User login
Is AFib ablation the fifth pillar in heart failure care? CASTLE-HTx
Recorded Aug. 28, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
John M. Mandrola, MD: I’m here at the European Society of Cardiology meeting, and I’m very excited to have two colleagues whom I met at the Western Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (Western AFib) and who presented the CASTLE-HTx study. This is Christian Sohns and Philipp Sommer, and the CASTLE-HTx study is very exciting.
Before I get into that, I really want to introduce the concept of atrial fibrillation in heart failure. I like to say that there are two big populations of patients with atrial fibrillation, and the vast majority can be treated slowly with reassurance and education. There is a group of patients who have heart failure who, when they develop atrial fibrillation, can degenerate rapidly. The CASTLE-HTx study looked at catheter ablation versus medical therapy in patients with advanced heart failure.
Christian, why don’t you tell us the top-line results and what you found.
CASTLE-HTx key findings
Christian Sohns, MD, PhD: Thanks, first of all, for mentioning this special cohort of patients in end-stage heart failure, which is very important. The endpoint of the study was a composite of death from any cause or left ventricular assist device (LVAD) implantation and heart transplantation. These are very hard, strong clinical endpoints, not the rate of rehospitalization or something like that.
Catheter ablation was superior to medical therapy alone in terms of this composite endpoint. That was driven by cardiovascular death and all-cause mortality, which highlights the fact that you should always consider atrial fibrillation ablation in the end-stage heart failure cohort. The findings were driven by the fact that we saw left ventricular reverse remodeling and the reduction of atrial fibrillation in these patients.
Dr. Mandrola: Tell me about how it came about. It was conducted at your center. Who were these patients?
Philipp Sommer, MD: As one of the biggest centers for heart transplantations all over Europe, with roughly 100 transplants per year, we had many patients being referred to our center with the questions of whether those patients are eligible for a heart transplantation. Not all of the patients in our study were listed for a transplant, but all of them were admitted in that end-stage heart failure status to evaluate their eligibility for transplant.
If we look at the baseline data of those patients, they had an ejection fraction of 29%. They had a 6-minute walk test as a functional capacity parameter of around 300 m. Approximately two thirds of them were New York Heart Association class III and IV, which is significantly worse than what we saw in the previous studies dealing with heart failure patients.
I think overall, if you also look at NT-proBNP levels, this is a really sick patient population where some people might doubt if they should admit and refer those patients for an ablation procedure. Therefore, it’s really interesting and fascinating to see the results.
Dr. Mandrola: I did read in the manuscript, and I heard from you, that these were recruited as outpatients. So they were stable outpatients who were referred to the center for consideration of an LVAD or transplant?
Dr. Sohns: The definition of stability is very difficult in these patients because they have hospital stays, they have a history of drug therapy, and they have a history of interventions also behind them – not atrial fibrillation ablation, but others. I think these patients are referred because the referring physicians are done with the case. They can no longer offer any option to the patients other than surgical treatment, assist device, pump implantation, or transplantation.
If you look at the guidelines, they do not comment on atrial fibrillation ablation in this cohort of patients. Also, they have different recommendations between the American societies and the European societies regarding what is end-stage heart failure and how to treat these patients. Therefore, it was a big benefit of CASTLE-HTx that we randomized a cohort of patients with advanced end-stage heart failure.
How can AFib ablation have such big, early effects?
Dr. Mandrola: These are very clinically significant findings, with large effect sizes and very early separation of the Kaplan-Meier curves. How do you explain how dramatic an effect that is, and how early of an effect?
Dr. Sommer: That’s one of the key questions at the end of the day. I think our job basically was to provide the data and to ensure that the data are clean and that it’s all perfectly done. The interpretation of these data is really kind of difficult, although we do not have the 100% perfect and obvious explanation why the curves separated so early. Our view on that is that we are talking about a pretty fragile patient population, so little differences like having a tachyarrhythmia of 110 day in, day out or being in sinus rhythm of 60 can make a huge difference. That’s obviously pretty early.
The one that remains in tachyarrhythmia will deteriorate and will require an LVAD after a couple of months, and the one that you may keep in sinus rhythm, even with reduced atrial fibrillation burden – not zero, but reduced atrial fibrillation burden – and improved LV function, all of a sudden this patient will still remain on a low level of being stable, but he or she will remain stable and will not require any surgical interventions for the next 1.5-2 years. If we can manage to do this, just postponing the natural cause of the disease, I think that is a great benefit for the patient.
Dr. Mandrola: One of the things that comes up in our center is that I look at some of these patients and think, there’s no way I can put this patient under general anesthetic and do all of this. Your ablation procedure wasn’t that extensive, was it?
Dr. Sohns: On the one hand, no. On the other hand, yes. You need to take into consideration that it has been performed by experienced physicians with experience in heart failure treatment and atrial fibrillation in heart transplantation centers, though it›s not sure that we can transfer these results one-to-one to all other centers in the world.
It is very clear that we have almost no major complications in these patients. We were able to do these ablation procedures without general anesthesia. We have 60% of patients who had pulmonary vein isolation only and 40% of patients who have PVI and additional therapy. We have a procedure duration of almost 90 minutes during radiofrequency ablation.
We have different categories. When you talk about the different patient cohorts, we also see different stages of myocardial tissue damage, which will be part of another publication for sure. It is, in part, surprising how normal some of the atria were despite having a volume of 180 mL, but they had no fibrosis. That was very interesting.
Dr. Mandrola: How did the persistent vs paroxysmal atrial fibrillation sort out? Were these mostly patients with persistent atrial fibrillation?
Dr. Sommer: Two-thirds were persistent. It would be expected in this patient population that you would not find so many paroxysmal cases. I think it›s very important what Christian was just mentioning that when we discussed the trial design, we were anticipating problems with the sedation, for example. With the follow-up of those procedures, would they decompensate because of the fluid that you have to deliver during such a procedure.
We were quite surprised at the end of the day that the procedures were quite straightforward. Fortunately, we had no major complications. I think there were four complications in the 100 ablated patients. I think we were really positive about how the procedures turned out.
I should mention that one of the exclusion criteria was a left atrial diameter of about 60 mm. The huge ones may be very diseased, and maybe the hopeless ones were excluded from the study. Below 60 mm, we did the ablation.
Rhythm control
Dr. Mandrola: One of my colleagues, who is even more skeptical than me, wanted me to ask you, why wouldn’t you take a patient with persistent atrial fibrillation who had heart failure and just cardiovert and use amiodarone and try and maintain sinus rhythm that way?
Dr. Sohns: It is important to mention that 50% of the patients have already had amiodarone before they were randomized and enrolled for the trial. It might bring you a couple of minutes or a couple of hours [of relief], but the patients would get recurrence.
It was very interesting also, and this is in line with the data from Jason Andrade, who demonstrated that we were able to reduce the percentage of patients with persistent atrial fibrillation to paroxysmal. We did a down-staging of the underlying disease. This is not possible with cardioversion or drugs, for example.
Dr. Sommer: What I really like about that question and that comment is the idea that rhythm control in this subset of patients obviously has a role and an importance. It may be a cardioversion initially, giving amiodarone if they didn’t have that before, and you can keep the patient in sinus rhythm with this therapy, I think we’re reaching the same goal.
I think the critical point to get into the mind of physicians who treat heart failure is that sinus rhythm is beneficial, however you get there. Ablation, of course, as in other studies, is the most powerful tool to get there. Cardioversion can be a really good thing to do; you just have to think about it and consider it.
Dr. Mandrola: I do want to say to everybody that there is a tension sometimes between the heart failure community and the electrophysiology community. I think the ideal situation is that we work together, because I think that we can help with the maintenance of sinus rhythm. The control group mortality at 1 year was 20%, and I’ve heard people say that that’s not advanced heart failure. Advanced heart failure patients have much higher mortality than that. My colleague who is a heart failure specialist was criticizing a selection bias in picking the best patients. How would you answer that?
Dr. Sohns: There are data available from Eurotransplant, for example, that the waiting list mortality is 18%, so I think we are almost in line with this 20% mortality in this conservative group. You cannot generalize it. All these patients have different histories. We have 60% dilated cardiomyopathy and 40% ischemic cardiomyopathy. I think it is a very representative group in contrast to your friend who suggests that it is not.
Dr. Sommer: What I like about the discussion is that some approach us to say that the mortality in the control group is much too high – like, what are you doing with those patients that you create so many endpoints? Then others say that it’s not high enough because that is not end-stage heart failure. Come on! We have a patient cohort that is very well described and very well characterized.
If the label is end-stage heart failure, advanced heart failure, or whatever, they are sicker than the patients that we had in earlier trials. The patients that we treated were mostly excluded from all other trials. We opened the door. We found a clear result. I think everyone can see whatever you like to see.
Dr. Mandrola: What would your take-home message be after having done this trial design, the trial was conducted in your single center, and you come up with these amazing results? What would your message be to the whole community?
Dr. Sohns: Taking into consideration how severely sick these patients are, I can just repeat it: They are one step away from death, more or less, or from surgical intervention that can prolong their life. You should also consider that there are options like atrial fibrillation ablation that can buy time, postpone the natural course, or even in some patients replace the destination therapy. Therefore, in my opinion the next guidelines should recommend that every patient should carefully be checked for sinus rhythm before bringing these patients into the environment of transplantation.
Dr. Sommer: My interpretation is that we have to try to bring into physicians’ minds that besides a well-established and well-documented effect of drug therapy with the fabulous four, we may now have the fabulous five, including an ablation option for patients with atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Mandrola is a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky. Dr. Sohns is deputy director of the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW, Ruhr University Bochum, Bad Oeynhausen, Germany. Dr. Sommer is professor of cardiology at the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW. Dr. Mandrola reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Sohns reported receiving research funding from Else Kröner–Fresenius–Stiftung. Dr. Sommer reported consulting with Abbott, Biosense Webster, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic USA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recorded Aug. 28, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
John M. Mandrola, MD: I’m here at the European Society of Cardiology meeting, and I’m very excited to have two colleagues whom I met at the Western Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (Western AFib) and who presented the CASTLE-HTx study. This is Christian Sohns and Philipp Sommer, and the CASTLE-HTx study is very exciting.
Before I get into that, I really want to introduce the concept of atrial fibrillation in heart failure. I like to say that there are two big populations of patients with atrial fibrillation, and the vast majority can be treated slowly with reassurance and education. There is a group of patients who have heart failure who, when they develop atrial fibrillation, can degenerate rapidly. The CASTLE-HTx study looked at catheter ablation versus medical therapy in patients with advanced heart failure.
Christian, why don’t you tell us the top-line results and what you found.
CASTLE-HTx key findings
Christian Sohns, MD, PhD: Thanks, first of all, for mentioning this special cohort of patients in end-stage heart failure, which is very important. The endpoint of the study was a composite of death from any cause or left ventricular assist device (LVAD) implantation and heart transplantation. These are very hard, strong clinical endpoints, not the rate of rehospitalization or something like that.
Catheter ablation was superior to medical therapy alone in terms of this composite endpoint. That was driven by cardiovascular death and all-cause mortality, which highlights the fact that you should always consider atrial fibrillation ablation in the end-stage heart failure cohort. The findings were driven by the fact that we saw left ventricular reverse remodeling and the reduction of atrial fibrillation in these patients.
Dr. Mandrola: Tell me about how it came about. It was conducted at your center. Who were these patients?
Philipp Sommer, MD: As one of the biggest centers for heart transplantations all over Europe, with roughly 100 transplants per year, we had many patients being referred to our center with the questions of whether those patients are eligible for a heart transplantation. Not all of the patients in our study were listed for a transplant, but all of them were admitted in that end-stage heart failure status to evaluate their eligibility for transplant.
If we look at the baseline data of those patients, they had an ejection fraction of 29%. They had a 6-minute walk test as a functional capacity parameter of around 300 m. Approximately two thirds of them were New York Heart Association class III and IV, which is significantly worse than what we saw in the previous studies dealing with heart failure patients.
I think overall, if you also look at NT-proBNP levels, this is a really sick patient population where some people might doubt if they should admit and refer those patients for an ablation procedure. Therefore, it’s really interesting and fascinating to see the results.
Dr. Mandrola: I did read in the manuscript, and I heard from you, that these were recruited as outpatients. So they were stable outpatients who were referred to the center for consideration of an LVAD or transplant?
Dr. Sohns: The definition of stability is very difficult in these patients because they have hospital stays, they have a history of drug therapy, and they have a history of interventions also behind them – not atrial fibrillation ablation, but others. I think these patients are referred because the referring physicians are done with the case. They can no longer offer any option to the patients other than surgical treatment, assist device, pump implantation, or transplantation.
If you look at the guidelines, they do not comment on atrial fibrillation ablation in this cohort of patients. Also, they have different recommendations between the American societies and the European societies regarding what is end-stage heart failure and how to treat these patients. Therefore, it was a big benefit of CASTLE-HTx that we randomized a cohort of patients with advanced end-stage heart failure.
How can AFib ablation have such big, early effects?
Dr. Mandrola: These are very clinically significant findings, with large effect sizes and very early separation of the Kaplan-Meier curves. How do you explain how dramatic an effect that is, and how early of an effect?
Dr. Sommer: That’s one of the key questions at the end of the day. I think our job basically was to provide the data and to ensure that the data are clean and that it’s all perfectly done. The interpretation of these data is really kind of difficult, although we do not have the 100% perfect and obvious explanation why the curves separated so early. Our view on that is that we are talking about a pretty fragile patient population, so little differences like having a tachyarrhythmia of 110 day in, day out or being in sinus rhythm of 60 can make a huge difference. That’s obviously pretty early.
The one that remains in tachyarrhythmia will deteriorate and will require an LVAD after a couple of months, and the one that you may keep in sinus rhythm, even with reduced atrial fibrillation burden – not zero, but reduced atrial fibrillation burden – and improved LV function, all of a sudden this patient will still remain on a low level of being stable, but he or she will remain stable and will not require any surgical interventions for the next 1.5-2 years. If we can manage to do this, just postponing the natural cause of the disease, I think that is a great benefit for the patient.
Dr. Mandrola: One of the things that comes up in our center is that I look at some of these patients and think, there’s no way I can put this patient under general anesthetic and do all of this. Your ablation procedure wasn’t that extensive, was it?
Dr. Sohns: On the one hand, no. On the other hand, yes. You need to take into consideration that it has been performed by experienced physicians with experience in heart failure treatment and atrial fibrillation in heart transplantation centers, though it›s not sure that we can transfer these results one-to-one to all other centers in the world.
It is very clear that we have almost no major complications in these patients. We were able to do these ablation procedures without general anesthesia. We have 60% of patients who had pulmonary vein isolation only and 40% of patients who have PVI and additional therapy. We have a procedure duration of almost 90 minutes during radiofrequency ablation.
We have different categories. When you talk about the different patient cohorts, we also see different stages of myocardial tissue damage, which will be part of another publication for sure. It is, in part, surprising how normal some of the atria were despite having a volume of 180 mL, but they had no fibrosis. That was very interesting.
Dr. Mandrola: How did the persistent vs paroxysmal atrial fibrillation sort out? Were these mostly patients with persistent atrial fibrillation?
Dr. Sommer: Two-thirds were persistent. It would be expected in this patient population that you would not find so many paroxysmal cases. I think it›s very important what Christian was just mentioning that when we discussed the trial design, we were anticipating problems with the sedation, for example. With the follow-up of those procedures, would they decompensate because of the fluid that you have to deliver during such a procedure.
We were quite surprised at the end of the day that the procedures were quite straightforward. Fortunately, we had no major complications. I think there were four complications in the 100 ablated patients. I think we were really positive about how the procedures turned out.
I should mention that one of the exclusion criteria was a left atrial diameter of about 60 mm. The huge ones may be very diseased, and maybe the hopeless ones were excluded from the study. Below 60 mm, we did the ablation.
Rhythm control
Dr. Mandrola: One of my colleagues, who is even more skeptical than me, wanted me to ask you, why wouldn’t you take a patient with persistent atrial fibrillation who had heart failure and just cardiovert and use amiodarone and try and maintain sinus rhythm that way?
Dr. Sohns: It is important to mention that 50% of the patients have already had amiodarone before they were randomized and enrolled for the trial. It might bring you a couple of minutes or a couple of hours [of relief], but the patients would get recurrence.
It was very interesting also, and this is in line with the data from Jason Andrade, who demonstrated that we were able to reduce the percentage of patients with persistent atrial fibrillation to paroxysmal. We did a down-staging of the underlying disease. This is not possible with cardioversion or drugs, for example.
Dr. Sommer: What I really like about that question and that comment is the idea that rhythm control in this subset of patients obviously has a role and an importance. It may be a cardioversion initially, giving amiodarone if they didn’t have that before, and you can keep the patient in sinus rhythm with this therapy, I think we’re reaching the same goal.
I think the critical point to get into the mind of physicians who treat heart failure is that sinus rhythm is beneficial, however you get there. Ablation, of course, as in other studies, is the most powerful tool to get there. Cardioversion can be a really good thing to do; you just have to think about it and consider it.
Dr. Mandrola: I do want to say to everybody that there is a tension sometimes between the heart failure community and the electrophysiology community. I think the ideal situation is that we work together, because I think that we can help with the maintenance of sinus rhythm. The control group mortality at 1 year was 20%, and I’ve heard people say that that’s not advanced heart failure. Advanced heart failure patients have much higher mortality than that. My colleague who is a heart failure specialist was criticizing a selection bias in picking the best patients. How would you answer that?
Dr. Sohns: There are data available from Eurotransplant, for example, that the waiting list mortality is 18%, so I think we are almost in line with this 20% mortality in this conservative group. You cannot generalize it. All these patients have different histories. We have 60% dilated cardiomyopathy and 40% ischemic cardiomyopathy. I think it is a very representative group in contrast to your friend who suggests that it is not.
Dr. Sommer: What I like about the discussion is that some approach us to say that the mortality in the control group is much too high – like, what are you doing with those patients that you create so many endpoints? Then others say that it’s not high enough because that is not end-stage heart failure. Come on! We have a patient cohort that is very well described and very well characterized.
If the label is end-stage heart failure, advanced heart failure, or whatever, they are sicker than the patients that we had in earlier trials. The patients that we treated were mostly excluded from all other trials. We opened the door. We found a clear result. I think everyone can see whatever you like to see.
Dr. Mandrola: What would your take-home message be after having done this trial design, the trial was conducted in your single center, and you come up with these amazing results? What would your message be to the whole community?
Dr. Sohns: Taking into consideration how severely sick these patients are, I can just repeat it: They are one step away from death, more or less, or from surgical intervention that can prolong their life. You should also consider that there are options like atrial fibrillation ablation that can buy time, postpone the natural course, or even in some patients replace the destination therapy. Therefore, in my opinion the next guidelines should recommend that every patient should carefully be checked for sinus rhythm before bringing these patients into the environment of transplantation.
Dr. Sommer: My interpretation is that we have to try to bring into physicians’ minds that besides a well-established and well-documented effect of drug therapy with the fabulous four, we may now have the fabulous five, including an ablation option for patients with atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Mandrola is a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky. Dr. Sohns is deputy director of the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW, Ruhr University Bochum, Bad Oeynhausen, Germany. Dr. Sommer is professor of cardiology at the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW. Dr. Mandrola reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Sohns reported receiving research funding from Else Kröner–Fresenius–Stiftung. Dr. Sommer reported consulting with Abbott, Biosense Webster, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic USA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recorded Aug. 28, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
John M. Mandrola, MD: I’m here at the European Society of Cardiology meeting, and I’m very excited to have two colleagues whom I met at the Western Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (Western AFib) and who presented the CASTLE-HTx study. This is Christian Sohns and Philipp Sommer, and the CASTLE-HTx study is very exciting.
Before I get into that, I really want to introduce the concept of atrial fibrillation in heart failure. I like to say that there are two big populations of patients with atrial fibrillation, and the vast majority can be treated slowly with reassurance and education. There is a group of patients who have heart failure who, when they develop atrial fibrillation, can degenerate rapidly. The CASTLE-HTx study looked at catheter ablation versus medical therapy in patients with advanced heart failure.
Christian, why don’t you tell us the top-line results and what you found.
CASTLE-HTx key findings
Christian Sohns, MD, PhD: Thanks, first of all, for mentioning this special cohort of patients in end-stage heart failure, which is very important. The endpoint of the study was a composite of death from any cause or left ventricular assist device (LVAD) implantation and heart transplantation. These are very hard, strong clinical endpoints, not the rate of rehospitalization or something like that.
Catheter ablation was superior to medical therapy alone in terms of this composite endpoint. That was driven by cardiovascular death and all-cause mortality, which highlights the fact that you should always consider atrial fibrillation ablation in the end-stage heart failure cohort. The findings were driven by the fact that we saw left ventricular reverse remodeling and the reduction of atrial fibrillation in these patients.
Dr. Mandrola: Tell me about how it came about. It was conducted at your center. Who were these patients?
Philipp Sommer, MD: As one of the biggest centers for heart transplantations all over Europe, with roughly 100 transplants per year, we had many patients being referred to our center with the questions of whether those patients are eligible for a heart transplantation. Not all of the patients in our study were listed for a transplant, but all of them were admitted in that end-stage heart failure status to evaluate their eligibility for transplant.
If we look at the baseline data of those patients, they had an ejection fraction of 29%. They had a 6-minute walk test as a functional capacity parameter of around 300 m. Approximately two thirds of them were New York Heart Association class III and IV, which is significantly worse than what we saw in the previous studies dealing with heart failure patients.
I think overall, if you also look at NT-proBNP levels, this is a really sick patient population where some people might doubt if they should admit and refer those patients for an ablation procedure. Therefore, it’s really interesting and fascinating to see the results.
Dr. Mandrola: I did read in the manuscript, and I heard from you, that these were recruited as outpatients. So they were stable outpatients who were referred to the center for consideration of an LVAD or transplant?
Dr. Sohns: The definition of stability is very difficult in these patients because they have hospital stays, they have a history of drug therapy, and they have a history of interventions also behind them – not atrial fibrillation ablation, but others. I think these patients are referred because the referring physicians are done with the case. They can no longer offer any option to the patients other than surgical treatment, assist device, pump implantation, or transplantation.
If you look at the guidelines, they do not comment on atrial fibrillation ablation in this cohort of patients. Also, they have different recommendations between the American societies and the European societies regarding what is end-stage heart failure and how to treat these patients. Therefore, it was a big benefit of CASTLE-HTx that we randomized a cohort of patients with advanced end-stage heart failure.
How can AFib ablation have such big, early effects?
Dr. Mandrola: These are very clinically significant findings, with large effect sizes and very early separation of the Kaplan-Meier curves. How do you explain how dramatic an effect that is, and how early of an effect?
Dr. Sommer: That’s one of the key questions at the end of the day. I think our job basically was to provide the data and to ensure that the data are clean and that it’s all perfectly done. The interpretation of these data is really kind of difficult, although we do not have the 100% perfect and obvious explanation why the curves separated so early. Our view on that is that we are talking about a pretty fragile patient population, so little differences like having a tachyarrhythmia of 110 day in, day out or being in sinus rhythm of 60 can make a huge difference. That’s obviously pretty early.
The one that remains in tachyarrhythmia will deteriorate and will require an LVAD after a couple of months, and the one that you may keep in sinus rhythm, even with reduced atrial fibrillation burden – not zero, but reduced atrial fibrillation burden – and improved LV function, all of a sudden this patient will still remain on a low level of being stable, but he or she will remain stable and will not require any surgical interventions for the next 1.5-2 years. If we can manage to do this, just postponing the natural cause of the disease, I think that is a great benefit for the patient.
Dr. Mandrola: One of the things that comes up in our center is that I look at some of these patients and think, there’s no way I can put this patient under general anesthetic and do all of this. Your ablation procedure wasn’t that extensive, was it?
Dr. Sohns: On the one hand, no. On the other hand, yes. You need to take into consideration that it has been performed by experienced physicians with experience in heart failure treatment and atrial fibrillation in heart transplantation centers, though it›s not sure that we can transfer these results one-to-one to all other centers in the world.
It is very clear that we have almost no major complications in these patients. We were able to do these ablation procedures without general anesthesia. We have 60% of patients who had pulmonary vein isolation only and 40% of patients who have PVI and additional therapy. We have a procedure duration of almost 90 minutes during radiofrequency ablation.
We have different categories. When you talk about the different patient cohorts, we also see different stages of myocardial tissue damage, which will be part of another publication for sure. It is, in part, surprising how normal some of the atria were despite having a volume of 180 mL, but they had no fibrosis. That was very interesting.
Dr. Mandrola: How did the persistent vs paroxysmal atrial fibrillation sort out? Were these mostly patients with persistent atrial fibrillation?
Dr. Sommer: Two-thirds were persistent. It would be expected in this patient population that you would not find so many paroxysmal cases. I think it›s very important what Christian was just mentioning that when we discussed the trial design, we were anticipating problems with the sedation, for example. With the follow-up of those procedures, would they decompensate because of the fluid that you have to deliver during such a procedure.
We were quite surprised at the end of the day that the procedures were quite straightforward. Fortunately, we had no major complications. I think there were four complications in the 100 ablated patients. I think we were really positive about how the procedures turned out.
I should mention that one of the exclusion criteria was a left atrial diameter of about 60 mm. The huge ones may be very diseased, and maybe the hopeless ones were excluded from the study. Below 60 mm, we did the ablation.
Rhythm control
Dr. Mandrola: One of my colleagues, who is even more skeptical than me, wanted me to ask you, why wouldn’t you take a patient with persistent atrial fibrillation who had heart failure and just cardiovert and use amiodarone and try and maintain sinus rhythm that way?
Dr. Sohns: It is important to mention that 50% of the patients have already had amiodarone before they were randomized and enrolled for the trial. It might bring you a couple of minutes or a couple of hours [of relief], but the patients would get recurrence.
It was very interesting also, and this is in line with the data from Jason Andrade, who demonstrated that we were able to reduce the percentage of patients with persistent atrial fibrillation to paroxysmal. We did a down-staging of the underlying disease. This is not possible with cardioversion or drugs, for example.
Dr. Sommer: What I really like about that question and that comment is the idea that rhythm control in this subset of patients obviously has a role and an importance. It may be a cardioversion initially, giving amiodarone if they didn’t have that before, and you can keep the patient in sinus rhythm with this therapy, I think we’re reaching the same goal.
I think the critical point to get into the mind of physicians who treat heart failure is that sinus rhythm is beneficial, however you get there. Ablation, of course, as in other studies, is the most powerful tool to get there. Cardioversion can be a really good thing to do; you just have to think about it and consider it.
Dr. Mandrola: I do want to say to everybody that there is a tension sometimes between the heart failure community and the electrophysiology community. I think the ideal situation is that we work together, because I think that we can help with the maintenance of sinus rhythm. The control group mortality at 1 year was 20%, and I’ve heard people say that that’s not advanced heart failure. Advanced heart failure patients have much higher mortality than that. My colleague who is a heart failure specialist was criticizing a selection bias in picking the best patients. How would you answer that?
Dr. Sohns: There are data available from Eurotransplant, for example, that the waiting list mortality is 18%, so I think we are almost in line with this 20% mortality in this conservative group. You cannot generalize it. All these patients have different histories. We have 60% dilated cardiomyopathy and 40% ischemic cardiomyopathy. I think it is a very representative group in contrast to your friend who suggests that it is not.
Dr. Sommer: What I like about the discussion is that some approach us to say that the mortality in the control group is much too high – like, what are you doing with those patients that you create so many endpoints? Then others say that it’s not high enough because that is not end-stage heart failure. Come on! We have a patient cohort that is very well described and very well characterized.
If the label is end-stage heart failure, advanced heart failure, or whatever, they are sicker than the patients that we had in earlier trials. The patients that we treated were mostly excluded from all other trials. We opened the door. We found a clear result. I think everyone can see whatever you like to see.
Dr. Mandrola: What would your take-home message be after having done this trial design, the trial was conducted in your single center, and you come up with these amazing results? What would your message be to the whole community?
Dr. Sohns: Taking into consideration how severely sick these patients are, I can just repeat it: They are one step away from death, more or less, or from surgical intervention that can prolong their life. You should also consider that there are options like atrial fibrillation ablation that can buy time, postpone the natural course, or even in some patients replace the destination therapy. Therefore, in my opinion the next guidelines should recommend that every patient should carefully be checked for sinus rhythm before bringing these patients into the environment of transplantation.
Dr. Sommer: My interpretation is that we have to try to bring into physicians’ minds that besides a well-established and well-documented effect of drug therapy with the fabulous four, we may now have the fabulous five, including an ablation option for patients with atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Mandrola is a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky. Dr. Sohns is deputy director of the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW, Ruhr University Bochum, Bad Oeynhausen, Germany. Dr. Sommer is professor of cardiology at the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW. Dr. Mandrola reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Sohns reported receiving research funding from Else Kröner–Fresenius–Stiftung. Dr. Sommer reported consulting with Abbott, Biosense Webster, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic USA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heart failure guidelines update: What the ESC got right
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This is my usual blog, except I am here from the absolutely beautiful city of Amsterdam, where the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology has been going on.
SGLT2 inhibitors for HFpEF and HFrEF
I’m going to review very briefly the 2023 focused update to the ESC heart failure guidelines. Theresa McDonagh was the first author of this and of the previous ESC or European guidelines. These are a little bit different than the American guidelines, which were presented in 2022. We know that we need an update. The Europeans have gotten ahead of us, and now we have the European update, which I find incredibly well written and it really highlights the areas that I think the takeaways are for the clinicians.
First, we have been seeing now for several years – since 2018 – the benefits of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Every time we lift the veil on something, there they are in a positive light. We have learned about heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) for both empagliflozin and dapagliflozin. There are very similar results. One population may be enriched with a little of this and a little of that, but the basic messages are the same. In HFrEF, both of these drugs improve outcomes and it happens quickly. You don’t have to wait 1 or 2 years to see this. Within months, and actually within days, you start to see the curves split apart statistically.
The next logical ground was heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). The definition, when we started the HFpEF trials, was 45% or greater. I want the audience to realize that, in the midst of all these trials, we came out – we meaning the American Heart Association, the American College of Cardiology, and the Heart Failure Society – with the new definition of heart failure, which said that true HFpEF is 50% or greater. That in-between zone of 40%-50% or 41%-49% is mRF, or mid-range, what I call middle of the road. I think the Europeans have really emphasized that to us. I believe that those patients really behave much more like a HFrEF population.
Now that we have very positive findings with the SGLT2 inhibitors, both dapagliflozin and empagliflozin, in HFpEF – defined, as I said, as 40% or 45% or greater, not necessarily 50% – with excellent point estimates that just line up, one on top of the other. It doesn’t matter if patients have diabetes or not; the results are exactly the same.
This has been so promising that I am not surprised that the Europeans elevated the SGLT2 inhibitors to a class 1A indication. In the United States in 2022, we thought we were really way ahead by calling it a class 2A indication. Well, now it’s a class 1A indication in Europe, and I have a feeling that the AHA and the ACC are going to start talking about an update because the data are so strong.
Now, we even have data on initiating these drugs in the hospital. EMPULSE was a very large trial about the benefits of starting these drugs in the hospital. You do not have to wait until the patient is in the outpatient setting. You can start it in the hospital.
When? I have no specific day that I start it. I used to try to do a good diuresis first, get the patients somewhat decongested, and then start it. I don’t want to deprive the patients of the benefits of these drugs that happen very early by waiting until the patients are in the outpatient setting.
In the United States, we’ve had some issues with coverage of some of these drugs. In my institution, we now have both on the formulary, and I pick the drug depending upon the patient’s coverage. Medicare pretty much covers most of them. If the patient is older but not yet a Medicare patient, they may have a very large copay. I advise you to get your offices or your health system to look into this so that, when you give the prescription to the patient, whether they’re leaving the hospital or are now in your clinics, they can actually get the drug.
Finerenone and intravenous iron
There is an additional recommendation in these guidelines for finerenone, the mineralocorticoid receptor agonist that I’ve discussed before, that has some really promising data on type 2 diabetes with chronic kidney disease. They have called that a class 1A indication for finerenone. I think there is more to come.
One more: the iron deficiency. Giving intravenous iron actually does improve symptoms and quality of life. I have seen this in my own patients, so I have been very diligent at looking for iron deficiency.
It is a new era. We have more tools, obviously, for our patients. It means one more drug, and that’s always a challenge. We’ve already been doing the pillars of care. This is the fourth pillar of care, but now with a class 1A indication.
Take a look. They’re easy to read. Dr. McDonagh is the first author, and I think they’ve been extremely well done.
Dr. Piña is professor of medicine at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital in Philadelphia. She is a heart failure and cardiac transplantation expert. She disclosed serving as an adviser/consultant to the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health and has been a volunteer for the American Heart Association since 1982.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This is my usual blog, except I am here from the absolutely beautiful city of Amsterdam, where the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology has been going on.
SGLT2 inhibitors for HFpEF and HFrEF
I’m going to review very briefly the 2023 focused update to the ESC heart failure guidelines. Theresa McDonagh was the first author of this and of the previous ESC or European guidelines. These are a little bit different than the American guidelines, which were presented in 2022. We know that we need an update. The Europeans have gotten ahead of us, and now we have the European update, which I find incredibly well written and it really highlights the areas that I think the takeaways are for the clinicians.
First, we have been seeing now for several years – since 2018 – the benefits of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Every time we lift the veil on something, there they are in a positive light. We have learned about heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) for both empagliflozin and dapagliflozin. There are very similar results. One population may be enriched with a little of this and a little of that, but the basic messages are the same. In HFrEF, both of these drugs improve outcomes and it happens quickly. You don’t have to wait 1 or 2 years to see this. Within months, and actually within days, you start to see the curves split apart statistically.
The next logical ground was heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). The definition, when we started the HFpEF trials, was 45% or greater. I want the audience to realize that, in the midst of all these trials, we came out – we meaning the American Heart Association, the American College of Cardiology, and the Heart Failure Society – with the new definition of heart failure, which said that true HFpEF is 50% or greater. That in-between zone of 40%-50% or 41%-49% is mRF, or mid-range, what I call middle of the road. I think the Europeans have really emphasized that to us. I believe that those patients really behave much more like a HFrEF population.
Now that we have very positive findings with the SGLT2 inhibitors, both dapagliflozin and empagliflozin, in HFpEF – defined, as I said, as 40% or 45% or greater, not necessarily 50% – with excellent point estimates that just line up, one on top of the other. It doesn’t matter if patients have diabetes or not; the results are exactly the same.
This has been so promising that I am not surprised that the Europeans elevated the SGLT2 inhibitors to a class 1A indication. In the United States in 2022, we thought we were really way ahead by calling it a class 2A indication. Well, now it’s a class 1A indication in Europe, and I have a feeling that the AHA and the ACC are going to start talking about an update because the data are so strong.
Now, we even have data on initiating these drugs in the hospital. EMPULSE was a very large trial about the benefits of starting these drugs in the hospital. You do not have to wait until the patient is in the outpatient setting. You can start it in the hospital.
When? I have no specific day that I start it. I used to try to do a good diuresis first, get the patients somewhat decongested, and then start it. I don’t want to deprive the patients of the benefits of these drugs that happen very early by waiting until the patients are in the outpatient setting.
In the United States, we’ve had some issues with coverage of some of these drugs. In my institution, we now have both on the formulary, and I pick the drug depending upon the patient’s coverage. Medicare pretty much covers most of them. If the patient is older but not yet a Medicare patient, they may have a very large copay. I advise you to get your offices or your health system to look into this so that, when you give the prescription to the patient, whether they’re leaving the hospital or are now in your clinics, they can actually get the drug.
Finerenone and intravenous iron
There is an additional recommendation in these guidelines for finerenone, the mineralocorticoid receptor agonist that I’ve discussed before, that has some really promising data on type 2 diabetes with chronic kidney disease. They have called that a class 1A indication for finerenone. I think there is more to come.
One more: the iron deficiency. Giving intravenous iron actually does improve symptoms and quality of life. I have seen this in my own patients, so I have been very diligent at looking for iron deficiency.
It is a new era. We have more tools, obviously, for our patients. It means one more drug, and that’s always a challenge. We’ve already been doing the pillars of care. This is the fourth pillar of care, but now with a class 1A indication.
Take a look. They’re easy to read. Dr. McDonagh is the first author, and I think they’ve been extremely well done.
Dr. Piña is professor of medicine at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital in Philadelphia. She is a heart failure and cardiac transplantation expert. She disclosed serving as an adviser/consultant to the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health and has been a volunteer for the American Heart Association since 1982.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This is my usual blog, except I am here from the absolutely beautiful city of Amsterdam, where the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology has been going on.
SGLT2 inhibitors for HFpEF and HFrEF
I’m going to review very briefly the 2023 focused update to the ESC heart failure guidelines. Theresa McDonagh was the first author of this and of the previous ESC or European guidelines. These are a little bit different than the American guidelines, which were presented in 2022. We know that we need an update. The Europeans have gotten ahead of us, and now we have the European update, which I find incredibly well written and it really highlights the areas that I think the takeaways are for the clinicians.
First, we have been seeing now for several years – since 2018 – the benefits of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Every time we lift the veil on something, there they are in a positive light. We have learned about heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) for both empagliflozin and dapagliflozin. There are very similar results. One population may be enriched with a little of this and a little of that, but the basic messages are the same. In HFrEF, both of these drugs improve outcomes and it happens quickly. You don’t have to wait 1 or 2 years to see this. Within months, and actually within days, you start to see the curves split apart statistically.
The next logical ground was heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). The definition, when we started the HFpEF trials, was 45% or greater. I want the audience to realize that, in the midst of all these trials, we came out – we meaning the American Heart Association, the American College of Cardiology, and the Heart Failure Society – with the new definition of heart failure, which said that true HFpEF is 50% or greater. That in-between zone of 40%-50% or 41%-49% is mRF, or mid-range, what I call middle of the road. I think the Europeans have really emphasized that to us. I believe that those patients really behave much more like a HFrEF population.
Now that we have very positive findings with the SGLT2 inhibitors, both dapagliflozin and empagliflozin, in HFpEF – defined, as I said, as 40% or 45% or greater, not necessarily 50% – with excellent point estimates that just line up, one on top of the other. It doesn’t matter if patients have diabetes or not; the results are exactly the same.
This has been so promising that I am not surprised that the Europeans elevated the SGLT2 inhibitors to a class 1A indication. In the United States in 2022, we thought we were really way ahead by calling it a class 2A indication. Well, now it’s a class 1A indication in Europe, and I have a feeling that the AHA and the ACC are going to start talking about an update because the data are so strong.
Now, we even have data on initiating these drugs in the hospital. EMPULSE was a very large trial about the benefits of starting these drugs in the hospital. You do not have to wait until the patient is in the outpatient setting. You can start it in the hospital.
When? I have no specific day that I start it. I used to try to do a good diuresis first, get the patients somewhat decongested, and then start it. I don’t want to deprive the patients of the benefits of these drugs that happen very early by waiting until the patients are in the outpatient setting.
In the United States, we’ve had some issues with coverage of some of these drugs. In my institution, we now have both on the formulary, and I pick the drug depending upon the patient’s coverage. Medicare pretty much covers most of them. If the patient is older but not yet a Medicare patient, they may have a very large copay. I advise you to get your offices or your health system to look into this so that, when you give the prescription to the patient, whether they’re leaving the hospital or are now in your clinics, they can actually get the drug.
Finerenone and intravenous iron
There is an additional recommendation in these guidelines for finerenone, the mineralocorticoid receptor agonist that I’ve discussed before, that has some really promising data on type 2 diabetes with chronic kidney disease. They have called that a class 1A indication for finerenone. I think there is more to come.
One more: the iron deficiency. Giving intravenous iron actually does improve symptoms and quality of life. I have seen this in my own patients, so I have been very diligent at looking for iron deficiency.
It is a new era. We have more tools, obviously, for our patients. It means one more drug, and that’s always a challenge. We’ve already been doing the pillars of care. This is the fourth pillar of care, but now with a class 1A indication.
Take a look. They’re easy to read. Dr. McDonagh is the first author, and I think they’ve been extremely well done.
Dr. Piña is professor of medicine at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital in Philadelphia. She is a heart failure and cardiac transplantation expert. She disclosed serving as an adviser/consultant to the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health and has been a volunteer for the American Heart Association since 1982.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is complete revascularization now compulsory? MULTISTARS-AMI and FIRE in context
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Michelle L. O’Donoghue, MD, MPH: Hi. This is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue reporting for Medscape. Joining me today is Dr. Sahil Parikh, who’s a cardiologist and an interventionalist at Columbia University. He’s an associate professor of medicine.
We’ll be discussing two interesting trials that were presented at the ESC Congress here in Amsterdam. They do have the potential to be very practice-changing, so I think it’s worth talking about.
The FIRE trial
The first trial we’ll be talking about is the FIRE trial. Perhaps setting the stage, Sahil, I’d love to get your thoughts. We’ve had data in this space to suggest that, for patients with STEMI [ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction], a strategy of complete revascularization – and not only treating the culprit lesion but also treating additional lesions – may be of benefit. Where does that lead us in terms of what we didn’t know?
Sahil A. Parikh, MD: I think that the practice has moved, at least in the United States, over the past two decades, from staging percutaneous coronary interventions over 30 days from index to intervention to now trying to do patients in the same hospitalization whenever possible to achieve complete revascularization.
I think these data support not only that complete revascularization is compulsory now in these patients, but also doing it sooner rather than later, and that the benefit applies to most of the patients that we see in clinical practice. In the earlier data, the patients were relatively youthful – under Medicare age, less than 65 – and now this dataset has a median age of 80. This is more like the real-world clinical practice that most of us are encountering, and it extends the benefit, perhaps, greater than we’ve ever seen before.
O’Donoghue: The FIRE trial is interesting. As you say, it enrolled patients who were over the age of 75, where I think that some proceduralists are probably a little bit hesitant to think about complete revascularization due to concerns about any additional contrast load on their kidneys and other types of comorbidities. Of course, for any trial, there’s going to be some patient selection.
I think it’s very reassuring that even in this older patient group, a strategy of treating all the lesions – and not only in STEMI but also in non-STEMI patients – reduced cardiovascular events and mortality. I was really quite impressed by the mortality benefit.
Parikh: The mortality curve is almost surprising to me. On the other hand, it emboldens us now that we can treat these patients more completely and earlier in their clinical presentation. Certainly, we worried about contrast exposure and the duration of procedures in this older population, but it seems that the benefit that’s derived, which we saw in younger patients where we had a natural inclination to be more aggressive, extends also to this older population.
MULTISTARS AMI
O’Donoghue: To the question of timing, as you mentioned, prior to this, we had a study presented earlier this year, the BIOVASC trial, which also was suggestive that maybe earlier complete revascularization was better. But it wasn’t a significant difference, at least for the primary outcome. Now we have MULTISTARS AMI, which is very supportive of what we saw earlier this year, suggesting that complete revascularization really at the time that you’re treating the culprit may be the way to go.
Parikh: All of us, as interventionalists, are circumspect about what we might do in the middle of the night versus what we would do in the light of day. Certainly it seems clear, particularly if it’s straightforward anatomy, that taking care of it in the index procedure is not only saving contrast and fluoroscopy time, but it’s also providing a clinical benefit to the patients. That’s something that will also impact how clinicians interpret these data. Previously, there was always a question about whether we should just do it in the same hospitalization or do it at the same time. I think now, increasingly, we’re emboldened to do more in the index procedure.
O’Donoghue: When you’re thinking about nonculprit lesions and which ones to treat, do you always make that determination based on physiologic guidance of some kind? Are you using instantaneous wave-free ratio? What’s your practice?
Parikh: In the acute setting, imaging is superior for at least the assessment of which is a culprit. If you see a ruptured atherothrombotic situation on optical coherence tomography, for example, that’s fairly convincing and definitive. In the absence of that physiology, we are taught to avoid in the infarct-related artery because of potential spuriously false-negative findings.
In this situation, certainly, an imaging subgroup probably would be helpful because some of the benefit is almost certainly derived from identifying the infarct-related artery by accident – in other words, doing what you thought was the nonculprit artery, which is, in fact, the culprit. I think that probably is part of this. As somebody who uses imaging in the overwhelming number of my cases, I think that imaging would be an important surrogate to this.
Index procedure versus staged
O’Donoghue: For the operator who is coming in to do their STEMI case at 2:00 in the morning, would these data now push you toward doing complete revascularization at that time of night, or do you think that there is wiggle room in terms of interpreting these results regarding timing, where as long as you were doing it before hospital discharge and not, let’s say, 30 days out, that you may be able to derive the same benefit? What are some of the pros and cons?
Parikh: There’s definitely a fatigue factor in the middle of the night if it’s a particularly arduous intervention for the index infarct-related artery. I think there’s a human element where it may make sense just to stop and then bring the patient back in the same hospitalization. It’s clear, though, that doing complete revascularization is better and doing it sooner is better. How soon one actually does it is a judgment call, as ever.
In our practice, we’ve been pushing ourselves to get most of the patients done in their index hospitalization. If you have a left-sided culprit, the left anterior descending artery, for example, and there’s a high-grade stenosis in the circumflex, it may make sense to take care of that in the same index procedure. If, on the other hand, it’s in the right coronary artery where you have to put a new guide in and spend more time, that may be a patient whom you stage. I think those nuances will come up as interventionalists look at the subgroup analysis data more carefully.
O’Donoghue: Those are great points, and I think they also underscore that we always need to think about what type of patient was enrolled in these studies. Certainly, if you have somebody with renal dysfunction, there might be more concern about giving them a large contrast load all in one sitting, albeit hard to know whether they do or not. But spacing that out by just a couple of days would really have a big impact.
Parikh: Very often in the STEMI patient, you don’t have the benefit of knowing the creatinine. The patient will come in immediately, if not directly from the ambulance to the cath lab, and there are no laboratories at all to work with. If the patient has never been seen in the system before, you won’t know. Again, in those situations, one may have pause, particularly if it’s an older patient. I think what’s reassuring, though, is that the data are supportive of being more aggressive earlier, and certainly this is the dataset that we were looking for.
O’Donoghue: To summarize, the two key takeaways are that, one, we now have more data to support a complete revascularization strategy and even extending that now to non-STEMI patients. Two, sooner appears to be better, so ideally, all done at the time of the index procedure. I think this is very interesting science and we’ll see how it changes practice.
Thanks for joining me today. Signing off for Medscape, this is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue.
Michelle O’Donoghue is a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and senior investigator with the TIMI Study Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Michelle L. O’Donoghue, MD, MPH: Hi. This is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue reporting for Medscape. Joining me today is Dr. Sahil Parikh, who’s a cardiologist and an interventionalist at Columbia University. He’s an associate professor of medicine.
We’ll be discussing two interesting trials that were presented at the ESC Congress here in Amsterdam. They do have the potential to be very practice-changing, so I think it’s worth talking about.
The FIRE trial
The first trial we’ll be talking about is the FIRE trial. Perhaps setting the stage, Sahil, I’d love to get your thoughts. We’ve had data in this space to suggest that, for patients with STEMI [ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction], a strategy of complete revascularization – and not only treating the culprit lesion but also treating additional lesions – may be of benefit. Where does that lead us in terms of what we didn’t know?
Sahil A. Parikh, MD: I think that the practice has moved, at least in the United States, over the past two decades, from staging percutaneous coronary interventions over 30 days from index to intervention to now trying to do patients in the same hospitalization whenever possible to achieve complete revascularization.
I think these data support not only that complete revascularization is compulsory now in these patients, but also doing it sooner rather than later, and that the benefit applies to most of the patients that we see in clinical practice. In the earlier data, the patients were relatively youthful – under Medicare age, less than 65 – and now this dataset has a median age of 80. This is more like the real-world clinical practice that most of us are encountering, and it extends the benefit, perhaps, greater than we’ve ever seen before.
O’Donoghue: The FIRE trial is interesting. As you say, it enrolled patients who were over the age of 75, where I think that some proceduralists are probably a little bit hesitant to think about complete revascularization due to concerns about any additional contrast load on their kidneys and other types of comorbidities. Of course, for any trial, there’s going to be some patient selection.
I think it’s very reassuring that even in this older patient group, a strategy of treating all the lesions – and not only in STEMI but also in non-STEMI patients – reduced cardiovascular events and mortality. I was really quite impressed by the mortality benefit.
Parikh: The mortality curve is almost surprising to me. On the other hand, it emboldens us now that we can treat these patients more completely and earlier in their clinical presentation. Certainly, we worried about contrast exposure and the duration of procedures in this older population, but it seems that the benefit that’s derived, which we saw in younger patients where we had a natural inclination to be more aggressive, extends also to this older population.
MULTISTARS AMI
O’Donoghue: To the question of timing, as you mentioned, prior to this, we had a study presented earlier this year, the BIOVASC trial, which also was suggestive that maybe earlier complete revascularization was better. But it wasn’t a significant difference, at least for the primary outcome. Now we have MULTISTARS AMI, which is very supportive of what we saw earlier this year, suggesting that complete revascularization really at the time that you’re treating the culprit may be the way to go.
Parikh: All of us, as interventionalists, are circumspect about what we might do in the middle of the night versus what we would do in the light of day. Certainly it seems clear, particularly if it’s straightforward anatomy, that taking care of it in the index procedure is not only saving contrast and fluoroscopy time, but it’s also providing a clinical benefit to the patients. That’s something that will also impact how clinicians interpret these data. Previously, there was always a question about whether we should just do it in the same hospitalization or do it at the same time. I think now, increasingly, we’re emboldened to do more in the index procedure.
O’Donoghue: When you’re thinking about nonculprit lesions and which ones to treat, do you always make that determination based on physiologic guidance of some kind? Are you using instantaneous wave-free ratio? What’s your practice?
Parikh: In the acute setting, imaging is superior for at least the assessment of which is a culprit. If you see a ruptured atherothrombotic situation on optical coherence tomography, for example, that’s fairly convincing and definitive. In the absence of that physiology, we are taught to avoid in the infarct-related artery because of potential spuriously false-negative findings.
In this situation, certainly, an imaging subgroup probably would be helpful because some of the benefit is almost certainly derived from identifying the infarct-related artery by accident – in other words, doing what you thought was the nonculprit artery, which is, in fact, the culprit. I think that probably is part of this. As somebody who uses imaging in the overwhelming number of my cases, I think that imaging would be an important surrogate to this.
Index procedure versus staged
O’Donoghue: For the operator who is coming in to do their STEMI case at 2:00 in the morning, would these data now push you toward doing complete revascularization at that time of night, or do you think that there is wiggle room in terms of interpreting these results regarding timing, where as long as you were doing it before hospital discharge and not, let’s say, 30 days out, that you may be able to derive the same benefit? What are some of the pros and cons?
Parikh: There’s definitely a fatigue factor in the middle of the night if it’s a particularly arduous intervention for the index infarct-related artery. I think there’s a human element where it may make sense just to stop and then bring the patient back in the same hospitalization. It’s clear, though, that doing complete revascularization is better and doing it sooner is better. How soon one actually does it is a judgment call, as ever.
In our practice, we’ve been pushing ourselves to get most of the patients done in their index hospitalization. If you have a left-sided culprit, the left anterior descending artery, for example, and there’s a high-grade stenosis in the circumflex, it may make sense to take care of that in the same index procedure. If, on the other hand, it’s in the right coronary artery where you have to put a new guide in and spend more time, that may be a patient whom you stage. I think those nuances will come up as interventionalists look at the subgroup analysis data more carefully.
O’Donoghue: Those are great points, and I think they also underscore that we always need to think about what type of patient was enrolled in these studies. Certainly, if you have somebody with renal dysfunction, there might be more concern about giving them a large contrast load all in one sitting, albeit hard to know whether they do or not. But spacing that out by just a couple of days would really have a big impact.
Parikh: Very often in the STEMI patient, you don’t have the benefit of knowing the creatinine. The patient will come in immediately, if not directly from the ambulance to the cath lab, and there are no laboratories at all to work with. If the patient has never been seen in the system before, you won’t know. Again, in those situations, one may have pause, particularly if it’s an older patient. I think what’s reassuring, though, is that the data are supportive of being more aggressive earlier, and certainly this is the dataset that we were looking for.
O’Donoghue: To summarize, the two key takeaways are that, one, we now have more data to support a complete revascularization strategy and even extending that now to non-STEMI patients. Two, sooner appears to be better, so ideally, all done at the time of the index procedure. I think this is very interesting science and we’ll see how it changes practice.
Thanks for joining me today. Signing off for Medscape, this is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue.
Michelle O’Donoghue is a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and senior investigator with the TIMI Study Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Michelle L. O’Donoghue, MD, MPH: Hi. This is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue reporting for Medscape. Joining me today is Dr. Sahil Parikh, who’s a cardiologist and an interventionalist at Columbia University. He’s an associate professor of medicine.
We’ll be discussing two interesting trials that were presented at the ESC Congress here in Amsterdam. They do have the potential to be very practice-changing, so I think it’s worth talking about.
The FIRE trial
The first trial we’ll be talking about is the FIRE trial. Perhaps setting the stage, Sahil, I’d love to get your thoughts. We’ve had data in this space to suggest that, for patients with STEMI [ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction], a strategy of complete revascularization – and not only treating the culprit lesion but also treating additional lesions – may be of benefit. Where does that lead us in terms of what we didn’t know?
Sahil A. Parikh, MD: I think that the practice has moved, at least in the United States, over the past two decades, from staging percutaneous coronary interventions over 30 days from index to intervention to now trying to do patients in the same hospitalization whenever possible to achieve complete revascularization.
I think these data support not only that complete revascularization is compulsory now in these patients, but also doing it sooner rather than later, and that the benefit applies to most of the patients that we see in clinical practice. In the earlier data, the patients were relatively youthful – under Medicare age, less than 65 – and now this dataset has a median age of 80. This is more like the real-world clinical practice that most of us are encountering, and it extends the benefit, perhaps, greater than we’ve ever seen before.
O’Donoghue: The FIRE trial is interesting. As you say, it enrolled patients who were over the age of 75, where I think that some proceduralists are probably a little bit hesitant to think about complete revascularization due to concerns about any additional contrast load on their kidneys and other types of comorbidities. Of course, for any trial, there’s going to be some patient selection.
I think it’s very reassuring that even in this older patient group, a strategy of treating all the lesions – and not only in STEMI but also in non-STEMI patients – reduced cardiovascular events and mortality. I was really quite impressed by the mortality benefit.
Parikh: The mortality curve is almost surprising to me. On the other hand, it emboldens us now that we can treat these patients more completely and earlier in their clinical presentation. Certainly, we worried about contrast exposure and the duration of procedures in this older population, but it seems that the benefit that’s derived, which we saw in younger patients where we had a natural inclination to be more aggressive, extends also to this older population.
MULTISTARS AMI
O’Donoghue: To the question of timing, as you mentioned, prior to this, we had a study presented earlier this year, the BIOVASC trial, which also was suggestive that maybe earlier complete revascularization was better. But it wasn’t a significant difference, at least for the primary outcome. Now we have MULTISTARS AMI, which is very supportive of what we saw earlier this year, suggesting that complete revascularization really at the time that you’re treating the culprit may be the way to go.
Parikh: All of us, as interventionalists, are circumspect about what we might do in the middle of the night versus what we would do in the light of day. Certainly it seems clear, particularly if it’s straightforward anatomy, that taking care of it in the index procedure is not only saving contrast and fluoroscopy time, but it’s also providing a clinical benefit to the patients. That’s something that will also impact how clinicians interpret these data. Previously, there was always a question about whether we should just do it in the same hospitalization or do it at the same time. I think now, increasingly, we’re emboldened to do more in the index procedure.
O’Donoghue: When you’re thinking about nonculprit lesions and which ones to treat, do you always make that determination based on physiologic guidance of some kind? Are you using instantaneous wave-free ratio? What’s your practice?
Parikh: In the acute setting, imaging is superior for at least the assessment of which is a culprit. If you see a ruptured atherothrombotic situation on optical coherence tomography, for example, that’s fairly convincing and definitive. In the absence of that physiology, we are taught to avoid in the infarct-related artery because of potential spuriously false-negative findings.
In this situation, certainly, an imaging subgroup probably would be helpful because some of the benefit is almost certainly derived from identifying the infarct-related artery by accident – in other words, doing what you thought was the nonculprit artery, which is, in fact, the culprit. I think that probably is part of this. As somebody who uses imaging in the overwhelming number of my cases, I think that imaging would be an important surrogate to this.
Index procedure versus staged
O’Donoghue: For the operator who is coming in to do their STEMI case at 2:00 in the morning, would these data now push you toward doing complete revascularization at that time of night, or do you think that there is wiggle room in terms of interpreting these results regarding timing, where as long as you were doing it before hospital discharge and not, let’s say, 30 days out, that you may be able to derive the same benefit? What are some of the pros and cons?
Parikh: There’s definitely a fatigue factor in the middle of the night if it’s a particularly arduous intervention for the index infarct-related artery. I think there’s a human element where it may make sense just to stop and then bring the patient back in the same hospitalization. It’s clear, though, that doing complete revascularization is better and doing it sooner is better. How soon one actually does it is a judgment call, as ever.
In our practice, we’ve been pushing ourselves to get most of the patients done in their index hospitalization. If you have a left-sided culprit, the left anterior descending artery, for example, and there’s a high-grade stenosis in the circumflex, it may make sense to take care of that in the same index procedure. If, on the other hand, it’s in the right coronary artery where you have to put a new guide in and spend more time, that may be a patient whom you stage. I think those nuances will come up as interventionalists look at the subgroup analysis data more carefully.
O’Donoghue: Those are great points, and I think they also underscore that we always need to think about what type of patient was enrolled in these studies. Certainly, if you have somebody with renal dysfunction, there might be more concern about giving them a large contrast load all in one sitting, albeit hard to know whether they do or not. But spacing that out by just a couple of days would really have a big impact.
Parikh: Very often in the STEMI patient, you don’t have the benefit of knowing the creatinine. The patient will come in immediately, if not directly from the ambulance to the cath lab, and there are no laboratories at all to work with. If the patient has never been seen in the system before, you won’t know. Again, in those situations, one may have pause, particularly if it’s an older patient. I think what’s reassuring, though, is that the data are supportive of being more aggressive earlier, and certainly this is the dataset that we were looking for.
O’Donoghue: To summarize, the two key takeaways are that, one, we now have more data to support a complete revascularization strategy and even extending that now to non-STEMI patients. Two, sooner appears to be better, so ideally, all done at the time of the index procedure. I think this is very interesting science and we’ll see how it changes practice.
Thanks for joining me today. Signing off for Medscape, this is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue.
Michelle O’Donoghue is a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and senior investigator with the TIMI Study Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dusty, but still cool
When I was 16, keeping my car shiny was a priority. I washed it every weekend and waxed it once a month. I was pretty good at it and got paid to do the occasional job for a neighbor, too.
In college I was busier, and my car was back at the house, so it didn’t need to be washed as much.
In medical school I think I washed the car once a year. Residency was probably the same.
Today I realized I couldn’t remember when I last had it washed (at my age I don’t have time to do it myself). So I looked it up in Quicken: Nov. 14, 2018.
Really? I’ve gone almost 5 years without washing my car? I can’t even blame that on the pandemic.
I mean, I still like my car. It’s comfortable, has good air conditioning (in Phoenix that’s critical), and gets me where I want to go. At my age those things are what’s really important. It’s hard to believe that 40 years ago, keeping a polished car was the center of my existence. Of course, it probably still is for most guys that age.
It’s a reminder of how much things change as life goes by.
Here in my little corner of neurology, multiple sclerosis has gone from steroids for relapses, to a few injections of mild benefit, to a bunch of drugs that are, literally, game-changing for many patients. And the Big Four epilepsy drugs (Dilantin, Tegretol, Depakote, and Phenobarb) are slowly fading into the background.
But back to changing priorities – it’s the way life rewrites our plans at each step. From a freshly waxed car to good grades to mortgages to kids – and then watching as they wax their cars.
Suddenly my car looks dusty. Am I the same way? I’m certainly not 16 anymore. Realistically, the majority of my life and career are behind me now. That doesn’t mean I’m not still having fun, it’s just the truth. I try not to think about it that much, as doing so won’t change anything.
In all honesty, neither did washing my car. I mean, the car looked good, but did it make me one of the cool kids? Or get me a girlfriend? Or invited to THE parties? Not at all. Like so many things about appearances, very few of them really matter. There’s only so far that style will get you, compared with substance.
Which doesn’t change the fact that I need to wash my car. But procrastination is for another column.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
When I was 16, keeping my car shiny was a priority. I washed it every weekend and waxed it once a month. I was pretty good at it and got paid to do the occasional job for a neighbor, too.
In college I was busier, and my car was back at the house, so it didn’t need to be washed as much.
In medical school I think I washed the car once a year. Residency was probably the same.
Today I realized I couldn’t remember when I last had it washed (at my age I don’t have time to do it myself). So I looked it up in Quicken: Nov. 14, 2018.
Really? I’ve gone almost 5 years without washing my car? I can’t even blame that on the pandemic.
I mean, I still like my car. It’s comfortable, has good air conditioning (in Phoenix that’s critical), and gets me where I want to go. At my age those things are what’s really important. It’s hard to believe that 40 years ago, keeping a polished car was the center of my existence. Of course, it probably still is for most guys that age.
It’s a reminder of how much things change as life goes by.
Here in my little corner of neurology, multiple sclerosis has gone from steroids for relapses, to a few injections of mild benefit, to a bunch of drugs that are, literally, game-changing for many patients. And the Big Four epilepsy drugs (Dilantin, Tegretol, Depakote, and Phenobarb) are slowly fading into the background.
But back to changing priorities – it’s the way life rewrites our plans at each step. From a freshly waxed car to good grades to mortgages to kids – and then watching as they wax their cars.
Suddenly my car looks dusty. Am I the same way? I’m certainly not 16 anymore. Realistically, the majority of my life and career are behind me now. That doesn’t mean I’m not still having fun, it’s just the truth. I try not to think about it that much, as doing so won’t change anything.
In all honesty, neither did washing my car. I mean, the car looked good, but did it make me one of the cool kids? Or get me a girlfriend? Or invited to THE parties? Not at all. Like so many things about appearances, very few of them really matter. There’s only so far that style will get you, compared with substance.
Which doesn’t change the fact that I need to wash my car. But procrastination is for another column.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
When I was 16, keeping my car shiny was a priority. I washed it every weekend and waxed it once a month. I was pretty good at it and got paid to do the occasional job for a neighbor, too.
In college I was busier, and my car was back at the house, so it didn’t need to be washed as much.
In medical school I think I washed the car once a year. Residency was probably the same.
Today I realized I couldn’t remember when I last had it washed (at my age I don’t have time to do it myself). So I looked it up in Quicken: Nov. 14, 2018.
Really? I’ve gone almost 5 years without washing my car? I can’t even blame that on the pandemic.
I mean, I still like my car. It’s comfortable, has good air conditioning (in Phoenix that’s critical), and gets me where I want to go. At my age those things are what’s really important. It’s hard to believe that 40 years ago, keeping a polished car was the center of my existence. Of course, it probably still is for most guys that age.
It’s a reminder of how much things change as life goes by.
Here in my little corner of neurology, multiple sclerosis has gone from steroids for relapses, to a few injections of mild benefit, to a bunch of drugs that are, literally, game-changing for many patients. And the Big Four epilepsy drugs (Dilantin, Tegretol, Depakote, and Phenobarb) are slowly fading into the background.
But back to changing priorities – it’s the way life rewrites our plans at each step. From a freshly waxed car to good grades to mortgages to kids – and then watching as they wax their cars.
Suddenly my car looks dusty. Am I the same way? I’m certainly not 16 anymore. Realistically, the majority of my life and career are behind me now. That doesn’t mean I’m not still having fun, it’s just the truth. I try not to think about it that much, as doing so won’t change anything.
In all honesty, neither did washing my car. I mean, the car looked good, but did it make me one of the cool kids? Or get me a girlfriend? Or invited to THE parties? Not at all. Like so many things about appearances, very few of them really matter. There’s only so far that style will get you, compared with substance.
Which doesn’t change the fact that I need to wash my car. But procrastination is for another column.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Should people who play sports pay higher medical insurance premiums?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’re anywhere near Seattle, anywhere near Florida, or anywhere where it might be not oppressively hot outside but encouraging some people who might want to go out and get a little exercise, you’ve undoubtedly seen or heard of pickleball.
This took off, I think, out of Bainbridge Island, Wash. It was meant as a gentlemanly game where people didn’t exert themselves too much. The joke is you could play it while holding a drink in one hand. It’s gotten more popular and more competitive. It’s kind of a miniature version of tennis, with a smaller court, a plastic ball, and a wooden paddle. The ball can go back and forth rapidly, but you’re always playing doubles and it doesn’t take as much energy, exertion, and, if you will, fitness as a game like singles tennis.
The upside is it’s gotten many people outdoors getting some exercise and socializing. That’s all to the good. But a recent study suggested that there are about $500 million worth of injuries coming into the health care system associated with pickleball. There have been leg sprains, broken bones, people getting hit in the eye, hamstring pulls, and many other problems. I’ve been told that many of the spectators who show up for pickleball matches are there with a cast or have some kind of a wrap on because they were injured.
Well, many people have argued in the past about what we are going to do about health care costs. Some suggest if you voluntarily incur health care damage, you ought to pay for that yourself and you ought to have a big copay.
If you decide you’re going to do cross-country skiing or downhill skiing and you injure yourself, you chose to do it, so you pay. If you’re not going to maintain your weight, you’re going to smoke, or you’re going to ride around without a helmet, that’s your choice. You ought to pay.
I think the pickleball example is really a good challenge to these views. You obviously want people to go out and get some exercise. Here, we’re talking about a population that’s a little older and oftentimes doesn’t get out there as much as doctors would like to get the exercise that’s still important that they need, and yet it does incur injuries and problems.
My suggestion would be to make the game a little safer. Let’s try to encourage people to warm up more before they get out there and jump out of the car and engage in their pickleball battles. Goggles might be important to prevent the eye injuries in a game that’s played up close. Maybe we want to make sure that people look out for one another out there. If they think they’re getting dehydrated or tired, they should say, “Let’s sit down.”
I’m not willing to put a tax or a copay on the pickleball players of America. I know they choose to do it. It’s got an upside and benefits, as many things like skiing and other behaviors that have some risk do, but I think we want to be encouraging, not discouraging, of it.
I don’t like a society where anybody who tries to do something that takes risk winds up bearing extra cost for doing that. I understand that that gets people irritated when it comes to dangerous, hyper-risky behavior like smoking and not wearing a motorcycle helmet. I think the way to engage is not to call out the sinner or to try and punish those who are trying to do things that bring them enjoyment, reward, or in some of these cases, physical fitness, but to try to make things safer and try to gradually improve and get rid of the risk side to capture the full benefit side.
I’m not sure I’ve come up with all the best ways to make pickleball safer, but I think that’s where our thinking in health care should go. My view is to get out there and play pickleball. If you do pull your hamstring, raise my insurance premium a little bit. I’ll help to pay for it. Better you get some enjoyment and some exercise.
I get the downside, but come on, folks, we ought to be, as a community, somewhat supportive of the fun and recreation that our fellow citizens engage in.
Dr. Caplan is director, division of medical ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center. He disclosed serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position); and as a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’re anywhere near Seattle, anywhere near Florida, or anywhere where it might be not oppressively hot outside but encouraging some people who might want to go out and get a little exercise, you’ve undoubtedly seen or heard of pickleball.
This took off, I think, out of Bainbridge Island, Wash. It was meant as a gentlemanly game where people didn’t exert themselves too much. The joke is you could play it while holding a drink in one hand. It’s gotten more popular and more competitive. It’s kind of a miniature version of tennis, with a smaller court, a plastic ball, and a wooden paddle. The ball can go back and forth rapidly, but you’re always playing doubles and it doesn’t take as much energy, exertion, and, if you will, fitness as a game like singles tennis.
The upside is it’s gotten many people outdoors getting some exercise and socializing. That’s all to the good. But a recent study suggested that there are about $500 million worth of injuries coming into the health care system associated with pickleball. There have been leg sprains, broken bones, people getting hit in the eye, hamstring pulls, and many other problems. I’ve been told that many of the spectators who show up for pickleball matches are there with a cast or have some kind of a wrap on because they were injured.
Well, many people have argued in the past about what we are going to do about health care costs. Some suggest if you voluntarily incur health care damage, you ought to pay for that yourself and you ought to have a big copay.
If you decide you’re going to do cross-country skiing or downhill skiing and you injure yourself, you chose to do it, so you pay. If you’re not going to maintain your weight, you’re going to smoke, or you’re going to ride around without a helmet, that’s your choice. You ought to pay.
I think the pickleball example is really a good challenge to these views. You obviously want people to go out and get some exercise. Here, we’re talking about a population that’s a little older and oftentimes doesn’t get out there as much as doctors would like to get the exercise that’s still important that they need, and yet it does incur injuries and problems.
My suggestion would be to make the game a little safer. Let’s try to encourage people to warm up more before they get out there and jump out of the car and engage in their pickleball battles. Goggles might be important to prevent the eye injuries in a game that’s played up close. Maybe we want to make sure that people look out for one another out there. If they think they’re getting dehydrated or tired, they should say, “Let’s sit down.”
I’m not willing to put a tax or a copay on the pickleball players of America. I know they choose to do it. It’s got an upside and benefits, as many things like skiing and other behaviors that have some risk do, but I think we want to be encouraging, not discouraging, of it.
I don’t like a society where anybody who tries to do something that takes risk winds up bearing extra cost for doing that. I understand that that gets people irritated when it comes to dangerous, hyper-risky behavior like smoking and not wearing a motorcycle helmet. I think the way to engage is not to call out the sinner or to try and punish those who are trying to do things that bring them enjoyment, reward, or in some of these cases, physical fitness, but to try to make things safer and try to gradually improve and get rid of the risk side to capture the full benefit side.
I’m not sure I’ve come up with all the best ways to make pickleball safer, but I think that’s where our thinking in health care should go. My view is to get out there and play pickleball. If you do pull your hamstring, raise my insurance premium a little bit. I’ll help to pay for it. Better you get some enjoyment and some exercise.
I get the downside, but come on, folks, we ought to be, as a community, somewhat supportive of the fun and recreation that our fellow citizens engage in.
Dr. Caplan is director, division of medical ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center. He disclosed serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position); and as a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’re anywhere near Seattle, anywhere near Florida, or anywhere where it might be not oppressively hot outside but encouraging some people who might want to go out and get a little exercise, you’ve undoubtedly seen or heard of pickleball.
This took off, I think, out of Bainbridge Island, Wash. It was meant as a gentlemanly game where people didn’t exert themselves too much. The joke is you could play it while holding a drink in one hand. It’s gotten more popular and more competitive. It’s kind of a miniature version of tennis, with a smaller court, a plastic ball, and a wooden paddle. The ball can go back and forth rapidly, but you’re always playing doubles and it doesn’t take as much energy, exertion, and, if you will, fitness as a game like singles tennis.
The upside is it’s gotten many people outdoors getting some exercise and socializing. That’s all to the good. But a recent study suggested that there are about $500 million worth of injuries coming into the health care system associated with pickleball. There have been leg sprains, broken bones, people getting hit in the eye, hamstring pulls, and many other problems. I’ve been told that many of the spectators who show up for pickleball matches are there with a cast or have some kind of a wrap on because they were injured.
Well, many people have argued in the past about what we are going to do about health care costs. Some suggest if you voluntarily incur health care damage, you ought to pay for that yourself and you ought to have a big copay.
If you decide you’re going to do cross-country skiing or downhill skiing and you injure yourself, you chose to do it, so you pay. If you’re not going to maintain your weight, you’re going to smoke, or you’re going to ride around without a helmet, that’s your choice. You ought to pay.
I think the pickleball example is really a good challenge to these views. You obviously want people to go out and get some exercise. Here, we’re talking about a population that’s a little older and oftentimes doesn’t get out there as much as doctors would like to get the exercise that’s still important that they need, and yet it does incur injuries and problems.
My suggestion would be to make the game a little safer. Let’s try to encourage people to warm up more before they get out there and jump out of the car and engage in their pickleball battles. Goggles might be important to prevent the eye injuries in a game that’s played up close. Maybe we want to make sure that people look out for one another out there. If they think they’re getting dehydrated or tired, they should say, “Let’s sit down.”
I’m not willing to put a tax or a copay on the pickleball players of America. I know they choose to do it. It’s got an upside and benefits, as many things like skiing and other behaviors that have some risk do, but I think we want to be encouraging, not discouraging, of it.
I don’t like a society where anybody who tries to do something that takes risk winds up bearing extra cost for doing that. I understand that that gets people irritated when it comes to dangerous, hyper-risky behavior like smoking and not wearing a motorcycle helmet. I think the way to engage is not to call out the sinner or to try and punish those who are trying to do things that bring them enjoyment, reward, or in some of these cases, physical fitness, but to try to make things safer and try to gradually improve and get rid of the risk side to capture the full benefit side.
I’m not sure I’ve come up with all the best ways to make pickleball safer, but I think that’s where our thinking in health care should go. My view is to get out there and play pickleball. If you do pull your hamstring, raise my insurance premium a little bit. I’ll help to pay for it. Better you get some enjoyment and some exercise.
I get the downside, but come on, folks, we ought to be, as a community, somewhat supportive of the fun and recreation that our fellow citizens engage in.
Dr. Caplan is director, division of medical ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center. He disclosed serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position); and as a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hepatic presentations of celiac disease
Liver biopsy findings may include variable degrees of steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis.
In one case we have seen, the patient presented with unexplained ascites and features suggestive of Budd-Chiari syndrome. The serum ascites albumin gradient was 2.3 with a total protein of 0.8 g/dL, and albumin 0.5 g/dL, with an ascitic WBC count of 88/mm3.
Echocardiography showed an ejection fraction of 80%. Transjugular liver biopsy revealed a normal hepatic venous pressure gradient but marked sinusoidal dilatation and congestion with hepatocyte atrophy and focal necrosis suggestive of vascular outlet obstruction (Figure 1).
Hepatic venography, however, showed no evidence of Budd-Chiari syndrome. When seen in consultation, pertinent observations included Irish ancestry, a history of occasional diarrhea, short stature, osteoporosis, and an atrophic spleen on computed tomography. An IgA transglutaminase antibody was positive, and a small-bowel biopsy confirmed celiac disease (Figure 2).
On a gluten-free diet, the patient’s symptoms resolved, with clinical and laboratory abnormalities returning to normal. She lived another 20 years before dying of primary pulmonary hypertension. Recognition of an unusual hepatic manifestation of celiac disease led to effective management.
Dr. Friedman is the Anton R. Fried, MD, Chair of the department of medicine at Newton-Wellesley Hospital in Newton, Mass., and assistant chief of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and Tufts University School of Medicine, all in Boston. Dr. Martin is chief of the division of digestive health and liver diseases at the Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami, where he is the Mandel Chair of Gastroenterology. The authors disclose no conflicts.
Previously published in Gastro Hep Advances. 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.03.018.
Liver biopsy findings may include variable degrees of steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis.
In one case we have seen, the patient presented with unexplained ascites and features suggestive of Budd-Chiari syndrome. The serum ascites albumin gradient was 2.3 with a total protein of 0.8 g/dL, and albumin 0.5 g/dL, with an ascitic WBC count of 88/mm3.
Echocardiography showed an ejection fraction of 80%. Transjugular liver biopsy revealed a normal hepatic venous pressure gradient but marked sinusoidal dilatation and congestion with hepatocyte atrophy and focal necrosis suggestive of vascular outlet obstruction (Figure 1).
Hepatic venography, however, showed no evidence of Budd-Chiari syndrome. When seen in consultation, pertinent observations included Irish ancestry, a history of occasional diarrhea, short stature, osteoporosis, and an atrophic spleen on computed tomography. An IgA transglutaminase antibody was positive, and a small-bowel biopsy confirmed celiac disease (Figure 2).
On a gluten-free diet, the patient’s symptoms resolved, with clinical and laboratory abnormalities returning to normal. She lived another 20 years before dying of primary pulmonary hypertension. Recognition of an unusual hepatic manifestation of celiac disease led to effective management.
Dr. Friedman is the Anton R. Fried, MD, Chair of the department of medicine at Newton-Wellesley Hospital in Newton, Mass., and assistant chief of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and Tufts University School of Medicine, all in Boston. Dr. Martin is chief of the division of digestive health and liver diseases at the Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami, where he is the Mandel Chair of Gastroenterology. The authors disclose no conflicts.
Previously published in Gastro Hep Advances. 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.03.018.
Liver biopsy findings may include variable degrees of steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis.
In one case we have seen, the patient presented with unexplained ascites and features suggestive of Budd-Chiari syndrome. The serum ascites albumin gradient was 2.3 with a total protein of 0.8 g/dL, and albumin 0.5 g/dL, with an ascitic WBC count of 88/mm3.
Echocardiography showed an ejection fraction of 80%. Transjugular liver biopsy revealed a normal hepatic venous pressure gradient but marked sinusoidal dilatation and congestion with hepatocyte atrophy and focal necrosis suggestive of vascular outlet obstruction (Figure 1).
Hepatic venography, however, showed no evidence of Budd-Chiari syndrome. When seen in consultation, pertinent observations included Irish ancestry, a history of occasional diarrhea, short stature, osteoporosis, and an atrophic spleen on computed tomography. An IgA transglutaminase antibody was positive, and a small-bowel biopsy confirmed celiac disease (Figure 2).
On a gluten-free diet, the patient’s symptoms resolved, with clinical and laboratory abnormalities returning to normal. She lived another 20 years before dying of primary pulmonary hypertension. Recognition of an unusual hepatic manifestation of celiac disease led to effective management.
Dr. Friedman is the Anton R. Fried, MD, Chair of the department of medicine at Newton-Wellesley Hospital in Newton, Mass., and assistant chief of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and Tufts University School of Medicine, all in Boston. Dr. Martin is chief of the division of digestive health and liver diseases at the Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami, where he is the Mandel Chair of Gastroenterology. The authors disclose no conflicts.
Previously published in Gastro Hep Advances. 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.03.018.
Barbie has an anxiety disorder
And it’s a great time to be a therapist
The Barbie movie is generating a lot of feelings, ranging from praise to vitriol. However one feels about the movie, let’s all pause and reflect for a moment on the fact that the number-one grossing film of 2023 is about our childhood doll trying to treat her anxiety disorder.
“Life imitates art more than art imitates life.” So said Oscar Wilde in 1889.
When my adult daughter, a childhood Barbie enthusiast, asked me to see the film, we put on pink and went. Twice. Little did I know that it would stir up so many thoughts and feelings. The one I want to share is how blessed I feel at this moment in time to be a mental health care provider! No longer is mental health something to be whispered about at the water cooler; instead, even Barbie is suffering. And with all the controversy in the press about the movie, no one seems at all surprised by this storyline.
I was raised by two child psychiatrists and have been practicing as an adult psychiatrist since 1991. The start of the pandemic was the most difficult time of my career, as almost every patient was struggling simultaneously, as was I. Three long years later, we are gradually emerging from our shared trauma. How ironic, now with the opportunity to go back to work, I have elected to maintain the majority of my practice online from home. It seems that most patients and providers prefer this mode of treatment, with a full 90 percent of practitioners saying they are using a hybrid model.
As mental health professionals, we know that anywhere from 3% to 49% of those experiencing trauma will develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and we have been trained to treat them.
But what happens when an entire global population is exposed simultaneously to trauma? Historians and social scientists refer to such events by many different names, such as: Singularity, Black Swan Event, and Tipping Point. These events are incredibly rare, and afterwards everything is different. These global traumas always lead to massive change.
I think we are at that tipping point. This is the singularity. This is our Black Swan Event. Within a 3-year span, we have experienced the following:
- A global traumatic event (COVID-19).
- A sudden and seemingly permanent shift from office to remote video meetings mostly from home.
- Upending of traditional fundamentals of the stock market as the game literally stopped in January 2021.
- Rapid and widespread availability of Artificial Intelligence.
- The first generation to be fully raised on the Internet and social media (Gen Z) is now entering the workforce.
- Ongoing war in Ukraine.
That’s already an overwhelming list, and I could go on, but let’s get back to Barbie’s anxiety disorder.
The awareness about and acceptance of mental health issues has never been higher. The access to treatment never greater. There are now more online therapy options than ever. Treatment options have dramatically expanded in recent years, from Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) to ketamine centers and psychedelics, as well as more mainstream options such as dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and so many more.
What is particularly unique about this moment is the direct access to care. Self-help books abound with many making it to the New York Times bestseller list. YouTube is loaded with fantastic content on overcoming many mental health issues, although one should be careful with selecting reliable sources. Apps like HeadSpace and Calm are being downloaded by millions of people around the globe. Investors provided a record-breaking $1.5 billion to mental health startups in 2020 alone.
For most practitioners, our phones have been ringing off the hook since 2020. Applications to psychology, psychiatric residency, social work, and counseling degree programs are on the rise, with workforce shortages expected to continue for decades. Psychological expertise has been embraced by businesses especially for DEI (diversity, equity, and inclusion). Mental health experts are the most asked-for experts through media request services. Elite athletes are talking openly about bringing us on their teams.
In this unique moment, when everything seems set to transform into something else, it is time for mental health professionals to exert some agency and influence over where mental health will go from here. I think the next frontier for mental health specialists is to figure out how to speak collectively and help guide society.
Neil Howe, in his sweeping book “The Fourth Turning is Here,” says we have another 10 years in this “Millennial Crisis” phase. He calls this our “winter,” and it remains to be seen how we will emerge from our current challenges. I think we can make a difference.
If the Barbie movie is indeed a canary in the coal mine, I see positive trends ahead as we move past some of the societal and structural issues facing us, and work together to create a more open and egalitarian society. We must find creative solutions that will solve truly massive problems threatening our well-being and perhaps even our existence.
I am so grateful to be able to continue to practice and share my thoughts with you here from my home office, and I hope you can take a break and see this movie, which is not only entertaining but also thought- and emotion-provoking.
Dr. Ritvo has almost 30 years’ experience in psychiatry and is currently practicing telemedicine. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018). She has no conflicts of interest.
And it’s a great time to be a therapist
And it’s a great time to be a therapist
The Barbie movie is generating a lot of feelings, ranging from praise to vitriol. However one feels about the movie, let’s all pause and reflect for a moment on the fact that the number-one grossing film of 2023 is about our childhood doll trying to treat her anxiety disorder.
“Life imitates art more than art imitates life.” So said Oscar Wilde in 1889.
When my adult daughter, a childhood Barbie enthusiast, asked me to see the film, we put on pink and went. Twice. Little did I know that it would stir up so many thoughts and feelings. The one I want to share is how blessed I feel at this moment in time to be a mental health care provider! No longer is mental health something to be whispered about at the water cooler; instead, even Barbie is suffering. And with all the controversy in the press about the movie, no one seems at all surprised by this storyline.
I was raised by two child psychiatrists and have been practicing as an adult psychiatrist since 1991. The start of the pandemic was the most difficult time of my career, as almost every patient was struggling simultaneously, as was I. Three long years later, we are gradually emerging from our shared trauma. How ironic, now with the opportunity to go back to work, I have elected to maintain the majority of my practice online from home. It seems that most patients and providers prefer this mode of treatment, with a full 90 percent of practitioners saying they are using a hybrid model.
As mental health professionals, we know that anywhere from 3% to 49% of those experiencing trauma will develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and we have been trained to treat them.
But what happens when an entire global population is exposed simultaneously to trauma? Historians and social scientists refer to such events by many different names, such as: Singularity, Black Swan Event, and Tipping Point. These events are incredibly rare, and afterwards everything is different. These global traumas always lead to massive change.
I think we are at that tipping point. This is the singularity. This is our Black Swan Event. Within a 3-year span, we have experienced the following:
- A global traumatic event (COVID-19).
- A sudden and seemingly permanent shift from office to remote video meetings mostly from home.
- Upending of traditional fundamentals of the stock market as the game literally stopped in January 2021.
- Rapid and widespread availability of Artificial Intelligence.
- The first generation to be fully raised on the Internet and social media (Gen Z) is now entering the workforce.
- Ongoing war in Ukraine.
That’s already an overwhelming list, and I could go on, but let’s get back to Barbie’s anxiety disorder.
The awareness about and acceptance of mental health issues has never been higher. The access to treatment never greater. There are now more online therapy options than ever. Treatment options have dramatically expanded in recent years, from Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) to ketamine centers and psychedelics, as well as more mainstream options such as dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and so many more.
What is particularly unique about this moment is the direct access to care. Self-help books abound with many making it to the New York Times bestseller list. YouTube is loaded with fantastic content on overcoming many mental health issues, although one should be careful with selecting reliable sources. Apps like HeadSpace and Calm are being downloaded by millions of people around the globe. Investors provided a record-breaking $1.5 billion to mental health startups in 2020 alone.
For most practitioners, our phones have been ringing off the hook since 2020. Applications to psychology, psychiatric residency, social work, and counseling degree programs are on the rise, with workforce shortages expected to continue for decades. Psychological expertise has been embraced by businesses especially for DEI (diversity, equity, and inclusion). Mental health experts are the most asked-for experts through media request services. Elite athletes are talking openly about bringing us on their teams.
In this unique moment, when everything seems set to transform into something else, it is time for mental health professionals to exert some agency and influence over where mental health will go from here. I think the next frontier for mental health specialists is to figure out how to speak collectively and help guide society.
Neil Howe, in his sweeping book “The Fourth Turning is Here,” says we have another 10 years in this “Millennial Crisis” phase. He calls this our “winter,” and it remains to be seen how we will emerge from our current challenges. I think we can make a difference.
If the Barbie movie is indeed a canary in the coal mine, I see positive trends ahead as we move past some of the societal and structural issues facing us, and work together to create a more open and egalitarian society. We must find creative solutions that will solve truly massive problems threatening our well-being and perhaps even our existence.
I am so grateful to be able to continue to practice and share my thoughts with you here from my home office, and I hope you can take a break and see this movie, which is not only entertaining but also thought- and emotion-provoking.
Dr. Ritvo has almost 30 years’ experience in psychiatry and is currently practicing telemedicine. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018). She has no conflicts of interest.
The Barbie movie is generating a lot of feelings, ranging from praise to vitriol. However one feels about the movie, let’s all pause and reflect for a moment on the fact that the number-one grossing film of 2023 is about our childhood doll trying to treat her anxiety disorder.
“Life imitates art more than art imitates life.” So said Oscar Wilde in 1889.
When my adult daughter, a childhood Barbie enthusiast, asked me to see the film, we put on pink and went. Twice. Little did I know that it would stir up so many thoughts and feelings. The one I want to share is how blessed I feel at this moment in time to be a mental health care provider! No longer is mental health something to be whispered about at the water cooler; instead, even Barbie is suffering. And with all the controversy in the press about the movie, no one seems at all surprised by this storyline.
I was raised by two child psychiatrists and have been practicing as an adult psychiatrist since 1991. The start of the pandemic was the most difficult time of my career, as almost every patient was struggling simultaneously, as was I. Three long years later, we are gradually emerging from our shared trauma. How ironic, now with the opportunity to go back to work, I have elected to maintain the majority of my practice online from home. It seems that most patients and providers prefer this mode of treatment, with a full 90 percent of practitioners saying they are using a hybrid model.
As mental health professionals, we know that anywhere from 3% to 49% of those experiencing trauma will develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and we have been trained to treat them.
But what happens when an entire global population is exposed simultaneously to trauma? Historians and social scientists refer to such events by many different names, such as: Singularity, Black Swan Event, and Tipping Point. These events are incredibly rare, and afterwards everything is different. These global traumas always lead to massive change.
I think we are at that tipping point. This is the singularity. This is our Black Swan Event. Within a 3-year span, we have experienced the following:
- A global traumatic event (COVID-19).
- A sudden and seemingly permanent shift from office to remote video meetings mostly from home.
- Upending of traditional fundamentals of the stock market as the game literally stopped in January 2021.
- Rapid and widespread availability of Artificial Intelligence.
- The first generation to be fully raised on the Internet and social media (Gen Z) is now entering the workforce.
- Ongoing war in Ukraine.
That’s already an overwhelming list, and I could go on, but let’s get back to Barbie’s anxiety disorder.
The awareness about and acceptance of mental health issues has never been higher. The access to treatment never greater. There are now more online therapy options than ever. Treatment options have dramatically expanded in recent years, from Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) to ketamine centers and psychedelics, as well as more mainstream options such as dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and so many more.
What is particularly unique about this moment is the direct access to care. Self-help books abound with many making it to the New York Times bestseller list. YouTube is loaded with fantastic content on overcoming many mental health issues, although one should be careful with selecting reliable sources. Apps like HeadSpace and Calm are being downloaded by millions of people around the globe. Investors provided a record-breaking $1.5 billion to mental health startups in 2020 alone.
For most practitioners, our phones have been ringing off the hook since 2020. Applications to psychology, psychiatric residency, social work, and counseling degree programs are on the rise, with workforce shortages expected to continue for decades. Psychological expertise has been embraced by businesses especially for DEI (diversity, equity, and inclusion). Mental health experts are the most asked-for experts through media request services. Elite athletes are talking openly about bringing us on their teams.
In this unique moment, when everything seems set to transform into something else, it is time for mental health professionals to exert some agency and influence over where mental health will go from here. I think the next frontier for mental health specialists is to figure out how to speak collectively and help guide society.
Neil Howe, in his sweeping book “The Fourth Turning is Here,” says we have another 10 years in this “Millennial Crisis” phase. He calls this our “winter,” and it remains to be seen how we will emerge from our current challenges. I think we can make a difference.
If the Barbie movie is indeed a canary in the coal mine, I see positive trends ahead as we move past some of the societal and structural issues facing us, and work together to create a more open and egalitarian society. We must find creative solutions that will solve truly massive problems threatening our well-being and perhaps even our existence.
I am so grateful to be able to continue to practice and share my thoughts with you here from my home office, and I hope you can take a break and see this movie, which is not only entertaining but also thought- and emotion-provoking.
Dr. Ritvo has almost 30 years’ experience in psychiatry and is currently practicing telemedicine. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018). She has no conflicts of interest.
The new normal in body temperature
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Every branch of science has its constants. Physics has the speed of light, the gravitational constant, the Planck constant. Chemistry gives us Avogadro’s number, Faraday’s constant, the charge of an electron. Medicine isn’t quite as reliable as physics when it comes to these things, but insofar as there are any constants in medicine, might I suggest normal body temperature: 37° Celsius, 98.6° Fahrenheit.
Sure, serum sodium may be less variable and lactate concentration more clinically relevant, but even my 7-year-old knows that normal body temperature is 98.6°.
Except, as it turns out, 98.6° isn’t normal at all.
How did we arrive at 37.0° C for normal body temperature? We got it from this guy – German physician Carl Reinhold August Wunderlich, who, in addition to looking eerily like Luciano Pavarotti, was the first to realize that fever was not itself a disease but a symptom of one.
In 1851, Dr. Wunderlich released his measurements of more than 1 million body temperatures taken from 25,000 Germans – a painstaking process at the time, which employed a foot-long thermometer and took 20 minutes to obtain a measurement.
The average temperature measured, of course, was 37° C.
We’re more than 150 years post-Wunderlich right now, and the average person in the United States might be quite a bit different from the average German in 1850. Moreover, we can do a lot better than just measuring a ton of people and taking the average, because we have statistics. The problem with measuring a bunch of people and taking the average temperature as normal is that you can’t be sure that the people you are measuring are normal. There are obvious causes of elevated temperature that you could exclude. Let’s not take people with a respiratory infection or who are taking Tylenol, for example. But as highlighted in this paper in JAMA Internal Medicine, we can do a lot better than that.
The study leverages the fact that body temperature is typically measured during all medical office visits and recorded in the ever-present electronic medical record.
Researchers from Stanford identified 724,199 patient encounters with outpatient temperature data. They excluded extreme temperatures – less than 34° C or greater than 40° C – excluded patients under 20 or above 80 years, and excluded those with extremes of height, weight, or body mass index.
You end up with a distribution like this. Note that the peak is clearly lower than 37° C.
But we’re still not at “normal.” Some people would be seeing their doctor for conditions that affect body temperature, such as infection. You could use diagnosis codes to flag these individuals and drop them, but that feels a bit arbitrary.
I really love how the researchers used data to fix this problem. They used a technique called LIMIT (Laboratory Information Mining for Individualized Thresholds). It works like this:
Take all the temperature measurements and then identify the outliers – the very tails of the distribution.
Look at all the diagnosis codes in those distributions. Determine which diagnosis codes are overrepresented in those distributions. Now you have a data-driven way to say that yes, these diagnoses are associated with weird temperatures. Next, eliminate everyone with those diagnoses from the dataset. What you are left with is a normal population, or at least a population that doesn’t have a condition that seems to meaningfully affect temperature.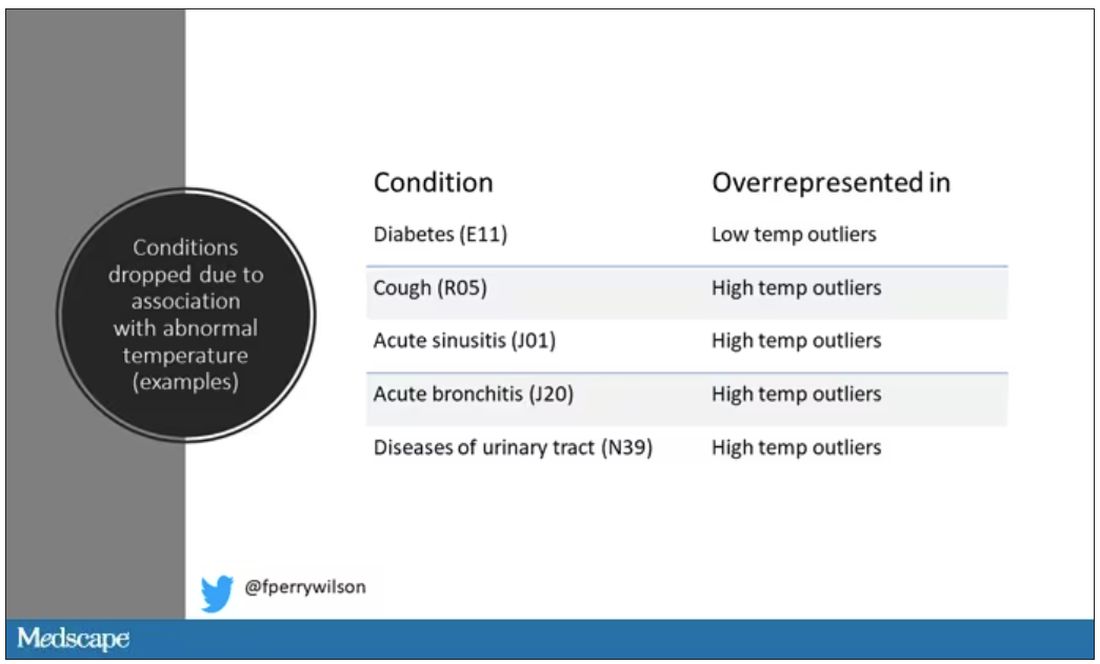
So, who was dropped? Well, a lot of people, actually. It turned out that diabetes was way overrepresented in the outlier group. Although 9.2% of the population had diabetes, 26% of people with very low temperatures did, so everyone with diabetes is removed from the dataset. While 5% of the population had a cough at their encounter, 7% of the people with very high temperature and 7% of the people with very low temperature had a cough, so everyone with cough gets thrown out.
The algorithm excluded people on antibiotics or who had sinusitis, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and, yes, a diagnosis of “fever.” The list makes sense, which is always nice when you have a purely algorithmic classification system.
What do we have left? What is the real normal temperature? Ready?
It’s 36.64° C, or about 98.0° F.
Of course, normal temperature varied depending on the time of day it was measured – higher in the afternoon.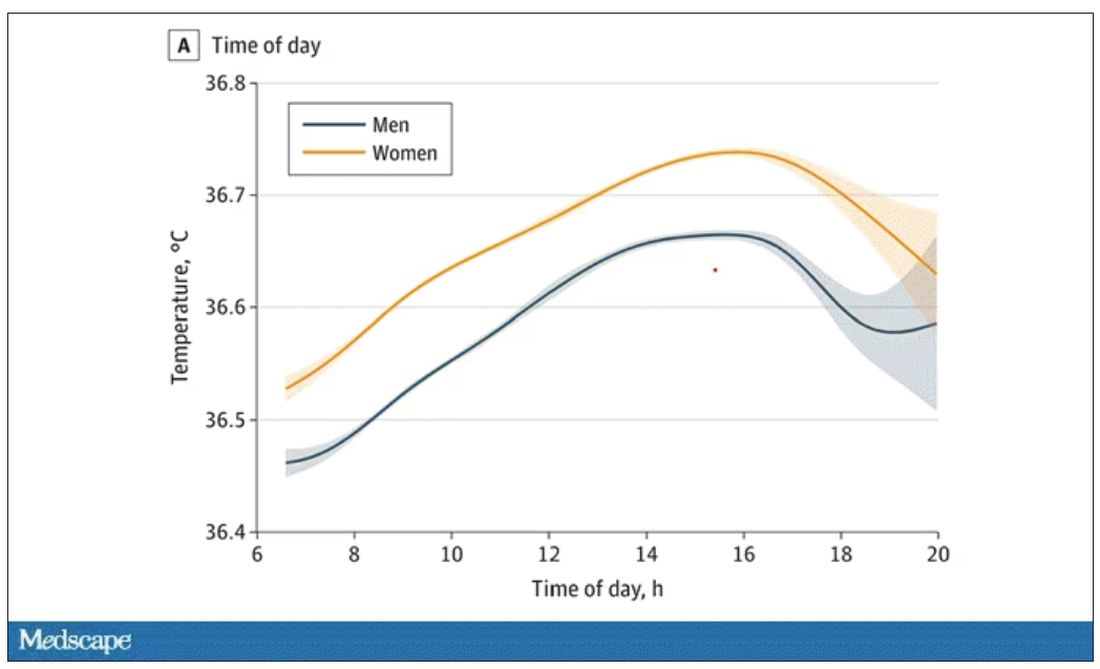
The normal temperature in women tended to be higher than in men. The normal temperature declined with age as well.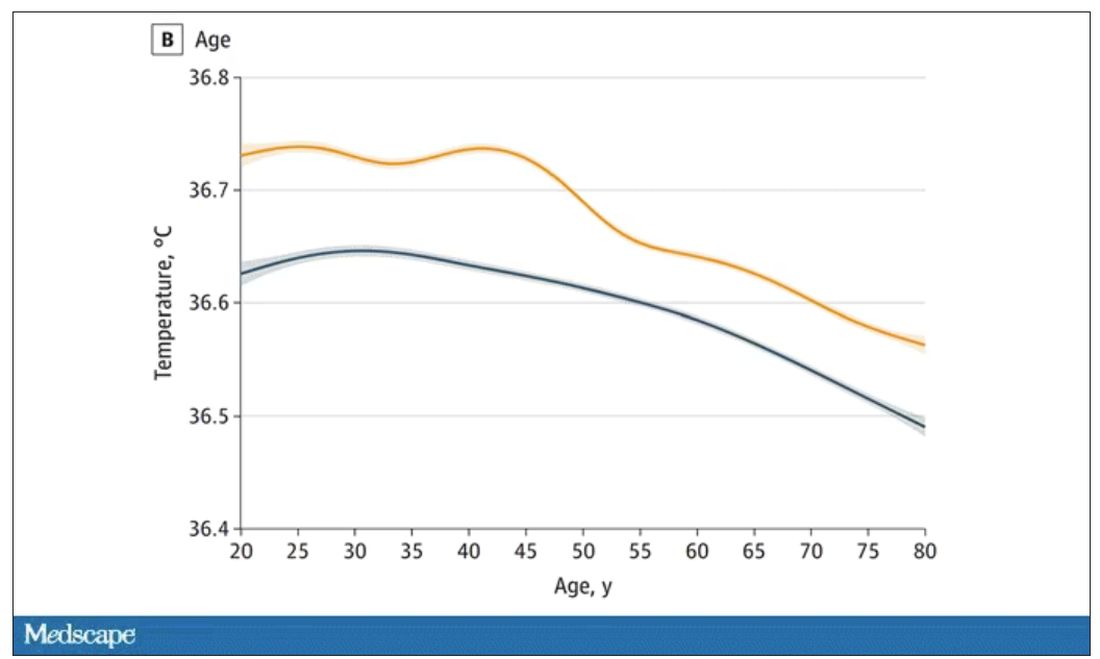
In fact, the researchers built a nice online calculator where you can enter your own, or your patient’s, parameters and calculate a normal body temperature for them. Here’s mine. My normal temperature at around 2 p.m. should be 36.7° C.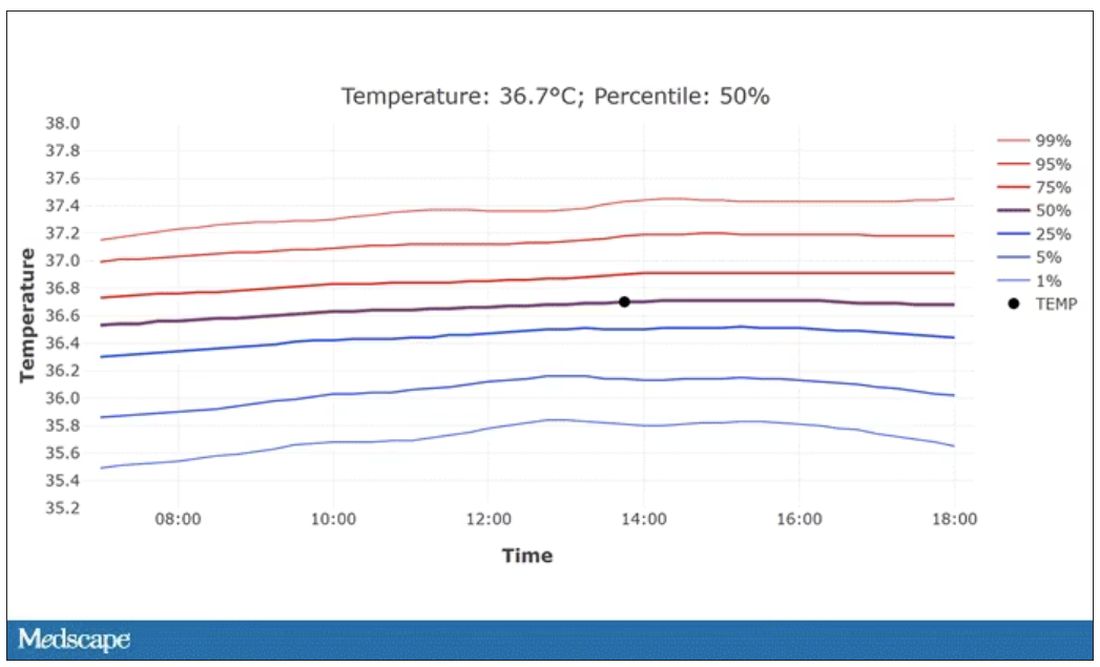
So, we’re all more cold-blooded than we thought. Is this just because of better methods? Maybe. But studies have actually shown that body temperature may be decreasing over time in humans, possibly because of the lower levels of inflammation we face in modern life (thanks to improvements in hygiene and antibiotics).
Of course, I’m sure some of you are asking yourselves whether any of this really matters. Is 37° C close enough?
Sure, this may be sort of puttering around the edges of physical diagnosis, but I think the methodology is really interesting and can obviously be applied to other broadly collected data points. But these data show us that thin, older individuals really do run cooler, and that we may need to pay more attention to a low-grade fever in that population than we otherwise would.
In any case, it’s time for a little re-education. If someone asks you what normal body temperature is, just say 36.6° C, 98.0° F. For his work in this area, I suggest we call it Wunderlich’s constant.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. He has no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Every branch of science has its constants. Physics has the speed of light, the gravitational constant, the Planck constant. Chemistry gives us Avogadro’s number, Faraday’s constant, the charge of an electron. Medicine isn’t quite as reliable as physics when it comes to these things, but insofar as there are any constants in medicine, might I suggest normal body temperature: 37° Celsius, 98.6° Fahrenheit.
Sure, serum sodium may be less variable and lactate concentration more clinically relevant, but even my 7-year-old knows that normal body temperature is 98.6°.
Except, as it turns out, 98.6° isn’t normal at all.
How did we arrive at 37.0° C for normal body temperature? We got it from this guy – German physician Carl Reinhold August Wunderlich, who, in addition to looking eerily like Luciano Pavarotti, was the first to realize that fever was not itself a disease but a symptom of one.
In 1851, Dr. Wunderlich released his measurements of more than 1 million body temperatures taken from 25,000 Germans – a painstaking process at the time, which employed a foot-long thermometer and took 20 minutes to obtain a measurement.
The average temperature measured, of course, was 37° C.
We’re more than 150 years post-Wunderlich right now, and the average person in the United States might be quite a bit different from the average German in 1850. Moreover, we can do a lot better than just measuring a ton of people and taking the average, because we have statistics. The problem with measuring a bunch of people and taking the average temperature as normal is that you can’t be sure that the people you are measuring are normal. There are obvious causes of elevated temperature that you could exclude. Let’s not take people with a respiratory infection or who are taking Tylenol, for example. But as highlighted in this paper in JAMA Internal Medicine, we can do a lot better than that.
The study leverages the fact that body temperature is typically measured during all medical office visits and recorded in the ever-present electronic medical record.
Researchers from Stanford identified 724,199 patient encounters with outpatient temperature data. They excluded extreme temperatures – less than 34° C or greater than 40° C – excluded patients under 20 or above 80 years, and excluded those with extremes of height, weight, or body mass index.
You end up with a distribution like this. Note that the peak is clearly lower than 37° C.
But we’re still not at “normal.” Some people would be seeing their doctor for conditions that affect body temperature, such as infection. You could use diagnosis codes to flag these individuals and drop them, but that feels a bit arbitrary.
I really love how the researchers used data to fix this problem. They used a technique called LIMIT (Laboratory Information Mining for Individualized Thresholds). It works like this:
Take all the temperature measurements and then identify the outliers – the very tails of the distribution.
Look at all the diagnosis codes in those distributions. Determine which diagnosis codes are overrepresented in those distributions. Now you have a data-driven way to say that yes, these diagnoses are associated with weird temperatures. Next, eliminate everyone with those diagnoses from the dataset. What you are left with is a normal population, or at least a population that doesn’t have a condition that seems to meaningfully affect temperature.
So, who was dropped? Well, a lot of people, actually. It turned out that diabetes was way overrepresented in the outlier group. Although 9.2% of the population had diabetes, 26% of people with very low temperatures did, so everyone with diabetes is removed from the dataset. While 5% of the population had a cough at their encounter, 7% of the people with very high temperature and 7% of the people with very low temperature had a cough, so everyone with cough gets thrown out.
The algorithm excluded people on antibiotics or who had sinusitis, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and, yes, a diagnosis of “fever.” The list makes sense, which is always nice when you have a purely algorithmic classification system.
What do we have left? What is the real normal temperature? Ready?
It’s 36.64° C, or about 98.0° F.
Of course, normal temperature varied depending on the time of day it was measured – higher in the afternoon.
The normal temperature in women tended to be higher than in men. The normal temperature declined with age as well.
In fact, the researchers built a nice online calculator where you can enter your own, or your patient’s, parameters and calculate a normal body temperature for them. Here’s mine. My normal temperature at around 2 p.m. should be 36.7° C.
So, we’re all more cold-blooded than we thought. Is this just because of better methods? Maybe. But studies have actually shown that body temperature may be decreasing over time in humans, possibly because of the lower levels of inflammation we face in modern life (thanks to improvements in hygiene and antibiotics).
Of course, I’m sure some of you are asking yourselves whether any of this really matters. Is 37° C close enough?
Sure, this may be sort of puttering around the edges of physical diagnosis, but I think the methodology is really interesting and can obviously be applied to other broadly collected data points. But these data show us that thin, older individuals really do run cooler, and that we may need to pay more attention to a low-grade fever in that population than we otherwise would.
In any case, it’s time for a little re-education. If someone asks you what normal body temperature is, just say 36.6° C, 98.0° F. For his work in this area, I suggest we call it Wunderlich’s constant.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. He has no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Every branch of science has its constants. Physics has the speed of light, the gravitational constant, the Planck constant. Chemistry gives us Avogadro’s number, Faraday’s constant, the charge of an electron. Medicine isn’t quite as reliable as physics when it comes to these things, but insofar as there are any constants in medicine, might I suggest normal body temperature: 37° Celsius, 98.6° Fahrenheit.
Sure, serum sodium may be less variable and lactate concentration more clinically relevant, but even my 7-year-old knows that normal body temperature is 98.6°.
Except, as it turns out, 98.6° isn’t normal at all.
How did we arrive at 37.0° C for normal body temperature? We got it from this guy – German physician Carl Reinhold August Wunderlich, who, in addition to looking eerily like Luciano Pavarotti, was the first to realize that fever was not itself a disease but a symptom of one.
In 1851, Dr. Wunderlich released his measurements of more than 1 million body temperatures taken from 25,000 Germans – a painstaking process at the time, which employed a foot-long thermometer and took 20 minutes to obtain a measurement.
The average temperature measured, of course, was 37° C.
We’re more than 150 years post-Wunderlich right now, and the average person in the United States might be quite a bit different from the average German in 1850. Moreover, we can do a lot better than just measuring a ton of people and taking the average, because we have statistics. The problem with measuring a bunch of people and taking the average temperature as normal is that you can’t be sure that the people you are measuring are normal. There are obvious causes of elevated temperature that you could exclude. Let’s not take people with a respiratory infection or who are taking Tylenol, for example. But as highlighted in this paper in JAMA Internal Medicine, we can do a lot better than that.
The study leverages the fact that body temperature is typically measured during all medical office visits and recorded in the ever-present electronic medical record.
Researchers from Stanford identified 724,199 patient encounters with outpatient temperature data. They excluded extreme temperatures – less than 34° C or greater than 40° C – excluded patients under 20 or above 80 years, and excluded those with extremes of height, weight, or body mass index.
You end up with a distribution like this. Note that the peak is clearly lower than 37° C.
But we’re still not at “normal.” Some people would be seeing their doctor for conditions that affect body temperature, such as infection. You could use diagnosis codes to flag these individuals and drop them, but that feels a bit arbitrary.
I really love how the researchers used data to fix this problem. They used a technique called LIMIT (Laboratory Information Mining for Individualized Thresholds). It works like this:
Take all the temperature measurements and then identify the outliers – the very tails of the distribution.
Look at all the diagnosis codes in those distributions. Determine which diagnosis codes are overrepresented in those distributions. Now you have a data-driven way to say that yes, these diagnoses are associated with weird temperatures. Next, eliminate everyone with those diagnoses from the dataset. What you are left with is a normal population, or at least a population that doesn’t have a condition that seems to meaningfully affect temperature.
So, who was dropped? Well, a lot of people, actually. It turned out that diabetes was way overrepresented in the outlier group. Although 9.2% of the population had diabetes, 26% of people with very low temperatures did, so everyone with diabetes is removed from the dataset. While 5% of the population had a cough at their encounter, 7% of the people with very high temperature and 7% of the people with very low temperature had a cough, so everyone with cough gets thrown out.
The algorithm excluded people on antibiotics or who had sinusitis, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and, yes, a diagnosis of “fever.” The list makes sense, which is always nice when you have a purely algorithmic classification system.
What do we have left? What is the real normal temperature? Ready?
It’s 36.64° C, or about 98.0° F.
Of course, normal temperature varied depending on the time of day it was measured – higher in the afternoon.
The normal temperature in women tended to be higher than in men. The normal temperature declined with age as well.
In fact, the researchers built a nice online calculator where you can enter your own, or your patient’s, parameters and calculate a normal body temperature for them. Here’s mine. My normal temperature at around 2 p.m. should be 36.7° C.
So, we’re all more cold-blooded than we thought. Is this just because of better methods? Maybe. But studies have actually shown that body temperature may be decreasing over time in humans, possibly because of the lower levels of inflammation we face in modern life (thanks to improvements in hygiene and antibiotics).
Of course, I’m sure some of you are asking yourselves whether any of this really matters. Is 37° C close enough?
Sure, this may be sort of puttering around the edges of physical diagnosis, but I think the methodology is really interesting and can obviously be applied to other broadly collected data points. But these data show us that thin, older individuals really do run cooler, and that we may need to pay more attention to a low-grade fever in that population than we otherwise would.
In any case, it’s time for a little re-education. If someone asks you what normal body temperature is, just say 36.6° C, 98.0° F. For his work in this area, I suggest we call it Wunderlich’s constant.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. He has no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The cult of the suicide risk assessment
Suicide is not a trivial matter – it upends families, robs partners of a loved one, prevents children from having a parent, and can destroy a parent’s most cherished being. It is not surprising that societies have repeatedly made it a goal to study and reduce suicide within their populations.
The suicide rate in the United States is trending upward, from about 10 per 100,000 in 2000 to about 15 per 100,000 in more recent reports. The increasing suicide rates have been accompanied by increasing distress among many strata of society. From a public health level, analysts are not just witnessing increasing suicide rates, but a shocking rise in all “deaths of despair,”1 among which suicide can be considered the ultimate example.
On an individual level, many know someone who has died of suicide or suffered from a serious suicide attempt. From the public health level to the individual level, advocacy has called for various interventions in the field of psychiatry to remedy this tragic problem.
Psychiatrists have been firsthand witnesses to this increasing demand for suicide interventions. When in residency, the norm was to perform a suicide risk assessment at the time of admission to the hospital and again at the time of discharge. As the years passed, the new normal within psychiatric hospitals has shifted to asking about suicidality on a daily basis.
In what seems to us like an escalating arms race, the emerging standard of care at many facilities is now not only for daily suicide risk assessments by each psychiatrist, but also to require nurses to ask about suicidality during every 8-hour shift – in addition to documented inquiries about suicidality by other allied staff on the psychiatric unit. As a result, it is not uncommon for a patient hospitalized at an academic center to receive more than half a dozen suicide risk assessments in a day (first by the medical student, at least once – often more than once – by the resident, again by the attending psychiatrist, then the social worker and three nurses in 24 hours).
One of the concerns about such an approach is the lack of logic inherent to many risk assessment tools and symptom scales. Many of us are familiar with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) to assess depression.2 The PHQ-9 asks to consider “over the last 2 weeks, how often have you ...” in relation to nine symptoms associated with depression. It has always defied reason to perform a PHQ-9 every day and expect the answers to change from “nearly every day” to “not at all,” considering only 1 day has passed since the last time the patient has answered the questions. Yet daily, or near daily, PHQ-9 scores are a frequently used tool of tracking symptom improvement in response to treatments, such as electroconvulsive therapy, performed multiple times a week.
One can argue that the patient’s perspective on how symptomatic he or she has been over the past 2 weeks may change rapidly with alleviation of a depressed mood. However, the PHQ-9 is both reported to be, and often regarded as, an objective score. If one wishes to utilize it as such, the defense of its use should not be that it is a subjective report with just as much utility as “Rate your depression on a scale of 0-27.”
Similarly, many suicide scales were intended to assess thoughts of suicide in the past month3 or have been re-tooled to address this particular concern by asking “since the last contact.”4 It is baffling to see a chart with many dozens of suicide risk assessments with at times widely differing answers, yet all measuring thoughts of suicide in the past month. Is one to expect the answer to “How many times have you had these thoughts [of suicide ideation]? (1) Less than once a week (2) Once a week ...” to change between 8 a.m. and noon? Furthermore, for the purpose of assessing acute risk of suicidality in the immediate future, to only consider symptoms since the last contact – or past 2 weeks, past month, etc. – is of unclear significance.
Provider liability
Another concern is the liability placed on providers. A common problem encountered in the inpatient setting is insurance companies refusing to reimburse a hospital stay for depressed patients denying suicidality.
Any provider in the position of caring for such a patient must ask: What is the likelihood of someone providing a false negative – a false denial of suicidality? Is the likelihood of a suicidal person denying suicidality different if asked 5 or 10 or more times in a day? There are innumerable instances where a patient at a very high risk of self-harm has denied suicidality, been discharged from the hospital, and suffered terrible consequences. Ethically, the psychiatrist aware of this risk is no more at ease discharging these patients, whether it is one suicide risk scale or a dozen that suggests a patient is at low risk.
Alternatively, it may feel untenable from a medicolegal perspective for a psychiatrist to discharge a patient denying suicidality when the chart includes over a dozen previously documented elevated suicide risk assessments in the past 72 hours. By placing the job of suicide risk assessment in the hands of providers of varying levels of training and responsibility, a situation is created in which the seasoned psychiatrist who would otherwise be comfortable discharging a patient feels unable to do so because every other note-writer in the record – from the triage nurse to the medical assistant to the sitter in the emergency department – has recorded the patient as high risk for suicide. When put in such a position, the thought often occurs that systems of care, rather than individual providers, are protected most by ever escalating requirements for suicide risk documentation. To make a clinical decision contrary to the body of suicide risk documentation puts the provider at risk of being scapegoated by the system of care, which can point to its illogical and ineffective, though profusely documented, suicide prevention protocols.
Limitations of risk assessments
Considering the ongoing rise in the use of suicide risk assessments, one would expect that the evidence for their efficacy was robust and well established. Yet a thorough review of suicide risk assessments funded by the MacArthur Foundation, which examined decades of research, came to disheartening conclusions: “predictive ability has not improved over the past 50 years”; “no risk factor category or subcategory is substantially stronger than any other”; and “predicting solely according to base rates may be comparable to prediction with current risk factors.”5
Those findings were consistent with the conclusions of many other studies, which have summarized the utility of suicide risk assessments as follows: “occurrence of suicide is too low to identify those individuals who are likely to die by suicide”;6 “suicide prediction models produce accurate overall classification models, but their accuracy of predicting a future event is near zero”;7 “risk stratification is too inaccurate to be clinically useful and might even be harmful”;8 “suicide risk prediction [lacks] any items or information that to a useful degree permit the identification of persons who will complete suicide”;9 “existing suicide prediction tools have little current clinical value”;10 “our current preoccupation with risk assessment has ... created a mythology with no evidence to support it.”11 And that’s to cite just a few.
Sadly, we have known about the limitations of suicide risk assessments for many decades. In 1983 a large VA prospective study, which aimed to identify veterans who will die by suicide, examined 4,800 patients with a wide range of instruments and measures.12 This study concluded that “discriminant analysis was clearly inadequate in correctly classifying the subjects. For an event as rare as suicide, our predictive tools and guides are simply not equal to the task.” The authors described the feelings of many in stating “courts and public opinion expect physicians to be able to pick out the particular persons who will later commit suicide. Although we may reconstruct causal chains and motives, we do not possess the tools to predict suicides.”
Yet, even several decades prior, in 1954, Dr. Albert Rosen performed an elegant statistical analysis and predicted that, considering the low base rate of suicide, suicide risk assessments are “of no practical value, for it would be impossible to treat the prodigious number of false positives.”13 It seems that we continue to be unable to accept Dr. Rosen’s premonition despite decades of confirmatory evidence.
“Quantity over quality”
Regardless of those sobering reports,
One can reasonably argue that the periodic performance of a suicide risk assessment may have clinical utility in reminding us of modifiable risk factors such as intoxication, social isolation, and access to lethal means. One can also reasonably argue that these risk assessments may provide useful education to patients and their families on epidemiological risk factors such as gender, age, and marital status. But our pursuit of serial suicide risk assessments throughout the day is encouraging providers to focus on a particular risk factor that changes from moment to moment and has particularly low validity, that being self-reported suicidality.
Reported suicidality is one of the few risk factors that can change from shift to shift. But 80% of people who die by suicide had not previously expressed suicidality, and 98.3% of people who have endorsed suicidality do not die by suicide.14 While the former statistic may improve with increased assessment, the later will likely worsen.
Suicide is not a trivial matter. We admire those that study it and advocate for better interventions. We have compassion for those who have suffered the loss of a loved one to suicide. Our patients have died as a result of the human limitations surrounding suicide prevention. Recognizing the weight of suicide and making an effort to avoid minimizing its immense consequences drive our desire to be honest with ourselves, our patients and their families, and society. That includes the unfortunate truth regarding the current state of the evidence and our ability to enact change.
It is our concern that the rising fascination with repeated suicide risk assessment is misguided in its current form and serves the purpose of appeasing administrators more than reflecting a scientific understanding of the literature. More sadly, we are concerned that this “quantity-over-quality” approach is yet another barrier to practicing what may be one of the few interventions with any hope of meaningfully impacting a patient’s risk of suicide in the clinical setting – spending time connecting with our patients.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. Dr. Compton is a member of the psychiatry faculty at University of California, San Diego. His background includes medical education, mental health advocacy, work with underserved populations, and brain cancer research. Dr. Badre and Dr. Compton have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Joint Economic Committee. (2019). Long Term Trends in Deaths of Despair. SCP Report 4-19.
2. Kroenke K and Spitzer RL. The PHQ-9: A new depression diagnostic and severity measure. Psychiatr Ann. 2013;32(9):509-15. doi: 10.3928/0048-5713-20020901-06.
3. Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) Full Lifetime/Recent.
4. Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) Full Since Last Contact.
5. Franklin JC et al. Risk factors for suicidal thoughts and behaviors: A meta-analysis of 50 years of research. Psychol Bull. 2017 Feb;143(2):187-232. doi: 10.1037/bul0000084.
6. Beautrais AL. Further suicidal behavior among medically serious suicide attempters. Suicide Life Threat Behav. 2004 Spring;34(1):1-11. doi: 10.1521/suli.34.1.1.27772.
7. Belsher BE. Prediction models for suicide attempts and deaths: A systematic review and simulation. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019 Jun 1;76(6):642-651. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.0174.
8. Carter G et al. Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists clinical practice guideline for the management of deliberate self-harm. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2016 Oct;50(10):939-1000. doi: 10.1177/0004867416661039.
9. Fosse R et al. Predictors of suicide in the patient population admitted to a locked-door psychiatric acute ward. PLoS One. 2017 Mar 16;12(3):e0173958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173958.
10. Kessler RC et al. Suicide prediction models: A critical review of recent research with recommendations for the way forward. Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Jan;25(1):168-79. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0531-0.
11. Mulder R. Problems with suicide risk assessment. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2011 Aug;45(8):605-7. doi: 10.3109/00048674.2011.594786.
12. Pokorny AD. Prediction of suicide in psychiatric patients: Report of a prospective study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983 Mar;40(3):249-57. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790030019002.
13. Rosen A. Detection of suicidal patients: An example of some limitations in the prediction of infrequent events. J Consult Psychol. 1954 Dec;18(6):397-403. doi: 10.1037/h0058579.
14. McHugh CM et al. (2019). Association between suicidal ideation and suicide: Meta-analyses of odds ratios, sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive value. BJPsych Open. 2019 Mar;5(2):e18. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2018.88.
Suicide is not a trivial matter – it upends families, robs partners of a loved one, prevents children from having a parent, and can destroy a parent’s most cherished being. It is not surprising that societies have repeatedly made it a goal to study and reduce suicide within their populations.
The suicide rate in the United States is trending upward, from about 10 per 100,000 in 2000 to about 15 per 100,000 in more recent reports. The increasing suicide rates have been accompanied by increasing distress among many strata of society. From a public health level, analysts are not just witnessing increasing suicide rates, but a shocking rise in all “deaths of despair,”1 among which suicide can be considered the ultimate example.
On an individual level, many know someone who has died of suicide or suffered from a serious suicide attempt. From the public health level to the individual level, advocacy has called for various interventions in the field of psychiatry to remedy this tragic problem.
Psychiatrists have been firsthand witnesses to this increasing demand for suicide interventions. When in residency, the norm was to perform a suicide risk assessment at the time of admission to the hospital and again at the time of discharge. As the years passed, the new normal within psychiatric hospitals has shifted to asking about suicidality on a daily basis.
In what seems to us like an escalating arms race, the emerging standard of care at many facilities is now not only for daily suicide risk assessments by each psychiatrist, but also to require nurses to ask about suicidality during every 8-hour shift – in addition to documented inquiries about suicidality by other allied staff on the psychiatric unit. As a result, it is not uncommon for a patient hospitalized at an academic center to receive more than half a dozen suicide risk assessments in a day (first by the medical student, at least once – often more than once – by the resident, again by the attending psychiatrist, then the social worker and three nurses in 24 hours).
One of the concerns about such an approach is the lack of logic inherent to many risk assessment tools and symptom scales. Many of us are familiar with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) to assess depression.2 The PHQ-9 asks to consider “over the last 2 weeks, how often have you ...” in relation to nine symptoms associated with depression. It has always defied reason to perform a PHQ-9 every day and expect the answers to change from “nearly every day” to “not at all,” considering only 1 day has passed since the last time the patient has answered the questions. Yet daily, or near daily, PHQ-9 scores are a frequently used tool of tracking symptom improvement in response to treatments, such as electroconvulsive therapy, performed multiple times a week.
One can argue that the patient’s perspective on how symptomatic he or she has been over the past 2 weeks may change rapidly with alleviation of a depressed mood. However, the PHQ-9 is both reported to be, and often regarded as, an objective score. If one wishes to utilize it as such, the defense of its use should not be that it is a subjective report with just as much utility as “Rate your depression on a scale of 0-27.”
Similarly, many suicide scales were intended to assess thoughts of suicide in the past month3 or have been re-tooled to address this particular concern by asking “since the last contact.”4 It is baffling to see a chart with many dozens of suicide risk assessments with at times widely differing answers, yet all measuring thoughts of suicide in the past month. Is one to expect the answer to “How many times have you had these thoughts [of suicide ideation]? (1) Less than once a week (2) Once a week ...” to change between 8 a.m. and noon? Furthermore, for the purpose of assessing acute risk of suicidality in the immediate future, to only consider symptoms since the last contact – or past 2 weeks, past month, etc. – is of unclear significance.
Provider liability
Another concern is the liability placed on providers. A common problem encountered in the inpatient setting is insurance companies refusing to reimburse a hospital stay for depressed patients denying suicidality.
Any provider in the position of caring for such a patient must ask: What is the likelihood of someone providing a false negative – a false denial of suicidality? Is the likelihood of a suicidal person denying suicidality different if asked 5 or 10 or more times in a day? There are innumerable instances where a patient at a very high risk of self-harm has denied suicidality, been discharged from the hospital, and suffered terrible consequences. Ethically, the psychiatrist aware of this risk is no more at ease discharging these patients, whether it is one suicide risk scale or a dozen that suggests a patient is at low risk.
Alternatively, it may feel untenable from a medicolegal perspective for a psychiatrist to discharge a patient denying suicidality when the chart includes over a dozen previously documented elevated suicide risk assessments in the past 72 hours. By placing the job of suicide risk assessment in the hands of providers of varying levels of training and responsibility, a situation is created in which the seasoned psychiatrist who would otherwise be comfortable discharging a patient feels unable to do so because every other note-writer in the record – from the triage nurse to the medical assistant to the sitter in the emergency department – has recorded the patient as high risk for suicide. When put in such a position, the thought often occurs that systems of care, rather than individual providers, are protected most by ever escalating requirements for suicide risk documentation. To make a clinical decision contrary to the body of suicide risk documentation puts the provider at risk of being scapegoated by the system of care, which can point to its illogical and ineffective, though profusely documented, suicide prevention protocols.
Limitations of risk assessments
Considering the ongoing rise in the use of suicide risk assessments, one would expect that the evidence for their efficacy was robust and well established. Yet a thorough review of suicide risk assessments funded by the MacArthur Foundation, which examined decades of research, came to disheartening conclusions: “predictive ability has not improved over the past 50 years”; “no risk factor category or subcategory is substantially stronger than any other”; and “predicting solely according to base rates may be comparable to prediction with current risk factors.”5
Those findings were consistent with the conclusions of many other studies, which have summarized the utility of suicide risk assessments as follows: “occurrence of suicide is too low to identify those individuals who are likely to die by suicide”;6 “suicide prediction models produce accurate overall classification models, but their accuracy of predicting a future event is near zero”;7 “risk stratification is too inaccurate to be clinically useful and might even be harmful”;8 “suicide risk prediction [lacks] any items or information that to a useful degree permit the identification of persons who will complete suicide”;9 “existing suicide prediction tools have little current clinical value”;10 “our current preoccupation with risk assessment has ... created a mythology with no evidence to support it.”11 And that’s to cite just a few.
Sadly, we have known about the limitations of suicide risk assessments for many decades. In 1983 a large VA prospective study, which aimed to identify veterans who will die by suicide, examined 4,800 patients with a wide range of instruments and measures.12 This study concluded that “discriminant analysis was clearly inadequate in correctly classifying the subjects. For an event as rare as suicide, our predictive tools and guides are simply not equal to the task.” The authors described the feelings of many in stating “courts and public opinion expect physicians to be able to pick out the particular persons who will later commit suicide. Although we may reconstruct causal chains and motives, we do not possess the tools to predict suicides.”
Yet, even several decades prior, in 1954, Dr. Albert Rosen performed an elegant statistical analysis and predicted that, considering the low base rate of suicide, suicide risk assessments are “of no practical value, for it would be impossible to treat the prodigious number of false positives.”13 It seems that we continue to be unable to accept Dr. Rosen’s premonition despite decades of confirmatory evidence.
“Quantity over quality”
Regardless of those sobering reports,
One can reasonably argue that the periodic performance of a suicide risk assessment may have clinical utility in reminding us of modifiable risk factors such as intoxication, social isolation, and access to lethal means. One can also reasonably argue that these risk assessments may provide useful education to patients and their families on epidemiological risk factors such as gender, age, and marital status. But our pursuit of serial suicide risk assessments throughout the day is encouraging providers to focus on a particular risk factor that changes from moment to moment and has particularly low validity, that being self-reported suicidality.
Reported suicidality is one of the few risk factors that can change from shift to shift. But 80% of people who die by suicide had not previously expressed suicidality, and 98.3% of people who have endorsed suicidality do not die by suicide.14 While the former statistic may improve with increased assessment, the later will likely worsen.
Suicide is not a trivial matter. We admire those that study it and advocate for better interventions. We have compassion for those who have suffered the loss of a loved one to suicide. Our patients have died as a result of the human limitations surrounding suicide prevention. Recognizing the weight of suicide and making an effort to avoid minimizing its immense consequences drive our desire to be honest with ourselves, our patients and their families, and society. That includes the unfortunate truth regarding the current state of the evidence and our ability to enact change.
It is our concern that the rising fascination with repeated suicide risk assessment is misguided in its current form and serves the purpose of appeasing administrators more than reflecting a scientific understanding of the literature. More sadly, we are concerned that this “quantity-over-quality” approach is yet another barrier to practicing what may be one of the few interventions with any hope of meaningfully impacting a patient’s risk of suicide in the clinical setting – spending time connecting with our patients.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. Dr. Compton is a member of the psychiatry faculty at University of California, San Diego. His background includes medical education, mental health advocacy, work with underserved populations, and brain cancer research. Dr. Badre and Dr. Compton have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Joint Economic Committee. (2019). Long Term Trends in Deaths of Despair. SCP Report 4-19.
2. Kroenke K and Spitzer RL. The PHQ-9: A new depression diagnostic and severity measure. Psychiatr Ann. 2013;32(9):509-15. doi: 10.3928/0048-5713-20020901-06.
3. Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) Full Lifetime/Recent.
4. Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) Full Since Last Contact.
5. Franklin JC et al. Risk factors for suicidal thoughts and behaviors: A meta-analysis of 50 years of research. Psychol Bull. 2017 Feb;143(2):187-232. doi: 10.1037/bul0000084.
6. Beautrais AL. Further suicidal behavior among medically serious suicide attempters. Suicide Life Threat Behav. 2004 Spring;34(1):1-11. doi: 10.1521/suli.34.1.1.27772.
7. Belsher BE. Prediction models for suicide attempts and deaths: A systematic review and simulation. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019 Jun 1;76(6):642-651. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.0174.
8. Carter G et al. Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists clinical practice guideline for the management of deliberate self-harm. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2016 Oct;50(10):939-1000. doi: 10.1177/0004867416661039.
9. Fosse R et al. Predictors of suicide in the patient population admitted to a locked-door psychiatric acute ward. PLoS One. 2017 Mar 16;12(3):e0173958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173958.
10. Kessler RC et al. Suicide prediction models: A critical review of recent research with recommendations for the way forward. Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Jan;25(1):168-79. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0531-0.
11. Mulder R. Problems with suicide risk assessment. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2011 Aug;45(8):605-7. doi: 10.3109/00048674.2011.594786.
12. Pokorny AD. Prediction of suicide in psychiatric patients: Report of a prospective study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983 Mar;40(3):249-57. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790030019002.
13. Rosen A. Detection of suicidal patients: An example of some limitations in the prediction of infrequent events. J Consult Psychol. 1954 Dec;18(6):397-403. doi: 10.1037/h0058579.
14. McHugh CM et al. (2019). Association between suicidal ideation and suicide: Meta-analyses of odds ratios, sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive value. BJPsych Open. 2019 Mar;5(2):e18. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2018.88.
Suicide is not a trivial matter – it upends families, robs partners of a loved one, prevents children from having a parent, and can destroy a parent’s most cherished being. It is not surprising that societies have repeatedly made it a goal to study and reduce suicide within their populations.
The suicide rate in the United States is trending upward, from about 10 per 100,000 in 2000 to about 15 per 100,000 in more recent reports. The increasing suicide rates have been accompanied by increasing distress among many strata of society. From a public health level, analysts are not just witnessing increasing suicide rates, but a shocking rise in all “deaths of despair,”1 among which suicide can be considered the ultimate example.
On an individual level, many know someone who has died of suicide or suffered from a serious suicide attempt. From the public health level to the individual level, advocacy has called for various interventions in the field of psychiatry to remedy this tragic problem.
Psychiatrists have been firsthand witnesses to this increasing demand for suicide interventions. When in residency, the norm was to perform a suicide risk assessment at the time of admission to the hospital and again at the time of discharge. As the years passed, the new normal within psychiatric hospitals has shifted to asking about suicidality on a daily basis.
In what seems to us like an escalating arms race, the emerging standard of care at many facilities is now not only for daily suicide risk assessments by each psychiatrist, but also to require nurses to ask about suicidality during every 8-hour shift – in addition to documented inquiries about suicidality by other allied staff on the psychiatric unit. As a result, it is not uncommon for a patient hospitalized at an academic center to receive more than half a dozen suicide risk assessments in a day (first by the medical student, at least once – often more than once – by the resident, again by the attending psychiatrist, then the social worker and three nurses in 24 hours).
One of the concerns about such an approach is the lack of logic inherent to many risk assessment tools and symptom scales. Many of us are familiar with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) to assess depression.2 The PHQ-9 asks to consider “over the last 2 weeks, how often have you ...” in relation to nine symptoms associated with depression. It has always defied reason to perform a PHQ-9 every day and expect the answers to change from “nearly every day” to “not at all,” considering only 1 day has passed since the last time the patient has answered the questions. Yet daily, or near daily, PHQ-9 scores are a frequently used tool of tracking symptom improvement in response to treatments, such as electroconvulsive therapy, performed multiple times a week.
One can argue that the patient’s perspective on how symptomatic he or she has been over the past 2 weeks may change rapidly with alleviation of a depressed mood. However, the PHQ-9 is both reported to be, and often regarded as, an objective score. If one wishes to utilize it as such, the defense of its use should not be that it is a subjective report with just as much utility as “Rate your depression on a scale of 0-27.”
Similarly, many suicide scales were intended to assess thoughts of suicide in the past month3 or have been re-tooled to address this particular concern by asking “since the last contact.”4 It is baffling to see a chart with many dozens of suicide risk assessments with at times widely differing answers, yet all measuring thoughts of suicide in the past month. Is one to expect the answer to “How many times have you had these thoughts [of suicide ideation]? (1) Less than once a week (2) Once a week ...” to change between 8 a.m. and noon? Furthermore, for the purpose of assessing acute risk of suicidality in the immediate future, to only consider symptoms since the last contact – or past 2 weeks, past month, etc. – is of unclear significance.
Provider liability
Another concern is the liability placed on providers. A common problem encountered in the inpatient setting is insurance companies refusing to reimburse a hospital stay for depressed patients denying suicidality.
Any provider in the position of caring for such a patient must ask: What is the likelihood of someone providing a false negative – a false denial of suicidality? Is the likelihood of a suicidal person denying suicidality different if asked 5 or 10 or more times in a day? There are innumerable instances where a patient at a very high risk of self-harm has denied suicidality, been discharged from the hospital, and suffered terrible consequences. Ethically, the psychiatrist aware of this risk is no more at ease discharging these patients, whether it is one suicide risk scale or a dozen that suggests a patient is at low risk.
Alternatively, it may feel untenable from a medicolegal perspective for a psychiatrist to discharge a patient denying suicidality when the chart includes over a dozen previously documented elevated suicide risk assessments in the past 72 hours. By placing the job of suicide risk assessment in the hands of providers of varying levels of training and responsibility, a situation is created in which the seasoned psychiatrist who would otherwise be comfortable discharging a patient feels unable to do so because every other note-writer in the record – from the triage nurse to the medical assistant to the sitter in the emergency department – has recorded the patient as high risk for suicide. When put in such a position, the thought often occurs that systems of care, rather than individual providers, are protected most by ever escalating requirements for suicide risk documentation. To make a clinical decision contrary to the body of suicide risk documentation puts the provider at risk of being scapegoated by the system of care, which can point to its illogical and ineffective, though profusely documented, suicide prevention protocols.
Limitations of risk assessments
Considering the ongoing rise in the use of suicide risk assessments, one would expect that the evidence for their efficacy was robust and well established. Yet a thorough review of suicide risk assessments funded by the MacArthur Foundation, which examined decades of research, came to disheartening conclusions: “predictive ability has not improved over the past 50 years”; “no risk factor category or subcategory is substantially stronger than any other”; and “predicting solely according to base rates may be comparable to prediction with current risk factors.”5
Those findings were consistent with the conclusions of many other studies, which have summarized the utility of suicide risk assessments as follows: “occurrence of suicide is too low to identify those individuals who are likely to die by suicide”;6 “suicide prediction models produce accurate overall classification models, but their accuracy of predicting a future event is near zero”;7 “risk stratification is too inaccurate to be clinically useful and might even be harmful”;8 “suicide risk prediction [lacks] any items or information that to a useful degree permit the identification of persons who will complete suicide”;9 “existing suicide prediction tools have little current clinical value”;10 “our current preoccupation with risk assessment has ... created a mythology with no evidence to support it.”11 And that’s to cite just a few.
Sadly, we have known about the limitations of suicide risk assessments for many decades. In 1983 a large VA prospective study, which aimed to identify veterans who will die by suicide, examined 4,800 patients with a wide range of instruments and measures.12 This study concluded that “discriminant analysis was clearly inadequate in correctly classifying the subjects. For an event as rare as suicide, our predictive tools and guides are simply not equal to the task.” The authors described the feelings of many in stating “courts and public opinion expect physicians to be able to pick out the particular persons who will later commit suicide. Although we may reconstruct causal chains and motives, we do not possess the tools to predict suicides.”
Yet, even several decades prior, in 1954, Dr. Albert Rosen performed an elegant statistical analysis and predicted that, considering the low base rate of suicide, suicide risk assessments are “of no practical value, for it would be impossible to treat the prodigious number of false positives.”13 It seems that we continue to be unable to accept Dr. Rosen’s premonition despite decades of confirmatory evidence.
“Quantity over quality”
Regardless of those sobering reports,
One can reasonably argue that the periodic performance of a suicide risk assessment may have clinical utility in reminding us of modifiable risk factors such as intoxication, social isolation, and access to lethal means. One can also reasonably argue that these risk assessments may provide useful education to patients and their families on epidemiological risk factors such as gender, age, and marital status. But our pursuit of serial suicide risk assessments throughout the day is encouraging providers to focus on a particular risk factor that changes from moment to moment and has particularly low validity, that being self-reported suicidality.
Reported suicidality is one of the few risk factors that can change from shift to shift. But 80% of people who die by suicide had not previously expressed suicidality, and 98.3% of people who have endorsed suicidality do not die by suicide.14 While the former statistic may improve with increased assessment, the later will likely worsen.
Suicide is not a trivial matter. We admire those that study it and advocate for better interventions. We have compassion for those who have suffered the loss of a loved one to suicide. Our patients have died as a result of the human limitations surrounding suicide prevention. Recognizing the weight of suicide and making an effort to avoid minimizing its immense consequences drive our desire to be honest with ourselves, our patients and their families, and society. That includes the unfortunate truth regarding the current state of the evidence and our ability to enact change.
It is our concern that the rising fascination with repeated suicide risk assessment is misguided in its current form and serves the purpose of appeasing administrators more than reflecting a scientific understanding of the literature. More sadly, we are concerned that this “quantity-over-quality” approach is yet another barrier to practicing what may be one of the few interventions with any hope of meaningfully impacting a patient’s risk of suicide in the clinical setting – spending time connecting with our patients.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. Dr. Compton is a member of the psychiatry faculty at University of California, San Diego. His background includes medical education, mental health advocacy, work with underserved populations, and brain cancer research. Dr. Badre and Dr. Compton have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Joint Economic Committee. (2019). Long Term Trends in Deaths of Despair. SCP Report 4-19.
2. Kroenke K and Spitzer RL. The PHQ-9: A new depression diagnostic and severity measure. Psychiatr Ann. 2013;32(9):509-15. doi: 10.3928/0048-5713-20020901-06.
3. Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) Full Lifetime/Recent.
4. Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) Full Since Last Contact.
5. Franklin JC et al. Risk factors for suicidal thoughts and behaviors: A meta-analysis of 50 years of research. Psychol Bull. 2017 Feb;143(2):187-232. doi: 10.1037/bul0000084.
6. Beautrais AL. Further suicidal behavior among medically serious suicide attempters. Suicide Life Threat Behav. 2004 Spring;34(1):1-11. doi: 10.1521/suli.34.1.1.27772.
7. Belsher BE. Prediction models for suicide attempts and deaths: A systematic review and simulation. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019 Jun 1;76(6):642-651. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.0174.
8. Carter G et al. Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists clinical practice guideline for the management of deliberate self-harm. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2016 Oct;50(10):939-1000. doi: 10.1177/0004867416661039.
9. Fosse R et al. Predictors of suicide in the patient population admitted to a locked-door psychiatric acute ward. PLoS One. 2017 Mar 16;12(3):e0173958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173958.
10. Kessler RC et al. Suicide prediction models: A critical review of recent research with recommendations for the way forward. Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Jan;25(1):168-79. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0531-0.
11. Mulder R. Problems with suicide risk assessment. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2011 Aug;45(8):605-7. doi: 10.3109/00048674.2011.594786.
12. Pokorny AD. Prediction of suicide in psychiatric patients: Report of a prospective study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983 Mar;40(3):249-57. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790030019002.
13. Rosen A. Detection of suicidal patients: An example of some limitations in the prediction of infrequent events. J Consult Psychol. 1954 Dec;18(6):397-403. doi: 10.1037/h0058579.
14. McHugh CM et al. (2019). Association between suicidal ideation and suicide: Meta-analyses of odds ratios, sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive value. BJPsych Open. 2019 Mar;5(2):e18. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2018.88.
IQ and concussion recovery
Pediatric concussion is one of those rare phenomena in which we may be witnessing its emergence and clarification in a generation. When I was serving as the game doctor for our local high school football team in the 1970s, I and many other physicians had a very simplistic view of concussion. If the patient never lost conscious and had a reasonably intact short-term memory, we didn’t seriously entertain concussion as a diagnosis. “What’s the score and who is the president?” Were my favorite screening questions.
Obviously, we were underdiagnosing and mismanaging concussion. In part thanks to some high-profile athletes who suffered multiple concussions and eventually chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) physicians began to realize that they should be looking more closely at children who sustained a head injury. The diagnostic criteria were expanded to include any injury that even temporarily effected brain function.
With the new appreciation for the risk of multiple concussions, the focus broadened to include the question of when is it safe for the athlete to return to competition. What signs or symptoms can the patient offer us so we can be sure his or her brain is sufficiently recovered? Here we stepped off into a deep abyss of ignorance. Fortunately, it became obvious fairly quickly that imaging studies weren’t going to help us, as they were invariably normal or at least didn’t tell us anything that wasn’t obvious on a physical exam.
If the patient had a headache, complained of dizziness, or manifested amnesia, monitoring the patient was fairly straightforward. But, in the absence of symptoms and no obvious way to determine the pace of recovery of an organ we couldn’t visualize, clinicians were pulling criteria and time tables out of thin air. Guessing that the concussed brain was in some ways like a torn muscle or overstretched tendon, “brain rest” was often suggested. So no TV, no reading, and certainly none of the cerebral challenging activity of school. Fortunately, we don’t hear much about the notion of brain rest anymore and there is at least one study that suggests that patients kept home from school recover more slowly.
But . Sometimes they describe headache or dizziness but often they complain of a vague mental unwellness. “Brain fog,” a term that has emerged in the wake of the COVID pandemic, might be an apt descriptor. Management of these slow recoverers has been a challenge.
However, two recent articles in the journal Pediatrics may provide some clarity and offer guidance in their management. In a study coming from the psychology department at Georgia State University, researchers reported that they have been able to find “no evidence of clinical meaningful differences in IQ after pediatric concussion.” In their words there is “strong evidence against reduced intelligence in the first few weeks to month after pediatric concussion.”
While their findings may simply toss the IQ onto the pile of worthless measures of healing, a companion commentary by Talin Babikian, PhD, a psychologist at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior at UCLA, provides a more nuanced interpretation. He writes that if we are looking for an explanation when a patient’s recovery is taking longer than we might expect we need to look beyond some structural damage. Maybe the patient has a previously undiagnosed premorbid condition effecting his or her intellectual, cognitive, or learning abilities. Could the stall in improvement be the result of other symptoms? Here fatigue and sleep deprivation may be the culprits. Could some underlying emotional factor such as anxiety or depression be the problem? For example, I have seen patients whose fear of re-injury has prevented their return to full function. And, finally, the patient may be avoiding a “nonpreferred or challenging situation” unrelated to the injury.
In other words, the concussion may simply be the most obvious rip in a fabric that was already frayed and under stress. This kind of broad holistic (a word I usually like to avoid) thinking may be what is lacking as we struggle to understand other mysterious and chronic conditions such as Lyme disease and chronic fatigue syndrome.
While these two papers help provide some clarity in the management of pediatric concussion, what they fail to address is the bigger question of the relationship between head injury and CTE. The answers to that conundrum are enshrouded in a mix of politics and publicity that I doubt will clear in the near future.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Pediatric concussion is one of those rare phenomena in which we may be witnessing its emergence and clarification in a generation. When I was serving as the game doctor for our local high school football team in the 1970s, I and many other physicians had a very simplistic view of concussion. If the patient never lost conscious and had a reasonably intact short-term memory, we didn’t seriously entertain concussion as a diagnosis. “What’s the score and who is the president?” Were my favorite screening questions.
Obviously, we were underdiagnosing and mismanaging concussion. In part thanks to some high-profile athletes who suffered multiple concussions and eventually chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) physicians began to realize that they should be looking more closely at children who sustained a head injury. The diagnostic criteria were expanded to include any injury that even temporarily effected brain function.
With the new appreciation for the risk of multiple concussions, the focus broadened to include the question of when is it safe for the athlete to return to competition. What signs or symptoms can the patient offer us so we can be sure his or her brain is sufficiently recovered? Here we stepped off into a deep abyss of ignorance. Fortunately, it became obvious fairly quickly that imaging studies weren’t going to help us, as they were invariably normal or at least didn’t tell us anything that wasn’t obvious on a physical exam.
If the patient had a headache, complained of dizziness, or manifested amnesia, monitoring the patient was fairly straightforward. But, in the absence of symptoms and no obvious way to determine the pace of recovery of an organ we couldn’t visualize, clinicians were pulling criteria and time tables out of thin air. Guessing that the concussed brain was in some ways like a torn muscle or overstretched tendon, “brain rest” was often suggested. So no TV, no reading, and certainly none of the cerebral challenging activity of school. Fortunately, we don’t hear much about the notion of brain rest anymore and there is at least one study that suggests that patients kept home from school recover more slowly.
But . Sometimes they describe headache or dizziness but often they complain of a vague mental unwellness. “Brain fog,” a term that has emerged in the wake of the COVID pandemic, might be an apt descriptor. Management of these slow recoverers has been a challenge.
However, two recent articles in the journal Pediatrics may provide some clarity and offer guidance in their management. In a study coming from the psychology department at Georgia State University, researchers reported that they have been able to find “no evidence of clinical meaningful differences in IQ after pediatric concussion.” In their words there is “strong evidence against reduced intelligence in the first few weeks to month after pediatric concussion.”
While their findings may simply toss the IQ onto the pile of worthless measures of healing, a companion commentary by Talin Babikian, PhD, a psychologist at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior at UCLA, provides a more nuanced interpretation. He writes that if we are looking for an explanation when a patient’s recovery is taking longer than we might expect we need to look beyond some structural damage. Maybe the patient has a previously undiagnosed premorbid condition effecting his or her intellectual, cognitive, or learning abilities. Could the stall in improvement be the result of other symptoms? Here fatigue and sleep deprivation may be the culprits. Could some underlying emotional factor such as anxiety or depression be the problem? For example, I have seen patients whose fear of re-injury has prevented their return to full function. And, finally, the patient may be avoiding a “nonpreferred or challenging situation” unrelated to the injury.
In other words, the concussion may simply be the most obvious rip in a fabric that was already frayed and under stress. This kind of broad holistic (a word I usually like to avoid) thinking may be what is lacking as we struggle to understand other mysterious and chronic conditions such as Lyme disease and chronic fatigue syndrome.
While these two papers help provide some clarity in the management of pediatric concussion, what they fail to address is the bigger question of the relationship between head injury and CTE. The answers to that conundrum are enshrouded in a mix of politics and publicity that I doubt will clear in the near future.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Pediatric concussion is one of those rare phenomena in which we may be witnessing its emergence and clarification in a generation. When I was serving as the game doctor for our local high school football team in the 1970s, I and many other physicians had a very simplistic view of concussion. If the patient never lost conscious and had a reasonably intact short-term memory, we didn’t seriously entertain concussion as a diagnosis. “What’s the score and who is the president?” Were my favorite screening questions.
Obviously, we were underdiagnosing and mismanaging concussion. In part thanks to some high-profile athletes who suffered multiple concussions and eventually chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) physicians began to realize that they should be looking more closely at children who sustained a head injury. The diagnostic criteria were expanded to include any injury that even temporarily effected brain function.
With the new appreciation for the risk of multiple concussions, the focus broadened to include the question of when is it safe for the athlete to return to competition. What signs or symptoms can the patient offer us so we can be sure his or her brain is sufficiently recovered? Here we stepped off into a deep abyss of ignorance. Fortunately, it became obvious fairly quickly that imaging studies weren’t going to help us, as they were invariably normal or at least didn’t tell us anything that wasn’t obvious on a physical exam.
If the patient had a headache, complained of dizziness, or manifested amnesia, monitoring the patient was fairly straightforward. But, in the absence of symptoms and no obvious way to determine the pace of recovery of an organ we couldn’t visualize, clinicians were pulling criteria and time tables out of thin air. Guessing that the concussed brain was in some ways like a torn muscle or overstretched tendon, “brain rest” was often suggested. So no TV, no reading, and certainly none of the cerebral challenging activity of school. Fortunately, we don’t hear much about the notion of brain rest anymore and there is at least one study that suggests that patients kept home from school recover more slowly.
But . Sometimes they describe headache or dizziness but often they complain of a vague mental unwellness. “Brain fog,” a term that has emerged in the wake of the COVID pandemic, might be an apt descriptor. Management of these slow recoverers has been a challenge.
However, two recent articles in the journal Pediatrics may provide some clarity and offer guidance in their management. In a study coming from the psychology department at Georgia State University, researchers reported that they have been able to find “no evidence of clinical meaningful differences in IQ after pediatric concussion.” In their words there is “strong evidence against reduced intelligence in the first few weeks to month after pediatric concussion.”
While their findings may simply toss the IQ onto the pile of worthless measures of healing, a companion commentary by Talin Babikian, PhD, a psychologist at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior at UCLA, provides a more nuanced interpretation. He writes that if we are looking for an explanation when a patient’s recovery is taking longer than we might expect we need to look beyond some structural damage. Maybe the patient has a previously undiagnosed premorbid condition effecting his or her intellectual, cognitive, or learning abilities. Could the stall in improvement be the result of other symptoms? Here fatigue and sleep deprivation may be the culprits. Could some underlying emotional factor such as anxiety or depression be the problem? For example, I have seen patients whose fear of re-injury has prevented their return to full function. And, finally, the patient may be avoiding a “nonpreferred or challenging situation” unrelated to the injury.
In other words, the concussion may simply be the most obvious rip in a fabric that was already frayed and under stress. This kind of broad holistic (a word I usually like to avoid) thinking may be what is lacking as we struggle to understand other mysterious and chronic conditions such as Lyme disease and chronic fatigue syndrome.
While these two papers help provide some clarity in the management of pediatric concussion, what they fail to address is the bigger question of the relationship between head injury and CTE. The answers to that conundrum are enshrouded in a mix of politics and publicity that I doubt will clear in the near future.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].