User login
Family violence patterns change during pandemic
Among adolescents treated for injuries caused by family-member violence, the proportion of incidents that involved illegal drugs or weapons more than doubled during the pandemic, and incidents that involved alcohol nearly doubled, according to data presented October 10 at the American Academy of Pediatrics 2021 National Conference.
“The COVID-19 pandemic amplified risk factors known to increase family interpersonal violence, such as increased need for parental supervision, parental stress, financial hardship, poor mental health, and isolation,” said investigator Mattea Miller, an MD candidate at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore.
To examine the issue, she and her colleagues “sought to characterize the prevalence and circumstances of adolescent injuries resulting from family interpersonal violence,” Ms. Miller told this news organization.
Their retrospective analysis involved children 10 to 15 years of age seen before or during the pandemic in the emergency department at Johns Hopkins Children’s Center for injuries that resulted from a violent incident with a family member.
Of the 819 incidents of violence-related injuries seen during the study period – the prepandemic ran from Jan. 1, 2019 to March 29, 2020, and the pandemic period ran from March 30, 2020, the date a stay-at-home order was first issued in Maryland, to Dec. 31, 2020 – 448 (54.7%) involved a family member. The proportion of such injuries was similar before and during the pandemic (54.6% vs. 54.9%; P = .99).
Most (83.9%) of these incidents occurred at home, 76.6% involved a parent or guardian, and 66.7% involved the youth being transported to the hospital by police.
It is surprising that families accounted for such a high level of violence involving adolescents, said Christopher S. Greeley, MD, MS, chief of the division of public health pediatrics at Texas Children’s Hospital and professor of pediatrics at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who was not involved in the research.
“The most common source of child physical abuse in younger children – infants and toddlers – [is the] parents,” who account for about 75% of cases, “but to see that amount of violence in adolescents was unexpected,” he told this news organization.
Patients in the study cohort were more likely to be Black than the hospital’s overall emergency-department population (84.4% vs. 60.0%), and more likely to be covered by public insurance (71.2% vs. 60.0%).
In the study cohort, 54.0% of the patients were female.
“We were surprised to see that 8% of visits did not have a referral to a social worker” – 92% of patients in the study cohort received a social work consult during their visit to the emergency department – and that number “did not vary during the COVID-19 pandemic,” Ms. Miller said. The pandemic exacerbated the types of stresses that social workers can help address, so “this potentially represents a gap in care that is important to address,” she added.
Increase in use of alcohol, drugs, weapons
The most significant increases from the prepandemic period to the pandemic period were in incidents that involved alcohol (10.0% vs. 18.8%; P ≤ .001), illegal drugs (6.5% vs. 14.9%; P ≤ .001), and weapons, most often a knife (10.7% vs. 23.8%; P ≤ .001).
“An obvious potential explanation for the increase in alcohol, drug, and weapons [involvement] would be the mental health impact of the pandemic in conjunction with the economic stressors that some families may be feeling,” Dr. Greeley said. Teachers are the most common reporters of child abuse, so it’s possible that reports of violence decreased when schools switched to remote learning. But with most schools back to in-person learning, data have not yet shown a surge in reporting, he noted.
The “epidemiology of family violence may be impacted by increased time at home, disruptions in school and family routines, exacerbations in mental health conditions, and financial stresses common during the pandemic,” said senior study investigator Leticia Ryan, MD, MPH, director of research in pediatrics at Johns Hopkins Medicine.
And research has shown increases in the use of alcohol and illegal drugs during the pandemic, she noted.
“As we transition to postpandemic life, it will be important to identify at-risk adolescents and families and provide supports,” Dr. Ryan told this news organization. “The emergency department is an appropriate setting to intervene with youth who have experienced family violence and initiate preventive strategies to avoid future violence.”
Among the strategies to identify and intervene for at-risk patients is the CRAFFT substance use screening tool. Furthermore, “case management, involvement of child protection services, and linkage with relevant support services may all be appropriate, depending on circumstances,” Ms. Miller added.
“Exposure to family violence at a young age increases the likelihood that a child will be exposed to additional violence or become a perpetrator of violence in the future, continuing a cycle of violence,” Ms. Miller explained. “Given that studies of adolescent violence often focus on peer violence, a better understanding of the epidemiology of violence-related injuries resulting from family violence is needed to better inform the development of more comprehensive prevention strategies.”
This study did not note any external funding. Ms. Miller, Dr. Greeley, and Dr. Ryan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among adolescents treated for injuries caused by family-member violence, the proportion of incidents that involved illegal drugs or weapons more than doubled during the pandemic, and incidents that involved alcohol nearly doubled, according to data presented October 10 at the American Academy of Pediatrics 2021 National Conference.
“The COVID-19 pandemic amplified risk factors known to increase family interpersonal violence, such as increased need for parental supervision, parental stress, financial hardship, poor mental health, and isolation,” said investigator Mattea Miller, an MD candidate at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore.
To examine the issue, she and her colleagues “sought to characterize the prevalence and circumstances of adolescent injuries resulting from family interpersonal violence,” Ms. Miller told this news organization.
Their retrospective analysis involved children 10 to 15 years of age seen before or during the pandemic in the emergency department at Johns Hopkins Children’s Center for injuries that resulted from a violent incident with a family member.
Of the 819 incidents of violence-related injuries seen during the study period – the prepandemic ran from Jan. 1, 2019 to March 29, 2020, and the pandemic period ran from March 30, 2020, the date a stay-at-home order was first issued in Maryland, to Dec. 31, 2020 – 448 (54.7%) involved a family member. The proportion of such injuries was similar before and during the pandemic (54.6% vs. 54.9%; P = .99).
Most (83.9%) of these incidents occurred at home, 76.6% involved a parent or guardian, and 66.7% involved the youth being transported to the hospital by police.
It is surprising that families accounted for such a high level of violence involving adolescents, said Christopher S. Greeley, MD, MS, chief of the division of public health pediatrics at Texas Children’s Hospital and professor of pediatrics at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who was not involved in the research.
“The most common source of child physical abuse in younger children – infants and toddlers – [is the] parents,” who account for about 75% of cases, “but to see that amount of violence in adolescents was unexpected,” he told this news organization.
Patients in the study cohort were more likely to be Black than the hospital’s overall emergency-department population (84.4% vs. 60.0%), and more likely to be covered by public insurance (71.2% vs. 60.0%).
In the study cohort, 54.0% of the patients were female.
“We were surprised to see that 8% of visits did not have a referral to a social worker” – 92% of patients in the study cohort received a social work consult during their visit to the emergency department – and that number “did not vary during the COVID-19 pandemic,” Ms. Miller said. The pandemic exacerbated the types of stresses that social workers can help address, so “this potentially represents a gap in care that is important to address,” she added.
Increase in use of alcohol, drugs, weapons
The most significant increases from the prepandemic period to the pandemic period were in incidents that involved alcohol (10.0% vs. 18.8%; P ≤ .001), illegal drugs (6.5% vs. 14.9%; P ≤ .001), and weapons, most often a knife (10.7% vs. 23.8%; P ≤ .001).
“An obvious potential explanation for the increase in alcohol, drug, and weapons [involvement] would be the mental health impact of the pandemic in conjunction with the economic stressors that some families may be feeling,” Dr. Greeley said. Teachers are the most common reporters of child abuse, so it’s possible that reports of violence decreased when schools switched to remote learning. But with most schools back to in-person learning, data have not yet shown a surge in reporting, he noted.
The “epidemiology of family violence may be impacted by increased time at home, disruptions in school and family routines, exacerbations in mental health conditions, and financial stresses common during the pandemic,” said senior study investigator Leticia Ryan, MD, MPH, director of research in pediatrics at Johns Hopkins Medicine.
And research has shown increases in the use of alcohol and illegal drugs during the pandemic, she noted.
“As we transition to postpandemic life, it will be important to identify at-risk adolescents and families and provide supports,” Dr. Ryan told this news organization. “The emergency department is an appropriate setting to intervene with youth who have experienced family violence and initiate preventive strategies to avoid future violence.”
Among the strategies to identify and intervene for at-risk patients is the CRAFFT substance use screening tool. Furthermore, “case management, involvement of child protection services, and linkage with relevant support services may all be appropriate, depending on circumstances,” Ms. Miller added.
“Exposure to family violence at a young age increases the likelihood that a child will be exposed to additional violence or become a perpetrator of violence in the future, continuing a cycle of violence,” Ms. Miller explained. “Given that studies of adolescent violence often focus on peer violence, a better understanding of the epidemiology of violence-related injuries resulting from family violence is needed to better inform the development of more comprehensive prevention strategies.”
This study did not note any external funding. Ms. Miller, Dr. Greeley, and Dr. Ryan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among adolescents treated for injuries caused by family-member violence, the proportion of incidents that involved illegal drugs or weapons more than doubled during the pandemic, and incidents that involved alcohol nearly doubled, according to data presented October 10 at the American Academy of Pediatrics 2021 National Conference.
“The COVID-19 pandemic amplified risk factors known to increase family interpersonal violence, such as increased need for parental supervision, parental stress, financial hardship, poor mental health, and isolation,” said investigator Mattea Miller, an MD candidate at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore.
To examine the issue, she and her colleagues “sought to characterize the prevalence and circumstances of adolescent injuries resulting from family interpersonal violence,” Ms. Miller told this news organization.
Their retrospective analysis involved children 10 to 15 years of age seen before or during the pandemic in the emergency department at Johns Hopkins Children’s Center for injuries that resulted from a violent incident with a family member.
Of the 819 incidents of violence-related injuries seen during the study period – the prepandemic ran from Jan. 1, 2019 to March 29, 2020, and the pandemic period ran from March 30, 2020, the date a stay-at-home order was first issued in Maryland, to Dec. 31, 2020 – 448 (54.7%) involved a family member. The proportion of such injuries was similar before and during the pandemic (54.6% vs. 54.9%; P = .99).
Most (83.9%) of these incidents occurred at home, 76.6% involved a parent or guardian, and 66.7% involved the youth being transported to the hospital by police.
It is surprising that families accounted for such a high level of violence involving adolescents, said Christopher S. Greeley, MD, MS, chief of the division of public health pediatrics at Texas Children’s Hospital and professor of pediatrics at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who was not involved in the research.
“The most common source of child physical abuse in younger children – infants and toddlers – [is the] parents,” who account for about 75% of cases, “but to see that amount of violence in adolescents was unexpected,” he told this news organization.
Patients in the study cohort were more likely to be Black than the hospital’s overall emergency-department population (84.4% vs. 60.0%), and more likely to be covered by public insurance (71.2% vs. 60.0%).
In the study cohort, 54.0% of the patients were female.
“We were surprised to see that 8% of visits did not have a referral to a social worker” – 92% of patients in the study cohort received a social work consult during their visit to the emergency department – and that number “did not vary during the COVID-19 pandemic,” Ms. Miller said. The pandemic exacerbated the types of stresses that social workers can help address, so “this potentially represents a gap in care that is important to address,” she added.
Increase in use of alcohol, drugs, weapons
The most significant increases from the prepandemic period to the pandemic period were in incidents that involved alcohol (10.0% vs. 18.8%; P ≤ .001), illegal drugs (6.5% vs. 14.9%; P ≤ .001), and weapons, most often a knife (10.7% vs. 23.8%; P ≤ .001).
“An obvious potential explanation for the increase in alcohol, drug, and weapons [involvement] would be the mental health impact of the pandemic in conjunction with the economic stressors that some families may be feeling,” Dr. Greeley said. Teachers are the most common reporters of child abuse, so it’s possible that reports of violence decreased when schools switched to remote learning. But with most schools back to in-person learning, data have not yet shown a surge in reporting, he noted.
The “epidemiology of family violence may be impacted by increased time at home, disruptions in school and family routines, exacerbations in mental health conditions, and financial stresses common during the pandemic,” said senior study investigator Leticia Ryan, MD, MPH, director of research in pediatrics at Johns Hopkins Medicine.
And research has shown increases in the use of alcohol and illegal drugs during the pandemic, she noted.
“As we transition to postpandemic life, it will be important to identify at-risk adolescents and families and provide supports,” Dr. Ryan told this news organization. “The emergency department is an appropriate setting to intervene with youth who have experienced family violence and initiate preventive strategies to avoid future violence.”
Among the strategies to identify and intervene for at-risk patients is the CRAFFT substance use screening tool. Furthermore, “case management, involvement of child protection services, and linkage with relevant support services may all be appropriate, depending on circumstances,” Ms. Miller added.
“Exposure to family violence at a young age increases the likelihood that a child will be exposed to additional violence or become a perpetrator of violence in the future, continuing a cycle of violence,” Ms. Miller explained. “Given that studies of adolescent violence often focus on peer violence, a better understanding of the epidemiology of violence-related injuries resulting from family violence is needed to better inform the development of more comprehensive prevention strategies.”
This study did not note any external funding. Ms. Miller, Dr. Greeley, and Dr. Ryan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Abaloparatide significantly reduced fractures, increased BMD in women at high fracture risk
Postmenopausal women at high or very high risk of fracture gained significantly more bone mineral density and were significantly less likely to experience a fracture when taking abaloparatide for 18 months, according to new research presented at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society.
“The findings showed that abaloparatide was better than teriparatide in a number of parameters important in osteoporosis treatment, and similar in others, in high-risk and very-high-risk postmenopausal women with osteoporosis,” Bart Clarke, MD, a professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., said in an interview. “Abaloparatide is safe and effective for use in high-risk or very-high-risk postmenopausal women,” as defined by the new American Association of Clinical Endocrinology/American College of Endocrinology osteoporosis guidelines.
Ricardo R. Correa, MD, of the department of endocrinology and director of diversity for graduate medical education at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, said that the study demonstrates that abaloparatide and teriparatide have a very similar effect with abaloparatide providing a slightly better absolute risk reduction in fracture. Dr. Correa was not involved in the research.
“What will drive my decision in what to prescribe will be the cost and insurance coverage,” Dr. Correa said. “At the Veterans Administration hospital, the option that we have is abaloparatide, so this is the option that we use.”
Among women at least 65 years old who have already had one fracture, 1 in 10 will experience another fracture within the next year, and 30% will have another fracture within the next 5 years, the authors noted in their background material. Since phase 3 ACTIVE study data in 2016 showed that abaloparatide reduces fracture risk while increasing bone mineral density, compared with placebo, the researchers reanalyzed that data to assess the drug’s efficacy in patients at high or very high risk for fracture.
The study involved 2,463 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who received one of three interventions: 80 mcg abaloparatide daily, placebo, or 20 mcg subcutaneous teriparatide daily. Only the abaloparatide and placebo groups were double blinded.
“Teriparatide was used as the comparator drug because teriparatide was previously approved as the first anabolic drug for osteoporosis,” Dr. Clarke said in an interview. “The hope was to show that abaloparatide was a better anabolic drug.”
Women were considered at high or very high risk of fracture if they met at least one of the following four criteria from the 2020 American Association of Clinical Endocrinology guidelines:
- Fracture within the past 12 months or prevalent vertebral fracture.
- Very low T-score (less than –3.0) at baseline at any site.
- Multiple fractures at baseline since age 45.
- Very high fracture risk based on the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) (at least 30% for major osteoporotic fracture or at least 4.5% for hip fracture).
Among the 2,026 patients who met at least one of these criteria, 664 received abaloparatide, 685 received teriparatide, and 677 received placebo. Both the abaloparatide and teriparatide significantly reduced new vertebral fracture risk, compared with placebo. In the abaloparatide group, 0.72% of women had a new vertebral fracture, compared with 0.99% in the teriparatide group and 4.77% in the placebo group (P < .0001).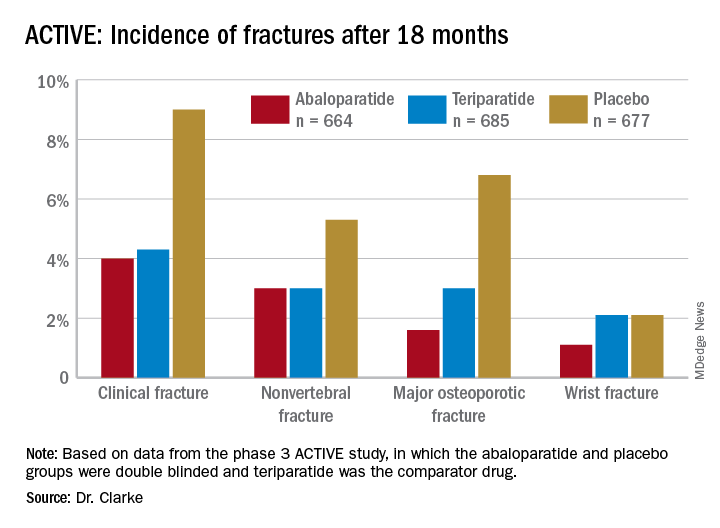
Abaloparatide and teriparatide also led to significant increases in lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck bone mineral density, compared with placebo (P < .0001).
The study was limited by its duration of 18 months and the Food and Drug Administration’s restriction on using abaloparatide for more than 2 years because of the theoretical risk of increasing osteosarcoma, although that risk has never been demonstrated in humans, Dr. Correa said. ”We need more data with abaloparitide in more than 2 years,” he added.
In determining which medication clinicians should first prescribe to manage osteoporosis, Dr. Correa said practitioners should consider the type of osteoporosis women have, their preferences, and their labs on kidney function.
With mild to moderate osteoporosis, bisphosphonates will be the first option while denosumab will be preferred for moderate to severe osteoporosis. Teriparatide and abaloparitide are the first-line options for severe osteoporosis, he said.
“If the glomerular filtration rate is low, we cannot use bisphosphonate and we will have to limit our use to denosumab,” he said. Route and frequency of delivery plays a role in patient preferences.
“If the patient prefers an infusion once a year or a pill, then bisphosphonate,” he said, but “if the patient is fine with an injection every 6 months, then denosumab.” Patients who need and can do an injection every day can take abaloparitide or teriparatide.
Failure of previous treatments also guide clinical decisions, he added. ”If the patient has been on one medication and has a fracture or the bone mineral density decreases, then we need to switch to another medication, usually teriparatide or abaloparitide, to build new bone.”
Contraindications for abaloparatide include a high serum calcium before therapy or prior allergic reactions to components in abaloparatide, Dr. Clarke said. No new safety signals showed up in the data analysis.
The research was funded by Radius Health. Dr. Clarke is an advisory board member of Amgen, and another author consults and speaks for Amgen and is a Radius Health Advisory Board member. Two other authors are Radius Health employees who own stock in the company. Dr Correa has no disclosures.
Postmenopausal women at high or very high risk of fracture gained significantly more bone mineral density and were significantly less likely to experience a fracture when taking abaloparatide for 18 months, according to new research presented at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society.
“The findings showed that abaloparatide was better than teriparatide in a number of parameters important in osteoporosis treatment, and similar in others, in high-risk and very-high-risk postmenopausal women with osteoporosis,” Bart Clarke, MD, a professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., said in an interview. “Abaloparatide is safe and effective for use in high-risk or very-high-risk postmenopausal women,” as defined by the new American Association of Clinical Endocrinology/American College of Endocrinology osteoporosis guidelines.
Ricardo R. Correa, MD, of the department of endocrinology and director of diversity for graduate medical education at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, said that the study demonstrates that abaloparatide and teriparatide have a very similar effect with abaloparatide providing a slightly better absolute risk reduction in fracture. Dr. Correa was not involved in the research.
“What will drive my decision in what to prescribe will be the cost and insurance coverage,” Dr. Correa said. “At the Veterans Administration hospital, the option that we have is abaloparatide, so this is the option that we use.”
Among women at least 65 years old who have already had one fracture, 1 in 10 will experience another fracture within the next year, and 30% will have another fracture within the next 5 years, the authors noted in their background material. Since phase 3 ACTIVE study data in 2016 showed that abaloparatide reduces fracture risk while increasing bone mineral density, compared with placebo, the researchers reanalyzed that data to assess the drug’s efficacy in patients at high or very high risk for fracture.
The study involved 2,463 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who received one of three interventions: 80 mcg abaloparatide daily, placebo, or 20 mcg subcutaneous teriparatide daily. Only the abaloparatide and placebo groups were double blinded.
“Teriparatide was used as the comparator drug because teriparatide was previously approved as the first anabolic drug for osteoporosis,” Dr. Clarke said in an interview. “The hope was to show that abaloparatide was a better anabolic drug.”
Women were considered at high or very high risk of fracture if they met at least one of the following four criteria from the 2020 American Association of Clinical Endocrinology guidelines:
- Fracture within the past 12 months or prevalent vertebral fracture.
- Very low T-score (less than –3.0) at baseline at any site.
- Multiple fractures at baseline since age 45.
- Very high fracture risk based on the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) (at least 30% for major osteoporotic fracture or at least 4.5% for hip fracture).
Among the 2,026 patients who met at least one of these criteria, 664 received abaloparatide, 685 received teriparatide, and 677 received placebo. Both the abaloparatide and teriparatide significantly reduced new vertebral fracture risk, compared with placebo. In the abaloparatide group, 0.72% of women had a new vertebral fracture, compared with 0.99% in the teriparatide group and 4.77% in the placebo group (P < .0001).
Abaloparatide and teriparatide also led to significant increases in lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck bone mineral density, compared with placebo (P < .0001).
The study was limited by its duration of 18 months and the Food and Drug Administration’s restriction on using abaloparatide for more than 2 years because of the theoretical risk of increasing osteosarcoma, although that risk has never been demonstrated in humans, Dr. Correa said. ”We need more data with abaloparitide in more than 2 years,” he added.
In determining which medication clinicians should first prescribe to manage osteoporosis, Dr. Correa said practitioners should consider the type of osteoporosis women have, their preferences, and their labs on kidney function.
With mild to moderate osteoporosis, bisphosphonates will be the first option while denosumab will be preferred for moderate to severe osteoporosis. Teriparatide and abaloparitide are the first-line options for severe osteoporosis, he said.
“If the glomerular filtration rate is low, we cannot use bisphosphonate and we will have to limit our use to denosumab,” he said. Route and frequency of delivery plays a role in patient preferences.
“If the patient prefers an infusion once a year or a pill, then bisphosphonate,” he said, but “if the patient is fine with an injection every 6 months, then denosumab.” Patients who need and can do an injection every day can take abaloparitide or teriparatide.
Failure of previous treatments also guide clinical decisions, he added. ”If the patient has been on one medication and has a fracture or the bone mineral density decreases, then we need to switch to another medication, usually teriparatide or abaloparitide, to build new bone.”
Contraindications for abaloparatide include a high serum calcium before therapy or prior allergic reactions to components in abaloparatide, Dr. Clarke said. No new safety signals showed up in the data analysis.
The research was funded by Radius Health. Dr. Clarke is an advisory board member of Amgen, and another author consults and speaks for Amgen and is a Radius Health Advisory Board member. Two other authors are Radius Health employees who own stock in the company. Dr Correa has no disclosures.
Postmenopausal women at high or very high risk of fracture gained significantly more bone mineral density and were significantly less likely to experience a fracture when taking abaloparatide for 18 months, according to new research presented at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society.
“The findings showed that abaloparatide was better than teriparatide in a number of parameters important in osteoporosis treatment, and similar in others, in high-risk and very-high-risk postmenopausal women with osteoporosis,” Bart Clarke, MD, a professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., said in an interview. “Abaloparatide is safe and effective for use in high-risk or very-high-risk postmenopausal women,” as defined by the new American Association of Clinical Endocrinology/American College of Endocrinology osteoporosis guidelines.
Ricardo R. Correa, MD, of the department of endocrinology and director of diversity for graduate medical education at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, said that the study demonstrates that abaloparatide and teriparatide have a very similar effect with abaloparatide providing a slightly better absolute risk reduction in fracture. Dr. Correa was not involved in the research.
“What will drive my decision in what to prescribe will be the cost and insurance coverage,” Dr. Correa said. “At the Veterans Administration hospital, the option that we have is abaloparatide, so this is the option that we use.”
Among women at least 65 years old who have already had one fracture, 1 in 10 will experience another fracture within the next year, and 30% will have another fracture within the next 5 years, the authors noted in their background material. Since phase 3 ACTIVE study data in 2016 showed that abaloparatide reduces fracture risk while increasing bone mineral density, compared with placebo, the researchers reanalyzed that data to assess the drug’s efficacy in patients at high or very high risk for fracture.
The study involved 2,463 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who received one of three interventions: 80 mcg abaloparatide daily, placebo, or 20 mcg subcutaneous teriparatide daily. Only the abaloparatide and placebo groups were double blinded.
“Teriparatide was used as the comparator drug because teriparatide was previously approved as the first anabolic drug for osteoporosis,” Dr. Clarke said in an interview. “The hope was to show that abaloparatide was a better anabolic drug.”
Women were considered at high or very high risk of fracture if they met at least one of the following four criteria from the 2020 American Association of Clinical Endocrinology guidelines:
- Fracture within the past 12 months or prevalent vertebral fracture.
- Very low T-score (less than –3.0) at baseline at any site.
- Multiple fractures at baseline since age 45.
- Very high fracture risk based on the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) (at least 30% for major osteoporotic fracture or at least 4.5% for hip fracture).
Among the 2,026 patients who met at least one of these criteria, 664 received abaloparatide, 685 received teriparatide, and 677 received placebo. Both the abaloparatide and teriparatide significantly reduced new vertebral fracture risk, compared with placebo. In the abaloparatide group, 0.72% of women had a new vertebral fracture, compared with 0.99% in the teriparatide group and 4.77% in the placebo group (P < .0001).
Abaloparatide and teriparatide also led to significant increases in lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck bone mineral density, compared with placebo (P < .0001).
The study was limited by its duration of 18 months and the Food and Drug Administration’s restriction on using abaloparatide for more than 2 years because of the theoretical risk of increasing osteosarcoma, although that risk has never been demonstrated in humans, Dr. Correa said. ”We need more data with abaloparitide in more than 2 years,” he added.
In determining which medication clinicians should first prescribe to manage osteoporosis, Dr. Correa said practitioners should consider the type of osteoporosis women have, their preferences, and their labs on kidney function.
With mild to moderate osteoporosis, bisphosphonates will be the first option while denosumab will be preferred for moderate to severe osteoporosis. Teriparatide and abaloparitide are the first-line options for severe osteoporosis, he said.
“If the glomerular filtration rate is low, we cannot use bisphosphonate and we will have to limit our use to denosumab,” he said. Route and frequency of delivery plays a role in patient preferences.
“If the patient prefers an infusion once a year or a pill, then bisphosphonate,” he said, but “if the patient is fine with an injection every 6 months, then denosumab.” Patients who need and can do an injection every day can take abaloparitide or teriparatide.
Failure of previous treatments also guide clinical decisions, he added. ”If the patient has been on one medication and has a fracture or the bone mineral density decreases, then we need to switch to another medication, usually teriparatide or abaloparitide, to build new bone.”
Contraindications for abaloparatide include a high serum calcium before therapy or prior allergic reactions to components in abaloparatide, Dr. Clarke said. No new safety signals showed up in the data analysis.
The research was funded by Radius Health. Dr. Clarke is an advisory board member of Amgen, and another author consults and speaks for Amgen and is a Radius Health Advisory Board member. Two other authors are Radius Health employees who own stock in the company. Dr Correa has no disclosures.
FROM NAMS 2021
New nonhormonal therapies for hot flashes on the horizon
Hot flashes affect three out of four women and can last 7-10 years, but the current standard of care treatment isn’t necessarily appropriate for all women who experience vasomotor symptoms, according to Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, director of the Mayo Clinic Women’s Health Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla.
For the majority of women under age 60 who are within 10 years of menopause, hormone therapy currently remains the most effective management option for hot flashes where the benefits outweigh the risks, Dr. Faubion told attendees Sept. 25 during a plenary at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. “But really, individualizing treatment is the goal, and there are some women who are going to need some other options.”
Contraindications for hormone therapy include having a history of breast cancer, coronary heart disease, active liver disease, unexplained vaginal bleeding, high-risk endometrial cancer, transient ischemic attack, and a previous venous thromboembolic event or stroke.
“Fortunately, we have things in development,” Dr. Faubion said. She reviewed a wide range of therapies that are not currently Food and Drug Administration approved for vasomotor symptoms but are either available off label or are in clinical trials.
One of these is oxybutynin, an antimuscarinic, anticholinergic agent currently used to treat overactive bladder and overactive sweating. In a 2016 trial, 73% of women taking 15 mg extended-release oxybutynin once daily rated their symptoms as “much better,” compared with 26% who received placebo. The women experienced reduced frequency and severity of hot flashes and better sleep.
Subsequent research found a 60% reduction in hot flash frequency with 2.5 mg twice a day and a 77% reduction with 5 mg twice a day, compared with a 27% reduction with placebo. The only reported side effect that occurred more often with oxybutynin was dry mouth, but there were no significant differences in reasons for discontinuation between the treatment and placebo groups.
There are, however, some potential long-term cognitive effects from oxybutynin, Dr. Faubion said. Some research has shown an increased risk of dementia from oxybutynin and from an overall higher cumulative use of anticholinergics.
“There’s some concern about that for long-term use,” she said, but it’s effective, it’s “probably not harmful [when] used short term in women with significant, bothersome hot flashes who are unwilling or unable to use hormone therapy, and the adverse effects are tolerable for most women.” Women with bladder symptoms would be especially ideal candidates since the drug already treats those.
Dr. Faubion then discussed a new estrogen called estetrol (E4), a naturally occurring estrogen with selection action in tissues that is produced by the fetal liver and crosses the placenta. It has a long half-life of 28-32 hours, and its potential mechanism may give it a different safety profile than estradiol (E2). “There may be a lower risk of drug-drug interactions; lower breast stimulation, pain or carcinogenic impact; lower impact on triglycerides; and a neutral impact on markers of coagulation,” she said.
Though estetrol was recently approved as an oral contraceptive under the name Estelle, it’s also under investigation as a postmenopausal regimen. Preliminary findings suggest it reduces vasomotor symptom severity by 44%, compared with 30% with placebo, at 15 mg, the apparent minimum effective dose. The safety profile showed no endometrial hyperplasia and no unexpected adverse events. In those taking 15 mg of estetrol, mean endometrial thickness increased from 2 to 6 mm but returned to baseline after progestin therapy.
“The 15-mg dose also positively influenced markers of bone turnover, increased HDL [cholesterol], improved glucose tolerance,” and had no effects on coagulation parameters or triglycerides, Dr. Faubion added.
Another group of potential agents being studied for hot flashes are NK3 antagonists, which aim to exploit the recent discovery that kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin (KNDy) neurons may play an important role in the etiology of vasomotor symptoms. Development of one of these, MLE 4901, was halted despite a 45% reduction in hot flashes because 3 of 28 women developed transiently elevated liver function tests, about four to six times the upper limit of normal.
Two others, fezolinetant and NT-814, are in phase 2 trials and have shown a significant reduction in symptoms, compared with placebo. The most commonly reported adverse effect in the phase 2a trial was gastrointestinal effects, but none of the participants stopped the drug because of these, and no elevated liver tests occurred. In the larger phase 2b trial, the most commonly reported treatment-emergent adverse events included nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, urinary tract infection, sinusitis, upper respiratory infection, headache, and cough. Five women discontinued the drug because of elevated liver enzymes.
“Overall, NK3 inhibitors appear to be generally well tolerated,” Dr. Faubion said. “There does seem to be mild transaminase elevation,” though it’s not yet known if this is an effect from this class of drugs as a whole. She noted that follicle-stimulating hormone does not significantly increase, which is important because elevated FSH is associated with poor bone health, nor does estradiol significantly increase, which is clinically relevant for women at high risk of breast cancer.
“We don’t know the effects on the heart, the brain, the bone, mood, weight, or sexual health, so there’s a lot that is still not known,” Dr. Faubion said. “We still don’t know about long-term safety and efficacy with these chemical compounds,” but clinical trials of them are ongoing.
They “would be a welcome alternative to hormone therapy for those who can’t or prefer not to use a hormonal option,” Dr. Faubion said. “However, we may need broad education of clinicians to caution against widespread abandonment of hormone therapy, particularly in women with premature or early menopause.”
Donna Klassen, LCSW, the cofounder of Let’s Talk Menopause, asked whether any of these new therapies were being tested in women with breast cancer and whether anything was known about taking oxybutynin at the same time as letrozole.
“I suspect that most women with chronic diseases would have been excluded from these initial studies, but I can’t speak to that,” Dr. Faubion said, and she wasn’t aware of any data related to taking oxybutynin and letrozole concurrently.
James Simon, MD, medical director and founder of IntimMedicine and one of those who led the research on oxybutynin, responded that his trials excluded breast cancer survivors and anyone taking aromatase inhibitors.
“It will be unlikely that, in the very near future, that data will be available because all the clinical developments on these NK3s or KNDy neuron-modulating drugs exclude cancer patients,” Dr. Simon said.
However, another attendee, Lisa Larkin, MD, of Cincinnati, introduced herself as a breast cancer survivor who takes tamoxifen and said she feels “completely comfortable” prescribing oxybutynin to breast cancer survivors.
“In terms of side effects and effectiveness in patients on tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors, I’ve had incredibly good luck with it, and I think it’s underutilized,” Dr. Larkin said. “The clinical pearl I would tell you is you can start really low, and the dry mouth really seems to improve with time.” She added that patients should be informed that it takes 2 weeks before it begins working, but the side effects eventually go away. “It becomes very tolerable, so I just encourage all of you to consider it as another great option.”
Dr. Faubion had no disclosures. Disclosure information was unavailable for Dr. Simon, Dr. Larkin, and Ms. Klassen.
Hot flashes affect three out of four women and can last 7-10 years, but the current standard of care treatment isn’t necessarily appropriate for all women who experience vasomotor symptoms, according to Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, director of the Mayo Clinic Women’s Health Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla.
For the majority of women under age 60 who are within 10 years of menopause, hormone therapy currently remains the most effective management option for hot flashes where the benefits outweigh the risks, Dr. Faubion told attendees Sept. 25 during a plenary at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. “But really, individualizing treatment is the goal, and there are some women who are going to need some other options.”
Contraindications for hormone therapy include having a history of breast cancer, coronary heart disease, active liver disease, unexplained vaginal bleeding, high-risk endometrial cancer, transient ischemic attack, and a previous venous thromboembolic event or stroke.
“Fortunately, we have things in development,” Dr. Faubion said. She reviewed a wide range of therapies that are not currently Food and Drug Administration approved for vasomotor symptoms but are either available off label or are in clinical trials.
One of these is oxybutynin, an antimuscarinic, anticholinergic agent currently used to treat overactive bladder and overactive sweating. In a 2016 trial, 73% of women taking 15 mg extended-release oxybutynin once daily rated their symptoms as “much better,” compared with 26% who received placebo. The women experienced reduced frequency and severity of hot flashes and better sleep.
Subsequent research found a 60% reduction in hot flash frequency with 2.5 mg twice a day and a 77% reduction with 5 mg twice a day, compared with a 27% reduction with placebo. The only reported side effect that occurred more often with oxybutynin was dry mouth, but there were no significant differences in reasons for discontinuation between the treatment and placebo groups.
There are, however, some potential long-term cognitive effects from oxybutynin, Dr. Faubion said. Some research has shown an increased risk of dementia from oxybutynin and from an overall higher cumulative use of anticholinergics.
“There’s some concern about that for long-term use,” she said, but it’s effective, it’s “probably not harmful [when] used short term in women with significant, bothersome hot flashes who are unwilling or unable to use hormone therapy, and the adverse effects are tolerable for most women.” Women with bladder symptoms would be especially ideal candidates since the drug already treats those.
Dr. Faubion then discussed a new estrogen called estetrol (E4), a naturally occurring estrogen with selection action in tissues that is produced by the fetal liver and crosses the placenta. It has a long half-life of 28-32 hours, and its potential mechanism may give it a different safety profile than estradiol (E2). “There may be a lower risk of drug-drug interactions; lower breast stimulation, pain or carcinogenic impact; lower impact on triglycerides; and a neutral impact on markers of coagulation,” she said.
Though estetrol was recently approved as an oral contraceptive under the name Estelle, it’s also under investigation as a postmenopausal regimen. Preliminary findings suggest it reduces vasomotor symptom severity by 44%, compared with 30% with placebo, at 15 mg, the apparent minimum effective dose. The safety profile showed no endometrial hyperplasia and no unexpected adverse events. In those taking 15 mg of estetrol, mean endometrial thickness increased from 2 to 6 mm but returned to baseline after progestin therapy.
“The 15-mg dose also positively influenced markers of bone turnover, increased HDL [cholesterol], improved glucose tolerance,” and had no effects on coagulation parameters or triglycerides, Dr. Faubion added.
Another group of potential agents being studied for hot flashes are NK3 antagonists, which aim to exploit the recent discovery that kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin (KNDy) neurons may play an important role in the etiology of vasomotor symptoms. Development of one of these, MLE 4901, was halted despite a 45% reduction in hot flashes because 3 of 28 women developed transiently elevated liver function tests, about four to six times the upper limit of normal.
Two others, fezolinetant and NT-814, are in phase 2 trials and have shown a significant reduction in symptoms, compared with placebo. The most commonly reported adverse effect in the phase 2a trial was gastrointestinal effects, but none of the participants stopped the drug because of these, and no elevated liver tests occurred. In the larger phase 2b trial, the most commonly reported treatment-emergent adverse events included nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, urinary tract infection, sinusitis, upper respiratory infection, headache, and cough. Five women discontinued the drug because of elevated liver enzymes.
“Overall, NK3 inhibitors appear to be generally well tolerated,” Dr. Faubion said. “There does seem to be mild transaminase elevation,” though it’s not yet known if this is an effect from this class of drugs as a whole. She noted that follicle-stimulating hormone does not significantly increase, which is important because elevated FSH is associated with poor bone health, nor does estradiol significantly increase, which is clinically relevant for women at high risk of breast cancer.
“We don’t know the effects on the heart, the brain, the bone, mood, weight, or sexual health, so there’s a lot that is still not known,” Dr. Faubion said. “We still don’t know about long-term safety and efficacy with these chemical compounds,” but clinical trials of them are ongoing.
They “would be a welcome alternative to hormone therapy for those who can’t or prefer not to use a hormonal option,” Dr. Faubion said. “However, we may need broad education of clinicians to caution against widespread abandonment of hormone therapy, particularly in women with premature or early menopause.”
Donna Klassen, LCSW, the cofounder of Let’s Talk Menopause, asked whether any of these new therapies were being tested in women with breast cancer and whether anything was known about taking oxybutynin at the same time as letrozole.
“I suspect that most women with chronic diseases would have been excluded from these initial studies, but I can’t speak to that,” Dr. Faubion said, and she wasn’t aware of any data related to taking oxybutynin and letrozole concurrently.
James Simon, MD, medical director and founder of IntimMedicine and one of those who led the research on oxybutynin, responded that his trials excluded breast cancer survivors and anyone taking aromatase inhibitors.
“It will be unlikely that, in the very near future, that data will be available because all the clinical developments on these NK3s or KNDy neuron-modulating drugs exclude cancer patients,” Dr. Simon said.
However, another attendee, Lisa Larkin, MD, of Cincinnati, introduced herself as a breast cancer survivor who takes tamoxifen and said she feels “completely comfortable” prescribing oxybutynin to breast cancer survivors.
“In terms of side effects and effectiveness in patients on tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors, I’ve had incredibly good luck with it, and I think it’s underutilized,” Dr. Larkin said. “The clinical pearl I would tell you is you can start really low, and the dry mouth really seems to improve with time.” She added that patients should be informed that it takes 2 weeks before it begins working, but the side effects eventually go away. “It becomes very tolerable, so I just encourage all of you to consider it as another great option.”
Dr. Faubion had no disclosures. Disclosure information was unavailable for Dr. Simon, Dr. Larkin, and Ms. Klassen.
Hot flashes affect three out of four women and can last 7-10 years, but the current standard of care treatment isn’t necessarily appropriate for all women who experience vasomotor symptoms, according to Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, director of the Mayo Clinic Women’s Health Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla.
For the majority of women under age 60 who are within 10 years of menopause, hormone therapy currently remains the most effective management option for hot flashes where the benefits outweigh the risks, Dr. Faubion told attendees Sept. 25 during a plenary at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. “But really, individualizing treatment is the goal, and there are some women who are going to need some other options.”
Contraindications for hormone therapy include having a history of breast cancer, coronary heart disease, active liver disease, unexplained vaginal bleeding, high-risk endometrial cancer, transient ischemic attack, and a previous venous thromboembolic event or stroke.
“Fortunately, we have things in development,” Dr. Faubion said. She reviewed a wide range of therapies that are not currently Food and Drug Administration approved for vasomotor symptoms but are either available off label or are in clinical trials.
One of these is oxybutynin, an antimuscarinic, anticholinergic agent currently used to treat overactive bladder and overactive sweating. In a 2016 trial, 73% of women taking 15 mg extended-release oxybutynin once daily rated their symptoms as “much better,” compared with 26% who received placebo. The women experienced reduced frequency and severity of hot flashes and better sleep.
Subsequent research found a 60% reduction in hot flash frequency with 2.5 mg twice a day and a 77% reduction with 5 mg twice a day, compared with a 27% reduction with placebo. The only reported side effect that occurred more often with oxybutynin was dry mouth, but there were no significant differences in reasons for discontinuation between the treatment and placebo groups.
There are, however, some potential long-term cognitive effects from oxybutynin, Dr. Faubion said. Some research has shown an increased risk of dementia from oxybutynin and from an overall higher cumulative use of anticholinergics.
“There’s some concern about that for long-term use,” she said, but it’s effective, it’s “probably not harmful [when] used short term in women with significant, bothersome hot flashes who are unwilling or unable to use hormone therapy, and the adverse effects are tolerable for most women.” Women with bladder symptoms would be especially ideal candidates since the drug already treats those.
Dr. Faubion then discussed a new estrogen called estetrol (E4), a naturally occurring estrogen with selection action in tissues that is produced by the fetal liver and crosses the placenta. It has a long half-life of 28-32 hours, and its potential mechanism may give it a different safety profile than estradiol (E2). “There may be a lower risk of drug-drug interactions; lower breast stimulation, pain or carcinogenic impact; lower impact on triglycerides; and a neutral impact on markers of coagulation,” she said.
Though estetrol was recently approved as an oral contraceptive under the name Estelle, it’s also under investigation as a postmenopausal regimen. Preliminary findings suggest it reduces vasomotor symptom severity by 44%, compared with 30% with placebo, at 15 mg, the apparent minimum effective dose. The safety profile showed no endometrial hyperplasia and no unexpected adverse events. In those taking 15 mg of estetrol, mean endometrial thickness increased from 2 to 6 mm but returned to baseline after progestin therapy.
“The 15-mg dose also positively influenced markers of bone turnover, increased HDL [cholesterol], improved glucose tolerance,” and had no effects on coagulation parameters or triglycerides, Dr. Faubion added.
Another group of potential agents being studied for hot flashes are NK3 antagonists, which aim to exploit the recent discovery that kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin (KNDy) neurons may play an important role in the etiology of vasomotor symptoms. Development of one of these, MLE 4901, was halted despite a 45% reduction in hot flashes because 3 of 28 women developed transiently elevated liver function tests, about four to six times the upper limit of normal.
Two others, fezolinetant and NT-814, are in phase 2 trials and have shown a significant reduction in symptoms, compared with placebo. The most commonly reported adverse effect in the phase 2a trial was gastrointestinal effects, but none of the participants stopped the drug because of these, and no elevated liver tests occurred. In the larger phase 2b trial, the most commonly reported treatment-emergent adverse events included nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, urinary tract infection, sinusitis, upper respiratory infection, headache, and cough. Five women discontinued the drug because of elevated liver enzymes.
“Overall, NK3 inhibitors appear to be generally well tolerated,” Dr. Faubion said. “There does seem to be mild transaminase elevation,” though it’s not yet known if this is an effect from this class of drugs as a whole. She noted that follicle-stimulating hormone does not significantly increase, which is important because elevated FSH is associated with poor bone health, nor does estradiol significantly increase, which is clinically relevant for women at high risk of breast cancer.
“We don’t know the effects on the heart, the brain, the bone, mood, weight, or sexual health, so there’s a lot that is still not known,” Dr. Faubion said. “We still don’t know about long-term safety and efficacy with these chemical compounds,” but clinical trials of them are ongoing.
They “would be a welcome alternative to hormone therapy for those who can’t or prefer not to use a hormonal option,” Dr. Faubion said. “However, we may need broad education of clinicians to caution against widespread abandonment of hormone therapy, particularly in women with premature or early menopause.”
Donna Klassen, LCSW, the cofounder of Let’s Talk Menopause, asked whether any of these new therapies were being tested in women with breast cancer and whether anything was known about taking oxybutynin at the same time as letrozole.
“I suspect that most women with chronic diseases would have been excluded from these initial studies, but I can’t speak to that,” Dr. Faubion said, and she wasn’t aware of any data related to taking oxybutynin and letrozole concurrently.
James Simon, MD, medical director and founder of IntimMedicine and one of those who led the research on oxybutynin, responded that his trials excluded breast cancer survivors and anyone taking aromatase inhibitors.
“It will be unlikely that, in the very near future, that data will be available because all the clinical developments on these NK3s or KNDy neuron-modulating drugs exclude cancer patients,” Dr. Simon said.
However, another attendee, Lisa Larkin, MD, of Cincinnati, introduced herself as a breast cancer survivor who takes tamoxifen and said she feels “completely comfortable” prescribing oxybutynin to breast cancer survivors.
“In terms of side effects and effectiveness in patients on tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors, I’ve had incredibly good luck with it, and I think it’s underutilized,” Dr. Larkin said. “The clinical pearl I would tell you is you can start really low, and the dry mouth really seems to improve with time.” She added that patients should be informed that it takes 2 weeks before it begins working, but the side effects eventually go away. “It becomes very tolerable, so I just encourage all of you to consider it as another great option.”
Dr. Faubion had no disclosures. Disclosure information was unavailable for Dr. Simon, Dr. Larkin, and Ms. Klassen.
FROM NAMS 2021
Migraine history linked to more severe hot flashes in postmenopausal women
Women with a history of migraine are more likely to experience severe or very severe hot flashes than women without migraines, according to research presented Sept. 24 at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. An estimated one in five women experience migraine, and women tend to have greater migraine symptoms and disability, the authors note in their background information. Since migraines are also linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, the authors sought to learn whether migraines were associated with vasomotor symptoms, another cardiovascular risk factor.
“The question in my mind is, can we do better at predicting cardiovascular risk in women because the risk prediction models that we have really don’t work all that well in women because they were designed for use in men,” Stephanie S. Faubion, MD, MBA, Penny and Bill George Director for Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health said in an interview. “My ultimate goal is to see if we can somehow use big data, artificial intelligence to figure out how to weight some of these female-specific or female-predominant factors to come up with a better model for cardiovascular risk prediction.”
The researchers analyzed cross-sectional data from 3,308 women who participated in the Data Registry on the Experiences of Aging, Menopause and Sexuality (DREAMS) study through Mayo Clinic sites in Rochester, Minn.; Scottsdale, Ariz.; and Jacksonville, Fla.. The women ranged in age from 45 to 60 years old, with an average age of 53, and the vast majority of them were white (95%) and had at least some college (93%). Most were also in a long-term relationship (85%), and a majority were employed (69%) and postmenopausal (67%).
The data, collected between May 2015 and December 2019, included a self-reported history of migraine and questionnaires that included the Menopause Rating Scale of menopause-related symptoms.
The researchers adjusted their findings to account for body mass index (BMI), menopause status, smoking status, depression, anxiety, current use of hormone therapy, and presence of low back pain within the past year. ”The diagnosis of low back pain, another pain disorder, was used to test the specificity of the association of migraine and vasomotor symptoms,” the authors write.
Just over a quarter of the women (27%) reported a history of migraine, and these women’s Menopause Rating Scale scores were an average 1.36 points greater than women without a history of migraines (P < .001). Women with self-reported migraine were also 40% more likely than women without migraines to report severe or very severe flashes versus reporting no hot flashes at all (odds ratio, 1.4; P = .02).
“The odds of reporting more severe hot flashes increased monotonically in women with a history of migraine,” the authors report. “In addition, women with low back pain had higher Menopause Rating Scale scores, but were no more likely to have severe/very severe hot flashes than those without back pain, confirming the specificity of the link between vasomotor symptoms and migraine.”
It’s not clear if migraine or hot flashes are risk factors that add to a woman’s existing cardiovascular risk profile or whether they are simply biomarkers of a shared pathway, Dr Faubion said in an interview. She speculates that the common link between migraine and vasomotor symptoms could be neurovascular dysregulation.
Rachael B. Smith, DO, of the department of ob.gyn. at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, was not involved in the research but found that hypothesis plausible as well.
“Our neurologic and vascular systems are coordinated physiologic processes working together for basic brain and body function,” Dr. Smith said in an interview. Some of the symptoms of migraines and menopause are similar and both are often explained by the dysfunction of these systems. The association between history of migraines and severity of vasomotor symptoms is very likely to be explained by this dysregulation between the neurologic and vascular systems.”
Dr. Smith also pointed out, however, that the largely homogeneous study population, all from the same national clinic system, makes it difficult to know how generalizable these findings are.
The primary clinical implications of these findings are that women’s providers need to be sure they’re asking their patients about migraine history and symptoms.
“The counseling we provide on menopausal symptoms should be better tailored to our patients’ medical history, specifically inquiring about history of migraines and how this may impact their symptoms,” Dr. Smith said.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Faubion and Dr. Smith had no disclosures.
Women with a history of migraine are more likely to experience severe or very severe hot flashes than women without migraines, according to research presented Sept. 24 at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. An estimated one in five women experience migraine, and women tend to have greater migraine symptoms and disability, the authors note in their background information. Since migraines are also linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, the authors sought to learn whether migraines were associated with vasomotor symptoms, another cardiovascular risk factor.
“The question in my mind is, can we do better at predicting cardiovascular risk in women because the risk prediction models that we have really don’t work all that well in women because they were designed for use in men,” Stephanie S. Faubion, MD, MBA, Penny and Bill George Director for Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health said in an interview. “My ultimate goal is to see if we can somehow use big data, artificial intelligence to figure out how to weight some of these female-specific or female-predominant factors to come up with a better model for cardiovascular risk prediction.”
The researchers analyzed cross-sectional data from 3,308 women who participated in the Data Registry on the Experiences of Aging, Menopause and Sexuality (DREAMS) study through Mayo Clinic sites in Rochester, Minn.; Scottsdale, Ariz.; and Jacksonville, Fla.. The women ranged in age from 45 to 60 years old, with an average age of 53, and the vast majority of them were white (95%) and had at least some college (93%). Most were also in a long-term relationship (85%), and a majority were employed (69%) and postmenopausal (67%).
The data, collected between May 2015 and December 2019, included a self-reported history of migraine and questionnaires that included the Menopause Rating Scale of menopause-related symptoms.
The researchers adjusted their findings to account for body mass index (BMI), menopause status, smoking status, depression, anxiety, current use of hormone therapy, and presence of low back pain within the past year. ”The diagnosis of low back pain, another pain disorder, was used to test the specificity of the association of migraine and vasomotor symptoms,” the authors write.
Just over a quarter of the women (27%) reported a history of migraine, and these women’s Menopause Rating Scale scores were an average 1.36 points greater than women without a history of migraines (P < .001). Women with self-reported migraine were also 40% more likely than women without migraines to report severe or very severe flashes versus reporting no hot flashes at all (odds ratio, 1.4; P = .02).
“The odds of reporting more severe hot flashes increased monotonically in women with a history of migraine,” the authors report. “In addition, women with low back pain had higher Menopause Rating Scale scores, but were no more likely to have severe/very severe hot flashes than those without back pain, confirming the specificity of the link between vasomotor symptoms and migraine.”
It’s not clear if migraine or hot flashes are risk factors that add to a woman’s existing cardiovascular risk profile or whether they are simply biomarkers of a shared pathway, Dr Faubion said in an interview. She speculates that the common link between migraine and vasomotor symptoms could be neurovascular dysregulation.
Rachael B. Smith, DO, of the department of ob.gyn. at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, was not involved in the research but found that hypothesis plausible as well.
“Our neurologic and vascular systems are coordinated physiologic processes working together for basic brain and body function,” Dr. Smith said in an interview. Some of the symptoms of migraines and menopause are similar and both are often explained by the dysfunction of these systems. The association between history of migraines and severity of vasomotor symptoms is very likely to be explained by this dysregulation between the neurologic and vascular systems.”
Dr. Smith also pointed out, however, that the largely homogeneous study population, all from the same national clinic system, makes it difficult to know how generalizable these findings are.
The primary clinical implications of these findings are that women’s providers need to be sure they’re asking their patients about migraine history and symptoms.
“The counseling we provide on menopausal symptoms should be better tailored to our patients’ medical history, specifically inquiring about history of migraines and how this may impact their symptoms,” Dr. Smith said.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Faubion and Dr. Smith had no disclosures.
Women with a history of migraine are more likely to experience severe or very severe hot flashes than women without migraines, according to research presented Sept. 24 at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. An estimated one in five women experience migraine, and women tend to have greater migraine symptoms and disability, the authors note in their background information. Since migraines are also linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, the authors sought to learn whether migraines were associated with vasomotor symptoms, another cardiovascular risk factor.
“The question in my mind is, can we do better at predicting cardiovascular risk in women because the risk prediction models that we have really don’t work all that well in women because they were designed for use in men,” Stephanie S. Faubion, MD, MBA, Penny and Bill George Director for Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health said in an interview. “My ultimate goal is to see if we can somehow use big data, artificial intelligence to figure out how to weight some of these female-specific or female-predominant factors to come up with a better model for cardiovascular risk prediction.”
The researchers analyzed cross-sectional data from 3,308 women who participated in the Data Registry on the Experiences of Aging, Menopause and Sexuality (DREAMS) study through Mayo Clinic sites in Rochester, Minn.; Scottsdale, Ariz.; and Jacksonville, Fla.. The women ranged in age from 45 to 60 years old, with an average age of 53, and the vast majority of them were white (95%) and had at least some college (93%). Most were also in a long-term relationship (85%), and a majority were employed (69%) and postmenopausal (67%).
The data, collected between May 2015 and December 2019, included a self-reported history of migraine and questionnaires that included the Menopause Rating Scale of menopause-related symptoms.
The researchers adjusted their findings to account for body mass index (BMI), menopause status, smoking status, depression, anxiety, current use of hormone therapy, and presence of low back pain within the past year. ”The diagnosis of low back pain, another pain disorder, was used to test the specificity of the association of migraine and vasomotor symptoms,” the authors write.
Just over a quarter of the women (27%) reported a history of migraine, and these women’s Menopause Rating Scale scores were an average 1.36 points greater than women without a history of migraines (P < .001). Women with self-reported migraine were also 40% more likely than women without migraines to report severe or very severe flashes versus reporting no hot flashes at all (odds ratio, 1.4; P = .02).
“The odds of reporting more severe hot flashes increased monotonically in women with a history of migraine,” the authors report. “In addition, women with low back pain had higher Menopause Rating Scale scores, but were no more likely to have severe/very severe hot flashes than those without back pain, confirming the specificity of the link between vasomotor symptoms and migraine.”
It’s not clear if migraine or hot flashes are risk factors that add to a woman’s existing cardiovascular risk profile or whether they are simply biomarkers of a shared pathway, Dr Faubion said in an interview. She speculates that the common link between migraine and vasomotor symptoms could be neurovascular dysregulation.
Rachael B. Smith, DO, of the department of ob.gyn. at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, was not involved in the research but found that hypothesis plausible as well.
“Our neurologic and vascular systems are coordinated physiologic processes working together for basic brain and body function,” Dr. Smith said in an interview. Some of the symptoms of migraines and menopause are similar and both are often explained by the dysfunction of these systems. The association between history of migraines and severity of vasomotor symptoms is very likely to be explained by this dysregulation between the neurologic and vascular systems.”
Dr. Smith also pointed out, however, that the largely homogeneous study population, all from the same national clinic system, makes it difficult to know how generalizable these findings are.
The primary clinical implications of these findings are that women’s providers need to be sure they’re asking their patients about migraine history and symptoms.
“The counseling we provide on menopausal symptoms should be better tailored to our patients’ medical history, specifically inquiring about history of migraines and how this may impact their symptoms,” Dr. Smith said.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Faubion and Dr. Smith had no disclosures.
FROM NAMS 2021
PCOS linked to menopausal urogenital symptoms but not hot flashes
Women with a history of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are more likely to experience somatic and urogenital symptoms post menopause, but they were no more likely to experience severe hot flashes than were other women with similar characteristics, according to research presented Sept. 24 at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society.
PCOS and vasomotor symptoms are each risk factors for cardiovascular disease, so researchers wanted to find out whether they were linked to one another, which might indicate that they are markers for the same underlying mechanisms that increase heart disease risk. The lack of an association, however, raises questions about how much each of these conditions might independently increase cardiovascular risk.
“Should we take a little more time to truly risk-assess these patients not just with their ASCVD risk score, but take into account that they have PCOS and they’re going through menopause, and how severe their hot flashes are?” asked Angie S. Lobo, MD, an internal medicine specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., when she discussed her findings in an interview.
The association between PCOS and urogenital symptoms was surprising, Dr. Lobo said, but she said she suspects the reason for the finding may be the self-reported nature of the study.
“If you ask the question, you get the answer,” Dr. Lobo said. ”Are we just not asking the right questions to our patients? And should we be doing this more often? This is an exciting finding because there’s so much room to improve the clinical care of our patients.”
The researchers analyzed data from 3,308 women, ages 45-60, in a cross-sectional study from the Data Registry on the Experiences of Aging, Menopause, and Sexuality (DREAMS). The study occurred at Mayo Clinic locations between May 2015 and December 2019 in Rochester, Minn., in Scottsdale, Ariz., and in Jacksonville, Fla.
The women were an average 53 years old and were primarily White, educated, and postmenopausal. Among the 4.6% of women with a self-reported history of PCOS, 56% of them reported depression symptoms, compared to 42% of women without PCOS. Those with PCOS also had nearly twice the prevalence of obesity – 42% versus 22.5% among women without PCOS – and had a higher average overall score on the Menopause Rating Scale (17.7 vs. 14.7; P < .001).
Although women with PCOS initially had a greater burden of psychological symptoms on the same scale, that association disappeared after adjustment for menopause status, body mass index, depression, anxiety, and current use of hormone therapy. Even after adjustment, however, women with PCOS had higher average scores for somatic symptoms (6.7 vs. 5.6) and urogenital symptoms (5.2 vs. 4.3) than those of women without PCOS (P < .001).
Severe or very severe hot flashes were no more likely in women with a history of PCOS than in the other women in the study.
”The mechanisms underlying the correlation between PCOS and menopause symptoms in the psychological and urogenital symptom domains requires further study, although the well-known association between PCOS and mood disorders may explain the high psychological symptom burden in these women during the menopause transition,” the authors concluded.
Rachael B. Smith, DO, clinical assistant professor of ob.gyn. at the University of Arizona in Phoenix, said she was not surprised to see an association between PCOS and menopause symptoms overall, but she was surprised that PCOS did not correlate with severity of vasomotor symptoms. But Dr. Smith pointed out that the sample size of women with PCOS is fairly small (n = 151).
“Given that PCOS prevalence is about 6%-10%, I feel this association should be further studied to improve our counseling and treatment for this PCOS population,” Dr. Smith, who was not involved in the research, said in an interview. “The take-home message for physicians is improved patient-tailored counseling that takes into account patients’ prior medical history of PCOS.”
Although it will require more research to find out, Dr. Smith said she suspects that PCOS and vasomotor symptoms are additive risk factors for cardiovascular disease. She also noted that the study is limited by the homogeneity of the study population.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Lobo and Dr. Smith had no disclosures.
Women with a history of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are more likely to experience somatic and urogenital symptoms post menopause, but they were no more likely to experience severe hot flashes than were other women with similar characteristics, according to research presented Sept. 24 at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society.
PCOS and vasomotor symptoms are each risk factors for cardiovascular disease, so researchers wanted to find out whether they were linked to one another, which might indicate that they are markers for the same underlying mechanisms that increase heart disease risk. The lack of an association, however, raises questions about how much each of these conditions might independently increase cardiovascular risk.
“Should we take a little more time to truly risk-assess these patients not just with their ASCVD risk score, but take into account that they have PCOS and they’re going through menopause, and how severe their hot flashes are?” asked Angie S. Lobo, MD, an internal medicine specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., when she discussed her findings in an interview.
The association between PCOS and urogenital symptoms was surprising, Dr. Lobo said, but she said she suspects the reason for the finding may be the self-reported nature of the study.
“If you ask the question, you get the answer,” Dr. Lobo said. ”Are we just not asking the right questions to our patients? And should we be doing this more often? This is an exciting finding because there’s so much room to improve the clinical care of our patients.”
The researchers analyzed data from 3,308 women, ages 45-60, in a cross-sectional study from the Data Registry on the Experiences of Aging, Menopause, and Sexuality (DREAMS). The study occurred at Mayo Clinic locations between May 2015 and December 2019 in Rochester, Minn., in Scottsdale, Ariz., and in Jacksonville, Fla.
The women were an average 53 years old and were primarily White, educated, and postmenopausal. Among the 4.6% of women with a self-reported history of PCOS, 56% of them reported depression symptoms, compared to 42% of women without PCOS. Those with PCOS also had nearly twice the prevalence of obesity – 42% versus 22.5% among women without PCOS – and had a higher average overall score on the Menopause Rating Scale (17.7 vs. 14.7; P < .001).
Although women with PCOS initially had a greater burden of psychological symptoms on the same scale, that association disappeared after adjustment for menopause status, body mass index, depression, anxiety, and current use of hormone therapy. Even after adjustment, however, women with PCOS had higher average scores for somatic symptoms (6.7 vs. 5.6) and urogenital symptoms (5.2 vs. 4.3) than those of women without PCOS (P < .001).
Severe or very severe hot flashes were no more likely in women with a history of PCOS than in the other women in the study.
”The mechanisms underlying the correlation between PCOS and menopause symptoms in the psychological and urogenital symptom domains requires further study, although the well-known association between PCOS and mood disorders may explain the high psychological symptom burden in these women during the menopause transition,” the authors concluded.
Rachael B. Smith, DO, clinical assistant professor of ob.gyn. at the University of Arizona in Phoenix, said she was not surprised to see an association between PCOS and menopause symptoms overall, but she was surprised that PCOS did not correlate with severity of vasomotor symptoms. But Dr. Smith pointed out that the sample size of women with PCOS is fairly small (n = 151).
“Given that PCOS prevalence is about 6%-10%, I feel this association should be further studied to improve our counseling and treatment for this PCOS population,” Dr. Smith, who was not involved in the research, said in an interview. “The take-home message for physicians is improved patient-tailored counseling that takes into account patients’ prior medical history of PCOS.”
Although it will require more research to find out, Dr. Smith said she suspects that PCOS and vasomotor symptoms are additive risk factors for cardiovascular disease. She also noted that the study is limited by the homogeneity of the study population.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Lobo and Dr. Smith had no disclosures.
Women with a history of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are more likely to experience somatic and urogenital symptoms post menopause, but they were no more likely to experience severe hot flashes than were other women with similar characteristics, according to research presented Sept. 24 at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society.
PCOS and vasomotor symptoms are each risk factors for cardiovascular disease, so researchers wanted to find out whether they were linked to one another, which might indicate that they are markers for the same underlying mechanisms that increase heart disease risk. The lack of an association, however, raises questions about how much each of these conditions might independently increase cardiovascular risk.
“Should we take a little more time to truly risk-assess these patients not just with their ASCVD risk score, but take into account that they have PCOS and they’re going through menopause, and how severe their hot flashes are?” asked Angie S. Lobo, MD, an internal medicine specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., when she discussed her findings in an interview.
The association between PCOS and urogenital symptoms was surprising, Dr. Lobo said, but she said she suspects the reason for the finding may be the self-reported nature of the study.
“If you ask the question, you get the answer,” Dr. Lobo said. ”Are we just not asking the right questions to our patients? And should we be doing this more often? This is an exciting finding because there’s so much room to improve the clinical care of our patients.”
The researchers analyzed data from 3,308 women, ages 45-60, in a cross-sectional study from the Data Registry on the Experiences of Aging, Menopause, and Sexuality (DREAMS). The study occurred at Mayo Clinic locations between May 2015 and December 2019 in Rochester, Minn., in Scottsdale, Ariz., and in Jacksonville, Fla.
The women were an average 53 years old and were primarily White, educated, and postmenopausal. Among the 4.6% of women with a self-reported history of PCOS, 56% of them reported depression symptoms, compared to 42% of women without PCOS. Those with PCOS also had nearly twice the prevalence of obesity – 42% versus 22.5% among women without PCOS – and had a higher average overall score on the Menopause Rating Scale (17.7 vs. 14.7; P < .001).
Although women with PCOS initially had a greater burden of psychological symptoms on the same scale, that association disappeared after adjustment for menopause status, body mass index, depression, anxiety, and current use of hormone therapy. Even after adjustment, however, women with PCOS had higher average scores for somatic symptoms (6.7 vs. 5.6) and urogenital symptoms (5.2 vs. 4.3) than those of women without PCOS (P < .001).
Severe or very severe hot flashes were no more likely in women with a history of PCOS than in the other women in the study.
”The mechanisms underlying the correlation between PCOS and menopause symptoms in the psychological and urogenital symptom domains requires further study, although the well-known association between PCOS and mood disorders may explain the high psychological symptom burden in these women during the menopause transition,” the authors concluded.
Rachael B. Smith, DO, clinical assistant professor of ob.gyn. at the University of Arizona in Phoenix, said she was not surprised to see an association between PCOS and menopause symptoms overall, but she was surprised that PCOS did not correlate with severity of vasomotor symptoms. But Dr. Smith pointed out that the sample size of women with PCOS is fairly small (n = 151).
“Given that PCOS prevalence is about 6%-10%, I feel this association should be further studied to improve our counseling and treatment for this PCOS population,” Dr. Smith, who was not involved in the research, said in an interview. “The take-home message for physicians is improved patient-tailored counseling that takes into account patients’ prior medical history of PCOS.”
Although it will require more research to find out, Dr. Smith said she suspects that PCOS and vasomotor symptoms are additive risk factors for cardiovascular disease. She also noted that the study is limited by the homogeneity of the study population.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Lobo and Dr. Smith had no disclosures.
FROM NAMS 2021
Updates to CDC’s STI guidelines relevant to midlife women too
Sexually transmitted infection rates have not increased as dramatically in older women as they have in women in their teens and 20s, but rates of chlamydia and gonorrhea in women over age 35 have seen a steady incline over the past decade, and syphilis rates have climbed steeply, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That makes the STI treatment guidelines released by the CDC in July even timelier for practitioners of menopause medicine, according to Michael S. Policar, MD, MPH, a professor emeritus of ob.gyn. and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco.
Dr. Policar discussed what clinicians need to know about STIs in midlife women at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. Even the nomenclature change in the guidelines from “sexually transmitted diseases” to “sexually transmitted infections” is important “because they want to acknowledge the fact that a lot of the sexually transmitted infections that we’re treating are asymptomatic, are colonizations, and are not yet diseases,” Dr. Policar said. “We’re trying to be much more expansive in thinking about finding these infections before they actually start causing morbidity in the form of a disease.”
Sexual history
The primary guidelines update for taking sexual history is the recommendation to ask patients about their intentions regarding pregnancy. The “5 Ps” of sexual history are now Partners, Practices, Protection from STIs, Past history of STIs, and Pregnancy intention.
“There should be a sixth P that has to do with pleasure questions,” Policar added. “We ask all the time for patients that we see in the context of perimenopausal and menopausal services, ‘Are you satisfied with your sexual relationship with your partner?’ Hopefully that will make it into the CDC guidelines as the sixth P at some point, but for now, that’s aspirational.”
In asking about partners, instead of asking patients whether they have sex with men, women, or both, clinicians should ask first if the patient is having sex of any kind – oral, vaginal, or anal – with anyone. From there, providers should ask how many sex partners the patient has had, the gender(s) of the partners, and whether they or their partners have other sex partners, using more gender-inclusive language.
When asking about practices, in addition to asking about the type of sexual contact patients have had, additional questions include whether the patient met their partners online or through apps, whether they or any of their partners use drugs, and whether the patient has exchanged sex for any needs, such as money, housing, or drugs. The additional questions can identify those at higher risk for STIs.
After reviewing the CDC’s list of risk factors for gonorrhea and chlamydia screening, Dr. Policar shared the screening list from the California Department of Public Health, which he finds more helpful:
- History of gonorrhea, chlamydia, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in the past 2 years.
- More than 1 sexual partner in the past year.
- New sexual partner within 90 days.
- Reason to believe that a sex partner has had other partners in the past year.
- Exchanging sex for drugs or money within the past year.
- Other factors identified locally, including prevalence of infection in the community.
STI screening guidelines
For those with a positive gonorrhea/chlamydia (GC/CT) screen, a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) vaginal swab is the preferred specimen source, and self-collection is fine for women of any age, Dr. Policar said. In addition, cis-women who received anal intercourse in the preceding year should consider undergoing a rectal GC/CT NAAT, and those who performed oral sex should consider a pharyngeal GC/CT NAAT, based on shared clinical decision-making. A rectal swab requires an insertion of 3-4 cm and a 360-degree twirl of the wrist, not the swab, to ensure you get a sample from the entire circumference. Pharyngeal samples require swabbing both tonsillar pillars while taking care for those who may gag.
For contact testing – asymptomatic people who have had a high-risk sexual exposure – providers should test for gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, and syphilis but not for herpes, high-risk HPV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, or bacterial vaginosis. “Maybe we’ll do a screen for trichomoniasis, and maybe we’ll offer herpes type 2 serology or antibody screening,” Dr. Policar said. Providers should also ask patients requesting contact testing if they have been vaccinated for hepatitis B. If not, “the conversation should be how can we get you vaccinated for hepatitis B,” Dr. Policar said.
HIV screening only needs to occur once between the ages of 15 and 65 for low-risk people and then once annually (or more often if necessary) for those who have a sex partner with HIV, use injectable drugs, engage in commercial sex work, have a new sex partner with unknown HIV status, received care at an STD or TB clinic, or were in a correctional facility or homeless shelter.
Those at increased risk for syphilis include men who have sex with men, men under age 29, and anyone living with HIV or who has a history of incarceration or a history of commercial sex work. In addition, African Americans have the greatest risk for syphilis of racial/ethnic groups, followed by Hispanics. Most adults only require hepatitis C screening with anti-hep C antibody testing once in their lifetime. Periodic hepatitis C screening should occur for people who inject drugs. If the screening is positive, providers should conduct an RNA polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test to determine whether a chronic infection is present.
Trichomoniasis screening should occur annually in women living with HIV or in correctional facilities. Others to consider screening include people with new or multiple sex partners, a history of STIs, inconsistent condom use, a history of sex work, and intravenous drug use. Dr. Policar also noted that several new assays, including NAAT, PCR, and a rapid test, are available for trichomoniasis.
STI treatment guidelines
For women with mucoprurulent cervicitis, the cause could be chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, trichomonas, mycoplasma, or even progesterone from pregnancy or contraception, Dr. Policar said. The new preferred treatment is 100 mg of doxycycline. The alternative, albeit less preferred, treatment is 1 g azithromycin.
The preferred treatment for chlamydia is now 100 mg oral doxycycline twice daily, or doxycycline 200 mg delayed-release once daily, for 7 days. Alternative regimens include 1 g oral azithromycin in a single dose or 500 mg oral levofloxacin once daily for 7 days. The switch to recommending doxycycline over azithromycin is based on recent evidence showing that doxycycline has a slightly higher efficacy for urogenital chlamydia and a substantially higher efficacy for rectal chlamydia. In addition, an increasing proportion of gonorrheal infections have shown resistance to azithromycin, particularly beginning in 2014.
Preferred treatment of new, uncomplicated gonorrhea infections of the cervix, urethra, rectum, and pharynx is one 500-mg dose of ceftriaxone for those weighing under 150 kg and 1 g for those weighing 150 kg or more. If ceftriaxone is unavailable, the new alternative recommended treatment for gonorrhea is 800 mg cefixime. For pharyngeal gonorrhea only, the CDC recommends a test-of-cure 7-14 days after treatment.
For gonorrheal infections, the CDC also recommends treatment with doxycycline if chlamydia has not been excluded, but the agency no longer recommends dual therapy with azithromycin unless it’s used in place of doxycycline for those who are pregnant, have an allergy, or may not be compliant with a 7-day doxycycline regimen.
The preferred treatment for bacterial vaginosis has not changed. The new recommended regimen for trichomoniasis is 500 mg oral metronidazole for 7 days, with the alternative being a single 2-g dose of tinidazole. Male partners should receive 2 g oral metronidazole. The CDC also notes that patients taking metronidazole no longer need to abstain from alcohol during treatment.
”Another area where the guidelines changed is in their description of expedited partner therapy, which means that, when we find an index case who has gonorrhea or chlamydia, we always have a discussion with her about getting her partners treated,” Dr. Policar said. “The CDC was quite clear that the responsibility for discussing partner treatment rests with us as the diagnosing provider” since city and county health departments don’t have the time or resources for contact tracing these STIs.
The two main ways to treat partners are to have the patient bring their partner(s) to the appointment with them or to do patient-delivered partner therapy. Ideally, clinicians who dispense their own medications can give the patient enough drugs to give her partner(s) a complete dose as well. Otherwise, providers can prescribe extra doses in the index patients’ name or write prescriptions in the partner’s name.
“In every state of the union now, it is legal for you to to prescribe antibiotics for partners sight unseen, Dr. Policar said.
Margaret Sullivan, MD, an ob.gyn. from rural western North Carolina, noted during the Q&A that an obstacle to partner therapy at her practice has been cost, particularly since many of the men don’t have insurance.
“I have not heard before of prescribing the extra doses for partners under the patient’s name,” Dr. Sullivan said. “I’ve thought about doing it, but [was worried about] it potentially being fraudulent if that patient has Medicaid and we’re prescribing extra doses under her name, so how do you work around that?”
Dr. Policar acknowledged that barrier and recommended that patients use the website/app Goodrx.com to find discounts for out-of-pocket generic medications. He also noted the occasional obstacle of pharmacists balking at filling a double or triple dose.
“What we’ve been suggesting in that circumstance is to literally copy that part of the CDC guidelines, which explains expedited partner therapy or patient-delivered partner therapy and send that off to the pharmacist so they can see that it’s a national recommendation of the CDC,” Dr. Policar said.
Claudia Rodriguez, MD, an ob.gyn. who works at Sherman Hospital in Elgin, Ill., asked about the CDC recommendations for HPV vaccination in older women. Although the CDC permits women over age 26 to receive the HPV vaccine, the agency does not “make a solid recommendation to have this done, which oftentimes makes a big difference in whether or not health insurance will actually pay for vaccination in that circumstance,” Dr. Policar said.
Patients are welcome to request the vaccine after shared decision-making, but “we should never present this as something which is routine,” he said. For women in their 50s, for example, “there’s virtually no data about any additional degree of protection that you would get” from HPV vaccination, Dr. Policar said in response to a similar question from Tara Allmen, MD, an ob.gyn. in New York City. “If you ask me for my personal clinical opinion about it, I would say it’s not going to be worth it,” he said.
Dr Policar had no disclosures. Disclosures were unavailable for attendees who spoke.
Sexually transmitted infection rates have not increased as dramatically in older women as they have in women in their teens and 20s, but rates of chlamydia and gonorrhea in women over age 35 have seen a steady incline over the past decade, and syphilis rates have climbed steeply, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That makes the STI treatment guidelines released by the CDC in July even timelier for practitioners of menopause medicine, according to Michael S. Policar, MD, MPH, a professor emeritus of ob.gyn. and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco.
Dr. Policar discussed what clinicians need to know about STIs in midlife women at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. Even the nomenclature change in the guidelines from “sexually transmitted diseases” to “sexually transmitted infections” is important “because they want to acknowledge the fact that a lot of the sexually transmitted infections that we’re treating are asymptomatic, are colonizations, and are not yet diseases,” Dr. Policar said. “We’re trying to be much more expansive in thinking about finding these infections before they actually start causing morbidity in the form of a disease.”
Sexual history
The primary guidelines update for taking sexual history is the recommendation to ask patients about their intentions regarding pregnancy. The “5 Ps” of sexual history are now Partners, Practices, Protection from STIs, Past history of STIs, and Pregnancy intention.
“There should be a sixth P that has to do with pleasure questions,” Policar added. “We ask all the time for patients that we see in the context of perimenopausal and menopausal services, ‘Are you satisfied with your sexual relationship with your partner?’ Hopefully that will make it into the CDC guidelines as the sixth P at some point, but for now, that’s aspirational.”
In asking about partners, instead of asking patients whether they have sex with men, women, or both, clinicians should ask first if the patient is having sex of any kind – oral, vaginal, or anal – with anyone. From there, providers should ask how many sex partners the patient has had, the gender(s) of the partners, and whether they or their partners have other sex partners, using more gender-inclusive language.
When asking about practices, in addition to asking about the type of sexual contact patients have had, additional questions include whether the patient met their partners online or through apps, whether they or any of their partners use drugs, and whether the patient has exchanged sex for any needs, such as money, housing, or drugs. The additional questions can identify those at higher risk for STIs.
After reviewing the CDC’s list of risk factors for gonorrhea and chlamydia screening, Dr. Policar shared the screening list from the California Department of Public Health, which he finds more helpful:
- History of gonorrhea, chlamydia, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in the past 2 years.
- More than 1 sexual partner in the past year.
- New sexual partner within 90 days.
- Reason to believe that a sex partner has had other partners in the past year.
- Exchanging sex for drugs or money within the past year.
- Other factors identified locally, including prevalence of infection in the community.
STI screening guidelines
For those with a positive gonorrhea/chlamydia (GC/CT) screen, a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) vaginal swab is the preferred specimen source, and self-collection is fine for women of any age, Dr. Policar said. In addition, cis-women who received anal intercourse in the preceding year should consider undergoing a rectal GC/CT NAAT, and those who performed oral sex should consider a pharyngeal GC/CT NAAT, based on shared clinical decision-making. A rectal swab requires an insertion of 3-4 cm and a 360-degree twirl of the wrist, not the swab, to ensure you get a sample from the entire circumference. Pharyngeal samples require swabbing both tonsillar pillars while taking care for those who may gag.
For contact testing – asymptomatic people who have had a high-risk sexual exposure – providers should test for gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, and syphilis but not for herpes, high-risk HPV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, or bacterial vaginosis. “Maybe we’ll do a screen for trichomoniasis, and maybe we’ll offer herpes type 2 serology or antibody screening,” Dr. Policar said. Providers should also ask patients requesting contact testing if they have been vaccinated for hepatitis B. If not, “the conversation should be how can we get you vaccinated for hepatitis B,” Dr. Policar said.
HIV screening only needs to occur once between the ages of 15 and 65 for low-risk people and then once annually (or more often if necessary) for those who have a sex partner with HIV, use injectable drugs, engage in commercial sex work, have a new sex partner with unknown HIV status, received care at an STD or TB clinic, or were in a correctional facility or homeless shelter.
Those at increased risk for syphilis include men who have sex with men, men under age 29, and anyone living with HIV or who has a history of incarceration or a history of commercial sex work. In addition, African Americans have the greatest risk for syphilis of racial/ethnic groups, followed by Hispanics. Most adults only require hepatitis C screening with anti-hep C antibody testing once in their lifetime. Periodic hepatitis C screening should occur for people who inject drugs. If the screening is positive, providers should conduct an RNA polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test to determine whether a chronic infection is present.
Trichomoniasis screening should occur annually in women living with HIV or in correctional facilities. Others to consider screening include people with new or multiple sex partners, a history of STIs, inconsistent condom use, a history of sex work, and intravenous drug use. Dr. Policar also noted that several new assays, including NAAT, PCR, and a rapid test, are available for trichomoniasis.
STI treatment guidelines
For women with mucoprurulent cervicitis, the cause could be chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, trichomonas, mycoplasma, or even progesterone from pregnancy or contraception, Dr. Policar said. The new preferred treatment is 100 mg of doxycycline. The alternative, albeit less preferred, treatment is 1 g azithromycin.
The preferred treatment for chlamydia is now 100 mg oral doxycycline twice daily, or doxycycline 200 mg delayed-release once daily, for 7 days. Alternative regimens include 1 g oral azithromycin in a single dose or 500 mg oral levofloxacin once daily for 7 days. The switch to recommending doxycycline over azithromycin is based on recent evidence showing that doxycycline has a slightly higher efficacy for urogenital chlamydia and a substantially higher efficacy for rectal chlamydia. In addition, an increasing proportion of gonorrheal infections have shown resistance to azithromycin, particularly beginning in 2014.
Preferred treatment of new, uncomplicated gonorrhea infections of the cervix, urethra, rectum, and pharynx is one 500-mg dose of ceftriaxone for those weighing under 150 kg and 1 g for those weighing 150 kg or more. If ceftriaxone is unavailable, the new alternative recommended treatment for gonorrhea is 800 mg cefixime. For pharyngeal gonorrhea only, the CDC recommends a test-of-cure 7-14 days after treatment.
For gonorrheal infections, the CDC also recommends treatment with doxycycline if chlamydia has not been excluded, but the agency no longer recommends dual therapy with azithromycin unless it’s used in place of doxycycline for those who are pregnant, have an allergy, or may not be compliant with a 7-day doxycycline regimen.
The preferred treatment for bacterial vaginosis has not changed. The new recommended regimen for trichomoniasis is 500 mg oral metronidazole for 7 days, with the alternative being a single 2-g dose of tinidazole. Male partners should receive 2 g oral metronidazole. The CDC also notes that patients taking metronidazole no longer need to abstain from alcohol during treatment.
”Another area where the guidelines changed is in their description of expedited partner therapy, which means that, when we find an index case who has gonorrhea or chlamydia, we always have a discussion with her about getting her partners treated,” Dr. Policar said. “The CDC was quite clear that the responsibility for discussing partner treatment rests with us as the diagnosing provider” since city and county health departments don’t have the time or resources for contact tracing these STIs.
The two main ways to treat partners are to have the patient bring their partner(s) to the appointment with them or to do patient-delivered partner therapy. Ideally, clinicians who dispense their own medications can give the patient enough drugs to give her partner(s) a complete dose as well. Otherwise, providers can prescribe extra doses in the index patients’ name or write prescriptions in the partner’s name.
“In every state of the union now, it is legal for you to to prescribe antibiotics for partners sight unseen, Dr. Policar said.
Margaret Sullivan, MD, an ob.gyn. from rural western North Carolina, noted during the Q&A that an obstacle to partner therapy at her practice has been cost, particularly since many of the men don’t have insurance.
“I have not heard before of prescribing the extra doses for partners under the patient’s name,” Dr. Sullivan said. “I’ve thought about doing it, but [was worried about] it potentially being fraudulent if that patient has Medicaid and we’re prescribing extra doses under her name, so how do you work around that?”
Dr. Policar acknowledged that barrier and recommended that patients use the website/app Goodrx.com to find discounts for out-of-pocket generic medications. He also noted the occasional obstacle of pharmacists balking at filling a double or triple dose.
“What we’ve been suggesting in that circumstance is to literally copy that part of the CDC guidelines, which explains expedited partner therapy or patient-delivered partner therapy and send that off to the pharmacist so they can see that it’s a national recommendation of the CDC,” Dr. Policar said.
Claudia Rodriguez, MD, an ob.gyn. who works at Sherman Hospital in Elgin, Ill., asked about the CDC recommendations for HPV vaccination in older women. Although the CDC permits women over age 26 to receive the HPV vaccine, the agency does not “make a solid recommendation to have this done, which oftentimes makes a big difference in whether or not health insurance will actually pay for vaccination in that circumstance,” Dr. Policar said.
Patients are welcome to request the vaccine after shared decision-making, but “we should never present this as something which is routine,” he said. For women in their 50s, for example, “there’s virtually no data about any additional degree of protection that you would get” from HPV vaccination, Dr. Policar said in response to a similar question from Tara Allmen, MD, an ob.gyn. in New York City. “If you ask me for my personal clinical opinion about it, I would say it’s not going to be worth it,” he said.
Dr Policar had no disclosures. Disclosures were unavailable for attendees who spoke.
Sexually transmitted infection rates have not increased as dramatically in older women as they have in women in their teens and 20s, but rates of chlamydia and gonorrhea in women over age 35 have seen a steady incline over the past decade, and syphilis rates have climbed steeply, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That makes the STI treatment guidelines released by the CDC in July even timelier for practitioners of menopause medicine, according to Michael S. Policar, MD, MPH, a professor emeritus of ob.gyn. and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco.
Dr. Policar discussed what clinicians need to know about STIs in midlife women at the hybrid annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. Even the nomenclature change in the guidelines from “sexually transmitted diseases” to “sexually transmitted infections” is important “because they want to acknowledge the fact that a lot of the sexually transmitted infections that we’re treating are asymptomatic, are colonizations, and are not yet diseases,” Dr. Policar said. “We’re trying to be much more expansive in thinking about finding these infections before they actually start causing morbidity in the form of a disease.”
Sexual history
The primary guidelines update for taking sexual history is the recommendation to ask patients about their intentions regarding pregnancy. The “5 Ps” of sexual history are now Partners, Practices, Protection from STIs, Past history of STIs, and Pregnancy intention.
“There should be a sixth P that has to do with pleasure questions,” Policar added. “We ask all the time for patients that we see in the context of perimenopausal and menopausal services, ‘Are you satisfied with your sexual relationship with your partner?’ Hopefully that will make it into the CDC guidelines as the sixth P at some point, but for now, that’s aspirational.”
In asking about partners, instead of asking patients whether they have sex with men, women, or both, clinicians should ask first if the patient is having sex of any kind – oral, vaginal, or anal – with anyone. From there, providers should ask how many sex partners the patient has had, the gender(s) of the partners, and whether they or their partners have other sex partners, using more gender-inclusive language.
When asking about practices, in addition to asking about the type of sexual contact patients have had, additional questions include whether the patient met their partners online or through apps, whether they or any of their partners use drugs, and whether the patient has exchanged sex for any needs, such as money, housing, or drugs. The additional questions can identify those at higher risk for STIs.
After reviewing the CDC’s list of risk factors for gonorrhea and chlamydia screening, Dr. Policar shared the screening list from the California Department of Public Health, which he finds more helpful:
- History of gonorrhea, chlamydia, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in the past 2 years.
- More than 1 sexual partner in the past year.
- New sexual partner within 90 days.
- Reason to believe that a sex partner has had other partners in the past year.
- Exchanging sex for drugs or money within the past year.
- Other factors identified locally, including prevalence of infection in the community.
STI screening guidelines
For those with a positive gonorrhea/chlamydia (GC/CT) screen, a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) vaginal swab is the preferred specimen source, and self-collection is fine for women of any age, Dr. Policar said. In addition, cis-women who received anal intercourse in the preceding year should consider undergoing a rectal GC/CT NAAT, and those who performed oral sex should consider a pharyngeal GC/CT NAAT, based on shared clinical decision-making. A rectal swab requires an insertion of 3-4 cm and a 360-degree twirl of the wrist, not the swab, to ensure you get a sample from the entire circumference. Pharyngeal samples require swabbing both tonsillar pillars while taking care for those who may gag.
For contact testing – asymptomatic people who have had a high-risk sexual exposure – providers should test for gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, and syphilis but not for herpes, high-risk HPV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, or bacterial vaginosis. “Maybe we’ll do a screen for trichomoniasis, and maybe we’ll offer herpes type 2 serology or antibody screening,” Dr. Policar said. Providers should also ask patients requesting contact testing if they have been vaccinated for hepatitis B. If not, “the conversation should be how can we get you vaccinated for hepatitis B,” Dr. Policar said.
HIV screening only needs to occur once between the ages of 15 and 65 for low-risk people and then once annually (or more often if necessary) for those who have a sex partner with HIV, use injectable drugs, engage in commercial sex work, have a new sex partner with unknown HIV status, received care at an STD or TB clinic, or were in a correctional facility or homeless shelter.
Those at increased risk for syphilis include men who have sex with men, men under age 29, and anyone living with HIV or who has a history of incarceration or a history of commercial sex work. In addition, African Americans have the greatest risk for syphilis of racial/ethnic groups, followed by Hispanics. Most adults only require hepatitis C screening with anti-hep C antibody testing once in their lifetime. Periodic hepatitis C screening should occur for people who inject drugs. If the screening is positive, providers should conduct an RNA polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test to determine whether a chronic infection is present.
Trichomoniasis screening should occur annually in women living with HIV or in correctional facilities. Others to consider screening include people with new or multiple sex partners, a history of STIs, inconsistent condom use, a history of sex work, and intravenous drug use. Dr. Policar also noted that several new assays, including NAAT, PCR, and a rapid test, are available for trichomoniasis.
STI treatment guidelines
For women with mucoprurulent cervicitis, the cause could be chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, trichomonas, mycoplasma, or even progesterone from pregnancy or contraception, Dr. Policar said. The new preferred treatment is 100 mg of doxycycline. The alternative, albeit less preferred, treatment is 1 g azithromycin.
The preferred treatment for chlamydia is now 100 mg oral doxycycline twice daily, or doxycycline 200 mg delayed-release once daily, for 7 days. Alternative regimens include 1 g oral azithromycin in a single dose or 500 mg oral levofloxacin once daily for 7 days. The switch to recommending doxycycline over azithromycin is based on recent evidence showing that doxycycline has a slightly higher efficacy for urogenital chlamydia and a substantially higher efficacy for rectal chlamydia. In addition, an increasing proportion of gonorrheal infections have shown resistance to azithromycin, particularly beginning in 2014.
Preferred treatment of new, uncomplicated gonorrhea infections of the cervix, urethra, rectum, and pharynx is one 500-mg dose of ceftriaxone for those weighing under 150 kg and 1 g for those weighing 150 kg or more. If ceftriaxone is unavailable, the new alternative recommended treatment for gonorrhea is 800 mg cefixime. For pharyngeal gonorrhea only, the CDC recommends a test-of-cure 7-14 days after treatment.
For gonorrheal infections, the CDC also recommends treatment with doxycycline if chlamydia has not been excluded, but the agency no longer recommends dual therapy with azithromycin unless it’s used in place of doxycycline for those who are pregnant, have an allergy, or may not be compliant with a 7-day doxycycline regimen.
The preferred treatment for bacterial vaginosis has not changed. The new recommended regimen for trichomoniasis is 500 mg oral metronidazole for 7 days, with the alternative being a single 2-g dose of tinidazole. Male partners should receive 2 g oral metronidazole. The CDC also notes that patients taking metronidazole no longer need to abstain from alcohol during treatment.
”Another area where the guidelines changed is in their description of expedited partner therapy, which means that, when we find an index case who has gonorrhea or chlamydia, we always have a discussion with her about getting her partners treated,” Dr. Policar said. “The CDC was quite clear that the responsibility for discussing partner treatment rests with us as the diagnosing provider” since city and county health departments don’t have the time or resources for contact tracing these STIs.
The two main ways to treat partners are to have the patient bring their partner(s) to the appointment with them or to do patient-delivered partner therapy. Ideally, clinicians who dispense their own medications can give the patient enough drugs to give her partner(s) a complete dose as well. Otherwise, providers can prescribe extra doses in the index patients’ name or write prescriptions in the partner’s name.
“In every state of the union now, it is legal for you to to prescribe antibiotics for partners sight unseen, Dr. Policar said.
Margaret Sullivan, MD, an ob.gyn. from rural western North Carolina, noted during the Q&A that an obstacle to partner therapy at her practice has been cost, particularly since many of the men don’t have insurance.
“I have not heard before of prescribing the extra doses for partners under the patient’s name,” Dr. Sullivan said. “I’ve thought about doing it, but [was worried about] it potentially being fraudulent if that patient has Medicaid and we’re prescribing extra doses under her name, so how do you work around that?”
Dr. Policar acknowledged that barrier and recommended that patients use the website/app Goodrx.com to find discounts for out-of-pocket generic medications. He also noted the occasional obstacle of pharmacists balking at filling a double or triple dose.
“What we’ve been suggesting in that circumstance is to literally copy that part of the CDC guidelines, which explains expedited partner therapy or patient-delivered partner therapy and send that off to the pharmacist so they can see that it’s a national recommendation of the CDC,” Dr. Policar said.
Claudia Rodriguez, MD, an ob.gyn. who works at Sherman Hospital in Elgin, Ill., asked about the CDC recommendations for HPV vaccination in older women. Although the CDC permits women over age 26 to receive the HPV vaccine, the agency does not “make a solid recommendation to have this done, which oftentimes makes a big difference in whether or not health insurance will actually pay for vaccination in that circumstance,” Dr. Policar said.
Patients are welcome to request the vaccine after shared decision-making, but “we should never present this as something which is routine,” he said. For women in their 50s, for example, “there’s virtually no data about any additional degree of protection that you would get” from HPV vaccination, Dr. Policar said in response to a similar question from Tara Allmen, MD, an ob.gyn. in New York City. “If you ask me for my personal clinical opinion about it, I would say it’s not going to be worth it,” he said.
Dr Policar had no disclosures. Disclosures were unavailable for attendees who spoke.
FROM NAMS 2021
COVID-19 disease may actually cause preeclampsia, suggests study
New evidence strongly suggests that COVID-19 disease causes an increased risk of preeclampsia and preterm birth in those who have an infection while pregnant, according to a retrospective observational study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Though the study was observational, its primary finding was a dose-response relationship between the severity of COVID-19 disease and the likelihood of preeclampsia or preterm birth, fulfilling a key criterion for establishing causality in an association.
“The fact that 43% (13/30) of the cases of preeclampsia diagnosed after SARS-Cov-2 infection were preterm preeclampsia (< 37 weeks) suggests that COVID-19 may be a cause for medically indicated preterm birth that contributes to the excess preterm birth delivery rate previously reported,” wrote Jonathan Lai, MD, of the Fetal Medicine Research Institute of King’s College Hospital, London, and colleagues. The study also found an increased likelihood of COVID-19 disease in those who had preeclampsia before their infection. “Whether preeclampsia can predispose COVID-19 some cases, or that the two conditions may co-occur because they share similar risk factors requires further investigation,” the authors wrote.
It’s also unclear whether the increased risk of pre-eclampsia is contributing to the higher preterm birth risk, according to Linda Eckert, MD, a professor of Ob.Gyn. at The University of Washington who specializes in maternal immunization.
“COVID is linked to preeclampsia in this study, and COVID is linked to preterm birth,” Dr. Eckert said in an interview. “The question of whether preeclampsia leading to preterm birth is also linked to infection is not possible to tease out in this study as all the factors are likely interrelated. There is a relationship between COVID and preterm birth absent preeclampsia.”
The researchers retrospectively examined data from 1,223 pregnant women who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 between February 2020 and March 2021 at any of 14 National Health Service maternity hospitals in the United Kingdom. The researchers compared the severity of disease among the women with their risk of preeclampsia as a primary outcome, followed by the outcomes of preterm birth and gestational age at delivery.
COVID-19 infections were classified as asymptomatic, mild illness (lacking shortness of breath, dyspnea, or abnormal chest imaging), moderate illness (evidence of lower respiratory disease but an oxygen saturation of at least 94%), and severe illness (requiring “high dependency or intensive care secondary to respiratory impairment/failure or multiorgan dysfunction”).
The researchers adjusted their analysis of preeclampsia to account for prior risk of preeclampsia based on maternal characteristics and medical history. Analysis of preterm birth risk included adjustment for maternal age, weight, height, race, method of conception, chronic hypertension, smoking, and diabetes.
Preeclampsia occurred in 4.2% of the women, and 17.6% of the women had a preterm birth. In addition, 1.3% of the cohort had a miscarriage, and there were 10 (0.81%) fetal deaths. Since 21 cases of preeclampsia occurred before the women tested positive, the researchers removed those cases from the analysis. Among the remaining 30 cases, 13 women had preterm preeclampsia and 17 had term preeclampsia.
When the researchers compared the study population’s risk of preeclampsia with that of a separate population with similar risk factors, they found a dose-response increased risk in those with COVID-19 infections. While 1.9% of asymptomatic patients had preeclampsia, incidence was 2.2% in patients with mild disease, 5.7% in those with moderate disease, and 11.1% in those with severe disease. Women with severe COVID-19 tended to be older and to have a higher body mass index.
After adjustments, women were nearly five times more likely to develop preeclampsia if they had severe COVID-19 compared to women with asymptomatic infection (adjusted relative risk [aRR] = 4.9). Those with moderate or severe disease had triple the risk of preeclampsia compared to those with mild or asymptomatic infection (aRR = 3.3).
To investigate whether having preeclampsia predisposes women to develop COVID-19 disease, the researchers compared the women who had preeclampsia before their infection with women in the study who never developed preeclampsia. Although they found a trend toward higher risk of moderate or severe COVID-19 following preeclampsia, the association was not significant before or after adjustment.
The researchers also found a dose-response relationship in risk of preterm birth. While 11.7% of asymptomatic patients had preterm birth, the incidence was 12.8% in those with mild COVID-19, 29.9% in those with moderate disease, and 69.4% in those with severe disease. Women with severe disease were more than five times more likely to have a preterm birth than were women with an asymptomatic infection (aRR = 5.64), and the risk of preterm birth was 2.5 times greater in women with moderate disease (aRR = 2.47).
“Moreover, there was a dose-response relationship between gestational age at delivery and the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection,” the authors reported. Mean gestational age at delivery was 38.7 weeks in asymptomatic women compared to 37.5 weeks for those with moderate disease and 33 weeks in those with severe disease (P < .001).
”The more severe the infection with SARS-CoV-2, the greater the risk of preeclampsia and preterm birth,” the authors wrote. “SARS-CoV-2 infection can lead to endothelial dysfunction, intravascular inflammation, proteinuria, activation of thrombin, and hypertension, which are all features of preeclampsia. Therefore, a causal relationship must be considered.”
A dose-response association is only one criterion for causality, however, so it’s still premature to say definitively that a causal relationship exists, Dr. Eckert said.
“More investigation in different populations across different ethnicities is needed before causality can be confidently assured,” she said.
Anthony Sciscione, DO, director of maternal-fetal medicine and the ob.gyn. residency at ChristianaCare in Delaware, agreed that the precise relationship between the two remains unresolved.
”We don’t know what causes preeclampsia,” but “we strongly suspect it has to do with a placental dysfunction, or endothelial dysfunction, and it’s really clear that women who get COVID have a much higher risk of preeclampsia,” Dr. Sciscione said in an interview. It’s possible that no real relationship exists between the two (or that greater surveillance of women with COVID-19 is picking up the relationship) but it’s more likely that one of two other situations is happening, Dr. Sciscione said. Either COVID-19 involves a syndrome that looks like preeclampsia in pregnant women, or the disease “leads to the cascade that causes preeclampsia,” he said.
One clear clinical implication of these findings is that “women who have severe COVID early in pregnancy may need to be watched more closely for signs of developing preeclampsia” and that “women with severe COVID are more likely to have preterm births,” Dr. Eckert said. “This absolutely lends support to the need for pregnant individuals to receive a COVID vaccine.”
Dr. Sciscione said his experience counseling pregnant patients about the vaccine has made it clear that patients generally want to do what’s safest for their babies and may feel uneasiness about the safety of the vaccine. “The truth is, now there’s mounting evidence that there are fetal effects, not just maternal effects” from COVID-19 disease. He added that preterm birth is associated with a variety of long-term adverse outcomes, such as cerebral palsy and learning disabilities.
“At this time it’s critically important that women be offered and get the vaccine because we know that people that are vaccinated don’t get as sick,” Dr. Sciscione said.
The research was funded by the Fetal Medicine Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Eckert have no disclosures. Dr. Sciscione is the associate editor of the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, where the study appeared.
New evidence strongly suggests that COVID-19 disease causes an increased risk of preeclampsia and preterm birth in those who have an infection while pregnant, according to a retrospective observational study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Though the study was observational, its primary finding was a dose-response relationship between the severity of COVID-19 disease and the likelihood of preeclampsia or preterm birth, fulfilling a key criterion for establishing causality in an association.
“The fact that 43% (13/30) of the cases of preeclampsia diagnosed after SARS-Cov-2 infection were preterm preeclampsia (< 37 weeks) suggests that COVID-19 may be a cause for medically indicated preterm birth that contributes to the excess preterm birth delivery rate previously reported,” wrote Jonathan Lai, MD, of the Fetal Medicine Research Institute of King’s College Hospital, London, and colleagues. The study also found an increased likelihood of COVID-19 disease in those who had preeclampsia before their infection. “Whether preeclampsia can predispose COVID-19 some cases, or that the two conditions may co-occur because they share similar risk factors requires further investigation,” the authors wrote.
It’s also unclear whether the increased risk of pre-eclampsia is contributing to the higher preterm birth risk, according to Linda Eckert, MD, a professor of Ob.Gyn. at The University of Washington who specializes in maternal immunization.
“COVID is linked to preeclampsia in this study, and COVID is linked to preterm birth,” Dr. Eckert said in an interview. “The question of whether preeclampsia leading to preterm birth is also linked to infection is not possible to tease out in this study as all the factors are likely interrelated. There is a relationship between COVID and preterm birth absent preeclampsia.”
The researchers retrospectively examined data from 1,223 pregnant women who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 between February 2020 and March 2021 at any of 14 National Health Service maternity hospitals in the United Kingdom. The researchers compared the severity of disease among the women with their risk of preeclampsia as a primary outcome, followed by the outcomes of preterm birth and gestational age at delivery.
COVID-19 infections were classified as asymptomatic, mild illness (lacking shortness of breath, dyspnea, or abnormal chest imaging), moderate illness (evidence of lower respiratory disease but an oxygen saturation of at least 94%), and severe illness (requiring “high dependency or intensive care secondary to respiratory impairment/failure or multiorgan dysfunction”).
The researchers adjusted their analysis of preeclampsia to account for prior risk of preeclampsia based on maternal characteristics and medical history. Analysis of preterm birth risk included adjustment for maternal age, weight, height, race, method of conception, chronic hypertension, smoking, and diabetes.
Preeclampsia occurred in 4.2% of the women, and 17.6% of the women had a preterm birth. In addition, 1.3% of the cohort had a miscarriage, and there were 10 (0.81%) fetal deaths. Since 21 cases of preeclampsia occurred before the women tested positive, the researchers removed those cases from the analysis. Among the remaining 30 cases, 13 women had preterm preeclampsia and 17 had term preeclampsia.
When the researchers compared the study population’s risk of preeclampsia with that of a separate population with similar risk factors, they found a dose-response increased risk in those with COVID-19 infections. While 1.9% of asymptomatic patients had preeclampsia, incidence was 2.2% in patients with mild disease, 5.7% in those with moderate disease, and 11.1% in those with severe disease. Women with severe COVID-19 tended to be older and to have a higher body mass index.
After adjustments, women were nearly five times more likely to develop preeclampsia if they had severe COVID-19 compared to women with asymptomatic infection (adjusted relative risk [aRR] = 4.9). Those with moderate or severe disease had triple the risk of preeclampsia compared to those with mild or asymptomatic infection (aRR = 3.3).
To investigate whether having preeclampsia predisposes women to develop COVID-19 disease, the researchers compared the women who had preeclampsia before their infection with women in the study who never developed preeclampsia. Although they found a trend toward higher risk of moderate or severe COVID-19 following preeclampsia, the association was not significant before or after adjustment.
The researchers also found a dose-response relationship in risk of preterm birth. While 11.7% of asymptomatic patients had preterm birth, the incidence was 12.8% in those with mild COVID-19, 29.9% in those with moderate disease, and 69.4% in those with severe disease. Women with severe disease were more than five times more likely to have a preterm birth than were women with an asymptomatic infection (aRR = 5.64), and the risk of preterm birth was 2.5 times greater in women with moderate disease (aRR = 2.47).
“Moreover, there was a dose-response relationship between gestational age at delivery and the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection,” the authors reported. Mean gestational age at delivery was 38.7 weeks in asymptomatic women compared to 37.5 weeks for those with moderate disease and 33 weeks in those with severe disease (P < .001).
”The more severe the infection with SARS-CoV-2, the greater the risk of preeclampsia and preterm birth,” the authors wrote. “SARS-CoV-2 infection can lead to endothelial dysfunction, intravascular inflammation, proteinuria, activation of thrombin, and hypertension, which are all features of preeclampsia. Therefore, a causal relationship must be considered.”
A dose-response association is only one criterion for causality, however, so it’s still premature to say definitively that a causal relationship exists, Dr. Eckert said.
“More investigation in different populations across different ethnicities is needed before causality can be confidently assured,” she said.
Anthony Sciscione, DO, director of maternal-fetal medicine and the ob.gyn. residency at ChristianaCare in Delaware, agreed that the precise relationship between the two remains unresolved.
”We don’t know what causes preeclampsia,” but “we strongly suspect it has to do with a placental dysfunction, or endothelial dysfunction, and it’s really clear that women who get COVID have a much higher risk of preeclampsia,” Dr. Sciscione said in an interview. It’s possible that no real relationship exists between the two (or that greater surveillance of women with COVID-19 is picking up the relationship) but it’s more likely that one of two other situations is happening, Dr. Sciscione said. Either COVID-19 involves a syndrome that looks like preeclampsia in pregnant women, or the disease “leads to the cascade that causes preeclampsia,” he said.
One clear clinical implication of these findings is that “women who have severe COVID early in pregnancy may need to be watched more closely for signs of developing preeclampsia” and that “women with severe COVID are more likely to have preterm births,” Dr. Eckert said. “This absolutely lends support to the need for pregnant individuals to receive a COVID vaccine.”
Dr. Sciscione said his experience counseling pregnant patients about the vaccine has made it clear that patients generally want to do what’s safest for their babies and may feel uneasiness about the safety of the vaccine. “The truth is, now there’s mounting evidence that there are fetal effects, not just maternal effects” from COVID-19 disease. He added that preterm birth is associated with a variety of long-term adverse outcomes, such as cerebral palsy and learning disabilities.
“At this time it’s critically important that women be offered and get the vaccine because we know that people that are vaccinated don’t get as sick,” Dr. Sciscione said.
The research was funded by the Fetal Medicine Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Eckert have no disclosures. Dr. Sciscione is the associate editor of the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, where the study appeared.
New evidence strongly suggests that COVID-19 disease causes an increased risk of preeclampsia and preterm birth in those who have an infection while pregnant, according to a retrospective observational study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Though the study was observational, its primary finding was a dose-response relationship between the severity of COVID-19 disease and the likelihood of preeclampsia or preterm birth, fulfilling a key criterion for establishing causality in an association.
“The fact that 43% (13/30) of the cases of preeclampsia diagnosed after SARS-Cov-2 infection were preterm preeclampsia (< 37 weeks) suggests that COVID-19 may be a cause for medically indicated preterm birth that contributes to the excess preterm birth delivery rate previously reported,” wrote Jonathan Lai, MD, of the Fetal Medicine Research Institute of King’s College Hospital, London, and colleagues. The study also found an increased likelihood of COVID-19 disease in those who had preeclampsia before their infection. “Whether preeclampsia can predispose COVID-19 some cases, or that the two conditions may co-occur because they share similar risk factors requires further investigation,” the authors wrote.
It’s also unclear whether the increased risk of pre-eclampsia is contributing to the higher preterm birth risk, according to Linda Eckert, MD, a professor of Ob.Gyn. at The University of Washington who specializes in maternal immunization.
“COVID is linked to preeclampsia in this study, and COVID is linked to preterm birth,” Dr. Eckert said in an interview. “The question of whether preeclampsia leading to preterm birth is also linked to infection is not possible to tease out in this study as all the factors are likely interrelated. There is a relationship between COVID and preterm birth absent preeclampsia.”
The researchers retrospectively examined data from 1,223 pregnant women who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 between February 2020 and March 2021 at any of 14 National Health Service maternity hospitals in the United Kingdom. The researchers compared the severity of disease among the women with their risk of preeclampsia as a primary outcome, followed by the outcomes of preterm birth and gestational age at delivery.
COVID-19 infections were classified as asymptomatic, mild illness (lacking shortness of breath, dyspnea, or abnormal chest imaging), moderate illness (evidence of lower respiratory disease but an oxygen saturation of at least 94%), and severe illness (requiring “high dependency or intensive care secondary to respiratory impairment/failure or multiorgan dysfunction”).
The researchers adjusted their analysis of preeclampsia to account for prior risk of preeclampsia based on maternal characteristics and medical history. Analysis of preterm birth risk included adjustment for maternal age, weight, height, race, method of conception, chronic hypertension, smoking, and diabetes.
Preeclampsia occurred in 4.2% of the women, and 17.6% of the women had a preterm birth. In addition, 1.3% of the cohort had a miscarriage, and there were 10 (0.81%) fetal deaths. Since 21 cases of preeclampsia occurred before the women tested positive, the researchers removed those cases from the analysis. Among the remaining 30 cases, 13 women had preterm preeclampsia and 17 had term preeclampsia.
When the researchers compared the study population’s risk of preeclampsia with that of a separate population with similar risk factors, they found a dose-response increased risk in those with COVID-19 infections. While 1.9% of asymptomatic patients had preeclampsia, incidence was 2.2% in patients with mild disease, 5.7% in those with moderate disease, and 11.1% in those with severe disease. Women with severe COVID-19 tended to be older and to have a higher body mass index.
After adjustments, women were nearly five times more likely to develop preeclampsia if they had severe COVID-19 compared to women with asymptomatic infection (adjusted relative risk [aRR] = 4.9). Those with moderate or severe disease had triple the risk of preeclampsia compared to those with mild or asymptomatic infection (aRR = 3.3).
To investigate whether having preeclampsia predisposes women to develop COVID-19 disease, the researchers compared the women who had preeclampsia before their infection with women in the study who never developed preeclampsia. Although they found a trend toward higher risk of moderate or severe COVID-19 following preeclampsia, the association was not significant before or after adjustment.
The researchers also found a dose-response relationship in risk of preterm birth. While 11.7% of asymptomatic patients had preterm birth, the incidence was 12.8% in those with mild COVID-19, 29.9% in those with moderate disease, and 69.4% in those with severe disease. Women with severe disease were more than five times more likely to have a preterm birth than were women with an asymptomatic infection (aRR = 5.64), and the risk of preterm birth was 2.5 times greater in women with moderate disease (aRR = 2.47).
“Moreover, there was a dose-response relationship between gestational age at delivery and the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection,” the authors reported. Mean gestational age at delivery was 38.7 weeks in asymptomatic women compared to 37.5 weeks for those with moderate disease and 33 weeks in those with severe disease (P < .001).
”The more severe the infection with SARS-CoV-2, the greater the risk of preeclampsia and preterm birth,” the authors wrote. “SARS-CoV-2 infection can lead to endothelial dysfunction, intravascular inflammation, proteinuria, activation of thrombin, and hypertension, which are all features of preeclampsia. Therefore, a causal relationship must be considered.”
A dose-response association is only one criterion for causality, however, so it’s still premature to say definitively that a causal relationship exists, Dr. Eckert said.
“More investigation in different populations across different ethnicities is needed before causality can be confidently assured,” she said.
Anthony Sciscione, DO, director of maternal-fetal medicine and the ob.gyn. residency at ChristianaCare in Delaware, agreed that the precise relationship between the two remains unresolved.
”We don’t know what causes preeclampsia,” but “we strongly suspect it has to do with a placental dysfunction, or endothelial dysfunction, and it’s really clear that women who get COVID have a much higher risk of preeclampsia,” Dr. Sciscione said in an interview. It’s possible that no real relationship exists between the two (or that greater surveillance of women with COVID-19 is picking up the relationship) but it’s more likely that one of two other situations is happening, Dr. Sciscione said. Either COVID-19 involves a syndrome that looks like preeclampsia in pregnant women, or the disease “leads to the cascade that causes preeclampsia,” he said.
One clear clinical implication of these findings is that “women who have severe COVID early in pregnancy may need to be watched more closely for signs of developing preeclampsia” and that “women with severe COVID are more likely to have preterm births,” Dr. Eckert said. “This absolutely lends support to the need for pregnant individuals to receive a COVID vaccine.”
Dr. Sciscione said his experience counseling pregnant patients about the vaccine has made it clear that patients generally want to do what’s safest for their babies and may feel uneasiness about the safety of the vaccine. “The truth is, now there’s mounting evidence that there are fetal effects, not just maternal effects” from COVID-19 disease. He added that preterm birth is associated with a variety of long-term adverse outcomes, such as cerebral palsy and learning disabilities.
“At this time it’s critically important that women be offered and get the vaccine because we know that people that are vaccinated don’t get as sick,” Dr. Sciscione said.
The research was funded by the Fetal Medicine Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Eckert have no disclosures. Dr. Sciscione is the associate editor of the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, where the study appeared.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
Bystander rescue breathing CPR in kids tied to better survival
Children who receive CPR with both rescue breathing and compressions from a bystander have greater odds of survival without serious brain damage than if they receive CPR with compressions only, according to a study published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Specifically, a child has a 61% better chance of surviving with good neurologic outcomes if they receive compression-only CPR versus no bystander resuscitation, but that child is more than twice as likely to survive if he or she receives rescue breathing as well.
The study’s clinical implications are most important for bystander CPR training, lead author Maryam Y. Naim, MD, MSCE, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Many programs teach compression-only CPR to lay rescuers, and there should be a renewed emphasis on rescue breathing for the possibility a lay rescuer has to perform CPR on a child,” Dr. Naim said.
That said, if a bystander is unfamiliar with how to properly administer rescue breathing or has concerns about hygiene or infection on someone they don’t know, Dr. Naim advises doing compression-only CPR, especially if the child is older than age 1 year. “If a child is younger than a year of age please consider giving rescue breaths with chest compressions,” she added.
Dr. Naim and colleagues analyzed 13,060 pediatric out-of-hospital cardiac arrests from the Cardiac Arrest Registry to Enhance Survival database, which includes data from 911 call centers, emergency medical services (EMS) providers, and receiving hospitals across 28 states. The data sample included all cases age 18 years or younger who experienced nontraumatic out-of-hospital cardiac arrest between January 2013 and December 2019, excluding those with obvious signs of death or a “do not resuscitate” order.
“Because the etiology of cardiac arrest in children is difficult to determine, especially in cases that result in death, all nontraumatic cases were included regardless of presumed etiology, including respiratory, cardiac, drowning, electrocution, or other,” the authors wrote. The researchers defined neurologically favorable survival, the primary endpoint, as “a cerebral performance category score of 1 (no neurologic disability) or 2 (moderate disability)” at discharge. Neurologically unfavorable survival included a score of 3 (severe disability), 4 (coma or vegetative state), or death.
Among the 10,429 cases ultimately analyzed after exclusions and missing data, 46.5% received bystander CPR. Slightly more than half of these (55.6%) received compression-only CPR while the other 45.3% received rescue-breathing CPR.
Dr. Naim was surprised that compression-only CPR was the most common form of CPR given to children with cardiac arrest because the current American Heart Association/International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation recommendations note rescue breathing as the preferred form in children.
That preference exists because respiratory failure occurs more often in children than in adults as a cause of cardiac arrest, explained Sandra Weiss, MD, an interventional cardiologist and the medical director of the cardiac intensive care unit at ChristianaCare’s Christiana Hospital in Newark, Del.
Because of that, “it’s not surprising that if you give respiratory resuscitation to a child who’s arresting from a respiratory cause that they’re going to do better than if you just do chest compressions,” said Dr. Weiss, who was not involved in the study.
The study found the most common presumed cause of arrest to be cardiac, occurring in 44.4% of cases, but it was closely followed by respiratory in nearly one-third of cases (32.8%).
Infants younger than age 1 year were the most common age group to have a cardiac arrest, making up more than all other ages combined. Most out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occurred in a home and were observed by someone when they happened. While rates of bystander CPR did not change during the study’s 6-year period, the incidence of compression-only CPR increased. Lay people without medical training provided the CPR in 93.6% of cases.
Only 8.6% of cardiac arrest cases resulted in neurologically favorable survival, a rate which remained steady throughout the study period. The rate increased with increasing age, at 4.6% of infants, 10.6% of children, and 16.5% of adolescents.
Those who received CPR with rescue breathing had more than double the odds of neurologically favorable survival than if they hadn’t received CPR at all (adjusted odds ratio, 2.16). Survival with a positive neurologic outcome was 1.6 times more likely with compression-only CPR than no CPR (aOR, 1.61). When researchers compared the two forms of CPR, inclusion of rescue breathing increased the child’s likelihood of survival without neurologic sequelae by 36% (aOR, 1.36).
Despite these findings, however, Dr. Weiss agrees with Dr. Naim that offering compression-only CPR is preferable to offering no CPR at all.
“All resuscitation is better than no resuscitation, regardless of whether it’s compression only or respiratory breathing,” Dr. Weiss said in an interview. “The average lay person is probably going to do the easiest thing, and survivability is going to be increased by doing anything rather than nothing.”
Dr. Weiss also noted that it’s easier to instruct people how to do chest compressions, especially, for example, during an emergency phone call with a dispatcher while waiting for EMS to arrive.
“It’s absolutely imperative for people to get the basics, and the basics are compressions,” she said. “That’s really what is the most vital component of all resuscitative efforts, regardless of whether it’s adult or pediatrics.”
Dr. Weiss also acknowledges that laypeople may feel particularly less comfortable administering rescue breaths to a child they don’t know in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. Even if the odds are low that the specific child experiencing a cardiac arrest is necessarily infectious, the AHA guidelines include the caveat that, “if there’s a concern for infection transmissibility, that compression only is acceptable,” Dr. Weiss said. “It’s a reality for our current state.”
The superiority of rescue-breathing CPR to compression-only CPR was true across all age groups, but compression-only CPR still resulted in better survival odds than no CPR at all for all age groups except infants, in whom only rescue breathing was associated with a statistically significant increased likelihood of neurologically favorable survival.
Protective factors for positive outcomes included being younger than age 1 year, the arrest being witnessed, and a having shockable rhythm. Risk factors reducing survival included being Black, being in a home, and cardiac arrests linked with automated external defibrillator use before EMS arrived.
The CARES program was previously funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and is now funded by the American Red Cross, the AHA, Stryker, and Emory University. Dr. Naim was further supported by Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the American Red Cross. The authors and Dr. Weiss disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children who receive CPR with both rescue breathing and compressions from a bystander have greater odds of survival without serious brain damage than if they receive CPR with compressions only, according to a study published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Specifically, a child has a 61% better chance of surviving with good neurologic outcomes if they receive compression-only CPR versus no bystander resuscitation, but that child is more than twice as likely to survive if he or she receives rescue breathing as well.
The study’s clinical implications are most important for bystander CPR training, lead author Maryam Y. Naim, MD, MSCE, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Many programs teach compression-only CPR to lay rescuers, and there should be a renewed emphasis on rescue breathing for the possibility a lay rescuer has to perform CPR on a child,” Dr. Naim said.
That said, if a bystander is unfamiliar with how to properly administer rescue breathing or has concerns about hygiene or infection on someone they don’t know, Dr. Naim advises doing compression-only CPR, especially if the child is older than age 1 year. “If a child is younger than a year of age please consider giving rescue breaths with chest compressions,” she added.
Dr. Naim and colleagues analyzed 13,060 pediatric out-of-hospital cardiac arrests from the Cardiac Arrest Registry to Enhance Survival database, which includes data from 911 call centers, emergency medical services (EMS) providers, and receiving hospitals across 28 states. The data sample included all cases age 18 years or younger who experienced nontraumatic out-of-hospital cardiac arrest between January 2013 and December 2019, excluding those with obvious signs of death or a “do not resuscitate” order.
“Because the etiology of cardiac arrest in children is difficult to determine, especially in cases that result in death, all nontraumatic cases were included regardless of presumed etiology, including respiratory, cardiac, drowning, electrocution, or other,” the authors wrote. The researchers defined neurologically favorable survival, the primary endpoint, as “a cerebral performance category score of 1 (no neurologic disability) or 2 (moderate disability)” at discharge. Neurologically unfavorable survival included a score of 3 (severe disability), 4 (coma or vegetative state), or death.
Among the 10,429 cases ultimately analyzed after exclusions and missing data, 46.5% received bystander CPR. Slightly more than half of these (55.6%) received compression-only CPR while the other 45.3% received rescue-breathing CPR.
Dr. Naim was surprised that compression-only CPR was the most common form of CPR given to children with cardiac arrest because the current American Heart Association/International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation recommendations note rescue breathing as the preferred form in children.
That preference exists because respiratory failure occurs more often in children than in adults as a cause of cardiac arrest, explained Sandra Weiss, MD, an interventional cardiologist and the medical director of the cardiac intensive care unit at ChristianaCare’s Christiana Hospital in Newark, Del.
Because of that, “it’s not surprising that if you give respiratory resuscitation to a child who’s arresting from a respiratory cause that they’re going to do better than if you just do chest compressions,” said Dr. Weiss, who was not involved in the study.
The study found the most common presumed cause of arrest to be cardiac, occurring in 44.4% of cases, but it was closely followed by respiratory in nearly one-third of cases (32.8%).
Infants younger than age 1 year were the most common age group to have a cardiac arrest, making up more than all other ages combined. Most out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occurred in a home and were observed by someone when they happened. While rates of bystander CPR did not change during the study’s 6-year period, the incidence of compression-only CPR increased. Lay people without medical training provided the CPR in 93.6% of cases.
Only 8.6% of cardiac arrest cases resulted in neurologically favorable survival, a rate which remained steady throughout the study period. The rate increased with increasing age, at 4.6% of infants, 10.6% of children, and 16.5% of adolescents.
Those who received CPR with rescue breathing had more than double the odds of neurologically favorable survival than if they hadn’t received CPR at all (adjusted odds ratio, 2.16). Survival with a positive neurologic outcome was 1.6 times more likely with compression-only CPR than no CPR (aOR, 1.61). When researchers compared the two forms of CPR, inclusion of rescue breathing increased the child’s likelihood of survival without neurologic sequelae by 36% (aOR, 1.36).
Despite these findings, however, Dr. Weiss agrees with Dr. Naim that offering compression-only CPR is preferable to offering no CPR at all.
“All resuscitation is better than no resuscitation, regardless of whether it’s compression only or respiratory breathing,” Dr. Weiss said in an interview. “The average lay person is probably going to do the easiest thing, and survivability is going to be increased by doing anything rather than nothing.”
Dr. Weiss also noted that it’s easier to instruct people how to do chest compressions, especially, for example, during an emergency phone call with a dispatcher while waiting for EMS to arrive.
“It’s absolutely imperative for people to get the basics, and the basics are compressions,” she said. “That’s really what is the most vital component of all resuscitative efforts, regardless of whether it’s adult or pediatrics.”
Dr. Weiss also acknowledges that laypeople may feel particularly less comfortable administering rescue breaths to a child they don’t know in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. Even if the odds are low that the specific child experiencing a cardiac arrest is necessarily infectious, the AHA guidelines include the caveat that, “if there’s a concern for infection transmissibility, that compression only is acceptable,” Dr. Weiss said. “It’s a reality for our current state.”
The superiority of rescue-breathing CPR to compression-only CPR was true across all age groups, but compression-only CPR still resulted in better survival odds than no CPR at all for all age groups except infants, in whom only rescue breathing was associated with a statistically significant increased likelihood of neurologically favorable survival.
Protective factors for positive outcomes included being younger than age 1 year, the arrest being witnessed, and a having shockable rhythm. Risk factors reducing survival included being Black, being in a home, and cardiac arrests linked with automated external defibrillator use before EMS arrived.
The CARES program was previously funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and is now funded by the American Red Cross, the AHA, Stryker, and Emory University. Dr. Naim was further supported by Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the American Red Cross. The authors and Dr. Weiss disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children who receive CPR with both rescue breathing and compressions from a bystander have greater odds of survival without serious brain damage than if they receive CPR with compressions only, according to a study published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Specifically, a child has a 61% better chance of surviving with good neurologic outcomes if they receive compression-only CPR versus no bystander resuscitation, but that child is more than twice as likely to survive if he or she receives rescue breathing as well.
The study’s clinical implications are most important for bystander CPR training, lead author Maryam Y. Naim, MD, MSCE, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Many programs teach compression-only CPR to lay rescuers, and there should be a renewed emphasis on rescue breathing for the possibility a lay rescuer has to perform CPR on a child,” Dr. Naim said.
That said, if a bystander is unfamiliar with how to properly administer rescue breathing or has concerns about hygiene or infection on someone they don’t know, Dr. Naim advises doing compression-only CPR, especially if the child is older than age 1 year. “If a child is younger than a year of age please consider giving rescue breaths with chest compressions,” she added.
Dr. Naim and colleagues analyzed 13,060 pediatric out-of-hospital cardiac arrests from the Cardiac Arrest Registry to Enhance Survival database, which includes data from 911 call centers, emergency medical services (EMS) providers, and receiving hospitals across 28 states. The data sample included all cases age 18 years or younger who experienced nontraumatic out-of-hospital cardiac arrest between January 2013 and December 2019, excluding those with obvious signs of death or a “do not resuscitate” order.
“Because the etiology of cardiac arrest in children is difficult to determine, especially in cases that result in death, all nontraumatic cases were included regardless of presumed etiology, including respiratory, cardiac, drowning, electrocution, or other,” the authors wrote. The researchers defined neurologically favorable survival, the primary endpoint, as “a cerebral performance category score of 1 (no neurologic disability) or 2 (moderate disability)” at discharge. Neurologically unfavorable survival included a score of 3 (severe disability), 4 (coma or vegetative state), or death.
Among the 10,429 cases ultimately analyzed after exclusions and missing data, 46.5% received bystander CPR. Slightly more than half of these (55.6%) received compression-only CPR while the other 45.3% received rescue-breathing CPR.
Dr. Naim was surprised that compression-only CPR was the most common form of CPR given to children with cardiac arrest because the current American Heart Association/International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation recommendations note rescue breathing as the preferred form in children.
That preference exists because respiratory failure occurs more often in children than in adults as a cause of cardiac arrest, explained Sandra Weiss, MD, an interventional cardiologist and the medical director of the cardiac intensive care unit at ChristianaCare’s Christiana Hospital in Newark, Del.
Because of that, “it’s not surprising that if you give respiratory resuscitation to a child who’s arresting from a respiratory cause that they’re going to do better than if you just do chest compressions,” said Dr. Weiss, who was not involved in the study.
The study found the most common presumed cause of arrest to be cardiac, occurring in 44.4% of cases, but it was closely followed by respiratory in nearly one-third of cases (32.8%).
Infants younger than age 1 year were the most common age group to have a cardiac arrest, making up more than all other ages combined. Most out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occurred in a home and were observed by someone when they happened. While rates of bystander CPR did not change during the study’s 6-year period, the incidence of compression-only CPR increased. Lay people without medical training provided the CPR in 93.6% of cases.
Only 8.6% of cardiac arrest cases resulted in neurologically favorable survival, a rate which remained steady throughout the study period. The rate increased with increasing age, at 4.6% of infants, 10.6% of children, and 16.5% of adolescents.
Those who received CPR with rescue breathing had more than double the odds of neurologically favorable survival than if they hadn’t received CPR at all (adjusted odds ratio, 2.16). Survival with a positive neurologic outcome was 1.6 times more likely with compression-only CPR than no CPR (aOR, 1.61). When researchers compared the two forms of CPR, inclusion of rescue breathing increased the child’s likelihood of survival without neurologic sequelae by 36% (aOR, 1.36).
Despite these findings, however, Dr. Weiss agrees with Dr. Naim that offering compression-only CPR is preferable to offering no CPR at all.
“All resuscitation is better than no resuscitation, regardless of whether it’s compression only or respiratory breathing,” Dr. Weiss said in an interview. “The average lay person is probably going to do the easiest thing, and survivability is going to be increased by doing anything rather than nothing.”
Dr. Weiss also noted that it’s easier to instruct people how to do chest compressions, especially, for example, during an emergency phone call with a dispatcher while waiting for EMS to arrive.
“It’s absolutely imperative for people to get the basics, and the basics are compressions,” she said. “That’s really what is the most vital component of all resuscitative efforts, regardless of whether it’s adult or pediatrics.”
Dr. Weiss also acknowledges that laypeople may feel particularly less comfortable administering rescue breaths to a child they don’t know in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. Even if the odds are low that the specific child experiencing a cardiac arrest is necessarily infectious, the AHA guidelines include the caveat that, “if there’s a concern for infection transmissibility, that compression only is acceptable,” Dr. Weiss said. “It’s a reality for our current state.”
The superiority of rescue-breathing CPR to compression-only CPR was true across all age groups, but compression-only CPR still resulted in better survival odds than no CPR at all for all age groups except infants, in whom only rescue breathing was associated with a statistically significant increased likelihood of neurologically favorable survival.
Protective factors for positive outcomes included being younger than age 1 year, the arrest being witnessed, and a having shockable rhythm. Risk factors reducing survival included being Black, being in a home, and cardiac arrests linked with automated external defibrillator use before EMS arrived.
The CARES program was previously funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and is now funded by the American Red Cross, the AHA, Stryker, and Emory University. Dr. Naim was further supported by Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the American Red Cross. The authors and Dr. Weiss disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Prevalence of high-risk HPV types dwindled since vaccine approval
Young women who received the quadrivalent human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine had fewer and fewer infections with high-risk HPV strains covered by the vaccine year after year, but the incidence of high-risk strains that were not covered by the vaccine increased over the same 12-year period, researchers report in a study published August 23 in JAMA Open Network.
“One of the unique contributions that this study provides is the evaluation of a real-world example of the HPV infection rates following immunization in a population of adolescent girls and young adult women at a single health center in a large U.S. city, reflecting strong evidence of vaccine effectiveness,” write Nicolas F. Schlecht, PhD, a professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, and his colleagues. “Previous surveillance studies from the U.S. have involved older women and populations with relatively low vaccine coverage.”
In addition to supporting the value of continuing to vaccinate teens against HPV, the findings underscore the importance of continuing to screen women for cervical cancer, Dr. Schlecht said in an interview.
“HPV has not and is not going away,” he said. “We need to keep on our toes with screening and other measures to continue to prevent the development of cervix cancer,” including monitoring different high-risk HPV types and keeping a close eye on cervical precancer rates, particularly CIN3 and cervix cancer, he said. “The vaccines are definitely a good thing. Just getting rid of HPV16 is an amazing accomplishment.”
Kevin Ault, MD, a professor of ob/gyn and academic specialist director of clinical and translational research at the University of Kansas, Kansas City, told this news organization that other studies have had similar findings, but this one is larger with longer follow-up.
“The take-home message is that vaccines work, and this is especially true for the HPV vaccine,” said Dr. Ault, who was not involved in the research. “The vaccine prevents HPV infections and the consequences of these infections, such as cervical cancer. The results are consistent with other studies in different settings, so they are likely generalizable.”
The researchers collected data from October 2007, shortly after the vaccine was approved, through September 2019 on sexually active adolescent and young women aged 13 to 21 years who had received the HPV vaccine and had agreed to follow-up assessments every 6 months until they turned 26. Each follow-up included the collecting of samples of cervical and anal cells for polymerase chain reaction testing for the presence of HPV types.
More than half of the 1,453 participants were Hispanic (58.8%), and half were Black (50.4%), including 15% Hispanic and Black patients. The average age of the participants was 18 years. They were tracked for a median 2.4 years. Nearly half the participants (48%) received the HPV vaccine prior to sexual debut.
For the longitudinal study, the researchers adjusted for participants’ age, the year they received the vaccine, and the years since they were vaccinated. They also tracked breakthrough infections for the four types of HPV covered by the vaccine in participants who received the vaccine before sexual debut.
“We evaluated whether infection rates for HPV have changed since the administration of the vaccine by assessing longitudinally the probability of HPV detection over time among vaccinated participants while adjusting for changes in cohort characteristics over time,” the researchers write. In their statistical analysis, they made adjustments for the number of vaccine doses participants received before their first study visit, age at sexual debut, age at first vaccine dose, number of sexual partners in the preceding 6 months, consistency of condom use during sex, history of a positive chlamydia test, and, for anal HPV analyses, whether the participants had had anal sex in the previous 6 months.
The average age at first intercourse remained steady at 15 years throughout the study, but the average age of vaccination dropped from 18 years in 2008 to 12 years in 2019 (P < .001). More than half the participants (64%) had had at least three lifetime sexual partners at baseline.
After adjustment for age, the researchers found that the incidence of the four HPV types covered by the vaccine – HPV-6, HPV-11, HPV-16, and HPV-18 – dropped more each year, shifting from 9.1% from 2008-2010 to 4.7% from 2017-2019. The effect was even greater among those vaccinated prior to sexual debut; for those patients, the incidence of the four vaccine types dropped from 8.8% to 1.7% over the course of the study. Declines over time also occurred for anal types HPV-31 (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 0.76) and HPV-45 (aOR = 0.77). Those vaccinated prior to any sexual intercourse had 19% lower odds of infection per year with a vaccine-covered HPV type.
“We were really excited to see that the types targeted by the vaccines were considerably lower over time in our population,” Dr. Schlecht told this news organization. “This is an important observation, since most of these types are the most worrisome for cervical cancer.”
They were surprised, however, to see overall HPV prevalence increase over time, particularly with the high-risk HPV types that were not covered by the quadrivalent vaccine.
Prevalence of cervical high-risk types not in the vaccine increased from 25.1% from 2008-2010 to 30.5% from 2017-2019. Odds of detection of high-risk HPV types not covered by the vaccine increased 8% each year, particularly for HPV-56 and HPV-68; anal HPV types increased 11% each year. Neither age nor recent number of sexual partners affected the findings.
“The underlying mechanisms for the observed increased detection of specific non-vaccine HPV types over time are not yet clear.”
“We hope this doesn’t translate into some increase in cervical neoplasia that is unanticipated,” Dr. Schlecht said. He noted that the attributable risks for cancer associated with nonvaccine high-risk HPV types remain low. “Theoretical concerns are one thing; actual data is what drives the show,” he said.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Schlecht has served on advisory boards for Merck, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), and PDS Biotechnology. One author previously served on a GSK advisory board, and another worked with Merck on an early vaccine trial. Dr. Ault has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Young women who received the quadrivalent human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine had fewer and fewer infections with high-risk HPV strains covered by the vaccine year after year, but the incidence of high-risk strains that were not covered by the vaccine increased over the same 12-year period, researchers report in a study published August 23 in JAMA Open Network.
“One of the unique contributions that this study provides is the evaluation of a real-world example of the HPV infection rates following immunization in a population of adolescent girls and young adult women at a single health center in a large U.S. city, reflecting strong evidence of vaccine effectiveness,” write Nicolas F. Schlecht, PhD, a professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, and his colleagues. “Previous surveillance studies from the U.S. have involved older women and populations with relatively low vaccine coverage.”
In addition to supporting the value of continuing to vaccinate teens against HPV, the findings underscore the importance of continuing to screen women for cervical cancer, Dr. Schlecht said in an interview.
“HPV has not and is not going away,” he said. “We need to keep on our toes with screening and other measures to continue to prevent the development of cervix cancer,” including monitoring different high-risk HPV types and keeping a close eye on cervical precancer rates, particularly CIN3 and cervix cancer, he said. “The vaccines are definitely a good thing. Just getting rid of HPV16 is an amazing accomplishment.”
Kevin Ault, MD, a professor of ob/gyn and academic specialist director of clinical and translational research at the University of Kansas, Kansas City, told this news organization that other studies have had similar findings, but this one is larger with longer follow-up.
“The take-home message is that vaccines work, and this is especially true for the HPV vaccine,” said Dr. Ault, who was not involved in the research. “The vaccine prevents HPV infections and the consequences of these infections, such as cervical cancer. The results are consistent with other studies in different settings, so they are likely generalizable.”
The researchers collected data from October 2007, shortly after the vaccine was approved, through September 2019 on sexually active adolescent and young women aged 13 to 21 years who had received the HPV vaccine and had agreed to follow-up assessments every 6 months until they turned 26. Each follow-up included the collecting of samples of cervical and anal cells for polymerase chain reaction testing for the presence of HPV types.
More than half of the 1,453 participants were Hispanic (58.8%), and half were Black (50.4%), including 15% Hispanic and Black patients. The average age of the participants was 18 years. They were tracked for a median 2.4 years. Nearly half the participants (48%) received the HPV vaccine prior to sexual debut.
For the longitudinal study, the researchers adjusted for participants’ age, the year they received the vaccine, and the years since they were vaccinated. They also tracked breakthrough infections for the four types of HPV covered by the vaccine in participants who received the vaccine before sexual debut.
“We evaluated whether infection rates for HPV have changed since the administration of the vaccine by assessing longitudinally the probability of HPV detection over time among vaccinated participants while adjusting for changes in cohort characteristics over time,” the researchers write. In their statistical analysis, they made adjustments for the number of vaccine doses participants received before their first study visit, age at sexual debut, age at first vaccine dose, number of sexual partners in the preceding 6 months, consistency of condom use during sex, history of a positive chlamydia test, and, for anal HPV analyses, whether the participants had had anal sex in the previous 6 months.
The average age at first intercourse remained steady at 15 years throughout the study, but the average age of vaccination dropped from 18 years in 2008 to 12 years in 2019 (P < .001). More than half the participants (64%) had had at least three lifetime sexual partners at baseline.
After adjustment for age, the researchers found that the incidence of the four HPV types covered by the vaccine – HPV-6, HPV-11, HPV-16, and HPV-18 – dropped more each year, shifting from 9.1% from 2008-2010 to 4.7% from 2017-2019. The effect was even greater among those vaccinated prior to sexual debut; for those patients, the incidence of the four vaccine types dropped from 8.8% to 1.7% over the course of the study. Declines over time also occurred for anal types HPV-31 (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 0.76) and HPV-45 (aOR = 0.77). Those vaccinated prior to any sexual intercourse had 19% lower odds of infection per year with a vaccine-covered HPV type.
“We were really excited to see that the types targeted by the vaccines were considerably lower over time in our population,” Dr. Schlecht told this news organization. “This is an important observation, since most of these types are the most worrisome for cervical cancer.”
They were surprised, however, to see overall HPV prevalence increase over time, particularly with the high-risk HPV types that were not covered by the quadrivalent vaccine.
Prevalence of cervical high-risk types not in the vaccine increased from 25.1% from 2008-2010 to 30.5% from 2017-2019. Odds of detection of high-risk HPV types not covered by the vaccine increased 8% each year, particularly for HPV-56 and HPV-68; anal HPV types increased 11% each year. Neither age nor recent number of sexual partners affected the findings.
“The underlying mechanisms for the observed increased detection of specific non-vaccine HPV types over time are not yet clear.”
“We hope this doesn’t translate into some increase in cervical neoplasia that is unanticipated,” Dr. Schlecht said. He noted that the attributable risks for cancer associated with nonvaccine high-risk HPV types remain low. “Theoretical concerns are one thing; actual data is what drives the show,” he said.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Schlecht has served on advisory boards for Merck, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), and PDS Biotechnology. One author previously served on a GSK advisory board, and another worked with Merck on an early vaccine trial. Dr. Ault has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Young women who received the quadrivalent human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine had fewer and fewer infections with high-risk HPV strains covered by the vaccine year after year, but the incidence of high-risk strains that were not covered by the vaccine increased over the same 12-year period, researchers report in a study published August 23 in JAMA Open Network.
“One of the unique contributions that this study provides is the evaluation of a real-world example of the HPV infection rates following immunization in a population of adolescent girls and young adult women at a single health center in a large U.S. city, reflecting strong evidence of vaccine effectiveness,” write Nicolas F. Schlecht, PhD, a professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, and his colleagues. “Previous surveillance studies from the U.S. have involved older women and populations with relatively low vaccine coverage.”
In addition to supporting the value of continuing to vaccinate teens against HPV, the findings underscore the importance of continuing to screen women for cervical cancer, Dr. Schlecht said in an interview.
“HPV has not and is not going away,” he said. “We need to keep on our toes with screening and other measures to continue to prevent the development of cervix cancer,” including monitoring different high-risk HPV types and keeping a close eye on cervical precancer rates, particularly CIN3 and cervix cancer, he said. “The vaccines are definitely a good thing. Just getting rid of HPV16 is an amazing accomplishment.”
Kevin Ault, MD, a professor of ob/gyn and academic specialist director of clinical and translational research at the University of Kansas, Kansas City, told this news organization that other studies have had similar findings, but this one is larger with longer follow-up.
“The take-home message is that vaccines work, and this is especially true for the HPV vaccine,” said Dr. Ault, who was not involved in the research. “The vaccine prevents HPV infections and the consequences of these infections, such as cervical cancer. The results are consistent with other studies in different settings, so they are likely generalizable.”
The researchers collected data from October 2007, shortly after the vaccine was approved, through September 2019 on sexually active adolescent and young women aged 13 to 21 years who had received the HPV vaccine and had agreed to follow-up assessments every 6 months until they turned 26. Each follow-up included the collecting of samples of cervical and anal cells for polymerase chain reaction testing for the presence of HPV types.
More than half of the 1,453 participants were Hispanic (58.8%), and half were Black (50.4%), including 15% Hispanic and Black patients. The average age of the participants was 18 years. They were tracked for a median 2.4 years. Nearly half the participants (48%) received the HPV vaccine prior to sexual debut.
For the longitudinal study, the researchers adjusted for participants’ age, the year they received the vaccine, and the years since they were vaccinated. They also tracked breakthrough infections for the four types of HPV covered by the vaccine in participants who received the vaccine before sexual debut.
“We evaluated whether infection rates for HPV have changed since the administration of the vaccine by assessing longitudinally the probability of HPV detection over time among vaccinated participants while adjusting for changes in cohort characteristics over time,” the researchers write. In their statistical analysis, they made adjustments for the number of vaccine doses participants received before their first study visit, age at sexual debut, age at first vaccine dose, number of sexual partners in the preceding 6 months, consistency of condom use during sex, history of a positive chlamydia test, and, for anal HPV analyses, whether the participants had had anal sex in the previous 6 months.
The average age at first intercourse remained steady at 15 years throughout the study, but the average age of vaccination dropped from 18 years in 2008 to 12 years in 2019 (P < .001). More than half the participants (64%) had had at least three lifetime sexual partners at baseline.
After adjustment for age, the researchers found that the incidence of the four HPV types covered by the vaccine – HPV-6, HPV-11, HPV-16, and HPV-18 – dropped more each year, shifting from 9.1% from 2008-2010 to 4.7% from 2017-2019. The effect was even greater among those vaccinated prior to sexual debut; for those patients, the incidence of the four vaccine types dropped from 8.8% to 1.7% over the course of the study. Declines over time also occurred for anal types HPV-31 (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 0.76) and HPV-45 (aOR = 0.77). Those vaccinated prior to any sexual intercourse had 19% lower odds of infection per year with a vaccine-covered HPV type.
“We were really excited to see that the types targeted by the vaccines were considerably lower over time in our population,” Dr. Schlecht told this news organization. “This is an important observation, since most of these types are the most worrisome for cervical cancer.”
They were surprised, however, to see overall HPV prevalence increase over time, particularly with the high-risk HPV types that were not covered by the quadrivalent vaccine.
Prevalence of cervical high-risk types not in the vaccine increased from 25.1% from 2008-2010 to 30.5% from 2017-2019. Odds of detection of high-risk HPV types not covered by the vaccine increased 8% each year, particularly for HPV-56 and HPV-68; anal HPV types increased 11% each year. Neither age nor recent number of sexual partners affected the findings.
“The underlying mechanisms for the observed increased detection of specific non-vaccine HPV types over time are not yet clear.”
“We hope this doesn’t translate into some increase in cervical neoplasia that is unanticipated,” Dr. Schlecht said. He noted that the attributable risks for cancer associated with nonvaccine high-risk HPV types remain low. “Theoretical concerns are one thing; actual data is what drives the show,” he said.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Schlecht has served on advisory boards for Merck, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), and PDS Biotechnology. One author previously served on a GSK advisory board, and another worked with Merck on an early vaccine trial. Dr. Ault has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 mitigation measures led to shifts in typical annual respiratory virus patterns
Nonpharmaceutical interventions, such as masking, staying home, limiting travel, and social distancing, have been doing more than reducing the risk for COVID-19. They’re also having an impact on infection rates and the timing of seasonal surges of other common respiratory diseases, according to an article published July 23 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Typically, respiratory pathogens such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), common cold coronaviruses, parainfluenza viruses, and respiratory adenoviruses increase in the fall and remain high throughout winter, following the same basic patterns as influenza. Although the historically low rates of influenza remained low into spring 2021, that’s not the case for several other common respiratory viruses.
“Clinicians should be aware of increases in some respiratory virus activity and remain vigilant for off-season increases,” wrote Sonja J. Olsen, PhD, and her colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. She told this news organization that clinicians should use multipathogen testing to help guide treatment.
The authors also underscore the importance of fall influenza vaccination campaigns for anyone aged 6 months or older.
Timothy Brewer, MD, MPH, a professor of medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), and of epidemiology at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health, agreed that it’s important for health care professionals to consider off-season illnesses in their patients.
“Practitioners should be aware that if they see a sick child in the summer, outside of what normally might be influenza season, but they look like they have influenza, consider potentially influenza and test for it, because it might be possible that we may have disrupted that natural pattern,” Dr. Brewer told this news organization. Dr. Brewer, who was not involved in the CDC research, said it’s also “critically important” to encourage influenza vaccination as the season approaches.
The CDC researchers used the U.S. World Health Organization Collaborating Laboratories System and the CDC’s National Respiratory and Enteric Virus Surveillance System to analyze virologic data from Oct. 3, 2020, to May 22, 2021, for influenza and Jan. 4, 2020, to May 22, 2021, for other respiratory viruses. The authors compared virus circulation during these periods to circulation during the same dates from four previous years.
Data to calculate influenza and RSV hospitalization rates came from the Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network and RSV Hospitalization Surveillance Network.
The authors report that flu activity dropped dramatically in March 2020 to its lowest levels since 1997, the earliest season for which data are available. Only 0.2% of more than 1 million specimens tested positive for influenza; the rate of hospitalizations for lab-confirmed flu was 0.8 per 100,000 people. Flu levels remained low through the summer, fall, and on to May 2021.
A potential drawback to this low activity, however, is a more prevalent and severe upcoming flu season, the authors write. The repeated exposure to flu viruses every year often “does not lead to illness, but it does serve to boost our immune response to influenza viruses,” Dr. Olsen said in an interview. “The absence of influenza viruses in the community over the last year means that we are not getting these regular boosts to our immune system. When we finally get exposed, our body may mount a weak response, and this could mean we develop a more clinically severe illness.”
Children are most susceptible to that phenomenon because they haven’t had a lifetime of exposure to flu viruses, Dr. Olsen said.
“An immunologically naive child may be more likely to develop a severe illness than someone who has lived through several influenza seasons,” she said. “This is why it is especially important for everyone 6 months and older to get vaccinated against influenza this season.”
Rhinovirus and enterovirus infections rebounded fairly quickly after their decline in March 2020 and started increasing in May 2020 until they reached “near prepandemic seasonal levels,” the authors write.
RSV infections dropped from 15.3% of weekly positive results in January 2020 to 1.4% by April and then stayed below 1% through the end of 2020. In past years, weekly positive results climbed to 3% in October and peaked at 12.5% to 16.7% in late December. Instead, RSV weekly positive results began increasing in April 2021, rising from 1.1% to 2.8% in May.
The “unusually timed” late spring increase in RSV “is probably associated with various nonpharmaceutical measures that have been in place but are now relaxing,” Dr. Olsen stated.
The RSV hospitalization rate was 0.3 per 100,000 people from October 2020 to April 2021, compared to 27.1 and 33.4 per 100,000 people in the previous 2 years. Of all RSV hospitalizations in the past year, 76.5% occurred in April-May 2021.
Rates of illness caused by the four common human coronaviruses (OC43, NL63, 229E, and HKU1) dropped from 7.5% of weekly positive results in January 2020 to 1.3% in April 2020 and stayed below 1% through February 2021. Then they climbed to 6.6% by May 2021. Infection rates of parainfluenza viruses types 1-4 similarly dropped from 2.6% in January 2020 to 1% in March 2020 and stayed below 1% until April 2021. Since then, rates of the common coronaviruses increased to 6.6% and parainfluenza viruses to 10.9% in May 2021.
Normally, parainfluenza viruses peak in October-November and May-June, so “the current increase could represent a return to prepandemic seasonality,” the authors write.
Human pneumoviruses’ weekly positive results initially increased from 4.2% in January 2020 to 7% in March and then fell to 1.9% the second week of April and remained below 1% through May 2021. In typical years, these viruses peak from 6.2% to 7.7% in March-April. Respiratory adenovirus activity similarly dropped to historically low levels in April 2021 and then began increasing to reach 3% by May 2021, the usual level for that month.
“The different circulation patterns observed across respiratory viruses probably also reflect differences in the virus transmission routes and how effective various nonpharmaceutical measures are at stopping transmission,” Dr. Olsen said in an interview. “As pandemic mitigation measures continue to be adjusted, we expect to see more changes in the circulation of these viruses, including a return to prepandemic circulation, as seen for rhinoviruses and enteroviruses.”
Rhinovirus and enterovirus rates dropped from 14.9% in March 2020 to 3.2% in May – lower than typical – and then climbed to a peak in October 2020. The peak (21.7% weekly positive results) was, however, still lower than the usual median of 32.8%. After dropping to 9.9% in January 2021, it then rose 19.1% in May, potentially reflecting “the usual spring peak that has occurred in previous years,” the authors write.
The authors note that it’s not yet clear how the COVID-19 pandemic and related mitigation measures will continue to affect respiratory virus circulation.
The authors hypothesize that the reasons for a seeming return to seasonal activity of respiratory adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, and enteroviruses could involve “different transmission mechanisms, the role of asymptomatic transmission, and prolonged survival of these nonenveloped viruses on surfaces, all of which might make these viruses less susceptible to nonpharmaceutical interventions.”
Dr. Brewer, of UCLA, agreed.
All the viruses basically “flatline except for adenoviruses and enteroviruses, and they behave a little differently in terms of how they spread,” he said. “Enteroviruses are much more likely to be fecal-oral spread than the other viruses [in the study].”
The delayed circulation of parainfluenza and human coronaviruses may have resulted from suspension of in-person classes through late winter 2020, they write, but that doesn’t explain the relative absence of pneumovirus activity, which usually affects the same young pediatric populations as RSV.
Dr. Brewer said California is seeing a surge of RSV right now, as are many states, especially throughout in the South. He’s not surprised by RSV’s deferred season, because those most affected – children younger than 2 years – are less likely to wear masks now and were “not going to daycare, not being out in public” in 2020. “As people are doing more activities, that’s probably why RSV has been starting to go up since April,” he said.
Despite the fact that, unlike many East Asian cultures, the United States has not traditionally been a mask-wearing culture, Dr. Brewer wouldn’t be surprised if more Americans begin wearing masks during flu season. “Hopefully another thing that will come out of this is better hand hygiene, with people just getting used to washing their hands more, particularly after they come home from being out,” he added.
Dr. Brewer similarly emphasized the importance of flu vaccination for the upcoming season, especially for younger children who may have poorer natural immunity to influenza, owing to its low circulation rates in 2020-2021.
The study was funded by the CDC. Dr. Brewer and Dr. Olsen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nonpharmaceutical interventions, such as masking, staying home, limiting travel, and social distancing, have been doing more than reducing the risk for COVID-19. They’re also having an impact on infection rates and the timing of seasonal surges of other common respiratory diseases, according to an article published July 23 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Typically, respiratory pathogens such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), common cold coronaviruses, parainfluenza viruses, and respiratory adenoviruses increase in the fall and remain high throughout winter, following the same basic patterns as influenza. Although the historically low rates of influenza remained low into spring 2021, that’s not the case for several other common respiratory viruses.
“Clinicians should be aware of increases in some respiratory virus activity and remain vigilant for off-season increases,” wrote Sonja J. Olsen, PhD, and her colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. She told this news organization that clinicians should use multipathogen testing to help guide treatment.
The authors also underscore the importance of fall influenza vaccination campaigns for anyone aged 6 months or older.
Timothy Brewer, MD, MPH, a professor of medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), and of epidemiology at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health, agreed that it’s important for health care professionals to consider off-season illnesses in their patients.
“Practitioners should be aware that if they see a sick child in the summer, outside of what normally might be influenza season, but they look like they have influenza, consider potentially influenza and test for it, because it might be possible that we may have disrupted that natural pattern,” Dr. Brewer told this news organization. Dr. Brewer, who was not involved in the CDC research, said it’s also “critically important” to encourage influenza vaccination as the season approaches.
The CDC researchers used the U.S. World Health Organization Collaborating Laboratories System and the CDC’s National Respiratory and Enteric Virus Surveillance System to analyze virologic data from Oct. 3, 2020, to May 22, 2021, for influenza and Jan. 4, 2020, to May 22, 2021, for other respiratory viruses. The authors compared virus circulation during these periods to circulation during the same dates from four previous years.
Data to calculate influenza and RSV hospitalization rates came from the Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network and RSV Hospitalization Surveillance Network.
The authors report that flu activity dropped dramatically in March 2020 to its lowest levels since 1997, the earliest season for which data are available. Only 0.2% of more than 1 million specimens tested positive for influenza; the rate of hospitalizations for lab-confirmed flu was 0.8 per 100,000 people. Flu levels remained low through the summer, fall, and on to May 2021.
A potential drawback to this low activity, however, is a more prevalent and severe upcoming flu season, the authors write. The repeated exposure to flu viruses every year often “does not lead to illness, but it does serve to boost our immune response to influenza viruses,” Dr. Olsen said in an interview. “The absence of influenza viruses in the community over the last year means that we are not getting these regular boosts to our immune system. When we finally get exposed, our body may mount a weak response, and this could mean we develop a more clinically severe illness.”
Children are most susceptible to that phenomenon because they haven’t had a lifetime of exposure to flu viruses, Dr. Olsen said.
“An immunologically naive child may be more likely to develop a severe illness than someone who has lived through several influenza seasons,” she said. “This is why it is especially important for everyone 6 months and older to get vaccinated against influenza this season.”
Rhinovirus and enterovirus infections rebounded fairly quickly after their decline in March 2020 and started increasing in May 2020 until they reached “near prepandemic seasonal levels,” the authors write.
RSV infections dropped from 15.3% of weekly positive results in January 2020 to 1.4% by April and then stayed below 1% through the end of 2020. In past years, weekly positive results climbed to 3% in October and peaked at 12.5% to 16.7% in late December. Instead, RSV weekly positive results began increasing in April 2021, rising from 1.1% to 2.8% in May.
The “unusually timed” late spring increase in RSV “is probably associated with various nonpharmaceutical measures that have been in place but are now relaxing,” Dr. Olsen stated.
The RSV hospitalization rate was 0.3 per 100,000 people from October 2020 to April 2021, compared to 27.1 and 33.4 per 100,000 people in the previous 2 years. Of all RSV hospitalizations in the past year, 76.5% occurred in April-May 2021.
Rates of illness caused by the four common human coronaviruses (OC43, NL63, 229E, and HKU1) dropped from 7.5% of weekly positive results in January 2020 to 1.3% in April 2020 and stayed below 1% through February 2021. Then they climbed to 6.6% by May 2021. Infection rates of parainfluenza viruses types 1-4 similarly dropped from 2.6% in January 2020 to 1% in March 2020 and stayed below 1% until April 2021. Since then, rates of the common coronaviruses increased to 6.6% and parainfluenza viruses to 10.9% in May 2021.
Normally, parainfluenza viruses peak in October-November and May-June, so “the current increase could represent a return to prepandemic seasonality,” the authors write.
Human pneumoviruses’ weekly positive results initially increased from 4.2% in January 2020 to 7% in March and then fell to 1.9% the second week of April and remained below 1% through May 2021. In typical years, these viruses peak from 6.2% to 7.7% in March-April. Respiratory adenovirus activity similarly dropped to historically low levels in April 2021 and then began increasing to reach 3% by May 2021, the usual level for that month.
“The different circulation patterns observed across respiratory viruses probably also reflect differences in the virus transmission routes and how effective various nonpharmaceutical measures are at stopping transmission,” Dr. Olsen said in an interview. “As pandemic mitigation measures continue to be adjusted, we expect to see more changes in the circulation of these viruses, including a return to prepandemic circulation, as seen for rhinoviruses and enteroviruses.”
Rhinovirus and enterovirus rates dropped from 14.9% in March 2020 to 3.2% in May – lower than typical – and then climbed to a peak in October 2020. The peak (21.7% weekly positive results) was, however, still lower than the usual median of 32.8%. After dropping to 9.9% in January 2021, it then rose 19.1% in May, potentially reflecting “the usual spring peak that has occurred in previous years,” the authors write.
The authors note that it’s not yet clear how the COVID-19 pandemic and related mitigation measures will continue to affect respiratory virus circulation.
The authors hypothesize that the reasons for a seeming return to seasonal activity of respiratory adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, and enteroviruses could involve “different transmission mechanisms, the role of asymptomatic transmission, and prolonged survival of these nonenveloped viruses on surfaces, all of which might make these viruses less susceptible to nonpharmaceutical interventions.”
Dr. Brewer, of UCLA, agreed.
All the viruses basically “flatline except for adenoviruses and enteroviruses, and they behave a little differently in terms of how they spread,” he said. “Enteroviruses are much more likely to be fecal-oral spread than the other viruses [in the study].”
The delayed circulation of parainfluenza and human coronaviruses may have resulted from suspension of in-person classes through late winter 2020, they write, but that doesn’t explain the relative absence of pneumovirus activity, which usually affects the same young pediatric populations as RSV.
Dr. Brewer said California is seeing a surge of RSV right now, as are many states, especially throughout in the South. He’s not surprised by RSV’s deferred season, because those most affected – children younger than 2 years – are less likely to wear masks now and were “not going to daycare, not being out in public” in 2020. “As people are doing more activities, that’s probably why RSV has been starting to go up since April,” he said.
Despite the fact that, unlike many East Asian cultures, the United States has not traditionally been a mask-wearing culture, Dr. Brewer wouldn’t be surprised if more Americans begin wearing masks during flu season. “Hopefully another thing that will come out of this is better hand hygiene, with people just getting used to washing their hands more, particularly after they come home from being out,” he added.
Dr. Brewer similarly emphasized the importance of flu vaccination for the upcoming season, especially for younger children who may have poorer natural immunity to influenza, owing to its low circulation rates in 2020-2021.
The study was funded by the CDC. Dr. Brewer and Dr. Olsen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nonpharmaceutical interventions, such as masking, staying home, limiting travel, and social distancing, have been doing more than reducing the risk for COVID-19. They’re also having an impact on infection rates and the timing of seasonal surges of other common respiratory diseases, according to an article published July 23 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Typically, respiratory pathogens such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), common cold coronaviruses, parainfluenza viruses, and respiratory adenoviruses increase in the fall and remain high throughout winter, following the same basic patterns as influenza. Although the historically low rates of influenza remained low into spring 2021, that’s not the case for several other common respiratory viruses.
“Clinicians should be aware of increases in some respiratory virus activity and remain vigilant for off-season increases,” wrote Sonja J. Olsen, PhD, and her colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. She told this news organization that clinicians should use multipathogen testing to help guide treatment.
The authors also underscore the importance of fall influenza vaccination campaigns for anyone aged 6 months or older.
Timothy Brewer, MD, MPH, a professor of medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), and of epidemiology at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health, agreed that it’s important for health care professionals to consider off-season illnesses in their patients.
“Practitioners should be aware that if they see a sick child in the summer, outside of what normally might be influenza season, but they look like they have influenza, consider potentially influenza and test for it, because it might be possible that we may have disrupted that natural pattern,” Dr. Brewer told this news organization. Dr. Brewer, who was not involved in the CDC research, said it’s also “critically important” to encourage influenza vaccination as the season approaches.
The CDC researchers used the U.S. World Health Organization Collaborating Laboratories System and the CDC’s National Respiratory and Enteric Virus Surveillance System to analyze virologic data from Oct. 3, 2020, to May 22, 2021, for influenza and Jan. 4, 2020, to May 22, 2021, for other respiratory viruses. The authors compared virus circulation during these periods to circulation during the same dates from four previous years.
Data to calculate influenza and RSV hospitalization rates came from the Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network and RSV Hospitalization Surveillance Network.
The authors report that flu activity dropped dramatically in March 2020 to its lowest levels since 1997, the earliest season for which data are available. Only 0.2% of more than 1 million specimens tested positive for influenza; the rate of hospitalizations for lab-confirmed flu was 0.8 per 100,000 people. Flu levels remained low through the summer, fall, and on to May 2021.
A potential drawback to this low activity, however, is a more prevalent and severe upcoming flu season, the authors write. The repeated exposure to flu viruses every year often “does not lead to illness, but it does serve to boost our immune response to influenza viruses,” Dr. Olsen said in an interview. “The absence of influenza viruses in the community over the last year means that we are not getting these regular boosts to our immune system. When we finally get exposed, our body may mount a weak response, and this could mean we develop a more clinically severe illness.”
Children are most susceptible to that phenomenon because they haven’t had a lifetime of exposure to flu viruses, Dr. Olsen said.
“An immunologically naive child may be more likely to develop a severe illness than someone who has lived through several influenza seasons,” she said. “This is why it is especially important for everyone 6 months and older to get vaccinated against influenza this season.”
Rhinovirus and enterovirus infections rebounded fairly quickly after their decline in March 2020 and started increasing in May 2020 until they reached “near prepandemic seasonal levels,” the authors write.
RSV infections dropped from 15.3% of weekly positive results in January 2020 to 1.4% by April and then stayed below 1% through the end of 2020. In past years, weekly positive results climbed to 3% in October and peaked at 12.5% to 16.7% in late December. Instead, RSV weekly positive results began increasing in April 2021, rising from 1.1% to 2.8% in May.
The “unusually timed” late spring increase in RSV “is probably associated with various nonpharmaceutical measures that have been in place but are now relaxing,” Dr. Olsen stated.
The RSV hospitalization rate was 0.3 per 100,000 people from October 2020 to April 2021, compared to 27.1 and 33.4 per 100,000 people in the previous 2 years. Of all RSV hospitalizations in the past year, 76.5% occurred in April-May 2021.
Rates of illness caused by the four common human coronaviruses (OC43, NL63, 229E, and HKU1) dropped from 7.5% of weekly positive results in January 2020 to 1.3% in April 2020 and stayed below 1% through February 2021. Then they climbed to 6.6% by May 2021. Infection rates of parainfluenza viruses types 1-4 similarly dropped from 2.6% in January 2020 to 1% in March 2020 and stayed below 1% until April 2021. Since then, rates of the common coronaviruses increased to 6.6% and parainfluenza viruses to 10.9% in May 2021.
Normally, parainfluenza viruses peak in October-November and May-June, so “the current increase could represent a return to prepandemic seasonality,” the authors write.
Human pneumoviruses’ weekly positive results initially increased from 4.2% in January 2020 to 7% in March and then fell to 1.9% the second week of April and remained below 1% through May 2021. In typical years, these viruses peak from 6.2% to 7.7% in March-April. Respiratory adenovirus activity similarly dropped to historically low levels in April 2021 and then began increasing to reach 3% by May 2021, the usual level for that month.
“The different circulation patterns observed across respiratory viruses probably also reflect differences in the virus transmission routes and how effective various nonpharmaceutical measures are at stopping transmission,” Dr. Olsen said in an interview. “As pandemic mitigation measures continue to be adjusted, we expect to see more changes in the circulation of these viruses, including a return to prepandemic circulation, as seen for rhinoviruses and enteroviruses.”
Rhinovirus and enterovirus rates dropped from 14.9% in March 2020 to 3.2% in May – lower than typical – and then climbed to a peak in October 2020. The peak (21.7% weekly positive results) was, however, still lower than the usual median of 32.8%. After dropping to 9.9% in January 2021, it then rose 19.1% in May, potentially reflecting “the usual spring peak that has occurred in previous years,” the authors write.
The authors note that it’s not yet clear how the COVID-19 pandemic and related mitigation measures will continue to affect respiratory virus circulation.
The authors hypothesize that the reasons for a seeming return to seasonal activity of respiratory adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, and enteroviruses could involve “different transmission mechanisms, the role of asymptomatic transmission, and prolonged survival of these nonenveloped viruses on surfaces, all of which might make these viruses less susceptible to nonpharmaceutical interventions.”
Dr. Brewer, of UCLA, agreed.
All the viruses basically “flatline except for adenoviruses and enteroviruses, and they behave a little differently in terms of how they spread,” he said. “Enteroviruses are much more likely to be fecal-oral spread than the other viruses [in the study].”
The delayed circulation of parainfluenza and human coronaviruses may have resulted from suspension of in-person classes through late winter 2020, they write, but that doesn’t explain the relative absence of pneumovirus activity, which usually affects the same young pediatric populations as RSV.
Dr. Brewer said California is seeing a surge of RSV right now, as are many states, especially throughout in the South. He’s not surprised by RSV’s deferred season, because those most affected – children younger than 2 years – are less likely to wear masks now and were “not going to daycare, not being out in public” in 2020. “As people are doing more activities, that’s probably why RSV has been starting to go up since April,” he said.
Despite the fact that, unlike many East Asian cultures, the United States has not traditionally been a mask-wearing culture, Dr. Brewer wouldn’t be surprised if more Americans begin wearing masks during flu season. “Hopefully another thing that will come out of this is better hand hygiene, with people just getting used to washing their hands more, particularly after they come home from being out,” he added.
Dr. Brewer similarly emphasized the importance of flu vaccination for the upcoming season, especially for younger children who may have poorer natural immunity to influenza, owing to its low circulation rates in 2020-2021.
The study was funded by the CDC. Dr. Brewer and Dr. Olsen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.