User login
-
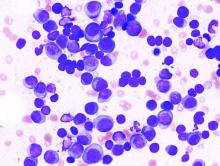
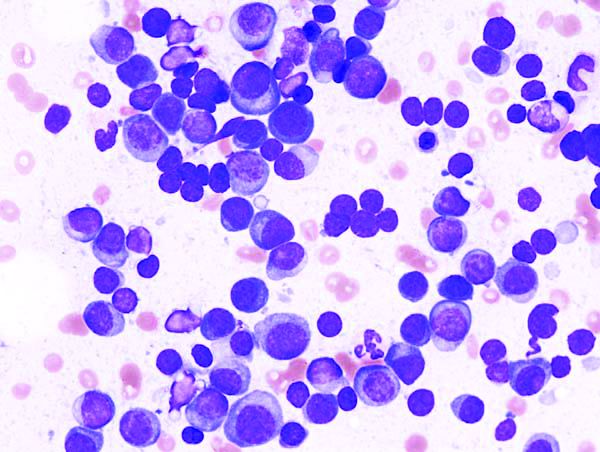
Socioeconomic factors affect survival of multiple myeloma patients
Disparities driven by socioeconomic factors have been shown to affect outcomes for patients with a variety of cancer types. Researchers found that this was also true for patients with multiple myeloma, according to a report published in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
In particular, survival was affected by a variety of socioeconomic factors.
Researchers conducting the study queried the National Cancer Database for patients diagnosed with multiple myeloma between 2004 and 2016. Only those 56,102 patients who received systemic therapy as the first-line treatment were included, according to Thejus T. Jayakrishnan, MD, of Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, and colleagues.
Enrollment rates for therapy were calculated using receiving systemic therapy as the incident event of interest (numerator) over time to initiation of therapy (denominator). The incident rate ratios were analyzed using Poisson regression. A multivariate Cox proportional hazards model was used for survival analysis of 50,543 patients, and differences were determined as hazard ratios.
Significant differences
The study showed that therapy enrollment was significantly affected by race and sex (P < .005), with the enrollment rate for women and for non-Hispanic Blacks both being lower versus men and non-Hispanic Whites, respectively.
Advanced age, earlier year of diagnosis, lack of insurance or Medicaid, and higher comorbidity were found to be associated with poor survival (HR >1), whereas being a woman or a non-Hispanic Black (who were speculated to have more favorable cytogenetic profiles), having a higher income, and having treatment at an academic center were all associated with improved survival (each category at HR <1).
“Disparities in [multiple myeloma] exist and are caused by a complex interplay of multiple factors, with socioeconomic factors such as insurance and income playing a dominant role. The disparities not only exact high human cost but also negatively impact the economics of health care,” the researchers concluded.
The study was not funded and the authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Jayakrishnan TT et al. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2020 Oct 10. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2020.09.005.
Disparities driven by socioeconomic factors have been shown to affect outcomes for patients with a variety of cancer types. Researchers found that this was also true for patients with multiple myeloma, according to a report published in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
In particular, survival was affected by a variety of socioeconomic factors.
Researchers conducting the study queried the National Cancer Database for patients diagnosed with multiple myeloma between 2004 and 2016. Only those 56,102 patients who received systemic therapy as the first-line treatment were included, according to Thejus T. Jayakrishnan, MD, of Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, and colleagues.
Enrollment rates for therapy were calculated using receiving systemic therapy as the incident event of interest (numerator) over time to initiation of therapy (denominator). The incident rate ratios were analyzed using Poisson regression. A multivariate Cox proportional hazards model was used for survival analysis of 50,543 patients, and differences were determined as hazard ratios.
Significant differences
The study showed that therapy enrollment was significantly affected by race and sex (P < .005), with the enrollment rate for women and for non-Hispanic Blacks both being lower versus men and non-Hispanic Whites, respectively.
Advanced age, earlier year of diagnosis, lack of insurance or Medicaid, and higher comorbidity were found to be associated with poor survival (HR >1), whereas being a woman or a non-Hispanic Black (who were speculated to have more favorable cytogenetic profiles), having a higher income, and having treatment at an academic center were all associated with improved survival (each category at HR <1).
“Disparities in [multiple myeloma] exist and are caused by a complex interplay of multiple factors, with socioeconomic factors such as insurance and income playing a dominant role. The disparities not only exact high human cost but also negatively impact the economics of health care,” the researchers concluded.
The study was not funded and the authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Jayakrishnan TT et al. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2020 Oct 10. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2020.09.005.
Disparities driven by socioeconomic factors have been shown to affect outcomes for patients with a variety of cancer types. Researchers found that this was also true for patients with multiple myeloma, according to a report published in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
In particular, survival was affected by a variety of socioeconomic factors.
Researchers conducting the study queried the National Cancer Database for patients diagnosed with multiple myeloma between 2004 and 2016. Only those 56,102 patients who received systemic therapy as the first-line treatment were included, according to Thejus T. Jayakrishnan, MD, of Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, and colleagues.
Enrollment rates for therapy were calculated using receiving systemic therapy as the incident event of interest (numerator) over time to initiation of therapy (denominator). The incident rate ratios were analyzed using Poisson regression. A multivariate Cox proportional hazards model was used for survival analysis of 50,543 patients, and differences were determined as hazard ratios.
Significant differences
The study showed that therapy enrollment was significantly affected by race and sex (P < .005), with the enrollment rate for women and for non-Hispanic Blacks both being lower versus men and non-Hispanic Whites, respectively.
Advanced age, earlier year of diagnosis, lack of insurance or Medicaid, and higher comorbidity were found to be associated with poor survival (HR >1), whereas being a woman or a non-Hispanic Black (who were speculated to have more favorable cytogenetic profiles), having a higher income, and having treatment at an academic center were all associated with improved survival (each category at HR <1).
“Disparities in [multiple myeloma] exist and are caused by a complex interplay of multiple factors, with socioeconomic factors such as insurance and income playing a dominant role. The disparities not only exact high human cost but also negatively impact the economics of health care,” the researchers concluded.
The study was not funded and the authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Jayakrishnan TT et al. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2020 Oct 10. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2020.09.005.
FROM HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY AND STEM CELL THERAPY
Cardiogenic shock rate soars in COVID-positive ACS
COVID-19–positive patients undergoing an invasive strategy for acute coronary syndrome presented hours later than uninfected historical controls, had a far higher incidence of cardiogenic shock, and their in-hospital mortality rate was four- to fivefold greater, according to data from the Global Multicenter Prospective COVID–ACS Registry. These phenomena are probably interrelated, according to Anthony Gershlick, MBBS, who presented the registry results at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics virtual annual meeting.
“We know that increasing ischemic time leads to bigger infarcts. And we know that bigger infarcts lead to cardiogenic shock, with its known higher mortality,” said Dr. Gershlick, professor of interventional cardiology at the University of Leicester (England).
“These data suggest that patients may have presented late, likely due to COVID concerns, and they had worse outcomes. If these data are borne out, future public information strategies need to be reassuring, proactive, simple, and more effective because we think patients stayed away,” the cardiologist added. “There are important public information messages to be taken from these data about getting patients to come to hospital during such pandemics.”
He presented prospectively collected registry data on 144 patients with confirmed ST-elevation MI (STEMI) and 122 with non-ST–elevation MI (NSTEMI), all COVID-19 positive on presentation at 85 hospitals in the United Kingdom, Europe, and North America during March through August of 2020. Since the initial message to the public early in the pandemic in many places was to try to avoid the hospital, the investigators selected for their no-COVID comparison group the data on more than 22,000 STEMI and NSTEMI patients included in two British national databases covering 2018-2019.
The COVID-positive STEMI patients were significantly younger, had more comorbidities, and had a higher mean heart rate and lower systolic blood pressure at admission than the non-COVID STEMI control group. Their median time from symptom onset to admission was 339 minutes, compared with 178 minutes in controls. Their door-to-balloon time averaged 83 minutes, versus 37 minutes in the era before the pandemic.
“I suspect that’s got something to do with the donning and doffing of personal protective equipment,” he said at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
The in-hospital mortality rates were strikingly different: 27.1% in COVID-positive STEMI patients versus 5.7% in controls. Bleeding Academic Research Consortium type 3-5 bleeding was increased as well, by a margin of 2.8% to 0.3%. So was stroke, with a 2.1% in-hospital incidence in COVID-positive STEMI patients and a 0.1% rate in the comparator arm.
“But the biggest headline here for me was that the cardiogenic shock rate was 20.1% in the COVID-positive patients versus 8.7% in the non-COVID STEMI patients,” the cardiologist continued.
The same pattern held true among the COVID-positive NSTEMI patients: They were younger, sicker, and slower to present to the hospital than the non-COVID group. The in-hospital mortality rate was 6.6% in the COVID-positive NSTEMI patients, compared with 1.2% in the reference group. The COVID-positive patients had a 2.5% bleeding rate versus 0.1% in the controls. And the incidence of cardiogenic shock was 5%, compared with 1.4% in the controls from before the pandemic.
“Even though NSTEMI is traditionally regarded as lower risk, this is really quite dramatic. These are sick patients,” Dr. Gershlick observed.
Nearly two-thirds of in-hospital deaths in COVID-positive ACS patients were cardiovascular, and three-quarters of those cardiovascular deaths occurred in patients with cardiogenic shock. Thirty-two percent of deaths in COVID-positive ACS patients were of respiratory causes, and 4.9% were neurologic.
Notably, the ischemic time of patients with cardiogenic shock who died – that is, the time from symptom onset to balloon deployment – averaged 1,271 minutes, compared with 441 minutes in those who died without being in cardiogenic shock.
Session comoderator Sahil A. Parikh, MD, director of endovascular services at Columbia University Medical Center in New York, commented, “One of the striking things that is resonating with me is the high incidence of cardiogenic shock and the mortality. It’s akin to what we’ve seen in New York.”
Discussant Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, said he doubts that the increased in-hospital mortality in the COVID–ACS registry is related to the prolonged time to presentation at the hospital. More likely, it’s related to the greater thrombotic burden various studies have shown accompanies COVID-positive ACS. It might even be caused by a direct effect of the virus on the myocardium, added Dr. Fuster, director of the Zena and Michael A. Wiener Cardiovascular Institute and professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York.
“I have to say I absolutely disagree,” responded Dr. Gershlick. “I think it’s important that we try to understand all the mechanisms, but we know that patients with COVID are anxious, and I think one of the messages from this registry is patients took longer to come to hospital, they were sicker, they had more cardiogenic shock, and they died. And I don’t think it’s anything more complicated than that.”
Another discussant, Mamas Mamas, MD, is involved with a 500-patient U.K. pandemic ACS registry nearing publication. The findings, he said, are similar to what Dr. Gershlick reported in terms of the high rate of presentation with cardiogenic shock and elevated in-hospital mortality. The COVID-positive ACS patients were also more likely to present with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. But like Dr. Fuster, he is skeptical that their worse outcomes can be explained by a delay in seeking care.
“I don’t think the delay in presentation is really associated with the high mortality rate that we see. The delay in our U.K. registry is maybe half an hour for STEMIs and maybe 2-3 hours for NSTEMIs. And I don’t think that can produce a 30%-40% increase in mortality,” asserted Dr. Mamas, professor of cardiology at Keele University in Staffordshire, England.
Dr. Gershlick reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
COVID-19–positive patients undergoing an invasive strategy for acute coronary syndrome presented hours later than uninfected historical controls, had a far higher incidence of cardiogenic shock, and their in-hospital mortality rate was four- to fivefold greater, according to data from the Global Multicenter Prospective COVID–ACS Registry. These phenomena are probably interrelated, according to Anthony Gershlick, MBBS, who presented the registry results at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics virtual annual meeting.
“We know that increasing ischemic time leads to bigger infarcts. And we know that bigger infarcts lead to cardiogenic shock, with its known higher mortality,” said Dr. Gershlick, professor of interventional cardiology at the University of Leicester (England).
“These data suggest that patients may have presented late, likely due to COVID concerns, and they had worse outcomes. If these data are borne out, future public information strategies need to be reassuring, proactive, simple, and more effective because we think patients stayed away,” the cardiologist added. “There are important public information messages to be taken from these data about getting patients to come to hospital during such pandemics.”
He presented prospectively collected registry data on 144 patients with confirmed ST-elevation MI (STEMI) and 122 with non-ST–elevation MI (NSTEMI), all COVID-19 positive on presentation at 85 hospitals in the United Kingdom, Europe, and North America during March through August of 2020. Since the initial message to the public early in the pandemic in many places was to try to avoid the hospital, the investigators selected for their no-COVID comparison group the data on more than 22,000 STEMI and NSTEMI patients included in two British national databases covering 2018-2019.
The COVID-positive STEMI patients were significantly younger, had more comorbidities, and had a higher mean heart rate and lower systolic blood pressure at admission than the non-COVID STEMI control group. Their median time from symptom onset to admission was 339 minutes, compared with 178 minutes in controls. Their door-to-balloon time averaged 83 minutes, versus 37 minutes in the era before the pandemic.
“I suspect that’s got something to do with the donning and doffing of personal protective equipment,” he said at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
The in-hospital mortality rates were strikingly different: 27.1% in COVID-positive STEMI patients versus 5.7% in controls. Bleeding Academic Research Consortium type 3-5 bleeding was increased as well, by a margin of 2.8% to 0.3%. So was stroke, with a 2.1% in-hospital incidence in COVID-positive STEMI patients and a 0.1% rate in the comparator arm.
“But the biggest headline here for me was that the cardiogenic shock rate was 20.1% in the COVID-positive patients versus 8.7% in the non-COVID STEMI patients,” the cardiologist continued.
The same pattern held true among the COVID-positive NSTEMI patients: They were younger, sicker, and slower to present to the hospital than the non-COVID group. The in-hospital mortality rate was 6.6% in the COVID-positive NSTEMI patients, compared with 1.2% in the reference group. The COVID-positive patients had a 2.5% bleeding rate versus 0.1% in the controls. And the incidence of cardiogenic shock was 5%, compared with 1.4% in the controls from before the pandemic.
“Even though NSTEMI is traditionally regarded as lower risk, this is really quite dramatic. These are sick patients,” Dr. Gershlick observed.
Nearly two-thirds of in-hospital deaths in COVID-positive ACS patients were cardiovascular, and three-quarters of those cardiovascular deaths occurred in patients with cardiogenic shock. Thirty-two percent of deaths in COVID-positive ACS patients were of respiratory causes, and 4.9% were neurologic.
Notably, the ischemic time of patients with cardiogenic shock who died – that is, the time from symptom onset to balloon deployment – averaged 1,271 minutes, compared with 441 minutes in those who died without being in cardiogenic shock.
Session comoderator Sahil A. Parikh, MD, director of endovascular services at Columbia University Medical Center in New York, commented, “One of the striking things that is resonating with me is the high incidence of cardiogenic shock and the mortality. It’s akin to what we’ve seen in New York.”
Discussant Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, said he doubts that the increased in-hospital mortality in the COVID–ACS registry is related to the prolonged time to presentation at the hospital. More likely, it’s related to the greater thrombotic burden various studies have shown accompanies COVID-positive ACS. It might even be caused by a direct effect of the virus on the myocardium, added Dr. Fuster, director of the Zena and Michael A. Wiener Cardiovascular Institute and professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York.
“I have to say I absolutely disagree,” responded Dr. Gershlick. “I think it’s important that we try to understand all the mechanisms, but we know that patients with COVID are anxious, and I think one of the messages from this registry is patients took longer to come to hospital, they were sicker, they had more cardiogenic shock, and they died. And I don’t think it’s anything more complicated than that.”
Another discussant, Mamas Mamas, MD, is involved with a 500-patient U.K. pandemic ACS registry nearing publication. The findings, he said, are similar to what Dr. Gershlick reported in terms of the high rate of presentation with cardiogenic shock and elevated in-hospital mortality. The COVID-positive ACS patients were also more likely to present with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. But like Dr. Fuster, he is skeptical that their worse outcomes can be explained by a delay in seeking care.
“I don’t think the delay in presentation is really associated with the high mortality rate that we see. The delay in our U.K. registry is maybe half an hour for STEMIs and maybe 2-3 hours for NSTEMIs. And I don’t think that can produce a 30%-40% increase in mortality,” asserted Dr. Mamas, professor of cardiology at Keele University in Staffordshire, England.
Dr. Gershlick reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
COVID-19–positive patients undergoing an invasive strategy for acute coronary syndrome presented hours later than uninfected historical controls, had a far higher incidence of cardiogenic shock, and their in-hospital mortality rate was four- to fivefold greater, according to data from the Global Multicenter Prospective COVID–ACS Registry. These phenomena are probably interrelated, according to Anthony Gershlick, MBBS, who presented the registry results at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics virtual annual meeting.
“We know that increasing ischemic time leads to bigger infarcts. And we know that bigger infarcts lead to cardiogenic shock, with its known higher mortality,” said Dr. Gershlick, professor of interventional cardiology at the University of Leicester (England).
“These data suggest that patients may have presented late, likely due to COVID concerns, and they had worse outcomes. If these data are borne out, future public information strategies need to be reassuring, proactive, simple, and more effective because we think patients stayed away,” the cardiologist added. “There are important public information messages to be taken from these data about getting patients to come to hospital during such pandemics.”
He presented prospectively collected registry data on 144 patients with confirmed ST-elevation MI (STEMI) and 122 with non-ST–elevation MI (NSTEMI), all COVID-19 positive on presentation at 85 hospitals in the United Kingdom, Europe, and North America during March through August of 2020. Since the initial message to the public early in the pandemic in many places was to try to avoid the hospital, the investigators selected for their no-COVID comparison group the data on more than 22,000 STEMI and NSTEMI patients included in two British national databases covering 2018-2019.
The COVID-positive STEMI patients were significantly younger, had more comorbidities, and had a higher mean heart rate and lower systolic blood pressure at admission than the non-COVID STEMI control group. Their median time from symptom onset to admission was 339 minutes, compared with 178 minutes in controls. Their door-to-balloon time averaged 83 minutes, versus 37 minutes in the era before the pandemic.
“I suspect that’s got something to do with the donning and doffing of personal protective equipment,” he said at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
The in-hospital mortality rates were strikingly different: 27.1% in COVID-positive STEMI patients versus 5.7% in controls. Bleeding Academic Research Consortium type 3-5 bleeding was increased as well, by a margin of 2.8% to 0.3%. So was stroke, with a 2.1% in-hospital incidence in COVID-positive STEMI patients and a 0.1% rate in the comparator arm.
“But the biggest headline here for me was that the cardiogenic shock rate was 20.1% in the COVID-positive patients versus 8.7% in the non-COVID STEMI patients,” the cardiologist continued.
The same pattern held true among the COVID-positive NSTEMI patients: They were younger, sicker, and slower to present to the hospital than the non-COVID group. The in-hospital mortality rate was 6.6% in the COVID-positive NSTEMI patients, compared with 1.2% in the reference group. The COVID-positive patients had a 2.5% bleeding rate versus 0.1% in the controls. And the incidence of cardiogenic shock was 5%, compared with 1.4% in the controls from before the pandemic.
“Even though NSTEMI is traditionally regarded as lower risk, this is really quite dramatic. These are sick patients,” Dr. Gershlick observed.
Nearly two-thirds of in-hospital deaths in COVID-positive ACS patients were cardiovascular, and three-quarters of those cardiovascular deaths occurred in patients with cardiogenic shock. Thirty-two percent of deaths in COVID-positive ACS patients were of respiratory causes, and 4.9% were neurologic.
Notably, the ischemic time of patients with cardiogenic shock who died – that is, the time from symptom onset to balloon deployment – averaged 1,271 minutes, compared with 441 minutes in those who died without being in cardiogenic shock.
Session comoderator Sahil A. Parikh, MD, director of endovascular services at Columbia University Medical Center in New York, commented, “One of the striking things that is resonating with me is the high incidence of cardiogenic shock and the mortality. It’s akin to what we’ve seen in New York.”
Discussant Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, said he doubts that the increased in-hospital mortality in the COVID–ACS registry is related to the prolonged time to presentation at the hospital. More likely, it’s related to the greater thrombotic burden various studies have shown accompanies COVID-positive ACS. It might even be caused by a direct effect of the virus on the myocardium, added Dr. Fuster, director of the Zena and Michael A. Wiener Cardiovascular Institute and professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York.
“I have to say I absolutely disagree,” responded Dr. Gershlick. “I think it’s important that we try to understand all the mechanisms, but we know that patients with COVID are anxious, and I think one of the messages from this registry is patients took longer to come to hospital, they were sicker, they had more cardiogenic shock, and they died. And I don’t think it’s anything more complicated than that.”
Another discussant, Mamas Mamas, MD, is involved with a 500-patient U.K. pandemic ACS registry nearing publication. The findings, he said, are similar to what Dr. Gershlick reported in terms of the high rate of presentation with cardiogenic shock and elevated in-hospital mortality. The COVID-positive ACS patients were also more likely to present with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. But like Dr. Fuster, he is skeptical that their worse outcomes can be explained by a delay in seeking care.
“I don’t think the delay in presentation is really associated with the high mortality rate that we see. The delay in our U.K. registry is maybe half an hour for STEMIs and maybe 2-3 hours for NSTEMIs. And I don’t think that can produce a 30%-40% increase in mortality,” asserted Dr. Mamas, professor of cardiology at Keele University in Staffordshire, England.
Dr. Gershlick reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
FROM TCT 2020
Brazil confirms death of volunteer in COVID-19 vaccine trial
The Brazilian National Health Surveillance Agency (Anvisa) announced Oct. 21 that it is investigating data received on the death of a volunteer in a clinical trial of the COVID-19 vaccine developed by Oxford University and the pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca.
In an email sent to Medscape Medical News, the agency states that it was formally informed of the death on October 19. It has already received data regarding the investigation of the case, which is now being conducted by the Brazilian International Security Assessment Committee.
The identity of the volunteer and cause of death have not yet been confirmed by any official source linked to the study. In the email, Anvisa reiterated that “according to national and international regulations on good clinical practices, data on clinical research volunteers must be kept confidential, in accordance with the principles of confidentiality, human dignity, and protection of participants.”
A report in the Brazilian newspaper O Globo, however, states that the patient who died is a 28-year-old doctor, recently graduated, who worked on the front line of combating COVID-19 in three hospitals in Rio de Janeiro. . Due to the study design, it is impossible to know whether the volunteer received the vaccine or placebo.
It is imperative to wait for the results of the investigations, said Sergio Cimerman, MD, the scientific coordinator of the Brazilian Society of Infectious Diseases (SBI), because death is possible during any vaccine trial, even more so in cases in which the final goal is to immunize the population in record time.
“It is precisely the phase 3 study that assesses efficacy and safety so that the vaccine can be used for the entire population. We cannot let ourselves lose hope, and we must move forward, as safely as possible, in search of an ideal vaccine,” said Cimerman, who works at the Instituto de Infectologia Emílio Ribas and is also an advisor to the Portuguese edition of Medscape.
This article was translated and adapted from the Portuguese edition of Medscape.
The Brazilian National Health Surveillance Agency (Anvisa) announced Oct. 21 that it is investigating data received on the death of a volunteer in a clinical trial of the COVID-19 vaccine developed by Oxford University and the pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca.
In an email sent to Medscape Medical News, the agency states that it was formally informed of the death on October 19. It has already received data regarding the investigation of the case, which is now being conducted by the Brazilian International Security Assessment Committee.
The identity of the volunteer and cause of death have not yet been confirmed by any official source linked to the study. In the email, Anvisa reiterated that “according to national and international regulations on good clinical practices, data on clinical research volunteers must be kept confidential, in accordance with the principles of confidentiality, human dignity, and protection of participants.”
A report in the Brazilian newspaper O Globo, however, states that the patient who died is a 28-year-old doctor, recently graduated, who worked on the front line of combating COVID-19 in three hospitals in Rio de Janeiro. . Due to the study design, it is impossible to know whether the volunteer received the vaccine or placebo.
It is imperative to wait for the results of the investigations, said Sergio Cimerman, MD, the scientific coordinator of the Brazilian Society of Infectious Diseases (SBI), because death is possible during any vaccine trial, even more so in cases in which the final goal is to immunize the population in record time.
“It is precisely the phase 3 study that assesses efficacy and safety so that the vaccine can be used for the entire population. We cannot let ourselves lose hope, and we must move forward, as safely as possible, in search of an ideal vaccine,” said Cimerman, who works at the Instituto de Infectologia Emílio Ribas and is also an advisor to the Portuguese edition of Medscape.
This article was translated and adapted from the Portuguese edition of Medscape.
The Brazilian National Health Surveillance Agency (Anvisa) announced Oct. 21 that it is investigating data received on the death of a volunteer in a clinical trial of the COVID-19 vaccine developed by Oxford University and the pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca.
In an email sent to Medscape Medical News, the agency states that it was formally informed of the death on October 19. It has already received data regarding the investigation of the case, which is now being conducted by the Brazilian International Security Assessment Committee.
The identity of the volunteer and cause of death have not yet been confirmed by any official source linked to the study. In the email, Anvisa reiterated that “according to national and international regulations on good clinical practices, data on clinical research volunteers must be kept confidential, in accordance with the principles of confidentiality, human dignity, and protection of participants.”
A report in the Brazilian newspaper O Globo, however, states that the patient who died is a 28-year-old doctor, recently graduated, who worked on the front line of combating COVID-19 in three hospitals in Rio de Janeiro. . Due to the study design, it is impossible to know whether the volunteer received the vaccine or placebo.
It is imperative to wait for the results of the investigations, said Sergio Cimerman, MD, the scientific coordinator of the Brazilian Society of Infectious Diseases (SBI), because death is possible during any vaccine trial, even more so in cases in which the final goal is to immunize the population in record time.
“It is precisely the phase 3 study that assesses efficacy and safety so that the vaccine can be used for the entire population. We cannot let ourselves lose hope, and we must move forward, as safely as possible, in search of an ideal vaccine,” said Cimerman, who works at the Instituto de Infectologia Emílio Ribas and is also an advisor to the Portuguese edition of Medscape.
This article was translated and adapted from the Portuguese edition of Medscape.
COVID-19 experience forced residents to quickly improve patient communication skills
While the spring peak of COVID-19 was tough and traumatic for many residents and interns in a New York City health system, the experience may have accelerated their patient communication skills regarding difficult goals-of-care discussions, results of a recent survey suggest.
Breaking bad news was an everyday or every-other-day occurrence at the peak of the pandemic for nearly all of 50 of the trainees surveyed, who had worked at hospitals affiliated with the internal medicine residency program at the at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai from March to June 2020.
However, trainees became significantly more comfortable and fluent in goals-of-care discussions during the pandemic, according to Patrick Tobin-Schnittger, MBBS, a third-year internal medicine resident in the Mount Sinai program.
“COVID-19 has obviously made a huge impact on the world, but I think it’s also made a huge impact on a whole generation of junior doctors,” said Dr. Tobin-Schnittger, who presented the findings in a late-breaking abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting, held virtually this year.
“It’ll be interesting to see what happens in the future as that generation matures, and I think one of the things is that we’re a lot more comfortable with end-of-life care,” he said in an interview conducted during the conference.
Nevertheless, coping with death may still be a challenge for many residents, according to Dr. Tobin-Schnittger. In the survey, internal medicine residents who had rarely encountered patient deaths suddenly found themselves experiencing deaths weekly, with more than one in five saying they were encountering it every day.
When asked to self-rate themselves according to Bugen’s Coping With Death scale, most participants had scores that suggested their ability to cope was suboptimal, the researcher said.
To help trainees cope with local COVID-19 surges, internal medicine residency programs should be implementing “breaking bad news” workshops and educating house staff on resilience in times of crisis, especially if it can be done virtually, according to Dr. Tobin-Schnittger.
“That could be done pretty quickly, and it could be done remotely so people could practice this from home,” he explained. “They wouldn’t even need to congregate in a big room.”
As a “mini-surge” of COVID-19 cases hits the United States, teaching self-care and coping techniques may also be important, said Mangala Narasimhan, DO, FCCP, director of critical care services at Northwell Health in New York City.
“We’ve had several sessions in our health system of letting people vent, talk about what happened, and tell stories about patients that they are still thinking about and haunted by – there was so much death,” Dr. Narasimhan said in an interview.
“People will be suffering for a long time thinking about what happened in March and April and May, so I think our focus now needs to be how to fix that in any way we can and to support people, as we’re dealing with these increases in numbers,” she said. “I think everyone’s panicking over the increase in numbers, but they’re panicking because of the fear of going through what they went through before.”
Dr. Tobin-Schnittger and colleagues sent their survey to 94 residents and interns in the Mount Sinai program who had worked through the peak of the pandemic. They received 50 responses. Of those individuals, the mean age was 29.5 years, and about 46% had worked for more than 3 years.
Before the pandemic, only 3 of the 50 respondents reported having goals-of-care conversations every day or every other day, while during the pandemic, those conversations were happening at least every other day for 38 of the respondents, survey data show.
Self-reported fluency and comfort with those discussions increased significantly, from a mean of about 50 on a scale of 100 before the pandemic to more than 75 during the pandemic, according to Dr. Tobin-Schnittger.
When asked how they remembered coping with patient death, one respondent described holding up a phone so a dying patient could hear his daughter’s voice. Another reported not being able to sleep at night.
“I constantly would have dreams that my patients were dying and there was nothing I could do about it,” the respondent said in a survey response.
A third respondent described the experience as ”humbling” but said there were rewarding aspects in patient care during the peak of the pandemic, which helped in being able to focus during difficult days.
Three participants (7.7%) said they changed their career plans as a result of the pandemic experience, the researchers reported.
Negative consequences of the peak pandemic experience included anger, anxiety, professional strain, trauma, and emotional distancing, some respondents reported.
However, others called attention to positive outcomes, such as more professional pride, resilience, confidence, and camaraderie.
“While we did encounter a lot of traumatic experiences, overall, there’s a huge sense that there is a lot more camaraderie within our department, but also within other departments,” said Dr. Tobin-Schnittger. “So I think there are some positives that come from this, and I think there’s been a bit of a culture change.”
Dr. Tobin-Schnittger said that he and his coauthors had no conflicts of interest or relationships with commercial interests to report.
SOURCE: Tobin-Schnittger P. CHEST 2020. Late-breaking abstract. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.09.040.
While the spring peak of COVID-19 was tough and traumatic for many residents and interns in a New York City health system, the experience may have accelerated their patient communication skills regarding difficult goals-of-care discussions, results of a recent survey suggest.
Breaking bad news was an everyday or every-other-day occurrence at the peak of the pandemic for nearly all of 50 of the trainees surveyed, who had worked at hospitals affiliated with the internal medicine residency program at the at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai from March to June 2020.
However, trainees became significantly more comfortable and fluent in goals-of-care discussions during the pandemic, according to Patrick Tobin-Schnittger, MBBS, a third-year internal medicine resident in the Mount Sinai program.
“COVID-19 has obviously made a huge impact on the world, but I think it’s also made a huge impact on a whole generation of junior doctors,” said Dr. Tobin-Schnittger, who presented the findings in a late-breaking abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting, held virtually this year.
“It’ll be interesting to see what happens in the future as that generation matures, and I think one of the things is that we’re a lot more comfortable with end-of-life care,” he said in an interview conducted during the conference.
Nevertheless, coping with death may still be a challenge for many residents, according to Dr. Tobin-Schnittger. In the survey, internal medicine residents who had rarely encountered patient deaths suddenly found themselves experiencing deaths weekly, with more than one in five saying they were encountering it every day.
When asked to self-rate themselves according to Bugen’s Coping With Death scale, most participants had scores that suggested their ability to cope was suboptimal, the researcher said.
To help trainees cope with local COVID-19 surges, internal medicine residency programs should be implementing “breaking bad news” workshops and educating house staff on resilience in times of crisis, especially if it can be done virtually, according to Dr. Tobin-Schnittger.
“That could be done pretty quickly, and it could be done remotely so people could practice this from home,” he explained. “They wouldn’t even need to congregate in a big room.”
As a “mini-surge” of COVID-19 cases hits the United States, teaching self-care and coping techniques may also be important, said Mangala Narasimhan, DO, FCCP, director of critical care services at Northwell Health in New York City.
“We’ve had several sessions in our health system of letting people vent, talk about what happened, and tell stories about patients that they are still thinking about and haunted by – there was so much death,” Dr. Narasimhan said in an interview.
“People will be suffering for a long time thinking about what happened in March and April and May, so I think our focus now needs to be how to fix that in any way we can and to support people, as we’re dealing with these increases in numbers,” she said. “I think everyone’s panicking over the increase in numbers, but they’re panicking because of the fear of going through what they went through before.”
Dr. Tobin-Schnittger and colleagues sent their survey to 94 residents and interns in the Mount Sinai program who had worked through the peak of the pandemic. They received 50 responses. Of those individuals, the mean age was 29.5 years, and about 46% had worked for more than 3 years.
Before the pandemic, only 3 of the 50 respondents reported having goals-of-care conversations every day or every other day, while during the pandemic, those conversations were happening at least every other day for 38 of the respondents, survey data show.
Self-reported fluency and comfort with those discussions increased significantly, from a mean of about 50 on a scale of 100 before the pandemic to more than 75 during the pandemic, according to Dr. Tobin-Schnittger.
When asked how they remembered coping with patient death, one respondent described holding up a phone so a dying patient could hear his daughter’s voice. Another reported not being able to sleep at night.
“I constantly would have dreams that my patients were dying and there was nothing I could do about it,” the respondent said in a survey response.
A third respondent described the experience as ”humbling” but said there were rewarding aspects in patient care during the peak of the pandemic, which helped in being able to focus during difficult days.
Three participants (7.7%) said they changed their career plans as a result of the pandemic experience, the researchers reported.
Negative consequences of the peak pandemic experience included anger, anxiety, professional strain, trauma, and emotional distancing, some respondents reported.
However, others called attention to positive outcomes, such as more professional pride, resilience, confidence, and camaraderie.
“While we did encounter a lot of traumatic experiences, overall, there’s a huge sense that there is a lot more camaraderie within our department, but also within other departments,” said Dr. Tobin-Schnittger. “So I think there are some positives that come from this, and I think there’s been a bit of a culture change.”
Dr. Tobin-Schnittger said that he and his coauthors had no conflicts of interest or relationships with commercial interests to report.
SOURCE: Tobin-Schnittger P. CHEST 2020. Late-breaking abstract. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.09.040.
While the spring peak of COVID-19 was tough and traumatic for many residents and interns in a New York City health system, the experience may have accelerated their patient communication skills regarding difficult goals-of-care discussions, results of a recent survey suggest.
Breaking bad news was an everyday or every-other-day occurrence at the peak of the pandemic for nearly all of 50 of the trainees surveyed, who had worked at hospitals affiliated with the internal medicine residency program at the at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai from March to June 2020.
However, trainees became significantly more comfortable and fluent in goals-of-care discussions during the pandemic, according to Patrick Tobin-Schnittger, MBBS, a third-year internal medicine resident in the Mount Sinai program.
“COVID-19 has obviously made a huge impact on the world, but I think it’s also made a huge impact on a whole generation of junior doctors,” said Dr. Tobin-Schnittger, who presented the findings in a late-breaking abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting, held virtually this year.
“It’ll be interesting to see what happens in the future as that generation matures, and I think one of the things is that we’re a lot more comfortable with end-of-life care,” he said in an interview conducted during the conference.
Nevertheless, coping with death may still be a challenge for many residents, according to Dr. Tobin-Schnittger. In the survey, internal medicine residents who had rarely encountered patient deaths suddenly found themselves experiencing deaths weekly, with more than one in five saying they were encountering it every day.
When asked to self-rate themselves according to Bugen’s Coping With Death scale, most participants had scores that suggested their ability to cope was suboptimal, the researcher said.
To help trainees cope with local COVID-19 surges, internal medicine residency programs should be implementing “breaking bad news” workshops and educating house staff on resilience in times of crisis, especially if it can be done virtually, according to Dr. Tobin-Schnittger.
“That could be done pretty quickly, and it could be done remotely so people could practice this from home,” he explained. “They wouldn’t even need to congregate in a big room.”
As a “mini-surge” of COVID-19 cases hits the United States, teaching self-care and coping techniques may also be important, said Mangala Narasimhan, DO, FCCP, director of critical care services at Northwell Health in New York City.
“We’ve had several sessions in our health system of letting people vent, talk about what happened, and tell stories about patients that they are still thinking about and haunted by – there was so much death,” Dr. Narasimhan said in an interview.
“People will be suffering for a long time thinking about what happened in March and April and May, so I think our focus now needs to be how to fix that in any way we can and to support people, as we’re dealing with these increases in numbers,” she said. “I think everyone’s panicking over the increase in numbers, but they’re panicking because of the fear of going through what they went through before.”
Dr. Tobin-Schnittger and colleagues sent their survey to 94 residents and interns in the Mount Sinai program who had worked through the peak of the pandemic. They received 50 responses. Of those individuals, the mean age was 29.5 years, and about 46% had worked for more than 3 years.
Before the pandemic, only 3 of the 50 respondents reported having goals-of-care conversations every day or every other day, while during the pandemic, those conversations were happening at least every other day for 38 of the respondents, survey data show.
Self-reported fluency and comfort with those discussions increased significantly, from a mean of about 50 on a scale of 100 before the pandemic to more than 75 during the pandemic, according to Dr. Tobin-Schnittger.
When asked how they remembered coping with patient death, one respondent described holding up a phone so a dying patient could hear his daughter’s voice. Another reported not being able to sleep at night.
“I constantly would have dreams that my patients were dying and there was nothing I could do about it,” the respondent said in a survey response.
A third respondent described the experience as ”humbling” but said there were rewarding aspects in patient care during the peak of the pandemic, which helped in being able to focus during difficult days.
Three participants (7.7%) said they changed their career plans as a result of the pandemic experience, the researchers reported.
Negative consequences of the peak pandemic experience included anger, anxiety, professional strain, trauma, and emotional distancing, some respondents reported.
However, others called attention to positive outcomes, such as more professional pride, resilience, confidence, and camaraderie.
“While we did encounter a lot of traumatic experiences, overall, there’s a huge sense that there is a lot more camaraderie within our department, but also within other departments,” said Dr. Tobin-Schnittger. “So I think there are some positives that come from this, and I think there’s been a bit of a culture change.”
Dr. Tobin-Schnittger said that he and his coauthors had no conflicts of interest or relationships with commercial interests to report.
SOURCE: Tobin-Schnittger P. CHEST 2020. Late-breaking abstract. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.09.040.
FROM CHEST 2020
Outpatient visits rebound for most specialties to pre-COVID-19 levels
, according to new data.
Overall visits plunged by almost 60% at the low point in late March and did not start recovering until late June, when visits were still off by 10%. Visits began to rise again – by 2% over the March 1 baseline – around Labor Day.
As of Oct. 4, visits had returned to that March 1 baseline, which was slightly higher than in late February, according to data analyzed by Harvard University, the Commonwealth Fund, and the healthcare technology company Phreesia, which helps medical practices with patient registration, insurance verification, and payments, and has data on 50,000 providers in all 50 states.
The study was published online by the Commonwealth Fund.
In-person visits are still down 6% from the March 1 baseline. Telemedicine visits – which surged in mid-April to account for some 13%-14% of visits – have subsided to 6% of visits.
Many states reopened businesses and lifted travel restrictions in early September, benefiting medical practices in some areas. But clinicians in some regions are still facing rising COVID-19 cases, as well as “the challenges of keeping patients and clinicians safe while also maintaining revenue,” wrote the report authors.
Some specialties are still hard hit. For the week starting Oct. 4, visits to pulmonologists were off 20% from March 1. Otolaryngology visits were down 17%, and behavioral health visits were down 14%. Cardiology, allergy/immunology, neurology, gastroenterology, and endocrinology also saw drops of 5%-10% from March.
Patients were flocking to dermatologists, however. Visits were up 17% over baseline. Primary care also was popular, with a 13% increase over March 1.
At the height of the pandemic shutdown in late March, Medicare beneficiaries stayed away from doctors the most. Visits dipped 63%, compared with 56% for the commercially insured, and 52% for those on Medicaid. Now, Medicare visits are up 3% over baseline, while Medicaid visits are down 1% and commercially insured visits have risen 1% from March.
The over-65 age group did not have the steepest drop in visits when analyzed by age. Children aged 3-17 years saw the biggest decline at the height of the shutdown. Infants to 5-year-olds have still not returned to prepandemic visit levels. Those visits are off by 10%-18%. The 65-and-older group is up 4% from March.
Larger practices – with more than six clinicians – have seen the biggest rebound, after having had the largest dip in visits, from a decline of 53% in late March to a 14% rise over that baseline. Practices with fewer than five clinicians are still 6% down from the March baseline.
Wide variation in telemedicine use
The researchers reported a massive gap in the percentage of various specialties that are using telemedicine. At the top end are behavioral health specialists, where 41% of visits are by telemedicine.
The next-closest specialty is endocrinology, which has 14% of visits via telemedicine, on par with rheumatology, neurology, and gastroenterology. At the low end: ophthalmology, with zero virtual visits; otolaryngology (1%), orthopedics (1%), surgery (2%), and dermatology and ob.gyn., both at 3%.
Smaller practices – with fewer than five clinicians – never adopted telemedicine at the rate of the larger practices. During the mid-April peak, about 10% of the smaller practices were using telemedicine in adult primary care practices, compared with 19% of those primary care practices with more than six clinicians.
The gap persists. Currently, 9% of the larger practices are using telemedicine, compared with 4% of small practices.
One-third of all provider organizations analyzed never-adopted telemedicine. And while use continues, it is now mostly minimal. At the April peak, 35% of the practices with telemedicine reported heavy use – that is, in more than 20% of visits. In September, 9% said they had such heavy use.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to new data.
Overall visits plunged by almost 60% at the low point in late March and did not start recovering until late June, when visits were still off by 10%. Visits began to rise again – by 2% over the March 1 baseline – around Labor Day.
As of Oct. 4, visits had returned to that March 1 baseline, which was slightly higher than in late February, according to data analyzed by Harvard University, the Commonwealth Fund, and the healthcare technology company Phreesia, which helps medical practices with patient registration, insurance verification, and payments, and has data on 50,000 providers in all 50 states.
The study was published online by the Commonwealth Fund.
In-person visits are still down 6% from the March 1 baseline. Telemedicine visits – which surged in mid-April to account for some 13%-14% of visits – have subsided to 6% of visits.
Many states reopened businesses and lifted travel restrictions in early September, benefiting medical practices in some areas. But clinicians in some regions are still facing rising COVID-19 cases, as well as “the challenges of keeping patients and clinicians safe while also maintaining revenue,” wrote the report authors.
Some specialties are still hard hit. For the week starting Oct. 4, visits to pulmonologists were off 20% from March 1. Otolaryngology visits were down 17%, and behavioral health visits were down 14%. Cardiology, allergy/immunology, neurology, gastroenterology, and endocrinology also saw drops of 5%-10% from March.
Patients were flocking to dermatologists, however. Visits were up 17% over baseline. Primary care also was popular, with a 13% increase over March 1.
At the height of the pandemic shutdown in late March, Medicare beneficiaries stayed away from doctors the most. Visits dipped 63%, compared with 56% for the commercially insured, and 52% for those on Medicaid. Now, Medicare visits are up 3% over baseline, while Medicaid visits are down 1% and commercially insured visits have risen 1% from March.
The over-65 age group did not have the steepest drop in visits when analyzed by age. Children aged 3-17 years saw the biggest decline at the height of the shutdown. Infants to 5-year-olds have still not returned to prepandemic visit levels. Those visits are off by 10%-18%. The 65-and-older group is up 4% from March.
Larger practices – with more than six clinicians – have seen the biggest rebound, after having had the largest dip in visits, from a decline of 53% in late March to a 14% rise over that baseline. Practices with fewer than five clinicians are still 6% down from the March baseline.
Wide variation in telemedicine use
The researchers reported a massive gap in the percentage of various specialties that are using telemedicine. At the top end are behavioral health specialists, where 41% of visits are by telemedicine.
The next-closest specialty is endocrinology, which has 14% of visits via telemedicine, on par with rheumatology, neurology, and gastroenterology. At the low end: ophthalmology, with zero virtual visits; otolaryngology (1%), orthopedics (1%), surgery (2%), and dermatology and ob.gyn., both at 3%.
Smaller practices – with fewer than five clinicians – never adopted telemedicine at the rate of the larger practices. During the mid-April peak, about 10% of the smaller practices were using telemedicine in adult primary care practices, compared with 19% of those primary care practices with more than six clinicians.
The gap persists. Currently, 9% of the larger practices are using telemedicine, compared with 4% of small practices.
One-third of all provider organizations analyzed never-adopted telemedicine. And while use continues, it is now mostly minimal. At the April peak, 35% of the practices with telemedicine reported heavy use – that is, in more than 20% of visits. In September, 9% said they had such heavy use.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to new data.
Overall visits plunged by almost 60% at the low point in late March and did not start recovering until late June, when visits were still off by 10%. Visits began to rise again – by 2% over the March 1 baseline – around Labor Day.
As of Oct. 4, visits had returned to that March 1 baseline, which was slightly higher than in late February, according to data analyzed by Harvard University, the Commonwealth Fund, and the healthcare technology company Phreesia, which helps medical practices with patient registration, insurance verification, and payments, and has data on 50,000 providers in all 50 states.
The study was published online by the Commonwealth Fund.
In-person visits are still down 6% from the March 1 baseline. Telemedicine visits – which surged in mid-April to account for some 13%-14% of visits – have subsided to 6% of visits.
Many states reopened businesses and lifted travel restrictions in early September, benefiting medical practices in some areas. But clinicians in some regions are still facing rising COVID-19 cases, as well as “the challenges of keeping patients and clinicians safe while also maintaining revenue,” wrote the report authors.
Some specialties are still hard hit. For the week starting Oct. 4, visits to pulmonologists were off 20% from March 1. Otolaryngology visits were down 17%, and behavioral health visits were down 14%. Cardiology, allergy/immunology, neurology, gastroenterology, and endocrinology also saw drops of 5%-10% from March.
Patients were flocking to dermatologists, however. Visits were up 17% over baseline. Primary care also was popular, with a 13% increase over March 1.
At the height of the pandemic shutdown in late March, Medicare beneficiaries stayed away from doctors the most. Visits dipped 63%, compared with 56% for the commercially insured, and 52% for those on Medicaid. Now, Medicare visits are up 3% over baseline, while Medicaid visits are down 1% and commercially insured visits have risen 1% from March.
The over-65 age group did not have the steepest drop in visits when analyzed by age. Children aged 3-17 years saw the biggest decline at the height of the shutdown. Infants to 5-year-olds have still not returned to prepandemic visit levels. Those visits are off by 10%-18%. The 65-and-older group is up 4% from March.
Larger practices – with more than six clinicians – have seen the biggest rebound, after having had the largest dip in visits, from a decline of 53% in late March to a 14% rise over that baseline. Practices with fewer than five clinicians are still 6% down from the March baseline.
Wide variation in telemedicine use
The researchers reported a massive gap in the percentage of various specialties that are using telemedicine. At the top end are behavioral health specialists, where 41% of visits are by telemedicine.
The next-closest specialty is endocrinology, which has 14% of visits via telemedicine, on par with rheumatology, neurology, and gastroenterology. At the low end: ophthalmology, with zero virtual visits; otolaryngology (1%), orthopedics (1%), surgery (2%), and dermatology and ob.gyn., both at 3%.
Smaller practices – with fewer than five clinicians – never adopted telemedicine at the rate of the larger practices. During the mid-April peak, about 10% of the smaller practices were using telemedicine in adult primary care practices, compared with 19% of those primary care practices with more than six clinicians.
The gap persists. Currently, 9% of the larger practices are using telemedicine, compared with 4% of small practices.
One-third of all provider organizations analyzed never-adopted telemedicine. And while use continues, it is now mostly minimal. At the April peak, 35% of the practices with telemedicine reported heavy use – that is, in more than 20% of visits. In September, 9% said they had such heavy use.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Teen vaping in the time of COVID-19
It’s an electronic cigarette maker’s dream, but a public health nightmare: The confluence of social isolation and anxiety resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic has the potential to make recent progress against e-cigarette use among teens go up in smoke.
“Stress and worsening mental health issues are well-known predisposing factors for smoking, both in quantity and frequency and in relapse,” said Mary Cataletto, MD, FCCP, clinical professor of pediatrics at New York University Winthrop Hospital, Mineola, during a webinar on e-cigarettes and vaping with asthma in the time of COVID-19, hosted by the Allergy & Asthma Network.
Prior to the pandemic, public health experts appeared to be making inroads into curbing e-cigarette use, according to results of the 2020 National Youth Tobacco Survey, a cross-sectional school-based survey of students from grades 6 to 12.
“In 2020, approximately 1 in 5 high school students and 1 in 20 middle school students currently used e-cigarettes. By comparison, in 2019, 27.5% of high school students (4.11 million) and 10.5% of middle school students (1.24 million) reported current e-cigarette use,” wrote Brian A. King, PhD, MPH, and colleagues, in an article reporting those results.
“We definitely believe that there was a real decline that occurred up until March. Those data from the National Youth Tobacco Survey were collected prior to youth leaving school settings and prior to the implementation of social distancing and other measures,” said Dr. King, deputy director for research translation in the Office on Smoking and Health within the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“That said, the jury’s still out on what’s going to happen with youth use during the coming year, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic” he said in an interview.
Flavor of the moment
Even though the data through March 2020 showed a distinct decline in e-cigarette use, Dr. King and colleagues found that 3.6 million U.S. adolescents still currently used e-cigarettes in 2020; among current users, more than 80% reported using flavored e-cigarettes.
Dr. Cataletto said in an interview that the 2020 National Youth Tobacco Survey continues to report widespread use of flavored e-cigarettes among young smokers despite Food and Drug Administration admonitions to manufacturers and retailers to remove unauthorized e-cigarettes from the market.
On Jan. 2, 2020, the FDA reported a finalized enforcement policy directed against “unauthorized flavored cartridge-based e-cigarettes that appeal to children, including fruit and mint.”
But as Dr. King and other investigators also mentioned in a separate analysis of e-cigarette unit sales, that enforcement policy applies only to prefilled cartridge e-cigarette products, such as those made by JUUL, and that while sales of mint- or fruit-flavored products of this type declined from September 2014 to May 2020, there was an increase in the sale of disposable e-cigarettes with flavors other than menthol or tobacco.
Dr. Cataletto pointed out that this vaping trend has coincided with the COVID-19 pandemic, noting that, on March 13, 2020, just 2 days after the World Health Organization declared that spread of COVID-19 was officially a pandemic, 16 states closed schools, leaving millions of middle school– and high school–age children at loose ends. She said: “This raised a number of concerns. Would students who used e-cigarettes be at increased risk of COVID-19? Would e-cigarette use increase again due to the social isolation and anxiety as predicted for tobacco smokers? How would access and availability impact e-cigarette use?
“It’s possible that use may go down, because youth may have less access to their typical social sources or other manners in which they obtain the product.” Dr. King said. “Alternatively, youth may have more disposable time on their hands and may be open to other sources of access to these products, and so use could increase.”
There is evidence to suggest that the latter scenario may be true, according to investigators who surveyed more than 1,000 Canadian adolescents about alcohol use, binge drinking, cannabis use, and vaping in the 3 weeks directly before and after social distancing measures took effect.
The investigators found that the frequency of both alcohol and cannabis use increased during social isolation, and that, although about half of respondents reported solitary substance use, 32% reported using substances with peers via technology, and 24% reported using substances face to face, despite social distancing mandates, reported Tara M. Dumas, PhD, from Huron University College, London, Ont.
“These authors suggest that teens who feared loss of friendships during quarantine might be more willing to engage in risky behaviors such as face to face substance use to maintain social status, while solitary substance use was related to both COVID19 fears and depressive symptomatology,” Dr. Cataletto said.
E-cigarettes and COVID-19
A recent survey of 4,351 adolescents and young adults in the United States showed that a COVID-19 diagnosis was five times more likely among those who had ever used e-cigarettes, seven times more likely among conventional cigarette and e-cigarette uses, and nearly seven times more likely among those who had used both within the past 30 days .
Perhaps not surprisingly, adolescents and young adults with asthma who also vape may be at especially high risk for COVID-19, but the exact effect may be hard to pin down with current levels of evidence.
“Prior to the pandemic we did see both new-onset asthma and asthma exacerbations in teens who reported either vaping or dual use with tobacco products,” Dr. Cataletto said. “However, numbers were small, were confounded by the bias of subspecialty practice, and the onset of the pandemic, which affected not only face-to-face visits but the opportunity to perform pulmonary function testing for a number of months.”
Dr. King noted: “There is an emerging body of science that does indicate that there could be some respiratory risks related to e-cigarette use, particularly among certain populations. ... That said, there’s no conclusive link between e-cigarette use and specific disease outcomes, which typically requires a robust body of different science conducted in multiple settings.”
He said that e-cigarette vapors contain ultrafine particles and heavy metals that can be inhaled deeply into the lungs, both of which have previously been associated with respiratory risk, including complications from asthma.
An ounce of prevention
“When it comes to cessation, we do know that about 50% of youth who are using tobacco products including e-cigarettes, want to quit, and about the same proportion make an effort to quit, so there’s certainly a will there, but we don’t clearly have an evidence-based way,” Dr. King said.
Combinations of behavioral interventions including face-to-face consultations and digital or telephone support can be helpful, Dr. Cataletto said, but both she and Dr. King agree that prevention is the most effective method of reducing e-cigarette use among teens and young adults, including peer support and education efforts.
Asked how she gets her patients to report honestly about their habits, Dr. Cataletto acknowledged that “this is a challenge for many kids. Some are unaware that many of the commercially available e-cigarette products contain nicotine and they are not ‘just vaping flavoring.’ Ongoing education is important, and it is happening in schools, in pediatrician’s offices, at home and in the community.”
Dr. Cataletto and Dr. King reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Cataletto serves on the editorial advisory board for Chest Physician.
It’s an electronic cigarette maker’s dream, but a public health nightmare: The confluence of social isolation and anxiety resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic has the potential to make recent progress against e-cigarette use among teens go up in smoke.
“Stress and worsening mental health issues are well-known predisposing factors for smoking, both in quantity and frequency and in relapse,” said Mary Cataletto, MD, FCCP, clinical professor of pediatrics at New York University Winthrop Hospital, Mineola, during a webinar on e-cigarettes and vaping with asthma in the time of COVID-19, hosted by the Allergy & Asthma Network.
Prior to the pandemic, public health experts appeared to be making inroads into curbing e-cigarette use, according to results of the 2020 National Youth Tobacco Survey, a cross-sectional school-based survey of students from grades 6 to 12.
“In 2020, approximately 1 in 5 high school students and 1 in 20 middle school students currently used e-cigarettes. By comparison, in 2019, 27.5% of high school students (4.11 million) and 10.5% of middle school students (1.24 million) reported current e-cigarette use,” wrote Brian A. King, PhD, MPH, and colleagues, in an article reporting those results.
“We definitely believe that there was a real decline that occurred up until March. Those data from the National Youth Tobacco Survey were collected prior to youth leaving school settings and prior to the implementation of social distancing and other measures,” said Dr. King, deputy director for research translation in the Office on Smoking and Health within the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“That said, the jury’s still out on what’s going to happen with youth use during the coming year, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic” he said in an interview.
Flavor of the moment
Even though the data through March 2020 showed a distinct decline in e-cigarette use, Dr. King and colleagues found that 3.6 million U.S. adolescents still currently used e-cigarettes in 2020; among current users, more than 80% reported using flavored e-cigarettes.
Dr. Cataletto said in an interview that the 2020 National Youth Tobacco Survey continues to report widespread use of flavored e-cigarettes among young smokers despite Food and Drug Administration admonitions to manufacturers and retailers to remove unauthorized e-cigarettes from the market.
On Jan. 2, 2020, the FDA reported a finalized enforcement policy directed against “unauthorized flavored cartridge-based e-cigarettes that appeal to children, including fruit and mint.”
But as Dr. King and other investigators also mentioned in a separate analysis of e-cigarette unit sales, that enforcement policy applies only to prefilled cartridge e-cigarette products, such as those made by JUUL, and that while sales of mint- or fruit-flavored products of this type declined from September 2014 to May 2020, there was an increase in the sale of disposable e-cigarettes with flavors other than menthol or tobacco.
Dr. Cataletto pointed out that this vaping trend has coincided with the COVID-19 pandemic, noting that, on March 13, 2020, just 2 days after the World Health Organization declared that spread of COVID-19 was officially a pandemic, 16 states closed schools, leaving millions of middle school– and high school–age children at loose ends. She said: “This raised a number of concerns. Would students who used e-cigarettes be at increased risk of COVID-19? Would e-cigarette use increase again due to the social isolation and anxiety as predicted for tobacco smokers? How would access and availability impact e-cigarette use?
“It’s possible that use may go down, because youth may have less access to their typical social sources or other manners in which they obtain the product.” Dr. King said. “Alternatively, youth may have more disposable time on their hands and may be open to other sources of access to these products, and so use could increase.”
There is evidence to suggest that the latter scenario may be true, according to investigators who surveyed more than 1,000 Canadian adolescents about alcohol use, binge drinking, cannabis use, and vaping in the 3 weeks directly before and after social distancing measures took effect.
The investigators found that the frequency of both alcohol and cannabis use increased during social isolation, and that, although about half of respondents reported solitary substance use, 32% reported using substances with peers via technology, and 24% reported using substances face to face, despite social distancing mandates, reported Tara M. Dumas, PhD, from Huron University College, London, Ont.
“These authors suggest that teens who feared loss of friendships during quarantine might be more willing to engage in risky behaviors such as face to face substance use to maintain social status, while solitary substance use was related to both COVID19 fears and depressive symptomatology,” Dr. Cataletto said.
E-cigarettes and COVID-19
A recent survey of 4,351 adolescents and young adults in the United States showed that a COVID-19 diagnosis was five times more likely among those who had ever used e-cigarettes, seven times more likely among conventional cigarette and e-cigarette uses, and nearly seven times more likely among those who had used both within the past 30 days .
Perhaps not surprisingly, adolescents and young adults with asthma who also vape may be at especially high risk for COVID-19, but the exact effect may be hard to pin down with current levels of evidence.
“Prior to the pandemic we did see both new-onset asthma and asthma exacerbations in teens who reported either vaping or dual use with tobacco products,” Dr. Cataletto said. “However, numbers were small, were confounded by the bias of subspecialty practice, and the onset of the pandemic, which affected not only face-to-face visits but the opportunity to perform pulmonary function testing for a number of months.”
Dr. King noted: “There is an emerging body of science that does indicate that there could be some respiratory risks related to e-cigarette use, particularly among certain populations. ... That said, there’s no conclusive link between e-cigarette use and specific disease outcomes, which typically requires a robust body of different science conducted in multiple settings.”
He said that e-cigarette vapors contain ultrafine particles and heavy metals that can be inhaled deeply into the lungs, both of which have previously been associated with respiratory risk, including complications from asthma.
An ounce of prevention
“When it comes to cessation, we do know that about 50% of youth who are using tobacco products including e-cigarettes, want to quit, and about the same proportion make an effort to quit, so there’s certainly a will there, but we don’t clearly have an evidence-based way,” Dr. King said.
Combinations of behavioral interventions including face-to-face consultations and digital or telephone support can be helpful, Dr. Cataletto said, but both she and Dr. King agree that prevention is the most effective method of reducing e-cigarette use among teens and young adults, including peer support and education efforts.
Asked how she gets her patients to report honestly about their habits, Dr. Cataletto acknowledged that “this is a challenge for many kids. Some are unaware that many of the commercially available e-cigarette products contain nicotine and they are not ‘just vaping flavoring.’ Ongoing education is important, and it is happening in schools, in pediatrician’s offices, at home and in the community.”
Dr. Cataletto and Dr. King reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Cataletto serves on the editorial advisory board for Chest Physician.
It’s an electronic cigarette maker’s dream, but a public health nightmare: The confluence of social isolation and anxiety resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic has the potential to make recent progress against e-cigarette use among teens go up in smoke.
“Stress and worsening mental health issues are well-known predisposing factors for smoking, both in quantity and frequency and in relapse,” said Mary Cataletto, MD, FCCP, clinical professor of pediatrics at New York University Winthrop Hospital, Mineola, during a webinar on e-cigarettes and vaping with asthma in the time of COVID-19, hosted by the Allergy & Asthma Network.
Prior to the pandemic, public health experts appeared to be making inroads into curbing e-cigarette use, according to results of the 2020 National Youth Tobacco Survey, a cross-sectional school-based survey of students from grades 6 to 12.
“In 2020, approximately 1 in 5 high school students and 1 in 20 middle school students currently used e-cigarettes. By comparison, in 2019, 27.5% of high school students (4.11 million) and 10.5% of middle school students (1.24 million) reported current e-cigarette use,” wrote Brian A. King, PhD, MPH, and colleagues, in an article reporting those results.
“We definitely believe that there was a real decline that occurred up until March. Those data from the National Youth Tobacco Survey were collected prior to youth leaving school settings and prior to the implementation of social distancing and other measures,” said Dr. King, deputy director for research translation in the Office on Smoking and Health within the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“That said, the jury’s still out on what’s going to happen with youth use during the coming year, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic” he said in an interview.
Flavor of the moment
Even though the data through March 2020 showed a distinct decline in e-cigarette use, Dr. King and colleagues found that 3.6 million U.S. adolescents still currently used e-cigarettes in 2020; among current users, more than 80% reported using flavored e-cigarettes.
Dr. Cataletto said in an interview that the 2020 National Youth Tobacco Survey continues to report widespread use of flavored e-cigarettes among young smokers despite Food and Drug Administration admonitions to manufacturers and retailers to remove unauthorized e-cigarettes from the market.
On Jan. 2, 2020, the FDA reported a finalized enforcement policy directed against “unauthorized flavored cartridge-based e-cigarettes that appeal to children, including fruit and mint.”
But as Dr. King and other investigators also mentioned in a separate analysis of e-cigarette unit sales, that enforcement policy applies only to prefilled cartridge e-cigarette products, such as those made by JUUL, and that while sales of mint- or fruit-flavored products of this type declined from September 2014 to May 2020, there was an increase in the sale of disposable e-cigarettes with flavors other than menthol or tobacco.
Dr. Cataletto pointed out that this vaping trend has coincided with the COVID-19 pandemic, noting that, on March 13, 2020, just 2 days after the World Health Organization declared that spread of COVID-19 was officially a pandemic, 16 states closed schools, leaving millions of middle school– and high school–age children at loose ends. She said: “This raised a number of concerns. Would students who used e-cigarettes be at increased risk of COVID-19? Would e-cigarette use increase again due to the social isolation and anxiety as predicted for tobacco smokers? How would access and availability impact e-cigarette use?
“It’s possible that use may go down, because youth may have less access to their typical social sources or other manners in which they obtain the product.” Dr. King said. “Alternatively, youth may have more disposable time on their hands and may be open to other sources of access to these products, and so use could increase.”
There is evidence to suggest that the latter scenario may be true, according to investigators who surveyed more than 1,000 Canadian adolescents about alcohol use, binge drinking, cannabis use, and vaping in the 3 weeks directly before and after social distancing measures took effect.
The investigators found that the frequency of both alcohol and cannabis use increased during social isolation, and that, although about half of respondents reported solitary substance use, 32% reported using substances with peers via technology, and 24% reported using substances face to face, despite social distancing mandates, reported Tara M. Dumas, PhD, from Huron University College, London, Ont.
“These authors suggest that teens who feared loss of friendships during quarantine might be more willing to engage in risky behaviors such as face to face substance use to maintain social status, while solitary substance use was related to both COVID19 fears and depressive symptomatology,” Dr. Cataletto said.
E-cigarettes and COVID-19
A recent survey of 4,351 adolescents and young adults in the United States showed that a COVID-19 diagnosis was five times more likely among those who had ever used e-cigarettes, seven times more likely among conventional cigarette and e-cigarette uses, and nearly seven times more likely among those who had used both within the past 30 days .
Perhaps not surprisingly, adolescents and young adults with asthma who also vape may be at especially high risk for COVID-19, but the exact effect may be hard to pin down with current levels of evidence.
“Prior to the pandemic we did see both new-onset asthma and asthma exacerbations in teens who reported either vaping or dual use with tobacco products,” Dr. Cataletto said. “However, numbers were small, were confounded by the bias of subspecialty practice, and the onset of the pandemic, which affected not only face-to-face visits but the opportunity to perform pulmonary function testing for a number of months.”
Dr. King noted: “There is an emerging body of science that does indicate that there could be some respiratory risks related to e-cigarette use, particularly among certain populations. ... That said, there’s no conclusive link between e-cigarette use and specific disease outcomes, which typically requires a robust body of different science conducted in multiple settings.”
He said that e-cigarette vapors contain ultrafine particles and heavy metals that can be inhaled deeply into the lungs, both of which have previously been associated with respiratory risk, including complications from asthma.
An ounce of prevention
“When it comes to cessation, we do know that about 50% of youth who are using tobacco products including e-cigarettes, want to quit, and about the same proportion make an effort to quit, so there’s certainly a will there, but we don’t clearly have an evidence-based way,” Dr. King said.
Combinations of behavioral interventions including face-to-face consultations and digital or telephone support can be helpful, Dr. Cataletto said, but both she and Dr. King agree that prevention is the most effective method of reducing e-cigarette use among teens and young adults, including peer support and education efforts.
Asked how she gets her patients to report honestly about their habits, Dr. Cataletto acknowledged that “this is a challenge for many kids. Some are unaware that many of the commercially available e-cigarette products contain nicotine and they are not ‘just vaping flavoring.’ Ongoing education is important, and it is happening in schools, in pediatrician’s offices, at home and in the community.”
Dr. Cataletto and Dr. King reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Cataletto serves on the editorial advisory board for Chest Physician.
Are oncologists ready to confront a second wave of COVID-19?
Canceled appointments, postponed surgeries, and delayed cancer diagnoses – all are a recipe for exhaustion for oncologists around the world, struggling to reach and treat their patients during the pandemic. Physicians and their teams felt the pain as COVID-19 took its initial march around the globe.
“We saw the distress of people with cancer who could no longer get to anyone on the phone. Their medical visit was usually canceled. Their radiotherapy session was postponed or modified, and chemotherapy postponed,” says Axel Kahn, MD, chairman of the board of directors of La Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (National League Against Cancer). “In the vast majority of cases, cancer treatment can be postponed or readjusted, without affecting the patient’s chances of survival, but there has been a lot of anxiety because the patients do not know that.”
The stay-at-home factor was one that played out across many months during the first wave.
“I believe that the ‘stay-home’ message that we transmitted was rigorously followed by patients who should have come to the emergency room much earlier and who, therefore, were admitted with a much more deteriorated general condition than in non-COVID-19 times,” says Benjamín Domingo Arrué, MD, from the department of medical oncology at Hospital Universitari i Politècnic La Fe in Valencia, Spain.
And in Brazil, some of the impact from the initial hit of COVID-19 on oncology is only now being felt, according to Laura Testa, MD, head of breast medical oncology, Instituto do Câncer do Estado de São Paulo.
“We are starting to see a lot of cancer cases that didn’t show up at the beginning of the pandemic, but now they are arriving to us already in advanced stages,” she said. “These patients need hospital care. If the situation worsens and goes back to what we saw at the peak of the curve, I fear the public system won’t be able to treat properly the oncology patients that need hospital care and the patients with cancer who also have COVID-19.”
But even as health care worker fatigue and concerns linger, oncologists say that what they have learned in the last 6 months has helped them prepare as COVID-19 cases increase and a second global wave kicks up.
Lessons from the first wave
In the United States, COVID-19 hit different regions at different times and to different degrees. One of the areas hit first was Seattle.
“We jumped on top of this, we were evidence based, we put things in place very, very quickly,” said Julie Gralow, MD, professor at the University of Washington and the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, both in Seattle.
“We did a really good job keeping COVID out of our cancer centers,” Dr. Gralow said. “We learned how to be super safe, and to keep symptomatic people out of the building, and to limit the extra people they could bring with them. It’s all about the number of contacts you have.”
The story was different, though, for oncologists in several other countries, and sometimes it varied immensely within each nation.
“We treated fewer patients with cancer during the first wave,” says Dirk Arnold, MD, medical director of the Asklepios Tumor Center Hamburg (Germany), in an interview. “In part, this was because staff were quarantined and because we had a completely different infrastructure in all of the hospitals. But also fewer patients with cancer came to the clinic at all. A lot of resources were directed toward COVID-19.”
In Spain, telemedicine helped keep up with visits, but other areas felt the effect of COVID-19 patient loads.
“At least in the oncology department of our center, we have practically maintained 100% of visits, mostly by telephone,” says Dr. Arrué, “but the reality is that our country has not yet been prepared for telemedicine.”
Laura Mezquita, MD, of the department of medical oncology at Hospital Clinic de Barcelona, describes a more dramatic situation: “We have seen how some of our patients, especially with metastatic disease, have been dismissed for intensive care and life-support treatments, as well as specific treatments against COVID-19 (tocilizumab, remdesivir, etc.) due to the general health collapse of the former wave,” she said. She adds that specific oncologic populations, such as those with thoracic tumors, have been more affected.
Distress among oncologists
Many oncologists are still feeling stressed and fatigued after the first wave, just as a second string of outbreaks is on its way.
A survey presented at last month’s ESMO 2020 Congress found that, in July-August, moral distress was reported by one-third of the oncologists who responded, and more than half reported a feeling of exhaustion.
“The tiredness and team exhaustion is noticeable,” said Dr. Arnold. “We recently had a task force discussion about what will happen when we have a second wave and how the department and our services will adapt. It was clear that those who were at the very front in the first wave had only a limited desire to do that again in the second wave.”
Another concern: COVID-19’s effect on staffing levels.
“We have a population of young caregivers who are affected by the COVID-19 disease with an absenteeism rate that is quite unprecedented,” said Sophie Beaupère, general delegate of Unicancer since January.
She said that, in general, the absenteeism rate in the cancer centers averages 5%-6%, depending on the year. But that rate is now skyrocketing.
Stop-start cycle for surgery
As caregivers quarantined around the world, more than 10% of patients with cancer had treatment canceled or delayed during the first wave of the pandemic, according to another survey from ESMO, involving 109 oncologists from 18 countries.
Difficulties were reported for surgeries by 34% of the centers, but also difficulties with delivering chemotherapy (22% of centers), radiotherapy (13.7%), and therapy with checkpoint inhibitors (9.1%), monoclonal antibodies (9%), and oral targeted therapy (3.7%).
Stopping surgery is a real concern in France, noted Dr. Kahn, the National League Against Cancer chair. He says that in regions that were badly hit by COVID-19, “it was not possible to have access to the operating room for people who absolutely needed surgery; for example, patients with lung cancer that was still operable. Most of the recovery rooms were mobilized for resuscitation.”
There may be some solutions, suggested Thierry Breton, director general of the National Institute of Cancer in France. “We are getting prepared, with the health ministry, for a possible increase in hospital tension, which would lead to a situation where we would have to reschedule operations. Nationally, regionally, and locally, we are seeing how we can resume and prioritize surgeries that have not been done.”
Delays in cancer diagnosis
While COVID-19 affected treatment, many oncologists say the major impact of the first wave was a delay in diagnosing cancer. Some of this was a result of the suspension of cancer screening programs, but there was also fear among the general public about visiting clinics and hospitals during a pandemic.
“We didn’t do so well with cancer during the first wave here in the U.K.,” said Karol Sikora, PhD, MBBChir, professor of cancer medicine and founding dean at the University of Buckingham Medical School, London. “Cancer diagnostic pathways virtually stalled partly because patients didn’t seek help, but getting scans and biopsies was also very difficult. Even patients referred urgently under the ‘2-weeks-wait’ rule were turned down.”
In France, “the delay in diagnosis is indisputable,” said Dr. Kahn. “About 50% of the cancer diagnoses one would expect during this period were missed.”
“I am worried that there remains a major traffic jam that has not been caught up with, and, in the meantime, the health crisis is worsening,” he added.
In Seattle, Dr. Gralow said the first COVID-19 wave had little impact on treatment for breast cancer, but it was in screening for breast cancer “where things really got messed up.”
“Even though we’ve been fully ramped up again,” she said, concerns remain. To ensure that screening mammography is maintained, “we have spaced out the visits to keep our waiting rooms less populated, with a longer time between using the machine so we can clean it. To do this, we have extended operating hours and are now opening on Saturday.
“So we’re actually at 100% of our capacity, but I’m really nervous, though, that a lot of people put off their screening mammogram and aren’t going to come in and get it.
“Not only did people get the message to stay home and not do nonessential things, but I think a lot of people lost their health insurance when they lost their jobs,” she said, and without health insurance, they are not covered for cancer screening.
Looking ahead, with a plan
Many oncologists agree that access to care can and must be improved – and there were some positive moves.
“Some regimens changed during the first months of the pandemic, and I don’t see them going back to the way they were anytime soon,” said Dr. Testa. “The changes/adaptations that were made to minimize the chance of SARS-CoV-2 infection are still in place and will go on for a while. In this context, telemedicine helped a lot. The pandemic forced the stakeholders to step up and put it in place in March. And now it’s here to stay.”
The experience gained in the last several months has driven preparation for the next wave.
“We are not going to see the disorganization that we saw during the first wave,” said Florence Joly, MD, PhD, head of medical oncology at the Centre François Baclesse in Caen, France. “The difference between now and earlier this year is that COVID diagnostic tests are available. That was one of the problems in the first wave. We had no way to diagnose.”
On the East Coast of the United States, medical oncologist Charu Aggarwal, MD, MPH, is also optimistic: “I think we’re at a place where we can manage.”
“I believe if there was going to be a new wave of COVID-19 cases we would be: better psychologically prepared and better organized,” said Dr. Aggarwal, assistant professor of medicine in the hematology-oncology division at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “We already have experience with all of the tools, we have telemedicine available, we have screening protocols available, we have testing, we are already universally masking, everyone’s hand-washing, so I do think that means we would be okay.”
Dr. Arnold agreed that “we are much better prepared than for the first wave, but … we have immense tasks in the area of patient management, the digitization of patient care, the clear allocation of resources when there is a second or third wave. In many areas of preparation, I believe, unfortunately, we are not as well positioned as we had actually hoped.”
The first wave of COVID hit cancer services in the United Kingdom particularly hard: One modeling study suggested that delays in cancer referrals will lead to thousands of additional deaths and tens of thousands of life-years lost.
“Cancer services are working at near normal levels now, but they are still fragile and could be severely compromised again if the NHS [National Health Service] gets flooded by COVID patients,” said Dr. Sikora.
The second wave may be different. “Although the number of infections has increased, the hospitalizations have only risen a little. Let’s see what happens,” he said in an interview. Since then, however, infections have continued to rise, and there has been an increase in hospitalizations. New social distancing measures in the United Kingdom were put into place on Oct. 12, with the aim of protecting the NHS from overload.
Dr. Arrué describes it this way: “The reality is that the ‘second wave’ has left behind the initial grief and shock that both patients and health professionals experienced when faced with something that, until now, we had only seen in the movies.” The second wave has led to new restrictions – including a partial lockdown since the beginning of October.
Dr. Aggarwal says her department recently had a conference with Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, about the impact of COVID-19 on oncology.
“I asked him what advice he’d give oncologists, and he said to go back to as much screening as you were doing previously as quickly as possible. That’s what must be relayed to our oncologists in the community – and also to primary care physicians – because they are often the ones who are ordering and championing the screening efforts.”
This article was originated by Aude Lecrubier, Medscape French edition, and developed by Zosia Chustecka, Medscape Oncology. With additional reporting by Kate Johnson, freelance medical journalist, Claudia Gottschling for Medscape Germany, Leoleli Schwartz for Medscape em português, Tim Locke for Medscape United Kingdom, and Carla Nieto Martínez, freelance medical journalist for Medscape Spanish edition.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Canceled appointments, postponed surgeries, and delayed cancer diagnoses – all are a recipe for exhaustion for oncologists around the world, struggling to reach and treat their patients during the pandemic. Physicians and their teams felt the pain as COVID-19 took its initial march around the globe.
“We saw the distress of people with cancer who could no longer get to anyone on the phone. Their medical visit was usually canceled. Their radiotherapy session was postponed or modified, and chemotherapy postponed,” says Axel Kahn, MD, chairman of the board of directors of La Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (National League Against Cancer). “In the vast majority of cases, cancer treatment can be postponed or readjusted, without affecting the patient’s chances of survival, but there has been a lot of anxiety because the patients do not know that.”
The stay-at-home factor was one that played out across many months during the first wave.
“I believe that the ‘stay-home’ message that we transmitted was rigorously followed by patients who should have come to the emergency room much earlier and who, therefore, were admitted with a much more deteriorated general condition than in non-COVID-19 times,” says Benjamín Domingo Arrué, MD, from the department of medical oncology at Hospital Universitari i Politècnic La Fe in Valencia, Spain.
And in Brazil, some of the impact from the initial hit of COVID-19 on oncology is only now being felt, according to Laura Testa, MD, head of breast medical oncology, Instituto do Câncer do Estado de São Paulo.
“We are starting to see a lot of cancer cases that didn’t show up at the beginning of the pandemic, but now they are arriving to us already in advanced stages,” she said. “These patients need hospital care. If the situation worsens and goes back to what we saw at the peak of the curve, I fear the public system won’t be able to treat properly the oncology patients that need hospital care and the patients with cancer who also have COVID-19.”
But even as health care worker fatigue and concerns linger, oncologists say that what they have learned in the last 6 months has helped them prepare as COVID-19 cases increase and a second global wave kicks up.
Lessons from the first wave
In the United States, COVID-19 hit different regions at different times and to different degrees. One of the areas hit first was Seattle.
“We jumped on top of this, we were evidence based, we put things in place very, very quickly,” said Julie Gralow, MD, professor at the University of Washington and the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, both in Seattle.
“We did a really good job keeping COVID out of our cancer centers,” Dr. Gralow said. “We learned how to be super safe, and to keep symptomatic people out of the building, and to limit the extra people they could bring with them. It’s all about the number of contacts you have.”
The story was different, though, for oncologists in several other countries, and sometimes it varied immensely within each nation.
“We treated fewer patients with cancer during the first wave,” says Dirk Arnold, MD, medical director of the Asklepios Tumor Center Hamburg (Germany), in an interview. “In part, this was because staff were quarantined and because we had a completely different infrastructure in all of the hospitals. But also fewer patients with cancer came to the clinic at all. A lot of resources were directed toward COVID-19.”
In Spain, telemedicine helped keep up with visits, but other areas felt the effect of COVID-19 patient loads.
“At least in the oncology department of our center, we have practically maintained 100% of visits, mostly by telephone,” says Dr. Arrué, “but the reality is that our country has not yet been prepared for telemedicine.”
Laura Mezquita, MD, of the department of medical oncology at Hospital Clinic de Barcelona, describes a more dramatic situation: “We have seen how some of our patients, especially with metastatic disease, have been dismissed for intensive care and life-support treatments, as well as specific treatments against COVID-19 (tocilizumab, remdesivir, etc.) due to the general health collapse of the former wave,” she said. She adds that specific oncologic populations, such as those with thoracic tumors, have been more affected.
Distress among oncologists
Many oncologists are still feeling stressed and fatigued after the first wave, just as a second string of outbreaks is on its way.
A survey presented at last month’s ESMO 2020 Congress found that, in July-August, moral distress was reported by one-third of the oncologists who responded, and more than half reported a feeling of exhaustion.
“The tiredness and team exhaustion is noticeable,” said Dr. Arnold. “We recently had a task force discussion about what will happen when we have a second wave and how the department and our services will adapt. It was clear that those who were at the very front in the first wave had only a limited desire to do that again in the second wave.”
Another concern: COVID-19’s effect on staffing levels.
“We have a population of young caregivers who are affected by the COVID-19 disease with an absenteeism rate that is quite unprecedented,” said Sophie Beaupère, general delegate of Unicancer since January.
She said that, in general, the absenteeism rate in the cancer centers averages 5%-6%, depending on the year. But that rate is now skyrocketing.
Stop-start cycle for surgery
As caregivers quarantined around the world, more than 10% of patients with cancer had treatment canceled or delayed during the first wave of the pandemic, according to another survey from ESMO, involving 109 oncologists from 18 countries.
Difficulties were reported for surgeries by 34% of the centers, but also difficulties with delivering chemotherapy (22% of centers), radiotherapy (13.7%), and therapy with checkpoint inhibitors (9.1%), monoclonal antibodies (9%), and oral targeted therapy (3.7%).
Stopping surgery is a real concern in France, noted Dr. Kahn, the National League Against Cancer chair. He says that in regions that were badly hit by COVID-19, “it was not possible to have access to the operating room for people who absolutely needed surgery; for example, patients with lung cancer that was still operable. Most of the recovery rooms were mobilized for resuscitation.”
There may be some solutions, suggested Thierry Breton, director general of the National Institute of Cancer in France. “We are getting prepared, with the health ministry, for a possible increase in hospital tension, which would lead to a situation where we would have to reschedule operations. Nationally, regionally, and locally, we are seeing how we can resume and prioritize surgeries that have not been done.”
Delays in cancer diagnosis
While COVID-19 affected treatment, many oncologists say the major impact of the first wave was a delay in diagnosing cancer. Some of this was a result of the suspension of cancer screening programs, but there was also fear among the general public about visiting clinics and hospitals during a pandemic.
“We didn’t do so well with cancer during the first wave here in the U.K.,” said Karol Sikora, PhD, MBBChir, professor of cancer medicine and founding dean at the University of Buckingham Medical School, London. “Cancer diagnostic pathways virtually stalled partly because patients didn’t seek help, but getting scans and biopsies was also very difficult. Even patients referred urgently under the ‘2-weeks-wait’ rule were turned down.”
In France, “the delay in diagnosis is indisputable,” said Dr. Kahn. “About 50% of the cancer diagnoses one would expect during this period were missed.”
“I am worried that there remains a major traffic jam that has not been caught up with, and, in the meantime, the health crisis is worsening,” he added.
In Seattle, Dr. Gralow said the first COVID-19 wave had little impact on treatment for breast cancer, but it was in screening for breast cancer “where things really got messed up.”
“Even though we’ve been fully ramped up again,” she said, concerns remain. To ensure that screening mammography is maintained, “we have spaced out the visits to keep our waiting rooms less populated, with a longer time between using the machine so we can clean it. To do this, we have extended operating hours and are now opening on Saturday.
“So we’re actually at 100% of our capacity, but I’m really nervous, though, that a lot of people put off their screening mammogram and aren’t going to come in and get it.
“Not only did people get the message to stay home and not do nonessential things, but I think a lot of people lost their health insurance when they lost their jobs,” she said, and without health insurance, they are not covered for cancer screening.
Looking ahead, with a plan
Many oncologists agree that access to care can and must be improved – and there were some positive moves.
“Some regimens changed during the first months of the pandemic, and I don’t see them going back to the way they were anytime soon,” said Dr. Testa. “The changes/adaptations that were made to minimize the chance of SARS-CoV-2 infection are still in place and will go on for a while. In this context, telemedicine helped a lot. The pandemic forced the stakeholders to step up and put it in place in March. And now it’s here to stay.”
The experience gained in the last several months has driven preparation for the next wave.
“We are not going to see the disorganization that we saw during the first wave,” said Florence Joly, MD, PhD, head of medical oncology at the Centre François Baclesse in Caen, France. “The difference between now and earlier this year is that COVID diagnostic tests are available. That was one of the problems in the first wave. We had no way to diagnose.”
On the East Coast of the United States, medical oncologist Charu Aggarwal, MD, MPH, is also optimistic: “I think we’re at a place where we can manage.”
“I believe if there was going to be a new wave of COVID-19 cases we would be: better psychologically prepared and better organized,” said Dr. Aggarwal, assistant professor of medicine in the hematology-oncology division at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “We already have experience with all of the tools, we have telemedicine available, we have screening protocols available, we have testing, we are already universally masking, everyone’s hand-washing, so I do think that means we would be okay.”
Dr. Arnold agreed that “we are much better prepared than for the first wave, but … we have immense tasks in the area of patient management, the digitization of patient care, the clear allocation of resources when there is a second or third wave. In many areas of preparation, I believe, unfortunately, we are not as well positioned as we had actually hoped.”
The first wave of COVID hit cancer services in the United Kingdom particularly hard: One modeling study suggested that delays in cancer referrals will lead to thousands of additional deaths and tens of thousands of life-years lost.
“Cancer services are working at near normal levels now, but they are still fragile and could be severely compromised again if the NHS [National Health Service] gets flooded by COVID patients,” said Dr. Sikora.
The second wave may be different. “Although the number of infections has increased, the hospitalizations have only risen a little. Let’s see what happens,” he said in an interview. Since then, however, infections have continued to rise, and there has been an increase in hospitalizations. New social distancing measures in the United Kingdom were put into place on Oct. 12, with the aim of protecting the NHS from overload.
Dr. Arrué describes it this way: “The reality is that the ‘second wave’ has left behind the initial grief and shock that both patients and health professionals experienced when faced with something that, until now, we had only seen in the movies.” The second wave has led to new restrictions – including a partial lockdown since the beginning of October.
Dr. Aggarwal says her department recently had a conference with Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, about the impact of COVID-19 on oncology.
“I asked him what advice he’d give oncologists, and he said to go back to as much screening as you were doing previously as quickly as possible. That’s what must be relayed to our oncologists in the community – and also to primary care physicians – because they are often the ones who are ordering and championing the screening efforts.”
This article was originated by Aude Lecrubier, Medscape French edition, and developed by Zosia Chustecka, Medscape Oncology. With additional reporting by Kate Johnson, freelance medical journalist, Claudia Gottschling for Medscape Germany, Leoleli Schwartz for Medscape em português, Tim Locke for Medscape United Kingdom, and Carla Nieto Martínez, freelance medical journalist for Medscape Spanish edition.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Canceled appointments, postponed surgeries, and delayed cancer diagnoses – all are a recipe for exhaustion for oncologists around the world, struggling to reach and treat their patients during the pandemic. Physicians and their teams felt the pain as COVID-19 took its initial march around the globe.
“We saw the distress of people with cancer who could no longer get to anyone on the phone. Their medical visit was usually canceled. Their radiotherapy session was postponed or modified, and chemotherapy postponed,” says Axel Kahn, MD, chairman of the board of directors of La Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (National League Against Cancer). “In the vast majority of cases, cancer treatment can be postponed or readjusted, without affecting the patient’s chances of survival, but there has been a lot of anxiety because the patients do not know that.”
The stay-at-home factor was one that played out across many months during the first wave.
“I believe that the ‘stay-home’ message that we transmitted was rigorously followed by patients who should have come to the emergency room much earlier and who, therefore, were admitted with a much more deteriorated general condition than in non-COVID-19 times,” says Benjamín Domingo Arrué, MD, from the department of medical oncology at Hospital Universitari i Politècnic La Fe in Valencia, Spain.
And in Brazil, some of the impact from the initial hit of COVID-19 on oncology is only now being felt, according to Laura Testa, MD, head of breast medical oncology, Instituto do Câncer do Estado de São Paulo.
“We are starting to see a lot of cancer cases that didn’t show up at the beginning of the pandemic, but now they are arriving to us already in advanced stages,” she said. “These patients need hospital care. If the situation worsens and goes back to what we saw at the peak of the curve, I fear the public system won’t be able to treat properly the oncology patients that need hospital care and the patients with cancer who also have COVID-19.”
But even as health care worker fatigue and concerns linger, oncologists say that what they have learned in the last 6 months has helped them prepare as COVID-19 cases increase and a second global wave kicks up.
Lessons from the first wave
In the United States, COVID-19 hit different regions at different times and to different degrees. One of the areas hit first was Seattle.
“We jumped on top of this, we were evidence based, we put things in place very, very quickly,” said Julie Gralow, MD, professor at the University of Washington and the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, both in Seattle.
“We did a really good job keeping COVID out of our cancer centers,” Dr. Gralow said. “We learned how to be super safe, and to keep symptomatic people out of the building, and to limit the extra people they could bring with them. It’s all about the number of contacts you have.”
The story was different, though, for oncologists in several other countries, and sometimes it varied immensely within each nation.
“We treated fewer patients with cancer during the first wave,” says Dirk Arnold, MD, medical director of the Asklepios Tumor Center Hamburg (Germany), in an interview. “In part, this was because staff were quarantined and because we had a completely different infrastructure in all of the hospitals. But also fewer patients with cancer came to the clinic at all. A lot of resources were directed toward COVID-19.”
In Spain, telemedicine helped keep up with visits, but other areas felt the effect of COVID-19 patient loads.
“At least in the oncology department of our center, we have practically maintained 100% of visits, mostly by telephone,” says Dr. Arrué, “but the reality is that our country has not yet been prepared for telemedicine.”
Laura Mezquita, MD, of the department of medical oncology at Hospital Clinic de Barcelona, describes a more dramatic situation: “We have seen how some of our patients, especially with metastatic disease, have been dismissed for intensive care and life-support treatments, as well as specific treatments against COVID-19 (tocilizumab, remdesivir, etc.) due to the general health collapse of the former wave,” she said. She adds that specific oncologic populations, such as those with thoracic tumors, have been more affected.
Distress among oncologists
Many oncologists are still feeling stressed and fatigued after the first wave, just as a second string of outbreaks is on its way.
A survey presented at last month’s ESMO 2020 Congress found that, in July-August, moral distress was reported by one-third of the oncologists who responded, and more than half reported a feeling of exhaustion.
“The tiredness and team exhaustion is noticeable,” said Dr. Arnold. “We recently had a task force discussion about what will happen when we have a second wave and how the department and our services will adapt. It was clear that those who were at the very front in the first wave had only a limited desire to do that again in the second wave.”
Another concern: COVID-19’s effect on staffing levels.
“We have a population of young caregivers who are affected by the COVID-19 disease with an absenteeism rate that is quite unprecedented,” said Sophie Beaupère, general delegate of Unicancer since January.
She said that, in general, the absenteeism rate in the cancer centers averages 5%-6%, depending on the year. But that rate is now skyrocketing.
Stop-start cycle for surgery
As caregivers quarantined around the world, more than 10% of patients with cancer had treatment canceled or delayed during the first wave of the pandemic, according to another survey from ESMO, involving 109 oncologists from 18 countries.
Difficulties were reported for surgeries by 34% of the centers, but also difficulties with delivering chemotherapy (22% of centers), radiotherapy (13.7%), and therapy with checkpoint inhibitors (9.1%), monoclonal antibodies (9%), and oral targeted therapy (3.7%).
Stopping surgery is a real concern in France, noted Dr. Kahn, the National League Against Cancer chair. He says that in regions that were badly hit by COVID-19, “it was not possible to have access to the operating room for people who absolutely needed surgery; for example, patients with lung cancer that was still operable. Most of the recovery rooms were mobilized for resuscitation.”
There may be some solutions, suggested Thierry Breton, director general of the National Institute of Cancer in France. “We are getting prepared, with the health ministry, for a possible increase in hospital tension, which would lead to a situation where we would have to reschedule operations. Nationally, regionally, and locally, we are seeing how we can resume and prioritize surgeries that have not been done.”
Delays in cancer diagnosis
While COVID-19 affected treatment, many oncologists say the major impact of the first wave was a delay in diagnosing cancer. Some of this was a result of the suspension of cancer screening programs, but there was also fear among the general public about visiting clinics and hospitals during a pandemic.
“We didn’t do so well with cancer during the first wave here in the U.K.,” said Karol Sikora, PhD, MBBChir, professor of cancer medicine and founding dean at the University of Buckingham Medical School, London. “Cancer diagnostic pathways virtually stalled partly because patients didn’t seek help, but getting scans and biopsies was also very difficult. Even patients referred urgently under the ‘2-weeks-wait’ rule were turned down.”
In France, “the delay in diagnosis is indisputable,” said Dr. Kahn. “About 50% of the cancer diagnoses one would expect during this period were missed.”
“I am worried that there remains a major traffic jam that has not been caught up with, and, in the meantime, the health crisis is worsening,” he added.
In Seattle, Dr. Gralow said the first COVID-19 wave had little impact on treatment for breast cancer, but it was in screening for breast cancer “where things really got messed up.”
“Even though we’ve been fully ramped up again,” she said, concerns remain. To ensure that screening mammography is maintained, “we have spaced out the visits to keep our waiting rooms less populated, with a longer time between using the machine so we can clean it. To do this, we have extended operating hours and are now opening on Saturday.
“So we’re actually at 100% of our capacity, but I’m really nervous, though, that a lot of people put off their screening mammogram and aren’t going to come in and get it.
“Not only did people get the message to stay home and not do nonessential things, but I think a lot of people lost their health insurance when they lost their jobs,” she said, and without health insurance, they are not covered for cancer screening.
Looking ahead, with a plan
Many oncologists agree that access to care can and must be improved – and there were some positive moves.
“Some regimens changed during the first months of the pandemic, and I don’t see them going back to the way they were anytime soon,” said Dr. Testa. “The changes/adaptations that were made to minimize the chance of SARS-CoV-2 infection are still in place and will go on for a while. In this context, telemedicine helped a lot. The pandemic forced the stakeholders to step up and put it in place in March. And now it’s here to stay.”
The experience gained in the last several months has driven preparation for the next wave.
“We are not going to see the disorganization that we saw during the first wave,” said Florence Joly, MD, PhD, head of medical oncology at the Centre François Baclesse in Caen, France. “The difference between now and earlier this year is that COVID diagnostic tests are available. That was one of the problems in the first wave. We had no way to diagnose.”
On the East Coast of the United States, medical oncologist Charu Aggarwal, MD, MPH, is also optimistic: “I think we’re at a place where we can manage.”
“I believe if there was going to be a new wave of COVID-19 cases we would be: better psychologically prepared and better organized,” said Dr. Aggarwal, assistant professor of medicine in the hematology-oncology division at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “We already have experience with all of the tools, we have telemedicine available, we have screening protocols available, we have testing, we are already universally masking, everyone’s hand-washing, so I do think that means we would be okay.”
Dr. Arnold agreed that “we are much better prepared than for the first wave, but … we have immense tasks in the area of patient management, the digitization of patient care, the clear allocation of resources when there is a second or third wave. In many areas of preparation, I believe, unfortunately, we are not as well positioned as we had actually hoped.”
The first wave of COVID hit cancer services in the United Kingdom particularly hard: One modeling study suggested that delays in cancer referrals will lead to thousands of additional deaths and tens of thousands of life-years lost.
“Cancer services are working at near normal levels now, but they are still fragile and could be severely compromised again if the NHS [National Health Service] gets flooded by COVID patients,” said Dr. Sikora.
The second wave may be different. “Although the number of infections has increased, the hospitalizations have only risen a little. Let’s see what happens,” he said in an interview. Since then, however, infections have continued to rise, and there has been an increase in hospitalizations. New social distancing measures in the United Kingdom were put into place on Oct. 12, with the aim of protecting the NHS from overload.
Dr. Arrué describes it this way: “The reality is that the ‘second wave’ has left behind the initial grief and shock that both patients and health professionals experienced when faced with something that, until now, we had only seen in the movies.” The second wave has led to new restrictions – including a partial lockdown since the beginning of October.
Dr. Aggarwal says her department recently had a conference with Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, about the impact of COVID-19 on oncology.
“I asked him what advice he’d give oncologists, and he said to go back to as much screening as you were doing previously as quickly as possible. That’s what must be relayed to our oncologists in the community – and also to primary care physicians – because they are often the ones who are ordering and championing the screening efforts.”
This article was originated by Aude Lecrubier, Medscape French edition, and developed by Zosia Chustecka, Medscape Oncology. With additional reporting by Kate Johnson, freelance medical journalist, Claudia Gottschling for Medscape Germany, Leoleli Schwartz for Medscape em português, Tim Locke for Medscape United Kingdom, and Carla Nieto Martínez, freelance medical journalist for Medscape Spanish edition.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ESMO offers new clinical practice guideline for CLL
An updated European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) clinical practice guidelines were released to provide key recommendations on the management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
The guidelines were developed by a multidisciplinary group of experts from different institutions and countries in Europe and provide levels of evidence and grades of recommendation where applicable for issues regarding prognosis and treatment decisions in CLL. Such decisions depend on genetic and clinical factors such as age, stage, and comorbidities. The guidelines also focus on new therapies targeting B-cell-receptor pathways or defect mechanism of apoptosis, which have been found to induce long-lasting remissions. The guidelines were endorsed by the European Hematology Association (EHA) through the Scientific Working Group on CLL/European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC), according to the report published online the Annals of Oncology.
These clinical practice guidelines were developed in accordance with the ESMO standard operating procedures for clinical practice guidelines development with use of relevant literature selected by the expert authors. Statements without grading were considered justified as standard clinical practice by the experts and the ESMO faculty.
Below are some highlights of the guidelines, which cover a wide array of topics regarding the diagnosis, staging, treatment, and progression of CLL disease.
Diagnosis
The guidelines indicate that CLL diagnosis is usually possible by immunophenotyping of peripheral blood only and that lymph node (LN) biopsy and/or bone marrow biopsy may be helpful if immunophenotyping is not conclusive for the diagnosis of CLL, according to Barbara Eichhorst, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany) and colleagues on behalf of the ESMO guidelines committee.
Staging and risk assessment
Early asymptomatic-stage disease does not need further risk assessment, but after the first year, when all patients should be seen at 3-monthly intervals, patients can be followed every 3-12 months. The interval would depend on burden and dynamics of the disease obtained by the using history and physical examinations, including a careful palpation of all LN areas, spleen, and liver, as well as assessing complete blood cell count and differential count, according to the report.
Advanced- and symptomatic-stage disease requires a broader examination including imaging, history and status of relevant infections, and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) assays for the detection of deletion of the chromosome 17 (del[17p]) affecting the tumor protein p53 expression and, in the absence of del(17p), TP53 sequencing for detection of TP53 gene mutation, according to the authors.
Prognostication
Two clinical staging systems are typically used in CLL. Both Binet and Rai staging systems separate three groups of patients with different prognosis, although “as a consequence of more effective therapy, the overall survival (OS) of patients with advanced stage has improved and the relevance of the staging systems for prognostication has decreased,” according to the report.
The recent addition of genetic markers has also proved highly relevant to identifying patients with different prognoses and to guide treatment.
Therapy
Although CLL is an incurable disease, choice and application of treatment are strongly tied to the length of survival, according to the authors. The guidelines recommend Binet and Rai staging with clinical symptoms as relevant for treatment indication. In addition, the identification of del(17p), TP53 mutations, and IGHV status are relevant for choice of therapy and should be assessed prior to treatment.
The guidelines discuss specific treatment modalities for various stages of the disease, from early stages to relapse.
For frontline therapy, different treatment strategies are available including continuous treatment with Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)–inhibitors, such as ibrutinib, until progression or time-limited therapy with ChT backbone and CD20 antibodies. In addition, the Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency have recently approved the combination of venetoclax plus obinutuzumab for first-line therapy of CLL.
Treatment decisions should include an assessment of IGHV and TP53 status, as well as patient-related factors such as comedication, comorbidities, preferences, drug availability, and potential of treatment adherence, according to the guidelines.
In case of symptomatic relapse within 3 years after fixed-duration therapy or nonresponse to therapy, the guidelines recommend that the therapeutic regimen should be changed, regardless of the type of first-line either to venetoclax plus rituximab for 24 months or to ibrutinib, acalabrutinib, or other BTK inhibitors (if available) as continuous therapy.
The guidelines also discuss the possible roles for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and cellular therapies, as well as the treatment of the various complications that can arise in patients with CLL, and dealing with various aspects of disease progression.
No external funds were provided for the production of the guidelines. The authors of the report and members of the ESMO Guidelines Committee reported numerous disclosures regarding pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
SOURCE: Eichhorst B et al. Ann Oncol. 2020 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.09.019.
An updated European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) clinical practice guidelines were released to provide key recommendations on the management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
The guidelines were developed by a multidisciplinary group of experts from different institutions and countries in Europe and provide levels of evidence and grades of recommendation where applicable for issues regarding prognosis and treatment decisions in CLL. Such decisions depend on genetic and clinical factors such as age, stage, and comorbidities. The guidelines also focus on new therapies targeting B-cell-receptor pathways or defect mechanism of apoptosis, which have been found to induce long-lasting remissions. The guidelines were endorsed by the European Hematology Association (EHA) through the Scientific Working Group on CLL/European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC), according to the report published online the Annals of Oncology.
These clinical practice guidelines were developed in accordance with the ESMO standard operating procedures for clinical practice guidelines development with use of relevant literature selected by the expert authors. Statements without grading were considered justified as standard clinical practice by the experts and the ESMO faculty.
Below are some highlights of the guidelines, which cover a wide array of topics regarding the diagnosis, staging, treatment, and progression of CLL disease.
Diagnosis
The guidelines indicate that CLL diagnosis is usually possible by immunophenotyping of peripheral blood only and that lymph node (LN) biopsy and/or bone marrow biopsy may be helpful if immunophenotyping is not conclusive for the diagnosis of CLL, according to Barbara Eichhorst, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany) and colleagues on behalf of the ESMO guidelines committee.
Staging and risk assessment
Early asymptomatic-stage disease does not need further risk assessment, but after the first year, when all patients should be seen at 3-monthly intervals, patients can be followed every 3-12 months. The interval would depend on burden and dynamics of the disease obtained by the using history and physical examinations, including a careful palpation of all LN areas, spleen, and liver, as well as assessing complete blood cell count and differential count, according to the report.
Advanced- and symptomatic-stage disease requires a broader examination including imaging, history and status of relevant infections, and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) assays for the detection of deletion of the chromosome 17 (del[17p]) affecting the tumor protein p53 expression and, in the absence of del(17p), TP53 sequencing for detection of TP53 gene mutation, according to the authors.
Prognostication
Two clinical staging systems are typically used in CLL. Both Binet and Rai staging systems separate three groups of patients with different prognosis, although “as a consequence of more effective therapy, the overall survival (OS) of patients with advanced stage has improved and the relevance of the staging systems for prognostication has decreased,” according to the report.
The recent addition of genetic markers has also proved highly relevant to identifying patients with different prognoses and to guide treatment.
Therapy
Although CLL is an incurable disease, choice and application of treatment are strongly tied to the length of survival, according to the authors. The guidelines recommend Binet and Rai staging with clinical symptoms as relevant for treatment indication. In addition, the identification of del(17p), TP53 mutations, and IGHV status are relevant for choice of therapy and should be assessed prior to treatment.
The guidelines discuss specific treatment modalities for various stages of the disease, from early stages to relapse.
For frontline therapy, different treatment strategies are available including continuous treatment with Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)–inhibitors, such as ibrutinib, until progression or time-limited therapy with ChT backbone and CD20 antibodies. In addition, the Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency have recently approved the combination of venetoclax plus obinutuzumab for first-line therapy of CLL.
Treatment decisions should include an assessment of IGHV and TP53 status, as well as patient-related factors such as comedication, comorbidities, preferences, drug availability, and potential of treatment adherence, according to the guidelines.
In case of symptomatic relapse within 3 years after fixed-duration therapy or nonresponse to therapy, the guidelines recommend that the therapeutic regimen should be changed, regardless of the type of first-line either to venetoclax plus rituximab for 24 months or to ibrutinib, acalabrutinib, or other BTK inhibitors (if available) as continuous therapy.
The guidelines also discuss the possible roles for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and cellular therapies, as well as the treatment of the various complications that can arise in patients with CLL, and dealing with various aspects of disease progression.
No external funds were provided for the production of the guidelines. The authors of the report and members of the ESMO Guidelines Committee reported numerous disclosures regarding pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
SOURCE: Eichhorst B et al. Ann Oncol. 2020 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.09.019.
An updated European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) clinical practice guidelines were released to provide key recommendations on the management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
The guidelines were developed by a multidisciplinary group of experts from different institutions and countries in Europe and provide levels of evidence and grades of recommendation where applicable for issues regarding prognosis and treatment decisions in CLL. Such decisions depend on genetic and clinical factors such as age, stage, and comorbidities. The guidelines also focus on new therapies targeting B-cell-receptor pathways or defect mechanism of apoptosis, which have been found to induce long-lasting remissions. The guidelines were endorsed by the European Hematology Association (EHA) through the Scientific Working Group on CLL/European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC), according to the report published online the Annals of Oncology.
These clinical practice guidelines were developed in accordance with the ESMO standard operating procedures for clinical practice guidelines development with use of relevant literature selected by the expert authors. Statements without grading were considered justified as standard clinical practice by the experts and the ESMO faculty.
Below are some highlights of the guidelines, which cover a wide array of topics regarding the diagnosis, staging, treatment, and progression of CLL disease.
Diagnosis
The guidelines indicate that CLL diagnosis is usually possible by immunophenotyping of peripheral blood only and that lymph node (LN) biopsy and/or bone marrow biopsy may be helpful if immunophenotyping is not conclusive for the diagnosis of CLL, according to Barbara Eichhorst, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany) and colleagues on behalf of the ESMO guidelines committee.
Staging and risk assessment
Early asymptomatic-stage disease does not need further risk assessment, but after the first year, when all patients should be seen at 3-monthly intervals, patients can be followed every 3-12 months. The interval would depend on burden and dynamics of the disease obtained by the using history and physical examinations, including a careful palpation of all LN areas, spleen, and liver, as well as assessing complete blood cell count and differential count, according to the report.
Advanced- and symptomatic-stage disease requires a broader examination including imaging, history and status of relevant infections, and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) assays for the detection of deletion of the chromosome 17 (del[17p]) affecting the tumor protein p53 expression and, in the absence of del(17p), TP53 sequencing for detection of TP53 gene mutation, according to the authors.
Prognostication
Two clinical staging systems are typically used in CLL. Both Binet and Rai staging systems separate three groups of patients with different prognosis, although “as a consequence of more effective therapy, the overall survival (OS) of patients with advanced stage has improved and the relevance of the staging systems for prognostication has decreased,” according to the report.
The recent addition of genetic markers has also proved highly relevant to identifying patients with different prognoses and to guide treatment.
Therapy
Although CLL is an incurable disease, choice and application of treatment are strongly tied to the length of survival, according to the authors. The guidelines recommend Binet and Rai staging with clinical symptoms as relevant for treatment indication. In addition, the identification of del(17p), TP53 mutations, and IGHV status are relevant for choice of therapy and should be assessed prior to treatment.
The guidelines discuss specific treatment modalities for various stages of the disease, from early stages to relapse.
For frontline therapy, different treatment strategies are available including continuous treatment with Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)–inhibitors, such as ibrutinib, until progression or time-limited therapy with ChT backbone and CD20 antibodies. In addition, the Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency have recently approved the combination of venetoclax plus obinutuzumab for first-line therapy of CLL.
Treatment decisions should include an assessment of IGHV and TP53 status, as well as patient-related factors such as comedication, comorbidities, preferences, drug availability, and potential of treatment adherence, according to the guidelines.
In case of symptomatic relapse within 3 years after fixed-duration therapy or nonresponse to therapy, the guidelines recommend that the therapeutic regimen should be changed, regardless of the type of first-line either to venetoclax plus rituximab for 24 months or to ibrutinib, acalabrutinib, or other BTK inhibitors (if available) as continuous therapy.
The guidelines also discuss the possible roles for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and cellular therapies, as well as the treatment of the various complications that can arise in patients with CLL, and dealing with various aspects of disease progression.
No external funds were provided for the production of the guidelines. The authors of the report and members of the ESMO Guidelines Committee reported numerous disclosures regarding pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
SOURCE: Eichhorst B et al. Ann Oncol. 2020 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.09.019.
FROM ANNALS OF ONCOLOGY
Can AML patients be too old for cell transplantation?
How old is too old for a patient to undergo hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)? That’s the wrong question to ask, a hematologist/oncologist told colleagues at the virtual Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus. Instead, he said, look at other factors such as disease status and genetics.
“Transplantation for older patients, even beyond the age of 70, is acceptable, as long as it’s done with caution, care, and wisdom. So we’re all not too old for transplantation, at least not today,” said Daniel Weisdorf, MD, professor of medicine and deputy director of the University of Minnesota Clinical and Translational Science Institute.
As he noted, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is often fatal. Among the general population, “the expected survival life expectancy at age 75 is 98% at 1 year, and most people living at 75 go on to live more than 10 years,” he said. “But if you have AML, at age 75, you have 20% survival at 1 year, 4% at 3 years. And since the median age of AML diagnosis is 68, and 75% of patients are diagnosed beyond the age of 55, this becomes relevant.”
Risk factors that affect survival after transplantation “certainly include age, but that interacts directly with the comorbidities people accumulate with age, their assessments of frailty, and their Karnofsky performance status, as well as the disease phenotype and molecular genetic markers,” Dr. Weisdorf said. “Perhaps most importantly, though not addressed very much, is patients’ willingness to undertake intensive therapy and their life outlook related to patient-reported outcomes when they get older.”
Despite the lack of indications that higher age by itself is an influential factor in survival after transplant, “we are generally reluctant to push the age of eligibility,” Dr. Weisdorf said. He noted that recently published American Society of Hematology guidelines for treatment of AML over the age of 55 “don’t discuss anything about transplantation fitness because they didn’t want to tackle that.”
Overall survival (OS) at 1 year after allogenic transplants only dipped slightly from ages 51-60 to 71 and above, according to Dr. Weisdorf’s analysis of U.S. data collected by the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research for the time period 2005-2019.
OS was 67.6% (66.8%-68.3%) for the 41-50 age group (n = 9,287) and 57.9% (56.1%-59.8%) for the 71 and older group, Dr. Weisdorf found. Overall, OS dropped by about 4 percentage points per decade of age, he said, revealing a “modest influence” of advancing years.
His analysis of autologous transplant data from the same source, also for 2005-2019, revealed “essentially no age influence.” OS was 90.8% (90.3%-91.2%) for the 41-50 age group (n = 15,075) and 86.6% (85.9%-87.3%) for the 71 and older group (n = 7,247).
Dr. Weisdorf also highlighted unpublished research that suggests that cord-blood transplant recipients older than 70 face a significantly higher risk of death than that of younger patients in the same category. Cord blood “may be option of last resort” because of a lack of other options, he explained. “And it may be part of the learning curve of cord blood transplantation, which grew a little bit in the early 2000s, and maybe past 2010, and then fell off as everybody got enamored with the haploidentical transplant option.”
How can physicians make decisions about transplants in older patients? “The transplant comorbidity index, the specific comorbidities themselves, performance score, and frailty are all measures of somebody’s fitness to be a good candidate for transplant, really at any age,” Dr. Weisdorf said. “But we also have to recognize that disease status, genetics, and the risk phenotype remain critical and should influence decision making.”
However, even as transplant survival improves overall, “very few people are incorporating any very specific biological markers” in decision-making, he said. “We’ve gotten to measures of frailty, but we haven’t gotten to any biologic measures of cytokines or other things that would predict poor chances for doing well. So I’m afraid we’re still standing at the foot of the bed saying: ‘You look okay.’ Or we’re measuring their comorbidity index. But it is disappointing that we’re using mostly very simple clinical measures to decide if somebody is sturdy enough to proceed, and we perhaps need something better. But I don’t have a great suggestion what it should be.”
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
Dr. Weisdorf disclosed consulting fees from Fate Therapeutics and Incyte Corp.
SOURCE: “The Ever-Increasing Upper Age for Transplant: Is This Evidence-Based?” Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus, Oct. 15, 2020.
How old is too old for a patient to undergo hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)? That’s the wrong question to ask, a hematologist/oncologist told colleagues at the virtual Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus. Instead, he said, look at other factors such as disease status and genetics.
“Transplantation for older patients, even beyond the age of 70, is acceptable, as long as it’s done with caution, care, and wisdom. So we’re all not too old for transplantation, at least not today,” said Daniel Weisdorf, MD, professor of medicine and deputy director of the University of Minnesota Clinical and Translational Science Institute.
As he noted, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is often fatal. Among the general population, “the expected survival life expectancy at age 75 is 98% at 1 year, and most people living at 75 go on to live more than 10 years,” he said. “But if you have AML, at age 75, you have 20% survival at 1 year, 4% at 3 years. And since the median age of AML diagnosis is 68, and 75% of patients are diagnosed beyond the age of 55, this becomes relevant.”
Risk factors that affect survival after transplantation “certainly include age, but that interacts directly with the comorbidities people accumulate with age, their assessments of frailty, and their Karnofsky performance status, as well as the disease phenotype and molecular genetic markers,” Dr. Weisdorf said. “Perhaps most importantly, though not addressed very much, is patients’ willingness to undertake intensive therapy and their life outlook related to patient-reported outcomes when they get older.”
Despite the lack of indications that higher age by itself is an influential factor in survival after transplant, “we are generally reluctant to push the age of eligibility,” Dr. Weisdorf said. He noted that recently published American Society of Hematology guidelines for treatment of AML over the age of 55 “don’t discuss anything about transplantation fitness because they didn’t want to tackle that.”
Overall survival (OS) at 1 year after allogenic transplants only dipped slightly from ages 51-60 to 71 and above, according to Dr. Weisdorf’s analysis of U.S. data collected by the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research for the time period 2005-2019.
OS was 67.6% (66.8%-68.3%) for the 41-50 age group (n = 9,287) and 57.9% (56.1%-59.8%) for the 71 and older group, Dr. Weisdorf found. Overall, OS dropped by about 4 percentage points per decade of age, he said, revealing a “modest influence” of advancing years.
His analysis of autologous transplant data from the same source, also for 2005-2019, revealed “essentially no age influence.” OS was 90.8% (90.3%-91.2%) for the 41-50 age group (n = 15,075) and 86.6% (85.9%-87.3%) for the 71 and older group (n = 7,247).
Dr. Weisdorf also highlighted unpublished research that suggests that cord-blood transplant recipients older than 70 face a significantly higher risk of death than that of younger patients in the same category. Cord blood “may be option of last resort” because of a lack of other options, he explained. “And it may be part of the learning curve of cord blood transplantation, which grew a little bit in the early 2000s, and maybe past 2010, and then fell off as everybody got enamored with the haploidentical transplant option.”
How can physicians make decisions about transplants in older patients? “The transplant comorbidity index, the specific comorbidities themselves, performance score, and frailty are all measures of somebody’s fitness to be a good candidate for transplant, really at any age,” Dr. Weisdorf said. “But we also have to recognize that disease status, genetics, and the risk phenotype remain critical and should influence decision making.”
However, even as transplant survival improves overall, “very few people are incorporating any very specific biological markers” in decision-making, he said. “We’ve gotten to measures of frailty, but we haven’t gotten to any biologic measures of cytokines or other things that would predict poor chances for doing well. So I’m afraid we’re still standing at the foot of the bed saying: ‘You look okay.’ Or we’re measuring their comorbidity index. But it is disappointing that we’re using mostly very simple clinical measures to decide if somebody is sturdy enough to proceed, and we perhaps need something better. But I don’t have a great suggestion what it should be.”
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
Dr. Weisdorf disclosed consulting fees from Fate Therapeutics and Incyte Corp.
SOURCE: “The Ever-Increasing Upper Age for Transplant: Is This Evidence-Based?” Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus, Oct. 15, 2020.
How old is too old for a patient to undergo hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)? That’s the wrong question to ask, a hematologist/oncologist told colleagues at the virtual Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus. Instead, he said, look at other factors such as disease status and genetics.
“Transplantation for older patients, even beyond the age of 70, is acceptable, as long as it’s done with caution, care, and wisdom. So we’re all not too old for transplantation, at least not today,” said Daniel Weisdorf, MD, professor of medicine and deputy director of the University of Minnesota Clinical and Translational Science Institute.
As he noted, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is often fatal. Among the general population, “the expected survival life expectancy at age 75 is 98% at 1 year, and most people living at 75 go on to live more than 10 years,” he said. “But if you have AML, at age 75, you have 20% survival at 1 year, 4% at 3 years. And since the median age of AML diagnosis is 68, and 75% of patients are diagnosed beyond the age of 55, this becomes relevant.”
Risk factors that affect survival after transplantation “certainly include age, but that interacts directly with the comorbidities people accumulate with age, their assessments of frailty, and their Karnofsky performance status, as well as the disease phenotype and molecular genetic markers,” Dr. Weisdorf said. “Perhaps most importantly, though not addressed very much, is patients’ willingness to undertake intensive therapy and their life outlook related to patient-reported outcomes when they get older.”
Despite the lack of indications that higher age by itself is an influential factor in survival after transplant, “we are generally reluctant to push the age of eligibility,” Dr. Weisdorf said. He noted that recently published American Society of Hematology guidelines for treatment of AML over the age of 55 “don’t discuss anything about transplantation fitness because they didn’t want to tackle that.”
Overall survival (OS) at 1 year after allogenic transplants only dipped slightly from ages 51-60 to 71 and above, according to Dr. Weisdorf’s analysis of U.S. data collected by the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research for the time period 2005-2019.
OS was 67.6% (66.8%-68.3%) for the 41-50 age group (n = 9,287) and 57.9% (56.1%-59.8%) for the 71 and older group, Dr. Weisdorf found. Overall, OS dropped by about 4 percentage points per decade of age, he said, revealing a “modest influence” of advancing years.
His analysis of autologous transplant data from the same source, also for 2005-2019, revealed “essentially no age influence.” OS was 90.8% (90.3%-91.2%) for the 41-50 age group (n = 15,075) and 86.6% (85.9%-87.3%) for the 71 and older group (n = 7,247).
Dr. Weisdorf also highlighted unpublished research that suggests that cord-blood transplant recipients older than 70 face a significantly higher risk of death than that of younger patients in the same category. Cord blood “may be option of last resort” because of a lack of other options, he explained. “And it may be part of the learning curve of cord blood transplantation, which grew a little bit in the early 2000s, and maybe past 2010, and then fell off as everybody got enamored with the haploidentical transplant option.”
How can physicians make decisions about transplants in older patients? “The transplant comorbidity index, the specific comorbidities themselves, performance score, and frailty are all measures of somebody’s fitness to be a good candidate for transplant, really at any age,” Dr. Weisdorf said. “But we also have to recognize that disease status, genetics, and the risk phenotype remain critical and should influence decision making.”
However, even as transplant survival improves overall, “very few people are incorporating any very specific biological markers” in decision-making, he said. “We’ve gotten to measures of frailty, but we haven’t gotten to any biologic measures of cytokines or other things that would predict poor chances for doing well. So I’m afraid we’re still standing at the foot of the bed saying: ‘You look okay.’ Or we’re measuring their comorbidity index. But it is disappointing that we’re using mostly very simple clinical measures to decide if somebody is sturdy enough to proceed, and we perhaps need something better. But I don’t have a great suggestion what it should be.”
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
Dr. Weisdorf disclosed consulting fees from Fate Therapeutics and Incyte Corp.
SOURCE: “The Ever-Increasing Upper Age for Transplant: Is This Evidence-Based?” Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus, Oct. 15, 2020.
FROM ALF 2020
COVID-19 antibody response not reduced with diabetes
Neither diabetes per se nor hyperglycemia appear to impair the antibody response to SARS-CoV-2, suggesting that a COVID-19 vaccine would be just as effective in people with diabetes as in those without, new research finds.
Results from a study involving 480 patients with confirmed COVID-19 seen at an Italian hospital between February 25 and April 19 were published online October 8 in Diabetologia by Vito Lampasona, MD, and colleagues.
Antibody responses against multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens among the 27% of patients with COVID-19 and diabetes (preexisting and newly diagnosed) were similar with regard to timing, titers, and classes to those of patients with COVID-19 and without diabetes, and the results did not differ by glucose levels.
Moreover, positivity for immunoglobulin G (IgG) against the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) was associated with improved survival regardless of diabetes status.
And as previously shown, high blood glucose levels were strongly associated with greater COVID-19 mortality even in those without diabetes.
This is the first study of the immunologic humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with hyperglycemia, the authors say.
“The immunological response to a future SARS-CoV-2 vaccine will be assessed when the vaccine becomes available. However, our data allow a cautious optimism regarding effective immunization in individuals with diabetes, as well as in the general population,” wrote Dr. Lampasona of San Raffaele Diabetes Research Institute, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele in Milan, and colleagues.
Diabetes and hyperglycemia worsen COVID-19 outcomes
The investigators analyzed the presence of three types of antibody to multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens in 509 participants: IgG, which is evidence of past infection; IgM, which indicates more recent or current infection; and IgA, which is involved in the mucosal immune response, for example, in the nose where the virus enters the body.
Overall, 452 (88.8%) patients were hospitalized, 79 (15.5%) patients were admitted to intensive care, and 93 (18.3%) patients died during follow-up.
Of the 139 patients with diabetes, 90 (17.7% of the study cohort) already had a diagnosis of diabetes, and 49 (9.6%) were newly diagnosed.
Those with diabetes were older, had a higher body mass index (BMI), and were more likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. As has been previously reported for diabetes and COVID-19, diabetes was also associated with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers, hypercoagulopathy, leukocytosis, and neutrophilia.
In multivariate analysis, diabetes status (hazard ratio, 2.32; P = .001), mean fasting plasma glucose (P < .001), and glucose variability (P = .002) were all independently associated with increased mortality and ICU admission. And fasting plasma glucose was associated with increased mortality risk even among those without diabetes (P < .001).
Antibody response similar in patients with and without diabetes
The humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with diabetes was present and superimposable in terms of timing and antibody titers to that of patients without diabetes, with marginal differences, and was not influenced by glucose levels.
After adjustment for sex, age, and diabetes status and stratification by symptom duration at time of sampling, the development of SARS-CoV-2 RBD IgG antibodies was associated with improved survival, with an HR for time to death of 0.4 (P = .002).
“Of the measured antibody responses, positivity for IgG against the SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD was predictive of survival rate, both in the presence or absence of diabetes,” the authors stressed, with similar HRs for those with diabetes (0.37; P = .013) and without diabetes (0.43; P = .038).
These data confirm “the relevance for patient survival rate of the specific antigen response against spike RBD even in the presence of diabetes, and it underlines how the mechanism explaining the worse clinical outcome in patients with diabetes is unrelated to the antibody response,” they explain.
They added, “This, together with evidence that increased blood glucose levels do predict a poor prognosis even in nondiabetic individuals and the association with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers and hypercoagulopathy, as well as leukocytosis and neutrophilia, support the speculation that glucose per se could be an independent biological negative factor, acting as a direct regulator of innate immunity.”
“The observed increased severity and mortality risk of COVID-19 pneumonia in patients with hyperglycemia was not the result of an impaired humoral response against SARS-CoV-2.”
“RBD IgG positivity was associated with a remarkable protective effect, allowing for a cautious optimism about the efficacy of future vaccines against SARS-COV-2 in people with diabetes,” they reiterated.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Neither diabetes per se nor hyperglycemia appear to impair the antibody response to SARS-CoV-2, suggesting that a COVID-19 vaccine would be just as effective in people with diabetes as in those without, new research finds.
Results from a study involving 480 patients with confirmed COVID-19 seen at an Italian hospital between February 25 and April 19 were published online October 8 in Diabetologia by Vito Lampasona, MD, and colleagues.
Antibody responses against multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens among the 27% of patients with COVID-19 and diabetes (preexisting and newly diagnosed) were similar with regard to timing, titers, and classes to those of patients with COVID-19 and without diabetes, and the results did not differ by glucose levels.
Moreover, positivity for immunoglobulin G (IgG) against the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) was associated with improved survival regardless of diabetes status.
And as previously shown, high blood glucose levels were strongly associated with greater COVID-19 mortality even in those without diabetes.
This is the first study of the immunologic humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with hyperglycemia, the authors say.
“The immunological response to a future SARS-CoV-2 vaccine will be assessed when the vaccine becomes available. However, our data allow a cautious optimism regarding effective immunization in individuals with diabetes, as well as in the general population,” wrote Dr. Lampasona of San Raffaele Diabetes Research Institute, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele in Milan, and colleagues.
Diabetes and hyperglycemia worsen COVID-19 outcomes
The investigators analyzed the presence of three types of antibody to multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens in 509 participants: IgG, which is evidence of past infection; IgM, which indicates more recent or current infection; and IgA, which is involved in the mucosal immune response, for example, in the nose where the virus enters the body.
Overall, 452 (88.8%) patients were hospitalized, 79 (15.5%) patients were admitted to intensive care, and 93 (18.3%) patients died during follow-up.
Of the 139 patients with diabetes, 90 (17.7% of the study cohort) already had a diagnosis of diabetes, and 49 (9.6%) were newly diagnosed.
Those with diabetes were older, had a higher body mass index (BMI), and were more likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. As has been previously reported for diabetes and COVID-19, diabetes was also associated with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers, hypercoagulopathy, leukocytosis, and neutrophilia.
In multivariate analysis, diabetes status (hazard ratio, 2.32; P = .001), mean fasting plasma glucose (P < .001), and glucose variability (P = .002) were all independently associated with increased mortality and ICU admission. And fasting plasma glucose was associated with increased mortality risk even among those without diabetes (P < .001).
Antibody response similar in patients with and without diabetes
The humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with diabetes was present and superimposable in terms of timing and antibody titers to that of patients without diabetes, with marginal differences, and was not influenced by glucose levels.
After adjustment for sex, age, and diabetes status and stratification by symptom duration at time of sampling, the development of SARS-CoV-2 RBD IgG antibodies was associated with improved survival, with an HR for time to death of 0.4 (P = .002).
“Of the measured antibody responses, positivity for IgG against the SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD was predictive of survival rate, both in the presence or absence of diabetes,” the authors stressed, with similar HRs for those with diabetes (0.37; P = .013) and without diabetes (0.43; P = .038).
These data confirm “the relevance for patient survival rate of the specific antigen response against spike RBD even in the presence of diabetes, and it underlines how the mechanism explaining the worse clinical outcome in patients with diabetes is unrelated to the antibody response,” they explain.
They added, “This, together with evidence that increased blood glucose levels do predict a poor prognosis even in nondiabetic individuals and the association with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers and hypercoagulopathy, as well as leukocytosis and neutrophilia, support the speculation that glucose per se could be an independent biological negative factor, acting as a direct regulator of innate immunity.”
“The observed increased severity and mortality risk of COVID-19 pneumonia in patients with hyperglycemia was not the result of an impaired humoral response against SARS-CoV-2.”
“RBD IgG positivity was associated with a remarkable protective effect, allowing for a cautious optimism about the efficacy of future vaccines against SARS-COV-2 in people with diabetes,” they reiterated.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Neither diabetes per se nor hyperglycemia appear to impair the antibody response to SARS-CoV-2, suggesting that a COVID-19 vaccine would be just as effective in people with diabetes as in those without, new research finds.
Results from a study involving 480 patients with confirmed COVID-19 seen at an Italian hospital between February 25 and April 19 were published online October 8 in Diabetologia by Vito Lampasona, MD, and colleagues.
Antibody responses against multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens among the 27% of patients with COVID-19 and diabetes (preexisting and newly diagnosed) were similar with regard to timing, titers, and classes to those of patients with COVID-19 and without diabetes, and the results did not differ by glucose levels.
Moreover, positivity for immunoglobulin G (IgG) against the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) was associated with improved survival regardless of diabetes status.
And as previously shown, high blood glucose levels were strongly associated with greater COVID-19 mortality even in those without diabetes.
This is the first study of the immunologic humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with hyperglycemia, the authors say.
“The immunological response to a future SARS-CoV-2 vaccine will be assessed when the vaccine becomes available. However, our data allow a cautious optimism regarding effective immunization in individuals with diabetes, as well as in the general population,” wrote Dr. Lampasona of San Raffaele Diabetes Research Institute, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele in Milan, and colleagues.
Diabetes and hyperglycemia worsen COVID-19 outcomes
The investigators analyzed the presence of three types of antibody to multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens in 509 participants: IgG, which is evidence of past infection; IgM, which indicates more recent or current infection; and IgA, which is involved in the mucosal immune response, for example, in the nose where the virus enters the body.
Overall, 452 (88.8%) patients were hospitalized, 79 (15.5%) patients were admitted to intensive care, and 93 (18.3%) patients died during follow-up.
Of the 139 patients with diabetes, 90 (17.7% of the study cohort) already had a diagnosis of diabetes, and 49 (9.6%) were newly diagnosed.
Those with diabetes were older, had a higher body mass index (BMI), and were more likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. As has been previously reported for diabetes and COVID-19, diabetes was also associated with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers, hypercoagulopathy, leukocytosis, and neutrophilia.
In multivariate analysis, diabetes status (hazard ratio, 2.32; P = .001), mean fasting plasma glucose (P < .001), and glucose variability (P = .002) were all independently associated with increased mortality and ICU admission. And fasting plasma glucose was associated with increased mortality risk even among those without diabetes (P < .001).
Antibody response similar in patients with and without diabetes
The humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with diabetes was present and superimposable in terms of timing and antibody titers to that of patients without diabetes, with marginal differences, and was not influenced by glucose levels.
After adjustment for sex, age, and diabetes status and stratification by symptom duration at time of sampling, the development of SARS-CoV-2 RBD IgG antibodies was associated with improved survival, with an HR for time to death of 0.4 (P = .002).
“Of the measured antibody responses, positivity for IgG against the SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD was predictive of survival rate, both in the presence or absence of diabetes,” the authors stressed, with similar HRs for those with diabetes (0.37; P = .013) and without diabetes (0.43; P = .038).
These data confirm “the relevance for patient survival rate of the specific antigen response against spike RBD even in the presence of diabetes, and it underlines how the mechanism explaining the worse clinical outcome in patients with diabetes is unrelated to the antibody response,” they explain.
They added, “This, together with evidence that increased blood glucose levels do predict a poor prognosis even in nondiabetic individuals and the association with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers and hypercoagulopathy, as well as leukocytosis and neutrophilia, support the speculation that glucose per se could be an independent biological negative factor, acting as a direct regulator of innate immunity.”
“The observed increased severity and mortality risk of COVID-19 pneumonia in patients with hyperglycemia was not the result of an impaired humoral response against SARS-CoV-2.”
“RBD IgG positivity was associated with a remarkable protective effect, allowing for a cautious optimism about the efficacy of future vaccines against SARS-COV-2 in people with diabetes,” they reiterated.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.