User login
Reticular Hyperpigmentation With Keratotic Papules in the Axillae and Groin
The Diagnosis: Galli-Galli Disease
Several cutaneous conditions can present as reticulated hyperpigmentation or keratotic papules. Although genetic testing can help identify some of these dermatoses, biopsy typically is sufficient for diagnosis, and genetic testing can be considered for more clinically challenging cases. In our case, the clinical evidence and histopathologic findings were diagnostic of Galli-Galli disease (GGD), an autosomal-dominant genodermatosis with incomplete penetrance. Our patient was unaware of any family members with a diagnosis of GGD; however, she reported a great uncle with similar clinical findings.
Galli-Galli disease is a rare allelic variant of Dowling- Degos disease (DDD), both caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the keratin 5 gene, KRT5. Both conditions present as reticulated papules distributed symmetrically in the flexural regions, most commonly the axillae and groin, but also as comedolike papules, typically in patients aged 30 to 50 years.1 Cutaneous lesions primarily are of cosmetic concern but can be extremely pruritic, especially for patients with GGD. Gene mutations in protein O-fucosyltransferase 1, POFUT1; protein O-glucosyltransferase 1, POGLUT1; and presenilin enhancer 2, PSENEN, also have been discovered in cases of DDD and GGD.2,3
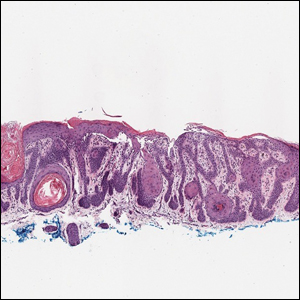
Galli-Galli disease and DDD are distinguishable by their histologic appearance. Both diseases show elongated fingerlike rete ridges and a thin suprapapillary epidermis. The basal projections often are described as bulbous or resembling antler horns.4 Galli-Galli disease can be differentiated from DDD by focal suprabasal acantholysis with minimal dyskeratosis (quiz images).5 Due to the genetic and clinical similarities, many consider GGD an acantholytic variant of DDD rather than its own entity. Indeed, some patients have shown acantholysis in one area of biopsy but not others.6
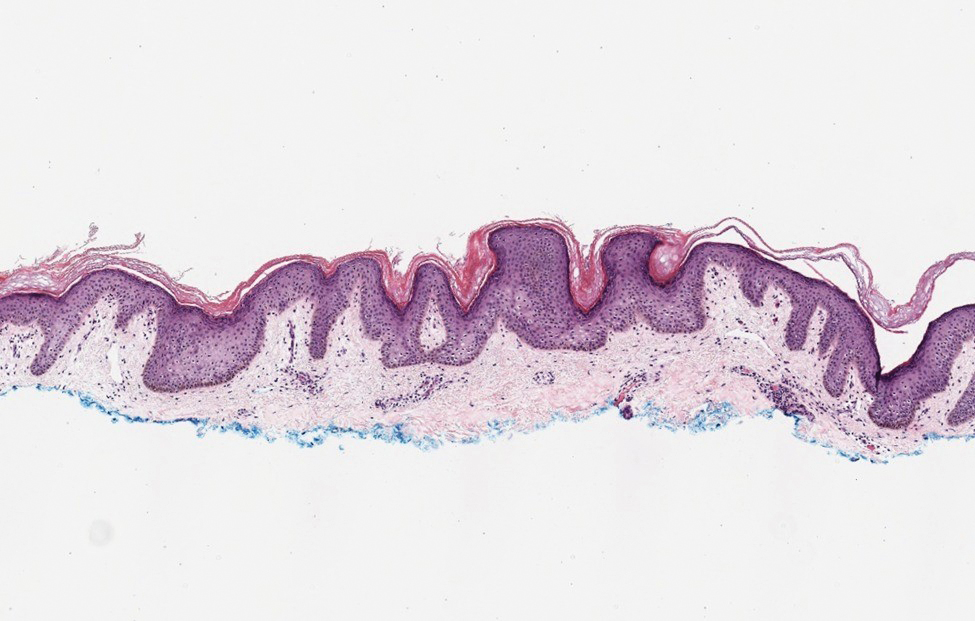
Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD)(also known as benign familial or benign chronic pemphigus) is an autosomaldominant disorder caused by mutation of the ATPase secretory pathway Ca2+ transporting 1 gene, ATP2C1. Clinically, patients tend to present at a wide age range with fragile flaccid vesicles that commonly develop on the neck, axillae, and groin. Histologically, the epidermis is acanthotic with a dilapidated brick wall– like appearance from a few persistent intercellular connections amid widespread acantholysis (Figure 1).7 Unlike in autoimmune pemphigus, direct immunofluorescence is negative, and acantholysis spares the adnexal structures. Hailey-Hailey disease does not involve reticulated hyperpigmentation or the elongated bulbous rete seen in GGD. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is a rare, typically asymptomatic, hyperpigmented dermatosis. It presents as a conglomeration of scaly hyperpigmented macules or papillomatous papules that coalesce centrally and are reticulated toward the periphery.
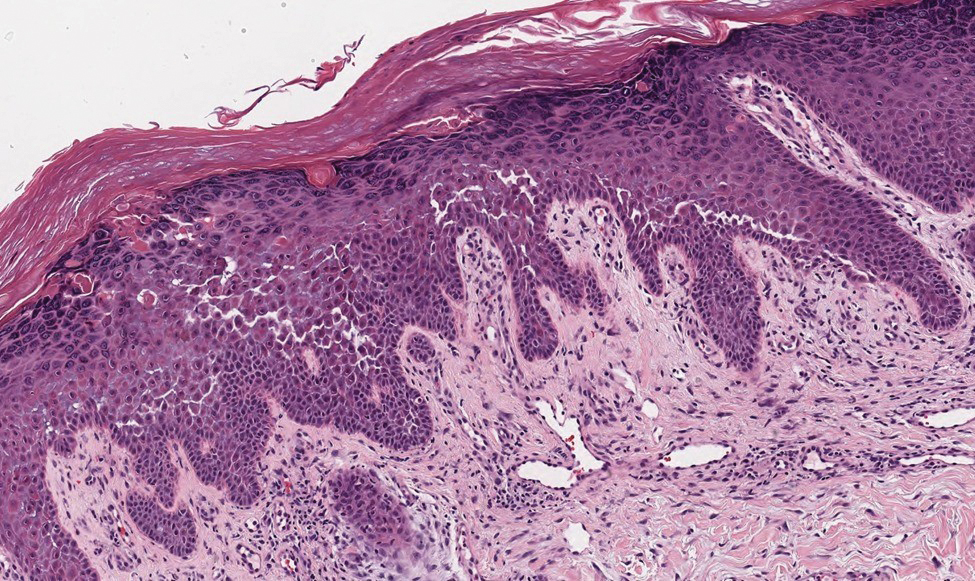
Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis most commonly is seen on the trunk, initially presenting in adolescents and young adults. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is histologically similar to acanthosis nigricans. Histopathology will show hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and minimal to no inflammatory infiltrate, with no elongated rete ridges or acantholysis (Figure 2).8
Pemphigus vulgaris is a blistering disease resulting from the development of autoantibodies against desmogleins 1 and 3. Similar to GGD, there is suprabasal acantholysis, which often results in a tombstonelike appearance consisting of separation between the basal layer cells of the epidermis but with maintained attachment to the underlying basement membrane zone. Unlike HHD, the acantholysis tends to involve the follicular epithelium in pemphigus vulgaris (Figure 3). Clinically, the blisters are positive for Nikolsky sign and can be both cutaneous or mucosal, commonly arising initially in the mouth during the fourth or fifth decades of life. Ruptured blisters can result in painful and hemorrhagic erosions.9 Direct immunofluorescence exhibits a classic chicken wire–like deposition of IgG and C3 between keratinocytes of the epidermis. Although sometimes difficult to appreciate, the deposition can be more prominent in the lower epidermis, in contrast to pemphigus foliaceus, which can have more prominent deposition in the upper epidermis.

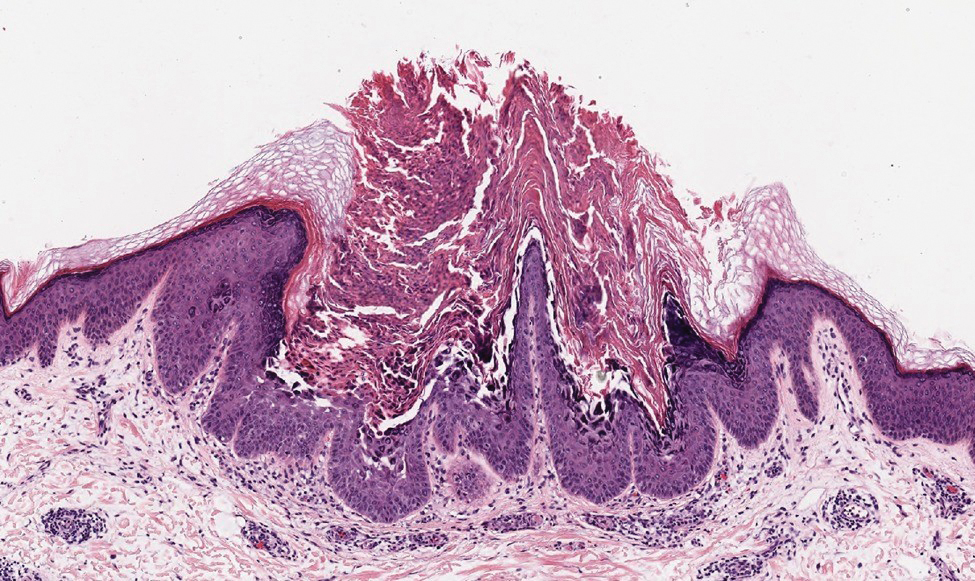
Darier disease (or dyskeratosis follicularis) is an autosomal-dominant genodermatosis caused by mutation of the ATPase sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transporting 2 gene, ATP2A2. Clinically, this disorder arises in adolescents as red-brown, greasy, crusted papules in seborrheic areas that may coalesce into papillomatous clusters. Palmar punctate keratoses and pits also are common. Histologically, Darier disease can appear similar to GGD, as both can show acantholysis and dyskeratosis. Darier disease will tend to show more prominent dyskeratosis with corps ronds and grains, as well as thicker villilike projections of keratinocytes into the papillary dermis, in contrast to the thinner, fingerlike or bulbous projections that hang down from the epidermis in GGD (Figure 4).10
- Hanneken S, Rütten A, Eigelshoven S, et al. Morbus Galli-Galli. Hautarzt. 2013;64:282.
- Wilson NJ, Cole C, Kroboth K, et al. Mutations in POGLUT1 in Galli- Galli/Dowling-Degos disease. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:270-274.
- Ralser DJ, Basmanav FB, Tafazzoli A, et al. Mutations in γ-secretase subunit–encoding PSENEN underlie Dowling-Degos disease associated with acne inversa. J Clin Invest. 2017;127:1485-1490.
- Desai CA, Virmani N, Sakhiya J, et al. An uncommon presentation of Galli-Galli disease. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016; 82:720-723.
- Joshi TP, Shaver S, Tschen J. Exacerbation of Galli-Galli disease following dialysis treatment: a case report and review of aggravating factors. Cureus. 2021;13:E15401.
- Muller CS, Pfohler C, Tilgen W. Changing a concept—controversy on the confusion spectrum of the reticulate pigmented disorders of the skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;36:44-48.
- Dai Y, Yu L, Wang Y, et al. Case report: a case of Hailey-Hailey disease mimicking condyloma acuminatum and a novel splice-site mutation of ATP2C1 gene. Front Genet. 2021;12:777630.
- Banjar TA, Abdulwahab RA, Al Hawsawi KA. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis of Gougerot and Carteaud: a case report and review of the literature. Cureus. 2022;14:E24557.
- Porro AM, Seque CA, Ferreira MCC, et al. Pemphigus vulgaris. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:264-278.
- Bachar-Wikström E, Wikström JD. Darier disease—a multi-organ condition? Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00430.
The Diagnosis: Galli-Galli Disease
Several cutaneous conditions can present as reticulated hyperpigmentation or keratotic papules. Although genetic testing can help identify some of these dermatoses, biopsy typically is sufficient for diagnosis, and genetic testing can be considered for more clinically challenging cases. In our case, the clinical evidence and histopathologic findings were diagnostic of Galli-Galli disease (GGD), an autosomal-dominant genodermatosis with incomplete penetrance. Our patient was unaware of any family members with a diagnosis of GGD; however, she reported a great uncle with similar clinical findings.
Galli-Galli disease is a rare allelic variant of Dowling- Degos disease (DDD), both caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the keratin 5 gene, KRT5. Both conditions present as reticulated papules distributed symmetrically in the flexural regions, most commonly the axillae and groin, but also as comedolike papules, typically in patients aged 30 to 50 years.1 Cutaneous lesions primarily are of cosmetic concern but can be extremely pruritic, especially for patients with GGD. Gene mutations in protein O-fucosyltransferase 1, POFUT1; protein O-glucosyltransferase 1, POGLUT1; and presenilin enhancer 2, PSENEN, also have been discovered in cases of DDD and GGD.2,3
Galli-Galli disease and DDD are distinguishable by their histologic appearance. Both diseases show elongated fingerlike rete ridges and a thin suprapapillary epidermis. The basal projections often are described as bulbous or resembling antler horns.4 Galli-Galli disease can be differentiated from DDD by focal suprabasal acantholysis with minimal dyskeratosis (quiz images).5 Due to the genetic and clinical similarities, many consider GGD an acantholytic variant of DDD rather than its own entity. Indeed, some patients have shown acantholysis in one area of biopsy but not others.6
Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD)(also known as benign familial or benign chronic pemphigus) is an autosomaldominant disorder caused by mutation of the ATPase secretory pathway Ca2+ transporting 1 gene, ATP2C1. Clinically, patients tend to present at a wide age range with fragile flaccid vesicles that commonly develop on the neck, axillae, and groin. Histologically, the epidermis is acanthotic with a dilapidated brick wall– like appearance from a few persistent intercellular connections amid widespread acantholysis (Figure 1).7 Unlike in autoimmune pemphigus, direct immunofluorescence is negative, and acantholysis spares the adnexal structures. Hailey-Hailey disease does not involve reticulated hyperpigmentation or the elongated bulbous rete seen in GGD. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is a rare, typically asymptomatic, hyperpigmented dermatosis. It presents as a conglomeration of scaly hyperpigmented macules or papillomatous papules that coalesce centrally and are reticulated toward the periphery.

Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis most commonly is seen on the trunk, initially presenting in adolescents and young adults. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is histologically similar to acanthosis nigricans. Histopathology will show hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and minimal to no inflammatory infiltrate, with no elongated rete ridges or acantholysis (Figure 2).8

Pemphigus vulgaris is a blistering disease resulting from the development of autoantibodies against desmogleins 1 and 3. Similar to GGD, there is suprabasal acantholysis, which often results in a tombstonelike appearance consisting of separation between the basal layer cells of the epidermis but with maintained attachment to the underlying basement membrane zone. Unlike HHD, the acantholysis tends to involve the follicular epithelium in pemphigus vulgaris (Figure 3). Clinically, the blisters are positive for Nikolsky sign and can be both cutaneous or mucosal, commonly arising initially in the mouth during the fourth or fifth decades of life. Ruptured blisters can result in painful and hemorrhagic erosions.9 Direct immunofluorescence exhibits a classic chicken wire–like deposition of IgG and C3 between keratinocytes of the epidermis. Although sometimes difficult to appreciate, the deposition can be more prominent in the lower epidermis, in contrast to pemphigus foliaceus, which can have more prominent deposition in the upper epidermis.

Darier disease (or dyskeratosis follicularis) is an autosomal-dominant genodermatosis caused by mutation of the ATPase sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transporting 2 gene, ATP2A2. Clinically, this disorder arises in adolescents as red-brown, greasy, crusted papules in seborrheic areas that may coalesce into papillomatous clusters. Palmar punctate keratoses and pits also are common. Histologically, Darier disease can appear similar to GGD, as both can show acantholysis and dyskeratosis. Darier disease will tend to show more prominent dyskeratosis with corps ronds and grains, as well as thicker villilike projections of keratinocytes into the papillary dermis, in contrast to the thinner, fingerlike or bulbous projections that hang down from the epidermis in GGD (Figure 4).10

The Diagnosis: Galli-Galli Disease
Several cutaneous conditions can present as reticulated hyperpigmentation or keratotic papules. Although genetic testing can help identify some of these dermatoses, biopsy typically is sufficient for diagnosis, and genetic testing can be considered for more clinically challenging cases. In our case, the clinical evidence and histopathologic findings were diagnostic of Galli-Galli disease (GGD), an autosomal-dominant genodermatosis with incomplete penetrance. Our patient was unaware of any family members with a diagnosis of GGD; however, she reported a great uncle with similar clinical findings.
Galli-Galli disease is a rare allelic variant of Dowling- Degos disease (DDD), both caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the keratin 5 gene, KRT5. Both conditions present as reticulated papules distributed symmetrically in the flexural regions, most commonly the axillae and groin, but also as comedolike papules, typically in patients aged 30 to 50 years.1 Cutaneous lesions primarily are of cosmetic concern but can be extremely pruritic, especially for patients with GGD. Gene mutations in protein O-fucosyltransferase 1, POFUT1; protein O-glucosyltransferase 1, POGLUT1; and presenilin enhancer 2, PSENEN, also have been discovered in cases of DDD and GGD.2,3
Galli-Galli disease and DDD are distinguishable by their histologic appearance. Both diseases show elongated fingerlike rete ridges and a thin suprapapillary epidermis. The basal projections often are described as bulbous or resembling antler horns.4 Galli-Galli disease can be differentiated from DDD by focal suprabasal acantholysis with minimal dyskeratosis (quiz images).5 Due to the genetic and clinical similarities, many consider GGD an acantholytic variant of DDD rather than its own entity. Indeed, some patients have shown acantholysis in one area of biopsy but not others.6
Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD)(also known as benign familial or benign chronic pemphigus) is an autosomaldominant disorder caused by mutation of the ATPase secretory pathway Ca2+ transporting 1 gene, ATP2C1. Clinically, patients tend to present at a wide age range with fragile flaccid vesicles that commonly develop on the neck, axillae, and groin. Histologically, the epidermis is acanthotic with a dilapidated brick wall– like appearance from a few persistent intercellular connections amid widespread acantholysis (Figure 1).7 Unlike in autoimmune pemphigus, direct immunofluorescence is negative, and acantholysis spares the adnexal structures. Hailey-Hailey disease does not involve reticulated hyperpigmentation or the elongated bulbous rete seen in GGD. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is a rare, typically asymptomatic, hyperpigmented dermatosis. It presents as a conglomeration of scaly hyperpigmented macules or papillomatous papules that coalesce centrally and are reticulated toward the periphery.

Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis most commonly is seen on the trunk, initially presenting in adolescents and young adults. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is histologically similar to acanthosis nigricans. Histopathology will show hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and minimal to no inflammatory infiltrate, with no elongated rete ridges or acantholysis (Figure 2).8

Pemphigus vulgaris is a blistering disease resulting from the development of autoantibodies against desmogleins 1 and 3. Similar to GGD, there is suprabasal acantholysis, which often results in a tombstonelike appearance consisting of separation between the basal layer cells of the epidermis but with maintained attachment to the underlying basement membrane zone. Unlike HHD, the acantholysis tends to involve the follicular epithelium in pemphigus vulgaris (Figure 3). Clinically, the blisters are positive for Nikolsky sign and can be both cutaneous or mucosal, commonly arising initially in the mouth during the fourth or fifth decades of life. Ruptured blisters can result in painful and hemorrhagic erosions.9 Direct immunofluorescence exhibits a classic chicken wire–like deposition of IgG and C3 between keratinocytes of the epidermis. Although sometimes difficult to appreciate, the deposition can be more prominent in the lower epidermis, in contrast to pemphigus foliaceus, which can have more prominent deposition in the upper epidermis.

Darier disease (or dyskeratosis follicularis) is an autosomal-dominant genodermatosis caused by mutation of the ATPase sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transporting 2 gene, ATP2A2. Clinically, this disorder arises in adolescents as red-brown, greasy, crusted papules in seborrheic areas that may coalesce into papillomatous clusters. Palmar punctate keratoses and pits also are common. Histologically, Darier disease can appear similar to GGD, as both can show acantholysis and dyskeratosis. Darier disease will tend to show more prominent dyskeratosis with corps ronds and grains, as well as thicker villilike projections of keratinocytes into the papillary dermis, in contrast to the thinner, fingerlike or bulbous projections that hang down from the epidermis in GGD (Figure 4).10

- Hanneken S, Rütten A, Eigelshoven S, et al. Morbus Galli-Galli. Hautarzt. 2013;64:282.
- Wilson NJ, Cole C, Kroboth K, et al. Mutations in POGLUT1 in Galli- Galli/Dowling-Degos disease. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:270-274.
- Ralser DJ, Basmanav FB, Tafazzoli A, et al. Mutations in γ-secretase subunit–encoding PSENEN underlie Dowling-Degos disease associated with acne inversa. J Clin Invest. 2017;127:1485-1490.
- Desai CA, Virmani N, Sakhiya J, et al. An uncommon presentation of Galli-Galli disease. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016; 82:720-723.
- Joshi TP, Shaver S, Tschen J. Exacerbation of Galli-Galli disease following dialysis treatment: a case report and review of aggravating factors. Cureus. 2021;13:E15401.
- Muller CS, Pfohler C, Tilgen W. Changing a concept—controversy on the confusion spectrum of the reticulate pigmented disorders of the skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;36:44-48.
- Dai Y, Yu L, Wang Y, et al. Case report: a case of Hailey-Hailey disease mimicking condyloma acuminatum and a novel splice-site mutation of ATP2C1 gene. Front Genet. 2021;12:777630.
- Banjar TA, Abdulwahab RA, Al Hawsawi KA. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis of Gougerot and Carteaud: a case report and review of the literature. Cureus. 2022;14:E24557.
- Porro AM, Seque CA, Ferreira MCC, et al. Pemphigus vulgaris. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:264-278.
- Bachar-Wikström E, Wikström JD. Darier disease—a multi-organ condition? Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00430.
- Hanneken S, Rütten A, Eigelshoven S, et al. Morbus Galli-Galli. Hautarzt. 2013;64:282.
- Wilson NJ, Cole C, Kroboth K, et al. Mutations in POGLUT1 in Galli- Galli/Dowling-Degos disease. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:270-274.
- Ralser DJ, Basmanav FB, Tafazzoli A, et al. Mutations in γ-secretase subunit–encoding PSENEN underlie Dowling-Degos disease associated with acne inversa. J Clin Invest. 2017;127:1485-1490.
- Desai CA, Virmani N, Sakhiya J, et al. An uncommon presentation of Galli-Galli disease. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016; 82:720-723.
- Joshi TP, Shaver S, Tschen J. Exacerbation of Galli-Galli disease following dialysis treatment: a case report and review of aggravating factors. Cureus. 2021;13:E15401.
- Muller CS, Pfohler C, Tilgen W. Changing a concept—controversy on the confusion spectrum of the reticulate pigmented disorders of the skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;36:44-48.
- Dai Y, Yu L, Wang Y, et al. Case report: a case of Hailey-Hailey disease mimicking condyloma acuminatum and a novel splice-site mutation of ATP2C1 gene. Front Genet. 2021;12:777630.
- Banjar TA, Abdulwahab RA, Al Hawsawi KA. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis of Gougerot and Carteaud: a case report and review of the literature. Cureus. 2022;14:E24557.
- Porro AM, Seque CA, Ferreira MCC, et al. Pemphigus vulgaris. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:264-278.
- Bachar-Wikström E, Wikström JD. Darier disease—a multi-organ condition? Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00430.
A 37-year-old woman presented with multiple hyperkeratotic small papules in the axillae and groin of 1 year’s duration. She reported pruritus and occasional sleep disruption. Subtle background reticulated hyperpigmentation was present. The patient reported that she had a great uncle with similar findings.


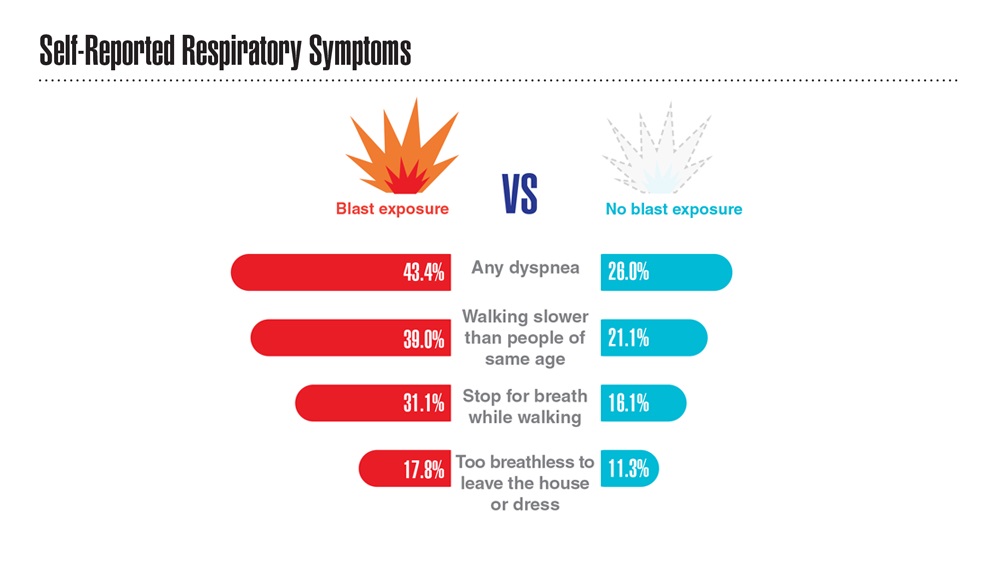
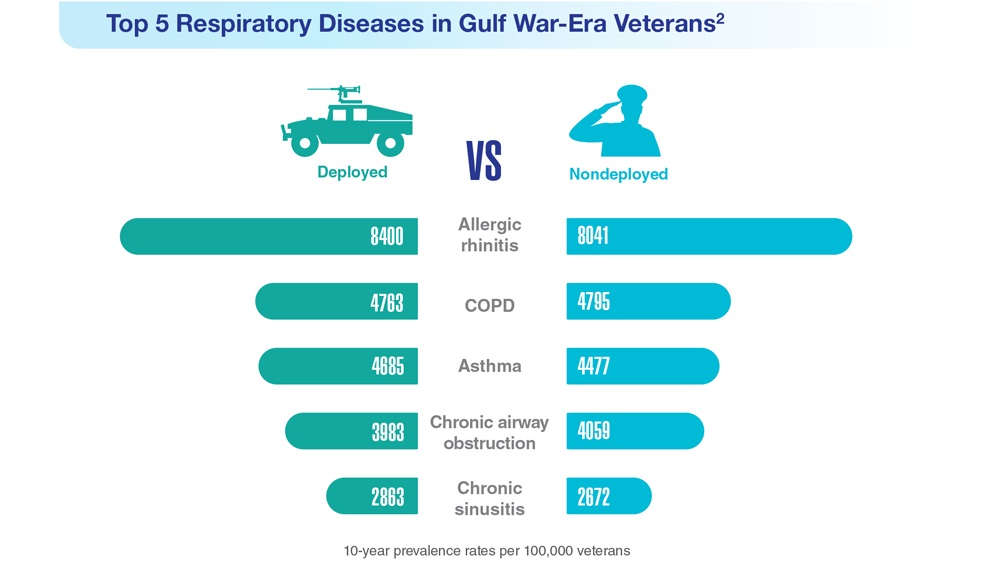
Data Trends 2023: Respiratory Illnesses
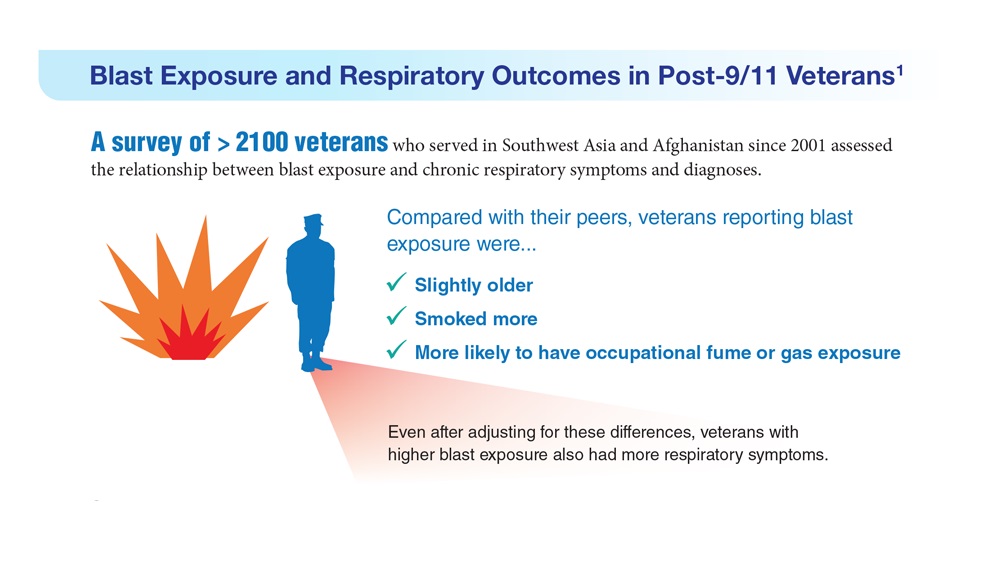
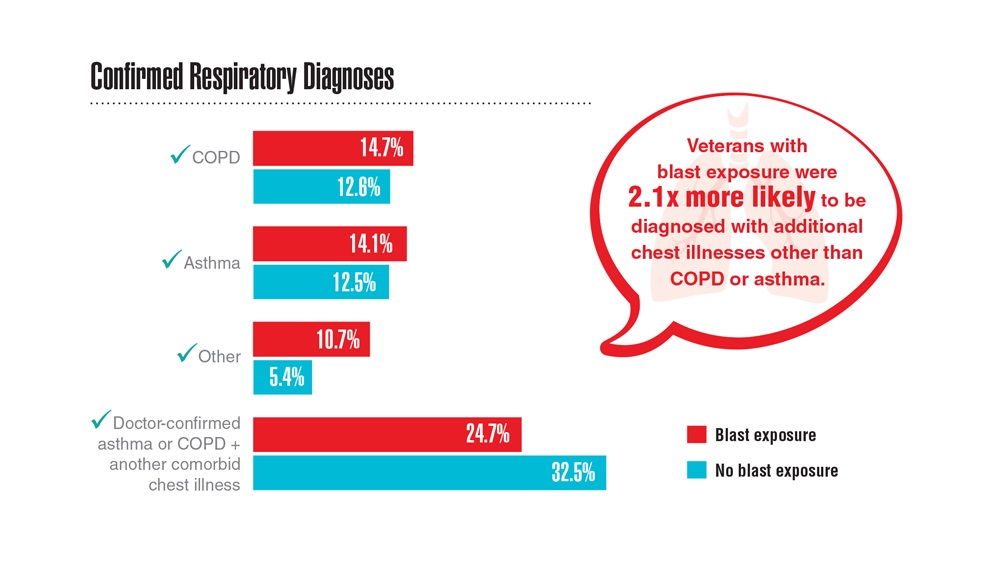
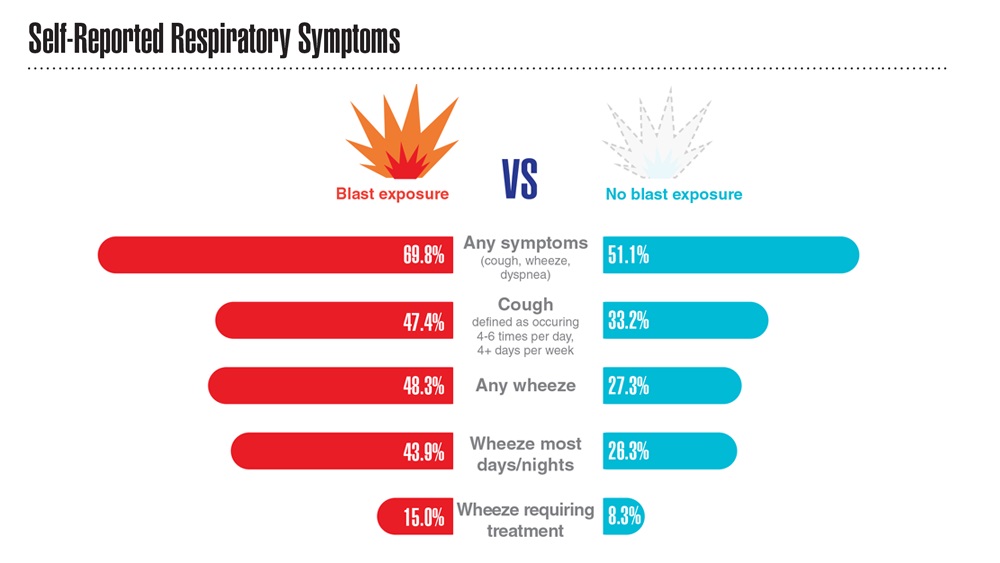
- Hines SE et al. Respir Med. 2022;202:106963. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106963
- Dursa EK et al. Am J Ind Med. 2020;63(11):980-987. doi:10.1002/ajim.23172
- Bamonti PM et al. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
- Hines SE et al. Respir Med. 2022;202:106963. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106963
- Dursa EK et al. Am J Ind Med. 2020;63(11):980-987. doi:10.1002/ajim.23172
- Bamonti PM et al. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
- Hines SE et al. Respir Med. 2022;202:106963. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106963
- Dursa EK et al. Am J Ind Med. 2020;63(11):980-987. doi:10.1002/ajim.23172
- Bamonti PM et al. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
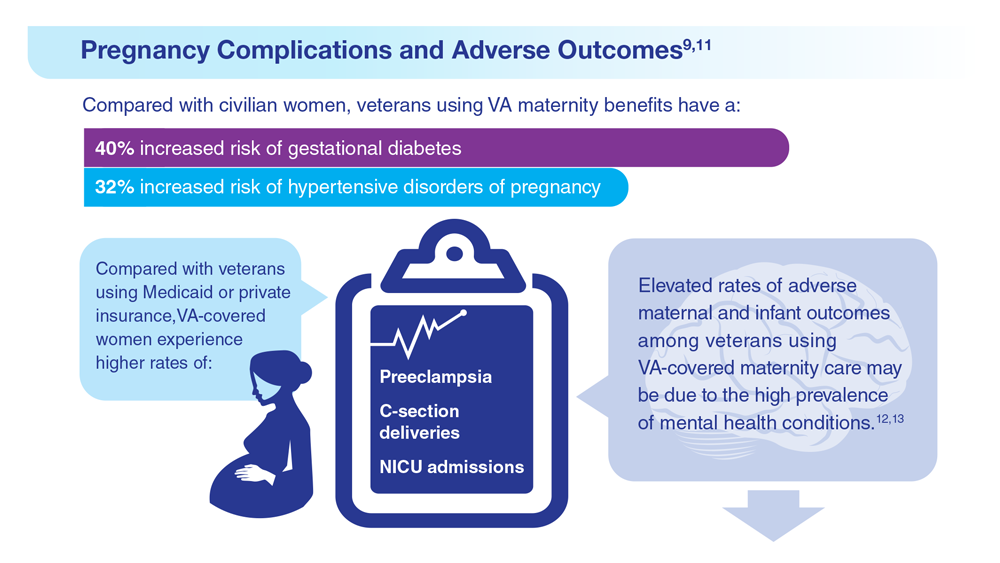
Data Trends 2023: Pregnancy
9. Frayne SM et al. Sourcebook: Women Veterans in the Veterans Health Administration. Volume 4: Longitudinal Trends in Sociodemographics, Utilization, Health Profile, and Geographic Distribution. Women’s Health Evaluation Initiative, Women’s Health Services, Veterans Health Administration. Published 2018. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.womenshealth.va.gov/WOMENSHEALTH/materials-and-resources/publications-and-reports.asp
10. Katon J et al. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2014;23(10):792-800. doi:10.1089/jwh.2013.4681
11. Day MA et al. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2023;93(1):41-49. doi:10.1037/ort0000654
12. Shaw JG et al. Health Serv Res. 2018;53(suppl 3):5260-5284. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13041
13. Shaw JG et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;124(6):1111-1119. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000000542
14. Shaw JG et al. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2017;31(3):185-194. doi:10.1111/ppe.12349
15. Kroll-Desrosiers A et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(suppl 3):762-769. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07573-7
16. Creech SK et al. Depress Anxiety. 2022;39(3):201-210. doi:10.1002/da.23218
17. US Department of Defense. Department of Defense Releases Annual Demographics Report — Upward Trend in Number of Women Serving Continues. Published December 14, 2022. Accessed June 12, 2023. https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/3246268/department-of-defense-releases-annual-demographics-report-upward-trend-in-numbe/
9. Frayne SM et al. Sourcebook: Women Veterans in the Veterans Health Administration. Volume 4: Longitudinal Trends in Sociodemographics, Utilization, Health Profile, and Geographic Distribution. Women’s Health Evaluation Initiative, Women’s Health Services, Veterans Health Administration. Published 2018. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.womenshealth.va.gov/WOMENSHEALTH/materials-and-resources/publications-and-reports.asp
10. Katon J et al. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2014;23(10):792-800. doi:10.1089/jwh.2013.4681
11. Day MA et al. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2023;93(1):41-49. doi:10.1037/ort0000654
12. Shaw JG et al. Health Serv Res. 2018;53(suppl 3):5260-5284. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13041
13. Shaw JG et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;124(6):1111-1119. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000000542
14. Shaw JG et al. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2017;31(3):185-194. doi:10.1111/ppe.12349
15. Kroll-Desrosiers A et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(suppl 3):762-769. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07573-7
16. Creech SK et al. Depress Anxiety. 2022;39(3):201-210. doi:10.1002/da.23218
17. US Department of Defense. Department of Defense Releases Annual Demographics Report — Upward Trend in Number of Women Serving Continues. Published December 14, 2022. Accessed June 12, 2023. https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/3246268/department-of-defense-releases-annual-demographics-report-upward-trend-in-numbe/
9. Frayne SM et al. Sourcebook: Women Veterans in the Veterans Health Administration. Volume 4: Longitudinal Trends in Sociodemographics, Utilization, Health Profile, and Geographic Distribution. Women’s Health Evaluation Initiative, Women’s Health Services, Veterans Health Administration. Published 2018. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.womenshealth.va.gov/WOMENSHEALTH/materials-and-resources/publications-and-reports.asp
10. Katon J et al. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2014;23(10):792-800. doi:10.1089/jwh.2013.4681
11. Day MA et al. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2023;93(1):41-49. doi:10.1037/ort0000654
12. Shaw JG et al. Health Serv Res. 2018;53(suppl 3):5260-5284. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13041
13. Shaw JG et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;124(6):1111-1119. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000000542
14. Shaw JG et al. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2017;31(3):185-194. doi:10.1111/ppe.12349
15. Kroll-Desrosiers A et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(suppl 3):762-769. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07573-7
16. Creech SK et al. Depress Anxiety. 2022;39(3):201-210. doi:10.1002/da.23218
17. US Department of Defense. Department of Defense Releases Annual Demographics Report — Upward Trend in Number of Women Serving Continues. Published December 14, 2022. Accessed June 12, 2023. https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/3246268/department-of-defense-releases-annual-demographics-report-upward-trend-in-numbe/
Federal Health Care Data Trends 2023
Federal Health Care Data Trends (click to view the digital edition) is a special supplement to Federal Practitioner, highlighting the latest research and study outcomes related to the health of veteran and active-duty populations.
In this issue:
- Limb Loss and Prostheses
- Neurology
- Cardiology
- Mental Health
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Respiratory illnesses
- Women's Health
- HPV and Related Cancers
Federal Health Care Data Trends (click to view the digital edition) is a special supplement to Federal Practitioner, highlighting the latest research and study outcomes related to the health of veteran and active-duty populations.
In this issue:
- Limb Loss and Prostheses
- Neurology
- Cardiology
- Mental Health
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Respiratory illnesses
- Women's Health
- HPV and Related Cancers
Federal Health Care Data Trends (click to view the digital edition) is a special supplement to Federal Practitioner, highlighting the latest research and study outcomes related to the health of veteran and active-duty populations.
In this issue:
- Limb Loss and Prostheses
- Neurology
- Cardiology
- Mental Health
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Respiratory illnesses
- Women's Health
- HPV and Related Cancers
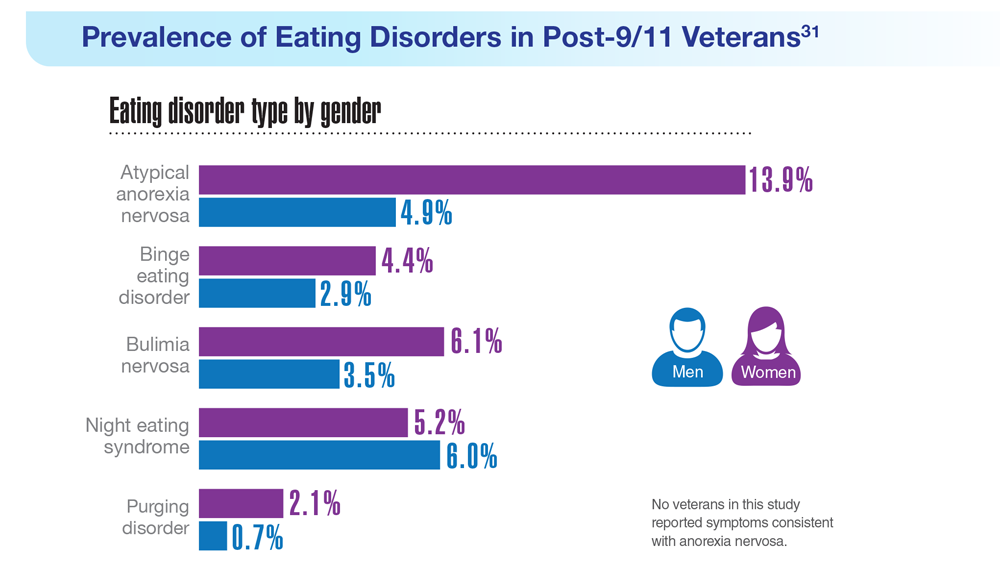
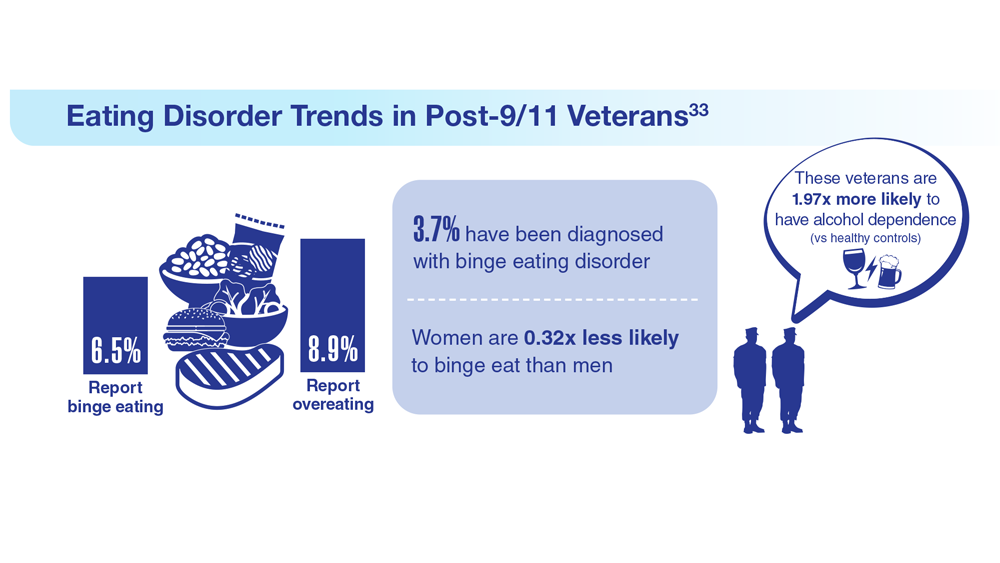
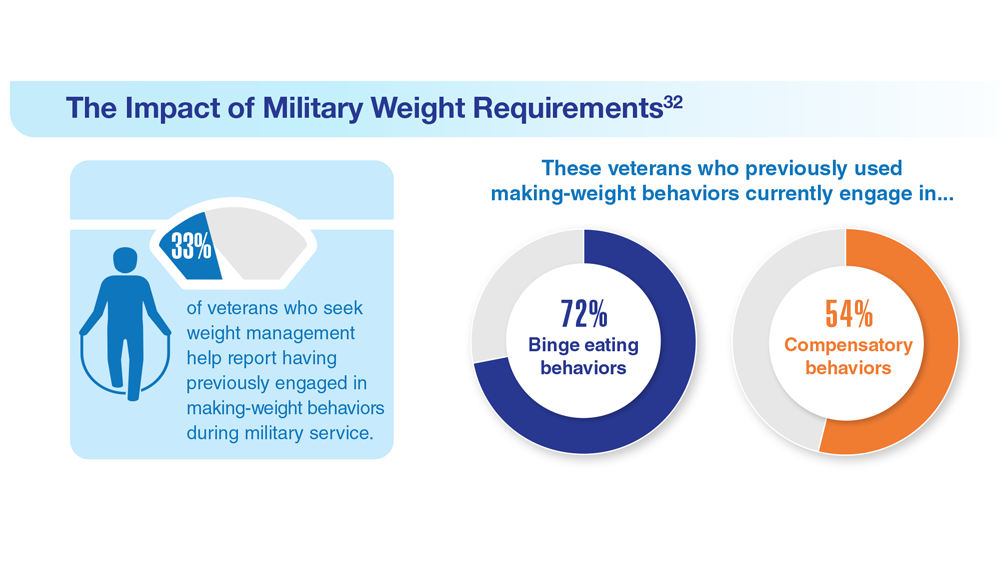
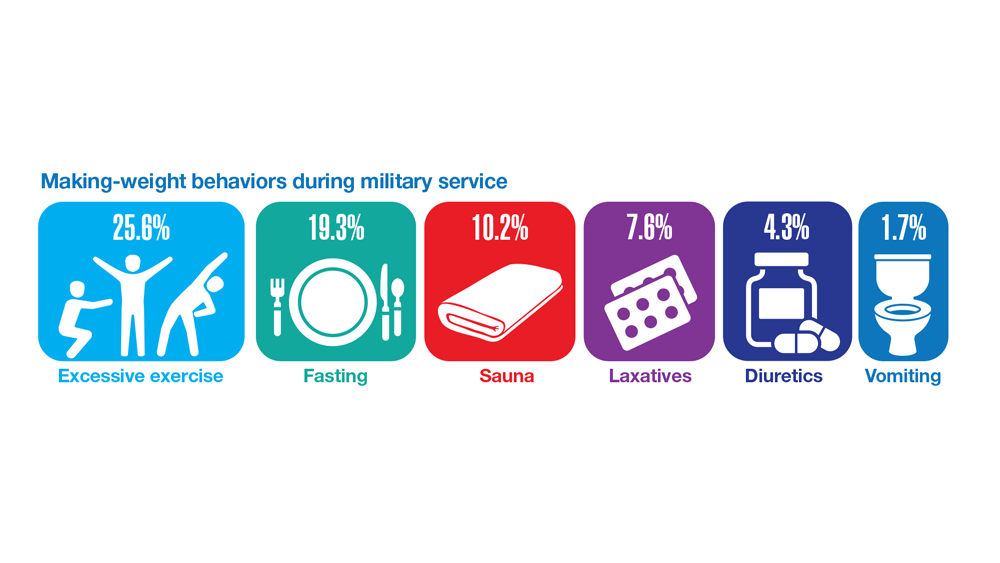
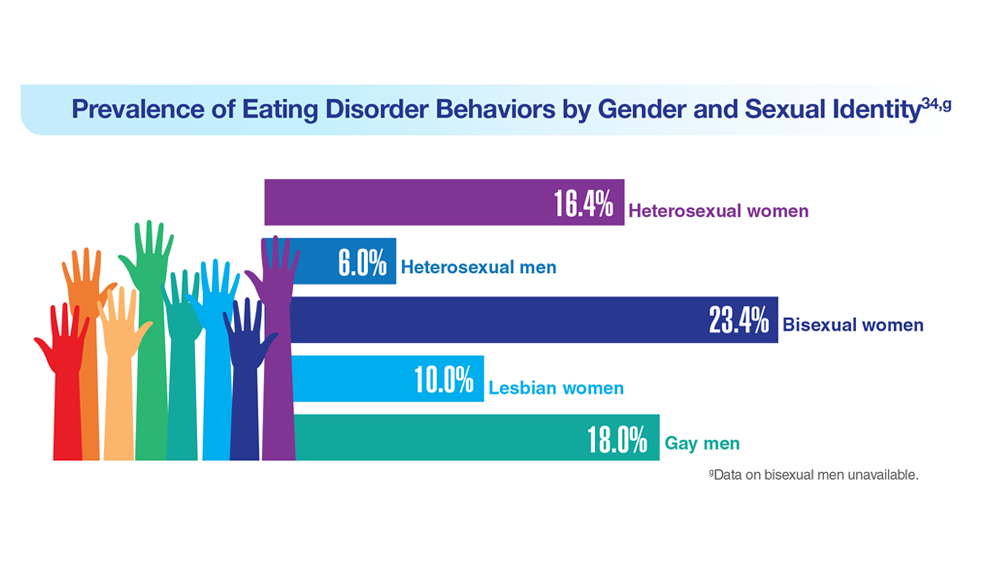
Data Trends 2023: Eating Disorders
29. Touma DA et al. Mil Med. 2022;usac180. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac180
30. Flatt RE et al. Eat Behav. 2021;43:101562. doi:10.1016/j.eatbeh.2021.101562
31. Masheb RM et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2021;54(7):1171-1180. doi:10.1002/eat.23501
32. Masheb RM et al. Eat Weight Disord. 2019;24(6):1063-1070. doi:10.1007/s40519-019-00766-w
33. Etuk R et al. Mil Med. 2022;187(3-4):297-303. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab533
34. Serier KN et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2022;55(4):470-480. doi:10.1002/eat.23680
29. Touma DA et al. Mil Med. 2022;usac180. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac180
30. Flatt RE et al. Eat Behav. 2021;43:101562. doi:10.1016/j.eatbeh.2021.101562
31. Masheb RM et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2021;54(7):1171-1180. doi:10.1002/eat.23501
32. Masheb RM et al. Eat Weight Disord. 2019;24(6):1063-1070. doi:10.1007/s40519-019-00766-w
33. Etuk R et al. Mil Med. 2022;187(3-4):297-303. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab533
34. Serier KN et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2022;55(4):470-480. doi:10.1002/eat.23680
29. Touma DA et al. Mil Med. 2022;usac180. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac180
30. Flatt RE et al. Eat Behav. 2021;43:101562. doi:10.1016/j.eatbeh.2021.101562
31. Masheb RM et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2021;54(7):1171-1180. doi:10.1002/eat.23501
32. Masheb RM et al. Eat Weight Disord. 2019;24(6):1063-1070. doi:10.1007/s40519-019-00766-w
33. Etuk R et al. Mil Med. 2022;187(3-4):297-303. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab533
34. Serier KN et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2022;55(4):470-480. doi:10.1002/eat.23680
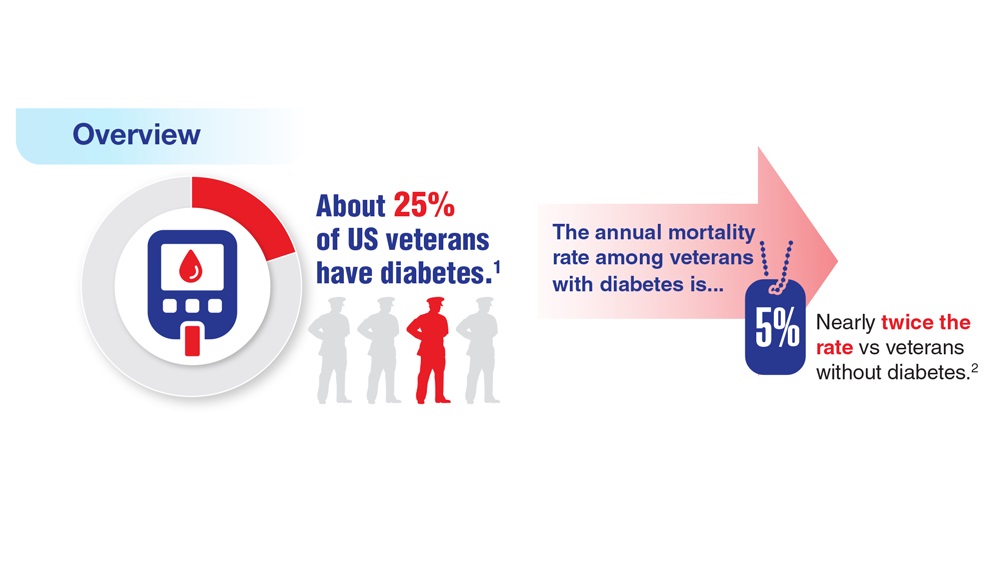
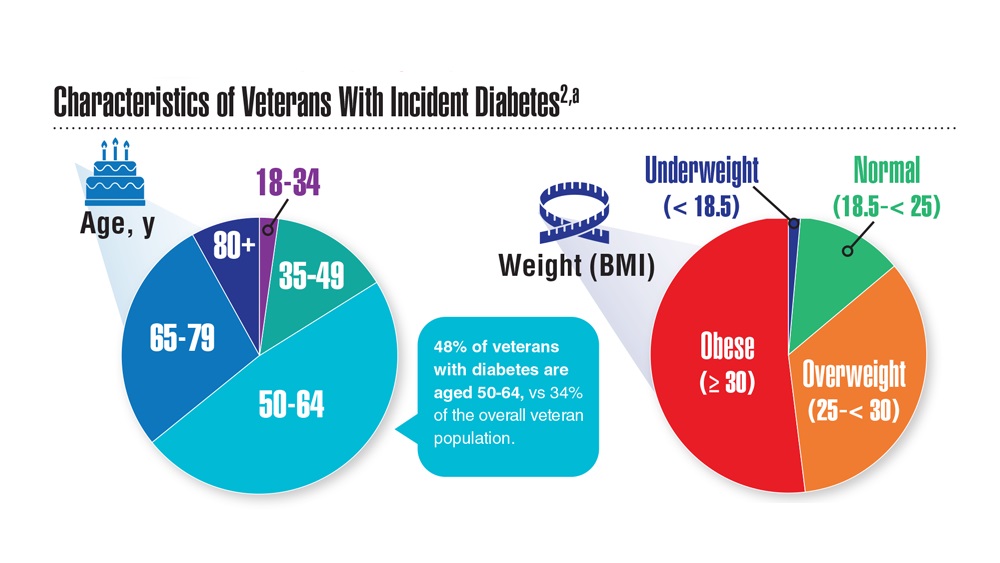
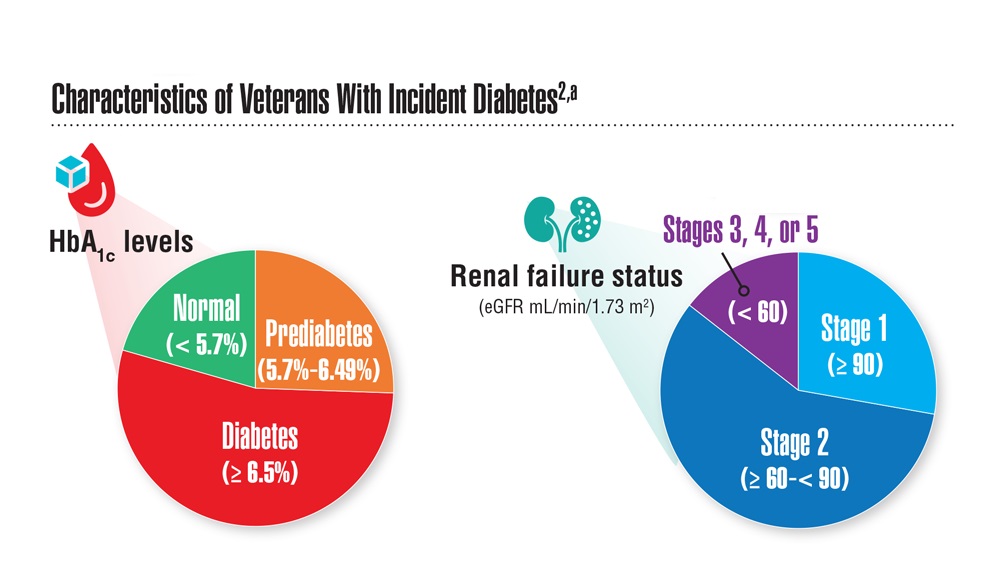
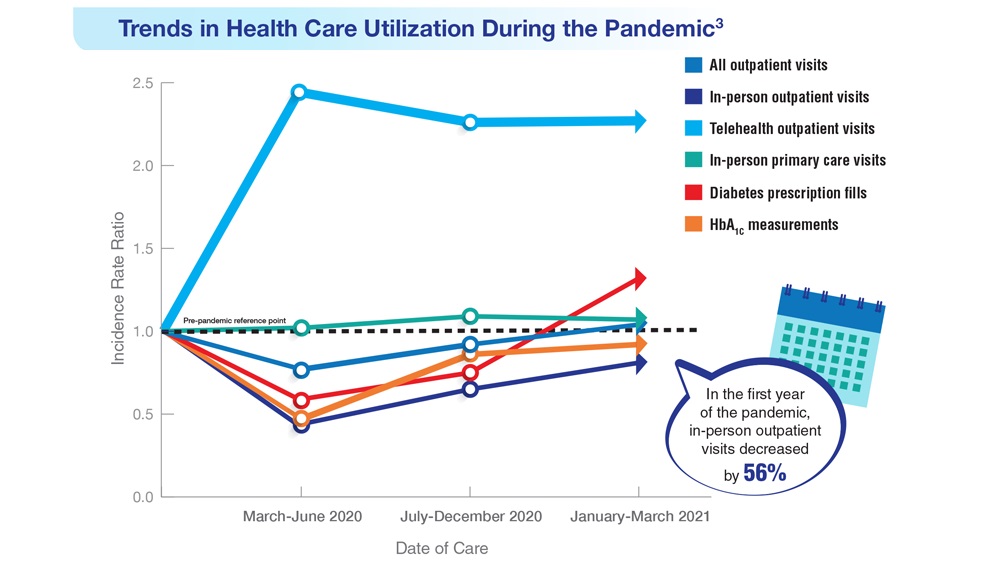
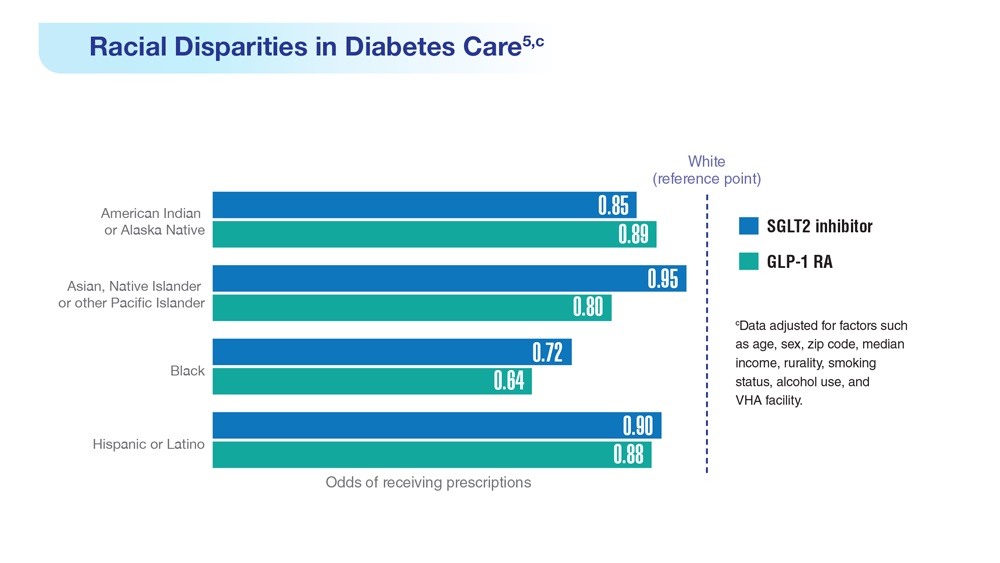
Data Trends 2023: Diabetes
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Nutrition and food services. Diabetes information. Updated December 1, 2022. Accessed April 14, 2023. https://www.nutrition.va.gov/Diabetes.asp
- Avramovic S et al. BMJ Open. 2020;10(12):e039489. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039489
- Adhikari S et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023;23(1):41. doi:10.1186/s12913-023-09057-8
- Zhou P et al. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022;21(1):759-768. doi:10.1007/s40200-022-01049-5
- Lamprea-Montealegre JA et al. JAMA. 2022;328(9):861-871. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.13885
- Fairman KA, Buckley K. Health Psychol. 2021;40(1):1-10. doi:10.1037/hea0000889
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Nutrition and food services. Diabetes information. Updated December 1, 2022. Accessed April 14, 2023. https://www.nutrition.va.gov/Diabetes.asp
- Avramovic S et al. BMJ Open. 2020;10(12):e039489. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039489
- Adhikari S et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023;23(1):41. doi:10.1186/s12913-023-09057-8
- Zhou P et al. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022;21(1):759-768. doi:10.1007/s40200-022-01049-5
- Lamprea-Montealegre JA et al. JAMA. 2022;328(9):861-871. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.13885
- Fairman KA, Buckley K. Health Psychol. 2021;40(1):1-10. doi:10.1037/hea0000889
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Nutrition and food services. Diabetes information. Updated December 1, 2022. Accessed April 14, 2023. https://www.nutrition.va.gov/Diabetes.asp
- Avramovic S et al. BMJ Open. 2020;10(12):e039489. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039489
- Adhikari S et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023;23(1):41. doi:10.1186/s12913-023-09057-8
- Zhou P et al. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022;21(1):759-768. doi:10.1007/s40200-022-01049-5
- Lamprea-Montealegre JA et al. JAMA. 2022;328(9):861-871. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.13885
- Fairman KA, Buckley K. Health Psychol. 2021;40(1):1-10. doi:10.1037/hea0000889
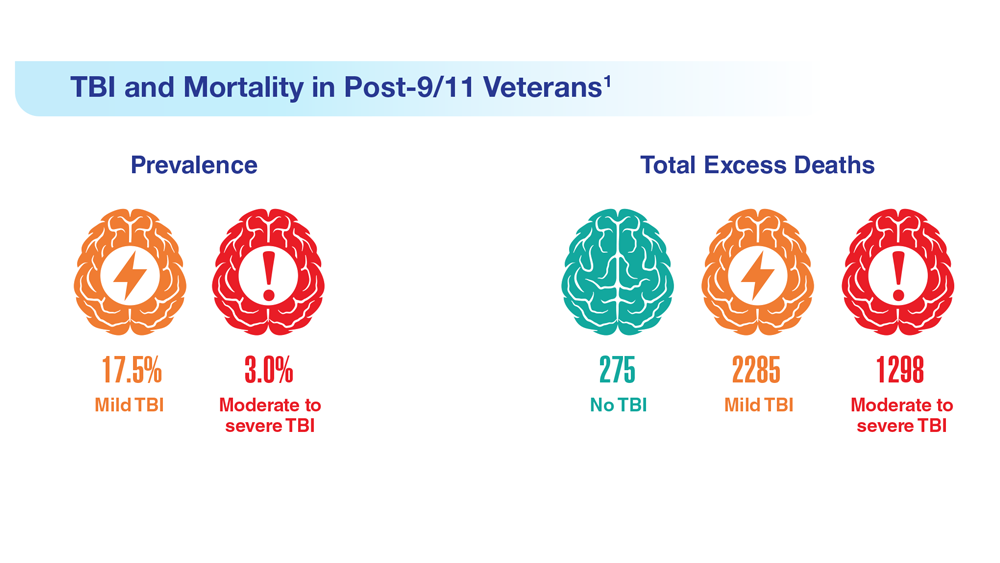
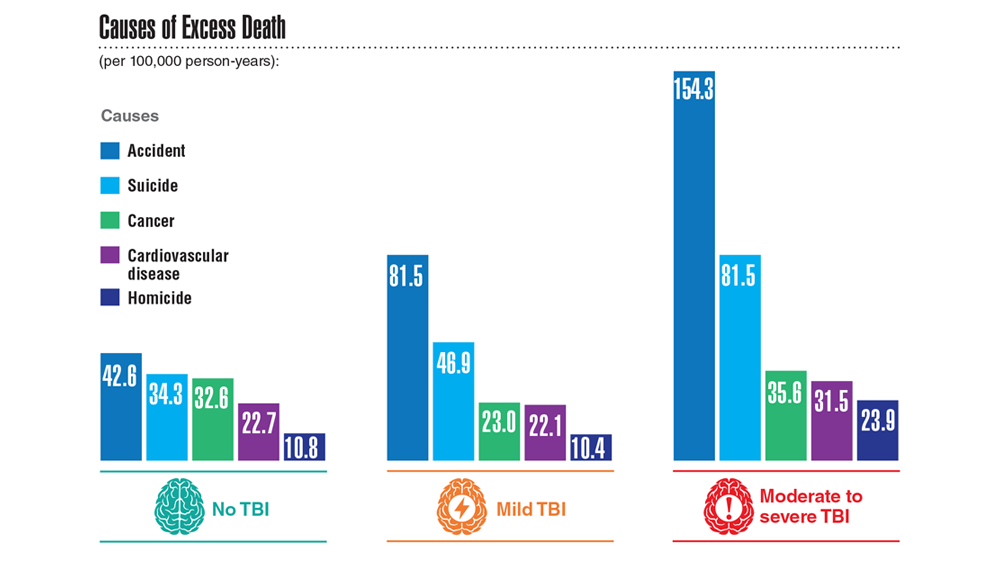
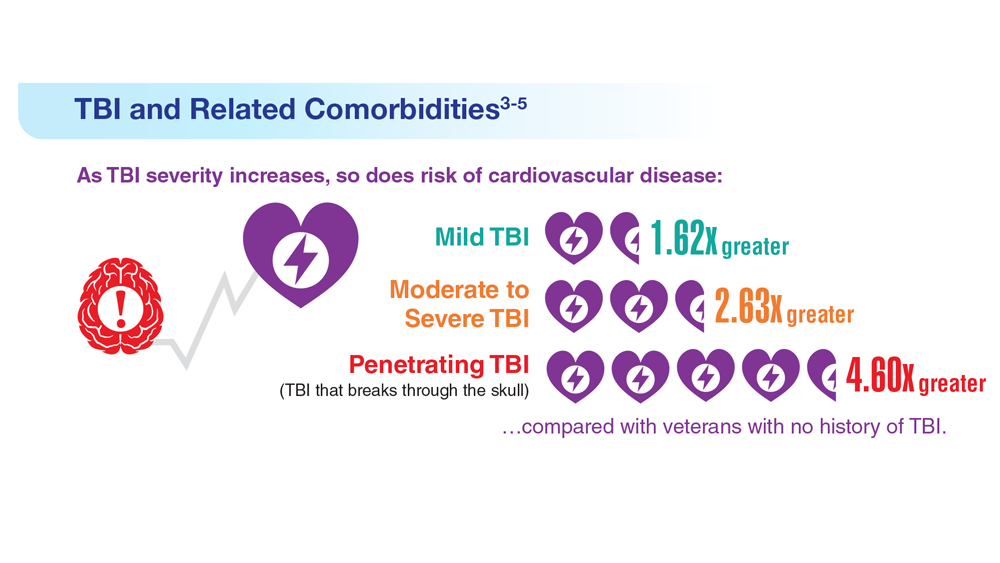
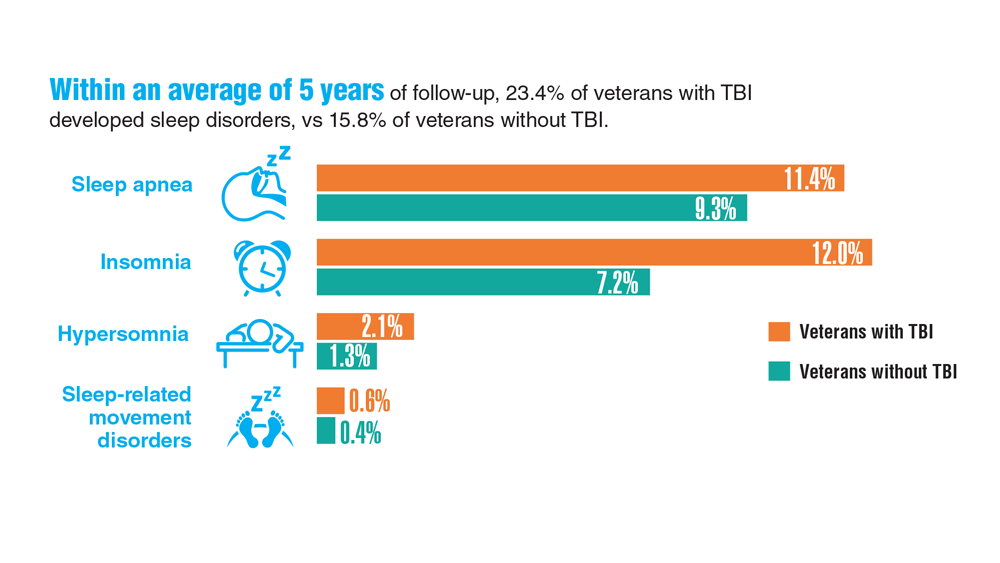
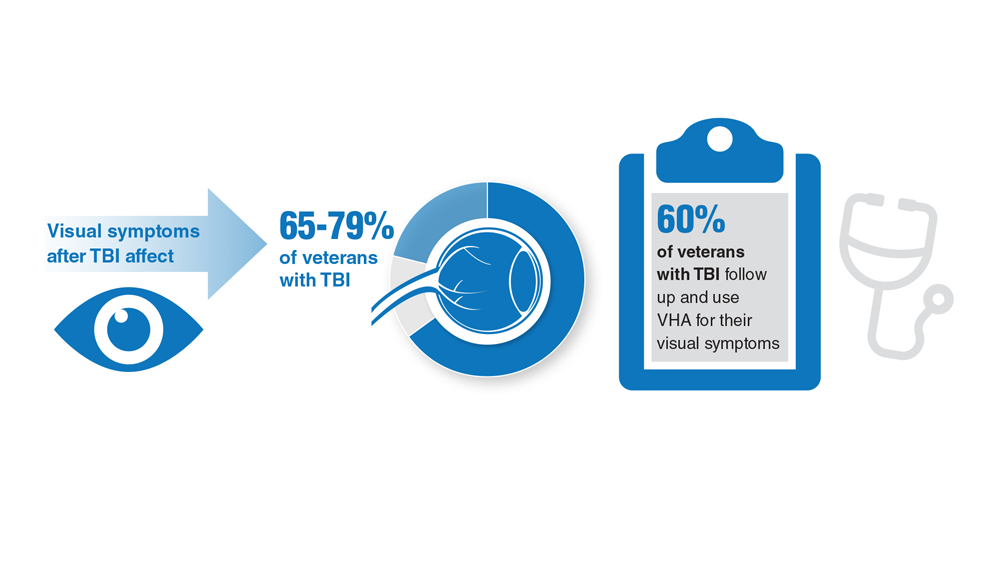
Data Trends 2023: Traumatic Brain Injury
- Howard JT et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(2):e2148150. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.48150
- Cogan AM et al. PM R. 2020;12(3):301-314. doi:10.1002/pmrj.12237
- Stewart IJ et al. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79(11):1122-1129. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.2682
- Leng Y et al. Neurology. 2021;96(13):e1792-e1799. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000011656
- Winkler SL et al. Optom Vis Sci. 2022;99(1):3-8. doi:10.1097/OPX.0000000000001824
- Howard JT et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(2):e2148150. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.48150
- Cogan AM et al. PM R. 2020;12(3):301-314. doi:10.1002/pmrj.12237
- Stewart IJ et al. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79(11):1122-1129. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.2682
- Leng Y et al. Neurology. 2021;96(13):e1792-e1799. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000011656
- Winkler SL et al. Optom Vis Sci. 2022;99(1):3-8. doi:10.1097/OPX.0000000000001824
- Howard JT et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(2):e2148150. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.48150
- Cogan AM et al. PM R. 2020;12(3):301-314. doi:10.1002/pmrj.12237
- Stewart IJ et al. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79(11):1122-1129. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.2682
- Leng Y et al. Neurology. 2021;96(13):e1792-e1799. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000011656
- Winkler SL et al. Optom Vis Sci. 2022;99(1):3-8. doi:10.1097/OPX.0000000000001824
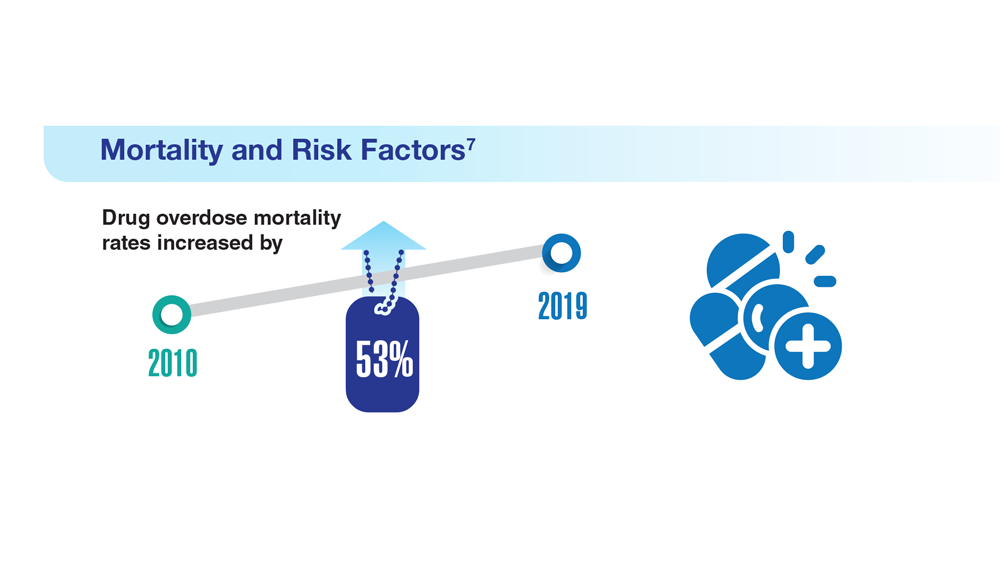
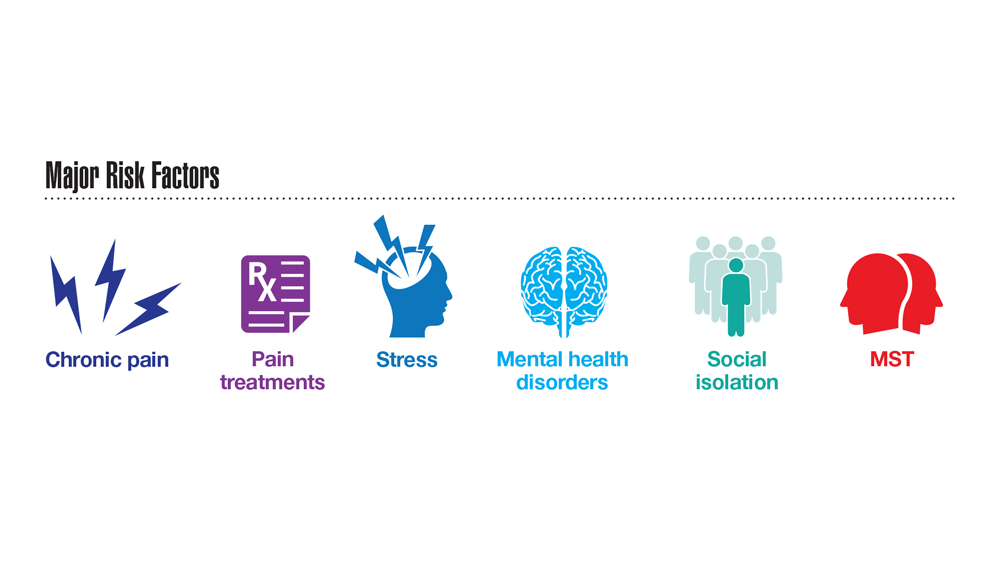
Data Trends 2023: Opioid Use Disorder
7. Bennett AS et al. Ann Med. 2022;54(1):1826-1838. doi:10.1080/07853890.2022.2092896
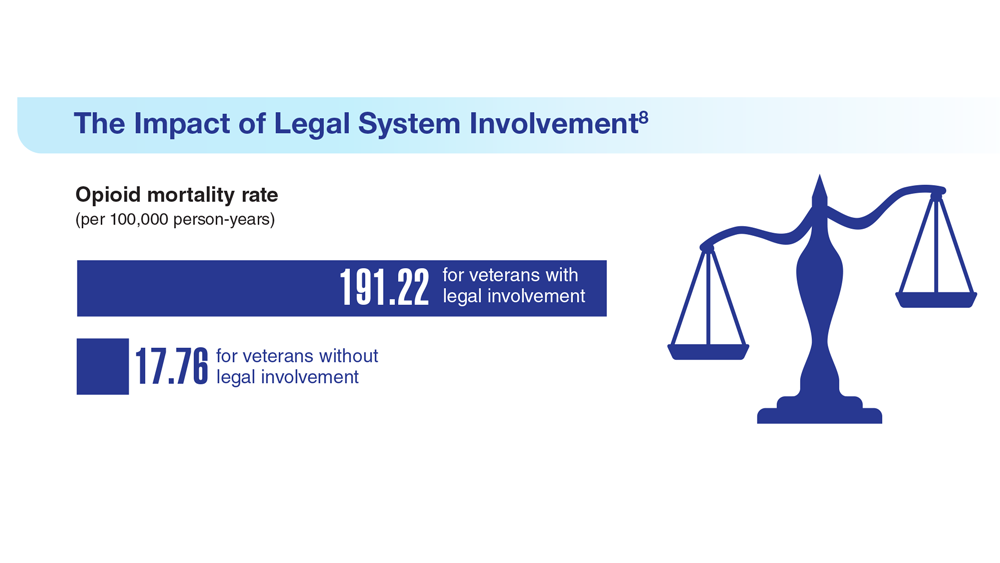
8. Finlay AK et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;62(1):e29-e37. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2021.06.014
9. Peltier MR et al. J Dual Diagn. 2021;17(2):124-134. doi:10.1080/15504263.2021.1904162
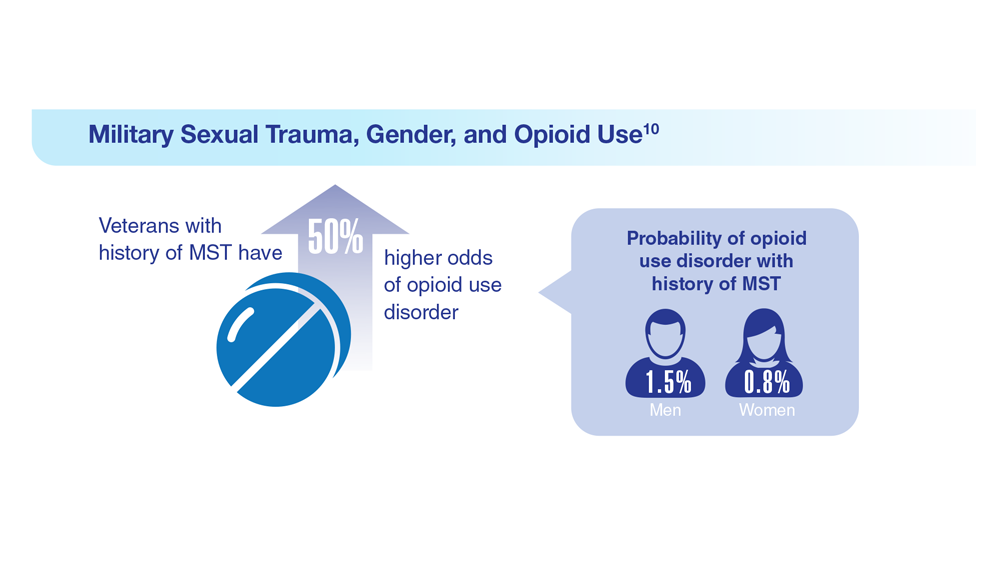
10. Beckman KL et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;62(3):377-386. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2021.08.020
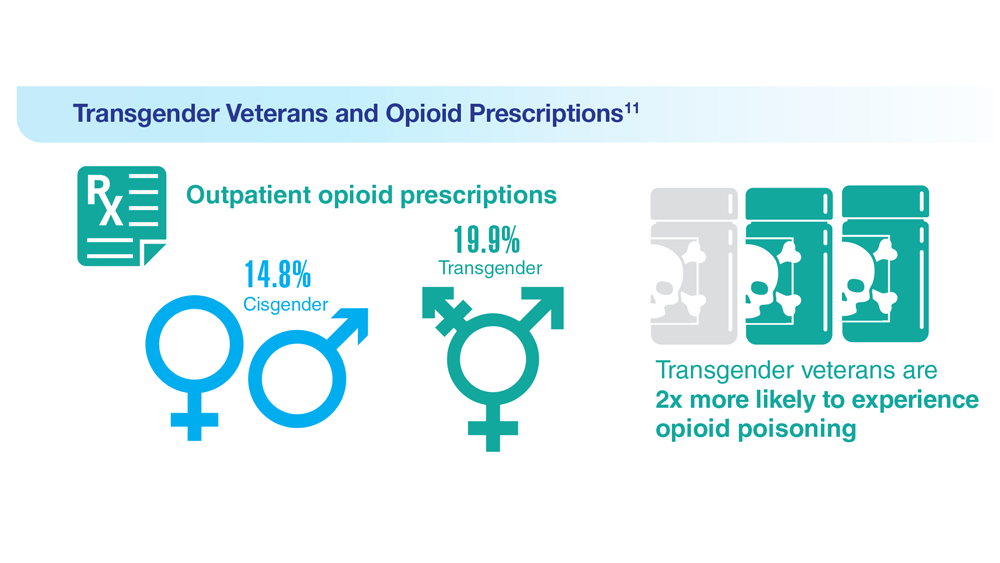
11. Boyer TL et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;63(2):168-177. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2022.02.011
12. Jasuja GK et al. Med Care. 2021;59(suppl 2):S165-S169. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001437
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Public and Intergovernmental Affairs. VA’s Rapid Naloxone Initiative recognized in fight against opioid overdose deaths. Published June 8, 2021. Accessed April 21, 2023. https://www.va.gov/opa/pressrel/pressrelease.cfm?id=5679
14. Chen EF, et. al. Fed Pract. 2022;39(3):136-141. doi:10.12788/fp.0236
7. Bennett AS et al. Ann Med. 2022;54(1):1826-1838. doi:10.1080/07853890.2022.2092896
8. Finlay AK et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;62(1):e29-e37. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2021.06.014
9. Peltier MR et al. J Dual Diagn. 2021;17(2):124-134. doi:10.1080/15504263.2021.1904162
10. Beckman KL et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;62(3):377-386. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2021.08.020
11. Boyer TL et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;63(2):168-177. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2022.02.011
12. Jasuja GK et al. Med Care. 2021;59(suppl 2):S165-S169. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001437
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Public and Intergovernmental Affairs. VA’s Rapid Naloxone Initiative recognized in fight against opioid overdose deaths. Published June 8, 2021. Accessed April 21, 2023. https://www.va.gov/opa/pressrel/pressrelease.cfm?id=5679
14. Chen EF, et. al. Fed Pract. 2022;39(3):136-141. doi:10.12788/fp.0236
7. Bennett AS et al. Ann Med. 2022;54(1):1826-1838. doi:10.1080/07853890.2022.2092896
8. Finlay AK et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;62(1):e29-e37. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2021.06.014
9. Peltier MR et al. J Dual Diagn. 2021;17(2):124-134. doi:10.1080/15504263.2021.1904162
10. Beckman KL et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;62(3):377-386. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2021.08.020
11. Boyer TL et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;63(2):168-177. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2022.02.011
12. Jasuja GK et al. Med Care. 2021;59(suppl 2):S165-S169. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001437
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Public and Intergovernmental Affairs. VA’s Rapid Naloxone Initiative recognized in fight against opioid overdose deaths. Published June 8, 2021. Accessed April 21, 2023. https://www.va.gov/opa/pressrel/pressrelease.cfm?id=5679
14. Chen EF, et. al. Fed Pract. 2022;39(3):136-141. doi:10.12788/fp.0236
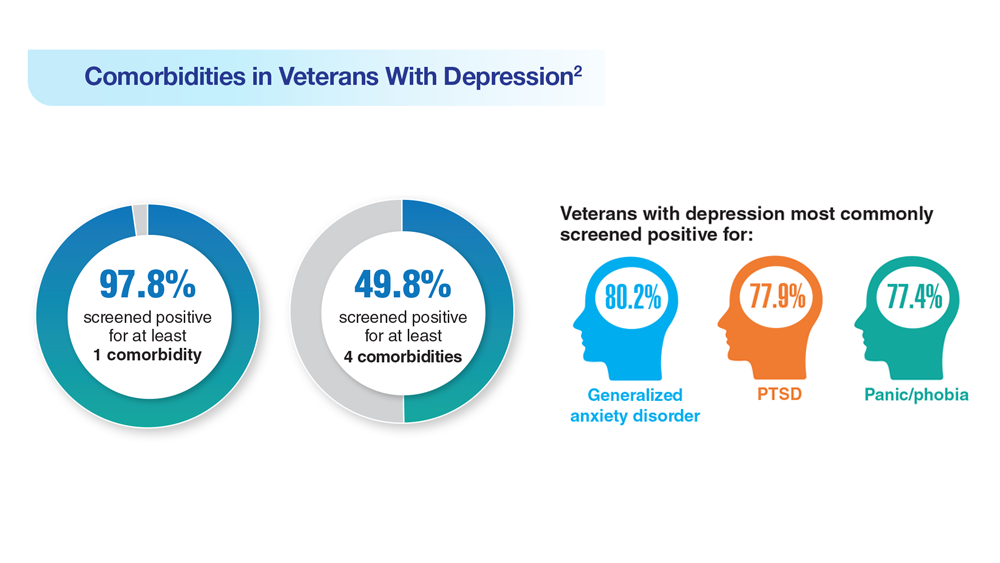
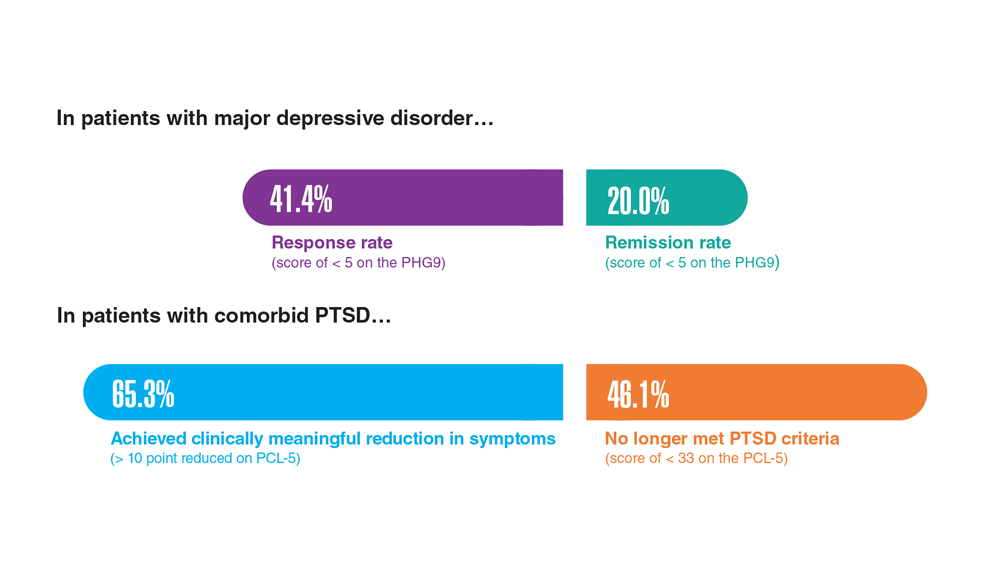
Data Trends 2023: Depression
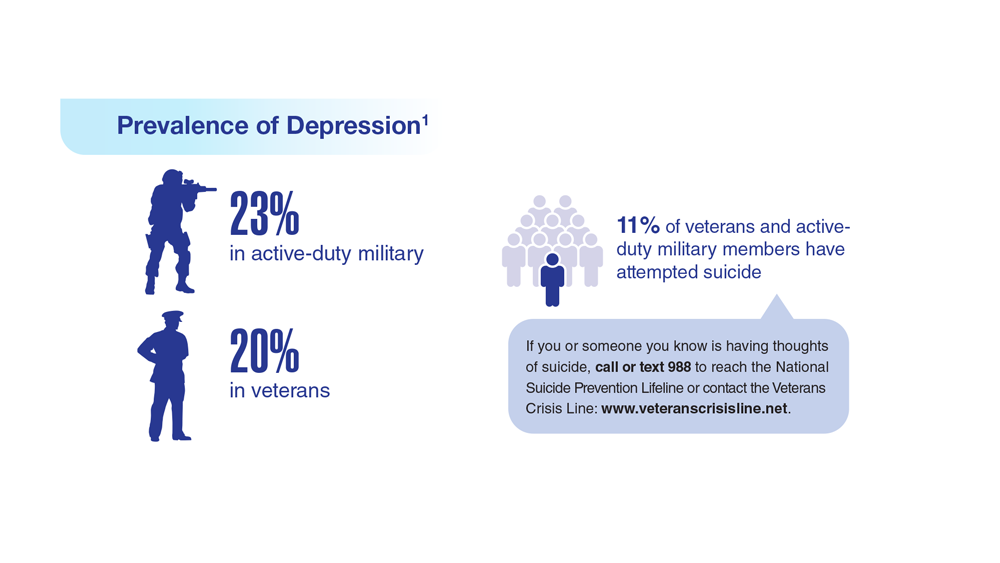
1. Moradi Y et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):510. doi:10.1186/s12888-021-03526-2
2. Ziobrowski HN et al. J Affect Disord. 2021;290:227-236. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2021.04.033
3. Szukis H et al. Curr Med Res Opin. 2021;37(8):1393-1401. doi:10.1080/03007995.2021.1918073
4. Levey DF et al. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24(7):954-963. doi:10.1038/s41593-021-00860-2
5. Madore MR et al. J Affect Disord. 2022;297:671-678. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2021.10.025
6. Cheng CM et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1305:333-349. doi:10.1007/978-981-33-6044-0_18
1. Moradi Y et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):510. doi:10.1186/s12888-021-03526-2
2. Ziobrowski HN et al. J Affect Disord. 2021;290:227-236. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2021.04.033
3. Szukis H et al. Curr Med Res Opin. 2021;37(8):1393-1401. doi:10.1080/03007995.2021.1918073
4. Levey DF et al. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24(7):954-963. doi:10.1038/s41593-021-00860-2
5. Madore MR et al. J Affect Disord. 2022;297:671-678. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2021.10.025
6. Cheng CM et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1305:333-349. doi:10.1007/978-981-33-6044-0_18
1. Moradi Y et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):510. doi:10.1186/s12888-021-03526-2
2. Ziobrowski HN et al. J Affect Disord. 2021;290:227-236. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2021.04.033
3. Szukis H et al. Curr Med Res Opin. 2021;37(8):1393-1401. doi:10.1080/03007995.2021.1918073
4. Levey DF et al. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24(7):954-963. doi:10.1038/s41593-021-00860-2
5. Madore MR et al. J Affect Disord. 2022;297:671-678. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2021.10.025
6. Cheng CM et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1305:333-349. doi:10.1007/978-981-33-6044-0_18
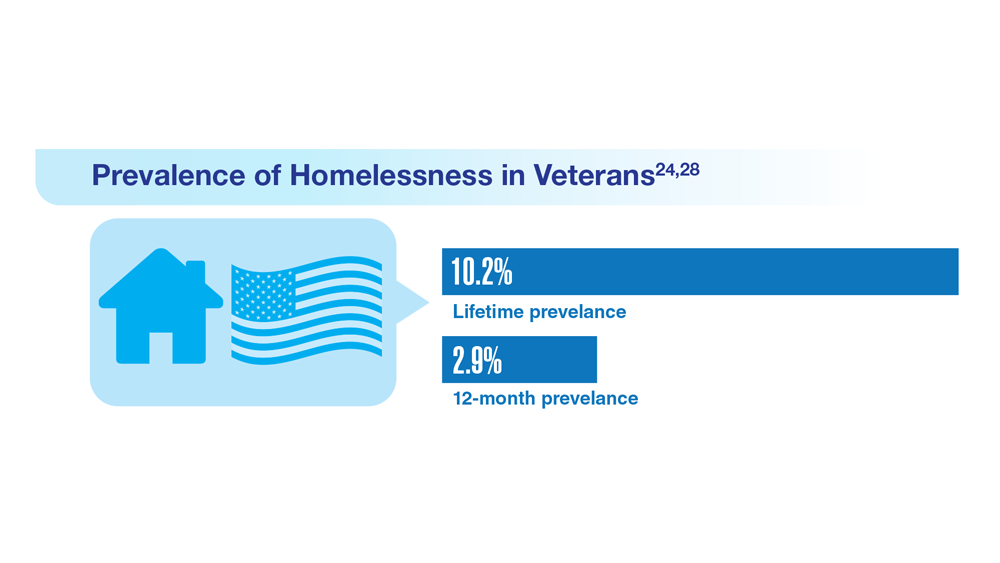
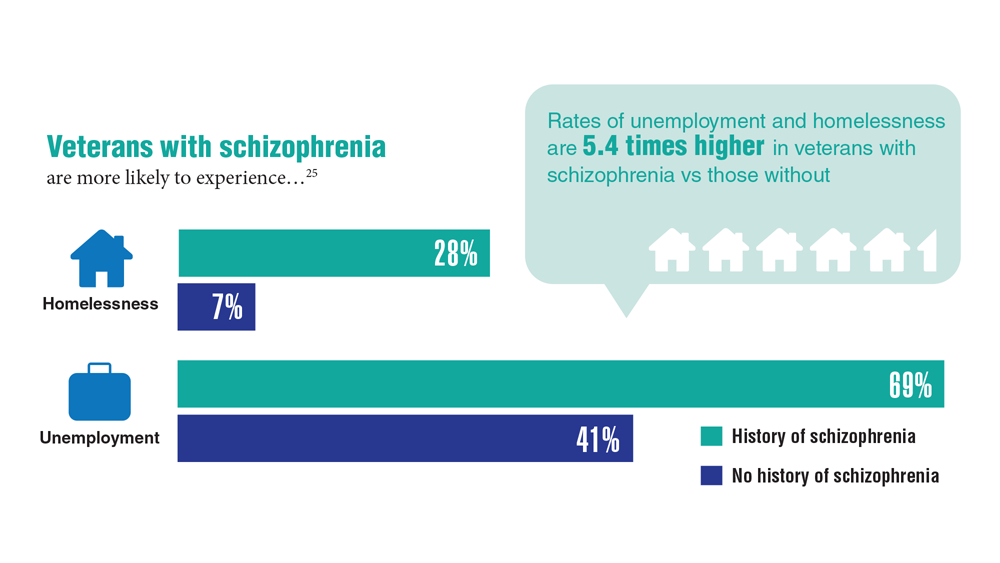
Data Trends 2023: Homelessness
24. Nichter B et al. Psychol Med. 2022;1-11. doi:10.1017/S0033291722000617
25. Lin D et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):458. doi:10.1186/s12888-022-04022-x
26. Jutkowitz E et al. R I Med J (2013). 2021;104(4):20-25. Published 2021 May 3.
27. Holliday R et al. Fed Pract. 2022;39(1):8-11. doi:10.12788/fp.0216
28. Koh KA et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;63(1):13-23. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2021.12.028
24. Nichter B et al. Psychol Med. 2022;1-11. doi:10.1017/S0033291722000617
25. Lin D et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):458. doi:10.1186/s12888-022-04022-x
26. Jutkowitz E et al. R I Med J (2013). 2021;104(4):20-25. Published 2021 May 3.
27. Holliday R et al. Fed Pract. 2022;39(1):8-11. doi:10.12788/fp.0216
28. Koh KA et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;63(1):13-23. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2021.12.028
24. Nichter B et al. Psychol Med. 2022;1-11. doi:10.1017/S0033291722000617
25. Lin D et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):458. doi:10.1186/s12888-022-04022-x
26. Jutkowitz E et al. R I Med J (2013). 2021;104(4):20-25. Published 2021 May 3.
27. Holliday R et al. Fed Pract. 2022;39(1):8-11. doi:10.12788/fp.0216
28. Koh KA et al. Am J Prev Med. 2022;63(1):13-23. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2021.12.028