User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
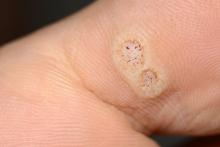
Isolated nail psoriasis may bring arthritis into play
for dermatologists to improve their diagnostic accuracy,” investigators said in a research letter.
Diagnosis of isolated NP was delayed by almost 3 years among the 87 cases recorded and “arthritis was most often diagnosed concurrently with NP,” at a major nail referral center between Jan. 1, 2001, and Dec. 21, 2022, Michelle J. Chang of Drexel University, Philadelphia, and associates reported.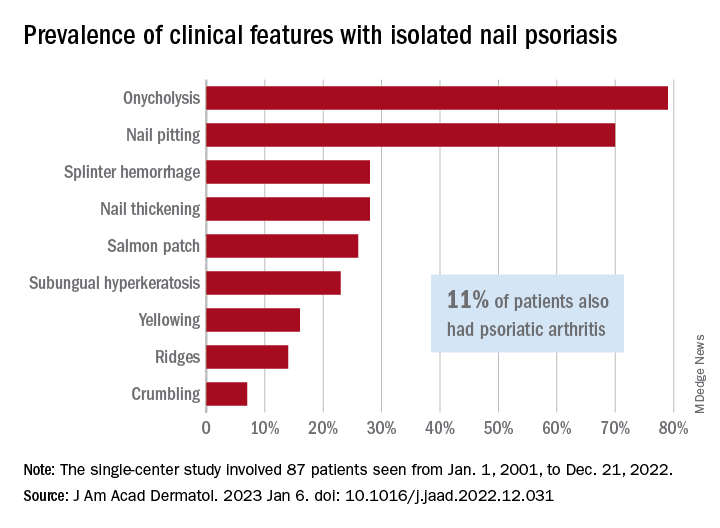
In what the authors say is, “the largest study documenting clinical and histologic features in patients with isolated NP,” the two most common clinical features were onycholysis and nail plate pitting, seen in 79% and 70% of cases, respectively. No other single feature had a prevalence higher than 28%.
The most frequent clinical dyad was onycholysis and pitting in 66% of patients, followed by onycholysis/nail thickening in 33% and onycholysis/splinter hemorrhage in 32%. The most common histologic features were parakeratosis in 79% and neutrophil infiltration in 48%, the investigators said.
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA), a focus of the study, occurred in 10 (11%) of the 87 individuals with isolated NP. Considering this finding, and “the close proximity between the nail apparatus and joint, we hypothesize a reciprocal relationship, with nail unit inflammation precipitating PsA,” Ms. Chang and associates wrote.
Senior author, Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, is a consultant for Ortho-Dermatologics, Hoth Therapeutics, and BelleTorus. Ms. Chang and the two other investigators had no conflicts of interest to declare.
for dermatologists to improve their diagnostic accuracy,” investigators said in a research letter.
Diagnosis of isolated NP was delayed by almost 3 years among the 87 cases recorded and “arthritis was most often diagnosed concurrently with NP,” at a major nail referral center between Jan. 1, 2001, and Dec. 21, 2022, Michelle J. Chang of Drexel University, Philadelphia, and associates reported.
In what the authors say is, “the largest study documenting clinical and histologic features in patients with isolated NP,” the two most common clinical features were onycholysis and nail plate pitting, seen in 79% and 70% of cases, respectively. No other single feature had a prevalence higher than 28%.
The most frequent clinical dyad was onycholysis and pitting in 66% of patients, followed by onycholysis/nail thickening in 33% and onycholysis/splinter hemorrhage in 32%. The most common histologic features were parakeratosis in 79% and neutrophil infiltration in 48%, the investigators said.
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA), a focus of the study, occurred in 10 (11%) of the 87 individuals with isolated NP. Considering this finding, and “the close proximity between the nail apparatus and joint, we hypothesize a reciprocal relationship, with nail unit inflammation precipitating PsA,” Ms. Chang and associates wrote.
Senior author, Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, is a consultant for Ortho-Dermatologics, Hoth Therapeutics, and BelleTorus. Ms. Chang and the two other investigators had no conflicts of interest to declare.
for dermatologists to improve their diagnostic accuracy,” investigators said in a research letter.
Diagnosis of isolated NP was delayed by almost 3 years among the 87 cases recorded and “arthritis was most often diagnosed concurrently with NP,” at a major nail referral center between Jan. 1, 2001, and Dec. 21, 2022, Michelle J. Chang of Drexel University, Philadelphia, and associates reported.
In what the authors say is, “the largest study documenting clinical and histologic features in patients with isolated NP,” the two most common clinical features were onycholysis and nail plate pitting, seen in 79% and 70% of cases, respectively. No other single feature had a prevalence higher than 28%.
The most frequent clinical dyad was onycholysis and pitting in 66% of patients, followed by onycholysis/nail thickening in 33% and onycholysis/splinter hemorrhage in 32%. The most common histologic features were parakeratosis in 79% and neutrophil infiltration in 48%, the investigators said.
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA), a focus of the study, occurred in 10 (11%) of the 87 individuals with isolated NP. Considering this finding, and “the close proximity between the nail apparatus and joint, we hypothesize a reciprocal relationship, with nail unit inflammation precipitating PsA,” Ms. Chang and associates wrote.
Senior author, Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, is a consultant for Ortho-Dermatologics, Hoth Therapeutics, and BelleTorus. Ms. Chang and the two other investigators had no conflicts of interest to declare.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Topical or intralesional cidofovir an option for recalcitrant warts
HONOLULU – Combining or those located in areas that are challenging to treat, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA.
“There are 5 million office visits per year in the United States for warts and molluscum, and they’re most common in pediatrics,” Dr. Barbieri, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “In fact, some studies have suggested that one in three children in primary school suffers from warts.”
According to a 2012 Cochrane review of topical therapies for warts, first-line treatments such as salicylic acid, cryotherapy, 5-FU, or Candida antigen injection often have modest efficacy when used alone. For example, the authors found that salicylic acid and cryotherapy cleared warts in about 60%-70% of cases, respectively, but clearance rates were improved by combining the two therapies.
In an earlier literature review and meta-analysis, investigators evaluated the effect of 5-FU plus salicylic acid or salicylic acid alone. The therapeutic effect for common warts across all studies was a 63.4% response rate (complete healing) for 5-FU/SA vversus 23.1% for the 5-FU–free controls, respectively. For plantar warts, the response rate was 63% versus 11%, respectively.
“But what about the person with multiple warts or those in challenging locations where you might worry about destructive treatments hurting the nail fold or causing nail dystrophy?” Dr. Barbieri asked. “Maybe they’ve used salicylic acid or intralesional Candida and they’re still not getting better. What can we do for these patients?”
Emerging research suggests that topical cidofovir can be a valuable option for recalcitrant warts or those in sensitive locations. In a case report of a 10-year-old boy with more than 50 severe verrucous papules on his hands and face that were recalcitrant to multiple conventional therapies, topical 1% cidofovir applied daily for 8 weeks was effective, with no adverse side effects. A young female patient who presented to Dr. Barbieri with multiple warts around the nail matrix of several fingers experienced complete clearance after treatment with topical cidofovir, he said. Other researchers found this approach to be effective for plantar warts as well, in a report of two brothers with severe combined immunodeficiency after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with persistent warts that did not respond to traditional topical treatments.
“Topical cidofovir is typically a painless treatment, which is nice, especially for our pediatric patients who might be afraid of other therapies like or cryotherapy or intralesional injections,” One limitation is that it is “a bit expensive,” Dr. Barbieri said. “To have topical cidofovir compounded is typically $100-$300, depending on the quantity and strength that you ask for.”
Intralesional cidofovir is another treatment option. In a retrospective study of 58 patients, Dr. Barbieri and colleagues evaluated the outcome of intralesional cidofovir treatment of warts in immunocompromised and nonimmunocompromised patients. Rates of improvement ranged from 98.3% to 100%, while resolution rates ranged from 75.9% to 97.6%.
“Most of the patients had warts for more than 5 years and almost half of them had recalcitrant warts,” Dr. Barbieri said. “These were mostly adult patients, but I think this is a treatment that can work in younger populations as well. About 10%-15% had HIV or cancer or diabetes or were transplant recipients, but despite these challenges and despite these recalcitrant warts, about 100% had improvement.”
He pointed out that cidofovir is available as a 75 mg/mL vial that comes with a 5 mL single-use vial. He dilutes this with normal saline to create a 15 mg/mL solution.
“If you want to be efficient you can try to schedule multiple patients together on the same day as a single vial is sufficient to treat about 25 patients,” assuming about 1 mL is injected per patient, he said. “The challenge with intralesional cidofovir is that it’s painful beyond just the needle part of the injection. Sometimes a nerve block can be helpful. But this can be an effective treatment for patients with recalcitrant warts or those with comorbidities.”
Other intralesional therapies to try for recalcitrant warts, he said, include bleomycin (1 U/mL solution, 1-2 mL per treatment, spaced every 2-4 weeks), and 5-FU (a 4:1 mixture of 5-FU [50 mg/mL] and 2% lidocaine).
Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel for work unrelated to his presentation. Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – Combining or those located in areas that are challenging to treat, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA.
“There are 5 million office visits per year in the United States for warts and molluscum, and they’re most common in pediatrics,” Dr. Barbieri, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “In fact, some studies have suggested that one in three children in primary school suffers from warts.”
According to a 2012 Cochrane review of topical therapies for warts, first-line treatments such as salicylic acid, cryotherapy, 5-FU, or Candida antigen injection often have modest efficacy when used alone. For example, the authors found that salicylic acid and cryotherapy cleared warts in about 60%-70% of cases, respectively, but clearance rates were improved by combining the two therapies.
In an earlier literature review and meta-analysis, investigators evaluated the effect of 5-FU plus salicylic acid or salicylic acid alone. The therapeutic effect for common warts across all studies was a 63.4% response rate (complete healing) for 5-FU/SA vversus 23.1% for the 5-FU–free controls, respectively. For plantar warts, the response rate was 63% versus 11%, respectively.
“But what about the person with multiple warts or those in challenging locations where you might worry about destructive treatments hurting the nail fold or causing nail dystrophy?” Dr. Barbieri asked. “Maybe they’ve used salicylic acid or intralesional Candida and they’re still not getting better. What can we do for these patients?”
Emerging research suggests that topical cidofovir can be a valuable option for recalcitrant warts or those in sensitive locations. In a case report of a 10-year-old boy with more than 50 severe verrucous papules on his hands and face that were recalcitrant to multiple conventional therapies, topical 1% cidofovir applied daily for 8 weeks was effective, with no adverse side effects. A young female patient who presented to Dr. Barbieri with multiple warts around the nail matrix of several fingers experienced complete clearance after treatment with topical cidofovir, he said. Other researchers found this approach to be effective for plantar warts as well, in a report of two brothers with severe combined immunodeficiency after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with persistent warts that did not respond to traditional topical treatments.
“Topical cidofovir is typically a painless treatment, which is nice, especially for our pediatric patients who might be afraid of other therapies like or cryotherapy or intralesional injections,” One limitation is that it is “a bit expensive,” Dr. Barbieri said. “To have topical cidofovir compounded is typically $100-$300, depending on the quantity and strength that you ask for.”
Intralesional cidofovir is another treatment option. In a retrospective study of 58 patients, Dr. Barbieri and colleagues evaluated the outcome of intralesional cidofovir treatment of warts in immunocompromised and nonimmunocompromised patients. Rates of improvement ranged from 98.3% to 100%, while resolution rates ranged from 75.9% to 97.6%.
“Most of the patients had warts for more than 5 years and almost half of them had recalcitrant warts,” Dr. Barbieri said. “These were mostly adult patients, but I think this is a treatment that can work in younger populations as well. About 10%-15% had HIV or cancer or diabetes or were transplant recipients, but despite these challenges and despite these recalcitrant warts, about 100% had improvement.”
He pointed out that cidofovir is available as a 75 mg/mL vial that comes with a 5 mL single-use vial. He dilutes this with normal saline to create a 15 mg/mL solution.
“If you want to be efficient you can try to schedule multiple patients together on the same day as a single vial is sufficient to treat about 25 patients,” assuming about 1 mL is injected per patient, he said. “The challenge with intralesional cidofovir is that it’s painful beyond just the needle part of the injection. Sometimes a nerve block can be helpful. But this can be an effective treatment for patients with recalcitrant warts or those with comorbidities.”
Other intralesional therapies to try for recalcitrant warts, he said, include bleomycin (1 U/mL solution, 1-2 mL per treatment, spaced every 2-4 weeks), and 5-FU (a 4:1 mixture of 5-FU [50 mg/mL] and 2% lidocaine).
Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel for work unrelated to his presentation. Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – Combining or those located in areas that are challenging to treat, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA.
“There are 5 million office visits per year in the United States for warts and molluscum, and they’re most common in pediatrics,” Dr. Barbieri, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “In fact, some studies have suggested that one in three children in primary school suffers from warts.”
According to a 2012 Cochrane review of topical therapies for warts, first-line treatments such as salicylic acid, cryotherapy, 5-FU, or Candida antigen injection often have modest efficacy when used alone. For example, the authors found that salicylic acid and cryotherapy cleared warts in about 60%-70% of cases, respectively, but clearance rates were improved by combining the two therapies.
In an earlier literature review and meta-analysis, investigators evaluated the effect of 5-FU plus salicylic acid or salicylic acid alone. The therapeutic effect for common warts across all studies was a 63.4% response rate (complete healing) for 5-FU/SA vversus 23.1% for the 5-FU–free controls, respectively. For plantar warts, the response rate was 63% versus 11%, respectively.
“But what about the person with multiple warts or those in challenging locations where you might worry about destructive treatments hurting the nail fold or causing nail dystrophy?” Dr. Barbieri asked. “Maybe they’ve used salicylic acid or intralesional Candida and they’re still not getting better. What can we do for these patients?”
Emerging research suggests that topical cidofovir can be a valuable option for recalcitrant warts or those in sensitive locations. In a case report of a 10-year-old boy with more than 50 severe verrucous papules on his hands and face that were recalcitrant to multiple conventional therapies, topical 1% cidofovir applied daily for 8 weeks was effective, with no adverse side effects. A young female patient who presented to Dr. Barbieri with multiple warts around the nail matrix of several fingers experienced complete clearance after treatment with topical cidofovir, he said. Other researchers found this approach to be effective for plantar warts as well, in a report of two brothers with severe combined immunodeficiency after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with persistent warts that did not respond to traditional topical treatments.
“Topical cidofovir is typically a painless treatment, which is nice, especially for our pediatric patients who might be afraid of other therapies like or cryotherapy or intralesional injections,” One limitation is that it is “a bit expensive,” Dr. Barbieri said. “To have topical cidofovir compounded is typically $100-$300, depending on the quantity and strength that you ask for.”
Intralesional cidofovir is another treatment option. In a retrospective study of 58 patients, Dr. Barbieri and colleagues evaluated the outcome of intralesional cidofovir treatment of warts in immunocompromised and nonimmunocompromised patients. Rates of improvement ranged from 98.3% to 100%, while resolution rates ranged from 75.9% to 97.6%.
“Most of the patients had warts for more than 5 years and almost half of them had recalcitrant warts,” Dr. Barbieri said. “These were mostly adult patients, but I think this is a treatment that can work in younger populations as well. About 10%-15% had HIV or cancer or diabetes or were transplant recipients, but despite these challenges and despite these recalcitrant warts, about 100% had improvement.”
He pointed out that cidofovir is available as a 75 mg/mL vial that comes with a 5 mL single-use vial. He dilutes this with normal saline to create a 15 mg/mL solution.
“If you want to be efficient you can try to schedule multiple patients together on the same day as a single vial is sufficient to treat about 25 patients,” assuming about 1 mL is injected per patient, he said. “The challenge with intralesional cidofovir is that it’s painful beyond just the needle part of the injection. Sometimes a nerve block can be helpful. But this can be an effective treatment for patients with recalcitrant warts or those with comorbidities.”
Other intralesional therapies to try for recalcitrant warts, he said, include bleomycin (1 U/mL solution, 1-2 mL per treatment, spaced every 2-4 weeks), and 5-FU (a 4:1 mixture of 5-FU [50 mg/mL] and 2% lidocaine).
Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel for work unrelated to his presentation. Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT THE MEDSCAPELIVE! HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Physician pleads guilty to 52 counts in opioid scheme
Jeffrey B. Sutton, DO, a neuromuscular medicine specialist, pled guilty on January 30 in federal court to 31 counts of illegally prescribing opioids and other controlled substances, 1 count of illegally distributing controlled substances, and 20 counts of health care fraud.
Prosecutors said Dr. Sutton admitted that he ignored warnings from prescription drug management organizations, insurers, and state authorities that he was prescribing excessively high dosages of opioids.
Dr. Sutton also admitted to ignoring patient requests to lower dosages and that he also ignored signs that patients were selling prescribed medications or otherwise engaging in illicit activity, including violations of a “pain management agreement” that he required them to sign.
The fraud counts pertained to Dr. Sutton billing Medicare, Medicaid, and other insurers for medically unnecessary visits that he required of patients so that he could prescribe inappropriate or unnecessary opioids.
In the charging document shared with this news organization, prosecutors said Dr. Sutton had sex with at least three patients, including during office visits and outside of the office. Occasionally, the physician would give opioids or other controlled substances – often benzodiazepines – to these patients, without a prescription or valid medical need.
Dr. Sutton escalated the dosage for one of those patients, even as the subjective pain score did not improve and when the patient’s urine tests showed the presence of THC and buprenorphine, but not any of the prescribed medications.
Another patient came to Dr. Sutton in 2007 with a warning that she had a history of “narcotic-seeking” behavior and diagnoses of depression, anxiety, paranoid schizophrenia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The patient was hospitalized in 2018 for complications from benzodiazepine use (prescribed by Dr. Sutton). She weighed 80 pounds at the time. Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe benzodiazepines and extreme doses of opioids – in excess of 2,000 morphine equivalent dose – “despite recognizing and documenting repeated instances of noncompliance with treatment for psychiatric conditions, and despite the known contraindications of long-term opioid use for patients with these mental illnesses,” according to the charging document.
Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe opioids despite two hospitalizations for overdoses, more than 20 failed urine drug screens that showed presence of illicit drugs such as cocaine, and documented excessive use of alprazolam (Xanax) and methadone.
The physician surrendered his Drug Enforcement Administration Certificate of Registration of Controlled Substances Privileges in February 2022 “as an indication of your good faith in desiring to remedy any incorrect or unlawful practices on your part,” according to a letter to Dr. Sutton from the State Medical Board of Ohio. In that September 2022 letter, the Board notified Dr. Sutton of its intention to possibly suspend or revoke his license.
Dr. Sutton did not request a hearing, and the Board permanently revoked his medical license on January 16.
The court will sentence Dr. Sutton on May 23, according to a report by WFMJ.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey B. Sutton, DO, a neuromuscular medicine specialist, pled guilty on January 30 in federal court to 31 counts of illegally prescribing opioids and other controlled substances, 1 count of illegally distributing controlled substances, and 20 counts of health care fraud.
Prosecutors said Dr. Sutton admitted that he ignored warnings from prescription drug management organizations, insurers, and state authorities that he was prescribing excessively high dosages of opioids.
Dr. Sutton also admitted to ignoring patient requests to lower dosages and that he also ignored signs that patients were selling prescribed medications or otherwise engaging in illicit activity, including violations of a “pain management agreement” that he required them to sign.
The fraud counts pertained to Dr. Sutton billing Medicare, Medicaid, and other insurers for medically unnecessary visits that he required of patients so that he could prescribe inappropriate or unnecessary opioids.
In the charging document shared with this news organization, prosecutors said Dr. Sutton had sex with at least three patients, including during office visits and outside of the office. Occasionally, the physician would give opioids or other controlled substances – often benzodiazepines – to these patients, without a prescription or valid medical need.
Dr. Sutton escalated the dosage for one of those patients, even as the subjective pain score did not improve and when the patient’s urine tests showed the presence of THC and buprenorphine, but not any of the prescribed medications.
Another patient came to Dr. Sutton in 2007 with a warning that she had a history of “narcotic-seeking” behavior and diagnoses of depression, anxiety, paranoid schizophrenia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The patient was hospitalized in 2018 for complications from benzodiazepine use (prescribed by Dr. Sutton). She weighed 80 pounds at the time. Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe benzodiazepines and extreme doses of opioids – in excess of 2,000 morphine equivalent dose – “despite recognizing and documenting repeated instances of noncompliance with treatment for psychiatric conditions, and despite the known contraindications of long-term opioid use for patients with these mental illnesses,” according to the charging document.
Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe opioids despite two hospitalizations for overdoses, more than 20 failed urine drug screens that showed presence of illicit drugs such as cocaine, and documented excessive use of alprazolam (Xanax) and methadone.
The physician surrendered his Drug Enforcement Administration Certificate of Registration of Controlled Substances Privileges in February 2022 “as an indication of your good faith in desiring to remedy any incorrect or unlawful practices on your part,” according to a letter to Dr. Sutton from the State Medical Board of Ohio. In that September 2022 letter, the Board notified Dr. Sutton of its intention to possibly suspend or revoke his license.
Dr. Sutton did not request a hearing, and the Board permanently revoked his medical license on January 16.
The court will sentence Dr. Sutton on May 23, according to a report by WFMJ.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey B. Sutton, DO, a neuromuscular medicine specialist, pled guilty on January 30 in federal court to 31 counts of illegally prescribing opioids and other controlled substances, 1 count of illegally distributing controlled substances, and 20 counts of health care fraud.
Prosecutors said Dr. Sutton admitted that he ignored warnings from prescription drug management organizations, insurers, and state authorities that he was prescribing excessively high dosages of opioids.
Dr. Sutton also admitted to ignoring patient requests to lower dosages and that he also ignored signs that patients were selling prescribed medications or otherwise engaging in illicit activity, including violations of a “pain management agreement” that he required them to sign.
The fraud counts pertained to Dr. Sutton billing Medicare, Medicaid, and other insurers for medically unnecessary visits that he required of patients so that he could prescribe inappropriate or unnecessary opioids.
In the charging document shared with this news organization, prosecutors said Dr. Sutton had sex with at least three patients, including during office visits and outside of the office. Occasionally, the physician would give opioids or other controlled substances – often benzodiazepines – to these patients, without a prescription or valid medical need.
Dr. Sutton escalated the dosage for one of those patients, even as the subjective pain score did not improve and when the patient’s urine tests showed the presence of THC and buprenorphine, but not any of the prescribed medications.
Another patient came to Dr. Sutton in 2007 with a warning that she had a history of “narcotic-seeking” behavior and diagnoses of depression, anxiety, paranoid schizophrenia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The patient was hospitalized in 2018 for complications from benzodiazepine use (prescribed by Dr. Sutton). She weighed 80 pounds at the time. Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe benzodiazepines and extreme doses of opioids – in excess of 2,000 morphine equivalent dose – “despite recognizing and documenting repeated instances of noncompliance with treatment for psychiatric conditions, and despite the known contraindications of long-term opioid use for patients with these mental illnesses,” according to the charging document.
Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe opioids despite two hospitalizations for overdoses, more than 20 failed urine drug screens that showed presence of illicit drugs such as cocaine, and documented excessive use of alprazolam (Xanax) and methadone.
The physician surrendered his Drug Enforcement Administration Certificate of Registration of Controlled Substances Privileges in February 2022 “as an indication of your good faith in desiring to remedy any incorrect or unlawful practices on your part,” according to a letter to Dr. Sutton from the State Medical Board of Ohio. In that September 2022 letter, the Board notified Dr. Sutton of its intention to possibly suspend or revoke his license.
Dr. Sutton did not request a hearing, and the Board permanently revoked his medical license on January 16.
The court will sentence Dr. Sutton on May 23, according to a report by WFMJ.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Toxic chemicals we consume without knowing it
Life expectancy is falling precipitously. Three-fourths of Americans are overweight or obese, half have diabetes or prediabetes, and a majority are metabolically unhealthy. Furthermore, the rates of allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases are rising at rates of 3%-9% per year in the West, far faster than the speed of genetic change in this population.
Of course, diet and lifestyle are major factors behind such trends, but a grossly underappreciated driver in what ails us is the role of environmental toxins and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. In years past, these factors have largely evaded the traditional Western medical establishment; however, mounting evidence now supports their significance in fertility, metabolic health, and cancer.
Although several industrial chemicals and toxins have been identified as carcinogens and have subsequently been regulated, many more remain persistent in the environment and continue to be freely used. It is therefore incumbent upon both the general public and clinicians to be knowledgeable about these exposures. Here, we review some of the most common exposures and the substantial health risks associated with them, along with some general guidance around best practices for how to minimize exposure.
Microplastics
“Microplastics” is a term used to describe small fragments or particles of plastic breakdown or microbeads from household or personal care products, measuring less than 5 mm in length.
Plastic waste is accumulating at alarming and devastating proportions – by 2050, it is estimated that by weight, there will be more plastic than fish in the oceans. That translates into hundreds of thousands of tons of microplastics and trillions of these particles in the seas. A recent study demonstrated that microplastics were present in the bloodstream in the majority of 22 otherwise healthy participants.
Since the 1950s, plastic exposure has been shown to promote tumorigenesis in animal studies, and in vitro studies have demonstrated the toxicity of microplastics at the cellular level. However, it is not well known whether the plastic itself is toxic or if it simply serves as a carrier for other environmental toxins to bioaccumulate.
According to Tasha Stoiber, a senior scientist at the Environmental Working Group, “Microplastics have been widely detected in fish and seafood, as well as other products like bottled water, beer, honey, and tap water.” The EWG states there are no formal advisories on fish consumption to avoid exposure to microplastics at the moment.
Pressure also is mounting for a ban on microbeads in personal care products.
Until such bans are put in place, it is advised to avoid single-use plastics, favor reusable tote bags for grocery shopping rather than plastic bags, and opt for loose leaf tea or paper tea bags rather than mesh-based alternatives.
Phthalates
Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastics soft and durable, as well as to bind fragrances. They are commonly found in household items such as vinyl (for example, flooring, shower curtains) and fragrances, air fresheners, and perfumes.
Phthalates are known hormone-disrupting chemicals, exposure to which has been associated with abnormal sexual and brain development in children, as well as lower levels of testosterone in men. Exposures are thought to occur via inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact; however, fasting studies demonstrate that a majority of exposure is probably food related.
To avoid phthalate exposures, recommendations include avoiding polyvinyl chloride plastics (particularly food containers, plastic wrap, and children’s toys), which are identifiable by the recycle code number 3, as well as air fresheners and fragranced products.
The EWG’s Skin Deep database provides an important resource on phthalate-free personal care products.
Despite pressure from consumer advocacy groups, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet banned phthalates in food packaging.
Bisphenol A (BPA)
BPA is a chemical additive used to make clear and hard polycarbonate plastics, as well as epoxy and thermal papers. BPA is one of the highest-volume chemicals, with roughly 6 billion pounds produced each year. BPA is traditionally found in many clear plastic bottles and sippy cups, as well as in the lining of canned foods.
Structurally, BPA acts as an estrogen mimetic and has been associated with cardiovascular disease, obesity, and male sexual dysfunction. Since 2012, BPA has been banned in sippy cups and baby bottles, but there is some debate as to whether its replacements (bisphenol S and bisphenol F) are any safer; they appear to have similar hormonal effects as BPA.
As with phthalates, the majority of ingestion is thought to be food related. BPA has been found in more than 90% of a representative study population in the United States.
Guidance advises avoiding polycarbonate plastics (identifiable with the recycling code number 7), as well as avoiding handling thermal papers such as tickets and receipts, if possible. Food and beverages should be stored in glass or stainless steel. If plastic must be used, opt for polycarbonate- and polyvinyl chloride–free plastics, and food and beverages should never be reheated in plastic containers or wrapping. Canned foods should ideally be avoided, particularly canned tunas and condensed soups. If canned products are bought, they should ideally be BPA free.
Dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
Dioxins are mainly the byproducts of industrial practices; they are released after incineration, trash burning, and fires. PCBs, which are somewhat structurally related to dioxins, were previously found in products such as flame retardants and coolants. Dioxins and PCBs are often grouped in the same category under the umbrella term “persistent organic pollutants” because they break down slowly and remain in the environment even after emissions have been curbed.
Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, perhaps the best-known dioxin, is a known carcinogen. Dioxins also have been associated with a host of health implications in development, immunity, and reproductive and endocrine systems. Higher levels of PCB exposure have also been associated with an increased risk for mortality from cardiovascular disease.
Notably, dioxin emissions have been reduced by 90% since the 1980s, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has banned the use of PCBs in industrial manufacturing since 1979. However, environmental dioxins and PCBs still enter the food chain and accumulate in fat.
The best ways to avoid exposures are through limiting meat, fish, and dairy consumption and trimming the skin and fat from meats. The level of dioxins and PCBs found in meat, eggs, fish, and dairy are approximately 5-10 times higher than they are in plant-based foods. Research has shown that farmed salmon is likely to be the most PCB-contaminated protein source in the U.S. diet; however, newer forms of land-based and sustainable aquaculture probably avoid this exposure.
Pesticides
The growth of modern monoculture agriculture in the United States over the past century has coincided with a dramatic surge in the use of industrial pesticides. In fact, over 90% of the U.S. population have pesticides in their urine and blood, regardless of where they live. Exposures are thought to be food related.
Approximately 1 billion pounds of pesticides are used annually in the United States, including nearly 300 million pounds of glyphosate, which has been identified as a probable carcinogen by European agencies. The EPA has not yet reached this conclusion, although the matter is currently being litigated.
A large European prospective cohort trial demonstrated a lower risk for cancer in those with a greater frequency of self-reported organic food consumption. In addition to cancer risk, relatively elevated blood levels of a pesticide known as beta-hexachlorocyclohexane (B-HCH) are associated with higher all-cause mortality. Also, exposure to DDE – a metabolite of DDT, a chlorinated pesticide heavily used in the 1940s-1960s that still persists in the environment today – has been shown to increase the risk for Alzheimer’s-type dementia as well as overall cognitive decline.
Because these chlorinated pesticides are often fat soluble, they seem to accumulate in animal products. Therefore, people consuming a vegetarian diet have been found to have lower levels of B-HCH. This has led to the recommendation that consumers of produce should favor organic over conventional, if possible. Here too, the EWG provides an important resource to consumers in the form of shopper guides regarding pesticides in produce.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)
PFAS are a group of fluorinated compounds discovered in the 1930s. Their chemical composition includes a durable carbon-fluoride bond, giving them a persistence within the environment that has led to their being referred to as “forever chemicals.”
PFAS have been detected in the blood of 98% of Americans, and in the rainwater of locations as far afield as Tibet and Antarctica. Even low levels of exposure have been associated with an increased risk for cancer, liver disease, low birth weight, and hormonal disruption.
The properties of PFAS also make them both durable at very high heat and water repellent. Notoriously, the chemical was used by 3M to make Scotchgard for carpets and fabrics and by Dupont to make Teflon for nonstick coating of pots and pans. Although perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was removed from nonstick cookware in 2013, PFAS – a family of thousands of synthetic compounds – remain common in fast-food packaging, water- and stain-repellent clothing, firefighting foam, and personal care products. PFAS are released into the environment during the breakdown of these consumer and industrial products, as well as from dumping from waste facilities.
Alarmingly, the EWG notes that up to 200 million Americans may be exposed to PFAS in their drinking water. In March 2021, the EPA announced that they will be regulating PFAS in drinking water; however, the regulations have not been finalized. Currently, it is up to individual states to test for its presence in the water. The EWG has compiled a map of all known PFAS contamination sites.
To avoid or prevent exposures from PFAS, recommendations include filtering tap water with either reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters, as well as avoiding fast food and carry-out food, if possible, and consumer products labeled as “water resistant,” “stain-resistant,” and “nonstick.”
In a testament to how harmful these chemicals are, the EPA recently revised their lifetime health advisories for PFAS, such as PFOA, to 0.004 parts per trillion, which is more than 10,000 times smaller than the previous limit of 70 parts per trillion. The EPA also has proposed formally designating certain PFAS chemicals as “hazardous substances.”
Dr. Goel, clinical assistant professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Life expectancy is falling precipitously. Three-fourths of Americans are overweight or obese, half have diabetes or prediabetes, and a majority are metabolically unhealthy. Furthermore, the rates of allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases are rising at rates of 3%-9% per year in the West, far faster than the speed of genetic change in this population.
Of course, diet and lifestyle are major factors behind such trends, but a grossly underappreciated driver in what ails us is the role of environmental toxins and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. In years past, these factors have largely evaded the traditional Western medical establishment; however, mounting evidence now supports their significance in fertility, metabolic health, and cancer.
Although several industrial chemicals and toxins have been identified as carcinogens and have subsequently been regulated, many more remain persistent in the environment and continue to be freely used. It is therefore incumbent upon both the general public and clinicians to be knowledgeable about these exposures. Here, we review some of the most common exposures and the substantial health risks associated with them, along with some general guidance around best practices for how to minimize exposure.
Microplastics
“Microplastics” is a term used to describe small fragments or particles of plastic breakdown or microbeads from household or personal care products, measuring less than 5 mm in length.
Plastic waste is accumulating at alarming and devastating proportions – by 2050, it is estimated that by weight, there will be more plastic than fish in the oceans. That translates into hundreds of thousands of tons of microplastics and trillions of these particles in the seas. A recent study demonstrated that microplastics were present in the bloodstream in the majority of 22 otherwise healthy participants.
Since the 1950s, plastic exposure has been shown to promote tumorigenesis in animal studies, and in vitro studies have demonstrated the toxicity of microplastics at the cellular level. However, it is not well known whether the plastic itself is toxic or if it simply serves as a carrier for other environmental toxins to bioaccumulate.
According to Tasha Stoiber, a senior scientist at the Environmental Working Group, “Microplastics have been widely detected in fish and seafood, as well as other products like bottled water, beer, honey, and tap water.” The EWG states there are no formal advisories on fish consumption to avoid exposure to microplastics at the moment.
Pressure also is mounting for a ban on microbeads in personal care products.
Until such bans are put in place, it is advised to avoid single-use plastics, favor reusable tote bags for grocery shopping rather than plastic bags, and opt for loose leaf tea or paper tea bags rather than mesh-based alternatives.
Phthalates
Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastics soft and durable, as well as to bind fragrances. They are commonly found in household items such as vinyl (for example, flooring, shower curtains) and fragrances, air fresheners, and perfumes.
Phthalates are known hormone-disrupting chemicals, exposure to which has been associated with abnormal sexual and brain development in children, as well as lower levels of testosterone in men. Exposures are thought to occur via inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact; however, fasting studies demonstrate that a majority of exposure is probably food related.
To avoid phthalate exposures, recommendations include avoiding polyvinyl chloride plastics (particularly food containers, plastic wrap, and children’s toys), which are identifiable by the recycle code number 3, as well as air fresheners and fragranced products.
The EWG’s Skin Deep database provides an important resource on phthalate-free personal care products.
Despite pressure from consumer advocacy groups, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet banned phthalates in food packaging.
Bisphenol A (BPA)
BPA is a chemical additive used to make clear and hard polycarbonate plastics, as well as epoxy and thermal papers. BPA is one of the highest-volume chemicals, with roughly 6 billion pounds produced each year. BPA is traditionally found in many clear plastic bottles and sippy cups, as well as in the lining of canned foods.
Structurally, BPA acts as an estrogen mimetic and has been associated with cardiovascular disease, obesity, and male sexual dysfunction. Since 2012, BPA has been banned in sippy cups and baby bottles, but there is some debate as to whether its replacements (bisphenol S and bisphenol F) are any safer; they appear to have similar hormonal effects as BPA.
As with phthalates, the majority of ingestion is thought to be food related. BPA has been found in more than 90% of a representative study population in the United States.
Guidance advises avoiding polycarbonate plastics (identifiable with the recycling code number 7), as well as avoiding handling thermal papers such as tickets and receipts, if possible. Food and beverages should be stored in glass or stainless steel. If plastic must be used, opt for polycarbonate- and polyvinyl chloride–free plastics, and food and beverages should never be reheated in plastic containers or wrapping. Canned foods should ideally be avoided, particularly canned tunas and condensed soups. If canned products are bought, they should ideally be BPA free.
Dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
Dioxins are mainly the byproducts of industrial practices; they are released after incineration, trash burning, and fires. PCBs, which are somewhat structurally related to dioxins, were previously found in products such as flame retardants and coolants. Dioxins and PCBs are often grouped in the same category under the umbrella term “persistent organic pollutants” because they break down slowly and remain in the environment even after emissions have been curbed.
Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, perhaps the best-known dioxin, is a known carcinogen. Dioxins also have been associated with a host of health implications in development, immunity, and reproductive and endocrine systems. Higher levels of PCB exposure have also been associated with an increased risk for mortality from cardiovascular disease.
Notably, dioxin emissions have been reduced by 90% since the 1980s, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has banned the use of PCBs in industrial manufacturing since 1979. However, environmental dioxins and PCBs still enter the food chain and accumulate in fat.
The best ways to avoid exposures are through limiting meat, fish, and dairy consumption and trimming the skin and fat from meats. The level of dioxins and PCBs found in meat, eggs, fish, and dairy are approximately 5-10 times higher than they are in plant-based foods. Research has shown that farmed salmon is likely to be the most PCB-contaminated protein source in the U.S. diet; however, newer forms of land-based and sustainable aquaculture probably avoid this exposure.
Pesticides
The growth of modern monoculture agriculture in the United States over the past century has coincided with a dramatic surge in the use of industrial pesticides. In fact, over 90% of the U.S. population have pesticides in their urine and blood, regardless of where they live. Exposures are thought to be food related.
Approximately 1 billion pounds of pesticides are used annually in the United States, including nearly 300 million pounds of glyphosate, which has been identified as a probable carcinogen by European agencies. The EPA has not yet reached this conclusion, although the matter is currently being litigated.
A large European prospective cohort trial demonstrated a lower risk for cancer in those with a greater frequency of self-reported organic food consumption. In addition to cancer risk, relatively elevated blood levels of a pesticide known as beta-hexachlorocyclohexane (B-HCH) are associated with higher all-cause mortality. Also, exposure to DDE – a metabolite of DDT, a chlorinated pesticide heavily used in the 1940s-1960s that still persists in the environment today – has been shown to increase the risk for Alzheimer’s-type dementia as well as overall cognitive decline.
Because these chlorinated pesticides are often fat soluble, they seem to accumulate in animal products. Therefore, people consuming a vegetarian diet have been found to have lower levels of B-HCH. This has led to the recommendation that consumers of produce should favor organic over conventional, if possible. Here too, the EWG provides an important resource to consumers in the form of shopper guides regarding pesticides in produce.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)
PFAS are a group of fluorinated compounds discovered in the 1930s. Their chemical composition includes a durable carbon-fluoride bond, giving them a persistence within the environment that has led to their being referred to as “forever chemicals.”
PFAS have been detected in the blood of 98% of Americans, and in the rainwater of locations as far afield as Tibet and Antarctica. Even low levels of exposure have been associated with an increased risk for cancer, liver disease, low birth weight, and hormonal disruption.
The properties of PFAS also make them both durable at very high heat and water repellent. Notoriously, the chemical was used by 3M to make Scotchgard for carpets and fabrics and by Dupont to make Teflon for nonstick coating of pots and pans. Although perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was removed from nonstick cookware in 2013, PFAS – a family of thousands of synthetic compounds – remain common in fast-food packaging, water- and stain-repellent clothing, firefighting foam, and personal care products. PFAS are released into the environment during the breakdown of these consumer and industrial products, as well as from dumping from waste facilities.
Alarmingly, the EWG notes that up to 200 million Americans may be exposed to PFAS in their drinking water. In March 2021, the EPA announced that they will be regulating PFAS in drinking water; however, the regulations have not been finalized. Currently, it is up to individual states to test for its presence in the water. The EWG has compiled a map of all known PFAS contamination sites.
To avoid or prevent exposures from PFAS, recommendations include filtering tap water with either reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters, as well as avoiding fast food and carry-out food, if possible, and consumer products labeled as “water resistant,” “stain-resistant,” and “nonstick.”
In a testament to how harmful these chemicals are, the EPA recently revised their lifetime health advisories for PFAS, such as PFOA, to 0.004 parts per trillion, which is more than 10,000 times smaller than the previous limit of 70 parts per trillion. The EPA also has proposed formally designating certain PFAS chemicals as “hazardous substances.”
Dr. Goel, clinical assistant professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Life expectancy is falling precipitously. Three-fourths of Americans are overweight or obese, half have diabetes or prediabetes, and a majority are metabolically unhealthy. Furthermore, the rates of allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases are rising at rates of 3%-9% per year in the West, far faster than the speed of genetic change in this population.
Of course, diet and lifestyle are major factors behind such trends, but a grossly underappreciated driver in what ails us is the role of environmental toxins and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. In years past, these factors have largely evaded the traditional Western medical establishment; however, mounting evidence now supports their significance in fertility, metabolic health, and cancer.
Although several industrial chemicals and toxins have been identified as carcinogens and have subsequently been regulated, many more remain persistent in the environment and continue to be freely used. It is therefore incumbent upon both the general public and clinicians to be knowledgeable about these exposures. Here, we review some of the most common exposures and the substantial health risks associated with them, along with some general guidance around best practices for how to minimize exposure.
Microplastics
“Microplastics” is a term used to describe small fragments or particles of plastic breakdown or microbeads from household or personal care products, measuring less than 5 mm in length.
Plastic waste is accumulating at alarming and devastating proportions – by 2050, it is estimated that by weight, there will be more plastic than fish in the oceans. That translates into hundreds of thousands of tons of microplastics and trillions of these particles in the seas. A recent study demonstrated that microplastics were present in the bloodstream in the majority of 22 otherwise healthy participants.
Since the 1950s, plastic exposure has been shown to promote tumorigenesis in animal studies, and in vitro studies have demonstrated the toxicity of microplastics at the cellular level. However, it is not well known whether the plastic itself is toxic or if it simply serves as a carrier for other environmental toxins to bioaccumulate.
According to Tasha Stoiber, a senior scientist at the Environmental Working Group, “Microplastics have been widely detected in fish and seafood, as well as other products like bottled water, beer, honey, and tap water.” The EWG states there are no formal advisories on fish consumption to avoid exposure to microplastics at the moment.
Pressure also is mounting for a ban on microbeads in personal care products.
Until such bans are put in place, it is advised to avoid single-use plastics, favor reusable tote bags for grocery shopping rather than plastic bags, and opt for loose leaf tea or paper tea bags rather than mesh-based alternatives.
Phthalates
Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastics soft and durable, as well as to bind fragrances. They are commonly found in household items such as vinyl (for example, flooring, shower curtains) and fragrances, air fresheners, and perfumes.
Phthalates are known hormone-disrupting chemicals, exposure to which has been associated with abnormal sexual and brain development in children, as well as lower levels of testosterone in men. Exposures are thought to occur via inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact; however, fasting studies demonstrate that a majority of exposure is probably food related.
To avoid phthalate exposures, recommendations include avoiding polyvinyl chloride plastics (particularly food containers, plastic wrap, and children’s toys), which are identifiable by the recycle code number 3, as well as air fresheners and fragranced products.
The EWG’s Skin Deep database provides an important resource on phthalate-free personal care products.
Despite pressure from consumer advocacy groups, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet banned phthalates in food packaging.
Bisphenol A (BPA)
BPA is a chemical additive used to make clear and hard polycarbonate plastics, as well as epoxy and thermal papers. BPA is one of the highest-volume chemicals, with roughly 6 billion pounds produced each year. BPA is traditionally found in many clear plastic bottles and sippy cups, as well as in the lining of canned foods.
Structurally, BPA acts as an estrogen mimetic and has been associated with cardiovascular disease, obesity, and male sexual dysfunction. Since 2012, BPA has been banned in sippy cups and baby bottles, but there is some debate as to whether its replacements (bisphenol S and bisphenol F) are any safer; they appear to have similar hormonal effects as BPA.
As with phthalates, the majority of ingestion is thought to be food related. BPA has been found in more than 90% of a representative study population in the United States.
Guidance advises avoiding polycarbonate plastics (identifiable with the recycling code number 7), as well as avoiding handling thermal papers such as tickets and receipts, if possible. Food and beverages should be stored in glass or stainless steel. If plastic must be used, opt for polycarbonate- and polyvinyl chloride–free plastics, and food and beverages should never be reheated in plastic containers or wrapping. Canned foods should ideally be avoided, particularly canned tunas and condensed soups. If canned products are bought, they should ideally be BPA free.
Dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
Dioxins are mainly the byproducts of industrial practices; they are released after incineration, trash burning, and fires. PCBs, which are somewhat structurally related to dioxins, were previously found in products such as flame retardants and coolants. Dioxins and PCBs are often grouped in the same category under the umbrella term “persistent organic pollutants” because they break down slowly and remain in the environment even after emissions have been curbed.
Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, perhaps the best-known dioxin, is a known carcinogen. Dioxins also have been associated with a host of health implications in development, immunity, and reproductive and endocrine systems. Higher levels of PCB exposure have also been associated with an increased risk for mortality from cardiovascular disease.
Notably, dioxin emissions have been reduced by 90% since the 1980s, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has banned the use of PCBs in industrial manufacturing since 1979. However, environmental dioxins and PCBs still enter the food chain and accumulate in fat.
The best ways to avoid exposures are through limiting meat, fish, and dairy consumption and trimming the skin and fat from meats. The level of dioxins and PCBs found in meat, eggs, fish, and dairy are approximately 5-10 times higher than they are in plant-based foods. Research has shown that farmed salmon is likely to be the most PCB-contaminated protein source in the U.S. diet; however, newer forms of land-based and sustainable aquaculture probably avoid this exposure.
Pesticides
The growth of modern monoculture agriculture in the United States over the past century has coincided with a dramatic surge in the use of industrial pesticides. In fact, over 90% of the U.S. population have pesticides in their urine and blood, regardless of where they live. Exposures are thought to be food related.
Approximately 1 billion pounds of pesticides are used annually in the United States, including nearly 300 million pounds of glyphosate, which has been identified as a probable carcinogen by European agencies. The EPA has not yet reached this conclusion, although the matter is currently being litigated.
A large European prospective cohort trial demonstrated a lower risk for cancer in those with a greater frequency of self-reported organic food consumption. In addition to cancer risk, relatively elevated blood levels of a pesticide known as beta-hexachlorocyclohexane (B-HCH) are associated with higher all-cause mortality. Also, exposure to DDE – a metabolite of DDT, a chlorinated pesticide heavily used in the 1940s-1960s that still persists in the environment today – has been shown to increase the risk for Alzheimer’s-type dementia as well as overall cognitive decline.
Because these chlorinated pesticides are often fat soluble, they seem to accumulate in animal products. Therefore, people consuming a vegetarian diet have been found to have lower levels of B-HCH. This has led to the recommendation that consumers of produce should favor organic over conventional, if possible. Here too, the EWG provides an important resource to consumers in the form of shopper guides regarding pesticides in produce.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)
PFAS are a group of fluorinated compounds discovered in the 1930s. Their chemical composition includes a durable carbon-fluoride bond, giving them a persistence within the environment that has led to their being referred to as “forever chemicals.”
PFAS have been detected in the blood of 98% of Americans, and in the rainwater of locations as far afield as Tibet and Antarctica. Even low levels of exposure have been associated with an increased risk for cancer, liver disease, low birth weight, and hormonal disruption.
The properties of PFAS also make them both durable at very high heat and water repellent. Notoriously, the chemical was used by 3M to make Scotchgard for carpets and fabrics and by Dupont to make Teflon for nonstick coating of pots and pans. Although perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was removed from nonstick cookware in 2013, PFAS – a family of thousands of synthetic compounds – remain common in fast-food packaging, water- and stain-repellent clothing, firefighting foam, and personal care products. PFAS are released into the environment during the breakdown of these consumer and industrial products, as well as from dumping from waste facilities.
Alarmingly, the EWG notes that up to 200 million Americans may be exposed to PFAS in their drinking water. In March 2021, the EPA announced that they will be regulating PFAS in drinking water; however, the regulations have not been finalized. Currently, it is up to individual states to test for its presence in the water. The EWG has compiled a map of all known PFAS contamination sites.
To avoid or prevent exposures from PFAS, recommendations include filtering tap water with either reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters, as well as avoiding fast food and carry-out food, if possible, and consumer products labeled as “water resistant,” “stain-resistant,” and “nonstick.”
In a testament to how harmful these chemicals are, the EPA recently revised their lifetime health advisories for PFAS, such as PFOA, to 0.004 parts per trillion, which is more than 10,000 times smaller than the previous limit of 70 parts per trillion. The EPA also has proposed formally designating certain PFAS chemicals as “hazardous substances.”
Dr. Goel, clinical assistant professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians and clinicians should be required to get flu shots: Ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Doxy PEP does not lower risk of STIs in cisgender women
The benefits of doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in men and transgender women do not appear to extend to cisgender women, who have disproportionately high rates of infection in many regions.
“This was the first trial to evaluate doxycycline PEP for cisgender women,” said first author Jenell Stewart, DO, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in discussing the findings at a press conference at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“Unfortunately, our primary outcome was not statistically significant – we did not see a reduction in STIs among cisgender women, which is in stark contrast to [reported effects] among cisgender men and transgender women,” she said.
The findings are from a study of 449 nonpregnant cisgender women (mean age, 24 years) in Kenya who had been taking daily oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for a median of about 7 months.
The women were randomly assigned to receive either Doxy PEP 200 mg, to be taken within 72 hours of sex (n = 224), or standard care, which included quarterly screening and treatment of STIs (n = 225).
Of the women, 36.7% reported transactional sex at enrollment; their baseline prevalence of STIs was 17.9%, including 14.1% with chlamydia, 3.8% gonorrhea, and 0.4% syphilis. There were no differences between the study groups.
In surveys, 78% of the women reported adherence to the use of Doxy PEP; they took the prophylaxis at least as many days as they had sex.
Nevertheless, there was no significant difference in the incidence of STIs, reported over 1 year, at quarterly visits that included genital STI testing, between groups, with 50 patients in the Doxy PEP group and 59 in the standard screening group developing STIs (relative risk, 0.88; P = .51).
Of the infections, 85 were chlamydia, including 35 in the Doxy PEP group and 50 with standard of care, while 31 were gonorrhea, including 19 in the Doxy PEP group and 12 with standard of care; 8 had both infections, and there was 1 syphilis infection.
The results were consistent across subanalyses of patients grouped according to STI, who became pregnant (n = 80), or sorted by other factors including age, contraceptive use, transactional sex, and STI at baseline.
None of the women developed HIV, and there were no serious events associated with the Doxy PEP treatment.
Cisgender women bear ‘highest burden’ of STIs
The findings are disappointing in light of the higher rates of STIs among cisgender women, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that women also disproportionately bear the long-term consequences of STIs.
“For example, each year, untreated sexually transmitted diseases cause infertility in at least 20,000 women in the United States, and a pregnant woman is highly likely to pass syphilis unto her unborn baby if left untested or untreated,” the CDC reports.
The STI rates are particularly high for women taking HIV PrEP in regions like East Africa, where rates of STIs among cisgender women in many cases are higher than rates for men taking PrEP in high income countries, Dr. Stewart said.
Previous studies of Doxy PEP in men and transgender women taking HIV PrEP, including new research presented at CROI, have shown highly encouraging reductions in STIs, at rates of up to approximately 80% for chlamydia and syphilis.
Adherence, anatomy, resistance
The key theories for the lack of a prevention of infections in cisgender women surround the issues of resistances, as well as anatomy and adherence, said Dr. Stewart.
In terms of bacterial resistances, while initial testing in a limited number of samples the study found no evidence of markers of resistance for chlamydia, all of the gonorrhea samples did show tetracycline-resistant N gonorrhea at baseline and follow-up in both groups.
Regarding anatomic differences, doxycycline may not prevent STIs in endocervical tissue among cisgender women, Dr. Stewart noted. Women are known to be at higher risk of infection because the lining of the vagina is thinner than the skin of the penis, allowing for easier penetration of bacteria and viruses.
The study was designed to optimize adherence to Doxy PEP. Measures included monitoring with weekly text message surveys, in which the women reported a high rate of adherence.
The overall retention rate in the study was high; as many as 97% of the quarterly follow-up visits were completed, including 95% in the Doxy PEP group and 98% of the standard care group. The response rate for the weekly surveys was 81%.
Of note, women reported the use of the treatment to be “imperfect,” suggesting social problems, such as biases toward the use of the prophylaxis.
The results underscore the need for ongoing efforts to make sure no groups of patients are left behind as interventions advance, Dr. Stewart said.
“The burden of STIs on cisgender women is large and growing,” she concluded. “STI prevention interventions are needed.”
Commenting on the study, Renee A. Heffron, PhD, MPH, said the findings “are somewhat surprising because results from trials in other populations have been positive.
“But cisgender women are exposed through the cervix, and this tissue is different from rectal or urethral tissue,” Dr. Heffron, a professor at the department of medicine and director of the Center for AIDS Research at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, told this news organization.
Further findings from the research should help shed light on key issues of adherence and drug concentration levels in cervical tissue, she added.
“For cisgender women, these data are the first and the beginning of understanding whether this is a viable strategy,” Dr. Heffron said.
“We have more to learn to better understand the results from the trial main outcomes, and if there are tweaks to this strategy that would improve efficacy.”
The authors and Dr. Heffron have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in men and transgender women do not appear to extend to cisgender women, who have disproportionately high rates of infection in many regions.
“This was the first trial to evaluate doxycycline PEP for cisgender women,” said first author Jenell Stewart, DO, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in discussing the findings at a press conference at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“Unfortunately, our primary outcome was not statistically significant – we did not see a reduction in STIs among cisgender women, which is in stark contrast to [reported effects] among cisgender men and transgender women,” she said.
The findings are from a study of 449 nonpregnant cisgender women (mean age, 24 years) in Kenya who had been taking daily oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for a median of about 7 months.
The women were randomly assigned to receive either Doxy PEP 200 mg, to be taken within 72 hours of sex (n = 224), or standard care, which included quarterly screening and treatment of STIs (n = 225).
Of the women, 36.7% reported transactional sex at enrollment; their baseline prevalence of STIs was 17.9%, including 14.1% with chlamydia, 3.8% gonorrhea, and 0.4% syphilis. There were no differences between the study groups.
In surveys, 78% of the women reported adherence to the use of Doxy PEP; they took the prophylaxis at least as many days as they had sex.
Nevertheless, there was no significant difference in the incidence of STIs, reported over 1 year, at quarterly visits that included genital STI testing, between groups, with 50 patients in the Doxy PEP group and 59 in the standard screening group developing STIs (relative risk, 0.88; P = .51).
Of the infections, 85 were chlamydia, including 35 in the Doxy PEP group and 50 with standard of care, while 31 were gonorrhea, including 19 in the Doxy PEP group and 12 with standard of care; 8 had both infections, and there was 1 syphilis infection.
The results were consistent across subanalyses of patients grouped according to STI, who became pregnant (n = 80), or sorted by other factors including age, contraceptive use, transactional sex, and STI at baseline.
None of the women developed HIV, and there were no serious events associated with the Doxy PEP treatment.
Cisgender women bear ‘highest burden’ of STIs
The findings are disappointing in light of the higher rates of STIs among cisgender women, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that women also disproportionately bear the long-term consequences of STIs.
“For example, each year, untreated sexually transmitted diseases cause infertility in at least 20,000 women in the United States, and a pregnant woman is highly likely to pass syphilis unto her unborn baby if left untested or untreated,” the CDC reports.
The STI rates are particularly high for women taking HIV PrEP in regions like East Africa, where rates of STIs among cisgender women in many cases are higher than rates for men taking PrEP in high income countries, Dr. Stewart said.
Previous studies of Doxy PEP in men and transgender women taking HIV PrEP, including new research presented at CROI, have shown highly encouraging reductions in STIs, at rates of up to approximately 80% for chlamydia and syphilis.
Adherence, anatomy, resistance
The key theories for the lack of a prevention of infections in cisgender women surround the issues of resistances, as well as anatomy and adherence, said Dr. Stewart.
In terms of bacterial resistances, while initial testing in a limited number of samples the study found no evidence of markers of resistance for chlamydia, all of the gonorrhea samples did show tetracycline-resistant N gonorrhea at baseline and follow-up in both groups.
Regarding anatomic differences, doxycycline may not prevent STIs in endocervical tissue among cisgender women, Dr. Stewart noted. Women are known to be at higher risk of infection because the lining of the vagina is thinner than the skin of the penis, allowing for easier penetration of bacteria and viruses.
The study was designed to optimize adherence to Doxy PEP. Measures included monitoring with weekly text message surveys, in which the women reported a high rate of adherence.
The overall retention rate in the study was high; as many as 97% of the quarterly follow-up visits were completed, including 95% in the Doxy PEP group and 98% of the standard care group. The response rate for the weekly surveys was 81%.
Of note, women reported the use of the treatment to be “imperfect,” suggesting social problems, such as biases toward the use of the prophylaxis.
The results underscore the need for ongoing efforts to make sure no groups of patients are left behind as interventions advance, Dr. Stewart said.
“The burden of STIs on cisgender women is large and growing,” she concluded. “STI prevention interventions are needed.”
Commenting on the study, Renee A. Heffron, PhD, MPH, said the findings “are somewhat surprising because results from trials in other populations have been positive.
“But cisgender women are exposed through the cervix, and this tissue is different from rectal or urethral tissue,” Dr. Heffron, a professor at the department of medicine and director of the Center for AIDS Research at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, told this news organization.
Further findings from the research should help shed light on key issues of adherence and drug concentration levels in cervical tissue, she added.
“For cisgender women, these data are the first and the beginning of understanding whether this is a viable strategy,” Dr. Heffron said.
“We have more to learn to better understand the results from the trial main outcomes, and if there are tweaks to this strategy that would improve efficacy.”
The authors and Dr. Heffron have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in men and transgender women do not appear to extend to cisgender women, who have disproportionately high rates of infection in many regions.
“This was the first trial to evaluate doxycycline PEP for cisgender women,” said first author Jenell Stewart, DO, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in discussing the findings at a press conference at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“Unfortunately, our primary outcome was not statistically significant – we did not see a reduction in STIs among cisgender women, which is in stark contrast to [reported effects] among cisgender men and transgender women,” she said.
The findings are from a study of 449 nonpregnant cisgender women (mean age, 24 years) in Kenya who had been taking daily oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for a median of about 7 months.
The women were randomly assigned to receive either Doxy PEP 200 mg, to be taken within 72 hours of sex (n = 224), or standard care, which included quarterly screening and treatment of STIs (n = 225).
Of the women, 36.7% reported transactional sex at enrollment; their baseline prevalence of STIs was 17.9%, including 14.1% with chlamydia, 3.8% gonorrhea, and 0.4% syphilis. There were no differences between the study groups.
In surveys, 78% of the women reported adherence to the use of Doxy PEP; they took the prophylaxis at least as many days as they had sex.
Nevertheless, there was no significant difference in the incidence of STIs, reported over 1 year, at quarterly visits that included genital STI testing, between groups, with 50 patients in the Doxy PEP group and 59 in the standard screening group developing STIs (relative risk, 0.88; P = .51).
Of the infections, 85 were chlamydia, including 35 in the Doxy PEP group and 50 with standard of care, while 31 were gonorrhea, including 19 in the Doxy PEP group and 12 with standard of care; 8 had both infections, and there was 1 syphilis infection.
The results were consistent across subanalyses of patients grouped according to STI, who became pregnant (n = 80), or sorted by other factors including age, contraceptive use, transactional sex, and STI at baseline.
None of the women developed HIV, and there were no serious events associated with the Doxy PEP treatment.
Cisgender women bear ‘highest burden’ of STIs
The findings are disappointing in light of the higher rates of STIs among cisgender women, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that women also disproportionately bear the long-term consequences of STIs.
“For example, each year, untreated sexually transmitted diseases cause infertility in at least 20,000 women in the United States, and a pregnant woman is highly likely to pass syphilis unto her unborn baby if left untested or untreated,” the CDC reports.
The STI rates are particularly high for women taking HIV PrEP in regions like East Africa, where rates of STIs among cisgender women in many cases are higher than rates for men taking PrEP in high income countries, Dr. Stewart said.
Previous studies of Doxy PEP in men and transgender women taking HIV PrEP, including new research presented at CROI, have shown highly encouraging reductions in STIs, at rates of up to approximately 80% for chlamydia and syphilis.
Adherence, anatomy, resistance
The key theories for the lack of a prevention of infections in cisgender women surround the issues of resistances, as well as anatomy and adherence, said Dr. Stewart.
In terms of bacterial resistances, while initial testing in a limited number of samples the study found no evidence of markers of resistance for chlamydia, all of the gonorrhea samples did show tetracycline-resistant N gonorrhea at baseline and follow-up in both groups.
Regarding anatomic differences, doxycycline may not prevent STIs in endocervical tissue among cisgender women, Dr. Stewart noted. Women are known to be at higher risk of infection because the lining of the vagina is thinner than the skin of the penis, allowing for easier penetration of bacteria and viruses.
The study was designed to optimize adherence to Doxy PEP. Measures included monitoring with weekly text message surveys, in which the women reported a high rate of adherence.
The overall retention rate in the study was high; as many as 97% of the quarterly follow-up visits were completed, including 95% in the Doxy PEP group and 98% of the standard care group. The response rate for the weekly surveys was 81%.
Of note, women reported the use of the treatment to be “imperfect,” suggesting social problems, such as biases toward the use of the prophylaxis.
The results underscore the need for ongoing efforts to make sure no groups of patients are left behind as interventions advance, Dr. Stewart said.
“The burden of STIs on cisgender women is large and growing,” she concluded. “STI prevention interventions are needed.”
Commenting on the study, Renee A. Heffron, PhD, MPH, said the findings “are somewhat surprising because results from trials in other populations have been positive.
“But cisgender women are exposed through the cervix, and this tissue is different from rectal or urethral tissue,” Dr. Heffron, a professor at the department of medicine and director of the Center for AIDS Research at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, told this news organization.
Further findings from the research should help shed light on key issues of adherence and drug concentration levels in cervical tissue, she added.
“For cisgender women, these data are the first and the beginning of understanding whether this is a viable strategy,” Dr. Heffron said.
“We have more to learn to better understand the results from the trial main outcomes, and if there are tweaks to this strategy that would improve efficacy.”
The authors and Dr. Heffron have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CROI 2023
Treating nail psoriasis: Intralesional injections and biologics
HONOLULU – combined with systemic therapy.
One might think of intralesional injections “as a torture method from the medieval days,” she said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE!, but intramatricial corticosteroid injections have been performed for many years as a treatment for nail psoriasis, typically with triamcinolone acetonide.
According to Dr. Armstrong, professor of dermatology and associate dean of clinical research at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, nail matrix psoriasis can present as pitting, leukonychia, red macules in the lunula, crumbling, or trachyonychia. Nail bed psoriasis can present as splinter hemorrhages and onycholysis, hyperkeratosis and splinter hemorrhages, salmon patch or oil spot dyschromia, or onycholysis and salmon patch dyschromia.
In a German cross-sectional study of patients with psoriasis, nails were one of the body sites that have the greatest impact on quality of life – especially those in younger age groups.
While topical treatments are generally considered first for limited disease involving special areas such as the nails, systemic therapy is warranted in patients with moderate-to-severe involvement of specific sites or in those refractory to topical therapy, Dr. Armstrong said.
In 2018, Indian researchers published results from an open-label study of 17 patients, with nail psoriasis, comparing three treatments . Patients were assigned to three groups of 30 nails each and treated with intramatricial injections of triamcinolone acetonide (10 mg/mL), methotrexate (25 mg/mL), and cyclosporine (50 mg/mL), respectively. Each nail was treated with two injections at 6-week intervals and graded at 24 weeks using the Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (NAPSI). In the triamcinolone acetonide and methotrexate groups, 50% of treated nails showed a greater than 75% improvement at 24 weeks, compared with 33% of those in the cyclosporine group. The most side effects occurred in the nails treated with cyclosporine.
When Dr. Armstrong performs intramatricial injections, she uses triamcinolone acetonide at 10 mg/mL. However, she said, “my favorite way of treating severe nail psoriasis is with biologics.”
In an early study of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis treated with the tumor necrosis factor blocker adalimumab 80 mg subcutaneously at week 0, followed by 40 mg subcutaneously every other week from weeks 1 to 15, a post hoc analysis on the effects on nail psoriasis showed a 10-point decrease in the median NAPSI score through week 16 – from 21 to 11 .
In VOYAGE 2, which compared the interleukin-23 blocker guselkumab and adalimumab in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis, the mean percent improvement from baseline in the NAPSI score was similar in patients treated with adalimumab or guselkumab at week 16 (39.6% vs. 46.9%, respectively) and at week 24 (55% vs. 53.7%).
In another study of patients with nail psoriasis, researchers evaluated the efficacy of the IL-17A antagonist secukinumab 150 mg, 300 mg, or placebo at weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4, and every 4 weeks thereafter for 2.5 years. At 2.5 years, the mean reduction in NAPSI score was 63.6% in the secukinumab 150 mg group and 73.3% in the secukinumab 300 mg group.
“I do have to tell my patients what to expect, because the nails grow out slowly, but over time we do see this increase in efficacy,” Dr. Armstrong said.
Studies of another IL-17A antagonist, ixekizumab, have yielded positive results as well, she noted. In 2021, Taiwanese researchers published a systematic review and network meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of small molecule inhibitors and biologics in treating nail psoriasis. They drew from 39 studies involving 15,673 patients with nail psoriasis and found that the oral Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib and ixekizumab had the best efficacy for treating nail psoriasis in 10-16 weeks and 24-26 weeks, respectively.
“They found that overall, the biologics have a good effect on nail psoriasis and that the treatment effects are overall quite similar,” Dr. Armstrong said.
Dr. Armstrong disclosed that she is a consultant or adviser for numerous pharmaceutical companies. She has also received research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Dermira, Leo, Lilly, Pfizer, and UCB Pharma.
HONOLULU – combined with systemic therapy.
One might think of intralesional injections “as a torture method from the medieval days,” she said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE!, but intramatricial corticosteroid injections have been performed for many years as a treatment for nail psoriasis, typically with triamcinolone acetonide.
According to Dr. Armstrong, professor of dermatology and associate dean of clinical research at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, nail matrix psoriasis can present as pitting, leukonychia, red macules in the lunula, crumbling, or trachyonychia. Nail bed psoriasis can present as splinter hemorrhages and onycholysis, hyperkeratosis and splinter hemorrhages, salmon patch or oil spot dyschromia, or onycholysis and salmon patch dyschromia.
In a German cross-sectional study of patients with psoriasis, nails were one of the body sites that have the greatest impact on quality of life – especially those in younger age groups.
While topical treatments are generally considered first for limited disease involving special areas such as the nails, systemic therapy is warranted in patients with moderate-to-severe involvement of specific sites or in those refractory to topical therapy, Dr. Armstrong said.
In 2018, Indian researchers published results from an open-label study of 17 patients, with nail psoriasis, comparing three treatments . Patients were assigned to three groups of 30 nails each and treated with intramatricial injections of triamcinolone acetonide (10 mg/mL), methotrexate (25 mg/mL), and cyclosporine (50 mg/mL), respectively. Each nail was treated with two injections at 6-week intervals and graded at 24 weeks using the Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (NAPSI). In the triamcinolone acetonide and methotrexate groups, 50% of treated nails showed a greater than 75% improvement at 24 weeks, compared with 33% of those in the cyclosporine group. The most side effects occurred in the nails treated with cyclosporine.
When Dr. Armstrong performs intramatricial injections, she uses triamcinolone acetonide at 10 mg/mL. However, she said, “my favorite way of treating severe nail psoriasis is with biologics.”
In an early study of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis treated with the tumor necrosis factor blocker adalimumab 80 mg subcutaneously at week 0, followed by 40 mg subcutaneously every other week from weeks 1 to 15, a post hoc analysis on the effects on nail psoriasis showed a 10-point decrease in the median NAPSI score through week 16 – from 21 to 11 .
In VOYAGE 2, which compared the interleukin-23 blocker guselkumab and adalimumab in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis, the mean percent improvement from baseline in the NAPSI score was similar in patients treated with adalimumab or guselkumab at week 16 (39.6% vs. 46.9%, respectively) and at week 24 (55% vs. 53.7%).
In another study of patients with nail psoriasis, researchers evaluated the efficacy of the IL-17A antagonist secukinumab 150 mg, 300 mg, or placebo at weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4, and every 4 weeks thereafter for 2.5 years. At 2.5 years, the mean reduction in NAPSI score was 63.6% in the secukinumab 150 mg group and 73.3% in the secukinumab 300 mg group.
“I do have to tell my patients what to expect, because the nails grow out slowly, but over time we do see this increase in efficacy,” Dr. Armstrong said.
Studies of another IL-17A antagonist, ixekizumab, have yielded positive results as well, she noted. In 2021, Taiwanese researchers published a systematic review and network meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of small molecule inhibitors and biologics in treating nail psoriasis. They drew from 39 studies involving 15,673 patients with nail psoriasis and found that the oral Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib and ixekizumab had the best efficacy for treating nail psoriasis in 10-16 weeks and 24-26 weeks, respectively.
“They found that overall, the biologics have a good effect on nail psoriasis and that the treatment effects are overall quite similar,” Dr. Armstrong said.
Dr. Armstrong disclosed that she is a consultant or adviser for numerous pharmaceutical companies. She has also received research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Dermira, Leo, Lilly, Pfizer, and UCB Pharma.
HONOLULU – combined with systemic therapy.
One might think of intralesional injections “as a torture method from the medieval days,” she said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE!, but intramatricial corticosteroid injections have been performed for many years as a treatment for nail psoriasis, typically with triamcinolone acetonide.
According to Dr. Armstrong, professor of dermatology and associate dean of clinical research at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, nail matrix psoriasis can present as pitting, leukonychia, red macules in the lunula, crumbling, or trachyonychia. Nail bed psoriasis can present as splinter hemorrhages and onycholysis, hyperkeratosis and splinter hemorrhages, salmon patch or oil spot dyschromia, or onycholysis and salmon patch dyschromia.
In a German cross-sectional study of patients with psoriasis, nails were one of the body sites that have the greatest impact on quality of life – especially those in younger age groups.
While topical treatments are generally considered first for limited disease involving special areas such as the nails, systemic therapy is warranted in patients with moderate-to-severe involvement of specific sites or in those refractory to topical therapy, Dr. Armstrong said.
In 2018, Indian researchers published results from an open-label study of 17 patients, with nail psoriasis, comparing three treatments . Patients were assigned to three groups of 30 nails each and treated with intramatricial injections of triamcinolone acetonide (10 mg/mL), methotrexate (25 mg/mL), and cyclosporine (50 mg/mL), respectively. Each nail was treated with two injections at 6-week intervals and graded at 24 weeks using the Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (NAPSI). In the triamcinolone acetonide and methotrexate groups, 50% of treated nails showed a greater than 75% improvement at 24 weeks, compared with 33% of those in the cyclosporine group. The most side effects occurred in the nails treated with cyclosporine.
When Dr. Armstrong performs intramatricial injections, she uses triamcinolone acetonide at 10 mg/mL. However, she said, “my favorite way of treating severe nail psoriasis is with biologics.”
In an early study of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis treated with the tumor necrosis factor blocker adalimumab 80 mg subcutaneously at week 0, followed by 40 mg subcutaneously every other week from weeks 1 to 15, a post hoc analysis on the effects on nail psoriasis showed a 10-point decrease in the median NAPSI score through week 16 – from 21 to 11 .
In VOYAGE 2, which compared the interleukin-23 blocker guselkumab and adalimumab in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis, the mean percent improvement from baseline in the NAPSI score was similar in patients treated with adalimumab or guselkumab at week 16 (39.6% vs. 46.9%, respectively) and at week 24 (55% vs. 53.7%).
In another study of patients with nail psoriasis, researchers evaluated the efficacy of the IL-17A antagonist secukinumab 150 mg, 300 mg, or placebo at weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4, and every 4 weeks thereafter for 2.5 years. At 2.5 years, the mean reduction in NAPSI score was 63.6% in the secukinumab 150 mg group and 73.3% in the secukinumab 300 mg group.
“I do have to tell my patients what to expect, because the nails grow out slowly, but over time we do see this increase in efficacy,” Dr. Armstrong said.
Studies of another IL-17A antagonist, ixekizumab, have yielded positive results as well, she noted. In 2021, Taiwanese researchers published a systematic review and network meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of small molecule inhibitors and biologics in treating nail psoriasis. They drew from 39 studies involving 15,673 patients with nail psoriasis and found that the oral Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib and ixekizumab had the best efficacy for treating nail psoriasis in 10-16 weeks and 24-26 weeks, respectively.
“They found that overall, the biologics have a good effect on nail psoriasis and that the treatment effects are overall quite similar,” Dr. Armstrong said.
Dr. Armstrong disclosed that she is a consultant or adviser for numerous pharmaceutical companies. She has also received research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Dermira, Leo, Lilly, Pfizer, and UCB Pharma.
AT THE MEDSCAPELIVE! HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
What’s holding back physicians from prescribing biosimilars? Four specialties weigh in
While most providers think that biosimilars will positively impact care, few feel that the economic benefits of biosimilars to date are enough to motivate switching.
In a new survey of over 350 dermatologists, gastroenterologists, ophthalmologists, and rheumatologists, clinicians shared their opinions on the rapidly evolving landscape of biosimilars, detailing top concerns about prescribing these medications and how they presently use biosimilars in clinical practice. Across all specialties, providers said they would be most likely to prescribe biosimilars to new patients or if a patient’s health plan mandated the switch. Most providers listed concerns about biosimilar efficacy and lack of economic benefit as the main barriers to adoption of biosimilars in clinical practice.
Cardinal Health, a health care services company based in Dublin, Ohio, conducted the surveys from July through October 2022.
Rheumatologists want cost-savings for patients
2023 is gearing up to be a big year for biosimilars for inflammatory diseases, with at least eight adalimumab biosimilars entering the market in the United States. Amjevita, manufactured by Amgen, was the first to become commercially available on Jan. 31. Out of 103 surveyed rheumatologists, 62% said they were very comfortable prescribing biosimilars to patients, and 32% said they were somewhat comfortable. Providers said they would be most likely to prescribe a biosimilar to new patients (40%) or if biosimilars were mandated by a patient’s health plan (41%). Nearly one-third (31%) of rheumatologists said that a discount of 21%-30% from a reference product would be necessary to consider switching a patient to a biosimilar.
There are several reasons why a rheumatologist might be wary of switching patients to biosimilars, said Marcus Snow, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s Committee on Rheumatologic Care. “Rheumatologists will always express concern about changing medications that work well for their patients. It is not ideal to ‘force switch’ to a different product, even if it is almost identical,” he told this news organization in an email. “Also, we must remember that a patient on a biologic has failed traditional medications, which speaks to the struggle a patient must endure to get their disease under control. Fail-first situations can cause a rheumatologist to be initially resistant or hesitant to any changes.”
The top concerns among rheumatologists about prescribing biosimilars were medication efficacy (36%), lack of economic benefit (24%), and evaluating when to prescribe a biosimilar versus a reference product (17%). For adalimumab biosimilars, rheumatologists said that interchangeability – a regulatory designation where a biosimilar can be automatically substituted for its reference product at the pharmacy – and citrate-free formulation were the most important product attributes. Sixty-four percent of providers also noted that patient out-of-pocket cost would be key when deciding to prescribe an adalimumab biosimilar.
“There needs to be a true reduction in price, to change providers’ opinions on the economic benefits of biosimilars – in the system generally and for the patient,” Dr. Snow said. “Things will get there eventually, but it is not there yet, based on the list prices we see for some biosimilars.”
Gastroenterologists emphasize patient education
Gastroenterology is another specialty to be affected by the influx of adalimumab biosimilars. Out of 72 surveyed gastroenterologists, 86% said they were very comfortable prescribing biosimilars. About half (49%) said they would be most likely to prescribe a biosimilar to patients with health plans mandating a biosimilar. More than 60% of surveyed gastroenterologists said that biosimilars would positively impact care; providers were divided on the current economic benefits of biosimilars, with 36% saying that the current discounts on biosimilars versus reference products were not favorable enough to motivate switching, and 35% stating that they were. A total of 40% of surveyed providers said that savings of 21%-30%, compared with savings of a reference product, would motivate them to switch patients to a biosimilar, with all other clinical factors being equal.
Gastroenterologists said that, along with the efficacy and cost savings of biosimilars, providing patient education (18%) was a top concern when prescribing biosimilars. Eighty-four percent of respondents said that educating patients about biosimilars as safe and effective treatment options was at least somewhat important. Nearly all participants (99%) cited device ease-of-use as at least somewhat important when considering prescribing adalimumab biosimilars, in addition to interchangeability (97%) and citrate-free formulation (93%).
“Despite general acceptance of biosimilars, there remains some uncertainty regarding their place in the current gastroenterology landscape,” wrote Vivek Kaul, MD, a professor of medicine at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, in the report. “This is likely because only half of the survey respondents believed that biosimilars will positively impact gastroenterology care, further highlighting the ongoing need for real-world data and incorporation of biosimilar use and interchangeability into clinical guidelines.”
Few dermatologists currently prescribe biosimilars
Eight out of ten dermatologists reported being at least somewhat comfortable prescribing biosimilars to patients, though fewer than 20% said they had prescribed a biosimilar in the past year. This indicates limited adoption of infliximab biosimilars, which were the only biosimilars with a dermatologic indication available in 2022, Alex Gross, MD, a dermatologist in Cumming, Ga., noted in his featured commentary in the report. Just 15% of respondents disagreed that biosimilars would have a positive impact on care, and 41% said they were excited about new biosimilars becoming available.
About half (47%) of dermatologists thought the economic benefits of biosimilars were not strong enough to motivate switching patients from reference products. Twenty-nine percent of respondents said that discounts of 21%-30% from a reference product would motivate them to switch patients to a biosimilar, with all other clinical factors being equal, while 20% said they were not likely to prescribe a biosimilar regardless of savings.
Dermatologists may be concerned that these cost savings may not be passed onto patients, said Alison Ehrlich, MD, a dermatologist in Washington, in an email to this news organization. Patient out-of-pocket cost savings would need to be “both significant and transparent” to begin to change providers’ minds, she noted.
Biosimilar efficacy was a top concern for 48% of dermatologists, while 13% said their main concern around prescribing biosimilars was lack of payer adoption. At least 95% of providers said that device ease-of-use and interchangeability were the most important attributes when considering adalimumab biosimilars. Nearly two-thirds (65%) reported that patient out-of-pocket cost would be key when deciding to prescribe an adalimumab biosimilar.
If both patients and providers are informed on biosimilar use and there are cost benefits, dermatologists’ opinions may become more favorable toward biosimilars, but that will take time, Dr. Ehrlich said. “We are very early in the game for biosimilar use in dermatology,” she added.
Ophthalmologists remain wary
Biosimilars have been relatively new to ophthalmology, with the first ranibizumab biosimilar becoming commercially available in July 2022. In the survey, 64 retina specialists were asked different questions than participants from other specialties to gauge ophthalmologists› familiarity with the biosimilars approval process and their overall comfort prescribing these medications. The primary concerns with prescribing biosimilars among respondents was payer coverage (52%), being uncomfortable with biosimilars from a clinical standpoint (48%), and administrative barriers (45%), such as prior authorization. Despite this lack of comfort with biosimilars, two-thirds of participants thought the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval process for these medications was sufficient to evaluate their efficacy and safety. Still, fewer than half (48%) of providers said they do or would prescribe biosimilars.
George Williams, MD, a spokesperson for the American Academy of Ophthalmology, noted that the FDA approval process for biosimilars was not as rigorous as for the respective reference product, and fewer patients are followed over a shorter time period. “Since anti–[vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)] therapy for indications such as neovascular age-related macular degeneration continues indefinitely over years, ophthalmologists may have concerns about the long-term efficacy and safety when applied to larger real-world populations. Ophthalmologists are well aware of safety issues with VEGF inhibitors arising after FDA approval,” he told this news organization in an email.
When asked about the likelihood of using either aflibercept or ranibizumab biosimilars in their clinical practice once commercially available, 70% of ophthalmologists said they would be at least somewhat likely to prescribe aflibercept biosimilars, and 64% said they would be at least somewhat likely to prescribe ranibizumab biosimilars. About half of respondents said they would not likely switch a currently stable patient on either aflibercept or ranibizumab to the corresponding biosimilar. More than half of ophthalmologists (56%) said they would prescribe a biosimilar only if it had an interchangeability designation.
Out of all four specialties, ophthalmologists more frequently reported that higher discounts from a reference product would be necessary to consider switching a patient to a biosimilar. Currently, many ophthalmologists are comfortable with the off-label use of bevacizumab (Avastin) for treating wet age-related macular degeneration, which also offers more cost savings than any currently available biosimilar on the market, Dr. Williams said.
While the limited number of respondents makes it difficult to draw concrete conclusions, Dr. Williams emphasized that the AAO supported the use of biosimilars. “We believe that with clinical experience ophthalmic biosimilars will become useful therapeutic agents,” he noted.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While most providers think that biosimilars will positively impact care, few feel that the economic benefits of biosimilars to date are enough to motivate switching.
In a new survey of over 350 dermatologists, gastroenterologists, ophthalmologists, and rheumatologists, clinicians shared their opinions on the rapidly evolving landscape of biosimilars, detailing top concerns about prescribing these medications and how they presently use biosimilars in clinical practice. Across all specialties, providers said they would be most likely to prescribe biosimilars to new patients or if a patient’s health plan mandated the switch. Most providers listed concerns about biosimilar efficacy and lack of economic benefit as the main barriers to adoption of biosimilars in clinical practice.
Cardinal Health, a health care services company based in Dublin, Ohio, conducted the surveys from July through October 2022.
Rheumatologists want cost-savings for patients
2023 is gearing up to be a big year for biosimilars for inflammatory diseases, with at least eight adalimumab biosimilars entering the market in the United States. Amjevita, manufactured by Amgen, was the first to become commercially available on Jan. 31. Out of 103 surveyed rheumatologists, 62% said they were very comfortable prescribing biosimilars to patients, and 32% said they were somewhat comfortable. Providers said they would be most likely to prescribe a biosimilar to new patients (40%) or if biosimilars were mandated by a patient’s health plan (41%). Nearly one-third (31%) of rheumatologists said that a discount of 21%-30% from a reference product would be necessary to consider switching a patient to a biosimilar.
There are several reasons why a rheumatologist might be wary of switching patients to biosimilars, said Marcus Snow, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s Committee on Rheumatologic Care. “Rheumatologists will always express concern about changing medications that work well for their patients. It is not ideal to ‘force switch’ to a different product, even if it is almost identical,” he told this news organization in an email. “Also, we must remember that a patient on a biologic has failed traditional medications, which speaks to the struggle a patient must endure to get their disease under control. Fail-first situations can cause a rheumatologist to be initially resistant or hesitant to any changes.”
The top concerns among rheumatologists about prescribing biosimilars were medication efficacy (36%), lack of economic benefit (24%), and evaluating when to prescribe a biosimilar versus a reference product (17%). For adalimumab biosimilars, rheumatologists said that interchangeability – a regulatory designation where a biosimilar can be automatically substituted for its reference product at the pharmacy – and citrate-free formulation were the most important product attributes. Sixty-four percent of providers also noted that patient out-of-pocket cost would be key when deciding to prescribe an adalimumab biosimilar.
“There needs to be a true reduction in price, to change providers’ opinions on the economic benefits of biosimilars – in the system generally and for the patient,” Dr. Snow said. “Things will get there eventually, but it is not there yet, based on the list prices we see for some biosimilars.”
Gastroenterologists emphasize patient education
Gastroenterology is another specialty to be affected by the influx of adalimumab biosimilars. Out of 72 surveyed gastroenterologists, 86% said they were very comfortable prescribing biosimilars. About half (49%) said they would be most likely to prescribe a biosimilar to patients with health plans mandating a biosimilar. More than 60% of surveyed gastroenterologists said that biosimilars would positively impact care; providers were divided on the current economic benefits of biosimilars, with 36% saying that the current discounts on biosimilars versus reference products were not favorable enough to motivate switching, and 35% stating that they were. A total of 40% of surveyed providers said that savings of 21%-30%, compared with savings of a reference product, would motivate them to switch patients to a biosimilar, with all other clinical factors being equal.
Gastroenterologists said that, along with the efficacy and cost savings of biosimilars, providing patient education (18%) was a top concern when prescribing biosimilars. Eighty-four percent of respondents said that educating patients about biosimilars as safe and effective treatment options was at least somewhat important. Nearly all participants (99%) cited device ease-of-use as at least somewhat important when considering prescribing adalimumab biosimilars, in addition to interchangeability (97%) and citrate-free formulation (93%).
“Despite general acceptance of biosimilars, there remains some uncertainty regarding their place in the current gastroenterology landscape,” wrote Vivek Kaul, MD, a professor of medicine at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, in the report. “This is likely because only half of the survey respondents believed that biosimilars will positively impact gastroenterology care, further highlighting the ongoing need for real-world data and incorporation of biosimilar use and interchangeability into clinical guidelines.”
Few dermatologists currently prescribe biosimilars
Eight out of ten dermatologists reported being at least somewhat comfortable prescribing biosimilars to patients, though fewer than 20% said they had prescribed a biosimilar in the past year. This indicates limited adoption of infliximab biosimilars, which were the only biosimilars with a dermatologic indication available in 2022, Alex Gross, MD, a dermatologist in Cumming, Ga., noted in his featured commentary in the report. Just 15% of respondents disagreed that biosimilars would have a positive impact on care, and 41% said they were excited about new biosimilars becoming available.
About half (47%) of dermatologists thought the economic benefits of biosimilars were not strong enough to motivate switching patients from reference products. Twenty-nine percent of respondents said that discounts of 21%-30% from a reference product would motivate them to switch patients to a biosimilar, with all other clinical factors being equal, while 20% said they were not likely to prescribe a biosimilar regardless of savings.
Dermatologists may be concerned that these cost savings may not be passed onto patients, said Alison Ehrlich, MD, a dermatologist in Washington, in an email to this news organization. Patient out-of-pocket cost savings would need to be “both significant and transparent” to begin to change providers’ minds, she noted.
Biosimilar efficacy was a top concern for 48% of dermatologists, while 13% said their main concern around prescribing biosimilars was lack of payer adoption. At least 95% of providers said that device ease-of-use and interchangeability were the most important attributes when considering adalimumab biosimilars. Nearly two-thirds (65%) reported that patient out-of-pocket cost would be key when deciding to prescribe an adalimumab biosimilar.
If both patients and providers are informed on biosimilar use and there are cost benefits, dermatologists’ opinions may become more favorable toward biosimilars, but that will take time, Dr. Ehrlich said. “We are very early in the game for biosimilar use in dermatology,” she added.
Ophthalmologists remain wary
Biosimilars have been relatively new to ophthalmology, with the first ranibizumab biosimilar becoming commercially available in July 2022. In the survey, 64 retina specialists were asked different questions than participants from other specialties to gauge ophthalmologists› familiarity with the biosimilars approval process and their overall comfort prescribing these medications. The primary concerns with prescribing biosimilars among respondents was payer coverage (52%), being uncomfortable with biosimilars from a clinical standpoint (48%), and administrative barriers (45%), such as prior authorization. Despite this lack of comfort with biosimilars, two-thirds of participants thought the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval process for these medications was sufficient to evaluate their efficacy and safety. Still, fewer than half (48%) of providers said they do or would prescribe biosimilars.
George Williams, MD, a spokesperson for the American Academy of Ophthalmology, noted that the FDA approval process for biosimilars was not as rigorous as for the respective reference product, and fewer patients are followed over a shorter time period. “Since anti–[vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)] therapy for indications such as neovascular age-related macular degeneration continues indefinitely over years, ophthalmologists may have concerns about the long-term efficacy and safety when applied to larger real-world populations. Ophthalmologists are well aware of safety issues with VEGF inhibitors arising after FDA approval,” he told this news organization in an email.
When asked about the likelihood of using either aflibercept or ranibizumab biosimilars in their clinical practice once commercially available, 70% of ophthalmologists said they would be at least somewhat likely to prescribe aflibercept biosimilars, and 64% said they would be at least somewhat likely to prescribe ranibizumab biosimilars. About half of respondents said they would not likely switch a currently stable patient on either aflibercept or ranibizumab to the corresponding biosimilar. More than half of ophthalmologists (56%) said they would prescribe a biosimilar only if it had an interchangeability designation.
Out of all four specialties, ophthalmologists more frequently reported that higher discounts from a reference product would be necessary to consider switching a patient to a biosimilar. Currently, many ophthalmologists are comfortable with the off-label use of bevacizumab (Avastin) for treating wet age-related macular degeneration, which also offers more cost savings than any currently available biosimilar on the market, Dr. Williams said.
While the limited number of respondents makes it difficult to draw concrete conclusions, Dr. Williams emphasized that the AAO supported the use of biosimilars. “We believe that with clinical experience ophthalmic biosimilars will become useful therapeutic agents,” he noted.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While most providers think that biosimilars will positively impact care, few feel that the economic benefits of biosimilars to date are enough to motivate switching.
In a new survey of over 350 dermatologists, gastroenterologists, ophthalmologists, and rheumatologists, clinicians shared their opinions on the rapidly evolving landscape of biosimilars, detailing top concerns about prescribing these medications and how they presently use biosimilars in clinical practice. Across all specialties, providers said they would be most likely to prescribe biosimilars to new patients or if a patient’s health plan mandated the switch. Most providers listed concerns about biosimilar efficacy and lack of economic benefit as the main barriers to adoption of biosimilars in clinical practice.
Cardinal Health, a health care services company based in Dublin, Ohio, conducted the surveys from July through October 2022.
Rheumatologists want cost-savings for patients
2023 is gearing up to be a big year for biosimilars for inflammatory diseases, with at least eight adalimumab biosimilars entering the market in the United States. Amjevita, manufactured by Amgen, was the first to become commercially available on Jan. 31. Out of 103 surveyed rheumatologists, 62% said they were very comfortable prescribing biosimilars to patients, and 32% said they were somewhat comfortable. Providers said they would be most likely to prescribe a biosimilar to new patients (40%) or if biosimilars were mandated by a patient’s health plan (41%). Nearly one-third (31%) of rheumatologists said that a discount of 21%-30% from a reference product would be necessary to consider switching a patient to a biosimilar.
There are several reasons why a rheumatologist might be wary of switching patients to biosimilars, said Marcus Snow, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s Committee on Rheumatologic Care. “Rheumatologists will always express concern about changing medications that work well for their patients. It is not ideal to ‘force switch’ to a different product, even if it is almost identical,” he told this news organization in an email. “Also, we must remember that a patient on a biologic has failed traditional medications, which speaks to the struggle a patient must endure to get their disease under control. Fail-first situations can cause a rheumatologist to be initially resistant or hesitant to any changes.”
The top concerns among rheumatologists about prescribing biosimilars were medication efficacy (36%), lack of economic benefit (24%), and evaluating when to prescribe a biosimilar versus a reference product (17%). For adalimumab biosimilars, rheumatologists said that interchangeability – a regulatory designation where a biosimilar can be automatically substituted for its reference product at the pharmacy – and citrate-free formulation were the most important product attributes. Sixty-four percent of providers also noted that patient out-of-pocket cost would be key when deciding to prescribe an adalimumab biosimilar.
“There needs to be a true reduction in price, to change providers’ opinions on the economic benefits of biosimilars – in the system generally and for the patient,” Dr. Snow said. “Things will get there eventually, but it is not there yet, based on the list prices we see for some biosimilars.”
Gastroenterologists emphasize patient education
Gastroenterology is another specialty to be affected by the influx of adalimumab biosimilars. Out of 72 surveyed gastroenterologists, 86% said they were very comfortable prescribing biosimilars. About half (49%) said they would be most likely to prescribe a biosimilar to patients with health plans mandating a biosimilar. More than 60% of surveyed gastroenterologists said that biosimilars would positively impact care; providers were divided on the current economic benefits of biosimilars, with 36% saying that the current discounts on biosimilars versus reference products were not favorable enough to motivate switching, and 35% stating that they were. A total of 40% of surveyed providers said that savings of 21%-30%, compared with savings of a reference product, would motivate them to switch patients to a biosimilar, with all other clinical factors being equal.
Gastroenterologists said that, along with the efficacy and cost savings of biosimilars, providing patient education (18%) was a top concern when prescribing biosimilars. Eighty-four percent of respondents said that educating patients about biosimilars as safe and effective treatment options was at least somewhat important. Nearly all participants (99%) cited device ease-of-use as at least somewhat important when considering prescribing adalimumab biosimilars, in addition to interchangeability (97%) and citrate-free formulation (93%).
“Despite general acceptance of biosimilars, there remains some uncertainty regarding their place in the current gastroenterology landscape,” wrote Vivek Kaul, MD, a professor of medicine at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, in the report. “This is likely because only half of the survey respondents believed that biosimilars will positively impact gastroenterology care, further highlighting the ongoing need for real-world data and incorporation of biosimilar use and interchangeability into clinical guidelines.”
Few dermatologists currently prescribe biosimilars
Eight out of ten dermatologists reported being at least somewhat comfortable prescribing biosimilars to patients, though fewer than 20% said they had prescribed a biosimilar in the past year. This indicates limited adoption of infliximab biosimilars, which were the only biosimilars with a dermatologic indication available in 2022, Alex Gross, MD, a dermatologist in Cumming, Ga., noted in his featured commentary in the report. Just 15% of respondents disagreed that biosimilars would have a positive impact on care, and 41% said they were excited about new biosimilars becoming available.
About half (47%) of dermatologists thought the economic benefits of biosimilars were not strong enough to motivate switching patients from reference products. Twenty-nine percent of respondents said that discounts of 21%-30% from a reference product would motivate them to switch patients to a biosimilar, with all other clinical factors being equal, while 20% said they were not likely to prescribe a biosimilar regardless of savings.
Dermatologists may be concerned that these cost savings may not be passed onto patients, said Alison Ehrlich, MD, a dermatologist in Washington, in an email to this news organization. Patient out-of-pocket cost savings would need to be “both significant and transparent” to begin to change providers’ minds, she noted.
Biosimilar efficacy was a top concern for 48% of dermatologists, while 13% said their main concern around prescribing biosimilars was lack of payer adoption. At least 95% of providers said that device ease-of-use and interchangeability were the most important attributes when considering adalimumab biosimilars. Nearly two-thirds (65%) reported that patient out-of-pocket cost would be key when deciding to prescribe an adalimumab biosimilar.
If both patients and providers are informed on biosimilar use and there are cost benefits, dermatologists’ opinions may become more favorable toward biosimilars, but that will take time, Dr. Ehrlich said. “We are very early in the game for biosimilar use in dermatology,” she added.
Ophthalmologists remain wary
Biosimilars have been relatively new to ophthalmology, with the first ranibizumab biosimilar becoming commercially available in July 2022. In the survey, 64 retina specialists were asked different questions than participants from other specialties to gauge ophthalmologists› familiarity with the biosimilars approval process and their overall comfort prescribing these medications. The primary concerns with prescribing biosimilars among respondents was payer coverage (52%), being uncomfortable with biosimilars from a clinical standpoint (48%), and administrative barriers (45%), such as prior authorization. Despite this lack of comfort with biosimilars, two-thirds of participants thought the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval process for these medications was sufficient to evaluate their efficacy and safety. Still, fewer than half (48%) of providers said they do or would prescribe biosimilars.
George Williams, MD, a spokesperson for the American Academy of Ophthalmology, noted that the FDA approval process for biosimilars was not as rigorous as for the respective reference product, and fewer patients are followed over a shorter time period. “Since anti–[vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)] therapy for indications such as neovascular age-related macular degeneration continues indefinitely over years, ophthalmologists may have concerns about the long-term efficacy and safety when applied to larger real-world populations. Ophthalmologists are well aware of safety issues with VEGF inhibitors arising after FDA approval,” he told this news organization in an email.
When asked about the likelihood of using either aflibercept or ranibizumab biosimilars in their clinical practice once commercially available, 70% of ophthalmologists said they would be at least somewhat likely to prescribe aflibercept biosimilars, and 64% said they would be at least somewhat likely to prescribe ranibizumab biosimilars. About half of respondents said they would not likely switch a currently stable patient on either aflibercept or ranibizumab to the corresponding biosimilar. More than half of ophthalmologists (56%) said they would prescribe a biosimilar only if it had an interchangeability designation.
Out of all four specialties, ophthalmologists more frequently reported that higher discounts from a reference product would be necessary to consider switching a patient to a biosimilar. Currently, many ophthalmologists are comfortable with the off-label use of bevacizumab (Avastin) for treating wet age-related macular degeneration, which also offers more cost savings than any currently available biosimilar on the market, Dr. Williams said.
While the limited number of respondents makes it difficult to draw concrete conclusions, Dr. Williams emphasized that the AAO supported the use of biosimilars. “We believe that with clinical experience ophthalmic biosimilars will become useful therapeutic agents,” he noted.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA broadens warning on potentially contaminated eye products
The announcement released Wednesday adds to a previous warning issued earlier this month for EzriCare Artificial Tears or Delsam Pharma’s Artificial Tears because of potential bacterial contamination. All three products are manufactured by the same company, Global Pharma Healthcare, based in Tamilnadu, India.
The FDA has faulted the company for multiple violations, including “lack of appropriate microbial testing” and “lack of proper controls concerning tamper-evident packaging,” and has banned imports to the United States.
The updated warning from the FDA did not give additional information about the over-the-counter eye ointment beyond potential bacterial contamination.
On Feb. 1, the CDC issued an alert about an outbreak of a drug-resistant strain of bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, linked to artificial tear products. To date, 58 patients across 13 states have been identified, and the most commonly reported artificial tear brand was EzriCare Artificial Tears. Five patients had permanent vision loss, and one patient died.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The announcement released Wednesday adds to a previous warning issued earlier this month for EzriCare Artificial Tears or Delsam Pharma’s Artificial Tears because of potential bacterial contamination. All three products are manufactured by the same company, Global Pharma Healthcare, based in Tamilnadu, India.
The FDA has faulted the company for multiple violations, including “lack of appropriate microbial testing” and “lack of proper controls concerning tamper-evident packaging,” and has banned imports to the United States.
The updated warning from the FDA did not give additional information about the over-the-counter eye ointment beyond potential bacterial contamination.
On Feb. 1, the CDC issued an alert about an outbreak of a drug-resistant strain of bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, linked to artificial tear products. To date, 58 patients across 13 states have been identified, and the most commonly reported artificial tear brand was EzriCare Artificial Tears. Five patients had permanent vision loss, and one patient died.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The announcement released Wednesday adds to a previous warning issued earlier this month for EzriCare Artificial Tears or Delsam Pharma’s Artificial Tears because of potential bacterial contamination. All three products are manufactured by the same company, Global Pharma Healthcare, based in Tamilnadu, India.
The FDA has faulted the company for multiple violations, including “lack of appropriate microbial testing” and “lack of proper controls concerning tamper-evident packaging,” and has banned imports to the United States.
The updated warning from the FDA did not give additional information about the over-the-counter eye ointment beyond potential bacterial contamination.
On Feb. 1, the CDC issued an alert about an outbreak of a drug-resistant strain of bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, linked to artificial tear products. To date, 58 patients across 13 states have been identified, and the most commonly reported artificial tear brand was EzriCare Artificial Tears. Five patients had permanent vision loss, and one patient died.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How spirituality guides these three doctors
Whether you’re spiritual, religious – or neither – the Medscape Physician Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2023 asked if you have a religious or spiritual belief. Turns out 69% of physicians shared that they have a spiritual or religious practice.
Tapping into the universe
Nick Shamie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery at University of California, Los Angeles, says the constant challenges of making life-and-death decisions offer an opportunity to check in with a higher power.
“Sometimes when I’m going into a tough surgery or have a tough situation, I pause and think about how this isn’t about me and the situation I’m in,” says Dr. Shamie, whose family is Muslim. “It’s about the whole universe. I feel like someone, or some being, is looking over my shoulders, and if my intentions are good, I’ll be fine. The person I’m going to take care of will be fine. That’s how I use my faith.”
Having a belief in something greater than herself also fuels Jill Carnahan, MD, a family medicine physician and functional medicine expert in Boulder, Colo.
“This is key for me as a physician,” says Dr. Carnahan, author of “Unexpected: Finding Resilience Through Functional Medicine, Science, and Faith.” “I urge physicians to think about their source of strength. That’s not necessarily even religious. It could be meditation or being in nature.”
Dr. Carnahan likes to share with patients that there are lessons that can come from being ill – whether treating ill patients or struggling with one’s own illness.
“I like to teach this idea of illness as a teacher,” says Dr. Carnahan, who has Crohn’s disease and is a cancer survivor. “This is tough, but what you’re saying here is that there is meaning or purpose to this experience. It brings awareness to your life that may not have been there before.”
Often illness is our body’s way of getting our attention that our life, relationships, or work needs adjustment. Illness can be a reminder to make changes. “For example, a diagnosis of autoimmunity may be a reminder to take better care of ourselves, or a diagnosis of cancer may cause us to get out of an unhealthy relationship or change jobs to do something more fulfilling, as we have increased awareness of the brevity of life.”
When patients are affected by illness, pain, reduced functionality, and even imminent death, understanding the experience is difficult, and finding any purpose in it may seem impossible. Still, studies show that those who find meaning in the experience cope better with their illness.
Finding that meaning may be a strong driver of survival and may be positively related to hope, belief, and happiness.
Spirituality supports patients
Even if you’re not religious yourself, it can be helpful to support a patient who opts to pray before an arduous procedure, says Sharyar Baradaran, DDS, a periodontist specializing in gum surgery in Beverly Hills, Calif.
“I’ve had patients who go into meditation mode, or they say a prayer before I start surgery,” he says. “I take that opportunity to connect. In that instance, we hold hands. I want them to know that I understand what they’re going through and how they’re trying to find the courage to undergo surgery.”
When Dr. Shamie was a child, his father described religion as embodying the basic tenet of being good to others. “I’ve taken that to heart,” he says. “All religions, all faiths have that as a central premise.”
These doctors agree that when you take the time to stop and hold a patient’s hand, bow your head during their prayer, or acknowledge or speak for a few moments about their faith, especially during a health crisis, surgery, or challenging diagnosis, patients appreciate it and develop an even deeper connection with you.
Dr. Baradaran believes spirituality can play an important role in how health care providers care for patients. Though it may not be widely discussed or reported, and physicians may find little time and space to address patients’ spiritual needs, there is growing sensitivity regarding spirituality in health care. One study found that while physicians understand its importance, nurses are more apt to integrate spirituality into practice.
“No matter the religion, if you’re spiritual, it means you’re listening and being respectful,” says Dr. Baradaran, who is Jewish. “There are times that I’m not familiar with the prayers my patients are saying, but I always take them in, absorb them, and respect them. This allows me to have a deeper connection with them, which is wonderful.”
Dr. Shamie says that he turns to his faith in good times as well as tough ones.
“I see a lot of people who are dealing with very difficult situations, and it’s not their choice to be in this position,” he says. “At those moments, I think to myself how fortunate I am that I’m not experiencing what this individual or family is going through. I do thank God at that time. I appreciate the life I have, and when I witness hardships, it resets my appreciation.”
For Dr. Carnahan, faith is about becoming comfortable with the inevitable uncertainty of life. It’s also about finding ways to tap into the day’s stresses.
“As physicians, we’re workaholics, and one in four of us are burnt out,” she says. “One solution that really works is to step back from the day-to-day grind and find time to pray or meditate or be in nature.”
There are times when a tragedy occurs, and despite your most intense efforts, a patient may die. Those experiences can be crushing to a physician. However, to guide you through the loss of a patient or the daily juggles of managing your practice, Dr. Carnahan suggests finding time every morning to focus on the day ahead and how you connect with the universe.
“I take 15 minutes in the morning and think about how I will bring love to the world,” she says. “If you look for the miracles and the good and the unexpected, that gratitude shift allows your mind to be transformed by what’s happening. It’s often in those moments that you’ll realize again why you went into medicine in the first place.”
Doctors without faith
So, what does this mean if you’re among the 25% of physicians in the Medscape report who do not have a religious or spiritual leaning and aren’t apt to be spiritually minded when it comes to your patients? An article on KevinMD.com points out that atheist physicians are often in the closet about their atheism because they usually bow their heads or keep a respectful silence when a patient or their family offers a prayer request before surgery or a prayer of thanks after a procedure.
The retired atheist physician who wrote the piece reminds us that nonreligious doctors are good people with a high moral compass who may not believe in an afterlife. However, that means they try to make their patients’ quality of life the best they can.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Whether you’re spiritual, religious – or neither – the Medscape Physician Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2023 asked if you have a religious or spiritual belief. Turns out 69% of physicians shared that they have a spiritual or religious practice.
Tapping into the universe
Nick Shamie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery at University of California, Los Angeles, says the constant challenges of making life-and-death decisions offer an opportunity to check in with a higher power.
“Sometimes when I’m going into a tough surgery or have a tough situation, I pause and think about how this isn’t about me and the situation I’m in,” says Dr. Shamie, whose family is Muslim. “It’s about the whole universe. I feel like someone, or some being, is looking over my shoulders, and if my intentions are good, I’ll be fine. The person I’m going to take care of will be fine. That’s how I use my faith.”
Having a belief in something greater than herself also fuels Jill Carnahan, MD, a family medicine physician and functional medicine expert in Boulder, Colo.
“This is key for me as a physician,” says Dr. Carnahan, author of “Unexpected: Finding Resilience Through Functional Medicine, Science, and Faith.” “I urge physicians to think about their source of strength. That’s not necessarily even religious. It could be meditation or being in nature.”
Dr. Carnahan likes to share with patients that there are lessons that can come from being ill – whether treating ill patients or struggling with one’s own illness.
“I like to teach this idea of illness as a teacher,” says Dr. Carnahan, who has Crohn’s disease and is a cancer survivor. “This is tough, but what you’re saying here is that there is meaning or purpose to this experience. It brings awareness to your life that may not have been there before.”
Often illness is our body’s way of getting our attention that our life, relationships, or work needs adjustment. Illness can be a reminder to make changes. “For example, a diagnosis of autoimmunity may be a reminder to take better care of ourselves, or a diagnosis of cancer may cause us to get out of an unhealthy relationship or change jobs to do something more fulfilling, as we have increased awareness of the brevity of life.”
When patients are affected by illness, pain, reduced functionality, and even imminent death, understanding the experience is difficult, and finding any purpose in it may seem impossible. Still, studies show that those who find meaning in the experience cope better with their illness.
Finding that meaning may be a strong driver of survival and may be positively related to hope, belief, and happiness.
Spirituality supports patients
Even if you’re not religious yourself, it can be helpful to support a patient who opts to pray before an arduous procedure, says Sharyar Baradaran, DDS, a periodontist specializing in gum surgery in Beverly Hills, Calif.
“I’ve had patients who go into meditation mode, or they say a prayer before I start surgery,” he says. “I take that opportunity to connect. In that instance, we hold hands. I want them to know that I understand what they’re going through and how they’re trying to find the courage to undergo surgery.”
When Dr. Shamie was a child, his father described religion as embodying the basic tenet of being good to others. “I’ve taken that to heart,” he says. “All religions, all faiths have that as a central premise.”
These doctors agree that when you take the time to stop and hold a patient’s hand, bow your head during their prayer, or acknowledge or speak for a few moments about their faith, especially during a health crisis, surgery, or challenging diagnosis, patients appreciate it and develop an even deeper connection with you.
Dr. Baradaran believes spirituality can play an important role in how health care providers care for patients. Though it may not be widely discussed or reported, and physicians may find little time and space to address patients’ spiritual needs, there is growing sensitivity regarding spirituality in health care. One study found that while physicians understand its importance, nurses are more apt to integrate spirituality into practice.
“No matter the religion, if you’re spiritual, it means you’re listening and being respectful,” says Dr. Baradaran, who is Jewish. “There are times that I’m not familiar with the prayers my patients are saying, but I always take them in, absorb them, and respect them. This allows me to have a deeper connection with them, which is wonderful.”
Dr. Shamie says that he turns to his faith in good times as well as tough ones.
“I see a lot of people who are dealing with very difficult situations, and it’s not their choice to be in this position,” he says. “At those moments, I think to myself how fortunate I am that I’m not experiencing what this individual or family is going through. I do thank God at that time. I appreciate the life I have, and when I witness hardships, it resets my appreciation.”
For Dr. Carnahan, faith is about becoming comfortable with the inevitable uncertainty of life. It’s also about finding ways to tap into the day’s stresses.
“As physicians, we’re workaholics, and one in four of us are burnt out,” she says. “One solution that really works is to step back from the day-to-day grind and find time to pray or meditate or be in nature.”
There are times when a tragedy occurs, and despite your most intense efforts, a patient may die. Those experiences can be crushing to a physician. However, to guide you through the loss of a patient or the daily juggles of managing your practice, Dr. Carnahan suggests finding time every morning to focus on the day ahead and how you connect with the universe.
“I take 15 minutes in the morning and think about how I will bring love to the world,” she says. “If you look for the miracles and the good and the unexpected, that gratitude shift allows your mind to be transformed by what’s happening. It’s often in those moments that you’ll realize again why you went into medicine in the first place.”
Doctors without faith
So, what does this mean if you’re among the 25% of physicians in the Medscape report who do not have a religious or spiritual leaning and aren’t apt to be spiritually minded when it comes to your patients? An article on KevinMD.com points out that atheist physicians are often in the closet about their atheism because they usually bow their heads or keep a respectful silence when a patient or their family offers a prayer request before surgery or a prayer of thanks after a procedure.
The retired atheist physician who wrote the piece reminds us that nonreligious doctors are good people with a high moral compass who may not believe in an afterlife. However, that means they try to make their patients’ quality of life the best they can.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Whether you’re spiritual, religious – or neither – the Medscape Physician Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2023 asked if you have a religious or spiritual belief. Turns out 69% of physicians shared that they have a spiritual or religious practice.
Tapping into the universe
Nick Shamie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery at University of California, Los Angeles, says the constant challenges of making life-and-death decisions offer an opportunity to check in with a higher power.
“Sometimes when I’m going into a tough surgery or have a tough situation, I pause and think about how this isn’t about me and the situation I’m in,” says Dr. Shamie, whose family is Muslim. “It’s about the whole universe. I feel like someone, or some being, is looking over my shoulders, and if my intentions are good, I’ll be fine. The person I’m going to take care of will be fine. That’s how I use my faith.”
Having a belief in something greater than herself also fuels Jill Carnahan, MD, a family medicine physician and functional medicine expert in Boulder, Colo.
“This is key for me as a physician,” says Dr. Carnahan, author of “Unexpected: Finding Resilience Through Functional Medicine, Science, and Faith.” “I urge physicians to think about their source of strength. That’s not necessarily even religious. It could be meditation or being in nature.”
Dr. Carnahan likes to share with patients that there are lessons that can come from being ill – whether treating ill patients or struggling with one’s own illness.
“I like to teach this idea of illness as a teacher,” says Dr. Carnahan, who has Crohn’s disease and is a cancer survivor. “This is tough, but what you’re saying here is that there is meaning or purpose to this experience. It brings awareness to your life that may not have been there before.”
Often illness is our body’s way of getting our attention that our life, relationships, or work needs adjustment. Illness can be a reminder to make changes. “For example, a diagnosis of autoimmunity may be a reminder to take better care of ourselves, or a diagnosis of cancer may cause us to get out of an unhealthy relationship or change jobs to do something more fulfilling, as we have increased awareness of the brevity of life.”
When patients are affected by illness, pain, reduced functionality, and even imminent death, understanding the experience is difficult, and finding any purpose in it may seem impossible. Still, studies show that those who find meaning in the experience cope better with their illness.
Finding that meaning may be a strong driver of survival and may be positively related to hope, belief, and happiness.
Spirituality supports patients
Even if you’re not religious yourself, it can be helpful to support a patient who opts to pray before an arduous procedure, says Sharyar Baradaran, DDS, a periodontist specializing in gum surgery in Beverly Hills, Calif.
“I’ve had patients who go into meditation mode, or they say a prayer before I start surgery,” he says. “I take that opportunity to connect. In that instance, we hold hands. I want them to know that I understand what they’re going through and how they’re trying to find the courage to undergo surgery.”
When Dr. Shamie was a child, his father described religion as embodying the basic tenet of being good to others. “I’ve taken that to heart,” he says. “All religions, all faiths have that as a central premise.”
These doctors agree that when you take the time to stop and hold a patient’s hand, bow your head during their prayer, or acknowledge or speak for a few moments about their faith, especially during a health crisis, surgery, or challenging diagnosis, patients appreciate it and develop an even deeper connection with you.
Dr. Baradaran believes spirituality can play an important role in how health care providers care for patients. Though it may not be widely discussed or reported, and physicians may find little time and space to address patients’ spiritual needs, there is growing sensitivity regarding spirituality in health care. One study found that while physicians understand its importance, nurses are more apt to integrate spirituality into practice.
“No matter the religion, if you’re spiritual, it means you’re listening and being respectful,” says Dr. Baradaran, who is Jewish. “There are times that I’m not familiar with the prayers my patients are saying, but I always take them in, absorb them, and respect them. This allows me to have a deeper connection with them, which is wonderful.”
Dr. Shamie says that he turns to his faith in good times as well as tough ones.
“I see a lot of people who are dealing with very difficult situations, and it’s not their choice to be in this position,” he says. “At those moments, I think to myself how fortunate I am that I’m not experiencing what this individual or family is going through. I do thank God at that time. I appreciate the life I have, and when I witness hardships, it resets my appreciation.”
For Dr. Carnahan, faith is about becoming comfortable with the inevitable uncertainty of life. It’s also about finding ways to tap into the day’s stresses.
“As physicians, we’re workaholics, and one in four of us are burnt out,” she says. “One solution that really works is to step back from the day-to-day grind and find time to pray or meditate or be in nature.”
There are times when a tragedy occurs, and despite your most intense efforts, a patient may die. Those experiences can be crushing to a physician. However, to guide you through the loss of a patient or the daily juggles of managing your practice, Dr. Carnahan suggests finding time every morning to focus on the day ahead and how you connect with the universe.
“I take 15 minutes in the morning and think about how I will bring love to the world,” she says. “If you look for the miracles and the good and the unexpected, that gratitude shift allows your mind to be transformed by what’s happening. It’s often in those moments that you’ll realize again why you went into medicine in the first place.”
Doctors without faith
So, what does this mean if you’re among the 25% of physicians in the Medscape report who do not have a religious or spiritual leaning and aren’t apt to be spiritually minded when it comes to your patients? An article on KevinMD.com points out that atheist physicians are often in the closet about their atheism because they usually bow their heads or keep a respectful silence when a patient or their family offers a prayer request before surgery or a prayer of thanks after a procedure.
The retired atheist physician who wrote the piece reminds us that nonreligious doctors are good people with a high moral compass who may not believe in an afterlife. However, that means they try to make their patients’ quality of life the best they can.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.