User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Vaccination alone won’t counter rise of resistant variants: Study
Relaxation of nonpharmaceutical interventions once vaccination of the population has reached a tipping point short of herd immunity can increase the probability of the emergence of a resistant strain that natural selection then favors, according to new findings of a modeling study published online on July 30, 2021, in Scientific Reports.
Although vaccination is the best strategy for controlling viral spread, changes in our behavior and mindset will be increasingly required to stay ahead of vaccine-resistant strains, according to the authors of the report.
“We have become accustomed to thinking of the pandemic from the point of view of epidemiology, and advised to reduce transmission and the number of people getting sick and the death rate. As the pandemic spreads across years, there will be a new dimension to our thinking, both for policymakers and the public. And that’s the evolutionary perspective,” coauthor Fyodor Kondrashov, PhD, an evolutionary biologist at the Institute of Science and Technology, Klosterneuburg, Austria, said at a press briefing on July 299.
The coming “change of mentality” that Dr. Kondrashov foresees should reassure people that masking and social distancing even after being vaccinated aren’t futile. “It decreases the possibility that a vaccine-resistant strain is running around. We’re not just trying to prevent the spread, but the evolution of novel variants, which are so rare at this point that we haven’t yet identified them,” he said.
The study focused on evolution generically, rather than on specific variants. “We took the classical model used to study epidemiology of pandemics, the SIR [susceptible, infected, recovered] model, and we modified it to study the dynamics of rare mutations associated with emergence of a vaccine-resistant strain,” Simon A. Rella, the lead author of the study and a PhD student at the Institute of Science and Technology, explained at the briefing.
The researchers simulated the probability that a vaccine-resistant strain will emerge in a population of 10,000,000 individuals over 3 years, with vaccinations beginning after the first year. For eight scenarios, rates of infection, recovery, death, vaccination, and mutation and the percentage of individuals with resistant viral strains were factors in the model.
The model also simulated waves of low and high transmission, similar to the effects of large-scale interventions such as lockdowns.
Three factors
The study showed that a trio of factors increases the probability of a vaccine-resistant strain taking hold: slow rates of vaccination, high number of infected individuals, and faster mutation rate
These factors, Mr. Rella said, are obvious to some degree. “Every infected individual is like a mini-bioreactor, increasing the risk that mutations will appear that will endow the virus with the property of avoiding the immune system primed by a vaccine.”
Not as obvious, Mr. Rella added, is that, when most people are vaccinated, a vaccine-resistant strain has an advantage over the original strain and spreads faster.
But we can stop it, he said. “Our model shows that if at the time a vaccine campaign is close to finishing and nonpharmacological interventions are maintained, then there’s a chance to completely remove the vaccine-resistant mutations from the virus population.”
In scenarios in which a resistant strain became established, resistance initially emerged after about 60% of the population had been vaccinated. That makes nonpharmaceutical interventions such as masking and social distancing vitally important. Just under 50% of the U.S. population over the age of 12 has been fully vaccinated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Our results suggest that policymakers and individuals should consider maintaining nonpharmaceutical interventions and transmission-reducing behaviors throughout the entire vaccination period,” the investigators concluded.
A ‘powerful force’
“We hope for the best, that vaccine resistance has not developed, but caution that evolution is a very powerful force, and maintaining some precautions during vaccination may help to control that evolution,” said Dr. Kondrashov.
The investigators are relying on epidemiologists to determine which measures are most effective.
“It’s necessary to vaccinate as many people as fast as possible and as globally as possible and to maintain some level of nonpharmaceutical intervention to ensure rare variants have a chance to be suppressed instead of spread,” concluded Dr. Kondrashov.
He’s pessimistic because many countries are still having difficulty accessing vaccines, and vaccine efficacy wanes slightly over time. The authors warned that “the emergence of a partially or fully vaccine-resistant strain and its eventual establishment appears inevitable.”
The worst-case scenario is familiar to population biologists: rounds of “vaccine development playing catch up in the evolutionary arms race against novel strains,” the authors wrote.
Limitations of the study are that some parameters of the rate of evolution for vaccine-resistant strains aren’t known, and in creating the model, consideration was not given to effects of increased testing, rigorous contact tracing, rates of viral genome sequencing, and travel restrictions.
Rather, the model illustrates general principals by which vaccine resistance can evolve, Dr. Kondrashov said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Relaxation of nonpharmaceutical interventions once vaccination of the population has reached a tipping point short of herd immunity can increase the probability of the emergence of a resistant strain that natural selection then favors, according to new findings of a modeling study published online on July 30, 2021, in Scientific Reports.
Although vaccination is the best strategy for controlling viral spread, changes in our behavior and mindset will be increasingly required to stay ahead of vaccine-resistant strains, according to the authors of the report.
“We have become accustomed to thinking of the pandemic from the point of view of epidemiology, and advised to reduce transmission and the number of people getting sick and the death rate. As the pandemic spreads across years, there will be a new dimension to our thinking, both for policymakers and the public. And that’s the evolutionary perspective,” coauthor Fyodor Kondrashov, PhD, an evolutionary biologist at the Institute of Science and Technology, Klosterneuburg, Austria, said at a press briefing on July 299.
The coming “change of mentality” that Dr. Kondrashov foresees should reassure people that masking and social distancing even after being vaccinated aren’t futile. “It decreases the possibility that a vaccine-resistant strain is running around. We’re not just trying to prevent the spread, but the evolution of novel variants, which are so rare at this point that we haven’t yet identified them,” he said.
The study focused on evolution generically, rather than on specific variants. “We took the classical model used to study epidemiology of pandemics, the SIR [susceptible, infected, recovered] model, and we modified it to study the dynamics of rare mutations associated with emergence of a vaccine-resistant strain,” Simon A. Rella, the lead author of the study and a PhD student at the Institute of Science and Technology, explained at the briefing.
The researchers simulated the probability that a vaccine-resistant strain will emerge in a population of 10,000,000 individuals over 3 years, with vaccinations beginning after the first year. For eight scenarios, rates of infection, recovery, death, vaccination, and mutation and the percentage of individuals with resistant viral strains were factors in the model.
The model also simulated waves of low and high transmission, similar to the effects of large-scale interventions such as lockdowns.
Three factors
The study showed that a trio of factors increases the probability of a vaccine-resistant strain taking hold: slow rates of vaccination, high number of infected individuals, and faster mutation rate
These factors, Mr. Rella said, are obvious to some degree. “Every infected individual is like a mini-bioreactor, increasing the risk that mutations will appear that will endow the virus with the property of avoiding the immune system primed by a vaccine.”
Not as obvious, Mr. Rella added, is that, when most people are vaccinated, a vaccine-resistant strain has an advantage over the original strain and spreads faster.
But we can stop it, he said. “Our model shows that if at the time a vaccine campaign is close to finishing and nonpharmacological interventions are maintained, then there’s a chance to completely remove the vaccine-resistant mutations from the virus population.”
In scenarios in which a resistant strain became established, resistance initially emerged after about 60% of the population had been vaccinated. That makes nonpharmaceutical interventions such as masking and social distancing vitally important. Just under 50% of the U.S. population over the age of 12 has been fully vaccinated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Our results suggest that policymakers and individuals should consider maintaining nonpharmaceutical interventions and transmission-reducing behaviors throughout the entire vaccination period,” the investigators concluded.
A ‘powerful force’
“We hope for the best, that vaccine resistance has not developed, but caution that evolution is a very powerful force, and maintaining some precautions during vaccination may help to control that evolution,” said Dr. Kondrashov.
The investigators are relying on epidemiologists to determine which measures are most effective.
“It’s necessary to vaccinate as many people as fast as possible and as globally as possible and to maintain some level of nonpharmaceutical intervention to ensure rare variants have a chance to be suppressed instead of spread,” concluded Dr. Kondrashov.
He’s pessimistic because many countries are still having difficulty accessing vaccines, and vaccine efficacy wanes slightly over time. The authors warned that “the emergence of a partially or fully vaccine-resistant strain and its eventual establishment appears inevitable.”
The worst-case scenario is familiar to population biologists: rounds of “vaccine development playing catch up in the evolutionary arms race against novel strains,” the authors wrote.
Limitations of the study are that some parameters of the rate of evolution for vaccine-resistant strains aren’t known, and in creating the model, consideration was not given to effects of increased testing, rigorous contact tracing, rates of viral genome sequencing, and travel restrictions.
Rather, the model illustrates general principals by which vaccine resistance can evolve, Dr. Kondrashov said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Relaxation of nonpharmaceutical interventions once vaccination of the population has reached a tipping point short of herd immunity can increase the probability of the emergence of a resistant strain that natural selection then favors, according to new findings of a modeling study published online on July 30, 2021, in Scientific Reports.
Although vaccination is the best strategy for controlling viral spread, changes in our behavior and mindset will be increasingly required to stay ahead of vaccine-resistant strains, according to the authors of the report.
“We have become accustomed to thinking of the pandemic from the point of view of epidemiology, and advised to reduce transmission and the number of people getting sick and the death rate. As the pandemic spreads across years, there will be a new dimension to our thinking, both for policymakers and the public. And that’s the evolutionary perspective,” coauthor Fyodor Kondrashov, PhD, an evolutionary biologist at the Institute of Science and Technology, Klosterneuburg, Austria, said at a press briefing on July 299.
The coming “change of mentality” that Dr. Kondrashov foresees should reassure people that masking and social distancing even after being vaccinated aren’t futile. “It decreases the possibility that a vaccine-resistant strain is running around. We’re not just trying to prevent the spread, but the evolution of novel variants, which are so rare at this point that we haven’t yet identified them,” he said.
The study focused on evolution generically, rather than on specific variants. “We took the classical model used to study epidemiology of pandemics, the SIR [susceptible, infected, recovered] model, and we modified it to study the dynamics of rare mutations associated with emergence of a vaccine-resistant strain,” Simon A. Rella, the lead author of the study and a PhD student at the Institute of Science and Technology, explained at the briefing.
The researchers simulated the probability that a vaccine-resistant strain will emerge in a population of 10,000,000 individuals over 3 years, with vaccinations beginning after the first year. For eight scenarios, rates of infection, recovery, death, vaccination, and mutation and the percentage of individuals with resistant viral strains were factors in the model.
The model also simulated waves of low and high transmission, similar to the effects of large-scale interventions such as lockdowns.
Three factors
The study showed that a trio of factors increases the probability of a vaccine-resistant strain taking hold: slow rates of vaccination, high number of infected individuals, and faster mutation rate
These factors, Mr. Rella said, are obvious to some degree. “Every infected individual is like a mini-bioreactor, increasing the risk that mutations will appear that will endow the virus with the property of avoiding the immune system primed by a vaccine.”
Not as obvious, Mr. Rella added, is that, when most people are vaccinated, a vaccine-resistant strain has an advantage over the original strain and spreads faster.
But we can stop it, he said. “Our model shows that if at the time a vaccine campaign is close to finishing and nonpharmacological interventions are maintained, then there’s a chance to completely remove the vaccine-resistant mutations from the virus population.”
In scenarios in which a resistant strain became established, resistance initially emerged after about 60% of the population had been vaccinated. That makes nonpharmaceutical interventions such as masking and social distancing vitally important. Just under 50% of the U.S. population over the age of 12 has been fully vaccinated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Our results suggest that policymakers and individuals should consider maintaining nonpharmaceutical interventions and transmission-reducing behaviors throughout the entire vaccination period,” the investigators concluded.
A ‘powerful force’
“We hope for the best, that vaccine resistance has not developed, but caution that evolution is a very powerful force, and maintaining some precautions during vaccination may help to control that evolution,” said Dr. Kondrashov.
The investigators are relying on epidemiologists to determine which measures are most effective.
“It’s necessary to vaccinate as many people as fast as possible and as globally as possible and to maintain some level of nonpharmaceutical intervention to ensure rare variants have a chance to be suppressed instead of spread,” concluded Dr. Kondrashov.
He’s pessimistic because many countries are still having difficulty accessing vaccines, and vaccine efficacy wanes slightly over time. The authors warned that “the emergence of a partially or fully vaccine-resistant strain and its eventual establishment appears inevitable.”
The worst-case scenario is familiar to population biologists: rounds of “vaccine development playing catch up in the evolutionary arms race against novel strains,” the authors wrote.
Limitations of the study are that some parameters of the rate of evolution for vaccine-resistant strains aren’t known, and in creating the model, consideration was not given to effects of increased testing, rigorous contact tracing, rates of viral genome sequencing, and travel restrictions.
Rather, the model illustrates general principals by which vaccine resistance can evolve, Dr. Kondrashov said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘War has changed’: CDC says Delta as contagious as chicken pox
Internal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention documents support the high transmission rate of the Delta variant and put the risk in easier to understand terms.
In addition, the agency released a new study that shows that breakthrough infections in the vaccinated make people about as contagious as those who are unvaccinated. The new report, published July 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), also reveals that the Delta variant likely causes more severe COVID-19 illness.
Given these recent findings, the internal CDC slide show advises that the agency should “acknowledge the war has changed.”
A ‘pivotal discovery’
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, said in a statement that the MMWR report demonstrates “that [D]elta infection resulted in similarly high SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in vaccinated and unvaccinated people.
“High viral loads suggest an increased risk of transmission and raised concern that, unlike with other variants, vaccinated people infected with [D]elta can transmit the virus,” she added. “This finding is concerning and was a pivotal discovery leading to CDC’s updated mask recommendation.”
The investigators analyzed 469 COVID-19 cases reported in Massachusetts residents July 3 through 17, 2021. The infections were associated with an outbreak following multiple events and large gatherings in Provincetown in that state’s easternmost Barnstable County, also known as Cape Cod.
Notably, 346 infections, or 74%, of the cases occurred in fully vaccinated individuals. This group had a median age of 42, and 87% were male. Also, 79% of the breakthrough infections were symptomatic.
Researchers also identified the Delta variant in 90% of 133 specimens collected for analysis. Furthermore, viral loads were about the same between samples taken from people who were fully vaccinated and those who were not.
Four of the five people hospitalized were fully vaccinated. No deaths were reported.
The publication of these results was highly anticipated following the CDC’s updated mask recommendations on July 27.
Outside the scope of the MMWR report is the total number of cases associated with the outbreak, including visitors from outside Massachusetts, which now approach 900 infections, NBC Boston reported.
‘Very sobering’ data
“The new information from the CDC around the [D]elta variant is very sobering,” David Hirschwerk, MD, infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said in an interview.
“The CDC is trying to convey and present this uncertain situation clearly to the public based on new, accumulated data,” he said. For example, given the evidence for higher contagiousness of the Delta variant, Dr. Hirschwerk added, “there will be situations where vaccinated people get infected, because the amount of the virus overwhelms the immune protection.
“What is new that is concerning is that people who are vaccinated still have the potential to transmit the virus to the same degree,” he said.
The MMWR study “helps us better understand the question related to whether or not a person who has completed a COVID-19 series can spread the infection,” agreed Michelle Barron, MD, a professor in the division of infectious disease at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
“The message is that, because the [D]elta variant is much more contagious than the original strain, unvaccinated persons need to get vaccinated because it is nearly impossible to avoid the virus indefinitely,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, infectious diseases specialist and epidemiologist at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said when asked to comment.
The new data highlight “that vaccinated persons, if they become sick, should still seek COVID-19 testing and should still isolate, as they are likely contagious,” Dr. Lin added.
More contagious than other infections
The internal CDC slide presentation also puts the new transmission risk in simple terms. Saying that the Delta variant is about as contagious as chicken pox, for example, immediately brings back vivid memories for some of staying indoors and away from friends during childhood or teenage outbreaks.
“A lot of people will remember getting chicken pox and then having their siblings get it shortly thereafter,” Dr. Barron said. “The only key thing to note is that this does not mean that the COVID-19 [D]elta variant mechanism of spread is the same as chicken pox and Ebola. The primary means of spread of COVID-19, even the Delta variant, is via droplets.”
This also means each person infected with the Delta variant could infect an average of eight or nine others.
In contrast, the original strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus was about as infectious as the common cold. In other words, someone was likely to infect about two other people on average.
In addition to the cold, the CDC notes that the Delta variant is now more contagious than Ebola, the seasonal flu, or small pox.
These Delta variant comparisons are one tangible way of explaining why the CDC on July 27 recommended a return to masking in schools and other indoor spaces for people – vaccinated and unvaccinated – in about 70% of the counties across the United States.
In comparing the Delta variant with other infections, “I think the CDC is trying to help people understand a little bit better the situation we now face since the information is so new. We are in a very different position now than just a few weeks ago, and it is hard for people to accept this,” Dr. Hirschwerk said.
The Delta variant is so different that the CDC considers it almost acting like a new virus altogether.
The CDC’s internal documents were first released by The Washington Post on July 29. The slides cite communication challenges for the agency to continue promoting vaccination while also acknowledging that breakthrough cases are occurring and therefore the fully vaccinated, in some instances, are likely infecting others.
Moving back to science talk, the CDC used the recent outbreak in Barnstable County as an example. The cycle threshold, or Ct values, a measure of viral load, were about the same between 80 vaccinated people linked to the outbreak who had a mean Ct value of 21.9, compared with 65 other unvaccinated people with a Ct of 21.5.
Many experts are quick to note that vaccination remains essential, in part because a vaccinated person also walks around with a much lower risk for severe outcomes, hospitalization, and death. In the internal slide show, the CDC points out that vaccination reduces the risk for infection threefold.
“Even with this high amount of virus, [the Delta variant] did not necessarily make the vaccinated individuals as sick,” Dr. Barron said.
In her statement, Dr. Walensky credited collaboration with the Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of Public Health and the CDC for the new data. She also thanked the residents of Barnstable County for participating in interviews done by contact tracers and their willingness to get tested and adhere to safety protocols after learning of their exposure.
Next moves by CDC?
The agency notes that next steps include consideration of prevention measures such as vaccine mandates for healthcare professionals to protect vulnerable populations, universal masking for source control and prevention, and reconsidering other community mitigation strategies.
Asked if this potential policy is appropriate and feasible, Dr. Lin said, “Yes, I believe that every person working in health care should be vaccinated for COVID-19, and it is feasible.”
Dr. Barron agreed as well. “We as health care providers choose to work in health care, and we should be doing everything feasible to ensure that we are protecting our patients and keeping our coworkers safe.”
“Whether you are a health care professional or not, I would urge everyone to get the COVID-19 vaccine, especially as cases across the country continue to rise,” Dr. Hirschwerk said. “Unequivocally vaccines protect you from the virus.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Internal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention documents support the high transmission rate of the Delta variant and put the risk in easier to understand terms.
In addition, the agency released a new study that shows that breakthrough infections in the vaccinated make people about as contagious as those who are unvaccinated. The new report, published July 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), also reveals that the Delta variant likely causes more severe COVID-19 illness.
Given these recent findings, the internal CDC slide show advises that the agency should “acknowledge the war has changed.”
A ‘pivotal discovery’
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, said in a statement that the MMWR report demonstrates “that [D]elta infection resulted in similarly high SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in vaccinated and unvaccinated people.
“High viral loads suggest an increased risk of transmission and raised concern that, unlike with other variants, vaccinated people infected with [D]elta can transmit the virus,” she added. “This finding is concerning and was a pivotal discovery leading to CDC’s updated mask recommendation.”
The investigators analyzed 469 COVID-19 cases reported in Massachusetts residents July 3 through 17, 2021. The infections were associated with an outbreak following multiple events and large gatherings in Provincetown in that state’s easternmost Barnstable County, also known as Cape Cod.
Notably, 346 infections, or 74%, of the cases occurred in fully vaccinated individuals. This group had a median age of 42, and 87% were male. Also, 79% of the breakthrough infections were symptomatic.
Researchers also identified the Delta variant in 90% of 133 specimens collected for analysis. Furthermore, viral loads were about the same between samples taken from people who were fully vaccinated and those who were not.
Four of the five people hospitalized were fully vaccinated. No deaths were reported.
The publication of these results was highly anticipated following the CDC’s updated mask recommendations on July 27.
Outside the scope of the MMWR report is the total number of cases associated with the outbreak, including visitors from outside Massachusetts, which now approach 900 infections, NBC Boston reported.
‘Very sobering’ data
“The new information from the CDC around the [D]elta variant is very sobering,” David Hirschwerk, MD, infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said in an interview.
“The CDC is trying to convey and present this uncertain situation clearly to the public based on new, accumulated data,” he said. For example, given the evidence for higher contagiousness of the Delta variant, Dr. Hirschwerk added, “there will be situations where vaccinated people get infected, because the amount of the virus overwhelms the immune protection.
“What is new that is concerning is that people who are vaccinated still have the potential to transmit the virus to the same degree,” he said.
The MMWR study “helps us better understand the question related to whether or not a person who has completed a COVID-19 series can spread the infection,” agreed Michelle Barron, MD, a professor in the division of infectious disease at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
“The message is that, because the [D]elta variant is much more contagious than the original strain, unvaccinated persons need to get vaccinated because it is nearly impossible to avoid the virus indefinitely,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, infectious diseases specialist and epidemiologist at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said when asked to comment.
The new data highlight “that vaccinated persons, if they become sick, should still seek COVID-19 testing and should still isolate, as they are likely contagious,” Dr. Lin added.
More contagious than other infections
The internal CDC slide presentation also puts the new transmission risk in simple terms. Saying that the Delta variant is about as contagious as chicken pox, for example, immediately brings back vivid memories for some of staying indoors and away from friends during childhood or teenage outbreaks.
“A lot of people will remember getting chicken pox and then having their siblings get it shortly thereafter,” Dr. Barron said. “The only key thing to note is that this does not mean that the COVID-19 [D]elta variant mechanism of spread is the same as chicken pox and Ebola. The primary means of spread of COVID-19, even the Delta variant, is via droplets.”
This also means each person infected with the Delta variant could infect an average of eight or nine others.
In contrast, the original strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus was about as infectious as the common cold. In other words, someone was likely to infect about two other people on average.
In addition to the cold, the CDC notes that the Delta variant is now more contagious than Ebola, the seasonal flu, or small pox.
These Delta variant comparisons are one tangible way of explaining why the CDC on July 27 recommended a return to masking in schools and other indoor spaces for people – vaccinated and unvaccinated – in about 70% of the counties across the United States.
In comparing the Delta variant with other infections, “I think the CDC is trying to help people understand a little bit better the situation we now face since the information is so new. We are in a very different position now than just a few weeks ago, and it is hard for people to accept this,” Dr. Hirschwerk said.
The Delta variant is so different that the CDC considers it almost acting like a new virus altogether.
The CDC’s internal documents were first released by The Washington Post on July 29. The slides cite communication challenges for the agency to continue promoting vaccination while also acknowledging that breakthrough cases are occurring and therefore the fully vaccinated, in some instances, are likely infecting others.
Moving back to science talk, the CDC used the recent outbreak in Barnstable County as an example. The cycle threshold, or Ct values, a measure of viral load, were about the same between 80 vaccinated people linked to the outbreak who had a mean Ct value of 21.9, compared with 65 other unvaccinated people with a Ct of 21.5.
Many experts are quick to note that vaccination remains essential, in part because a vaccinated person also walks around with a much lower risk for severe outcomes, hospitalization, and death. In the internal slide show, the CDC points out that vaccination reduces the risk for infection threefold.
“Even with this high amount of virus, [the Delta variant] did not necessarily make the vaccinated individuals as sick,” Dr. Barron said.
In her statement, Dr. Walensky credited collaboration with the Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of Public Health and the CDC for the new data. She also thanked the residents of Barnstable County for participating in interviews done by contact tracers and their willingness to get tested and adhere to safety protocols after learning of their exposure.
Next moves by CDC?
The agency notes that next steps include consideration of prevention measures such as vaccine mandates for healthcare professionals to protect vulnerable populations, universal masking for source control and prevention, and reconsidering other community mitigation strategies.
Asked if this potential policy is appropriate and feasible, Dr. Lin said, “Yes, I believe that every person working in health care should be vaccinated for COVID-19, and it is feasible.”
Dr. Barron agreed as well. “We as health care providers choose to work in health care, and we should be doing everything feasible to ensure that we are protecting our patients and keeping our coworkers safe.”
“Whether you are a health care professional or not, I would urge everyone to get the COVID-19 vaccine, especially as cases across the country continue to rise,” Dr. Hirschwerk said. “Unequivocally vaccines protect you from the virus.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Internal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention documents support the high transmission rate of the Delta variant and put the risk in easier to understand terms.
In addition, the agency released a new study that shows that breakthrough infections in the vaccinated make people about as contagious as those who are unvaccinated. The new report, published July 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), also reveals that the Delta variant likely causes more severe COVID-19 illness.
Given these recent findings, the internal CDC slide show advises that the agency should “acknowledge the war has changed.”
A ‘pivotal discovery’
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, said in a statement that the MMWR report demonstrates “that [D]elta infection resulted in similarly high SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in vaccinated and unvaccinated people.
“High viral loads suggest an increased risk of transmission and raised concern that, unlike with other variants, vaccinated people infected with [D]elta can transmit the virus,” she added. “This finding is concerning and was a pivotal discovery leading to CDC’s updated mask recommendation.”
The investigators analyzed 469 COVID-19 cases reported in Massachusetts residents July 3 through 17, 2021. The infections were associated with an outbreak following multiple events and large gatherings in Provincetown in that state’s easternmost Barnstable County, also known as Cape Cod.
Notably, 346 infections, or 74%, of the cases occurred in fully vaccinated individuals. This group had a median age of 42, and 87% were male. Also, 79% of the breakthrough infections were symptomatic.
Researchers also identified the Delta variant in 90% of 133 specimens collected for analysis. Furthermore, viral loads were about the same between samples taken from people who were fully vaccinated and those who were not.
Four of the five people hospitalized were fully vaccinated. No deaths were reported.
The publication of these results was highly anticipated following the CDC’s updated mask recommendations on July 27.
Outside the scope of the MMWR report is the total number of cases associated with the outbreak, including visitors from outside Massachusetts, which now approach 900 infections, NBC Boston reported.
‘Very sobering’ data
“The new information from the CDC around the [D]elta variant is very sobering,” David Hirschwerk, MD, infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said in an interview.
“The CDC is trying to convey and present this uncertain situation clearly to the public based on new, accumulated data,” he said. For example, given the evidence for higher contagiousness of the Delta variant, Dr. Hirschwerk added, “there will be situations where vaccinated people get infected, because the amount of the virus overwhelms the immune protection.
“What is new that is concerning is that people who are vaccinated still have the potential to transmit the virus to the same degree,” he said.
The MMWR study “helps us better understand the question related to whether or not a person who has completed a COVID-19 series can spread the infection,” agreed Michelle Barron, MD, a professor in the division of infectious disease at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
“The message is that, because the [D]elta variant is much more contagious than the original strain, unvaccinated persons need to get vaccinated because it is nearly impossible to avoid the virus indefinitely,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, infectious diseases specialist and epidemiologist at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said when asked to comment.
The new data highlight “that vaccinated persons, if they become sick, should still seek COVID-19 testing and should still isolate, as they are likely contagious,” Dr. Lin added.
More contagious than other infections
The internal CDC slide presentation also puts the new transmission risk in simple terms. Saying that the Delta variant is about as contagious as chicken pox, for example, immediately brings back vivid memories for some of staying indoors and away from friends during childhood or teenage outbreaks.
“A lot of people will remember getting chicken pox and then having their siblings get it shortly thereafter,” Dr. Barron said. “The only key thing to note is that this does not mean that the COVID-19 [D]elta variant mechanism of spread is the same as chicken pox and Ebola. The primary means of spread of COVID-19, even the Delta variant, is via droplets.”
This also means each person infected with the Delta variant could infect an average of eight or nine others.
In contrast, the original strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus was about as infectious as the common cold. In other words, someone was likely to infect about two other people on average.
In addition to the cold, the CDC notes that the Delta variant is now more contagious than Ebola, the seasonal flu, or small pox.
These Delta variant comparisons are one tangible way of explaining why the CDC on July 27 recommended a return to masking in schools and other indoor spaces for people – vaccinated and unvaccinated – in about 70% of the counties across the United States.
In comparing the Delta variant with other infections, “I think the CDC is trying to help people understand a little bit better the situation we now face since the information is so new. We are in a very different position now than just a few weeks ago, and it is hard for people to accept this,” Dr. Hirschwerk said.
The Delta variant is so different that the CDC considers it almost acting like a new virus altogether.
The CDC’s internal documents were first released by The Washington Post on July 29. The slides cite communication challenges for the agency to continue promoting vaccination while also acknowledging that breakthrough cases are occurring and therefore the fully vaccinated, in some instances, are likely infecting others.
Moving back to science talk, the CDC used the recent outbreak in Barnstable County as an example. The cycle threshold, or Ct values, a measure of viral load, were about the same between 80 vaccinated people linked to the outbreak who had a mean Ct value of 21.9, compared with 65 other unvaccinated people with a Ct of 21.5.
Many experts are quick to note that vaccination remains essential, in part because a vaccinated person also walks around with a much lower risk for severe outcomes, hospitalization, and death. In the internal slide show, the CDC points out that vaccination reduces the risk for infection threefold.
“Even with this high amount of virus, [the Delta variant] did not necessarily make the vaccinated individuals as sick,” Dr. Barron said.
In her statement, Dr. Walensky credited collaboration with the Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of Public Health and the CDC for the new data. She also thanked the residents of Barnstable County for participating in interviews done by contact tracers and their willingness to get tested and adhere to safety protocols after learning of their exposure.
Next moves by CDC?
The agency notes that next steps include consideration of prevention measures such as vaccine mandates for healthcare professionals to protect vulnerable populations, universal masking for source control and prevention, and reconsidering other community mitigation strategies.
Asked if this potential policy is appropriate and feasible, Dr. Lin said, “Yes, I believe that every person working in health care should be vaccinated for COVID-19, and it is feasible.”
Dr. Barron agreed as well. “We as health care providers choose to work in health care, and we should be doing everything feasible to ensure that we are protecting our patients and keeping our coworkers safe.”
“Whether you are a health care professional or not, I would urge everyone to get the COVID-19 vaccine, especially as cases across the country continue to rise,” Dr. Hirschwerk said. “Unequivocally vaccines protect you from the virus.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DOACs best aspirin after ventricular ablation: STROKE-VT
Catheter ablation has been around a lot longer for ventricular arrhythmia than for atrial fibrillation, but far less is settled about what antithrombotic therapy should follow ventricular ablations, as there have been no big, randomized trials for guidance.
But the evidence base grew stronger this week, and it favors postprocedure treatment with a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) over antiplatelet therapy with aspirin for patients undergoing radiofrequency (RF) ablation to treat left ventricular (LV) arrhythmias.
The 30-day risk for ischemic stroke or transient ischemia attack (TIA) was sharply higher for patients who took daily aspirin after RF ablation for ventricular tachycardia (VT) or premature ventricular contractions (PVC) in a multicenter randomized trial.
Those of its 246 patients who received aspirin were also far more likely to show asymptomatic lesions on cerebral MRI scans performed both 24 hours and 30 days after the procedure.
The findings show the importance of DOAC therapy after ventricular ablation procedures, a setting for which there are no evidence-based guidelines, “to mitigate the risk of systemic thromboembolic events,” said Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park. He spoke at a media presentation on the trial, called STROKE-VT, during the Heart Rhythm Society 2021 Scientific Sessions, held virtually and on-site in Boston.
The risk for stroke and TIA went up in association with several procedural issues, including some that operators might be able to change in order to reach for better outcomes, Dr. Lakkireddy observed.
“Prolonged radiofrequency ablation times, especially in those with low left ventricle ejection fractions, are definitely higher risk,” as are procedures that involved the retrograde transaortic approach for advancing the ablation catheter, rather than a trans-septal approach.
The retrograde transaortic approach should be avoided in such procedures, “whenever it can be avoided,” said Dr. Lakkireddy, who formally presented STROKE-VT at the HRS sessions and is lead author on its report published about the same time in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
The trial has limitations, but “it’s a very important study, and I think that this could become our standard of care for managing anticoagulation after VT and PVC left-sided ablations,” Mina K. Chung, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s presentation.
How patients are treated with antithrombotics after ventricular ablations can vary widely, sometimes based on the operator’s “subjective feeling of how extensive the ablation is,” Christine M. Albert, MD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, not involved in the study, said during the STROKE-VT media briefing.
That’s consistent with the guidelines, which propose oral anticoagulation therapy after more extensive ventricular ablations and antiplatelets when the ablation is more limited – based more on consensus than firm evidence – as described by Jeffrey R. Winterfield, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and Usha Tedrow, MD, MSc, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
“This is really the first randomized trial data, that I know of, that we have on this. So I do think it will be guideline-influencing,” Dr. Albert said.
“This should change practice,” agreed Jonathan P. Piccini, MD, MHS, Duke University, Durham, N.C., also not part of STROKE-VT. “A lot of evidence in the trial is consistent and provides a compelling story, not to mention that, in my opinion, the study probably underestimates the value of DOACs,” he told this news organization.
That’s because patients assigned to DOACs had far longer ablation times, “so their risk was even greater than in the aspirin arm,” Dr. Piccini said. Ablation times averaged 2,095 seconds in the DOAC group, compared with only 1,708 seconds in the aspirin group, probably because the preponderance of VT over PVC ablations for those getting a DOAC was even greater in the aspirin group.
Of the 246 patients assigned to either aspirin or a DOAC, usually a factor Xa inhibitor, 75% had undergone VT ablation and the remainder ablation for PVCs. Their mean age was 60 years and only 18% were women. None had experienced a cerebrovascular event in the previous 3 months.
The 30-day odds ratio for TIA or ischemic stroke in patients who received aspirin, compared with a DOAC, was 12.6 (95% confidence interval, 4.10-39.11; P < .001).
The corresponding OR for asymptomatic cerebral lesions by MRI at 24 hours was 2.15 (95% CI, 1.02-4.54; P = .04) and at 30 days was 3.48 (95% CI, 1.38-8.80; P = .008).
The rate of stroke or TIA was similar in patients who underwent ablation for VT and for PVCs (14% vs. 16%, respectively; P = .70). There were fewer asymptomatic cerebrovascular events by MRI at 24 hours for those undergoing VT ablations (14.7% and 25.8%, respectively; P = .046); but difference between rates attenuated by 30 days (11.4% and 14.5%, respectively; P = .52).
The OR for TIA or stroke associated with the retrograde transaortic approach, performed in about 40% of the patients, compared with the trans-septal approach in the remainder was 2.60 (95% CI, 1.06-6.37; P = .04).
“The study tells us it’s safe and indeed preferable to anticoagulate after an ablation procedure. But the more important finding, perhaps, wasn’t the one related to the core hypothesis. And that was the effect of retrograde access,” Paul A. Friedman, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s formal presentation of the trial.
Whether a ventricular ablation is performed using the retrograde transaortic or trans-septal approach often depends on the location of the ablation targets in the left ventricle. But in some cases it’s a matter of operator preference, Dr. Piccini observed.
“There are some situations where, really, it is better to do retrograde aortic, and there are some cases that are better to do trans-septal. But now there’s going to be a higher burden of proof,” he said. Given the findings of STROKE-VT, operators may need to consider that a ventricular ablation procedure that can be done by the trans-septal route perhaps ought to be consistently done that way.
Dr. Lakkireddy discloses financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Biosense Webster, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and more. Dr. Chung had “nothing relevant to disclose.” Dr. Piccini discloses receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Sanofi, Abbott, ARCA Biopharma, Medtronic, Philips, Biotronik, Allergan, LivaNova, and Myokardia; and research in conjunction with Bayer Healthcare, Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Philips. Dr. Friedman discloses conducting research in conjunction with Medtronic and Abbott; holding intellectual property rights with AliveCor, Inference, Medicool, Eko, and Anumana; and receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Boston Scientific. Dr. Winterfield and Dr. Tedrow had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Catheter ablation has been around a lot longer for ventricular arrhythmia than for atrial fibrillation, but far less is settled about what antithrombotic therapy should follow ventricular ablations, as there have been no big, randomized trials for guidance.
But the evidence base grew stronger this week, and it favors postprocedure treatment with a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) over antiplatelet therapy with aspirin for patients undergoing radiofrequency (RF) ablation to treat left ventricular (LV) arrhythmias.
The 30-day risk for ischemic stroke or transient ischemia attack (TIA) was sharply higher for patients who took daily aspirin after RF ablation for ventricular tachycardia (VT) or premature ventricular contractions (PVC) in a multicenter randomized trial.
Those of its 246 patients who received aspirin were also far more likely to show asymptomatic lesions on cerebral MRI scans performed both 24 hours and 30 days after the procedure.
The findings show the importance of DOAC therapy after ventricular ablation procedures, a setting for which there are no evidence-based guidelines, “to mitigate the risk of systemic thromboembolic events,” said Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park. He spoke at a media presentation on the trial, called STROKE-VT, during the Heart Rhythm Society 2021 Scientific Sessions, held virtually and on-site in Boston.
The risk for stroke and TIA went up in association with several procedural issues, including some that operators might be able to change in order to reach for better outcomes, Dr. Lakkireddy observed.
“Prolonged radiofrequency ablation times, especially in those with low left ventricle ejection fractions, are definitely higher risk,” as are procedures that involved the retrograde transaortic approach for advancing the ablation catheter, rather than a trans-septal approach.
The retrograde transaortic approach should be avoided in such procedures, “whenever it can be avoided,” said Dr. Lakkireddy, who formally presented STROKE-VT at the HRS sessions and is lead author on its report published about the same time in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
The trial has limitations, but “it’s a very important study, and I think that this could become our standard of care for managing anticoagulation after VT and PVC left-sided ablations,” Mina K. Chung, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s presentation.
How patients are treated with antithrombotics after ventricular ablations can vary widely, sometimes based on the operator’s “subjective feeling of how extensive the ablation is,” Christine M. Albert, MD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, not involved in the study, said during the STROKE-VT media briefing.
That’s consistent with the guidelines, which propose oral anticoagulation therapy after more extensive ventricular ablations and antiplatelets when the ablation is more limited – based more on consensus than firm evidence – as described by Jeffrey R. Winterfield, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and Usha Tedrow, MD, MSc, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
“This is really the first randomized trial data, that I know of, that we have on this. So I do think it will be guideline-influencing,” Dr. Albert said.
“This should change practice,” agreed Jonathan P. Piccini, MD, MHS, Duke University, Durham, N.C., also not part of STROKE-VT. “A lot of evidence in the trial is consistent and provides a compelling story, not to mention that, in my opinion, the study probably underestimates the value of DOACs,” he told this news organization.
That’s because patients assigned to DOACs had far longer ablation times, “so their risk was even greater than in the aspirin arm,” Dr. Piccini said. Ablation times averaged 2,095 seconds in the DOAC group, compared with only 1,708 seconds in the aspirin group, probably because the preponderance of VT over PVC ablations for those getting a DOAC was even greater in the aspirin group.
Of the 246 patients assigned to either aspirin or a DOAC, usually a factor Xa inhibitor, 75% had undergone VT ablation and the remainder ablation for PVCs. Their mean age was 60 years and only 18% were women. None had experienced a cerebrovascular event in the previous 3 months.
The 30-day odds ratio for TIA or ischemic stroke in patients who received aspirin, compared with a DOAC, was 12.6 (95% confidence interval, 4.10-39.11; P < .001).
The corresponding OR for asymptomatic cerebral lesions by MRI at 24 hours was 2.15 (95% CI, 1.02-4.54; P = .04) and at 30 days was 3.48 (95% CI, 1.38-8.80; P = .008).
The rate of stroke or TIA was similar in patients who underwent ablation for VT and for PVCs (14% vs. 16%, respectively; P = .70). There were fewer asymptomatic cerebrovascular events by MRI at 24 hours for those undergoing VT ablations (14.7% and 25.8%, respectively; P = .046); but difference between rates attenuated by 30 days (11.4% and 14.5%, respectively; P = .52).
The OR for TIA or stroke associated with the retrograde transaortic approach, performed in about 40% of the patients, compared with the trans-septal approach in the remainder was 2.60 (95% CI, 1.06-6.37; P = .04).
“The study tells us it’s safe and indeed preferable to anticoagulate after an ablation procedure. But the more important finding, perhaps, wasn’t the one related to the core hypothesis. And that was the effect of retrograde access,” Paul A. Friedman, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s formal presentation of the trial.
Whether a ventricular ablation is performed using the retrograde transaortic or trans-septal approach often depends on the location of the ablation targets in the left ventricle. But in some cases it’s a matter of operator preference, Dr. Piccini observed.
“There are some situations where, really, it is better to do retrograde aortic, and there are some cases that are better to do trans-septal. But now there’s going to be a higher burden of proof,” he said. Given the findings of STROKE-VT, operators may need to consider that a ventricular ablation procedure that can be done by the trans-septal route perhaps ought to be consistently done that way.
Dr. Lakkireddy discloses financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Biosense Webster, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and more. Dr. Chung had “nothing relevant to disclose.” Dr. Piccini discloses receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Sanofi, Abbott, ARCA Biopharma, Medtronic, Philips, Biotronik, Allergan, LivaNova, and Myokardia; and research in conjunction with Bayer Healthcare, Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Philips. Dr. Friedman discloses conducting research in conjunction with Medtronic and Abbott; holding intellectual property rights with AliveCor, Inference, Medicool, Eko, and Anumana; and receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Boston Scientific. Dr. Winterfield and Dr. Tedrow had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Catheter ablation has been around a lot longer for ventricular arrhythmia than for atrial fibrillation, but far less is settled about what antithrombotic therapy should follow ventricular ablations, as there have been no big, randomized trials for guidance.
But the evidence base grew stronger this week, and it favors postprocedure treatment with a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) over antiplatelet therapy with aspirin for patients undergoing radiofrequency (RF) ablation to treat left ventricular (LV) arrhythmias.
The 30-day risk for ischemic stroke or transient ischemia attack (TIA) was sharply higher for patients who took daily aspirin after RF ablation for ventricular tachycardia (VT) or premature ventricular contractions (PVC) in a multicenter randomized trial.
Those of its 246 patients who received aspirin were also far more likely to show asymptomatic lesions on cerebral MRI scans performed both 24 hours and 30 days after the procedure.
The findings show the importance of DOAC therapy after ventricular ablation procedures, a setting for which there are no evidence-based guidelines, “to mitigate the risk of systemic thromboembolic events,” said Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park. He spoke at a media presentation on the trial, called STROKE-VT, during the Heart Rhythm Society 2021 Scientific Sessions, held virtually and on-site in Boston.
The risk for stroke and TIA went up in association with several procedural issues, including some that operators might be able to change in order to reach for better outcomes, Dr. Lakkireddy observed.
“Prolonged radiofrequency ablation times, especially in those with low left ventricle ejection fractions, are definitely higher risk,” as are procedures that involved the retrograde transaortic approach for advancing the ablation catheter, rather than a trans-septal approach.
The retrograde transaortic approach should be avoided in such procedures, “whenever it can be avoided,” said Dr. Lakkireddy, who formally presented STROKE-VT at the HRS sessions and is lead author on its report published about the same time in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
The trial has limitations, but “it’s a very important study, and I think that this could become our standard of care for managing anticoagulation after VT and PVC left-sided ablations,” Mina K. Chung, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s presentation.
How patients are treated with antithrombotics after ventricular ablations can vary widely, sometimes based on the operator’s “subjective feeling of how extensive the ablation is,” Christine M. Albert, MD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, not involved in the study, said during the STROKE-VT media briefing.
That’s consistent with the guidelines, which propose oral anticoagulation therapy after more extensive ventricular ablations and antiplatelets when the ablation is more limited – based more on consensus than firm evidence – as described by Jeffrey R. Winterfield, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and Usha Tedrow, MD, MSc, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
“This is really the first randomized trial data, that I know of, that we have on this. So I do think it will be guideline-influencing,” Dr. Albert said.
“This should change practice,” agreed Jonathan P. Piccini, MD, MHS, Duke University, Durham, N.C., also not part of STROKE-VT. “A lot of evidence in the trial is consistent and provides a compelling story, not to mention that, in my opinion, the study probably underestimates the value of DOACs,” he told this news organization.
That’s because patients assigned to DOACs had far longer ablation times, “so their risk was even greater than in the aspirin arm,” Dr. Piccini said. Ablation times averaged 2,095 seconds in the DOAC group, compared with only 1,708 seconds in the aspirin group, probably because the preponderance of VT over PVC ablations for those getting a DOAC was even greater in the aspirin group.
Of the 246 patients assigned to either aspirin or a DOAC, usually a factor Xa inhibitor, 75% had undergone VT ablation and the remainder ablation for PVCs. Their mean age was 60 years and only 18% were women. None had experienced a cerebrovascular event in the previous 3 months.
The 30-day odds ratio for TIA or ischemic stroke in patients who received aspirin, compared with a DOAC, was 12.6 (95% confidence interval, 4.10-39.11; P < .001).
The corresponding OR for asymptomatic cerebral lesions by MRI at 24 hours was 2.15 (95% CI, 1.02-4.54; P = .04) and at 30 days was 3.48 (95% CI, 1.38-8.80; P = .008).
The rate of stroke or TIA was similar in patients who underwent ablation for VT and for PVCs (14% vs. 16%, respectively; P = .70). There were fewer asymptomatic cerebrovascular events by MRI at 24 hours for those undergoing VT ablations (14.7% and 25.8%, respectively; P = .046); but difference between rates attenuated by 30 days (11.4% and 14.5%, respectively; P = .52).
The OR for TIA or stroke associated with the retrograde transaortic approach, performed in about 40% of the patients, compared with the trans-septal approach in the remainder was 2.60 (95% CI, 1.06-6.37; P = .04).
“The study tells us it’s safe and indeed preferable to anticoagulate after an ablation procedure. But the more important finding, perhaps, wasn’t the one related to the core hypothesis. And that was the effect of retrograde access,” Paul A. Friedman, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s formal presentation of the trial.
Whether a ventricular ablation is performed using the retrograde transaortic or trans-septal approach often depends on the location of the ablation targets in the left ventricle. But in some cases it’s a matter of operator preference, Dr. Piccini observed.
“There are some situations where, really, it is better to do retrograde aortic, and there are some cases that are better to do trans-septal. But now there’s going to be a higher burden of proof,” he said. Given the findings of STROKE-VT, operators may need to consider that a ventricular ablation procedure that can be done by the trans-septal route perhaps ought to be consistently done that way.
Dr. Lakkireddy discloses financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Biosense Webster, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and more. Dr. Chung had “nothing relevant to disclose.” Dr. Piccini discloses receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Sanofi, Abbott, ARCA Biopharma, Medtronic, Philips, Biotronik, Allergan, LivaNova, and Myokardia; and research in conjunction with Bayer Healthcare, Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Philips. Dr. Friedman discloses conducting research in conjunction with Medtronic and Abbott; holding intellectual property rights with AliveCor, Inference, Medicool, Eko, and Anumana; and receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Boston Scientific. Dr. Winterfield and Dr. Tedrow had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Even 10 minutes of daily exercise beneficial after ICD implantation
Small increases in daily physical activity are associated with a boost in 1-year survival in patients with heart failure and coronary disease who received an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), new research suggests.
“Our study looked at how much exercise was necessary for a better outcome in patients with prior ICD implantation and, for every 10 minutes of exercise, we saw a 1% reduction in the likelihood of death or hospitalization, which is a pretty profound impact on outcome for just a small amount of additional physical activity per day,” lead author Brett Atwater, MD, told this news organization.
“These improvements were achieved outside of a formal cardiac rehabilitation program, suggesting that the benefits of increased physical activity obtained in cardiac rehabilitation programs may also be achievable at home,” he said.
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) programs have been shown to improve short- and long-term outcomes in patients with heart failure (HF) but continue to be underutilized, especially by women, the elderly, and minorities. Home-based CR could help overcome this limitation but the science behind it is relatively new, noted Dr. Atwater, director of electrophysiology and electrophysiology research, Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Fairfax, Va.
As reported in Circulation Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, the study involved 41,731 Medicare beneficiaries (mean age, 73.5 years) who received an ICD from 2014 to 2016.
ICD heart rate and activity sensor measurements were used to establish a personalized physical activity (PA) threshold for each patient in the first 3 weeks after ICD implantation. Thereafter, the ICD logged PA when the personalized PA threshold was exceeded. The mean baseline PA level was 128.9 minutes/day.
At 3 years’ follow-up, one-quarter of the patients had died and half had been hospitalized for HF. Of the total population, only 3.2% participated in CR.
Compared with nonparticipants, CR participants were more likely to be White (91.0% versus 87.3%), male (75.5% versus 72.2%), and to have diabetes (48.8% versus 44.1%), ischemic heart disease (91.4% versus 82.1%), or congestive heart failure (90.4% versus 83.4%).
CR participants attended a median of 24 sessions, during which time daily PA increased by a mean of 9.7 minutes per day. During the same time, PA decreased by a mean of 1.0 minute per day in non-CR participants (P < .001).
PA levels remained “relatively constant” for the first 36 months of follow-up among CR participants before showing a steep decline, whereas levels gradually declined throughout follow-up among nonparticipants, with a median annual change of –4.5 min/day.
In adjusted analysis, every 10 minutes of increased daily PA was associated with a 1.1% reduced risk for death (hazard ratio, 0.989; 95% confidence interval, 0.979-0.996) and a 1% reduced risk for HF hospitalization (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.986-0.995) at 1-year follow-up (P < .001).
After propensity score was used to match CR participants with nonparticipants by demographic characteristics, comorbidities, and baseline PA level, CR participants had a significantly lower risk for death at 1 year (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.69-0.85). This difference in risk remained at 2- and 3-year follow-ups.
However, when the researchers further adjusted for change in PA during CR or the same time period after device implantation, no differences in mortality were found between CR participants and nonparticipants at 1 year (HR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.82-1.21) or at 2 or 3 years.
The risk for HF hospitalization did not differ between the two groups in either propensity score model.
Unlike wearable devices, implanted devices “don’t give that type of feedback to patients regarding PA levels – only to providers – and it will be interesting to discover whether providing feedback to patients can motivate them to do more physical activity,” Dr. Atwater commented.
The team is currently enrolling patients in a follow-up trial, in which patients will be given feedback from their ICD “to move these data from an interesting observation to something that can drive outcomes,” he said.
Commenting for this news organization, Melissa Tracy, MD, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said the study reiterates the “profound” underutilization of CR.
“Only about 3% of patients who should have qualified for cardiac rehabilitation actually attended, which is startling considering that it has class 1A level of evidence supporting its use,” she said.
Dr. Tracy, who is also a member of the American College of Cardiology’s Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Section Leadership Council, described the study as “another notch in the belt of positive outcomes supporting the need for cardiac rehabilitation” and emphasizing the importance of a home-based alternative.
“One of the reasons women, minorities, and older patients don’t go to cardiac rehabilitation is they have to get there, rely on someone to drive them, or they have other responsibilities – especially women, who are often primary caretakers of others,” she said. “For women and men, the pressure to get back to work and support their families means they don’t have the luxury to go to cardiac rehabilitation.”
Dr. Tracy noted that home-based CR is covered by CMS until the end of 2021. “An important take-home is for providers and patients to understand that they do have a home-based option,” she stated.
Limitations of the study are that only 24% of patients were women, only 6% were Black, and the results might not be generalizable to patients younger than 65 years, note Dr. Atwater and colleagues. Also, previous implantation might have protected the cohort from experiencing arrhythmic death, and it remains unclear if similar results would be obtained in patients without a previous ICD.
This research was funded through the unrestricted Abbott Medical-Duke Health Strategic Alliance Research Grant. Dr. Atwater receives significant research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott Medical, and modest honoraria from Abbott Medical, Medtronic, and Biotronik. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tracy has created cardiac prevention programs with Virtual Health Partners (VHP) and owns the intellectual property and consults with VHP but receives no monetary compensation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Small increases in daily physical activity are associated with a boost in 1-year survival in patients with heart failure and coronary disease who received an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), new research suggests.
“Our study looked at how much exercise was necessary for a better outcome in patients with prior ICD implantation and, for every 10 minutes of exercise, we saw a 1% reduction in the likelihood of death or hospitalization, which is a pretty profound impact on outcome for just a small amount of additional physical activity per day,” lead author Brett Atwater, MD, told this news organization.
“These improvements were achieved outside of a formal cardiac rehabilitation program, suggesting that the benefits of increased physical activity obtained in cardiac rehabilitation programs may also be achievable at home,” he said.
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) programs have been shown to improve short- and long-term outcomes in patients with heart failure (HF) but continue to be underutilized, especially by women, the elderly, and minorities. Home-based CR could help overcome this limitation but the science behind it is relatively new, noted Dr. Atwater, director of electrophysiology and electrophysiology research, Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Fairfax, Va.
As reported in Circulation Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, the study involved 41,731 Medicare beneficiaries (mean age, 73.5 years) who received an ICD from 2014 to 2016.
ICD heart rate and activity sensor measurements were used to establish a personalized physical activity (PA) threshold for each patient in the first 3 weeks after ICD implantation. Thereafter, the ICD logged PA when the personalized PA threshold was exceeded. The mean baseline PA level was 128.9 minutes/day.
At 3 years’ follow-up, one-quarter of the patients had died and half had been hospitalized for HF. Of the total population, only 3.2% participated in CR.
Compared with nonparticipants, CR participants were more likely to be White (91.0% versus 87.3%), male (75.5% versus 72.2%), and to have diabetes (48.8% versus 44.1%), ischemic heart disease (91.4% versus 82.1%), or congestive heart failure (90.4% versus 83.4%).
CR participants attended a median of 24 sessions, during which time daily PA increased by a mean of 9.7 minutes per day. During the same time, PA decreased by a mean of 1.0 minute per day in non-CR participants (P < .001).
PA levels remained “relatively constant” for the first 36 months of follow-up among CR participants before showing a steep decline, whereas levels gradually declined throughout follow-up among nonparticipants, with a median annual change of –4.5 min/day.
In adjusted analysis, every 10 minutes of increased daily PA was associated with a 1.1% reduced risk for death (hazard ratio, 0.989; 95% confidence interval, 0.979-0.996) and a 1% reduced risk for HF hospitalization (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.986-0.995) at 1-year follow-up (P < .001).
After propensity score was used to match CR participants with nonparticipants by demographic characteristics, comorbidities, and baseline PA level, CR participants had a significantly lower risk for death at 1 year (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.69-0.85). This difference in risk remained at 2- and 3-year follow-ups.
However, when the researchers further adjusted for change in PA during CR or the same time period after device implantation, no differences in mortality were found between CR participants and nonparticipants at 1 year (HR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.82-1.21) or at 2 or 3 years.
The risk for HF hospitalization did not differ between the two groups in either propensity score model.
Unlike wearable devices, implanted devices “don’t give that type of feedback to patients regarding PA levels – only to providers – and it will be interesting to discover whether providing feedback to patients can motivate them to do more physical activity,” Dr. Atwater commented.
The team is currently enrolling patients in a follow-up trial, in which patients will be given feedback from their ICD “to move these data from an interesting observation to something that can drive outcomes,” he said.
Commenting for this news organization, Melissa Tracy, MD, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said the study reiterates the “profound” underutilization of CR.
“Only about 3% of patients who should have qualified for cardiac rehabilitation actually attended, which is startling considering that it has class 1A level of evidence supporting its use,” she said.
Dr. Tracy, who is also a member of the American College of Cardiology’s Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Section Leadership Council, described the study as “another notch in the belt of positive outcomes supporting the need for cardiac rehabilitation” and emphasizing the importance of a home-based alternative.
“One of the reasons women, minorities, and older patients don’t go to cardiac rehabilitation is they have to get there, rely on someone to drive them, or they have other responsibilities – especially women, who are often primary caretakers of others,” she said. “For women and men, the pressure to get back to work and support their families means they don’t have the luxury to go to cardiac rehabilitation.”
Dr. Tracy noted that home-based CR is covered by CMS until the end of 2021. “An important take-home is for providers and patients to understand that they do have a home-based option,” she stated.
Limitations of the study are that only 24% of patients were women, only 6% were Black, and the results might not be generalizable to patients younger than 65 years, note Dr. Atwater and colleagues. Also, previous implantation might have protected the cohort from experiencing arrhythmic death, and it remains unclear if similar results would be obtained in patients without a previous ICD.
This research was funded through the unrestricted Abbott Medical-Duke Health Strategic Alliance Research Grant. Dr. Atwater receives significant research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott Medical, and modest honoraria from Abbott Medical, Medtronic, and Biotronik. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tracy has created cardiac prevention programs with Virtual Health Partners (VHP) and owns the intellectual property and consults with VHP but receives no monetary compensation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Small increases in daily physical activity are associated with a boost in 1-year survival in patients with heart failure and coronary disease who received an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), new research suggests.
“Our study looked at how much exercise was necessary for a better outcome in patients with prior ICD implantation and, for every 10 minutes of exercise, we saw a 1% reduction in the likelihood of death or hospitalization, which is a pretty profound impact on outcome for just a small amount of additional physical activity per day,” lead author Brett Atwater, MD, told this news organization.
“These improvements were achieved outside of a formal cardiac rehabilitation program, suggesting that the benefits of increased physical activity obtained in cardiac rehabilitation programs may also be achievable at home,” he said.
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) programs have been shown to improve short- and long-term outcomes in patients with heart failure (HF) but continue to be underutilized, especially by women, the elderly, and minorities. Home-based CR could help overcome this limitation but the science behind it is relatively new, noted Dr. Atwater, director of electrophysiology and electrophysiology research, Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Fairfax, Va.
As reported in Circulation Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, the study involved 41,731 Medicare beneficiaries (mean age, 73.5 years) who received an ICD from 2014 to 2016.
ICD heart rate and activity sensor measurements were used to establish a personalized physical activity (PA) threshold for each patient in the first 3 weeks after ICD implantation. Thereafter, the ICD logged PA when the personalized PA threshold was exceeded. The mean baseline PA level was 128.9 minutes/day.
At 3 years’ follow-up, one-quarter of the patients had died and half had been hospitalized for HF. Of the total population, only 3.2% participated in CR.
Compared with nonparticipants, CR participants were more likely to be White (91.0% versus 87.3%), male (75.5% versus 72.2%), and to have diabetes (48.8% versus 44.1%), ischemic heart disease (91.4% versus 82.1%), or congestive heart failure (90.4% versus 83.4%).
CR participants attended a median of 24 sessions, during which time daily PA increased by a mean of 9.7 minutes per day. During the same time, PA decreased by a mean of 1.0 minute per day in non-CR participants (P < .001).
PA levels remained “relatively constant” for the first 36 months of follow-up among CR participants before showing a steep decline, whereas levels gradually declined throughout follow-up among nonparticipants, with a median annual change of –4.5 min/day.
In adjusted analysis, every 10 minutes of increased daily PA was associated with a 1.1% reduced risk for death (hazard ratio, 0.989; 95% confidence interval, 0.979-0.996) and a 1% reduced risk for HF hospitalization (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.986-0.995) at 1-year follow-up (P < .001).
After propensity score was used to match CR participants with nonparticipants by demographic characteristics, comorbidities, and baseline PA level, CR participants had a significantly lower risk for death at 1 year (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.69-0.85). This difference in risk remained at 2- and 3-year follow-ups.
However, when the researchers further adjusted for change in PA during CR or the same time period after device implantation, no differences in mortality were found between CR participants and nonparticipants at 1 year (HR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.82-1.21) or at 2 or 3 years.
The risk for HF hospitalization did not differ between the two groups in either propensity score model.
Unlike wearable devices, implanted devices “don’t give that type of feedback to patients regarding PA levels – only to providers – and it will be interesting to discover whether providing feedback to patients can motivate them to do more physical activity,” Dr. Atwater commented.
The team is currently enrolling patients in a follow-up trial, in which patients will be given feedback from their ICD “to move these data from an interesting observation to something that can drive outcomes,” he said.
Commenting for this news organization, Melissa Tracy, MD, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said the study reiterates the “profound” underutilization of CR.
“Only about 3% of patients who should have qualified for cardiac rehabilitation actually attended, which is startling considering that it has class 1A level of evidence supporting its use,” she said.
Dr. Tracy, who is also a member of the American College of Cardiology’s Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Section Leadership Council, described the study as “another notch in the belt of positive outcomes supporting the need for cardiac rehabilitation” and emphasizing the importance of a home-based alternative.
“One of the reasons women, minorities, and older patients don’t go to cardiac rehabilitation is they have to get there, rely on someone to drive them, or they have other responsibilities – especially women, who are often primary caretakers of others,” she said. “For women and men, the pressure to get back to work and support their families means they don’t have the luxury to go to cardiac rehabilitation.”
Dr. Tracy noted that home-based CR is covered by CMS until the end of 2021. “An important take-home is for providers and patients to understand that they do have a home-based option,” she stated.
Limitations of the study are that only 24% of patients were women, only 6% were Black, and the results might not be generalizable to patients younger than 65 years, note Dr. Atwater and colleagues. Also, previous implantation might have protected the cohort from experiencing arrhythmic death, and it remains unclear if similar results would be obtained in patients without a previous ICD.
This research was funded through the unrestricted Abbott Medical-Duke Health Strategic Alliance Research Grant. Dr. Atwater receives significant research support from Boston Scientific and Abbott Medical, and modest honoraria from Abbott Medical, Medtronic, and Biotronik. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tracy has created cardiac prevention programs with Virtual Health Partners (VHP) and owns the intellectual property and consults with VHP but receives no monetary compensation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA’s fast-track approval process exposed as lax, in need of reform
an in-depth investigation published in The BMJ has determined.
“Despite the pathway’s good intentions to accelerate ‘the availability of drugs that treat serious diseases,’ experts are concerned that it is now being exploited – to the detriment of patients, who may be prescribed a drug that offers little benefit and possible harm, and to taxpayers,” writes Elisabeth Mahase, clinical reporter at The BMJ, who carried out the analysis.
The FDA’s accelerated approval pathway is intended to provide earlier access to drugs for serious diseases when there is lingering uncertainty at the time of approval regarding the drug’s ultimate clinical benefit.
Required studies rarely completed
As part of this fast-track pathway, drug manufacturers must conduct postapproval, phase 4 confirmatory trials to verify the anticipated clinical benefit. If these trials indicate no benefit, FDA approval can be withdrawn.
However, the analysis of FDA data shows once they are approved drugs are rarely taken off the market.
The BMJ investigation that analyzed data up to the end of 2020 shows that 112 of the 253 (44%) medications granted accelerated approval have not been confirmed to be effective.
In addition, 24 (21%) of these questionable drugs have been on the market for more than 5 years and some have been on the market for more than 20 years – often with a hefty price tag.
Furthermore, only 16 drugs approved through the accelerated approval process have ever been withdrawn, and most were shown to be ineffective, but in some cases the confirmatory trials were never done, Ms. Mahase reports.
For example, the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib (Celebrex), which was granted accelerated approval in 1999 for the treatment of familial adenomatous polyposis, was on the market for 12 years before the FDA finally asked Pfizer to voluntarily withdraw it for this indication because efficacy trials were never completed.
As part of The BMJ’s investigation, Ms. Mahase asked manufacturers of the 24 drugs that have remained on the market for more than 5 years whether they had conducted the required phase 4 confirmatory trials. Six of the drugs had been withdrawn, approved, or postponed.
Of the remaining 18 drugs, the manufacturers provided the relevant trial information for only six. Only four drugmakers had started to recruit patients; two said they were still in discussion with the FDA over the final trial design.
“These products routinely have side effects, but the benefit information is a lot less certain. That’s what we’re concerned about – that we may have drugs on the market that don’t have any benefits, but certainly predictably have harms associated with them,” Huseyin Naci, PhD, MHS, with the London School of Economics, comments in the report.
Call for reform
As reported by this news organization, a 2015 report by the General Accountability Office (GAO) concluded that the FDA does not do an effective job of tracking the clinical efficacy or the safety of drugs with expedited approval after they hit the market.
In April of this year, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) cited a lack of “credible threats” to withdraw approval if companies don’t do confirmatory trials – meaning drugmakers have little incentive to do the trials.
“There are some instances where the companies really do seem to be taking advantage of the accelerated approval pathway and are using it in a way that makes it harder to get at the truth about whether these products really are safe and effective,” Rachel Sachs, JD, MPH, Washington University, St. Louis, said in The BMJ article.
In addition, the authors of a recent viewpoint article in JAMA Internal Medicine assert the recent approval of the controversial anti-amyloid drug aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen) shows that the accelerated approval pathway needs to be reformed.
Despite the concerns, Ms. Mahase said all experts who spoke to The BMJ believe the accelerated approval pathway is still useful and can be beneficial to patients, although some changes are needed.
One effective reform might be to have confirmatory trials designed, and even started, as part of accelerated approval.
“One important piece of the puzzle is for the FDA itself to be tougher on these companies, to hold them to the bargain that they have agreed to, and to take action when the company has not met their obligations,” Ms. Sachs told the journal.
An FDA spokesperson told the BMJ that the agency is “committed to working with sponsors to ensure that confirmatory studies are completed in a timely manner.”
“We expect sponsors to commit all resources needed to move trials forward as effectively as possible, with the aim of completing trials as soon as is feasible, while assuring the quality of the data and the robustness of the results,” the agency said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
an in-depth investigation published in The BMJ has determined.
“Despite the pathway’s good intentions to accelerate ‘the availability of drugs that treat serious diseases,’ experts are concerned that it is now being exploited – to the detriment of patients, who may be prescribed a drug that offers little benefit and possible harm, and to taxpayers,” writes Elisabeth Mahase, clinical reporter at The BMJ, who carried out the analysis.
The FDA’s accelerated approval pathway is intended to provide earlier access to drugs for serious diseases when there is lingering uncertainty at the time of approval regarding the drug’s ultimate clinical benefit.
Required studies rarely completed
As part of this fast-track pathway, drug manufacturers must conduct postapproval, phase 4 confirmatory trials to verify the anticipated clinical benefit. If these trials indicate no benefit, FDA approval can be withdrawn.
However, the analysis of FDA data shows once they are approved drugs are rarely taken off the market.
The BMJ investigation that analyzed data up to the end of 2020 shows that 112 of the 253 (44%) medications granted accelerated approval have not been confirmed to be effective.
In addition, 24 (21%) of these questionable drugs have been on the market for more than 5 years and some have been on the market for more than 20 years – often with a hefty price tag.
Furthermore, only 16 drugs approved through the accelerated approval process have ever been withdrawn, and most were shown to be ineffective, but in some cases the confirmatory trials were never done, Ms. Mahase reports.
For example, the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib (Celebrex), which was granted accelerated approval in 1999 for the treatment of familial adenomatous polyposis, was on the market for 12 years before the FDA finally asked Pfizer to voluntarily withdraw it for this indication because efficacy trials were never completed.
As part of The BMJ’s investigation, Ms. Mahase asked manufacturers of the 24 drugs that have remained on the market for more than 5 years whether they had conducted the required phase 4 confirmatory trials. Six of the drugs had been withdrawn, approved, or postponed.
Of the remaining 18 drugs, the manufacturers provided the relevant trial information for only six. Only four drugmakers had started to recruit patients; two said they were still in discussion with the FDA over the final trial design.
“These products routinely have side effects, but the benefit information is a lot less certain. That’s what we’re concerned about – that we may have drugs on the market that don’t have any benefits, but certainly predictably have harms associated with them,” Huseyin Naci, PhD, MHS, with the London School of Economics, comments in the report.
Call for reform
As reported by this news organization, a 2015 report by the General Accountability Office (GAO) concluded that the FDA does not do an effective job of tracking the clinical efficacy or the safety of drugs with expedited approval after they hit the market.
In April of this year, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) cited a lack of “credible threats” to withdraw approval if companies don’t do confirmatory trials – meaning drugmakers have little incentive to do the trials.
“There are some instances where the companies really do seem to be taking advantage of the accelerated approval pathway and are using it in a way that makes it harder to get at the truth about whether these products really are safe and effective,” Rachel Sachs, JD, MPH, Washington University, St. Louis, said in The BMJ article.
In addition, the authors of a recent viewpoint article in JAMA Internal Medicine assert the recent approval of the controversial anti-amyloid drug aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen) shows that the accelerated approval pathway needs to be reformed.
Despite the concerns, Ms. Mahase said all experts who spoke to The BMJ believe the accelerated approval pathway is still useful and can be beneficial to patients, although some changes are needed.
One effective reform might be to have confirmatory trials designed, and even started, as part of accelerated approval.
“One important piece of the puzzle is for the FDA itself to be tougher on these companies, to hold them to the bargain that they have agreed to, and to take action when the company has not met their obligations,” Ms. Sachs told the journal.
An FDA spokesperson told the BMJ that the agency is “committed to working with sponsors to ensure that confirmatory studies are completed in a timely manner.”
“We expect sponsors to commit all resources needed to move trials forward as effectively as possible, with the aim of completing trials as soon as is feasible, while assuring the quality of the data and the robustness of the results,” the agency said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
an in-depth investigation published in The BMJ has determined.
“Despite the pathway’s good intentions to accelerate ‘the availability of drugs that treat serious diseases,’ experts are concerned that it is now being exploited – to the detriment of patients, who may be prescribed a drug that offers little benefit and possible harm, and to taxpayers,” writes Elisabeth Mahase, clinical reporter at The BMJ, who carried out the analysis.
The FDA’s accelerated approval pathway is intended to provide earlier access to drugs for serious diseases when there is lingering uncertainty at the time of approval regarding the drug’s ultimate clinical benefit.
Required studies rarely completed
As part of this fast-track pathway, drug manufacturers must conduct postapproval, phase 4 confirmatory trials to verify the anticipated clinical benefit. If these trials indicate no benefit, FDA approval can be withdrawn.
However, the analysis of FDA data shows once they are approved drugs are rarely taken off the market.
The BMJ investigation that analyzed data up to the end of 2020 shows that 112 of the 253 (44%) medications granted accelerated approval have not been confirmed to be effective.
In addition, 24 (21%) of these questionable drugs have been on the market for more than 5 years and some have been on the market for more than 20 years – often with a hefty price tag.
Furthermore, only 16 drugs approved through the accelerated approval process have ever been withdrawn, and most were shown to be ineffective, but in some cases the confirmatory trials were never done, Ms. Mahase reports.
For example, the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib (Celebrex), which was granted accelerated approval in 1999 for the treatment of familial adenomatous polyposis, was on the market for 12 years before the FDA finally asked Pfizer to voluntarily withdraw it for this indication because efficacy trials were never completed.
As part of The BMJ’s investigation, Ms. Mahase asked manufacturers of the 24 drugs that have remained on the market for more than 5 years whether they had conducted the required phase 4 confirmatory trials. Six of the drugs had been withdrawn, approved, or postponed.
Of the remaining 18 drugs, the manufacturers provided the relevant trial information for only six. Only four drugmakers had started to recruit patients; two said they were still in discussion with the FDA over the final trial design.
“These products routinely have side effects, but the benefit information is a lot less certain. That’s what we’re concerned about – that we may have drugs on the market that don’t have any benefits, but certainly predictably have harms associated with them,” Huseyin Naci, PhD, MHS, with the London School of Economics, comments in the report.
Call for reform
As reported by this news organization, a 2015 report by the General Accountability Office (GAO) concluded that the FDA does not do an effective job of tracking the clinical efficacy or the safety of drugs with expedited approval after they hit the market.
In April of this year, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) cited a lack of “credible threats” to withdraw approval if companies don’t do confirmatory trials – meaning drugmakers have little incentive to do the trials.
“There are some instances where the companies really do seem to be taking advantage of the accelerated approval pathway and are using it in a way that makes it harder to get at the truth about whether these products really are safe and effective,” Rachel Sachs, JD, MPH, Washington University, St. Louis, said in The BMJ article.
In addition, the authors of a recent viewpoint article in JAMA Internal Medicine assert the recent approval of the controversial anti-amyloid drug aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen) shows that the accelerated approval pathway needs to be reformed.
Despite the concerns, Ms. Mahase said all experts who spoke to The BMJ believe the accelerated approval pathway is still useful and can be beneficial to patients, although some changes are needed.
One effective reform might be to have confirmatory trials designed, and even started, as part of accelerated approval.
“One important piece of the puzzle is for the FDA itself to be tougher on these companies, to hold them to the bargain that they have agreed to, and to take action when the company has not met their obligations,” Ms. Sachs told the journal.
An FDA spokesperson told the BMJ that the agency is “committed to working with sponsors to ensure that confirmatory studies are completed in a timely manner.”
“We expect sponsors to commit all resources needed to move trials forward as effectively as possible, with the aim of completing trials as soon as is feasible, while assuring the quality of the data and the robustness of the results,” the agency said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘A few mutations away’: The threat of a vaccine-proof variant
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, made a dire prediction during a media briefing this week that, if we weren’t already living within the reality of the COVID-19 pandemic, would sound more like a pitch for a movie about a dystopian future.
“For the amount of virus circulating in this country right now largely among unvaccinated people, the largest concern that we in public health and science are worried about is that the virus … [becomes] a very transmissible virus that has the potential to evade our vaccines in terms of how it protects us from severe disease and death,” Dr. Walensky told reporters on July 27.
A new, more elusive variant could be “just a few mutations away,” she said.
“That’s a very prescient comment,” Lewis Nelson, MD, professor and clinical chair of emergency medicine and chief of the division of medical toxicology at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, told this news organization.
“We’ve gone through a few mutations already that have been named, and each one of them gets a little more transmissible,” he said. “That’s normal, natural selection and what you would expect to happen as viruses mutate from one strain to another.”
“What we’ve mostly seen this virus do is evolve to become more infectious,” said Stuart Ray, MD, when also asked to comment. “That is the remarkable feature of Delta – that it is so infectious.”
He said that the SARS-CoV-2 has evolved largely as expected, at least so far. “The potential for this virus to mutate has been something that has been a concern from early on.”
“The viral evolution is a bit like a ticking clock. The more we allow infections to occur, the more likely changes will occur. When we have lots of people infected, we give more chances to the virus to diversify and then adapt to selective pressures,” said Dr. Ray, vice-chair of medicine for data integrity and analytics and professor in the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore.
Dr. Nelson said.
If this occurs, he added, “we will have an ineffective vaccine, essentially. And we’ll be back to where we were last March with a brand-new disease.”
Technology to the rescue?
The flexibility of mRNA vaccines is one potential solution. These vaccines could be more easily and quickly adapted to respond to a new, more vaccine-elusive variant.
“That’s absolutely reassuring,” Dr. Nelson said. For example, if a mutation changes the spike protein and vaccines no longer recognize it, a manufacturer could identify the new protein and incorporate that in a new mRNA vaccine.
“The problem is that some people are not taking the current vaccine,” he added. “I’m not sure what is going to make them take the next vaccine.”
Nothing appears certain
When asked how likely a new strain of SARS-CoV-2 could emerge that gets around vaccine protection, Dr. Nelson said, “I think [what] we’ve learned so far there is no way to predict anything” about this pandemic.
“The best way to prevent the virus from mutating is to prevent hosts, people, from getting sick with it,” he said. “That’s why it’s so important people should get immunized and wear masks.”
Both Dr. Nelson and Dr. Ray pointed out that it is in the best interest of the virus to evolve to be more transmissible and spread to more people. In contrast, a virus that causes people to get so sick that they isolate or die, thus halting transmission, works against viruses surviving evolutionarily.
Some viruses also mutate to become milder over time, but that has not been the case with SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Ray said.
Mutations not the only concern
Viruses have another mechanism that produces new strains, and it works even more quickly than mutations. Recombination, as it’s known, can occur when a person is infected with two different strains of the same virus. If the two versions enter the same cell, the viruses can swap genetic material and produce a third, altogether different strain.
Recombination has already been seen with influenza strains, where H and N genetic segments are swapped to yield H1N1, H1N2, and H3N2 versions of the flu, for example.
“In the early days of SARS-CoV-2 there was so little diversity that recombination did not matter,” Dr. Ray said. However, there are now distinct lineages of the virus circulating globally. If two of these lineages swap segments “this would make a very new viral sequence in one step without having to mutate to gain those differences.”
“The more diverse the strains that are circulating, the bigger a possibility this is,” Dr. Ray said.
Protected, for now
Dr. Walensky’s sober warning came at the same time the CDC released new guidance calling for the wearing of masks indoors in schools and in any location in the country where COVID-19 cases surpass 50 people per 100,000, also known as substantial or high transmission areas.
On a positive note, Dr. Walensky said: “Right now, fortunately, we are not there. The vaccines operate really well in protecting us from severe disease and death.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, made a dire prediction during a media briefing this week that, if we weren’t already living within the reality of the COVID-19 pandemic, would sound more like a pitch for a movie about a dystopian future.
“For the amount of virus circulating in this country right now largely among unvaccinated people, the largest concern that we in public health and science are worried about is that the virus … [becomes] a very transmissible virus that has the potential to evade our vaccines in terms of how it protects us from severe disease and death,” Dr. Walensky told reporters on July 27.
A new, more elusive variant could be “just a few mutations away,” she said.
“That’s a very prescient comment,” Lewis Nelson, MD, professor and clinical chair of emergency medicine and chief of the division of medical toxicology at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, told this news organization.
“We’ve gone through a few mutations already that have been named, and each one of them gets a little more transmissible,” he said. “That’s normal, natural selection and what you would expect to happen as viruses mutate from one strain to another.”
“What we’ve mostly seen this virus do is evolve to become more infectious,” said Stuart Ray, MD, when also asked to comment. “That is the remarkable feature of Delta – that it is so infectious.”
He said that the SARS-CoV-2 has evolved largely as expected, at least so far. “The potential for this virus to mutate has been something that has been a concern from early on.”
“The viral evolution is a bit like a ticking clock. The more we allow infections to occur, the more likely changes will occur. When we have lots of people infected, we give more chances to the virus to diversify and then adapt to selective pressures,” said Dr. Ray, vice-chair of medicine for data integrity and analytics and professor in the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore.
Dr. Nelson said.
If this occurs, he added, “we will have an ineffective vaccine, essentially. And we’ll be back to where we were last March with a brand-new disease.”
Technology to the rescue?
The flexibility of mRNA vaccines is one potential solution. These vaccines could be more easily and quickly adapted to respond to a new, more vaccine-elusive variant.
“That’s absolutely reassuring,” Dr. Nelson said. For example, if a mutation changes the spike protein and vaccines no longer recognize it, a manufacturer could identify the new protein and incorporate that in a new mRNA vaccine.
“The problem is that some people are not taking the current vaccine,” he added. “I’m not sure what is going to make them take the next vaccine.”
Nothing appears certain
When asked how likely a new strain of SARS-CoV-2 could emerge that gets around vaccine protection, Dr. Nelson said, “I think [what] we’ve learned so far there is no way to predict anything” about this pandemic.
“The best way to prevent the virus from mutating is to prevent hosts, people, from getting sick with it,” he said. “That’s why it’s so important people should get immunized and wear masks.”
Both Dr. Nelson and Dr. Ray pointed out that it is in the best interest of the virus to evolve to be more transmissible and spread to more people. In contrast, a virus that causes people to get so sick that they isolate or die, thus halting transmission, works against viruses surviving evolutionarily.
Some viruses also mutate to become milder over time, but that has not been the case with SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Ray said.
Mutations not the only concern
Viruses have another mechanism that produces new strains, and it works even more quickly than mutations. Recombination, as it’s known, can occur when a person is infected with two different strains of the same virus. If the two versions enter the same cell, the viruses can swap genetic material and produce a third, altogether different strain.
Recombination has already been seen with influenza strains, where H and N genetic segments are swapped to yield H1N1, H1N2, and H3N2 versions of the flu, for example.
“In the early days of SARS-CoV-2 there was so little diversity that recombination did not matter,” Dr. Ray said. However, there are now distinct lineages of the virus circulating globally. If two of these lineages swap segments “this would make a very new viral sequence in one step without having to mutate to gain those differences.”
“The more diverse the strains that are circulating, the bigger a possibility this is,” Dr. Ray said.
Protected, for now
Dr. Walensky’s sober warning came at the same time the CDC released new guidance calling for the wearing of masks indoors in schools and in any location in the country where COVID-19 cases surpass 50 people per 100,000, also known as substantial or high transmission areas.
On a positive note, Dr. Walensky said: “Right now, fortunately, we are not there. The vaccines operate really well in protecting us from severe disease and death.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, made a dire prediction during a media briefing this week that, if we weren’t already living within the reality of the COVID-19 pandemic, would sound more like a pitch for a movie about a dystopian future.
“For the amount of virus circulating in this country right now largely among unvaccinated people, the largest concern that we in public health and science are worried about is that the virus … [becomes] a very transmissible virus that has the potential to evade our vaccines in terms of how it protects us from severe disease and death,” Dr. Walensky told reporters on July 27.
A new, more elusive variant could be “just a few mutations away,” she said.
“That’s a very prescient comment,” Lewis Nelson, MD, professor and clinical chair of emergency medicine and chief of the division of medical toxicology at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, told this news organization.
“We’ve gone through a few mutations already that have been named, and each one of them gets a little more transmissible,” he said. “That’s normal, natural selection and what you would expect to happen as viruses mutate from one strain to another.”
“What we’ve mostly seen this virus do is evolve to become more infectious,” said Stuart Ray, MD, when also asked to comment. “That is the remarkable feature of Delta – that it is so infectious.”
He said that the SARS-CoV-2 has evolved largely as expected, at least so far. “The potential for this virus to mutate has been something that has been a concern from early on.”
“The viral evolution is a bit like a ticking clock. The more we allow infections to occur, the more likely changes will occur. When we have lots of people infected, we give more chances to the virus to diversify and then adapt to selective pressures,” said Dr. Ray, vice-chair of medicine for data integrity and analytics and professor in the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore.
Dr. Nelson said.
If this occurs, he added, “we will have an ineffective vaccine, essentially. And we’ll be back to where we were last March with a brand-new disease.”
Technology to the rescue?
The flexibility of mRNA vaccines is one potential solution. These vaccines could be more easily and quickly adapted to respond to a new, more vaccine-elusive variant.
“That’s absolutely reassuring,” Dr. Nelson said. For example, if a mutation changes the spike protein and vaccines no longer recognize it, a manufacturer could identify the new protein and incorporate that in a new mRNA vaccine.
“The problem is that some people are not taking the current vaccine,” he added. “I’m not sure what is going to make them take the next vaccine.”
Nothing appears certain
When asked how likely a new strain of SARS-CoV-2 could emerge that gets around vaccine protection, Dr. Nelson said, “I think [what] we’ve learned so far there is no way to predict anything” about this pandemic.
“The best way to prevent the virus from mutating is to prevent hosts, people, from getting sick with it,” he said. “That’s why it’s so important people should get immunized and wear masks.”
Both Dr. Nelson and Dr. Ray pointed out that it is in the best interest of the virus to evolve to be more transmissible and spread to more people. In contrast, a virus that causes people to get so sick that they isolate or die, thus halting transmission, works against viruses surviving evolutionarily.
Some viruses also mutate to become milder over time, but that has not been the case with SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Ray said.
Mutations not the only concern
Viruses have another mechanism that produces new strains, and it works even more quickly than mutations. Recombination, as it’s known, can occur when a person is infected with two different strains of the same virus. If the two versions enter the same cell, the viruses can swap genetic material and produce a third, altogether different strain.
Recombination has already been seen with influenza strains, where H and N genetic segments are swapped to yield H1N1, H1N2, and H3N2 versions of the flu, for example.
“In the early days of SARS-CoV-2 there was so little diversity that recombination did not matter,” Dr. Ray said. However, there are now distinct lineages of the virus circulating globally. If two of these lineages swap segments “this would make a very new viral sequence in one step without having to mutate to gain those differences.”
“The more diverse the strains that are circulating, the bigger a possibility this is,” Dr. Ray said.
Protected, for now
Dr. Walensky’s sober warning came at the same time the CDC released new guidance calling for the wearing of masks indoors in schools and in any location in the country where COVID-19 cases surpass 50 people per 100,000, also known as substantial or high transmission areas.
On a positive note, Dr. Walensky said: “Right now, fortunately, we are not there. The vaccines operate really well in protecting us from severe disease and death.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Shocking’ early complications from teen-onset type 2 diabetes
Newly published data show alarmingly high rates and severity of early diabetes-specific complications in individuals who develop type 2 diabetes at a young age. This suggests intervention should be early and aggressive among these youngsters, said the researchers.
The results for the 500 young adult participants in the Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth 2 (TODAY 2) study were published online July 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine by the TODAY study group.
At follow-up – after originally participating in the TODAY trial when they were young teenagers – they had a mean age of 26.4 years.
At this time, more than two thirds had hypertension and half had dyslipidemia.
Overall, 60% had at least one diabetic microvascular complication (retinal disease, neuropathy, or diabetic kidney disease), and more than a quarter had two or more such complications.
“These data illustrate the serious personal and public health consequences of youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the transition to adulthood,” the researchers noted.
Don’t tread lightly just because they are young
“The fact that these youth are accumulating complications at a rapid rate and are broadly affected early in adulthood certainly suggests that aggressive therapy is needed, both for glycemic control and treatment of risk factors like hypertension and dyslipidemia,” study coauthor Philip S. Zeitler, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
“In the absence of studies specifically addressing this, we need to take a more aggressive approach than people might be inclined to, given that the age at diagnosis is young, around 14 years,” he added.
“Contrary to the inclination to be ‘gentle’ in treating them because they are kids, these data suggest that we can’t let these initial years go by without strong intervention, and we need to be prepared for polypharmacy.”
Unfortunately, as Dr. Zeitler and coauthors explained, youth-onset type 2 diabetes is characterized by a suboptimal response to currently approved diabetes medications.
New pediatric indications in the United States for drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes in adults, including the recent Food and Drug Administration approval of extended-release exenatide for children as young as 10 years of age, “helps, but only marginally,” said Dr. Zeitler, of the Clinical & Translational Research Center, Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora.
“In some cases, it will help get them covered by carriers, which is always good. But this is still a very limited set of medications. It doesn’t include more recently approved more potent glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, like semaglutide, and doesn’t include the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Pediatricians are used to using medications off label and that is necessary here while we await further approvals,” he said.
And he noted that most individuals with youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the United States are covered by public insurance or are uninsured, depending on which state they live in. While the two major Medicaid programs in Colorado allow full access to adult formularies, that’s not the case everywhere. Moreover, patients often face further access barriers in states without expanded Medicaid.
Follow-up shows all metrics worsening over time
In TODAY 2, patients participated in an observational follow-up in their usual care settings in 2011-2020. At the start, they were receiving metformin with or without insulin for diabetes, but whether this continued and whether they were treated for other risk factors was down to individual circumstances.
Participants’ median A1c increased over time, and the percentage with A1c < 6% (< 48 mmol/mol) declined from 75% at the time of TODAY entry to just 19% at the 15-year end of follow-up.
The proportion with an A1c ≤ 10% (≤ 86 mmol/mol) rose from 0% at baseline to 34% at 15 years.
At that time, nearly 50% were taking both metformin and insulin, while more than a quarter were taking no medications.
The prevalence of hypertension increased from 19.2% at baseline to 67.5% at 15 years, while dyslipidemia rose from 20.8% to 51.6%.
Kidney disease prevalence increased from 8.0% at baseline to 54.8% at 15 years. Nerve disease rose from 1.0% to 32.4%. Retinal disease jumped from 13.7% with milder nonproliferative retinopathy in 2010-2011 to 51.0% with any eye disease in 2017-2018, including 8.8% with moderate to severe retinal changes and 3.5% with macular edema.
Overall, at the time of the last visit, 39.9% had no diabetes complications, 31.8% had one, 21.3% had two, and 7.1% had three complications.
Serious cardiovascular events in mid-20s
There were 17 adjudicated serious cardiovascular events, including four myocardial infarctions, six heart failure events, three diagnoses of coronary artery disease, and four strokes.
Six participants died, one each from myocardial infarction, kidney failure, and drug overdose, and three from sepsis.
Dr. Zeitler called the macrovascular events “shocking,” noting that although the numbers are small, for people in their mid-20s “they should be zero ... While we don’t yet know if the rates are the same or faster than in adults, even if they are the same, these kids are only in their late 20s, as opposed to adults experiencing these problems in their 50s, 60s, and 70s.
“The fact that these complications are occurring when these individuals should be in the prime of their life for both family and work has huge implications,” he stressed.
Findings have multiple causes
The reasons for the findings are both biologic and socioeconomic, Dr. Zeitler said.
“We know already that many kids with type 2 have rapid [deterioration of] beta-cell [function], which is probably very biologic. It stands to reason that an individual who can get diabetes as an adolescent probably has more fragile beta cells in some way,” he noted.
“But we also know that many other things contribute: stress, social determinants, access to quality care and medications, access to healthy foods and physical activity, availability of family supervision given the realities of families’ economic status and jobs, etc.”
It’s also known that youth with type 2 diabetes have much more severe insulin resistance than that of adults with the condition, and that “once the kids left ... the [TODAY] study, risk factor treatment in the community was less than ideal, and a lot of kids who met criteria for treatment of their blood pressure or lipids were not being treated. This is likely at least partly sociologic and partly the general pediatric hesitancy to use medications.”
He said the TODAY team will soon have some new data to show that “glycemia during the early years makes a difference, again supporting intensive intervention early on.”
The TODAY study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Zeitler had no further disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Newly published data show alarmingly high rates and severity of early diabetes-specific complications in individuals who develop type 2 diabetes at a young age. This suggests intervention should be early and aggressive among these youngsters, said the researchers.
The results for the 500 young adult participants in the Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth 2 (TODAY 2) study were published online July 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine by the TODAY study group.
At follow-up – after originally participating in the TODAY trial when they were young teenagers – they had a mean age of 26.4 years.
At this time, more than two thirds had hypertension and half had dyslipidemia.
Overall, 60% had at least one diabetic microvascular complication (retinal disease, neuropathy, or diabetic kidney disease), and more than a quarter had two or more such complications.
“These data illustrate the serious personal and public health consequences of youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the transition to adulthood,” the researchers noted.
Don’t tread lightly just because they are young
“The fact that these youth are accumulating complications at a rapid rate and are broadly affected early in adulthood certainly suggests that aggressive therapy is needed, both for glycemic control and treatment of risk factors like hypertension and dyslipidemia,” study coauthor Philip S. Zeitler, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
“In the absence of studies specifically addressing this, we need to take a more aggressive approach than people might be inclined to, given that the age at diagnosis is young, around 14 years,” he added.
“Contrary to the inclination to be ‘gentle’ in treating them because they are kids, these data suggest that we can’t let these initial years go by without strong intervention, and we need to be prepared for polypharmacy.”
Unfortunately, as Dr. Zeitler and coauthors explained, youth-onset type 2 diabetes is characterized by a suboptimal response to currently approved diabetes medications.
New pediatric indications in the United States for drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes in adults, including the recent Food and Drug Administration approval of extended-release exenatide for children as young as 10 years of age, “helps, but only marginally,” said Dr. Zeitler, of the Clinical & Translational Research Center, Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora.
“In some cases, it will help get them covered by carriers, which is always good. But this is still a very limited set of medications. It doesn’t include more recently approved more potent glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, like semaglutide, and doesn’t include the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Pediatricians are used to using medications off label and that is necessary here while we await further approvals,” he said.
And he noted that most individuals with youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the United States are covered by public insurance or are uninsured, depending on which state they live in. While the two major Medicaid programs in Colorado allow full access to adult formularies, that’s not the case everywhere. Moreover, patients often face further access barriers in states without expanded Medicaid.
Follow-up shows all metrics worsening over time
In TODAY 2, patients participated in an observational follow-up in their usual care settings in 2011-2020. At the start, they were receiving metformin with or without insulin for diabetes, but whether this continued and whether they were treated for other risk factors was down to individual circumstances.
Participants’ median A1c increased over time, and the percentage with A1c < 6% (< 48 mmol/mol) declined from 75% at the time of TODAY entry to just 19% at the 15-year end of follow-up.
The proportion with an A1c ≤ 10% (≤ 86 mmol/mol) rose from 0% at baseline to 34% at 15 years.
At that time, nearly 50% were taking both metformin and insulin, while more than a quarter were taking no medications.
The prevalence of hypertension increased from 19.2% at baseline to 67.5% at 15 years, while dyslipidemia rose from 20.8% to 51.6%.
Kidney disease prevalence increased from 8.0% at baseline to 54.8% at 15 years. Nerve disease rose from 1.0% to 32.4%. Retinal disease jumped from 13.7% with milder nonproliferative retinopathy in 2010-2011 to 51.0% with any eye disease in 2017-2018, including 8.8% with moderate to severe retinal changes and 3.5% with macular edema.
Overall, at the time of the last visit, 39.9% had no diabetes complications, 31.8% had one, 21.3% had two, and 7.1% had three complications.
Serious cardiovascular events in mid-20s
There were 17 adjudicated serious cardiovascular events, including four myocardial infarctions, six heart failure events, three diagnoses of coronary artery disease, and four strokes.
Six participants died, one each from myocardial infarction, kidney failure, and drug overdose, and three from sepsis.
Dr. Zeitler called the macrovascular events “shocking,” noting that although the numbers are small, for people in their mid-20s “they should be zero ... While we don’t yet know if the rates are the same or faster than in adults, even if they are the same, these kids are only in their late 20s, as opposed to adults experiencing these problems in their 50s, 60s, and 70s.
“The fact that these complications are occurring when these individuals should be in the prime of their life for both family and work has huge implications,” he stressed.
Findings have multiple causes
The reasons for the findings are both biologic and socioeconomic, Dr. Zeitler said.
“We know already that many kids with type 2 have rapid [deterioration of] beta-cell [function], which is probably very biologic. It stands to reason that an individual who can get diabetes as an adolescent probably has more fragile beta cells in some way,” he noted.
“But we also know that many other things contribute: stress, social determinants, access to quality care and medications, access to healthy foods and physical activity, availability of family supervision given the realities of families’ economic status and jobs, etc.”
It’s also known that youth with type 2 diabetes have much more severe insulin resistance than that of adults with the condition, and that “once the kids left ... the [TODAY] study, risk factor treatment in the community was less than ideal, and a lot of kids who met criteria for treatment of their blood pressure or lipids were not being treated. This is likely at least partly sociologic and partly the general pediatric hesitancy to use medications.”
He said the TODAY team will soon have some new data to show that “glycemia during the early years makes a difference, again supporting intensive intervention early on.”
The TODAY study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Zeitler had no further disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Newly published data show alarmingly high rates and severity of early diabetes-specific complications in individuals who develop type 2 diabetes at a young age. This suggests intervention should be early and aggressive among these youngsters, said the researchers.
The results for the 500 young adult participants in the Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth 2 (TODAY 2) study were published online July 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine by the TODAY study group.
At follow-up – after originally participating in the TODAY trial when they were young teenagers – they had a mean age of 26.4 years.
At this time, more than two thirds had hypertension and half had dyslipidemia.
Overall, 60% had at least one diabetic microvascular complication (retinal disease, neuropathy, or diabetic kidney disease), and more than a quarter had two or more such complications.
“These data illustrate the serious personal and public health consequences of youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the transition to adulthood,” the researchers noted.
Don’t tread lightly just because they are young
“The fact that these youth are accumulating complications at a rapid rate and are broadly affected early in adulthood certainly suggests that aggressive therapy is needed, both for glycemic control and treatment of risk factors like hypertension and dyslipidemia,” study coauthor Philip S. Zeitler, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
“In the absence of studies specifically addressing this, we need to take a more aggressive approach than people might be inclined to, given that the age at diagnosis is young, around 14 years,” he added.
“Contrary to the inclination to be ‘gentle’ in treating them because they are kids, these data suggest that we can’t let these initial years go by without strong intervention, and we need to be prepared for polypharmacy.”
Unfortunately, as Dr. Zeitler and coauthors explained, youth-onset type 2 diabetes is characterized by a suboptimal response to currently approved diabetes medications.
New pediatric indications in the United States for drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes in adults, including the recent Food and Drug Administration approval of extended-release exenatide for children as young as 10 years of age, “helps, but only marginally,” said Dr. Zeitler, of the Clinical & Translational Research Center, Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora.
“In some cases, it will help get them covered by carriers, which is always good. But this is still a very limited set of medications. It doesn’t include more recently approved more potent glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, like semaglutide, and doesn’t include the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Pediatricians are used to using medications off label and that is necessary here while we await further approvals,” he said.
And he noted that most individuals with youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the United States are covered by public insurance or are uninsured, depending on which state they live in. While the two major Medicaid programs in Colorado allow full access to adult formularies, that’s not the case everywhere. Moreover, patients often face further access barriers in states without expanded Medicaid.
Follow-up shows all metrics worsening over time
In TODAY 2, patients participated in an observational follow-up in their usual care settings in 2011-2020. At the start, they were receiving metformin with or without insulin for diabetes, but whether this continued and whether they were treated for other risk factors was down to individual circumstances.
Participants’ median A1c increased over time, and the percentage with A1c < 6% (< 48 mmol/mol) declined from 75% at the time of TODAY entry to just 19% at the 15-year end of follow-up.
The proportion with an A1c ≤ 10% (≤ 86 mmol/mol) rose from 0% at baseline to 34% at 15 years.
At that time, nearly 50% were taking both metformin and insulin, while more than a quarter were taking no medications.
The prevalence of hypertension increased from 19.2% at baseline to 67.5% at 15 years, while dyslipidemia rose from 20.8% to 51.6%.
Kidney disease prevalence increased from 8.0% at baseline to 54.8% at 15 years. Nerve disease rose from 1.0% to 32.4%. Retinal disease jumped from 13.7% with milder nonproliferative retinopathy in 2010-2011 to 51.0% with any eye disease in 2017-2018, including 8.8% with moderate to severe retinal changes and 3.5% with macular edema.
Overall, at the time of the last visit, 39.9% had no diabetes complications, 31.8% had one, 21.3% had two, and 7.1% had three complications.
Serious cardiovascular events in mid-20s
There were 17 adjudicated serious cardiovascular events, including four myocardial infarctions, six heart failure events, three diagnoses of coronary artery disease, and four strokes.
Six participants died, one each from myocardial infarction, kidney failure, and drug overdose, and three from sepsis.
Dr. Zeitler called the macrovascular events “shocking,” noting that although the numbers are small, for people in their mid-20s “they should be zero ... While we don’t yet know if the rates are the same or faster than in adults, even if they are the same, these kids are only in their late 20s, as opposed to adults experiencing these problems in their 50s, 60s, and 70s.
“The fact that these complications are occurring when these individuals should be in the prime of their life for both family and work has huge implications,” he stressed.
Findings have multiple causes
The reasons for the findings are both biologic and socioeconomic, Dr. Zeitler said.
“We know already that many kids with type 2 have rapid [deterioration of] beta-cell [function], which is probably very biologic. It stands to reason that an individual who can get diabetes as an adolescent probably has more fragile beta cells in some way,” he noted.
“But we also know that many other things contribute: stress, social determinants, access to quality care and medications, access to healthy foods and physical activity, availability of family supervision given the realities of families’ economic status and jobs, etc.”
It’s also known that youth with type 2 diabetes have much more severe insulin resistance than that of adults with the condition, and that “once the kids left ... the [TODAY] study, risk factor treatment in the community was less than ideal, and a lot of kids who met criteria for treatment of their blood pressure or lipids were not being treated. This is likely at least partly sociologic and partly the general pediatric hesitancy to use medications.”
He said the TODAY team will soon have some new data to show that “glycemia during the early years makes a difference, again supporting intensive intervention early on.”
The TODAY study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Zeitler had no further disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 leaves wake of medical debt among U.S. adults
Despite the passage of four major relief bills in 2020 and 2021 and federal efforts to offset pandemic- and job-related coverage loss, many people continued to face financial challenges, especially those with a low income and those who are Black or Latino.
The survey, which included responses from 5,450 adults, revealed that 10% of adults aged 19-64 were uninsured during the first half of 2021, a rate lower than what was recorded in 2020 and 2019 in both federal and private surveys. However, uninsured rates were highest among those with low income, those younger than 50 years old, and Black and Latino adults.
For most adults who lost employee health insurance, the coverage gap was relatively brief, with 54% saying their coverage gap lasted 3-4 months. Only 16% of adults said coverage gaps lasted a year or longer.
“The good news is that this survey is suggesting that the coverage losses during the pandemic may have been offset by federal efforts to help people get and maintain health insurance coverage,” lead author Sara Collins, PhD, Commonwealth Fund vice president for health care coverage, access, and tracking, said in an interview.
“The bad news is that a third of Americans continue to struggle with medical bills and medical debt, even among those who have health insurance coverage,” Dr. Collins added.
Indeed, the survey found that about one-third of insured adults reported a medical bill problem or that they were paying off medical debt, as did approximately half of those who were uninsured. Medical debt caused 35% of respondents to use up most or all of their savings to pay it off.
Meanwhile, 27% of adults said medical bills left them unable to pay for necessities such as food, heat, or rent. What surprised Dr. Collins was that 43% of adults said they received a lower credit rating as a result of their medical debt, and 35% said they had taken on more credit card debt to pay off these bills.
“The fact that it’s bleeding over into people’s financial security in terms of their credit scores, I think is something that really needs to be looked at by policymakers,” Dr. Collins said.
When analyzed by race/ethnicity, the researchers found that 55% of Black adults and 44% of Latino/Hispanic adults reported medical bills and debt problems, compared with 32% of White adults. In addition, 47% of those living below the poverty line also reported problems with medical bills.
According to the survey, 45% of respondents were directly affected by the pandemic in at least one of three ways – testing positive or getting sick from COVID-19, losing income, or losing employer coverage – with Black and Latinx adults and those with lower incomes at greater risk.
George Abraham, MD, president of the American College of Physicians, said the Commonwealth Fund’s findings were not surprising because it has always been known that underrepresented populations struggle for access to care because of socioeconomic factors. He said these populations were more vulnerable in terms of more severe infections and disease burden during the pandemic.
“[This study] validates what primary care physicians have been saying all along in regard to our patients’ access to care and their ability to cover health care costs,” said Dr. Abraham, who was not involved with the study. “This will hopefully be an eye-opener and wake-up call that reiterates that we still do not have equitable access to care and vulnerable populations are disproportionately affected.”
He believes that, although people are insured, many of them may contend with medical debt when they fall ill because they can’t afford the premiums.
“Even though they may have been registered for health coverage, they may not have active coverage at the time of illness simply because they weren’t able to make their last premium payments because they’ve been down, because they lost their job, or whatever else,” Dr. Abraham explained. “On paper, they appear to have health care coverage. But in reality, clearly, that coverage does not match their needs or it’s not affordable.”
For Dr. Abraham, the study emphasizes the need to continue support for health care reform, including pricing it so that insurance is available for those with fewer socioeconomic resources.
Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, medical director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies, Washington, said high-deductible health plans need to be “reined in” because they can lead to greater debt, particularly among vulnerable populations.
“Hopefully this will encourage policymakers to look more closely at the problem of medical debt as a contributing factor to financial instability,” Dr. Jabbarpour said. “Federal relief is important, so is expanding access to comprehensive, affordable health care coverage.”
Dr. Collins said there should also be a way to raise awareness of the health care marketplace and coverage options so that people have an easier time getting insured.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite the passage of four major relief bills in 2020 and 2021 and federal efforts to offset pandemic- and job-related coverage loss, many people continued to face financial challenges, especially those with a low income and those who are Black or Latino.
The survey, which included responses from 5,450 adults, revealed that 10% of adults aged 19-64 were uninsured during the first half of 2021, a rate lower than what was recorded in 2020 and 2019 in both federal and private surveys. However, uninsured rates were highest among those with low income, those younger than 50 years old, and Black and Latino adults.
For most adults who lost employee health insurance, the coverage gap was relatively brief, with 54% saying their coverage gap lasted 3-4 months. Only 16% of adults said coverage gaps lasted a year or longer.
“The good news is that this survey is suggesting that the coverage losses during the pandemic may have been offset by federal efforts to help people get and maintain health insurance coverage,” lead author Sara Collins, PhD, Commonwealth Fund vice president for health care coverage, access, and tracking, said in an interview.
“The bad news is that a third of Americans continue to struggle with medical bills and medical debt, even among those who have health insurance coverage,” Dr. Collins added.
Indeed, the survey found that about one-third of insured adults reported a medical bill problem or that they were paying off medical debt, as did approximately half of those who were uninsured. Medical debt caused 35% of respondents to use up most or all of their savings to pay it off.
Meanwhile, 27% of adults said medical bills left them unable to pay for necessities such as food, heat, or rent. What surprised Dr. Collins was that 43% of adults said they received a lower credit rating as a result of their medical debt, and 35% said they had taken on more credit card debt to pay off these bills.
“The fact that it’s bleeding over into people’s financial security in terms of their credit scores, I think is something that really needs to be looked at by policymakers,” Dr. Collins said.
When analyzed by race/ethnicity, the researchers found that 55% of Black adults and 44% of Latino/Hispanic adults reported medical bills and debt problems, compared with 32% of White adults. In addition, 47% of those living below the poverty line also reported problems with medical bills.
According to the survey, 45% of respondents were directly affected by the pandemic in at least one of three ways – testing positive or getting sick from COVID-19, losing income, or losing employer coverage – with Black and Latinx adults and those with lower incomes at greater risk.
George Abraham, MD, president of the American College of Physicians, said the Commonwealth Fund’s findings were not surprising because it has always been known that underrepresented populations struggle for access to care because of socioeconomic factors. He said these populations were more vulnerable in terms of more severe infections and disease burden during the pandemic.
“[This study] validates what primary care physicians have been saying all along in regard to our patients’ access to care and their ability to cover health care costs,” said Dr. Abraham, who was not involved with the study. “This will hopefully be an eye-opener and wake-up call that reiterates that we still do not have equitable access to care and vulnerable populations are disproportionately affected.”
He believes that, although people are insured, many of them may contend with medical debt when they fall ill because they can’t afford the premiums.
“Even though they may have been registered for health coverage, they may not have active coverage at the time of illness simply because they weren’t able to make their last premium payments because they’ve been down, because they lost their job, or whatever else,” Dr. Abraham explained. “On paper, they appear to have health care coverage. But in reality, clearly, that coverage does not match their needs or it’s not affordable.”
For Dr. Abraham, the study emphasizes the need to continue support for health care reform, including pricing it so that insurance is available for those with fewer socioeconomic resources.
Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, medical director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies, Washington, said high-deductible health plans need to be “reined in” because they can lead to greater debt, particularly among vulnerable populations.
“Hopefully this will encourage policymakers to look more closely at the problem of medical debt as a contributing factor to financial instability,” Dr. Jabbarpour said. “Federal relief is important, so is expanding access to comprehensive, affordable health care coverage.”
Dr. Collins said there should also be a way to raise awareness of the health care marketplace and coverage options so that people have an easier time getting insured.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite the passage of four major relief bills in 2020 and 2021 and federal efforts to offset pandemic- and job-related coverage loss, many people continued to face financial challenges, especially those with a low income and those who are Black or Latino.
The survey, which included responses from 5,450 adults, revealed that 10% of adults aged 19-64 were uninsured during the first half of 2021, a rate lower than what was recorded in 2020 and 2019 in both federal and private surveys. However, uninsured rates were highest among those with low income, those younger than 50 years old, and Black and Latino adults.
For most adults who lost employee health insurance, the coverage gap was relatively brief, with 54% saying their coverage gap lasted 3-4 months. Only 16% of adults said coverage gaps lasted a year or longer.
“The good news is that this survey is suggesting that the coverage losses during the pandemic may have been offset by federal efforts to help people get and maintain health insurance coverage,” lead author Sara Collins, PhD, Commonwealth Fund vice president for health care coverage, access, and tracking, said in an interview.
“The bad news is that a third of Americans continue to struggle with medical bills and medical debt, even among those who have health insurance coverage,” Dr. Collins added.
Indeed, the survey found that about one-third of insured adults reported a medical bill problem or that they were paying off medical debt, as did approximately half of those who were uninsured. Medical debt caused 35% of respondents to use up most or all of their savings to pay it off.
Meanwhile, 27% of adults said medical bills left them unable to pay for necessities such as food, heat, or rent. What surprised Dr. Collins was that 43% of adults said they received a lower credit rating as a result of their medical debt, and 35% said they had taken on more credit card debt to pay off these bills.
“The fact that it’s bleeding over into people’s financial security in terms of their credit scores, I think is something that really needs to be looked at by policymakers,” Dr. Collins said.
When analyzed by race/ethnicity, the researchers found that 55% of Black adults and 44% of Latino/Hispanic adults reported medical bills and debt problems, compared with 32% of White adults. In addition, 47% of those living below the poverty line also reported problems with medical bills.
According to the survey, 45% of respondents were directly affected by the pandemic in at least one of three ways – testing positive or getting sick from COVID-19, losing income, or losing employer coverage – with Black and Latinx adults and those with lower incomes at greater risk.
George Abraham, MD, president of the American College of Physicians, said the Commonwealth Fund’s findings were not surprising because it has always been known that underrepresented populations struggle for access to care because of socioeconomic factors. He said these populations were more vulnerable in terms of more severe infections and disease burden during the pandemic.
“[This study] validates what primary care physicians have been saying all along in regard to our patients’ access to care and their ability to cover health care costs,” said Dr. Abraham, who was not involved with the study. “This will hopefully be an eye-opener and wake-up call that reiterates that we still do not have equitable access to care and vulnerable populations are disproportionately affected.”
He believes that, although people are insured, many of them may contend with medical debt when they fall ill because they can’t afford the premiums.
“Even though they may have been registered for health coverage, they may not have active coverage at the time of illness simply because they weren’t able to make their last premium payments because they’ve been down, because they lost their job, or whatever else,” Dr. Abraham explained. “On paper, they appear to have health care coverage. But in reality, clearly, that coverage does not match their needs or it’s not affordable.”
For Dr. Abraham, the study emphasizes the need to continue support for health care reform, including pricing it so that insurance is available for those with fewer socioeconomic resources.
Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, medical director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies, Washington, said high-deductible health plans need to be “reined in” because they can lead to greater debt, particularly among vulnerable populations.
“Hopefully this will encourage policymakers to look more closely at the problem of medical debt as a contributing factor to financial instability,” Dr. Jabbarpour said. “Federal relief is important, so is expanding access to comprehensive, affordable health care coverage.”
Dr. Collins said there should also be a way to raise awareness of the health care marketplace and coverage options so that people have an easier time getting insured.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vaccinated people infected with Delta remain contagious
, The New York Times reported late on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data show people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on July 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak in Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
, The New York Times reported late on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data show people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on July 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak in Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
, The New York Times reported late on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data show people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on July 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak in Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
ESC heart failure guideline to integrate bounty of new meds
Today there are so many evidence-based drug therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) that physicians treating HF patients almost don’t know what to do them.
It’s an exciting new age that way, but to many vexingly unclear how best to merge the shiny new options with mainstay regimens based on time-honored renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors and beta-blockers.
To impart some clarity, the authors of a new HF guideline document recently took center stage at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) annual meeting to preview their updated recommendations, with novel twists based on recent major trials, for the new age of HF pharmacotherapeutics.
The guideline committee considered the evidence base that existed “up until the end of March of this year,” Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, said during the presentation. The document “is now finalized, it’s with the publishers, and it will be presented in full with simultaneous publication at the ESC meeting” that starts August 27.
It describes a game plan, already followed by some clinicians in practice without official guidance, for initiating drugs from each of four classes in virtually all patients with HFrEF.
New indicated drugs, new perspective for HFrEF
Three of the drug categories are old acquaintances. Among them are the RAS inhibitors, which include angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors, beta-blockers, and the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. The latter drugs are gaining new respect after having been underplayed in HF prescribing despite longstanding evidence of efficacy.
Completing the quartet of first-line HFrEF drug classes is a recent arrival to the HF arena, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“We now have new data and a simplified treatment algorithm for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction based on the early administration of the four major classes of drugs,” said Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia (Italy), previewing the medical-therapy portions of the new guideline at the ESC-HFA sessions, which launched virtually and live in Florence, Italy, on July 29.
The new game plan offers a simple answer to a once-common but complex question: How and in what order are the different drug classes initiated in patients with HFrEF? In the new document, the stated goal is to get them all on board expeditiously and safely, by any means possible.
The guideline writers did not specify a sequence, preferring to leave that decision to physicians, said Dr. Metra, who stated only two guiding principles. The first is to consider the patient’s unique circumstances. The order in which the drugs are introduced might vary, depending on, for example, whether the patient has low or high blood pressure or renal dysfunction.
Second, “it is very important that we try to give all four classes of drugs to the patient in the shortest time possible, because this saves lives,” he said.
That there is no recommendation on sequencing the drugs has led some to the wrong interpretation that all should be started at once, observed coauthor Javed Butler, MD, MPH, University of Mississippi, Jackson, as a panelist during the presentation. Far from it, he said. “The doctor with the patient in front of you can make the best decision. The idea here is to get all the therapies on as soon as possible, as safely as possible.”
“The order in which they are introduced is not really important,” agreed Vijay Chopra, MD, Max Super Specialty Hospital Saket, New Delhi, another coauthor on the panel. “The important thing is that at least some dose of all the four drugs needs to be introduced in the first 4-6 weeks, and then up-titrated.”
Other medical therapy can be more tailored, Dr. Metra noted, such as loop diuretics for patients with congestion, iron for those with iron deficiency, and other drugs depending on whether there is, for example, atrial fibrillation or coronary disease.
Adoption of emerging definitions
The document adopts the emerging characterization of HFrEF by a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) up to 40%.
And it will leverage an expanding evidence base for medication in a segment of patients once said to have HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who had therefore lacked specific, guideline-directed medical therapies. Now, patients with an LVEF of 41%-49% will be said to have HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF), a tweak to the recently introduced HF with “mid-range” LVEF that is designed to assert its nature as something to treat. The new document’s HFmrEF recommendations come with various class and level-of-evidence ratings.
That leaves HFpEF to be characterized by an LVEF of 50% in combination with structural or functional abnormalities associated with LV diastolic dysfunction or raised LV filling pressures, including raised natriuretic peptide levels.
The definitions are consistent with those proposed internationally by the ESC-HFA, the Heart Failure Society of America, and other groups in a statement published in March.
Expanded HFrEF med landscape
Since the 2016 ESC guideline on HF therapy, Dr. McDonagh said, “there’s been no substantial change in the evidence for many of the classical drugs that we use in heart failure. However, we had a lot of new and exciting evidence to consider,” especially in support of the SGLT2 inhibitors as one of the core medications in HFrEF.
The new data came from two controlled trials in particular. In DAPA-HF, patients with HFrEF who were initially without diabetes and who went on dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) showed a 27% drop in cardiovascular (CV) death or worsening-HF events over a median of 18 months.
“That was followed up with very concordant results with empagliflozin [Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly] in HFrEF in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial,” Dr. McDonagh said. In that trial, comparable patients who took empagliflozin showed a 25% drop in a primary endpoint similar to that in DAPA-HF over the median 16-month follow-up.
Other HFrEF recommendations are for selected patients. They include ivabradine, already in the guidelines, for patients in sinus rhythm with an elevated resting heart rate who can’t take beta-blockers for whatever reason. But, Dr. McDonagh noted, “we had some new classes of drugs to consider as well.”
In particular, the oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo) emerged about a year ago from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization. In the trial with more than 5,000 patients, treatment with vericiguat atop standard drug and device therapy was followed by a significant 10% drop in risk for CV death or HF hospitalization.
Available now or likely to be available in the United States, the European Union, Japan, and other countries, vericiguat is recommended in the new guideline for VICTORIA-like patients who don’t adequately respond to other indicated medications.
Little for HFpEF as newly defined
“Almost nothing is new” in the guidelines for HFpEF, Dr. Metra said. The document recommends screening for and treatment of any underlying disorder and comorbidities, plus diuretics for any congestion. “That’s what we have to date.”
But that evidence base might soon change. The new HFpEF recommendations could possibly be up-staged at the ESC sessions by the August 27 scheduled presentation of EMPEROR-Preserved, a randomized test of empagliflozin in HFpEF and – it could be said – HFmrEF. The trial entered patients with chronic HF and an LVEF greater than 40%.
Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim offered the world a peek at the results, which suggest the SGLT2 inhibitor had a positive impact on the primary endpoint of CV death or HF hospitalization. They announced the cursory top-line outcomes in early July as part of its regulatory obligations, noting that the trial had “met” its primary endpoint.
But many unknowns remain, including the degree of benefit and whether it varied among subgroups, and especially whether outcomes were different for HFmrEF than for HFpEF.
Upgrades for familiar agents
Still, HFmrEF gets noteworthy attention in the document. “For the first time, we have recommendations for these patients,” Dr. Metra said. “We already knew that diuretics are indicated for the treatment of congestion. But now, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid antagonists, as well as sacubitril/valsartan, may be considered to improve outcomes in these patients.” Their upgrades in the new guidelines were based on review of trials in the CHARM program and of TOPCAT and PARAGON-HF, among others, he said.
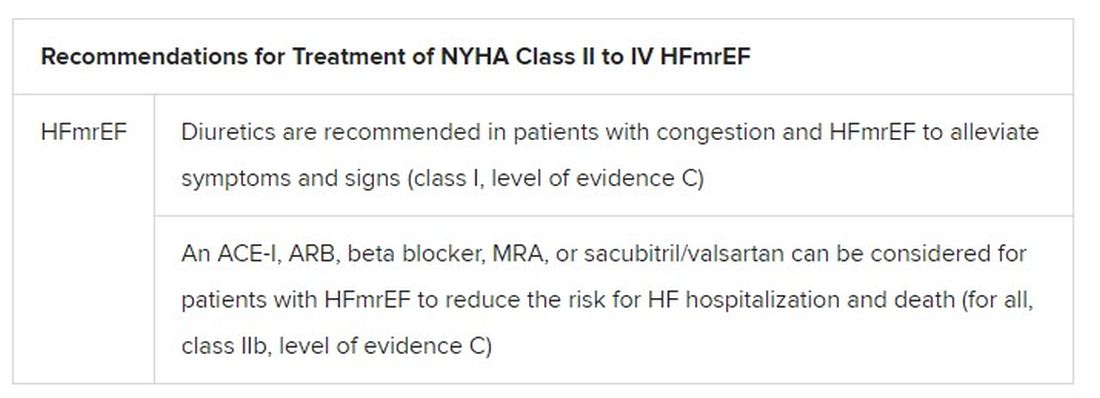
The new document also includes “treatment algorithms based on phenotypes”; that is, comorbidities and less common HF precipitants. For example, “assessment of iron status is now mandated in all patients with heart failure,” Dr. Metra said.
AFFIRM-HF is the key trial in this arena, with its more than 1,100 iron-deficient patients with LVEF less than 50% who had been recently hospitalized for HF. A year of treatment with ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject/Injectafer, Vifor) led to a 26% drop in risk for HF hospitalization, but without affecting mortality.
For those who are iron deficient, Dr. Metra said, “ferric carboxymaltose intravenously should be considered not only in patients with low ejection fraction and outpatients, but also in patients recently hospitalized for acute heart failure.”
The SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended in HFrEF patients with type 2 diabetes. And treatment with tafamidis (Vyndaqel, Pfizer) in patients with genetic or wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis gets a class I recommendation based on survival gains seen in the ATTR-ACT trial.
Also recommended is a full CV assessment for patients with cancer who are on cardiotoxic agents or otherwise might be at risk for chemotherapy cardiotoxicity. “Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors should be considered in those who develop left ventricular systolic dysfunction after anticancer therapy,” Dr. Metra said.
The ongoing pandemic made its mark on the document’s genesis, as it has with most everything else. “For better or worse, we were a ‘COVID guideline,’ ” Dr. McDonagh said. The writing committee consisted of “a large task force of 31 individuals, including two patients,” and there were “only two face-to-face meetings prior to the first wave of COVID hitting Europe.”
The committee voted on each of the recommendations, “and we had to have agreement of more than 75% of the task force to assign a class of recommendation or level of evidence,” she said. “I think we did the best we could in the circumstances. We had the benefit of many discussions over Zoom, and I think at the end of the day we have achieved a consensus.”
With such a large body of participants and the 75% threshold for agreement, “you end up with perhaps a conservative guideline. But that’s not a bad thing for clinical practice, for guidelines to be conservative,” Dr. McDonagh said. “They’re mainly concerned with looking at evidence and safety.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Today there are so many evidence-based drug therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) that physicians treating HF patients almost don’t know what to do them.
It’s an exciting new age that way, but to many vexingly unclear how best to merge the shiny new options with mainstay regimens based on time-honored renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors and beta-blockers.
To impart some clarity, the authors of a new HF guideline document recently took center stage at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) annual meeting to preview their updated recommendations, with novel twists based on recent major trials, for the new age of HF pharmacotherapeutics.
The guideline committee considered the evidence base that existed “up until the end of March of this year,” Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, said during the presentation. The document “is now finalized, it’s with the publishers, and it will be presented in full with simultaneous publication at the ESC meeting” that starts August 27.
It describes a game plan, already followed by some clinicians in practice without official guidance, for initiating drugs from each of four classes in virtually all patients with HFrEF.
New indicated drugs, new perspective for HFrEF
Three of the drug categories are old acquaintances. Among them are the RAS inhibitors, which include angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors, beta-blockers, and the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. The latter drugs are gaining new respect after having been underplayed in HF prescribing despite longstanding evidence of efficacy.
Completing the quartet of first-line HFrEF drug classes is a recent arrival to the HF arena, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“We now have new data and a simplified treatment algorithm for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction based on the early administration of the four major classes of drugs,” said Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia (Italy), previewing the medical-therapy portions of the new guideline at the ESC-HFA sessions, which launched virtually and live in Florence, Italy, on July 29.
The new game plan offers a simple answer to a once-common but complex question: How and in what order are the different drug classes initiated in patients with HFrEF? In the new document, the stated goal is to get them all on board expeditiously and safely, by any means possible.
The guideline writers did not specify a sequence, preferring to leave that decision to physicians, said Dr. Metra, who stated only two guiding principles. The first is to consider the patient’s unique circumstances. The order in which the drugs are introduced might vary, depending on, for example, whether the patient has low or high blood pressure or renal dysfunction.
Second, “it is very important that we try to give all four classes of drugs to the patient in the shortest time possible, because this saves lives,” he said.
That there is no recommendation on sequencing the drugs has led some to the wrong interpretation that all should be started at once, observed coauthor Javed Butler, MD, MPH, University of Mississippi, Jackson, as a panelist during the presentation. Far from it, he said. “The doctor with the patient in front of you can make the best decision. The idea here is to get all the therapies on as soon as possible, as safely as possible.”
“The order in which they are introduced is not really important,” agreed Vijay Chopra, MD, Max Super Specialty Hospital Saket, New Delhi, another coauthor on the panel. “The important thing is that at least some dose of all the four drugs needs to be introduced in the first 4-6 weeks, and then up-titrated.”
Other medical therapy can be more tailored, Dr. Metra noted, such as loop diuretics for patients with congestion, iron for those with iron deficiency, and other drugs depending on whether there is, for example, atrial fibrillation or coronary disease.
Adoption of emerging definitions
The document adopts the emerging characterization of HFrEF by a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) up to 40%.
And it will leverage an expanding evidence base for medication in a segment of patients once said to have HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who had therefore lacked specific, guideline-directed medical therapies. Now, patients with an LVEF of 41%-49% will be said to have HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF), a tweak to the recently introduced HF with “mid-range” LVEF that is designed to assert its nature as something to treat. The new document’s HFmrEF recommendations come with various class and level-of-evidence ratings.
That leaves HFpEF to be characterized by an LVEF of 50% in combination with structural or functional abnormalities associated with LV diastolic dysfunction or raised LV filling pressures, including raised natriuretic peptide levels.
The definitions are consistent with those proposed internationally by the ESC-HFA, the Heart Failure Society of America, and other groups in a statement published in March.
Expanded HFrEF med landscape
Since the 2016 ESC guideline on HF therapy, Dr. McDonagh said, “there’s been no substantial change in the evidence for many of the classical drugs that we use in heart failure. However, we had a lot of new and exciting evidence to consider,” especially in support of the SGLT2 inhibitors as one of the core medications in HFrEF.
The new data came from two controlled trials in particular. In DAPA-HF, patients with HFrEF who were initially without diabetes and who went on dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) showed a 27% drop in cardiovascular (CV) death or worsening-HF events over a median of 18 months.
“That was followed up with very concordant results with empagliflozin [Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly] in HFrEF in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial,” Dr. McDonagh said. In that trial, comparable patients who took empagliflozin showed a 25% drop in a primary endpoint similar to that in DAPA-HF over the median 16-month follow-up.
Other HFrEF recommendations are for selected patients. They include ivabradine, already in the guidelines, for patients in sinus rhythm with an elevated resting heart rate who can’t take beta-blockers for whatever reason. But, Dr. McDonagh noted, “we had some new classes of drugs to consider as well.”
In particular, the oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo) emerged about a year ago from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization. In the trial with more than 5,000 patients, treatment with vericiguat atop standard drug and device therapy was followed by a significant 10% drop in risk for CV death or HF hospitalization.
Available now or likely to be available in the United States, the European Union, Japan, and other countries, vericiguat is recommended in the new guideline for VICTORIA-like patients who don’t adequately respond to other indicated medications.
Little for HFpEF as newly defined
“Almost nothing is new” in the guidelines for HFpEF, Dr. Metra said. The document recommends screening for and treatment of any underlying disorder and comorbidities, plus diuretics for any congestion. “That’s what we have to date.”
But that evidence base might soon change. The new HFpEF recommendations could possibly be up-staged at the ESC sessions by the August 27 scheduled presentation of EMPEROR-Preserved, a randomized test of empagliflozin in HFpEF and – it could be said – HFmrEF. The trial entered patients with chronic HF and an LVEF greater than 40%.
Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim offered the world a peek at the results, which suggest the SGLT2 inhibitor had a positive impact on the primary endpoint of CV death or HF hospitalization. They announced the cursory top-line outcomes in early July as part of its regulatory obligations, noting that the trial had “met” its primary endpoint.
But many unknowns remain, including the degree of benefit and whether it varied among subgroups, and especially whether outcomes were different for HFmrEF than for HFpEF.
Upgrades for familiar agents
Still, HFmrEF gets noteworthy attention in the document. “For the first time, we have recommendations for these patients,” Dr. Metra said. “We already knew that diuretics are indicated for the treatment of congestion. But now, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid antagonists, as well as sacubitril/valsartan, may be considered to improve outcomes in these patients.” Their upgrades in the new guidelines were based on review of trials in the CHARM program and of TOPCAT and PARAGON-HF, among others, he said.

The new document also includes “treatment algorithms based on phenotypes”; that is, comorbidities and less common HF precipitants. For example, “assessment of iron status is now mandated in all patients with heart failure,” Dr. Metra said.
AFFIRM-HF is the key trial in this arena, with its more than 1,100 iron-deficient patients with LVEF less than 50% who had been recently hospitalized for HF. A year of treatment with ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject/Injectafer, Vifor) led to a 26% drop in risk for HF hospitalization, but without affecting mortality.
For those who are iron deficient, Dr. Metra said, “ferric carboxymaltose intravenously should be considered not only in patients with low ejection fraction and outpatients, but also in patients recently hospitalized for acute heart failure.”
The SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended in HFrEF patients with type 2 diabetes. And treatment with tafamidis (Vyndaqel, Pfizer) in patients with genetic or wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis gets a class I recommendation based on survival gains seen in the ATTR-ACT trial.
Also recommended is a full CV assessment for patients with cancer who are on cardiotoxic agents or otherwise might be at risk for chemotherapy cardiotoxicity. “Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors should be considered in those who develop left ventricular systolic dysfunction after anticancer therapy,” Dr. Metra said.
The ongoing pandemic made its mark on the document’s genesis, as it has with most everything else. “For better or worse, we were a ‘COVID guideline,’ ” Dr. McDonagh said. The writing committee consisted of “a large task force of 31 individuals, including two patients,” and there were “only two face-to-face meetings prior to the first wave of COVID hitting Europe.”
The committee voted on each of the recommendations, “and we had to have agreement of more than 75% of the task force to assign a class of recommendation or level of evidence,” she said. “I think we did the best we could in the circumstances. We had the benefit of many discussions over Zoom, and I think at the end of the day we have achieved a consensus.”
With such a large body of participants and the 75% threshold for agreement, “you end up with perhaps a conservative guideline. But that’s not a bad thing for clinical practice, for guidelines to be conservative,” Dr. McDonagh said. “They’re mainly concerned with looking at evidence and safety.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Today there are so many evidence-based drug therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) that physicians treating HF patients almost don’t know what to do them.
It’s an exciting new age that way, but to many vexingly unclear how best to merge the shiny new options with mainstay regimens based on time-honored renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors and beta-blockers.
To impart some clarity, the authors of a new HF guideline document recently took center stage at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) annual meeting to preview their updated recommendations, with novel twists based on recent major trials, for the new age of HF pharmacotherapeutics.
The guideline committee considered the evidence base that existed “up until the end of March of this year,” Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, said during the presentation. The document “is now finalized, it’s with the publishers, and it will be presented in full with simultaneous publication at the ESC meeting” that starts August 27.
It describes a game plan, already followed by some clinicians in practice without official guidance, for initiating drugs from each of four classes in virtually all patients with HFrEF.
New indicated drugs, new perspective for HFrEF
Three of the drug categories are old acquaintances. Among them are the RAS inhibitors, which include angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors, beta-blockers, and the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. The latter drugs are gaining new respect after having been underplayed in HF prescribing despite longstanding evidence of efficacy.
Completing the quartet of first-line HFrEF drug classes is a recent arrival to the HF arena, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“We now have new data and a simplified treatment algorithm for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction based on the early administration of the four major classes of drugs,” said Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia (Italy), previewing the medical-therapy portions of the new guideline at the ESC-HFA sessions, which launched virtually and live in Florence, Italy, on July 29.
The new game plan offers a simple answer to a once-common but complex question: How and in what order are the different drug classes initiated in patients with HFrEF? In the new document, the stated goal is to get them all on board expeditiously and safely, by any means possible.
The guideline writers did not specify a sequence, preferring to leave that decision to physicians, said Dr. Metra, who stated only two guiding principles. The first is to consider the patient’s unique circumstances. The order in which the drugs are introduced might vary, depending on, for example, whether the patient has low or high blood pressure or renal dysfunction.
Second, “it is very important that we try to give all four classes of drugs to the patient in the shortest time possible, because this saves lives,” he said.
That there is no recommendation on sequencing the drugs has led some to the wrong interpretation that all should be started at once, observed coauthor Javed Butler, MD, MPH, University of Mississippi, Jackson, as a panelist during the presentation. Far from it, he said. “The doctor with the patient in front of you can make the best decision. The idea here is to get all the therapies on as soon as possible, as safely as possible.”
“The order in which they are introduced is not really important,” agreed Vijay Chopra, MD, Max Super Specialty Hospital Saket, New Delhi, another coauthor on the panel. “The important thing is that at least some dose of all the four drugs needs to be introduced in the first 4-6 weeks, and then up-titrated.”
Other medical therapy can be more tailored, Dr. Metra noted, such as loop diuretics for patients with congestion, iron for those with iron deficiency, and other drugs depending on whether there is, for example, atrial fibrillation or coronary disease.
Adoption of emerging definitions
The document adopts the emerging characterization of HFrEF by a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) up to 40%.
And it will leverage an expanding evidence base for medication in a segment of patients once said to have HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who had therefore lacked specific, guideline-directed medical therapies. Now, patients with an LVEF of 41%-49% will be said to have HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF), a tweak to the recently introduced HF with “mid-range” LVEF that is designed to assert its nature as something to treat. The new document’s HFmrEF recommendations come with various class and level-of-evidence ratings.
That leaves HFpEF to be characterized by an LVEF of 50% in combination with structural or functional abnormalities associated with LV diastolic dysfunction or raised LV filling pressures, including raised natriuretic peptide levels.
The definitions are consistent with those proposed internationally by the ESC-HFA, the Heart Failure Society of America, and other groups in a statement published in March.
Expanded HFrEF med landscape
Since the 2016 ESC guideline on HF therapy, Dr. McDonagh said, “there’s been no substantial change in the evidence for many of the classical drugs that we use in heart failure. However, we had a lot of new and exciting evidence to consider,” especially in support of the SGLT2 inhibitors as one of the core medications in HFrEF.
The new data came from two controlled trials in particular. In DAPA-HF, patients with HFrEF who were initially without diabetes and who went on dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) showed a 27% drop in cardiovascular (CV) death or worsening-HF events over a median of 18 months.
“That was followed up with very concordant results with empagliflozin [Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly] in HFrEF in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial,” Dr. McDonagh said. In that trial, comparable patients who took empagliflozin showed a 25% drop in a primary endpoint similar to that in DAPA-HF over the median 16-month follow-up.
Other HFrEF recommendations are for selected patients. They include ivabradine, already in the guidelines, for patients in sinus rhythm with an elevated resting heart rate who can’t take beta-blockers for whatever reason. But, Dr. McDonagh noted, “we had some new classes of drugs to consider as well.”
In particular, the oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo) emerged about a year ago from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization. In the trial with more than 5,000 patients, treatment with vericiguat atop standard drug and device therapy was followed by a significant 10% drop in risk for CV death or HF hospitalization.
Available now or likely to be available in the United States, the European Union, Japan, and other countries, vericiguat is recommended in the new guideline for VICTORIA-like patients who don’t adequately respond to other indicated medications.
Little for HFpEF as newly defined
“Almost nothing is new” in the guidelines for HFpEF, Dr. Metra said. The document recommends screening for and treatment of any underlying disorder and comorbidities, plus diuretics for any congestion. “That’s what we have to date.”
But that evidence base might soon change. The new HFpEF recommendations could possibly be up-staged at the ESC sessions by the August 27 scheduled presentation of EMPEROR-Preserved, a randomized test of empagliflozin in HFpEF and – it could be said – HFmrEF. The trial entered patients with chronic HF and an LVEF greater than 40%.
Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim offered the world a peek at the results, which suggest the SGLT2 inhibitor had a positive impact on the primary endpoint of CV death or HF hospitalization. They announced the cursory top-line outcomes in early July as part of its regulatory obligations, noting that the trial had “met” its primary endpoint.
But many unknowns remain, including the degree of benefit and whether it varied among subgroups, and especially whether outcomes were different for HFmrEF than for HFpEF.
Upgrades for familiar agents
Still, HFmrEF gets noteworthy attention in the document. “For the first time, we have recommendations for these patients,” Dr. Metra said. “We already knew that diuretics are indicated for the treatment of congestion. But now, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid antagonists, as well as sacubitril/valsartan, may be considered to improve outcomes in these patients.” Their upgrades in the new guidelines were based on review of trials in the CHARM program and of TOPCAT and PARAGON-HF, among others, he said.

The new document also includes “treatment algorithms based on phenotypes”; that is, comorbidities and less common HF precipitants. For example, “assessment of iron status is now mandated in all patients with heart failure,” Dr. Metra said.
AFFIRM-HF is the key trial in this arena, with its more than 1,100 iron-deficient patients with LVEF less than 50% who had been recently hospitalized for HF. A year of treatment with ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject/Injectafer, Vifor) led to a 26% drop in risk for HF hospitalization, but without affecting mortality.
For those who are iron deficient, Dr. Metra said, “ferric carboxymaltose intravenously should be considered not only in patients with low ejection fraction and outpatients, but also in patients recently hospitalized for acute heart failure.”
The SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended in HFrEF patients with type 2 diabetes. And treatment with tafamidis (Vyndaqel, Pfizer) in patients with genetic or wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis gets a class I recommendation based on survival gains seen in the ATTR-ACT trial.
Also recommended is a full CV assessment for patients with cancer who are on cardiotoxic agents or otherwise might be at risk for chemotherapy cardiotoxicity. “Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors should be considered in those who develop left ventricular systolic dysfunction after anticancer therapy,” Dr. Metra said.
The ongoing pandemic made its mark on the document’s genesis, as it has with most everything else. “For better or worse, we were a ‘COVID guideline,’ ” Dr. McDonagh said. The writing committee consisted of “a large task force of 31 individuals, including two patients,” and there were “only two face-to-face meetings prior to the first wave of COVID hitting Europe.”
The committee voted on each of the recommendations, “and we had to have agreement of more than 75% of the task force to assign a class of recommendation or level of evidence,” she said. “I think we did the best we could in the circumstances. We had the benefit of many discussions over Zoom, and I think at the end of the day we have achieved a consensus.”
With such a large body of participants and the 75% threshold for agreement, “you end up with perhaps a conservative guideline. But that’s not a bad thing for clinical practice, for guidelines to be conservative,” Dr. McDonagh said. “They’re mainly concerned with looking at evidence and safety.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.






