nation. In 2019, the breast cancer mortality rate among Black women in Louisiana was 29.3 per 100,000 women compared with the national rate of 19.4 per 100,000.
Although Louisiana has made strides in improving access to breast cancer screening in recent years, the use of advanced imaging – specifically breast MRI – remains underused in this high-risk population. A major barrier to wider use of breast MRI has been cost, and ACA expansion led to higher, not lower, out-of-pocket costs for this screening modality.
“Breast MRI is a powerful imaging tool for early detection and for screening women at high risk for breast cancer,” wrote the researchers, led by Brooke L. Morrell, MD, of Louisiana State University Health and Sciences Center, New Orleans.
However, greater access to health care has not necessarily translated to increased breast MRI screening or improved survival among Black women. Even years after the adoption of the ACA, “Black women in Louisiana continue to die of breast cancer at rates significantly greater than the national average,” the authors wrote.
The position statement was published in Cancer.
Breast MRI is known to provide the highest rate of breast cancer detection among commonly used imaging options, with a sensitivity ranging from 81% to 100%. That’s about twice as high as the sensitivity range for mammography after factoring in breast density.
“This is of particular importance when we consider the risk‐based screening of younger populations, in which dense breasts are more prevalent,” the authors explained.
For Black women in particular, studies show nearly a quarter (23%) who develop breast cancer are diagnosed under the age of 50, compared with 16% of White women. Black women are also more likely to develop more aggressive, premenopausal breast cancers, including triple-negative breast cancer, that are more easily detected on MRI.
“Adding supplemental screening breast MRI to annual mammography in higher risk women has been shown to detect up to 18 additional cancers out of 1,000 patients,” Dr. Morrell said. And “many of these cancers are detected much earlier than with mammography alone.”
Still, with ACA expansion, out-of-pocket costs for breast MRI actually increased. This increase likely occurred, in part, because the financial protections outlined in the ACA’s Women’s Preventive Services Guidelines covered mammograms but not breast MRI.
More specifically, under the ACA, Medicaid and most private health insurance plans are required to provide coverage for mammograms at no cost to the patient. The percentage of health plans providing zero cost sharing for mammograms increased under the ACA from 81.9% to 96.8%, but the corresponding rates of zero cost sharing for breast MRI screening went in the opposite direction – from 43.1% in 2009 to only 26.2% in 2017, a 2022 study found.
This study also highlighted geographic variations in zero cost sharing and out-of-pocket costs for screening breast MRI, with a higher financial burden observed for women living in the South. In addition, studies have demonstrated that race and socioeconomic factors, including education and income, play a role in the underuse of screening, including breast MRI.
These factors all likely contribute to screening breast MRI remaining inaccessible to many women, Dr. Morrell and colleagues said.
The authors also outlined three key action items that could help address barriers to MRI breast screening, which include reducing the high cost of breast MRI, lobbying to include breast MRI in ACA protections, and addressing knowledge gaps among patients and clinicians to better identify women who might benefit from breast MRI.
On the financial front, the team explained that a central driver for high costs is the scan time for breast MRI, which could be substantially reduced from 30 to 5 minutes, using an abbreviated protocol.
“Widespread use of low‐cost breast abbreviated MRI screening could remove the cost barrier of adding breast MRI screening to ACA coverage,” without compromising diagnostic accuracy, the authors noted.
Further efforts should focus on overcoming cultural barriers, including fear and mistrust of the health care system among Black women. Outreach efforts could include public campaigns or town hall and church gatherings that enlist patient navigators, advocates, or community members.
“Our visibility in the community builds trust and affords us the opportunity to share knowledge that may empower women to be their own health advocates,” the authors wrote.
In terms of the feasibility of revising ACA policies to improve breast MRI access and affordability, Dr. Morrell pointed to improvements made in colon cancer screening.
“Studies have demonstrated that after ACA policy changes lowering out-of-pocket cost for colonoscopies, screening colonoscopy rates significantly increased among men, predominantly in socioeconomically disadvantaged population,” she noted. “Similarly, we should investigate how to this can be applied to screening breast MRI.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite improvements in access to health coverage under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), racial disparities in breast cancer mortality rates persist and the underuse of advanced breast imaging may be one culprit, experts say.
In a recent position statement, researchers highlighted the disproportionally high breast cancer mortality rates among Black women in Louisiana – a state that has one of the highest breast cancer mortality rates in the nation. In 2019, the breast cancer mortality rate among Black women in Louisiana was 29.3 per 100,000 women compared with the national rate of 19.4 per 100,000.
Although Louisiana has made strides in improving access to breast cancer screening in recent years, the use of advanced imaging – specifically breast MRI – remains underused in this high-risk population. A major barrier to wider use of breast MRI has been cost, and ACA expansion led to higher, not lower, out-of-pocket costs for this screening modality.
“Breast MRI is a powerful imaging tool for early detection and for screening women at high risk for breast cancer,” wrote the researchers, led by Brooke L. Morrell, MD, of Louisiana State University Health and Sciences Center, New Orleans.
However, greater access to health care has not necessarily translated to increased breast MRI screening or improved survival among Black women. Even years after the adoption of the ACA, “Black women in Louisiana continue to die of breast cancer at rates significantly greater than the national average,” the authors wrote.
The position statement was published in Cancer.
Breast MRI is known to provide the highest rate of breast cancer detection among commonly used imaging options, with a sensitivity ranging from 81% to 100%. That’s about twice as high as the sensitivity range for mammography after factoring in breast density.
“This is of particular importance when we consider the risk‐based screening of younger populations, in which dense breasts are more prevalent,” the authors explained.
For Black women in particular, studies show nearly a quarter (23%) who develop breast cancer are diagnosed under the age of 50, compared with 16% of White women. Black women are also more likely to develop more aggressive, premenopausal breast cancers, including triple-negative breast cancer, that are more easily detected on MRI.
“Adding supplemental screening breast MRI to annual mammography in higher risk women has been shown to detect up to 18 additional cancers out of 1,000 patients,” Dr. Morrell said. And “many of these cancers are detected much earlier than with mammography alone.”
Still, with ACA expansion, out-of-pocket costs for breast MRI actually increased. This increase likely occurred, in part, because the financial protections outlined in the ACA’s Women’s Preventive Services Guidelines covered mammograms but not breast MRI.
More specifically, under the ACA, Medicaid and most private health insurance plans are required to provide coverage for mammograms at no cost to the patient. The percentage of health plans providing zero cost sharing for mammograms increased under the ACA from 81.9% to 96.8%, but the corresponding rates of zero cost sharing for breast MRI screening went in the opposite direction – from 43.1% in 2009 to only 26.2% in 2017, a 2022 study found.
This study also highlighted geographic variations in zero cost sharing and out-of-pocket costs for screening breast MRI, with a higher financial burden observed for women living in the South. In addition, studies have demonstrated that race and socioeconomic factors, including education and income, play a role in the underuse of screening, including breast MRI.
These factors all likely contribute to screening breast MRI remaining inaccessible to many women, Dr. Morrell and colleagues said.
The authors also outlined three key action items that could help address barriers to MRI breast screening, which include reducing the high cost of breast MRI, lobbying to include breast MRI in ACA protections, and addressing knowledge gaps among patients and clinicians to better identify women who might benefit from breast MRI.
On the financial front, the team explained that a central driver for high costs is the scan time for breast MRI, which could be substantially reduced from 30 to 5 minutes, using an abbreviated protocol.
“Widespread use of low‐cost breast abbreviated MRI screening could remove the cost barrier of adding breast MRI screening to ACA coverage,” without compromising diagnostic accuracy, the authors noted.
Further efforts should focus on overcoming cultural barriers, including fear and mistrust of the health care system among Black women. Outreach efforts could include public campaigns or town hall and church gatherings that enlist patient navigators, advocates, or community members.
“Our visibility in the community builds trust and affords us the opportunity to share knowledge that may empower women to be their own health advocates,” the authors wrote.
In terms of the feasibility of revising ACA policies to improve breast MRI access and affordability, Dr. Morrell pointed to improvements made in colon cancer screening.
“Studies have demonstrated that after ACA policy changes lowering out-of-pocket cost for colonoscopies, screening colonoscopy rates significantly increased among men, predominantly in socioeconomically disadvantaged population,” she noted. “Similarly, we should investigate how to this can be applied to screening breast MRI.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CANCER
Novel nomogram distinguishes pneumonias
A model incorporating factors such as lymphocytes and lung lesions differentiated adenovirus pneumonias from Chlamydia psittaci (CPP) in a multicenter study of nearly 200 individuals.
Symptoms of pneumonia caused by CPP are often confused with other respiratory infections, particularly adenovirus pneumonia (AVP), which can delay correct diagnosis and impact treatment, Yi Li, MD, of Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, and colleagues wrote. Detailed comparisons of the two conditions are lacking.
In a retrospective study published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases, the researchers examined laboratory, clinical, and radiological differences and created a nomogram to distinguish CPP from AVP. The study population included 78 adults with CPP and 102 with AVP who were seen at a single center in China. The mean ages of the CPP and AVP patients were 61.0 years and 38.5 years, and 57.7% men and 91.2% men, respectively. Patients with CPP were significantly more likely to have hypertension and diabetes at baseline, compared with the AVP group.
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality after hospital admission, which was 10.3% and 14.7% for the CPP and AVP patients, respectively (P = 0.376). However, the incidence of cardiac injury was significantly higher in AVP patients versus those with CPP (48.0% vs. 11.5%; P < 0.001).
In a multivariate analysis, age, sex, nervous system symptoms, lymphocyte count, C-reactive protein level (CRP), and bilateral lung lesions were risk factors for CPP. The researchers combined these factors into a nomogram that showed a concordance value of 0.949 for differentiating between the CPP and AVP groups.
Overall, CPP patients were older, had more nervous system symptoms, and had higher CRP levels, compared with patients with AVP, who were more likely to be men and to have higher lymphocyte percentages and more bilateral lung lesions on chest imaging.
The current study is the first known to provide a way to distinguish CPP and AVP, the researchers wrote. “The antibiotic treatments, prognoses, and life support measures of CPP and AVP are considerably different. Therefore, differentiating the two diseases through early identification of specific clinical characteristics is vital.”
The findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size, retrospective design, and the use of mNGS to diagnose CPP in the absence of standard clinical diagnostic kits, which may have resulted in underestimated CPP incidence, the researchers noted.
However, “the nomogram we established combines patient data on age, sex, and readily available laboratory results to reasonably predict CPP, thus making rapid and direct diagnosis possible,” they said.
The study was supported by the Key R&D Program of Hunan Province, Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Hunan Natural Science Youth Foundation, and the national key clinical specialist construction programs of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A model incorporating factors such as lymphocytes and lung lesions differentiated adenovirus pneumonias from Chlamydia psittaci (CPP) in a multicenter study of nearly 200 individuals.
Symptoms of pneumonia caused by CPP are often confused with other respiratory infections, particularly adenovirus pneumonia (AVP), which can delay correct diagnosis and impact treatment, Yi Li, MD, of Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, and colleagues wrote. Detailed comparisons of the two conditions are lacking.
In a retrospective study published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases, the researchers examined laboratory, clinical, and radiological differences and created a nomogram to distinguish CPP from AVP. The study population included 78 adults with CPP and 102 with AVP who were seen at a single center in China. The mean ages of the CPP and AVP patients were 61.0 years and 38.5 years, and 57.7% men and 91.2% men, respectively. Patients with CPP were significantly more likely to have hypertension and diabetes at baseline, compared with the AVP group.
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality after hospital admission, which was 10.3% and 14.7% for the CPP and AVP patients, respectively (P = 0.376). However, the incidence of cardiac injury was significantly higher in AVP patients versus those with CPP (48.0% vs. 11.5%; P < 0.001).
In a multivariate analysis, age, sex, nervous system symptoms, lymphocyte count, C-reactive protein level (CRP), and bilateral lung lesions were risk factors for CPP. The researchers combined these factors into a nomogram that showed a concordance value of 0.949 for differentiating between the CPP and AVP groups.
Overall, CPP patients were older, had more nervous system symptoms, and had higher CRP levels, compared with patients with AVP, who were more likely to be men and to have higher lymphocyte percentages and more bilateral lung lesions on chest imaging.
The current study is the first known to provide a way to distinguish CPP and AVP, the researchers wrote. “The antibiotic treatments, prognoses, and life support measures of CPP and AVP are considerably different. Therefore, differentiating the two diseases through early identification of specific clinical characteristics is vital.”
The findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size, retrospective design, and the use of mNGS to diagnose CPP in the absence of standard clinical diagnostic kits, which may have resulted in underestimated CPP incidence, the researchers noted.
However, “the nomogram we established combines patient data on age, sex, and readily available laboratory results to reasonably predict CPP, thus making rapid and direct diagnosis possible,” they said.
The study was supported by the Key R&D Program of Hunan Province, Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Hunan Natural Science Youth Foundation, and the national key clinical specialist construction programs of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A model incorporating factors such as lymphocytes and lung lesions differentiated adenovirus pneumonias from Chlamydia psittaci (CPP) in a multicenter study of nearly 200 individuals.
Symptoms of pneumonia caused by CPP are often confused with other respiratory infections, particularly adenovirus pneumonia (AVP), which can delay correct diagnosis and impact treatment, Yi Li, MD, of Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, and colleagues wrote. Detailed comparisons of the two conditions are lacking.
In a retrospective study published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases, the researchers examined laboratory, clinical, and radiological differences and created a nomogram to distinguish CPP from AVP. The study population included 78 adults with CPP and 102 with AVP who were seen at a single center in China. The mean ages of the CPP and AVP patients were 61.0 years and 38.5 years, and 57.7% men and 91.2% men, respectively. Patients with CPP were significantly more likely to have hypertension and diabetes at baseline, compared with the AVP group.
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality after hospital admission, which was 10.3% and 14.7% for the CPP and AVP patients, respectively (P = 0.376). However, the incidence of cardiac injury was significantly higher in AVP patients versus those with CPP (48.0% vs. 11.5%; P < 0.001).
In a multivariate analysis, age, sex, nervous system symptoms, lymphocyte count, C-reactive protein level (CRP), and bilateral lung lesions were risk factors for CPP. The researchers combined these factors into a nomogram that showed a concordance value of 0.949 for differentiating between the CPP and AVP groups.
Overall, CPP patients were older, had more nervous system symptoms, and had higher CRP levels, compared with patients with AVP, who were more likely to be men and to have higher lymphocyte percentages and more bilateral lung lesions on chest imaging.
The current study is the first known to provide a way to distinguish CPP and AVP, the researchers wrote. “The antibiotic treatments, prognoses, and life support measures of CPP and AVP are considerably different. Therefore, differentiating the two diseases through early identification of specific clinical characteristics is vital.”
The findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size, retrospective design, and the use of mNGS to diagnose CPP in the absence of standard clinical diagnostic kits, which may have resulted in underestimated CPP incidence, the researchers noted.
However, “the nomogram we established combines patient data on age, sex, and readily available laboratory results to reasonably predict CPP, thus making rapid and direct diagnosis possible,” they said.
The study was supported by the Key R&D Program of Hunan Province, Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Hunan Natural Science Youth Foundation, and the national key clinical specialist construction programs of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Dermatologists address cultural competence and unconscious biases in the specialty
ORLANDO – When he was applying for residency, Omar N. Qutub, MD, eagerly arrived at his first interview of the day. But he was quickly thrown off his game.
The interviewer, he said, spent a surprising amount of time asking about his ethnicity and his last name. “I think I spent about 3-5 minutes in the first interview talking about my last name,” said Dr. Qutub, who practices in Portland, Ore., during a session titled “unconscious bias and microaggressions in dermatology” at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic and Surgical Conference. “I really would have rather talked about my research interests.” The interaction threw him off for the rest of the interview process, he said.
The experience is an example of how the field has a ways to go in acquiring cultural competence and in overcoming unconscious biases, said Dr. Qutub. In 2020, a review in Clinics in Dermatology referred to a report that dermatology was the second-least diverse medical specialty, only behind orthopedic surgery, because of its low numbers of residents and faculty from groups underrepresented in medicine.
“We really need to put cultural competency at the forefront in order to do better for our patients,” he said.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology and director of the residency program at George Washington University, Washington, who also spoke during the session, said that the process of diversifying the field has to go deeper than the resident interviewing process. “If we just focus on trying to increase the diversity of our applicant pool for residents, it’s too late.”
Nada Elbuluk, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, pointed to USC’s Derm RISES initiative, a service program that aims to reach inner-city students through education in the sciences, starting from kindergarten to 12th grade. The program also includes premed undergraduate and medical students, “with the goal of increasing exposure to the sciences, medicine, and dermatology,” according to the USC website. “It’s crucial to begin the process early to get a high yield of students who reach medical school and eventually dermatology, she said, because of the inevitable attrition at each level of the education process.
“It’s incredibly rewarding,” added Dr. Elbuluk, who is also director of the dermatology diversity and inclusion program at USC. “And we get these thank-you letters back from students who [say], ‘I didn’t know I could be a doctor.’ ”
In another presentation, Kavita Mariwalla, MD, who practices in West Islip, N.Y., provided tips on boosting cultural competence during aesthetic consults.
One was to “know your fillers,” she said, noting that fillers have different effects on different skin tones, because of differences in fibroblast content, and fat cells will interact with fillers in different ways across skin tones.
Another is to “understand the shortfall of facial canons,” the idea that you can divide a face into sections that can be viewed and enhanced discretely. This concept was based on a White European model and has to be expanded when considering other ethnicities, Dr. Mariwalla said.
Overgeneralizing categories is another pitfall, she said. “Asian” is a term that covers countries from India to Japan, but within that category are a multitude of notions and nuances about aesthetics, and dermatologists have to be sensitive to all of them.
When meeting with a patient, Dr. Mariwalla said, asking the typical “Where are you from?” is not a helpful question. Instead, she suggested asking: “What is your cultural background? Can you tell me more about what your expectations are?”
“I ask for pictures,” she said. “I want to know what they looked like as a kid. I want to know what their family looks like. And I always hand patients a mirror. Patients will say to me: ‘I want to do what you think.’ It’s not about what I think, because what I see, and what you see in your magnifying mirror, are totally different things.”
After the session ended, a member of the audience, Sharon Stokes, MD, a dermatologist in the Orlando area, provided her view of the presentations, noting that it was an important discussion.
“I think it’s past time in medicine for cultural diversity training and awareness for physicians to understand their patients better and getting to know them – and how to even approach the patient and not to offensively and microaggressively approach the patient,” she said.
Dr. Elbuluk reported relevant relationships with Avita, Incyte, Beiersdorf, and other companies. Dr. Friedman reported financial relationships with Sanova, Pfizer, Novartis and other companies. Dr. Mariwalla reported relevant financial relationships with Abbvie, Sanofi, Regeneron and other companies. Dr. Qutub reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Qutub is the ODAC director of equity, diversity, and inclusion.
ORLANDO – When he was applying for residency, Omar N. Qutub, MD, eagerly arrived at his first interview of the day. But he was quickly thrown off his game.
The interviewer, he said, spent a surprising amount of time asking about his ethnicity and his last name. “I think I spent about 3-5 minutes in the first interview talking about my last name,” said Dr. Qutub, who practices in Portland, Ore., during a session titled “unconscious bias and microaggressions in dermatology” at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic and Surgical Conference. “I really would have rather talked about my research interests.” The interaction threw him off for the rest of the interview process, he said.
The experience is an example of how the field has a ways to go in acquiring cultural competence and in overcoming unconscious biases, said Dr. Qutub. In 2020, a review in Clinics in Dermatology referred to a report that dermatology was the second-least diverse medical specialty, only behind orthopedic surgery, because of its low numbers of residents and faculty from groups underrepresented in medicine.
“We really need to put cultural competency at the forefront in order to do better for our patients,” he said.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology and director of the residency program at George Washington University, Washington, who also spoke during the session, said that the process of diversifying the field has to go deeper than the resident interviewing process. “If we just focus on trying to increase the diversity of our applicant pool for residents, it’s too late.”
Nada Elbuluk, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, pointed to USC’s Derm RISES initiative, a service program that aims to reach inner-city students through education in the sciences, starting from kindergarten to 12th grade. The program also includes premed undergraduate and medical students, “with the goal of increasing exposure to the sciences, medicine, and dermatology,” according to the USC website. “It’s crucial to begin the process early to get a high yield of students who reach medical school and eventually dermatology, she said, because of the inevitable attrition at each level of the education process.
“It’s incredibly rewarding,” added Dr. Elbuluk, who is also director of the dermatology diversity and inclusion program at USC. “And we get these thank-you letters back from students who [say], ‘I didn’t know I could be a doctor.’ ”
In another presentation, Kavita Mariwalla, MD, who practices in West Islip, N.Y., provided tips on boosting cultural competence during aesthetic consults.
One was to “know your fillers,” she said, noting that fillers have different effects on different skin tones, because of differences in fibroblast content, and fat cells will interact with fillers in different ways across skin tones.
Another is to “understand the shortfall of facial canons,” the idea that you can divide a face into sections that can be viewed and enhanced discretely. This concept was based on a White European model and has to be expanded when considering other ethnicities, Dr. Mariwalla said.
Overgeneralizing categories is another pitfall, she said. “Asian” is a term that covers countries from India to Japan, but within that category are a multitude of notions and nuances about aesthetics, and dermatologists have to be sensitive to all of them.
When meeting with a patient, Dr. Mariwalla said, asking the typical “Where are you from?” is not a helpful question. Instead, she suggested asking: “What is your cultural background? Can you tell me more about what your expectations are?”
“I ask for pictures,” she said. “I want to know what they looked like as a kid. I want to know what their family looks like. And I always hand patients a mirror. Patients will say to me: ‘I want to do what you think.’ It’s not about what I think, because what I see, and what you see in your magnifying mirror, are totally different things.”
After the session ended, a member of the audience, Sharon Stokes, MD, a dermatologist in the Orlando area, provided her view of the presentations, noting that it was an important discussion.
“I think it’s past time in medicine for cultural diversity training and awareness for physicians to understand their patients better and getting to know them – and how to even approach the patient and not to offensively and microaggressively approach the patient,” she said.
Dr. Elbuluk reported relevant relationships with Avita, Incyte, Beiersdorf, and other companies. Dr. Friedman reported financial relationships with Sanova, Pfizer, Novartis and other companies. Dr. Mariwalla reported relevant financial relationships with Abbvie, Sanofi, Regeneron and other companies. Dr. Qutub reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Qutub is the ODAC director of equity, diversity, and inclusion.
ORLANDO – When he was applying for residency, Omar N. Qutub, MD, eagerly arrived at his first interview of the day. But he was quickly thrown off his game.
The interviewer, he said, spent a surprising amount of time asking about his ethnicity and his last name. “I think I spent about 3-5 minutes in the first interview talking about my last name,” said Dr. Qutub, who practices in Portland, Ore., during a session titled “unconscious bias and microaggressions in dermatology” at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic and Surgical Conference. “I really would have rather talked about my research interests.” The interaction threw him off for the rest of the interview process, he said.
The experience is an example of how the field has a ways to go in acquiring cultural competence and in overcoming unconscious biases, said Dr. Qutub. In 2020, a review in Clinics in Dermatology referred to a report that dermatology was the second-least diverse medical specialty, only behind orthopedic surgery, because of its low numbers of residents and faculty from groups underrepresented in medicine.
“We really need to put cultural competency at the forefront in order to do better for our patients,” he said.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology and director of the residency program at George Washington University, Washington, who also spoke during the session, said that the process of diversifying the field has to go deeper than the resident interviewing process. “If we just focus on trying to increase the diversity of our applicant pool for residents, it’s too late.”
Nada Elbuluk, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, pointed to USC’s Derm RISES initiative, a service program that aims to reach inner-city students through education in the sciences, starting from kindergarten to 12th grade. The program also includes premed undergraduate and medical students, “with the goal of increasing exposure to the sciences, medicine, and dermatology,” according to the USC website. “It’s crucial to begin the process early to get a high yield of students who reach medical school and eventually dermatology, she said, because of the inevitable attrition at each level of the education process.
“It’s incredibly rewarding,” added Dr. Elbuluk, who is also director of the dermatology diversity and inclusion program at USC. “And we get these thank-you letters back from students who [say], ‘I didn’t know I could be a doctor.’ ”
In another presentation, Kavita Mariwalla, MD, who practices in West Islip, N.Y., provided tips on boosting cultural competence during aesthetic consults.
One was to “know your fillers,” she said, noting that fillers have different effects on different skin tones, because of differences in fibroblast content, and fat cells will interact with fillers in different ways across skin tones.
Another is to “understand the shortfall of facial canons,” the idea that you can divide a face into sections that can be viewed and enhanced discretely. This concept was based on a White European model and has to be expanded when considering other ethnicities, Dr. Mariwalla said.
Overgeneralizing categories is another pitfall, she said. “Asian” is a term that covers countries from India to Japan, but within that category are a multitude of notions and nuances about aesthetics, and dermatologists have to be sensitive to all of them.
When meeting with a patient, Dr. Mariwalla said, asking the typical “Where are you from?” is not a helpful question. Instead, she suggested asking: “What is your cultural background? Can you tell me more about what your expectations are?”
“I ask for pictures,” she said. “I want to know what they looked like as a kid. I want to know what their family looks like. And I always hand patients a mirror. Patients will say to me: ‘I want to do what you think.’ It’s not about what I think, because what I see, and what you see in your magnifying mirror, are totally different things.”
After the session ended, a member of the audience, Sharon Stokes, MD, a dermatologist in the Orlando area, provided her view of the presentations, noting that it was an important discussion.
“I think it’s past time in medicine for cultural diversity training and awareness for physicians to understand their patients better and getting to know them – and how to even approach the patient and not to offensively and microaggressively approach the patient,” she said.
Dr. Elbuluk reported relevant relationships with Avita, Incyte, Beiersdorf, and other companies. Dr. Friedman reported financial relationships with Sanova, Pfizer, Novartis and other companies. Dr. Mariwalla reported relevant financial relationships with Abbvie, Sanofi, Regeneron and other companies. Dr. Qutub reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Qutub is the ODAC director of equity, diversity, and inclusion.
AT ODAC 2023
Two AI optical diagnosis systems appear clinically comparable for small colorectal polyps
In a head-to-head comparison, two commercially available computer-aided diagnosis systems appeared clinically equivalent for the optical diagnosis of small colorectal polyps, according to a research letter published in Gastroenterology.
For the optical diagnosis of diminutive colorectal polyps, the comparable performances of both CAD EYE (Fujifilm Co.) and GI Genius (Medtronic) met cutoff guidelines to implement the cost-saving leave-in-situ and resect-and-discard strategies, wrote Cesare Hassan, MD, PhD, associate professor of gastroenterology at Humanitas University and member of the endoscopy unit at Humanitas Clinical Research Hospital in Milan, and colleagues.
“Screening colonoscopy is effective in reducing colorectal cancer risk but also represents a substantial financial burden,” the authors wrote. “Novel strategies based on artificial intelligence may enable targeted removal only of polyps deemed to be neoplastic, thus reducing patient burden for unnecessary removal of nonneoplastic polyps and reducing costs for histopathology.”
Several computer-aided diagnosis (CADx) systems are commercially available for optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps, the authors wrote. However, each artificial intelligence (AI) system has been trained and validated with different polyp datasets, which may contribute to variability and affect the clinical outcome of optical diagnosis-based strategies.
Dr. Hassan and colleagues conducted a prospective comparison trial at a single center to look at the real-life performances of two CADx systems on optical diagnosis of polyps smaller than 5 mm.
At colonoscopy, the same polyp was visualized by the same endoscopist on two different monitors simultaneously with the respective output from each of the two CADx systems. Pre- and post-CADx human diagnoses were also collected.
Between January 2022 and March 2022, 176 consecutive patients age 40 and older underwent colonoscopy for colorectal cancer screening, polypectomy surveillance, or gastrointestinal symptoms. About 60.8% of participants were men, and the average age was 60.
Among 543 polyps detected and removed, 169 (31.3%) were adenomas, and 373 (68.7%) were nonadenomas. Of those, 325 (59.9%) were rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less in diameter and eligible for analyses in the study. This included 44 adenomas (13.5%) and 281 nonadenomas (86.5%).
The two CADx systems were grouped as CADx-A for CAD EYE and CADx-B for GI Genius. CADx-A provided prediction output for all 325 rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less, whereas CADx-B wasn’t able to provide output for six of the nonadenomas, which were excluded from the analysis.
The negative predictive value (NPV) for rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less was 97% for CADx-A and 97.7% for CADx-B, the authors wrote. The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommends a threshold for optical diagnosis of at least 90%.
In addition, the sensitivity for adenomas was 81.8% for CADx-A and 86.4% for CADx-B. The accuracy of CADx-A was slightly higher, at 93.2%, as compared with 91.5% for CADx-B.
Based on AI prediction alone, 269 of 319 polyps (84.3%) with CADx-A and 260 of 319 polyps (81.5%) with CADx-B would have been classified as nonneoplastic and avoided removal. This corresponded to a specificity of 94.9% for CADx-A and 92.4% for CADx-B, which wasn’t significantly different, the authors wrote. Concordance in histology prediction between the two systems was 94.7%.
Based on the 2020 U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer (USMSTF) guidelines, the agreement with histopathology in surveillance interval assignment was 84.7% for CADx-A and 89.2% for CADx-B. Based on the 2020 European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) guidelines, the agreement was 98.3% for both systems.
For rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less, the NPV of unassisted optical diagnosis was 97.8% for a high-confidence diagnosis, but it wasn’t significantly different from the NPV of CADx-A (96.9%) or CADx-B (97.6%). The NPV of a CADx-assisted optical diagnosis at high confidence was 97.7%, without statistically significant differences as compared with unassisted interpretation.
Based on the 2020 USMSTF and ESGE guidelines, the agreement between unassisted interpretation and histopathology in surveillance interval assignment was 92.6% and 98.9%, respectively. There was total agreement between unassisted interpretation and CADx-assisted interpretation in surveillance interval assignment based on both guidelines.
As in previous findings, unassisted endoscopic diagnosis was on par with CADx-assisted, both in technical accuracy and clinical outcomes. The study authors attributed the lack of additional benefit from CADx to a high performance of unassisted-endoscopist diagnosis, with the 97.8% NPV for rectosigmoid polyps and 90% or greater concordance in postpolypectomy surveillance intervals with histology. In addition, a human endoscopist was the only one to achieve 90% or greater agreement in postpolypectomy surveillance intervals under the U.S. guidelines, mainly due to a very high specificity.
“This confirms the complexity of the human-machine interaction that should not be marginalized in the stand-alone performance of the machine,” the authors wrote.
However, the high accuracy of unassisted endoscopists in the academic center in Italy is unlikely to mirror the real performance in community settings, they added. Future studies should focus on nontertiary centers to show the additional benefit, if any, that CADx provides for leave-in-situ colorectal polyps.
“A high degree of concordance in clinical outcomes was shown when directly comparing in vivo two different systems of CADx,” the authors concluded. “This reassured our confidence in the standardization of performance that may be achieved with the incorporation of AI in clinical practice, irrespective of the availability of multiple systems.”
The study authors declared no funding source for this study. Several authors reported consulting relationships with numerous companies, including Fuji and Medtronic, which make the CAD EYE and GI Genius systems, respectively.
Colonoscopy is the gold standard test to reduce an individual’s chance of developing colorectal cancer. The latest tool to improve colonoscopy outcomes is integrating artificial intelligence (AI) during the exam. AI systems offer both computer aided detection (CADe) as well as diagnosis (CADx). Accurate CADx could lead to a cost-effective strategy of removing only neoplastic polyps.
The study by Hassan et al. compared two AI CADx systems for optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps ≤ 5 mm. Polyps were simultaneously evaluated by both AI systems, but initially the endoscopist performed a CADx unassisted diagnosis. The two systems (CAD EYE [Fujifilm Co.] and GI Genius [Medtronic]) had similar specificity: 94.9% and 92.4%, respectively. Furthermore, the systems demonstrated negative predictive values of 96.9% and 97.6%, respectively, which exceeds the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy’s threshold of at least 90%.
A surprising finding was the unassisted endoscopist before CADx interpretation had a polyp diagnosis accuracy of 97.8%, resulting in negligible benefit when CADx was activated. However, this level of polyp interpretation is likely lower in community practice, but clinical trials will be needed.
There is rapid development of CADx and CADe systems entering the clinical realm of colonoscopy. It is critical to have the ability to objectively review the performance of these AI systems in a real-life clinical setting to assess accuracy for both CADx and CADe. Clinicians must balance striving for high quality colonoscopy outcomes with the cost of innovative technology like AI. However, it is reassuring that the initial CADx systems have similar high-performance accuracy for polyp interpretation, since most practices will incorporate a single system. Future studies will be needed to compare not only the accuracy of AI platforms offering CADx and CADe, but also the many other features that will be entering the endoscopy space.
Seth A. Gross, MD, is professor of medicine at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and clinical chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at NYU Langone Health. He disclosed financial relationships with Medtronic, Olympus, Iterative Scopes, and Micro-Tech Endoscopy.
Colonoscopy is the gold standard test to reduce an individual’s chance of developing colorectal cancer. The latest tool to improve colonoscopy outcomes is integrating artificial intelligence (AI) during the exam. AI systems offer both computer aided detection (CADe) as well as diagnosis (CADx). Accurate CADx could lead to a cost-effective strategy of removing only neoplastic polyps.
The study by Hassan et al. compared two AI CADx systems for optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps ≤ 5 mm. Polyps were simultaneously evaluated by both AI systems, but initially the endoscopist performed a CADx unassisted diagnosis. The two systems (CAD EYE [Fujifilm Co.] and GI Genius [Medtronic]) had similar specificity: 94.9% and 92.4%, respectively. Furthermore, the systems demonstrated negative predictive values of 96.9% and 97.6%, respectively, which exceeds the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy’s threshold of at least 90%.
A surprising finding was the unassisted endoscopist before CADx interpretation had a polyp diagnosis accuracy of 97.8%, resulting in negligible benefit when CADx was activated. However, this level of polyp interpretation is likely lower in community practice, but clinical trials will be needed.
There is rapid development of CADx and CADe systems entering the clinical realm of colonoscopy. It is critical to have the ability to objectively review the performance of these AI systems in a real-life clinical setting to assess accuracy for both CADx and CADe. Clinicians must balance striving for high quality colonoscopy outcomes with the cost of innovative technology like AI. However, it is reassuring that the initial CADx systems have similar high-performance accuracy for polyp interpretation, since most practices will incorporate a single system. Future studies will be needed to compare not only the accuracy of AI platforms offering CADx and CADe, but also the many other features that will be entering the endoscopy space.
Seth A. Gross, MD, is professor of medicine at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and clinical chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at NYU Langone Health. He disclosed financial relationships with Medtronic, Olympus, Iterative Scopes, and Micro-Tech Endoscopy.
Colonoscopy is the gold standard test to reduce an individual’s chance of developing colorectal cancer. The latest tool to improve colonoscopy outcomes is integrating artificial intelligence (AI) during the exam. AI systems offer both computer aided detection (CADe) as well as diagnosis (CADx). Accurate CADx could lead to a cost-effective strategy of removing only neoplastic polyps.
The study by Hassan et al. compared two AI CADx systems for optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps ≤ 5 mm. Polyps were simultaneously evaluated by both AI systems, but initially the endoscopist performed a CADx unassisted diagnosis. The two systems (CAD EYE [Fujifilm Co.] and GI Genius [Medtronic]) had similar specificity: 94.9% and 92.4%, respectively. Furthermore, the systems demonstrated negative predictive values of 96.9% and 97.6%, respectively, which exceeds the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy’s threshold of at least 90%.
A surprising finding was the unassisted endoscopist before CADx interpretation had a polyp diagnosis accuracy of 97.8%, resulting in negligible benefit when CADx was activated. However, this level of polyp interpretation is likely lower in community practice, but clinical trials will be needed.
There is rapid development of CADx and CADe systems entering the clinical realm of colonoscopy. It is critical to have the ability to objectively review the performance of these AI systems in a real-life clinical setting to assess accuracy for both CADx and CADe. Clinicians must balance striving for high quality colonoscopy outcomes with the cost of innovative technology like AI. However, it is reassuring that the initial CADx systems have similar high-performance accuracy for polyp interpretation, since most practices will incorporate a single system. Future studies will be needed to compare not only the accuracy of AI platforms offering CADx and CADe, but also the many other features that will be entering the endoscopy space.
Seth A. Gross, MD, is professor of medicine at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and clinical chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at NYU Langone Health. He disclosed financial relationships with Medtronic, Olympus, Iterative Scopes, and Micro-Tech Endoscopy.
In a head-to-head comparison, two commercially available computer-aided diagnosis systems appeared clinically equivalent for the optical diagnosis of small colorectal polyps, according to a research letter published in Gastroenterology.
For the optical diagnosis of diminutive colorectal polyps, the comparable performances of both CAD EYE (Fujifilm Co.) and GI Genius (Medtronic) met cutoff guidelines to implement the cost-saving leave-in-situ and resect-and-discard strategies, wrote Cesare Hassan, MD, PhD, associate professor of gastroenterology at Humanitas University and member of the endoscopy unit at Humanitas Clinical Research Hospital in Milan, and colleagues.
“Screening colonoscopy is effective in reducing colorectal cancer risk but also represents a substantial financial burden,” the authors wrote. “Novel strategies based on artificial intelligence may enable targeted removal only of polyps deemed to be neoplastic, thus reducing patient burden for unnecessary removal of nonneoplastic polyps and reducing costs for histopathology.”
Several computer-aided diagnosis (CADx) systems are commercially available for optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps, the authors wrote. However, each artificial intelligence (AI) system has been trained and validated with different polyp datasets, which may contribute to variability and affect the clinical outcome of optical diagnosis-based strategies.
Dr. Hassan and colleagues conducted a prospective comparison trial at a single center to look at the real-life performances of two CADx systems on optical diagnosis of polyps smaller than 5 mm.
At colonoscopy, the same polyp was visualized by the same endoscopist on two different monitors simultaneously with the respective output from each of the two CADx systems. Pre- and post-CADx human diagnoses were also collected.
Between January 2022 and March 2022, 176 consecutive patients age 40 and older underwent colonoscopy for colorectal cancer screening, polypectomy surveillance, or gastrointestinal symptoms. About 60.8% of participants were men, and the average age was 60.
Among 543 polyps detected and removed, 169 (31.3%) were adenomas, and 373 (68.7%) were nonadenomas. Of those, 325 (59.9%) were rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less in diameter and eligible for analyses in the study. This included 44 adenomas (13.5%) and 281 nonadenomas (86.5%).
The two CADx systems were grouped as CADx-A for CAD EYE and CADx-B for GI Genius. CADx-A provided prediction output for all 325 rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less, whereas CADx-B wasn’t able to provide output for six of the nonadenomas, which were excluded from the analysis.
The negative predictive value (NPV) for rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less was 97% for CADx-A and 97.7% for CADx-B, the authors wrote. The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommends a threshold for optical diagnosis of at least 90%.
In addition, the sensitivity for adenomas was 81.8% for CADx-A and 86.4% for CADx-B. The accuracy of CADx-A was slightly higher, at 93.2%, as compared with 91.5% for CADx-B.
Based on AI prediction alone, 269 of 319 polyps (84.3%) with CADx-A and 260 of 319 polyps (81.5%) with CADx-B would have been classified as nonneoplastic and avoided removal. This corresponded to a specificity of 94.9% for CADx-A and 92.4% for CADx-B, which wasn’t significantly different, the authors wrote. Concordance in histology prediction between the two systems was 94.7%.
Based on the 2020 U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer (USMSTF) guidelines, the agreement with histopathology in surveillance interval assignment was 84.7% for CADx-A and 89.2% for CADx-B. Based on the 2020 European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) guidelines, the agreement was 98.3% for both systems.
For rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less, the NPV of unassisted optical diagnosis was 97.8% for a high-confidence diagnosis, but it wasn’t significantly different from the NPV of CADx-A (96.9%) or CADx-B (97.6%). The NPV of a CADx-assisted optical diagnosis at high confidence was 97.7%, without statistically significant differences as compared with unassisted interpretation.
Based on the 2020 USMSTF and ESGE guidelines, the agreement between unassisted interpretation and histopathology in surveillance interval assignment was 92.6% and 98.9%, respectively. There was total agreement between unassisted interpretation and CADx-assisted interpretation in surveillance interval assignment based on both guidelines.
As in previous findings, unassisted endoscopic diagnosis was on par with CADx-assisted, both in technical accuracy and clinical outcomes. The study authors attributed the lack of additional benefit from CADx to a high performance of unassisted-endoscopist diagnosis, with the 97.8% NPV for rectosigmoid polyps and 90% or greater concordance in postpolypectomy surveillance intervals with histology. In addition, a human endoscopist was the only one to achieve 90% or greater agreement in postpolypectomy surveillance intervals under the U.S. guidelines, mainly due to a very high specificity.
“This confirms the complexity of the human-machine interaction that should not be marginalized in the stand-alone performance of the machine,” the authors wrote.
However, the high accuracy of unassisted endoscopists in the academic center in Italy is unlikely to mirror the real performance in community settings, they added. Future studies should focus on nontertiary centers to show the additional benefit, if any, that CADx provides for leave-in-situ colorectal polyps.
“A high degree of concordance in clinical outcomes was shown when directly comparing in vivo two different systems of CADx,” the authors concluded. “This reassured our confidence in the standardization of performance that may be achieved with the incorporation of AI in clinical practice, irrespective of the availability of multiple systems.”
The study authors declared no funding source for this study. Several authors reported consulting relationships with numerous companies, including Fuji and Medtronic, which make the CAD EYE and GI Genius systems, respectively.
In a head-to-head comparison, two commercially available computer-aided diagnosis systems appeared clinically equivalent for the optical diagnosis of small colorectal polyps, according to a research letter published in Gastroenterology.
For the optical diagnosis of diminutive colorectal polyps, the comparable performances of both CAD EYE (Fujifilm Co.) and GI Genius (Medtronic) met cutoff guidelines to implement the cost-saving leave-in-situ and resect-and-discard strategies, wrote Cesare Hassan, MD, PhD, associate professor of gastroenterology at Humanitas University and member of the endoscopy unit at Humanitas Clinical Research Hospital in Milan, and colleagues.
“Screening colonoscopy is effective in reducing colorectal cancer risk but also represents a substantial financial burden,” the authors wrote. “Novel strategies based on artificial intelligence may enable targeted removal only of polyps deemed to be neoplastic, thus reducing patient burden for unnecessary removal of nonneoplastic polyps and reducing costs for histopathology.”
Several computer-aided diagnosis (CADx) systems are commercially available for optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps, the authors wrote. However, each artificial intelligence (AI) system has been trained and validated with different polyp datasets, which may contribute to variability and affect the clinical outcome of optical diagnosis-based strategies.
Dr. Hassan and colleagues conducted a prospective comparison trial at a single center to look at the real-life performances of two CADx systems on optical diagnosis of polyps smaller than 5 mm.
At colonoscopy, the same polyp was visualized by the same endoscopist on two different monitors simultaneously with the respective output from each of the two CADx systems. Pre- and post-CADx human diagnoses were also collected.
Between January 2022 and March 2022, 176 consecutive patients age 40 and older underwent colonoscopy for colorectal cancer screening, polypectomy surveillance, or gastrointestinal symptoms. About 60.8% of participants were men, and the average age was 60.
Among 543 polyps detected and removed, 169 (31.3%) were adenomas, and 373 (68.7%) were nonadenomas. Of those, 325 (59.9%) were rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less in diameter and eligible for analyses in the study. This included 44 adenomas (13.5%) and 281 nonadenomas (86.5%).
The two CADx systems were grouped as CADx-A for CAD EYE and CADx-B for GI Genius. CADx-A provided prediction output for all 325 rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less, whereas CADx-B wasn’t able to provide output for six of the nonadenomas, which were excluded from the analysis.
The negative predictive value (NPV) for rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less was 97% for CADx-A and 97.7% for CADx-B, the authors wrote. The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommends a threshold for optical diagnosis of at least 90%.
In addition, the sensitivity for adenomas was 81.8% for CADx-A and 86.4% for CADx-B. The accuracy of CADx-A was slightly higher, at 93.2%, as compared with 91.5% for CADx-B.
Based on AI prediction alone, 269 of 319 polyps (84.3%) with CADx-A and 260 of 319 polyps (81.5%) with CADx-B would have been classified as nonneoplastic and avoided removal. This corresponded to a specificity of 94.9% for CADx-A and 92.4% for CADx-B, which wasn’t significantly different, the authors wrote. Concordance in histology prediction between the two systems was 94.7%.
Based on the 2020 U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer (USMSTF) guidelines, the agreement with histopathology in surveillance interval assignment was 84.7% for CADx-A and 89.2% for CADx-B. Based on the 2020 European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) guidelines, the agreement was 98.3% for both systems.
For rectosigmoid polyps of 5 mm or less, the NPV of unassisted optical diagnosis was 97.8% for a high-confidence diagnosis, but it wasn’t significantly different from the NPV of CADx-A (96.9%) or CADx-B (97.6%). The NPV of a CADx-assisted optical diagnosis at high confidence was 97.7%, without statistically significant differences as compared with unassisted interpretation.
Based on the 2020 USMSTF and ESGE guidelines, the agreement between unassisted interpretation and histopathology in surveillance interval assignment was 92.6% and 98.9%, respectively. There was total agreement between unassisted interpretation and CADx-assisted interpretation in surveillance interval assignment based on both guidelines.
As in previous findings, unassisted endoscopic diagnosis was on par with CADx-assisted, both in technical accuracy and clinical outcomes. The study authors attributed the lack of additional benefit from CADx to a high performance of unassisted-endoscopist diagnosis, with the 97.8% NPV for rectosigmoid polyps and 90% or greater concordance in postpolypectomy surveillance intervals with histology. In addition, a human endoscopist was the only one to achieve 90% or greater agreement in postpolypectomy surveillance intervals under the U.S. guidelines, mainly due to a very high specificity.
“This confirms the complexity of the human-machine interaction that should not be marginalized in the stand-alone performance of the machine,” the authors wrote.
However, the high accuracy of unassisted endoscopists in the academic center in Italy is unlikely to mirror the real performance in community settings, they added. Future studies should focus on nontertiary centers to show the additional benefit, if any, that CADx provides for leave-in-situ colorectal polyps.
“A high degree of concordance in clinical outcomes was shown when directly comparing in vivo two different systems of CADx,” the authors concluded. “This reassured our confidence in the standardization of performance that may be achieved with the incorporation of AI in clinical practice, irrespective of the availability of multiple systems.”
The study authors declared no funding source for this study. Several authors reported consulting relationships with numerous companies, including Fuji and Medtronic, which make the CAD EYE and GI Genius systems, respectively.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Even one head injury boosts all-cause mortality risk
An analysis of more than 13,000 adult participants in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study showed a dose-response pattern in which one head injury was linked to a 66% increased risk for all-cause mortality, and two or more head injuries were associated with twice the risk in comparison with no head injuries.
These findings underscore the importance of preventing head injuries and of swift clinical intervention once a head injury occurs, lead author Holly Elser, MD, PhD, department of neurology, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Clinicians should counsel patients who are at risk for falls about head injuries and ensure patients are promptly evaluated in the hospital setting if they do have a fall – especially with loss of consciousness or other symptoms, such as headache or dizziness,” Dr. Elser added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Consistent evidence
There is “pretty consistent evidence” that mortality rates are increased in the short term after head injury, predominantly among hospitalized patients, Dr. Elser noted.
“But there’s less evidence about the long-term mortality implications of head injuries and less evidence from adults living in the community,” she added.
The analysis included 13,037 participants in the ARIC study, an ongoing study involving adults aged 45-65 years who were recruited from four geographically and racially diverse U.S. communities. The mean age at baseline (1987-1989) was 54 years; 57.7% were women; and 27.9% were Black.
Study participants are followed at routine in-person visits and semiannually via telephone.
Data on head injuries came from hospital diagnostic codes and self-reports. These reports included information on the number of injuries and whether the injury required medical care and involved loss of consciousness.
During the 27-year follow-up, 18.4% of the study sample had at least one head injury. Injuries occurred more frequently among women, which may reflect the predominance of women in the study population, said Dr. Elser.
Overall, about 56% of participants died during the study period. The estimated median amount of survival time after head injury was 4.7 years.
The most common causes of death were neoplasm, cardiovascular disease, and neurologic disorders. Regarding specific neurologic causes of death, the researchers found that 62.2% of deaths were due to neurodegenerative disease among individuals with head injury, vs. 51.4% among those without head injury.
This, said Dr. Elser, raises the possibility of reverse causality. “If you have a neurodegenerative disorder like Alzheimer’s disease dementia or Parkinson’s disease that leads to difficulty walking, you may be more likely to fall and have a head injury. The head injury in turn may lead to increased mortality,” she noted.
However, she stressed that the data on cause-specific mortality are exploratory. “Our research motivates future studies that really examine this time-dependent relationship between neurodegenerative disease and head injuries,” Dr. Elser said.
Dose-dependent response
In the unadjusted analysis, the hazard ratio of mortality among individuals with head injury was 2.21 (95% confidence interval, 2.09-2.34) compared with those who did not have head injury.
The association remained significant with adjustment for sociodemographic factors (HR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.88-2.11) and with additional adjustment for vascular risk factors (HR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.81-2.03).
The findings also showed a dose-response pattern in the association of head injuries with mortality. Compared with participants who did not have head injury, the HR was 1.66 (95% CI, 1.56-1.77) for those with one head injury and 2.11 (95% CI, 1.89-2.37) for those with two or more head injuries.
“It’s not as though once you’ve had one head injury, you’ve accrued all the damage you possibly can. We see pretty clearly here that recurrent head injury further increased the rate of deaths from all causes,” said Dr. Elser.
Injury severity was determined from hospital diagnostic codes using established algorithms. Results showed that mortality rates were increased with even mild head injury.
Interestingly, the association between head injury and all-cause mortality was weaker among those whose injuries were self-reported. One possibility is that these injuries were less severe, Dr. Elser noted.
“If you have head injury that’s mild enough that you don’t need to go to the hospital, it’s probably going to confer less long-term health risks than one that’s severe enough that you needed to be examined in an acute care setting,” she said.
Results were similar by race and for sex. “Even though there were more women with head injuries, the rate of mortality associated with head injury doesn’t differ from the rate among men,” Dr. Elser reported.
However, the association was stronger among those younger than 54 years at baseline (HR, 2.26) compared with older individuals (HR, 2.0) in the model that adjusted for demographics and lifestyle factors.
This may be explained by the reference group (those without a head injury) – the mortality rate was in general higher for the older participants, said Dr. Elser. It could also be that younger adults are more likely to have severe head injuries from, for example, motor vehicle accidents or violence, she added.
These new findings underscore the importance of public health measures, such as seatbelt laws, to reduce head injuries, the investigators note.
They add that clinicians with patients at risk for head injuries may recommend steps to lessen the risk of falls, such as having access to durable medical equipment, and ensuring driver safety.
Shorter life span
Commenting for this news organization, Frank Conidi, MD, director of the Florida Center for Headache and Sports Neurology in Port St. Lucie and past president of the Florida Society of Neurology, said the large number of participants “adds validity” to the finding that individuals with head injury are likely to have a shorter life span than those who do not suffer head trauma – and that this “was not purely by chance or from other causes.”
However, patients may not have accurately reported head injuries, in which case the rate of injury in the self-report subgroup would not reflect the actual incidence, noted Dr. Conidi, who was not involved with the research.
“In my practice, most patients have little knowledge as to the signs and symptoms of concussion and traumatic brain injury. Most think there needs to be some form of loss of consciousness to have a head injury, which is of course not true,” he said.
Dr. Conidi added that the finding of a higher incidence of death from neurodegenerative disorders supports the generally accepted consensus view that about 30% of patients with traumatic brain injury experience progression of symptoms and are at risk for early dementia.
The ARIC study is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Elser and Dr. Conidi have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
An analysis of more than 13,000 adult participants in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study showed a dose-response pattern in which one head injury was linked to a 66% increased risk for all-cause mortality, and two or more head injuries were associated with twice the risk in comparison with no head injuries.
These findings underscore the importance of preventing head injuries and of swift clinical intervention once a head injury occurs, lead author Holly Elser, MD, PhD, department of neurology, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Clinicians should counsel patients who are at risk for falls about head injuries and ensure patients are promptly evaluated in the hospital setting if they do have a fall – especially with loss of consciousness or other symptoms, such as headache or dizziness,” Dr. Elser added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Consistent evidence
There is “pretty consistent evidence” that mortality rates are increased in the short term after head injury, predominantly among hospitalized patients, Dr. Elser noted.
“But there’s less evidence about the long-term mortality implications of head injuries and less evidence from adults living in the community,” she added.
The analysis included 13,037 participants in the ARIC study, an ongoing study involving adults aged 45-65 years who were recruited from four geographically and racially diverse U.S. communities. The mean age at baseline (1987-1989) was 54 years; 57.7% were women; and 27.9% were Black.
Study participants are followed at routine in-person visits and semiannually via telephone.
Data on head injuries came from hospital diagnostic codes and self-reports. These reports included information on the number of injuries and whether the injury required medical care and involved loss of consciousness.
During the 27-year follow-up, 18.4% of the study sample had at least one head injury. Injuries occurred more frequently among women, which may reflect the predominance of women in the study population, said Dr. Elser.
Overall, about 56% of participants died during the study period. The estimated median amount of survival time after head injury was 4.7 years.
The most common causes of death were neoplasm, cardiovascular disease, and neurologic disorders. Regarding specific neurologic causes of death, the researchers found that 62.2% of deaths were due to neurodegenerative disease among individuals with head injury, vs. 51.4% among those without head injury.
This, said Dr. Elser, raises the possibility of reverse causality. “If you have a neurodegenerative disorder like Alzheimer’s disease dementia or Parkinson’s disease that leads to difficulty walking, you may be more likely to fall and have a head injury. The head injury in turn may lead to increased mortality,” she noted.
However, she stressed that the data on cause-specific mortality are exploratory. “Our research motivates future studies that really examine this time-dependent relationship between neurodegenerative disease and head injuries,” Dr. Elser said.
Dose-dependent response
In the unadjusted analysis, the hazard ratio of mortality among individuals with head injury was 2.21 (95% confidence interval, 2.09-2.34) compared with those who did not have head injury.
The association remained significant with adjustment for sociodemographic factors (HR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.88-2.11) and with additional adjustment for vascular risk factors (HR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.81-2.03).
The findings also showed a dose-response pattern in the association of head injuries with mortality. Compared with participants who did not have head injury, the HR was 1.66 (95% CI, 1.56-1.77) for those with one head injury and 2.11 (95% CI, 1.89-2.37) for those with two or more head injuries.
“It’s not as though once you’ve had one head injury, you’ve accrued all the damage you possibly can. We see pretty clearly here that recurrent head injury further increased the rate of deaths from all causes,” said Dr. Elser.
Injury severity was determined from hospital diagnostic codes using established algorithms. Results showed that mortality rates were increased with even mild head injury.
Interestingly, the association between head injury and all-cause mortality was weaker among those whose injuries were self-reported. One possibility is that these injuries were less severe, Dr. Elser noted.
“If you have head injury that’s mild enough that you don’t need to go to the hospital, it’s probably going to confer less long-term health risks than one that’s severe enough that you needed to be examined in an acute care setting,” she said.
Results were similar by race and for sex. “Even though there were more women with head injuries, the rate of mortality associated with head injury doesn’t differ from the rate among men,” Dr. Elser reported.
However, the association was stronger among those younger than 54 years at baseline (HR, 2.26) compared with older individuals (HR, 2.0) in the model that adjusted for demographics and lifestyle factors.
This may be explained by the reference group (those without a head injury) – the mortality rate was in general higher for the older participants, said Dr. Elser. It could also be that younger adults are more likely to have severe head injuries from, for example, motor vehicle accidents or violence, she added.
These new findings underscore the importance of public health measures, such as seatbelt laws, to reduce head injuries, the investigators note.
They add that clinicians with patients at risk for head injuries may recommend steps to lessen the risk of falls, such as having access to durable medical equipment, and ensuring driver safety.
Shorter life span
Commenting for this news organization, Frank Conidi, MD, director of the Florida Center for Headache and Sports Neurology in Port St. Lucie and past president of the Florida Society of Neurology, said the large number of participants “adds validity” to the finding that individuals with head injury are likely to have a shorter life span than those who do not suffer head trauma – and that this “was not purely by chance or from other causes.”
However, patients may not have accurately reported head injuries, in which case the rate of injury in the self-report subgroup would not reflect the actual incidence, noted Dr. Conidi, who was not involved with the research.
“In my practice, most patients have little knowledge as to the signs and symptoms of concussion and traumatic brain injury. Most think there needs to be some form of loss of consciousness to have a head injury, which is of course not true,” he said.
Dr. Conidi added that the finding of a higher incidence of death from neurodegenerative disorders supports the generally accepted consensus view that about 30% of patients with traumatic brain injury experience progression of symptoms and are at risk for early dementia.
The ARIC study is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Elser and Dr. Conidi have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
An analysis of more than 13,000 adult participants in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study showed a dose-response pattern in which one head injury was linked to a 66% increased risk for all-cause mortality, and two or more head injuries were associated with twice the risk in comparison with no head injuries.
These findings underscore the importance of preventing head injuries and of swift clinical intervention once a head injury occurs, lead author Holly Elser, MD, PhD, department of neurology, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Clinicians should counsel patients who are at risk for falls about head injuries and ensure patients are promptly evaluated in the hospital setting if they do have a fall – especially with loss of consciousness or other symptoms, such as headache or dizziness,” Dr. Elser added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Consistent evidence
There is “pretty consistent evidence” that mortality rates are increased in the short term after head injury, predominantly among hospitalized patients, Dr. Elser noted.
“But there’s less evidence about the long-term mortality implications of head injuries and less evidence from adults living in the community,” she added.
The analysis included 13,037 participants in the ARIC study, an ongoing study involving adults aged 45-65 years who were recruited from four geographically and racially diverse U.S. communities. The mean age at baseline (1987-1989) was 54 years; 57.7% were women; and 27.9% were Black.
Study participants are followed at routine in-person visits and semiannually via telephone.
Data on head injuries came from hospital diagnostic codes and self-reports. These reports included information on the number of injuries and whether the injury required medical care and involved loss of consciousness.
During the 27-year follow-up, 18.4% of the study sample had at least one head injury. Injuries occurred more frequently among women, which may reflect the predominance of women in the study population, said Dr. Elser.
Overall, about 56% of participants died during the study period. The estimated median amount of survival time after head injury was 4.7 years.
The most common causes of death were neoplasm, cardiovascular disease, and neurologic disorders. Regarding specific neurologic causes of death, the researchers found that 62.2% of deaths were due to neurodegenerative disease among individuals with head injury, vs. 51.4% among those without head injury.
This, said Dr. Elser, raises the possibility of reverse causality. “If you have a neurodegenerative disorder like Alzheimer’s disease dementia or Parkinson’s disease that leads to difficulty walking, you may be more likely to fall and have a head injury. The head injury in turn may lead to increased mortality,” she noted.
However, she stressed that the data on cause-specific mortality are exploratory. “Our research motivates future studies that really examine this time-dependent relationship between neurodegenerative disease and head injuries,” Dr. Elser said.
Dose-dependent response
In the unadjusted analysis, the hazard ratio of mortality among individuals with head injury was 2.21 (95% confidence interval, 2.09-2.34) compared with those who did not have head injury.
The association remained significant with adjustment for sociodemographic factors (HR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.88-2.11) and with additional adjustment for vascular risk factors (HR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.81-2.03).
The findings also showed a dose-response pattern in the association of head injuries with mortality. Compared with participants who did not have head injury, the HR was 1.66 (95% CI, 1.56-1.77) for those with one head injury and 2.11 (95% CI, 1.89-2.37) for those with two or more head injuries.
“It’s not as though once you’ve had one head injury, you’ve accrued all the damage you possibly can. We see pretty clearly here that recurrent head injury further increased the rate of deaths from all causes,” said Dr. Elser.
Injury severity was determined from hospital diagnostic codes using established algorithms. Results showed that mortality rates were increased with even mild head injury.
Interestingly, the association between head injury and all-cause mortality was weaker among those whose injuries were self-reported. One possibility is that these injuries were less severe, Dr. Elser noted.
“If you have head injury that’s mild enough that you don’t need to go to the hospital, it’s probably going to confer less long-term health risks than one that’s severe enough that you needed to be examined in an acute care setting,” she said.
Results were similar by race and for sex. “Even though there were more women with head injuries, the rate of mortality associated with head injury doesn’t differ from the rate among men,” Dr. Elser reported.
However, the association was stronger among those younger than 54 years at baseline (HR, 2.26) compared with older individuals (HR, 2.0) in the model that adjusted for demographics and lifestyle factors.
This may be explained by the reference group (those without a head injury) – the mortality rate was in general higher for the older participants, said Dr. Elser. It could also be that younger adults are more likely to have severe head injuries from, for example, motor vehicle accidents or violence, she added.
These new findings underscore the importance of public health measures, such as seatbelt laws, to reduce head injuries, the investigators note.
They add that clinicians with patients at risk for head injuries may recommend steps to lessen the risk of falls, such as having access to durable medical equipment, and ensuring driver safety.
Shorter life span
Commenting for this news organization, Frank Conidi, MD, director of the Florida Center for Headache and Sports Neurology in Port St. Lucie and past president of the Florida Society of Neurology, said the large number of participants “adds validity” to the finding that individuals with head injury are likely to have a shorter life span than those who do not suffer head trauma – and that this “was not purely by chance or from other causes.”
However, patients may not have accurately reported head injuries, in which case the rate of injury in the self-report subgroup would not reflect the actual incidence, noted Dr. Conidi, who was not involved with the research.
“In my practice, most patients have little knowledge as to the signs and symptoms of concussion and traumatic brain injury. Most think there needs to be some form of loss of consciousness to have a head injury, which is of course not true,” he said.
Dr. Conidi added that the finding of a higher incidence of death from neurodegenerative disorders supports the generally accepted consensus view that about 30% of patients with traumatic brain injury experience progression of symptoms and are at risk for early dementia.
The ARIC study is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Elser and Dr. Conidi have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Long COVID affecting more than one-third of college students, faculty
With a median age of 23 years, the study is unique for evaluating mostly healthy, young adults and for its rare look at long COVID in a university community.
The more symptoms during a bout with COVID, the greater the risk for long COVID, the researchers found. That lines up with previous studies. Also, the more vaccinations and booster shots against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID, the lower the long COVID risk.
Women were more likely than men to be affected. Current or prior smoking, seeking medical care for COVID, and receiving antibody treatment also were linked to higher chances for developing long COVID.
Lead author Megan Landry, DrPH, MPH, and colleagues were already assessing students, staff, and faculty at George Washington University, Washington, who tested positive for COVID. Then they started seeing symptoms that lasted 28 days or more after their 10-day isolation period.
“We were starting to recognize that individuals ... were still having symptoms longer than the typical isolation period,” said Dr. Landry. So they developed a questionnaire to figure out the how long these symptoms last and how many people are affected by them.
The list of potential symptoms was long and included trouble thinking, fatigue, loss of smell or taste, shortness of breath, and more.
The study was published online in Emerging Infectious Diseases. Results are based on records and responses from 1,388 students, faculty, and staff from July 2021 to March 2022.
People had a median of four long COVID symptoms, about 63% were women, and 56% were non-Hispanic White. About three-quarters were students and the remainder were faculty and staff.
The finding that 36% of people with a history of COVID reported long COVID symptoms did not surprise Dr. Landry.
“Based on the literature that’s currently out there, it ranges from a 10% to an 80% prevalence of long COVID,” she said. “We kind of figured that we would fall somewhere in there.”
In contrast, that figure seemed high to Eric Topol, MD.
“That’s really high,” said Dr. Topol, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He added most studies estimate that about 10% of people with a history of acute infection develop long COVID.
Even at 10%, which could be an underestimate, that’s a lot of affected people globally.
“At least 65 million individuals around the world have long COVID, based on a conservative estimated incidence of 10% of infected people and more than 651 million documented COVID-19 cases worldwide; the number is likely much higher due to many undocumented cases,” Dr. Topol and colleagues wrote in a long COVID review article published in Nature Reviews Microbiology.
About 30% of study participants were fully vaccinated with an initial vaccine series, 42% had received a booster dose, and 29% were not fully vaccinated at the time of their first positive test for COVID. Those who were not fully vaccinated were significantly more likely to report symptoms of long COVID.
“I know a lot of people wish they could put COVID on the back burner or brush it under the rug, but COVID is still a real thing. We need to continue supporting vaccines and boosters and make sure people are up to date. Not only for COVID, but for flu as well,” Dr. Topol said
Research continues
“Long COVID is still evolving and we continue to learn more about it every day,” Landry said. “It’s just so new and there are still a lot of unknowns. That’s why it’s important to get this information out.”
People with long COVID often have a hard time with occupational, educational, social, or personal activities, compared with before COVID, with effects that can last for more than 6 months, the authors noted.
“I think across the board, universities in general need to consider the possibility of folks on their campuses are having symptoms of long COVID,” Dr. Landry said.
Moving forward, Dr. Landry and colleagues would like to continue investigating long COVID. For example, in the current study, they did not ask about severity of symptoms or how the symptoms affected daily functioning.
“I would like to continue this and dive deeper into how disruptive their symptoms of long COVID are to their everyday studying, teaching, or their activities to keeping a university running,” Dr. Landry said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
With a median age of 23 years, the study is unique for evaluating mostly healthy, young adults and for its rare look at long COVID in a university community.
The more symptoms during a bout with COVID, the greater the risk for long COVID, the researchers found. That lines up with previous studies. Also, the more vaccinations and booster shots against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID, the lower the long COVID risk.
Women were more likely than men to be affected. Current or prior smoking, seeking medical care for COVID, and receiving antibody treatment also were linked to higher chances for developing long COVID.
Lead author Megan Landry, DrPH, MPH, and colleagues were already assessing students, staff, and faculty at George Washington University, Washington, who tested positive for COVID. Then they started seeing symptoms that lasted 28 days or more after their 10-day isolation period.
“We were starting to recognize that individuals ... were still having symptoms longer than the typical isolation period,” said Dr. Landry. So they developed a questionnaire to figure out the how long these symptoms last and how many people are affected by them.
The list of potential symptoms was long and included trouble thinking, fatigue, loss of smell or taste, shortness of breath, and more.
The study was published online in Emerging Infectious Diseases. Results are based on records and responses from 1,388 students, faculty, and staff from July 2021 to March 2022.
People had a median of four long COVID symptoms, about 63% were women, and 56% were non-Hispanic White. About three-quarters were students and the remainder were faculty and staff.
The finding that 36% of people with a history of COVID reported long COVID symptoms did not surprise Dr. Landry.
“Based on the literature that’s currently out there, it ranges from a 10% to an 80% prevalence of long COVID,” she said. “We kind of figured that we would fall somewhere in there.”
In contrast, that figure seemed high to Eric Topol, MD.
“That’s really high,” said Dr. Topol, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He added most studies estimate that about 10% of people with a history of acute infection develop long COVID.
Even at 10%, which could be an underestimate, that’s a lot of affected people globally.
“At least 65 million individuals around the world have long COVID, based on a conservative estimated incidence of 10% of infected people and more than 651 million documented COVID-19 cases worldwide; the number is likely much higher due to many undocumented cases,” Dr. Topol and colleagues wrote in a long COVID review article published in Nature Reviews Microbiology.
About 30% of study participants were fully vaccinated with an initial vaccine series, 42% had received a booster dose, and 29% were not fully vaccinated at the time of their first positive test for COVID. Those who were not fully vaccinated were significantly more likely to report symptoms of long COVID.
“I know a lot of people wish they could put COVID on the back burner or brush it under the rug, but COVID is still a real thing. We need to continue supporting vaccines and boosters and make sure people are up to date. Not only for COVID, but for flu as well,” Dr. Topol said
Research continues
“Long COVID is still evolving and we continue to learn more about it every day,” Landry said. “It’s just so new and there are still a lot of unknowns. That’s why it’s important to get this information out.”
People with long COVID often have a hard time with occupational, educational, social, or personal activities, compared with before COVID, with effects that can last for more than 6 months, the authors noted.
“I think across the board, universities in general need to consider the possibility of folks on their campuses are having symptoms of long COVID,” Dr. Landry said.
Moving forward, Dr. Landry and colleagues would like to continue investigating long COVID. For example, in the current study, they did not ask about severity of symptoms or how the symptoms affected daily functioning.
“I would like to continue this and dive deeper into how disruptive their symptoms of long COVID are to their everyday studying, teaching, or their activities to keeping a university running,” Dr. Landry said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
With a median age of 23 years, the study is unique for evaluating mostly healthy, young adults and for its rare look at long COVID in a university community.
The more symptoms during a bout with COVID, the greater the risk for long COVID, the researchers found. That lines up with previous studies. Also, the more vaccinations and booster shots against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID, the lower the long COVID risk.
Women were more likely than men to be affected. Current or prior smoking, seeking medical care for COVID, and receiving antibody treatment also were linked to higher chances for developing long COVID.
Lead author Megan Landry, DrPH, MPH, and colleagues were already assessing students, staff, and faculty at George Washington University, Washington, who tested positive for COVID. Then they started seeing symptoms that lasted 28 days or more after their 10-day isolation period.
“We were starting to recognize that individuals ... were still having symptoms longer than the typical isolation period,” said Dr. Landry. So they developed a questionnaire to figure out the how long these symptoms last and how many people are affected by them.
The list of potential symptoms was long and included trouble thinking, fatigue, loss of smell or taste, shortness of breath, and more.
The study was published online in Emerging Infectious Diseases. Results are based on records and responses from 1,388 students, faculty, and staff from July 2021 to March 2022.
People had a median of four long COVID symptoms, about 63% were women, and 56% were non-Hispanic White. About three-quarters were students and the remainder were faculty and staff.
The finding that 36% of people with a history of COVID reported long COVID symptoms did not surprise Dr. Landry.
“Based on the literature that’s currently out there, it ranges from a 10% to an 80% prevalence of long COVID,” she said. “We kind of figured that we would fall somewhere in there.”
In contrast, that figure seemed high to Eric Topol, MD.
“That’s really high,” said Dr. Topol, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He added most studies estimate that about 10% of people with a history of acute infection develop long COVID.
Even at 10%, which could be an underestimate, that’s a lot of affected people globally.
“At least 65 million individuals around the world have long COVID, based on a conservative estimated incidence of 10% of infected people and more than 651 million documented COVID-19 cases worldwide; the number is likely much higher due to many undocumented cases,” Dr. Topol and colleagues wrote in a long COVID review article published in Nature Reviews Microbiology.
About 30% of study participants were fully vaccinated with an initial vaccine series, 42% had received a booster dose, and 29% were not fully vaccinated at the time of their first positive test for COVID. Those who were not fully vaccinated were significantly more likely to report symptoms of long COVID.
“I know a lot of people wish they could put COVID on the back burner or brush it under the rug, but COVID is still a real thing. We need to continue supporting vaccines and boosters and make sure people are up to date. Not only for COVID, but for flu as well,” Dr. Topol said
Research continues
“Long COVID is still evolving and we continue to learn more about it every day,” Landry said. “It’s just so new and there are still a lot of unknowns. That’s why it’s important to get this information out.”
People with long COVID often have a hard time with occupational, educational, social, or personal activities, compared with before COVID, with effects that can last for more than 6 months, the authors noted.
“I think across the board, universities in general need to consider the possibility of folks on their campuses are having symptoms of long COVID,” Dr. Landry said.
Moving forward, Dr. Landry and colleagues would like to continue investigating long COVID. For example, in the current study, they did not ask about severity of symptoms or how the symptoms affected daily functioning.
“I would like to continue this and dive deeper into how disruptive their symptoms of long COVID are to their everyday studying, teaching, or their activities to keeping a university running,” Dr. Landry said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Noninvasive liver test may help select asymptomatic candidates for heart failure tests
A noninvasive test for liver disease may be a useful, low-cost screening tool to select asymptomatic candidates for a detailed examination of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), say authors of a report published in Gastro Hep Advances.
The fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk, wrote Chisato Okamoto, MD, of the department of medical biochemistry at Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine and the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center in Japan, and colleagues.
“Recognition of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction at an early stage in mass screening is desirable, but difficult to achieve,” the authors wrote. “The FIB-4 index is calculated using only four parameters that are routinely evaluated in general health check-up programs.”
HFpEF is an emerging disease in recent years with a poor prognosis, they wrote. Early diagnosis can be challenging for several reasons, particularly because HFpEF patients are often asymptomatic until late in the disease process and have normal left ventricular filling pressures at rest. By using a tool to select probable cases from subclinical participants in a health check-up program, clinicians can refer patients for a diastolic stress test, which is considered the gold standard for diagnosing HFpEF.
Previous studies have found that the FIB-4 index, a noninvasive tool to estimate liver stiffness and fibrosis, is associated with a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with HFpEF. In addition, patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) have a twofold higher prevalence of HFpEF than the general population.
Dr. Okamoto and colleagues examined the association between the FIB-4 index and HFpEF risk based on the Heart Failure Association’s diagnostic algorithm for HFpEF in patients with breathlessness (HFA-PEFF). The researchers looked at the prognostic impact of the FIB-4 index in 710 patients who participated in a health check-up program in the rural community of Arita-cho, Japan, between 2006 and 2007. They excluded participants with a history of cardiovascular disease or reduced left ventricular systolic function (LVEF < 50%). Researchers calculated the FIB-4 index and HFA-PEFF score for all participants.
First, using the HFA-PEFF scores, the researchers sorted participants into five groups by HFpEF risk: 215 (30%) with zero points, 100 (14%) with 1 point, 171 (24%) with 2 points, 163 (23%) with 3 points, and 61 (9%) with 4-6 points. Participants in the high-risk group (scores 4-6) were older, mostly men, and had higher blood pressure, alcohol intake, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and liver disease. The higher the HFpEF risk group, the higher the rates of all-cause mortality, hospitalization for heart failure, and MACE.
Overall, the FIB-4 index was correlated with the HFpEF risk groups and showed a stepwise increase across the groups, with .94 for the low-risk group, 1.45 for the intermediate-risk group, and 1.99 for the high-risk group, the authors wrote. The FIB-4 index also correlated with markers associated with components of the HFA-PEFF scoring system.
Using multivariate logistic regression analysis, the FIB-4 index was associated with a high HFpEF risk, and an increase in FIB-4 was associated with increased odds of high HFpEF risk. The association remained significant across four separate models that accounted for risk factors associated with lifestyle-related diseases, blood parameters associated with liver disease, and chronic conditions such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and liver disease.
In additional area under the curve (AUC) analyses, the FIB-4 index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk. At cutoff values typically used for advanced liver fibrosis in NAFLD, a FIB-4 cutoff of 1.3 or less had a sensitivity of 85.2%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of 2.67 or higher had a specificity of 94.8%. At alternate cutoff values typically used for patients with HIV/hepatitis C virus infection, a FIB-4 cutoff of less than 1.45 had a sensitivity of 75.4%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of greater than 3.25 had a specificity of 98%.
Using cutoffs of 1.3 and 2.67, a higher FIB-4 was associated with higher rates of clinical events and MACE, as well as a higher HFpEF risk. Using the alternate cutoffs of 1.45 and 3.25, prognostic stratification of clinical events and MACE was also possible.
When all variables were included in the multivariate model, the FIB-4 index remained a significant prognostic predictor. The FIB-4 index stratified clinical prognosis was also an independent predictor of all-cause mortality and hospitalization for heart failure.
Although additional studies are needed to reveal the interaction between liver and heart function, the study authors wrote, the findings provide valuable insights that can help discover the cardiohepatic interaction to reduce the development of HFpEF.
“Since it can be easily, quickly, and inexpensively measured, routine or repeated measurements of the FIB-4 index could help in selecting preferred candidates for detailed examination of HFpEF risk, which may improve clinical outcomes by diagnosing HFpEF at an early stage,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the Osaka Medical Research Foundation for Intractable Disease, the Japan Arteriosclerosis Prevention Fund, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and the Japan Heart Foundation. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
The 2021 NAFLD clinical care pathway is a shining example of how a simple score like the fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index – paired sequentially with a second noninvasive test like vibration-controlled elastography – can provide an accurate, cost-effective screening tool and risk stratification and further limit invasive testing such as liver biopsy.
Broader use of FIB-4 by cardiovascular and hepatology providers may increase earlier identification of NAFLD or HFpEF or both.
Anand S. Shah, MD, is director of hepatology at Atlanta VA Healthcare and assistant professor of medicine, division of digestive disease, department of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta. He has no financial conflicts.
The 2021 NAFLD clinical care pathway is a shining example of how a simple score like the fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index – paired sequentially with a second noninvasive test like vibration-controlled elastography – can provide an accurate, cost-effective screening tool and risk stratification and further limit invasive testing such as liver biopsy.
Broader use of FIB-4 by cardiovascular and hepatology providers may increase earlier identification of NAFLD or HFpEF or both.
Anand S. Shah, MD, is director of hepatology at Atlanta VA Healthcare and assistant professor of medicine, division of digestive disease, department of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta. He has no financial conflicts.
The 2021 NAFLD clinical care pathway is a shining example of how a simple score like the fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index – paired sequentially with a second noninvasive test like vibration-controlled elastography – can provide an accurate, cost-effective screening tool and risk stratification and further limit invasive testing such as liver biopsy.
Broader use of FIB-4 by cardiovascular and hepatology providers may increase earlier identification of NAFLD or HFpEF or both.
Anand S. Shah, MD, is director of hepatology at Atlanta VA Healthcare and assistant professor of medicine, division of digestive disease, department of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta. He has no financial conflicts.
A noninvasive test for liver disease may be a useful, low-cost screening tool to select asymptomatic candidates for a detailed examination of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), say authors of a report published in Gastro Hep Advances.
The fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk, wrote Chisato Okamoto, MD, of the department of medical biochemistry at Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine and the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center in Japan, and colleagues.
“Recognition of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction at an early stage in mass screening is desirable, but difficult to achieve,” the authors wrote. “The FIB-4 index is calculated using only four parameters that are routinely evaluated in general health check-up programs.”
HFpEF is an emerging disease in recent years with a poor prognosis, they wrote. Early diagnosis can be challenging for several reasons, particularly because HFpEF patients are often asymptomatic until late in the disease process and have normal left ventricular filling pressures at rest. By using a tool to select probable cases from subclinical participants in a health check-up program, clinicians can refer patients for a diastolic stress test, which is considered the gold standard for diagnosing HFpEF.
Previous studies have found that the FIB-4 index, a noninvasive tool to estimate liver stiffness and fibrosis, is associated with a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with HFpEF. In addition, patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) have a twofold higher prevalence of HFpEF than the general population.
Dr. Okamoto and colleagues examined the association between the FIB-4 index and HFpEF risk based on the Heart Failure Association’s diagnostic algorithm for HFpEF in patients with breathlessness (HFA-PEFF). The researchers looked at the prognostic impact of the FIB-4 index in 710 patients who participated in a health check-up program in the rural community of Arita-cho, Japan, between 2006 and 2007. They excluded participants with a history of cardiovascular disease or reduced left ventricular systolic function (LVEF < 50%). Researchers calculated the FIB-4 index and HFA-PEFF score for all participants.
First, using the HFA-PEFF scores, the researchers sorted participants into five groups by HFpEF risk: 215 (30%) with zero points, 100 (14%) with 1 point, 171 (24%) with 2 points, 163 (23%) with 3 points, and 61 (9%) with 4-6 points. Participants in the high-risk group (scores 4-6) were older, mostly men, and had higher blood pressure, alcohol intake, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and liver disease. The higher the HFpEF risk group, the higher the rates of all-cause mortality, hospitalization for heart failure, and MACE.
Overall, the FIB-4 index was correlated with the HFpEF risk groups and showed a stepwise increase across the groups, with .94 for the low-risk group, 1.45 for the intermediate-risk group, and 1.99 for the high-risk group, the authors wrote. The FIB-4 index also correlated with markers associated with components of the HFA-PEFF scoring system.
Using multivariate logistic regression analysis, the FIB-4 index was associated with a high HFpEF risk, and an increase in FIB-4 was associated with increased odds of high HFpEF risk. The association remained significant across four separate models that accounted for risk factors associated with lifestyle-related diseases, blood parameters associated with liver disease, and chronic conditions such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and liver disease.
In additional area under the curve (AUC) analyses, the FIB-4 index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk. At cutoff values typically used for advanced liver fibrosis in NAFLD, a FIB-4 cutoff of 1.3 or less had a sensitivity of 85.2%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of 2.67 or higher had a specificity of 94.8%. At alternate cutoff values typically used for patients with HIV/hepatitis C virus infection, a FIB-4 cutoff of less than 1.45 had a sensitivity of 75.4%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of greater than 3.25 had a specificity of 98%.
Using cutoffs of 1.3 and 2.67, a higher FIB-4 was associated with higher rates of clinical events and MACE, as well as a higher HFpEF risk. Using the alternate cutoffs of 1.45 and 3.25, prognostic stratification of clinical events and MACE was also possible.
When all variables were included in the multivariate model, the FIB-4 index remained a significant prognostic predictor. The FIB-4 index stratified clinical prognosis was also an independent predictor of all-cause mortality and hospitalization for heart failure.
Although additional studies are needed to reveal the interaction between liver and heart function, the study authors wrote, the findings provide valuable insights that can help discover the cardiohepatic interaction to reduce the development of HFpEF.
“Since it can be easily, quickly, and inexpensively measured, routine or repeated measurements of the FIB-4 index could help in selecting preferred candidates for detailed examination of HFpEF risk, which may improve clinical outcomes by diagnosing HFpEF at an early stage,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the Osaka Medical Research Foundation for Intractable Disease, the Japan Arteriosclerosis Prevention Fund, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and the Japan Heart Foundation. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
A noninvasive test for liver disease may be a useful, low-cost screening tool to select asymptomatic candidates for a detailed examination of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), say authors of a report published in Gastro Hep Advances.
The fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk, wrote Chisato Okamoto, MD, of the department of medical biochemistry at Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine and the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center in Japan, and colleagues.
“Recognition of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction at an early stage in mass screening is desirable, but difficult to achieve,” the authors wrote. “The FIB-4 index is calculated using only four parameters that are routinely evaluated in general health check-up programs.”
HFpEF is an emerging disease in recent years with a poor prognosis, they wrote. Early diagnosis can be challenging for several reasons, particularly because HFpEF patients are often asymptomatic until late in the disease process and have normal left ventricular filling pressures at rest. By using a tool to select probable cases from subclinical participants in a health check-up program, clinicians can refer patients for a diastolic stress test, which is considered the gold standard for diagnosing HFpEF.
Previous studies have found that the FIB-4 index, a noninvasive tool to estimate liver stiffness and fibrosis, is associated with a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with HFpEF. In addition, patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) have a twofold higher prevalence of HFpEF than the general population.
Dr. Okamoto and colleagues examined the association between the FIB-4 index and HFpEF risk based on the Heart Failure Association’s diagnostic algorithm for HFpEF in patients with breathlessness (HFA-PEFF). The researchers looked at the prognostic impact of the FIB-4 index in 710 patients who participated in a health check-up program in the rural community of Arita-cho, Japan, between 2006 and 2007. They excluded participants with a history of cardiovascular disease or reduced left ventricular systolic function (LVEF < 50%). Researchers calculated the FIB-4 index and HFA-PEFF score for all participants.
First, using the HFA-PEFF scores, the researchers sorted participants into five groups by HFpEF risk: 215 (30%) with zero points, 100 (14%) with 1 point, 171 (24%) with 2 points, 163 (23%) with 3 points, and 61 (9%) with 4-6 points. Participants in the high-risk group (scores 4-6) were older, mostly men, and had higher blood pressure, alcohol intake, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and liver disease. The higher the HFpEF risk group, the higher the rates of all-cause mortality, hospitalization for heart failure, and MACE.
Overall, the FIB-4 index was correlated with the HFpEF risk groups and showed a stepwise increase across the groups, with .94 for the low-risk group, 1.45 for the intermediate-risk group, and 1.99 for the high-risk group, the authors wrote. The FIB-4 index also correlated with markers associated with components of the HFA-PEFF scoring system.
Using multivariate logistic regression analysis, the FIB-4 index was associated with a high HFpEF risk, and an increase in FIB-4 was associated with increased odds of high HFpEF risk. The association remained significant across four separate models that accounted for risk factors associated with lifestyle-related diseases, blood parameters associated with liver disease, and chronic conditions such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and liver disease.
In additional area under the curve (AUC) analyses, the FIB-4 index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk. At cutoff values typically used for advanced liver fibrosis in NAFLD, a FIB-4 cutoff of 1.3 or less had a sensitivity of 85.2%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of 2.67 or higher had a specificity of 94.8%. At alternate cutoff values typically used for patients with HIV/hepatitis C virus infection, a FIB-4 cutoff of less than 1.45 had a sensitivity of 75.4%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of greater than 3.25 had a specificity of 98%.
Using cutoffs of 1.3 and 2.67, a higher FIB-4 was associated with higher rates of clinical events and MACE, as well as a higher HFpEF risk. Using the alternate cutoffs of 1.45 and 3.25, prognostic stratification of clinical events and MACE was also possible.
When all variables were included in the multivariate model, the FIB-4 index remained a significant prognostic predictor. The FIB-4 index stratified clinical prognosis was also an independent predictor of all-cause mortality and hospitalization for heart failure.
Although additional studies are needed to reveal the interaction between liver and heart function, the study authors wrote, the findings provide valuable insights that can help discover the cardiohepatic interaction to reduce the development of HFpEF.
“Since it can be easily, quickly, and inexpensively measured, routine or repeated measurements of the FIB-4 index could help in selecting preferred candidates for detailed examination of HFpEF risk, which may improve clinical outcomes by diagnosing HFpEF at an early stage,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the Osaka Medical Research Foundation for Intractable Disease, the Japan Arteriosclerosis Prevention Fund, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and the Japan Heart Foundation. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
FROM GASTRO HEP ADVANCES
New cancer data spark outcry from patient advocates
The American Cancer Society on Jan. 13 revealed what it called “alarming” news about prostate cancer: After 2 decades of decline, the number of men diagnosed with the disease in the United States rose by 15% from 2014 to 2019.
“Most concerning,” according to the group’s CEO Karen Knudsen, PhD, MBA, is that the increase is being driven by diagnoses of advanced disease.
“Since 2011, the diagnosis of advanced-stage (regional- or distant-stage) prostate cancer has increased by 4%-5% annually and the proportion of men diagnosed with distant-stage disease has doubled,” said Dr. Knudsen at a press conference concerning the figures. “These findings underscore the importance of understanding and reducing this trend.”
The increase, which works out to be an additional 99,000 cases of prostate cancer, did not take the ACS by surprise; the group has been predicting a jump in diagnoses of the disease, which is the most common cancer in men after skin cancer, and the second most common cause of cancer death for that group.
The ACS announced a new action plan, “Improving Mortality from Prostate Cancer Together” – or IMPACT – to address the rise, especially in Black men, and to curb the increasing rate of advanced, difficult-to-treat cases.
“We must address these shifts in prostate cancer, especially in the Black community, since the incidence of prostate cancer in Black men is 70% higher than in White men and prostate cancer mortality rates in Black men are approximately two to four times higher than those in every other racial and ethnic group,” William Dahut, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer for the ACS, said at the press conference.
A study published in JAMA Network Open challenged that claim, finding that, after controlling for socioeconomic factors, race does not appear to be a significant predictor of mortality for prostate cancer.
Dr. Dahut said in an interview that IMPACT “is still [in the] early days for this initiative and more details will be coming out soon.”
Charles Ryan, MD, CEO of the Prostate Cancer Foundation, the world’s largest prostate cancer research charity, called IMPACT “extremely important work. Highlighting the disparities can only serve to benefit all men with prostate cancer, especially Black men.”
Bold action ... or passivity?
Overall cancer mortality has dropped 33% since 1991, averting an estimated 3.8 million deaths, according to ACS. But the story for prostate cancer is different.
The society and advocates had warned as recently as 2 years ago that prostate cancer was poised to rise again, especially advanced cases that may be too late to treat.
Leaders in the prostate cancer advocacy community praised the ACS plan for IMPACT, but some expressed frustration over what they said was ACS’ passivity in the face of long-anticipated increases in cases of the disease.
“I think prostate cancer was not high on their agenda,” said Rick Davis, founder of AnCan, which offers several support groups for patients with prostate cancer. “It’s good to see ACS get back into the prostate cancer game.”
Mr. Davis and patient advocate Darryl Mitteldorf, LCSW, founder of Malecare, another prostate support organization, said ACS dropped patient services for prostate cancer patients a decade ago and has not been a vocal supporter of screening for levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) to detect prostate cancer early.
“Early detection is supposed to be their goal,” Mr. Davis said.
In 2012, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommended against PSA screening, giving it a D-rating. The move prompted attacks on the task force from most advocates and many urologists.
Following this criticism, the task force recommended shared decision-making between patient and doctor, while giving PSA screening a C-rating. Now, the ACS recommends men in general at age 50 discuss prostate cancer screening with their doctor and that Black men do the same at age 45.
Mr. Mitteldorf said ACS “owes prostate cancer patients an explanation and analysis of its response to the USPTF’s downgrade of PSA testing and how that response might be related to death and instance rates.”
Mr. Mitteldorf added that male patients lost key support from ACS when the group dismantled its Man to Man group for prostate cancer patients and its Brother to Brother group for Blacks in particular.
Dr. Dahut said Man to Man “sunsetted” and was turned over to any local organization that chose to offer it. He said longtime staff didn’t have “a lot of information about [the demise of] Brother to Brother.”
For Mr. Davis, those smaller cuts add up to a much larger insult.
“Today, in 2023, ACS continues to poke a finger in the eyes of prostate cancer patients,” he said. “Since 2010, they have not given us any respect. ACS dumped its support.”
He pointed to the group’s funding priorities, noting that outlays for prostate cancer have consistently lagged behind those for breast cancer.
The ACS spent $25.3 million on breast cancer research and $6.7 million for prostate cancer in 2018, and in 2023 will designate $126.5 for breast cancer research and $43.9 million for prostate cancer.
ACS has earmarked $62 million this year for lung cancer programs and $61 million for colorectal cancer.
“Parity between breast cancer and prostate cancer would be a good start in sizing the IMPACT program,” Mr. Davis said. “After all, breast cancer and prostate cancer are hardly different in numbers today.”
Dr. Dahut denied any gender bias in research funding. He said the group makes funding decisions “based on finding the most impactful science regardless of tumor type. Our mission includes funding every cancer, every day; thus, we generally do not go into our funding cycle with any set-asides for a particular cancer.”
Mr. Davis also said the ACS data suggest the growing number of prostate cancer cases is even worse than the group has said. Although the society cites a 3% annual increase in prostate cancer diagnoses from 2014 to 2019, since 2019 the annual increase is a much more dramatic 16%. Meanwhile, the number of new cases of the disease is projected to rise from 175,000 per year in 2019 to 288,000 this year.
Dr. Dahut said the society used the 2014-2019 time frame for technical reasons, separating confirmed cases in the earlier period from estimated cases in recent years.
“We discourage comparing projected cases over time because these cases are model-based and subject to fluctuations,” Dr. Dahut said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Cancer Society on Jan. 13 revealed what it called “alarming” news about prostate cancer: After 2 decades of decline, the number of men diagnosed with the disease in the United States rose by 15% from 2014 to 2019.
“Most concerning,” according to the group’s CEO Karen Knudsen, PhD, MBA, is that the increase is being driven by diagnoses of advanced disease.
“Since 2011, the diagnosis of advanced-stage (regional- or distant-stage) prostate cancer has increased by 4%-5% annually and the proportion of men diagnosed with distant-stage disease has doubled,” said Dr. Knudsen at a press conference concerning the figures. “These findings underscore the importance of understanding and reducing this trend.”
The increase, which works out to be an additional 99,000 cases of prostate cancer, did not take the ACS by surprise; the group has been predicting a jump in diagnoses of the disease, which is the most common cancer in men after skin cancer, and the second most common cause of cancer death for that group.
The ACS announced a new action plan, “Improving Mortality from Prostate Cancer Together” – or IMPACT – to address the rise, especially in Black men, and to curb the increasing rate of advanced, difficult-to-treat cases.
“We must address these shifts in prostate cancer, especially in the Black community, since the incidence of prostate cancer in Black men is 70% higher than in White men and prostate cancer mortality rates in Black men are approximately two to four times higher than those in every other racial and ethnic group,” William Dahut, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer for the ACS, said at the press conference.
A study published in JAMA Network Open challenged that claim, finding that, after controlling for socioeconomic factors, race does not appear to be a significant predictor of mortality for prostate cancer.
Dr. Dahut said in an interview that IMPACT “is still [in the] early days for this initiative and more details will be coming out soon.”
Charles Ryan, MD, CEO of the Prostate Cancer Foundation, the world’s largest prostate cancer research charity, called IMPACT “extremely important work. Highlighting the disparities can only serve to benefit all men with prostate cancer, especially Black men.”
Bold action ... or passivity?
Overall cancer mortality has dropped 33% since 1991, averting an estimated 3.8 million deaths, according to ACS. But the story for prostate cancer is different.
The society and advocates had warned as recently as 2 years ago that prostate cancer was poised to rise again, especially advanced cases that may be too late to treat.
Leaders in the prostate cancer advocacy community praised the ACS plan for IMPACT, but some expressed frustration over what they said was ACS’ passivity in the face of long-anticipated increases in cases of the disease.
“I think prostate cancer was not high on their agenda,” said Rick Davis, founder of AnCan, which offers several support groups for patients with prostate cancer. “It’s good to see ACS get back into the prostate cancer game.”
Mr. Davis and patient advocate Darryl Mitteldorf, LCSW, founder of Malecare, another prostate support organization, said ACS dropped patient services for prostate cancer patients a decade ago and has not been a vocal supporter of screening for levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) to detect prostate cancer early.
“Early detection is supposed to be their goal,” Mr. Davis said.
In 2012, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommended against PSA screening, giving it a D-rating. The move prompted attacks on the task force from most advocates and many urologists.
Following this criticism, the task force recommended shared decision-making between patient and doctor, while giving PSA screening a C-rating. Now, the ACS recommends men in general at age 50 discuss prostate cancer screening with their doctor and that Black men do the same at age 45.
Mr. Mitteldorf said ACS “owes prostate cancer patients an explanation and analysis of its response to the USPTF’s downgrade of PSA testing and how that response might be related to death and instance rates.”
Mr. Mitteldorf added that male patients lost key support from ACS when the group dismantled its Man to Man group for prostate cancer patients and its Brother to Brother group for Blacks in particular.
Dr. Dahut said Man to Man “sunsetted” and was turned over to any local organization that chose to offer it. He said longtime staff didn’t have “a lot of information about [the demise of] Brother to Brother.”
For Mr. Davis, those smaller cuts add up to a much larger insult.
“Today, in 2023, ACS continues to poke a finger in the eyes of prostate cancer patients,” he said. “Since 2010, they have not given us any respect. ACS dumped its support.”
He pointed to the group’s funding priorities, noting that outlays for prostate cancer have consistently lagged behind those for breast cancer.
The ACS spent $25.3 million on breast cancer research and $6.7 million for prostate cancer in 2018, and in 2023 will designate $126.5 for breast cancer research and $43.9 million for prostate cancer.
ACS has earmarked $62 million this year for lung cancer programs and $61 million for colorectal cancer.
“Parity between breast cancer and prostate cancer would be a good start in sizing the IMPACT program,” Mr. Davis said. “After all, breast cancer and prostate cancer are hardly different in numbers today.”
Dr. Dahut denied any gender bias in research funding. He said the group makes funding decisions “based on finding the most impactful science regardless of tumor type. Our mission includes funding every cancer, every day; thus, we generally do not go into our funding cycle with any set-asides for a particular cancer.”
Mr. Davis also said the ACS data suggest the growing number of prostate cancer cases is even worse than the group has said. Although the society cites a 3% annual increase in prostate cancer diagnoses from 2014 to 2019, since 2019 the annual increase is a much more dramatic 16%. Meanwhile, the number of new cases of the disease is projected to rise from 175,000 per year in 2019 to 288,000 this year.
Dr. Dahut said the society used the 2014-2019 time frame for technical reasons, separating confirmed cases in the earlier period from estimated cases in recent years.
“We discourage comparing projected cases over time because these cases are model-based and subject to fluctuations,” Dr. Dahut said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Cancer Society on Jan. 13 revealed what it called “alarming” news about prostate cancer: After 2 decades of decline, the number of men diagnosed with the disease in the United States rose by 15% from 2014 to 2019.
“Most concerning,” according to the group’s CEO Karen Knudsen, PhD, MBA, is that the increase is being driven by diagnoses of advanced disease.
“Since 2011, the diagnosis of advanced-stage (regional- or distant-stage) prostate cancer has increased by 4%-5% annually and the proportion of men diagnosed with distant-stage disease has doubled,” said Dr. Knudsen at a press conference concerning the figures. “These findings underscore the importance of understanding and reducing this trend.”
The increase, which works out to be an additional 99,000 cases of prostate cancer, did not take the ACS by surprise; the group has been predicting a jump in diagnoses of the disease, which is the most common cancer in men after skin cancer, and the second most common cause of cancer death for that group.
The ACS announced a new action plan, “Improving Mortality from Prostate Cancer Together” – or IMPACT – to address the rise, especially in Black men, and to curb the increasing rate of advanced, difficult-to-treat cases.
“We must address these shifts in prostate cancer, especially in the Black community, since the incidence of prostate cancer in Black men is 70% higher than in White men and prostate cancer mortality rates in Black men are approximately two to four times higher than those in every other racial and ethnic group,” William Dahut, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer for the ACS, said at the press conference.
A study published in JAMA Network Open challenged that claim, finding that, after controlling for socioeconomic factors, race does not appear to be a significant predictor of mortality for prostate cancer.
Dr. Dahut said in an interview that IMPACT “is still [in the] early days for this initiative and more details will be coming out soon.”
Charles Ryan, MD, CEO of the Prostate Cancer Foundation, the world’s largest prostate cancer research charity, called IMPACT “extremely important work. Highlighting the disparities can only serve to benefit all men with prostate cancer, especially Black men.”
Bold action ... or passivity?
Overall cancer mortality has dropped 33% since 1991, averting an estimated 3.8 million deaths, according to ACS. But the story for prostate cancer is different.
The society and advocates had warned as recently as 2 years ago that prostate cancer was poised to rise again, especially advanced cases that may be too late to treat.
Leaders in the prostate cancer advocacy community praised the ACS plan for IMPACT, but some expressed frustration over what they said was ACS’ passivity in the face of long-anticipated increases in cases of the disease.
“I think prostate cancer was not high on their agenda,” said Rick Davis, founder of AnCan, which offers several support groups for patients with prostate cancer. “It’s good to see ACS get back into the prostate cancer game.”
Mr. Davis and patient advocate Darryl Mitteldorf, LCSW, founder of Malecare, another prostate support organization, said ACS dropped patient services for prostate cancer patients a decade ago and has not been a vocal supporter of screening for levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) to detect prostate cancer early.
“Early detection is supposed to be their goal,” Mr. Davis said.
In 2012, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommended against PSA screening, giving it a D-rating. The move prompted attacks on the task force from most advocates and many urologists.
Following this criticism, the task force recommended shared decision-making between patient and doctor, while giving PSA screening a C-rating. Now, the ACS recommends men in general at age 50 discuss prostate cancer screening with their doctor and that Black men do the same at age 45.
Mr. Mitteldorf said ACS “owes prostate cancer patients an explanation and analysis of its response to the USPTF’s downgrade of PSA testing and how that response might be related to death and instance rates.”
Mr. Mitteldorf added that male patients lost key support from ACS when the group dismantled its Man to Man group for prostate cancer patients and its Brother to Brother group for Blacks in particular.
Dr. Dahut said Man to Man “sunsetted” and was turned over to any local organization that chose to offer it. He said longtime staff didn’t have “a lot of information about [the demise of] Brother to Brother.”
For Mr. Davis, those smaller cuts add up to a much larger insult.
“Today, in 2023, ACS continues to poke a finger in the eyes of prostate cancer patients,” he said. “Since 2010, they have not given us any respect. ACS dumped its support.”
He pointed to the group’s funding priorities, noting that outlays for prostate cancer have consistently lagged behind those for breast cancer.
The ACS spent $25.3 million on breast cancer research and $6.7 million for prostate cancer in 2018, and in 2023 will designate $126.5 for breast cancer research and $43.9 million for prostate cancer.
ACS has earmarked $62 million this year for lung cancer programs and $61 million for colorectal cancer.
“Parity between breast cancer and prostate cancer would be a good start in sizing the IMPACT program,” Mr. Davis said. “After all, breast cancer and prostate cancer are hardly different in numbers today.”
Dr. Dahut denied any gender bias in research funding. He said the group makes funding decisions “based on finding the most impactful science regardless of tumor type. Our mission includes funding every cancer, every day; thus, we generally do not go into our funding cycle with any set-asides for a particular cancer.”
Mr. Davis also said the ACS data suggest the growing number of prostate cancer cases is even worse than the group has said. Although the society cites a 3% annual increase in prostate cancer diagnoses from 2014 to 2019, since 2019 the annual increase is a much more dramatic 16%. Meanwhile, the number of new cases of the disease is projected to rise from 175,000 per year in 2019 to 288,000 this year.
Dr. Dahut said the society used the 2014-2019 time frame for technical reasons, separating confirmed cases in the earlier period from estimated cases in recent years.
“We discourage comparing projected cases over time because these cases are model-based and subject to fluctuations,” Dr. Dahut said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.










