User login
Clinical Psychiatry News is the online destination and multimedia properties of Clinica Psychiatry News, the independent news publication for psychiatrists. Since 1971, Clinical Psychiatry News has been the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in psychiatry as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the physician's practice.
Dear Drupal User: You're seeing this because you're logged in to Drupal, and not redirected to MDedge.com/psychiatry.
Depression
adolescent depression
adolescent major depressive disorder
adolescent schizophrenia
adolescent with major depressive disorder
animals
autism
baby
brexpiprazole
child
child bipolar
child depression
child schizophrenia
children with bipolar disorder
children with depression
children with major depressive disorder
compulsive behaviors
cure
elderly bipolar
elderly depression
elderly major depressive disorder
elderly schizophrenia
elderly with dementia
first break
first episode
gambling
gaming
geriatric depression
geriatric major depressive disorder
geriatric schizophrenia
infant
ketamine
kid
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder in adolescents
major depressive disorder in children
parenting
pediatric
pediatric bipolar
pediatric depression
pediatric major depressive disorder
pediatric schizophrenia
pregnancy
pregnant
rexulti
skin care
suicide
teen
wine
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
How to identify, evaluate, and treat patients with ‘Percocet use disorder’
In recent years, Percocet (oxycodone/paracetamol) has experienced a meteoric rise to prominence because of the presence of conspicuous references in pop culture and the ever-evolving hip-hop scene,1 so much so that even propafenone is being mislabeled as the agent.2 It is of utmost importance for clinicians to be made aware of the adverse effects and the treatment protocols associated with Percocet as well as propafenone.
Propafenone is identified as a class 1C antiarrhythmic with adverse effects associated with that particular class of drugs (e.g., generalized tonic-clonic seizures coupled with widened QRS complex), however, Percocet’s toxidrome is the product of the opioid/nonopioid (in the form of oxycodone/acetaminophen) components found within the formulation. Percocet is often recreationally used with MDMA (“molly”) or ecstasy as popularized by the lyrics of “Mask Off” by Future (“Percocets, Molly, Percocets”).3,4
Addressing the challenge of imitation Percocet pills
Differentiating the untoward effects of Percocet and propafenone isn’t too challenging because the agents belong to separate classes – the problem is the use of deceitful labels on propafenone with both medications sporting the “512 imprint” on their respective pills. Initial symptoms of propafenone ingestion may include weakness and dizziness followed by seizures.5As an emergent situation, the patient should be immediately treated with a sodium bicarbonate infusion to effectively reverse the sodium channel blockade associated with the widened QRS.
However, a more likely scenario is that of Percocet counterfeit pills designed to illicitly emulate the properties of officially marketed Percocet. As expected, Percocet overdose management will require that the clinician be familiar with treating general opioid toxicity (in this case, derived from the oxycodone component), in particular respiratory or CNS depression. Symptoms of opioid overdose also include the loss of consciousness with pupillary miosis. Therapy entails the use of naloxone and/or mechanical ventilation for respiratory support. The patient can also exhibit cardiovascular compromise. If further information is elicited during a patient interview, it may reveal a history of drug procurement from the streets.
Epidemiologists from Georgia collaborated with the state’s department of public health’s office of emergency services, forensic experts, and drug enforcement professionals to evaluate almost 40 cases of counterfeit Percocet overdoses during the period spanning the second week of June 2017. Of these cases, a cluster triad was identified consisting of general opioid toxicity symptoms (for example, CNS or respiratory depression with concomitant pupillary constriction, a history of drug procurement, and a history of ingesting only one or two pills with rapid deterioration.6 Unfortunately, the screening process is often hindered by the fact that synthetic opioids such as Percocet are not readily identified on urine drug screens (UDS).
Despite shortcomings in assessment procedures, a UDS will yield positive results for multiple drugs, a feature that is common to seasoned opioid users and serves as an instrumental diagnostic clue in the investigative process. To address the crisis and prevent further spread, numerous Georgia agencies (e.g., drug trafficking and legal authorities) worked with the health care community to expediently identify cases of interest and bring forth public awareness concerning the ongoing perils of counterfeit drug intake. Future investigations might benefit from the implementation of DNA-verified UDS, because those screens are versatile enough to detect the presence of synthetic urine substitutes within the context of opioid use.7,8 Moreover, an expanded panel could be tailored to provide coverage for semisynthetics, including hydrocodone, oxycodone, hydromorphone, and oxymorphone.9
As a well-received painkiller from the opioid family, Percocet derives its analgesic properties from the fast-acting oxycodone; hepatic failure is also possible from Percocet (because of the acetaminophen component) or counterfeit Percocet overdose but is less common unless the Tylenol content approaches 4 grams. By binding to the brain’s opiate receptors, Percocet modulates pain pathways leading to a dulling of pain sensation along with euphoria, which is particularly attractive to drug seekers. Chronic Percocet use corresponds with a myriad of psychological and physical consequences, and the Drug Enforcement Administration recognizes oxycodone as a Schedule II drug.
A chronic Percocet user may try to disrupt the cycle of symptoms by abruptly ceasing use of the offending agent. This can precipitate the development of classical opioid-based withdrawal symptoms, including but not limited to nausea, vomiting, irritability, tachycardia, body aches, and episodes of cold sweats. Physicians have noted that misuse (i.e., deviations from intended prescribed) might include crushing and snorting as well as “doctor-shopping” behaviors for a continuous supply of Percocet.
Treatment recommendations
According to Sarah Wakeman, MD, medical director of the substance use disorders initiative at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, there are apparently two clinical manifestations of Percocet use. The primary consequence is derived from the oxycodone component of Percocet; as an opioid, oxycodone toxicity leads to disrupted breathing and oxygenation, negatively impacting vital organs such as the brain or the heart. Patients experiencing a lack of oxygen will often display cyanosis and may not respond appropriately to stimuli. For individuals suspected of succumbing to overdose, Dr. Wakeman reportedly advised that the clinician or trained professional rub his or her knuckles along the breastbone of the potential user – a drug overdose patient will fail to wake up. On the other hand, a Percocet user may exhibit the symptoms of liver failure depending on the overall level of acetaminophen in the formulation. To prevent relapses, Percocet use disorder is best managed in a professional setting under the direction of trained clinicians; users are provided medications to address ongoing cravings and symptoms associated with the withdrawal process. A detoxification center can tailor the treatment with opioid-based medications such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone to help patients be weaned off Percocet.
Clinicians may further improve the efficacy of a therapeutic regimen by incorporating a personalized plan with a comprehensive substance UDS panel for monitoring and treatment purposes. This may prove to be beneficial in the event of suspected polysubstance use, as is the case with patients who dabble with Percocet and “molly.” Preparations can also be instituted at the outset of therapy with genetic testing implemented in high-risk patients who exhibit an inclination for opioid use disorder.10 Genetic polymorphisms provide robust clinical assets for evaluating patients most at risk for relapse. For individuals with biological susceptibility, arrangements can be made to incorporate nonopioid treatment alternatives.
References
1. Thomas BB. The death of Lil Peep: How the U.S. prescription drug epidemic is changing hip-hop. The Guardian. 2017 Nov 16.
2. D’Orazio JL and Curtis JA. J Emer Med. 2011 Aug 1;41(2):172-5.
3. Levy L. These are the drugs influencing pop culture now. Vulture. 2018 Feb 6.
4. Kounang N and Bender M. “What is Percocet? Drug facts, side effects, abuse and more.” CNN. 2018 Jul 12.
5. The dangers of Percocet use and overdose. American Addiction Centers. Last updated 2020 Feb 3. https://americanaddictioncenters.org/percocet-treatment/dangers-of-use-and-overdose.
6. Edison L et al. MMWR. 2017 Oct 20;66(41):1119-20.
7. Choudhry Z et al. J Psychiatry. 2015. doi: 10.4172/2378-5756.10000319.
8. Islam F and Choudhry Z. Current Psychiatry. 2018 Dec;17(12):43-4.
9. Jupe N. Ask the Experts: DOT 5-panel drug test regimen. Quest Diagnostics. 2018 Mar 21. https://blog.employersolutions.com/ask-experts-dot-5-panel-drug-test-regimen/.
10. Ahmed S et al. Pharmacogenomics. 2019 Jun 28;20(9):685-703.
Dr. Islam is a medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Islam reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the IMCHF. He reported no relevant disclosures.
In recent years, Percocet (oxycodone/paracetamol) has experienced a meteoric rise to prominence because of the presence of conspicuous references in pop culture and the ever-evolving hip-hop scene,1 so much so that even propafenone is being mislabeled as the agent.2 It is of utmost importance for clinicians to be made aware of the adverse effects and the treatment protocols associated with Percocet as well as propafenone.
Propafenone is identified as a class 1C antiarrhythmic with adverse effects associated with that particular class of drugs (e.g., generalized tonic-clonic seizures coupled with widened QRS complex), however, Percocet’s toxidrome is the product of the opioid/nonopioid (in the form of oxycodone/acetaminophen) components found within the formulation. Percocet is often recreationally used with MDMA (“molly”) or ecstasy as popularized by the lyrics of “Mask Off” by Future (“Percocets, Molly, Percocets”).3,4
Addressing the challenge of imitation Percocet pills
Differentiating the untoward effects of Percocet and propafenone isn’t too challenging because the agents belong to separate classes – the problem is the use of deceitful labels on propafenone with both medications sporting the “512 imprint” on their respective pills. Initial symptoms of propafenone ingestion may include weakness and dizziness followed by seizures.5As an emergent situation, the patient should be immediately treated with a sodium bicarbonate infusion to effectively reverse the sodium channel blockade associated with the widened QRS.
However, a more likely scenario is that of Percocet counterfeit pills designed to illicitly emulate the properties of officially marketed Percocet. As expected, Percocet overdose management will require that the clinician be familiar with treating general opioid toxicity (in this case, derived from the oxycodone component), in particular respiratory or CNS depression. Symptoms of opioid overdose also include the loss of consciousness with pupillary miosis. Therapy entails the use of naloxone and/or mechanical ventilation for respiratory support. The patient can also exhibit cardiovascular compromise. If further information is elicited during a patient interview, it may reveal a history of drug procurement from the streets.
Epidemiologists from Georgia collaborated with the state’s department of public health’s office of emergency services, forensic experts, and drug enforcement professionals to evaluate almost 40 cases of counterfeit Percocet overdoses during the period spanning the second week of June 2017. Of these cases, a cluster triad was identified consisting of general opioid toxicity symptoms (for example, CNS or respiratory depression with concomitant pupillary constriction, a history of drug procurement, and a history of ingesting only one or two pills with rapid deterioration.6 Unfortunately, the screening process is often hindered by the fact that synthetic opioids such as Percocet are not readily identified on urine drug screens (UDS).
Despite shortcomings in assessment procedures, a UDS will yield positive results for multiple drugs, a feature that is common to seasoned opioid users and serves as an instrumental diagnostic clue in the investigative process. To address the crisis and prevent further spread, numerous Georgia agencies (e.g., drug trafficking and legal authorities) worked with the health care community to expediently identify cases of interest and bring forth public awareness concerning the ongoing perils of counterfeit drug intake. Future investigations might benefit from the implementation of DNA-verified UDS, because those screens are versatile enough to detect the presence of synthetic urine substitutes within the context of opioid use.7,8 Moreover, an expanded panel could be tailored to provide coverage for semisynthetics, including hydrocodone, oxycodone, hydromorphone, and oxymorphone.9
As a well-received painkiller from the opioid family, Percocet derives its analgesic properties from the fast-acting oxycodone; hepatic failure is also possible from Percocet (because of the acetaminophen component) or counterfeit Percocet overdose but is less common unless the Tylenol content approaches 4 grams. By binding to the brain’s opiate receptors, Percocet modulates pain pathways leading to a dulling of pain sensation along with euphoria, which is particularly attractive to drug seekers. Chronic Percocet use corresponds with a myriad of psychological and physical consequences, and the Drug Enforcement Administration recognizes oxycodone as a Schedule II drug.
A chronic Percocet user may try to disrupt the cycle of symptoms by abruptly ceasing use of the offending agent. This can precipitate the development of classical opioid-based withdrawal symptoms, including but not limited to nausea, vomiting, irritability, tachycardia, body aches, and episodes of cold sweats. Physicians have noted that misuse (i.e., deviations from intended prescribed) might include crushing and snorting as well as “doctor-shopping” behaviors for a continuous supply of Percocet.
Treatment recommendations
According to Sarah Wakeman, MD, medical director of the substance use disorders initiative at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, there are apparently two clinical manifestations of Percocet use. The primary consequence is derived from the oxycodone component of Percocet; as an opioid, oxycodone toxicity leads to disrupted breathing and oxygenation, negatively impacting vital organs such as the brain or the heart. Patients experiencing a lack of oxygen will often display cyanosis and may not respond appropriately to stimuli. For individuals suspected of succumbing to overdose, Dr. Wakeman reportedly advised that the clinician or trained professional rub his or her knuckles along the breastbone of the potential user – a drug overdose patient will fail to wake up. On the other hand, a Percocet user may exhibit the symptoms of liver failure depending on the overall level of acetaminophen in the formulation. To prevent relapses, Percocet use disorder is best managed in a professional setting under the direction of trained clinicians; users are provided medications to address ongoing cravings and symptoms associated with the withdrawal process. A detoxification center can tailor the treatment with opioid-based medications such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone to help patients be weaned off Percocet.
Clinicians may further improve the efficacy of a therapeutic regimen by incorporating a personalized plan with a comprehensive substance UDS panel for monitoring and treatment purposes. This may prove to be beneficial in the event of suspected polysubstance use, as is the case with patients who dabble with Percocet and “molly.” Preparations can also be instituted at the outset of therapy with genetic testing implemented in high-risk patients who exhibit an inclination for opioid use disorder.10 Genetic polymorphisms provide robust clinical assets for evaluating patients most at risk for relapse. For individuals with biological susceptibility, arrangements can be made to incorporate nonopioid treatment alternatives.
References
1. Thomas BB. The death of Lil Peep: How the U.S. prescription drug epidemic is changing hip-hop. The Guardian. 2017 Nov 16.
2. D’Orazio JL and Curtis JA. J Emer Med. 2011 Aug 1;41(2):172-5.
3. Levy L. These are the drugs influencing pop culture now. Vulture. 2018 Feb 6.
4. Kounang N and Bender M. “What is Percocet? Drug facts, side effects, abuse and more.” CNN. 2018 Jul 12.
5. The dangers of Percocet use and overdose. American Addiction Centers. Last updated 2020 Feb 3. https://americanaddictioncenters.org/percocet-treatment/dangers-of-use-and-overdose.
6. Edison L et al. MMWR. 2017 Oct 20;66(41):1119-20.
7. Choudhry Z et al. J Psychiatry. 2015. doi: 10.4172/2378-5756.10000319.
8. Islam F and Choudhry Z. Current Psychiatry. 2018 Dec;17(12):43-4.
9. Jupe N. Ask the Experts: DOT 5-panel drug test regimen. Quest Diagnostics. 2018 Mar 21. https://blog.employersolutions.com/ask-experts-dot-5-panel-drug-test-regimen/.
10. Ahmed S et al. Pharmacogenomics. 2019 Jun 28;20(9):685-703.
Dr. Islam is a medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Islam reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the IMCHF. He reported no relevant disclosures.
In recent years, Percocet (oxycodone/paracetamol) has experienced a meteoric rise to prominence because of the presence of conspicuous references in pop culture and the ever-evolving hip-hop scene,1 so much so that even propafenone is being mislabeled as the agent.2 It is of utmost importance for clinicians to be made aware of the adverse effects and the treatment protocols associated with Percocet as well as propafenone.
Propafenone is identified as a class 1C antiarrhythmic with adverse effects associated with that particular class of drugs (e.g., generalized tonic-clonic seizures coupled with widened QRS complex), however, Percocet’s toxidrome is the product of the opioid/nonopioid (in the form of oxycodone/acetaminophen) components found within the formulation. Percocet is often recreationally used with MDMA (“molly”) or ecstasy as popularized by the lyrics of “Mask Off” by Future (“Percocets, Molly, Percocets”).3,4
Addressing the challenge of imitation Percocet pills
Differentiating the untoward effects of Percocet and propafenone isn’t too challenging because the agents belong to separate classes – the problem is the use of deceitful labels on propafenone with both medications sporting the “512 imprint” on their respective pills. Initial symptoms of propafenone ingestion may include weakness and dizziness followed by seizures.5As an emergent situation, the patient should be immediately treated with a sodium bicarbonate infusion to effectively reverse the sodium channel blockade associated with the widened QRS.
However, a more likely scenario is that of Percocet counterfeit pills designed to illicitly emulate the properties of officially marketed Percocet. As expected, Percocet overdose management will require that the clinician be familiar with treating general opioid toxicity (in this case, derived from the oxycodone component), in particular respiratory or CNS depression. Symptoms of opioid overdose also include the loss of consciousness with pupillary miosis. Therapy entails the use of naloxone and/or mechanical ventilation for respiratory support. The patient can also exhibit cardiovascular compromise. If further information is elicited during a patient interview, it may reveal a history of drug procurement from the streets.
Epidemiologists from Georgia collaborated with the state’s department of public health’s office of emergency services, forensic experts, and drug enforcement professionals to evaluate almost 40 cases of counterfeit Percocet overdoses during the period spanning the second week of June 2017. Of these cases, a cluster triad was identified consisting of general opioid toxicity symptoms (for example, CNS or respiratory depression with concomitant pupillary constriction, a history of drug procurement, and a history of ingesting only one or two pills with rapid deterioration.6 Unfortunately, the screening process is often hindered by the fact that synthetic opioids such as Percocet are not readily identified on urine drug screens (UDS).
Despite shortcomings in assessment procedures, a UDS will yield positive results for multiple drugs, a feature that is common to seasoned opioid users and serves as an instrumental diagnostic clue in the investigative process. To address the crisis and prevent further spread, numerous Georgia agencies (e.g., drug trafficking and legal authorities) worked with the health care community to expediently identify cases of interest and bring forth public awareness concerning the ongoing perils of counterfeit drug intake. Future investigations might benefit from the implementation of DNA-verified UDS, because those screens are versatile enough to detect the presence of synthetic urine substitutes within the context of opioid use.7,8 Moreover, an expanded panel could be tailored to provide coverage for semisynthetics, including hydrocodone, oxycodone, hydromorphone, and oxymorphone.9
As a well-received painkiller from the opioid family, Percocet derives its analgesic properties from the fast-acting oxycodone; hepatic failure is also possible from Percocet (because of the acetaminophen component) or counterfeit Percocet overdose but is less common unless the Tylenol content approaches 4 grams. By binding to the brain’s opiate receptors, Percocet modulates pain pathways leading to a dulling of pain sensation along with euphoria, which is particularly attractive to drug seekers. Chronic Percocet use corresponds with a myriad of psychological and physical consequences, and the Drug Enforcement Administration recognizes oxycodone as a Schedule II drug.
A chronic Percocet user may try to disrupt the cycle of symptoms by abruptly ceasing use of the offending agent. This can precipitate the development of classical opioid-based withdrawal symptoms, including but not limited to nausea, vomiting, irritability, tachycardia, body aches, and episodes of cold sweats. Physicians have noted that misuse (i.e., deviations from intended prescribed) might include crushing and snorting as well as “doctor-shopping” behaviors for a continuous supply of Percocet.
Treatment recommendations
According to Sarah Wakeman, MD, medical director of the substance use disorders initiative at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, there are apparently two clinical manifestations of Percocet use. The primary consequence is derived from the oxycodone component of Percocet; as an opioid, oxycodone toxicity leads to disrupted breathing and oxygenation, negatively impacting vital organs such as the brain or the heart. Patients experiencing a lack of oxygen will often display cyanosis and may not respond appropriately to stimuli. For individuals suspected of succumbing to overdose, Dr. Wakeman reportedly advised that the clinician or trained professional rub his or her knuckles along the breastbone of the potential user – a drug overdose patient will fail to wake up. On the other hand, a Percocet user may exhibit the symptoms of liver failure depending on the overall level of acetaminophen in the formulation. To prevent relapses, Percocet use disorder is best managed in a professional setting under the direction of trained clinicians; users are provided medications to address ongoing cravings and symptoms associated with the withdrawal process. A detoxification center can tailor the treatment with opioid-based medications such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone to help patients be weaned off Percocet.
Clinicians may further improve the efficacy of a therapeutic regimen by incorporating a personalized plan with a comprehensive substance UDS panel for monitoring and treatment purposes. This may prove to be beneficial in the event of suspected polysubstance use, as is the case with patients who dabble with Percocet and “molly.” Preparations can also be instituted at the outset of therapy with genetic testing implemented in high-risk patients who exhibit an inclination for opioid use disorder.10 Genetic polymorphisms provide robust clinical assets for evaluating patients most at risk for relapse. For individuals with biological susceptibility, arrangements can be made to incorporate nonopioid treatment alternatives.
References
1. Thomas BB. The death of Lil Peep: How the U.S. prescription drug epidemic is changing hip-hop. The Guardian. 2017 Nov 16.
2. D’Orazio JL and Curtis JA. J Emer Med. 2011 Aug 1;41(2):172-5.
3. Levy L. These are the drugs influencing pop culture now. Vulture. 2018 Feb 6.
4. Kounang N and Bender M. “What is Percocet? Drug facts, side effects, abuse and more.” CNN. 2018 Jul 12.
5. The dangers of Percocet use and overdose. American Addiction Centers. Last updated 2020 Feb 3. https://americanaddictioncenters.org/percocet-treatment/dangers-of-use-and-overdose.
6. Edison L et al. MMWR. 2017 Oct 20;66(41):1119-20.
7. Choudhry Z et al. J Psychiatry. 2015. doi: 10.4172/2378-5756.10000319.
8. Islam F and Choudhry Z. Current Psychiatry. 2018 Dec;17(12):43-4.
9. Jupe N. Ask the Experts: DOT 5-panel drug test regimen. Quest Diagnostics. 2018 Mar 21. https://blog.employersolutions.com/ask-experts-dot-5-panel-drug-test-regimen/.
10. Ahmed S et al. Pharmacogenomics. 2019 Jun 28;20(9):685-703.
Dr. Islam is a medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Islam reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the IMCHF. He reported no relevant disclosures.
COVID-19: Hand sanitizer poisonings soar, psych patients at high risk
Cases of poisoning – intentional and unintentional – from ingestion of alcohol-based hand sanitizer have soared during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the United Kingdom alone, alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisonings reported to the National Poisons Information Service jumped 157% – from 155 between January 1 and September 16, 2019, to 398 between Jan. 1 and Sept. 14, 2020, new research shows.
More needs to be done to protect those at risk of unintentional and intentional swallowing of alcohol-based hand sanitizer, including children, people with dementia/confusion, and those with mental health issues, according to Georgia Richards, DPhil student, Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford (England).
“If providers are supplying alcohol-based hand sanitizers in the community to reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2, Ms. Richards said in an interview.
The study was published online Dec. 1 in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
European, U.S. poisoning rates soar
In the paper Ms. Richards described two deaths that occurred in hospitals in England.
In one case, a 30-year-old woman, detained in a psychiatric unit who received the antidepressant venlafaxine was found dead in her hospital bed with a container of hand-sanitizing gel beside her.
“The gel was readily accessible to patients on the ward from a communal dispenser, and patients were allowed to fill cups or other containers with it to keep in their rooms,” Ms. Richards reported.
A postmortem analysis found a high level of alcohol in her blood (214 mg of alcohol in 100 mL of blood). The medical cause of death was listed as “ingestion of alcohol and venlafaxine.” The coroner concluded that the combination of these substances suppressed the patient’s breathing, leading to her death.
The other case involved a 76-year-old man who unintentionally swallowed an unknown quantity of alcohol-based hand-sanitizing foam attached to the foot of his hospital bed.
The patient had a history of agitation and depression and was treated with antidepressants. He had become increasingly confused over the preceding 9 months, possibly because of vascular dementia.
His blood ethanol concentration was 463 mg/dL (100 mmol/L) initially and 354 mg/dL (77mmol/L) 10 hours later. He was admitted to the ICU, where he received lorazepam and haloperidol and treated with ventilation, with a plan to allow the alcohol to be naturally metabolized.
The patient developed complications and died 6 days later. The primary causes of death were bronchopneumonia and acute alcohol toxicity, secondary to acute delirium and coronary artery disease.
Since COVID-19 started, alcohol-based hand sanitizers are among the most sought-after commodities around the world. The volume of these products – now found in homes, hospitals, schools, workplaces, and elsewhere – “may be a cause for concern,” Ms. Richards wrote.
Yet, warnings about the toxicity and lethality of intentional or unintentional ingestion of these products have not been widely disseminated, she noted.
To reduce the risk of harm, Ms. Richards suggested educating the public and health care professionals, improving warning labels on products, and increasing the awareness and reporting of such exposures to public health authorities.
“While governments and public health authorities have successfully heightened our awareness of, and need for, better hand hygiene during the COVID-19 outbreak, they must also make the public aware of the potential harms and encourage the reporting of such harms to poisons information centers,” she noted.
Increases in alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisoning during the pandemic have also been reported in the United States.
The American Association of Poison Control Centers reports that data from the National Poison Data System show 32,892 hand sanitizer exposure cases reported to the 55 U.S. poison control centers from Jan. 1 to Nov. 15, 2020 – an increase of 73%, compared with the same time period during the previous year.
An increase in self-harm
Weighing in on this issue, Robert Bassett, DO, associate medical director of the Poison Control Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview that “cleaning agents and disinfectants have been around for eons and their potential for toxicity hasn’t changed.
“Now with COVID, and this hypervigilance when it comes to cleanliness, there is increased access and the exposure risk has gone up,” he said.
“One of the sad casualties of an overstressed health care system and a globally depressed environment is worsening behavioral health emergencies and, as part of that, the risk of self-harm goes up,” Dr. Bassett added.
“The consensus is that there has been an exacerbation of behavioral health emergencies and behavioral health needs since COVID started and hand sanitizers are readily accessible to someone who may be looking to self-harm,” he said.
This research had no specific funding. Ms. Richards is the editorial registrar of BMJ Evidence Based Medicine and is developing a website to track preventable deaths. Dr. Bassett disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Cases of poisoning – intentional and unintentional – from ingestion of alcohol-based hand sanitizer have soared during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the United Kingdom alone, alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisonings reported to the National Poisons Information Service jumped 157% – from 155 between January 1 and September 16, 2019, to 398 between Jan. 1 and Sept. 14, 2020, new research shows.
More needs to be done to protect those at risk of unintentional and intentional swallowing of alcohol-based hand sanitizer, including children, people with dementia/confusion, and those with mental health issues, according to Georgia Richards, DPhil student, Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford (England).
“If providers are supplying alcohol-based hand sanitizers in the community to reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2, Ms. Richards said in an interview.
The study was published online Dec. 1 in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
European, U.S. poisoning rates soar
In the paper Ms. Richards described two deaths that occurred in hospitals in England.
In one case, a 30-year-old woman, detained in a psychiatric unit who received the antidepressant venlafaxine was found dead in her hospital bed with a container of hand-sanitizing gel beside her.
“The gel was readily accessible to patients on the ward from a communal dispenser, and patients were allowed to fill cups or other containers with it to keep in their rooms,” Ms. Richards reported.
A postmortem analysis found a high level of alcohol in her blood (214 mg of alcohol in 100 mL of blood). The medical cause of death was listed as “ingestion of alcohol and venlafaxine.” The coroner concluded that the combination of these substances suppressed the patient’s breathing, leading to her death.
The other case involved a 76-year-old man who unintentionally swallowed an unknown quantity of alcohol-based hand-sanitizing foam attached to the foot of his hospital bed.
The patient had a history of agitation and depression and was treated with antidepressants. He had become increasingly confused over the preceding 9 months, possibly because of vascular dementia.
His blood ethanol concentration was 463 mg/dL (100 mmol/L) initially and 354 mg/dL (77mmol/L) 10 hours later. He was admitted to the ICU, where he received lorazepam and haloperidol and treated with ventilation, with a plan to allow the alcohol to be naturally metabolized.
The patient developed complications and died 6 days later. The primary causes of death were bronchopneumonia and acute alcohol toxicity, secondary to acute delirium and coronary artery disease.
Since COVID-19 started, alcohol-based hand sanitizers are among the most sought-after commodities around the world. The volume of these products – now found in homes, hospitals, schools, workplaces, and elsewhere – “may be a cause for concern,” Ms. Richards wrote.
Yet, warnings about the toxicity and lethality of intentional or unintentional ingestion of these products have not been widely disseminated, she noted.
To reduce the risk of harm, Ms. Richards suggested educating the public and health care professionals, improving warning labels on products, and increasing the awareness and reporting of such exposures to public health authorities.
“While governments and public health authorities have successfully heightened our awareness of, and need for, better hand hygiene during the COVID-19 outbreak, they must also make the public aware of the potential harms and encourage the reporting of such harms to poisons information centers,” she noted.
Increases in alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisoning during the pandemic have also been reported in the United States.
The American Association of Poison Control Centers reports that data from the National Poison Data System show 32,892 hand sanitizer exposure cases reported to the 55 U.S. poison control centers from Jan. 1 to Nov. 15, 2020 – an increase of 73%, compared with the same time period during the previous year.
An increase in self-harm
Weighing in on this issue, Robert Bassett, DO, associate medical director of the Poison Control Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview that “cleaning agents and disinfectants have been around for eons and their potential for toxicity hasn’t changed.
“Now with COVID, and this hypervigilance when it comes to cleanliness, there is increased access and the exposure risk has gone up,” he said.
“One of the sad casualties of an overstressed health care system and a globally depressed environment is worsening behavioral health emergencies and, as part of that, the risk of self-harm goes up,” Dr. Bassett added.
“The consensus is that there has been an exacerbation of behavioral health emergencies and behavioral health needs since COVID started and hand sanitizers are readily accessible to someone who may be looking to self-harm,” he said.
This research had no specific funding. Ms. Richards is the editorial registrar of BMJ Evidence Based Medicine and is developing a website to track preventable deaths. Dr. Bassett disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Cases of poisoning – intentional and unintentional – from ingestion of alcohol-based hand sanitizer have soared during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the United Kingdom alone, alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisonings reported to the National Poisons Information Service jumped 157% – from 155 between January 1 and September 16, 2019, to 398 between Jan. 1 and Sept. 14, 2020, new research shows.
More needs to be done to protect those at risk of unintentional and intentional swallowing of alcohol-based hand sanitizer, including children, people with dementia/confusion, and those with mental health issues, according to Georgia Richards, DPhil student, Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford (England).
“If providers are supplying alcohol-based hand sanitizers in the community to reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2, Ms. Richards said in an interview.
The study was published online Dec. 1 in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
European, U.S. poisoning rates soar
In the paper Ms. Richards described two deaths that occurred in hospitals in England.
In one case, a 30-year-old woman, detained in a psychiatric unit who received the antidepressant venlafaxine was found dead in her hospital bed with a container of hand-sanitizing gel beside her.
“The gel was readily accessible to patients on the ward from a communal dispenser, and patients were allowed to fill cups or other containers with it to keep in their rooms,” Ms. Richards reported.
A postmortem analysis found a high level of alcohol in her blood (214 mg of alcohol in 100 mL of blood). The medical cause of death was listed as “ingestion of alcohol and venlafaxine.” The coroner concluded that the combination of these substances suppressed the patient’s breathing, leading to her death.
The other case involved a 76-year-old man who unintentionally swallowed an unknown quantity of alcohol-based hand-sanitizing foam attached to the foot of his hospital bed.
The patient had a history of agitation and depression and was treated with antidepressants. He had become increasingly confused over the preceding 9 months, possibly because of vascular dementia.
His blood ethanol concentration was 463 mg/dL (100 mmol/L) initially and 354 mg/dL (77mmol/L) 10 hours later. He was admitted to the ICU, where he received lorazepam and haloperidol and treated with ventilation, with a plan to allow the alcohol to be naturally metabolized.
The patient developed complications and died 6 days later. The primary causes of death were bronchopneumonia and acute alcohol toxicity, secondary to acute delirium and coronary artery disease.
Since COVID-19 started, alcohol-based hand sanitizers are among the most sought-after commodities around the world. The volume of these products – now found in homes, hospitals, schools, workplaces, and elsewhere – “may be a cause for concern,” Ms. Richards wrote.
Yet, warnings about the toxicity and lethality of intentional or unintentional ingestion of these products have not been widely disseminated, she noted.
To reduce the risk of harm, Ms. Richards suggested educating the public and health care professionals, improving warning labels on products, and increasing the awareness and reporting of such exposures to public health authorities.
“While governments and public health authorities have successfully heightened our awareness of, and need for, better hand hygiene during the COVID-19 outbreak, they must also make the public aware of the potential harms and encourage the reporting of such harms to poisons information centers,” she noted.
Increases in alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisoning during the pandemic have also been reported in the United States.
The American Association of Poison Control Centers reports that data from the National Poison Data System show 32,892 hand sanitizer exposure cases reported to the 55 U.S. poison control centers from Jan. 1 to Nov. 15, 2020 – an increase of 73%, compared with the same time period during the previous year.
An increase in self-harm
Weighing in on this issue, Robert Bassett, DO, associate medical director of the Poison Control Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview that “cleaning agents and disinfectants have been around for eons and their potential for toxicity hasn’t changed.
“Now with COVID, and this hypervigilance when it comes to cleanliness, there is increased access and the exposure risk has gone up,” he said.
“One of the sad casualties of an overstressed health care system and a globally depressed environment is worsening behavioral health emergencies and, as part of that, the risk of self-harm goes up,” Dr. Bassett added.
“The consensus is that there has been an exacerbation of behavioral health emergencies and behavioral health needs since COVID started and hand sanitizers are readily accessible to someone who may be looking to self-harm,” he said.
This research had no specific funding. Ms. Richards is the editorial registrar of BMJ Evidence Based Medicine and is developing a website to track preventable deaths. Dr. Bassett disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Infant’s COVID-19–related myocardial injury reversed
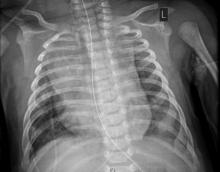
Reports of signs of heart failure in adults with COVID-19 have been rare – just four such cases have been published since the outbreak started in China – and now a team of pediatric cardiologists in New York have reported a case of acute but reversible myocardial injury in an infant with COVID-19.
and right upper lobe atelectasis.
The 2-month-old infant went home after more than 2 weeks in the hospital with no apparent lingering cardiac effects of the illness and not needing any oral heart failure medications, Madhu Sharma, MD, of the Children’s Hospital and Montefiore in New York and colleagues reported in JACC Case Reports. With close follow-up, the child’s left ventricle size and systolic function have remained normal and mitral regurgitation resolved. The case report didn’t mention the infant’s gender.
But before the straightforward postdischarge course emerged, the infant was in a precarious state, and Dr. Sharma and her team were challenged to diagnose the underlying causes.
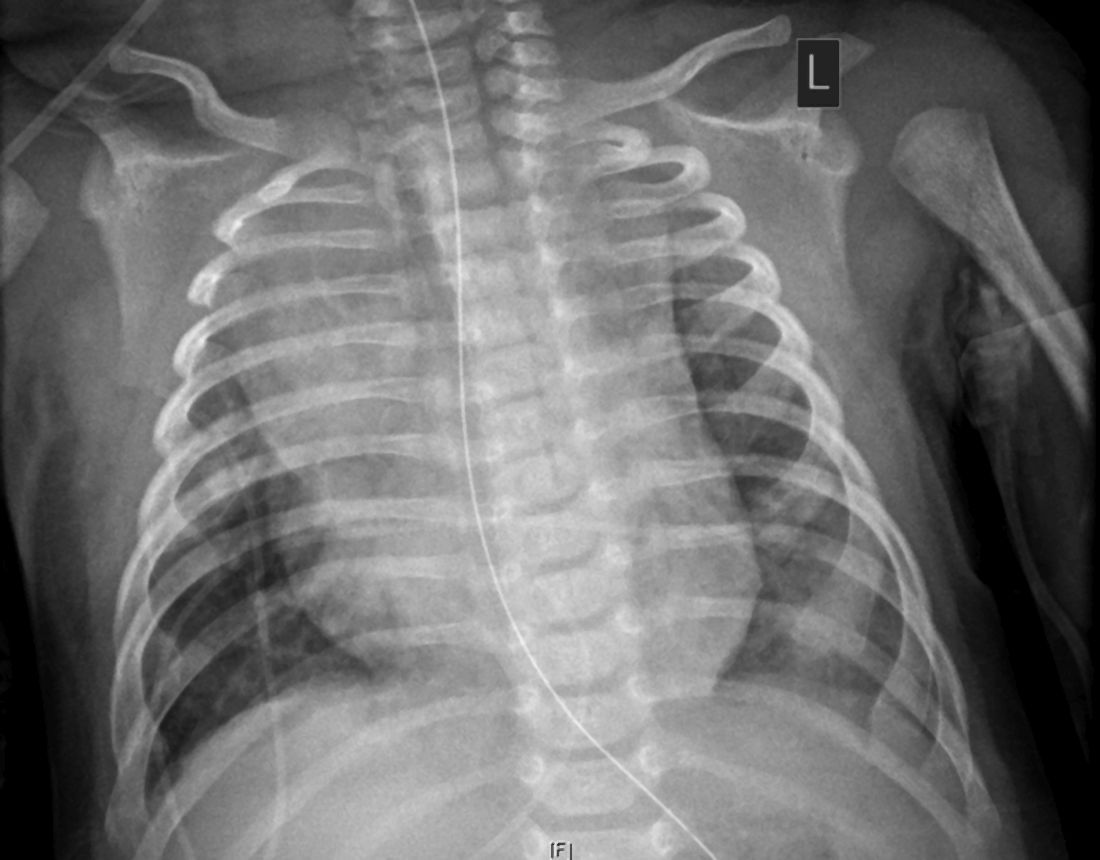
The child, who was born about 7 weeks premature, first came to the hospital having turned blue after choking on food. Nonrebreather mask ventilation was initiated in the ED, and an examination detected a holosystolic murmur. A test for COVID-19 was negative, but a later test was positive, and a chest x-ray exhibited cardiomegaly and signs of fluid and inflammation in the lungs.
An electrocardiogram detected sinus tachycardia, ST-segment depression and other anomalies in cardiac function. Further investigation with a transthoracic ECG showed severely depressed left ventricle systolic function with an ejection fraction of 30%, severe mitral regurgitation, and normal right ventricular systolic function.
Treatment included remdesivir and intravenous antibiotics. Through the hospital course, the patient was extubated to noninvasive ventilation, reintubated, put on intravenous steroid (methylprednisolone) and low-molecular-weight heparin, extubated, and tested throughout for cardiac function.
By day 14, left ventricle size and function normalized, and while the mitral regurgitation remained severe, it improved later without HF therapies. Left ventricle ejection fraction had recovered to 60%, and key cardiac biomarkers had normalized. On day 16, milrinone was discontinued, and the care team determined the patient no longer needed oral heart failure therapies.
“Most children with COVID-19 are either asymptomatic or have mild symptoms, but our case shows the potential for reversible myocardial injury in infants with COVID-19,” said Dr. Sharma. “Testing for COVID-19 in children presenting with signs and symptoms of heart failure is very important as we learn more about the impact of this virus.”
Dr. Sharma and coauthors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.
Reports of signs of heart failure in adults with COVID-19 have been rare – just four such cases have been published since the outbreak started in China – and now a team of pediatric cardiologists in New York have reported a case of acute but reversible myocardial injury in an infant with COVID-19.
and right upper lobe atelectasis.
The 2-month-old infant went home after more than 2 weeks in the hospital with no apparent lingering cardiac effects of the illness and not needing any oral heart failure medications, Madhu Sharma, MD, of the Children’s Hospital and Montefiore in New York and colleagues reported in JACC Case Reports. With close follow-up, the child’s left ventricle size and systolic function have remained normal and mitral regurgitation resolved. The case report didn’t mention the infant’s gender.
But before the straightforward postdischarge course emerged, the infant was in a precarious state, and Dr. Sharma and her team were challenged to diagnose the underlying causes.
The child, who was born about 7 weeks premature, first came to the hospital having turned blue after choking on food. Nonrebreather mask ventilation was initiated in the ED, and an examination detected a holosystolic murmur. A test for COVID-19 was negative, but a later test was positive, and a chest x-ray exhibited cardiomegaly and signs of fluid and inflammation in the lungs.
An electrocardiogram detected sinus tachycardia, ST-segment depression and other anomalies in cardiac function. Further investigation with a transthoracic ECG showed severely depressed left ventricle systolic function with an ejection fraction of 30%, severe mitral regurgitation, and normal right ventricular systolic function.
Treatment included remdesivir and intravenous antibiotics. Through the hospital course, the patient was extubated to noninvasive ventilation, reintubated, put on intravenous steroid (methylprednisolone) and low-molecular-weight heparin, extubated, and tested throughout for cardiac function.
By day 14, left ventricle size and function normalized, and while the mitral regurgitation remained severe, it improved later without HF therapies. Left ventricle ejection fraction had recovered to 60%, and key cardiac biomarkers had normalized. On day 16, milrinone was discontinued, and the care team determined the patient no longer needed oral heart failure therapies.
“Most children with COVID-19 are either asymptomatic or have mild symptoms, but our case shows the potential for reversible myocardial injury in infants with COVID-19,” said Dr. Sharma. “Testing for COVID-19 in children presenting with signs and symptoms of heart failure is very important as we learn more about the impact of this virus.”
Dr. Sharma and coauthors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.
Reports of signs of heart failure in adults with COVID-19 have been rare – just four such cases have been published since the outbreak started in China – and now a team of pediatric cardiologists in New York have reported a case of acute but reversible myocardial injury in an infant with COVID-19.
and right upper lobe atelectasis.
The 2-month-old infant went home after more than 2 weeks in the hospital with no apparent lingering cardiac effects of the illness and not needing any oral heart failure medications, Madhu Sharma, MD, of the Children’s Hospital and Montefiore in New York and colleagues reported in JACC Case Reports. With close follow-up, the child’s left ventricle size and systolic function have remained normal and mitral regurgitation resolved. The case report didn’t mention the infant’s gender.
But before the straightforward postdischarge course emerged, the infant was in a precarious state, and Dr. Sharma and her team were challenged to diagnose the underlying causes.
The child, who was born about 7 weeks premature, first came to the hospital having turned blue after choking on food. Nonrebreather mask ventilation was initiated in the ED, and an examination detected a holosystolic murmur. A test for COVID-19 was negative, but a later test was positive, and a chest x-ray exhibited cardiomegaly and signs of fluid and inflammation in the lungs.
An electrocardiogram detected sinus tachycardia, ST-segment depression and other anomalies in cardiac function. Further investigation with a transthoracic ECG showed severely depressed left ventricle systolic function with an ejection fraction of 30%, severe mitral regurgitation, and normal right ventricular systolic function.
Treatment included remdesivir and intravenous antibiotics. Through the hospital course, the patient was extubated to noninvasive ventilation, reintubated, put on intravenous steroid (methylprednisolone) and low-molecular-weight heparin, extubated, and tested throughout for cardiac function.
By day 14, left ventricle size and function normalized, and while the mitral regurgitation remained severe, it improved later without HF therapies. Left ventricle ejection fraction had recovered to 60%, and key cardiac biomarkers had normalized. On day 16, milrinone was discontinued, and the care team determined the patient no longer needed oral heart failure therapies.
“Most children with COVID-19 are either asymptomatic or have mild symptoms, but our case shows the potential for reversible myocardial injury in infants with COVID-19,” said Dr. Sharma. “Testing for COVID-19 in children presenting with signs and symptoms of heart failure is very important as we learn more about the impact of this virus.”
Dr. Sharma and coauthors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.
FROM JACC CASE REPORTS
Key clinical point: Children presenting with COVID-19 should be tested for heart failure.
Major finding: A 2-month-old infant with COVID-19 had acute but reversible myocardial injury.
Study details: Single case report.
Disclosures: Dr. Sharma, MD, has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Source: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.
Obesity, hypoxia predict severity in children with COVID-19
based on data from 281 patients at 8 locations.
Manifestations of COVID-19 in children include respiratory disease similar to that seen in adults, but the full spectrum of disease in children has been studied mainly in single settings or with a focus on one clinical manifestation, wrote Danielle M. Fernandes, MD, of Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Pediatrics, the researchers identified 281 children hospitalized with COVID-19 and/or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) at 8 sites in Connecticut, New Jersey, and New York. A total of 143 (51%) had respiratory disease, 69 (25%) had MIS-C, and 69 (25%) had other manifestations of illness including 32 patients with gastrointestinal problems, 21 infants with fever, 6 cases of neurologic disease, 6 cases of diabetic ketoacidosis, and 4 patients with other indications. The median age of the patients was 10 years, 60% were male, 51% were Hispanic, and 23% were non-Hispanic Black. The most common comorbidities were obesity (34%) and asthma (14%).
Independent predictors of disease severity in children found
After controlling for multiple variables, obesity and hypoxia at hospital admission were significant independent predictors of severe respiratory disease, with odds ratios of 3.39 and 4.01, respectively. In addition, lower absolute lymphocyte count (OR, 8.33 per unit decrease in 109 cells/L) and higher C-reactive protein (OR, 1.06 per unit increase in mg/dL) were significantly predictive of severe MIS-C (P = .001 and P = .017, respectively).
“The association between weight and severe respiratory COVID-19 is consistent with the adult literature; however, the mechanisms of this association require further study,” Dr. Fernandes and associates noted.
Overall, children with MIS-C were significantly more likely to be non-Hispanic Black, compared with children with respiratory disease, an 18% difference. However, neither race/ethnicity nor socioeconomic status were significant predictors of disease severity, the researchers wrote.
During the study period, 7 patients (2%) died and 114 (41%) were admitted to the ICU.
“We found a wide array of clinical manifestations in children and youth hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2,” Dr. Fernandes and associates wrote. Notably, gastrointestinal symptoms, ocular symptoms, and dermatologic symptoms have rarely been noted in adults with COVID-19, but occurred in more than 30% of the pediatric patients.
“We also found that SARS-CoV-2 can be an incidental finding in a substantial number of hospitalized pediatric patients,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including a population of patients only from Connecticut, New Jersey, and New York, and the possibility that decisions on hospital and ICU admission may have varied by location, the researchers said. In addition, approaches may have varied in the absence of data on the optimal treatment of MIS-C.
“This study builds on the growing body of evidence showing that mortality in hospitalized pediatric patients is low, compared with adults,” Dr. Fernandes and associates said. “However, it highlights that the young population is not universally spared from morbidity, and that even previously healthy children and youth can develop severe disease requiring supportive therapy.”
Findings confirm other clinical experience
The study was important to show that, “although most children are spared severe illness from COVID-19, some children are hospitalized both with acute COVID-19 respiratory disease, with MIS-C and with a range of other complications,” Adrienne Randolph, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Dr. Randolph said she was not surprised by the study findings, “as we are also seeing these types of complications at Boston Children’s Hospital where I work.”
Additional research is needed on the outcomes of these patients, “especially the longer-term sequelae of having COVID-19 or MIS-C early in life,” she emphasized.
The take-home message to clinicians from the findings at this time is to be aware that children and adolescents can become severely ill from COVID-19–related complications, said Dr. Randolph. “Some of the laboratory values on presentation appear to be associated with disease severity.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Randolph disclosed funding from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to lead the Overcoming COVID-19 Study in U.S. Children and Adults.
SOURCE: Fernandes DM et al. J Pediatr. 2020 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.11.016.
based on data from 281 patients at 8 locations.
Manifestations of COVID-19 in children include respiratory disease similar to that seen in adults, but the full spectrum of disease in children has been studied mainly in single settings or with a focus on one clinical manifestation, wrote Danielle M. Fernandes, MD, of Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Pediatrics, the researchers identified 281 children hospitalized with COVID-19 and/or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) at 8 sites in Connecticut, New Jersey, and New York. A total of 143 (51%) had respiratory disease, 69 (25%) had MIS-C, and 69 (25%) had other manifestations of illness including 32 patients with gastrointestinal problems, 21 infants with fever, 6 cases of neurologic disease, 6 cases of diabetic ketoacidosis, and 4 patients with other indications. The median age of the patients was 10 years, 60% were male, 51% were Hispanic, and 23% were non-Hispanic Black. The most common comorbidities were obesity (34%) and asthma (14%).
Independent predictors of disease severity in children found
After controlling for multiple variables, obesity and hypoxia at hospital admission were significant independent predictors of severe respiratory disease, with odds ratios of 3.39 and 4.01, respectively. In addition, lower absolute lymphocyte count (OR, 8.33 per unit decrease in 109 cells/L) and higher C-reactive protein (OR, 1.06 per unit increase in mg/dL) were significantly predictive of severe MIS-C (P = .001 and P = .017, respectively).
“The association between weight and severe respiratory COVID-19 is consistent with the adult literature; however, the mechanisms of this association require further study,” Dr. Fernandes and associates noted.
Overall, children with MIS-C were significantly more likely to be non-Hispanic Black, compared with children with respiratory disease, an 18% difference. However, neither race/ethnicity nor socioeconomic status were significant predictors of disease severity, the researchers wrote.
During the study period, 7 patients (2%) died and 114 (41%) were admitted to the ICU.
“We found a wide array of clinical manifestations in children and youth hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2,” Dr. Fernandes and associates wrote. Notably, gastrointestinal symptoms, ocular symptoms, and dermatologic symptoms have rarely been noted in adults with COVID-19, but occurred in more than 30% of the pediatric patients.
“We also found that SARS-CoV-2 can be an incidental finding in a substantial number of hospitalized pediatric patients,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including a population of patients only from Connecticut, New Jersey, and New York, and the possibility that decisions on hospital and ICU admission may have varied by location, the researchers said. In addition, approaches may have varied in the absence of data on the optimal treatment of MIS-C.
“This study builds on the growing body of evidence showing that mortality in hospitalized pediatric patients is low, compared with adults,” Dr. Fernandes and associates said. “However, it highlights that the young population is not universally spared from morbidity, and that even previously healthy children and youth can develop severe disease requiring supportive therapy.”
Findings confirm other clinical experience
The study was important to show that, “although most children are spared severe illness from COVID-19, some children are hospitalized both with acute COVID-19 respiratory disease, with MIS-C and with a range of other complications,” Adrienne Randolph, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Dr. Randolph said she was not surprised by the study findings, “as we are also seeing these types of complications at Boston Children’s Hospital where I work.”
Additional research is needed on the outcomes of these patients, “especially the longer-term sequelae of having COVID-19 or MIS-C early in life,” she emphasized.
The take-home message to clinicians from the findings at this time is to be aware that children and adolescents can become severely ill from COVID-19–related complications, said Dr. Randolph. “Some of the laboratory values on presentation appear to be associated with disease severity.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Randolph disclosed funding from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to lead the Overcoming COVID-19 Study in U.S. Children and Adults.
SOURCE: Fernandes DM et al. J Pediatr. 2020 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.11.016.
based on data from 281 patients at 8 locations.
Manifestations of COVID-19 in children include respiratory disease similar to that seen in adults, but the full spectrum of disease in children has been studied mainly in single settings or with a focus on one clinical manifestation, wrote Danielle M. Fernandes, MD, of Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Pediatrics, the researchers identified 281 children hospitalized with COVID-19 and/or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) at 8 sites in Connecticut, New Jersey, and New York. A total of 143 (51%) had respiratory disease, 69 (25%) had MIS-C, and 69 (25%) had other manifestations of illness including 32 patients with gastrointestinal problems, 21 infants with fever, 6 cases of neurologic disease, 6 cases of diabetic ketoacidosis, and 4 patients with other indications. The median age of the patients was 10 years, 60% were male, 51% were Hispanic, and 23% were non-Hispanic Black. The most common comorbidities were obesity (34%) and asthma (14%).
Independent predictors of disease severity in children found
After controlling for multiple variables, obesity and hypoxia at hospital admission were significant independent predictors of severe respiratory disease, with odds ratios of 3.39 and 4.01, respectively. In addition, lower absolute lymphocyte count (OR, 8.33 per unit decrease in 109 cells/L) and higher C-reactive protein (OR, 1.06 per unit increase in mg/dL) were significantly predictive of severe MIS-C (P = .001 and P = .017, respectively).
“The association between weight and severe respiratory COVID-19 is consistent with the adult literature; however, the mechanisms of this association require further study,” Dr. Fernandes and associates noted.
Overall, children with MIS-C were significantly more likely to be non-Hispanic Black, compared with children with respiratory disease, an 18% difference. However, neither race/ethnicity nor socioeconomic status were significant predictors of disease severity, the researchers wrote.
During the study period, 7 patients (2%) died and 114 (41%) were admitted to the ICU.
“We found a wide array of clinical manifestations in children and youth hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2,” Dr. Fernandes and associates wrote. Notably, gastrointestinal symptoms, ocular symptoms, and dermatologic symptoms have rarely been noted in adults with COVID-19, but occurred in more than 30% of the pediatric patients.
“We also found that SARS-CoV-2 can be an incidental finding in a substantial number of hospitalized pediatric patients,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including a population of patients only from Connecticut, New Jersey, and New York, and the possibility that decisions on hospital and ICU admission may have varied by location, the researchers said. In addition, approaches may have varied in the absence of data on the optimal treatment of MIS-C.
“This study builds on the growing body of evidence showing that mortality in hospitalized pediatric patients is low, compared with adults,” Dr. Fernandes and associates said. “However, it highlights that the young population is not universally spared from morbidity, and that even previously healthy children and youth can develop severe disease requiring supportive therapy.”
Findings confirm other clinical experience
The study was important to show that, “although most children are spared severe illness from COVID-19, some children are hospitalized both with acute COVID-19 respiratory disease, with MIS-C and with a range of other complications,” Adrienne Randolph, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Dr. Randolph said she was not surprised by the study findings, “as we are also seeing these types of complications at Boston Children’s Hospital where I work.”
Additional research is needed on the outcomes of these patients, “especially the longer-term sequelae of having COVID-19 or MIS-C early in life,” she emphasized.
The take-home message to clinicians from the findings at this time is to be aware that children and adolescents can become severely ill from COVID-19–related complications, said Dr. Randolph. “Some of the laboratory values on presentation appear to be associated with disease severity.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Randolph disclosed funding from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to lead the Overcoming COVID-19 Study in U.S. Children and Adults.
SOURCE: Fernandes DM et al. J Pediatr. 2020 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.11.016.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PEDIATRICS
An alternative path to recertification
Recertification will include physicians who were initially board certified with UCNS in the subspecialties of autonomic disorders, behavioral neurology and neuropsychiatry, clinical neuromuscular pathology, geriatric neurology, headache medicine, neurocritical care, neuroimaging, and neuro-oncology.
In 2020, UCNS transitioned to a new continuous-certification (C-cert) model that requires its diplomates to pay an annual fee of $175 and complete a 25-question online quiz based on preselected journal articles with an 80% passing grade. In a press release outlining the details of the new C-cert program, UCNS said that diplomates began the transition last year by “attesting they have participated in subspecialty-specific continuing medical education (CME) requirements from the time their most recent certificate was issued through 2019.” Diplomates have a 2-year window, which began in 2019, to meet these transitional CME requirements and complete an attestation statement before their certification lapses. “Diplomates with a status of ‘meeting requirements’ will be issued a replacement certificate that shows their original certification date and will reflect there is no expiration date after they pay the first annual C-cert fee in 2020,” UCNS said in the press release.
“It is unfortunate that despite requests from diplomates and other stakeholders, UCNS has decided to impose new requirements and additional fees on diplomates who have unexpired certificates based on passing an examination that granted a 10-year certification,” Paul G. Mathew, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School in Boston and Director of Legislative Affairs at NBPAS, said in an interview. “A one-size-fits-all approach for learning with preselected articles is not ideal, and physicians should be able to choose CME and other learning activities that best suit their individual interests and practice.”
The added requirements and fees have caused some UCNS diplomates to consider letting their certification lapse, Dr. Mathew said, but the NBPAS decision offers them a new path to recertification. “Many physicians who would have otherwise let their certification lapse and would no longer be considered board certified in headache medicine and other UCNS subspecialties will now have the option to recertify with NBPAS,” he said.
NBPAS was formed in 2014 in response to controversial American Board of Medical Specialties Maintenance of Certification (MOC) programs. NBPAS recertifies diplomates of all specialties and subspecialties offered by the ABMS and its member boards, including board certification in neurology and neurologic subspecialties offered by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology.
Board recertification with NBPAS requires an unrestricted license to practice medicine in the United States, an initial certification with ABPN, the American Osteopathic Association, and/or UCNS, a medical staff appointment/membership in good standing, active hospital privileges based on specialty, and 50 hours of relevant CME credits every 2 years.
“Although MOC compliance is not required for licensure, the vast majority of insurance carriers in the United States require to some extent that their physicians be MOC compliant. As such, the ABMS has a monopoly in that a physician cannot practice medicine without complying with MOC,” Dr. Mathew said. “That’s very gradually changing.”
So far, 13 states have passed legislation limiting ABMS MOC compliance as a requirement for credentialing or licensure, and 136 healthcare institutions have recognized NBPAS as a pathway for physician credentialing, according to an NBPAS press release.
Changing the rules
Alan Rapoport, MD, was asked to comment on the recertification situtaion. Dr. Rapoport is clinical professor of neurology at UCLA and the Editor in Chief of Neurology Reviews. “As Dr. Mathew aptly states, it is unfortunate that despite requests from diplomates and other stakeholders, UCNS has decided to impose new requirements and additional fees on diplomates who have unexpired certificates based on passing an examination that granted a 10-year certification,”
For context, Dr. Rapoport explained what has happened to him and about 200 neurologists and a few other specialists who took the first UCNS certifying exam in Headache Medicine. “I sat for the first exam in a testing center in 2006, after paying a large fee. I passed and was granted a certificate for a 10-year certification in Headache Medicine. Prior to the expiration of that certificate, I was told I had to pay about $1,800 and take a similar examination to certify for another 10 years. I was not sure I needed to do that, but I did so anyway and passed and was granted a new, dated certificate for another 10 years of certification in Headache Medicine. Shortly after that I began to get notices from UCNS saying that they were changing their certification process and I would soon have to read their designated articles, take an examination on that literature, pay $175 for this privilege of C-Cert yearly, all in spite of the fact that I had a valid certificate for 10 years of certification.”
After complaints from Dr. Rapoport and many others, “UCNS said we would only have to do this when we had 5 years left on our certification. When they advertised this new C-Cert plan on the AAN Headache Listserv, even though advertising was against the rules of the Listserv, I complained about it saying we had paid for a 10-year certification. Their response was to abruptly take me off the Listserv. Then they temporarily shut it down when others agreed with what I had written.”
Dr. Rapoport has the certificate that proves that he has 6 years left on his certification, but UCNS will not recognize this, he said. “I believe that to be unfair, unethical, and probably illegal, as do many senior Headache specialists in the country who have the same issue. The attorney for the UCNS, who is also the attorney for the AAN, has disregarded our objections to this move.”
Now the NBPAS will be recertifying Headache Medicine doctors and those of other specialties who are in a similar situation and do not want to pay for the privilege of taking exams yearly when they have already been certified. “I expect many specialists will switch to this new way of certifying,” Dr. Rapoport said.
“I believe the UCNS has cheapened the value of their certifications by not honoring them,” Dr. Rapoort said.
Dr. Mathew reports that he collects no salary for his role with NBPAS, but receives reimbursement for travel expenses, and occasionally receives honoraria for speaking on behalf of NBPAS.
Recertification will include physicians who were initially board certified with UCNS in the subspecialties of autonomic disorders, behavioral neurology and neuropsychiatry, clinical neuromuscular pathology, geriatric neurology, headache medicine, neurocritical care, neuroimaging, and neuro-oncology.
In 2020, UCNS transitioned to a new continuous-certification (C-cert) model that requires its diplomates to pay an annual fee of $175 and complete a 25-question online quiz based on preselected journal articles with an 80% passing grade. In a press release outlining the details of the new C-cert program, UCNS said that diplomates began the transition last year by “attesting they have participated in subspecialty-specific continuing medical education (CME) requirements from the time their most recent certificate was issued through 2019.” Diplomates have a 2-year window, which began in 2019, to meet these transitional CME requirements and complete an attestation statement before their certification lapses. “Diplomates with a status of ‘meeting requirements’ will be issued a replacement certificate that shows their original certification date and will reflect there is no expiration date after they pay the first annual C-cert fee in 2020,” UCNS said in the press release.
“It is unfortunate that despite requests from diplomates and other stakeholders, UCNS has decided to impose new requirements and additional fees on diplomates who have unexpired certificates based on passing an examination that granted a 10-year certification,” Paul G. Mathew, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School in Boston and Director of Legislative Affairs at NBPAS, said in an interview. “A one-size-fits-all approach for learning with preselected articles is not ideal, and physicians should be able to choose CME and other learning activities that best suit their individual interests and practice.”
The added requirements and fees have caused some UCNS diplomates to consider letting their certification lapse, Dr. Mathew said, but the NBPAS decision offers them a new path to recertification. “Many physicians who would have otherwise let their certification lapse and would no longer be considered board certified in headache medicine and other UCNS subspecialties will now have the option to recertify with NBPAS,” he said.
NBPAS was formed in 2014 in response to controversial American Board of Medical Specialties Maintenance of Certification (MOC) programs. NBPAS recertifies diplomates of all specialties and subspecialties offered by the ABMS and its member boards, including board certification in neurology and neurologic subspecialties offered by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology.
Board recertification with NBPAS requires an unrestricted license to practice medicine in the United States, an initial certification with ABPN, the American Osteopathic Association, and/or UCNS, a medical staff appointment/membership in good standing, active hospital privileges based on specialty, and 50 hours of relevant CME credits every 2 years.
“Although MOC compliance is not required for licensure, the vast majority of insurance carriers in the United States require to some extent that their physicians be MOC compliant. As such, the ABMS has a monopoly in that a physician cannot practice medicine without complying with MOC,” Dr. Mathew said. “That’s very gradually changing.”
So far, 13 states have passed legislation limiting ABMS MOC compliance as a requirement for credentialing or licensure, and 136 healthcare institutions have recognized NBPAS as a pathway for physician credentialing, according to an NBPAS press release.
Changing the rules
Alan Rapoport, MD, was asked to comment on the recertification situtaion. Dr. Rapoport is clinical professor of neurology at UCLA and the Editor in Chief of Neurology Reviews. “As Dr. Mathew aptly states, it is unfortunate that despite requests from diplomates and other stakeholders, UCNS has decided to impose new requirements and additional fees on diplomates who have unexpired certificates based on passing an examination that granted a 10-year certification,”
For context, Dr. Rapoport explained what has happened to him and about 200 neurologists and a few other specialists who took the first UCNS certifying exam in Headache Medicine. “I sat for the first exam in a testing center in 2006, after paying a large fee. I passed and was granted a certificate for a 10-year certification in Headache Medicine. Prior to the expiration of that certificate, I was told I had to pay about $1,800 and take a similar examination to certify for another 10 years. I was not sure I needed to do that, but I did so anyway and passed and was granted a new, dated certificate for another 10 years of certification in Headache Medicine. Shortly after that I began to get notices from UCNS saying that they were changing their certification process and I would soon have to read their designated articles, take an examination on that literature, pay $175 for this privilege of C-Cert yearly, all in spite of the fact that I had a valid certificate for 10 years of certification.”
After complaints from Dr. Rapoport and many others, “UCNS said we would only have to do this when we had 5 years left on our certification. When they advertised this new C-Cert plan on the AAN Headache Listserv, even though advertising was against the rules of the Listserv, I complained about it saying we had paid for a 10-year certification. Their response was to abruptly take me off the Listserv. Then they temporarily shut it down when others agreed with what I had written.”
Dr. Rapoport has the certificate that proves that he has 6 years left on his certification, but UCNS will not recognize this, he said. “I believe that to be unfair, unethical, and probably illegal, as do many senior Headache specialists in the country who have the same issue. The attorney for the UCNS, who is also the attorney for the AAN, has disregarded our objections to this move.”
Now the NBPAS will be recertifying Headache Medicine doctors and those of other specialties who are in a similar situation and do not want to pay for the privilege of taking exams yearly when they have already been certified. “I expect many specialists will switch to this new way of certifying,” Dr. Rapoport said.
“I believe the UCNS has cheapened the value of their certifications by not honoring them,” Dr. Rapoort said.
Dr. Mathew reports that he collects no salary for his role with NBPAS, but receives reimbursement for travel expenses, and occasionally receives honoraria for speaking on behalf of NBPAS.
Recertification will include physicians who were initially board certified with UCNS in the subspecialties of autonomic disorders, behavioral neurology and neuropsychiatry, clinical neuromuscular pathology, geriatric neurology, headache medicine, neurocritical care, neuroimaging, and neuro-oncology.
In 2020, UCNS transitioned to a new continuous-certification (C-cert) model that requires its diplomates to pay an annual fee of $175 and complete a 25-question online quiz based on preselected journal articles with an 80% passing grade. In a press release outlining the details of the new C-cert program, UCNS said that diplomates began the transition last year by “attesting they have participated in subspecialty-specific continuing medical education (CME) requirements from the time their most recent certificate was issued through 2019.” Diplomates have a 2-year window, which began in 2019, to meet these transitional CME requirements and complete an attestation statement before their certification lapses. “Diplomates with a status of ‘meeting requirements’ will be issued a replacement certificate that shows their original certification date and will reflect there is no expiration date after they pay the first annual C-cert fee in 2020,” UCNS said in the press release.
“It is unfortunate that despite requests from diplomates and other stakeholders, UCNS has decided to impose new requirements and additional fees on diplomates who have unexpired certificates based on passing an examination that granted a 10-year certification,” Paul G. Mathew, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School in Boston and Director of Legislative Affairs at NBPAS, said in an interview. “A one-size-fits-all approach for learning with preselected articles is not ideal, and physicians should be able to choose CME and other learning activities that best suit their individual interests and practice.”
The added requirements and fees have caused some UCNS diplomates to consider letting their certification lapse, Dr. Mathew said, but the NBPAS decision offers them a new path to recertification. “Many physicians who would have otherwise let their certification lapse and would no longer be considered board certified in headache medicine and other UCNS subspecialties will now have the option to recertify with NBPAS,” he said.
NBPAS was formed in 2014 in response to controversial American Board of Medical Specialties Maintenance of Certification (MOC) programs. NBPAS recertifies diplomates of all specialties and subspecialties offered by the ABMS and its member boards, including board certification in neurology and neurologic subspecialties offered by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology.
Board recertification with NBPAS requires an unrestricted license to practice medicine in the United States, an initial certification with ABPN, the American Osteopathic Association, and/or UCNS, a medical staff appointment/membership in good standing, active hospital privileges based on specialty, and 50 hours of relevant CME credits every 2 years.
“Although MOC compliance is not required for licensure, the vast majority of insurance carriers in the United States require to some extent that their physicians be MOC compliant. As such, the ABMS has a monopoly in that a physician cannot practice medicine without complying with MOC,” Dr. Mathew said. “That’s very gradually changing.”
So far, 13 states have passed legislation limiting ABMS MOC compliance as a requirement for credentialing or licensure, and 136 healthcare institutions have recognized NBPAS as a pathway for physician credentialing, according to an NBPAS press release.
Changing the rules
Alan Rapoport, MD, was asked to comment on the recertification situtaion. Dr. Rapoport is clinical professor of neurology at UCLA and the Editor in Chief of Neurology Reviews. “As Dr. Mathew aptly states, it is unfortunate that despite requests from diplomates and other stakeholders, UCNS has decided to impose new requirements and additional fees on diplomates who have unexpired certificates based on passing an examination that granted a 10-year certification,”
For context, Dr. Rapoport explained what has happened to him and about 200 neurologists and a few other specialists who took the first UCNS certifying exam in Headache Medicine. “I sat for the first exam in a testing center in 2006, after paying a large fee. I passed and was granted a certificate for a 10-year certification in Headache Medicine. Prior to the expiration of that certificate, I was told I had to pay about $1,800 and take a similar examination to certify for another 10 years. I was not sure I needed to do that, but I did so anyway and passed and was granted a new, dated certificate for another 10 years of certification in Headache Medicine. Shortly after that I began to get notices from UCNS saying that they were changing their certification process and I would soon have to read their designated articles, take an examination on that literature, pay $175 for this privilege of C-Cert yearly, all in spite of the fact that I had a valid certificate for 10 years of certification.”
After complaints from Dr. Rapoport and many others, “UCNS said we would only have to do this when we had 5 years left on our certification. When they advertised this new C-Cert plan on the AAN Headache Listserv, even though advertising was against the rules of the Listserv, I complained about it saying we had paid for a 10-year certification. Their response was to abruptly take me off the Listserv. Then they temporarily shut it down when others agreed with what I had written.”
Dr. Rapoport has the certificate that proves that he has 6 years left on his certification, but UCNS will not recognize this, he said. “I believe that to be unfair, unethical, and probably illegal, as do many senior Headache specialists in the country who have the same issue. The attorney for the UCNS, who is also the attorney for the AAN, has disregarded our objections to this move.”
Now the NBPAS will be recertifying Headache Medicine doctors and those of other specialties who are in a similar situation and do not want to pay for the privilege of taking exams yearly when they have already been certified. “I expect many specialists will switch to this new way of certifying,” Dr. Rapoport said.
“I believe the UCNS has cheapened the value of their certifications by not honoring them,” Dr. Rapoort said.
Dr. Mathew reports that he collects no salary for his role with NBPAS, but receives reimbursement for travel expenses, and occasionally receives honoraria for speaking on behalf of NBPAS.
Several strategies can prevent pandemic-related weight gain
If you have been faithfully following the COVID-19 stay-at-home restrictive orders, you may have become a victim of “COVID-15,” the additional, unexpected, unwanted 10- to 15-pound weight gain that is making your clothes not fit so well any more.
A change in routine; being home in comfy, stretchable clothing in front of the TV; and having unhealthy, processed foods ready to grab have set us up to lose the battle with COVID-15. We are set up to gain the weight because of excessive or unhealthful eating, taking an extra daily shot of alcohol, and being inactive, bored, depressed, anxious, and isolated from coworkers and family. Beware – weight gain can be “catching”; we tend to adopt the same poor eating habits and eat the same junk foods as those around us.
Since psychiatry can be a sedentary profession, I’ve (R.W.C.) kept myself very active and physically fit. Prior to the pandemic, I played tennis and ran every day. I was obese only once in my life. I had not realized that I had gained a lot of weight.
Thankfully, a physician called me “obese.” Initially, I was angry at the doctor, however, I realized that he did me the biggest favor of my life. I changed my diet and eating habits, and for the past 20 years, kept my weight between 135-140 pounds and my BMI at 23 consistently – until the pandemic stress caused me to fall into the same bad eating habits that have caused many others to gain the COVID-15.
I was surprised to see that when I weighed myself, and I had gained 12 pounds! I immediately modified my diet and increased my physical activity. I have now lost the extra 12 pounds and will offer suggestions that may help you and your patients exceed your prepandemic physical condition.
Possible solutions
1. Keep a food journal. Write down what you eat, the amount of food you eat, the time you are eating, and your mood at that moment. Keeping a small notebook to record what and when you eat is important because upon review, it will make you face reality and be accountable for what you put in your mouth. Until you review your journal, you may have underestimated the amount, as well as the kinds, of food and drinks you actually consume. A food journal can show your areas of struggle and unhealthy eating habits and help you make necessary changes in your habits and diet to eventually lose weight. You will be less likely to eat junk food or have an extra serving of food. If you do not want to use paper and pencil, you can download an app on your phone, such as myplate tracker to keep track of your food and calorie intake. Do your journaling immediately after you eat and include snacks; do not wait until night time to record your food and journal. Include your mood or how you felt during your meal or snack (for example, were you bored, sad, or anxious) since this information will indicate why you may be overeating.
2. Develop healthful eating habits. Eat a maximum of three meals and three snacks per day but eat only when you are hungry (that is, when your stomach growls or you feel light headed). Limiting yourself to eating only when you are hungry will help eliminate emotional eating to fill a loss in your life or to deal with feelings of stress, anxiety, sadness, or isolation, which have been exacerbated by the pandemic. Buy eat only healthful foods and not items with empty calories, such as chips, cake, and items with sugar. When you are eating, devote yourself to that activity only, eat slowly, and savor each bite. Do not watch television during your meal time.
3. Record the amount and type of exercise you engage in each day and determine the number of calories burned. Walk, run, or bicycle outside, or exercise inside with stretching, weights, or an exercycle. You may use a website, such as diet tool on WebMD.com to calculate daily calories burned. To lose weight, calories burned during a day must exceed caloric intake. You may want to invest in a Fitbit or an Apple Watch and use the health section to determine your caloric intake versus output. Analyzing your caloric data will provide a concrete measure of your progress.
4. Do not overconsume calories or underconsume protein. Protein plays a key role in the creation and maintenance of every cell of your body, and because the body does not store protein, it is important to consume it every day. To meet basic protein requirements, the DRI (Dietary Reference Intake) recommends 0.36 grams of protein per pound (0.8 grams per kg) of body weight. This amounts to: 56 grams per day for the average sedentary man, and 46 grams per day for the average sedentary woman. There is also an app entitled the Protein Tracker that can simplify your calculations.
5. Drink water. It is important to be hydrated to regulate body temperature, keep joints lubricated, prevent infections, deliver nutrients to cells, and keep organs functioning properly. Being well hydrated also improves sleep, cognition, and mood. Your daily water intake by ounce should be equal to your weight in pounds multiplied by two-thirds (or 67%) to determine the amount of water to drink daily. For example, if you weigh 175 pounds, you would multiply 175 by two-thirds and learn that you should be drinking about 117 ounces of water every day. You can also meet some of your daily water requirements by consuming fruits and vegetables, such as tomatoes, watermelon, lettuce, etc.
Also, drink 2 cups (16 oz.) of water before every meal: Often when you feel hungry, it is because your body simply needs water. Science has proven that drinking 2 cups of water before every meal helps you to eat less during meal time and lose weight. If you do this three times daily – at breakfast, lunch, and dinner – you have already consumed 48 ounces of water.
6. Keep track of your progress. In addition to keeping and analyzing your food journal, weigh yourself once or twice a week. Do not weigh yourself every day; you will not see any results on a day-to-day basis, but once a week gives your body time to regulate and show progress. Always calibrate/zero your scale before each use, and weigh yourself at the same time of the day (preferably after you first wake up in the morning) while wearing the same type of clothing. Keep a record of your weight in your journal to track your progress. Do not panic if the scale indicates you gained 1, 2, or 3 pounds, your weight can fluctuate because of glycogen storage, sodium retention, human bias, reporting or recall errors, and home scales can have a plus or minus 3 pound margin of error. Look at your weight trend over time. You may prefer buying a scale that indicates both weight and body mass index.
7. Celebrate and reward yourself with nonfood items. A healthful fitness and diet regime requires energy and dedication, so if you are able to follow a healthful routine, reward yourself with nonfood rewards for your good choices and new habits as an incentive to maintain your healthful behavior.
8. Don’t buy it if you can’t stop eating it. The biggest decision you make is when you decide what you are going to buy. Don’t lie to yourself in the store that you will only eat one at a time. Only buy what you can afford to binge eat if you can’t stop yourself from eating any particular type of food.
9. Have someone hide the food you can’t resist. You can’t eat what you can’t find. If you can’t avoid having irresistible food around, ask another adult to hide the food from you.
10. Learn what harm foods can cause in your body. Read about the effects of high blood sugar and high blood pressure can cause in your body. Find out which foods boost your immune system. Demonize the bad foods in your mind. Make up your mind before you go into the store that you are going to read food labels and find the best quality food with the lowest amount of sugar or saturated fat. Appreciate the flavor of vegetables and fruit.
11. Treat sugar as if it were an addictive drug. You can’t have just one. If you reduce your craving for sugar by slowly reducing your intake of sugar, you will find that you don’t crave sugar any more. This won’t be easy, but once it is done, you will be preventing many of the ravages that sugar takes on your body over time. But you can’t have one piece of pie because the craving will come back. At some point, it may be more likely that you find that piece of pie too sweet.
Here are a few other ideas: Buy a gift for yourself or new clothes, makeup, a plant or flowers, running shoes, exercise clothes, fitness tracker, water bottle, book, movie or network subscription. Improve your home décor. Or treat yourself to online lessons for painting, music, and so on. Or you might adopt a dog, donate food to a shelter or food bank; or organize and declutter your home since staying busy will give you a reason not to eat. In nice weather, enjoy the outdoors by going for a walk, run, bikeride or by gardening.
We are all worried about getting COVID-19. Preventing COVID-15 will go a long way toward boosting our immune systems to help protect us from the coronavirus.
Dr. Cohen is board-certified in psychiatry and has had a private practice in Philadelphia for more than 35 years. His areas of specialty include sports psychiatry, agoraphobia, depression, and substance abuse. In addition, Dr. Cohen is a former professor of psychiatry, family medicine, and otolaryngology at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia. He has no conflicts of interest. Ms. Cohen holds an MBA from Temple University in Philadelphia with a focus on health care administration. Previously, Ms. Cohen was an associate administrator at Hahnemann University Hospital and an executive at the Health Services Council, both in Philadelphia. She currently writes biographical summaries of notable 18th- and 19th-century women. Ms. Cohen has no conflicts of interest.
If you have been faithfully following the COVID-19 stay-at-home restrictive orders, you may have become a victim of “COVID-15,” the additional, unexpected, unwanted 10- to 15-pound weight gain that is making your clothes not fit so well any more.
A change in routine; being home in comfy, stretchable clothing in front of the TV; and having unhealthy, processed foods ready to grab have set us up to lose the battle with COVID-15. We are set up to gain the weight because of excessive or unhealthful eating, taking an extra daily shot of alcohol, and being inactive, bored, depressed, anxious, and isolated from coworkers and family. Beware – weight gain can be “catching”; we tend to adopt the same poor eating habits and eat the same junk foods as those around us.
Since psychiatry can be a sedentary profession, I’ve (R.W.C.) kept myself very active and physically fit. Prior to the pandemic, I played tennis and ran every day. I was obese only once in my life. I had not realized that I had gained a lot of weight.
Thankfully, a physician called me “obese.” Initially, I was angry at the doctor, however, I realized that he did me the biggest favor of my life. I changed my diet and eating habits, and for the past 20 years, kept my weight between 135-140 pounds and my BMI at 23 consistently – until the pandemic stress caused me to fall into the same bad eating habits that have caused many others to gain the COVID-15.
I was surprised to see that when I weighed myself, and I had gained 12 pounds! I immediately modified my diet and increased my physical activity. I have now lost the extra 12 pounds and will offer suggestions that may help you and your patients exceed your prepandemic physical condition.
Possible solutions
1. Keep a food journal. Write down what you eat, the amount of food you eat, the time you are eating, and your mood at that moment. Keeping a small notebook to record what and when you eat is important because upon review, it will make you face reality and be accountable for what you put in your mouth. Until you review your journal, you may have underestimated the amount, as well as the kinds, of food and drinks you actually consume. A food journal can show your areas of struggle and unhealthy eating habits and help you make necessary changes in your habits and diet to eventually lose weight. You will be less likely to eat junk food or have an extra serving of food. If you do not want to use paper and pencil, you can download an app on your phone, such as myplate tracker to keep track of your food and calorie intake. Do your journaling immediately after you eat and include snacks; do not wait until night time to record your food and journal. Include your mood or how you felt during your meal or snack (for example, were you bored, sad, or anxious) since this information will indicate why you may be overeating.
2. Develop healthful eating habits. Eat a maximum of three meals and three snacks per day but eat only when you are hungry (that is, when your stomach growls or you feel light headed). Limiting yourself to eating only when you are hungry will help eliminate emotional eating to fill a loss in your life or to deal with feelings of stress, anxiety, sadness, or isolation, which have been exacerbated by the pandemic. Buy eat only healthful foods and not items with empty calories, such as chips, cake, and items with sugar. When you are eating, devote yourself to that activity only, eat slowly, and savor each bite. Do not watch television during your meal time.
3. Record the amount and type of exercise you engage in each day and determine the number of calories burned. Walk, run, or bicycle outside, or exercise inside with stretching, weights, or an exercycle. You may use a website, such as diet tool on WebMD.com to calculate daily calories burned. To lose weight, calories burned during a day must exceed caloric intake. You may want to invest in a Fitbit or an Apple Watch and use the health section to determine your caloric intake versus output. Analyzing your caloric data will provide a concrete measure of your progress.
4. Do not overconsume calories or underconsume protein. Protein plays a key role in the creation and maintenance of every cell of your body, and because the body does not store protein, it is important to consume it every day. To meet basic protein requirements, the DRI (Dietary Reference Intake) recommends 0.36 grams of protein per pound (0.8 grams per kg) of body weight. This amounts to: 56 grams per day for the average sedentary man, and 46 grams per day for the average sedentary woman. There is also an app entitled the Protein Tracker that can simplify your calculations.
5. Drink water. It is important to be hydrated to regulate body temperature, keep joints lubricated, prevent infections, deliver nutrients to cells, and keep organs functioning properly. Being well hydrated also improves sleep, cognition, and mood. Your daily water intake by ounce should be equal to your weight in pounds multiplied by two-thirds (or 67%) to determine the amount of water to drink daily. For example, if you weigh 175 pounds, you would multiply 175 by two-thirds and learn that you should be drinking about 117 ounces of water every day. You can also meet some of your daily water requirements by consuming fruits and vegetables, such as tomatoes, watermelon, lettuce, etc.
Also, drink 2 cups (16 oz.) of water before every meal: Often when you feel hungry, it is because your body simply needs water. Science has proven that drinking 2 cups of water before every meal helps you to eat less during meal time and lose weight. If you do this three times daily – at breakfast, lunch, and dinner – you have already consumed 48 ounces of water.
6. Keep track of your progress. In addition to keeping and analyzing your food journal, weigh yourself once or twice a week. Do not weigh yourself every day; you will not see any results on a day-to-day basis, but once a week gives your body time to regulate and show progress. Always calibrate/zero your scale before each use, and weigh yourself at the same time of the day (preferably after you first wake up in the morning) while wearing the same type of clothing. Keep a record of your weight in your journal to track your progress. Do not panic if the scale indicates you gained 1, 2, or 3 pounds, your weight can fluctuate because of glycogen storage, sodium retention, human bias, reporting or recall errors, and home scales can have a plus or minus 3 pound margin of error. Look at your weight trend over time. You may prefer buying a scale that indicates both weight and body mass index.
7. Celebrate and reward yourself with nonfood items. A healthful fitness and diet regime requires energy and dedication, so if you are able to follow a healthful routine, reward yourself with nonfood rewards for your good choices and new habits as an incentive to maintain your healthful behavior.
8. Don’t buy it if you can’t stop eating it. The biggest decision you make is when you decide what you are going to buy. Don’t lie to yourself in the store that you will only eat one at a time. Only buy what you can afford to binge eat if you can’t stop yourself from eating any particular type of food.
9. Have someone hide the food you can’t resist. You can’t eat what you can’t find. If you can’t avoid having irresistible food around, ask another adult to hide the food from you.
10. Learn what harm foods can cause in your body. Read about the effects of high blood sugar and high blood pressure can cause in your body. Find out which foods boost your immune system. Demonize the bad foods in your mind. Make up your mind before you go into the store that you are going to read food labels and find the best quality food with the lowest amount of sugar or saturated fat. Appreciate the flavor of vegetables and fruit.
11. Treat sugar as if it were an addictive drug. You can’t have just one. If you reduce your craving for sugar by slowly reducing your intake of sugar, you will find that you don’t crave sugar any more. This won’t be easy, but once it is done, you will be preventing many of the ravages that sugar takes on your body over time. But you can’t have one piece of pie because the craving will come back. At some point, it may be more likely that you find that piece of pie too sweet.
Here are a few other ideas: Buy a gift for yourself or new clothes, makeup, a plant or flowers, running shoes, exercise clothes, fitness tracker, water bottle, book, movie or network subscription. Improve your home décor. Or treat yourself to online lessons for painting, music, and so on. Or you might adopt a dog, donate food to a shelter or food bank; or organize and declutter your home since staying busy will give you a reason not to eat. In nice weather, enjoy the outdoors by going for a walk, run, bikeride or by gardening.
We are all worried about getting COVID-19. Preventing COVID-15 will go a long way toward boosting our immune systems to help protect us from the coronavirus.
Dr. Cohen is board-certified in psychiatry and has had a private practice in Philadelphia for more than 35 years. His areas of specialty include sports psychiatry, agoraphobia, depression, and substance abuse. In addition, Dr. Cohen is a former professor of psychiatry, family medicine, and otolaryngology at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia. He has no conflicts of interest. Ms. Cohen holds an MBA from Temple University in Philadelphia with a focus on health care administration. Previously, Ms. Cohen was an associate administrator at Hahnemann University Hospital and an executive at the Health Services Council, both in Philadelphia. She currently writes biographical summaries of notable 18th- and 19th-century women. Ms. Cohen has no conflicts of interest.
If you have been faithfully following the COVID-19 stay-at-home restrictive orders, you may have become a victim of “COVID-15,” the additional, unexpected, unwanted 10- to 15-pound weight gain that is making your clothes not fit so well any more.
A change in routine; being home in comfy, stretchable clothing in front of the TV; and having unhealthy, processed foods ready to grab have set us up to lose the battle with COVID-15. We are set up to gain the weight because of excessive or unhealthful eating, taking an extra daily shot of alcohol, and being inactive, bored, depressed, anxious, and isolated from coworkers and family. Beware – weight gain can be “catching”; we tend to adopt the same poor eating habits and eat the same junk foods as those around us.
Since psychiatry can be a sedentary profession, I’ve (R.W.C.) kept myself very active and physically fit. Prior to the pandemic, I played tennis and ran every day. I was obese only once in my life. I had not realized that I had gained a lot of weight.
Thankfully, a physician called me “obese.” Initially, I was angry at the doctor, however, I realized that he did me the biggest favor of my life. I changed my diet and eating habits, and for the past 20 years, kept my weight between 135-140 pounds and my BMI at 23 consistently – until the pandemic stress caused me to fall into the same bad eating habits that have caused many others to gain the COVID-15.
I was surprised to see that when I weighed myself, and I had gained 12 pounds! I immediately modified my diet and increased my physical activity. I have now lost the extra 12 pounds and will offer suggestions that may help you and your patients exceed your prepandemic physical condition.
Possible solutions
1. Keep a food journal. Write down what you eat, the amount of food you eat, the time you are eating, and your mood at that moment. Keeping a small notebook to record what and when you eat is important because upon review, it will make you face reality and be accountable for what you put in your mouth. Until you review your journal, you may have underestimated the amount, as well as the kinds, of food and drinks you actually consume. A food journal can show your areas of struggle and unhealthy eating habits and help you make necessary changes in your habits and diet to eventually lose weight. You will be less likely to eat junk food or have an extra serving of food. If you do not want to use paper and pencil, you can download an app on your phone, such as myplate tracker to keep track of your food and calorie intake. Do your journaling immediately after you eat and include snacks; do not wait until night time to record your food and journal. Include your mood or how you felt during your meal or snack (for example, were you bored, sad, or anxious) since this information will indicate why you may be overeating.
2. Develop healthful eating habits. Eat a maximum of three meals and three snacks per day but eat only when you are hungry (that is, when your stomach growls or you feel light headed). Limiting yourself to eating only when you are hungry will help eliminate emotional eating to fill a loss in your life or to deal with feelings of stress, anxiety, sadness, or isolation, which have been exacerbated by the pandemic. Buy eat only healthful foods and not items with empty calories, such as chips, cake, and items with sugar. When you are eating, devote yourself to that activity only, eat slowly, and savor each bite. Do not watch television during your meal time.
3. Record the amount and type of exercise you engage in each day and determine the number of calories burned. Walk, run, or bicycle outside, or exercise inside with stretching, weights, or an exercycle. You may use a website, such as diet tool on WebMD.com to calculate daily calories burned. To lose weight, calories burned during a day must exceed caloric intake. You may want to invest in a Fitbit or an Apple Watch and use the health section to determine your caloric intake versus output. Analyzing your caloric data will provide a concrete measure of your progress.
4. Do not overconsume calories or underconsume protein. Protein plays a key role in the creation and maintenance of every cell of your body, and because the body does not store protein, it is important to consume it every day. To meet basic protein requirements, the DRI (Dietary Reference Intake) recommends 0.36 grams of protein per pound (0.8 grams per kg) of body weight. This amounts to: 56 grams per day for the average sedentary man, and 46 grams per day for the average sedentary woman. There is also an app entitled the Protein Tracker that can simplify your calculations.
5. Drink water. It is important to be hydrated to regulate body temperature, keep joints lubricated, prevent infections, deliver nutrients to cells, and keep organs functioning properly. Being well hydrated also improves sleep, cognition, and mood. Your daily water intake by ounce should be equal to your weight in pounds multiplied by two-thirds (or 67%) to determine the amount of water to drink daily. For example, if you weigh 175 pounds, you would multiply 175 by two-thirds and learn that you should be drinking about 117 ounces of water every day. You can also meet some of your daily water requirements by consuming fruits and vegetables, such as tomatoes, watermelon, lettuce, etc.
Also, drink 2 cups (16 oz.) of water before every meal: Often when you feel hungry, it is because your body simply needs water. Science has proven that drinking 2 cups of water before every meal helps you to eat less during meal time and lose weight. If you do this three times daily – at breakfast, lunch, and dinner – you have already consumed 48 ounces of water.
6. Keep track of your progress. In addition to keeping and analyzing your food journal, weigh yourself once or twice a week. Do not weigh yourself every day; you will not see any results on a day-to-day basis, but once a week gives your body time to regulate and show progress. Always calibrate/zero your scale before each use, and weigh yourself at the same time of the day (preferably after you first wake up in the morning) while wearing the same type of clothing. Keep a record of your weight in your journal to track your progress. Do not panic if the scale indicates you gained 1, 2, or 3 pounds, your weight can fluctuate because of glycogen storage, sodium retention, human bias, reporting or recall errors, and home scales can have a plus or minus 3 pound margin of error. Look at your weight trend over time. You may prefer buying a scale that indicates both weight and body mass index.
7. Celebrate and reward yourself with nonfood items. A healthful fitness and diet regime requires energy and dedication, so if you are able to follow a healthful routine, reward yourself with nonfood rewards for your good choices and new habits as an incentive to maintain your healthful behavior.
8. Don’t buy it if you can’t stop eating it. The biggest decision you make is when you decide what you are going to buy. Don’t lie to yourself in the store that you will only eat one at a time. Only buy what you can afford to binge eat if you can’t stop yourself from eating any particular type of food.
9. Have someone hide the food you can’t resist. You can’t eat what you can’t find. If you can’t avoid having irresistible food around, ask another adult to hide the food from you.
10. Learn what harm foods can cause in your body. Read about the effects of high blood sugar and high blood pressure can cause in your body. Find out which foods boost your immune system. Demonize the bad foods in your mind. Make up your mind before you go into the store that you are going to read food labels and find the best quality food with the lowest amount of sugar or saturated fat. Appreciate the flavor of vegetables and fruit.
11. Treat sugar as if it were an addictive drug. You can’t have just one. If you reduce your craving for sugar by slowly reducing your intake of sugar, you will find that you don’t crave sugar any more. This won’t be easy, but once it is done, you will be preventing many of the ravages that sugar takes on your body over time. But you can’t have one piece of pie because the craving will come back. At some point, it may be more likely that you find that piece of pie too sweet.
Here are a few other ideas: Buy a gift for yourself or new clothes, makeup, a plant or flowers, running shoes, exercise clothes, fitness tracker, water bottle, book, movie or network subscription. Improve your home décor. Or treat yourself to online lessons for painting, music, and so on. Or you might adopt a dog, donate food to a shelter or food bank; or organize and declutter your home since staying busy will give you a reason not to eat. In nice weather, enjoy the outdoors by going for a walk, run, bikeride or by gardening.
We are all worried about getting COVID-19. Preventing COVID-15 will go a long way toward boosting our immune systems to help protect us from the coronavirus.
Dr. Cohen is board-certified in psychiatry and has had a private practice in Philadelphia for more than 35 years. His areas of specialty include sports psychiatry, agoraphobia, depression, and substance abuse. In addition, Dr. Cohen is a former professor of psychiatry, family medicine, and otolaryngology at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia. He has no conflicts of interest. Ms. Cohen holds an MBA from Temple University in Philadelphia with a focus on health care administration. Previously, Ms. Cohen was an associate administrator at Hahnemann University Hospital and an executive at the Health Services Council, both in Philadelphia. She currently writes biographical summaries of notable 18th- and 19th-century women. Ms. Cohen has no conflicts of interest.
Diabetic retinopathy may predict greater risk of COVID-19 severity
Risk of intubation for COVID-19 in very sick hospitalized patients was increased over fivefold in those with diabetic retinopathy, compared with those without, in a small single-center study from the United Kingdom.
Importantly, the risk of intubation was independent of conventional risk factors for poor COVID-19 outcomes.
“People with preexisting diabetes-related vascular damage, such as retinopathy, might be predisposed to a more severe form of COVID-19 requiring ventilation in the intensive therapy unit,” said lead investigator Janaka Karalliedde, MBBS, PhD.
Dr. Karalliedde and colleagues note that this is “the first description of diabetic retinopathy as a potential risk factor for poor COVID-19 outcomes.”
“For this reason, looking for the presence or history of retinopathy or other vascular complications of diabetes may help health care professionals identify patients at high risk of severe COVID-19,” added Dr. Karalliedde, of Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London.
The study was published online in Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.
Preexisting diabetic retinopathy and COVID-19 outcomes
The prevalence of diabetic retinopathy is thought to be around 55% in people with type 1 diabetes and 30% in people with type 2 diabetes, on average.
Dr. Karalliedde is part of a research group at King’s College London that has been focused on how vascular disease may predispose to more severe COVID-19.
“COVID-19 affects the blood vessels all over the body,” he said, so they wondered whether having preexisting retinopathy “would predispose to a severe manifestation of COVID-19.”
The observational study included 187 patients with diabetes (179 patients with type 2 diabetes and 8 patients with type 1 diabetes) hospitalized with COVID-19 at Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust between March 12 and April 7 (the peak of the first wave of the pandemic in the United Kingdom).
“It was an ethnically diverse population who were very sick and provides a clinical observation of real life,” Dr. Karalliedde said.
Nearly half of patients were African Caribbean (44%), 39% were White, and 17% were of other ethnicities, including 8% who were Asian. The mean age of the cohort was 68 years (range, 22-97 years), and 60% were men.
Diabetic retinopathy was reported in 67 (36%) patients, of whom 80% had background retinopathy and 20% had more advanced retinopathy.
They then looked at whether the presence of retinopathy was associated with a more severe manifestation of COVID-19 as defined by the need for tracheal intubation.
Of the 187 patients, 26% were intubated and 45% of these patients had diabetic retinopathy.
The analysis showed those with diabetic retinopathy had an over-fivefold increased risk for intubation (odds ratio, 5.81; 95% confidence interval, 1.37-24.66).
Of the entire cohort, 32% of patients died, although no association was observed between retinopathy and mortality.
“A greater number of diabetes patients with COVID-19 ended up on the intensive therapy unit. Upon multivariate analysis, we found retinopathy was independently associated with ending up on the intensive therapy unit,” stressed Dr. Karalliedde.
However, they noted that, “due to the cross-sectional design of our study, we cannot prove causality [between retinopathy and intubation]. Further studies are required to understand the mechanisms that explain the associations between retinopathy and other indices of microangiopathy with severe COVID-19.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Risk of intubation for COVID-19 in very sick hospitalized patients was increased over fivefold in those with diabetic retinopathy, compared with those without, in a small single-center study from the United Kingdom.
Importantly, the risk of intubation was independent of conventional risk factors for poor COVID-19 outcomes.
“People with preexisting diabetes-related vascular damage, such as retinopathy, might be predisposed to a more severe form of COVID-19 requiring ventilation in the intensive therapy unit,” said lead investigator Janaka Karalliedde, MBBS, PhD.
Dr. Karalliedde and colleagues note that this is “the first description of diabetic retinopathy as a potential risk factor for poor COVID-19 outcomes.”
“For this reason, looking for the presence or history of retinopathy or other vascular complications of diabetes may help health care professionals identify patients at high risk of severe COVID-19,” added Dr. Karalliedde, of Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London.
The study was published online in Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.
Preexisting diabetic retinopathy and COVID-19 outcomes
The prevalence of diabetic retinopathy is thought to be around 55% in people with type 1 diabetes and 30% in people with type 2 diabetes, on average.
Dr. Karalliedde is part of a research group at King’s College London that has been focused on how vascular disease may predispose to more severe COVID-19.
“COVID-19 affects the blood vessels all over the body,” he said, so they wondered whether having preexisting retinopathy “would predispose to a severe manifestation of COVID-19.”
The observational study included 187 patients with diabetes (179 patients with type 2 diabetes and 8 patients with type 1 diabetes) hospitalized with COVID-19 at Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust between March 12 and April 7 (the peak of the first wave of the pandemic in the United Kingdom).
“It was an ethnically diverse population who were very sick and provides a clinical observation of real life,” Dr. Karalliedde said.
Nearly half of patients were African Caribbean (44%), 39% were White, and 17% were of other ethnicities, including 8% who were Asian. The mean age of the cohort was 68 years (range, 22-97 years), and 60% were men.
Diabetic retinopathy was reported in 67 (36%) patients, of whom 80% had background retinopathy and 20% had more advanced retinopathy.
They then looked at whether the presence of retinopathy was associated with a more severe manifestation of COVID-19 as defined by the need for tracheal intubation.
Of the 187 patients, 26% were intubated and 45% of these patients had diabetic retinopathy.
The analysis showed those with diabetic retinopathy had an over-fivefold increased risk for intubation (odds ratio, 5.81; 95% confidence interval, 1.37-24.66).
Of the entire cohort, 32% of patients died, although no association was observed between retinopathy and mortality.
“A greater number of diabetes patients with COVID-19 ended up on the intensive therapy unit. Upon multivariate analysis, we found retinopathy was independently associated with ending up on the intensive therapy unit,” stressed Dr. Karalliedde.
However, they noted that, “due to the cross-sectional design of our study, we cannot prove causality [between retinopathy and intubation]. Further studies are required to understand the mechanisms that explain the associations between retinopathy and other indices of microangiopathy with severe COVID-19.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Risk of intubation for COVID-19 in very sick hospitalized patients was increased over fivefold in those with diabetic retinopathy, compared with those without, in a small single-center study from the United Kingdom.
Importantly, the risk of intubation was independent of conventional risk factors for poor COVID-19 outcomes.
“People with preexisting diabetes-related vascular damage, such as retinopathy, might be predisposed to a more severe form of COVID-19 requiring ventilation in the intensive therapy unit,” said lead investigator Janaka Karalliedde, MBBS, PhD.
Dr. Karalliedde and colleagues note that this is “the first description of diabetic retinopathy as a potential risk factor for poor COVID-19 outcomes.”
“For this reason, looking for the presence or history of retinopathy or other vascular complications of diabetes may help health care professionals identify patients at high risk of severe COVID-19,” added Dr. Karalliedde, of Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London.
The study was published online in Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.
Preexisting diabetic retinopathy and COVID-19 outcomes
The prevalence of diabetic retinopathy is thought to be around 55% in people with type 1 diabetes and 30% in people with type 2 diabetes, on average.
Dr. Karalliedde is part of a research group at King’s College London that has been focused on how vascular disease may predispose to more severe COVID-19.
“COVID-19 affects the blood vessels all over the body,” he said, so they wondered whether having preexisting retinopathy “would predispose to a severe manifestation of COVID-19.”
The observational study included 187 patients with diabetes (179 patients with type 2 diabetes and 8 patients with type 1 diabetes) hospitalized with COVID-19 at Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust between March 12 and April 7 (the peak of the first wave of the pandemic in the United Kingdom).
“It was an ethnically diverse population who were very sick and provides a clinical observation of real life,” Dr. Karalliedde said.
Nearly half of patients were African Caribbean (44%), 39% were White, and 17% were of other ethnicities, including 8% who were Asian. The mean age of the cohort was 68 years (range, 22-97 years), and 60% were men.
Diabetic retinopathy was reported in 67 (36%) patients, of whom 80% had background retinopathy and 20% had more advanced retinopathy.
They then looked at whether the presence of retinopathy was associated with a more severe manifestation of COVID-19 as defined by the need for tracheal intubation.
Of the 187 patients, 26% were intubated and 45% of these patients had diabetic retinopathy.
The analysis showed those with diabetic retinopathy had an over-fivefold increased risk for intubation (odds ratio, 5.81; 95% confidence interval, 1.37-24.66).
Of the entire cohort, 32% of patients died, although no association was observed between retinopathy and mortality.
“A greater number of diabetes patients with COVID-19 ended up on the intensive therapy unit. Upon multivariate analysis, we found retinopathy was independently associated with ending up on the intensive therapy unit,” stressed Dr. Karalliedde.
However, they noted that, “due to the cross-sectional design of our study, we cannot prove causality [between retinopathy and intubation]. Further studies are required to understand the mechanisms that explain the associations between retinopathy and other indices of microangiopathy with severe COVID-19.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
How Twitter amplifies my doctor and human voice
When I graduated from residency in 2007, Facebook had just become “a thing,” and my cohort decided to use it to keep in touch. These days, Twitter seems to be the social media platform of choice for health care professionals.
When I started on Twitter a few years ago, it was in reaction to the current political climate. I wanted to keep track of what my favorite thinkers were writing. I was anonymous and tweeted about politics mostly. My husband was my only follower for a while.
I deanonymized when, at last year’s American College of Rheumatology meeting, I presented a poster and wanted to reach a wider audience. I could have created two different personas on Twitter, like many doctors apparently do. Initially, I resisted doing that because I am frankly too lazy to keep track of two different social media profiles, but now I resist because I see my profession as an extension of my political self, and have no problem with using my (very low) profile to amplify both my doctor voice and my human voice.
Professionally, Twitter is rewarding. It is a space for networking and for promoting one’s work. It is a fantastic learning format, as evidenced by the popularity of tweetorials. The international consortium that has worked to collect information on rheumatology patients with COVID started as an idea on Twitter. The fact that ACR Convergence 2020 abstracts are now available? I only know because of the #ACRambassadors that I follow.
But I find that I cannot separate who I am from what I do. As a rheumatologist, I build long-term relationships with patients. I cannot care for their medical conditions in isolation without also concerning myself with their nonmedical circumstances. For that reason, I have opinions that one might call humanist, and I suspect that I am not alone among rheumatologists.
I can think of three areas, broadly construed but with huge overlaps, that concern me a great deal.
First, there are things that affect all physicians: race and gender discrimination in the workplace; advancement of women in science, technology, engineering, or math; Medicare reimbursement; COVID-19 preparedness; immigration issues (an issue near and dear to me, as I am an immigrant and a foreign medical graduate); and federal funding (including funding for training programs and community health centers, funding for the National Institutes of Health, and funding for stem cell research).
Then there are the things that affect rheumatologists in particular. Access to medications and procedures is one thing. (I did say these categories hugely overlap.) If you›ve ever tried to prescribe even a drug as old as oral cyclophosphamide, you’ll have experienced the difficulty of getting it for Medicare patients. Patients who need biologics are limited by insurance contracts with pharmaceutical companies, but also by requirements such as step therapy. I am all varieties of annoyed, incredulous, and apologetic that when a patient asks me how much a treatment will cost him/her, I do not have an answer.
Speaking of pricing, don’t even get me started on pharmaceutical company price gouging. Yes, the H.P. Acthar gel may be the most egregious offender among rheumatology medications, but it’s easy to not prescribe a drug that costs $80,000 a vial and which does not do much more than prednisone does. On the other hand, I remember a time when colchicine cost $0.10 cents a pill and patients did not have to jump through hoops to get it.
And what of reproductive freedom? Our patients rely on us for advice about their childbearing options, including birth control, in vitro fertilization, and pregnancy termination.
Finally, and most important, the things that affect me most are the issues that affect patients. The lowest-hanging fruit here is the abject incompetence of the federal response to the ongoing pandemic. How many of our patients’ lives have been lost or adversely affected? And what of coverage for preexisting conditions for the vast majority of our patients, whose illnesses are chronic?
While we’re at it, the fact of health insurance being tied to employment, something that seemingly no other country in the developed world does, makes living with chronic conditions outright scary, doesn’t it? It isn’t quite so easy to remain employed when one cannot get the right medications for RA.
I could go on. Gun violence and health care disparities, vaccine denialism, coverage for mental health issues, LGBTQ rights, refugee rights, police brutality … there is a seemingly endless list of things to care about. It’s exhausting.
While I do use my Twitter account to learn from colleagues and to promote work that interests me, my primary aim is to participate in civil society as a person. Critics will use “stay in your lane” as shorthand to say x professionals should stick to x (actors to acting, musicians to music, athletes to sports). If only I could. But my humanity won’t let me. Aristotle said man is a political animal; even the venerable New England Journal of Medicine has found it impossible to keep silent.
Karmela Kim Chan, MD, is an assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, and an attending physician at the Hospital for Special Surgery and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, both in New York. Before moving to New York City, she spent 7 years in private practice in Rhode Island and was a past columnist for MDedge Rheumatology, writing about the challenges of starting life as a full-fledged rheumatologist in a private practice.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
When I graduated from residency in 2007, Facebook had just become “a thing,” and my cohort decided to use it to keep in touch. These days, Twitter seems to be the social media platform of choice for health care professionals.
When I started on Twitter a few years ago, it was in reaction to the current political climate. I wanted to keep track of what my favorite thinkers were writing. I was anonymous and tweeted about politics mostly. My husband was my only follower for a while.
I deanonymized when, at last year’s American College of Rheumatology meeting, I presented a poster and wanted to reach a wider audience. I could have created two different personas on Twitter, like many doctors apparently do. Initially, I resisted doing that because I am frankly too lazy to keep track of two different social media profiles, but now I resist because I see my profession as an extension of my political self, and have no problem with using my (very low) profile to amplify both my doctor voice and my human voice.
Professionally, Twitter is rewarding. It is a space for networking and for promoting one’s work. It is a fantastic learning format, as evidenced by the popularity of tweetorials. The international consortium that has worked to collect information on rheumatology patients with COVID started as an idea on Twitter. The fact that ACR Convergence 2020 abstracts are now available? I only know because of the #ACRambassadors that I follow.
But I find that I cannot separate who I am from what I do. As a rheumatologist, I build long-term relationships with patients. I cannot care for their medical conditions in isolation without also concerning myself with their nonmedical circumstances. For that reason, I have opinions that one might call humanist, and I suspect that I am not alone among rheumatologists.
I can think of three areas, broadly construed but with huge overlaps, that concern me a great deal.
First, there are things that affect all physicians: race and gender discrimination in the workplace; advancement of women in science, technology, engineering, or math; Medicare reimbursement; COVID-19 preparedness; immigration issues (an issue near and dear to me, as I am an immigrant and a foreign medical graduate); and federal funding (including funding for training programs and community health centers, funding for the National Institutes of Health, and funding for stem cell research).
Then there are the things that affect rheumatologists in particular. Access to medications and procedures is one thing. (I did say these categories hugely overlap.) If you›ve ever tried to prescribe even a drug as old as oral cyclophosphamide, you’ll have experienced the difficulty of getting it for Medicare patients. Patients who need biologics are limited by insurance contracts with pharmaceutical companies, but also by requirements such as step therapy. I am all varieties of annoyed, incredulous, and apologetic that when a patient asks me how much a treatment will cost him/her, I do not have an answer.
Speaking of pricing, don’t even get me started on pharmaceutical company price gouging. Yes, the H.P. Acthar gel may be the most egregious offender among rheumatology medications, but it’s easy to not prescribe a drug that costs $80,000 a vial and which does not do much more than prednisone does. On the other hand, I remember a time when colchicine cost $0.10 cents a pill and patients did not have to jump through hoops to get it.
And what of reproductive freedom? Our patients rely on us for advice about their childbearing options, including birth control, in vitro fertilization, and pregnancy termination.
Finally, and most important, the things that affect me most are the issues that affect patients. The lowest-hanging fruit here is the abject incompetence of the federal response to the ongoing pandemic. How many of our patients’ lives have been lost or adversely affected? And what of coverage for preexisting conditions for the vast majority of our patients, whose illnesses are chronic?
While we’re at it, the fact of health insurance being tied to employment, something that seemingly no other country in the developed world does, makes living with chronic conditions outright scary, doesn’t it? It isn’t quite so easy to remain employed when one cannot get the right medications for RA.
I could go on. Gun violence and health care disparities, vaccine denialism, coverage for mental health issues, LGBTQ rights, refugee rights, police brutality … there is a seemingly endless list of things to care about. It’s exhausting.
While I do use my Twitter account to learn from colleagues and to promote work that interests me, my primary aim is to participate in civil society as a person. Critics will use “stay in your lane” as shorthand to say x professionals should stick to x (actors to acting, musicians to music, athletes to sports). If only I could. But my humanity won’t let me. Aristotle said man is a political animal; even the venerable New England Journal of Medicine has found it impossible to keep silent.
Karmela Kim Chan, MD, is an assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, and an attending physician at the Hospital for Special Surgery and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, both in New York. Before moving to New York City, she spent 7 years in private practice in Rhode Island and was a past columnist for MDedge Rheumatology, writing about the challenges of starting life as a full-fledged rheumatologist in a private practice.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
When I graduated from residency in 2007, Facebook had just become “a thing,” and my cohort decided to use it to keep in touch. These days, Twitter seems to be the social media platform of choice for health care professionals.
When I started on Twitter a few years ago, it was in reaction to the current political climate. I wanted to keep track of what my favorite thinkers were writing. I was anonymous and tweeted about politics mostly. My husband was my only follower for a while.
I deanonymized when, at last year’s American College of Rheumatology meeting, I presented a poster and wanted to reach a wider audience. I could have created two different personas on Twitter, like many doctors apparently do. Initially, I resisted doing that because I am frankly too lazy to keep track of two different social media profiles, but now I resist because I see my profession as an extension of my political self, and have no problem with using my (very low) profile to amplify both my doctor voice and my human voice.
Professionally, Twitter is rewarding. It is a space for networking and for promoting one’s work. It is a fantastic learning format, as evidenced by the popularity of tweetorials. The international consortium that has worked to collect information on rheumatology patients with COVID started as an idea on Twitter. The fact that ACR Convergence 2020 abstracts are now available? I only know because of the #ACRambassadors that I follow.
But I find that I cannot separate who I am from what I do. As a rheumatologist, I build long-term relationships with patients. I cannot care for their medical conditions in isolation without also concerning myself with their nonmedical circumstances. For that reason, I have opinions that one might call humanist, and I suspect that I am not alone among rheumatologists.
I can think of three areas, broadly construed but with huge overlaps, that concern me a great deal.
First, there are things that affect all physicians: race and gender discrimination in the workplace; advancement of women in science, technology, engineering, or math; Medicare reimbursement; COVID-19 preparedness; immigration issues (an issue near and dear to me, as I am an immigrant and a foreign medical graduate); and federal funding (including funding for training programs and community health centers, funding for the National Institutes of Health, and funding for stem cell research).
Then there are the things that affect rheumatologists in particular. Access to medications and procedures is one thing. (I did say these categories hugely overlap.) If you›ve ever tried to prescribe even a drug as old as oral cyclophosphamide, you’ll have experienced the difficulty of getting it for Medicare patients. Patients who need biologics are limited by insurance contracts with pharmaceutical companies, but also by requirements such as step therapy. I am all varieties of annoyed, incredulous, and apologetic that when a patient asks me how much a treatment will cost him/her, I do not have an answer.
Speaking of pricing, don’t even get me started on pharmaceutical company price gouging. Yes, the H.P. Acthar gel may be the most egregious offender among rheumatology medications, but it’s easy to not prescribe a drug that costs $80,000 a vial and which does not do much more than prednisone does. On the other hand, I remember a time when colchicine cost $0.10 cents a pill and patients did not have to jump through hoops to get it.
And what of reproductive freedom? Our patients rely on us for advice about their childbearing options, including birth control, in vitro fertilization, and pregnancy termination.
Finally, and most important, the things that affect me most are the issues that affect patients. The lowest-hanging fruit here is the abject incompetence of the federal response to the ongoing pandemic. How many of our patients’ lives have been lost or adversely affected? And what of coverage for preexisting conditions for the vast majority of our patients, whose illnesses are chronic?
While we’re at it, the fact of health insurance being tied to employment, something that seemingly no other country in the developed world does, makes living with chronic conditions outright scary, doesn’t it? It isn’t quite so easy to remain employed when one cannot get the right medications for RA.
I could go on. Gun violence and health care disparities, vaccine denialism, coverage for mental health issues, LGBTQ rights, refugee rights, police brutality … there is a seemingly endless list of things to care about. It’s exhausting.
While I do use my Twitter account to learn from colleagues and to promote work that interests me, my primary aim is to participate in civil society as a person. Critics will use “stay in your lane” as shorthand to say x professionals should stick to x (actors to acting, musicians to music, athletes to sports). If only I could. But my humanity won’t let me. Aristotle said man is a political animal; even the venerable New England Journal of Medicine has found it impossible to keep silent.
Karmela Kim Chan, MD, is an assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, and an attending physician at the Hospital for Special Surgery and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, both in New York. Before moving to New York City, she spent 7 years in private practice in Rhode Island and was a past columnist for MDedge Rheumatology, writing about the challenges of starting life as a full-fledged rheumatologist in a private practice.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 vaccine distribution could start in 2 weeks, Pence says
Initial doses of a coronavirus vaccine could be sent out as early as mid-December, Vice President Mike Pence told governors during a call on Monday.
The distribution process could start during the week of Dec. 14, according to audio of a White House Coronavirus Task Force call obtained by CBS News. The call focused on the timeline of vaccine approval and distribution.
“With this morning’s news that Moderna is joining Pfizer in submitting an emergency-use authorization [to the Food and Drug Administration], we continue to be on pace,” Pence said.
The FDA is scheduled to make a decision about Pfizer’s emergency use authorization after an advisory panel meets on Dec. 10 to review the company’s application. FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, didn’t commit to the Dec. 14 date, CBS News reported.
“We do all the number crunching ourselves,” Dr. Hahn said. “We look line by line by line on all the data, on all the patients and manufacturing. We do statistical analyses and we come to our own conclusions to support a decision of either thumbs-up or thumbs-down.”
According to a meeting agenda, Pfizer vaccine deliveries should start on Dec. 15, followed by the Moderna vaccine on Dec. 22, CBS News reported.
Between Dec. 13-19, Pfizer is slated to deliver 6.4 million doses, which is enough to immunize about 3 million people with two shots. An “undetermined number” are reserved for backup doses, the news outlet reported.
During the next week, Pfizer and Moderna are scheduled to produce enough doses to vaccinate an additional 10 million people. By the end of the month, about 30 million people should receive doses.
As vaccines begin to roll out, Mr. Pence said “we have a ways to go” in reassuring the public about immunization. He urged governors to use their “bully pulpit” to educate their states and “develop public confidence” in the vaccines.
During the call, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases, supported the safety and efficacy of the vaccines. Although the vaccine development and approval process was accelerated this year, he said, it “does not at all compromise safety, nor does it compromise scientific integrity.”
“Any misrepresentation that the vaccines had government interference or company interference is patently untrue,” he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Initial doses of a coronavirus vaccine could be sent out as early as mid-December, Vice President Mike Pence told governors during a call on Monday.
The distribution process could start during the week of Dec. 14, according to audio of a White House Coronavirus Task Force call obtained by CBS News. The call focused on the timeline of vaccine approval and distribution.
“With this morning’s news that Moderna is joining Pfizer in submitting an emergency-use authorization [to the Food and Drug Administration], we continue to be on pace,” Pence said.
The FDA is scheduled to make a decision about Pfizer’s emergency use authorization after an advisory panel meets on Dec. 10 to review the company’s application. FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, didn’t commit to the Dec. 14 date, CBS News reported.
“We do all the number crunching ourselves,” Dr. Hahn said. “We look line by line by line on all the data, on all the patients and manufacturing. We do statistical analyses and we come to our own conclusions to support a decision of either thumbs-up or thumbs-down.”
According to a meeting agenda, Pfizer vaccine deliveries should start on Dec. 15, followed by the Moderna vaccine on Dec. 22, CBS News reported.
Between Dec. 13-19, Pfizer is slated to deliver 6.4 million doses, which is enough to immunize about 3 million people with two shots. An “undetermined number” are reserved for backup doses, the news outlet reported.
During the next week, Pfizer and Moderna are scheduled to produce enough doses to vaccinate an additional 10 million people. By the end of the month, about 30 million people should receive doses.
As vaccines begin to roll out, Mr. Pence said “we have a ways to go” in reassuring the public about immunization. He urged governors to use their “bully pulpit” to educate their states and “develop public confidence” in the vaccines.
During the call, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases, supported the safety and efficacy of the vaccines. Although the vaccine development and approval process was accelerated this year, he said, it “does not at all compromise safety, nor does it compromise scientific integrity.”
“Any misrepresentation that the vaccines had government interference or company interference is patently untrue,” he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Initial doses of a coronavirus vaccine could be sent out as early as mid-December, Vice President Mike Pence told governors during a call on Monday.
The distribution process could start during the week of Dec. 14, according to audio of a White House Coronavirus Task Force call obtained by CBS News. The call focused on the timeline of vaccine approval and distribution.
“With this morning’s news that Moderna is joining Pfizer in submitting an emergency-use authorization [to the Food and Drug Administration], we continue to be on pace,” Pence said.
The FDA is scheduled to make a decision about Pfizer’s emergency use authorization after an advisory panel meets on Dec. 10 to review the company’s application. FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, didn’t commit to the Dec. 14 date, CBS News reported.
“We do all the number crunching ourselves,” Dr. Hahn said. “We look line by line by line on all the data, on all the patients and manufacturing. We do statistical analyses and we come to our own conclusions to support a decision of either thumbs-up or thumbs-down.”
According to a meeting agenda, Pfizer vaccine deliveries should start on Dec. 15, followed by the Moderna vaccine on Dec. 22, CBS News reported.
Between Dec. 13-19, Pfizer is slated to deliver 6.4 million doses, which is enough to immunize about 3 million people with two shots. An “undetermined number” are reserved for backup doses, the news outlet reported.
During the next week, Pfizer and Moderna are scheduled to produce enough doses to vaccinate an additional 10 million people. By the end of the month, about 30 million people should receive doses.
As vaccines begin to roll out, Mr. Pence said “we have a ways to go” in reassuring the public about immunization. He urged governors to use their “bully pulpit” to educate their states and “develop public confidence” in the vaccines.
During the call, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases, supported the safety and efficacy of the vaccines. Although the vaccine development and approval process was accelerated this year, he said, it “does not at all compromise safety, nor does it compromise scientific integrity.”
“Any misrepresentation that the vaccines had government interference or company interference is patently untrue,” he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medicare finalizes 2021 physician pay rule with E/M changes
Medicare officials stuck with their plan to increase payments for office visits for primary care and several other specialties that focus on helping patients manage complex conditions such as diabetes. In doing so, Medicare also finalized cuts for other fields, triggering a new wave of protests.
The final version of the 2021 Medicare physician fee schedule was unveiled on the night of Dec. 1. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services posted an unofficial copy of the rule, which will later be published in the Federal Register.
CMS said it completed work on this massive annual review of payments for clinicians later than it usually does because of the demands of the federal response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The 2021 physician fee rule will take effect within a 30-day period instead of the usual 60-day time frame.
The most contentious item proposed for 2021 was a reshuffling of payments among specialties as part of an overhaul of Medicare’s approach to valuing evaluation and management (E/M) services. There was broader support for other aspects of the E/M overhaul, which are intended to cut some of the administrative hassle clinicians face.
“This finalized policy marks the most significant updates to E/M codes in 30 years, reducing burden on doctors imposed by the coding system and rewarding time spent evaluating and managing their patients’ care,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a statement. “In the past, the system has rewarded interventions and procedures over time spent with patients – time taken preventing disease and managing chronic illnesses.”
In the final rule, CMS summarized these results of the E/M changes in Table 106. CMS largely stuck with the approach outlined in a draft rule released in August, with minor changes in the amounts of cuts and increases.
Specialties in line for increases under the 2021 final physician fee schedule include allergy/immunology (9%), endocrinology (16%), family practice (13%), general practice (7%), geriatrics (3%), hematology/oncology (14%), internal medicine (4%), nephrology (6%), physician assistants (8%), psychiatry (7%), rheumatology (15%), and urology (8%).
In line for cuts would be anesthesiology (–8%), cardiac surgery (–8%), emergency medicine (–6%), general surgery (–6%), infectious disease (–4%), neurosurgery (–6%), physical/occupational therapy (–9%), plastic surgery (–7%), radiology (–10%), and thoracic surgery (–8%).
CMS had initially set these changes in 2021 pay in motion in the 2020 physician fee schedule. The agency subsequently faced significant opposition to its plans. Many physician groups sought to waive a “budget-neutral” approach to the E/M overhaul, which makes the offsetting of cuts necessary. They argued this would allow increased compensation for clinicians whose practices focus on office visits without requiring offsetting cuts from other fields of medicine.
The American Medical Association is among those urging Congress to prevent or postpone the payment reductions resulting from Medicare’s budget neutrality requirement as applied to the E/M overhaul.
In a Tuesday statement, AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD, noted that many physicians are facing “substantial economic hardships due to COVID-19.”
By AMA’s calculations, CMS’ planned 2021 E/M overhaul could result in “a shocking reduction of 10.2% to Medicare payment rates,” according to Bailey’s statement. The AMA strongly supports other aspects of the E/M changes CMS finalized, which Bailey said will result in “simpler and more flexible” coding and documentation.
The Surgical Care Coalition, which represents about a dozen medical specialty associations, is asking members of Congress to block the full implementation of the E/M overhaul.
In a Dec. 1 statement, the coalition urged the passage of a bill (HR 8702) that has been introduced in the House by a bipartisan duo of physicians, Rep. Ami Bera, MD (D-Calif.), and Rep. Larry Bucshon, MD (R-Ind.). Their bill would effectively block the cuts from going into effect on January 1, 2021. It would provide an additional Medicare payment for certain services in 2021 and 2022 if the otherwise applicable payment is less than it would have been in 2020.
The Medicare E/M overhaul “was a dangerous policy even before the pandemic, and enacting it during the worst health care crisis in a century is unconscionable. If Congress fails to act, it will further strain a health care system that’s already been pushed to the brink due to the COVID-19 pandemic and undermine patient care,” said John A. Wilson, MD, president of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons, in a statement.
Also backing the Bera-Bucshon bill is the American College of Emergency Physicians. In a statement on Tuesday, ACEP President Mark Rosenberg, DO, MBA, urged Congress to act on this measure.
“Emergency physicians and other health care providers battling on the front lines of the ongoing pandemic are already under unprecedented financial strain as they continue to bear the brunt of COVID-19,” Dr. Rosenberg said. “These cuts would have a devastating impact for the future of emergency medicine and could seriously impede patients’ access to emergency care when they need it most.”
“Long overdue”
But there also are champions for the approach CMS took in the E/M overhaul. The influential Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) has argued strongly for keeping the budget-neutral approach to the E/M overhaul.
In an Oct. 2 comment to CMS about the draft 2021 physician fee schedule, MedPAC Chairman Michael E. Chernew, PhD, said this approach would “help rebalance the fee schedule from services that have become overvalued to services that have become undervalued.”
This budget-neutral approach also “will go further in reducing the large gap in compensation between primary care physicians (who had a median income of $243,000 in 2018) and specialists such as surgeons (whose median income was $426,000 in 2018),” Dr. Chernew wrote.
In a Tuesday tweet, Robert B. Doherty, senior vice president of governmental affairs and public policy for the American College of Physicians, said CMS had “finalized long overdue payment increases for primary and comprehensive care including an add-in for more complex visits.”
The American Academy of Family Physicians joined ACP in a November 30 letter to congressional leaders, urging them to allow Medicare “to increase investment in primary care, benefiting millions of Medicare patients and the program itself, and reject last minute efforts to prevent these essential and long-overdue changes from going fully into effect on January 1, 2021.”
In the letter, AAFP and ACP and their cosigners argued for a need to address “underinvestment” in primary care by finalizing the E/M overhaul.
“Given that six in ten American adults have a chronic disease and four in ten have two or more chronic conditions, why would we, as a country, accept such an inadequate investment in the very care model that stands to provide maximum value to these patients?” they wrote. “Since we know that individuals with a longitudinal relationship with a primary care physician have better health outcomes and use fewer health care resources, why would we continue to direct money to higher-cost, marginal value services?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Medicare officials stuck with their plan to increase payments for office visits for primary care and several other specialties that focus on helping patients manage complex conditions such as diabetes. In doing so, Medicare also finalized cuts for other fields, triggering a new wave of protests.
The final version of the 2021 Medicare physician fee schedule was unveiled on the night of Dec. 1. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services posted an unofficial copy of the rule, which will later be published in the Federal Register.
CMS said it completed work on this massive annual review of payments for clinicians later than it usually does because of the demands of the federal response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The 2021 physician fee rule will take effect within a 30-day period instead of the usual 60-day time frame.
The most contentious item proposed for 2021 was a reshuffling of payments among specialties as part of an overhaul of Medicare’s approach to valuing evaluation and management (E/M) services. There was broader support for other aspects of the E/M overhaul, which are intended to cut some of the administrative hassle clinicians face.
“This finalized policy marks the most significant updates to E/M codes in 30 years, reducing burden on doctors imposed by the coding system and rewarding time spent evaluating and managing their patients’ care,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a statement. “In the past, the system has rewarded interventions and procedures over time spent with patients – time taken preventing disease and managing chronic illnesses.”
In the final rule, CMS summarized these results of the E/M changes in Table 106. CMS largely stuck with the approach outlined in a draft rule released in August, with minor changes in the amounts of cuts and increases.
Specialties in line for increases under the 2021 final physician fee schedule include allergy/immunology (9%), endocrinology (16%), family practice (13%), general practice (7%), geriatrics (3%), hematology/oncology (14%), internal medicine (4%), nephrology (6%), physician assistants (8%), psychiatry (7%), rheumatology (15%), and urology (8%).
In line for cuts would be anesthesiology (–8%), cardiac surgery (–8%), emergency medicine (–6%), general surgery (–6%), infectious disease (–4%), neurosurgery (–6%), physical/occupational therapy (–9%), plastic surgery (–7%), radiology (–10%), and thoracic surgery (–8%).
CMS had initially set these changes in 2021 pay in motion in the 2020 physician fee schedule. The agency subsequently faced significant opposition to its plans. Many physician groups sought to waive a “budget-neutral” approach to the E/M overhaul, which makes the offsetting of cuts necessary. They argued this would allow increased compensation for clinicians whose practices focus on office visits without requiring offsetting cuts from other fields of medicine.
The American Medical Association is among those urging Congress to prevent or postpone the payment reductions resulting from Medicare’s budget neutrality requirement as applied to the E/M overhaul.
In a Tuesday statement, AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD, noted that many physicians are facing “substantial economic hardships due to COVID-19.”
By AMA’s calculations, CMS’ planned 2021 E/M overhaul could result in “a shocking reduction of 10.2% to Medicare payment rates,” according to Bailey’s statement. The AMA strongly supports other aspects of the E/M changes CMS finalized, which Bailey said will result in “simpler and more flexible” coding and documentation.
The Surgical Care Coalition, which represents about a dozen medical specialty associations, is asking members of Congress to block the full implementation of the E/M overhaul.
In a Dec. 1 statement, the coalition urged the passage of a bill (HR 8702) that has been introduced in the House by a bipartisan duo of physicians, Rep. Ami Bera, MD (D-Calif.), and Rep. Larry Bucshon, MD (R-Ind.). Their bill would effectively block the cuts from going into effect on January 1, 2021. It would provide an additional Medicare payment for certain services in 2021 and 2022 if the otherwise applicable payment is less than it would have been in 2020.
The Medicare E/M overhaul “was a dangerous policy even before the pandemic, and enacting it during the worst health care crisis in a century is unconscionable. If Congress fails to act, it will further strain a health care system that’s already been pushed to the brink due to the COVID-19 pandemic and undermine patient care,” said John A. Wilson, MD, president of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons, in a statement.
Also backing the Bera-Bucshon bill is the American College of Emergency Physicians. In a statement on Tuesday, ACEP President Mark Rosenberg, DO, MBA, urged Congress to act on this measure.
“Emergency physicians and other health care providers battling on the front lines of the ongoing pandemic are already under unprecedented financial strain as they continue to bear the brunt of COVID-19,” Dr. Rosenberg said. “These cuts would have a devastating impact for the future of emergency medicine and could seriously impede patients’ access to emergency care when they need it most.”
“Long overdue”
But there also are champions for the approach CMS took in the E/M overhaul. The influential Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) has argued strongly for keeping the budget-neutral approach to the E/M overhaul.
In an Oct. 2 comment to CMS about the draft 2021 physician fee schedule, MedPAC Chairman Michael E. Chernew, PhD, said this approach would “help rebalance the fee schedule from services that have become overvalued to services that have become undervalued.”
This budget-neutral approach also “will go further in reducing the large gap in compensation between primary care physicians (who had a median income of $243,000 in 2018) and specialists such as surgeons (whose median income was $426,000 in 2018),” Dr. Chernew wrote.
In a Tuesday tweet, Robert B. Doherty, senior vice president of governmental affairs and public policy for the American College of Physicians, said CMS had “finalized long overdue payment increases for primary and comprehensive care including an add-in for more complex visits.”
The American Academy of Family Physicians joined ACP in a November 30 letter to congressional leaders, urging them to allow Medicare “to increase investment in primary care, benefiting millions of Medicare patients and the program itself, and reject last minute efforts to prevent these essential and long-overdue changes from going fully into effect on January 1, 2021.”
In the letter, AAFP and ACP and their cosigners argued for a need to address “underinvestment” in primary care by finalizing the E/M overhaul.
“Given that six in ten American adults have a chronic disease and four in ten have two or more chronic conditions, why would we, as a country, accept such an inadequate investment in the very care model that stands to provide maximum value to these patients?” they wrote. “Since we know that individuals with a longitudinal relationship with a primary care physician have better health outcomes and use fewer health care resources, why would we continue to direct money to higher-cost, marginal value services?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Medicare officials stuck with their plan to increase payments for office visits for primary care and several other specialties that focus on helping patients manage complex conditions such as diabetes. In doing so, Medicare also finalized cuts for other fields, triggering a new wave of protests.
The final version of the 2021 Medicare physician fee schedule was unveiled on the night of Dec. 1. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services posted an unofficial copy of the rule, which will later be published in the Federal Register.
CMS said it completed work on this massive annual review of payments for clinicians later than it usually does because of the demands of the federal response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The 2021 physician fee rule will take effect within a 30-day period instead of the usual 60-day time frame.
The most contentious item proposed for 2021 was a reshuffling of payments among specialties as part of an overhaul of Medicare’s approach to valuing evaluation and management (E/M) services. There was broader support for other aspects of the E/M overhaul, which are intended to cut some of the administrative hassle clinicians face.
“This finalized policy marks the most significant updates to E/M codes in 30 years, reducing burden on doctors imposed by the coding system and rewarding time spent evaluating and managing their patients’ care,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a statement. “In the past, the system has rewarded interventions and procedures over time spent with patients – time taken preventing disease and managing chronic illnesses.”
In the final rule, CMS summarized these results of the E/M changes in Table 106. CMS largely stuck with the approach outlined in a draft rule released in August, with minor changes in the amounts of cuts and increases.
Specialties in line for increases under the 2021 final physician fee schedule include allergy/immunology (9%), endocrinology (16%), family practice (13%), general practice (7%), geriatrics (3%), hematology/oncology (14%), internal medicine (4%), nephrology (6%), physician assistants (8%), psychiatry (7%), rheumatology (15%), and urology (8%).
In line for cuts would be anesthesiology (–8%), cardiac surgery (–8%), emergency medicine (–6%), general surgery (–6%), infectious disease (–4%), neurosurgery (–6%), physical/occupational therapy (–9%), plastic surgery (–7%), radiology (–10%), and thoracic surgery (–8%).
CMS had initially set these changes in 2021 pay in motion in the 2020 physician fee schedule. The agency subsequently faced significant opposition to its plans. Many physician groups sought to waive a “budget-neutral” approach to the E/M overhaul, which makes the offsetting of cuts necessary. They argued this would allow increased compensation for clinicians whose practices focus on office visits without requiring offsetting cuts from other fields of medicine.
The American Medical Association is among those urging Congress to prevent or postpone the payment reductions resulting from Medicare’s budget neutrality requirement as applied to the E/M overhaul.
In a Tuesday statement, AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD, noted that many physicians are facing “substantial economic hardships due to COVID-19.”
By AMA’s calculations, CMS’ planned 2021 E/M overhaul could result in “a shocking reduction of 10.2% to Medicare payment rates,” according to Bailey’s statement. The AMA strongly supports other aspects of the E/M changes CMS finalized, which Bailey said will result in “simpler and more flexible” coding and documentation.
The Surgical Care Coalition, which represents about a dozen medical specialty associations, is asking members of Congress to block the full implementation of the E/M overhaul.
In a Dec. 1 statement, the coalition urged the passage of a bill (HR 8702) that has been introduced in the House by a bipartisan duo of physicians, Rep. Ami Bera, MD (D-Calif.), and Rep. Larry Bucshon, MD (R-Ind.). Their bill would effectively block the cuts from going into effect on January 1, 2021. It would provide an additional Medicare payment for certain services in 2021 and 2022 if the otherwise applicable payment is less than it would have been in 2020.
The Medicare E/M overhaul “was a dangerous policy even before the pandemic, and enacting it during the worst health care crisis in a century is unconscionable. If Congress fails to act, it will further strain a health care system that’s already been pushed to the brink due to the COVID-19 pandemic and undermine patient care,” said John A. Wilson, MD, president of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons, in a statement.
Also backing the Bera-Bucshon bill is the American College of Emergency Physicians. In a statement on Tuesday, ACEP President Mark Rosenberg, DO, MBA, urged Congress to act on this measure.
“Emergency physicians and other health care providers battling on the front lines of the ongoing pandemic are already under unprecedented financial strain as they continue to bear the brunt of COVID-19,” Dr. Rosenberg said. “These cuts would have a devastating impact for the future of emergency medicine and could seriously impede patients’ access to emergency care when they need it most.”
“Long overdue”
But there also are champions for the approach CMS took in the E/M overhaul. The influential Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) has argued strongly for keeping the budget-neutral approach to the E/M overhaul.
In an Oct. 2 comment to CMS about the draft 2021 physician fee schedule, MedPAC Chairman Michael E. Chernew, PhD, said this approach would “help rebalance the fee schedule from services that have become overvalued to services that have become undervalued.”
This budget-neutral approach also “will go further in reducing the large gap in compensation between primary care physicians (who had a median income of $243,000 in 2018) and specialists such as surgeons (whose median income was $426,000 in 2018),” Dr. Chernew wrote.
In a Tuesday tweet, Robert B. Doherty, senior vice president of governmental affairs and public policy for the American College of Physicians, said CMS had “finalized long overdue payment increases for primary and comprehensive care including an add-in for more complex visits.”
The American Academy of Family Physicians joined ACP in a November 30 letter to congressional leaders, urging them to allow Medicare “to increase investment in primary care, benefiting millions of Medicare patients and the program itself, and reject last minute efforts to prevent these essential and long-overdue changes from going fully into effect on January 1, 2021.”
In the letter, AAFP and ACP and their cosigners argued for a need to address “underinvestment” in primary care by finalizing the E/M overhaul.
“Given that six in ten American adults have a chronic disease and four in ten have two or more chronic conditions, why would we, as a country, accept such an inadequate investment in the very care model that stands to provide maximum value to these patients?” they wrote. “Since we know that individuals with a longitudinal relationship with a primary care physician have better health outcomes and use fewer health care resources, why would we continue to direct money to higher-cost, marginal value services?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.