User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Seeing is bleeding, and smelling is perceiving
True Blood casting call!
If you’ve seen the show True Blood on HBO, you’re probably familiar with blood coming out instead of tears when any of the vampires start crying. Apparently, this interesting phenomenon isn’t unique to vampires on TV.
If you know about female anatomy, you know that the eyes aren’t usually involved in the menstrual cycle. However, a 25-year-old woman went to the ED when she experienced haemolacria, the term for blood tears, for the second time in 2 months during her cycle. She did not appear to have any injuries or illnesses that caused the eye bleeding, but physicians noted that both times she had eye bleeding, she also had her period.
Menstrual bleeding outside of the uterus, called vicarious menstruation, can occur, and it seems that the patient may have had that condition.
Since there are rumors of a True Blood remake circling, perhaps the show’s writers could blend in a little medical fact with vampire fiction.
What does skinny smell like? Lemons apparently
When you smell a lemon, what comes to your mind? How does it make you feel? Now think of the scent of vanilla. How does that one make you feel? Current research suggests certain smells may have an effect on how you perceive your body image.
Researchers from the University of Sussex (England) have found that certain olfactory stimuli (such as lemons and vanilla) and audio stimuli (light steps vs. heavy steps), have a moderate effect on self-image.
During their study, participants were put through a series of auditory and olfactory tests, from listening to stilettos and boots walking across the floor, to being exposed to certain essential oils with different sound pitches.
Exposure to lemon and higher-pitched sounds (like stilettos) made participants feel lighter and was associated with thin, spiky shapes. Exposure to vanilla and lower-pitched sounds was more associated with thicker, rounded shapes. This made researchers believe that multisensory stimuli, such as scents and sounds, can have a bigger role in treating eating disorders.
Our brain functions with multiple “mental models” of ourselves. Based on sensory stimuli from our day-to-day lives, those images and perceptions of ourselves change. Someone complimenting your snazzy new sweater provokes one self-perception, while someone letting you know that your fly is down provokes another.
Well, the researchers believe that, through a sense of smell, we can alter that perception of ourselves when paired with positive influence. Doing this through wearable “interactive clothes” could help boost the confidence and self-esteem of patients struggling with body image. Light smells equals light feelings. Of course, this won’t help the nearly 5% of the world who have some kind of smell disorder.
The researchers said that more research needs to be done, but you can do your own little experiment at home. Think about yourself and how you react to certain smells. How do they make you feel? If it makes you feel good, stop and smell more often.
Pregnancy with a side of pregnancy
It was a great day when Rebecca Roberts and her partner went to the obstetrician to confirm their positive pregnancy test. They’d been trying for more than a year without success, and now they would be having a baby. Note the usage of the singular there. That will become important in a moment.
When Ms. Roberts went back for her 12-week ultrasound appointment, there was an unexpected complication: Baby had become babies. The original fetus was there and doing fine, but there was now a second, less-developed fetus who’d invited herself in unannounced. While they were technically twins, the second fetus did not form at the same time, like normal fraternal twins, instead forming from an egg that was released weeks after the first egg was fertilized.
The phenomenon, called superfetation, is incredibly rare. Prior to 2008, there were fewer than 10 reported cases in the world, according to the European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology. The odds of an egg being released during pregnancy, something that’s not supposed to happen, and then having that egg also become fertilized and successfully implanted in the uterus, is astronomically small.
It was not an easy pregnancy for Ms. Roberts, and at 33 weeks into the first pregnancy, the younger fetus’s umbilical cord began to malfunction, so delivery for both was induced in September 2020. Both infants spent time in the neonatal ICU, with the younger baby being in for 3 months, but after 6 months both are doing well and developing quickly. It’s always nice to have a happy ending to one of these weird medical phenomena, especially one with such an unpleasant-sounding name. If we didn’t know better, we’d think superfetation was something really, really smelly.
What’s a little misinformation among neighbors?
Vaccination will, hopefully, get the COVID-19 pandemic under control at some point, but the related misinformation floating around the Internet is another story. Already rampant in the United States, it’s now spreading … to Canada.
Investigators from that northern land took a look at the Twitter accounts of the platform’s 187,000 most active Canadian users and eventually ended up with a database of 147 million tweets, of which 154,000 contained terms associated with misinformation.
The Canadian social media users had more exposure to information from the United States than from Canada, and the exposure to U.S. outlets was more likely to involve misperceptions about COVID-19. “Most of the misinformation circulating on Twitter shared by Canadians was retweeted from U.S. sources,” the researchers said, and “Canadians who followed more American users were more likely to post misinformation.”
The study’s lead investigator, Aengus Bridgman of McGill University in Montreal, put it this way: “It’s hard for Canadian journalists, scientists, and public health experts to be heard by the average Canadian, given all the noise generated by American sources.”
People generally don’t take the time to read the fine print on contracts, and it looks like the Canadians have fallen into that trap. Not entirely their fault, of course, because most people coming from Canada to America don’t pass the Statue of Liberty, but she’s got some fine print of her own.
That poem written on the pedestal, the one that says, “Give me your tired, your poor, your huddled masses yearning to breathe free”? It’s actually a contract, and at the bottom, in very small print, it says, “In return for acceptance of the aforementioned ‘huddled masses,’ countries of origin agree to accept all of the social media noise generated by American sources.”
Sorry, Canada, but we gotcha.
True Blood casting call!
If you’ve seen the show True Blood on HBO, you’re probably familiar with blood coming out instead of tears when any of the vampires start crying. Apparently, this interesting phenomenon isn’t unique to vampires on TV.
If you know about female anatomy, you know that the eyes aren’t usually involved in the menstrual cycle. However, a 25-year-old woman went to the ED when she experienced haemolacria, the term for blood tears, for the second time in 2 months during her cycle. She did not appear to have any injuries or illnesses that caused the eye bleeding, but physicians noted that both times she had eye bleeding, she also had her period.
Menstrual bleeding outside of the uterus, called vicarious menstruation, can occur, and it seems that the patient may have had that condition.
Since there are rumors of a True Blood remake circling, perhaps the show’s writers could blend in a little medical fact with vampire fiction.
What does skinny smell like? Lemons apparently
When you smell a lemon, what comes to your mind? How does it make you feel? Now think of the scent of vanilla. How does that one make you feel? Current research suggests certain smells may have an effect on how you perceive your body image.
Researchers from the University of Sussex (England) have found that certain olfactory stimuli (such as lemons and vanilla) and audio stimuli (light steps vs. heavy steps), have a moderate effect on self-image.
During their study, participants were put through a series of auditory and olfactory tests, from listening to stilettos and boots walking across the floor, to being exposed to certain essential oils with different sound pitches.
Exposure to lemon and higher-pitched sounds (like stilettos) made participants feel lighter and was associated with thin, spiky shapes. Exposure to vanilla and lower-pitched sounds was more associated with thicker, rounded shapes. This made researchers believe that multisensory stimuli, such as scents and sounds, can have a bigger role in treating eating disorders.
Our brain functions with multiple “mental models” of ourselves. Based on sensory stimuli from our day-to-day lives, those images and perceptions of ourselves change. Someone complimenting your snazzy new sweater provokes one self-perception, while someone letting you know that your fly is down provokes another.
Well, the researchers believe that, through a sense of smell, we can alter that perception of ourselves when paired with positive influence. Doing this through wearable “interactive clothes” could help boost the confidence and self-esteem of patients struggling with body image. Light smells equals light feelings. Of course, this won’t help the nearly 5% of the world who have some kind of smell disorder.
The researchers said that more research needs to be done, but you can do your own little experiment at home. Think about yourself and how you react to certain smells. How do they make you feel? If it makes you feel good, stop and smell more often.
Pregnancy with a side of pregnancy
It was a great day when Rebecca Roberts and her partner went to the obstetrician to confirm their positive pregnancy test. They’d been trying for more than a year without success, and now they would be having a baby. Note the usage of the singular there. That will become important in a moment.
When Ms. Roberts went back for her 12-week ultrasound appointment, there was an unexpected complication: Baby had become babies. The original fetus was there and doing fine, but there was now a second, less-developed fetus who’d invited herself in unannounced. While they were technically twins, the second fetus did not form at the same time, like normal fraternal twins, instead forming from an egg that was released weeks after the first egg was fertilized.
The phenomenon, called superfetation, is incredibly rare. Prior to 2008, there were fewer than 10 reported cases in the world, according to the European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology. The odds of an egg being released during pregnancy, something that’s not supposed to happen, and then having that egg also become fertilized and successfully implanted in the uterus, is astronomically small.
It was not an easy pregnancy for Ms. Roberts, and at 33 weeks into the first pregnancy, the younger fetus’s umbilical cord began to malfunction, so delivery for both was induced in September 2020. Both infants spent time in the neonatal ICU, with the younger baby being in for 3 months, but after 6 months both are doing well and developing quickly. It’s always nice to have a happy ending to one of these weird medical phenomena, especially one with such an unpleasant-sounding name. If we didn’t know better, we’d think superfetation was something really, really smelly.
What’s a little misinformation among neighbors?
Vaccination will, hopefully, get the COVID-19 pandemic under control at some point, but the related misinformation floating around the Internet is another story. Already rampant in the United States, it’s now spreading … to Canada.
Investigators from that northern land took a look at the Twitter accounts of the platform’s 187,000 most active Canadian users and eventually ended up with a database of 147 million tweets, of which 154,000 contained terms associated with misinformation.
The Canadian social media users had more exposure to information from the United States than from Canada, and the exposure to U.S. outlets was more likely to involve misperceptions about COVID-19. “Most of the misinformation circulating on Twitter shared by Canadians was retweeted from U.S. sources,” the researchers said, and “Canadians who followed more American users were more likely to post misinformation.”
The study’s lead investigator, Aengus Bridgman of McGill University in Montreal, put it this way: “It’s hard for Canadian journalists, scientists, and public health experts to be heard by the average Canadian, given all the noise generated by American sources.”
People generally don’t take the time to read the fine print on contracts, and it looks like the Canadians have fallen into that trap. Not entirely their fault, of course, because most people coming from Canada to America don’t pass the Statue of Liberty, but she’s got some fine print of her own.
That poem written on the pedestal, the one that says, “Give me your tired, your poor, your huddled masses yearning to breathe free”? It’s actually a contract, and at the bottom, in very small print, it says, “In return for acceptance of the aforementioned ‘huddled masses,’ countries of origin agree to accept all of the social media noise generated by American sources.”
Sorry, Canada, but we gotcha.
True Blood casting call!
If you’ve seen the show True Blood on HBO, you’re probably familiar with blood coming out instead of tears when any of the vampires start crying. Apparently, this interesting phenomenon isn’t unique to vampires on TV.
If you know about female anatomy, you know that the eyes aren’t usually involved in the menstrual cycle. However, a 25-year-old woman went to the ED when she experienced haemolacria, the term for blood tears, for the second time in 2 months during her cycle. She did not appear to have any injuries or illnesses that caused the eye bleeding, but physicians noted that both times she had eye bleeding, she also had her period.
Menstrual bleeding outside of the uterus, called vicarious menstruation, can occur, and it seems that the patient may have had that condition.
Since there are rumors of a True Blood remake circling, perhaps the show’s writers could blend in a little medical fact with vampire fiction.
What does skinny smell like? Lemons apparently
When you smell a lemon, what comes to your mind? How does it make you feel? Now think of the scent of vanilla. How does that one make you feel? Current research suggests certain smells may have an effect on how you perceive your body image.
Researchers from the University of Sussex (England) have found that certain olfactory stimuli (such as lemons and vanilla) and audio stimuli (light steps vs. heavy steps), have a moderate effect on self-image.
During their study, participants were put through a series of auditory and olfactory tests, from listening to stilettos and boots walking across the floor, to being exposed to certain essential oils with different sound pitches.
Exposure to lemon and higher-pitched sounds (like stilettos) made participants feel lighter and was associated with thin, spiky shapes. Exposure to vanilla and lower-pitched sounds was more associated with thicker, rounded shapes. This made researchers believe that multisensory stimuli, such as scents and sounds, can have a bigger role in treating eating disorders.
Our brain functions with multiple “mental models” of ourselves. Based on sensory stimuli from our day-to-day lives, those images and perceptions of ourselves change. Someone complimenting your snazzy new sweater provokes one self-perception, while someone letting you know that your fly is down provokes another.
Well, the researchers believe that, through a sense of smell, we can alter that perception of ourselves when paired with positive influence. Doing this through wearable “interactive clothes” could help boost the confidence and self-esteem of patients struggling with body image. Light smells equals light feelings. Of course, this won’t help the nearly 5% of the world who have some kind of smell disorder.
The researchers said that more research needs to be done, but you can do your own little experiment at home. Think about yourself and how you react to certain smells. How do they make you feel? If it makes you feel good, stop and smell more often.
Pregnancy with a side of pregnancy
It was a great day when Rebecca Roberts and her partner went to the obstetrician to confirm their positive pregnancy test. They’d been trying for more than a year without success, and now they would be having a baby. Note the usage of the singular there. That will become important in a moment.
When Ms. Roberts went back for her 12-week ultrasound appointment, there was an unexpected complication: Baby had become babies. The original fetus was there and doing fine, but there was now a second, less-developed fetus who’d invited herself in unannounced. While they were technically twins, the second fetus did not form at the same time, like normal fraternal twins, instead forming from an egg that was released weeks after the first egg was fertilized.
The phenomenon, called superfetation, is incredibly rare. Prior to 2008, there were fewer than 10 reported cases in the world, according to the European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology. The odds of an egg being released during pregnancy, something that’s not supposed to happen, and then having that egg also become fertilized and successfully implanted in the uterus, is astronomically small.
It was not an easy pregnancy for Ms. Roberts, and at 33 weeks into the first pregnancy, the younger fetus’s umbilical cord began to malfunction, so delivery for both was induced in September 2020. Both infants spent time in the neonatal ICU, with the younger baby being in for 3 months, but after 6 months both are doing well and developing quickly. It’s always nice to have a happy ending to one of these weird medical phenomena, especially one with such an unpleasant-sounding name. If we didn’t know better, we’d think superfetation was something really, really smelly.
What’s a little misinformation among neighbors?
Vaccination will, hopefully, get the COVID-19 pandemic under control at some point, but the related misinformation floating around the Internet is another story. Already rampant in the United States, it’s now spreading … to Canada.
Investigators from that northern land took a look at the Twitter accounts of the platform’s 187,000 most active Canadian users and eventually ended up with a database of 147 million tweets, of which 154,000 contained terms associated with misinformation.
The Canadian social media users had more exposure to information from the United States than from Canada, and the exposure to U.S. outlets was more likely to involve misperceptions about COVID-19. “Most of the misinformation circulating on Twitter shared by Canadians was retweeted from U.S. sources,” the researchers said, and “Canadians who followed more American users were more likely to post misinformation.”
The study’s lead investigator, Aengus Bridgman of McGill University in Montreal, put it this way: “It’s hard for Canadian journalists, scientists, and public health experts to be heard by the average Canadian, given all the noise generated by American sources.”
People generally don’t take the time to read the fine print on contracts, and it looks like the Canadians have fallen into that trap. Not entirely their fault, of course, because most people coming from Canada to America don’t pass the Statue of Liberty, but she’s got some fine print of her own.
That poem written on the pedestal, the one that says, “Give me your tired, your poor, your huddled masses yearning to breathe free”? It’s actually a contract, and at the bottom, in very small print, it says, “In return for acceptance of the aforementioned ‘huddled masses,’ countries of origin agree to accept all of the social media noise generated by American sources.”
Sorry, Canada, but we gotcha.
How some COVID-19 vaccines could cause rare blood clots
on April 14, 2021, after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that states hold off on using it pending a detailed review of six cases of the same kind of rare but serious event – a blood clot in the vessels that drain blood from the brain combined with a large drop in platelets, which increases the risk for bleeding.
This combination can lead to severe strokes that can lead to brain damage or death. Among the six cases reported, which came to light over the past 3 weeks, one person died, according to the CDC. All six were women and ranged in age from 18 to 48 years.
According to a report from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), which is maintained by the Department of Health & Human Services, the woman who died was 45. She developed a gradually worsening headache about a week after receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
On March 17, the day she came to the hospital, she was dry heaving. Her headache had suddenly gotten much worse, and the left side of her body was weak, which are signs of a stroke. A CT scan revealed both bleeding in her brain and a clot in her cortical vein. She died the following day.
In addition to VAERS, which accepts reports from anyone, the CDC and FDA are monitoring at least eight other safety systems maintained by hospitals, research centers, long-term care facilities, and insurance companies for signs of trouble with the vaccines. VAERS data is searchable and open to the public. Most of these systems are not publicly available to protect patient privacy. It’s unclear which systems detected the six cases cited by federal regulators.
“These are very serious and potentially fatal problems occurring in a healthy young adult. It’s serious and we need to get to the bottom of it,” said Ed Belongia, MD, director of the Center for Clinical Epidemiology and Population Health at the Marshfield (Wis.) Clinic Research Institute. Dr. Belongia leads a research team that helps the CDC monitor vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“Safety is always the highest priority, and I think what we’ve seen here in the past 24 hours is our vaccine safety monitoring system is working,” he said.
Others agree. “I think what CDC and FDA have detected is a rare, but likely real adverse event associated with this vaccine,” said Paul Offit, MD, director of vaccine education at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Although much is still unknown about these events, they follow a similar pattern of blood clots reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine in Europe. That vaccine is now sold under the brand name Vaxzevria.
This has experts questioning whether all vaccines of this type may cause these rare clots.
“I think it’s likely a class effect,” said Dr. Offit, who was a member of the FDA advisory committee that reviewed clinical trial data on the J&J vaccine before it was authorized for use.
Adenovirus vaccines scrutinized
Both the Johnson & Johnson and Vaxzevria vaccines use an adenovirus to ferry genetic instructions for making the coronaviruses spike protein into our cells.
Adenoviruses are common, relatively simple viruses that normally cause mild cold or flu symptoms. The ones used in the vaccine are disabled so they can’t make us sick. They’re more like Trojan horses.
Once inside our cells, they release the DNA instructions they carry to make the spike protein of the new coronavirus. Those cells then crank out copies of the spike protein, which then get displayed on the outer surface of the cell membrane where they are recognized by the immune system.
The immune system then makes antibodies and other defenses against the spike so that, when the real coronavirus comes along, our bodies are ready to fight the infection.
There’s no question the vaccine works. In clinical trials, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine was 66% percent effective at preventing against moderate to severe COVID-19 infection, and none of the patients who got COVID-19 after vaccination had to be admitted to the hospital or died.
The idea behind using adenoviruses in vaccines isn’t a new one. In a kind of fight-fire-with-fire approach, the idea is to use a virus, which is good at infecting us, to fight a different kind of virus.
Researchers have been working on the concept for about 10 years, but the COVID-19 vaccines that use this technology are some of the first adenovirus-vector vaccines deployed in humans.
Only one other adenovirus vaccine, for Ebola, has been approved for use in humans. It was approved in Europe last year. Before the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, no other adenovirus vector has been available for use in humans in the United States.
There are six adenovirus-vector vaccines for COVID-19. In addition to AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson, there’s the Russian-developed vaccine Sputnik V, along with CanSino from China, and the Covishield vaccine in India.
Adenovirus vaccines are more stable than the mRNA vaccines. That makes them easier to store and transport.
But they have a significant downside, too. Because adenoviruses infect humans out in the world, we already make antibodies against them. So there’s always a danger that our immune systems might recognize and react to the vaccine, rendering it ineffective. For that reason, scientists try to carefully select the adenovirus vectors, or carriers, they use.
The two vaccines under investigation for blood clots are slightly different. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine uses the vector AD26, because most of the population lacks preexisting immunity to it. Vaxzevria uses an adenovirus that infects chimpanzees, called ChAdOx1.
Vaxzevria has been widely used in Europe but has not yet been authorized in the United States.
On April 7, the European Medicines Agency, Europe’s counterpart to the FDA, ruled that unusual blood clots with low blood platelets should be listed as rare side effects on the Vaxzevria vaccine.
The decision came after reviewing 62 cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) linked to the vaccine and 25 cases of another rare type of clot, called a splanchnic vein thrombosis. Splanchnic veins drain blood from the major organs in the digestive system, including the stomach, liver, and intestines; 18 of those events were fatal.
The reports were culled from reporting in Europe and the United Kingdom, where around 25 million people have received the Vaxzevria vaccine, making these clots exceptionally rare, but serious.
So far, six cases of CVST have been reported in the United States, after more than 7 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccines have been administered.
A key question for U.S. regulators will be the background rate for these types of rare combinations of clots and deplenished platelets. The background rate is the number of events that would be expected to occur naturally in a population of unvaccinated people. On a press call on April 13, Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, was asked about the frequency of this dangerous combination. He said the combination of low platelets and clots was so rare that it was hard to pinpoint, but might be somewhere between 2 and 14 cases per million people over the course of a year.
The first Johnson & Johnson doses were given in early March. That means the six cases came to light within the first few weeks of use of the vaccine in the United States, a very short amount of time.
“These were six cases per million people for 2 weeks, which is the same thing as 25 million per year, so it’s clearly above the background rate,” Dr. Offit said.
Studies suggest possible mechanism
On April 9, the New England Journal of Medicine published a detailed evaluation of the 11 patients in Germany and Austria who developed the rare clots after their Vaxzevria vaccines.
The study detected rare antibodies to a signaling protein called platelet factor 4, which helps to coordinate clot formation.
These same type of antibodies form in some people given the blood thinning drug heparin. In those reactions, which are also exceptionally rare, the same type of syndrome develops, leading to large, devastating clots that consume circulating platelets.
It’s not yet clear whether people who develop reactions to the vaccines already have some platelet factor 4 antibodies before they are vaccinated, or whether the vaccines somehow spur the body to make these antibodies, which then launch a kind of autoimmune attack.
The researchers on the paper gave the syndrome a name, vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT).
It’s also not clear why more cases seem to be in women than in men. Andrew Eisenberger, MD, an associate professor of hematology and oncology at Columbia University, New York, said the most common causes of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis have to do with conditions that raise estrogen levels, like pregnancy and hormonal contraception.
“Estrogen naturally leads to changes in several clotting proteins in the blood that may predispose to abnormal blood clotting in a few different sites in the body,” he said. “The clotting changes we are encountering with some of COVID-19 vaccines are likely to be synergistic with the effects of estrogen on the blood.”
No matter the cause, the CDC on April 13 alerted doctors to keep a high index of suspicion for VITT in patients who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccination within the last 2 weeks. In those patients, the usual course of treatment with blood thinning drugs like heparin may be harmful.
Symptoms to watch for include severe headache or backache, new neurologic symptoms, severe abdominal pain, shortness of breath, leg swelling, tiny red spots on the skin, or easy bruising.
Grappling with evidence
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet today in an emergency session to review the cases and see if any changes are needed to use of the J&J vaccine in the United States.
Last week, for example, the United Kingdom restricted the use of the AstraZeneca vaccine in people aged younger than 30 years, saying the risks and benefits of vaccination are “more finely balanced” for this age group.
With cases of COVID-19 rising again in the United States, and the Johnson & Johnson vaccine currently the most convenient form of protection against the virus, the committee will have to weigh the risks of that infection against the risk of rare clots caused by vaccination.
They will also likely have to rule out whether any of the cases had COVID. At least one study has reported CVST clots in three patients with confirmed COVID infections. In Europe, COVID infection did not seem to play a role in the formation of the clots with low platelets.
Hilda Bastian, PhD, a clinical trials expert who cofounded the Cochrane Collaboration, said it won’t be an easy task. Much will depend on how certain the committee members feel they know about all the events linked to the vaccine.
“That’s the really, really hard issue from my point of view for them right this moment. Have we missed any? Or how many are we likely to have missed?” asked Dr. Bastian, who lives in Australia.
“In a country that size with that fragmented [of] a health care system, how sure can you be that you know them all? That’s going to be a really difficult situation for them to grapple with, the quality of information that they’ve got,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
on April 14, 2021, after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that states hold off on using it pending a detailed review of six cases of the same kind of rare but serious event – a blood clot in the vessels that drain blood from the brain combined with a large drop in platelets, which increases the risk for bleeding.
This combination can lead to severe strokes that can lead to brain damage or death. Among the six cases reported, which came to light over the past 3 weeks, one person died, according to the CDC. All six were women and ranged in age from 18 to 48 years.
According to a report from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), which is maintained by the Department of Health & Human Services, the woman who died was 45. She developed a gradually worsening headache about a week after receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
On March 17, the day she came to the hospital, she was dry heaving. Her headache had suddenly gotten much worse, and the left side of her body was weak, which are signs of a stroke. A CT scan revealed both bleeding in her brain and a clot in her cortical vein. She died the following day.
In addition to VAERS, which accepts reports from anyone, the CDC and FDA are monitoring at least eight other safety systems maintained by hospitals, research centers, long-term care facilities, and insurance companies for signs of trouble with the vaccines. VAERS data is searchable and open to the public. Most of these systems are not publicly available to protect patient privacy. It’s unclear which systems detected the six cases cited by federal regulators.
“These are very serious and potentially fatal problems occurring in a healthy young adult. It’s serious and we need to get to the bottom of it,” said Ed Belongia, MD, director of the Center for Clinical Epidemiology and Population Health at the Marshfield (Wis.) Clinic Research Institute. Dr. Belongia leads a research team that helps the CDC monitor vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“Safety is always the highest priority, and I think what we’ve seen here in the past 24 hours is our vaccine safety monitoring system is working,” he said.
Others agree. “I think what CDC and FDA have detected is a rare, but likely real adverse event associated with this vaccine,” said Paul Offit, MD, director of vaccine education at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Although much is still unknown about these events, they follow a similar pattern of blood clots reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine in Europe. That vaccine is now sold under the brand name Vaxzevria.
This has experts questioning whether all vaccines of this type may cause these rare clots.
“I think it’s likely a class effect,” said Dr. Offit, who was a member of the FDA advisory committee that reviewed clinical trial data on the J&J vaccine before it was authorized for use.
Adenovirus vaccines scrutinized
Both the Johnson & Johnson and Vaxzevria vaccines use an adenovirus to ferry genetic instructions for making the coronaviruses spike protein into our cells.
Adenoviruses are common, relatively simple viruses that normally cause mild cold or flu symptoms. The ones used in the vaccine are disabled so they can’t make us sick. They’re more like Trojan horses.
Once inside our cells, they release the DNA instructions they carry to make the spike protein of the new coronavirus. Those cells then crank out copies of the spike protein, which then get displayed on the outer surface of the cell membrane where they are recognized by the immune system.
The immune system then makes antibodies and other defenses against the spike so that, when the real coronavirus comes along, our bodies are ready to fight the infection.
There’s no question the vaccine works. In clinical trials, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine was 66% percent effective at preventing against moderate to severe COVID-19 infection, and none of the patients who got COVID-19 after vaccination had to be admitted to the hospital or died.
The idea behind using adenoviruses in vaccines isn’t a new one. In a kind of fight-fire-with-fire approach, the idea is to use a virus, which is good at infecting us, to fight a different kind of virus.
Researchers have been working on the concept for about 10 years, but the COVID-19 vaccines that use this technology are some of the first adenovirus-vector vaccines deployed in humans.
Only one other adenovirus vaccine, for Ebola, has been approved for use in humans. It was approved in Europe last year. Before the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, no other adenovirus vector has been available for use in humans in the United States.
There are six adenovirus-vector vaccines for COVID-19. In addition to AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson, there’s the Russian-developed vaccine Sputnik V, along with CanSino from China, and the Covishield vaccine in India.
Adenovirus vaccines are more stable than the mRNA vaccines. That makes them easier to store and transport.
But they have a significant downside, too. Because adenoviruses infect humans out in the world, we already make antibodies against them. So there’s always a danger that our immune systems might recognize and react to the vaccine, rendering it ineffective. For that reason, scientists try to carefully select the adenovirus vectors, or carriers, they use.
The two vaccines under investigation for blood clots are slightly different. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine uses the vector AD26, because most of the population lacks preexisting immunity to it. Vaxzevria uses an adenovirus that infects chimpanzees, called ChAdOx1.
Vaxzevria has been widely used in Europe but has not yet been authorized in the United States.
On April 7, the European Medicines Agency, Europe’s counterpart to the FDA, ruled that unusual blood clots with low blood platelets should be listed as rare side effects on the Vaxzevria vaccine.
The decision came after reviewing 62 cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) linked to the vaccine and 25 cases of another rare type of clot, called a splanchnic vein thrombosis. Splanchnic veins drain blood from the major organs in the digestive system, including the stomach, liver, and intestines; 18 of those events were fatal.
The reports were culled from reporting in Europe and the United Kingdom, where around 25 million people have received the Vaxzevria vaccine, making these clots exceptionally rare, but serious.
So far, six cases of CVST have been reported in the United States, after more than 7 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccines have been administered.
A key question for U.S. regulators will be the background rate for these types of rare combinations of clots and deplenished platelets. The background rate is the number of events that would be expected to occur naturally in a population of unvaccinated people. On a press call on April 13, Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, was asked about the frequency of this dangerous combination. He said the combination of low platelets and clots was so rare that it was hard to pinpoint, but might be somewhere between 2 and 14 cases per million people over the course of a year.
The first Johnson & Johnson doses were given in early March. That means the six cases came to light within the first few weeks of use of the vaccine in the United States, a very short amount of time.
“These were six cases per million people for 2 weeks, which is the same thing as 25 million per year, so it’s clearly above the background rate,” Dr. Offit said.
Studies suggest possible mechanism
On April 9, the New England Journal of Medicine published a detailed evaluation of the 11 patients in Germany and Austria who developed the rare clots after their Vaxzevria vaccines.
The study detected rare antibodies to a signaling protein called platelet factor 4, which helps to coordinate clot formation.
These same type of antibodies form in some people given the blood thinning drug heparin. In those reactions, which are also exceptionally rare, the same type of syndrome develops, leading to large, devastating clots that consume circulating platelets.
It’s not yet clear whether people who develop reactions to the vaccines already have some platelet factor 4 antibodies before they are vaccinated, or whether the vaccines somehow spur the body to make these antibodies, which then launch a kind of autoimmune attack.
The researchers on the paper gave the syndrome a name, vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT).
It’s also not clear why more cases seem to be in women than in men. Andrew Eisenberger, MD, an associate professor of hematology and oncology at Columbia University, New York, said the most common causes of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis have to do with conditions that raise estrogen levels, like pregnancy and hormonal contraception.
“Estrogen naturally leads to changes in several clotting proteins in the blood that may predispose to abnormal blood clotting in a few different sites in the body,” he said. “The clotting changes we are encountering with some of COVID-19 vaccines are likely to be synergistic with the effects of estrogen on the blood.”
No matter the cause, the CDC on April 13 alerted doctors to keep a high index of suspicion for VITT in patients who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccination within the last 2 weeks. In those patients, the usual course of treatment with blood thinning drugs like heparin may be harmful.
Symptoms to watch for include severe headache or backache, new neurologic symptoms, severe abdominal pain, shortness of breath, leg swelling, tiny red spots on the skin, or easy bruising.
Grappling with evidence
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet today in an emergency session to review the cases and see if any changes are needed to use of the J&J vaccine in the United States.
Last week, for example, the United Kingdom restricted the use of the AstraZeneca vaccine in people aged younger than 30 years, saying the risks and benefits of vaccination are “more finely balanced” for this age group.
With cases of COVID-19 rising again in the United States, and the Johnson & Johnson vaccine currently the most convenient form of protection against the virus, the committee will have to weigh the risks of that infection against the risk of rare clots caused by vaccination.
They will also likely have to rule out whether any of the cases had COVID. At least one study has reported CVST clots in three patients with confirmed COVID infections. In Europe, COVID infection did not seem to play a role in the formation of the clots with low platelets.
Hilda Bastian, PhD, a clinical trials expert who cofounded the Cochrane Collaboration, said it won’t be an easy task. Much will depend on how certain the committee members feel they know about all the events linked to the vaccine.
“That’s the really, really hard issue from my point of view for them right this moment. Have we missed any? Or how many are we likely to have missed?” asked Dr. Bastian, who lives in Australia.
“In a country that size with that fragmented [of] a health care system, how sure can you be that you know them all? That’s going to be a really difficult situation for them to grapple with, the quality of information that they’ve got,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
on April 14, 2021, after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that states hold off on using it pending a detailed review of six cases of the same kind of rare but serious event – a blood clot in the vessels that drain blood from the brain combined with a large drop in platelets, which increases the risk for bleeding.
This combination can lead to severe strokes that can lead to brain damage or death. Among the six cases reported, which came to light over the past 3 weeks, one person died, according to the CDC. All six were women and ranged in age from 18 to 48 years.
According to a report from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), which is maintained by the Department of Health & Human Services, the woman who died was 45. She developed a gradually worsening headache about a week after receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
On March 17, the day she came to the hospital, she was dry heaving. Her headache had suddenly gotten much worse, and the left side of her body was weak, which are signs of a stroke. A CT scan revealed both bleeding in her brain and a clot in her cortical vein. She died the following day.
In addition to VAERS, which accepts reports from anyone, the CDC and FDA are monitoring at least eight other safety systems maintained by hospitals, research centers, long-term care facilities, and insurance companies for signs of trouble with the vaccines. VAERS data is searchable and open to the public. Most of these systems are not publicly available to protect patient privacy. It’s unclear which systems detected the six cases cited by federal regulators.
“These are very serious and potentially fatal problems occurring in a healthy young adult. It’s serious and we need to get to the bottom of it,” said Ed Belongia, MD, director of the Center for Clinical Epidemiology and Population Health at the Marshfield (Wis.) Clinic Research Institute. Dr. Belongia leads a research team that helps the CDC monitor vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“Safety is always the highest priority, and I think what we’ve seen here in the past 24 hours is our vaccine safety monitoring system is working,” he said.
Others agree. “I think what CDC and FDA have detected is a rare, but likely real adverse event associated with this vaccine,” said Paul Offit, MD, director of vaccine education at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Although much is still unknown about these events, they follow a similar pattern of blood clots reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine in Europe. That vaccine is now sold under the brand name Vaxzevria.
This has experts questioning whether all vaccines of this type may cause these rare clots.
“I think it’s likely a class effect,” said Dr. Offit, who was a member of the FDA advisory committee that reviewed clinical trial data on the J&J vaccine before it was authorized for use.
Adenovirus vaccines scrutinized
Both the Johnson & Johnson and Vaxzevria vaccines use an adenovirus to ferry genetic instructions for making the coronaviruses spike protein into our cells.
Adenoviruses are common, relatively simple viruses that normally cause mild cold or flu symptoms. The ones used in the vaccine are disabled so they can’t make us sick. They’re more like Trojan horses.
Once inside our cells, they release the DNA instructions they carry to make the spike protein of the new coronavirus. Those cells then crank out copies of the spike protein, which then get displayed on the outer surface of the cell membrane where they are recognized by the immune system.
The immune system then makes antibodies and other defenses against the spike so that, when the real coronavirus comes along, our bodies are ready to fight the infection.
There’s no question the vaccine works. In clinical trials, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine was 66% percent effective at preventing against moderate to severe COVID-19 infection, and none of the patients who got COVID-19 after vaccination had to be admitted to the hospital or died.
The idea behind using adenoviruses in vaccines isn’t a new one. In a kind of fight-fire-with-fire approach, the idea is to use a virus, which is good at infecting us, to fight a different kind of virus.
Researchers have been working on the concept for about 10 years, but the COVID-19 vaccines that use this technology are some of the first adenovirus-vector vaccines deployed in humans.
Only one other adenovirus vaccine, for Ebola, has been approved for use in humans. It was approved in Europe last year. Before the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, no other adenovirus vector has been available for use in humans in the United States.
There are six adenovirus-vector vaccines for COVID-19. In addition to AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson, there’s the Russian-developed vaccine Sputnik V, along with CanSino from China, and the Covishield vaccine in India.
Adenovirus vaccines are more stable than the mRNA vaccines. That makes them easier to store and transport.
But they have a significant downside, too. Because adenoviruses infect humans out in the world, we already make antibodies against them. So there’s always a danger that our immune systems might recognize and react to the vaccine, rendering it ineffective. For that reason, scientists try to carefully select the adenovirus vectors, or carriers, they use.
The two vaccines under investigation for blood clots are slightly different. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine uses the vector AD26, because most of the population lacks preexisting immunity to it. Vaxzevria uses an adenovirus that infects chimpanzees, called ChAdOx1.
Vaxzevria has been widely used in Europe but has not yet been authorized in the United States.
On April 7, the European Medicines Agency, Europe’s counterpart to the FDA, ruled that unusual blood clots with low blood platelets should be listed as rare side effects on the Vaxzevria vaccine.
The decision came after reviewing 62 cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) linked to the vaccine and 25 cases of another rare type of clot, called a splanchnic vein thrombosis. Splanchnic veins drain blood from the major organs in the digestive system, including the stomach, liver, and intestines; 18 of those events were fatal.
The reports were culled from reporting in Europe and the United Kingdom, where around 25 million people have received the Vaxzevria vaccine, making these clots exceptionally rare, but serious.
So far, six cases of CVST have been reported in the United States, after more than 7 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccines have been administered.
A key question for U.S. regulators will be the background rate for these types of rare combinations of clots and deplenished platelets. The background rate is the number of events that would be expected to occur naturally in a population of unvaccinated people. On a press call on April 13, Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, was asked about the frequency of this dangerous combination. He said the combination of low platelets and clots was so rare that it was hard to pinpoint, but might be somewhere between 2 and 14 cases per million people over the course of a year.
The first Johnson & Johnson doses were given in early March. That means the six cases came to light within the first few weeks of use of the vaccine in the United States, a very short amount of time.
“These were six cases per million people for 2 weeks, which is the same thing as 25 million per year, so it’s clearly above the background rate,” Dr. Offit said.
Studies suggest possible mechanism
On April 9, the New England Journal of Medicine published a detailed evaluation of the 11 patients in Germany and Austria who developed the rare clots after their Vaxzevria vaccines.
The study detected rare antibodies to a signaling protein called platelet factor 4, which helps to coordinate clot formation.
These same type of antibodies form in some people given the blood thinning drug heparin. In those reactions, which are also exceptionally rare, the same type of syndrome develops, leading to large, devastating clots that consume circulating platelets.
It’s not yet clear whether people who develop reactions to the vaccines already have some platelet factor 4 antibodies before they are vaccinated, or whether the vaccines somehow spur the body to make these antibodies, which then launch a kind of autoimmune attack.
The researchers on the paper gave the syndrome a name, vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT).
It’s also not clear why more cases seem to be in women than in men. Andrew Eisenberger, MD, an associate professor of hematology and oncology at Columbia University, New York, said the most common causes of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis have to do with conditions that raise estrogen levels, like pregnancy and hormonal contraception.
“Estrogen naturally leads to changes in several clotting proteins in the blood that may predispose to abnormal blood clotting in a few different sites in the body,” he said. “The clotting changes we are encountering with some of COVID-19 vaccines are likely to be synergistic with the effects of estrogen on the blood.”
No matter the cause, the CDC on April 13 alerted doctors to keep a high index of suspicion for VITT in patients who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccination within the last 2 weeks. In those patients, the usual course of treatment with blood thinning drugs like heparin may be harmful.
Symptoms to watch for include severe headache or backache, new neurologic symptoms, severe abdominal pain, shortness of breath, leg swelling, tiny red spots on the skin, or easy bruising.
Grappling with evidence
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet today in an emergency session to review the cases and see if any changes are needed to use of the J&J vaccine in the United States.
Last week, for example, the United Kingdom restricted the use of the AstraZeneca vaccine in people aged younger than 30 years, saying the risks and benefits of vaccination are “more finely balanced” for this age group.
With cases of COVID-19 rising again in the United States, and the Johnson & Johnson vaccine currently the most convenient form of protection against the virus, the committee will have to weigh the risks of that infection against the risk of rare clots caused by vaccination.
They will also likely have to rule out whether any of the cases had COVID. At least one study has reported CVST clots in three patients with confirmed COVID infections. In Europe, COVID infection did not seem to play a role in the formation of the clots with low platelets.
Hilda Bastian, PhD, a clinical trials expert who cofounded the Cochrane Collaboration, said it won’t be an easy task. Much will depend on how certain the committee members feel they know about all the events linked to the vaccine.
“That’s the really, really hard issue from my point of view for them right this moment. Have we missed any? Or how many are we likely to have missed?” asked Dr. Bastian, who lives in Australia.
“In a country that size with that fragmented [of] a health care system, how sure can you be that you know them all? That’s going to be a really difficult situation for them to grapple with, the quality of information that they’ve got,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitalization not rare for children with COVID, study says
Nearly a third of those had severe disease that required mechanical ventilation or admission to an intensive care unit, according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open on April 9.*
That means about 1 in 9 kids with COVID-19 in this cohort needed hospitalization, and about 1 in 28 had severe COVID-19.
“Although most children with COVID-19 experience mild illness, some children develop serious illness that leads to hospitalization, use of invasive mechanical ventilation, and death,” the researchers wrote.
The research team analyzed discharge data from 869 medical facilities in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. They looked for COVID-19 patients ages 18 and under who had an in-patient or emergency department visit between March and October 2020.
More than 20,700 children with COVID-19 had an in-patient or an emergency department visit, and 2,430 were hospitalized with COVID-19. Among those, 756 children had severe COVID-19 and were admitted to an intensive care unit or needed mechanical ventilation.
About 53% of the COVID-19 patients were girls, and about 54% were between ages 12-18. In addition, about 29% had at least one chronic condition.
Similar to COVID-19 studies in adults, Hispanic, Latino and Black patients were overrepresented. About 39% of the children were Hispanic or Latino, and 24% were Black. However, the researchers didn’t find an association between severe COVID-19 and race or ethnicity.
The likelihood of severe COVID-19 increased if the patient had at least one chronic condition, was male, or was between ages 2-11.
“Understanding factors associated with severe COVID-19 disease among children could help inform prevention and control strategies,” they added. “Reducing infection risk through community mitigation strategies is critical for protecting children from COVID-19 and preventing poor outcomes.”
As of April 8, more than 3.54 million U.S. children have tested positive for COVID-19, according to the latest report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and Children’s Hospital Association. Cases among children are increasing slightly, with about 73,000 new cases reported during the first week of April.
Children represent about 13.5% of the COVID-19 cases in the country, according to the report. Among the 24 states that provide data, children represented 1% to 3% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations, and less than 2% of all child COVID-19 cases resulted in hospitalization.
“At this time, it appears that severe illness due to COVID-19 is rare among children,” the two groups wrote.
“However, there is an urgent need to collect more data on longer-term impacts of the pandemic on children, including ways the virus may harm the long-term physical health of infected children, as well as its emotional and mental health effects,” they added.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
*CORRECTION, 6/7/21 – This story has been corrected to clarify that the patient sample study reflects only those children who presented to an emergency department or received inpatient care for COVID-19 in a hospital network and were included in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. A previous version of the story incorrectly implied that 12% of all U.S. children with COVID-19 had required inpatient care.
Nearly a third of those had severe disease that required mechanical ventilation or admission to an intensive care unit, according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open on April 9.*
That means about 1 in 9 kids with COVID-19 in this cohort needed hospitalization, and about 1 in 28 had severe COVID-19.
“Although most children with COVID-19 experience mild illness, some children develop serious illness that leads to hospitalization, use of invasive mechanical ventilation, and death,” the researchers wrote.
The research team analyzed discharge data from 869 medical facilities in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. They looked for COVID-19 patients ages 18 and under who had an in-patient or emergency department visit between March and October 2020.
More than 20,700 children with COVID-19 had an in-patient or an emergency department visit, and 2,430 were hospitalized with COVID-19. Among those, 756 children had severe COVID-19 and were admitted to an intensive care unit or needed mechanical ventilation.
About 53% of the COVID-19 patients were girls, and about 54% were between ages 12-18. In addition, about 29% had at least one chronic condition.
Similar to COVID-19 studies in adults, Hispanic, Latino and Black patients were overrepresented. About 39% of the children were Hispanic or Latino, and 24% were Black. However, the researchers didn’t find an association between severe COVID-19 and race or ethnicity.
The likelihood of severe COVID-19 increased if the patient had at least one chronic condition, was male, or was between ages 2-11.
“Understanding factors associated with severe COVID-19 disease among children could help inform prevention and control strategies,” they added. “Reducing infection risk through community mitigation strategies is critical for protecting children from COVID-19 and preventing poor outcomes.”
As of April 8, more than 3.54 million U.S. children have tested positive for COVID-19, according to the latest report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and Children’s Hospital Association. Cases among children are increasing slightly, with about 73,000 new cases reported during the first week of April.
Children represent about 13.5% of the COVID-19 cases in the country, according to the report. Among the 24 states that provide data, children represented 1% to 3% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations, and less than 2% of all child COVID-19 cases resulted in hospitalization.
“At this time, it appears that severe illness due to COVID-19 is rare among children,” the two groups wrote.
“However, there is an urgent need to collect more data on longer-term impacts of the pandemic on children, including ways the virus may harm the long-term physical health of infected children, as well as its emotional and mental health effects,” they added.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
*CORRECTION, 6/7/21 – This story has been corrected to clarify that the patient sample study reflects only those children who presented to an emergency department or received inpatient care for COVID-19 in a hospital network and were included in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. A previous version of the story incorrectly implied that 12% of all U.S. children with COVID-19 had required inpatient care.
Nearly a third of those had severe disease that required mechanical ventilation or admission to an intensive care unit, according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open on April 9.*
That means about 1 in 9 kids with COVID-19 in this cohort needed hospitalization, and about 1 in 28 had severe COVID-19.
“Although most children with COVID-19 experience mild illness, some children develop serious illness that leads to hospitalization, use of invasive mechanical ventilation, and death,” the researchers wrote.
The research team analyzed discharge data from 869 medical facilities in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. They looked for COVID-19 patients ages 18 and under who had an in-patient or emergency department visit between March and October 2020.
More than 20,700 children with COVID-19 had an in-patient or an emergency department visit, and 2,430 were hospitalized with COVID-19. Among those, 756 children had severe COVID-19 and were admitted to an intensive care unit or needed mechanical ventilation.
About 53% of the COVID-19 patients were girls, and about 54% were between ages 12-18. In addition, about 29% had at least one chronic condition.
Similar to COVID-19 studies in adults, Hispanic, Latino and Black patients were overrepresented. About 39% of the children were Hispanic or Latino, and 24% were Black. However, the researchers didn’t find an association between severe COVID-19 and race or ethnicity.
The likelihood of severe COVID-19 increased if the patient had at least one chronic condition, was male, or was between ages 2-11.
“Understanding factors associated with severe COVID-19 disease among children could help inform prevention and control strategies,” they added. “Reducing infection risk through community mitigation strategies is critical for protecting children from COVID-19 and preventing poor outcomes.”
As of April 8, more than 3.54 million U.S. children have tested positive for COVID-19, according to the latest report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and Children’s Hospital Association. Cases among children are increasing slightly, with about 73,000 new cases reported during the first week of April.
Children represent about 13.5% of the COVID-19 cases in the country, according to the report. Among the 24 states that provide data, children represented 1% to 3% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations, and less than 2% of all child COVID-19 cases resulted in hospitalization.
“At this time, it appears that severe illness due to COVID-19 is rare among children,” the two groups wrote.
“However, there is an urgent need to collect more data on longer-term impacts of the pandemic on children, including ways the virus may harm the long-term physical health of infected children, as well as its emotional and mental health effects,” they added.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
*CORRECTION, 6/7/21 – This story has been corrected to clarify that the patient sample study reflects only those children who presented to an emergency department or received inpatient care for COVID-19 in a hospital network and were included in the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release. A previous version of the story incorrectly implied that 12% of all U.S. children with COVID-19 had required inpatient care.
Data about COVID-19-related skin manifestations in children continue to emerge
Two and stratifying children at risk for serious, systemic illness due to the virus.
In a single-center descriptive study carried out over a 9-month period, researchers in Madrid found that of 50 hospitalized children infected with COVID-19, 21 (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly exanthem, followed by conjunctival hyperemia without secretion and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue. In addition, 18 (36%) fulfilled criteria for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
“Based on findings in adult patients, the skin manifestations of COVID-19 have been classified under five categories: acral pseudo-chilblain, vesicular eruptions, urticarial lesions, maculopapular eruptions, and livedo or necrosis,” David Andina-Martinez, MD, of Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online on April 2 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Chilblain lesions in healthy children and adolescents have received much attention; these lesions resolve without complications after a few weeks,” they added. “Besides, other cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 in children have been the matter of case reports or small case series. Nevertheless, the mucocutaneous manifestations in hospitalized children infected with SARS-CoV-2 and their implications on the clinical course have not yet been extensively described.”
In an effort to describe the mucocutaneous manifestations in children hospitalized for COVID-19, the researchers evaluated 50 children up to 18 years of age who were admitted between March 1 and Nov. 30, 2020, to Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, which was designated as a pediatric reference center during the peak of the pandemic. The main reasons for admission were respiratory illness (40%) and MIS-C (40%).
Of the 50 patients, 44 (88%) had a positive RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 and 6 (12%) met clinical suspicion criteria and had a negative RT-PCR with a positive IgG serology. In 34 patients (68%), a close contact with a suspected or confirmed case of COVID-19 was referred, while the source of the infection remained unknown in the remaining 16 patients (32%).
The researchers reported that 21 patients (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly maculopapular exanthem (86%), conjunctival hyperemia (81%), and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue (43%). In addition, 18 of the 21 patients (86%) fulfilled criteria for MIS-C.
“A tricky thing about MIS-C is that it often manifests 4-5 weeks after a child had COVID-19,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study. “MIS-C is associated with characteristic bright red lips and a red tongue that might resemble a strawberry. Such oral findings should prompt rapid evaluation for other signs and symptoms. There can be redness of the eyes or other more nonspecific skin findings (large or small areas of redness on the trunk or limbs, sometimes with surface change), but more importantly, fever, a rapid heartbeat, diarrhea, or breathing issues. The risk with MIS-C is a rapid decline in a child’s health, with admission to an intensive care unit.”
Dr. Andina-Martinez and his colleagues also contrast the skin findings of MIS-C, which are not generally on the hands or feet, with the so-called “COVID toe” or finger phenomenon, which has also been associated with SARS-CoV-2, particularly in children. “Only one of the patients in this series had skin involvement of a finger, and it only appeared after recovery from MIS-C,” Dr. Ko noted. “Distinguishing COVID toes from MIS-C is important, as COVID toes has a very good outcome, while MIS-C can have severe consequences, including protracted heart disease.”
In other findings, patients who presented with mucocutaneous signs tended to be older than those without skin signs and they presented at the emergency department with poor general status and extreme tachycardia. They also had higher C-reactive protein and D-dimer levels and lower lymphocyte counts and faced a more than a 10-fold increased risk of being admitted to the PICU, compared with patients who did not have skin signs (OR, 10.24; P = .003).
In a separate study published online on April 7 in JAMA Dermatology, Zachary E. Holcomb, MD, of the combined dermatology residency program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues presented what is believed to be the first case report of reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) triggered by SARS-CoV-2. RIME is the preferred term for pediatric patients who present with mucositis and rash (often a scant or even absent skin eruption) triggered by various infectious agents.
The patient, a 17-year-old male, presented to the emergency department with 3 days of mouth pain and nonpainful penile erosions. “One week prior, he experienced transient anosmia and ageusia that had since spontaneously resolved,” the researchers wrote. “At that time, he was tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection via nasopharyngeal polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the results of which were positive.”
At presentation, the patient had no fever, his vital signs were normal, and the physical exam revealed shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities. Serum analysis revealed a normal white blood cell count with mild absolute lymphopenia, slightly elevated creatinine level, normal liver function, slightly elevated C-reactive protein level, and normal ferritin level.
Dr. Holcomb and colleagues made a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2–associated RIME based on microbiological results, which revealed positive repeated SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal PCR and negative nasopharyngeal PCR testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, adenovirus, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, human metapneumovirus, influenza A/B, parainfluenza 1 to 4, rhinovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. In addition, titers of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM levels were negative, but Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG levels were elevated.
The lesions resolved with 60 mg of oral prednisone taken daily for 4 days. A recurrence of oral mucositis 3 months later responded to 80 mg oral prednisone taken daily for 6 days.
“It’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 is yet another trigger for RIME,” said Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of the division of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was asked to comment about the case report.
“The take-home message is for clinicians to be aware of this association and distinguish these patients from those with MIS-C, because patients with MIS-C require monitoring and urgent systemic treatment. RIME and MIS-C may potentially be distinguished clinically based on the nature of the mucositis (hemorrhagic and erosive in RIME, dry, cracked lips with ‘strawberry tongue’ in MIS-C) but more importantly patients with RIME lack laboratory evidence of severe systemic inflammation,” such as ESR, CRP, or ferritin, she said.
“A final interesting point in this article was the recurrence of mucositis in this patient, which could mean that recurrent mucositis/recurrent RIME might be yet another manifestation of ‘long-COVID’ (now called post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection) in some patients,” Dr. Kirkorian added. She noted that the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatologic Societies COVID-19 Dermatology Registry and articles like these “provide invaluable ‘hot off the presses’ information for clinicians who are facing the protean manifestations of a novel viral epidemic.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Two and stratifying children at risk for serious, systemic illness due to the virus.
In a single-center descriptive study carried out over a 9-month period, researchers in Madrid found that of 50 hospitalized children infected with COVID-19, 21 (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly exanthem, followed by conjunctival hyperemia without secretion and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue. In addition, 18 (36%) fulfilled criteria for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
“Based on findings in adult patients, the skin manifestations of COVID-19 have been classified under five categories: acral pseudo-chilblain, vesicular eruptions, urticarial lesions, maculopapular eruptions, and livedo or necrosis,” David Andina-Martinez, MD, of Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online on April 2 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Chilblain lesions in healthy children and adolescents have received much attention; these lesions resolve without complications after a few weeks,” they added. “Besides, other cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 in children have been the matter of case reports or small case series. Nevertheless, the mucocutaneous manifestations in hospitalized children infected with SARS-CoV-2 and their implications on the clinical course have not yet been extensively described.”
In an effort to describe the mucocutaneous manifestations in children hospitalized for COVID-19, the researchers evaluated 50 children up to 18 years of age who were admitted between March 1 and Nov. 30, 2020, to Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, which was designated as a pediatric reference center during the peak of the pandemic. The main reasons for admission were respiratory illness (40%) and MIS-C (40%).
Of the 50 patients, 44 (88%) had a positive RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 and 6 (12%) met clinical suspicion criteria and had a negative RT-PCR with a positive IgG serology. In 34 patients (68%), a close contact with a suspected or confirmed case of COVID-19 was referred, while the source of the infection remained unknown in the remaining 16 patients (32%).
The researchers reported that 21 patients (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly maculopapular exanthem (86%), conjunctival hyperemia (81%), and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue (43%). In addition, 18 of the 21 patients (86%) fulfilled criteria for MIS-C.
“A tricky thing about MIS-C is that it often manifests 4-5 weeks after a child had COVID-19,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study. “MIS-C is associated with characteristic bright red lips and a red tongue that might resemble a strawberry. Such oral findings should prompt rapid evaluation for other signs and symptoms. There can be redness of the eyes or other more nonspecific skin findings (large or small areas of redness on the trunk or limbs, sometimes with surface change), but more importantly, fever, a rapid heartbeat, diarrhea, or breathing issues. The risk with MIS-C is a rapid decline in a child’s health, with admission to an intensive care unit.”
Dr. Andina-Martinez and his colleagues also contrast the skin findings of MIS-C, which are not generally on the hands or feet, with the so-called “COVID toe” or finger phenomenon, which has also been associated with SARS-CoV-2, particularly in children. “Only one of the patients in this series had skin involvement of a finger, and it only appeared after recovery from MIS-C,” Dr. Ko noted. “Distinguishing COVID toes from MIS-C is important, as COVID toes has a very good outcome, while MIS-C can have severe consequences, including protracted heart disease.”
In other findings, patients who presented with mucocutaneous signs tended to be older than those without skin signs and they presented at the emergency department with poor general status and extreme tachycardia. They also had higher C-reactive protein and D-dimer levels and lower lymphocyte counts and faced a more than a 10-fold increased risk of being admitted to the PICU, compared with patients who did not have skin signs (OR, 10.24; P = .003).
In a separate study published online on April 7 in JAMA Dermatology, Zachary E. Holcomb, MD, of the combined dermatology residency program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues presented what is believed to be the first case report of reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) triggered by SARS-CoV-2. RIME is the preferred term for pediatric patients who present with mucositis and rash (often a scant or even absent skin eruption) triggered by various infectious agents.
The patient, a 17-year-old male, presented to the emergency department with 3 days of mouth pain and nonpainful penile erosions. “One week prior, he experienced transient anosmia and ageusia that had since spontaneously resolved,” the researchers wrote. “At that time, he was tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection via nasopharyngeal polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the results of which were positive.”
At presentation, the patient had no fever, his vital signs were normal, and the physical exam revealed shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities. Serum analysis revealed a normal white blood cell count with mild absolute lymphopenia, slightly elevated creatinine level, normal liver function, slightly elevated C-reactive protein level, and normal ferritin level.
Dr. Holcomb and colleagues made a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2–associated RIME based on microbiological results, which revealed positive repeated SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal PCR and negative nasopharyngeal PCR testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, adenovirus, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, human metapneumovirus, influenza A/B, parainfluenza 1 to 4, rhinovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. In addition, titers of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM levels were negative, but Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG levels were elevated.
The lesions resolved with 60 mg of oral prednisone taken daily for 4 days. A recurrence of oral mucositis 3 months later responded to 80 mg oral prednisone taken daily for 6 days.
“It’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 is yet another trigger for RIME,” said Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of the division of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was asked to comment about the case report.
“The take-home message is for clinicians to be aware of this association and distinguish these patients from those with MIS-C, because patients with MIS-C require monitoring and urgent systemic treatment. RIME and MIS-C may potentially be distinguished clinically based on the nature of the mucositis (hemorrhagic and erosive in RIME, dry, cracked lips with ‘strawberry tongue’ in MIS-C) but more importantly patients with RIME lack laboratory evidence of severe systemic inflammation,” such as ESR, CRP, or ferritin, she said.
“A final interesting point in this article was the recurrence of mucositis in this patient, which could mean that recurrent mucositis/recurrent RIME might be yet another manifestation of ‘long-COVID’ (now called post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection) in some patients,” Dr. Kirkorian added. She noted that the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatologic Societies COVID-19 Dermatology Registry and articles like these “provide invaluable ‘hot off the presses’ information for clinicians who are facing the protean manifestations of a novel viral epidemic.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Two and stratifying children at risk for serious, systemic illness due to the virus.
In a single-center descriptive study carried out over a 9-month period, researchers in Madrid found that of 50 hospitalized children infected with COVID-19, 21 (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly exanthem, followed by conjunctival hyperemia without secretion and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue. In addition, 18 (36%) fulfilled criteria for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
“Based on findings in adult patients, the skin manifestations of COVID-19 have been classified under five categories: acral pseudo-chilblain, vesicular eruptions, urticarial lesions, maculopapular eruptions, and livedo or necrosis,” David Andina-Martinez, MD, of Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online on April 2 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Chilblain lesions in healthy children and adolescents have received much attention; these lesions resolve without complications after a few weeks,” they added. “Besides, other cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 in children have been the matter of case reports or small case series. Nevertheless, the mucocutaneous manifestations in hospitalized children infected with SARS-CoV-2 and their implications on the clinical course have not yet been extensively described.”
In an effort to describe the mucocutaneous manifestations in children hospitalized for COVID-19, the researchers evaluated 50 children up to 18 years of age who were admitted between March 1 and Nov. 30, 2020, to Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, which was designated as a pediatric reference center during the peak of the pandemic. The main reasons for admission were respiratory illness (40%) and MIS-C (40%).
Of the 50 patients, 44 (88%) had a positive RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 and 6 (12%) met clinical suspicion criteria and had a negative RT-PCR with a positive IgG serology. In 34 patients (68%), a close contact with a suspected or confirmed case of COVID-19 was referred, while the source of the infection remained unknown in the remaining 16 patients (32%).
The researchers reported that 21 patients (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly maculopapular exanthem (86%), conjunctival hyperemia (81%), and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue (43%). In addition, 18 of the 21 patients (86%) fulfilled criteria for MIS-C.
“A tricky thing about MIS-C is that it often manifests 4-5 weeks after a child had COVID-19,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study. “MIS-C is associated with characteristic bright red lips and a red tongue that might resemble a strawberry. Such oral findings should prompt rapid evaluation for other signs and symptoms. There can be redness of the eyes or other more nonspecific skin findings (large or small areas of redness on the trunk or limbs, sometimes with surface change), but more importantly, fever, a rapid heartbeat, diarrhea, or breathing issues. The risk with MIS-C is a rapid decline in a child’s health, with admission to an intensive care unit.”
Dr. Andina-Martinez and his colleagues also contrast the skin findings of MIS-C, which are not generally on the hands or feet, with the so-called “COVID toe” or finger phenomenon, which has also been associated with SARS-CoV-2, particularly in children. “Only one of the patients in this series had skin involvement of a finger, and it only appeared after recovery from MIS-C,” Dr. Ko noted. “Distinguishing COVID toes from MIS-C is important, as COVID toes has a very good outcome, while MIS-C can have severe consequences, including protracted heart disease.”
In other findings, patients who presented with mucocutaneous signs tended to be older than those without skin signs and they presented at the emergency department with poor general status and extreme tachycardia. They also had higher C-reactive protein and D-dimer levels and lower lymphocyte counts and faced a more than a 10-fold increased risk of being admitted to the PICU, compared with patients who did not have skin signs (OR, 10.24; P = .003).
In a separate study published online on April 7 in JAMA Dermatology, Zachary E. Holcomb, MD, of the combined dermatology residency program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues presented what is believed to be the first case report of reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) triggered by SARS-CoV-2. RIME is the preferred term for pediatric patients who present with mucositis and rash (often a scant or even absent skin eruption) triggered by various infectious agents.
The patient, a 17-year-old male, presented to the emergency department with 3 days of mouth pain and nonpainful penile erosions. “One week prior, he experienced transient anosmia and ageusia that had since spontaneously resolved,” the researchers wrote. “At that time, he was tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection via nasopharyngeal polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the results of which were positive.”
At presentation, the patient had no fever, his vital signs were normal, and the physical exam revealed shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities. Serum analysis revealed a normal white blood cell count with mild absolute lymphopenia, slightly elevated creatinine level, normal liver function, slightly elevated C-reactive protein level, and normal ferritin level.
Dr. Holcomb and colleagues made a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2–associated RIME based on microbiological results, which revealed positive repeated SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal PCR and negative nasopharyngeal PCR testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, adenovirus, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, human metapneumovirus, influenza A/B, parainfluenza 1 to 4, rhinovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. In addition, titers of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM levels were negative, but Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG levels were elevated.
The lesions resolved with 60 mg of oral prednisone taken daily for 4 days. A recurrence of oral mucositis 3 months later responded to 80 mg oral prednisone taken daily for 6 days.
“It’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 is yet another trigger for RIME,” said Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of the division of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was asked to comment about the case report.
“The take-home message is for clinicians to be aware of this association and distinguish these patients from those with MIS-C, because patients with MIS-C require monitoring and urgent systemic treatment. RIME and MIS-C may potentially be distinguished clinically based on the nature of the mucositis (hemorrhagic and erosive in RIME, dry, cracked lips with ‘strawberry tongue’ in MIS-C) but more importantly patients with RIME lack laboratory evidence of severe systemic inflammation,” such as ESR, CRP, or ferritin, she said.
“A final interesting point in this article was the recurrence of mucositis in this patient, which could mean that recurrent mucositis/recurrent RIME might be yet another manifestation of ‘long-COVID’ (now called post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection) in some patients,” Dr. Kirkorian added. She noted that the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatologic Societies COVID-19 Dermatology Registry and articles like these “provide invaluable ‘hot off the presses’ information for clinicians who are facing the protean manifestations of a novel viral epidemic.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
COVID-19 in children: New cases on the rise again
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children rose for the third time in the last 4 weeks, reaching the highest point since mid-February, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
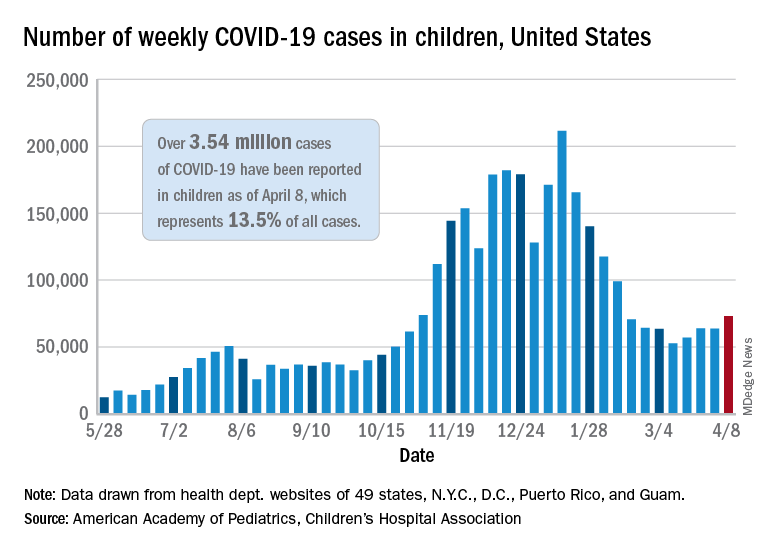
Just over 73,000 cases were reported during the week of April 2-8, up by 14.6% over the previous week. For the latest week, children represented 18.8% of all COVID-19 cases in the United States – also up from the week before and the second-highest proportion seen during the entire pandemic, based on data in the weekly AAP/CHA report.
The 3.54 million children who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 make up 13.5% of all cases reported in the United States during the pandemic, a figure that climbed again after 2 weeks at 13.4%. The overall rate of infection was just over 4,700 cases per 100,000 children as of April 8, the AAP and CHA said.
State-level data show that Vermont, Michigan, and Maine have been the COVID-19 hotspots over the past 2 weeks. The total number of cases has jumped by almost 19% in Vermont since the week of March 19-25, by 18% in Michigan, and by 12% in Maine, according to the report.
Cumulative data also indicate that the children of Vermont are bearing a greater share of the COVID-19 burden – 21.5% of all cases – than in any other state. North Dakota, meanwhile, has the highest cumulative rate of infection at 9,057 cases per 100,000 children, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The number of COVID-19–related deaths in children increased by 8 during the week of April 2-8 and now stands at 292, just 0.06% of all deaths reported in the 43 states (along with New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that provide age distributions for mortality data, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children rose for the third time in the last 4 weeks, reaching the highest point since mid-February, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Just over 73,000 cases were reported during the week of April 2-8, up by 14.6% over the previous week. For the latest week, children represented 18.8% of all COVID-19 cases in the United States – also up from the week before and the second-highest proportion seen during the entire pandemic, based on data in the weekly AAP/CHA report.
The 3.54 million children who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 make up 13.5% of all cases reported in the United States during the pandemic, a figure that climbed again after 2 weeks at 13.4%. The overall rate of infection was just over 4,700 cases per 100,000 children as of April 8, the AAP and CHA said.
State-level data show that Vermont, Michigan, and Maine have been the COVID-19 hotspots over the past 2 weeks. The total number of cases has jumped by almost 19% in Vermont since the week of March 19-25, by 18% in Michigan, and by 12% in Maine, according to the report.
Cumulative data also indicate that the children of Vermont are bearing a greater share of the COVID-19 burden – 21.5% of all cases – than in any other state. North Dakota, meanwhile, has the highest cumulative rate of infection at 9,057 cases per 100,000 children, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The number of COVID-19–related deaths in children increased by 8 during the week of April 2-8 and now stands at 292, just 0.06% of all deaths reported in the 43 states (along with New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that provide age distributions for mortality data, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children rose for the third time in the last 4 weeks, reaching the highest point since mid-February, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Just over 73,000 cases were reported during the week of April 2-8, up by 14.6% over the previous week. For the latest week, children represented 18.8% of all COVID-19 cases in the United States – also up from the week before and the second-highest proportion seen during the entire pandemic, based on data in the weekly AAP/CHA report.
The 3.54 million children who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 make up 13.5% of all cases reported in the United States during the pandemic, a figure that climbed again after 2 weeks at 13.4%. The overall rate of infection was just over 4,700 cases per 100,000 children as of April 8, the AAP and CHA said.
State-level data show that Vermont, Michigan, and Maine have been the COVID-19 hotspots over the past 2 weeks. The total number of cases has jumped by almost 19% in Vermont since the week of March 19-25, by 18% in Michigan, and by 12% in Maine, according to the report.
Cumulative data also indicate that the children of Vermont are bearing a greater share of the COVID-19 burden – 21.5% of all cases – than in any other state. North Dakota, meanwhile, has the highest cumulative rate of infection at 9,057 cases per 100,000 children, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The number of COVID-19–related deaths in children increased by 8 during the week of April 2-8 and now stands at 292, just 0.06% of all deaths reported in the 43 states (along with New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that provide age distributions for mortality data, the AAP and CHA said.
Arthritis drug may curb myocardial damage in acute STEMI
Early use of tocilizumab (Actemra) does not reduce myocardial infarct size but modestly increases myocardial salvage in patients with acute ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI), results of the ASSAIL-MI trial suggest.
“We’re among the first to show that you can actually affect the reperfusion injury through anti-inflammatory treatment – it’s sort of a new attack point for treatments in STEMI,” lead author Kaspar Broch, MD, PhD, Oslo University Hospital Rikshospitalet, said in an interview. “What we do now is reperfuse as soon as we can and then add drugs in order to prevent new events, but we don’t really attack the reperfusion injury that occurs when you perform PCI [percutaneous coronary intervention], which has been shown to actually account for some 50% of the final injury.”
The phase 2, proof-of-concept study was prompted by the team’s earlier work in non-STEMI patients, in which a single dose of the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist cut C-reactive protein (CRP) levels by more than 50% during hospitalization and reduced troponin T release after PCI.
For ASSAIL-MI, Dr. Broch and colleagues randomly assigned 199 patients presenting with acute STEMI within 6 hours of symptom onset to a single intravenous injection of 280 mg tocilizumab or placebo during PCI. Patients, study personnel, and caretakers were blinded to treatment. Data were available for 195 patients for the primary endpoint of myocardial salvage index.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, tocilizumab was associated with a higher adjusted myocardial salvage index on cardiac MRI 3-7 days after PCI than placebo (69.3% vs. 63.6%; P = .04).
The extent of microvascular obstruction was less with tocilizumab (0% vs. 4%; P = .03), as was the area under the curve of CRP during hospitalization (1.9 vs. 8.6 mg/L per hour; P < .001).
The final infarct size at 6 months was 21% lower in the tocilizumab group but the difference did not reach statistical significance (7.2% vs. 9.1% of left ventricular mass; P = .08).
There were no between-group differences in troponin T area under the curve during hospitalization (1,614 vs. 2,357 ng/L per hour; P = .13), N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide concentrations at 6 months (79 vs. 63 ng/L; P = .25), or baseline-adjusted left ventricular end-diastolic volume at 6 months (157 vs. 160 mL; P = .54).
Subgroup analyses suggested the positive effect of tocilizumab on myocardial salvage index is limited to patients presenting at least 3 hours after symptom onset versus 3 hours or less (P = .034), with a trend for greater benefit among men versus women (P = .053).
Dr. Broch noted that the absolute effect of tocilizumab on myocardial necrosis was smaller than anticipated when the trial was designed, which may explain the lack of significant reduction in infarct size.
“We were aiming for patients with larger infarctions than we actually ended up with, which is partly due to the strict inclusion criteria and the fact that, with modern treatments, patients don’t end up with large myocardial infarctions,” he said. “But if they had been larger, I think that 20% absolute reduction would have meant a lot in terms of clinical events.”
The study also used a very modest dose of tocilizumab, compared with that used for inflammatory diseases, to minimize a potential negative effect on myocardial healing, for instance, myocardial ruptures, Dr. Broch said. “I’m not sure whether you gain anything by giving a larger dose.”
Serious adverse events were similar in the tocilizumab and placebo groups (19 vs. 15; P = .57). There were no myocardial ruptures, and no patient died or developed heart failure. LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and liver enzymes increased in the tocilizumab group but were similar at 3 and 6 months.
“IL-6 is a central cytokine involved in all stages of plaque growth, progression, and rupture,” Paul Ridker, MD, MPH, of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and a long-standing investigator in inflammation and atherothrombosis, said in an interview. “These preliminary data in STEMI, like the authors’ prior data in non-STEMI, are consistent with the idea that inhibiting IL-6 could have clinical benefit, a concept that will be taken into a major cardiovascular outcomes trial later this year.”
The cardiovascular outcomes trial, known as ZEUS, will test the novel IL-6 inhibitor ziltivekimab among more than 6,000 very-high-risk atherosclerosis patients who have moderate to severe chronic kidney disease and high sensitivity CRP greater than 2 mg/L, he noted.
Moving beyond IL-1b blockade as done in CANTOS to direct downstream inhibition of IL-6 represents a “logical next scientific step” in the development of anti-inflammatory therapies for acute ischemia and chronic atherosclerosis, Dr. Ridker, who led the CANTOS trial, noted in an accompanying editorial.
“Preventive cardiologists, however, need not wait until outcome trials are complete to use this evolving biological knowledge to their patient’s advantage,” he wrote. “As recently confirmed in the pages of the Journal, exercise, smoking cessation, and a healthy diet reduce both C-reactive protein and IL-6, and clearly have lifelong benefits. Our immediate task is thus to incorporate inflammation inhibition through lifestyle management into our daily practice.”
The study was supported by the South-Eastern Norway Regional Health Authority, Central Norway Regional Health Authority, and Roche, which provided the medicinal products and an unrestricted grant. Dr. Broch has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Ridker has received investigator-initiated research grant support from Kowa, Novartis, Amarin, Pfizer, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and has served as a consultant to Novartis, Janssen, Agepha, Flame, Civi Biopharma, Inflazome, Corvidia, Novo Nordisk, SOCAR, IQVIA, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early use of tocilizumab (Actemra) does not reduce myocardial infarct size but modestly increases myocardial salvage in patients with acute ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI), results of the ASSAIL-MI trial suggest.
“We’re among the first to show that you can actually affect the reperfusion injury through anti-inflammatory treatment – it’s sort of a new attack point for treatments in STEMI,” lead author Kaspar Broch, MD, PhD, Oslo University Hospital Rikshospitalet, said in an interview. “What we do now is reperfuse as soon as we can and then add drugs in order to prevent new events, but we don’t really attack the reperfusion injury that occurs when you perform PCI [percutaneous coronary intervention], which has been shown to actually account for some 50% of the final injury.”
The phase 2, proof-of-concept study was prompted by the team’s earlier work in non-STEMI patients, in which a single dose of the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist cut C-reactive protein (CRP) levels by more than 50% during hospitalization and reduced troponin T release after PCI.
For ASSAIL-MI, Dr. Broch and colleagues randomly assigned 199 patients presenting with acute STEMI within 6 hours of symptom onset to a single intravenous injection of 280 mg tocilizumab or placebo during PCI. Patients, study personnel, and caretakers were blinded to treatment. Data were available for 195 patients for the primary endpoint of myocardial salvage index.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, tocilizumab was associated with a higher adjusted myocardial salvage index on cardiac MRI 3-7 days after PCI than placebo (69.3% vs. 63.6%; P = .04).
The extent of microvascular obstruction was less with tocilizumab (0% vs. 4%; P = .03), as was the area under the curve of CRP during hospitalization (1.9 vs. 8.6 mg/L per hour; P < .001).
The final infarct size at 6 months was 21% lower in the tocilizumab group but the difference did not reach statistical significance (7.2% vs. 9.1% of left ventricular mass; P = .08).
There were no between-group differences in troponin T area under the curve during hospitalization (1,614 vs. 2,357 ng/L per hour; P = .13), N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide concentrations at 6 months (79 vs. 63 ng/L; P = .25), or baseline-adjusted left ventricular end-diastolic volume at 6 months (157 vs. 160 mL; P = .54).
Subgroup analyses suggested the positive effect of tocilizumab on myocardial salvage index is limited to patients presenting at least 3 hours after symptom onset versus 3 hours or less (P = .034), with a trend for greater benefit among men versus women (P = .053).
Dr. Broch noted that the absolute effect of tocilizumab on myocardial necrosis was smaller than anticipated when the trial was designed, which may explain the lack of significant reduction in infarct size.
“We were aiming for patients with larger infarctions than we actually ended up with, which is partly due to the strict inclusion criteria and the fact that, with modern treatments, patients don’t end up with large myocardial infarctions,” he said. “But if they had been larger, I think that 20% absolute reduction would have meant a lot in terms of clinical events.”
The study also used a very modest dose of tocilizumab, compared with that used for inflammatory diseases, to minimize a potential negative effect on myocardial healing, for instance, myocardial ruptures, Dr. Broch said. “I’m not sure whether you gain anything by giving a larger dose.”
Serious adverse events were similar in the tocilizumab and placebo groups (19 vs. 15; P = .57). There were no myocardial ruptures, and no patient died or developed heart failure. LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and liver enzymes increased in the tocilizumab group but were similar at 3 and 6 months.
“IL-6 is a central cytokine involved in all stages of plaque growth, progression, and rupture,” Paul Ridker, MD, MPH, of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and a long-standing investigator in inflammation and atherothrombosis, said in an interview. “These preliminary data in STEMI, like the authors’ prior data in non-STEMI, are consistent with the idea that inhibiting IL-6 could have clinical benefit, a concept that will be taken into a major cardiovascular outcomes trial later this year.”
The cardiovascular outcomes trial, known as ZEUS, will test the novel IL-6 inhibitor ziltivekimab among more than 6,000 very-high-risk atherosclerosis patients who have moderate to severe chronic kidney disease and high sensitivity CRP greater than 2 mg/L, he noted.
Moving beyond IL-1b blockade as done in CANTOS to direct downstream inhibition of IL-6 represents a “logical next scientific step” in the development of anti-inflammatory therapies for acute ischemia and chronic atherosclerosis, Dr. Ridker, who led the CANTOS trial, noted in an accompanying editorial.
“Preventive cardiologists, however, need not wait until outcome trials are complete to use this evolving biological knowledge to their patient’s advantage,” he wrote. “As recently confirmed in the pages of the Journal, exercise, smoking cessation, and a healthy diet reduce both C-reactive protein and IL-6, and clearly have lifelong benefits. Our immediate task is thus to incorporate inflammation inhibition through lifestyle management into our daily practice.”
The study was supported by the South-Eastern Norway Regional Health Authority, Central Norway Regional Health Authority, and Roche, which provided the medicinal products and an unrestricted grant. Dr. Broch has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Ridker has received investigator-initiated research grant support from Kowa, Novartis, Amarin, Pfizer, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and has served as a consultant to Novartis, Janssen, Agepha, Flame, Civi Biopharma, Inflazome, Corvidia, Novo Nordisk, SOCAR, IQVIA, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early use of tocilizumab (Actemra) does not reduce myocardial infarct size but modestly increases myocardial salvage in patients with acute ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI), results of the ASSAIL-MI trial suggest.
“We’re among the first to show that you can actually affect the reperfusion injury through anti-inflammatory treatment – it’s sort of a new attack point for treatments in STEMI,” lead author Kaspar Broch, MD, PhD, Oslo University Hospital Rikshospitalet, said in an interview. “What we do now is reperfuse as soon as we can and then add drugs in order to prevent new events, but we don’t really attack the reperfusion injury that occurs when you perform PCI [percutaneous coronary intervention], which has been shown to actually account for some 50% of the final injury.”
The phase 2, proof-of-concept study was prompted by the team’s earlier work in non-STEMI patients, in which a single dose of the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist cut C-reactive protein (CRP) levels by more than 50% during hospitalization and reduced troponin T release after PCI.
For ASSAIL-MI, Dr. Broch and colleagues randomly assigned 199 patients presenting with acute STEMI within 6 hours of symptom onset to a single intravenous injection of 280 mg tocilizumab or placebo during PCI. Patients, study personnel, and caretakers were blinded to treatment. Data were available for 195 patients for the primary endpoint of myocardial salvage index.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, tocilizumab was associated with a higher adjusted myocardial salvage index on cardiac MRI 3-7 days after PCI than placebo (69.3% vs. 63.6%; P = .04).
The extent of microvascular obstruction was less with tocilizumab (0% vs. 4%; P = .03), as was the area under the curve of CRP during hospitalization (1.9 vs. 8.6 mg/L per hour; P < .001).
The final infarct size at 6 months was 21% lower in the tocilizumab group but the difference did not reach statistical significance (7.2% vs. 9.1% of left ventricular mass; P = .08).
There were no between-group differences in troponin T area under the curve during hospitalization (1,614 vs. 2,357 ng/L per hour; P = .13), N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide concentrations at 6 months (79 vs. 63 ng/L; P = .25), or baseline-adjusted left ventricular end-diastolic volume at 6 months (157 vs. 160 mL; P = .54).
Subgroup analyses suggested the positive effect of tocilizumab on myocardial salvage index is limited to patients presenting at least 3 hours after symptom onset versus 3 hours or less (P = .034), with a trend for greater benefit among men versus women (P = .053).
Dr. Broch noted that the absolute effect of tocilizumab on myocardial necrosis was smaller than anticipated when the trial was designed, which may explain the lack of significant reduction in infarct size.
“We were aiming for patients with larger infarctions than we actually ended up with, which is partly due to the strict inclusion criteria and the fact that, with modern treatments, patients don’t end up with large myocardial infarctions,” he said. “But if they had been larger, I think that 20% absolute reduction would have meant a lot in terms of clinical events.”
The study also used a very modest dose of tocilizumab, compared with that used for inflammatory diseases, to minimize a potential negative effect on myocardial healing, for instance, myocardial ruptures, Dr. Broch said. “I’m not sure whether you gain anything by giving a larger dose.”
Serious adverse events were similar in the tocilizumab and placebo groups (19 vs. 15; P = .57). There were no myocardial ruptures, and no patient died or developed heart failure. LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and liver enzymes increased in the tocilizumab group but were similar at 3 and 6 months.
“IL-6 is a central cytokine involved in all stages of plaque growth, progression, and rupture,” Paul Ridker, MD, MPH, of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and a long-standing investigator in inflammation and atherothrombosis, said in an interview. “These preliminary data in STEMI, like the authors’ prior data in non-STEMI, are consistent with the idea that inhibiting IL-6 could have clinical benefit, a concept that will be taken into a major cardiovascular outcomes trial later this year.”
The cardiovascular outcomes trial, known as ZEUS, will test the novel IL-6 inhibitor ziltivekimab among more than 6,000 very-high-risk atherosclerosis patients who have moderate to severe chronic kidney disease and high sensitivity CRP greater than 2 mg/L, he noted.
Moving beyond IL-1b blockade as done in CANTOS to direct downstream inhibition of IL-6 represents a “logical next scientific step” in the development of anti-inflammatory therapies for acute ischemia and chronic atherosclerosis, Dr. Ridker, who led the CANTOS trial, noted in an accompanying editorial.
“Preventive cardiologists, however, need not wait until outcome trials are complete to use this evolving biological knowledge to their patient’s advantage,” he wrote. “As recently confirmed in the pages of the Journal, exercise, smoking cessation, and a healthy diet reduce both C-reactive protein and IL-6, and clearly have lifelong benefits. Our immediate task is thus to incorporate inflammation inhibition through lifestyle management into our daily practice.”
The study was supported by the South-Eastern Norway Regional Health Authority, Central Norway Regional Health Authority, and Roche, which provided the medicinal products and an unrestricted grant. Dr. Broch has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Ridker has received investigator-initiated research grant support from Kowa, Novartis, Amarin, Pfizer, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and has served as a consultant to Novartis, Janssen, Agepha, Flame, Civi Biopharma, Inflazome, Corvidia, Novo Nordisk, SOCAR, IQVIA, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medtronic recall of almost 240,000 ICDs is class I, FDA says
The Food and Drug Administration has declared Medtronic’s recall of seven models of defibrillating cardiac rhythm devices, caused by a risk for premature battery depletion, as class I, which implies a potential risk for serious injury or death. A total of 444 complaints, but no deaths, have been reported in association with the 239,171 affected devices, the agency said in a statement on April 12, 2021.
Physicians were notified of the company’s recall in early February. It covered implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) and cardiac resynchronization therapy–defibrillator (CRT-D) models Evera, Viva, Brava, Claria, Amplia, Compia, and Visia distributed from Aug. 31, 2012 to May 9, 2018.
The devices could be subject to “an unexpected and rapid decrease in battery life” because of a possible short circuit that could lead to a device-replacement alert “earlier than expected.” Some devices may experience full battery depletion “within as little as 1 day” after such an alert.
“If the user does not respond to the first warning, the device may stop functioning. The likelihood that this issue will occur is constant after approximately 3 years after device use,” the announcement said.
Medtronic recommends device replacement no more than 1 week after such an early warning for patients who are not pacing dependent or who have them for primary prevention, but right away for pacing-dependent patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
The Food and Drug Administration has declared Medtronic’s recall of seven models of defibrillating cardiac rhythm devices, caused by a risk for premature battery depletion, as class I, which implies a potential risk for serious injury or death. A total of 444 complaints, but no deaths, have been reported in association with the 239,171 affected devices, the agency said in a statement on April 12, 2021.
Physicians were notified of the company’s recall in early February. It covered implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) and cardiac resynchronization therapy–defibrillator (CRT-D) models Evera, Viva, Brava, Claria, Amplia, Compia, and Visia distributed from Aug. 31, 2012 to May 9, 2018.
The devices could be subject to “an unexpected and rapid decrease in battery life” because of a possible short circuit that could lead to a device-replacement alert “earlier than expected.” Some devices may experience full battery depletion “within as little as 1 day” after such an alert.
“If the user does not respond to the first warning, the device may stop functioning. The likelihood that this issue will occur is constant after approximately 3 years after device use,” the announcement said.
Medtronic recommends device replacement no more than 1 week after such an early warning for patients who are not pacing dependent or who have them for primary prevention, but right away for pacing-dependent patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
The Food and Drug Administration has declared Medtronic’s recall of seven models of defibrillating cardiac rhythm devices, caused by a risk for premature battery depletion, as class I, which implies a potential risk for serious injury or death. A total of 444 complaints, but no deaths, have been reported in association with the 239,171 affected devices, the agency said in a statement on April 12, 2021.
Physicians were notified of the company’s recall in early February. It covered implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) and cardiac resynchronization therapy–defibrillator (CRT-D) models Evera, Viva, Brava, Claria, Amplia, Compia, and Visia distributed from Aug. 31, 2012 to May 9, 2018.
The devices could be subject to “an unexpected and rapid decrease in battery life” because of a possible short circuit that could lead to a device-replacement alert “earlier than expected.” Some devices may experience full battery depletion “within as little as 1 day” after such an alert.
“If the user does not respond to the first warning, the device may stop functioning. The likelihood that this issue will occur is constant after approximately 3 years after device use,” the announcement said.
Medtronic recommends device replacement no more than 1 week after such an early warning for patients who are not pacing dependent or who have them for primary prevention, but right away for pacing-dependent patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
Next winter may be rough: Models predict ‘considerable surge’ of COVID
It’s likely the United States will see another surge of COVID-19 this winter, warned Christopher Murray, MD, director of the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington in Seattle.
Speaking at the national conference of State of Reform on April 8, Dr. Murray cited the seasonality of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which wanes in the summer and waxes in the winter. The “optimistic forecast” of IHME, which has modeled the course of the pandemic for the past 13 months, is that daily deaths will rise a bit in the next month, then decline from May through August, he said.
“Summer should be fairly quiet in terms of COVID, if vaccinations rise and people don’t stop wearing masks,” Dr. Murray said.
But he added that “a considerable surge will occur over next winter,” because the new variants are more transmissible, and people will likely relax social distancing and mask wearing. The IHME predicts that the percentage of Americans who usually don masks will decline from 73% today to 21% by Aug. 1.
With a rapid decline in mask use and a rise in mobility, there will still be more than 1,000 deaths each day by July 1, Dr. Murray said. In a forecast released the day after Dr. Murray spoke, the IHME predicted that by Aug. 1, there will be a total of 618,523 U.S. deaths from COVID-19. Deaths could be as high as 696,651 if mobility among the vaccinated returns to prepandemic levels, the institute forecasts.
Based on cell phone data, Dr. Murray said, the amount of mobility in the United States has already risen to the level of March 2020, when the pandemic was just getting underway.
Decreased infections
If there’s one piece of good news in the latest IHME report, it’s that the estimated number of people infected (including those not tested) will drop from 111,581 today to a projected 17,502 on Aug. 1. But in a worst-case scenario, with sharply higher mobility among vaccinated people, the case count on that date would only fall to 73,842.
The SARS-CoV-2 variants are another factor of concern. Dr. Murray distinguished between variants like the one first identified in the U.K. (B.1.1.7) and other “escape variants.”
B.1.1.7, which is now the dominant strain in the United States, increases transmission but doesn’t necessarily escape the immune system or vaccines, he explained.
In contrast, if someone is infected with a variant such as the South African or the Brazilian mutations, he said, a previous COVID-19 infection might not protect the person, and vaccines are less effective against those variants.
Cross-variant immunity may range from 0% to 60% for escape variants, based on the slim amount of data now available, Dr. Murray said. In his view, these variants will be the long-term driver of the pandemic in the United States, while the United Kingdom variant is the short-term driver.
The latest data, he said, show that the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines are 75% effective against the escape variants, with lower efficacy for other vaccines. But booster shots may still be required to protect people against some variants.
Human factors
Human behavior will also help determine the course of the pandemic, he noted. Vaccine hesitancy, for example, is still high in the United States.
By the end of May, he predicted, about 180 million people will have received about two doses of vaccine. After that, he said, “vaccination will flatline due to lack of demand.” The two unknowns are how much campaigns to promote vaccination will increase vaccine confidence, and when children will be vaccinated.
In the United States, he said, 69% of adults have been vaccinated or want to get a shot. But that percentage has dropped 5 points since February, and vaccine confidence varies by state.
Dr. Murray emphasized that the winter surge he predicts can be blocked if people change their behaviors. These include a rise in vaccine confidence to 80% and continued mask wearing by most people.
However, if vaccine confidence and mask wearing decline, state governments continue to drop social distancing rules, and the uptake of boosters is low, the winter surge could be more serious, he said.
Double surge
Murray also raised the possibility of a double surge of COVID-19 and influenza this winter. Widely expected last winter, this double surge never materialized here or elsewhere, partly because of mask wearing. But Dr. Murray said it could happen this year: History shows that the flu tends to be stronger in years after weak outbreaks.
He advised hospitals to prepare now for whatever might come later this year. Public health authorities, he said, should speed up vaccination, monitor variants closely with additional sequencing, and try to modify behavior in high-risk groups.
Asked to explain the recent surge of COVID-19 cases in Michigan, Dr. Murray attributed it partly to the spread of the B.1.1.7 (U.K.) variant. But he noted that the U.K. variant has expanded even more widely in some other states that haven’t had an explosive surge like Michigan’s.
Moreover, he noted, Michigan doesn’t have low mask use or high mobility. So the upward spiral of COVID-19 infections there is very concerning, he said.
In regard to the role of children as reservoirs of the virus, Dr. Murray pointed out that views on this have changed around the world. For a while, people thought kids didn’t spread COVID-19 very much. That view shifted when U.K. data showed that child transmission of the B.1.1.7 variant increased by half to 9% of contacts in comparison with the original virus strain.
Dutch data, similarly, showed schools contributing to the latest outbreaks, and some European nations have closed schools. In the United States, the trend is to open them.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s likely the United States will see another surge of COVID-19 this winter, warned Christopher Murray, MD, director of the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington in Seattle.
Speaking at the national conference of State of Reform on April 8, Dr. Murray cited the seasonality of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which wanes in the summer and waxes in the winter. The “optimistic forecast” of IHME, which has modeled the course of the pandemic for the past 13 months, is that daily deaths will rise a bit in the next month, then decline from May through August, he said.
“Summer should be fairly quiet in terms of COVID, if vaccinations rise and people don’t stop wearing masks,” Dr. Murray said.
But he added that “a considerable surge will occur over next winter,” because the new variants are more transmissible, and people will likely relax social distancing and mask wearing. The IHME predicts that the percentage of Americans who usually don masks will decline from 73% today to 21% by Aug. 1.
With a rapid decline in mask use and a rise in mobility, there will still be more than 1,000 deaths each day by July 1, Dr. Murray said. In a forecast released the day after Dr. Murray spoke, the IHME predicted that by Aug. 1, there will be a total of 618,523 U.S. deaths from COVID-19. Deaths could be as high as 696,651 if mobility among the vaccinated returns to prepandemic levels, the institute forecasts.
Based on cell phone data, Dr. Murray said, the amount of mobility in the United States has already risen to the level of March 2020, when the pandemic was just getting underway.
Decreased infections
If there’s one piece of good news in the latest IHME report, it’s that the estimated number of people infected (including those not tested) will drop from 111,581 today to a projected 17,502 on Aug. 1. But in a worst-case scenario, with sharply higher mobility among vaccinated people, the case count on that date would only fall to 73,842.
The SARS-CoV-2 variants are another factor of concern. Dr. Murray distinguished between variants like the one first identified in the U.K. (B.1.1.7) and other “escape variants.”
B.1.1.7, which is now the dominant strain in the United States, increases transmission but doesn’t necessarily escape the immune system or vaccines, he explained.
In contrast, if someone is infected with a variant such as the South African or the Brazilian mutations, he said, a previous COVID-19 infection might not protect the person, and vaccines are less effective against those variants.
Cross-variant immunity may range from 0% to 60% for escape variants, based on the slim amount of data now available, Dr. Murray said. In his view, these variants will be the long-term driver of the pandemic in the United States, while the United Kingdom variant is the short-term driver.
The latest data, he said, show that the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines are 75% effective against the escape variants, with lower efficacy for other vaccines. But booster shots may still be required to protect people against some variants.
Human factors
Human behavior will also help determine the course of the pandemic, he noted. Vaccine hesitancy, for example, is still high in the United States.
By the end of May, he predicted, about 180 million people will have received about two doses of vaccine. After that, he said, “vaccination will flatline due to lack of demand.” The two unknowns are how much campaigns to promote vaccination will increase vaccine confidence, and when children will be vaccinated.
In the United States, he said, 69% of adults have been vaccinated or want to get a shot. But that percentage has dropped 5 points since February, and vaccine confidence varies by state.
Dr. Murray emphasized that the winter surge he predicts can be blocked if people change their behaviors. These include a rise in vaccine confidence to 80% and continued mask wearing by most people.
However, if vaccine confidence and mask wearing decline, state governments continue to drop social distancing rules, and the uptake of boosters is low, the winter surge could be more serious, he said.
Double surge
Murray also raised the possibility of a double surge of COVID-19 and influenza this winter. Widely expected last winter, this double surge never materialized here or elsewhere, partly because of mask wearing. But Dr. Murray said it could happen this year: History shows that the flu tends to be stronger in years after weak outbreaks.
He advised hospitals to prepare now for whatever might come later this year. Public health authorities, he said, should speed up vaccination, monitor variants closely with additional sequencing, and try to modify behavior in high-risk groups.
Asked to explain the recent surge of COVID-19 cases in Michigan, Dr. Murray attributed it partly to the spread of the B.1.1.7 (U.K.) variant. But he noted that the U.K. variant has expanded even more widely in some other states that haven’t had an explosive surge like Michigan’s.
Moreover, he noted, Michigan doesn’t have low mask use or high mobility. So the upward spiral of COVID-19 infections there is very concerning, he said.
In regard to the role of children as reservoirs of the virus, Dr. Murray pointed out that views on this have changed around the world. For a while, people thought kids didn’t spread COVID-19 very much. That view shifted when U.K. data showed that child transmission of the B.1.1.7 variant increased by half to 9% of contacts in comparison with the original virus strain.
Dutch data, similarly, showed schools contributing to the latest outbreaks, and some European nations have closed schools. In the United States, the trend is to open them.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s likely the United States will see another surge of COVID-19 this winter, warned Christopher Murray, MD, director of the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington in Seattle.
Speaking at the national conference of State of Reform on April 8, Dr. Murray cited the seasonality of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which wanes in the summer and waxes in the winter. The “optimistic forecast” of IHME, which has modeled the course of the pandemic for the past 13 months, is that daily deaths will rise a bit in the next month, then decline from May through August, he said.
“Summer should be fairly quiet in terms of COVID, if vaccinations rise and people don’t stop wearing masks,” Dr. Murray said.
But he added that “a considerable surge will occur over next winter,” because the new variants are more transmissible, and people will likely relax social distancing and mask wearing. The IHME predicts that the percentage of Americans who usually don masks will decline from 73% today to 21% by Aug. 1.
With a rapid decline in mask use and a rise in mobility, there will still be more than 1,000 deaths each day by July 1, Dr. Murray said. In a forecast released the day after Dr. Murray spoke, the IHME predicted that by Aug. 1, there will be a total of 618,523 U.S. deaths from COVID-19. Deaths could be as high as 696,651 if mobility among the vaccinated returns to prepandemic levels, the institute forecasts.
Based on cell phone data, Dr. Murray said, the amount of mobility in the United States has already risen to the level of March 2020, when the pandemic was just getting underway.
Decreased infections
If there’s one piece of good news in the latest IHME report, it’s that the estimated number of people infected (including those not tested) will drop from 111,581 today to a projected 17,502 on Aug. 1. But in a worst-case scenario, with sharply higher mobility among vaccinated people, the case count on that date would only fall to 73,842.
The SARS-CoV-2 variants are another factor of concern. Dr. Murray distinguished between variants like the one first identified in the U.K. (B.1.1.7) and other “escape variants.”
B.1.1.7, which is now the dominant strain in the United States, increases transmission but doesn’t necessarily escape the immune system or vaccines, he explained.
In contrast, if someone is infected with a variant such as the South African or the Brazilian mutations, he said, a previous COVID-19 infection might not protect the person, and vaccines are less effective against those variants.
Cross-variant immunity may range from 0% to 60% for escape variants, based on the slim amount of data now available, Dr. Murray said. In his view, these variants will be the long-term driver of the pandemic in the United States, while the United Kingdom variant is the short-term driver.
The latest data, he said, show that the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines are 75% effective against the escape variants, with lower efficacy for other vaccines. But booster shots may still be required to protect people against some variants.
Human factors
Human behavior will also help determine the course of the pandemic, he noted. Vaccine hesitancy, for example, is still high in the United States.
By the end of May, he predicted, about 180 million people will have received about two doses of vaccine. After that, he said, “vaccination will flatline due to lack of demand.” The two unknowns are how much campaigns to promote vaccination will increase vaccine confidence, and when children will be vaccinated.
In the United States, he said, 69% of adults have been vaccinated or want to get a shot. But that percentage has dropped 5 points since February, and vaccine confidence varies by state.
Dr. Murray emphasized that the winter surge he predicts can be blocked if people change their behaviors. These include a rise in vaccine confidence to 80% and continued mask wearing by most people.
However, if vaccine confidence and mask wearing decline, state governments continue to drop social distancing rules, and the uptake of boosters is low, the winter surge could be more serious, he said.
Double surge
Murray also raised the possibility of a double surge of COVID-19 and influenza this winter. Widely expected last winter, this double surge never materialized here or elsewhere, partly because of mask wearing. But Dr. Murray said it could happen this year: History shows that the flu tends to be stronger in years after weak outbreaks.
He advised hospitals to prepare now for whatever might come later this year. Public health authorities, he said, should speed up vaccination, monitor variants closely with additional sequencing, and try to modify behavior in high-risk groups.
Asked to explain the recent surge of COVID-19 cases in Michigan, Dr. Murray attributed it partly to the spread of the B.1.1.7 (U.K.) variant. But he noted that the U.K. variant has expanded even more widely in some other states that haven’t had an explosive surge like Michigan’s.
Moreover, he noted, Michigan doesn’t have low mask use or high mobility. So the upward spiral of COVID-19 infections there is very concerning, he said.
In regard to the role of children as reservoirs of the virus, Dr. Murray pointed out that views on this have changed around the world. For a while, people thought kids didn’t spread COVID-19 very much. That view shifted when U.K. data showed that child transmission of the B.1.1.7 variant increased by half to 9% of contacts in comparison with the original virus strain.
Dutch data, similarly, showed schools contributing to the latest outbreaks, and some European nations have closed schools. In the United States, the trend is to open them.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Remote cardio visits expand access for underserved during COVID
Remote cardiology clinic visits during COVID-19 were used more often by certain traditionally underserved patient groups, but were also associated with less frequent testing and prescribing, new research shows.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has led to an unprecedented shift in ambulatory cardiovascular care from in-person to remote visits,” lead author Neal Yuan, MD, a cardiology fellow at the Smidt Heart Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Their findings were published online April 5 in JAMA Network Open.
“We wanted to explore whether the transition to remote visits was associated with disparities in how patients accessed care, and also how this transition affected diagnostic test ordering and medication prescribing,” Dr. Yuan said.
The researchers used electronic health records data for all ambulatory cardiology visits at an urban, multisite health system in Los Angeles County during two periods: April 1 to Dec. 31, 2019, the pre-COVID era; and April 1 to Dec. 31, 2020, the COVID era.
The investigators compared patient characteristics and frequencies of medication ordering and cardiology-specific testing across four visit types: pre-COVID in person, used as reference; COVID-era in person; COVID-era video; and COVID-era telephone.
The study looked at 176,781 ambulatory cardiology visits. Of these visits, 87,182 were conducted in person in the pre-COVID period; 74,498 were conducted in person in the COVID era; 4,720 were COVID-era video visits; and 10,381 were COVID-era telephone visits.
In the study cohort, 79,572 patients (45.0%) were female, 127,080 patients (71.9%) were non-Hispanic White, and the mean age was 68.1 years (standard deviation, 17.0).
Patients accessing COVID-era remote visits were more likely to be Asian, Black, or Hispanic, to have private insurance, and to have cardiovascular comorbidities, such as hypertension and heart failure.
Also, patients whose visits were conducted by video were significantly younger than patients whose visits were conducted in person or by telephone (P < .001).
In addition, the study found that clinicians ordered fewer diagnostic tests, such as electrocardiograms and echocardiograms, and were less likely to order any medication, in the pre-COVID era than during the COVID era.
“If you don’t have a patient in front of you, it’s much more difficult to get a physical exam or obtain reliable vital signs,” said Dr. Yuan. Communication can sometimes be difficult, often because of technical issues, like a bad connection. “You might be more reticent to get testing or to prescribe medications if you don’t feel confident knowing what the patient’s vital signs are.”
In addition, he added, “a lot of medications used in the cardiology setting require monitoring patients’ kidney function and electrolytes, and if you can’t do that reliably, you might be more cautious about prescribing those types of medications.”
An eye-opening study
Cardiologist Nieca Goldberg, MD, medical director of the New York University Langone womens’ heart program and spokesperson for the American Heart Association, recounted her experience with telemedicine at the height of the pandemic in New York, when everything, including medical outpatient offices, had to close.
“We were experienced with telemedicine because we had started a virtual urgent care program well ahead of the pandemic,” she said. “We started using that to screen people with potential COVID symptoms so that they wouldn’t have to come into the hospital, the medical center, or to the offices and expose people. We learned that it was great to have the telemedicine option from the infectious disease standpoint, and I did visits like that for my own patient population.”
An equally if not more important finding from the study is the fact that telemedicine increased access to care among traditionally underserved demographics, she said.
“This is eye-opening, that you can actually improve access to care by doing telemedicine visits. It was really important to see that telemedicine has added benefit to the way we can see people in the health care system.”
Telemedicine visits had a positive impact at a time when people were isolated at home, Dr. Goldberg said.
“It was a way for them to connect with their doctor and in some ways it was more personal,” she added. “I actually got to meet some of my patients’ family members. It was like making a remote house call.”
Stable cardiology patients can take their blood pressure at home, weigh themselves, and take their own pulse to give an excellent set of vital signs that will indicate how they are doing, said Dr. Goldberg.
“During a remote visit, we can talk to the patient and notice whether or not they are short of breath or coughing, but we can’t listen to their heart or do an EKG or any of the traditional cardiac testing. Still, for someone who is not having symptoms and is able to reliably monitor their blood pressure and weight, a remote visit is sufficient to give you a good sense of how that patient is doing,” she said. “We can talk to them about their medications, any potential side effects, and we can use their blood pressure information to adjust their medications.”
Many patients are becoming more savvy about using tech gadgets and devices to monitor their health.
“Some of my patients were using Apple watches and the Kardia app to address their heart rate. Many had purchased inexpensive pulse oximeters to check their oxygen during the pandemic, and that also reads the pulse,” Dr. Goldberg said.
In-person visits were reserved for symptomatic cardiac patients, she explained.
“Initially during the pandemic, we did mostly telemedicine visits and we organized the office so that each cardiologist would come in 1 day a week to take care of symptomatic cardiac patients. In that way, we were able to socially distance – they provided us with [personal protective equipment]; at NYU there was no problem with that – and nobody waited in the waiting room. To this day, office issues are more efficient and people are not waiting in the waiting room,” she added. “Telemedicine improves access to health care in populations where such access is limited.”
Dr. Yuan’s research is supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Goldberg reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Remote cardiology clinic visits during COVID-19 were used more often by certain traditionally underserved patient groups, but were also associated with less frequent testing and prescribing, new research shows.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has led to an unprecedented shift in ambulatory cardiovascular care from in-person to remote visits,” lead author Neal Yuan, MD, a cardiology fellow at the Smidt Heart Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Their findings were published online April 5 in JAMA Network Open.
“We wanted to explore whether the transition to remote visits was associated with disparities in how patients accessed care, and also how this transition affected diagnostic test ordering and medication prescribing,” Dr. Yuan said.
The researchers used electronic health records data for all ambulatory cardiology visits at an urban, multisite health system in Los Angeles County during two periods: April 1 to Dec. 31, 2019, the pre-COVID era; and April 1 to Dec. 31, 2020, the COVID era.
The investigators compared patient characteristics and frequencies of medication ordering and cardiology-specific testing across four visit types: pre-COVID in person, used as reference; COVID-era in person; COVID-era video; and COVID-era telephone.
The study looked at 176,781 ambulatory cardiology visits. Of these visits, 87,182 were conducted in person in the pre-COVID period; 74,498 were conducted in person in the COVID era; 4,720 were COVID-era video visits; and 10,381 were COVID-era telephone visits.
In the study cohort, 79,572 patients (45.0%) were female, 127,080 patients (71.9%) were non-Hispanic White, and the mean age was 68.1 years (standard deviation, 17.0).
Patients accessing COVID-era remote visits were more likely to be Asian, Black, or Hispanic, to have private insurance, and to have cardiovascular comorbidities, such as hypertension and heart failure.
Also, patients whose visits were conducted by video were significantly younger than patients whose visits were conducted in person or by telephone (P < .001).
In addition, the study found that clinicians ordered fewer diagnostic tests, such as electrocardiograms and echocardiograms, and were less likely to order any medication, in the pre-COVID era than during the COVID era.
“If you don’t have a patient in front of you, it’s much more difficult to get a physical exam or obtain reliable vital signs,” said Dr. Yuan. Communication can sometimes be difficult, often because of technical issues, like a bad connection. “You might be more reticent to get testing or to prescribe medications if you don’t feel confident knowing what the patient’s vital signs are.”
In addition, he added, “a lot of medications used in the cardiology setting require monitoring patients’ kidney function and electrolytes, and if you can’t do that reliably, you might be more cautious about prescribing those types of medications.”
An eye-opening study
Cardiologist Nieca Goldberg, MD, medical director of the New York University Langone womens’ heart program and spokesperson for the American Heart Association, recounted her experience with telemedicine at the height of the pandemic in New York, when everything, including medical outpatient offices, had to close.
“We were experienced with telemedicine because we had started a virtual urgent care program well ahead of the pandemic,” she said. “We started using that to screen people with potential COVID symptoms so that they wouldn’t have to come into the hospital, the medical center, or to the offices and expose people. We learned that it was great to have the telemedicine option from the infectious disease standpoint, and I did visits like that for my own patient population.”
An equally if not more important finding from the study is the fact that telemedicine increased access to care among traditionally underserved demographics, she said.
“This is eye-opening, that you can actually improve access to care by doing telemedicine visits. It was really important to see that telemedicine has added benefit to the way we can see people in the health care system.”
Telemedicine visits had a positive impact at a time when people were isolated at home, Dr. Goldberg said.
“It was a way for them to connect with their doctor and in some ways it was more personal,” she added. “I actually got to meet some of my patients’ family members. It was like making a remote house call.”
Stable cardiology patients can take their blood pressure at home, weigh themselves, and take their own pulse to give an excellent set of vital signs that will indicate how they are doing, said Dr. Goldberg.
“During a remote visit, we can talk to the patient and notice whether or not they are short of breath or coughing, but we can’t listen to their heart or do an EKG or any of the traditional cardiac testing. Still, for someone who is not having symptoms and is able to reliably monitor their blood pressure and weight, a remote visit is sufficient to give you a good sense of how that patient is doing,” she said. “We can talk to them about their medications, any potential side effects, and we can use their blood pressure information to adjust their medications.”
Many patients are becoming more savvy about using tech gadgets and devices to monitor their health.
“Some of my patients were using Apple watches and the Kardia app to address their heart rate. Many had purchased inexpensive pulse oximeters to check their oxygen during the pandemic, and that also reads the pulse,” Dr. Goldberg said.
In-person visits were reserved for symptomatic cardiac patients, she explained.
“Initially during the pandemic, we did mostly telemedicine visits and we organized the office so that each cardiologist would come in 1 day a week to take care of symptomatic cardiac patients. In that way, we were able to socially distance – they provided us with [personal protective equipment]; at NYU there was no problem with that – and nobody waited in the waiting room. To this day, office issues are more efficient and people are not waiting in the waiting room,” she added. “Telemedicine improves access to health care in populations where such access is limited.”
Dr. Yuan’s research is supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Goldberg reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Remote cardiology clinic visits during COVID-19 were used more often by certain traditionally underserved patient groups, but were also associated with less frequent testing and prescribing, new research shows.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has led to an unprecedented shift in ambulatory cardiovascular care from in-person to remote visits,” lead author Neal Yuan, MD, a cardiology fellow at the Smidt Heart Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Their findings were published online April 5 in JAMA Network Open.
“We wanted to explore whether the transition to remote visits was associated with disparities in how patients accessed care, and also how this transition affected diagnostic test ordering and medication prescribing,” Dr. Yuan said.
The researchers used electronic health records data for all ambulatory cardiology visits at an urban, multisite health system in Los Angeles County during two periods: April 1 to Dec. 31, 2019, the pre-COVID era; and April 1 to Dec. 31, 2020, the COVID era.
The investigators compared patient characteristics and frequencies of medication ordering and cardiology-specific testing across four visit types: pre-COVID in person, used as reference; COVID-era in person; COVID-era video; and COVID-era telephone.
The study looked at 176,781 ambulatory cardiology visits. Of these visits, 87,182 were conducted in person in the pre-COVID period; 74,498 were conducted in person in the COVID era; 4,720 were COVID-era video visits; and 10,381 were COVID-era telephone visits.
In the study cohort, 79,572 patients (45.0%) were female, 127,080 patients (71.9%) were non-Hispanic White, and the mean age was 68.1 years (standard deviation, 17.0).
Patients accessing COVID-era remote visits were more likely to be Asian, Black, or Hispanic, to have private insurance, and to have cardiovascular comorbidities, such as hypertension and heart failure.
Also, patients whose visits were conducted by video were significantly younger than patients whose visits were conducted in person or by telephone (P < .001).
In addition, the study found that clinicians ordered fewer diagnostic tests, such as electrocardiograms and echocardiograms, and were less likely to order any medication, in the pre-COVID era than during the COVID era.
“If you don’t have a patient in front of you, it’s much more difficult to get a physical exam or obtain reliable vital signs,” said Dr. Yuan. Communication can sometimes be difficult, often because of technical issues, like a bad connection. “You might be more reticent to get testing or to prescribe medications if you don’t feel confident knowing what the patient’s vital signs are.”
In addition, he added, “a lot of medications used in the cardiology setting require monitoring patients’ kidney function and electrolytes, and if you can’t do that reliably, you might be more cautious about prescribing those types of medications.”
An eye-opening study
Cardiologist Nieca Goldberg, MD, medical director of the New York University Langone womens’ heart program and spokesperson for the American Heart Association, recounted her experience with telemedicine at the height of the pandemic in New York, when everything, including medical outpatient offices, had to close.
“We were experienced with telemedicine because we had started a virtual urgent care program well ahead of the pandemic,” she said. “We started using that to screen people with potential COVID symptoms so that they wouldn’t have to come into the hospital, the medical center, or to the offices and expose people. We learned that it was great to have the telemedicine option from the infectious disease standpoint, and I did visits like that for my own patient population.”
An equally if not more important finding from the study is the fact that telemedicine increased access to care among traditionally underserved demographics, she said.
“This is eye-opening, that you can actually improve access to care by doing telemedicine visits. It was really important to see that telemedicine has added benefit to the way we can see people in the health care system.”
Telemedicine visits had a positive impact at a time when people were isolated at home, Dr. Goldberg said.
“It was a way for them to connect with their doctor and in some ways it was more personal,” she added. “I actually got to meet some of my patients’ family members. It was like making a remote house call.”
Stable cardiology patients can take their blood pressure at home, weigh themselves, and take their own pulse to give an excellent set of vital signs that will indicate how they are doing, said Dr. Goldberg.
“During a remote visit, we can talk to the patient and notice whether or not they are short of breath or coughing, but we can’t listen to their heart or do an EKG or any of the traditional cardiac testing. Still, for someone who is not having symptoms and is able to reliably monitor their blood pressure and weight, a remote visit is sufficient to give you a good sense of how that patient is doing,” she said. “We can talk to them about their medications, any potential side effects, and we can use their blood pressure information to adjust their medications.”
Many patients are becoming more savvy about using tech gadgets and devices to monitor their health.
“Some of my patients were using Apple watches and the Kardia app to address their heart rate. Many had purchased inexpensive pulse oximeters to check their oxygen during the pandemic, and that also reads the pulse,” Dr. Goldberg said.
In-person visits were reserved for symptomatic cardiac patients, she explained.
“Initially during the pandemic, we did mostly telemedicine visits and we organized the office so that each cardiologist would come in 1 day a week to take care of symptomatic cardiac patients. In that way, we were able to socially distance – they provided us with [personal protective equipment]; at NYU there was no problem with that – and nobody waited in the waiting room. To this day, office issues are more efficient and people are not waiting in the waiting room,” she added. “Telemedicine improves access to health care in populations where such access is limited.”
Dr. Yuan’s research is supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Goldberg reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA, CDC urge pause of J&J COVID vaccine
The Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on April 13 recommended that use of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine be paused after reports of blood clots in patients receiving the shot, the agencies have announced.
In a statement, FDA said 6.8 million doses of the J&J vaccine have been administered and the agency is investigating six reported cases of a rare and severe blood clot occurring in patients who received the vaccine.
The pause is intended to give time to alert the public to this "very rare" condition, experts said during a joint CDC-FDA media briefing April 13.
"It was clear to us that we needed to alert the public," Janet Woodcock, MD, acting FDA commissioner, said. The move also will allow "time for the healthcare community to learn what they need to know about how to diagnose, treat and report" any additional cases.
The CDC will convene a meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on April 14 to review the cases.
"I know the information today will be very concerning to Americans who have already received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine," said Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director at the CDC.
"For people who got the vaccine more than one month ago, the risk is very low at this time," she added. "For people who recently got the vaccine, in the last couple of weeks, look for symptoms."
Headache, leg pain, abdominal pain, and shortness of breath were among the reported symptoms. All six cases arose within 6 to 13 days of receipt of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
Traditional treatment dangerous
Importantly, treatment for traditional blood clots, such as the drug heparin, should not be used for these clots. "The issue here with these types of blood clots is that if one administers the standard treatment we give for blood clots, one can cause tremendous harm or it can be fatal," said Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research.
If health care providers see people with these symptoms along with a low platelet count or blood clots, they should ask about any recent vaccinations, Dr. Marks added.
Headache is a common side effect of COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Marks said, but it typically happens within a day or two. In contrast, the headaches associated with these blood clots come 1 to 2 weeks later and were very severe.
Not all of the six women involved in the events had a pre-existing condition or risk factor, Dr. Schuchat said.
Severe but 'extremely rare'
To put the numbers in context, the six reported events occurred among millions of people who received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine to date.
"There have been six reports of a severe stroke-like illness due to low platelet count and more than six million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine have been administered so far," Dr. Schuchat said.
"I would like to stress these events are extremely rare," Dr. Woodcock said, "but we take all reports of adverse events after vaccination very seriously."
The company response
Johnson & Johnson in a statement said, "We are aware of an extremely rare disorder involving people with blood clots in combination with low platelets in a small number of individuals who have received our COVID-19 vaccine. The United States Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are reviewing data involving six reported U.S. cases out of more than 6.8 million doses administered. Out of an abundance of caution, the CDC and FDA have recommended a pause in the use of our vaccine."
The company said they are also reviewing these cases with European regulators and "we have made the decision to proactively delay the rollout of our vaccine in Europe."
Overall vaccinations continuing apace
"This announcement will not have a significant impact on our vaccination plan. Johnson & Johnson vaccine makes up less than 5% of the recorded shots in arms in the United States to date," Jeff Zients, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator, said in a statement.
"Based on actions taken by the president earlier this year, the United States has secured enough Pfizer and Moderna doses for 300 million Americans. We are working now with our state and federal partners to get anyone scheduled for a J&J vaccine quickly rescheduled for a Pfizer or Moderna vaccine," he added.
The likely duration of the pause remains unclear.
"I know this has been a long and difficult pandemic, and people are tired of the steps they have to take," Dr. Schuchat said. "Steps taken today make sure the health care system is ready to diagnose, treat and report [any additional cases] and the public has the information necessary to stay safe."
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
This article was updated 4/13/21.
The Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on April 13 recommended that use of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine be paused after reports of blood clots in patients receiving the shot, the agencies have announced.
In a statement, FDA said 6.8 million doses of the J&J vaccine have been administered and the agency is investigating six reported cases of a rare and severe blood clot occurring in patients who received the vaccine.
The pause is intended to give time to alert the public to this "very rare" condition, experts said during a joint CDC-FDA media briefing April 13.
"It was clear to us that we needed to alert the public," Janet Woodcock, MD, acting FDA commissioner, said. The move also will allow "time for the healthcare community to learn what they need to know about how to diagnose, treat and report" any additional cases.
The CDC will convene a meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on April 14 to review the cases.
"I know the information today will be very concerning to Americans who have already received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine," said Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director at the CDC.
"For people who got the vaccine more than one month ago, the risk is very low at this time," she added. "For people who recently got the vaccine, in the last couple of weeks, look for symptoms."
Headache, leg pain, abdominal pain, and shortness of breath were among the reported symptoms. All six cases arose within 6 to 13 days of receipt of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
Traditional treatment dangerous
Importantly, treatment for traditional blood clots, such as the drug heparin, should not be used for these clots. "The issue here with these types of blood clots is that if one administers the standard treatment we give for blood clots, one can cause tremendous harm or it can be fatal," said Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research.
If health care providers see people with these symptoms along with a low platelet count or blood clots, they should ask about any recent vaccinations, Dr. Marks added.
Headache is a common side effect of COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Marks said, but it typically happens within a day or two. In contrast, the headaches associated with these blood clots come 1 to 2 weeks later and were very severe.
Not all of the six women involved in the events had a pre-existing condition or risk factor, Dr. Schuchat said.
Severe but 'extremely rare'
To put the numbers in context, the six reported events occurred among millions of people who received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine to date.
"There have been six reports of a severe stroke-like illness due to low platelet count and more than six million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine have been administered so far," Dr. Schuchat said.
"I would like to stress these events are extremely rare," Dr. Woodcock said, "but we take all reports of adverse events after vaccination very seriously."
The company response
Johnson & Johnson in a statement said, "We are aware of an extremely rare disorder involving people with blood clots in combination with low platelets in a small number of individuals who have received our COVID-19 vaccine. The United States Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are reviewing data involving six reported U.S. cases out of more than 6.8 million doses administered. Out of an abundance of caution, the CDC and FDA have recommended a pause in the use of our vaccine."
The company said they are also reviewing these cases with European regulators and "we have made the decision to proactively delay the rollout of our vaccine in Europe."
Overall vaccinations continuing apace
"This announcement will not have a significant impact on our vaccination plan. Johnson & Johnson vaccine makes up less than 5% of the recorded shots in arms in the United States to date," Jeff Zients, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator, said in a statement.
"Based on actions taken by the president earlier this year, the United States has secured enough Pfizer and Moderna doses for 300 million Americans. We are working now with our state and federal partners to get anyone scheduled for a J&J vaccine quickly rescheduled for a Pfizer or Moderna vaccine," he added.
The likely duration of the pause remains unclear.
"I know this has been a long and difficult pandemic, and people are tired of the steps they have to take," Dr. Schuchat said. "Steps taken today make sure the health care system is ready to diagnose, treat and report [any additional cases] and the public has the information necessary to stay safe."
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
This article was updated 4/13/21.
The Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on April 13 recommended that use of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine be paused after reports of blood clots in patients receiving the shot, the agencies have announced.
In a statement, FDA said 6.8 million doses of the J&J vaccine have been administered and the agency is investigating six reported cases of a rare and severe blood clot occurring in patients who received the vaccine.
The pause is intended to give time to alert the public to this "very rare" condition, experts said during a joint CDC-FDA media briefing April 13.
"It was clear to us that we needed to alert the public," Janet Woodcock, MD, acting FDA commissioner, said. The move also will allow "time for the healthcare community to learn what they need to know about how to diagnose, treat and report" any additional cases.
The CDC will convene a meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on April 14 to review the cases.
"I know the information today will be very concerning to Americans who have already received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine," said Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director at the CDC.
"For people who got the vaccine more than one month ago, the risk is very low at this time," she added. "For people who recently got the vaccine, in the last couple of weeks, look for symptoms."
Headache, leg pain, abdominal pain, and shortness of breath were among the reported symptoms. All six cases arose within 6 to 13 days of receipt of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
Traditional treatment dangerous
Importantly, treatment for traditional blood clots, such as the drug heparin, should not be used for these clots. "The issue here with these types of blood clots is that if one administers the standard treatment we give for blood clots, one can cause tremendous harm or it can be fatal," said Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research.
If health care providers see people with these symptoms along with a low platelet count or blood clots, they should ask about any recent vaccinations, Dr. Marks added.
Headache is a common side effect of COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Marks said, but it typically happens within a day or two. In contrast, the headaches associated with these blood clots come 1 to 2 weeks later and were very severe.
Not all of the six women involved in the events had a pre-existing condition or risk factor, Dr. Schuchat said.
Severe but 'extremely rare'
To put the numbers in context, the six reported events occurred among millions of people who received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine to date.
"There have been six reports of a severe stroke-like illness due to low platelet count and more than six million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine have been administered so far," Dr. Schuchat said.
"I would like to stress these events are extremely rare," Dr. Woodcock said, "but we take all reports of adverse events after vaccination very seriously."
The company response
Johnson & Johnson in a statement said, "We are aware of an extremely rare disorder involving people with blood clots in combination with low platelets in a small number of individuals who have received our COVID-19 vaccine. The United States Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are reviewing data involving six reported U.S. cases out of more than 6.8 million doses administered. Out of an abundance of caution, the CDC and FDA have recommended a pause in the use of our vaccine."
The company said they are also reviewing these cases with European regulators and "we have made the decision to proactively delay the rollout of our vaccine in Europe."
Overall vaccinations continuing apace
"This announcement will not have a significant impact on our vaccination plan. Johnson & Johnson vaccine makes up less than 5% of the recorded shots in arms in the United States to date," Jeff Zients, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator, said in a statement.
"Based on actions taken by the president earlier this year, the United States has secured enough Pfizer and Moderna doses for 300 million Americans. We are working now with our state and federal partners to get anyone scheduled for a J&J vaccine quickly rescheduled for a Pfizer or Moderna vaccine," he added.
The likely duration of the pause remains unclear.
"I know this has been a long and difficult pandemic, and people are tired of the steps they have to take," Dr. Schuchat said. "Steps taken today make sure the health care system is ready to diagnose, treat and report [any additional cases] and the public has the information necessary to stay safe."
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
This article was updated 4/13/21.