User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Please interrupt me, but don't heat your fish
Bother me, I’m working
Although some of us have been comfortably functioning in a virtual work environment, others are now trickling back into the office. And you know what that means? People come to your desk to show you pictures of their cat or tell you about their kid’s birthday party. You may sneer at the interruption, but a study shows you actually like it.
A team of researchers at the University of Cincinnati surveyed 111 full-time employees twice a day for 3 weeks about their work experience. They asked about mental exhaustion, workplace interruptions, sense of belonging, and overall job satisfaction. They found that employees had a higher sense of belonging and job satisfaction when interrupted with a social versus work interruption.
“Interruptions can actually benefit individuals from an interpersonal perspective – people feel like they belong when others come and talk to them or ask them questions, even while being distracted from their tasks,” said Heather C. Vough, senior investigator and a former university faculty member.
Chitchatting at work is often seen as a distraction, but this study suggests that it’s not like heating up fish in the breakroom microwave.
So the next time someone hits you with the “Hey, do you have a sec?,” do yourself a favor and enjoy the interruption.
A smorgasbord of science
It’s probably difficult to recruit patients for some medical trials. Try this new drug and potentially get all sorts of interesting and unpleasant side effects. Pass. We suggest the approach a group of researchers from the University of Kansas took for a recent study into weight gain: Invite a bunch of 20-something adults to an all-you-can-eat buffet. They’ll be beating down your door in no time.
Their study, published in Appetite, focused on hyperpalatable food – the sort of food you can keep eating – and compared it with high-energy-dense food and ultra processed food. The test patients had their body composition measured, were let loose on the buffet, and were measured again a year later.
The patients who favored salty/carbohydrate-filled hyperpalatable food (such as pretzels or popcorn) were much more likely to gain weight, compared with those who focused on salty/fat-filled food of any variety. As a matter of fact, those who stuck to fatty food during the buffet had no change in weight over the 1-year study period. The researchers noted that those who ate the carb-filled food tended more toward hedonic eating, or the act of eating simply for pleasure.
The study is no doubt helpful in the long battle against obesity and overeating, but it’s also a very helpful guide to getting the most bang for your buck at the buffet. Stay away from the cheap salty snack food. Go for the steak and seafood. Get your money’s worth. In the long run you won’t even gain any weight. No promises about tomorrow though.
There’s a cheat code for that
For a large percentage of kids and young adults, and maybe even older adults (we don’t judge), a storm warning means a cozy night in playing video games. Staying inside is probably the safest bet when there’s a storm, and the weatherman never says to avoid playing video games when there’s lightning.
Maybe he should, though, since a man from Tennessee reportedly got struck by lightning through his game controller. Emergency crews determined that lightning either hit the man’s house or struck near it and went through the controller. The type of console was not revealed, even though some people may want to know the specifics before playing during the next storm.
Luckily, the man was not seriously hurt and did not need to go to the hospital. This is apparently not unheard of, as a professional gamer was shocked through a wired controller last year, causing burns on her hands and a broken controller.
This might be our cue to do less electrical types of activities during thunderstorms, like knitting or reading by candlelight.
Freeze, squeeze, and enjoy … cramping
As you were ingesting last week’s installment of the never-ending buffet that is LOTME, you probably wondered: What’s going on? Where’s the latest bodily insult being perpetuated by the gang over at TikTok?
Have no fear, good readers. We would never make you go 2 straight weeks without serving up some hyperpalatable TikTok tidbits.
Our bodily insult du jour is frozen honey, and it’s exploding all over TikTok … and a few other places. “The hashtag ‘#FrozenHoney’ has been viewed nearly 600 million times, and the hashtag ‘#FrozenHoneyChallenge’ has been viewed more than 80 million times,” NBC News recently reported.
After a few hours in the freezer, honey can be squeezed out of a plastic bottle as a semisolid, toothpastelike goo – it’s stiff enough to rise out of a container that’s pointed straight up – and bitten off in large chunks. And therein lies the problem.
Some people are overdoing it. “Honey is great, but having it in small amounts to sweeten is really a healthy relationship with food, and using it to get a lot of followers and a lot of attention and having it in excess amounts is crazy,” Kristin Kirkpatrick, a registered dietitian at the Cleveland Clinic, told NBC.
Besides the possible weight gain from eating massive amounts of sugar, experts warned that “gobbling up bottles of frozen honey” could lead to stomach cramping, bloating, and diarrhea. Some TikTokers, NBC noted, said that they “were running for the bathroom.”
As we said, it’s a trend that is exploding.
Be sure to tune in next week, when we learn how TikTokers use ground meat as a skin moisturizer.
Bother me, I’m working
Although some of us have been comfortably functioning in a virtual work environment, others are now trickling back into the office. And you know what that means? People come to your desk to show you pictures of their cat or tell you about their kid’s birthday party. You may sneer at the interruption, but a study shows you actually like it.
A team of researchers at the University of Cincinnati surveyed 111 full-time employees twice a day for 3 weeks about their work experience. They asked about mental exhaustion, workplace interruptions, sense of belonging, and overall job satisfaction. They found that employees had a higher sense of belonging and job satisfaction when interrupted with a social versus work interruption.
“Interruptions can actually benefit individuals from an interpersonal perspective – people feel like they belong when others come and talk to them or ask them questions, even while being distracted from their tasks,” said Heather C. Vough, senior investigator and a former university faculty member.
Chitchatting at work is often seen as a distraction, but this study suggests that it’s not like heating up fish in the breakroom microwave.
So the next time someone hits you with the “Hey, do you have a sec?,” do yourself a favor and enjoy the interruption.
A smorgasbord of science
It’s probably difficult to recruit patients for some medical trials. Try this new drug and potentially get all sorts of interesting and unpleasant side effects. Pass. We suggest the approach a group of researchers from the University of Kansas took for a recent study into weight gain: Invite a bunch of 20-something adults to an all-you-can-eat buffet. They’ll be beating down your door in no time.
Their study, published in Appetite, focused on hyperpalatable food – the sort of food you can keep eating – and compared it with high-energy-dense food and ultra processed food. The test patients had their body composition measured, were let loose on the buffet, and were measured again a year later.
The patients who favored salty/carbohydrate-filled hyperpalatable food (such as pretzels or popcorn) were much more likely to gain weight, compared with those who focused on salty/fat-filled food of any variety. As a matter of fact, those who stuck to fatty food during the buffet had no change in weight over the 1-year study period. The researchers noted that those who ate the carb-filled food tended more toward hedonic eating, or the act of eating simply for pleasure.
The study is no doubt helpful in the long battle against obesity and overeating, but it’s also a very helpful guide to getting the most bang for your buck at the buffet. Stay away from the cheap salty snack food. Go for the steak and seafood. Get your money’s worth. In the long run you won’t even gain any weight. No promises about tomorrow though.
There’s a cheat code for that
For a large percentage of kids and young adults, and maybe even older adults (we don’t judge), a storm warning means a cozy night in playing video games. Staying inside is probably the safest bet when there’s a storm, and the weatherman never says to avoid playing video games when there’s lightning.
Maybe he should, though, since a man from Tennessee reportedly got struck by lightning through his game controller. Emergency crews determined that lightning either hit the man’s house or struck near it and went through the controller. The type of console was not revealed, even though some people may want to know the specifics before playing during the next storm.
Luckily, the man was not seriously hurt and did not need to go to the hospital. This is apparently not unheard of, as a professional gamer was shocked through a wired controller last year, causing burns on her hands and a broken controller.
This might be our cue to do less electrical types of activities during thunderstorms, like knitting or reading by candlelight.
Freeze, squeeze, and enjoy … cramping
As you were ingesting last week’s installment of the never-ending buffet that is LOTME, you probably wondered: What’s going on? Where’s the latest bodily insult being perpetuated by the gang over at TikTok?
Have no fear, good readers. We would never make you go 2 straight weeks without serving up some hyperpalatable TikTok tidbits.
Our bodily insult du jour is frozen honey, and it’s exploding all over TikTok … and a few other places. “The hashtag ‘#FrozenHoney’ has been viewed nearly 600 million times, and the hashtag ‘#FrozenHoneyChallenge’ has been viewed more than 80 million times,” NBC News recently reported.
After a few hours in the freezer, honey can be squeezed out of a plastic bottle as a semisolid, toothpastelike goo – it’s stiff enough to rise out of a container that’s pointed straight up – and bitten off in large chunks. And therein lies the problem.
Some people are overdoing it. “Honey is great, but having it in small amounts to sweeten is really a healthy relationship with food, and using it to get a lot of followers and a lot of attention and having it in excess amounts is crazy,” Kristin Kirkpatrick, a registered dietitian at the Cleveland Clinic, told NBC.
Besides the possible weight gain from eating massive amounts of sugar, experts warned that “gobbling up bottles of frozen honey” could lead to stomach cramping, bloating, and diarrhea. Some TikTokers, NBC noted, said that they “were running for the bathroom.”
As we said, it’s a trend that is exploding.
Be sure to tune in next week, when we learn how TikTokers use ground meat as a skin moisturizer.
Bother me, I’m working
Although some of us have been comfortably functioning in a virtual work environment, others are now trickling back into the office. And you know what that means? People come to your desk to show you pictures of their cat or tell you about their kid’s birthday party. You may sneer at the interruption, but a study shows you actually like it.
A team of researchers at the University of Cincinnati surveyed 111 full-time employees twice a day for 3 weeks about their work experience. They asked about mental exhaustion, workplace interruptions, sense of belonging, and overall job satisfaction. They found that employees had a higher sense of belonging and job satisfaction when interrupted with a social versus work interruption.
“Interruptions can actually benefit individuals from an interpersonal perspective – people feel like they belong when others come and talk to them or ask them questions, even while being distracted from their tasks,” said Heather C. Vough, senior investigator and a former university faculty member.
Chitchatting at work is often seen as a distraction, but this study suggests that it’s not like heating up fish in the breakroom microwave.
So the next time someone hits you with the “Hey, do you have a sec?,” do yourself a favor and enjoy the interruption.
A smorgasbord of science
It’s probably difficult to recruit patients for some medical trials. Try this new drug and potentially get all sorts of interesting and unpleasant side effects. Pass. We suggest the approach a group of researchers from the University of Kansas took for a recent study into weight gain: Invite a bunch of 20-something adults to an all-you-can-eat buffet. They’ll be beating down your door in no time.
Their study, published in Appetite, focused on hyperpalatable food – the sort of food you can keep eating – and compared it with high-energy-dense food and ultra processed food. The test patients had their body composition measured, were let loose on the buffet, and were measured again a year later.
The patients who favored salty/carbohydrate-filled hyperpalatable food (such as pretzels or popcorn) were much more likely to gain weight, compared with those who focused on salty/fat-filled food of any variety. As a matter of fact, those who stuck to fatty food during the buffet had no change in weight over the 1-year study period. The researchers noted that those who ate the carb-filled food tended more toward hedonic eating, or the act of eating simply for pleasure.
The study is no doubt helpful in the long battle against obesity and overeating, but it’s also a very helpful guide to getting the most bang for your buck at the buffet. Stay away from the cheap salty snack food. Go for the steak and seafood. Get your money’s worth. In the long run you won’t even gain any weight. No promises about tomorrow though.
There’s a cheat code for that
For a large percentage of kids and young adults, and maybe even older adults (we don’t judge), a storm warning means a cozy night in playing video games. Staying inside is probably the safest bet when there’s a storm, and the weatherman never says to avoid playing video games when there’s lightning.
Maybe he should, though, since a man from Tennessee reportedly got struck by lightning through his game controller. Emergency crews determined that lightning either hit the man’s house or struck near it and went through the controller. The type of console was not revealed, even though some people may want to know the specifics before playing during the next storm.
Luckily, the man was not seriously hurt and did not need to go to the hospital. This is apparently not unheard of, as a professional gamer was shocked through a wired controller last year, causing burns on her hands and a broken controller.
This might be our cue to do less electrical types of activities during thunderstorms, like knitting or reading by candlelight.
Freeze, squeeze, and enjoy … cramping
As you were ingesting last week’s installment of the never-ending buffet that is LOTME, you probably wondered: What’s going on? Where’s the latest bodily insult being perpetuated by the gang over at TikTok?
Have no fear, good readers. We would never make you go 2 straight weeks without serving up some hyperpalatable TikTok tidbits.
Our bodily insult du jour is frozen honey, and it’s exploding all over TikTok … and a few other places. “The hashtag ‘#FrozenHoney’ has been viewed nearly 600 million times, and the hashtag ‘#FrozenHoneyChallenge’ has been viewed more than 80 million times,” NBC News recently reported.
After a few hours in the freezer, honey can be squeezed out of a plastic bottle as a semisolid, toothpastelike goo – it’s stiff enough to rise out of a container that’s pointed straight up – and bitten off in large chunks. And therein lies the problem.
Some people are overdoing it. “Honey is great, but having it in small amounts to sweeten is really a healthy relationship with food, and using it to get a lot of followers and a lot of attention and having it in excess amounts is crazy,” Kristin Kirkpatrick, a registered dietitian at the Cleveland Clinic, told NBC.
Besides the possible weight gain from eating massive amounts of sugar, experts warned that “gobbling up bottles of frozen honey” could lead to stomach cramping, bloating, and diarrhea. Some TikTokers, NBC noted, said that they “were running for the bathroom.”
As we said, it’s a trend that is exploding.
Be sure to tune in next week, when we learn how TikTokers use ground meat as a skin moisturizer.
Certain gut bacteria tied to lower risk of diabetes
Having more diverse gut bacteria (greater microbiome richness) and specifically a greater abundance of 12 types of butyrate-producing bacteria were both associated with less insulin resistance and less type 2 diabetes, in a population-based observational study from the Netherlands.
Several studies have reported that there is less microbiome diversity in type 2 diabetes, Zhangling Chen, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues note.
Their study also identified a dozen types of bacteria that ferment dietary fiber (undigested carbohydrates) in the gut to produce butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, which may play a role in protection against type 2 diabetes.
“The current study is the first, to our knowledge, to comprehensively investigate the associations between gut microbiome composition [and] type 2 diabetes in a large population-based sample … which we adjusted for a series of key confounders,” the researchers write.
“These findings suggest that higher gut microbial diversity, along with specifically more butyrate-producing bacteria, may play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes, which may help guide future prevention and treatment strategies,” they conclude in their study published online July 29 in JAMA Network Open.
Confirmation of previous work, plus some new findings
The study confirms what many smaller ones have repeatedly shown – that low gut microbiome diversity is associated with increased risks of obesity and type 2 diabetes, Nanette I. Steinle, MD, RDN, who was not involved in the research, said in an interview.
A diet rich in fiber and prebiotics promotes gut biome diversity, added Dr. Steinle, chief of the endocrinology and diabetes section at Maryland Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Baltimore.
The findings add to other research, she noted, such as a prospective trial in which a high-fiber diet induced changes in the gut microbe that were linked to better glycemic regulation (Science. 2018;359:1151-6) and a study of a promising probiotic formula to treat diabetes.
“An important next step,” according to Dr. Steinle, “is to provide interventions like healthy diet or specific fiber types to see what can be done to produce lasting shifts in the gut microbiome and if these shifts result in improved metabolic health.”
Natalia Shulzhenko, MD, PhD, said: “Some of associations of taxa [bacteria groupings] with type 2 diabetes reported by this study are new.”
Dr. Shulzhenko and colleagues recently published a review of the role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology that summarized evidence from 42 human studies as well as preclinical studies and clinical trials of probiotic treatments (EBioMedicine. 2020;51:102590).
“Besides adding new microbes to the list of potential pathobionts [organisms that can cause harm] and beneficial microbes for type 2 diabetes,” the findings by Dr. Chen and colleagues “support a notion that different members of the gut microbial community may have similar effects on type 2 diabetes in different individuals,” commonly known as “functional redundancy,” Dr. Shulzhenko, associate professor, Carlson College of Veterinary Medicine, Oregon State University, Corvallis, pointed out in an email.
Also “in line with previous studies,” the study shows that butyrate-producing bacteria are associated with type 2 diabetes.
She speculated that “these results will probably contribute to the body of knowledge that is needed to develop microbiota-based therapy and diagnostics.”
Which gut bacteria are linked with diabetes?
It is unclear which gut bacteria are associated with the development of type 2 diabetes, Dr. Chen and colleagues write.
To investigate this, they identified 1,418 participants from the Rotterdam Study and 748 participants from the LifeLines-DEEP study enrolled from January 2018 to December 2020. Of these participants, 193 had type 2 diabetes.
The participants provided stool samples that were used to measure gut microbiome composition using the 16S ribosomal RNA method. They also had blood tests to measure glucose and insulin, and researchers collected other demographic and medical data.
Participants in the Rotterdam study were older than in the LifeLines Deep study (mean age, 62 vs. 45 years). Both cohorts included slightly more men than women (58%).
Dr. Chen and colleagues identified 126 (bacteria) genera in the gut microbiome in the Rotterdam study and 184 genera in the LifeLines Deep study.
After correcting for age, sex, smoking, education, physical activity, alcohol intake, daily calories, body mass index, and use of lipid-lowering medication or proton pump inhibitors, higher microbiome diversity was associated with lower insulin resistance and a lower prevalence of type 2 diabetes.
A higher abundance of each of seven types of butyrate-producing bacteria – Christensenellaceae, Christensenellaceae R7 group, Marvinbryantia, Ruminococcaceae UCG-005, Ruminococcaceae UCG-008, Ruminococcaceae UCG-010, and Ruminococcaceae NK4A214 group – was associated with lower insulin resistance, after adjusting for confounders such as diet and medications (all P < .001).
And a higher abundance of each of five other types of butyrate-producing bacteria – Clostridiaceae 1, Peptostreptococcaceae, Clostridium sensu stricto 1, Intestinibacter, and Romboutsia – was associated with less type 2 diabetes (all P < .001).
Study limitations include that gut microbiome composition was determined from stool (fecal) samples, whereas the actual composition varies in different locations along the intestine, and the study also lacked information about butyrate concentrations in stool or blood, the researchers note.
They call for “future research [to] validate the hypothesis of butyrate-producing bacteria affecting glucose metabolism and diabetes risk via production of butyrate.”
The authors and Dr. Shulzhenko have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Steinle has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health and conducting a study funded by Kowa through the VA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having more diverse gut bacteria (greater microbiome richness) and specifically a greater abundance of 12 types of butyrate-producing bacteria were both associated with less insulin resistance and less type 2 diabetes, in a population-based observational study from the Netherlands.
Several studies have reported that there is less microbiome diversity in type 2 diabetes, Zhangling Chen, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues note.
Their study also identified a dozen types of bacteria that ferment dietary fiber (undigested carbohydrates) in the gut to produce butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, which may play a role in protection against type 2 diabetes.
“The current study is the first, to our knowledge, to comprehensively investigate the associations between gut microbiome composition [and] type 2 diabetes in a large population-based sample … which we adjusted for a series of key confounders,” the researchers write.
“These findings suggest that higher gut microbial diversity, along with specifically more butyrate-producing bacteria, may play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes, which may help guide future prevention and treatment strategies,” they conclude in their study published online July 29 in JAMA Network Open.
Confirmation of previous work, plus some new findings
The study confirms what many smaller ones have repeatedly shown – that low gut microbiome diversity is associated with increased risks of obesity and type 2 diabetes, Nanette I. Steinle, MD, RDN, who was not involved in the research, said in an interview.
A diet rich in fiber and prebiotics promotes gut biome diversity, added Dr. Steinle, chief of the endocrinology and diabetes section at Maryland Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Baltimore.
The findings add to other research, she noted, such as a prospective trial in which a high-fiber diet induced changes in the gut microbe that were linked to better glycemic regulation (Science. 2018;359:1151-6) and a study of a promising probiotic formula to treat diabetes.
“An important next step,” according to Dr. Steinle, “is to provide interventions like healthy diet or specific fiber types to see what can be done to produce lasting shifts in the gut microbiome and if these shifts result in improved metabolic health.”
Natalia Shulzhenko, MD, PhD, said: “Some of associations of taxa [bacteria groupings] with type 2 diabetes reported by this study are new.”
Dr. Shulzhenko and colleagues recently published a review of the role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology that summarized evidence from 42 human studies as well as preclinical studies and clinical trials of probiotic treatments (EBioMedicine. 2020;51:102590).
“Besides adding new microbes to the list of potential pathobionts [organisms that can cause harm] and beneficial microbes for type 2 diabetes,” the findings by Dr. Chen and colleagues “support a notion that different members of the gut microbial community may have similar effects on type 2 diabetes in different individuals,” commonly known as “functional redundancy,” Dr. Shulzhenko, associate professor, Carlson College of Veterinary Medicine, Oregon State University, Corvallis, pointed out in an email.
Also “in line with previous studies,” the study shows that butyrate-producing bacteria are associated with type 2 diabetes.
She speculated that “these results will probably contribute to the body of knowledge that is needed to develop microbiota-based therapy and diagnostics.”
Which gut bacteria are linked with diabetes?
It is unclear which gut bacteria are associated with the development of type 2 diabetes, Dr. Chen and colleagues write.
To investigate this, they identified 1,418 participants from the Rotterdam Study and 748 participants from the LifeLines-DEEP study enrolled from January 2018 to December 2020. Of these participants, 193 had type 2 diabetes.
The participants provided stool samples that were used to measure gut microbiome composition using the 16S ribosomal RNA method. They also had blood tests to measure glucose and insulin, and researchers collected other demographic and medical data.
Participants in the Rotterdam study were older than in the LifeLines Deep study (mean age, 62 vs. 45 years). Both cohorts included slightly more men than women (58%).
Dr. Chen and colleagues identified 126 (bacteria) genera in the gut microbiome in the Rotterdam study and 184 genera in the LifeLines Deep study.
After correcting for age, sex, smoking, education, physical activity, alcohol intake, daily calories, body mass index, and use of lipid-lowering medication or proton pump inhibitors, higher microbiome diversity was associated with lower insulin resistance and a lower prevalence of type 2 diabetes.
A higher abundance of each of seven types of butyrate-producing bacteria – Christensenellaceae, Christensenellaceae R7 group, Marvinbryantia, Ruminococcaceae UCG-005, Ruminococcaceae UCG-008, Ruminococcaceae UCG-010, and Ruminococcaceae NK4A214 group – was associated with lower insulin resistance, after adjusting for confounders such as diet and medications (all P < .001).
And a higher abundance of each of five other types of butyrate-producing bacteria – Clostridiaceae 1, Peptostreptococcaceae, Clostridium sensu stricto 1, Intestinibacter, and Romboutsia – was associated with less type 2 diabetes (all P < .001).
Study limitations include that gut microbiome composition was determined from stool (fecal) samples, whereas the actual composition varies in different locations along the intestine, and the study also lacked information about butyrate concentrations in stool or blood, the researchers note.
They call for “future research [to] validate the hypothesis of butyrate-producing bacteria affecting glucose metabolism and diabetes risk via production of butyrate.”
The authors and Dr. Shulzhenko have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Steinle has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health and conducting a study funded by Kowa through the VA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having more diverse gut bacteria (greater microbiome richness) and specifically a greater abundance of 12 types of butyrate-producing bacteria were both associated with less insulin resistance and less type 2 diabetes, in a population-based observational study from the Netherlands.
Several studies have reported that there is less microbiome diversity in type 2 diabetes, Zhangling Chen, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues note.
Their study also identified a dozen types of bacteria that ferment dietary fiber (undigested carbohydrates) in the gut to produce butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, which may play a role in protection against type 2 diabetes.
“The current study is the first, to our knowledge, to comprehensively investigate the associations between gut microbiome composition [and] type 2 diabetes in a large population-based sample … which we adjusted for a series of key confounders,” the researchers write.
“These findings suggest that higher gut microbial diversity, along with specifically more butyrate-producing bacteria, may play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes, which may help guide future prevention and treatment strategies,” they conclude in their study published online July 29 in JAMA Network Open.
Confirmation of previous work, plus some new findings
The study confirms what many smaller ones have repeatedly shown – that low gut microbiome diversity is associated with increased risks of obesity and type 2 diabetes, Nanette I. Steinle, MD, RDN, who was not involved in the research, said in an interview.
A diet rich in fiber and prebiotics promotes gut biome diversity, added Dr. Steinle, chief of the endocrinology and diabetes section at Maryland Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Baltimore.
The findings add to other research, she noted, such as a prospective trial in which a high-fiber diet induced changes in the gut microbe that were linked to better glycemic regulation (Science. 2018;359:1151-6) and a study of a promising probiotic formula to treat diabetes.
“An important next step,” according to Dr. Steinle, “is to provide interventions like healthy diet or specific fiber types to see what can be done to produce lasting shifts in the gut microbiome and if these shifts result in improved metabolic health.”
Natalia Shulzhenko, MD, PhD, said: “Some of associations of taxa [bacteria groupings] with type 2 diabetes reported by this study are new.”
Dr. Shulzhenko and colleagues recently published a review of the role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology that summarized evidence from 42 human studies as well as preclinical studies and clinical trials of probiotic treatments (EBioMedicine. 2020;51:102590).
“Besides adding new microbes to the list of potential pathobionts [organisms that can cause harm] and beneficial microbes for type 2 diabetes,” the findings by Dr. Chen and colleagues “support a notion that different members of the gut microbial community may have similar effects on type 2 diabetes in different individuals,” commonly known as “functional redundancy,” Dr. Shulzhenko, associate professor, Carlson College of Veterinary Medicine, Oregon State University, Corvallis, pointed out in an email.
Also “in line with previous studies,” the study shows that butyrate-producing bacteria are associated with type 2 diabetes.
She speculated that “these results will probably contribute to the body of knowledge that is needed to develop microbiota-based therapy and diagnostics.”
Which gut bacteria are linked with diabetes?
It is unclear which gut bacteria are associated with the development of type 2 diabetes, Dr. Chen and colleagues write.
To investigate this, they identified 1,418 participants from the Rotterdam Study and 748 participants from the LifeLines-DEEP study enrolled from January 2018 to December 2020. Of these participants, 193 had type 2 diabetes.
The participants provided stool samples that were used to measure gut microbiome composition using the 16S ribosomal RNA method. They also had blood tests to measure glucose and insulin, and researchers collected other demographic and medical data.
Participants in the Rotterdam study were older than in the LifeLines Deep study (mean age, 62 vs. 45 years). Both cohorts included slightly more men than women (58%).
Dr. Chen and colleagues identified 126 (bacteria) genera in the gut microbiome in the Rotterdam study and 184 genera in the LifeLines Deep study.
After correcting for age, sex, smoking, education, physical activity, alcohol intake, daily calories, body mass index, and use of lipid-lowering medication or proton pump inhibitors, higher microbiome diversity was associated with lower insulin resistance and a lower prevalence of type 2 diabetes.
A higher abundance of each of seven types of butyrate-producing bacteria – Christensenellaceae, Christensenellaceae R7 group, Marvinbryantia, Ruminococcaceae UCG-005, Ruminococcaceae UCG-008, Ruminococcaceae UCG-010, and Ruminococcaceae NK4A214 group – was associated with lower insulin resistance, after adjusting for confounders such as diet and medications (all P < .001).
And a higher abundance of each of five other types of butyrate-producing bacteria – Clostridiaceae 1, Peptostreptococcaceae, Clostridium sensu stricto 1, Intestinibacter, and Romboutsia – was associated with less type 2 diabetes (all P < .001).
Study limitations include that gut microbiome composition was determined from stool (fecal) samples, whereas the actual composition varies in different locations along the intestine, and the study also lacked information about butyrate concentrations in stool or blood, the researchers note.
They call for “future research [to] validate the hypothesis of butyrate-producing bacteria affecting glucose metabolism and diabetes risk via production of butyrate.”
The authors and Dr. Shulzhenko have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Steinle has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health and conducting a study funded by Kowa through the VA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Delta variant could drive herd immunity threshold over 80%
Because the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 spreads more easily than the original virus, the proportion of the population that needs to be vaccinated to reach herd immunity could be upward of 80% or more, experts say.
Also, it could be time to consider wearing an N95 mask in public indoor spaces regardless of vaccination status, according to a media briefing on Aug. 3 sponsored by the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Furthermore, giving booster shots to the fully vaccinated is not the top public health priority now. Instead, third vaccinations should be reserved for more vulnerable populations – and efforts should focus on getting first vaccinations to unvaccinated people in the United States and around the world.
“The problem here is that the Delta variant is ... more transmissible than the original virus. That pushes the overall population herd immunity threshold much higher,” Ricardo Franco, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said during the briefing.
“For Delta, those threshold estimates go well over 80% and may be approaching 90%,” he said.
To put that figure in context, the original SARS-CoV-2 virus required an estimated 67% of the population to be vaccinated to achieve herd immunity. Also, measles has one of the highest herd immunity thresholds at 95%, Dr. Franco added.
Herd immunity is the point at which enough people are immunized that the entire population gains protection. And it’s already happening. “Unvaccinated people are actually benefiting from greater herd immunity protection in high-vaccination counties compared to low-vaccination ones,” he said.
Maximize mask protection
Unlike early in the COVID-19 pandemic with widespread shortages of personal protective equipment, face masks are now readily available. This includes N95 masks, which offer enhanced protection against SARS-CoV-2, Ezekiel J. Emanuel, MD, PhD, said during the briefing.
Following the July 27 CDC recommendation that most Americans wear masks indoors when in public places, “I do think we need to upgrade our masks,” said Dr. Emanuel, who is Diane v.S. Levy & Robert M. Levy professor at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“It’s not just any mask,” he added. “Good masks make a big difference and are very important.”
Mask protection is about blocking 0.3-mcm particles, “and I think we need to make sure that people have masks that can filter that out,” he said. Although surgical masks are very good, he added, “they’re not quite as good as N95s.” As their name implies, N95s filter out 95% of these particles.
Dr. Emanuel acknowledged that people are tired of COVID-19 and complying with public health measures but urged perseverance. “We’ve sacrificed a lot. We should not throw it away in just a few months because we are tired. We’re all tired, but we do have to do the little bit extra getting vaccinated, wearing masks indoors, and protecting ourselves, our families, and our communities.”
Dealing with a disconnect
In response to a reporter’s question about the possibility that the large crowd at the Lollapalooza music festival in Chicago could become a superspreader event, Dr. Emanuel said, “it is worrisome.”
“I would say that, if you’re going to go to a gathering like that, wearing an N95 mask is wise, and not spending too long at any one place is also wise,” he said.
On the plus side, the event was held outdoors with lots of air circulation, Dr. Emanuel said.
However, “this is the kind of thing where we’ve got a sort of disconnect between people’s desire to get back to normal ... and the fact that we’re in the middle of this upsurge.”
Another potential problem is the event brought people together from many different locations, so when they travel home, they could be “potentially seeding lots of other communities.”
Boosters for some, for now
Even though not officially recommended, some fully vaccinated Americans are seeking a third or booster vaccination on their own.
Asked for his opinion, Dr. Emanuel said: “We’re probably going to have to be giving boosters to immunocompromised people and people who are susceptible. That’s where we are going to start.”
More research is needed regarding booster shots, he said. “There are very small studies – and the ‘very small’ should be emphasized – given that we’ve given shots to over 160 million people.”
“But it does appear that the boosters increase the antibodies and protection,” he said.
Instead of boosters, it is more important for people who haven’t been vaccinated to get fully vaccinated.
“We need to put our priorities in the right places,” he said.
Emanuel noted that, except for people in rural areas that might have to travel long distances, access to vaccines is no longer an issue. “It’s very hard not to find a vaccine if you want it.”
A remaining hurdle is “battling a major disinformation initiative. I don’t think this is misinformation. I think there’s very clear evidence that it is disinformation – false facts about the vaccines being spread,” Dr. Emanuel said.
The breakthrough infection dilemma
Breakthrough cases “remain the vast minority of infections at this time ... that is reassuring,” Dr. Franco said.
Also, tracking symptomatic breakthrough infections remains easier than studying fully vaccinated people who become infected with SARS-CoV-2 but remain symptom free.
“We really don’t have a good handle on the frequency of asymptomatic cases,” Dr. Emanuel said. “If you’re missing breakthrough infections, a lot of them, you may be missing some [virus] evolution that would be very important for us to follow.” This missing information could include the emergence of new variants.
The asymptomatic breakthrough cases are the most worrisome group,” Dr. Emanuel said. “You get infected, you’re feeling fine. Maybe you’ve got a little sneeze or cough, but nothing unusual. And then you’re still able to transmit the Delta variant.”
The big picture
The upsurge in cases, hospitalizations, and deaths is a major challenge, Dr. Emanuel said. “We need to address that by getting many more people vaccinated right now with what are very good vaccines.”
“But it also means that we have to stop being U.S. focused alone.” He pointed out that Delta and other variants originated overseas, “so getting the world vaccinated ... has to be a top priority.”
“We are obviously all facing a challenge as we move into the fall,” Dr. Emanuel said. “With schools opening and employers bringing their employees back together, even if these groups are vaccinated, there are going to be major challenges for all of us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Because the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 spreads more easily than the original virus, the proportion of the population that needs to be vaccinated to reach herd immunity could be upward of 80% or more, experts say.
Also, it could be time to consider wearing an N95 mask in public indoor spaces regardless of vaccination status, according to a media briefing on Aug. 3 sponsored by the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Furthermore, giving booster shots to the fully vaccinated is not the top public health priority now. Instead, third vaccinations should be reserved for more vulnerable populations – and efforts should focus on getting first vaccinations to unvaccinated people in the United States and around the world.
“The problem here is that the Delta variant is ... more transmissible than the original virus. That pushes the overall population herd immunity threshold much higher,” Ricardo Franco, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said during the briefing.
“For Delta, those threshold estimates go well over 80% and may be approaching 90%,” he said.
To put that figure in context, the original SARS-CoV-2 virus required an estimated 67% of the population to be vaccinated to achieve herd immunity. Also, measles has one of the highest herd immunity thresholds at 95%, Dr. Franco added.
Herd immunity is the point at which enough people are immunized that the entire population gains protection. And it’s already happening. “Unvaccinated people are actually benefiting from greater herd immunity protection in high-vaccination counties compared to low-vaccination ones,” he said.
Maximize mask protection
Unlike early in the COVID-19 pandemic with widespread shortages of personal protective equipment, face masks are now readily available. This includes N95 masks, which offer enhanced protection against SARS-CoV-2, Ezekiel J. Emanuel, MD, PhD, said during the briefing.
Following the July 27 CDC recommendation that most Americans wear masks indoors when in public places, “I do think we need to upgrade our masks,” said Dr. Emanuel, who is Diane v.S. Levy & Robert M. Levy professor at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“It’s not just any mask,” he added. “Good masks make a big difference and are very important.”
Mask protection is about blocking 0.3-mcm particles, “and I think we need to make sure that people have masks that can filter that out,” he said. Although surgical masks are very good, he added, “they’re not quite as good as N95s.” As their name implies, N95s filter out 95% of these particles.
Dr. Emanuel acknowledged that people are tired of COVID-19 and complying with public health measures but urged perseverance. “We’ve sacrificed a lot. We should not throw it away in just a few months because we are tired. We’re all tired, but we do have to do the little bit extra getting vaccinated, wearing masks indoors, and protecting ourselves, our families, and our communities.”
Dealing with a disconnect
In response to a reporter’s question about the possibility that the large crowd at the Lollapalooza music festival in Chicago could become a superspreader event, Dr. Emanuel said, “it is worrisome.”
“I would say that, if you’re going to go to a gathering like that, wearing an N95 mask is wise, and not spending too long at any one place is also wise,” he said.
On the plus side, the event was held outdoors with lots of air circulation, Dr. Emanuel said.
However, “this is the kind of thing where we’ve got a sort of disconnect between people’s desire to get back to normal ... and the fact that we’re in the middle of this upsurge.”
Another potential problem is the event brought people together from many different locations, so when they travel home, they could be “potentially seeding lots of other communities.”
Boosters for some, for now
Even though not officially recommended, some fully vaccinated Americans are seeking a third or booster vaccination on their own.
Asked for his opinion, Dr. Emanuel said: “We’re probably going to have to be giving boosters to immunocompromised people and people who are susceptible. That’s where we are going to start.”
More research is needed regarding booster shots, he said. “There are very small studies – and the ‘very small’ should be emphasized – given that we’ve given shots to over 160 million people.”
“But it does appear that the boosters increase the antibodies and protection,” he said.
Instead of boosters, it is more important for people who haven’t been vaccinated to get fully vaccinated.
“We need to put our priorities in the right places,” he said.
Emanuel noted that, except for people in rural areas that might have to travel long distances, access to vaccines is no longer an issue. “It’s very hard not to find a vaccine if you want it.”
A remaining hurdle is “battling a major disinformation initiative. I don’t think this is misinformation. I think there’s very clear evidence that it is disinformation – false facts about the vaccines being spread,” Dr. Emanuel said.
The breakthrough infection dilemma
Breakthrough cases “remain the vast minority of infections at this time ... that is reassuring,” Dr. Franco said.
Also, tracking symptomatic breakthrough infections remains easier than studying fully vaccinated people who become infected with SARS-CoV-2 but remain symptom free.
“We really don’t have a good handle on the frequency of asymptomatic cases,” Dr. Emanuel said. “If you’re missing breakthrough infections, a lot of them, you may be missing some [virus] evolution that would be very important for us to follow.” This missing information could include the emergence of new variants.
The asymptomatic breakthrough cases are the most worrisome group,” Dr. Emanuel said. “You get infected, you’re feeling fine. Maybe you’ve got a little sneeze or cough, but nothing unusual. And then you’re still able to transmit the Delta variant.”
The big picture
The upsurge in cases, hospitalizations, and deaths is a major challenge, Dr. Emanuel said. “We need to address that by getting many more people vaccinated right now with what are very good vaccines.”
“But it also means that we have to stop being U.S. focused alone.” He pointed out that Delta and other variants originated overseas, “so getting the world vaccinated ... has to be a top priority.”
“We are obviously all facing a challenge as we move into the fall,” Dr. Emanuel said. “With schools opening and employers bringing their employees back together, even if these groups are vaccinated, there are going to be major challenges for all of us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Because the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 spreads more easily than the original virus, the proportion of the population that needs to be vaccinated to reach herd immunity could be upward of 80% or more, experts say.
Also, it could be time to consider wearing an N95 mask in public indoor spaces regardless of vaccination status, according to a media briefing on Aug. 3 sponsored by the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Furthermore, giving booster shots to the fully vaccinated is not the top public health priority now. Instead, third vaccinations should be reserved for more vulnerable populations – and efforts should focus on getting first vaccinations to unvaccinated people in the United States and around the world.
“The problem here is that the Delta variant is ... more transmissible than the original virus. That pushes the overall population herd immunity threshold much higher,” Ricardo Franco, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said during the briefing.
“For Delta, those threshold estimates go well over 80% and may be approaching 90%,” he said.
To put that figure in context, the original SARS-CoV-2 virus required an estimated 67% of the population to be vaccinated to achieve herd immunity. Also, measles has one of the highest herd immunity thresholds at 95%, Dr. Franco added.
Herd immunity is the point at which enough people are immunized that the entire population gains protection. And it’s already happening. “Unvaccinated people are actually benefiting from greater herd immunity protection in high-vaccination counties compared to low-vaccination ones,” he said.
Maximize mask protection
Unlike early in the COVID-19 pandemic with widespread shortages of personal protective equipment, face masks are now readily available. This includes N95 masks, which offer enhanced protection against SARS-CoV-2, Ezekiel J. Emanuel, MD, PhD, said during the briefing.
Following the July 27 CDC recommendation that most Americans wear masks indoors when in public places, “I do think we need to upgrade our masks,” said Dr. Emanuel, who is Diane v.S. Levy & Robert M. Levy professor at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“It’s not just any mask,” he added. “Good masks make a big difference and are very important.”
Mask protection is about blocking 0.3-mcm particles, “and I think we need to make sure that people have masks that can filter that out,” he said. Although surgical masks are very good, he added, “they’re not quite as good as N95s.” As their name implies, N95s filter out 95% of these particles.
Dr. Emanuel acknowledged that people are tired of COVID-19 and complying with public health measures but urged perseverance. “We’ve sacrificed a lot. We should not throw it away in just a few months because we are tired. We’re all tired, but we do have to do the little bit extra getting vaccinated, wearing masks indoors, and protecting ourselves, our families, and our communities.”
Dealing with a disconnect
In response to a reporter’s question about the possibility that the large crowd at the Lollapalooza music festival in Chicago could become a superspreader event, Dr. Emanuel said, “it is worrisome.”
“I would say that, if you’re going to go to a gathering like that, wearing an N95 mask is wise, and not spending too long at any one place is also wise,” he said.
On the plus side, the event was held outdoors with lots of air circulation, Dr. Emanuel said.
However, “this is the kind of thing where we’ve got a sort of disconnect between people’s desire to get back to normal ... and the fact that we’re in the middle of this upsurge.”
Another potential problem is the event brought people together from many different locations, so when they travel home, they could be “potentially seeding lots of other communities.”
Boosters for some, for now
Even though not officially recommended, some fully vaccinated Americans are seeking a third or booster vaccination on their own.
Asked for his opinion, Dr. Emanuel said: “We’re probably going to have to be giving boosters to immunocompromised people and people who are susceptible. That’s where we are going to start.”
More research is needed regarding booster shots, he said. “There are very small studies – and the ‘very small’ should be emphasized – given that we’ve given shots to over 160 million people.”
“But it does appear that the boosters increase the antibodies and protection,” he said.
Instead of boosters, it is more important for people who haven’t been vaccinated to get fully vaccinated.
“We need to put our priorities in the right places,” he said.
Emanuel noted that, except for people in rural areas that might have to travel long distances, access to vaccines is no longer an issue. “It’s very hard not to find a vaccine if you want it.”
A remaining hurdle is “battling a major disinformation initiative. I don’t think this is misinformation. I think there’s very clear evidence that it is disinformation – false facts about the vaccines being spread,” Dr. Emanuel said.
The breakthrough infection dilemma
Breakthrough cases “remain the vast minority of infections at this time ... that is reassuring,” Dr. Franco said.
Also, tracking symptomatic breakthrough infections remains easier than studying fully vaccinated people who become infected with SARS-CoV-2 but remain symptom free.
“We really don’t have a good handle on the frequency of asymptomatic cases,” Dr. Emanuel said. “If you’re missing breakthrough infections, a lot of them, you may be missing some [virus] evolution that would be very important for us to follow.” This missing information could include the emergence of new variants.
The asymptomatic breakthrough cases are the most worrisome group,” Dr. Emanuel said. “You get infected, you’re feeling fine. Maybe you’ve got a little sneeze or cough, but nothing unusual. And then you’re still able to transmit the Delta variant.”
The big picture
The upsurge in cases, hospitalizations, and deaths is a major challenge, Dr. Emanuel said. “We need to address that by getting many more people vaccinated right now with what are very good vaccines.”
“But it also means that we have to stop being U.S. focused alone.” He pointed out that Delta and other variants originated overseas, “so getting the world vaccinated ... has to be a top priority.”
“We are obviously all facing a challenge as we move into the fall,” Dr. Emanuel said. “With schools opening and employers bringing their employees back together, even if these groups are vaccinated, there are going to be major challenges for all of us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
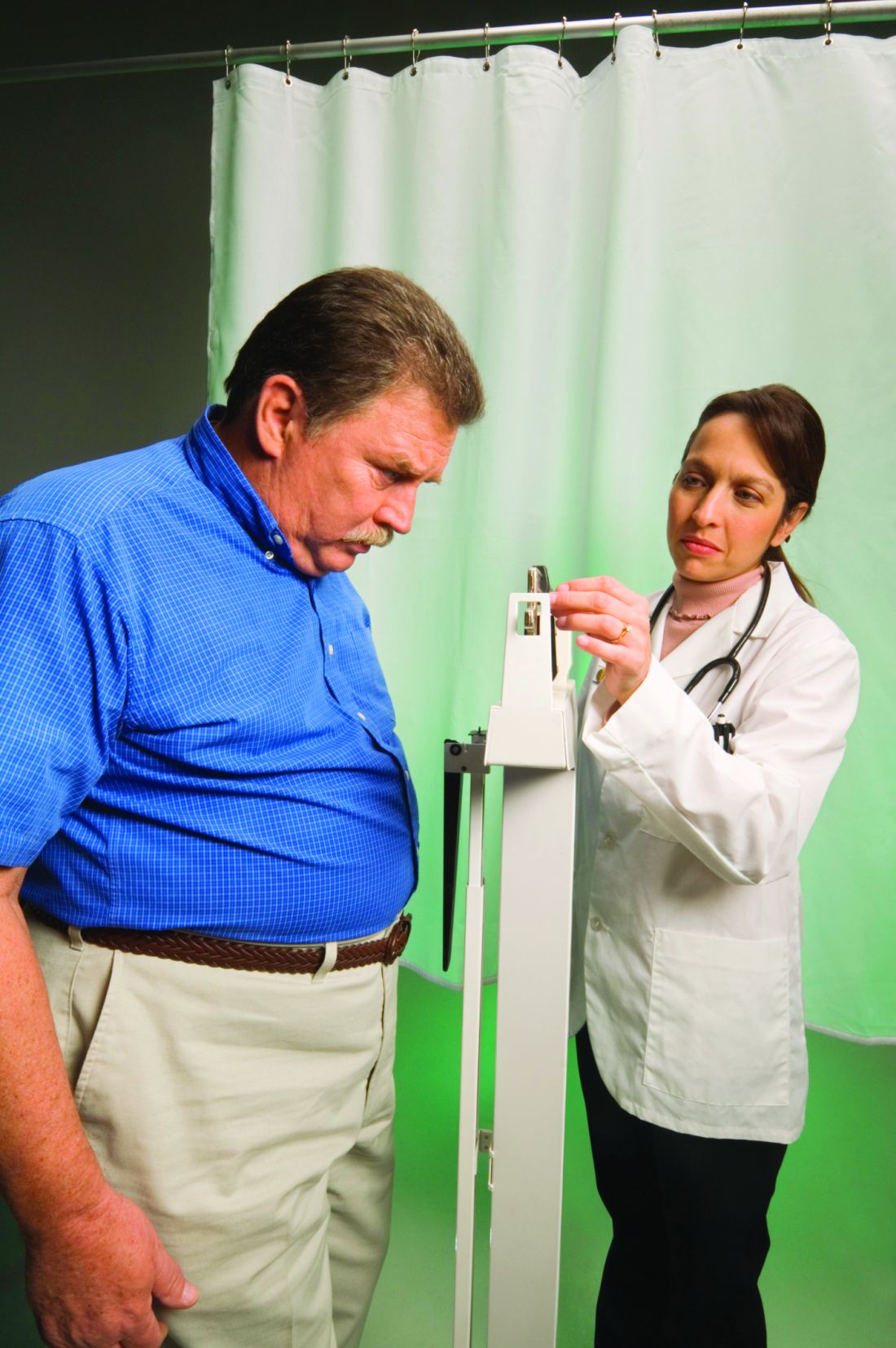
Diabetes drug’s new weight-loss indication fuels cost-benefit debate
The long list of side effects that follow ads for newer expensive drugs to treat type 2 diabetes sometimes include an unusual warning: They might cause weight loss. That side effect is one that many people – especially those with type 2 diabetes, which is associated with obesity – may desperately want.
So it’s no surprise that some of the same drugs are being reformulated and renamed by manufacturers as a new obesity treatment. No longer limited to the crowded field of treatments for type 2 diabetes, which affects about 10% of Americans, they join the far smaller number of drugs for obesity, which affects 42% of Americans and is ready to be mined for profit.
One that recently hit the market – winning Food and Drug Administration approval in June – is Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy (semaglutide), a higher-dose version of the company’s injectable diabetes drug, Ozempic.
Ozempic’s peppy ads suggest that people who use it might lose weight, but also include a disclaimer: that it “is not a weight-loss drug.” Now – with a new name – it is. And clinical trials showed using it leads to significant weight loss for many patients.
“People who go on this medication lose more weight than with any drug we’ve seen, ever,” said Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, who was not involved with any of the clinical trials.
But that leaves employers and insurers in the uncomfortable position of deciding if it’s worth it.
Wegovy’s monthly wholesale price tag – set at $1,349 – is about 58% more than Ozempic’s, although, the company pointed out, the drug’s injector pens contain more than twice as much of the active ingredient. Studies so far show that patients may need to take it indefinitely to maintain weight loss, translating to a tab that could top $323,000 over 20 years at the current price. Weight-loss treatments are not universally covered by insurance policies.
The arrival of this new class of weight-loss drugs – one from Lilly may soon follow – has created a thicket of issues for those who will pay for them. The decision is complicated by many unknowables concerning their long-term use and whether competition might eventually lower the price.
“The metric we try to use is value,” said James Gelfand, senior vice president for health policy at the ERISA Industry Committee, which represents large, self-insured employers. “If we pay for this drug, how much is this going to cost and how much value will it provide to the beneficiaries?”
Weight-loss treatments have had a lackluster past in this regard, with only modest results. Many employers and insurers likely remember Fen-Phen, a combination of fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine that was pulled from the market in the late 1990s for causing heart valve problems.
New drugs like Wegovy, more effective but also pricier than previous weight-loss treatments, will add more fuel to that debate.
Past treatments were shown to prompt weight loss in the range of 5%-10% of body weight. But many had relatively serious or unpleasant side effects.
Wegovy, however, helped patients lose an average of 15% of their body weight over 68 weeks in the main clinical trial that led to its approval. A comparison group that got a placebo injection lost an average of 2.5% over the same period. On the high end, nearly a third of patients in the treatment group lost 20% or more. Both groups had counseling on diet and exercise.
Side effects, generally considered mild, included nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation. A few patients developed pancreatitis, a serious inflammation of the pancreas. Like the diabetes medication, the drug carries a warning about a potential risk of a type of thyroid cancer.
Weight loss in those taking Wegovy puts it close to the 20%-25% losses seen with bariatric surgery, said Stanford, and well above the 3%-4% seen with diet and other lifestyle changes alone.
Participants also saw reductions in their waistlines and improvements in their blood pressure and blood sugar levels, which may mean they won’t develop diabetes, said Sean Wharton, MD, an internal medicine specialist and adjunct professor at York University in Toronto who was among the coauthors of the report outlining the results of the first clinical trial on Wegovy.
Since weight loss is known to reduce the risk of heart attack, high blood pressure and diabetes, might the new drug type be worth it?
Covering such treatment would be a sea change for Medicare, which specifically bars coverage for obesity medications or drugs for “anorexia, weight loss, or weight gain,” although it does pay for bariatric surgery. Pharmaceutical companies, patient advocates, and some medical professionals are backing proposed federal legislation to allow coverage. But the legislation, the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act, has not made progress despite being reintroduced every year since 2012, and sponsors are now asking federal officials instead to rewrite existing rules.
Private insurers will have to consider a cost-benefit analysis of adding Wegovy to their list of covered treatments, either broadly or with limits. Obesity was first recognized as a disease by the American Medical Association, easing the path for insurance coverage, in 2013.
“Employers are going to have a bit of a challenge” deciding whether to add the benefit to insurance offerings, said Steve Pearson, founder and president of the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, which provides cost-benefit analyses of medical treatments but has not yet looked at Wegovy.
The trade-offs are embodied in patients like Phylander Pannell, a 49-year-old Largo, Md., woman who said she lost 65 pounds in a clinical trial of Wegovy. That study gave the drug to all participants for the first 20 weeks, then randomly assigned patients to get either the drug or a placebo for the next 48 weeks to determine what happens when the medication is stopped. Only after the trial ended did she find out she was in the treatment group the entire time.
Her weight fell slowly at first, then ramped up, eventually bringing her 190-pound frame down to about 125. Pains in her joints eased; she felt better all around.
“I definitely feel the drug was it for me,” said Ms. Pannell, who also followed the trial’s guidance on diet and exercise.
The study found that both groups lost weight in the initial 20 weeks, but those who continued to get the drug lost an additional average of 7.9% of their body weight. Those who got a placebo gained back nearly 7%.
After the trial ended, and the COVID-19 pandemic hit, Ms. Pannell regained some weight and is now at 155. She is eager to get back on the medication and hopes her job-based insurance will cover it.
Many employers do cover obesity drugs. For example, about 40% of private employer plans include Novo Nordisk’s once-daily injection called Saxenda on their health plans, said Michael Bachner, Novo Nordisk’s director of media relations.
He said the $1,349-a-month wholesale acquisition price of Wegovy was determined by making it equivalent to that of Saxenda, which is less effective.
Still, that is more than the $851 monthly wholesale price of Ozempic. But, he pointed out, the recommended dosage of Wegovy is more than twice that of Ozempic. Four milligrams come in the Ozempic injector pens for the month, while Wegovy has 9.6.
“There’s more drug in the pen,” Mr. Bachner said. “That drives the price up.”
He added: “This is not a 20-year-old drug that we now have a new indication for and are pricing it higher. It’s a whole different clinical program,” which required new trials.
Now scientists, employers, physicians, and patients will have to decide whether the new drugs are worth it.
Earlier estimates – some commissioned by Novo Nordisk – of the potential cost of adding an obesity drug benefit to Medicare showed an overall reduction in spending when better health from the resulting weight loss was factored in.
Still, those earlier estimates considered much less expensive drugs, including a range of generic and branded drugs costing as little as $7 a month to more than $300, a small fraction of Wegovy’s cost.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The long list of side effects that follow ads for newer expensive drugs to treat type 2 diabetes sometimes include an unusual warning: They might cause weight loss. That side effect is one that many people – especially those with type 2 diabetes, which is associated with obesity – may desperately want.
So it’s no surprise that some of the same drugs are being reformulated and renamed by manufacturers as a new obesity treatment. No longer limited to the crowded field of treatments for type 2 diabetes, which affects about 10% of Americans, they join the far smaller number of drugs for obesity, which affects 42% of Americans and is ready to be mined for profit.
One that recently hit the market – winning Food and Drug Administration approval in June – is Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy (semaglutide), a higher-dose version of the company’s injectable diabetes drug, Ozempic.
Ozempic’s peppy ads suggest that people who use it might lose weight, but also include a disclaimer: that it “is not a weight-loss drug.” Now – with a new name – it is. And clinical trials showed using it leads to significant weight loss for many patients.
“People who go on this medication lose more weight than with any drug we’ve seen, ever,” said Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, who was not involved with any of the clinical trials.
But that leaves employers and insurers in the uncomfortable position of deciding if it’s worth it.
Wegovy’s monthly wholesale price tag – set at $1,349 – is about 58% more than Ozempic’s, although, the company pointed out, the drug’s injector pens contain more than twice as much of the active ingredient. Studies so far show that patients may need to take it indefinitely to maintain weight loss, translating to a tab that could top $323,000 over 20 years at the current price. Weight-loss treatments are not universally covered by insurance policies.
The arrival of this new class of weight-loss drugs – one from Lilly may soon follow – has created a thicket of issues for those who will pay for them. The decision is complicated by many unknowables concerning their long-term use and whether competition might eventually lower the price.
“The metric we try to use is value,” said James Gelfand, senior vice president for health policy at the ERISA Industry Committee, which represents large, self-insured employers. “If we pay for this drug, how much is this going to cost and how much value will it provide to the beneficiaries?”
Weight-loss treatments have had a lackluster past in this regard, with only modest results. Many employers and insurers likely remember Fen-Phen, a combination of fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine that was pulled from the market in the late 1990s for causing heart valve problems.
New drugs like Wegovy, more effective but also pricier than previous weight-loss treatments, will add more fuel to that debate.
Past treatments were shown to prompt weight loss in the range of 5%-10% of body weight. But many had relatively serious or unpleasant side effects.
Wegovy, however, helped patients lose an average of 15% of their body weight over 68 weeks in the main clinical trial that led to its approval. A comparison group that got a placebo injection lost an average of 2.5% over the same period. On the high end, nearly a third of patients in the treatment group lost 20% or more. Both groups had counseling on diet and exercise.
Side effects, generally considered mild, included nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation. A few patients developed pancreatitis, a serious inflammation of the pancreas. Like the diabetes medication, the drug carries a warning about a potential risk of a type of thyroid cancer.
Weight loss in those taking Wegovy puts it close to the 20%-25% losses seen with bariatric surgery, said Stanford, and well above the 3%-4% seen with diet and other lifestyle changes alone.
Participants also saw reductions in their waistlines and improvements in their blood pressure and blood sugar levels, which may mean they won’t develop diabetes, said Sean Wharton, MD, an internal medicine specialist and adjunct professor at York University in Toronto who was among the coauthors of the report outlining the results of the first clinical trial on Wegovy.
Since weight loss is known to reduce the risk of heart attack, high blood pressure and diabetes, might the new drug type be worth it?
Covering such treatment would be a sea change for Medicare, which specifically bars coverage for obesity medications or drugs for “anorexia, weight loss, or weight gain,” although it does pay for bariatric surgery. Pharmaceutical companies, patient advocates, and some medical professionals are backing proposed federal legislation to allow coverage. But the legislation, the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act, has not made progress despite being reintroduced every year since 2012, and sponsors are now asking federal officials instead to rewrite existing rules.
Private insurers will have to consider a cost-benefit analysis of adding Wegovy to their list of covered treatments, either broadly or with limits. Obesity was first recognized as a disease by the American Medical Association, easing the path for insurance coverage, in 2013.
“Employers are going to have a bit of a challenge” deciding whether to add the benefit to insurance offerings, said Steve Pearson, founder and president of the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, which provides cost-benefit analyses of medical treatments but has not yet looked at Wegovy.
The trade-offs are embodied in patients like Phylander Pannell, a 49-year-old Largo, Md., woman who said she lost 65 pounds in a clinical trial of Wegovy. That study gave the drug to all participants for the first 20 weeks, then randomly assigned patients to get either the drug or a placebo for the next 48 weeks to determine what happens when the medication is stopped. Only after the trial ended did she find out she was in the treatment group the entire time.
Her weight fell slowly at first, then ramped up, eventually bringing her 190-pound frame down to about 125. Pains in her joints eased; she felt better all around.
“I definitely feel the drug was it for me,” said Ms. Pannell, who also followed the trial’s guidance on diet and exercise.
The study found that both groups lost weight in the initial 20 weeks, but those who continued to get the drug lost an additional average of 7.9% of their body weight. Those who got a placebo gained back nearly 7%.
After the trial ended, and the COVID-19 pandemic hit, Ms. Pannell regained some weight and is now at 155. She is eager to get back on the medication and hopes her job-based insurance will cover it.
Many employers do cover obesity drugs. For example, about 40% of private employer plans include Novo Nordisk’s once-daily injection called Saxenda on their health plans, said Michael Bachner, Novo Nordisk’s director of media relations.
He said the $1,349-a-month wholesale acquisition price of Wegovy was determined by making it equivalent to that of Saxenda, which is less effective.
Still, that is more than the $851 monthly wholesale price of Ozempic. But, he pointed out, the recommended dosage of Wegovy is more than twice that of Ozempic. Four milligrams come in the Ozempic injector pens for the month, while Wegovy has 9.6.
“There’s more drug in the pen,” Mr. Bachner said. “That drives the price up.”
He added: “This is not a 20-year-old drug that we now have a new indication for and are pricing it higher. It’s a whole different clinical program,” which required new trials.
Now scientists, employers, physicians, and patients will have to decide whether the new drugs are worth it.
Earlier estimates – some commissioned by Novo Nordisk – of the potential cost of adding an obesity drug benefit to Medicare showed an overall reduction in spending when better health from the resulting weight loss was factored in.
Still, those earlier estimates considered much less expensive drugs, including a range of generic and branded drugs costing as little as $7 a month to more than $300, a small fraction of Wegovy’s cost.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The long list of side effects that follow ads for newer expensive drugs to treat type 2 diabetes sometimes include an unusual warning: They might cause weight loss. That side effect is one that many people – especially those with type 2 diabetes, which is associated with obesity – may desperately want.
So it’s no surprise that some of the same drugs are being reformulated and renamed by manufacturers as a new obesity treatment. No longer limited to the crowded field of treatments for type 2 diabetes, which affects about 10% of Americans, they join the far smaller number of drugs for obesity, which affects 42% of Americans and is ready to be mined for profit.
One that recently hit the market – winning Food and Drug Administration approval in June – is Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy (semaglutide), a higher-dose version of the company’s injectable diabetes drug, Ozempic.
Ozempic’s peppy ads suggest that people who use it might lose weight, but also include a disclaimer: that it “is not a weight-loss drug.” Now – with a new name – it is. And clinical trials showed using it leads to significant weight loss for many patients.
“People who go on this medication lose more weight than with any drug we’ve seen, ever,” said Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, who was not involved with any of the clinical trials.
But that leaves employers and insurers in the uncomfortable position of deciding if it’s worth it.
Wegovy’s monthly wholesale price tag – set at $1,349 – is about 58% more than Ozempic’s, although, the company pointed out, the drug’s injector pens contain more than twice as much of the active ingredient. Studies so far show that patients may need to take it indefinitely to maintain weight loss, translating to a tab that could top $323,000 over 20 years at the current price. Weight-loss treatments are not universally covered by insurance policies.
The arrival of this new class of weight-loss drugs – one from Lilly may soon follow – has created a thicket of issues for those who will pay for them. The decision is complicated by many unknowables concerning their long-term use and whether competition might eventually lower the price.
“The metric we try to use is value,” said James Gelfand, senior vice president for health policy at the ERISA Industry Committee, which represents large, self-insured employers. “If we pay for this drug, how much is this going to cost and how much value will it provide to the beneficiaries?”
Weight-loss treatments have had a lackluster past in this regard, with only modest results. Many employers and insurers likely remember Fen-Phen, a combination of fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine that was pulled from the market in the late 1990s for causing heart valve problems.
New drugs like Wegovy, more effective but also pricier than previous weight-loss treatments, will add more fuel to that debate.
Past treatments were shown to prompt weight loss in the range of 5%-10% of body weight. But many had relatively serious or unpleasant side effects.
Wegovy, however, helped patients lose an average of 15% of their body weight over 68 weeks in the main clinical trial that led to its approval. A comparison group that got a placebo injection lost an average of 2.5% over the same period. On the high end, nearly a third of patients in the treatment group lost 20% or more. Both groups had counseling on diet and exercise.
Side effects, generally considered mild, included nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation. A few patients developed pancreatitis, a serious inflammation of the pancreas. Like the diabetes medication, the drug carries a warning about a potential risk of a type of thyroid cancer.
Weight loss in those taking Wegovy puts it close to the 20%-25% losses seen with bariatric surgery, said Stanford, and well above the 3%-4% seen with diet and other lifestyle changes alone.
Participants also saw reductions in their waistlines and improvements in their blood pressure and blood sugar levels, which may mean they won’t develop diabetes, said Sean Wharton, MD, an internal medicine specialist and adjunct professor at York University in Toronto who was among the coauthors of the report outlining the results of the first clinical trial on Wegovy.
Since weight loss is known to reduce the risk of heart attack, high blood pressure and diabetes, might the new drug type be worth it?
Covering such treatment would be a sea change for Medicare, which specifically bars coverage for obesity medications or drugs for “anorexia, weight loss, or weight gain,” although it does pay for bariatric surgery. Pharmaceutical companies, patient advocates, and some medical professionals are backing proposed federal legislation to allow coverage. But the legislation, the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act, has not made progress despite being reintroduced every year since 2012, and sponsors are now asking federal officials instead to rewrite existing rules.
Private insurers will have to consider a cost-benefit analysis of adding Wegovy to their list of covered treatments, either broadly or with limits. Obesity was first recognized as a disease by the American Medical Association, easing the path for insurance coverage, in 2013.
“Employers are going to have a bit of a challenge” deciding whether to add the benefit to insurance offerings, said Steve Pearson, founder and president of the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, which provides cost-benefit analyses of medical treatments but has not yet looked at Wegovy.
The trade-offs are embodied in patients like Phylander Pannell, a 49-year-old Largo, Md., woman who said she lost 65 pounds in a clinical trial of Wegovy. That study gave the drug to all participants for the first 20 weeks, then randomly assigned patients to get either the drug or a placebo for the next 48 weeks to determine what happens when the medication is stopped. Only after the trial ended did she find out she was in the treatment group the entire time.
Her weight fell slowly at first, then ramped up, eventually bringing her 190-pound frame down to about 125. Pains in her joints eased; she felt better all around.
“I definitely feel the drug was it for me,” said Ms. Pannell, who also followed the trial’s guidance on diet and exercise.
The study found that both groups lost weight in the initial 20 weeks, but those who continued to get the drug lost an additional average of 7.9% of their body weight. Those who got a placebo gained back nearly 7%.
After the trial ended, and the COVID-19 pandemic hit, Ms. Pannell regained some weight and is now at 155. She is eager to get back on the medication and hopes her job-based insurance will cover it.
Many employers do cover obesity drugs. For example, about 40% of private employer plans include Novo Nordisk’s once-daily injection called Saxenda on their health plans, said Michael Bachner, Novo Nordisk’s director of media relations.
He said the $1,349-a-month wholesale acquisition price of Wegovy was determined by making it equivalent to that of Saxenda, which is less effective.
Still, that is more than the $851 monthly wholesale price of Ozempic. But, he pointed out, the recommended dosage of Wegovy is more than twice that of Ozempic. Four milligrams come in the Ozempic injector pens for the month, while Wegovy has 9.6.
“There’s more drug in the pen,” Mr. Bachner said. “That drives the price up.”
He added: “This is not a 20-year-old drug that we now have a new indication for and are pricing it higher. It’s a whole different clinical program,” which required new trials.
Now scientists, employers, physicians, and patients will have to decide whether the new drugs are worth it.
Earlier estimates – some commissioned by Novo Nordisk – of the potential cost of adding an obesity drug benefit to Medicare showed an overall reduction in spending when better health from the resulting weight loss was factored in.
Still, those earlier estimates considered much less expensive drugs, including a range of generic and branded drugs costing as little as $7 a month to more than $300, a small fraction of Wegovy’s cost.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Indoor masking needed in almost 70% of U.S. counties: CDC data
In announcing new guidance on July 27, the CDC said vaccinated people should wear face masks in indoor public places with “high” or “substantial” community transmission rates of COVID-19.
Data from the CDC shows that designation covers 69.3% of all counties in the United States – 52.2% (1,680 counties) with high community transmission rates and 17.1% (551 counties) with substantial rates.
A county has “high transmission” if it reports 100 or more weekly cases per 100,000 residents or a 10% or higher test positivity rate in the last 7 days, the CDC said. “Substantial transmission” means a county reports 50-99 weekly cases per 100,000 residents or has a positivity rate between 8% and 9.9% in the last 7 days.
About 23% of U.S. counties had moderate rates of community transmission, and 7.67% had low rates.
To find out the transmission rate in your county, go to the CDC COVID data tracker.
Smithsonian requiring masks again
The Smithsonian now requires all visitors over age 2, regardless of vaccination status, to wear face masks indoors and in all museum spaces.
The Smithsonian said in a news release that fully vaccinated visitors won’t have to wear masks at the National Zoo or outdoor gardens for museums.
The new rule goes into effect Aug. 6. It reverses a rule that said fully vaccinated visitors didn’t have to wear masks indoors beginning June 28.
Indoor face masks will be required throughout the District of Columbia beginning July 31., D.C. Mayor Muriel Bowser.
House Republicans protest face mask policy
About 40 maskless Republican members of the U.S. House of Representatives filed onto the Senate floor on July 29 to protest a new rule requiring House members to wear face masks, the Hill reported.
Congress’s attending doctor said in a memo that the 435 members of the House, plus workers, must wear masks indoors, but not the 100 members of the Senate. The Senate is a smaller body and has had better mask compliance than the House.
Rep. Ronny Jackson (R-Tex.), told the Hill that Republicans wanted to show “what it was like on the floor of the Senate versus the floor of the House. Obviously, it’s vastly different.”
Among the group of Republicans who filed onto the Senate floor were Rep. Lauren Boebert of Colorado, Rep. Matt Gaetz and Rep. Byron Donalds of Florida, Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene of Georgia, Rep. Chip Roy and Rep. Louie Gohmert of Texas, Rep. Madison Cawthorn of North Carolina, Rep. Warren Davidson of Ohio, and Rep. Andy Biggs of Arizona.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In announcing new guidance on July 27, the CDC said vaccinated people should wear face masks in indoor public places with “high” or “substantial” community transmission rates of COVID-19.
Data from the CDC shows that designation covers 69.3% of all counties in the United States – 52.2% (1,680 counties) with high community transmission rates and 17.1% (551 counties) with substantial rates.
A county has “high transmission” if it reports 100 or more weekly cases per 100,000 residents or a 10% or higher test positivity rate in the last 7 days, the CDC said. “Substantial transmission” means a county reports 50-99 weekly cases per 100,000 residents or has a positivity rate between 8% and 9.9% in the last 7 days.
About 23% of U.S. counties had moderate rates of community transmission, and 7.67% had low rates.
To find out the transmission rate in your county, go to the CDC COVID data tracker.
Smithsonian requiring masks again
The Smithsonian now requires all visitors over age 2, regardless of vaccination status, to wear face masks indoors and in all museum spaces.
The Smithsonian said in a news release that fully vaccinated visitors won’t have to wear masks at the National Zoo or outdoor gardens for museums.
The new rule goes into effect Aug. 6. It reverses a rule that said fully vaccinated visitors didn’t have to wear masks indoors beginning June 28.
Indoor face masks will be required throughout the District of Columbia beginning July 31., D.C. Mayor Muriel Bowser.
House Republicans protest face mask policy
About 40 maskless Republican members of the U.S. House of Representatives filed onto the Senate floor on July 29 to protest a new rule requiring House members to wear face masks, the Hill reported.
Congress’s attending doctor said in a memo that the 435 members of the House, plus workers, must wear masks indoors, but not the 100 members of the Senate. The Senate is a smaller body and has had better mask compliance than the House.
Rep. Ronny Jackson (R-Tex.), told the Hill that Republicans wanted to show “what it was like on the floor of the Senate versus the floor of the House. Obviously, it’s vastly different.”
Among the group of Republicans who filed onto the Senate floor were Rep. Lauren Boebert of Colorado, Rep. Matt Gaetz and Rep. Byron Donalds of Florida, Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene of Georgia, Rep. Chip Roy and Rep. Louie Gohmert of Texas, Rep. Madison Cawthorn of North Carolina, Rep. Warren Davidson of Ohio, and Rep. Andy Biggs of Arizona.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In announcing new guidance on July 27, the CDC said vaccinated people should wear face masks in indoor public places with “high” or “substantial” community transmission rates of COVID-19.
Data from the CDC shows that designation covers 69.3% of all counties in the United States – 52.2% (1,680 counties) with high community transmission rates and 17.1% (551 counties) with substantial rates.
A county has “high transmission” if it reports 100 or more weekly cases per 100,000 residents or a 10% or higher test positivity rate in the last 7 days, the CDC said. “Substantial transmission” means a county reports 50-99 weekly cases per 100,000 residents or has a positivity rate between 8% and 9.9% in the last 7 days.
About 23% of U.S. counties had moderate rates of community transmission, and 7.67% had low rates.
To find out the transmission rate in your county, go to the CDC COVID data tracker.
Smithsonian requiring masks again
The Smithsonian now requires all visitors over age 2, regardless of vaccination status, to wear face masks indoors and in all museum spaces.
The Smithsonian said in a news release that fully vaccinated visitors won’t have to wear masks at the National Zoo or outdoor gardens for museums.
The new rule goes into effect Aug. 6. It reverses a rule that said fully vaccinated visitors didn’t have to wear masks indoors beginning June 28.
Indoor face masks will be required throughout the District of Columbia beginning July 31., D.C. Mayor Muriel Bowser.
House Republicans protest face mask policy
About 40 maskless Republican members of the U.S. House of Representatives filed onto the Senate floor on July 29 to protest a new rule requiring House members to wear face masks, the Hill reported.
Congress’s attending doctor said in a memo that the 435 members of the House, plus workers, must wear masks indoors, but not the 100 members of the Senate. The Senate is a smaller body and has had better mask compliance than the House.
Rep. Ronny Jackson (R-Tex.), told the Hill that Republicans wanted to show “what it was like on the floor of the Senate versus the floor of the House. Obviously, it’s vastly different.”
Among the group of Republicans who filed onto the Senate floor were Rep. Lauren Boebert of Colorado, Rep. Matt Gaetz and Rep. Byron Donalds of Florida, Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene of Georgia, Rep. Chip Roy and Rep. Louie Gohmert of Texas, Rep. Madison Cawthorn of North Carolina, Rep. Warren Davidson of Ohio, and Rep. Andy Biggs of Arizona.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
‘War has changed’: CDC says Delta as contagious as chicken pox
Internal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention documents support the high transmission rate of the Delta variant and put the risk in easier to understand terms.
In addition, the agency released a new study that shows that breakthrough infections in the vaccinated make people about as contagious as those who are unvaccinated. The new report, published July 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), also reveals that the Delta variant likely causes more severe COVID-19 illness.
Given these recent findings, the internal CDC slide show advises that the agency should “acknowledge the war has changed.”
A ‘pivotal discovery’
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, said in a statement that the MMWR report demonstrates “that [D]elta infection resulted in similarly high SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in vaccinated and unvaccinated people.
“High viral loads suggest an increased risk of transmission and raised concern that, unlike with other variants, vaccinated people infected with [D]elta can transmit the virus,” she added. “This finding is concerning and was a pivotal discovery leading to CDC’s updated mask recommendation.”
The investigators analyzed 469 COVID-19 cases reported in Massachusetts residents July 3 through 17, 2021. The infections were associated with an outbreak following multiple events and large gatherings in Provincetown in that state’s easternmost Barnstable County, also known as Cape Cod.
Notably, 346 infections, or 74%, of the cases occurred in fully vaccinated individuals. This group had a median age of 42, and 87% were male. Also, 79% of the breakthrough infections were symptomatic.
Researchers also identified the Delta variant in 90% of 133 specimens collected for analysis. Furthermore, viral loads were about the same between samples taken from people who were fully vaccinated and those who were not.
Four of the five people hospitalized were fully vaccinated. No deaths were reported.
The publication of these results was highly anticipated following the CDC’s updated mask recommendations on July 27.
Outside the scope of the MMWR report is the total number of cases associated with the outbreak, including visitors from outside Massachusetts, which now approach 900 infections, NBC Boston reported.
‘Very sobering’ data
“The new information from the CDC around the [D]elta variant is very sobering,” David Hirschwerk, MD, infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said in an interview.
“The CDC is trying to convey and present this uncertain situation clearly to the public based on new, accumulated data,” he said. For example, given the evidence for higher contagiousness of the Delta variant, Dr. Hirschwerk added, “there will be situations where vaccinated people get infected, because the amount of the virus overwhelms the immune protection.
“What is new that is concerning is that people who are vaccinated still have the potential to transmit the virus to the same degree,” he said.
The MMWR study “helps us better understand the question related to whether or not a person who has completed a COVID-19 series can spread the infection,” agreed Michelle Barron, MD, a professor in the division of infectious disease at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
“The message is that, because the [D]elta variant is much more contagious than the original strain, unvaccinated persons need to get vaccinated because it is nearly impossible to avoid the virus indefinitely,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, infectious diseases specialist and epidemiologist at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said when asked to comment.
The new data highlight “that vaccinated persons, if they become sick, should still seek COVID-19 testing and should still isolate, as they are likely contagious,” Dr. Lin added.
More contagious than other infections
The internal CDC slide presentation also puts the new transmission risk in simple terms. Saying that the Delta variant is about as contagious as chicken pox, for example, immediately brings back vivid memories for some of staying indoors and away from friends during childhood or teenage outbreaks.
“A lot of people will remember getting chicken pox and then having their siblings get it shortly thereafter,” Dr. Barron said. “The only key thing to note is that this does not mean that the COVID-19 [D]elta variant mechanism of spread is the same as chicken pox and Ebola. The primary means of spread of COVID-19, even the Delta variant, is via droplets.”
This also means each person infected with the Delta variant could infect an average of eight or nine others.
In contrast, the original strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus was about as infectious as the common cold. In other words, someone was likely to infect about two other people on average.
In addition to the cold, the CDC notes that the Delta variant is now more contagious than Ebola, the seasonal flu, or small pox.
These Delta variant comparisons are one tangible way of explaining why the CDC on July 27 recommended a return to masking in schools and other indoor spaces for people – vaccinated and unvaccinated – in about 70% of the counties across the United States.
In comparing the Delta variant with other infections, “I think the CDC is trying to help people understand a little bit better the situation we now face since the information is so new. We are in a very different position now than just a few weeks ago, and it is hard for people to accept this,” Dr. Hirschwerk said.
The Delta variant is so different that the CDC considers it almost acting like a new virus altogether.
The CDC’s internal documents were first released by The Washington Post on July 29. The slides cite communication challenges for the agency to continue promoting vaccination while also acknowledging that breakthrough cases are occurring and therefore the fully vaccinated, in some instances, are likely infecting others.
Moving back to science talk, the CDC used the recent outbreak in Barnstable County as an example. The cycle threshold, or Ct values, a measure of viral load, were about the same between 80 vaccinated people linked to the outbreak who had a mean Ct value of 21.9, compared with 65 other unvaccinated people with a Ct of 21.5.
Many experts are quick to note that vaccination remains essential, in part because a vaccinated person also walks around with a much lower risk for severe outcomes, hospitalization, and death. In the internal slide show, the CDC points out that vaccination reduces the risk for infection threefold.
“Even with this high amount of virus, [the Delta variant] did not necessarily make the vaccinated individuals as sick,” Dr. Barron said.
In her statement, Dr. Walensky credited collaboration with the Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of Public Health and the CDC for the new data. She also thanked the residents of Barnstable County for participating in interviews done by contact tracers and their willingness to get tested and adhere to safety protocols after learning of their exposure.
Next moves by CDC?
The agency notes that next steps include consideration of prevention measures such as vaccine mandates for healthcare professionals to protect vulnerable populations, universal masking for source control and prevention, and reconsidering other community mitigation strategies.
Asked if this potential policy is appropriate and feasible, Dr. Lin said, “Yes, I believe that every person working in health care should be vaccinated for COVID-19, and it is feasible.”
Dr. Barron agreed as well. “We as health care providers choose to work in health care, and we should be doing everything feasible to ensure that we are protecting our patients and keeping our coworkers safe.”
“Whether you are a health care professional or not, I would urge everyone to get the COVID-19 vaccine, especially as cases across the country continue to rise,” Dr. Hirschwerk said. “Unequivocally vaccines protect you from the virus.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Internal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention documents support the high transmission rate of the Delta variant and put the risk in easier to understand terms.
In addition, the agency released a new study that shows that breakthrough infections in the vaccinated make people about as contagious as those who are unvaccinated. The new report, published July 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), also reveals that the Delta variant likely causes more severe COVID-19 illness.
Given these recent findings, the internal CDC slide show advises that the agency should “acknowledge the war has changed.”
A ‘pivotal discovery’
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, said in a statement that the MMWR report demonstrates “that [D]elta infection resulted in similarly high SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in vaccinated and unvaccinated people.
“High viral loads suggest an increased risk of transmission and raised concern that, unlike with other variants, vaccinated people infected with [D]elta can transmit the virus,” she added. “This finding is concerning and was a pivotal discovery leading to CDC’s updated mask recommendation.”
The investigators analyzed 469 COVID-19 cases reported in Massachusetts residents July 3 through 17, 2021. The infections were associated with an outbreak following multiple events and large gatherings in Provincetown in that state’s easternmost Barnstable County, also known as Cape Cod.
Notably, 346 infections, or 74%, of the cases occurred in fully vaccinated individuals. This group had a median age of 42, and 87% were male. Also, 79% of the breakthrough infections were symptomatic.
Researchers also identified the Delta variant in 90% of 133 specimens collected for analysis. Furthermore, viral loads were about the same between samples taken from people who were fully vaccinated and those who were not.
Four of the five people hospitalized were fully vaccinated. No deaths were reported.
The publication of these results was highly anticipated following the CDC’s updated mask recommendations on July 27.
Outside the scope of the MMWR report is the total number of cases associated with the outbreak, including visitors from outside Massachusetts, which now approach 900 infections, NBC Boston reported.
‘Very sobering’ data
“The new information from the CDC around the [D]elta variant is very sobering,” David Hirschwerk, MD, infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said in an interview.
“The CDC is trying to convey and present this uncertain situation clearly to the public based on new, accumulated data,” he said. For example, given the evidence for higher contagiousness of the Delta variant, Dr. Hirschwerk added, “there will be situations where vaccinated people get infected, because the amount of the virus overwhelms the immune protection.
“What is new that is concerning is that people who are vaccinated still have the potential to transmit the virus to the same degree,” he said.
The MMWR study “helps us better understand the question related to whether or not a person who has completed a COVID-19 series can spread the infection,” agreed Michelle Barron, MD, a professor in the division of infectious disease at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
“The message is that, because the [D]elta variant is much more contagious than the original strain, unvaccinated persons need to get vaccinated because it is nearly impossible to avoid the virus indefinitely,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, infectious diseases specialist and epidemiologist at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said when asked to comment.
The new data highlight “that vaccinated persons, if they become sick, should still seek COVID-19 testing and should still isolate, as they are likely contagious,” Dr. Lin added.
More contagious than other infections
The internal CDC slide presentation also puts the new transmission risk in simple terms. Saying that the Delta variant is about as contagious as chicken pox, for example, immediately brings back vivid memories for some of staying indoors and away from friends during childhood or teenage outbreaks.
“A lot of people will remember getting chicken pox and then having their siblings get it shortly thereafter,” Dr. Barron said. “The only key thing to note is that this does not mean that the COVID-19 [D]elta variant mechanism of spread is the same as chicken pox and Ebola. The primary means of spread of COVID-19, even the Delta variant, is via droplets.”
This also means each person infected with the Delta variant could infect an average of eight or nine others.
In contrast, the original strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus was about as infectious as the common cold. In other words, someone was likely to infect about two other people on average.
In addition to the cold, the CDC notes that the Delta variant is now more contagious than Ebola, the seasonal flu, or small pox.
These Delta variant comparisons are one tangible way of explaining why the CDC on July 27 recommended a return to masking in schools and other indoor spaces for people – vaccinated and unvaccinated – in about 70% of the counties across the United States.
In comparing the Delta variant with other infections, “I think the CDC is trying to help people understand a little bit better the situation we now face since the information is so new. We are in a very different position now than just a few weeks ago, and it is hard for people to accept this,” Dr. Hirschwerk said.
The Delta variant is so different that the CDC considers it almost acting like a new virus altogether.
The CDC’s internal documents were first released by The Washington Post on July 29. The slides cite communication challenges for the agency to continue promoting vaccination while also acknowledging that breakthrough cases are occurring and therefore the fully vaccinated, in some instances, are likely infecting others.
Moving back to science talk, the CDC used the recent outbreak in Barnstable County as an example. The cycle threshold, or Ct values, a measure of viral load, were about the same between 80 vaccinated people linked to the outbreak who had a mean Ct value of 21.9, compared with 65 other unvaccinated people with a Ct of 21.5.
Many experts are quick to note that vaccination remains essential, in part because a vaccinated person also walks around with a much lower risk for severe outcomes, hospitalization, and death. In the internal slide show, the CDC points out that vaccination reduces the risk for infection threefold.
“Even with this high amount of virus, [the Delta variant] did not necessarily make the vaccinated individuals as sick,” Dr. Barron said.
In her statement, Dr. Walensky credited collaboration with the Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of Public Health and the CDC for the new data. She also thanked the residents of Barnstable County for participating in interviews done by contact tracers and their willingness to get tested and adhere to safety protocols after learning of their exposure.
Next moves by CDC?
The agency notes that next steps include consideration of prevention measures such as vaccine mandates for healthcare professionals to protect vulnerable populations, universal masking for source control and prevention, and reconsidering other community mitigation strategies.
Asked if this potential policy is appropriate and feasible, Dr. Lin said, “Yes, I believe that every person working in health care should be vaccinated for COVID-19, and it is feasible.”
Dr. Barron agreed as well. “We as health care providers choose to work in health care, and we should be doing everything feasible to ensure that we are protecting our patients and keeping our coworkers safe.”
“Whether you are a health care professional or not, I would urge everyone to get the COVID-19 vaccine, especially as cases across the country continue to rise,” Dr. Hirschwerk said. “Unequivocally vaccines protect you from the virus.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Internal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention documents support the high transmission rate of the Delta variant and put the risk in easier to understand terms.
In addition, the agency released a new study that shows that breakthrough infections in the vaccinated make people about as contagious as those who are unvaccinated. The new report, published July 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), also reveals that the Delta variant likely causes more severe COVID-19 illness.
Given these recent findings, the internal CDC slide show advises that the agency should “acknowledge the war has changed.”
A ‘pivotal discovery’
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, said in a statement that the MMWR report demonstrates “that [D]elta infection resulted in similarly high SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in vaccinated and unvaccinated people.
“High viral loads suggest an increased risk of transmission and raised concern that, unlike with other variants, vaccinated people infected with [D]elta can transmit the virus,” she added. “This finding is concerning and was a pivotal discovery leading to CDC’s updated mask recommendation.”
The investigators analyzed 469 COVID-19 cases reported in Massachusetts residents July 3 through 17, 2021. The infections were associated with an outbreak following multiple events and large gatherings in Provincetown in that state’s easternmost Barnstable County, also known as Cape Cod.
Notably, 346 infections, or 74%, of the cases occurred in fully vaccinated individuals. This group had a median age of 42, and 87% were male. Also, 79% of the breakthrough infections were symptomatic.
Researchers also identified the Delta variant in 90% of 133 specimens collected for analysis. Furthermore, viral loads were about the same between samples taken from people who were fully vaccinated and those who were not.
Four of the five people hospitalized were fully vaccinated. No deaths were reported.
The publication of these results was highly anticipated following the CDC’s updated mask recommendations on July 27.
Outside the scope of the MMWR report is the total number of cases associated with the outbreak, including visitors from outside Massachusetts, which now approach 900 infections, NBC Boston reported.
‘Very sobering’ data
“The new information from the CDC around the [D]elta variant is very sobering,” David Hirschwerk, MD, infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said in an interview.
“The CDC is trying to convey and present this uncertain situation clearly to the public based on new, accumulated data,” he said. For example, given the evidence for higher contagiousness of the Delta variant, Dr. Hirschwerk added, “there will be situations where vaccinated people get infected, because the amount of the virus overwhelms the immune protection.
“What is new that is concerning is that people who are vaccinated still have the potential to transmit the virus to the same degree,” he said.
The MMWR study “helps us better understand the question related to whether or not a person who has completed a COVID-19 series can spread the infection,” agreed Michelle Barron, MD, a professor in the division of infectious disease at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
“The message is that, because the [D]elta variant is much more contagious than the original strain, unvaccinated persons need to get vaccinated because it is nearly impossible to avoid the virus indefinitely,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, infectious diseases specialist and epidemiologist at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said when asked to comment.
The new data highlight “that vaccinated persons, if they become sick, should still seek COVID-19 testing and should still isolate, as they are likely contagious,” Dr. Lin added.
More contagious than other infections
The internal CDC slide presentation also puts the new transmission risk in simple terms. Saying that the Delta variant is about as contagious as chicken pox, for example, immediately brings back vivid memories for some of staying indoors and away from friends during childhood or teenage outbreaks.
“A lot of people will remember getting chicken pox and then having their siblings get it shortly thereafter,” Dr. Barron said. “The only key thing to note is that this does not mean that the COVID-19 [D]elta variant mechanism of spread is the same as chicken pox and Ebola. The primary means of spread of COVID-19, even the Delta variant, is via droplets.”
This also means each person infected with the Delta variant could infect an average of eight or nine others.
In contrast, the original strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus was about as infectious as the common cold. In other words, someone was likely to infect about two other people on average.
In addition to the cold, the CDC notes that the Delta variant is now more contagious than Ebola, the seasonal flu, or small pox.
These Delta variant comparisons are one tangible way of explaining why the CDC on July 27 recommended a return to masking in schools and other indoor spaces for people – vaccinated and unvaccinated – in about 70% of the counties across the United States.
In comparing the Delta variant with other infections, “I think the CDC is trying to help people understand a little bit better the situation we now face since the information is so new. We are in a very different position now than just a few weeks ago, and it is hard for people to accept this,” Dr. Hirschwerk said.
The Delta variant is so different that the CDC considers it almost acting like a new virus altogether.
The CDC’s internal documents were first released by The Washington Post on July 29. The slides cite communication challenges for the agency to continue promoting vaccination while also acknowledging that breakthrough cases are occurring and therefore the fully vaccinated, in some instances, are likely infecting others.
Moving back to science talk, the CDC used the recent outbreak in Barnstable County as an example. The cycle threshold, or Ct values, a measure of viral load, were about the same between 80 vaccinated people linked to the outbreak who had a mean Ct value of 21.9, compared with 65 other unvaccinated people with a Ct of 21.5.
Many experts are quick to note that vaccination remains essential, in part because a vaccinated person also walks around with a much lower risk for severe outcomes, hospitalization, and death. In the internal slide show, the CDC points out that vaccination reduces the risk for infection threefold.
“Even with this high amount of virus, [the Delta variant] did not necessarily make the vaccinated individuals as sick,” Dr. Barron said.
In her statement, Dr. Walensky credited collaboration with the Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of Public Health and the CDC for the new data. She also thanked the residents of Barnstable County for participating in interviews done by contact tracers and their willingness to get tested and adhere to safety protocols after learning of their exposure.
Next moves by CDC?
The agency notes that next steps include consideration of prevention measures such as vaccine mandates for healthcare professionals to protect vulnerable populations, universal masking for source control and prevention, and reconsidering other community mitigation strategies.
Asked if this potential policy is appropriate and feasible, Dr. Lin said, “Yes, I believe that every person working in health care should be vaccinated for COVID-19, and it is feasible.”
Dr. Barron agreed as well. “We as health care providers choose to work in health care, and we should be doing everything feasible to ensure that we are protecting our patients and keeping our coworkers safe.”
“Whether you are a health care professional or not, I would urge everyone to get the COVID-19 vaccine, especially as cases across the country continue to rise,” Dr. Hirschwerk said. “Unequivocally vaccines protect you from the virus.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians wearing white coats rated more experienced
Physicians wearing white coats were rated as significantly more experienced and professional than peers wearing casual attire. Regardless of their attire, however, female physicians were more likely to be judged as appearing less professional and were more likely to be misidentified as medical technicians, physician assistants, or nurses, found research published in JAMA Network Open.
“A white coat with scrubs attire was most preferred for surgeons (mean preference index, 1.3), whereas a white coat with business attire was preferred for family physicians and dermatologists (mean preference indexes, 1.6 and 1.2, respectively; P < .001),” Helen Xun, MD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote. “A male model wearing business inner wear with a white coat, fleece jacket, or softshell jacket was perceived as significantly more professional than a female model wearing the same attire (mean professionalism score: male, 65.8; female, 56.2; mean difference in professionalism score: white coat, 12.06; fleece, 7.89; softshell, 8.82; P < .001). ... A male model wearing hospital scrubs or fashion scrubs alone was also perceived as more professional than a female model in the same attire.”
While casual attire, such as fleece or softshell jackets emblazoned with the names of the institution and wearer, has become more popular attire for physicians in recent years, the researchers noted theirs is the first published research to identify associations between gender, attire, and how people distinguish between various health care roles. The study authors launched their web-based survey from May to June 2020 and asked people aged 18 years and older to rate a series of photographs of deidentified models wearing health care attire. Inner wear choices were business attire versus scrubs with and without outer wear options of a long white coat, gray fleece jacket, or black softshell jackets. Survey respondents ranked the images on a 6-point Likert scale with 1 being the least experienced, professional, and friendly and 6 being the most experienced, professional, and friendly. Survey respondents also viewed individual images of male or female models and were asked to rate their professionalism on a scale of 0-100 – with 100 as the “most professional” as well as to identify their profession as either physician, surgeon, nurse, medical technician, or physician assistant.
The study team included 487 (93.3%) of 522 completed surveys in their analyses. Respondents’ mean age was 36.2 years; 260 (53.4%) were female; 372 (76.4%) were White; 33 (6.8%) were Black or African American. Younger respondents and those living in the Western United States who had more exposure to physician casual attire appeared more accepting of it, the authors wrote.
“I remember attending my white-coat ceremony as a medical student, and the symbolism of it all representing me entering the profession. It felt very emotional and heavy and I felt very proud to be there. I also remember taking a ‘selfie’ in my long white coat as a doctor for the first time before my first shift as a resident. But, I’ve also been wearing that same white coat, and a large badge with a ‘DOCTOR’ label on it, and been mistaken by a patient or parent for something other than the physician,” Alexandra M. Sims, a pediatrician and health equity researcher in Cincinnati, said in an interview. “So, I’d really hope that the take-home here is not simply that we must wear our white coats to be considered more professional. I think we have to unpack and dismantle how we’ve even built this notion of ‘professionalism’ in the first place. Women, people of color, and other marginalized groups were certainly not a part of the defining, but we must be a part of the reimagining of an equitable health care profession in this new era.”
As sartorial trends usher in more casual attire, clinicians should redouble efforts to build rapport and enhance communication with patients, such as clarifying team members’ roles when introducing themselves. Dr. Xun and coauthors noted that addressing gender bias is important for all clinicians – not just women – and point to the need for institutional and organizational support for disciplines where gender bias is “especially prevalent,” like surgery. “This responsibility should not be undertaken only by the individuals that experience the biases, which may result in additional cumulative career disadvantages. The promotion of equality and diversity begins with recognition, characterization, and evidence-supported interventions and is a community operation,” Dr. Xun and colleagues concluded.
“I do not equate attire to professionalism or experience, nor is it connected to my satisfaction with the physician. For myself and my daughter, it is the experience of care that ultimately influences our perceptions regarding the professionalism of the physician,” Hala H. Durrah, MTA, parent to a chronically ill child with special health care needs and a Patient and Family Engagement Consultant, said in an interview. “My respect for a physician will ultimately be determined by how my daughter and I were treated, not just from a clinical perspective, but how we felt during those interactions.”
Physicians wearing white coats were rated as significantly more experienced and professional than peers wearing casual attire. Regardless of their attire, however, female physicians were more likely to be judged as appearing less professional and were more likely to be misidentified as medical technicians, physician assistants, or nurses, found research published in JAMA Network Open.
“A white coat with scrubs attire was most preferred for surgeons (mean preference index, 1.3), whereas a white coat with business attire was preferred for family physicians and dermatologists (mean preference indexes, 1.6 and 1.2, respectively; P < .001),” Helen Xun, MD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote. “A male model wearing business inner wear with a white coat, fleece jacket, or softshell jacket was perceived as significantly more professional than a female model wearing the same attire (mean professionalism score: male, 65.8; female, 56.2; mean difference in professionalism score: white coat, 12.06; fleece, 7.89; softshell, 8.82; P < .001). ... A male model wearing hospital scrubs or fashion scrubs alone was also perceived as more professional than a female model in the same attire.”
While casual attire, such as fleece or softshell jackets emblazoned with the names of the institution and wearer, has become more popular attire for physicians in recent years, the researchers noted theirs is the first published research to identify associations between gender, attire, and how people distinguish between various health care roles. The study authors launched their web-based survey from May to June 2020 and asked people aged 18 years and older to rate a series of photographs of deidentified models wearing health care attire. Inner wear choices were business attire versus scrubs with and without outer wear options of a long white coat, gray fleece jacket, or black softshell jackets. Survey respondents ranked the images on a 6-point Likert scale with 1 being the least experienced, professional, and friendly and 6 being the most experienced, professional, and friendly. Survey respondents also viewed individual images of male or female models and were asked to rate their professionalism on a scale of 0-100 – with 100 as the “most professional” as well as to identify their profession as either physician, surgeon, nurse, medical technician, or physician assistant.
The study team included 487 (93.3%) of 522 completed surveys in their analyses. Respondents’ mean age was 36.2 years; 260 (53.4%) were female; 372 (76.4%) were White; 33 (6.8%) were Black or African American. Younger respondents and those living in the Western United States who had more exposure to physician casual attire appeared more accepting of it, the authors wrote.
“I remember attending my white-coat ceremony as a medical student, and the symbolism of it all representing me entering the profession. It felt very emotional and heavy and I felt very proud to be there. I also remember taking a ‘selfie’ in my long white coat as a doctor for the first time before my first shift as a resident. But, I’ve also been wearing that same white coat, and a large badge with a ‘DOCTOR’ label on it, and been mistaken by a patient or parent for something other than the physician,” Alexandra M. Sims, a pediatrician and health equity researcher in Cincinnati, said in an interview. “So, I’d really hope that the take-home here is not simply that we must wear our white coats to be considered more professional. I think we have to unpack and dismantle how we’ve even built this notion of ‘professionalism’ in the first place. Women, people of color, and other marginalized groups were certainly not a part of the defining, but we must be a part of the reimagining of an equitable health care profession in this new era.”
As sartorial trends usher in more casual attire, clinicians should redouble efforts to build rapport and enhance communication with patients, such as clarifying team members’ roles when introducing themselves. Dr. Xun and coauthors noted that addressing gender bias is important for all clinicians – not just women – and point to the need for institutional and organizational support for disciplines where gender bias is “especially prevalent,” like surgery. “This responsibility should not be undertaken only by the individuals that experience the biases, which may result in additional cumulative career disadvantages. The promotion of equality and diversity begins with recognition, characterization, and evidence-supported interventions and is a community operation,” Dr. Xun and colleagues concluded.
“I do not equate attire to professionalism or experience, nor is it connected to my satisfaction with the physician. For myself and my daughter, it is the experience of care that ultimately influences our perceptions regarding the professionalism of the physician,” Hala H. Durrah, MTA, parent to a chronically ill child with special health care needs and a Patient and Family Engagement Consultant, said in an interview. “My respect for a physician will ultimately be determined by how my daughter and I were treated, not just from a clinical perspective, but how we felt during those interactions.”
Physicians wearing white coats were rated as significantly more experienced and professional than peers wearing casual attire. Regardless of their attire, however, female physicians were more likely to be judged as appearing less professional and were more likely to be misidentified as medical technicians, physician assistants, or nurses, found research published in JAMA Network Open.
“A white coat with scrubs attire was most preferred for surgeons (mean preference index, 1.3), whereas a white coat with business attire was preferred for family physicians and dermatologists (mean preference indexes, 1.6 and 1.2, respectively; P < .001),” Helen Xun, MD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote. “A male model wearing business inner wear with a white coat, fleece jacket, or softshell jacket was perceived as significantly more professional than a female model wearing the same attire (mean professionalism score: male, 65.8; female, 56.2; mean difference in professionalism score: white coat, 12.06; fleece, 7.89; softshell, 8.82; P < .001). ... A male model wearing hospital scrubs or fashion scrubs alone was also perceived as more professional than a female model in the same attire.”
While casual attire, such as fleece or softshell jackets emblazoned with the names of the institution and wearer, has become more popular attire for physicians in recent years, the researchers noted theirs is the first published research to identify associations between gender, attire, and how people distinguish between various health care roles. The study authors launched their web-based survey from May to June 2020 and asked people aged 18 years and older to rate a series of photographs of deidentified models wearing health care attire. Inner wear choices were business attire versus scrubs with and without outer wear options of a long white coat, gray fleece jacket, or black softshell jackets. Survey respondents ranked the images on a 6-point Likert scale with 1 being the least experienced, professional, and friendly and 6 being the most experienced, professional, and friendly. Survey respondents also viewed individual images of male or female models and were asked to rate their professionalism on a scale of 0-100 – with 100 as the “most professional” as well as to identify their profession as either physician, surgeon, nurse, medical technician, or physician assistant.
The study team included 487 (93.3%) of 522 completed surveys in their analyses. Respondents’ mean age was 36.2 years; 260 (53.4%) were female; 372 (76.4%) were White; 33 (6.8%) were Black or African American. Younger respondents and those living in the Western United States who had more exposure to physician casual attire appeared more accepting of it, the authors wrote.
“I remember attending my white-coat ceremony as a medical student, and the symbolism of it all representing me entering the profession. It felt very emotional and heavy and I felt very proud to be there. I also remember taking a ‘selfie’ in my long white coat as a doctor for the first time before my first shift as a resident. But, I’ve also been wearing that same white coat, and a large badge with a ‘DOCTOR’ label on it, and been mistaken by a patient or parent for something other than the physician,” Alexandra M. Sims, a pediatrician and health equity researcher in Cincinnati, said in an interview. “So, I’d really hope that the take-home here is not simply that we must wear our white coats to be considered more professional. I think we have to unpack and dismantle how we’ve even built this notion of ‘professionalism’ in the first place. Women, people of color, and other marginalized groups were certainly not a part of the defining, but we must be a part of the reimagining of an equitable health care profession in this new era.”
As sartorial trends usher in more casual attire, clinicians should redouble efforts to build rapport and enhance communication with patients, such as clarifying team members’ roles when introducing themselves. Dr. Xun and coauthors noted that addressing gender bias is important for all clinicians – not just women – and point to the need for institutional and organizational support for disciplines where gender bias is “especially prevalent,” like surgery. “This responsibility should not be undertaken only by the individuals that experience the biases, which may result in additional cumulative career disadvantages. The promotion of equality and diversity begins with recognition, characterization, and evidence-supported interventions and is a community operation,” Dr. Xun and colleagues concluded.
“I do not equate attire to professionalism or experience, nor is it connected to my satisfaction with the physician. For myself and my daughter, it is the experience of care that ultimately influences our perceptions regarding the professionalism of the physician,” Hala H. Durrah, MTA, parent to a chronically ill child with special health care needs and a Patient and Family Engagement Consultant, said in an interview. “My respect for a physician will ultimately be determined by how my daughter and I were treated, not just from a clinical perspective, but how we felt during those interactions.”
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Modest calorie reduction plus exercise linked with improved vascular health
Finding applies to seniors with obesity, who were part of a new study
The authors of the paper, published in Circulation, found a link between greater vascular benefits and exercise with modest – rather than intense – calorie restriction (CR) in elderly individuals with obesity.
“The finding that higher-intensity calorie restriction may not be necessary or advised has important implications for weight loss recommendations,” noted Tina E. Brinkley, Ph.D., lead author of the study and associate professor of gerontology and geriatric medicine at the Sticht Center for Healthy Aging and Alzheimer’s Prevention at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
It’s “not entirely clear” why greater calorie restriction did not translate to greater vascular benefit, but it “could be related in part to potentially adverse effects of severe CR on vascular function,” she noted. “These findings have important implications for reducing cardiovascular risk with nonpharmacological interventions in high-risk populations.”
Methods and findings
The study included 160 men and women aged 65-79 years, with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 to 45 kg/m2. The subjects were randomized to one of three groups for 20 weeks of aerobic exercise only, aerobic exercise plus moderate CR, or aerobic exercise plus more intensive CR. Their exercise regimen involved 30 minutes of supervised treadmill walking for 4 days per week at 65%-70% of heart rate reserve.
Subjects in the moderate CR group decreased caloric intake by 250 kcals a day, while the intense calorie reduction group cut 600 kcals per day. Their meals contained less than 30% of calories from fat and at least 0.8 g of protein per kg of ideal body weight. They were also provided with supplemental calcium (1,200 mg/day) and vitamin D (800 IU/day).
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging was used to assess various aspects of aortic structure and function, including aortic arch pulse wave velocity, aortic distensibility and dimensions, and periaortic fat.
Weight loss was greater among subjects with CR plus exercise, compared with that of patients in the exercise-only group. The degree of weight loss was not significantly different between those with moderate versus intense CR ( 8.02 kg vs. 8.98 kg).
Among the exercise-only group, researchers observed no changes in aortic stiffness. However, adding moderate CR significantly improved this measure, while intense CR did not.
Specifically, subjects in the moderate-CR group had a “robust” 21% increase in distensibility in the descending aorta (DA), and an 8% decrease in aortic arch pulse wave velocity, whereas there were no significant vascular changes in the intense-CR group.
Bests results seen in exercise plus modest CR group
“Collectively, these data suggest that combining exercise with modest CR (as opposed to more intensive CR or no CR) provides the greatest benefit for proximal aortic stiffness, while also optimizing weight loss and improvements in body composition and body fat distribution,” noted the authors in their paper.
“Our data support the growing number of studies indicating that intentional weight loss can be safe for older adults with obesity and extend our previous findings, suggesting that obesity may blunt the beneficial effects of exercise for not only cardiorespiratory fitness, but likely vascular health as well.”
William E. Kraus, MD, professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology at Duke University Medical Center, in Durham, NC, described the study as important and interesting for several reasons.
“First, it demonstrates one can change aortic vascular function with a combined diet and exercise program, even in older, obese Americans. This implies it is never too late to make meaningful lifestyle changes that will benefit cardiovascular health,” he said. “Second, it is among an increasing number of studies demonstrating that more is not always better than less in exercise and diet lifestyle changes - and in fact the converse is true.”
“This gives hope that more people can benefit from modest lifestyle changes - in this case following guidelines for physical activity and only a modest reduction of 250 kilocalories per day resulted in benefit,” Dr. Kraus added.
The authors of the paper and Dr. Kraus disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Finding applies to seniors with obesity, who were part of a new study
Finding applies to seniors with obesity, who were part of a new study
The authors of the paper, published in Circulation, found a link between greater vascular benefits and exercise with modest – rather than intense – calorie restriction (CR) in elderly individuals with obesity.
“The finding that higher-intensity calorie restriction may not be necessary or advised has important implications for weight loss recommendations,” noted Tina E. Brinkley, Ph.D., lead author of the study and associate professor of gerontology and geriatric medicine at the Sticht Center for Healthy Aging and Alzheimer’s Prevention at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
It’s “not entirely clear” why greater calorie restriction did not translate to greater vascular benefit, but it “could be related in part to potentially adverse effects of severe CR on vascular function,” she noted. “These findings have important implications for reducing cardiovascular risk with nonpharmacological interventions in high-risk populations.”
Methods and findings
The study included 160 men and women aged 65-79 years, with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 to 45 kg/m2. The subjects were randomized to one of three groups for 20 weeks of aerobic exercise only, aerobic exercise plus moderate CR, or aerobic exercise plus more intensive CR. Their exercise regimen involved 30 minutes of supervised treadmill walking for 4 days per week at 65%-70% of heart rate reserve.
Subjects in the moderate CR group decreased caloric intake by 250 kcals a day, while the intense calorie reduction group cut 600 kcals per day. Their meals contained less than 30% of calories from fat and at least 0.8 g of protein per kg of ideal body weight. They were also provided with supplemental calcium (1,200 mg/day) and vitamin D (800 IU/day).
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging was used to assess various aspects of aortic structure and function, including aortic arch pulse wave velocity, aortic distensibility and dimensions, and periaortic fat.
Weight loss was greater among subjects with CR plus exercise, compared with that of patients in the exercise-only group. The degree of weight loss was not significantly different between those with moderate versus intense CR ( 8.02 kg vs. 8.98 kg).
Among the exercise-only group, researchers observed no changes in aortic stiffness. However, adding moderate CR significantly improved this measure, while intense CR did not.
Specifically, subjects in the moderate-CR group had a “robust” 21% increase in distensibility in the descending aorta (DA), and an 8% decrease in aortic arch pulse wave velocity, whereas there were no significant vascular changes in the intense-CR group.
Bests results seen in exercise plus modest CR group
“Collectively, these data suggest that combining exercise with modest CR (as opposed to more intensive CR or no CR) provides the greatest benefit for proximal aortic stiffness, while also optimizing weight loss and improvements in body composition and body fat distribution,” noted the authors in their paper.
“Our data support the growing number of studies indicating that intentional weight loss can be safe for older adults with obesity and extend our previous findings, suggesting that obesity may blunt the beneficial effects of exercise for not only cardiorespiratory fitness, but likely vascular health as well.”
William E. Kraus, MD, professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology at Duke University Medical Center, in Durham, NC, described the study as important and interesting for several reasons.
“First, it demonstrates one can change aortic vascular function with a combined diet and exercise program, even in older, obese Americans. This implies it is never too late to make meaningful lifestyle changes that will benefit cardiovascular health,” he said. “Second, it is among an increasing number of studies demonstrating that more is not always better than less in exercise and diet lifestyle changes - and in fact the converse is true.”
“This gives hope that more people can benefit from modest lifestyle changes - in this case following guidelines for physical activity and only a modest reduction of 250 kilocalories per day resulted in benefit,” Dr. Kraus added.
The authors of the paper and Dr. Kraus disclosed no conflicts of interest.
The authors of the paper, published in Circulation, found a link between greater vascular benefits and exercise with modest – rather than intense – calorie restriction (CR) in elderly individuals with obesity.
“The finding that higher-intensity calorie restriction may not be necessary or advised has important implications for weight loss recommendations,” noted Tina E. Brinkley, Ph.D., lead author of the study and associate professor of gerontology and geriatric medicine at the Sticht Center for Healthy Aging and Alzheimer’s Prevention at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
It’s “not entirely clear” why greater calorie restriction did not translate to greater vascular benefit, but it “could be related in part to potentially adverse effects of severe CR on vascular function,” she noted. “These findings have important implications for reducing cardiovascular risk with nonpharmacological interventions in high-risk populations.”
Methods and findings
The study included 160 men and women aged 65-79 years, with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 to 45 kg/m2. The subjects were randomized to one of three groups for 20 weeks of aerobic exercise only, aerobic exercise plus moderate CR, or aerobic exercise plus more intensive CR. Their exercise regimen involved 30 minutes of supervised treadmill walking for 4 days per week at 65%-70% of heart rate reserve.
Subjects in the moderate CR group decreased caloric intake by 250 kcals a day, while the intense calorie reduction group cut 600 kcals per day. Their meals contained less than 30% of calories from fat and at least 0.8 g of protein per kg of ideal body weight. They were also provided with supplemental calcium (1,200 mg/day) and vitamin D (800 IU/day).
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging was used to assess various aspects of aortic structure and function, including aortic arch pulse wave velocity, aortic distensibility and dimensions, and periaortic fat.
Weight loss was greater among subjects with CR plus exercise, compared with that of patients in the exercise-only group. The degree of weight loss was not significantly different between those with moderate versus intense CR ( 8.02 kg vs. 8.98 kg).
Among the exercise-only group, researchers observed no changes in aortic stiffness. However, adding moderate CR significantly improved this measure, while intense CR did not.
Specifically, subjects in the moderate-CR group had a “robust” 21% increase in distensibility in the descending aorta (DA), and an 8% decrease in aortic arch pulse wave velocity, whereas there were no significant vascular changes in the intense-CR group.
Bests results seen in exercise plus modest CR group
“Collectively, these data suggest that combining exercise with modest CR (as opposed to more intensive CR or no CR) provides the greatest benefit for proximal aortic stiffness, while also optimizing weight loss and improvements in body composition and body fat distribution,” noted the authors in their paper.
“Our data support the growing number of studies indicating that intentional weight loss can be safe for older adults with obesity and extend our previous findings, suggesting that obesity may blunt the beneficial effects of exercise for not only cardiorespiratory fitness, but likely vascular health as well.”
William E. Kraus, MD, professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology at Duke University Medical Center, in Durham, NC, described the study as important and interesting for several reasons.
“First, it demonstrates one can change aortic vascular function with a combined diet and exercise program, even in older, obese Americans. This implies it is never too late to make meaningful lifestyle changes that will benefit cardiovascular health,” he said. “Second, it is among an increasing number of studies demonstrating that more is not always better than less in exercise and diet lifestyle changes - and in fact the converse is true.”
“This gives hope that more people can benefit from modest lifestyle changes - in this case following guidelines for physical activity and only a modest reduction of 250 kilocalories per day resulted in benefit,” Dr. Kraus added.
The authors of the paper and Dr. Kraus disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM CIRCULATION
Even 10 minutes of daily exercise beneficial after ICD implantation
Small increases in daily physical activity are associated with a boost in 1-year survival in patients with heart failure and coronary disease who received an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), new research suggests.
“Our study looked at how much exercise was necessary for a better outcome in patients with prior ICD implantation and, for every 10 minutes of exercise, we saw a 1% reduction in the likelihood of death or hospitalization, which is a pretty profound impact on outcome for just a small amount of additional physical activity per day,” lead author Brett Atwater, MD, told this news organization.
“These improvements were achieved outside of a formal cardiac rehabilitation program, suggesting that the benefits of increased physical activity obtained in cardiac rehabilitation programs may also be achievable at home,” he said.
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) programs have been shown to improve short- and long-term outcomes in patients with heart failure (HF) but continue to be underutilized, especially by women, the elderly, and minorities. Home-based CR could help overcome this limitation but the science behind it is relatively new, noted Dr. Atwater, director of electrophysiology and electrophysiology research, Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Fairfax, Va.
As reported in Circulation Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, the study involved 41,731 Medicare beneficiaries (mean age, 73.5 years) who received an ICD from 2014 to 2016.
ICD heart rate and activity sensor measurements were used to establish a personalized physical activity (PA) threshold for each patient in the first 3 weeks after ICD implantation. Thereafter, the ICD logged PA when the personalized PA threshold was exceeded. The mean baseline PA level was 128.9 minutes/day.
At 3 years’ follow-up, one-quarter of the patients had died and half had been hospitalized for HF. Of the total population, only 3.2% participated in CR.
Compared with nonparticipants, CR participants were more likely to be White (91.0% versus 87.3%), male (75.5% versus 72.2%), and to have diabetes (48.8% versus 44.1%), ischemic heart disease (91.4% versus 82.1%), or congestive heart failure (90.4% versus 83.4%).
CR participants attended a median of 24 sessions, during which time daily PA increased by a mean of 9.7 minutes per day. During the same time, PA decreased by a mean of 1.0 minute per day in non-CR participants (P < .001).
PA levels remained “relatively constant” for the first 36 months of follow-up among CR participants before showing a steep decline, whereas levels gradually declined throughout follow-up among nonparticipants, with a median annual change of –4.5 min/day.
In adjusted analysis, every 10 minutes of increased daily PA was associated with a 1.1% reduced risk for death (hazard ratio, 0.989; 95% confidence interval, 0.979-0.996) and a 1% reduced risk for HF hospitalization (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.986-0.995) at 1-year follow-up (P < .001).
After propensity score was used to match CR participants with nonparticipants by demographic characteristics, comorbidities, and baseline PA level, CR participants had a significantly lower risk for death at 1 year (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.69-0.85). This difference in risk remained at 2- and 3-year follow-ups.
However, when the researchers further adjusted for change in PA during CR or the same time period after device implantation, no differences in mortality were found between CR participants and nonparticipants at 1 year (HR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.82-1.21) or at 2 or 3 years.
The risk for HF hospitalization did not differ between the two groups in either propensity score model.
Unlike wearable devices, implanted devices “don’t give that type of feedback to patients regarding PA levels – only to providers – and it will be interesting to discover whether providing feedback to patients can motivate them to do more physical activity,” Dr. Atwater commented.
The team is currently enrolling patients in a follow-up trial, in which patients will be given feedback from their ICD “to move these data from an interesting observation to something that can drive outcomes,” he said.
Commenting for this news organization, Melissa Tracy, MD, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said the study reiterates the “profound” underutilization of CR.
“Only about 3% of patients who should have qualified for cardiac rehabilitation actually attended, which is startling considering that it has class 1A level of evidence supporting its use,” she said.
Dr. Tracy, who is also a member of the American College of Cardiology’s Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Section Leadership Council, described the study as “another notch in the belt of positive outcomes supporting the need for cardiac rehabilitation” and emphasizing the importance of a home-based alternative.
“One of the reasons women, minorities, and older patients don’t go to cardiac rehabilitation is they have to get there, rely on someone to drive them, or they have other responsibilities – especially women, who are often primary caretakers of others,” she said. “For women and men, the pressure to get back to work and support their families means they don’t have the luxury to go to cardiac rehabilitation.”
Dr. Tracy noted that home-based CR is covered by CMS until the end of 2021. “An important take-home is for providers and patients to understand that they do have a home-based option,” she stated.
Limitations of the study are that only 24% of patients were women, only 6% were Black, and the results might not be generalizable to patients younger than 65 years, note Dr. Atwater and colleagues. Also, previous implantation might have protected the cohort from experiencing arrhythmic death, and it remains unclear if similar results would be obtained in patients without a previous ICD.
This research was funded through the unrestricted Abbott Medical-Duke Health Strategic Alliance Research Grant. Dr. Atwater receives significant research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott Medical, and modest honoraria from Abbott Medical, Medtronic, and Biotronik. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tracy has created cardiac prevention programs with Virtual Health Partners (VHP) and owns the intellectual property and consults with VHP but receives no monetary compensation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Small increases in daily physical activity are associated with a boost in 1-year survival in patients with heart failure and coronary disease who received an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), new research suggests.
“Our study looked at how much exercise was necessary for a better outcome in patients with prior ICD implantation and, for every 10 minutes of exercise, we saw a 1% reduction in the likelihood of death or hospitalization, which is a pretty profound impact on outcome for just a small amount of additional physical activity per day,” lead author Brett Atwater, MD, told this news organization.
“These improvements were achieved outside of a formal cardiac rehabilitation program, suggesting that the benefits of increased physical activity obtained in cardiac rehabilitation programs may also be achievable at home,” he said.
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) programs have been shown to improve short- and long-term outcomes in patients with heart failure (HF) but continue to be underutilized, especially by women, the elderly, and minorities. Home-based CR could help overcome this limitation but the science behind it is relatively new, noted Dr. Atwater, director of electrophysiology and electrophysiology research, Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Fairfax, Va.
As reported in Circulation Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, the study involved 41,731 Medicare beneficiaries (mean age, 73.5 years) who received an ICD from 2014 to 2016.
ICD heart rate and activity sensor measurements were used to establish a personalized physical activity (PA) threshold for each patient in the first 3 weeks after ICD implantation. Thereafter, the ICD logged PA when the personalized PA threshold was exceeded. The mean baseline PA level was 128.9 minutes/day.
At 3 years’ follow-up, one-quarter of the patients had died and half had been hospitalized for HF. Of the total population, only 3.2% participated in CR.
Compared with nonparticipants, CR participants were more likely to be White (91.0% versus 87.3%), male (75.5% versus 72.2%), and to have diabetes (48.8% versus 44.1%), ischemic heart disease (91.4% versus 82.1%), or congestive heart failure (90.4% versus 83.4%).
CR participants attended a median of 24 sessions, during which time daily PA increased by a mean of 9.7 minutes per day. During the same time, PA decreased by a mean of 1.0 minute per day in non-CR participants (P < .001).
PA levels remained “relatively constant” for the first 36 months of follow-up among CR participants before showing a steep decline, whereas levels gradually declined throughout follow-up among nonparticipants, with a median annual change of –4.5 min/day.
In adjusted analysis, every 10 minutes of increased daily PA was associated with a 1.1% reduced risk for death (hazard ratio, 0.989; 95% confidence interval, 0.979-0.996) and a 1% reduced risk for HF hospitalization (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.986-0.995) at 1-year follow-up (P < .001).
After propensity score was used to match CR participants with nonparticipants by demographic characteristics, comorbidities, and baseline PA level, CR participants had a significantly lower risk for death at 1 year (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.69-0.85). This difference in risk remained at 2- and 3-year follow-ups.
However, when the researchers further adjusted for change in PA during CR or the same time period after device implantation, no differences in mortality were found between CR participants and nonparticipants at 1 year (HR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.82-1.21) or at 2 or 3 years.
The risk for HF hospitalization did not differ between the two groups in either propensity score model.
Unlike wearable devices, implanted devices “don’t give that type of feedback to patients regarding PA levels – only to providers – and it will be interesting to discover whether providing feedback to patients can motivate them to do more physical activity,” Dr. Atwater commented.
The team is currently enrolling patients in a follow-up trial, in which patients will be given feedback from their ICD “to move these data from an interesting observation to something that can drive outcomes,” he said.
Commenting for this news organization, Melissa Tracy, MD, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said the study reiterates the “profound” underutilization of CR.
“Only about 3% of patients who should have qualified for cardiac rehabilitation actually attended, which is startling considering that it has class 1A level of evidence supporting its use,” she said.
Dr. Tracy, who is also a member of the American College of Cardiology’s Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Section Leadership Council, described the study as “another notch in the belt of positive outcomes supporting the need for cardiac rehabilitation” and emphasizing the importance of a home-based alternative.
“One of the reasons women, minorities, and older patients don’t go to cardiac rehabilitation is they have to get there, rely on someone to drive them, or they have other responsibilities – especially women, who are often primary caretakers of others,” she said. “For women and men, the pressure to get back to work and support their families means they don’t have the luxury to go to cardiac rehabilitation.”
Dr. Tracy noted that home-based CR is covered by CMS until the end of 2021. “An important take-home is for providers and patients to understand that they do have a home-based option,” she stated.
Limitations of the study are that only 24% of patients were women, only 6% were Black, and the results might not be generalizable to patients younger than 65 years, note Dr. Atwater and colleagues. Also, previous implantation might have protected the cohort from experiencing arrhythmic death, and it remains unclear if similar results would be obtained in patients without a previous ICD.
This research was funded through the unrestricted Abbott Medical-Duke Health Strategic Alliance Research Grant. Dr. Atwater receives significant research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott Medical, and modest honoraria from Abbott Medical, Medtronic, and Biotronik. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tracy has created cardiac prevention programs with Virtual Health Partners (VHP) and owns the intellectual property and consults with VHP but receives no monetary compensation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Small increases in daily physical activity are associated with a boost in 1-year survival in patients with heart failure and coronary disease who received an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), new research suggests.
“Our study looked at how much exercise was necessary for a better outcome in patients with prior ICD implantation and, for every 10 minutes of exercise, we saw a 1% reduction in the likelihood of death or hospitalization, which is a pretty profound impact on outcome for just a small amount of additional physical activity per day,” lead author Brett Atwater, MD, told this news organization.
“These improvements were achieved outside of a formal cardiac rehabilitation program, suggesting that the benefits of increased physical activity obtained in cardiac rehabilitation programs may also be achievable at home,” he said.
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) programs have been shown to improve short- and long-term outcomes in patients with heart failure (HF) but continue to be underutilized, especially by women, the elderly, and minorities. Home-based CR could help overcome this limitation but the science behind it is relatively new, noted Dr. Atwater, director of electrophysiology and electrophysiology research, Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Fairfax, Va.
As reported in Circulation Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, the study involved 41,731 Medicare beneficiaries (mean age, 73.5 years) who received an ICD from 2014 to 2016.
ICD heart rate and activity sensor measurements were used to establish a personalized physical activity (PA) threshold for each patient in the first 3 weeks after ICD implantation. Thereafter, the ICD logged PA when the personalized PA threshold was exceeded. The mean baseline PA level was 128.9 minutes/day.
At 3 years’ follow-up, one-quarter of the patients had died and half had been hospitalized for HF. Of the total population, only 3.2% participated in CR.
Compared with nonparticipants, CR participants were more likely to be White (91.0% versus 87.3%), male (75.5% versus 72.2%), and to have diabetes (48.8% versus 44.1%), ischemic heart disease (91.4% versus 82.1%), or congestive heart failure (90.4% versus 83.4%).
CR participants attended a median of 24 sessions, during which time daily PA increased by a mean of 9.7 minutes per day. During the same time, PA decreased by a mean of 1.0 minute per day in non-CR participants (P < .001).
PA levels remained “relatively constant” for the first 36 months of follow-up among CR participants before showing a steep decline, whereas levels gradually declined throughout follow-up among nonparticipants, with a median annual change of –4.5 min/day.
In adjusted analysis, every 10 minutes of increased daily PA was associated with a 1.1% reduced risk for death (hazard ratio, 0.989; 95% confidence interval, 0.979-0.996) and a 1% reduced risk for HF hospitalization (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.986-0.995) at 1-year follow-up (P < .001).
After propensity score was used to match CR participants with nonparticipants by demographic characteristics, comorbidities, and baseline PA level, CR participants had a significantly lower risk for death at 1 year (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.69-0.85). This difference in risk remained at 2- and 3-year follow-ups.
However, when the researchers further adjusted for change in PA during CR or the same time period after device implantation, no differences in mortality were found between CR participants and nonparticipants at 1 year (HR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.82-1.21) or at 2 or 3 years.
The risk for HF hospitalization did not differ between the two groups in either propensity score model.
Unlike wearable devices, implanted devices “don’t give that type of feedback to patients regarding PA levels – only to providers – and it will be interesting to discover whether providing feedback to patients can motivate them to do more physical activity,” Dr. Atwater commented.
The team is currently enrolling patients in a follow-up trial, in which patients will be given feedback from their ICD “to move these data from an interesting observation to something that can drive outcomes,” he said.
Commenting for this news organization, Melissa Tracy, MD, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said the study reiterates the “profound” underutilization of CR.
“Only about 3% of patients who should have qualified for cardiac rehabilitation actually attended, which is startling considering that it has class 1A level of evidence supporting its use,” she said.
Dr. Tracy, who is also a member of the American College of Cardiology’s Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Section Leadership Council, described the study as “another notch in the belt of positive outcomes supporting the need for cardiac rehabilitation” and emphasizing the importance of a home-based alternative.
“One of the reasons women, minorities, and older patients don’t go to cardiac rehabilitation is they have to get there, rely on someone to drive them, or they have other responsibilities – especially women, who are often primary caretakers of others,” she said. “For women and men, the pressure to get back to work and support their families means they don’t have the luxury to go to cardiac rehabilitation.”
Dr. Tracy noted that home-based CR is covered by CMS until the end of 2021. “An important take-home is for providers and patients to understand that they do have a home-based option,” she stated.
Limitations of the study are that only 24% of patients were women, only 6% were Black, and the results might not be generalizable to patients younger than 65 years, note Dr. Atwater and colleagues. Also, previous implantation might have protected the cohort from experiencing arrhythmic death, and it remains unclear if similar results would be obtained in patients without a previous ICD.
This research was funded through the unrestricted Abbott Medical-Duke Health Strategic Alliance Research Grant. Dr. Atwater receives significant research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott Medical, and modest honoraria from Abbott Medical, Medtronic, and Biotronik. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tracy has created cardiac prevention programs with Virtual Health Partners (VHP) and owns the intellectual property and consults with VHP but receives no monetary compensation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA’s fast-track approval process exposed as lax, in need of reform
an in-depth investigation published in The BMJ has determined.
“Despite the pathway’s good intentions to accelerate ‘the availability of drugs that treat serious diseases,’ experts are concerned that it is now being exploited – to the detriment of patients, who may be prescribed a drug that offers little benefit and possible harm, and to taxpayers,” writes Elisabeth Mahase, clinical reporter at The BMJ, who carried out the analysis.
The FDA’s accelerated approval pathway is intended to provide earlier access to drugs for serious diseases when there is lingering uncertainty at the time of approval regarding the drug’s ultimate clinical benefit.
Required studies rarely completed
As part of this fast-track pathway, drug manufacturers must conduct postapproval, phase 4 confirmatory trials to verify the anticipated clinical benefit. If these trials indicate no benefit, FDA approval can be withdrawn.
However, the analysis of FDA data shows once they are approved drugs are rarely taken off the market.
The BMJ investigation that analyzed data up to the end of 2020 shows that 112 of the 253 (44%) medications granted accelerated approval have not been confirmed to be effective.
In addition, 24 (21%) of these questionable drugs have been on the market for more than 5 years and some have been on the market for more than 20 years – often with a hefty price tag.
Furthermore, only 16 drugs approved through the accelerated approval process have ever been withdrawn, and most were shown to be ineffective, but in some cases the confirmatory trials were never done, Ms. Mahase reports.
For example, the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib (Celebrex), which was granted accelerated approval in 1999 for the treatment of familial adenomatous polyposis, was on the market for 12 years before the FDA finally asked Pfizer to voluntarily withdraw it for this indication because efficacy trials were never completed.
As part of The BMJ’s investigation, Ms. Mahase asked manufacturers of the 24 drugs that have remained on the market for more than 5 years whether they had conducted the required phase 4 confirmatory trials. Six of the drugs had been withdrawn, approved, or postponed.
Of the remaining 18 drugs, the manufacturers provided the relevant trial information for only six. Only four drugmakers had started to recruit patients; two said they were still in discussion with the FDA over the final trial design.
“These products routinely have side effects, but the benefit information is a lot less certain. That’s what we’re concerned about – that we may have drugs on the market that don’t have any benefits, but certainly predictably have harms associated with them,” Huseyin Naci, PhD, MHS, with the London School of Economics, comments in the report.
Call for reform
As reported by this news organization, a 2015 report by the General Accountability Office (GAO) concluded that the FDA does not do an effective job of tracking the clinical efficacy or the safety of drugs with expedited approval after they hit the market.
In April of this year, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) cited a lack of “credible threats” to withdraw approval if companies don’t do confirmatory trials – meaning drugmakers have little incentive to do the trials.
“There are some instances where the companies really do seem to be taking advantage of the accelerated approval pathway and are using it in a way that makes it harder to get at the truth about whether these products really are safe and effective,” Rachel Sachs, JD, MPH, Washington University, St. Louis, said in The BMJ article.
In addition, the authors of a recent viewpoint article in JAMA Internal Medicine assert the recent approval of the controversial anti-amyloid drug aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen) shows that the accelerated approval pathway needs to be reformed.
Despite the concerns, Ms. Mahase said all experts who spoke to The BMJ believe the accelerated approval pathway is still useful and can be beneficial to patients, although some changes are needed.
One effective reform might be to have confirmatory trials designed, and even started, as part of accelerated approval.
“One important piece of the puzzle is for the FDA itself to be tougher on these companies, to hold them to the bargain that they have agreed to, and to take action when the company has not met their obligations,” Ms. Sachs told the journal.
An FDA spokesperson told the BMJ that the agency is “committed to working with sponsors to ensure that confirmatory studies are completed in a timely manner.”
“We expect sponsors to commit all resources needed to move trials forward as effectively as possible, with the aim of completing trials as soon as is feasible, while assuring the quality of the data and the robustness of the results,” the agency said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
an in-depth investigation published in The BMJ has determined.
“Despite the pathway’s good intentions to accelerate ‘the availability of drugs that treat serious diseases,’ experts are concerned that it is now being exploited – to the detriment of patients, who may be prescribed a drug that offers little benefit and possible harm, and to taxpayers,” writes Elisabeth Mahase, clinical reporter at The BMJ, who carried out the analysis.
The FDA’s accelerated approval pathway is intended to provide earlier access to drugs for serious diseases when there is lingering uncertainty at the time of approval regarding the drug’s ultimate clinical benefit.
Required studies rarely completed
As part of this fast-track pathway, drug manufacturers must conduct postapproval, phase 4 confirmatory trials to verify the anticipated clinical benefit. If these trials indicate no benefit, FDA approval can be withdrawn.
However, the analysis of FDA data shows once they are approved drugs are rarely taken off the market.
The BMJ investigation that analyzed data up to the end of 2020 shows that 112 of the 253 (44%) medications granted accelerated approval have not been confirmed to be effective.
In addition, 24 (21%) of these questionable drugs have been on the market for more than 5 years and some have been on the market for more than 20 years – often with a hefty price tag.
Furthermore, only 16 drugs approved through the accelerated approval process have ever been withdrawn, and most were shown to be ineffective, but in some cases the confirmatory trials were never done, Ms. Mahase reports.
For example, the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib (Celebrex), which was granted accelerated approval in 1999 for the treatment of familial adenomatous polyposis, was on the market for 12 years before the FDA finally asked Pfizer to voluntarily withdraw it for this indication because efficacy trials were never completed.
As part of The BMJ’s investigation, Ms. Mahase asked manufacturers of the 24 drugs that have remained on the market for more than 5 years whether they had conducted the required phase 4 confirmatory trials. Six of the drugs had been withdrawn, approved, or postponed.
Of the remaining 18 drugs, the manufacturers provided the relevant trial information for only six. Only four drugmakers had started to recruit patients; two said they were still in discussion with the FDA over the final trial design.
“These products routinely have side effects, but the benefit information is a lot less certain. That’s what we’re concerned about – that we may have drugs on the market that don’t have any benefits, but certainly predictably have harms associated with them,” Huseyin Naci, PhD, MHS, with the London School of Economics, comments in the report.
Call for reform
As reported by this news organization, a 2015 report by the General Accountability Office (GAO) concluded that the FDA does not do an effective job of tracking the clinical efficacy or the safety of drugs with expedited approval after they hit the market.
In April of this year, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) cited a lack of “credible threats” to withdraw approval if companies don’t do confirmatory trials – meaning drugmakers have little incentive to do the trials.
“There are some instances where the companies really do seem to be taking advantage of the accelerated approval pathway and are using it in a way that makes it harder to get at the truth about whether these products really are safe and effective,” Rachel Sachs, JD, MPH, Washington University, St. Louis, said in The BMJ article.
In addition, the authors of a recent viewpoint article in JAMA Internal Medicine assert the recent approval of the controversial anti-amyloid drug aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen) shows that the accelerated approval pathway needs to be reformed.
Despite the concerns, Ms. Mahase said all experts who spoke to The BMJ believe the accelerated approval pathway is still useful and can be beneficial to patients, although some changes are needed.
One effective reform might be to have confirmatory trials designed, and even started, as part of accelerated approval.
“One important piece of the puzzle is for the FDA itself to be tougher on these companies, to hold them to the bargain that they have agreed to, and to take action when the company has not met their obligations,” Ms. Sachs told the journal.
An FDA spokesperson told the BMJ that the agency is “committed to working with sponsors to ensure that confirmatory studies are completed in a timely manner.”
“We expect sponsors to commit all resources needed to move trials forward as effectively as possible, with the aim of completing trials as soon as is feasible, while assuring the quality of the data and the robustness of the results,” the agency said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
an in-depth investigation published in The BMJ has determined.
“Despite the pathway’s good intentions to accelerate ‘the availability of drugs that treat serious diseases,’ experts are concerned that it is now being exploited – to the detriment of patients, who may be prescribed a drug that offers little benefit and possible harm, and to taxpayers,” writes Elisabeth Mahase, clinical reporter at The BMJ, who carried out the analysis.
The FDA’s accelerated approval pathway is intended to provide earlier access to drugs for serious diseases when there is lingering uncertainty at the time of approval regarding the drug’s ultimate clinical benefit.
Required studies rarely completed
As part of this fast-track pathway, drug manufacturers must conduct postapproval, phase 4 confirmatory trials to verify the anticipated clinical benefit. If these trials indicate no benefit, FDA approval can be withdrawn.
However, the analysis of FDA data shows once they are approved drugs are rarely taken off the market.
The BMJ investigation that analyzed data up to the end of 2020 shows that 112 of the 253 (44%) medications granted accelerated approval have not been confirmed to be effective.
In addition, 24 (21%) of these questionable drugs have been on the market for more than 5 years and some have been on the market for more than 20 years – often with a hefty price tag.
Furthermore, only 16 drugs approved through the accelerated approval process have ever been withdrawn, and most were shown to be ineffective, but in some cases the confirmatory trials were never done, Ms. Mahase reports.
For example, the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib (Celebrex), which was granted accelerated approval in 1999 for the treatment of familial adenomatous polyposis, was on the market for 12 years before the FDA finally asked Pfizer to voluntarily withdraw it for this indication because efficacy trials were never completed.
As part of The BMJ’s investigation, Ms. Mahase asked manufacturers of the 24 drugs that have remained on the market for more than 5 years whether they had conducted the required phase 4 confirmatory trials. Six of the drugs had been withdrawn, approved, or postponed.
Of the remaining 18 drugs, the manufacturers provided the relevant trial information for only six. Only four drugmakers had started to recruit patients; two said they were still in discussion with the FDA over the final trial design.
“These products routinely have side effects, but the benefit information is a lot less certain. That’s what we’re concerned about – that we may have drugs on the market that don’t have any benefits, but certainly predictably have harms associated with them,” Huseyin Naci, PhD, MHS, with the London School of Economics, comments in the report.
Call for reform
As reported by this news organization, a 2015 report by the General Accountability Office (GAO) concluded that the FDA does not do an effective job of tracking the clinical efficacy or the safety of drugs with expedited approval after they hit the market.
In April of this year, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) cited a lack of “credible threats” to withdraw approval if companies don’t do confirmatory trials – meaning drugmakers have little incentive to do the trials.
“There are some instances where the companies really do seem to be taking advantage of the accelerated approval pathway and are using it in a way that makes it harder to get at the truth about whether these products really are safe and effective,” Rachel Sachs, JD, MPH, Washington University, St. Louis, said in The BMJ article.
In addition, the authors of a recent viewpoint article in JAMA Internal Medicine assert the recent approval of the controversial anti-amyloid drug aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen) shows that the accelerated approval pathway needs to be reformed.
Despite the concerns, Ms. Mahase said all experts who spoke to The BMJ believe the accelerated approval pathway is still useful and can be beneficial to patients, although some changes are needed.
One effective reform might be to have confirmatory trials designed, and even started, as part of accelerated approval.
“One important piece of the puzzle is for the FDA itself to be tougher on these companies, to hold them to the bargain that they have agreed to, and to take action when the company has not met their obligations,” Ms. Sachs told the journal.
An FDA spokesperson told the BMJ that the agency is “committed to working with sponsors to ensure that confirmatory studies are completed in a timely manner.”
“We expect sponsors to commit all resources needed to move trials forward as effectively as possible, with the aim of completing trials as soon as is feasible, while assuring the quality of the data and the robustness of the results,” the agency said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.