User login
Cutis is a peer-reviewed clinical journal for the dermatologist, allergist, and general practitioner published monthly since 1965. Concise clinical articles present the practical side of dermatology, helping physicians to improve patient care. Cutis is referenced in Index Medicus/MEDLINE and is written and edited by industry leaders.
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')
A peer-reviewed, indexed journal for dermatologists with original research, image quizzes, cases and reviews, and columns.
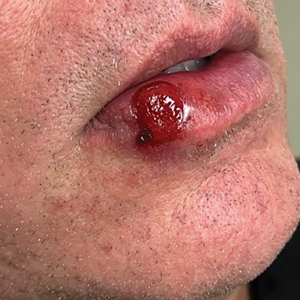
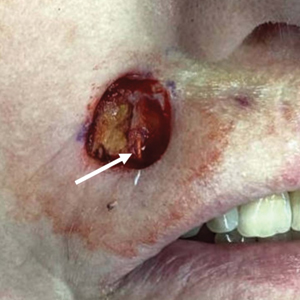
Nonhealing Ulcer on the Lower Lip
Nonhealing Ulcer on the Lower Lip
THE DIAGNOSIS: Syphilis
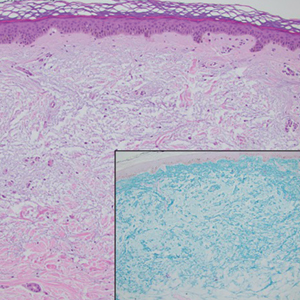
The differential diagnosis of oral lesions can be complex; in our patient, we considered conditions such as pyogenic granuloma, herpes simplex virus, and syphilis, despite the presence of pain. Immunohistochemical staining for spirochete antigens was positive, and serologic confirmation through a positive rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test confirmed the diagnosis of primary syphilis. The patient was promptly referred back to the primary care physician for treatment with intramuscular penicillin, leading to resolution of the lesion. At 3 months’ follow-up in our clinic, the lesion was fully resolved.
A primary syphilitic chancre is the initial lesion caused by Treponema pallidum, typically manifesting as a painless ulcer at the infection site, usually in the genital area; however, chancres also may manifest in other locations (eg, the anus or oral cavity) due to direct contact with infectious lesions on another individual. Our case represents an atypical presentation of an oral syphilitic chancre.
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection with various clinical manifestations. It is crucial to consider syphilis in the differential diagnosis of ulcerative lesions even when pain is present, especially in high-risk individuals such as those who engage in unprotected sex.1,2 Oral syphilitic chancres have been documented in the medical literature for more than a century, underscoring the importance of maintaining a high index of suspicion for diagnosis and a low threshold for obtaining an RPR test to facilitate early detection and treatment.2,3 Notably, the prevalence of syphilis is higher in men who have sex with men, particularly among those who engage in unprotected oral and anal sex. Increased screening and early treatment are essential to control the spread of disease within all populations. Doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (doxyPEP) is used as a preventive measure for syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea.4 This regimen consists of 200 mg of doxycycline taken within 24 hours but no later than 72 hours after unprotected anal, vaginal, or oral sex.
Our case highlights the importance of considering the differential diagnosis of oral ulcers, particularly in high-risk populations such as men who have sex with men. Prompt diagnosis, effective treatment, and preventive strategies such as doxyPEP are essential for controlling syphilis. Comprehensive patient education and regular follow-up appointments are critical components of successful management.
The United States has experienced a considerable rise in primary and congenital syphilis cases, with an 80% increase between 2018 and 2022.6 Serologic testing is the primary method for diagnosing, staging, and managing syphilis. Sexually active patients with suspected syphilis or unexplained symptoms should undergo testing. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent systemic complications, including ocular involvement and permanent blindness.
Syphilis is transmitted through direct contact with a syphilitic ulcer or saliva or blood from an infected individual. Oral syphilitic ulcers can develop on the lips, tongue, oral mucosa, and tonsils. Chancres can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters, with an incubation period of 10 to 90 days (average, 21 days). The chancre lasts 3 to 6 weeks and heals spontaneously. Without treatment, primary syphilis can progress to secondary syphilis, characterized by a papulosquamous eruption and mucosal involvement, and potentially tertiary syphilis, which can affect the central nervous system, heart, bones, and skin.7
Immunocompromised patients, especially those diagnosed with HIV, face increased risks including altered clinical presentations (eg, multiple or deep chancres), delayed healing, overlapping stages of disease, and increased severity of organ involvement. All sexually active individuals should be screened for syphilis every 3 to 6 months, particularly those with unexplained oral ulcers.
Serologic testing is fundamental for syphilis diagnosis and management. Nontreponemal tests such as RPR and treponemal tests such as the fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test provide comprehensive diagnostic information. Early diagnosis and empiric treatment are crucial in suspected cases. Ocular screening is recommended for suspected or confirmed syphilis cases.7
Management of syphilis includes treating all sexual partners and providing thorough patient education on the disease. Monitoring for the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction—an acute febrile reaction following penicillin therapy—is important, especially in pregnant patients.5 Serologic evaluation at 6 and 12 months posttreatment is recommended, with more frequent evaluations if follow-up is uncertain, particularly for those with inconsistent access to health care or in whom reinfection is suspected. Guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advocate for intramuscular penicillin G benzathine as the preferred treatment, with specific dosing for adults and children.7 Due to the ongoing bicillin shortage, alternatives such as extencilline have temporarily been allowed for use in the United States.8
The rising incidence of syphilis in the United States underscores the critical need for enhanced public health initiatives focusing on education, screening, and early intervention. Comprehensive sexual education that includes information about syphilis and other sexually transmitted infections, proper use of prophylactic measures such as condoms, and the benefits of doxyPEP can considerably reduce transmission rates. Health care providers should routinely discuss these preventive measures with their patients, especially those in high-risk groups.
Our case highlights the importance of considering syphilis in the differential diagnosis of oral ulcers, particularly in high-risk populations. Timely diagnosis, effective treatment, and preventive measures such as doxyPEP are essential for managing and controlling syphilis. The rising incidence of syphilis in the United States warrants increased screening, patient education, and public health interventions to address this notable health challenge. The syphilis crisis calls for coordinated efforts from health care providers, public health officials, and community leaders to curb the spread of this infection and protect public health.
- Mayer KH, Traeger M, Marcus JL. Doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis and sexually transmitted infections. JAMA. 2023;330:1381-1382. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.16416
- Cossman JP, Fournier JB. Frequency of syphilis diagnoses by dermatologists. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:718-719. doi:10.1001 /jamadermatol.2017.0460
- Porterfield C, Brodell D, Dolohanty L, et al. Primary syphilis presenting as a chronic lip ulcer. Cureus. 2020;12:E7086. doi:10.7759 /cureus.7086
- Schamberg JF. An epidemic of chancres of the lip from kissing. JAMA. 1911;LVII:783-784. doi:10.1001/jama.1911.04260090005002
- Farmer TW. Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction in early syphilis. JAMA. 1948;138:480–485. doi:10.1001/jama.1948.02900070012003
- Winney A. Why is syphilis spiking in the U.S.? Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Published March 13, 2024. Accessed April 30, 2025. https://publichealth.jhu.edu/why-is-syphilis-spiking-in-the-us
- Koundanya VV, Tripathy K. Syphilis ocular manifestations. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Updated August 25, 2023. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558957/
- CDC. FDA announcement on availability of extencilline. National Center for HIV, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and Tuberculosis Prevention. Published July 19, 2024. Accessed April 30, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/nchhstp/director-letters/extencilline-during-bicillin-l-a-shortage.html
THE DIAGNOSIS: Syphilis
The differential diagnosis of oral lesions can be complex; in our patient, we considered conditions such as pyogenic granuloma, herpes simplex virus, and syphilis, despite the presence of pain. Immunohistochemical staining for spirochete antigens was positive, and serologic confirmation through a positive rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test confirmed the diagnosis of primary syphilis. The patient was promptly referred back to the primary care physician for treatment with intramuscular penicillin, leading to resolution of the lesion. At 3 months’ follow-up in our clinic, the lesion was fully resolved.
A primary syphilitic chancre is the initial lesion caused by Treponema pallidum, typically manifesting as a painless ulcer at the infection site, usually in the genital area; however, chancres also may manifest in other locations (eg, the anus or oral cavity) due to direct contact with infectious lesions on another individual. Our case represents an atypical presentation of an oral syphilitic chancre.
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection with various clinical manifestations. It is crucial to consider syphilis in the differential diagnosis of ulcerative lesions even when pain is present, especially in high-risk individuals such as those who engage in unprotected sex.1,2 Oral syphilitic chancres have been documented in the medical literature for more than a century, underscoring the importance of maintaining a high index of suspicion for diagnosis and a low threshold for obtaining an RPR test to facilitate early detection and treatment.2,3 Notably, the prevalence of syphilis is higher in men who have sex with men, particularly among those who engage in unprotected oral and anal sex. Increased screening and early treatment are essential to control the spread of disease within all populations. Doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (doxyPEP) is used as a preventive measure for syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea.4 This regimen consists of 200 mg of doxycycline taken within 24 hours but no later than 72 hours after unprotected anal, vaginal, or oral sex.
Our case highlights the importance of considering the differential diagnosis of oral ulcers, particularly in high-risk populations such as men who have sex with men. Prompt diagnosis, effective treatment, and preventive strategies such as doxyPEP are essential for controlling syphilis. Comprehensive patient education and regular follow-up appointments are critical components of successful management.
The United States has experienced a considerable rise in primary and congenital syphilis cases, with an 80% increase between 2018 and 2022.6 Serologic testing is the primary method for diagnosing, staging, and managing syphilis. Sexually active patients with suspected syphilis or unexplained symptoms should undergo testing. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent systemic complications, including ocular involvement and permanent blindness.
Syphilis is transmitted through direct contact with a syphilitic ulcer or saliva or blood from an infected individual. Oral syphilitic ulcers can develop on the lips, tongue, oral mucosa, and tonsils. Chancres can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters, with an incubation period of 10 to 90 days (average, 21 days). The chancre lasts 3 to 6 weeks and heals spontaneously. Without treatment, primary syphilis can progress to secondary syphilis, characterized by a papulosquamous eruption and mucosal involvement, and potentially tertiary syphilis, which can affect the central nervous system, heart, bones, and skin.7
Immunocompromised patients, especially those diagnosed with HIV, face increased risks including altered clinical presentations (eg, multiple or deep chancres), delayed healing, overlapping stages of disease, and increased severity of organ involvement. All sexually active individuals should be screened for syphilis every 3 to 6 months, particularly those with unexplained oral ulcers.
Serologic testing is fundamental for syphilis diagnosis and management. Nontreponemal tests such as RPR and treponemal tests such as the fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test provide comprehensive diagnostic information. Early diagnosis and empiric treatment are crucial in suspected cases. Ocular screening is recommended for suspected or confirmed syphilis cases.7
Management of syphilis includes treating all sexual partners and providing thorough patient education on the disease. Monitoring for the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction—an acute febrile reaction following penicillin therapy—is important, especially in pregnant patients.5 Serologic evaluation at 6 and 12 months posttreatment is recommended, with more frequent evaluations if follow-up is uncertain, particularly for those with inconsistent access to health care or in whom reinfection is suspected. Guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advocate for intramuscular penicillin G benzathine as the preferred treatment, with specific dosing for adults and children.7 Due to the ongoing bicillin shortage, alternatives such as extencilline have temporarily been allowed for use in the United States.8
The rising incidence of syphilis in the United States underscores the critical need for enhanced public health initiatives focusing on education, screening, and early intervention. Comprehensive sexual education that includes information about syphilis and other sexually transmitted infections, proper use of prophylactic measures such as condoms, and the benefits of doxyPEP can considerably reduce transmission rates. Health care providers should routinely discuss these preventive measures with their patients, especially those in high-risk groups.
Our case highlights the importance of considering syphilis in the differential diagnosis of oral ulcers, particularly in high-risk populations. Timely diagnosis, effective treatment, and preventive measures such as doxyPEP are essential for managing and controlling syphilis. The rising incidence of syphilis in the United States warrants increased screening, patient education, and public health interventions to address this notable health challenge. The syphilis crisis calls for coordinated efforts from health care providers, public health officials, and community leaders to curb the spread of this infection and protect public health.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Syphilis
The differential diagnosis of oral lesions can be complex; in our patient, we considered conditions such as pyogenic granuloma, herpes simplex virus, and syphilis, despite the presence of pain. Immunohistochemical staining for spirochete antigens was positive, and serologic confirmation through a positive rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test confirmed the diagnosis of primary syphilis. The patient was promptly referred back to the primary care physician for treatment with intramuscular penicillin, leading to resolution of the lesion. At 3 months’ follow-up in our clinic, the lesion was fully resolved.
A primary syphilitic chancre is the initial lesion caused by Treponema pallidum, typically manifesting as a painless ulcer at the infection site, usually in the genital area; however, chancres also may manifest in other locations (eg, the anus or oral cavity) due to direct contact with infectious lesions on another individual. Our case represents an atypical presentation of an oral syphilitic chancre.
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection with various clinical manifestations. It is crucial to consider syphilis in the differential diagnosis of ulcerative lesions even when pain is present, especially in high-risk individuals such as those who engage in unprotected sex.1,2 Oral syphilitic chancres have been documented in the medical literature for more than a century, underscoring the importance of maintaining a high index of suspicion for diagnosis and a low threshold for obtaining an RPR test to facilitate early detection and treatment.2,3 Notably, the prevalence of syphilis is higher in men who have sex with men, particularly among those who engage in unprotected oral and anal sex. Increased screening and early treatment are essential to control the spread of disease within all populations. Doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (doxyPEP) is used as a preventive measure for syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea.4 This regimen consists of 200 mg of doxycycline taken within 24 hours but no later than 72 hours after unprotected anal, vaginal, or oral sex.
Our case highlights the importance of considering the differential diagnosis of oral ulcers, particularly in high-risk populations such as men who have sex with men. Prompt diagnosis, effective treatment, and preventive strategies such as doxyPEP are essential for controlling syphilis. Comprehensive patient education and regular follow-up appointments are critical components of successful management.
The United States has experienced a considerable rise in primary and congenital syphilis cases, with an 80% increase between 2018 and 2022.6 Serologic testing is the primary method for diagnosing, staging, and managing syphilis. Sexually active patients with suspected syphilis or unexplained symptoms should undergo testing. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent systemic complications, including ocular involvement and permanent blindness.
Syphilis is transmitted through direct contact with a syphilitic ulcer or saliva or blood from an infected individual. Oral syphilitic ulcers can develop on the lips, tongue, oral mucosa, and tonsils. Chancres can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters, with an incubation period of 10 to 90 days (average, 21 days). The chancre lasts 3 to 6 weeks and heals spontaneously. Without treatment, primary syphilis can progress to secondary syphilis, characterized by a papulosquamous eruption and mucosal involvement, and potentially tertiary syphilis, which can affect the central nervous system, heart, bones, and skin.7
Immunocompromised patients, especially those diagnosed with HIV, face increased risks including altered clinical presentations (eg, multiple or deep chancres), delayed healing, overlapping stages of disease, and increased severity of organ involvement. All sexually active individuals should be screened for syphilis every 3 to 6 months, particularly those with unexplained oral ulcers.
Serologic testing is fundamental for syphilis diagnosis and management. Nontreponemal tests such as RPR and treponemal tests such as the fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test provide comprehensive diagnostic information. Early diagnosis and empiric treatment are crucial in suspected cases. Ocular screening is recommended for suspected or confirmed syphilis cases.7
Management of syphilis includes treating all sexual partners and providing thorough patient education on the disease. Monitoring for the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction—an acute febrile reaction following penicillin therapy—is important, especially in pregnant patients.5 Serologic evaluation at 6 and 12 months posttreatment is recommended, with more frequent evaluations if follow-up is uncertain, particularly for those with inconsistent access to health care or in whom reinfection is suspected. Guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advocate for intramuscular penicillin G benzathine as the preferred treatment, with specific dosing for adults and children.7 Due to the ongoing bicillin shortage, alternatives such as extencilline have temporarily been allowed for use in the United States.8
The rising incidence of syphilis in the United States underscores the critical need for enhanced public health initiatives focusing on education, screening, and early intervention. Comprehensive sexual education that includes information about syphilis and other sexually transmitted infections, proper use of prophylactic measures such as condoms, and the benefits of doxyPEP can considerably reduce transmission rates. Health care providers should routinely discuss these preventive measures with their patients, especially those in high-risk groups.
Our case highlights the importance of considering syphilis in the differential diagnosis of oral ulcers, particularly in high-risk populations. Timely diagnosis, effective treatment, and preventive measures such as doxyPEP are essential for managing and controlling syphilis. The rising incidence of syphilis in the United States warrants increased screening, patient education, and public health interventions to address this notable health challenge. The syphilis crisis calls for coordinated efforts from health care providers, public health officials, and community leaders to curb the spread of this infection and protect public health.
- Mayer KH, Traeger M, Marcus JL. Doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis and sexually transmitted infections. JAMA. 2023;330:1381-1382. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.16416
- Cossman JP, Fournier JB. Frequency of syphilis diagnoses by dermatologists. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:718-719. doi:10.1001 /jamadermatol.2017.0460
- Porterfield C, Brodell D, Dolohanty L, et al. Primary syphilis presenting as a chronic lip ulcer. Cureus. 2020;12:E7086. doi:10.7759 /cureus.7086
- Schamberg JF. An epidemic of chancres of the lip from kissing. JAMA. 1911;LVII:783-784. doi:10.1001/jama.1911.04260090005002
- Farmer TW. Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction in early syphilis. JAMA. 1948;138:480–485. doi:10.1001/jama.1948.02900070012003
- Winney A. Why is syphilis spiking in the U.S.? Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Published March 13, 2024. Accessed April 30, 2025. https://publichealth.jhu.edu/why-is-syphilis-spiking-in-the-us
- Koundanya VV, Tripathy K. Syphilis ocular manifestations. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Updated August 25, 2023. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558957/
- CDC. FDA announcement on availability of extencilline. National Center for HIV, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and Tuberculosis Prevention. Published July 19, 2024. Accessed April 30, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/nchhstp/director-letters/extencilline-during-bicillin-l-a-shortage.html
- Mayer KH, Traeger M, Marcus JL. Doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis and sexually transmitted infections. JAMA. 2023;330:1381-1382. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.16416
- Cossman JP, Fournier JB. Frequency of syphilis diagnoses by dermatologists. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:718-719. doi:10.1001 /jamadermatol.2017.0460
- Porterfield C, Brodell D, Dolohanty L, et al. Primary syphilis presenting as a chronic lip ulcer. Cureus. 2020;12:E7086. doi:10.7759 /cureus.7086
- Schamberg JF. An epidemic of chancres of the lip from kissing. JAMA. 1911;LVII:783-784. doi:10.1001/jama.1911.04260090005002
- Farmer TW. Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction in early syphilis. JAMA. 1948;138:480–485. doi:10.1001/jama.1948.02900070012003
- Winney A. Why is syphilis spiking in the U.S.? Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Published March 13, 2024. Accessed April 30, 2025. https://publichealth.jhu.edu/why-is-syphilis-spiking-in-the-us
- Koundanya VV, Tripathy K. Syphilis ocular manifestations. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Updated August 25, 2023. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558957/
- CDC. FDA announcement on availability of extencilline. National Center for HIV, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and Tuberculosis Prevention. Published July 19, 2024. Accessed April 30, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/nchhstp/director-letters/extencilline-during-bicillin-l-a-shortage.html
Nonhealing Ulcer on the Lower Lip
Nonhealing Ulcer on the Lower Lip
A 54-year-old HIV-negative man with a history of having sex with men presented to his primary care physician with an ulcer on the lower lip of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient reported that the lesion had appeared as a typical cold sore with pain in the area. A 9-day course of oral valacyclovir prescribed by the primary care physician provided no relief or improvement. A 2-mm punch biopsy was performed.
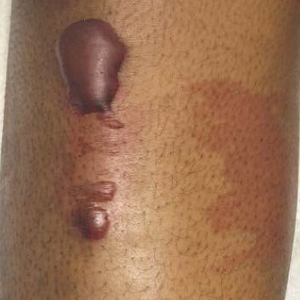
Large Bullae on the Legs in a Hospitalized Patient Following a Gunshot Wound
Large Bullae on the Legs in a Hospitalized Patient Following a Gunshot Wound
THE DIAGNOSIS: Bullous Hemorrhagic Dermatosis
Biopsy results showed an intraepidermal blister with a floor composed of maturing epidermis. The roof of the blister was composed of necrotic keratinocytes with overlying orthokeratosis, and the cavity was filled with a moderate amount of fibrin and dead cells with neutrophils. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) using specific antihuman IgG, IgM, IgA, C3, and fibrin was negative. Aerobic, anaerobic, and fungal cultures also were negative. With these histopathologic findings, medication exposure, and timing of bullae onset, our patient was diagnosed with bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis (BHD) secondary to enoxaparin administration. Enoxaparin was continued due to increased risk for coagulopathy, and there was complete resolution of the bullae after 5 weeks with no residual symptoms.
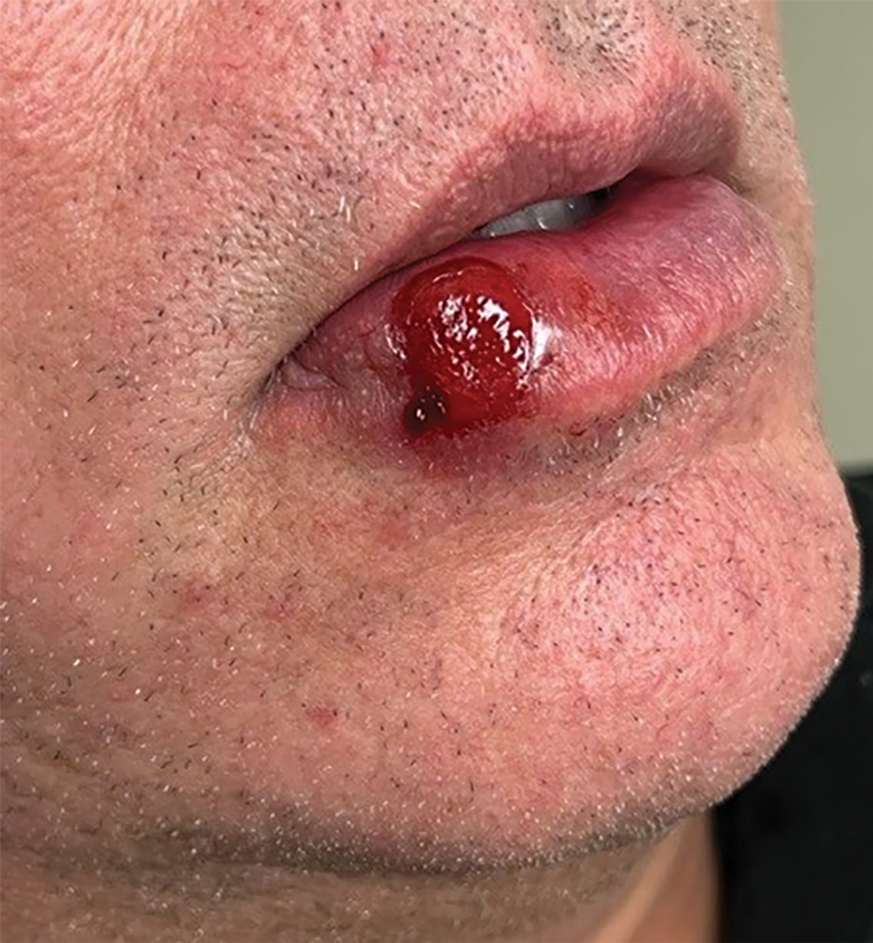
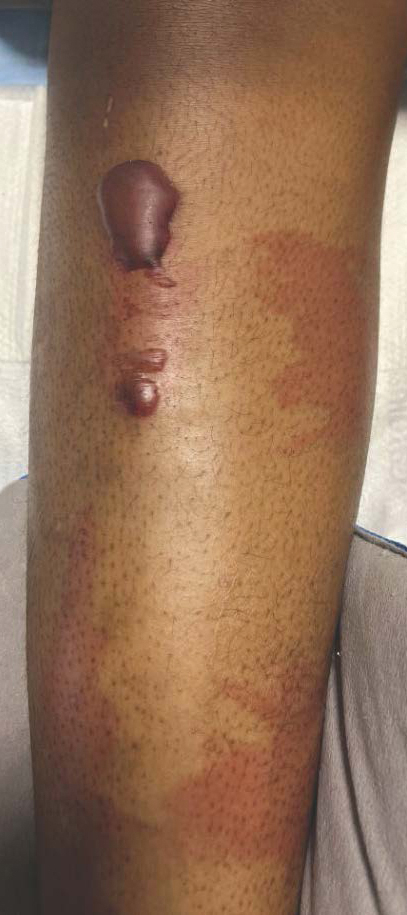
Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis is a rare eruption that can occur after administration of heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin, with enoxaparin being the most commonly implicated drug.1 The lesions typically are seen in elderly men in the seventh decade of life and appear within a median of 7 days after drug exposure. The time course for the postexposure eruption can vary from 2 to 21 days, with reports of skin lesions appearing up to 4 months after exposure.1,2 hemorrhagic bullae (Figure) typically on the arms and legs, though lesions also can develop on the trunk. The lesions can occur in distant areas from the injection site, suggesting BHD may be a systemic reaction, although the etiology is poorly understood.1
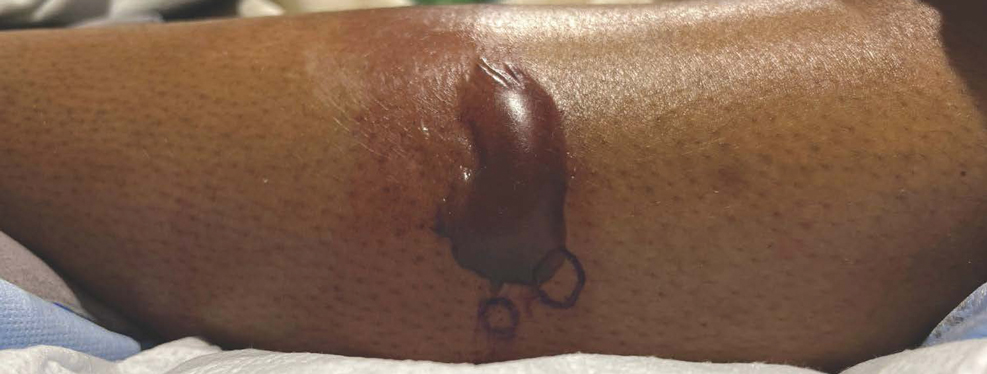
Another heparin reaction that can manifest similarly to BHD is heparin-induced skin necrosis.3 Patients with this condition also may have associated heparin-induced thrombocytopenia upon laboratory investigation and have a more aggressive clinical course than BHD. Biopsy can help differentiate BHD and early heparin-induced skin necrosis if the clinical manifestation is unclear. Histopathologically, BHD typically has intraepidermal bullae filled with blood, whereas heparin-induced skin necrosis has dermal thrombi.1,4 Treatment of both conditions differs in whether to discontinue anticoagulants: heparin-induced skin necrosis requires discontinuation of the medication, while BHD does not.2,3
In patients with BHD, the lesions are self-resolving, and treatment is supportive, although whether enoxaparin is discontinued varies among physicians.2 Lesions typically resolve within 2 weeks of onset, although it is unclear whether continuing anticoagulants delays resolution.1 Discontinuing anticoagulants in certain patients can be life-threatening due to complex comorbidities (eg, risk for venous thromboembolism or pulmonary embolism from prolonged hospitalization or severe trauma) and is not necessary for the resolution of BHD.
In addition to BHD and heparin-induced skin necrosis, our differential diagnosis included bullous pemphigoid, coma blisters, and Vibrio vulnificus infection. Although bullous pemphigoid can manifest with tense bullae that are pauci-inflammatory on histology, DIF would show linear IgG and C3 deposition at the dermal-epidermal junction. In our patient, DIF was negative and favored another etiology for the lesions. Coma blisters can occur in areas of sustained pressure and typically develop in patients with a prolonged hospitalization or those who are sedentary for long periods of time. The distribution of bullae on our patient’s bilateral pretibial shins made this diagnosis unlikely. Vibrio vulnificus infection can manifest as hemorrhagic bullae, though typically after a break in the skin exposed to brackish water. Vibrio vulnificus infection can be life-threatening, resulting in septicemia and increased mortality, and a thorough patient history is important for diagnosis.5
- Russo A, Curtis S, Balbuena-Merle R, et al. Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis is an under-recognized side effect of full dose lowmolecular weight heparin: a case report and review of the literature. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2018;7:15. doi:10.1186/s40164-018-0108-7
- Dhattarwal N, Gurjar R. Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis: a rare cutaneous reaction of heparin. J Postgrad Med. 2023;69:97-98. doi:10.4103/jpgm.jpgm_282_22
- Maldonado Cid P, Alonso de Celada RM, Noguera Morel L, et al. Cutaneous adverse events associated with heparin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37:707-711. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2012.04395.x
- Handschin AE, Trentz O, Kock HJ, et al. Low molecular weight heparininduced skin necrosis-a systematic review. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2005;390:249-254. doi:10.1007/s00423-004-0522-7
- Jones MK, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 2009;77:1723-1733. doi:10.1128/IAI.01046-08
THE DIAGNOSIS: Bullous Hemorrhagic Dermatosis
Biopsy results showed an intraepidermal blister with a floor composed of maturing epidermis. The roof of the blister was composed of necrotic keratinocytes with overlying orthokeratosis, and the cavity was filled with a moderate amount of fibrin and dead cells with neutrophils. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) using specific antihuman IgG, IgM, IgA, C3, and fibrin was negative. Aerobic, anaerobic, and fungal cultures also were negative. With these histopathologic findings, medication exposure, and timing of bullae onset, our patient was diagnosed with bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis (BHD) secondary to enoxaparin administration. Enoxaparin was continued due to increased risk for coagulopathy, and there was complete resolution of the bullae after 5 weeks with no residual symptoms.
Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis is a rare eruption that can occur after administration of heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin, with enoxaparin being the most commonly implicated drug.1 The lesions typically are seen in elderly men in the seventh decade of life and appear within a median of 7 days after drug exposure. The time course for the postexposure eruption can vary from 2 to 21 days, with reports of skin lesions appearing up to 4 months after exposure.1,2 hemorrhagic bullae (Figure) typically on the arms and legs, though lesions also can develop on the trunk. The lesions can occur in distant areas from the injection site, suggesting BHD may be a systemic reaction, although the etiology is poorly understood.1

Another heparin reaction that can manifest similarly to BHD is heparin-induced skin necrosis.3 Patients with this condition also may have associated heparin-induced thrombocytopenia upon laboratory investigation and have a more aggressive clinical course than BHD. Biopsy can help differentiate BHD and early heparin-induced skin necrosis if the clinical manifestation is unclear. Histopathologically, BHD typically has intraepidermal bullae filled with blood, whereas heparin-induced skin necrosis has dermal thrombi.1,4 Treatment of both conditions differs in whether to discontinue anticoagulants: heparin-induced skin necrosis requires discontinuation of the medication, while BHD does not.2,3
In patients with BHD, the lesions are self-resolving, and treatment is supportive, although whether enoxaparin is discontinued varies among physicians.2 Lesions typically resolve within 2 weeks of onset, although it is unclear whether continuing anticoagulants delays resolution.1 Discontinuing anticoagulants in certain patients can be life-threatening due to complex comorbidities (eg, risk for venous thromboembolism or pulmonary embolism from prolonged hospitalization or severe trauma) and is not necessary for the resolution of BHD.
In addition to BHD and heparin-induced skin necrosis, our differential diagnosis included bullous pemphigoid, coma blisters, and Vibrio vulnificus infection. Although bullous pemphigoid can manifest with tense bullae that are pauci-inflammatory on histology, DIF would show linear IgG and C3 deposition at the dermal-epidermal junction. In our patient, DIF was negative and favored another etiology for the lesions. Coma blisters can occur in areas of sustained pressure and typically develop in patients with a prolonged hospitalization or those who are sedentary for long periods of time. The distribution of bullae on our patient’s bilateral pretibial shins made this diagnosis unlikely. Vibrio vulnificus infection can manifest as hemorrhagic bullae, though typically after a break in the skin exposed to brackish water. Vibrio vulnificus infection can be life-threatening, resulting in septicemia and increased mortality, and a thorough patient history is important for diagnosis.5
THE DIAGNOSIS: Bullous Hemorrhagic Dermatosis
Biopsy results showed an intraepidermal blister with a floor composed of maturing epidermis. The roof of the blister was composed of necrotic keratinocytes with overlying orthokeratosis, and the cavity was filled with a moderate amount of fibrin and dead cells with neutrophils. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) using specific antihuman IgG, IgM, IgA, C3, and fibrin was negative. Aerobic, anaerobic, and fungal cultures also were negative. With these histopathologic findings, medication exposure, and timing of bullae onset, our patient was diagnosed with bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis (BHD) secondary to enoxaparin administration. Enoxaparin was continued due to increased risk for coagulopathy, and there was complete resolution of the bullae after 5 weeks with no residual symptoms.
Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis is a rare eruption that can occur after administration of heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin, with enoxaparin being the most commonly implicated drug.1 The lesions typically are seen in elderly men in the seventh decade of life and appear within a median of 7 days after drug exposure. The time course for the postexposure eruption can vary from 2 to 21 days, with reports of skin lesions appearing up to 4 months after exposure.1,2 hemorrhagic bullae (Figure) typically on the arms and legs, though lesions also can develop on the trunk. The lesions can occur in distant areas from the injection site, suggesting BHD may be a systemic reaction, although the etiology is poorly understood.1

Another heparin reaction that can manifest similarly to BHD is heparin-induced skin necrosis.3 Patients with this condition also may have associated heparin-induced thrombocytopenia upon laboratory investigation and have a more aggressive clinical course than BHD. Biopsy can help differentiate BHD and early heparin-induced skin necrosis if the clinical manifestation is unclear. Histopathologically, BHD typically has intraepidermal bullae filled with blood, whereas heparin-induced skin necrosis has dermal thrombi.1,4 Treatment of both conditions differs in whether to discontinue anticoagulants: heparin-induced skin necrosis requires discontinuation of the medication, while BHD does not.2,3
In patients with BHD, the lesions are self-resolving, and treatment is supportive, although whether enoxaparin is discontinued varies among physicians.2 Lesions typically resolve within 2 weeks of onset, although it is unclear whether continuing anticoagulants delays resolution.1 Discontinuing anticoagulants in certain patients can be life-threatening due to complex comorbidities (eg, risk for venous thromboembolism or pulmonary embolism from prolonged hospitalization or severe trauma) and is not necessary for the resolution of BHD.
In addition to BHD and heparin-induced skin necrosis, our differential diagnosis included bullous pemphigoid, coma blisters, and Vibrio vulnificus infection. Although bullous pemphigoid can manifest with tense bullae that are pauci-inflammatory on histology, DIF would show linear IgG and C3 deposition at the dermal-epidermal junction. In our patient, DIF was negative and favored another etiology for the lesions. Coma blisters can occur in areas of sustained pressure and typically develop in patients with a prolonged hospitalization or those who are sedentary for long periods of time. The distribution of bullae on our patient’s bilateral pretibial shins made this diagnosis unlikely. Vibrio vulnificus infection can manifest as hemorrhagic bullae, though typically after a break in the skin exposed to brackish water. Vibrio vulnificus infection can be life-threatening, resulting in septicemia and increased mortality, and a thorough patient history is important for diagnosis.5
- Russo A, Curtis S, Balbuena-Merle R, et al. Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis is an under-recognized side effect of full dose lowmolecular weight heparin: a case report and review of the literature. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2018;7:15. doi:10.1186/s40164-018-0108-7
- Dhattarwal N, Gurjar R. Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis: a rare cutaneous reaction of heparin. J Postgrad Med. 2023;69:97-98. doi:10.4103/jpgm.jpgm_282_22
- Maldonado Cid P, Alonso de Celada RM, Noguera Morel L, et al. Cutaneous adverse events associated with heparin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37:707-711. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2012.04395.x
- Handschin AE, Trentz O, Kock HJ, et al. Low molecular weight heparininduced skin necrosis-a systematic review. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2005;390:249-254. doi:10.1007/s00423-004-0522-7
- Jones MK, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 2009;77:1723-1733. doi:10.1128/IAI.01046-08
- Russo A, Curtis S, Balbuena-Merle R, et al. Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis is an under-recognized side effect of full dose lowmolecular weight heparin: a case report and review of the literature. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2018;7:15. doi:10.1186/s40164-018-0108-7
- Dhattarwal N, Gurjar R. Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis: a rare cutaneous reaction of heparin. J Postgrad Med. 2023;69:97-98. doi:10.4103/jpgm.jpgm_282_22
- Maldonado Cid P, Alonso de Celada RM, Noguera Morel L, et al. Cutaneous adverse events associated with heparin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37:707-711. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2012.04395.x
- Handschin AE, Trentz O, Kock HJ, et al. Low molecular weight heparininduced skin necrosis-a systematic review. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2005;390:249-254. doi:10.1007/s00423-004-0522-7
- Jones MK, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 2009;77:1723-1733. doi:10.1128/IAI.01046-08
Large Bullae on the Legs in a Hospitalized Patient Following a Gunshot Wound
Large Bullae on the Legs in a Hospitalized Patient Following a Gunshot Wound
A 19-year-old man developed fluid-filled blisters on both legs within 1 month of a prolonged hospitalization following a gunshot wound that resulted in complete paralysis of the legs. His medical history was otherwise unremarkable. Medications started during hospitalization included moxifloxacin, levetiracetam, and prophylactic subcutaneous enoxaparin. Physical examination by dermatology revealed tense blood-filled bullae measuring several centimeters with well-demarcated, pink to red, irregularly shaped patches on both legs. A biopsy of a blister was taken.
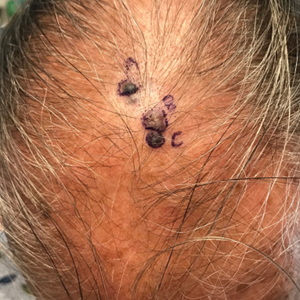
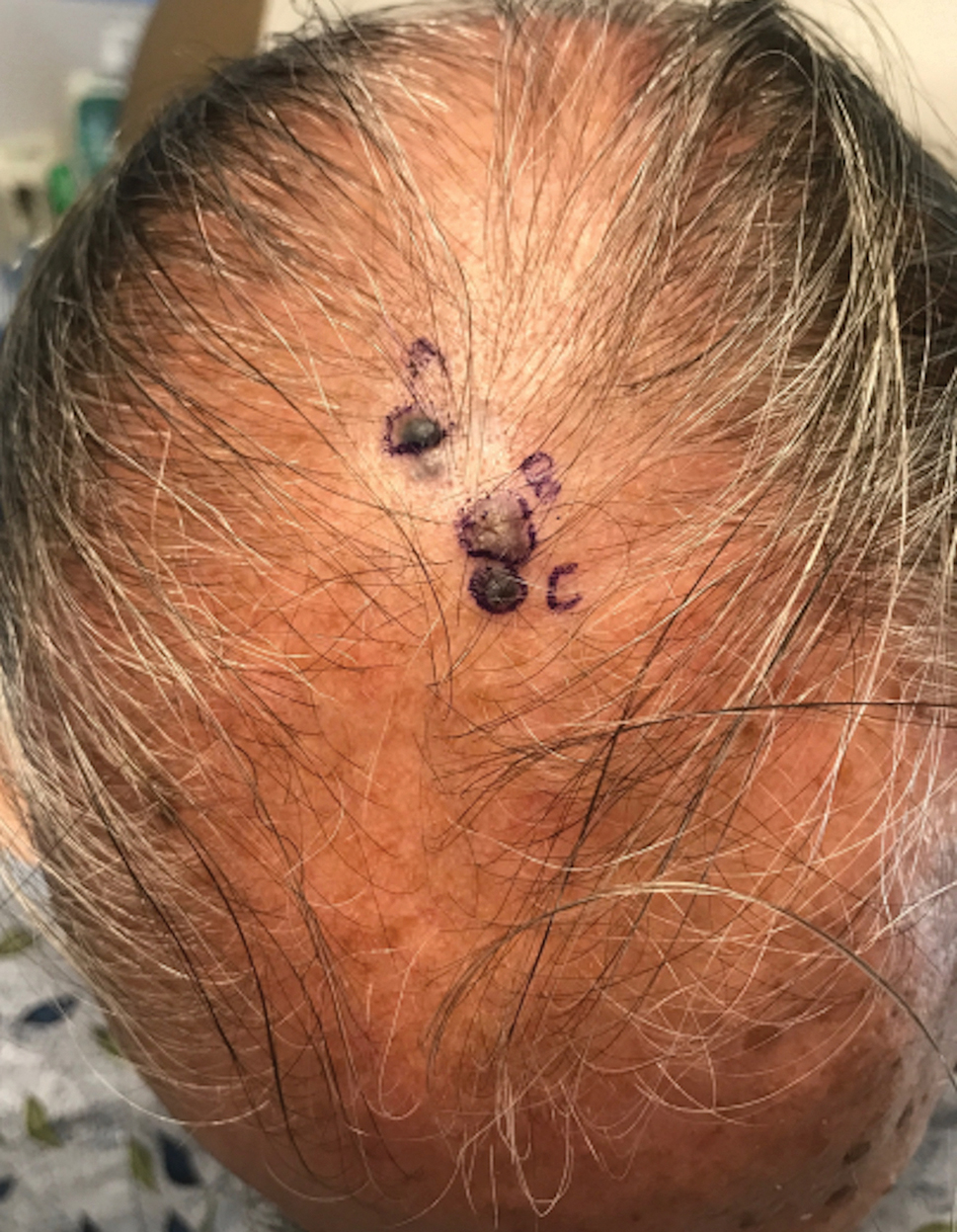
Pigmented Cystic Masses on the Scalp
THE DIAGNOSIS: Apocrine Hidrocystoma
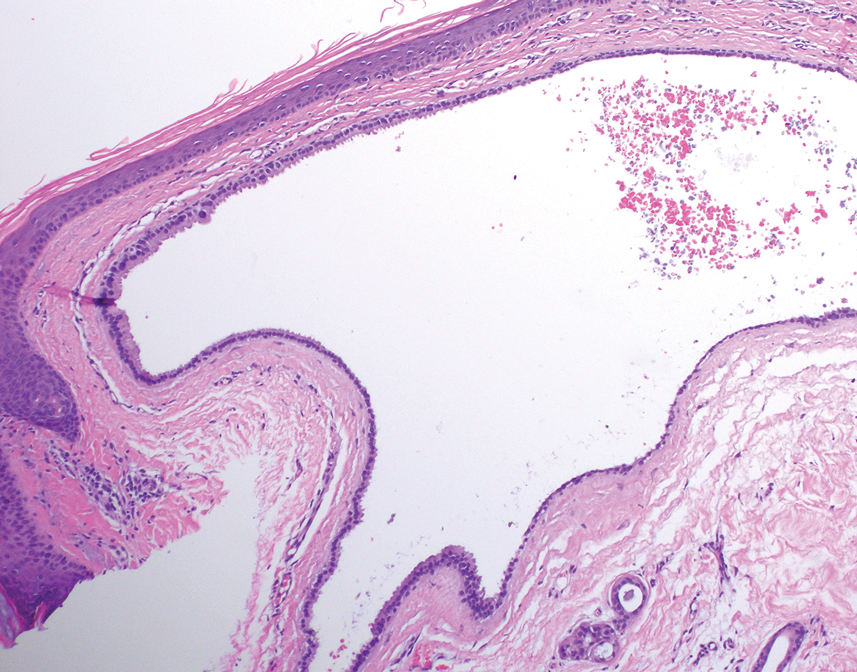
Histology for all 3 lesions demonstrated similar cystic structures lined by a dual layer of epithelial cells, with the outermost layer composed of flattened myoepithelial cells and the inner layer composed of cells with apocrine features (Figure 1). Based on these findings, a diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma was made. The patient underwent successful surgical excision shortly thereafter without recurrence at follow-up 1 year later.
Apocrine hidrocystomas are rare benign cystic lesions that are considered to be adenomatous proliferations of apocrine glands. They typically manifest as solitary asymptomatic lesions measuring 3 to 15 mm.1 They tend to appear on the face, usually in the periorbital region, but also have been described on the neck, scalp, trunk, arms, and legs.2-4 Multiple apocrine hidrocystomas can be a marker of 2 rare inherited disorders: Gorlin-Goltz syndrome and Schopf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome.5 Apocrine hidrocystomas may be flesh colored or may have a blue, black, or brown appearance due to the Tyndall effect, in which light with shorter wavelengths is scattered by the contents of the lesions.2 Histologically, apocrine hidrocystomas are cysts lined by a dual layer of epithelial cells. The inner layer is composed of cells with apocrine features, and the outer layer is composed of flattened myoepithelial cells. Due to their range of colors and predilection for sun-exposed surfaces, apocrine hidrocystomas may be mistaken for various malignant neoplasms, including melanoma.6,7
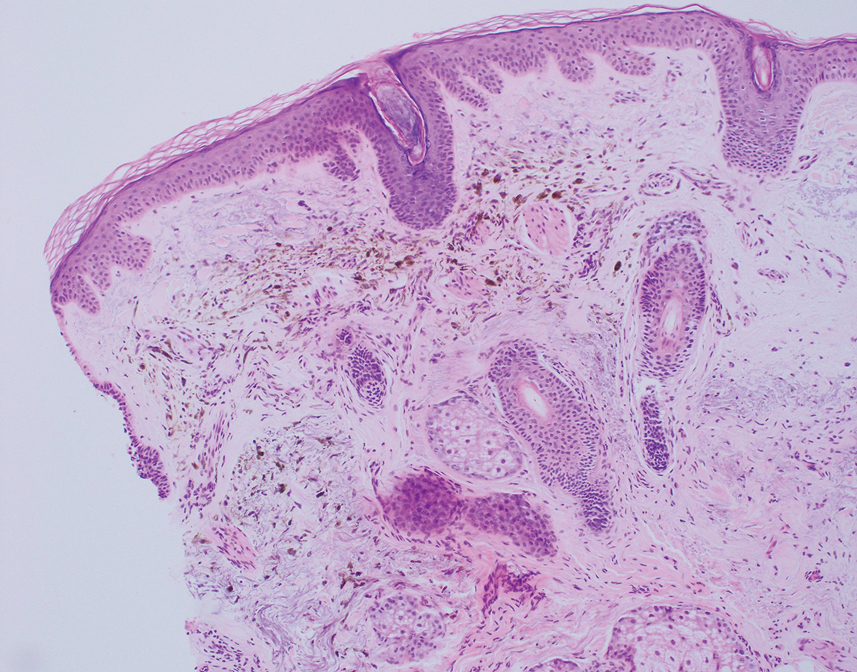
The differential diagnosis for our patient included agminated blue nevi, melanoma, pigmented basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and seborrheic keratosis. A blue nevus is a dermal melanocytic lesion that manifests as a well-demarcated, blue to blue-black papule that typically appears on the face, scalp, arms, legs, lower back, and buttocks. Although there are several histologic subtypes, the common blue nevus usually manifests as a solitary lesion measuring less than 1 cm, often developing during childhood to young adulthood.8 Histologically, common blue nevi are characterized by a dermal proliferation of deeply pigmented bipolar spindled melanocytes embedded in thickened collagen bundles, often with scattered epithelioid melanophages, and no conspicuous mitotic activity (Figure 2).9 There are other types of blue nevi, including cellular blue nevi, which tend to be larger and manifest commonly on the buttocks and sacrococcygeal region in early adulthood.9 Histologically, cellular blue nevi contain oval to spindled melanocytes with scattered melanophages forming a well-demarcated nodule typically in the reticular dermis. There may be bulbous extension into the subcutaneous adipose tissue. Occasional mitoses may be seen.9,10 Melanoma can arise from common or cellular blue nevi, though it more frequently occurs with cellular blue nevi. Other subtypes of blue nevi have been described, including the sclerosing, plaque-type, combined, hypomelanotic/amelanotic, and pigmented epithelioid melanocytoma.11 However, they typically have features of the common blue nevus or cellular blue nevus, such as oval/spindle cell morphology, some degree of melanin, and biphasic architecture, but are classified according to their dominant histologic characteristics.
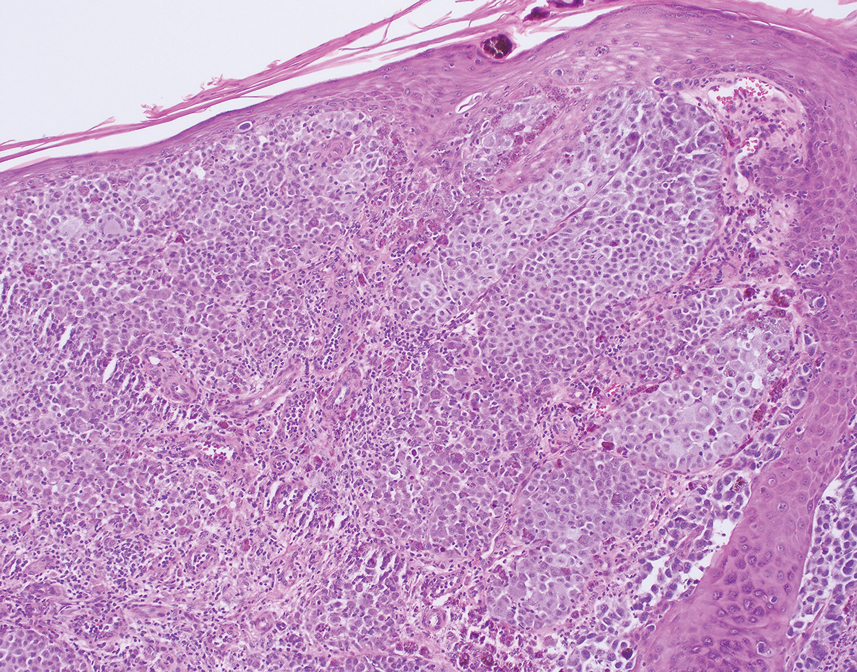
Given the location of our patient’s lesions on the scalp and his extensive history of sun exposure, malignancy was high in the differential. Multiple synchronous primary melanomas including nodular melanoma, blue nevus–like metastatic melanoma, and metastatic melanoma were considered. The leg and the scalp have the highest reported incidence of cutaneous metastases of melanoma, with many cases presenting as dermal or subcutaneous nodules and eruptive blue nevus–like papules, similar to our patient’s clinical presentation.12,13 Nodular melanoma (NM) is one of 4 major types of melanoma, accounting for approximately 15% to 30% of cases in the United States.14 Nodular melanoma typically manifests as a smooth, raised, symmetric, well-circumscribed lesion with variable pigmentation, from very dark to amelanotic. Histologically, NM is defined as a dermal mass, either in isolation or with an epidermal component, not to exceed 3 rete ridges beyond the dermal component.15 Tumor cells have a high cell density with pleomorphism, usually with atypical epithelioid cells with vesicular nuclei and irregular cytoplasm, and occasionally spindle cells (Figure 2).16 Mitoses and necrosis are frequent. Scalp location independently is responsible for worse survival, both overall and melanoma specific.17 Nodular melanoma tends to have greater Breslow thickness at diagnosis than other melanoma subtypes and often carries a worse prognosis.
Malignant melanomas that develop from or in conjunction with or bear histologic resemblance to blue nevi are termed blue nevus–like melanoma or blue nevus–associated melanoma. These malignancies are exceedingly rare, accounting for only 0.3% of melanomas in one Turkey-based multicenter study.18 The histologic criteria for diagnosing blue nevus–like melanoma are poorly defined, and terminology of these lesions has led to some debate in naming conventions.19 Nevertheless, unlike blue nevus, blue nevus–like melanoma demonstrates histologic features of malignancy, including pleomorphism, prominent nucleoli, mitotic activity, vascular invasion, and potential necrosis.10 The lack of an inflammatory infiltrate, surrounding fibrosis, junctional activity, and pre-existing nevus can help distinguish cutaneous melanoma metastases from primary nodular melanoma. Immunohistochemical stains such as S100, Melan-A/MART1, or SOX-10 can help confirm melanocytic lineage.12
Pigmented BCC is a clinical and histologic variant of BCC characterized by increased melanin pigmentation due to melanocytes admixed with tumor cells. Dermoscopically, the pigment can have a maple leaf–like appearance with spoke-wheel areas, in-focus dots, and concentric structures at the dermoepidermal junction, which is more characteristic of superficial and infiltrating BCC.20 In nodular BCC, the pigment occurs as blue-gray ovoid nests and globules in deeper layers of the dermis.20
Seborrheic keratoses (SKs) can vary widely in clinical appearance, with pigmentation ranging from flesh colored to yellow to brown to black. Melanoacanthomas are acanthotic SKs that are highly pigmented due to intermixed epidermal melanocytes and subepidermal melanophages.21 Dermoscopy can help distinguish cutaneous malignancies from SKs, which often demonstrate fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and milialike cysts. Biopsy sometimes is required to assess for malignancy, as was the case in our patient. The classic histologic features of SKs include acanthosis, papillomatosis, and hyperkeratosis.22
This case highlights the need to consider apocrine hidrocystoma, along with malignancy, in the differential diagnosis of pigmented cystic masses of the face and scalp. Because apocrine hidrocystomas are benign, they do not need to be treated but often are surgically excised for cosmesis or complete histopathologic examination. Destruction via electrodessication, carbon dioxide ablation, trichloroacetic acid chemical ablation, botulinum toxin injection, and anticholinergic creams sometimes is used, especially for cosmetic treatment of multiple small lesions.5 Our patient was treated with surgical excision with no evidence of recurrence on follow-up 1 year later.
- Ioannidis DG, Drivas EI, Papadakis CE, et al. Hidrocystoma of the external auditory canal: a case report. Cases J. 2009;2:79. doi:10.1186/1757- 1626-2-79
- Nguyen HP, Barker HS, Bloomquist L, et al. Giant pigmented apocrine hidrocystoma of the scalp. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26. doi:10.5070/D3268049895
- Mendoza-Cembranos MD, Haro R, Requena L, et al. Digital apocrine hidrocystoma: the exception confirms the rule. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:79. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000001044
- May C, Chang O, Compton N. A giant apocrine hidrocystoma of the trunk. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23. doi:10.5070/D3239036497
- Sarabi K, Khachemoune A. Hidrocystomas—a brief review. Medscape Gen Med. 2006;8:57.
- Kruse ALD, Zwahlen R, Bredell MG, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma of the cheek. J Craniofac Surg. 2010;21:594-596. doi:10.1097 /SCS.0b013e3181d08c77
- Zaballos P, Bañuls J, Medina C, et al. Dermoscopy of apocrine hidrocystomas: a morphological study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:378-381. doi:10.1111/jdv.12044
- Rodriguez HA, Ackerman LV. Cellular blue nevus. clinicopathologic study of forty-five cases. Cancer. 1968;21:393-405. doi:10.1002 /1097-0142(196803)21:3<393::aid-cncr2820210309>3.0.co;2-k
- Murali R, McCarthy SW, Scolyer RA. Blue nevi and related lesions: a review highlighting atypical and newly described variants, distinguishing features and diagnostic pitfalls. Adv Anat Pathol. 2009;16:365. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e3181bb6b53
- Borgenvik TL, Karlsvik TM, Ray S, et al. Blue nevus-like and blue nevusassociated melanoma: a comprehensive review of the literature. ANZ J Surg. 2017;87:345-349. doi:10.1111/ans.13946
- de la Fouchardiere A. Blue naevi and the blue tumour spectrum. Pathology. 2023;55:187-195. doi:10.1016/j.pathol.2022.12.342
- Lowe L. Metastatic melanoma and rare melanoma variants: a review. Pathology (Phila). 2023;55:236-244. doi:10.1016/j.pathol.2022.11.006
- Plaza JA, Torres-Cabala C, Evans H, et al. Cutaneous metastases of malignant melanoma: a clinicopathologic study of 192 cases with emphasis on the morphologic spectrum. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:129-136. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181b34a19
- Shaikh WR, Xiong M, Weinstock MA. The contribution of nodular subtype to melanoma mortality in the United States, 1978 to 2007. Archives of Dermatology. 2012;148:30-36. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2011.264
- Clark WH, From L, Bernardino EA, et al. The histogenesis and biologic behavior of primary human malignant melanomas of the skin. Cancer Res. 1969;29:705-727.
- Bobos M. Histopathologic classification and prognostic factors of melanoma: a 2021 update. Ital J Dermatol Venereol. 2021;156:300-321. doi:10.23736/S2784-8671.21.06958-3
- Ozao-Choy J, Nelson DW, Hiles J, et al. The prognostic importance of scalp location in primary head and neck melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 2017;116:337-343. doi:10.1002/jso.24679
- Gamsizkan M, Yilmaz I, Buyukbabani N, et al. A retrospective multicenter evaluation of cutaneous melanomas in Turkey. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP. 2014;15:10451-10456. doi:10.7314 /apjcp.2014.15.23.10451
- Mones JM, Ackerman AB. “Atypical” blue nevus, “malignant” blue nevus, and “metastasizing” blue nevus: a critique in historical perspective of three concepts flawed fatally. Am J Dermatopathol. 2004;26:407-430. doi:10.1097/00000372-200410000-00012
- Tanese K. Diagnosis and management of basal cell carcinoma Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2019;20:13. doi:10.1007/s11864 -019-0610-0
- Barthelmann S, Butsch F, Lang BM, et al. Seborrheic keratosis. JDDG J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2023;21:265-277. doi:10.1111/ddg.14984
- Taylor S. Advancing the understanding of seborrheic keratosis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:419-424.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Apocrine Hidrocystoma
Histology for all 3 lesions demonstrated similar cystic structures lined by a dual layer of epithelial cells, with the outermost layer composed of flattened myoepithelial cells and the inner layer composed of cells with apocrine features (Figure 1). Based on these findings, a diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma was made. The patient underwent successful surgical excision shortly thereafter without recurrence at follow-up 1 year later.
Apocrine hidrocystomas are rare benign cystic lesions that are considered to be adenomatous proliferations of apocrine glands. They typically manifest as solitary asymptomatic lesions measuring 3 to 15 mm.1 They tend to appear on the face, usually in the periorbital region, but also have been described on the neck, scalp, trunk, arms, and legs.2-4 Multiple apocrine hidrocystomas can be a marker of 2 rare inherited disorders: Gorlin-Goltz syndrome and Schopf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome.5 Apocrine hidrocystomas may be flesh colored or may have a blue, black, or brown appearance due to the Tyndall effect, in which light with shorter wavelengths is scattered by the contents of the lesions.2 Histologically, apocrine hidrocystomas are cysts lined by a dual layer of epithelial cells. The inner layer is composed of cells with apocrine features, and the outer layer is composed of flattened myoepithelial cells. Due to their range of colors and predilection for sun-exposed surfaces, apocrine hidrocystomas may be mistaken for various malignant neoplasms, including melanoma.6,7

The differential diagnosis for our patient included agminated blue nevi, melanoma, pigmented basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and seborrheic keratosis. A blue nevus is a dermal melanocytic lesion that manifests as a well-demarcated, blue to blue-black papule that typically appears on the face, scalp, arms, legs, lower back, and buttocks. Although there are several histologic subtypes, the common blue nevus usually manifests as a solitary lesion measuring less than 1 cm, often developing during childhood to young adulthood.8 Histologically, common blue nevi are characterized by a dermal proliferation of deeply pigmented bipolar spindled melanocytes embedded in thickened collagen bundles, often with scattered epithelioid melanophages, and no conspicuous mitotic activity (Figure 2).9 There are other types of blue nevi, including cellular blue nevi, which tend to be larger and manifest commonly on the buttocks and sacrococcygeal region in early adulthood.9 Histologically, cellular blue nevi contain oval to spindled melanocytes with scattered melanophages forming a well-demarcated nodule typically in the reticular dermis. There may be bulbous extension into the subcutaneous adipose tissue. Occasional mitoses may be seen.9,10 Melanoma can arise from common or cellular blue nevi, though it more frequently occurs with cellular blue nevi. Other subtypes of blue nevi have been described, including the sclerosing, plaque-type, combined, hypomelanotic/amelanotic, and pigmented epithelioid melanocytoma.11 However, they typically have features of the common blue nevus or cellular blue nevus, such as oval/spindle cell morphology, some degree of melanin, and biphasic architecture, but are classified according to their dominant histologic characteristics.

Given the location of our patient’s lesions on the scalp and his extensive history of sun exposure, malignancy was high in the differential. Multiple synchronous primary melanomas including nodular melanoma, blue nevus–like metastatic melanoma, and metastatic melanoma were considered. The leg and the scalp have the highest reported incidence of cutaneous metastases of melanoma, with many cases presenting as dermal or subcutaneous nodules and eruptive blue nevus–like papules, similar to our patient’s clinical presentation.12,13 Nodular melanoma (NM) is one of 4 major types of melanoma, accounting for approximately 15% to 30% of cases in the United States.14 Nodular melanoma typically manifests as a smooth, raised, symmetric, well-circumscribed lesion with variable pigmentation, from very dark to amelanotic. Histologically, NM is defined as a dermal mass, either in isolation or with an epidermal component, not to exceed 3 rete ridges beyond the dermal component.15 Tumor cells have a high cell density with pleomorphism, usually with atypical epithelioid cells with vesicular nuclei and irregular cytoplasm, and occasionally spindle cells (Figure 2).16 Mitoses and necrosis are frequent. Scalp location independently is responsible for worse survival, both overall and melanoma specific.17 Nodular melanoma tends to have greater Breslow thickness at diagnosis than other melanoma subtypes and often carries a worse prognosis.

Malignant melanomas that develop from or in conjunction with or bear histologic resemblance to blue nevi are termed blue nevus–like melanoma or blue nevus–associated melanoma. These malignancies are exceedingly rare, accounting for only 0.3% of melanomas in one Turkey-based multicenter study.18 The histologic criteria for diagnosing blue nevus–like melanoma are poorly defined, and terminology of these lesions has led to some debate in naming conventions.19 Nevertheless, unlike blue nevus, blue nevus–like melanoma demonstrates histologic features of malignancy, including pleomorphism, prominent nucleoli, mitotic activity, vascular invasion, and potential necrosis.10 The lack of an inflammatory infiltrate, surrounding fibrosis, junctional activity, and pre-existing nevus can help distinguish cutaneous melanoma metastases from primary nodular melanoma. Immunohistochemical stains such as S100, Melan-A/MART1, or SOX-10 can help confirm melanocytic lineage.12
Pigmented BCC is a clinical and histologic variant of BCC characterized by increased melanin pigmentation due to melanocytes admixed with tumor cells. Dermoscopically, the pigment can have a maple leaf–like appearance with spoke-wheel areas, in-focus dots, and concentric structures at the dermoepidermal junction, which is more characteristic of superficial and infiltrating BCC.20 In nodular BCC, the pigment occurs as blue-gray ovoid nests and globules in deeper layers of the dermis.20
Seborrheic keratoses (SKs) can vary widely in clinical appearance, with pigmentation ranging from flesh colored to yellow to brown to black. Melanoacanthomas are acanthotic SKs that are highly pigmented due to intermixed epidermal melanocytes and subepidermal melanophages.21 Dermoscopy can help distinguish cutaneous malignancies from SKs, which often demonstrate fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and milialike cysts. Biopsy sometimes is required to assess for malignancy, as was the case in our patient. The classic histologic features of SKs include acanthosis, papillomatosis, and hyperkeratosis.22
This case highlights the need to consider apocrine hidrocystoma, along with malignancy, in the differential diagnosis of pigmented cystic masses of the face and scalp. Because apocrine hidrocystomas are benign, they do not need to be treated but often are surgically excised for cosmesis or complete histopathologic examination. Destruction via electrodessication, carbon dioxide ablation, trichloroacetic acid chemical ablation, botulinum toxin injection, and anticholinergic creams sometimes is used, especially for cosmetic treatment of multiple small lesions.5 Our patient was treated with surgical excision with no evidence of recurrence on follow-up 1 year later.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Apocrine Hidrocystoma
Histology for all 3 lesions demonstrated similar cystic structures lined by a dual layer of epithelial cells, with the outermost layer composed of flattened myoepithelial cells and the inner layer composed of cells with apocrine features (Figure 1). Based on these findings, a diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma was made. The patient underwent successful surgical excision shortly thereafter without recurrence at follow-up 1 year later.
Apocrine hidrocystomas are rare benign cystic lesions that are considered to be adenomatous proliferations of apocrine glands. They typically manifest as solitary asymptomatic lesions measuring 3 to 15 mm.1 They tend to appear on the face, usually in the periorbital region, but also have been described on the neck, scalp, trunk, arms, and legs.2-4 Multiple apocrine hidrocystomas can be a marker of 2 rare inherited disorders: Gorlin-Goltz syndrome and Schopf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome.5 Apocrine hidrocystomas may be flesh colored or may have a blue, black, or brown appearance due to the Tyndall effect, in which light with shorter wavelengths is scattered by the contents of the lesions.2 Histologically, apocrine hidrocystomas are cysts lined by a dual layer of epithelial cells. The inner layer is composed of cells with apocrine features, and the outer layer is composed of flattened myoepithelial cells. Due to their range of colors and predilection for sun-exposed surfaces, apocrine hidrocystomas may be mistaken for various malignant neoplasms, including melanoma.6,7

The differential diagnosis for our patient included agminated blue nevi, melanoma, pigmented basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and seborrheic keratosis. A blue nevus is a dermal melanocytic lesion that manifests as a well-demarcated, blue to blue-black papule that typically appears on the face, scalp, arms, legs, lower back, and buttocks. Although there are several histologic subtypes, the common blue nevus usually manifests as a solitary lesion measuring less than 1 cm, often developing during childhood to young adulthood.8 Histologically, common blue nevi are characterized by a dermal proliferation of deeply pigmented bipolar spindled melanocytes embedded in thickened collagen bundles, often with scattered epithelioid melanophages, and no conspicuous mitotic activity (Figure 2).9 There are other types of blue nevi, including cellular blue nevi, which tend to be larger and manifest commonly on the buttocks and sacrococcygeal region in early adulthood.9 Histologically, cellular blue nevi contain oval to spindled melanocytes with scattered melanophages forming a well-demarcated nodule typically in the reticular dermis. There may be bulbous extension into the subcutaneous adipose tissue. Occasional mitoses may be seen.9,10 Melanoma can arise from common or cellular blue nevi, though it more frequently occurs with cellular blue nevi. Other subtypes of blue nevi have been described, including the sclerosing, plaque-type, combined, hypomelanotic/amelanotic, and pigmented epithelioid melanocytoma.11 However, they typically have features of the common blue nevus or cellular blue nevus, such as oval/spindle cell morphology, some degree of melanin, and biphasic architecture, but are classified according to their dominant histologic characteristics.

Given the location of our patient’s lesions on the scalp and his extensive history of sun exposure, malignancy was high in the differential. Multiple synchronous primary melanomas including nodular melanoma, blue nevus–like metastatic melanoma, and metastatic melanoma were considered. The leg and the scalp have the highest reported incidence of cutaneous metastases of melanoma, with many cases presenting as dermal or subcutaneous nodules and eruptive blue nevus–like papules, similar to our patient’s clinical presentation.12,13 Nodular melanoma (NM) is one of 4 major types of melanoma, accounting for approximately 15% to 30% of cases in the United States.14 Nodular melanoma typically manifests as a smooth, raised, symmetric, well-circumscribed lesion with variable pigmentation, from very dark to amelanotic. Histologically, NM is defined as a dermal mass, either in isolation or with an epidermal component, not to exceed 3 rete ridges beyond the dermal component.15 Tumor cells have a high cell density with pleomorphism, usually with atypical epithelioid cells with vesicular nuclei and irregular cytoplasm, and occasionally spindle cells (Figure 2).16 Mitoses and necrosis are frequent. Scalp location independently is responsible for worse survival, both overall and melanoma specific.17 Nodular melanoma tends to have greater Breslow thickness at diagnosis than other melanoma subtypes and often carries a worse prognosis.

Malignant melanomas that develop from or in conjunction with or bear histologic resemblance to blue nevi are termed blue nevus–like melanoma or blue nevus–associated melanoma. These malignancies are exceedingly rare, accounting for only 0.3% of melanomas in one Turkey-based multicenter study.18 The histologic criteria for diagnosing blue nevus–like melanoma are poorly defined, and terminology of these lesions has led to some debate in naming conventions.19 Nevertheless, unlike blue nevus, blue nevus–like melanoma demonstrates histologic features of malignancy, including pleomorphism, prominent nucleoli, mitotic activity, vascular invasion, and potential necrosis.10 The lack of an inflammatory infiltrate, surrounding fibrosis, junctional activity, and pre-existing nevus can help distinguish cutaneous melanoma metastases from primary nodular melanoma. Immunohistochemical stains such as S100, Melan-A/MART1, or SOX-10 can help confirm melanocytic lineage.12
Pigmented BCC is a clinical and histologic variant of BCC characterized by increased melanin pigmentation due to melanocytes admixed with tumor cells. Dermoscopically, the pigment can have a maple leaf–like appearance with spoke-wheel areas, in-focus dots, and concentric structures at the dermoepidermal junction, which is more characteristic of superficial and infiltrating BCC.20 In nodular BCC, the pigment occurs as blue-gray ovoid nests and globules in deeper layers of the dermis.20
Seborrheic keratoses (SKs) can vary widely in clinical appearance, with pigmentation ranging from flesh colored to yellow to brown to black. Melanoacanthomas are acanthotic SKs that are highly pigmented due to intermixed epidermal melanocytes and subepidermal melanophages.21 Dermoscopy can help distinguish cutaneous malignancies from SKs, which often demonstrate fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and milialike cysts. Biopsy sometimes is required to assess for malignancy, as was the case in our patient. The classic histologic features of SKs include acanthosis, papillomatosis, and hyperkeratosis.22
This case highlights the need to consider apocrine hidrocystoma, along with malignancy, in the differential diagnosis of pigmented cystic masses of the face and scalp. Because apocrine hidrocystomas are benign, they do not need to be treated but often are surgically excised for cosmesis or complete histopathologic examination. Destruction via electrodessication, carbon dioxide ablation, trichloroacetic acid chemical ablation, botulinum toxin injection, and anticholinergic creams sometimes is used, especially for cosmetic treatment of multiple small lesions.5 Our patient was treated with surgical excision with no evidence of recurrence on follow-up 1 year later.
- Ioannidis DG, Drivas EI, Papadakis CE, et al. Hidrocystoma of the external auditory canal: a case report. Cases J. 2009;2:79. doi:10.1186/1757- 1626-2-79
- Nguyen HP, Barker HS, Bloomquist L, et al. Giant pigmented apocrine hidrocystoma of the scalp. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26. doi:10.5070/D3268049895
- Mendoza-Cembranos MD, Haro R, Requena L, et al. Digital apocrine hidrocystoma: the exception confirms the rule. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:79. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000001044
- May C, Chang O, Compton N. A giant apocrine hidrocystoma of the trunk. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23. doi:10.5070/D3239036497
- Sarabi K, Khachemoune A. Hidrocystomas—a brief review. Medscape Gen Med. 2006;8:57.
- Kruse ALD, Zwahlen R, Bredell MG, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma of the cheek. J Craniofac Surg. 2010;21:594-596. doi:10.1097 /SCS.0b013e3181d08c77
- Zaballos P, Bañuls J, Medina C, et al. Dermoscopy of apocrine hidrocystomas: a morphological study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:378-381. doi:10.1111/jdv.12044
- Rodriguez HA, Ackerman LV. Cellular blue nevus. clinicopathologic study of forty-five cases. Cancer. 1968;21:393-405. doi:10.1002 /1097-0142(196803)21:3<393::aid-cncr2820210309>3.0.co;2-k
- Murali R, McCarthy SW, Scolyer RA. Blue nevi and related lesions: a review highlighting atypical and newly described variants, distinguishing features and diagnostic pitfalls. Adv Anat Pathol. 2009;16:365. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e3181bb6b53
- Borgenvik TL, Karlsvik TM, Ray S, et al. Blue nevus-like and blue nevusassociated melanoma: a comprehensive review of the literature. ANZ J Surg. 2017;87:345-349. doi:10.1111/ans.13946
- de la Fouchardiere A. Blue naevi and the blue tumour spectrum. Pathology. 2023;55:187-195. doi:10.1016/j.pathol.2022.12.342
- Lowe L. Metastatic melanoma and rare melanoma variants: a review. Pathology (Phila). 2023;55:236-244. doi:10.1016/j.pathol.2022.11.006
- Plaza JA, Torres-Cabala C, Evans H, et al. Cutaneous metastases of malignant melanoma: a clinicopathologic study of 192 cases with emphasis on the morphologic spectrum. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:129-136. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181b34a19
- Shaikh WR, Xiong M, Weinstock MA. The contribution of nodular subtype to melanoma mortality in the United States, 1978 to 2007. Archives of Dermatology. 2012;148:30-36. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2011.264
- Clark WH, From L, Bernardino EA, et al. The histogenesis and biologic behavior of primary human malignant melanomas of the skin. Cancer Res. 1969;29:705-727.
- Bobos M. Histopathologic classification and prognostic factors of melanoma: a 2021 update. Ital J Dermatol Venereol. 2021;156:300-321. doi:10.23736/S2784-8671.21.06958-3
- Ozao-Choy J, Nelson DW, Hiles J, et al. The prognostic importance of scalp location in primary head and neck melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 2017;116:337-343. doi:10.1002/jso.24679
- Gamsizkan M, Yilmaz I, Buyukbabani N, et al. A retrospective multicenter evaluation of cutaneous melanomas in Turkey. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP. 2014;15:10451-10456. doi:10.7314 /apjcp.2014.15.23.10451
- Mones JM, Ackerman AB. “Atypical” blue nevus, “malignant” blue nevus, and “metastasizing” blue nevus: a critique in historical perspective of three concepts flawed fatally. Am J Dermatopathol. 2004;26:407-430. doi:10.1097/00000372-200410000-00012
- Tanese K. Diagnosis and management of basal cell carcinoma Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2019;20:13. doi:10.1007/s11864 -019-0610-0
- Barthelmann S, Butsch F, Lang BM, et al. Seborrheic keratosis. JDDG J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2023;21:265-277. doi:10.1111/ddg.14984
- Taylor S. Advancing the understanding of seborrheic keratosis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:419-424.
- Ioannidis DG, Drivas EI, Papadakis CE, et al. Hidrocystoma of the external auditory canal: a case report. Cases J. 2009;2:79. doi:10.1186/1757- 1626-2-79
- Nguyen HP, Barker HS, Bloomquist L, et al. Giant pigmented apocrine hidrocystoma of the scalp. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26. doi:10.5070/D3268049895
- Mendoza-Cembranos MD, Haro R, Requena L, et al. Digital apocrine hidrocystoma: the exception confirms the rule. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:79. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000001044
- May C, Chang O, Compton N. A giant apocrine hidrocystoma of the trunk. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23. doi:10.5070/D3239036497
- Sarabi K, Khachemoune A. Hidrocystomas—a brief review. Medscape Gen Med. 2006;8:57.
- Kruse ALD, Zwahlen R, Bredell MG, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma of the cheek. J Craniofac Surg. 2010;21:594-596. doi:10.1097 /SCS.0b013e3181d08c77
- Zaballos P, Bañuls J, Medina C, et al. Dermoscopy of apocrine hidrocystomas: a morphological study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:378-381. doi:10.1111/jdv.12044
- Rodriguez HA, Ackerman LV. Cellular blue nevus. clinicopathologic study of forty-five cases. Cancer. 1968;21:393-405. doi:10.1002 /1097-0142(196803)21:3<393::aid-cncr2820210309>3.0.co;2-k
- Murali R, McCarthy SW, Scolyer RA. Blue nevi and related lesions: a review highlighting atypical and newly described variants, distinguishing features and diagnostic pitfalls. Adv Anat Pathol. 2009;16:365. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e3181bb6b53
- Borgenvik TL, Karlsvik TM, Ray S, et al. Blue nevus-like and blue nevusassociated melanoma: a comprehensive review of the literature. ANZ J Surg. 2017;87:345-349. doi:10.1111/ans.13946
- de la Fouchardiere A. Blue naevi and the blue tumour spectrum. Pathology. 2023;55:187-195. doi:10.1016/j.pathol.2022.12.342
- Lowe L. Metastatic melanoma and rare melanoma variants: a review. Pathology (Phila). 2023;55:236-244. doi:10.1016/j.pathol.2022.11.006
- Plaza JA, Torres-Cabala C, Evans H, et al. Cutaneous metastases of malignant melanoma: a clinicopathologic study of 192 cases with emphasis on the morphologic spectrum. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:129-136. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181b34a19
- Shaikh WR, Xiong M, Weinstock MA. The contribution of nodular subtype to melanoma mortality in the United States, 1978 to 2007. Archives of Dermatology. 2012;148:30-36. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2011.264
- Clark WH, From L, Bernardino EA, et al. The histogenesis and biologic behavior of primary human malignant melanomas of the skin. Cancer Res. 1969;29:705-727.
- Bobos M. Histopathologic classification and prognostic factors of melanoma: a 2021 update. Ital J Dermatol Venereol. 2021;156:300-321. doi:10.23736/S2784-8671.21.06958-3
- Ozao-Choy J, Nelson DW, Hiles J, et al. The prognostic importance of scalp location in primary head and neck melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 2017;116:337-343. doi:10.1002/jso.24679
- Gamsizkan M, Yilmaz I, Buyukbabani N, et al. A retrospective multicenter evaluation of cutaneous melanomas in Turkey. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP. 2014;15:10451-10456. doi:10.7314 /apjcp.2014.15.23.10451
- Mones JM, Ackerman AB. “Atypical” blue nevus, “malignant” blue nevus, and “metastasizing” blue nevus: a critique in historical perspective of three concepts flawed fatally. Am J Dermatopathol. 2004;26:407-430. doi:10.1097/00000372-200410000-00012
- Tanese K. Diagnosis and management of basal cell carcinoma Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2019;20:13. doi:10.1007/s11864 -019-0610-0
- Barthelmann S, Butsch F, Lang BM, et al. Seborrheic keratosis. JDDG J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2023;21:265-277. doi:10.1111/ddg.14984
- Taylor S. Advancing the understanding of seborrheic keratosis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:419-424.
A 67-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic with 3 asymptomatic pigmented papules on the scalp. The patient reported that he was unaware of the lesions until they were pointed out weeks earlier by his primary care physician during a routine visit. He then was referred to dermatology for follow-up. Physical examination at the current presentation revealed clustered firm, smooth, well-circumscribed, pigmented papules on the scalp measuring 5 to 8 mm. The patient reported no personal or family history of skin cancer but stated that he spent a lot of time outdoors and had a history of 6 blistering sunburns in his life. A punch biopsy of each lesion was performed.
Low-Dose Oral Naltrexone for Darier Disease
To the Editor:
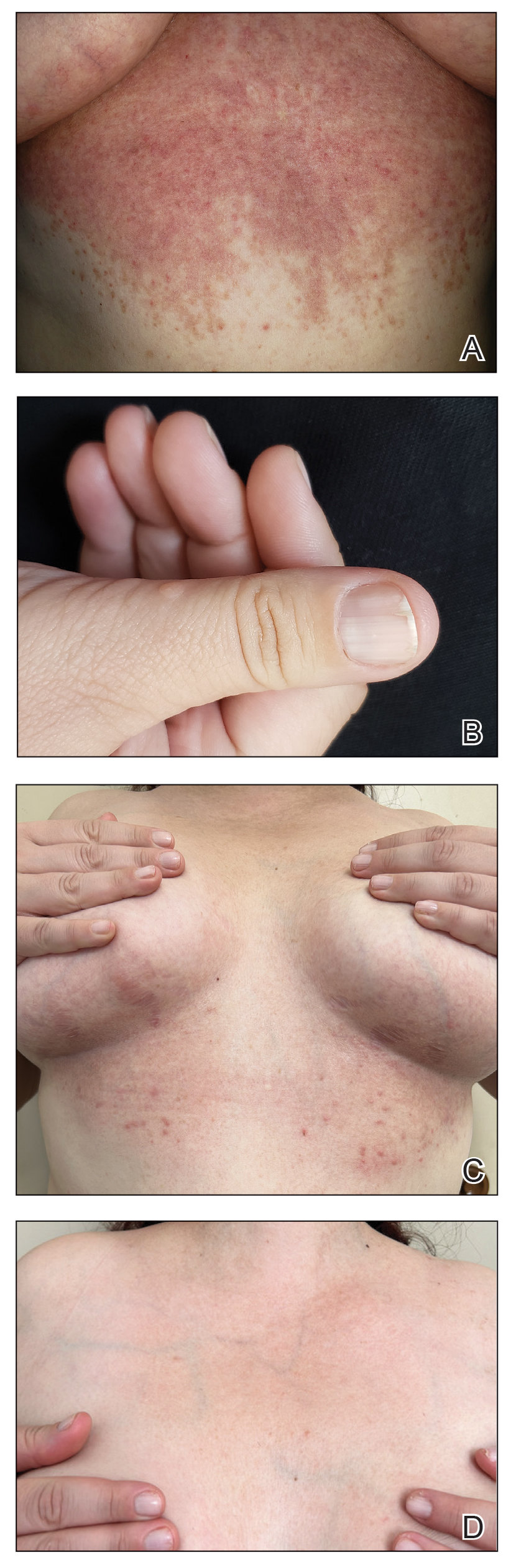
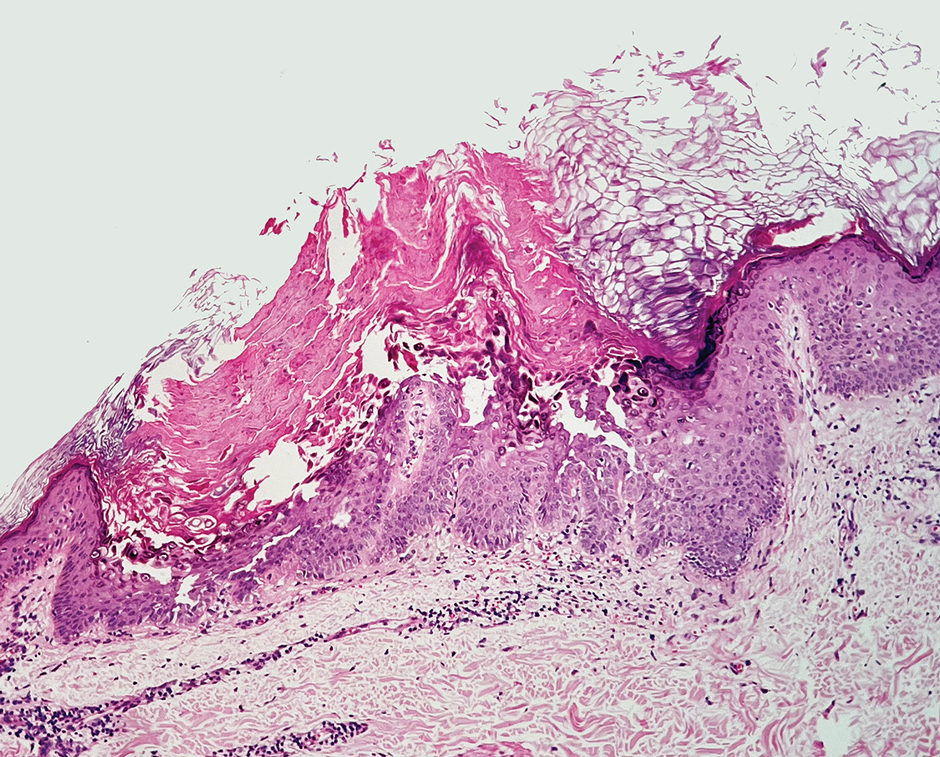
A 34-year-old Brazilian woman presented to the dermatology department with pruritic lesions on the neck and chest that had been present since adolescence. She reported a family history of Darier disease in her father. Physical examination revealed erythematous follicular papules on the neck, inframammary region, and abdomen (Figure 1A), as well as longitudinal bandlike leukonychia and distal nail splits on the fingernails (Figure 1B). Histopathology of a lesion on the back revealed compact hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis above an acantholytic cleft accompanied by dyskeratotic keratinocytes, including some corps ronds and grains, which supported the clinical impression of Darier disease (Figure 2). The typical clinical presentation along with the family history and histopathology confirmed the diagnosis. After therapeutic failure with topical corticosteroids and oral antibiotics for 3 months, low-dose oral naltrexone (4.5 mg/d) as monotherapy noticeably improved the lesions and pruritus within 2 months, with near-complete regression at 6 months, achieving disease stability (Figures 1C and 1D). The patient remained stable with no recurrence after 1 year of follow-up.
Darier disease is an autosomal-dominant genodermatosis caused by a mutation in the ATP2A2 gene, which encodes the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase, leading to defective intracellular calcium signaling and alterations in epidermal adhesion and keratinization.1 Darier disease typically begins in adolescence and is aggravated by exposure to heat and friction. It is characterized by seborrheic distribution of painful and pruritic red-brown keratotic papules. Nail manifestations include longitudinal ridges—erythronychia and/or leukonychia—and grooves that end in a V-shaped notch. The differential diagnosis includes Hailey-Hailey disease, psoriasis, and pityriasis rubra pilaris.1,2 The diagnosis is clinical and is confirmed by histopathology, which reveals suprabasal cleavage, acantholytic dyskeratosis, corps ronds, and grains. Treatment options are limited and include corticosteroids, oral and/or topical antibiotics, and systemic retinoids.2
Oral naltrexone has been used in Darier disease based on its observed effectiveness in Hailey-Hailey disease, considering the histopathologic similarities and alterations in calcium homeostasis in both conditions. Low-dose oral naltrexone (1-5 mg/d) increases the expression of opioid receptors (δ, μ, κ), enhancing its immunomodulatory and antinociceptive effects. The δ opioid receptor regulates the expression of desmoglein, improving epidermal differentiation and wound healing.3 Activation of the δ and μ receptors increases intracellular calcium through the inositol phosphate pathway, which contributes to calcium homeostasis.4 Naltrexone blocks the nonopioid toll-like receptor 4 found in keratinocytes and macrophages, exerting an anti-inflammatory effect by reducing proinflammatory cytokines.3 Adverse events associated with low-dose naltrexone are minimal, mostly mild, and often related to sleep disorders3,5; however, patients should undergo screening for prior opioid dependence, recent opioid usage, and signs of opioid withdrawal before initiating naltrexone treatment.5
Boehmer et al6 used naltrexone (4.5 mg/d) and oral magnesium (200 mg/d) in 6 patients with inconsistent results, except for 1 case that concurrently used acitretin (25 mg/d) with satisfactory improvement. Pessoa et al7 added naltrexone (4.5 mg/d) to oral isotretinoin (0.5 mg/kg/d) in 1 patient, resulting in notable improvement of lesions within 3 months.
In our patient with Darier disease, low-dose naltrexone demonstrated a substantial response as monotherapy after 2 months of treatment and nearly complete regression of lesions within 6 months, with no reported side effects after 1 year of follow-up. The use of low-dose naltrexone could be a promising and safe treatment option as monotherapy or in combination with conventional therapy for Darier disease; however, further studies are needed.
Sakuntabhai A, Ruiz-Perez V, Carter S, et al. Mutations in ATP2A2, encoding a Ca2+ pump, cause Darier disease. Nat Genet. 1999;21:271-277. doi:10.1038/6784
Burge SM, Wilkinson JD. Darier-White disease: a review of the clinical features in 163 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:40-50. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(92)70154-8
Lee B, Elston DM. The uses of naltrexone in dermatologic conditions. Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1746-1752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.031
Samways DSK, Henderson G. Opioid elevation of intracellular free calcium: possible mechanisms and physiological relevance. Cell Signal. 2006;18:151-161. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.08.005
Ekelem C, Juhasz M, Khera P, et al. Utility of naltrexone treatment for chronic inflammatory dermatologic conditions: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:229-236. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4093
Boehmer D, Eyerich K, Darsow U, et al. Variable response to low‐dose naltrexone in patients with Darier disease: a case series. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:950-953. doi:10.1111/jdv.15457
Pessoa T, Rebelo C, Gabriela Marques Pinto, et al. Combination of naltrexone and isotretinoin for the treatment of Darier disease. Cureus. 2023;15:E33321. doi:10.7759/cureus.33321
To the Editor:
A 34-year-old Brazilian woman presented to the dermatology department with pruritic lesions on the neck and chest that had been present since adolescence. She reported a family history of Darier disease in her father. Physical examination revealed erythematous follicular papules on the neck, inframammary region, and abdomen (Figure 1A), as well as longitudinal bandlike leukonychia and distal nail splits on the fingernails (Figure 1B). Histopathology of a lesion on the back revealed compact hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis above an acantholytic cleft accompanied by dyskeratotic keratinocytes, including some corps ronds and grains, which supported the clinical impression of Darier disease (Figure 2). The typical clinical presentation along with the family history and histopathology confirmed the diagnosis. After therapeutic failure with topical corticosteroids and oral antibiotics for 3 months, low-dose oral naltrexone (4.5 mg/d) as monotherapy noticeably improved the lesions and pruritus within 2 months, with near-complete regression at 6 months, achieving disease stability (Figures 1C and 1D). The patient remained stable with no recurrence after 1 year of follow-up.

Darier disease is an autosomal-dominant genodermatosis caused by a mutation in the ATP2A2 gene, which encodes the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase, leading to defective intracellular calcium signaling and alterations in epidermal adhesion and keratinization.1 Darier disease typically begins in adolescence and is aggravated by exposure to heat and friction. It is characterized by seborrheic distribution of painful and pruritic red-brown keratotic papules. Nail manifestations include longitudinal ridges—erythronychia and/or leukonychia—and grooves that end in a V-shaped notch. The differential diagnosis includes Hailey-Hailey disease, psoriasis, and pityriasis rubra pilaris.1,2 The diagnosis is clinical and is confirmed by histopathology, which reveals suprabasal cleavage, acantholytic dyskeratosis, corps ronds, and grains. Treatment options are limited and include corticosteroids, oral and/or topical antibiotics, and systemic retinoids.2

Oral naltrexone has been used in Darier disease based on its observed effectiveness in Hailey-Hailey disease, considering the histopathologic similarities and alterations in calcium homeostasis in both conditions. Low-dose oral naltrexone (1-5 mg/d) increases the expression of opioid receptors (δ, μ, κ), enhancing its immunomodulatory and antinociceptive effects. The δ opioid receptor regulates the expression of desmoglein, improving epidermal differentiation and wound healing.3 Activation of the δ and μ receptors increases intracellular calcium through the inositol phosphate pathway, which contributes to calcium homeostasis.4 Naltrexone blocks the nonopioid toll-like receptor 4 found in keratinocytes and macrophages, exerting an anti-inflammatory effect by reducing proinflammatory cytokines.3 Adverse events associated with low-dose naltrexone are minimal, mostly mild, and often related to sleep disorders3,5; however, patients should undergo screening for prior opioid dependence, recent opioid usage, and signs of opioid withdrawal before initiating naltrexone treatment.5
Boehmer et al6 used naltrexone (4.5 mg/d) and oral magnesium (200 mg/d) in 6 patients with inconsistent results, except for 1 case that concurrently used acitretin (25 mg/d) with satisfactory improvement. Pessoa et al7 added naltrexone (4.5 mg/d) to oral isotretinoin (0.5 mg/kg/d) in 1 patient, resulting in notable improvement of lesions within 3 months.
In our patient with Darier disease, low-dose naltrexone demonstrated a substantial response as monotherapy after 2 months of treatment and nearly complete regression of lesions within 6 months, with no reported side effects after 1 year of follow-up. The use of low-dose naltrexone could be a promising and safe treatment option as monotherapy or in combination with conventional therapy for Darier disease; however, further studies are needed.
To the Editor:
A 34-year-old Brazilian woman presented to the dermatology department with pruritic lesions on the neck and chest that had been present since adolescence. She reported a family history of Darier disease in her father. Physical examination revealed erythematous follicular papules on the neck, inframammary region, and abdomen (Figure 1A), as well as longitudinal bandlike leukonychia and distal nail splits on the fingernails (Figure 1B). Histopathology of a lesion on the back revealed compact hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis above an acantholytic cleft accompanied by dyskeratotic keratinocytes, including some corps ronds and grains, which supported the clinical impression of Darier disease (Figure 2). The typical clinical presentation along with the family history and histopathology confirmed the diagnosis. After therapeutic failure with topical corticosteroids and oral antibiotics for 3 months, low-dose oral naltrexone (4.5 mg/d) as monotherapy noticeably improved the lesions and pruritus within 2 months, with near-complete regression at 6 months, achieving disease stability (Figures 1C and 1D). The patient remained stable with no recurrence after 1 year of follow-up.

Darier disease is an autosomal-dominant genodermatosis caused by a mutation in the ATP2A2 gene, which encodes the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase, leading to defective intracellular calcium signaling and alterations in epidermal adhesion and keratinization.1 Darier disease typically begins in adolescence and is aggravated by exposure to heat and friction. It is characterized by seborrheic distribution of painful and pruritic red-brown keratotic papules. Nail manifestations include longitudinal ridges—erythronychia and/or leukonychia—and grooves that end in a V-shaped notch. The differential diagnosis includes Hailey-Hailey disease, psoriasis, and pityriasis rubra pilaris.1,2 The diagnosis is clinical and is confirmed by histopathology, which reveals suprabasal cleavage, acantholytic dyskeratosis, corps ronds, and grains. Treatment options are limited and include corticosteroids, oral and/or topical antibiotics, and systemic retinoids.2

Oral naltrexone has been used in Darier disease based on its observed effectiveness in Hailey-Hailey disease, considering the histopathologic similarities and alterations in calcium homeostasis in both conditions. Low-dose oral naltrexone (1-5 mg/d) increases the expression of opioid receptors (δ, μ, κ), enhancing its immunomodulatory and antinociceptive effects. The δ opioid receptor regulates the expression of desmoglein, improving epidermal differentiation and wound healing.3 Activation of the δ and μ receptors increases intracellular calcium through the inositol phosphate pathway, which contributes to calcium homeostasis.4 Naltrexone blocks the nonopioid toll-like receptor 4 found in keratinocytes and macrophages, exerting an anti-inflammatory effect by reducing proinflammatory cytokines.3 Adverse events associated with low-dose naltrexone are minimal, mostly mild, and often related to sleep disorders3,5; however, patients should undergo screening for prior opioid dependence, recent opioid usage, and signs of opioid withdrawal before initiating naltrexone treatment.5
Boehmer et al6 used naltrexone (4.5 mg/d) and oral magnesium (200 mg/d) in 6 patients with inconsistent results, except for 1 case that concurrently used acitretin (25 mg/d) with satisfactory improvement. Pessoa et al7 added naltrexone (4.5 mg/d) to oral isotretinoin (0.5 mg/kg/d) in 1 patient, resulting in notable improvement of lesions within 3 months.
In our patient with Darier disease, low-dose naltrexone demonstrated a substantial response as monotherapy after 2 months of treatment and nearly complete regression of lesions within 6 months, with no reported side effects after 1 year of follow-up. The use of low-dose naltrexone could be a promising and safe treatment option as monotherapy or in combination with conventional therapy for Darier disease; however, further studies are needed.
Sakuntabhai A, Ruiz-Perez V, Carter S, et al. Mutations in ATP2A2, encoding a Ca2+ pump, cause Darier disease. Nat Genet. 1999;21:271-277. doi:10.1038/6784
Burge SM, Wilkinson JD. Darier-White disease: a review of the clinical features in 163 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:40-50. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(92)70154-8
Lee B, Elston DM. The uses of naltrexone in dermatologic conditions. Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1746-1752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.031
Samways DSK, Henderson G. Opioid elevation of intracellular free calcium: possible mechanisms and physiological relevance. Cell Signal. 2006;18:151-161. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.08.005
Ekelem C, Juhasz M, Khera P, et al. Utility of naltrexone treatment for chronic inflammatory dermatologic conditions: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:229-236. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4093
Boehmer D, Eyerich K, Darsow U, et al. Variable response to low‐dose naltrexone in patients with Darier disease: a case series. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:950-953. doi:10.1111/jdv.15457
Pessoa T, Rebelo C, Gabriela Marques Pinto, et al. Combination of naltrexone and isotretinoin for the treatment of Darier disease. Cureus. 2023;15:E33321. doi:10.7759/cureus.33321
Sakuntabhai A, Ruiz-Perez V, Carter S, et al. Mutations in ATP2A2, encoding a Ca2+ pump, cause Darier disease. Nat Genet. 1999;21:271-277. doi:10.1038/6784
Burge SM, Wilkinson JD. Darier-White disease: a review of the clinical features in 163 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:40-50. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(92)70154-8
Lee B, Elston DM. The uses of naltrexone in dermatologic conditions. Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1746-1752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.031
Samways DSK, Henderson G. Opioid elevation of intracellular free calcium: possible mechanisms and physiological relevance. Cell Signal. 2006;18:151-161. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.08.005
Ekelem C, Juhasz M, Khera P, et al. Utility of naltrexone treatment for chronic inflammatory dermatologic conditions: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:229-236. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4093
Boehmer D, Eyerich K, Darsow U, et al. Variable response to low‐dose naltrexone in patients with Darier disease: a case series. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:950-953. doi:10.1111/jdv.15457
Pessoa T, Rebelo C, Gabriela Marques Pinto, et al. Combination of naltrexone and isotretinoin for the treatment of Darier disease. Cureus. 2023;15:E33321. doi:10.7759/cureus.33321
Practice Points
- Consider low-dose naltrexone as a potential treatment option for patients with Darier disease, as it regulates opioid receptors and has shown benefits in enhancing epidermal differentiation, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Further research is needed to validate the efficacy and safety of low-dose naltrexone in treating Darier disease considering its observed clinical improvement in this single patient case.
Evaluating Factors Impacting Hidradenitis Suppurativa Disease Severity in Patients With Darker Skin Types
Evaluating Factors Impacting Hidradenitis Suppurativa Disease Severity in Patients With Darker Skin Types
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a debilitating chronic skin disease that often affects apocrinebearing regions of the skin such as the axillae, perineum, and groin.1 Although current research on the etiology and pathogenesis of HS is limited, the disease is known to have a considerable psychosocial impact on patient quality of life.
Clinically, HS lesions manifest as tender subcutaneous nodules that rupture to form painful and deep dermal abscesses.2 These lesions typically develop due to hair follicle occlusion, followed by a cyclic process of inflammation, healing, re-inflammation, and scarring. Often, they are mistaken for cysts or a simple abscess in the early stages of the disease, leading to a delay in diagnosis.1 Disease severity is categorized based on Hurley staging: stage 1 involves abscess formation without scarring; stage 2 involves limited sinus tracts and recurrent abscesses with scarring and/or multiple separated lesions; and stage 3 is the most advanced stage, with diffuse involvement or multiple interconnected sinus tracts across an area with scarring. The condition primarily is medically managed with antibiotics and immunomodulators, but patients who have refractory disease can benefit from surgical excision.1,2
The prevalence of HS in the United States ranges from 0.77% to 1.19%, and individuals who self-identify as Black have 3-fold higher odds of having this condition compared with all other racial groups.3-5 Black patients also are thought to have a greater number and size of apocrine glands compared with patients who self-identify as White, suggesting an anatomic predisposition to developing HS and greater disease severity.6 However, despite HS disproportionately impacting individuals with skin of color (SOC), the majority of published HS research includes predominantly White patient cohorts.5 There is insufficient research assessing HS epidemiology, comorbidities, and treatment responses in patients with SOC.
A 2020 review reported the notable lack of clinical trials that sufficiently examine systemic medication treatment response in HS patients with SOC.7 Of the 15 HS treatment trials published from 2000 to 2019, only 16.4% (138/840) of the patient population were of African descent.7 Clinical trials investigating the efficacy of adalimumab in reducing HS burden also did not adequately evaluate clinical response in patients with SOC. One clinical trial did not include any Black patients as part of the cohort,8 and in 3 other studies, 80% to 85% of the study participants self-identified as White.9 The current literature does not reflect the patient populations most affected by HS, as several studies have reported that 65% of patients diagnosed with HS in the United States annually are Black.5,7 These results emphasize the underrepresentation of SOC populations in the current HS literature and the need for more research that investigates the disease processes, comorbidities, and treatment outcomes of the diverse patient population impacted by HS.
Methods
Study Population and Data Extraction—Following a protocol reviewed and approved by the MedStar Health/Georgetown University institutional review board (IRB #00006783), a retrospective chart review of 31 adult patients with HS who underwent surgery at a regional verified burn center from April 2014 to April 2023 was conducted. The following variables were collected from the electronic medical record (EMR): baseline demographics including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), obesity status, race, ethnicity, Fitzpatrick skin type, smoking status, substance use, employment status, and family history of HS; HS-specific details including Hurley staging, affected areas, and age at initial diagnosis; comorbidities such as dermatologic conditions, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, cardiovascular and associated diseases, ovarian disorders, gastrointestinal diseases, and othother common chronic comorbidities (psychiatric illness, kidney disease, type 2 diabetes [T2D], asthma, allergies, lymphedema, and inflammatory eye disease); and use of pharmacologics such as topical medications, oral antibiotics, immunomodulators, and steroids.
Study Definitions—Obesity was defined as both a continuous and categorical variable. Each patient’s BMI at the surgery date was recorded from the EMR as a continuous variable. Patients with obesity also had this condition listed under their complaints and problem list in the EMR, which was recorded as a categorical variable. Race and ethnicity were self-reported by patients. Comorbidity data, including T2D and hyperlipidemia, were defined by previously diagnosed diseases listed in the EMR. Pharmacologic medication data were included in the study if a patient was recommended/prescribed a medication and they had confirmed use of the medication in a subsequent office visit.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were calculated for demographics, HS characteristics (eg, location, Hurley stage), and comorbidities. Continuous variables were presented as mean and standard deviation or median and interquartile range and were evaluated using a t test or Mann-Whitney U test when appropriate. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages and tested for associations using the X2 or Fisher exact test. Data analyses were performed using SAS software version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc.).
Results
Thirty-one patients (17 females, 14 males; mean age, 40.9 years) were included in the study. Twenty-nine (93.5%) patients identified as Black. All study patients had at least 1 comorbidity. Obesity was diagnosed in 22 (71.0%) patients (mean BMI, 35.5 kg/m2). A total of 16 (51.6%) patients were current smokers, 3 (9.7%) were past smokers, 22 (71%) reported alcohol use, and 17 (54.8%) were active marijuana users. Only 3 (9.7%) patients had a family history of HS (Table 1).
Other common comorbidities associated with HS were anemia (64.5% [20/31]), a non–inflammatory bowel disease gastrointestinal disease (61.3% [19/31]), allergies (54.8% [17/31]), hypertension (41.9% [13/31]), cardiovascular disease (41.9% [13/31]), T2D (32.3% [10/31]), asthma (32.3% [10/31]), kidney disease (29.0% [9/31]), and atopic dermatitis (25.8% [8/31]). More than half (54.8% [17/31]) of patients were diagnosed with psychiatric illnesses, including depression, anxiety, bipolar depression, psychosis, anorexia, impulsive anger, hallucinations, delusion, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder, and panic disorder (Table 2). Depression was diagnosed in 38.7% (12/31) of patients, and 22.6% (7/31) were diagnosed with anxiety.
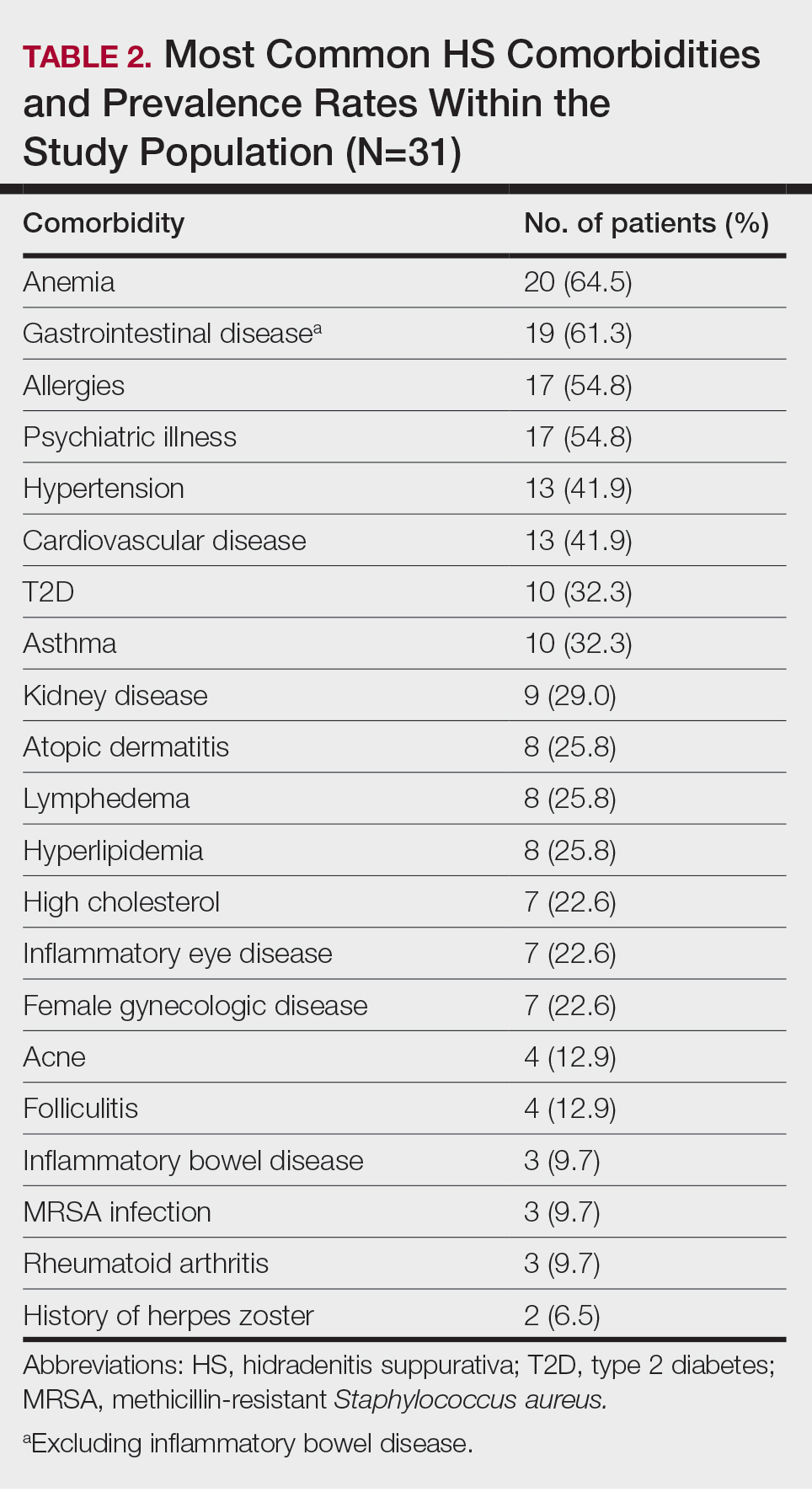
The most common anatomic locations for HS were the right axilla (74.2% [23/31]), left axilla (74.2% [23/31]), groin (71% [22/31]), perineum (61.3% [19/31]), buttocks (41.9% [13/31]), and thigh (41.9% [13/31]). Other locations included the breast, lower back, posterior neck, dorsal foot, and scalp (all 3.2% [1/31])(Table 3). Twenty (64.5%) patients had Hurley staging recorded in the EMR. Seventeen (54.8%) were categorized as Hurley stage 3, and 3 (9.7%) were categorized as Hurley stage 2.
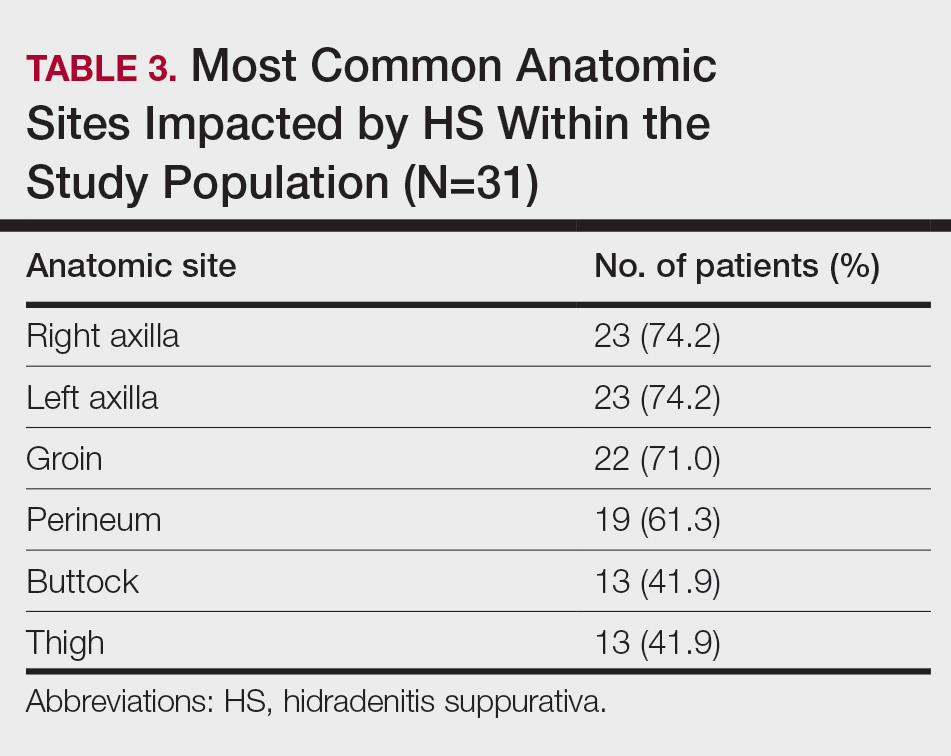
Twenty-nine (93.5%) patients were prescribed an oral antibiotic regimen. The most common oral antibiotics were clindamycin (35.5% [11/31]), doxycycline (35.5% [11/31]), rifampin (29% [9/31]), trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (22.6% [7/31]), and cephalexin (22.6% [7/31]). Of the patients who were prescribed rifampin, 87.5% (8/9) also were prescribed an adjunct oral clindamycin regimen. Twenty-nine percent (9/31) of patients were prescribed a biologic regimen; 22.6% (7/31) were prescribed adalimumab, 3.2% (1/31) were prescribed secukinumab, and 3.2% (1/31) were prescribed ustekinumab (Table 4).
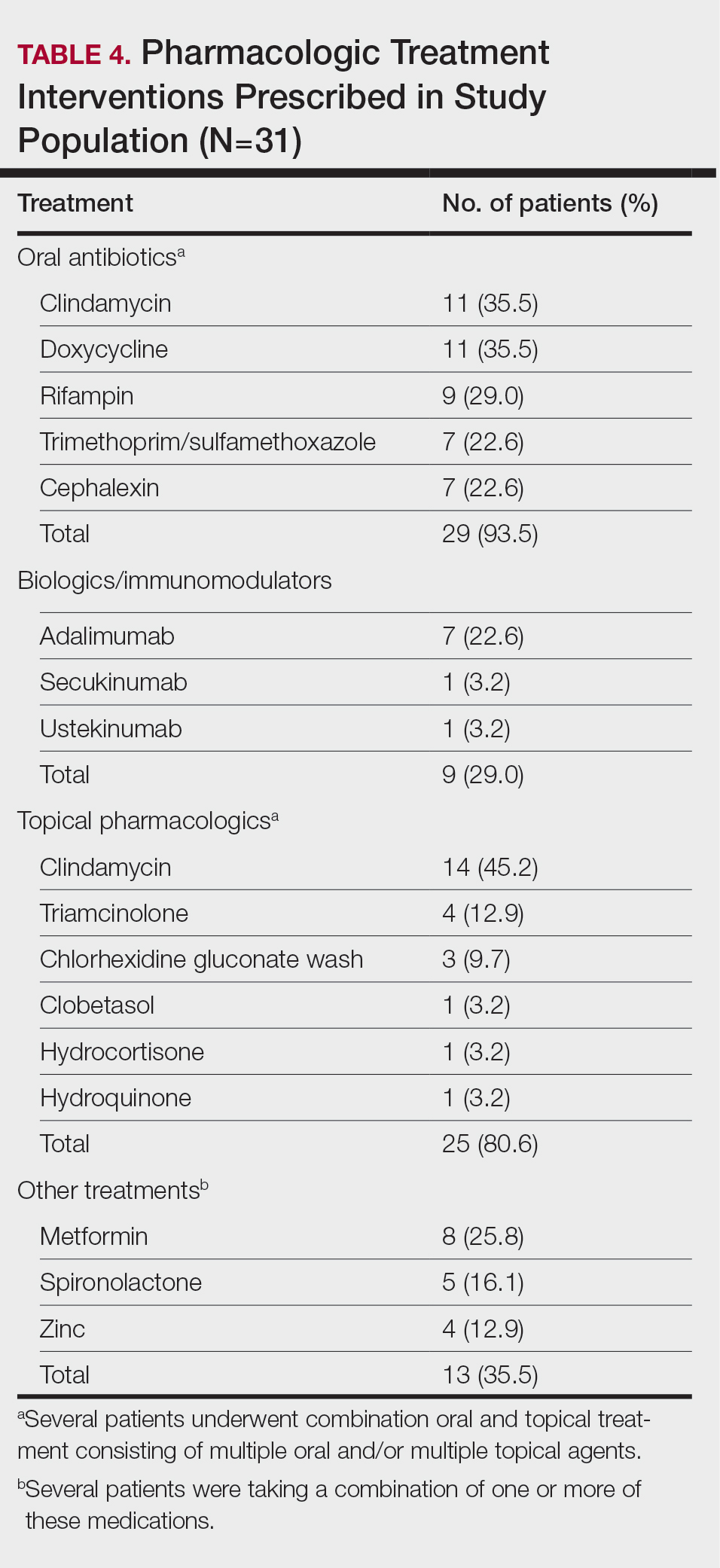
Twenty-five (80.6%) patients were prescribed a topical treatment regimen, the most common being topical clindamycin (45.2% [14/31]). Other topical medications included triamcinolone (12.9% [4/31]), chlorhexidine gluconate wash (9.7% [3/31]), clobetasol (3.2% [1/31]), hydrocortisone (3.2% [1/31]), and hydroquinone (3.2% [1/31])(Table 4).
Other medical treatments for HS included metformin (25.8% [8/31]), spironolactone (16.1% [5/31]), and zinc supplements (12.9% [4/31]). Four patients (12.9%) were prescribed clindamycin plus rifampin as well as a combination of metformin, spironolactone, and/or zinc (Table 4).
Twenty-two (71.0%) patients had a history of receiving incision and drainage procedures as treatment for HS. All 31 patients underwent excisional surgery followed by appropriate reconstruction. The total number of excisional surgeries a single patient underwent for HS treatment ranged from 1 to 9, with a mean of 2 excisional surgeries per patient.
Comment
Our regional verified burn center in Washington, DC, serves a large population of patients with SOC, making it a unique and important sample to study for HS. Our results suggest that Black patients with HS may be at a higher risk for depression and anxiety. Twelve (38.7%) of our patients were diagnosed with depression, which is substantially higher than the 17% to 21% depression prevalence rate among all HS patients reported in meta-analyses.10,11 Additionally, 22.6% (7/31) of our patients were diagnosed with anxiety, which is higher than the 5% to 12% prevalence rate of anxiety among HS patients reported in meta-analyses.10,11 The stress of chronic disease management, psychosocial impact of living with HS, social stigma, sexual dysfunction, pain, and financial concerns make mental illness a debilitating yet common comorbidity for patients with HS. The results of our study suggest that anxiety and depression are highly prevalent among Black patients with HS. It is important to identify if this finding is due to the interplay of health care disparities and social determinants of health; the cause likely is multifactorial, as race and ethnicity may be potential predictors for increased disease severity. Hidradenitis suppurativa is known to be a major economic burden on patients, and race-dependent structural and societal inequalities may be influencing the increased prevalence of anxiety and depression among Black patients with HS.12 Therefore, clinicians must be vigilant for the signs and symptoms of mental illnesses to refer patients for psychiatric treatment when appropriate. Implementing self-report Patient Health Questionnaire-9, General Anxiety Disorder-7 depression and anxiety screening tools, and Dermatology Life Quality Index questionnaires at primary care and dermatology office visits may be a beneficial step toward identifying patients who could benefit from additional mental health resources.13
The patients included in our study predominantly self-identified as Black, and the current smoker prevalence rate was 51.6% (16/31). This percentage is lower than the smoking rates of other published HS studies conducted in predominantly White patient populations, which report up to a 76.5% smoking prevalence rate.14-16 One review article published in 2022 reported that approximately 90% of HS patients are current or former smokers.17 Additionally, a retrospective cohort analysis identifying HS cases among 3,924,310 tobacco smokers in the United States reported that tobacco smokers diagnosed with HS most commonly racially self-identified as White (66.2%).18 Tobacco chemicals and smoke can increase inflammatory cytokine levels, and the activation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors surrounding pilosebaceous-apocrine units can increase follicular occlusion.14 While several studies1-3,14,19,20 support the strong correlation between tobacco smoking and HS, there are very few that specifically investigate the association between smoking and HS disease in SOC populations. It is possible that smoking rates may be lower in Black patients with HS compared with White patients with HS, which would suggest a multifactorial nature of HS disease pathophysiology. Future large, multicenter studies are needed that investigate smoking rates and HS disease severity in patients across various racial groups.
Prior research has shown a strong correlation between cigarette smoking and HS, but there is minimal data on the role of use of marijuana and other illicit drugs in HS disease pathophysiology.21 A total of 54.8% of our patients were active marijuana users with daily or weekly usage. Further research is needed to investigate whether marijuana use is linked with HS disease pathophysiology and severity or if patients with HS may be using marijuana to relieve pain, anxiety, and depression. Additional studies that survey the method of marijuana use (eg, joint, vape devices, or edibles) would clarify the relationship between not only HS and marijuana but also a potential link between disease severity and the process of inhaling large amounts of smoke vs a link with the active ingredients in the marijuana plant itself.
Approximately 61% (19/31) of our patients were diagnosed with a gastrointestinal disease in addition to HS. Current research reports the link between HS and inflammatory bowel disease, but few studies have investigated if a relationship exists between the gut microbiome and HS, as well as the incidence of general gastrointestinal disease among Black patients with HS.14,22 Our patients were diagnosed with gastrointestinal conditions such as colonic polyps, gastroesophageal reflux disease, benign neoplasms of the cecum and sigmoid colons, small bowel obstruction and perforation, biliary tract diseases, ileus, abdominal hernia, peritonitis, and diverticulosis. Further research is warranted to identify if there is a true relationship between gastrointestinal disease, the gut microbiome, and skin conditions such as HS.22 Biochemical research on the common genetic and inflammatory cytokine pathways involved in HS and gastrointestinal manifestations could help predict disease severity and management in HS patients with SOC.
Several research studies have reported the association between obesity and HS, likely due to adipose cells producing increased estrogen and leading to an estrogen-dominant hormone profile and increased local androgen production in adipose tissue.14,23,24 Antiandrogenic drugs such as finasteride and spironolactone lead to positive results in HS treatment compared to oral antibiotics alone.24 While 71.9% (22/31) of our patients were diagnosed with obesity, only 16.1% (5/31) were prescribed antiandrogen therapy such as spironolactone. It is unclear if this result reflects a health disparity due to insufficient insurance coverage and low prescribing rates or if there is patient hesitancy to taking antiandrogen medications. Additional clinical trials are needed to investigate the efficacy of antiandrogen therapies for HS. If proven to be efficacious, providers should consider adding these medications to the pharmacologic regimen of HS patients with SOC prior to recommending wide-excision surgeries. Furthermore, in addition to antiandrogen medication, weight-management interventions may be helpful in reducing HS disease. The results of a survey conducted in 35 HS patients who underwent bariatric surgery reported 48.6% (17/35) experienced complete disease remission after more than a 15% weight reduction.25,26 Investigating the impact of weight-management practices on disease severity would be helpful in outlining nonpharmacologic treatments for patients with HS.
Limitations
Our study was limited by the constraints of a retrospective chart review and small sample size. Retrospective chart reviews are susceptible to recall bias, variability in providers’ charting practices, and human error from data collectors. We acknowledge that a control group of non-HS patients should be the next step in furthering our research on HS disease comorbidities. Also, since 35.5% (11/31) of our patients did not have Hurley staging recorded in the EMR, it would be beneficial to conduct a future study comprehensive of all 3 Hurley stages. Since 93.5% (29/31) of the patients in our study racially identified as Black, having a control group of racially diverse HS patients would help further our understanding of HS pathophysiology. Lastly, since the inclusion criteria required patients to have undergone excisional surgery for HS, future studies that consider comorbidities among both surgical and nonsurgical patients with HS will aid in our understanding of HS patients with SOC.
Conclusion
The results of our study demonstrate a descriptive analysis of the demographics, most common comorbidities, lesion sites, pharmacologic treatments, and surgical profiles in patients with SOC who underwent surgical treatment for HS. Our data show that HS patients with SOC may be more likely to experience anxiety, depression, and gastrointestinal disease than other HS patients. Additionally, our patients had a high prevalence of marijuana use but lower prevalence of current cigarette use compared to studies conducted in predominantly White HS patient populations, emphasizing the multifactorial nature of HS pathophysiology. Furthermore, despite published research on the efficacy of immunomodulator therapy for HS, most of our HS patients with SOC underwent surgical intervention without first attempting biologic treatment regimens, indicating possible gaps in health care access for minority patients that may be impacting disease severity and outcomes. Studies such as this one that investigate disease pathophysiology and risk factors in SOC patient populations with HS are imperative in minimizing the health care disparity gap, improving disease outcomes, and providing more equitable health care for all patients.
- Wieczorek M, Walecka I. Hidradenitis suppurativa—known and unknown disease. Reumatologia. 2018;56:337-339. doi:10.5114/reum.2018.80709
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-563. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2008.11.911
- Garg A, Lavian J, Lin G, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States: a sex- and age-adjusted population analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:118-122. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.005
- Ingram JR, Jenkins-Jones S, Knipe DW, et al. Population-based Clinical Practice Research Datalink study using algorithm modelling to identify the true burden of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:917-924. doi:10.1111/bjd.16101
- Lee DE, Clark AK, Shi VY. Hidradenitis suppurativa: disease burden and etiology in skin of color. Dermatology. 2017;233:456-461. doi:10.1159/000486741
- Brown-Korsah JB, McKenzie S, Omar D, et al. Variations in genetics, biology, and phenotype of cutaneous disorders in skin of color—part I: genetic, biologic, and structural differences in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1239-1258. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.06.1193
- Narla S, Lyons AB, Hamzavi IH. The most recent advances in understanding and managing hidradenitis suppurativa. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-1049. doi:10.12688/f1000research.26083.1
- Arenbergerova M, Gkalpakiotis S, Arenberger P. Effective long-term control of refractory hidradenitis suppurativa with adalimumab after failure of conventional therapy. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49:1445-1449. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04638.x
- Kimball AB, Okun MM, Williams DA, et al. Two phase 3 trials of adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:422-434. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1504370
- Jalenques I, Ciortianu L, Pereira B, et al. The prevalence and odds of anxiety and depression in children and adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:542-553. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.041
- Machado MO, Stergiopoulos V, Maes M, et al. Depression and anxiety in adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:939-945. doi:10.1001 /jamadermatol.2019.0759
- Kilgour JM, Li S, Sarin KY. Hidradenitis suppurativa in patients of color is associated with increased disease severity and healthcare utilization: a retrospective analysis of 2 U.S. cohorts. JAAD Int. 2021;3:42-52. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.01.007
- Rymaszewska JE, Krajewski PK, Szcze² ch J, et al. Depression and anxiety in hidradenitis suppurativa patients: a cross-sectional study among Polish patients. Postep Dermatol Alergol. 2023;40:35-39. doi:10.5114ada.2022.119080
- Johnston LA, Alhusayen R, Bourcier M, et al. Practical guidelines for managing patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: an update. J Cutan Med Surg. 2022;26(2 suppl):2S-24S. doi:10.1177/12034754221116115
- Vazquez BG, Alikhan A, Weaver AL, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa and associated factors: a population-based study of Olmsted County, Minnesota. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:97-103. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.255
- Seyed Jafari SM, Knüsel E, Cazzaniga S, et al. A retrospective cohort study on patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatology. 2018;234:71-78. doi:10.1159/000488344
- Lewandowski M, S´ wierczewska Z, Baran´ ska-Rybak W. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of current treatment options. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:1152-1164. doi:10.1111/ijd.16115
- Garg A, Papagermanos V, Midura M, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa among tobacco smokers: a population-based retrospective analysis in the U.S.A. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:709-714. doi:10.1111/bjd.15939
- Garg A, Malviya N, Strunk A, et al. Comorbidity screening in hidradenitis suppurativa: evidence-based recommendations from the US and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1092-1101. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.01.059
- Tzellos T, Zouboulis CC. Which hidradenitis suppurativa comorbidities should I take into account? Exp Dermatol. 2022;31(suppl 1):29-32. doi:10.1111/exd.14633
- Metko D, Mehta S, Piguet V. Cannabis usage among patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a scoping review. J Cutan Med Surg. 2024;28:307-308. doi:10.1177/12034754241238719
- Mahmud MR, Akter S, Tamanna SK, et al. Impact of gut microbiome on skin health: gut-skin axis observed through the lenses of therapeutics and skin diseases. Gut Microbes. 2022;14:2096995. doi:10.1080/194 90976.2022.2096995
- Mair KM, Gaw R, MacLean MR. Obesity, estrogens and adipose tissue dysfunction—implications for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm Circ. 2020;10:2045894020952019. doi:10.1177/2045894020952023
- Abu Rached N, Gambichler T, Dietrich JW, et al. The role of hormones in hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:15250. doi:10.3390/ijms232315250
- Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: a publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations: part I: diagnosis, evaluation, and the use of complementary and procedural management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:76-90. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2019.02.067
- Choi ECE, Phan PHC, Oon HH. Hidradenitis suppurativa: racial and socioeconomic considerations in management. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:1452-1457. doi:10.1111/ijd.16163
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a debilitating chronic skin disease that often affects apocrinebearing regions of the skin such as the axillae, perineum, and groin.1 Although current research on the etiology and pathogenesis of HS is limited, the disease is known to have a considerable psychosocial impact on patient quality of life.
Clinically, HS lesions manifest as tender subcutaneous nodules that rupture to form painful and deep dermal abscesses.2 These lesions typically develop due to hair follicle occlusion, followed by a cyclic process of inflammation, healing, re-inflammation, and scarring. Often, they are mistaken for cysts or a simple abscess in the early stages of the disease, leading to a delay in diagnosis.1 Disease severity is categorized based on Hurley staging: stage 1 involves abscess formation without scarring; stage 2 involves limited sinus tracts and recurrent abscesses with scarring and/or multiple separated lesions; and stage 3 is the most advanced stage, with diffuse involvement or multiple interconnected sinus tracts across an area with scarring. The condition primarily is medically managed with antibiotics and immunomodulators, but patients who have refractory disease can benefit from surgical excision.1,2
The prevalence of HS in the United States ranges from 0.77% to 1.19%, and individuals who self-identify as Black have 3-fold higher odds of having this condition compared with all other racial groups.3-5 Black patients also are thought to have a greater number and size of apocrine glands compared with patients who self-identify as White, suggesting an anatomic predisposition to developing HS and greater disease severity.6 However, despite HS disproportionately impacting individuals with skin of color (SOC), the majority of published HS research includes predominantly White patient cohorts.5 There is insufficient research assessing HS epidemiology, comorbidities, and treatment responses in patients with SOC.
A 2020 review reported the notable lack of clinical trials that sufficiently examine systemic medication treatment response in HS patients with SOC.7 Of the 15 HS treatment trials published from 2000 to 2019, only 16.4% (138/840) of the patient population were of African descent.7 Clinical trials investigating the efficacy of adalimumab in reducing HS burden also did not adequately evaluate clinical response in patients with SOC. One clinical trial did not include any Black patients as part of the cohort,8 and in 3 other studies, 80% to 85% of the study participants self-identified as White.9 The current literature does not reflect the patient populations most affected by HS, as several studies have reported that 65% of patients diagnosed with HS in the United States annually are Black.5,7 These results emphasize the underrepresentation of SOC populations in the current HS literature and the need for more research that investigates the disease processes, comorbidities, and treatment outcomes of the diverse patient population impacted by HS.
Methods
Study Population and Data Extraction—Following a protocol reviewed and approved by the MedStar Health/Georgetown University institutional review board (IRB #00006783), a retrospective chart review of 31 adult patients with HS who underwent surgery at a regional verified burn center from April 2014 to April 2023 was conducted. The following variables were collected from the electronic medical record (EMR): baseline demographics including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), obesity status, race, ethnicity, Fitzpatrick skin type, smoking status, substance use, employment status, and family history of HS; HS-specific details including Hurley staging, affected areas, and age at initial diagnosis; comorbidities such as dermatologic conditions, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, cardiovascular and associated diseases, ovarian disorders, gastrointestinal diseases, and othother common chronic comorbidities (psychiatric illness, kidney disease, type 2 diabetes [T2D], asthma, allergies, lymphedema, and inflammatory eye disease); and use of pharmacologics such as topical medications, oral antibiotics, immunomodulators, and steroids.
Study Definitions—Obesity was defined as both a continuous and categorical variable. Each patient’s BMI at the surgery date was recorded from the EMR as a continuous variable. Patients with obesity also had this condition listed under their complaints and problem list in the EMR, which was recorded as a categorical variable. Race and ethnicity were self-reported by patients. Comorbidity data, including T2D and hyperlipidemia, were defined by previously diagnosed diseases listed in the EMR. Pharmacologic medication data were included in the study if a patient was recommended/prescribed a medication and they had confirmed use of the medication in a subsequent office visit.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were calculated for demographics, HS characteristics (eg, location, Hurley stage), and comorbidities. Continuous variables were presented as mean and standard deviation or median and interquartile range and were evaluated using a t test or Mann-Whitney U test when appropriate. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages and tested for associations using the X2 or Fisher exact test. Data analyses were performed using SAS software version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc.).
Results
Thirty-one patients (17 females, 14 males; mean age, 40.9 years) were included in the study. Twenty-nine (93.5%) patients identified as Black. All study patients had at least 1 comorbidity. Obesity was diagnosed in 22 (71.0%) patients (mean BMI, 35.5 kg/m2). A total of 16 (51.6%) patients were current smokers, 3 (9.7%) were past smokers, 22 (71%) reported alcohol use, and 17 (54.8%) were active marijuana users. Only 3 (9.7%) patients had a family history of HS (Table 1).

Other common comorbidities associated with HS were anemia (64.5% [20/31]), a non–inflammatory bowel disease gastrointestinal disease (61.3% [19/31]), allergies (54.8% [17/31]), hypertension (41.9% [13/31]), cardiovascular disease (41.9% [13/31]), T2D (32.3% [10/31]), asthma (32.3% [10/31]), kidney disease (29.0% [9/31]), and atopic dermatitis (25.8% [8/31]). More than half (54.8% [17/31]) of patients were diagnosed with psychiatric illnesses, including depression, anxiety, bipolar depression, psychosis, anorexia, impulsive anger, hallucinations, delusion, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder, and panic disorder (Table 2). Depression was diagnosed in 38.7% (12/31) of patients, and 22.6% (7/31) were diagnosed with anxiety.

The most common anatomic locations for HS were the right axilla (74.2% [23/31]), left axilla (74.2% [23/31]), groin (71% [22/31]), perineum (61.3% [19/31]), buttocks (41.9% [13/31]), and thigh (41.9% [13/31]). Other locations included the breast, lower back, posterior neck, dorsal foot, and scalp (all 3.2% [1/31])(Table 3). Twenty (64.5%) patients had Hurley staging recorded in the EMR. Seventeen (54.8%) were categorized as Hurley stage 3, and 3 (9.7%) were categorized as Hurley stage 2.

Twenty-nine (93.5%) patients were prescribed an oral antibiotic regimen. The most common oral antibiotics were clindamycin (35.5% [11/31]), doxycycline (35.5% [11/31]), rifampin (29% [9/31]), trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (22.6% [7/31]), and cephalexin (22.6% [7/31]). Of the patients who were prescribed rifampin, 87.5% (8/9) also were prescribed an adjunct oral clindamycin regimen. Twenty-nine percent (9/31) of patients were prescribed a biologic regimen; 22.6% (7/31) were prescribed adalimumab, 3.2% (1/31) were prescribed secukinumab, and 3.2% (1/31) were prescribed ustekinumab (Table 4).

Twenty-five (80.6%) patients were prescribed a topical treatment regimen, the most common being topical clindamycin (45.2% [14/31]). Other topical medications included triamcinolone (12.9% [4/31]), chlorhexidine gluconate wash (9.7% [3/31]), clobetasol (3.2% [1/31]), hydrocortisone (3.2% [1/31]), and hydroquinone (3.2% [1/31])(Table 4).
Other medical treatments for HS included metformin (25.8% [8/31]), spironolactone (16.1% [5/31]), and zinc supplements (12.9% [4/31]). Four patients (12.9%) were prescribed clindamycin plus rifampin as well as a combination of metformin, spironolactone, and/or zinc (Table 4).
Twenty-two (71.0%) patients had a history of receiving incision and drainage procedures as treatment for HS. All 31 patients underwent excisional surgery followed by appropriate reconstruction. The total number of excisional surgeries a single patient underwent for HS treatment ranged from 1 to 9, with a mean of 2 excisional surgeries per patient.
Comment
Our regional verified burn center in Washington, DC, serves a large population of patients with SOC, making it a unique and important sample to study for HS. Our results suggest that Black patients with HS may be at a higher risk for depression and anxiety. Twelve (38.7%) of our patients were diagnosed with depression, which is substantially higher than the 17% to 21% depression prevalence rate among all HS patients reported in meta-analyses.10,11 Additionally, 22.6% (7/31) of our patients were diagnosed with anxiety, which is higher than the 5% to 12% prevalence rate of anxiety among HS patients reported in meta-analyses.10,11 The stress of chronic disease management, psychosocial impact of living with HS, social stigma, sexual dysfunction, pain, and financial concerns make mental illness a debilitating yet common comorbidity for patients with HS. The results of our study suggest that anxiety and depression are highly prevalent among Black patients with HS. It is important to identify if this finding is due to the interplay of health care disparities and social determinants of health; the cause likely is multifactorial, as race and ethnicity may be potential predictors for increased disease severity. Hidradenitis suppurativa is known to be a major economic burden on patients, and race-dependent structural and societal inequalities may be influencing the increased prevalence of anxiety and depression among Black patients with HS.12 Therefore, clinicians must be vigilant for the signs and symptoms of mental illnesses to refer patients for psychiatric treatment when appropriate. Implementing self-report Patient Health Questionnaire-9, General Anxiety Disorder-7 depression and anxiety screening tools, and Dermatology Life Quality Index questionnaires at primary care and dermatology office visits may be a beneficial step toward identifying patients who could benefit from additional mental health resources.13
The patients included in our study predominantly self-identified as Black, and the current smoker prevalence rate was 51.6% (16/31). This percentage is lower than the smoking rates of other published HS studies conducted in predominantly White patient populations, which report up to a 76.5% smoking prevalence rate.14-16 One review article published in 2022 reported that approximately 90% of HS patients are current or former smokers.17 Additionally, a retrospective cohort analysis identifying HS cases among 3,924,310 tobacco smokers in the United States reported that tobacco smokers diagnosed with HS most commonly racially self-identified as White (66.2%).18 Tobacco chemicals and smoke can increase inflammatory cytokine levels, and the activation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors surrounding pilosebaceous-apocrine units can increase follicular occlusion.14 While several studies1-3,14,19,20 support the strong correlation between tobacco smoking and HS, there are very few that specifically investigate the association between smoking and HS disease in SOC populations. It is possible that smoking rates may be lower in Black patients with HS compared with White patients with HS, which would suggest a multifactorial nature of HS disease pathophysiology. Future large, multicenter studies are needed that investigate smoking rates and HS disease severity in patients across various racial groups.
Prior research has shown a strong correlation between cigarette smoking and HS, but there is minimal data on the role of use of marijuana and other illicit drugs in HS disease pathophysiology.21 A total of 54.8% of our patients were active marijuana users with daily or weekly usage. Further research is needed to investigate whether marijuana use is linked with HS disease pathophysiology and severity or if patients with HS may be using marijuana to relieve pain, anxiety, and depression. Additional studies that survey the method of marijuana use (eg, joint, vape devices, or edibles) would clarify the relationship between not only HS and marijuana but also a potential link between disease severity and the process of inhaling large amounts of smoke vs a link with the active ingredients in the marijuana plant itself.
Approximately 61% (19/31) of our patients were diagnosed with a gastrointestinal disease in addition to HS. Current research reports the link between HS and inflammatory bowel disease, but few studies have investigated if a relationship exists between the gut microbiome and HS, as well as the incidence of general gastrointestinal disease among Black patients with HS.14,22 Our patients were diagnosed with gastrointestinal conditions such as colonic polyps, gastroesophageal reflux disease, benign neoplasms of the cecum and sigmoid colons, small bowel obstruction and perforation, biliary tract diseases, ileus, abdominal hernia, peritonitis, and diverticulosis. Further research is warranted to identify if there is a true relationship between gastrointestinal disease, the gut microbiome, and skin conditions such as HS.22 Biochemical research on the common genetic and inflammatory cytokine pathways involved in HS and gastrointestinal manifestations could help predict disease severity and management in HS patients with SOC.
Several research studies have reported the association between obesity and HS, likely due to adipose cells producing increased estrogen and leading to an estrogen-dominant hormone profile and increased local androgen production in adipose tissue.14,23,24 Antiandrogenic drugs such as finasteride and spironolactone lead to positive results in HS treatment compared to oral antibiotics alone.24 While 71.9% (22/31) of our patients were diagnosed with obesity, only 16.1% (5/31) were prescribed antiandrogen therapy such as spironolactone. It is unclear if this result reflects a health disparity due to insufficient insurance coverage and low prescribing rates or if there is patient hesitancy to taking antiandrogen medications. Additional clinical trials are needed to investigate the efficacy of antiandrogen therapies for HS. If proven to be efficacious, providers should consider adding these medications to the pharmacologic regimen of HS patients with SOC prior to recommending wide-excision surgeries. Furthermore, in addition to antiandrogen medication, weight-management interventions may be helpful in reducing HS disease. The results of a survey conducted in 35 HS patients who underwent bariatric surgery reported 48.6% (17/35) experienced complete disease remission after more than a 15% weight reduction.25,26 Investigating the impact of weight-management practices on disease severity would be helpful in outlining nonpharmacologic treatments for patients with HS.
Limitations
Our study was limited by the constraints of a retrospective chart review and small sample size. Retrospective chart reviews are susceptible to recall bias, variability in providers’ charting practices, and human error from data collectors. We acknowledge that a control group of non-HS patients should be the next step in furthering our research on HS disease comorbidities. Also, since 35.5% (11/31) of our patients did not have Hurley staging recorded in the EMR, it would be beneficial to conduct a future study comprehensive of all 3 Hurley stages. Since 93.5% (29/31) of the patients in our study racially identified as Black, having a control group of racially diverse HS patients would help further our understanding of HS pathophysiology. Lastly, since the inclusion criteria required patients to have undergone excisional surgery for HS, future studies that consider comorbidities among both surgical and nonsurgical patients with HS will aid in our understanding of HS patients with SOC.
Conclusion
The results of our study demonstrate a descriptive analysis of the demographics, most common comorbidities, lesion sites, pharmacologic treatments, and surgical profiles in patients with SOC who underwent surgical treatment for HS. Our data show that HS patients with SOC may be more likely to experience anxiety, depression, and gastrointestinal disease than other HS patients. Additionally, our patients had a high prevalence of marijuana use but lower prevalence of current cigarette use compared to studies conducted in predominantly White HS patient populations, emphasizing the multifactorial nature of HS pathophysiology. Furthermore, despite published research on the efficacy of immunomodulator therapy for HS, most of our HS patients with SOC underwent surgical intervention without first attempting biologic treatment regimens, indicating possible gaps in health care access for minority patients that may be impacting disease severity and outcomes. Studies such as this one that investigate disease pathophysiology and risk factors in SOC patient populations with HS are imperative in minimizing the health care disparity gap, improving disease outcomes, and providing more equitable health care for all patients.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a debilitating chronic skin disease that often affects apocrinebearing regions of the skin such as the axillae, perineum, and groin.1 Although current research on the etiology and pathogenesis of HS is limited, the disease is known to have a considerable psychosocial impact on patient quality of life.
Clinically, HS lesions manifest as tender subcutaneous nodules that rupture to form painful and deep dermal abscesses.2 These lesions typically develop due to hair follicle occlusion, followed by a cyclic process of inflammation, healing, re-inflammation, and scarring. Often, they are mistaken for cysts or a simple abscess in the early stages of the disease, leading to a delay in diagnosis.1 Disease severity is categorized based on Hurley staging: stage 1 involves abscess formation without scarring; stage 2 involves limited sinus tracts and recurrent abscesses with scarring and/or multiple separated lesions; and stage 3 is the most advanced stage, with diffuse involvement or multiple interconnected sinus tracts across an area with scarring. The condition primarily is medically managed with antibiotics and immunomodulators, but patients who have refractory disease can benefit from surgical excision.1,2
The prevalence of HS in the United States ranges from 0.77% to 1.19%, and individuals who self-identify as Black have 3-fold higher odds of having this condition compared with all other racial groups.3-5 Black patients also are thought to have a greater number and size of apocrine glands compared with patients who self-identify as White, suggesting an anatomic predisposition to developing HS and greater disease severity.6 However, despite HS disproportionately impacting individuals with skin of color (SOC), the majority of published HS research includes predominantly White patient cohorts.5 There is insufficient research assessing HS epidemiology, comorbidities, and treatment responses in patients with SOC.
A 2020 review reported the notable lack of clinical trials that sufficiently examine systemic medication treatment response in HS patients with SOC.7 Of the 15 HS treatment trials published from 2000 to 2019, only 16.4% (138/840) of the patient population were of African descent.7 Clinical trials investigating the efficacy of adalimumab in reducing HS burden also did not adequately evaluate clinical response in patients with SOC. One clinical trial did not include any Black patients as part of the cohort,8 and in 3 other studies, 80% to 85% of the study participants self-identified as White.9 The current literature does not reflect the patient populations most affected by HS, as several studies have reported that 65% of patients diagnosed with HS in the United States annually are Black.5,7 These results emphasize the underrepresentation of SOC populations in the current HS literature and the need for more research that investigates the disease processes, comorbidities, and treatment outcomes of the diverse patient population impacted by HS.
Methods
Study Population and Data Extraction—Following a protocol reviewed and approved by the MedStar Health/Georgetown University institutional review board (IRB #00006783), a retrospective chart review of 31 adult patients with HS who underwent surgery at a regional verified burn center from April 2014 to April 2023 was conducted. The following variables were collected from the electronic medical record (EMR): baseline demographics including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), obesity status, race, ethnicity, Fitzpatrick skin type, smoking status, substance use, employment status, and family history of HS; HS-specific details including Hurley staging, affected areas, and age at initial diagnosis; comorbidities such as dermatologic conditions, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, cardiovascular and associated diseases, ovarian disorders, gastrointestinal diseases, and othother common chronic comorbidities (psychiatric illness, kidney disease, type 2 diabetes [T2D], asthma, allergies, lymphedema, and inflammatory eye disease); and use of pharmacologics such as topical medications, oral antibiotics, immunomodulators, and steroids.
Study Definitions—Obesity was defined as both a continuous and categorical variable. Each patient’s BMI at the surgery date was recorded from the EMR as a continuous variable. Patients with obesity also had this condition listed under their complaints and problem list in the EMR, which was recorded as a categorical variable. Race and ethnicity were self-reported by patients. Comorbidity data, including T2D and hyperlipidemia, were defined by previously diagnosed diseases listed in the EMR. Pharmacologic medication data were included in the study if a patient was recommended/prescribed a medication and they had confirmed use of the medication in a subsequent office visit.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were calculated for demographics, HS characteristics (eg, location, Hurley stage), and comorbidities. Continuous variables were presented as mean and standard deviation or median and interquartile range and were evaluated using a t test or Mann-Whitney U test when appropriate. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages and tested for associations using the X2 or Fisher exact test. Data analyses were performed using SAS software version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc.).
Results
Thirty-one patients (17 females, 14 males; mean age, 40.9 years) were included in the study. Twenty-nine (93.5%) patients identified as Black. All study patients had at least 1 comorbidity. Obesity was diagnosed in 22 (71.0%) patients (mean BMI, 35.5 kg/m2). A total of 16 (51.6%) patients were current smokers, 3 (9.7%) were past smokers, 22 (71%) reported alcohol use, and 17 (54.8%) were active marijuana users. Only 3 (9.7%) patients had a family history of HS (Table 1).

Other common comorbidities associated with HS were anemia (64.5% [20/31]), a non–inflammatory bowel disease gastrointestinal disease (61.3% [19/31]), allergies (54.8% [17/31]), hypertension (41.9% [13/31]), cardiovascular disease (41.9% [13/31]), T2D (32.3% [10/31]), asthma (32.3% [10/31]), kidney disease (29.0% [9/31]), and atopic dermatitis (25.8% [8/31]). More than half (54.8% [17/31]) of patients were diagnosed with psychiatric illnesses, including depression, anxiety, bipolar depression, psychosis, anorexia, impulsive anger, hallucinations, delusion, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder, and panic disorder (Table 2). Depression was diagnosed in 38.7% (12/31) of patients, and 22.6% (7/31) were diagnosed with anxiety.

The most common anatomic locations for HS were the right axilla (74.2% [23/31]), left axilla (74.2% [23/31]), groin (71% [22/31]), perineum (61.3% [19/31]), buttocks (41.9% [13/31]), and thigh (41.9% [13/31]). Other locations included the breast, lower back, posterior neck, dorsal foot, and scalp (all 3.2% [1/31])(Table 3). Twenty (64.5%) patients had Hurley staging recorded in the EMR. Seventeen (54.8%) were categorized as Hurley stage 3, and 3 (9.7%) were categorized as Hurley stage 2.

Twenty-nine (93.5%) patients were prescribed an oral antibiotic regimen. The most common oral antibiotics were clindamycin (35.5% [11/31]), doxycycline (35.5% [11/31]), rifampin (29% [9/31]), trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (22.6% [7/31]), and cephalexin (22.6% [7/31]). Of the patients who were prescribed rifampin, 87.5% (8/9) also were prescribed an adjunct oral clindamycin regimen. Twenty-nine percent (9/31) of patients were prescribed a biologic regimen; 22.6% (7/31) were prescribed adalimumab, 3.2% (1/31) were prescribed secukinumab, and 3.2% (1/31) were prescribed ustekinumab (Table 4).

Twenty-five (80.6%) patients were prescribed a topical treatment regimen, the most common being topical clindamycin (45.2% [14/31]). Other topical medications included triamcinolone (12.9% [4/31]), chlorhexidine gluconate wash (9.7% [3/31]), clobetasol (3.2% [1/31]), hydrocortisone (3.2% [1/31]), and hydroquinone (3.2% [1/31])(Table 4).
Other medical treatments for HS included metformin (25.8% [8/31]), spironolactone (16.1% [5/31]), and zinc supplements (12.9% [4/31]). Four patients (12.9%) were prescribed clindamycin plus rifampin as well as a combination of metformin, spironolactone, and/or zinc (Table 4).
Twenty-two (71.0%) patients had a history of receiving incision and drainage procedures as treatment for HS. All 31 patients underwent excisional surgery followed by appropriate reconstruction. The total number of excisional surgeries a single patient underwent for HS treatment ranged from 1 to 9, with a mean of 2 excisional surgeries per patient.
Comment
Our regional verified burn center in Washington, DC, serves a large population of patients with SOC, making it a unique and important sample to study for HS. Our results suggest that Black patients with HS may be at a higher risk for depression and anxiety. Twelve (38.7%) of our patients were diagnosed with depression, which is substantially higher than the 17% to 21% depression prevalence rate among all HS patients reported in meta-analyses.10,11 Additionally, 22.6% (7/31) of our patients were diagnosed with anxiety, which is higher than the 5% to 12% prevalence rate of anxiety among HS patients reported in meta-analyses.10,11 The stress of chronic disease management, psychosocial impact of living with HS, social stigma, sexual dysfunction, pain, and financial concerns make mental illness a debilitating yet common comorbidity for patients with HS. The results of our study suggest that anxiety and depression are highly prevalent among Black patients with HS. It is important to identify if this finding is due to the interplay of health care disparities and social determinants of health; the cause likely is multifactorial, as race and ethnicity may be potential predictors for increased disease severity. Hidradenitis suppurativa is known to be a major economic burden on patients, and race-dependent structural and societal inequalities may be influencing the increased prevalence of anxiety and depression among Black patients with HS.12 Therefore, clinicians must be vigilant for the signs and symptoms of mental illnesses to refer patients for psychiatric treatment when appropriate. Implementing self-report Patient Health Questionnaire-9, General Anxiety Disorder-7 depression and anxiety screening tools, and Dermatology Life Quality Index questionnaires at primary care and dermatology office visits may be a beneficial step toward identifying patients who could benefit from additional mental health resources.13
The patients included in our study predominantly self-identified as Black, and the current smoker prevalence rate was 51.6% (16/31). This percentage is lower than the smoking rates of other published HS studies conducted in predominantly White patient populations, which report up to a 76.5% smoking prevalence rate.14-16 One review article published in 2022 reported that approximately 90% of HS patients are current or former smokers.17 Additionally, a retrospective cohort analysis identifying HS cases among 3,924,310 tobacco smokers in the United States reported that tobacco smokers diagnosed with HS most commonly racially self-identified as White (66.2%).18 Tobacco chemicals and smoke can increase inflammatory cytokine levels, and the activation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors surrounding pilosebaceous-apocrine units can increase follicular occlusion.14 While several studies1-3,14,19,20 support the strong correlation between tobacco smoking and HS, there are very few that specifically investigate the association between smoking and HS disease in SOC populations. It is possible that smoking rates may be lower in Black patients with HS compared with White patients with HS, which would suggest a multifactorial nature of HS disease pathophysiology. Future large, multicenter studies are needed that investigate smoking rates and HS disease severity in patients across various racial groups.
Prior research has shown a strong correlation between cigarette smoking and HS, but there is minimal data on the role of use of marijuana and other illicit drugs in HS disease pathophysiology.21 A total of 54.8% of our patients were active marijuana users with daily or weekly usage. Further research is needed to investigate whether marijuana use is linked with HS disease pathophysiology and severity or if patients with HS may be using marijuana to relieve pain, anxiety, and depression. Additional studies that survey the method of marijuana use (eg, joint, vape devices, or edibles) would clarify the relationship between not only HS and marijuana but also a potential link between disease severity and the process of inhaling large amounts of smoke vs a link with the active ingredients in the marijuana plant itself.
Approximately 61% (19/31) of our patients were diagnosed with a gastrointestinal disease in addition to HS. Current research reports the link between HS and inflammatory bowel disease, but few studies have investigated if a relationship exists between the gut microbiome and HS, as well as the incidence of general gastrointestinal disease among Black patients with HS.14,22 Our patients were diagnosed with gastrointestinal conditions such as colonic polyps, gastroesophageal reflux disease, benign neoplasms of the cecum and sigmoid colons, small bowel obstruction and perforation, biliary tract diseases, ileus, abdominal hernia, peritonitis, and diverticulosis. Further research is warranted to identify if there is a true relationship between gastrointestinal disease, the gut microbiome, and skin conditions such as HS.22 Biochemical research on the common genetic and inflammatory cytokine pathways involved in HS and gastrointestinal manifestations could help predict disease severity and management in HS patients with SOC.
Several research studies have reported the association between obesity and HS, likely due to adipose cells producing increased estrogen and leading to an estrogen-dominant hormone profile and increased local androgen production in adipose tissue.14,23,24 Antiandrogenic drugs such as finasteride and spironolactone lead to positive results in HS treatment compared to oral antibiotics alone.24 While 71.9% (22/31) of our patients were diagnosed with obesity, only 16.1% (5/31) were prescribed antiandrogen therapy such as spironolactone. It is unclear if this result reflects a health disparity due to insufficient insurance coverage and low prescribing rates or if there is patient hesitancy to taking antiandrogen medications. Additional clinical trials are needed to investigate the efficacy of antiandrogen therapies for HS. If proven to be efficacious, providers should consider adding these medications to the pharmacologic regimen of HS patients with SOC prior to recommending wide-excision surgeries. Furthermore, in addition to antiandrogen medication, weight-management interventions may be helpful in reducing HS disease. The results of a survey conducted in 35 HS patients who underwent bariatric surgery reported 48.6% (17/35) experienced complete disease remission after more than a 15% weight reduction.25,26 Investigating the impact of weight-management practices on disease severity would be helpful in outlining nonpharmacologic treatments for patients with HS.
Limitations
Our study was limited by the constraints of a retrospective chart review and small sample size. Retrospective chart reviews are susceptible to recall bias, variability in providers’ charting practices, and human error from data collectors. We acknowledge that a control group of non-HS patients should be the next step in furthering our research on HS disease comorbidities. Also, since 35.5% (11/31) of our patients did not have Hurley staging recorded in the EMR, it would be beneficial to conduct a future study comprehensive of all 3 Hurley stages. Since 93.5% (29/31) of the patients in our study racially identified as Black, having a control group of racially diverse HS patients would help further our understanding of HS pathophysiology. Lastly, since the inclusion criteria required patients to have undergone excisional surgery for HS, future studies that consider comorbidities among both surgical and nonsurgical patients with HS will aid in our understanding of HS patients with SOC.
Conclusion
The results of our study demonstrate a descriptive analysis of the demographics, most common comorbidities, lesion sites, pharmacologic treatments, and surgical profiles in patients with SOC who underwent surgical treatment for HS. Our data show that HS patients with SOC may be more likely to experience anxiety, depression, and gastrointestinal disease than other HS patients. Additionally, our patients had a high prevalence of marijuana use but lower prevalence of current cigarette use compared to studies conducted in predominantly White HS patient populations, emphasizing the multifactorial nature of HS pathophysiology. Furthermore, despite published research on the efficacy of immunomodulator therapy for HS, most of our HS patients with SOC underwent surgical intervention without first attempting biologic treatment regimens, indicating possible gaps in health care access for minority patients that may be impacting disease severity and outcomes. Studies such as this one that investigate disease pathophysiology and risk factors in SOC patient populations with HS are imperative in minimizing the health care disparity gap, improving disease outcomes, and providing more equitable health care for all patients.
- Wieczorek M, Walecka I. Hidradenitis suppurativa—known and unknown disease. Reumatologia. 2018;56:337-339. doi:10.5114/reum.2018.80709
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-563. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2008.11.911
- Garg A, Lavian J, Lin G, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States: a sex- and age-adjusted population analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:118-122. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.005
- Ingram JR, Jenkins-Jones S, Knipe DW, et al. Population-based Clinical Practice Research Datalink study using algorithm modelling to identify the true burden of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:917-924. doi:10.1111/bjd.16101
- Lee DE, Clark AK, Shi VY. Hidradenitis suppurativa: disease burden and etiology in skin of color. Dermatology. 2017;233:456-461. doi:10.1159/000486741
- Brown-Korsah JB, McKenzie S, Omar D, et al. Variations in genetics, biology, and phenotype of cutaneous disorders in skin of color—part I: genetic, biologic, and structural differences in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1239-1258. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.06.1193
- Narla S, Lyons AB, Hamzavi IH. The most recent advances in understanding and managing hidradenitis suppurativa. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-1049. doi:10.12688/f1000research.26083.1
- Arenbergerova M, Gkalpakiotis S, Arenberger P. Effective long-term control of refractory hidradenitis suppurativa with adalimumab after failure of conventional therapy. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49:1445-1449. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04638.x
- Kimball AB, Okun MM, Williams DA, et al. Two phase 3 trials of adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:422-434. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1504370
- Jalenques I, Ciortianu L, Pereira B, et al. The prevalence and odds of anxiety and depression in children and adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:542-553. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.041
- Machado MO, Stergiopoulos V, Maes M, et al. Depression and anxiety in adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:939-945. doi:10.1001 /jamadermatol.2019.0759
- Kilgour JM, Li S, Sarin KY. Hidradenitis suppurativa in patients of color is associated with increased disease severity and healthcare utilization: a retrospective analysis of 2 U.S. cohorts. JAAD Int. 2021;3:42-52. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.01.007
- Rymaszewska JE, Krajewski PK, Szcze² ch J, et al. Depression and anxiety in hidradenitis suppurativa patients: a cross-sectional study among Polish patients. Postep Dermatol Alergol. 2023;40:35-39. doi:10.5114ada.2022.119080
- Johnston LA, Alhusayen R, Bourcier M, et al. Practical guidelines for managing patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: an update. J Cutan Med Surg. 2022;26(2 suppl):2S-24S. doi:10.1177/12034754221116115
- Vazquez BG, Alikhan A, Weaver AL, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa and associated factors: a population-based study of Olmsted County, Minnesota. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:97-103. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.255
- Seyed Jafari SM, Knüsel E, Cazzaniga S, et al. A retrospective cohort study on patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatology. 2018;234:71-78. doi:10.1159/000488344
- Lewandowski M, S´ wierczewska Z, Baran´ ska-Rybak W. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of current treatment options. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:1152-1164. doi:10.1111/ijd.16115
- Garg A, Papagermanos V, Midura M, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa among tobacco smokers: a population-based retrospective analysis in the U.S.A. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:709-714. doi:10.1111/bjd.15939
- Garg A, Malviya N, Strunk A, et al. Comorbidity screening in hidradenitis suppurativa: evidence-based recommendations from the US and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1092-1101. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.01.059
- Tzellos T, Zouboulis CC. Which hidradenitis suppurativa comorbidities should I take into account? Exp Dermatol. 2022;31(suppl 1):29-32. doi:10.1111/exd.14633
- Metko D, Mehta S, Piguet V. Cannabis usage among patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a scoping review. J Cutan Med Surg. 2024;28:307-308. doi:10.1177/12034754241238719
- Mahmud MR, Akter S, Tamanna SK, et al. Impact of gut microbiome on skin health: gut-skin axis observed through the lenses of therapeutics and skin diseases. Gut Microbes. 2022;14:2096995. doi:10.1080/194 90976.2022.2096995
- Mair KM, Gaw R, MacLean MR. Obesity, estrogens and adipose tissue dysfunction—implications for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm Circ. 2020;10:2045894020952019. doi:10.1177/2045894020952023
- Abu Rached N, Gambichler T, Dietrich JW, et al. The role of hormones in hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:15250. doi:10.3390/ijms232315250
- Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: a publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations: part I: diagnosis, evaluation, and the use of complementary and procedural management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:76-90. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2019.02.067
- Choi ECE, Phan PHC, Oon HH. Hidradenitis suppurativa: racial and socioeconomic considerations in management. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:1452-1457. doi:10.1111/ijd.16163
- Wieczorek M, Walecka I. Hidradenitis suppurativa—known and unknown disease. Reumatologia. 2018;56:337-339. doi:10.5114/reum.2018.80709
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-563. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2008.11.911
- Garg A, Lavian J, Lin G, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States: a sex- and age-adjusted population analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:118-122. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.005
- Ingram JR, Jenkins-Jones S, Knipe DW, et al. Population-based Clinical Practice Research Datalink study using algorithm modelling to identify the true burden of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:917-924. doi:10.1111/bjd.16101
- Lee DE, Clark AK, Shi VY. Hidradenitis suppurativa: disease burden and etiology in skin of color. Dermatology. 2017;233:456-461. doi:10.1159/000486741
- Brown-Korsah JB, McKenzie S, Omar D, et al. Variations in genetics, biology, and phenotype of cutaneous disorders in skin of color—part I: genetic, biologic, and structural differences in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1239-1258. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.06.1193
- Narla S, Lyons AB, Hamzavi IH. The most recent advances in understanding and managing hidradenitis suppurativa. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-1049. doi:10.12688/f1000research.26083.1
- Arenbergerova M, Gkalpakiotis S, Arenberger P. Effective long-term control of refractory hidradenitis suppurativa with adalimumab after failure of conventional therapy. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49:1445-1449. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04638.x
- Kimball AB, Okun MM, Williams DA, et al. Two phase 3 trials of adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:422-434. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1504370
- Jalenques I, Ciortianu L, Pereira B, et al. The prevalence and odds of anxiety and depression in children and adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:542-553. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.041
- Machado MO, Stergiopoulos V, Maes M, et al. Depression and anxiety in adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:939-945. doi:10.1001 /jamadermatol.2019.0759
- Kilgour JM, Li S, Sarin KY. Hidradenitis suppurativa in patients of color is associated with increased disease severity and healthcare utilization: a retrospective analysis of 2 U.S. cohorts. JAAD Int. 2021;3:42-52. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.01.007
- Rymaszewska JE, Krajewski PK, Szcze² ch J, et al. Depression and anxiety in hidradenitis suppurativa patients: a cross-sectional study among Polish patients. Postep Dermatol Alergol. 2023;40:35-39. doi:10.5114ada.2022.119080
- Johnston LA, Alhusayen R, Bourcier M, et al. Practical guidelines for managing patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: an update. J Cutan Med Surg. 2022;26(2 suppl):2S-24S. doi:10.1177/12034754221116115
- Vazquez BG, Alikhan A, Weaver AL, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa and associated factors: a population-based study of Olmsted County, Minnesota. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:97-103. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.255
- Seyed Jafari SM, Knüsel E, Cazzaniga S, et al. A retrospective cohort study on patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatology. 2018;234:71-78. doi:10.1159/000488344
- Lewandowski M, S´ wierczewska Z, Baran´ ska-Rybak W. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of current treatment options. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:1152-1164. doi:10.1111/ijd.16115
- Garg A, Papagermanos V, Midura M, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa among tobacco smokers: a population-based retrospective analysis in the U.S.A. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:709-714. doi:10.1111/bjd.15939
- Garg A, Malviya N, Strunk A, et al. Comorbidity screening in hidradenitis suppurativa: evidence-based recommendations from the US and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1092-1101. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.01.059
- Tzellos T, Zouboulis CC. Which hidradenitis suppurativa comorbidities should I take into account? Exp Dermatol. 2022;31(suppl 1):29-32. doi:10.1111/exd.14633
- Metko D, Mehta S, Piguet V. Cannabis usage among patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a scoping review. J Cutan Med Surg. 2024;28:307-308. doi:10.1177/12034754241238719
- Mahmud MR, Akter S, Tamanna SK, et al. Impact of gut microbiome on skin health: gut-skin axis observed through the lenses of therapeutics and skin diseases. Gut Microbes. 2022;14:2096995. doi:10.1080/194 90976.2022.2096995
- Mair KM, Gaw R, MacLean MR. Obesity, estrogens and adipose tissue dysfunction—implications for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm Circ. 2020;10:2045894020952019. doi:10.1177/2045894020952023
- Abu Rached N, Gambichler T, Dietrich JW, et al. The role of hormones in hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:15250. doi:10.3390/ijms232315250
- Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: a publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations: part I: diagnosis, evaluation, and the use of complementary and procedural management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:76-90. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2019.02.067
- Choi ECE, Phan PHC, Oon HH. Hidradenitis suppurativa: racial and socioeconomic considerations in management. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:1452-1457. doi:10.1111/ijd.16163
Evaluating Factors Impacting Hidradenitis Suppurativa Disease Severity in Patients With Darker Skin Types
Evaluating Factors Impacting Hidradenitis Suppurativa Disease Severity in Patients With Darker Skin Types
PRACTICE POINTS
- Anxiety and depression are highly prevalent among Black patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). Implementing self-report questionnaires at medical office visits are crucial to identifying patients who could benefit from additional psychiatric resources.
- Hidradenitis suppurativa patients with skin of color may have a higher incidence of comorbid gastrointestinal disease than other HS patients.
- Investigating the impact of weight-management practices on disease severity would be helpful in outlining nonpharmacologic treatments for patients with HS.
- The patient cohort described here had a high prevalence of marijuana use but lower prevalence of current cigarette use compared to studies conducted in predominantly White HS patient populations, emphasizing the multifactorial nature of HS pathophysiology.
Evaluating Access to Full-Body Skin Examinations in Los Angeles County, California
Evaluating Access to Full-Body Skin Examinations in Los Angeles County, California
To the Editor:
Early skin cancer detection improves patient outcomes1; however, socioeconomic and racial disparities may impact access to dermatologic care.2 Although non-Hispanic White individuals have a high incidence of skin cancer, they experience higher melanoma-specific survival rates than non-White patients, who often receive later-stage diagnoses and experience higher mortality.2 Furthermore, racial/ ethnic minorities often face longer surgery wait times after diagnosis and have lower socioeconomic status (SES) and less favorable health insurance coverage, contributing to poorer outcomes.2,3
To examine access to full-body skin examinations (FBSEs) by board-certified dermatologists in Los Angeles (LA) County, California, we analyzed the availability of FBSEs based on racial demographics, income, and insurance type (Medicaid [Medi-Cal] vs private [Blue Cross Blue Shield (BCBS)]). Demographic data by zip code were obtained from the US Census Bureau.4 This validated metric highlights socioeconomic disparities and minimizes data gaps5,6 and was used to assess health care access among different population subgroups. Dermatologists’ contact information was obtained from the Find a Dermatologist page on the American Academy of Dermatology website and the listed phone numbers of their practice were used to contact them. Practices with board-certified dermatologists accepting new patients were included in the study; practices were not included if they had exclusive insurance plans; were pediatric, cosmetic, or research only; or were nonresponsive to calls. From August 2022 to September 2022, each practice was called twice within a 36-hour period—once by a simulated patient with Medi-Cal and once by a simulated patient with BCBS—and were asked about availability for new patient FBSE appointments and accepted insurance types. Data were analyzed using SAS software (SAS Institute Inc.).
Los Angeles County comprises 269 zip codes, of which 82 (30.5%) have dermatology practices. Of 213 total dermatologists in LA County listed on the American Academy of Dermatology website, 193 (90.6%) met preliminary criteria, and 169 (79.3%) were successfully contacted. Almost all (94.6% [160/169]) accepted new patients for FBSEs; of those, 63.1% (101/160) accepted only private insurance, 16.9% (27/160) accepted both private insurance and Medi-Cal, and 16.2% (26/160) did not accept any insurance. Racial predominance for each dermatology practice was analyzed by zip code (Table). Dermatologists included in our study were significantly more concentrated in predominantly non- Hispanic White areas of LA County vs predominantly Hispanic areas (P<.0001). Notably, the average income in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes ($114,757.74) was significantly higher than in predominantly Hispanic areas ($58,278.54)(P=.001)(Table).4
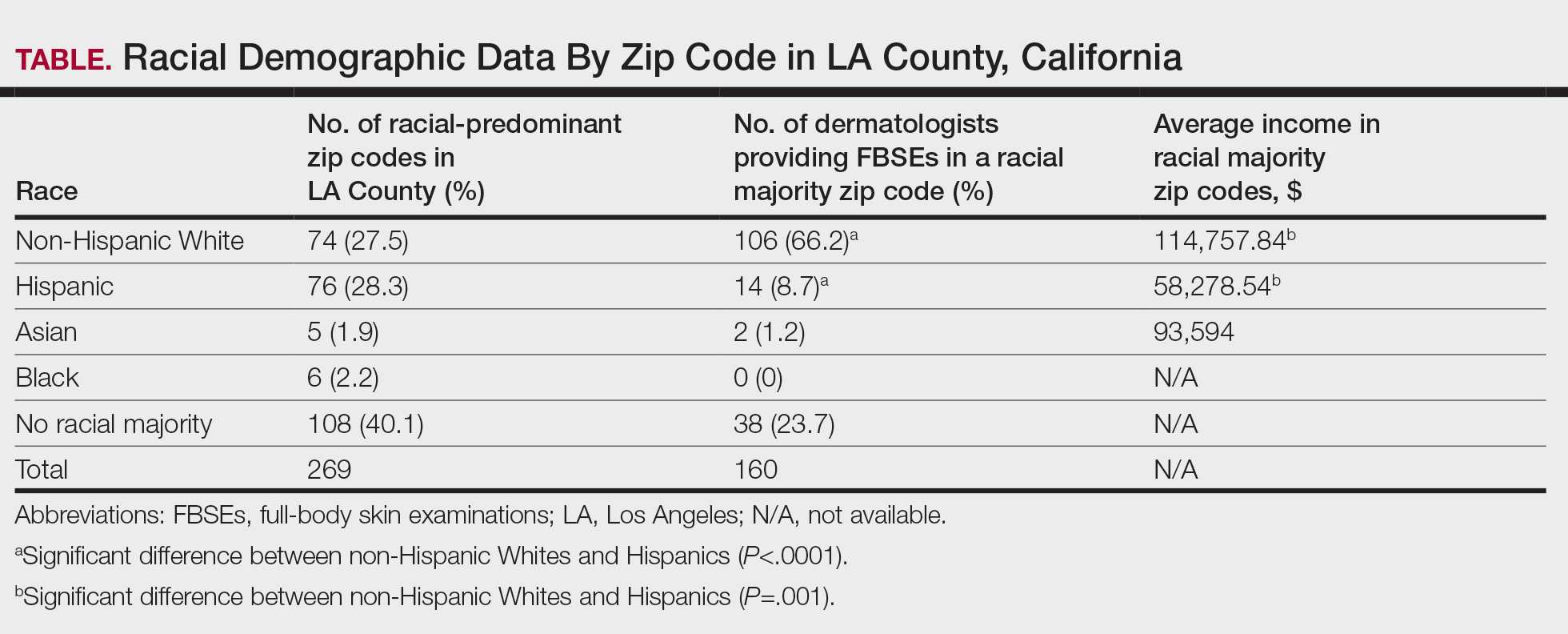
In LA County, 40.1% (108/269) of zip codes have no racial majority, 28.2% (76/269) are predominantly Hispanic, 27.5% (74/269) are predominantly non-Hispanic White, 2.2% (6/269) are predominantly Black, and 1.9% (5/269) are predominantly Asian.4 There are no dermatologists in predominantly Black zip codes, 2 in predominantly Asian zip codes, 14 in predominantly Hispanic zip codes, 38 in zip codes with no racial majority, and 106 in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes. There are significantly more dermatologists in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes compared to predominantly Hispanic zip codes (P<.0001). In LA County, the average income in predominantly Asian, non-Hispanic White, and Hispanic zip codes was $93,594, $114,757.84, and $58,278.54, respectively, in 2021.4 The average income in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes was significantly higher than in predominantly Hispanic zip codes (P=.001). There were no income data available for predominantly Black zip codes or zip codes with no racial majority.
The results from our study revealed potential barriers to FBSEs for racial and ethnic minorities in LA County, which supports previous research on the impact of SES, race, and insurance on access to dermatologic care.2,3 Predominantly Hispanic zip codes have significantly lower income (P<.0001) and fewer dermatologists (P=.001) compared to zip codes that are predominantly non-Hispanic White, reflecting how lower SES correlates with worse health outcomes and higher melanoma mortality. Conversely, predominantly non-Hispanic White areas with higher income have better access to dermatologists, which may contribute to the improved melanoma survival rates among White patients. Additionally, most dermatologists accept only private insurance, further highlighting the disparity in FBSE access for non-White patients across LA County. While our study focused on FBSE access, our findings may point to a wider barrier to dermatologic care, especially in zip codes with fewer dermatologists. Further studies are needed to determine whether these areas also face barriers to accessing primary care.
Our study was limited by the exclusion of nonphysician providers (eg, nurse practitioners, physician assistants), a small sample size, and lack of available economic data for predominantly Black zip codes.4 Additionally, the exclusion of practices with exclusive insurance plans (eg, Kaiser Permanente) limited the generalizability of our findings, as our results did not account for the populations served by these practices. Furthermore, our analysis did not account for variations in practice size or the proportion of care provided to patients with different insurance types, which could impact overall accessibility. Additional studies are needed to explore the impact of these factors on access to general dermatologic care and not just FBSEs.
Racial/ethnic minorities and lower SES populations face major barriers to FBSE access in LA County, such as difficulty finding a dermatologist in their area or one who accepts Medi-Cal. Addressing these disparities is crucial for improving skin cancer outcomes. Further research is needed to develop strategies to eliminate these barriers to dermatologic care, such as increasing access to teledermatology, offering mobile dermatology clinics, and improving insurance coverage.
- Chiaravalloti AJ, Laduca JR. Melanoma screening by means of complete skin exams for all patients in a dermatology practice reduces the thickness of primary melanomas at diagnosis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:18-22.
- Qian Y, Johannet P, Sawyers A, et al. The ongoing racial disparities in melanoma: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (1975-2016). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1585-1593.
- Baranowski MLH, Yeung H, Chen SC, et al. Factors associated with time to surgery in melanoma: an analysis of the National Cancer Database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:908-916.
- United States Census Bureau. Explore census data. Accessed March 17, 2025. https://data.census.gov/all?q=los+angeles+county
- Berkowitz SA, Traore CY, Singer DE, et al. Evaluating area-based socioeconomic status indicators for monitoring disparities within health care systems: results from a primary care network. Health Serv Res. 2015;50:398-417.
- Jacobs B, Ir P, Bigdeli M, et al. Addressing access barriers to health services: an analytical framework for selecting appropriate interventions in lowincome Asian countries. Health Policy Plan. 2012;27:288-300.
To the Editor:
Early skin cancer detection improves patient outcomes1; however, socioeconomic and racial disparities may impact access to dermatologic care.2 Although non-Hispanic White individuals have a high incidence of skin cancer, they experience higher melanoma-specific survival rates than non-White patients, who often receive later-stage diagnoses and experience higher mortality.2 Furthermore, racial/ ethnic minorities often face longer surgery wait times after diagnosis and have lower socioeconomic status (SES) and less favorable health insurance coverage, contributing to poorer outcomes.2,3
To examine access to full-body skin examinations (FBSEs) by board-certified dermatologists in Los Angeles (LA) County, California, we analyzed the availability of FBSEs based on racial demographics, income, and insurance type (Medicaid [Medi-Cal] vs private [Blue Cross Blue Shield (BCBS)]). Demographic data by zip code were obtained from the US Census Bureau.4 This validated metric highlights socioeconomic disparities and minimizes data gaps5,6 and was used to assess health care access among different population subgroups. Dermatologists’ contact information was obtained from the Find a Dermatologist page on the American Academy of Dermatology website and the listed phone numbers of their practice were used to contact them. Practices with board-certified dermatologists accepting new patients were included in the study; practices were not included if they had exclusive insurance plans; were pediatric, cosmetic, or research only; or were nonresponsive to calls. From August 2022 to September 2022, each practice was called twice within a 36-hour period—once by a simulated patient with Medi-Cal and once by a simulated patient with BCBS—and were asked about availability for new patient FBSE appointments and accepted insurance types. Data were analyzed using SAS software (SAS Institute Inc.).
Los Angeles County comprises 269 zip codes, of which 82 (30.5%) have dermatology practices. Of 213 total dermatologists in LA County listed on the American Academy of Dermatology website, 193 (90.6%) met preliminary criteria, and 169 (79.3%) were successfully contacted. Almost all (94.6% [160/169]) accepted new patients for FBSEs; of those, 63.1% (101/160) accepted only private insurance, 16.9% (27/160) accepted both private insurance and Medi-Cal, and 16.2% (26/160) did not accept any insurance. Racial predominance for each dermatology practice was analyzed by zip code (Table). Dermatologists included in our study were significantly more concentrated in predominantly non- Hispanic White areas of LA County vs predominantly Hispanic areas (P<.0001). Notably, the average income in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes ($114,757.74) was significantly higher than in predominantly Hispanic areas ($58,278.54)(P=.001)(Table).4

In LA County, 40.1% (108/269) of zip codes have no racial majority, 28.2% (76/269) are predominantly Hispanic, 27.5% (74/269) are predominantly non-Hispanic White, 2.2% (6/269) are predominantly Black, and 1.9% (5/269) are predominantly Asian.4 There are no dermatologists in predominantly Black zip codes, 2 in predominantly Asian zip codes, 14 in predominantly Hispanic zip codes, 38 in zip codes with no racial majority, and 106 in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes. There are significantly more dermatologists in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes compared to predominantly Hispanic zip codes (P<.0001). In LA County, the average income in predominantly Asian, non-Hispanic White, and Hispanic zip codes was $93,594, $114,757.84, and $58,278.54, respectively, in 2021.4 The average income in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes was significantly higher than in predominantly Hispanic zip codes (P=.001). There were no income data available for predominantly Black zip codes or zip codes with no racial majority.
The results from our study revealed potential barriers to FBSEs for racial and ethnic minorities in LA County, which supports previous research on the impact of SES, race, and insurance on access to dermatologic care.2,3 Predominantly Hispanic zip codes have significantly lower income (P<.0001) and fewer dermatologists (P=.001) compared to zip codes that are predominantly non-Hispanic White, reflecting how lower SES correlates with worse health outcomes and higher melanoma mortality. Conversely, predominantly non-Hispanic White areas with higher income have better access to dermatologists, which may contribute to the improved melanoma survival rates among White patients. Additionally, most dermatologists accept only private insurance, further highlighting the disparity in FBSE access for non-White patients across LA County. While our study focused on FBSE access, our findings may point to a wider barrier to dermatologic care, especially in zip codes with fewer dermatologists. Further studies are needed to determine whether these areas also face barriers to accessing primary care.
Our study was limited by the exclusion of nonphysician providers (eg, nurse practitioners, physician assistants), a small sample size, and lack of available economic data for predominantly Black zip codes.4 Additionally, the exclusion of practices with exclusive insurance plans (eg, Kaiser Permanente) limited the generalizability of our findings, as our results did not account for the populations served by these practices. Furthermore, our analysis did not account for variations in practice size or the proportion of care provided to patients with different insurance types, which could impact overall accessibility. Additional studies are needed to explore the impact of these factors on access to general dermatologic care and not just FBSEs.
Racial/ethnic minorities and lower SES populations face major barriers to FBSE access in LA County, such as difficulty finding a dermatologist in their area or one who accepts Medi-Cal. Addressing these disparities is crucial for improving skin cancer outcomes. Further research is needed to develop strategies to eliminate these barriers to dermatologic care, such as increasing access to teledermatology, offering mobile dermatology clinics, and improving insurance coverage.
To the Editor:
Early skin cancer detection improves patient outcomes1; however, socioeconomic and racial disparities may impact access to dermatologic care.2 Although non-Hispanic White individuals have a high incidence of skin cancer, they experience higher melanoma-specific survival rates than non-White patients, who often receive later-stage diagnoses and experience higher mortality.2 Furthermore, racial/ ethnic minorities often face longer surgery wait times after diagnosis and have lower socioeconomic status (SES) and less favorable health insurance coverage, contributing to poorer outcomes.2,3
To examine access to full-body skin examinations (FBSEs) by board-certified dermatologists in Los Angeles (LA) County, California, we analyzed the availability of FBSEs based on racial demographics, income, and insurance type (Medicaid [Medi-Cal] vs private [Blue Cross Blue Shield (BCBS)]). Demographic data by zip code were obtained from the US Census Bureau.4 This validated metric highlights socioeconomic disparities and minimizes data gaps5,6 and was used to assess health care access among different population subgroups. Dermatologists’ contact information was obtained from the Find a Dermatologist page on the American Academy of Dermatology website and the listed phone numbers of their practice were used to contact them. Practices with board-certified dermatologists accepting new patients were included in the study; practices were not included if they had exclusive insurance plans; were pediatric, cosmetic, or research only; or were nonresponsive to calls. From August 2022 to September 2022, each practice was called twice within a 36-hour period—once by a simulated patient with Medi-Cal and once by a simulated patient with BCBS—and were asked about availability for new patient FBSE appointments and accepted insurance types. Data were analyzed using SAS software (SAS Institute Inc.).
Los Angeles County comprises 269 zip codes, of which 82 (30.5%) have dermatology practices. Of 213 total dermatologists in LA County listed on the American Academy of Dermatology website, 193 (90.6%) met preliminary criteria, and 169 (79.3%) were successfully contacted. Almost all (94.6% [160/169]) accepted new patients for FBSEs; of those, 63.1% (101/160) accepted only private insurance, 16.9% (27/160) accepted both private insurance and Medi-Cal, and 16.2% (26/160) did not accept any insurance. Racial predominance for each dermatology practice was analyzed by zip code (Table). Dermatologists included in our study were significantly more concentrated in predominantly non- Hispanic White areas of LA County vs predominantly Hispanic areas (P<.0001). Notably, the average income in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes ($114,757.74) was significantly higher than in predominantly Hispanic areas ($58,278.54)(P=.001)(Table).4

In LA County, 40.1% (108/269) of zip codes have no racial majority, 28.2% (76/269) are predominantly Hispanic, 27.5% (74/269) are predominantly non-Hispanic White, 2.2% (6/269) are predominantly Black, and 1.9% (5/269) are predominantly Asian.4 There are no dermatologists in predominantly Black zip codes, 2 in predominantly Asian zip codes, 14 in predominantly Hispanic zip codes, 38 in zip codes with no racial majority, and 106 in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes. There are significantly more dermatologists in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes compared to predominantly Hispanic zip codes (P<.0001). In LA County, the average income in predominantly Asian, non-Hispanic White, and Hispanic zip codes was $93,594, $114,757.84, and $58,278.54, respectively, in 2021.4 The average income in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes was significantly higher than in predominantly Hispanic zip codes (P=.001). There were no income data available for predominantly Black zip codes or zip codes with no racial majority.
The results from our study revealed potential barriers to FBSEs for racial and ethnic minorities in LA County, which supports previous research on the impact of SES, race, and insurance on access to dermatologic care.2,3 Predominantly Hispanic zip codes have significantly lower income (P<.0001) and fewer dermatologists (P=.001) compared to zip codes that are predominantly non-Hispanic White, reflecting how lower SES correlates with worse health outcomes and higher melanoma mortality. Conversely, predominantly non-Hispanic White areas with higher income have better access to dermatologists, which may contribute to the improved melanoma survival rates among White patients. Additionally, most dermatologists accept only private insurance, further highlighting the disparity in FBSE access for non-White patients across LA County. While our study focused on FBSE access, our findings may point to a wider barrier to dermatologic care, especially in zip codes with fewer dermatologists. Further studies are needed to determine whether these areas also face barriers to accessing primary care.
Our study was limited by the exclusion of nonphysician providers (eg, nurse practitioners, physician assistants), a small sample size, and lack of available economic data for predominantly Black zip codes.4 Additionally, the exclusion of practices with exclusive insurance plans (eg, Kaiser Permanente) limited the generalizability of our findings, as our results did not account for the populations served by these practices. Furthermore, our analysis did not account for variations in practice size or the proportion of care provided to patients with different insurance types, which could impact overall accessibility. Additional studies are needed to explore the impact of these factors on access to general dermatologic care and not just FBSEs.
Racial/ethnic minorities and lower SES populations face major barriers to FBSE access in LA County, such as difficulty finding a dermatologist in their area or one who accepts Medi-Cal. Addressing these disparities is crucial for improving skin cancer outcomes. Further research is needed to develop strategies to eliminate these barriers to dermatologic care, such as increasing access to teledermatology, offering mobile dermatology clinics, and improving insurance coverage.
- Chiaravalloti AJ, Laduca JR. Melanoma screening by means of complete skin exams for all patients in a dermatology practice reduces the thickness of primary melanomas at diagnosis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:18-22.
- Qian Y, Johannet P, Sawyers A, et al. The ongoing racial disparities in melanoma: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (1975-2016). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1585-1593.
- Baranowski MLH, Yeung H, Chen SC, et al. Factors associated with time to surgery in melanoma: an analysis of the National Cancer Database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:908-916.
- United States Census Bureau. Explore census data. Accessed March 17, 2025. https://data.census.gov/all?q=los+angeles+county
- Berkowitz SA, Traore CY, Singer DE, et al. Evaluating area-based socioeconomic status indicators for monitoring disparities within health care systems: results from a primary care network. Health Serv Res. 2015;50:398-417.
- Jacobs B, Ir P, Bigdeli M, et al. Addressing access barriers to health services: an analytical framework for selecting appropriate interventions in lowincome Asian countries. Health Policy Plan. 2012;27:288-300.
- Chiaravalloti AJ, Laduca JR. Melanoma screening by means of complete skin exams for all patients in a dermatology practice reduces the thickness of primary melanomas at diagnosis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:18-22.
- Qian Y, Johannet P, Sawyers A, et al. The ongoing racial disparities in melanoma: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (1975-2016). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1585-1593.
- Baranowski MLH, Yeung H, Chen SC, et al. Factors associated with time to surgery in melanoma: an analysis of the National Cancer Database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:908-916.
- United States Census Bureau. Explore census data. Accessed March 17, 2025. https://data.census.gov/all?q=los+angeles+county
- Berkowitz SA, Traore CY, Singer DE, et al. Evaluating area-based socioeconomic status indicators for monitoring disparities within health care systems: results from a primary care network. Health Serv Res. 2015;50:398-417.
- Jacobs B, Ir P, Bigdeli M, et al. Addressing access barriers to health services: an analytical framework for selecting appropriate interventions in lowincome Asian countries. Health Policy Plan. 2012;27:288-300.
Evaluating Access to Full-Body Skin Examinations in Los Angeles County, California
Evaluating Access to Full-Body Skin Examinations in Los Angeles County, California
PRACTICE POINTS
- Socioeconomic and racial disparities impact access to full-body skin examinations (FBSEs) in Los Angeles County.
- Most dermatologists included in this study were accepting new patients for a FBSE.
- There are significantly more dermatologists in predominantly non-Hispanic White zip codes than in predominantly Hispanic zip codes in Los Angeles County.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Arising From an Infantile Hemangioma Treated With Gold Radon Seeds
Basal Cell Carcinoma Arising From an Infantile Hemangioma Treated With Gold Radon Seeds
To the Editor:
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC), which is the most common type of skin cancer, typically arises on sun-damaged skin as a result of long-term exposure to UV radiation. Another known risk factor for BCC is exposure to ionizing radiation, though this is less commonly encountered.1 We present a unique case of a BCC arising at the site of an involuted infantile hemangioma that had been treated with implanted and retained gold radon seeds more than 7 decades prior. This case highlights the importance of obtaining a detailed history of radiation exposures to better counsel patients about skin cancer risk and manage disease in complex skin locations.
A 75-year-old woman presented to an outside dermatologist for evaluation of a pink papule on the right upper cutaneous lip that had enlarged over several months (Figure 1). The patient’s medical history was remarkable for an infantile hemangioma present since shortly after birth in the same location that had been treated with 10 implanted gold radon seeds when she was 6 years old. Over her lifetime, several seeds had self-extruded from the area, but some remained within the subcutaneous tissue as confirmed by dental radiographs. A shave biopsy of the papule demonstrated a superficial BCC, and the patient was referred to our institution for Mohs micrographic surgery.
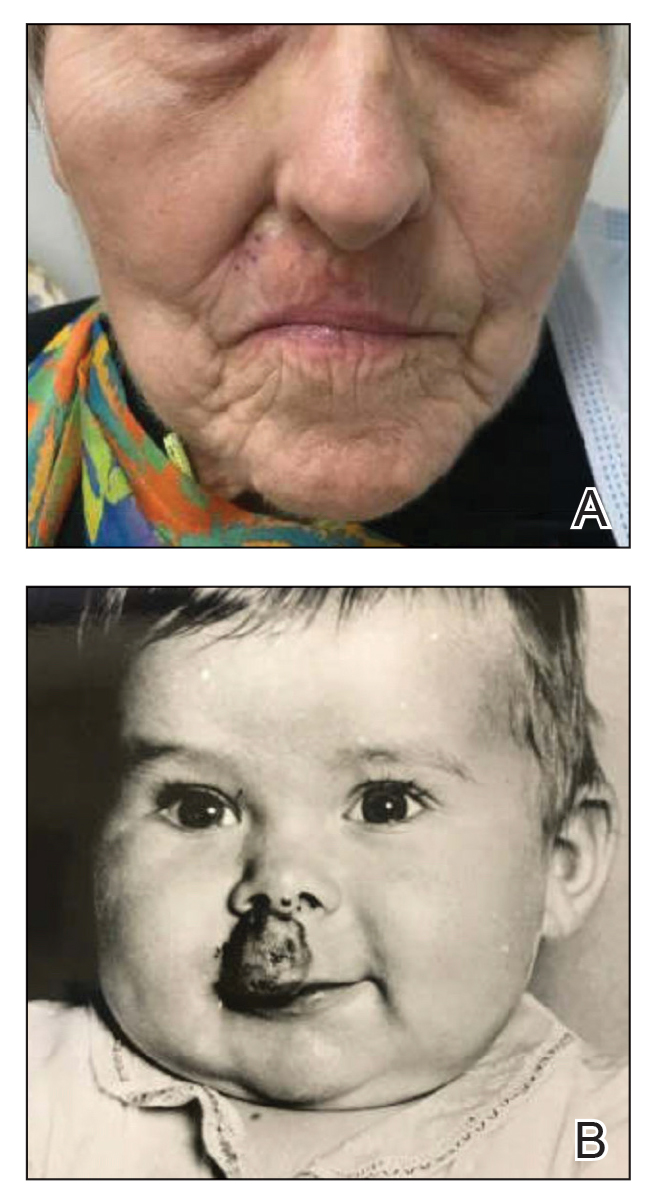
Intraoperative frozen sections revealed both superficial and nodular BCC, and the tumor was cleared in 3 stages. During surgery, a gold radon seed was visualized at the base of the excised BCC and was removed from the subcutaneous tissue (Figure 2). The primary defect on the upper lip was closed with a rotation flap. The patient returned for follow-up 2 months later and showed good healing and cosmetic outcome.
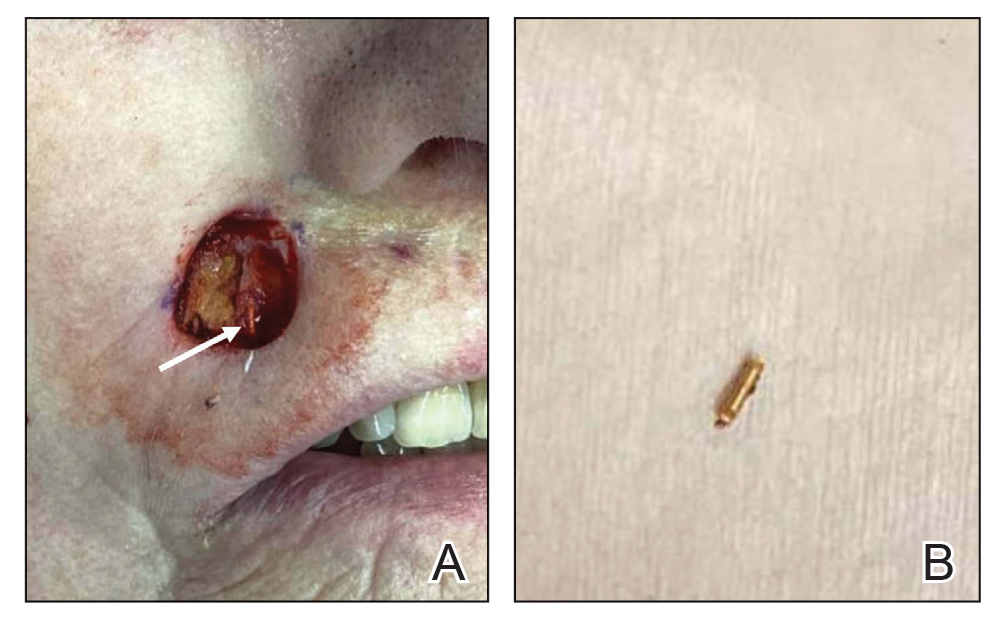
Although not commonly encountered, ionizing radiation is a known risk factor for BCC.1 Basal cell carcinoma arising from implanted gold radon seeds represents a minority of reported cases.2,3 Radium was first used to treat skin disease in the early 1900s.1 The radioactive decay of radium produced tissue destruction via alpha, beta, and gamma particles, which slowly released over weeks when radium was packaged into a capsule.4 Following implantation of the capsule, DNA damage occurred due to double-stranded breaks, chromosomal aberrations, and generation of reactive oxygen species. The downstream effect of these cellular insults resulted in cell-cycle shortening, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis.5
Gold radon seeds were used to treat infantile hemangiomas in the United States and Europe from the early 1940s to the 1960s; their use declined dramatically in the 1950s due to adverse effects and discovery of the potential for future malignancies as well as the development of safer and more effective treatments.1,3 Our patient received a substantial dose of ionizing radiation from the implantation of gold radon seeds at the site of the infantile hemangioma, which dramatically increased her risk for BCC in this location.
Infantile hemangiomas are the most common vascular tumors in children. Most infantile hemangiomas regress spontaneously and are stably involuted by about 5 or 6 years of age.6 Treatment is indicated for rapidly growing hemangiomas that are at risk for ulceration or are located by critical structures (eg, the eyes or airway). Hemangiomas located on or near the lips should be treated to avoid disfigurement and loss of function as a consequence of rapid growth and involution.7 The treatment of choice for large or high-risk infantile hemangiomas over the past 10 to 15 years has been beta blockers.6-8 Propranolol hydrochloride, a systemic beta blocker, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for the treatment of infantile hemangiomas and has demonstrated safety and effectiveness in promoting involution in these lesions.8 Unlike radiation therapy from implanted gold radon seeds, propranolol does not increase the risk for BCC. Although other risk factors such as skin type and cumulative UV exposure contribute to the development of BCC, the exact location of the BCC overlying the residual gold radon seeds was highly suggestive of ionizing radiation playing a major role in the carcinogenesis of the tumor in our patient.
Our case highlights the importance of screening elderly patients for exposures that may increase the risk for skin carcinogenesis. Dermatologists are accustomed to asking about history of UV exposure, sunburns, and use of sun-protective measures; however, direct questioning about less common sources of radiation exposure also may help stratify a patient’s risk for developing BCC. Although the US Preventive Services Task Force 2023 guidelines determined there is insufficient evidence to recommend visual skin cancer screening examinations in asymptomatic adults,9 we advocate for verbal screening of radiation exposure in both primary care and dermatology office settings. At a time when access to care, particularly dermatology services, is challenging, determining the appropriate interval for follow-up based on the patient’s skin cancer risk is imperative.
- Fürst CJ, Lundell M, Holm LE. Radiation therapy of hemangiomas, 1909- 1959. a cohort based on 50 years of clinical practice at Radiumhemmet, Stockholm. Acta Oncol. 1987;26:33-36. doi:10.3109/02841868709092974
- Bräuner EV, Loft S, Sørensen M, et al. Residential radon exposure and skin cancer incidence in a prospective Danish cohort. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:E0135642. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0135642
- Weiss E, Sukal SA, Zimbler MS, et al. Basal cell carcinoma arising 57 years after interstitial radiotherapy of a nasal hemangioma. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:1137-1140. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2008.34229.x
- Lavery MJ, Lorenzelli D, Crema J. A radon seed identified during skin surgery: an unusual finding. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46:604-606. doi:10.1111/ced.14454
- Robertson A, Allen J, Laney R, et al. The cellular and molecular carcinogenic effects of radon exposure: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:14024-14063. doi:10.3390/ijms140714024
- Rodríguez Bandera AI, Sebaratnam DF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 1: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1379-1392. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2021.08.019
- Krowchuk DP, Frieden IJ, Mancini AJ, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019;143:E20183475. doi:10.1542/peds.2018-3475
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AL, Wong LF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 2: management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85: 1395-1404. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.08.020
- US Preventive Services Task Force, Mangione CM, Barry MJ, Nicholson WK, et al. Screening for skin cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2023;329:1290-1295. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.4342
To the Editor:
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC), which is the most common type of skin cancer, typically arises on sun-damaged skin as a result of long-term exposure to UV radiation. Another known risk factor for BCC is exposure to ionizing radiation, though this is less commonly encountered.1 We present a unique case of a BCC arising at the site of an involuted infantile hemangioma that had been treated with implanted and retained gold radon seeds more than 7 decades prior. This case highlights the importance of obtaining a detailed history of radiation exposures to better counsel patients about skin cancer risk and manage disease in complex skin locations.
A 75-year-old woman presented to an outside dermatologist for evaluation of a pink papule on the right upper cutaneous lip that had enlarged over several months (Figure 1). The patient’s medical history was remarkable for an infantile hemangioma present since shortly after birth in the same location that had been treated with 10 implanted gold radon seeds when she was 6 years old. Over her lifetime, several seeds had self-extruded from the area, but some remained within the subcutaneous tissue as confirmed by dental radiographs. A shave biopsy of the papule demonstrated a superficial BCC, and the patient was referred to our institution for Mohs micrographic surgery.

Intraoperative frozen sections revealed both superficial and nodular BCC, and the tumor was cleared in 3 stages. During surgery, a gold radon seed was visualized at the base of the excised BCC and was removed from the subcutaneous tissue (Figure 2). The primary defect on the upper lip was closed with a rotation flap. The patient returned for follow-up 2 months later and showed good healing and cosmetic outcome.

Although not commonly encountered, ionizing radiation is a known risk factor for BCC.1 Basal cell carcinoma arising from implanted gold radon seeds represents a minority of reported cases.2,3 Radium was first used to treat skin disease in the early 1900s.1 The radioactive decay of radium produced tissue destruction via alpha, beta, and gamma particles, which slowly released over weeks when radium was packaged into a capsule.4 Following implantation of the capsule, DNA damage occurred due to double-stranded breaks, chromosomal aberrations, and generation of reactive oxygen species. The downstream effect of these cellular insults resulted in cell-cycle shortening, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis.5
Gold radon seeds were used to treat infantile hemangiomas in the United States and Europe from the early 1940s to the 1960s; their use declined dramatically in the 1950s due to adverse effects and discovery of the potential for future malignancies as well as the development of safer and more effective treatments.1,3 Our patient received a substantial dose of ionizing radiation from the implantation of gold radon seeds at the site of the infantile hemangioma, which dramatically increased her risk for BCC in this location.
Infantile hemangiomas are the most common vascular tumors in children. Most infantile hemangiomas regress spontaneously and are stably involuted by about 5 or 6 years of age.6 Treatment is indicated for rapidly growing hemangiomas that are at risk for ulceration or are located by critical structures (eg, the eyes or airway). Hemangiomas located on or near the lips should be treated to avoid disfigurement and loss of function as a consequence of rapid growth and involution.7 The treatment of choice for large or high-risk infantile hemangiomas over the past 10 to 15 years has been beta blockers.6-8 Propranolol hydrochloride, a systemic beta blocker, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for the treatment of infantile hemangiomas and has demonstrated safety and effectiveness in promoting involution in these lesions.8 Unlike radiation therapy from implanted gold radon seeds, propranolol does not increase the risk for BCC. Although other risk factors such as skin type and cumulative UV exposure contribute to the development of BCC, the exact location of the BCC overlying the residual gold radon seeds was highly suggestive of ionizing radiation playing a major role in the carcinogenesis of the tumor in our patient.
Our case highlights the importance of screening elderly patients for exposures that may increase the risk for skin carcinogenesis. Dermatologists are accustomed to asking about history of UV exposure, sunburns, and use of sun-protective measures; however, direct questioning about less common sources of radiation exposure also may help stratify a patient’s risk for developing BCC. Although the US Preventive Services Task Force 2023 guidelines determined there is insufficient evidence to recommend visual skin cancer screening examinations in asymptomatic adults,9 we advocate for verbal screening of radiation exposure in both primary care and dermatology office settings. At a time when access to care, particularly dermatology services, is challenging, determining the appropriate interval for follow-up based on the patient’s skin cancer risk is imperative.
To the Editor:
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC), which is the most common type of skin cancer, typically arises on sun-damaged skin as a result of long-term exposure to UV radiation. Another known risk factor for BCC is exposure to ionizing radiation, though this is less commonly encountered.1 We present a unique case of a BCC arising at the site of an involuted infantile hemangioma that had been treated with implanted and retained gold radon seeds more than 7 decades prior. This case highlights the importance of obtaining a detailed history of radiation exposures to better counsel patients about skin cancer risk and manage disease in complex skin locations.
A 75-year-old woman presented to an outside dermatologist for evaluation of a pink papule on the right upper cutaneous lip that had enlarged over several months (Figure 1). The patient’s medical history was remarkable for an infantile hemangioma present since shortly after birth in the same location that had been treated with 10 implanted gold radon seeds when she was 6 years old. Over her lifetime, several seeds had self-extruded from the area, but some remained within the subcutaneous tissue as confirmed by dental radiographs. A shave biopsy of the papule demonstrated a superficial BCC, and the patient was referred to our institution for Mohs micrographic surgery.

Intraoperative frozen sections revealed both superficial and nodular BCC, and the tumor was cleared in 3 stages. During surgery, a gold radon seed was visualized at the base of the excised BCC and was removed from the subcutaneous tissue (Figure 2). The primary defect on the upper lip was closed with a rotation flap. The patient returned for follow-up 2 months later and showed good healing and cosmetic outcome.

Although not commonly encountered, ionizing radiation is a known risk factor for BCC.1 Basal cell carcinoma arising from implanted gold radon seeds represents a minority of reported cases.2,3 Radium was first used to treat skin disease in the early 1900s.1 The radioactive decay of radium produced tissue destruction via alpha, beta, and gamma particles, which slowly released over weeks when radium was packaged into a capsule.4 Following implantation of the capsule, DNA damage occurred due to double-stranded breaks, chromosomal aberrations, and generation of reactive oxygen species. The downstream effect of these cellular insults resulted in cell-cycle shortening, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis.5
Gold radon seeds were used to treat infantile hemangiomas in the United States and Europe from the early 1940s to the 1960s; their use declined dramatically in the 1950s due to adverse effects and discovery of the potential for future malignancies as well as the development of safer and more effective treatments.1,3 Our patient received a substantial dose of ionizing radiation from the implantation of gold radon seeds at the site of the infantile hemangioma, which dramatically increased her risk for BCC in this location.
Infantile hemangiomas are the most common vascular tumors in children. Most infantile hemangiomas regress spontaneously and are stably involuted by about 5 or 6 years of age.6 Treatment is indicated for rapidly growing hemangiomas that are at risk for ulceration or are located by critical structures (eg, the eyes or airway). Hemangiomas located on or near the lips should be treated to avoid disfigurement and loss of function as a consequence of rapid growth and involution.7 The treatment of choice for large or high-risk infantile hemangiomas over the past 10 to 15 years has been beta blockers.6-8 Propranolol hydrochloride, a systemic beta blocker, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for the treatment of infantile hemangiomas and has demonstrated safety and effectiveness in promoting involution in these lesions.8 Unlike radiation therapy from implanted gold radon seeds, propranolol does not increase the risk for BCC. Although other risk factors such as skin type and cumulative UV exposure contribute to the development of BCC, the exact location of the BCC overlying the residual gold radon seeds was highly suggestive of ionizing radiation playing a major role in the carcinogenesis of the tumor in our patient.
Our case highlights the importance of screening elderly patients for exposures that may increase the risk for skin carcinogenesis. Dermatologists are accustomed to asking about history of UV exposure, sunburns, and use of sun-protective measures; however, direct questioning about less common sources of radiation exposure also may help stratify a patient’s risk for developing BCC. Although the US Preventive Services Task Force 2023 guidelines determined there is insufficient evidence to recommend visual skin cancer screening examinations in asymptomatic adults,9 we advocate for verbal screening of radiation exposure in both primary care and dermatology office settings. At a time when access to care, particularly dermatology services, is challenging, determining the appropriate interval for follow-up based on the patient’s skin cancer risk is imperative.
- Fürst CJ, Lundell M, Holm LE. Radiation therapy of hemangiomas, 1909- 1959. a cohort based on 50 years of clinical practice at Radiumhemmet, Stockholm. Acta Oncol. 1987;26:33-36. doi:10.3109/02841868709092974
- Bräuner EV, Loft S, Sørensen M, et al. Residential radon exposure and skin cancer incidence in a prospective Danish cohort. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:E0135642. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0135642
- Weiss E, Sukal SA, Zimbler MS, et al. Basal cell carcinoma arising 57 years after interstitial radiotherapy of a nasal hemangioma. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:1137-1140. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2008.34229.x
- Lavery MJ, Lorenzelli D, Crema J. A radon seed identified during skin surgery: an unusual finding. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46:604-606. doi:10.1111/ced.14454
- Robertson A, Allen J, Laney R, et al. The cellular and molecular carcinogenic effects of radon exposure: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:14024-14063. doi:10.3390/ijms140714024
- Rodríguez Bandera AI, Sebaratnam DF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 1: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1379-1392. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2021.08.019
- Krowchuk DP, Frieden IJ, Mancini AJ, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019;143:E20183475. doi:10.1542/peds.2018-3475
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AL, Wong LF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 2: management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85: 1395-1404. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.08.020
- US Preventive Services Task Force, Mangione CM, Barry MJ, Nicholson WK, et al. Screening for skin cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2023;329:1290-1295. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.4342
- Fürst CJ, Lundell M, Holm LE. Radiation therapy of hemangiomas, 1909- 1959. a cohort based on 50 years of clinical practice at Radiumhemmet, Stockholm. Acta Oncol. 1987;26:33-36. doi:10.3109/02841868709092974
- Bräuner EV, Loft S, Sørensen M, et al. Residential radon exposure and skin cancer incidence in a prospective Danish cohort. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:E0135642. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0135642
- Weiss E, Sukal SA, Zimbler MS, et al. Basal cell carcinoma arising 57 years after interstitial radiotherapy of a nasal hemangioma. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:1137-1140. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2008.34229.x
- Lavery MJ, Lorenzelli D, Crema J. A radon seed identified during skin surgery: an unusual finding. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46:604-606. doi:10.1111/ced.14454
- Robertson A, Allen J, Laney R, et al. The cellular and molecular carcinogenic effects of radon exposure: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:14024-14063. doi:10.3390/ijms140714024
- Rodríguez Bandera AI, Sebaratnam DF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 1: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1379-1392. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2021.08.019
- Krowchuk DP, Frieden IJ, Mancini AJ, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019;143:E20183475. doi:10.1542/peds.2018-3475
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AL, Wong LF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 2: management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85: 1395-1404. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.08.020
- US Preventive Services Task Force, Mangione CM, Barry MJ, Nicholson WK, et al. Screening for skin cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2023;329:1290-1295. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.4342
Basal Cell Carcinoma Arising From an Infantile Hemangioma Treated With Gold Radon Seeds
Basal Cell Carcinoma Arising From an Infantile Hemangioma Treated With Gold Radon Seeds
PRACTICE POINTS
- Historical use of ionizing radiation to treat skin disease is a risk factor for basal cell carcinoma (BCC).
- Mohs micrographic surgery is the treatment of choice for BCC in high-risk areas such as the nose, eyelids, and lips, where tissue conservation and complete margin control are essential.
- Elderly patients should be screened for less common sources of radiation exposure for better risk stratification and to determine appropriate intervals for follow-up with a dermatologist.
Multiple Firm Papules on the Wrists and Forearms
Multiple Firm Papules on the Wrists and Forearms
THE DIAGNOSIS: Acral Persistent Papular Mucinosis
Histopathologic analysis revealed conspicuous interstitial mucin deposition throughout the upper to mid reticular dermis in the absence of a cellular infiltrate or fibroplasia. Colloidal iron staining confirmed the presence of mucin. In correlation with the clinical presentation, a diagnosis of acral persistent papular mucinosis (APPM) was made. The patient was counseled on the benign disease course and lack of associated comorbidities, and additional treatment was not pursued.
Acral persistent papular mucinosis is a rare distinct subtype of cutaneous mucinosis that initially was described by Rongioletti et al1 in 1986. As a localized form of lichen myxedematosus, APPM is characterized by mucin deposition in the dermis with no systemic involvement. The precise pathogenesis remains unclear, although some investigators have suggested that cytokine-mediated stimulation of glycosaminoglycan production may contribute to increased mucin accumulation in the dermis.2 Acral persistent papular mucinosis predominantly affects middle-aged women with a 5:1 female-to-male predominance.3 Clinically, patients present with discrete, nonfollicular, waxy papules that typically measure 2 to 5 mm and are distributed symmetrically on the extensor surfaces of the wrists and forearms. While the lesions generally are asymptomatic, some patients may report mild pruritus. The condition is chronic, with lesions seldom resolving and often increasing in number over time.3
Histologically, APPM is characterized by focal deposits of mucin in the upper reticular dermis with no evidence of increased fibroblast proliferation or fibrosis.4 This feature is pivotal in differentiating APPM from other subtypes of localized lichen myxedematosus and similar dermatoses. Diagnosis of APPM requires exclusion of systemic involvement, including thyroid abnormalities and monoclonal gammopathy, aligning with its classification as a purely cutaneous condition.5 Management of APPM is unclear due to its rarity. Reassurance for patients of its benign nature as well as clinical observation are recommended, though some reports cite benefits of treatment with topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors.6,7 The long-term prognosis for patients with APPM is favorable, although the persistence of and potential increase in lesions over time can be a cosmetic concern.
The differential diagnoses for APPM include scleromyxedema, scleredema, and other cutaneous eruptions that manifest as smooth flesh-colored papules, such as granuloma annulare and lichen nitidus.3 Scleromyxedema is a systemic cutaneous mucinosis that is part of the same disease spectrum as lichen myxedematosus. The papular eruption of scleromyxedema is much more widespread, and coalescing of the lesions may lead to characteristic skin thickening, creating leonine facies and deep furrowing over the trunk.8 Extracutaneous manifestations are frequent in scleromyxedema, and up to 90% of patients exhibit evidence of an underlying plasma cell dyscrasia.2 Histopathologically, scleromyxedema shows extensive fibroblast proliferation and fibrosis, in contrast to the findings of APPM (Figure 1).
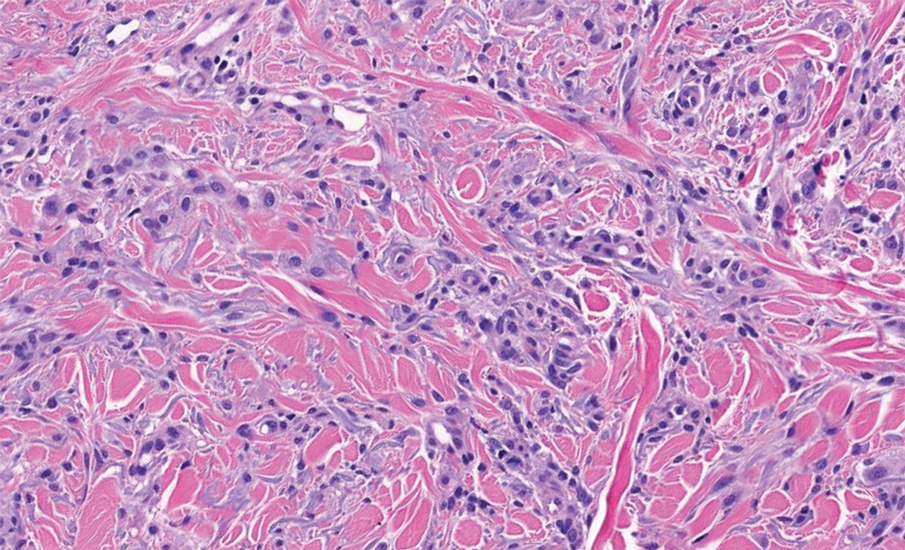
The histopathology of APPM is most similar to scleredema, a rare fibromucinous disorder of the skin associated with diabetes, infection (especially poststreptococcal), or monoclonal gammopathy.9 Biopsy evaluation of scleredema reveals a normal epidermis with mucin deposition between collagen bundles predominantly in the deep reticular dermis as well as absent fibroblast proliferation (Figure 2). Unlike APPM, scleredema manifests with diffuse woody induration with erythema and hyperpigmentation on the posterior neck and upper back.9 On physical examination, the distinct clinical features of scleredema distinguish this condition from APPM and scleromyxedema.
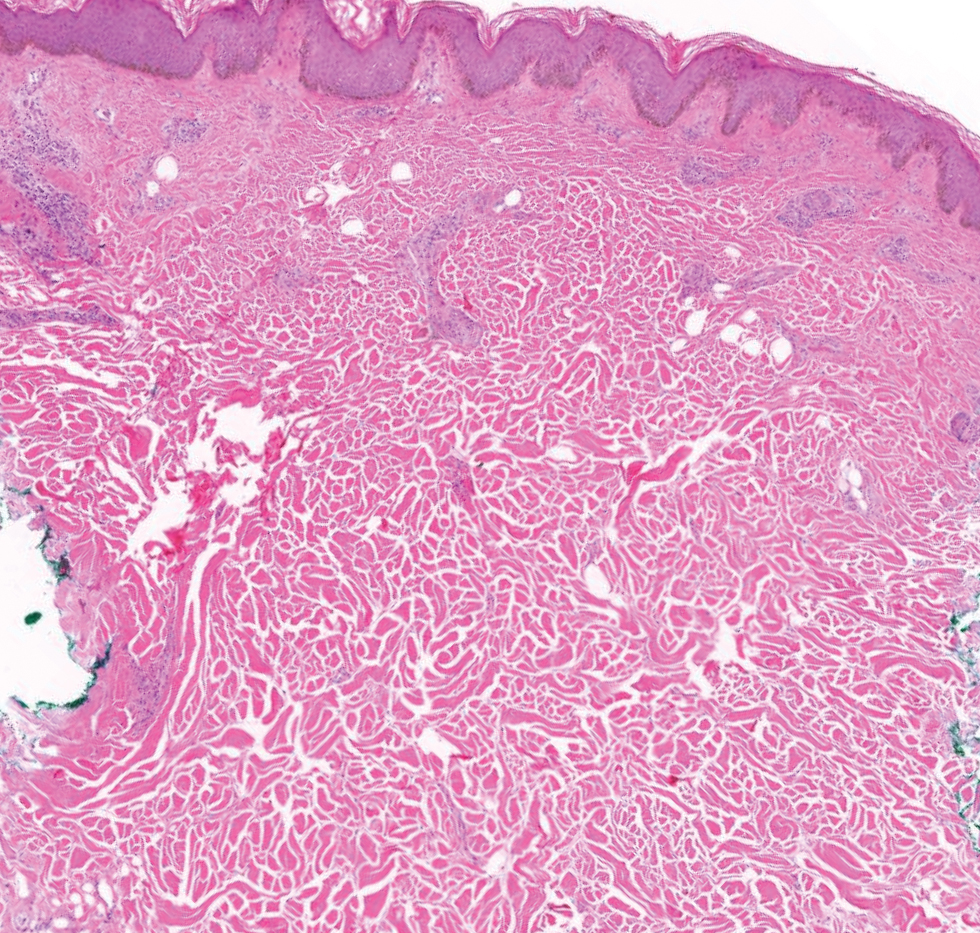
Papular granuloma annulare also was considered in our patient due to the presence of small flesh-colored papules. Histologically, granuloma annulare is characterized by palisading granulomas and mucin deposition in the dermis.10 However, the pattern of mucin deposition differs from that seen in APPM. In granuloma annulare, mucin is observed around foci of degenerated collagen (Figure 3), which was not observed in our patient.10 Additionally, the absence of an inflammatory infiltrate in our patient further ruled out this diagnosis.
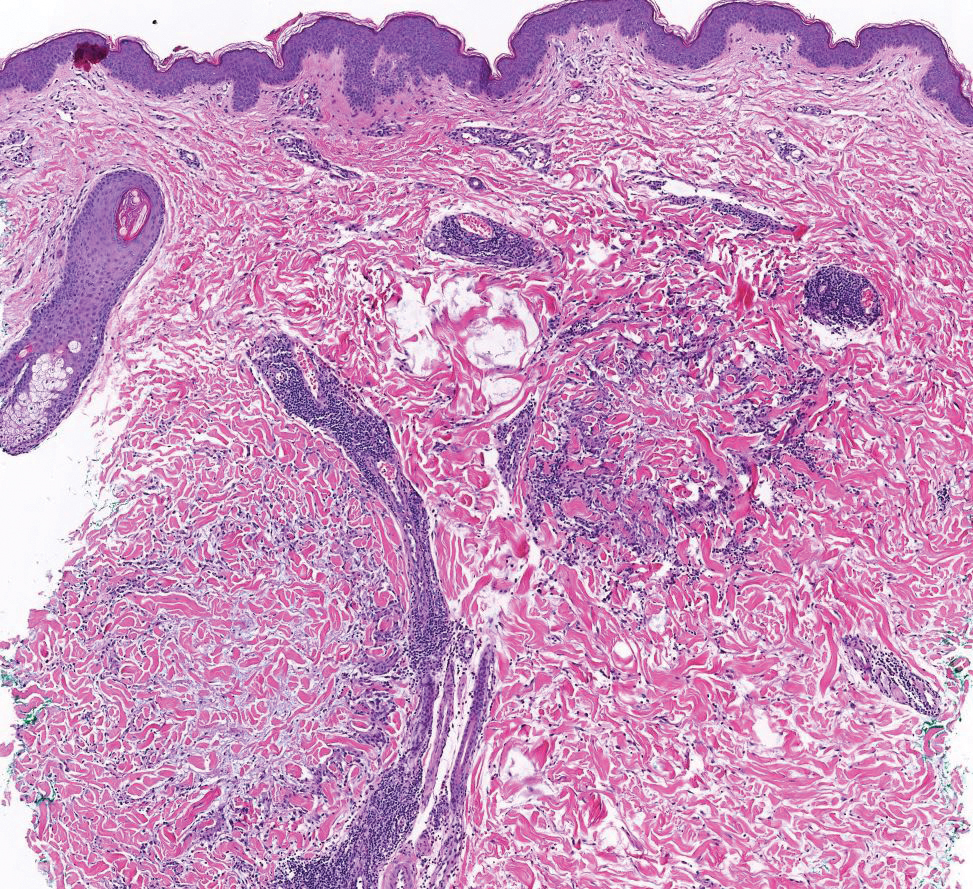
Lichen nitidus also could be considered in the differential diagnosis for ACCM. It typically manifests with minute, clustered, monomorphous papules with a predilection for the chest, abdomen, flexural forearms, and genitalia. The histology of lichen nitidus is distinct, showing a well-circumscribed lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the papillary dermis bordered by epidermal ridges, resembling a ball and clutch appearance (Figure 4).11
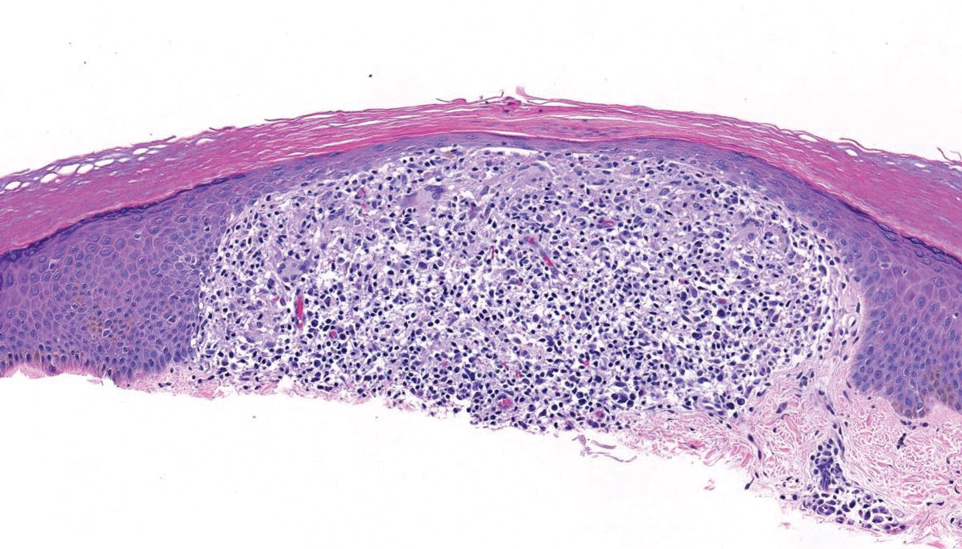
Although the clinical differential diagnosis in our patient was broad, histopathologic evaluation played a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis of APPM. This benign condition could be overlooked by patients and physicians; thorough clinical evaluation is necessary to rule out systemic mucinoses, which are associated with higher risks of morbidity and mortality.
- Rongioletti F, Rebora A. Acral persistent papular mucinosis: a new entity. Arch Dermatol. 1986;122:1237-1239. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1986.01660230027002
- Christman MP, Sukhdeo K, Kim RH, et al. Papular mucinosis, or localized lichen myxedematosus (LM)(discrete papular type). Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3xp109qd.
- Rongioletti F, Ferreli C, Atzori L. Acral persistent papular mucinosis. Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:211-214. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.10.001
- Rongioletti F, Rebora A. Cutaneous mucinoses: microscopic criteria for diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:257-267. doi:10.1097/00000372- 200106000-00022
- Rongioletti F. Lichen myxedematosus (papular mucinosis): new concepts and perspectives for an old disease. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2006;25:100-104. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2006.04.001
- Jun JY, Oh SH, Shim JH, et al. Acral persistent papular mucinosis with partial response to tacrolimus ointment. Ann Dermatol. 2016;28:517-519. doi:10.5021/ad.2016.28.4.517
- Rongioletti F, Zaccaria E, Cozzani E, et al. Treatment of localized lichen myxedematosus of discrete type with tacrolimus ointment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:530-532. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.10.021
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2013.01.007
- Rongioletti F, Kaiser F, Cinotti E, et al. Scleredema. a multicentre study of characteristics, comorbidities, course and therapy in 44 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:2399-2404. doi:10.1111/jdv.13272
- Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: clinical and histologic variants, epidemiology, and genetics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:457-465. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.054
- Al-Mutairi N, Hassanein A, Nour-Eldin O, et al. Generalized lichen nitidus. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:158-160. doi:10.1111 /j.1525-1470.2005.22215.x
THE DIAGNOSIS: Acral Persistent Papular Mucinosis
Histopathologic analysis revealed conspicuous interstitial mucin deposition throughout the upper to mid reticular dermis in the absence of a cellular infiltrate or fibroplasia. Colloidal iron staining confirmed the presence of mucin. In correlation with the clinical presentation, a diagnosis of acral persistent papular mucinosis (APPM) was made. The patient was counseled on the benign disease course and lack of associated comorbidities, and additional treatment was not pursued.
Acral persistent papular mucinosis is a rare distinct subtype of cutaneous mucinosis that initially was described by Rongioletti et al1 in 1986. As a localized form of lichen myxedematosus, APPM is characterized by mucin deposition in the dermis with no systemic involvement. The precise pathogenesis remains unclear, although some investigators have suggested that cytokine-mediated stimulation of glycosaminoglycan production may contribute to increased mucin accumulation in the dermis.2 Acral persistent papular mucinosis predominantly affects middle-aged women with a 5:1 female-to-male predominance.3 Clinically, patients present with discrete, nonfollicular, waxy papules that typically measure 2 to 5 mm and are distributed symmetrically on the extensor surfaces of the wrists and forearms. While the lesions generally are asymptomatic, some patients may report mild pruritus. The condition is chronic, with lesions seldom resolving and often increasing in number over time.3
Histologically, APPM is characterized by focal deposits of mucin in the upper reticular dermis with no evidence of increased fibroblast proliferation or fibrosis.4 This feature is pivotal in differentiating APPM from other subtypes of localized lichen myxedematosus and similar dermatoses. Diagnosis of APPM requires exclusion of systemic involvement, including thyroid abnormalities and monoclonal gammopathy, aligning with its classification as a purely cutaneous condition.5 Management of APPM is unclear due to its rarity. Reassurance for patients of its benign nature as well as clinical observation are recommended, though some reports cite benefits of treatment with topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors.6,7 The long-term prognosis for patients with APPM is favorable, although the persistence of and potential increase in lesions over time can be a cosmetic concern.
The differential diagnoses for APPM include scleromyxedema, scleredema, and other cutaneous eruptions that manifest as smooth flesh-colored papules, such as granuloma annulare and lichen nitidus.3 Scleromyxedema is a systemic cutaneous mucinosis that is part of the same disease spectrum as lichen myxedematosus. The papular eruption of scleromyxedema is much more widespread, and coalescing of the lesions may lead to characteristic skin thickening, creating leonine facies and deep furrowing over the trunk.8 Extracutaneous manifestations are frequent in scleromyxedema, and up to 90% of patients exhibit evidence of an underlying plasma cell dyscrasia.2 Histopathologically, scleromyxedema shows extensive fibroblast proliferation and fibrosis, in contrast to the findings of APPM (Figure 1).

The histopathology of APPM is most similar to scleredema, a rare fibromucinous disorder of the skin associated with diabetes, infection (especially poststreptococcal), or monoclonal gammopathy.9 Biopsy evaluation of scleredema reveals a normal epidermis with mucin deposition between collagen bundles predominantly in the deep reticular dermis as well as absent fibroblast proliferation (Figure 2). Unlike APPM, scleredema manifests with diffuse woody induration with erythema and hyperpigmentation on the posterior neck and upper back.9 On physical examination, the distinct clinical features of scleredema distinguish this condition from APPM and scleromyxedema.

Papular granuloma annulare also was considered in our patient due to the presence of small flesh-colored papules. Histologically, granuloma annulare is characterized by palisading granulomas and mucin deposition in the dermis.10 However, the pattern of mucin deposition differs from that seen in APPM. In granuloma annulare, mucin is observed around foci of degenerated collagen (Figure 3), which was not observed in our patient.10 Additionally, the absence of an inflammatory infiltrate in our patient further ruled out this diagnosis.

Lichen nitidus also could be considered in the differential diagnosis for ACCM. It typically manifests with minute, clustered, monomorphous papules with a predilection for the chest, abdomen, flexural forearms, and genitalia. The histology of lichen nitidus is distinct, showing a well-circumscribed lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the papillary dermis bordered by epidermal ridges, resembling a ball and clutch appearance (Figure 4).11

Although the clinical differential diagnosis in our patient was broad, histopathologic evaluation played a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis of APPM. This benign condition could be overlooked by patients and physicians; thorough clinical evaluation is necessary to rule out systemic mucinoses, which are associated with higher risks of morbidity and mortality.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Acral Persistent Papular Mucinosis
Histopathologic analysis revealed conspicuous interstitial mucin deposition throughout the upper to mid reticular dermis in the absence of a cellular infiltrate or fibroplasia. Colloidal iron staining confirmed the presence of mucin. In correlation with the clinical presentation, a diagnosis of acral persistent papular mucinosis (APPM) was made. The patient was counseled on the benign disease course and lack of associated comorbidities, and additional treatment was not pursued.
Acral persistent papular mucinosis is a rare distinct subtype of cutaneous mucinosis that initially was described by Rongioletti et al1 in 1986. As a localized form of lichen myxedematosus, APPM is characterized by mucin deposition in the dermis with no systemic involvement. The precise pathogenesis remains unclear, although some investigators have suggested that cytokine-mediated stimulation of glycosaminoglycan production may contribute to increased mucin accumulation in the dermis.2 Acral persistent papular mucinosis predominantly affects middle-aged women with a 5:1 female-to-male predominance.3 Clinically, patients present with discrete, nonfollicular, waxy papules that typically measure 2 to 5 mm and are distributed symmetrically on the extensor surfaces of the wrists and forearms. While the lesions generally are asymptomatic, some patients may report mild pruritus. The condition is chronic, with lesions seldom resolving and often increasing in number over time.3
Histologically, APPM is characterized by focal deposits of mucin in the upper reticular dermis with no evidence of increased fibroblast proliferation or fibrosis.4 This feature is pivotal in differentiating APPM from other subtypes of localized lichen myxedematosus and similar dermatoses. Diagnosis of APPM requires exclusion of systemic involvement, including thyroid abnormalities and monoclonal gammopathy, aligning with its classification as a purely cutaneous condition.5 Management of APPM is unclear due to its rarity. Reassurance for patients of its benign nature as well as clinical observation are recommended, though some reports cite benefits of treatment with topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors.6,7 The long-term prognosis for patients with APPM is favorable, although the persistence of and potential increase in lesions over time can be a cosmetic concern.
The differential diagnoses for APPM include scleromyxedema, scleredema, and other cutaneous eruptions that manifest as smooth flesh-colored papules, such as granuloma annulare and lichen nitidus.3 Scleromyxedema is a systemic cutaneous mucinosis that is part of the same disease spectrum as lichen myxedematosus. The papular eruption of scleromyxedema is much more widespread, and coalescing of the lesions may lead to characteristic skin thickening, creating leonine facies and deep furrowing over the trunk.8 Extracutaneous manifestations are frequent in scleromyxedema, and up to 90% of patients exhibit evidence of an underlying plasma cell dyscrasia.2 Histopathologically, scleromyxedema shows extensive fibroblast proliferation and fibrosis, in contrast to the findings of APPM (Figure 1).

The histopathology of APPM is most similar to scleredema, a rare fibromucinous disorder of the skin associated with diabetes, infection (especially poststreptococcal), or monoclonal gammopathy.9 Biopsy evaluation of scleredema reveals a normal epidermis with mucin deposition between collagen bundles predominantly in the deep reticular dermis as well as absent fibroblast proliferation (Figure 2). Unlike APPM, scleredema manifests with diffuse woody induration with erythema and hyperpigmentation on the posterior neck and upper back.9 On physical examination, the distinct clinical features of scleredema distinguish this condition from APPM and scleromyxedema.

Papular granuloma annulare also was considered in our patient due to the presence of small flesh-colored papules. Histologically, granuloma annulare is characterized by palisading granulomas and mucin deposition in the dermis.10 However, the pattern of mucin deposition differs from that seen in APPM. In granuloma annulare, mucin is observed around foci of degenerated collagen (Figure 3), which was not observed in our patient.10 Additionally, the absence of an inflammatory infiltrate in our patient further ruled out this diagnosis.

Lichen nitidus also could be considered in the differential diagnosis for ACCM. It typically manifests with minute, clustered, monomorphous papules with a predilection for the chest, abdomen, flexural forearms, and genitalia. The histology of lichen nitidus is distinct, showing a well-circumscribed lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the papillary dermis bordered by epidermal ridges, resembling a ball and clutch appearance (Figure 4).11

Although the clinical differential diagnosis in our patient was broad, histopathologic evaluation played a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis of APPM. This benign condition could be overlooked by patients and physicians; thorough clinical evaluation is necessary to rule out systemic mucinoses, which are associated with higher risks of morbidity and mortality.
- Rongioletti F, Rebora A. Acral persistent papular mucinosis: a new entity. Arch Dermatol. 1986;122:1237-1239. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1986.01660230027002
- Christman MP, Sukhdeo K, Kim RH, et al. Papular mucinosis, or localized lichen myxedematosus (LM)(discrete papular type). Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3xp109qd.
- Rongioletti F, Ferreli C, Atzori L. Acral persistent papular mucinosis. Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:211-214. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.10.001
- Rongioletti F, Rebora A. Cutaneous mucinoses: microscopic criteria for diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:257-267. doi:10.1097/00000372- 200106000-00022
- Rongioletti F. Lichen myxedematosus (papular mucinosis): new concepts and perspectives for an old disease. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2006;25:100-104. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2006.04.001
- Jun JY, Oh SH, Shim JH, et al. Acral persistent papular mucinosis with partial response to tacrolimus ointment. Ann Dermatol. 2016;28:517-519. doi:10.5021/ad.2016.28.4.517
- Rongioletti F, Zaccaria E, Cozzani E, et al. Treatment of localized lichen myxedematosus of discrete type with tacrolimus ointment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:530-532. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.10.021
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2013.01.007
- Rongioletti F, Kaiser F, Cinotti E, et al. Scleredema. a multicentre study of characteristics, comorbidities, course and therapy in 44 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:2399-2404. doi:10.1111/jdv.13272
- Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: clinical and histologic variants, epidemiology, and genetics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:457-465. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.054
- Al-Mutairi N, Hassanein A, Nour-Eldin O, et al. Generalized lichen nitidus. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:158-160. doi:10.1111 /j.1525-1470.2005.22215.x
- Rongioletti F, Rebora A. Acral persistent papular mucinosis: a new entity. Arch Dermatol. 1986;122:1237-1239. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1986.01660230027002
- Christman MP, Sukhdeo K, Kim RH, et al. Papular mucinosis, or localized lichen myxedematosus (LM)(discrete papular type). Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3xp109qd.
- Rongioletti F, Ferreli C, Atzori L. Acral persistent papular mucinosis. Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:211-214. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.10.001
- Rongioletti F, Rebora A. Cutaneous mucinoses: microscopic criteria for diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:257-267. doi:10.1097/00000372- 200106000-00022
- Rongioletti F. Lichen myxedematosus (papular mucinosis): new concepts and perspectives for an old disease. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2006;25:100-104. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2006.04.001
- Jun JY, Oh SH, Shim JH, et al. Acral persistent papular mucinosis with partial response to tacrolimus ointment. Ann Dermatol. 2016;28:517-519. doi:10.5021/ad.2016.28.4.517
- Rongioletti F, Zaccaria E, Cozzani E, et al. Treatment of localized lichen myxedematosus of discrete type with tacrolimus ointment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:530-532. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.10.021
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2013.01.007
- Rongioletti F, Kaiser F, Cinotti E, et al. Scleredema. a multicentre study of characteristics, comorbidities, course and therapy in 44 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:2399-2404. doi:10.1111/jdv.13272
- Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: clinical and histologic variants, epidemiology, and genetics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:457-465. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.054
- Al-Mutairi N, Hassanein A, Nour-Eldin O, et al. Generalized lichen nitidus. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:158-160. doi:10.1111 /j.1525-1470.2005.22215.x
Multiple Firm Papules on the Wrists and Forearms
Multiple Firm Papules on the Wrists and Forearms
A 69-year-old woman presented to the dermatology department with persistent asymptomatic skin lesions on the wrists and forearms of several months’ duration. The lesions had slowly grown in number over the past few months with no identifiable triggers. The patient reported no known history of injury or trauma to the affected sites and was not taking any prescription medications other than daily vitamins. She denied any family history of similar lesions and was otherwise healthy. Physical examination revealed multiple waxy, firm, hypopigmented, 3- to 5-mm papules located exclusively on the dorsal wrists and forearms. No extracutaneous involvement was observed. A 4-mm punch biopsy from the forearm was obtained.
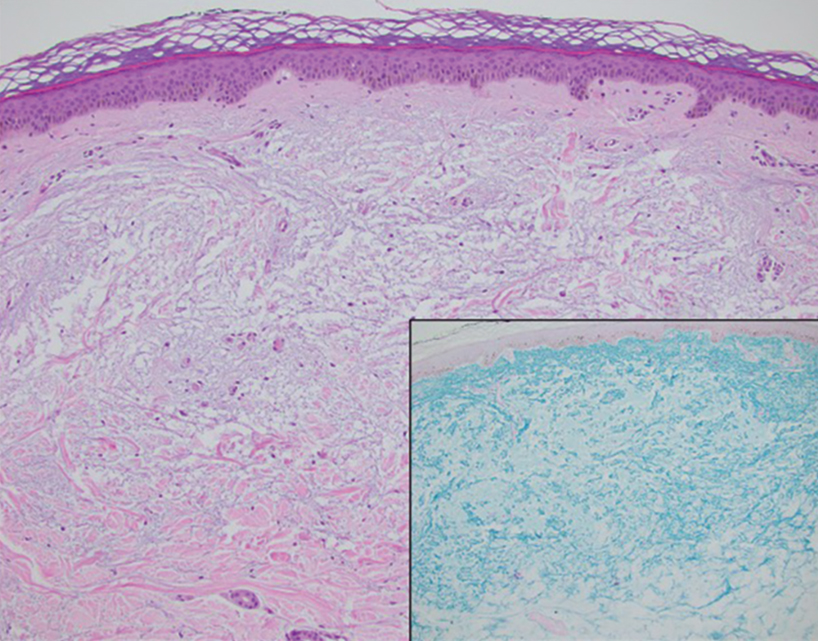
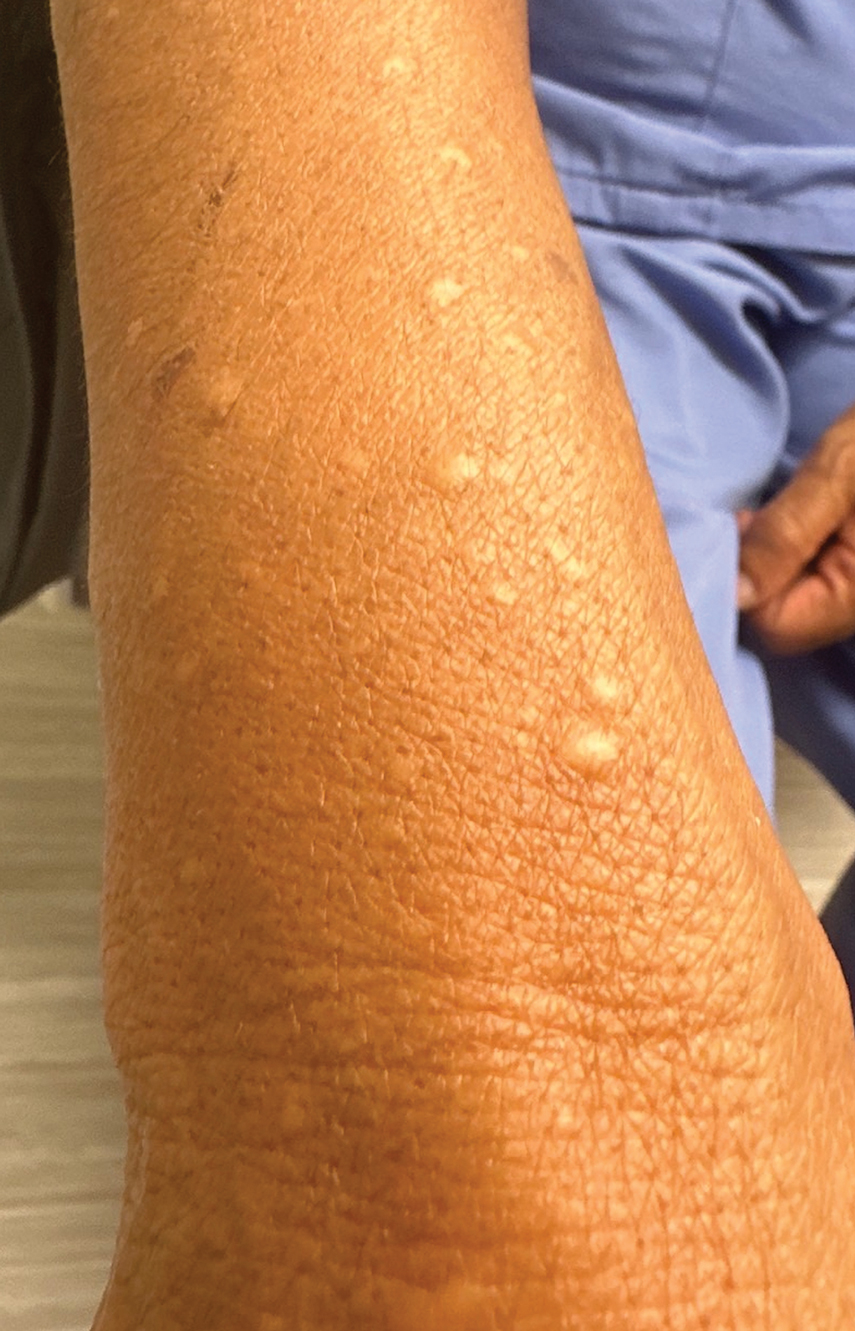
Bridging the Knowledge-Action Gap in Skin Cancer Prevention Among US Military Personnel
Bridging the Knowledge-Action Gap in Skin Cancer Prevention Among US Military Personnel
Skin cancer is a major health concern for military service members, who experience notably higher incidence rates than the general population.1 Active-duty military personnel are particularly vulnerable to prolonged sun exposure due to deployments, specialized training, and everyday outdoor duties.1 Despite skin cancer being the most commonly diagnosed malignancy in active-duty service members,2 tracking and documenting the quantity and diversity of these risk factors remain limited. This knowledge gap comes at high cost, simultaneously impairing military medicine preventive measures while burdening the military health care system with substantial expenditures.3 These findings underscore the critical need for targeted surveillance, early-detection programs, and policy-driven interventions to mitigate these medical and economic concerns.
Skin cancer has been recognized as a major health risk to the military population for decades, yet incidence and prevalence remain high. This phenomenon is closely linked to the inherent responsibilities and expectations of active-duty military members, including outdoor physical training, field exercises, standing in formation, and outdoor working environments—all of which can occur during peak sunlight hours. These risks are further elevated at duty stations in geographic regions with high levels of UV exposure, such as those in tropical and arid regions of the world. Certain military occupational specialties and missions may further introduce unique risk factors; for instance, pilots with frequent high-altitude missions experience heightened UV exposure and melanoma risk.4 Secondary to compounding determinants, the aviation, diving, and nuclear subgroups of the military community are particularly vulnerable to skin cancer.5
Despite well-documented risks, considerable gaps remain in quantifying and analyzing variations in UV exposure across military occupations, duty locations, and operational roles. Factors such as the existence of over 150 distinct military occupational specialties, frequent geographic relocations, and routine work in austere environments contribute to a wide range of UV exposure profiles that remain insufficiently characterized. This lack of comprehensive exposure data hinders the development of large-scale, targeted skin cancer prevention strategies. Initial approaches to addressing these challenges include enhanced surveillance, education, and policy initiatives. The Table presents practical recommendations for military leadership to consider in implementing preventive measures for skin cancer. Herein, we outline broader systemic strategies to bridge knowledge gaps and address underrecognized occupational risk factors for skin cancer in military service members; these elements include proposed modifications to the electronic Periodic Health Assessment (ePHA) and the development of standardized, military-specific screening and prevention guidelines to support early detection and resource optimization.
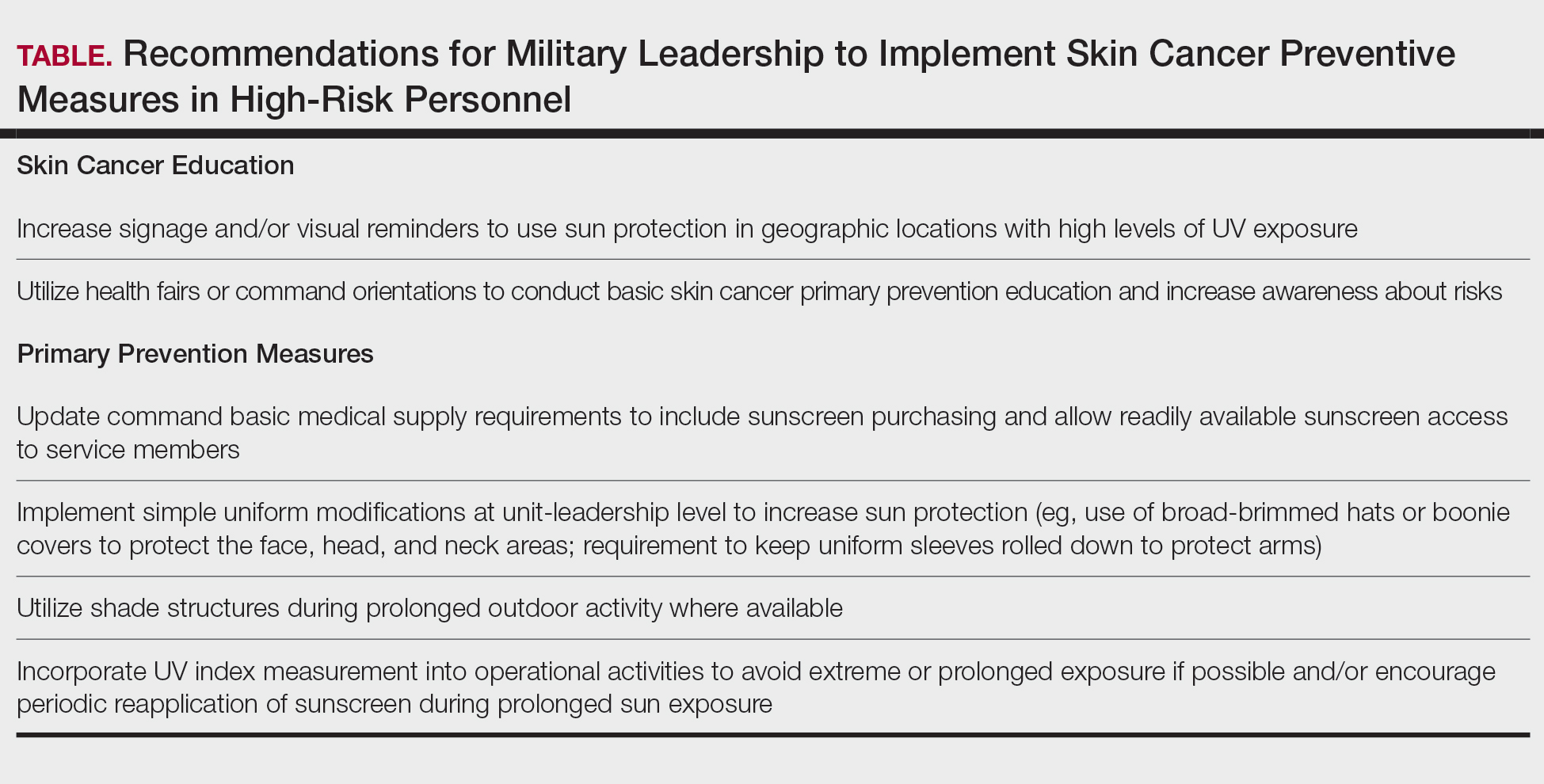
Skin Cancer Education for Service Members
Sunscreen and Signage—Diligent primary prevention offers a promising avenue for mitigating skin cancer incidence in military service members. Basic education and precautionary messaging on photoprotection can be widely implemented to simultaneously educate service members on the dangers of sun exposure while reinforcing healthy behaviors in real time. Simple low-cost initiatives such as strategically placed visual signage reminding service members to apply sunscreen in high UV environments can support consistent sun-safe practices. Educational efforts also should emphasize proper sunscreen use, including application on high-risk anatomic sites (eg, the face, neck, scalp, dorsal hands, and ears) and the essentiality of using sufficient quantities of broad-spectrum sunscreen for effective protection. Incorporating this guidance into training materials, briefings, and visual reminders allow seamless integration of photoprotection into service members’ daily routines without compromising operational efficiency.6 Younger service members, who may be less likely to prioritize preventive behaviors, may be particularly responsive to sun safety reminders in training areas, bases, and deployment zones.7 Health fairs and orientation briefs in high-UV regions also offer potential opportunities for targeted education.
Resources for Sun Protection in the Military
Sunscreen—Although sunscreen is critical in minimizing the risk for UV-induced skin cancer, its widespread use in the military is hindered by practical challenges related to accessibility and the need for consistent reapplication; for instance, providing free sunscreen dispensers at institutions for staff working under intense or prolonged UV exposure may improve sunscreen accessibility and use.8 Including sunscreen in standard-issue gear offers another logical way to embed its use into operational readiness as part of the routine protective measures.
Uniform Modifications—Adapting military uniforms and practices to improve sun protection plays a critical role in reducing skin cancer risk. Targeted protective gear for commonly sun-exposed areas can help mitigate UV exposure. One practical option is the use of wide-brimmed headgear (eg, boonie hats), which provide more face and neck coverage than standard-issue military caps, or covers. The wide-brimmed headgear currently is only selectively authorized during specific scenarios, such as field operations and training exercises, or at the discretion of unit-level leadership. Wide-brimmed headgear, already used by many service members, has been associated with up to a 17% reduction in UV exposure to inadequately protected areas, potentially lowering skin cancer risk.9,10 Similarly, a “sleeves-down” policy—requiring sleeves to remain unrolled and covering the forearms during outdoor activities—offers a simple way to minimize sun exposure without necessitating additional gear. Other specialized clothing items, including UV-blocking neck gaiters, photoprotective clothing, and lightweight gloves, also may be appropriate for high-risk groups and can be implemented in a relatively straightforward manner.
Shade Structures and UV Index Monitoring—Aside from uniform adaptation, physical barrier intervention can further complement skin cancer prevention efforts in the military. Shade structures offer a straightforward way to reduce UV exposure during prolonged outdoor activities. Incorporating daily UV index monitoring into operational guidance can help inform adjustments to training schedules and guide the implementation of additional sun protection measures, such as mandatory sunscreen application, use of wide-brimmed hats, or increased access to shaded rest areas during heavy sunlight hours. Currently, outdoor physical training is restricted during periods of high heat index, measured via Wet Bulb Globe Temperature, to reduce heat-related injuries. We argue that avoidance of nonoperational outdoor activity during peak UV index hours also should be incorporated into standardized policies. This intervention is of particular benefit to service members stationed in regions with a high UV index year-round, such as those stationed in the Middle East, Guam, Okinawa, and southern coastal United States bases.
Policy Changes to Support Photoprotective Measures
Annual Risk Factor Screening‐Screening—Effective secondary prevention efforts by military dermatologists remain an important measure in reducing the burden of skin cancer among military personnel; however, these efforts have become increasingly challenging due to 2 main factors—the diversity of military occupational specialties and their associated unique occupational risks as well as the limited availability of military dermatologists across all branches (approximately 100 active-duty dermatologists for nearly 3 million service members).11 Therefore, targeted interventions that enhance risk assessment, refined screening protocols, and leveraging of existing military health networks can improve early skin cancer detection while optimizing resource allocation.
The ePHA is an online screening tool used annually by all service members to evaluate their overall health. Presently, the ePHA lacks specific questions to assess sun exposure and skin cancer risks. Integrating annual skin cancer risk factor assessments into the ePHA would offer a practical and straightforward approach to identifying at-risk individuals, as suggested by Newnam et al12 in 2022. Skin cancer risk factor assessments allow for targeted data collection related to sun exposure history, family history, and personal risk factors, which can be used to determine individualized risk stratification to assess the need for early secondary prevention measures and specialist referral. These ePHA data can also support population-based analyses to inform preventive strategies and address knowledge gaps related to high-risk exposures, such as extended field exercises or assignments in high-UV regions, that may impede effective skin cancer prevention.
Development of Military-Specific Screening Guidelines—Given the limited number of military dermatologists, a standardized risk-assessment tool could enhance early detection of skin cancer and streamline the referral process. We propose a military-specific skin cancer screening algorithm or risk nomogram that could help to consolidate risk factors into a clear and actionable framework for more efficient triage and appropriate allocation of dermatologic resources and manpower. This nomogram could be developed by military dermatologists and then implemented on a command level, affording primary care providers a useful tool to expedite evaluation of individuals at higher risk for skin cancer while simultaneously promoting judicious use of limited dermatology resources.
Although the United States Preventive Services Task Force does not universally recommend routine skin cancer screenings for asymptomatic adults, military service members are exposed to higher occupational risks than the general population, as previously mentioned. Currently, there is no standardized screening guideline across all military services due to the unique nature and exposure risks for each branch of service and their varied occupations; however, we propose the development of basic standardized screening guidelines by adapting the framework of the United States Preventive Services Task Force and adjusting for military-specific UV exposure and occupational risks to improve early detection of skin cancer. These guidelines could be updated and tailored appropriately when additional population-based data are collected and analyzed through ePHA.
Critiques and Limitations of Implementation
Several challenges and limitations must be considered when attempting to integrate large-scale preventive measures for skin cancer within the US military. A primary concern is the extent to which military resources should be allocated to prevention when off-duty sun exposure remains largely beyond institutional control. Although military health initiatives can address workplace risk through education and policy, individual decisions during both work and leisure time remain a major variable that cannot be feasibly controlled. Cultural and operational barriers also pose challenges; for instance, the US Marine Corps maintains a strong cultural identity tied to uniform appearance, making it difficult to implement widespread changes to clothing-based sun-protection measures. Institutional changes, particularly those involving uniforms, likely will face substantial administrative resistance and potential operational limitations. When broad uniform modifications are unattainable, a more feasible approach may be to encourage unit-level leadership to authorize and promote the frequent use of nonuniform protective measures.
Furthermore, integrating additional skin cancer risk questions into the already extensive ePHA means extra time required to complete the assessment; this adds to service members’ administrative burden, potentially leading to reduced timely compliance, rushed responses, and survey fatigue, which threaten data quality. If new items are to be included, they should be carefully selected for efficiency and clinical relevance. Existing validated questionnaires such as those from the study by Lyford et al7 published in 2021 can serve as a foundation.
Another critical limitation is access to dermatologic care for active-duty service members. Raising awareness of skin cancer risk without ensuring adequate resources may create ethical concerns, particularly in high-risk environments such as the Middle East and Indo-Pacific. Additionally, because skin cancer often develops years or decades after exposure, securing early buy-in from service members and their leaders can be challenging. These concerns make it clear that, while skin cancer prevention is important, implementing widespread measures is not straightforward and requires a practical and balanced approach.
Final Thoughts
Implementing prevention strategies for skin cancer in the military requires balancing evidence-based recommendations with the practical realities of military culture, resource limitations, and operational demands. Challenges remain for dermatologists in providing targeted recommendations due to the multifaceted nature of military roles, including over 150 Navy Military Occupational Specialties, limited familiarity with the unique UV exposure risks associated with each occupation, and variability in local and regional policies on uniform wear, physical training requirements, and other operational practices. Although targeted prevention measures are difficult to establish in the setting of these knowledge gaps, leveraging unit-level leadership to align with existing screening guidelines and optimizing primary prevention measures can be meaningful steps toward reducing skin cancer risk for military service members while maintaining mission readiness.
- Riemenschneider K, Liu J, Powers JG. Skin cancer in the military: a systematic review of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancerincidence, prevention, and screening among active duty and veteran personnel. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1185-1192. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.062
- Lee T, Taubman SB, Williams VF. Incident diagnoses of non-melanoma skin cancer, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2005-2014. MSMR. 2016;23:2-6.
- Krivda KR, Watson NL, Lyford WH, et al. The burden of skin cancer in the military health system, 2017-2022. Cutis. 2024;113:200-215. doi:10.12788/cutis.1015
- Sanlorenzo M, Wehner MR, Linos E, et al. The risk of melanoma in airline pilots and cabin crew: a meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:51-58. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1077
- Brundage JF, Williams VF, Stahlman S, et al. Incidence rates of malignant melanoma in relation to years of military service, overall and in selected military occupational groups, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2001-2015. MMSR. 2017;24:8-14.
- Subramaniam P, Olsen CM, Thompson BS, et al, for the QSkin Sun and Health Study Investigators. Anatomical distributions of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma in a population-based study in Queensland, Australia. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:175-182. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.4070
- Lyford WH, Crotty A, Logemann NF. Sun exposure prevention practices within U.S. naval aviation. Mil Med. 2021;186:1169-1175. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab099
- Wood M, Raisanen T, Polcari I. Observational study of free public sunscreen dispenser use at a major US outdoor event. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:164-166.
- Schissel D. Operation shadow warrior: a quantitative analysis of the ultraviolet radiation protection demonstrated by various headgear. Mil Med. 2001;166:783-785.
- Milch JM, Logemann NF. Photoprotection prevents skin cancer: let’s make it fashionable to wear sun-protective clothing. Cutis. 2017;99:89-92.
- Association of Military Dermatologists. (n.d.). Military dermatology. https://militaryderm.org/military-dermatology/
- Newnam R, Le-Jenkins U, Rutledge C, et al. The association of skin cancer prevention knowledge, sun-protective attitudes, and sunprotective behaviors in a Navy population. Mil Med. 2024;189:1-7. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac285
Skin cancer is a major health concern for military service members, who experience notably higher incidence rates than the general population.1 Active-duty military personnel are particularly vulnerable to prolonged sun exposure due to deployments, specialized training, and everyday outdoor duties.1 Despite skin cancer being the most commonly diagnosed malignancy in active-duty service members,2 tracking and documenting the quantity and diversity of these risk factors remain limited. This knowledge gap comes at high cost, simultaneously impairing military medicine preventive measures while burdening the military health care system with substantial expenditures.3 These findings underscore the critical need for targeted surveillance, early-detection programs, and policy-driven interventions to mitigate these medical and economic concerns.
Skin cancer has been recognized as a major health risk to the military population for decades, yet incidence and prevalence remain high. This phenomenon is closely linked to the inherent responsibilities and expectations of active-duty military members, including outdoor physical training, field exercises, standing in formation, and outdoor working environments—all of which can occur during peak sunlight hours. These risks are further elevated at duty stations in geographic regions with high levels of UV exposure, such as those in tropical and arid regions of the world. Certain military occupational specialties and missions may further introduce unique risk factors; for instance, pilots with frequent high-altitude missions experience heightened UV exposure and melanoma risk.4 Secondary to compounding determinants, the aviation, diving, and nuclear subgroups of the military community are particularly vulnerable to skin cancer.5
Despite well-documented risks, considerable gaps remain in quantifying and analyzing variations in UV exposure across military occupations, duty locations, and operational roles. Factors such as the existence of over 150 distinct military occupational specialties, frequent geographic relocations, and routine work in austere environments contribute to a wide range of UV exposure profiles that remain insufficiently characterized. This lack of comprehensive exposure data hinders the development of large-scale, targeted skin cancer prevention strategies. Initial approaches to addressing these challenges include enhanced surveillance, education, and policy initiatives. The Table presents practical recommendations for military leadership to consider in implementing preventive measures for skin cancer. Herein, we outline broader systemic strategies to bridge knowledge gaps and address underrecognized occupational risk factors for skin cancer in military service members; these elements include proposed modifications to the electronic Periodic Health Assessment (ePHA) and the development of standardized, military-specific screening and prevention guidelines to support early detection and resource optimization.

Skin Cancer Education for Service Members
Sunscreen and Signage—Diligent primary prevention offers a promising avenue for mitigating skin cancer incidence in military service members. Basic education and precautionary messaging on photoprotection can be widely implemented to simultaneously educate service members on the dangers of sun exposure while reinforcing healthy behaviors in real time. Simple low-cost initiatives such as strategically placed visual signage reminding service members to apply sunscreen in high UV environments can support consistent sun-safe practices. Educational efforts also should emphasize proper sunscreen use, including application on high-risk anatomic sites (eg, the face, neck, scalp, dorsal hands, and ears) and the essentiality of using sufficient quantities of broad-spectrum sunscreen for effective protection. Incorporating this guidance into training materials, briefings, and visual reminders allow seamless integration of photoprotection into service members’ daily routines without compromising operational efficiency.6 Younger service members, who may be less likely to prioritize preventive behaviors, may be particularly responsive to sun safety reminders in training areas, bases, and deployment zones.7 Health fairs and orientation briefs in high-UV regions also offer potential opportunities for targeted education.
Resources for Sun Protection in the Military
Sunscreen—Although sunscreen is critical in minimizing the risk for UV-induced skin cancer, its widespread use in the military is hindered by practical challenges related to accessibility and the need for consistent reapplication; for instance, providing free sunscreen dispensers at institutions for staff working under intense or prolonged UV exposure may improve sunscreen accessibility and use.8 Including sunscreen in standard-issue gear offers another logical way to embed its use into operational readiness as part of the routine protective measures.
Uniform Modifications—Adapting military uniforms and practices to improve sun protection plays a critical role in reducing skin cancer risk. Targeted protective gear for commonly sun-exposed areas can help mitigate UV exposure. One practical option is the use of wide-brimmed headgear (eg, boonie hats), which provide more face and neck coverage than standard-issue military caps, or covers. The wide-brimmed headgear currently is only selectively authorized during specific scenarios, such as field operations and training exercises, or at the discretion of unit-level leadership. Wide-brimmed headgear, already used by many service members, has been associated with up to a 17% reduction in UV exposure to inadequately protected areas, potentially lowering skin cancer risk.9,10 Similarly, a “sleeves-down” policy—requiring sleeves to remain unrolled and covering the forearms during outdoor activities—offers a simple way to minimize sun exposure without necessitating additional gear. Other specialized clothing items, including UV-blocking neck gaiters, photoprotective clothing, and lightweight gloves, also may be appropriate for high-risk groups and can be implemented in a relatively straightforward manner.
Shade Structures and UV Index Monitoring—Aside from uniform adaptation, physical barrier intervention can further complement skin cancer prevention efforts in the military. Shade structures offer a straightforward way to reduce UV exposure during prolonged outdoor activities. Incorporating daily UV index monitoring into operational guidance can help inform adjustments to training schedules and guide the implementation of additional sun protection measures, such as mandatory sunscreen application, use of wide-brimmed hats, or increased access to shaded rest areas during heavy sunlight hours. Currently, outdoor physical training is restricted during periods of high heat index, measured via Wet Bulb Globe Temperature, to reduce heat-related injuries. We argue that avoidance of nonoperational outdoor activity during peak UV index hours also should be incorporated into standardized policies. This intervention is of particular benefit to service members stationed in regions with a high UV index year-round, such as those stationed in the Middle East, Guam, Okinawa, and southern coastal United States bases.
Policy Changes to Support Photoprotective Measures
Annual Risk Factor Screening‐Screening—Effective secondary prevention efforts by military dermatologists remain an important measure in reducing the burden of skin cancer among military personnel; however, these efforts have become increasingly challenging due to 2 main factors—the diversity of military occupational specialties and their associated unique occupational risks as well as the limited availability of military dermatologists across all branches (approximately 100 active-duty dermatologists for nearly 3 million service members).11 Therefore, targeted interventions that enhance risk assessment, refined screening protocols, and leveraging of existing military health networks can improve early skin cancer detection while optimizing resource allocation.
The ePHA is an online screening tool used annually by all service members to evaluate their overall health. Presently, the ePHA lacks specific questions to assess sun exposure and skin cancer risks. Integrating annual skin cancer risk factor assessments into the ePHA would offer a practical and straightforward approach to identifying at-risk individuals, as suggested by Newnam et al12 in 2022. Skin cancer risk factor assessments allow for targeted data collection related to sun exposure history, family history, and personal risk factors, which can be used to determine individualized risk stratification to assess the need for early secondary prevention measures and specialist referral. These ePHA data can also support population-based analyses to inform preventive strategies and address knowledge gaps related to high-risk exposures, such as extended field exercises or assignments in high-UV regions, that may impede effective skin cancer prevention.
Development of Military-Specific Screening Guidelines—Given the limited number of military dermatologists, a standardized risk-assessment tool could enhance early detection of skin cancer and streamline the referral process. We propose a military-specific skin cancer screening algorithm or risk nomogram that could help to consolidate risk factors into a clear and actionable framework for more efficient triage and appropriate allocation of dermatologic resources and manpower. This nomogram could be developed by military dermatologists and then implemented on a command level, affording primary care providers a useful tool to expedite evaluation of individuals at higher risk for skin cancer while simultaneously promoting judicious use of limited dermatology resources.
Although the United States Preventive Services Task Force does not universally recommend routine skin cancer screenings for asymptomatic adults, military service members are exposed to higher occupational risks than the general population, as previously mentioned. Currently, there is no standardized screening guideline across all military services due to the unique nature and exposure risks for each branch of service and their varied occupations; however, we propose the development of basic standardized screening guidelines by adapting the framework of the United States Preventive Services Task Force and adjusting for military-specific UV exposure and occupational risks to improve early detection of skin cancer. These guidelines could be updated and tailored appropriately when additional population-based data are collected and analyzed through ePHA.
Critiques and Limitations of Implementation
Several challenges and limitations must be considered when attempting to integrate large-scale preventive measures for skin cancer within the US military. A primary concern is the extent to which military resources should be allocated to prevention when off-duty sun exposure remains largely beyond institutional control. Although military health initiatives can address workplace risk through education and policy, individual decisions during both work and leisure time remain a major variable that cannot be feasibly controlled. Cultural and operational barriers also pose challenges; for instance, the US Marine Corps maintains a strong cultural identity tied to uniform appearance, making it difficult to implement widespread changes to clothing-based sun-protection measures. Institutional changes, particularly those involving uniforms, likely will face substantial administrative resistance and potential operational limitations. When broad uniform modifications are unattainable, a more feasible approach may be to encourage unit-level leadership to authorize and promote the frequent use of nonuniform protective measures.
Furthermore, integrating additional skin cancer risk questions into the already extensive ePHA means extra time required to complete the assessment; this adds to service members’ administrative burden, potentially leading to reduced timely compliance, rushed responses, and survey fatigue, which threaten data quality. If new items are to be included, they should be carefully selected for efficiency and clinical relevance. Existing validated questionnaires such as those from the study by Lyford et al7 published in 2021 can serve as a foundation.
Another critical limitation is access to dermatologic care for active-duty service members. Raising awareness of skin cancer risk without ensuring adequate resources may create ethical concerns, particularly in high-risk environments such as the Middle East and Indo-Pacific. Additionally, because skin cancer often develops years or decades after exposure, securing early buy-in from service members and their leaders can be challenging. These concerns make it clear that, while skin cancer prevention is important, implementing widespread measures is not straightforward and requires a practical and balanced approach.
Final Thoughts
Implementing prevention strategies for skin cancer in the military requires balancing evidence-based recommendations with the practical realities of military culture, resource limitations, and operational demands. Challenges remain for dermatologists in providing targeted recommendations due to the multifaceted nature of military roles, including over 150 Navy Military Occupational Specialties, limited familiarity with the unique UV exposure risks associated with each occupation, and variability in local and regional policies on uniform wear, physical training requirements, and other operational practices. Although targeted prevention measures are difficult to establish in the setting of these knowledge gaps, leveraging unit-level leadership to align with existing screening guidelines and optimizing primary prevention measures can be meaningful steps toward reducing skin cancer risk for military service members while maintaining mission readiness.
Skin cancer is a major health concern for military service members, who experience notably higher incidence rates than the general population.1 Active-duty military personnel are particularly vulnerable to prolonged sun exposure due to deployments, specialized training, and everyday outdoor duties.1 Despite skin cancer being the most commonly diagnosed malignancy in active-duty service members,2 tracking and documenting the quantity and diversity of these risk factors remain limited. This knowledge gap comes at high cost, simultaneously impairing military medicine preventive measures while burdening the military health care system with substantial expenditures.3 These findings underscore the critical need for targeted surveillance, early-detection programs, and policy-driven interventions to mitigate these medical and economic concerns.
Skin cancer has been recognized as a major health risk to the military population for decades, yet incidence and prevalence remain high. This phenomenon is closely linked to the inherent responsibilities and expectations of active-duty military members, including outdoor physical training, field exercises, standing in formation, and outdoor working environments—all of which can occur during peak sunlight hours. These risks are further elevated at duty stations in geographic regions with high levels of UV exposure, such as those in tropical and arid regions of the world. Certain military occupational specialties and missions may further introduce unique risk factors; for instance, pilots with frequent high-altitude missions experience heightened UV exposure and melanoma risk.4 Secondary to compounding determinants, the aviation, diving, and nuclear subgroups of the military community are particularly vulnerable to skin cancer.5
Despite well-documented risks, considerable gaps remain in quantifying and analyzing variations in UV exposure across military occupations, duty locations, and operational roles. Factors such as the existence of over 150 distinct military occupational specialties, frequent geographic relocations, and routine work in austere environments contribute to a wide range of UV exposure profiles that remain insufficiently characterized. This lack of comprehensive exposure data hinders the development of large-scale, targeted skin cancer prevention strategies. Initial approaches to addressing these challenges include enhanced surveillance, education, and policy initiatives. The Table presents practical recommendations for military leadership to consider in implementing preventive measures for skin cancer. Herein, we outline broader systemic strategies to bridge knowledge gaps and address underrecognized occupational risk factors for skin cancer in military service members; these elements include proposed modifications to the electronic Periodic Health Assessment (ePHA) and the development of standardized, military-specific screening and prevention guidelines to support early detection and resource optimization.

Skin Cancer Education for Service Members
Sunscreen and Signage—Diligent primary prevention offers a promising avenue for mitigating skin cancer incidence in military service members. Basic education and precautionary messaging on photoprotection can be widely implemented to simultaneously educate service members on the dangers of sun exposure while reinforcing healthy behaviors in real time. Simple low-cost initiatives such as strategically placed visual signage reminding service members to apply sunscreen in high UV environments can support consistent sun-safe practices. Educational efforts also should emphasize proper sunscreen use, including application on high-risk anatomic sites (eg, the face, neck, scalp, dorsal hands, and ears) and the essentiality of using sufficient quantities of broad-spectrum sunscreen for effective protection. Incorporating this guidance into training materials, briefings, and visual reminders allow seamless integration of photoprotection into service members’ daily routines without compromising operational efficiency.6 Younger service members, who may be less likely to prioritize preventive behaviors, may be particularly responsive to sun safety reminders in training areas, bases, and deployment zones.7 Health fairs and orientation briefs in high-UV regions also offer potential opportunities for targeted education.
Resources for Sun Protection in the Military
Sunscreen—Although sunscreen is critical in minimizing the risk for UV-induced skin cancer, its widespread use in the military is hindered by practical challenges related to accessibility and the need for consistent reapplication; for instance, providing free sunscreen dispensers at institutions for staff working under intense or prolonged UV exposure may improve sunscreen accessibility and use.8 Including sunscreen in standard-issue gear offers another logical way to embed its use into operational readiness as part of the routine protective measures.
Uniform Modifications—Adapting military uniforms and practices to improve sun protection plays a critical role in reducing skin cancer risk. Targeted protective gear for commonly sun-exposed areas can help mitigate UV exposure. One practical option is the use of wide-brimmed headgear (eg, boonie hats), which provide more face and neck coverage than standard-issue military caps, or covers. The wide-brimmed headgear currently is only selectively authorized during specific scenarios, such as field operations and training exercises, or at the discretion of unit-level leadership. Wide-brimmed headgear, already used by many service members, has been associated with up to a 17% reduction in UV exposure to inadequately protected areas, potentially lowering skin cancer risk.9,10 Similarly, a “sleeves-down” policy—requiring sleeves to remain unrolled and covering the forearms during outdoor activities—offers a simple way to minimize sun exposure without necessitating additional gear. Other specialized clothing items, including UV-blocking neck gaiters, photoprotective clothing, and lightweight gloves, also may be appropriate for high-risk groups and can be implemented in a relatively straightforward manner.
Shade Structures and UV Index Monitoring—Aside from uniform adaptation, physical barrier intervention can further complement skin cancer prevention efforts in the military. Shade structures offer a straightforward way to reduce UV exposure during prolonged outdoor activities. Incorporating daily UV index monitoring into operational guidance can help inform adjustments to training schedules and guide the implementation of additional sun protection measures, such as mandatory sunscreen application, use of wide-brimmed hats, or increased access to shaded rest areas during heavy sunlight hours. Currently, outdoor physical training is restricted during periods of high heat index, measured via Wet Bulb Globe Temperature, to reduce heat-related injuries. We argue that avoidance of nonoperational outdoor activity during peak UV index hours also should be incorporated into standardized policies. This intervention is of particular benefit to service members stationed in regions with a high UV index year-round, such as those stationed in the Middle East, Guam, Okinawa, and southern coastal United States bases.
Policy Changes to Support Photoprotective Measures
Annual Risk Factor Screening‐Screening—Effective secondary prevention efforts by military dermatologists remain an important measure in reducing the burden of skin cancer among military personnel; however, these efforts have become increasingly challenging due to 2 main factors—the diversity of military occupational specialties and their associated unique occupational risks as well as the limited availability of military dermatologists across all branches (approximately 100 active-duty dermatologists for nearly 3 million service members).11 Therefore, targeted interventions that enhance risk assessment, refined screening protocols, and leveraging of existing military health networks can improve early skin cancer detection while optimizing resource allocation.
The ePHA is an online screening tool used annually by all service members to evaluate their overall health. Presently, the ePHA lacks specific questions to assess sun exposure and skin cancer risks. Integrating annual skin cancer risk factor assessments into the ePHA would offer a practical and straightforward approach to identifying at-risk individuals, as suggested by Newnam et al12 in 2022. Skin cancer risk factor assessments allow for targeted data collection related to sun exposure history, family history, and personal risk factors, which can be used to determine individualized risk stratification to assess the need for early secondary prevention measures and specialist referral. These ePHA data can also support population-based analyses to inform preventive strategies and address knowledge gaps related to high-risk exposures, such as extended field exercises or assignments in high-UV regions, that may impede effective skin cancer prevention.
Development of Military-Specific Screening Guidelines—Given the limited number of military dermatologists, a standardized risk-assessment tool could enhance early detection of skin cancer and streamline the referral process. We propose a military-specific skin cancer screening algorithm or risk nomogram that could help to consolidate risk factors into a clear and actionable framework for more efficient triage and appropriate allocation of dermatologic resources and manpower. This nomogram could be developed by military dermatologists and then implemented on a command level, affording primary care providers a useful tool to expedite evaluation of individuals at higher risk for skin cancer while simultaneously promoting judicious use of limited dermatology resources.
Although the United States Preventive Services Task Force does not universally recommend routine skin cancer screenings for asymptomatic adults, military service members are exposed to higher occupational risks than the general population, as previously mentioned. Currently, there is no standardized screening guideline across all military services due to the unique nature and exposure risks for each branch of service and their varied occupations; however, we propose the development of basic standardized screening guidelines by adapting the framework of the United States Preventive Services Task Force and adjusting for military-specific UV exposure and occupational risks to improve early detection of skin cancer. These guidelines could be updated and tailored appropriately when additional population-based data are collected and analyzed through ePHA.
Critiques and Limitations of Implementation
Several challenges and limitations must be considered when attempting to integrate large-scale preventive measures for skin cancer within the US military. A primary concern is the extent to which military resources should be allocated to prevention when off-duty sun exposure remains largely beyond institutional control. Although military health initiatives can address workplace risk through education and policy, individual decisions during both work and leisure time remain a major variable that cannot be feasibly controlled. Cultural and operational barriers also pose challenges; for instance, the US Marine Corps maintains a strong cultural identity tied to uniform appearance, making it difficult to implement widespread changes to clothing-based sun-protection measures. Institutional changes, particularly those involving uniforms, likely will face substantial administrative resistance and potential operational limitations. When broad uniform modifications are unattainable, a more feasible approach may be to encourage unit-level leadership to authorize and promote the frequent use of nonuniform protective measures.
Furthermore, integrating additional skin cancer risk questions into the already extensive ePHA means extra time required to complete the assessment; this adds to service members’ administrative burden, potentially leading to reduced timely compliance, rushed responses, and survey fatigue, which threaten data quality. If new items are to be included, they should be carefully selected for efficiency and clinical relevance. Existing validated questionnaires such as those from the study by Lyford et al7 published in 2021 can serve as a foundation.
Another critical limitation is access to dermatologic care for active-duty service members. Raising awareness of skin cancer risk without ensuring adequate resources may create ethical concerns, particularly in high-risk environments such as the Middle East and Indo-Pacific. Additionally, because skin cancer often develops years or decades after exposure, securing early buy-in from service members and their leaders can be challenging. These concerns make it clear that, while skin cancer prevention is important, implementing widespread measures is not straightforward and requires a practical and balanced approach.
Final Thoughts
Implementing prevention strategies for skin cancer in the military requires balancing evidence-based recommendations with the practical realities of military culture, resource limitations, and operational demands. Challenges remain for dermatologists in providing targeted recommendations due to the multifaceted nature of military roles, including over 150 Navy Military Occupational Specialties, limited familiarity with the unique UV exposure risks associated with each occupation, and variability in local and regional policies on uniform wear, physical training requirements, and other operational practices. Although targeted prevention measures are difficult to establish in the setting of these knowledge gaps, leveraging unit-level leadership to align with existing screening guidelines and optimizing primary prevention measures can be meaningful steps toward reducing skin cancer risk for military service members while maintaining mission readiness.
- Riemenschneider K, Liu J, Powers JG. Skin cancer in the military: a systematic review of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancerincidence, prevention, and screening among active duty and veteran personnel. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1185-1192. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.062
- Lee T, Taubman SB, Williams VF. Incident diagnoses of non-melanoma skin cancer, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2005-2014. MSMR. 2016;23:2-6.
- Krivda KR, Watson NL, Lyford WH, et al. The burden of skin cancer in the military health system, 2017-2022. Cutis. 2024;113:200-215. doi:10.12788/cutis.1015
- Sanlorenzo M, Wehner MR, Linos E, et al. The risk of melanoma in airline pilots and cabin crew: a meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:51-58. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1077
- Brundage JF, Williams VF, Stahlman S, et al. Incidence rates of malignant melanoma in relation to years of military service, overall and in selected military occupational groups, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2001-2015. MMSR. 2017;24:8-14.
- Subramaniam P, Olsen CM, Thompson BS, et al, for the QSkin Sun and Health Study Investigators. Anatomical distributions of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma in a population-based study in Queensland, Australia. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:175-182. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.4070
- Lyford WH, Crotty A, Logemann NF. Sun exposure prevention practices within U.S. naval aviation. Mil Med. 2021;186:1169-1175. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab099
- Wood M, Raisanen T, Polcari I. Observational study of free public sunscreen dispenser use at a major US outdoor event. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:164-166.
- Schissel D. Operation shadow warrior: a quantitative analysis of the ultraviolet radiation protection demonstrated by various headgear. Mil Med. 2001;166:783-785.
- Milch JM, Logemann NF. Photoprotection prevents skin cancer: let’s make it fashionable to wear sun-protective clothing. Cutis. 2017;99:89-92.
- Association of Military Dermatologists. (n.d.). Military dermatology. https://militaryderm.org/military-dermatology/
- Newnam R, Le-Jenkins U, Rutledge C, et al. The association of skin cancer prevention knowledge, sun-protective attitudes, and sunprotective behaviors in a Navy population. Mil Med. 2024;189:1-7. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac285
- Riemenschneider K, Liu J, Powers JG. Skin cancer in the military: a systematic review of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancerincidence, prevention, and screening among active duty and veteran personnel. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1185-1192. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.062
- Lee T, Taubman SB, Williams VF. Incident diagnoses of non-melanoma skin cancer, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2005-2014. MSMR. 2016;23:2-6.
- Krivda KR, Watson NL, Lyford WH, et al. The burden of skin cancer in the military health system, 2017-2022. Cutis. 2024;113:200-215. doi:10.12788/cutis.1015
- Sanlorenzo M, Wehner MR, Linos E, et al. The risk of melanoma in airline pilots and cabin crew: a meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:51-58. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1077
- Brundage JF, Williams VF, Stahlman S, et al. Incidence rates of malignant melanoma in relation to years of military service, overall and in selected military occupational groups, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2001-2015. MMSR. 2017;24:8-14.
- Subramaniam P, Olsen CM, Thompson BS, et al, for the QSkin Sun and Health Study Investigators. Anatomical distributions of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma in a population-based study in Queensland, Australia. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:175-182. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.4070
- Lyford WH, Crotty A, Logemann NF. Sun exposure prevention practices within U.S. naval aviation. Mil Med. 2021;186:1169-1175. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab099
- Wood M, Raisanen T, Polcari I. Observational study of free public sunscreen dispenser use at a major US outdoor event. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:164-166.
- Schissel D. Operation shadow warrior: a quantitative analysis of the ultraviolet radiation protection demonstrated by various headgear. Mil Med. 2001;166:783-785.
- Milch JM, Logemann NF. Photoprotection prevents skin cancer: let’s make it fashionable to wear sun-protective clothing. Cutis. 2017;99:89-92.
- Association of Military Dermatologists. (n.d.). Military dermatology. https://militaryderm.org/military-dermatology/
- Newnam R, Le-Jenkins U, Rutledge C, et al. The association of skin cancer prevention knowledge, sun-protective attitudes, and sunprotective behaviors in a Navy population. Mil Med. 2024;189:1-7. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac285
Bridging the Knowledge-Action Gap in Skin Cancer Prevention Among US Military Personnel
Bridging the Knowledge-Action Gap in Skin Cancer Prevention Among US Military Personnel
PRACTICE POINTS
- Military personnel face elevated skin cancer risks due to prolonged occupational UV exposure.
- Medical providers can partner with unit-level leadership to implement low-cost interventions such as shade structures and uniform modifications.
- Annual sun exposure risk assessments should be integrated into the military Electronic Periodic Health Assessment for targeted screening and early intervention of risk factors.
- Photoprotective gear and signage in high—UV index areas can improve service member awareness and adherence to preventive measures.