User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Decline in weekly child COVID-19 cases has almost stopped
A third COVID-19 vaccine is now in circulation and states are starting to drop mask mandates, but the latest decline in weekly child cases barely registers as a decline, according to new data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.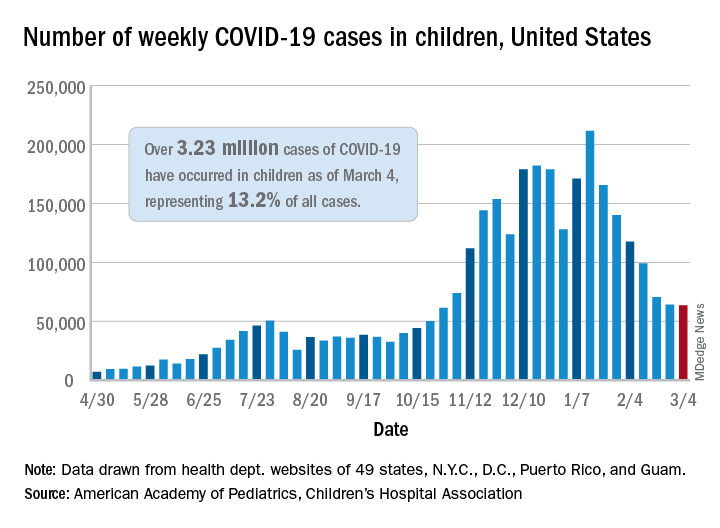
That’s only 702 cases – a drop of just 1.1% – the smallest by far since weekly cases peaked in mid-January, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. Since that peak, the last 7 weeks of declines have looked like this: 21.7%, 15.3%, 16.2%, 15.7%, 28.7%, 9.0%, and 1.1%.
Meanwhile, children’s share of the COVID-19 burden increased to its highest point ever: 18.0% of all new cases occurred in children during the week ending March 4, climbing from 15.7% the week before and eclipsing the previous high of 16.9%. Cumulatively, the 3.23 million cases in children represent 13.2% of all COVID-19 cases reported in 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
At the state level, the new leader in cumulative share of cases is Vermont at 19.4%, which just edged past Wyoming’s 19.3% as of the week ending March 4. The other states above 18% are Alaska (19.2%) and South Carolina (18.2%). The lowest rates can be found in Florida (8.1%), New Jersey (10.2%), Iowa (10.4%), and Utah (10.5%), the AAP and CHA said.
The overall rate of COVID-19 cases nationwide was 4,294 cases per 100,000 children as of March 4, up from 4,209 per 100,000 the week before. That measure had doubled between Dec. 3 (1,941 per 100,000) and Feb. 4 (3,899) but has only risen about 10% in the last month, the AAP/CHA data show.
Perhaps the most surprising news of the week involves the number of COVID-19 deaths in children, which went from 256 the previous week to 253 after Ohio made a downward revision of its mortality data. So far, children represent just 0.06% of all coronavirus-related deaths, a figure that has held steady since last summer in the 43 states (along with New York City and Guam) that are reporting mortality data by age, the AAP and CHA said.
A third COVID-19 vaccine is now in circulation and states are starting to drop mask mandates, but the latest decline in weekly child cases barely registers as a decline, according to new data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
That’s only 702 cases – a drop of just 1.1% – the smallest by far since weekly cases peaked in mid-January, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. Since that peak, the last 7 weeks of declines have looked like this: 21.7%, 15.3%, 16.2%, 15.7%, 28.7%, 9.0%, and 1.1%.
Meanwhile, children’s share of the COVID-19 burden increased to its highest point ever: 18.0% of all new cases occurred in children during the week ending March 4, climbing from 15.7% the week before and eclipsing the previous high of 16.9%. Cumulatively, the 3.23 million cases in children represent 13.2% of all COVID-19 cases reported in 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
At the state level, the new leader in cumulative share of cases is Vermont at 19.4%, which just edged past Wyoming’s 19.3% as of the week ending March 4. The other states above 18% are Alaska (19.2%) and South Carolina (18.2%). The lowest rates can be found in Florida (8.1%), New Jersey (10.2%), Iowa (10.4%), and Utah (10.5%), the AAP and CHA said.
The overall rate of COVID-19 cases nationwide was 4,294 cases per 100,000 children as of March 4, up from 4,209 per 100,000 the week before. That measure had doubled between Dec. 3 (1,941 per 100,000) and Feb. 4 (3,899) but has only risen about 10% in the last month, the AAP/CHA data show.
Perhaps the most surprising news of the week involves the number of COVID-19 deaths in children, which went from 256 the previous week to 253 after Ohio made a downward revision of its mortality data. So far, children represent just 0.06% of all coronavirus-related deaths, a figure that has held steady since last summer in the 43 states (along with New York City and Guam) that are reporting mortality data by age, the AAP and CHA said.
A third COVID-19 vaccine is now in circulation and states are starting to drop mask mandates, but the latest decline in weekly child cases barely registers as a decline, according to new data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
That’s only 702 cases – a drop of just 1.1% – the smallest by far since weekly cases peaked in mid-January, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. Since that peak, the last 7 weeks of declines have looked like this: 21.7%, 15.3%, 16.2%, 15.7%, 28.7%, 9.0%, and 1.1%.
Meanwhile, children’s share of the COVID-19 burden increased to its highest point ever: 18.0% of all new cases occurred in children during the week ending March 4, climbing from 15.7% the week before and eclipsing the previous high of 16.9%. Cumulatively, the 3.23 million cases in children represent 13.2% of all COVID-19 cases reported in 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
At the state level, the new leader in cumulative share of cases is Vermont at 19.4%, which just edged past Wyoming’s 19.3% as of the week ending March 4. The other states above 18% are Alaska (19.2%) and South Carolina (18.2%). The lowest rates can be found in Florida (8.1%), New Jersey (10.2%), Iowa (10.4%), and Utah (10.5%), the AAP and CHA said.
The overall rate of COVID-19 cases nationwide was 4,294 cases per 100,000 children as of March 4, up from 4,209 per 100,000 the week before. That measure had doubled between Dec. 3 (1,941 per 100,000) and Feb. 4 (3,899) but has only risen about 10% in the last month, the AAP/CHA data show.
Perhaps the most surprising news of the week involves the number of COVID-19 deaths in children, which went from 256 the previous week to 253 after Ohio made a downward revision of its mortality data. So far, children represent just 0.06% of all coronavirus-related deaths, a figure that has held steady since last summer in the 43 states (along with New York City and Guam) that are reporting mortality data by age, the AAP and CHA said.
Call to action on obesity amid COVID-19 pandemic
Hundreds of thousands of deaths worldwide from COVID-19 could have been avoided if obesity rates were lower, a new report says.
An analysis by the World Obesity Federation found that of the 2.5 million COVID-19 deaths reported by the end of February 2021, almost 90% (2.2 million) were in countries where more than half the population is classified as overweight.
The report, released to coincide with World Obesity Day, calls for obesity to be recognized as a disease in its own right around the world, and for people with obesity to be included in priority lists for COVID-19 testing and vaccination.
“Overweight is a highly significant predictor of developing complications from COVID-19, including the need for hospitalization, for intensive care and for mechanical ventilation,” the WOF notes in the report.
It adds that in countries where less than half the adult population is classified as overweight (body mass index > 25 mg/kg2), for example, Vietnam, the likelihood of death from COVID-19 is a small fraction – around one-tenth – of the level seen in countries where more than half the population is classified as overweight.
And while it acknowledges that figures for COVID-19 deaths are affected by the age structure of national populations and a country’s relative wealth and reporting capacity, “our findings appear to be independent of these contributory factors. Furthermore, other studies have found that overweight remains a highly significant predictor of the need for COVID-19 health care after accounting for these other influences.”
As an example, based on the U.K. experience, where an estimated 36% of COVID-19 hospitalizations have been attributed to lack of physical activity and excess body weight, it can be suggested that up to a third of the costs – between $6 trillion and $7 trillion over the longer period – might be attributable to these predisposing risks.
The report said the prevalence of obesity in the United Kingdom is expected to rise from 27.8% in 2016 to more than 35% by 2025.
Rachel Batterham, lead adviser on obesity at the Royal College of Physicians, commented: “The link between high levels of obesity and deaths from COVID-19 in the U.K. is indisputable, as is the urgent need to address the factors that lead so many people to be living with obesity.
“With 30% of COVID-19 hospitalizations in the U.K. directly attributed to overweight and obesity, and three-quarters of all critically ill patients having overweight or obesity, the human and financial costs are high.”
Window of opportunity to prioritize obesity as a disease
WOF says that evolving evidence on the close association between COVID-19 and underlying obesity “provides a new urgency … for political and collective action.”
“Obesity is a disease that does not receive prioritization commensurate with its prevalence and impact, which is rising fastest in emerging economies. It is a gateway to many other noncommunicable diseases and mental-health illness and is now a major factor in COVID-19 complications and mortality.”
The WOF also shows that COVID-19 is not a special case, noting that several other respiratory viruses lead to more severe consequences in people living with excess bodyweight, giving good reasons to expect the next pandemic to have similar effects. “For these reasons we need to recognize overweight as a major risk factor for infectious diseases including respiratory viruses.”
“To prevent pandemic health crises in future requires action now: we call on all readers to support the World Obesity Federation’s call for stronger, more resilient economies that prioritize investment in people’s health.”
There is, it stresses, “a window of opportunity to advocate for, fund and implement these actions in all countries to ensure better, more resilient and sustainable health for all, “now and in our postCOVID-19 future.”
It proposes a ROOTS approach:
- Recognize that obesity is a disease in its own right.
- Obesity monitoring and surveillance must be enhanced.
- Obesity prevention strategies must be developed.
- Treatment of obesity.
- Systems-based approaches should be applied.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hundreds of thousands of deaths worldwide from COVID-19 could have been avoided if obesity rates were lower, a new report says.
An analysis by the World Obesity Federation found that of the 2.5 million COVID-19 deaths reported by the end of February 2021, almost 90% (2.2 million) were in countries where more than half the population is classified as overweight.
The report, released to coincide with World Obesity Day, calls for obesity to be recognized as a disease in its own right around the world, and for people with obesity to be included in priority lists for COVID-19 testing and vaccination.
“Overweight is a highly significant predictor of developing complications from COVID-19, including the need for hospitalization, for intensive care and for mechanical ventilation,” the WOF notes in the report.
It adds that in countries where less than half the adult population is classified as overweight (body mass index > 25 mg/kg2), for example, Vietnam, the likelihood of death from COVID-19 is a small fraction – around one-tenth – of the level seen in countries where more than half the population is classified as overweight.
And while it acknowledges that figures for COVID-19 deaths are affected by the age structure of national populations and a country’s relative wealth and reporting capacity, “our findings appear to be independent of these contributory factors. Furthermore, other studies have found that overweight remains a highly significant predictor of the need for COVID-19 health care after accounting for these other influences.”
As an example, based on the U.K. experience, where an estimated 36% of COVID-19 hospitalizations have been attributed to lack of physical activity and excess body weight, it can be suggested that up to a third of the costs – between $6 trillion and $7 trillion over the longer period – might be attributable to these predisposing risks.
The report said the prevalence of obesity in the United Kingdom is expected to rise from 27.8% in 2016 to more than 35% by 2025.
Rachel Batterham, lead adviser on obesity at the Royal College of Physicians, commented: “The link between high levels of obesity and deaths from COVID-19 in the U.K. is indisputable, as is the urgent need to address the factors that lead so many people to be living with obesity.
“With 30% of COVID-19 hospitalizations in the U.K. directly attributed to overweight and obesity, and three-quarters of all critically ill patients having overweight or obesity, the human and financial costs are high.”
Window of opportunity to prioritize obesity as a disease
WOF says that evolving evidence on the close association between COVID-19 and underlying obesity “provides a new urgency … for political and collective action.”
“Obesity is a disease that does not receive prioritization commensurate with its prevalence and impact, which is rising fastest in emerging economies. It is a gateway to many other noncommunicable diseases and mental-health illness and is now a major factor in COVID-19 complications and mortality.”
The WOF also shows that COVID-19 is not a special case, noting that several other respiratory viruses lead to more severe consequences in people living with excess bodyweight, giving good reasons to expect the next pandemic to have similar effects. “For these reasons we need to recognize overweight as a major risk factor for infectious diseases including respiratory viruses.”
“To prevent pandemic health crises in future requires action now: we call on all readers to support the World Obesity Federation’s call for stronger, more resilient economies that prioritize investment in people’s health.”
There is, it stresses, “a window of opportunity to advocate for, fund and implement these actions in all countries to ensure better, more resilient and sustainable health for all, “now and in our postCOVID-19 future.”
It proposes a ROOTS approach:
- Recognize that obesity is a disease in its own right.
- Obesity monitoring and surveillance must be enhanced.
- Obesity prevention strategies must be developed.
- Treatment of obesity.
- Systems-based approaches should be applied.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hundreds of thousands of deaths worldwide from COVID-19 could have been avoided if obesity rates were lower, a new report says.
An analysis by the World Obesity Federation found that of the 2.5 million COVID-19 deaths reported by the end of February 2021, almost 90% (2.2 million) were in countries where more than half the population is classified as overweight.
The report, released to coincide with World Obesity Day, calls for obesity to be recognized as a disease in its own right around the world, and for people with obesity to be included in priority lists for COVID-19 testing and vaccination.
“Overweight is a highly significant predictor of developing complications from COVID-19, including the need for hospitalization, for intensive care and for mechanical ventilation,” the WOF notes in the report.
It adds that in countries where less than half the adult population is classified as overweight (body mass index > 25 mg/kg2), for example, Vietnam, the likelihood of death from COVID-19 is a small fraction – around one-tenth – of the level seen in countries where more than half the population is classified as overweight.
And while it acknowledges that figures for COVID-19 deaths are affected by the age structure of national populations and a country’s relative wealth and reporting capacity, “our findings appear to be independent of these contributory factors. Furthermore, other studies have found that overweight remains a highly significant predictor of the need for COVID-19 health care after accounting for these other influences.”
As an example, based on the U.K. experience, where an estimated 36% of COVID-19 hospitalizations have been attributed to lack of physical activity and excess body weight, it can be suggested that up to a third of the costs – between $6 trillion and $7 trillion over the longer period – might be attributable to these predisposing risks.
The report said the prevalence of obesity in the United Kingdom is expected to rise from 27.8% in 2016 to more than 35% by 2025.
Rachel Batterham, lead adviser on obesity at the Royal College of Physicians, commented: “The link between high levels of obesity and deaths from COVID-19 in the U.K. is indisputable, as is the urgent need to address the factors that lead so many people to be living with obesity.
“With 30% of COVID-19 hospitalizations in the U.K. directly attributed to overweight and obesity, and three-quarters of all critically ill patients having overweight or obesity, the human and financial costs are high.”
Window of opportunity to prioritize obesity as a disease
WOF says that evolving evidence on the close association between COVID-19 and underlying obesity “provides a new urgency … for political and collective action.”
“Obesity is a disease that does not receive prioritization commensurate with its prevalence and impact, which is rising fastest in emerging economies. It is a gateway to many other noncommunicable diseases and mental-health illness and is now a major factor in COVID-19 complications and mortality.”
The WOF also shows that COVID-19 is not a special case, noting that several other respiratory viruses lead to more severe consequences in people living with excess bodyweight, giving good reasons to expect the next pandemic to have similar effects. “For these reasons we need to recognize overweight as a major risk factor for infectious diseases including respiratory viruses.”
“To prevent pandemic health crises in future requires action now: we call on all readers to support the World Obesity Federation’s call for stronger, more resilient economies that prioritize investment in people’s health.”
There is, it stresses, “a window of opportunity to advocate for, fund and implement these actions in all countries to ensure better, more resilient and sustainable health for all, “now and in our postCOVID-19 future.”
It proposes a ROOTS approach:
- Recognize that obesity is a disease in its own right.
- Obesity monitoring and surveillance must be enhanced.
- Obesity prevention strategies must be developed.
- Treatment of obesity.
- Systems-based approaches should be applied.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Potential COVID-19 variant surge looms over U.S.
Another coronavirus surge may be on the way in the United States as daily COVID-19 cases continue to plateau around 60,000, states begin to lift restrictions, and people embark on spring break trips this week, according to CNN.
Outbreaks will likely stem from the B.1.1.7 variant, which was first identified in the United Kingdom, and gain momentum during the next 6-14 weeks.
“Four weeks ago, the B.1.1.7 variant made up about 1%-4% of the virus that we were seeing in communities across the country. Today it’s up to 30%-40%,” Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, told NBC’s Meet the Press on March 7.
Dr. Osterholm compared the current situation with the “eye of the hurricane,” where the skies appear clear but more storms are on the way. Across Europe, 27 countries are seeing significant B.1.1.7 case increases, and 10 are getting hit hard, he said.
“What we’ve seen in Europe, when we hit that 50% mark, you see cases surge,” he said. “So right now, we do have to keep America as safe as we can from this virus by not letting up on any of the public health measures we’ve taken.”
In January, the CDC warned that B.1.1.7 variant cases would increase in 2021 and become the dominant variant in the country by this month. The United States has now reported more than 3,000 cases across 46 states, according to the latest CDC tally updated on March 7. More than 600 cases have been found in Florida, followed by more than 400 in Michigan.
The CDC has said the tally doesn’t represent the total number of B.1.1.7 cases in the United States, only the ones that have been identified by analyzing samples through genomic sequencing.
“Where it has hit in the U.K. and now elsewhere in Europe, it has been catastrophic,” Celine Gounder, MD, an infectious disease specialist with New York University Langone Health, told CNN on March 7.
The variant is more transmissible than the original novel coronavirus, and the cases in the United States are “increasing exponentially,” she said.
“It has driven up rates of hospitalizations and deaths and it’s very difficult to control,” Dr. Gounder said.
Vaccination numbers aren’t yet high enough to stop the predicted surge, she added. The United States has shipped more than 116 million vaccine doses, according to the latest CDC update on March 7. Nearly 59 million people have received at least one dose, and 30.6 million people have received two vaccine doses. About 9% of the U.S. population has been fully vaccinated.
States shouldn’t ease restrictions until the vaccination numbers are much higher and daily COVID-19 cases fall below 10,000 – and maybe “considerably less than that,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, told CNN on March 4.
Several states have already begun to lift COVID-19 safety protocols, with Texas and Mississippi removing mask mandates last week. Businesses in Texas will be able to reopen at full capacity on March 10. For now, public health officials are urging Americans to continue to wear masks, avoid crowds, and follow social distancing guidelines as vaccines roll out across the country.
“This is sort of like we’ve been running this really long marathon, and we’re 100 yards from the finish line and we sit down and we give up,” Dr. Gounder told CNN on Sunday. ‘We’re almost there, we just need to give ourselves a bit more time to get a larger proportion of the population covered with vaccines.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Another coronavirus surge may be on the way in the United States as daily COVID-19 cases continue to plateau around 60,000, states begin to lift restrictions, and people embark on spring break trips this week, according to CNN.
Outbreaks will likely stem from the B.1.1.7 variant, which was first identified in the United Kingdom, and gain momentum during the next 6-14 weeks.
“Four weeks ago, the B.1.1.7 variant made up about 1%-4% of the virus that we were seeing in communities across the country. Today it’s up to 30%-40%,” Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, told NBC’s Meet the Press on March 7.
Dr. Osterholm compared the current situation with the “eye of the hurricane,” where the skies appear clear but more storms are on the way. Across Europe, 27 countries are seeing significant B.1.1.7 case increases, and 10 are getting hit hard, he said.
“What we’ve seen in Europe, when we hit that 50% mark, you see cases surge,” he said. “So right now, we do have to keep America as safe as we can from this virus by not letting up on any of the public health measures we’ve taken.”
In January, the CDC warned that B.1.1.7 variant cases would increase in 2021 and become the dominant variant in the country by this month. The United States has now reported more than 3,000 cases across 46 states, according to the latest CDC tally updated on March 7. More than 600 cases have been found in Florida, followed by more than 400 in Michigan.
The CDC has said the tally doesn’t represent the total number of B.1.1.7 cases in the United States, only the ones that have been identified by analyzing samples through genomic sequencing.
“Where it has hit in the U.K. and now elsewhere in Europe, it has been catastrophic,” Celine Gounder, MD, an infectious disease specialist with New York University Langone Health, told CNN on March 7.
The variant is more transmissible than the original novel coronavirus, and the cases in the United States are “increasing exponentially,” she said.
“It has driven up rates of hospitalizations and deaths and it’s very difficult to control,” Dr. Gounder said.
Vaccination numbers aren’t yet high enough to stop the predicted surge, she added. The United States has shipped more than 116 million vaccine doses, according to the latest CDC update on March 7. Nearly 59 million people have received at least one dose, and 30.6 million people have received two vaccine doses. About 9% of the U.S. population has been fully vaccinated.
States shouldn’t ease restrictions until the vaccination numbers are much higher and daily COVID-19 cases fall below 10,000 – and maybe “considerably less than that,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, told CNN on March 4.
Several states have already begun to lift COVID-19 safety protocols, with Texas and Mississippi removing mask mandates last week. Businesses in Texas will be able to reopen at full capacity on March 10. For now, public health officials are urging Americans to continue to wear masks, avoid crowds, and follow social distancing guidelines as vaccines roll out across the country.
“This is sort of like we’ve been running this really long marathon, and we’re 100 yards from the finish line and we sit down and we give up,” Dr. Gounder told CNN on Sunday. ‘We’re almost there, we just need to give ourselves a bit more time to get a larger proportion of the population covered with vaccines.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Another coronavirus surge may be on the way in the United States as daily COVID-19 cases continue to plateau around 60,000, states begin to lift restrictions, and people embark on spring break trips this week, according to CNN.
Outbreaks will likely stem from the B.1.1.7 variant, which was first identified in the United Kingdom, and gain momentum during the next 6-14 weeks.
“Four weeks ago, the B.1.1.7 variant made up about 1%-4% of the virus that we were seeing in communities across the country. Today it’s up to 30%-40%,” Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, told NBC’s Meet the Press on March 7.
Dr. Osterholm compared the current situation with the “eye of the hurricane,” where the skies appear clear but more storms are on the way. Across Europe, 27 countries are seeing significant B.1.1.7 case increases, and 10 are getting hit hard, he said.
“What we’ve seen in Europe, when we hit that 50% mark, you see cases surge,” he said. “So right now, we do have to keep America as safe as we can from this virus by not letting up on any of the public health measures we’ve taken.”
In January, the CDC warned that B.1.1.7 variant cases would increase in 2021 and become the dominant variant in the country by this month. The United States has now reported more than 3,000 cases across 46 states, according to the latest CDC tally updated on March 7. More than 600 cases have been found in Florida, followed by more than 400 in Michigan.
The CDC has said the tally doesn’t represent the total number of B.1.1.7 cases in the United States, only the ones that have been identified by analyzing samples through genomic sequencing.
“Where it has hit in the U.K. and now elsewhere in Europe, it has been catastrophic,” Celine Gounder, MD, an infectious disease specialist with New York University Langone Health, told CNN on March 7.
The variant is more transmissible than the original novel coronavirus, and the cases in the United States are “increasing exponentially,” she said.
“It has driven up rates of hospitalizations and deaths and it’s very difficult to control,” Dr. Gounder said.
Vaccination numbers aren’t yet high enough to stop the predicted surge, she added. The United States has shipped more than 116 million vaccine doses, according to the latest CDC update on March 7. Nearly 59 million people have received at least one dose, and 30.6 million people have received two vaccine doses. About 9% of the U.S. population has been fully vaccinated.
States shouldn’t ease restrictions until the vaccination numbers are much higher and daily COVID-19 cases fall below 10,000 – and maybe “considerably less than that,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, told CNN on March 4.
Several states have already begun to lift COVID-19 safety protocols, with Texas and Mississippi removing mask mandates last week. Businesses in Texas will be able to reopen at full capacity on March 10. For now, public health officials are urging Americans to continue to wear masks, avoid crowds, and follow social distancing guidelines as vaccines roll out across the country.
“This is sort of like we’ve been running this really long marathon, and we’re 100 yards from the finish line and we sit down and we give up,” Dr. Gounder told CNN on Sunday. ‘We’re almost there, we just need to give ourselves a bit more time to get a larger proportion of the population covered with vaccines.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
DOACs offered after heart valve surgery despite absence of data
Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are used in about 1% of patients undergoing surgical mechanical aortic and mitral valve replacement, but in up to 6% of surgical bioprosthetic valve replacements, according to registry data presented at CRT 2021.
In an analysis of the Society of Thoracic Surgery (STS) registry during 2014-2017, DOAC use increased steadily among those undergoing surgical bioprosthetic valve replacement, reaching a number that is potentially clinically significant, according to Ankur Kalra, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Akron General Hospital who has an academic appointment at the Cleveland Clinic.
There was no increase in the use of DOACs observed among patients undergoing mechanical valve replacement, “but even if the number is 1%, they should probably not be used at all until we accrue more data,” Dr. Kalra said.
DOACs discouraged in patients with mechanical or bioprosthetic valves
In Food and Drug Administration labeling, DOACs are contraindicated or not recommended. This can be traced to the randomized RE-ALIGN trial, which was stopped prematurely due to evidence of harm from a DOAC, according to Dr. Kalra.
In RE-ALIGN, which enrolled patients undergoing mechanical aortic or mitral valve replacement, dabigatran was associated not only with more bleeding events than warfarin, but also more thromboembolic events.
There are no randomized data comparing the factor Xa inhibitors rivaroxaban or apixaban to warfarin in heart valve surgery, but Dr. Kalra noted cautionary language is found in the labeling of both, “perhaps due to the RE-ALIGN data.”
Registry shows trends in prescribing
In the STS registry data, 193 (1.1%) of the 18,142 patients undergoing mechanical aortic valve surgery, 139 (1.0%) of the 13,942 patients undergoing mechanical mitral valve surgery, 5,625 (4.7%) of the 116,203 patients undergoing aortic bioprosthetic aortic valve surgery, and 2,180 (5.9%) of the 39,243 patients undergoing bioprosthetic mitral valve surgery were on a DOAC at discharge.
Among those receiving a mechanical value and placed on a DOAC, about two-thirds were on a factor Xa inhibitor rather than dabigatran. For those receiving a bioprosthetic value, the proportion was greater than 80%. Dr. Kalra speculated that the RE-ALIGN trial might be the reason factor Xa inhibitors were favored.
In both types of valves, whether mechanical or bioprosthetic, more comorbidities predicted a greater likelihood of receiving a DOAC rather than warfarin. For those receiving mechanical values, the comorbidities with a significant association with greater DOAC use included hypertension (P = .003), dyslipidemia (P = .02), arrhythmia (P < .001), and peripheral arterial disease (P < 0.001).
The same factors were significant for predicting increased likelihood of a DOAC following bioprosthetic valve replacement, but there were additional factors, including atrial fibrillation independent of other types of arrhythmias (P < .001), a factor not significant for mechanical valves, as well as diabetes (P < .001), cerebrovascular disease (P < .001), dialysis (P < .001), and endocarditis (P < .001).
“This is probably intuitive, but patients who were on a factor Xa inhibitor before their valve replacement were also more likely to be discharged on a factor Xa inhibitor,” Dr. Kalra said at the virtual meeting, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
The year-to-year increase in DOAC use among those undergoing bioprosthetic valve replacement over the study period, which was a significant trend, was not observed among those undergoing mechanical valve replacement. Rather, the 1% proportion remained stable over the study period.
“We wanted to look at outcomes, but we found that the STS database, which only includes data out to 30 days, is not structured for this type of analysis,” Dr. Kalra said. He was also concerned about the limitations of a comparison in which 1% of the sample was being compared to 99%.
Expert: One percent is ‘very small number’
David J. Cohen, MD, commented on the 1% figure, which was so low that a moderator questioned whether it could be due mostly to coding errors.
“This is a very, very small number so at some level it is reassuring that it is so low in the mechanical valves,” Dr. Cohen said. However, he was more circumspect about the larger number in bioprosthetic valves.
“I have always thought it was a bit strange there was a warning against using them in bioprosthetic valves, especially in the aortic position,” he said.
“The trials that established the benefits of DOACs were all in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation, but this did not mean non–aortic stenosis; it meant non–mitral valvular. There have been articles written about how that has been misinterpreted,” said Dr. Cohen, director of clinical and outcomes research at the Cardiovascular Research Foundation and director of academic affairs at St. Francis Hospital, Roslyn, N.Y.
For his part, Dr. Kalra reported that he does not consider DOACs in patients who have undergone a surgical mechanical valve replacement. For bioprosthetic valves, he “prefers” warfarin over DOACs.
Overall, the evidence from the registry led Dr. Kalra to suggest that physicians should continue to “exercise caution” in using DOACs instead of warfarin after any surgical valve replacement “until randomized clinical trials provide sufficient evidence” to make a judgment about relative efficacy and safety.
Results of the study were published online as a research letter in Jama Network Open after Dr. Kalra’s presentation. Dr. Kalra and Dr. Cohen report no potential conflicts of interest.
Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are used in about 1% of patients undergoing surgical mechanical aortic and mitral valve replacement, but in up to 6% of surgical bioprosthetic valve replacements, according to registry data presented at CRT 2021.
In an analysis of the Society of Thoracic Surgery (STS) registry during 2014-2017, DOAC use increased steadily among those undergoing surgical bioprosthetic valve replacement, reaching a number that is potentially clinically significant, according to Ankur Kalra, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Akron General Hospital who has an academic appointment at the Cleveland Clinic.
There was no increase in the use of DOACs observed among patients undergoing mechanical valve replacement, “but even if the number is 1%, they should probably not be used at all until we accrue more data,” Dr. Kalra said.
DOACs discouraged in patients with mechanical or bioprosthetic valves
In Food and Drug Administration labeling, DOACs are contraindicated or not recommended. This can be traced to the randomized RE-ALIGN trial, which was stopped prematurely due to evidence of harm from a DOAC, according to Dr. Kalra.
In RE-ALIGN, which enrolled patients undergoing mechanical aortic or mitral valve replacement, dabigatran was associated not only with more bleeding events than warfarin, but also more thromboembolic events.
There are no randomized data comparing the factor Xa inhibitors rivaroxaban or apixaban to warfarin in heart valve surgery, but Dr. Kalra noted cautionary language is found in the labeling of both, “perhaps due to the RE-ALIGN data.”
Registry shows trends in prescribing
In the STS registry data, 193 (1.1%) of the 18,142 patients undergoing mechanical aortic valve surgery, 139 (1.0%) of the 13,942 patients undergoing mechanical mitral valve surgery, 5,625 (4.7%) of the 116,203 patients undergoing aortic bioprosthetic aortic valve surgery, and 2,180 (5.9%) of the 39,243 patients undergoing bioprosthetic mitral valve surgery were on a DOAC at discharge.
Among those receiving a mechanical value and placed on a DOAC, about two-thirds were on a factor Xa inhibitor rather than dabigatran. For those receiving a bioprosthetic value, the proportion was greater than 80%. Dr. Kalra speculated that the RE-ALIGN trial might be the reason factor Xa inhibitors were favored.
In both types of valves, whether mechanical or bioprosthetic, more comorbidities predicted a greater likelihood of receiving a DOAC rather than warfarin. For those receiving mechanical values, the comorbidities with a significant association with greater DOAC use included hypertension (P = .003), dyslipidemia (P = .02), arrhythmia (P < .001), and peripheral arterial disease (P < 0.001).
The same factors were significant for predicting increased likelihood of a DOAC following bioprosthetic valve replacement, but there were additional factors, including atrial fibrillation independent of other types of arrhythmias (P < .001), a factor not significant for mechanical valves, as well as diabetes (P < .001), cerebrovascular disease (P < .001), dialysis (P < .001), and endocarditis (P < .001).
“This is probably intuitive, but patients who were on a factor Xa inhibitor before their valve replacement were also more likely to be discharged on a factor Xa inhibitor,” Dr. Kalra said at the virtual meeting, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
The year-to-year increase in DOAC use among those undergoing bioprosthetic valve replacement over the study period, which was a significant trend, was not observed among those undergoing mechanical valve replacement. Rather, the 1% proportion remained stable over the study period.
“We wanted to look at outcomes, but we found that the STS database, which only includes data out to 30 days, is not structured for this type of analysis,” Dr. Kalra said. He was also concerned about the limitations of a comparison in which 1% of the sample was being compared to 99%.
Expert: One percent is ‘very small number’
David J. Cohen, MD, commented on the 1% figure, which was so low that a moderator questioned whether it could be due mostly to coding errors.
“This is a very, very small number so at some level it is reassuring that it is so low in the mechanical valves,” Dr. Cohen said. However, he was more circumspect about the larger number in bioprosthetic valves.
“I have always thought it was a bit strange there was a warning against using them in bioprosthetic valves, especially in the aortic position,” he said.
“The trials that established the benefits of DOACs were all in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation, but this did not mean non–aortic stenosis; it meant non–mitral valvular. There have been articles written about how that has been misinterpreted,” said Dr. Cohen, director of clinical and outcomes research at the Cardiovascular Research Foundation and director of academic affairs at St. Francis Hospital, Roslyn, N.Y.
For his part, Dr. Kalra reported that he does not consider DOACs in patients who have undergone a surgical mechanical valve replacement. For bioprosthetic valves, he “prefers” warfarin over DOACs.
Overall, the evidence from the registry led Dr. Kalra to suggest that physicians should continue to “exercise caution” in using DOACs instead of warfarin after any surgical valve replacement “until randomized clinical trials provide sufficient evidence” to make a judgment about relative efficacy and safety.
Results of the study were published online as a research letter in Jama Network Open after Dr. Kalra’s presentation. Dr. Kalra and Dr. Cohen report no potential conflicts of interest.
Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are used in about 1% of patients undergoing surgical mechanical aortic and mitral valve replacement, but in up to 6% of surgical bioprosthetic valve replacements, according to registry data presented at CRT 2021.
In an analysis of the Society of Thoracic Surgery (STS) registry during 2014-2017, DOAC use increased steadily among those undergoing surgical bioprosthetic valve replacement, reaching a number that is potentially clinically significant, according to Ankur Kalra, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Akron General Hospital who has an academic appointment at the Cleveland Clinic.
There was no increase in the use of DOACs observed among patients undergoing mechanical valve replacement, “but even if the number is 1%, they should probably not be used at all until we accrue more data,” Dr. Kalra said.
DOACs discouraged in patients with mechanical or bioprosthetic valves
In Food and Drug Administration labeling, DOACs are contraindicated or not recommended. This can be traced to the randomized RE-ALIGN trial, which was stopped prematurely due to evidence of harm from a DOAC, according to Dr. Kalra.
In RE-ALIGN, which enrolled patients undergoing mechanical aortic or mitral valve replacement, dabigatran was associated not only with more bleeding events than warfarin, but also more thromboembolic events.
There are no randomized data comparing the factor Xa inhibitors rivaroxaban or apixaban to warfarin in heart valve surgery, but Dr. Kalra noted cautionary language is found in the labeling of both, “perhaps due to the RE-ALIGN data.”
Registry shows trends in prescribing
In the STS registry data, 193 (1.1%) of the 18,142 patients undergoing mechanical aortic valve surgery, 139 (1.0%) of the 13,942 patients undergoing mechanical mitral valve surgery, 5,625 (4.7%) of the 116,203 patients undergoing aortic bioprosthetic aortic valve surgery, and 2,180 (5.9%) of the 39,243 patients undergoing bioprosthetic mitral valve surgery were on a DOAC at discharge.
Among those receiving a mechanical value and placed on a DOAC, about two-thirds were on a factor Xa inhibitor rather than dabigatran. For those receiving a bioprosthetic value, the proportion was greater than 80%. Dr. Kalra speculated that the RE-ALIGN trial might be the reason factor Xa inhibitors were favored.
In both types of valves, whether mechanical or bioprosthetic, more comorbidities predicted a greater likelihood of receiving a DOAC rather than warfarin. For those receiving mechanical values, the comorbidities with a significant association with greater DOAC use included hypertension (P = .003), dyslipidemia (P = .02), arrhythmia (P < .001), and peripheral arterial disease (P < 0.001).
The same factors were significant for predicting increased likelihood of a DOAC following bioprosthetic valve replacement, but there were additional factors, including atrial fibrillation independent of other types of arrhythmias (P < .001), a factor not significant for mechanical valves, as well as diabetes (P < .001), cerebrovascular disease (P < .001), dialysis (P < .001), and endocarditis (P < .001).
“This is probably intuitive, but patients who were on a factor Xa inhibitor before their valve replacement were also more likely to be discharged on a factor Xa inhibitor,” Dr. Kalra said at the virtual meeting, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
The year-to-year increase in DOAC use among those undergoing bioprosthetic valve replacement over the study period, which was a significant trend, was not observed among those undergoing mechanical valve replacement. Rather, the 1% proportion remained stable over the study period.
“We wanted to look at outcomes, but we found that the STS database, which only includes data out to 30 days, is not structured for this type of analysis,” Dr. Kalra said. He was also concerned about the limitations of a comparison in which 1% of the sample was being compared to 99%.
Expert: One percent is ‘very small number’
David J. Cohen, MD, commented on the 1% figure, which was so low that a moderator questioned whether it could be due mostly to coding errors.
“This is a very, very small number so at some level it is reassuring that it is so low in the mechanical valves,” Dr. Cohen said. However, he was more circumspect about the larger number in bioprosthetic valves.
“I have always thought it was a bit strange there was a warning against using them in bioprosthetic valves, especially in the aortic position,” he said.
“The trials that established the benefits of DOACs were all in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation, but this did not mean non–aortic stenosis; it meant non–mitral valvular. There have been articles written about how that has been misinterpreted,” said Dr. Cohen, director of clinical and outcomes research at the Cardiovascular Research Foundation and director of academic affairs at St. Francis Hospital, Roslyn, N.Y.
For his part, Dr. Kalra reported that he does not consider DOACs in patients who have undergone a surgical mechanical valve replacement. For bioprosthetic valves, he “prefers” warfarin over DOACs.
Overall, the evidence from the registry led Dr. Kalra to suggest that physicians should continue to “exercise caution” in using DOACs instead of warfarin after any surgical valve replacement “until randomized clinical trials provide sufficient evidence” to make a judgment about relative efficacy and safety.
Results of the study were published online as a research letter in Jama Network Open after Dr. Kalra’s presentation. Dr. Kalra and Dr. Cohen report no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM CRT 2021
Five-day course of oral antiviral appears to stop SARS-CoV-2 in its tracks
A single pill of the investigational drug molnupiravir taken twice a day for 5 days eliminated SARS-CoV-2 from the nasopharynx of 49 participants.
That led Carlos del Rio, MD, distinguished professor of medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, to suggest a future in which a drug like molnupiravir could be taken in the first few days of symptoms to prevent severe disease, similar to Tamiflu for influenza.
“I think it’s critically important,” he said of the data. Emory University was involved in the trial of molnupiravir but Dr. del Rio was not part of that team. “This drug offers the first antiviral oral drug that then could be used in an outpatient setting.”
Still, Dr. del Rio said it’s too soon to call this particular drug the breakthrough clinicians need to keep people out of the ICU. “It has the potential to be practice changing; it’s not practice changing at the moment.”
Wendy Painter, MD, of Ridgeback Biotherapeutics, who presented the data at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, agreed. While the data are promising, “We will need to see if people get better from actual illness” to assess the real value of the drug in clinical care.
“That’s a phase 3 objective we’ll need to prove,” she said in an interview.
Phase 2/3 efficacy and safety studies of the drug are now underway in hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients.
In a brief prerecorded presentation of the data, Dr. Painter laid out what researchers know so far: Preclinical studies suggest that molnupiravir is effective against a number of viruses, including coronaviruses and specifically SARS-CoV-2. It prevents a virus from replicating by inducing viral error catastrophe (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 15;99[21]:13374-6) – essentially overloading the virus with replication and mutation until the virus burns itself out and can’t produce replicable copies.
In this phase 2a, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial, researchers recruited 202 adults who were treated at an outpatient clinic with fever or other symptoms of a respiratory virus and confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection by day 4. Participants were randomly assigned to three different groups: 200 mg of molnupiravir, 400 mg, or 800 mg. The 200-mg arm was matched 1:1 with a placebo-controlled group, and the other two groups had three participants in the active group for every one control.
Participants took the pills twice daily for 5 days, and then were followed for a total of 28 days to monitor for complications or adverse events. At days 3, 5, 7, 14, and 28, researchers also took nasopharyngeal swabs for polymerase chain reaction tests, to sequence the virus, and to grow cultures of SARS-CoV-2 to see if the virus that’s present is actually capable of infecting others.
Notably, the pills do not have to be refrigerated at any point in the process, alleviating the cold-chain challenges that have plagued vaccines.
“There’s an urgent need for an easily produced, transported, stored, and administered antiviral drug against SARS-CoV-2,” Dr. Painter said.
Of the 202 people recruited, 182 had swabs that could be evaluated, of which 78 showed infection at baseline. The results are based on labs of those 78 participants.
By day 3, 28% of patients in the placebo arm had SARS-CoV-2 in their nasopharynx, compared with 20.4% of patients receiving any dose of molnupiravir. But by day 5, none of the participants receiving the active drug had evidence of SARS-CoV-2 in their nasopharynx. In comparison, 24% of people in the placebo arm still had detectable virus.
Halfway through the treatment course, differences in the presence of infectious virus were already evident. By day 3 of the 5-day course, 36.4% of participants in the 200-mg group had detectable virus in the nasopharynx, compared with 21% in the 400-mg group and just 12.5% in the 800-mg group. And although the reduction in SARS-CoV-2 was noticeable in the 200-mg and the 400-mg arms, it was only statistically significant in the 800-mg arm.
In contrast, by the end of the 5 days in the placebo groups, infectious virus varied from 18.2% in the 200-mg placebo group to 30% in the 800-mg group. This points out the variability of the disease course of SARS-CoV-2.
“You just don’t know” which infections will lead to serious disease, Dr. Painter said in an interview. “And don’t you wish we did?”
Seven participants discontinued treatment, though only four experienced adverse events. Three of those discontinued the trial because of adverse events. The study is still blinded, so it’s unclear what those events were, but Dr. Painter said that they were not thought to be related to the study drug.
The bottom line, said Dr. Painter, was that people treated with molnupiravir had starkly different outcomes in lab measures during the study.
“An average of 10 days after symptom onset, 24% of placebo patients remained culture positive” for SARS-CoV-2 – meaning there wasn’t just virus in the nasopharynx, but it was capable of replicating, Dr. Painter said. “In contrast, no infectious virus could be recovered at study day 5 in any molnupiravir-treated patients.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A single pill of the investigational drug molnupiravir taken twice a day for 5 days eliminated SARS-CoV-2 from the nasopharynx of 49 participants.
That led Carlos del Rio, MD, distinguished professor of medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, to suggest a future in which a drug like molnupiravir could be taken in the first few days of symptoms to prevent severe disease, similar to Tamiflu for influenza.
“I think it’s critically important,” he said of the data. Emory University was involved in the trial of molnupiravir but Dr. del Rio was not part of that team. “This drug offers the first antiviral oral drug that then could be used in an outpatient setting.”
Still, Dr. del Rio said it’s too soon to call this particular drug the breakthrough clinicians need to keep people out of the ICU. “It has the potential to be practice changing; it’s not practice changing at the moment.”
Wendy Painter, MD, of Ridgeback Biotherapeutics, who presented the data at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, agreed. While the data are promising, “We will need to see if people get better from actual illness” to assess the real value of the drug in clinical care.
“That’s a phase 3 objective we’ll need to prove,” she said in an interview.
Phase 2/3 efficacy and safety studies of the drug are now underway in hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients.
In a brief prerecorded presentation of the data, Dr. Painter laid out what researchers know so far: Preclinical studies suggest that molnupiravir is effective against a number of viruses, including coronaviruses and specifically SARS-CoV-2. It prevents a virus from replicating by inducing viral error catastrophe (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 15;99[21]:13374-6) – essentially overloading the virus with replication and mutation until the virus burns itself out and can’t produce replicable copies.
In this phase 2a, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial, researchers recruited 202 adults who were treated at an outpatient clinic with fever or other symptoms of a respiratory virus and confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection by day 4. Participants were randomly assigned to three different groups: 200 mg of molnupiravir, 400 mg, or 800 mg. The 200-mg arm was matched 1:1 with a placebo-controlled group, and the other two groups had three participants in the active group for every one control.
Participants took the pills twice daily for 5 days, and then were followed for a total of 28 days to monitor for complications or adverse events. At days 3, 5, 7, 14, and 28, researchers also took nasopharyngeal swabs for polymerase chain reaction tests, to sequence the virus, and to grow cultures of SARS-CoV-2 to see if the virus that’s present is actually capable of infecting others.
Notably, the pills do not have to be refrigerated at any point in the process, alleviating the cold-chain challenges that have plagued vaccines.
“There’s an urgent need for an easily produced, transported, stored, and administered antiviral drug against SARS-CoV-2,” Dr. Painter said.
Of the 202 people recruited, 182 had swabs that could be evaluated, of which 78 showed infection at baseline. The results are based on labs of those 78 participants.
By day 3, 28% of patients in the placebo arm had SARS-CoV-2 in their nasopharynx, compared with 20.4% of patients receiving any dose of molnupiravir. But by day 5, none of the participants receiving the active drug had evidence of SARS-CoV-2 in their nasopharynx. In comparison, 24% of people in the placebo arm still had detectable virus.
Halfway through the treatment course, differences in the presence of infectious virus were already evident. By day 3 of the 5-day course, 36.4% of participants in the 200-mg group had detectable virus in the nasopharynx, compared with 21% in the 400-mg group and just 12.5% in the 800-mg group. And although the reduction in SARS-CoV-2 was noticeable in the 200-mg and the 400-mg arms, it was only statistically significant in the 800-mg arm.
In contrast, by the end of the 5 days in the placebo groups, infectious virus varied from 18.2% in the 200-mg placebo group to 30% in the 800-mg group. This points out the variability of the disease course of SARS-CoV-2.
“You just don’t know” which infections will lead to serious disease, Dr. Painter said in an interview. “And don’t you wish we did?”
Seven participants discontinued treatment, though only four experienced adverse events. Three of those discontinued the trial because of adverse events. The study is still blinded, so it’s unclear what those events were, but Dr. Painter said that they were not thought to be related to the study drug.
The bottom line, said Dr. Painter, was that people treated with molnupiravir had starkly different outcomes in lab measures during the study.
“An average of 10 days after symptom onset, 24% of placebo patients remained culture positive” for SARS-CoV-2 – meaning there wasn’t just virus in the nasopharynx, but it was capable of replicating, Dr. Painter said. “In contrast, no infectious virus could be recovered at study day 5 in any molnupiravir-treated patients.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A single pill of the investigational drug molnupiravir taken twice a day for 5 days eliminated SARS-CoV-2 from the nasopharynx of 49 participants.
That led Carlos del Rio, MD, distinguished professor of medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, to suggest a future in which a drug like molnupiravir could be taken in the first few days of symptoms to prevent severe disease, similar to Tamiflu for influenza.
“I think it’s critically important,” he said of the data. Emory University was involved in the trial of molnupiravir but Dr. del Rio was not part of that team. “This drug offers the first antiviral oral drug that then could be used in an outpatient setting.”
Still, Dr. del Rio said it’s too soon to call this particular drug the breakthrough clinicians need to keep people out of the ICU. “It has the potential to be practice changing; it’s not practice changing at the moment.”
Wendy Painter, MD, of Ridgeback Biotherapeutics, who presented the data at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, agreed. While the data are promising, “We will need to see if people get better from actual illness” to assess the real value of the drug in clinical care.
“That’s a phase 3 objective we’ll need to prove,” she said in an interview.
Phase 2/3 efficacy and safety studies of the drug are now underway in hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients.
In a brief prerecorded presentation of the data, Dr. Painter laid out what researchers know so far: Preclinical studies suggest that molnupiravir is effective against a number of viruses, including coronaviruses and specifically SARS-CoV-2. It prevents a virus from replicating by inducing viral error catastrophe (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 15;99[21]:13374-6) – essentially overloading the virus with replication and mutation until the virus burns itself out and can’t produce replicable copies.
In this phase 2a, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial, researchers recruited 202 adults who were treated at an outpatient clinic with fever or other symptoms of a respiratory virus and confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection by day 4. Participants were randomly assigned to three different groups: 200 mg of molnupiravir, 400 mg, or 800 mg. The 200-mg arm was matched 1:1 with a placebo-controlled group, and the other two groups had three participants in the active group for every one control.
Participants took the pills twice daily for 5 days, and then were followed for a total of 28 days to monitor for complications or adverse events. At days 3, 5, 7, 14, and 28, researchers also took nasopharyngeal swabs for polymerase chain reaction tests, to sequence the virus, and to grow cultures of SARS-CoV-2 to see if the virus that’s present is actually capable of infecting others.
Notably, the pills do not have to be refrigerated at any point in the process, alleviating the cold-chain challenges that have plagued vaccines.
“There’s an urgent need for an easily produced, transported, stored, and administered antiviral drug against SARS-CoV-2,” Dr. Painter said.
Of the 202 people recruited, 182 had swabs that could be evaluated, of which 78 showed infection at baseline. The results are based on labs of those 78 participants.
By day 3, 28% of patients in the placebo arm had SARS-CoV-2 in their nasopharynx, compared with 20.4% of patients receiving any dose of molnupiravir. But by day 5, none of the participants receiving the active drug had evidence of SARS-CoV-2 in their nasopharynx. In comparison, 24% of people in the placebo arm still had detectable virus.
Halfway through the treatment course, differences in the presence of infectious virus were already evident. By day 3 of the 5-day course, 36.4% of participants in the 200-mg group had detectable virus in the nasopharynx, compared with 21% in the 400-mg group and just 12.5% in the 800-mg group. And although the reduction in SARS-CoV-2 was noticeable in the 200-mg and the 400-mg arms, it was only statistically significant in the 800-mg arm.
In contrast, by the end of the 5 days in the placebo groups, infectious virus varied from 18.2% in the 200-mg placebo group to 30% in the 800-mg group. This points out the variability of the disease course of SARS-CoV-2.
“You just don’t know” which infections will lead to serious disease, Dr. Painter said in an interview. “And don’t you wish we did?”
Seven participants discontinued treatment, though only four experienced adverse events. Three of those discontinued the trial because of adverse events. The study is still blinded, so it’s unclear what those events were, but Dr. Painter said that they were not thought to be related to the study drug.
The bottom line, said Dr. Painter, was that people treated with molnupiravir had starkly different outcomes in lab measures during the study.
“An average of 10 days after symptom onset, 24% of placebo patients remained culture positive” for SARS-CoV-2 – meaning there wasn’t just virus in the nasopharynx, but it was capable of replicating, Dr. Painter said. “In contrast, no infectious virus could be recovered at study day 5 in any molnupiravir-treated patients.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Assessing Psychological Interventions for Hidradenitis Suppurativa as a First Step Toward Patient-Centered Practice
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)(also known as acne inversa) is a chronic, recurrent, and debilitating inflammatory dermatologic disease of the hair follicle. It usually presents after puberty, with painful, deep-seated, inflamed lesions in apocrine gland–bearing areas of the body, most commonly the axillae and inguinal and anogenital regions.1
Hidradenitis suppurativa patients have a high rate of psychologic and psychiatric comorbidities that often are interrelated and multidirectional. Approximately 1 in 4 adults with HS also experience depression (prevalence among all HS patients, 16.9%), and 1 in 5 experience anxiety (prevalence, 4.9%).2,3 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been associated with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and suicidality.2,4
These comorbidity factors have a remarkable impact on HS patients’ quality of life (QOL). Compared to other diseases, including psoriasis, stroke, and conditions that create candidacy for heart transplantation, HS was identified as the most impairing condition.5,6 It is estimated that more than 50% of HS patients experience a very or extremely large effect on their QOL, as measured by the dermatology life quality index.6
Pain, a major component of low QOL in HS patients, has an adverse impact on emotional health. Hidradenitis suppurativa causes body image dissatisfaction, leading to shame, embarrassment, lack of self-confidence, stigmatization, and social isolation.7-9 Furthermore, patients with HS have an increased risk for antidepressant drug use, completed suicide, and suicidal behavior compared to the general population.10
Focusing therapy on physical manifestations of HS only while ignoring the psychologic aspect could lead to a vicious cycle in which stress triggers flares, leading to worsening HS, leading to more stress, and so on.11 Therefore, psychological support for HS patients is critical, and we believe it should be an integral part of managing the disease.
There is no evidence to support effective therapeutic intervention for psychological aspects of HS. We conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term hidradenitis in combination with psychology, psychological, mindfulness, and cognitive behavioral therapy. No relevant articles were found. Most articles on HS focused on the low QOL associated with the disease and patient coping mechanisms. However, there are a number of psychological therapies to consider and evaluate for the management of HS.
Psychological Therapies to Consider in HS
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment
Cognitive behavioral treatment has been successfully used to manage skin diseases other than HS.12 Patients’ shame and stigmatization due to body dissatisfaction often cause social isolation, which might appear as social anxiety.9,13 Cognitive behavioral treatment, or compassion-focused therapy, could increase patients’ self-acceptance and reduce shameful feelings.13
Group Therapy
Alternatively, group therapy might be beneficial for HS patients. Research has shown that most HS patients know others affected by the same disease or attend an HS support group, and patients value the support of peers with the disease.13 Therefore, group therapy meetings with HS patients that are directed by a health care professional might reduce feelings of shame and stigmatization and increase feelings of social acceptance.
Mindfulness
Another approach for managing psychological aspects of skin diseases that might be useful in HS is mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), developed by Kabat-Zinn and colleagues,14 which helps patients develop mindfulness through training in meditation. It is an intensive, structured, patient-centered approach that has been successfully used in a variety of settings.14,15
Current evidence supports the use of MBSR in the adjunct treatment of chronic pain, anxiety, and depression—symptoms that have a great impact on HS patients’ QOL.16 Furthermore, MBSR is offered in a group setting, which is potentially an opportunity for peer support and understanding; social support has been reported to be highly beneficial for HS patients.17
Can the Placebo Effect Aid in Managing HS?
A recent review that assessed the placebo effect in randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of treatments for cutaneous disease demonstrated that the placebo effect in HS therapy trials is higher than in RCTs of therapies for psoriasis and eczema. This finding highlights the importance of the physician-patient relationship when managing HS, which can result in greater treatment adherence and more patient education, empowerment, and encouragement toward beneficial lifestyle changes.18
Complementary psychological interventions for managing HS might maximize the placebo effect in clinical practice.18 The placebo effect in RCTs is higher for HS treatments than for psoriasis treatments, and if patients with psoriasis improved with psychological interventions,12 it would be reasonable to expect an improvement in QOL with psychological interventions for HS.
Final Thoughts
Although a number of studies have been published in the medical literature regarding psychological intervention in psoriasis management,12 we found no clinical studies assessing the psychological management of HS. We conclude that more research is necessary to develop psychological interventions targeting HS patients because a multidisciplinary and patient-centered approach is essential for the management of HS.
- Zouboulis CC, Desai N, Emtestam L, et al. European S1 guideline for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:619-644.
- Patel KR, Lee HH, Rastogi S, et al. Association between hidradenitis suppurativa, depression, anxiety, and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:737-744.
- Machado MO, Stergiopoulos V, Maes M, et al. Depression and anxiety in adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:939-945.
- Huilaja L, Tiri H, Jokelainen J, et al. Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have a high psychiatric disease burden: a Finnish nationwide registry study. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:46-51.
- Sampogna F, Fania L, Mazzanti C, et al. The broad-spectrum impact of hidradenitis suppurativa on quality of life: a comparison with psoriasis. Dermatology. 2019;235:308-314.
- von der Werth JM, Jemec GB. Morbidity in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:809-813.
- Esmann S, Jemec GBE. Psychosocial impact of hidradenitis suppurativa: a qualitative study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:328-332.
- Schneider-Burrus S, Jost A, Peters EMJ, et al. Association of hidradenitis suppurativa with body image. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:447-451.
- Koumaki D, Efthymiou O, Bozi E, et al. Perspectives on perceived stigma and self-stigma in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:785-790.
- Thorlacius L, Cohen AD, Gislason GH, et al. Increased suicide risk in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:52-57.
- Gill L, Williams M, Hamzavi I. Update on hidradenitis suppurativa: connecting the tracts. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6:112.
- Qureshi AA, Awosika O, Baruffi F, et al. Psychological therapies in management of psoriatic skin disease: a systematic review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019;20:607-624.
- Keary E, Hevey D, Tobin AM. A qualitative analysis of psychological distress in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:342-347.
- Kabat-Zinn J, Massion AO, Kristeller J, et al. Effectiveness of a meditation-based stress reduction program in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 1992;149:936-943.
- Evans S, Ferrando S, Findler M, et al. Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22:716-721.
- Gotink RA, Chu P, Busschbach JJV, et al. Standardised mindfulness-based interventions in healthcare: an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of RCTs. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124344.
- Golbari NM, Porter ML, Kimball AM. Online communications among hidradenitis suppurativa patients reflect community needs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1760-1762.
- Ali AA, Seng EK, Alavi A, et al. Exploring changes in placebo treatment arms in hidradenitis suppurativa randomized clinical trials: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:45-53.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)(also known as acne inversa) is a chronic, recurrent, and debilitating inflammatory dermatologic disease of the hair follicle. It usually presents after puberty, with painful, deep-seated, inflamed lesions in apocrine gland–bearing areas of the body, most commonly the axillae and inguinal and anogenital regions.1
Hidradenitis suppurativa patients have a high rate of psychologic and psychiatric comorbidities that often are interrelated and multidirectional. Approximately 1 in 4 adults with HS also experience depression (prevalence among all HS patients, 16.9%), and 1 in 5 experience anxiety (prevalence, 4.9%).2,3 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been associated with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and suicidality.2,4
These comorbidity factors have a remarkable impact on HS patients’ quality of life (QOL). Compared to other diseases, including psoriasis, stroke, and conditions that create candidacy for heart transplantation, HS was identified as the most impairing condition.5,6 It is estimated that more than 50% of HS patients experience a very or extremely large effect on their QOL, as measured by the dermatology life quality index.6
Pain, a major component of low QOL in HS patients, has an adverse impact on emotional health. Hidradenitis suppurativa causes body image dissatisfaction, leading to shame, embarrassment, lack of self-confidence, stigmatization, and social isolation.7-9 Furthermore, patients with HS have an increased risk for antidepressant drug use, completed suicide, and suicidal behavior compared to the general population.10
Focusing therapy on physical manifestations of HS only while ignoring the psychologic aspect could lead to a vicious cycle in which stress triggers flares, leading to worsening HS, leading to more stress, and so on.11 Therefore, psychological support for HS patients is critical, and we believe it should be an integral part of managing the disease.
There is no evidence to support effective therapeutic intervention for psychological aspects of HS. We conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term hidradenitis in combination with psychology, psychological, mindfulness, and cognitive behavioral therapy. No relevant articles were found. Most articles on HS focused on the low QOL associated with the disease and patient coping mechanisms. However, there are a number of psychological therapies to consider and evaluate for the management of HS.
Psychological Therapies to Consider in HS
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment
Cognitive behavioral treatment has been successfully used to manage skin diseases other than HS.12 Patients’ shame and stigmatization due to body dissatisfaction often cause social isolation, which might appear as social anxiety.9,13 Cognitive behavioral treatment, or compassion-focused therapy, could increase patients’ self-acceptance and reduce shameful feelings.13
Group Therapy
Alternatively, group therapy might be beneficial for HS patients. Research has shown that most HS patients know others affected by the same disease or attend an HS support group, and patients value the support of peers with the disease.13 Therefore, group therapy meetings with HS patients that are directed by a health care professional might reduce feelings of shame and stigmatization and increase feelings of social acceptance.
Mindfulness
Another approach for managing psychological aspects of skin diseases that might be useful in HS is mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), developed by Kabat-Zinn and colleagues,14 which helps patients develop mindfulness through training in meditation. It is an intensive, structured, patient-centered approach that has been successfully used in a variety of settings.14,15
Current evidence supports the use of MBSR in the adjunct treatment of chronic pain, anxiety, and depression—symptoms that have a great impact on HS patients’ QOL.16 Furthermore, MBSR is offered in a group setting, which is potentially an opportunity for peer support and understanding; social support has been reported to be highly beneficial for HS patients.17
Can the Placebo Effect Aid in Managing HS?
A recent review that assessed the placebo effect in randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of treatments for cutaneous disease demonstrated that the placebo effect in HS therapy trials is higher than in RCTs of therapies for psoriasis and eczema. This finding highlights the importance of the physician-patient relationship when managing HS, which can result in greater treatment adherence and more patient education, empowerment, and encouragement toward beneficial lifestyle changes.18
Complementary psychological interventions for managing HS might maximize the placebo effect in clinical practice.18 The placebo effect in RCTs is higher for HS treatments than for psoriasis treatments, and if patients with psoriasis improved with psychological interventions,12 it would be reasonable to expect an improvement in QOL with psychological interventions for HS.
Final Thoughts
Although a number of studies have been published in the medical literature regarding psychological intervention in psoriasis management,12 we found no clinical studies assessing the psychological management of HS. We conclude that more research is necessary to develop psychological interventions targeting HS patients because a multidisciplinary and patient-centered approach is essential for the management of HS.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)(also known as acne inversa) is a chronic, recurrent, and debilitating inflammatory dermatologic disease of the hair follicle. It usually presents after puberty, with painful, deep-seated, inflamed lesions in apocrine gland–bearing areas of the body, most commonly the axillae and inguinal and anogenital regions.1
Hidradenitis suppurativa patients have a high rate of psychologic and psychiatric comorbidities that often are interrelated and multidirectional. Approximately 1 in 4 adults with HS also experience depression (prevalence among all HS patients, 16.9%), and 1 in 5 experience anxiety (prevalence, 4.9%).2,3 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been associated with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and suicidality.2,4
These comorbidity factors have a remarkable impact on HS patients’ quality of life (QOL). Compared to other diseases, including psoriasis, stroke, and conditions that create candidacy for heart transplantation, HS was identified as the most impairing condition.5,6 It is estimated that more than 50% of HS patients experience a very or extremely large effect on their QOL, as measured by the dermatology life quality index.6
Pain, a major component of low QOL in HS patients, has an adverse impact on emotional health. Hidradenitis suppurativa causes body image dissatisfaction, leading to shame, embarrassment, lack of self-confidence, stigmatization, and social isolation.7-9 Furthermore, patients with HS have an increased risk for antidepressant drug use, completed suicide, and suicidal behavior compared to the general population.10
Focusing therapy on physical manifestations of HS only while ignoring the psychologic aspect could lead to a vicious cycle in which stress triggers flares, leading to worsening HS, leading to more stress, and so on.11 Therefore, psychological support for HS patients is critical, and we believe it should be an integral part of managing the disease.
There is no evidence to support effective therapeutic intervention for psychological aspects of HS. We conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term hidradenitis in combination with psychology, psychological, mindfulness, and cognitive behavioral therapy. No relevant articles were found. Most articles on HS focused on the low QOL associated with the disease and patient coping mechanisms. However, there are a number of psychological therapies to consider and evaluate for the management of HS.
Psychological Therapies to Consider in HS
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment
Cognitive behavioral treatment has been successfully used to manage skin diseases other than HS.12 Patients’ shame and stigmatization due to body dissatisfaction often cause social isolation, which might appear as social anxiety.9,13 Cognitive behavioral treatment, or compassion-focused therapy, could increase patients’ self-acceptance and reduce shameful feelings.13
Group Therapy
Alternatively, group therapy might be beneficial for HS patients. Research has shown that most HS patients know others affected by the same disease or attend an HS support group, and patients value the support of peers with the disease.13 Therefore, group therapy meetings with HS patients that are directed by a health care professional might reduce feelings of shame and stigmatization and increase feelings of social acceptance.
Mindfulness
Another approach for managing psychological aspects of skin diseases that might be useful in HS is mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), developed by Kabat-Zinn and colleagues,14 which helps patients develop mindfulness through training in meditation. It is an intensive, structured, patient-centered approach that has been successfully used in a variety of settings.14,15
Current evidence supports the use of MBSR in the adjunct treatment of chronic pain, anxiety, and depression—symptoms that have a great impact on HS patients’ QOL.16 Furthermore, MBSR is offered in a group setting, which is potentially an opportunity for peer support and understanding; social support has been reported to be highly beneficial for HS patients.17
Can the Placebo Effect Aid in Managing HS?
A recent review that assessed the placebo effect in randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of treatments for cutaneous disease demonstrated that the placebo effect in HS therapy trials is higher than in RCTs of therapies for psoriasis and eczema. This finding highlights the importance of the physician-patient relationship when managing HS, which can result in greater treatment adherence and more patient education, empowerment, and encouragement toward beneficial lifestyle changes.18
Complementary psychological interventions for managing HS might maximize the placebo effect in clinical practice.18 The placebo effect in RCTs is higher for HS treatments than for psoriasis treatments, and if patients with psoriasis improved with psychological interventions,12 it would be reasonable to expect an improvement in QOL with psychological interventions for HS.
Final Thoughts
Although a number of studies have been published in the medical literature regarding psychological intervention in psoriasis management,12 we found no clinical studies assessing the psychological management of HS. We conclude that more research is necessary to develop psychological interventions targeting HS patients because a multidisciplinary and patient-centered approach is essential for the management of HS.
- Zouboulis CC, Desai N, Emtestam L, et al. European S1 guideline for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:619-644.
- Patel KR, Lee HH, Rastogi S, et al. Association between hidradenitis suppurativa, depression, anxiety, and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:737-744.
- Machado MO, Stergiopoulos V, Maes M, et al. Depression and anxiety in adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:939-945.
- Huilaja L, Tiri H, Jokelainen J, et al. Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have a high psychiatric disease burden: a Finnish nationwide registry study. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:46-51.
- Sampogna F, Fania L, Mazzanti C, et al. The broad-spectrum impact of hidradenitis suppurativa on quality of life: a comparison with psoriasis. Dermatology. 2019;235:308-314.
- von der Werth JM, Jemec GB. Morbidity in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:809-813.
- Esmann S, Jemec GBE. Psychosocial impact of hidradenitis suppurativa: a qualitative study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:328-332.
- Schneider-Burrus S, Jost A, Peters EMJ, et al. Association of hidradenitis suppurativa with body image. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:447-451.
- Koumaki D, Efthymiou O, Bozi E, et al. Perspectives on perceived stigma and self-stigma in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:785-790.
- Thorlacius L, Cohen AD, Gislason GH, et al. Increased suicide risk in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:52-57.
- Gill L, Williams M, Hamzavi I. Update on hidradenitis suppurativa: connecting the tracts. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6:112.
- Qureshi AA, Awosika O, Baruffi F, et al. Psychological therapies in management of psoriatic skin disease: a systematic review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019;20:607-624.
- Keary E, Hevey D, Tobin AM. A qualitative analysis of psychological distress in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:342-347.
- Kabat-Zinn J, Massion AO, Kristeller J, et al. Effectiveness of a meditation-based stress reduction program in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 1992;149:936-943.
- Evans S, Ferrando S, Findler M, et al. Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22:716-721.
- Gotink RA, Chu P, Busschbach JJV, et al. Standardised mindfulness-based interventions in healthcare: an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of RCTs. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124344.
- Golbari NM, Porter ML, Kimball AM. Online communications among hidradenitis suppurativa patients reflect community needs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1760-1762.
- Ali AA, Seng EK, Alavi A, et al. Exploring changes in placebo treatment arms in hidradenitis suppurativa randomized clinical trials: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:45-53.
- Zouboulis CC, Desai N, Emtestam L, et al. European S1 guideline for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:619-644.
- Patel KR, Lee HH, Rastogi S, et al. Association between hidradenitis suppurativa, depression, anxiety, and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:737-744.
- Machado MO, Stergiopoulos V, Maes M, et al. Depression and anxiety in adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:939-945.
- Huilaja L, Tiri H, Jokelainen J, et al. Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have a high psychiatric disease burden: a Finnish nationwide registry study. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:46-51.
- Sampogna F, Fania L, Mazzanti C, et al. The broad-spectrum impact of hidradenitis suppurativa on quality of life: a comparison with psoriasis. Dermatology. 2019;235:308-314.
- von der Werth JM, Jemec GB. Morbidity in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:809-813.
- Esmann S, Jemec GBE. Psychosocial impact of hidradenitis suppurativa: a qualitative study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:328-332.
- Schneider-Burrus S, Jost A, Peters EMJ, et al. Association of hidradenitis suppurativa with body image. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:447-451.
- Koumaki D, Efthymiou O, Bozi E, et al. Perspectives on perceived stigma and self-stigma in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:785-790.
- Thorlacius L, Cohen AD, Gislason GH, et al. Increased suicide risk in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:52-57.
- Gill L, Williams M, Hamzavi I. Update on hidradenitis suppurativa: connecting the tracts. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6:112.
- Qureshi AA, Awosika O, Baruffi F, et al. Psychological therapies in management of psoriatic skin disease: a systematic review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019;20:607-624.
- Keary E, Hevey D, Tobin AM. A qualitative analysis of psychological distress in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:342-347.
- Kabat-Zinn J, Massion AO, Kristeller J, et al. Effectiveness of a meditation-based stress reduction program in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 1992;149:936-943.
- Evans S, Ferrando S, Findler M, et al. Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22:716-721.
- Gotink RA, Chu P, Busschbach JJV, et al. Standardised mindfulness-based interventions in healthcare: an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of RCTs. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124344.
- Golbari NM, Porter ML, Kimball AM. Online communications among hidradenitis suppurativa patients reflect community needs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1760-1762.
- Ali AA, Seng EK, Alavi A, et al. Exploring changes in placebo treatment arms in hidradenitis suppurativa randomized clinical trials: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:45-53.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Although hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) has high rates of psychological comorbidities, management of the psychological aspects of the disease has not been studied extensively.
- Complementary psychological interventions should be evaluated for the management of HS.
How to make resident mental health care stigma free
Sarah Sofka, MD, FACP, noticed a pattern. As program director for the internal medicine (IM) residency at West Virginia University, Morgantown, she was informed when residents were sent to counseling because they were affected by burnout, depression, or anxiety. When trainees returned from these visits, many told her the same thing: They wished they had sought help sooner.
IM residents and their families had access to free counseling at WVU, but few used the resource, says Dr. Sofka. “So, we thought, let’s just schedule all of our residents for a therapy visit so they can go and see what it’s like,” she said. “This will hopefully decrease the stigma for seeking mental health care. If everybody’s going, it’s not a big deal.”
In July 2015, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues launched a universal well-being assessment program for the IM residents at WVU. The program leaders automatically scheduled first- and second-year residents for a visit to the faculty staff assistance program counselors. The visits were not mandatory, and residents could choose not to go; but if they did go, they received the entire day of their visit off from work.
Five and a half years after launching their program, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues conducted one of the first studies of the efficacy of an opt-out approach for resident mental wellness. They found that , suggesting that residents were seeking help proactively after having to at least consider it.
Opt-out counseling is a recent concept in residency programs – one that’s attracting interest from training programs across the country. Brown University, Providence, R.I.; the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora; University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia; and the University of California, San Francisco have at least one residency program that uses the approach.
Lisa Meeks, PhD, an assistant professor of family medicine at Michigan Medicine, in Ann Arbor, and other experts also believe opt-out counseling could decrease stigma and help normalize seeking care for mental health problems in the medical community while lowering the barriers for trainees who need help.
No time, no access, plenty of stigma
Burnout and mental health are known to be major concerns for health care workers, especially trainees. College graduates starting medical education have lower rates of burnout and depression, compared with demographically matched peers; however, once they’ve started training, medical students, residents, and fellows are more likely to be burned out and exhibit symptoms of depression. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic is further fraying the well-being of overworked and traumatized health care professionals, and experts predict a mental health crisis will follow the viral crisis.
The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education recently mandated that programs offer wellness services to trainees. Yet this doesn’t mean they are always used; well-known barriers stand between residents, medical students, and physicians and their receiving effective mental health treatment.
Two of the most obvious are access and time, given the grueling and often inflexible schedules of most trainees, says Jessica Gold, MD, a psychiatrist at Washington University, St. Louis, who specializes in treating medical professionals. Dr. Gold also points out that, to be done correctly, these programs require institutional support and investment – resources that aren’t always adequate.
“A lack of transparency and clear messaging around what is available, who provides the services, and how to access these services can be a major barrier,” says Erene Stergiopoulos, MD, a second-year psychiatry resident at the University of Toronto. In addition, there can be considerable lag between when a resident realizes they need help and when they manage to find a provider and schedule an appointment, says Dr. Meeks.
Even when these logistical barriers are overcome, trainees and physicians have to contend with the persistent stigma associated with mental health treatment in the culture of medicine, says Dr. Gold. A recent survey by the American College of Emergency Physicians found that 73% of surveyed physicians feel there is stigma in their workplace about seeking mental health treatment. Many state medical licensing boards still require physicians to disclose mental health treatment, which discourages many trainees and providers from seeking proactive care, says Mary Moffit, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and director of the resident and faculty wellness program at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
How the opt-out approach works
“The idea is by making it opt-out, you really normalize it,” says Maneesh Batra, MD, MPH, associate director of the University of Washington, Seattle, Children’s Hospital residency program. Similar approaches have proven effective at shaping human behavior in other health care settings, including boosting testing rates for HIV and increasing immunization rates for childhood vaccines, Dr. Batra says.
In general, opt-out programs acknowledge that people are busy and won’t take that extra step or click that extra button if they don’t have to, says Oana Tomescu, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical medicine and pediatrics at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
In 2018, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues at WVU conducted a survey that showed that a majority of residents thought favorably of their opt-out program and said they would return to counseling for follow-up care. In their most recent study, published in the Journal of Graduate Medical Education in 2021, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues found that residents did just that – only 8 of 239 opted out of universally scheduled visits. Resident-initiated visits increased significantly from zero during the 2014-2015 academic year to 23 in 2018-2019. Between those periods, program-mandated visits decreased significantly from 12 to 3.
The initiative has succeeded in creating a culture of openness and caring at WVU, says 2nd-year internal medicine resident Nistha Modi, MD. “It sets the tone for the program – we talk about mental health openly,” says Dr. Modi.
Crucially, the counselors work out of a different building than the hospital where Dr. Modi and her fellow residents work and use a separate electronic medical record system to protect resident privacy. This is hugely important for medical trainees, note Dr. Tomescu, Dr. Gold, and many other experts. The therapists understand residency and medical education, and there is no limit to the number of visits a resident or fellow can make with the program counselors, says Dr. Modi.
Opt-out programs offer a counterbalance to many negative tendencies in residency, says Dr. Meeks. “We’ve normalized so many things that are not healthy and productive. ... We need to counterbalance that with normalizing help seeking. And it’s really difficult to normalize something that’s not part of a system.”
Costs, concerns, and systematic support
Providing unlimited, free counseling for trainees can be very beneficial, but it requires adequate funding and personnel resources. Offering unlimited access means that an institution has to follow through in making this degree of care available while also ensuring that the system doesn’t get overwhelmed or is unable to accommodate very sick individuals, says Dr. Gold.
Another concern that experts like Dr. Batra, Dr. Moffit, and Dr. Gold share is that residents who go to their scheduled appointments may not completely buy into the experience because it wasn’t their idea in the first place. Participation alone doesn’t necessarily indicate full acceptance. Program personnel don’t intend for these appointments to be thought of as mandatory, yet residents may still experience them that way. Several leading resident well-being programs instead emphasize outreach to trainees, institutional support, and accessible mental health resources that are – and feel – entirely voluntary.
“If I tell someone that they have to do something, it’s very different than if they arrive at that conclusion for themselves,” says Dr. Batra. “That’s how life works.”
When it comes to cost, a recent study published in Academic Medicine provides encouraging data. At the University of Colorado, an opt-out pilot program for IM and pediatrics interns during the 2017-2018 academic year cost just $940 total, equal to $11.75 per intern. As in West Virginia, the program in Colorado covered the cost of the visit, interns were provided a half day off (whether they attended their appointment or not), and the visits and surveys were entirely optional and confidential. During the 1-year pilot program, 29% of 80 interns attended the scheduled appointment, 56% opted out in advance, and 15% didn’t show up. The majority of interns who were surveyed (85%), however, thought the program should continue and that it had a positive effect on their wellness even if they didn’t attend their appointment.
In West Virginia, program costs are higher. The program has $20,000 in annual funding to cover the opt-out program and unlimited counseling visits for residents and fellows. With that funding, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues were also able to expand the program slightly last year to schedule all the critical care faculty for counseling visits. Cost is a barrier to expanding these services to the entire institution, which Dr. Sofka says she hopes to do one day.
Research in this area is still preliminary. The WVU and Colorado studies provide some of the first evidence in support of an opt-out approach. Eventually, it would be beneficial for multicenter studies and longitudinal research to track the effects of such programs over time, say Dr. Sofka and Ajay Major, MD, MBA, one of the study’s coauthors and a hematology/oncology fellow at the University of Chicago.
Whether a program goes with an opt-out approach or not, the systematic supports – protecting resident privacy, providing flexible scheduling, and more – are crucial.
As Dr. Tomescu notes, wellness shouldn’t be just something trainees have to do. “The key with really working on burnout at a huge level is for all programs and schools to recognize that it’s a shared responsibility.”
“I felt very fortunate that I was able to get some help throughout residency,” says Dr. Modi. “About how to be a better daughter. How to be content with things I have in life. How to be happy, and grateful. With the kind of job we have, I think we sometimes forget to be grateful.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sarah Sofka, MD, FACP, noticed a pattern. As program director for the internal medicine (IM) residency at West Virginia University, Morgantown, she was informed when residents were sent to counseling because they were affected by burnout, depression, or anxiety. When trainees returned from these visits, many told her the same thing: They wished they had sought help sooner.
IM residents and their families had access to free counseling at WVU, but few used the resource, says Dr. Sofka. “So, we thought, let’s just schedule all of our residents for a therapy visit so they can go and see what it’s like,” she said. “This will hopefully decrease the stigma for seeking mental health care. If everybody’s going, it’s not a big deal.”
In July 2015, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues launched a universal well-being assessment program for the IM residents at WVU. The program leaders automatically scheduled first- and second-year residents for a visit to the faculty staff assistance program counselors. The visits were not mandatory, and residents could choose not to go; but if they did go, they received the entire day of their visit off from work.
Five and a half years after launching their program, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues conducted one of the first studies of the efficacy of an opt-out approach for resident mental wellness. They found that , suggesting that residents were seeking help proactively after having to at least consider it.
Opt-out counseling is a recent concept in residency programs – one that’s attracting interest from training programs across the country. Brown University, Providence, R.I.; the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora; University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia; and the University of California, San Francisco have at least one residency program that uses the approach.
Lisa Meeks, PhD, an assistant professor of family medicine at Michigan Medicine, in Ann Arbor, and other experts also believe opt-out counseling could decrease stigma and help normalize seeking care for mental health problems in the medical community while lowering the barriers for trainees who need help.
No time, no access, plenty of stigma
Burnout and mental health are known to be major concerns for health care workers, especially trainees. College graduates starting medical education have lower rates of burnout and depression, compared with demographically matched peers; however, once they’ve started training, medical students, residents, and fellows are more likely to be burned out and exhibit symptoms of depression. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic is further fraying the well-being of overworked and traumatized health care professionals, and experts predict a mental health crisis will follow the viral crisis.
The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education recently mandated that programs offer wellness services to trainees. Yet this doesn’t mean they are always used; well-known barriers stand between residents, medical students, and physicians and their receiving effective mental health treatment.
Two of the most obvious are access and time, given the grueling and often inflexible schedules of most trainees, says Jessica Gold, MD, a psychiatrist at Washington University, St. Louis, who specializes in treating medical professionals. Dr. Gold also points out that, to be done correctly, these programs require institutional support and investment – resources that aren’t always adequate.
“A lack of transparency and clear messaging around what is available, who provides the services, and how to access these services can be a major barrier,” says Erene Stergiopoulos, MD, a second-year psychiatry resident at the University of Toronto. In addition, there can be considerable lag between when a resident realizes they need help and when they manage to find a provider and schedule an appointment, says Dr. Meeks.
Even when these logistical barriers are overcome, trainees and physicians have to contend with the persistent stigma associated with mental health treatment in the culture of medicine, says Dr. Gold. A recent survey by the American College of Emergency Physicians found that 73% of surveyed physicians feel there is stigma in their workplace about seeking mental health treatment. Many state medical licensing boards still require physicians to disclose mental health treatment, which discourages many trainees and providers from seeking proactive care, says Mary Moffit, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and director of the resident and faculty wellness program at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
How the opt-out approach works
“The idea is by making it opt-out, you really normalize it,” says Maneesh Batra, MD, MPH, associate director of the University of Washington, Seattle, Children’s Hospital residency program. Similar approaches have proven effective at shaping human behavior in other health care settings, including boosting testing rates for HIV and increasing immunization rates for childhood vaccines, Dr. Batra says.
In general, opt-out programs acknowledge that people are busy and won’t take that extra step or click that extra button if they don’t have to, says Oana Tomescu, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical medicine and pediatrics at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
In 2018, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues at WVU conducted a survey that showed that a majority of residents thought favorably of their opt-out program and said they would return to counseling for follow-up care. In their most recent study, published in the Journal of Graduate Medical Education in 2021, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues found that residents did just that – only 8 of 239 opted out of universally scheduled visits. Resident-initiated visits increased significantly from zero during the 2014-2015 academic year to 23 in 2018-2019. Between those periods, program-mandated visits decreased significantly from 12 to 3.
The initiative has succeeded in creating a culture of openness and caring at WVU, says 2nd-year internal medicine resident Nistha Modi, MD. “It sets the tone for the program – we talk about mental health openly,” says Dr. Modi.
Crucially, the counselors work out of a different building than the hospital where Dr. Modi and her fellow residents work and use a separate electronic medical record system to protect resident privacy. This is hugely important for medical trainees, note Dr. Tomescu, Dr. Gold, and many other experts. The therapists understand residency and medical education, and there is no limit to the number of visits a resident or fellow can make with the program counselors, says Dr. Modi.
Opt-out programs offer a counterbalance to many negative tendencies in residency, says Dr. Meeks. “We’ve normalized so many things that are not healthy and productive. ... We need to counterbalance that with normalizing help seeking. And it’s really difficult to normalize something that’s not part of a system.”
Costs, concerns, and systematic support
Providing unlimited, free counseling for trainees can be very beneficial, but it requires adequate funding and personnel resources. Offering unlimited access means that an institution has to follow through in making this degree of care available while also ensuring that the system doesn’t get overwhelmed or is unable to accommodate very sick individuals, says Dr. Gold.
Another concern that experts like Dr. Batra, Dr. Moffit, and Dr. Gold share is that residents who go to their scheduled appointments may not completely buy into the experience because it wasn’t their idea in the first place. Participation alone doesn’t necessarily indicate full acceptance. Program personnel don’t intend for these appointments to be thought of as mandatory, yet residents may still experience them that way. Several leading resident well-being programs instead emphasize outreach to trainees, institutional support, and accessible mental health resources that are – and feel – entirely voluntary.
“If I tell someone that they have to do something, it’s very different than if they arrive at that conclusion for themselves,” says Dr. Batra. “That’s how life works.”
When it comes to cost, a recent study published in Academic Medicine provides encouraging data. At the University of Colorado, an opt-out pilot program for IM and pediatrics interns during the 2017-2018 academic year cost just $940 total, equal to $11.75 per intern. As in West Virginia, the program in Colorado covered the cost of the visit, interns were provided a half day off (whether they attended their appointment or not), and the visits and surveys were entirely optional and confidential. During the 1-year pilot program, 29% of 80 interns attended the scheduled appointment, 56% opted out in advance, and 15% didn’t show up. The majority of interns who were surveyed (85%), however, thought the program should continue and that it had a positive effect on their wellness even if they didn’t attend their appointment.
In West Virginia, program costs are higher. The program has $20,000 in annual funding to cover the opt-out program and unlimited counseling visits for residents and fellows. With that funding, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues were also able to expand the program slightly last year to schedule all the critical care faculty for counseling visits. Cost is a barrier to expanding these services to the entire institution, which Dr. Sofka says she hopes to do one day.
Research in this area is still preliminary. The WVU and Colorado studies provide some of the first evidence in support of an opt-out approach. Eventually, it would be beneficial for multicenter studies and longitudinal research to track the effects of such programs over time, say Dr. Sofka and Ajay Major, MD, MBA, one of the study’s coauthors and a hematology/oncology fellow at the University of Chicago.
Whether a program goes with an opt-out approach or not, the systematic supports – protecting resident privacy, providing flexible scheduling, and more – are crucial.
As Dr. Tomescu notes, wellness shouldn’t be just something trainees have to do. “The key with really working on burnout at a huge level is for all programs and schools to recognize that it’s a shared responsibility.”
“I felt very fortunate that I was able to get some help throughout residency,” says Dr. Modi. “About how to be a better daughter. How to be content with things I have in life. How to be happy, and grateful. With the kind of job we have, I think we sometimes forget to be grateful.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sarah Sofka, MD, FACP, noticed a pattern. As program director for the internal medicine (IM) residency at West Virginia University, Morgantown, she was informed when residents were sent to counseling because they were affected by burnout, depression, or anxiety. When trainees returned from these visits, many told her the same thing: They wished they had sought help sooner.
IM residents and their families had access to free counseling at WVU, but few used the resource, says Dr. Sofka. “So, we thought, let’s just schedule all of our residents for a therapy visit so they can go and see what it’s like,” she said. “This will hopefully decrease the stigma for seeking mental health care. If everybody’s going, it’s not a big deal.”
In July 2015, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues launched a universal well-being assessment program for the IM residents at WVU. The program leaders automatically scheduled first- and second-year residents for a visit to the faculty staff assistance program counselors. The visits were not mandatory, and residents could choose not to go; but if they did go, they received the entire day of their visit off from work.
Five and a half years after launching their program, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues conducted one of the first studies of the efficacy of an opt-out approach for resident mental wellness. They found that , suggesting that residents were seeking help proactively after having to at least consider it.
Opt-out counseling is a recent concept in residency programs – one that’s attracting interest from training programs across the country. Brown University, Providence, R.I.; the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora; University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia; and the University of California, San Francisco have at least one residency program that uses the approach.
Lisa Meeks, PhD, an assistant professor of family medicine at Michigan Medicine, in Ann Arbor, and other experts also believe opt-out counseling could decrease stigma and help normalize seeking care for mental health problems in the medical community while lowering the barriers for trainees who need help.
No time, no access, plenty of stigma
Burnout and mental health are known to be major concerns for health care workers, especially trainees. College graduates starting medical education have lower rates of burnout and depression, compared with demographically matched peers; however, once they’ve started training, medical students, residents, and fellows are more likely to be burned out and exhibit symptoms of depression. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic is further fraying the well-being of overworked and traumatized health care professionals, and experts predict a mental health crisis will follow the viral crisis.
The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education recently mandated that programs offer wellness services to trainees. Yet this doesn’t mean they are always used; well-known barriers stand between residents, medical students, and physicians and their receiving effective mental health treatment.
Two of the most obvious are access and time, given the grueling and often inflexible schedules of most trainees, says Jessica Gold, MD, a psychiatrist at Washington University, St. Louis, who specializes in treating medical professionals. Dr. Gold also points out that, to be done correctly, these programs require institutional support and investment – resources that aren’t always adequate.
“A lack of transparency and clear messaging around what is available, who provides the services, and how to access these services can be a major barrier,” says Erene Stergiopoulos, MD, a second-year psychiatry resident at the University of Toronto. In addition, there can be considerable lag between when a resident realizes they need help and when they manage to find a provider and schedule an appointment, says Dr. Meeks.
Even when these logistical barriers are overcome, trainees and physicians have to contend with the persistent stigma associated with mental health treatment in the culture of medicine, says Dr. Gold. A recent survey by the American College of Emergency Physicians found that 73% of surveyed physicians feel there is stigma in their workplace about seeking mental health treatment. Many state medical licensing boards still require physicians to disclose mental health treatment, which discourages many trainees and providers from seeking proactive care, says Mary Moffit, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and director of the resident and faculty wellness program at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
How the opt-out approach works
“The idea is by making it opt-out, you really normalize it,” says Maneesh Batra, MD, MPH, associate director of the University of Washington, Seattle, Children’s Hospital residency program. Similar approaches have proven effective at shaping human behavior in other health care settings, including boosting testing rates for HIV and increasing immunization rates for childhood vaccines, Dr. Batra says.
In general, opt-out programs acknowledge that people are busy and won’t take that extra step or click that extra button if they don’t have to, says Oana Tomescu, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical medicine and pediatrics at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
In 2018, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues at WVU conducted a survey that showed that a majority of residents thought favorably of their opt-out program and said they would return to counseling for follow-up care. In their most recent study, published in the Journal of Graduate Medical Education in 2021, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues found that residents did just that – only 8 of 239 opted out of universally scheduled visits. Resident-initiated visits increased significantly from zero during the 2014-2015 academic year to 23 in 2018-2019. Between those periods, program-mandated visits decreased significantly from 12 to 3.
The initiative has succeeded in creating a culture of openness and caring at WVU, says 2nd-year internal medicine resident Nistha Modi, MD. “It sets the tone for the program – we talk about mental health openly,” says Dr. Modi.
Crucially, the counselors work out of a different building than the hospital where Dr. Modi and her fellow residents work and use a separate electronic medical record system to protect resident privacy. This is hugely important for medical trainees, note Dr. Tomescu, Dr. Gold, and many other experts. The therapists understand residency and medical education, and there is no limit to the number of visits a resident or fellow can make with the program counselors, says Dr. Modi.
Opt-out programs offer a counterbalance to many negative tendencies in residency, says Dr. Meeks. “We’ve normalized so many things that are not healthy and productive. ... We need to counterbalance that with normalizing help seeking. And it’s really difficult to normalize something that’s not part of a system.”
Costs, concerns, and systematic support
Providing unlimited, free counseling for trainees can be very beneficial, but it requires adequate funding and personnel resources. Offering unlimited access means that an institution has to follow through in making this degree of care available while also ensuring that the system doesn’t get overwhelmed or is unable to accommodate very sick individuals, says Dr. Gold.
Another concern that experts like Dr. Batra, Dr. Moffit, and Dr. Gold share is that residents who go to their scheduled appointments may not completely buy into the experience because it wasn’t their idea in the first place. Participation alone doesn’t necessarily indicate full acceptance. Program personnel don’t intend for these appointments to be thought of as mandatory, yet residents may still experience them that way. Several leading resident well-being programs instead emphasize outreach to trainees, institutional support, and accessible mental health resources that are – and feel – entirely voluntary.
“If I tell someone that they have to do something, it’s very different than if they arrive at that conclusion for themselves,” says Dr. Batra. “That’s how life works.”
When it comes to cost, a recent study published in Academic Medicine provides encouraging data. At the University of Colorado, an opt-out pilot program for IM and pediatrics interns during the 2017-2018 academic year cost just $940 total, equal to $11.75 per intern. As in West Virginia, the program in Colorado covered the cost of the visit, interns were provided a half day off (whether they attended their appointment or not), and the visits and surveys were entirely optional and confidential. During the 1-year pilot program, 29% of 80 interns attended the scheduled appointment, 56% opted out in advance, and 15% didn’t show up. The majority of interns who were surveyed (85%), however, thought the program should continue and that it had a positive effect on their wellness even if they didn’t attend their appointment.
In West Virginia, program costs are higher. The program has $20,000 in annual funding to cover the opt-out program and unlimited counseling visits for residents and fellows. With that funding, Dr. Sofka and her colleagues were also able to expand the program slightly last year to schedule all the critical care faculty for counseling visits. Cost is a barrier to expanding these services to the entire institution, which Dr. Sofka says she hopes to do one day.
Research in this area is still preliminary. The WVU and Colorado studies provide some of the first evidence in support of an opt-out approach. Eventually, it would be beneficial for multicenter studies and longitudinal research to track the effects of such programs over time, say Dr. Sofka and Ajay Major, MD, MBA, one of the study’s coauthors and a hematology/oncology fellow at the University of Chicago.
Whether a program goes with an opt-out approach or not, the systematic supports – protecting resident privacy, providing flexible scheduling, and more – are crucial.
As Dr. Tomescu notes, wellness shouldn’t be just something trainees have to do. “The key with really working on burnout at a huge level is for all programs and schools to recognize that it’s a shared responsibility.”
“I felt very fortunate that I was able to get some help throughout residency,” says Dr. Modi. “About how to be a better daughter. How to be content with things I have in life. How to be happy, and grateful. With the kind of job we have, I think we sometimes forget to be grateful.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
RECOVERY trial of COVID-19 treatments stops colchicine arm
On the advice of its independent data monitoring committee (DMC), the RECOVERY trial has stopped recruitment to the colchicine arm for lack of efficacy in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
“The DMC saw no convincing evidence that further recruitment would provide conclusive proof of worthwhile mortality benefit either overall or in any prespecified subgroup,” the British investigators announced on March 5.
“The RECOVERY trial has already identified two anti-inflammatory drugs – dexamethasone and tocilizumab – that improve the chances of survival for patients with severe COVID-19. So, it is disappointing that colchicine, which is widely used to treat gout and other inflammatory conditions, has no effect in these patients,” cochief investigator Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, said in a statement.
“We do large, randomized trials to establish whether a drug that seems promising in theory has real benefits for patients in practice. Unfortunately, colchicine is not one of those,” said Dr. Landry, University of Oxford (England).
The RECOVERY trial is evaluating a range of potential treatments for COVID-19 at 180 hospitals in the United Kingdom, Indonesia, and Nepal, and was designed with the expectation that drugs would be added or dropped as the evidence changes. Since November 2020, the trial has included an arm comparing colchicine with usual care alone.
As part of a routine meeting March 4, the DMC reviewed data from a preliminary analysis based on 2,178 deaths among 11,162 patients, 94% of whom were being treated with a corticosteroid such as dexamethasone.
The results showed no significant difference in the primary endpoint of 28-day mortality in patients randomized to colchicine versus usual care alone (20% vs. 19%; risk ratio, 1.02; 95% confidence interval, 0.94-1.11; P = .63).
Follow-up is ongoing and final results will be published as soon as possible, the investigators said. Thus far, there has been no convincing evidence of an effect of colchicine on clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Recruitment will continue to all other treatment arms – aspirin, baricitinib, Regeneron’s antibody cocktail, and, in select hospitals, dimethyl fumarate – the investigators said.
Cochief investigator Peter Hornby, MD, PhD, also from the University of Oxford, noted that this has been the largest trial ever of colchicine. “Whilst we are disappointed that the overall result is negative, it is still important information for the future care of patients in the U.K. and worldwide.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On the advice of its independent data monitoring committee (DMC), the RECOVERY trial has stopped recruitment to the colchicine arm for lack of efficacy in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
“The DMC saw no convincing evidence that further recruitment would provide conclusive proof of worthwhile mortality benefit either overall or in any prespecified subgroup,” the British investigators announced on March 5.
“The RECOVERY trial has already identified two anti-inflammatory drugs – dexamethasone and tocilizumab – that improve the chances of survival for patients with severe COVID-19. So, it is disappointing that colchicine, which is widely used to treat gout and other inflammatory conditions, has no effect in these patients,” cochief investigator Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, said in a statement.
“We do large, randomized trials to establish whether a drug that seems promising in theory has real benefits for patients in practice. Unfortunately, colchicine is not one of those,” said Dr. Landry, University of Oxford (England).
The RECOVERY trial is evaluating a range of potential treatments for COVID-19 at 180 hospitals in the United Kingdom, Indonesia, and Nepal, and was designed with the expectation that drugs would be added or dropped as the evidence changes. Since November 2020, the trial has included an arm comparing colchicine with usual care alone.
As part of a routine meeting March 4, the DMC reviewed data from a preliminary analysis based on 2,178 deaths among 11,162 patients, 94% of whom were being treated with a corticosteroid such as dexamethasone.
The results showed no significant difference in the primary endpoint of 28-day mortality in patients randomized to colchicine versus usual care alone (20% vs. 19%; risk ratio, 1.02; 95% confidence interval, 0.94-1.11; P = .63).
Follow-up is ongoing and final results will be published as soon as possible, the investigators said. Thus far, there has been no convincing evidence of an effect of colchicine on clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Recruitment will continue to all other treatment arms – aspirin, baricitinib, Regeneron’s antibody cocktail, and, in select hospitals, dimethyl fumarate – the investigators said.
Cochief investigator Peter Hornby, MD, PhD, also from the University of Oxford, noted that this has been the largest trial ever of colchicine. “Whilst we are disappointed that the overall result is negative, it is still important information for the future care of patients in the U.K. and worldwide.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On the advice of its independent data monitoring committee (DMC), the RECOVERY trial has stopped recruitment to the colchicine arm for lack of efficacy in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
“The DMC saw no convincing evidence that further recruitment would provide conclusive proof of worthwhile mortality benefit either overall or in any prespecified subgroup,” the British investigators announced on March 5.
“The RECOVERY trial has already identified two anti-inflammatory drugs – dexamethasone and tocilizumab – that improve the chances of survival for patients with severe COVID-19. So, it is disappointing that colchicine, which is widely used to treat gout and other inflammatory conditions, has no effect in these patients,” cochief investigator Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, said in a statement.
“We do large, randomized trials to establish whether a drug that seems promising in theory has real benefits for patients in practice. Unfortunately, colchicine is not one of those,” said Dr. Landry, University of Oxford (England).
The RECOVERY trial is evaluating a range of potential treatments for COVID-19 at 180 hospitals in the United Kingdom, Indonesia, and Nepal, and was designed with the expectation that drugs would be added or dropped as the evidence changes. Since November 2020, the trial has included an arm comparing colchicine with usual care alone.
As part of a routine meeting March 4, the DMC reviewed data from a preliminary analysis based on 2,178 deaths among 11,162 patients, 94% of whom were being treated with a corticosteroid such as dexamethasone.
The results showed no significant difference in the primary endpoint of 28-day mortality in patients randomized to colchicine versus usual care alone (20% vs. 19%; risk ratio, 1.02; 95% confidence interval, 0.94-1.11; P = .63).
Follow-up is ongoing and final results will be published as soon as possible, the investigators said. Thus far, there has been no convincing evidence of an effect of colchicine on clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Recruitment will continue to all other treatment arms – aspirin, baricitinib, Regeneron’s antibody cocktail, and, in select hospitals, dimethyl fumarate – the investigators said.
Cochief investigator Peter Hornby, MD, PhD, also from the University of Oxford, noted that this has been the largest trial ever of colchicine. “Whilst we are disappointed that the overall result is negative, it is still important information for the future care of patients in the U.K. and worldwide.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heart failure redefined with new classifications, staging
The terminology and classification scheme for heart failure (HF) is changing in ways that experts hope will directly impact patient outcomes.
In a new consensus statement, a multisociety group of experts proposed a new universal definition of heart failure and made substantial revisions to the way in which the disease is staged and classified.
The authors of the statement, led by writing committee chair and immediate past president of the Heart Failure Society of America Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, hope their efforts will go far to improve standardization of terminology, but more importantly will facilitate better management of the disease in ways that keep pace with current knowledge and advances in the field.
“There is a great need for reframing and standardizing the terminology across societies and different stakeholders, and importantly for patients because a lot of the terminology we were using was understood by academicians, but were not being translated in important ways to ensure patients are being appropriately treated,” said Dr. Bozkurt, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
The consensus statement was a group effort led by the HFSA, the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Japanese Heart Failure Society, with endorsements from the Canadian Heart Failure Society, the Heart Failure Association of India, the Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand, and the Chinese Heart Failure Association.
The article was published March 1 in the Journal of Cardiac Failure and the European Journal of Heart Failure, authored by a writing committee of 38 individuals with domain expertise in HF, cardiomyopathy, and cardiovascular disease.
“This is a very thorough and very carefully written document that I think will be helpful for clinicians because they’ve tapped into important changes in the field that have occurred over the past 10 years and that now allow us to do more for patients than we could before,” Eugene Braunwald, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Braunwald and Elliott M. Antman, MD, both from TIMI Study Group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, wrote an editorial that accompanied the European Journal of Heart Failure article.
A new universal definition
“[Heart failure] is a clinical syndrome with symptoms and or signs caused by a structural and/or functional cardiac abnormality and corroborated by elevated natriuretic peptide levels and/or objective evidence of pulmonary or systemic congestion.”
This proposed definition, said the authors, is designed to be contemporary and simple “but conceptually comprehensive, with near universal applicability, prognostic and therapeutic viability, and acceptable sensitivity and specificity.”
Both left and right HF qualifies under this definition, said the authors, but conditions that result in marked volume overload, such as chronic kidney disease, which may present with signs and symptoms of HF, do not.
“Although some of these patients may have concomitant HF, these patients have a primary abnormality that may require a specific treatment beyond that for HF,” said the consensus statement authors.
For his part, Douglas L. Mann, MD, is happy to see what he considers a more accurate and practical definition for heart failure.
“We’ve had some wacky definitions in heart failure that haven’t made sense for 30 years, the principal of which is the definition of heart failure that says it’s the inability of the heart to meet the metabolic demands of the body,” Dr. Mann, of Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview.
“I think this description was developed thinking about people with end-stage heart failure, but it makes no sense in clinical practice. Does it make sense to say about someone with New York Heart Association class I heart failure that their heart can’t meet the metabolic demands of the body?” said Dr. Mann, who was not involved with the writing of the consensus statement.
Proposed revised stages of the HF continuum
Overall, minimal changes have been made to the HF stages, with tweaks intended to enhance understanding and address the evolving role of biomarkers.
The authors proposed an approach to staging of HF:
- At-risk for HF (stage A), for patients at risk for HF but without current or prior symptoms or signs of HF and without structural or biomarkers evidence of heart disease.
- Pre-HF (stage B), for patients without current or prior symptoms or signs of HF, but evidence of structural heart disease or abnormal cardiac function, or elevated natriuretic peptide levels.
- HF (stage C), for patients with current or prior symptoms and/or signs of HF caused by a structural and/or functional cardiac abnormality.
- Advanced HF (stage D), for patients with severe symptoms and/or signs of HF at rest, recurrent hospitalizations despite guideline-directed management and therapy (GDMT), refractory or intolerant to GDMT, requiring advanced therapies such as consideration for transplant, mechanical circulatory support, or palliative care.
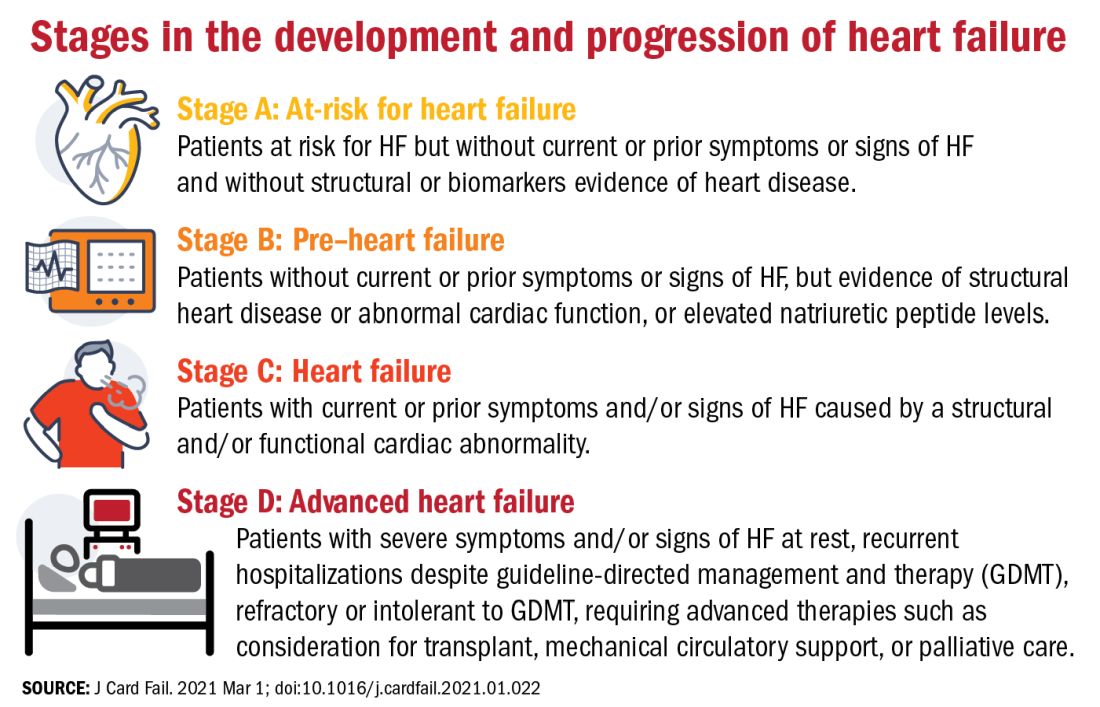
One notable change to the staging scheme is stage B, which the authors have reframed as “pre–heart failure.”
“Pre-cancer is a term widely understood and considered actionable and we wanted to tap into this successful messaging and embrace the pre–heart failure concept as something that is treatable and preventable,” said Dr. Bozkurt.
“We want patients and clinicians to understand that there are things we can do to prevent heart failure, strategies we didn’t have before, like SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with diabetes at risk for HF,” she added.
The revision also avoids the stigma of HF before the symptoms are manifest.
“Not calling it stage A and stage B heart failure you might say is semantics, but it’s important semantics,” said Dr. Braunwald. “When you’re talking to a patient or a relative and tell them they have stage A heart failure, it’s scares them unnecessarily. They don’t hear the stage A or B part, just the heart failure part.”
New classifications according to LVEF
And finally, in what some might consider the most obviously needed modification, the document proposes a new and revised classification of HF according to left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Most agree on how to classify heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), but although the middle range has long been understood to be a clinically relevant, it has no proper name or clear delineation.
“For standardization across practice guidelines, to recognize clinical trajectories in HF, and to facilitate the recognition of different heart failure entities in a sensitive and specific manner that can guide therapy, we want to formalize the heart failure categories according to ejection fraction,” said Dr. Bozkurt.
To this end, the authors propose the following four classifications of EF:
- HF with reduced EF (HFrEF): LVEF of up to 40%.
- HF with mildly reduced EF (HFmrEF): LVEF of 41-49%.
- HF with preserved EF (HFpEF)HF with an LVEF of at least 50%.
- HF with improved EF (HFimpEF): HF with a baseline LVEF of 40% or less, an increase of at least 10 points from baseline LVEF, and a second measurement of LVEF of greater than 40%.
HFmrEF is usually a transition period, noted Dr. Bozkurt. “Patients with HF in this range may represent a population whose EF is likely to change, either increase or decrease over time and it’s important to be cognizant of that trajectory. Understanding where your patient is headed is crucial for prognosis and optimization of guideline-directed treatment,” she said.
Improved, not recovered, HF
The last classification of heart failure with improved ejection fraction (HFimpEF) represents an important change to the current classification scheme.
“We want to clarify what terms to use but also which not to use. For example, we don’t want people to use recovered heart failure or heart failure in remission, partly because we don’t want the medication to be stopped. We don’t want to give the false message that there has been full recovery,” said Dr. Bozkurt.
As seen in the TRED-HF trial, guideline-directed medical therapy should be continued in patients with HF with improved EF regardless of whether it has improved to a normal range of above 50% in subsequent measurements.
“This is a distinct group of people, and for a while the guidelines were lumping them in with HFpEF, which I think is totally wrong,” said Dr. Mann.
“I think it’s very important that we emphasize heart failure as a continuum, rather than a one-way street of [inevitable] progression. Because we do see improvements in ejection fraction and we do see that we can prevent heart failure if we do the right things, and this should be reflected in the terminology we use,” he added.
Dr. Bozkurt stressed that HFimpEF only applies if the EF improves to above 40%. A move from an EF of 10%-20% would still see the patient classified as having HFrEF, but a patient whose EF improved from, say, 30% to 45% would be classified as HFimpEF.
“The reason for this, again, is because a transition from, say an EF of 10%-20% does not change therapy, but a move upward over 40% might, especially regarding decisions for device therapies, so the trajectory as well as the absolute EF is important,” she added.
“Particularly in the early stages, people are responsive to therapy and it’s possible in some cases to reverse heart failure, so I think this change helps us understand when that’s happened,” said Dr. Braunwald.
One step toward universality
“The implementation of this terminology and nomenclature into practice will require a variety of tactics,” said Dr. Bozkurt. “For example, the current ICD 10 codes need to incorporate the at-risk and pre–heart failure categories, as well as the mid-range EF, preserved, and improved EF classifications, because the treatment differs between those three domains.”
In terms of how these proposed changes will be worked into practice guidelines, Dr. Bozkurt declined to comment on this to avoid any perception of conflict of interest as she is the cochair of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association HF guideline writing committee.
Dr. Braunwald and Dr. Antman suggest it may be premature to call the new terminology and classifications “universal.” In an interview, Dr. Braunwald lamented the absence of the World Heart Federation, the ACC, and the AHA as active participants in this effort and suggested this paper is only the first step of a multistep process that requires input from many stakeholders.
“It’s important that these organizations be involved, not just to bless it, but to contribute their expertise to the process,” he said.
For his part, Dr. Mann hopes these changes will gain widespread acceptance and clinical traction. “The problem sometimes with guidelines is that they’re so data driven that you just can’t come out and say the obvious, so making a position statement is a good first step. And they got good international representation on this, so I think these changes will be accepted in the next heart failure guidelines.”
To encourage further discussion and acceptance, Robert J. Mentz, MD, and Anuradha Lala, MD, editor-in-chief and deputy editor of the Journal of Cardiac Failure, respectively, announced a series of multidisciplinary perspective pieces to be published in the journal monthly, starting in May with editorials from Dr. Clyde W Yancy, MD, MSc, and Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, both of whom were authors of the consensus statement.
Dr. Bozkurt reports being a consultant for Abbott, Amgen, Baxter, Bristol Myers Squibb, Liva Nova Relypsa/Vifor Pharma, Respicardia, and being on the registry steering committee for Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Braunwald reports research grant support through Brigham and Women’s Hospital from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Merck, and Novartis; and consulting for Amgen, Boehringer-Ingelheim/Lilly, Cardurion, MyoKardia, Novo Nordisk, and Verve. Dr. Mann has been a consultant to Novartis, is on the steering committee for the PARADISE trial, and is on the scientific advisory board for MyoKardia/Bristol Myers Squibb.
The terminology and classification scheme for heart failure (HF) is changing in ways that experts hope will directly impact patient outcomes.
In a new consensus statement, a multisociety group of experts proposed a new universal definition of heart failure and made substantial revisions to the way in which the disease is staged and classified.
The authors of the statement, led by writing committee chair and immediate past president of the Heart Failure Society of America Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, hope their efforts will go far to improve standardization of terminology, but more importantly will facilitate better management of the disease in ways that keep pace with current knowledge and advances in the field.
“There is a great need for reframing and standardizing the terminology across societies and different stakeholders, and importantly for patients because a lot of the terminology we were using was understood by academicians, but were not being translated in important ways to ensure patients are being appropriately treated,” said Dr. Bozkurt, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
The consensus statement was a group effort led by the HFSA, the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Japanese Heart Failure Society, with endorsements from the Canadian Heart Failure Society, the Heart Failure Association of India, the Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand, and the Chinese Heart Failure Association.
The article was published March 1 in the Journal of Cardiac Failure and the European Journal of Heart Failure, authored by a writing committee of 38 individuals with domain expertise in HF, cardiomyopathy, and cardiovascular disease.
“This is a very thorough and very carefully written document that I think will be helpful for clinicians because they’ve tapped into important changes in the field that have occurred over the past 10 years and that now allow us to do more for patients than we could before,” Eugene Braunwald, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Braunwald and Elliott M. Antman, MD, both from TIMI Study Group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, wrote an editorial that accompanied the European Journal of Heart Failure article.
A new universal definition
“[Heart failure] is a clinical syndrome with symptoms and or signs caused by a structural and/or functional cardiac abnormality and corroborated by elevated natriuretic peptide levels and/or objective evidence of pulmonary or systemic congestion.”
This proposed definition, said the authors, is designed to be contemporary and simple “but conceptually comprehensive, with near universal applicability, prognostic and therapeutic viability, and acceptable sensitivity and specificity.”
Both left and right HF qualifies under this definition, said the authors, but conditions that result in marked volume overload, such as chronic kidney disease, which may present with signs and symptoms of HF, do not.
“Although some of these patients may have concomitant HF, these patients have a primary abnormality that may require a specific treatment beyond that for HF,” said the consensus statement authors.
For his part, Douglas L. Mann, MD, is happy to see what he considers a more accurate and practical definition for heart failure.
“We’ve had some wacky definitions in heart failure that haven’t made sense for 30 years, the principal of which is the definition of heart failure that says it’s the inability of the heart to meet the metabolic demands of the body,” Dr. Mann, of Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview.
“I think this description was developed thinking about people with end-stage heart failure, but it makes no sense in clinical practice. Does it make sense to say about someone with New York Heart Association class I heart failure that their heart can’t meet the metabolic demands of the body?” said Dr. Mann, who was not involved with the writing of the consensus statement.
Proposed revised stages of the HF continuum
Overall, minimal changes have been made to the HF stages, with tweaks intended to enhance understanding and address the evolving role of biomarkers.
The authors proposed an approach to staging of HF:
- At-risk for HF (stage A), for patients at risk for HF but without current or prior symptoms or signs of HF and without structural or biomarkers evidence of heart disease.
- Pre-HF (stage B), for patients without current or prior symptoms or signs of HF, but evidence of structural heart disease or abnormal cardiac function, or elevated natriuretic peptide levels.
- HF (stage C), for patients with current or prior symptoms and/or signs of HF caused by a structural and/or functional cardiac abnormality.
- Advanced HF (stage D), for patients with severe symptoms and/or signs of HF at rest, recurrent hospitalizations despite guideline-directed management and therapy (GDMT), refractory or intolerant to GDMT, requiring advanced therapies such as consideration for transplant, mechanical circulatory support, or palliative care.

One notable change to the staging scheme is stage B, which the authors have reframed as “pre–heart failure.”
“Pre-cancer is a term widely understood and considered actionable and we wanted to tap into this successful messaging and embrace the pre–heart failure concept as something that is treatable and preventable,” said Dr. Bozkurt.
“We want patients and clinicians to understand that there are things we can do to prevent heart failure, strategies we didn’t have before, like SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with diabetes at risk for HF,” she added.
The revision also avoids the stigma of HF before the symptoms are manifest.
“Not calling it stage A and stage B heart failure you might say is semantics, but it’s important semantics,” said Dr. Braunwald. “When you’re talking to a patient or a relative and tell them they have stage A heart failure, it’s scares them unnecessarily. They don’t hear the stage A or B part, just the heart failure part.”
New classifications according to LVEF
And finally, in what some might consider the most obviously needed modification, the document proposes a new and revised classification of HF according to left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Most agree on how to classify heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), but although the middle range has long been understood to be a clinically relevant, it has no proper name or clear delineation.
“For standardization across practice guidelines, to recognize clinical trajectories in HF, and to facilitate the recognition of different heart failure entities in a sensitive and specific manner that can guide therapy, we want to formalize the heart failure categories according to ejection fraction,” said Dr. Bozkurt.
To this end, the authors propose the following four classifications of EF:
- HF with reduced EF (HFrEF): LVEF of up to 40%.
- HF with mildly reduced EF (HFmrEF): LVEF of 41-49%.
- HF with preserved EF (HFpEF)HF with an LVEF of at least 50%.
- HF with improved EF (HFimpEF): HF with a baseline LVEF of 40% or less, an increase of at least 10 points from baseline LVEF, and a second measurement of LVEF of greater than 40%.
HFmrEF is usually a transition period, noted Dr. Bozkurt. “Patients with HF in this range may represent a population whose EF is likely to change, either increase or decrease over time and it’s important to be cognizant of that trajectory. Understanding where your patient is headed is crucial for prognosis and optimization of guideline-directed treatment,” she said.
Improved, not recovered, HF
The last classification of heart failure with improved ejection fraction (HFimpEF) represents an important change to the current classification scheme.
“We want to clarify what terms to use but also which not to use. For example, we don’t want people to use recovered heart failure or heart failure in remission, partly because we don’t want the medication to be stopped. We don’t want to give the false message that there has been full recovery,” said Dr. Bozkurt.
As seen in the TRED-HF trial, guideline-directed medical therapy should be continued in patients with HF with improved EF regardless of whether it has improved to a normal range of above 50% in subsequent measurements.
“This is a distinct group of people, and for a while the guidelines were lumping them in with HFpEF, which I think is totally wrong,” said Dr. Mann.
“I think it’s very important that we emphasize heart failure as a continuum, rather than a one-way street of [inevitable] progression. Because we do see improvements in ejection fraction and we do see that we can prevent heart failure if we do the right things, and this should be reflected in the terminology we use,” he added.
Dr. Bozkurt stressed that HFimpEF only applies if the EF improves to above 40%. A move from an EF of 10%-20% would still see the patient classified as having HFrEF, but a patient whose EF improved from, say, 30% to 45% would be classified as HFimpEF.
“The reason for this, again, is because a transition from, say an EF of 10%-20% does not change therapy, but a move upward over 40% might, especially regarding decisions for device therapies, so the trajectory as well as the absolute EF is important,” she added.
“Particularly in the early stages, people are responsive to therapy and it’s possible in some cases to reverse heart failure, so I think this change helps us understand when that’s happened,” said Dr. Braunwald.
One step toward universality
“The implementation of this terminology and nomenclature into practice will require a variety of tactics,” said Dr. Bozkurt. “For example, the current ICD 10 codes need to incorporate the at-risk and pre–heart failure categories, as well as the mid-range EF, preserved, and improved EF classifications, because the treatment differs between those three domains.”
In terms of how these proposed changes will be worked into practice guidelines, Dr. Bozkurt declined to comment on this to avoid any perception of conflict of interest as she is the cochair of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association HF guideline writing committee.
Dr. Braunwald and Dr. Antman suggest it may be premature to call the new terminology and classifications “universal.” In an interview, Dr. Braunwald lamented the absence of the World Heart Federation, the ACC, and the AHA as active participants in this effort and suggested this paper is only the first step of a multistep process that requires input from many stakeholders.
“It’s important that these organizations be involved, not just to bless it, but to contribute their expertise to the process,” he said.
For his part, Dr. Mann hopes these changes will gain widespread acceptance and clinical traction. “The problem sometimes with guidelines is that they’re so data driven that you just can’t come out and say the obvious, so making a position statement is a good first step. And they got good international representation on this, so I think these changes will be accepted in the next heart failure guidelines.”
To encourage further discussion and acceptance, Robert J. Mentz, MD, and Anuradha Lala, MD, editor-in-chief and deputy editor of the Journal of Cardiac Failure, respectively, announced a series of multidisciplinary perspective pieces to be published in the journal monthly, starting in May with editorials from Dr. Clyde W Yancy, MD, MSc, and Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, both of whom were authors of the consensus statement.
Dr. Bozkurt reports being a consultant for Abbott, Amgen, Baxter, Bristol Myers Squibb, Liva Nova Relypsa/Vifor Pharma, Respicardia, and being on the registry steering committee for Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Braunwald reports research grant support through Brigham and Women’s Hospital from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Merck, and Novartis; and consulting for Amgen, Boehringer-Ingelheim/Lilly, Cardurion, MyoKardia, Novo Nordisk, and Verve. Dr. Mann has been a consultant to Novartis, is on the steering committee for the PARADISE trial, and is on the scientific advisory board for MyoKardia/Bristol Myers Squibb.
The terminology and classification scheme for heart failure (HF) is changing in ways that experts hope will directly impact patient outcomes.
In a new consensus statement, a multisociety group of experts proposed a new universal definition of heart failure and made substantial revisions to the way in which the disease is staged and classified.
The authors of the statement, led by writing committee chair and immediate past president of the Heart Failure Society of America Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, hope their efforts will go far to improve standardization of terminology, but more importantly will facilitate better management of the disease in ways that keep pace with current knowledge and advances in the field.
“There is a great need for reframing and standardizing the terminology across societies and different stakeholders, and importantly for patients because a lot of the terminology we were using was understood by academicians, but were not being translated in important ways to ensure patients are being appropriately treated,” said Dr. Bozkurt, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
The consensus statement was a group effort led by the HFSA, the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Japanese Heart Failure Society, with endorsements from the Canadian Heart Failure Society, the Heart Failure Association of India, the Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand, and the Chinese Heart Failure Association.
The article was published March 1 in the Journal of Cardiac Failure and the European Journal of Heart Failure, authored by a writing committee of 38 individuals with domain expertise in HF, cardiomyopathy, and cardiovascular disease.
“This is a very thorough and very carefully written document that I think will be helpful for clinicians because they’ve tapped into important changes in the field that have occurred over the past 10 years and that now allow us to do more for patients than we could before,” Eugene Braunwald, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Braunwald and Elliott M. Antman, MD, both from TIMI Study Group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, wrote an editorial that accompanied the European Journal of Heart Failure article.
A new universal definition
“[Heart failure] is a clinical syndrome with symptoms and or signs caused by a structural and/or functional cardiac abnormality and corroborated by elevated natriuretic peptide levels and/or objective evidence of pulmonary or systemic congestion.”
This proposed definition, said the authors, is designed to be contemporary and simple “but conceptually comprehensive, with near universal applicability, prognostic and therapeutic viability, and acceptable sensitivity and specificity.”
Both left and right HF qualifies under this definition, said the authors, but conditions that result in marked volume overload, such as chronic kidney disease, which may present with signs and symptoms of HF, do not.
“Although some of these patients may have concomitant HF, these patients have a primary abnormality that may require a specific treatment beyond that for HF,” said the consensus statement authors.
For his part, Douglas L. Mann, MD, is happy to see what he considers a more accurate and practical definition for heart failure.
“We’ve had some wacky definitions in heart failure that haven’t made sense for 30 years, the principal of which is the definition of heart failure that says it’s the inability of the heart to meet the metabolic demands of the body,” Dr. Mann, of Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview.
“I think this description was developed thinking about people with end-stage heart failure, but it makes no sense in clinical practice. Does it make sense to say about someone with New York Heart Association class I heart failure that their heart can’t meet the metabolic demands of the body?” said Dr. Mann, who was not involved with the writing of the consensus statement.
Proposed revised stages of the HF continuum
Overall, minimal changes have been made to the HF stages, with tweaks intended to enhance understanding and address the evolving role of biomarkers.
The authors proposed an approach to staging of HF:
- At-risk for HF (stage A), for patients at risk for HF but without current or prior symptoms or signs of HF and without structural or biomarkers evidence of heart disease.
- Pre-HF (stage B), for patients without current or prior symptoms or signs of HF, but evidence of structural heart disease or abnormal cardiac function, or elevated natriuretic peptide levels.
- HF (stage C), for patients with current or prior symptoms and/or signs of HF caused by a structural and/or functional cardiac abnormality.
- Advanced HF (stage D), for patients with severe symptoms and/or signs of HF at rest, recurrent hospitalizations despite guideline-directed management and therapy (GDMT), refractory or intolerant to GDMT, requiring advanced therapies such as consideration for transplant, mechanical circulatory support, or palliative care.

One notable change to the staging scheme is stage B, which the authors have reframed as “pre–heart failure.”
“Pre-cancer is a term widely understood and considered actionable and we wanted to tap into this successful messaging and embrace the pre–heart failure concept as something that is treatable and preventable,” said Dr. Bozkurt.
“We want patients and clinicians to understand that there are things we can do to prevent heart failure, strategies we didn’t have before, like SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with diabetes at risk for HF,” she added.
The revision also avoids the stigma of HF before the symptoms are manifest.
“Not calling it stage A and stage B heart failure you might say is semantics, but it’s important semantics,” said Dr. Braunwald. “When you’re talking to a patient or a relative and tell them they have stage A heart failure, it’s scares them unnecessarily. They don’t hear the stage A or B part, just the heart failure part.”
New classifications according to LVEF
And finally, in what some might consider the most obviously needed modification, the document proposes a new and revised classification of HF according to left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Most agree on how to classify heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), but although the middle range has long been understood to be a clinically relevant, it has no proper name or clear delineation.
“For standardization across practice guidelines, to recognize clinical trajectories in HF, and to facilitate the recognition of different heart failure entities in a sensitive and specific manner that can guide therapy, we want to formalize the heart failure categories according to ejection fraction,” said Dr. Bozkurt.
To this end, the authors propose the following four classifications of EF:
- HF with reduced EF (HFrEF): LVEF of up to 40%.
- HF with mildly reduced EF (HFmrEF): LVEF of 41-49%.
- HF with preserved EF (HFpEF)HF with an LVEF of at least 50%.
- HF with improved EF (HFimpEF): HF with a baseline LVEF of 40% or less, an increase of at least 10 points from baseline LVEF, and a second measurement of LVEF of greater than 40%.
HFmrEF is usually a transition period, noted Dr. Bozkurt. “Patients with HF in this range may represent a population whose EF is likely to change, either increase or decrease over time and it’s important to be cognizant of that trajectory. Understanding where your patient is headed is crucial for prognosis and optimization of guideline-directed treatment,” she said.
Improved, not recovered, HF
The last classification of heart failure with improved ejection fraction (HFimpEF) represents an important change to the current classification scheme.
“We want to clarify what terms to use but also which not to use. For example, we don’t want people to use recovered heart failure or heart failure in remission, partly because we don’t want the medication to be stopped. We don’t want to give the false message that there has been full recovery,” said Dr. Bozkurt.
As seen in the TRED-HF trial, guideline-directed medical therapy should be continued in patients with HF with improved EF regardless of whether it has improved to a normal range of above 50% in subsequent measurements.
“This is a distinct group of people, and for a while the guidelines were lumping them in with HFpEF, which I think is totally wrong,” said Dr. Mann.
“I think it’s very important that we emphasize heart failure as a continuum, rather than a one-way street of [inevitable] progression. Because we do see improvements in ejection fraction and we do see that we can prevent heart failure if we do the right things, and this should be reflected in the terminology we use,” he added.
Dr. Bozkurt stressed that HFimpEF only applies if the EF improves to above 40%. A move from an EF of 10%-20% would still see the patient classified as having HFrEF, but a patient whose EF improved from, say, 30% to 45% would be classified as HFimpEF.
“The reason for this, again, is because a transition from, say an EF of 10%-20% does not change therapy, but a move upward over 40% might, especially regarding decisions for device therapies, so the trajectory as well as the absolute EF is important,” she added.
“Particularly in the early stages, people are responsive to therapy and it’s possible in some cases to reverse heart failure, so I think this change helps us understand when that’s happened,” said Dr. Braunwald.
One step toward universality
“The implementation of this terminology and nomenclature into practice will require a variety of tactics,” said Dr. Bozkurt. “For example, the current ICD 10 codes need to incorporate the at-risk and pre–heart failure categories, as well as the mid-range EF, preserved, and improved EF classifications, because the treatment differs between those three domains.”
In terms of how these proposed changes will be worked into practice guidelines, Dr. Bozkurt declined to comment on this to avoid any perception of conflict of interest as she is the cochair of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association HF guideline writing committee.
Dr. Braunwald and Dr. Antman suggest it may be premature to call the new terminology and classifications “universal.” In an interview, Dr. Braunwald lamented the absence of the World Heart Federation, the ACC, and the AHA as active participants in this effort and suggested this paper is only the first step of a multistep process that requires input from many stakeholders.
“It’s important that these organizations be involved, not just to bless it, but to contribute their expertise to the process,” he said.
For his part, Dr. Mann hopes these changes will gain widespread acceptance and clinical traction. “The problem sometimes with guidelines is that they’re so data driven that you just can’t come out and say the obvious, so making a position statement is a good first step. And they got good international representation on this, so I think these changes will be accepted in the next heart failure guidelines.”
To encourage further discussion and acceptance, Robert J. Mentz, MD, and Anuradha Lala, MD, editor-in-chief and deputy editor of the Journal of Cardiac Failure, respectively, announced a series of multidisciplinary perspective pieces to be published in the journal monthly, starting in May with editorials from Dr. Clyde W Yancy, MD, MSc, and Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, both of whom were authors of the consensus statement.
Dr. Bozkurt reports being a consultant for Abbott, Amgen, Baxter, Bristol Myers Squibb, Liva Nova Relypsa/Vifor Pharma, Respicardia, and being on the registry steering committee for Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Braunwald reports research grant support through Brigham and Women’s Hospital from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Merck, and Novartis; and consulting for Amgen, Boehringer-Ingelheim/Lilly, Cardurion, MyoKardia, Novo Nordisk, and Verve. Dr. Mann has been a consultant to Novartis, is on the steering committee for the PARADISE trial, and is on the scientific advisory board for MyoKardia/Bristol Myers Squibb.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CARDIAC FAILURE
BMI, age, and sex affect COVID-19 vaccine antibody response
The capacity to mount humoral immune responses to COVID-19 vaccinations may be reduced among people who are heavier, older, and male, new findings suggest.
The data pertain specifically to the mRNA vaccine, BNT162b2, developed by BioNTech and Pfizer. The study was conducted by Italian researchers and was published Feb. 26 as a preprint.
The study involved 248 health care workers who each received two doses of the vaccine. Of the participants, 99.5% developed a humoral immune response after the second dose. Those responses varied by body mass index (BMI), age, and sex.
“The findings imply that female, lean, and young people have an increased capacity to mount humoral immune responses, compared to male, overweight, and older populations,” Raul Pellini, MD, professor at the IRCCS Regina Elena National Cancer Institute, Rome, and colleagues said.
“To our knowledge, this study is the first to analyze Covid-19 vaccine response in correlation to BMI,” they noted.
“Although further studies are needed, this data may have important implications to the development of vaccination strategies for COVID-19, particularly in obese people,” they wrote. If the data are confirmed by larger studies, “giving obese people an extra dose of the vaccine or a higher dose could be options to be evaluated in this population.”
Results contrast with Pfizer trials of vaccine
The BMI finding seemingly contrasts with final data from the phase 3 clinical trial of the vaccine, which were reported in a supplement to an article published Dec. 31, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine. In that study, vaccine efficacy did not differ by obesity status.
Akiko Iwasaki, PhD, professor of immunology at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and an investigator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., noted that, although the current Italian study showed somewhat lower levels of antibodies in people with obesity, compared with people who did not have obesity, the phase 3 trial found no difference in symptomatic infection rates.
“These results indicate that even with a slightly lower level of antibody induced in obese people, that level was sufficient to protect against symptomatic infection,” Dr. Iwasaki said in an interview.
Indeed, Dr. Pellini and colleagues pointed out that responses to vaccines against influenza, hepatitis B, and rabies are also reduced in those with obesity, compared with lean individuals.
However, they said, it was especially important to study the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in people with obesity, because obesity is a major risk factor for morbidity and mortality in COVID-19.
“The constant state of low-grade inflammation, present in overweight people, can weaken some immune responses, including those launched by T cells, which can directly kill infected cells,” the authors noted.
Findings reported in British newspapers
The findings of the Italian study were widely covered in the lay press in the United Kingdom, with headlines such as “Pfizer Vaccine May Be Less Effective in People With Obesity, Says Study” and “Pfizer Vaccine: Overweight People Might Need Bigger Dose, Italian Study Says.” In tabloid newspapers, some headlines were slightly more stigmatizing.
The reports do stress that the Italian research was published as a preprint and has not been peer reviewed, or “is yet to be scrutinized by fellow scientists.”
Most make the point that there were only 26 people with obesity among the 248 persons in the study.
“We always knew that BMI was an enormous predictor of poor immune response to vaccines, so this paper is definitely interesting, although it is based on a rather small preliminary dataset,” Danny Altmann, PhD, a professor of immunology at Imperial College London, told the Guardian.
“It confirms that having a vaccinated population isn’t synonymous with having an immune population, especially in a country with high obesity, and emphasizes the vital need for long-term immune monitoring programs,” he added.
Antibody responses differ by BMI, age, and sex
In the Italian study, the participants – 158 women and 90 men – were assigned to receive a priming BNT162b2 vaccine dose with a booster at day 21. Blood and nasopharyngeal swabs were collected at baseline and 7 days after the second vaccine dose.
After the second dose, 99.5% of participants developed a humoral immune response; one person did not respond. None tested positive for SARS-CoV-2.
Titers of SARS-CoV-2–binding antibodies were greater in younger than in older participants. There were statistically significant differences between those aged 37 years and younger (453.5 AU/mL) and those aged 47-56 years (239.8 AU/mL; P = .005), those aged 37 years and younger versus those older than 56 years (453.5 vs 182.4 AU/mL; P < .0001), and those aged 37-47 years versus those older than 56 years (330.9 vs. 182.4 AU/mL; P = .01).
Antibody response was significantly greater for women than for men (338.5 vs. 212.6 AU/mL; P = .001).
Humoral responses were greater in persons of normal-weight BMI (18.5-24.9 kg/m2; 325.8 AU/mL) and those of underweight BMI (<18.5 kg/m2; 455.4 AU/mL), compared with persons with preobesity, defined as BMI of 25-29.9 (222.4 AU/mL), and those with obesity (BMI ≥30; 167.0 AU/mL; P < .0001). This association remained after adjustment for age (P = .003).
“Our data stresses the importance of close vaccination monitoring of obese people, considering the growing list of countries with obesity problems,” the researchers noted.
Hypertension was also associated with lower antibody titers (P = .006), but that lost statistical significance after matching for age (P = .22).
“We strongly believe that our results are extremely encouraging and useful for the scientific community,” Dr. Pellini and colleagues concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Iwasaki is a cofounder of RIGImmune and is a member of its scientific advisory board.
This article was updated on 3/8/21.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The capacity to mount humoral immune responses to COVID-19 vaccinations may be reduced among people who are heavier, older, and male, new findings suggest.
The data pertain specifically to the mRNA vaccine, BNT162b2, developed by BioNTech and Pfizer. The study was conducted by Italian researchers and was published Feb. 26 as a preprint.
The study involved 248 health care workers who each received two doses of the vaccine. Of the participants, 99.5% developed a humoral immune response after the second dose. Those responses varied by body mass index (BMI), age, and sex.
“The findings imply that female, lean, and young people have an increased capacity to mount humoral immune responses, compared to male, overweight, and older populations,” Raul Pellini, MD, professor at the IRCCS Regina Elena National Cancer Institute, Rome, and colleagues said.
“To our knowledge, this study is the first to analyze Covid-19 vaccine response in correlation to BMI,” they noted.
“Although further studies are needed, this data may have important implications to the development of vaccination strategies for COVID-19, particularly in obese people,” they wrote. If the data are confirmed by larger studies, “giving obese people an extra dose of the vaccine or a higher dose could be options to be evaluated in this population.”
Results contrast with Pfizer trials of vaccine
The BMI finding seemingly contrasts with final data from the phase 3 clinical trial of the vaccine, which were reported in a supplement to an article published Dec. 31, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine. In that study, vaccine efficacy did not differ by obesity status.
Akiko Iwasaki, PhD, professor of immunology at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and an investigator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., noted that, although the current Italian study showed somewhat lower levels of antibodies in people with obesity, compared with people who did not have obesity, the phase 3 trial found no difference in symptomatic infection rates.
“These results indicate that even with a slightly lower level of antibody induced in obese people, that level was sufficient to protect against symptomatic infection,” Dr. Iwasaki said in an interview.
Indeed, Dr. Pellini and colleagues pointed out that responses to vaccines against influenza, hepatitis B, and rabies are also reduced in those with obesity, compared with lean individuals.
However, they said, it was especially important to study the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in people with obesity, because obesity is a major risk factor for morbidity and mortality in COVID-19.
“The constant state of low-grade inflammation, present in overweight people, can weaken some immune responses, including those launched by T cells, which can directly kill infected cells,” the authors noted.
Findings reported in British newspapers
The findings of the Italian study were widely covered in the lay press in the United Kingdom, with headlines such as “Pfizer Vaccine May Be Less Effective in People With Obesity, Says Study” and “Pfizer Vaccine: Overweight People Might Need Bigger Dose, Italian Study Says.” In tabloid newspapers, some headlines were slightly more stigmatizing.
The reports do stress that the Italian research was published as a preprint and has not been peer reviewed, or “is yet to be scrutinized by fellow scientists.”
Most make the point that there were only 26 people with obesity among the 248 persons in the study.
“We always knew that BMI was an enormous predictor of poor immune response to vaccines, so this paper is definitely interesting, although it is based on a rather small preliminary dataset,” Danny Altmann, PhD, a professor of immunology at Imperial College London, told the Guardian.
“It confirms that having a vaccinated population isn’t synonymous with having an immune population, especially in a country with high obesity, and emphasizes the vital need for long-term immune monitoring programs,” he added.
Antibody responses differ by BMI, age, and sex
In the Italian study, the participants – 158 women and 90 men – were assigned to receive a priming BNT162b2 vaccine dose with a booster at day 21. Blood and nasopharyngeal swabs were collected at baseline and 7 days after the second vaccine dose.
After the second dose, 99.5% of participants developed a humoral immune response; one person did not respond. None tested positive for SARS-CoV-2.
Titers of SARS-CoV-2–binding antibodies were greater in younger than in older participants. There were statistically significant differences between those aged 37 years and younger (453.5 AU/mL) and those aged 47-56 years (239.8 AU/mL; P = .005), those aged 37 years and younger versus those older than 56 years (453.5 vs 182.4 AU/mL; P < .0001), and those aged 37-47 years versus those older than 56 years (330.9 vs. 182.4 AU/mL; P = .01).
Antibody response was significantly greater for women than for men (338.5 vs. 212.6 AU/mL; P = .001).
Humoral responses were greater in persons of normal-weight BMI (18.5-24.9 kg/m2; 325.8 AU/mL) and those of underweight BMI (<18.5 kg/m2; 455.4 AU/mL), compared with persons with preobesity, defined as BMI of 25-29.9 (222.4 AU/mL), and those with obesity (BMI ≥30; 167.0 AU/mL; P < .0001). This association remained after adjustment for age (P = .003).
“Our data stresses the importance of close vaccination monitoring of obese people, considering the growing list of countries with obesity problems,” the researchers noted.
Hypertension was also associated with lower antibody titers (P = .006), but that lost statistical significance after matching for age (P = .22).
“We strongly believe that our results are extremely encouraging and useful for the scientific community,” Dr. Pellini and colleagues concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Iwasaki is a cofounder of RIGImmune and is a member of its scientific advisory board.
This article was updated on 3/8/21.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The capacity to mount humoral immune responses to COVID-19 vaccinations may be reduced among people who are heavier, older, and male, new findings suggest.
The data pertain specifically to the mRNA vaccine, BNT162b2, developed by BioNTech and Pfizer. The study was conducted by Italian researchers and was published Feb. 26 as a preprint.
The study involved 248 health care workers who each received two doses of the vaccine. Of the participants, 99.5% developed a humoral immune response after the second dose. Those responses varied by body mass index (BMI), age, and sex.
“The findings imply that female, lean, and young people have an increased capacity to mount humoral immune responses, compared to male, overweight, and older populations,” Raul Pellini, MD, professor at the IRCCS Regina Elena National Cancer Institute, Rome, and colleagues said.
“To our knowledge, this study is the first to analyze Covid-19 vaccine response in correlation to BMI,” they noted.
“Although further studies are needed, this data may have important implications to the development of vaccination strategies for COVID-19, particularly in obese people,” they wrote. If the data are confirmed by larger studies, “giving obese people an extra dose of the vaccine or a higher dose could be options to be evaluated in this population.”
Results contrast with Pfizer trials of vaccine
The BMI finding seemingly contrasts with final data from the phase 3 clinical trial of the vaccine, which were reported in a supplement to an article published Dec. 31, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine. In that study, vaccine efficacy did not differ by obesity status.
Akiko Iwasaki, PhD, professor of immunology at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and an investigator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., noted that, although the current Italian study showed somewhat lower levels of antibodies in people with obesity, compared with people who did not have obesity, the phase 3 trial found no difference in symptomatic infection rates.
“These results indicate that even with a slightly lower level of antibody induced in obese people, that level was sufficient to protect against symptomatic infection,” Dr. Iwasaki said in an interview.
Indeed, Dr. Pellini and colleagues pointed out that responses to vaccines against influenza, hepatitis B, and rabies are also reduced in those with obesity, compared with lean individuals.
However, they said, it was especially important to study the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in people with obesity, because obesity is a major risk factor for morbidity and mortality in COVID-19.
“The constant state of low-grade inflammation, present in overweight people, can weaken some immune responses, including those launched by T cells, which can directly kill infected cells,” the authors noted.
Findings reported in British newspapers
The findings of the Italian study were widely covered in the lay press in the United Kingdom, with headlines such as “Pfizer Vaccine May Be Less Effective in People With Obesity, Says Study” and “Pfizer Vaccine: Overweight People Might Need Bigger Dose, Italian Study Says.” In tabloid newspapers, some headlines were slightly more stigmatizing.
The reports do stress that the Italian research was published as a preprint and has not been peer reviewed, or “is yet to be scrutinized by fellow scientists.”
Most make the point that there were only 26 people with obesity among the 248 persons in the study.
“We always knew that BMI was an enormous predictor of poor immune response to vaccines, so this paper is definitely interesting, although it is based on a rather small preliminary dataset,” Danny Altmann, PhD, a professor of immunology at Imperial College London, told the Guardian.
“It confirms that having a vaccinated population isn’t synonymous with having an immune population, especially in a country with high obesity, and emphasizes the vital need for long-term immune monitoring programs,” he added.
Antibody responses differ by BMI, age, and sex
In the Italian study, the participants – 158 women and 90 men – were assigned to receive a priming BNT162b2 vaccine dose with a booster at day 21. Blood and nasopharyngeal swabs were collected at baseline and 7 days after the second vaccine dose.
After the second dose, 99.5% of participants developed a humoral immune response; one person did not respond. None tested positive for SARS-CoV-2.
Titers of SARS-CoV-2–binding antibodies were greater in younger than in older participants. There were statistically significant differences between those aged 37 years and younger (453.5 AU/mL) and those aged 47-56 years (239.8 AU/mL; P = .005), those aged 37 years and younger versus those older than 56 years (453.5 vs 182.4 AU/mL; P < .0001), and those aged 37-47 years versus those older than 56 years (330.9 vs. 182.4 AU/mL; P = .01).
Antibody response was significantly greater for women than for men (338.5 vs. 212.6 AU/mL; P = .001).
Humoral responses were greater in persons of normal-weight BMI (18.5-24.9 kg/m2; 325.8 AU/mL) and those of underweight BMI (<18.5 kg/m2; 455.4 AU/mL), compared with persons with preobesity, defined as BMI of 25-29.9 (222.4 AU/mL), and those with obesity (BMI ≥30; 167.0 AU/mL; P < .0001). This association remained after adjustment for age (P = .003).
“Our data stresses the importance of close vaccination monitoring of obese people, considering the growing list of countries with obesity problems,” the researchers noted.
Hypertension was also associated with lower antibody titers (P = .006), but that lost statistical significance after matching for age (P = .22).
“We strongly believe that our results are extremely encouraging and useful for the scientific community,” Dr. Pellini and colleagues concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Iwasaki is a cofounder of RIGImmune and is a member of its scientific advisory board.
This article was updated on 3/8/21.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.