User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
Zero tolerance for patient bias: Too harsh? Clinicians respond
If a patient refuses care from a health care practitioner because of their race or sex, should their request be accommodated?
In a recent blog on Medscape titled “No, You Can’t See a Different Doctor: We Need Zero Tolerance of Patient Bias,” Cleveland Francis Jr., MD, argued no.
Dr. Francis, who is Black, is a recently retired cardiologist who practiced for 50 years. He is currently Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Advisor at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va.
When Francis was a medical student and was preparing to take a patient’s history and perform a medical exam, the patient refused and requested a “White doctor,” he recounted.
“I can remember the hurt and embarrassment as if it were yesterday,” he wrote.
The blog, especially the title, drew strong reactions. Close to 500 readers weighed in.
“The title of my blog sounds harsh,” Dr. Francis said, “but in reality, a simple conversation with the patient usually resolves these issues. The difference is that in the old days, there was utter silence, and the wishes of the patient would be granted”
Health care practitioners “should expect to be treated with respect,” he concluded his blog.
Readers agreed on that point, but they debated whether being uncomfortable with a health care practitioner of a different sex or race always constituted “patient bias.”
Some noted that difficulty understanding a practitioner’s accent, for example, is a legitimate reason for asking for another clinician.
Accents and understanding
“If I am struggling to understand you because your accent is too thick or ... because hearing aids can only do so much, I need to ask for someone else,” a reader commented.
Another chimed in: “My elderly parents changed PCPs frequently during the final years of their lives, mainly due to language barriers encountered with foreign-born providers. Due to progressive hearing loss, they simply couldn’t understand them.”
“It is important to remember that there is a Patient Bill of Rights,” she noted, “the first part of which states, ‘You have the right to safe, considerate, and respectful care, provided in a manner consistent with your beliefs.’ ”
A former charge nurse added: “If a request for change was substantive (poor communication, perceived incompetence, trauma history, etc.), I would move mountains to accommodate it, but IMHO [in my humble opinion], the belief in honoring patient preference doesn’t necessarily need to include rearranging the world in order to accommodate racism, sexism, etc.”
Bias against female doctors, male nurses
Many commenters described how they gladly traded when a patient requested a practitioner of the opposite sex.
A female hospitalist related how she contacted the senior male doctor working with her to arrange a patient trade, adding, “I do agree that racial discrimination ought to be discouraged.”
Similarly, a male ICU RN commented: “Over 13 years, I have had a handful of female (usually older) patients request a female nurse. I have always strived to make this happen.”
However, an older woman related how at first she “had some bias against a male nurse touching me and also felt self-conscious,” she said. “So, I tried to relax ... and let him do his job. He was one of the most compassionate, kind, and sensitive nurses I’ve ever had.”
“I think in some cases,” she noted, “some women have had a history of some sort of abuse by a male, whether it’s sexual or psychological,” but in other cases, “it’s often just a personal preference, not a bias.”
A physician assistant (PA) who worked in a rural ED recounted how “there was only one physician and one PA on at any given evening/night shift, both usually White males.”
“Sometimes, you just have to cope as best you can with whomever is available, and in doing so,” he said, “they might just end up being pleasantly surprised.”
Don’t take it personally, move on
“If a patient doesn’t want to see me for whatever reason, then I would rather not treat them,” was a common sentiment.
Patients “should feel comfortable with their provider even if it’s with someone other than myself,” a reader wrote.
A female physician chimed in: “I frequently have older male patients refuse to see me. ... While this is irritating on several levels, I recognize that it is the patient’s choice, sigh, and move on to the next patient.”
“There are many more patients who specifically ask to see me, so I don’t waste my time and energy on being bothered by those who refuse.”
Similarly, a female mental health provider and sometimes patient wrote: “If any patient tells me that they prefer a male ... or someone of a particular race or religion or whatever, I don’t take it personally.”
A female Hispanic doctor chimed in: “Honestly, if a patient does not want to see me due to my race, I’m OK with that. Patients need to feel comfortable with me for the relationship to be therapeutic and effective,” she said.
“Forcing the patient to see me is adding injury to insult to ME! Not to mention increase[d] workload since that patient will take [so] much more time.”
Similarly, an Asian American doctor commented: “There are people who choose not to see me because of my ethnicity. However, I strongly believe that it should always be the patient’s preference. Whatever the reason, do not force the patient to see you in the name of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, or whatever hurts your feeling. Let the patient go.”
Patient bias vs. patient preference
A physician referring to Dr. Francis’s experience suggested that “perhaps there was an opportunity to explore this misconception directly with the patient. If not, your supervising senior resident or attending should have been informed and brought into the process and conversation.”
“If/when I were rejected by a patient for whatever reason,” another physician commented, “I would gracefully accede, and hope that my colleague would tactfully point out to the patient their error.”
“Having a nurse ask the patient ... what they need style-wise (keeping race, gender, etc., out of it) might help identify whether or not the underlying issue(s) are based on style/needs mismatch match rather than bias,” a reader suggested.
A health care worker commented: “We generally assure patients that we are professionals and think nothing of situations that they might find uncomfortable, but don’t realize that our comfort does not translate to theirs.”
Maybe a different strategy is needed
“Having been the target of bias many times,” a reader said, “I understand the pain that is inflicted. Unfortunately, a patient bias policy, while a good idea, will not prevent patient bias. This is a much larger societal problem. But we can at least tell patients that it is not okay. On the other hand, I would not want to be the provider for a patient who was biased against me and held me in disdain.”
“I do not like Zero Tolerance policies ever. They are too absolute,” another reader commented. “Sometimes, there are reasons and we do have to listen to our patients for why. ... I do not think a policy of zero tolerance will fix the problem of racism.”
“Instead of trying to educate the general public about how not to be jerks,” another reader suggested, “perhaps it would be easier to provide elective classes for doctors and employees who believe themselves to be at-risk for discrimination, providing them with a ‘toolkit’ of strategies for responding to discrimination in the moment, processing it emotionally later on, and reporting the most egregious events through designated channels.”
Another commenter agreed and wrote that, “While we as doctors need and deserve protection, we are also called to act with compassion. So, rather than ask the system for ‘zero-tolerance’ in either direction, we could encourage our health systems to provide education, support, and mediation to any party who feels or fears that they are not being well served. Such a model would include support for physicians who have been the victims of bias and hurt.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If a patient refuses care from a health care practitioner because of their race or sex, should their request be accommodated?
In a recent blog on Medscape titled “No, You Can’t See a Different Doctor: We Need Zero Tolerance of Patient Bias,” Cleveland Francis Jr., MD, argued no.
Dr. Francis, who is Black, is a recently retired cardiologist who practiced for 50 years. He is currently Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Advisor at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va.
When Francis was a medical student and was preparing to take a patient’s history and perform a medical exam, the patient refused and requested a “White doctor,” he recounted.
“I can remember the hurt and embarrassment as if it were yesterday,” he wrote.
The blog, especially the title, drew strong reactions. Close to 500 readers weighed in.
“The title of my blog sounds harsh,” Dr. Francis said, “but in reality, a simple conversation with the patient usually resolves these issues. The difference is that in the old days, there was utter silence, and the wishes of the patient would be granted”
Health care practitioners “should expect to be treated with respect,” he concluded his blog.
Readers agreed on that point, but they debated whether being uncomfortable with a health care practitioner of a different sex or race always constituted “patient bias.”
Some noted that difficulty understanding a practitioner’s accent, for example, is a legitimate reason for asking for another clinician.
Accents and understanding
“If I am struggling to understand you because your accent is too thick or ... because hearing aids can only do so much, I need to ask for someone else,” a reader commented.
Another chimed in: “My elderly parents changed PCPs frequently during the final years of their lives, mainly due to language barriers encountered with foreign-born providers. Due to progressive hearing loss, they simply couldn’t understand them.”
“It is important to remember that there is a Patient Bill of Rights,” she noted, “the first part of which states, ‘You have the right to safe, considerate, and respectful care, provided in a manner consistent with your beliefs.’ ”
A former charge nurse added: “If a request for change was substantive (poor communication, perceived incompetence, trauma history, etc.), I would move mountains to accommodate it, but IMHO [in my humble opinion], the belief in honoring patient preference doesn’t necessarily need to include rearranging the world in order to accommodate racism, sexism, etc.”
Bias against female doctors, male nurses
Many commenters described how they gladly traded when a patient requested a practitioner of the opposite sex.
A female hospitalist related how she contacted the senior male doctor working with her to arrange a patient trade, adding, “I do agree that racial discrimination ought to be discouraged.”
Similarly, a male ICU RN commented: “Over 13 years, I have had a handful of female (usually older) patients request a female nurse. I have always strived to make this happen.”
However, an older woman related how at first she “had some bias against a male nurse touching me and also felt self-conscious,” she said. “So, I tried to relax ... and let him do his job. He was one of the most compassionate, kind, and sensitive nurses I’ve ever had.”
“I think in some cases,” she noted, “some women have had a history of some sort of abuse by a male, whether it’s sexual or psychological,” but in other cases, “it’s often just a personal preference, not a bias.”
A physician assistant (PA) who worked in a rural ED recounted how “there was only one physician and one PA on at any given evening/night shift, both usually White males.”
“Sometimes, you just have to cope as best you can with whomever is available, and in doing so,” he said, “they might just end up being pleasantly surprised.”
Don’t take it personally, move on
“If a patient doesn’t want to see me for whatever reason, then I would rather not treat them,” was a common sentiment.
Patients “should feel comfortable with their provider even if it’s with someone other than myself,” a reader wrote.
A female physician chimed in: “I frequently have older male patients refuse to see me. ... While this is irritating on several levels, I recognize that it is the patient’s choice, sigh, and move on to the next patient.”
“There are many more patients who specifically ask to see me, so I don’t waste my time and energy on being bothered by those who refuse.”
Similarly, a female mental health provider and sometimes patient wrote: “If any patient tells me that they prefer a male ... or someone of a particular race or religion or whatever, I don’t take it personally.”
A female Hispanic doctor chimed in: “Honestly, if a patient does not want to see me due to my race, I’m OK with that. Patients need to feel comfortable with me for the relationship to be therapeutic and effective,” she said.
“Forcing the patient to see me is adding injury to insult to ME! Not to mention increase[d] workload since that patient will take [so] much more time.”
Similarly, an Asian American doctor commented: “There are people who choose not to see me because of my ethnicity. However, I strongly believe that it should always be the patient’s preference. Whatever the reason, do not force the patient to see you in the name of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, or whatever hurts your feeling. Let the patient go.”
Patient bias vs. patient preference
A physician referring to Dr. Francis’s experience suggested that “perhaps there was an opportunity to explore this misconception directly with the patient. If not, your supervising senior resident or attending should have been informed and brought into the process and conversation.”
“If/when I were rejected by a patient for whatever reason,” another physician commented, “I would gracefully accede, and hope that my colleague would tactfully point out to the patient their error.”
“Having a nurse ask the patient ... what they need style-wise (keeping race, gender, etc., out of it) might help identify whether or not the underlying issue(s) are based on style/needs mismatch match rather than bias,” a reader suggested.
A health care worker commented: “We generally assure patients that we are professionals and think nothing of situations that they might find uncomfortable, but don’t realize that our comfort does not translate to theirs.”
Maybe a different strategy is needed
“Having been the target of bias many times,” a reader said, “I understand the pain that is inflicted. Unfortunately, a patient bias policy, while a good idea, will not prevent patient bias. This is a much larger societal problem. But we can at least tell patients that it is not okay. On the other hand, I would not want to be the provider for a patient who was biased against me and held me in disdain.”
“I do not like Zero Tolerance policies ever. They are too absolute,” another reader commented. “Sometimes, there are reasons and we do have to listen to our patients for why. ... I do not think a policy of zero tolerance will fix the problem of racism.”
“Instead of trying to educate the general public about how not to be jerks,” another reader suggested, “perhaps it would be easier to provide elective classes for doctors and employees who believe themselves to be at-risk for discrimination, providing them with a ‘toolkit’ of strategies for responding to discrimination in the moment, processing it emotionally later on, and reporting the most egregious events through designated channels.”
Another commenter agreed and wrote that, “While we as doctors need and deserve protection, we are also called to act with compassion. So, rather than ask the system for ‘zero-tolerance’ in either direction, we could encourage our health systems to provide education, support, and mediation to any party who feels or fears that they are not being well served. Such a model would include support for physicians who have been the victims of bias and hurt.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If a patient refuses care from a health care practitioner because of their race or sex, should their request be accommodated?
In a recent blog on Medscape titled “No, You Can’t See a Different Doctor: We Need Zero Tolerance of Patient Bias,” Cleveland Francis Jr., MD, argued no.
Dr. Francis, who is Black, is a recently retired cardiologist who practiced for 50 years. He is currently Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Advisor at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va.
When Francis was a medical student and was preparing to take a patient’s history and perform a medical exam, the patient refused and requested a “White doctor,” he recounted.
“I can remember the hurt and embarrassment as if it were yesterday,” he wrote.
The blog, especially the title, drew strong reactions. Close to 500 readers weighed in.
“The title of my blog sounds harsh,” Dr. Francis said, “but in reality, a simple conversation with the patient usually resolves these issues. The difference is that in the old days, there was utter silence, and the wishes of the patient would be granted”
Health care practitioners “should expect to be treated with respect,” he concluded his blog.
Readers agreed on that point, but they debated whether being uncomfortable with a health care practitioner of a different sex or race always constituted “patient bias.”
Some noted that difficulty understanding a practitioner’s accent, for example, is a legitimate reason for asking for another clinician.
Accents and understanding
“If I am struggling to understand you because your accent is too thick or ... because hearing aids can only do so much, I need to ask for someone else,” a reader commented.
Another chimed in: “My elderly parents changed PCPs frequently during the final years of their lives, mainly due to language barriers encountered with foreign-born providers. Due to progressive hearing loss, they simply couldn’t understand them.”
“It is important to remember that there is a Patient Bill of Rights,” she noted, “the first part of which states, ‘You have the right to safe, considerate, and respectful care, provided in a manner consistent with your beliefs.’ ”
A former charge nurse added: “If a request for change was substantive (poor communication, perceived incompetence, trauma history, etc.), I would move mountains to accommodate it, but IMHO [in my humble opinion], the belief in honoring patient preference doesn’t necessarily need to include rearranging the world in order to accommodate racism, sexism, etc.”
Bias against female doctors, male nurses
Many commenters described how they gladly traded when a patient requested a practitioner of the opposite sex.
A female hospitalist related how she contacted the senior male doctor working with her to arrange a patient trade, adding, “I do agree that racial discrimination ought to be discouraged.”
Similarly, a male ICU RN commented: “Over 13 years, I have had a handful of female (usually older) patients request a female nurse. I have always strived to make this happen.”
However, an older woman related how at first she “had some bias against a male nurse touching me and also felt self-conscious,” she said. “So, I tried to relax ... and let him do his job. He was one of the most compassionate, kind, and sensitive nurses I’ve ever had.”
“I think in some cases,” she noted, “some women have had a history of some sort of abuse by a male, whether it’s sexual or psychological,” but in other cases, “it’s often just a personal preference, not a bias.”
A physician assistant (PA) who worked in a rural ED recounted how “there was only one physician and one PA on at any given evening/night shift, both usually White males.”
“Sometimes, you just have to cope as best you can with whomever is available, and in doing so,” he said, “they might just end up being pleasantly surprised.”
Don’t take it personally, move on
“If a patient doesn’t want to see me for whatever reason, then I would rather not treat them,” was a common sentiment.
Patients “should feel comfortable with their provider even if it’s with someone other than myself,” a reader wrote.
A female physician chimed in: “I frequently have older male patients refuse to see me. ... While this is irritating on several levels, I recognize that it is the patient’s choice, sigh, and move on to the next patient.”
“There are many more patients who specifically ask to see me, so I don’t waste my time and energy on being bothered by those who refuse.”
Similarly, a female mental health provider and sometimes patient wrote: “If any patient tells me that they prefer a male ... or someone of a particular race or religion or whatever, I don’t take it personally.”
A female Hispanic doctor chimed in: “Honestly, if a patient does not want to see me due to my race, I’m OK with that. Patients need to feel comfortable with me for the relationship to be therapeutic and effective,” she said.
“Forcing the patient to see me is adding injury to insult to ME! Not to mention increase[d] workload since that patient will take [so] much more time.”
Similarly, an Asian American doctor commented: “There are people who choose not to see me because of my ethnicity. However, I strongly believe that it should always be the patient’s preference. Whatever the reason, do not force the patient to see you in the name of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, or whatever hurts your feeling. Let the patient go.”
Patient bias vs. patient preference
A physician referring to Dr. Francis’s experience suggested that “perhaps there was an opportunity to explore this misconception directly with the patient. If not, your supervising senior resident or attending should have been informed and brought into the process and conversation.”
“If/when I were rejected by a patient for whatever reason,” another physician commented, “I would gracefully accede, and hope that my colleague would tactfully point out to the patient their error.”
“Having a nurse ask the patient ... what they need style-wise (keeping race, gender, etc., out of it) might help identify whether or not the underlying issue(s) are based on style/needs mismatch match rather than bias,” a reader suggested.
A health care worker commented: “We generally assure patients that we are professionals and think nothing of situations that they might find uncomfortable, but don’t realize that our comfort does not translate to theirs.”
Maybe a different strategy is needed
“Having been the target of bias many times,” a reader said, “I understand the pain that is inflicted. Unfortunately, a patient bias policy, while a good idea, will not prevent patient bias. This is a much larger societal problem. But we can at least tell patients that it is not okay. On the other hand, I would not want to be the provider for a patient who was biased against me and held me in disdain.”
“I do not like Zero Tolerance policies ever. They are too absolute,” another reader commented. “Sometimes, there are reasons and we do have to listen to our patients for why. ... I do not think a policy of zero tolerance will fix the problem of racism.”
“Instead of trying to educate the general public about how not to be jerks,” another reader suggested, “perhaps it would be easier to provide elective classes for doctors and employees who believe themselves to be at-risk for discrimination, providing them with a ‘toolkit’ of strategies for responding to discrimination in the moment, processing it emotionally later on, and reporting the most egregious events through designated channels.”
Another commenter agreed and wrote that, “While we as doctors need and deserve protection, we are also called to act with compassion. So, rather than ask the system for ‘zero-tolerance’ in either direction, we could encourage our health systems to provide education, support, and mediation to any party who feels or fears that they are not being well served. Such a model would include support for physicians who have been the victims of bias and hurt.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
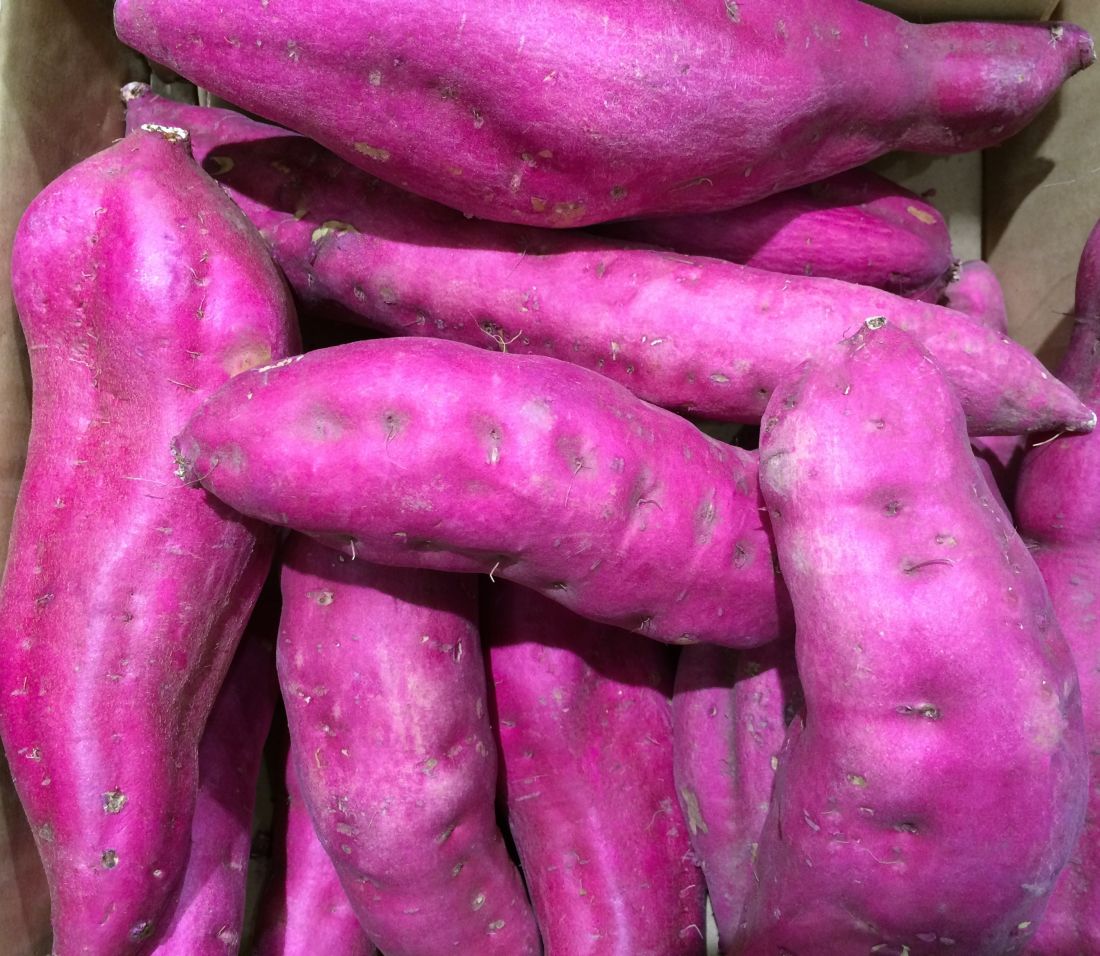
A purple warrior rises in the battle against diabetes
One-eyed, one-horned, flying purple veggie eater
Big Fruits and Vegetables is at it again. You notice how they’re always like “Oh, vegetables are good for your health,” and “Eating fruits every day makes you live longer,” but come on. It’s a marketing ploy, leading us astray from our personal savior, McDonald’s.
Just look at this latest bit of research: According to researchers from Finland, eating purple vegetables can protect against diabetes. Considering nearly 40 million Americans have diabetes (and nearly 100 million have prediabetes), anything to reduce the incidence of diabetes (people with diabetes account for one-fourth of every dollar spent in U.S. health care) would be beneficial. So, let’s humor the fruits and veggies people this time and hear them out.
It all comes down to a chemical called anthocyanin, which is a pigment that gives fruits and vegetables such as blueberries, radishes, and red cabbages their purplish color. Anthocyanin also has probiotic and anti-inflammatory effects, meaning it can help improve intestinal lining health and regulate glucose and lipid metabolic pathways. Obviously, good things if you want to avoid diabetes.
The investigators also found that, while standard anthocyanin was beneficial, acylated anthocyanin (which has an acyl group added to the sugar molecules of anthocyanin) is really what you want to go for. The acylated version, found in abundance in purple potatoes, purple carrots, radishes, and red cabbages, is tougher to digest, but the positive effects it has in the body are enhanced over the standard version.
Now, this all a compelling bit of research, but at the end of the day, you’re still eating fruits and vegetables, and we are red-blooded Americans here. We don’t do healthy foods. Although, if you were to dye our burgers with anthocyanin and make them purple, you’d have our attention. Purple is our favorite color.
Manuka honey better as building material than antibiotic
Milk, according to the old saying, builds strong bones, but when it comes to patients with bone loss caused by various medical reasons, researchers found that manuka honey, produced only in New Zealand and some parts of Australia, may also do the job. They soaked collagen scaffolds used for bone implants in various concentrations of the honey and found that 5% led to higher mineral formation and osteoprotegerin production, which suggests increased bone production.
But, and this is a pretty big one, the other half of the study – testing manuka honey’s ability to ward off bacteria – wasn’t so successful. Bone implants, apparently, count for almost half of all hospital-acquired infections, which obviously can put a damper on the healing process. The hope was that a biomaterial would be more effective than something like metal in lessening bacteria formation. Nope.
When the researchers soaked paper disks in honey and added them to cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, none of the various concentrations stopped bacterial growth in the scaffolding, even when they added antibiotics.
The sticky conclusion, you could say, is more bitter than sweet.
It may sound like Korn, but can it play ‘Freak on a Leash’?
Like all right-thinking Americans, we love corn, corn-based products, and almost corn. Corn on the cob grilled in the husk? Mmm. Plus, we’re big fans of the band Korn. Also, we once had a reporter here named Tim Kirn. And don’t even get us started with Karn. Best Family Feud host ever.
But what about Quorn? Oh sure, the fungi-based meat alternative is full of yummy mycoprotein, but can it prevent colorectal cancer? Can we add Quorn to our favorites list? Let’s see what Science has to say.
Researchers at Northumbria University in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, fed a group of 20 men some meat (240 g/day) for 2 weeks – hopefully, they were allowed to eat some other food as well – and then gave them the same amount of Quorn, excuse us, fungi-derived mycoprotein equivalents, for 2 more weeks, with a 4-week washout period in between.
Levels of cancer-causing chemicals known as genotoxins fell significantly in the mycoprotein phase but rose during the meat phase. The mycoprotein diet also improved gut health “by increasing the abundance of protective bacteria such as Lactobacilli, Roseburia, and Akkermansia, which are associated with offering protection against chemically induced tumours, inflammation and bowel cancer,” they said in a statement from the university.
The meat phase, on the other hand, resulted in an increase in “gut bacteria linked with issues such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, weight gain and other negative health outcomes,” they noted.
Science, then, seems to approve of Quorn, and that’s good enough for us. We’re adding Quorn to our diet, starting with a fungi-derived mycoproteinburger tonight while we’re watching the Cornell Big Red take the court against their archrivals, the Big Green of Dartmouth College. GO RED!
One-eyed, one-horned, flying purple veggie eater
Big Fruits and Vegetables is at it again. You notice how they’re always like “Oh, vegetables are good for your health,” and “Eating fruits every day makes you live longer,” but come on. It’s a marketing ploy, leading us astray from our personal savior, McDonald’s.
Just look at this latest bit of research: According to researchers from Finland, eating purple vegetables can protect against diabetes. Considering nearly 40 million Americans have diabetes (and nearly 100 million have prediabetes), anything to reduce the incidence of diabetes (people with diabetes account for one-fourth of every dollar spent in U.S. health care) would be beneficial. So, let’s humor the fruits and veggies people this time and hear them out.
It all comes down to a chemical called anthocyanin, which is a pigment that gives fruits and vegetables such as blueberries, radishes, and red cabbages their purplish color. Anthocyanin also has probiotic and anti-inflammatory effects, meaning it can help improve intestinal lining health and regulate glucose and lipid metabolic pathways. Obviously, good things if you want to avoid diabetes.
The investigators also found that, while standard anthocyanin was beneficial, acylated anthocyanin (which has an acyl group added to the sugar molecules of anthocyanin) is really what you want to go for. The acylated version, found in abundance in purple potatoes, purple carrots, radishes, and red cabbages, is tougher to digest, but the positive effects it has in the body are enhanced over the standard version.
Now, this all a compelling bit of research, but at the end of the day, you’re still eating fruits and vegetables, and we are red-blooded Americans here. We don’t do healthy foods. Although, if you were to dye our burgers with anthocyanin and make them purple, you’d have our attention. Purple is our favorite color.
Manuka honey better as building material than antibiotic
Milk, according to the old saying, builds strong bones, but when it comes to patients with bone loss caused by various medical reasons, researchers found that manuka honey, produced only in New Zealand and some parts of Australia, may also do the job. They soaked collagen scaffolds used for bone implants in various concentrations of the honey and found that 5% led to higher mineral formation and osteoprotegerin production, which suggests increased bone production.
But, and this is a pretty big one, the other half of the study – testing manuka honey’s ability to ward off bacteria – wasn’t so successful. Bone implants, apparently, count for almost half of all hospital-acquired infections, which obviously can put a damper on the healing process. The hope was that a biomaterial would be more effective than something like metal in lessening bacteria formation. Nope.
When the researchers soaked paper disks in honey and added them to cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, none of the various concentrations stopped bacterial growth in the scaffolding, even when they added antibiotics.
The sticky conclusion, you could say, is more bitter than sweet.
It may sound like Korn, but can it play ‘Freak on a Leash’?
Like all right-thinking Americans, we love corn, corn-based products, and almost corn. Corn on the cob grilled in the husk? Mmm. Plus, we’re big fans of the band Korn. Also, we once had a reporter here named Tim Kirn. And don’t even get us started with Karn. Best Family Feud host ever.
But what about Quorn? Oh sure, the fungi-based meat alternative is full of yummy mycoprotein, but can it prevent colorectal cancer? Can we add Quorn to our favorites list? Let’s see what Science has to say.
Researchers at Northumbria University in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, fed a group of 20 men some meat (240 g/day) for 2 weeks – hopefully, they were allowed to eat some other food as well – and then gave them the same amount of Quorn, excuse us, fungi-derived mycoprotein equivalents, for 2 more weeks, with a 4-week washout period in between.
Levels of cancer-causing chemicals known as genotoxins fell significantly in the mycoprotein phase but rose during the meat phase. The mycoprotein diet also improved gut health “by increasing the abundance of protective bacteria such as Lactobacilli, Roseburia, and Akkermansia, which are associated with offering protection against chemically induced tumours, inflammation and bowel cancer,” they said in a statement from the university.
The meat phase, on the other hand, resulted in an increase in “gut bacteria linked with issues such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, weight gain and other negative health outcomes,” they noted.
Science, then, seems to approve of Quorn, and that’s good enough for us. We’re adding Quorn to our diet, starting with a fungi-derived mycoproteinburger tonight while we’re watching the Cornell Big Red take the court against their archrivals, the Big Green of Dartmouth College. GO RED!
One-eyed, one-horned, flying purple veggie eater
Big Fruits and Vegetables is at it again. You notice how they’re always like “Oh, vegetables are good for your health,” and “Eating fruits every day makes you live longer,” but come on. It’s a marketing ploy, leading us astray from our personal savior, McDonald’s.
Just look at this latest bit of research: According to researchers from Finland, eating purple vegetables can protect against diabetes. Considering nearly 40 million Americans have diabetes (and nearly 100 million have prediabetes), anything to reduce the incidence of diabetes (people with diabetes account for one-fourth of every dollar spent in U.S. health care) would be beneficial. So, let’s humor the fruits and veggies people this time and hear them out.
It all comes down to a chemical called anthocyanin, which is a pigment that gives fruits and vegetables such as blueberries, radishes, and red cabbages their purplish color. Anthocyanin also has probiotic and anti-inflammatory effects, meaning it can help improve intestinal lining health and regulate glucose and lipid metabolic pathways. Obviously, good things if you want to avoid diabetes.
The investigators also found that, while standard anthocyanin was beneficial, acylated anthocyanin (which has an acyl group added to the sugar molecules of anthocyanin) is really what you want to go for. The acylated version, found in abundance in purple potatoes, purple carrots, radishes, and red cabbages, is tougher to digest, but the positive effects it has in the body are enhanced over the standard version.
Now, this all a compelling bit of research, but at the end of the day, you’re still eating fruits and vegetables, and we are red-blooded Americans here. We don’t do healthy foods. Although, if you were to dye our burgers with anthocyanin and make them purple, you’d have our attention. Purple is our favorite color.
Manuka honey better as building material than antibiotic
Milk, according to the old saying, builds strong bones, but when it comes to patients with bone loss caused by various medical reasons, researchers found that manuka honey, produced only in New Zealand and some parts of Australia, may also do the job. They soaked collagen scaffolds used for bone implants in various concentrations of the honey and found that 5% led to higher mineral formation and osteoprotegerin production, which suggests increased bone production.
But, and this is a pretty big one, the other half of the study – testing manuka honey’s ability to ward off bacteria – wasn’t so successful. Bone implants, apparently, count for almost half of all hospital-acquired infections, which obviously can put a damper on the healing process. The hope was that a biomaterial would be more effective than something like metal in lessening bacteria formation. Nope.
When the researchers soaked paper disks in honey and added them to cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, none of the various concentrations stopped bacterial growth in the scaffolding, even when they added antibiotics.
The sticky conclusion, you could say, is more bitter than sweet.
It may sound like Korn, but can it play ‘Freak on a Leash’?
Like all right-thinking Americans, we love corn, corn-based products, and almost corn. Corn on the cob grilled in the husk? Mmm. Plus, we’re big fans of the band Korn. Also, we once had a reporter here named Tim Kirn. And don’t even get us started with Karn. Best Family Feud host ever.
But what about Quorn? Oh sure, the fungi-based meat alternative is full of yummy mycoprotein, but can it prevent colorectal cancer? Can we add Quorn to our favorites list? Let’s see what Science has to say.
Researchers at Northumbria University in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, fed a group of 20 men some meat (240 g/day) for 2 weeks – hopefully, they were allowed to eat some other food as well – and then gave them the same amount of Quorn, excuse us, fungi-derived mycoprotein equivalents, for 2 more weeks, with a 4-week washout period in between.
Levels of cancer-causing chemicals known as genotoxins fell significantly in the mycoprotein phase but rose during the meat phase. The mycoprotein diet also improved gut health “by increasing the abundance of protective bacteria such as Lactobacilli, Roseburia, and Akkermansia, which are associated with offering protection against chemically induced tumours, inflammation and bowel cancer,” they said in a statement from the university.
The meat phase, on the other hand, resulted in an increase in “gut bacteria linked with issues such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, weight gain and other negative health outcomes,” they noted.
Science, then, seems to approve of Quorn, and that’s good enough for us. We’re adding Quorn to our diet, starting with a fungi-derived mycoproteinburger tonight while we’re watching the Cornell Big Red take the court against their archrivals, the Big Green of Dartmouth College. GO RED!
Meningococcal vaccine shows benefit in STI prevention
The latest study to show high efficacy of doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing sexually transmitted infections among men who have sex with men (MSM) adds a new twist, showing – for the first time – reductions in gonorrhea among those receiving the meningococcal B vaccine.
said first author Jean-Michel Molina, MD, PhD, in presenting the findings at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections.
In addition, “two doses of the meningococcal B vaccine reduced the incidence of a first episode of gonorrhea by roughly 50% among men who have sex with men,” said Dr. Molina, a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Paris, and head of the Infectious Diseases Department at the Saint-Louis and Lariboisière Hospitals, Paris.
Whereas the advent of PrEP has been associated with significant reductions in HIV transmission, rates of STIs have conversely been on the rise among MSM, specifically among those receiving PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis with Doxy PEP has been shown to reduce the incidence of chlamydia and syphilis by approximately 70%; however, effects on prevention of gonorrhea have been less clear.
Meningococcal B vaccination has, meanwhile, shown intriguing reductions of gonorrhea incidence of as much as 26%-46% in some observational studies.
Therefore, Dr. Molina and colleagues decided to further investigate Doxy PEP as well as the meningococcal B vaccine in prevention of STIs.
For the ANRS 174 DOXYVAC trial, they enrolled 546 MSM in the open-label, multicenter study between January 2021 and July 2022.
The men were randomly assigned to one of 4 groups: doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP: 200 mg; n = 332), no Doxy PEP (n = 170), two shots of meningococcal B vaccine (4CMenB vaccine; n = 257), or no 4CMenB vaccine (n = 245).
All participants were assigned to their groups within 72 hours of condomless sex.
The men, who had a median age of 39, had a median time of PrEP use of 42 months, a history of an STI in the past year, and their median number of sexual partners in the past 3 months was 10.
Their characteristics were well-balanced across the treatment groups. After discontinuations of 54 patients across the groups, the final analysis included 502 participants.
With a median follow-up of 9 months, the intent-to-treat analysis showed 13 subjects had a first episode of chlamydia or syphilis in the Doxy PEP group, versus 49 subjects infected in the no Doxy PEP arm, for an incidence of 5.6 versus 35.4 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.16; P < .0001).
Infection specifically with chlamydia occurred among 21 men with no Doxy PEP versus 5 receiving Dox PEP (19.3 vs. 2.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.11; P < .0001).
And infection with syphilis occurred in 18 men receiving no Doxy PEP versus 8 receiving the treatment (16.3 vs. 3.4 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.21; P < .001).
The corresponding rates for gonorrhea infection were an incidence 41.3 versus 20.5 per 100 person-years, in the no Doxy PEP versus Doxy PEP arms, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .001), and 29.4 versus 16.8 per 100 person-years for Mycoplasma genitalium infection (aHR, 0.55; P = .015).
Throughout the study, about 80% of patients in the Doxy PEP group reported using the prophylaxis treatment after their most recent sexual intercourse, with subjects reporting taking a median of seven pills per month.
In the vaccine/no vaccine comparisons, 32 subjects in the no meningococcal vaccine group were infected with a first gonorrhea infection, compared with 17 in the vaccine group, representing an incidence of 19.7 versus 9.8 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .016), which Dr. Molina called “highly significant.”
An analysis of the cumulative incidence of gonorrhea infection with the meningococcal vaccine showed rates in the no vaccine versus vaccine groups of 30.4 versus 20.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; however, statistical significance was not reached (aHR, 0.66; P = .052).
Importantly, there were no significant interactions in the results between those receiving Doxy PEP or the 4CMenB vaccine group, and there were no significant differences in drug-related serious adverse events between the groups.
Dr. Molina noted that the meningococcal B vaccine is known to contain key antigens that are shared between meningitis and gonorrhea, which could explain the benefits.
Although chlamydia and syphilis thus far appear to remain susceptible to Doxy PEP, resistances with gonorrhea remain a concern, hence the ability of the vaccine to provide some protection could be an added bonus.
“We know that [gonorrhea] is able to very quickly develop resistances to any antibiotics, so that was why we wanted to look beyond the antibiotic prophylaxis,” said Dr. Molina.
Among questions to explore looking ahead is the potential longevity of protection with the vaccine.
“We don’t know at this point how long the protection with the vaccine could last, or if [people] may need booster injections, for instance, but the literature suggests benefits for at least a year,” Dr. Molina said. “We are still monitoring the patients in the study to see what happens.”
He added that combination of the interventions may be of benefit.
“In the future, we think we may need to combine these approaches if we want to meet the WHO/UNAIDS targets to reduce the incidence of HIV and STIs by 90% by 2030.”
Commenting on the study, CROI vice-chair Landon Myer, MD, PhD, noted that “gonorrhea develops resistance quickly and can be hard to treat or prophylaxis, so the vaccine finding, which was hinted at by previous observational data, is really important.”
He agrees that “the duration of protective efficacy – a big thing in vaccines – is unknown.”
“Still, this is really significant,” Dr. Myer stressed. “An efficacious vaccine against a stubborn sexually transmitted infection.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The latest study to show high efficacy of doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing sexually transmitted infections among men who have sex with men (MSM) adds a new twist, showing – for the first time – reductions in gonorrhea among those receiving the meningococcal B vaccine.
said first author Jean-Michel Molina, MD, PhD, in presenting the findings at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections.
In addition, “two doses of the meningococcal B vaccine reduced the incidence of a first episode of gonorrhea by roughly 50% among men who have sex with men,” said Dr. Molina, a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Paris, and head of the Infectious Diseases Department at the Saint-Louis and Lariboisière Hospitals, Paris.
Whereas the advent of PrEP has been associated with significant reductions in HIV transmission, rates of STIs have conversely been on the rise among MSM, specifically among those receiving PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis with Doxy PEP has been shown to reduce the incidence of chlamydia and syphilis by approximately 70%; however, effects on prevention of gonorrhea have been less clear.
Meningococcal B vaccination has, meanwhile, shown intriguing reductions of gonorrhea incidence of as much as 26%-46% in some observational studies.
Therefore, Dr. Molina and colleagues decided to further investigate Doxy PEP as well as the meningococcal B vaccine in prevention of STIs.
For the ANRS 174 DOXYVAC trial, they enrolled 546 MSM in the open-label, multicenter study between January 2021 and July 2022.
The men were randomly assigned to one of 4 groups: doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP: 200 mg; n = 332), no Doxy PEP (n = 170), two shots of meningococcal B vaccine (4CMenB vaccine; n = 257), or no 4CMenB vaccine (n = 245).
All participants were assigned to their groups within 72 hours of condomless sex.
The men, who had a median age of 39, had a median time of PrEP use of 42 months, a history of an STI in the past year, and their median number of sexual partners in the past 3 months was 10.
Their characteristics were well-balanced across the treatment groups. After discontinuations of 54 patients across the groups, the final analysis included 502 participants.
With a median follow-up of 9 months, the intent-to-treat analysis showed 13 subjects had a first episode of chlamydia or syphilis in the Doxy PEP group, versus 49 subjects infected in the no Doxy PEP arm, for an incidence of 5.6 versus 35.4 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.16; P < .0001).
Infection specifically with chlamydia occurred among 21 men with no Doxy PEP versus 5 receiving Dox PEP (19.3 vs. 2.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.11; P < .0001).
And infection with syphilis occurred in 18 men receiving no Doxy PEP versus 8 receiving the treatment (16.3 vs. 3.4 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.21; P < .001).
The corresponding rates for gonorrhea infection were an incidence 41.3 versus 20.5 per 100 person-years, in the no Doxy PEP versus Doxy PEP arms, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .001), and 29.4 versus 16.8 per 100 person-years for Mycoplasma genitalium infection (aHR, 0.55; P = .015).
Throughout the study, about 80% of patients in the Doxy PEP group reported using the prophylaxis treatment after their most recent sexual intercourse, with subjects reporting taking a median of seven pills per month.
In the vaccine/no vaccine comparisons, 32 subjects in the no meningococcal vaccine group were infected with a first gonorrhea infection, compared with 17 in the vaccine group, representing an incidence of 19.7 versus 9.8 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .016), which Dr. Molina called “highly significant.”
An analysis of the cumulative incidence of gonorrhea infection with the meningococcal vaccine showed rates in the no vaccine versus vaccine groups of 30.4 versus 20.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; however, statistical significance was not reached (aHR, 0.66; P = .052).
Importantly, there were no significant interactions in the results between those receiving Doxy PEP or the 4CMenB vaccine group, and there were no significant differences in drug-related serious adverse events between the groups.
Dr. Molina noted that the meningococcal B vaccine is known to contain key antigens that are shared between meningitis and gonorrhea, which could explain the benefits.
Although chlamydia and syphilis thus far appear to remain susceptible to Doxy PEP, resistances with gonorrhea remain a concern, hence the ability of the vaccine to provide some protection could be an added bonus.
“We know that [gonorrhea] is able to very quickly develop resistances to any antibiotics, so that was why we wanted to look beyond the antibiotic prophylaxis,” said Dr. Molina.
Among questions to explore looking ahead is the potential longevity of protection with the vaccine.
“We don’t know at this point how long the protection with the vaccine could last, or if [people] may need booster injections, for instance, but the literature suggests benefits for at least a year,” Dr. Molina said. “We are still monitoring the patients in the study to see what happens.”
He added that combination of the interventions may be of benefit.
“In the future, we think we may need to combine these approaches if we want to meet the WHO/UNAIDS targets to reduce the incidence of HIV and STIs by 90% by 2030.”
Commenting on the study, CROI vice-chair Landon Myer, MD, PhD, noted that “gonorrhea develops resistance quickly and can be hard to treat or prophylaxis, so the vaccine finding, which was hinted at by previous observational data, is really important.”
He agrees that “the duration of protective efficacy – a big thing in vaccines – is unknown.”
“Still, this is really significant,” Dr. Myer stressed. “An efficacious vaccine against a stubborn sexually transmitted infection.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The latest study to show high efficacy of doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing sexually transmitted infections among men who have sex with men (MSM) adds a new twist, showing – for the first time – reductions in gonorrhea among those receiving the meningococcal B vaccine.
said first author Jean-Michel Molina, MD, PhD, in presenting the findings at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections.
In addition, “two doses of the meningococcal B vaccine reduced the incidence of a first episode of gonorrhea by roughly 50% among men who have sex with men,” said Dr. Molina, a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Paris, and head of the Infectious Diseases Department at the Saint-Louis and Lariboisière Hospitals, Paris.
Whereas the advent of PrEP has been associated with significant reductions in HIV transmission, rates of STIs have conversely been on the rise among MSM, specifically among those receiving PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis with Doxy PEP has been shown to reduce the incidence of chlamydia and syphilis by approximately 70%; however, effects on prevention of gonorrhea have been less clear.
Meningococcal B vaccination has, meanwhile, shown intriguing reductions of gonorrhea incidence of as much as 26%-46% in some observational studies.
Therefore, Dr. Molina and colleagues decided to further investigate Doxy PEP as well as the meningococcal B vaccine in prevention of STIs.
For the ANRS 174 DOXYVAC trial, they enrolled 546 MSM in the open-label, multicenter study between January 2021 and July 2022.
The men were randomly assigned to one of 4 groups: doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP: 200 mg; n = 332), no Doxy PEP (n = 170), two shots of meningococcal B vaccine (4CMenB vaccine; n = 257), or no 4CMenB vaccine (n = 245).
All participants were assigned to their groups within 72 hours of condomless sex.
The men, who had a median age of 39, had a median time of PrEP use of 42 months, a history of an STI in the past year, and their median number of sexual partners in the past 3 months was 10.
Their characteristics were well-balanced across the treatment groups. After discontinuations of 54 patients across the groups, the final analysis included 502 participants.
With a median follow-up of 9 months, the intent-to-treat analysis showed 13 subjects had a first episode of chlamydia or syphilis in the Doxy PEP group, versus 49 subjects infected in the no Doxy PEP arm, for an incidence of 5.6 versus 35.4 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.16; P < .0001).
Infection specifically with chlamydia occurred among 21 men with no Doxy PEP versus 5 receiving Dox PEP (19.3 vs. 2.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.11; P < .0001).
And infection with syphilis occurred in 18 men receiving no Doxy PEP versus 8 receiving the treatment (16.3 vs. 3.4 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.21; P < .001).
The corresponding rates for gonorrhea infection were an incidence 41.3 versus 20.5 per 100 person-years, in the no Doxy PEP versus Doxy PEP arms, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .001), and 29.4 versus 16.8 per 100 person-years for Mycoplasma genitalium infection (aHR, 0.55; P = .015).
Throughout the study, about 80% of patients in the Doxy PEP group reported using the prophylaxis treatment after their most recent sexual intercourse, with subjects reporting taking a median of seven pills per month.
In the vaccine/no vaccine comparisons, 32 subjects in the no meningococcal vaccine group were infected with a first gonorrhea infection, compared with 17 in the vaccine group, representing an incidence of 19.7 versus 9.8 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .016), which Dr. Molina called “highly significant.”
An analysis of the cumulative incidence of gonorrhea infection with the meningococcal vaccine showed rates in the no vaccine versus vaccine groups of 30.4 versus 20.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; however, statistical significance was not reached (aHR, 0.66; P = .052).
Importantly, there were no significant interactions in the results between those receiving Doxy PEP or the 4CMenB vaccine group, and there were no significant differences in drug-related serious adverse events between the groups.
Dr. Molina noted that the meningococcal B vaccine is known to contain key antigens that are shared between meningitis and gonorrhea, which could explain the benefits.
Although chlamydia and syphilis thus far appear to remain susceptible to Doxy PEP, resistances with gonorrhea remain a concern, hence the ability of the vaccine to provide some protection could be an added bonus.
“We know that [gonorrhea] is able to very quickly develop resistances to any antibiotics, so that was why we wanted to look beyond the antibiotic prophylaxis,” said Dr. Molina.
Among questions to explore looking ahead is the potential longevity of protection with the vaccine.
“We don’t know at this point how long the protection with the vaccine could last, or if [people] may need booster injections, for instance, but the literature suggests benefits for at least a year,” Dr. Molina said. “We are still monitoring the patients in the study to see what happens.”
He added that combination of the interventions may be of benefit.
“In the future, we think we may need to combine these approaches if we want to meet the WHO/UNAIDS targets to reduce the incidence of HIV and STIs by 90% by 2030.”
Commenting on the study, CROI vice-chair Landon Myer, MD, PhD, noted that “gonorrhea develops resistance quickly and can be hard to treat or prophylaxis, so the vaccine finding, which was hinted at by previous observational data, is really important.”
He agrees that “the duration of protective efficacy – a big thing in vaccines – is unknown.”
“Still, this is really significant,” Dr. Myer stressed. “An efficacious vaccine against a stubborn sexually transmitted infection.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CROI 2023
Physician group staffing down, expenses up, new reports show
Physician groups saw staff-to-physician ratios decline even as their workforce expenses rose between 2019 and 2021, according to recent reports from the American Medical Group Association (AMGA) and the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA).
As patients started to return to doctors’ offices as the pandemic eased in 2021, physician groups found it increasingly difficult to recruit and retain lower-level clinicians, including medical assistants and LPNs, officials from both associations told this news organization. Many clinics had to raise their pay scales to be competitive with employers in other fields, and some had to hire higher-priced RNs to keep their practices running.
The AMGA report was based largely on data from groups of over 500 physicians, mostly affiliated with health systems. According to a news release accompanying the report, the ratio between full-time equivalent (FTE) clinic staff and health care professionals in direct patient care dropped by 11.3% between 2019 and 2021. The ratio of medical assistants (MAs) to clinicians declined by a greater percentage.
In the MGMA report, which represented about 4,000 practices ranging from very small (two doctors) to very large groups, total support staff per FTE primary-care physician dropped by 18% from 2019 to 2021 in independent groups and by 13% in hospital-affiliated groups. The ratios decreased by smaller amounts in surgical practices.
In contrast, nonsurgical specialty groups under both types of ownership saw their staffing ratios rise slightly.
Although it’s unclear why medical specialties increased their staff while other types of specialties lost employees, Ron Holder, MHA, chief operating officer of MGMA, said that some specialists may have opened more ancillary facilities and hired new employees to recoup revenue lost during the pandemic.
Expenses rise sharply
The AMGA report found that staffing expenses for the surveyed groups increased by 15% between 2019 and 2021.
“We saw a decrease in staff and an increase in expenses during that time period, and there are a few reasons for that,” Rose Wagner, RN, chief operating officer of AMGA, said. “Groups increased salaries to maintain staff. We also saw lower-paid staff find other jobs outside of health care. For example, medical assistants and receptionists could find jobs outside of health care that paid more. [Open positions] got back-filled with other higher paid staff, such as RNs, doing lower skilled jobs.”
Mr. Holder added that rising wages in other sectors made leaving physician groups more attractive for employees.
“Three years ago, there weren’t many positions in a medical practice where you were competing with Chick-fil-A or Taco Bell,” he said. In Denver, where Mr. Holder is based, “every restaurant in town is now advertising $17-$19 [hourly] starting pay just to do fast food. That causes practices to either lose employees or pay more for the employees they have. So that raises per-employee expense significantly,” he said.
Mr. Holder noted that inflation also has driven up wages as employees demand higher pay to keep up with the cost of living.
Unusual exodus of employees
Fred Horton, MHA, president of AMGA Consulting, said he has never seen so many people leaving health care for other occupations.
Some exits resulted from practices laying people off early in the pandemic, but most staff members who left practices were seeking higher pay, he said. In addition, Ms. Wagner noted, some staff members didn’t want to be exposed to COVID at work.
“There was an exodus from health care that was different from what we’d experienced in the past,” Mr. Horton added. “It’s still extremely challenging to get up to the staffing levels that are appropriate.”
Mr. Holder, however, said that the situation is slowly improving. “Health care is fairly recession-proof, because people need it. So when you see companies in other industries closing shop or reducing their head count, that actually helps health care recruiting in some jobs. And people are coming back to the workplace who previously were worried about COVID or didn’t want to get the vaccine.”
Paying more for nurses
In 2021, groups adopted a variety of tactics to adapt to the pandemic and respond to patient demand, the AMGA survey shows. Forty percent of system-affiliated groups and 18% of independent practices changed registered nurses’ responsibilities, in many cases having them do the work of medical assistants who were in short supply.
Some practices hired RNs, who have historically been utilized less by primary care than by surgical specialties, Mr. Holder noted. Other clinics paid temp agencies to supply nurses at a steep cost.
“When you’re short staffed, you end up paying more overtime, you end up paying temporary agencies at higher dollars, and you hire higher skilled people to do lower-skilled work,” Ms. Wagner said.
Meanwhile, many physician groups tried to cope with the physician shortage by bringing on more advanced practice clinicians (APCs), including nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Seventy percent of the AMGA groups used this strategy, the report revealed.
“The use of APCs has been steadily increasing as groups try to adopt a lower-cost care model in the midst of a nationwide physician shortage,” Ms. Wagner said in the press release.
Changes in patient care
About half of the groups in the AMGA survey said they changed their staff structure to allow APCs to carry their own patient panels. Although most of these clinicians were probably under physician supervision, nearly half of the states now allow NPs to practice autonomously.
Mr. Horton cautioned that APCs can’t fully substitute for physicians and require the same support staff that doctors do if they have their own panels. In primary care groups, Mr. Holder noted, the average salary of an APC “is continuing to rise, and there isn’t a huge difference between what they and doctors make.”
Nevertheless, he added, “there are more NPs and PAs being added to the marketplace all the time, whereas [physician] residency programs aren’t really growing. There are caps on the number of residency positions, and some physicians are retiring. So the clock is ticking to the point where someday doctors will be grossly outnumbered by NPs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician groups saw staff-to-physician ratios decline even as their workforce expenses rose between 2019 and 2021, according to recent reports from the American Medical Group Association (AMGA) and the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA).
As patients started to return to doctors’ offices as the pandemic eased in 2021, physician groups found it increasingly difficult to recruit and retain lower-level clinicians, including medical assistants and LPNs, officials from both associations told this news organization. Many clinics had to raise their pay scales to be competitive with employers in other fields, and some had to hire higher-priced RNs to keep their practices running.
The AMGA report was based largely on data from groups of over 500 physicians, mostly affiliated with health systems. According to a news release accompanying the report, the ratio between full-time equivalent (FTE) clinic staff and health care professionals in direct patient care dropped by 11.3% between 2019 and 2021. The ratio of medical assistants (MAs) to clinicians declined by a greater percentage.
In the MGMA report, which represented about 4,000 practices ranging from very small (two doctors) to very large groups, total support staff per FTE primary-care physician dropped by 18% from 2019 to 2021 in independent groups and by 13% in hospital-affiliated groups. The ratios decreased by smaller amounts in surgical practices.
In contrast, nonsurgical specialty groups under both types of ownership saw their staffing ratios rise slightly.
Although it’s unclear why medical specialties increased their staff while other types of specialties lost employees, Ron Holder, MHA, chief operating officer of MGMA, said that some specialists may have opened more ancillary facilities and hired new employees to recoup revenue lost during the pandemic.
Expenses rise sharply
The AMGA report found that staffing expenses for the surveyed groups increased by 15% between 2019 and 2021.
“We saw a decrease in staff and an increase in expenses during that time period, and there are a few reasons for that,” Rose Wagner, RN, chief operating officer of AMGA, said. “Groups increased salaries to maintain staff. We also saw lower-paid staff find other jobs outside of health care. For example, medical assistants and receptionists could find jobs outside of health care that paid more. [Open positions] got back-filled with other higher paid staff, such as RNs, doing lower skilled jobs.”
Mr. Holder added that rising wages in other sectors made leaving physician groups more attractive for employees.
“Three years ago, there weren’t many positions in a medical practice where you were competing with Chick-fil-A or Taco Bell,” he said. In Denver, where Mr. Holder is based, “every restaurant in town is now advertising $17-$19 [hourly] starting pay just to do fast food. That causes practices to either lose employees or pay more for the employees they have. So that raises per-employee expense significantly,” he said.
Mr. Holder noted that inflation also has driven up wages as employees demand higher pay to keep up with the cost of living.
Unusual exodus of employees
Fred Horton, MHA, president of AMGA Consulting, said he has never seen so many people leaving health care for other occupations.
Some exits resulted from practices laying people off early in the pandemic, but most staff members who left practices were seeking higher pay, he said. In addition, Ms. Wagner noted, some staff members didn’t want to be exposed to COVID at work.
“There was an exodus from health care that was different from what we’d experienced in the past,” Mr. Horton added. “It’s still extremely challenging to get up to the staffing levels that are appropriate.”
Mr. Holder, however, said that the situation is slowly improving. “Health care is fairly recession-proof, because people need it. So when you see companies in other industries closing shop or reducing their head count, that actually helps health care recruiting in some jobs. And people are coming back to the workplace who previously were worried about COVID or didn’t want to get the vaccine.”
Paying more for nurses
In 2021, groups adopted a variety of tactics to adapt to the pandemic and respond to patient demand, the AMGA survey shows. Forty percent of system-affiliated groups and 18% of independent practices changed registered nurses’ responsibilities, in many cases having them do the work of medical assistants who were in short supply.
Some practices hired RNs, who have historically been utilized less by primary care than by surgical specialties, Mr. Holder noted. Other clinics paid temp agencies to supply nurses at a steep cost.
“When you’re short staffed, you end up paying more overtime, you end up paying temporary agencies at higher dollars, and you hire higher skilled people to do lower-skilled work,” Ms. Wagner said.
Meanwhile, many physician groups tried to cope with the physician shortage by bringing on more advanced practice clinicians (APCs), including nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Seventy percent of the AMGA groups used this strategy, the report revealed.
“The use of APCs has been steadily increasing as groups try to adopt a lower-cost care model in the midst of a nationwide physician shortage,” Ms. Wagner said in the press release.
Changes in patient care
About half of the groups in the AMGA survey said they changed their staff structure to allow APCs to carry their own patient panels. Although most of these clinicians were probably under physician supervision, nearly half of the states now allow NPs to practice autonomously.
Mr. Horton cautioned that APCs can’t fully substitute for physicians and require the same support staff that doctors do if they have their own panels. In primary care groups, Mr. Holder noted, the average salary of an APC “is continuing to rise, and there isn’t a huge difference between what they and doctors make.”
Nevertheless, he added, “there are more NPs and PAs being added to the marketplace all the time, whereas [physician] residency programs aren’t really growing. There are caps on the number of residency positions, and some physicians are retiring. So the clock is ticking to the point where someday doctors will be grossly outnumbered by NPs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician groups saw staff-to-physician ratios decline even as their workforce expenses rose between 2019 and 2021, according to recent reports from the American Medical Group Association (AMGA) and the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA).
As patients started to return to doctors’ offices as the pandemic eased in 2021, physician groups found it increasingly difficult to recruit and retain lower-level clinicians, including medical assistants and LPNs, officials from both associations told this news organization. Many clinics had to raise their pay scales to be competitive with employers in other fields, and some had to hire higher-priced RNs to keep their practices running.
The AMGA report was based largely on data from groups of over 500 physicians, mostly affiliated with health systems. According to a news release accompanying the report, the ratio between full-time equivalent (FTE) clinic staff and health care professionals in direct patient care dropped by 11.3% between 2019 and 2021. The ratio of medical assistants (MAs) to clinicians declined by a greater percentage.
In the MGMA report, which represented about 4,000 practices ranging from very small (two doctors) to very large groups, total support staff per FTE primary-care physician dropped by 18% from 2019 to 2021 in independent groups and by 13% in hospital-affiliated groups. The ratios decreased by smaller amounts in surgical practices.
In contrast, nonsurgical specialty groups under both types of ownership saw their staffing ratios rise slightly.
Although it’s unclear why medical specialties increased their staff while other types of specialties lost employees, Ron Holder, MHA, chief operating officer of MGMA, said that some specialists may have opened more ancillary facilities and hired new employees to recoup revenue lost during the pandemic.
Expenses rise sharply
The AMGA report found that staffing expenses for the surveyed groups increased by 15% between 2019 and 2021.
“We saw a decrease in staff and an increase in expenses during that time period, and there are a few reasons for that,” Rose Wagner, RN, chief operating officer of AMGA, said. “Groups increased salaries to maintain staff. We also saw lower-paid staff find other jobs outside of health care. For example, medical assistants and receptionists could find jobs outside of health care that paid more. [Open positions] got back-filled with other higher paid staff, such as RNs, doing lower skilled jobs.”
Mr. Holder added that rising wages in other sectors made leaving physician groups more attractive for employees.
“Three years ago, there weren’t many positions in a medical practice where you were competing with Chick-fil-A or Taco Bell,” he said. In Denver, where Mr. Holder is based, “every restaurant in town is now advertising $17-$19 [hourly] starting pay just to do fast food. That causes practices to either lose employees or pay more for the employees they have. So that raises per-employee expense significantly,” he said.
Mr. Holder noted that inflation also has driven up wages as employees demand higher pay to keep up with the cost of living.
Unusual exodus of employees
Fred Horton, MHA, president of AMGA Consulting, said he has never seen so many people leaving health care for other occupations.
Some exits resulted from practices laying people off early in the pandemic, but most staff members who left practices were seeking higher pay, he said. In addition, Ms. Wagner noted, some staff members didn’t want to be exposed to COVID at work.
“There was an exodus from health care that was different from what we’d experienced in the past,” Mr. Horton added. “It’s still extremely challenging to get up to the staffing levels that are appropriate.”
Mr. Holder, however, said that the situation is slowly improving. “Health care is fairly recession-proof, because people need it. So when you see companies in other industries closing shop or reducing their head count, that actually helps health care recruiting in some jobs. And people are coming back to the workplace who previously were worried about COVID or didn’t want to get the vaccine.”
Paying more for nurses
In 2021, groups adopted a variety of tactics to adapt to the pandemic and respond to patient demand, the AMGA survey shows. Forty percent of system-affiliated groups and 18% of independent practices changed registered nurses’ responsibilities, in many cases having them do the work of medical assistants who were in short supply.
Some practices hired RNs, who have historically been utilized less by primary care than by surgical specialties, Mr. Holder noted. Other clinics paid temp agencies to supply nurses at a steep cost.
“When you’re short staffed, you end up paying more overtime, you end up paying temporary agencies at higher dollars, and you hire higher skilled people to do lower-skilled work,” Ms. Wagner said.
Meanwhile, many physician groups tried to cope with the physician shortage by bringing on more advanced practice clinicians (APCs), including nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Seventy percent of the AMGA groups used this strategy, the report revealed.
“The use of APCs has been steadily increasing as groups try to adopt a lower-cost care model in the midst of a nationwide physician shortage,” Ms. Wagner said in the press release.
Changes in patient care
About half of the groups in the AMGA survey said they changed their staff structure to allow APCs to carry their own patient panels. Although most of these clinicians were probably under physician supervision, nearly half of the states now allow NPs to practice autonomously.
Mr. Horton cautioned that APCs can’t fully substitute for physicians and require the same support staff that doctors do if they have their own panels. In primary care groups, Mr. Holder noted, the average salary of an APC “is continuing to rise, and there isn’t a huge difference between what they and doctors make.”
Nevertheless, he added, “there are more NPs and PAs being added to the marketplace all the time, whereas [physician] residency programs aren’t really growing. There are caps on the number of residency positions, and some physicians are retiring. So the clock is ticking to the point where someday doctors will be grossly outnumbered by NPs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors and their families tend to ignore medical guidelines
according to a study by economic professors from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge; Stanford (Calif.) University; and the George Gund Professor of Economics and Business Administration at Harvard University, Boston.
What to know
- Doctors’ medical knowledge may influence them and their families to often ignore medical advice while the rest of the population adheres to general medication guidelines.
- Of the 63 guidelines used in the study, doctors and their families followed the standards less than a third of the time.
- The difference in adherence to guidelines between experts and nonexperts is largest with respect to antibiotics, in which doctors and their families are 5.2 percentage points less in compliance than everyone else.
- Doctors could be more likely to prescribe broader-spectrum antibiotics for themselves and their families, whereas most patients receive more narrow-spectrum antibiotics.
- Many members of the general public don’t understand medical guidelines, finding them too complex to follow, and many people don’t trust their doctors.
This is a summary of the article, “A Taste of Their Own Medicine: Guideline Adherence and Access to Expertise,” published in the American Economic Review: Insights on December 13, 2022. The full article can be found on aeaweb.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a study by economic professors from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge; Stanford (Calif.) University; and the George Gund Professor of Economics and Business Administration at Harvard University, Boston.
What to know
- Doctors’ medical knowledge may influence them and their families to often ignore medical advice while the rest of the population adheres to general medication guidelines.
- Of the 63 guidelines used in the study, doctors and their families followed the standards less than a third of the time.
- The difference in adherence to guidelines between experts and nonexperts is largest with respect to antibiotics, in which doctors and their families are 5.2 percentage points less in compliance than everyone else.
- Doctors could be more likely to prescribe broader-spectrum antibiotics for themselves and their families, whereas most patients receive more narrow-spectrum antibiotics.
- Many members of the general public don’t understand medical guidelines, finding them too complex to follow, and many people don’t trust their doctors.
This is a summary of the article, “A Taste of Their Own Medicine: Guideline Adherence and Access to Expertise,” published in the American Economic Review: Insights on December 13, 2022. The full article can be found on aeaweb.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a study by economic professors from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge; Stanford (Calif.) University; and the George Gund Professor of Economics and Business Administration at Harvard University, Boston.
What to know
- Doctors’ medical knowledge may influence them and their families to often ignore medical advice while the rest of the population adheres to general medication guidelines.
- Of the 63 guidelines used in the study, doctors and their families followed the standards less than a third of the time.
- The difference in adherence to guidelines between experts and nonexperts is largest with respect to antibiotics, in which doctors and their families are 5.2 percentage points less in compliance than everyone else.
- Doctors could be more likely to prescribe broader-spectrum antibiotics for themselves and their families, whereas most patients receive more narrow-spectrum antibiotics.
- Many members of the general public don’t understand medical guidelines, finding them too complex to follow, and many people don’t trust their doctors.
This is a summary of the article, “A Taste of Their Own Medicine: Guideline Adherence and Access to Expertise,” published in the American Economic Review: Insights on December 13, 2022. The full article can be found on aeaweb.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Docs with one paid malpractice claim are four times more likely to have another
In this retrospective case-control study, law and public health researchers from Georgetown University, the National Opinion Research Center, the University of Colorado, and Northwestern University analyzed paid malpractice claims for all licensed U.S. physicians.
The findings suggest that a single malpractice claim may not be a random stroke of bad luck but instead holds some predictive power into the risk for future paid claims.
“A four times increase in risk is huge, particularly since we observe a similar increase in both high-risk and lower-risk specialties,” David Hyman, JD, MD, professor of health law and policy at Georgetown University, Washington, and lead researcher on the study, told this news organization. “There are surely some false positives, but there must be lots of actual negligence too, or we would not see these results.”
For the 881,876 physicians analyzed, researchers looked at malpractice claims paid during two 5-year periods: 2009-2013 and 2014-2018. Nearly 96% of physicians had no paid malpractice claims between 2009 and 2013; 3% had one, and less than 1% had multiple claims. The proportion of physicians with paid claims between 2014 and 2018 was similar.
Compared with physicians with no 2009-2013 claims, a physician with just one paid claim in that time period had a 3.7 times higher risk for a future paid claim. Physicians with two paid claims were nearly 7 times more likely to have a future paid claim, and those with three or more paid claims were more than 11 times more likely to have one.
Approximately 3% of physicians with no paid claims between 2009 and 2013 had a future paid claim, growing to 12.4% of those with one paid claim during that time.
The study’s findings may have implications for medical licensing boards and hospitals granting staff privileges.
“After some number of paid claims, there should be an official response” from these entities, such as a hands-on assessment of technical skills or assignment of a peer mentor, said Dr. Hyman, who is also coauthor of a book titled “Medical Malpractice Litigation: How It Works, Why Tort Reform Hasn’t Helped.” A graduated set of interventions, whether voluntary or mandatory, can reduce future claim risk and patient harm, Dr. Hyman added.
Interventions may include error avoidance and post-error communication training, counseling to improve bedside skills, and encouragement to move into nonclinical practice. Either way, Dr. Hyman says a nuanced intervention strategy would be a welcome shift away from the current “all or nothing approach” that too often ends in the revocation of a physician’s medical license.
Although there are strategies to proactively identify physicians with excess risk for malpractice claims and implement preventive measures – like Vanderbilt University’s Patient Advocacy Reporting System, for example – most hospitals and physician groups fail to initiate even informal interventions after a malpractice settlement or verdict, which is a missed opportunity, Dr. Hyman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In this retrospective case-control study, law and public health researchers from Georgetown University, the National Opinion Research Center, the University of Colorado, and Northwestern University analyzed paid malpractice claims for all licensed U.S. physicians.
The findings suggest that a single malpractice claim may not be a random stroke of bad luck but instead holds some predictive power into the risk for future paid claims.
“A four times increase in risk is huge, particularly since we observe a similar increase in both high-risk and lower-risk specialties,” David Hyman, JD, MD, professor of health law and policy at Georgetown University, Washington, and lead researcher on the study, told this news organization. “There are surely some false positives, but there must be lots of actual negligence too, or we would not see these results.”
For the 881,876 physicians analyzed, researchers looked at malpractice claims paid during two 5-year periods: 2009-2013 and 2014-2018. Nearly 96% of physicians had no paid malpractice claims between 2009 and 2013; 3% had one, and less than 1% had multiple claims. The proportion of physicians with paid claims between 2014 and 2018 was similar.
Compared with physicians with no 2009-2013 claims, a physician with just one paid claim in that time period had a 3.7 times higher risk for a future paid claim. Physicians with two paid claims were nearly 7 times more likely to have a future paid claim, and those with three or more paid claims were more than 11 times more likely to have one.
Approximately 3% of physicians with no paid claims between 2009 and 2013 had a future paid claim, growing to 12.4% of those with one paid claim during that time.
The study’s findings may have implications for medical licensing boards and hospitals granting staff privileges.
“After some number of paid claims, there should be an official response” from these entities, such as a hands-on assessment of technical skills or assignment of a peer mentor, said Dr. Hyman, who is also coauthor of a book titled “Medical Malpractice Litigation: How It Works, Why Tort Reform Hasn’t Helped.” A graduated set of interventions, whether voluntary or mandatory, can reduce future claim risk and patient harm, Dr. Hyman added.
Interventions may include error avoidance and post-error communication training, counseling to improve bedside skills, and encouragement to move into nonclinical practice. Either way, Dr. Hyman says a nuanced intervention strategy would be a welcome shift away from the current “all or nothing approach” that too often ends in the revocation of a physician’s medical license.
Although there are strategies to proactively identify physicians with excess risk for malpractice claims and implement preventive measures – like Vanderbilt University’s Patient Advocacy Reporting System, for example – most hospitals and physician groups fail to initiate even informal interventions after a malpractice settlement or verdict, which is a missed opportunity, Dr. Hyman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In this retrospective case-control study, law and public health researchers from Georgetown University, the National Opinion Research Center, the University of Colorado, and Northwestern University analyzed paid malpractice claims for all licensed U.S. physicians.
The findings suggest that a single malpractice claim may not be a random stroke of bad luck but instead holds some predictive power into the risk for future paid claims.
“A four times increase in risk is huge, particularly since we observe a similar increase in both high-risk and lower-risk specialties,” David Hyman, JD, MD, professor of health law and policy at Georgetown University, Washington, and lead researcher on the study, told this news organization. “There are surely some false positives, but there must be lots of actual negligence too, or we would not see these results.”
For the 881,876 physicians analyzed, researchers looked at malpractice claims paid during two 5-year periods: 2009-2013 and 2014-2018. Nearly 96% of physicians had no paid malpractice claims between 2009 and 2013; 3% had one, and less than 1% had multiple claims. The proportion of physicians with paid claims between 2014 and 2018 was similar.
Compared with physicians with no 2009-2013 claims, a physician with just one paid claim in that time period had a 3.7 times higher risk for a future paid claim. Physicians with two paid claims were nearly 7 times more likely to have a future paid claim, and those with three or more paid claims were more than 11 times more likely to have one.
Approximately 3% of physicians with no paid claims between 2009 and 2013 had a future paid claim, growing to 12.4% of those with one paid claim during that time.
The study’s findings may have implications for medical licensing boards and hospitals granting staff privileges.
“After some number of paid claims, there should be an official response” from these entities, such as a hands-on assessment of technical skills or assignment of a peer mentor, said Dr. Hyman, who is also coauthor of a book titled “Medical Malpractice Litigation: How It Works, Why Tort Reform Hasn’t Helped.” A graduated set of interventions, whether voluntary or mandatory, can reduce future claim risk and patient harm, Dr. Hyman added.
Interventions may include error avoidance and post-error communication training, counseling to improve bedside skills, and encouragement to move into nonclinical practice. Either way, Dr. Hyman says a nuanced intervention strategy would be a welcome shift away from the current “all or nothing approach” that too often ends in the revocation of a physician’s medical license.
Although there are strategies to proactively identify physicians with excess risk for malpractice claims and implement preventive measures – like Vanderbilt University’s Patient Advocacy Reporting System, for example – most hospitals and physician groups fail to initiate even informal interventions after a malpractice settlement or verdict, which is a missed opportunity, Dr. Hyman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
Autoantibodies signal reduced cancer risk in dermatomyositis
Adults with the inflammatory autoimmune myopathy dermatomyositis are at increased for concurrent cancers, but new research suggests that certain autoantibodies in patients with a specific dermatomyositis subtype may actually protect against cancer.
A study of cohorts of patients with dermatomyositis, other rheumatic diseases, and those without disease showed that among patients with dermatomyositis positive for antitranscriptional intermediary factor 1 (anti–TIF1-gamma) autoantibodies – a disease subtype associated with increased cancer risk – the presence of autoantibodies directed against cell division cycle and apoptosis regulator 1 (CCAR1) was associated with reduced cancer risk “to a level comparable to that seen in the general population,” Christopher A. Mecoli, MD, MHS, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues reported.
“Our prior data suggest that there are autoantigens that, when targeted simultaneously with CCAR1, provide additional cancer protection. Although these autoantigens are less frequently targeted, it is likely that additional, more prevalent ‘autoantigen hubs’ remain undiscovered,” they wrote in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Identification of other autoantibodies both in the anti–TIF1-gamma–positive and other dermatomyositis subgroups may help with cancer risk stratification in patients with the disease and may ultimately improve cancer screening for adults with dermatomyositis, the investigators said.
Toward precision medicine
“I think this is a step toward precision medicine in patients with rheumatic disease, specifically myositis,” Dr. Mecoli said in an interview.
The study supports earlier work showing that dermatomyositis and related myopathies are heterogeneous, he said, noting that, “if you put 10 myositis patients in the same room, you wouldn’t get that they all have the same disease because they can look so different from one another.”
The association of dermatomyositis with concurrent cancers has been known for decades, but in recent years his team and other investigators have noted that the association holds true for only some patients with dermatomyositis, most notably those patients positive for anti–TIF1-gamma autoantibodies.
“And then, of course, once you really start studying just one gamma-positive dermatomyositis patient, you realize that even among that group it is heterogeneous in terms of their cancer risk, and that was the main focus of this study: to reconcile this clinical observation that I had a lot of patients with TIF1-gamma dermatomyositis who never get diagnosed with cancer,” Dr. Mecoli said.
Study details
Dr. Dr. Mecoli and colleagues previously reported that immune responses to CCAR1 and other autoantigens seen in patients with dermatomyositis were associated with lower probability of cancer occurrence.
In the current study, they focused on the disease specificity, clinical phenotype, and cancer risk for patients with dermatomyositis and anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies.
They looked at all patients aged 18 or older with a probable or definite finding of dermatomyositis, according to 2017 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy criteria, who were seen at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center from August 2004 to April 2020 (101 patients), or the Johns Hopkins Myositis Center (141 patients) from January 2007 to December 2020.
Controls included 44 patients evaluated at the Johns Hopkins Myositis Center with immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy, 186 patients with anti–TIF1-gamma–negative dermatomyositis (defined as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay readout of less than seven units) evaluated at either Stanford or Johns Hopkins, 44 patients with inclusion body myositis evaluated at Johns Hopkins, and 46 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus from the Hopkins Lupus Cohort. The investigators also assayed serum from 32 healthy individuals.
They found that patients with anti–TIF1-gamma–positive dermatomyositis were significantly more likely than those with anti–TIF1-gamma–negative dermatomyositis to have anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies (32% vs. 8%; P < .001). Additionally, they noted that the anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies were not seen in serum from healthy controls and were found at only very low frequencies among patients with other rheumatic diseases.
When they looked at the incidence of cancer from the time of dermatomyositis onset (defined as the first patient-reported symptoms of rash, weakness, myalgia, or dyspnea) they found that the standardized incidence ratio in anti–TIF1-gamma–positive patients in both the Stanford and Hopkins cohorts was higher than expected, with SIRs of 3.49 and 4.54, respectively (P < .001 for each comparison).
However, among those patients who were both anti–TIF1-gamma positive and anti-CCAR1 positive, the SIRs were 1.78 in the Stanford cohort and 1.61 in the Hopkins cohort, and neither SIR was significantly higher than that of the general population.
Risk prediction
Their findings suggest that autoantibody profiles might be used for cancer risk stratification in patients with anti–TIF1-gamma–positive dermatomyositis, Dr. Mecoli said.
“Are we overscreening? What is the cost in terms of patient anxiety, in terms of radiation, and in terms of false positive results?” he asked. “If I had a patient in front of me with anti–TIF1-gamma dermatomyositis, I would probably manage them differently if I knew that they were CCAR1 positive, because the presence of that additional autoantibody attenuates their cancer risk relative to the general population.”
In an editorial accompanying the study, Manabu Fujimoto, MD, of the department of dermatology at Osaka (Japan) University, commented that it “is of clinical importance in that combination of autoantibodies can predict cancer risk with more accuracy. At the same time, this study will give an insight into the pathomechanisms of how antitumor activity may shape autoimmunity in dermatomyositis.”
It will be “intriguing” to discover whether anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies act only against tumors or might also have an impact on dermatomyositis itself, Dr. Fujimoto said.
The research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health; Huayi and Siuling Zhang Discovery Fund; Peter Buck, MD; and the Donald B. and Dorothy L. Stabler Foundation. The authors and Dr. Fujimoto reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adults with the inflammatory autoimmune myopathy dermatomyositis are at increased for concurrent cancers, but new research suggests that certain autoantibodies in patients with a specific dermatomyositis subtype may actually protect against cancer.
A study of cohorts of patients with dermatomyositis, other rheumatic diseases, and those without disease showed that among patients with dermatomyositis positive for antitranscriptional intermediary factor 1 (anti–TIF1-gamma) autoantibodies – a disease subtype associated with increased cancer risk – the presence of autoantibodies directed against cell division cycle and apoptosis regulator 1 (CCAR1) was associated with reduced cancer risk “to a level comparable to that seen in the general population,” Christopher A. Mecoli, MD, MHS, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues reported.
“Our prior data suggest that there are autoantigens that, when targeted simultaneously with CCAR1, provide additional cancer protection. Although these autoantigens are less frequently targeted, it is likely that additional, more prevalent ‘autoantigen hubs’ remain undiscovered,” they wrote in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Identification of other autoantibodies both in the anti–TIF1-gamma–positive and other dermatomyositis subgroups may help with cancer risk stratification in patients with the disease and may ultimately improve cancer screening for adults with dermatomyositis, the investigators said.
Toward precision medicine
“I think this is a step toward precision medicine in patients with rheumatic disease, specifically myositis,” Dr. Mecoli said in an interview.
The study supports earlier work showing that dermatomyositis and related myopathies are heterogeneous, he said, noting that, “if you put 10 myositis patients in the same room, you wouldn’t get that they all have the same disease because they can look so different from one another.”
The association of dermatomyositis with concurrent cancers has been known for decades, but in recent years his team and other investigators have noted that the association holds true for only some patients with dermatomyositis, most notably those patients positive for anti–TIF1-gamma autoantibodies.
“And then, of course, once you really start studying just one gamma-positive dermatomyositis patient, you realize that even among that group it is heterogeneous in terms of their cancer risk, and that was the main focus of this study: to reconcile this clinical observation that I had a lot of patients with TIF1-gamma dermatomyositis who never get diagnosed with cancer,” Dr. Mecoli said.
Study details
Dr. Dr. Mecoli and colleagues previously reported that immune responses to CCAR1 and other autoantigens seen in patients with dermatomyositis were associated with lower probability of cancer occurrence.
In the current study, they focused on the disease specificity, clinical phenotype, and cancer risk for patients with dermatomyositis and anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies.
They looked at all patients aged 18 or older with a probable or definite finding of dermatomyositis, according to 2017 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy criteria, who were seen at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center from August 2004 to April 2020 (101 patients), or the Johns Hopkins Myositis Center (141 patients) from January 2007 to December 2020.
Controls included 44 patients evaluated at the Johns Hopkins Myositis Center with immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy, 186 patients with anti–TIF1-gamma–negative dermatomyositis (defined as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay readout of less than seven units) evaluated at either Stanford or Johns Hopkins, 44 patients with inclusion body myositis evaluated at Johns Hopkins, and 46 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus from the Hopkins Lupus Cohort. The investigators also assayed serum from 32 healthy individuals.
They found that patients with anti–TIF1-gamma–positive dermatomyositis were significantly more likely than those with anti–TIF1-gamma–negative dermatomyositis to have anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies (32% vs. 8%; P < .001). Additionally, they noted that the anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies were not seen in serum from healthy controls and were found at only very low frequencies among patients with other rheumatic diseases.
When they looked at the incidence of cancer from the time of dermatomyositis onset (defined as the first patient-reported symptoms of rash, weakness, myalgia, or dyspnea) they found that the standardized incidence ratio in anti–TIF1-gamma–positive patients in both the Stanford and Hopkins cohorts was higher than expected, with SIRs of 3.49 and 4.54, respectively (P < .001 for each comparison).
However, among those patients who were both anti–TIF1-gamma positive and anti-CCAR1 positive, the SIRs were 1.78 in the Stanford cohort and 1.61 in the Hopkins cohort, and neither SIR was significantly higher than that of the general population.
Risk prediction
Their findings suggest that autoantibody profiles might be used for cancer risk stratification in patients with anti–TIF1-gamma–positive dermatomyositis, Dr. Mecoli said.
“Are we overscreening? What is the cost in terms of patient anxiety, in terms of radiation, and in terms of false positive results?” he asked. “If I had a patient in front of me with anti–TIF1-gamma dermatomyositis, I would probably manage them differently if I knew that they were CCAR1 positive, because the presence of that additional autoantibody attenuates their cancer risk relative to the general population.”
In an editorial accompanying the study, Manabu Fujimoto, MD, of the department of dermatology at Osaka (Japan) University, commented that it “is of clinical importance in that combination of autoantibodies can predict cancer risk with more accuracy. At the same time, this study will give an insight into the pathomechanisms of how antitumor activity may shape autoimmunity in dermatomyositis.”
It will be “intriguing” to discover whether anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies act only against tumors or might also have an impact on dermatomyositis itself, Dr. Fujimoto said.
The research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health; Huayi and Siuling Zhang Discovery Fund; Peter Buck, MD; and the Donald B. and Dorothy L. Stabler Foundation. The authors and Dr. Fujimoto reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adults with the inflammatory autoimmune myopathy dermatomyositis are at increased for concurrent cancers, but new research suggests that certain autoantibodies in patients with a specific dermatomyositis subtype may actually protect against cancer.
A study of cohorts of patients with dermatomyositis, other rheumatic diseases, and those without disease showed that among patients with dermatomyositis positive for antitranscriptional intermediary factor 1 (anti–TIF1-gamma) autoantibodies – a disease subtype associated with increased cancer risk – the presence of autoantibodies directed against cell division cycle and apoptosis regulator 1 (CCAR1) was associated with reduced cancer risk “to a level comparable to that seen in the general population,” Christopher A. Mecoli, MD, MHS, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues reported.
“Our prior data suggest that there are autoantigens that, when targeted simultaneously with CCAR1, provide additional cancer protection. Although these autoantigens are less frequently targeted, it is likely that additional, more prevalent ‘autoantigen hubs’ remain undiscovered,” they wrote in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Identification of other autoantibodies both in the anti–TIF1-gamma–positive and other dermatomyositis subgroups may help with cancer risk stratification in patients with the disease and may ultimately improve cancer screening for adults with dermatomyositis, the investigators said.
Toward precision medicine
“I think this is a step toward precision medicine in patients with rheumatic disease, specifically myositis,” Dr. Mecoli said in an interview.
The study supports earlier work showing that dermatomyositis and related myopathies are heterogeneous, he said, noting that, “if you put 10 myositis patients in the same room, you wouldn’t get that they all have the same disease because they can look so different from one another.”
The association of dermatomyositis with concurrent cancers has been known for decades, but in recent years his team and other investigators have noted that the association holds true for only some patients with dermatomyositis, most notably those patients positive for anti–TIF1-gamma autoantibodies.
“And then, of course, once you really start studying just one gamma-positive dermatomyositis patient, you realize that even among that group it is heterogeneous in terms of their cancer risk, and that was the main focus of this study: to reconcile this clinical observation that I had a lot of patients with TIF1-gamma dermatomyositis who never get diagnosed with cancer,” Dr. Mecoli said.
Study details
Dr. Dr. Mecoli and colleagues previously reported that immune responses to CCAR1 and other autoantigens seen in patients with dermatomyositis were associated with lower probability of cancer occurrence.
In the current study, they focused on the disease specificity, clinical phenotype, and cancer risk for patients with dermatomyositis and anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies.
They looked at all patients aged 18 or older with a probable or definite finding of dermatomyositis, according to 2017 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy criteria, who were seen at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center from August 2004 to April 2020 (101 patients), or the Johns Hopkins Myositis Center (141 patients) from January 2007 to December 2020.
Controls included 44 patients evaluated at the Johns Hopkins Myositis Center with immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy, 186 patients with anti–TIF1-gamma–negative dermatomyositis (defined as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay readout of less than seven units) evaluated at either Stanford or Johns Hopkins, 44 patients with inclusion body myositis evaluated at Johns Hopkins, and 46 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus from the Hopkins Lupus Cohort. The investigators also assayed serum from 32 healthy individuals.
They found that patients with anti–TIF1-gamma–positive dermatomyositis were significantly more likely than those with anti–TIF1-gamma–negative dermatomyositis to have anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies (32% vs. 8%; P < .001). Additionally, they noted that the anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies were not seen in serum from healthy controls and were found at only very low frequencies among patients with other rheumatic diseases.
When they looked at the incidence of cancer from the time of dermatomyositis onset (defined as the first patient-reported symptoms of rash, weakness, myalgia, or dyspnea) they found that the standardized incidence ratio in anti–TIF1-gamma–positive patients in both the Stanford and Hopkins cohorts was higher than expected, with SIRs of 3.49 and 4.54, respectively (P < .001 for each comparison).
However, among those patients who were both anti–TIF1-gamma positive and anti-CCAR1 positive, the SIRs were 1.78 in the Stanford cohort and 1.61 in the Hopkins cohort, and neither SIR was significantly higher than that of the general population.
Risk prediction
Their findings suggest that autoantibody profiles might be used for cancer risk stratification in patients with anti–TIF1-gamma–positive dermatomyositis, Dr. Mecoli said.
“Are we overscreening? What is the cost in terms of patient anxiety, in terms of radiation, and in terms of false positive results?” he asked. “If I had a patient in front of me with anti–TIF1-gamma dermatomyositis, I would probably manage them differently if I knew that they were CCAR1 positive, because the presence of that additional autoantibody attenuates their cancer risk relative to the general population.”
In an editorial accompanying the study, Manabu Fujimoto, MD, of the department of dermatology at Osaka (Japan) University, commented that it “is of clinical importance in that combination of autoantibodies can predict cancer risk with more accuracy. At the same time, this study will give an insight into the pathomechanisms of how antitumor activity may shape autoimmunity in dermatomyositis.”
It will be “intriguing” to discover whether anti-CCAR1 autoantibodies act only against tumors or might also have an impact on dermatomyositis itself, Dr. Fujimoto said.
The research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health; Huayi and Siuling Zhang Discovery Fund; Peter Buck, MD; and the Donald B. and Dorothy L. Stabler Foundation. The authors and Dr. Fujimoto reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Treating rosacea: Combination therapy, benzoyl peroxide, and the ‘STOP’ mnemonic
HONOLULU – More often than not, patients with rosacea require a combination of treatments to optimize the management of the disease, according to Julie C. Harper, MD.
“We’ve been more comfortable with the idea of combination therapy for acne than we have been for rosacea,” Dr. Harper, who practices in Birmingham, Ala., said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “If patients are doing great on one treatment, then don’t change it. But if there’s room for improvement, think about combinations.”
Treatment options for papules and pustules include ivermectin, metronidazole, azelaic acid, sodium sulfacetamide/sulfur, modified release doxycycline, minocycline foam, and microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide, 5%. Options for persistent background erythema include brimonidine and oxymetazoline, as well as device-based treatments, which include the pulsed dye laser, the KTP laser, intense pulsed light, and electrosurgery.
Dr. Harper said that she has been especially surprised by the effectiveness of one of these options, microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream, 5% (Epsolay), which is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating inflammatory lesions of rosacea in adults. In two identical, phase 3 randomized clinical trials of patients with inflammatory rosacea lesions, those treated with microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide achieved a 68.8% reduction in inflammatory lesions at 12 weeks (including 42.5% at week 2), compared with 38%-46% of those on the vehicle, according to the April 2022 announcement of the approval from the manufacturers, Sol-Gel Technologies and Galderma.
“A common drug is playing a key role,” Dr. Harper said. “What’s the mechanism of action? I have no idea. I wonder if there may be a bacterial pathogen after all,” possibly Staphylococcus epidermidis, she added. However, she noted, “it does appear that benzoyl peroxide has an impact on Demodex, so maybe that’s the primary way it’s working.”
In her opinion, a key standout from the clinical trial data is the drug’s rapid onset of action, with a 42.5% reduction of lesions at week 2. “What makes this different is that the 5% microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream is wrapped up in a silica shell,” said Dr. Harper, a past president of the American Acne and Rosacea Society. “The silica shell kind of acts like a speed bump that slows the release of drug onto the skin. We think that’s what may be giving us this better tolerability.”
In an interview at the meeting, Linda Stein Gold, MD, director of clinical research and division head of dermatology at the Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, said that prior to the approval of Epsolay, benzoyl peroxide was never considered a first-line treatment for rosacea. “The problem is, the conventional formulation is irritating to the skin,” said Dr. Stein Gold, who was involved in clinical trials of Epsolay.
“The benzoyl peroxide encapsulated in the silica shell allows for a slow and steady delivery of medication to the skin in a very controlled manner. It is exceptionally good at getting rosacea under control. In the clinical trials, when we looked at the baseline irritation of the skin and followed those patients when they used the benzoyl 5% microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream, the irritation improved.”
‘STOP’ mnemonic
When treating her patients with rosacea, Dr. Harper incorporates the mnemonic “STOP” to these patient visits:
S: Identify signs and symptoms of rosacea.
T: Discuss triggers. “We cannot make this disease triggerless, so when you’re talking to your patients, you need to find out what’s triggering their rosacea,” she said.
O: Agree on a treatment outcome. “What is it that’s important to the patient?” she said. “They may tell you, ‘I want to be able to not be so red,’ or ‘I want to get rid of the bumps,’ or ‘I want my eyes to not feel so dry.’ ”
P: Develop a plan that helps achieve that desired outcome with patients.
Dr. Harper disclosed ties with Almirall, Cassiopeia, Cutera, Galderma, EPI, L’Oréal, Ortho Dermatologics, Sol Gel, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, and Vyne.
Dr. Stein Gold disclosed ties with Almirall, Cutera, Dermata, Galderma, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – More often than not, patients with rosacea require a combination of treatments to optimize the management of the disease, according to Julie C. Harper, MD.
“We’ve been more comfortable with the idea of combination therapy for acne than we have been for rosacea,” Dr. Harper, who practices in Birmingham, Ala., said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “If patients are doing great on one treatment, then don’t change it. But if there’s room for improvement, think about combinations.”
Treatment options for papules and pustules include ivermectin, metronidazole, azelaic acid, sodium sulfacetamide/sulfur, modified release doxycycline, minocycline foam, and microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide, 5%. Options for persistent background erythema include brimonidine and oxymetazoline, as well as device-based treatments, which include the pulsed dye laser, the KTP laser, intense pulsed light, and electrosurgery.
Dr. Harper said that she has been especially surprised by the effectiveness of one of these options, microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream, 5% (Epsolay), which is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating inflammatory lesions of rosacea in adults. In two identical, phase 3 randomized clinical trials of patients with inflammatory rosacea lesions, those treated with microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide achieved a 68.8% reduction in inflammatory lesions at 12 weeks (including 42.5% at week 2), compared with 38%-46% of those on the vehicle, according to the April 2022 announcement of the approval from the manufacturers, Sol-Gel Technologies and Galderma.
“A common drug is playing a key role,” Dr. Harper said. “What’s the mechanism of action? I have no idea. I wonder if there may be a bacterial pathogen after all,” possibly Staphylococcus epidermidis, she added. However, she noted, “it does appear that benzoyl peroxide has an impact on Demodex, so maybe that’s the primary way it’s working.”
In her opinion, a key standout from the clinical trial data is the drug’s rapid onset of action, with a 42.5% reduction of lesions at week 2. “What makes this different is that the 5% microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream is wrapped up in a silica shell,” said Dr. Harper, a past president of the American Acne and Rosacea Society. “The silica shell kind of acts like a speed bump that slows the release of drug onto the skin. We think that’s what may be giving us this better tolerability.”
In an interview at the meeting, Linda Stein Gold, MD, director of clinical research and division head of dermatology at the Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, said that prior to the approval of Epsolay, benzoyl peroxide was never considered a first-line treatment for rosacea. “The problem is, the conventional formulation is irritating to the skin,” said Dr. Stein Gold, who was involved in clinical trials of Epsolay.
“The benzoyl peroxide encapsulated in the silica shell allows for a slow and steady delivery of medication to the skin in a very controlled manner. It is exceptionally good at getting rosacea under control. In the clinical trials, when we looked at the baseline irritation of the skin and followed those patients when they used the benzoyl 5% microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream, the irritation improved.”
‘STOP’ mnemonic
When treating her patients with rosacea, Dr. Harper incorporates the mnemonic “STOP” to these patient visits:
S: Identify signs and symptoms of rosacea.
T: Discuss triggers. “We cannot make this disease triggerless, so when you’re talking to your patients, you need to find out what’s triggering their rosacea,” she said.
O: Agree on a treatment outcome. “What is it that’s important to the patient?” she said. “They may tell you, ‘I want to be able to not be so red,’ or ‘I want to get rid of the bumps,’ or ‘I want my eyes to not feel so dry.’ ”
P: Develop a plan that helps achieve that desired outcome with patients.
Dr. Harper disclosed ties with Almirall, Cassiopeia, Cutera, Galderma, EPI, L’Oréal, Ortho Dermatologics, Sol Gel, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, and Vyne.
Dr. Stein Gold disclosed ties with Almirall, Cutera, Dermata, Galderma, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – More often than not, patients with rosacea require a combination of treatments to optimize the management of the disease, according to Julie C. Harper, MD.
“We’ve been more comfortable with the idea of combination therapy for acne than we have been for rosacea,” Dr. Harper, who practices in Birmingham, Ala., said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “If patients are doing great on one treatment, then don’t change it. But if there’s room for improvement, think about combinations.”
Treatment options for papules and pustules include ivermectin, metronidazole, azelaic acid, sodium sulfacetamide/sulfur, modified release doxycycline, minocycline foam, and microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide, 5%. Options for persistent background erythema include brimonidine and oxymetazoline, as well as device-based treatments, which include the pulsed dye laser, the KTP laser, intense pulsed light, and electrosurgery.
Dr. Harper said that she has been especially surprised by the effectiveness of one of these options, microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream, 5% (Epsolay), which is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating inflammatory lesions of rosacea in adults. In two identical, phase 3 randomized clinical trials of patients with inflammatory rosacea lesions, those treated with microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide achieved a 68.8% reduction in inflammatory lesions at 12 weeks (including 42.5% at week 2), compared with 38%-46% of those on the vehicle, according to the April 2022 announcement of the approval from the manufacturers, Sol-Gel Technologies and Galderma.
“A common drug is playing a key role,” Dr. Harper said. “What’s the mechanism of action? I have no idea. I wonder if there may be a bacterial pathogen after all,” possibly Staphylococcus epidermidis, she added. However, she noted, “it does appear that benzoyl peroxide has an impact on Demodex, so maybe that’s the primary way it’s working.”
In her opinion, a key standout from the clinical trial data is the drug’s rapid onset of action, with a 42.5% reduction of lesions at week 2. “What makes this different is that the 5% microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream is wrapped up in a silica shell,” said Dr. Harper, a past president of the American Acne and Rosacea Society. “The silica shell kind of acts like a speed bump that slows the release of drug onto the skin. We think that’s what may be giving us this better tolerability.”
In an interview at the meeting, Linda Stein Gold, MD, director of clinical research and division head of dermatology at the Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, said that prior to the approval of Epsolay, benzoyl peroxide was never considered a first-line treatment for rosacea. “The problem is, the conventional formulation is irritating to the skin,” said Dr. Stein Gold, who was involved in clinical trials of Epsolay.
“The benzoyl peroxide encapsulated in the silica shell allows for a slow and steady delivery of medication to the skin in a very controlled manner. It is exceptionally good at getting rosacea under control. In the clinical trials, when we looked at the baseline irritation of the skin and followed those patients when they used the benzoyl 5% microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream, the irritation improved.”
‘STOP’ mnemonic
When treating her patients with rosacea, Dr. Harper incorporates the mnemonic “STOP” to these patient visits:
S: Identify signs and symptoms of rosacea.
T: Discuss triggers. “We cannot make this disease triggerless, so when you’re talking to your patients, you need to find out what’s triggering their rosacea,” she said.
O: Agree on a treatment outcome. “What is it that’s important to the patient?” she said. “They may tell you, ‘I want to be able to not be so red,’ or ‘I want to get rid of the bumps,’ or ‘I want my eyes to not feel so dry.’ ”
P: Develop a plan that helps achieve that desired outcome with patients.
Dr. Harper disclosed ties with Almirall, Cassiopeia, Cutera, Galderma, EPI, L’Oréal, Ortho Dermatologics, Sol Gel, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, and Vyne.
Dr. Stein Gold disclosed ties with Almirall, Cutera, Dermata, Galderma, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT THE MEDSCAPE LIVE! HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Zika virus still calls for preparedness and vaccine development
Warming U.S. temperatures, the resumption of travel, and new knowledge about Zika’s long-term effects on children signal that Zika prevention and vaccine development should be on public health officials’, doctors’, and communities’ radar, even when community infection is not occurring.
“Although we haven’t seen confirmed Zika virus circulation in the continental United States or its territories for several years, it’s still something that we are closely monitoring, particularly as we move into the summer months,” Erin Staples, MD, PhD, medical epidemiologist at the Arboviral Diseases Branch of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Fort Collins, Colo., told this news organization.
“This is because cases are still being reported in other countries, particularly in South America. Travel to these places is increasing following the pandemic, leaving more potential for individuals who might have acquired the infection to come back and restart community transmission.”
How Zika might reemerge
The Aedes aegypti mosquito is the vector by which Zika spreads, and “during the COVID pandemic, these mosquitoes moved further north in the United States, into southern California, and were identified as far north as Washington, D.C.,” said Neil Silverman, MD, professor of clinical obstetrics and gynecology and director of the Infections in Pregnancy Program at UCLA Medical Center in Los Angeles.
“On a population level, Americans have essentially no immunity to Zika from prior infection, and there is no vaccine yet approved. If individuals infected with Zika came into a U.S. region where the Aedes aegypti mosquito was present, that population could be very susceptible to infection spread and even another outbreak. This would be a confluence of bad circumstances, but that’s exactly what infectious disease specialists continue to be watchful about, especially because Zika is so dangerous for fetuses,” said Dr. Silverman.
How the public can prepare
The CDC recommends that pregnant women or women who plan to become pregnant avoid traveling to regions where there are currently outbreaks of Zika, but this is not the only way that individuals can protect themselves.
“The message we want to deliver to people is that in the United States, people are at risk for several mosquito-borne diseases every summer beyond just Zika,” Dr. Staples said. “It’s really important that people are instructed to make a habit of wearing EPA [U.S. Environmental Protection Agency)–registered insect repellents when they go outside. Right now, that is the single best tool that we have to prevent mosquito-borne diseases in the U.S.
“From a community standpoint, there are several emerging mosquito control methods that are being evaluated right now, such as genetic modification and irradiation of mosquitoes. These methods are aimed at producing sterile mosquitoes that are released into the wild to mate with the local mosquito population, which will render them infertile. This leads, over time, to suppression of the overall Aedes aegypti mosquito population – the main vector of Zika transmission,” said Dr. Staples.
Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, professor of medicine and associate chief of the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, encourages her patients to wear mosquito repellent but cautioned that “there’s no antiviral that you can take for Zika. Until we have a vaccine, the key to controlling/preventing Zika is controlling the mosquitoes that spread the virus.”
Vaccines
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) is currently investigating a variety of Zika vaccines, including a DNA-based vaccine, (phase 2), a purified inactivated virus vaccine (phase 1), live attenuated vaccines (phase 2), and mRNA vaccines (phase 2).
“I’m most excited about mRNA vaccines because they help patients produce a lot of proteins. The protein from a typical protein-adjuvant vaccine will break down, and patients can only raise an immune response to whatever proteins are left. On the other hand, mRNA vaccines provide the body [with] a recipe to make the protein from the pathogen in high amounts, so that a strong immune response can be raised for protection,” noted Dr. Gandhi.
Moderna’s mRNA-1893 vaccine was recently studied in a randomized, observer-blind, controlled, phase 1 trial among 120 adults in the United States and Puerto Rico, the results of which were published online in The Lancet. “The vaccine was found to be generally well tolerated with no serious adverse events considered related to vaccine. Furthermore, the vaccine was able to generate a potent immune response that was capable of neutralizing the virus in vitro,” said Brett Leav, MD, executive director of clinical development for public health vaccines at Moderna.
“Our mRNA platform technology ... can be very helpful against emerging pandemic threats, as we saw in response to COVID-19. What is unique in our approach is that if the genetic sequence of the virus is known, we can quickly generate vaccines to test for their capability to generate a functional immune response. In the case of the mRNA-1893 trial, the vaccine was developed with antigens that were present in the strain of virus circulating in 2016, but we could easily match whatever strain reemerges,” said Dr. Leav.
A phase 2 trial to confirm the dose of mRNA-1893 in a larger study population is underway.
Although it’s been demonstrated that Moderna’s mRNA vaccine is safe and effective, moving from a phase 2 to a phase 3 study presents a challenge, given the fact that currently, the disease burden from Zika is low. If an outbreak were to occur in the future, these mRNA vaccines could potentially be given emergency approval, as occurred during the COVID pandemic, according to Dr. Silverman.
If approved, provisionally or through a traditional route, the vaccine would “accelerate the ability to tamp down any further outbreaks, because vaccine-based immunity could be made available to a large portion of the population who were pregnant or planning a pregnancy, not just in the U.S. but also in these endemic areas,” said Dr. Silverman.
Takeaways from the last Zika outbreak
Practical steps such as mosquito eradication and development of vaccines are not the only takeaway from the recent Zika epidemics inside and outside the United States. A clearer picture of the short- and long-term stakes of the disease has emerged.
According to the CDC, most people who become infected with Zika experience only mild symptoms, such as fever, rash, headache, and muscle pain, but babies conceived by mothers infected with Zika are at risk for stillbirth, miscarriage, and microcephaly and other brain defects.
Although a pregnant woman who tests positive for Zika is in a very high-risk situation, “data show that only about 30% of mothers with Zika have a baby with birth defects. If a pregnant woman contracted Zika, what would happen is we would just do very close screening by ultrasound of the fetus. If microcephaly in utero or fetal brain defects were observed, then a mother would be counseled on her options,” said Dr. Gandhi.
Dr. Silverman noted that “new data on children who were exposed in utero and had normal exams, including head measurements when they were born, have raised concerns. In recently published long-term follow-up studies, even when children born to mothers infected with Zika during pregnancy had normal head growth at least 3 years after birth, they were still at risk for neurodevelopmental delay and behavioral disorders, including impact on coordination and executive function.
“This is another good reason to keep the potential risks of Zika active in the public’s consciousness and in public health planning.”
Dr. Silverman, Dr. Gandhi, and Dr. Staples have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leav is an employee of Moderna and owns stock in the company.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Warming U.S. temperatures, the resumption of travel, and new knowledge about Zika’s long-term effects on children signal that Zika prevention and vaccine development should be on public health officials’, doctors’, and communities’ radar, even when community infection is not occurring.
“Although we haven’t seen confirmed Zika virus circulation in the continental United States or its territories for several years, it’s still something that we are closely monitoring, particularly as we move into the summer months,” Erin Staples, MD, PhD, medical epidemiologist at the Arboviral Diseases Branch of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Fort Collins, Colo., told this news organization.
“This is because cases are still being reported in other countries, particularly in South America. Travel to these places is increasing following the pandemic, leaving more potential for individuals who might have acquired the infection to come back and restart community transmission.”
How Zika might reemerge
The Aedes aegypti mosquito is the vector by which Zika spreads, and “during the COVID pandemic, these mosquitoes moved further north in the United States, into southern California, and were identified as far north as Washington, D.C.,” said Neil Silverman, MD, professor of clinical obstetrics and gynecology and director of the Infections in Pregnancy Program at UCLA Medical Center in Los Angeles.
“On a population level, Americans have essentially no immunity to Zika from prior infection, and there is no vaccine yet approved. If individuals infected with Zika came into a U.S. region where the Aedes aegypti mosquito was present, that population could be very susceptible to infection spread and even another outbreak. This would be a confluence of bad circumstances, but that’s exactly what infectious disease specialists continue to be watchful about, especially because Zika is so dangerous for fetuses,” said Dr. Silverman.
How the public can prepare
The CDC recommends that pregnant women or women who plan to become pregnant avoid traveling to regions where there are currently outbreaks of Zika, but this is not the only way that individuals can protect themselves.
“The message we want to deliver to people is that in the United States, people are at risk for several mosquito-borne diseases every summer beyond just Zika,” Dr. Staples said. “It’s really important that people are instructed to make a habit of wearing EPA [U.S. Environmental Protection Agency)–registered insect repellents when they go outside. Right now, that is the single best tool that we have to prevent mosquito-borne diseases in the U.S.
“From a community standpoint, there are several emerging mosquito control methods that are being evaluated right now, such as genetic modification and irradiation of mosquitoes. These methods are aimed at producing sterile mosquitoes that are released into the wild to mate with the local mosquito population, which will render them infertile. This leads, over time, to suppression of the overall Aedes aegypti mosquito population – the main vector of Zika transmission,” said Dr. Staples.
Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, professor of medicine and associate chief of the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, encourages her patients to wear mosquito repellent but cautioned that “there’s no antiviral that you can take for Zika. Until we have a vaccine, the key to controlling/preventing Zika is controlling the mosquitoes that spread the virus.”
Vaccines
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) is currently investigating a variety of Zika vaccines, including a DNA-based vaccine, (phase 2), a purified inactivated virus vaccine (phase 1), live attenuated vaccines (phase 2), and mRNA vaccines (phase 2).
“I’m most excited about mRNA vaccines because they help patients produce a lot of proteins. The protein from a typical protein-adjuvant vaccine will break down, and patients can only raise an immune response to whatever proteins are left. On the other hand, mRNA vaccines provide the body [with] a recipe to make the protein from the pathogen in high amounts, so that a strong immune response can be raised for protection,” noted Dr. Gandhi.
Moderna’s mRNA-1893 vaccine was recently studied in a randomized, observer-blind, controlled, phase 1 trial among 120 adults in the United States and Puerto Rico, the results of which were published online in The Lancet. “The vaccine was found to be generally well tolerated with no serious adverse events considered related to vaccine. Furthermore, the vaccine was able to generate a potent immune response that was capable of neutralizing the virus in vitro,” said Brett Leav, MD, executive director of clinical development for public health vaccines at Moderna.
“Our mRNA platform technology ... can be very helpful against emerging pandemic threats, as we saw in response to COVID-19. What is unique in our approach is that if the genetic sequence of the virus is known, we can quickly generate vaccines to test for their capability to generate a functional immune response. In the case of the mRNA-1893 trial, the vaccine was developed with antigens that were present in the strain of virus circulating in 2016, but we could easily match whatever strain reemerges,” said Dr. Leav.
A phase 2 trial to confirm the dose of mRNA-1893 in a larger study population is underway.
Although it’s been demonstrated that Moderna’s mRNA vaccine is safe and effective, moving from a phase 2 to a phase 3 study presents a challenge, given the fact that currently, the disease burden from Zika is low. If an outbreak were to occur in the future, these mRNA vaccines could potentially be given emergency approval, as occurred during the COVID pandemic, according to Dr. Silverman.
If approved, provisionally or through a traditional route, the vaccine would “accelerate the ability to tamp down any further outbreaks, because vaccine-based immunity could be made available to a large portion of the population who were pregnant or planning a pregnancy, not just in the U.S. but also in these endemic areas,” said Dr. Silverman.
Takeaways from the last Zika outbreak
Practical steps such as mosquito eradication and development of vaccines are not the only takeaway from the recent Zika epidemics inside and outside the United States. A clearer picture of the short- and long-term stakes of the disease has emerged.
According to the CDC, most people who become infected with Zika experience only mild symptoms, such as fever, rash, headache, and muscle pain, but babies conceived by mothers infected with Zika are at risk for stillbirth, miscarriage, and microcephaly and other brain defects.
Although a pregnant woman who tests positive for Zika is in a very high-risk situation, “data show that only about 30% of mothers with Zika have a baby with birth defects. If a pregnant woman contracted Zika, what would happen is we would just do very close screening by ultrasound of the fetus. If microcephaly in utero or fetal brain defects were observed, then a mother would be counseled on her options,” said Dr. Gandhi.
Dr. Silverman noted that “new data on children who were exposed in utero and had normal exams, including head measurements when they were born, have raised concerns. In recently published long-term follow-up studies, even when children born to mothers infected with Zika during pregnancy had normal head growth at least 3 years after birth, they were still at risk for neurodevelopmental delay and behavioral disorders, including impact on coordination and executive function.
“This is another good reason to keep the potential risks of Zika active in the public’s consciousness and in public health planning.”
Dr. Silverman, Dr. Gandhi, and Dr. Staples have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leav is an employee of Moderna and owns stock in the company.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Warming U.S. temperatures, the resumption of travel, and new knowledge about Zika’s long-term effects on children signal that Zika prevention and vaccine development should be on public health officials’, doctors’, and communities’ radar, even when community infection is not occurring.
“Although we haven’t seen confirmed Zika virus circulation in the continental United States or its territories for several years, it’s still something that we are closely monitoring, particularly as we move into the summer months,” Erin Staples, MD, PhD, medical epidemiologist at the Arboviral Diseases Branch of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Fort Collins, Colo., told this news organization.
“This is because cases are still being reported in other countries, particularly in South America. Travel to these places is increasing following the pandemic, leaving more potential for individuals who might have acquired the infection to come back and restart community transmission.”
How Zika might reemerge
The Aedes aegypti mosquito is the vector by which Zika spreads, and “during the COVID pandemic, these mosquitoes moved further north in the United States, into southern California, and were identified as far north as Washington, D.C.,” said Neil Silverman, MD, professor of clinical obstetrics and gynecology and director of the Infections in Pregnancy Program at UCLA Medical Center in Los Angeles.
“On a population level, Americans have essentially no immunity to Zika from prior infection, and there is no vaccine yet approved. If individuals infected with Zika came into a U.S. region where the Aedes aegypti mosquito was present, that population could be very susceptible to infection spread and even another outbreak. This would be a confluence of bad circumstances, but that’s exactly what infectious disease specialists continue to be watchful about, especially because Zika is so dangerous for fetuses,” said Dr. Silverman.
How the public can prepare
The CDC recommends that pregnant women or women who plan to become pregnant avoid traveling to regions where there are currently outbreaks of Zika, but this is not the only way that individuals can protect themselves.
“The message we want to deliver to people is that in the United States, people are at risk for several mosquito-borne diseases every summer beyond just Zika,” Dr. Staples said. “It’s really important that people are instructed to make a habit of wearing EPA [U.S. Environmental Protection Agency)–registered insect repellents when they go outside. Right now, that is the single best tool that we have to prevent mosquito-borne diseases in the U.S.
“From a community standpoint, there are several emerging mosquito control methods that are being evaluated right now, such as genetic modification and irradiation of mosquitoes. These methods are aimed at producing sterile mosquitoes that are released into the wild to mate with the local mosquito population, which will render them infertile. This leads, over time, to suppression of the overall Aedes aegypti mosquito population – the main vector of Zika transmission,” said Dr. Staples.
Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, professor of medicine and associate chief of the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, encourages her patients to wear mosquito repellent but cautioned that “there’s no antiviral that you can take for Zika. Until we have a vaccine, the key to controlling/preventing Zika is controlling the mosquitoes that spread the virus.”
Vaccines
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) is currently investigating a variety of Zika vaccines, including a DNA-based vaccine, (phase 2), a purified inactivated virus vaccine (phase 1), live attenuated vaccines (phase 2), and mRNA vaccines (phase 2).
“I’m most excited about mRNA vaccines because they help patients produce a lot of proteins. The protein from a typical protein-adjuvant vaccine will break down, and patients can only raise an immune response to whatever proteins are left. On the other hand, mRNA vaccines provide the body [with] a recipe to make the protein from the pathogen in high amounts, so that a strong immune response can be raised for protection,” noted Dr. Gandhi.
Moderna’s mRNA-1893 vaccine was recently studied in a randomized, observer-blind, controlled, phase 1 trial among 120 adults in the United States and Puerto Rico, the results of which were published online in The Lancet. “The vaccine was found to be generally well tolerated with no serious adverse events considered related to vaccine. Furthermore, the vaccine was able to generate a potent immune response that was capable of neutralizing the virus in vitro,” said Brett Leav, MD, executive director of clinical development for public health vaccines at Moderna.
“Our mRNA platform technology ... can be very helpful against emerging pandemic threats, as we saw in response to COVID-19. What is unique in our approach is that if the genetic sequence of the virus is known, we can quickly generate vaccines to test for their capability to generate a functional immune response. In the case of the mRNA-1893 trial, the vaccine was developed with antigens that were present in the strain of virus circulating in 2016, but we could easily match whatever strain reemerges,” said Dr. Leav.
A phase 2 trial to confirm the dose of mRNA-1893 in a larger study population is underway.
Although it’s been demonstrated that Moderna’s mRNA vaccine is safe and effective, moving from a phase 2 to a phase 3 study presents a challenge, given the fact that currently, the disease burden from Zika is low. If an outbreak were to occur in the future, these mRNA vaccines could potentially be given emergency approval, as occurred during the COVID pandemic, according to Dr. Silverman.
If approved, provisionally or through a traditional route, the vaccine would “accelerate the ability to tamp down any further outbreaks, because vaccine-based immunity could be made available to a large portion of the population who were pregnant or planning a pregnancy, not just in the U.S. but also in these endemic areas,” said Dr. Silverman.
Takeaways from the last Zika outbreak
Practical steps such as mosquito eradication and development of vaccines are not the only takeaway from the recent Zika epidemics inside and outside the United States. A clearer picture of the short- and long-term stakes of the disease has emerged.
According to the CDC, most people who become infected with Zika experience only mild symptoms, such as fever, rash, headache, and muscle pain, but babies conceived by mothers infected with Zika are at risk for stillbirth, miscarriage, and microcephaly and other brain defects.
Although a pregnant woman who tests positive for Zika is in a very high-risk situation, “data show that only about 30% of mothers with Zika have a baby with birth defects. If a pregnant woman contracted Zika, what would happen is we would just do very close screening by ultrasound of the fetus. If microcephaly in utero or fetal brain defects were observed, then a mother would be counseled on her options,” said Dr. Gandhi.
Dr. Silverman noted that “new data on children who were exposed in utero and had normal exams, including head measurements when they were born, have raised concerns. In recently published long-term follow-up studies, even when children born to mothers infected with Zika during pregnancy had normal head growth at least 3 years after birth, they were still at risk for neurodevelopmental delay and behavioral disorders, including impact on coordination and executive function.
“This is another good reason to keep the potential risks of Zika active in the public’s consciousness and in public health planning.”
Dr. Silverman, Dr. Gandhi, and Dr. Staples have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leav is an employee of Moderna and owns stock in the company.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New influx of Humira biosimilars may not drive immediate change
Gastroenterologists in 2023 will have more tools in their arsenal to treat patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. As many as 8-10 adalimumab biosimilars are anticipated to come on the market this year, giving mainstay drug Humira some vigorous competition.
Three scenarios will drive adalimumab biosimilar initiation: Insurance preference for the initial treatment of a newly diagnosed condition, a change in a patient’s insurance plan, or an insurance-mandated switch, said Edward C. Oldfield IV, MD, assistant professor at Eastern Virginia Medical School’s division of gastroenterology in Norfolk.
“Outside of these scenarios, I would encourage patients to remain on their current biologic so long as cost and accessibility remain stable,” said Dr. Oldfield.
Many factors will contribute to the success of biosimilars. Will physicians be prescribing them? How are biosimilars placed on formularies and will they be given preferred status? How will manufacturers price their biosimilars? “We have to wait and see to get the answers to these questions,” said Steven Newmark, JD, MPA, chief legal officer and director of policy, Global Healthy Living Foundation/CreakyJoints, a nonprofit advocacy organization based in New York.
Prescribing biosimilars is no different than prescribing originator biologics, so providers should know how to use them, said Mr. Newmark. “Most important will be the availability of patient-friendly resources that providers can share with their patients to provide education about and confidence in using biosimilars,” he added.
Overall, biosimilars are a good thing, said Dr. Oldfield. “In the long run they should bring down costs and increase access to medications for our patients.”
Others are skeptical that the adalimumab biosimilars will save patients much money.
Biosimilar laws were created to lower costs. However, if a patient with insurance pays only $5 a month out of pocket for Humira – a drug that normally costs $7,000 without coverage – it’s unlikely they would want to switch unless there’s comparable savings from the biosimilar, said Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, medical director of the Digestive Health Center and professor of medicine at Northwestern Medicine, Northwestern University, Evanston, Ill.
Like generics, Humira biosimilars may face some initial backlash, said Dr. Hanauer.
2023 broadens scope of adalimumab treatments
The American Gastroenterological Association describes a biosimilar as something that’s “highly similar to, but not an exact copy of, a biologic reference product already approved” by the Food and Drug Administration. Congress under the 2010 Affordable Care Act created a special, abbreviated pathway to approval for biosimilars.
AbbVie’s Humira, the global revenue for which exceeded $20 billion in 2021, has long dominated the U.S. market on injectable treatments for autoimmune diseases. The popular drug faces some competition in 2023, however, following a series of legal settlements that allowed AbbVie competitors to release their own adalimumab biosimilars.
“So far, we haven’t seen biosimilars live up to their potential in the U.S. in the inflammatory space,” said Mr. Newmark. This may change, however. Previously, biosimilars have required infusion, which demanded more time, commitment, and travel from patients. “The new set of forthcoming Humira biosimilars are injectables, an administration method preferred by patients,” he said.
The FDA will approve a biosimilar if it determines that the biological product is highly similar to the reference product, and that there are no clinically meaningful differences between the biological and reference product in terms of the safety, purity, and potency of the product.
The agency to date has approved 8 adalimumab biosimilars. These include: Idacio (adalimumab-aacf, Fresenius Kabi); Amjevita (adalimumab-atto, Amgen); Hadlima (adalimumab-bwwd, Organon); Cyltezo (adalimumab-adbm, Boehringer Ingelheim); Yusimry (adalimumab-aqvh from Coherus BioSciences); Hulio (adalimumab-fkjp; Mylan/Fujifilm Kyowa Kirin Biologics); Hyrimoz (adalimumab-adaz, Sandoz), and Abrilada (adalimumab-afzb, Pfizer).
“While FDA doesn’t formally track when products come to market, we know based on published reports that application holders for many of the currently FDA-approved biosimilars plan to market this year, starting with Amjevita being the first adalimumab biosimilar launched” in January, said Sarah Yim, MD, director of the Office of Therapeutic Biologics and Biosimilars at the agency.
At press time, two other companies (Celltrion and Alvotech/Teva) were awaiting FDA approval for their adalimumab biosimilar drugs.
Among the eight approved drugs, Cyltezo is the only one that has a designation for interchangeability with Humira.
An interchangeable biosimilar may be substituted at the pharmacy without the intervention of the prescriber – much like generics are substituted, depending on state laws, said Dr. Yim. “However, in terms of safety and effectiveness, FDA’s standards for approval mean that biosimilar or interchangeable biosimilar products can be used in place of the reference product they were compared to.”
FDA-approved biosimilars undergo a rigorous evaluation for safety, effectiveness, and quality for their approved conditions of use, she continued. “Therefore, patients and health care providers can rely on a biosimilar to be as safe and effective for its approved uses as the original biological product.”
Remicade as a yard stick
Gastroenterologists dealt with this situation once before, when Remicade (infliximab) biosimilars came on the market in 2016, noted Miguel Regueiro, MD, chair of the Digestive Disease and Surgery Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
Remicade and Humira are both tumor necrosis factor inhibitors with the same mechanism of action and many of the same indications. “We already had that experience with Remicade and biosimilar switch 2 or 3 years ago. Now we’re talking about Humira,” said Dr. Regueiro.
Most GI doctors have prescribed one of the more common infliximab biosimilars (Inflectra or Renflexis), noted Dr. Oldfield.
Cardinal Health, which recently surveyed 300 gastroenterologists, rheumatologists, and dermatologists about adalimumab biosimilars, found that gastroenterologists had the highest comfort level in prescribing them. Their top concern, however, was changing a patient from adalimumab to an adalimumab biosimilar.
For most patients, Dr. Oldfield sees the Humira reference biologic and biosimilar as equivalent.
However, he said he would change a patient’s drug only if there were a good reason or if his hand was forced by insurance. He would not make the change for a patient who recently began induction with the reference biologic or a patient with highly active clinical disease.
“While there is limited data to support this, I would also have some qualms about changing a patient from reference biologic to a biosimilar if they previously had immune-mediated pharmacokinetic failure due to antibody development with a biologic and were currently doing well on their new biologic,” he said.
Those with a new ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s diagnosis who are initiating a biologic for the first time might consider a biosimilar. If a patient is transitioning from a reference biologic to a biosimilar, “I would want to make that change during a time of stable remission and with the recognition that the switch is not a temporary switch, but a long-term switch,” he continued.
A paper that reviewed 23 observational studies of adalimumab and other biosimilars found that switching biosimilars was safe and effective. But if possible, patients should minimize the number of switches until more robust long-term data are available, added Dr. Oldfield.
If a patient is apprehensive about switching to a new therapy, “one may need to be cognizant of the ‘nocebo’ effect in which there is an unexplained or unfavorable therapeutic effect after switching,” he said.
Other gastroenterologists voiced similar reservations about switching. “I won’t use an adalimumab biosimilar unless the patient requests it, the insurance requires it, or there is a cost advantage for the patient such that they prefer it,” said Doug Wolf, MD, an Atlanta gastroenterologist.
“There is no medical treatment advantage to a biosimilar, especially if switching from Humira,” added Dr. Wolf.
Insurance will guide treatment
Once a drug is approved for use by the FDA, that drug will be available in all 50 states. “Different private insurance formularies, as well as state Medicaid formularies, might affect the actual ability of patients to receive such drugs,” said Mr. Newmark.
Patients should consult with their providers and insurance companies to see what therapies are available, he advised.
Dr. Hanauer anticipates some headaches arising for patients and doctors alike when negotiating for a specific drug.
Cyltezo may be the only biosimilar interchangeable with Humira, but the third-party pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) could negotiate for one of the noninterchangeable ones. “On a yearly basis they could switch their preference,” said Dr. Hanauer.
In the Cardinal Health survey, more than 60% of respondents said they would feel comfortable prescribing an adalimumab biosimilar only with an interchangeability designation.
A PBM may offer a patient Cyltezo if it’s cheaper than Humira. If the patient insists on staying on Humira, then they’ll have to pay more for that drug on their payer’s formulary, said Dr. Hanauer. In a worst-case scenario, a physician may have to appeal on a patient’s behalf to get Humira if the insurer offers only the biosimilar.
Taking that step to appeal is a major hassle for the physician, and leads to extra back door costs as well, said Dr. Hanauer.
Humira manufacturer AbbVie, in turn, may offer discounts and rebates to the PBMs to put Humira on their formulary. “That’s the AbbVie negotiating power. It’s not that the cost is going to be that much different. It’s going to be that there are rebates and discounts that are going to make the cost different,” he added.
As a community physician, Dr. Oldfield has specific concerns about accessibility.
The ever-increasing burden of insurance documentation and prior authorization means it can take weeks or months to get these medications approved. “The addition of new biosimilars is a welcome entrance if it can get patients the medications they need when they need it,” he said.
When it comes to prescribing biologics, many physicians rely on ancillary staff for assistance. It’s a team effort to sift through all the paperwork, observed Dr. Oldfield.
“While many community GI practices have specialized staff to deal with prior authorizations, they are still a far cry from the IBD [inflammatory bowel disease] academic centers where there are often pharmacists, nursing specialists, and home-monitoring programs to check in on patients,” he explained.
Landscape on cost is uncertain
At present, little is known about the cost of the biosimilars and impact on future drug pricing, said Dr. Oldfield.
At least for Medicare, Humira biosimilars will be considered Medicare Part D drugs if used for a medically accepted indication, said a spokesperson for the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
Part D sponsors (pharmacy and therapeutic committees) “will make the determination as to whether Amjevita and other products will be added to their formularies,” said the spokesperson.
Patients never saw a significant cost savings with Remicade biosimilars. “I imagine the same would be true with biosimilars for Humira,” said Dr. Regueiro. Patients may see greater access to these drugs, however, because the insurance plan or the pharmacy plan will make them more readily available, he added.
The hope is that, as biosimilars are introduced, the price of the originator biologic will go down, said Mr. Newmark. “Therefore, we can expect Humira to be offered at a lower price as it faces competition. Where it will sit in comparison to the forthcoming biosimilars will depend on how much biosimilar companies drop their price and how much pressure will be on PBMs and insurers to cover the lowest list price drug,” he said.
AbbVie did not respond to several requests for comment.
Charitable patient assistance programs for biosimilars or biologics can help offset the price of copayments, Mr. Newmark offered.
Ideally, insurers will offer designated biosimilars at a reduced or even no out-of-pocket expense on their formularies. This should lead to a decreased administrative burden for approval with streamlined (or even removal) of prior authorizations for certain medications, said Dr. Oldfield.
Without insurance or medication assistance programs, the cost of biosimilars is prohibitively expensive, he added.
“Biosimilars have higher research, development, and manufacturing costs than what people conventionally think of [for] a generic medication.”
Educating, advising patients
Dr. Oldfield advised that gastroenterologists refer to biologics by the generic name rather than branded name when initiating therapy unless there is a very specific reason not to. “This approach should make the process more streamlined and less subjected to quick denials for brand-only requests as biosimilars start to assume a larger market share,” he said.
Uptake of the Humira biosimilars also will depend on proper education of physicians and patients and their comfort level with the biosimilars, said Dr. Regueiro. Cleveland Clinic uses a team approach to educate on this topic, relying on pharmacists, clinicians, and nurses to explain that there’s no real difference between the reference drug and its biosimilars, based on efficacy and safety data.
Physicians can also direct patients to patient-friendly resources, said Mr. Newmark. “By starting the conversation early, it ensures that when/if the time comes that your patient is switched to or chooses a biosimilar they will feel more confident because they have the knowledge to make decisions about their care.”
The Global Healthy Living Foundation’s podcast, Breaking Down Biosimilars , is a free resource for patients, he added.
It’s important that doctors also understand these products so they can explain to their patients what to expect, said the FDA’s Dr. Yim. The FDA provides educational materials on its website, including a comprehensive curriculum toolkit.
Dr. Hanauer has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Amgen, American College of Gastroenterology, GlaxoSmithKline, American Gastroenterological Association, Pfizer, and a host of other companies . Dr. Regueiro has served on advisory boards and as a consultant for Abbvie, Janssen, UCB, Takeda, Pfizer, BMS, Organon, Amgen, Genentech, Gilead, Salix, Prometheus, Lilly, Celgene, TARGET Pharma Solutions,Trellis, and Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Wolf, Dr. Yim, Dr. Oldfield, and Mr. Newmark have no financial conflicts of interest.
Gastroenterologists in 2023 will have more tools in their arsenal to treat patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. As many as 8-10 adalimumab biosimilars are anticipated to come on the market this year, giving mainstay drug Humira some vigorous competition.
Three scenarios will drive adalimumab biosimilar initiation: Insurance preference for the initial treatment of a newly diagnosed condition, a change in a patient’s insurance plan, or an insurance-mandated switch, said Edward C. Oldfield IV, MD, assistant professor at Eastern Virginia Medical School’s division of gastroenterology in Norfolk.
“Outside of these scenarios, I would encourage patients to remain on their current biologic so long as cost and accessibility remain stable,” said Dr. Oldfield.
Many factors will contribute to the success of biosimilars. Will physicians be prescribing them? How are biosimilars placed on formularies and will they be given preferred status? How will manufacturers price their biosimilars? “We have to wait and see to get the answers to these questions,” said Steven Newmark, JD, MPA, chief legal officer and director of policy, Global Healthy Living Foundation/CreakyJoints, a nonprofit advocacy organization based in New York.
Prescribing biosimilars is no different than prescribing originator biologics, so providers should know how to use them, said Mr. Newmark. “Most important will be the availability of patient-friendly resources that providers can share with their patients to provide education about and confidence in using biosimilars,” he added.
Overall, biosimilars are a good thing, said Dr. Oldfield. “In the long run they should bring down costs and increase access to medications for our patients.”
Others are skeptical that the adalimumab biosimilars will save patients much money.
Biosimilar laws were created to lower costs. However, if a patient with insurance pays only $5 a month out of pocket for Humira – a drug that normally costs $7,000 without coverage – it’s unlikely they would want to switch unless there’s comparable savings from the biosimilar, said Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, medical director of the Digestive Health Center and professor of medicine at Northwestern Medicine, Northwestern University, Evanston, Ill.
Like generics, Humira biosimilars may face some initial backlash, said Dr. Hanauer.
2023 broadens scope of adalimumab treatments
The American Gastroenterological Association describes a biosimilar as something that’s “highly similar to, but not an exact copy of, a biologic reference product already approved” by the Food and Drug Administration. Congress under the 2010 Affordable Care Act created a special, abbreviated pathway to approval for biosimilars.
AbbVie’s Humira, the global revenue for which exceeded $20 billion in 2021, has long dominated the U.S. market on injectable treatments for autoimmune diseases. The popular drug faces some competition in 2023, however, following a series of legal settlements that allowed AbbVie competitors to release their own adalimumab biosimilars.
“So far, we haven’t seen biosimilars live up to their potential in the U.S. in the inflammatory space,” said Mr. Newmark. This may change, however. Previously, biosimilars have required infusion, which demanded more time, commitment, and travel from patients. “The new set of forthcoming Humira biosimilars are injectables, an administration method preferred by patients,” he said.
The FDA will approve a biosimilar if it determines that the biological product is highly similar to the reference product, and that there are no clinically meaningful differences between the biological and reference product in terms of the safety, purity, and potency of the product.
The agency to date has approved 8 adalimumab biosimilars. These include: Idacio (adalimumab-aacf, Fresenius Kabi); Amjevita (adalimumab-atto, Amgen); Hadlima (adalimumab-bwwd, Organon); Cyltezo (adalimumab-adbm, Boehringer Ingelheim); Yusimry (adalimumab-aqvh from Coherus BioSciences); Hulio (adalimumab-fkjp; Mylan/Fujifilm Kyowa Kirin Biologics); Hyrimoz (adalimumab-adaz, Sandoz), and Abrilada (adalimumab-afzb, Pfizer).
“While FDA doesn’t formally track when products come to market, we know based on published reports that application holders for many of the currently FDA-approved biosimilars plan to market this year, starting with Amjevita being the first adalimumab biosimilar launched” in January, said Sarah Yim, MD, director of the Office of Therapeutic Biologics and Biosimilars at the agency.
At press time, two other companies (Celltrion and Alvotech/Teva) were awaiting FDA approval for their adalimumab biosimilar drugs.
Among the eight approved drugs, Cyltezo is the only one that has a designation for interchangeability with Humira.
An interchangeable biosimilar may be substituted at the pharmacy without the intervention of the prescriber – much like generics are substituted, depending on state laws, said Dr. Yim. “However, in terms of safety and effectiveness, FDA’s standards for approval mean that biosimilar or interchangeable biosimilar products can be used in place of the reference product they were compared to.”
FDA-approved biosimilars undergo a rigorous evaluation for safety, effectiveness, and quality for their approved conditions of use, she continued. “Therefore, patients and health care providers can rely on a biosimilar to be as safe and effective for its approved uses as the original biological product.”
Remicade as a yard stick
Gastroenterologists dealt with this situation once before, when Remicade (infliximab) biosimilars came on the market in 2016, noted Miguel Regueiro, MD, chair of the Digestive Disease and Surgery Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
Remicade and Humira are both tumor necrosis factor inhibitors with the same mechanism of action and many of the same indications. “We already had that experience with Remicade and biosimilar switch 2 or 3 years ago. Now we’re talking about Humira,” said Dr. Regueiro.
Most GI doctors have prescribed one of the more common infliximab biosimilars (Inflectra or Renflexis), noted Dr. Oldfield.
Cardinal Health, which recently surveyed 300 gastroenterologists, rheumatologists, and dermatologists about adalimumab biosimilars, found that gastroenterologists had the highest comfort level in prescribing them. Their top concern, however, was changing a patient from adalimumab to an adalimumab biosimilar.
For most patients, Dr. Oldfield sees the Humira reference biologic and biosimilar as equivalent.
However, he said he would change a patient’s drug only if there were a good reason or if his hand was forced by insurance. He would not make the change for a patient who recently began induction with the reference biologic or a patient with highly active clinical disease.
“While there is limited data to support this, I would also have some qualms about changing a patient from reference biologic to a biosimilar if they previously had immune-mediated pharmacokinetic failure due to antibody development with a biologic and were currently doing well on their new biologic,” he said.
Those with a new ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s diagnosis who are initiating a biologic for the first time might consider a biosimilar. If a patient is transitioning from a reference biologic to a biosimilar, “I would want to make that change during a time of stable remission and with the recognition that the switch is not a temporary switch, but a long-term switch,” he continued.
A paper that reviewed 23 observational studies of adalimumab and other biosimilars found that switching biosimilars was safe and effective. But if possible, patients should minimize the number of switches until more robust long-term data are available, added Dr. Oldfield.
If a patient is apprehensive about switching to a new therapy, “one may need to be cognizant of the ‘nocebo’ effect in which there is an unexplained or unfavorable therapeutic effect after switching,” he said.
Other gastroenterologists voiced similar reservations about switching. “I won’t use an adalimumab biosimilar unless the patient requests it, the insurance requires it, or there is a cost advantage for the patient such that they prefer it,” said Doug Wolf, MD, an Atlanta gastroenterologist.
“There is no medical treatment advantage to a biosimilar, especially if switching from Humira,” added Dr. Wolf.
Insurance will guide treatment
Once a drug is approved for use by the FDA, that drug will be available in all 50 states. “Different private insurance formularies, as well as state Medicaid formularies, might affect the actual ability of patients to receive such drugs,” said Mr. Newmark.
Patients should consult with their providers and insurance companies to see what therapies are available, he advised.
Dr. Hanauer anticipates some headaches arising for patients and doctors alike when negotiating for a specific drug.
Cyltezo may be the only biosimilar interchangeable with Humira, but the third-party pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) could negotiate for one of the noninterchangeable ones. “On a yearly basis they could switch their preference,” said Dr. Hanauer.
In the Cardinal Health survey, more than 60% of respondents said they would feel comfortable prescribing an adalimumab biosimilar only with an interchangeability designation.
A PBM may offer a patient Cyltezo if it’s cheaper than Humira. If the patient insists on staying on Humira, then they’ll have to pay more for that drug on their payer’s formulary, said Dr. Hanauer. In a worst-case scenario, a physician may have to appeal on a patient’s behalf to get Humira if the insurer offers only the biosimilar.
Taking that step to appeal is a major hassle for the physician, and leads to extra back door costs as well, said Dr. Hanauer.
Humira manufacturer AbbVie, in turn, may offer discounts and rebates to the PBMs to put Humira on their formulary. “That’s the AbbVie negotiating power. It’s not that the cost is going to be that much different. It’s going to be that there are rebates and discounts that are going to make the cost different,” he added.
As a community physician, Dr. Oldfield has specific concerns about accessibility.
The ever-increasing burden of insurance documentation and prior authorization means it can take weeks or months to get these medications approved. “The addition of new biosimilars is a welcome entrance if it can get patients the medications they need when they need it,” he said.
When it comes to prescribing biologics, many physicians rely on ancillary staff for assistance. It’s a team effort to sift through all the paperwork, observed Dr. Oldfield.
“While many community GI practices have specialized staff to deal with prior authorizations, they are still a far cry from the IBD [inflammatory bowel disease] academic centers where there are often pharmacists, nursing specialists, and home-monitoring programs to check in on patients,” he explained.
Landscape on cost is uncertain
At present, little is known about the cost of the biosimilars and impact on future drug pricing, said Dr. Oldfield.
At least for Medicare, Humira biosimilars will be considered Medicare Part D drugs if used for a medically accepted indication, said a spokesperson for the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
Part D sponsors (pharmacy and therapeutic committees) “will make the determination as to whether Amjevita and other products will be added to their formularies,” said the spokesperson.
Patients never saw a significant cost savings with Remicade biosimilars. “I imagine the same would be true with biosimilars for Humira,” said Dr. Regueiro. Patients may see greater access to these drugs, however, because the insurance plan or the pharmacy plan will make them more readily available, he added.
The hope is that, as biosimilars are introduced, the price of the originator biologic will go down, said Mr. Newmark. “Therefore, we can expect Humira to be offered at a lower price as it faces competition. Where it will sit in comparison to the forthcoming biosimilars will depend on how much biosimilar companies drop their price and how much pressure will be on PBMs and insurers to cover the lowest list price drug,” he said.
AbbVie did not respond to several requests for comment.
Charitable patient assistance programs for biosimilars or biologics can help offset the price of copayments, Mr. Newmark offered.
Ideally, insurers will offer designated biosimilars at a reduced or even no out-of-pocket expense on their formularies. This should lead to a decreased administrative burden for approval with streamlined (or even removal) of prior authorizations for certain medications, said Dr. Oldfield.
Without insurance or medication assistance programs, the cost of biosimilars is prohibitively expensive, he added.
“Biosimilars have higher research, development, and manufacturing costs than what people conventionally think of [for] a generic medication.”
Educating, advising patients
Dr. Oldfield advised that gastroenterologists refer to biologics by the generic name rather than branded name when initiating therapy unless there is a very specific reason not to. “This approach should make the process more streamlined and less subjected to quick denials for brand-only requests as biosimilars start to assume a larger market share,” he said.
Uptake of the Humira biosimilars also will depend on proper education of physicians and patients and their comfort level with the biosimilars, said Dr. Regueiro. Cleveland Clinic uses a team approach to educate on this topic, relying on pharmacists, clinicians, and nurses to explain that there’s no real difference between the reference drug and its biosimilars, based on efficacy and safety data.
Physicians can also direct patients to patient-friendly resources, said Mr. Newmark. “By starting the conversation early, it ensures that when/if the time comes that your patient is switched to or chooses a biosimilar they will feel more confident because they have the knowledge to make decisions about their care.”
The Global Healthy Living Foundation’s podcast, Breaking Down Biosimilars , is a free resource for patients, he added.
It’s important that doctors also understand these products so they can explain to their patients what to expect, said the FDA’s Dr. Yim. The FDA provides educational materials on its website, including a comprehensive curriculum toolkit.
Dr. Hanauer has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Amgen, American College of Gastroenterology, GlaxoSmithKline, American Gastroenterological Association, Pfizer, and a host of other companies . Dr. Regueiro has served on advisory boards and as a consultant for Abbvie, Janssen, UCB, Takeda, Pfizer, BMS, Organon, Amgen, Genentech, Gilead, Salix, Prometheus, Lilly, Celgene, TARGET Pharma Solutions,Trellis, and Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Wolf, Dr. Yim, Dr. Oldfield, and Mr. Newmark have no financial conflicts of interest.
Gastroenterologists in 2023 will have more tools in their arsenal to treat patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. As many as 8-10 adalimumab biosimilars are anticipated to come on the market this year, giving mainstay drug Humira some vigorous competition.
Three scenarios will drive adalimumab biosimilar initiation: Insurance preference for the initial treatment of a newly diagnosed condition, a change in a patient’s insurance plan, or an insurance-mandated switch, said Edward C. Oldfield IV, MD, assistant professor at Eastern Virginia Medical School’s division of gastroenterology in Norfolk.
“Outside of these scenarios, I would encourage patients to remain on their current biologic so long as cost and accessibility remain stable,” said Dr. Oldfield.
Many factors will contribute to the success of biosimilars. Will physicians be prescribing them? How are biosimilars placed on formularies and will they be given preferred status? How will manufacturers price their biosimilars? “We have to wait and see to get the answers to these questions,” said Steven Newmark, JD, MPA, chief legal officer and director of policy, Global Healthy Living Foundation/CreakyJoints, a nonprofit advocacy organization based in New York.
Prescribing biosimilars is no different than prescribing originator biologics, so providers should know how to use them, said Mr. Newmark. “Most important will be the availability of patient-friendly resources that providers can share with their patients to provide education about and confidence in using biosimilars,” he added.
Overall, biosimilars are a good thing, said Dr. Oldfield. “In the long run they should bring down costs and increase access to medications for our patients.”
Others are skeptical that the adalimumab biosimilars will save patients much money.
Biosimilar laws were created to lower costs. However, if a patient with insurance pays only $5 a month out of pocket for Humira – a drug that normally costs $7,000 without coverage – it’s unlikely they would want to switch unless there’s comparable savings from the biosimilar, said Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, medical director of the Digestive Health Center and professor of medicine at Northwestern Medicine, Northwestern University, Evanston, Ill.
Like generics, Humira biosimilars may face some initial backlash, said Dr. Hanauer.
2023 broadens scope of adalimumab treatments
The American Gastroenterological Association describes a biosimilar as something that’s “highly similar to, but not an exact copy of, a biologic reference product already approved” by the Food and Drug Administration. Congress under the 2010 Affordable Care Act created a special, abbreviated pathway to approval for biosimilars.
AbbVie’s Humira, the global revenue for which exceeded $20 billion in 2021, has long dominated the U.S. market on injectable treatments for autoimmune diseases. The popular drug faces some competition in 2023, however, following a series of legal settlements that allowed AbbVie competitors to release their own adalimumab biosimilars.
“So far, we haven’t seen biosimilars live up to their potential in the U.S. in the inflammatory space,” said Mr. Newmark. This may change, however. Previously, biosimilars have required infusion, which demanded more time, commitment, and travel from patients. “The new set of forthcoming Humira biosimilars are injectables, an administration method preferred by patients,” he said.
The FDA will approve a biosimilar if it determines that the biological product is highly similar to the reference product, and that there are no clinically meaningful differences between the biological and reference product in terms of the safety, purity, and potency of the product.
The agency to date has approved 8 adalimumab biosimilars. These include: Idacio (adalimumab-aacf, Fresenius Kabi); Amjevita (adalimumab-atto, Amgen); Hadlima (adalimumab-bwwd, Organon); Cyltezo (adalimumab-adbm, Boehringer Ingelheim); Yusimry (adalimumab-aqvh from Coherus BioSciences); Hulio (adalimumab-fkjp; Mylan/Fujifilm Kyowa Kirin Biologics); Hyrimoz (adalimumab-adaz, Sandoz), and Abrilada (adalimumab-afzb, Pfizer).
“While FDA doesn’t formally track when products come to market, we know based on published reports that application holders for many of the currently FDA-approved biosimilars plan to market this year, starting with Amjevita being the first adalimumab biosimilar launched” in January, said Sarah Yim, MD, director of the Office of Therapeutic Biologics and Biosimilars at the agency.
At press time, two other companies (Celltrion and Alvotech/Teva) were awaiting FDA approval for their adalimumab biosimilar drugs.
Among the eight approved drugs, Cyltezo is the only one that has a designation for interchangeability with Humira.
An interchangeable biosimilar may be substituted at the pharmacy without the intervention of the prescriber – much like generics are substituted, depending on state laws, said Dr. Yim. “However, in terms of safety and effectiveness, FDA’s standards for approval mean that biosimilar or interchangeable biosimilar products can be used in place of the reference product they were compared to.”
FDA-approved biosimilars undergo a rigorous evaluation for safety, effectiveness, and quality for their approved conditions of use, she continued. “Therefore, patients and health care providers can rely on a biosimilar to be as safe and effective for its approved uses as the original biological product.”
Remicade as a yard stick
Gastroenterologists dealt with this situation once before, when Remicade (infliximab) biosimilars came on the market in 2016, noted Miguel Regueiro, MD, chair of the Digestive Disease and Surgery Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
Remicade and Humira are both tumor necrosis factor inhibitors with the same mechanism of action and many of the same indications. “We already had that experience with Remicade and biosimilar switch 2 or 3 years ago. Now we’re talking about Humira,” said Dr. Regueiro.
Most GI doctors have prescribed one of the more common infliximab biosimilars (Inflectra or Renflexis), noted Dr. Oldfield.
Cardinal Health, which recently surveyed 300 gastroenterologists, rheumatologists, and dermatologists about adalimumab biosimilars, found that gastroenterologists had the highest comfort level in prescribing them. Their top concern, however, was changing a patient from adalimumab to an adalimumab biosimilar.
For most patients, Dr. Oldfield sees the Humira reference biologic and biosimilar as equivalent.
However, he said he would change a patient’s drug only if there were a good reason or if his hand was forced by insurance. He would not make the change for a patient who recently began induction with the reference biologic or a patient with highly active clinical disease.
“While there is limited data to support this, I would also have some qualms about changing a patient from reference biologic to a biosimilar if they previously had immune-mediated pharmacokinetic failure due to antibody development with a biologic and were currently doing well on their new biologic,” he said.
Those with a new ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s diagnosis who are initiating a biologic for the first time might consider a biosimilar. If a patient is transitioning from a reference biologic to a biosimilar, “I would want to make that change during a time of stable remission and with the recognition that the switch is not a temporary switch, but a long-term switch,” he continued.
A paper that reviewed 23 observational studies of adalimumab and other biosimilars found that switching biosimilars was safe and effective. But if possible, patients should minimize the number of switches until more robust long-term data are available, added Dr. Oldfield.
If a patient is apprehensive about switching to a new therapy, “one may need to be cognizant of the ‘nocebo’ effect in which there is an unexplained or unfavorable therapeutic effect after switching,” he said.
Other gastroenterologists voiced similar reservations about switching. “I won’t use an adalimumab biosimilar unless the patient requests it, the insurance requires it, or there is a cost advantage for the patient such that they prefer it,” said Doug Wolf, MD, an Atlanta gastroenterologist.
“There is no medical treatment advantage to a biosimilar, especially if switching from Humira,” added Dr. Wolf.
Insurance will guide treatment
Once a drug is approved for use by the FDA, that drug will be available in all 50 states. “Different private insurance formularies, as well as state Medicaid formularies, might affect the actual ability of patients to receive such drugs,” said Mr. Newmark.
Patients should consult with their providers and insurance companies to see what therapies are available, he advised.
Dr. Hanauer anticipates some headaches arising for patients and doctors alike when negotiating for a specific drug.
Cyltezo may be the only biosimilar interchangeable with Humira, but the third-party pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) could negotiate for one of the noninterchangeable ones. “On a yearly basis they could switch their preference,” said Dr. Hanauer.
In the Cardinal Health survey, more than 60% of respondents said they would feel comfortable prescribing an adalimumab biosimilar only with an interchangeability designation.
A PBM may offer a patient Cyltezo if it’s cheaper than Humira. If the patient insists on staying on Humira, then they’ll have to pay more for that drug on their payer’s formulary, said Dr. Hanauer. In a worst-case scenario, a physician may have to appeal on a patient’s behalf to get Humira if the insurer offers only the biosimilar.
Taking that step to appeal is a major hassle for the physician, and leads to extra back door costs as well, said Dr. Hanauer.
Humira manufacturer AbbVie, in turn, may offer discounts and rebates to the PBMs to put Humira on their formulary. “That’s the AbbVie negotiating power. It’s not that the cost is going to be that much different. It’s going to be that there are rebates and discounts that are going to make the cost different,” he added.
As a community physician, Dr. Oldfield has specific concerns about accessibility.
The ever-increasing burden of insurance documentation and prior authorization means it can take weeks or months to get these medications approved. “The addition of new biosimilars is a welcome entrance if it can get patients the medications they need when they need it,” he said.
When it comes to prescribing biologics, many physicians rely on ancillary staff for assistance. It’s a team effort to sift through all the paperwork, observed Dr. Oldfield.
“While many community GI practices have specialized staff to deal with prior authorizations, they are still a far cry from the IBD [inflammatory bowel disease] academic centers where there are often pharmacists, nursing specialists, and home-monitoring programs to check in on patients,” he explained.
Landscape on cost is uncertain
At present, little is known about the cost of the biosimilars and impact on future drug pricing, said Dr. Oldfield.
At least for Medicare, Humira biosimilars will be considered Medicare Part D drugs if used for a medically accepted indication, said a spokesperson for the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
Part D sponsors (pharmacy and therapeutic committees) “will make the determination as to whether Amjevita and other products will be added to their formularies,” said the spokesperson.
Patients never saw a significant cost savings with Remicade biosimilars. “I imagine the same would be true with biosimilars for Humira,” said Dr. Regueiro. Patients may see greater access to these drugs, however, because the insurance plan or the pharmacy plan will make them more readily available, he added.
The hope is that, as biosimilars are introduced, the price of the originator biologic will go down, said Mr. Newmark. “Therefore, we can expect Humira to be offered at a lower price as it faces competition. Where it will sit in comparison to the forthcoming biosimilars will depend on how much biosimilar companies drop their price and how much pressure will be on PBMs and insurers to cover the lowest list price drug,” he said.
AbbVie did not respond to several requests for comment.
Charitable patient assistance programs for biosimilars or biologics can help offset the price of copayments, Mr. Newmark offered.
Ideally, insurers will offer designated biosimilars at a reduced or even no out-of-pocket expense on their formularies. This should lead to a decreased administrative burden for approval with streamlined (or even removal) of prior authorizations for certain medications, said Dr. Oldfield.
Without insurance or medication assistance programs, the cost of biosimilars is prohibitively expensive, he added.
“Biosimilars have higher research, development, and manufacturing costs than what people conventionally think of [for] a generic medication.”
Educating, advising patients
Dr. Oldfield advised that gastroenterologists refer to biologics by the generic name rather than branded name when initiating therapy unless there is a very specific reason not to. “This approach should make the process more streamlined and less subjected to quick denials for brand-only requests as biosimilars start to assume a larger market share,” he said.
Uptake of the Humira biosimilars also will depend on proper education of physicians and patients and their comfort level with the biosimilars, said Dr. Regueiro. Cleveland Clinic uses a team approach to educate on this topic, relying on pharmacists, clinicians, and nurses to explain that there’s no real difference between the reference drug and its biosimilars, based on efficacy and safety data.
Physicians can also direct patients to patient-friendly resources, said Mr. Newmark. “By starting the conversation early, it ensures that when/if the time comes that your patient is switched to or chooses a biosimilar they will feel more confident because they have the knowledge to make decisions about their care.”
The Global Healthy Living Foundation’s podcast, Breaking Down Biosimilars , is a free resource for patients, he added.
It’s important that doctors also understand these products so they can explain to their patients what to expect, said the FDA’s Dr. Yim. The FDA provides educational materials on its website, including a comprehensive curriculum toolkit.
Dr. Hanauer has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Amgen, American College of Gastroenterology, GlaxoSmithKline, American Gastroenterological Association, Pfizer, and a host of other companies . Dr. Regueiro has served on advisory boards and as a consultant for Abbvie, Janssen, UCB, Takeda, Pfizer, BMS, Organon, Amgen, Genentech, Gilead, Salix, Prometheus, Lilly, Celgene, TARGET Pharma Solutions,Trellis, and Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Wolf, Dr. Yim, Dr. Oldfield, and Mr. Newmark have no financial conflicts of interest.