User login
ID Practitioner is an independent news source that provides infectious disease specialists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the infectious disease specialist’s practice. Specialty focus topics include antimicrobial resistance, emerging infections, global ID, hepatitis, HIV, hospital-acquired infections, immunizations and vaccines, influenza, mycoses, pediatric infections, and STIs. Infectious Diseases News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
sofosbuvir
ritonavir with dasabuvir
discount
support path
program
ritonavir
greedy
ledipasvir
assistance
viekira pak
vpak
advocacy
needy
protest
abbvie
paritaprevir
ombitasvir
direct-acting antivirals
dasabuvir
gilead
fake-ovir
support
v pak
oasis
harvoni
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-medstat-latest-articles-articles-section')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-idp')]
Who can sue docs for wrongful death? Some states are trying to expand that group
In addition, the types of emotional damage that physicians can be sued for is expanding in pockets across the nation. The latest effort to expand the capacity to sue, a bill in New York state, failed when it was not signed by the governor – but a toned-down bill is in the works.
The impact of New York’s proposed expansion of wrongful death lawsuits would have been widespread. The New York legislation would have expanded the definition of “close family members” to include spouses, domestic partners, children, parents, stepparents, siblings, grandparents, and perhaps more. Additionally, lawsuits could have allowed juries to determine “close family members” of the deceased patient on the basis of specific circumstances of the person’s relationship with the decedent.
Currently, every state allows a wrongful death claim to be filed by immediate family members. If the patient who died was married, a surviving spouse could bring the lawsuit. If the patient had been unmarried, an adult child could bring the lawsuit in some states. A parent typically brings a lawsuit if their minor child has died from alleged wrongful death. In some states, one member of a civil union or domestic partnership may bring a wrongful death lawsuit. And if a single adult has no children or spouse/partner, more distant family members, including aunts, uncles, siblings, or grandparents, may file the suit.
The New York bill would also have expanded compensable damages to include loss of affection and companionship, and it would have expanded emotional damages, which are not currently included in New York. It would also have extended the statute of limitations of a wrongful death claim from 2 years to 3.5 years.
In general, in states that allow emotional distress to be included in wrongful death lawsuits, attorneys must demonstrate that survivors have suffered mental harm, such as depression, loss of sleep, fear, and anger, says Russ Haven, JD, general counsel for the New York Public Interest Research Group. While mental harm is not particularly easy to prove, attorneys must show that survivors have ongoing distress that is the direct result of the loss of the loved one and that the distress is significant enough to severely affect their quality of life.
Mr. Haven gives an example of emotional distress: “We worked with a woman who lost her fiancé in a motor vehicle accident,” he says. “The funeral ended up on the day she had scheduled her wedding dress fitting. A situation like that causes a good deal of lasting emotional distress.”
Expanding family members who can bring the lawsuit
The fact that a fiancé could be included in a wrongful death settlement is another aspect of the New York bill that was central to arguments both for and against the expansion of family members who can make claims. “We think a modern society includes unmarried partners, grandparents, siblings, and others,” says Mr. Haven.
“The language of who is a close family member might seem clear, but to a defense attorney, it isn’t,” says Tom Stebbins, executive director of the Lawsuit Reform Alliance of New York. “This could end up being a situation where someone has 40 grandchildren, and all could be considered close family members.”
Many states currently allow damages for claims of grief and mental anguish resulting from a wrongful death.
In her recent veto of the Grieving Families Act, New York Gov. Kathy Hochul took fire for her choices. The bill represented years of effort by the state legislature to expand the qualifiers for wrongful death lawsuits. Those supporting what ultimately became Senate Bill S74A believed they finally had the law over the finish line. Those opposed breathed a sigh of relief when the bill was vetoed.
Had Gov. Hochul signed Bill 274A, the effect on costs would have been enormous for physicians. New York already has the highest cumulative medical liability payouts in the nation, according to the Medical Society of the State of New York.
The MSSNY was among many parties that fought against the law. The Greater New York Hospital Association, insurance companies, the Defense Association of New York, and the New York Conference of Mayors all joined in lobbying against the bill.
“Gov. Hochul, in her veto message, correctly noted that the proposed New York legislation represented an extraordinary departure from New York’s wrongful death jurisprudence,” says Remi Stone, director of government relations at The Doctors Company, part of the TDC Group. “I would add that while there are some other states that allow grief damages, none are as wide-ranging as the proposed legislation.”
The NYPIRG, the AARP, and the New York Immigration Coalition supported the bill. In a statement following the veto, the New York State Trial Lawyers Association said: “By vetoing the Grieving Families Act, Gov. Hochul has sided with insurance companies, the health care industry, big corporations, and anyone else who doesn’t want to be held accountable for the negligent killing of a person. This bill passed with overwhelming bipartisan support and would rectify over a century of injustice.”
Following Gov. Hochul’s veto, the bill’s proponents and the state legislature vowed to return to the drawing board and construct a bill that the governor would eventually approve. For now, however, the controversial legislation has been put to rest.
Mr. Haven and the NYPIRG argue that New York lags behind many other states in allowing survivors to claim loss for their emotional distress. “When there is relationship loss, it has a great impact on your life,” Mr. Haven says, “and this goes beyond simply the financial impact.”
“The bill was well intended but completely vague on who could bring lawsuits and would have increased medical malpractice insurance by far too much,” says MSSNY President Parag Mehta, MD. “For safety net hospitals, one lawsuit would halt their ability to provide many programs aimed at underserved populations.”
Peter Kolbert, JD, senior vice president of claim and litigation services at Healthcare Risk Advisors (part of the TDC Group), had this to say: “The current ‘recoverable’ damages in New York in a wrongful death case include loss of guidance and support for minor children of a decedent. Those damages have been sustained at $2 million per child. It is rationally very challenging, if not impossible, to distinguish between those damages and the proposed damages that the very same people would have been entitled to under the proposed statute.”
What will happen in the future?
While the veto has stalled New York’s wrongful death expansion for now, supporters in and out of the legislature remain determined to continue their fight. “Advocates argue that the bill would have brought the state in line with wrongful death law in others,” says Brian Whitelaw, JD, a partner at Michigan’s Foley, Baron, Metzger & Juip. “But if the bill had become law as written, the economic impact would have been substantial.”
Mr. Whitelaw says that such wide-ranging lawsuits can have consequences that extend far beyond physicians’ insurance premiums. “This could impact the average person on the street’s ability to obtain the medical care they need, because doctors will go elsewhere to practice,” he says. “Beyond impacting the health care system, it can hurt small businesses as well.”
Mr. Haven says supporters of the expansion are far from finished with their efforts. “New York’s current law dates back to 1847, and it was cutting edge then,” he says. “It was designed for an agrarian society where if the husband died, his widow and children wouldn’t become destitute. Now, 175 years later, we realize that the law has biases, and tort law has evolved. The state needs to evolve as well.”
For his part, Dr. Mehta is open to a dialogue with lawmakers to revise the law in a manner agreeable to all parties. “We want to work together to make the system right,” he says. “The liability system in New York needs an overall holistic change, and we are available at any time to have discussions. The vetoed bill was a Band-Aid and didn’t address the main, underlying issues in the state.”
Mr. Stebbins, too, says he would like to continue the debate over how an expansion should look. “We hope to go through a discussion on caps to these suits,” he explains. “We have already seen the cap of $10 million broken four times in the past few years through nuclear verdicts. That’s something we need to address.”
Given the legislature’s overwhelming support for the bill, some version of it will likely make another appearance in the coming session. Whether or not it can strike the middle ground that will make all parties happy – including the governor – is yet to be seen. “Is it wrong to seek compensation for pain and suffering from a wrongful death?” asks Mr. Whitelaw. “No. But there must be limits to such laws, or where does it end?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In addition, the types of emotional damage that physicians can be sued for is expanding in pockets across the nation. The latest effort to expand the capacity to sue, a bill in New York state, failed when it was not signed by the governor – but a toned-down bill is in the works.
The impact of New York’s proposed expansion of wrongful death lawsuits would have been widespread. The New York legislation would have expanded the definition of “close family members” to include spouses, domestic partners, children, parents, stepparents, siblings, grandparents, and perhaps more. Additionally, lawsuits could have allowed juries to determine “close family members” of the deceased patient on the basis of specific circumstances of the person’s relationship with the decedent.
Currently, every state allows a wrongful death claim to be filed by immediate family members. If the patient who died was married, a surviving spouse could bring the lawsuit. If the patient had been unmarried, an adult child could bring the lawsuit in some states. A parent typically brings a lawsuit if their minor child has died from alleged wrongful death. In some states, one member of a civil union or domestic partnership may bring a wrongful death lawsuit. And if a single adult has no children or spouse/partner, more distant family members, including aunts, uncles, siblings, or grandparents, may file the suit.
The New York bill would also have expanded compensable damages to include loss of affection and companionship, and it would have expanded emotional damages, which are not currently included in New York. It would also have extended the statute of limitations of a wrongful death claim from 2 years to 3.5 years.
In general, in states that allow emotional distress to be included in wrongful death lawsuits, attorneys must demonstrate that survivors have suffered mental harm, such as depression, loss of sleep, fear, and anger, says Russ Haven, JD, general counsel for the New York Public Interest Research Group. While mental harm is not particularly easy to prove, attorneys must show that survivors have ongoing distress that is the direct result of the loss of the loved one and that the distress is significant enough to severely affect their quality of life.
Mr. Haven gives an example of emotional distress: “We worked with a woman who lost her fiancé in a motor vehicle accident,” he says. “The funeral ended up on the day she had scheduled her wedding dress fitting. A situation like that causes a good deal of lasting emotional distress.”
Expanding family members who can bring the lawsuit
The fact that a fiancé could be included in a wrongful death settlement is another aspect of the New York bill that was central to arguments both for and against the expansion of family members who can make claims. “We think a modern society includes unmarried partners, grandparents, siblings, and others,” says Mr. Haven.
“The language of who is a close family member might seem clear, but to a defense attorney, it isn’t,” says Tom Stebbins, executive director of the Lawsuit Reform Alliance of New York. “This could end up being a situation where someone has 40 grandchildren, and all could be considered close family members.”
Many states currently allow damages for claims of grief and mental anguish resulting from a wrongful death.
In her recent veto of the Grieving Families Act, New York Gov. Kathy Hochul took fire for her choices. The bill represented years of effort by the state legislature to expand the qualifiers for wrongful death lawsuits. Those supporting what ultimately became Senate Bill S74A believed they finally had the law over the finish line. Those opposed breathed a sigh of relief when the bill was vetoed.
Had Gov. Hochul signed Bill 274A, the effect on costs would have been enormous for physicians. New York already has the highest cumulative medical liability payouts in the nation, according to the Medical Society of the State of New York.
The MSSNY was among many parties that fought against the law. The Greater New York Hospital Association, insurance companies, the Defense Association of New York, and the New York Conference of Mayors all joined in lobbying against the bill.
“Gov. Hochul, in her veto message, correctly noted that the proposed New York legislation represented an extraordinary departure from New York’s wrongful death jurisprudence,” says Remi Stone, director of government relations at The Doctors Company, part of the TDC Group. “I would add that while there are some other states that allow grief damages, none are as wide-ranging as the proposed legislation.”
The NYPIRG, the AARP, and the New York Immigration Coalition supported the bill. In a statement following the veto, the New York State Trial Lawyers Association said: “By vetoing the Grieving Families Act, Gov. Hochul has sided with insurance companies, the health care industry, big corporations, and anyone else who doesn’t want to be held accountable for the negligent killing of a person. This bill passed with overwhelming bipartisan support and would rectify over a century of injustice.”
Following Gov. Hochul’s veto, the bill’s proponents and the state legislature vowed to return to the drawing board and construct a bill that the governor would eventually approve. For now, however, the controversial legislation has been put to rest.
Mr. Haven and the NYPIRG argue that New York lags behind many other states in allowing survivors to claim loss for their emotional distress. “When there is relationship loss, it has a great impact on your life,” Mr. Haven says, “and this goes beyond simply the financial impact.”
“The bill was well intended but completely vague on who could bring lawsuits and would have increased medical malpractice insurance by far too much,” says MSSNY President Parag Mehta, MD. “For safety net hospitals, one lawsuit would halt their ability to provide many programs aimed at underserved populations.”
Peter Kolbert, JD, senior vice president of claim and litigation services at Healthcare Risk Advisors (part of the TDC Group), had this to say: “The current ‘recoverable’ damages in New York in a wrongful death case include loss of guidance and support for minor children of a decedent. Those damages have been sustained at $2 million per child. It is rationally very challenging, if not impossible, to distinguish between those damages and the proposed damages that the very same people would have been entitled to under the proposed statute.”
What will happen in the future?
While the veto has stalled New York’s wrongful death expansion for now, supporters in and out of the legislature remain determined to continue their fight. “Advocates argue that the bill would have brought the state in line with wrongful death law in others,” says Brian Whitelaw, JD, a partner at Michigan’s Foley, Baron, Metzger & Juip. “But if the bill had become law as written, the economic impact would have been substantial.”
Mr. Whitelaw says that such wide-ranging lawsuits can have consequences that extend far beyond physicians’ insurance premiums. “This could impact the average person on the street’s ability to obtain the medical care they need, because doctors will go elsewhere to practice,” he says. “Beyond impacting the health care system, it can hurt small businesses as well.”
Mr. Haven says supporters of the expansion are far from finished with their efforts. “New York’s current law dates back to 1847, and it was cutting edge then,” he says. “It was designed for an agrarian society where if the husband died, his widow and children wouldn’t become destitute. Now, 175 years later, we realize that the law has biases, and tort law has evolved. The state needs to evolve as well.”
For his part, Dr. Mehta is open to a dialogue with lawmakers to revise the law in a manner agreeable to all parties. “We want to work together to make the system right,” he says. “The liability system in New York needs an overall holistic change, and we are available at any time to have discussions. The vetoed bill was a Band-Aid and didn’t address the main, underlying issues in the state.”
Mr. Stebbins, too, says he would like to continue the debate over how an expansion should look. “We hope to go through a discussion on caps to these suits,” he explains. “We have already seen the cap of $10 million broken four times in the past few years through nuclear verdicts. That’s something we need to address.”
Given the legislature’s overwhelming support for the bill, some version of it will likely make another appearance in the coming session. Whether or not it can strike the middle ground that will make all parties happy – including the governor – is yet to be seen. “Is it wrong to seek compensation for pain and suffering from a wrongful death?” asks Mr. Whitelaw. “No. But there must be limits to such laws, or where does it end?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In addition, the types of emotional damage that physicians can be sued for is expanding in pockets across the nation. The latest effort to expand the capacity to sue, a bill in New York state, failed when it was not signed by the governor – but a toned-down bill is in the works.
The impact of New York’s proposed expansion of wrongful death lawsuits would have been widespread. The New York legislation would have expanded the definition of “close family members” to include spouses, domestic partners, children, parents, stepparents, siblings, grandparents, and perhaps more. Additionally, lawsuits could have allowed juries to determine “close family members” of the deceased patient on the basis of specific circumstances of the person’s relationship with the decedent.
Currently, every state allows a wrongful death claim to be filed by immediate family members. If the patient who died was married, a surviving spouse could bring the lawsuit. If the patient had been unmarried, an adult child could bring the lawsuit in some states. A parent typically brings a lawsuit if their minor child has died from alleged wrongful death. In some states, one member of a civil union or domestic partnership may bring a wrongful death lawsuit. And if a single adult has no children or spouse/partner, more distant family members, including aunts, uncles, siblings, or grandparents, may file the suit.
The New York bill would also have expanded compensable damages to include loss of affection and companionship, and it would have expanded emotional damages, which are not currently included in New York. It would also have extended the statute of limitations of a wrongful death claim from 2 years to 3.5 years.
In general, in states that allow emotional distress to be included in wrongful death lawsuits, attorneys must demonstrate that survivors have suffered mental harm, such as depression, loss of sleep, fear, and anger, says Russ Haven, JD, general counsel for the New York Public Interest Research Group. While mental harm is not particularly easy to prove, attorneys must show that survivors have ongoing distress that is the direct result of the loss of the loved one and that the distress is significant enough to severely affect their quality of life.
Mr. Haven gives an example of emotional distress: “We worked with a woman who lost her fiancé in a motor vehicle accident,” he says. “The funeral ended up on the day she had scheduled her wedding dress fitting. A situation like that causes a good deal of lasting emotional distress.”
Expanding family members who can bring the lawsuit
The fact that a fiancé could be included in a wrongful death settlement is another aspect of the New York bill that was central to arguments both for and against the expansion of family members who can make claims. “We think a modern society includes unmarried partners, grandparents, siblings, and others,” says Mr. Haven.
“The language of who is a close family member might seem clear, but to a defense attorney, it isn’t,” says Tom Stebbins, executive director of the Lawsuit Reform Alliance of New York. “This could end up being a situation where someone has 40 grandchildren, and all could be considered close family members.”
Many states currently allow damages for claims of grief and mental anguish resulting from a wrongful death.
In her recent veto of the Grieving Families Act, New York Gov. Kathy Hochul took fire for her choices. The bill represented years of effort by the state legislature to expand the qualifiers for wrongful death lawsuits. Those supporting what ultimately became Senate Bill S74A believed they finally had the law over the finish line. Those opposed breathed a sigh of relief when the bill was vetoed.
Had Gov. Hochul signed Bill 274A, the effect on costs would have been enormous for physicians. New York already has the highest cumulative medical liability payouts in the nation, according to the Medical Society of the State of New York.
The MSSNY was among many parties that fought against the law. The Greater New York Hospital Association, insurance companies, the Defense Association of New York, and the New York Conference of Mayors all joined in lobbying against the bill.
“Gov. Hochul, in her veto message, correctly noted that the proposed New York legislation represented an extraordinary departure from New York’s wrongful death jurisprudence,” says Remi Stone, director of government relations at The Doctors Company, part of the TDC Group. “I would add that while there are some other states that allow grief damages, none are as wide-ranging as the proposed legislation.”
The NYPIRG, the AARP, and the New York Immigration Coalition supported the bill. In a statement following the veto, the New York State Trial Lawyers Association said: “By vetoing the Grieving Families Act, Gov. Hochul has sided with insurance companies, the health care industry, big corporations, and anyone else who doesn’t want to be held accountable for the negligent killing of a person. This bill passed with overwhelming bipartisan support and would rectify over a century of injustice.”
Following Gov. Hochul’s veto, the bill’s proponents and the state legislature vowed to return to the drawing board and construct a bill that the governor would eventually approve. For now, however, the controversial legislation has been put to rest.
Mr. Haven and the NYPIRG argue that New York lags behind many other states in allowing survivors to claim loss for their emotional distress. “When there is relationship loss, it has a great impact on your life,” Mr. Haven says, “and this goes beyond simply the financial impact.”
“The bill was well intended but completely vague on who could bring lawsuits and would have increased medical malpractice insurance by far too much,” says MSSNY President Parag Mehta, MD. “For safety net hospitals, one lawsuit would halt their ability to provide many programs aimed at underserved populations.”
Peter Kolbert, JD, senior vice president of claim and litigation services at Healthcare Risk Advisors (part of the TDC Group), had this to say: “The current ‘recoverable’ damages in New York in a wrongful death case include loss of guidance and support for minor children of a decedent. Those damages have been sustained at $2 million per child. It is rationally very challenging, if not impossible, to distinguish between those damages and the proposed damages that the very same people would have been entitled to under the proposed statute.”
What will happen in the future?
While the veto has stalled New York’s wrongful death expansion for now, supporters in and out of the legislature remain determined to continue their fight. “Advocates argue that the bill would have brought the state in line with wrongful death law in others,” says Brian Whitelaw, JD, a partner at Michigan’s Foley, Baron, Metzger & Juip. “But if the bill had become law as written, the economic impact would have been substantial.”
Mr. Whitelaw says that such wide-ranging lawsuits can have consequences that extend far beyond physicians’ insurance premiums. “This could impact the average person on the street’s ability to obtain the medical care they need, because doctors will go elsewhere to practice,” he says. “Beyond impacting the health care system, it can hurt small businesses as well.”
Mr. Haven says supporters of the expansion are far from finished with their efforts. “New York’s current law dates back to 1847, and it was cutting edge then,” he says. “It was designed for an agrarian society where if the husband died, his widow and children wouldn’t become destitute. Now, 175 years later, we realize that the law has biases, and tort law has evolved. The state needs to evolve as well.”
For his part, Dr. Mehta is open to a dialogue with lawmakers to revise the law in a manner agreeable to all parties. “We want to work together to make the system right,” he says. “The liability system in New York needs an overall holistic change, and we are available at any time to have discussions. The vetoed bill was a Band-Aid and didn’t address the main, underlying issues in the state.”
Mr. Stebbins, too, says he would like to continue the debate over how an expansion should look. “We hope to go through a discussion on caps to these suits,” he explains. “We have already seen the cap of $10 million broken four times in the past few years through nuclear verdicts. That’s something we need to address.”
Given the legislature’s overwhelming support for the bill, some version of it will likely make another appearance in the coming session. Whether or not it can strike the middle ground that will make all parties happy – including the governor – is yet to be seen. “Is it wrong to seek compensation for pain and suffering from a wrongful death?” asks Mr. Whitelaw. “No. But there must be limits to such laws, or where does it end?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Breakthrough’ study: Diabetes drug helps prevent long COVID
with The Lancet on SSRN. The preprint hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed or published in a journal.
In particular, metformin led to a 42% drop in long COVID among people who had a mild to moderate COVID-19 infection.
“Long COVID affects millions of people, and preventing long COVID through a treatment like metformin could prevent significant disruptions in people’s lives,” said lead author Carolyn Bramante, MD, assistant professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Between January 2021 and February 2022, Dr. Bramante and colleagues tested three oral medications – metformin (typically used to treat type 2 diabetes), ivermectin (an antiparasitic), and fluvoxamine (an antidepressant) – in a clinical trial across the United States called COVID-OUT. The people being studied, investigators, care providers, and others involved in the study were blinded to the randomized treatments. The trial was decentralized, with no in-person contact with participants.
The researchers included patients who were aged 30-85 with overweight or obesity, had documentation of a confirmed COVID-19 infection, had fewer than 7 days of symptoms, had no known prior infection, and joined the study within 3 days of their positive test. The study included monthly follow-up for 300 days, and participants indicated whether they received a long COVID diagnosis from a medical doctor, which the researchers confirmed in medical records after participants gave consent.
The medications were prepackaged into pill boxes for fast delivery to participants and to ensure they took the correct number of each type of pill. The packages were sent via same-day courier or overnight shipping.
The metformin doses were doled out over 14 days, with 500 milligrams on the first day, 500 milligrams twice a day for the next 4 days, and then 500 milligrams in the morning and 1,000 milligrams in the evening for the remaining 9 days.
Among the 1,323 people studied, 1,125 agreed to do long-term follow-up for long COVID: 564 in the metformin group and 561 in the blinded placebo group. The average age was 45, and 56% were women, including 7% who were pregnant.
The average time from the start of symptoms to starting medication was 5 days, and 47% began taking the drug within 4 days or less. About 55% had received the primary COVID-19 vaccination series, including 5.1% who received an initial booster, before enrolling in the study.
Overall, 8.4% of participants reported that a medical provider diagnosed them with long COVID. Of those who took metformin, 6.3% developed long COVID, compared to 10.6% among those who took the identical-matched placebo.
The risk reduction for metformin was 42% versus the placebo, which was consistent across subgroups, including vaccination status and different COVID-19 variants.
When metformin was started less than 4 days after COVID-19 symptoms started, the effect was potentially even greater, with a 64% reduction, as compared with a 36% reduction among those who started metformin after 4 or more days after symptoms.
Neither ivermectin nor fluvoxamine showed any benefits for preventing long COVID.
At the same time, the study authors caution that more research is needed.
“The COVID-OUT trial does not indicate whether or not metformin would be effective at preventing long COVID if started at the time of emergency department visit or hospitalization for COVID-19, nor whether metformin would be effective as treatment in persons who already have long COVID,” they wrote. “With the burden of long COVID on society, confirmation is urgently needed in a trial that addresses our study’s limitations in order to translate these results into practice and policy.”
Several risk factors for long COVID emerged in the analysis. About 11.1% of the women had a long COVID diagnosis, compared with 4.9% of the men. Also, those who had received at least the primary vaccine series had a lower risk of developing long COVID, at 6.6%, as compared with 10.5% among the unvaccinated. Only 1 of the 57 people who received a booster shot developed long COVID.
Notably, pregnant and lactating people were included in this study, which is important given that pregnant people face higher risks for poor COVID-19 outcomes and are excluded from most nonobstetric clinical trials, the study authors wrote. In this study, they were randomized to metformin or placebo but not ivermectin or fluvoxamine due to limited research about the safety of those drugs during pregnancy and lactation.
The results are now under journal review but show findings consistent with those from other recent studies. Also, in August 2022, the authors published results from COVID-OUT that showed metformin led to a 42% reduction in hospital visits, emergency department visits, and deaths related to severe COVID-19.
“Given the lack of side effects and cost for a 2-week course, I think these data support use of metformin now,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health care professionals.
Dr. Topol, who wasn’t involved with this study, has been a leading voice on COVID-19 research throughout the pandemic. He noted the need for more studies, including a factorial design trial to test metformin and Paxlovid, which has shown promise in preventing long COVID. Dr. Topol also wrote about the preprint in Ground Truths, his online newsletter.
“As I’ve written in the past, I don’t use the term ‘breakthrough’ lightly,” he wrote. “But to see such a pronounced benefit in the current randomized trial of metformin, in the context of its being so safe and low cost, I’d give it a breakthrough categorization.”
Another way to put it, Dr. Topol wrote, is that based on this study, he would take metformin if he became infected with COVID-19.
Jeremy Faust, MD, an emergency medicine doctor at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, also wrote about the study in his newsletter, Inside Medicine. He noted that the 42% reduction in long COVID means that 23 COVID-19 patients need to be treated with metformin to prevent one long COVID diagnosis, which is an “important reduction.”
“Bottom line: If a person who meets criteria for obesity or overweight status were to ask me if they should take metformin (for 2 weeks) starting as soon as they learn they have COVID-19, I would say yes in many if not most cases, based on this new data,” he wrote. “This is starting to look like a real win.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
with The Lancet on SSRN. The preprint hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed or published in a journal.
In particular, metformin led to a 42% drop in long COVID among people who had a mild to moderate COVID-19 infection.
“Long COVID affects millions of people, and preventing long COVID through a treatment like metformin could prevent significant disruptions in people’s lives,” said lead author Carolyn Bramante, MD, assistant professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Between January 2021 and February 2022, Dr. Bramante and colleagues tested three oral medications – metformin (typically used to treat type 2 diabetes), ivermectin (an antiparasitic), and fluvoxamine (an antidepressant) – in a clinical trial across the United States called COVID-OUT. The people being studied, investigators, care providers, and others involved in the study were blinded to the randomized treatments. The trial was decentralized, with no in-person contact with participants.
The researchers included patients who were aged 30-85 with overweight or obesity, had documentation of a confirmed COVID-19 infection, had fewer than 7 days of symptoms, had no known prior infection, and joined the study within 3 days of their positive test. The study included monthly follow-up for 300 days, and participants indicated whether they received a long COVID diagnosis from a medical doctor, which the researchers confirmed in medical records after participants gave consent.
The medications were prepackaged into pill boxes for fast delivery to participants and to ensure they took the correct number of each type of pill. The packages were sent via same-day courier or overnight shipping.
The metformin doses were doled out over 14 days, with 500 milligrams on the first day, 500 milligrams twice a day for the next 4 days, and then 500 milligrams in the morning and 1,000 milligrams in the evening for the remaining 9 days.
Among the 1,323 people studied, 1,125 agreed to do long-term follow-up for long COVID: 564 in the metformin group and 561 in the blinded placebo group. The average age was 45, and 56% were women, including 7% who were pregnant.
The average time from the start of symptoms to starting medication was 5 days, and 47% began taking the drug within 4 days or less. About 55% had received the primary COVID-19 vaccination series, including 5.1% who received an initial booster, before enrolling in the study.
Overall, 8.4% of participants reported that a medical provider diagnosed them with long COVID. Of those who took metformin, 6.3% developed long COVID, compared to 10.6% among those who took the identical-matched placebo.
The risk reduction for metformin was 42% versus the placebo, which was consistent across subgroups, including vaccination status and different COVID-19 variants.
When metformin was started less than 4 days after COVID-19 symptoms started, the effect was potentially even greater, with a 64% reduction, as compared with a 36% reduction among those who started metformin after 4 or more days after symptoms.
Neither ivermectin nor fluvoxamine showed any benefits for preventing long COVID.
At the same time, the study authors caution that more research is needed.
“The COVID-OUT trial does not indicate whether or not metformin would be effective at preventing long COVID if started at the time of emergency department visit or hospitalization for COVID-19, nor whether metformin would be effective as treatment in persons who already have long COVID,” they wrote. “With the burden of long COVID on society, confirmation is urgently needed in a trial that addresses our study’s limitations in order to translate these results into practice and policy.”
Several risk factors for long COVID emerged in the analysis. About 11.1% of the women had a long COVID diagnosis, compared with 4.9% of the men. Also, those who had received at least the primary vaccine series had a lower risk of developing long COVID, at 6.6%, as compared with 10.5% among the unvaccinated. Only 1 of the 57 people who received a booster shot developed long COVID.
Notably, pregnant and lactating people were included in this study, which is important given that pregnant people face higher risks for poor COVID-19 outcomes and are excluded from most nonobstetric clinical trials, the study authors wrote. In this study, they were randomized to metformin or placebo but not ivermectin or fluvoxamine due to limited research about the safety of those drugs during pregnancy and lactation.
The results are now under journal review but show findings consistent with those from other recent studies. Also, in August 2022, the authors published results from COVID-OUT that showed metformin led to a 42% reduction in hospital visits, emergency department visits, and deaths related to severe COVID-19.
“Given the lack of side effects and cost for a 2-week course, I think these data support use of metformin now,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health care professionals.
Dr. Topol, who wasn’t involved with this study, has been a leading voice on COVID-19 research throughout the pandemic. He noted the need for more studies, including a factorial design trial to test metformin and Paxlovid, which has shown promise in preventing long COVID. Dr. Topol also wrote about the preprint in Ground Truths, his online newsletter.
“As I’ve written in the past, I don’t use the term ‘breakthrough’ lightly,” he wrote. “But to see such a pronounced benefit in the current randomized trial of metformin, in the context of its being so safe and low cost, I’d give it a breakthrough categorization.”
Another way to put it, Dr. Topol wrote, is that based on this study, he would take metformin if he became infected with COVID-19.
Jeremy Faust, MD, an emergency medicine doctor at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, also wrote about the study in his newsletter, Inside Medicine. He noted that the 42% reduction in long COVID means that 23 COVID-19 patients need to be treated with metformin to prevent one long COVID diagnosis, which is an “important reduction.”
“Bottom line: If a person who meets criteria for obesity or overweight status were to ask me if they should take metformin (for 2 weeks) starting as soon as they learn they have COVID-19, I would say yes in many if not most cases, based on this new data,” he wrote. “This is starting to look like a real win.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
with The Lancet on SSRN. The preprint hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed or published in a journal.
In particular, metformin led to a 42% drop in long COVID among people who had a mild to moderate COVID-19 infection.
“Long COVID affects millions of people, and preventing long COVID through a treatment like metformin could prevent significant disruptions in people’s lives,” said lead author Carolyn Bramante, MD, assistant professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Between January 2021 and February 2022, Dr. Bramante and colleagues tested three oral medications – metformin (typically used to treat type 2 diabetes), ivermectin (an antiparasitic), and fluvoxamine (an antidepressant) – in a clinical trial across the United States called COVID-OUT. The people being studied, investigators, care providers, and others involved in the study were blinded to the randomized treatments. The trial was decentralized, with no in-person contact with participants.
The researchers included patients who were aged 30-85 with overweight or obesity, had documentation of a confirmed COVID-19 infection, had fewer than 7 days of symptoms, had no known prior infection, and joined the study within 3 days of their positive test. The study included monthly follow-up for 300 days, and participants indicated whether they received a long COVID diagnosis from a medical doctor, which the researchers confirmed in medical records after participants gave consent.
The medications were prepackaged into pill boxes for fast delivery to participants and to ensure they took the correct number of each type of pill. The packages were sent via same-day courier or overnight shipping.
The metformin doses were doled out over 14 days, with 500 milligrams on the first day, 500 milligrams twice a day for the next 4 days, and then 500 milligrams in the morning and 1,000 milligrams in the evening for the remaining 9 days.
Among the 1,323 people studied, 1,125 agreed to do long-term follow-up for long COVID: 564 in the metformin group and 561 in the blinded placebo group. The average age was 45, and 56% were women, including 7% who were pregnant.
The average time from the start of symptoms to starting medication was 5 days, and 47% began taking the drug within 4 days or less. About 55% had received the primary COVID-19 vaccination series, including 5.1% who received an initial booster, before enrolling in the study.
Overall, 8.4% of participants reported that a medical provider diagnosed them with long COVID. Of those who took metformin, 6.3% developed long COVID, compared to 10.6% among those who took the identical-matched placebo.
The risk reduction for metformin was 42% versus the placebo, which was consistent across subgroups, including vaccination status and different COVID-19 variants.
When metformin was started less than 4 days after COVID-19 symptoms started, the effect was potentially even greater, with a 64% reduction, as compared with a 36% reduction among those who started metformin after 4 or more days after symptoms.
Neither ivermectin nor fluvoxamine showed any benefits for preventing long COVID.
At the same time, the study authors caution that more research is needed.
“The COVID-OUT trial does not indicate whether or not metformin would be effective at preventing long COVID if started at the time of emergency department visit or hospitalization for COVID-19, nor whether metformin would be effective as treatment in persons who already have long COVID,” they wrote. “With the burden of long COVID on society, confirmation is urgently needed in a trial that addresses our study’s limitations in order to translate these results into practice and policy.”
Several risk factors for long COVID emerged in the analysis. About 11.1% of the women had a long COVID diagnosis, compared with 4.9% of the men. Also, those who had received at least the primary vaccine series had a lower risk of developing long COVID, at 6.6%, as compared with 10.5% among the unvaccinated. Only 1 of the 57 people who received a booster shot developed long COVID.
Notably, pregnant and lactating people were included in this study, which is important given that pregnant people face higher risks for poor COVID-19 outcomes and are excluded from most nonobstetric clinical trials, the study authors wrote. In this study, they were randomized to metformin or placebo but not ivermectin or fluvoxamine due to limited research about the safety of those drugs during pregnancy and lactation.
The results are now under journal review but show findings consistent with those from other recent studies. Also, in August 2022, the authors published results from COVID-OUT that showed metformin led to a 42% reduction in hospital visits, emergency department visits, and deaths related to severe COVID-19.
“Given the lack of side effects and cost for a 2-week course, I think these data support use of metformin now,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health care professionals.
Dr. Topol, who wasn’t involved with this study, has been a leading voice on COVID-19 research throughout the pandemic. He noted the need for more studies, including a factorial design trial to test metformin and Paxlovid, which has shown promise in preventing long COVID. Dr. Topol also wrote about the preprint in Ground Truths, his online newsletter.
“As I’ve written in the past, I don’t use the term ‘breakthrough’ lightly,” he wrote. “But to see such a pronounced benefit in the current randomized trial of metformin, in the context of its being so safe and low cost, I’d give it a breakthrough categorization.”
Another way to put it, Dr. Topol wrote, is that based on this study, he would take metformin if he became infected with COVID-19.
Jeremy Faust, MD, an emergency medicine doctor at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, also wrote about the study in his newsletter, Inside Medicine. He noted that the 42% reduction in long COVID means that 23 COVID-19 patients need to be treated with metformin to prevent one long COVID diagnosis, which is an “important reduction.”
“Bottom line: If a person who meets criteria for obesity or overweight status were to ask me if they should take metformin (for 2 weeks) starting as soon as they learn they have COVID-19, I would say yes in many if not most cases, based on this new data,” he wrote. “This is starting to look like a real win.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Telehealth doctor indicted on health care fraud, opioid distribution charges
Sangita Patel, MD, 50, practiced at Advance Medical Home Physicians in Troy.
According to court documents, between July 2020 and June 2022 Patel was responsible for submitting Medicare claims for improper telehealth visits she didn’t conduct herself.
Dr. Patel, who accepted patients who paid in cash as well as those with Medicare and Medicaid coverage, billed approximately $3.4 million to Medicare between 2018 and 2022, according to court documents. An unusual number of these visits were billed using complex codes, an indication of health care fraud. The investigation also found that on many days, Dr. Patel billed for more than 24 hours of services. During this period, according to the document, 76% of Dr. Patel’s Medicare reimbursements were for telehealth.
Prosecutors say that Dr. Patel prescribed Schedule II controlled substances to more than 90% of the patients in these telehealth visits. She delegated her prescription authority to an unlicensed medical assistant. Through undercover visits and cell site search warrant data, the investigation found that Dr. Patel directed patients to contact, via cell phone, this assistant, who then entered electronic prescriptions into the electronic medical records system. Dr. Patel then signed the prescriptions and sent them to the pharmacies without ever interacting with the patients. Prosecutors also used text messages, obtained by search warrant, between Dr. Patel and her assistant and between the assistant and undercover informers to build their case.
Dr. Patel is also accused of referring patients to other providers, who in turn billed Medicare for claims associated with those patients. Advance Medical received $143,000 from these providers, potentially in violation of anti-kickback laws, according to bank records obtained by subpoena.
If convicted, Dr. Patel could be sentenced to up to 10 years in federal prison.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sangita Patel, MD, 50, practiced at Advance Medical Home Physicians in Troy.
According to court documents, between July 2020 and June 2022 Patel was responsible for submitting Medicare claims for improper telehealth visits she didn’t conduct herself.
Dr. Patel, who accepted patients who paid in cash as well as those with Medicare and Medicaid coverage, billed approximately $3.4 million to Medicare between 2018 and 2022, according to court documents. An unusual number of these visits were billed using complex codes, an indication of health care fraud. The investigation also found that on many days, Dr. Patel billed for more than 24 hours of services. During this period, according to the document, 76% of Dr. Patel’s Medicare reimbursements were for telehealth.
Prosecutors say that Dr. Patel prescribed Schedule II controlled substances to more than 90% of the patients in these telehealth visits. She delegated her prescription authority to an unlicensed medical assistant. Through undercover visits and cell site search warrant data, the investigation found that Dr. Patel directed patients to contact, via cell phone, this assistant, who then entered electronic prescriptions into the electronic medical records system. Dr. Patel then signed the prescriptions and sent them to the pharmacies without ever interacting with the patients. Prosecutors also used text messages, obtained by search warrant, between Dr. Patel and her assistant and between the assistant and undercover informers to build their case.
Dr. Patel is also accused of referring patients to other providers, who in turn billed Medicare for claims associated with those patients. Advance Medical received $143,000 from these providers, potentially in violation of anti-kickback laws, according to bank records obtained by subpoena.
If convicted, Dr. Patel could be sentenced to up to 10 years in federal prison.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sangita Patel, MD, 50, practiced at Advance Medical Home Physicians in Troy.
According to court documents, between July 2020 and June 2022 Patel was responsible for submitting Medicare claims for improper telehealth visits she didn’t conduct herself.
Dr. Patel, who accepted patients who paid in cash as well as those with Medicare and Medicaid coverage, billed approximately $3.4 million to Medicare between 2018 and 2022, according to court documents. An unusual number of these visits were billed using complex codes, an indication of health care fraud. The investigation also found that on many days, Dr. Patel billed for more than 24 hours of services. During this period, according to the document, 76% of Dr. Patel’s Medicare reimbursements were for telehealth.
Prosecutors say that Dr. Patel prescribed Schedule II controlled substances to more than 90% of the patients in these telehealth visits. She delegated her prescription authority to an unlicensed medical assistant. Through undercover visits and cell site search warrant data, the investigation found that Dr. Patel directed patients to contact, via cell phone, this assistant, who then entered electronic prescriptions into the electronic medical records system. Dr. Patel then signed the prescriptions and sent them to the pharmacies without ever interacting with the patients. Prosecutors also used text messages, obtained by search warrant, between Dr. Patel and her assistant and between the assistant and undercover informers to build their case.
Dr. Patel is also accused of referring patients to other providers, who in turn billed Medicare for claims associated with those patients. Advance Medical received $143,000 from these providers, potentially in violation of anti-kickback laws, according to bank records obtained by subpoena.
If convicted, Dr. Patel could be sentenced to up to 10 years in federal prison.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
We have seen the future of healthy muffins, and its name is Roselle
Get ‘em while they’re hot … for your health
Today on the Eating Channel, it’s a very special episode of “Much Ado About Muffin.”
The muffin. For some of us, it’s a good way to pretend we’re not having dessert for breakfast. A bran muffin can be loaded with calcium and fiber, and our beloved blueberry is full of yummy antioxidants and vitamins. Definitely not dessert.
Well, the muffin denial can stop there because there’s a new flavor on the scene, and research suggests it may actually be healthy. (Disclaimer: Muffin may not be considered healthy in Norway.) This new muffin has a name, Roselle, that comes from the calyx extract used in it, which is found in the Hibiscus sabdariffa plant of the same name.
Now, when it comes to new foods, especially ones that are supposed to be healthy, the No. 1 criteria is the same: It has to taste good. Researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology and Amity University in India agreed, but they also set out to make it nutritionally valuable and give it a long shelf life without the addition of preservatives.
Sounds like a tall order, but they figured it out.
Not only is it tasty, but the properties of it could rival your morning multivitamin. Hibiscus extract has huge amounts of antioxidants, like phenolics, which are believed to help prevent cell membrane damage. Foods like vegetables, flax seed, and whole grains also have these antioxidants, but why not just have a Roselle muffin instead? You also get a dose of ascorbic acid without the glass of OJ in the morning.
The ascorbic acid, however, is not there just to help you. It also helps to check the researcher’s third box, shelf life. These naturally rosy-colored pastries will stay mold-free for 6 days without refrigeration at room temperature and without added preservatives.
Our guess, though, is they won’t be on the kitchen counter long enough to find out.
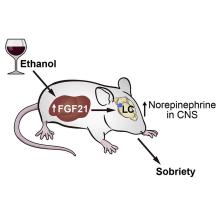
A sobering proposition
If Hollywood is to be believed, there’s no amount of drunkenness that can’t be cured with a cup of coffee or a stern slap in the face. Unfortunately, here in the real world the only thing that can make you less drunk is time. Maybe next time you’ll stop after that seventh Manhattan.
But what if we could beat time? What if there’s an actual sobriety drug out there?
Say hello to fibroblast growth factor 21. Although the liver already does good work filtering out what is essentially poison, it then goes the extra mile and produces fibroblast growth factor 21 (or, as her friends call her, FGF21), a hormone that suppresses the desire to drink, makes you desire water, and protects the liver all at the same time.
Now, FGF21 in its current role is great, but if you’ve ever seen or been a drunk person before, you’ve experienced the lack of interest in listening to reason, especially when it comes from within our own bodies. Who are you to tell us what to do, body? You’re not the boss of us! So a group of scientists decided to push the limits of FGF21. Could it do more than it already does?
First off, they genetically altered a group of mice so that they didn’t produce FGF21 on their own. Then they got them drunk. We’re going to assume they built a scale model of the bar from Cheers and had the mice filter in through the front door as they served their subjects beer out of tiny little glasses.
Once the mice were nice and liquored up, some were given a treatment of FGF21 while others were given a placebo. Lo and behold, the mice given FGF21 recovered about 50% faster than those that received the control treatment. Not exactly instant, but 50% is nothing to sniff at.
Before you bring your FGF21 supplement to the bar, though, this research only applies to mice. We don’t know if it works in people. And make sure you stick to booze. If your choice of intoxication is a bit more exotic, FGF21 isn’t going to do anything for you. Yes, the scientists tried. Yes, those mice are living a very interesting life. And yes, we are jealous of drugged-up lab mice.
Supersize your imagination, shrink your snacks
Have you ever heard of the meal-recall effect? Did you know that, in England, a biscuit is really a cookie? Did you also know that the magazine Bon Appétit is not the same as the peer-reviewed journal Appetite? We do … now.
The meal-recall effect is the subsequent reduction in snacking that comes from remembering a recent meal. It was used to great effect in a recent study conducted at the University of Cambridge, which is in England, where they feed their experimental humans cookies but, for some reason, call them biscuits.
For the first part of the study, the participants were invited to dine at Che Laboratory, where they “were given a microwave ready meal of rice and sauce and a cup of water,” according to a statement from the university. As our Uncle Ernie would say, “Gourmet all the way.”
The test subjects were instructed not to eat anything for 3 hours and “then invited back to the lab to perform imagination tasks.” Those who did come back were randomly divided into five different groups, each with a different task:
- Imagine moving their recent lunch at the lab around a plate.
- Recall eating their recent lunch in detail.
- Imagine that the lunch was twice as big and filling as it really was.
- Look at a photograph of spaghetti hoops in tomato sauce and write a description of it before imagining moving the food around a plate.
- Look at a photo of paper clips and rubber bands and imagine moving them around.
Now, at last, we get to the biscuits/cookies, which were the subject of a taste test that “was simply a rouse for covertly assessing snacking,” the investigators explained. As part of that test, participants were told they could eat as many biscuits as they wanted.
When the tables were cleared and the leftovers examined, the group that imagined spaghetti hoops had eaten the most biscuits (75.9 g), followed by the group that imagined paper clips (75.5 g), the moving-their-lunch-around-the-plate group (72.0 g), and the group that relived eating their lunch (70.0 g).
In a victory for the meal-recall effect, the people who imagined their meal being twice as big ate the fewest biscuits (51.1 g). “Your mind can be more powerful than your stomach in dictating how much you eat,” lead author Joanna Szypula, PhD, said in the university statement.
Oh! One more thing. The study appeared in Appetite, which is a peer-reviewed journal, not in Bon Appétit, which is not a peer-reviewed journal. Thanks to the fine folks at both publications for pointing that out to us.
Get ‘em while they’re hot … for your health
Today on the Eating Channel, it’s a very special episode of “Much Ado About Muffin.”
The muffin. For some of us, it’s a good way to pretend we’re not having dessert for breakfast. A bran muffin can be loaded with calcium and fiber, and our beloved blueberry is full of yummy antioxidants and vitamins. Definitely not dessert.
Well, the muffin denial can stop there because there’s a new flavor on the scene, and research suggests it may actually be healthy. (Disclaimer: Muffin may not be considered healthy in Norway.) This new muffin has a name, Roselle, that comes from the calyx extract used in it, which is found in the Hibiscus sabdariffa plant of the same name.
Now, when it comes to new foods, especially ones that are supposed to be healthy, the No. 1 criteria is the same: It has to taste good. Researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology and Amity University in India agreed, but they also set out to make it nutritionally valuable and give it a long shelf life without the addition of preservatives.
Sounds like a tall order, but they figured it out.
Not only is it tasty, but the properties of it could rival your morning multivitamin. Hibiscus extract has huge amounts of antioxidants, like phenolics, which are believed to help prevent cell membrane damage. Foods like vegetables, flax seed, and whole grains also have these antioxidants, but why not just have a Roselle muffin instead? You also get a dose of ascorbic acid without the glass of OJ in the morning.
The ascorbic acid, however, is not there just to help you. It also helps to check the researcher’s third box, shelf life. These naturally rosy-colored pastries will stay mold-free for 6 days without refrigeration at room temperature and without added preservatives.
Our guess, though, is they won’t be on the kitchen counter long enough to find out.
A sobering proposition
If Hollywood is to be believed, there’s no amount of drunkenness that can’t be cured with a cup of coffee or a stern slap in the face. Unfortunately, here in the real world the only thing that can make you less drunk is time. Maybe next time you’ll stop after that seventh Manhattan.
But what if we could beat time? What if there’s an actual sobriety drug out there?
Say hello to fibroblast growth factor 21. Although the liver already does good work filtering out what is essentially poison, it then goes the extra mile and produces fibroblast growth factor 21 (or, as her friends call her, FGF21), a hormone that suppresses the desire to drink, makes you desire water, and protects the liver all at the same time.
Now, FGF21 in its current role is great, but if you’ve ever seen or been a drunk person before, you’ve experienced the lack of interest in listening to reason, especially when it comes from within our own bodies. Who are you to tell us what to do, body? You’re not the boss of us! So a group of scientists decided to push the limits of FGF21. Could it do more than it already does?
First off, they genetically altered a group of mice so that they didn’t produce FGF21 on their own. Then they got them drunk. We’re going to assume they built a scale model of the bar from Cheers and had the mice filter in through the front door as they served their subjects beer out of tiny little glasses.
Once the mice were nice and liquored up, some were given a treatment of FGF21 while others were given a placebo. Lo and behold, the mice given FGF21 recovered about 50% faster than those that received the control treatment. Not exactly instant, but 50% is nothing to sniff at.
Before you bring your FGF21 supplement to the bar, though, this research only applies to mice. We don’t know if it works in people. And make sure you stick to booze. If your choice of intoxication is a bit more exotic, FGF21 isn’t going to do anything for you. Yes, the scientists tried. Yes, those mice are living a very interesting life. And yes, we are jealous of drugged-up lab mice.
Supersize your imagination, shrink your snacks
Have you ever heard of the meal-recall effect? Did you know that, in England, a biscuit is really a cookie? Did you also know that the magazine Bon Appétit is not the same as the peer-reviewed journal Appetite? We do … now.
The meal-recall effect is the subsequent reduction in snacking that comes from remembering a recent meal. It was used to great effect in a recent study conducted at the University of Cambridge, which is in England, where they feed their experimental humans cookies but, for some reason, call them biscuits.
For the first part of the study, the participants were invited to dine at Che Laboratory, where they “were given a microwave ready meal of rice and sauce and a cup of water,” according to a statement from the university. As our Uncle Ernie would say, “Gourmet all the way.”
The test subjects were instructed not to eat anything for 3 hours and “then invited back to the lab to perform imagination tasks.” Those who did come back were randomly divided into five different groups, each with a different task:
- Imagine moving their recent lunch at the lab around a plate.
- Recall eating their recent lunch in detail.
- Imagine that the lunch was twice as big and filling as it really was.
- Look at a photograph of spaghetti hoops in tomato sauce and write a description of it before imagining moving the food around a plate.
- Look at a photo of paper clips and rubber bands and imagine moving them around.
Now, at last, we get to the biscuits/cookies, which were the subject of a taste test that “was simply a rouse for covertly assessing snacking,” the investigators explained. As part of that test, participants were told they could eat as many biscuits as they wanted.
When the tables were cleared and the leftovers examined, the group that imagined spaghetti hoops had eaten the most biscuits (75.9 g), followed by the group that imagined paper clips (75.5 g), the moving-their-lunch-around-the-plate group (72.0 g), and the group that relived eating their lunch (70.0 g).
In a victory for the meal-recall effect, the people who imagined their meal being twice as big ate the fewest biscuits (51.1 g). “Your mind can be more powerful than your stomach in dictating how much you eat,” lead author Joanna Szypula, PhD, said in the university statement.
Oh! One more thing. The study appeared in Appetite, which is a peer-reviewed journal, not in Bon Appétit, which is not a peer-reviewed journal. Thanks to the fine folks at both publications for pointing that out to us.
Get ‘em while they’re hot … for your health
Today on the Eating Channel, it’s a very special episode of “Much Ado About Muffin.”
The muffin. For some of us, it’s a good way to pretend we’re not having dessert for breakfast. A bran muffin can be loaded with calcium and fiber, and our beloved blueberry is full of yummy antioxidants and vitamins. Definitely not dessert.
Well, the muffin denial can stop there because there’s a new flavor on the scene, and research suggests it may actually be healthy. (Disclaimer: Muffin may not be considered healthy in Norway.) This new muffin has a name, Roselle, that comes from the calyx extract used in it, which is found in the Hibiscus sabdariffa plant of the same name.
Now, when it comes to new foods, especially ones that are supposed to be healthy, the No. 1 criteria is the same: It has to taste good. Researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology and Amity University in India agreed, but they also set out to make it nutritionally valuable and give it a long shelf life without the addition of preservatives.
Sounds like a tall order, but they figured it out.
Not only is it tasty, but the properties of it could rival your morning multivitamin. Hibiscus extract has huge amounts of antioxidants, like phenolics, which are believed to help prevent cell membrane damage. Foods like vegetables, flax seed, and whole grains also have these antioxidants, but why not just have a Roselle muffin instead? You also get a dose of ascorbic acid without the glass of OJ in the morning.
The ascorbic acid, however, is not there just to help you. It also helps to check the researcher’s third box, shelf life. These naturally rosy-colored pastries will stay mold-free for 6 days without refrigeration at room temperature and without added preservatives.
Our guess, though, is they won’t be on the kitchen counter long enough to find out.
A sobering proposition
If Hollywood is to be believed, there’s no amount of drunkenness that can’t be cured with a cup of coffee or a stern slap in the face. Unfortunately, here in the real world the only thing that can make you less drunk is time. Maybe next time you’ll stop after that seventh Manhattan.
But what if we could beat time? What if there’s an actual sobriety drug out there?
Say hello to fibroblast growth factor 21. Although the liver already does good work filtering out what is essentially poison, it then goes the extra mile and produces fibroblast growth factor 21 (or, as her friends call her, FGF21), a hormone that suppresses the desire to drink, makes you desire water, and protects the liver all at the same time.
Now, FGF21 in its current role is great, but if you’ve ever seen or been a drunk person before, you’ve experienced the lack of interest in listening to reason, especially when it comes from within our own bodies. Who are you to tell us what to do, body? You’re not the boss of us! So a group of scientists decided to push the limits of FGF21. Could it do more than it already does?
First off, they genetically altered a group of mice so that they didn’t produce FGF21 on their own. Then they got them drunk. We’re going to assume they built a scale model of the bar from Cheers and had the mice filter in through the front door as they served their subjects beer out of tiny little glasses.
Once the mice were nice and liquored up, some were given a treatment of FGF21 while others were given a placebo. Lo and behold, the mice given FGF21 recovered about 50% faster than those that received the control treatment. Not exactly instant, but 50% is nothing to sniff at.
Before you bring your FGF21 supplement to the bar, though, this research only applies to mice. We don’t know if it works in people. And make sure you stick to booze. If your choice of intoxication is a bit more exotic, FGF21 isn’t going to do anything for you. Yes, the scientists tried. Yes, those mice are living a very interesting life. And yes, we are jealous of drugged-up lab mice.
Supersize your imagination, shrink your snacks
Have you ever heard of the meal-recall effect? Did you know that, in England, a biscuit is really a cookie? Did you also know that the magazine Bon Appétit is not the same as the peer-reviewed journal Appetite? We do … now.
The meal-recall effect is the subsequent reduction in snacking that comes from remembering a recent meal. It was used to great effect in a recent study conducted at the University of Cambridge, which is in England, where they feed their experimental humans cookies but, for some reason, call them biscuits.
For the first part of the study, the participants were invited to dine at Che Laboratory, where they “were given a microwave ready meal of rice and sauce and a cup of water,” according to a statement from the university. As our Uncle Ernie would say, “Gourmet all the way.”
The test subjects were instructed not to eat anything for 3 hours and “then invited back to the lab to perform imagination tasks.” Those who did come back were randomly divided into five different groups, each with a different task:
- Imagine moving their recent lunch at the lab around a plate.
- Recall eating their recent lunch in detail.
- Imagine that the lunch was twice as big and filling as it really was.
- Look at a photograph of spaghetti hoops in tomato sauce and write a description of it before imagining moving the food around a plate.
- Look at a photo of paper clips and rubber bands and imagine moving them around.
Now, at last, we get to the biscuits/cookies, which were the subject of a taste test that “was simply a rouse for covertly assessing snacking,” the investigators explained. As part of that test, participants were told they could eat as many biscuits as they wanted.
When the tables were cleared and the leftovers examined, the group that imagined spaghetti hoops had eaten the most biscuits (75.9 g), followed by the group that imagined paper clips (75.5 g), the moving-their-lunch-around-the-plate group (72.0 g), and the group that relived eating their lunch (70.0 g).
In a victory for the meal-recall effect, the people who imagined their meal being twice as big ate the fewest biscuits (51.1 g). “Your mind can be more powerful than your stomach in dictating how much you eat,” lead author Joanna Szypula, PhD, said in the university statement.
Oh! One more thing. The study appeared in Appetite, which is a peer-reviewed journal, not in Bon Appétit, which is not a peer-reviewed journal. Thanks to the fine folks at both publications for pointing that out to us.
Specialty and age may contribute to suicidal thoughts among physicians
A physician’s specialty can make a difference when it comes to having suicidal thoughts. Doctors who specialize in family medicine, obstetrics-gynecology, and psychiatry reported double the rates of suicidal thoughts than doctors in oncology, rheumatology, and pulmonary medicine, according to Doctors’ Burden: Medscape Physician Suicide Report 2023.
“The specialties with the highest reporting of physician suicidal thoughts are also those with the greatest physician shortages, based on the number of job openings posted by recruiting sites,” said Peter Yellowlees, MD, professor of psychiatry and chief wellness officer at UC Davis Health.
Doctors in those specialties are overworked, which can lead to burnout, he said.
There’s also a generational divide among physicians who reported suicidal thoughts. Millennials (age 27-41) and Gen-X physicians (age 42-56) were more likely to report these thoughts than were Baby Boomers (age 57-75) and the Silent Generation (age 76-95).
“Younger physicians are more burned out – they may have less control over their lives and less meaning than some older doctors who can do what they want,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
One millennial respondent commented that being on call and being required to chart detailed notes in the EHR has contributed to her burnout. “I’m more impatient and make less time and effort to see my friends and family.”
One Silent Generation respondent commented, “I am semi-retired, I take no call, I work no weekends, I provide anesthesia care in my area of special expertise, I work clinically about 46 days a year. Life is good, particularly compared to my younger colleagues who are working 60-plus hours a week with evening work, weekend work, and call. I feel really sorry for them.”
When young people enter medical school, they’re quite healthy, with low rates of depression and burnout, said Dr. Yellowlees. Yet, studies have shown that rates of burnout and suicidal thoughts increased within 2 years. “That reflects what happens when a group of idealistic young people hit a horrible system,” he said.
Who’s responsible?
Millennials were three times as likely as baby boomers to say that a medical school or health care organization should be responsible when a student or physician commits suicide.
“Young physicians may expect more of their employers than my generation did, which we see in residency programs that have unionized,” said Dr. Yellowlees, a Baby Boomer.
“As more young doctors are employed by health care organizations, they also may expect more resources to be available to them, such as wellness programs,” he added.
Younger doctors also focus more on work-life balance than older doctors, including time off and having hobbies, he said. “They are much more rational in terms of their overall beliefs and expectations than the older generation.”
Whom doctors confide in
Nearly 60% of physician-respondents with suicidal thoughts said they confided in a professional or someone they knew. Men were just as likely as women to reach out to a therapist (38%), whereas men were slightly more likely to confide in a family member and women were slightly more likely to confide in a colleague.
“It’s interesting that women are more active in seeking support at work – they often have developed a network of colleagues to support each other’s careers and whom they can confide in,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
He emphasized that 40% of physicians said they didn’t confide in anyone when they had suicidal thoughts. Of those, just over half said they could cope without professional help.
One respondent commented, “It’s just a thought; nothing I would actually do.” Another commented, “Mental health professionals can’t fix the underlying reason for the problem.”
Many doctors were concerned about risking disclosure to their medical boards (42%); that it would show up on their insurance records (33%); and that their colleagues would find out (25%), according to the report.
One respondent commented, “I don’t trust doctors to keep it to themselves.”
Another barrier doctors mentioned was a lack of time to seek help. One commented, “Time. I have none, when am I supposed to find an hour for counseling?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A physician’s specialty can make a difference when it comes to having suicidal thoughts. Doctors who specialize in family medicine, obstetrics-gynecology, and psychiatry reported double the rates of suicidal thoughts than doctors in oncology, rheumatology, and pulmonary medicine, according to Doctors’ Burden: Medscape Physician Suicide Report 2023.
“The specialties with the highest reporting of physician suicidal thoughts are also those with the greatest physician shortages, based on the number of job openings posted by recruiting sites,” said Peter Yellowlees, MD, professor of psychiatry and chief wellness officer at UC Davis Health.
Doctors in those specialties are overworked, which can lead to burnout, he said.
There’s also a generational divide among physicians who reported suicidal thoughts. Millennials (age 27-41) and Gen-X physicians (age 42-56) were more likely to report these thoughts than were Baby Boomers (age 57-75) and the Silent Generation (age 76-95).
“Younger physicians are more burned out – they may have less control over their lives and less meaning than some older doctors who can do what they want,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
One millennial respondent commented that being on call and being required to chart detailed notes in the EHR has contributed to her burnout. “I’m more impatient and make less time and effort to see my friends and family.”
One Silent Generation respondent commented, “I am semi-retired, I take no call, I work no weekends, I provide anesthesia care in my area of special expertise, I work clinically about 46 days a year. Life is good, particularly compared to my younger colleagues who are working 60-plus hours a week with evening work, weekend work, and call. I feel really sorry for them.”
When young people enter medical school, they’re quite healthy, with low rates of depression and burnout, said Dr. Yellowlees. Yet, studies have shown that rates of burnout and suicidal thoughts increased within 2 years. “That reflects what happens when a group of idealistic young people hit a horrible system,” he said.
Who’s responsible?
Millennials were three times as likely as baby boomers to say that a medical school or health care organization should be responsible when a student or physician commits suicide.
“Young physicians may expect more of their employers than my generation did, which we see in residency programs that have unionized,” said Dr. Yellowlees, a Baby Boomer.
“As more young doctors are employed by health care organizations, they also may expect more resources to be available to them, such as wellness programs,” he added.
Younger doctors also focus more on work-life balance than older doctors, including time off and having hobbies, he said. “They are much more rational in terms of their overall beliefs and expectations than the older generation.”
Whom doctors confide in
Nearly 60% of physician-respondents with suicidal thoughts said they confided in a professional or someone they knew. Men were just as likely as women to reach out to a therapist (38%), whereas men were slightly more likely to confide in a family member and women were slightly more likely to confide in a colleague.
“It’s interesting that women are more active in seeking support at work – they often have developed a network of colleagues to support each other’s careers and whom they can confide in,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
He emphasized that 40% of physicians said they didn’t confide in anyone when they had suicidal thoughts. Of those, just over half said they could cope without professional help.
One respondent commented, “It’s just a thought; nothing I would actually do.” Another commented, “Mental health professionals can’t fix the underlying reason for the problem.”
Many doctors were concerned about risking disclosure to their medical boards (42%); that it would show up on their insurance records (33%); and that their colleagues would find out (25%), according to the report.
One respondent commented, “I don’t trust doctors to keep it to themselves.”
Another barrier doctors mentioned was a lack of time to seek help. One commented, “Time. I have none, when am I supposed to find an hour for counseling?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A physician’s specialty can make a difference when it comes to having suicidal thoughts. Doctors who specialize in family medicine, obstetrics-gynecology, and psychiatry reported double the rates of suicidal thoughts than doctors in oncology, rheumatology, and pulmonary medicine, according to Doctors’ Burden: Medscape Physician Suicide Report 2023.
“The specialties with the highest reporting of physician suicidal thoughts are also those with the greatest physician shortages, based on the number of job openings posted by recruiting sites,” said Peter Yellowlees, MD, professor of psychiatry and chief wellness officer at UC Davis Health.
Doctors in those specialties are overworked, which can lead to burnout, he said.
There’s also a generational divide among physicians who reported suicidal thoughts. Millennials (age 27-41) and Gen-X physicians (age 42-56) were more likely to report these thoughts than were Baby Boomers (age 57-75) and the Silent Generation (age 76-95).
“Younger physicians are more burned out – they may have less control over their lives and less meaning than some older doctors who can do what they want,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
One millennial respondent commented that being on call and being required to chart detailed notes in the EHR has contributed to her burnout. “I’m more impatient and make less time and effort to see my friends and family.”
One Silent Generation respondent commented, “I am semi-retired, I take no call, I work no weekends, I provide anesthesia care in my area of special expertise, I work clinically about 46 days a year. Life is good, particularly compared to my younger colleagues who are working 60-plus hours a week with evening work, weekend work, and call. I feel really sorry for them.”
When young people enter medical school, they’re quite healthy, with low rates of depression and burnout, said Dr. Yellowlees. Yet, studies have shown that rates of burnout and suicidal thoughts increased within 2 years. “That reflects what happens when a group of idealistic young people hit a horrible system,” he said.
Who’s responsible?
Millennials were three times as likely as baby boomers to say that a medical school or health care organization should be responsible when a student or physician commits suicide.
“Young physicians may expect more of their employers than my generation did, which we see in residency programs that have unionized,” said Dr. Yellowlees, a Baby Boomer.
“As more young doctors are employed by health care organizations, they also may expect more resources to be available to them, such as wellness programs,” he added.
Younger doctors also focus more on work-life balance than older doctors, including time off and having hobbies, he said. “They are much more rational in terms of their overall beliefs and expectations than the older generation.”
Whom doctors confide in
Nearly 60% of physician-respondents with suicidal thoughts said they confided in a professional or someone they knew. Men were just as likely as women to reach out to a therapist (38%), whereas men were slightly more likely to confide in a family member and women were slightly more likely to confide in a colleague.
“It’s interesting that women are more active in seeking support at work – they often have developed a network of colleagues to support each other’s careers and whom they can confide in,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
He emphasized that 40% of physicians said they didn’t confide in anyone when they had suicidal thoughts. Of those, just over half said they could cope without professional help.
One respondent commented, “It’s just a thought; nothing I would actually do.” Another commented, “Mental health professionals can’t fix the underlying reason for the problem.”
Many doctors were concerned about risking disclosure to their medical boards (42%); that it would show up on their insurance records (33%); and that their colleagues would find out (25%), according to the report.
One respondent commented, “I don’t trust doctors to keep it to themselves.”
Another barrier doctors mentioned was a lack of time to seek help. One commented, “Time. I have none, when am I supposed to find an hour for counseling?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Measles exposures in Kentucky have CDC on alert
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has issued a Health Alert Network (HAN) health advisory notifying clinicians and public health officials of a confirmed measles case in an individual who for 2 days (February 17-18) attended a large religious gathering that was attended by an estimated 20,000 people at Asbury University in Wilmore, Ky.
Given that large numbers of people might have been exposed to the attendee (who was not vaccinated) and that the individual had a history of recent international travel, the CDC has encouraged clinicians to be vigilant for patients presenting with symptoms that meet the measles case definition. A steady increase in measles cases from 49 in 2021 to 121 in 2022 in children who were not fully vaccinated – coupled with outbreaks in Ohio and Minnesota – underscores the potential gravity of the CDC advisory as well as the need to mitigate the risk of ongoing or secondary transmission.
Currently, little is known about the individual who contracted measles other than the fact that he is a resident of Jessamine County, Ky., according to a news release issued by the Kentucky Department of Public Health. It is the third confirmed case in Kentucky over the past 3 months. State and national health officials are concerned that the individual might have transmitted measles to attendees visiting from other states.
David Sugerman, MD, MPH, a medical officer in CDC’s division of viral diseases and lead for the measles, rubella, and cytomegalovirus team, noted that the timing of the alert coincides with the period in which persons who had had contact with the initial case patient might be expected to develop symptoms.
For clinicians, “It’s really about considering measles in any un- or undervaccinated patient that arrives at a clinic and recently traveled internationally,” Dr. Sugerman told this news organization. He explained that “when doctors are seeing patients, they’re not going to necessarily share that information off the bat when they present with fever or rash, or if their child has fever and rash, or that they traveled internationally. So, eliciting that history from the patient or their parents is really critical.”
The CDC recommends that measles be considered in anyone presenting with a febrile illness and symptoms that are clinically compatible with measles (that is, rash, cough, coryza, or conjunctivitis), as well as in patients who have recently traveled abroad, especially to countries with ongoing outbreaks, including India, Somalia, and Yemen.
“In general, if they’ve traveled internationally and they are undervaccinated, measles should be part of the differential diagnosis,” Sugerman said. He also emphasized the need to follow airborne isolation precautions in addition to general infection control measures.
Immediate triage is critical, especially since overcrowded waiting rooms might be filled with patients who are not yet eligible for vaccination or are not up to date or fully vaccinated.
“Measles is under airborne isolation criteria and precautions, and therefore, [patients] need to be placed as soon as possible into a negative pressure or airborne infection isolation room – and that should be a single room,” he explained. He noted, “In some settings, there may not be a negative pressure room, e.g., an outpatient pediatrics or family medicine office.”
Dr. Sugerman said that in these circumstances, patients should be placed in a room with masked health care providers who have received two doses of measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and that they should wear an N95 mask when entering the room and interviewing the patient.
Clinicians should follow CDC’s testing recommendations and collect a nasopharyngeal or throat swab or a urine specimen for PCR testing and a blood specimen for serology. In addition, they should immediately report cases to local and state public health authorities.
For all patients, it’s critical to be up to date on MMR vaccines, especially persons who are going to be traveling internationally. “We recommend that when they’ve got infants traveling with them who are 6-11 months of age, that they get a first dose (which we consider a zero dose), because they need a routine dose at 12-15 months, and then 4-6 years,” said Dr. Sugerman. He said that it’s safe for adults who are unsure of their status to receive an MMR dose as well.
Dr. Sugerman stressed that despite major strides, “we just don’t have enough coverage in all individuals in this country. Because people are traveling as often as they are, it can be imported. Until measles is eliminated globally, there’s going to be an ongoing risk of importation and potential spread amongst others in their household or community, especially amongst individuals who are not fully vaccinated and, in particular, amongst those who are unvaccinated,” he said.
Dr. Sugerman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has issued a Health Alert Network (HAN) health advisory notifying clinicians and public health officials of a confirmed measles case in an individual who for 2 days (February 17-18) attended a large religious gathering that was attended by an estimated 20,000 people at Asbury University in Wilmore, Ky.
Given that large numbers of people might have been exposed to the attendee (who was not vaccinated) and that the individual had a history of recent international travel, the CDC has encouraged clinicians to be vigilant for patients presenting with symptoms that meet the measles case definition. A steady increase in measles cases from 49 in 2021 to 121 in 2022 in children who were not fully vaccinated – coupled with outbreaks in Ohio and Minnesota – underscores the potential gravity of the CDC advisory as well as the need to mitigate the risk of ongoing or secondary transmission.
Currently, little is known about the individual who contracted measles other than the fact that he is a resident of Jessamine County, Ky., according to a news release issued by the Kentucky Department of Public Health. It is the third confirmed case in Kentucky over the past 3 months. State and national health officials are concerned that the individual might have transmitted measles to attendees visiting from other states.
David Sugerman, MD, MPH, a medical officer in CDC’s division of viral diseases and lead for the measles, rubella, and cytomegalovirus team, noted that the timing of the alert coincides with the period in which persons who had had contact with the initial case patient might be expected to develop symptoms.
For clinicians, “It’s really about considering measles in any un- or undervaccinated patient that arrives at a clinic and recently traveled internationally,” Dr. Sugerman told this news organization. He explained that “when doctors are seeing patients, they’re not going to necessarily share that information off the bat when they present with fever or rash, or if their child has fever and rash, or that they traveled internationally. So, eliciting that history from the patient or their parents is really critical.”
The CDC recommends that measles be considered in anyone presenting with a febrile illness and symptoms that are clinically compatible with measles (that is, rash, cough, coryza, or conjunctivitis), as well as in patients who have recently traveled abroad, especially to countries with ongoing outbreaks, including India, Somalia, and Yemen.
“In general, if they’ve traveled internationally and they are undervaccinated, measles should be part of the differential diagnosis,” Sugerman said. He also emphasized the need to follow airborne isolation precautions in addition to general infection control measures.
Immediate triage is critical, especially since overcrowded waiting rooms might be filled with patients who are not yet eligible for vaccination or are not up to date or fully vaccinated.
“Measles is under airborne isolation criteria and precautions, and therefore, [patients] need to be placed as soon as possible into a negative pressure or airborne infection isolation room – and that should be a single room,” he explained. He noted, “In some settings, there may not be a negative pressure room, e.g., an outpatient pediatrics or family medicine office.”
Dr. Sugerman said that in these circumstances, patients should be placed in a room with masked health care providers who have received two doses of measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and that they should wear an N95 mask when entering the room and interviewing the patient.
Clinicians should follow CDC’s testing recommendations and collect a nasopharyngeal or throat swab or a urine specimen for PCR testing and a blood specimen for serology. In addition, they should immediately report cases to local and state public health authorities.
For all patients, it’s critical to be up to date on MMR vaccines, especially persons who are going to be traveling internationally. “We recommend that when they’ve got infants traveling with them who are 6-11 months of age, that they get a first dose (which we consider a zero dose), because they need a routine dose at 12-15 months, and then 4-6 years,” said Dr. Sugerman. He said that it’s safe for adults who are unsure of their status to receive an MMR dose as well.
Dr. Sugerman stressed that despite major strides, “we just don’t have enough coverage in all individuals in this country. Because people are traveling as often as they are, it can be imported. Until measles is eliminated globally, there’s going to be an ongoing risk of importation and potential spread amongst others in their household or community, especially amongst individuals who are not fully vaccinated and, in particular, amongst those who are unvaccinated,” he said.
Dr. Sugerman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has issued a Health Alert Network (HAN) health advisory notifying clinicians and public health officials of a confirmed measles case in an individual who for 2 days (February 17-18) attended a large religious gathering that was attended by an estimated 20,000 people at Asbury University in Wilmore, Ky.
Given that large numbers of people might have been exposed to the attendee (who was not vaccinated) and that the individual had a history of recent international travel, the CDC has encouraged clinicians to be vigilant for patients presenting with symptoms that meet the measles case definition. A steady increase in measles cases from 49 in 2021 to 121 in 2022 in children who were not fully vaccinated – coupled with outbreaks in Ohio and Minnesota – underscores the potential gravity of the CDC advisory as well as the need to mitigate the risk of ongoing or secondary transmission.
Currently, little is known about the individual who contracted measles other than the fact that he is a resident of Jessamine County, Ky., according to a news release issued by the Kentucky Department of Public Health. It is the third confirmed case in Kentucky over the past 3 months. State and national health officials are concerned that the individual might have transmitted measles to attendees visiting from other states.
David Sugerman, MD, MPH, a medical officer in CDC’s division of viral diseases and lead for the measles, rubella, and cytomegalovirus team, noted that the timing of the alert coincides with the period in which persons who had had contact with the initial case patient might be expected to develop symptoms.
For clinicians, “It’s really about considering measles in any un- or undervaccinated patient that arrives at a clinic and recently traveled internationally,” Dr. Sugerman told this news organization. He explained that “when doctors are seeing patients, they’re not going to necessarily share that information off the bat when they present with fever or rash, or if their child has fever and rash, or that they traveled internationally. So, eliciting that history from the patient or their parents is really critical.”
The CDC recommends that measles be considered in anyone presenting with a febrile illness and symptoms that are clinically compatible with measles (that is, rash, cough, coryza, or conjunctivitis), as well as in patients who have recently traveled abroad, especially to countries with ongoing outbreaks, including India, Somalia, and Yemen.
“In general, if they’ve traveled internationally and they are undervaccinated, measles should be part of the differential diagnosis,” Sugerman said. He also emphasized the need to follow airborne isolation precautions in addition to general infection control measures.
Immediate triage is critical, especially since overcrowded waiting rooms might be filled with patients who are not yet eligible for vaccination or are not up to date or fully vaccinated.
“Measles is under airborne isolation criteria and precautions, and therefore, [patients] need to be placed as soon as possible into a negative pressure or airborne infection isolation room – and that should be a single room,” he explained. He noted, “In some settings, there may not be a negative pressure room, e.g., an outpatient pediatrics or family medicine office.”
Dr. Sugerman said that in these circumstances, patients should be placed in a room with masked health care providers who have received two doses of measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and that they should wear an N95 mask when entering the room and interviewing the patient.
Clinicians should follow CDC’s testing recommendations and collect a nasopharyngeal or throat swab or a urine specimen for PCR testing and a blood specimen for serology. In addition, they should immediately report cases to local and state public health authorities.
For all patients, it’s critical to be up to date on MMR vaccines, especially persons who are going to be traveling internationally. “We recommend that when they’ve got infants traveling with them who are 6-11 months of age, that they get a first dose (which we consider a zero dose), because they need a routine dose at 12-15 months, and then 4-6 years,” said Dr. Sugerman. He said that it’s safe for adults who are unsure of their status to receive an MMR dose as well.
Dr. Sugerman stressed that despite major strides, “we just don’t have enough coverage in all individuals in this country. Because people are traveling as often as they are, it can be imported. Until measles is eliminated globally, there’s going to be an ongoing risk of importation and potential spread amongst others in their household or community, especially amongst individuals who are not fully vaccinated and, in particular, amongst those who are unvaccinated,” he said.
Dr. Sugerman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in four parents lied about kids’ COVID status: Survey
More than 1 in 4 parents lied to school officials about their children’s COVID-19 status or refused to comply with public health rules during the height of the pandemic, a new study found. Researchers said they suspected the 26% of parents who misrepresented their children’s health status may have undercounted the actual figure.
“If anything, 26% is probably the minimum” of parents who misled school officials, said Angela Fagerlin, PhD, a researcher at the University of Utah Medical School, Salt Lake City.
In the survey, many parents said they considered it their right as parents to make their own decision about their children’s health status, said Dr. Fagerlin, who is also the chair of the department of population health sciences at the University of Utah School of Medicine.
“It appears that many parents were concerned about their children missing school,” she said. “At the same time, they’re potentially exposing other kids to a serious illness.”
In the survey, parents were asked whether they lied or misrepresented information about their children on seven different COVID-19 topics, including illness and vaccination status and if they followed quarantine protocols. Researchers tallied survey responses collected in December 2021 from 580 parents, whose average age was 36 and of whom 70% were women. Results were published in the journal JAMA Network Open.
Overall, 24% of parents said they lied to people that their children were with while knowing or suspecting the children had COVID. About half of parents cited at least one of the following reasons for doing so: parental freedom, child did not feel very sick, or wanted the child’s life to feel “normal.”
About 20% of parents said they avoided testing when they thought their child had COVID, and parents also reported allowing children to break quarantine rules at a similar rate. More than half of parents who avoided testing said they were worried testing would hurt or feel uncomfortable.
About 4 in 10 parents who lied about their child’s illness status or who lied about whether their child should be in quarantine said they did so because of guidance from a public figure such as a celebrity or politician. At least 3 in 10 said they lied because they could not miss work to stay home with their child.
“We need to do a better job of providing support mechanisms like paid sick leave for family illness so that parents don’t feel like their only option is to engage in misrepresentation or non-adherence to public health guidelines during a future infectious disease outbreak that matches or exceeds the magnitude of COVID-19,” says researcher Andrea Gurmankin Levy, PhD, of Middlesex (Conn.) Community College.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More than 1 in 4 parents lied to school officials about their children’s COVID-19 status or refused to comply with public health rules during the height of the pandemic, a new study found. Researchers said they suspected the 26% of parents who misrepresented their children’s health status may have undercounted the actual figure.
“If anything, 26% is probably the minimum” of parents who misled school officials, said Angela Fagerlin, PhD, a researcher at the University of Utah Medical School, Salt Lake City.
In the survey, many parents said they considered it their right as parents to make their own decision about their children’s health status, said Dr. Fagerlin, who is also the chair of the department of population health sciences at the University of Utah School of Medicine.
“It appears that many parents were concerned about their children missing school,” she said. “At the same time, they’re potentially exposing other kids to a serious illness.”
In the survey, parents were asked whether they lied or misrepresented information about their children on seven different COVID-19 topics, including illness and vaccination status and if they followed quarantine protocols. Researchers tallied survey responses collected in December 2021 from 580 parents, whose average age was 36 and of whom 70% were women. Results were published in the journal JAMA Network Open.
Overall, 24% of parents said they lied to people that their children were with while knowing or suspecting the children had COVID. About half of parents cited at least one of the following reasons for doing so: parental freedom, child did not feel very sick, or wanted the child’s life to feel “normal.”
About 20% of parents said they avoided testing when they thought their child had COVID, and parents also reported allowing children to break quarantine rules at a similar rate. More than half of parents who avoided testing said they were worried testing would hurt or feel uncomfortable.
About 4 in 10 parents who lied about their child’s illness status or who lied about whether their child should be in quarantine said they did so because of guidance from a public figure such as a celebrity or politician. At least 3 in 10 said they lied because they could not miss work to stay home with their child.
“We need to do a better job of providing support mechanisms like paid sick leave for family illness so that parents don’t feel like their only option is to engage in misrepresentation or non-adherence to public health guidelines during a future infectious disease outbreak that matches or exceeds the magnitude of COVID-19,” says researcher Andrea Gurmankin Levy, PhD, of Middlesex (Conn.) Community College.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More than 1 in 4 parents lied to school officials about their children’s COVID-19 status or refused to comply with public health rules during the height of the pandemic, a new study found. Researchers said they suspected the 26% of parents who misrepresented their children’s health status may have undercounted the actual figure.
“If anything, 26% is probably the minimum” of parents who misled school officials, said Angela Fagerlin, PhD, a researcher at the University of Utah Medical School, Salt Lake City.
In the survey, many parents said they considered it their right as parents to make their own decision about their children’s health status, said Dr. Fagerlin, who is also the chair of the department of population health sciences at the University of Utah School of Medicine.
“It appears that many parents were concerned about their children missing school,” she said. “At the same time, they’re potentially exposing other kids to a serious illness.”
In the survey, parents were asked whether they lied or misrepresented information about their children on seven different COVID-19 topics, including illness and vaccination status and if they followed quarantine protocols. Researchers tallied survey responses collected in December 2021 from 580 parents, whose average age was 36 and of whom 70% were women. Results were published in the journal JAMA Network Open.
Overall, 24% of parents said they lied to people that their children were with while knowing or suspecting the children had COVID. About half of parents cited at least one of the following reasons for doing so: parental freedom, child did not feel very sick, or wanted the child’s life to feel “normal.”
About 20% of parents said they avoided testing when they thought their child had COVID, and parents also reported allowing children to break quarantine rules at a similar rate. More than half of parents who avoided testing said they were worried testing would hurt or feel uncomfortable.
About 4 in 10 parents who lied about their child’s illness status or who lied about whether their child should be in quarantine said they did so because of guidance from a public figure such as a celebrity or politician. At least 3 in 10 said they lied because they could not miss work to stay home with their child.
“We need to do a better job of providing support mechanisms like paid sick leave for family illness so that parents don’t feel like their only option is to engage in misrepresentation or non-adherence to public health guidelines during a future infectious disease outbreak that matches or exceeds the magnitude of COVID-19,” says researcher Andrea Gurmankin Levy, PhD, of Middlesex (Conn.) Community College.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Even mild COVID is hard on the brain
early research suggests.
“Our results suggest a severe pattern of changes in how the brain communicates as well as its structure, mainly in people with anxiety and depression with long-COVID syndrome, which affects so many people,” study investigator Clarissa Yasuda, MD, PhD, from University of Campinas, São Paulo, said in a news release.
“The magnitude of these changes suggests that they could lead to problems with memory and thinking skills, so we need to be exploring holistic treatments even for people mildly affected by COVID-19,” Dr. Yasuda added.
The findings were released March 6 ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Brain shrinkage
Some studies have shown a high prevalence of symptoms of anxiety and depression in COVID-19 survivors, but few have investigated the associated cerebral changes, Dr. Yasuda told this news organization.
The study included 254 adults (177 women, 77 men, median age 41 years) who had mild COVID-19 a median of 82 days earlier. A total of 102 had symptoms of both anxiety and depression, and 152 had no such symptoms.
On brain imaging, those with COVID-19 and anxiety and depression had atrophy in the limbic area of the brain, which plays a role in memory and emotional processing.
No shrinkage in this area was evident in people who had COVID-19 without anxiety and depression or in a healthy control group of individuals without COVID-19.
The researchers also observed a “severe” pattern of abnormal cerebral functional connectivity in those with COVID-19 and anxiety and depression.
In this functional connectivity analysis, individuals with COVID-19 and anxiety and depression had widespread functional changes in each of the 12 networks assessed, while those with COVID-19 but without symptoms of anxiety and depression showed changes in only 5 networks.
Mechanisms unclear
“Unfortunately, the underpinning mechanisms associated with brain changes and neuropsychiatric dysfunction after COVID-19 infection are unclear,” Dr. Yasuda told this news organization.
“Some studies have demonstrated an association between symptoms of anxiety and depression with inflammation. However, we hypothesize that these cerebral alterations may result from a more complex interaction of social, psychological, and systemic stressors, including inflammation. It is indeed intriguing that such alterations are present in individuals who presented mild acute infection,” Dr. Yasuda added.
“Symptoms of anxiety and depression are frequently observed after COVID-19 and are part of long-COVID syndrome for some individuals. These symptoms require adequate treatment to improve the quality of life, cognition, and work capacity,” she said.
Treating these symptoms may induce “brain plasticity, which may result in some degree of gray matter increase and eventually prevent further structural and functional damage,” Dr. Yasuda said.
A limitation of the study was that symptoms of anxiety and depression were self-reported, meaning people may have misjudged or misreported symptoms.
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, Cyrus Raji, MD, PhD, with the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University, St. Louis, said the idea that COVID-19 is bad for the brain isn’t new. Dr. Raji was not involved with the study.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Raji and colleagues published a paper detailing COVID-19’s effects on the brain, and Dr. Raji followed it up with a TED talk on the subject.
“Within the growing framework of what we already know about COVID-19 infection and its adverse effects on the brain, this work incrementally adds to this knowledge by identifying functional and structural neuroimaging abnormalities related to anxiety and depression in persons suffering from COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Raji said.
The study was supported by the São Paulo Research Foundation. The authors have no relevant disclosures. Raji is a consultant for Brainreader, Apollo Health, Pacific Neuroscience Foundation, and Neurevolution LLC.
early research suggests.
“Our results suggest a severe pattern of changes in how the brain communicates as well as its structure, mainly in people with anxiety and depression with long-COVID syndrome, which affects so many people,” study investigator Clarissa Yasuda, MD, PhD, from University of Campinas, São Paulo, said in a news release.
“The magnitude of these changes suggests that they could lead to problems with memory and thinking skills, so we need to be exploring holistic treatments even for people mildly affected by COVID-19,” Dr. Yasuda added.
The findings were released March 6 ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Brain shrinkage
Some studies have shown a high prevalence of symptoms of anxiety and depression in COVID-19 survivors, but few have investigated the associated cerebral changes, Dr. Yasuda told this news organization.
The study included 254 adults (177 women, 77 men, median age 41 years) who had mild COVID-19 a median of 82 days earlier. A total of 102 had symptoms of both anxiety and depression, and 152 had no such symptoms.
On brain imaging, those with COVID-19 and anxiety and depression had atrophy in the limbic area of the brain, which plays a role in memory and emotional processing.
No shrinkage in this area was evident in people who had COVID-19 without anxiety and depression or in a healthy control group of individuals without COVID-19.
The researchers also observed a “severe” pattern of abnormal cerebral functional connectivity in those with COVID-19 and anxiety and depression.
In this functional connectivity analysis, individuals with COVID-19 and anxiety and depression had widespread functional changes in each of the 12 networks assessed, while those with COVID-19 but without symptoms of anxiety and depression showed changes in only 5 networks.
Mechanisms unclear
“Unfortunately, the underpinning mechanisms associated with brain changes and neuropsychiatric dysfunction after COVID-19 infection are unclear,” Dr. Yasuda told this news organization.
“Some studies have demonstrated an association between symptoms of anxiety and depression with inflammation. However, we hypothesize that these cerebral alterations may result from a more complex interaction of social, psychological, and systemic stressors, including inflammation. It is indeed intriguing that such alterations are present in individuals who presented mild acute infection,” Dr. Yasuda added.
“Symptoms of anxiety and depression are frequently observed after COVID-19 and are part of long-COVID syndrome for some individuals. These symptoms require adequate treatment to improve the quality of life, cognition, and work capacity,” she said.
Treating these symptoms may induce “brain plasticity, which may result in some degree of gray matter increase and eventually prevent further structural and functional damage,” Dr. Yasuda said.
A limitation of the study was that symptoms of anxiety and depression were self-reported, meaning people may have misjudged or misreported symptoms.
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, Cyrus Raji, MD, PhD, with the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University, St. Louis, said the idea that COVID-19 is bad for the brain isn’t new. Dr. Raji was not involved with the study.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Raji and colleagues published a paper detailing COVID-19’s effects on the brain, and Dr. Raji followed it up with a TED talk on the subject.
“Within the growing framework of what we already know about COVID-19 infection and its adverse effects on the brain, this work incrementally adds to this knowledge by identifying functional and structural neuroimaging abnormalities related to anxiety and depression in persons suffering from COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Raji said.
The study was supported by the São Paulo Research Foundation. The authors have no relevant disclosures. Raji is a consultant for Brainreader, Apollo Health, Pacific Neuroscience Foundation, and Neurevolution LLC.
early research suggests.
“Our results suggest a severe pattern of changes in how the brain communicates as well as its structure, mainly in people with anxiety and depression with long-COVID syndrome, which affects so many people,” study investigator Clarissa Yasuda, MD, PhD, from University of Campinas, São Paulo, said in a news release.
“The magnitude of these changes suggests that they could lead to problems with memory and thinking skills, so we need to be exploring holistic treatments even for people mildly affected by COVID-19,” Dr. Yasuda added.
The findings were released March 6 ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Brain shrinkage
Some studies have shown a high prevalence of symptoms of anxiety and depression in COVID-19 survivors, but few have investigated the associated cerebral changes, Dr. Yasuda told this news organization.
The study included 254 adults (177 women, 77 men, median age 41 years) who had mild COVID-19 a median of 82 days earlier. A total of 102 had symptoms of both anxiety and depression, and 152 had no such symptoms.
On brain imaging, those with COVID-19 and anxiety and depression had atrophy in the limbic area of the brain, which plays a role in memory and emotional processing.
No shrinkage in this area was evident in people who had COVID-19 without anxiety and depression or in a healthy control group of individuals without COVID-19.
The researchers also observed a “severe” pattern of abnormal cerebral functional connectivity in those with COVID-19 and anxiety and depression.
In this functional connectivity analysis, individuals with COVID-19 and anxiety and depression had widespread functional changes in each of the 12 networks assessed, while those with COVID-19 but without symptoms of anxiety and depression showed changes in only 5 networks.
Mechanisms unclear
“Unfortunately, the underpinning mechanisms associated with brain changes and neuropsychiatric dysfunction after COVID-19 infection are unclear,” Dr. Yasuda told this news organization.
“Some studies have demonstrated an association between symptoms of anxiety and depression with inflammation. However, we hypothesize that these cerebral alterations may result from a more complex interaction of social, psychological, and systemic stressors, including inflammation. It is indeed intriguing that such alterations are present in individuals who presented mild acute infection,” Dr. Yasuda added.
“Symptoms of anxiety and depression are frequently observed after COVID-19 and are part of long-COVID syndrome for some individuals. These symptoms require adequate treatment to improve the quality of life, cognition, and work capacity,” she said.
Treating these symptoms may induce “brain plasticity, which may result in some degree of gray matter increase and eventually prevent further structural and functional damage,” Dr. Yasuda said.
A limitation of the study was that symptoms of anxiety and depression were self-reported, meaning people may have misjudged or misreported symptoms.
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, Cyrus Raji, MD, PhD, with the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University, St. Louis, said the idea that COVID-19 is bad for the brain isn’t new. Dr. Raji was not involved with the study.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Raji and colleagues published a paper detailing COVID-19’s effects on the brain, and Dr. Raji followed it up with a TED talk on the subject.
“Within the growing framework of what we already know about COVID-19 infection and its adverse effects on the brain, this work incrementally adds to this knowledge by identifying functional and structural neuroimaging abnormalities related to anxiety and depression in persons suffering from COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Raji said.
The study was supported by the São Paulo Research Foundation. The authors have no relevant disclosures. Raji is a consultant for Brainreader, Apollo Health, Pacific Neuroscience Foundation, and Neurevolution LLC.
Shaved costs, high risk, maximum profits: Regulators worry about Florida’s butt lift boom
The office in Miami where she scheduled what’s known as a Brazilian butt lift had closed and transferred her records to a different facility, she said. The price she was quoted – and paid upfront – increased the day of the procedure, and she said she did not meet her surgeon until she was about to be placed under general anesthesia.
“I was ready to walk out,” said Ms. Ruston, 44, of Lake Alfred in Central Florida. “But I had paid everything.”
A few days after the July procedure, Ms. Ruston was hospitalized because of infection, blood loss, and nausea, her medical records show.
“I went cheap. That’s what I did,” Ms. Ruston recalled recently. “I looked for the lowest price, and I found him on Instagram.”

People like Ms. Ruston are commonly lured to office-based surgery centers in South Florida through social media marketing that makes Brazilian butt lifts and other cosmetic surgery look deceptively painless, safe, and affordable, say researchers, patient advocates, and surgeon groups.
Unlike ambulatory surgery centers and hospitals, where a patient might stay overnight for observation after treatment, office-based surgery centers offer procedures that don’t typically require an inpatient stay and are regulated as an extension of a doctor’s private practice.

But such surgical offices are often owned by corporations that can offer discount prices by contracting with surgeons who are incentivized to work on as many patients per day as possible, in as little time as possible, according to state regulators and physicians critical of the facilities.
After a rash of deaths, and in the absence of national standards, Florida regulators were the first in the nation to enact rules in 2019 meant to make the procedures safer. More than 3 years later, data shows deaths still occur.

Patient advocates and some surgeons – including those who perform the procedure themselves – anticipate the problem will only get worse. Emergency restrictions imposed by the state’s medical board in June expired in September, and the corporate business model popularized in Miami is spreading to other cities.
“We’re seeing entities that have a strong footprint in low-cost, high-volume cosmetic surgery, based in South Florida, manifesting in other parts of the country,” said Bob Basu, MD, MPH, a vice president of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons and a practicing physician in Houston.
During a Brazilian butt lift, fat is taken via liposuction from other areas of the body – such as the torso, back, or thighs – and injected into the buttocks. More than 61,000 buttock augmentation procedures, both butt lifts and implants, were performed nationwide in 2021, a 37% increase from the previous year, according to data from the Aesthetic Society, a trade group of plastic surgeons.
As with all surgery, complications can occur. Miami-Dade County’s medical examiner has documented nearly three dozen cosmetic surgery patient deaths since 2009, of which 26 resulted from a Brazilian butt lift. In each case, the person died from a pulmonary fat embolism, when fat entered the bloodstream through veins in the gluteal muscles and stopped blood from flowing to the lungs.
No national reporting system or insurance code tracks outcomes and patient demographics for a Brazilian butt lift. About 3% of surgeons worldwide had a patient die as a result of the procedure, according to a 2017 report from an Aesthetic Surgery Education and Research Foundation task force.
Medical experts said the problem is driven, in part, by having medical professionals like physician assistants and nurse practitioners perform key parts of the butt lift instead of doctors. It’s also driven by a business model that is motivated by profit, not safety, and incentivizes surgeons to exceed the number of surgeries outlined in their contracts.
In May, after a fifth patient in as many months died of complications in Miami-Dade County, Kevin Cairns, MD, proposed the state’s emergency rule to limit the number of butt lifts a surgeon could perform each day.
“I was getting sick of reading about women dying and seeing cases come before the board,” said Dr. Cairns, a physician and former member of the Florida Board of Medicine.
Some doctors performed as many as seven, according to disciplinary cases against surgeons prosecuted by the Florida Department of Health. The emergency rule limited them to no more than three, and required the use of an ultrasound to help surgeons lower the risk of a pulmonary fat clot.
But a group of physicians who perform Brazilian butt lifts in South Florida clapped back and formed Surgeons for Safety. They argued the new requirements would make the situation worse. Qualified doctors would have to do fewer procedures, they said, thus driving patients to dangerous medical professionals who don’t follow rules.
The group has since donated more than $350,000 to the state’s Republican Party, Republican candidates, and Republican political action committees, according to campaign contribution data from the Florida Department of State.
Surgeons for Safety declined KHN’s repeated interview requests. Although the group’s president, Constantino Mendieta, MD, wrote in an August editorial that he agreed not all surgeons have followed the standard of care, he called the limits put on surgeons “arbitrary.” The rule sets “a historic precedent of controlling surgeons,” he said during a meeting with Florida’s medical board.
In January, Florida state Sen. Ileana Garcia, a Republican, filed a draft bill with the state legislature that proposes no limit on the number of Brazilian butt lifts a surgeon can perform in a day. Instead, it requires office surgery centers where the procedures are performed to staff one physician per patient and prohibits surgeons from working on more than one person at a time.
The bill would also allow surgeons to delegate some parts of the procedure to other clinicians under their direct supervision.
Florida’s legislature convenes on March 7.
Consumers considering cosmetic procedures are urged to be cautious. Like Ms. Ruston, many people base their expectations on before-and-after photos and marketing videos posted on social media platforms such as Facebook, Snapchat, and Instagram.
“That’s very dangerous,” said Dr. Basu, of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons. “They’re excited about a low price and they forget about doing their homework,” he said.
The average price of a buttocks augmentation in 2021 was $4,000, according to data from the Aesthetic Society. But that’s only for the physician’s fee and does not cover anesthesia, operating room fees, prescriptions, or other expenses. A “safe” Brazilian butt lift, performed in an accredited facility and with proper aftercare, costs between $12,000 and $18,000, according to a recent article on the American Society of Plastic Surgeons’ website.
Although Florida requires a physician’s license to perform liposuction on patients who are under general anesthesia, it’s common in the medical field for midlevel medical practitioners, such as physician assistants and nurse practitioners, to do the procedure in office settings, according to Mark Mofid, MD, who coauthored the 2017 Aesthetic Surgery Education and Research Foundation task force study.
By relying on staffers who don’t have the same specialty training and get paid less, office-based surgeons can complete more butt lifts per day and charge a lower price.
“They’re doing all of them simultaneously in three or four different rooms, and it’s being staffed by one surgeon,” said Dr. Mofid, a plastic surgeon in San Diego, who added that he does not perform more than one Brazilian butt lift in a day. “The surgeon isn’t doing the actual case. It’s assistants.”
Dr. Basu said patients should ask whether their doctor holds privileges to perform the same procedure at a hospital or ambulatory surgery center, which have stricter rules than office surgery centers in terms of who can perform butt lifts and how they should be done.
People in search of bargains are reminded that cosmetic surgery can have other serious risks beyond the deadly fat clots, such as infection and organ puncture, plus problems with the kidneys, heart, and lungs.
Ms. Ruston’s surgery was performed by a board-certified plastic surgeon she said she found on Instagram. She was originally quoted $4,995, which she said she paid in full before surgery. But when she arrived in Miami, she said, the clinic tacked on fees for liposuction and for postsurgical garments and devices.
“I ended up having to pay, like, $8,000,” Ms. Ruston said. A few days after Ms. Ruston returned home to Lake Alfred, she said, she started to feel dizzy and weak and called 911.
Paramedics took her to an emergency room, where doctors diagnosed her with anemia due to blood loss, and blood and abdominal infections, her medical records show.
“If I could go back in time,” she said, “I wouldn’t have had it done.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The office in Miami where she scheduled what’s known as a Brazilian butt lift had closed and transferred her records to a different facility, she said. The price she was quoted – and paid upfront – increased the day of the procedure, and she said she did not meet her surgeon until she was about to be placed under general anesthesia.
“I was ready to walk out,” said Ms. Ruston, 44, of Lake Alfred in Central Florida. “But I had paid everything.”
A few days after the July procedure, Ms. Ruston was hospitalized because of infection, blood loss, and nausea, her medical records show.
“I went cheap. That’s what I did,” Ms. Ruston recalled recently. “I looked for the lowest price, and I found him on Instagram.”

People like Ms. Ruston are commonly lured to office-based surgery centers in South Florida through social media marketing that makes Brazilian butt lifts and other cosmetic surgery look deceptively painless, safe, and affordable, say researchers, patient advocates, and surgeon groups.
Unlike ambulatory surgery centers and hospitals, where a patient might stay overnight for observation after treatment, office-based surgery centers offer procedures that don’t typically require an inpatient stay and are regulated as an extension of a doctor’s private practice.

But such surgical offices are often owned by corporations that can offer discount prices by contracting with surgeons who are incentivized to work on as many patients per day as possible, in as little time as possible, according to state regulators and physicians critical of the facilities.
After a rash of deaths, and in the absence of national standards, Florida regulators were the first in the nation to enact rules in 2019 meant to make the procedures safer. More than 3 years later, data shows deaths still occur.

Patient advocates and some surgeons – including those who perform the procedure themselves – anticipate the problem will only get worse. Emergency restrictions imposed by the state’s medical board in June expired in September, and the corporate business model popularized in Miami is spreading to other cities.
“We’re seeing entities that have a strong footprint in low-cost, high-volume cosmetic surgery, based in South Florida, manifesting in other parts of the country,” said Bob Basu, MD, MPH, a vice president of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons and a practicing physician in Houston.
During a Brazilian butt lift, fat is taken via liposuction from other areas of the body – such as the torso, back, or thighs – and injected into the buttocks. More than 61,000 buttock augmentation procedures, both butt lifts and implants, were performed nationwide in 2021, a 37% increase from the previous year, according to data from the Aesthetic Society, a trade group of plastic surgeons.
As with all surgery, complications can occur. Miami-Dade County’s medical examiner has documented nearly three dozen cosmetic surgery patient deaths since 2009, of which 26 resulted from a Brazilian butt lift. In each case, the person died from a pulmonary fat embolism, when fat entered the bloodstream through veins in the gluteal muscles and stopped blood from flowing to the lungs.
No national reporting system or insurance code tracks outcomes and patient demographics for a Brazilian butt lift. About 3% of surgeons worldwide had a patient die as a result of the procedure, according to a 2017 report from an Aesthetic Surgery Education and Research Foundation task force.
Medical experts said the problem is driven, in part, by having medical professionals like physician assistants and nurse practitioners perform key parts of the butt lift instead of doctors. It’s also driven by a business model that is motivated by profit, not safety, and incentivizes surgeons to exceed the number of surgeries outlined in their contracts.
In May, after a fifth patient in as many months died of complications in Miami-Dade County, Kevin Cairns, MD, proposed the state’s emergency rule to limit the number of butt lifts a surgeon could perform each day.
“I was getting sick of reading about women dying and seeing cases come before the board,” said Dr. Cairns, a physician and former member of the Florida Board of Medicine.
Some doctors performed as many as seven, according to disciplinary cases against surgeons prosecuted by the Florida Department of Health. The emergency rule limited them to no more than three, and required the use of an ultrasound to help surgeons lower the risk of a pulmonary fat clot.
But a group of physicians who perform Brazilian butt lifts in South Florida clapped back and formed Surgeons for Safety. They argued the new requirements would make the situation worse. Qualified doctors would have to do fewer procedures, they said, thus driving patients to dangerous medical professionals who don’t follow rules.
The group has since donated more than $350,000 to the state’s Republican Party, Republican candidates, and Republican political action committees, according to campaign contribution data from the Florida Department of State.
Surgeons for Safety declined KHN’s repeated interview requests. Although the group’s president, Constantino Mendieta, MD, wrote in an August editorial that he agreed not all surgeons have followed the standard of care, he called the limits put on surgeons “arbitrary.” The rule sets “a historic precedent of controlling surgeons,” he said during a meeting with Florida’s medical board.
In January, Florida state Sen. Ileana Garcia, a Republican, filed a draft bill with the state legislature that proposes no limit on the number of Brazilian butt lifts a surgeon can perform in a day. Instead, it requires office surgery centers where the procedures are performed to staff one physician per patient and prohibits surgeons from working on more than one person at a time.
The bill would also allow surgeons to delegate some parts of the procedure to other clinicians under their direct supervision.
Florida’s legislature convenes on March 7.
Consumers considering cosmetic procedures are urged to be cautious. Like Ms. Ruston, many people base their expectations on before-and-after photos and marketing videos posted on social media platforms such as Facebook, Snapchat, and Instagram.
“That’s very dangerous,” said Dr. Basu, of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons. “They’re excited about a low price and they forget about doing their homework,” he said.
The average price of a buttocks augmentation in 2021 was $4,000, according to data from the Aesthetic Society. But that’s only for the physician’s fee and does not cover anesthesia, operating room fees, prescriptions, or other expenses. A “safe” Brazilian butt lift, performed in an accredited facility and with proper aftercare, costs between $12,000 and $18,000, according to a recent article on the American Society of Plastic Surgeons’ website.
Although Florida requires a physician’s license to perform liposuction on patients who are under general anesthesia, it’s common in the medical field for midlevel medical practitioners, such as physician assistants and nurse practitioners, to do the procedure in office settings, according to Mark Mofid, MD, who coauthored the 2017 Aesthetic Surgery Education and Research Foundation task force study.
By relying on staffers who don’t have the same specialty training and get paid less, office-based surgeons can complete more butt lifts per day and charge a lower price.
“They’re doing all of them simultaneously in three or four different rooms, and it’s being staffed by one surgeon,” said Dr. Mofid, a plastic surgeon in San Diego, who added that he does not perform more than one Brazilian butt lift in a day. “The surgeon isn’t doing the actual case. It’s assistants.”
Dr. Basu said patients should ask whether their doctor holds privileges to perform the same procedure at a hospital or ambulatory surgery center, which have stricter rules than office surgery centers in terms of who can perform butt lifts and how they should be done.
People in search of bargains are reminded that cosmetic surgery can have other serious risks beyond the deadly fat clots, such as infection and organ puncture, plus problems with the kidneys, heart, and lungs.
Ms. Ruston’s surgery was performed by a board-certified plastic surgeon she said she found on Instagram. She was originally quoted $4,995, which she said she paid in full before surgery. But when she arrived in Miami, she said, the clinic tacked on fees for liposuction and for postsurgical garments and devices.
“I ended up having to pay, like, $8,000,” Ms. Ruston said. A few days after Ms. Ruston returned home to Lake Alfred, she said, she started to feel dizzy and weak and called 911.
Paramedics took her to an emergency room, where doctors diagnosed her with anemia due to blood loss, and blood and abdominal infections, her medical records show.
“If I could go back in time,” she said, “I wouldn’t have had it done.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The office in Miami where she scheduled what’s known as a Brazilian butt lift had closed and transferred her records to a different facility, she said. The price she was quoted – and paid upfront – increased the day of the procedure, and she said she did not meet her surgeon until she was about to be placed under general anesthesia.
“I was ready to walk out,” said Ms. Ruston, 44, of Lake Alfred in Central Florida. “But I had paid everything.”
A few days after the July procedure, Ms. Ruston was hospitalized because of infection, blood loss, and nausea, her medical records show.
“I went cheap. That’s what I did,” Ms. Ruston recalled recently. “I looked for the lowest price, and I found him on Instagram.”

People like Ms. Ruston are commonly lured to office-based surgery centers in South Florida through social media marketing that makes Brazilian butt lifts and other cosmetic surgery look deceptively painless, safe, and affordable, say researchers, patient advocates, and surgeon groups.
Unlike ambulatory surgery centers and hospitals, where a patient might stay overnight for observation after treatment, office-based surgery centers offer procedures that don’t typically require an inpatient stay and are regulated as an extension of a doctor’s private practice.

But such surgical offices are often owned by corporations that can offer discount prices by contracting with surgeons who are incentivized to work on as many patients per day as possible, in as little time as possible, according to state regulators and physicians critical of the facilities.
After a rash of deaths, and in the absence of national standards, Florida regulators were the first in the nation to enact rules in 2019 meant to make the procedures safer. More than 3 years later, data shows deaths still occur.

Patient advocates and some surgeons – including those who perform the procedure themselves – anticipate the problem will only get worse. Emergency restrictions imposed by the state’s medical board in June expired in September, and the corporate business model popularized in Miami is spreading to other cities.
“We’re seeing entities that have a strong footprint in low-cost, high-volume cosmetic surgery, based in South Florida, manifesting in other parts of the country,” said Bob Basu, MD, MPH, a vice president of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons and a practicing physician in Houston.
During a Brazilian butt lift, fat is taken via liposuction from other areas of the body – such as the torso, back, or thighs – and injected into the buttocks. More than 61,000 buttock augmentation procedures, both butt lifts and implants, were performed nationwide in 2021, a 37% increase from the previous year, according to data from the Aesthetic Society, a trade group of plastic surgeons.
As with all surgery, complications can occur. Miami-Dade County’s medical examiner has documented nearly three dozen cosmetic surgery patient deaths since 2009, of which 26 resulted from a Brazilian butt lift. In each case, the person died from a pulmonary fat embolism, when fat entered the bloodstream through veins in the gluteal muscles and stopped blood from flowing to the lungs.
No national reporting system or insurance code tracks outcomes and patient demographics for a Brazilian butt lift. About 3% of surgeons worldwide had a patient die as a result of the procedure, according to a 2017 report from an Aesthetic Surgery Education and Research Foundation task force.
Medical experts said the problem is driven, in part, by having medical professionals like physician assistants and nurse practitioners perform key parts of the butt lift instead of doctors. It’s also driven by a business model that is motivated by profit, not safety, and incentivizes surgeons to exceed the number of surgeries outlined in their contracts.
In May, after a fifth patient in as many months died of complications in Miami-Dade County, Kevin Cairns, MD, proposed the state’s emergency rule to limit the number of butt lifts a surgeon could perform each day.
“I was getting sick of reading about women dying and seeing cases come before the board,” said Dr. Cairns, a physician and former member of the Florida Board of Medicine.
Some doctors performed as many as seven, according to disciplinary cases against surgeons prosecuted by the Florida Department of Health. The emergency rule limited them to no more than three, and required the use of an ultrasound to help surgeons lower the risk of a pulmonary fat clot.
But a group of physicians who perform Brazilian butt lifts in South Florida clapped back and formed Surgeons for Safety. They argued the new requirements would make the situation worse. Qualified doctors would have to do fewer procedures, they said, thus driving patients to dangerous medical professionals who don’t follow rules.
The group has since donated more than $350,000 to the state’s Republican Party, Republican candidates, and Republican political action committees, according to campaign contribution data from the Florida Department of State.
Surgeons for Safety declined KHN’s repeated interview requests. Although the group’s president, Constantino Mendieta, MD, wrote in an August editorial that he agreed not all surgeons have followed the standard of care, he called the limits put on surgeons “arbitrary.” The rule sets “a historic precedent of controlling surgeons,” he said during a meeting with Florida’s medical board.
In January, Florida state Sen. Ileana Garcia, a Republican, filed a draft bill with the state legislature that proposes no limit on the number of Brazilian butt lifts a surgeon can perform in a day. Instead, it requires office surgery centers where the procedures are performed to staff one physician per patient and prohibits surgeons from working on more than one person at a time.
The bill would also allow surgeons to delegate some parts of the procedure to other clinicians under their direct supervision.
Florida’s legislature convenes on March 7.
Consumers considering cosmetic procedures are urged to be cautious. Like Ms. Ruston, many people base their expectations on before-and-after photos and marketing videos posted on social media platforms such as Facebook, Snapchat, and Instagram.
“That’s very dangerous,” said Dr. Basu, of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons. “They’re excited about a low price and they forget about doing their homework,” he said.
The average price of a buttocks augmentation in 2021 was $4,000, according to data from the Aesthetic Society. But that’s only for the physician’s fee and does not cover anesthesia, operating room fees, prescriptions, or other expenses. A “safe” Brazilian butt lift, performed in an accredited facility and with proper aftercare, costs between $12,000 and $18,000, according to a recent article on the American Society of Plastic Surgeons’ website.
Although Florida requires a physician’s license to perform liposuction on patients who are under general anesthesia, it’s common in the medical field for midlevel medical practitioners, such as physician assistants and nurse practitioners, to do the procedure in office settings, according to Mark Mofid, MD, who coauthored the 2017 Aesthetic Surgery Education and Research Foundation task force study.
By relying on staffers who don’t have the same specialty training and get paid less, office-based surgeons can complete more butt lifts per day and charge a lower price.
“They’re doing all of them simultaneously in three or four different rooms, and it’s being staffed by one surgeon,” said Dr. Mofid, a plastic surgeon in San Diego, who added that he does not perform more than one Brazilian butt lift in a day. “The surgeon isn’t doing the actual case. It’s assistants.”
Dr. Basu said patients should ask whether their doctor holds privileges to perform the same procedure at a hospital or ambulatory surgery center, which have stricter rules than office surgery centers in terms of who can perform butt lifts and how they should be done.
People in search of bargains are reminded that cosmetic surgery can have other serious risks beyond the deadly fat clots, such as infection and organ puncture, plus problems with the kidneys, heart, and lungs.
Ms. Ruston’s surgery was performed by a board-certified plastic surgeon she said she found on Instagram. She was originally quoted $4,995, which she said she paid in full before surgery. But when she arrived in Miami, she said, the clinic tacked on fees for liposuction and for postsurgical garments and devices.
“I ended up having to pay, like, $8,000,” Ms. Ruston said. A few days after Ms. Ruston returned home to Lake Alfred, she said, she started to feel dizzy and weak and called 911.
Paramedics took her to an emergency room, where doctors diagnosed her with anemia due to blood loss, and blood and abdominal infections, her medical records show.
“If I could go back in time,” she said, “I wouldn’t have had it done.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
NP-PA turf fights: Where the relationship can improve
– The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics forecasts a 40% increase in the NP workforce by 2031, coupled with a 28% rise in PAs.
In recent reports on the quality of the relationships involving these health care professions, survey respondents mostly gave positive accounts of collaboration, using words such as like “comradery,” “teamwork,” “congenial,” and “cohesion.” But all was not perfect. Where and how could these important health care provider relationships improve?
PAs: “Competition and collaboration’ with RNs
In a Medscape survey of more than 770 PAs about their working relationships with other health care professionals; 83% of them supported the idea of PAs and NPs practicing more independently from physicians, but sometimes it’s not easy to stay in their individual lanes.
One PA respondent complained that NPs get “more opportunities and preference,” another pointed to PA-NP “turf issues,” and a third griped about NPs’ “strong unions,” which have stoked more fighting about practice abilities and available settings.
Robert Blumm, MA, PA-C, a retired surgical and emergency medicine PA who regards himself as an advocate for both PAs and NPs, describes their interaction as a “mixture of competition and collaboration.”
On one hand, the two groups typically “cooperate and do an excellent job, incurring patient errors similar to or less than physician colleagues or senior residents.” On the other hand, Mr. Blumm conceded, there is some jealousy among PAs over NPs’ advantage in staffing and hiring decisions, “since they don’t need [direct physician] supervision ... and there are limits on how many PAs can be supervised by one physician.”
Most PA-NP interactions are collaborative, although many people emphasize the relatively few conflicts, said Jennifer Orozco, DMSc, PA-C, president and chair of the American Academy of PAs.
“We see that a lot in this country,” she said. “People try to drive a wedge, but it’s often a misnomer that there’s a lot of arguing and infighting.”
NPs: Different backgrounds, same goal
The Medscape survey also included information from 750 NPs on working relationships; 93% of them favored nurses and PAs working more independently from doctors.
April Kapu, DNP, ARPN, has worked closely with PAs for more than 20 years. “In my experience ... they complement one another as health team members, although the education and training are somewhat different,” said Ms. Kapu, , president of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners.
Some respondents noted the different educational trajectories for NPs and PAs. “Doctors and PAs are taught using the same model, but NPs are taught under the nursing model,” wrote a family medicine PA.
In emergency departments where Mr. Blumm has worked, ICU NPs have an edge over PAs in terms of preparation, organization, and the tabulation of formulas. On the other hand, some of Mr. Blumm’s fellow PAs were also emergency medicine technicians or respiratory therapists, who had “2 years of classroom training, on par with that of medical students.”
Must these differences in training and education foment conflict between NPs and PAs? “We all bring something different to the table,” said Ms. Kapu, who also is associate dean for clinical and community partnerships at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “It is important to respect each person’s entry point, education, and training.”
Differing personalities and environments
Numerous PA respondents said that individual personalities and work environments are more likely to trigger issues with NPs than are differences in training.
“It depends on the team and situation and who the people are, not the letters behind their names,” an emergency medicine PA wrote. A surgical PA noted that “group dynamics and work culture differ from place to place,” while a third PA agreed that “it’s personality dependent, not title dependent.”
No single formula will resolve areas of NP-PA conflict, Ms. Orozco said. “What works in Chicago might not work in rural Colorado or Texas or California, but we do have to come together. The overall focus should be on greater flexibility for PAs and NPs. Patients will fare better.”
Joint research, publishing could help
About a decade ago, Mr. Blumm joined with another PA and an NP to form the American College of Clinicians, the first joint PA-NP national professional organization. Although it disbanded after 6 years, owing to low membership, he hopes a similar collaboration will take off in the future.
“I also recommend that PAs and NPs publish articles together, with research as an excellent place to start,” he added. “PAs and NPs should stand together and be a source of healing for all our patients. Regardless of our titles, our responsibility is to bring healing together.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics forecasts a 40% increase in the NP workforce by 2031, coupled with a 28% rise in PAs.
In recent reports on the quality of the relationships involving these health care professions, survey respondents mostly gave positive accounts of collaboration, using words such as like “comradery,” “teamwork,” “congenial,” and “cohesion.” But all was not perfect. Where and how could these important health care provider relationships improve?
PAs: “Competition and collaboration’ with RNs
In a Medscape survey of more than 770 PAs about their working relationships with other health care professionals; 83% of them supported the idea of PAs and NPs practicing more independently from physicians, but sometimes it’s not easy to stay in their individual lanes.
One PA respondent complained that NPs get “more opportunities and preference,” another pointed to PA-NP “turf issues,” and a third griped about NPs’ “strong unions,” which have stoked more fighting about practice abilities and available settings.
Robert Blumm, MA, PA-C, a retired surgical and emergency medicine PA who regards himself as an advocate for both PAs and NPs, describes their interaction as a “mixture of competition and collaboration.”
On one hand, the two groups typically “cooperate and do an excellent job, incurring patient errors similar to or less than physician colleagues or senior residents.” On the other hand, Mr. Blumm conceded, there is some jealousy among PAs over NPs’ advantage in staffing and hiring decisions, “since they don’t need [direct physician] supervision ... and there are limits on how many PAs can be supervised by one physician.”
Most PA-NP interactions are collaborative, although many people emphasize the relatively few conflicts, said Jennifer Orozco, DMSc, PA-C, president and chair of the American Academy of PAs.
“We see that a lot in this country,” she said. “People try to drive a wedge, but it’s often a misnomer that there’s a lot of arguing and infighting.”
NPs: Different backgrounds, same goal
The Medscape survey also included information from 750 NPs on working relationships; 93% of them favored nurses and PAs working more independently from doctors.
April Kapu, DNP, ARPN, has worked closely with PAs for more than 20 years. “In my experience ... they complement one another as health team members, although the education and training are somewhat different,” said Ms. Kapu, , president of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners.
Some respondents noted the different educational trajectories for NPs and PAs. “Doctors and PAs are taught using the same model, but NPs are taught under the nursing model,” wrote a family medicine PA.
In emergency departments where Mr. Blumm has worked, ICU NPs have an edge over PAs in terms of preparation, organization, and the tabulation of formulas. On the other hand, some of Mr. Blumm’s fellow PAs were also emergency medicine technicians or respiratory therapists, who had “2 years of classroom training, on par with that of medical students.”
Must these differences in training and education foment conflict between NPs and PAs? “We all bring something different to the table,” said Ms. Kapu, who also is associate dean for clinical and community partnerships at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “It is important to respect each person’s entry point, education, and training.”
Differing personalities and environments
Numerous PA respondents said that individual personalities and work environments are more likely to trigger issues with NPs than are differences in training.
“It depends on the team and situation and who the people are, not the letters behind their names,” an emergency medicine PA wrote. A surgical PA noted that “group dynamics and work culture differ from place to place,” while a third PA agreed that “it’s personality dependent, not title dependent.”
No single formula will resolve areas of NP-PA conflict, Ms. Orozco said. “What works in Chicago might not work in rural Colorado or Texas or California, but we do have to come together. The overall focus should be on greater flexibility for PAs and NPs. Patients will fare better.”
Joint research, publishing could help
About a decade ago, Mr. Blumm joined with another PA and an NP to form the American College of Clinicians, the first joint PA-NP national professional organization. Although it disbanded after 6 years, owing to low membership, he hopes a similar collaboration will take off in the future.
“I also recommend that PAs and NPs publish articles together, with research as an excellent place to start,” he added. “PAs and NPs should stand together and be a source of healing for all our patients. Regardless of our titles, our responsibility is to bring healing together.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics forecasts a 40% increase in the NP workforce by 2031, coupled with a 28% rise in PAs.
In recent reports on the quality of the relationships involving these health care professions, survey respondents mostly gave positive accounts of collaboration, using words such as like “comradery,” “teamwork,” “congenial,” and “cohesion.” But all was not perfect. Where and how could these important health care provider relationships improve?
PAs: “Competition and collaboration’ with RNs
In a Medscape survey of more than 770 PAs about their working relationships with other health care professionals; 83% of them supported the idea of PAs and NPs practicing more independently from physicians, but sometimes it’s not easy to stay in their individual lanes.
One PA respondent complained that NPs get “more opportunities and preference,” another pointed to PA-NP “turf issues,” and a third griped about NPs’ “strong unions,” which have stoked more fighting about practice abilities and available settings.
Robert Blumm, MA, PA-C, a retired surgical and emergency medicine PA who regards himself as an advocate for both PAs and NPs, describes their interaction as a “mixture of competition and collaboration.”
On one hand, the two groups typically “cooperate and do an excellent job, incurring patient errors similar to or less than physician colleagues or senior residents.” On the other hand, Mr. Blumm conceded, there is some jealousy among PAs over NPs’ advantage in staffing and hiring decisions, “since they don’t need [direct physician] supervision ... and there are limits on how many PAs can be supervised by one physician.”
Most PA-NP interactions are collaborative, although many people emphasize the relatively few conflicts, said Jennifer Orozco, DMSc, PA-C, president and chair of the American Academy of PAs.
“We see that a lot in this country,” she said. “People try to drive a wedge, but it’s often a misnomer that there’s a lot of arguing and infighting.”
NPs: Different backgrounds, same goal
The Medscape survey also included information from 750 NPs on working relationships; 93% of them favored nurses and PAs working more independently from doctors.
April Kapu, DNP, ARPN, has worked closely with PAs for more than 20 years. “In my experience ... they complement one another as health team members, although the education and training are somewhat different,” said Ms. Kapu, , president of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners.
Some respondents noted the different educational trajectories for NPs and PAs. “Doctors and PAs are taught using the same model, but NPs are taught under the nursing model,” wrote a family medicine PA.
In emergency departments where Mr. Blumm has worked, ICU NPs have an edge over PAs in terms of preparation, organization, and the tabulation of formulas. On the other hand, some of Mr. Blumm’s fellow PAs were also emergency medicine technicians or respiratory therapists, who had “2 years of classroom training, on par with that of medical students.”
Must these differences in training and education foment conflict between NPs and PAs? “We all bring something different to the table,” said Ms. Kapu, who also is associate dean for clinical and community partnerships at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “It is important to respect each person’s entry point, education, and training.”
Differing personalities and environments
Numerous PA respondents said that individual personalities and work environments are more likely to trigger issues with NPs than are differences in training.
“It depends on the team and situation and who the people are, not the letters behind their names,” an emergency medicine PA wrote. A surgical PA noted that “group dynamics and work culture differ from place to place,” while a third PA agreed that “it’s personality dependent, not title dependent.”
No single formula will resolve areas of NP-PA conflict, Ms. Orozco said. “What works in Chicago might not work in rural Colorado or Texas or California, but we do have to come together. The overall focus should be on greater flexibility for PAs and NPs. Patients will fare better.”
Joint research, publishing could help
About a decade ago, Mr. Blumm joined with another PA and an NP to form the American College of Clinicians, the first joint PA-NP national professional organization. Although it disbanded after 6 years, owing to low membership, he hopes a similar collaboration will take off in the future.
“I also recommend that PAs and NPs publish articles together, with research as an excellent place to start,” he added. “PAs and NPs should stand together and be a source of healing for all our patients. Regardless of our titles, our responsibility is to bring healing together.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.