User login
Cutis is a peer-reviewed clinical journal for the dermatologist, allergist, and general practitioner published monthly since 1965. Concise clinical articles present the practical side of dermatology, helping physicians to improve patient care. Cutis is referenced in Index Medicus/MEDLINE and is written and edited by industry leaders.
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')
A peer-reviewed, indexed journal for dermatologists with original research, image quizzes, cases and reviews, and columns.
Lesions on the Thigh After an Organ Transplant
The Diagnosis: Microcystic Lymphatic Malformation
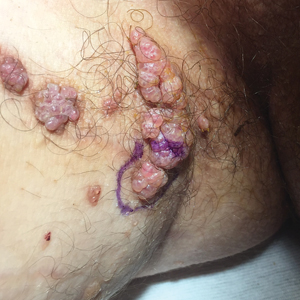
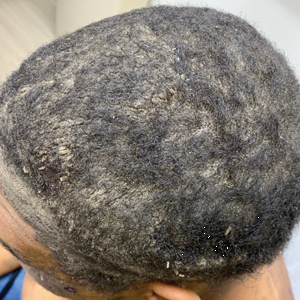
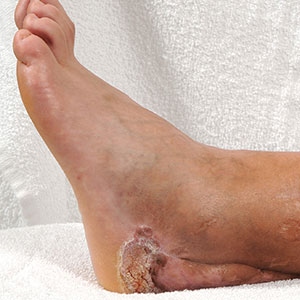
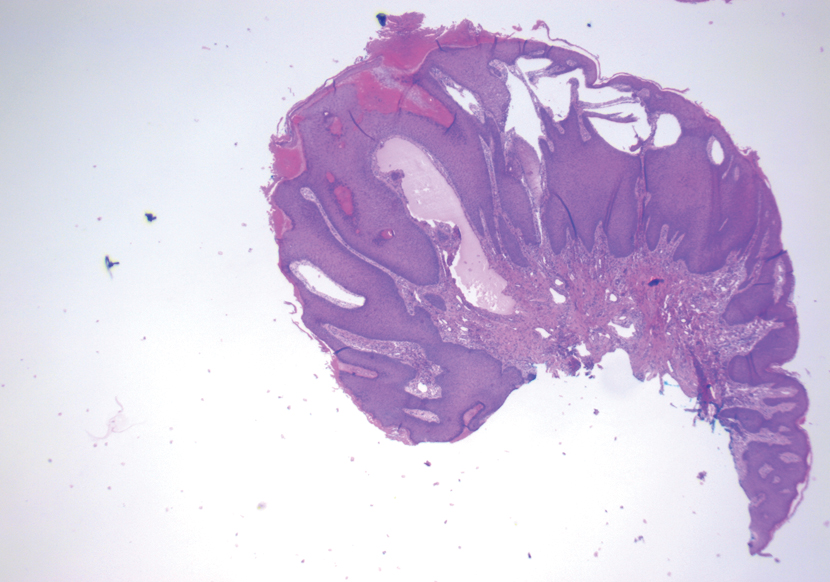
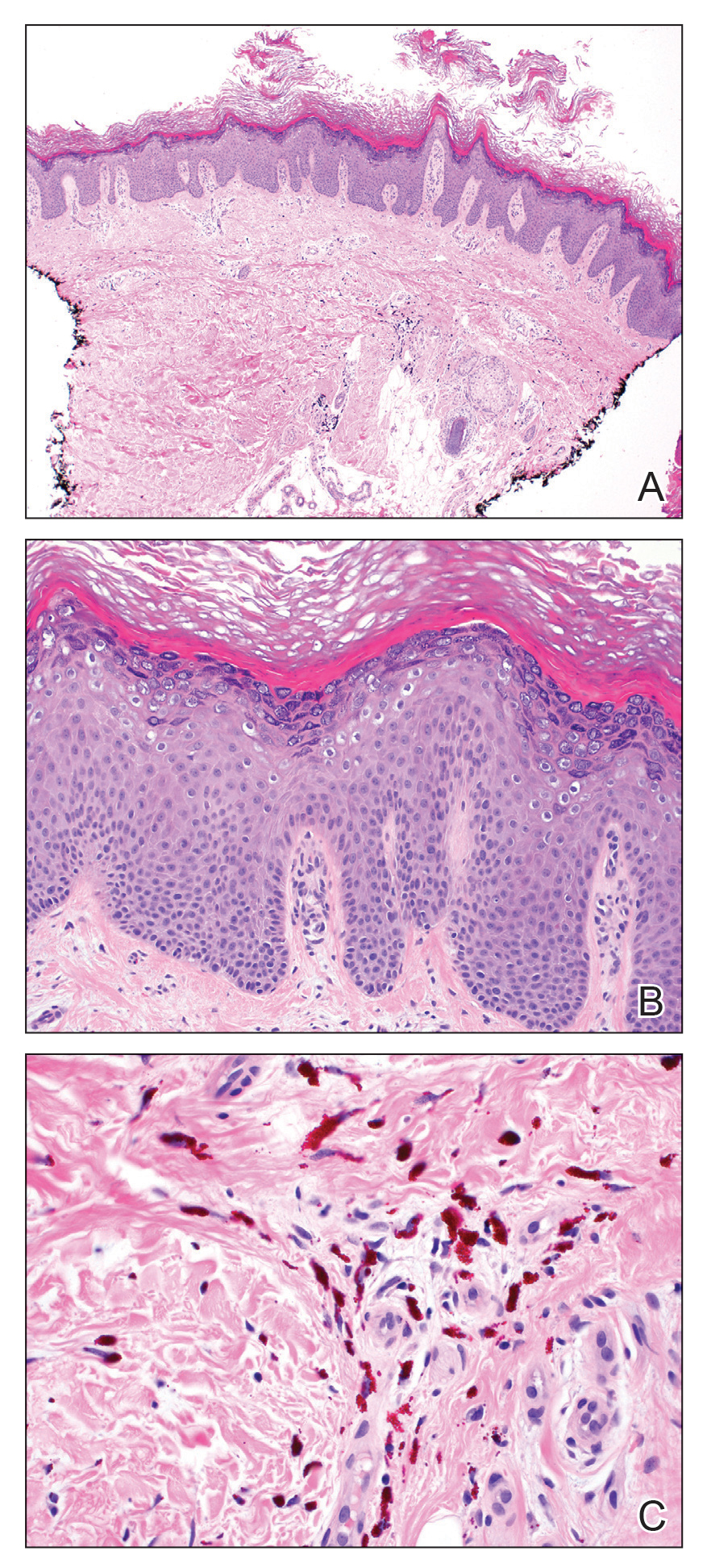
The shave biopsy demonstrated numerous thin-walled vascular spaces filled with lymphatic fluid within the dermis (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of microcystic lymphatic malformation (LM). Lymphatic malformations represent a class of benign vascular lesions consisting of anomalous or dilated lymphatic vessels, which can be broadly categorized as macrocystic (formerly cavernous lymphangioma or cystic hygroma), microcystic (formerly lymphangioma circumscriptum), or mixed.1 Patients often will present with pruritus, crusting, secondary infection, edema, or oozing.2 The superficial blebs of microcystic LMs resemble frog spawn and range in color from clear to pink, brawny, or deep maroon.3 Although the lymphatic vessels involved in microcystic LMs appear disconnected from the major lymphatic circulation,3 systemic fluid overload could plausibly promote lesional swelling and tenderness; we attributed our patient's worsening symptoms to the cumulative 7.8 L of intravenous fluid he received intraoperatively during his cardiac transplant. The excess fluid allowed communication between lymphatic cisterns and thin-walled vesicles on the skin surface through dilated channels. Overall, LMs represent roughly 26% of pediatric benign vascular tumors and approximately 4% of all vascular tumors.4
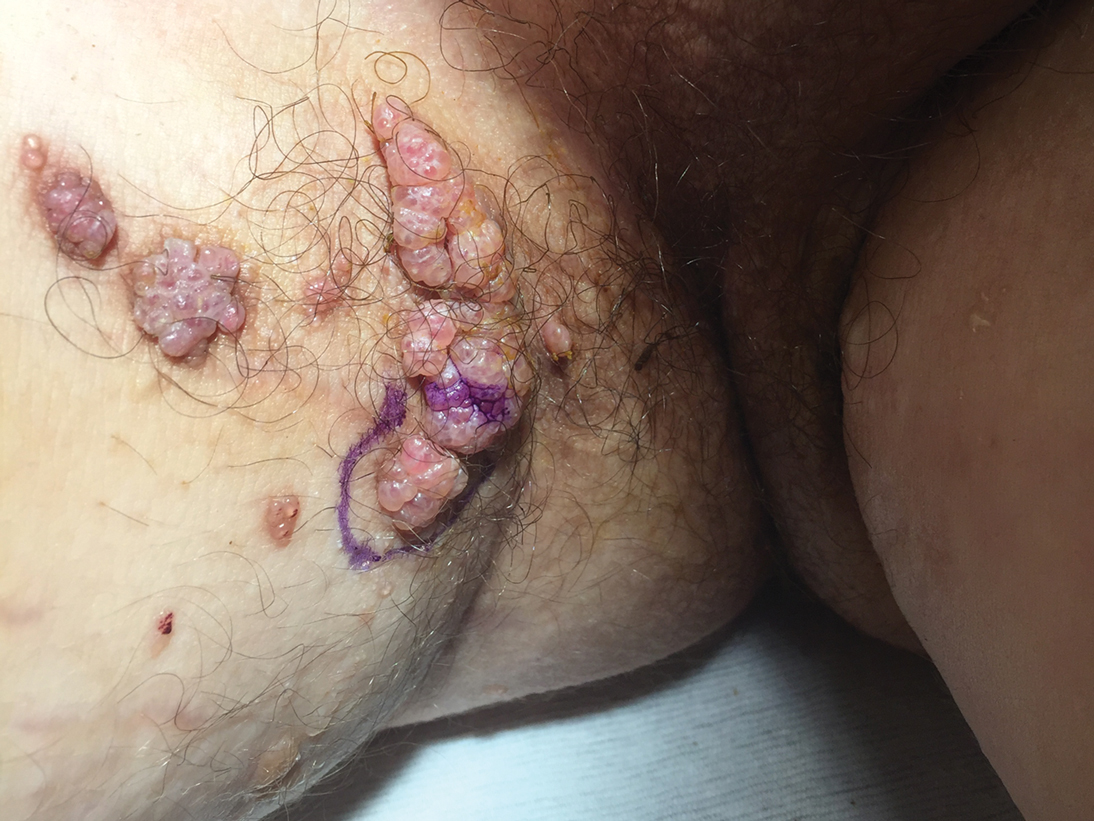
Although microcystic LMs may appear especially vascular or verrucous, the differential diagnosis for our patient's LM included condyloma acuminatum,5,6 condyloma lata,7 epidermal nevus, and lymphangiosarcoma. Epidermal nevi are congenital lesions, varying in appearance from velvety to verrucous patches and plaques that often evolve during puberty and become thicker, more verrucous, and hyperpigmented. Keratinocytic epidermal nevus syndromes and other entities such as nevus sebaceous have been associated with somatic mutations affecting proteins in the fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway (eg, FGFR3, HRAS).8 Although the clinical appearance alone may be similar, lymphangiosarcoma can be distinguished from LM via biopsy.
There are several methods to diagnose LM. Duplex sonography is possibly the best noninvasive method to identify the flow between venous valves. Magnetic resonance imaging can detect larger occurrences of LM, and lymphangiography can be utilized to confirm a normal or abnormal lymphatic network.4 Treatment options are broad, including surgical excision, laser ablation, and topical sirolimus. Hypertonic saline sclerotherapy can be injected into the afflicted lymphatic channels to decrease inflammation, erythema, and hyperpigmentation without further treatment or major side effects.4
However, the benefits of sclerotherapy alone in the treatment of LM often come gradually, and radiofrequency ablation may need to be utilized to achieve more immediate results.2 Overall, outcomes are highly variable, but favorable outcomes often can be difficult to obtain due to a high recurrence rate.2,8 Our patient's symptoms improved during his postoperative recovery, and he declined further intervention.
- Elluru RG, Balakrishnan K, Padua HM. Lymphatic malformations: diagnosis and management. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014;23:178-185. doi:10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2014.07.002
- Niti K, Manish P. Microcystic lymphatic malformation (lymphangioma circumscriptum) treated using a minimally invasive technique of radiofrequency ablation and sclerotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1711-1717. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2010.01723.x
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Bikowski JB, Dumont AM. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: treatment with hypertonic saline sclerotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:442-444. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.04.086
- Costa-Silva M, Fernandes I, Rodrigues AG, et al. Anogenital warts in pediatric population. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:675-681. doi:10.1590 /abd1806-4841.201756411
- Darmstadt GL. Perianal lymphangioma circumscriptum mistaken for genital warts. Pediatrics 1996;98;461.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJA, de Vries HJC. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259. doi:10.1136 /bmj.h1259
- Asch S, Sugarman JL. Epidermal nevus syndromes: new insights into whorls and swirls. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:21-29. doi:10.1111 /pde.13273
The Diagnosis: Microcystic Lymphatic Malformation
The shave biopsy demonstrated numerous thin-walled vascular spaces filled with lymphatic fluid within the dermis (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of microcystic lymphatic malformation (LM). Lymphatic malformations represent a class of benign vascular lesions consisting of anomalous or dilated lymphatic vessels, which can be broadly categorized as macrocystic (formerly cavernous lymphangioma or cystic hygroma), microcystic (formerly lymphangioma circumscriptum), or mixed.1 Patients often will present with pruritus, crusting, secondary infection, edema, or oozing.2 The superficial blebs of microcystic LMs resemble frog spawn and range in color from clear to pink, brawny, or deep maroon.3 Although the lymphatic vessels involved in microcystic LMs appear disconnected from the major lymphatic circulation,3 systemic fluid overload could plausibly promote lesional swelling and tenderness; we attributed our patient's worsening symptoms to the cumulative 7.8 L of intravenous fluid he received intraoperatively during his cardiac transplant. The excess fluid allowed communication between lymphatic cisterns and thin-walled vesicles on the skin surface through dilated channels. Overall, LMs represent roughly 26% of pediatric benign vascular tumors and approximately 4% of all vascular tumors.4

Although microcystic LMs may appear especially vascular or verrucous, the differential diagnosis for our patient's LM included condyloma acuminatum,5,6 condyloma lata,7 epidermal nevus, and lymphangiosarcoma. Epidermal nevi are congenital lesions, varying in appearance from velvety to verrucous patches and plaques that often evolve during puberty and become thicker, more verrucous, and hyperpigmented. Keratinocytic epidermal nevus syndromes and other entities such as nevus sebaceous have been associated with somatic mutations affecting proteins in the fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway (eg, FGFR3, HRAS).8 Although the clinical appearance alone may be similar, lymphangiosarcoma can be distinguished from LM via biopsy.
There are several methods to diagnose LM. Duplex sonography is possibly the best noninvasive method to identify the flow between venous valves. Magnetic resonance imaging can detect larger occurrences of LM, and lymphangiography can be utilized to confirm a normal or abnormal lymphatic network.4 Treatment options are broad, including surgical excision, laser ablation, and topical sirolimus. Hypertonic saline sclerotherapy can be injected into the afflicted lymphatic channels to decrease inflammation, erythema, and hyperpigmentation without further treatment or major side effects.4
However, the benefits of sclerotherapy alone in the treatment of LM often come gradually, and radiofrequency ablation may need to be utilized to achieve more immediate results.2 Overall, outcomes are highly variable, but favorable outcomes often can be difficult to obtain due to a high recurrence rate.2,8 Our patient's symptoms improved during his postoperative recovery, and he declined further intervention.
The Diagnosis: Microcystic Lymphatic Malformation
The shave biopsy demonstrated numerous thin-walled vascular spaces filled with lymphatic fluid within the dermis (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of microcystic lymphatic malformation (LM). Lymphatic malformations represent a class of benign vascular lesions consisting of anomalous or dilated lymphatic vessels, which can be broadly categorized as macrocystic (formerly cavernous lymphangioma or cystic hygroma), microcystic (formerly lymphangioma circumscriptum), or mixed.1 Patients often will present with pruritus, crusting, secondary infection, edema, or oozing.2 The superficial blebs of microcystic LMs resemble frog spawn and range in color from clear to pink, brawny, or deep maroon.3 Although the lymphatic vessels involved in microcystic LMs appear disconnected from the major lymphatic circulation,3 systemic fluid overload could plausibly promote lesional swelling and tenderness; we attributed our patient's worsening symptoms to the cumulative 7.8 L of intravenous fluid he received intraoperatively during his cardiac transplant. The excess fluid allowed communication between lymphatic cisterns and thin-walled vesicles on the skin surface through dilated channels. Overall, LMs represent roughly 26% of pediatric benign vascular tumors and approximately 4% of all vascular tumors.4

Although microcystic LMs may appear especially vascular or verrucous, the differential diagnosis for our patient's LM included condyloma acuminatum,5,6 condyloma lata,7 epidermal nevus, and lymphangiosarcoma. Epidermal nevi are congenital lesions, varying in appearance from velvety to verrucous patches and plaques that often evolve during puberty and become thicker, more verrucous, and hyperpigmented. Keratinocytic epidermal nevus syndromes and other entities such as nevus sebaceous have been associated with somatic mutations affecting proteins in the fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway (eg, FGFR3, HRAS).8 Although the clinical appearance alone may be similar, lymphangiosarcoma can be distinguished from LM via biopsy.
There are several methods to diagnose LM. Duplex sonography is possibly the best noninvasive method to identify the flow between venous valves. Magnetic resonance imaging can detect larger occurrences of LM, and lymphangiography can be utilized to confirm a normal or abnormal lymphatic network.4 Treatment options are broad, including surgical excision, laser ablation, and topical sirolimus. Hypertonic saline sclerotherapy can be injected into the afflicted lymphatic channels to decrease inflammation, erythema, and hyperpigmentation without further treatment or major side effects.4
However, the benefits of sclerotherapy alone in the treatment of LM often come gradually, and radiofrequency ablation may need to be utilized to achieve more immediate results.2 Overall, outcomes are highly variable, but favorable outcomes often can be difficult to obtain due to a high recurrence rate.2,8 Our patient's symptoms improved during his postoperative recovery, and he declined further intervention.
- Elluru RG, Balakrishnan K, Padua HM. Lymphatic malformations: diagnosis and management. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014;23:178-185. doi:10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2014.07.002
- Niti K, Manish P. Microcystic lymphatic malformation (lymphangioma circumscriptum) treated using a minimally invasive technique of radiofrequency ablation and sclerotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1711-1717. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2010.01723.x
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Bikowski JB, Dumont AM. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: treatment with hypertonic saline sclerotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:442-444. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.04.086
- Costa-Silva M, Fernandes I, Rodrigues AG, et al. Anogenital warts in pediatric population. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:675-681. doi:10.1590 /abd1806-4841.201756411
- Darmstadt GL. Perianal lymphangioma circumscriptum mistaken for genital warts. Pediatrics 1996;98;461.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJA, de Vries HJC. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259. doi:10.1136 /bmj.h1259
- Asch S, Sugarman JL. Epidermal nevus syndromes: new insights into whorls and swirls. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:21-29. doi:10.1111 /pde.13273
- Elluru RG, Balakrishnan K, Padua HM. Lymphatic malformations: diagnosis and management. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014;23:178-185. doi:10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2014.07.002
- Niti K, Manish P. Microcystic lymphatic malformation (lymphangioma circumscriptum) treated using a minimally invasive technique of radiofrequency ablation and sclerotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1711-1717. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2010.01723.x
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Bikowski JB, Dumont AM. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: treatment with hypertonic saline sclerotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:442-444. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.04.086
- Costa-Silva M, Fernandes I, Rodrigues AG, et al. Anogenital warts in pediatric population. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:675-681. doi:10.1590 /abd1806-4841.201756411
- Darmstadt GL. Perianal lymphangioma circumscriptum mistaken for genital warts. Pediatrics 1996;98;461.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJA, de Vries HJC. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259. doi:10.1136 /bmj.h1259
- Asch S, Sugarman JL. Epidermal nevus syndromes: new insights into whorls and swirls. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:21-29. doi:10.1111 /pde.13273
A 17-year-old adolescent boy presented with increasingly painful genital warts on the right thigh, groin, and scrotum that had been present since birth. The patient had a medical history of cardiac transplantation in the months prior to presentation and was on immunosuppressive therapy. The lesions had become more swollen and bothersome in the weeks following the transplantation and now prevented him from ambulating due to discomfort. He denied any history of sexual contact or oral lesions. Physical examination revealed numerous translucent and hemorrhagic vesicles clustered and linearly distributed on the right medial thigh. A shave biopsy of a vesicle was performed.
A Severe Presentation of Plasma Cell Cheilitis
Plasma cell cheilitis (PCC), also known as plasmocytosis circumorificialis and plasmocytosis mucosae,1 is a poorly understood, uncommon inflammatory condition characterized by dense infiltration of mature plasma cells in the mucosal dermis of the lip.2-5 The etiology of PCC is unknown but is thought to be a reactive immune process triggered by infection, mechanical friction, trauma, or solar damage.1,5,6
The most common presentation of PCC is a slowly evolving, red-brown patch or plaque on the lower lip in older individuals.2,3,5,7 Secondary changes with disease progression can include erosion, ulceration, fissures, edema, bleeding, or crusting.5 The diagnosis of PCC is challenging because it can mimic neoplastic, infectious, and inflammatory conditions.8,9
Treatment strategies for PCC described in the literature vary, as does therapeutic response. Resolution of PCC has been documented after systemic steroids, intralesional steroids, systemic griseofulvin, and topical calcineurin inhibitors, among other agents.6,7,10-16
We present the case of a patient with a lip lesion who ultimately was diagnosed with PCC after it progressed to an advanced necrotic stage.
Case Report
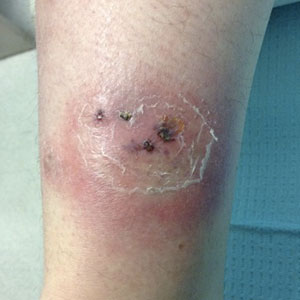
An 80-year-old male veteran of the Armed Services initially presented to our institution via teledermatology with redness and crusting of the lower lip (Figure 1). He had a history of myelodysplastic syndrome and anemia requiring iron transfusion. The process appeared to be consistent with actinic cheilitis vs squamous cell carcinoma. In-person dermatology consultation was recommended; however, the patient did not follow through with that appointment.
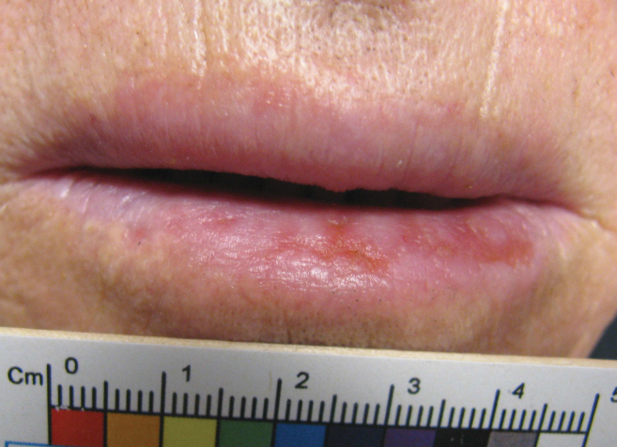
Five months later, additional photographs of the lesion were taken by the patient's primary care physician and sent through teledermatology, revealing progression to an erythematous, yellow-crusted erosion (Figure 2). The medical record indicated that a punch biopsy performed by the patient’s primary care physician showed hyperkeratosis and fungal organisms on periodic acid–Schiff staining. He subsequently applied ketoconazole and terbinafine cream to the lower lip without improvement. Prompt in-person evaluation by dermatology was again recommended.
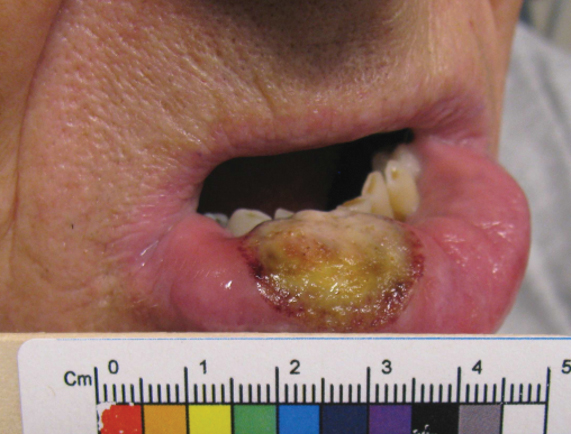
Ten days later, the patient was seen in our dermatology clinic, at which point his condition had rapidly progressed. The lower lip displayed a 3.0×2.5-cm, yellow and black, crusted, ulcerated plaque (Figure 3). He reported severe burning and pain of the lip as well as spontaneous bleeding. He had lost approximately 10 pounds over the last month due to poor oral intake. A second punch biopsy showed benign mucosa with extensive ulceration and formation of full-thickness granulation tissue. No fungi or bacteria were identified.
Consultation and Histologic Analysis
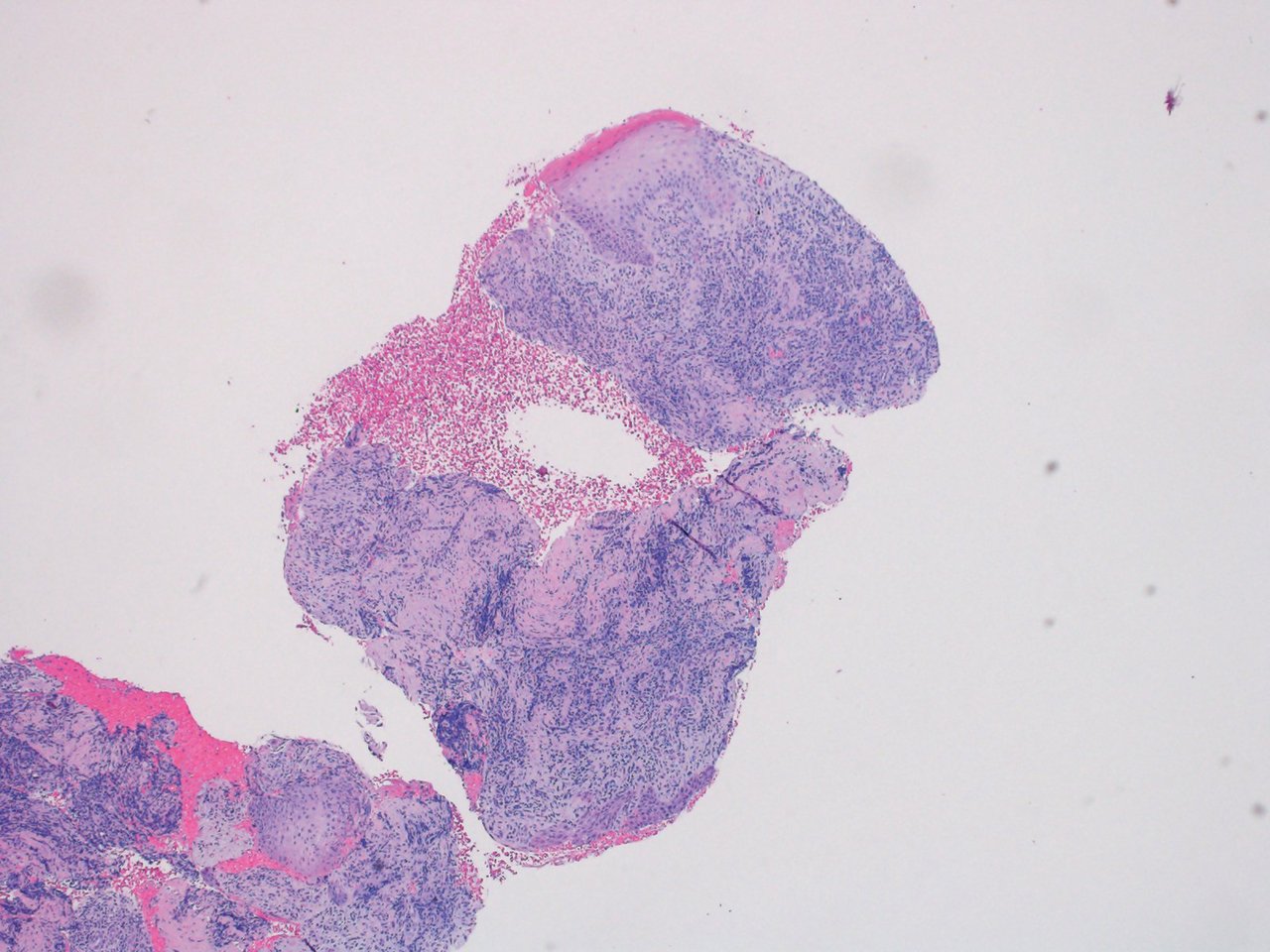
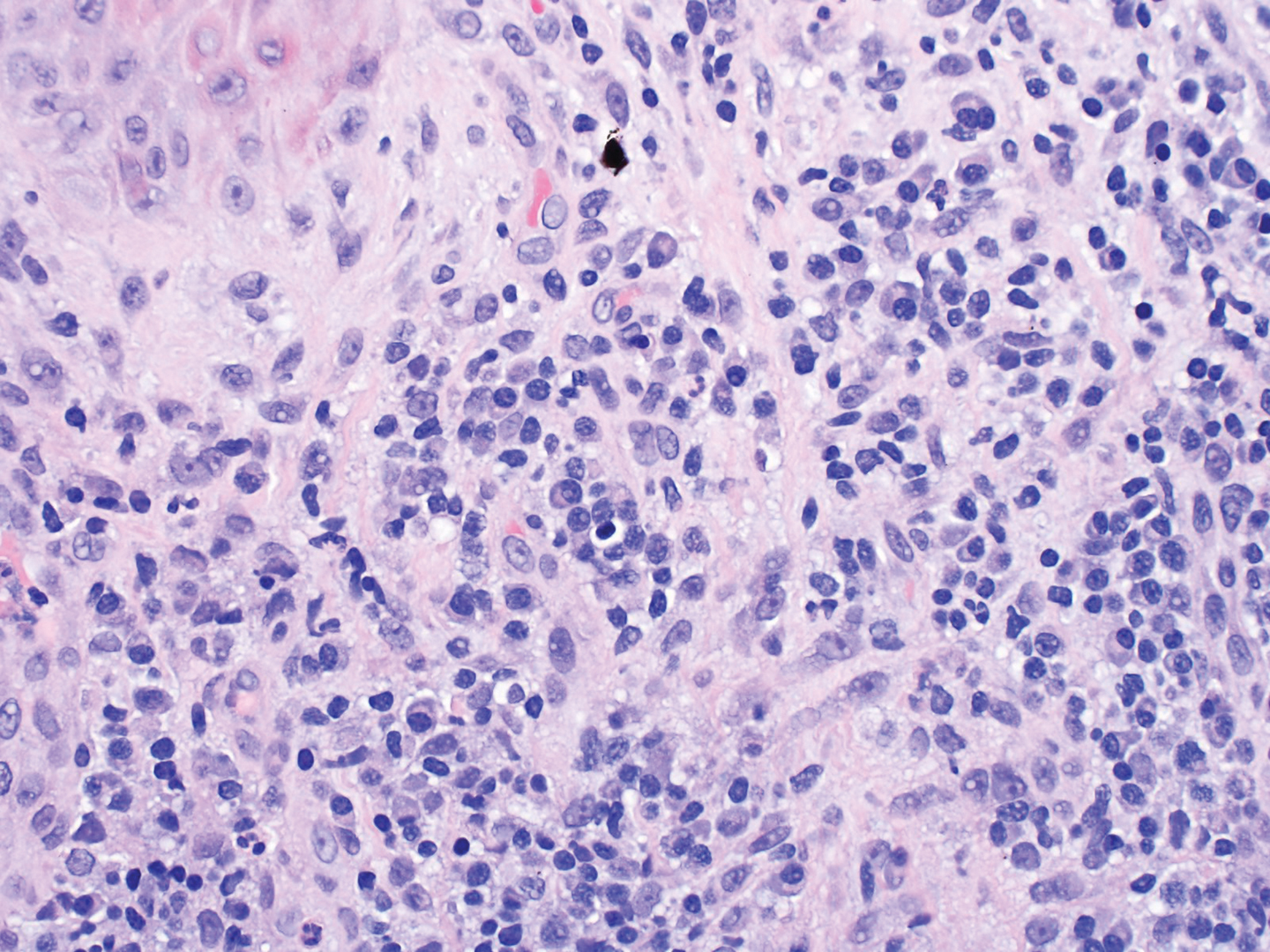
Dermatopathology was consulted and recommended a third punch biopsy for additional testing. A repeat biopsy demonstrated ulceration with lateral elements of retained epidermis and a dense submucosal chronic inflammatory infiltrate comprising plasma cells and lymphocytes (Figures 4 and 5). Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated a mixed inflammatory infiltrate with CD3+ T cells and CD20+ B cells. In situ hybridization studies demonstrated numerous lambda-positive and kappa-positive plasma cells without chain restriction. Periodic acid–Schiff with diastase and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver staining demonstrated no fungi. Findings were interpreted to be most consistent with a diagnosis of PCC.
Treatment and Follow-up
The patient was treated with clobetasol ointment 0.05% twice daily for 6 weeks and topical lidocaine as needed for pain. At 6-week follow-up, he displayed substantial improvement, with normal-appearing lips and complete resolution of symptoms.
Comment
The diagnosis and management of PCC is difficult because the condition is uncommon (though its true incidence is unknown) and the presentation is nonspecific, invoking a wide differential diagnosis. In the literature, PCC presents as a slowly progressive, red-brown patch or plaque on the lower lip in older individuals.2,3,5,7 The lesion can progress to become eroded, ulcerated, fissured, or edematous.5
Differential Diagnosis
The clinical differential diagnosis of PCC is broad and includes inflammatory, infectious, and neoplastic causes, such as actinic cheilitis, allergic contact cheilitis, exfoliative cheilitis, granulomatous cheilitis, lichen planus, candidiasis, syphilis, and squamous cell carcinoma of the lip.7,9 The histologic differential diagnosis includes allergic contact cheilitis, secondary syphilis, actinic cheilitis, squamous cell carcinoma, cheilitis granulomatosa, and plasmacytoma.17-19
Histopathology
On biopsy, PCC usually is characterized by plasma cells in a bandlike pattern in the upper submucosa or even more diffusely throughout the submucosa.20 In earlier studies, polyclonality of plasma cells with kappa and lambda light chains has been demonstrated5; in this case, such polyclonality militated against a plasma cell dyscrasia. There have been reports of a various number of eosinophils in PCC,5,20 but eosinophils were not a prominent feature in our case.
Treatment
As reported in the literature, treatment of PCC has been attempted using a broad range of strategies; however, the optimal regimen has yet to be elucidated.15 Numerous therapies, including excision, radiation, electrocauterization, cryotherapy, steroids, systemic griseofulvin, topical fusidic acid, and topical calcineurin inhibitors, have yielded variable success.6,7,10-16
The success of topical corticosteroids, as demonstrated in our case, has been unpredictable; the reported response has ranged from complete resolution to failure.9 This variability is thought to be related to epithelial width and the degree of acanthosis, with ulcerative lesions demonstrating a superior response to topical corticosteroids.9
Conclusion
Our case highlights the challenges of diagnosing and managing PCC, especially through teledermatology. Initial photographs of the lesion (Figure 1) that were submitted demonstrated a nonspecific erosion, which was concerning for any of several infectious, inflammatory, and malignant causes. Prompt in-person evaluation was warranted; regrettably, the patient’s condition worsened rapidly in the 10 days it took for him to be seen in-person by dermatology.
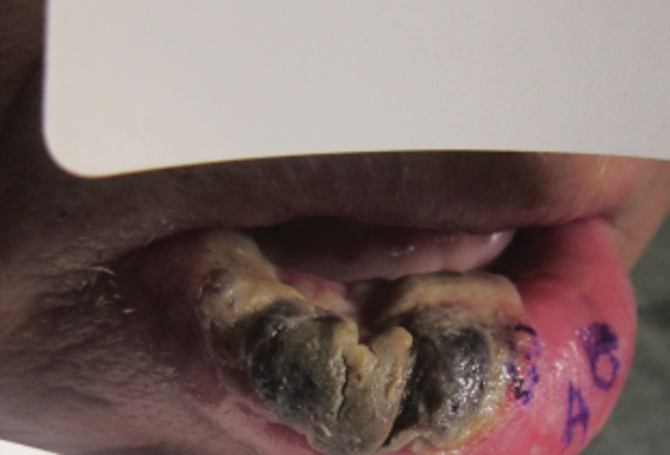
Furthermore, this case necessitated 3 separate biopsies because the pathology on the first 2 biopsies initially was equivocal, demonstrating ulceration and granulation tissue. The diagnosis was finally made after a third biopsy was recommended by a dermatopathologist, who eventually identified a bandlike distribution of polyclonal plasma cells in the upper submucosa, consistent with a diagnosis of PCC. Our patient’s final disease presentation (Figure 3) was exuberant and may represent the end point of untreated PCC.
- Senol M, Ozcan A, Aydin NE, et al. Intertriginous plasmacytosis with plasmoacanthoma: report of a typical case and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:265-268. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2008.03385.x
- Rocha N, Mota F, Horta M, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:96-98. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2004.00791.x
- Farrier JN, Perkins CS. Plasma cell cheilitis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46:679-680. doi:10.1016/j.bjoms.2008.03.009
- Baughman RD, Berger P, Pringle WM. Plasma cell cheilitis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;110:725-726.
- Lee JY, Kim KH, Hahm JE, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 13 cases. Ann Dermatol. 2017;29:536-542. doi:10.5021/ad.2017.29.5.536
- da Cunha Filho RR, Tochetto LB, Tochetto BB, et al. “Angular” plasma cell cheilitis. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:doj_21759.
- Yang JH, Lee UH, Jang SJ, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis treated with intralesional injection of corticosteroids. J Dermatol. 2005;32:987-990. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2005.tb00887.x
- Solomon LW, Wein RO, Rosenwald I, et al. Plasma cell mucositis of the oral cavity: report of a case and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;106:853-860. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.08.016
- Dos Santos HT, Cunha JLS, Santana LAM, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis: the diagnosis of a disorder mimicking lip cancer. Autops Case Rep. 2019;9:e2018075. doi:10.4322/acr.2018.075
- Fujimura T, Furudate S, Ishibashi M, et al. Successful treatment of plasmacytosis circumorificialis with topical tacrolimus: two case reports and an immunohistochemical study. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013;5:79-83. doi:10.1159/000350184
- Tamaki K, Osada A, Tsukamoto K, et al. Treatment of plasma cell cheilitis with griseofulvin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:789-790. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)81515-0
- Choi JW, Choi M, Cho KH. Successful treatment of plasma cell cheilitis with topical calcineurin inhibitors. J Dermatol. 2009;36:669-671. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00733.x
- Hanami Y, Motoki Y, Yamamoto T. Successful treatment of plasma cell cheilitis with topical tacrolimus: report of two cases. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:6.
- Jin SP, Cho KH, Huh CH. Plasma cell cheilitis, successfully treated with topical 0.03% tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatolog Treat. 2010;21:130-132. doi:10.1080/09546630903200620
- Tseng JT-P, Cheng C-J, Lee W-R, et al. Plasma-cell cheilitis: successful treatment with intralesional injections of corticosteroids. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:174-177. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2008.02765.x
- Yoshimura K, Nakano S, Tsuruta D, et al. Successful treatment with 308-nm monochromatic excimer light and subsequent tacrolimus 0.03% ointment in refractory plasma cell cheilitis. J Dermatol. 2013;40:471-474. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.12152
- Fujimura Y, Natsuga K, Abe R, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis extending beyond vermillion border. J Dermatol. 2015;42:935-936. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.12985
- White JW Jr, Olsen KD, Banks PM. Plasma cell orificial mucositis. report of a case and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 1986;122:1321-1324. doi:10.1001/archderm.122.11.1321
- Román CC, Yuste CM, Gonzalez MA, et al. Plasma cell gingivitis. Cutis. 2002;69:41-45.
- Choe HC, Park HJ, Oh ST, et al. Clinicopathologic study of 8 patients with plasma cell cheilitis. Korean J Dermatol. 2003;41:174-178.
Plasma cell cheilitis (PCC), also known as plasmocytosis circumorificialis and plasmocytosis mucosae,1 is a poorly understood, uncommon inflammatory condition characterized by dense infiltration of mature plasma cells in the mucosal dermis of the lip.2-5 The etiology of PCC is unknown but is thought to be a reactive immune process triggered by infection, mechanical friction, trauma, or solar damage.1,5,6
The most common presentation of PCC is a slowly evolving, red-brown patch or plaque on the lower lip in older individuals.2,3,5,7 Secondary changes with disease progression can include erosion, ulceration, fissures, edema, bleeding, or crusting.5 The diagnosis of PCC is challenging because it can mimic neoplastic, infectious, and inflammatory conditions.8,9
Treatment strategies for PCC described in the literature vary, as does therapeutic response. Resolution of PCC has been documented after systemic steroids, intralesional steroids, systemic griseofulvin, and topical calcineurin inhibitors, among other agents.6,7,10-16
We present the case of a patient with a lip lesion who ultimately was diagnosed with PCC after it progressed to an advanced necrotic stage.
Case Report
An 80-year-old male veteran of the Armed Services initially presented to our institution via teledermatology with redness and crusting of the lower lip (Figure 1). He had a history of myelodysplastic syndrome and anemia requiring iron transfusion. The process appeared to be consistent with actinic cheilitis vs squamous cell carcinoma. In-person dermatology consultation was recommended; however, the patient did not follow through with that appointment.

Five months later, additional photographs of the lesion were taken by the patient's primary care physician and sent through teledermatology, revealing progression to an erythematous, yellow-crusted erosion (Figure 2). The medical record indicated that a punch biopsy performed by the patient’s primary care physician showed hyperkeratosis and fungal organisms on periodic acid–Schiff staining. He subsequently applied ketoconazole and terbinafine cream to the lower lip without improvement. Prompt in-person evaluation by dermatology was again recommended.

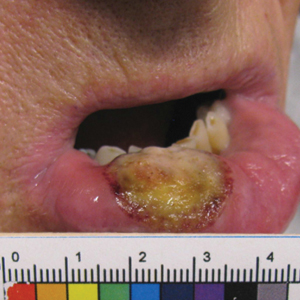
Ten days later, the patient was seen in our dermatology clinic, at which point his condition had rapidly progressed. The lower lip displayed a 3.0×2.5-cm, yellow and black, crusted, ulcerated plaque (Figure 3). He reported severe burning and pain of the lip as well as spontaneous bleeding. He had lost approximately 10 pounds over the last month due to poor oral intake. A second punch biopsy showed benign mucosa with extensive ulceration and formation of full-thickness granulation tissue. No fungi or bacteria were identified.

Consultation and Histologic Analysis
Dermatopathology was consulted and recommended a third punch biopsy for additional testing. A repeat biopsy demonstrated ulceration with lateral elements of retained epidermis and a dense submucosal chronic inflammatory infiltrate comprising plasma cells and lymphocytes (Figures 4 and 5). Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated a mixed inflammatory infiltrate with CD3+ T cells and CD20+ B cells. In situ hybridization studies demonstrated numerous lambda-positive and kappa-positive plasma cells without chain restriction. Periodic acid–Schiff with diastase and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver staining demonstrated no fungi. Findings were interpreted to be most consistent with a diagnosis of PCC.


Treatment and Follow-up
The patient was treated with clobetasol ointment 0.05% twice daily for 6 weeks and topical lidocaine as needed for pain. At 6-week follow-up, he displayed substantial improvement, with normal-appearing lips and complete resolution of symptoms.
Comment
The diagnosis and management of PCC is difficult because the condition is uncommon (though its true incidence is unknown) and the presentation is nonspecific, invoking a wide differential diagnosis. In the literature, PCC presents as a slowly progressive, red-brown patch or plaque on the lower lip in older individuals.2,3,5,7 The lesion can progress to become eroded, ulcerated, fissured, or edematous.5
Differential Diagnosis
The clinical differential diagnosis of PCC is broad and includes inflammatory, infectious, and neoplastic causes, such as actinic cheilitis, allergic contact cheilitis, exfoliative cheilitis, granulomatous cheilitis, lichen planus, candidiasis, syphilis, and squamous cell carcinoma of the lip.7,9 The histologic differential diagnosis includes allergic contact cheilitis, secondary syphilis, actinic cheilitis, squamous cell carcinoma, cheilitis granulomatosa, and plasmacytoma.17-19
Histopathology
On biopsy, PCC usually is characterized by plasma cells in a bandlike pattern in the upper submucosa or even more diffusely throughout the submucosa.20 In earlier studies, polyclonality of plasma cells with kappa and lambda light chains has been demonstrated5; in this case, such polyclonality militated against a plasma cell dyscrasia. There have been reports of a various number of eosinophils in PCC,5,20 but eosinophils were not a prominent feature in our case.
Treatment
As reported in the literature, treatment of PCC has been attempted using a broad range of strategies; however, the optimal regimen has yet to be elucidated.15 Numerous therapies, including excision, radiation, electrocauterization, cryotherapy, steroids, systemic griseofulvin, topical fusidic acid, and topical calcineurin inhibitors, have yielded variable success.6,7,10-16
The success of topical corticosteroids, as demonstrated in our case, has been unpredictable; the reported response has ranged from complete resolution to failure.9 This variability is thought to be related to epithelial width and the degree of acanthosis, with ulcerative lesions demonstrating a superior response to topical corticosteroids.9
Conclusion
Our case highlights the challenges of diagnosing and managing PCC, especially through teledermatology. Initial photographs of the lesion (Figure 1) that were submitted demonstrated a nonspecific erosion, which was concerning for any of several infectious, inflammatory, and malignant causes. Prompt in-person evaluation was warranted; regrettably, the patient’s condition worsened rapidly in the 10 days it took for him to be seen in-person by dermatology.
Furthermore, this case necessitated 3 separate biopsies because the pathology on the first 2 biopsies initially was equivocal, demonstrating ulceration and granulation tissue. The diagnosis was finally made after a third biopsy was recommended by a dermatopathologist, who eventually identified a bandlike distribution of polyclonal plasma cells in the upper submucosa, consistent with a diagnosis of PCC. Our patient’s final disease presentation (Figure 3) was exuberant and may represent the end point of untreated PCC.
Plasma cell cheilitis (PCC), also known as plasmocytosis circumorificialis and plasmocytosis mucosae,1 is a poorly understood, uncommon inflammatory condition characterized by dense infiltration of mature plasma cells in the mucosal dermis of the lip.2-5 The etiology of PCC is unknown but is thought to be a reactive immune process triggered by infection, mechanical friction, trauma, or solar damage.1,5,6
The most common presentation of PCC is a slowly evolving, red-brown patch or plaque on the lower lip in older individuals.2,3,5,7 Secondary changes with disease progression can include erosion, ulceration, fissures, edema, bleeding, or crusting.5 The diagnosis of PCC is challenging because it can mimic neoplastic, infectious, and inflammatory conditions.8,9
Treatment strategies for PCC described in the literature vary, as does therapeutic response. Resolution of PCC has been documented after systemic steroids, intralesional steroids, systemic griseofulvin, and topical calcineurin inhibitors, among other agents.6,7,10-16
We present the case of a patient with a lip lesion who ultimately was diagnosed with PCC after it progressed to an advanced necrotic stage.
Case Report
An 80-year-old male veteran of the Armed Services initially presented to our institution via teledermatology with redness and crusting of the lower lip (Figure 1). He had a history of myelodysplastic syndrome and anemia requiring iron transfusion. The process appeared to be consistent with actinic cheilitis vs squamous cell carcinoma. In-person dermatology consultation was recommended; however, the patient did not follow through with that appointment.

Five months later, additional photographs of the lesion were taken by the patient's primary care physician and sent through teledermatology, revealing progression to an erythematous, yellow-crusted erosion (Figure 2). The medical record indicated that a punch biopsy performed by the patient’s primary care physician showed hyperkeratosis and fungal organisms on periodic acid–Schiff staining. He subsequently applied ketoconazole and terbinafine cream to the lower lip without improvement. Prompt in-person evaluation by dermatology was again recommended.

Ten days later, the patient was seen in our dermatology clinic, at which point his condition had rapidly progressed. The lower lip displayed a 3.0×2.5-cm, yellow and black, crusted, ulcerated plaque (Figure 3). He reported severe burning and pain of the lip as well as spontaneous bleeding. He had lost approximately 10 pounds over the last month due to poor oral intake. A second punch biopsy showed benign mucosa with extensive ulceration and formation of full-thickness granulation tissue. No fungi or bacteria were identified.

Consultation and Histologic Analysis
Dermatopathology was consulted and recommended a third punch biopsy for additional testing. A repeat biopsy demonstrated ulceration with lateral elements of retained epidermis and a dense submucosal chronic inflammatory infiltrate comprising plasma cells and lymphocytes (Figures 4 and 5). Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated a mixed inflammatory infiltrate with CD3+ T cells and CD20+ B cells. In situ hybridization studies demonstrated numerous lambda-positive and kappa-positive plasma cells without chain restriction. Periodic acid–Schiff with diastase and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver staining demonstrated no fungi. Findings were interpreted to be most consistent with a diagnosis of PCC.


Treatment and Follow-up
The patient was treated with clobetasol ointment 0.05% twice daily for 6 weeks and topical lidocaine as needed for pain. At 6-week follow-up, he displayed substantial improvement, with normal-appearing lips and complete resolution of symptoms.
Comment
The diagnosis and management of PCC is difficult because the condition is uncommon (though its true incidence is unknown) and the presentation is nonspecific, invoking a wide differential diagnosis. In the literature, PCC presents as a slowly progressive, red-brown patch or plaque on the lower lip in older individuals.2,3,5,7 The lesion can progress to become eroded, ulcerated, fissured, or edematous.5
Differential Diagnosis
The clinical differential diagnosis of PCC is broad and includes inflammatory, infectious, and neoplastic causes, such as actinic cheilitis, allergic contact cheilitis, exfoliative cheilitis, granulomatous cheilitis, lichen planus, candidiasis, syphilis, and squamous cell carcinoma of the lip.7,9 The histologic differential diagnosis includes allergic contact cheilitis, secondary syphilis, actinic cheilitis, squamous cell carcinoma, cheilitis granulomatosa, and plasmacytoma.17-19
Histopathology
On biopsy, PCC usually is characterized by plasma cells in a bandlike pattern in the upper submucosa or even more diffusely throughout the submucosa.20 In earlier studies, polyclonality of plasma cells with kappa and lambda light chains has been demonstrated5; in this case, such polyclonality militated against a plasma cell dyscrasia. There have been reports of a various number of eosinophils in PCC,5,20 but eosinophils were not a prominent feature in our case.
Treatment
As reported in the literature, treatment of PCC has been attempted using a broad range of strategies; however, the optimal regimen has yet to be elucidated.15 Numerous therapies, including excision, radiation, electrocauterization, cryotherapy, steroids, systemic griseofulvin, topical fusidic acid, and topical calcineurin inhibitors, have yielded variable success.6,7,10-16
The success of topical corticosteroids, as demonstrated in our case, has been unpredictable; the reported response has ranged from complete resolution to failure.9 This variability is thought to be related to epithelial width and the degree of acanthosis, with ulcerative lesions demonstrating a superior response to topical corticosteroids.9
Conclusion
Our case highlights the challenges of diagnosing and managing PCC, especially through teledermatology. Initial photographs of the lesion (Figure 1) that were submitted demonstrated a nonspecific erosion, which was concerning for any of several infectious, inflammatory, and malignant causes. Prompt in-person evaluation was warranted; regrettably, the patient’s condition worsened rapidly in the 10 days it took for him to be seen in-person by dermatology.
Furthermore, this case necessitated 3 separate biopsies because the pathology on the first 2 biopsies initially was equivocal, demonstrating ulceration and granulation tissue. The diagnosis was finally made after a third biopsy was recommended by a dermatopathologist, who eventually identified a bandlike distribution of polyclonal plasma cells in the upper submucosa, consistent with a diagnosis of PCC. Our patient’s final disease presentation (Figure 3) was exuberant and may represent the end point of untreated PCC.
- Senol M, Ozcan A, Aydin NE, et al. Intertriginous plasmacytosis with plasmoacanthoma: report of a typical case and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:265-268. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2008.03385.x
- Rocha N, Mota F, Horta M, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:96-98. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2004.00791.x
- Farrier JN, Perkins CS. Plasma cell cheilitis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46:679-680. doi:10.1016/j.bjoms.2008.03.009
- Baughman RD, Berger P, Pringle WM. Plasma cell cheilitis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;110:725-726.
- Lee JY, Kim KH, Hahm JE, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 13 cases. Ann Dermatol. 2017;29:536-542. doi:10.5021/ad.2017.29.5.536
- da Cunha Filho RR, Tochetto LB, Tochetto BB, et al. “Angular” plasma cell cheilitis. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:doj_21759.
- Yang JH, Lee UH, Jang SJ, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis treated with intralesional injection of corticosteroids. J Dermatol. 2005;32:987-990. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2005.tb00887.x
- Solomon LW, Wein RO, Rosenwald I, et al. Plasma cell mucositis of the oral cavity: report of a case and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;106:853-860. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.08.016
- Dos Santos HT, Cunha JLS, Santana LAM, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis: the diagnosis of a disorder mimicking lip cancer. Autops Case Rep. 2019;9:e2018075. doi:10.4322/acr.2018.075
- Fujimura T, Furudate S, Ishibashi M, et al. Successful treatment of plasmacytosis circumorificialis with topical tacrolimus: two case reports and an immunohistochemical study. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013;5:79-83. doi:10.1159/000350184
- Tamaki K, Osada A, Tsukamoto K, et al. Treatment of plasma cell cheilitis with griseofulvin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:789-790. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)81515-0
- Choi JW, Choi M, Cho KH. Successful treatment of plasma cell cheilitis with topical calcineurin inhibitors. J Dermatol. 2009;36:669-671. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00733.x
- Hanami Y, Motoki Y, Yamamoto T. Successful treatment of plasma cell cheilitis with topical tacrolimus: report of two cases. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:6.
- Jin SP, Cho KH, Huh CH. Plasma cell cheilitis, successfully treated with topical 0.03% tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatolog Treat. 2010;21:130-132. doi:10.1080/09546630903200620
- Tseng JT-P, Cheng C-J, Lee W-R, et al. Plasma-cell cheilitis: successful treatment with intralesional injections of corticosteroids. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:174-177. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2008.02765.x
- Yoshimura K, Nakano S, Tsuruta D, et al. Successful treatment with 308-nm monochromatic excimer light and subsequent tacrolimus 0.03% ointment in refractory plasma cell cheilitis. J Dermatol. 2013;40:471-474. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.12152
- Fujimura Y, Natsuga K, Abe R, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis extending beyond vermillion border. J Dermatol. 2015;42:935-936. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.12985
- White JW Jr, Olsen KD, Banks PM. Plasma cell orificial mucositis. report of a case and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 1986;122:1321-1324. doi:10.1001/archderm.122.11.1321
- Román CC, Yuste CM, Gonzalez MA, et al. Plasma cell gingivitis. Cutis. 2002;69:41-45.
- Choe HC, Park HJ, Oh ST, et al. Clinicopathologic study of 8 patients with plasma cell cheilitis. Korean J Dermatol. 2003;41:174-178.
- Senol M, Ozcan A, Aydin NE, et al. Intertriginous plasmacytosis with plasmoacanthoma: report of a typical case and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:265-268. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2008.03385.x
- Rocha N, Mota F, Horta M, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:96-98. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2004.00791.x
- Farrier JN, Perkins CS. Plasma cell cheilitis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46:679-680. doi:10.1016/j.bjoms.2008.03.009
- Baughman RD, Berger P, Pringle WM. Plasma cell cheilitis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;110:725-726.
- Lee JY, Kim KH, Hahm JE, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 13 cases. Ann Dermatol. 2017;29:536-542. doi:10.5021/ad.2017.29.5.536
- da Cunha Filho RR, Tochetto LB, Tochetto BB, et al. “Angular” plasma cell cheilitis. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:doj_21759.
- Yang JH, Lee UH, Jang SJ, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis treated with intralesional injection of corticosteroids. J Dermatol. 2005;32:987-990. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2005.tb00887.x
- Solomon LW, Wein RO, Rosenwald I, et al. Plasma cell mucositis of the oral cavity: report of a case and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;106:853-860. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.08.016
- Dos Santos HT, Cunha JLS, Santana LAM, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis: the diagnosis of a disorder mimicking lip cancer. Autops Case Rep. 2019;9:e2018075. doi:10.4322/acr.2018.075
- Fujimura T, Furudate S, Ishibashi M, et al. Successful treatment of plasmacytosis circumorificialis with topical tacrolimus: two case reports and an immunohistochemical study. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013;5:79-83. doi:10.1159/000350184
- Tamaki K, Osada A, Tsukamoto K, et al. Treatment of plasma cell cheilitis with griseofulvin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:789-790. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)81515-0
- Choi JW, Choi M, Cho KH. Successful treatment of plasma cell cheilitis with topical calcineurin inhibitors. J Dermatol. 2009;36:669-671. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00733.x
- Hanami Y, Motoki Y, Yamamoto T. Successful treatment of plasma cell cheilitis with topical tacrolimus: report of two cases. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:6.
- Jin SP, Cho KH, Huh CH. Plasma cell cheilitis, successfully treated with topical 0.03% tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatolog Treat. 2010;21:130-132. doi:10.1080/09546630903200620
- Tseng JT-P, Cheng C-J, Lee W-R, et al. Plasma-cell cheilitis: successful treatment with intralesional injections of corticosteroids. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:174-177. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2008.02765.x
- Yoshimura K, Nakano S, Tsuruta D, et al. Successful treatment with 308-nm monochromatic excimer light and subsequent tacrolimus 0.03% ointment in refractory plasma cell cheilitis. J Dermatol. 2013;40:471-474. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.12152
- Fujimura Y, Natsuga K, Abe R, et al. Plasma cell cheilitis extending beyond vermillion border. J Dermatol. 2015;42:935-936. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.12985
- White JW Jr, Olsen KD, Banks PM. Plasma cell orificial mucositis. report of a case and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 1986;122:1321-1324. doi:10.1001/archderm.122.11.1321
- Román CC, Yuste CM, Gonzalez MA, et al. Plasma cell gingivitis. Cutis. 2002;69:41-45.
- Choe HC, Park HJ, Oh ST, et al. Clinicopathologic study of 8 patients with plasma cell cheilitis. Korean J Dermatol. 2003;41:174-178.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Plasma cell cheilitis (PCC) is a benign condition that affects the lower lip in older individuals, presenting as a nonspecific, red-brown patch or plaque that can progress slowly to erosions and edema.
- Our patient with PCC experienced full resolution of symptoms with application of a class I topical corticosteroid.
Verruca Vulgaris Arising Within the Red Portion of a Multicolored Tattoo
To the Editor:
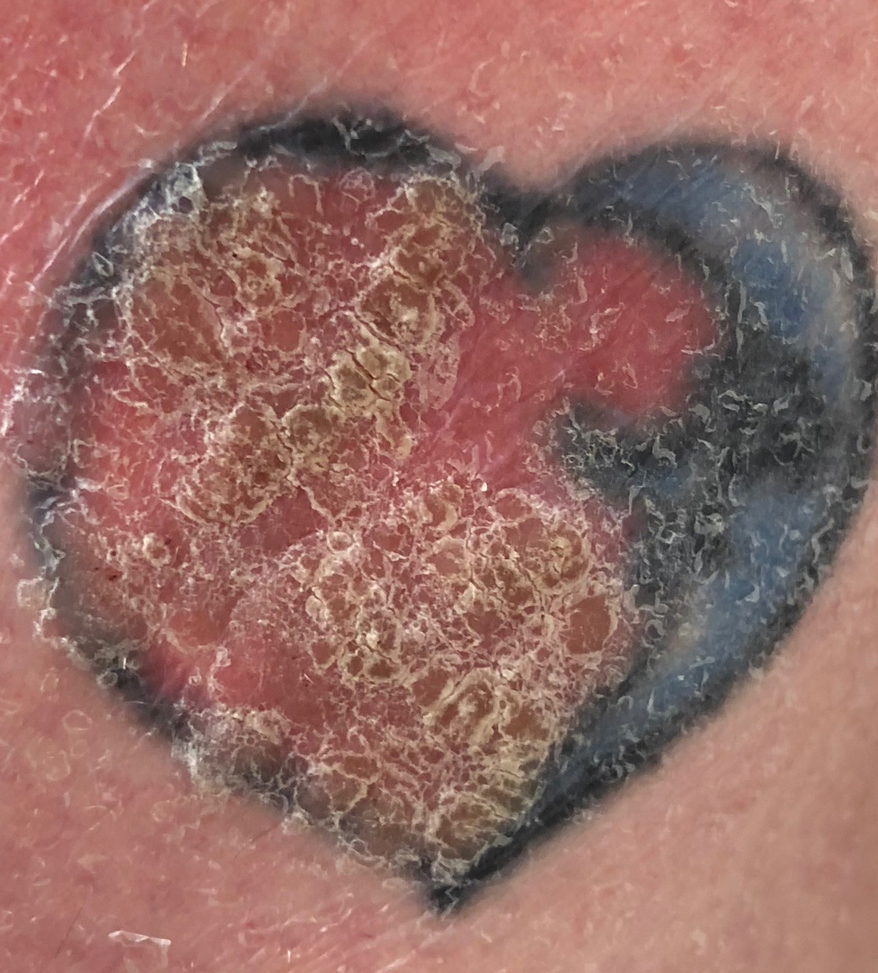
The art of tattooing continues to gain popularity in the 21st century, albeit with accompanying hazards.1 Reported adverse reactions to tattoos include infections, tumors, and hypersensitivity and granulomatous reactions.2 Various infectious agents may involve tattoos, including human papillomavirus (HPV), molluscum contagiosum, herpes simplex virus, hepatitis C virus, tuberculoid and nontuberculoid mycobacteria, and Staphylococcus aureus.2 Verruca vulgaris infrequently has been reported to develop in tattoos.3,4 Previously reported cases of verruca in tattoos suggest a predilection for blue or black pigment.1-5 We report a case of verruca vulgaris occurring within the red-inked areas of a tattoo that first appeared approximately 18 years after the initial tattoo placement.
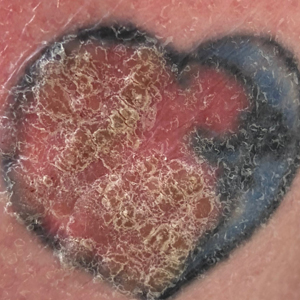
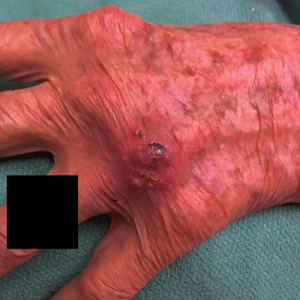
A 44-year-old woman presented with erythema, induration, and irritation of a tattoo on the left leg of 2 years’ duration. The tattoo initially was inscribed more than 20 years prior. The patient had a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. She reported no prior trauma to the area, prior rash or irritation, or similar changes to her other tattoos, including those with red ink. The affected tattoo was inscribed at a separate time from the other tattoos. Physical examination of the irritated tattoo revealed hyperkeratotic papules with firm scaling in the zone of dermal red pigment (Figure 1). Notable nodularity or deep induration was not present. The clinical differential diagnosis included a hypersensitivity reaction to red tattoo ink, sarcoidosis, and an infectious process, such as an atypical mycobacterial infection. A punch biopsy demonstrated papillomatous epidermal hyperplasia with hyperkeratosis, focal parakeratosis, and frequent vacuolization of keratinocytes with enlarged keratohyalin granules, diagnostic of verruca vulgaris (Figure 2). Of note, the patient did not have clinically apparent viral warts elsewhere on physical examination. The patient was successfully managedwith a combination of 2 treatments of intralesional Candida antigen and 3 treatments of cryotherapy with resolution of most lesions over the course of 8 months. Over the following several months, the patient applied topical salicylic acid, which led to the resolution of the remaining lesions. The verrucae had not recurred 19 months after the initial presentation.
The development of verruca vulgaris within a tattoo may occur secondary to various mechanisms of HPV inoculation, including introduction of the virus through contaminated ink, the tattoo artist’s saliva, autoinoculation, or koebnerization of a pre-existing verruca vulgaris.4 Local immune system dysregulation secondary to tattoo ink also has been proposed as a mechanism for HPV infection in this setting.1,5 The contents of darker tattoo pigments may promote formation of reactive oxygen species inducing local immunocompromise.5
The pathogenic mechanism was elusive in our patient. Although the localization of verruca vulgaris to the zones of red pigment may be merely coincidental, this phenomenon raised suspicion for direct inoculation via contaminated red ink. The patient’s other red ink–containing tattoos that were inscribed separately were spared, compatible with contamination of the red ink used for the affected tattoo. However, the delayed onset of nearly 2 decades was exceptional, given the shorter previously reported latencies ranging from months to 10 years.4 Autoinoculation or koebnerization is plausible, though greater involvement of nonred pigments would be expected as well as a briefer latency. Finally, the possibility of local immune dysregulation seemed feasible, given the slow evolution of the lesions largely restricted to one pigment type.
We report a case of verruca vulgaris within the red area of a multicolored tattoo that occurred approximately 18 years after tattoo placement. This case highlights a rare presentation of an infectious agent that may complicate tattoos. Both predilection for red pigment rather than black or blue pigment and the long latency period raised interesting questions regarding pathogenesis. Confirmatory biopsy enables effective management of this tattoo complication.
- Huynh TN, Jackson JD, Brodell RT. Tattoo and vaccination sites: possible nest for opportunistic infections, tumors, and dysimmune reactions. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:678-684.
- Wenzel SM, Rittmann I, Landthaler M, et al. Adverse reactions after tattooing: review of the literature and comparison to results of a survey. Dermatology. 2013;226:138-147.
- Trefzer U, Schmollack K, Stockfleth E, et al. Verrucae in a multicolored decorative tattoo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:478-479.
- Wanat KA, Tyring S, Rady P, et al. Human papillomavirus type 27 associated with multiple verruca within a tattoo: report of a case and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:882-884.
- Ramey K, Ibrahim J, Brodell RT. Verruca localization predominately in black tattoo ink: a retrospective case series. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:E34-E36.
To the Editor:
The art of tattooing continues to gain popularity in the 21st century, albeit with accompanying hazards.1 Reported adverse reactions to tattoos include infections, tumors, and hypersensitivity and granulomatous reactions.2 Various infectious agents may involve tattoos, including human papillomavirus (HPV), molluscum contagiosum, herpes simplex virus, hepatitis C virus, tuberculoid and nontuberculoid mycobacteria, and Staphylococcus aureus.2 Verruca vulgaris infrequently has been reported to develop in tattoos.3,4 Previously reported cases of verruca in tattoos suggest a predilection for blue or black pigment.1-5 We report a case of verruca vulgaris occurring within the red-inked areas of a tattoo that first appeared approximately 18 years after the initial tattoo placement.
A 44-year-old woman presented with erythema, induration, and irritation of a tattoo on the left leg of 2 years’ duration. The tattoo initially was inscribed more than 20 years prior. The patient had a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. She reported no prior trauma to the area, prior rash or irritation, or similar changes to her other tattoos, including those with red ink. The affected tattoo was inscribed at a separate time from the other tattoos. Physical examination of the irritated tattoo revealed hyperkeratotic papules with firm scaling in the zone of dermal red pigment (Figure 1). Notable nodularity or deep induration was not present. The clinical differential diagnosis included a hypersensitivity reaction to red tattoo ink, sarcoidosis, and an infectious process, such as an atypical mycobacterial infection. A punch biopsy demonstrated papillomatous epidermal hyperplasia with hyperkeratosis, focal parakeratosis, and frequent vacuolization of keratinocytes with enlarged keratohyalin granules, diagnostic of verruca vulgaris (Figure 2). Of note, the patient did not have clinically apparent viral warts elsewhere on physical examination. The patient was successfully managedwith a combination of 2 treatments of intralesional Candida antigen and 3 treatments of cryotherapy with resolution of most lesions over the course of 8 months. Over the following several months, the patient applied topical salicylic acid, which led to the resolution of the remaining lesions. The verrucae had not recurred 19 months after the initial presentation.


The development of verruca vulgaris within a tattoo may occur secondary to various mechanisms of HPV inoculation, including introduction of the virus through contaminated ink, the tattoo artist’s saliva, autoinoculation, or koebnerization of a pre-existing verruca vulgaris.4 Local immune system dysregulation secondary to tattoo ink also has been proposed as a mechanism for HPV infection in this setting.1,5 The contents of darker tattoo pigments may promote formation of reactive oxygen species inducing local immunocompromise.5
The pathogenic mechanism was elusive in our patient. Although the localization of verruca vulgaris to the zones of red pigment may be merely coincidental, this phenomenon raised suspicion for direct inoculation via contaminated red ink. The patient’s other red ink–containing tattoos that were inscribed separately were spared, compatible with contamination of the red ink used for the affected tattoo. However, the delayed onset of nearly 2 decades was exceptional, given the shorter previously reported latencies ranging from months to 10 years.4 Autoinoculation or koebnerization is plausible, though greater involvement of nonred pigments would be expected as well as a briefer latency. Finally, the possibility of local immune dysregulation seemed feasible, given the slow evolution of the lesions largely restricted to one pigment type.
We report a case of verruca vulgaris within the red area of a multicolored tattoo that occurred approximately 18 years after tattoo placement. This case highlights a rare presentation of an infectious agent that may complicate tattoos. Both predilection for red pigment rather than black or blue pigment and the long latency period raised interesting questions regarding pathogenesis. Confirmatory biopsy enables effective management of this tattoo complication.
To the Editor:
The art of tattooing continues to gain popularity in the 21st century, albeit with accompanying hazards.1 Reported adverse reactions to tattoos include infections, tumors, and hypersensitivity and granulomatous reactions.2 Various infectious agents may involve tattoos, including human papillomavirus (HPV), molluscum contagiosum, herpes simplex virus, hepatitis C virus, tuberculoid and nontuberculoid mycobacteria, and Staphylococcus aureus.2 Verruca vulgaris infrequently has been reported to develop in tattoos.3,4 Previously reported cases of verruca in tattoos suggest a predilection for blue or black pigment.1-5 We report a case of verruca vulgaris occurring within the red-inked areas of a tattoo that first appeared approximately 18 years after the initial tattoo placement.
A 44-year-old woman presented with erythema, induration, and irritation of a tattoo on the left leg of 2 years’ duration. The tattoo initially was inscribed more than 20 years prior. The patient had a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. She reported no prior trauma to the area, prior rash or irritation, or similar changes to her other tattoos, including those with red ink. The affected tattoo was inscribed at a separate time from the other tattoos. Physical examination of the irritated tattoo revealed hyperkeratotic papules with firm scaling in the zone of dermal red pigment (Figure 1). Notable nodularity or deep induration was not present. The clinical differential diagnosis included a hypersensitivity reaction to red tattoo ink, sarcoidosis, and an infectious process, such as an atypical mycobacterial infection. A punch biopsy demonstrated papillomatous epidermal hyperplasia with hyperkeratosis, focal parakeratosis, and frequent vacuolization of keratinocytes with enlarged keratohyalin granules, diagnostic of verruca vulgaris (Figure 2). Of note, the patient did not have clinically apparent viral warts elsewhere on physical examination. The patient was successfully managedwith a combination of 2 treatments of intralesional Candida antigen and 3 treatments of cryotherapy with resolution of most lesions over the course of 8 months. Over the following several months, the patient applied topical salicylic acid, which led to the resolution of the remaining lesions. The verrucae had not recurred 19 months after the initial presentation.


The development of verruca vulgaris within a tattoo may occur secondary to various mechanisms of HPV inoculation, including introduction of the virus through contaminated ink, the tattoo artist’s saliva, autoinoculation, or koebnerization of a pre-existing verruca vulgaris.4 Local immune system dysregulation secondary to tattoo ink also has been proposed as a mechanism for HPV infection in this setting.1,5 The contents of darker tattoo pigments may promote formation of reactive oxygen species inducing local immunocompromise.5
The pathogenic mechanism was elusive in our patient. Although the localization of verruca vulgaris to the zones of red pigment may be merely coincidental, this phenomenon raised suspicion for direct inoculation via contaminated red ink. The patient’s other red ink–containing tattoos that were inscribed separately were spared, compatible with contamination of the red ink used for the affected tattoo. However, the delayed onset of nearly 2 decades was exceptional, given the shorter previously reported latencies ranging from months to 10 years.4 Autoinoculation or koebnerization is plausible, though greater involvement of nonred pigments would be expected as well as a briefer latency. Finally, the possibility of local immune dysregulation seemed feasible, given the slow evolution of the lesions largely restricted to one pigment type.
We report a case of verruca vulgaris within the red area of a multicolored tattoo that occurred approximately 18 years after tattoo placement. This case highlights a rare presentation of an infectious agent that may complicate tattoos. Both predilection for red pigment rather than black or blue pigment and the long latency period raised interesting questions regarding pathogenesis. Confirmatory biopsy enables effective management of this tattoo complication.
- Huynh TN, Jackson JD, Brodell RT. Tattoo and vaccination sites: possible nest for opportunistic infections, tumors, and dysimmune reactions. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:678-684.
- Wenzel SM, Rittmann I, Landthaler M, et al. Adverse reactions after tattooing: review of the literature and comparison to results of a survey. Dermatology. 2013;226:138-147.
- Trefzer U, Schmollack K, Stockfleth E, et al. Verrucae in a multicolored decorative tattoo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:478-479.
- Wanat KA, Tyring S, Rady P, et al. Human papillomavirus type 27 associated with multiple verruca within a tattoo: report of a case and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:882-884.
- Ramey K, Ibrahim J, Brodell RT. Verruca localization predominately in black tattoo ink: a retrospective case series. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:E34-E36.
- Huynh TN, Jackson JD, Brodell RT. Tattoo and vaccination sites: possible nest for opportunistic infections, tumors, and dysimmune reactions. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:678-684.
- Wenzel SM, Rittmann I, Landthaler M, et al. Adverse reactions after tattooing: review of the literature and comparison to results of a survey. Dermatology. 2013;226:138-147.
- Trefzer U, Schmollack K, Stockfleth E, et al. Verrucae in a multicolored decorative tattoo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:478-479.
- Wanat KA, Tyring S, Rady P, et al. Human papillomavirus type 27 associated with multiple verruca within a tattoo: report of a case and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:882-884.
- Ramey K, Ibrahim J, Brodell RT. Verruca localization predominately in black tattoo ink: a retrospective case series. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:E34-E36.
Practice Points
- Various adverse reactions and infectious agents may involve tattoos.
- Verruca vulgaris may affect tattoos in a color-restricted manner and demonstrate latency of many years after tattoo placement.
- Timely diagnosis of the tattoo-involving process, confirmed by biopsy, allows for appropriate management.
Pediatric-Onset Refractory Lupus Erythematosus Panniculitis Treated With Rituximab
To the Editor:
Lupus erythematosus panniculitis (LEP) is rare in the pediatric population. It can be difficult to manage, as patients may not respond to conventional treatments including hydroxychloroquine and prednisone. We report the use of rituximab in the treatment of a 20-year-old woman with LEP of the face, legs, and arms that was refractory to standard treatments. She also had a history of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). Further studies are warranted to determine the role of rituximab in the treatment of pediatric patients with LEP.
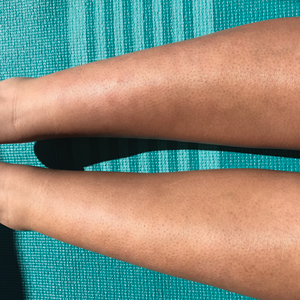
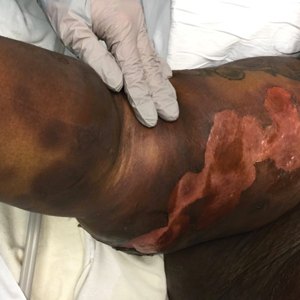
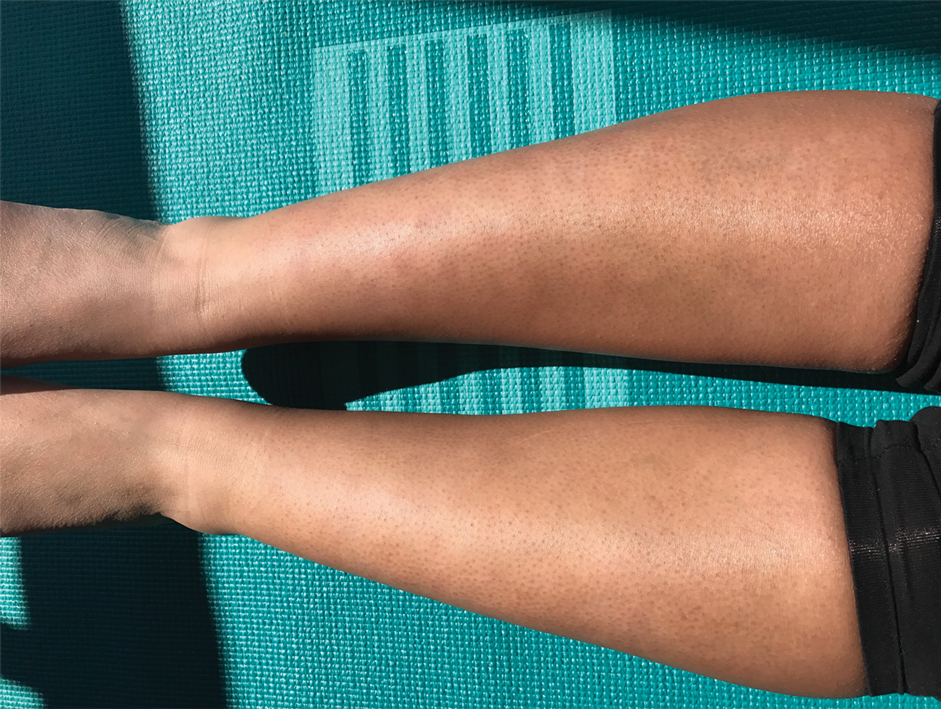
A 20-year-old woman with history of LEP and HLH initially presented with migratory violaceous nodules on the face 16 years prior to the current presentation. A skin biopsy 3 years after that initial presentation suggested a diagnosis of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Six years later, numerous asymptomatic lesions appeared on the legs, predominantly on the calves; she was successfully treated with hydroxychloroquine and high-dose prednisone. Four years prior to the current presentation, a febrile illness prompted discontinuation of hydroxychloroquine and hospitalization, where she was first was diagnosed with HLH; she achieved remission with cyclosporine. At the current presentation, she continued to have persistent violaceous lesions on the face, lower arms, and legs with underlying nodularity (Figure 1). Skin biopsies revealed LEP and were less suggestive of HLH. She was restarted on hydroxychloroquine, which did not adequately control the disease. Rheumatologic workup was only notable for an antinuclear antibody titer of 1:80 (reference range, <1:80) in a speckled pattern.
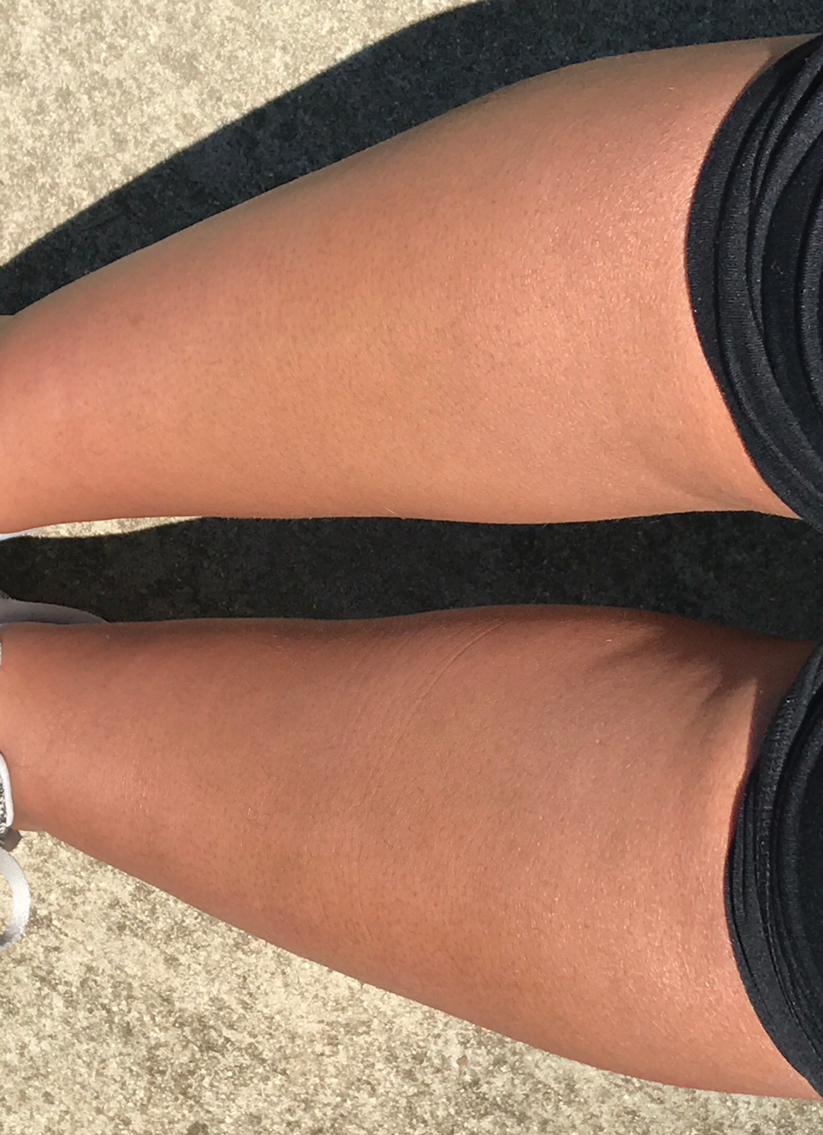
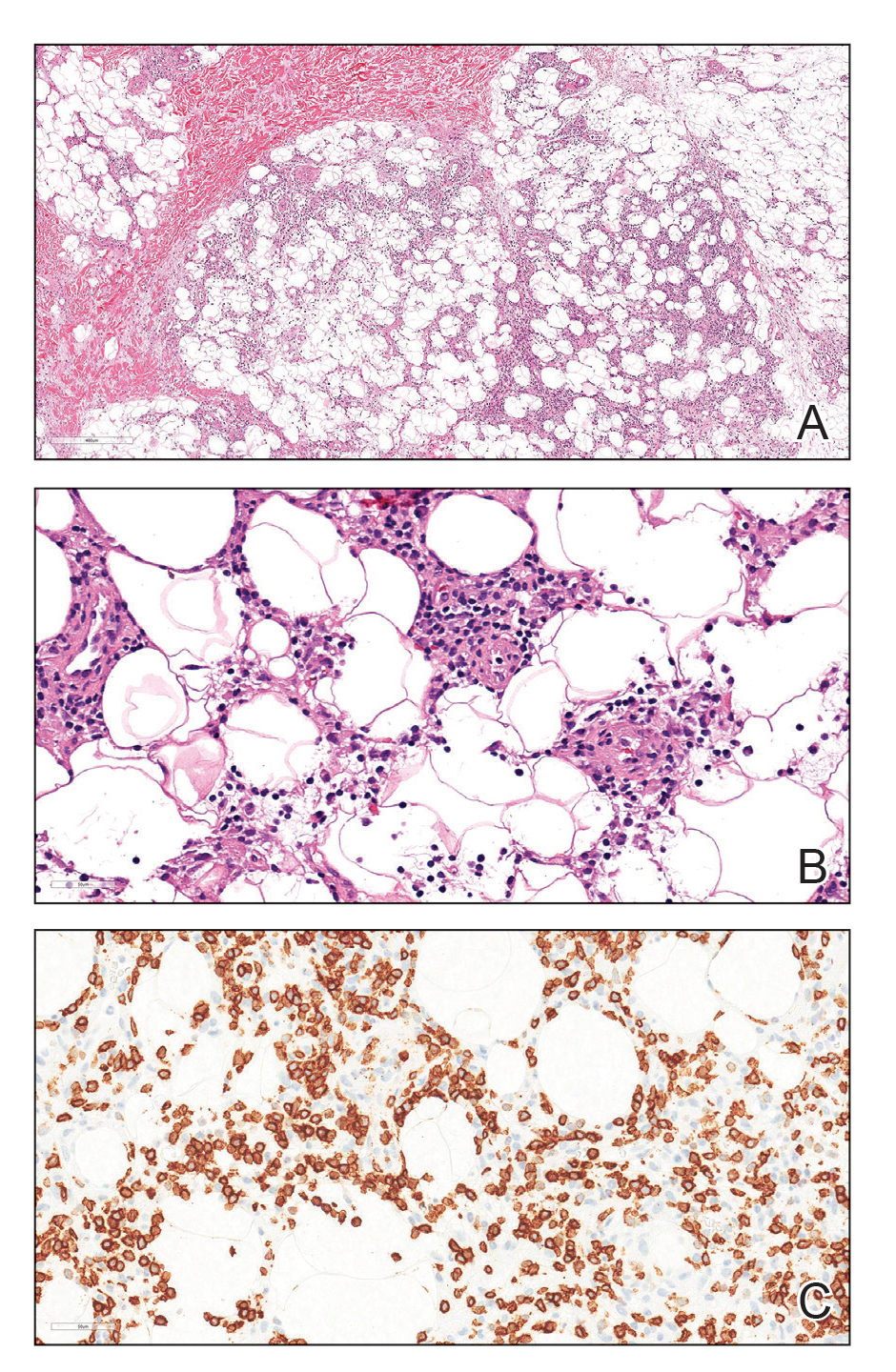
Due to the refractory nature of her condition, continued lesion development despite standard treatment, and concerns of possible scarring, we considered a trial of rituximab. Because HLH and LEP can mimic subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma, another skin biopsy was performed, which revealed a deep dermal and subcutaneous lymphohistiocytic infiltrate composed of predominantly CD3+ T cells with a mixed population of CD4+ and CD8+ cells (Figure 2). There was no evidence of transformation into lymphoma. Pathologic findings were most compatible with LEP rather than an HLH-associated panniculitis due to the lack of definitive phagocytosis. She received rituximab using body surface area–based dosing at 375 mg/m2. CD19 levels decreased to undetectable levels after the first dose. Rituximab was dosed based on clinical response; she tolerated treatment well and experienced considerable improvement in the number of lesions following completion of 4 doses at weeks 0, 1, 5, and 7 (Figure 3). She developed a flare at 7 months and improved again after another dose of rituximab.

Lupus erythematosus panniculitis is a rare variant of lupus erythematosus with an average age of presentation between 30 and 60 years.1 In children, LEP presents as recurrent subcutaneous nodules and plaques, commonly involving the face and upper arms.1,2 Long-term sequelae include local swelling and skin atrophy.3 Conventional treatment options for pediatric patients include hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroids.1 Management can be challenging due to the lack of response to conventional treatments as well as the chronic progressive nature of LEP.2 In refractory cases, cyclosporine, azathioprine, sulfones, thalidomide, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclophosphamide are alternative treatment options.1-4
Rituximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting B-cell surface marker CD20, results in depletion of mature B cells. Use of rituximab for LEP has been described in multiple case reports involving an 8-year-old boy, 22-year-old girl, and 2 middle-aged women.2-4 In addition, a recently published case series of 4 patients with childhood-onset refractory LEP described improvement of disease activity with rituximab.5 It is important to rule out subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma before treatment with rituximab, as its histopathology can closely resemble that seen in LEP and HLH-associated cytophagic histiocytic panniculitis.1,6
Rituximab may be an effective treatment option in pediatric patients with refractory LEP. Larger studies on the use of rituximab in the pediatric population are necessary.
- Weingartner JS, Zedek DC, Burkhart CN, et al. Lupus erythematosus panniculitis in children: report of three cases and review of previously reported cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;29:169-176.
- Moreno-Suárez F, Pulpillo-Ruiz Á. Rituximab for the treatment of lupus erythematosus panniculitis. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:415-418.
- Guissa VR, Trudes G, Jesus AA, et al. Lupus erythematosus panniculitis in children and adolescents. Acta Reumatol Port. 2012;37:82-85.
- Mcardle A, Baker JF. A case of “refractory” lupus erythematosus profundus responsive to rituximab. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28:745-746.
- Correll CK, Miller DD, Maguiness SM. Treatment of childhood-onset lupus erythematosus panniculitis with rituximab. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:566-569.
- Aronson IK, Worobec SM. Cytophagic histiocytic panniculitis and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: an overview. Dermatol Ther. 2010;23:389-402.
To the Editor:
Lupus erythematosus panniculitis (LEP) is rare in the pediatric population. It can be difficult to manage, as patients may not respond to conventional treatments including hydroxychloroquine and prednisone. We report the use of rituximab in the treatment of a 20-year-old woman with LEP of the face, legs, and arms that was refractory to standard treatments. She also had a history of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). Further studies are warranted to determine the role of rituximab in the treatment of pediatric patients with LEP.
A 20-year-old woman with history of LEP and HLH initially presented with migratory violaceous nodules on the face 16 years prior to the current presentation. A skin biopsy 3 years after that initial presentation suggested a diagnosis of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Six years later, numerous asymptomatic lesions appeared on the legs, predominantly on the calves; she was successfully treated with hydroxychloroquine and high-dose prednisone. Four years prior to the current presentation, a febrile illness prompted discontinuation of hydroxychloroquine and hospitalization, where she was first was diagnosed with HLH; she achieved remission with cyclosporine. At the current presentation, she continued to have persistent violaceous lesions on the face, lower arms, and legs with underlying nodularity (Figure 1). Skin biopsies revealed LEP and were less suggestive of HLH. She was restarted on hydroxychloroquine, which did not adequately control the disease. Rheumatologic workup was only notable for an antinuclear antibody titer of 1:80 (reference range, <1:80) in a speckled pattern.

Due to the refractory nature of her condition, continued lesion development despite standard treatment, and concerns of possible scarring, we considered a trial of rituximab. Because HLH and LEP can mimic subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma, another skin biopsy was performed, which revealed a deep dermal and subcutaneous lymphohistiocytic infiltrate composed of predominantly CD3+ T cells with a mixed population of CD4+ and CD8+ cells (Figure 2). There was no evidence of transformation into lymphoma. Pathologic findings were most compatible with LEP rather than an HLH-associated panniculitis due to the lack of definitive phagocytosis. She received rituximab using body surface area–based dosing at 375 mg/m2. CD19 levels decreased to undetectable levels after the first dose. Rituximab was dosed based on clinical response; she tolerated treatment well and experienced considerable improvement in the number of lesions following completion of 4 doses at weeks 0, 1, 5, and 7 (Figure 3). She developed a flare at 7 months and improved again after another dose of rituximab.


Lupus erythematosus panniculitis is a rare variant of lupus erythematosus with an average age of presentation between 30 and 60 years.1 In children, LEP presents as recurrent subcutaneous nodules and plaques, commonly involving the face and upper arms.1,2 Long-term sequelae include local swelling and skin atrophy.3 Conventional treatment options for pediatric patients include hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroids.1 Management can be challenging due to the lack of response to conventional treatments as well as the chronic progressive nature of LEP.2 In refractory cases, cyclosporine, azathioprine, sulfones, thalidomide, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclophosphamide are alternative treatment options.1-4
Rituximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting B-cell surface marker CD20, results in depletion of mature B cells. Use of rituximab for LEP has been described in multiple case reports involving an 8-year-old boy, 22-year-old girl, and 2 middle-aged women.2-4 In addition, a recently published case series of 4 patients with childhood-onset refractory LEP described improvement of disease activity with rituximab.5 It is important to rule out subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma before treatment with rituximab, as its histopathology can closely resemble that seen in LEP and HLH-associated cytophagic histiocytic panniculitis.1,6
Rituximab may be an effective treatment option in pediatric patients with refractory LEP. Larger studies on the use of rituximab in the pediatric population are necessary.
To the Editor:
Lupus erythematosus panniculitis (LEP) is rare in the pediatric population. It can be difficult to manage, as patients may not respond to conventional treatments including hydroxychloroquine and prednisone. We report the use of rituximab in the treatment of a 20-year-old woman with LEP of the face, legs, and arms that was refractory to standard treatments. She also had a history of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). Further studies are warranted to determine the role of rituximab in the treatment of pediatric patients with LEP.
A 20-year-old woman with history of LEP and HLH initially presented with migratory violaceous nodules on the face 16 years prior to the current presentation. A skin biopsy 3 years after that initial presentation suggested a diagnosis of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Six years later, numerous asymptomatic lesions appeared on the legs, predominantly on the calves; she was successfully treated with hydroxychloroquine and high-dose prednisone. Four years prior to the current presentation, a febrile illness prompted discontinuation of hydroxychloroquine and hospitalization, where she was first was diagnosed with HLH; she achieved remission with cyclosporine. At the current presentation, she continued to have persistent violaceous lesions on the face, lower arms, and legs with underlying nodularity (Figure 1). Skin biopsies revealed LEP and were less suggestive of HLH. She was restarted on hydroxychloroquine, which did not adequately control the disease. Rheumatologic workup was only notable for an antinuclear antibody titer of 1:80 (reference range, <1:80) in a speckled pattern.

Due to the refractory nature of her condition, continued lesion development despite standard treatment, and concerns of possible scarring, we considered a trial of rituximab. Because HLH and LEP can mimic subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma, another skin biopsy was performed, which revealed a deep dermal and subcutaneous lymphohistiocytic infiltrate composed of predominantly CD3+ T cells with a mixed population of CD4+ and CD8+ cells (Figure 2). There was no evidence of transformation into lymphoma. Pathologic findings were most compatible with LEP rather than an HLH-associated panniculitis due to the lack of definitive phagocytosis. She received rituximab using body surface area–based dosing at 375 mg/m2. CD19 levels decreased to undetectable levels after the first dose. Rituximab was dosed based on clinical response; she tolerated treatment well and experienced considerable improvement in the number of lesions following completion of 4 doses at weeks 0, 1, 5, and 7 (Figure 3). She developed a flare at 7 months and improved again after another dose of rituximab.


Lupus erythematosus panniculitis is a rare variant of lupus erythematosus with an average age of presentation between 30 and 60 years.1 In children, LEP presents as recurrent subcutaneous nodules and plaques, commonly involving the face and upper arms.1,2 Long-term sequelae include local swelling and skin atrophy.3 Conventional treatment options for pediatric patients include hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroids.1 Management can be challenging due to the lack of response to conventional treatments as well as the chronic progressive nature of LEP.2 In refractory cases, cyclosporine, azathioprine, sulfones, thalidomide, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclophosphamide are alternative treatment options.1-4
Rituximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting B-cell surface marker CD20, results in depletion of mature B cells. Use of rituximab for LEP has been described in multiple case reports involving an 8-year-old boy, 22-year-old girl, and 2 middle-aged women.2-4 In addition, a recently published case series of 4 patients with childhood-onset refractory LEP described improvement of disease activity with rituximab.5 It is important to rule out subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma before treatment with rituximab, as its histopathology can closely resemble that seen in LEP and HLH-associated cytophagic histiocytic panniculitis.1,6
Rituximab may be an effective treatment option in pediatric patients with refractory LEP. Larger studies on the use of rituximab in the pediatric population are necessary.
- Weingartner JS, Zedek DC, Burkhart CN, et al. Lupus erythematosus panniculitis in children: report of three cases and review of previously reported cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;29:169-176.
- Moreno-Suárez F, Pulpillo-Ruiz Á. Rituximab for the treatment of lupus erythematosus panniculitis. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:415-418.
- Guissa VR, Trudes G, Jesus AA, et al. Lupus erythematosus panniculitis in children and adolescents. Acta Reumatol Port. 2012;37:82-85.
- Mcardle A, Baker JF. A case of “refractory” lupus erythematosus profundus responsive to rituximab. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28:745-746.
- Correll CK, Miller DD, Maguiness SM. Treatment of childhood-onset lupus erythematosus panniculitis with rituximab. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:566-569.
- Aronson IK, Worobec SM. Cytophagic histiocytic panniculitis and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: an overview. Dermatol Ther. 2010;23:389-402.
- Weingartner JS, Zedek DC, Burkhart CN, et al. Lupus erythematosus panniculitis in children: report of three cases and review of previously reported cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;29:169-176.
- Moreno-Suárez F, Pulpillo-Ruiz Á. Rituximab for the treatment of lupus erythematosus panniculitis. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:415-418.
- Guissa VR, Trudes G, Jesus AA, et al. Lupus erythematosus panniculitis in children and adolescents. Acta Reumatol Port. 2012;37:82-85.
- Mcardle A, Baker JF. A case of “refractory” lupus erythematosus profundus responsive to rituximab. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28:745-746.
- Correll CK, Miller DD, Maguiness SM. Treatment of childhood-onset lupus erythematosus panniculitis with rituximab. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:566-569.
- Aronson IK, Worobec SM. Cytophagic histiocytic panniculitis and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: an overview. Dermatol Ther. 2010;23:389-402.
Practice Points
- Lupus erythematosus panniculitis (LEP) is rare in the pediatric population and often is difficult to treat.
- Rituximab can be an effective treatment option for refractory LEP.
- Before the initiation of rituximab, a biopsy is warranted to rule out subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma, which can mimic LEP and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis–associated panniculitis.
Volunteer Opportunities Within Dermatology: More than Skin Deep
The adage “so much to do, so little time” aptly describes the daily challenges facing dermatologists and dermatology residents. The time and attention required by direct patient care, writing notes, navigating electronic health records, and engaging in education and research as well as family commitments can drain even the most tireless clinician. In addition, dermatologists are expected to play a critical role in clinic and practice management to successfully curate an online presence and adapt their skills to successfully manage a teledermatology practice. Coupled with the time spent socializing with friends or colleagues and time for personal hobbies or exercise, it’s easy to see how sleep deprivation is common in many of our colleagues.
What’s being left out of these jam-packed schedules? Increasingly, it is the time and expertise dedicated to volunteering in our local communities. Two recent research letters highlighted how a dramatic increase in the number of research projects and publications is not mirrored by a similar increase in volunteer experiences as dermatology residency selection becomes more competitive.1,2
Although the rate of volunteerism among practicing dermatologists has yet to be studied, a brief review suggests a component of unmet dermatology need within our communities. It’s estimated that approximately 5% to 10% of all emergency department visits are for dermatologic concerns.3-5 In many cases, the reason for the visit is nonurgent and instead reflects a lack of other options for care. However, the need for dermatologists extends beyond the emergency department setting. A review of the prevalence of patients presenting for care to a group of regional free clinics found that 8% (N=5553) of all visitors sought care for dermatologic concerns.6 The benefit is not just for those seated on the examination table; research has shown that while many of the underlying factors resulting in physician burnout stem from systemic issues, participating in volunteer opportunities helps combat burnout in ourselves and our colleagues.7-9 Herein, opportunities that exist for dermatologists to reconnect with their communities, advocate for causes distinctive to the specialty, and care for neighbors most in need are highlighted.
Camp Wonder
Every year, children from across the United States living with chronic and debilitating skin conditions get the opportunity to join fellow campers and spend a week just being kids without the constant focus on being a patient. Camp Wonder’s founder and director, Francesca Tenconi, describes the camp as a place where kids “can form a community and can feel free to be themselves, without judgment, without stares. They get the chance to forget about their skin disease and be themselves” (oral communication, June 18, 2021). Tenconi and the camp’s cofounders and medical directors, Drs. Jenny Kim and Stefani Takahashi, envisioned the camp as a place for all campers regardless of their skin condition to feel safe and welcome. This overall mission guides camp leadership and staff every year over the course of the camp week where campers participate in a mix of traditional and nontraditional summer activities that are safe and accessible for all, from spending time in the pool to arts and crafts and a ropes course.
Camp Wonder is in its 21st year of hosting children and adolescents from across North America at its camp in Livermore, California. This year, Tenconi expects about 100 campers during the last week in July. Camp Wonder relies on medical staff volunteers to make the camp setting safe, inclusive, and fun. “Our dermatology residents and dermatology volunteers are a huge part of why we’re able to have camp,” said Tenconi. “A lot of our kids require very specific medical care throughout the week. We are able to provide this camp experience for them because we have this medical support system available, this specialized dermatology knowledge.” She also noted the benefit to the volunteers themselves, saying,“The feedback we get a lot from residents and dermatologists is that camp gave them a chance to understand the true-life impact of some of the skin diseases these kids and families are living with. Kids will open up to them and tell them how their disease has impacted them personally” (oral communication, June 18, 2021).
Volunteer medical providers help manage the medical needs of the campers beginning at check-in and work shifts in the infirmary as well as help with dispensing and administering medications, changing dressings, and applying ointments or other topical medications. When not assisting with medical care, medical staff can get to know the campers; help out with arts and crafts, games, sports, and other camp activities; and put on skits and plays for campers at nightly camp hangouts (Figure 1).

How to Get Involved
Visit the website (https://www.csdf.org/camp-wonder) for information on becoming a medical volunteer for 2022. Donations to help keep the camp running also are greatly appreciated, as attendance, including travel costs, is free for families through the Children’s Skin Disease Foundation. Finally, dermatologists can help by keeping their young patients with skin disease in mind as future campers. The camp welcomes kids from across the United States and Canada and invites questions from dermatologists and families on how to become a camper and what the experience is like.
Native American Health Services Rotation
Located in the southwestern United States, the Navajo Nation is North America’s largest Native American tribe by enrollment and resides on the largest reservation in the United States.10 Comprised of 27,000 square miles within portions of Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah, the reservation’s total area is greater than that of Massachusetts, Vermont, and New Hampshire combined.11 The reservation is home to an estimated 180,000 Navajo people, a population roughly the size of Salt Lake City, Utah. Yet, many homes on the reservation are without electricity, running water, telephones, or broadband access, and many roads on the reservation remain unpaved. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, 4 dermatology residents were selected each year to travel to this unique and remote location to work with the staff of the Chinle Comprehensive Health Care Facility (Chinle, Arizona), an Indian Health Service facility, as part of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)–sponsored Native American Health Services Resident Rotation (NAHSRR).
Dr. Lucinda Kohn, Assistant Professor of Dermatology at the University of Colorado and the director of the NAHSRR program discovered the value of this rotation firsthand as a dermatology resident. In 2017, she traveled to the area to spend 2 weeks serving within the community. “I went because of a personal connection. My husband is Native American, although not Navajo. I wanted to experience what it was like to provide dermatologic care for Native Americans. I found the Navajo people to be so friendly and so grateful for our care. The clinicians we worked with at Chinle were excited to have us share our expertise and to pass on their knowledge to us,” said Dr. Kohn (personal communication, June 24, 2021).
Rotating residents provide dermatologic care for the Navajo people and share their unique medical skill set to local primary care clinicians serving as preceptors. They also may have an opportunity to learn from Native healers about traditional Navajo beliefs and ceremonies used as part of a holistic approach to healing.
The program, similar to volunteer programs across the country, was put on hold during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. “The Navajo nation witnessed a really tragic surge of COVID cases that required that limited medical resources be diverted to help cope with the pandemic,” says Dr. Kohn. “It really wasn’t safe for residents to travel to the reservation either, so the rotation had to be put on hold.” However, in April 2021, the health care staff of the Chinle Comprehensive Care Facility reached out to revive the program, which is now pending the green light from the AAD. It is unclear if or when AAD leadership will allow this rotation to restart. Dr. Kohn hopes to be able to start accepting new applications soon. “This rotation provides a wealth of benefits to all those involved, from the residents who get the chance to work with a unique population in need to the clinicians who gain a diverse understanding of dermatology treatment techniques. And of course, for the patients, who are so appreciative of the care they receive from our volunteers” (personal communication, June 25, 2021).
How to Get Involved
Dr. Kohn is happy to field questions regarding the rotation and requests for more information via email ([email protected]). Residents interested in this program also may reach out to the AAD’s Education and Volunteers Abroad Committee to express interest in the NAHSRR program’s reinstatement.
Destination Healthy Skin
Since 2017, the Skin Cancer Foundation’s Destination Healthy Skin (DHS) RV has been the setting for more than 3800 free skin cancer screenings provided by volunteers within underserved populations across the United States (Figure 2). After a year hiatus due to the pandemic, DHS hit the road again, starting in New York City on August 1 to 3, 2021. From there, the DHS RV will traverse the country in one large loop, starting with visits to large and small cities in the Midwest and the West Coast. Following a visit to San Diego, California, in early October, the RV will turn east, with stops in Arizona, Texas, and several southern states before ending in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Dr. Elizabeth Hale, Senior Vice President of the Skin Cancer Foundation, feels that increasing awareness of the importance of regular skin cancer screening for those at risk is more important than ever. “We know that many people in the past year put routine cancer screening on the back burner, but we’re beginning to appreciate that this has led to significant delays in skin cancer diagnosis and potentially more significant disease when cases are diagnosed.” Dr. Hale noted that as the country continues to return to a degree of normalcy, the backlog of patients now seeking their routine screening has led to longer wait times. She expects DHS may offer some relief. “There are no appointments necessary. If the RV is close to their hometown, patients have an advantage in being able to be seen first come, first served, without having to wait for an appointment or make sure their insurance is accepted. It’s a free screening that can increase access to dermatologists” (personal communication, June 21, 2021).

The program’s organizers acknowledge that DHS is not a long-term solution for improving dermatology access in the United States and recognize that more needs to be done to raise awareness, both of the value that screenings can provide and the importance of sun-protective behavior. “This is an important first step,” says Dr. Hale. “It’s important that we disseminate that no one is immune to skin cancer. It’s about education, and this is a tool to educate patients that everyone should have a skin check once a year, regardless of where you live or what your skin type is” (personal communication, June 21, 2021).
Volunteer dermatologists are needed to assist with screenings when the DHS RV arrives in their community. Providers complete a screening form identifying any concerning lesions and can document specific lesions using the patient’s cell phone. Following the screenings, participating dermatologists are welcome to invite participants to make appointments at their practices or suggest local clinics for follow-up care.
How to Get Involved
The schedule for this year’s screening events can be found online (https://www.skincancer.org/early-detection/destination-healthy-skin/). Consider volunteering (https://www.skincancer.org/early-detection/destination-healthy-skin/physician-volunteers/) or helping to raise awareness by reaching out to local dermatology societies or free clinics in your area. Residents and physician’s assistants are welcome to volunteer as well, as long as they are under the on-site supervision of a board-certified dermatologist.
Final Thoughts
As medical professionals, we all recognize there are valuable contributions we can make to groups and organizations that need our help. The stresses and pressure of work and everyday life can make finding the time to offer that help seem impossible. Although it may seem counterintuitive, volunteering our time to help others can help us better navigate the professional burnout that many medical professionals experience today.
- Ezekor M, Pona A, Cline A, et al. An increasing trend in the number of publications and research projects among dermatology residency applicants. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:214-216.
- Atluri S, Seivright JR, Shi VY, et al. Volunteer and work experiences among dermatology residency applicants. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E97-E98.
- Abokwidir M, Davis SA, Fleischer AB, et al. Use of the emergency department for dermatologic care in the United States by ethnic group. J Dermatolog Treat. 2015;26:392-394.
- Uscher-Pines L, Pines J, Kellermann A, et al. Emergency department visits for nonurgent conditions: systematic literature review. Am J Manag Care. 2013;19:47-59.
- Jack AR, Spence AA, Nichols BJ, et al. Cutaneous conditions leading to dermatology consultations in the emergency department. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:551-555.
- Ayoubi N, Mirza A-S, Swanson J, et al. Dermatologic care of uninsured patients managed at free clinics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:433-437.
- Wright AA, Katz IT. Beyond burnout—redesigning care to restore meaning and sanity for physicians. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:309-311.
- Bull C, Aucoin JB. Voluntary association participation and life satisfaction: a replication note. J Gerontol. 1975;30:73-76.
- Iserson KV. Burnout syndrome: global medicine volunteering as a possible treatment strategy. J Emerg Med. 2018;54:516-521.
- Romero S. Navajo Nation becomes largest tribe in U.S. after pandemic enrollment surge. New York Times. May 21, 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/05/21/us/navajo-cherokee-population.html
- Moore GR, Benally J, Tuttle S. The Navajo Nation: quick facts. University of Arizona website. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1471.pdf
The adage “so much to do, so little time” aptly describes the daily challenges facing dermatologists and dermatology residents. The time and attention required by direct patient care, writing notes, navigating electronic health records, and engaging in education and research as well as family commitments can drain even the most tireless clinician. In addition, dermatologists are expected to play a critical role in clinic and practice management to successfully curate an online presence and adapt their skills to successfully manage a teledermatology practice. Coupled with the time spent socializing with friends or colleagues and time for personal hobbies or exercise, it’s easy to see how sleep deprivation is common in many of our colleagues.
What’s being left out of these jam-packed schedules? Increasingly, it is the time and expertise dedicated to volunteering in our local communities. Two recent research letters highlighted how a dramatic increase in the number of research projects and publications is not mirrored by a similar increase in volunteer experiences as dermatology residency selection becomes more competitive.1,2
Although the rate of volunteerism among practicing dermatologists has yet to be studied, a brief review suggests a component of unmet dermatology need within our communities. It’s estimated that approximately 5% to 10% of all emergency department visits are for dermatologic concerns.3-5 In many cases, the reason for the visit is nonurgent and instead reflects a lack of other options for care. However, the need for dermatologists extends beyond the emergency department setting. A review of the prevalence of patients presenting for care to a group of regional free clinics found that 8% (N=5553) of all visitors sought care for dermatologic concerns.6 The benefit is not just for those seated on the examination table; research has shown that while many of the underlying factors resulting in physician burnout stem from systemic issues, participating in volunteer opportunities helps combat burnout in ourselves and our colleagues.7-9 Herein, opportunities that exist for dermatologists to reconnect with their communities, advocate for causes distinctive to the specialty, and care for neighbors most in need are highlighted.
Camp Wonder
Every year, children from across the United States living with chronic and debilitating skin conditions get the opportunity to join fellow campers and spend a week just being kids without the constant focus on being a patient. Camp Wonder’s founder and director, Francesca Tenconi, describes the camp as a place where kids “can form a community and can feel free to be themselves, without judgment, without stares. They get the chance to forget about their skin disease and be themselves” (oral communication, June 18, 2021). Tenconi and the camp’s cofounders and medical directors, Drs. Jenny Kim and Stefani Takahashi, envisioned the camp as a place for all campers regardless of their skin condition to feel safe and welcome. This overall mission guides camp leadership and staff every year over the course of the camp week where campers participate in a mix of traditional and nontraditional summer activities that are safe and accessible for all, from spending time in the pool to arts and crafts and a ropes course.
Camp Wonder is in its 21st year of hosting children and adolescents from across North America at its camp in Livermore, California. This year, Tenconi expects about 100 campers during the last week in July. Camp Wonder relies on medical staff volunteers to make the camp setting safe, inclusive, and fun. “Our dermatology residents and dermatology volunteers are a huge part of why we’re able to have camp,” said Tenconi. “A lot of our kids require very specific medical care throughout the week. We are able to provide this camp experience for them because we have this medical support system available, this specialized dermatology knowledge.” She also noted the benefit to the volunteers themselves, saying,“The feedback we get a lot from residents and dermatologists is that camp gave them a chance to understand the true-life impact of some of the skin diseases these kids and families are living with. Kids will open up to them and tell them how their disease has impacted them personally” (oral communication, June 18, 2021).
Volunteer medical providers help manage the medical needs of the campers beginning at check-in and work shifts in the infirmary as well as help with dispensing and administering medications, changing dressings, and applying ointments or other topical medications. When not assisting with medical care, medical staff can get to know the campers; help out with arts and crafts, games, sports, and other camp activities; and put on skits and plays for campers at nightly camp hangouts (Figure 1).

How to Get Involved
Visit the website (https://www.csdf.org/camp-wonder) for information on becoming a medical volunteer for 2022. Donations to help keep the camp running also are greatly appreciated, as attendance, including travel costs, is free for families through the Children’s Skin Disease Foundation. Finally, dermatologists can help by keeping their young patients with skin disease in mind as future campers. The camp welcomes kids from across the United States and Canada and invites questions from dermatologists and families on how to become a camper and what the experience is like.
Native American Health Services Rotation
Located in the southwestern United States, the Navajo Nation is North America’s largest Native American tribe by enrollment and resides on the largest reservation in the United States.10 Comprised of 27,000 square miles within portions of Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah, the reservation’s total area is greater than that of Massachusetts, Vermont, and New Hampshire combined.11 The reservation is home to an estimated 180,000 Navajo people, a population roughly the size of Salt Lake City, Utah. Yet, many homes on the reservation are without electricity, running water, telephones, or broadband access, and many roads on the reservation remain unpaved. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, 4 dermatology residents were selected each year to travel to this unique and remote location to work with the staff of the Chinle Comprehensive Health Care Facility (Chinle, Arizona), an Indian Health Service facility, as part of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)–sponsored Native American Health Services Resident Rotation (NAHSRR).
Dr. Lucinda Kohn, Assistant Professor of Dermatology at the University of Colorado and the director of the NAHSRR program discovered the value of this rotation firsthand as a dermatology resident. In 2017, she traveled to the area to spend 2 weeks serving within the community. “I went because of a personal connection. My husband is Native American, although not Navajo. I wanted to experience what it was like to provide dermatologic care for Native Americans. I found the Navajo people to be so friendly and so grateful for our care. The clinicians we worked with at Chinle were excited to have us share our expertise and to pass on their knowledge to us,” said Dr. Kohn (personal communication, June 24, 2021).
Rotating residents provide dermatologic care for the Navajo people and share their unique medical skill set to local primary care clinicians serving as preceptors. They also may have an opportunity to learn from Native healers about traditional Navajo beliefs and ceremonies used as part of a holistic approach to healing.
The program, similar to volunteer programs across the country, was put on hold during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. “The Navajo nation witnessed a really tragic surge of COVID cases that required that limited medical resources be diverted to help cope with the pandemic,” says Dr. Kohn. “It really wasn’t safe for residents to travel to the reservation either, so the rotation had to be put on hold.” However, in April 2021, the health care staff of the Chinle Comprehensive Care Facility reached out to revive the program, which is now pending the green light from the AAD. It is unclear if or when AAD leadership will allow this rotation to restart. Dr. Kohn hopes to be able to start accepting new applications soon. “This rotation provides a wealth of benefits to all those involved, from the residents who get the chance to work with a unique population in need to the clinicians who gain a diverse understanding of dermatology treatment techniques. And of course, for the patients, who are so appreciative of the care they receive from our volunteers” (personal communication, June 25, 2021).
How to Get Involved
Dr. Kohn is happy to field questions regarding the rotation and requests for more information via email ([email protected]). Residents interested in this program also may reach out to the AAD’s Education and Volunteers Abroad Committee to express interest in the NAHSRR program’s reinstatement.
Destination Healthy Skin
Since 2017, the Skin Cancer Foundation’s Destination Healthy Skin (DHS) RV has been the setting for more than 3800 free skin cancer screenings provided by volunteers within underserved populations across the United States (Figure 2). After a year hiatus due to the pandemic, DHS hit the road again, starting in New York City on August 1 to 3, 2021. From there, the DHS RV will traverse the country in one large loop, starting with visits to large and small cities in the Midwest and the West Coast. Following a visit to San Diego, California, in early October, the RV will turn east, with stops in Arizona, Texas, and several southern states before ending in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Dr. Elizabeth Hale, Senior Vice President of the Skin Cancer Foundation, feels that increasing awareness of the importance of regular skin cancer screening for those at risk is more important than ever. “We know that many people in the past year put routine cancer screening on the back burner, but we’re beginning to appreciate that this has led to significant delays in skin cancer diagnosis and potentially more significant disease when cases are diagnosed.” Dr. Hale noted that as the country continues to return to a degree of normalcy, the backlog of patients now seeking their routine screening has led to longer wait times. She expects DHS may offer some relief. “There are no appointments necessary. If the RV is close to their hometown, patients have an advantage in being able to be seen first come, first served, without having to wait for an appointment or make sure their insurance is accepted. It’s a free screening that can increase access to dermatologists” (personal communication, June 21, 2021).

The program’s organizers acknowledge that DHS is not a long-term solution for improving dermatology access in the United States and recognize that more needs to be done to raise awareness, both of the value that screenings can provide and the importance of sun-protective behavior. “This is an important first step,” says Dr. Hale. “It’s important that we disseminate that no one is immune to skin cancer. It’s about education, and this is a tool to educate patients that everyone should have a skin check once a year, regardless of where you live or what your skin type is” (personal communication, June 21, 2021).
Volunteer dermatologists are needed to assist with screenings when the DHS RV arrives in their community. Providers complete a screening form identifying any concerning lesions and can document specific lesions using the patient’s cell phone. Following the screenings, participating dermatologists are welcome to invite participants to make appointments at their practices or suggest local clinics for follow-up care.
How to Get Involved
The schedule for this year’s screening events can be found online (https://www.skincancer.org/early-detection/destination-healthy-skin/). Consider volunteering (https://www.skincancer.org/early-detection/destination-healthy-skin/physician-volunteers/) or helping to raise awareness by reaching out to local dermatology societies or free clinics in your area. Residents and physician’s assistants are welcome to volunteer as well, as long as they are under the on-site supervision of a board-certified dermatologist.
Final Thoughts
As medical professionals, we all recognize there are valuable contributions we can make to groups and organizations that need our help. The stresses and pressure of work and everyday life can make finding the time to offer that help seem impossible. Although it may seem counterintuitive, volunteering our time to help others can help us better navigate the professional burnout that many medical professionals experience today.
The adage “so much to do, so little time” aptly describes the daily challenges facing dermatologists and dermatology residents. The time and attention required by direct patient care, writing notes, navigating electronic health records, and engaging in education and research as well as family commitments can drain even the most tireless clinician. In addition, dermatologists are expected to play a critical role in clinic and practice management to successfully curate an online presence and adapt their skills to successfully manage a teledermatology practice. Coupled with the time spent socializing with friends or colleagues and time for personal hobbies or exercise, it’s easy to see how sleep deprivation is common in many of our colleagues.
What’s being left out of these jam-packed schedules? Increasingly, it is the time and expertise dedicated to volunteering in our local communities. Two recent research letters highlighted how a dramatic increase in the number of research projects and publications is not mirrored by a similar increase in volunteer experiences as dermatology residency selection becomes more competitive.1,2
Although the rate of volunteerism among practicing dermatologists has yet to be studied, a brief review suggests a component of unmet dermatology need within our communities. It’s estimated that approximately 5% to 10% of all emergency department visits are for dermatologic concerns.3-5 In many cases, the reason for the visit is nonurgent and instead reflects a lack of other options for care. However, the need for dermatologists extends beyond the emergency department setting. A review of the prevalence of patients presenting for care to a group of regional free clinics found that 8% (N=5553) of all visitors sought care for dermatologic concerns.6 The benefit is not just for those seated on the examination table; research has shown that while many of the underlying factors resulting in physician burnout stem from systemic issues, participating in volunteer opportunities helps combat burnout in ourselves and our colleagues.7-9 Herein, opportunities that exist for dermatologists to reconnect with their communities, advocate for causes distinctive to the specialty, and care for neighbors most in need are highlighted.
Camp Wonder
Every year, children from across the United States living with chronic and debilitating skin conditions get the opportunity to join fellow campers and spend a week just being kids without the constant focus on being a patient. Camp Wonder’s founder and director, Francesca Tenconi, describes the camp as a place where kids “can form a community and can feel free to be themselves, without judgment, without stares. They get the chance to forget about their skin disease and be themselves” (oral communication, June 18, 2021). Tenconi and the camp’s cofounders and medical directors, Drs. Jenny Kim and Stefani Takahashi, envisioned the camp as a place for all campers regardless of their skin condition to feel safe and welcome. This overall mission guides camp leadership and staff every year over the course of the camp week where campers participate in a mix of traditional and nontraditional summer activities that are safe and accessible for all, from spending time in the pool to arts and crafts and a ropes course.
Camp Wonder is in its 21st year of hosting children and adolescents from across North America at its camp in Livermore, California. This year, Tenconi expects about 100 campers during the last week in July. Camp Wonder relies on medical staff volunteers to make the camp setting safe, inclusive, and fun. “Our dermatology residents and dermatology volunteers are a huge part of why we’re able to have camp,” said Tenconi. “A lot of our kids require very specific medical care throughout the week. We are able to provide this camp experience for them because we have this medical support system available, this specialized dermatology knowledge.” She also noted the benefit to the volunteers themselves, saying,“The feedback we get a lot from residents and dermatologists is that camp gave them a chance to understand the true-life impact of some of the skin diseases these kids and families are living with. Kids will open up to them and tell them how their disease has impacted them personally” (oral communication, June 18, 2021).
Volunteer medical providers help manage the medical needs of the campers beginning at check-in and work shifts in the infirmary as well as help with dispensing and administering medications, changing dressings, and applying ointments or other topical medications. When not assisting with medical care, medical staff can get to know the campers; help out with arts and crafts, games, sports, and other camp activities; and put on skits and plays for campers at nightly camp hangouts (Figure 1).

How to Get Involved
Visit the website (https://www.csdf.org/camp-wonder) for information on becoming a medical volunteer for 2022. Donations to help keep the camp running also are greatly appreciated, as attendance, including travel costs, is free for families through the Children’s Skin Disease Foundation. Finally, dermatologists can help by keeping their young patients with skin disease in mind as future campers. The camp welcomes kids from across the United States and Canada and invites questions from dermatologists and families on how to become a camper and what the experience is like.
Native American Health Services Rotation
Located in the southwestern United States, the Navajo Nation is North America’s largest Native American tribe by enrollment and resides on the largest reservation in the United States.10 Comprised of 27,000 square miles within portions of Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah, the reservation’s total area is greater than that of Massachusetts, Vermont, and New Hampshire combined.11 The reservation is home to an estimated 180,000 Navajo people, a population roughly the size of Salt Lake City, Utah. Yet, many homes on the reservation are without electricity, running water, telephones, or broadband access, and many roads on the reservation remain unpaved. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, 4 dermatology residents were selected each year to travel to this unique and remote location to work with the staff of the Chinle Comprehensive Health Care Facility (Chinle, Arizona), an Indian Health Service facility, as part of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)–sponsored Native American Health Services Resident Rotation (NAHSRR).
Dr. Lucinda Kohn, Assistant Professor of Dermatology at the University of Colorado and the director of the NAHSRR program discovered the value of this rotation firsthand as a dermatology resident. In 2017, she traveled to the area to spend 2 weeks serving within the community. “I went because of a personal connection. My husband is Native American, although not Navajo. I wanted to experience what it was like to provide dermatologic care for Native Americans. I found the Navajo people to be so friendly and so grateful for our care. The clinicians we worked with at Chinle were excited to have us share our expertise and to pass on their knowledge to us,” said Dr. Kohn (personal communication, June 24, 2021).
Rotating residents provide dermatologic care for the Navajo people and share their unique medical skill set to local primary care clinicians serving as preceptors. They also may have an opportunity to learn from Native healers about traditional Navajo beliefs and ceremonies used as part of a holistic approach to healing.
The program, similar to volunteer programs across the country, was put on hold during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. “The Navajo nation witnessed a really tragic surge of COVID cases that required that limited medical resources be diverted to help cope with the pandemic,” says Dr. Kohn. “It really wasn’t safe for residents to travel to the reservation either, so the rotation had to be put on hold.” However, in April 2021, the health care staff of the Chinle Comprehensive Care Facility reached out to revive the program, which is now pending the green light from the AAD. It is unclear if or when AAD leadership will allow this rotation to restart. Dr. Kohn hopes to be able to start accepting new applications soon. “This rotation provides a wealth of benefits to all those involved, from the residents who get the chance to work with a unique population in need to the clinicians who gain a diverse understanding of dermatology treatment techniques. And of course, for the patients, who are so appreciative of the care they receive from our volunteers” (personal communication, June 25, 2021).
How to Get Involved
Dr. Kohn is happy to field questions regarding the rotation and requests for more information via email ([email protected]). Residents interested in this program also may reach out to the AAD’s Education and Volunteers Abroad Committee to express interest in the NAHSRR program’s reinstatement.
Destination Healthy Skin
Since 2017, the Skin Cancer Foundation’s Destination Healthy Skin (DHS) RV has been the setting for more than 3800 free skin cancer screenings provided by volunteers within underserved populations across the United States (Figure 2). After a year hiatus due to the pandemic, DHS hit the road again, starting in New York City on August 1 to 3, 2021. From there, the DHS RV will traverse the country in one large loop, starting with visits to large and small cities in the Midwest and the West Coast. Following a visit to San Diego, California, in early October, the RV will turn east, with stops in Arizona, Texas, and several southern states before ending in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Dr. Elizabeth Hale, Senior Vice President of the Skin Cancer Foundation, feels that increasing awareness of the importance of regular skin cancer screening for those at risk is more important than ever. “We know that many people in the past year put routine cancer screening on the back burner, but we’re beginning to appreciate that this has led to significant delays in skin cancer diagnosis and potentially more significant disease when cases are diagnosed.” Dr. Hale noted that as the country continues to return to a degree of normalcy, the backlog of patients now seeking their routine screening has led to longer wait times. She expects DHS may offer some relief. “There are no appointments necessary. If the RV is close to their hometown, patients have an advantage in being able to be seen first come, first served, without having to wait for an appointment or make sure their insurance is accepted. It’s a free screening that can increase access to dermatologists” (personal communication, June 21, 2021).

The program’s organizers acknowledge that DHS is not a long-term solution for improving dermatology access in the United States and recognize that more needs to be done to raise awareness, both of the value that screenings can provide and the importance of sun-protective behavior. “This is an important first step,” says Dr. Hale. “It’s important that we disseminate that no one is immune to skin cancer. It’s about education, and this is a tool to educate patients that everyone should have a skin check once a year, regardless of where you live or what your skin type is” (personal communication, June 21, 2021).
Volunteer dermatologists are needed to assist with screenings when the DHS RV arrives in their community. Providers complete a screening form identifying any concerning lesions and can document specific lesions using the patient’s cell phone. Following the screenings, participating dermatologists are welcome to invite participants to make appointments at their practices or suggest local clinics for follow-up care.
How to Get Involved
The schedule for this year’s screening events can be found online (https://www.skincancer.org/early-detection/destination-healthy-skin/). Consider volunteering (https://www.skincancer.org/early-detection/destination-healthy-skin/physician-volunteers/) or helping to raise awareness by reaching out to local dermatology societies or free clinics in your area. Residents and physician’s assistants are welcome to volunteer as well, as long as they are under the on-site supervision of a board-certified dermatologist.
Final Thoughts
As medical professionals, we all recognize there are valuable contributions we can make to groups and organizations that need our help. The stresses and pressure of work and everyday life can make finding the time to offer that help seem impossible. Although it may seem counterintuitive, volunteering our time to help others can help us better navigate the professional burnout that many medical professionals experience today.
- Ezekor M, Pona A, Cline A, et al. An increasing trend in the number of publications and research projects among dermatology residency applicants. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:214-216.
- Atluri S, Seivright JR, Shi VY, et al. Volunteer and work experiences among dermatology residency applicants. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E97-E98.
- Abokwidir M, Davis SA, Fleischer AB, et al. Use of the emergency department for dermatologic care in the United States by ethnic group. J Dermatolog Treat. 2015;26:392-394.
- Uscher-Pines L, Pines J, Kellermann A, et al. Emergency department visits for nonurgent conditions: systematic literature review. Am J Manag Care. 2013;19:47-59.
- Jack AR, Spence AA, Nichols BJ, et al. Cutaneous conditions leading to dermatology consultations in the emergency department. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:551-555.
- Ayoubi N, Mirza A-S, Swanson J, et al. Dermatologic care of uninsured patients managed at free clinics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:433-437.
- Wright AA, Katz IT. Beyond burnout—redesigning care to restore meaning and sanity for physicians. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:309-311.
- Bull C, Aucoin JB. Voluntary association participation and life satisfaction: a replication note. J Gerontol. 1975;30:73-76.
- Iserson KV. Burnout syndrome: global medicine volunteering as a possible treatment strategy. J Emerg Med. 2018;54:516-521.
- Romero S. Navajo Nation becomes largest tribe in U.S. after pandemic enrollment surge. New York Times. May 21, 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/05/21/us/navajo-cherokee-population.html
- Moore GR, Benally J, Tuttle S. The Navajo Nation: quick facts. University of Arizona website. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1471.pdf
- Ezekor M, Pona A, Cline A, et al. An increasing trend in the number of publications and research projects among dermatology residency applicants. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:214-216.
- Atluri S, Seivright JR, Shi VY, et al. Volunteer and work experiences among dermatology residency applicants. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E97-E98.
- Abokwidir M, Davis SA, Fleischer AB, et al. Use of the emergency department for dermatologic care in the United States by ethnic group. J Dermatolog Treat. 2015;26:392-394.
- Uscher-Pines L, Pines J, Kellermann A, et al. Emergency department visits for nonurgent conditions: systematic literature review. Am J Manag Care. 2013;19:47-59.
- Jack AR, Spence AA, Nichols BJ, et al. Cutaneous conditions leading to dermatology consultations in the emergency department. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:551-555.
- Ayoubi N, Mirza A-S, Swanson J, et al. Dermatologic care of uninsured patients managed at free clinics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:433-437.
- Wright AA, Katz IT. Beyond burnout—redesigning care to restore meaning and sanity for physicians. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:309-311.
- Bull C, Aucoin JB. Voluntary association participation and life satisfaction: a replication note. J Gerontol. 1975;30:73-76.
- Iserson KV. Burnout syndrome: global medicine volunteering as a possible treatment strategy. J Emerg Med. 2018;54:516-521.
- Romero S. Navajo Nation becomes largest tribe in U.S. after pandemic enrollment surge. New York Times. May 21, 2021. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/05/21/us/navajo-cherokee-population.html
- Moore GR, Benally J, Tuttle S. The Navajo Nation: quick facts. University of Arizona website. Accessed August 19, 2021. https://extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1471.pdf
Resident Pearl
- Volunteerism rates among dermatology residents seem to be decreasing. We should work to combat this trend by finding ways to give back to our communities and spur our colleagues to do the same.
Verrucous Scalp Plaque and Widespread Eruption
The Diagnosis: Pemphigus Foliaceous
Laboratory workup including a complete blood cell count with differential, comprehensive metabolic panel, antinuclear antibodies, Sjögren syndrome A and B antibodies, hepatitis profile, rapid plasma reagin, HIV screen, aldolase, anti–Jo-1, T-Spot TB test (Quest Diagnostics), and tissue cultures was unremarkable. Two 4-mm punch biopsies were obtained from the left cheek and upper back, both of which demonstrated intragranular acantholysis suggestive of pemphigus foliaceous (Figure 1A). A subsequent punch biopsy from the right lower abdomen sent for direct immunofluorescence demonstrated netlike positivity of IgG and C3 in the upper epidermis (Figure 1B), and serum sent for indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated intercellular IgG antibodies to desmoglein (Dsg) 1 on monkey esophagus and positive Dsg-1 antibodies on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, confirming the diagnosis.
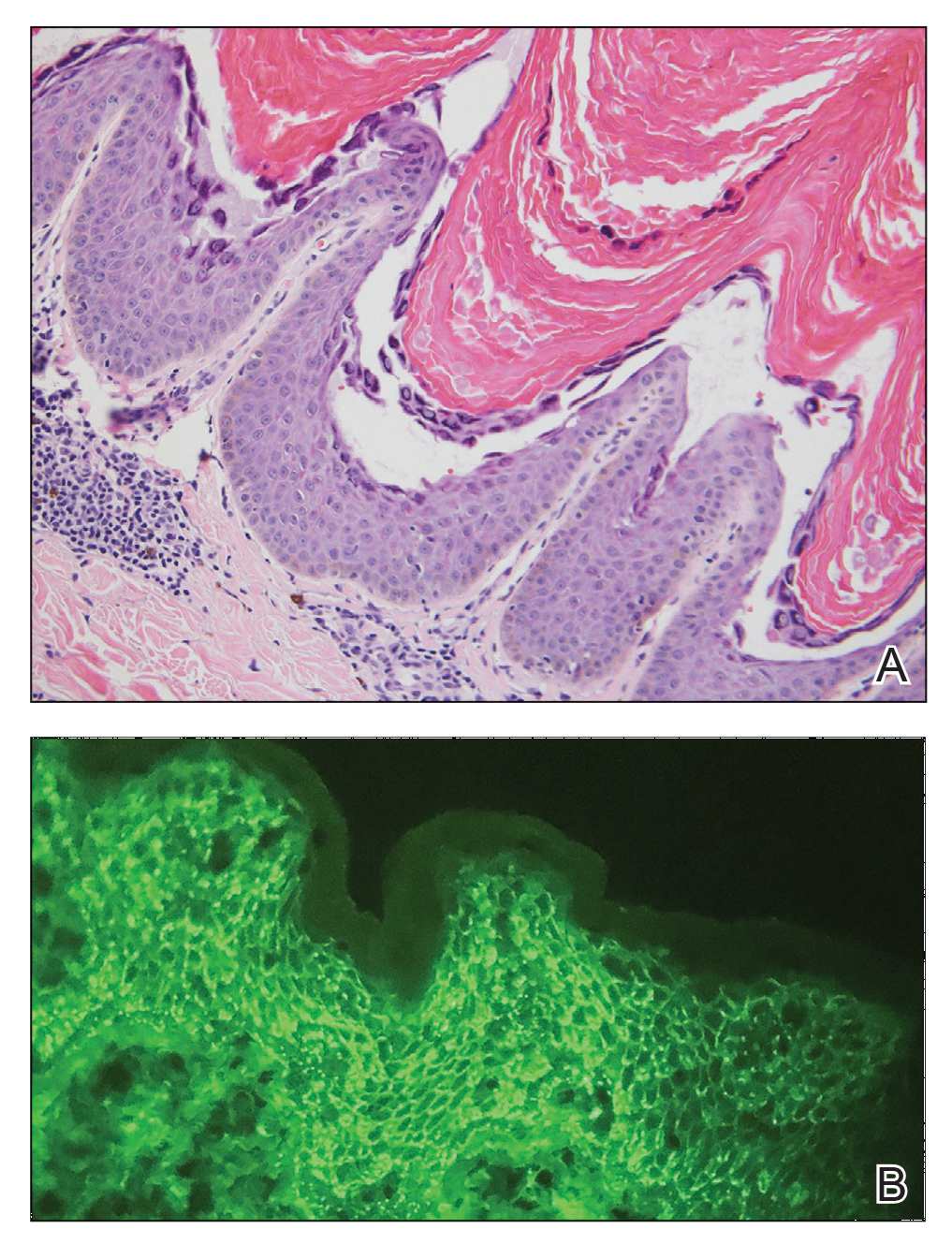
The patient was started on a 60-mg prednisone taper as well as dapsone 50 mg daily; the dapsone was titrated up to 100 mg daily. After tapering down to 10 mg daily of prednisone over 2 months and continuing dapsone with minimal improvement, he was given 2 infusions of rituximab 1000 mg 2 weeks apart. The scalp plaque was dramatically improved at 3-month follow-up (Figure 2), with partial improvement of the cheek plaques (Figure 3). Dapsone was increased to 150 mg daily, and he was encouraged to use triamcinolone acetonide ointment 0.1% twice daily, which led to further improvement.
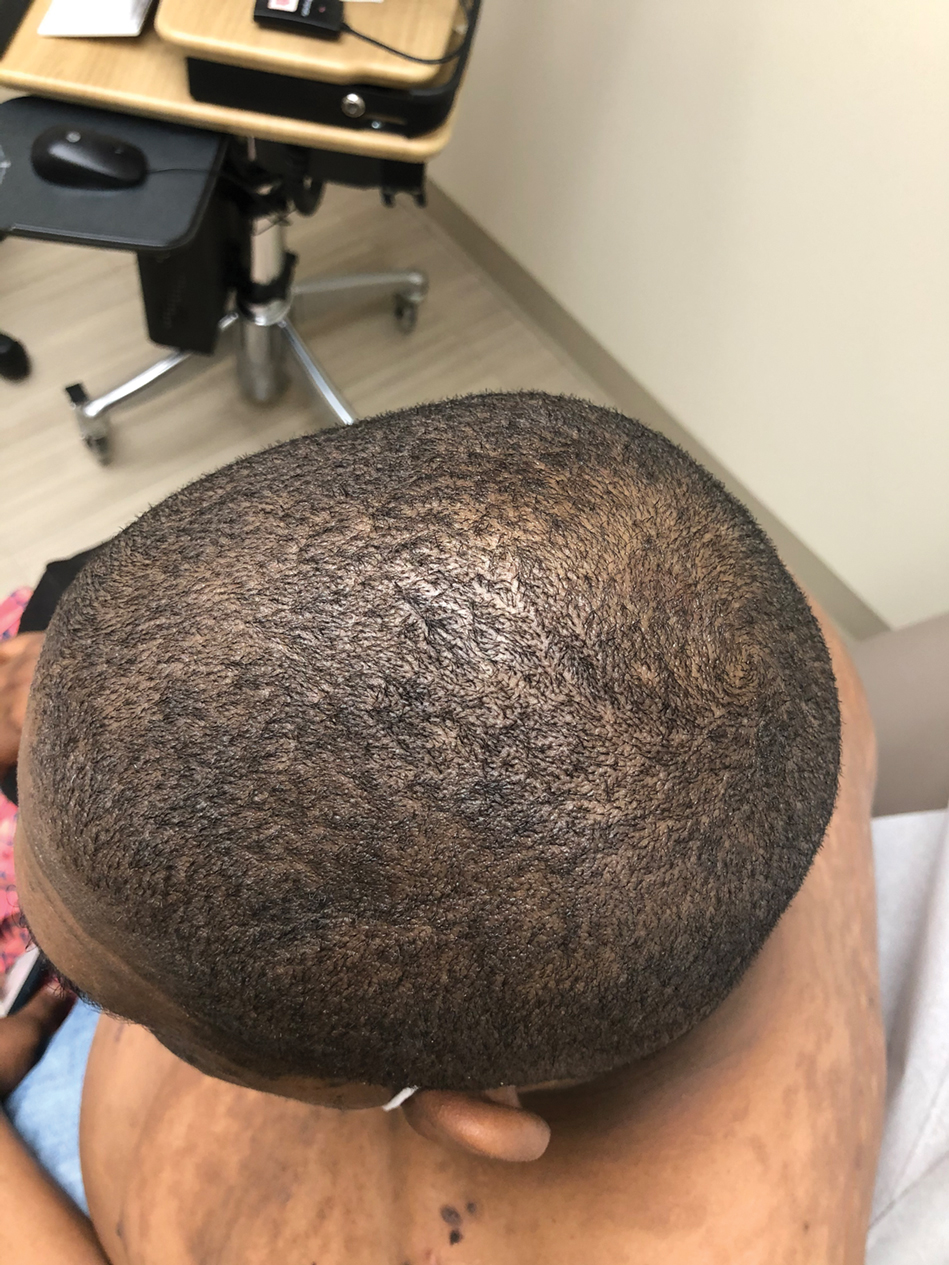
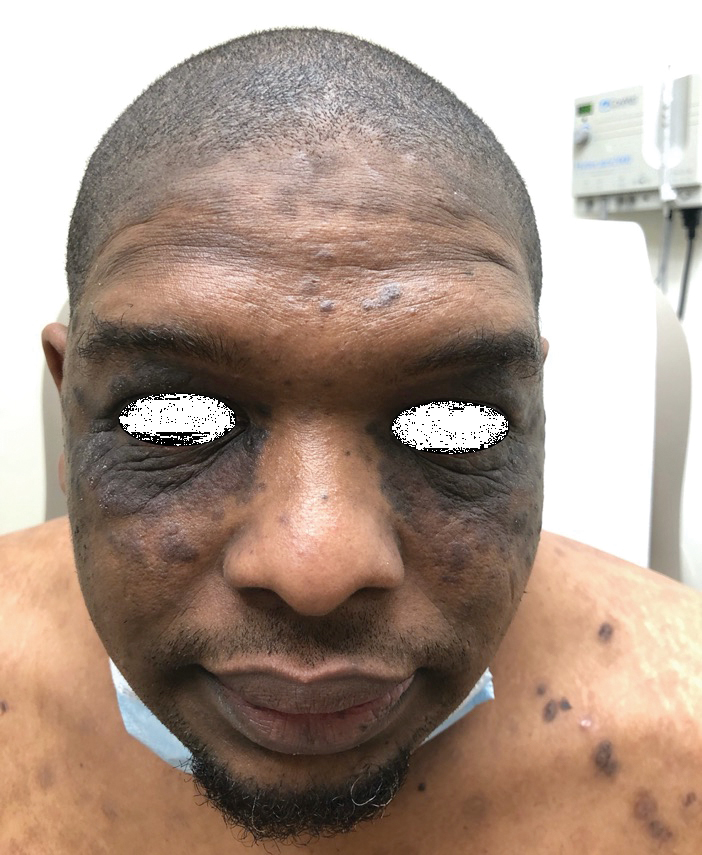
Pemphigus foliaceus is an autoimmune blistering disease that most commonly occurs in middle-aged adults. It generally is less common than pemphigus vulgaris, except in Finland, Tunisia, and Brazil, where there is an endemic condition with an identical clinical and histological presentation known as fogo selvagem.1
The pathogenesis of pemphigus foliaceous is characterized by IgG autoantibodies against Dsg-1, a transmembrane glycoprotein involved in the cellular adhesion of keratinocytes, which is preferentially expressed in the superficial epidermis.2-7 Dysfunction of Dsg-1 results in the separation of superficial epidermal cells, resulting in intraepidermal blisters.2,7 In contrast to pemphigus vulgaris, there typically is a lack of oral mucosal involvement due to compensation by Dsg-3 in the mucosa.4 Potential triggers for pemphigus foliaceous include exposure to UV radiation; radiotherapy; pregnancy; physiologic stress; and drugs, most commonly captopril, penicillamine, and thiols.8
Pemphigus foliaceous lesions clinically appear as eroded and crusted lesions on an erythematous base, commonly in a seborrheic distribution on the face, scalp, and trunk with sparing of the oral mucosa,2,6 but lesions can progress to a widespread and more severe exfoliative dermatitis.7 Lesions also can appear as psoriasiform plaques and often are initially misdiagnosed as psoriasis, particularly in patients with skin of color.9,10
Diagnosis of pemphigus foliaceous typically is made using a combination of histology as well as both direct and indirect immunofluorescence. Histologically, pemphigus foliaceus presents with subcorneal acantholysis, which is most prominent in the granular layer and occasionally the presence of neutrophils and eosinophils in the blister cavity.7 Direct immunofluorescence demonstrates netlike intercellular IgG and C3 in the upper portion of the epidermis.11 Indirect immunofluorescence can help detect circulating IgG antibodies to Dsg-1, with guinea pig esophagus being the ideal substrate.11,12
First-line treatment of pemphigus foliaceus consists of systemic glucocorticoid therapy, often administered with azathioprine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil.2,6,13 Although first-line treatment is effective in 60% to 80% of patients,2 relapsing cases can be treated with cyclophosphamide, intravenous immunoglobulin, immunoadsorption, plasmapheresis, or rituximab.2
Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting CD20+ B cells, leading to decreased antibody production, which has been shown to be effective in treating severe and refractory cases of pemphigus foliaceus.6,13Rituximab with short-course prednisone has been found to be more effective in achieving complete remission at 24 months than prednisone alone.14 In patients with contraindications to systemic glucocorticoid therapy, rituximab has been shown as an effective first-line therapy.15 One-quarter of patients treated with rituximab relapsed within 2 years of treatment6 (average time to relapse, 6–26 months).16 High-dose rituximab regimens, along with a higher number of rituximab treatment cycles, have been shown to prolong time to relapse.6 Further, higher baseline levels of Dsg-1 antibody have been correlated to earlier relapse and can be used following rituximab therapy to monitor disease progression.6,16
The differential diagnosis for pemphigus foliaceous includes disseminated blastomycosis, hypertrophic lupus erythematosus, sebopsoriasis, and secondary syphilis. Disseminated blastomycosis presents with cutaneous manifestations such as nodules, papules, or pustules evolving over weeks to months into ulcers with subsequent scarring.17 Hypertrophic lupus erythematosus presents with papules and nodules with associated keratotic scaling on the face, palms, and extensor surfaces of the limbs.18 Sebopsoriasis is characterized by well-defined lesions with an overlying scale distributed on the scalp, face, and chest.19 Secondary syphilis presents as early hyperpigmented macules transitioning to acral papulosquamous lesions involving the palms and soles.20
- Hans-Filho G, Aoki V, Hans Bittner NR, et al. Fogo selvagem: endemic pemphigus foliaceus. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:638-650.
- Jenson KK, Burr DM, Edwards BC. Case report: reatment of refractory pemphigus foliaceus with rituximab. Practical Dermatology. February 2016:33-36. Accessed August 27, 2021. https://practicaldermatology.com/articles/2016-feb/case-report -treatment-of-refractory-pemphigus-foliaceus-with-rituximab -financial-matters-aad-asds-resources
- Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Green KJ, et al. Antigen-specific immunoadsorption of pathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;104:895-901.
- Mahoney MG, Wang Z, Rothenberger K, et al. Explanations for the clinical and microscopic localization of lesions in pemphigus foliaceus and vulgaris. J Clin Invest. 1999;103:461-468.
- Oktarina DAM, Sokol E, Kramer D, et al. Endocytosis of IgG, desmoglein 1, and plakoglobin in pemphigus foliaceus patient skin. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1-12.
- Kraft M, Worm M. Pemphigus foliaceus-repeated treatment with rituximab 7 years after initial response: a case report. Front Med. 2018;5:315.
- Hale EK. Pemphigus foliaceous. Dermatol Online J. 2002;8:9.
- Tavakolpour S. Pemphigus trigger factors: special focus on pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2018;310:95-106.
- A boobaker J, Morar N, Ramdial PK, et al. Pemphigus in South Africa. Int J Dermatol. 2001;40:115-119.
- Austin E, Millsop JW, Ely H, et al. Psoriasiform pemphigus foliaceus in an African American female: an important clinical manifestation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:471.
- Arbache ST, Nogueira TG, Delgado L, et al. Immunofluorescence testing in the diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases: overview of 10-year experience. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:885-889.
- Sabolinski ML, Beutner EH, Krasny S, et al. Substrate specificity of antiepithelial antibodies of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus sera in immunofluorescence tests on monkey and guinea pig esophagus sections. J Invest Dermatol. 1987;88:545-549.
- Palacios-Álvarez I, Riquelme-McLoughlin C, Curto-Barredo L, et al. Rituximab treatment of pemphigus foliaceus: a retrospective study of 12 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:484-486.
- Murrell DF, Sprecher E. Rituximab and short-course prednisone as the new gold standard for new-onset pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:1143-1144.
- Gregoriou S, Efthymiou O, Stefanaki C, et al. Management of pemphigus vulgaris: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:521-527.
- Saleh MA. A prospective study comparing patients with early and late relapsing pemphigus treated with rituximab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:97-103.
- Castillo CG, Kauffman CA, Miceli MH. Blastomycosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016;30:247-264.
- Herzum A, Gasparini G, Emanuele C, et al. Atypical and rare forms of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: the importance of the diagnosis for the best management of patients. Dermatology. 2013;1-10.
- Tull TJ, Noy M, Bunker CB, et al. Sebopsoriasis in patients with HIV: a case series of 20 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2016; 173:813-815.
- Balagula Y, Mattei P, Wisco OJ, et al. The great imitator revised: the spectrum of atypical cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1434-1441.
The Diagnosis: Pemphigus Foliaceous
Laboratory workup including a complete blood cell count with differential, comprehensive metabolic panel, antinuclear antibodies, Sjögren syndrome A and B antibodies, hepatitis profile, rapid plasma reagin, HIV screen, aldolase, anti–Jo-1, T-Spot TB test (Quest Diagnostics), and tissue cultures was unremarkable. Two 4-mm punch biopsies were obtained from the left cheek and upper back, both of which demonstrated intragranular acantholysis suggestive of pemphigus foliaceous (Figure 1A). A subsequent punch biopsy from the right lower abdomen sent for direct immunofluorescence demonstrated netlike positivity of IgG and C3 in the upper epidermis (Figure 1B), and serum sent for indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated intercellular IgG antibodies to desmoglein (Dsg) 1 on monkey esophagus and positive Dsg-1 antibodies on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, confirming the diagnosis.

The patient was started on a 60-mg prednisone taper as well as dapsone 50 mg daily; the dapsone was titrated up to 100 mg daily. After tapering down to 10 mg daily of prednisone over 2 months and continuing dapsone with minimal improvement, he was given 2 infusions of rituximab 1000 mg 2 weeks apart. The scalp plaque was dramatically improved at 3-month follow-up (Figure 2), with partial improvement of the cheek plaques (Figure 3). Dapsone was increased to 150 mg daily, and he was encouraged to use triamcinolone acetonide ointment 0.1% twice daily, which led to further improvement.


Pemphigus foliaceus is an autoimmune blistering disease that most commonly occurs in middle-aged adults. It generally is less common than pemphigus vulgaris, except in Finland, Tunisia, and Brazil, where there is an endemic condition with an identical clinical and histological presentation known as fogo selvagem.1
The pathogenesis of pemphigus foliaceous is characterized by IgG autoantibodies against Dsg-1, a transmembrane glycoprotein involved in the cellular adhesion of keratinocytes, which is preferentially expressed in the superficial epidermis.2-7 Dysfunction of Dsg-1 results in the separation of superficial epidermal cells, resulting in intraepidermal blisters.2,7 In contrast to pemphigus vulgaris, there typically is a lack of oral mucosal involvement due to compensation by Dsg-3 in the mucosa.4 Potential triggers for pemphigus foliaceous include exposure to UV radiation; radiotherapy; pregnancy; physiologic stress; and drugs, most commonly captopril, penicillamine, and thiols.8
Pemphigus foliaceous lesions clinically appear as eroded and crusted lesions on an erythematous base, commonly in a seborrheic distribution on the face, scalp, and trunk with sparing of the oral mucosa,2,6 but lesions can progress to a widespread and more severe exfoliative dermatitis.7 Lesions also can appear as psoriasiform plaques and often are initially misdiagnosed as psoriasis, particularly in patients with skin of color.9,10
Diagnosis of pemphigus foliaceous typically is made using a combination of histology as well as both direct and indirect immunofluorescence. Histologically, pemphigus foliaceus presents with subcorneal acantholysis, which is most prominent in the granular layer and occasionally the presence of neutrophils and eosinophils in the blister cavity.7 Direct immunofluorescence demonstrates netlike intercellular IgG and C3 in the upper portion of the epidermis.11 Indirect immunofluorescence can help detect circulating IgG antibodies to Dsg-1, with guinea pig esophagus being the ideal substrate.11,12
First-line treatment of pemphigus foliaceus consists of systemic glucocorticoid therapy, often administered with azathioprine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil.2,6,13 Although first-line treatment is effective in 60% to 80% of patients,2 relapsing cases can be treated with cyclophosphamide, intravenous immunoglobulin, immunoadsorption, plasmapheresis, or rituximab.2
Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting CD20+ B cells, leading to decreased antibody production, which has been shown to be effective in treating severe and refractory cases of pemphigus foliaceus.6,13Rituximab with short-course prednisone has been found to be more effective in achieving complete remission at 24 months than prednisone alone.14 In patients with contraindications to systemic glucocorticoid therapy, rituximab has been shown as an effective first-line therapy.15 One-quarter of patients treated with rituximab relapsed within 2 years of treatment6 (average time to relapse, 6–26 months).16 High-dose rituximab regimens, along with a higher number of rituximab treatment cycles, have been shown to prolong time to relapse.6 Further, higher baseline levels of Dsg-1 antibody have been correlated to earlier relapse and can be used following rituximab therapy to monitor disease progression.6,16
The differential diagnosis for pemphigus foliaceous includes disseminated blastomycosis, hypertrophic lupus erythematosus, sebopsoriasis, and secondary syphilis. Disseminated blastomycosis presents with cutaneous manifestations such as nodules, papules, or pustules evolving over weeks to months into ulcers with subsequent scarring.17 Hypertrophic lupus erythematosus presents with papules and nodules with associated keratotic scaling on the face, palms, and extensor surfaces of the limbs.18 Sebopsoriasis is characterized by well-defined lesions with an overlying scale distributed on the scalp, face, and chest.19 Secondary syphilis presents as early hyperpigmented macules transitioning to acral papulosquamous lesions involving the palms and soles.20
The Diagnosis: Pemphigus Foliaceous
Laboratory workup including a complete blood cell count with differential, comprehensive metabolic panel, antinuclear antibodies, Sjögren syndrome A and B antibodies, hepatitis profile, rapid plasma reagin, HIV screen, aldolase, anti–Jo-1, T-Spot TB test (Quest Diagnostics), and tissue cultures was unremarkable. Two 4-mm punch biopsies were obtained from the left cheek and upper back, both of which demonstrated intragranular acantholysis suggestive of pemphigus foliaceous (Figure 1A). A subsequent punch biopsy from the right lower abdomen sent for direct immunofluorescence demonstrated netlike positivity of IgG and C3 in the upper epidermis (Figure 1B), and serum sent for indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated intercellular IgG antibodies to desmoglein (Dsg) 1 on monkey esophagus and positive Dsg-1 antibodies on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, confirming the diagnosis.

The patient was started on a 60-mg prednisone taper as well as dapsone 50 mg daily; the dapsone was titrated up to 100 mg daily. After tapering down to 10 mg daily of prednisone over 2 months and continuing dapsone with minimal improvement, he was given 2 infusions of rituximab 1000 mg 2 weeks apart. The scalp plaque was dramatically improved at 3-month follow-up (Figure 2), with partial improvement of the cheek plaques (Figure 3). Dapsone was increased to 150 mg daily, and he was encouraged to use triamcinolone acetonide ointment 0.1% twice daily, which led to further improvement.


Pemphigus foliaceus is an autoimmune blistering disease that most commonly occurs in middle-aged adults. It generally is less common than pemphigus vulgaris, except in Finland, Tunisia, and Brazil, where there is an endemic condition with an identical clinical and histological presentation known as fogo selvagem.1
The pathogenesis of pemphigus foliaceous is characterized by IgG autoantibodies against Dsg-1, a transmembrane glycoprotein involved in the cellular adhesion of keratinocytes, which is preferentially expressed in the superficial epidermis.2-7 Dysfunction of Dsg-1 results in the separation of superficial epidermal cells, resulting in intraepidermal blisters.2,7 In contrast to pemphigus vulgaris, there typically is a lack of oral mucosal involvement due to compensation by Dsg-3 in the mucosa.4 Potential triggers for pemphigus foliaceous include exposure to UV radiation; radiotherapy; pregnancy; physiologic stress; and drugs, most commonly captopril, penicillamine, and thiols.8
Pemphigus foliaceous lesions clinically appear as eroded and crusted lesions on an erythematous base, commonly in a seborrheic distribution on the face, scalp, and trunk with sparing of the oral mucosa,2,6 but lesions can progress to a widespread and more severe exfoliative dermatitis.7 Lesions also can appear as psoriasiform plaques and often are initially misdiagnosed as psoriasis, particularly in patients with skin of color.9,10
Diagnosis of pemphigus foliaceous typically is made using a combination of histology as well as both direct and indirect immunofluorescence. Histologically, pemphigus foliaceus presents with subcorneal acantholysis, which is most prominent in the granular layer and occasionally the presence of neutrophils and eosinophils in the blister cavity.7 Direct immunofluorescence demonstrates netlike intercellular IgG and C3 in the upper portion of the epidermis.11 Indirect immunofluorescence can help detect circulating IgG antibodies to Dsg-1, with guinea pig esophagus being the ideal substrate.11,12
First-line treatment of pemphigus foliaceus consists of systemic glucocorticoid therapy, often administered with azathioprine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil.2,6,13 Although first-line treatment is effective in 60% to 80% of patients,2 relapsing cases can be treated with cyclophosphamide, intravenous immunoglobulin, immunoadsorption, plasmapheresis, or rituximab.2
Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting CD20+ B cells, leading to decreased antibody production, which has been shown to be effective in treating severe and refractory cases of pemphigus foliaceus.6,13Rituximab with short-course prednisone has been found to be more effective in achieving complete remission at 24 months than prednisone alone.14 In patients with contraindications to systemic glucocorticoid therapy, rituximab has been shown as an effective first-line therapy.15 One-quarter of patients treated with rituximab relapsed within 2 years of treatment6 (average time to relapse, 6–26 months).16 High-dose rituximab regimens, along with a higher number of rituximab treatment cycles, have been shown to prolong time to relapse.6 Further, higher baseline levels of Dsg-1 antibody have been correlated to earlier relapse and can be used following rituximab therapy to monitor disease progression.6,16
The differential diagnosis for pemphigus foliaceous includes disseminated blastomycosis, hypertrophic lupus erythematosus, sebopsoriasis, and secondary syphilis. Disseminated blastomycosis presents with cutaneous manifestations such as nodules, papules, or pustules evolving over weeks to months into ulcers with subsequent scarring.17 Hypertrophic lupus erythematosus presents with papules and nodules with associated keratotic scaling on the face, palms, and extensor surfaces of the limbs.18 Sebopsoriasis is characterized by well-defined lesions with an overlying scale distributed on the scalp, face, and chest.19 Secondary syphilis presents as early hyperpigmented macules transitioning to acral papulosquamous lesions involving the palms and soles.20
- Hans-Filho G, Aoki V, Hans Bittner NR, et al. Fogo selvagem: endemic pemphigus foliaceus. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:638-650.
- Jenson KK, Burr DM, Edwards BC. Case report: reatment of refractory pemphigus foliaceus with rituximab. Practical Dermatology. February 2016:33-36. Accessed August 27, 2021. https://practicaldermatology.com/articles/2016-feb/case-report -treatment-of-refractory-pemphigus-foliaceus-with-rituximab -financial-matters-aad-asds-resources
- Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Green KJ, et al. Antigen-specific immunoadsorption of pathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;104:895-901.
- Mahoney MG, Wang Z, Rothenberger K, et al. Explanations for the clinical and microscopic localization of lesions in pemphigus foliaceus and vulgaris. J Clin Invest. 1999;103:461-468.
- Oktarina DAM, Sokol E, Kramer D, et al. Endocytosis of IgG, desmoglein 1, and plakoglobin in pemphigus foliaceus patient skin. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1-12.
- Kraft M, Worm M. Pemphigus foliaceus-repeated treatment with rituximab 7 years after initial response: a case report. Front Med. 2018;5:315.
- Hale EK. Pemphigus foliaceous. Dermatol Online J. 2002;8:9.
- Tavakolpour S. Pemphigus trigger factors: special focus on pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2018;310:95-106.
- A boobaker J, Morar N, Ramdial PK, et al. Pemphigus in South Africa. Int J Dermatol. 2001;40:115-119.
- Austin E, Millsop JW, Ely H, et al. Psoriasiform pemphigus foliaceus in an African American female: an important clinical manifestation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:471.
- Arbache ST, Nogueira TG, Delgado L, et al. Immunofluorescence testing in the diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases: overview of 10-year experience. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:885-889.
- Sabolinski ML, Beutner EH, Krasny S, et al. Substrate specificity of antiepithelial antibodies of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus sera in immunofluorescence tests on monkey and guinea pig esophagus sections. J Invest Dermatol. 1987;88:545-549.
- Palacios-Álvarez I, Riquelme-McLoughlin C, Curto-Barredo L, et al. Rituximab treatment of pemphigus foliaceus: a retrospective study of 12 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:484-486.
- Murrell DF, Sprecher E. Rituximab and short-course prednisone as the new gold standard for new-onset pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:1143-1144.
- Gregoriou S, Efthymiou O, Stefanaki C, et al. Management of pemphigus vulgaris: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:521-527.
- Saleh MA. A prospective study comparing patients with early and late relapsing pemphigus treated with rituximab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:97-103.
- Castillo CG, Kauffman CA, Miceli MH. Blastomycosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016;30:247-264.
- Herzum A, Gasparini G, Emanuele C, et al. Atypical and rare forms of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: the importance of the diagnosis for the best management of patients. Dermatology. 2013;1-10.
- Tull TJ, Noy M, Bunker CB, et al. Sebopsoriasis in patients with HIV: a case series of 20 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2016; 173:813-815.
- Balagula Y, Mattei P, Wisco OJ, et al. The great imitator revised: the spectrum of atypical cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1434-1441.
- Hans-Filho G, Aoki V, Hans Bittner NR, et al. Fogo selvagem: endemic pemphigus foliaceus. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:638-650.
- Jenson KK, Burr DM, Edwards BC. Case report: reatment of refractory pemphigus foliaceus with rituximab. Practical Dermatology. February 2016:33-36. Accessed August 27, 2021. https://practicaldermatology.com/articles/2016-feb/case-report -treatment-of-refractory-pemphigus-foliaceus-with-rituximab -financial-matters-aad-asds-resources
- Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Green KJ, et al. Antigen-specific immunoadsorption of pathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;104:895-901.
- Mahoney MG, Wang Z, Rothenberger K, et al. Explanations for the clinical and microscopic localization of lesions in pemphigus foliaceus and vulgaris. J Clin Invest. 1999;103:461-468.
- Oktarina DAM, Sokol E, Kramer D, et al. Endocytosis of IgG, desmoglein 1, and plakoglobin in pemphigus foliaceus patient skin. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1-12.
- Kraft M, Worm M. Pemphigus foliaceus-repeated treatment with rituximab 7 years after initial response: a case report. Front Med. 2018;5:315.
- Hale EK. Pemphigus foliaceous. Dermatol Online J. 2002;8:9.
- Tavakolpour S. Pemphigus trigger factors: special focus on pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2018;310:95-106.
- A boobaker J, Morar N, Ramdial PK, et al. Pemphigus in South Africa. Int J Dermatol. 2001;40:115-119.
- Austin E, Millsop JW, Ely H, et al. Psoriasiform pemphigus foliaceus in an African American female: an important clinical manifestation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:471.
- Arbache ST, Nogueira TG, Delgado L, et al. Immunofluorescence testing in the diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases: overview of 10-year experience. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:885-889.
- Sabolinski ML, Beutner EH, Krasny S, et al. Substrate specificity of antiepithelial antibodies of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus sera in immunofluorescence tests on monkey and guinea pig esophagus sections. J Invest Dermatol. 1987;88:545-549.
- Palacios-Álvarez I, Riquelme-McLoughlin C, Curto-Barredo L, et al. Rituximab treatment of pemphigus foliaceus: a retrospective study of 12 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:484-486.
- Murrell DF, Sprecher E. Rituximab and short-course prednisone as the new gold standard for new-onset pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:1143-1144.
- Gregoriou S, Efthymiou O, Stefanaki C, et al. Management of pemphigus vulgaris: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:521-527.
- Saleh MA. A prospective study comparing patients with early and late relapsing pemphigus treated with rituximab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:97-103.
- Castillo CG, Kauffman CA, Miceli MH. Blastomycosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016;30:247-264.
- Herzum A, Gasparini G, Emanuele C, et al. Atypical and rare forms of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: the importance of the diagnosis for the best management of patients. Dermatology. 2013;1-10.
- Tull TJ, Noy M, Bunker CB, et al. Sebopsoriasis in patients with HIV: a case series of 20 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2016; 173:813-815.
- Balagula Y, Mattei P, Wisco OJ, et al. The great imitator revised: the spectrum of atypical cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1434-1441.
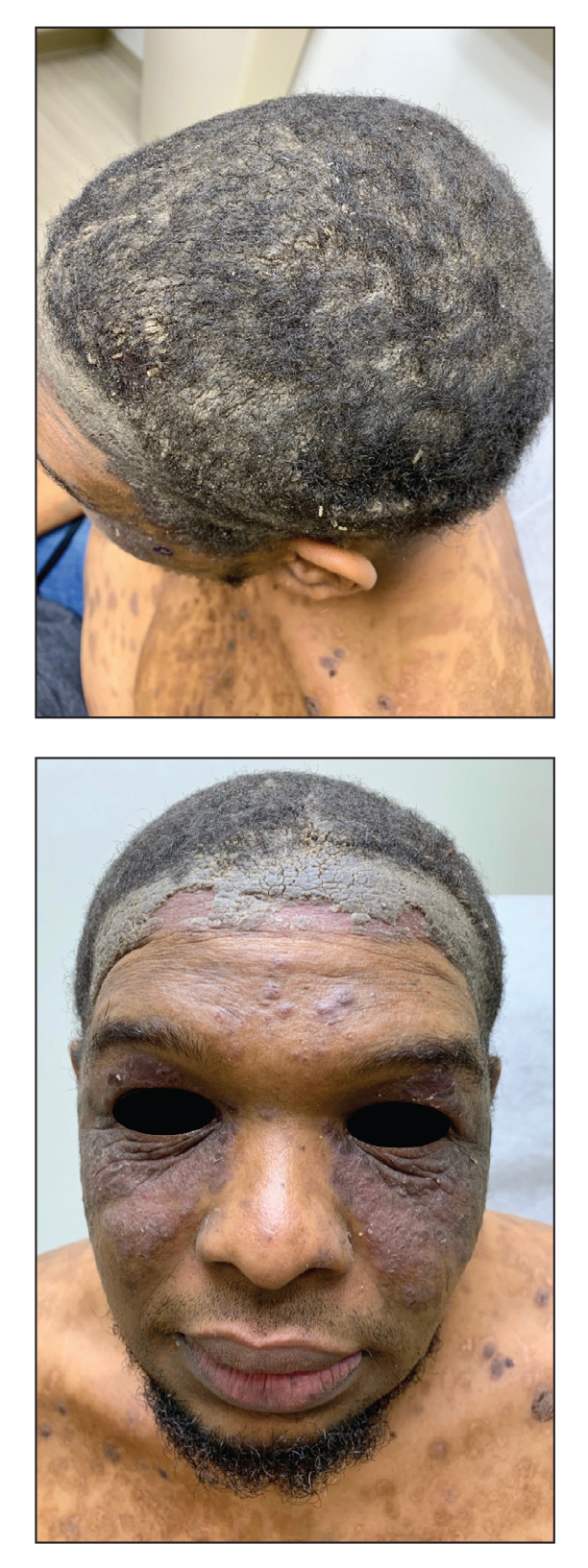
A 40-year-old Black man presented for evaluation of a thick plaque throughout the scalp (top), scaly plaques on the cheeks (bottom), and a spreading rash on the trunk that had progressed over the last few months. He had no relevant medical history, took no medications, and was in a monogamous relationship with a female partner. He previously saw an outside dermatologist who gave him triamcinolone cream, which was mildly helpful. Physical examination revealed a thick verrucous plaque throughout the scalp extending onto the forehead; thick plaques on the cheeks; and numerous, thinly eroded lesions on the trunk. Biopsies and a laboratory workup were performed.
Cutaneous Protothecosis
To the Editor:
Protothecosis infections are caused by an achlorophyllic algae of the species Prototheca. Prototheca organisms are found mostly in soil and water.1 Human infections are rare and involve 2 species, Prototheca wickerhamii and Prototheca zopfii. The former most commonly is responsible for human infections, though P zopfii results in more serious systemic infections with a poor prognosis. There are various types of Prototheca infection presentations, with a 2007 review of 117 cases reporting that cutaneous infections are most common (66%), followed by systemic infections (19%), and olecranon bursitis (15%).2 Skin lesions most commonly occur on the extremities and face, and they present as vesiculobullous and ulcerative lesions with purulent drainage. The skin lesions also may appear as erythematous plaques or nodules, subcutaneous papules, verrucous or herpetiformis lesions, or pyogenic granuloma–like lesions.3 Protothecosis typically affects immunocompromised individuals, especially those with a history of chronic corticosteroid use, malignancy, diabetes mellitus, AIDS, and/or organ transplant.1 We present a case of cutaneous protothecosis on the dorsal distal extremity of a 94-year-old woman. History of exposure to soil while gardening was elicited from the patient, and no immunosuppressive history was present aside from the patient’s age. This case may prompt workup for malignancy or immunosuppression in this patient subset.
A 94-year-old woman with a medical history of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) presented with a growing lesion on the dorsal surface of the left fourth digit of 2 months’ duration. The patient reported the lesion was painful, and she noted preceding trauma to the area that was suspected to have occurred while gardening. Physical examination revealed an ulcerated, hypertrophic, erythematous nodule on the dorsal surface of the left fourth metacarpophalangeal joint. The differential diagnosis included SCC, inflamed cyst, verruca vulgaris, and orf virus due to the clinical presentation. A shave biopsy was performed, and the lesion subsequently was treated with electrodesiccation and curettage.
Histopathologic evaluation revealed pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with a mixed inflammatory infiltrate including lymphocytes and histiocytes. A morula within the dermis was characteristic of a protothecosis infection (Figure 1). On follow-up visit 6 weeks later, the lesion had grown back to its original size and morphology (Figure 2). At this time, the lesion was again treated with shave removal, followed by electrodesiccation and curettage, and the patient was placed on oral fluconazole 200 mg daily for 1 month. When the lesion did not resolve with fluconazole, she was referred to infectious disease as well as general surgery for surgical removal and debridement of the lesion. Unfortunately, the patient was lost to follow-up.
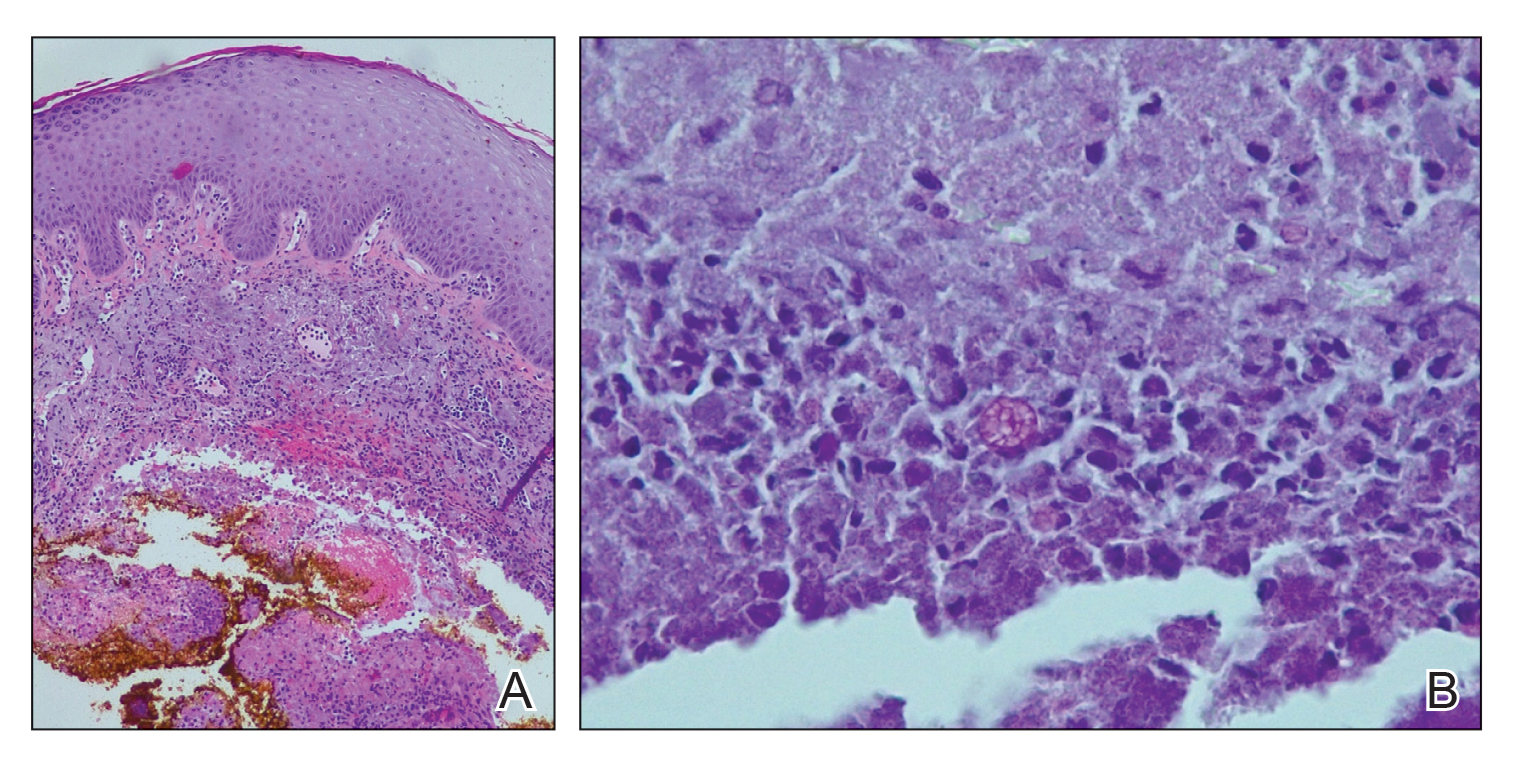
Protothecosis is an infectious disease comprised of achlorophyllic algae found in soil and water that rarely affects humans. When it does affect humans, cutaneous infections are most common. All human cases in which organisms were identified to species level have been caused by P wickerhamii or P zopfii species.2 Inoculation is suspected to occur through trauma to affected skin, especially when in the context of contaminated water. Our patient reported history of trauma to the hand, with soil from gardening as the potential aquagenic source of the infection.

The clinical presentation of protothecosis ranges from localized cutaneous to disseminated systemic infections, with most reported cases of systemic disease occurring in immunocompromised individuals. The cutaneous lesions of protothecosis vary greatly in clinical appearance including ulcerative nodules (as in our case), papules, plaques, pustules, and vesicles with erosion or crusting.4
Cutaneous protothecosis has the potential to mimic many other skin diseases and lesions, and, given its rarity, it may not be on the radar of dermatologists. Our patient’s lesion was presumed to be a skin cancer and was treated as such because of the history of SCC and clinical presentation. Although excision of individual lesions of protothecosis can be curative, electrodesiccation and curettage does not appear to be an adequate treatment, as the lesion subsequently recurred. It also is possible that this case represents P zopfii infection, as it did not respond to treatment with oral fluconazole, though in vitro studies with fluconazole to both P zopfii and P wickerhamii had variable treatment success.2 Also, the histopathologic findings were most consistent with P wickerhamii, revealing small, round, symmetrical morula, compared to P zopfii, which typically will display oval or cylindrical, asymmetrical, random internal segmentation.5 This case may warrant determination of species, which can be accomplished by a culture on Sabouraud dextrose agar, carbohydrate and alcohol assimilation test, yeast biochemical card, serological typing by immunoblotting, immunofluorescence study using species-specific antibodies, or amplification by polymerase chain reaction for small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences.2,6-8
The natural history of isolated skin disease is an indolent progressive course; however, reports do exist noting spontaneous resolution.4,9 Treatment options for Prototheca infections can be disappointing and consist of both surgical and medical management, or a combination of the 2 approaches. Reports in the literature support the use of antifungals including ketoconazole, voriconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, and amphotericin B, with the latter displaying the best activity against Prototheca species.2 Tetracycline has been used in combination with oral or topical amphotericin B and was found to be synergistic in vitro and in case reports at successfully treating cutaneous protothecosis infections. It is possible that our patient was not treated with fluconazole long enough for it to become therapeutic, as most reported treatment regimens are weeks to months in length. Conversely, it may have been of benefit to transition the patient to topical amphotericin B and tetracycline, as fluconazole failed in this patient. However, treatment successes and failures are limited to case reports/case series and in vitro studies, with prospective studies lacking. Due to the variability with in vitro susceptibility profiles for Prototheca species, it generally is not recommended to pursue in vitro susceptibility testing in the management of Prototheca skin infections due to the inconsistency demonstrated between in vitro activity and clinical response to therapy.2
- Silva PC, Costa e Silva SB, Lima RB, et al. Cutaneous protothecosis—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:183-185.
- Lass-Flörl C, Mayr A. Human protothecosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007;20:230-242.
- Seok JY, Lee Y, Lee H, et al. Human cutaneous protothecosis: report of a case and literature review. Korean J Pathol. 2013;47:575-578.
- Mayorga J, Barba-Gómez JF, Verduzco-Martínez AP, et al. Protothecosis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:432-436.
- Walsh SV, Johnson RA, Tahan SR. Protothecosis: an unusual cause of chronic subcutaneous and soft tissue infection. Am J Dermatopathol. 1998;20:379-382.
- Casal MJ, Gutierrez J. Simple new test for rapid differentiation of Prototheca wickerhamii from Prototheca zopfii. J Clin Microbiol. 1983;18:992-993.
- Arnold, P, Ahearn, DG. The systematics of the genus Prototheca with a description of a new species P. filamenta. Mycologia 1972;64:265-275.
- Roesler U, Scholz H, Hensel H. Emended phenotypic characterization of Prototheca zopfii: a proposal for three biotypes and standards for their identification. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2003;53:1195-1199.
- Todd JR, King JW, Oberle A, et al. Protothecosis: report of a case with 20-year follow-up, and review of previously published cases. Med Mycol. 2012;50:673-689.
To the Editor:
Protothecosis infections are caused by an achlorophyllic algae of the species Prototheca. Prototheca organisms are found mostly in soil and water.1 Human infections are rare and involve 2 species, Prototheca wickerhamii and Prototheca zopfii. The former most commonly is responsible for human infections, though P zopfii results in more serious systemic infections with a poor prognosis. There are various types of Prototheca infection presentations, with a 2007 review of 117 cases reporting that cutaneous infections are most common (66%), followed by systemic infections (19%), and olecranon bursitis (15%).2 Skin lesions most commonly occur on the extremities and face, and they present as vesiculobullous and ulcerative lesions with purulent drainage. The skin lesions also may appear as erythematous plaques or nodules, subcutaneous papules, verrucous or herpetiformis lesions, or pyogenic granuloma–like lesions.3 Protothecosis typically affects immunocompromised individuals, especially those with a history of chronic corticosteroid use, malignancy, diabetes mellitus, AIDS, and/or organ transplant.1 We present a case of cutaneous protothecosis on the dorsal distal extremity of a 94-year-old woman. History of exposure to soil while gardening was elicited from the patient, and no immunosuppressive history was present aside from the patient’s age. This case may prompt workup for malignancy or immunosuppression in this patient subset.
A 94-year-old woman with a medical history of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) presented with a growing lesion on the dorsal surface of the left fourth digit of 2 months’ duration. The patient reported the lesion was painful, and she noted preceding trauma to the area that was suspected to have occurred while gardening. Physical examination revealed an ulcerated, hypertrophic, erythematous nodule on the dorsal surface of the left fourth metacarpophalangeal joint. The differential diagnosis included SCC, inflamed cyst, verruca vulgaris, and orf virus due to the clinical presentation. A shave biopsy was performed, and the lesion subsequently was treated with electrodesiccation and curettage.
Histopathologic evaluation revealed pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with a mixed inflammatory infiltrate including lymphocytes and histiocytes. A morula within the dermis was characteristic of a protothecosis infection (Figure 1). On follow-up visit 6 weeks later, the lesion had grown back to its original size and morphology (Figure 2). At this time, the lesion was again treated with shave removal, followed by electrodesiccation and curettage, and the patient was placed on oral fluconazole 200 mg daily for 1 month. When the lesion did not resolve with fluconazole, she was referred to infectious disease as well as general surgery for surgical removal and debridement of the lesion. Unfortunately, the patient was lost to follow-up.

Protothecosis is an infectious disease comprised of achlorophyllic algae found in soil and water that rarely affects humans. When it does affect humans, cutaneous infections are most common. All human cases in which organisms were identified to species level have been caused by P wickerhamii or P zopfii species.2 Inoculation is suspected to occur through trauma to affected skin, especially when in the context of contaminated water. Our patient reported history of trauma to the hand, with soil from gardening as the potential aquagenic source of the infection.

The clinical presentation of protothecosis ranges from localized cutaneous to disseminated systemic infections, with most reported cases of systemic disease occurring in immunocompromised individuals. The cutaneous lesions of protothecosis vary greatly in clinical appearance including ulcerative nodules (as in our case), papules, plaques, pustules, and vesicles with erosion or crusting.4
Cutaneous protothecosis has the potential to mimic many other skin diseases and lesions, and, given its rarity, it may not be on the radar of dermatologists. Our patient’s lesion was presumed to be a skin cancer and was treated as such because of the history of SCC and clinical presentation. Although excision of individual lesions of protothecosis can be curative, electrodesiccation and curettage does not appear to be an adequate treatment, as the lesion subsequently recurred. It also is possible that this case represents P zopfii infection, as it did not respond to treatment with oral fluconazole, though in vitro studies with fluconazole to both P zopfii and P wickerhamii had variable treatment success.2 Also, the histopathologic findings were most consistent with P wickerhamii, revealing small, round, symmetrical morula, compared to P zopfii, which typically will display oval or cylindrical, asymmetrical, random internal segmentation.5 This case may warrant determination of species, which can be accomplished by a culture on Sabouraud dextrose agar, carbohydrate and alcohol assimilation test, yeast biochemical card, serological typing by immunoblotting, immunofluorescence study using species-specific antibodies, or amplification by polymerase chain reaction for small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences.2,6-8
The natural history of isolated skin disease is an indolent progressive course; however, reports do exist noting spontaneous resolution.4,9 Treatment options for Prototheca infections can be disappointing and consist of both surgical and medical management, or a combination of the 2 approaches. Reports in the literature support the use of antifungals including ketoconazole, voriconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, and amphotericin B, with the latter displaying the best activity against Prototheca species.2 Tetracycline has been used in combination with oral or topical amphotericin B and was found to be synergistic in vitro and in case reports at successfully treating cutaneous protothecosis infections. It is possible that our patient was not treated with fluconazole long enough for it to become therapeutic, as most reported treatment regimens are weeks to months in length. Conversely, it may have been of benefit to transition the patient to topical amphotericin B and tetracycline, as fluconazole failed in this patient. However, treatment successes and failures are limited to case reports/case series and in vitro studies, with prospective studies lacking. Due to the variability with in vitro susceptibility profiles for Prototheca species, it generally is not recommended to pursue in vitro susceptibility testing in the management of Prototheca skin infections due to the inconsistency demonstrated between in vitro activity and clinical response to therapy.2
To the Editor:
Protothecosis infections are caused by an achlorophyllic algae of the species Prototheca. Prototheca organisms are found mostly in soil and water.1 Human infections are rare and involve 2 species, Prototheca wickerhamii and Prototheca zopfii. The former most commonly is responsible for human infections, though P zopfii results in more serious systemic infections with a poor prognosis. There are various types of Prototheca infection presentations, with a 2007 review of 117 cases reporting that cutaneous infections are most common (66%), followed by systemic infections (19%), and olecranon bursitis (15%).2 Skin lesions most commonly occur on the extremities and face, and they present as vesiculobullous and ulcerative lesions with purulent drainage. The skin lesions also may appear as erythematous plaques or nodules, subcutaneous papules, verrucous or herpetiformis lesions, or pyogenic granuloma–like lesions.3 Protothecosis typically affects immunocompromised individuals, especially those with a history of chronic corticosteroid use, malignancy, diabetes mellitus, AIDS, and/or organ transplant.1 We present a case of cutaneous protothecosis on the dorsal distal extremity of a 94-year-old woman. History of exposure to soil while gardening was elicited from the patient, and no immunosuppressive history was present aside from the patient’s age. This case may prompt workup for malignancy or immunosuppression in this patient subset.
A 94-year-old woman with a medical history of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) presented with a growing lesion on the dorsal surface of the left fourth digit of 2 months’ duration. The patient reported the lesion was painful, and she noted preceding trauma to the area that was suspected to have occurred while gardening. Physical examination revealed an ulcerated, hypertrophic, erythematous nodule on the dorsal surface of the left fourth metacarpophalangeal joint. The differential diagnosis included SCC, inflamed cyst, verruca vulgaris, and orf virus due to the clinical presentation. A shave biopsy was performed, and the lesion subsequently was treated with electrodesiccation and curettage.
Histopathologic evaluation revealed pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with a mixed inflammatory infiltrate including lymphocytes and histiocytes. A morula within the dermis was characteristic of a protothecosis infection (Figure 1). On follow-up visit 6 weeks later, the lesion had grown back to its original size and morphology (Figure 2). At this time, the lesion was again treated with shave removal, followed by electrodesiccation and curettage, and the patient was placed on oral fluconazole 200 mg daily for 1 month. When the lesion did not resolve with fluconazole, she was referred to infectious disease as well as general surgery for surgical removal and debridement of the lesion. Unfortunately, the patient was lost to follow-up.

Protothecosis is an infectious disease comprised of achlorophyllic algae found in soil and water that rarely affects humans. When it does affect humans, cutaneous infections are most common. All human cases in which organisms were identified to species level have been caused by P wickerhamii or P zopfii species.2 Inoculation is suspected to occur through trauma to affected skin, especially when in the context of contaminated water. Our patient reported history of trauma to the hand, with soil from gardening as the potential aquagenic source of the infection.

The clinical presentation of protothecosis ranges from localized cutaneous to disseminated systemic infections, with most reported cases of systemic disease occurring in immunocompromised individuals. The cutaneous lesions of protothecosis vary greatly in clinical appearance including ulcerative nodules (as in our case), papules, plaques, pustules, and vesicles with erosion or crusting.4
Cutaneous protothecosis has the potential to mimic many other skin diseases and lesions, and, given its rarity, it may not be on the radar of dermatologists. Our patient’s lesion was presumed to be a skin cancer and was treated as such because of the history of SCC and clinical presentation. Although excision of individual lesions of protothecosis can be curative, electrodesiccation and curettage does not appear to be an adequate treatment, as the lesion subsequently recurred. It also is possible that this case represents P zopfii infection, as it did not respond to treatment with oral fluconazole, though in vitro studies with fluconazole to both P zopfii and P wickerhamii had variable treatment success.2 Also, the histopathologic findings were most consistent with P wickerhamii, revealing small, round, symmetrical morula, compared to P zopfii, which typically will display oval or cylindrical, asymmetrical, random internal segmentation.5 This case may warrant determination of species, which can be accomplished by a culture on Sabouraud dextrose agar, carbohydrate and alcohol assimilation test, yeast biochemical card, serological typing by immunoblotting, immunofluorescence study using species-specific antibodies, or amplification by polymerase chain reaction for small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences.2,6-8
The natural history of isolated skin disease is an indolent progressive course; however, reports do exist noting spontaneous resolution.4,9 Treatment options for Prototheca infections can be disappointing and consist of both surgical and medical management, or a combination of the 2 approaches. Reports in the literature support the use of antifungals including ketoconazole, voriconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, and amphotericin B, with the latter displaying the best activity against Prototheca species.2 Tetracycline has been used in combination with oral or topical amphotericin B and was found to be synergistic in vitro and in case reports at successfully treating cutaneous protothecosis infections. It is possible that our patient was not treated with fluconazole long enough for it to become therapeutic, as most reported treatment regimens are weeks to months in length. Conversely, it may have been of benefit to transition the patient to topical amphotericin B and tetracycline, as fluconazole failed in this patient. However, treatment successes and failures are limited to case reports/case series and in vitro studies, with prospective studies lacking. Due to the variability with in vitro susceptibility profiles for Prototheca species, it generally is not recommended to pursue in vitro susceptibility testing in the management of Prototheca skin infections due to the inconsistency demonstrated between in vitro activity and clinical response to therapy.2
- Silva PC, Costa e Silva SB, Lima RB, et al. Cutaneous protothecosis—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:183-185.
- Lass-Flörl C, Mayr A. Human protothecosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007;20:230-242.
- Seok JY, Lee Y, Lee H, et al. Human cutaneous protothecosis: report of a case and literature review. Korean J Pathol. 2013;47:575-578.
- Mayorga J, Barba-Gómez JF, Verduzco-Martínez AP, et al. Protothecosis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:432-436.
- Walsh SV, Johnson RA, Tahan SR. Protothecosis: an unusual cause of chronic subcutaneous and soft tissue infection. Am J Dermatopathol. 1998;20:379-382.
- Casal MJ, Gutierrez J. Simple new test for rapid differentiation of Prototheca wickerhamii from Prototheca zopfii. J Clin Microbiol. 1983;18:992-993.
- Arnold, P, Ahearn, DG. The systematics of the genus Prototheca with a description of a new species P. filamenta. Mycologia 1972;64:265-275.
- Roesler U, Scholz H, Hensel H. Emended phenotypic characterization of Prototheca zopfii: a proposal for three biotypes and standards for their identification. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2003;53:1195-1199.
- Todd JR, King JW, Oberle A, et al. Protothecosis: report of a case with 20-year follow-up, and review of previously published cases. Med Mycol. 2012;50:673-689.
- Silva PC, Costa e Silva SB, Lima RB, et al. Cutaneous protothecosis—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:183-185.
- Lass-Flörl C, Mayr A. Human protothecosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007;20:230-242.
- Seok JY, Lee Y, Lee H, et al. Human cutaneous protothecosis: report of a case and literature review. Korean J Pathol. 2013;47:575-578.
- Mayorga J, Barba-Gómez JF, Verduzco-Martínez AP, et al. Protothecosis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:432-436.
- Walsh SV, Johnson RA, Tahan SR. Protothecosis: an unusual cause of chronic subcutaneous and soft tissue infection. Am J Dermatopathol. 1998;20:379-382.
- Casal MJ, Gutierrez J. Simple new test for rapid differentiation of Prototheca wickerhamii from Prototheca zopfii. J Clin Microbiol. 1983;18:992-993.
- Arnold, P, Ahearn, DG. The systematics of the genus Prototheca with a description of a new species P. filamenta. Mycologia 1972;64:265-275.
- Roesler U, Scholz H, Hensel H. Emended phenotypic characterization of Prototheca zopfii: a proposal for three biotypes and standards for their identification. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2003;53:1195-1199.
- Todd JR, King JW, Oberle A, et al. Protothecosis: report of a case with 20-year follow-up, and review of previously published cases. Med Mycol. 2012;50:673-689.
Practice Points
- Cutaneous protothecosis is a rare skin infection most commonly reported in immunocompromised individuals with recent exposure to contaminated soil or water. Cutaneous protothecosis has the potential to mimic many other skin diseases and lesions, including eczema; nonmelanoma skin cancer; or bacterial, viral, and fungal skin infections.
- A skin biopsy is essential for diagnosis, and histopathology is characteristic with soccer ball–appearing morula noted in a mixed inflammatory infiltrate.
Sudden-Onset Blistering Rash
The Diagnosis: Generalized Bullous Fixed Drug Eruption
A punch biopsy from the left thigh revealed a vacuolar interface dermatitis with full-thickness necrosis of the epidermis and a patchy lichenoid inflammatory cell infiltrate in the superficial dermis consistent with a generalized bullous fixed drug eruption (GBFDE). The patient received supportive care and methylprednisolone with improvement of symptoms.
Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption is a rare, potentially life-threatening form of a fixed drug eruption (FDE), a cutaneous drug reaction that occurs in response to a causative medication. It typically presents with welldemarcated, dusky, erythematous patches or plaques that recur in the same sites with repeat exposure.1 The pathogenesis of FDE has been hypothesized to involve epidermal CD8+ T cells, which are activated by drug exposure and release cytotoxic molecules including Fas, Fas ligand, perforin, and granzyme B, resulting in lysis of the surrounding keratinocytes.1-3 Common eliciting drugs include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibacterial agents (particularly trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole), barbiturates, acetaminophen, and antimalarials.1 In addition to the findings seen in FDE, GBFDE is characterized by widespread bullous skin lesions.1-4 Typical histologic patterns seen in GBFDE are dispersed epidermal apoptotic keratinocytes, prominent dermal eosinophilic and lymphocytic infiltrates, and dermal melanophages.3 Discontinuing the causative agent and diligent prevention of re-exposure are the most important steps in management, as additional exposures can increase the number of lesions and overall severity. Symptoms typically resolve 7 to 14 days after drug discontinuation, often with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.3
Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption presents a diagnostic challenge, as it sometimes involves the oral mucosa and can exhibit the Nikolsky sign. Thus, it often is confused with Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) or toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).1,4 Stevens-Johnson syndrome and TEN are severe cutaneous drug eruptions that also can present with diffuse bullous skin lesions. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and TEN are thought to be a spectrum of the same disease that initially presents with dusky red macules that can coalesce, develop central blistering, and lead to skin detachment.5 Stevens-Johnson syndrome is defined as skin detachment of less than 10% body surface area (BSA); TEN is defined as skin detachment of more than 30% BSA. Stevens-Johnson syndrome/TEN overlap syndrome includes skin detachment of 10% to 30% BSA.5
Causative medications overlap substantially with GBFDE and include anticonvulsants, sulfa-containing drugs, antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and uric acid–lowering agents. The histology of SJS/TEN also is quite similar to GBFDE, and these entities may be indistinguishable without clinical information.5 Lee et al1 found that absence of grouped necrotic keratinocytes (fire flag sign), deep inflammatory infiltrates, notable pigment incontinence, and higher eosinophil counts appear to be more common in GBFDE than SJS/TEN. Constitutional symptoms and mucosal involvement also were more frequent in SJS/TEN.
The timing of clinical presentation and medical history can be useful in differentiating between SJS/TEN and GBFDE. In SJS/TEN, drug exposure typically occurs 1 to 3 weeks before onset of symptoms vs 30 minutes to 24 hours in GBFDE.3 Additionally, a history of similar eruption in the same location is pathognomonic for GBFDE. Although GBFDE has been thought to have a better prognosis than SJS/TEN, more recent data suggest mortality rates may be similar.3 A case-control study found a mortality rate of 22% (13/58) in patients with GBFDE compared to 28% (n=170) in SJS/TEN patients.4
Erythema multiforme (EM) is an uncommon immunemediated disorder that typically presents as targetoid lesions with central epidermal necrosis in an acral distribution. Erythema multiforme can arise from a variety of factors, but up to 90% of cases are due to infection, most commonly herpes simplex virus; medications account for less than 10% of cases.6 Previously, EM has been thought to be on the same disease spectrum as SJS and TEN. It is now clear that EM is a separate entity with similar mucosal erosions but different cutaneous findings,6 mainly typical target lesions that differ from the atypical targets seen in SJS.
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is a blistering skin disorder associated with local Staphylococcus aureus infection. It most commonly is seen in children and rarely occurs in adults who are not on dialysis. Some Staphylococcus strains produce exfoliative toxins A and B, which are serine proteases that target and cleave desmoglein 1, a mediator of keratinocyte adhesion. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome initially presents with erythema accentuated in the skin folds that becomes generalized. The disruption of keratinocyte adhesion leads to bullae formation in areas of erythema and diffuse sheetlike desquamation. Pathology reveals subcorneal rather than subepidermal blistering, which is seen in GBFDE and SJS/TEN. Treatment involves antistaphylococcal antibiotics and supportive care. With proper treatment, most cases resolve within 2 to 3 weeks.7
Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis presents with prominent mucositis and can have cutaneous findings of sparse vesiculobullous or targetoid eruption.8 Mycoplasma pneumoniae typically infects the lungs and is a leading cause of community-acquired pneumonia. However, a subset of patients can have extrapulmonary disease presenting as mucocutaneous eruptions, which is preceded by an approximately weeklong prodrome of fever, cough, and malaise.7 Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis also affect children and young patients and is more common in males.8
- Lee CH, Chen YC, Cho YT, et al. Fixed-drug eruption: a retrospective study in a single referral center in northern Taiwan. Dermatologica Sinica. 2012;30:11-15. doi:10.1016/j.dsi.2012.02.002
- Cho Y-T, Lin J-W, Chen Y-C, et al. Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption is distinct from Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis by immunohistopathological features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:539-548. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.11.015
- Mitre V, Applebaum DS, Albahrani Y, et al. Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption imitating toxic epidermal necrolysis: a case report and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23: 13030/qt25v009gs.
- Lipowicz S, Sekula P, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, et al. Prognosis of generalized bullous fixed drug eruption: comparison with StevensJohnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:726-732. doi:10.1111/bjd.12133
- Cho Y-T, Chu C-Y. Treatments for severe cutaneous adverse reactions [published online December 27, 2017]. J Immunol Res. doi:10.1155/2017/1503709
- Sokumbi O, Wetter DA. Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of erythema multiforme: a review for the practicing dermatologist. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:889-902. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05348.x
- Leung AKC, Barankin B, Leong KF. Staphylococcal-scalded skin syndrome: evaluation, diagnosis, and management. World J Pediatr. 2018;14:116-120.
- Canavan TN, Mathes EF, Frieden I, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis as a syndrome distinct from Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:239-245. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2014.06.026
The Diagnosis: Generalized Bullous Fixed Drug Eruption
A punch biopsy from the left thigh revealed a vacuolar interface dermatitis with full-thickness necrosis of the epidermis and a patchy lichenoid inflammatory cell infiltrate in the superficial dermis consistent with a generalized bullous fixed drug eruption (GBFDE). The patient received supportive care and methylprednisolone with improvement of symptoms.
Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption is a rare, potentially life-threatening form of a fixed drug eruption (FDE), a cutaneous drug reaction that occurs in response to a causative medication. It typically presents with welldemarcated, dusky, erythematous patches or plaques that recur in the same sites with repeat exposure.1 The pathogenesis of FDE has been hypothesized to involve epidermal CD8+ T cells, which are activated by drug exposure and release cytotoxic molecules including Fas, Fas ligand, perforin, and granzyme B, resulting in lysis of the surrounding keratinocytes.1-3 Common eliciting drugs include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibacterial agents (particularly trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole), barbiturates, acetaminophen, and antimalarials.1 In addition to the findings seen in FDE, GBFDE is characterized by widespread bullous skin lesions.1-4 Typical histologic patterns seen in GBFDE are dispersed epidermal apoptotic keratinocytes, prominent dermal eosinophilic and lymphocytic infiltrates, and dermal melanophages.3 Discontinuing the causative agent and diligent prevention of re-exposure are the most important steps in management, as additional exposures can increase the number of lesions and overall severity. Symptoms typically resolve 7 to 14 days after drug discontinuation, often with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.3
Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption presents a diagnostic challenge, as it sometimes involves the oral mucosa and can exhibit the Nikolsky sign. Thus, it often is confused with Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) or toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).1,4 Stevens-Johnson syndrome and TEN are severe cutaneous drug eruptions that also can present with diffuse bullous skin lesions. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and TEN are thought to be a spectrum of the same disease that initially presents with dusky red macules that can coalesce, develop central blistering, and lead to skin detachment.5 Stevens-Johnson syndrome is defined as skin detachment of less than 10% body surface area (BSA); TEN is defined as skin detachment of more than 30% BSA. Stevens-Johnson syndrome/TEN overlap syndrome includes skin detachment of 10% to 30% BSA.5
Causative medications overlap substantially with GBFDE and include anticonvulsants, sulfa-containing drugs, antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and uric acid–lowering agents. The histology of SJS/TEN also is quite similar to GBFDE, and these entities may be indistinguishable without clinical information.5 Lee et al1 found that absence of grouped necrotic keratinocytes (fire flag sign), deep inflammatory infiltrates, notable pigment incontinence, and higher eosinophil counts appear to be more common in GBFDE than SJS/TEN. Constitutional symptoms and mucosal involvement also were more frequent in SJS/TEN.
The timing of clinical presentation and medical history can be useful in differentiating between SJS/TEN and GBFDE. In SJS/TEN, drug exposure typically occurs 1 to 3 weeks before onset of symptoms vs 30 minutes to 24 hours in GBFDE.3 Additionally, a history of similar eruption in the same location is pathognomonic for GBFDE. Although GBFDE has been thought to have a better prognosis than SJS/TEN, more recent data suggest mortality rates may be similar.3 A case-control study found a mortality rate of 22% (13/58) in patients with GBFDE compared to 28% (n=170) in SJS/TEN patients.4
Erythema multiforme (EM) is an uncommon immunemediated disorder that typically presents as targetoid lesions with central epidermal necrosis in an acral distribution. Erythema multiforme can arise from a variety of factors, but up to 90% of cases are due to infection, most commonly herpes simplex virus; medications account for less than 10% of cases.6 Previously, EM has been thought to be on the same disease spectrum as SJS and TEN. It is now clear that EM is a separate entity with similar mucosal erosions but different cutaneous findings,6 mainly typical target lesions that differ from the atypical targets seen in SJS.
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is a blistering skin disorder associated with local Staphylococcus aureus infection. It most commonly is seen in children and rarely occurs in adults who are not on dialysis. Some Staphylococcus strains produce exfoliative toxins A and B, which are serine proteases that target and cleave desmoglein 1, a mediator of keratinocyte adhesion. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome initially presents with erythema accentuated in the skin folds that becomes generalized. The disruption of keratinocyte adhesion leads to bullae formation in areas of erythema and diffuse sheetlike desquamation. Pathology reveals subcorneal rather than subepidermal blistering, which is seen in GBFDE and SJS/TEN. Treatment involves antistaphylococcal antibiotics and supportive care. With proper treatment, most cases resolve within 2 to 3 weeks.7
Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis presents with prominent mucositis and can have cutaneous findings of sparse vesiculobullous or targetoid eruption.8 Mycoplasma pneumoniae typically infects the lungs and is a leading cause of community-acquired pneumonia. However, a subset of patients can have extrapulmonary disease presenting as mucocutaneous eruptions, which is preceded by an approximately weeklong prodrome of fever, cough, and malaise.7 Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis also affect children and young patients and is more common in males.8
The Diagnosis: Generalized Bullous Fixed Drug Eruption
A punch biopsy from the left thigh revealed a vacuolar interface dermatitis with full-thickness necrosis of the epidermis and a patchy lichenoid inflammatory cell infiltrate in the superficial dermis consistent with a generalized bullous fixed drug eruption (GBFDE). The patient received supportive care and methylprednisolone with improvement of symptoms.
Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption is a rare, potentially life-threatening form of a fixed drug eruption (FDE), a cutaneous drug reaction that occurs in response to a causative medication. It typically presents with welldemarcated, dusky, erythematous patches or plaques that recur in the same sites with repeat exposure.1 The pathogenesis of FDE has been hypothesized to involve epidermal CD8+ T cells, which are activated by drug exposure and release cytotoxic molecules including Fas, Fas ligand, perforin, and granzyme B, resulting in lysis of the surrounding keratinocytes.1-3 Common eliciting drugs include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibacterial agents (particularly trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole), barbiturates, acetaminophen, and antimalarials.1 In addition to the findings seen in FDE, GBFDE is characterized by widespread bullous skin lesions.1-4 Typical histologic patterns seen in GBFDE are dispersed epidermal apoptotic keratinocytes, prominent dermal eosinophilic and lymphocytic infiltrates, and dermal melanophages.3 Discontinuing the causative agent and diligent prevention of re-exposure are the most important steps in management, as additional exposures can increase the number of lesions and overall severity. Symptoms typically resolve 7 to 14 days after drug discontinuation, often with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.3
Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption presents a diagnostic challenge, as it sometimes involves the oral mucosa and can exhibit the Nikolsky sign. Thus, it often is confused with Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) or toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).1,4 Stevens-Johnson syndrome and TEN are severe cutaneous drug eruptions that also can present with diffuse bullous skin lesions. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and TEN are thought to be a spectrum of the same disease that initially presents with dusky red macules that can coalesce, develop central blistering, and lead to skin detachment.5 Stevens-Johnson syndrome is defined as skin detachment of less than 10% body surface area (BSA); TEN is defined as skin detachment of more than 30% BSA. Stevens-Johnson syndrome/TEN overlap syndrome includes skin detachment of 10% to 30% BSA.5
Causative medications overlap substantially with GBFDE and include anticonvulsants, sulfa-containing drugs, antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and uric acid–lowering agents. The histology of SJS/TEN also is quite similar to GBFDE, and these entities may be indistinguishable without clinical information.5 Lee et al1 found that absence of grouped necrotic keratinocytes (fire flag sign), deep inflammatory infiltrates, notable pigment incontinence, and higher eosinophil counts appear to be more common in GBFDE than SJS/TEN. Constitutional symptoms and mucosal involvement also were more frequent in SJS/TEN.
The timing of clinical presentation and medical history can be useful in differentiating between SJS/TEN and GBFDE. In SJS/TEN, drug exposure typically occurs 1 to 3 weeks before onset of symptoms vs 30 minutes to 24 hours in GBFDE.3 Additionally, a history of similar eruption in the same location is pathognomonic for GBFDE. Although GBFDE has been thought to have a better prognosis than SJS/TEN, more recent data suggest mortality rates may be similar.3 A case-control study found a mortality rate of 22% (13/58) in patients with GBFDE compared to 28% (n=170) in SJS/TEN patients.4
Erythema multiforme (EM) is an uncommon immunemediated disorder that typically presents as targetoid lesions with central epidermal necrosis in an acral distribution. Erythema multiforme can arise from a variety of factors, but up to 90% of cases are due to infection, most commonly herpes simplex virus; medications account for less than 10% of cases.6 Previously, EM has been thought to be on the same disease spectrum as SJS and TEN. It is now clear that EM is a separate entity with similar mucosal erosions but different cutaneous findings,6 mainly typical target lesions that differ from the atypical targets seen in SJS.
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is a blistering skin disorder associated with local Staphylococcus aureus infection. It most commonly is seen in children and rarely occurs in adults who are not on dialysis. Some Staphylococcus strains produce exfoliative toxins A and B, which are serine proteases that target and cleave desmoglein 1, a mediator of keratinocyte adhesion. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome initially presents with erythema accentuated in the skin folds that becomes generalized. The disruption of keratinocyte adhesion leads to bullae formation in areas of erythema and diffuse sheetlike desquamation. Pathology reveals subcorneal rather than subepidermal blistering, which is seen in GBFDE and SJS/TEN. Treatment involves antistaphylococcal antibiotics and supportive care. With proper treatment, most cases resolve within 2 to 3 weeks.7
Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis presents with prominent mucositis and can have cutaneous findings of sparse vesiculobullous or targetoid eruption.8 Mycoplasma pneumoniae typically infects the lungs and is a leading cause of community-acquired pneumonia. However, a subset of patients can have extrapulmonary disease presenting as mucocutaneous eruptions, which is preceded by an approximately weeklong prodrome of fever, cough, and malaise.7 Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis also affect children and young patients and is more common in males.8
- Lee CH, Chen YC, Cho YT, et al. Fixed-drug eruption: a retrospective study in a single referral center in northern Taiwan. Dermatologica Sinica. 2012;30:11-15. doi:10.1016/j.dsi.2012.02.002
- Cho Y-T, Lin J-W, Chen Y-C, et al. Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption is distinct from Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis by immunohistopathological features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:539-548. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.11.015
- Mitre V, Applebaum DS, Albahrani Y, et al. Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption imitating toxic epidermal necrolysis: a case report and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23: 13030/qt25v009gs.
- Lipowicz S, Sekula P, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, et al. Prognosis of generalized bullous fixed drug eruption: comparison with StevensJohnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:726-732. doi:10.1111/bjd.12133
- Cho Y-T, Chu C-Y. Treatments for severe cutaneous adverse reactions [published online December 27, 2017]. J Immunol Res. doi:10.1155/2017/1503709
- Sokumbi O, Wetter DA. Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of erythema multiforme: a review for the practicing dermatologist. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:889-902. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05348.x
- Leung AKC, Barankin B, Leong KF. Staphylococcal-scalded skin syndrome: evaluation, diagnosis, and management. World J Pediatr. 2018;14:116-120.
- Canavan TN, Mathes EF, Frieden I, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis as a syndrome distinct from Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:239-245. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2014.06.026
- Lee CH, Chen YC, Cho YT, et al. Fixed-drug eruption: a retrospective study in a single referral center in northern Taiwan. Dermatologica Sinica. 2012;30:11-15. doi:10.1016/j.dsi.2012.02.002
- Cho Y-T, Lin J-W, Chen Y-C, et al. Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption is distinct from Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis by immunohistopathological features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:539-548. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.11.015
- Mitre V, Applebaum DS, Albahrani Y, et al. Generalized bullous fixed drug eruption imitating toxic epidermal necrolysis: a case report and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23: 13030/qt25v009gs.
- Lipowicz S, Sekula P, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, et al. Prognosis of generalized bullous fixed drug eruption: comparison with StevensJohnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:726-732. doi:10.1111/bjd.12133
- Cho Y-T, Chu C-Y. Treatments for severe cutaneous adverse reactions [published online December 27, 2017]. J Immunol Res. doi:10.1155/2017/1503709
- Sokumbi O, Wetter DA. Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of erythema multiforme: a review for the practicing dermatologist. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:889-902. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05348.x
- Leung AKC, Barankin B, Leong KF. Staphylococcal-scalded skin syndrome: evaluation, diagnosis, and management. World J Pediatr. 2018;14:116-120.
- Canavan TN, Mathes EF, Frieden I, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis as a syndrome distinct from Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:239-245. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2014.06.026
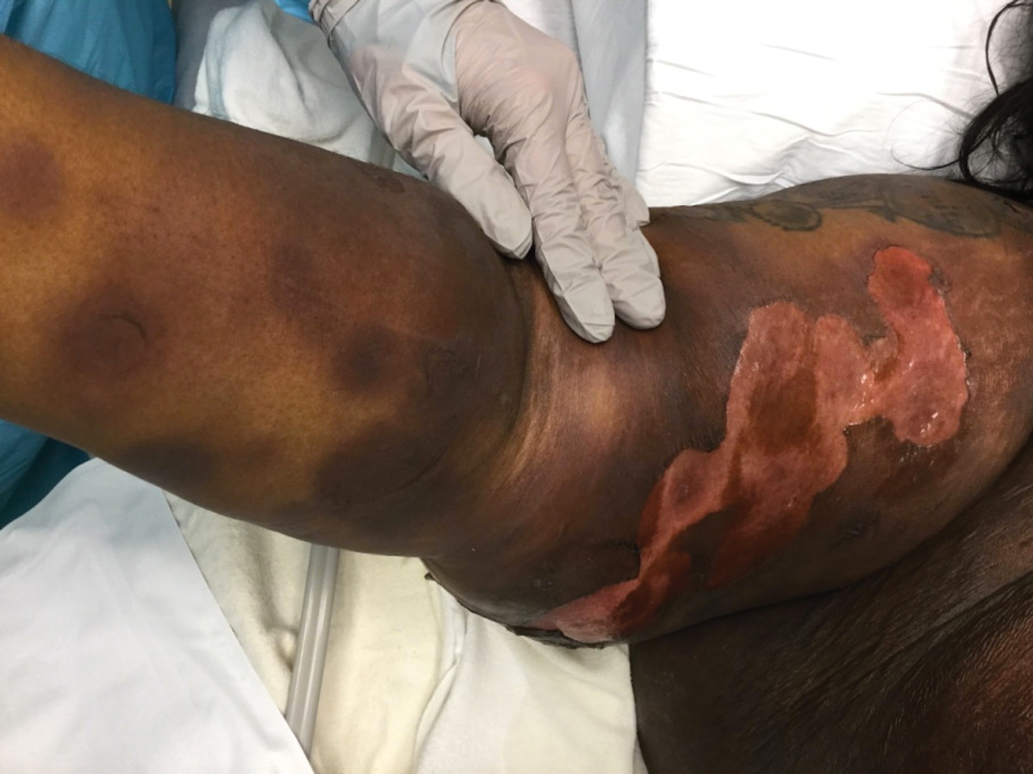
A 45-year-old woman presented with a diffuse rash 2 days after receiving ondansetron. She developed blisters on the arms, legs, trunk, and face 2 hours after exposure. There was no oral or vaginal involvement. She reported a history of leg blisters after prior exposure to ondansetron that were not as severe or numerous as the current episode. Physical examination revealed innumerable coalescing, ovoid and circular, dusky patches, some with central flaccid bullae, along with large areas of denuded skin on the trunk, arms, legs, and face. There were erosions on the lower eyelids without conjunctival or other mucosal involvement.
Cutaneous Chaetomium globosum Infection in a Vedolizumab-Treated Patient
To the Editor:
Broader availability and utilization of novel biologic treatments has heralded the emergence of unusual infections, including skin and soft tissue infections. These unusual infections may not be seen in clinical trials due to their overall rare incidence. In modern society, exposure to unusual pathogens can occur in locations far from their natural habitat.1 Tissue culture remains the gold standard, as histopathology and smears may not identify the organisms. Tissue culture of these less-common pathogens is challenging and may require multiple samples and specialized laboratory evaluations.2 In some cases, a skin biopsy with histopathologic examination is an efficient means to confirm or exclude a dermatologic manifestation of an inflammatory disease. This information can quickly change the course of treatment, especially for those on immunosuppressive medications.3 We report a case of unusual cutaneous infection with Chaetomium globosum in a patient concomitantly treated with vedolizumab, a gut-specific integrin inhibitor, alongside traditional immunosuppressive therapy.
A 33-year-old woman with Crohn disease on vedolizumab and mercaptopurine was referred to the dermatology clinic with firm, tender, erythematous lesions on the legs of 1 month’s duration (Figure, A). She had a history of inflammatory bowel disease with perianal fistula, sacroiliitis, uveitis, guttate psoriasis, and erythema nodosum. She denied recent medication changes, foreign travel, swimming in freshwater or a hot tub, chills, fever, malaise, night sweats, and weight loss. Physical examination revealed several tender, indurated, erythematous plaques across the legs, ranging in size from 4 to 12 cm. The plaques had central hyperpigmentation, atrophy, and scant scale without ulceration, drainage, or pustules. The largest plaque demonstrated a well-defined area of central fluctuance. Prednisone (60 mg) with taper was initiated for presumed recurrence of erythema nodosum with close follow-up.
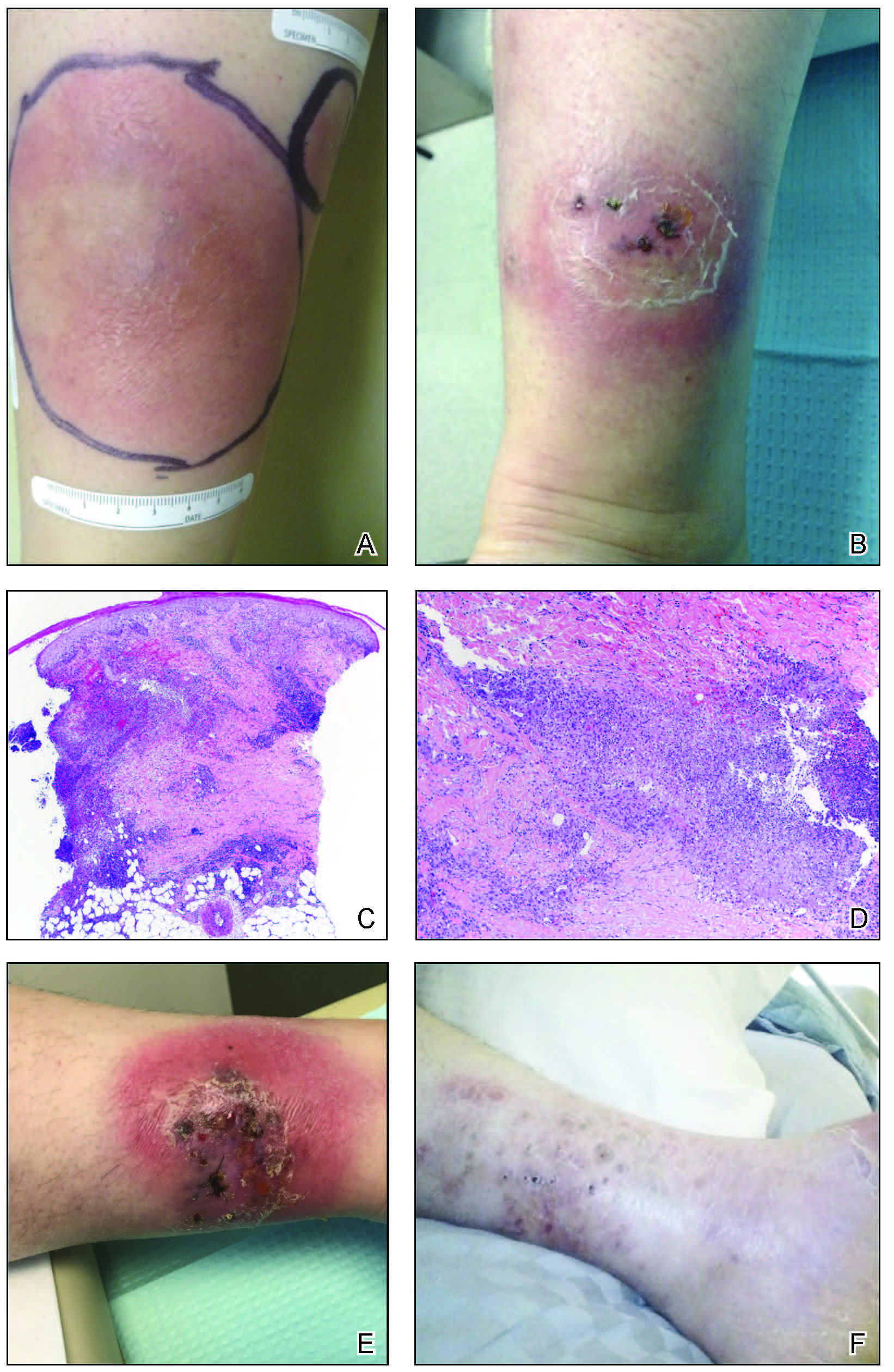
Five weeks later, most indurated plaques healed, leaving depressed scars; however, at 10 mg of prednisone she developed 2 additional nodules on the shin that, unlike earlier plaques, developed a central pustule and drained. The prednisone dose was increased to control the new areas and tapered thereafter to 20 mg daily. Despite the overall improvement, 2 plaques remained on the left side of the shin. Initially, erythema nodosum recurrence was considered, given the setting of inflammatory bowel disease and recent more classic presentation4; however, the disease progression and lack of response to standard treatment suggested an alternate pathology. Further history revealed that the patient had a pedicure 3 weeks prior to initial symptom onset. A swab was sent for routine bacterial culture at an outside clinic; no infectious agents were identified.
Three weeks later, the patient's condition had worsened again with increased edema, pain with standing, and more drainage (Figure, B). She did not report fevers or joint swelling. A punch biopsy was performed for tissue culture and histopathologic evaluation, which revealed granulomatous and suppurative inflammation and excluded erythema nodosum. Special stains for organisms were negative (Figure, C and D). Two weeks later, tissue culture began growing an unspecified mold. Mercaptopurine and prednisone were immediately discontinued. The patient remained on vedolizumab, started itraconazole (200 mg), and was referred to an infectious disease (ID) specialist. The sample was eventually identified as C globosum (Figure, E) at a specialized facility (University of Texas, San Antonio). Despite several weeks of itraconazole therapy, the patient developed edema surrounding the knee. Upon evaluation by orthopedics, the patient was diagnosed with reactive arthritis in the left knee and ankle. The knee fluid was drained, and cultures were negative. At recommendation of the ID physician, the itraconazole dosage was doubled given the limited clinical response. After several weeks at the increased dosage, she began to experience slow improvement (Figure, F). Because Chaetomium species infections are rare and have limited response to many antifungal agents,5 no standard treatment protocol was available. Initial recommendations for treatment were for 1 year, based on the experience and expertise of the ID physician. Treatment with itraconazole was continued for 10 months, at which point the patient chose to discontinue therapy prior to her follow-up appointments. The patient had no evidence of infection recurrence 2 months after discontinuing therapy.
In the expanding landscape of targeted biologic therapies for chronic inflammatory disease, physicians of various specialties are increasingly encountering unanticipated cutaneous eruptions and infections. Chaetomium is a dematiaceous mold found primarily in soil, water, decaying plants, paper, or dung. Based on its habitat, populations at risk for infection with Chaetomium species include farmers (plant and animal husbandry), children who play on the ground, and people with inadequate foot protection.1,2Chaetomium globosum has been identified in indoor environments, such as moldy rugs and mattresses. In one report, it was cultured from the environmental air in a bone marrow transplant patient’s room after the patient presented with delayed infection.6 Although human infection is uncommon, clinical isolation of Chaetomium species has occurred mainly in superficial samples from the skin, hair, nails, eyes, and respiratory tract.1 It been reported as a causative agent of onychomycosis in several immunocompetent patients7,8 but rarely is a cause of deep-skin infection. Chaetomium is thought to cause superficial infections, as it uses extracellular keratinases1 to degrade protective keratin structures, such as human nails. Infections in the brain, blood, and lymph nodes also have been noted but are quite rare. Deep skin infections present as painful papules and nodules to nonhealing ulcers that develop into inflammatory granulomas on the extremities.3 Local edema and yellow-brown crust often is present and fevers have been reported. Hyphae may be identified in skin biopsy.8 We posit that our patient may have been exposed to Chaetomium during her pedicure, as recirculating baths in nail salons have been a reported site of other infectious organisms, such as atypical mycobacteria.9
Vedolizumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody used in the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease. It targets the α4β7 integrin, a specific modulator of gut-trafficking lymphocytes. In vedolizumab’s clinical trial for Crohn disease, there was no increased incidence of life-threatening, severe infection.10,11 Often, new biologic treatments are used with known immunosuppressive medications. Mercaptopurine and prednisone are implicated in infections; however, recovery from the immune suppression usually is seen at 1 month after discontinuation.12 Our patient continued to worsen for several weeks and required increased dosing of itraconazole, despite stopping both prednisone and mercaptopurine. It opens the question as to whether vedolizumab played a role in the recalcitrant disease.
This case illustrates the importance of a high index of suspicion for unusual infections in the setting of biologic therapy. An infectious etiology of a cutaneous eruption in an immunosuppressed patient should always be included in the differential diagnosis and actively pursued early on; tissue culture may shorten the treatment course and decrease severity of the disease. Although a direct link between the mechanism of action of vedolizumab and cutaneous infection is not clear, given the rare incidence of this infection, a report of such a case is important to the practicing clinician.
- de Hoog GS, Ahmed SA, Najafzadeh MJ, et al. Phylogenetic findings suggest possible new habitat and routes of infection of human eumycetoma. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:e2229. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002229
- Zhang H, Ran Y, Li D, et al. Clavispora lusitaniae and Chaetomium atrobrunneum as rare agents of cutaneous infection. Mycopathologia. 2010;169:373-380. doi:10.1007/s11046-009-9266-9
- Schieffelin JS, Garcia-Diaz JB, Loss GE, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis fungal infections in solid organ transplant recipients: clinical presentation, pathology, and treatment. Transpl Infect Dis Off J Transplant Soc. 2014;16:270-278. doi:10.1111/tid.12197
- Farhi D, Cosnes J, Zizi N, et al. Significance of erythema nodosum and pyoderma gangrenosum in inflammatory bowel diseases: a cohort study of 2402 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2008;87:281-293. doi:10.1097/MD.0b013e318187cc9c
- Guarro J, Soler L, Rinaldi MG. Pathogenicity and antifungal susceptibility of Chaetomium species. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis Off Publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol. 1995;14:613-618.
- Teixeira ABA, Trabasso P, Moretti-Branchini ML, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Chaetomium globosum in an allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipient. Mycopathologia. 2003;156:309-312.
- Falcón CS, Falcón MDMS, Ceballos JD, et al. Onychomycosis by Chaetomium spp. Mycoses. 2009;52:77-79. doi:10.1111/j.14390507.2008.01519.x
- Kim DM, Lee MH, Suh MK, et al. Onychomycosis caused by Chaetomium globosum. Ann Dermatol. 2013;25:232-236. doi:10.5021/ad.2013.25.2.232
- Vugia DJ, Jang Y, Zizek C, et al. Mycobacteria in nail salon whirlpool footbaths, California. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:616-618. doi:10.3201/eid1104.040936
- Luthra P, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Ford AC. Systematic review and meta-analysis: opportunistic infections and malignancies during treatment with anti-integrin antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41:1227-1236. doi:10.1111/apt.13215
- Colombel J-F, Sands BE, Rutgeerts P, et al. The safety of vedolizumab for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2017;66:839-851. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2015-311079
- Connell WR, Kamm MA, Ritchie JK, et al. Bone marrow toxicity caused by azathioprine in inflammatory bowel disease: 27 years of experience. Gut. 1993;34:1081-1085.
To the Editor:
Broader availability and utilization of novel biologic treatments has heralded the emergence of unusual infections, including skin and soft tissue infections. These unusual infections may not be seen in clinical trials due to their overall rare incidence. In modern society, exposure to unusual pathogens can occur in locations far from their natural habitat.1 Tissue culture remains the gold standard, as histopathology and smears may not identify the organisms. Tissue culture of these less-common pathogens is challenging and may require multiple samples and specialized laboratory evaluations.2 In some cases, a skin biopsy with histopathologic examination is an efficient means to confirm or exclude a dermatologic manifestation of an inflammatory disease. This information can quickly change the course of treatment, especially for those on immunosuppressive medications.3 We report a case of unusual cutaneous infection with Chaetomium globosum in a patient concomitantly treated with vedolizumab, a gut-specific integrin inhibitor, alongside traditional immunosuppressive therapy.
A 33-year-old woman with Crohn disease on vedolizumab and mercaptopurine was referred to the dermatology clinic with firm, tender, erythematous lesions on the legs of 1 month’s duration (Figure, A). She had a history of inflammatory bowel disease with perianal fistula, sacroiliitis, uveitis, guttate psoriasis, and erythema nodosum. She denied recent medication changes, foreign travel, swimming in freshwater or a hot tub, chills, fever, malaise, night sweats, and weight loss. Physical examination revealed several tender, indurated, erythematous plaques across the legs, ranging in size from 4 to 12 cm. The plaques had central hyperpigmentation, atrophy, and scant scale without ulceration, drainage, or pustules. The largest plaque demonstrated a well-defined area of central fluctuance. Prednisone (60 mg) with taper was initiated for presumed recurrence of erythema nodosum with close follow-up.

Five weeks later, most indurated plaques healed, leaving depressed scars; however, at 10 mg of prednisone she developed 2 additional nodules on the shin that, unlike earlier plaques, developed a central pustule and drained. The prednisone dose was increased to control the new areas and tapered thereafter to 20 mg daily. Despite the overall improvement, 2 plaques remained on the left side of the shin. Initially, erythema nodosum recurrence was considered, given the setting of inflammatory bowel disease and recent more classic presentation4; however, the disease progression and lack of response to standard treatment suggested an alternate pathology. Further history revealed that the patient had a pedicure 3 weeks prior to initial symptom onset. A swab was sent for routine bacterial culture at an outside clinic; no infectious agents were identified.
Three weeks later, the patient's condition had worsened again with increased edema, pain with standing, and more drainage (Figure, B). She did not report fevers or joint swelling. A punch biopsy was performed for tissue culture and histopathologic evaluation, which revealed granulomatous and suppurative inflammation and excluded erythema nodosum. Special stains for organisms were negative (Figure, C and D). Two weeks later, tissue culture began growing an unspecified mold. Mercaptopurine and prednisone were immediately discontinued. The patient remained on vedolizumab, started itraconazole (200 mg), and was referred to an infectious disease (ID) specialist. The sample was eventually identified as C globosum (Figure, E) at a specialized facility (University of Texas, San Antonio). Despite several weeks of itraconazole therapy, the patient developed edema surrounding the knee. Upon evaluation by orthopedics, the patient was diagnosed with reactive arthritis in the left knee and ankle. The knee fluid was drained, and cultures were negative. At recommendation of the ID physician, the itraconazole dosage was doubled given the limited clinical response. After several weeks at the increased dosage, she began to experience slow improvement (Figure, F). Because Chaetomium species infections are rare and have limited response to many antifungal agents,5 no standard treatment protocol was available. Initial recommendations for treatment were for 1 year, based on the experience and expertise of the ID physician. Treatment with itraconazole was continued for 10 months, at which point the patient chose to discontinue therapy prior to her follow-up appointments. The patient had no evidence of infection recurrence 2 months after discontinuing therapy.
In the expanding landscape of targeted biologic therapies for chronic inflammatory disease, physicians of various specialties are increasingly encountering unanticipated cutaneous eruptions and infections. Chaetomium is a dematiaceous mold found primarily in soil, water, decaying plants, paper, or dung. Based on its habitat, populations at risk for infection with Chaetomium species include farmers (plant and animal husbandry), children who play on the ground, and people with inadequate foot protection.1,2Chaetomium globosum has been identified in indoor environments, such as moldy rugs and mattresses. In one report, it was cultured from the environmental air in a bone marrow transplant patient’s room after the patient presented with delayed infection.6 Although human infection is uncommon, clinical isolation of Chaetomium species has occurred mainly in superficial samples from the skin, hair, nails, eyes, and respiratory tract.1 It been reported as a causative agent of onychomycosis in several immunocompetent patients7,8 but rarely is a cause of deep-skin infection. Chaetomium is thought to cause superficial infections, as it uses extracellular keratinases1 to degrade protective keratin structures, such as human nails. Infections in the brain, blood, and lymph nodes also have been noted but are quite rare. Deep skin infections present as painful papules and nodules to nonhealing ulcers that develop into inflammatory granulomas on the extremities.3 Local edema and yellow-brown crust often is present and fevers have been reported. Hyphae may be identified in skin biopsy.8 We posit that our patient may have been exposed to Chaetomium during her pedicure, as recirculating baths in nail salons have been a reported site of other infectious organisms, such as atypical mycobacteria.9
Vedolizumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody used in the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease. It targets the α4β7 integrin, a specific modulator of gut-trafficking lymphocytes. In vedolizumab’s clinical trial for Crohn disease, there was no increased incidence of life-threatening, severe infection.10,11 Often, new biologic treatments are used with known immunosuppressive medications. Mercaptopurine and prednisone are implicated in infections; however, recovery from the immune suppression usually is seen at 1 month after discontinuation.12 Our patient continued to worsen for several weeks and required increased dosing of itraconazole, despite stopping both prednisone and mercaptopurine. It opens the question as to whether vedolizumab played a role in the recalcitrant disease.
This case illustrates the importance of a high index of suspicion for unusual infections in the setting of biologic therapy. An infectious etiology of a cutaneous eruption in an immunosuppressed patient should always be included in the differential diagnosis and actively pursued early on; tissue culture may shorten the treatment course and decrease severity of the disease. Although a direct link between the mechanism of action of vedolizumab and cutaneous infection is not clear, given the rare incidence of this infection, a report of such a case is important to the practicing clinician.
To the Editor:
Broader availability and utilization of novel biologic treatments has heralded the emergence of unusual infections, including skin and soft tissue infections. These unusual infections may not be seen in clinical trials due to their overall rare incidence. In modern society, exposure to unusual pathogens can occur in locations far from their natural habitat.1 Tissue culture remains the gold standard, as histopathology and smears may not identify the organisms. Tissue culture of these less-common pathogens is challenging and may require multiple samples and specialized laboratory evaluations.2 In some cases, a skin biopsy with histopathologic examination is an efficient means to confirm or exclude a dermatologic manifestation of an inflammatory disease. This information can quickly change the course of treatment, especially for those on immunosuppressive medications.3 We report a case of unusual cutaneous infection with Chaetomium globosum in a patient concomitantly treated with vedolizumab, a gut-specific integrin inhibitor, alongside traditional immunosuppressive therapy.
A 33-year-old woman with Crohn disease on vedolizumab and mercaptopurine was referred to the dermatology clinic with firm, tender, erythematous lesions on the legs of 1 month’s duration (Figure, A). She had a history of inflammatory bowel disease with perianal fistula, sacroiliitis, uveitis, guttate psoriasis, and erythema nodosum. She denied recent medication changes, foreign travel, swimming in freshwater or a hot tub, chills, fever, malaise, night sweats, and weight loss. Physical examination revealed several tender, indurated, erythematous plaques across the legs, ranging in size from 4 to 12 cm. The plaques had central hyperpigmentation, atrophy, and scant scale without ulceration, drainage, or pustules. The largest plaque demonstrated a well-defined area of central fluctuance. Prednisone (60 mg) with taper was initiated for presumed recurrence of erythema nodosum with close follow-up.

Five weeks later, most indurated plaques healed, leaving depressed scars; however, at 10 mg of prednisone she developed 2 additional nodules on the shin that, unlike earlier plaques, developed a central pustule and drained. The prednisone dose was increased to control the new areas and tapered thereafter to 20 mg daily. Despite the overall improvement, 2 plaques remained on the left side of the shin. Initially, erythema nodosum recurrence was considered, given the setting of inflammatory bowel disease and recent more classic presentation4; however, the disease progression and lack of response to standard treatment suggested an alternate pathology. Further history revealed that the patient had a pedicure 3 weeks prior to initial symptom onset. A swab was sent for routine bacterial culture at an outside clinic; no infectious agents were identified.
Three weeks later, the patient's condition had worsened again with increased edema, pain with standing, and more drainage (Figure, B). She did not report fevers or joint swelling. A punch biopsy was performed for tissue culture and histopathologic evaluation, which revealed granulomatous and suppurative inflammation and excluded erythema nodosum. Special stains for organisms were negative (Figure, C and D). Two weeks later, tissue culture began growing an unspecified mold. Mercaptopurine and prednisone were immediately discontinued. The patient remained on vedolizumab, started itraconazole (200 mg), and was referred to an infectious disease (ID) specialist. The sample was eventually identified as C globosum (Figure, E) at a specialized facility (University of Texas, San Antonio). Despite several weeks of itraconazole therapy, the patient developed edema surrounding the knee. Upon evaluation by orthopedics, the patient was diagnosed with reactive arthritis in the left knee and ankle. The knee fluid was drained, and cultures were negative. At recommendation of the ID physician, the itraconazole dosage was doubled given the limited clinical response. After several weeks at the increased dosage, she began to experience slow improvement (Figure, F). Because Chaetomium species infections are rare and have limited response to many antifungal agents,5 no standard treatment protocol was available. Initial recommendations for treatment were for 1 year, based on the experience and expertise of the ID physician. Treatment with itraconazole was continued for 10 months, at which point the patient chose to discontinue therapy prior to her follow-up appointments. The patient had no evidence of infection recurrence 2 months after discontinuing therapy.
In the expanding landscape of targeted biologic therapies for chronic inflammatory disease, physicians of various specialties are increasingly encountering unanticipated cutaneous eruptions and infections. Chaetomium is a dematiaceous mold found primarily in soil, water, decaying plants, paper, or dung. Based on its habitat, populations at risk for infection with Chaetomium species include farmers (plant and animal husbandry), children who play on the ground, and people with inadequate foot protection.1,2Chaetomium globosum has been identified in indoor environments, such as moldy rugs and mattresses. In one report, it was cultured from the environmental air in a bone marrow transplant patient’s room after the patient presented with delayed infection.6 Although human infection is uncommon, clinical isolation of Chaetomium species has occurred mainly in superficial samples from the skin, hair, nails, eyes, and respiratory tract.1 It been reported as a causative agent of onychomycosis in several immunocompetent patients7,8 but rarely is a cause of deep-skin infection. Chaetomium is thought to cause superficial infections, as it uses extracellular keratinases1 to degrade protective keratin structures, such as human nails. Infections in the brain, blood, and lymph nodes also have been noted but are quite rare. Deep skin infections present as painful papules and nodules to nonhealing ulcers that develop into inflammatory granulomas on the extremities.3 Local edema and yellow-brown crust often is present and fevers have been reported. Hyphae may be identified in skin biopsy.8 We posit that our patient may have been exposed to Chaetomium during her pedicure, as recirculating baths in nail salons have been a reported site of other infectious organisms, such as atypical mycobacteria.9
Vedolizumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody used in the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease. It targets the α4β7 integrin, a specific modulator of gut-trafficking lymphocytes. In vedolizumab’s clinical trial for Crohn disease, there was no increased incidence of life-threatening, severe infection.10,11 Often, new biologic treatments are used with known immunosuppressive medications. Mercaptopurine and prednisone are implicated in infections; however, recovery from the immune suppression usually is seen at 1 month after discontinuation.12 Our patient continued to worsen for several weeks and required increased dosing of itraconazole, despite stopping both prednisone and mercaptopurine. It opens the question as to whether vedolizumab played a role in the recalcitrant disease.
This case illustrates the importance of a high index of suspicion for unusual infections in the setting of biologic therapy. An infectious etiology of a cutaneous eruption in an immunosuppressed patient should always be included in the differential diagnosis and actively pursued early on; tissue culture may shorten the treatment course and decrease severity of the disease. Although a direct link between the mechanism of action of vedolizumab and cutaneous infection is not clear, given the rare incidence of this infection, a report of such a case is important to the practicing clinician.
- de Hoog GS, Ahmed SA, Najafzadeh MJ, et al. Phylogenetic findings suggest possible new habitat and routes of infection of human eumycetoma. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:e2229. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002229
- Zhang H, Ran Y, Li D, et al. Clavispora lusitaniae and Chaetomium atrobrunneum as rare agents of cutaneous infection. Mycopathologia. 2010;169:373-380. doi:10.1007/s11046-009-9266-9
- Schieffelin JS, Garcia-Diaz JB, Loss GE, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis fungal infections in solid organ transplant recipients: clinical presentation, pathology, and treatment. Transpl Infect Dis Off J Transplant Soc. 2014;16:270-278. doi:10.1111/tid.12197
- Farhi D, Cosnes J, Zizi N, et al. Significance of erythema nodosum and pyoderma gangrenosum in inflammatory bowel diseases: a cohort study of 2402 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2008;87:281-293. doi:10.1097/MD.0b013e318187cc9c
- Guarro J, Soler L, Rinaldi MG. Pathogenicity and antifungal susceptibility of Chaetomium species. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis Off Publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol. 1995;14:613-618.
- Teixeira ABA, Trabasso P, Moretti-Branchini ML, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Chaetomium globosum in an allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipient. Mycopathologia. 2003;156:309-312.
- Falcón CS, Falcón MDMS, Ceballos JD, et al. Onychomycosis by Chaetomium spp. Mycoses. 2009;52:77-79. doi:10.1111/j.14390507.2008.01519.x
- Kim DM, Lee MH, Suh MK, et al. Onychomycosis caused by Chaetomium globosum. Ann Dermatol. 2013;25:232-236. doi:10.5021/ad.2013.25.2.232
- Vugia DJ, Jang Y, Zizek C, et al. Mycobacteria in nail salon whirlpool footbaths, California. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:616-618. doi:10.3201/eid1104.040936
- Luthra P, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Ford AC. Systematic review and meta-analysis: opportunistic infections and malignancies during treatment with anti-integrin antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41:1227-1236. doi:10.1111/apt.13215
- Colombel J-F, Sands BE, Rutgeerts P, et al. The safety of vedolizumab for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2017;66:839-851. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2015-311079
- Connell WR, Kamm MA, Ritchie JK, et al. Bone marrow toxicity caused by azathioprine in inflammatory bowel disease: 27 years of experience. Gut. 1993;34:1081-1085.
- de Hoog GS, Ahmed SA, Najafzadeh MJ, et al. Phylogenetic findings suggest possible new habitat and routes of infection of human eumycetoma. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:e2229. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002229
- Zhang H, Ran Y, Li D, et al. Clavispora lusitaniae and Chaetomium atrobrunneum as rare agents of cutaneous infection. Mycopathologia. 2010;169:373-380. doi:10.1007/s11046-009-9266-9
- Schieffelin JS, Garcia-Diaz JB, Loss GE, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis fungal infections in solid organ transplant recipients: clinical presentation, pathology, and treatment. Transpl Infect Dis Off J Transplant Soc. 2014;16:270-278. doi:10.1111/tid.12197
- Farhi D, Cosnes J, Zizi N, et al. Significance of erythema nodosum and pyoderma gangrenosum in inflammatory bowel diseases: a cohort study of 2402 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2008;87:281-293. doi:10.1097/MD.0b013e318187cc9c
- Guarro J, Soler L, Rinaldi MG. Pathogenicity and antifungal susceptibility of Chaetomium species. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis Off Publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol. 1995;14:613-618.
- Teixeira ABA, Trabasso P, Moretti-Branchini ML, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Chaetomium globosum in an allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipient. Mycopathologia. 2003;156:309-312.
- Falcón CS, Falcón MDMS, Ceballos JD, et al. Onychomycosis by Chaetomium spp. Mycoses. 2009;52:77-79. doi:10.1111/j.14390507.2008.01519.x
- Kim DM, Lee MH, Suh MK, et al. Onychomycosis caused by Chaetomium globosum. Ann Dermatol. 2013;25:232-236. doi:10.5021/ad.2013.25.2.232
- Vugia DJ, Jang Y, Zizek C, et al. Mycobacteria in nail salon whirlpool footbaths, California. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:616-618. doi:10.3201/eid1104.040936
- Luthra P, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Ford AC. Systematic review and meta-analysis: opportunistic infections and malignancies during treatment with anti-integrin antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41:1227-1236. doi:10.1111/apt.13215
- Colombel J-F, Sands BE, Rutgeerts P, et al. The safety of vedolizumab for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2017;66:839-851. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2015-311079
- Connell WR, Kamm MA, Ritchie JK, et al. Bone marrow toxicity caused by azathioprine in inflammatory bowel disease: 27 years of experience. Gut. 1993;34:1081-1085.
Practice Points
- Tissue culture remains the gold standard for deep fungal infections.
- Physicians must maintain a high index of suspicion for alternate diagnoses when a disease progresses along an unexpected course.
- Biologic medications may have low-incidence side effects that emerge in postmarket use.
Verrucous Carcinoma in a Wounded Military Amputee
To the Editor:
Verrucous carcinoma is a rare, well-differentiated, locally aggressive squamous cell carcinoma first described by Ackerman in 1948.1 There are 4 main clinicopathologic types: oral florid papillomatosis or Ackerman tumor, giant condyloma acuminatum or Buschke-Lowenstein tumor, plantar verrucous carcinoma, and cutaneous verrucous carcinoma.2,3 Historically, most patients are older white men. The lesion commonly occurs in sites of inflammation4 or chronic irritation/trauma. Clinically, patients present with a slowly enlarging, exophytic, verrucous plaque violating the skin, fascia, and occasionally bone. Although these lesions have little tendency to metastasize, substantial morbidity can be seen due to local invasion. Despite surgical excision, recurrence is not uncommon and is associated with a poor prognosis and higher infiltrative potential.5
A 45-year-old male veteran initially presented to our dermatology clinic with a 4-cm, macerated, verrucous plaque on the left lateral ankle in the area of a skin graft placed during a prior limb salvage surgery (Figure 1). The patient experienced a traumatic blast injury while deployed 7 years prior with a subsequent right-sided below-the-knee amputation and left lower limb salvage. The lesion was clinically diagnosed as verruca vulgaris and treated with daily salicylic acid. Six weeks after the initial presentation, the lesion remained largely unchanged. A biopsy subsequently was obtained to confirm the diagnosis. At that time, the histopathology was consistent with verruca vulgaris without evidence of carcinoma. Due to the persistence of the lesion, lack of improvement with topical treatment, and overall size, the patient opted for surgical excision.
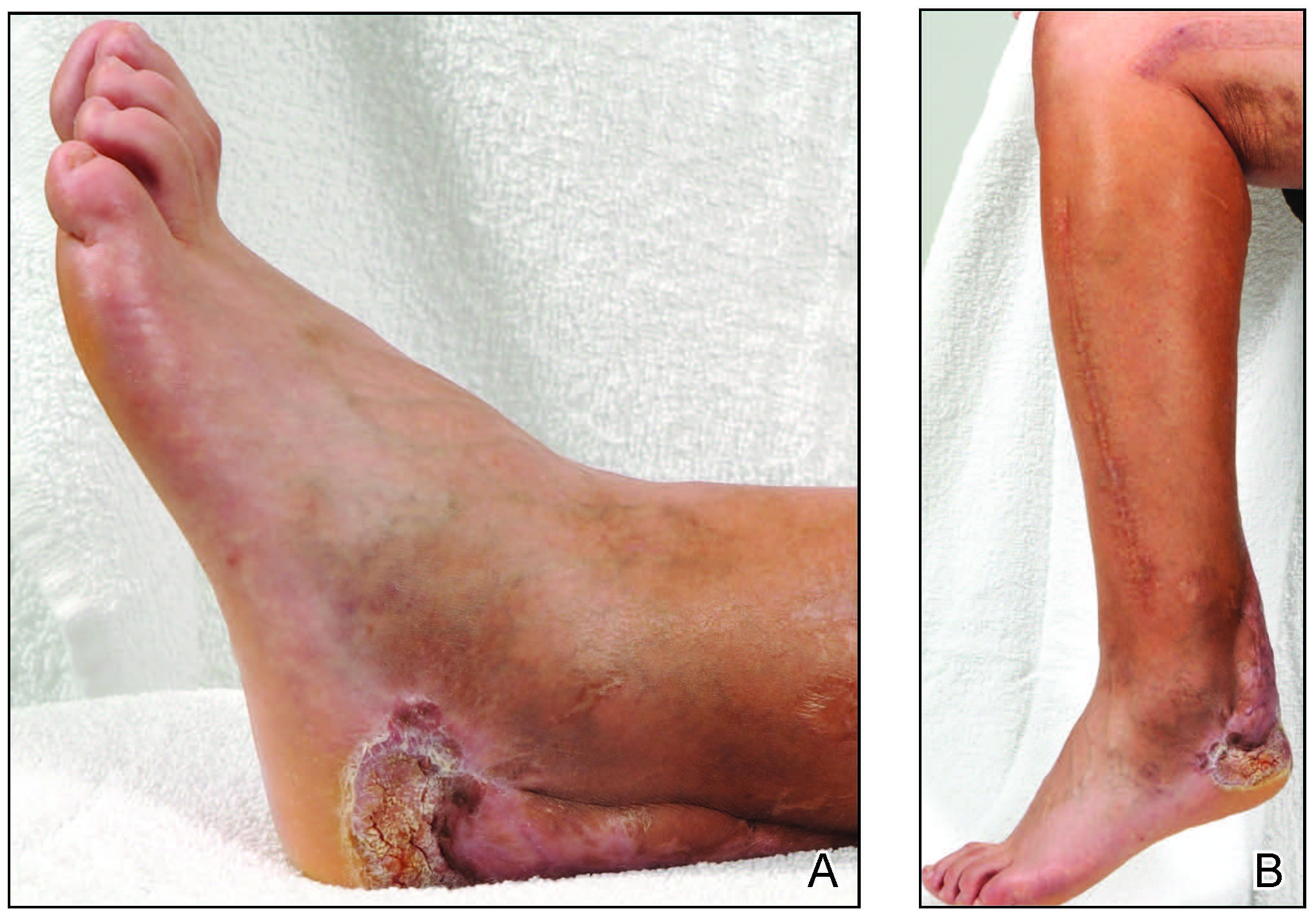
A year later, the lesion was excised again by orthopedic surgery, and the tissue was submitted for histopathologic evaluation, which was suggestive of a verrucous neoplasm with some disagreement on whether it was consistent with verrucous hyperplasia or verrucous carcinoma. Following excision, the patient sustained a nonhealing chronic ulcer that required wound care for a total of 6 months. The lesion recurred a year later and was surgically excised a third time. A split-thickness skin graft was utilized to repair the defect. Histopathology again was consistent with verrucous carcinoma. With a fourth and final recurrence of the verrucous plaque 6 months later, the patient elected to undergo a left-sided below-the-knee amputation.
Verrucous carcinoma can represent a diagnostic dilemma, as histologic sections may mimic benign entities. The features of a well-differentiated squamous epithelium with hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis can be mistaken for verruca vulgaris, keratoacanthoma, and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia,6 which are characteristic of verrucous hyperplasia. Accurate diagnosis can be difficult with a superficial biopsy because of the mature appearance of the epithelium,7 prompting the need for multiple and deeper biopsies8 to include sampling of the base of the hyperplastic epithelium in which the characteristic bulbous pushing growth pattern of the rete ridges is visualized. Precise histologic diagnosis can be further confounded by external mechanical factors, such as pressure, which can distort the classic histopathology.7 The histopathologic features leading to the diagnosis of verrucous carcinoma in our specimen were minimal squamous atypia present in a predominantly exophytic squamous proliferation with human papillomavirus cytopathic effect and focal endophytic pushing borders by rounded bulbous rete ridges into the mid and deep dermis (Figure 2).

Diagnostic uncertainty can delay surgical excision and lead to progression of verrucous carcinoma. Unfortunately, even with appropriate surgical intervention, recurrence has been documented; therefore, close clinical follow-up is recommended. The tumor spreads by local invasion and may follow the path of least resistance.4 In our patient, the frequent tissue manipulation may have facilitated aggressive infiltration of the tumor, ultimately resulting in the loss of his remaining leg. Therefore, it is important for clinicians to recognize that verrucous carcinoma, especially one that develops on a refractory ulcer or scar tissue, may be a complex malignant neoplasm that requires extensive treatment at onset to prevent the amputation of a limb.
- Ackerman LV. Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Surgery. 1948;23:670-678.
- Yoshitasu S, Takagi T, Ohata C, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: report of a case treated with Boyd amputation followed by reconstruction with a free forearm flap. J Dermatol. 2001;28:226-230.
- Schwartz R. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-14.
- Bernstein SC, Lim KK, Brodland DG, et al. The many faces of squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 1996;22:243-254.
- Costache M, Tatiana D, Mitrache L, et al. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma—report of three cases with review of literature. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014;55:383-388.
- Shenoy A, Waghmare R, Kavishwar V, et al. Carcinoma cuniculatum of foot. Foot. 2011;21:207-208.
- Klima M, Kurtis B, Jordan P. Verrucous carcinoma of skin. J Cutan Pathol.1980;7:88-98.
- Pleat J, Sacks L, Rigby H. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma. Br J Plast Surg. 2001;54:554-555.
To the Editor:
Verrucous carcinoma is a rare, well-differentiated, locally aggressive squamous cell carcinoma first described by Ackerman in 1948.1 There are 4 main clinicopathologic types: oral florid papillomatosis or Ackerman tumor, giant condyloma acuminatum or Buschke-Lowenstein tumor, plantar verrucous carcinoma, and cutaneous verrucous carcinoma.2,3 Historically, most patients are older white men. The lesion commonly occurs in sites of inflammation4 or chronic irritation/trauma. Clinically, patients present with a slowly enlarging, exophytic, verrucous plaque violating the skin, fascia, and occasionally bone. Although these lesions have little tendency to metastasize, substantial morbidity can be seen due to local invasion. Despite surgical excision, recurrence is not uncommon and is associated with a poor prognosis and higher infiltrative potential.5
A 45-year-old male veteran initially presented to our dermatology clinic with a 4-cm, macerated, verrucous plaque on the left lateral ankle in the area of a skin graft placed during a prior limb salvage surgery (Figure 1). The patient experienced a traumatic blast injury while deployed 7 years prior with a subsequent right-sided below-the-knee amputation and left lower limb salvage. The lesion was clinically diagnosed as verruca vulgaris and treated with daily salicylic acid. Six weeks after the initial presentation, the lesion remained largely unchanged. A biopsy subsequently was obtained to confirm the diagnosis. At that time, the histopathology was consistent with verruca vulgaris without evidence of carcinoma. Due to the persistence of the lesion, lack of improvement with topical treatment, and overall size, the patient opted for surgical excision.

A year later, the lesion was excised again by orthopedic surgery, and the tissue was submitted for histopathologic evaluation, which was suggestive of a verrucous neoplasm with some disagreement on whether it was consistent with verrucous hyperplasia or verrucous carcinoma. Following excision, the patient sustained a nonhealing chronic ulcer that required wound care for a total of 6 months. The lesion recurred a year later and was surgically excised a third time. A split-thickness skin graft was utilized to repair the defect. Histopathology again was consistent with verrucous carcinoma. With a fourth and final recurrence of the verrucous plaque 6 months later, the patient elected to undergo a left-sided below-the-knee amputation.
Verrucous carcinoma can represent a diagnostic dilemma, as histologic sections may mimic benign entities. The features of a well-differentiated squamous epithelium with hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis can be mistaken for verruca vulgaris, keratoacanthoma, and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia,6 which are characteristic of verrucous hyperplasia. Accurate diagnosis can be difficult with a superficial biopsy because of the mature appearance of the epithelium,7 prompting the need for multiple and deeper biopsies8 to include sampling of the base of the hyperplastic epithelium in which the characteristic bulbous pushing growth pattern of the rete ridges is visualized. Precise histologic diagnosis can be further confounded by external mechanical factors, such as pressure, which can distort the classic histopathology.7 The histopathologic features leading to the diagnosis of verrucous carcinoma in our specimen were minimal squamous atypia present in a predominantly exophytic squamous proliferation with human papillomavirus cytopathic effect and focal endophytic pushing borders by rounded bulbous rete ridges into the mid and deep dermis (Figure 2).

Diagnostic uncertainty can delay surgical excision and lead to progression of verrucous carcinoma. Unfortunately, even with appropriate surgical intervention, recurrence has been documented; therefore, close clinical follow-up is recommended. The tumor spreads by local invasion and may follow the path of least resistance.4 In our patient, the frequent tissue manipulation may have facilitated aggressive infiltration of the tumor, ultimately resulting in the loss of his remaining leg. Therefore, it is important for clinicians to recognize that verrucous carcinoma, especially one that develops on a refractory ulcer or scar tissue, may be a complex malignant neoplasm that requires extensive treatment at onset to prevent the amputation of a limb.
To the Editor:
Verrucous carcinoma is a rare, well-differentiated, locally aggressive squamous cell carcinoma first described by Ackerman in 1948.1 There are 4 main clinicopathologic types: oral florid papillomatosis or Ackerman tumor, giant condyloma acuminatum or Buschke-Lowenstein tumor, plantar verrucous carcinoma, and cutaneous verrucous carcinoma.2,3 Historically, most patients are older white men. The lesion commonly occurs in sites of inflammation4 or chronic irritation/trauma. Clinically, patients present with a slowly enlarging, exophytic, verrucous plaque violating the skin, fascia, and occasionally bone. Although these lesions have little tendency to metastasize, substantial morbidity can be seen due to local invasion. Despite surgical excision, recurrence is not uncommon and is associated with a poor prognosis and higher infiltrative potential.5
A 45-year-old male veteran initially presented to our dermatology clinic with a 4-cm, macerated, verrucous plaque on the left lateral ankle in the area of a skin graft placed during a prior limb salvage surgery (Figure 1). The patient experienced a traumatic blast injury while deployed 7 years prior with a subsequent right-sided below-the-knee amputation and left lower limb salvage. The lesion was clinically diagnosed as verruca vulgaris and treated with daily salicylic acid. Six weeks after the initial presentation, the lesion remained largely unchanged. A biopsy subsequently was obtained to confirm the diagnosis. At that time, the histopathology was consistent with verruca vulgaris without evidence of carcinoma. Due to the persistence of the lesion, lack of improvement with topical treatment, and overall size, the patient opted for surgical excision.

A year later, the lesion was excised again by orthopedic surgery, and the tissue was submitted for histopathologic evaluation, which was suggestive of a verrucous neoplasm with some disagreement on whether it was consistent with verrucous hyperplasia or verrucous carcinoma. Following excision, the patient sustained a nonhealing chronic ulcer that required wound care for a total of 6 months. The lesion recurred a year later and was surgically excised a third time. A split-thickness skin graft was utilized to repair the defect. Histopathology again was consistent with verrucous carcinoma. With a fourth and final recurrence of the verrucous plaque 6 months later, the patient elected to undergo a left-sided below-the-knee amputation.
Verrucous carcinoma can represent a diagnostic dilemma, as histologic sections may mimic benign entities. The features of a well-differentiated squamous epithelium with hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis can be mistaken for verruca vulgaris, keratoacanthoma, and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia,6 which are characteristic of verrucous hyperplasia. Accurate diagnosis can be difficult with a superficial biopsy because of the mature appearance of the epithelium,7 prompting the need for multiple and deeper biopsies8 to include sampling of the base of the hyperplastic epithelium in which the characteristic bulbous pushing growth pattern of the rete ridges is visualized. Precise histologic diagnosis can be further confounded by external mechanical factors, such as pressure, which can distort the classic histopathology.7 The histopathologic features leading to the diagnosis of verrucous carcinoma in our specimen were minimal squamous atypia present in a predominantly exophytic squamous proliferation with human papillomavirus cytopathic effect and focal endophytic pushing borders by rounded bulbous rete ridges into the mid and deep dermis (Figure 2).

Diagnostic uncertainty can delay surgical excision and lead to progression of verrucous carcinoma. Unfortunately, even with appropriate surgical intervention, recurrence has been documented; therefore, close clinical follow-up is recommended. The tumor spreads by local invasion and may follow the path of least resistance.4 In our patient, the frequent tissue manipulation may have facilitated aggressive infiltration of the tumor, ultimately resulting in the loss of his remaining leg. Therefore, it is important for clinicians to recognize that verrucous carcinoma, especially one that develops on a refractory ulcer or scar tissue, may be a complex malignant neoplasm that requires extensive treatment at onset to prevent the amputation of a limb.
- Ackerman LV. Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Surgery. 1948;23:670-678.
- Yoshitasu S, Takagi T, Ohata C, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: report of a case treated with Boyd amputation followed by reconstruction with a free forearm flap. J Dermatol. 2001;28:226-230.
- Schwartz R. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-14.
- Bernstein SC, Lim KK, Brodland DG, et al. The many faces of squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 1996;22:243-254.
- Costache M, Tatiana D, Mitrache L, et al. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma—report of three cases with review of literature. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014;55:383-388.
- Shenoy A, Waghmare R, Kavishwar V, et al. Carcinoma cuniculatum of foot. Foot. 2011;21:207-208.
- Klima M, Kurtis B, Jordan P. Verrucous carcinoma of skin. J Cutan Pathol.1980;7:88-98.
- Pleat J, Sacks L, Rigby H. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma. Br J Plast Surg. 2001;54:554-555.
- Ackerman LV. Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Surgery. 1948;23:670-678.
- Yoshitasu S, Takagi T, Ohata C, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: report of a case treated with Boyd amputation followed by reconstruction with a free forearm flap. J Dermatol. 2001;28:226-230.
- Schwartz R. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-14.
- Bernstein SC, Lim KK, Brodland DG, et al. The many faces of squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 1996;22:243-254.
- Costache M, Tatiana D, Mitrache L, et al. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma—report of three cases with review of literature. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014;55:383-388.
- Shenoy A, Waghmare R, Kavishwar V, et al. Carcinoma cuniculatum of foot. Foot. 2011;21:207-208.
- Klima M, Kurtis B, Jordan P. Verrucous carcinoma of skin. J Cutan Pathol.1980;7:88-98.
- Pleat J, Sacks L, Rigby H. Cutaneous verrucous carcinoma. Br J Plast Surg. 2001;54:554-555.
Practice Points
- Verrucous carcinoma is a rare, well-differentiated, locally aggressive squamous cell carcinoma that commonly occurs in sites of inflammation or chronic irritation.
- Histologically, verrucous carcinoma can be mistaken for other entities including verruca vulgaris, keratoacanthoma, and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, often delaying the appropriate diagnosis and treatment.