User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
ACR issues guidances for MIS-C and pediatric rheumatic disease during pandemic
Two new clinical guidance documents from the American College of Rheumatology provide evidence-based recommendations for managing pediatric rheumatic disease during the COVID-19 pandemic as well as diagnostic and treatment recommendations for multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) associated with COVID-19 infection.
Although several children’s hospitals have published their treatment protocols for MIS-C since the condition’s initial discovery, the ACR appears to be the first medical organization to review all the most current evidence to issue interim guidance with the expectations that it will change as more data become available.
“It is challenging having to make recommendations not having a lot of scientific evidence, but we still felt we had to use whatever’s out there to the best of our ability and use our experience to put together these recommendations,” Dawn M. Wahezi, MD, chief of pediatric rheumatology at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore and an associate professor of pediatrics at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said in an interview.
“We wanted to be mindful of the fact that there are things we know and things we don’t know, and we have to be careful about what we’re recommending,” said Dr. Wahezi, a member of the ACR working group that assembled the recommendations for pediatric rheumatic disease management during the pandemic. “We’re recommending the best we can at this moment, but if there are new studies that come out and suggest otherwise, we will definitely have to go back and amend the document.”
The foremost priority of the pediatric rheumatic disease guidance focuses on maintaining control of the disease and avoiding flares that may put children at greater risk of infection. Dr. Wahezi said the ACR has received many calls from patients and clinicians asking whether patients should continue their immunosuppressant medications. Fear of the coronavirus infection, medication shortages, difficulty getting to the pharmacy, uneasiness about going to the clinic or hospital for infusions, and other barriers may have led to gaps in medication.
“We didn’t want people to be too quick to hold patients’ medications just because they were scared of COVID,” Dr. Wahezi said. “If they did have medication stopped for one reason or another and their disease flared, having active disease, regardless of which disease it is, actually puts you at higher risk for infection. By controlling their disease, that would be the way to protect them the most.”
A key takeaway in the guidance on MIS-C, meanwhile, is an emphasis on its rarity lest physicians be too quick to diagnose it and miss another serious condition with overlapping symptoms, explained Lauren Henderson, MD, an attending rheumatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital and assistant professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Henderson participated in the ACR group that wrote the MIS-C guidance.
“The first thing we want to be thoughtful about clinically is to recognize that children in general with the acute infectious phase of SARS-CoV-2 have mild symptoms and generally do well,” Dr. Henderson said. “From what we can tell from all the data, MIS-C is rare. That really needs to be considered when clinicians on the ground are doing the diagnostic evaluation” because of concerns that clinicians “could rush to diagnose and treat patients with MIS-C and miss important diagnoses like malignancies and infections.”
Management of pediatric rheumatic disease during the pandemic
The COVID-19 clinical guidance for managing pediatric rheumatic disease grew from the work of the North American Pediatric Rheumatology Clinical Guidance Task Force, which included seven pediatric rheumatologists, two pediatric infectious disease physicians, one adult rheumatologist, and one pediatric nurse practitioner. The general guidance covers usual preventive measures for reducing risk for COVID-19 infection, the recommendation that children continue to receive recommended vaccines unless contraindicated by medication, and routine in-person visits for ophthalmologic surveillance of those with a history of uveitis or at high risk for chronic uveitis. The guidance also notes the risk of mental health concerns, such as depression and anxiety, related to quarantine and the pandemic.
The top recommendation is initiation or continuation of all medications necessary to control underlying disease, including NSAIDs, hydroxychloroquine, ACE inhibitors/angiotensin II receptor blockers, colchicine, conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (cDMARDs), biologic DMARDs, and targeted synthetic DMARDs. Even patients who may have had exposure to COVID-19 or who have an asymptomatic COVID-19 infection should continue to take these medications with the exception of ACEi/ARBs.
In those with pediatric rheumatic disease who have a symptomatic COVID-19 infection, “NSAIDs, HCQ, and colchicine may be continued, if necessary, to control underlying disease,” as can interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-6 inhibitors, but “cDMARDs, bDMARDs [except IL-1 and IL-6 inhibitors] and tsDMARDs should be temporarily delayed or withheld,” according to the guidance. Glucocorticoids can be continued at the lowest possible dose to control disease.
“There’s nothing in the literature that suggests people who have rheumatic disease, especially children, and people who are on these medications, really are at increased risk for COVID-19,” Dr. Wahezi said. “That’s why we didn’t want people to be overcautious in stopping medications when the main priority is to control their disease.”
She noted some experts’ speculations that these medications may actually benefit patients with rheumatic disease who develop a COVID-19 infection because the medications keep the immune response in check. “If you allow them to have this dysregulated immune response and have active disease, you’re potentially putting them at greater risk,” Dr. Wahezi said, although she stressed that inadequate evidence exists to support these speculations right now.
Lack of evidence has been the biggest challenge all around with developing this guidance, she said.
“Because this is such an unprecedented situation and because people are so desperate to find treatments both for the illness and to protect those at risk for it, there are lots of people trying to put evidence out there, but it may not be the best-quality evidence,” Dr. Wahezi said.
Insufficient evidence also drove the group’s determination that “SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing is not useful in informing on the history of infection or risk of reinfection,” as the guidance states. Too much variability in the assays exist, Dr. Wahezi said, and, further, it’s unclear what the clinical significance of a positive test would be.
“We didn’t want anyone to feel they had to make clinical decisions based on the results of that antibody testing,” she said. “Even if the test is accurate, we don’t know how to interpret it because it’s so new.”
The guidance also notes that patients with stable disease and previously stable lab markers on stable doses of their medication may be able to extend the interval for medication toxicity lab testing a few months if there is concern about exposure to COVID-19 to get the blood work.
“If you’re just starting a medicine or there’s someone who’s had abnormalities with the medicine in the past or you’re making medication adjustments, you wouldn’t do it in those scenarios, but if there’s someone who’s been on the drug for a long time and are nervous to get [blood] drawn, it’s probably okay to delay it,” Dr. Wahezi said. Lab work for disease activity measures, on the other hand, remain particularly important, especially since telemedicine visits may require clinicians to rely on lab results more than previously.
Management of MIS-C associated with COVID-19
The task force that developed guidance for the new inflammatory condition recently linked to SARS-CoV-2 infections in children included nine pediatric rheumatologists, two adult rheumatologists, two pediatric cardiologists, two pediatric infectious disease specialists, and one pediatric critical care physician.
The guidance includes a figure for the diagnostic pathway in evaluating children suspected of having MIS-C and extensive detail on diagnostic work-up, but the task force intentionally avoided providing a case definition for the condition. Existing case definitions from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, World Health Organization, and the United Kingdom’s Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health differ from one another and are based on unclear evidence, Dr. Henderson noted. “We really don’t have enough data to know the sensitivity and specificity of each parameter, and until that’s available, we didn’t want to add to the confusion,” she said.
The guidance also stresses that MIS-C is a rare complication, so patients suspected of having the condition who do not have “life-threatening manifestations should undergo diagnostic evaluation for MIS-C as well as other possible infectious and noninfectious etiologies before immunomodulatory treatment is initiated,” the guidance states.
Unless a child is in shock or otherwise requires urgent care, physicians should take the time to complete the diagnostic work-up while monitoring the child, Dr. Henderson said. If the child does have MIS-C, the guidance currently recommends intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and/or glucocorticoids to prevent coronary artery aneurysms, the same treatment other institutions have been recommending.
“We don’t have rigorous comparative studies looking at different types of treatments,” Dr. Henderson said, noting that the vast majority of children in the literature received IVIG and/or glucocorticoid treatment. “Often children really responded quite forcefully to those treatments, but we don’t have high-quality data yet to know that this treatment is better than supportive care or another medication.”
Dr. Henderson also stressed the importance of children receiving care at a facility with the necessary expertise to manage MIS-C and receiving long-term follow-up care from a multidisciplinary clinical team that includes a rheumatologist, an infectious disease doctor, a cardiologist, and possibly a hematologist.
“Making sure children are admitted to a hospital that has the resources and are followed by physicians with expertise or understanding of the intricacies of MIS-C is really important,” she said, particularly for children with cardiac involvement. “We don’t know if all the kids presenting with left ventricular dysfunction and shock are at risk for having myocardial fibrosis down the line,” she noted. “There is so much we do not understand and very little data to guide us on what to do, so these children really need to be under the care of a cardiologist and rheumatologist to make sure that their care is tailored to them.”
Although MIS-C shares overlapping symptoms with Kawasaki disease, it’s still unclear how similar or different the two conditions are, Dr. Henderson said.
“We can definitely say that when we look at MIS-C and compare it to historical groups of Kawasaki disease before the pandemic, there are definitely different features in the MIS-C group,” she said. Kawasaki disease generally only affects children under age 5, whereas MIS-C patients run the gamut from age 1-17. Racial demographics are also different, with a higher proportion of black children affected by MIS-C.
It’s possible that the pathophysiology of both conditions will turn out to be similar, particularly given the hypothesis that Kawasaki disease is triggered by infections in genetically predisposed people. However, the severity of symptoms and risk of aneurysms appear greater with MIS-C so far.
“The degree to which these patients are presenting with left ventricular dysfunction and shock is much higher than what we’ve seen previously,” Dr. Henderson said. “Children can have aneurysms even if they don’t meet all the Kawasaki disease features, which makes it feel that this is somehow clinically different from what we’ve seen before. It’s not just the kids who have the rash and the conjunctivitis and the extremity changes and oral changes who have the aneurysms.”
The reason for including both IVIG and glucocorticoids as possible first-line drugs to prevent aneurysms is that some evidence suggests children with MIS-C may have higher levels of IVIG resistance, she said.
Like Dr. Wahezi, Dr. Henderson emphasized the necessarily transient nature of these recommendations.
“These recommendations will almost certainly change based on evolving understanding of MIS-C and the data,” Dr. Henderson said, adding that this new, unique condition highlights the importance of including children in allocating funding for research and in clinical trials.
“Children are not always identical to adults, and it’s really important that we have high-quality data to inform our decisions about how to care for them,” she said.
Dr. Wahezi had no disclosures. Dr. Henderson has consulted for Sobi and Adaptive Technologies. The guidelines did not note other disclosures for members of the ACR groups.
SOURCES: COVID-19 Clinical Guidance for Pediatric Patients with Rheumatic Disease and Clinical Guidance for Pediatric Patients with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Associated with SARS-CoV-2 and Hyperinflammation in COVID-19
Two new clinical guidance documents from the American College of Rheumatology provide evidence-based recommendations for managing pediatric rheumatic disease during the COVID-19 pandemic as well as diagnostic and treatment recommendations for multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) associated with COVID-19 infection.
Although several children’s hospitals have published their treatment protocols for MIS-C since the condition’s initial discovery, the ACR appears to be the first medical organization to review all the most current evidence to issue interim guidance with the expectations that it will change as more data become available.
“It is challenging having to make recommendations not having a lot of scientific evidence, but we still felt we had to use whatever’s out there to the best of our ability and use our experience to put together these recommendations,” Dawn M. Wahezi, MD, chief of pediatric rheumatology at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore and an associate professor of pediatrics at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said in an interview.
“We wanted to be mindful of the fact that there are things we know and things we don’t know, and we have to be careful about what we’re recommending,” said Dr. Wahezi, a member of the ACR working group that assembled the recommendations for pediatric rheumatic disease management during the pandemic. “We’re recommending the best we can at this moment, but if there are new studies that come out and suggest otherwise, we will definitely have to go back and amend the document.”
The foremost priority of the pediatric rheumatic disease guidance focuses on maintaining control of the disease and avoiding flares that may put children at greater risk of infection. Dr. Wahezi said the ACR has received many calls from patients and clinicians asking whether patients should continue their immunosuppressant medications. Fear of the coronavirus infection, medication shortages, difficulty getting to the pharmacy, uneasiness about going to the clinic or hospital for infusions, and other barriers may have led to gaps in medication.
“We didn’t want people to be too quick to hold patients’ medications just because they were scared of COVID,” Dr. Wahezi said. “If they did have medication stopped for one reason or another and their disease flared, having active disease, regardless of which disease it is, actually puts you at higher risk for infection. By controlling their disease, that would be the way to protect them the most.”
A key takeaway in the guidance on MIS-C, meanwhile, is an emphasis on its rarity lest physicians be too quick to diagnose it and miss another serious condition with overlapping symptoms, explained Lauren Henderson, MD, an attending rheumatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital and assistant professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Henderson participated in the ACR group that wrote the MIS-C guidance.
“The first thing we want to be thoughtful about clinically is to recognize that children in general with the acute infectious phase of SARS-CoV-2 have mild symptoms and generally do well,” Dr. Henderson said. “From what we can tell from all the data, MIS-C is rare. That really needs to be considered when clinicians on the ground are doing the diagnostic evaluation” because of concerns that clinicians “could rush to diagnose and treat patients with MIS-C and miss important diagnoses like malignancies and infections.”
Management of pediatric rheumatic disease during the pandemic
The COVID-19 clinical guidance for managing pediatric rheumatic disease grew from the work of the North American Pediatric Rheumatology Clinical Guidance Task Force, which included seven pediatric rheumatologists, two pediatric infectious disease physicians, one adult rheumatologist, and one pediatric nurse practitioner. The general guidance covers usual preventive measures for reducing risk for COVID-19 infection, the recommendation that children continue to receive recommended vaccines unless contraindicated by medication, and routine in-person visits for ophthalmologic surveillance of those with a history of uveitis or at high risk for chronic uveitis. The guidance also notes the risk of mental health concerns, such as depression and anxiety, related to quarantine and the pandemic.
The top recommendation is initiation or continuation of all medications necessary to control underlying disease, including NSAIDs, hydroxychloroquine, ACE inhibitors/angiotensin II receptor blockers, colchicine, conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (cDMARDs), biologic DMARDs, and targeted synthetic DMARDs. Even patients who may have had exposure to COVID-19 or who have an asymptomatic COVID-19 infection should continue to take these medications with the exception of ACEi/ARBs.
In those with pediatric rheumatic disease who have a symptomatic COVID-19 infection, “NSAIDs, HCQ, and colchicine may be continued, if necessary, to control underlying disease,” as can interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-6 inhibitors, but “cDMARDs, bDMARDs [except IL-1 and IL-6 inhibitors] and tsDMARDs should be temporarily delayed or withheld,” according to the guidance. Glucocorticoids can be continued at the lowest possible dose to control disease.
“There’s nothing in the literature that suggests people who have rheumatic disease, especially children, and people who are on these medications, really are at increased risk for COVID-19,” Dr. Wahezi said. “That’s why we didn’t want people to be overcautious in stopping medications when the main priority is to control their disease.”
She noted some experts’ speculations that these medications may actually benefit patients with rheumatic disease who develop a COVID-19 infection because the medications keep the immune response in check. “If you allow them to have this dysregulated immune response and have active disease, you’re potentially putting them at greater risk,” Dr. Wahezi said, although she stressed that inadequate evidence exists to support these speculations right now.
Lack of evidence has been the biggest challenge all around with developing this guidance, she said.
“Because this is such an unprecedented situation and because people are so desperate to find treatments both for the illness and to protect those at risk for it, there are lots of people trying to put evidence out there, but it may not be the best-quality evidence,” Dr. Wahezi said.
Insufficient evidence also drove the group’s determination that “SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing is not useful in informing on the history of infection or risk of reinfection,” as the guidance states. Too much variability in the assays exist, Dr. Wahezi said, and, further, it’s unclear what the clinical significance of a positive test would be.
“We didn’t want anyone to feel they had to make clinical decisions based on the results of that antibody testing,” she said. “Even if the test is accurate, we don’t know how to interpret it because it’s so new.”
The guidance also notes that patients with stable disease and previously stable lab markers on stable doses of their medication may be able to extend the interval for medication toxicity lab testing a few months if there is concern about exposure to COVID-19 to get the blood work.
“If you’re just starting a medicine or there’s someone who’s had abnormalities with the medicine in the past or you’re making medication adjustments, you wouldn’t do it in those scenarios, but if there’s someone who’s been on the drug for a long time and are nervous to get [blood] drawn, it’s probably okay to delay it,” Dr. Wahezi said. Lab work for disease activity measures, on the other hand, remain particularly important, especially since telemedicine visits may require clinicians to rely on lab results more than previously.
Management of MIS-C associated with COVID-19
The task force that developed guidance for the new inflammatory condition recently linked to SARS-CoV-2 infections in children included nine pediatric rheumatologists, two adult rheumatologists, two pediatric cardiologists, two pediatric infectious disease specialists, and one pediatric critical care physician.
The guidance includes a figure for the diagnostic pathway in evaluating children suspected of having MIS-C and extensive detail on diagnostic work-up, but the task force intentionally avoided providing a case definition for the condition. Existing case definitions from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, World Health Organization, and the United Kingdom’s Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health differ from one another and are based on unclear evidence, Dr. Henderson noted. “We really don’t have enough data to know the sensitivity and specificity of each parameter, and until that’s available, we didn’t want to add to the confusion,” she said.
The guidance also stresses that MIS-C is a rare complication, so patients suspected of having the condition who do not have “life-threatening manifestations should undergo diagnostic evaluation for MIS-C as well as other possible infectious and noninfectious etiologies before immunomodulatory treatment is initiated,” the guidance states.
Unless a child is in shock or otherwise requires urgent care, physicians should take the time to complete the diagnostic work-up while monitoring the child, Dr. Henderson said. If the child does have MIS-C, the guidance currently recommends intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and/or glucocorticoids to prevent coronary artery aneurysms, the same treatment other institutions have been recommending.
“We don’t have rigorous comparative studies looking at different types of treatments,” Dr. Henderson said, noting that the vast majority of children in the literature received IVIG and/or glucocorticoid treatment. “Often children really responded quite forcefully to those treatments, but we don’t have high-quality data yet to know that this treatment is better than supportive care or another medication.”
Dr. Henderson also stressed the importance of children receiving care at a facility with the necessary expertise to manage MIS-C and receiving long-term follow-up care from a multidisciplinary clinical team that includes a rheumatologist, an infectious disease doctor, a cardiologist, and possibly a hematologist.
“Making sure children are admitted to a hospital that has the resources and are followed by physicians with expertise or understanding of the intricacies of MIS-C is really important,” she said, particularly for children with cardiac involvement. “We don’t know if all the kids presenting with left ventricular dysfunction and shock are at risk for having myocardial fibrosis down the line,” she noted. “There is so much we do not understand and very little data to guide us on what to do, so these children really need to be under the care of a cardiologist and rheumatologist to make sure that their care is tailored to them.”
Although MIS-C shares overlapping symptoms with Kawasaki disease, it’s still unclear how similar or different the two conditions are, Dr. Henderson said.
“We can definitely say that when we look at MIS-C and compare it to historical groups of Kawasaki disease before the pandemic, there are definitely different features in the MIS-C group,” she said. Kawasaki disease generally only affects children under age 5, whereas MIS-C patients run the gamut from age 1-17. Racial demographics are also different, with a higher proportion of black children affected by MIS-C.
It’s possible that the pathophysiology of both conditions will turn out to be similar, particularly given the hypothesis that Kawasaki disease is triggered by infections in genetically predisposed people. However, the severity of symptoms and risk of aneurysms appear greater with MIS-C so far.
“The degree to which these patients are presenting with left ventricular dysfunction and shock is much higher than what we’ve seen previously,” Dr. Henderson said. “Children can have aneurysms even if they don’t meet all the Kawasaki disease features, which makes it feel that this is somehow clinically different from what we’ve seen before. It’s not just the kids who have the rash and the conjunctivitis and the extremity changes and oral changes who have the aneurysms.”
The reason for including both IVIG and glucocorticoids as possible first-line drugs to prevent aneurysms is that some evidence suggests children with MIS-C may have higher levels of IVIG resistance, she said.
Like Dr. Wahezi, Dr. Henderson emphasized the necessarily transient nature of these recommendations.
“These recommendations will almost certainly change based on evolving understanding of MIS-C and the data,” Dr. Henderson said, adding that this new, unique condition highlights the importance of including children in allocating funding for research and in clinical trials.
“Children are not always identical to adults, and it’s really important that we have high-quality data to inform our decisions about how to care for them,” she said.
Dr. Wahezi had no disclosures. Dr. Henderson has consulted for Sobi and Adaptive Technologies. The guidelines did not note other disclosures for members of the ACR groups.
SOURCES: COVID-19 Clinical Guidance for Pediatric Patients with Rheumatic Disease and Clinical Guidance for Pediatric Patients with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Associated with SARS-CoV-2 and Hyperinflammation in COVID-19
Two new clinical guidance documents from the American College of Rheumatology provide evidence-based recommendations for managing pediatric rheumatic disease during the COVID-19 pandemic as well as diagnostic and treatment recommendations for multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) associated with COVID-19 infection.
Although several children’s hospitals have published their treatment protocols for MIS-C since the condition’s initial discovery, the ACR appears to be the first medical organization to review all the most current evidence to issue interim guidance with the expectations that it will change as more data become available.
“It is challenging having to make recommendations not having a lot of scientific evidence, but we still felt we had to use whatever’s out there to the best of our ability and use our experience to put together these recommendations,” Dawn M. Wahezi, MD, chief of pediatric rheumatology at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore and an associate professor of pediatrics at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said in an interview.
“We wanted to be mindful of the fact that there are things we know and things we don’t know, and we have to be careful about what we’re recommending,” said Dr. Wahezi, a member of the ACR working group that assembled the recommendations for pediatric rheumatic disease management during the pandemic. “We’re recommending the best we can at this moment, but if there are new studies that come out and suggest otherwise, we will definitely have to go back and amend the document.”
The foremost priority of the pediatric rheumatic disease guidance focuses on maintaining control of the disease and avoiding flares that may put children at greater risk of infection. Dr. Wahezi said the ACR has received many calls from patients and clinicians asking whether patients should continue their immunosuppressant medications. Fear of the coronavirus infection, medication shortages, difficulty getting to the pharmacy, uneasiness about going to the clinic or hospital for infusions, and other barriers may have led to gaps in medication.
“We didn’t want people to be too quick to hold patients’ medications just because they were scared of COVID,” Dr. Wahezi said. “If they did have medication stopped for one reason or another and their disease flared, having active disease, regardless of which disease it is, actually puts you at higher risk for infection. By controlling their disease, that would be the way to protect them the most.”
A key takeaway in the guidance on MIS-C, meanwhile, is an emphasis on its rarity lest physicians be too quick to diagnose it and miss another serious condition with overlapping symptoms, explained Lauren Henderson, MD, an attending rheumatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital and assistant professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Henderson participated in the ACR group that wrote the MIS-C guidance.
“The first thing we want to be thoughtful about clinically is to recognize that children in general with the acute infectious phase of SARS-CoV-2 have mild symptoms and generally do well,” Dr. Henderson said. “From what we can tell from all the data, MIS-C is rare. That really needs to be considered when clinicians on the ground are doing the diagnostic evaluation” because of concerns that clinicians “could rush to diagnose and treat patients with MIS-C and miss important diagnoses like malignancies and infections.”
Management of pediatric rheumatic disease during the pandemic
The COVID-19 clinical guidance for managing pediatric rheumatic disease grew from the work of the North American Pediatric Rheumatology Clinical Guidance Task Force, which included seven pediatric rheumatologists, two pediatric infectious disease physicians, one adult rheumatologist, and one pediatric nurse practitioner. The general guidance covers usual preventive measures for reducing risk for COVID-19 infection, the recommendation that children continue to receive recommended vaccines unless contraindicated by medication, and routine in-person visits for ophthalmologic surveillance of those with a history of uveitis or at high risk for chronic uveitis. The guidance also notes the risk of mental health concerns, such as depression and anxiety, related to quarantine and the pandemic.
The top recommendation is initiation or continuation of all medications necessary to control underlying disease, including NSAIDs, hydroxychloroquine, ACE inhibitors/angiotensin II receptor blockers, colchicine, conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (cDMARDs), biologic DMARDs, and targeted synthetic DMARDs. Even patients who may have had exposure to COVID-19 or who have an asymptomatic COVID-19 infection should continue to take these medications with the exception of ACEi/ARBs.
In those with pediatric rheumatic disease who have a symptomatic COVID-19 infection, “NSAIDs, HCQ, and colchicine may be continued, if necessary, to control underlying disease,” as can interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-6 inhibitors, but “cDMARDs, bDMARDs [except IL-1 and IL-6 inhibitors] and tsDMARDs should be temporarily delayed or withheld,” according to the guidance. Glucocorticoids can be continued at the lowest possible dose to control disease.
“There’s nothing in the literature that suggests people who have rheumatic disease, especially children, and people who are on these medications, really are at increased risk for COVID-19,” Dr. Wahezi said. “That’s why we didn’t want people to be overcautious in stopping medications when the main priority is to control their disease.”
She noted some experts’ speculations that these medications may actually benefit patients with rheumatic disease who develop a COVID-19 infection because the medications keep the immune response in check. “If you allow them to have this dysregulated immune response and have active disease, you’re potentially putting them at greater risk,” Dr. Wahezi said, although she stressed that inadequate evidence exists to support these speculations right now.
Lack of evidence has been the biggest challenge all around with developing this guidance, she said.
“Because this is such an unprecedented situation and because people are so desperate to find treatments both for the illness and to protect those at risk for it, there are lots of people trying to put evidence out there, but it may not be the best-quality evidence,” Dr. Wahezi said.
Insufficient evidence also drove the group’s determination that “SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing is not useful in informing on the history of infection or risk of reinfection,” as the guidance states. Too much variability in the assays exist, Dr. Wahezi said, and, further, it’s unclear what the clinical significance of a positive test would be.
“We didn’t want anyone to feel they had to make clinical decisions based on the results of that antibody testing,” she said. “Even if the test is accurate, we don’t know how to interpret it because it’s so new.”
The guidance also notes that patients with stable disease and previously stable lab markers on stable doses of their medication may be able to extend the interval for medication toxicity lab testing a few months if there is concern about exposure to COVID-19 to get the blood work.
“If you’re just starting a medicine or there’s someone who’s had abnormalities with the medicine in the past or you’re making medication adjustments, you wouldn’t do it in those scenarios, but if there’s someone who’s been on the drug for a long time and are nervous to get [blood] drawn, it’s probably okay to delay it,” Dr. Wahezi said. Lab work for disease activity measures, on the other hand, remain particularly important, especially since telemedicine visits may require clinicians to rely on lab results more than previously.
Management of MIS-C associated with COVID-19
The task force that developed guidance for the new inflammatory condition recently linked to SARS-CoV-2 infections in children included nine pediatric rheumatologists, two adult rheumatologists, two pediatric cardiologists, two pediatric infectious disease specialists, and one pediatric critical care physician.
The guidance includes a figure for the diagnostic pathway in evaluating children suspected of having MIS-C and extensive detail on diagnostic work-up, but the task force intentionally avoided providing a case definition for the condition. Existing case definitions from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, World Health Organization, and the United Kingdom’s Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health differ from one another and are based on unclear evidence, Dr. Henderson noted. “We really don’t have enough data to know the sensitivity and specificity of each parameter, and until that’s available, we didn’t want to add to the confusion,” she said.
The guidance also stresses that MIS-C is a rare complication, so patients suspected of having the condition who do not have “life-threatening manifestations should undergo diagnostic evaluation for MIS-C as well as other possible infectious and noninfectious etiologies before immunomodulatory treatment is initiated,” the guidance states.
Unless a child is in shock or otherwise requires urgent care, physicians should take the time to complete the diagnostic work-up while monitoring the child, Dr. Henderson said. If the child does have MIS-C, the guidance currently recommends intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and/or glucocorticoids to prevent coronary artery aneurysms, the same treatment other institutions have been recommending.
“We don’t have rigorous comparative studies looking at different types of treatments,” Dr. Henderson said, noting that the vast majority of children in the literature received IVIG and/or glucocorticoid treatment. “Often children really responded quite forcefully to those treatments, but we don’t have high-quality data yet to know that this treatment is better than supportive care or another medication.”
Dr. Henderson also stressed the importance of children receiving care at a facility with the necessary expertise to manage MIS-C and receiving long-term follow-up care from a multidisciplinary clinical team that includes a rheumatologist, an infectious disease doctor, a cardiologist, and possibly a hematologist.
“Making sure children are admitted to a hospital that has the resources and are followed by physicians with expertise or understanding of the intricacies of MIS-C is really important,” she said, particularly for children with cardiac involvement. “We don’t know if all the kids presenting with left ventricular dysfunction and shock are at risk for having myocardial fibrosis down the line,” she noted. “There is so much we do not understand and very little data to guide us on what to do, so these children really need to be under the care of a cardiologist and rheumatologist to make sure that their care is tailored to them.”
Although MIS-C shares overlapping symptoms with Kawasaki disease, it’s still unclear how similar or different the two conditions are, Dr. Henderson said.
“We can definitely say that when we look at MIS-C and compare it to historical groups of Kawasaki disease before the pandemic, there are definitely different features in the MIS-C group,” she said. Kawasaki disease generally only affects children under age 5, whereas MIS-C patients run the gamut from age 1-17. Racial demographics are also different, with a higher proportion of black children affected by MIS-C.
It’s possible that the pathophysiology of both conditions will turn out to be similar, particularly given the hypothesis that Kawasaki disease is triggered by infections in genetically predisposed people. However, the severity of symptoms and risk of aneurysms appear greater with MIS-C so far.
“The degree to which these patients are presenting with left ventricular dysfunction and shock is much higher than what we’ve seen previously,” Dr. Henderson said. “Children can have aneurysms even if they don’t meet all the Kawasaki disease features, which makes it feel that this is somehow clinically different from what we’ve seen before. It’s not just the kids who have the rash and the conjunctivitis and the extremity changes and oral changes who have the aneurysms.”
The reason for including both IVIG and glucocorticoids as possible first-line drugs to prevent aneurysms is that some evidence suggests children with MIS-C may have higher levels of IVIG resistance, she said.
Like Dr. Wahezi, Dr. Henderson emphasized the necessarily transient nature of these recommendations.
“These recommendations will almost certainly change based on evolving understanding of MIS-C and the data,” Dr. Henderson said, adding that this new, unique condition highlights the importance of including children in allocating funding for research and in clinical trials.
“Children are not always identical to adults, and it’s really important that we have high-quality data to inform our decisions about how to care for them,” she said.
Dr. Wahezi had no disclosures. Dr. Henderson has consulted for Sobi and Adaptive Technologies. The guidelines did not note other disclosures for members of the ACR groups.
SOURCES: COVID-19 Clinical Guidance for Pediatric Patients with Rheumatic Disease and Clinical Guidance for Pediatric Patients with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Associated with SARS-CoV-2 and Hyperinflammation in COVID-19
Experts publish imaging recommendations for pediatric COVID-19
A team of pulmonologists has synthesized the clinical and imaging characteristics of COVID-19 in children, and has devised recommendations for ordering imaging studies in suspected cases of the infection.
The review also included useful radiographic findings to help in the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other respiratory infections. Alexandra M. Foust, DO, of Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues reported the summary of findings and recommendations in Pediatric Pulmonology.
“Pediatricians face numerous challenges created by increasing reports of severe COVID-19 related findings in affected children,” said Mary Cataletto, MD, of NYU Langone Health in Mineola, N.Y. “[The current review] represents a multinational collaboration to provide up to date information and key imaging findings to guide chest physicians caring for children with pneumonia symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Clinical presentation in children
In general, pediatric patients infected with the virus show milder symptoms compared with adults, and based on the limited evidence reported to date, the most common clinical symptoms of COVID-19 in children are rhinorrhea and/or nasal congestion, fever and cough with sore throat, fatigue or dyspnea, and diarrhea.
As with other viral pneumonias in children, the laboratory parameters are usually nonspecific; however, while the complete blood count (CBC) is often normal, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia have been reported in some cases of pediatric COVID-19, the authors noted.
The current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendation for initial diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 is obtaining a nasopharyngeal swab, followed by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing, they explained.
Role of imaging in diagnosis
The researchers reported that current recommendations from the American College of Radiology (ACR) do not include chest computed tomography (CT) or chest radiography (CXR) as a upfront test to diagnose pediatric COVID-19, but they may still have a role in clinical monitoring, especially in patients with a moderate to severe disease course.
The potential benefits of utilizing radiologic evaluation, such as establishing a baseline for monitoring disease progression, must be balanced with potential drawbacks, which include radiation exposure, and reduced availability of imaging resources owing to necessary cleaning and air turnover time.
Recommendations for ordering imaging studies
Based on the most recent international guidelines for pediatric COVID-19 patient management, the authors developed an algorithm for performing imaging studies in suspected cases of COVID-19 pneumonia.
The purpose of the tool is to support clinical decision-making around the utilization of CXR and CT to evaluate pediatric COVID-19 pneumonia.
“The step by step algorithm addresses the selection, sequence and timing of imaging studies with multiple images illustrating key findings of COVID-19 pneumonia in the pediatric age group,” said Dr. Cataletto. “By synthesizing the available imaging case series and guidelines, this primer provides a useful tool for the practicing pulmonologist,” she explained.
Key recommendations: CXR
“For pediatric patients with suspected or known COVID-19 infection with moderate to severe clinical symptoms requiring hospitalization (i.e., hypoxia, moderate or severe dyspnea, signs of sepsis, shock, cardiovascular compromise, altered mentation), CXR is usually indicated to establish an imaging baseline and to assess for an alternative diagnosis,” they recommended.
“Sequential CXRs may be helpful to assess pediatric patients with COVID-19 who demonstrate worsening clinical symptoms or to assess response to supportive therapy,” they wrote.
Key recommendations: CT
“Due to the increased radiation sensitivity of pediatric patients, chest CT is not recommended as an initial diagnostic test for pediatric patients with known or suspected COVID-19 pneumonia,” they explained.
The guide also included several considerations around the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other pediatric lung disorders, including immune-related conditions, infectious etiologies, hematological dyscrasias, and inhalation-related lung injury.
As best practice recommendations for COVID-19 continue to evolve, the availability of practical clinical decision-making tools becomes essential to ensure optimal patient care.
No funding sources or financial disclosures were reported in the manuscript.
SOURCE: Foust AM et al. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020 May 28. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24870.
A team of pulmonologists has synthesized the clinical and imaging characteristics of COVID-19 in children, and has devised recommendations for ordering imaging studies in suspected cases of the infection.
The review also included useful radiographic findings to help in the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other respiratory infections. Alexandra M. Foust, DO, of Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues reported the summary of findings and recommendations in Pediatric Pulmonology.
“Pediatricians face numerous challenges created by increasing reports of severe COVID-19 related findings in affected children,” said Mary Cataletto, MD, of NYU Langone Health in Mineola, N.Y. “[The current review] represents a multinational collaboration to provide up to date information and key imaging findings to guide chest physicians caring for children with pneumonia symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Clinical presentation in children
In general, pediatric patients infected with the virus show milder symptoms compared with adults, and based on the limited evidence reported to date, the most common clinical symptoms of COVID-19 in children are rhinorrhea and/or nasal congestion, fever and cough with sore throat, fatigue or dyspnea, and diarrhea.
As with other viral pneumonias in children, the laboratory parameters are usually nonspecific; however, while the complete blood count (CBC) is often normal, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia have been reported in some cases of pediatric COVID-19, the authors noted.
The current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendation for initial diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 is obtaining a nasopharyngeal swab, followed by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing, they explained.
Role of imaging in diagnosis
The researchers reported that current recommendations from the American College of Radiology (ACR) do not include chest computed tomography (CT) or chest radiography (CXR) as a upfront test to diagnose pediatric COVID-19, but they may still have a role in clinical monitoring, especially in patients with a moderate to severe disease course.
The potential benefits of utilizing radiologic evaluation, such as establishing a baseline for monitoring disease progression, must be balanced with potential drawbacks, which include radiation exposure, and reduced availability of imaging resources owing to necessary cleaning and air turnover time.
Recommendations for ordering imaging studies
Based on the most recent international guidelines for pediatric COVID-19 patient management, the authors developed an algorithm for performing imaging studies in suspected cases of COVID-19 pneumonia.
The purpose of the tool is to support clinical decision-making around the utilization of CXR and CT to evaluate pediatric COVID-19 pneumonia.
“The step by step algorithm addresses the selection, sequence and timing of imaging studies with multiple images illustrating key findings of COVID-19 pneumonia in the pediatric age group,” said Dr. Cataletto. “By synthesizing the available imaging case series and guidelines, this primer provides a useful tool for the practicing pulmonologist,” she explained.
Key recommendations: CXR
“For pediatric patients with suspected or known COVID-19 infection with moderate to severe clinical symptoms requiring hospitalization (i.e., hypoxia, moderate or severe dyspnea, signs of sepsis, shock, cardiovascular compromise, altered mentation), CXR is usually indicated to establish an imaging baseline and to assess for an alternative diagnosis,” they recommended.
“Sequential CXRs may be helpful to assess pediatric patients with COVID-19 who demonstrate worsening clinical symptoms or to assess response to supportive therapy,” they wrote.
Key recommendations: CT
“Due to the increased radiation sensitivity of pediatric patients, chest CT is not recommended as an initial diagnostic test for pediatric patients with known or suspected COVID-19 pneumonia,” they explained.
The guide also included several considerations around the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other pediatric lung disorders, including immune-related conditions, infectious etiologies, hematological dyscrasias, and inhalation-related lung injury.
As best practice recommendations for COVID-19 continue to evolve, the availability of practical clinical decision-making tools becomes essential to ensure optimal patient care.
No funding sources or financial disclosures were reported in the manuscript.
SOURCE: Foust AM et al. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020 May 28. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24870.
A team of pulmonologists has synthesized the clinical and imaging characteristics of COVID-19 in children, and has devised recommendations for ordering imaging studies in suspected cases of the infection.
The review also included useful radiographic findings to help in the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other respiratory infections. Alexandra M. Foust, DO, of Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues reported the summary of findings and recommendations in Pediatric Pulmonology.
“Pediatricians face numerous challenges created by increasing reports of severe COVID-19 related findings in affected children,” said Mary Cataletto, MD, of NYU Langone Health in Mineola, N.Y. “[The current review] represents a multinational collaboration to provide up to date information and key imaging findings to guide chest physicians caring for children with pneumonia symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Clinical presentation in children
In general, pediatric patients infected with the virus show milder symptoms compared with adults, and based on the limited evidence reported to date, the most common clinical symptoms of COVID-19 in children are rhinorrhea and/or nasal congestion, fever and cough with sore throat, fatigue or dyspnea, and diarrhea.
As with other viral pneumonias in children, the laboratory parameters are usually nonspecific; however, while the complete blood count (CBC) is often normal, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia have been reported in some cases of pediatric COVID-19, the authors noted.
The current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendation for initial diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 is obtaining a nasopharyngeal swab, followed by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing, they explained.
Role of imaging in diagnosis
The researchers reported that current recommendations from the American College of Radiology (ACR) do not include chest computed tomography (CT) or chest radiography (CXR) as a upfront test to diagnose pediatric COVID-19, but they may still have a role in clinical monitoring, especially in patients with a moderate to severe disease course.
The potential benefits of utilizing radiologic evaluation, such as establishing a baseline for monitoring disease progression, must be balanced with potential drawbacks, which include radiation exposure, and reduced availability of imaging resources owing to necessary cleaning and air turnover time.
Recommendations for ordering imaging studies
Based on the most recent international guidelines for pediatric COVID-19 patient management, the authors developed an algorithm for performing imaging studies in suspected cases of COVID-19 pneumonia.
The purpose of the tool is to support clinical decision-making around the utilization of CXR and CT to evaluate pediatric COVID-19 pneumonia.
“The step by step algorithm addresses the selection, sequence and timing of imaging studies with multiple images illustrating key findings of COVID-19 pneumonia in the pediatric age group,” said Dr. Cataletto. “By synthesizing the available imaging case series and guidelines, this primer provides a useful tool for the practicing pulmonologist,” she explained.
Key recommendations: CXR
“For pediatric patients with suspected or known COVID-19 infection with moderate to severe clinical symptoms requiring hospitalization (i.e., hypoxia, moderate or severe dyspnea, signs of sepsis, shock, cardiovascular compromise, altered mentation), CXR is usually indicated to establish an imaging baseline and to assess for an alternative diagnosis,” they recommended.
“Sequential CXRs may be helpful to assess pediatric patients with COVID-19 who demonstrate worsening clinical symptoms or to assess response to supportive therapy,” they wrote.
Key recommendations: CT
“Due to the increased radiation sensitivity of pediatric patients, chest CT is not recommended as an initial diagnostic test for pediatric patients with known or suspected COVID-19 pneumonia,” they explained.
The guide also included several considerations around the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other pediatric lung disorders, including immune-related conditions, infectious etiologies, hematological dyscrasias, and inhalation-related lung injury.
As best practice recommendations for COVID-19 continue to evolve, the availability of practical clinical decision-making tools becomes essential to ensure optimal patient care.
No funding sources or financial disclosures were reported in the manuscript.
SOURCE: Foust AM et al. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020 May 28. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24870.
FROM PEDIATRIC PULMONOLOGY
ED visits for life-threatening conditions declined early in COVID-19 pandemic
ED visits for myocardial infarction, stroke, and hyperglycemic crisis dropped substantially in the 10 weeks after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency on March 13, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
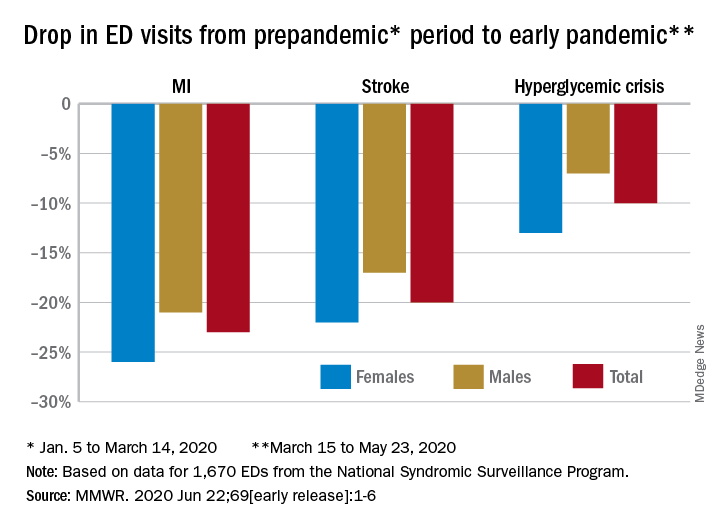
Compared with the 10-week period from Jan. 5 to March 14, ED visits were down by 23% for MI, 20% for stroke, and 10% for hyperglycemic crisis from March 15 to May 23, Samantha J. Lange, MPH, and associates at the CDC reported June 22 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
“A short-term decline of this magnitude … is biologically implausible for MI and stroke, especially for older adults, and unlikely for hyperglycemic crisis, and the finding suggests that patients with these conditions either could not access care or were delaying or avoiding seeking care during the early pandemic period,” they wrote.
The largest decreases in the actual number of visits for MI occurred among both men (down by 2,114, –24%) and women (down by 1,459, –25%) aged 65-74 years. For stroke, men aged 65-74 years had 1,406 (–19%) fewer visits to the ED and women 75-84 years had 1,642 (–23%) fewer visits, the CDC researchers said.
For hypoglycemic crisis, the largest declines during the early pandemic period occurred among younger adults: ED visits for men and women aged 18-44 years were down, respectively, by 419 (–8%) and 775 (–16%), they reported based on data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
“Decreases in ED visits for hyperglycemic crisis might be less striking because patient recognition of this crisis is typically augmented by home glucose monitoring and not reliant upon symptoms alone, as is the case for MI and stroke,” Ms. Lange and her associates noted.
Charting weekly visit numbers showed that the drop for all three conditions actually started the week before the emergency was declared and reached its nadir the week after (March 22) for MI and 2 weeks later (March 29) for stroke and hypoglycemic crisis.
Visits for hypoglycemic crisis have largely returned to normal since those low points, but MI and stroke visits “remain below prepandemic levels” despite gradual increases through April and May, they said.
It has been reported that “deaths not associated with confirmed or probable COVID-19 might have been directly or indirectly attributed to the pandemic. The striking decline in ED visits for acute life-threatening conditions might partially explain observed excess mortality not associated with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote.
ED visits for myocardial infarction, stroke, and hyperglycemic crisis dropped substantially in the 10 weeks after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency on March 13, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Compared with the 10-week period from Jan. 5 to March 14, ED visits were down by 23% for MI, 20% for stroke, and 10% for hyperglycemic crisis from March 15 to May 23, Samantha J. Lange, MPH, and associates at the CDC reported June 22 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
“A short-term decline of this magnitude … is biologically implausible for MI and stroke, especially for older adults, and unlikely for hyperglycemic crisis, and the finding suggests that patients with these conditions either could not access care or were delaying or avoiding seeking care during the early pandemic period,” they wrote.
The largest decreases in the actual number of visits for MI occurred among both men (down by 2,114, –24%) and women (down by 1,459, –25%) aged 65-74 years. For stroke, men aged 65-74 years had 1,406 (–19%) fewer visits to the ED and women 75-84 years had 1,642 (–23%) fewer visits, the CDC researchers said.
For hypoglycemic crisis, the largest declines during the early pandemic period occurred among younger adults: ED visits for men and women aged 18-44 years were down, respectively, by 419 (–8%) and 775 (–16%), they reported based on data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
“Decreases in ED visits for hyperglycemic crisis might be less striking because patient recognition of this crisis is typically augmented by home glucose monitoring and not reliant upon symptoms alone, as is the case for MI and stroke,” Ms. Lange and her associates noted.
Charting weekly visit numbers showed that the drop for all three conditions actually started the week before the emergency was declared and reached its nadir the week after (March 22) for MI and 2 weeks later (March 29) for stroke and hypoglycemic crisis.
Visits for hypoglycemic crisis have largely returned to normal since those low points, but MI and stroke visits “remain below prepandemic levels” despite gradual increases through April and May, they said.
It has been reported that “deaths not associated with confirmed or probable COVID-19 might have been directly or indirectly attributed to the pandemic. The striking decline in ED visits for acute life-threatening conditions might partially explain observed excess mortality not associated with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote.
ED visits for myocardial infarction, stroke, and hyperglycemic crisis dropped substantially in the 10 weeks after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency on March 13, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Compared with the 10-week period from Jan. 5 to March 14, ED visits were down by 23% for MI, 20% for stroke, and 10% for hyperglycemic crisis from March 15 to May 23, Samantha J. Lange, MPH, and associates at the CDC reported June 22 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
“A short-term decline of this magnitude … is biologically implausible for MI and stroke, especially for older adults, and unlikely for hyperglycemic crisis, and the finding suggests that patients with these conditions either could not access care or were delaying or avoiding seeking care during the early pandemic period,” they wrote.
The largest decreases in the actual number of visits for MI occurred among both men (down by 2,114, –24%) and women (down by 1,459, –25%) aged 65-74 years. For stroke, men aged 65-74 years had 1,406 (–19%) fewer visits to the ED and women 75-84 years had 1,642 (–23%) fewer visits, the CDC researchers said.
For hypoglycemic crisis, the largest declines during the early pandemic period occurred among younger adults: ED visits for men and women aged 18-44 years were down, respectively, by 419 (–8%) and 775 (–16%), they reported based on data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
“Decreases in ED visits for hyperglycemic crisis might be less striking because patient recognition of this crisis is typically augmented by home glucose monitoring and not reliant upon symptoms alone, as is the case for MI and stroke,” Ms. Lange and her associates noted.
Charting weekly visit numbers showed that the drop for all three conditions actually started the week before the emergency was declared and reached its nadir the week after (March 22) for MI and 2 weeks later (March 29) for stroke and hypoglycemic crisis.
Visits for hypoglycemic crisis have largely returned to normal since those low points, but MI and stroke visits “remain below prepandemic levels” despite gradual increases through April and May, they said.
It has been reported that “deaths not associated with confirmed or probable COVID-19 might have been directly or indirectly attributed to the pandemic. The striking decline in ED visits for acute life-threatening conditions might partially explain observed excess mortality not associated with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote.
FROM MMWR
T2D plus heart failure packs a deadly punch
It’s bad news for patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes when they then develop heart failure during the next few years.
Patients with incident type 2 diabetes (T2D) who soon after also had heart failure appear faced a dramatically elevated mortality risk, higher than the incremental risk from any other cardiovascular or renal comorbidity that appeared following diabetes onset, in an analysis of more than 150,000 Danish patients with incident type 2 diabetes during 1998-2015.
The 5-year risk of death in patients who developed heart failure during the first 5 years following an initial diagnosis of T2D was about 48%, about threefold higher than in patients with newly diagnosed T2D who remained free of heart failure or any of the other studied comorbidities, Bochra Zareini, MD, and associates reported in a study published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. The studied patients had no known cardiovascular or renal disease at the time of their first T2D diagnosis.
“Our study reports not only on the absolute 5-year risk” of mortality, “but also takes into consideration when patients developed” a comorbidity. “What is surprising and worrying is the very high risk of death following heart failure and the potential life years lost when compared to T2D patients who do not develop heart failure,” said Dr. Zareini, a cardiologist at Herlev and Gentofte University Hospital in Copenhagen. “The implications of our study are to create awareness and highlight the importance of early detection of heart failure development in patients with T2D.” The results also showed that “heart failure is a common cardiovascular disease” in patients with newly diagnosed T2D, she added in an interview.
The data she and her associates reported came from a retrospective analysis of 153,403 Danish citizens in national health records who received a prescription for an antidiabetes drug for the first time during 1998-2015, excluding patients with a prior diagnosis of heart failure, ischemic heart disease (IHD), stroke, peripheral artery disease (PAD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), or gestational diabetes. They followed these patients for a median of just under 10 years, during which time 45% of the cohort had an incident diagnosis of at least one of these cardiovascular and renal conditions, based on medical-record entries from hospitalization discharges or ambulatory contacts.
Nearly two-thirds of the T2D patients with an incident comorbidity during follow-up had a single new diagnosis, a quarter had two new comorbidities appear during follow-up, and 13% developed at least three new comorbidities.
Heart failure, least common but deadliest comorbidity
The most common of the tracked comorbidities was IHD, which appeared in 8% of the T2D patients within 5 years and in 13% after 10 years. Next most common was stroke, affecting 3% of patients after 5 years and 5% after 10 years. CKD occurred in 2.2% after 5 years and in 4.0% after 10 years, PAD occurred in 2.1% after 5 years and in 3.0% at 10 years, and heart failure occurred in 1.6% at 5 years and in 2.2% after 10 years.
But despite being the least common of the studied comorbidities, heart failure was by far the most deadly, roughly tripling the 5-year mortality rate, compared with T2D patients with no comorbidities, regardless of exactly when it first appeared during the first 5 years after the initial T2D diagnosis. The next most deadly comorbidities were stroke and PAD, which each roughly doubled mortality, compared with the patients who remained free of any studied comorbidity. CKD boosted mortality by 70%-110%, depending on exactly when it appeared during the first 5 years of follow-up, and IHD, while the most frequent comorbidity was also the most benign, increasing mortality by about 30%.
The most deadly combinations of two comorbidities were when heart failure appeared with either CKD or with PAD; each of these combinations boosted mortality by 300%-400% when it occurred during the first few years after a T2D diagnosis.
The findings came from “a very big and unselected patient group of patients, making our results highly generalizable in terms of assessing the prognostic consequences of heart failure,” Dr. Zareini stressed.
Management implications
The dangerous combination of T2D and heart failure has been documented for several years, and prompted a focused statement in 2019 about best practices for managing these patients (Circulation. 2019 Aug 3;140[7]:e294-324). “Heart failure has been known for some time to predict poorer outcomes in patients with T2D. Not much surprising” in the new findings reported by Dr. Zareini and associates, commented Robert H. Eckel, MD, a cardiovascular endocrinologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Heart failure “rarely acts alone, but in combination with other forms of heart or renal disease,” he noted in an interview.
Earlier studies may have “overlooked” heart failure’s importance compared with other comorbidities because they often “only investigated one cardiovascular disease in patients with T2D,” Dr. Zareini noted. In recent years the importance of heart failure occurring in patients with T2D also gained heightened significance because of the growing role of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor drug class in treating patients with T2D and the documented ability of these drugs to significantly reduce hospitalizations for heart failure (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 28;75[16]:1956-74). Dr. Zareini and associates put it this way in their report: “Heart failure has in recent years been recognized as an important clinical endpoint ... in patients with T2D, in particular, after the results from randomized, controlled trials of SGLT2 inhibitors showed benefit on cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations.”
Despite this, the new findings “do not address treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T2D, nor can we use our data to address which patients should not be treated,” with this drug class, which instead should rely on “current evidence and expert consensus,” she said.
“Guidelines favor SGLT2 inhibitors or [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists in patients with a history of or high risk for major adverse coronary events,” and SGLT2 inhibitors are also “preferable in patients with renal disease,” Dr. Eckel noted.
Other avenues also exist for minimizing the onset of heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases in patients with T2D, Dr. Zareini said, citing modifiable risks that lead to heart failure that include hypertension, “diabetic cardiomyopathy,” and ISD. “Clinicians must treat all modifiable risk factors in patients with T2D in order to improve prognosis and limit development of cardiovascular and renal disease.”
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Zareini and Dr. Eckel had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Zareini B et al. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020 Jun 23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.119.006260.
It’s bad news for patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes when they then develop heart failure during the next few years.
Patients with incident type 2 diabetes (T2D) who soon after also had heart failure appear faced a dramatically elevated mortality risk, higher than the incremental risk from any other cardiovascular or renal comorbidity that appeared following diabetes onset, in an analysis of more than 150,000 Danish patients with incident type 2 diabetes during 1998-2015.
The 5-year risk of death in patients who developed heart failure during the first 5 years following an initial diagnosis of T2D was about 48%, about threefold higher than in patients with newly diagnosed T2D who remained free of heart failure or any of the other studied comorbidities, Bochra Zareini, MD, and associates reported in a study published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. The studied patients had no known cardiovascular or renal disease at the time of their first T2D diagnosis.
“Our study reports not only on the absolute 5-year risk” of mortality, “but also takes into consideration when patients developed” a comorbidity. “What is surprising and worrying is the very high risk of death following heart failure and the potential life years lost when compared to T2D patients who do not develop heart failure,” said Dr. Zareini, a cardiologist at Herlev and Gentofte University Hospital in Copenhagen. “The implications of our study are to create awareness and highlight the importance of early detection of heart failure development in patients with T2D.” The results also showed that “heart failure is a common cardiovascular disease” in patients with newly diagnosed T2D, she added in an interview.
The data she and her associates reported came from a retrospective analysis of 153,403 Danish citizens in national health records who received a prescription for an antidiabetes drug for the first time during 1998-2015, excluding patients with a prior diagnosis of heart failure, ischemic heart disease (IHD), stroke, peripheral artery disease (PAD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), or gestational diabetes. They followed these patients for a median of just under 10 years, during which time 45% of the cohort had an incident diagnosis of at least one of these cardiovascular and renal conditions, based on medical-record entries from hospitalization discharges or ambulatory contacts.
Nearly two-thirds of the T2D patients with an incident comorbidity during follow-up had a single new diagnosis, a quarter had two new comorbidities appear during follow-up, and 13% developed at least three new comorbidities.
Heart failure, least common but deadliest comorbidity
The most common of the tracked comorbidities was IHD, which appeared in 8% of the T2D patients within 5 years and in 13% after 10 years. Next most common was stroke, affecting 3% of patients after 5 years and 5% after 10 years. CKD occurred in 2.2% after 5 years and in 4.0% after 10 years, PAD occurred in 2.1% after 5 years and in 3.0% at 10 years, and heart failure occurred in 1.6% at 5 years and in 2.2% after 10 years.
But despite being the least common of the studied comorbidities, heart failure was by far the most deadly, roughly tripling the 5-year mortality rate, compared with T2D patients with no comorbidities, regardless of exactly when it first appeared during the first 5 years after the initial T2D diagnosis. The next most deadly comorbidities were stroke and PAD, which each roughly doubled mortality, compared with the patients who remained free of any studied comorbidity. CKD boosted mortality by 70%-110%, depending on exactly when it appeared during the first 5 years of follow-up, and IHD, while the most frequent comorbidity was also the most benign, increasing mortality by about 30%.
The most deadly combinations of two comorbidities were when heart failure appeared with either CKD or with PAD; each of these combinations boosted mortality by 300%-400% when it occurred during the first few years after a T2D diagnosis.
The findings came from “a very big and unselected patient group of patients, making our results highly generalizable in terms of assessing the prognostic consequences of heart failure,” Dr. Zareini stressed.
Management implications
The dangerous combination of T2D and heart failure has been documented for several years, and prompted a focused statement in 2019 about best practices for managing these patients (Circulation. 2019 Aug 3;140[7]:e294-324). “Heart failure has been known for some time to predict poorer outcomes in patients with T2D. Not much surprising” in the new findings reported by Dr. Zareini and associates, commented Robert H. Eckel, MD, a cardiovascular endocrinologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Heart failure “rarely acts alone, but in combination with other forms of heart or renal disease,” he noted in an interview.
Earlier studies may have “overlooked” heart failure’s importance compared with other comorbidities because they often “only investigated one cardiovascular disease in patients with T2D,” Dr. Zareini noted. In recent years the importance of heart failure occurring in patients with T2D also gained heightened significance because of the growing role of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor drug class in treating patients with T2D and the documented ability of these drugs to significantly reduce hospitalizations for heart failure (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 28;75[16]:1956-74). Dr. Zareini and associates put it this way in their report: “Heart failure has in recent years been recognized as an important clinical endpoint ... in patients with T2D, in particular, after the results from randomized, controlled trials of SGLT2 inhibitors showed benefit on cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations.”
Despite this, the new findings “do not address treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T2D, nor can we use our data to address which patients should not be treated,” with this drug class, which instead should rely on “current evidence and expert consensus,” she said.
“Guidelines favor SGLT2 inhibitors or [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists in patients with a history of or high risk for major adverse coronary events,” and SGLT2 inhibitors are also “preferable in patients with renal disease,” Dr. Eckel noted.
Other avenues also exist for minimizing the onset of heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases in patients with T2D, Dr. Zareini said, citing modifiable risks that lead to heart failure that include hypertension, “diabetic cardiomyopathy,” and ISD. “Clinicians must treat all modifiable risk factors in patients with T2D in order to improve prognosis and limit development of cardiovascular and renal disease.”
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Zareini and Dr. Eckel had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Zareini B et al. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020 Jun 23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.119.006260.
It’s bad news for patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes when they then develop heart failure during the next few years.
Patients with incident type 2 diabetes (T2D) who soon after also had heart failure appear faced a dramatically elevated mortality risk, higher than the incremental risk from any other cardiovascular or renal comorbidity that appeared following diabetes onset, in an analysis of more than 150,000 Danish patients with incident type 2 diabetes during 1998-2015.
The 5-year risk of death in patients who developed heart failure during the first 5 years following an initial diagnosis of T2D was about 48%, about threefold higher than in patients with newly diagnosed T2D who remained free of heart failure or any of the other studied comorbidities, Bochra Zareini, MD, and associates reported in a study published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. The studied patients had no known cardiovascular or renal disease at the time of their first T2D diagnosis.
“Our study reports not only on the absolute 5-year risk” of mortality, “but also takes into consideration when patients developed” a comorbidity. “What is surprising and worrying is the very high risk of death following heart failure and the potential life years lost when compared to T2D patients who do not develop heart failure,” said Dr. Zareini, a cardiologist at Herlev and Gentofte University Hospital in Copenhagen. “The implications of our study are to create awareness and highlight the importance of early detection of heart failure development in patients with T2D.” The results also showed that “heart failure is a common cardiovascular disease” in patients with newly diagnosed T2D, she added in an interview.
The data she and her associates reported came from a retrospective analysis of 153,403 Danish citizens in national health records who received a prescription for an antidiabetes drug for the first time during 1998-2015, excluding patients with a prior diagnosis of heart failure, ischemic heart disease (IHD), stroke, peripheral artery disease (PAD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), or gestational diabetes. They followed these patients for a median of just under 10 years, during which time 45% of the cohort had an incident diagnosis of at least one of these cardiovascular and renal conditions, based on medical-record entries from hospitalization discharges or ambulatory contacts.
Nearly two-thirds of the T2D patients with an incident comorbidity during follow-up had a single new diagnosis, a quarter had two new comorbidities appear during follow-up, and 13% developed at least three new comorbidities.
Heart failure, least common but deadliest comorbidity
The most common of the tracked comorbidities was IHD, which appeared in 8% of the T2D patients within 5 years and in 13% after 10 years. Next most common was stroke, affecting 3% of patients after 5 years and 5% after 10 years. CKD occurred in 2.2% after 5 years and in 4.0% after 10 years, PAD occurred in 2.1% after 5 years and in 3.0% at 10 years, and heart failure occurred in 1.6% at 5 years and in 2.2% after 10 years.
But despite being the least common of the studied comorbidities, heart failure was by far the most deadly, roughly tripling the 5-year mortality rate, compared with T2D patients with no comorbidities, regardless of exactly when it first appeared during the first 5 years after the initial T2D diagnosis. The next most deadly comorbidities were stroke and PAD, which each roughly doubled mortality, compared with the patients who remained free of any studied comorbidity. CKD boosted mortality by 70%-110%, depending on exactly when it appeared during the first 5 years of follow-up, and IHD, while the most frequent comorbidity was also the most benign, increasing mortality by about 30%.
The most deadly combinations of two comorbidities were when heart failure appeared with either CKD or with PAD; each of these combinations boosted mortality by 300%-400% when it occurred during the first few years after a T2D diagnosis.
The findings came from “a very big and unselected patient group of patients, making our results highly generalizable in terms of assessing the prognostic consequences of heart failure,” Dr. Zareini stressed.
Management implications
The dangerous combination of T2D and heart failure has been documented for several years, and prompted a focused statement in 2019 about best practices for managing these patients (Circulation. 2019 Aug 3;140[7]:e294-324). “Heart failure has been known for some time to predict poorer outcomes in patients with T2D. Not much surprising” in the new findings reported by Dr. Zareini and associates, commented Robert H. Eckel, MD, a cardiovascular endocrinologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Heart failure “rarely acts alone, but in combination with other forms of heart or renal disease,” he noted in an interview.
Earlier studies may have “overlooked” heart failure’s importance compared with other comorbidities because they often “only investigated one cardiovascular disease in patients with T2D,” Dr. Zareini noted. In recent years the importance of heart failure occurring in patients with T2D also gained heightened significance because of the growing role of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor drug class in treating patients with T2D and the documented ability of these drugs to significantly reduce hospitalizations for heart failure (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 28;75[16]:1956-74). Dr. Zareini and associates put it this way in their report: “Heart failure has in recent years been recognized as an important clinical endpoint ... in patients with T2D, in particular, after the results from randomized, controlled trials of SGLT2 inhibitors showed benefit on cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations.”
Despite this, the new findings “do not address treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T2D, nor can we use our data to address which patients should not be treated,” with this drug class, which instead should rely on “current evidence and expert consensus,” she said.
“Guidelines favor SGLT2 inhibitors or [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists in patients with a history of or high risk for major adverse coronary events,” and SGLT2 inhibitors are also “preferable in patients with renal disease,” Dr. Eckel noted.
Other avenues also exist for minimizing the onset of heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases in patients with T2D, Dr. Zareini said, citing modifiable risks that lead to heart failure that include hypertension, “diabetic cardiomyopathy,” and ISD. “Clinicians must treat all modifiable risk factors in patients with T2D in order to improve prognosis and limit development of cardiovascular and renal disease.”
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Zareini and Dr. Eckel had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Zareini B et al. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020 Jun 23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.119.006260.
FROM CIRCULATION: CARDIOVASCULAR QUALITY AND OUTCOMES
Cost of preventable adult hospital stays topped $33 billion in 2017
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
That year, there were 27.4 million inpatient visits by adults with a total cost of $380.1 billion, although obstetric stays were not included in the analysis. Of those inpatient admissions, 3.5 million (12.9%) were deemed to be “avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in a recent AHRQ statistical brief.
The charges for those 3.5 million visits came to $33.7 billion, or 8.9% of aggregate hospital costs in 2017, based on data from the AHRQ Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project’s state inpatient databases.
“Determining the volume and costs of potentially preventable inpatient stays can identify where potential cost savings might be found associated with reducing these hospitalizations overall and among specific subpopulations,” the investigators pointed out.
Of the seven conditions that are potentially avoidable, heart failure was the most expensive, producing more than 1.1 million inpatient admissions at a cost of $11.2 billion. Diabetes was next with a cost of almost $7.4 billion, followed by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at nearly $7.3 billion, they said.
Those three conditions, along with hypertension and asthma in younger adults, brought the total cost of the preventable-stay equation’s chronic side to $27.3 billion in 2017, versus $6.4 billion for the two acute conditions, community-acquired pneumonia and urinary tract infections, said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ.
The rate of potentially avoidable stays for chronic conditions was higher for men (1,112/100,000 population) than for women (954/100,000), but women had a higher rate for acute conditions, 346 vs. 257, which made the overall rates similar (1,369 for men and 1,300 for women), they reported.
Differences by race/ethnicity were more striking. The rate of potentially avoidable stays for blacks was 2,573/100,000 in 2017, compared with 1,315 for Hispanics, 1,173 for whites, and 581 for Asians/Pacific Islanders. The considerable margins between those figures, however, were far eclipsed by the “other” category, which had 4,911 stays per 100,000, the researchers said.
Large disparities also can be seen when looking at community-level income. Communities with income in the lowest quartile had a preventable-hospitalization rate of 2,013/100,000, and the rate dropped with each successive quartile until it reached 878/100,000 for the highest-income communities, according to the report.
“High hospital admission rates for these conditions may indicate areas where changes to the healthcare delivery system could be implemented to improve patient outcomes and lower costs,” Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang wrote.
SOURCE: McDermott KW and Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

That year, there were 27.4 million inpatient visits by adults with a total cost of $380.1 billion, although obstetric stays were not included in the analysis. Of those inpatient admissions, 3.5 million (12.9%) were deemed to be “avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in a recent AHRQ statistical brief.
The charges for those 3.5 million visits came to $33.7 billion, or 8.9% of aggregate hospital costs in 2017, based on data from the AHRQ Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project’s state inpatient databases.
“Determining the volume and costs of potentially preventable inpatient stays can identify where potential cost savings might be found associated with reducing these hospitalizations overall and among specific subpopulations,” the investigators pointed out.
Of the seven conditions that are potentially avoidable, heart failure was the most expensive, producing more than 1.1 million inpatient admissions at a cost of $11.2 billion. Diabetes was next with a cost of almost $7.4 billion, followed by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at nearly $7.3 billion, they said.
Those three conditions, along with hypertension and asthma in younger adults, brought the total cost of the preventable-stay equation’s chronic side to $27.3 billion in 2017, versus $6.4 billion for the two acute conditions, community-acquired pneumonia and urinary tract infections, said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ.
The rate of potentially avoidable stays for chronic conditions was higher for men (1,112/100,000 population) than for women (954/100,000), but women had a higher rate for acute conditions, 346 vs. 257, which made the overall rates similar (1,369 for men and 1,300 for women), they reported.
Differences by race/ethnicity were more striking. The rate of potentially avoidable stays for blacks was 2,573/100,000 in 2017, compared with 1,315 for Hispanics, 1,173 for whites, and 581 for Asians/Pacific Islanders. The considerable margins between those figures, however, were far eclipsed by the “other” category, which had 4,911 stays per 100,000, the researchers said.
Large disparities also can be seen when looking at community-level income. Communities with income in the lowest quartile had a preventable-hospitalization rate of 2,013/100,000, and the rate dropped with each successive quartile until it reached 878/100,000 for the highest-income communities, according to the report.
“High hospital admission rates for these conditions may indicate areas where changes to the healthcare delivery system could be implemented to improve patient outcomes and lower costs,” Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang wrote.
SOURCE: McDermott KW and Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

That year, there were 27.4 million inpatient visits by adults with a total cost of $380.1 billion, although obstetric stays were not included in the analysis. Of those inpatient admissions, 3.5 million (12.9%) were deemed to be “avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in a recent AHRQ statistical brief.
The charges for those 3.5 million visits came to $33.7 billion, or 8.9% of aggregate hospital costs in 2017, based on data from the AHRQ Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project’s state inpatient databases.
“Determining the volume and costs of potentially preventable inpatient stays can identify where potential cost savings might be found associated with reducing these hospitalizations overall and among specific subpopulations,” the investigators pointed out.
Of the seven conditions that are potentially avoidable, heart failure was the most expensive, producing more than 1.1 million inpatient admissions at a cost of $11.2 billion. Diabetes was next with a cost of almost $7.4 billion, followed by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at nearly $7.3 billion, they said.
Those three conditions, along with hypertension and asthma in younger adults, brought the total cost of the preventable-stay equation’s chronic side to $27.3 billion in 2017, versus $6.4 billion for the two acute conditions, community-acquired pneumonia and urinary tract infections, said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ.
The rate of potentially avoidable stays for chronic conditions was higher for men (1,112/100,000 population) than for women (954/100,000), but women had a higher rate for acute conditions, 346 vs. 257, which made the overall rates similar (1,369 for men and 1,300 for women), they reported.
Differences by race/ethnicity were more striking. The rate of potentially avoidable stays for blacks was 2,573/100,000 in 2017, compared with 1,315 for Hispanics, 1,173 for whites, and 581 for Asians/Pacific Islanders. The considerable margins between those figures, however, were far eclipsed by the “other” category, which had 4,911 stays per 100,000, the researchers said.
Large disparities also can be seen when looking at community-level income. Communities with income in the lowest quartile had a preventable-hospitalization rate of 2,013/100,000, and the rate dropped with each successive quartile until it reached 878/100,000 for the highest-income communities, according to the report.
“High hospital admission rates for these conditions may indicate areas where changes to the healthcare delivery system could be implemented to improve patient outcomes and lower costs,” Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang wrote.
SOURCE: McDermott KW and Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
U.S. adults reach Healthy People 2020 cholesterol goal
Good news: High cholesterol is down in the United States. More good news: Low HDL cholesterol is down in the United States.
The prevalence of high total cholesterol in adults aged 20 years and older dropped from 18.3% in 1999-2000 to 10.5% in 2017-2018. And starting in 2007-2008, the prevalence of low HDL cholesterol declined from 22.2% to 16.0% in 2017-2018, the National Center for Health Statistics reported.
HDL cholesterol data before 2007 were not presented because of changes in laboratories and methods, but both trends are significant, and the decline in high total cholesterol means that the Healthy People 2020 goal of dropping prevalence to 13.5% has been met, said Margaret D. Carroll, MSPH, and Cheryl D. Fryar, MSPH, of the NCHS.
The demographic details, however, show some disparities hidden by the broader measures. The prevalence of low HDL cholesterol for women in 2015-2018 was 8.5%, but for men it was 26.6%, the NCHS investigators said.
And that Healthy People 2020 goal for total cholesterol? Age makes a difference: 7.5% of adults aged 20-39 years had high total cholesterol in 2015-2018, as did 11.4% of those aged 60 years and older, but those aged 40-59 years had a significantly higher prevalence of 15.7%, they reported.
Race/ethnicity was also a factor. Prevalence of low HDL was similar for white (16.6%) and Asian (15.8%) adults in 2015-2018, but black adults’ low HDL prevalence was significantly lower (11.9%) and Hispanics’ was significantly higher (21.9%), the researchers said.
The analysis was based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The investigators defined high total cholesterol as a level of 240 mg/dL or more, and low HDL cholesterol as less than 40 mg/dL. LDL cholesterol was not included in the analysis.
Good news: High cholesterol is down in the United States. More good news: Low HDL cholesterol is down in the United States.

The prevalence of high total cholesterol in adults aged 20 years and older dropped from 18.3% in 1999-2000 to 10.5% in 2017-2018. And starting in 2007-2008, the prevalence of low HDL cholesterol declined from 22.2% to 16.0% in 2017-2018, the National Center for Health Statistics reported.
HDL cholesterol data before 2007 were not presented because of changes in laboratories and methods, but both trends are significant, and the decline in high total cholesterol means that the Healthy People 2020 goal of dropping prevalence to 13.5% has been met, said Margaret D. Carroll, MSPH, and Cheryl D. Fryar, MSPH, of the NCHS.
The demographic details, however, show some disparities hidden by the broader measures. The prevalence of low HDL cholesterol for women in 2015-2018 was 8.5%, but for men it was 26.6%, the NCHS investigators said.
And that Healthy People 2020 goal for total cholesterol? Age makes a difference: 7.5% of adults aged 20-39 years had high total cholesterol in 2015-2018, as did 11.4% of those aged 60 years and older, but those aged 40-59 years had a significantly higher prevalence of 15.7%, they reported.
Race/ethnicity was also a factor. Prevalence of low HDL was similar for white (16.6%) and Asian (15.8%) adults in 2015-2018, but black adults’ low HDL prevalence was significantly lower (11.9%) and Hispanics’ was significantly higher (21.9%), the researchers said.
The analysis was based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The investigators defined high total cholesterol as a level of 240 mg/dL or more, and low HDL cholesterol as less than 40 mg/dL. LDL cholesterol was not included in the analysis.
Good news: High cholesterol is down in the United States. More good news: Low HDL cholesterol is down in the United States.

The prevalence of high total cholesterol in adults aged 20 years and older dropped from 18.3% in 1999-2000 to 10.5% in 2017-2018. And starting in 2007-2008, the prevalence of low HDL cholesterol declined from 22.2% to 16.0% in 2017-2018, the National Center for Health Statistics reported.
HDL cholesterol data before 2007 were not presented because of changes in laboratories and methods, but both trends are significant, and the decline in high total cholesterol means that the Healthy People 2020 goal of dropping prevalence to 13.5% has been met, said Margaret D. Carroll, MSPH, and Cheryl D. Fryar, MSPH, of the NCHS.
The demographic details, however, show some disparities hidden by the broader measures. The prevalence of low HDL cholesterol for women in 2015-2018 was 8.5%, but for men it was 26.6%, the NCHS investigators said.
And that Healthy People 2020 goal for total cholesterol? Age makes a difference: 7.5% of adults aged 20-39 years had high total cholesterol in 2015-2018, as did 11.4% of those aged 60 years and older, but those aged 40-59 years had a significantly higher prevalence of 15.7%, they reported.
Race/ethnicity was also a factor. Prevalence of low HDL was similar for white (16.6%) and Asian (15.8%) adults in 2015-2018, but black adults’ low HDL prevalence was significantly lower (11.9%) and Hispanics’ was significantly higher (21.9%), the researchers said.
The analysis was based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The investigators defined high total cholesterol as a level of 240 mg/dL or more, and low HDL cholesterol as less than 40 mg/dL. LDL cholesterol was not included in the analysis.
LAA Closure noninferior to DOACs to prevent AF-related events
Left atrial appendage closure was noninferior to use of direct oral anticoagulants for the prevention of atrial fibrillation (AFib)–related events in high-risk patients, based on data from 402 adults.
Given the limitations of vitamin K antagonists for preventing stroke in AFib, “a novel site-specific therapeutic alternative, mechanical left atrial appendage occlusion [LAAO], entered clinical practice,” but has not been compared with current safe and effective oral anticoagulants, wrote Pavel Osmancik, MD, of University Hospital Kralovske Vinohrady, Prague, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers randomized 201 moderate- or high-risk adults with nonvalvular AFib to LAAO and another 201 to direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC).
Patients in the LAAO group underwent transesophageal echocardiography to exclude left atrial thrombi and underwent implantation with Boston Scientific’s Watchman, Watchman-FLX, or Abbott’s Amulet devices. Patients in the DOAC group received rivaroxaban, apixaban, or dabigatran at the manufacturer-recommended dose.
The primary outcome was a composite of complications related to procedures or devices, thromboembolic events (including stroke), and clinically significant bleeding. After an average of 20 months follow-up, 35 patients in the LAAO group and 41 in the DOAC group met the primary outcome (11% per 100 patient-years vs. 13% per 100 patient-years).
In addition, no differences appeared between the groups for the endpoint components of all-stroke/transient ischemic attack event (subdistribution hazard ratio, 1.00), clinically significantly bleeding (sHR, 0.81), or cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75).
Nine patients experienced major complications related to LAAO, including clinically significant bleeding (sHR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.44-1.52) and cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.34-1.62). Major LAAO-related complications occurred in nine (4.5%) patients, with a short-term (up to 7 days or hospital discharge) complication rate of 2.1% and a 2.7% late complication rate. The late complications included three pericardial effusions, one of which resulted in death, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to assess the differences among the components of the composite primary endpoint. For example, “Regarding the primary endpoint, stroke reduction may be more important than bleeding reduction,” the investigators wrote.
The results were strengthened, however, by the enrollment of a high-risk AF population and is the first known randomized trial to compare percutaneous LAAO and DOACs for stroke prevention in this group. But the late complication rate of 2.7% is “suboptimal” and safety issues reinforce the need for refinement of operator technique and device technology with LAAO, they concluded.
‘Important step forward,’ with caveats
“How LAAO might stack up against DOAC therapy has remained an open question: Compared with warfarin, DOACs are easier to use and are associated with a reduction in mortality, driven by a substantially lower risk of intracranial hemorrhage and fatal bleeding,” wrote Matthew J. Price, MD, of the Scripps Clinic in La Jolla, Calif., and Jacqueline Saw, MD, of Vancouver General Hospital, in an accompanying editorial.
Previous studies of LAAO have shown a reduced risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, but procedure hazards interfered with long-term benefits, they said. The current study findings of similar rates of stroke and lower bleeding rates with LAAO, compared with DOAC, “are provocative given the clinical consensus that DOACs are safer, well tolerated, and generally better than warfarin, which was an easy target for transcatheter LAAO, given warfarin’s extensive limitations,” the editorialists wrote. Although the findings lend support to the use of LAAO, clinicians should consider several caveats such as the inclusion of patients who were “not optimal candidates for long-term OAC but were selected because they were at high risk for bleeding or because OAC treatment had already failed.”
However, “despite its imperfections, PRAGUE-17 is an important step forward and reinforces the role of transcatheter LAAO as a stroke-prevention strategy for patients with [AFib] at high risk of bleeding or medical treatment failure, even in the modern era of the DOACs,” they concluded. “Going forward, successful enrollment in ongoing and planned clinical trials while avoiding off-label procedures will be critical to define the appropriate use of transcatheter LAAO in expanded patient populations.”
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. Dr. Osmancik disclosed speaking honoraria from Bayer and Abbot. Dr. Price’s financial disclosures included honoraria, speaker bureau fees, and/or research grants from Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Chiesi USA, Daiichi Sankyo, and Medtronic. Dr. Saw disclosed receiving unrestricted research grant support several Canadian research institutes and fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and Servier, among other drug companies.
SOURCES: Osmancik P et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3122-35; Price MJ, Saw J. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3136-9.
Left atrial appendage closure was noninferior to use of direct oral anticoagulants for the prevention of atrial fibrillation (AFib)–related events in high-risk patients, based on data from 402 adults.
Given the limitations of vitamin K antagonists for preventing stroke in AFib, “a novel site-specific therapeutic alternative, mechanical left atrial appendage occlusion [LAAO], entered clinical practice,” but has not been compared with current safe and effective oral anticoagulants, wrote Pavel Osmancik, MD, of University Hospital Kralovske Vinohrady, Prague, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers randomized 201 moderate- or high-risk adults with nonvalvular AFib to LAAO and another 201 to direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC).
Patients in the LAAO group underwent transesophageal echocardiography to exclude left atrial thrombi and underwent implantation with Boston Scientific’s Watchman, Watchman-FLX, or Abbott’s Amulet devices. Patients in the DOAC group received rivaroxaban, apixaban, or dabigatran at the manufacturer-recommended dose.
The primary outcome was a composite of complications related to procedures or devices, thromboembolic events (including stroke), and clinically significant bleeding. After an average of 20 months follow-up, 35 patients in the LAAO group and 41 in the DOAC group met the primary outcome (11% per 100 patient-years vs. 13% per 100 patient-years).
In addition, no differences appeared between the groups for the endpoint components of all-stroke/transient ischemic attack event (subdistribution hazard ratio, 1.00), clinically significantly bleeding (sHR, 0.81), or cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75).
Nine patients experienced major complications related to LAAO, including clinically significant bleeding (sHR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.44-1.52) and cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.34-1.62). Major LAAO-related complications occurred in nine (4.5%) patients, with a short-term (up to 7 days or hospital discharge) complication rate of 2.1% and a 2.7% late complication rate. The late complications included three pericardial effusions, one of which resulted in death, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to assess the differences among the components of the composite primary endpoint. For example, “Regarding the primary endpoint, stroke reduction may be more important than bleeding reduction,” the investigators wrote.
The results were strengthened, however, by the enrollment of a high-risk AF population and is the first known randomized trial to compare percutaneous LAAO and DOACs for stroke prevention in this group. But the late complication rate of 2.7% is “suboptimal” and safety issues reinforce the need for refinement of operator technique and device technology with LAAO, they concluded.
‘Important step forward,’ with caveats
“How LAAO might stack up against DOAC therapy has remained an open question: Compared with warfarin, DOACs are easier to use and are associated with a reduction in mortality, driven by a substantially lower risk of intracranial hemorrhage and fatal bleeding,” wrote Matthew J. Price, MD, of the Scripps Clinic in La Jolla, Calif., and Jacqueline Saw, MD, of Vancouver General Hospital, in an accompanying editorial.
Previous studies of LAAO have shown a reduced risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, but procedure hazards interfered with long-term benefits, they said. The current study findings of similar rates of stroke and lower bleeding rates with LAAO, compared with DOAC, “are provocative given the clinical consensus that DOACs are safer, well tolerated, and generally better than warfarin, which was an easy target for transcatheter LAAO, given warfarin’s extensive limitations,” the editorialists wrote. Although the findings lend support to the use of LAAO, clinicians should consider several caveats such as the inclusion of patients who were “not optimal candidates for long-term OAC but were selected because they were at high risk for bleeding or because OAC treatment had already failed.”
However, “despite its imperfections, PRAGUE-17 is an important step forward and reinforces the role of transcatheter LAAO as a stroke-prevention strategy for patients with [AFib] at high risk of bleeding or medical treatment failure, even in the modern era of the DOACs,” they concluded. “Going forward, successful enrollment in ongoing and planned clinical trials while avoiding off-label procedures will be critical to define the appropriate use of transcatheter LAAO in expanded patient populations.”
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. Dr. Osmancik disclosed speaking honoraria from Bayer and Abbot. Dr. Price’s financial disclosures included honoraria, speaker bureau fees, and/or research grants from Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Chiesi USA, Daiichi Sankyo, and Medtronic. Dr. Saw disclosed receiving unrestricted research grant support several Canadian research institutes and fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and Servier, among other drug companies.
SOURCES: Osmancik P et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3122-35; Price MJ, Saw J. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3136-9.
Left atrial appendage closure was noninferior to use of direct oral anticoagulants for the prevention of atrial fibrillation (AFib)–related events in high-risk patients, based on data from 402 adults.
Given the limitations of vitamin K antagonists for preventing stroke in AFib, “a novel site-specific therapeutic alternative, mechanical left atrial appendage occlusion [LAAO], entered clinical practice,” but has not been compared with current safe and effective oral anticoagulants, wrote Pavel Osmancik, MD, of University Hospital Kralovske Vinohrady, Prague, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers randomized 201 moderate- or high-risk adults with nonvalvular AFib to LAAO and another 201 to direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC).
Patients in the LAAO group underwent transesophageal echocardiography to exclude left atrial thrombi and underwent implantation with Boston Scientific’s Watchman, Watchman-FLX, or Abbott’s Amulet devices. Patients in the DOAC group received rivaroxaban, apixaban, or dabigatran at the manufacturer-recommended dose.
The primary outcome was a composite of complications related to procedures or devices, thromboembolic events (including stroke), and clinically significant bleeding. After an average of 20 months follow-up, 35 patients in the LAAO group and 41 in the DOAC group met the primary outcome (11% per 100 patient-years vs. 13% per 100 patient-years).
In addition, no differences appeared between the groups for the endpoint components of all-stroke/transient ischemic attack event (subdistribution hazard ratio, 1.00), clinically significantly bleeding (sHR, 0.81), or cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75).
Nine patients experienced major complications related to LAAO, including clinically significant bleeding (sHR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.44-1.52) and cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.34-1.62). Major LAAO-related complications occurred in nine (4.5%) patients, with a short-term (up to 7 days or hospital discharge) complication rate of 2.1% and a 2.7% late complication rate. The late complications included three pericardial effusions, one of which resulted in death, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to assess the differences among the components of the composite primary endpoint. For example, “Regarding the primary endpoint, stroke reduction may be more important than bleeding reduction,” the investigators wrote.
The results were strengthened, however, by the enrollment of a high-risk AF population and is the first known randomized trial to compare percutaneous LAAO and DOACs for stroke prevention in this group. But the late complication rate of 2.7% is “suboptimal” and safety issues reinforce the need for refinement of operator technique and device technology with LAAO, they concluded.
‘Important step forward,’ with caveats
“How LAAO might stack up against DOAC therapy has remained an open question: Compared with warfarin, DOACs are easier to use and are associated with a reduction in mortality, driven by a substantially lower risk of intracranial hemorrhage and fatal bleeding,” wrote Matthew J. Price, MD, of the Scripps Clinic in La Jolla, Calif., and Jacqueline Saw, MD, of Vancouver General Hospital, in an accompanying editorial.
Previous studies of LAAO have shown a reduced risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, but procedure hazards interfered with long-term benefits, they said. The current study findings of similar rates of stroke and lower bleeding rates with LAAO, compared with DOAC, “are provocative given the clinical consensus that DOACs are safer, well tolerated, and generally better than warfarin, which was an easy target for transcatheter LAAO, given warfarin’s extensive limitations,” the editorialists wrote. Although the findings lend support to the use of LAAO, clinicians should consider several caveats such as the inclusion of patients who were “not optimal candidates for long-term OAC but were selected because they were at high risk for bleeding or because OAC treatment had already failed.”
However, “despite its imperfections, PRAGUE-17 is an important step forward and reinforces the role of transcatheter LAAO as a stroke-prevention strategy for patients with [AFib] at high risk of bleeding or medical treatment failure, even in the modern era of the DOACs,” they concluded. “Going forward, successful enrollment in ongoing and planned clinical trials while avoiding off-label procedures will be critical to define the appropriate use of transcatheter LAAO in expanded patient populations.”
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. Dr. Osmancik disclosed speaking honoraria from Bayer and Abbot. Dr. Price’s financial disclosures included honoraria, speaker bureau fees, and/or research grants from Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Chiesi USA, Daiichi Sankyo, and Medtronic. Dr. Saw disclosed receiving unrestricted research grant support several Canadian research institutes and fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and Servier, among other drug companies.
SOURCES: Osmancik P et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3122-35; Price MJ, Saw J. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3136-9.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: A composite primary outcome including stroke and death was not significantly different in high-risk patients randomized to left atrial appendage occlusion or direct oral anticoagulants at roughly 20 months’ follow-up (11% vs. 13%, respectively).
Study details: The data come from the PRAGUE-17 study, a randomized trial of 402 adults at increased risk for atrial fibrillation.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. Dr. Osmancik disclosed speaking honoraria from Bayer and Abbot.
Sources: Osmancik P et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3122-35; Price MJ, Saw J. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3136-9.
Hashtag medicine: #ShareTheMicNowMed highlights Black female physicians on social media
Prominent female physicians are handing over their social media platforms today to black female physicians as part of a campaign called #ShareTheMicNowMed.
The social media event, which will play out on both Twitter and Instagram, is an offshoot of #ShareTheMicNow, held earlier this month. For that event, more than 90 women, including A-list celebrities like Ellen DeGeneres, Julia Roberts, and Senator Elizabeth Warren, swapped accounts with women of color, such as “I’m Still Here” author Austin Channing Brown, Olympic fencer Ibtihaj Muhammad, and #MeToo founder Tarana Burke.
The physician event will feature 10 teams of two, with one physician handing over her account to her black female counterpart for the day. The takeover will allow the black physician to share her thoughts about the successes and challenges she faces as a woman of color in medicine.
“It was such an honor to be contacted by Arghavan Salles, MD, PhD, to participate in an event that has a goal of connecting like-minded women from various backgrounds to share a diverse perspective with a different audience,” Minnesota family medicine physician Jay-Sheree Allen, MD, told Medscape Medical News. “This event is not only incredibly important but timely.”
Only about 5% of all active physicians in 2018 identified as Black or African American, according to a report by the Association of American Medical Colleges. And of those, just over a third are female, the report found.
“I think that as we hear those small numbers we often celebrate the success of those people without looking back and understanding where all of the barriers are that are limiting talented black women from entering medicine at every stage,” another campaign participant, Chicago pediatrician Rebekah Fenton, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
Allen says that, amid continuing worldwide protests over racial injustice, prompted by the death of George Floyd while in Minneapolis police custody last month, the online event is very timely and an important way to advocate for black lives and engage in a productive conversation.
“I believe that with the #ShareTheMicNowMed movement we will start to show people how they can become allies. I always say that a candle loses nothing by lighting another candle, and sharing that stage is one of the many ways you can support the Black Lives Matters movement by amplifying black voices,” she said.
Allen went on to add that women in medicine have many of the same experiences as any other doctor but do face some unique challenges. This is especially true for female physicians of color, she noted.
To join the conversation follow the hashtag #ShareTheMicNowMed all day on Monday, June 22, 2020.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Prominent female physicians are handing over their social media platforms today to black female physicians as part of a campaign called #ShareTheMicNowMed.
The social media event, which will play out on both Twitter and Instagram, is an offshoot of #ShareTheMicNow, held earlier this month. For that event, more than 90 women, including A-list celebrities like Ellen DeGeneres, Julia Roberts, and Senator Elizabeth Warren, swapped accounts with women of color, such as “I’m Still Here” author Austin Channing Brown, Olympic fencer Ibtihaj Muhammad, and #MeToo founder Tarana Burke.
The physician event will feature 10 teams of two, with one physician handing over her account to her black female counterpart for the day. The takeover will allow the black physician to share her thoughts about the successes and challenges she faces as a woman of color in medicine.
“It was such an honor to be contacted by Arghavan Salles, MD, PhD, to participate in an event that has a goal of connecting like-minded women from various backgrounds to share a diverse perspective with a different audience,” Minnesota family medicine physician Jay-Sheree Allen, MD, told Medscape Medical News. “This event is not only incredibly important but timely.”
Only about 5% of all active physicians in 2018 identified as Black or African American, according to a report by the Association of American Medical Colleges. And of those, just over a third are female, the report found.
“I think that as we hear those small numbers we often celebrate the success of those people without looking back and understanding where all of the barriers are that are limiting talented black women from entering medicine at every stage,” another campaign participant, Chicago pediatrician Rebekah Fenton, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
Allen says that, amid continuing worldwide protests over racial injustice, prompted by the death of George Floyd while in Minneapolis police custody last month, the online event is very timely and an important way to advocate for black lives and engage in a productive conversation.
“I believe that with the #ShareTheMicNowMed movement we will start to show people how they can become allies. I always say that a candle loses nothing by lighting another candle, and sharing that stage is one of the many ways you can support the Black Lives Matters movement by amplifying black voices,” she said.
Allen went on to add that women in medicine have many of the same experiences as any other doctor but do face some unique challenges. This is especially true for female physicians of color, she noted.
To join the conversation follow the hashtag #ShareTheMicNowMed all day on Monday, June 22, 2020.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Prominent female physicians are handing over their social media platforms today to black female physicians as part of a campaign called #ShareTheMicNowMed.
The social media event, which will play out on both Twitter and Instagram, is an offshoot of #ShareTheMicNow, held earlier this month. For that event, more than 90 women, including A-list celebrities like Ellen DeGeneres, Julia Roberts, and Senator Elizabeth Warren, swapped accounts with women of color, such as “I’m Still Here” author Austin Channing Brown, Olympic fencer Ibtihaj Muhammad, and #MeToo founder Tarana Burke.
The physician event will feature 10 teams of two, with one physician handing over her account to her black female counterpart for the day. The takeover will allow the black physician to share her thoughts about the successes and challenges she faces as a woman of color in medicine.
“It was such an honor to be contacted by Arghavan Salles, MD, PhD, to participate in an event that has a goal of connecting like-minded women from various backgrounds to share a diverse perspective with a different audience,” Minnesota family medicine physician Jay-Sheree Allen, MD, told Medscape Medical News. “This event is not only incredibly important but timely.”
Only about 5% of all active physicians in 2018 identified as Black or African American, according to a report by the Association of American Medical Colleges. And of those, just over a third are female, the report found.
“I think that as we hear those small numbers we often celebrate the success of those people without looking back and understanding where all of the barriers are that are limiting talented black women from entering medicine at every stage,” another campaign participant, Chicago pediatrician Rebekah Fenton, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
Allen says that, amid continuing worldwide protests over racial injustice, prompted by the death of George Floyd while in Minneapolis police custody last month, the online event is very timely and an important way to advocate for black lives and engage in a productive conversation.
“I believe that with the #ShareTheMicNowMed movement we will start to show people how they can become allies. I always say that a candle loses nothing by lighting another candle, and sharing that stage is one of the many ways you can support the Black Lives Matters movement by amplifying black voices,” she said.
Allen went on to add that women in medicine have many of the same experiences as any other doctor but do face some unique challenges. This is especially true for female physicians of color, she noted.
To join the conversation follow the hashtag #ShareTheMicNowMed all day on Monday, June 22, 2020.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Daily Recap: Headache as COVID evolution predictor; psoriasis drug treats canker sores
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Headache may predict clinical evolution of COVID-19
Headache may be a key symptom of COVID-19 that predicts the disease’s clinical evolution, new research suggests. An observational study of more than 100 patients showed that headache onset could occur during the presymptomatic or symptomatic phase of COVID-19.
Headache itself was associated with a shorter symptomatic period, while headache and anosmia were associated with a shorter hospitalization period.
It seems that those patients who start early on, during the asymptomatic or early symptomatic period of COVID-19, with headache have a more localized inflammatory response that may reflect the ability of the body to better control and respond to the infection,” lead investigator Patricia Pozo-Rosich, MD, PhD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Read more.
More tops news from the AHS meeting is available on our website.
Pilot study shows apremilast effective for severe recurrent canker sores
Apremilast was highly effective in treating patients with severe recurrent aphthous stomatitis, with rapid response and an excellent safety profile, results from a small pilot study showed.
Apremilast is approved by the FDA for psoriasis and was shown in a recent phase 2 trial to be effective for Behçet’s disease aphthosis.
Dr. Alison Bruce and colleagues found that, within 4 weeks of therapy, complete clearance of RAS lesions occurred in all patients except one in whom ulcers were reported to be less severe. Remission in all patients was sustained during 16 weeks of treatment, Dr. Bruce noted at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. Read more.
For more top news from the AAD virtual conference, visit our website.
Where does dexamethasone fit in with diabetic ketoacidosis in COVID-19?
A new article in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM) addresses unique concerns and considerations regarding diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in the setting of COVID-19.
“Hospitals and clinicians need to be able to quickly identify and manage DKA in COVID patients to save lives. This involves determining the options for management, including when less intensive subcutaneous insulin is indicated, and understanding how to guide patients on avoiding this serious complication,” corresponding author Marie E. McDonnell, MD, said in an Endocrine Society statement.
The new article briefly touches on the fact that upward adjustments to intensive intravenous insulin therapy for DKA may be necessary in patients with COVID-19 who are receiving concomitant corticosteroids or vasopressors. But it was written prior to the June 16 announcement of the “RECOVERY” trial results with dexamethasone. The UK National Health Service immediately approved the drug’s use in the COVID-19 setting, despite the fact that there has been no published article on the findings yet.
“The peer review will be critical. It looks as if it only benefits people who need respiratory support, but I want to understand that in much more detail,” said Dr. McDonnell. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Headache may predict clinical evolution of COVID-19
Headache may be a key symptom of COVID-19 that predicts the disease’s clinical evolution, new research suggests. An observational study of more than 100 patients showed that headache onset could occur during the presymptomatic or symptomatic phase of COVID-19.
Headache itself was associated with a shorter symptomatic period, while headache and anosmia were associated with a shorter hospitalization period.
It seems that those patients who start early on, during the asymptomatic or early symptomatic period of COVID-19, with headache have a more localized inflammatory response that may reflect the ability of the body to better control and respond to the infection,” lead investigator Patricia Pozo-Rosich, MD, PhD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Read more.
More tops news from the AHS meeting is available on our website.
Pilot study shows apremilast effective for severe recurrent canker sores
Apremilast was highly effective in treating patients with severe recurrent aphthous stomatitis, with rapid response and an excellent safety profile, results from a small pilot study showed.
Apremilast is approved by the FDA for psoriasis and was shown in a recent phase 2 trial to be effective for Behçet’s disease aphthosis.
Dr. Alison Bruce and colleagues found that, within 4 weeks of therapy, complete clearance of RAS lesions occurred in all patients except one in whom ulcers were reported to be less severe. Remission in all patients was sustained during 16 weeks of treatment, Dr. Bruce noted at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. Read more.
For more top news from the AAD virtual conference, visit our website.
Where does dexamethasone fit in with diabetic ketoacidosis in COVID-19?
A new article in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM) addresses unique concerns and considerations regarding diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in the setting of COVID-19.
“Hospitals and clinicians need to be able to quickly identify and manage DKA in COVID patients to save lives. This involves determining the options for management, including when less intensive subcutaneous insulin is indicated, and understanding how to guide patients on avoiding this serious complication,” corresponding author Marie E. McDonnell, MD, said in an Endocrine Society statement.
The new article briefly touches on the fact that upward adjustments to intensive intravenous insulin therapy for DKA may be necessary in patients with COVID-19 who are receiving concomitant corticosteroids or vasopressors. But it was written prior to the June 16 announcement of the “RECOVERY” trial results with dexamethasone. The UK National Health Service immediately approved the drug’s use in the COVID-19 setting, despite the fact that there has been no published article on the findings yet.
“The peer review will be critical. It looks as if it only benefits people who need respiratory support, but I want to understand that in much more detail,” said Dr. McDonnell. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Headache may predict clinical evolution of COVID-19
Headache may be a key symptom of COVID-19 that predicts the disease’s clinical evolution, new research suggests. An observational study of more than 100 patients showed that headache onset could occur during the presymptomatic or symptomatic phase of COVID-19.
Headache itself was associated with a shorter symptomatic period, while headache and anosmia were associated with a shorter hospitalization period.
It seems that those patients who start early on, during the asymptomatic or early symptomatic period of COVID-19, with headache have a more localized inflammatory response that may reflect the ability of the body to better control and respond to the infection,” lead investigator Patricia Pozo-Rosich, MD, PhD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Read more.
More tops news from the AHS meeting is available on our website.
Pilot study shows apremilast effective for severe recurrent canker sores
Apremilast was highly effective in treating patients with severe recurrent aphthous stomatitis, with rapid response and an excellent safety profile, results from a small pilot study showed.
Apremilast is approved by the FDA for psoriasis and was shown in a recent phase 2 trial to be effective for Behçet’s disease aphthosis.
Dr. Alison Bruce and colleagues found that, within 4 weeks of therapy, complete clearance of RAS lesions occurred in all patients except one in whom ulcers were reported to be less severe. Remission in all patients was sustained during 16 weeks of treatment, Dr. Bruce noted at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. Read more.
For more top news from the AAD virtual conference, visit our website.
Where does dexamethasone fit in with diabetic ketoacidosis in COVID-19?
A new article in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM) addresses unique concerns and considerations regarding diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in the setting of COVID-19.
“Hospitals and clinicians need to be able to quickly identify and manage DKA in COVID patients to save lives. This involves determining the options for management, including when less intensive subcutaneous insulin is indicated, and understanding how to guide patients on avoiding this serious complication,” corresponding author Marie E. McDonnell, MD, said in an Endocrine Society statement.
The new article briefly touches on the fact that upward adjustments to intensive intravenous insulin therapy for DKA may be necessary in patients with COVID-19 who are receiving concomitant corticosteroids or vasopressors. But it was written prior to the June 16 announcement of the “RECOVERY” trial results with dexamethasone. The UK National Health Service immediately approved the drug’s use in the COVID-19 setting, despite the fact that there has been no published article on the findings yet.
“The peer review will be critical. It looks as if it only benefits people who need respiratory support, but I want to understand that in much more detail,” said Dr. McDonnell. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
‘Collateral damage’: COVID-19 threatens patients with COPD
according to a commentary published in CHEST (2020 May 28. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.05.549) by a group of physicians who study COPD.
Not only is COPD among the most prevalent underlying diseases among hospitalized COVID-19 patients (Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Jun 8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.05.041), but other unanticipated factors of treatment put these patients at extra risk. Valerie Press, MD, assistant professor of medicine and pediatrics at the University of Chicago, and colleagues aimed to alert physicians to be aware of potential negative effects, or collateral damage, that the pandemic can have on their patients with COPD, even those without a COVID-19 diagnosis.
These concerns include that patients may delay presenting to the ED with acute exacerbations of COPD and once they present they may be at later stages of the exacerbation. Further, evaluation for COVID-19 as a possible trigger of acute exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD) is essential; however, implementing proven AECOPD therapies remains challenging. For instance, routine therapy with corticosteroids for AECOPD may be delayed due to diagnostic uncertainty and hesitation to treat COVID-19 with steroids while COVID-19 testing is pending,” Dr. Press and her colleagues stated.
Shortages and scarcity of medications such as albuterol inhalers to treat COPD have been reported. In addition, patients with COPD are currently less likely to access their health care providers because of fear of COVID-19 infection. This barrier to care and the current higher threshold for presenting to the hospital may to lead to more cases of AECOPD and worsening health in these patients, according to the authors.
Dr. Press said in an interview: “Access to medications delivered through inhalers is challenging even without the pandemic due to high cost of medications. Generic medications are key to improving access for patients with chronic lung disease, so once the generic albuterol becomes available, this should help with access. In the meantime, some companies help provide medications at reduced cost, but usually only on a short time basis. In addition, some pharmacies have lower-cost albuterol inhalers, but these are often not supplied with a full month of dosing.”
In addition to all these concerns is the economic toll this pandemic is taking on patients. The association between COPD and socioeconomic status has been studied in depth (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019; 199[8]:961-69) and would indicate that low-income patients with COPD would face an increased burden during an economic downturn. The authors noted, “Historic rapid job loss and unemployment in the U.S., coupled with a health system of employment-integrated health insurance coverage, makes it more likely that people with COPD will not be able to afford their medication.”
Dr. Press stressed that the COVID pandemic has highlighted critically important disparities in access to health care and disparities in health. “Many of the recommendations regarding stay-at-home and other safety mechanisms to prevent contracting and spreading COVID-19 have not been feasible for all sub-populations in the United States. Those that were essential workers did not have the ability to stay home. Further, those that rely on public transportation had less opportunities to social distance. Finally, while telemedicine opportunities have advanced for clinical care, not all patients have equal access to these capabilities and health disparities could widen in this regard as well. Clinicians have a responsibility to identify social determinants of health that increase risks to our patients’ health and limit their safety.”*
The authors offer some concrete suggestions of how physicians can address some of these concerns, including the following:
- Be alert to potential barriers to accessing medication and be aware of generic albuterol inhaler recently approved by the FDA in response to COVID-19–related shortages.
- Use telemedicine to monitor patients and improvement of home self-management. Clinicians should help patients “seek care with worsening symptoms and have clear management guidelines regarding seeking phone/video visits; implementing therapy with corticosteroids, antibiotics, or inhalers and nebulizers; COVID-19 testing recommendations; and thresholds for seeking emergent, urgent, or outpatient care in person,” Dr. Press added, “Building on the work of nurse advice lines and case management and other support services for high-risk patients with COPD may continue via telehealth and telephone visits.”
- Ensure that untried therapy for COVID-19 “does not displace proven and necessary treatments for patients with COPD, hence placing them at increased risk for poor outcomes.”
Dr. Press is also concerned about the post–COVID-19 period for patients with COPD. “It is too early to know if there are specific after effects of the COVID infection on patients with COPD, but given the damage the virus does to even healthy lungs, there is reason to have concern that COVID could cause worsening damage to the lungs of individuals with COPD.”
She noted, “Post-ICU [PICU] syndrome has been recognized in patients with ARDS generally, and patients who recover from critical illness may have long-lasting (and permanent) effects on strength, cognition, disability, and pulmonary function. Whether the PICU syndrome in patients with ARDS due to COVID-19 specifically is different from the PICU syndrome due to other causes remains unknown. But clinicians whose patients with COPD survive COVID-19 may expect long-lasting effects and slow recovery in cases where COVID-19 led to severe ARDS and a prolonged ICU stay. Assessment of overall patient recovery and functional capacity (beyond lung function and dyspnea symptoms) including deconditioning, anxiety, PTSD, weakness, and malnutrition will need to be addressed. Additionally, clinicians may help patients and their families understand the expected recovery and help facilitate family conversations about residual effects of COVID-19.”
The authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Press V et al. Chest. 2020 May 28. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.05.549.
CORRECTION: *This story was updated with further comments and clarifications from Dr. Press. 6/23/2020
according to a commentary published in CHEST (2020 May 28. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.05.549) by a group of physicians who study COPD.
Not only is COPD among the most prevalent underlying diseases among hospitalized COVID-19 patients (Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Jun 8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.05.041), but other unanticipated factors of treatment put these patients at extra risk. Valerie Press, MD, assistant professor of medicine and pediatrics at the University of Chicago, and colleagues aimed to alert physicians to be aware of potential negative effects, or collateral damage, that the pandemic can have on their patients with COPD, even those without a COVID-19 diagnosis.
These concerns include that patients may delay presenting to the ED with acute exacerbations of COPD and once they present they may be at later stages of the exacerbation. Further, evaluation for COVID-19 as a possible trigger of acute exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD) is essential; however, implementing proven AECOPD therapies remains challenging. For instance, routine therapy with corticosteroids for AECOPD may be delayed due to diagnostic uncertainty and hesitation to treat COVID-19 with steroids while COVID-19 testing is pending,” Dr. Press and her colleagues stated.
Shortages and scarcity of medications such as albuterol inhalers to treat COPD have been reported. In addition, patients with COPD are currently less likely to access their health care providers because of fear of COVID-19 infection. This barrier to care and the current higher threshold for presenting to the hospital may to lead to more cases of AECOPD and worsening health in these patients, according to the authors.
Dr. Press said in an interview: “Access to medications delivered through inhalers is challenging even without the pandemic due to high cost of medications. Generic medications are key to improving access for patients with chronic lung disease, so once the generic albuterol becomes available, this should help with access. In the meantime, some companies help provide medications at reduced cost, but usually only on a short time basis. In addition, some pharmacies have lower-cost albuterol inhalers, but these are often not supplied with a full month of dosing.”
In addition to all these concerns is the economic toll this pandemic is taking on patients. The association between COPD and socioeconomic status has been studied in depth (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019; 199[8]:961-69) and would indicate that low-income patients with COPD would face an increased burden during an economic downturn. The authors noted, “Historic rapid job loss and unemployment in the U.S., coupled with a health system of employment-integrated health insurance coverage, makes it more likely that people with COPD will not be able to afford their medication.”
Dr. Press stressed that the COVID pandemic has highlighted critically important disparities in access to health care and disparities in health. “Many of the recommendations regarding stay-at-home and other safety mechanisms to prevent contracting and spreading COVID-19 have not been feasible for all sub-populations in the United States. Those that were essential workers did not have the ability to stay home. Further, those that rely on public transportation had less opportunities to social distance. Finally, while telemedicine opportunities have advanced for clinical care, not all patients have equal access to these capabilities and health disparities could widen in this regard as well. Clinicians have a responsibility to identify social determinants of health that increase risks to our patients’ health and limit their safety.”*
The authors offer some concrete suggestions of how physicians can address some of these concerns, including the following:
- Be alert to potential barriers to accessing medication and be aware of generic albuterol inhaler recently approved by the FDA in response to COVID-19–related shortages.
- Use telemedicine to monitor patients and improvement of home self-management. Clinicians should help patients “seek care with worsening symptoms and have clear management guidelines regarding seeking phone/video visits; implementing therapy with corticosteroids, antibiotics, or inhalers and nebulizers; COVID-19 testing recommendations; and thresholds for seeking emergent, urgent, or outpatient care in person,” Dr. Press added, “Building on the work of nurse advice lines and case management and other support services for high-risk patients with COPD may continue via telehealth and telephone visits.”
- Ensure that untried therapy for COVID-19 “does not displace proven and necessary treatments for patients with COPD, hence placing them at increased risk for poor outcomes.”
Dr. Press is also concerned about the post–COVID-19 period for patients with COPD. “It is too early to know if there are specific after effects of the COVID infection on patients with COPD, but given the damage the virus does to even healthy lungs, there is reason to have concern that COVID could cause worsening damage to the lungs of individuals with COPD.”
She noted, “Post-ICU [PICU] syndrome has been recognized in patients with ARDS generally, and patients who recover from critical illness may have long-lasting (and permanent) effects on strength, cognition, disability, and pulmonary function. Whether the PICU syndrome in patients with ARDS due to COVID-19 specifically is different from the PICU syndrome due to other causes remains unknown. But clinicians whose patients with COPD survive COVID-19 may expect long-lasting effects and slow recovery in cases where COVID-19 led to severe ARDS and a prolonged ICU stay. Assessment of overall patient recovery and functional capacity (beyond lung function and dyspnea symptoms) including deconditioning, anxiety, PTSD, weakness, and malnutrition will need to be addressed. Additionally, clinicians may help patients and their families understand the expected recovery and help facilitate family conversations about residual effects of COVID-19.”
The authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Press V et al. Chest. 2020 May 28. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.05.549.
CORRECTION: *This story was updated with further comments and clarifications from Dr. Press. 6/23/2020
according to a commentary published in CHEST (2020 May 28. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.05.549) by a group of physicians who study COPD.
Not only is COPD among the most prevalent underlying diseases among hospitalized COVID-19 patients (Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Jun 8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.05.041), but other unanticipated factors of treatment put these patients at extra risk. Valerie Press, MD, assistant professor of medicine and pediatrics at the University of Chicago, and colleagues aimed to alert physicians to be aware of potential negative effects, or collateral damage, that the pandemic can have on their patients with COPD, even those without a COVID-19 diagnosis.
These concerns include that patients may delay presenting to the ED with acute exacerbations of COPD and once they present they may be at later stages of the exacerbation. Further, evaluation for COVID-19 as a possible trigger of acute exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD) is essential; however, implementing proven AECOPD therapies remains challenging. For instance, routine therapy with corticosteroids for AECOPD may be delayed due to diagnostic uncertainty and hesitation to treat COVID-19 with steroids while COVID-19 testing is pending,” Dr. Press and her colleagues stated.
Shortages and scarcity of medications such as albuterol inhalers to treat COPD have been reported. In addition, patients with COPD are currently less likely to access their health care providers because of fear of COVID-19 infection. This barrier to care and the current higher threshold for presenting to the hospital may to lead to more cases of AECOPD and worsening health in these patients, according to the authors.
Dr. Press said in an interview: “Access to medications delivered through inhalers is challenging even without the pandemic due to high cost of medications. Generic medications are key to improving access for patients with chronic lung disease, so once the generic albuterol becomes available, this should help with access. In the meantime, some companies help provide medications at reduced cost, but usually only on a short time basis. In addition, some pharmacies have lower-cost albuterol inhalers, but these are often not supplied with a full month of dosing.”
In addition to all these concerns is the economic toll this pandemic is taking on patients. The association between COPD and socioeconomic status has been studied in depth (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019; 199[8]:961-69) and would indicate that low-income patients with COPD would face an increased burden during an economic downturn. The authors noted, “Historic rapid job loss and unemployment in the U.S., coupled with a health system of employment-integrated health insurance coverage, makes it more likely that people with COPD will not be able to afford their medication.”
Dr. Press stressed that the COVID pandemic has highlighted critically important disparities in access to health care and disparities in health. “Many of the recommendations regarding stay-at-home and other safety mechanisms to prevent contracting and spreading COVID-19 have not been feasible for all sub-populations in the United States. Those that were essential workers did not have the ability to stay home. Further, those that rely on public transportation had less opportunities to social distance. Finally, while telemedicine opportunities have advanced for clinical care, not all patients have equal access to these capabilities and health disparities could widen in this regard as well. Clinicians have a responsibility to identify social determinants of health that increase risks to our patients’ health and limit their safety.”*
The authors offer some concrete suggestions of how physicians can address some of these concerns, including the following:
- Be alert to potential barriers to accessing medication and be aware of generic albuterol inhaler recently approved by the FDA in response to COVID-19–related shortages.
- Use telemedicine to monitor patients and improvement of home self-management. Clinicians should help patients “seek care with worsening symptoms and have clear management guidelines regarding seeking phone/video visits; implementing therapy with corticosteroids, antibiotics, or inhalers and nebulizers; COVID-19 testing recommendations; and thresholds for seeking emergent, urgent, or outpatient care in person,” Dr. Press added, “Building on the work of nurse advice lines and case management and other support services for high-risk patients with COPD may continue via telehealth and telephone visits.”
- Ensure that untried therapy for COVID-19 “does not displace proven and necessary treatments for patients with COPD, hence placing them at increased risk for poor outcomes.”
Dr. Press is also concerned about the post–COVID-19 period for patients with COPD. “It is too early to know if there are specific after effects of the COVID infection on patients with COPD, but given the damage the virus does to even healthy lungs, there is reason to have concern that COVID could cause worsening damage to the lungs of individuals with COPD.”
She noted, “Post-ICU [PICU] syndrome has been recognized in patients with ARDS generally, and patients who recover from critical illness may have long-lasting (and permanent) effects on strength, cognition, disability, and pulmonary function. Whether the PICU syndrome in patients with ARDS due to COVID-19 specifically is different from the PICU syndrome due to other causes remains unknown. But clinicians whose patients with COPD survive COVID-19 may expect long-lasting effects and slow recovery in cases where COVID-19 led to severe ARDS and a prolonged ICU stay. Assessment of overall patient recovery and functional capacity (beyond lung function and dyspnea symptoms) including deconditioning, anxiety, PTSD, weakness, and malnutrition will need to be addressed. Additionally, clinicians may help patients and their families understand the expected recovery and help facilitate family conversations about residual effects of COVID-19.”
The authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Press V et al. Chest. 2020 May 28. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.05.549.
CORRECTION: *This story was updated with further comments and clarifications from Dr. Press. 6/23/2020
FROM CHEST











