User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Supreme Court Justices seem skeptical of case to overturn ACA
The Justices conducted arguments by telephone in the case, California v Texas (previously California v US), which was brought by 18 Republican state officials and two individual plaintiffs. The Trump administration joined the plaintiffs in June, arguing that the entire law should be overturned. The ACA is being defended by Democratic state officials from 16 states and Washington, D.C.
The Republican plaintiffs have essentially argued that the ACA cannot stand without the individual mandate requirement – that it is not possible to “sever” it from the rest of the Act. In 2017, Congress set the tax penalty to $0 if an individual did not buy insurance. The mandate to buy insurance was left in place, but there were no longer any consequences. The plaintiffs said that congressional act was equivalent to severing the mandate.
But many Justices appeared to take a dim view of that argument.
“It’s a very straightforward case for severability under our precedents,” said Justice Brett Kavanaugh. “Meaning that we would excise the mandate and leave the rest of the Act in play. Congress knows how to write an inseverability clause and that is not the language that they chose here,” he said.
Justice Elena Kagan also questioned how it would jibe with legal precedent to allow the severing of one part of a law when there was no clear instruction from Congress on the issue. She also raised the concern that it would open the door to all sorts of challenges.
“It would seem a big deal to say that, if you can point to injury with respect to one provision and you can concoct some kind of inseverability argument, that allows you to challenge anything else in the statute,” she said.
“Isn’t that something that really cuts against all of our doctrine?” asked Kagan.
“I think it’s hard for you to argue that Congress intended the entire Act to fall if the mandate was struck down when the same Congress that lowered the penalty to zero did not even try to repeal the rest of the act,” said Chief Justice John Roberts.
“I think, frankly, that they wanted the Court to do that but that’s not our job,” he added.
Proof of harm?
To have the standing to sue, the plaintiffs have to prove they have been harmed by the ACA. Texas Solicitor General Kyle Hawkins said that individuals feel compelled to buy insurance – even without a penalty hanging over their heads.
Justice Stephen Breyer argued that many laws include what he called “precatory” language – that is, they seek to compel citizens to do something. But most don’t penalize those who fail to act – just like the ACA currently.
If, as the Texas plaintiffs argued, it’s still unconstitutional to make such a request, “I think there will be an awful lot of language in an awful lot of statutes that will suddenly be the subject of court constitutional challenge,” he said.
Hawkins disagreed. He said the ACA’s mandate “is not some suggestion, not some hortatory statement. It is the law of the United States of America today that you have to purchase health insurance and not just any health insurance, but health insurance that the federal government has decided would be best for you.”
Hawkins said that, if just one additional person signed up for Medicaid, the state of Texas and the other plaintiff states would be harmed. He said people were continuing to enroll in the program because they believed the law required them to get health insurance.
Justice Sonia Sotomayor said that defied common sense. “The problem is that your theory assumes people that people are going to pay a tax and break the law by not buying insurance, but they wouldn’t do it when the tax is zero.”
What’s at stake
It’s unlikely the justices will issue a decision immediately. They have until the end of the term in June to rule.
Katie Keith, JD, MPH, a principal at Keith Policy Solutions, LLC, outlined the potential outcomes in Health Affairs .
“The most likely scenario is that the Court maintains the status quo,” she wrote. They could get there by deciding Texas et al. did not have standing to bring the case. Or they could decide that either the mandate is constitutional or that it is unconstitutional but can be severed from the rest of the ACA.
The Court could alternatively find that some or all of the law’s insurance provisions – such as protections for people with pre-existing conditions – can’t be severed from the mandate. Or the justices could strike down all of the insurance consumer protections, the health insurance marketplaces, premium tax credits, and other provisions, which would force states to come up with the money to help people buy insurance. And states are unlikely to be able to do so, especially with the pandemic stretching their budgets.
Finally, the Court could find that the mandate can’t be separated, which would essentially overturn the law.
If that happens, some 15 million people could lose Medicaid coverage, 11 million who buy on health insurance exchanges could lose coverage, and 2.3 million young adults would no longer be able to stay on parents’ policies, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. Kaiser also estimates that 54 million people under age 65 who have pre-existing conditions would no longer be guaranteed coverage.
The Urban Institute estimates that 21 million people could lose insurance – 15 million through Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) and 7.6 million through private nongroup coverage.
Medical societies weigh in
Multiple physicians’ groups, patient advocates, and hospital organizations have filed briefs with the Court in favor of keeping the law intact.
Twenty patient groups representing millions with pre-existing conditions – including the American Cancer Society, American Diabetes Association, American Heart Association, National Alliance on Mental Illness, National Organization for Rare Disorders, and the Kennedy Forum – filed a court brief in May arguing that the law has expanded access to insurance and improved patient outcomes.
“The coronavirus pandemic has only served to underscore the necessity of meaningful coverage – especially for those who are at high risk of being severely affected by the virus – including countless Americans who have pre-existing, acute or chronic conditions like heart disease, cancer, diabetes, lung diseases and multiple sclerosis,” they said in a statement.
Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, MACP, president of the American College of Physicians, which joined a court brief in support of the law with 19 other medical organizations, said the law has worked.
“The coverage, protections and benefits provided by the ACA are critical to the well-being of millions of Americans,” she said in a statement.
“If the ACA were to be thrown out at the same time that we face the pandemic, it would cause chaos for physicians and our patients, and for the entire health care system,” said Fincher, adding that millions of Americans who have been infected could lose insurance if protections for pre-existing conditions disappeared.
“The ACA has revolutionized access to care for tens of millions of women by helping them obtain meaningful health coverage, ensuring that essential care is covered by insurers, and protecting patients from unfair insurance practices,” said Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), in a statement.
Overturning the ACA “would be one of the most singularly disruptive acts to be committed during this public health crisis,” she said.
American Psychiatric Association President Jeffrey Geller, MD, MPH, also warned of disruptions to care, especially for those with mental health and substance use disorders. “We urge the Supreme Court to preserve the entire Act, including the individual mandate,” he said, in a statement.
“In the midst of COVID is no time to let down the millions who we serve as our patients,” said Chip Kahn, Federation of American Health Systems president and CEO, in a statement.
“As caregivers, the goal of hospitals for our patients is to see increased access to affordable coverage for all Americans – not new obstacles,” he said, adding that the ACA “can accomplish this goal. We hope the Supreme Court will see its way clear to allow it to go forward.”
For the defense
Many legal analysts on social media who listened in to today’s hearing agreed that the tenor of the proceedings seemed to lean toward survival of the ACA.
“At this point I would say it is *extremely* likely that the ACA will be upheld, but the mandate struck down and severed out,” tweeted Raffi Melkonian, an appellate lawyer in Houston, Texas. “A decision on standing (throwing out the case entirely) is also possible. The chance that the ACA is struck down v. low.”
“Both Kavanaugh and Roberts have suggested this morning that they may view the individual mandate as severable from the rest of the law. If those two justices join the court’s three liberals in finding that the mandate is severable, that would be five votes to save the ACA,” tweeted the analysts at SCOTUS Blog.
Sean Marotta, a lawyer with Hogan Lovells’ Supreme Court group, agreed. “Oral argument is always an imperfect measure, but the Act’s defenders should feel good today,” he tweeted.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Justices conducted arguments by telephone in the case, California v Texas (previously California v US), which was brought by 18 Republican state officials and two individual plaintiffs. The Trump administration joined the plaintiffs in June, arguing that the entire law should be overturned. The ACA is being defended by Democratic state officials from 16 states and Washington, D.C.
The Republican plaintiffs have essentially argued that the ACA cannot stand without the individual mandate requirement – that it is not possible to “sever” it from the rest of the Act. In 2017, Congress set the tax penalty to $0 if an individual did not buy insurance. The mandate to buy insurance was left in place, but there were no longer any consequences. The plaintiffs said that congressional act was equivalent to severing the mandate.
But many Justices appeared to take a dim view of that argument.
“It’s a very straightforward case for severability under our precedents,” said Justice Brett Kavanaugh. “Meaning that we would excise the mandate and leave the rest of the Act in play. Congress knows how to write an inseverability clause and that is not the language that they chose here,” he said.
Justice Elena Kagan also questioned how it would jibe with legal precedent to allow the severing of one part of a law when there was no clear instruction from Congress on the issue. She also raised the concern that it would open the door to all sorts of challenges.
“It would seem a big deal to say that, if you can point to injury with respect to one provision and you can concoct some kind of inseverability argument, that allows you to challenge anything else in the statute,” she said.
“Isn’t that something that really cuts against all of our doctrine?” asked Kagan.
“I think it’s hard for you to argue that Congress intended the entire Act to fall if the mandate was struck down when the same Congress that lowered the penalty to zero did not even try to repeal the rest of the act,” said Chief Justice John Roberts.
“I think, frankly, that they wanted the Court to do that but that’s not our job,” he added.
Proof of harm?
To have the standing to sue, the plaintiffs have to prove they have been harmed by the ACA. Texas Solicitor General Kyle Hawkins said that individuals feel compelled to buy insurance – even without a penalty hanging over their heads.
Justice Stephen Breyer argued that many laws include what he called “precatory” language – that is, they seek to compel citizens to do something. But most don’t penalize those who fail to act – just like the ACA currently.
If, as the Texas plaintiffs argued, it’s still unconstitutional to make such a request, “I think there will be an awful lot of language in an awful lot of statutes that will suddenly be the subject of court constitutional challenge,” he said.
Hawkins disagreed. He said the ACA’s mandate “is not some suggestion, not some hortatory statement. It is the law of the United States of America today that you have to purchase health insurance and not just any health insurance, but health insurance that the federal government has decided would be best for you.”
Hawkins said that, if just one additional person signed up for Medicaid, the state of Texas and the other plaintiff states would be harmed. He said people were continuing to enroll in the program because they believed the law required them to get health insurance.
Justice Sonia Sotomayor said that defied common sense. “The problem is that your theory assumes people that people are going to pay a tax and break the law by not buying insurance, but they wouldn’t do it when the tax is zero.”
What’s at stake
It’s unlikely the justices will issue a decision immediately. They have until the end of the term in June to rule.
Katie Keith, JD, MPH, a principal at Keith Policy Solutions, LLC, outlined the potential outcomes in Health Affairs .
“The most likely scenario is that the Court maintains the status quo,” she wrote. They could get there by deciding Texas et al. did not have standing to bring the case. Or they could decide that either the mandate is constitutional or that it is unconstitutional but can be severed from the rest of the ACA.
The Court could alternatively find that some or all of the law’s insurance provisions – such as protections for people with pre-existing conditions – can’t be severed from the mandate. Or the justices could strike down all of the insurance consumer protections, the health insurance marketplaces, premium tax credits, and other provisions, which would force states to come up with the money to help people buy insurance. And states are unlikely to be able to do so, especially with the pandemic stretching their budgets.
Finally, the Court could find that the mandate can’t be separated, which would essentially overturn the law.
If that happens, some 15 million people could lose Medicaid coverage, 11 million who buy on health insurance exchanges could lose coverage, and 2.3 million young adults would no longer be able to stay on parents’ policies, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. Kaiser also estimates that 54 million people under age 65 who have pre-existing conditions would no longer be guaranteed coverage.
The Urban Institute estimates that 21 million people could lose insurance – 15 million through Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) and 7.6 million through private nongroup coverage.
Medical societies weigh in
Multiple physicians’ groups, patient advocates, and hospital organizations have filed briefs with the Court in favor of keeping the law intact.
Twenty patient groups representing millions with pre-existing conditions – including the American Cancer Society, American Diabetes Association, American Heart Association, National Alliance on Mental Illness, National Organization for Rare Disorders, and the Kennedy Forum – filed a court brief in May arguing that the law has expanded access to insurance and improved patient outcomes.
“The coronavirus pandemic has only served to underscore the necessity of meaningful coverage – especially for those who are at high risk of being severely affected by the virus – including countless Americans who have pre-existing, acute or chronic conditions like heart disease, cancer, diabetes, lung diseases and multiple sclerosis,” they said in a statement.
Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, MACP, president of the American College of Physicians, which joined a court brief in support of the law with 19 other medical organizations, said the law has worked.
“The coverage, protections and benefits provided by the ACA are critical to the well-being of millions of Americans,” she said in a statement.
“If the ACA were to be thrown out at the same time that we face the pandemic, it would cause chaos for physicians and our patients, and for the entire health care system,” said Fincher, adding that millions of Americans who have been infected could lose insurance if protections for pre-existing conditions disappeared.
“The ACA has revolutionized access to care for tens of millions of women by helping them obtain meaningful health coverage, ensuring that essential care is covered by insurers, and protecting patients from unfair insurance practices,” said Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), in a statement.
Overturning the ACA “would be one of the most singularly disruptive acts to be committed during this public health crisis,” she said.
American Psychiatric Association President Jeffrey Geller, MD, MPH, also warned of disruptions to care, especially for those with mental health and substance use disorders. “We urge the Supreme Court to preserve the entire Act, including the individual mandate,” he said, in a statement.
“In the midst of COVID is no time to let down the millions who we serve as our patients,” said Chip Kahn, Federation of American Health Systems president and CEO, in a statement.
“As caregivers, the goal of hospitals for our patients is to see increased access to affordable coverage for all Americans – not new obstacles,” he said, adding that the ACA “can accomplish this goal. We hope the Supreme Court will see its way clear to allow it to go forward.”
For the defense
Many legal analysts on social media who listened in to today’s hearing agreed that the tenor of the proceedings seemed to lean toward survival of the ACA.
“At this point I would say it is *extremely* likely that the ACA will be upheld, but the mandate struck down and severed out,” tweeted Raffi Melkonian, an appellate lawyer in Houston, Texas. “A decision on standing (throwing out the case entirely) is also possible. The chance that the ACA is struck down v. low.”
“Both Kavanaugh and Roberts have suggested this morning that they may view the individual mandate as severable from the rest of the law. If those two justices join the court’s three liberals in finding that the mandate is severable, that would be five votes to save the ACA,” tweeted the analysts at SCOTUS Blog.
Sean Marotta, a lawyer with Hogan Lovells’ Supreme Court group, agreed. “Oral argument is always an imperfect measure, but the Act’s defenders should feel good today,” he tweeted.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Justices conducted arguments by telephone in the case, California v Texas (previously California v US), which was brought by 18 Republican state officials and two individual plaintiffs. The Trump administration joined the plaintiffs in June, arguing that the entire law should be overturned. The ACA is being defended by Democratic state officials from 16 states and Washington, D.C.
The Republican plaintiffs have essentially argued that the ACA cannot stand without the individual mandate requirement – that it is not possible to “sever” it from the rest of the Act. In 2017, Congress set the tax penalty to $0 if an individual did not buy insurance. The mandate to buy insurance was left in place, but there were no longer any consequences. The plaintiffs said that congressional act was equivalent to severing the mandate.
But many Justices appeared to take a dim view of that argument.
“It’s a very straightforward case for severability under our precedents,” said Justice Brett Kavanaugh. “Meaning that we would excise the mandate and leave the rest of the Act in play. Congress knows how to write an inseverability clause and that is not the language that they chose here,” he said.
Justice Elena Kagan also questioned how it would jibe with legal precedent to allow the severing of one part of a law when there was no clear instruction from Congress on the issue. She also raised the concern that it would open the door to all sorts of challenges.
“It would seem a big deal to say that, if you can point to injury with respect to one provision and you can concoct some kind of inseverability argument, that allows you to challenge anything else in the statute,” she said.
“Isn’t that something that really cuts against all of our doctrine?” asked Kagan.
“I think it’s hard for you to argue that Congress intended the entire Act to fall if the mandate was struck down when the same Congress that lowered the penalty to zero did not even try to repeal the rest of the act,” said Chief Justice John Roberts.
“I think, frankly, that they wanted the Court to do that but that’s not our job,” he added.
Proof of harm?
To have the standing to sue, the plaintiffs have to prove they have been harmed by the ACA. Texas Solicitor General Kyle Hawkins said that individuals feel compelled to buy insurance – even without a penalty hanging over their heads.
Justice Stephen Breyer argued that many laws include what he called “precatory” language – that is, they seek to compel citizens to do something. But most don’t penalize those who fail to act – just like the ACA currently.
If, as the Texas plaintiffs argued, it’s still unconstitutional to make such a request, “I think there will be an awful lot of language in an awful lot of statutes that will suddenly be the subject of court constitutional challenge,” he said.
Hawkins disagreed. He said the ACA’s mandate “is not some suggestion, not some hortatory statement. It is the law of the United States of America today that you have to purchase health insurance and not just any health insurance, but health insurance that the federal government has decided would be best for you.”
Hawkins said that, if just one additional person signed up for Medicaid, the state of Texas and the other plaintiff states would be harmed. He said people were continuing to enroll in the program because they believed the law required them to get health insurance.
Justice Sonia Sotomayor said that defied common sense. “The problem is that your theory assumes people that people are going to pay a tax and break the law by not buying insurance, but they wouldn’t do it when the tax is zero.”
What’s at stake
It’s unlikely the justices will issue a decision immediately. They have until the end of the term in June to rule.
Katie Keith, JD, MPH, a principal at Keith Policy Solutions, LLC, outlined the potential outcomes in Health Affairs .
“The most likely scenario is that the Court maintains the status quo,” she wrote. They could get there by deciding Texas et al. did not have standing to bring the case. Or they could decide that either the mandate is constitutional or that it is unconstitutional but can be severed from the rest of the ACA.
The Court could alternatively find that some or all of the law’s insurance provisions – such as protections for people with pre-existing conditions – can’t be severed from the mandate. Or the justices could strike down all of the insurance consumer protections, the health insurance marketplaces, premium tax credits, and other provisions, which would force states to come up with the money to help people buy insurance. And states are unlikely to be able to do so, especially with the pandemic stretching their budgets.
Finally, the Court could find that the mandate can’t be separated, which would essentially overturn the law.
If that happens, some 15 million people could lose Medicaid coverage, 11 million who buy on health insurance exchanges could lose coverage, and 2.3 million young adults would no longer be able to stay on parents’ policies, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. Kaiser also estimates that 54 million people under age 65 who have pre-existing conditions would no longer be guaranteed coverage.
The Urban Institute estimates that 21 million people could lose insurance – 15 million through Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) and 7.6 million through private nongroup coverage.
Medical societies weigh in
Multiple physicians’ groups, patient advocates, and hospital organizations have filed briefs with the Court in favor of keeping the law intact.
Twenty patient groups representing millions with pre-existing conditions – including the American Cancer Society, American Diabetes Association, American Heart Association, National Alliance on Mental Illness, National Organization for Rare Disorders, and the Kennedy Forum – filed a court brief in May arguing that the law has expanded access to insurance and improved patient outcomes.
“The coronavirus pandemic has only served to underscore the necessity of meaningful coverage – especially for those who are at high risk of being severely affected by the virus – including countless Americans who have pre-existing, acute or chronic conditions like heart disease, cancer, diabetes, lung diseases and multiple sclerosis,” they said in a statement.
Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, MACP, president of the American College of Physicians, which joined a court brief in support of the law with 19 other medical organizations, said the law has worked.
“The coverage, protections and benefits provided by the ACA are critical to the well-being of millions of Americans,” she said in a statement.
“If the ACA were to be thrown out at the same time that we face the pandemic, it would cause chaos for physicians and our patients, and for the entire health care system,” said Fincher, adding that millions of Americans who have been infected could lose insurance if protections for pre-existing conditions disappeared.
“The ACA has revolutionized access to care for tens of millions of women by helping them obtain meaningful health coverage, ensuring that essential care is covered by insurers, and protecting patients from unfair insurance practices,” said Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), in a statement.
Overturning the ACA “would be one of the most singularly disruptive acts to be committed during this public health crisis,” she said.
American Psychiatric Association President Jeffrey Geller, MD, MPH, also warned of disruptions to care, especially for those with mental health and substance use disorders. “We urge the Supreme Court to preserve the entire Act, including the individual mandate,” he said, in a statement.
“In the midst of COVID is no time to let down the millions who we serve as our patients,” said Chip Kahn, Federation of American Health Systems president and CEO, in a statement.
“As caregivers, the goal of hospitals for our patients is to see increased access to affordable coverage for all Americans – not new obstacles,” he said, adding that the ACA “can accomplish this goal. We hope the Supreme Court will see its way clear to allow it to go forward.”
For the defense
Many legal analysts on social media who listened in to today’s hearing agreed that the tenor of the proceedings seemed to lean toward survival of the ACA.
“At this point I would say it is *extremely* likely that the ACA will be upheld, but the mandate struck down and severed out,” tweeted Raffi Melkonian, an appellate lawyer in Houston, Texas. “A decision on standing (throwing out the case entirely) is also possible. The chance that the ACA is struck down v. low.”
“Both Kavanaugh and Roberts have suggested this morning that they may view the individual mandate as severable from the rest of the law. If those two justices join the court’s three liberals in finding that the mandate is severable, that would be five votes to save the ACA,” tweeted the analysts at SCOTUS Blog.
Sean Marotta, a lawyer with Hogan Lovells’ Supreme Court group, agreed. “Oral argument is always an imperfect measure, but the Act’s defenders should feel good today,” he tweeted.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA grants emergency use authorization to Lilly’s antibody COVID-19 therapy
The monoclonal antibody therapy has emergency authorization for treating patients who have tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection and who are considered to be at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19 or hospitalization. To be eligible for treatment with bamlanivimab, patients must be at least 12 years of age and weigh at least 40 kg (approximately 88 lb). The agency notes that this includes patients aged 65 years and older or people with certain chronic conditions.
Bamlanivimab is not authorized for use in patients who are hospitalized or who require oxygen therapy because of COVID-19. The FDA’s action comes less than 2 weeks after Eli Lilly halted the ACTIV-3 study of the therapy for severe, hospitalized COVID-19 patients after evidence showed that adding the antibody therapy to standard care did not improve outcomes over standard care alone for patients with advanced COVID-19.
The government contract with Eli Lilly involves the purchase of 300,000 doses through December, with the option to procure another 650,000 doses through June 2021.
Because of Operation Warp Speed, “we have supplies to distribute now. Product distribution will begin this week,” US Health & Human Services (HHS) Secretary Alex Azar said at a news conference today.
“We talked about building the bridge to safe and effective vaccines” for COVID-19, Azar added. “With this therapeutic, the bridge is taking shape.”
Bamlanivimab 700 mg will be administered as a 1-hour infusion followed by a 1-hour observation period for detecting any infusion-related side effects. The authorized dose is 700 mg, which was on the lower end of the dose range evaluated in studies.
During the press conference, a reporter asked whether the lower dose was chosen in order that more doses of the antibody could be made available. “The lower dose is a rational choice in this situation because we don’t want to give more of a drug than you need,” said Janet Woodcock, MD, the therapeutics lead for Operation Warp Speed. “I think we could probably go lower.”
Bamlanivimab works by attaching to the virus and blocking its entry into the cells and possibly by helping the patients’ immune system clear the virus, said Woodcock, who is also director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“The goal is to treat high-risk people as soon as possible after they show symptoms and are diagnosed,” she added.
Infusions an initial challenge?
There could be some logistic challenges at first because the antibody is administered via infusion. “We expect there will initially be a challenge in administering ... these infusions and setting up infusion centers,” Woodcock said.
Outpatient intravenous infusions are normally performed at infusion centers for patients with cancer and immune disorders, she noted. “You really don’t want them mixing with people who have COVID-19 disease, so we will need to set up separate sites.”
Bamlanivimab will be provided free of cost to patients, Azar said. Patients should be aware that coinsurance may be required for the infusion.
“Fair and equitable” distribution planned
During phase 1 of distribution, the agent will first be allocated to hospitals and hospital-affiliated locations only, John Redd, MD, MPH, chief medical officer, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response at HHS, said at the press conference.
During phase 2, “there will be expanded distribution to outpatient sites,” he said. In an effort to keep the process transparent, a new website features the latest updates on the distribution of bamlanivimab.
Allocation will be based on two factors: the number of new cases reported in a state or territory in the prior 7 days, and rates of COVID-19 hospitalization during the same period.
Asked why the government would determine distribution of the antibody on the basis of the number of hospitalized patients when the indication includes prevention of admission, Woodcock replied that hospitalization is a surrogate measure that can reflect risk factors in a particular state population, such as obesity, diabetes, or the proportion of older people.
Furthermore, the confirmed cases are a “leading indicator,” she said, that can help identify a steep rise in COVID-19 cases that could indicate more hospitalizations are likely soon. “We don’t want to miss that.”
Data underlying the EUA decision
A decrease in hospitalizations or emergency department visits within 28 days of treatment in preclinical studies was “the most important evidence that bamlanivimab may be effective,” the agency noted in the press release announcing the EUA. Among patients at high risk for progression, 3% required such interventions, compared with 10% of placebo-treated patients.
Potential side effects of bamlanivimab include anaphylaxis, infusion-related reactions, nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, headache, itching, and vomiting.
“As illustrated by today’s action, the FDA remains committed to expediting the development and availability of potential COVID-19 treatments and providing sick patients timely access to new therapies where appropriate,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in the news release.
Healthcare providers can download a detailed FDA fact sheet on the EUA for bamlanivimab, which includes dosing instructions.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The monoclonal antibody therapy has emergency authorization for treating patients who have tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection and who are considered to be at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19 or hospitalization. To be eligible for treatment with bamlanivimab, patients must be at least 12 years of age and weigh at least 40 kg (approximately 88 lb). The agency notes that this includes patients aged 65 years and older or people with certain chronic conditions.
Bamlanivimab is not authorized for use in patients who are hospitalized or who require oxygen therapy because of COVID-19. The FDA’s action comes less than 2 weeks after Eli Lilly halted the ACTIV-3 study of the therapy for severe, hospitalized COVID-19 patients after evidence showed that adding the antibody therapy to standard care did not improve outcomes over standard care alone for patients with advanced COVID-19.
The government contract with Eli Lilly involves the purchase of 300,000 doses through December, with the option to procure another 650,000 doses through June 2021.
Because of Operation Warp Speed, “we have supplies to distribute now. Product distribution will begin this week,” US Health & Human Services (HHS) Secretary Alex Azar said at a news conference today.
“We talked about building the bridge to safe and effective vaccines” for COVID-19, Azar added. “With this therapeutic, the bridge is taking shape.”
Bamlanivimab 700 mg will be administered as a 1-hour infusion followed by a 1-hour observation period for detecting any infusion-related side effects. The authorized dose is 700 mg, which was on the lower end of the dose range evaluated in studies.
During the press conference, a reporter asked whether the lower dose was chosen in order that more doses of the antibody could be made available. “The lower dose is a rational choice in this situation because we don’t want to give more of a drug than you need,” said Janet Woodcock, MD, the therapeutics lead for Operation Warp Speed. “I think we could probably go lower.”
Bamlanivimab works by attaching to the virus and blocking its entry into the cells and possibly by helping the patients’ immune system clear the virus, said Woodcock, who is also director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“The goal is to treat high-risk people as soon as possible after they show symptoms and are diagnosed,” she added.
Infusions an initial challenge?
There could be some logistic challenges at first because the antibody is administered via infusion. “We expect there will initially be a challenge in administering ... these infusions and setting up infusion centers,” Woodcock said.
Outpatient intravenous infusions are normally performed at infusion centers for patients with cancer and immune disorders, she noted. “You really don’t want them mixing with people who have COVID-19 disease, so we will need to set up separate sites.”
Bamlanivimab will be provided free of cost to patients, Azar said. Patients should be aware that coinsurance may be required for the infusion.
“Fair and equitable” distribution planned
During phase 1 of distribution, the agent will first be allocated to hospitals and hospital-affiliated locations only, John Redd, MD, MPH, chief medical officer, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response at HHS, said at the press conference.
During phase 2, “there will be expanded distribution to outpatient sites,” he said. In an effort to keep the process transparent, a new website features the latest updates on the distribution of bamlanivimab.
Allocation will be based on two factors: the number of new cases reported in a state or territory in the prior 7 days, and rates of COVID-19 hospitalization during the same period.
Asked why the government would determine distribution of the antibody on the basis of the number of hospitalized patients when the indication includes prevention of admission, Woodcock replied that hospitalization is a surrogate measure that can reflect risk factors in a particular state population, such as obesity, diabetes, or the proportion of older people.
Furthermore, the confirmed cases are a “leading indicator,” she said, that can help identify a steep rise in COVID-19 cases that could indicate more hospitalizations are likely soon. “We don’t want to miss that.”
Data underlying the EUA decision
A decrease in hospitalizations or emergency department visits within 28 days of treatment in preclinical studies was “the most important evidence that bamlanivimab may be effective,” the agency noted in the press release announcing the EUA. Among patients at high risk for progression, 3% required such interventions, compared with 10% of placebo-treated patients.
Potential side effects of bamlanivimab include anaphylaxis, infusion-related reactions, nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, headache, itching, and vomiting.
“As illustrated by today’s action, the FDA remains committed to expediting the development and availability of potential COVID-19 treatments and providing sick patients timely access to new therapies where appropriate,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in the news release.
Healthcare providers can download a detailed FDA fact sheet on the EUA for bamlanivimab, which includes dosing instructions.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The monoclonal antibody therapy has emergency authorization for treating patients who have tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection and who are considered to be at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19 or hospitalization. To be eligible for treatment with bamlanivimab, patients must be at least 12 years of age and weigh at least 40 kg (approximately 88 lb). The agency notes that this includes patients aged 65 years and older or people with certain chronic conditions.
Bamlanivimab is not authorized for use in patients who are hospitalized or who require oxygen therapy because of COVID-19. The FDA’s action comes less than 2 weeks after Eli Lilly halted the ACTIV-3 study of the therapy for severe, hospitalized COVID-19 patients after evidence showed that adding the antibody therapy to standard care did not improve outcomes over standard care alone for patients with advanced COVID-19.
The government contract with Eli Lilly involves the purchase of 300,000 doses through December, with the option to procure another 650,000 doses through June 2021.
Because of Operation Warp Speed, “we have supplies to distribute now. Product distribution will begin this week,” US Health & Human Services (HHS) Secretary Alex Azar said at a news conference today.
“We talked about building the bridge to safe and effective vaccines” for COVID-19, Azar added. “With this therapeutic, the bridge is taking shape.”
Bamlanivimab 700 mg will be administered as a 1-hour infusion followed by a 1-hour observation period for detecting any infusion-related side effects. The authorized dose is 700 mg, which was on the lower end of the dose range evaluated in studies.
During the press conference, a reporter asked whether the lower dose was chosen in order that more doses of the antibody could be made available. “The lower dose is a rational choice in this situation because we don’t want to give more of a drug than you need,” said Janet Woodcock, MD, the therapeutics lead for Operation Warp Speed. “I think we could probably go lower.”
Bamlanivimab works by attaching to the virus and blocking its entry into the cells and possibly by helping the patients’ immune system clear the virus, said Woodcock, who is also director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“The goal is to treat high-risk people as soon as possible after they show symptoms and are diagnosed,” she added.
Infusions an initial challenge?
There could be some logistic challenges at first because the antibody is administered via infusion. “We expect there will initially be a challenge in administering ... these infusions and setting up infusion centers,” Woodcock said.
Outpatient intravenous infusions are normally performed at infusion centers for patients with cancer and immune disorders, she noted. “You really don’t want them mixing with people who have COVID-19 disease, so we will need to set up separate sites.”
Bamlanivimab will be provided free of cost to patients, Azar said. Patients should be aware that coinsurance may be required for the infusion.
“Fair and equitable” distribution planned
During phase 1 of distribution, the agent will first be allocated to hospitals and hospital-affiliated locations only, John Redd, MD, MPH, chief medical officer, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response at HHS, said at the press conference.
During phase 2, “there will be expanded distribution to outpatient sites,” he said. In an effort to keep the process transparent, a new website features the latest updates on the distribution of bamlanivimab.
Allocation will be based on two factors: the number of new cases reported in a state or territory in the prior 7 days, and rates of COVID-19 hospitalization during the same period.
Asked why the government would determine distribution of the antibody on the basis of the number of hospitalized patients when the indication includes prevention of admission, Woodcock replied that hospitalization is a surrogate measure that can reflect risk factors in a particular state population, such as obesity, diabetes, or the proportion of older people.
Furthermore, the confirmed cases are a “leading indicator,” she said, that can help identify a steep rise in COVID-19 cases that could indicate more hospitalizations are likely soon. “We don’t want to miss that.”
Data underlying the EUA decision
A decrease in hospitalizations or emergency department visits within 28 days of treatment in preclinical studies was “the most important evidence that bamlanivimab may be effective,” the agency noted in the press release announcing the EUA. Among patients at high risk for progression, 3% required such interventions, compared with 10% of placebo-treated patients.
Potential side effects of bamlanivimab include anaphylaxis, infusion-related reactions, nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, headache, itching, and vomiting.
“As illustrated by today’s action, the FDA remains committed to expediting the development and availability of potential COVID-19 treatments and providing sick patients timely access to new therapies where appropriate,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in the news release.
Healthcare providers can download a detailed FDA fact sheet on the EUA for bamlanivimab, which includes dosing instructions.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Triple combination therapy for cystic fibrosis linked to plunging hospitalizations
.
The triple combination therapy elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor was associated with a near elimination of hospital stays in one hospital in Oregon, according to a new report. The hospital savings still weren’t nearly enough to pay for the cost of therapy, but the study underscores what many institutions have observed and adds a new layer to the view of quality of life improvements that the new therapy brings.
“After we started prescribing it, we noticed pretty quickly that hospitalizations appeared to be declining after patients started triple combination therapy, and we were hearing [similar reports] from other centers as well. We wanted to quantify this,” Eric C. Walter, MD, a pulmonologist at the Kaiser Permanente Cystic Fibrosis Clinic in Portland, Ore., said during a presentation of the results at the virtual North American Cystic Fibrosis Conference.
“We’re seeing that across the board in real practice, the number of cystic fibrosis patients that have to be hospitalized since starting this triple combination has gone down,” Robert Giusti, MD, said in an interview. “When they’ve had pulmonary exacerbations in the past, it was frequently because they failed outpatient antibiotics, but I think with triple combination therapy, if they do get sick, the likelihood is they will respond to oral antibiotics, so they may not need that prolonged IV course in the hospital.” Dr. Giusti is clinical professor of pediatrics at New York University and director of the Pediatric Cystic Fibrosis Center. He was not involved in the study.
The therapy gained Food and Drug Administration approval in 2019 for the treatment of individuals with CF who are aged 12 years and older, and who have at least one copy of the F508del mutation. Its cost is about $317,000 per year within the Kaiser Permanente system, according to Dr. Walter. His group compared hospitalization days for CF-related diagnoses from Jan. 1 through Aug. 31, 2020, before and after initiation of triple combination therapy.
Of 47 eligible patients, 32 initiated therapy during the study period; 38% had severe lung disease, defined by forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) value less than 40%. In 2020, before initiation of therapy, there were an average of 27 hospital days per month, all among patients with severe lung disease.
Among the therapy group, there were no hospitalizations after initiation of therapy through Aug. 31. Dr. Walter noted that the first hospitalization of a patient on triple combination therapy didn’t occur until early October.
At an average daily cost of $6,700, the researchers calculated that triple combination therapy saved about $189,000 per month in this group of patients. Comparing numbers to previous years, in which some patients with FEV1 greater than 40% were hospitalized, the researchers calculated that the therapy saved about $151,000 per month among individuals with severe lung disease: Patients with severe lung disease contributed about 80% to total hospital costs.
The drug itself for the whole group cost $845,000, dwarfing the $189,000 savings overall. But among patients with severe disease, hospitalization savings were about $151,000 per month, while the drug cost in this group was $316,800 per month.
Cost savings are important, but the improvement in quality of life for a patient – avoiding hospitalization, fewer impacts on work and education – should not be overlooked, according to Ryan Perkins, MD, a pediatric and adult pulmonary fellow at Boston Children’s Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, who moderated the session. “Some of these aren’t things people typically quantify and assign a price tag to,” Dr. Perkins said in an interview.
A big limitation of the work is that it was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, which may have reduced hospitalizations. “We did have patients that called in, told us they were sick, that they needed to be treated for an exacerbation but didn’t want to go to the hospital,” said Dr. Walter. To help adjust for this, Dr. Walter’s team plans to compare intravenous antibiotic exposure before and after triple combination therapy, reasoning that it could help clarify the pandemic’s impact on hospitalizations.
Dr. Walter, Dr. Giusti, and Dr. Perkins have no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Walter E et al. NACFC 2020. Abstract 795.
.
The triple combination therapy elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor was associated with a near elimination of hospital stays in one hospital in Oregon, according to a new report. The hospital savings still weren’t nearly enough to pay for the cost of therapy, but the study underscores what many institutions have observed and adds a new layer to the view of quality of life improvements that the new therapy brings.
“After we started prescribing it, we noticed pretty quickly that hospitalizations appeared to be declining after patients started triple combination therapy, and we were hearing [similar reports] from other centers as well. We wanted to quantify this,” Eric C. Walter, MD, a pulmonologist at the Kaiser Permanente Cystic Fibrosis Clinic in Portland, Ore., said during a presentation of the results at the virtual North American Cystic Fibrosis Conference.
“We’re seeing that across the board in real practice, the number of cystic fibrosis patients that have to be hospitalized since starting this triple combination has gone down,” Robert Giusti, MD, said in an interview. “When they’ve had pulmonary exacerbations in the past, it was frequently because they failed outpatient antibiotics, but I think with triple combination therapy, if they do get sick, the likelihood is they will respond to oral antibiotics, so they may not need that prolonged IV course in the hospital.” Dr. Giusti is clinical professor of pediatrics at New York University and director of the Pediatric Cystic Fibrosis Center. He was not involved in the study.
The therapy gained Food and Drug Administration approval in 2019 for the treatment of individuals with CF who are aged 12 years and older, and who have at least one copy of the F508del mutation. Its cost is about $317,000 per year within the Kaiser Permanente system, according to Dr. Walter. His group compared hospitalization days for CF-related diagnoses from Jan. 1 through Aug. 31, 2020, before and after initiation of triple combination therapy.
Of 47 eligible patients, 32 initiated therapy during the study period; 38% had severe lung disease, defined by forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) value less than 40%. In 2020, before initiation of therapy, there were an average of 27 hospital days per month, all among patients with severe lung disease.
Among the therapy group, there were no hospitalizations after initiation of therapy through Aug. 31. Dr. Walter noted that the first hospitalization of a patient on triple combination therapy didn’t occur until early October.
At an average daily cost of $6,700, the researchers calculated that triple combination therapy saved about $189,000 per month in this group of patients. Comparing numbers to previous years, in which some patients with FEV1 greater than 40% were hospitalized, the researchers calculated that the therapy saved about $151,000 per month among individuals with severe lung disease: Patients with severe lung disease contributed about 80% to total hospital costs.
The drug itself for the whole group cost $845,000, dwarfing the $189,000 savings overall. But among patients with severe disease, hospitalization savings were about $151,000 per month, while the drug cost in this group was $316,800 per month.
Cost savings are important, but the improvement in quality of life for a patient – avoiding hospitalization, fewer impacts on work and education – should not be overlooked, according to Ryan Perkins, MD, a pediatric and adult pulmonary fellow at Boston Children’s Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, who moderated the session. “Some of these aren’t things people typically quantify and assign a price tag to,” Dr. Perkins said in an interview.
A big limitation of the work is that it was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, which may have reduced hospitalizations. “We did have patients that called in, told us they were sick, that they needed to be treated for an exacerbation but didn’t want to go to the hospital,” said Dr. Walter. To help adjust for this, Dr. Walter’s team plans to compare intravenous antibiotic exposure before and after triple combination therapy, reasoning that it could help clarify the pandemic’s impact on hospitalizations.
Dr. Walter, Dr. Giusti, and Dr. Perkins have no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Walter E et al. NACFC 2020. Abstract 795.
.
The triple combination therapy elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor was associated with a near elimination of hospital stays in one hospital in Oregon, according to a new report. The hospital savings still weren’t nearly enough to pay for the cost of therapy, but the study underscores what many institutions have observed and adds a new layer to the view of quality of life improvements that the new therapy brings.
“After we started prescribing it, we noticed pretty quickly that hospitalizations appeared to be declining after patients started triple combination therapy, and we were hearing [similar reports] from other centers as well. We wanted to quantify this,” Eric C. Walter, MD, a pulmonologist at the Kaiser Permanente Cystic Fibrosis Clinic in Portland, Ore., said during a presentation of the results at the virtual North American Cystic Fibrosis Conference.
“We’re seeing that across the board in real practice, the number of cystic fibrosis patients that have to be hospitalized since starting this triple combination has gone down,” Robert Giusti, MD, said in an interview. “When they’ve had pulmonary exacerbations in the past, it was frequently because they failed outpatient antibiotics, but I think with triple combination therapy, if they do get sick, the likelihood is they will respond to oral antibiotics, so they may not need that prolonged IV course in the hospital.” Dr. Giusti is clinical professor of pediatrics at New York University and director of the Pediatric Cystic Fibrosis Center. He was not involved in the study.
The therapy gained Food and Drug Administration approval in 2019 for the treatment of individuals with CF who are aged 12 years and older, and who have at least one copy of the F508del mutation. Its cost is about $317,000 per year within the Kaiser Permanente system, according to Dr. Walter. His group compared hospitalization days for CF-related diagnoses from Jan. 1 through Aug. 31, 2020, before and after initiation of triple combination therapy.
Of 47 eligible patients, 32 initiated therapy during the study period; 38% had severe lung disease, defined by forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) value less than 40%. In 2020, before initiation of therapy, there were an average of 27 hospital days per month, all among patients with severe lung disease.
Among the therapy group, there were no hospitalizations after initiation of therapy through Aug. 31. Dr. Walter noted that the first hospitalization of a patient on triple combination therapy didn’t occur until early October.
At an average daily cost of $6,700, the researchers calculated that triple combination therapy saved about $189,000 per month in this group of patients. Comparing numbers to previous years, in which some patients with FEV1 greater than 40% were hospitalized, the researchers calculated that the therapy saved about $151,000 per month among individuals with severe lung disease: Patients with severe lung disease contributed about 80% to total hospital costs.
The drug itself for the whole group cost $845,000, dwarfing the $189,000 savings overall. But among patients with severe disease, hospitalization savings were about $151,000 per month, while the drug cost in this group was $316,800 per month.
Cost savings are important, but the improvement in quality of life for a patient – avoiding hospitalization, fewer impacts on work and education – should not be overlooked, according to Ryan Perkins, MD, a pediatric and adult pulmonary fellow at Boston Children’s Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, who moderated the session. “Some of these aren’t things people typically quantify and assign a price tag to,” Dr. Perkins said in an interview.
A big limitation of the work is that it was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, which may have reduced hospitalizations. “We did have patients that called in, told us they were sick, that they needed to be treated for an exacerbation but didn’t want to go to the hospital,” said Dr. Walter. To help adjust for this, Dr. Walter’s team plans to compare intravenous antibiotic exposure before and after triple combination therapy, reasoning that it could help clarify the pandemic’s impact on hospitalizations.
Dr. Walter, Dr. Giusti, and Dr. Perkins have no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Walter E et al. NACFC 2020. Abstract 795.
FROM NACFC 2020
FDA clears smartphone app to interrupt PTSD-related nightmares
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared for marketing a smartphone app that can detect and interrupt nightmares in adults with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The NightWare app, from Minneapolis-based NightWare Inc., runs on the Apple Watch and Apple iPhone.
During sleep, Apple Watch sensors monitor heart rate and body movement. These data are used to create a unique sleep profile using a proprietary algorithm.
When the NightWare app detects that a patient is experiencing a nightmare based on changes in heart rate and movement, it provides slight vibrations through the Apple Watch to arouse the patient and interrupt the nightmare, without fully awakening the patient, the company notes.
NightWare is available by prescription only and is intended for use in adults aged 22 years and older with PTSD.
“Sleep is an essential part of a person’s daily routine. However, certain adults who have a nightmare disorder or who experience nightmares from PTSD are not able to get the rest they need,” Carlos Peña, PhD, director, Office of Neurological and Physical Medicine Devices, Center for Devices and Radiological Health at the FDA, said in a news release.
This authorization “offers a new, low-risk treatment option that uses digital technology in an effort to provide temporary relief from sleep disturbance related to nightmares,” said Dr. Peña.
NightWare was tested in a 30-day randomized, sham-controlled trial of 70 patients. Patients in the sham group wore the device, but no vibrations were provided.
Both the sham and active groups showed improvement in sleep on standard sleep scales, with the active group showing greater improvement than sham. “The evidence demonstrated the probable benefits outweighed the probable risks,” the FDA said in a statement.
and other recommended therapies for PTSD-associated nightmares and nightmare disorder, the agency said.
NightWare was granted breakthrough device designation for the treatment of nightmares in patients with PTSD. The device reviewed through the de novo premarket pathway, a regulatory pathway for some low- to moderate-risk devices of a new type.
Along with this marketing authorization, the FDA is establishing “special controls” designed to provide a “reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness for tests of this type,” the agency said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared for marketing a smartphone app that can detect and interrupt nightmares in adults with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The NightWare app, from Minneapolis-based NightWare Inc., runs on the Apple Watch and Apple iPhone.
During sleep, Apple Watch sensors monitor heart rate and body movement. These data are used to create a unique sleep profile using a proprietary algorithm.
When the NightWare app detects that a patient is experiencing a nightmare based on changes in heart rate and movement, it provides slight vibrations through the Apple Watch to arouse the patient and interrupt the nightmare, without fully awakening the patient, the company notes.
NightWare is available by prescription only and is intended for use in adults aged 22 years and older with PTSD.
“Sleep is an essential part of a person’s daily routine. However, certain adults who have a nightmare disorder or who experience nightmares from PTSD are not able to get the rest they need,” Carlos Peña, PhD, director, Office of Neurological and Physical Medicine Devices, Center for Devices and Radiological Health at the FDA, said in a news release.
This authorization “offers a new, low-risk treatment option that uses digital technology in an effort to provide temporary relief from sleep disturbance related to nightmares,” said Dr. Peña.
NightWare was tested in a 30-day randomized, sham-controlled trial of 70 patients. Patients in the sham group wore the device, but no vibrations were provided.
Both the sham and active groups showed improvement in sleep on standard sleep scales, with the active group showing greater improvement than sham. “The evidence demonstrated the probable benefits outweighed the probable risks,” the FDA said in a statement.
and other recommended therapies for PTSD-associated nightmares and nightmare disorder, the agency said.
NightWare was granted breakthrough device designation for the treatment of nightmares in patients with PTSD. The device reviewed through the de novo premarket pathway, a regulatory pathway for some low- to moderate-risk devices of a new type.
Along with this marketing authorization, the FDA is establishing “special controls” designed to provide a “reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness for tests of this type,” the agency said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared for marketing a smartphone app that can detect and interrupt nightmares in adults with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The NightWare app, from Minneapolis-based NightWare Inc., runs on the Apple Watch and Apple iPhone.
During sleep, Apple Watch sensors monitor heart rate and body movement. These data are used to create a unique sleep profile using a proprietary algorithm.
When the NightWare app detects that a patient is experiencing a nightmare based on changes in heart rate and movement, it provides slight vibrations through the Apple Watch to arouse the patient and interrupt the nightmare, without fully awakening the patient, the company notes.
NightWare is available by prescription only and is intended for use in adults aged 22 years and older with PTSD.
“Sleep is an essential part of a person’s daily routine. However, certain adults who have a nightmare disorder or who experience nightmares from PTSD are not able to get the rest they need,” Carlos Peña, PhD, director, Office of Neurological and Physical Medicine Devices, Center for Devices and Radiological Health at the FDA, said in a news release.
This authorization “offers a new, low-risk treatment option that uses digital technology in an effort to provide temporary relief from sleep disturbance related to nightmares,” said Dr. Peña.
NightWare was tested in a 30-day randomized, sham-controlled trial of 70 patients. Patients in the sham group wore the device, but no vibrations were provided.
Both the sham and active groups showed improvement in sleep on standard sleep scales, with the active group showing greater improvement than sham. “The evidence demonstrated the probable benefits outweighed the probable risks,” the FDA said in a statement.
and other recommended therapies for PTSD-associated nightmares and nightmare disorder, the agency said.
NightWare was granted breakthrough device designation for the treatment of nightmares in patients with PTSD. The device reviewed through the de novo premarket pathway, a regulatory pathway for some low- to moderate-risk devices of a new type.
Along with this marketing authorization, the FDA is establishing “special controls” designed to provide a “reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness for tests of this type,” the agency said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Great Barrington coauthor backs off strict reliance on herd immunity
A coauthor of the Great Barrington Declaration says that he and colleagues have never argued against using mitigation strategies to keep COVID-19 from spreading, and that critics have mischaracterized the document as a “let it rip” strategy.
Jay Bhattacharya, MD, PhD, a professor and public health policy expert in infectious diseases at Stanford University in California, spoke on a JAMA Livestream debate on November 6. Marc Lipsitch, MD, an epidemiology professor at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, Massachusetts, represented the 6900 signatories of the John Snow Memorandum, a rebuttal to the Great Barrington document.
The Great Barrington approach of “Focused Protection” advocates isolation and protection of people who are most vulnerable to COVID-19 while avoiding what they characterize as lockdowns. “The most compassionate approach that balances the risks and benefits of reaching herd immunity, is to allow those who are at minimal risk of death to live their lives normally to build up immunity to the virus through natural infection, while better protecting those who are at highest risk,” the document reads.
The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and its HIV Medicine Association denounced the declaration, as reported by Medscape Medical News, and the World Health Organization (WHO) Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus called the proposal “unethical.” But the idea has gained some traction at the White House, where Coronavirus Task Force Member and Stanford professor Scott Atlas, MD, has been advising President Donald J. Trump.
On the JAMA debate, Bhattacharya said, “I think all of the mitigation measures are really important,” listing social distancing, hand washing, and masks when distancing is not possible as chief among those strategies for the less vulnerable. “I don’t want to create infections intentionally, but I want us to allow people to go back to their lives as best they can, understanding of the risks they are taking when they do it,” he said, claiming that 99.95% of the population will survive infection.
“The harmful lockdowns are worse for many, many people,” Bhattacharya said.
“I think Jay is moving towards a middle ground which is not really what the Great Barrington Declaration seems to promote,” countered Lipsitch. The declaration does not say use masks or social distance, he said. “It just says we need to go back to a normal life.”
Bhattacharya’s statements to JAMA mean that “maybe we are approaching some common ground,” Lipsitch said.
Definition of a lockdown
Both men were asked to give their definition of a “lockdown.” To Lipsitch, it means people are not allowed out except for essential services and that most businesses are closed, with exceptions for those deemed essential.
Bhattacharya, however, said he views that as a quarantine. Lockdowns “are what we’re currently doing,” he said. Schools, churches, businesses, and arts and culture organizations are shuttered, and “almost every aspect of society is restricted in some way,” Bhattacharya said.
He blamed these lockdowns for most of the excess deaths over and above the COVID-19 deaths and said they had failed to control the pandemic.
Lipsitch said that “it feels to me that Jay is describing as lockdown everything that causes harm, even when it’s not locked down.” He noted that the country was truly closed down for 2 months or so in the spring.
“All of these harms I agree are real,” said Lipsitch. “But they are because the normal life of our society is being interfered with by viral transmission and by people’s inability to live their normal lives.”
Closures and lockdowns are essential to delaying cases and deaths, said Lipsitch. “A case today is worse than a case tomorrow and a lot worse than a case 6 months from now,” he said, noting that a vaccine or improved therapeutics could evolve.
“Delay is not nothing,” Lipsitch added. “It’s actually the goal as I see it, and as the John Snow memo says, we want to keep the virus under control in such a way as that the vulnerable people are not at risk.”
He predicted that cases will continue to grow exponentially because the nation is “not even close to herd immunity.” And, if intensive care units fill up, “there will be a responsive lockdown,” he said, adding that he did not endorse that as a general matter or favor it as a default position.
Bhattacharya claimed that Sweden has tallied only 1800 excess deaths since the pandemic began. “That’s lockdown harm avoided,” he said, advocating a similar strategy for the United States. But, infections have been on the rise in Sweden, and the nation has a higher COVID-19 death rate — with 6000 deaths — than other Nordic countries.
“If we keep this policy of lockdown we will have the same kind of outcomes we’ve already had — high excess deaths and sort of indifferent control of COVID,” Bhattacharya said.
“We’re still going to have misery and death going forward until we reach a point where there’s sufficient immunity either though a vaccine or through natural infection,” he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A coauthor of the Great Barrington Declaration says that he and colleagues have never argued against using mitigation strategies to keep COVID-19 from spreading, and that critics have mischaracterized the document as a “let it rip” strategy.
Jay Bhattacharya, MD, PhD, a professor and public health policy expert in infectious diseases at Stanford University in California, spoke on a JAMA Livestream debate on November 6. Marc Lipsitch, MD, an epidemiology professor at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, Massachusetts, represented the 6900 signatories of the John Snow Memorandum, a rebuttal to the Great Barrington document.
The Great Barrington approach of “Focused Protection” advocates isolation and protection of people who are most vulnerable to COVID-19 while avoiding what they characterize as lockdowns. “The most compassionate approach that balances the risks and benefits of reaching herd immunity, is to allow those who are at minimal risk of death to live their lives normally to build up immunity to the virus through natural infection, while better protecting those who are at highest risk,” the document reads.
The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and its HIV Medicine Association denounced the declaration, as reported by Medscape Medical News, and the World Health Organization (WHO) Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus called the proposal “unethical.” But the idea has gained some traction at the White House, where Coronavirus Task Force Member and Stanford professor Scott Atlas, MD, has been advising President Donald J. Trump.
On the JAMA debate, Bhattacharya said, “I think all of the mitigation measures are really important,” listing social distancing, hand washing, and masks when distancing is not possible as chief among those strategies for the less vulnerable. “I don’t want to create infections intentionally, but I want us to allow people to go back to their lives as best they can, understanding of the risks they are taking when they do it,” he said, claiming that 99.95% of the population will survive infection.
“The harmful lockdowns are worse for many, many people,” Bhattacharya said.
“I think Jay is moving towards a middle ground which is not really what the Great Barrington Declaration seems to promote,” countered Lipsitch. The declaration does not say use masks or social distance, he said. “It just says we need to go back to a normal life.”
Bhattacharya’s statements to JAMA mean that “maybe we are approaching some common ground,” Lipsitch said.
Definition of a lockdown
Both men were asked to give their definition of a “lockdown.” To Lipsitch, it means people are not allowed out except for essential services and that most businesses are closed, with exceptions for those deemed essential.
Bhattacharya, however, said he views that as a quarantine. Lockdowns “are what we’re currently doing,” he said. Schools, churches, businesses, and arts and culture organizations are shuttered, and “almost every aspect of society is restricted in some way,” Bhattacharya said.
He blamed these lockdowns for most of the excess deaths over and above the COVID-19 deaths and said they had failed to control the pandemic.
Lipsitch said that “it feels to me that Jay is describing as lockdown everything that causes harm, even when it’s not locked down.” He noted that the country was truly closed down for 2 months or so in the spring.
“All of these harms I agree are real,” said Lipsitch. “But they are because the normal life of our society is being interfered with by viral transmission and by people’s inability to live their normal lives.”
Closures and lockdowns are essential to delaying cases and deaths, said Lipsitch. “A case today is worse than a case tomorrow and a lot worse than a case 6 months from now,” he said, noting that a vaccine or improved therapeutics could evolve.
“Delay is not nothing,” Lipsitch added. “It’s actually the goal as I see it, and as the John Snow memo says, we want to keep the virus under control in such a way as that the vulnerable people are not at risk.”
He predicted that cases will continue to grow exponentially because the nation is “not even close to herd immunity.” And, if intensive care units fill up, “there will be a responsive lockdown,” he said, adding that he did not endorse that as a general matter or favor it as a default position.
Bhattacharya claimed that Sweden has tallied only 1800 excess deaths since the pandemic began. “That’s lockdown harm avoided,” he said, advocating a similar strategy for the United States. But, infections have been on the rise in Sweden, and the nation has a higher COVID-19 death rate — with 6000 deaths — than other Nordic countries.
“If we keep this policy of lockdown we will have the same kind of outcomes we’ve already had — high excess deaths and sort of indifferent control of COVID,” Bhattacharya said.
“We’re still going to have misery and death going forward until we reach a point where there’s sufficient immunity either though a vaccine or through natural infection,” he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A coauthor of the Great Barrington Declaration says that he and colleagues have never argued against using mitigation strategies to keep COVID-19 from spreading, and that critics have mischaracterized the document as a “let it rip” strategy.
Jay Bhattacharya, MD, PhD, a professor and public health policy expert in infectious diseases at Stanford University in California, spoke on a JAMA Livestream debate on November 6. Marc Lipsitch, MD, an epidemiology professor at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, Massachusetts, represented the 6900 signatories of the John Snow Memorandum, a rebuttal to the Great Barrington document.
The Great Barrington approach of “Focused Protection” advocates isolation and protection of people who are most vulnerable to COVID-19 while avoiding what they characterize as lockdowns. “The most compassionate approach that balances the risks and benefits of reaching herd immunity, is to allow those who are at minimal risk of death to live their lives normally to build up immunity to the virus through natural infection, while better protecting those who are at highest risk,” the document reads.
The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and its HIV Medicine Association denounced the declaration, as reported by Medscape Medical News, and the World Health Organization (WHO) Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus called the proposal “unethical.” But the idea has gained some traction at the White House, where Coronavirus Task Force Member and Stanford professor Scott Atlas, MD, has been advising President Donald J. Trump.
On the JAMA debate, Bhattacharya said, “I think all of the mitigation measures are really important,” listing social distancing, hand washing, and masks when distancing is not possible as chief among those strategies for the less vulnerable. “I don’t want to create infections intentionally, but I want us to allow people to go back to their lives as best they can, understanding of the risks they are taking when they do it,” he said, claiming that 99.95% of the population will survive infection.
“The harmful lockdowns are worse for many, many people,” Bhattacharya said.
“I think Jay is moving towards a middle ground which is not really what the Great Barrington Declaration seems to promote,” countered Lipsitch. The declaration does not say use masks or social distance, he said. “It just says we need to go back to a normal life.”
Bhattacharya’s statements to JAMA mean that “maybe we are approaching some common ground,” Lipsitch said.
Definition of a lockdown
Both men were asked to give their definition of a “lockdown.” To Lipsitch, it means people are not allowed out except for essential services and that most businesses are closed, with exceptions for those deemed essential.
Bhattacharya, however, said he views that as a quarantine. Lockdowns “are what we’re currently doing,” he said. Schools, churches, businesses, and arts and culture organizations are shuttered, and “almost every aspect of society is restricted in some way,” Bhattacharya said.
He blamed these lockdowns for most of the excess deaths over and above the COVID-19 deaths and said they had failed to control the pandemic.
Lipsitch said that “it feels to me that Jay is describing as lockdown everything that causes harm, even when it’s not locked down.” He noted that the country was truly closed down for 2 months or so in the spring.
“All of these harms I agree are real,” said Lipsitch. “But they are because the normal life of our society is being interfered with by viral transmission and by people’s inability to live their normal lives.”
Closures and lockdowns are essential to delaying cases and deaths, said Lipsitch. “A case today is worse than a case tomorrow and a lot worse than a case 6 months from now,” he said, noting that a vaccine or improved therapeutics could evolve.
“Delay is not nothing,” Lipsitch added. “It’s actually the goal as I see it, and as the John Snow memo says, we want to keep the virus under control in such a way as that the vulnerable people are not at risk.”
He predicted that cases will continue to grow exponentially because the nation is “not even close to herd immunity.” And, if intensive care units fill up, “there will be a responsive lockdown,” he said, adding that he did not endorse that as a general matter or favor it as a default position.
Bhattacharya claimed that Sweden has tallied only 1800 excess deaths since the pandemic began. “That’s lockdown harm avoided,” he said, advocating a similar strategy for the United States. But, infections have been on the rise in Sweden, and the nation has a higher COVID-19 death rate — with 6000 deaths — than other Nordic countries.
“If we keep this policy of lockdown we will have the same kind of outcomes we’ve already had — high excess deaths and sort of indifferent control of COVID,” Bhattacharya said.
“We’re still going to have misery and death going forward until we reach a point where there’s sufficient immunity either though a vaccine or through natural infection,” he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitals poised to launch first COVID-19 vaccines in clinicians
At first, when news spread of a 28-year-old doctor on the COVID-19 front lines in Brazil who died after receiving an experimental vaccine, doubts arose about the safety of one of the most promising coronavirus vaccine candidates. But then the story flipped. Although the vaccine maker wouldn’t confirm it, the doctor appeared to have been in the control group and had received a dose of an established meningitis vaccine. The danger came from exposure to the coronavirus itself.
That tragedy underscores the ongoing risk of COVID-19 to healthcare workers, who have been designated by US advisory panels as part of phase 1A – the first to receive doses of any approved vaccine. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently reported that 6% of adults hospitalized with COVID from March to May were healthcare workers. The report was based on surveillance data from 13 states. The average age of the patients was 49 years. The agency set a November 15 vaccination “readiness date” for jurisdictions, such as state health departments, even though a vaccine isn’t likely to be authorized by then.
As hospitals scramble to prepare, their watchword is flexibility. They don’t yet know how many initial doses they will get, of which vaccine, or in what time frame. They have a sophisticated infrastructure to deliver flu vaccines each fall, but that framework doesn’t align with the likely scenarios of limited supply, additional reporting requirements, two-dose regimens, and differing storage needs.
“Healthcare organizations have consistently risen to the challenge. I wholeheartedly believe in their potential to do this,” Anna Legreid Dopp, PharmD, senior director of quality improvement and guidelines for the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, told Medscape Medical News.
Healthcare workers won’t face a vaccine mandate
Even after months of caring for COVID patients, most clinicians remain vulnerable to infection – at work and in their communities. That was what occupational medicine physician Kevin Smith, MD, realized when his health system, Toledo, Ohio–based ProMedica, offered antibody testing to all its 50,000 employees. About 2% of the 6933 tests given came back positive, he says.
Yet many physicians, nurses, and other healthcare workers share the public’s skepticism about the safety and effectiveness of a vaccine that receives swift US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for emergency use. About half of nurses (47%) and almost 1 in 3 physicians (30%) say that they don’t want to get the vaccine when it first becomes available or that they’re unsure about vaccination, according to a Medscape survey.
Because vaccination of healthcare workers will set the stage for public acceptance of the vaccine, hospital epidemiologists are concerned. “We know that there will be some hesitancy in the healthcare workforce, just as there will be in the broader public,” said Marci Drees, MD, chief infection prevention officer and hospital epidemiologist for ChristianaCare in Newark, Delaware, and liaison from the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America to the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.* “I do not think we can expect anyone to be vaccinated if we’re not willing to vaccinate ourselves.”
Healthcare workers are typically required to receive a range of vaccines, including measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) and pertussis shots. Each year, close to half of US healthcare workers receive a flu vaccine under a workplace mandate. But COVID-19 will be different. The FDA requires anyone given products under an emergency use authorization (EUA) to receive information about risks and benefits and to have the option to decline. Hospitals instead will rely on education as they offer a novel vaccine (or more than one) that will have a minimum effectiveness of 50%.
ProMedica doesn’t require employees to be vaccinated against flu, but employees who decline must get a note from a doctor indicating that they have talked about the risks and benefits of the vaccine. A similar approach may be used with a COVID-19 vaccine, in which employees may be required to learn about the vaccine before they decline, Smith says. “I do believe some people will say they don’t want to get it,” he added.
Like colleagues across the country, Smith is identifying healthcare workers who are involved in direct care of COVID-19 patients and are at highest risk for exposure. Even within the top tier, those performing the riskiest tasks, such as respiratory therapists who provide breathing treatments that spread aerosols and droplets, will be tagged as a priority group, he says. Healthcare workers who spend the most time in proximity to COVID patients, such as nurses in a COVID unit, also are likely to get the first doses, he says.
Swirl, don’t shake, the vaccine
Hospitals are adept at ramping up vaccination campaigns. For example, last year, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, in Nashville, Tennessee, vaccinated nearly 16,000 employees against influenza in their 1-day “Flulapalooza” event. The medical center even earned a Guinness world record in 2011 at the first Flulapalooza for giving the most vaccinations ever within 8 hours.
The 10th anniversary of the event was canceled this year because of COVID restrictions. Instead, nurses, pharmacists, and other clinicians pitched in to vaccinate their coworkers against influenza. Now, plans for COVID-19 vaccination move forward amid uncertainty.
Instead of holding a mass event, “the delivery mechanisms will need to be more targeted and focused,” said Lori Rolando, MD, MPH, director of the Vanderbilt Occupational Health Clinic. In the CDC’s most recent version of its vaccination program “playbook,” the agency recommends giving the vaccines in an area that allows people to remain 6 feet apart and for them to wait for 15 minutes after receiving the shot to make sure they don’t faint, a potential risk common to almost all vaccines.
That’s the easy part. Planning becomes more complex, given the uncertainty as to which vaccines will receive approval and which one a hospital will receive.
If the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine receives EUA in 2020, about 10 to 20 million doses could be available in November and 20 to 30 million doses in December. The ultracold containers used to ship the vaccines have to be replenished with dry ice within 24 hours of receipt and every 5 days thereafter. Hospitals will need temperature probes to monitor storage in the containers. The five-dose vials can be refrigerated before administering, but only for 5 days. The product must be diluted, and it then must be used within 6 hours.
The Moderna vaccine will be somewhat less plentiful at first. About 10 million doses are expected in November and 15 million doses by the end of December. The 10-dose vials are stored in a freezer. Once they are placed in a refrigerator to thaw, they have to be used within 7 days, and once they’re removed from the refrigerator, they have to be used within 12 hours. The pharmacist or other vaccinator must swirl – but not shake! – the vial before delivering a dose, according to the CDC playbook.
As more information emerges about the vaccines, instructions may change, and Smith is steeled for shifting scenarios. “These are all draft plans. We’re going to modify as we go along,” he says.
The Pfizer vaccine requires a second dose at 21 days, and the Moderna vaccine targets the second dose at 28 days. In addition to using information systems to track vaccinations and any adverse effects, hospitals will give employees a card indicating what vaccine they received, the date it was administered, and the date on which they need to return. (At this point, the time frame for the second dose doesn’t appear to be flexible.)
Regardless of the vaccine, one message stays the same: COVID precautions must continue. That means mask wearing, social distancing, and hand washing – practices that also must be followed by healthcare workers who test positive for naturally acquired antibodies.
“I don’t think anyone expects the COVID vaccine to be 100% effective at preventing COVID,” says Rolando. “So all of the other tools in our toolbox are going to need to be continued to be used as well.”
*Correction, 11/12/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the name of Dr. Drees' institution.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At first, when news spread of a 28-year-old doctor on the COVID-19 front lines in Brazil who died after receiving an experimental vaccine, doubts arose about the safety of one of the most promising coronavirus vaccine candidates. But then the story flipped. Although the vaccine maker wouldn’t confirm it, the doctor appeared to have been in the control group and had received a dose of an established meningitis vaccine. The danger came from exposure to the coronavirus itself.
That tragedy underscores the ongoing risk of COVID-19 to healthcare workers, who have been designated by US advisory panels as part of phase 1A – the first to receive doses of any approved vaccine. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently reported that 6% of adults hospitalized with COVID from March to May were healthcare workers. The report was based on surveillance data from 13 states. The average age of the patients was 49 years. The agency set a November 15 vaccination “readiness date” for jurisdictions, such as state health departments, even though a vaccine isn’t likely to be authorized by then.
As hospitals scramble to prepare, their watchword is flexibility. They don’t yet know how many initial doses they will get, of which vaccine, or in what time frame. They have a sophisticated infrastructure to deliver flu vaccines each fall, but that framework doesn’t align with the likely scenarios of limited supply, additional reporting requirements, two-dose regimens, and differing storage needs.
“Healthcare organizations have consistently risen to the challenge. I wholeheartedly believe in their potential to do this,” Anna Legreid Dopp, PharmD, senior director of quality improvement and guidelines for the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, told Medscape Medical News.
Healthcare workers won’t face a vaccine mandate
Even after months of caring for COVID patients, most clinicians remain vulnerable to infection – at work and in their communities. That was what occupational medicine physician Kevin Smith, MD, realized when his health system, Toledo, Ohio–based ProMedica, offered antibody testing to all its 50,000 employees. About 2% of the 6933 tests given came back positive, he says.
Yet many physicians, nurses, and other healthcare workers share the public’s skepticism about the safety and effectiveness of a vaccine that receives swift US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for emergency use. About half of nurses (47%) and almost 1 in 3 physicians (30%) say that they don’t want to get the vaccine when it first becomes available or that they’re unsure about vaccination, according to a Medscape survey.
Because vaccination of healthcare workers will set the stage for public acceptance of the vaccine, hospital epidemiologists are concerned. “We know that there will be some hesitancy in the healthcare workforce, just as there will be in the broader public,” said Marci Drees, MD, chief infection prevention officer and hospital epidemiologist for ChristianaCare in Newark, Delaware, and liaison from the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America to the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.* “I do not think we can expect anyone to be vaccinated if we’re not willing to vaccinate ourselves.”
Healthcare workers are typically required to receive a range of vaccines, including measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) and pertussis shots. Each year, close to half of US healthcare workers receive a flu vaccine under a workplace mandate. But COVID-19 will be different. The FDA requires anyone given products under an emergency use authorization (EUA) to receive information about risks and benefits and to have the option to decline. Hospitals instead will rely on education as they offer a novel vaccine (or more than one) that will have a minimum effectiveness of 50%.
ProMedica doesn’t require employees to be vaccinated against flu, but employees who decline must get a note from a doctor indicating that they have talked about the risks and benefits of the vaccine. A similar approach may be used with a COVID-19 vaccine, in which employees may be required to learn about the vaccine before they decline, Smith says. “I do believe some people will say they don’t want to get it,” he added.
Like colleagues across the country, Smith is identifying healthcare workers who are involved in direct care of COVID-19 patients and are at highest risk for exposure. Even within the top tier, those performing the riskiest tasks, such as respiratory therapists who provide breathing treatments that spread aerosols and droplets, will be tagged as a priority group, he says. Healthcare workers who spend the most time in proximity to COVID patients, such as nurses in a COVID unit, also are likely to get the first doses, he says.
Swirl, don’t shake, the vaccine
Hospitals are adept at ramping up vaccination campaigns. For example, last year, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, in Nashville, Tennessee, vaccinated nearly 16,000 employees against influenza in their 1-day “Flulapalooza” event. The medical center even earned a Guinness world record in 2011 at the first Flulapalooza for giving the most vaccinations ever within 8 hours.
The 10th anniversary of the event was canceled this year because of COVID restrictions. Instead, nurses, pharmacists, and other clinicians pitched in to vaccinate their coworkers against influenza. Now, plans for COVID-19 vaccination move forward amid uncertainty.
Instead of holding a mass event, “the delivery mechanisms will need to be more targeted and focused,” said Lori Rolando, MD, MPH, director of the Vanderbilt Occupational Health Clinic. In the CDC’s most recent version of its vaccination program “playbook,” the agency recommends giving the vaccines in an area that allows people to remain 6 feet apart and for them to wait for 15 minutes after receiving the shot to make sure they don’t faint, a potential risk common to almost all vaccines.
That’s the easy part. Planning becomes more complex, given the uncertainty as to which vaccines will receive approval and which one a hospital will receive.
If the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine receives EUA in 2020, about 10 to 20 million doses could be available in November and 20 to 30 million doses in December. The ultracold containers used to ship the vaccines have to be replenished with dry ice within 24 hours of receipt and every 5 days thereafter. Hospitals will need temperature probes to monitor storage in the containers. The five-dose vials can be refrigerated before administering, but only for 5 days. The product must be diluted, and it then must be used within 6 hours.
The Moderna vaccine will be somewhat less plentiful at first. About 10 million doses are expected in November and 15 million doses by the end of December. The 10-dose vials are stored in a freezer. Once they are placed in a refrigerator to thaw, they have to be used within 7 days, and once they’re removed from the refrigerator, they have to be used within 12 hours. The pharmacist or other vaccinator must swirl – but not shake! – the vial before delivering a dose, according to the CDC playbook.
As more information emerges about the vaccines, instructions may change, and Smith is steeled for shifting scenarios. “These are all draft plans. We’re going to modify as we go along,” he says.
The Pfizer vaccine requires a second dose at 21 days, and the Moderna vaccine targets the second dose at 28 days. In addition to using information systems to track vaccinations and any adverse effects, hospitals will give employees a card indicating what vaccine they received, the date it was administered, and the date on which they need to return. (At this point, the time frame for the second dose doesn’t appear to be flexible.)
Regardless of the vaccine, one message stays the same: COVID precautions must continue. That means mask wearing, social distancing, and hand washing – practices that also must be followed by healthcare workers who test positive for naturally acquired antibodies.
“I don’t think anyone expects the COVID vaccine to be 100% effective at preventing COVID,” says Rolando. “So all of the other tools in our toolbox are going to need to be continued to be used as well.”
*Correction, 11/12/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the name of Dr. Drees' institution.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At first, when news spread of a 28-year-old doctor on the COVID-19 front lines in Brazil who died after receiving an experimental vaccine, doubts arose about the safety of one of the most promising coronavirus vaccine candidates. But then the story flipped. Although the vaccine maker wouldn’t confirm it, the doctor appeared to have been in the control group and had received a dose of an established meningitis vaccine. The danger came from exposure to the coronavirus itself.
That tragedy underscores the ongoing risk of COVID-19 to healthcare workers, who have been designated by US advisory panels as part of phase 1A – the first to receive doses of any approved vaccine. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently reported that 6% of adults hospitalized with COVID from March to May were healthcare workers. The report was based on surveillance data from 13 states. The average age of the patients was 49 years. The agency set a November 15 vaccination “readiness date” for jurisdictions, such as state health departments, even though a vaccine isn’t likely to be authorized by then.
As hospitals scramble to prepare, their watchword is flexibility. They don’t yet know how many initial doses they will get, of which vaccine, or in what time frame. They have a sophisticated infrastructure to deliver flu vaccines each fall, but that framework doesn’t align with the likely scenarios of limited supply, additional reporting requirements, two-dose regimens, and differing storage needs.
“Healthcare organizations have consistently risen to the challenge. I wholeheartedly believe in their potential to do this,” Anna Legreid Dopp, PharmD, senior director of quality improvement and guidelines for the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, told Medscape Medical News.
Healthcare workers won’t face a vaccine mandate
Even after months of caring for COVID patients, most clinicians remain vulnerable to infection – at work and in their communities. That was what occupational medicine physician Kevin Smith, MD, realized when his health system, Toledo, Ohio–based ProMedica, offered antibody testing to all its 50,000 employees. About 2% of the 6933 tests given came back positive, he says.
Yet many physicians, nurses, and other healthcare workers share the public’s skepticism about the safety and effectiveness of a vaccine that receives swift US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for emergency use. About half of nurses (47%) and almost 1 in 3 physicians (30%) say that they don’t want to get the vaccine when it first becomes available or that they’re unsure about vaccination, according to a Medscape survey.
Because vaccination of healthcare workers will set the stage for public acceptance of the vaccine, hospital epidemiologists are concerned. “We know that there will be some hesitancy in the healthcare workforce, just as there will be in the broader public,” said Marci Drees, MD, chief infection prevention officer and hospital epidemiologist for ChristianaCare in Newark, Delaware, and liaison from the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America to the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.* “I do not think we can expect anyone to be vaccinated if we’re not willing to vaccinate ourselves.”
Healthcare workers are typically required to receive a range of vaccines, including measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) and pertussis shots. Each year, close to half of US healthcare workers receive a flu vaccine under a workplace mandate. But COVID-19 will be different. The FDA requires anyone given products under an emergency use authorization (EUA) to receive information about risks and benefits and to have the option to decline. Hospitals instead will rely on education as they offer a novel vaccine (or more than one) that will have a minimum effectiveness of 50%.
ProMedica doesn’t require employees to be vaccinated against flu, but employees who decline must get a note from a doctor indicating that they have talked about the risks and benefits of the vaccine. A similar approach may be used with a COVID-19 vaccine, in which employees may be required to learn about the vaccine before they decline, Smith says. “I do believe some people will say they don’t want to get it,” he added.
Like colleagues across the country, Smith is identifying healthcare workers who are involved in direct care of COVID-19 patients and are at highest risk for exposure. Even within the top tier, those performing the riskiest tasks, such as respiratory therapists who provide breathing treatments that spread aerosols and droplets, will be tagged as a priority group, he says. Healthcare workers who spend the most time in proximity to COVID patients, such as nurses in a COVID unit, also are likely to get the first doses, he says.
Swirl, don’t shake, the vaccine
Hospitals are adept at ramping up vaccination campaigns. For example, last year, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, in Nashville, Tennessee, vaccinated nearly 16,000 employees against influenza in their 1-day “Flulapalooza” event. The medical center even earned a Guinness world record in 2011 at the first Flulapalooza for giving the most vaccinations ever within 8 hours.
The 10th anniversary of the event was canceled this year because of COVID restrictions. Instead, nurses, pharmacists, and other clinicians pitched in to vaccinate their coworkers against influenza. Now, plans for COVID-19 vaccination move forward amid uncertainty.
Instead of holding a mass event, “the delivery mechanisms will need to be more targeted and focused,” said Lori Rolando, MD, MPH, director of the Vanderbilt Occupational Health Clinic. In the CDC’s most recent version of its vaccination program “playbook,” the agency recommends giving the vaccines in an area that allows people to remain 6 feet apart and for them to wait for 15 minutes after receiving the shot to make sure they don’t faint, a potential risk common to almost all vaccines.
That’s the easy part. Planning becomes more complex, given the uncertainty as to which vaccines will receive approval and which one a hospital will receive.
If the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine receives EUA in 2020, about 10 to 20 million doses could be available in November and 20 to 30 million doses in December. The ultracold containers used to ship the vaccines have to be replenished with dry ice within 24 hours of receipt and every 5 days thereafter. Hospitals will need temperature probes to monitor storage in the containers. The five-dose vials can be refrigerated before administering, but only for 5 days. The product must be diluted, and it then must be used within 6 hours.
The Moderna vaccine will be somewhat less plentiful at first. About 10 million doses are expected in November and 15 million doses by the end of December. The 10-dose vials are stored in a freezer. Once they are placed in a refrigerator to thaw, they have to be used within 7 days, and once they’re removed from the refrigerator, they have to be used within 12 hours. The pharmacist or other vaccinator must swirl – but not shake! – the vial before delivering a dose, according to the CDC playbook.
As more information emerges about the vaccines, instructions may change, and Smith is steeled for shifting scenarios. “These are all draft plans. We’re going to modify as we go along,” he says.
The Pfizer vaccine requires a second dose at 21 days, and the Moderna vaccine targets the second dose at 28 days. In addition to using information systems to track vaccinations and any adverse effects, hospitals will give employees a card indicating what vaccine they received, the date it was administered, and the date on which they need to return. (At this point, the time frame for the second dose doesn’t appear to be flexible.)
Regardless of the vaccine, one message stays the same: COVID precautions must continue. That means mask wearing, social distancing, and hand washing – practices that also must be followed by healthcare workers who test positive for naturally acquired antibodies.
“I don’t think anyone expects the COVID vaccine to be 100% effective at preventing COVID,” says Rolando. “So all of the other tools in our toolbox are going to need to be continued to be used as well.”
*Correction, 11/12/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the name of Dr. Drees' institution.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
United States adds nearly 74,000 more children with COVID-19
The new weekly high for COVID-19 cases in children announced last week has been surpassed already, as the United States experienced almost 74,000 new pediatric cases for the week ending Nov. 5, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
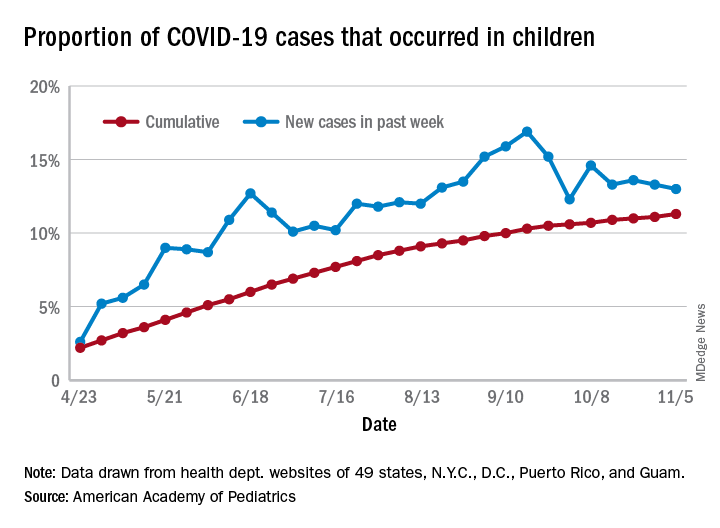
The total number of COVID-19 cases in children is now 927,518 in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report.
Cumulatively, children represent 11.3% of all COVID-19 cases in those jurisdictions, up from 11.1% a week ago. For just the past week, those 73,883 children represent 13.0% of the 567,672 new cases reported among all ages. That proportion peaked at 16.9% in mid-September, the AAP/CHA data show.
Dropping down to the state level, cumulative proportions as of Nov. 5 range from 5.2% in New Jersey to 23.3% in Wyoming, with 11 other states over 15%. California has had more cases, 100,856, than any other state, and Vermont the fewest at 329, the AAP and CHA said.
The national rate per 100,000 children is now 1,232, up from 1,134 the previous week and more than doubled since mid-August (582.2 per 100,000 on Aug. 20). North Dakota’s rate of 3,990 per 100,000 children is the highest of any state (South Dakota is next at 2,779), while Vermont is again the lowest at 245 per 100,000, based on data collected from state health department websites.
Two COVID-19–related deaths in children were reported during the week ending Nov. 5, bringing the total to 123 but leaving the overall proportion of deaths in children unchanged at 0.06% of all deaths. Texas has reported the most COVID-19 deaths in children with 29, while 15 states have recorded no deaths so far (mortality data in children reported by 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA said.
The new weekly high for COVID-19 cases in children announced last week has been surpassed already, as the United States experienced almost 74,000 new pediatric cases for the week ending Nov. 5, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of COVID-19 cases in children is now 927,518 in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report.
Cumulatively, children represent 11.3% of all COVID-19 cases in those jurisdictions, up from 11.1% a week ago. For just the past week, those 73,883 children represent 13.0% of the 567,672 new cases reported among all ages. That proportion peaked at 16.9% in mid-September, the AAP/CHA data show.
Dropping down to the state level, cumulative proportions as of Nov. 5 range from 5.2% in New Jersey to 23.3% in Wyoming, with 11 other states over 15%. California has had more cases, 100,856, than any other state, and Vermont the fewest at 329, the AAP and CHA said.
The national rate per 100,000 children is now 1,232, up from 1,134 the previous week and more than doubled since mid-August (582.2 per 100,000 on Aug. 20). North Dakota’s rate of 3,990 per 100,000 children is the highest of any state (South Dakota is next at 2,779), while Vermont is again the lowest at 245 per 100,000, based on data collected from state health department websites.
Two COVID-19–related deaths in children were reported during the week ending Nov. 5, bringing the total to 123 but leaving the overall proportion of deaths in children unchanged at 0.06% of all deaths. Texas has reported the most COVID-19 deaths in children with 29, while 15 states have recorded no deaths so far (mortality data in children reported by 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA said.
The new weekly high for COVID-19 cases in children announced last week has been surpassed already, as the United States experienced almost 74,000 new pediatric cases for the week ending Nov. 5, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of COVID-19 cases in children is now 927,518 in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report.
Cumulatively, children represent 11.3% of all COVID-19 cases in those jurisdictions, up from 11.1% a week ago. For just the past week, those 73,883 children represent 13.0% of the 567,672 new cases reported among all ages. That proportion peaked at 16.9% in mid-September, the AAP/CHA data show.
Dropping down to the state level, cumulative proportions as of Nov. 5 range from 5.2% in New Jersey to 23.3% in Wyoming, with 11 other states over 15%. California has had more cases, 100,856, than any other state, and Vermont the fewest at 329, the AAP and CHA said.
The national rate per 100,000 children is now 1,232, up from 1,134 the previous week and more than doubled since mid-August (582.2 per 100,000 on Aug. 20). North Dakota’s rate of 3,990 per 100,000 children is the highest of any state (South Dakota is next at 2,779), while Vermont is again the lowest at 245 per 100,000, based on data collected from state health department websites.
Two COVID-19–related deaths in children were reported during the week ending Nov. 5, bringing the total to 123 but leaving the overall proportion of deaths in children unchanged at 0.06% of all deaths. Texas has reported the most COVID-19 deaths in children with 29, while 15 states have recorded no deaths so far (mortality data in children reported by 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA said.
Food insecurity called urgent issue you must address
and advocate on behalf of those experiencing or at risk of food insecurity, according to Kofi Essel, MD, MPH, a pediatrician at Children’s National Hospital in Washington.
More than one in four adults are dealing with food access hardships during the pandemic, Dr. Essel said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Food insecurity is often interchangeable with hunger and refers to limited or uncertain availability of foods that are nutritious and safe.
“Food insecurity is as much about the threat of deprivation as it is about deprivation itself: A food-insecure life means a life lived in fear of hunger, and the psychological toll that takes,” according to a 2020 New York Times photo feature on food insecurity by Brenda Ann Kenneally that Dr. Essel quoted.
The lived experience of food insecure households includes food anxiety, a preoccupation with being able to get enough food that takes up cognitive bandwidth and prevents people from being able to focus on other important things. Another feature of food-insecure homes is a monotony of diet, which often involves an increase in caloric density and decrease in nutritional quality. As food insecurity grows more dire, adults’ food intake decreases, and then children’s intake decreases as adults seek out any way to get food, including “socially unacceptable” ways, which can include food pantries and bartering for food.
Food insecurity is associated with a wide range of negative outcomes even after accounting for other confounders, including decreased overall health, mental health, and educational outcomes. It’s also associated with an increase in developmental delays, hospitalizations, iron deficiency, asthma, and birth defects, among other problems. Somewhat paradoxically, it’s associated with both an increase and a decrease in obesity in the research.
Megan J. Gray, MD, MPH, assistant professor of pediatrics and population health at Dell Medical School at the The University of Texas at Austin, attended Dr. Essel’s session because food insecurity during COVID-19 now affects about half her patients, according to screening research she’s conducted.
“I wanted to learn more about the nuances of screening and using language and talking points that are helpful with families and with staff in building a culture of discussing food insecurity in our clinics,” Dr. Gray said in an interview. “What I’ve learned in my clinic is that if we don’t ask about it, families aren’t telling us – food insecurity is hiding in plain sight.”
She particularly appreciated Dr. Essel’s slides on the progression of food insecurity and how they acknowledged the mental health burden of food insecurity among parents.
“Right now during COVID-19, I see more patients I would call ‘socially complex’ rather than ‘medically complex,’ ” she said. “We all need to get a crash course in social work and Dr. Essel’s presentation is a great starting place.”
Screening for food insecurity
Beginning in 2015, an AAP policy statement charged pediatricians to “screen and intervene” with regard to food insecurity and their patients, Dr. Essel said. The statement also called for pediatricians to advocate for programs and policies that end childhood food insecurity.
The policy statement recommended a validated two-question screening tool called the Hunger Vital Sign:
1. “Within the past 12 months, we worried whether our food would run out before we got money to buy more.”
2. “Within the past 12 months, the food that we bought just didn’t last and we didn’t have money to get more.”
But in screening, you need to be conscious of how dignity intersects with food insecurity concerns, Dr. Essel said.
“We need to create dignity for our families,” he said. “We need to create a safe environment for our families and use appropriate tools when necessary to be able to identify families that are struggling with food insecurity.”
That need is seen in research on food screening. The Hunger Vital Signs questions can be asked with a dichotomous variable, as a yes/no question, or on a Likert scale, though the latter is a more complex way to ask.
A 2017 study found, however, that asking with “yes/no” answers missed more than a quarter of at-risk families. In the AAP survey using “yes/no” answers, 31% of families screened positive for being at risk of food insecurity, compared with 46% when the same question was asked on a Likert scale. It seems the ability to answer with “sometimes” feels “safer” than answering “yes,” Dr. Essel said.
Another factor that potentially affects answers is how doctors ask. In a March 2020 study at a single primary care practice, 16% of families screened positive with yes/no responses to a food insecurity screen when the questions were written, compared with 10% of positive screens with verbal responses (P < .001).
Epidemiology of food insecurity
The most updated United States Department of Agriculture report on food insecurity released in September shows the United States finally reached prerecession levels in 2019, with 11% of families designated as “food insecure.” But 2019 data cannot show what has occurred since the pandemic.
Further, the numbers are higher in households with children: Fourteen percent, or one in seven households with children, are experiencing food insecurity. Racial and ethnic disparities in food insecurity have remained consistent over the past 2 decades, with about twice as many Black and Hispanic homes experiencing food insecurity as White homes.
More recent research using Census Household Pulse Surveys has found a tremendous increase in food insecurity for children in 2020. One in three Black children and one in four Hispanic children are food insecure, according to these surveys. The rates are one in six for Asian households and one in ten for White households.
“The disparity is consistent,” Dr. Essel said. “We see what COVID has done. We once may have described it as a great equalizer – everyone is touched in the same way – but the reality is, this is actually a great magnifier. It’s revealing to us and magnifying disparities that have existed for far too long and has really allowed us to see it in a new way.”
A big part of disparities in food insecurity is disparities in wealth, “the safety net or cushion for families when things go wrong,” Dr. Essel said. The median wealth of White Americans in 2016 was $171,000, compared to $20,700 among Latinx Americans and $17,600 among Black Americans, according to the Federal Reserve Board Survey of Consumer Finances.
Food insecurity interventions
Federal nutrition programs – such as Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC), and school meal programs – are key to addressing food insecurity, Dr. Essel said.
“They have a long track record of rescuing families out of poverty, of rescuing families from food security and improving overall health of families,” he said.
But emergency food relief programs are important as well. Four in 10 families currently coming into food pantries are new recipients, and these resources have seen a 60% increase in clients, he said.
“This is utterly unreasonable for them to be able to manage,” he said. “Food pantries are essential but inadequate to compensate for large numbers of families,” even while they also may be the only option for families unable or unwilling to access federal programs. For example, for every one meal that food banks can provide, SNAP can provide nine meals, Dr. Essel said. Further, during times of economic downtown, every SNAP $1 spent generates $1.50 to $2 in economic activity.
Currently, the Pandemic Electronic Benefit Transfer (P-EBT) program provides benefits to families for school breakfast and lunch and has been extended through December 2021. Another federal pandemic response was to increase SNAP to the maximum household benefit for families, about $646 for a family of four, although 40% of households were already receiving the maximum benefit.
Food insecurity advocacy
You can advocate for any one of multiple pillars when it comes to food insecurity, Dr. Essel said. “Food cannot solve food insecurity by itself,” he said. “We have to think about root causes – systemic causes – and think about unemployment, livable wage, systemic racism, oppression, an inequitable food system. All of these things are pillars that any of you can advocate for when recognizing a family that is struggling with food insecurity.”
He offered several suggestions for advocacy:
- Join your local AAP chapter and prioritize food insecurity.
- Join a local antihunger task force.
- Make your clinical environment as safe as possible for families to respond to questions about food insecurity.
- Know what’s happening in your community immigrant populations.
- Provide up-to-date information to families about eligibility for federal programs.
- Share stories through op-eds and letters to the editor, and by contacting congressional representatives and providing expert testimony to school boards and city councils.
- Educate others about food insecurity through the above channels and on social media.
Jessica Lazerov, MD, a general pediatrician at Children’s National Anacostia and assistant professor of pediatrics at George Washington University, Washington, said the session was fantastic.
“Dr. Essel went beyond the basics of food insecurity, delving into the root causes, potential solutions, and important considerations when screening for food insecurity in practice,” Dr. Lazerov said in an interview. “I enjoyed his focus on advocacy, as well as the fact that he spent a bit of time reviewing how the COVID pandemic has affected food insecurity. I truly felt empowered to take my advocacy efforts a step further as Dr. Essel laid out concrete, actionable next steps, as well as a review of the most relevant and current information about food insecurity.”
Dr. Essel, Dr. Lazerov, and Dr. Gray have no relevant financial disclosures.
and advocate on behalf of those experiencing or at risk of food insecurity, according to Kofi Essel, MD, MPH, a pediatrician at Children’s National Hospital in Washington.
More than one in four adults are dealing with food access hardships during the pandemic, Dr. Essel said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Food insecurity is often interchangeable with hunger and refers to limited or uncertain availability of foods that are nutritious and safe.
“Food insecurity is as much about the threat of deprivation as it is about deprivation itself: A food-insecure life means a life lived in fear of hunger, and the psychological toll that takes,” according to a 2020 New York Times photo feature on food insecurity by Brenda Ann Kenneally that Dr. Essel quoted.
The lived experience of food insecure households includes food anxiety, a preoccupation with being able to get enough food that takes up cognitive bandwidth and prevents people from being able to focus on other important things. Another feature of food-insecure homes is a monotony of diet, which often involves an increase in caloric density and decrease in nutritional quality. As food insecurity grows more dire, adults’ food intake decreases, and then children’s intake decreases as adults seek out any way to get food, including “socially unacceptable” ways, which can include food pantries and bartering for food.
Food insecurity is associated with a wide range of negative outcomes even after accounting for other confounders, including decreased overall health, mental health, and educational outcomes. It’s also associated with an increase in developmental delays, hospitalizations, iron deficiency, asthma, and birth defects, among other problems. Somewhat paradoxically, it’s associated with both an increase and a decrease in obesity in the research.
Megan J. Gray, MD, MPH, assistant professor of pediatrics and population health at Dell Medical School at the The University of Texas at Austin, attended Dr. Essel’s session because food insecurity during COVID-19 now affects about half her patients, according to screening research she’s conducted.
“I wanted to learn more about the nuances of screening and using language and talking points that are helpful with families and with staff in building a culture of discussing food insecurity in our clinics,” Dr. Gray said in an interview. “What I’ve learned in my clinic is that if we don’t ask about it, families aren’t telling us – food insecurity is hiding in plain sight.”
She particularly appreciated Dr. Essel’s slides on the progression of food insecurity and how they acknowledged the mental health burden of food insecurity among parents.
“Right now during COVID-19, I see more patients I would call ‘socially complex’ rather than ‘medically complex,’ ” she said. “We all need to get a crash course in social work and Dr. Essel’s presentation is a great starting place.”
Screening for food insecurity
Beginning in 2015, an AAP policy statement charged pediatricians to “screen and intervene” with regard to food insecurity and their patients, Dr. Essel said. The statement also called for pediatricians to advocate for programs and policies that end childhood food insecurity.
The policy statement recommended a validated two-question screening tool called the Hunger Vital Sign:
1. “Within the past 12 months, we worried whether our food would run out before we got money to buy more.”
2. “Within the past 12 months, the food that we bought just didn’t last and we didn’t have money to get more.”
But in screening, you need to be conscious of how dignity intersects with food insecurity concerns, Dr. Essel said.
“We need to create dignity for our families,” he said. “We need to create a safe environment for our families and use appropriate tools when necessary to be able to identify families that are struggling with food insecurity.”
That need is seen in research on food screening. The Hunger Vital Signs questions can be asked with a dichotomous variable, as a yes/no question, or on a Likert scale, though the latter is a more complex way to ask.
A 2017 study found, however, that asking with “yes/no” answers missed more than a quarter of at-risk families. In the AAP survey using “yes/no” answers, 31% of families screened positive for being at risk of food insecurity, compared with 46% when the same question was asked on a Likert scale. It seems the ability to answer with “sometimes” feels “safer” than answering “yes,” Dr. Essel said.
Another factor that potentially affects answers is how doctors ask. In a March 2020 study at a single primary care practice, 16% of families screened positive with yes/no responses to a food insecurity screen when the questions were written, compared with 10% of positive screens with verbal responses (P < .001).
Epidemiology of food insecurity
The most updated United States Department of Agriculture report on food insecurity released in September shows the United States finally reached prerecession levels in 2019, with 11% of families designated as “food insecure.” But 2019 data cannot show what has occurred since the pandemic.
Further, the numbers are higher in households with children: Fourteen percent, or one in seven households with children, are experiencing food insecurity. Racial and ethnic disparities in food insecurity have remained consistent over the past 2 decades, with about twice as many Black and Hispanic homes experiencing food insecurity as White homes.
More recent research using Census Household Pulse Surveys has found a tremendous increase in food insecurity for children in 2020. One in three Black children and one in four Hispanic children are food insecure, according to these surveys. The rates are one in six for Asian households and one in ten for White households.
“The disparity is consistent,” Dr. Essel said. “We see what COVID has done. We once may have described it as a great equalizer – everyone is touched in the same way – but the reality is, this is actually a great magnifier. It’s revealing to us and magnifying disparities that have existed for far too long and has really allowed us to see it in a new way.”
A big part of disparities in food insecurity is disparities in wealth, “the safety net or cushion for families when things go wrong,” Dr. Essel said. The median wealth of White Americans in 2016 was $171,000, compared to $20,700 among Latinx Americans and $17,600 among Black Americans, according to the Federal Reserve Board Survey of Consumer Finances.
Food insecurity interventions
Federal nutrition programs – such as Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC), and school meal programs – are key to addressing food insecurity, Dr. Essel said.
“They have a long track record of rescuing families out of poverty, of rescuing families from food security and improving overall health of families,” he said.
But emergency food relief programs are important as well. Four in 10 families currently coming into food pantries are new recipients, and these resources have seen a 60% increase in clients, he said.
“This is utterly unreasonable for them to be able to manage,” he said. “Food pantries are essential but inadequate to compensate for large numbers of families,” even while they also may be the only option for families unable or unwilling to access federal programs. For example, for every one meal that food banks can provide, SNAP can provide nine meals, Dr. Essel said. Further, during times of economic downtown, every SNAP $1 spent generates $1.50 to $2 in economic activity.
Currently, the Pandemic Electronic Benefit Transfer (P-EBT) program provides benefits to families for school breakfast and lunch and has been extended through December 2021. Another federal pandemic response was to increase SNAP to the maximum household benefit for families, about $646 for a family of four, although 40% of households were already receiving the maximum benefit.
Food insecurity advocacy
You can advocate for any one of multiple pillars when it comes to food insecurity, Dr. Essel said. “Food cannot solve food insecurity by itself,” he said. “We have to think about root causes – systemic causes – and think about unemployment, livable wage, systemic racism, oppression, an inequitable food system. All of these things are pillars that any of you can advocate for when recognizing a family that is struggling with food insecurity.”
He offered several suggestions for advocacy:
- Join your local AAP chapter and prioritize food insecurity.
- Join a local antihunger task force.
- Make your clinical environment as safe as possible for families to respond to questions about food insecurity.
- Know what’s happening in your community immigrant populations.
- Provide up-to-date information to families about eligibility for federal programs.
- Share stories through op-eds and letters to the editor, and by contacting congressional representatives and providing expert testimony to school boards and city councils.
- Educate others about food insecurity through the above channels and on social media.
Jessica Lazerov, MD, a general pediatrician at Children’s National Anacostia and assistant professor of pediatrics at George Washington University, Washington, said the session was fantastic.
“Dr. Essel went beyond the basics of food insecurity, delving into the root causes, potential solutions, and important considerations when screening for food insecurity in practice,” Dr. Lazerov said in an interview. “I enjoyed his focus on advocacy, as well as the fact that he spent a bit of time reviewing how the COVID pandemic has affected food insecurity. I truly felt empowered to take my advocacy efforts a step further as Dr. Essel laid out concrete, actionable next steps, as well as a review of the most relevant and current information about food insecurity.”
Dr. Essel, Dr. Lazerov, and Dr. Gray have no relevant financial disclosures.
and advocate on behalf of those experiencing or at risk of food insecurity, according to Kofi Essel, MD, MPH, a pediatrician at Children’s National Hospital in Washington.
More than one in four adults are dealing with food access hardships during the pandemic, Dr. Essel said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Food insecurity is often interchangeable with hunger and refers to limited or uncertain availability of foods that are nutritious and safe.
“Food insecurity is as much about the threat of deprivation as it is about deprivation itself: A food-insecure life means a life lived in fear of hunger, and the psychological toll that takes,” according to a 2020 New York Times photo feature on food insecurity by Brenda Ann Kenneally that Dr. Essel quoted.
The lived experience of food insecure households includes food anxiety, a preoccupation with being able to get enough food that takes up cognitive bandwidth and prevents people from being able to focus on other important things. Another feature of food-insecure homes is a monotony of diet, which often involves an increase in caloric density and decrease in nutritional quality. As food insecurity grows more dire, adults’ food intake decreases, and then children’s intake decreases as adults seek out any way to get food, including “socially unacceptable” ways, which can include food pantries and bartering for food.
Food insecurity is associated with a wide range of negative outcomes even after accounting for other confounders, including decreased overall health, mental health, and educational outcomes. It’s also associated with an increase in developmental delays, hospitalizations, iron deficiency, asthma, and birth defects, among other problems. Somewhat paradoxically, it’s associated with both an increase and a decrease in obesity in the research.
Megan J. Gray, MD, MPH, assistant professor of pediatrics and population health at Dell Medical School at the The University of Texas at Austin, attended Dr. Essel’s session because food insecurity during COVID-19 now affects about half her patients, according to screening research she’s conducted.
“I wanted to learn more about the nuances of screening and using language and talking points that are helpful with families and with staff in building a culture of discussing food insecurity in our clinics,” Dr. Gray said in an interview. “What I’ve learned in my clinic is that if we don’t ask about it, families aren’t telling us – food insecurity is hiding in plain sight.”
She particularly appreciated Dr. Essel’s slides on the progression of food insecurity and how they acknowledged the mental health burden of food insecurity among parents.
“Right now during COVID-19, I see more patients I would call ‘socially complex’ rather than ‘medically complex,’ ” she said. “We all need to get a crash course in social work and Dr. Essel’s presentation is a great starting place.”
Screening for food insecurity
Beginning in 2015, an AAP policy statement charged pediatricians to “screen and intervene” with regard to food insecurity and their patients, Dr. Essel said. The statement also called for pediatricians to advocate for programs and policies that end childhood food insecurity.
The policy statement recommended a validated two-question screening tool called the Hunger Vital Sign:
1. “Within the past 12 months, we worried whether our food would run out before we got money to buy more.”
2. “Within the past 12 months, the food that we bought just didn’t last and we didn’t have money to get more.”
But in screening, you need to be conscious of how dignity intersects with food insecurity concerns, Dr. Essel said.
“We need to create dignity for our families,” he said. “We need to create a safe environment for our families and use appropriate tools when necessary to be able to identify families that are struggling with food insecurity.”
That need is seen in research on food screening. The Hunger Vital Signs questions can be asked with a dichotomous variable, as a yes/no question, or on a Likert scale, though the latter is a more complex way to ask.
A 2017 study found, however, that asking with “yes/no” answers missed more than a quarter of at-risk families. In the AAP survey using “yes/no” answers, 31% of families screened positive for being at risk of food insecurity, compared with 46% when the same question was asked on a Likert scale. It seems the ability to answer with “sometimes” feels “safer” than answering “yes,” Dr. Essel said.
Another factor that potentially affects answers is how doctors ask. In a March 2020 study at a single primary care practice, 16% of families screened positive with yes/no responses to a food insecurity screen when the questions were written, compared with 10% of positive screens with verbal responses (P < .001).
Epidemiology of food insecurity
The most updated United States Department of Agriculture report on food insecurity released in September shows the United States finally reached prerecession levels in 2019, with 11% of families designated as “food insecure.” But 2019 data cannot show what has occurred since the pandemic.
Further, the numbers are higher in households with children: Fourteen percent, or one in seven households with children, are experiencing food insecurity. Racial and ethnic disparities in food insecurity have remained consistent over the past 2 decades, with about twice as many Black and Hispanic homes experiencing food insecurity as White homes.
More recent research using Census Household Pulse Surveys has found a tremendous increase in food insecurity for children in 2020. One in three Black children and one in four Hispanic children are food insecure, according to these surveys. The rates are one in six for Asian households and one in ten for White households.
“The disparity is consistent,” Dr. Essel said. “We see what COVID has done. We once may have described it as a great equalizer – everyone is touched in the same way – but the reality is, this is actually a great magnifier. It’s revealing to us and magnifying disparities that have existed for far too long and has really allowed us to see it in a new way.”
A big part of disparities in food insecurity is disparities in wealth, “the safety net or cushion for families when things go wrong,” Dr. Essel said. The median wealth of White Americans in 2016 was $171,000, compared to $20,700 among Latinx Americans and $17,600 among Black Americans, according to the Federal Reserve Board Survey of Consumer Finances.
Food insecurity interventions
Federal nutrition programs – such as Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC), and school meal programs – are key to addressing food insecurity, Dr. Essel said.
“They have a long track record of rescuing families out of poverty, of rescuing families from food security and improving overall health of families,” he said.
But emergency food relief programs are important as well. Four in 10 families currently coming into food pantries are new recipients, and these resources have seen a 60% increase in clients, he said.
“This is utterly unreasonable for them to be able to manage,” he said. “Food pantries are essential but inadequate to compensate for large numbers of families,” even while they also may be the only option for families unable or unwilling to access federal programs. For example, for every one meal that food banks can provide, SNAP can provide nine meals, Dr. Essel said. Further, during times of economic downtown, every SNAP $1 spent generates $1.50 to $2 in economic activity.
Currently, the Pandemic Electronic Benefit Transfer (P-EBT) program provides benefits to families for school breakfast and lunch and has been extended through December 2021. Another federal pandemic response was to increase SNAP to the maximum household benefit for families, about $646 for a family of four, although 40% of households were already receiving the maximum benefit.
Food insecurity advocacy
You can advocate for any one of multiple pillars when it comes to food insecurity, Dr. Essel said. “Food cannot solve food insecurity by itself,” he said. “We have to think about root causes – systemic causes – and think about unemployment, livable wage, systemic racism, oppression, an inequitable food system. All of these things are pillars that any of you can advocate for when recognizing a family that is struggling with food insecurity.”
He offered several suggestions for advocacy:
- Join your local AAP chapter and prioritize food insecurity.
- Join a local antihunger task force.
- Make your clinical environment as safe as possible for families to respond to questions about food insecurity.
- Know what’s happening in your community immigrant populations.
- Provide up-to-date information to families about eligibility for federal programs.
- Share stories through op-eds and letters to the editor, and by contacting congressional representatives and providing expert testimony to school boards and city councils.
- Educate others about food insecurity through the above channels and on social media.
Jessica Lazerov, MD, a general pediatrician at Children’s National Anacostia and assistant professor of pediatrics at George Washington University, Washington, said the session was fantastic.
“Dr. Essel went beyond the basics of food insecurity, delving into the root causes, potential solutions, and important considerations when screening for food insecurity in practice,” Dr. Lazerov said in an interview. “I enjoyed his focus on advocacy, as well as the fact that he spent a bit of time reviewing how the COVID pandemic has affected food insecurity. I truly felt empowered to take my advocacy efforts a step further as Dr. Essel laid out concrete, actionable next steps, as well as a review of the most relevant and current information about food insecurity.”
Dr. Essel, Dr. Lazerov, and Dr. Gray have no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AAP 2020
Whales, seals, and dolphins: Will SARS-CoV-2–contaminated wastewater prove a killer?
Zoonoses are no respecter of biological boundaries and are notorious for crossing genus and even higher taxonomic boundaries. SARS-CoV-2 is no exception, the current outbreak most probably having originated in bats, a common source of human-affecting zoonoses throughout history. But it is not a one-way street, and the virus has been shown to spread from infected humans to a variety of other land mammals, including our domesticated animals and kept zoo species.
A recent troubling report, however, has indicated that sea mammals may be part of a next wave of likely candidates for infection, put at risk by the current human pandemic and environmental degradation on a global scale, according to a the results of a genomic analysis of four major groups of sea mammals.
Researchers Sabateeshan Mathavarajah and colleagues from Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., examined the sequences of the ACE2 receptors in the various marine mammal species. The ACE2 receptor has recently been identified as the SARS-CoV-2 receptor, which allows for infection.
The researchers examined genomic databases of the marine species to determine if their ACE2 receptor sequences indicated the potential for high, medium, or low susceptibility to infection, as reported in Science of the Total Environment. Database analysis was performed for four groups: Cetacea (whales and dolphins), Pinnepidia (seals), Sirenia (sea cows), and Fissipedia (sea otters and polar bears).
The researchers defined susceptibility values based on comparable binding with the receptor and came up with the following subgroups: higher than human, high (resembles human ACE2), medium (resembles cat ACE2), and low (resembles dog ACE2). It has yet to be established if these marine mammals actually are infected with SARS-CoV-2 and what the impact of such an infection might have on animal health or humans who come in contact with infected animals.
They also cross-referenced for the level of species endangerment and with maps of potential wastewater contamination for certain areas that species came in contact with, using Alaska as the model.
Populations in danger
The researchers found 15 species that are already at risk globally that fall under the categories of near threatened, vulnerable, endangered, and critically endangered that were predicted to be medium to higher susceptibility to the SARS-CoV-2 virus than humans. Cross infection is of particular concern because other coronaviruses have been shown to have severe and lethal effects among many of these species.
Among the potentially impacted species were the near threatened–status Antarctic Mink whale and the stellar sea lion; the vulnerable sperm whale, northern fur seal, and Atlantic walrus; the endangered northern and southern sea otters, the North Pacific right whale, and the Amazon River dolphin; and the critically threatened Baiji and Vaquita dolphin species.
Pollution risks
In Alaska, as of Aug. 7th, 2020, there were 4,221 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and this number continues to rise, according to the researchers. Since there is a diversity of marine mammals in Alaska and their populations are well documented, they compared this information with available data on the wastewater treatment plants in the state. They were thus able to determine the potential geographic locations and species at high risk for transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via wastewater effluent.
Among their findings, the city of Cold Bay discharges wastewater into Cold Bay, where there are Northern sea otter populations that are predicted to be highly susceptible to the virus. Beluga whales are also predicted to have high susceptibility and they can be found in Bristol Bay near Naknek, a city which relies only on lagoon treatment prior to the discharge of wastewater effluent; the city of Dillingham discharges wastewater into the Nushagak River where beluga whales are found. In Palmer, wastewater effluent flows into the Talkeetna River, which is a tributary to the Susitna River and home to two species predicted to have high susceptibility, beluga whales and harbor seals, the authors added.
Based on these results, the researchers predicted that there was likely a significant risk to sea mammals across the globe, especially where less-adequate treatment facilities and high population densities may lead to greater wastewater contamination.
“Given the proximity of marine animals to high-risk environments where viral spill over is likely, we must act with foresight to protect marine mammal species predicted to be at risk and mitigate the environmental impact of the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mathavarajah S et al. Sci Total Environ. 2020 Oct 29. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143346.
Zoonoses are no respecter of biological boundaries and are notorious for crossing genus and even higher taxonomic boundaries. SARS-CoV-2 is no exception, the current outbreak most probably having originated in bats, a common source of human-affecting zoonoses throughout history. But it is not a one-way street, and the virus has been shown to spread from infected humans to a variety of other land mammals, including our domesticated animals and kept zoo species.
A recent troubling report, however, has indicated that sea mammals may be part of a next wave of likely candidates for infection, put at risk by the current human pandemic and environmental degradation on a global scale, according to a the results of a genomic analysis of four major groups of sea mammals.
Researchers Sabateeshan Mathavarajah and colleagues from Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., examined the sequences of the ACE2 receptors in the various marine mammal species. The ACE2 receptor has recently been identified as the SARS-CoV-2 receptor, which allows for infection.
The researchers examined genomic databases of the marine species to determine if their ACE2 receptor sequences indicated the potential for high, medium, or low susceptibility to infection, as reported in Science of the Total Environment. Database analysis was performed for four groups: Cetacea (whales and dolphins), Pinnepidia (seals), Sirenia (sea cows), and Fissipedia (sea otters and polar bears).
The researchers defined susceptibility values based on comparable binding with the receptor and came up with the following subgroups: higher than human, high (resembles human ACE2), medium (resembles cat ACE2), and low (resembles dog ACE2). It has yet to be established if these marine mammals actually are infected with SARS-CoV-2 and what the impact of such an infection might have on animal health or humans who come in contact with infected animals.
They also cross-referenced for the level of species endangerment and with maps of potential wastewater contamination for certain areas that species came in contact with, using Alaska as the model.
Populations in danger
The researchers found 15 species that are already at risk globally that fall under the categories of near threatened, vulnerable, endangered, and critically endangered that were predicted to be medium to higher susceptibility to the SARS-CoV-2 virus than humans. Cross infection is of particular concern because other coronaviruses have been shown to have severe and lethal effects among many of these species.
Among the potentially impacted species were the near threatened–status Antarctic Mink whale and the stellar sea lion; the vulnerable sperm whale, northern fur seal, and Atlantic walrus; the endangered northern and southern sea otters, the North Pacific right whale, and the Amazon River dolphin; and the critically threatened Baiji and Vaquita dolphin species.
Pollution risks
In Alaska, as of Aug. 7th, 2020, there were 4,221 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and this number continues to rise, according to the researchers. Since there is a diversity of marine mammals in Alaska and their populations are well documented, they compared this information with available data on the wastewater treatment plants in the state. They were thus able to determine the potential geographic locations and species at high risk for transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via wastewater effluent.
Among their findings, the city of Cold Bay discharges wastewater into Cold Bay, where there are Northern sea otter populations that are predicted to be highly susceptible to the virus. Beluga whales are also predicted to have high susceptibility and they can be found in Bristol Bay near Naknek, a city which relies only on lagoon treatment prior to the discharge of wastewater effluent; the city of Dillingham discharges wastewater into the Nushagak River where beluga whales are found. In Palmer, wastewater effluent flows into the Talkeetna River, which is a tributary to the Susitna River and home to two species predicted to have high susceptibility, beluga whales and harbor seals, the authors added.
Based on these results, the researchers predicted that there was likely a significant risk to sea mammals across the globe, especially where less-adequate treatment facilities and high population densities may lead to greater wastewater contamination.
“Given the proximity of marine animals to high-risk environments where viral spill over is likely, we must act with foresight to protect marine mammal species predicted to be at risk and mitigate the environmental impact of the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mathavarajah S et al. Sci Total Environ. 2020 Oct 29. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143346.
Zoonoses are no respecter of biological boundaries and are notorious for crossing genus and even higher taxonomic boundaries. SARS-CoV-2 is no exception, the current outbreak most probably having originated in bats, a common source of human-affecting zoonoses throughout history. But it is not a one-way street, and the virus has been shown to spread from infected humans to a variety of other land mammals, including our domesticated animals and kept zoo species.
A recent troubling report, however, has indicated that sea mammals may be part of a next wave of likely candidates for infection, put at risk by the current human pandemic and environmental degradation on a global scale, according to a the results of a genomic analysis of four major groups of sea mammals.
Researchers Sabateeshan Mathavarajah and colleagues from Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., examined the sequences of the ACE2 receptors in the various marine mammal species. The ACE2 receptor has recently been identified as the SARS-CoV-2 receptor, which allows for infection.
The researchers examined genomic databases of the marine species to determine if their ACE2 receptor sequences indicated the potential for high, medium, or low susceptibility to infection, as reported in Science of the Total Environment. Database analysis was performed for four groups: Cetacea (whales and dolphins), Pinnepidia (seals), Sirenia (sea cows), and Fissipedia (sea otters and polar bears).
The researchers defined susceptibility values based on comparable binding with the receptor and came up with the following subgroups: higher than human, high (resembles human ACE2), medium (resembles cat ACE2), and low (resembles dog ACE2). It has yet to be established if these marine mammals actually are infected with SARS-CoV-2 and what the impact of such an infection might have on animal health or humans who come in contact with infected animals.
They also cross-referenced for the level of species endangerment and with maps of potential wastewater contamination for certain areas that species came in contact with, using Alaska as the model.
Populations in danger
The researchers found 15 species that are already at risk globally that fall under the categories of near threatened, vulnerable, endangered, and critically endangered that were predicted to be medium to higher susceptibility to the SARS-CoV-2 virus than humans. Cross infection is of particular concern because other coronaviruses have been shown to have severe and lethal effects among many of these species.
Among the potentially impacted species were the near threatened–status Antarctic Mink whale and the stellar sea lion; the vulnerable sperm whale, northern fur seal, and Atlantic walrus; the endangered northern and southern sea otters, the North Pacific right whale, and the Amazon River dolphin; and the critically threatened Baiji and Vaquita dolphin species.
Pollution risks
In Alaska, as of Aug. 7th, 2020, there were 4,221 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and this number continues to rise, according to the researchers. Since there is a diversity of marine mammals in Alaska and their populations are well documented, they compared this information with available data on the wastewater treatment plants in the state. They were thus able to determine the potential geographic locations and species at high risk for transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via wastewater effluent.
Among their findings, the city of Cold Bay discharges wastewater into Cold Bay, where there are Northern sea otter populations that are predicted to be highly susceptible to the virus. Beluga whales are also predicted to have high susceptibility and they can be found in Bristol Bay near Naknek, a city which relies only on lagoon treatment prior to the discharge of wastewater effluent; the city of Dillingham discharges wastewater into the Nushagak River where beluga whales are found. In Palmer, wastewater effluent flows into the Talkeetna River, which is a tributary to the Susitna River and home to two species predicted to have high susceptibility, beluga whales and harbor seals, the authors added.
Based on these results, the researchers predicted that there was likely a significant risk to sea mammals across the globe, especially where less-adequate treatment facilities and high population densities may lead to greater wastewater contamination.
“Given the proximity of marine animals to high-risk environments where viral spill over is likely, we must act with foresight to protect marine mammal species predicted to be at risk and mitigate the environmental impact of the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mathavarajah S et al. Sci Total Environ. 2020 Oct 29. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143346.
FROM SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT
Pfizer vaccine data show 90% efficacy in early results
A vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2 has been found to be 90% effective in preventing COVID-19 in trial volunteers who were without evidence of prior infection of the virus, results from an interim analysis of a phase 3 study demonstrated.
BTN162b2, a messenger RNA–based vaccine candidate that requires two doses, is being developed by Pfizer and BioNTech SE independently of the Trump administration’s Operation Warp Speed. A global phase 3 clinical trial of BTN162b2 began on July 27 and has enrolled 43,538 participants to date; 42% of enrollees have racially and ethnically diverse backgrounds.
According to a press release issued by the two companies, 38,955 trial volunteers had received a second dose of either vaccine or placebo as of Nov. 8. An interim analysis of 94 individuals conducted by an independent data monitoring committee (DMC) found that the vaccine efficacy rate was above 90% 7 days after the second dose. This means that protection was achieved 28 days after the first vaccine dose.
“It’s promising in that it validates the genetic strategy – whether it’s mRNA vaccines or DNA vaccines,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told Medscape Medical News. Offit is a member of the US Food and Drug Administraiton’s COVID-19 Vaccine Advisory Committee. “All of them have the same approach, which is that they introduce the gene that codes for the coronavirus spike protein into the cell. Your cell makes the spike protein, and your immune system makes antibodies to the spike protein. At least in these preliminary data, which involved 94 people getting sick, it looks like it’s effective. That’s good. We knew that it seemed to work in experimental animals, but you never know until you put it into people.”
According to Pfizer and BioNTech SE, a final data analysis is planned once 164 confirmed COVID-19 cases have accrued. So far, the DMC has not reported any serious safety concerns. It recommends that the study continue to collect safety and efficacy data as planned. The companies plan to apply to the FDA for emergency use authorization soon after the required safety milestone is achieved.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, added in a separate press release, “It’s important to note that we cannot apply for FDA Emergency Use Authorization based on these efficacy results alone. More data on safety is also needed, and we are continuing to accumulate that safety data as part of our ongoing clinical study.
“We estimate that a median of two months of safety data following the second and final dose of the vaccine candidate – required by FDA’s guidance for potential Emergency Use Authorization – will be available by the third week of November.”
Offit, professor of pediatrics in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said that, if BTN162b2 is approved, administering it will be tricky. “This particular vaccine has to be shipped and stored at –70° C or –80° C, which we’ve never done before in this country,” he said. “That means maintaining the product on dry ice. That’s going to be a challenge for distribution, I think.”
Good news, but…
In the press release, BioNTech SE’s cofounder and CEO, Ugur Sahin, MD, characterized the findings as “a victory for innovation, science and a global collaborative effort. When we embarked on this journey 10 months ago this is what we aspired to achieve. Especially today, while we are all in the midst of a second wave and many of us in lockdown, we appreciate even more how important this milestone is on our path towards ending this pandemic and for all of us to regain a sense of normality.”
President-elect Joe Biden also weighed in, calling the results “excellent news” in a news release.
“At the same time, it is also important to understand that the end of the battle against COVID-19 is still months away,” he said. “This news follows a previously announced timeline by industry officials that forecast vaccine approval by late November. Even if that is achieved, and some Americans are vaccinated later this year, it will be many more months before there is widespread vaccination in this country.
“Today’s news does not change this urgent reality. Americans will have to rely on masking, distancing, contact tracing, hand washing, and other measures to keep themselves safe well into next year,” Biden added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2 has been found to be 90% effective in preventing COVID-19 in trial volunteers who were without evidence of prior infection of the virus, results from an interim analysis of a phase 3 study demonstrated.
BTN162b2, a messenger RNA–based vaccine candidate that requires two doses, is being developed by Pfizer and BioNTech SE independently of the Trump administration’s Operation Warp Speed. A global phase 3 clinical trial of BTN162b2 began on July 27 and has enrolled 43,538 participants to date; 42% of enrollees have racially and ethnically diverse backgrounds.
According to a press release issued by the two companies, 38,955 trial volunteers had received a second dose of either vaccine or placebo as of Nov. 8. An interim analysis of 94 individuals conducted by an independent data monitoring committee (DMC) found that the vaccine efficacy rate was above 90% 7 days after the second dose. This means that protection was achieved 28 days after the first vaccine dose.
“It’s promising in that it validates the genetic strategy – whether it’s mRNA vaccines or DNA vaccines,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told Medscape Medical News. Offit is a member of the US Food and Drug Administraiton’s COVID-19 Vaccine Advisory Committee. “All of them have the same approach, which is that they introduce the gene that codes for the coronavirus spike protein into the cell. Your cell makes the spike protein, and your immune system makes antibodies to the spike protein. At least in these preliminary data, which involved 94 people getting sick, it looks like it’s effective. That’s good. We knew that it seemed to work in experimental animals, but you never know until you put it into people.”
According to Pfizer and BioNTech SE, a final data analysis is planned once 164 confirmed COVID-19 cases have accrued. So far, the DMC has not reported any serious safety concerns. It recommends that the study continue to collect safety and efficacy data as planned. The companies plan to apply to the FDA for emergency use authorization soon after the required safety milestone is achieved.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, added in a separate press release, “It’s important to note that we cannot apply for FDA Emergency Use Authorization based on these efficacy results alone. More data on safety is also needed, and we are continuing to accumulate that safety data as part of our ongoing clinical study.
“We estimate that a median of two months of safety data following the second and final dose of the vaccine candidate – required by FDA’s guidance for potential Emergency Use Authorization – will be available by the third week of November.”
Offit, professor of pediatrics in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said that, if BTN162b2 is approved, administering it will be tricky. “This particular vaccine has to be shipped and stored at –70° C or –80° C, which we’ve never done before in this country,” he said. “That means maintaining the product on dry ice. That’s going to be a challenge for distribution, I think.”
Good news, but…
In the press release, BioNTech SE’s cofounder and CEO, Ugur Sahin, MD, characterized the findings as “a victory for innovation, science and a global collaborative effort. When we embarked on this journey 10 months ago this is what we aspired to achieve. Especially today, while we are all in the midst of a second wave and many of us in lockdown, we appreciate even more how important this milestone is on our path towards ending this pandemic and for all of us to regain a sense of normality.”
President-elect Joe Biden also weighed in, calling the results “excellent news” in a news release.
“At the same time, it is also important to understand that the end of the battle against COVID-19 is still months away,” he said. “This news follows a previously announced timeline by industry officials that forecast vaccine approval by late November. Even if that is achieved, and some Americans are vaccinated later this year, it will be many more months before there is widespread vaccination in this country.
“Today’s news does not change this urgent reality. Americans will have to rely on masking, distancing, contact tracing, hand washing, and other measures to keep themselves safe well into next year,” Biden added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2 has been found to be 90% effective in preventing COVID-19 in trial volunteers who were without evidence of prior infection of the virus, results from an interim analysis of a phase 3 study demonstrated.
BTN162b2, a messenger RNA–based vaccine candidate that requires two doses, is being developed by Pfizer and BioNTech SE independently of the Trump administration’s Operation Warp Speed. A global phase 3 clinical trial of BTN162b2 began on July 27 and has enrolled 43,538 participants to date; 42% of enrollees have racially and ethnically diverse backgrounds.
According to a press release issued by the two companies, 38,955 trial volunteers had received a second dose of either vaccine or placebo as of Nov. 8. An interim analysis of 94 individuals conducted by an independent data monitoring committee (DMC) found that the vaccine efficacy rate was above 90% 7 days after the second dose. This means that protection was achieved 28 days after the first vaccine dose.
“It’s promising in that it validates the genetic strategy – whether it’s mRNA vaccines or DNA vaccines,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told Medscape Medical News. Offit is a member of the US Food and Drug Administraiton’s COVID-19 Vaccine Advisory Committee. “All of them have the same approach, which is that they introduce the gene that codes for the coronavirus spike protein into the cell. Your cell makes the spike protein, and your immune system makes antibodies to the spike protein. At least in these preliminary data, which involved 94 people getting sick, it looks like it’s effective. That’s good. We knew that it seemed to work in experimental animals, but you never know until you put it into people.”
According to Pfizer and BioNTech SE, a final data analysis is planned once 164 confirmed COVID-19 cases have accrued. So far, the DMC has not reported any serious safety concerns. It recommends that the study continue to collect safety and efficacy data as planned. The companies plan to apply to the FDA for emergency use authorization soon after the required safety milestone is achieved.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, added in a separate press release, “It’s important to note that we cannot apply for FDA Emergency Use Authorization based on these efficacy results alone. More data on safety is also needed, and we are continuing to accumulate that safety data as part of our ongoing clinical study.
“We estimate that a median of two months of safety data following the second and final dose of the vaccine candidate – required by FDA’s guidance for potential Emergency Use Authorization – will be available by the third week of November.”
Offit, professor of pediatrics in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said that, if BTN162b2 is approved, administering it will be tricky. “This particular vaccine has to be shipped and stored at –70° C or –80° C, which we’ve never done before in this country,” he said. “That means maintaining the product on dry ice. That’s going to be a challenge for distribution, I think.”
Good news, but…
In the press release, BioNTech SE’s cofounder and CEO, Ugur Sahin, MD, characterized the findings as “a victory for innovation, science and a global collaborative effort. When we embarked on this journey 10 months ago this is what we aspired to achieve. Especially today, while we are all in the midst of a second wave and many of us in lockdown, we appreciate even more how important this milestone is on our path towards ending this pandemic and for all of us to regain a sense of normality.”
President-elect Joe Biden also weighed in, calling the results “excellent news” in a news release.
“At the same time, it is also important to understand that the end of the battle against COVID-19 is still months away,” he said. “This news follows a previously announced timeline by industry officials that forecast vaccine approval by late November. Even if that is achieved, and some Americans are vaccinated later this year, it will be many more months before there is widespread vaccination in this country.
“Today’s news does not change this urgent reality. Americans will have to rely on masking, distancing, contact tracing, hand washing, and other measures to keep themselves safe well into next year,” Biden added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.

