User login
New Vitamin D Recs: Testing, Supplementing, Dosing
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik, and today I’m going to talk about the Endocrine Society Guideline on Vitamin D. The question of who and when to test for vitamin D, and when to prescribe vitamin D, comes up frequently. There have been a lot of studies, and many people I know have opinions about this, but I haven’t seen a lot of clear, evidence-based guidance. This much-needed guideline provides guidance, though I’m not sure that everyone is going to be happy with the recommendations. That said, the society did conduct a comprehensive assessment and systematic review of the evidence that was impressive and well done. For our discussion, I will focus on the recommendations for nonpregnant adults.
The assumption for all of the recommendations is that these are for individuals who are already getting the Institute of Medicine’s recommended amount of vitamin D, which is 600 IU daily for those 50-70 years of age and 800 IU daily for those above 80 years.
For adults aged 18-74 years, who do not have prediabetes, the guidelines suggest against routinely testing for vitamin D deficiency and recommend against routine supplementation. For the older part of this cohort, adults aged 50-74 years, there is abundant randomized trial evidence showing little to no significant differences with vitamin D supplementation on outcomes of fracture, cancer, cardiovascular disease, kidney stones, or mortality. While supplementation is safe, there does not appear to be any benefit to routine supplementation or testing. It is important to note that the trials were done in populations that were meeting the daily recommended intake of vitamin D and who did not have low vitamin D levels at baseline, so individuals who may not be meeting the recommended daily intake though their diet or through sun exposure may consider vitamin D supplementation.
For adults with prediabetes, vitamin D supplementation is recommended to reduce the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes. This is about 1 in 3 adults in the United States. A number of trials have looked at vitamin D supplementation for adults with prediabetes in addition to lifestyle modification (diet and exercise). Vitamin D decreases the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes by approximately 10%-15%. The effect may be greater in those who are over age 60 and who have lower initial vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D in older adults (aged 75 or older) has a separate recommendation. In this age group, low vitamin D levels are common, with up to 20% of older adults having low levels. The guidelines suggest against testing vitamin D in adults aged 75 or over and recommend empiric vitamin D supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. While observational studies have shown a relationship between low vitamin D levels in this age group and adverse outcomes, including falls, fractures, and respiratory infections, evidence from randomized placebo-controlled trials of vitamin D supplementation have been inconsistent in regard to benefit. That said, a meta-analysis has shown that vitamin D supplementation lowers mortality compared with placebo, with a relative risk of 0.96 (confidence interval, 0.93-1.00). There was no difference in effect according to setting (community vs nursing home), vitamin D dosage, or baseline vitamin D level.
There appeared to be a benefit of low-dose vitamin D supplementation on fall risk, with possibly greater fall risk when high-dose supplementation was used. No significant effect on fracture rate was seen with vitamin D supplementation alone, although there was a decrease in fractures when vitamin D was combined with calcium. In these studies, the median dose of calcium was 1000 mg per day.
Based on the probability of a “slight decrease in all-cause mortality” and its safety, as well as possible benefit to decrease falls, the recommendation is for supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. Since there was not a consistent difference by vitamin D level, testing is not necessary.
Let’s now discuss dosage. The guidelines recommend daily lower-dose vitamin D over nondaily higher-dose vitamin D. Unfortunately, the guideline does not specify a specific dose of vitamin D. The supplementation dose used in trials of adults aged 75 or older ranged from 400 to 3333 IU daily, with an average dose of 900 IU daily, so it seems to me that a dose of 1000-2000 IU daily is a reasonable choice for older adults. In the prediabetes trials, a higher average dose was used, with a mean of 3500 IU daily, so a higher dose might make sense in this group.
Dr. Skolnik, is a professor in the Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik, and today I’m going to talk about the Endocrine Society Guideline on Vitamin D. The question of who and when to test for vitamin D, and when to prescribe vitamin D, comes up frequently. There have been a lot of studies, and many people I know have opinions about this, but I haven’t seen a lot of clear, evidence-based guidance. This much-needed guideline provides guidance, though I’m not sure that everyone is going to be happy with the recommendations. That said, the society did conduct a comprehensive assessment and systematic review of the evidence that was impressive and well done. For our discussion, I will focus on the recommendations for nonpregnant adults.
The assumption for all of the recommendations is that these are for individuals who are already getting the Institute of Medicine’s recommended amount of vitamin D, which is 600 IU daily for those 50-70 years of age and 800 IU daily for those above 80 years.
For adults aged 18-74 years, who do not have prediabetes, the guidelines suggest against routinely testing for vitamin D deficiency and recommend against routine supplementation. For the older part of this cohort, adults aged 50-74 years, there is abundant randomized trial evidence showing little to no significant differences with vitamin D supplementation on outcomes of fracture, cancer, cardiovascular disease, kidney stones, or mortality. While supplementation is safe, there does not appear to be any benefit to routine supplementation or testing. It is important to note that the trials were done in populations that were meeting the daily recommended intake of vitamin D and who did not have low vitamin D levels at baseline, so individuals who may not be meeting the recommended daily intake though their diet or through sun exposure may consider vitamin D supplementation.
For adults with prediabetes, vitamin D supplementation is recommended to reduce the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes. This is about 1 in 3 adults in the United States. A number of trials have looked at vitamin D supplementation for adults with prediabetes in addition to lifestyle modification (diet and exercise). Vitamin D decreases the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes by approximately 10%-15%. The effect may be greater in those who are over age 60 and who have lower initial vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D in older adults (aged 75 or older) has a separate recommendation. In this age group, low vitamin D levels are common, with up to 20% of older adults having low levels. The guidelines suggest against testing vitamin D in adults aged 75 or over and recommend empiric vitamin D supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. While observational studies have shown a relationship between low vitamin D levels in this age group and adverse outcomes, including falls, fractures, and respiratory infections, evidence from randomized placebo-controlled trials of vitamin D supplementation have been inconsistent in regard to benefit. That said, a meta-analysis has shown that vitamin D supplementation lowers mortality compared with placebo, with a relative risk of 0.96 (confidence interval, 0.93-1.00). There was no difference in effect according to setting (community vs nursing home), vitamin D dosage, or baseline vitamin D level.
There appeared to be a benefit of low-dose vitamin D supplementation on fall risk, with possibly greater fall risk when high-dose supplementation was used. No significant effect on fracture rate was seen with vitamin D supplementation alone, although there was a decrease in fractures when vitamin D was combined with calcium. In these studies, the median dose of calcium was 1000 mg per day.
Based on the probability of a “slight decrease in all-cause mortality” and its safety, as well as possible benefit to decrease falls, the recommendation is for supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. Since there was not a consistent difference by vitamin D level, testing is not necessary.
Let’s now discuss dosage. The guidelines recommend daily lower-dose vitamin D over nondaily higher-dose vitamin D. Unfortunately, the guideline does not specify a specific dose of vitamin D. The supplementation dose used in trials of adults aged 75 or older ranged from 400 to 3333 IU daily, with an average dose of 900 IU daily, so it seems to me that a dose of 1000-2000 IU daily is a reasonable choice for older adults. In the prediabetes trials, a higher average dose was used, with a mean of 3500 IU daily, so a higher dose might make sense in this group.
Dr. Skolnik, is a professor in the Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik, and today I’m going to talk about the Endocrine Society Guideline on Vitamin D. The question of who and when to test for vitamin D, and when to prescribe vitamin D, comes up frequently. There have been a lot of studies, and many people I know have opinions about this, but I haven’t seen a lot of clear, evidence-based guidance. This much-needed guideline provides guidance, though I’m not sure that everyone is going to be happy with the recommendations. That said, the society did conduct a comprehensive assessment and systematic review of the evidence that was impressive and well done. For our discussion, I will focus on the recommendations for nonpregnant adults.
The assumption for all of the recommendations is that these are for individuals who are already getting the Institute of Medicine’s recommended amount of vitamin D, which is 600 IU daily for those 50-70 years of age and 800 IU daily for those above 80 years.
For adults aged 18-74 years, who do not have prediabetes, the guidelines suggest against routinely testing for vitamin D deficiency and recommend against routine supplementation. For the older part of this cohort, adults aged 50-74 years, there is abundant randomized trial evidence showing little to no significant differences with vitamin D supplementation on outcomes of fracture, cancer, cardiovascular disease, kidney stones, or mortality. While supplementation is safe, there does not appear to be any benefit to routine supplementation or testing. It is important to note that the trials were done in populations that were meeting the daily recommended intake of vitamin D and who did not have low vitamin D levels at baseline, so individuals who may not be meeting the recommended daily intake though their diet or through sun exposure may consider vitamin D supplementation.
For adults with prediabetes, vitamin D supplementation is recommended to reduce the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes. This is about 1 in 3 adults in the United States. A number of trials have looked at vitamin D supplementation for adults with prediabetes in addition to lifestyle modification (diet and exercise). Vitamin D decreases the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes by approximately 10%-15%. The effect may be greater in those who are over age 60 and who have lower initial vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D in older adults (aged 75 or older) has a separate recommendation. In this age group, low vitamin D levels are common, with up to 20% of older adults having low levels. The guidelines suggest against testing vitamin D in adults aged 75 or over and recommend empiric vitamin D supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. While observational studies have shown a relationship between low vitamin D levels in this age group and adverse outcomes, including falls, fractures, and respiratory infections, evidence from randomized placebo-controlled trials of vitamin D supplementation have been inconsistent in regard to benefit. That said, a meta-analysis has shown that vitamin D supplementation lowers mortality compared with placebo, with a relative risk of 0.96 (confidence interval, 0.93-1.00). There was no difference in effect according to setting (community vs nursing home), vitamin D dosage, or baseline vitamin D level.
There appeared to be a benefit of low-dose vitamin D supplementation on fall risk, with possibly greater fall risk when high-dose supplementation was used. No significant effect on fracture rate was seen with vitamin D supplementation alone, although there was a decrease in fractures when vitamin D was combined with calcium. In these studies, the median dose of calcium was 1000 mg per day.
Based on the probability of a “slight decrease in all-cause mortality” and its safety, as well as possible benefit to decrease falls, the recommendation is for supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. Since there was not a consistent difference by vitamin D level, testing is not necessary.
Let’s now discuss dosage. The guidelines recommend daily lower-dose vitamin D over nondaily higher-dose vitamin D. Unfortunately, the guideline does not specify a specific dose of vitamin D. The supplementation dose used in trials of adults aged 75 or older ranged from 400 to 3333 IU daily, with an average dose of 900 IU daily, so it seems to me that a dose of 1000-2000 IU daily is a reasonable choice for older adults. In the prediabetes trials, a higher average dose was used, with a mean of 3500 IU daily, so a higher dose might make sense in this group.
Dr. Skolnik, is a professor in the Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Let ’em Play: In Defense of Youth Football
Over the last couple of decades, I have become increasingly more uncomfortable watching American-style football on television. Lax refereeing coupled with over-juiced players who can generate g-forces previously attainable only on a NASA rocket sled has resulted in a spate of injuries I find unacceptable. The revolving door of transfers from college to college has made the term scholar-athlete a relic that can be applied to only a handful of players at the smallest uncompetitive schools.
Many of you who are regular readers of Letters from Maine have probably tired of my boasting that when I played football in high school we wore leather helmets. I enjoyed playing football and continued playing in college for a couple of years until it became obvious that “bench” was going to be my usual position. But, I would not want my grandson to play college football. Certainly, not at the elite college level. Were he to do so, he would be putting himself at risk for significant injury by participating in what I no longer view as an appealing activity. Let me add that I am not including chronic traumatic encephalopathy among my concerns, because I think its association with football injuries is far from settled. My concern is more about spinal cord injuries, which, although infrequent, are almost always devastating.
I should also make it perfectly clear that my lack of enthusiasm for college and professional football does not place me among the increasingly vocal throng calling for the elimination of youth football. For the 5- to 12-year-olds, putting on pads and a helmet and scrambling around on a grassy field bumping shoulders and heads with their peers is a wonderful way to burn off energy and satisfies a need for roughhousing that comes naturally to most young boys (and many girls). The chance of anyone of those kids playing youth football reaching the elite college or professional level is extremely unlikely. Other activities and the realization that football is not in their future weeds the field during adolescence.
Although there have been some studies suggesting that starting football at an early age is associated with increased injury risk, a recent and well-controlled study published in the journal Sports Medicine has found no such association in professional football players. This finding makes some sense when you consider that most of the children in this age group are not mustering g-forces anywhere close to those a college or professional athlete can generate.
Another recent study published in the Journal of Pediatrics offers more evidence to consider before one passes judgment on youth football. When reviewing the records of nearly 1500 patients in a specialty-care concussion setting at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, investigators found that recreation-related concussions and non–sport- or recreation-related concussions were more prevalent than sports-related concussions. The authors propose that “less supervision at the time of injury and less access to established concussion healthcare following injury” may explain their observations.
Of course as a card-carrying AARP old fogey, I long for the good old days when youth sports were organized by the kids in backyards and playgrounds. There we learned to pick teams and deal with the disappointment of not being a first-round pick and the embarrassment of being a last rounder. We settled out-of-bounds calls and arguments about ball possession without adults’ assistance — or video replays for that matter. But those days are gone and likely never to return, with parental anxiety running at record highs. We must accept youth sports organized for kids by adults is the way it’s going to be for the foreseeable future.
As long as the program is organized with the emphasis on fun nor structured as a fast track to elite play it will be healthier for the kids than sitting on the couch at home watching the carnage on TV.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Over the last couple of decades, I have become increasingly more uncomfortable watching American-style football on television. Lax refereeing coupled with over-juiced players who can generate g-forces previously attainable only on a NASA rocket sled has resulted in a spate of injuries I find unacceptable. The revolving door of transfers from college to college has made the term scholar-athlete a relic that can be applied to only a handful of players at the smallest uncompetitive schools.
Many of you who are regular readers of Letters from Maine have probably tired of my boasting that when I played football in high school we wore leather helmets. I enjoyed playing football and continued playing in college for a couple of years until it became obvious that “bench” was going to be my usual position. But, I would not want my grandson to play college football. Certainly, not at the elite college level. Were he to do so, he would be putting himself at risk for significant injury by participating in what I no longer view as an appealing activity. Let me add that I am not including chronic traumatic encephalopathy among my concerns, because I think its association with football injuries is far from settled. My concern is more about spinal cord injuries, which, although infrequent, are almost always devastating.
I should also make it perfectly clear that my lack of enthusiasm for college and professional football does not place me among the increasingly vocal throng calling for the elimination of youth football. For the 5- to 12-year-olds, putting on pads and a helmet and scrambling around on a grassy field bumping shoulders and heads with their peers is a wonderful way to burn off energy and satisfies a need for roughhousing that comes naturally to most young boys (and many girls). The chance of anyone of those kids playing youth football reaching the elite college or professional level is extremely unlikely. Other activities and the realization that football is not in their future weeds the field during adolescence.
Although there have been some studies suggesting that starting football at an early age is associated with increased injury risk, a recent and well-controlled study published in the journal Sports Medicine has found no such association in professional football players. This finding makes some sense when you consider that most of the children in this age group are not mustering g-forces anywhere close to those a college or professional athlete can generate.
Another recent study published in the Journal of Pediatrics offers more evidence to consider before one passes judgment on youth football. When reviewing the records of nearly 1500 patients in a specialty-care concussion setting at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, investigators found that recreation-related concussions and non–sport- or recreation-related concussions were more prevalent than sports-related concussions. The authors propose that “less supervision at the time of injury and less access to established concussion healthcare following injury” may explain their observations.
Of course as a card-carrying AARP old fogey, I long for the good old days when youth sports were organized by the kids in backyards and playgrounds. There we learned to pick teams and deal with the disappointment of not being a first-round pick and the embarrassment of being a last rounder. We settled out-of-bounds calls and arguments about ball possession without adults’ assistance — or video replays for that matter. But those days are gone and likely never to return, with parental anxiety running at record highs. We must accept youth sports organized for kids by adults is the way it’s going to be for the foreseeable future.
As long as the program is organized with the emphasis on fun nor structured as a fast track to elite play it will be healthier for the kids than sitting on the couch at home watching the carnage on TV.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Over the last couple of decades, I have become increasingly more uncomfortable watching American-style football on television. Lax refereeing coupled with over-juiced players who can generate g-forces previously attainable only on a NASA rocket sled has resulted in a spate of injuries I find unacceptable. The revolving door of transfers from college to college has made the term scholar-athlete a relic that can be applied to only a handful of players at the smallest uncompetitive schools.
Many of you who are regular readers of Letters from Maine have probably tired of my boasting that when I played football in high school we wore leather helmets. I enjoyed playing football and continued playing in college for a couple of years until it became obvious that “bench” was going to be my usual position. But, I would not want my grandson to play college football. Certainly, not at the elite college level. Were he to do so, he would be putting himself at risk for significant injury by participating in what I no longer view as an appealing activity. Let me add that I am not including chronic traumatic encephalopathy among my concerns, because I think its association with football injuries is far from settled. My concern is more about spinal cord injuries, which, although infrequent, are almost always devastating.
I should also make it perfectly clear that my lack of enthusiasm for college and professional football does not place me among the increasingly vocal throng calling for the elimination of youth football. For the 5- to 12-year-olds, putting on pads and a helmet and scrambling around on a grassy field bumping shoulders and heads with their peers is a wonderful way to burn off energy and satisfies a need for roughhousing that comes naturally to most young boys (and many girls). The chance of anyone of those kids playing youth football reaching the elite college or professional level is extremely unlikely. Other activities and the realization that football is not in their future weeds the field during adolescence.
Although there have been some studies suggesting that starting football at an early age is associated with increased injury risk, a recent and well-controlled study published in the journal Sports Medicine has found no such association in professional football players. This finding makes some sense when you consider that most of the children in this age group are not mustering g-forces anywhere close to those a college or professional athlete can generate.
Another recent study published in the Journal of Pediatrics offers more evidence to consider before one passes judgment on youth football. When reviewing the records of nearly 1500 patients in a specialty-care concussion setting at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, investigators found that recreation-related concussions and non–sport- or recreation-related concussions were more prevalent than sports-related concussions. The authors propose that “less supervision at the time of injury and less access to established concussion healthcare following injury” may explain their observations.
Of course as a card-carrying AARP old fogey, I long for the good old days when youth sports were organized by the kids in backyards and playgrounds. There we learned to pick teams and deal with the disappointment of not being a first-round pick and the embarrassment of being a last rounder. We settled out-of-bounds calls and arguments about ball possession without adults’ assistance — or video replays for that matter. But those days are gone and likely never to return, with parental anxiety running at record highs. We must accept youth sports organized for kids by adults is the way it’s going to be for the foreseeable future.
As long as the program is organized with the emphasis on fun nor structured as a fast track to elite play it will be healthier for the kids than sitting on the couch at home watching the carnage on TV.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Managing Cancer in Pregnancy: Improvements and Considerations
Introduction: Tremendous Progress on Cancer Extends to Cancer in Pregnancy
The biomedical research enterprise that took shape in the United States after World War II has had numerous positive effects, including significant progress made during the past 75-plus years in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of cancer.
President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s 1944 request of Dr. Vannevar Bush, director of the then Office of Scientific Research and Development, to organize a program that would advance and apply scientific knowledge for times of peace — just as it been advanced and applied in times of war — culminated in a historic report, Science – The Endless Frontier. Presented in 1945 to President Harry S. Truman, this report helped fuel decades of broad, bold, and coordinated government-sponsored biomedical research aimed at addressing disease and improving the health of the American people (National Science Foundation, 1945).
Discoveries made from research in basic and translational sciences deepened our knowledge of the cellular and molecular underpinnings of cancer, leading to advances in chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and other treatment approaches as well as continual refinements in their application. Similarly, our diagnostic armamentarium has significantly improved.
As a result, we have reduced both the incidence and mortality of cancer. Today, some cancers can be prevented. Others can be reversed or put in remission. Granted, progress has been variable, with some cancers such as ovarian cancer still having relatively low survival rates. Much more needs to be done. Overall, however, the positive effects of the U.S. biomedical research enterprise on cancer are evident. According to the National Cancer Institute’s most recent report on the status of cancer, death rates from cancer fell 1.9% per year on average in females from 2015 to 2019 (Cancer. 2022 Oct 22. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34479).
It is not only patients whose cancer occurs outside of pregnancy who have benefited. When treatment is appropriately selected and timing considerations are made, patients whose cancer is diagnosed during pregnancy — and their children — can have good outcomes.
To explain how the management of cancer in pregnancy has improved, we have invited Gautam G. Rao, MD, gynecologic oncologist and associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, to write this installment of the Master Class in Obstetrics. As Dr. Rao explains, radiation is not as dangerous to the fetus as once thought, and the safety of many chemotherapeutic regimens in pregnancy has been documented. Obstetricians can and should counsel patients, he explains, about the likelihood of good maternal and fetal outcomes.
E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist, is dean emeritus of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, former university executive vice president; currently the endowed professor and director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI), and senior scientist in the Center for Birth Defects Research. Dr. Reece reported no relevant disclosures. He is the medical editor of this column. Contact him at [email protected].
Managing Cancer in Pregnancy
Cancer can cause fear and distress for any patient, but when cancer is diagnosed during pregnancy, an expectant mother fears not only for her own health but for the health of her unborn child. Fortunately, ob.gyn.s and multidisciplinary teams have good reason to reassure patients about the likelihood of good outcomes.
Cancer treatment in pregnancy has improved with advancements in imaging and chemotherapy, and while maternal and fetal outcomes of prenatal cancer treatment are not well reported, evidence acquired in recent years from case series and retrospective studies shows that most imaging studies and procedural diagnostic tests – and many treatments – can be performed safely in pregnancy.
Decades ago, we avoided CT scans during pregnancy because of concerns about radiation exposure to the fetus, leaving some patients without an accurate staging of their cancer. Today, we have evidence that a CT scan is generally safe in pregnancy. Similarly, the safety of many chemotherapeutic regimens in pregnancy has been documented in recent decades,and the use of chemotherapy during pregnancy has increased progressively. Radiation is also commonly utilized in the management of cancers that may occur during pregnancy, such as breast cancer.1
Considerations of timing are often central to decision-making; chemotherapy and radiotherapy are generally avoided in the first trimester to prevent structural fetal anomalies, for instance, and delaying cancer treatment is often warranted when the patient is a few weeks away from delivery. On occasion, iatrogenic preterm birth is considered when the risks to the mother of delaying a necessary cancer treatment outweigh the risks to the fetus of prematurity.1
Pregnancy termination is rarely indicated, however, and information gathered over the past 2 decades suggests that fetal and placental metastases are rare.1 There is broad agreement that prenatal treatment of cancer in pregnancy should adhere as much as possible to protocols and guidelines for nonpregnant patients and that treatment delays driven by fear of fetal anomalies and miscarriage are unnecessary.
Cancer Incidence, Use of Diagnostic Imaging
Data on the incidence of cancer in pregnancy comes from population-based cancer registries, and unfortunately, these data are not standardized and are often incomplete. Many studies include cancer diagnosed up to 1 year after pregnancy, and some include preinvasive disease. Estimates therefore vary considerably (see Table 1 for a sampling of estimates incidences.)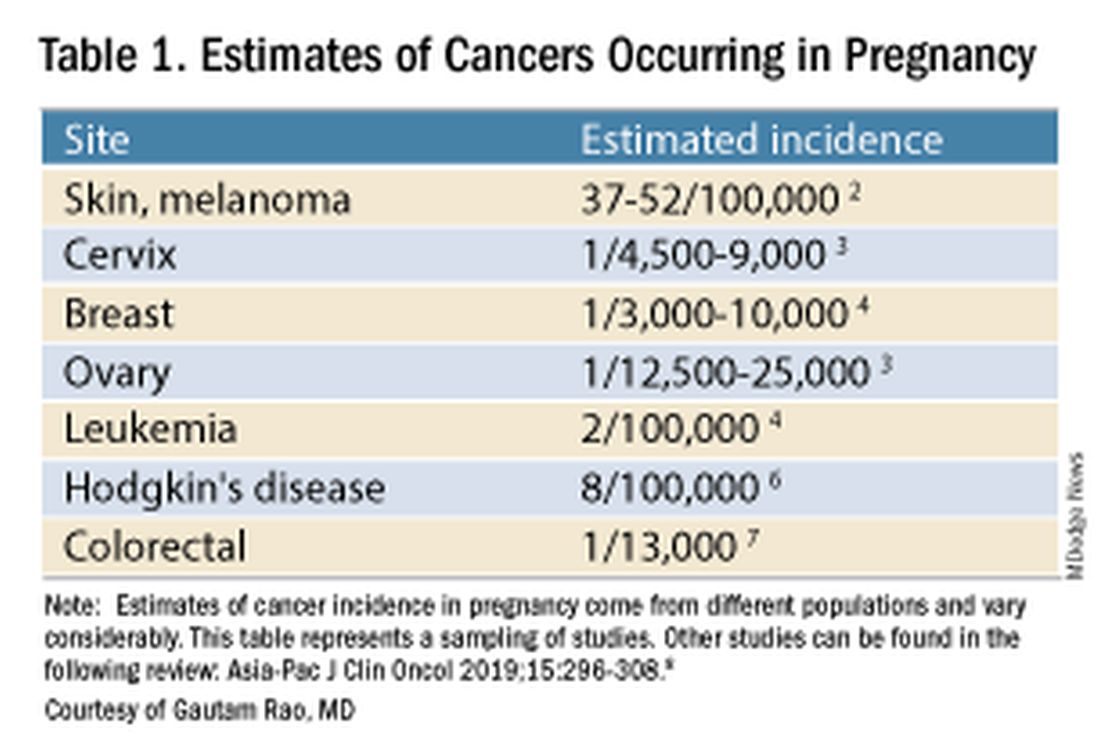
It has been reported, and often cited in the literature, that invasive malignancy complicates one in 1,000 pregnancies and that the incidence of cancer in pregnancy (invasive and noninvasive malignancies) has been rising over time.8 Increasing maternal age is believed to be playing a role in this rise; as women delay childbearing, they enter the age range in which some cancers become more common. Additionally, improvements in screening and diagnostics have led to earlier cancer detection. The incidence of ovarian neoplasms found during pregnancy has increased, for instance, with the routine use of diagnostic ultrasound in pregnancy.1
Among the studies showing an increased incidence of pregnancy-associated cancer is a population-based study in Australia, which found that from 1994 to 2007 the crude incidence of pregnancy-associated cancer increased from 112.3 to 191.5 per 100,000 pregnancies (P < .001).9 A cohort study in the United States documented an increase in incidence from 75.0 per 100,000 pregnancies in 2002 to 138.5 per 100,000 pregnancies in 2012.10
Overall, the literature shows us that the skin, cervix, and breast are also common sites for malignancy during pregnancy.1 According to a 2022 review, breast cancer during pregnancy is less often hormone receptor–positive and more frequently triple negative compared with age-matched controls.11 The frequencies of other pregnancy-associated cancers appear overall to be similar to that of cancer occurring in all women across their reproductive years.1
Too often, diagnosis is delayed because cancer symptoms can be masked by or can mimic normal physiological changes in pregnancy. For instance, breast cancer can be difficult to diagnose during pregnancy and lactation due to anatomic changes in the breast parenchyma. Several studies published in the 1990s showed that breast cancer presents at a more advanced stage in pregnant patients than in nonpregnant patients because of this delay.1 Skin changes suggestive of melanoma can be attributed to hyperpigmentation of pregnancy, for instance. Several observational studies have suggested that thicker melanomas found in pregnancy may be because of delayed diagnosis.8
It is important that we thoroughly investigate signs and symptoms suggestive of a malignancy and not automatically attribute these symptoms to the pregnancy itself. Cervical biopsy of a mass or lesion suspicious for cervical cancer can be done safely during pregnancy and should not be delayed or deferred.
Fetal radiation exposure from radiologic examinations has long been a concern, but we know today that while the imaging modality should be chosen to minimize fetal radiation exposure, CT scans and even PET scans should be performed if these exams are deemed best for evaluation. Embryonic exposure to a dose of less than 50 mGy is rarely if at all associated with fetal malformations or miscarriage and a radiation dose of 100 mGy may be considered a floor for consideration of therapeutic termination of pregnancy.1,8
CT exams are associated with a fetal dose far less than 50 mGy (see Table 2 for radiation doses).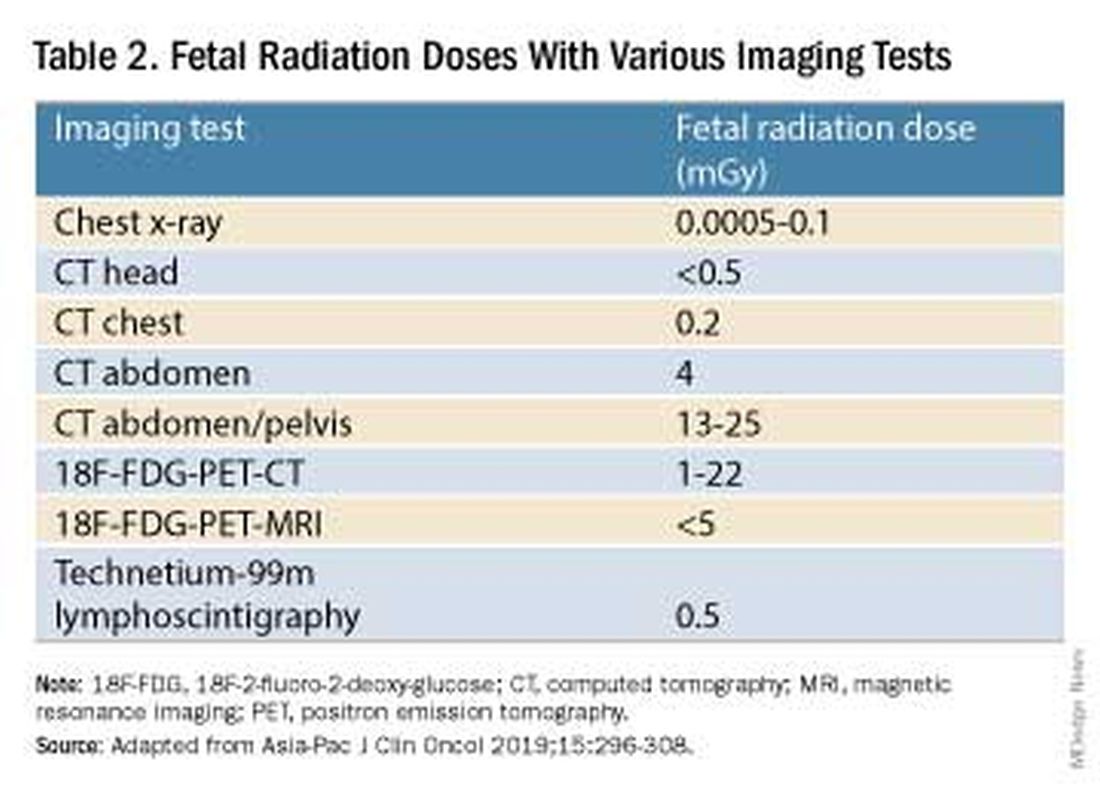
Magnetic resonance imaging with a magnet strength of 3 Tesla or less in any trimester is not associated with an increased risk of harm to the fetus or in early childhood, but the contrast agent gadolinium should be avoided in pregnancy as it has been associated with an increased risk of stillbirth, neonatal death, and childhood inflammatory, rheumatologic, and infiltrative skin lesions.1,8,12
Chemotherapy, Surgery, and Radiation in Pregnancy
The management of cancer during pregnancy requires a multidisciplinary team including medical, gynecologic, or radiation oncologists, and maternal-fetal medicine specialists (Figure 1). Prematurity and low birth weight are frequent complications for fetuses exposed to chemotherapy, although there is some uncertainty as to whether the treatment is causative. However, congenital anomalies no longer are a major concern, provided that drugs are appropriately selected and that fetal exposure occurs during the second or third trimester.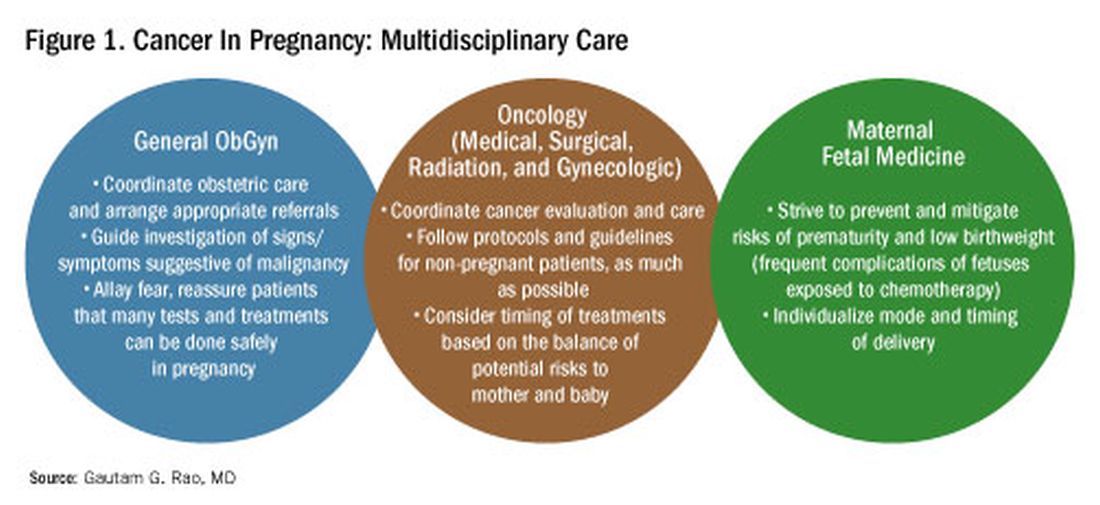
For instance, alkylating agents including cisplatin (an important drug in the management of gynecologic malignancies) have been associated with congenital anomalies in the first trimester but not in the second and third trimesters, and a variety of antimetabolites — excluding methotrexate and aminopterin — similarly have been shown to be relatively safe when used after the first trimester.1
Small studies have shown no long-term effects of chemotherapy exposure on postnatal growth and long-term neurologic/neurocognitive function,1 but this is an area that needs more research.
Also in need of investigation is the safety of newer agents in pregnancy. Data are limited on the use of new targeted treatments, monoclonal antibodies, and immunotherapies in pregnancy and their effects on the fetus, with current knowledge coming mainly from single case reports.13
Until more is learned — a challenge given that pregnant women are generally excluded from clinical trials — management teams are generally postponing use of these therapies until after delivery. Considering the pace of new developments revolutionizing cancer treatment, this topic will likely get more complex and confusing before we begin acquiring sufficient knowledge.
The timing of surgery for malignancy in pregnancy is similarly based on the balance of maternal and fetal risks, including the risk of maternal disease progression, the risk of preterm delivery, and the prevention of fetal metastases. In general, the safest time is the second trimester.
Maternal surgery in the third trimester may be associated with a risk of premature labor and altered uteroplacental perfusion. A 2005 systematic review of 12,452 women who underwent nonobstetric surgery during pregnancy provides some reassurance, however; compared with the general obstetric population, there was no increase in the rate of miscarriage or major birth defects.14
Radiotherapy used to be contraindicated in pregnancy but many experts today believe it can be safely utilized provided the uterus is out of field and is protected from scattered radiation. The head, neck, and breast, for instance, can be treated with newer radiotherapies, including stereotactic ablative radiation therapy.8 Patients with advanced cervical cancer often receive chemotherapy during pregnancy to slow metastatic growth followed by definitive treatment with postpartum radiation or surgery.
More research is needed, but available data on maternal outcomes are encouraging. For instance, there appear to be no significant differences in short- and long-term complications or survival between women who are pregnant and nonpregnant when treated for invasive cervical cancer.8 Similarly, while earlier studies of breast cancer diagnosed during pregnancy suggested a poor prognosis, data now show similar prognoses for pregnant and nonpregnant patients when controlled for stage.1
Dr. Rao is a gynecologic oncologist and associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. He reported no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Rao GG. Chapter 42. Clinical Obstetrics: The Fetus & Mother, 4th ed. Reece EA et al. (eds): 2021.
2. Bannister-Tyrrell M et al. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;55:116-122.
3. Oehler MK et al. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2003;43(6):414-420.
4. Ruiz R et al. Breast. 2017;35:136-141. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2017.07.008.
5. Nolan S et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;220(1):S480. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2018.11.752.
6. El-Messidi A et al. J Perinat Med. 2015;43(6):683-688. doi: 10.1515/jpm-2014-0133.
7. Pellino G et al. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;29(7):743-753. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000863.
8. Eastwood-Wilshere N et al. Asia-Pac J Clin Oncol. 2019;15:296-308.
9. Lee YY et al. BJOG. 2012;119(13):1572-1582.
10. Cottreau CM et al. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2019 Feb;28(2):250-257.
11. Boere I et al. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2022;82:46-59.
12. Ray JG et al. JAMA 2016;316(9):952-961.
13. Schwab R et al. Cancers. (Basel) 2021;13(12):3048.
14. Cohen-Kerem et al. Am J Surg. 2005;190(3):467-473.
Introduction: Tremendous Progress on Cancer Extends to Cancer in Pregnancy
The biomedical research enterprise that took shape in the United States after World War II has had numerous positive effects, including significant progress made during the past 75-plus years in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of cancer.
President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s 1944 request of Dr. Vannevar Bush, director of the then Office of Scientific Research and Development, to organize a program that would advance and apply scientific knowledge for times of peace — just as it been advanced and applied in times of war — culminated in a historic report, Science – The Endless Frontier. Presented in 1945 to President Harry S. Truman, this report helped fuel decades of broad, bold, and coordinated government-sponsored biomedical research aimed at addressing disease and improving the health of the American people (National Science Foundation, 1945).
Discoveries made from research in basic and translational sciences deepened our knowledge of the cellular and molecular underpinnings of cancer, leading to advances in chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and other treatment approaches as well as continual refinements in their application. Similarly, our diagnostic armamentarium has significantly improved.
As a result, we have reduced both the incidence and mortality of cancer. Today, some cancers can be prevented. Others can be reversed or put in remission. Granted, progress has been variable, with some cancers such as ovarian cancer still having relatively low survival rates. Much more needs to be done. Overall, however, the positive effects of the U.S. biomedical research enterprise on cancer are evident. According to the National Cancer Institute’s most recent report on the status of cancer, death rates from cancer fell 1.9% per year on average in females from 2015 to 2019 (Cancer. 2022 Oct 22. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34479).
It is not only patients whose cancer occurs outside of pregnancy who have benefited. When treatment is appropriately selected and timing considerations are made, patients whose cancer is diagnosed during pregnancy — and their children — can have good outcomes.
To explain how the management of cancer in pregnancy has improved, we have invited Gautam G. Rao, MD, gynecologic oncologist and associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, to write this installment of the Master Class in Obstetrics. As Dr. Rao explains, radiation is not as dangerous to the fetus as once thought, and the safety of many chemotherapeutic regimens in pregnancy has been documented. Obstetricians can and should counsel patients, he explains, about the likelihood of good maternal and fetal outcomes.
E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist, is dean emeritus of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, former university executive vice president; currently the endowed professor and director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI), and senior scientist in the Center for Birth Defects Research. Dr. Reece reported no relevant disclosures. He is the medical editor of this column. Contact him at [email protected].
Managing Cancer in Pregnancy
Cancer can cause fear and distress for any patient, but when cancer is diagnosed during pregnancy, an expectant mother fears not only for her own health but for the health of her unborn child. Fortunately, ob.gyn.s and multidisciplinary teams have good reason to reassure patients about the likelihood of good outcomes.
Cancer treatment in pregnancy has improved with advancements in imaging and chemotherapy, and while maternal and fetal outcomes of prenatal cancer treatment are not well reported, evidence acquired in recent years from case series and retrospective studies shows that most imaging studies and procedural diagnostic tests – and many treatments – can be performed safely in pregnancy.
Decades ago, we avoided CT scans during pregnancy because of concerns about radiation exposure to the fetus, leaving some patients without an accurate staging of their cancer. Today, we have evidence that a CT scan is generally safe in pregnancy. Similarly, the safety of many chemotherapeutic regimens in pregnancy has been documented in recent decades,and the use of chemotherapy during pregnancy has increased progressively. Radiation is also commonly utilized in the management of cancers that may occur during pregnancy, such as breast cancer.1
Considerations of timing are often central to decision-making; chemotherapy and radiotherapy are generally avoided in the first trimester to prevent structural fetal anomalies, for instance, and delaying cancer treatment is often warranted when the patient is a few weeks away from delivery. On occasion, iatrogenic preterm birth is considered when the risks to the mother of delaying a necessary cancer treatment outweigh the risks to the fetus of prematurity.1
Pregnancy termination is rarely indicated, however, and information gathered over the past 2 decades suggests that fetal and placental metastases are rare.1 There is broad agreement that prenatal treatment of cancer in pregnancy should adhere as much as possible to protocols and guidelines for nonpregnant patients and that treatment delays driven by fear of fetal anomalies and miscarriage are unnecessary.
Cancer Incidence, Use of Diagnostic Imaging
Data on the incidence of cancer in pregnancy comes from population-based cancer registries, and unfortunately, these data are not standardized and are often incomplete. Many studies include cancer diagnosed up to 1 year after pregnancy, and some include preinvasive disease. Estimates therefore vary considerably (see Table 1 for a sampling of estimates incidences.)
It has been reported, and often cited in the literature, that invasive malignancy complicates one in 1,000 pregnancies and that the incidence of cancer in pregnancy (invasive and noninvasive malignancies) has been rising over time.8 Increasing maternal age is believed to be playing a role in this rise; as women delay childbearing, they enter the age range in which some cancers become more common. Additionally, improvements in screening and diagnostics have led to earlier cancer detection. The incidence of ovarian neoplasms found during pregnancy has increased, for instance, with the routine use of diagnostic ultrasound in pregnancy.1
Among the studies showing an increased incidence of pregnancy-associated cancer is a population-based study in Australia, which found that from 1994 to 2007 the crude incidence of pregnancy-associated cancer increased from 112.3 to 191.5 per 100,000 pregnancies (P < .001).9 A cohort study in the United States documented an increase in incidence from 75.0 per 100,000 pregnancies in 2002 to 138.5 per 100,000 pregnancies in 2012.10
Overall, the literature shows us that the skin, cervix, and breast are also common sites for malignancy during pregnancy.1 According to a 2022 review, breast cancer during pregnancy is less often hormone receptor–positive and more frequently triple negative compared with age-matched controls.11 The frequencies of other pregnancy-associated cancers appear overall to be similar to that of cancer occurring in all women across their reproductive years.1
Too often, diagnosis is delayed because cancer symptoms can be masked by or can mimic normal physiological changes in pregnancy. For instance, breast cancer can be difficult to diagnose during pregnancy and lactation due to anatomic changes in the breast parenchyma. Several studies published in the 1990s showed that breast cancer presents at a more advanced stage in pregnant patients than in nonpregnant patients because of this delay.1 Skin changes suggestive of melanoma can be attributed to hyperpigmentation of pregnancy, for instance. Several observational studies have suggested that thicker melanomas found in pregnancy may be because of delayed diagnosis.8
It is important that we thoroughly investigate signs and symptoms suggestive of a malignancy and not automatically attribute these symptoms to the pregnancy itself. Cervical biopsy of a mass or lesion suspicious for cervical cancer can be done safely during pregnancy and should not be delayed or deferred.
Fetal radiation exposure from radiologic examinations has long been a concern, but we know today that while the imaging modality should be chosen to minimize fetal radiation exposure, CT scans and even PET scans should be performed if these exams are deemed best for evaluation. Embryonic exposure to a dose of less than 50 mGy is rarely if at all associated with fetal malformations or miscarriage and a radiation dose of 100 mGy may be considered a floor for consideration of therapeutic termination of pregnancy.1,8
CT exams are associated with a fetal dose far less than 50 mGy (see Table 2 for radiation doses).
Magnetic resonance imaging with a magnet strength of 3 Tesla or less in any trimester is not associated with an increased risk of harm to the fetus or in early childhood, but the contrast agent gadolinium should be avoided in pregnancy as it has been associated with an increased risk of stillbirth, neonatal death, and childhood inflammatory, rheumatologic, and infiltrative skin lesions.1,8,12
Chemotherapy, Surgery, and Radiation in Pregnancy
The management of cancer during pregnancy requires a multidisciplinary team including medical, gynecologic, or radiation oncologists, and maternal-fetal medicine specialists (Figure 1). Prematurity and low birth weight are frequent complications for fetuses exposed to chemotherapy, although there is some uncertainty as to whether the treatment is causative. However, congenital anomalies no longer are a major concern, provided that drugs are appropriately selected and that fetal exposure occurs during the second or third trimester.
For instance, alkylating agents including cisplatin (an important drug in the management of gynecologic malignancies) have been associated with congenital anomalies in the first trimester but not in the second and third trimesters, and a variety of antimetabolites — excluding methotrexate and aminopterin — similarly have been shown to be relatively safe when used after the first trimester.1
Small studies have shown no long-term effects of chemotherapy exposure on postnatal growth and long-term neurologic/neurocognitive function,1 but this is an area that needs more research.
Also in need of investigation is the safety of newer agents in pregnancy. Data are limited on the use of new targeted treatments, monoclonal antibodies, and immunotherapies in pregnancy and their effects on the fetus, with current knowledge coming mainly from single case reports.13
Until more is learned — a challenge given that pregnant women are generally excluded from clinical trials — management teams are generally postponing use of these therapies until after delivery. Considering the pace of new developments revolutionizing cancer treatment, this topic will likely get more complex and confusing before we begin acquiring sufficient knowledge.
The timing of surgery for malignancy in pregnancy is similarly based on the balance of maternal and fetal risks, including the risk of maternal disease progression, the risk of preterm delivery, and the prevention of fetal metastases. In general, the safest time is the second trimester.
Maternal surgery in the third trimester may be associated with a risk of premature labor and altered uteroplacental perfusion. A 2005 systematic review of 12,452 women who underwent nonobstetric surgery during pregnancy provides some reassurance, however; compared with the general obstetric population, there was no increase in the rate of miscarriage or major birth defects.14
Radiotherapy used to be contraindicated in pregnancy but many experts today believe it can be safely utilized provided the uterus is out of field and is protected from scattered radiation. The head, neck, and breast, for instance, can be treated with newer radiotherapies, including stereotactic ablative radiation therapy.8 Patients with advanced cervical cancer often receive chemotherapy during pregnancy to slow metastatic growth followed by definitive treatment with postpartum radiation or surgery.
More research is needed, but available data on maternal outcomes are encouraging. For instance, there appear to be no significant differences in short- and long-term complications or survival between women who are pregnant and nonpregnant when treated for invasive cervical cancer.8 Similarly, while earlier studies of breast cancer diagnosed during pregnancy suggested a poor prognosis, data now show similar prognoses for pregnant and nonpregnant patients when controlled for stage.1
Dr. Rao is a gynecologic oncologist and associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. He reported no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Rao GG. Chapter 42. Clinical Obstetrics: The Fetus & Mother, 4th ed. Reece EA et al. (eds): 2021.
2. Bannister-Tyrrell M et al. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;55:116-122.
3. Oehler MK et al. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2003;43(6):414-420.
4. Ruiz R et al. Breast. 2017;35:136-141. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2017.07.008.
5. Nolan S et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;220(1):S480. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2018.11.752.
6. El-Messidi A et al. J Perinat Med. 2015;43(6):683-688. doi: 10.1515/jpm-2014-0133.
7. Pellino G et al. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;29(7):743-753. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000863.
8. Eastwood-Wilshere N et al. Asia-Pac J Clin Oncol. 2019;15:296-308.
9. Lee YY et al. BJOG. 2012;119(13):1572-1582.
10. Cottreau CM et al. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2019 Feb;28(2):250-257.
11. Boere I et al. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2022;82:46-59.
12. Ray JG et al. JAMA 2016;316(9):952-961.
13. Schwab R et al. Cancers. (Basel) 2021;13(12):3048.
14. Cohen-Kerem et al. Am J Surg. 2005;190(3):467-473.
Introduction: Tremendous Progress on Cancer Extends to Cancer in Pregnancy
The biomedical research enterprise that took shape in the United States after World War II has had numerous positive effects, including significant progress made during the past 75-plus years in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of cancer.
President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s 1944 request of Dr. Vannevar Bush, director of the then Office of Scientific Research and Development, to organize a program that would advance and apply scientific knowledge for times of peace — just as it been advanced and applied in times of war — culminated in a historic report, Science – The Endless Frontier. Presented in 1945 to President Harry S. Truman, this report helped fuel decades of broad, bold, and coordinated government-sponsored biomedical research aimed at addressing disease and improving the health of the American people (National Science Foundation, 1945).
Discoveries made from research in basic and translational sciences deepened our knowledge of the cellular and molecular underpinnings of cancer, leading to advances in chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and other treatment approaches as well as continual refinements in their application. Similarly, our diagnostic armamentarium has significantly improved.
As a result, we have reduced both the incidence and mortality of cancer. Today, some cancers can be prevented. Others can be reversed or put in remission. Granted, progress has been variable, with some cancers such as ovarian cancer still having relatively low survival rates. Much more needs to be done. Overall, however, the positive effects of the U.S. biomedical research enterprise on cancer are evident. According to the National Cancer Institute’s most recent report on the status of cancer, death rates from cancer fell 1.9% per year on average in females from 2015 to 2019 (Cancer. 2022 Oct 22. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34479).
It is not only patients whose cancer occurs outside of pregnancy who have benefited. When treatment is appropriately selected and timing considerations are made, patients whose cancer is diagnosed during pregnancy — and their children — can have good outcomes.
To explain how the management of cancer in pregnancy has improved, we have invited Gautam G. Rao, MD, gynecologic oncologist and associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, to write this installment of the Master Class in Obstetrics. As Dr. Rao explains, radiation is not as dangerous to the fetus as once thought, and the safety of many chemotherapeutic regimens in pregnancy has been documented. Obstetricians can and should counsel patients, he explains, about the likelihood of good maternal and fetal outcomes.
E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist, is dean emeritus of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, former university executive vice president; currently the endowed professor and director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI), and senior scientist in the Center for Birth Defects Research. Dr. Reece reported no relevant disclosures. He is the medical editor of this column. Contact him at [email protected].
Managing Cancer in Pregnancy
Cancer can cause fear and distress for any patient, but when cancer is diagnosed during pregnancy, an expectant mother fears not only for her own health but for the health of her unborn child. Fortunately, ob.gyn.s and multidisciplinary teams have good reason to reassure patients about the likelihood of good outcomes.
Cancer treatment in pregnancy has improved with advancements in imaging and chemotherapy, and while maternal and fetal outcomes of prenatal cancer treatment are not well reported, evidence acquired in recent years from case series and retrospective studies shows that most imaging studies and procedural diagnostic tests – and many treatments – can be performed safely in pregnancy.
Decades ago, we avoided CT scans during pregnancy because of concerns about radiation exposure to the fetus, leaving some patients without an accurate staging of their cancer. Today, we have evidence that a CT scan is generally safe in pregnancy. Similarly, the safety of many chemotherapeutic regimens in pregnancy has been documented in recent decades,and the use of chemotherapy during pregnancy has increased progressively. Radiation is also commonly utilized in the management of cancers that may occur during pregnancy, such as breast cancer.1
Considerations of timing are often central to decision-making; chemotherapy and radiotherapy are generally avoided in the first trimester to prevent structural fetal anomalies, for instance, and delaying cancer treatment is often warranted when the patient is a few weeks away from delivery. On occasion, iatrogenic preterm birth is considered when the risks to the mother of delaying a necessary cancer treatment outweigh the risks to the fetus of prematurity.1
Pregnancy termination is rarely indicated, however, and information gathered over the past 2 decades suggests that fetal and placental metastases are rare.1 There is broad agreement that prenatal treatment of cancer in pregnancy should adhere as much as possible to protocols and guidelines for nonpregnant patients and that treatment delays driven by fear of fetal anomalies and miscarriage are unnecessary.
Cancer Incidence, Use of Diagnostic Imaging
Data on the incidence of cancer in pregnancy comes from population-based cancer registries, and unfortunately, these data are not standardized and are often incomplete. Many studies include cancer diagnosed up to 1 year after pregnancy, and some include preinvasive disease. Estimates therefore vary considerably (see Table 1 for a sampling of estimates incidences.)
It has been reported, and often cited in the literature, that invasive malignancy complicates one in 1,000 pregnancies and that the incidence of cancer in pregnancy (invasive and noninvasive malignancies) has been rising over time.8 Increasing maternal age is believed to be playing a role in this rise; as women delay childbearing, they enter the age range in which some cancers become more common. Additionally, improvements in screening and diagnostics have led to earlier cancer detection. The incidence of ovarian neoplasms found during pregnancy has increased, for instance, with the routine use of diagnostic ultrasound in pregnancy.1
Among the studies showing an increased incidence of pregnancy-associated cancer is a population-based study in Australia, which found that from 1994 to 2007 the crude incidence of pregnancy-associated cancer increased from 112.3 to 191.5 per 100,000 pregnancies (P < .001).9 A cohort study in the United States documented an increase in incidence from 75.0 per 100,000 pregnancies in 2002 to 138.5 per 100,000 pregnancies in 2012.10
Overall, the literature shows us that the skin, cervix, and breast are also common sites for malignancy during pregnancy.1 According to a 2022 review, breast cancer during pregnancy is less often hormone receptor–positive and more frequently triple negative compared with age-matched controls.11 The frequencies of other pregnancy-associated cancers appear overall to be similar to that of cancer occurring in all women across their reproductive years.1
Too often, diagnosis is delayed because cancer symptoms can be masked by or can mimic normal physiological changes in pregnancy. For instance, breast cancer can be difficult to diagnose during pregnancy and lactation due to anatomic changes in the breast parenchyma. Several studies published in the 1990s showed that breast cancer presents at a more advanced stage in pregnant patients than in nonpregnant patients because of this delay.1 Skin changes suggestive of melanoma can be attributed to hyperpigmentation of pregnancy, for instance. Several observational studies have suggested that thicker melanomas found in pregnancy may be because of delayed diagnosis.8
It is important that we thoroughly investigate signs and symptoms suggestive of a malignancy and not automatically attribute these symptoms to the pregnancy itself. Cervical biopsy of a mass or lesion suspicious for cervical cancer can be done safely during pregnancy and should not be delayed or deferred.
Fetal radiation exposure from radiologic examinations has long been a concern, but we know today that while the imaging modality should be chosen to minimize fetal radiation exposure, CT scans and even PET scans should be performed if these exams are deemed best for evaluation. Embryonic exposure to a dose of less than 50 mGy is rarely if at all associated with fetal malformations or miscarriage and a radiation dose of 100 mGy may be considered a floor for consideration of therapeutic termination of pregnancy.1,8
CT exams are associated with a fetal dose far less than 50 mGy (see Table 2 for radiation doses).
Magnetic resonance imaging with a magnet strength of 3 Tesla or less in any trimester is not associated with an increased risk of harm to the fetus or in early childhood, but the contrast agent gadolinium should be avoided in pregnancy as it has been associated with an increased risk of stillbirth, neonatal death, and childhood inflammatory, rheumatologic, and infiltrative skin lesions.1,8,12
Chemotherapy, Surgery, and Radiation in Pregnancy
The management of cancer during pregnancy requires a multidisciplinary team including medical, gynecologic, or radiation oncologists, and maternal-fetal medicine specialists (Figure 1). Prematurity and low birth weight are frequent complications for fetuses exposed to chemotherapy, although there is some uncertainty as to whether the treatment is causative. However, congenital anomalies no longer are a major concern, provided that drugs are appropriately selected and that fetal exposure occurs during the second or third trimester.
For instance, alkylating agents including cisplatin (an important drug in the management of gynecologic malignancies) have been associated with congenital anomalies in the first trimester but not in the second and third trimesters, and a variety of antimetabolites — excluding methotrexate and aminopterin — similarly have been shown to be relatively safe when used after the first trimester.1
Small studies have shown no long-term effects of chemotherapy exposure on postnatal growth and long-term neurologic/neurocognitive function,1 but this is an area that needs more research.
Also in need of investigation is the safety of newer agents in pregnancy. Data are limited on the use of new targeted treatments, monoclonal antibodies, and immunotherapies in pregnancy and their effects on the fetus, with current knowledge coming mainly from single case reports.13
Until more is learned — a challenge given that pregnant women are generally excluded from clinical trials — management teams are generally postponing use of these therapies until after delivery. Considering the pace of new developments revolutionizing cancer treatment, this topic will likely get more complex and confusing before we begin acquiring sufficient knowledge.
The timing of surgery for malignancy in pregnancy is similarly based on the balance of maternal and fetal risks, including the risk of maternal disease progression, the risk of preterm delivery, and the prevention of fetal metastases. In general, the safest time is the second trimester.
Maternal surgery in the third trimester may be associated with a risk of premature labor and altered uteroplacental perfusion. A 2005 systematic review of 12,452 women who underwent nonobstetric surgery during pregnancy provides some reassurance, however; compared with the general obstetric population, there was no increase in the rate of miscarriage or major birth defects.14
Radiotherapy used to be contraindicated in pregnancy but many experts today believe it can be safely utilized provided the uterus is out of field and is protected from scattered radiation. The head, neck, and breast, for instance, can be treated with newer radiotherapies, including stereotactic ablative radiation therapy.8 Patients with advanced cervical cancer often receive chemotherapy during pregnancy to slow metastatic growth followed by definitive treatment with postpartum radiation or surgery.
More research is needed, but available data on maternal outcomes are encouraging. For instance, there appear to be no significant differences in short- and long-term complications or survival between women who are pregnant and nonpregnant when treated for invasive cervical cancer.8 Similarly, while earlier studies of breast cancer diagnosed during pregnancy suggested a poor prognosis, data now show similar prognoses for pregnant and nonpregnant patients when controlled for stage.1
Dr. Rao is a gynecologic oncologist and associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. He reported no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Rao GG. Chapter 42. Clinical Obstetrics: The Fetus & Mother, 4th ed. Reece EA et al. (eds): 2021.
2. Bannister-Tyrrell M et al. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;55:116-122.
3. Oehler MK et al. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2003;43(6):414-420.
4. Ruiz R et al. Breast. 2017;35:136-141. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2017.07.008.
5. Nolan S et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;220(1):S480. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2018.11.752.
6. El-Messidi A et al. J Perinat Med. 2015;43(6):683-688. doi: 10.1515/jpm-2014-0133.
7. Pellino G et al. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;29(7):743-753. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000863.
8. Eastwood-Wilshere N et al. Asia-Pac J Clin Oncol. 2019;15:296-308.
9. Lee YY et al. BJOG. 2012;119(13):1572-1582.
10. Cottreau CM et al. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2019 Feb;28(2):250-257.
11. Boere I et al. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2022;82:46-59.
12. Ray JG et al. JAMA 2016;316(9):952-961.
13. Schwab R et al. Cancers. (Basel) 2021;13(12):3048.
14. Cohen-Kerem et al. Am J Surg. 2005;190(3):467-473.
Mounjaro Beats Ozempic, So Why Isn’t It More Popular?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 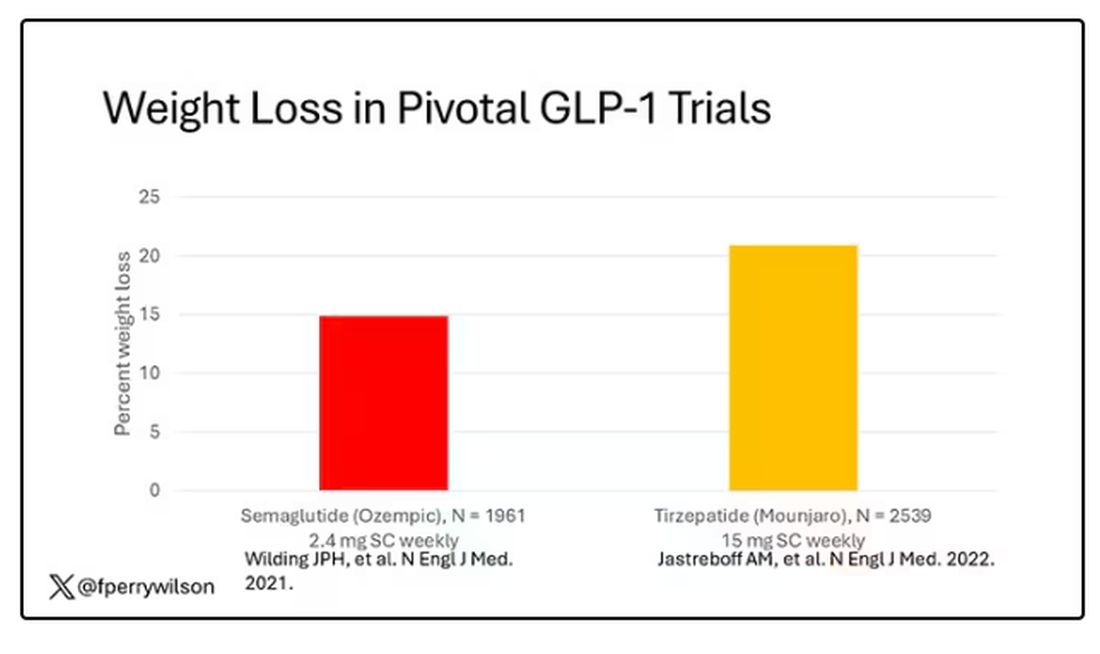
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 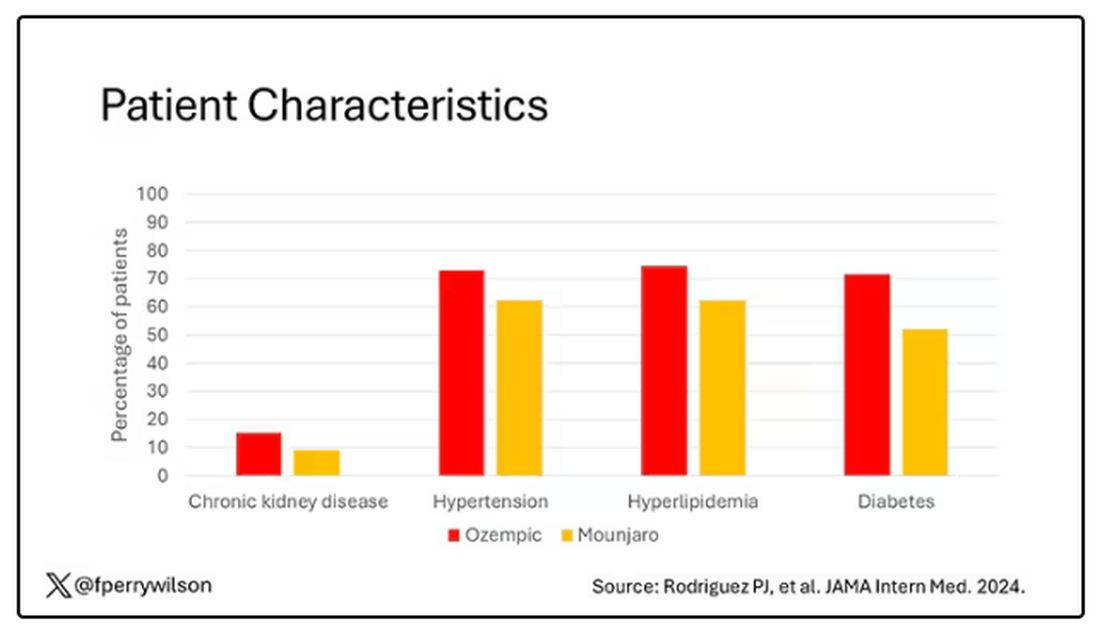
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.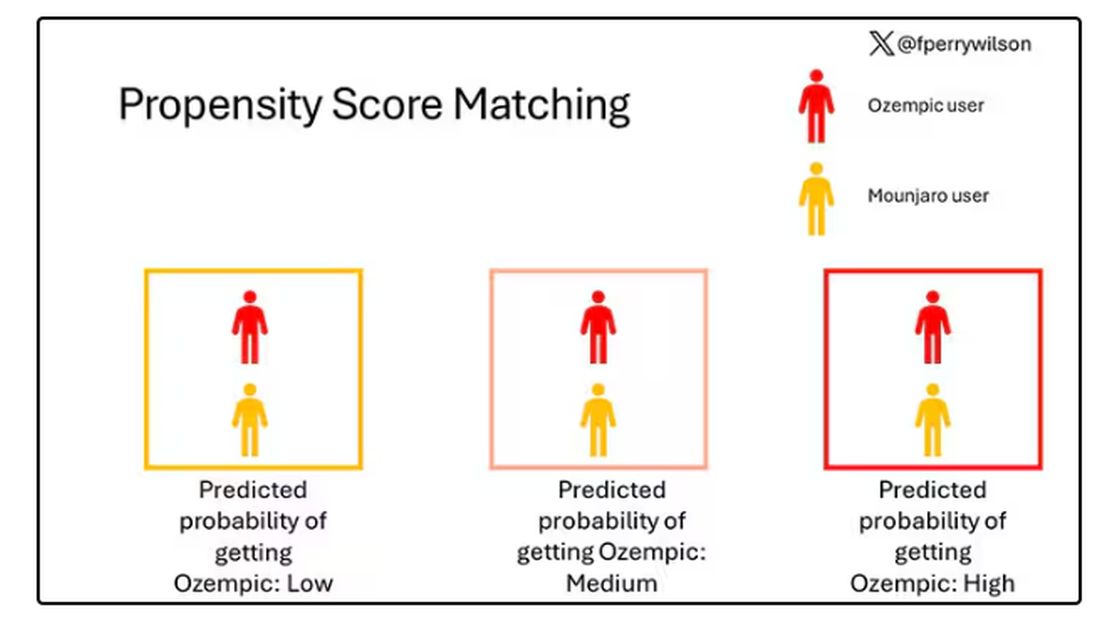
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.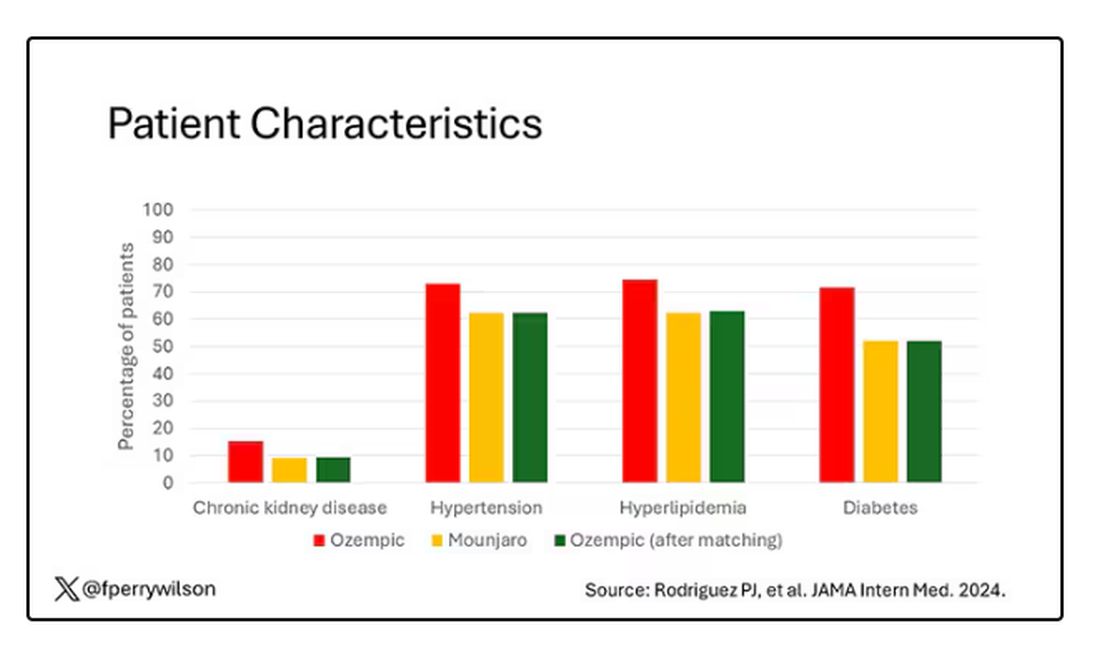
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 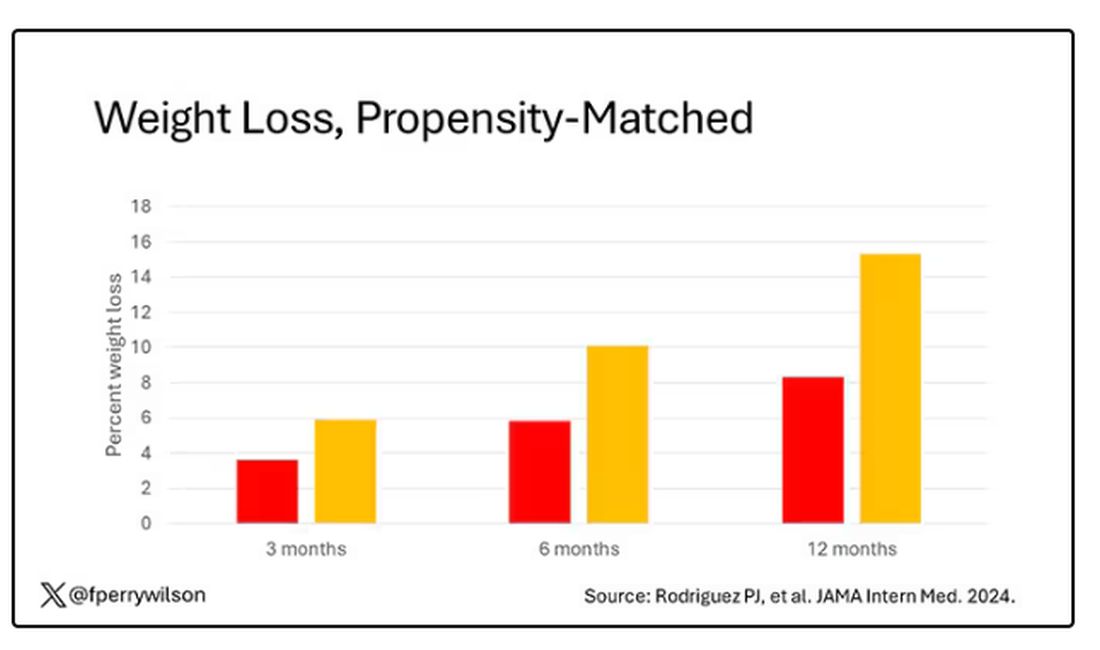
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.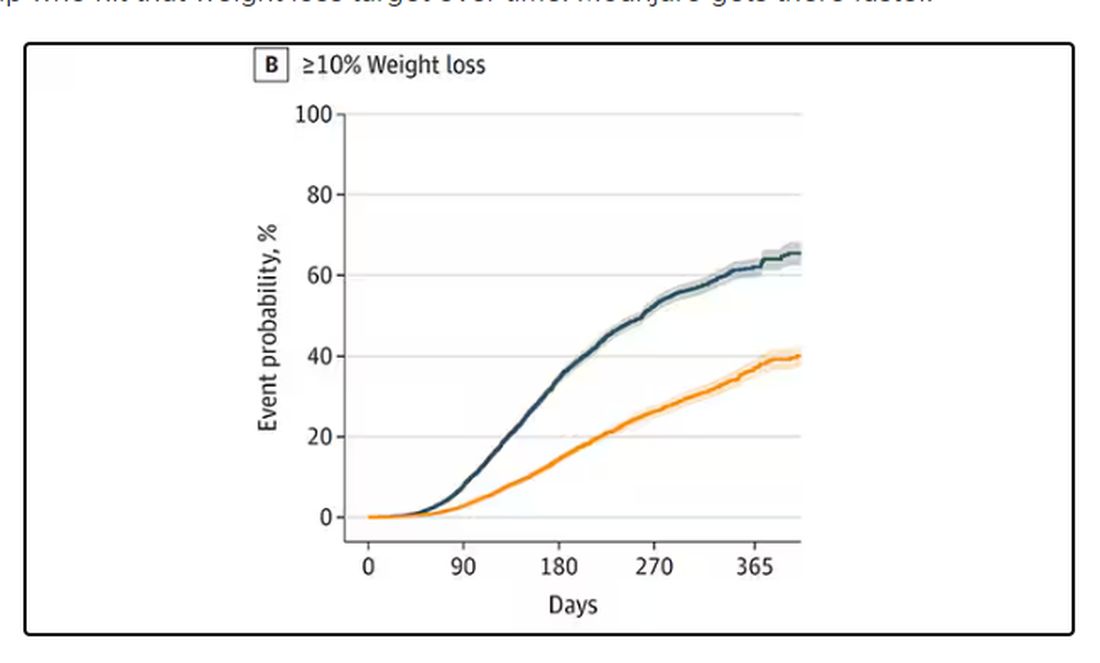
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic Neck Pain: A Primary Care Approach
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome to The Curbsiders. I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. We’re going to be talking about the evaluation of chronic neck pain, which is a really common complaint in primary care. So, Paul, what are the three buckets of neck pain?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Well, as our listeners probably know, neck pain is extraordinarily common. There are three big buckets. There is mechanical neck pain, which is sort of the bread-and-butter “my neck just hurts” — probably the one you’re going to see most commonly in the office. We’ll get into that in just a second.
The second bucket is cervical radiculopathy. We see a little bit more neurologic symptoms as part of the presentation. They may have weakness. They may have pain.
The third type of neck pain is cervical myelopathy, which is the one that probably warrants more aggressive follow-up and evaluation, and potentially even management. And that is typically your older patients in nontraumatic cases, who have bony impingement on the central spinal cord, often with upper motor neuron signs, and it can ultimately be very devastating. It’s almost a spectrum of presentations to worry about in terms of severity and outcomes.
We’ll start with the mechanical neck pain. It’s the one that we see the most commonly in the primary care office. We’ve all dealt with this. This is the patient who’s got localized neck pain that doesn’t really radiate anywhere; it kind of sits in the middle of the neck. In fact, if you actually poke back there where the patient says “ouch,” you’re probably in the right ballpark. The etiology and pathophysiology, weirdly, are still not super well-defined, but it’s probably mostly myofascial in etiology. And as such, it often gets better no matter what you do. It will probably get better with time.
You are not going to have neurologic deficits with this type of neck pain. There’s not going to be weakness, or radiation down the arm, or upper motor neuron signs. No one is mentioning the urinary symptoms with this. You can treat it with NSAIDs and physical therapy, which may be necessary if it persists. Massage can sometimes be helpful, but basically you’re just kind of supporting the patients through their own natural healing process. Physical therapy might help with the ergonomics and help make sure that they position themselves and move in a way that does not exacerbate the underlying structures. That is probably the one that we see the most and in some ways is probably the easiest to manage.
Dr. Watto: This is the one that we generally should be least worried about. But cervical radiculopathy, which is the second bucket, is not as severe as cervical myelopathy, so it’s kind of in between the two. Cervical radiculopathy is basically the patient who has neck pain that’s going down one arm or the other, usually not both arms because that would be weird for them to have symmetric radiculopathy. It’s a nerve being pinched somewhere, usually more on one side than the other.
The good news for patients is that the natural history is that it’s going to get better over time, almost no matter what we do. I almost think of this akin to sciatica. Usually sciatica and cervical radiculopathy do not have any motor weakness along with them. It’s really just the pain and maybe a little bit of mild sensory symptoms. So, you can reassure the patient that this usually goes away. Our guest said he sometimes gives gabapentin for this. That’s not my practice. I would be more likely to refer to physical therapy or try some NSAIDs if they’re really having trouble functioning or maybe some muscle relaxants. But they aren’t going to need to go to surgery.
What about cervical myelopathy, Paul? Do those patients need surgery?
Dr. Williams: Yes. The idea with cervical myelopathy is to keep it from progressing. It typically occurs in older patients. It’s like arthritis — a sort of bony buildup that compresses on the spinal cord itself. These patients will often have neck pain but not always. It’s also associated with impairments in motor function and other neurologic deficits. So, the patients may report that they have difficulty buttoning their buttons or managing fine-motor skills. They may have radicular symptoms down their arms. They may have an abnormal physical examination. They may have weakness on exam, but they’ll have a positive Hoffmann’s test where you flick the middle finger and look for flexion of the first finger and the thumb. They may have abnormal tandem gait, or patellar or Achilles hyperreflexia. Their neuro exam will not be normal much of the time, and in later cases because it’s upper motor neuron disease, they may even report urinary symptoms like urinary hesitancy or just a feeling of general unsteadiness of the gait, even though we’re at the cervical level. If you suspect myelopathy — and the trick is to think about it and recognize it when you see it — then you should send them for an MRI. If it persists or they have rapid regression, you get the MRI and refer them to neurosurgery. It’s not necessarily a neurosurgical emergency, but things should move along fairly briskly once you’ve actually identified it.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Mikula made the point that if someone comes to you in a wheelchair, they are probably not going to regain the ability to walk. You’re really trying to prevent progression. If they are already severely disabled, they’re probably not going to get totally back to full functioning, even with surgery. You’re just trying to prevent things from getting worse. That’s the main reason to identify this and get the patient to surgery.
We covered a lot more about neck pain. This was a very superficial review of what we talked about with Dr. Anthony Mikula. Click here to listen to the full podcast.
Matthew F. Watto is clinical assistant professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania, and internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams is associate professor of clinical medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine, and staff physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders; received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome to The Curbsiders. I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. We’re going to be talking about the evaluation of chronic neck pain, which is a really common complaint in primary care. So, Paul, what are the three buckets of neck pain?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Well, as our listeners probably know, neck pain is extraordinarily common. There are three big buckets. There is mechanical neck pain, which is sort of the bread-and-butter “my neck just hurts” — probably the one you’re going to see most commonly in the office. We’ll get into that in just a second.
The second bucket is cervical radiculopathy. We see a little bit more neurologic symptoms as part of the presentation. They may have weakness. They may have pain.
The third type of neck pain is cervical myelopathy, which is the one that probably warrants more aggressive follow-up and evaluation, and potentially even management. And that is typically your older patients in nontraumatic cases, who have bony impingement on the central spinal cord, often with upper motor neuron signs, and it can ultimately be very devastating. It’s almost a spectrum of presentations to worry about in terms of severity and outcomes.
We’ll start with the mechanical neck pain. It’s the one that we see the most commonly in the primary care office. We’ve all dealt with this. This is the patient who’s got localized neck pain that doesn’t really radiate anywhere; it kind of sits in the middle of the neck. In fact, if you actually poke back there where the patient says “ouch,” you’re probably in the right ballpark. The etiology and pathophysiology, weirdly, are still not super well-defined, but it’s probably mostly myofascial in etiology. And as such, it often gets better no matter what you do. It will probably get better with time.
You are not going to have neurologic deficits with this type of neck pain. There’s not going to be weakness, or radiation down the arm, or upper motor neuron signs. No one is mentioning the urinary symptoms with this. You can treat it with NSAIDs and physical therapy, which may be necessary if it persists. Massage can sometimes be helpful, but basically you’re just kind of supporting the patients through their own natural healing process. Physical therapy might help with the ergonomics and help make sure that they position themselves and move in a way that does not exacerbate the underlying structures. That is probably the one that we see the most and in some ways is probably the easiest to manage.
Dr. Watto: This is the one that we generally should be least worried about. But cervical radiculopathy, which is the second bucket, is not as severe as cervical myelopathy, so it’s kind of in between the two. Cervical radiculopathy is basically the patient who has neck pain that’s going down one arm or the other, usually not both arms because that would be weird for them to have symmetric radiculopathy. It’s a nerve being pinched somewhere, usually more on one side than the other.
The good news for patients is that the natural history is that it’s going to get better over time, almost no matter what we do. I almost think of this akin to sciatica. Usually sciatica and cervical radiculopathy do not have any motor weakness along with them. It’s really just the pain and maybe a little bit of mild sensory symptoms. So, you can reassure the patient that this usually goes away. Our guest said he sometimes gives gabapentin for this. That’s not my practice. I would be more likely to refer to physical therapy or try some NSAIDs if they’re really having trouble functioning or maybe some muscle relaxants. But they aren’t going to need to go to surgery.
What about cervical myelopathy, Paul? Do those patients need surgery?
Dr. Williams: Yes. The idea with cervical myelopathy is to keep it from progressing. It typically occurs in older patients. It’s like arthritis — a sort of bony buildup that compresses on the spinal cord itself. These patients will often have neck pain but not always. It’s also associated with impairments in motor function and other neurologic deficits. So, the patients may report that they have difficulty buttoning their buttons or managing fine-motor skills. They may have radicular symptoms down their arms. They may have an abnormal physical examination. They may have weakness on exam, but they’ll have a positive Hoffmann’s test where you flick the middle finger and look for flexion of the first finger and the thumb. They may have abnormal tandem gait, or patellar or Achilles hyperreflexia. Their neuro exam will not be normal much of the time, and in later cases because it’s upper motor neuron disease, they may even report urinary symptoms like urinary hesitancy or just a feeling of general unsteadiness of the gait, even though we’re at the cervical level. If you suspect myelopathy — and the trick is to think about it and recognize it when you see it — then you should send them for an MRI. If it persists or they have rapid regression, you get the MRI and refer them to neurosurgery. It’s not necessarily a neurosurgical emergency, but things should move along fairly briskly once you’ve actually identified it.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Mikula made the point that if someone comes to you in a wheelchair, they are probably not going to regain the ability to walk. You’re really trying to prevent progression. If they are already severely disabled, they’re probably not going to get totally back to full functioning, even with surgery. You’re just trying to prevent things from getting worse. That’s the main reason to identify this and get the patient to surgery.
We covered a lot more about neck pain. This was a very superficial review of what we talked about with Dr. Anthony Mikula. Click here to listen to the full podcast.
Matthew F. Watto is clinical assistant professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania, and internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams is associate professor of clinical medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine, and staff physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders; received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome to The Curbsiders. I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. We’re going to be talking about the evaluation of chronic neck pain, which is a really common complaint in primary care. So, Paul, what are the three buckets of neck pain?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Well, as our listeners probably know, neck pain is extraordinarily common. There are three big buckets. There is mechanical neck pain, which is sort of the bread-and-butter “my neck just hurts” — probably the one you’re going to see most commonly in the office. We’ll get into that in just a second.
The second bucket is cervical radiculopathy. We see a little bit more neurologic symptoms as part of the presentation. They may have weakness. They may have pain.
The third type of neck pain is cervical myelopathy, which is the one that probably warrants more aggressive follow-up and evaluation, and potentially even management. And that is typically your older patients in nontraumatic cases, who have bony impingement on the central spinal cord, often with upper motor neuron signs, and it can ultimately be very devastating. It’s almost a spectrum of presentations to worry about in terms of severity and outcomes.
We’ll start with the mechanical neck pain. It’s the one that we see the most commonly in the primary care office. We’ve all dealt with this. This is the patient who’s got localized neck pain that doesn’t really radiate anywhere; it kind of sits in the middle of the neck. In fact, if you actually poke back there where the patient says “ouch,” you’re probably in the right ballpark. The etiology and pathophysiology, weirdly, are still not super well-defined, but it’s probably mostly myofascial in etiology. And as such, it often gets better no matter what you do. It will probably get better with time.
You are not going to have neurologic deficits with this type of neck pain. There’s not going to be weakness, or radiation down the arm, or upper motor neuron signs. No one is mentioning the urinary symptoms with this. You can treat it with NSAIDs and physical therapy, which may be necessary if it persists. Massage can sometimes be helpful, but basically you’re just kind of supporting the patients through their own natural healing process. Physical therapy might help with the ergonomics and help make sure that they position themselves and move in a way that does not exacerbate the underlying structures. That is probably the one that we see the most and in some ways is probably the easiest to manage.
Dr. Watto: This is the one that we generally should be least worried about. But cervical radiculopathy, which is the second bucket, is not as severe as cervical myelopathy, so it’s kind of in between the two. Cervical radiculopathy is basically the patient who has neck pain that’s going down one arm or the other, usually not both arms because that would be weird for them to have symmetric radiculopathy. It’s a nerve being pinched somewhere, usually more on one side than the other.
The good news for patients is that the natural history is that it’s going to get better over time, almost no matter what we do. I almost think of this akin to sciatica. Usually sciatica and cervical radiculopathy do not have any motor weakness along with them. It’s really just the pain and maybe a little bit of mild sensory symptoms. So, you can reassure the patient that this usually goes away. Our guest said he sometimes gives gabapentin for this. That’s not my practice. I would be more likely to refer to physical therapy or try some NSAIDs if they’re really having trouble functioning or maybe some muscle relaxants. But they aren’t going to need to go to surgery.
What about cervical myelopathy, Paul? Do those patients need surgery?
Dr. Williams: Yes. The idea with cervical myelopathy is to keep it from progressing. It typically occurs in older patients. It’s like arthritis — a sort of bony buildup that compresses on the spinal cord itself. These patients will often have neck pain but not always. It’s also associated with impairments in motor function and other neurologic deficits. So, the patients may report that they have difficulty buttoning their buttons or managing fine-motor skills. They may have radicular symptoms down their arms. They may have an abnormal physical examination. They may have weakness on exam, but they’ll have a positive Hoffmann’s test where you flick the middle finger and look for flexion of the first finger and the thumb. They may have abnormal tandem gait, or patellar or Achilles hyperreflexia. Their neuro exam will not be normal much of the time, and in later cases because it’s upper motor neuron disease, they may even report urinary symptoms like urinary hesitancy or just a feeling of general unsteadiness of the gait, even though we’re at the cervical level. If you suspect myelopathy — and the trick is to think about it and recognize it when you see it — then you should send them for an MRI. If it persists or they have rapid regression, you get the MRI and refer them to neurosurgery. It’s not necessarily a neurosurgical emergency, but things should move along fairly briskly once you’ve actually identified it.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Mikula made the point that if someone comes to you in a wheelchair, they are probably not going to regain the ability to walk. You’re really trying to prevent progression. If they are already severely disabled, they’re probably not going to get totally back to full functioning, even with surgery. You’re just trying to prevent things from getting worse. That’s the main reason to identify this and get the patient to surgery.
We covered a lot more about neck pain. This was a very superficial review of what we talked about with Dr. Anthony Mikula. Click here to listen to the full podcast.
Matthew F. Watto is clinical assistant professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania, and internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams is associate professor of clinical medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine, and staff physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders; received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioids Post T&A
I recently encountered a study that reviewed return visits of pediatric patients after undergoing adenotonsillectomy. The investigators discovered that pain-related visits were higher for patients who had received prescriptions for opioids. After the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a boxed warning about the use of codeine in postoperative pediatric tonsillectomy with adenoidectomy (T&A), patients pain-related return visits declined and steroid prescriptions increased.
On the surface, this inverse relationship between opioid prescriptions and pain-related visits seems counterintuitive. This is particularly true if you believe that opioids are effective pain medications. The relationship between pain-related visits, steroid use, and the boxed warning is a bit easier to understand and most likely points to the effectiveness of the steroids.
Keeping in mind this was a single-institution study that included more than 5000 patients and more than 700 return visits, we should be careful in reading too much into these results. However, I can’t resist the temptation to use it as a springboard from which to launch a short dissertation on pain management.
First, let’s consider whether there was something about the opioids that was causing more pain for the patients. I’m not aware of any studies that suggest pain as a side effect of codeine. Nausea and vomiting, yes. And, although the investigators were focusing on pain, it may have been that the general discomfort associated with the gastrointestinal effects of the drug were lowering the patients’ pain threshold. I certainly know of many adults who have said that they now avoid opioids postoperatively because of the general sense of unwellness they have experienced during previous surgical adventures.
However, my bias leads me to focus on this question: If the patients didn’t receive opioids postoperatively, were they receiving something else that was making them less likely to arrive at the hospital or clinic complaining of pain? I assume the researchers would have told us about some new alternative miracle painkiller that was being prescribed.
As a card-carrying nihilist in good standing, I am tempted to claim that this is another example of nothing is better than most well-intentioned somethings. However, I am going to posit that these patients were receiving something that lessened their need to seek help with their pain.
Most likely that something was a thoughtful preemptive dialogue postoperatively about what they (and in most cases their parents) might expect in the way of symptoms. And ... an easy-to-reach contact point preferably with a person with whom they were familiar. And ... were scheduled to receive follow up phone calls at intervals relevant to the details of their surgery.
I know many of you are going to say, “We are already doing those things.” And, if so, you are to be commended. And, I’m sure that every outpatient postoperative manual includes all of those common-sense ingredients of good follow-up care. However, you know as well as I do that not all postoperative instructions are delivered with same degree of thoroughness nor with sufficient pauses thoughtfully delivered to make it a real dialogue. Nor is the follow-up contact person as easy to reach as promised.
I’m not sure how much we can thank the FDA boxed warning about codeine for the decrease in postoperative pain-generated visits. However, it could be that when physicians were discouraged from prescribing postoperative opioids, they may have felt the need to lean more heavily on good old-fashioned postoperative follow-up care. Instructions presented more as a dialogue and preemptive follow-up calls made with an aura of caring are well known deterrents of middle-of-the-night calls for help.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I recently encountered a study that reviewed return visits of pediatric patients after undergoing adenotonsillectomy. The investigators discovered that pain-related visits were higher for patients who had received prescriptions for opioids. After the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a boxed warning about the use of codeine in postoperative pediatric tonsillectomy with adenoidectomy (T&A), patients pain-related return visits declined and steroid prescriptions increased.
On the surface, this inverse relationship between opioid prescriptions and pain-related visits seems counterintuitive. This is particularly true if you believe that opioids are effective pain medications. The relationship between pain-related visits, steroid use, and the boxed warning is a bit easier to understand and most likely points to the effectiveness of the steroids.
Keeping in mind this was a single-institution study that included more than 5000 patients and more than 700 return visits, we should be careful in reading too much into these results. However, I can’t resist the temptation to use it as a springboard from which to launch a short dissertation on pain management.
First, let’s consider whether there was something about the opioids that was causing more pain for the patients. I’m not aware of any studies that suggest pain as a side effect of codeine. Nausea and vomiting, yes. And, although the investigators were focusing on pain, it may have been that the general discomfort associated with the gastrointestinal effects of the drug were lowering the patients’ pain threshold. I certainly know of many adults who have said that they now avoid opioids postoperatively because of the general sense of unwellness they have experienced during previous surgical adventures.
However, my bias leads me to focus on this question: If the patients didn’t receive opioids postoperatively, were they receiving something else that was making them less likely to arrive at the hospital or clinic complaining of pain? I assume the researchers would have told us about some new alternative miracle painkiller that was being prescribed.
As a card-carrying nihilist in good standing, I am tempted to claim that this is another example of nothing is better than most well-intentioned somethings. However, I am going to posit that these patients were receiving something that lessened their need to seek help with their pain.
Most likely that something was a thoughtful preemptive dialogue postoperatively about what they (and in most cases their parents) might expect in the way of symptoms. And ... an easy-to-reach contact point preferably with a person with whom they were familiar. And ... were scheduled to receive follow up phone calls at intervals relevant to the details of their surgery.
I know many of you are going to say, “We are already doing those things.” And, if so, you are to be commended. And, I’m sure that every outpatient postoperative manual includes all of those common-sense ingredients of good follow-up care. However, you know as well as I do that not all postoperative instructions are delivered with same degree of thoroughness nor with sufficient pauses thoughtfully delivered to make it a real dialogue. Nor is the follow-up contact person as easy to reach as promised.
I’m not sure how much we can thank the FDA boxed warning about codeine for the decrease in postoperative pain-generated visits. However, it could be that when physicians were discouraged from prescribing postoperative opioids, they may have felt the need to lean more heavily on good old-fashioned postoperative follow-up care. Instructions presented more as a dialogue and preemptive follow-up calls made with an aura of caring are well known deterrents of middle-of-the-night calls for help.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I recently encountered a study that reviewed return visits of pediatric patients after undergoing adenotonsillectomy. The investigators discovered that pain-related visits were higher for patients who had received prescriptions for opioids. After the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a boxed warning about the use of codeine in postoperative pediatric tonsillectomy with adenoidectomy (T&A), patients pain-related return visits declined and steroid prescriptions increased.
On the surface, this inverse relationship between opioid prescriptions and pain-related visits seems counterintuitive. This is particularly true if you believe that opioids are effective pain medications. The relationship between pain-related visits, steroid use, and the boxed warning is a bit easier to understand and most likely points to the effectiveness of the steroids.
Keeping in mind this was a single-institution study that included more than 5000 patients and more than 700 return visits, we should be careful in reading too much into these results. However, I can’t resist the temptation to use it as a springboard from which to launch a short dissertation on pain management.
First, let’s consider whether there was something about the opioids that was causing more pain for the patients. I’m not aware of any studies that suggest pain as a side effect of codeine. Nausea and vomiting, yes. And, although the investigators were focusing on pain, it may have been that the general discomfort associated with the gastrointestinal effects of the drug were lowering the patients’ pain threshold. I certainly know of many adults who have said that they now avoid opioids postoperatively because of the general sense of unwellness they have experienced during previous surgical adventures.
However, my bias leads me to focus on this question: If the patients didn’t receive opioids postoperatively, were they receiving something else that was making them less likely to arrive at the hospital or clinic complaining of pain? I assume the researchers would have told us about some new alternative miracle painkiller that was being prescribed.
As a card-carrying nihilist in good standing, I am tempted to claim that this is another example of nothing is better than most well-intentioned somethings. However, I am going to posit that these patients were receiving something that lessened their need to seek help with their pain.
Most likely that something was a thoughtful preemptive dialogue postoperatively about what they (and in most cases their parents) might expect in the way of symptoms. And ... an easy-to-reach contact point preferably with a person with whom they were familiar. And ... were scheduled to receive follow up phone calls at intervals relevant to the details of their surgery.
I know many of you are going to say, “We are already doing those things.” And, if so, you are to be commended. And, I’m sure that every outpatient postoperative manual includes all of those common-sense ingredients of good follow-up care. However, you know as well as I do that not all postoperative instructions are delivered with same degree of thoroughness nor with sufficient pauses thoughtfully delivered to make it a real dialogue. Nor is the follow-up contact person as easy to reach as promised.
I’m not sure how much we can thank the FDA boxed warning about codeine for the decrease in postoperative pain-generated visits. However, it could be that when physicians were discouraged from prescribing postoperative opioids, they may have felt the need to lean more heavily on good old-fashioned postoperative follow-up care. Instructions presented more as a dialogue and preemptive follow-up calls made with an aura of caring are well known deterrents of middle-of-the-night calls for help.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
‘The Oncologist Without the Pathologist Is Blind’: GI Cancer Updates at ASCO 2024
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m Mark Lewis, director of gastrointestinal (GI) oncology at Intermountain Health in Utah.
If you allow me, I’d like to go in a craniocaudal fashion. It’s my anatomic mnemonic. I think that’s appropriate because our plenary session yesterday kicked off with some exciting data in esophageal cancer, specifically esophageal adenocarcinoma.
This was the long-awaited ESOPEC trial. It’s a phase 3 study looking at perioperative FLOT (5-FU/leucovorin/oxaliplatin/docetaxel), a chemo triplet, vs the CROSS protocol, which is neoadjuvant chemoradiation with carboplatin and paclitaxel. The primary endpoint was overall survival, and at first blush, FLOT looked to be the true winner. There were some really remarkable milestones in this study, and I have some reservations about the FLOT arm that I’ll raise in just a second.
The investigators are to be commended because in a truly deadly disease, they reported a 5-year overall survival in half of the patients who were receiving FLOT. That is truly commendable and really a milestone in our field. The reason I take a little bit of issue with the trial is that I still have some questions about methodology.
It wasn’t that long ago at ASCO GI that there was a really heated debate called “FLOT or Not” — not in this precise setting, but asking the question, do we think that patients with upper GI malignancy are even fit enough to handle a chemo triplet like FLOT?
The reason I bring that up now in 2024 is that, to my surprise, and I think to many others’, there was a lower-than-expected completion rate of the patients in this trial who were receiving the CROSS regimen. The number of people who were able to complete that in full was about two-thirds, which compared with a historical control from a trial scheme that first emerged over a decade ago that used to be over 90% completion. I found that quite strange.
I also think this trial suffers a little bit, and unavoidably, from the evolution of care that’s happened since it was first enrolling. Of course, I refer to adjuvant immunotherapy. Now, the real question is whether there is synergy between patients who receive radiation upfront and then adjuvant nivolumab, as per CheckMate 577.
In her plenary discussion, I thought Dr. Karyn Goodman did a masterful job — I would encourage you to watch it on ASCO’s website —discussing how we can take all these data and reconcile them for optimal patient outcome. She ultimately suggested that we might deploy all four modalities in the management of these people.
She proposed a paradigm with a PET-adapted, upfront induction chemotherapy, then moving to chemoradiation, then moving to surgery, and finally moving to immunotherapy. That is all four of the traditional arms of oncology. I find that really rather remarkable. Watch that space. This is a great trial with really remarkable survival data, but I’m not entirely convinced that the CROSS arm was given its due.
Next up, I want to talk about pancreas cancer, which is something near and dear to my heart. It affects about one in four of my patients and it remains, unfortunately, a highly lethal disease. I think the top-line news from this meeting is that the KRAS mutation is druggable. I’m probably showing my age, but when I did my fellowship in 2009 through 2012, I was taught that KRAS was sort of the undruggable mutation par excellence. At this meeting, we’ve seen maturing data in regard to targeting KRAS G12C with both sotorasib and adagrasib. The disease control rates are astounding, at 80% and more, which is really remarkable. I wouldn’t have believed that even a few years ago.
I’m even more excited about how we bring a rising tide that can lift all boats and apply this to other KRAS mutations, and not just KRAS G12C but all KRAS mutations. I think that’s coming, hopefully, with the pan-RAS inhibitors, because once that happens — if that happens; I’ll try not to be irrationally exuberant — that would take the traditional mutation found in almost all pancreas cancers and really make it its own Achilles heel. I think that could be such a huge leap forward.
Another matter, however, that remains unresolved at this meeting is in the neoadjuvant setting with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. There’s still equipoise, actually, between neoadjuvant gemcitabine, paclitaxel, and FOLFIRINOX. I thought that that was very well spelled out by some of our Dutch colleagues, who continue to do great work in a variety of cancers, including colorectal.
Where I’d like to move next is colorectal cancer. Of course, immunotherapy remains a hot topic at all of these conferences. There were three different aspects of immunotherapy I’d like to highlight at this conference in regard to colon and rectal cancer.
First, Dr. Heinz-Josef Lenz presented updated data from CheckMate 8HW, which looked at nivolumab and ipilimumab (nivo/ipi) vs chemotherapy in the first line for MSI-high or mismatch repair–deficient colon cancer. Once again, the data we’ve had now for several years at the 2-year mark are incredibly impressive. The 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates for nivo/ipi are above 70% and down at around 14% for chemo.
What was impressive about this meeting is that Dr. Lenz presented PFS2, trying to determine the impact, if any, of subsequent therapy. What was going on here, which I think was ethically responsible by the investigators, was crossover. About two-thirds of the chemo arm crossed over to any form of immuno-oncology (IO), and just under a half crossed over to nivo and ipi. The PFS benefits continued with up-front IO. The way that Dr. Lenz phrased it is that you really never get the chance to win back the benefit that you would derive by giving immunotherapy first line to someone who has MSI-high or mismatch repair–deficient metastatic colon cancer.
One thing that’s still not settled in my mind, though, is, does this really dethrone single-agent immunotherapy, such as pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-177? What I’m really driving at is the ipilimumab. Is the juice worth the squeeze? Is the addition of an anti-CTLA4 agent worth the toxicity that we know comes along with that mechanism of action? Watch this space.
I was also really interested in NEOPRISM-CRC, which looked at the role of immunotherapy in neoadjuvant down-staging of radiographically high-risk stage II or stage III colon cancer. Here, the investigators really make a strong case that, up front in these potentially respectable cases, not only should we know about mismatch repair deficiency but we should actually be interrogating further for tumor mutational burden (TMB).
They had TMB-high patients. In fact, the median TMB was 42 mutations per megabase, with really impressive down-staging using three cycles of every-3-week pembrolizumab before surgery. Again, I really think we’re at an exciting time where, even for colon cancer that looks operable up front, we might actually have the opportunity to improve pathologic and clinical complete responses before and after surgery.
Finally, I want to bring up what continues to amaze me. Two years ago, at ASCO 2022, we heard from Dr. Andrea Cercek and the Memorial Sloan Kettering group about the incredible experience they were having with neoadjuvant, or frankly, definitive dostarlimab in mismatch repair–deficient locally advanced rectal cancer.
I remember being at the conference and there was simultaneous publication of that abstract in The New York Times because it was so remarkable. There was a 100% clinical complete response. The patients didn’t require radiation, they didn’t require chemotherapy, and they didn’t require surgery for locally advanced rectal cancer, provided there was this vulnerability of mismatch-repair deficiency.
Now, 2 years later, Dr. Cercek and her group have updated those data with more than 40 patients, and again, a 100% clinical complete response, including mature, complete responses at over a year in about 20 patients. Again, we are really doing our rectal cancer patients a disservice if we’re not checking for mismatch-repair deficiency upfront, and especially if we’re not talking about them in multidisciplinary conferences.
One of the things that absolutely blows my mind about rectal cancer is just how complicated it’s becoming. I think it is the standard of care to discuss these cases upfront with radiation oncology, surgical oncology, medical oncology, and pathology.
Maybe the overarching message I would take from everything I’ve said today is that the oncologist without the pathologist is blind. It’s really a dyad, a partnership that guides optimal medical oncology care. As much as I love ASCO, I often wish we had more of our pathology colleagues here. I look forward to taking all the findings from this meeting back to the tumor board and really having a dynamic dialogue.
Dr. Lewis is director, Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Intermountain Health, Salt Lake City, Utah. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m Mark Lewis, director of gastrointestinal (GI) oncology at Intermountain Health in Utah.
If you allow me, I’d like to go in a craniocaudal fashion. It’s my anatomic mnemonic. I think that’s appropriate because our plenary session yesterday kicked off with some exciting data in esophageal cancer, specifically esophageal adenocarcinoma.
This was the long-awaited ESOPEC trial. It’s a phase 3 study looking at perioperative FLOT (5-FU/leucovorin/oxaliplatin/docetaxel), a chemo triplet, vs the CROSS protocol, which is neoadjuvant chemoradiation with carboplatin and paclitaxel. The primary endpoint was overall survival, and at first blush, FLOT looked to be the true winner. There were some really remarkable milestones in this study, and I have some reservations about the FLOT arm that I’ll raise in just a second.
The investigators are to be commended because in a truly deadly disease, they reported a 5-year overall survival in half of the patients who were receiving FLOT. That is truly commendable and really a milestone in our field. The reason I take a little bit of issue with the trial is that I still have some questions about methodology.
It wasn’t that long ago at ASCO GI that there was a really heated debate called “FLOT or Not” — not in this precise setting, but asking the question, do we think that patients with upper GI malignancy are even fit enough to handle a chemo triplet like FLOT?
The reason I bring that up now in 2024 is that, to my surprise, and I think to many others’, there was a lower-than-expected completion rate of the patients in this trial who were receiving the CROSS regimen. The number of people who were able to complete that in full was about two-thirds, which compared with a historical control from a trial scheme that first emerged over a decade ago that used to be over 90% completion. I found that quite strange.
I also think this trial suffers a little bit, and unavoidably, from the evolution of care that’s happened since it was first enrolling. Of course, I refer to adjuvant immunotherapy. Now, the real question is whether there is synergy between patients who receive radiation upfront and then adjuvant nivolumab, as per CheckMate 577.
In her plenary discussion, I thought Dr. Karyn Goodman did a masterful job — I would encourage you to watch it on ASCO’s website —discussing how we can take all these data and reconcile them for optimal patient outcome. She ultimately suggested that we might deploy all four modalities in the management of these people.
She proposed a paradigm with a PET-adapted, upfront induction chemotherapy, then moving to chemoradiation, then moving to surgery, and finally moving to immunotherapy. That is all four of the traditional arms of oncology. I find that really rather remarkable. Watch that space. This is a great trial with really remarkable survival data, but I’m not entirely convinced that the CROSS arm was given its due.
Next up, I want to talk about pancreas cancer, which is something near and dear to my heart. It affects about one in four of my patients and it remains, unfortunately, a highly lethal disease. I think the top-line news from this meeting is that the KRAS mutation is druggable. I’m probably showing my age, but when I did my fellowship in 2009 through 2012, I was taught that KRAS was sort of the undruggable mutation par excellence. At this meeting, we’ve seen maturing data in regard to targeting KRAS G12C with both sotorasib and adagrasib. The disease control rates are astounding, at 80% and more, which is really remarkable. I wouldn’t have believed that even a few years ago.
I’m even more excited about how we bring a rising tide that can lift all boats and apply this to other KRAS mutations, and not just KRAS G12C but all KRAS mutations. I think that’s coming, hopefully, with the pan-RAS inhibitors, because once that happens — if that happens; I’ll try not to be irrationally exuberant — that would take the traditional mutation found in almost all pancreas cancers and really make it its own Achilles heel. I think that could be such a huge leap forward.
Another matter, however, that remains unresolved at this meeting is in the neoadjuvant setting with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. There’s still equipoise, actually, between neoadjuvant gemcitabine, paclitaxel, and FOLFIRINOX. I thought that that was very well spelled out by some of our Dutch colleagues, who continue to do great work in a variety of cancers, including colorectal.
Where I’d like to move next is colorectal cancer. Of course, immunotherapy remains a hot topic at all of these conferences. There were three different aspects of immunotherapy I’d like to highlight at this conference in regard to colon and rectal cancer.
First, Dr. Heinz-Josef Lenz presented updated data from CheckMate 8HW, which looked at nivolumab and ipilimumab (nivo/ipi) vs chemotherapy in the first line for MSI-high or mismatch repair–deficient colon cancer. Once again, the data we’ve had now for several years at the 2-year mark are incredibly impressive. The 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates for nivo/ipi are above 70% and down at around 14% for chemo.
What was impressive about this meeting is that Dr. Lenz presented PFS2, trying to determine the impact, if any, of subsequent therapy. What was going on here, which I think was ethically responsible by the investigators, was crossover. About two-thirds of the chemo arm crossed over to any form of immuno-oncology (IO), and just under a half crossed over to nivo and ipi. The PFS benefits continued with up-front IO. The way that Dr. Lenz phrased it is that you really never get the chance to win back the benefit that you would derive by giving immunotherapy first line to someone who has MSI-high or mismatch repair–deficient metastatic colon cancer.
One thing that’s still not settled in my mind, though, is, does this really dethrone single-agent immunotherapy, such as pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-177? What I’m really driving at is the ipilimumab. Is the juice worth the squeeze? Is the addition of an anti-CTLA4 agent worth the toxicity that we know comes along with that mechanism of action? Watch this space.
I was also really interested in NEOPRISM-CRC, which looked at the role of immunotherapy in neoadjuvant down-staging of radiographically high-risk stage II or stage III colon cancer. Here, the investigators really make a strong case that, up front in these potentially respectable cases, not only should we know about mismatch repair deficiency but we should actually be interrogating further for tumor mutational burden (TMB).
They had TMB-high patients. In fact, the median TMB was 42 mutations per megabase, with really impressive down-staging using three cycles of every-3-week pembrolizumab before surgery. Again, I really think we’re at an exciting time where, even for colon cancer that looks operable up front, we might actually have the opportunity to improve pathologic and clinical complete responses before and after surgery.
Finally, I want to bring up what continues to amaze me. Two years ago, at ASCO 2022, we heard from Dr. Andrea Cercek and the Memorial Sloan Kettering group about the incredible experience they were having with neoadjuvant, or frankly, definitive dostarlimab in mismatch repair–deficient locally advanced rectal cancer.
I remember being at the conference and there was simultaneous publication of that abstract in The New York Times because it was so remarkable. There was a 100% clinical complete response. The patients didn’t require radiation, they didn’t require chemotherapy, and they didn’t require surgery for locally advanced rectal cancer, provided there was this vulnerability of mismatch-repair deficiency.
Now, 2 years later, Dr. Cercek and her group have updated those data with more than 40 patients, and again, a 100% clinical complete response, including mature, complete responses at over a year in about 20 patients. Again, we are really doing our rectal cancer patients a disservice if we’re not checking for mismatch-repair deficiency upfront, and especially if we’re not talking about them in multidisciplinary conferences.
One of the things that absolutely blows my mind about rectal cancer is just how complicated it’s becoming. I think it is the standard of care to discuss these cases upfront with radiation oncology, surgical oncology, medical oncology, and pathology.
Maybe the overarching message I would take from everything I’ve said today is that the oncologist without the pathologist is blind. It’s really a dyad, a partnership that guides optimal medical oncology care. As much as I love ASCO, I often wish we had more of our pathology colleagues here. I look forward to taking all the findings from this meeting back to the tumor board and really having a dynamic dialogue.
Dr. Lewis is director, Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Intermountain Health, Salt Lake City, Utah. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m Mark Lewis, director of gastrointestinal (GI) oncology at Intermountain Health in Utah.
If you allow me, I’d like to go in a craniocaudal fashion. It’s my anatomic mnemonic. I think that’s appropriate because our plenary session yesterday kicked off with some exciting data in esophageal cancer, specifically esophageal adenocarcinoma.
This was the long-awaited ESOPEC trial. It’s a phase 3 study looking at perioperative FLOT (5-FU/leucovorin/oxaliplatin/docetaxel), a chemo triplet, vs the CROSS protocol, which is neoadjuvant chemoradiation with carboplatin and paclitaxel. The primary endpoint was overall survival, and at first blush, FLOT looked to be the true winner. There were some really remarkable milestones in this study, and I have some reservations about the FLOT arm that I’ll raise in just a second.
The investigators are to be commended because in a truly deadly disease, they reported a 5-year overall survival in half of the patients who were receiving FLOT. That is truly commendable and really a milestone in our field. The reason I take a little bit of issue with the trial is that I still have some questions about methodology.
It wasn’t that long ago at ASCO GI that there was a really heated debate called “FLOT or Not” — not in this precise setting, but asking the question, do we think that patients with upper GI malignancy are even fit enough to handle a chemo triplet like FLOT?
The reason I bring that up now in 2024 is that, to my surprise, and I think to many others’, there was a lower-than-expected completion rate of the patients in this trial who were receiving the CROSS regimen. The number of people who were able to complete that in full was about two-thirds, which compared with a historical control from a trial scheme that first emerged over a decade ago that used to be over 90% completion. I found that quite strange.
I also think this trial suffers a little bit, and unavoidably, from the evolution of care that’s happened since it was first enrolling. Of course, I refer to adjuvant immunotherapy. Now, the real question is whether there is synergy between patients who receive radiation upfront and then adjuvant nivolumab, as per CheckMate 577.
In her plenary discussion, I thought Dr. Karyn Goodman did a masterful job — I would encourage you to watch it on ASCO’s website —discussing how we can take all these data and reconcile them for optimal patient outcome. She ultimately suggested that we might deploy all four modalities in the management of these people.
She proposed a paradigm with a PET-adapted, upfront induction chemotherapy, then moving to chemoradiation, then moving to surgery, and finally moving to immunotherapy. That is all four of the traditional arms of oncology. I find that really rather remarkable. Watch that space. This is a great trial with really remarkable survival data, but I’m not entirely convinced that the CROSS arm was given its due.
Next up, I want to talk about pancreas cancer, which is something near and dear to my heart. It affects about one in four of my patients and it remains, unfortunately, a highly lethal disease. I think the top-line news from this meeting is that the KRAS mutation is druggable. I’m probably showing my age, but when I did my fellowship in 2009 through 2012, I was taught that KRAS was sort of the undruggable mutation par excellence. At this meeting, we’ve seen maturing data in regard to targeting KRAS G12C with both sotorasib and adagrasib. The disease control rates are astounding, at 80% and more, which is really remarkable. I wouldn’t have believed that even a few years ago.
I’m even more excited about how we bring a rising tide that can lift all boats and apply this to other KRAS mutations, and not just KRAS G12C but all KRAS mutations. I think that’s coming, hopefully, with the pan-RAS inhibitors, because once that happens — if that happens; I’ll try not to be irrationally exuberant — that would take the traditional mutation found in almost all pancreas cancers and really make it its own Achilles heel. I think that could be such a huge leap forward.
Another matter, however, that remains unresolved at this meeting is in the neoadjuvant setting with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. There’s still equipoise, actually, between neoadjuvant gemcitabine, paclitaxel, and FOLFIRINOX. I thought that that was very well spelled out by some of our Dutch colleagues, who continue to do great work in a variety of cancers, including colorectal.
Where I’d like to move next is colorectal cancer. Of course, immunotherapy remains a hot topic at all of these conferences. There were three different aspects of immunotherapy I’d like to highlight at this conference in regard to colon and rectal cancer.
First, Dr. Heinz-Josef Lenz presented updated data from CheckMate 8HW, which looked at nivolumab and ipilimumab (nivo/ipi) vs chemotherapy in the first line for MSI-high or mismatch repair–deficient colon cancer. Once again, the data we’ve had now for several years at the 2-year mark are incredibly impressive. The 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates for nivo/ipi are above 70% and down at around 14% for chemo.
What was impressive about this meeting is that Dr. Lenz presented PFS2, trying to determine the impact, if any, of subsequent therapy. What was going on here, which I think was ethically responsible by the investigators, was crossover. About two-thirds of the chemo arm crossed over to any form of immuno-oncology (IO), and just under a half crossed over to nivo and ipi. The PFS benefits continued with up-front IO. The way that Dr. Lenz phrased it is that you really never get the chance to win back the benefit that you would derive by giving immunotherapy first line to someone who has MSI-high or mismatch repair–deficient metastatic colon cancer.
One thing that’s still not settled in my mind, though, is, does this really dethrone single-agent immunotherapy, such as pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-177? What I’m really driving at is the ipilimumab. Is the juice worth the squeeze? Is the addition of an anti-CTLA4 agent worth the toxicity that we know comes along with that mechanism of action? Watch this space.
I was also really interested in NEOPRISM-CRC, which looked at the role of immunotherapy in neoadjuvant down-staging of radiographically high-risk stage II or stage III colon cancer. Here, the investigators really make a strong case that, up front in these potentially respectable cases, not only should we know about mismatch repair deficiency but we should actually be interrogating further for tumor mutational burden (TMB).
They had TMB-high patients. In fact, the median TMB was 42 mutations per megabase, with really impressive down-staging using three cycles of every-3-week pembrolizumab before surgery. Again, I really think we’re at an exciting time where, even for colon cancer that looks operable up front, we might actually have the opportunity to improve pathologic and clinical complete responses before and after surgery.
Finally, I want to bring up what continues to amaze me. Two years ago, at ASCO 2022, we heard from Dr. Andrea Cercek and the Memorial Sloan Kettering group about the incredible experience they were having with neoadjuvant, or frankly, definitive dostarlimab in mismatch repair–deficient locally advanced rectal cancer.
I remember being at the conference and there was simultaneous publication of that abstract in The New York Times because it was so remarkable. There was a 100% clinical complete response. The patients didn’t require radiation, they didn’t require chemotherapy, and they didn’t require surgery for locally advanced rectal cancer, provided there was this vulnerability of mismatch-repair deficiency.
Now, 2 years later, Dr. Cercek and her group have updated those data with more than 40 patients, and again, a 100% clinical complete response, including mature, complete responses at over a year in about 20 patients. Again, we are really doing our rectal cancer patients a disservice if we’re not checking for mismatch-repair deficiency upfront, and especially if we’re not talking about them in multidisciplinary conferences.
One of the things that absolutely blows my mind about rectal cancer is just how complicated it’s becoming. I think it is the standard of care to discuss these cases upfront with radiation oncology, surgical oncology, medical oncology, and pathology.
Maybe the overarching message I would take from everything I’ve said today is that the oncologist without the pathologist is blind. It’s really a dyad, a partnership that guides optimal medical oncology care. As much as I love ASCO, I often wish we had more of our pathology colleagues here. I look forward to taking all the findings from this meeting back to the tumor board and really having a dynamic dialogue.
Dr. Lewis is director, Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Intermountain Health, Salt Lake City, Utah. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An Overview of Gender-Affirming Care for Children and Adolescents
As Pride Month drew to a close, the Supreme Court made a shocking announcement. For the first time in the history of the court, it is willing to hear a legal challenge regarding gender-affirming care for minors. The justices will review whether a 2023 Tennessee law, SB1, which bans hormone therapy, puberty blockers, and surgery for transgender minors, is unconstitutional. This is the first time the Supreme Court will directly weigh in on gender-affirming care.
There are few topics as politically and medically divisive as gender-affirming care for minors. When the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) released its updated Standards of Care, SOC8, one of the noticeable changes to the document was its approach to caring for transgender children and adolescents.
Before I highlight these recommendations and the ensuing controversy, it is imperative to establish proper terminology. Unfortunately, medical and legal terms often differ. Both activists and opponents use these terms interchangeably, which makes discourse about an already emotionally charged topic extremely difficult. From a legal perspective, the terms “minor” and “child” often refer to individuals under the age of majority. In the United States, the age of majority is 18. However, the term child also has a well-established medical definition. A child is an individual between the stages of infancy and puberty. Adolescence is a transitional period marked by the onset of puberty until adulthood (typically the age of majority). As medical providers, understanding these definitions is essential to identifying misinformation pertaining to this type of healthcare.
For the purposes of this article, I will be adhering to the medical terminology. Now, I want to be very clear. WPATH does not endorse surgical procedures on children. Furthermore, surgeons are not performing gender-affirming surgeries on children. On adolescents, rarely. But children, never.
According to the updated SOC8, the only acceptable gender-affirming intervention for children is psychosocial support.1 This does not include puberty blockers, hormones, or surgery, but rather allowing a child to explore their gender identity by experimenting with different clothing, toys, hairstyles, and even an alternative name that aligns more closely with their gender identity.1
It is only after children reach adolescence that medical, and in rare cases, surgical interventions, can be considered. Puberty blockers are appropriate for patients who have started puberty and experience gender dysphoria. These medications are reversible, and their purpose is to temporarily pause puberty to allow the adolescent to further explore their gender identity.
The most significant side effect of puberty blockers is decreased bone density.1 As a result, providers typically do not prescribe these medications for more than 2-3 years. After discontinuation of the medication, bone density returns to baseline.1 If the adolescent’s gender identity is marked and sustained over time, hormone therapy, such as testosterone or estrogen is then considered. Unlike puberty blockers, these medications can have permanent side effects. Testosterone use can lead to irreversible hair growth, alopecia, clitoromegaly, and voice deepening, while estrogen can cause permanent breast growth and halt sperm production.1 Future fertility and these side effects are discussed with the patient in detail prior to the initiation of these medications.
Contrary to the current political narrative, gender-affirming care for children and adolescents is not taken lightly. These individuals often receive years of multidisciplinary assessments, with a focus on gender identity development, social development and support, and diagnostic assessment of possible co-occurring mental health or developmental concerns and capacity for decision making.1 The clinical visits also occur with parental support and consent.
WPATH SOC8 also delineates the provider qualifications for health care professionals assessing these patients. Providers must be licensed by their statutory bodies and hold a postgraduate degree by a nationally accredited statutory institution; receive theoretical and evidence-based training and develop expertise in child, adolescent, and family mental health across the developmental spectrum; receive training and have expertise in gender identity development and gender diversity in children and adolescence; have the ability to assess capacity to assent/consent; receive training and develop expertise in autism spectrum disorders and other neurodevelopmental presentations; and to continue engaging in professional development in all areas relevant to gender-diverse children, adolescents, and families.1
The most controversial aspect of gender-affirming care for children and adolescents relates to surgical treatment. While the rates of gender-affirming surgeries have increased for this age group over the years, the overall rate of gender-affirming surgery for adolescents is markedly lower compared with other adolescents seeking cosmetic surgeries and compared with transgender adults undergoing gender-affirming surgery.
In a cohort study conducted between 2016 to 2020, 48,019 patients were identified who had undergone gender-affirming surgery.2 Only 3678 or 7.7% of patients were aged between 12 and 18, with the most common procedure being chest/breast surgery.2 So, under about 1000 cases per year were gender-affirming surgeries on patients under 18.
During 2020 alone, the number of cisgender adolescents between the ages of 13 and 19 who underwent breast augmentation and breast reduction was 3233 and 4666, respectively.3 The outrage about gender-affirming surgeries on transgender youth, yet the silence on cosmetic procedures in this same age group, speaks volumes.
All surgeries on adolescents should be taken seriously and with caution, regardless of gender identity. However, current legislation disproportionately targets only transgender youth. For whatever reason, surgeries on transgender individuals are labeled as “body mutilation,” whereas surgeries on cisgender youth are not even discussed. Such inflammatory rhetoric and complete lack of empathy impedes the common goal of all parties: what is in the best interest of the minor? Unfortunately, in a few short months, the answer to this question will be determined by a group of nine justices who have no experience in medicine or transgender health care, instead of by medical experts and the parents who care for these individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pennsylvania. She has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Coleman E et al. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, version 8. Int J Transgender Health. 2022;23(sup):S1-S259.
2. Wright JD et al. National estimates of gender affirming surgery in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Aug 1;6(8):e2330348.
3. American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Plastic Surgery Statistics Report. ASPS National Clearinghouse of Plastic Surgery Procedural Statistics. 2020.
As Pride Month drew to a close, the Supreme Court made a shocking announcement. For the first time in the history of the court, it is willing to hear a legal challenge regarding gender-affirming care for minors. The justices will review whether a 2023 Tennessee law, SB1, which bans hormone therapy, puberty blockers, and surgery for transgender minors, is unconstitutional. This is the first time the Supreme Court will directly weigh in on gender-affirming care.
There are few topics as politically and medically divisive as gender-affirming care for minors. When the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) released its updated Standards of Care, SOC8, one of the noticeable changes to the document was its approach to caring for transgender children and adolescents.
Before I highlight these recommendations and the ensuing controversy, it is imperative to establish proper terminology. Unfortunately, medical and legal terms often differ. Both activists and opponents use these terms interchangeably, which makes discourse about an already emotionally charged topic extremely difficult. From a legal perspective, the terms “minor” and “child” often refer to individuals under the age of majority. In the United States, the age of majority is 18. However, the term child also has a well-established medical definition. A child is an individual between the stages of infancy and puberty. Adolescence is a transitional period marked by the onset of puberty until adulthood (typically the age of majority). As medical providers, understanding these definitions is essential to identifying misinformation pertaining to this type of healthcare.
For the purposes of this article, I will be adhering to the medical terminology. Now, I want to be very clear. WPATH does not endorse surgical procedures on children. Furthermore, surgeons are not performing gender-affirming surgeries on children. On adolescents, rarely. But children, never.
According to the updated SOC8, the only acceptable gender-affirming intervention for children is psychosocial support.1 This does not include puberty blockers, hormones, or surgery, but rather allowing a child to explore their gender identity by experimenting with different clothing, toys, hairstyles, and even an alternative name that aligns more closely with their gender identity.1
It is only after children reach adolescence that medical, and in rare cases, surgical interventions, can be considered. Puberty blockers are appropriate for patients who have started puberty and experience gender dysphoria. These medications are reversible, and their purpose is to temporarily pause puberty to allow the adolescent to further explore their gender identity.
The most significant side effect of puberty blockers is decreased bone density.1 As a result, providers typically do not prescribe these medications for more than 2-3 years. After discontinuation of the medication, bone density returns to baseline.1 If the adolescent’s gender identity is marked and sustained over time, hormone therapy, such as testosterone or estrogen is then considered. Unlike puberty blockers, these medications can have permanent side effects. Testosterone use can lead to irreversible hair growth, alopecia, clitoromegaly, and voice deepening, while estrogen can cause permanent breast growth and halt sperm production.1 Future fertility and these side effects are discussed with the patient in detail prior to the initiation of these medications.
Contrary to the current political narrative, gender-affirming care for children and adolescents is not taken lightly. These individuals often receive years of multidisciplinary assessments, with a focus on gender identity development, social development and support, and diagnostic assessment of possible co-occurring mental health or developmental concerns and capacity for decision making.1 The clinical visits also occur with parental support and consent.
WPATH SOC8 also delineates the provider qualifications for health care professionals assessing these patients. Providers must be licensed by their statutory bodies and hold a postgraduate degree by a nationally accredited statutory institution; receive theoretical and evidence-based training and develop expertise in child, adolescent, and family mental health across the developmental spectrum; receive training and have expertise in gender identity development and gender diversity in children and adolescence; have the ability to assess capacity to assent/consent; receive training and develop expertise in autism spectrum disorders and other neurodevelopmental presentations; and to continue engaging in professional development in all areas relevant to gender-diverse children, adolescents, and families.1
The most controversial aspect of gender-affirming care for children and adolescents relates to surgical treatment. While the rates of gender-affirming surgeries have increased for this age group over the years, the overall rate of gender-affirming surgery for adolescents is markedly lower compared with other adolescents seeking cosmetic surgeries and compared with transgender adults undergoing gender-affirming surgery.
In a cohort study conducted between 2016 to 2020, 48,019 patients were identified who had undergone gender-affirming surgery.2 Only 3678 or 7.7% of patients were aged between 12 and 18, with the most common procedure being chest/breast surgery.2 So, under about 1000 cases per year were gender-affirming surgeries on patients under 18.
During 2020 alone, the number of cisgender adolescents between the ages of 13 and 19 who underwent breast augmentation and breast reduction was 3233 and 4666, respectively.3 The outrage about gender-affirming surgeries on transgender youth, yet the silence on cosmetic procedures in this same age group, speaks volumes.
All surgeries on adolescents should be taken seriously and with caution, regardless of gender identity. However, current legislation disproportionately targets only transgender youth. For whatever reason, surgeries on transgender individuals are labeled as “body mutilation,” whereas surgeries on cisgender youth are not even discussed. Such inflammatory rhetoric and complete lack of empathy impedes the common goal of all parties: what is in the best interest of the minor? Unfortunately, in a few short months, the answer to this question will be determined by a group of nine justices who have no experience in medicine or transgender health care, instead of by medical experts and the parents who care for these individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pennsylvania. She has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Coleman E et al. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, version 8. Int J Transgender Health. 2022;23(sup):S1-S259.
2. Wright JD et al. National estimates of gender affirming surgery in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Aug 1;6(8):e2330348.
3. American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Plastic Surgery Statistics Report. ASPS National Clearinghouse of Plastic Surgery Procedural Statistics. 2020.
As Pride Month drew to a close, the Supreme Court made a shocking announcement. For the first time in the history of the court, it is willing to hear a legal challenge regarding gender-affirming care for minors. The justices will review whether a 2023 Tennessee law, SB1, which bans hormone therapy, puberty blockers, and surgery for transgender minors, is unconstitutional. This is the first time the Supreme Court will directly weigh in on gender-affirming care.
There are few topics as politically and medically divisive as gender-affirming care for minors. When the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) released its updated Standards of Care, SOC8, one of the noticeable changes to the document was its approach to caring for transgender children and adolescents.
Before I highlight these recommendations and the ensuing controversy, it is imperative to establish proper terminology. Unfortunately, medical and legal terms often differ. Both activists and opponents use these terms interchangeably, which makes discourse about an already emotionally charged topic extremely difficult. From a legal perspective, the terms “minor” and “child” often refer to individuals under the age of majority. In the United States, the age of majority is 18. However, the term child also has a well-established medical definition. A child is an individual between the stages of infancy and puberty. Adolescence is a transitional period marked by the onset of puberty until adulthood (typically the age of majority). As medical providers, understanding these definitions is essential to identifying misinformation pertaining to this type of healthcare.
For the purposes of this article, I will be adhering to the medical terminology. Now, I want to be very clear. WPATH does not endorse surgical procedures on children. Furthermore, surgeons are not performing gender-affirming surgeries on children. On adolescents, rarely. But children, never.
According to the updated SOC8, the only acceptable gender-affirming intervention for children is psychosocial support.1 This does not include puberty blockers, hormones, or surgery, but rather allowing a child to explore their gender identity by experimenting with different clothing, toys, hairstyles, and even an alternative name that aligns more closely with their gender identity.1
It is only after children reach adolescence that medical, and in rare cases, surgical interventions, can be considered. Puberty blockers are appropriate for patients who have started puberty and experience gender dysphoria. These medications are reversible, and their purpose is to temporarily pause puberty to allow the adolescent to further explore their gender identity.
The most significant side effect of puberty blockers is decreased bone density.1 As a result, providers typically do not prescribe these medications for more than 2-3 years. After discontinuation of the medication, bone density returns to baseline.1 If the adolescent’s gender identity is marked and sustained over time, hormone therapy, such as testosterone or estrogen is then considered. Unlike puberty blockers, these medications can have permanent side effects. Testosterone use can lead to irreversible hair growth, alopecia, clitoromegaly, and voice deepening, while estrogen can cause permanent breast growth and halt sperm production.1 Future fertility and these side effects are discussed with the patient in detail prior to the initiation of these medications.
Contrary to the current political narrative, gender-affirming care for children and adolescents is not taken lightly. These individuals often receive years of multidisciplinary assessments, with a focus on gender identity development, social development and support, and diagnostic assessment of possible co-occurring mental health or developmental concerns and capacity for decision making.1 The clinical visits also occur with parental support and consent.
WPATH SOC8 also delineates the provider qualifications for health care professionals assessing these patients. Providers must be licensed by their statutory bodies and hold a postgraduate degree by a nationally accredited statutory institution; receive theoretical and evidence-based training and develop expertise in child, adolescent, and family mental health across the developmental spectrum; receive training and have expertise in gender identity development and gender diversity in children and adolescence; have the ability to assess capacity to assent/consent; receive training and develop expertise in autism spectrum disorders and other neurodevelopmental presentations; and to continue engaging in professional development in all areas relevant to gender-diverse children, adolescents, and families.1
The most controversial aspect of gender-affirming care for children and adolescents relates to surgical treatment. While the rates of gender-affirming surgeries have increased for this age group over the years, the overall rate of gender-affirming surgery for adolescents is markedly lower compared with other adolescents seeking cosmetic surgeries and compared with transgender adults undergoing gender-affirming surgery.
In a cohort study conducted between 2016 to 2020, 48,019 patients were identified who had undergone gender-affirming surgery.2 Only 3678 or 7.7% of patients were aged between 12 and 18, with the most common procedure being chest/breast surgery.2 So, under about 1000 cases per year were gender-affirming surgeries on patients under 18.
During 2020 alone, the number of cisgender adolescents between the ages of 13 and 19 who underwent breast augmentation and breast reduction was 3233 and 4666, respectively.3 The outrage about gender-affirming surgeries on transgender youth, yet the silence on cosmetic procedures in this same age group, speaks volumes.
All surgeries on adolescents should be taken seriously and with caution, regardless of gender identity. However, current legislation disproportionately targets only transgender youth. For whatever reason, surgeries on transgender individuals are labeled as “body mutilation,” whereas surgeries on cisgender youth are not even discussed. Such inflammatory rhetoric and complete lack of empathy impedes the common goal of all parties: what is in the best interest of the minor? Unfortunately, in a few short months, the answer to this question will be determined by a group of nine justices who have no experience in medicine or transgender health care, instead of by medical experts and the parents who care for these individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pennsylvania. She has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Coleman E et al. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, version 8. Int J Transgender Health. 2022;23(sup):S1-S259.
2. Wright JD et al. National estimates of gender affirming surgery in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Aug 1;6(8):e2330348.
3. American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Plastic Surgery Statistics Report. ASPS National Clearinghouse of Plastic Surgery Procedural Statistics. 2020.
Another Social Media Snowball
Recently, the British Journal of General Practice published a paper that claimed that anxiety may be a prodromal feature of Parkinson’s disease). That news was widely picked up and spread.
The researchers certainly have some interesting data, but this sort of article, once enough general and social media websites get a hold of it, is bound to cause panic in the streets. And phone calls to my office.
An anxious-by-nature friend even emailed me the link with a laconic “Well, I’m screwed” in the subject line.
Is there a correlation between Parkinson’s disease and anxiety? Probably. Any of us practicing neurology have seen it. Some of it is likely from the anxiety of the situation, but the biochemical changes brought by the disease are also likely a big part.
But does that mean everyone with anxiety has Parkinson’s disease? Of course not. Anxiety is common, probably more common in our current era than ever before (this is why I tell patients not to watch the news and to avoid social media — they’re bad for your sanity and blood pressure).
Stories like this, once they start getting forwarded on Facebook (or another social media outlet), only raise anxiety, which results in more forwarding, and the snowball begins rolling downhill before crashing into my office (obviously this is a figure of speech, as it’s July in Phoenix).
The research is interesting. The point is valid. But the leaps the public makes are ... problematic. It’s only a matter of time before someone comes in demanding a DaT scan because they’re anxious. At $4K a test, that’s not happening.
Which raises anxiety all around.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Recently, the British Journal of General Practice published a paper that claimed that anxiety may be a prodromal feature of Parkinson’s disease). That news was widely picked up and spread.
The researchers certainly have some interesting data, but this sort of article, once enough general and social media websites get a hold of it, is bound to cause panic in the streets. And phone calls to my office.
An anxious-by-nature friend even emailed me the link with a laconic “Well, I’m screwed” in the subject line.
Is there a correlation between Parkinson’s disease and anxiety? Probably. Any of us practicing neurology have seen it. Some of it is likely from the anxiety of the situation, but the biochemical changes brought by the disease are also likely a big part.
But does that mean everyone with anxiety has Parkinson’s disease? Of course not. Anxiety is common, probably more common in our current era than ever before (this is why I tell patients not to watch the news and to avoid social media — they’re bad for your sanity and blood pressure).
Stories like this, once they start getting forwarded on Facebook (or another social media outlet), only raise anxiety, which results in more forwarding, and the snowball begins rolling downhill before crashing into my office (obviously this is a figure of speech, as it’s July in Phoenix).
The research is interesting. The point is valid. But the leaps the public makes are ... problematic. It’s only a matter of time before someone comes in demanding a DaT scan because they’re anxious. At $4K a test, that’s not happening.
Which raises anxiety all around.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Recently, the British Journal of General Practice published a paper that claimed that anxiety may be a prodromal feature of Parkinson’s disease). That news was widely picked up and spread.
The researchers certainly have some interesting data, but this sort of article, once enough general and social media websites get a hold of it, is bound to cause panic in the streets. And phone calls to my office.
An anxious-by-nature friend even emailed me the link with a laconic “Well, I’m screwed” in the subject line.
Is there a correlation between Parkinson’s disease and anxiety? Probably. Any of us practicing neurology have seen it. Some of it is likely from the anxiety of the situation, but the biochemical changes brought by the disease are also likely a big part.
But does that mean everyone with anxiety has Parkinson’s disease? Of course not. Anxiety is common, probably more common in our current era than ever before (this is why I tell patients not to watch the news and to avoid social media — they’re bad for your sanity and blood pressure).
Stories like this, once they start getting forwarded on Facebook (or another social media outlet), only raise anxiety, which results in more forwarding, and the snowball begins rolling downhill before crashing into my office (obviously this is a figure of speech, as it’s July in Phoenix).
The research is interesting. The point is valid. But the leaps the public makes are ... problematic. It’s only a matter of time before someone comes in demanding a DaT scan because they’re anxious. At $4K a test, that’s not happening.
Which raises anxiety all around.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Should South Park: The End of Obesity Be Required Viewing in Medical School?
Yes, there’s still much to find offensive, but South Park: The End of Obesity, in just 51 minutes, does more to explain some of obesity’s realities, its pharmacotherapy, and weight bias than the mainstream media has done perhaps ever.
The mini-movie follows the plight of Eric Cartman, the fictional South Parkian child with severe obesity.
South Park got everything right. The movie starts in a medical center where discussions with Cartman, his mother, and his doctor make it clear that obesity isn’t something that Cartman chose and is perhaps the most distressing aspect of his life. This certainly echoes study findings which report that quality-of-life scores in children with severe obesity are lower than those of children with newly diagnosed on-treatment cancers. As to how obesity erodes a child’s quality of life, no doubt part of its impact stems from obesity being a top source of schoolyard bullying, which is reflected by Cartman as he imagines his life without it.
Cartman’s mother explains that of course they’ve tried diet and exercise, but that intentional behavior change alone hasn’t been sufficient to sustainably move the scale’s needle — a truth for the vast majority of people with obesity. But here, unlike in many actual doctors’ offices, Cartman’s doctor doesn’t spend time doubting or cajoling; instead, he does his job — which is to inform his patient, without judgment, about a pharmaceutical option that has proved to be beneficial. He accurately describes these medications as ushering in “a whole new era of medicine, a miracle really” that can “help people lose vast amounts of weight.”
The kicker, though, comes next. The doctor explains that insurance companies cover the medications only for patients with diabetes, “so if you can’t afford them, you’re just kind of out of luck.” This is changing somewhat now, at least here in Canada, where two of our main private insurers have changed their base coverages to make antiobesity medications something employers need to opt out of rather than opt into, but certainly they’re not covered by US Medicare for weight management, nor by our version of the same here in Canada.
But even for those who have coverage, there are hoops to jump through, which is highlighted by the incredible efforts made by Cartman and his friends to get his insurance plan to cover the medications. Thwarted at every turn, despite the undeniable benefits of these medications to health and quality of life, they are forced to turn to compounding — a phenomenon certainly pervasive here in North America whereby compounding pharmacies claim to be able to provide glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs with comparable efficacy at a fraction of the price, but without the same rigor of proof of purity or efficacy.
Also covered by South Park is that the GLP-1 analog supply is impacted by use by people who don’t meet approved medical criteria and are using the medications for aesthetic purposes. This speaks to the incredible societal pressure to be thin and to the comfort of some physicians to inappropriately prescribe these medications. This is covered by the subplot of South Park’s weed farmer, Randy, who in turn delivers an important insight into how it feels to use a GLP-1 analog: “I think there’s something wrong with these drugs ... I feel satisfied. With any drugs I want to do more and more, but with these drugs I feel like I want things less. With these drugs you don’t really crave anything.” The sentiment is echoed by Cartman, who exclaims, “I think I’m full. I’ve never known that feeling before in my life, but I’m full.”
It’s remarkable that South Park, a show built on serving up politically incorrect offense, covers obesity and its treatment with more accuracy, nuance, and compassion than does society as a whole. The show notes that obesity is a biological condition (it is), that when it comes to health (in America) “you have to have some f-ing willpower.” But where they explicitly mean having willpower in terms of filing and pursing insurance claims (you do), explains that drug companies are making antiobesity medications more expensive in America than anywhere else in the world (they are), and finally delivers this quote, which, while missing the biological basis of behavior and hunger with respect to obesity, certainly sums up why blame has no place in the discourse:
“We have sugar companies, pharmaceutical companies, and insurance companies all just trying to figure out how to make money off our health. It isn’t fair to put the blame on anyone for their weight.”
No, it’s not.
This movie should be required viewing in medical schools.
Dr. Freedhoff is associate professor, department of family medicine, University of Ottawa, and medical director, Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. He disclosed ties with Bariatric Medical Institute, Constant Health, Novo Nordisk, and Weighty Matters.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Yes, there’s still much to find offensive, but South Park: The End of Obesity, in just 51 minutes, does more to explain some of obesity’s realities, its pharmacotherapy, and weight bias than the mainstream media has done perhaps ever.
The mini-movie follows the plight of Eric Cartman, the fictional South Parkian child with severe obesity.
South Park got everything right. The movie starts in a medical center where discussions with Cartman, his mother, and his doctor make it clear that obesity isn’t something that Cartman chose and is perhaps the most distressing aspect of his life. This certainly echoes study findings which report that quality-of-life scores in children with severe obesity are lower than those of children with newly diagnosed on-treatment cancers. As to how obesity erodes a child’s quality of life, no doubt part of its impact stems from obesity being a top source of schoolyard bullying, which is reflected by Cartman as he imagines his life without it.
Cartman’s mother explains that of course they’ve tried diet and exercise, but that intentional behavior change alone hasn’t been sufficient to sustainably move the scale’s needle — a truth for the vast majority of people with obesity. But here, unlike in many actual doctors’ offices, Cartman’s doctor doesn’t spend time doubting or cajoling; instead, he does his job — which is to inform his patient, without judgment, about a pharmaceutical option that has proved to be beneficial. He accurately describes these medications as ushering in “a whole new era of medicine, a miracle really” that can “help people lose vast amounts of weight.”
The kicker, though, comes next. The doctor explains that insurance companies cover the medications only for patients with diabetes, “so if you can’t afford them, you’re just kind of out of luck.” This is changing somewhat now, at least here in Canada, where two of our main private insurers have changed their base coverages to make antiobesity medications something employers need to opt out of rather than opt into, but certainly they’re not covered by US Medicare for weight management, nor by our version of the same here in Canada.
But even for those who have coverage, there are hoops to jump through, which is highlighted by the incredible efforts made by Cartman and his friends to get his insurance plan to cover the medications. Thwarted at every turn, despite the undeniable benefits of these medications to health and quality of life, they are forced to turn to compounding — a phenomenon certainly pervasive here in North America whereby compounding pharmacies claim to be able to provide glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs with comparable efficacy at a fraction of the price, but without the same rigor of proof of purity or efficacy.
Also covered by South Park is that the GLP-1 analog supply is impacted by use by people who don’t meet approved medical criteria and are using the medications for aesthetic purposes. This speaks to the incredible societal pressure to be thin and to the comfort of some physicians to inappropriately prescribe these medications. This is covered by the subplot of South Park’s weed farmer, Randy, who in turn delivers an important insight into how it feels to use a GLP-1 analog: “I think there’s something wrong with these drugs ... I feel satisfied. With any drugs I want to do more and more, but with these drugs I feel like I want things less. With these drugs you don’t really crave anything.” The sentiment is echoed by Cartman, who exclaims, “I think I’m full. I’ve never known that feeling before in my life, but I’m full.”
It’s remarkable that South Park, a show built on serving up politically incorrect offense, covers obesity and its treatment with more accuracy, nuance, and compassion than does society as a whole. The show notes that obesity is a biological condition (it is), that when it comes to health (in America) “you have to have some f-ing willpower.” But where they explicitly mean having willpower in terms of filing and pursing insurance claims (you do), explains that drug companies are making antiobesity medications more expensive in America than anywhere else in the world (they are), and finally delivers this quote, which, while missing the biological basis of behavior and hunger with respect to obesity, certainly sums up why blame has no place in the discourse:
“We have sugar companies, pharmaceutical companies, and insurance companies all just trying to figure out how to make money off our health. It isn’t fair to put the blame on anyone for their weight.”
No, it’s not.
This movie should be required viewing in medical schools.
Dr. Freedhoff is associate professor, department of family medicine, University of Ottawa, and medical director, Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. He disclosed ties with Bariatric Medical Institute, Constant Health, Novo Nordisk, and Weighty Matters.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Yes, there’s still much to find offensive, but South Park: The End of Obesity, in just 51 minutes, does more to explain some of obesity’s realities, its pharmacotherapy, and weight bias than the mainstream media has done perhaps ever.
The mini-movie follows the plight of Eric Cartman, the fictional South Parkian child with severe obesity.
South Park got everything right. The movie starts in a medical center where discussions with Cartman, his mother, and his doctor make it clear that obesity isn’t something that Cartman chose and is perhaps the most distressing aspect of his life. This certainly echoes study findings which report that quality-of-life scores in children with severe obesity are lower than those of children with newly diagnosed on-treatment cancers. As to how obesity erodes a child’s quality of life, no doubt part of its impact stems from obesity being a top source of schoolyard bullying, which is reflected by Cartman as he imagines his life without it.
Cartman’s mother explains that of course they’ve tried diet and exercise, but that intentional behavior change alone hasn’t been sufficient to sustainably move the scale’s needle — a truth for the vast majority of people with obesity. But here, unlike in many actual doctors’ offices, Cartman’s doctor doesn’t spend time doubting or cajoling; instead, he does his job — which is to inform his patient, without judgment, about a pharmaceutical option that has proved to be beneficial. He accurately describes these medications as ushering in “a whole new era of medicine, a miracle really” that can “help people lose vast amounts of weight.”
The kicker, though, comes next. The doctor explains that insurance companies cover the medications only for patients with diabetes, “so if you can’t afford them, you’re just kind of out of luck.” This is changing somewhat now, at least here in Canada, where two of our main private insurers have changed their base coverages to make antiobesity medications something employers need to opt out of rather than opt into, but certainly they’re not covered by US Medicare for weight management, nor by our version of the same here in Canada.
But even for those who have coverage, there are hoops to jump through, which is highlighted by the incredible efforts made by Cartman and his friends to get his insurance plan to cover the medications. Thwarted at every turn, despite the undeniable benefits of these medications to health and quality of life, they are forced to turn to compounding — a phenomenon certainly pervasive here in North America whereby compounding pharmacies claim to be able to provide glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs with comparable efficacy at a fraction of the price, but without the same rigor of proof of purity or efficacy.
Also covered by South Park is that the GLP-1 analog supply is impacted by use by people who don’t meet approved medical criteria and are using the medications for aesthetic purposes. This speaks to the incredible societal pressure to be thin and to the comfort of some physicians to inappropriately prescribe these medications. This is covered by the subplot of South Park’s weed farmer, Randy, who in turn delivers an important insight into how it feels to use a GLP-1 analog: “I think there’s something wrong with these drugs ... I feel satisfied. With any drugs I want to do more and more, but with these drugs I feel like I want things less. With these drugs you don’t really crave anything.” The sentiment is echoed by Cartman, who exclaims, “I think I’m full. I’ve never known that feeling before in my life, but I’m full.”
It’s remarkable that South Park, a show built on serving up politically incorrect offense, covers obesity and its treatment with more accuracy, nuance, and compassion than does society as a whole. The show notes that obesity is a biological condition (it is), that when it comes to health (in America) “you have to have some f-ing willpower.” But where they explicitly mean having willpower in terms of filing and pursing insurance claims (you do), explains that drug companies are making antiobesity medications more expensive in America than anywhere else in the world (they are), and finally delivers this quote, which, while missing the biological basis of behavior and hunger with respect to obesity, certainly sums up why blame has no place in the discourse:
“We have sugar companies, pharmaceutical companies, and insurance companies all just trying to figure out how to make money off our health. It isn’t fair to put the blame on anyone for their weight.”
No, it’s not.
This movie should be required viewing in medical schools.
Dr. Freedhoff is associate professor, department of family medicine, University of Ottawa, and medical director, Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. He disclosed ties with Bariatric Medical Institute, Constant Health, Novo Nordisk, and Weighty Matters.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.








