User login
Clinical Endocrinology News is an independent news source that provides endocrinologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the endocrinologist's practice. Specialty topics include Diabetes, Lipid & Metabolic Disorders Menopause, Obesity, Osteoporosis, Pediatric Endocrinology, Pituitary, Thyroid & Adrenal Disorders, and Reproductive Endocrinology. Featured content includes Commentaries, Implementin Health Reform, Law & Medicine, and In the Loop, the blog of Clinical Endocrinology News. Clinical Endocrinology News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
addict
addicted
addicting
addiction
adult sites
alcohol
antibody
ass
attorney
audit
auditor
babies
babpa
baby
ban
banned
banning
best
bisexual
bitch
bleach
blog
blow job
bondage
boobs
booty
buy
cannabis
certificate
certification
certified
cheap
cheapest
class action
cocaine
cock
counterfeit drug
crack
crap
crime
criminal
cunt
curable
cure
dangerous
dangers
dead
deadly
death
defend
defended
depedent
dependence
dependent
detergent
dick
die
dildo
drug abuse
drug recall
dying
fag
fake
fatal
fatalities
fatality
free
fuck
gangs
gingivitis
guns
hardcore
herbal
herbs
heroin
herpes
home remedies
homo
horny
hypersensitivity
hypoglycemia treatment
illegal drug use
illegal use of prescription
incest
infant
infants
job
ketoacidosis
kill
killer
killing
kinky
law suit
lawsuit
lawyer
lesbian
marijuana
medicine for hypoglycemia
murder
naked
natural
newborn
nigger
noise
nude
nudity
orgy
over the counter
overdosage
overdose
overdosed
overdosing
penis
pimp
pistol
porn
porno
pornographic
pornography
prison
profanity
purchase
purchasing
pussy
queer
rape
rapist
recall
recreational drug
rob
robberies
sale
sales
sex
sexual
shit
shoot
slut
slutty
stole
stolen
store
sue
suicidal
suicide
supplements
supply company
theft
thief
thieves
tit
toddler
toddlers
toxic
toxin
tragedy
treating dka
treating hypoglycemia
treatment for hypoglycemia
vagina
violence
whore
withdrawal
without prescription
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
New calculator tool estimates fracture risk on dialysis
VANCOUVER – A new calculator that predicts short-term fracture risk at both 1 year and 3 years in patients on dialysis performed well in a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
The tool will soon be available on QxMD Calculate, which provides free decision-support tools for physicians, said presenter Andrea Cowan, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Western Ontario, London.
Dialysis patients have an approximately fivefold increased risk for fracture, Dr. Cowan noted, compared with the general population. However, treatments to prevent fracture risk are relatively limited and can have significant side effects. Therefore, “you really want to make sure that the person you’re targeting for treatment is actually going to be at a reasonable risk of fracture,” she said.
The Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) is useful, but it estimates 10-year fracture risk, which is too long of a time frame to be useful for dialysis patients who experience a 50% 5-year mortality, according to Dr. Cowan. It does not take kidney failure or severe hyperparathyroidism into account, and it also requires information like bone mineral density, which poses an additional burden for a dialysis patient already undergoing multiple tests.
The new calculator could also be useful for research because it doesn’t rely on clinical data that might not be generally available, such as parental fracture, smoking status, or body mass index. “There’s a move towards things like pragmatic trials, which use more routinely collected data, have broader inclusion criteria, and are often more cost efficient to run. This calculator should be relatively easy to implement in trials using routinely collected data to perhaps define a subgroup of patients who may be at high risk of fracture without having to apply really cumbersome tools,” Dr. Cowan said.
The researchers included 11,599 patients between ages 40 and 89 years who were treated at a single center in Ontario between 2010 and 2017. The mean age was 66.18 years, 38.6% were women, 64.1% had diabetes, 11.9% had liver disease, and median time on dialysis was 0.81 years. The patients’ median parathyroid hormone level was 30 pmol/L.
At 3 years, the cumulative incidence of any fracture was 7.36% (95% confidence interval, 6.89-7.85), including 2.62% for hip fracture (95% CI, 2.34-2.93), 1.36% for spine fracture (95% CI, 1.16-1.59), 1.93% for wrist or forearm (95% CI, 1.69-2.20), and 2.15% for the pelvis (95% CI, 1.89-2.43). The incidence for all fractures at 1 year was 2.93 (95% CI, 2.62-3.26).
Variables associated with fracture risk included female sex (hazard ratio, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.27-1.67), a previous fracture more than 1 year in the past (HR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.37-2.00), a fracture in the past year (HR, 3.63; 95% CI, 2.86-4.60), and proton pump inhibitor use (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.04-1.45). After inclusion of vitamin D use, steroid use, time on dialysis, calcium levels, phosphate levels, presence of diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and chronic liver disease, the full model had an area under the curve of 77.7 at 1 year (95% CI, 73.3-84.4) and 69.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 68.0-72.2). For hip fracture, the model had an AUC of 80.1 at 1 year (95% CI, 77.0-83.5) and 71.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 70.1-74.2).
During the Q&A session, Dr. Cowan was asked how the tool could be implemented clinically. She said that it could have value in discussing fracture prediction and prevention with patients, but it could also increase fracture risk awareness among nephrologists. “I need to convince a lot of my colleagues because they’re focused on other things, so having this [calculator] I think is both good from a patient as well as a practitioner perspective. And the treatments that we have in people with end-stage renal disease are limited, so you want to know that you’re really targeting the high-risk person before you potentially put them on denosumab and increase the risk of severe hypercalcemia and things like that,” Dr. Cowan said.
The study points out the challenges of predicting fracture risk for specific populations, according to session comoderator Evelyn Hsieh, MD. She noted that the study needs follow-up. “I don’t think they had gotten to a validation [in a separate cohort] yet,” said Dr. Hsieh, an associate professor of medicine (rheumatology) and epidemiology (chronic diseases) at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Cowan and Dr. Hsieh have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER – A new calculator that predicts short-term fracture risk at both 1 year and 3 years in patients on dialysis performed well in a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
The tool will soon be available on QxMD Calculate, which provides free decision-support tools for physicians, said presenter Andrea Cowan, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Western Ontario, London.
Dialysis patients have an approximately fivefold increased risk for fracture, Dr. Cowan noted, compared with the general population. However, treatments to prevent fracture risk are relatively limited and can have significant side effects. Therefore, “you really want to make sure that the person you’re targeting for treatment is actually going to be at a reasonable risk of fracture,” she said.
The Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) is useful, but it estimates 10-year fracture risk, which is too long of a time frame to be useful for dialysis patients who experience a 50% 5-year mortality, according to Dr. Cowan. It does not take kidney failure or severe hyperparathyroidism into account, and it also requires information like bone mineral density, which poses an additional burden for a dialysis patient already undergoing multiple tests.
The new calculator could also be useful for research because it doesn’t rely on clinical data that might not be generally available, such as parental fracture, smoking status, or body mass index. “There’s a move towards things like pragmatic trials, which use more routinely collected data, have broader inclusion criteria, and are often more cost efficient to run. This calculator should be relatively easy to implement in trials using routinely collected data to perhaps define a subgroup of patients who may be at high risk of fracture without having to apply really cumbersome tools,” Dr. Cowan said.
The researchers included 11,599 patients between ages 40 and 89 years who were treated at a single center in Ontario between 2010 and 2017. The mean age was 66.18 years, 38.6% were women, 64.1% had diabetes, 11.9% had liver disease, and median time on dialysis was 0.81 years. The patients’ median parathyroid hormone level was 30 pmol/L.
At 3 years, the cumulative incidence of any fracture was 7.36% (95% confidence interval, 6.89-7.85), including 2.62% for hip fracture (95% CI, 2.34-2.93), 1.36% for spine fracture (95% CI, 1.16-1.59), 1.93% for wrist or forearm (95% CI, 1.69-2.20), and 2.15% for the pelvis (95% CI, 1.89-2.43). The incidence for all fractures at 1 year was 2.93 (95% CI, 2.62-3.26).
Variables associated with fracture risk included female sex (hazard ratio, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.27-1.67), a previous fracture more than 1 year in the past (HR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.37-2.00), a fracture in the past year (HR, 3.63; 95% CI, 2.86-4.60), and proton pump inhibitor use (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.04-1.45). After inclusion of vitamin D use, steroid use, time on dialysis, calcium levels, phosphate levels, presence of diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and chronic liver disease, the full model had an area under the curve of 77.7 at 1 year (95% CI, 73.3-84.4) and 69.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 68.0-72.2). For hip fracture, the model had an AUC of 80.1 at 1 year (95% CI, 77.0-83.5) and 71.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 70.1-74.2).
During the Q&A session, Dr. Cowan was asked how the tool could be implemented clinically. She said that it could have value in discussing fracture prediction and prevention with patients, but it could also increase fracture risk awareness among nephrologists. “I need to convince a lot of my colleagues because they’re focused on other things, so having this [calculator] I think is both good from a patient as well as a practitioner perspective. And the treatments that we have in people with end-stage renal disease are limited, so you want to know that you’re really targeting the high-risk person before you potentially put them on denosumab and increase the risk of severe hypercalcemia and things like that,” Dr. Cowan said.
The study points out the challenges of predicting fracture risk for specific populations, according to session comoderator Evelyn Hsieh, MD. She noted that the study needs follow-up. “I don’t think they had gotten to a validation [in a separate cohort] yet,” said Dr. Hsieh, an associate professor of medicine (rheumatology) and epidemiology (chronic diseases) at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Cowan and Dr. Hsieh have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER – A new calculator that predicts short-term fracture risk at both 1 year and 3 years in patients on dialysis performed well in a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
The tool will soon be available on QxMD Calculate, which provides free decision-support tools for physicians, said presenter Andrea Cowan, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Western Ontario, London.
Dialysis patients have an approximately fivefold increased risk for fracture, Dr. Cowan noted, compared with the general population. However, treatments to prevent fracture risk are relatively limited and can have significant side effects. Therefore, “you really want to make sure that the person you’re targeting for treatment is actually going to be at a reasonable risk of fracture,” she said.
The Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) is useful, but it estimates 10-year fracture risk, which is too long of a time frame to be useful for dialysis patients who experience a 50% 5-year mortality, according to Dr. Cowan. It does not take kidney failure or severe hyperparathyroidism into account, and it also requires information like bone mineral density, which poses an additional burden for a dialysis patient already undergoing multiple tests.
The new calculator could also be useful for research because it doesn’t rely on clinical data that might not be generally available, such as parental fracture, smoking status, or body mass index. “There’s a move towards things like pragmatic trials, which use more routinely collected data, have broader inclusion criteria, and are often more cost efficient to run. This calculator should be relatively easy to implement in trials using routinely collected data to perhaps define a subgroup of patients who may be at high risk of fracture without having to apply really cumbersome tools,” Dr. Cowan said.
The researchers included 11,599 patients between ages 40 and 89 years who were treated at a single center in Ontario between 2010 and 2017. The mean age was 66.18 years, 38.6% were women, 64.1% had diabetes, 11.9% had liver disease, and median time on dialysis was 0.81 years. The patients’ median parathyroid hormone level was 30 pmol/L.
At 3 years, the cumulative incidence of any fracture was 7.36% (95% confidence interval, 6.89-7.85), including 2.62% for hip fracture (95% CI, 2.34-2.93), 1.36% for spine fracture (95% CI, 1.16-1.59), 1.93% for wrist or forearm (95% CI, 1.69-2.20), and 2.15% for the pelvis (95% CI, 1.89-2.43). The incidence for all fractures at 1 year was 2.93 (95% CI, 2.62-3.26).
Variables associated with fracture risk included female sex (hazard ratio, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.27-1.67), a previous fracture more than 1 year in the past (HR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.37-2.00), a fracture in the past year (HR, 3.63; 95% CI, 2.86-4.60), and proton pump inhibitor use (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.04-1.45). After inclusion of vitamin D use, steroid use, time on dialysis, calcium levels, phosphate levels, presence of diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and chronic liver disease, the full model had an area under the curve of 77.7 at 1 year (95% CI, 73.3-84.4) and 69.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 68.0-72.2). For hip fracture, the model had an AUC of 80.1 at 1 year (95% CI, 77.0-83.5) and 71.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 70.1-74.2).
During the Q&A session, Dr. Cowan was asked how the tool could be implemented clinically. She said that it could have value in discussing fracture prediction and prevention with patients, but it could also increase fracture risk awareness among nephrologists. “I need to convince a lot of my colleagues because they’re focused on other things, so having this [calculator] I think is both good from a patient as well as a practitioner perspective. And the treatments that we have in people with end-stage renal disease are limited, so you want to know that you’re really targeting the high-risk person before you potentially put them on denosumab and increase the risk of severe hypercalcemia and things like that,” Dr. Cowan said.
The study points out the challenges of predicting fracture risk for specific populations, according to session comoderator Evelyn Hsieh, MD. She noted that the study needs follow-up. “I don’t think they had gotten to a validation [in a separate cohort] yet,” said Dr. Hsieh, an associate professor of medicine (rheumatology) and epidemiology (chronic diseases) at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Cowan and Dr. Hsieh have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASBMR 2023
What predicts successful weight loss maintenance in WeightWatchers?
DALLAS – Researchers identified behavioral, psychological, and environmental predictors of continued weight loss maintenance vs. weight regain in a large cohort of members of WeightWatchers who had successful long-term weight loss.
On average, the participants had lost 25.5 kg (56 lb) and kept it off for 3.5 years, when they entered the 1-year study.
At study entry and 1 year later, the participants replied to several questionnaires that asked about predictors of weight loss maintenance.
Compared with people who gained weight over the 1-year study,
They also had reduced disinhibition (tendency to overeat) when faced with food cues, as well as less pain and a more positive body image “at any weight, shape, or size,” Suzanne Phelan, MD, PhD, reported.
Dr. Phelan, from the department of kinesiology and public health, California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, presented the study in an Obesity symposium at the annual meeting of the Obesity Society, and it was simultaneously published in the journal. The study was selected as one of five top papers submitted to the journal to coincide with the meeting.
Future interventions to prevent weight regain should target overeating in response to internal and external food cues and declines in self-monitoring and body image, Dr. Phelan said.
The study aimed to identify behaviors that might predict who might “beat the odds” and sustain long-term weight loss, she said in an interview.
The findings suggest that the people who maintained their weight loss had developed skills to help them cope with cravings and not respond by eating, she said. Continued self-monitoring and body acceptance and appreciation (all body sizes are beautiful) were key elements of successful weight-loss maintenance.
No antiobesity drugs or surgery; don’t forget behavioral stuff
Importantly, although 43% of the study participants regained more than five pounds during this 1-year study, they still remained at 18% below their starting weight, “indicating that they were largely successful at weight loss,” Dr. Phelan said.
Michael D. Jensen, MD, editor-in-chief of Obesity, echoed this.
The researchers “did find some weak predictors of success,” said Dr. Jensen, from Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “But perhaps as important,” he said, “was that at the end of the trial, even those who had regained some slight weight still had 18% weight loss – which is not trivial – after, on average, 4.5 years with a standard commercial weight management program.
“At every talk I go to here,” the message is, “Let’s stampede towards use of the drugs and skip diet and exercise and behavioral stuff,” he observed. “I would argue,” he said, “that when it works, it works really well, and it’s free. So this idea that we shouldn’t even try it, because we know it’s going to fail, is wrong.
“If you have the right group, they have a decent chance of having a sufficiently good response that you don’t have to give the medications and you don’t have to send them for bariatric surgery.
“Once you learn from these programs what to do, you’re not paying $1,000 a month for a drug and you haven’t had bariatric surgery,” Dr. Jensen noted. “Their 3 years of follow-up of WeightWatchers cost less than 1 month worth of one of these [antiobesity medications].”
The predictive findings were like ‘”icing on the cake,” he said. Anybody can find five people who’ve done well with therapy, but this study was in more than 2,800 people who did well with a commercial program that is not expensive.
Study design and findings
Between 2019 and 2020, WeightWatchers invited adult members who had maintained weight loss of at least 9.1 kg (20 lb) for at least 1 year to participate in this study.
Of 7,025 participants who entered the study, 4,004 individuals (57%) who did not complete the 1-year questionnaires and others with implausible weight were excluded, leaving a final sample of 2,843 participants.
Most participants were women (92%), non-Hispanic White (95%), married (92%), and college educated. They had a mean age of 56 years.
On average, the participants had a body mass index (BMI) of 35.9 kg/m2 (grade 2 obesity) at the start of the WeightWatchers program and a BMI of 26.7 when they entered the current study.
At the 1-year follow-up, 57% of the participants had maintained the same weight (within 2.3 kg) as when they enrolled in the study, and 43% had gained ≥ 2.3 kg.
On average, the weight-loss maintainers had gained 0.4 kg (0.88 lb). The weight gainers had gained 7.2 kg (15.9 lb) but were still 19.1 kg (42.1 lb) below the weight they had when they started the WeightWatchers program.
At baseline, compared with the weight gainers, the weight-loss maintainers were on average older (58 vs. 52 years), had a lower initial BMI (26 vs. 28), and had longer duration of weight loss maintenance (4 vs. 3 years).
At 1 year, those who had maintained their weight loss had greater self-monitoring, psychological coping, physical activity strategies, dietary choice strategies, and eating and physical activity habits, and they had less eating initiation in the absence of hunger.
They also had less disinhibition, more willingness to ignore cravings and accept food urges, more future orientation, more mindfulness, more positive body image and body satisfaction, better general health and mental health, and less bodily pain.
This research was supported by a grant to Dr. Phelan from WeightWatchers (WW) International, and three study authors are employees and shareholders of the company. Dr. Jensen discloses consulting for Biohaven Pharmaceuticals and for Seattle Gummy Co.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DALLAS – Researchers identified behavioral, psychological, and environmental predictors of continued weight loss maintenance vs. weight regain in a large cohort of members of WeightWatchers who had successful long-term weight loss.
On average, the participants had lost 25.5 kg (56 lb) and kept it off for 3.5 years, when they entered the 1-year study.
At study entry and 1 year later, the participants replied to several questionnaires that asked about predictors of weight loss maintenance.
Compared with people who gained weight over the 1-year study,
They also had reduced disinhibition (tendency to overeat) when faced with food cues, as well as less pain and a more positive body image “at any weight, shape, or size,” Suzanne Phelan, MD, PhD, reported.
Dr. Phelan, from the department of kinesiology and public health, California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, presented the study in an Obesity symposium at the annual meeting of the Obesity Society, and it was simultaneously published in the journal. The study was selected as one of five top papers submitted to the journal to coincide with the meeting.
Future interventions to prevent weight regain should target overeating in response to internal and external food cues and declines in self-monitoring and body image, Dr. Phelan said.
The study aimed to identify behaviors that might predict who might “beat the odds” and sustain long-term weight loss, she said in an interview.
The findings suggest that the people who maintained their weight loss had developed skills to help them cope with cravings and not respond by eating, she said. Continued self-monitoring and body acceptance and appreciation (all body sizes are beautiful) were key elements of successful weight-loss maintenance.
No antiobesity drugs or surgery; don’t forget behavioral stuff
Importantly, although 43% of the study participants regained more than five pounds during this 1-year study, they still remained at 18% below their starting weight, “indicating that they were largely successful at weight loss,” Dr. Phelan said.
Michael D. Jensen, MD, editor-in-chief of Obesity, echoed this.
The researchers “did find some weak predictors of success,” said Dr. Jensen, from Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “But perhaps as important,” he said, “was that at the end of the trial, even those who had regained some slight weight still had 18% weight loss – which is not trivial – after, on average, 4.5 years with a standard commercial weight management program.
“At every talk I go to here,” the message is, “Let’s stampede towards use of the drugs and skip diet and exercise and behavioral stuff,” he observed. “I would argue,” he said, “that when it works, it works really well, and it’s free. So this idea that we shouldn’t even try it, because we know it’s going to fail, is wrong.
“If you have the right group, they have a decent chance of having a sufficiently good response that you don’t have to give the medications and you don’t have to send them for bariatric surgery.
“Once you learn from these programs what to do, you’re not paying $1,000 a month for a drug and you haven’t had bariatric surgery,” Dr. Jensen noted. “Their 3 years of follow-up of WeightWatchers cost less than 1 month worth of one of these [antiobesity medications].”
The predictive findings were like ‘”icing on the cake,” he said. Anybody can find five people who’ve done well with therapy, but this study was in more than 2,800 people who did well with a commercial program that is not expensive.
Study design and findings
Between 2019 and 2020, WeightWatchers invited adult members who had maintained weight loss of at least 9.1 kg (20 lb) for at least 1 year to participate in this study.
Of 7,025 participants who entered the study, 4,004 individuals (57%) who did not complete the 1-year questionnaires and others with implausible weight were excluded, leaving a final sample of 2,843 participants.
Most participants were women (92%), non-Hispanic White (95%), married (92%), and college educated. They had a mean age of 56 years.
On average, the participants had a body mass index (BMI) of 35.9 kg/m2 (grade 2 obesity) at the start of the WeightWatchers program and a BMI of 26.7 when they entered the current study.
At the 1-year follow-up, 57% of the participants had maintained the same weight (within 2.3 kg) as when they enrolled in the study, and 43% had gained ≥ 2.3 kg.
On average, the weight-loss maintainers had gained 0.4 kg (0.88 lb). The weight gainers had gained 7.2 kg (15.9 lb) but were still 19.1 kg (42.1 lb) below the weight they had when they started the WeightWatchers program.
At baseline, compared with the weight gainers, the weight-loss maintainers were on average older (58 vs. 52 years), had a lower initial BMI (26 vs. 28), and had longer duration of weight loss maintenance (4 vs. 3 years).
At 1 year, those who had maintained their weight loss had greater self-monitoring, psychological coping, physical activity strategies, dietary choice strategies, and eating and physical activity habits, and they had less eating initiation in the absence of hunger.
They also had less disinhibition, more willingness to ignore cravings and accept food urges, more future orientation, more mindfulness, more positive body image and body satisfaction, better general health and mental health, and less bodily pain.
This research was supported by a grant to Dr. Phelan from WeightWatchers (WW) International, and three study authors are employees and shareholders of the company. Dr. Jensen discloses consulting for Biohaven Pharmaceuticals and for Seattle Gummy Co.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DALLAS – Researchers identified behavioral, psychological, and environmental predictors of continued weight loss maintenance vs. weight regain in a large cohort of members of WeightWatchers who had successful long-term weight loss.
On average, the participants had lost 25.5 kg (56 lb) and kept it off for 3.5 years, when they entered the 1-year study.
At study entry and 1 year later, the participants replied to several questionnaires that asked about predictors of weight loss maintenance.
Compared with people who gained weight over the 1-year study,
They also had reduced disinhibition (tendency to overeat) when faced with food cues, as well as less pain and a more positive body image “at any weight, shape, or size,” Suzanne Phelan, MD, PhD, reported.
Dr. Phelan, from the department of kinesiology and public health, California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, presented the study in an Obesity symposium at the annual meeting of the Obesity Society, and it was simultaneously published in the journal. The study was selected as one of five top papers submitted to the journal to coincide with the meeting.
Future interventions to prevent weight regain should target overeating in response to internal and external food cues and declines in self-monitoring and body image, Dr. Phelan said.
The study aimed to identify behaviors that might predict who might “beat the odds” and sustain long-term weight loss, she said in an interview.
The findings suggest that the people who maintained their weight loss had developed skills to help them cope with cravings and not respond by eating, she said. Continued self-monitoring and body acceptance and appreciation (all body sizes are beautiful) were key elements of successful weight-loss maintenance.
No antiobesity drugs or surgery; don’t forget behavioral stuff
Importantly, although 43% of the study participants regained more than five pounds during this 1-year study, they still remained at 18% below their starting weight, “indicating that they were largely successful at weight loss,” Dr. Phelan said.
Michael D. Jensen, MD, editor-in-chief of Obesity, echoed this.
The researchers “did find some weak predictors of success,” said Dr. Jensen, from Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “But perhaps as important,” he said, “was that at the end of the trial, even those who had regained some slight weight still had 18% weight loss – which is not trivial – after, on average, 4.5 years with a standard commercial weight management program.
“At every talk I go to here,” the message is, “Let’s stampede towards use of the drugs and skip diet and exercise and behavioral stuff,” he observed. “I would argue,” he said, “that when it works, it works really well, and it’s free. So this idea that we shouldn’t even try it, because we know it’s going to fail, is wrong.
“If you have the right group, they have a decent chance of having a sufficiently good response that you don’t have to give the medications and you don’t have to send them for bariatric surgery.
“Once you learn from these programs what to do, you’re not paying $1,000 a month for a drug and you haven’t had bariatric surgery,” Dr. Jensen noted. “Their 3 years of follow-up of WeightWatchers cost less than 1 month worth of one of these [antiobesity medications].”
The predictive findings were like ‘”icing on the cake,” he said. Anybody can find five people who’ve done well with therapy, but this study was in more than 2,800 people who did well with a commercial program that is not expensive.
Study design and findings
Between 2019 and 2020, WeightWatchers invited adult members who had maintained weight loss of at least 9.1 kg (20 lb) for at least 1 year to participate in this study.
Of 7,025 participants who entered the study, 4,004 individuals (57%) who did not complete the 1-year questionnaires and others with implausible weight were excluded, leaving a final sample of 2,843 participants.
Most participants were women (92%), non-Hispanic White (95%), married (92%), and college educated. They had a mean age of 56 years.
On average, the participants had a body mass index (BMI) of 35.9 kg/m2 (grade 2 obesity) at the start of the WeightWatchers program and a BMI of 26.7 when they entered the current study.
At the 1-year follow-up, 57% of the participants had maintained the same weight (within 2.3 kg) as when they enrolled in the study, and 43% had gained ≥ 2.3 kg.
On average, the weight-loss maintainers had gained 0.4 kg (0.88 lb). The weight gainers had gained 7.2 kg (15.9 lb) but were still 19.1 kg (42.1 lb) below the weight they had when they started the WeightWatchers program.
At baseline, compared with the weight gainers, the weight-loss maintainers were on average older (58 vs. 52 years), had a lower initial BMI (26 vs. 28), and had longer duration of weight loss maintenance (4 vs. 3 years).
At 1 year, those who had maintained their weight loss had greater self-monitoring, psychological coping, physical activity strategies, dietary choice strategies, and eating and physical activity habits, and they had less eating initiation in the absence of hunger.
They also had less disinhibition, more willingness to ignore cravings and accept food urges, more future orientation, more mindfulness, more positive body image and body satisfaction, better general health and mental health, and less bodily pain.
This research was supported by a grant to Dr. Phelan from WeightWatchers (WW) International, and three study authors are employees and shareholders of the company. Dr. Jensen discloses consulting for Biohaven Pharmaceuticals and for Seattle Gummy Co.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM OBESITY WEEK® 2023
Treatment order evidence comes to light for premenopausal idiopathic osteoporosis: What to do after denosumab
VANCOUVER – With treatment with a bisphosphonate following sequential use of teriparatide (Forteo) and denosumab (Prolia) for premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis, bone mineral density (BMD) was maintained over the first year following denosumab cessation, according to results from a small, nonrandomized extension of a phase 2 study.
Bisphosphonates are recommended for patients after they have completed a course of denosumab because cessation of the bone resorption blocker is known to increase bone turnover markers, decrease BMD, and raise the risk of vertebral fractures. Although there is evidence to support this treatment sequence for postmenopausal women, there was no evidence regarding premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis, said Adi Cohen, MD, who presented the results of the study at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
In the extension study, neither length of treatment with denosumab nor transition to menopause affected BMD results. Weekly doses of alendronate (ALN) better suppressed C-terminal telopeptide (CTX) than did zoledronic acid (ZOL) and led to better maintenance of BMD than did a single dose of ZOL. The researchers suggested that single-dose ZOL may not prevent bone loss for an entire year.
It is too early to call the results practice changing, said Dr. Cohen, professor of medicine and endocrinology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, but she noted, “It’s important just to provide information about how sequences of osteoporosis medications might be used in a rare but certainly understudied group of premenopausal women with osteoporosis who need treatment, and these data hopefully will help make some treatment decisions.”
In the early 2000s, researchers initially believed that premenopausal women with low BMD had experienced some kind of temporary event and that they would likely improve on their own over time. “I think we now recognize that whatever it is that causes this is an ongoing issue and that this is a problem they’re going to have to deal with for the rest of their lives. This is something that they have to stay on top of,” said coauthor Elizabeth Shane, MD, who is a professor of medicine at CUIMC.
However, there are no practice guidelines for the management of osteoporosis in premenopausal women, according to Dr. Shane. She noted that there is controversy as to whether to treat women with low bone density who do not have a history of fractures. “I think that there’s pretty much agreement that anybody who has a lot of fractures has an early-onset form of osteoporosis. The controversy is what to do about the person who just has a low bone density and hasn’t yet fractured and what is the utility of trying to treat them at that point and perhaps prevent a fracture. I don’t think we have enough data to address that,” Dr. Shane said.
Still, the research has provided some clarity in her own practice. “I think if somebody would come to my office who had very low bone density, I would probably treat them. If they have fractures, I would definitely treat them. I think that our work has provided a framework for people to approach that,” she said.
The study was an extension of a sequential treatment approach that began with 2 years of teriparatide (20 mcg daily) followed by an extension study of 2–3 years of treatment with denosumab (60 mg every 6 months). Seven months after the last dose of denosumab, patients underwent 1 year of treatment with ALN (70 mg weekly; n = 18) or a single dose of ZOL (5 mg IV; n = 6), according to patient choice.
The original phase 2 study started with 41 women. At 24 months, teriparatide treatment led to BMD increases of 13% in the lumbar spine (LS), 5% in the total hip (TH), and 5% in the femoral neck (FN). There was a 2% decline in BMD in the forearm (distal radius [DR]). A group of 32 of the women participated in an extension study and took denosumab for 12 months. Of those patients, 29 continued to take it for another 12 months. At 12 months, BMD increased 5% in the LS, 3% in the TH, 3% in the FN, and 1% in the DR (P < .05 for all). At 24 months, BMD rose by 22%, 10%, and 10% at the first three of those locations. BMD in the DR remained stable, compared with the baseline after taking teriparatide.
The bisphosphonate phase of the extension study included 24 women (mean age, 43 years). The mean body mass index of the patients was 23.0 kg/m2. The patients had experienced a mean of 3.0 fractures in adulthood, and 38% of patients had a history of vertebral fracture.
Over 12 months of follow-up, the researchers found no statistically significant difference in BMD in the LS, TH, or FN, compared with bisphosphonate extension baseline. There was also no statistically significant change in serum CTX. There was evidence that, among patients with higher rates of bone turnover, there were higher rates of LS and FN bone loss during bisphosphonate treatment.
Among patients taking ZOL, at 12 months there was a statistically significant rise in CTX levels, but not among patients taking ALN. There were no new vertebral fractures among any participants during the bisphosphonate extension period.
The results represent critical data for an understudied population, according to Yumie Rhee, MD, PhD, who was comoderator of the session in which the study was presented. “They are showing that by using a bisphosphonate [patients] have this just slight decrease, but within error, so it’s maintaining the BMD, at least. I think it’s very important. It will be fascinating to see next year’s follow-up,” said Dr. Rhee, a professor of endocrinology at Yonsei University College of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea. “The problem with premenopausal osteoporosis is that we don’t have good evidence. Even though this study is very small, we’re just following that data, all of us.”
Comoderator Maria Zanchetta, MD, a professor of osteology at the Institute of Diagnostics and Metabolic Research, Universidad del Salvador, Buenos Aires, agreed. “We know what to do when we stop denosumab in postmenopausal women. We didn’t have any work about what to do when we stopped in premenopausal women. You can think that probably it’s going to be the same, but this is the first time you have the evidence that if you give bisphosphonate, you will maintain BMD.”
Limitations to the study include its small size and the lack of a placebo-treated control group. In addition, the bisphosphonate extension was not randomized.
The studies were funded by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and Amgen. Dr. Cohen and Dr. Shane received research funding from Amgen. Dr. Rhee and Dr. Zanchetta have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER – With treatment with a bisphosphonate following sequential use of teriparatide (Forteo) and denosumab (Prolia) for premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis, bone mineral density (BMD) was maintained over the first year following denosumab cessation, according to results from a small, nonrandomized extension of a phase 2 study.
Bisphosphonates are recommended for patients after they have completed a course of denosumab because cessation of the bone resorption blocker is known to increase bone turnover markers, decrease BMD, and raise the risk of vertebral fractures. Although there is evidence to support this treatment sequence for postmenopausal women, there was no evidence regarding premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis, said Adi Cohen, MD, who presented the results of the study at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
In the extension study, neither length of treatment with denosumab nor transition to menopause affected BMD results. Weekly doses of alendronate (ALN) better suppressed C-terminal telopeptide (CTX) than did zoledronic acid (ZOL) and led to better maintenance of BMD than did a single dose of ZOL. The researchers suggested that single-dose ZOL may not prevent bone loss for an entire year.
It is too early to call the results practice changing, said Dr. Cohen, professor of medicine and endocrinology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, but she noted, “It’s important just to provide information about how sequences of osteoporosis medications might be used in a rare but certainly understudied group of premenopausal women with osteoporosis who need treatment, and these data hopefully will help make some treatment decisions.”
In the early 2000s, researchers initially believed that premenopausal women with low BMD had experienced some kind of temporary event and that they would likely improve on their own over time. “I think we now recognize that whatever it is that causes this is an ongoing issue and that this is a problem they’re going to have to deal with for the rest of their lives. This is something that they have to stay on top of,” said coauthor Elizabeth Shane, MD, who is a professor of medicine at CUIMC.
However, there are no practice guidelines for the management of osteoporosis in premenopausal women, according to Dr. Shane. She noted that there is controversy as to whether to treat women with low bone density who do not have a history of fractures. “I think that there’s pretty much agreement that anybody who has a lot of fractures has an early-onset form of osteoporosis. The controversy is what to do about the person who just has a low bone density and hasn’t yet fractured and what is the utility of trying to treat them at that point and perhaps prevent a fracture. I don’t think we have enough data to address that,” Dr. Shane said.
Still, the research has provided some clarity in her own practice. “I think if somebody would come to my office who had very low bone density, I would probably treat them. If they have fractures, I would definitely treat them. I think that our work has provided a framework for people to approach that,” she said.
The study was an extension of a sequential treatment approach that began with 2 years of teriparatide (20 mcg daily) followed by an extension study of 2–3 years of treatment with denosumab (60 mg every 6 months). Seven months after the last dose of denosumab, patients underwent 1 year of treatment with ALN (70 mg weekly; n = 18) or a single dose of ZOL (5 mg IV; n = 6), according to patient choice.
The original phase 2 study started with 41 women. At 24 months, teriparatide treatment led to BMD increases of 13% in the lumbar spine (LS), 5% in the total hip (TH), and 5% in the femoral neck (FN). There was a 2% decline in BMD in the forearm (distal radius [DR]). A group of 32 of the women participated in an extension study and took denosumab for 12 months. Of those patients, 29 continued to take it for another 12 months. At 12 months, BMD increased 5% in the LS, 3% in the TH, 3% in the FN, and 1% in the DR (P < .05 for all). At 24 months, BMD rose by 22%, 10%, and 10% at the first three of those locations. BMD in the DR remained stable, compared with the baseline after taking teriparatide.
The bisphosphonate phase of the extension study included 24 women (mean age, 43 years). The mean body mass index of the patients was 23.0 kg/m2. The patients had experienced a mean of 3.0 fractures in adulthood, and 38% of patients had a history of vertebral fracture.
Over 12 months of follow-up, the researchers found no statistically significant difference in BMD in the LS, TH, or FN, compared with bisphosphonate extension baseline. There was also no statistically significant change in serum CTX. There was evidence that, among patients with higher rates of bone turnover, there were higher rates of LS and FN bone loss during bisphosphonate treatment.
Among patients taking ZOL, at 12 months there was a statistically significant rise in CTX levels, but not among patients taking ALN. There were no new vertebral fractures among any participants during the bisphosphonate extension period.
The results represent critical data for an understudied population, according to Yumie Rhee, MD, PhD, who was comoderator of the session in which the study was presented. “They are showing that by using a bisphosphonate [patients] have this just slight decrease, but within error, so it’s maintaining the BMD, at least. I think it’s very important. It will be fascinating to see next year’s follow-up,” said Dr. Rhee, a professor of endocrinology at Yonsei University College of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea. “The problem with premenopausal osteoporosis is that we don’t have good evidence. Even though this study is very small, we’re just following that data, all of us.”
Comoderator Maria Zanchetta, MD, a professor of osteology at the Institute of Diagnostics and Metabolic Research, Universidad del Salvador, Buenos Aires, agreed. “We know what to do when we stop denosumab in postmenopausal women. We didn’t have any work about what to do when we stopped in premenopausal women. You can think that probably it’s going to be the same, but this is the first time you have the evidence that if you give bisphosphonate, you will maintain BMD.”
Limitations to the study include its small size and the lack of a placebo-treated control group. In addition, the bisphosphonate extension was not randomized.
The studies were funded by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and Amgen. Dr. Cohen and Dr. Shane received research funding from Amgen. Dr. Rhee and Dr. Zanchetta have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER – With treatment with a bisphosphonate following sequential use of teriparatide (Forteo) and denosumab (Prolia) for premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis, bone mineral density (BMD) was maintained over the first year following denosumab cessation, according to results from a small, nonrandomized extension of a phase 2 study.
Bisphosphonates are recommended for patients after they have completed a course of denosumab because cessation of the bone resorption blocker is known to increase bone turnover markers, decrease BMD, and raise the risk of vertebral fractures. Although there is evidence to support this treatment sequence for postmenopausal women, there was no evidence regarding premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis, said Adi Cohen, MD, who presented the results of the study at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
In the extension study, neither length of treatment with denosumab nor transition to menopause affected BMD results. Weekly doses of alendronate (ALN) better suppressed C-terminal telopeptide (CTX) than did zoledronic acid (ZOL) and led to better maintenance of BMD than did a single dose of ZOL. The researchers suggested that single-dose ZOL may not prevent bone loss for an entire year.
It is too early to call the results practice changing, said Dr. Cohen, professor of medicine and endocrinology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, but she noted, “It’s important just to provide information about how sequences of osteoporosis medications might be used in a rare but certainly understudied group of premenopausal women with osteoporosis who need treatment, and these data hopefully will help make some treatment decisions.”
In the early 2000s, researchers initially believed that premenopausal women with low BMD had experienced some kind of temporary event and that they would likely improve on their own over time. “I think we now recognize that whatever it is that causes this is an ongoing issue and that this is a problem they’re going to have to deal with for the rest of their lives. This is something that they have to stay on top of,” said coauthor Elizabeth Shane, MD, who is a professor of medicine at CUIMC.
However, there are no practice guidelines for the management of osteoporosis in premenopausal women, according to Dr. Shane. She noted that there is controversy as to whether to treat women with low bone density who do not have a history of fractures. “I think that there’s pretty much agreement that anybody who has a lot of fractures has an early-onset form of osteoporosis. The controversy is what to do about the person who just has a low bone density and hasn’t yet fractured and what is the utility of trying to treat them at that point and perhaps prevent a fracture. I don’t think we have enough data to address that,” Dr. Shane said.
Still, the research has provided some clarity in her own practice. “I think if somebody would come to my office who had very low bone density, I would probably treat them. If they have fractures, I would definitely treat them. I think that our work has provided a framework for people to approach that,” she said.
The study was an extension of a sequential treatment approach that began with 2 years of teriparatide (20 mcg daily) followed by an extension study of 2–3 years of treatment with denosumab (60 mg every 6 months). Seven months after the last dose of denosumab, patients underwent 1 year of treatment with ALN (70 mg weekly; n = 18) or a single dose of ZOL (5 mg IV; n = 6), according to patient choice.
The original phase 2 study started with 41 women. At 24 months, teriparatide treatment led to BMD increases of 13% in the lumbar spine (LS), 5% in the total hip (TH), and 5% in the femoral neck (FN). There was a 2% decline in BMD in the forearm (distal radius [DR]). A group of 32 of the women participated in an extension study and took denosumab for 12 months. Of those patients, 29 continued to take it for another 12 months. At 12 months, BMD increased 5% in the LS, 3% in the TH, 3% in the FN, and 1% in the DR (P < .05 for all). At 24 months, BMD rose by 22%, 10%, and 10% at the first three of those locations. BMD in the DR remained stable, compared with the baseline after taking teriparatide.
The bisphosphonate phase of the extension study included 24 women (mean age, 43 years). The mean body mass index of the patients was 23.0 kg/m2. The patients had experienced a mean of 3.0 fractures in adulthood, and 38% of patients had a history of vertebral fracture.
Over 12 months of follow-up, the researchers found no statistically significant difference in BMD in the LS, TH, or FN, compared with bisphosphonate extension baseline. There was also no statistically significant change in serum CTX. There was evidence that, among patients with higher rates of bone turnover, there were higher rates of LS and FN bone loss during bisphosphonate treatment.
Among patients taking ZOL, at 12 months there was a statistically significant rise in CTX levels, but not among patients taking ALN. There were no new vertebral fractures among any participants during the bisphosphonate extension period.
The results represent critical data for an understudied population, according to Yumie Rhee, MD, PhD, who was comoderator of the session in which the study was presented. “They are showing that by using a bisphosphonate [patients] have this just slight decrease, but within error, so it’s maintaining the BMD, at least. I think it’s very important. It will be fascinating to see next year’s follow-up,” said Dr. Rhee, a professor of endocrinology at Yonsei University College of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea. “The problem with premenopausal osteoporosis is that we don’t have good evidence. Even though this study is very small, we’re just following that data, all of us.”
Comoderator Maria Zanchetta, MD, a professor of osteology at the Institute of Diagnostics and Metabolic Research, Universidad del Salvador, Buenos Aires, agreed. “We know what to do when we stop denosumab in postmenopausal women. We didn’t have any work about what to do when we stopped in premenopausal women. You can think that probably it’s going to be the same, but this is the first time you have the evidence that if you give bisphosphonate, you will maintain BMD.”
Limitations to the study include its small size and the lack of a placebo-treated control group. In addition, the bisphosphonate extension was not randomized.
The studies were funded by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and Amgen. Dr. Cohen and Dr. Shane received research funding from Amgen. Dr. Rhee and Dr. Zanchetta have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASBMR 2023
ESG yields significant, sustained weight loss across obesity classes
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective analysis of 1,506 adults (85% female, 70% White) with severe obesity (501 class I, 546 class II, and 459 class III) who underwent ESG at seven academic and private U.S. centers from 2013 to 2022.
- Average percent total body weight loss (%TBWL) was evaluated at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months after the procedure.
- Weight loss and safety outcomes were evaluated according to obesity class.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 months, 83.2% of patients achieved ≥10% TBWL and 60.9% achieved ≥15% TBWL across all obesity classes.
- There was a significant difference in TBWL by baseline obesity class, with average weight loss significantly greater in class III than classes I and II at all time points. At 24 months, class III patients had mean TBWL of 20.4%, compared with 13.3% for class I and 13.6% for class II patients.
- As early as 6 months post-ESG, patients in all BMI classes were able to drop to the next lower BMI class and remained there through 2 years. However, ongoing improvement in BMI until the end of follow-up was seen only in class III patients. Notably, class III patients were significantly younger and taller than class I and class II patients.
- There were no differences in adverse events between obesity classes. Only 2.6% of patients had an adverse event requiring hospitalization. Most of these events (86%) were for symptom management and/or fluid replacement.
IN PRACTICE:
“Traditionally, ESG has been proposed as a treatment choice for patients with class I and II obesity because of its modest weight loss outcomes. However, our data show a %TBWL crossing 20% in patients with class III disease, which may push the envelope of perceived utility of ESG,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Khushboo Gala, MBBS, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., was published online in Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include the retrospective design, with outcomes only out to 2 years, and loss of follow-up, with only 339 of the 1506 patients evaluated at 2 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no financial support. Several study authors reported ties to industry. The full list can be found with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective analysis of 1,506 adults (85% female, 70% White) with severe obesity (501 class I, 546 class II, and 459 class III) who underwent ESG at seven academic and private U.S. centers from 2013 to 2022.
- Average percent total body weight loss (%TBWL) was evaluated at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months after the procedure.
- Weight loss and safety outcomes were evaluated according to obesity class.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 months, 83.2% of patients achieved ≥10% TBWL and 60.9% achieved ≥15% TBWL across all obesity classes.
- There was a significant difference in TBWL by baseline obesity class, with average weight loss significantly greater in class III than classes I and II at all time points. At 24 months, class III patients had mean TBWL of 20.4%, compared with 13.3% for class I and 13.6% for class II patients.
- As early as 6 months post-ESG, patients in all BMI classes were able to drop to the next lower BMI class and remained there through 2 years. However, ongoing improvement in BMI until the end of follow-up was seen only in class III patients. Notably, class III patients were significantly younger and taller than class I and class II patients.
- There were no differences in adverse events between obesity classes. Only 2.6% of patients had an adverse event requiring hospitalization. Most of these events (86%) were for symptom management and/or fluid replacement.
IN PRACTICE:
“Traditionally, ESG has been proposed as a treatment choice for patients with class I and II obesity because of its modest weight loss outcomes. However, our data show a %TBWL crossing 20% in patients with class III disease, which may push the envelope of perceived utility of ESG,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Khushboo Gala, MBBS, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., was published online in Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include the retrospective design, with outcomes only out to 2 years, and loss of follow-up, with only 339 of the 1506 patients evaluated at 2 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no financial support. Several study authors reported ties to industry. The full list can be found with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective analysis of 1,506 adults (85% female, 70% White) with severe obesity (501 class I, 546 class II, and 459 class III) who underwent ESG at seven academic and private U.S. centers from 2013 to 2022.
- Average percent total body weight loss (%TBWL) was evaluated at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months after the procedure.
- Weight loss and safety outcomes were evaluated according to obesity class.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 months, 83.2% of patients achieved ≥10% TBWL and 60.9% achieved ≥15% TBWL across all obesity classes.
- There was a significant difference in TBWL by baseline obesity class, with average weight loss significantly greater in class III than classes I and II at all time points. At 24 months, class III patients had mean TBWL of 20.4%, compared with 13.3% for class I and 13.6% for class II patients.
- As early as 6 months post-ESG, patients in all BMI classes were able to drop to the next lower BMI class and remained there through 2 years. However, ongoing improvement in BMI until the end of follow-up was seen only in class III patients. Notably, class III patients were significantly younger and taller than class I and class II patients.
- There were no differences in adverse events between obesity classes. Only 2.6% of patients had an adverse event requiring hospitalization. Most of these events (86%) were for symptom management and/or fluid replacement.
IN PRACTICE:
“Traditionally, ESG has been proposed as a treatment choice for patients with class I and II obesity because of its modest weight loss outcomes. However, our data show a %TBWL crossing 20% in patients with class III disease, which may push the envelope of perceived utility of ESG,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Khushboo Gala, MBBS, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., was published online in Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include the retrospective design, with outcomes only out to 2 years, and loss of follow-up, with only 339 of the 1506 patients evaluated at 2 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no financial support. Several study authors reported ties to industry. The full list can be found with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA proposes ban on hair straightener ingredients
The
The proposal specifies that formaldehyde would be banned, as well as other chemicals that release formaldehyde, such as methylene glycol. Using hair smoothing products containing formaldehyde and formaldehyde-releasing chemicals “is linked to short-term adverse health effects, such as sensitization reactions and breathing problems, and long-term adverse health effects, including an increased risk of certain cancers,” the proposal states.
One study published last year showed that repeated use of hair straightening products, also called relaxers, could more than double the risk of uterine cancer. Although that study didn’t find that the uterine cancer risk varied based on a person’s race, the researchers noted that women who are Black are among the most likely to use the products and tend to start using them at younger ages, compared with people of other races and ethnicities.
Hair straightening products have also been linked to elevated risks of hormone-sensitive cancers, such as breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Rep. Ayanna Pressley (D-Mass.) and Rep. Shontel Brown (D-Ohio) applauded the proposed rule in a statement issued jointly on Oct. 6. “The FDA’s proposal to ban these harmful chemicals in hair straighteners and relaxers is a win for public health – especially the health of Black women who are disproportionately put at risk by these products as a result of systemic racism and anti–Black hair sentiment,” Rep. Pressley said The two congresswomen wrote a letter to the FDA earlier this year requesting the topic be investigated.
“Regardless of how we wear our hair, we should be allowed to show up in the world without putting our health at risk. I applaud the FDA for being responsive to our calls and advancing a rule that will help prevent manufacturers from making a profit at the expense of our health,” Rep. Pressley said in the statement. “The administration should finalize this rule without delay.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com
The
The proposal specifies that formaldehyde would be banned, as well as other chemicals that release formaldehyde, such as methylene glycol. Using hair smoothing products containing formaldehyde and formaldehyde-releasing chemicals “is linked to short-term adverse health effects, such as sensitization reactions and breathing problems, and long-term adverse health effects, including an increased risk of certain cancers,” the proposal states.
One study published last year showed that repeated use of hair straightening products, also called relaxers, could more than double the risk of uterine cancer. Although that study didn’t find that the uterine cancer risk varied based on a person’s race, the researchers noted that women who are Black are among the most likely to use the products and tend to start using them at younger ages, compared with people of other races and ethnicities.
Hair straightening products have also been linked to elevated risks of hormone-sensitive cancers, such as breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Rep. Ayanna Pressley (D-Mass.) and Rep. Shontel Brown (D-Ohio) applauded the proposed rule in a statement issued jointly on Oct. 6. “The FDA’s proposal to ban these harmful chemicals in hair straighteners and relaxers is a win for public health – especially the health of Black women who are disproportionately put at risk by these products as a result of systemic racism and anti–Black hair sentiment,” Rep. Pressley said The two congresswomen wrote a letter to the FDA earlier this year requesting the topic be investigated.
“Regardless of how we wear our hair, we should be allowed to show up in the world without putting our health at risk. I applaud the FDA for being responsive to our calls and advancing a rule that will help prevent manufacturers from making a profit at the expense of our health,” Rep. Pressley said in the statement. “The administration should finalize this rule without delay.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com
The
The proposal specifies that formaldehyde would be banned, as well as other chemicals that release formaldehyde, such as methylene glycol. Using hair smoothing products containing formaldehyde and formaldehyde-releasing chemicals “is linked to short-term adverse health effects, such as sensitization reactions and breathing problems, and long-term adverse health effects, including an increased risk of certain cancers,” the proposal states.
One study published last year showed that repeated use of hair straightening products, also called relaxers, could more than double the risk of uterine cancer. Although that study didn’t find that the uterine cancer risk varied based on a person’s race, the researchers noted that women who are Black are among the most likely to use the products and tend to start using them at younger ages, compared with people of other races and ethnicities.
Hair straightening products have also been linked to elevated risks of hormone-sensitive cancers, such as breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Rep. Ayanna Pressley (D-Mass.) and Rep. Shontel Brown (D-Ohio) applauded the proposed rule in a statement issued jointly on Oct. 6. “The FDA’s proposal to ban these harmful chemicals in hair straighteners and relaxers is a win for public health – especially the health of Black women who are disproportionately put at risk by these products as a result of systemic racism and anti–Black hair sentiment,” Rep. Pressley said The two congresswomen wrote a letter to the FDA earlier this year requesting the topic be investigated.
“Regardless of how we wear our hair, we should be allowed to show up in the world without putting our health at risk. I applaud the FDA for being responsive to our calls and advancing a rule that will help prevent manufacturers from making a profit at the expense of our health,” Rep. Pressley said in the statement. “The administration should finalize this rule without delay.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com
Higher fracture risk not seen with SGLT2 inhibitors
VANCOUVER – In patients with type 2 diabetes, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors as an adjunct to metformin were not associated with an increase in fracture risk, according to a new real-world study.
There have been some reports of an increase in fracture risk associated with SGLT2 inhibitors, and it was observed in the phase 3 CANVAS trial of canagliflozin (Invokana), which led to a Food and Drug Administration warning of fracture risks associated with canagliflozin use. Some ensuing studies did not show an increased risk, but these studies were generally less than a year in duration and may have missed longer-term risk, according to Veerle van Hulten, MSc.
“Fracture risk is something that takes a long time to develop, so we wanted to have a longer follow-up. We looked into the CPRD [Clinical Practice Research Datalink], which is a beautiful database containing real-world data from primary care practices,” said Ms. van Hulten, a PhD student at Maastricht (the Netherlands) University, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Ms. van Hulten and colleagues compared SGLT2 inhibitors with dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors because the latter are used in similar populations and have been shown to have no effect on fracture risk.
“What we found is that SGLT2 inhibitors are not associated with an increased fracture risk. Even with a duration of use of over 811 days, we did not observe an increased hazard ratio for fractures when compared DPP-4 inhibitor users,” Ms. van Hulten said.
SGLT2 inhibitors reduce blood sugar by increasing elimination of sugar in the urine. They also increase phosphate, reduce calcium, and increase parathyroid hormone, which could in turn negatively affect bone turnover, according to Ms. van Hulten.
In the new study, conducted between January 2013 and June 2020, the researchers used propensity score matching to compare adult patients, including 13,807 who were prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors and 28,524 who were prescribed DPP-4 inhibitors for the first time. They matched patients based on demographics, comorbidities, comedication, and lifestyle factors.
There was no association between SGLT2 inhibitor use and overall fracture risk or major osteoporotic, hip, vertebral, humerus, radius, or ulna fractures. There was no difference in risk for any duration of use, even with the longest duration of use of 811 days (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.0). There were no differences among specific SGLT2 inhibitors, including canagliflozin (aHR, 1.12; 95% confidence interval, 0.73-1.72). Analyses by sex and age also revealed no statistically significant differences between the two drug classes.
During the Q&A session after the presentation, Sarah Berry, MD, MPH, an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a clinical researcher at the Marcus Institute for Aging Research, both in Boston, noted the trend toward an increase in fracture risk in the first 90 days. “It looked like there was something going on in the first 90 days, and then after that the results were much closer to the null. I would put out maybe another potential mechanism whereby the SGLT2 inhibitors might cause fracture, and that’s falls. They cause polyuria, and any drug you give that causes women to rush to the bathroom may well cause fractures, particularly in the short term,” Dr. Berry said.
Ms. van Hulten agreed, and also brought up that the drugs can cause osmotic diuresis. That can lead to hypovolemia, the symptoms of which include weakness, fatigue, and dizziness. “And increased falls, of course, increases fracture risk. We do not expect anything to happen to bone metabolism in the first 90 days. I think we can agree that there would be more time needed to alter the bone enough to increase fracture risk, so we expect that this trend toward an increased risk might be attributable to that increased fall risk that might occur with SGLT2 inhibitor use,” she said.
It’s possible that such a mechanism explains increased fracture risk seen in some earlier short-term studies, she added.
Overall, Ms. van Hulten said that the results should provide some confidence in SGLT2 inhibitors, though more work needs to be done. “I think we provide reassurance that SGLT2 inhibitors are safe to use. However, we still only have a median follow-up of 1.6 years. It’s not as long as we maybe would like, but it’s the best we can do with the data available, since the SGLT2 inhibitors have only been used since 2013. So maybe it’s best to prescribe it and keep [fall risk] in mind and look into the effects later on again, but it seems to be safe to use.”
The study received funding from the Novo Nordisk Foundation. Ms. van Hulten and Dr. Berry reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER – In patients with type 2 diabetes, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors as an adjunct to metformin were not associated with an increase in fracture risk, according to a new real-world study.
There have been some reports of an increase in fracture risk associated with SGLT2 inhibitors, and it was observed in the phase 3 CANVAS trial of canagliflozin (Invokana), which led to a Food and Drug Administration warning of fracture risks associated with canagliflozin use. Some ensuing studies did not show an increased risk, but these studies were generally less than a year in duration and may have missed longer-term risk, according to Veerle van Hulten, MSc.
“Fracture risk is something that takes a long time to develop, so we wanted to have a longer follow-up. We looked into the CPRD [Clinical Practice Research Datalink], which is a beautiful database containing real-world data from primary care practices,” said Ms. van Hulten, a PhD student at Maastricht (the Netherlands) University, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Ms. van Hulten and colleagues compared SGLT2 inhibitors with dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors because the latter are used in similar populations and have been shown to have no effect on fracture risk.
“What we found is that SGLT2 inhibitors are not associated with an increased fracture risk. Even with a duration of use of over 811 days, we did not observe an increased hazard ratio for fractures when compared DPP-4 inhibitor users,” Ms. van Hulten said.
SGLT2 inhibitors reduce blood sugar by increasing elimination of sugar in the urine. They also increase phosphate, reduce calcium, and increase parathyroid hormone, which could in turn negatively affect bone turnover, according to Ms. van Hulten.
In the new study, conducted between January 2013 and June 2020, the researchers used propensity score matching to compare adult patients, including 13,807 who were prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors and 28,524 who were prescribed DPP-4 inhibitors for the first time. They matched patients based on demographics, comorbidities, comedication, and lifestyle factors.
There was no association between SGLT2 inhibitor use and overall fracture risk or major osteoporotic, hip, vertebral, humerus, radius, or ulna fractures. There was no difference in risk for any duration of use, even with the longest duration of use of 811 days (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.0). There were no differences among specific SGLT2 inhibitors, including canagliflozin (aHR, 1.12; 95% confidence interval, 0.73-1.72). Analyses by sex and age also revealed no statistically significant differences between the two drug classes.
During the Q&A session after the presentation, Sarah Berry, MD, MPH, an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a clinical researcher at the Marcus Institute for Aging Research, both in Boston, noted the trend toward an increase in fracture risk in the first 90 days. “It looked like there was something going on in the first 90 days, and then after that the results were much closer to the null. I would put out maybe another potential mechanism whereby the SGLT2 inhibitors might cause fracture, and that’s falls. They cause polyuria, and any drug you give that causes women to rush to the bathroom may well cause fractures, particularly in the short term,” Dr. Berry said.
Ms. van Hulten agreed, and also brought up that the drugs can cause osmotic diuresis. That can lead to hypovolemia, the symptoms of which include weakness, fatigue, and dizziness. “And increased falls, of course, increases fracture risk. We do not expect anything to happen to bone metabolism in the first 90 days. I think we can agree that there would be more time needed to alter the bone enough to increase fracture risk, so we expect that this trend toward an increased risk might be attributable to that increased fall risk that might occur with SGLT2 inhibitor use,” she said.
It’s possible that such a mechanism explains increased fracture risk seen in some earlier short-term studies, she added.
Overall, Ms. van Hulten said that the results should provide some confidence in SGLT2 inhibitors, though more work needs to be done. “I think we provide reassurance that SGLT2 inhibitors are safe to use. However, we still only have a median follow-up of 1.6 years. It’s not as long as we maybe would like, but it’s the best we can do with the data available, since the SGLT2 inhibitors have only been used since 2013. So maybe it’s best to prescribe it and keep [fall risk] in mind and look into the effects later on again, but it seems to be safe to use.”
The study received funding from the Novo Nordisk Foundation. Ms. van Hulten and Dr. Berry reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER – In patients with type 2 diabetes, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors as an adjunct to metformin were not associated with an increase in fracture risk, according to a new real-world study.
There have been some reports of an increase in fracture risk associated with SGLT2 inhibitors, and it was observed in the phase 3 CANVAS trial of canagliflozin (Invokana), which led to a Food and Drug Administration warning of fracture risks associated with canagliflozin use. Some ensuing studies did not show an increased risk, but these studies were generally less than a year in duration and may have missed longer-term risk, according to Veerle van Hulten, MSc.
“Fracture risk is something that takes a long time to develop, so we wanted to have a longer follow-up. We looked into the CPRD [Clinical Practice Research Datalink], which is a beautiful database containing real-world data from primary care practices,” said Ms. van Hulten, a PhD student at Maastricht (the Netherlands) University, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Ms. van Hulten and colleagues compared SGLT2 inhibitors with dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors because the latter are used in similar populations and have been shown to have no effect on fracture risk.
“What we found is that SGLT2 inhibitors are not associated with an increased fracture risk. Even with a duration of use of over 811 days, we did not observe an increased hazard ratio for fractures when compared DPP-4 inhibitor users,” Ms. van Hulten said.
SGLT2 inhibitors reduce blood sugar by increasing elimination of sugar in the urine. They also increase phosphate, reduce calcium, and increase parathyroid hormone, which could in turn negatively affect bone turnover, according to Ms. van Hulten.
In the new study, conducted between January 2013 and June 2020, the researchers used propensity score matching to compare adult patients, including 13,807 who were prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors and 28,524 who were prescribed DPP-4 inhibitors for the first time. They matched patients based on demographics, comorbidities, comedication, and lifestyle factors.
There was no association between SGLT2 inhibitor use and overall fracture risk or major osteoporotic, hip, vertebral, humerus, radius, or ulna fractures. There was no difference in risk for any duration of use, even with the longest duration of use of 811 days (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.0). There were no differences among specific SGLT2 inhibitors, including canagliflozin (aHR, 1.12; 95% confidence interval, 0.73-1.72). Analyses by sex and age also revealed no statistically significant differences between the two drug classes.
During the Q&A session after the presentation, Sarah Berry, MD, MPH, an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a clinical researcher at the Marcus Institute for Aging Research, both in Boston, noted the trend toward an increase in fracture risk in the first 90 days. “It looked like there was something going on in the first 90 days, and then after that the results were much closer to the null. I would put out maybe another potential mechanism whereby the SGLT2 inhibitors might cause fracture, and that’s falls. They cause polyuria, and any drug you give that causes women to rush to the bathroom may well cause fractures, particularly in the short term,” Dr. Berry said.
Ms. van Hulten agreed, and also brought up that the drugs can cause osmotic diuresis. That can lead to hypovolemia, the symptoms of which include weakness, fatigue, and dizziness. “And increased falls, of course, increases fracture risk. We do not expect anything to happen to bone metabolism in the first 90 days. I think we can agree that there would be more time needed to alter the bone enough to increase fracture risk, so we expect that this trend toward an increased risk might be attributable to that increased fall risk that might occur with SGLT2 inhibitor use,” she said.
It’s possible that such a mechanism explains increased fracture risk seen in some earlier short-term studies, she added.
Overall, Ms. van Hulten said that the results should provide some confidence in SGLT2 inhibitors, though more work needs to be done. “I think we provide reassurance that SGLT2 inhibitors are safe to use. However, we still only have a median follow-up of 1.6 years. It’s not as long as we maybe would like, but it’s the best we can do with the data available, since the SGLT2 inhibitors have only been used since 2013. So maybe it’s best to prescribe it and keep [fall risk] in mind and look into the effects later on again, but it seems to be safe to use.”
The study received funding from the Novo Nordisk Foundation. Ms. van Hulten and Dr. Berry reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASBMR 2023
A focus on women with diabetes and their offspring
In 2021, diabetes and related complications was the 8th leading cause of death in the United States.1 As of 2022, more than 11% of the U.S. population had diabetes and 38% of the adult U.S. population had prediabetes.2 Diabetes is the most expensive chronic condition in the United States, where $1 of every $4 in health care costs is spent on care.3
Where this is most concerning is diabetes in pregnancy. While childbirth rates in the United States have decreased since the 2007 high of 4.32 million births4 to 3.66 million in 2021,5 the incidence of diabetes in pregnancy – both pregestational and gestational – has increased. The rate of pregestational diabetes in 2021 was 10.9 per 1,000 births, a 27% increase from 2016 (8.6 per 1,000).6 The percentage of those giving birth who also were diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) was 8.3% in 2021, up from 6.0% in 2016.7
Adverse outcomes for an infant born to a mother with diabetes include a higher risk of obesity and diabetes as adults, potentially leading to a forward-feeding cycle.
We and our colleagues established the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America in 1997 because we had witnessed too frequently the devastating diabetes-induced pregnancy complications in our patients. The mission we set forth was to provide a forum for dialogue among maternal-fetal medicine subspecialists. The three main goals we set forth to support this mission were to provide a catalyst for research, contribute to the creation and refinement of medical policies, and influence professional practices in diabetes in pregnancy.8
In the last quarter century, DPSG-NA, through its annual and biennial meetings, has brought together several hundred practitioners that include physicians, nurses, statisticians, researchers, nutritionists, and allied health professionals, among others. As a group, it has improved the detection and management of diabetes in pregnant women and their offspring through knowledge sharing and influencing policies on GDM screening, diagnosis, management, and treatment. Our members have shown that preconceptional counseling for women with diabetes can significantly reduce congenital malformation and perinatal mortality compared with those women with pregestational diabetes who receive no counseling.9,10
We have addressed a wide variety of topics including the paucity of data in determining the timing of delivery for women with diabetes and the Institute of Medicine/National Academy of Medicine recommendations of gestational weight gain and risks of not adhering to them. We have learned about new scientific discoveries that reveal underlying mechanisms to diabetes-related birth defects and potential therapeutic targets; and we have discussed the health literacy requirements, ethics, and opportunities for lifestyle intervention.11-16
But we need to do more.
Two risk factors are at play: Women continue to choose to have babies at later ages and their pregnancies continue to be complicated by the rising incidence of obesity (see Figure 1 and Figure 2). 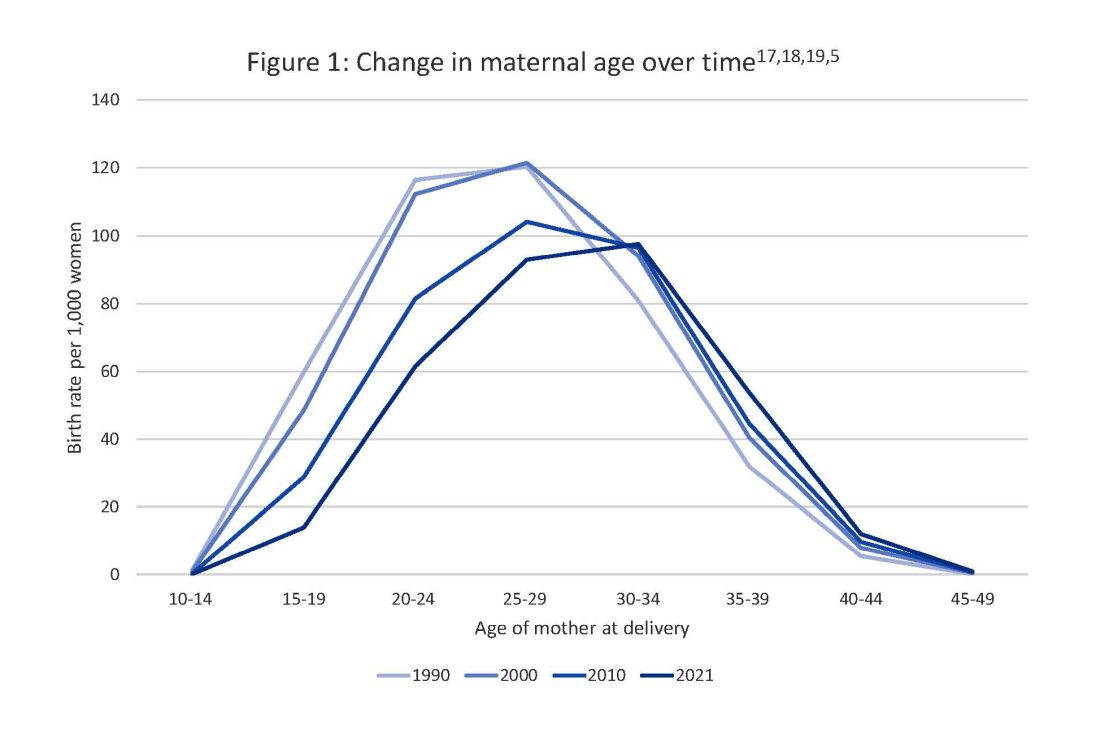
The global obesity epidemic has become a significant concern for all aspects of health and particularly for diabetes in pregnancy. 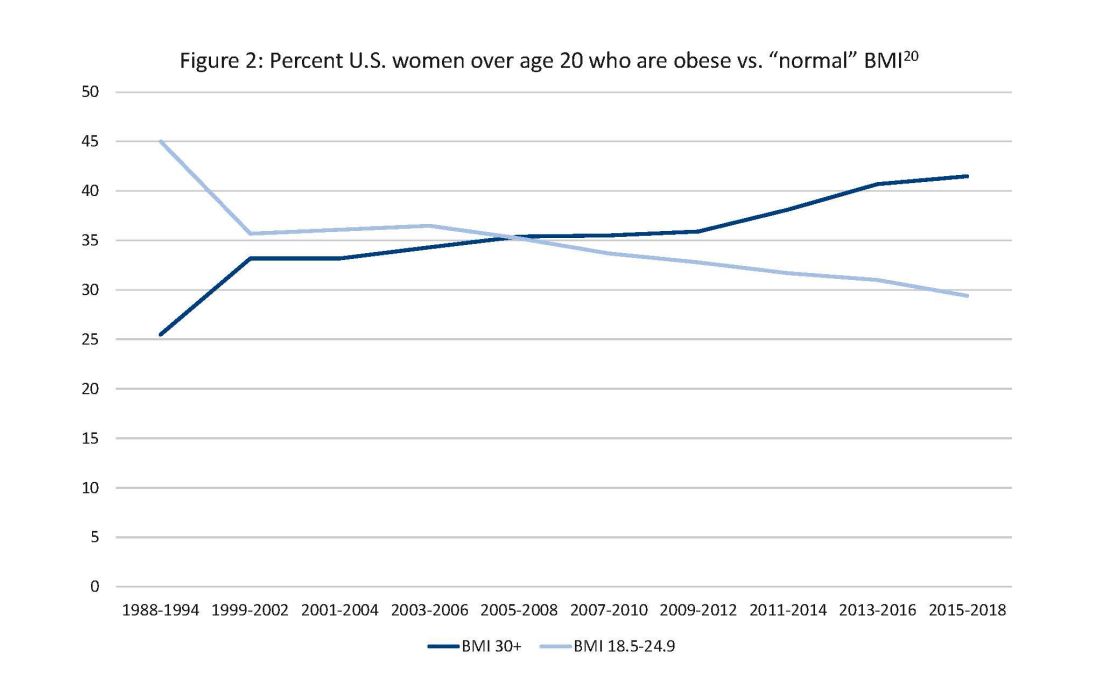
In 1990, 24.9% of women in the United States were obese; in 2010, 35.8%; and now more than 41%. Some experts project that by 2030 more than 80% of women in the United States will be overweight or obese.21
If we are to stop this cycle of diabetes begets more diabetes, now more than ever we need to come together and accelerate the research and education around the diabetes in pregnancy. Join us at this year’s DPSG-NA meeting Oct. 26-28 to take part in the knowledge sharing, discussions, and planning. More information can be found online at https://events.dpsg-na.com/home.
Dr. Miodovnik is adjunct professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at University of Maryland School of Medicine. Dr. Reece is professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences and senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research at University of Maryland School of Medicine.
References
1. Xu J et al. Mortality in the United States, 2021. NCHS Data Brief. 2022 Dec;(456):1-8. PMID: 36598387.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, diabetes data and statistics.
3. American Diabetes Association. The Cost of Diabetes.
4. Martin JA et al. Births: Final data for 2007. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2010 Aug 9;58(24):1-85. PMID: 21254725.
5. Osterman MJK et al. Births: Final data for 2021. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2023 Jan;72(1):1-53. PMID: 36723449.
6. Gregory ECW and Ely DM. Trends and characteristics in prepregnancy diabetes: United States, 2016-2021. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2023 May;72(6):1-13. PMID: 37256333.
7. QuickStats: Percentage of mothers with gestational diabetes, by maternal age – National Vital Statistics System, United States, 2016 and 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Jan 6;72(1):16. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7201a4.
8. Langer O et al. The Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America – Introduction and summary statement. Prenat Neonat Med. 1998;3(6):514-6.
9. Willhoite MB et al. The impact of preconception counseling on pregnancy outcomes. The experience of the Maine Diabetes in Pregnancy Program. Diabetes Care. 1993 Feb;16(2):450-5. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.2.450.
10. McElvy SS et al. A focused preconceptional and early pregnancy program in women with type 1 diabetes reduces perinatal mortality and malformation rates to general population levels. J Matern Fetal Med. 2000 Jan-Feb;9(1):14-20. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6661(200001/02)9:1<14::AID-MFM5>3.0.CO;2-K.
11. Rosen JA et al. The history and contributions of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (1997-2015). Am J Perinatol. 2016 Nov;33(13):1223-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1585082.
12. Driggers RW and Baschat A. The 12th meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG-NA): Introduction and overview. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012 Jan;25(1):3-4. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2012.626917.
13. Langer O et al. The proceedings of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America 2009 conference. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010 Mar;23(3):196-8. doi: 10.3109/14767050903550634.
14. Reece EA et al. A consensus report of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America Conference, Little Rock, Ark., May 2002. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2002 Dec;12(6):362-4. doi: 10.1080/jmf.12.6.362.364.
15. Reece EA and Maulik D. A consensus conference of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2002 Dec;12(6):361. doi: 10.1080/jmf.12.6.361.361.
16. Gabbe SG. Summation of the second meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG-NA). J Matern Fetal Med. 2000 Jan-Feb;9(1):3-9.
17. Vital Statistics of the United States 1990: Volume I – Natality.
18. Martin JA et al. Births: final data for 2000. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2002 Feb 12;50(5):1-101. PMID: 11876093.
19. Martin JA et al. Births: final data for 2010. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2012 Aug 28;61(1):1-72. PMID: 24974589.
20. CDC Website. Normal weight, overweight, and obesity among adults aged 20 and over, by selected characteristics: United States.
21. Wang Y et al. Has the prevalence of overweight, obesity, and central obesity levelled off in the United States? Trends, patterns, disparities, and future projections for the obesity epidemic. Int J Epidemiol. 2020 Jun 1;49(3):810-23. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyz273.
In 2021, diabetes and related complications was the 8th leading cause of death in the United States.1 As of 2022, more than 11% of the U.S. population had diabetes and 38% of the adult U.S. population had prediabetes.2 Diabetes is the most expensive chronic condition in the United States, where $1 of every $4 in health care costs is spent on care.3
Where this is most concerning is diabetes in pregnancy. While childbirth rates in the United States have decreased since the 2007 high of 4.32 million births4 to 3.66 million in 2021,5 the incidence of diabetes in pregnancy – both pregestational and gestational – has increased. The rate of pregestational diabetes in 2021 was 10.9 per 1,000 births, a 27% increase from 2016 (8.6 per 1,000).6 The percentage of those giving birth who also were diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) was 8.3% in 2021, up from 6.0% in 2016.7
Adverse outcomes for an infant born to a mother with diabetes include a higher risk of obesity and diabetes as adults, potentially leading to a forward-feeding cycle.
We and our colleagues established the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America in 1997 because we had witnessed too frequently the devastating diabetes-induced pregnancy complications in our patients. The mission we set forth was to provide a forum for dialogue among maternal-fetal medicine subspecialists. The three main goals we set forth to support this mission were to provide a catalyst for research, contribute to the creation and refinement of medical policies, and influence professional practices in diabetes in pregnancy.8
In the last quarter century, DPSG-NA, through its annual and biennial meetings, has brought together several hundred practitioners that include physicians, nurses, statisticians, researchers, nutritionists, and allied health professionals, among others. As a group, it has improved the detection and management of diabetes in pregnant women and their offspring through knowledge sharing and influencing policies on GDM screening, diagnosis, management, and treatment. Our members have shown that preconceptional counseling for women with diabetes can significantly reduce congenital malformation and perinatal mortality compared with those women with pregestational diabetes who receive no counseling.9,10
We have addressed a wide variety of topics including the paucity of data in determining the timing of delivery for women with diabetes and the Institute of Medicine/National Academy of Medicine recommendations of gestational weight gain and risks of not adhering to them. We have learned about new scientific discoveries that reveal underlying mechanisms to diabetes-related birth defects and potential therapeutic targets; and we have discussed the health literacy requirements, ethics, and opportunities for lifestyle intervention.11-16
But we need to do more.
Two risk factors are at play: Women continue to choose to have babies at later ages and their pregnancies continue to be complicated by the rising incidence of obesity (see Figure 1 and Figure 2). 
The global obesity epidemic has become a significant concern for all aspects of health and particularly for diabetes in pregnancy. 
In 1990, 24.9% of women in the United States were obese; in 2010, 35.8%; and now more than 41%. Some experts project that by 2030 more than 80% of women in the United States will be overweight or obese.21
If we are to stop this cycle of diabetes begets more diabetes, now more than ever we need to come together and accelerate the research and education around the diabetes in pregnancy. Join us at this year’s DPSG-NA meeting Oct. 26-28 to take part in the knowledge sharing, discussions, and planning. More information can be found online at https://events.dpsg-na.com/home.
Dr. Miodovnik is adjunct professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at University of Maryland School of Medicine. Dr. Reece is professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences and senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research at University of Maryland School of Medicine.
References
1. Xu J et al. Mortality in the United States, 2021. NCHS Data Brief. 2022 Dec;(456):1-8. PMID: 36598387.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, diabetes data and statistics.
3. American Diabetes Association. The Cost of Diabetes.
4. Martin JA et al. Births: Final data for 2007. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2010 Aug 9;58(24):1-85. PMID: 21254725.
5. Osterman MJK et al. Births: Final data for 2021. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2023 Jan;72(1):1-53. PMID: 36723449.
6. Gregory ECW and Ely DM. Trends and characteristics in prepregnancy diabetes: United States, 2016-2021. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2023 May;72(6):1-13. PMID: 37256333.
7. QuickStats: Percentage of mothers with gestational diabetes, by maternal age – National Vital Statistics System, United States, 2016 and 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Jan 6;72(1):16. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7201a4.
8. Langer O et al. The Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America – Introduction and summary statement. Prenat Neonat Med. 1998;3(6):514-6.
9. Willhoite MB et al. The impact of preconception counseling on pregnancy outcomes. The experience of the Maine Diabetes in Pregnancy Program. Diabetes Care. 1993 Feb;16(2):450-5. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.2.450.
10. McElvy SS et al. A focused preconceptional and early pregnancy program in women with type 1 diabetes reduces perinatal mortality and malformation rates to general population levels. J Matern Fetal Med. 2000 Jan-Feb;9(1):14-20. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6661(200001/02)9:1<14::AID-MFM5>3.0.CO;2-K.
11. Rosen JA et al. The history and contributions of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (1997-2015). Am J Perinatol. 2016 Nov;33(13):1223-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1585082.
12. Driggers RW and Baschat A. The 12th meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG-NA): Introduction and overview. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012 Jan;25(1):3-4. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2012.626917.
13. Langer O et al. The proceedings of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America 2009 conference. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010 Mar;23(3):196-8. doi: 10.3109/14767050903550634.
14. Reece EA et al. A consensus report of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America Conference, Little Rock, Ark., May 2002. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2002 Dec;12(6):362-4. doi: 10.1080/jmf.12.6.362.364.
15. Reece EA and Maulik D. A consensus conference of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2002 Dec;12(6):361. doi: 10.1080/jmf.12.6.361.361.
16. Gabbe SG. Summation of the second meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG-NA). J Matern Fetal Med. 2000 Jan-Feb;9(1):3-9.
17. Vital Statistics of the United States 1990: Volume I – Natality.
18. Martin JA et al. Births: final data for 2000. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2002 Feb 12;50(5):1-101. PMID: 11876093.
19. Martin JA et al. Births: final data for 2010. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2012 Aug 28;61(1):1-72. PMID: 24974589.
20. CDC Website. Normal weight, overweight, and obesity among adults aged 20 and over, by selected characteristics: United States.
21. Wang Y et al. Has the prevalence of overweight, obesity, and central obesity levelled off in the United States? Trends, patterns, disparities, and future projections for the obesity epidemic. Int J Epidemiol. 2020 Jun 1;49(3):810-23. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyz273.
In 2021, diabetes and related complications was the 8th leading cause of death in the United States.1 As of 2022, more than 11% of the U.S. population had diabetes and 38% of the adult U.S. population had prediabetes.2 Diabetes is the most expensive chronic condition in the United States, where $1 of every $4 in health care costs is spent on care.3
Where this is most concerning is diabetes in pregnancy. While childbirth rates in the United States have decreased since the 2007 high of 4.32 million births4 to 3.66 million in 2021,5 the incidence of diabetes in pregnancy – both pregestational and gestational – has increased. The rate of pregestational diabetes in 2021 was 10.9 per 1,000 births, a 27% increase from 2016 (8.6 per 1,000).6 The percentage of those giving birth who also were diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) was 8.3% in 2021, up from 6.0% in 2016.7
Adverse outcomes for an infant born to a mother with diabetes include a higher risk of obesity and diabetes as adults, potentially leading to a forward-feeding cycle.
We and our colleagues established the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America in 1997 because we had witnessed too frequently the devastating diabetes-induced pregnancy complications in our patients. The mission we set forth was to provide a forum for dialogue among maternal-fetal medicine subspecialists. The three main goals we set forth to support this mission were to provide a catalyst for research, contribute to the creation and refinement of medical policies, and influence professional practices in diabetes in pregnancy.8
In the last quarter century, DPSG-NA, through its annual and biennial meetings, has brought together several hundred practitioners that include physicians, nurses, statisticians, researchers, nutritionists, and allied health professionals, among others. As a group, it has improved the detection and management of diabetes in pregnant women and their offspring through knowledge sharing and influencing policies on GDM screening, diagnosis, management, and treatment. Our members have shown that preconceptional counseling for women with diabetes can significantly reduce congenital malformation and perinatal mortality compared with those women with pregestational diabetes who receive no counseling.9,10
We have addressed a wide variety of topics including the paucity of data in determining the timing of delivery for women with diabetes and the Institute of Medicine/National Academy of Medicine recommendations of gestational weight gain and risks of not adhering to them. We have learned about new scientific discoveries that reveal underlying mechanisms to diabetes-related birth defects and potential therapeutic targets; and we have discussed the health literacy requirements, ethics, and opportunities for lifestyle intervention.11-16
But we need to do more.
Two risk factors are at play: Women continue to choose to have babies at later ages and their pregnancies continue to be complicated by the rising incidence of obesity (see Figure 1 and Figure 2). 
The global obesity epidemic has become a significant concern for all aspects of health and particularly for diabetes in pregnancy. 
In 1990, 24.9% of women in the United States were obese; in 2010, 35.8%; and now more than 41%. Some experts project that by 2030 more than 80% of women in the United States will be overweight or obese.21
If we are to stop this cycle of diabetes begets more diabetes, now more than ever we need to come together and accelerate the research and education around the diabetes in pregnancy. Join us at this year’s DPSG-NA meeting Oct. 26-28 to take part in the knowledge sharing, discussions, and planning. More information can be found online at https://events.dpsg-na.com/home.
Dr. Miodovnik is adjunct professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at University of Maryland School of Medicine. Dr. Reece is professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences and senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research at University of Maryland School of Medicine.
References
1. Xu J et al. Mortality in the United States, 2021. NCHS Data Brief. 2022 Dec;(456):1-8. PMID: 36598387.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, diabetes data and statistics.
3. American Diabetes Association. The Cost of Diabetes.
4. Martin JA et al. Births: Final data for 2007. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2010 Aug 9;58(24):1-85. PMID: 21254725.
5. Osterman MJK et al. Births: Final data for 2021. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2023 Jan;72(1):1-53. PMID: 36723449.
6. Gregory ECW and Ely DM. Trends and characteristics in prepregnancy diabetes: United States, 2016-2021. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2023 May;72(6):1-13. PMID: 37256333.
7. QuickStats: Percentage of mothers with gestational diabetes, by maternal age – National Vital Statistics System, United States, 2016 and 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Jan 6;72(1):16. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7201a4.
8. Langer O et al. The Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America – Introduction and summary statement. Prenat Neonat Med. 1998;3(6):514-6.
9. Willhoite MB et al. The impact of preconception counseling on pregnancy outcomes. The experience of the Maine Diabetes in Pregnancy Program. Diabetes Care. 1993 Feb;16(2):450-5. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.2.450.
10. McElvy SS et al. A focused preconceptional and early pregnancy program in women with type 1 diabetes reduces perinatal mortality and malformation rates to general population levels. J Matern Fetal Med. 2000 Jan-Feb;9(1):14-20. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6661(200001/02)9:1<14::AID-MFM5>3.0.CO;2-K.
11. Rosen JA et al. The history and contributions of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (1997-2015). Am J Perinatol. 2016 Nov;33(13):1223-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1585082.
12. Driggers RW and Baschat A. The 12th meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG-NA): Introduction and overview. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012 Jan;25(1):3-4. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2012.626917.
13. Langer O et al. The proceedings of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America 2009 conference. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010 Mar;23(3):196-8. doi: 10.3109/14767050903550634.
14. Reece EA et al. A consensus report of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America Conference, Little Rock, Ark., May 2002. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2002 Dec;12(6):362-4. doi: 10.1080/jmf.12.6.362.364.
15. Reece EA and Maulik D. A consensus conference of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2002 Dec;12(6):361. doi: 10.1080/jmf.12.6.361.361.
16. Gabbe SG. Summation of the second meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG-NA). J Matern Fetal Med. 2000 Jan-Feb;9(1):3-9.
17. Vital Statistics of the United States 1990: Volume I – Natality.
18. Martin JA et al. Births: final data for 2000. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2002 Feb 12;50(5):1-101. PMID: 11876093.
19. Martin JA et al. Births: final data for 2010. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2012 Aug 28;61(1):1-72. PMID: 24974589.
20. CDC Website. Normal weight, overweight, and obesity among adults aged 20 and over, by selected characteristics: United States.
21. Wang Y et al. Has the prevalence of overweight, obesity, and central obesity levelled off in the United States? Trends, patterns, disparities, and future projections for the obesity epidemic. Int J Epidemiol. 2020 Jun 1;49(3):810-23. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyz273.
Antidepressants ‘don’t blunt’ semaglutide and weight loss
in a post hoc analysis of the Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity (STEP) program.
Adverse events, including psychiatric events, were slightly more usual in the patients on antidepressants, Robert Kushner, MD, noted, in an oral session at the annual meeting of the Obesity Society.
“It is very common that patients who present for weight management are taking antidepressants for various reasons, including depression, anxiety, insomnia, or chronic pain,”Dr. Kushner, from Northwestern University in Chicago, said in an email. “We wanted to see if these participants responded differently to semaglutide, compared to those not on antidepressants.”
“We found that antidepressants do not blunt the effect of semaglutide for weight loss,” he said. “However, there is a slight increase in reported adverse effects.”
“Semaglutide 2.4 mg provides an effective treatment option for weight management, regardless of antidepressant use at baseline,” Dr. Kushner summarized. “Clinicians should be assured that we can use semaglutide in this population of patients.”
Jack Yanovski, MD, PhD, said this was a “great presentation,” noting that “it’s really important that we understand what goes on in patients with depression.”
“Of course, all these trials still had rules that prevent the folks with the most severe depressive symptoms or past suicidality to participate,” added Dr. Yanovski, chief of the Growth and Obesity Section, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Rockville, Md. “We need specific trials to know exactly how well we do.”
Dr. Kushner agreed, but also noted that, ever since some earlier antidepressants were associated with risk for suicidal ideation and death, strict guidelines were put in place that exclude certain patients from participating in clinical trials.
Dr. Yanovski suggested that now that the drugs are approved, it would be possible to study this, and the information would be important for clinicians.
Dr. Kushner said he hopes that such studies are forthcoming. In the meantime, “data like this will add some support and understanding,” he suggested.
36,000 Patients with obesity, 500 on antidepressants
Many people living with obesity report taking antidepressants for depression, anxiety, chronic pain, obsessive-compulsive disorder, sleep disturbance, neuropathy, panic disorder, or posttraumatic stress disorder, Dr. Kushner noted.
However, some of these medications can cause weight gain, and little is known about treatment outcomes for people with obesity who are on antidepressants, since most weight-loss studies exclude people with active major depressive disorder.
The researchers analyzed data from 1,961 patients in STEP 1 and 807 patients in STEP 2 as well as 611 patients in STEP 3 and 304 patients in STEP 5 – 3,683 participants in total, of which 539 were on antidepressants at baseline.
The patients were randomly assigned to 2.4 mg semaglutide vs. placebo plus a lifestyle intervention (STEP 1, 2, and 5) or intensive behavioral therapy (STEP 3 only), for 68 weeks, except STEP 5, which was 104 weeks.
Patients were included if they were aged 18 or older with a body mass index ≥30 kg/m2, or ≥27 kg/m2 with more than one weight-related complication (STEP 1, 3, and 5) or BMI ≥27 kg/m2 with type 2 diabetes (STEP 2 only), and at least one self-reported unsuccessful effort to lose weight by diet.
They were excluded if they had active major depressive disorder within 2 years prior to screening (or other severe psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder) or a Patient Health Questionnaire-9 score of 15 or higher (indicating moderately severe or severe depression), or suicide ideation (type 4 or 5 on the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale) or suicide behavior, within 30 days of screening.
From baseline to week 68, patients on semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) had a significantly greater change in weight vs. patients on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: –15.7% / –14.7% vs. –0.2% / –2.8%
- STEP 2: –10.7% / –9.5% vs. –3.3% / –3.4%
- STEP 3: –16.2% / –15.9% vs. –5.0% / –5.9%
- STEP 5: –19.0% / –14.1% vs. +1.6% / – 4.0%.
The proportion of reported adverse events was generally slightly greater in patients receiving semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) than those on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: 97.7% vs 88.6% and 92.9% vs. 86%
- STEP 2: 97.6% vs 86.5% and 88.6% vs. 77.2%
- STEP 3: 97.6% vs 95.3% and 100% vs. 95.8%
- STEP 5: 100% vs 94.8% and 95.5% vs. 89.2%.
Gastrointestinal adverse events were more frequently reported in the semaglutide group and in patients on antidepressants at baseline. The proportion of patients with psychiatric adverse events was greater in participants on antidepressants at baseline. There were no differences in suicidal ideation/behavior in patients with/without antidepressant use at baseline.
The STEP trials were funded by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Kushner discloses that he served as a consultant for Novo Nordisk, WeightWatchers, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer, and received a research grant from Epitomee.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
in a post hoc analysis of the Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity (STEP) program.
Adverse events, including psychiatric events, were slightly more usual in the patients on antidepressants, Robert Kushner, MD, noted, in an oral session at the annual meeting of the Obesity Society.
“It is very common that patients who present for weight management are taking antidepressants for various reasons, including depression, anxiety, insomnia, or chronic pain,”Dr. Kushner, from Northwestern University in Chicago, said in an email. “We wanted to see if these participants responded differently to semaglutide, compared to those not on antidepressants.”
“We found that antidepressants do not blunt the effect of semaglutide for weight loss,” he said. “However, there is a slight increase in reported adverse effects.”
“Semaglutide 2.4 mg provides an effective treatment option for weight management, regardless of antidepressant use at baseline,” Dr. Kushner summarized. “Clinicians should be assured that we can use semaglutide in this population of patients.”
Jack Yanovski, MD, PhD, said this was a “great presentation,” noting that “it’s really important that we understand what goes on in patients with depression.”
“Of course, all these trials still had rules that prevent the folks with the most severe depressive symptoms or past suicidality to participate,” added Dr. Yanovski, chief of the Growth and Obesity Section, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Rockville, Md. “We need specific trials to know exactly how well we do.”
Dr. Kushner agreed, but also noted that, ever since some earlier antidepressants were associated with risk for suicidal ideation and death, strict guidelines were put in place that exclude certain patients from participating in clinical trials.
Dr. Yanovski suggested that now that the drugs are approved, it would be possible to study this, and the information would be important for clinicians.
Dr. Kushner said he hopes that such studies are forthcoming. In the meantime, “data like this will add some support and understanding,” he suggested.
36,000 Patients with obesity, 500 on antidepressants
Many people living with obesity report taking antidepressants for depression, anxiety, chronic pain, obsessive-compulsive disorder, sleep disturbance, neuropathy, panic disorder, or posttraumatic stress disorder, Dr. Kushner noted.
However, some of these medications can cause weight gain, and little is known about treatment outcomes for people with obesity who are on antidepressants, since most weight-loss studies exclude people with active major depressive disorder.
The researchers analyzed data from 1,961 patients in STEP 1 and 807 patients in STEP 2 as well as 611 patients in STEP 3 and 304 patients in STEP 5 – 3,683 participants in total, of which 539 were on antidepressants at baseline.
The patients were randomly assigned to 2.4 mg semaglutide vs. placebo plus a lifestyle intervention (STEP 1, 2, and 5) or intensive behavioral therapy (STEP 3 only), for 68 weeks, except STEP 5, which was 104 weeks.
Patients were included if they were aged 18 or older with a body mass index ≥30 kg/m2, or ≥27 kg/m2 with more than one weight-related complication (STEP 1, 3, and 5) or BMI ≥27 kg/m2 with type 2 diabetes (STEP 2 only), and at least one self-reported unsuccessful effort to lose weight by diet.
They were excluded if they had active major depressive disorder within 2 years prior to screening (or other severe psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder) or a Patient Health Questionnaire-9 score of 15 or higher (indicating moderately severe or severe depression), or suicide ideation (type 4 or 5 on the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale) or suicide behavior, within 30 days of screening.
From baseline to week 68, patients on semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) had a significantly greater change in weight vs. patients on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: –15.7% / –14.7% vs. –0.2% / –2.8%
- STEP 2: –10.7% / –9.5% vs. –3.3% / –3.4%
- STEP 3: –16.2% / –15.9% vs. –5.0% / –5.9%
- STEP 5: –19.0% / –14.1% vs. +1.6% / – 4.0%.
The proportion of reported adverse events was generally slightly greater in patients receiving semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) than those on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: 97.7% vs 88.6% and 92.9% vs. 86%
- STEP 2: 97.6% vs 86.5% and 88.6% vs. 77.2%
- STEP 3: 97.6% vs 95.3% and 100% vs. 95.8%
- STEP 5: 100% vs 94.8% and 95.5% vs. 89.2%.
Gastrointestinal adverse events were more frequently reported in the semaglutide group and in patients on antidepressants at baseline. The proportion of patients with psychiatric adverse events was greater in participants on antidepressants at baseline. There were no differences in suicidal ideation/behavior in patients with/without antidepressant use at baseline.
The STEP trials were funded by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Kushner discloses that he served as a consultant for Novo Nordisk, WeightWatchers, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer, and received a research grant from Epitomee.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
in a post hoc analysis of the Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity (STEP) program.
Adverse events, including psychiatric events, were slightly more usual in the patients on antidepressants, Robert Kushner, MD, noted, in an oral session at the annual meeting of the Obesity Society.
“It is very common that patients who present for weight management are taking antidepressants for various reasons, including depression, anxiety, insomnia, or chronic pain,”Dr. Kushner, from Northwestern University in Chicago, said in an email. “We wanted to see if these participants responded differently to semaglutide, compared to those not on antidepressants.”
“We found that antidepressants do not blunt the effect of semaglutide for weight loss,” he said. “However, there is a slight increase in reported adverse effects.”
“Semaglutide 2.4 mg provides an effective treatment option for weight management, regardless of antidepressant use at baseline,” Dr. Kushner summarized. “Clinicians should be assured that we can use semaglutide in this population of patients.”
Jack Yanovski, MD, PhD, said this was a “great presentation,” noting that “it’s really important that we understand what goes on in patients with depression.”
“Of course, all these trials still had rules that prevent the folks with the most severe depressive symptoms or past suicidality to participate,” added Dr. Yanovski, chief of the Growth and Obesity Section, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Rockville, Md. “We need specific trials to know exactly how well we do.”
Dr. Kushner agreed, but also noted that, ever since some earlier antidepressants were associated with risk for suicidal ideation and death, strict guidelines were put in place that exclude certain patients from participating in clinical trials.
Dr. Yanovski suggested that now that the drugs are approved, it would be possible to study this, and the information would be important for clinicians.
Dr. Kushner said he hopes that such studies are forthcoming. In the meantime, “data like this will add some support and understanding,” he suggested.
36,000 Patients with obesity, 500 on antidepressants
Many people living with obesity report taking antidepressants for depression, anxiety, chronic pain, obsessive-compulsive disorder, sleep disturbance, neuropathy, panic disorder, or posttraumatic stress disorder, Dr. Kushner noted.
However, some of these medications can cause weight gain, and little is known about treatment outcomes for people with obesity who are on antidepressants, since most weight-loss studies exclude people with active major depressive disorder.
The researchers analyzed data from 1,961 patients in STEP 1 and 807 patients in STEP 2 as well as 611 patients in STEP 3 and 304 patients in STEP 5 – 3,683 participants in total, of which 539 were on antidepressants at baseline.
The patients were randomly assigned to 2.4 mg semaglutide vs. placebo plus a lifestyle intervention (STEP 1, 2, and 5) or intensive behavioral therapy (STEP 3 only), for 68 weeks, except STEP 5, which was 104 weeks.
Patients were included if they were aged 18 or older with a body mass index ≥30 kg/m2, or ≥27 kg/m2 with more than one weight-related complication (STEP 1, 3, and 5) or BMI ≥27 kg/m2 with type 2 diabetes (STEP 2 only), and at least one self-reported unsuccessful effort to lose weight by diet.
They were excluded if they had active major depressive disorder within 2 years prior to screening (or other severe psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder) or a Patient Health Questionnaire-9 score of 15 or higher (indicating moderately severe or severe depression), or suicide ideation (type 4 or 5 on the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale) or suicide behavior, within 30 days of screening.
From baseline to week 68, patients on semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) had a significantly greater change in weight vs. patients on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: –15.7% / –14.7% vs. –0.2% / –2.8%
- STEP 2: –10.7% / –9.5% vs. –3.3% / –3.4%
- STEP 3: –16.2% / –15.9% vs. –5.0% / –5.9%
- STEP 5: –19.0% / –14.1% vs. +1.6% / – 4.0%.
The proportion of reported adverse events was generally slightly greater in patients receiving semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) than those on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: 97.7% vs 88.6% and 92.9% vs. 86%
- STEP 2: 97.6% vs 86.5% and 88.6% vs. 77.2%
- STEP 3: 97.6% vs 95.3% and 100% vs. 95.8%
- STEP 5: 100% vs 94.8% and 95.5% vs. 89.2%.
Gastrointestinal adverse events were more frequently reported in the semaglutide group and in patients on antidepressants at baseline. The proportion of patients with psychiatric adverse events was greater in participants on antidepressants at baseline. There were no differences in suicidal ideation/behavior in patients with/without antidepressant use at baseline.
The STEP trials were funded by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Kushner discloses that he served as a consultant for Novo Nordisk, WeightWatchers, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer, and received a research grant from Epitomee.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM OBESITYWEEK® 2023
Taking a new obesity drug and birth control pills? Be careful
For women who are obese, daily life is wrought with landmines. Whether it’s the challenges of air travel because plane seats are too small, the need to shield themselves from the world’s discriminating eyes, or the great lengths many will go to achieve better health and the promise of longevity, navigating life as an obese person requires a thick skin.
So, it’s no wonder so many are willing to pay more than $1,000 a month out of pocket to get their hands on drugs like semaglutide (Ozempic and Wegovy) or tirzepatide (Mounjaro). The benefits of these drugs, which are part of a new class called glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, include significant and rapid weight loss, blood sugar control, and improved life quality; they are unprecedented in a setting where surgery has long been considered the most effective long-term option.
On the flip side, the desire for rapid weight loss and better blood sugar control also comes with an unexpected cost. , making an unintended pregnancy more likely.
Neel Shah, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, said he has had several patients become pregnant without intending to.
“It was when Mounjaro came out on the market when we started using it,” he said of the drug the Food and Drug Administration approved for type 2 diabetes in 2022. “It [the warning] was in the product insert, but clinically speaking, I don’t know if it was at the top of providers’ minds when they were prescribing Mounjaro.”
When asked if he believed that we were going to be seeing a significant increase in so-called Mounjaro babies, Dr. Shah was sure in his response.
“Absolutely. We will because the sheer volume [of patients] will increase,” he said.
It’s all in the gut
One of the ways that drugs like Mounjaro work is by delaying the time that it takes for food to move from the stomach to the small intestine. Although data are still evolving, it is believed that this process – delayed gastric emptying – may affect the absorption of birth control pills.
Dr. Shah said another theory is that vomiting, which is a common side effect of these types of drugs, also affects the pills’ ability to prevent pregnancy.
And “there’s a prolonged period of ramping up the dose because of the GI side effects,” said Pinar Kodaman, MD, PhD, a reproductive endocrinologist and assistant professor of gynecology at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
“Initially, at the lowest dose, there may not be a lot of potential effect on absorption and gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes more common, and it can cause diarrhea, which is another condition that can affect the absorption of any medication,” she said.
Unanticipated outcomes, extra prevention
Roughly 42% of women in the United States are obese, 40% of whom are between the ages of 20 and 39. Although these new drugs can improve fertility outcomes for women who are obese (especially those with polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS), only one – Mounjaro – currently carries a warning about birth control pill effectiveness on its label. Unfortunately, it appears that some doctors are unaware or not counseling patients about this risk, and the data are unclear about whether other drugs in this class, like Ozempic and Wegovy, have the same risks.
“To date, it hasn’t been a typical thing that we counsel about,” said Dr. Kodaman. “It’s all fairly new, but when we have patients on birth control pills, we do review other medications that they are on because some can affect efficacy, and it’s something to keep in mind.”
It’s also unclear if other forms of birth control – for example, birth control patches that deliver through the skin – might carry similar pregnancy risks. Dr. Shah said some of his patients who became pregnant without intending to were using these patches. This raises even more questions, since they deliver drugs through the skin directly into the bloodstream and not through the GI system.
What can women do to help ensure that they don’t become pregnant while using these drugs?
“I really think that if patients want to protect themselves from an unplanned pregnancy, that as soon as they start the GLP receptor agonists, it wouldn’t be a bad idea to use condoms, because the onset of action is pretty quick,” said Dr. Kodaman, noting also that “at the lowest dose there may not be a lot of potential effect on gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes much more common or can cause diarrhea.”
Dr. Shah said that in his practice he’s “been telling patients to add barrier contraception” 4 weeks before they start their first dose “and at any dose adjustment.”
Zoobia Chaudhry, an obesity medicine doctor and assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, recommends that “patients just make sure that the injection and medication that they take are at least 1 hour apart.”
“Most of the time, patients do take birth control before bedtime, so if the two are spaced, it should be OK,” she said.
Another option is for women to speak to their doctors about other contraceptive options like IUDs or implantable rods, where gastric absorption is not going to be an issue.
“There’s very little research on this class of drugs,” said Emily Goodstein, a 40-year-old small-business owner in Washington, who recently switched from Ozempic to Mounjaro. “Being a person who lives in a larger body is such a horrifying experience because of the way that the world discriminates against you.”
She appreciates the feeling of being proactive that these new drugs grant. It has “opened up a bunch of opportunities for me to be seen as a full individual by the medical establishment,” she said. “I was willing to take the risk, knowing that I would be on these drugs for the rest of my life.”
In addition to being what Dr. Goodstein refers to as a guinea pig, she said she made sure that her primary care doctor was aware that she was not trying or planning to become pregnant again. (She has a 3-year-old child.) Still, her doctor mentioned only the most common side effects linked to these drugs, like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, and did not mention the risk of pregnancy.
“Folks are really not talking about the reproductive implications,” she said, referring to members of a Facebook group on these drugs that she belongs to.
Like patients themselves, many doctors are just beginning to get their arms around these agents. “Awareness, education, provider involvement, and having a multidisciplinary team could help patients achieve the goals that they set out for themselves,” said Dr. Shah.
Clear conversations are key.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
For women who are obese, daily life is wrought with landmines. Whether it’s the challenges of air travel because plane seats are too small, the need to shield themselves from the world’s discriminating eyes, or the great lengths many will go to achieve better health and the promise of longevity, navigating life as an obese person requires a thick skin.
So, it’s no wonder so many are willing to pay more than $1,000 a month out of pocket to get their hands on drugs like semaglutide (Ozempic and Wegovy) or tirzepatide (Mounjaro). The benefits of these drugs, which are part of a new class called glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, include significant and rapid weight loss, blood sugar control, and improved life quality; they are unprecedented in a setting where surgery has long been considered the most effective long-term option.
On the flip side, the desire for rapid weight loss and better blood sugar control also comes with an unexpected cost. , making an unintended pregnancy more likely.
Neel Shah, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, said he has had several patients become pregnant without intending to.
“It was when Mounjaro came out on the market when we started using it,” he said of the drug the Food and Drug Administration approved for type 2 diabetes in 2022. “It [the warning] was in the product insert, but clinically speaking, I don’t know if it was at the top of providers’ minds when they were prescribing Mounjaro.”
When asked if he believed that we were going to be seeing a significant increase in so-called Mounjaro babies, Dr. Shah was sure in his response.
“Absolutely. We will because the sheer volume [of patients] will increase,” he said.
It’s all in the gut
One of the ways that drugs like Mounjaro work is by delaying the time that it takes for food to move from the stomach to the small intestine. Although data are still evolving, it is believed that this process – delayed gastric emptying – may affect the absorption of birth control pills.
Dr. Shah said another theory is that vomiting, which is a common side effect of these types of drugs, also affects the pills’ ability to prevent pregnancy.
And “there’s a prolonged period of ramping up the dose because of the GI side effects,” said Pinar Kodaman, MD, PhD, a reproductive endocrinologist and assistant professor of gynecology at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
“Initially, at the lowest dose, there may not be a lot of potential effect on absorption and gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes more common, and it can cause diarrhea, which is another condition that can affect the absorption of any medication,” she said.
Unanticipated outcomes, extra prevention
Roughly 42% of women in the United States are obese, 40% of whom are between the ages of 20 and 39. Although these new drugs can improve fertility outcomes for women who are obese (especially those with polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS), only one – Mounjaro – currently carries a warning about birth control pill effectiveness on its label. Unfortunately, it appears that some doctors are unaware or not counseling patients about this risk, and the data are unclear about whether other drugs in this class, like Ozempic and Wegovy, have the same risks.
“To date, it hasn’t been a typical thing that we counsel about,” said Dr. Kodaman. “It’s all fairly new, but when we have patients on birth control pills, we do review other medications that they are on because some can affect efficacy, and it’s something to keep in mind.”
It’s also unclear if other forms of birth control – for example, birth control patches that deliver through the skin – might carry similar pregnancy risks. Dr. Shah said some of his patients who became pregnant without intending to were using these patches. This raises even more questions, since they deliver drugs through the skin directly into the bloodstream and not through the GI system.
What can women do to help ensure that they don’t become pregnant while using these drugs?
“I really think that if patients want to protect themselves from an unplanned pregnancy, that as soon as they start the GLP receptor agonists, it wouldn’t be a bad idea to use condoms, because the onset of action is pretty quick,” said Dr. Kodaman, noting also that “at the lowest dose there may not be a lot of potential effect on gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes much more common or can cause diarrhea.”
Dr. Shah said that in his practice he’s “been telling patients to add barrier contraception” 4 weeks before they start their first dose “and at any dose adjustment.”
Zoobia Chaudhry, an obesity medicine doctor and assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, recommends that “patients just make sure that the injection and medication that they take are at least 1 hour apart.”
“Most of the time, patients do take birth control before bedtime, so if the two are spaced, it should be OK,” she said.
Another option is for women to speak to their doctors about other contraceptive options like IUDs or implantable rods, where gastric absorption is not going to be an issue.
“There’s very little research on this class of drugs,” said Emily Goodstein, a 40-year-old small-business owner in Washington, who recently switched from Ozempic to Mounjaro. “Being a person who lives in a larger body is such a horrifying experience because of the way that the world discriminates against you.”
She appreciates the feeling of being proactive that these new drugs grant. It has “opened up a bunch of opportunities for me to be seen as a full individual by the medical establishment,” she said. “I was willing to take the risk, knowing that I would be on these drugs for the rest of my life.”
In addition to being what Dr. Goodstein refers to as a guinea pig, she said she made sure that her primary care doctor was aware that she was not trying or planning to become pregnant again. (She has a 3-year-old child.) Still, her doctor mentioned only the most common side effects linked to these drugs, like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, and did not mention the risk of pregnancy.
“Folks are really not talking about the reproductive implications,” she said, referring to members of a Facebook group on these drugs that she belongs to.
Like patients themselves, many doctors are just beginning to get their arms around these agents. “Awareness, education, provider involvement, and having a multidisciplinary team could help patients achieve the goals that they set out for themselves,” said Dr. Shah.
Clear conversations are key.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
For women who are obese, daily life is wrought with landmines. Whether it’s the challenges of air travel because plane seats are too small, the need to shield themselves from the world’s discriminating eyes, or the great lengths many will go to achieve better health and the promise of longevity, navigating life as an obese person requires a thick skin.
So, it’s no wonder so many are willing to pay more than $1,000 a month out of pocket to get their hands on drugs like semaglutide (Ozempic and Wegovy) or tirzepatide (Mounjaro). The benefits of these drugs, which are part of a new class called glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, include significant and rapid weight loss, blood sugar control, and improved life quality; they are unprecedented in a setting where surgery has long been considered the most effective long-term option.
On the flip side, the desire for rapid weight loss and better blood sugar control also comes with an unexpected cost. , making an unintended pregnancy more likely.
Neel Shah, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, said he has had several patients become pregnant without intending to.
“It was when Mounjaro came out on the market when we started using it,” he said of the drug the Food and Drug Administration approved for type 2 diabetes in 2022. “It [the warning] was in the product insert, but clinically speaking, I don’t know if it was at the top of providers’ minds when they were prescribing Mounjaro.”
When asked if he believed that we were going to be seeing a significant increase in so-called Mounjaro babies, Dr. Shah was sure in his response.
“Absolutely. We will because the sheer volume [of patients] will increase,” he said.
It’s all in the gut
One of the ways that drugs like Mounjaro work is by delaying the time that it takes for food to move from the stomach to the small intestine. Although data are still evolving, it is believed that this process – delayed gastric emptying – may affect the absorption of birth control pills.
Dr. Shah said another theory is that vomiting, which is a common side effect of these types of drugs, also affects the pills’ ability to prevent pregnancy.
And “there’s a prolonged period of ramping up the dose because of the GI side effects,” said Pinar Kodaman, MD, PhD, a reproductive endocrinologist and assistant professor of gynecology at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
“Initially, at the lowest dose, there may not be a lot of potential effect on absorption and gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes more common, and it can cause diarrhea, which is another condition that can affect the absorption of any medication,” she said.
Unanticipated outcomes, extra prevention
Roughly 42% of women in the United States are obese, 40% of whom are between the ages of 20 and 39. Although these new drugs can improve fertility outcomes for women who are obese (especially those with polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS), only one – Mounjaro – currently carries a warning about birth control pill effectiveness on its label. Unfortunately, it appears that some doctors are unaware or not counseling patients about this risk, and the data are unclear about whether other drugs in this class, like Ozempic and Wegovy, have the same risks.
“To date, it hasn’t been a typical thing that we counsel about,” said Dr. Kodaman. “It’s all fairly new, but when we have patients on birth control pills, we do review other medications that they are on because some can affect efficacy, and it’s something to keep in mind.”
It’s also unclear if other forms of birth control – for example, birth control patches that deliver through the skin – might carry similar pregnancy risks. Dr. Shah said some of his patients who became pregnant without intending to were using these patches. This raises even more questions, since they deliver drugs through the skin directly into the bloodstream and not through the GI system.
What can women do to help ensure that they don’t become pregnant while using these drugs?
“I really think that if patients want to protect themselves from an unplanned pregnancy, that as soon as they start the GLP receptor agonists, it wouldn’t be a bad idea to use condoms, because the onset of action is pretty quick,” said Dr. Kodaman, noting also that “at the lowest dose there may not be a lot of potential effect on gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes much more common or can cause diarrhea.”
Dr. Shah said that in his practice he’s “been telling patients to add barrier contraception” 4 weeks before they start their first dose “and at any dose adjustment.”
Zoobia Chaudhry, an obesity medicine doctor and assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, recommends that “patients just make sure that the injection and medication that they take are at least 1 hour apart.”
“Most of the time, patients do take birth control before bedtime, so if the two are spaced, it should be OK,” she said.
Another option is for women to speak to their doctors about other contraceptive options like IUDs or implantable rods, where gastric absorption is not going to be an issue.
“There’s very little research on this class of drugs,” said Emily Goodstein, a 40-year-old small-business owner in Washington, who recently switched from Ozempic to Mounjaro. “Being a person who lives in a larger body is such a horrifying experience because of the way that the world discriminates against you.”
She appreciates the feeling of being proactive that these new drugs grant. It has “opened up a bunch of opportunities for me to be seen as a full individual by the medical establishment,” she said. “I was willing to take the risk, knowing that I would be on these drugs for the rest of my life.”
In addition to being what Dr. Goodstein refers to as a guinea pig, she said she made sure that her primary care doctor was aware that she was not trying or planning to become pregnant again. (She has a 3-year-old child.) Still, her doctor mentioned only the most common side effects linked to these drugs, like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, and did not mention the risk of pregnancy.
“Folks are really not talking about the reproductive implications,” she said, referring to members of a Facebook group on these drugs that she belongs to.
Like patients themselves, many doctors are just beginning to get their arms around these agents. “Awareness, education, provider involvement, and having a multidisciplinary team could help patients achieve the goals that they set out for themselves,” said Dr. Shah.
Clear conversations are key.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Employed physicians: A survival guide
The strike by health care workers at Kaiser Permanente may not involve physicians (yet). But as more doctors in the United States are finding themselves working as salaried employees, physicians can – and probably will – become a powerful force for change in a health care system that has shown itself to be increasingly hostile to employee concerns over issues involving patient care, wages and benefits, safety, and well-being.
Salaried employment has its challenges. Physician-employees may have less autonomy and voice in decision-making that affects patients. They may splinter into fragmented work groups; feel isolated; and have different imperatives based on who they are, what they want, and where they work. They may feel more removed from their patients and struggle to build strong relationships, with their employers in the way.
Yet important opportunities exist for doctors when embracing their employee side. Examples of these interests include adequate compensation, wellness, job security, patient and worker safety, health care quality, reasonable workloads and schedules, and fair treatment by employers, including the need to exhibit a strong collective voice in organizational decision-making.
Some believe that physician-employees must be unionized to maximize their rights and power as employees. Many expect physician unionization to take hold more fully over time. Medical residents, the doctors of tomorrow, are already considering unionization in greater numbers. Some are also doing it in the same employment setting alongside other health professionals, such as nurses.
Having studied doctors and their employment situations for years, I am convinced that whether through unionization or another approach, physicians must also change how they think about control; train and learn alongside other health care workers who share similar interests; and elevate at an early career stage their knowledge of the business side of health care.
Adopt a more pragmatic definition of autonomy
Doctors must embrace an updated definition of autonomy – one that matches their status as highly paid labor.
When I have spoken to physicians in my research about what autonomy means to them, many seem unable to reconceptualize it from a vague and absolute form of their profession’s strategic control over their economic fates and technical skills toward an individualized control that is situation-specific, one centered on winning the daily fights about workplace bread-and-butter issues such as those mentioned above.
But a more pragmatic definition of autonomy could get doctors focused on influencing important issues of the patient-care day and enhance their negotiating power with employers. It would allow physicians to break out of what often seems a paralysis of inaction – waiting for employers, insurers, or the government to reinstate the profession’s idealized version of control by handing it back the keys to the health care system through major regulatory, structural, and reimbursement-related changes. This fantasy is unlikely to become reality.
Physician-employees I’ve talked to over the years understand their everyday challenges. But when it comes to engaging in localized and sustained action to overcome them, they often perform less well, leading to feelings of helplessness and burnout. Valuing tactical control over their jobs and work setting will yield smaller but more impactful wins as employees intent on making their everyday work lives better.
Train alongside other health care professionals
Physicians must accept that how they are trained no longer prepares them for the employee world into which most are dropped. For instance, unless doctors are trained collaboratively alongside other health care professionals – such as nurses – they are less likely to identify closely with these colleagues once in practice. There is strength in numbers, so this mutual identification empowers both groups of employees. Yet, medical education remains largely the same: training young medical students in isolation for the first couple of years, then placing them into clerkships and residencies where true interprofessional care opportunities remain stunted and secondary to the “physician as captain of the team” mantra.
Unfortunately, the “hidden curriculum” of medicine helps convince medical students and residents early in their careers that they are the unquestioned leaders in patient care settings. This hierarchy encourages some doctors to keep their psychological distance from other members of the health care team and to resist sharing power, concerns, or insights with less skilled health care workers. This socialization harms the ability of physicians to act in a unified fashion alongside these other workers. Having physicians learn and train alongside other health professionals yields positive benefits for collective advocacy, including a shared sense of purpose, positive views on collaboration with others in the health setting, and greater development of bonds with nonphysician coworkers.
Integrate business with medical training in real time
Medical students and residents generally lack exposure to the everyday business realities of the U.S. health care system. This gap hinders their ability to understand the employee world and push for the types of changes and work conditions that benefit all health care workers. Formal business and management training should be a required part of every U.S. medical school and residency curriculum from day one. If you see it at all in medical schools now, it is mostly by accident, or given separate treatment in the form of standalone MBA or MPH degrees that rarely integrate organically and in real time with actual medical training. Not every doctor needs an MBA or MPH degree. However, all of them require a stronger contextual understanding of how the medicine they wish to practice is shaped by the economic and fiscal circumstances surrounding it – circumstances they do not control.
This is another reason why young doctors are unhappy and burned out. They cannot push for specific changes or properly critique the pros and cons of how their work is structured because they have not been made aware, in real time as they learn clinical practice, how their jobs are shaped by realities such as insurance coverage and reimbursement, the fragmentation of the care delivery system, their employer’s financial health , and the socioeconomic circumstances of their patients. They aren’t given the methods and tools related to process and quality improvement, budgeting, negotiation, risk management, leadership, and talent management that might help them navigate these undermining forces. They also get little advance exposure in their training to important workplace “soft” skills in such areas as how to work in teams, networking, communication and listening, empathy, and problem-solving – all necessary foci for bringing them closer to other health care workers and advocating alongside them effectively with health care employers.
Now is the time for physicians to embrace their identity as employees. Doing so is in their own best interest as professionals. It will help others in the health care workforce as well as patients. Moreover, it provides a needed counterbalance to the powerful corporate ethos now ascendant in U.S. health care.
Timothy Hoff, PhD, is a professor of management and healthcare systems at Northeastern University, Boston, and an associate fellow at the University of Oxford, England. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The strike by health care workers at Kaiser Permanente may not involve physicians (yet). But as more doctors in the United States are finding themselves working as salaried employees, physicians can – and probably will – become a powerful force for change in a health care system that has shown itself to be increasingly hostile to employee concerns over issues involving patient care, wages and benefits, safety, and well-being.
Salaried employment has its challenges. Physician-employees may have less autonomy and voice in decision-making that affects patients. They may splinter into fragmented work groups; feel isolated; and have different imperatives based on who they are, what they want, and where they work. They may feel more removed from their patients and struggle to build strong relationships, with their employers in the way.
Yet important opportunities exist for doctors when embracing their employee side. Examples of these interests include adequate compensation, wellness, job security, patient and worker safety, health care quality, reasonable workloads and schedules, and fair treatment by employers, including the need to exhibit a strong collective voice in organizational decision-making.
Some believe that physician-employees must be unionized to maximize their rights and power as employees. Many expect physician unionization to take hold more fully over time. Medical residents, the doctors of tomorrow, are already considering unionization in greater numbers. Some are also doing it in the same employment setting alongside other health professionals, such as nurses.
Having studied doctors and their employment situations for years, I am convinced that whether through unionization or another approach, physicians must also change how they think about control; train and learn alongside other health care workers who share similar interests; and elevate at an early career stage their knowledge of the business side of health care.
Adopt a more pragmatic definition of autonomy
Doctors must embrace an updated definition of autonomy – one that matches their status as highly paid labor.
When I have spoken to physicians in my research about what autonomy means to them, many seem unable to reconceptualize it from a vague and absolute form of their profession’s strategic control over their economic fates and technical skills toward an individualized control that is situation-specific, one centered on winning the daily fights about workplace bread-and-butter issues such as those mentioned above.
But a more pragmatic definition of autonomy could get doctors focused on influencing important issues of the patient-care day and enhance their negotiating power with employers. It would allow physicians to break out of what often seems a paralysis of inaction – waiting for employers, insurers, or the government to reinstate the profession’s idealized version of control by handing it back the keys to the health care system through major regulatory, structural, and reimbursement-related changes. This fantasy is unlikely to become reality.
Physician-employees I’ve talked to over the years understand their everyday challenges. But when it comes to engaging in localized and sustained action to overcome them, they often perform less well, leading to feelings of helplessness and burnout. Valuing tactical control over their jobs and work setting will yield smaller but more impactful wins as employees intent on making their everyday work lives better.
Train alongside other health care professionals
Physicians must accept that how they are trained no longer prepares them for the employee world into which most are dropped. For instance, unless doctors are trained collaboratively alongside other health care professionals – such as nurses – they are less likely to identify closely with these colleagues once in practice. There is strength in numbers, so this mutual identification empowers both groups of employees. Yet, medical education remains largely the same: training young medical students in isolation for the first couple of years, then placing them into clerkships and residencies where true interprofessional care opportunities remain stunted and secondary to the “physician as captain of the team” mantra.
Unfortunately, the “hidden curriculum” of medicine helps convince medical students and residents early in their careers that they are the unquestioned leaders in patient care settings. This hierarchy encourages some doctors to keep their psychological distance from other members of the health care team and to resist sharing power, concerns, or insights with less skilled health care workers. This socialization harms the ability of physicians to act in a unified fashion alongside these other workers. Having physicians learn and train alongside other health professionals yields positive benefits for collective advocacy, including a shared sense of purpose, positive views on collaboration with others in the health setting, and greater development of bonds with nonphysician coworkers.
Integrate business with medical training in real time
Medical students and residents generally lack exposure to the everyday business realities of the U.S. health care system. This gap hinders their ability to understand the employee world and push for the types of changes and work conditions that benefit all health care workers. Formal business and management training should be a required part of every U.S. medical school and residency curriculum from day one. If you see it at all in medical schools now, it is mostly by accident, or given separate treatment in the form of standalone MBA or MPH degrees that rarely integrate organically and in real time with actual medical training. Not every doctor needs an MBA or MPH degree. However, all of them require a stronger contextual understanding of how the medicine they wish to practice is shaped by the economic and fiscal circumstances surrounding it – circumstances they do not control.
This is another reason why young doctors are unhappy and burned out. They cannot push for specific changes or properly critique the pros and cons of how their work is structured because they have not been made aware, in real time as they learn clinical practice, how their jobs are shaped by realities such as insurance coverage and reimbursement, the fragmentation of the care delivery system, their employer’s financial health , and the socioeconomic circumstances of their patients. They aren’t given the methods and tools related to process and quality improvement, budgeting, negotiation, risk management, leadership, and talent management that might help them navigate these undermining forces. They also get little advance exposure in their training to important workplace “soft” skills in such areas as how to work in teams, networking, communication and listening, empathy, and problem-solving – all necessary foci for bringing them closer to other health care workers and advocating alongside them effectively with health care employers.
Now is the time for physicians to embrace their identity as employees. Doing so is in their own best interest as professionals. It will help others in the health care workforce as well as patients. Moreover, it provides a needed counterbalance to the powerful corporate ethos now ascendant in U.S. health care.
Timothy Hoff, PhD, is a professor of management and healthcare systems at Northeastern University, Boston, and an associate fellow at the University of Oxford, England. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The strike by health care workers at Kaiser Permanente may not involve physicians (yet). But as more doctors in the United States are finding themselves working as salaried employees, physicians can – and probably will – become a powerful force for change in a health care system that has shown itself to be increasingly hostile to employee concerns over issues involving patient care, wages and benefits, safety, and well-being.
Salaried employment has its challenges. Physician-employees may have less autonomy and voice in decision-making that affects patients. They may splinter into fragmented work groups; feel isolated; and have different imperatives based on who they are, what they want, and where they work. They may feel more removed from their patients and struggle to build strong relationships, with their employers in the way.
Yet important opportunities exist for doctors when embracing their employee side. Examples of these interests include adequate compensation, wellness, job security, patient and worker safety, health care quality, reasonable workloads and schedules, and fair treatment by employers, including the need to exhibit a strong collective voice in organizational decision-making.
Some believe that physician-employees must be unionized to maximize their rights and power as employees. Many expect physician unionization to take hold more fully over time. Medical residents, the doctors of tomorrow, are already considering unionization in greater numbers. Some are also doing it in the same employment setting alongside other health professionals, such as nurses.
Having studied doctors and their employment situations for years, I am convinced that whether through unionization or another approach, physicians must also change how they think about control; train and learn alongside other health care workers who share similar interests; and elevate at an early career stage their knowledge of the business side of health care.
Adopt a more pragmatic definition of autonomy
Doctors must embrace an updated definition of autonomy – one that matches their status as highly paid labor.
When I have spoken to physicians in my research about what autonomy means to them, many seem unable to reconceptualize it from a vague and absolute form of their profession’s strategic control over their economic fates and technical skills toward an individualized control that is situation-specific, one centered on winning the daily fights about workplace bread-and-butter issues such as those mentioned above.
But a more pragmatic definition of autonomy could get doctors focused on influencing important issues of the patient-care day and enhance their negotiating power with employers. It would allow physicians to break out of what often seems a paralysis of inaction – waiting for employers, insurers, or the government to reinstate the profession’s idealized version of control by handing it back the keys to the health care system through major regulatory, structural, and reimbursement-related changes. This fantasy is unlikely to become reality.
Physician-employees I’ve talked to over the years understand their everyday challenges. But when it comes to engaging in localized and sustained action to overcome them, they often perform less well, leading to feelings of helplessness and burnout. Valuing tactical control over their jobs and work setting will yield smaller but more impactful wins as employees intent on making their everyday work lives better.
Train alongside other health care professionals
Physicians must accept that how they are trained no longer prepares them for the employee world into which most are dropped. For instance, unless doctors are trained collaboratively alongside other health care professionals – such as nurses – they are less likely to identify closely with these colleagues once in practice. There is strength in numbers, so this mutual identification empowers both groups of employees. Yet, medical education remains largely the same: training young medical students in isolation for the first couple of years, then placing them into clerkships and residencies where true interprofessional care opportunities remain stunted and secondary to the “physician as captain of the team” mantra.
Unfortunately, the “hidden curriculum” of medicine helps convince medical students and residents early in their careers that they are the unquestioned leaders in patient care settings. This hierarchy encourages some doctors to keep their psychological distance from other members of the health care team and to resist sharing power, concerns, or insights with less skilled health care workers. This socialization harms the ability of physicians to act in a unified fashion alongside these other workers. Having physicians learn and train alongside other health professionals yields positive benefits for collective advocacy, including a shared sense of purpose, positive views on collaboration with others in the health setting, and greater development of bonds with nonphysician coworkers.
Integrate business with medical training in real time
Medical students and residents generally lack exposure to the everyday business realities of the U.S. health care system. This gap hinders their ability to understand the employee world and push for the types of changes and work conditions that benefit all health care workers. Formal business and management training should be a required part of every U.S. medical school and residency curriculum from day one. If you see it at all in medical schools now, it is mostly by accident, or given separate treatment in the form of standalone MBA or MPH degrees that rarely integrate organically and in real time with actual medical training. Not every doctor needs an MBA or MPH degree. However, all of them require a stronger contextual understanding of how the medicine they wish to practice is shaped by the economic and fiscal circumstances surrounding it – circumstances they do not control.
This is another reason why young doctors are unhappy and burned out. They cannot push for specific changes or properly critique the pros and cons of how their work is structured because they have not been made aware, in real time as they learn clinical practice, how their jobs are shaped by realities such as insurance coverage and reimbursement, the fragmentation of the care delivery system, their employer’s financial health , and the socioeconomic circumstances of their patients. They aren’t given the methods and tools related to process and quality improvement, budgeting, negotiation, risk management, leadership, and talent management that might help them navigate these undermining forces. They also get little advance exposure in their training to important workplace “soft” skills in such areas as how to work in teams, networking, communication and listening, empathy, and problem-solving – all necessary foci for bringing them closer to other health care workers and advocating alongside them effectively with health care employers.
Now is the time for physicians to embrace their identity as employees. Doing so is in their own best interest as professionals. It will help others in the health care workforce as well as patients. Moreover, it provides a needed counterbalance to the powerful corporate ethos now ascendant in U.S. health care.
Timothy Hoff, PhD, is a professor of management and healthcare systems at Northeastern University, Boston, and an associate fellow at the University of Oxford, England. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

