User login
Top 5 Tips for Becoming an Effective Gastroenterology Consultant
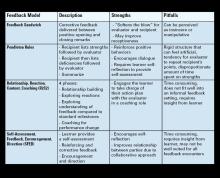
Gastroenterology (GI) subspecialty training is carefully designed to develop expertise in digestive diseases and gastrointestinal endoscopy, while facilitating the transition from generalist to subspecialty consultant. The concept of effective consultation extends far beyond clinical expertise and has been explored repeatedly, beginning with Goldman’s “Ten Commandments” in 1983.1,2 How should these best practices be specifically applied to GI? More importantly, what kind of experience would you want if you were the referring provider or the patient themselves?
Below are
1. Be Kind
Survey studies of medical/surgical residents and attending hospitalists have demonstrated that willingness to accept consultation requests was the single factor consistently rated as most important in determining the quality of the consultation interaction.3,4 Unfortunately, nearly 65% of respondents reported encountering pushback when requesting subspecialty consultation. It is critical to recognize that when you receive a GI consult request, the requester has already decided that it is needed. Whether that request comports with our individual notion of “necessary” or “important,” this is a colleague’s request for help. There are myriad reasons why a request may be made, but they are unified in this principle.
Effective teamwork in healthcare settings enhances clinical performance and patient safety. Positive relationships with colleagues and healthcare team members also mitigate the emotional basis for physician burnout.5 Be kind and courteous to those who seek your assistance. Move beyond the notion of the “bad” or “soft” consult and seek instead to understand how you can help.
A requesting physician may phrase the consult question vaguely or may know that the patient is having a GI-related issue, but simply lack the specific knowledge to know what is needed. In these instances, it is our role to listen and help guide them to the correct thought process to ensure the best care of the patient. These important interactions establish our reputation, create our referral bases, and directly affect our sense of personal satisfaction.
2. Be Timely
GI presents an appealing breadth of pathology, but this also corresponds to a wide variety of indications for consultation and, therefore, urgency of need. In a busy clinical practice, not all requests can be urgently prioritized. However, it is the consultant’s responsibility to identify patients that require urgent evaluation and intervention to avert a potential adverse outcome.
We are well-trained in the medical triage of consultations. There are explicit guidelines for assessing urgency for GI bleeding, foreign body ingestion, choledocholithiasis, and many other indications. However, there are often special contextual circumstances that will elevate the urgency of a seemingly non-urgent consult request. Does the patient have an upcoming surgery or treatment that will depend on your input? Are they facing an imminent loss of insurance coverage? Is their non-severe GI disease leading to more severe impact on non-GI organ systems? The referring provider knows the patient better than you – seek to understand the context of the consult request.
Timeliness also applies to our communication. Communicate recommendations directly to the consulting service as soon as the patient is seen. When a colleague reaches out with a concern about a patient, make sure to take that request seriously. If you are unable to address the concern immediately, at least provide acknowledgment and an estimated timeline for response. As the maxim states, the effectiveness of a consultant is just as dependent on availability as it is on ability.
3. Be Specific
The same survey studies indicate that the second most critical aspect of successful subspecialty consultation is delivering clear recommendations. Accordingly, I always urge my trainees to challenge me when we leave a consult interaction if they feel that our plan is vague or imprecise.
Specificity in consult recommendations is an essential way to demonstrate your expertise and provide value. Clear and definitive recommendations enhance others’ perception of your skill, reduce the need for additional clarifying communication, and lead to more efficient, higher quality care. Avoid vague language, such as asking the requester to “consider” a test or intervention. When recommending medication, specify the dose, frequency, duration, and expected timeline of effect. Rather than recommending “cross-sectional imaging,” specify what modality and protocol. Instead of recommending “adequate resuscitation,” specify your target endpoints. If you engage in multidisciplinary discussion, ensure you strive for a specific group consensus plan and communicate this to all members of the team.
Specificity also applies to the quality of your documentation. Ensure that your clinical notes outline your rationale for your recommended plan, specific contingencies based on results of recommended testing, and a plan for follow-up care. When referring for open-access endoscopy, specifically outline what to look for and which specimens or endoscopic interventions are needed. Be precise in your procedure documentation – avoid vague terms such as small/medium/large and instead quantify in terms of millimeter/centimeter measurement. If you do not adopt specific classification schemes (e.g. Prague classification, Paris classification, Eosinophilic Esophagitis Endoscopic Reference Score, etc.), ensure you provide enough descriptive language to convey an adequate understanding of the findings.
4. Be Helpful
A consultant’s primary directive is to be of service to the consulting provider and the patient. As an educational leader, I am often asked what attributes separate a high-performing trainee from an average one. My feeling is that the most critical attribute is a sense of ownership over patient care.
As a consultant, when others feel we are exhibiting engagement and ownership in a patient’s care, they perceive that we are working together as an effective healthcare team. Interestingly, survey studies of inpatient care show that primary services do not necessarily value assistance with orders or care coordination – they consider these as core aspects of their daily work. What they did value was ongoing daily progress notes/communication, regardless of patient acuity or consulting specialty. This is a potent signal that our continued engagement (both inpatient and outpatient) is perceived as helpful.
Helpfulness is further aided by ensuring mutual understanding. While survey data indicate that sharing specific literature citations may not always be perceived positively, explaining the consultant’s rationale for their recommendations is highly valued. Take the time to tactfully explain your assessment of the patient and why you arrived at your specific recommendations. If your recommendations differ from what the requester expected (e.g. a procedure was expected but is not offered), ensure you explain why and answer questions they may have. This fosters mutual respect and proactively averts conflict or discontent from misunderstanding.
Multidisciplinary collaboration is another important avenue for aiding our patients and colleagues. Studies across a wide range of disease processes (including GI bleeding, IBD, etc.) and medical settings have demonstrated that multidisciplinary collaboration unequivocally improves patient outcomes.6 The success of these collaborations relies on our willingness to fully engage in these conversations, despite the fact that they may often be logistically challenging.
We all know how difficult it can be to locate and organize multiple medical specialists with complex varying clinical schedules and busy personal lives. Choosing to do so demonstrates a dedication to providing the highest level of care and elevates both patient and physician satisfaction. Having chosen to cultivate several ongoing multidisciplinary conferences/collaborations, I can attest to the notion that the outcome is well worth the effort.
5. Be Honest
While we always strive to provide the answers for our patients and colleagues, we must also acknowledge our limitations. Be honest with yourself when you encounter a scenario that pushes beyond the boundaries of your knowledge and comfort. Be willing to admit when you yourself need to consult others or seek an outside referral to provide the care a patient needs. Aspiring physicians often espouse that a devotion to lifelong learning is a key driver of their desire to pursue a career in medicine. These scenarios provide a key opportunity to expand our knowledge while doing what is right for our patients.
Be equally honest about your comfort with “curbside” consultations. Studies show that subspecialists receive on average of 3-4 such requests per week.7 The perception of these interactions is starkly discrepant between the requester and recipient. While over 80% of surveyed primary nonsurgical services felt that curbside consultations were helpful in patient care, a similar proportion of subspecialists expressed concern that insufficient clinical information was provided, even leading to a fear of litigation. While straightforward, informal conversations on narrow, well-defined questions can be helpful and efficient, the consultant should always feel comfortable seeking an opportunity for formal consultation when the details are unclear or the case/question is complex.
Closing Thoughts
Being an effective GI consultant isn’t just about what you know—it’s about how you apply it, how you communicate it, and how you make others feel in the process.
The attributes outlined above are not ancillary traits—they are essential components of high-quality consultation. When consistently applied, they enhance collaboration, improve patient outcomes, and reinforce trust within the healthcare system. By committing to them, you establish your reputation of excellence and play a role in elevating the field of gastroenterology more broadly.
Dr. Kahn is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Arizona. He reports no conflicts of interest in regard to this article.
References
1. Goldman L, et al. Ten commandments for effective consultations. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Sep.
2. Salerno SM, et al. Principles of effective consultation: an update for the 21st-century consultant. Arch Intern Med. 2007 Feb. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.3.271.
3. Adams TN, et al. Hospitalist Perspective of Interactions with Medicine Subspecialty Consult Services. J Hosp Med. 2018 May. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2882.
4. Matsuo T, et al. Essential consultants’ skills and attitudes (Willing CONSULT): a cross-sectional survey. BMC Med Educ. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02810-9.
5. Welp A, Manser T. Integrating teamwork, clinician occupational well-being and patient safety - development of a conceptual framework based on a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016 Jul. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1535-y.
6. Webster CS, et al. Interprofessional Learning in Multidisciplinary Healthcare Teams Is Associated With Reduced Patient Mortality: A Quantitative Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Patient Saf. 2024 Jan. doi: 10.1097/PTS.0000000000001170.
7. Lin M, et al. Curbside Consultations: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.09.026.
Gastroenterology (GI) subspecialty training is carefully designed to develop expertise in digestive diseases and gastrointestinal endoscopy, while facilitating the transition from generalist to subspecialty consultant. The concept of effective consultation extends far beyond clinical expertise and has been explored repeatedly, beginning with Goldman’s “Ten Commandments” in 1983.1,2 How should these best practices be specifically applied to GI? More importantly, what kind of experience would you want if you were the referring provider or the patient themselves?
Below are
1. Be Kind
Survey studies of medical/surgical residents and attending hospitalists have demonstrated that willingness to accept consultation requests was the single factor consistently rated as most important in determining the quality of the consultation interaction.3,4 Unfortunately, nearly 65% of respondents reported encountering pushback when requesting subspecialty consultation. It is critical to recognize that when you receive a GI consult request, the requester has already decided that it is needed. Whether that request comports with our individual notion of “necessary” or “important,” this is a colleague’s request for help. There are myriad reasons why a request may be made, but they are unified in this principle.
Effective teamwork in healthcare settings enhances clinical performance and patient safety. Positive relationships with colleagues and healthcare team members also mitigate the emotional basis for physician burnout.5 Be kind and courteous to those who seek your assistance. Move beyond the notion of the “bad” or “soft” consult and seek instead to understand how you can help.
A requesting physician may phrase the consult question vaguely or may know that the patient is having a GI-related issue, but simply lack the specific knowledge to know what is needed. In these instances, it is our role to listen and help guide them to the correct thought process to ensure the best care of the patient. These important interactions establish our reputation, create our referral bases, and directly affect our sense of personal satisfaction.
2. Be Timely
GI presents an appealing breadth of pathology, but this also corresponds to a wide variety of indications for consultation and, therefore, urgency of need. In a busy clinical practice, not all requests can be urgently prioritized. However, it is the consultant’s responsibility to identify patients that require urgent evaluation and intervention to avert a potential adverse outcome.
We are well-trained in the medical triage of consultations. There are explicit guidelines for assessing urgency for GI bleeding, foreign body ingestion, choledocholithiasis, and many other indications. However, there are often special contextual circumstances that will elevate the urgency of a seemingly non-urgent consult request. Does the patient have an upcoming surgery or treatment that will depend on your input? Are they facing an imminent loss of insurance coverage? Is their non-severe GI disease leading to more severe impact on non-GI organ systems? The referring provider knows the patient better than you – seek to understand the context of the consult request.
Timeliness also applies to our communication. Communicate recommendations directly to the consulting service as soon as the patient is seen. When a colleague reaches out with a concern about a patient, make sure to take that request seriously. If you are unable to address the concern immediately, at least provide acknowledgment and an estimated timeline for response. As the maxim states, the effectiveness of a consultant is just as dependent on availability as it is on ability.
3. Be Specific
The same survey studies indicate that the second most critical aspect of successful subspecialty consultation is delivering clear recommendations. Accordingly, I always urge my trainees to challenge me when we leave a consult interaction if they feel that our plan is vague or imprecise.
Specificity in consult recommendations is an essential way to demonstrate your expertise and provide value. Clear and definitive recommendations enhance others’ perception of your skill, reduce the need for additional clarifying communication, and lead to more efficient, higher quality care. Avoid vague language, such as asking the requester to “consider” a test or intervention. When recommending medication, specify the dose, frequency, duration, and expected timeline of effect. Rather than recommending “cross-sectional imaging,” specify what modality and protocol. Instead of recommending “adequate resuscitation,” specify your target endpoints. If you engage in multidisciplinary discussion, ensure you strive for a specific group consensus plan and communicate this to all members of the team.
Specificity also applies to the quality of your documentation. Ensure that your clinical notes outline your rationale for your recommended plan, specific contingencies based on results of recommended testing, and a plan for follow-up care. When referring for open-access endoscopy, specifically outline what to look for and which specimens or endoscopic interventions are needed. Be precise in your procedure documentation – avoid vague terms such as small/medium/large and instead quantify in terms of millimeter/centimeter measurement. If you do not adopt specific classification schemes (e.g. Prague classification, Paris classification, Eosinophilic Esophagitis Endoscopic Reference Score, etc.), ensure you provide enough descriptive language to convey an adequate understanding of the findings.
4. Be Helpful
A consultant’s primary directive is to be of service to the consulting provider and the patient. As an educational leader, I am often asked what attributes separate a high-performing trainee from an average one. My feeling is that the most critical attribute is a sense of ownership over patient care.
As a consultant, when others feel we are exhibiting engagement and ownership in a patient’s care, they perceive that we are working together as an effective healthcare team. Interestingly, survey studies of inpatient care show that primary services do not necessarily value assistance with orders or care coordination – they consider these as core aspects of their daily work. What they did value was ongoing daily progress notes/communication, regardless of patient acuity or consulting specialty. This is a potent signal that our continued engagement (both inpatient and outpatient) is perceived as helpful.
Helpfulness is further aided by ensuring mutual understanding. While survey data indicate that sharing specific literature citations may not always be perceived positively, explaining the consultant’s rationale for their recommendations is highly valued. Take the time to tactfully explain your assessment of the patient and why you arrived at your specific recommendations. If your recommendations differ from what the requester expected (e.g. a procedure was expected but is not offered), ensure you explain why and answer questions they may have. This fosters mutual respect and proactively averts conflict or discontent from misunderstanding.
Multidisciplinary collaboration is another important avenue for aiding our patients and colleagues. Studies across a wide range of disease processes (including GI bleeding, IBD, etc.) and medical settings have demonstrated that multidisciplinary collaboration unequivocally improves patient outcomes.6 The success of these collaborations relies on our willingness to fully engage in these conversations, despite the fact that they may often be logistically challenging.
We all know how difficult it can be to locate and organize multiple medical specialists with complex varying clinical schedules and busy personal lives. Choosing to do so demonstrates a dedication to providing the highest level of care and elevates both patient and physician satisfaction. Having chosen to cultivate several ongoing multidisciplinary conferences/collaborations, I can attest to the notion that the outcome is well worth the effort.
5. Be Honest
While we always strive to provide the answers for our patients and colleagues, we must also acknowledge our limitations. Be honest with yourself when you encounter a scenario that pushes beyond the boundaries of your knowledge and comfort. Be willing to admit when you yourself need to consult others or seek an outside referral to provide the care a patient needs. Aspiring physicians often espouse that a devotion to lifelong learning is a key driver of their desire to pursue a career in medicine. These scenarios provide a key opportunity to expand our knowledge while doing what is right for our patients.
Be equally honest about your comfort with “curbside” consultations. Studies show that subspecialists receive on average of 3-4 such requests per week.7 The perception of these interactions is starkly discrepant between the requester and recipient. While over 80% of surveyed primary nonsurgical services felt that curbside consultations were helpful in patient care, a similar proportion of subspecialists expressed concern that insufficient clinical information was provided, even leading to a fear of litigation. While straightforward, informal conversations on narrow, well-defined questions can be helpful and efficient, the consultant should always feel comfortable seeking an opportunity for formal consultation when the details are unclear or the case/question is complex.
Closing Thoughts
Being an effective GI consultant isn’t just about what you know—it’s about how you apply it, how you communicate it, and how you make others feel in the process.
The attributes outlined above are not ancillary traits—they are essential components of high-quality consultation. When consistently applied, they enhance collaboration, improve patient outcomes, and reinforce trust within the healthcare system. By committing to them, you establish your reputation of excellence and play a role in elevating the field of gastroenterology more broadly.
Dr. Kahn is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Arizona. He reports no conflicts of interest in regard to this article.
References
1. Goldman L, et al. Ten commandments for effective consultations. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Sep.
2. Salerno SM, et al. Principles of effective consultation: an update for the 21st-century consultant. Arch Intern Med. 2007 Feb. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.3.271.
3. Adams TN, et al. Hospitalist Perspective of Interactions with Medicine Subspecialty Consult Services. J Hosp Med. 2018 May. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2882.
4. Matsuo T, et al. Essential consultants’ skills and attitudes (Willing CONSULT): a cross-sectional survey. BMC Med Educ. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02810-9.
5. Welp A, Manser T. Integrating teamwork, clinician occupational well-being and patient safety - development of a conceptual framework based on a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016 Jul. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1535-y.
6. Webster CS, et al. Interprofessional Learning in Multidisciplinary Healthcare Teams Is Associated With Reduced Patient Mortality: A Quantitative Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Patient Saf. 2024 Jan. doi: 10.1097/PTS.0000000000001170.
7. Lin M, et al. Curbside Consultations: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.09.026.
Gastroenterology (GI) subspecialty training is carefully designed to develop expertise in digestive diseases and gastrointestinal endoscopy, while facilitating the transition from generalist to subspecialty consultant. The concept of effective consultation extends far beyond clinical expertise and has been explored repeatedly, beginning with Goldman’s “Ten Commandments” in 1983.1,2 How should these best practices be specifically applied to GI? More importantly, what kind of experience would you want if you were the referring provider or the patient themselves?
Below are
1. Be Kind
Survey studies of medical/surgical residents and attending hospitalists have demonstrated that willingness to accept consultation requests was the single factor consistently rated as most important in determining the quality of the consultation interaction.3,4 Unfortunately, nearly 65% of respondents reported encountering pushback when requesting subspecialty consultation. It is critical to recognize that when you receive a GI consult request, the requester has already decided that it is needed. Whether that request comports with our individual notion of “necessary” or “important,” this is a colleague’s request for help. There are myriad reasons why a request may be made, but they are unified in this principle.
Effective teamwork in healthcare settings enhances clinical performance and patient safety. Positive relationships with colleagues and healthcare team members also mitigate the emotional basis for physician burnout.5 Be kind and courteous to those who seek your assistance. Move beyond the notion of the “bad” or “soft” consult and seek instead to understand how you can help.
A requesting physician may phrase the consult question vaguely or may know that the patient is having a GI-related issue, but simply lack the specific knowledge to know what is needed. In these instances, it is our role to listen and help guide them to the correct thought process to ensure the best care of the patient. These important interactions establish our reputation, create our referral bases, and directly affect our sense of personal satisfaction.
2. Be Timely
GI presents an appealing breadth of pathology, but this also corresponds to a wide variety of indications for consultation and, therefore, urgency of need. In a busy clinical practice, not all requests can be urgently prioritized. However, it is the consultant’s responsibility to identify patients that require urgent evaluation and intervention to avert a potential adverse outcome.
We are well-trained in the medical triage of consultations. There are explicit guidelines for assessing urgency for GI bleeding, foreign body ingestion, choledocholithiasis, and many other indications. However, there are often special contextual circumstances that will elevate the urgency of a seemingly non-urgent consult request. Does the patient have an upcoming surgery or treatment that will depend on your input? Are they facing an imminent loss of insurance coverage? Is their non-severe GI disease leading to more severe impact on non-GI organ systems? The referring provider knows the patient better than you – seek to understand the context of the consult request.
Timeliness also applies to our communication. Communicate recommendations directly to the consulting service as soon as the patient is seen. When a colleague reaches out with a concern about a patient, make sure to take that request seriously. If you are unable to address the concern immediately, at least provide acknowledgment and an estimated timeline for response. As the maxim states, the effectiveness of a consultant is just as dependent on availability as it is on ability.
3. Be Specific
The same survey studies indicate that the second most critical aspect of successful subspecialty consultation is delivering clear recommendations. Accordingly, I always urge my trainees to challenge me when we leave a consult interaction if they feel that our plan is vague or imprecise.
Specificity in consult recommendations is an essential way to demonstrate your expertise and provide value. Clear and definitive recommendations enhance others’ perception of your skill, reduce the need for additional clarifying communication, and lead to more efficient, higher quality care. Avoid vague language, such as asking the requester to “consider” a test or intervention. When recommending medication, specify the dose, frequency, duration, and expected timeline of effect. Rather than recommending “cross-sectional imaging,” specify what modality and protocol. Instead of recommending “adequate resuscitation,” specify your target endpoints. If you engage in multidisciplinary discussion, ensure you strive for a specific group consensus plan and communicate this to all members of the team.
Specificity also applies to the quality of your documentation. Ensure that your clinical notes outline your rationale for your recommended plan, specific contingencies based on results of recommended testing, and a plan for follow-up care. When referring for open-access endoscopy, specifically outline what to look for and which specimens or endoscopic interventions are needed. Be precise in your procedure documentation – avoid vague terms such as small/medium/large and instead quantify in terms of millimeter/centimeter measurement. If you do not adopt specific classification schemes (e.g. Prague classification, Paris classification, Eosinophilic Esophagitis Endoscopic Reference Score, etc.), ensure you provide enough descriptive language to convey an adequate understanding of the findings.
4. Be Helpful
A consultant’s primary directive is to be of service to the consulting provider and the patient. As an educational leader, I am often asked what attributes separate a high-performing trainee from an average one. My feeling is that the most critical attribute is a sense of ownership over patient care.
As a consultant, when others feel we are exhibiting engagement and ownership in a patient’s care, they perceive that we are working together as an effective healthcare team. Interestingly, survey studies of inpatient care show that primary services do not necessarily value assistance with orders or care coordination – they consider these as core aspects of their daily work. What they did value was ongoing daily progress notes/communication, regardless of patient acuity or consulting specialty. This is a potent signal that our continued engagement (both inpatient and outpatient) is perceived as helpful.
Helpfulness is further aided by ensuring mutual understanding. While survey data indicate that sharing specific literature citations may not always be perceived positively, explaining the consultant’s rationale for their recommendations is highly valued. Take the time to tactfully explain your assessment of the patient and why you arrived at your specific recommendations. If your recommendations differ from what the requester expected (e.g. a procedure was expected but is not offered), ensure you explain why and answer questions they may have. This fosters mutual respect and proactively averts conflict or discontent from misunderstanding.
Multidisciplinary collaboration is another important avenue for aiding our patients and colleagues. Studies across a wide range of disease processes (including GI bleeding, IBD, etc.) and medical settings have demonstrated that multidisciplinary collaboration unequivocally improves patient outcomes.6 The success of these collaborations relies on our willingness to fully engage in these conversations, despite the fact that they may often be logistically challenging.
We all know how difficult it can be to locate and organize multiple medical specialists with complex varying clinical schedules and busy personal lives. Choosing to do so demonstrates a dedication to providing the highest level of care and elevates both patient and physician satisfaction. Having chosen to cultivate several ongoing multidisciplinary conferences/collaborations, I can attest to the notion that the outcome is well worth the effort.
5. Be Honest
While we always strive to provide the answers for our patients and colleagues, we must also acknowledge our limitations. Be honest with yourself when you encounter a scenario that pushes beyond the boundaries of your knowledge and comfort. Be willing to admit when you yourself need to consult others or seek an outside referral to provide the care a patient needs. Aspiring physicians often espouse that a devotion to lifelong learning is a key driver of their desire to pursue a career in medicine. These scenarios provide a key opportunity to expand our knowledge while doing what is right for our patients.
Be equally honest about your comfort with “curbside” consultations. Studies show that subspecialists receive on average of 3-4 such requests per week.7 The perception of these interactions is starkly discrepant between the requester and recipient. While over 80% of surveyed primary nonsurgical services felt that curbside consultations were helpful in patient care, a similar proportion of subspecialists expressed concern that insufficient clinical information was provided, even leading to a fear of litigation. While straightforward, informal conversations on narrow, well-defined questions can be helpful and efficient, the consultant should always feel comfortable seeking an opportunity for formal consultation when the details are unclear or the case/question is complex.
Closing Thoughts
Being an effective GI consultant isn’t just about what you know—it’s about how you apply it, how you communicate it, and how you make others feel in the process.
The attributes outlined above are not ancillary traits—they are essential components of high-quality consultation. When consistently applied, they enhance collaboration, improve patient outcomes, and reinforce trust within the healthcare system. By committing to them, you establish your reputation of excellence and play a role in elevating the field of gastroenterology more broadly.
Dr. Kahn is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Arizona. He reports no conflicts of interest in regard to this article.
References
1. Goldman L, et al. Ten commandments for effective consultations. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Sep.
2. Salerno SM, et al. Principles of effective consultation: an update for the 21st-century consultant. Arch Intern Med. 2007 Feb. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.3.271.
3. Adams TN, et al. Hospitalist Perspective of Interactions with Medicine Subspecialty Consult Services. J Hosp Med. 2018 May. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2882.
4. Matsuo T, et al. Essential consultants’ skills and attitudes (Willing CONSULT): a cross-sectional survey. BMC Med Educ. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02810-9.
5. Welp A, Manser T. Integrating teamwork, clinician occupational well-being and patient safety - development of a conceptual framework based on a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016 Jul. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1535-y.
6. Webster CS, et al. Interprofessional Learning in Multidisciplinary Healthcare Teams Is Associated With Reduced Patient Mortality: A Quantitative Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Patient Saf. 2024 Jan. doi: 10.1097/PTS.0000000000001170.
7. Lin M, et al. Curbside Consultations: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.09.026.
Choosing the Best Formalin-Resistant Ink for Biopsy Specimen Labeling
Choosing the Best Formalin-Resistant Ink for Biopsy Specimen Labeling
Practice Gap
Many dermatology practices utilize pens and markers to label biopsy specimen containers, but the ink may have variable susceptibility to fading and smearing when exposed to moisture before processing. Specimen containers often are placed in plastic bags for transport. If formalin accidentally spills into the bag during this time, the labels may be exposed to moisture for hours, overnight, or even over a weekend. Effective labeling with formalin-resistant ink is crucial for maintaining the clarity of anatomic location and planning treatment, especially when multiple samples are obtained.
The Technique
We tested 12 pens and markers commonly used when labeling specimen containers to determine their susceptibility to fading due to accidental formalin exposure (Figure). Various inks were allowed to dry on sample specimen labels for 5 minutes before a thin layer of 10% buffered formalin was evenly distributed over the dried ink. Photographs of the labels were taken at baseline as well as 15 minutes, 1 hour, 3 hours, and 24 hours after formalin exposure.
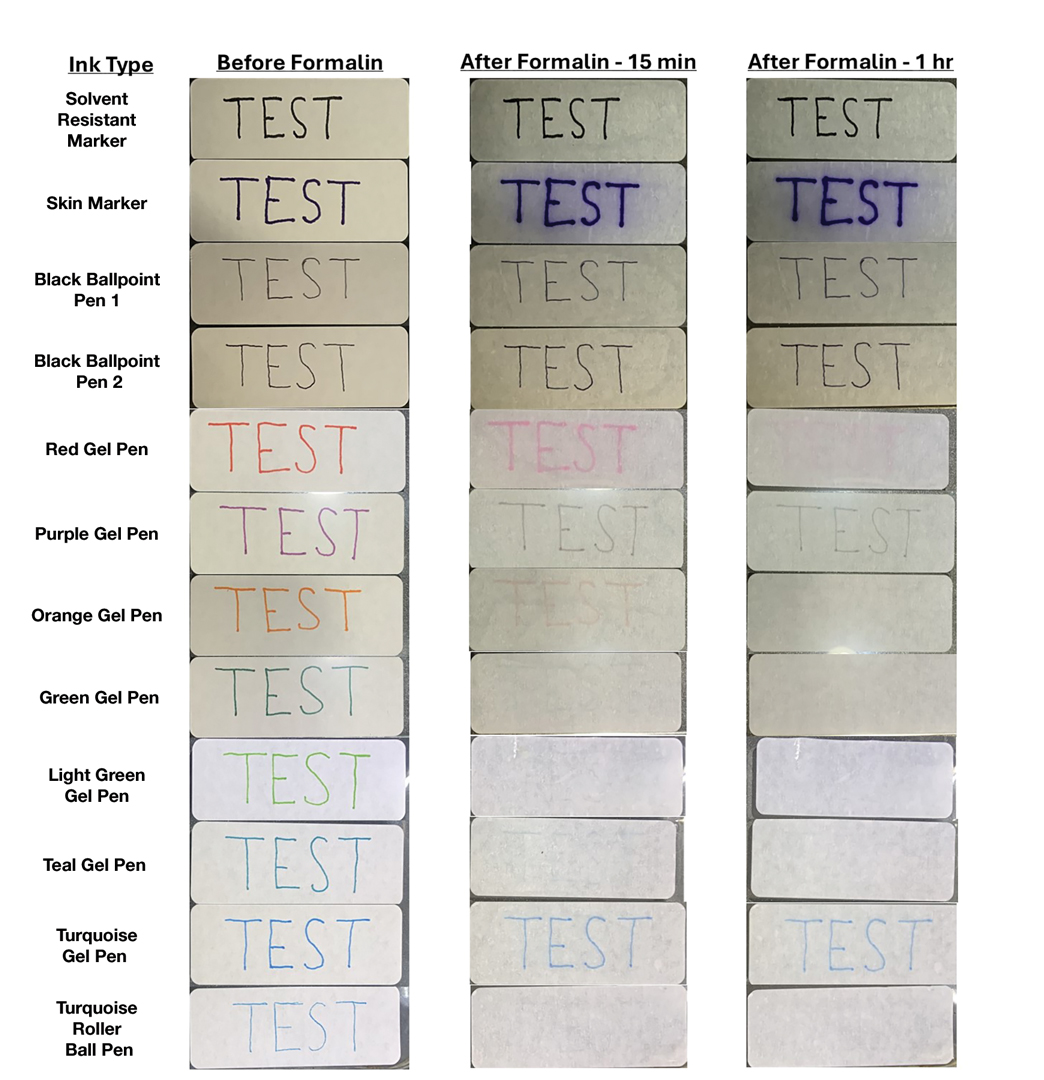
Fading was observed in both the skin marker and gel panes after 15 minutes and peaked after 1 hour. Gel pens were most susceptible to fading on exposure to formalin, and the level of fading varied by ink color, with certain colors disappearing almost entirely (Figure). The solvent-resistant marker had a robust defense to formalin, as did both ballpoint pens.
Practice Implications
Given our findings, dermatology practices should avoid using gel pens to label specimen containers. Solvent-resistant markers performed as expected; however, ballpoint pens appeared to withstand formalin exposure to a similar degree and often are more readily available. Labeling biopsy specimens with an appropriate ink ensures that each sample is clearly identified with the appropriate anatomic location and any other relevant patient information.
Practice Gap
Many dermatology practices utilize pens and markers to label biopsy specimen containers, but the ink may have variable susceptibility to fading and smearing when exposed to moisture before processing. Specimen containers often are placed in plastic bags for transport. If formalin accidentally spills into the bag during this time, the labels may be exposed to moisture for hours, overnight, or even over a weekend. Effective labeling with formalin-resistant ink is crucial for maintaining the clarity of anatomic location and planning treatment, especially when multiple samples are obtained.
The Technique
We tested 12 pens and markers commonly used when labeling specimen containers to determine their susceptibility to fading due to accidental formalin exposure (Figure). Various inks were allowed to dry on sample specimen labels for 5 minutes before a thin layer of 10% buffered formalin was evenly distributed over the dried ink. Photographs of the labels were taken at baseline as well as 15 minutes, 1 hour, 3 hours, and 24 hours after formalin exposure.

Fading was observed in both the skin marker and gel panes after 15 minutes and peaked after 1 hour. Gel pens were most susceptible to fading on exposure to formalin, and the level of fading varied by ink color, with certain colors disappearing almost entirely (Figure). The solvent-resistant marker had a robust defense to formalin, as did both ballpoint pens.
Practice Implications
Given our findings, dermatology practices should avoid using gel pens to label specimen containers. Solvent-resistant markers performed as expected; however, ballpoint pens appeared to withstand formalin exposure to a similar degree and often are more readily available. Labeling biopsy specimens with an appropriate ink ensures that each sample is clearly identified with the appropriate anatomic location and any other relevant patient information.
Practice Gap
Many dermatology practices utilize pens and markers to label biopsy specimen containers, but the ink may have variable susceptibility to fading and smearing when exposed to moisture before processing. Specimen containers often are placed in plastic bags for transport. If formalin accidentally spills into the bag during this time, the labels may be exposed to moisture for hours, overnight, or even over a weekend. Effective labeling with formalin-resistant ink is crucial for maintaining the clarity of anatomic location and planning treatment, especially when multiple samples are obtained.
The Technique
We tested 12 pens and markers commonly used when labeling specimen containers to determine their susceptibility to fading due to accidental formalin exposure (Figure). Various inks were allowed to dry on sample specimen labels for 5 minutes before a thin layer of 10% buffered formalin was evenly distributed over the dried ink. Photographs of the labels were taken at baseline as well as 15 minutes, 1 hour, 3 hours, and 24 hours after formalin exposure.

Fading was observed in both the skin marker and gel panes after 15 minutes and peaked after 1 hour. Gel pens were most susceptible to fading on exposure to formalin, and the level of fading varied by ink color, with certain colors disappearing almost entirely (Figure). The solvent-resistant marker had a robust defense to formalin, as did both ballpoint pens.
Practice Implications
Given our findings, dermatology practices should avoid using gel pens to label specimen containers. Solvent-resistant markers performed as expected; however, ballpoint pens appeared to withstand formalin exposure to a similar degree and often are more readily available. Labeling biopsy specimens with an appropriate ink ensures that each sample is clearly identified with the appropriate anatomic location and any other relevant patient information.
Choosing the Best Formalin-Resistant Ink for Biopsy Specimen Labeling
Choosing the Best Formalin-Resistant Ink for Biopsy Specimen Labeling
Colonoscopy Costs Rise When Private Equity Acquires GI Practices, but Quality Does Not
Price increases ranged from about 5% to about 7%.
In view of the growing trend to such acquisitions, policy makers should monitor the impact of PE investment in medical practices, according to researchers led by health economist Daniel R. Arnold, PhD, of the Department of Health Services, Policy & Practice in the School of Public Health at Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island. “In a previous study of ours, gastroenterology stood out as a particularly attractive specialty to private equity,” Arnold told GI & Hepatology News.
Published in JAMA Health Forum, the economic evaluation of more than 1.1 million patients and 1.3 million colonoscopies concluded that PE acquisitions of GI sites are difficult to justify.
The Study
This difference-in-differences event study and economic evaluation analyzed data from US GI practices acquired by PE firms from 2015 to 2021. Commercial insurance claims covering more than 50 million enrollees were used to calculate price, spending, utilization, and quality measures from 2012 to 2021, with all data analyzed from April to September 2024.
The main outcomes were price, spending per physician, number of colonoscopies per physician, number of unique patients per physician, and quality, as defined by polyp detection, incomplete colonoscopies, and four adverse event measures: cardiovascular, serious and nonserious GI events, and any other adverse events.
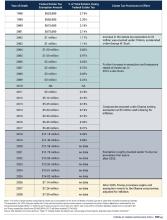
The mean age of patients was 47.1 years, and 47.8% were men. The sample included 718, 851 colonoscopies conducted by 1494 physicians in 590, 900 patients across 1240 PE-acquired practice sites and 637, 990 control colonoscopies conducted by 2550 physicians in 527,380 patients across 2657 independent practice sites.
Among the findings:
- Colonoscopy prices at PE-acquired sites increased by 4.5% (95% CI, 2.5-6.6; P < .001) vs independent practices. That increase was much lower than that reported by Singh and colleagues for .
- The estimated price increase was 6.7% (95% CI, 4.2-9.3; P < .001) when only colonoscopies at PE practices with market shares above the 75th percentile (24.4%) in 2021 were considered. Both increases were in line with other research, Arnold said.
- Colonoscopy spending per physician increased by 16.0% (95% CI, 8.4%-24.0%; P < .001), while the number of colonoscopies and the number of unique patients per physician increased by 12.1% (95% CI, 5.3-19.4; P < .001) and 11.3% (95% CI, 4.4%-18.5%; P < .001), respectively. These measures, however, were already increasing before PE acquisition.
- No statistically significant associations were detected for the six quality measures analyzed.
Could such cost-raising acquisitions potentially be blocked by concerned regulators?
“No. Generally the purchases are at prices below what would require notification to federal authorities,” Arnold said. “The Department of Justice/Federal Trade Commission hinted at being willing to look at serial acquisitions in their 2023 Merger Guidelines, but until that happens, these will likely continue to fly under the radar.”
Still, as evidence of PE-associated poorer quality outcomes as well as clinician burnout continues to emerge, Arnold added, “I would advise physicians who get buyout offers from PE to educate themselves on what could happen to patients and staff if they choose to sell.”
Offering an outsider’s perspective on the study, health economist Atul Gupta, PhD, an assistant professor of healthcare management in the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, called it an “excellent addition to the developing literature examining the effects of private equity ownership of healthcare providers.” Very few studies have examined the effects on prices and quality for the same set of deals and providers. “This is important because we want to be able to do an apples-to-apples comparison of the effects on both outcomes before judging PE ownership,” he told GI & Hepatology News.
In an accompanying editorial , primary care physician Jane M. Zhu, MD, an associate professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, Oregon, and not involved in the commercial-insurance-based study, said one interpretation of the findings may be that PE acquisition focuses on reducing inefficiencies, improving access by expanding practice capacity, and increasing throughput. “Another interpretation may be that PE acquisition is focused on the strategic exploitation of market and pricing power. The latter may have less of an impact on clinical measures like quality of care, but potentially, both strategies could be at play.”
Since this analysis focused on the commercial population, understanding how patient demographics may change after PE acquisition is a future avenue for exploration. “For instance, a potential explanation for both the price and utilization shifts might be if payer mix shifted toward more commercially insured patients at the expense of Medicaid or Medicare patients,” she wrote.
Zhu added that the impact of PE on prices and spending, by now replicated across different settings and specialties, is far clearer than the effect of PE on access and quality. “The analysis by Arnold et al is a welcome addition to the literature, generating important questions for future study and transparent monitoring as investor-owners become increasingly influential in healthcare.”
Going forward, said Gupta, an open question is whether the harmful effects of PE ownership of practices are differentially worse than those of other corporate entities such as insurers and hospital systems.
“There are reasons to believe that PE could be worse in theory. For example, their short-term investment horizon may force them to take measures that others will not as well as avoid investing into capital improvements that have a long-run payoff,” he said. “Their uniquely high dependence on debt and unbundling of real estate can severely hurt financial solvency of providers.” But high-quality evidence is lacking to compare the effects from these two distinct forms of corporatization.
The trend away from individual private practice is a reality, Arnold said. “The administrative burden on solo docs is becoming too much and physicians just seem to want to treat patients and not deal with it. So the options at this point really become selling to a hospital system or private equity.”
This study was funded by a grant from the philanthropic foundation Arnold Ventures (no family relation to Daniel Arnold).
Arnold reported receiving grants from Arnold Ventures during the conduct of the study. Gupta had no competing interests to declare. Zhu reported receiving grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality during the submitted work and from the National Institutes of Health, National Institute for Health Care Management Foundation, and American Psychological Association, as well as personal fees from Cambia outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Price increases ranged from about 5% to about 7%.
In view of the growing trend to such acquisitions, policy makers should monitor the impact of PE investment in medical practices, according to researchers led by health economist Daniel R. Arnold, PhD, of the Department of Health Services, Policy & Practice in the School of Public Health at Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island. “In a previous study of ours, gastroenterology stood out as a particularly attractive specialty to private equity,” Arnold told GI & Hepatology News.
Published in JAMA Health Forum, the economic evaluation of more than 1.1 million patients and 1.3 million colonoscopies concluded that PE acquisitions of GI sites are difficult to justify.
The Study
This difference-in-differences event study and economic evaluation analyzed data from US GI practices acquired by PE firms from 2015 to 2021. Commercial insurance claims covering more than 50 million enrollees were used to calculate price, spending, utilization, and quality measures from 2012 to 2021, with all data analyzed from April to September 2024.
The main outcomes were price, spending per physician, number of colonoscopies per physician, number of unique patients per physician, and quality, as defined by polyp detection, incomplete colonoscopies, and four adverse event measures: cardiovascular, serious and nonserious GI events, and any other adverse events.
The mean age of patients was 47.1 years, and 47.8% were men. The sample included 718, 851 colonoscopies conducted by 1494 physicians in 590, 900 patients across 1240 PE-acquired practice sites and 637, 990 control colonoscopies conducted by 2550 physicians in 527,380 patients across 2657 independent practice sites.
Among the findings:
- Colonoscopy prices at PE-acquired sites increased by 4.5% (95% CI, 2.5-6.6; P < .001) vs independent practices. That increase was much lower than that reported by Singh and colleagues for .
- The estimated price increase was 6.7% (95% CI, 4.2-9.3; P < .001) when only colonoscopies at PE practices with market shares above the 75th percentile (24.4%) in 2021 were considered. Both increases were in line with other research, Arnold said.
- Colonoscopy spending per physician increased by 16.0% (95% CI, 8.4%-24.0%; P < .001), while the number of colonoscopies and the number of unique patients per physician increased by 12.1% (95% CI, 5.3-19.4; P < .001) and 11.3% (95% CI, 4.4%-18.5%; P < .001), respectively. These measures, however, were already increasing before PE acquisition.
- No statistically significant associations were detected for the six quality measures analyzed.
Could such cost-raising acquisitions potentially be blocked by concerned regulators?
“No. Generally the purchases are at prices below what would require notification to federal authorities,” Arnold said. “The Department of Justice/Federal Trade Commission hinted at being willing to look at serial acquisitions in their 2023 Merger Guidelines, but until that happens, these will likely continue to fly under the radar.”
Still, as evidence of PE-associated poorer quality outcomes as well as clinician burnout continues to emerge, Arnold added, “I would advise physicians who get buyout offers from PE to educate themselves on what could happen to patients and staff if they choose to sell.”
Offering an outsider’s perspective on the study, health economist Atul Gupta, PhD, an assistant professor of healthcare management in the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, called it an “excellent addition to the developing literature examining the effects of private equity ownership of healthcare providers.” Very few studies have examined the effects on prices and quality for the same set of deals and providers. “This is important because we want to be able to do an apples-to-apples comparison of the effects on both outcomes before judging PE ownership,” he told GI & Hepatology News.
In an accompanying editorial , primary care physician Jane M. Zhu, MD, an associate professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, Oregon, and not involved in the commercial-insurance-based study, said one interpretation of the findings may be that PE acquisition focuses on reducing inefficiencies, improving access by expanding practice capacity, and increasing throughput. “Another interpretation may be that PE acquisition is focused on the strategic exploitation of market and pricing power. The latter may have less of an impact on clinical measures like quality of care, but potentially, both strategies could be at play.”
Since this analysis focused on the commercial population, understanding how patient demographics may change after PE acquisition is a future avenue for exploration. “For instance, a potential explanation for both the price and utilization shifts might be if payer mix shifted toward more commercially insured patients at the expense of Medicaid or Medicare patients,” she wrote.
Zhu added that the impact of PE on prices and spending, by now replicated across different settings and specialties, is far clearer than the effect of PE on access and quality. “The analysis by Arnold et al is a welcome addition to the literature, generating important questions for future study and transparent monitoring as investor-owners become increasingly influential in healthcare.”
Going forward, said Gupta, an open question is whether the harmful effects of PE ownership of practices are differentially worse than those of other corporate entities such as insurers and hospital systems.
“There are reasons to believe that PE could be worse in theory. For example, their short-term investment horizon may force them to take measures that others will not as well as avoid investing into capital improvements that have a long-run payoff,” he said. “Their uniquely high dependence on debt and unbundling of real estate can severely hurt financial solvency of providers.” But high-quality evidence is lacking to compare the effects from these two distinct forms of corporatization.
The trend away from individual private practice is a reality, Arnold said. “The administrative burden on solo docs is becoming too much and physicians just seem to want to treat patients and not deal with it. So the options at this point really become selling to a hospital system or private equity.”
This study was funded by a grant from the philanthropic foundation Arnold Ventures (no family relation to Daniel Arnold).
Arnold reported receiving grants from Arnold Ventures during the conduct of the study. Gupta had no competing interests to declare. Zhu reported receiving grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality during the submitted work and from the National Institutes of Health, National Institute for Health Care Management Foundation, and American Psychological Association, as well as personal fees from Cambia outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Price increases ranged from about 5% to about 7%.
In view of the growing trend to such acquisitions, policy makers should monitor the impact of PE investment in medical practices, according to researchers led by health economist Daniel R. Arnold, PhD, of the Department of Health Services, Policy & Practice in the School of Public Health at Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island. “In a previous study of ours, gastroenterology stood out as a particularly attractive specialty to private equity,” Arnold told GI & Hepatology News.
Published in JAMA Health Forum, the economic evaluation of more than 1.1 million patients and 1.3 million colonoscopies concluded that PE acquisitions of GI sites are difficult to justify.
The Study
This difference-in-differences event study and economic evaluation analyzed data from US GI practices acquired by PE firms from 2015 to 2021. Commercial insurance claims covering more than 50 million enrollees were used to calculate price, spending, utilization, and quality measures from 2012 to 2021, with all data analyzed from April to September 2024.
The main outcomes were price, spending per physician, number of colonoscopies per physician, number of unique patients per physician, and quality, as defined by polyp detection, incomplete colonoscopies, and four adverse event measures: cardiovascular, serious and nonserious GI events, and any other adverse events.
The mean age of patients was 47.1 years, and 47.8% were men. The sample included 718, 851 colonoscopies conducted by 1494 physicians in 590, 900 patients across 1240 PE-acquired practice sites and 637, 990 control colonoscopies conducted by 2550 physicians in 527,380 patients across 2657 independent practice sites.
Among the findings:
- Colonoscopy prices at PE-acquired sites increased by 4.5% (95% CI, 2.5-6.6; P < .001) vs independent practices. That increase was much lower than that reported by Singh and colleagues for .
- The estimated price increase was 6.7% (95% CI, 4.2-9.3; P < .001) when only colonoscopies at PE practices with market shares above the 75th percentile (24.4%) in 2021 were considered. Both increases were in line with other research, Arnold said.
- Colonoscopy spending per physician increased by 16.0% (95% CI, 8.4%-24.0%; P < .001), while the number of colonoscopies and the number of unique patients per physician increased by 12.1% (95% CI, 5.3-19.4; P < .001) and 11.3% (95% CI, 4.4%-18.5%; P < .001), respectively. These measures, however, were already increasing before PE acquisition.
- No statistically significant associations were detected for the six quality measures analyzed.
Could such cost-raising acquisitions potentially be blocked by concerned regulators?
“No. Generally the purchases are at prices below what would require notification to federal authorities,” Arnold said. “The Department of Justice/Federal Trade Commission hinted at being willing to look at serial acquisitions in their 2023 Merger Guidelines, but until that happens, these will likely continue to fly under the radar.”
Still, as evidence of PE-associated poorer quality outcomes as well as clinician burnout continues to emerge, Arnold added, “I would advise physicians who get buyout offers from PE to educate themselves on what could happen to patients and staff if they choose to sell.”
Offering an outsider’s perspective on the study, health economist Atul Gupta, PhD, an assistant professor of healthcare management in the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, called it an “excellent addition to the developing literature examining the effects of private equity ownership of healthcare providers.” Very few studies have examined the effects on prices and quality for the same set of deals and providers. “This is important because we want to be able to do an apples-to-apples comparison of the effects on both outcomes before judging PE ownership,” he told GI & Hepatology News.
In an accompanying editorial , primary care physician Jane M. Zhu, MD, an associate professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, Oregon, and not involved in the commercial-insurance-based study, said one interpretation of the findings may be that PE acquisition focuses on reducing inefficiencies, improving access by expanding practice capacity, and increasing throughput. “Another interpretation may be that PE acquisition is focused on the strategic exploitation of market and pricing power. The latter may have less of an impact on clinical measures like quality of care, but potentially, both strategies could be at play.”
Since this analysis focused on the commercial population, understanding how patient demographics may change after PE acquisition is a future avenue for exploration. “For instance, a potential explanation for both the price and utilization shifts might be if payer mix shifted toward more commercially insured patients at the expense of Medicaid or Medicare patients,” she wrote.
Zhu added that the impact of PE on prices and spending, by now replicated across different settings and specialties, is far clearer than the effect of PE on access and quality. “The analysis by Arnold et al is a welcome addition to the literature, generating important questions for future study and transparent monitoring as investor-owners become increasingly influential in healthcare.”
Going forward, said Gupta, an open question is whether the harmful effects of PE ownership of practices are differentially worse than those of other corporate entities such as insurers and hospital systems.
“There are reasons to believe that PE could be worse in theory. For example, their short-term investment horizon may force them to take measures that others will not as well as avoid investing into capital improvements that have a long-run payoff,” he said. “Their uniquely high dependence on debt and unbundling of real estate can severely hurt financial solvency of providers.” But high-quality evidence is lacking to compare the effects from these two distinct forms of corporatization.
The trend away from individual private practice is a reality, Arnold said. “The administrative burden on solo docs is becoming too much and physicians just seem to want to treat patients and not deal with it. So the options at this point really become selling to a hospital system or private equity.”
This study was funded by a grant from the philanthropic foundation Arnold Ventures (no family relation to Daniel Arnold).
Arnold reported receiving grants from Arnold Ventures during the conduct of the study. Gupta had no competing interests to declare. Zhu reported receiving grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality during the submitted work and from the National Institutes of Health, National Institute for Health Care Management Foundation, and American Psychological Association, as well as personal fees from Cambia outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Navigating Moonlighting Opportunities During Dermatology Training
Navigating Moonlighting Opportunities During Dermatology Training
Residents and fellows in training have to navigate time management to balance reading, hands-on training, family responsibilities, exercise, diet, and sleep requirements. In addition, they grapple with the stress of financial commitments for food, housing, clothing, family members, transportation, and student loans. A brilliant friend of mine once said that she struggled throughout residency and her early career to find balance until it finally occurred to her that, while balance was aspirational, resilience was key. All that said, residents in training may find it appealing to earn a little extra money and gain additional clinical experience through moonlighting. This article discusses some key considerations when embarking on such a decision, including the effects of moonlighting on other commitments and some logistical factors to consider.
Will Moonlighting Adversely Affect My Other Commitments?
Residency and fellowship are precious opportunities to gain medical knowledge, hone your ability to make diagnoses through complex pattern recognition, and refine the necessary surgical and interpersonal skills to carry you through a successful career. Dermatology encompasses a vast array of conditions related only by their manifestation in skin. Dermatology residents and fellows may spend fewer sleepless hours on call, but the reading requirements are massive. Our treatment armamentarium has expanded rapidly with highly effective treatments for chronic conditions that have a dramatic impact on quality of life. With so many effective agents available, the choice often relates as much to comorbidities as to disease severity and location. There is so much to learn.
While making a full commitment to acquiring the skills of an expert clinician, it is important for residents to remain aware of those who depend on you—in particular, the fleeting time you have with your growing children. They grow up fast, and your interactions with them determine who they will grow up to be. In the past, salt, silk, gold, and jewels were the world’s greatest luxuries. Now, it’s time—time with family, time for self-care, time to reflect, and time to rest and renew. Be careful how you squander time in exchange for material possessions.
What Logistical Factors Should You Consider When Embarking on Moonlighting?
There are clearly stated policies from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education for when moonlighting can occur during training.1 It should not occur during typical residency or fellowship work hours, and the individual must be in good standing academically and progressing well on their journey to becoming a competent dermatologist. They must also have the appropriate skills to practice in the field of medicine chosen for moonlighting.
Moonlighting opportunities may exist in the form of emergency department or “quick clinic” coverage, especially for the evaluation and treatment of acute minor illnesses. Fellows who have completed a dermatology residency may supervise dermatology residents in afterhours or weekend clinics, offering enhanced opportunities for autonomy, additional clinical experience, and some welcome cash. To make such clinics viable, the office space must be available; the building must be open; and the costs of the space, scheduling, reception, and security services must be covered as well as nursing support (which should be voluntary and likely will require overtime pay scales). After all of these—as well as supplies—have been paid for, what is left is what is available to distribute as pay for service. Working through these factors provides valuable experience in resource management and helps prepare trainees for the economic realities of private practice. Large organizations may be able to provide the space and support, but all of that needs to be paid for through the proceeds that come from the patient care provided. No-show rates often are quite high for after-hours and weekend clinics, but the expenses for those unfilled appointment slots remain and must be paid in full. Be sure the demand exists and that you plan appropriately with strategic overbooking based on historical data on patient mix, procedural needs, and no-show rates.
My department has supported resident and fellow requests for moonlighting opportunities in the past. The most successful model was to have a limited number of early morning appointment slots prior to the start of morning didactics. Security typically already exists, rooms are available, and patients can be seen and still get to work or get their kids to school. No-show rates remained very low for morning appointments, and strategic overbooking was unnecessary.
In contrast, evening and weekend clinics start out strong with high patient satisfaction and deteriorate fairly quickly with accelerating no-show rates. People are busy at the end of the day, and unforeseen circumstances often affect their ability to keep an appointment. Weekends are precious; potential patients may be less schedule minded in the evenings and on weekends, and the residents and fellows themselves often find it stressful to commit to giving up a chunk of weekend time on a scheduled basis.
Before you commit to a moonlighting job, be sure to weigh all of the above factors and be sure the juice is worth the squeeze.
Final Thoughts
Moonlighting opportunities are a way to acquire both clinical and management skills and can provide a welcome extra bit of cash to ease financial burdens, but these benefits should be balanced with other time commitments and overall quality of life. Time is precious—choose wisely and be sure you spend it well.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Common Program Requirements (Residency). Updated September 17, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/cprresidency_2023v3.pdf
Residents and fellows in training have to navigate time management to balance reading, hands-on training, family responsibilities, exercise, diet, and sleep requirements. In addition, they grapple with the stress of financial commitments for food, housing, clothing, family members, transportation, and student loans. A brilliant friend of mine once said that she struggled throughout residency and her early career to find balance until it finally occurred to her that, while balance was aspirational, resilience was key. All that said, residents in training may find it appealing to earn a little extra money and gain additional clinical experience through moonlighting. This article discusses some key considerations when embarking on such a decision, including the effects of moonlighting on other commitments and some logistical factors to consider.
Will Moonlighting Adversely Affect My Other Commitments?
Residency and fellowship are precious opportunities to gain medical knowledge, hone your ability to make diagnoses through complex pattern recognition, and refine the necessary surgical and interpersonal skills to carry you through a successful career. Dermatology encompasses a vast array of conditions related only by their manifestation in skin. Dermatology residents and fellows may spend fewer sleepless hours on call, but the reading requirements are massive. Our treatment armamentarium has expanded rapidly with highly effective treatments for chronic conditions that have a dramatic impact on quality of life. With so many effective agents available, the choice often relates as much to comorbidities as to disease severity and location. There is so much to learn.
While making a full commitment to acquiring the skills of an expert clinician, it is important for residents to remain aware of those who depend on you—in particular, the fleeting time you have with your growing children. They grow up fast, and your interactions with them determine who they will grow up to be. In the past, salt, silk, gold, and jewels were the world’s greatest luxuries. Now, it’s time—time with family, time for self-care, time to reflect, and time to rest and renew. Be careful how you squander time in exchange for material possessions.
What Logistical Factors Should You Consider When Embarking on Moonlighting?
There are clearly stated policies from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education for when moonlighting can occur during training.1 It should not occur during typical residency or fellowship work hours, and the individual must be in good standing academically and progressing well on their journey to becoming a competent dermatologist. They must also have the appropriate skills to practice in the field of medicine chosen for moonlighting.
Moonlighting opportunities may exist in the form of emergency department or “quick clinic” coverage, especially for the evaluation and treatment of acute minor illnesses. Fellows who have completed a dermatology residency may supervise dermatology residents in afterhours or weekend clinics, offering enhanced opportunities for autonomy, additional clinical experience, and some welcome cash. To make such clinics viable, the office space must be available; the building must be open; and the costs of the space, scheduling, reception, and security services must be covered as well as nursing support (which should be voluntary and likely will require overtime pay scales). After all of these—as well as supplies—have been paid for, what is left is what is available to distribute as pay for service. Working through these factors provides valuable experience in resource management and helps prepare trainees for the economic realities of private practice. Large organizations may be able to provide the space and support, but all of that needs to be paid for through the proceeds that come from the patient care provided. No-show rates often are quite high for after-hours and weekend clinics, but the expenses for those unfilled appointment slots remain and must be paid in full. Be sure the demand exists and that you plan appropriately with strategic overbooking based on historical data on patient mix, procedural needs, and no-show rates.
My department has supported resident and fellow requests for moonlighting opportunities in the past. The most successful model was to have a limited number of early morning appointment slots prior to the start of morning didactics. Security typically already exists, rooms are available, and patients can be seen and still get to work or get their kids to school. No-show rates remained very low for morning appointments, and strategic overbooking was unnecessary.
In contrast, evening and weekend clinics start out strong with high patient satisfaction and deteriorate fairly quickly with accelerating no-show rates. People are busy at the end of the day, and unforeseen circumstances often affect their ability to keep an appointment. Weekends are precious; potential patients may be less schedule minded in the evenings and on weekends, and the residents and fellows themselves often find it stressful to commit to giving up a chunk of weekend time on a scheduled basis.
Before you commit to a moonlighting job, be sure to weigh all of the above factors and be sure the juice is worth the squeeze.
Final Thoughts
Moonlighting opportunities are a way to acquire both clinical and management skills and can provide a welcome extra bit of cash to ease financial burdens, but these benefits should be balanced with other time commitments and overall quality of life. Time is precious—choose wisely and be sure you spend it well.
Residents and fellows in training have to navigate time management to balance reading, hands-on training, family responsibilities, exercise, diet, and sleep requirements. In addition, they grapple with the stress of financial commitments for food, housing, clothing, family members, transportation, and student loans. A brilliant friend of mine once said that she struggled throughout residency and her early career to find balance until it finally occurred to her that, while balance was aspirational, resilience was key. All that said, residents in training may find it appealing to earn a little extra money and gain additional clinical experience through moonlighting. This article discusses some key considerations when embarking on such a decision, including the effects of moonlighting on other commitments and some logistical factors to consider.
Will Moonlighting Adversely Affect My Other Commitments?
Residency and fellowship are precious opportunities to gain medical knowledge, hone your ability to make diagnoses through complex pattern recognition, and refine the necessary surgical and interpersonal skills to carry you through a successful career. Dermatology encompasses a vast array of conditions related only by their manifestation in skin. Dermatology residents and fellows may spend fewer sleepless hours on call, but the reading requirements are massive. Our treatment armamentarium has expanded rapidly with highly effective treatments for chronic conditions that have a dramatic impact on quality of life. With so many effective agents available, the choice often relates as much to comorbidities as to disease severity and location. There is so much to learn.
While making a full commitment to acquiring the skills of an expert clinician, it is important for residents to remain aware of those who depend on you—in particular, the fleeting time you have with your growing children. They grow up fast, and your interactions with them determine who they will grow up to be. In the past, salt, silk, gold, and jewels were the world’s greatest luxuries. Now, it’s time—time with family, time for self-care, time to reflect, and time to rest and renew. Be careful how you squander time in exchange for material possessions.
What Logistical Factors Should You Consider When Embarking on Moonlighting?
There are clearly stated policies from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education for when moonlighting can occur during training.1 It should not occur during typical residency or fellowship work hours, and the individual must be in good standing academically and progressing well on their journey to becoming a competent dermatologist. They must also have the appropriate skills to practice in the field of medicine chosen for moonlighting.
Moonlighting opportunities may exist in the form of emergency department or “quick clinic” coverage, especially for the evaluation and treatment of acute minor illnesses. Fellows who have completed a dermatology residency may supervise dermatology residents in afterhours or weekend clinics, offering enhanced opportunities for autonomy, additional clinical experience, and some welcome cash. To make such clinics viable, the office space must be available; the building must be open; and the costs of the space, scheduling, reception, and security services must be covered as well as nursing support (which should be voluntary and likely will require overtime pay scales). After all of these—as well as supplies—have been paid for, what is left is what is available to distribute as pay for service. Working through these factors provides valuable experience in resource management and helps prepare trainees for the economic realities of private practice. Large organizations may be able to provide the space and support, but all of that needs to be paid for through the proceeds that come from the patient care provided. No-show rates often are quite high for after-hours and weekend clinics, but the expenses for those unfilled appointment slots remain and must be paid in full. Be sure the demand exists and that you plan appropriately with strategic overbooking based on historical data on patient mix, procedural needs, and no-show rates.
My department has supported resident and fellow requests for moonlighting opportunities in the past. The most successful model was to have a limited number of early morning appointment slots prior to the start of morning didactics. Security typically already exists, rooms are available, and patients can be seen and still get to work or get their kids to school. No-show rates remained very low for morning appointments, and strategic overbooking was unnecessary.
In contrast, evening and weekend clinics start out strong with high patient satisfaction and deteriorate fairly quickly with accelerating no-show rates. People are busy at the end of the day, and unforeseen circumstances often affect their ability to keep an appointment. Weekends are precious; potential patients may be less schedule minded in the evenings and on weekends, and the residents and fellows themselves often find it stressful to commit to giving up a chunk of weekend time on a scheduled basis.
Before you commit to a moonlighting job, be sure to weigh all of the above factors and be sure the juice is worth the squeeze.
Final Thoughts
Moonlighting opportunities are a way to acquire both clinical and management skills and can provide a welcome extra bit of cash to ease financial burdens, but these benefits should be balanced with other time commitments and overall quality of life. Time is precious—choose wisely and be sure you spend it well.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Common Program Requirements (Residency). Updated September 17, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/cprresidency_2023v3.pdf
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Common Program Requirements (Residency). Updated September 17, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/cprresidency_2023v3.pdf
Navigating Moonlighting Opportunities During Dermatology Training
Navigating Moonlighting Opportunities During Dermatology Training
PRACTICE POINTS
- Dermatology training demands extensive study and hands-on skill development, which need to be balanced with family time, finances, and self-care.
- Before moonlighting, ensure it will not compromise your family’s quality of life or your core residency/fellowship commitments and that your program’s policies permit it.
- Carefully assess logistics to determine if an afterhours or weekend clinic can be a financially viable moonlighting opportunity.
Practical Tips on Delivering Feedback to Trainees and Colleagues
Feedback is the purposeful practice of offering constructive, goal-directed input rooted in the power of observation and behavioral assessment. Healthcare inherently fosters a broad range of interactions among people with unique insights, and feedback can naturally emerge from this milieu. In medical training, feedback is an indispensable element that personalizes the learning process and drives the professional development of physicians through all career stages.
If delivered effectively, feedback can strengthen the relationship between the evaluator and recipient, promote self-reflection, and enhance motivation. As such, it has the potential to impact us and those we serve for a lifetime. Feedback has been invaluable to our growth as clinicians and has been embedded into our roles as educators. However, Here, we provide some “tried and true” practical tips on delivering feedback to trainees and co-workers and on navigating potential barriers based on lessons learned.
Barriers to Effective Feedback
- Time: Feedback is predicated on observation over time and consideration of repetitive processes rather than isolated events. Perhaps the most challenging factor faced by both parties is that of time constraints, leading to limited ability to engage and build rapport.
- Fear: Hesitancy by evaluators to provide feedback in fear of negative impacts on the recipient’s morale or rapport can lead them to shy away from personalized corrective feedback strategies and choose to rely on written evaluations or generic advice.
- Varying approaches: Feedback strategies have evolved from unidirectional, critique-based, hierarchical practices that emphasize the evaluator’s skills to models that prioritize the recipient’s goals and participation (see Table 1). Traditionally employed feedback models such as the “Feedback Sandwich” or the “Pendleton Rules” are criticized because of a lack of proven benefit on performance, recipient goal prioritization, and open communication.1,2 Studies showing incongruent perceptions of feedback adequacy between trainees and faculty further support the need for recipient-focused strategies.3 Recognition of the foundational role of the reciprocal learner-teacher alliance in feedback integration inspired newer feedback models, such as the “R2C2” and the “Self-Assessment, Feedback, Encouragement, Direction.”4,5
But which way is best? With increasing abundance and complexity of feedback frameworks, selecting an approach can feel overwhelming and impractical. A generic “one-size-fits-all” strategy or avoidance of feedback altogether can be detrimental. Structured feedback models can also lead to rigid, inauthentic interactions. Below, we suggest a more practical approach through our tips that unifies the common themes of various feedback models and embeds them into daily practice habits while leaving room for personalization.
Our Practical Feedback Tips
Tip 1: Set the scene: Create a positive feedback culture
Proactively creating a culture in which feedback is embedded and encouraged is perhaps the most important step. Priming both parties for feedback clarifies intent, increases receptiveness, and paves the way for growth and open communication. It also prevents the misinterpretation of unexpected feedback as an expression of disapproval. To do this, start by regularly stating your intentions at the start of every experience. Explicitly expressing your vision for mutual learning, bidirectional feedback, and growth in your respective roles attaches a positive intention to feedback. Providing a reminder that we are all works in progress and acknowledging this on a regular basis sets the stage for structured growth opportunities.
Scheduling future feedback encounters from the start maintains accountability and prevents feedback from being perceived as the consequence of a particular behavior. The number and timing of feedback sessions can be customized to the duration of the working relationship, generally allowing enough time for a second interaction (at the end of each week, halfway point, etc.).
Tip 2: Build rapport
Increasing clinical workloads and pressure to teach in time-constrained settings often results in insufficient time to engage in conversation and trust building. However, a foundational relationship is an essential precursor to meaningful feedback. Ramani et al. state that “relationships, not recipes, are more likely to promote feedback that has an impact on learner performance and ultimately patient care.”6 Building this rapport can begin by dedicating a few minutes (before/during rounds, between cases) to exchange information about career interests, hobbies, favorite restaurants, etc. This “small talk” is the beginning of a two-way exchange that ultimately develops into more meaningful exchanges.
In our experience, this simple step is impactful and fulfilling to both parties. This is also a good time for shared vulnerability by talking about what you are currently working on or have worked on at their stage to affirm that feedback is a continuous part of professional development and not a reflection of how far they are from competence at a given point in time.
Tip 3: Consider Timing, assess readiness, and preschedule sessions
Lack of attention to timing can hinder feedback acceptance. We suggest adhering to delivering positive feedback publicly and corrective feedback privately (“Praise in public, perfect in private”). This reinforces positive behaviors, increases motivation, and minimizes demoralization. Prolonged delays between the observed behavior and feedback can decrease its relevance. Conversely, delivering feedback too soon after an emotionally charged experience can be perceived as blame. Pre-designated times for feedback can minimize the guesswork and maintain your accountability for giving feedback without inadvertently linking it to one particular behavior. If the recipient does not appear to be in a state to receive feedback at the predesignated time, you can pivot to a “check-in” session to show support and strengthen rapport.
Tip 4: Customize to the learner and set shared goals
Diversity in backgrounds, perspectives, and personalities can impact how people perceive their own performances and experience feedback. Given the profound impact of sociocultural factors on feedback assimilation, maintaining the recipient and their goals at the core of performance evaluations is key to feedback acceptance.
A. Trainees
We suggest starting by introducing the idea of feedback as a partnership and something you feel privileged to do to help them achieve mutual goals. It helps to ask them to use the first day to get oriented with the experience, general expectations, challenges they expect to encounter, and their feedback goals. Tailoring your feedback to their goals creates a sense of shared purpose which increases motivation. Encouraging them to develop their own strategies allows them to play an active role in their growth. Giving them the opportunity to share their perceived strengths and deficiencies provides you with valuable information regarding their insight and ability to self-evaluate. This can help you predict their readiness for your feedback and to tailor your approach when there is a mismatch.
Examples:
- Medical student: Start with “What do you think you are doing well?” and “What do you think you need to work on?” Build on their response with encouragement and empathy. This helps make them more deliberate with what they work on because being a medical student can be overwhelming and can feel as though they have everything to work on.
- Resident/Fellow: By this point, trainees usually have an increased awareness of their strengths and deficiencies. Your questions can then be more specific, giving them autonomy over their learning, such as “What are some of the things you are working on that you want me to give you feedback on this week?” This makes them more aware, intentional, and receptive to your feedback because it is framed as something that they sought out.
B. Colleagues/Staff
Unlike the training environment in which feedback is built-in, giving feedback to co-workers requires you to establish a feedback-conducive environment and to develop a more in-depth understanding of coworkers’ personalities. Similar strategies can be applied, such as proactively setting the scene for open communication, scheduling check-ins, demonstrating receptiveness to feedback, and investing in trust-building.
Longer working relationships allow for strong foundational connections that make feedback less threatening. Personality assessment testing like Myers-Briggs Type Indicator or DiSC Assessment can aid in tailoring feedback to different individuals.7,8 An analytical thinker may appreciate direct, data-driven feedback. Relationship-oriented individuals might respond better to softer, encouragement-based approaches. Always maintain shared goals at the center of your interactions and consider collaborative opportunities such as quality improvement projects. This can improve your working relationship in a constructive way without casting blame.
Tip 5: Work on delivery: Bidirectional communication and body language
Non-verbal cues can have a profound impact on how your feedback is interpreted and on the recipient’s comfort to engage in conversation. Sitting down, making eye contact, nodding, and avoiding closed-off body posture can project support and feel less judgmental. Creating a safe and non-distracted environment with privacy can make them feel valued. Use motivating, respectful language focused on directly observed behaviors rather than personal attributes or second-hand reports.
Remember that focusing on repetitive patterns is likely more helpful than isolated incidents. Validate their hard work and give them a global idea of where they stand before diving into individual behaviors. Encourage their participation and empower them to suggest changes they plan to implement. Conclude by having them summarize their action plan to give them ownership and to verify that your feedback was interpreted as you intended. Thank them for being a part of the process, as it does take a partnership for feedback to be effective.
Tip 6: Be open to feedback
Demonstrating your willingness to accept and act on feedback reinforces a positive culture where feedback is normalized and valued. After an unintended outcome, initiate a two-way conversation and ask their input on anything they wish you would have done differently. This reaffirms your commitment to maintaining culture that does not revolve around one-sided critiques. Frequently soliciting feedback about your feedback skills can also guide you to adapt your approach and to recognize any ineffective feedback practices.
Tip 7: When things don’t go as planned
Receiving feedback, no matter how thoughtfully it is delivered, can be an emotionally-charged experience ending in hurt feelings. This happens because of misinterpretation of feedback as an indicator of inadequacy, heightened awareness of underlying insecurities, sociocultural or personal circumstances, frustration with oneself, needing additional guidance, or being caught off-guard by the assessment.
The evaluator should always acknowledge the recipient’s feelings, show compassion, and allow time for processing. When they are ready to talk, it is important to help reframe the recipients’ mindsets to recognize that feedback is not personal or defining and is not a “one and done” reflection of whether they have “made it.” Instead, it is a continual process that we benefit from through all career stages. Again, shared vulnerability can help to normalize feedback and maintain open dialogue. Setting an opportunity for a future check-in can reinforce support and lead to a more productive conversation after they have had time to process.
Conclusion
Effective feedback delivery is an invaluable skill that can result in meaningful goal-directed changes while strengthening professional relationships. Given the complexity of feedback interactions and the many factors that influence its acceptance, no single approach is suitable for all recipients and frequent adaptation of the approach is essential.
In our experience, adhering to these general overarching feedback principles (see Figure 1) has allowed us to have more successful interactions with trainees and colleagues.
Dr. Baliss is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri. Dr. Hachem is director of the Division of Gastroenterology and Digestive Health at Intermountain Medical, Sandy, Utah. Both authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Parkes J, et al. Feedback sandwiches affect perceptions but not performance. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2013 Aug. doi:10.1007/s10459-012-9377-9.
2. van de Ridder JMM and Wijnen-Meijer M. Pendleton’s Rules: A Mini Review of a Feedback Method. Am J Biomed Sci & Res. 2023 May. doi: 10.34297/AJBSR.2023.19.002542.
3. Sender Liberman A, et al. Surgery residents and attending surgeons have different perceptions of feedback. Med Teach. 2005 Aug. doi: 10.1080/0142590500129183.
4. Sargeant J, et al. R2C2 in Action: Testing an Evidence-Based Model to Facilitate Feedback and Coaching in Residency. J Grad Med Educ. 2017 Apr. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-16-00398.1.
5. Liakos W, et al. Frameworks for Effective Feedback in Health Professions Education. Acad Med. 2023 May. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000004884.
6. Ramani S, et al. Feedback Redefined: Principles and Practice. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 May. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04874-2.
7. Woods RA and Hill PB. Myers-Briggs Type Indicator. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. 2022 Sept. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554596/
8. Slowikowski MK. Using the DISC behavioral instrument to guide leadership and communication. AORN J. 2005 Nov. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2092(06)60276-7.
Feedback is the purposeful practice of offering constructive, goal-directed input rooted in the power of observation and behavioral assessment. Healthcare inherently fosters a broad range of interactions among people with unique insights, and feedback can naturally emerge from this milieu. In medical training, feedback is an indispensable element that personalizes the learning process and drives the professional development of physicians through all career stages.
If delivered effectively, feedback can strengthen the relationship between the evaluator and recipient, promote self-reflection, and enhance motivation. As such, it has the potential to impact us and those we serve for a lifetime. Feedback has been invaluable to our growth as clinicians and has been embedded into our roles as educators. However, Here, we provide some “tried and true” practical tips on delivering feedback to trainees and co-workers and on navigating potential barriers based on lessons learned.
Barriers to Effective Feedback
- Time: Feedback is predicated on observation over time and consideration of repetitive processes rather than isolated events. Perhaps the most challenging factor faced by both parties is that of time constraints, leading to limited ability to engage and build rapport.
- Fear: Hesitancy by evaluators to provide feedback in fear of negative impacts on the recipient’s morale or rapport can lead them to shy away from personalized corrective feedback strategies and choose to rely on written evaluations or generic advice.
- Varying approaches: Feedback strategies have evolved from unidirectional, critique-based, hierarchical practices that emphasize the evaluator’s skills to models that prioritize the recipient’s goals and participation (see Table 1). Traditionally employed feedback models such as the “Feedback Sandwich” or the “Pendleton Rules” are criticized because of a lack of proven benefit on performance, recipient goal prioritization, and open communication.1,2 Studies showing incongruent perceptions of feedback adequacy between trainees and faculty further support the need for recipient-focused strategies.3 Recognition of the foundational role of the reciprocal learner-teacher alliance in feedback integration inspired newer feedback models, such as the “R2C2” and the “Self-Assessment, Feedback, Encouragement, Direction.”4,5
But which way is best? With increasing abundance and complexity of feedback frameworks, selecting an approach can feel overwhelming and impractical. A generic “one-size-fits-all” strategy or avoidance of feedback altogether can be detrimental. Structured feedback models can also lead to rigid, inauthentic interactions. Below, we suggest a more practical approach through our tips that unifies the common themes of various feedback models and embeds them into daily practice habits while leaving room for personalization.
Our Practical Feedback Tips
Tip 1: Set the scene: Create a positive feedback culture
Proactively creating a culture in which feedback is embedded and encouraged is perhaps the most important step. Priming both parties for feedback clarifies intent, increases receptiveness, and paves the way for growth and open communication. It also prevents the misinterpretation of unexpected feedback as an expression of disapproval. To do this, start by regularly stating your intentions at the start of every experience. Explicitly expressing your vision for mutual learning, bidirectional feedback, and growth in your respective roles attaches a positive intention to feedback. Providing a reminder that we are all works in progress and acknowledging this on a regular basis sets the stage for structured growth opportunities.
Scheduling future feedback encounters from the start maintains accountability and prevents feedback from being perceived as the consequence of a particular behavior. The number and timing of feedback sessions can be customized to the duration of the working relationship, generally allowing enough time for a second interaction (at the end of each week, halfway point, etc.).
Tip 2: Build rapport
Increasing clinical workloads and pressure to teach in time-constrained settings often results in insufficient time to engage in conversation and trust building. However, a foundational relationship is an essential precursor to meaningful feedback. Ramani et al. state that “relationships, not recipes, are more likely to promote feedback that has an impact on learner performance and ultimately patient care.”6 Building this rapport can begin by dedicating a few minutes (before/during rounds, between cases) to exchange information about career interests, hobbies, favorite restaurants, etc. This “small talk” is the beginning of a two-way exchange that ultimately develops into more meaningful exchanges.
In our experience, this simple step is impactful and fulfilling to both parties. This is also a good time for shared vulnerability by talking about what you are currently working on or have worked on at their stage to affirm that feedback is a continuous part of professional development and not a reflection of how far they are from competence at a given point in time.
Tip 3: Consider Timing, assess readiness, and preschedule sessions
Lack of attention to timing can hinder feedback acceptance. We suggest adhering to delivering positive feedback publicly and corrective feedback privately (“Praise in public, perfect in private”). This reinforces positive behaviors, increases motivation, and minimizes demoralization. Prolonged delays between the observed behavior and feedback can decrease its relevance. Conversely, delivering feedback too soon after an emotionally charged experience can be perceived as blame. Pre-designated times for feedback can minimize the guesswork and maintain your accountability for giving feedback without inadvertently linking it to one particular behavior. If the recipient does not appear to be in a state to receive feedback at the predesignated time, you can pivot to a “check-in” session to show support and strengthen rapport.
Tip 4: Customize to the learner and set shared goals
Diversity in backgrounds, perspectives, and personalities can impact how people perceive their own performances and experience feedback. Given the profound impact of sociocultural factors on feedback assimilation, maintaining the recipient and their goals at the core of performance evaluations is key to feedback acceptance.
A. Trainees
We suggest starting by introducing the idea of feedback as a partnership and something you feel privileged to do to help them achieve mutual goals. It helps to ask them to use the first day to get oriented with the experience, general expectations, challenges they expect to encounter, and their feedback goals. Tailoring your feedback to their goals creates a sense of shared purpose which increases motivation. Encouraging them to develop their own strategies allows them to play an active role in their growth. Giving them the opportunity to share their perceived strengths and deficiencies provides you with valuable information regarding their insight and ability to self-evaluate. This can help you predict their readiness for your feedback and to tailor your approach when there is a mismatch.
Examples:
- Medical student: Start with “What do you think you are doing well?” and “What do you think you need to work on?” Build on their response with encouragement and empathy. This helps make them more deliberate with what they work on because being a medical student can be overwhelming and can feel as though they have everything to work on.
- Resident/Fellow: By this point, trainees usually have an increased awareness of their strengths and deficiencies. Your questions can then be more specific, giving them autonomy over their learning, such as “What are some of the things you are working on that you want me to give you feedback on this week?” This makes them more aware, intentional, and receptive to your feedback because it is framed as something that they sought out.
B. Colleagues/Staff
Unlike the training environment in which feedback is built-in, giving feedback to co-workers requires you to establish a feedback-conducive environment and to develop a more in-depth understanding of coworkers’ personalities. Similar strategies can be applied, such as proactively setting the scene for open communication, scheduling check-ins, demonstrating receptiveness to feedback, and investing in trust-building.
Longer working relationships allow for strong foundational connections that make feedback less threatening. Personality assessment testing like Myers-Briggs Type Indicator or DiSC Assessment can aid in tailoring feedback to different individuals.7,8 An analytical thinker may appreciate direct, data-driven feedback. Relationship-oriented individuals might respond better to softer, encouragement-based approaches. Always maintain shared goals at the center of your interactions and consider collaborative opportunities such as quality improvement projects. This can improve your working relationship in a constructive way without casting blame.
Tip 5: Work on delivery: Bidirectional communication and body language
Non-verbal cues can have a profound impact on how your feedback is interpreted and on the recipient’s comfort to engage in conversation. Sitting down, making eye contact, nodding, and avoiding closed-off body posture can project support and feel less judgmental. Creating a safe and non-distracted environment with privacy can make them feel valued. Use motivating, respectful language focused on directly observed behaviors rather than personal attributes or second-hand reports.
Remember that focusing on repetitive patterns is likely more helpful than isolated incidents. Validate their hard work and give them a global idea of where they stand before diving into individual behaviors. Encourage their participation and empower them to suggest changes they plan to implement. Conclude by having them summarize their action plan to give them ownership and to verify that your feedback was interpreted as you intended. Thank them for being a part of the process, as it does take a partnership for feedback to be effective.
Tip 6: Be open to feedback
Demonstrating your willingness to accept and act on feedback reinforces a positive culture where feedback is normalized and valued. After an unintended outcome, initiate a two-way conversation and ask their input on anything they wish you would have done differently. This reaffirms your commitment to maintaining culture that does not revolve around one-sided critiques. Frequently soliciting feedback about your feedback skills can also guide you to adapt your approach and to recognize any ineffective feedback practices.
Tip 7: When things don’t go as planned
Receiving feedback, no matter how thoughtfully it is delivered, can be an emotionally-charged experience ending in hurt feelings. This happens because of misinterpretation of feedback as an indicator of inadequacy, heightened awareness of underlying insecurities, sociocultural or personal circumstances, frustration with oneself, needing additional guidance, or being caught off-guard by the assessment.
The evaluator should always acknowledge the recipient’s feelings, show compassion, and allow time for processing. When they are ready to talk, it is important to help reframe the recipients’ mindsets to recognize that feedback is not personal or defining and is not a “one and done” reflection of whether they have “made it.” Instead, it is a continual process that we benefit from through all career stages. Again, shared vulnerability can help to normalize feedback and maintain open dialogue. Setting an opportunity for a future check-in can reinforce support and lead to a more productive conversation after they have had time to process.
Conclusion
Effective feedback delivery is an invaluable skill that can result in meaningful goal-directed changes while strengthening professional relationships. Given the complexity of feedback interactions and the many factors that influence its acceptance, no single approach is suitable for all recipients and frequent adaptation of the approach is essential.
In our experience, adhering to these general overarching feedback principles (see Figure 1) has allowed us to have more successful interactions with trainees and colleagues.
Dr. Baliss is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri. Dr. Hachem is director of the Division of Gastroenterology and Digestive Health at Intermountain Medical, Sandy, Utah. Both authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Parkes J, et al. Feedback sandwiches affect perceptions but not performance. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2013 Aug. doi:10.1007/s10459-012-9377-9.
2. van de Ridder JMM and Wijnen-Meijer M. Pendleton’s Rules: A Mini Review of a Feedback Method. Am J Biomed Sci & Res. 2023 May. doi: 10.34297/AJBSR.2023.19.002542.
3. Sender Liberman A, et al. Surgery residents and attending surgeons have different perceptions of feedback. Med Teach. 2005 Aug. doi: 10.1080/0142590500129183.
4. Sargeant J, et al. R2C2 in Action: Testing an Evidence-Based Model to Facilitate Feedback and Coaching in Residency. J Grad Med Educ. 2017 Apr. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-16-00398.1.
5. Liakos W, et al. Frameworks for Effective Feedback in Health Professions Education. Acad Med. 2023 May. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000004884.
6. Ramani S, et al. Feedback Redefined: Principles and Practice. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 May. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04874-2.
7. Woods RA and Hill PB. Myers-Briggs Type Indicator. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. 2022 Sept. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554596/
8. Slowikowski MK. Using the DISC behavioral instrument to guide leadership and communication. AORN J. 2005 Nov. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2092(06)60276-7.
Feedback is the purposeful practice of offering constructive, goal-directed input rooted in the power of observation and behavioral assessment. Healthcare inherently fosters a broad range of interactions among people with unique insights, and feedback can naturally emerge from this milieu. In medical training, feedback is an indispensable element that personalizes the learning process and drives the professional development of physicians through all career stages.
If delivered effectively, feedback can strengthen the relationship between the evaluator and recipient, promote self-reflection, and enhance motivation. As such, it has the potential to impact us and those we serve for a lifetime. Feedback has been invaluable to our growth as clinicians and has been embedded into our roles as educators. However, Here, we provide some “tried and true” practical tips on delivering feedback to trainees and co-workers and on navigating potential barriers based on lessons learned.
Barriers to Effective Feedback
- Time: Feedback is predicated on observation over time and consideration of repetitive processes rather than isolated events. Perhaps the most challenging factor faced by both parties is that of time constraints, leading to limited ability to engage and build rapport.
- Fear: Hesitancy by evaluators to provide feedback in fear of negative impacts on the recipient’s morale or rapport can lead them to shy away from personalized corrective feedback strategies and choose to rely on written evaluations or generic advice.
- Varying approaches: Feedback strategies have evolved from unidirectional, critique-based, hierarchical practices that emphasize the evaluator’s skills to models that prioritize the recipient’s goals and participation (see Table 1). Traditionally employed feedback models such as the “Feedback Sandwich” or the “Pendleton Rules” are criticized because of a lack of proven benefit on performance, recipient goal prioritization, and open communication.1,2 Studies showing incongruent perceptions of feedback adequacy between trainees and faculty further support the need for recipient-focused strategies.3 Recognition of the foundational role of the reciprocal learner-teacher alliance in feedback integration inspired newer feedback models, such as the “R2C2” and the “Self-Assessment, Feedback, Encouragement, Direction.”4,5
But which way is best? With increasing abundance and complexity of feedback frameworks, selecting an approach can feel overwhelming and impractical. A generic “one-size-fits-all” strategy or avoidance of feedback altogether can be detrimental. Structured feedback models can also lead to rigid, inauthentic interactions. Below, we suggest a more practical approach through our tips that unifies the common themes of various feedback models and embeds them into daily practice habits while leaving room for personalization.
Our Practical Feedback Tips
Tip 1: Set the scene: Create a positive feedback culture
Proactively creating a culture in which feedback is embedded and encouraged is perhaps the most important step. Priming both parties for feedback clarifies intent, increases receptiveness, and paves the way for growth and open communication. It also prevents the misinterpretation of unexpected feedback as an expression of disapproval. To do this, start by regularly stating your intentions at the start of every experience. Explicitly expressing your vision for mutual learning, bidirectional feedback, and growth in your respective roles attaches a positive intention to feedback. Providing a reminder that we are all works in progress and acknowledging this on a regular basis sets the stage for structured growth opportunities.
Scheduling future feedback encounters from the start maintains accountability and prevents feedback from being perceived as the consequence of a particular behavior. The number and timing of feedback sessions can be customized to the duration of the working relationship, generally allowing enough time for a second interaction (at the end of each week, halfway point, etc.).
Tip 2: Build rapport
Increasing clinical workloads and pressure to teach in time-constrained settings often results in insufficient time to engage in conversation and trust building. However, a foundational relationship is an essential precursor to meaningful feedback. Ramani et al. state that “relationships, not recipes, are more likely to promote feedback that has an impact on learner performance and ultimately patient care.”6 Building this rapport can begin by dedicating a few minutes (before/during rounds, between cases) to exchange information about career interests, hobbies, favorite restaurants, etc. This “small talk” is the beginning of a two-way exchange that ultimately develops into more meaningful exchanges.
In our experience, this simple step is impactful and fulfilling to both parties. This is also a good time for shared vulnerability by talking about what you are currently working on or have worked on at their stage to affirm that feedback is a continuous part of professional development and not a reflection of how far they are from competence at a given point in time.
Tip 3: Consider Timing, assess readiness, and preschedule sessions
Lack of attention to timing can hinder feedback acceptance. We suggest adhering to delivering positive feedback publicly and corrective feedback privately (“Praise in public, perfect in private”). This reinforces positive behaviors, increases motivation, and minimizes demoralization. Prolonged delays between the observed behavior and feedback can decrease its relevance. Conversely, delivering feedback too soon after an emotionally charged experience can be perceived as blame. Pre-designated times for feedback can minimize the guesswork and maintain your accountability for giving feedback without inadvertently linking it to one particular behavior. If the recipient does not appear to be in a state to receive feedback at the predesignated time, you can pivot to a “check-in” session to show support and strengthen rapport.
Tip 4: Customize to the learner and set shared goals
Diversity in backgrounds, perspectives, and personalities can impact how people perceive their own performances and experience feedback. Given the profound impact of sociocultural factors on feedback assimilation, maintaining the recipient and their goals at the core of performance evaluations is key to feedback acceptance.
A. Trainees
We suggest starting by introducing the idea of feedback as a partnership and something you feel privileged to do to help them achieve mutual goals. It helps to ask them to use the first day to get oriented with the experience, general expectations, challenges they expect to encounter, and their feedback goals. Tailoring your feedback to their goals creates a sense of shared purpose which increases motivation. Encouraging them to develop their own strategies allows them to play an active role in their growth. Giving them the opportunity to share their perceived strengths and deficiencies provides you with valuable information regarding their insight and ability to self-evaluate. This can help you predict their readiness for your feedback and to tailor your approach when there is a mismatch.
Examples:
- Medical student: Start with “What do you think you are doing well?” and “What do you think you need to work on?” Build on their response with encouragement and empathy. This helps make them more deliberate with what they work on because being a medical student can be overwhelming and can feel as though they have everything to work on.
- Resident/Fellow: By this point, trainees usually have an increased awareness of their strengths and deficiencies. Your questions can then be more specific, giving them autonomy over their learning, such as “What are some of the things you are working on that you want me to give you feedback on this week?” This makes them more aware, intentional, and receptive to your feedback because it is framed as something that they sought out.
B. Colleagues/Staff
Unlike the training environment in which feedback is built-in, giving feedback to co-workers requires you to establish a feedback-conducive environment and to develop a more in-depth understanding of coworkers’ personalities. Similar strategies can be applied, such as proactively setting the scene for open communication, scheduling check-ins, demonstrating receptiveness to feedback, and investing in trust-building.
Longer working relationships allow for strong foundational connections that make feedback less threatening. Personality assessment testing like Myers-Briggs Type Indicator or DiSC Assessment can aid in tailoring feedback to different individuals.7,8 An analytical thinker may appreciate direct, data-driven feedback. Relationship-oriented individuals might respond better to softer, encouragement-based approaches. Always maintain shared goals at the center of your interactions and consider collaborative opportunities such as quality improvement projects. This can improve your working relationship in a constructive way without casting blame.
Tip 5: Work on delivery: Bidirectional communication and body language
Non-verbal cues can have a profound impact on how your feedback is interpreted and on the recipient’s comfort to engage in conversation. Sitting down, making eye contact, nodding, and avoiding closed-off body posture can project support and feel less judgmental. Creating a safe and non-distracted environment with privacy can make them feel valued. Use motivating, respectful language focused on directly observed behaviors rather than personal attributes or second-hand reports.
Remember that focusing on repetitive patterns is likely more helpful than isolated incidents. Validate their hard work and give them a global idea of where they stand before diving into individual behaviors. Encourage their participation and empower them to suggest changes they plan to implement. Conclude by having them summarize their action plan to give them ownership and to verify that your feedback was interpreted as you intended. Thank them for being a part of the process, as it does take a partnership for feedback to be effective.
Tip 6: Be open to feedback
Demonstrating your willingness to accept and act on feedback reinforces a positive culture where feedback is normalized and valued. After an unintended outcome, initiate a two-way conversation and ask their input on anything they wish you would have done differently. This reaffirms your commitment to maintaining culture that does not revolve around one-sided critiques. Frequently soliciting feedback about your feedback skills can also guide you to adapt your approach and to recognize any ineffective feedback practices.
Tip 7: When things don’t go as planned
Receiving feedback, no matter how thoughtfully it is delivered, can be an emotionally-charged experience ending in hurt feelings. This happens because of misinterpretation of feedback as an indicator of inadequacy, heightened awareness of underlying insecurities, sociocultural or personal circumstances, frustration with oneself, needing additional guidance, or being caught off-guard by the assessment.
The evaluator should always acknowledge the recipient’s feelings, show compassion, and allow time for processing. When they are ready to talk, it is important to help reframe the recipients’ mindsets to recognize that feedback is not personal or defining and is not a “one and done” reflection of whether they have “made it.” Instead, it is a continual process that we benefit from through all career stages. Again, shared vulnerability can help to normalize feedback and maintain open dialogue. Setting an opportunity for a future check-in can reinforce support and lead to a more productive conversation after they have had time to process.
Conclusion
Effective feedback delivery is an invaluable skill that can result in meaningful goal-directed changes while strengthening professional relationships. Given the complexity of feedback interactions and the many factors that influence its acceptance, no single approach is suitable for all recipients and frequent adaptation of the approach is essential.
In our experience, adhering to these general overarching feedback principles (see Figure 1) has allowed us to have more successful interactions with trainees and colleagues.
Dr. Baliss is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri. Dr. Hachem is director of the Division of Gastroenterology and Digestive Health at Intermountain Medical, Sandy, Utah. Both authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Parkes J, et al. Feedback sandwiches affect perceptions but not performance. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2013 Aug. doi:10.1007/s10459-012-9377-9.
2. van de Ridder JMM and Wijnen-Meijer M. Pendleton’s Rules: A Mini Review of a Feedback Method. Am J Biomed Sci & Res. 2023 May. doi: 10.34297/AJBSR.2023.19.002542.
3. Sender Liberman A, et al. Surgery residents and attending surgeons have different perceptions of feedback. Med Teach. 2005 Aug. doi: 10.1080/0142590500129183.
4. Sargeant J, et al. R2C2 in Action: Testing an Evidence-Based Model to Facilitate Feedback and Coaching in Residency. J Grad Med Educ. 2017 Apr. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-16-00398.1.
5. Liakos W, et al. Frameworks for Effective Feedback in Health Professions Education. Acad Med. 2023 May. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000004884.
6. Ramani S, et al. Feedback Redefined: Principles and Practice. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 May. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04874-2.
7. Woods RA and Hill PB. Myers-Briggs Type Indicator. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. 2022 Sept. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554596/
8. Slowikowski MK. Using the DISC behavioral instrument to guide leadership and communication. AORN J. 2005 Nov. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2092(06)60276-7.
The Essential Guide to Estate Planning for Physicians: Securing Your Legacy and Protecting Your Wealth
As a physician, you’ve spent years building a career that not only provides financial security for your family but also allows you to make a meaningful impact in your community. However, without a comprehensive estate plan in place, much of what you’ve worked so hard to build may not be preserved according to your wishes.
Many physicians delay estate planning, assuming it’s something to consider later in life. However, the most successful estate plans are those that are established early and evolve over time. Proper planning ensures that your assets are protected, your loved ones are provided for, and your legacy is preserved in the most tax-efficient and legally-sound manner possible.1
This article explores why estate planning is particularly crucial for physicians, the key elements of a strong estate plan, and how beginning early can create long-term financial advantages.
Why Estate Planning Matters for Physicians
Physicians are in a unique financial position compared to many other professionals. With high earning potential, specialized assets, and significant liability exposure, their estate planning needs differ from those of the average individual. A well-structured estate plan not only facilitates the smooth transfer of wealth but also protects assets from excessive taxation, legal complications, and potential risks such as malpractice claims.
1. High Net-Worth Considerations
Physicians often accumulate substantial wealth over time. Without a clear estate plan, your estate could face excessive taxation, with a large portion of your assets potentially going to the government rather than your heirs. Estate taxes, probate costs, and legal fees can significantly erode your legacy if not properly planned for.
2. Asset Protection from Liability Risks
Unlike most professionals, physicians are at a higher risk of litigation. A comprehensive estate plan can incorporate asset protection strategies, such as irrevocable trusts, family limited partnerships, or liability insurance, to shield your wealth from lawsuits or creditor claims.
3. Family and Generational Wealth Planning
Many physicians prioritize ensuring their family’s financial stability. Whether you want to provide for your spouse, children, or even charitable causes, estate planning allows you to dictate how your wealth is distributed. Establishing trusts for your children or grandchildren can help manage how and when they receive their inheritance, preventing mismanagement and ensuring financial responsibility.
4. Business and Practice Continuity
If you own a medical practice, succession planning should be part of your estate plan. Without clear directives, the future of your practice may be uncertain in the event of your passing or incapacitation. A well-drafted estate plan provides a roadmap for ownership transition, ensuring continuity for patients, employees, and business partners.
Key Elements of an Effective Estate Plan
Every estate plan should be customized based on your financial situation, goals, and family dynamics. However, certain fundamental components apply to nearly all high-net-worth individuals, including physicians.
1. Revocable Living Trusts
A revocable living trust allows you to manage your assets during your lifetime while providing a clear path for distribution after your passing. Unlike a will, a trust helps your estate avoid probate, ensuring a smoother and more private transition of wealth. You maintain control over your assets while also establishing clear rules for distribution, particularly useful if you have minor children or complex family structures.2
2. Irrevocable Trusts for Asset Protection
For physicians concerned about lawsuits or estate tax exposure, irrevocable trusts can offer robust asset protection. Since assets placed in these trusts are no longer legally owned by you, they are shielded from creditors and legal claims while also reducing your taxable estate.2
3. Powers of Attorney and Healthcare Directives
Estate planning isn’t just about what happens after your passing—it’s also about protecting you and your family if you become incapacitated. A durable power of attorney allows a trusted individual to manage your financial affairs, while a healthcare directive ensures your medical decisions align with your wishes.3
4. Life Insurance Planning
Life insurance is an essential estate planning tool for physicians, providing liquidity to cover estate taxes, debts, or income replacement for your family. A properly structured life insurance trust can help ensure that policy proceeds remain outside of your taxable estate while being efficiently distributed according to your wishes.4
5. Business Succession Planning
If you own a medical practice, a well-designed succession plan can ensure that your business continues to operate smoothly in your absence. This may involve buy-sell agreements, key-person insurance, or identifying a successor to take over your role.5
The Long-Term Benefits of Early Estate Planning
Estate planning is not a one-time event—it’s a process that should evolve with your career, financial growth, and family dynamics. The earlier you begin, the more control you have over your financial future. Here’s why starting early is a strategic advantage:
1. Maximizing Tax Efficiency
Many estate planning strategies, such as gifting assets or establishing irrevocable trusts, are most effective when implemented over time. By spreading out wealth transfers and taking advantage of annual gift exclusions, you can significantly reduce estate tax liability while maintaining financial security.
2. Adjusting for Life Changes
Your financial situation and family needs will change over the years. Marriages, births, career advancements, and new investments all impact your estate planning needs. By starting early, you can make gradual adjustments rather than facing an overwhelming restructuring later in life.1
3. Ensuring Asset Protection Strategies Are in Place
Many asset protection strategies require time to be effective. For instance, certain types of trusts must be in place for a number of years before they fully shield assets from legal claims. Delaying planning could leave your wealth unnecessarily exposed.
4. Creating a Legacy Beyond Wealth
Estate planning is not just about finances—it’s about legacy. Whether you want to support a charitable cause, endow a scholarship, or establish a foundation, early planning gives you the ability to shape your long-term impact.
5. Adapt to Ever Changing Legislation
Estate planning needs to be adaptable. The federal government can change the estate tax exemption at any time; this was even a topic of the last election cycle. Early planning allows you to implement necessary changes throughout your life to minimize estate taxes. At present, unless new policy is enacted, the exemption per individual will reduce by half in 2026 (see Figure 1).
Final Thoughts: Taking Action Today
The complexity of physician finances—ranging from high income and significant assets to legal risks—makes individualized estate planning an absolute necessity.
By taking proactive steps today, you can maximize tax efficiency, safeguard your assets, and ensure your wishes are carried out without unnecessary delays or legal battles. Working with a financial advisor and estate planning attorney who understands the unique needs of physicians can help you craft a plan that aligns with your goals and evolves as your career progresses.
Mr. Gardner is a financial advisor at Lifetime Financial Growth, LLC, in Columbus, Ohio, one of the largest privately held wealth management firms in the country. John has had a passion for finance since his early years in college when his tennis coach introduced him. He also has a passion for helping physicians, as his wife is a gastroenterologist at Ohio State University. He reports no relevant disclosures relevant to this article. If you have additional questions, please contact John at 740-403-4891 or [email protected].
References
1. The Law Offices of Diron Rutty, LLC. https://www.dironruttyllc.com/reasons-to-start-estate-planning-early/.
2. Physician Side Gigs. https://www.physiciansidegigs.com/estateplanning.
3. Afshar, A & MacBeth, S. https://www.schwabe.com/publication/estate-planning-for-physicians-why-its-important-and-how-to-get-started/. December 2024.
4. Skeeles, JC. https://ohioline.osu.edu/factsheet/ep-1. July 2012.
5. Rosenfeld, J. Physician estate planning guide. Medical Economics. 2022 Nov. https://www.medicaleconomics.com/view/physician-estate-planning-guide.
As a physician, you’ve spent years building a career that not only provides financial security for your family but also allows you to make a meaningful impact in your community. However, without a comprehensive estate plan in place, much of what you’ve worked so hard to build may not be preserved according to your wishes.
Many physicians delay estate planning, assuming it’s something to consider later in life. However, the most successful estate plans are those that are established early and evolve over time. Proper planning ensures that your assets are protected, your loved ones are provided for, and your legacy is preserved in the most tax-efficient and legally-sound manner possible.1
This article explores why estate planning is particularly crucial for physicians, the key elements of a strong estate plan, and how beginning early can create long-term financial advantages.
Why Estate Planning Matters for Physicians
Physicians are in a unique financial position compared to many other professionals. With high earning potential, specialized assets, and significant liability exposure, their estate planning needs differ from those of the average individual. A well-structured estate plan not only facilitates the smooth transfer of wealth but also protects assets from excessive taxation, legal complications, and potential risks such as malpractice claims.
1. High Net-Worth Considerations
Physicians often accumulate substantial wealth over time. Without a clear estate plan, your estate could face excessive taxation, with a large portion of your assets potentially going to the government rather than your heirs. Estate taxes, probate costs, and legal fees can significantly erode your legacy if not properly planned for.
2. Asset Protection from Liability Risks
Unlike most professionals, physicians are at a higher risk of litigation. A comprehensive estate plan can incorporate asset protection strategies, such as irrevocable trusts, family limited partnerships, or liability insurance, to shield your wealth from lawsuits or creditor claims.
3. Family and Generational Wealth Planning
Many physicians prioritize ensuring their family’s financial stability. Whether you want to provide for your spouse, children, or even charitable causes, estate planning allows you to dictate how your wealth is distributed. Establishing trusts for your children or grandchildren can help manage how and when they receive their inheritance, preventing mismanagement and ensuring financial responsibility.
4. Business and Practice Continuity
If you own a medical practice, succession planning should be part of your estate plan. Without clear directives, the future of your practice may be uncertain in the event of your passing or incapacitation. A well-drafted estate plan provides a roadmap for ownership transition, ensuring continuity for patients, employees, and business partners.
Key Elements of an Effective Estate Plan
Every estate plan should be customized based on your financial situation, goals, and family dynamics. However, certain fundamental components apply to nearly all high-net-worth individuals, including physicians.
1. Revocable Living Trusts
A revocable living trust allows you to manage your assets during your lifetime while providing a clear path for distribution after your passing. Unlike a will, a trust helps your estate avoid probate, ensuring a smoother and more private transition of wealth. You maintain control over your assets while also establishing clear rules for distribution, particularly useful if you have minor children or complex family structures.2
2. Irrevocable Trusts for Asset Protection
For physicians concerned about lawsuits or estate tax exposure, irrevocable trusts can offer robust asset protection. Since assets placed in these trusts are no longer legally owned by you, they are shielded from creditors and legal claims while also reducing your taxable estate.2
3. Powers of Attorney and Healthcare Directives
Estate planning isn’t just about what happens after your passing—it’s also about protecting you and your family if you become incapacitated. A durable power of attorney allows a trusted individual to manage your financial affairs, while a healthcare directive ensures your medical decisions align with your wishes.3
4. Life Insurance Planning
Life insurance is an essential estate planning tool for physicians, providing liquidity to cover estate taxes, debts, or income replacement for your family. A properly structured life insurance trust can help ensure that policy proceeds remain outside of your taxable estate while being efficiently distributed according to your wishes.4
5. Business Succession Planning
If you own a medical practice, a well-designed succession plan can ensure that your business continues to operate smoothly in your absence. This may involve buy-sell agreements, key-person insurance, or identifying a successor to take over your role.5
The Long-Term Benefits of Early Estate Planning
Estate planning is not a one-time event—it’s a process that should evolve with your career, financial growth, and family dynamics. The earlier you begin, the more control you have over your financial future. Here’s why starting early is a strategic advantage:
1. Maximizing Tax Efficiency
Many estate planning strategies, such as gifting assets or establishing irrevocable trusts, are most effective when implemented over time. By spreading out wealth transfers and taking advantage of annual gift exclusions, you can significantly reduce estate tax liability while maintaining financial security.
2. Adjusting for Life Changes
Your financial situation and family needs will change over the years. Marriages, births, career advancements, and new investments all impact your estate planning needs. By starting early, you can make gradual adjustments rather than facing an overwhelming restructuring later in life.1
3. Ensuring Asset Protection Strategies Are in Place
Many asset protection strategies require time to be effective. For instance, certain types of trusts must be in place for a number of years before they fully shield assets from legal claims. Delaying planning could leave your wealth unnecessarily exposed.
4. Creating a Legacy Beyond Wealth
Estate planning is not just about finances—it’s about legacy. Whether you want to support a charitable cause, endow a scholarship, or establish a foundation, early planning gives you the ability to shape your long-term impact.
5. Adapt to Ever Changing Legislation
Estate planning needs to be adaptable. The federal government can change the estate tax exemption at any time; this was even a topic of the last election cycle. Early planning allows you to implement necessary changes throughout your life to minimize estate taxes. At present, unless new policy is enacted, the exemption per individual will reduce by half in 2026 (see Figure 1).
Final Thoughts: Taking Action Today
The complexity of physician finances—ranging from high income and significant assets to legal risks—makes individualized estate planning an absolute necessity.
By taking proactive steps today, you can maximize tax efficiency, safeguard your assets, and ensure your wishes are carried out without unnecessary delays or legal battles. Working with a financial advisor and estate planning attorney who understands the unique needs of physicians can help you craft a plan that aligns with your goals and evolves as your career progresses.
Mr. Gardner is a financial advisor at Lifetime Financial Growth, LLC, in Columbus, Ohio, one of the largest privately held wealth management firms in the country. John has had a passion for finance since his early years in college when his tennis coach introduced him. He also has a passion for helping physicians, as his wife is a gastroenterologist at Ohio State University. He reports no relevant disclosures relevant to this article. If you have additional questions, please contact John at 740-403-4891 or [email protected].
References
1. The Law Offices of Diron Rutty, LLC. https://www.dironruttyllc.com/reasons-to-start-estate-planning-early/.
2. Physician Side Gigs. https://www.physiciansidegigs.com/estateplanning.
3. Afshar, A & MacBeth, S. https://www.schwabe.com/publication/estate-planning-for-physicians-why-its-important-and-how-to-get-started/. December 2024.
4. Skeeles, JC. https://ohioline.osu.edu/factsheet/ep-1. July 2012.
5. Rosenfeld, J. Physician estate planning guide. Medical Economics. 2022 Nov. https://www.medicaleconomics.com/view/physician-estate-planning-guide.
As a physician, you’ve spent years building a career that not only provides financial security for your family but also allows you to make a meaningful impact in your community. However, without a comprehensive estate plan in place, much of what you’ve worked so hard to build may not be preserved according to your wishes.
Many physicians delay estate planning, assuming it’s something to consider later in life. However, the most successful estate plans are those that are established early and evolve over time. Proper planning ensures that your assets are protected, your loved ones are provided for, and your legacy is preserved in the most tax-efficient and legally-sound manner possible.1
This article explores why estate planning is particularly crucial for physicians, the key elements of a strong estate plan, and how beginning early can create long-term financial advantages.
Why Estate Planning Matters for Physicians
Physicians are in a unique financial position compared to many other professionals. With high earning potential, specialized assets, and significant liability exposure, their estate planning needs differ from those of the average individual. A well-structured estate plan not only facilitates the smooth transfer of wealth but also protects assets from excessive taxation, legal complications, and potential risks such as malpractice claims.
1. High Net-Worth Considerations
Physicians often accumulate substantial wealth over time. Without a clear estate plan, your estate could face excessive taxation, with a large portion of your assets potentially going to the government rather than your heirs. Estate taxes, probate costs, and legal fees can significantly erode your legacy if not properly planned for.
2. Asset Protection from Liability Risks
Unlike most professionals, physicians are at a higher risk of litigation. A comprehensive estate plan can incorporate asset protection strategies, such as irrevocable trusts, family limited partnerships, or liability insurance, to shield your wealth from lawsuits or creditor claims.
3. Family and Generational Wealth Planning
Many physicians prioritize ensuring their family’s financial stability. Whether you want to provide for your spouse, children, or even charitable causes, estate planning allows you to dictate how your wealth is distributed. Establishing trusts for your children or grandchildren can help manage how and when they receive their inheritance, preventing mismanagement and ensuring financial responsibility.
4. Business and Practice Continuity
If you own a medical practice, succession planning should be part of your estate plan. Without clear directives, the future of your practice may be uncertain in the event of your passing or incapacitation. A well-drafted estate plan provides a roadmap for ownership transition, ensuring continuity for patients, employees, and business partners.
Key Elements of an Effective Estate Plan
Every estate plan should be customized based on your financial situation, goals, and family dynamics. However, certain fundamental components apply to nearly all high-net-worth individuals, including physicians.
1. Revocable Living Trusts
A revocable living trust allows you to manage your assets during your lifetime while providing a clear path for distribution after your passing. Unlike a will, a trust helps your estate avoid probate, ensuring a smoother and more private transition of wealth. You maintain control over your assets while also establishing clear rules for distribution, particularly useful if you have minor children or complex family structures.2
2. Irrevocable Trusts for Asset Protection
For physicians concerned about lawsuits or estate tax exposure, irrevocable trusts can offer robust asset protection. Since assets placed in these trusts are no longer legally owned by you, they are shielded from creditors and legal claims while also reducing your taxable estate.2
3. Powers of Attorney and Healthcare Directives
Estate planning isn’t just about what happens after your passing—it’s also about protecting you and your family if you become incapacitated. A durable power of attorney allows a trusted individual to manage your financial affairs, while a healthcare directive ensures your medical decisions align with your wishes.3
4. Life Insurance Planning
Life insurance is an essential estate planning tool for physicians, providing liquidity to cover estate taxes, debts, or income replacement for your family. A properly structured life insurance trust can help ensure that policy proceeds remain outside of your taxable estate while being efficiently distributed according to your wishes.4
5. Business Succession Planning
If you own a medical practice, a well-designed succession plan can ensure that your business continues to operate smoothly in your absence. This may involve buy-sell agreements, key-person insurance, or identifying a successor to take over your role.5
The Long-Term Benefits of Early Estate Planning
Estate planning is not a one-time event—it’s a process that should evolve with your career, financial growth, and family dynamics. The earlier you begin, the more control you have over your financial future. Here’s why starting early is a strategic advantage:
1. Maximizing Tax Efficiency
Many estate planning strategies, such as gifting assets or establishing irrevocable trusts, are most effective when implemented over time. By spreading out wealth transfers and taking advantage of annual gift exclusions, you can significantly reduce estate tax liability while maintaining financial security.
2. Adjusting for Life Changes
Your financial situation and family needs will change over the years. Marriages, births, career advancements, and new investments all impact your estate planning needs. By starting early, you can make gradual adjustments rather than facing an overwhelming restructuring later in life.1
3. Ensuring Asset Protection Strategies Are in Place
Many asset protection strategies require time to be effective. For instance, certain types of trusts must be in place for a number of years before they fully shield assets from legal claims. Delaying planning could leave your wealth unnecessarily exposed.
4. Creating a Legacy Beyond Wealth
Estate planning is not just about finances—it’s about legacy. Whether you want to support a charitable cause, endow a scholarship, or establish a foundation, early planning gives you the ability to shape your long-term impact.
5. Adapt to Ever Changing Legislation
Estate planning needs to be adaptable. The federal government can change the estate tax exemption at any time; this was even a topic of the last election cycle. Early planning allows you to implement necessary changes throughout your life to minimize estate taxes. At present, unless new policy is enacted, the exemption per individual will reduce by half in 2026 (see Figure 1).
Final Thoughts: Taking Action Today
The complexity of physician finances—ranging from high income and significant assets to legal risks—makes individualized estate planning an absolute necessity.
By taking proactive steps today, you can maximize tax efficiency, safeguard your assets, and ensure your wishes are carried out without unnecessary delays or legal battles. Working with a financial advisor and estate planning attorney who understands the unique needs of physicians can help you craft a plan that aligns with your goals and evolves as your career progresses.
Mr. Gardner is a financial advisor at Lifetime Financial Growth, LLC, in Columbus, Ohio, one of the largest privately held wealth management firms in the country. John has had a passion for finance since his early years in college when his tennis coach introduced him. He also has a passion for helping physicians, as his wife is a gastroenterologist at Ohio State University. He reports no relevant disclosures relevant to this article. If you have additional questions, please contact John at 740-403-4891 or [email protected].
References
1. The Law Offices of Diron Rutty, LLC. https://www.dironruttyllc.com/reasons-to-start-estate-planning-early/.
2. Physician Side Gigs. https://www.physiciansidegigs.com/estateplanning.
3. Afshar, A & MacBeth, S. https://www.schwabe.com/publication/estate-planning-for-physicians-why-its-important-and-how-to-get-started/. December 2024.
4. Skeeles, JC. https://ohioline.osu.edu/factsheet/ep-1. July 2012.
5. Rosenfeld, J. Physician estate planning guide. Medical Economics. 2022 Nov. https://www.medicaleconomics.com/view/physician-estate-planning-guide.
Winning Strategies to Retain Private Practice Gastroenterologists
SAN DIEGO — With the recently updated recommendations by the US Preventive Services Task Force lowering the age for colorectal cancer screening to 45 instead of 50, an additional 19 million patients now require screening, Asma Khapra, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist at Gastro Health in Fairfax, Virginia, told attendees at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2025.
That change, coupled with the expected shortage of gastroenterologists, means one thing: The current workforce can’t meet patient demand, she said. , Khapra added.
The private practice model is already declining, she said. The fraction of US gastroenterologists in “fully independent” private practice was about 30% in 2019, Khapra noted. Then, “COVID really changed the landscape even more.” By 2022, “that number has shrunk to 13%.” Meanwhile, 67% are employed gastroenterologists (not in private practice), 7% work in large group practices, and 13% are private equity (PE) backed.
That makes effective retention strategies crucial for private practices, Khapra said. She first addressed the common attractions of private practices, then the challenges, and finally the winning strategies to retain and keep a viable private practice gastroenterology workforce.
The Attractions of Private Practice
The reasons for choosing private practice are many, Khapra said, including:
- Autonomy,
- Flexibility,
- Competitive compensation,
- Ownership mindset,
- Partnership paths, and
- Work-life balance including involvement in community and culture.
On the other hand, private practices have unique challenges, including:
- Administrative burdens such as EHR documentation, paperwork, prior authorizations, and staffing issues,
- Financial pressures, including competition with the employment packages offered by hospitals, as reimbursements continue to drop and staffing costs increase,
- Burnout,
- Variety of buy-ins and partnership tracks,
- Limited career development, and
- The strains of aging and endoscopy. “We used to joke in our practice that at any given time, three staff members are in physical therapy due to injuries and disabilities.”
Employing the Iceberg Model
One strategy, Khapra said, is to follow Edward T. Hall’s Iceberg Model of Culture , which focuses on the importance of both visible and invisible elements.
“The key to retention in private practice is to develop a value system where everyone is treated well and respected and compensated fairly,” she said. “That doesn’t mean you split the pie [equally].”
“Visible” elements of the model include the physical environment, policies and practices, symbols and behaviors, she said. While under the surface (“invisible” elements) are shared values, perceptions and attitudes, leadership style, conflict resolution, decision making and unwritten rules.
The key, she said, is to provide physicians an actual voice in decision making and to avoid favouritism, thus avoiding comments such as “Why do the same two people always get the prime scoping blocks?”
Financial transparency is also important, Khapra said. And people want flexibility without it being called special treatment. She provided several practical suggestions to accomplish the invisible Iceberg goals.
For instance, she suggested paying for activities outside the practice that physicians do, such as serving on committees. If the practice can’t afford that, she suggested asking the affiliated hospitals to do so, noting that such an initiative can often build community support.
Paying more attention to early associates than is typical can also benefit the practice, Khapra said. “So much effort is made to recruit them, and then once there, we’re on to the next [recruits].” Instead, she suggested, “pay attention to their needs.”
Providing support to physicians who are injured is also crucial and can foster a community culture, she said. For example, one Gastro Health physician was out for 4 weeks due to complications from surgery. “Everyone jumped in” to help fill the injured physician’s shifts, she said, reassuring the physician that the money would be figured out later. “That’s the culture you want to instill.”
To prevent burnout, another key to retaining physicians, “you have to provide support staff.” And offering good benefits, including parental and maternal leave and disability benefits, is also crucial, Khapra said. Consider practices such as having social dinners, another way to build a sense of community.
Finally, bring in national and local gastroenterologist organizations for discussions, including advocating for fair reimbursement for private practice. Consider working with the Digestive Health Physicians Alliance, which describes itself as the voice of independent gastroenterology, she suggested.
More Perspectives
Jami Kinnucan, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist and associate professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville , Florida, spoke about optimizing recruitment of young gastroenterologists and provided perspective on Khapra’s talk.
“I think there’s a lot of overlap” with her topic and retaining private practice gastroenterologists, she said in an interview with GI & Hepatology News. Most important, she said, is having an efficient system in which the administrative flow is left to digital tools or other staff, not physicians. “That will also help to reduce burnout,” she said, and allow physicians to do what they most want to do, which is to focus on providing care to patients.
“People want to feel valued for their work,” she agreed. “People want opportunity for career development, opportunities for growth.”
As gastroenterologists age, flexibility is important, as it in in general for all physicians, Kinnucan said. She suggested schedule flexibility as one way. For instance, “if I tell 10 providers, ‘I need you to see 100 patients this week, but you can do it however you want,’ that promotes flexibility. They might want to see all of them on Monday and Tuesday, for instance. If you give people choice and autonomy, they are more likely to feel like they are part of the decision.”
How do you build a high-functioning team? “You do it by letting them operate autonomously,” and “you let people do the things they are really excited about.” And always, as Khapra said, focus on the invisible elements that are so crucial.
Khapra and Kinnucan had no relevant disclosures. Khapra received no funding for her presentation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — With the recently updated recommendations by the US Preventive Services Task Force lowering the age for colorectal cancer screening to 45 instead of 50, an additional 19 million patients now require screening, Asma Khapra, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist at Gastro Health in Fairfax, Virginia, told attendees at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2025.
That change, coupled with the expected shortage of gastroenterologists, means one thing: The current workforce can’t meet patient demand, she said. , Khapra added.
The private practice model is already declining, she said. The fraction of US gastroenterologists in “fully independent” private practice was about 30% in 2019, Khapra noted. Then, “COVID really changed the landscape even more.” By 2022, “that number has shrunk to 13%.” Meanwhile, 67% are employed gastroenterologists (not in private practice), 7% work in large group practices, and 13% are private equity (PE) backed.
That makes effective retention strategies crucial for private practices, Khapra said. She first addressed the common attractions of private practices, then the challenges, and finally the winning strategies to retain and keep a viable private practice gastroenterology workforce.
The Attractions of Private Practice
The reasons for choosing private practice are many, Khapra said, including:
- Autonomy,
- Flexibility,
- Competitive compensation,
- Ownership mindset,
- Partnership paths, and
- Work-life balance including involvement in community and culture.
On the other hand, private practices have unique challenges, including:
- Administrative burdens such as EHR documentation, paperwork, prior authorizations, and staffing issues,
- Financial pressures, including competition with the employment packages offered by hospitals, as reimbursements continue to drop and staffing costs increase,
- Burnout,
- Variety of buy-ins and partnership tracks,
- Limited career development, and
- The strains of aging and endoscopy. “We used to joke in our practice that at any given time, three staff members are in physical therapy due to injuries and disabilities.”
Employing the Iceberg Model
One strategy, Khapra said, is to follow Edward T. Hall’s Iceberg Model of Culture , which focuses on the importance of both visible and invisible elements.
“The key to retention in private practice is to develop a value system where everyone is treated well and respected and compensated fairly,” she said. “That doesn’t mean you split the pie [equally].”
“Visible” elements of the model include the physical environment, policies and practices, symbols and behaviors, she said. While under the surface (“invisible” elements) are shared values, perceptions and attitudes, leadership style, conflict resolution, decision making and unwritten rules.
The key, she said, is to provide physicians an actual voice in decision making and to avoid favouritism, thus avoiding comments such as “Why do the same two people always get the prime scoping blocks?”
Financial transparency is also important, Khapra said. And people want flexibility without it being called special treatment. She provided several practical suggestions to accomplish the invisible Iceberg goals.
For instance, she suggested paying for activities outside the practice that physicians do, such as serving on committees. If the practice can’t afford that, she suggested asking the affiliated hospitals to do so, noting that such an initiative can often build community support.
Paying more attention to early associates than is typical can also benefit the practice, Khapra said. “So much effort is made to recruit them, and then once there, we’re on to the next [recruits].” Instead, she suggested, “pay attention to their needs.”
Providing support to physicians who are injured is also crucial and can foster a community culture, she said. For example, one Gastro Health physician was out for 4 weeks due to complications from surgery. “Everyone jumped in” to help fill the injured physician’s shifts, she said, reassuring the physician that the money would be figured out later. “That’s the culture you want to instill.”
To prevent burnout, another key to retaining physicians, “you have to provide support staff.” And offering good benefits, including parental and maternal leave and disability benefits, is also crucial, Khapra said. Consider practices such as having social dinners, another way to build a sense of community.
Finally, bring in national and local gastroenterologist organizations for discussions, including advocating for fair reimbursement for private practice. Consider working with the Digestive Health Physicians Alliance, which describes itself as the voice of independent gastroenterology, she suggested.
More Perspectives
Jami Kinnucan, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist and associate professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville , Florida, spoke about optimizing recruitment of young gastroenterologists and provided perspective on Khapra’s talk.
“I think there’s a lot of overlap” with her topic and retaining private practice gastroenterologists, she said in an interview with GI & Hepatology News. Most important, she said, is having an efficient system in which the administrative flow is left to digital tools or other staff, not physicians. “That will also help to reduce burnout,” she said, and allow physicians to do what they most want to do, which is to focus on providing care to patients.
“People want to feel valued for their work,” she agreed. “People want opportunity for career development, opportunities for growth.”
As gastroenterologists age, flexibility is important, as it in in general for all physicians, Kinnucan said. She suggested schedule flexibility as one way. For instance, “if I tell 10 providers, ‘I need you to see 100 patients this week, but you can do it however you want,’ that promotes flexibility. They might want to see all of them on Monday and Tuesday, for instance. If you give people choice and autonomy, they are more likely to feel like they are part of the decision.”
How do you build a high-functioning team? “You do it by letting them operate autonomously,” and “you let people do the things they are really excited about.” And always, as Khapra said, focus on the invisible elements that are so crucial.
Khapra and Kinnucan had no relevant disclosures. Khapra received no funding for her presentation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — With the recently updated recommendations by the US Preventive Services Task Force lowering the age for colorectal cancer screening to 45 instead of 50, an additional 19 million patients now require screening, Asma Khapra, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist at Gastro Health in Fairfax, Virginia, told attendees at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2025.
That change, coupled with the expected shortage of gastroenterologists, means one thing: The current workforce can’t meet patient demand, she said. , Khapra added.
The private practice model is already declining, she said. The fraction of US gastroenterologists in “fully independent” private practice was about 30% in 2019, Khapra noted. Then, “COVID really changed the landscape even more.” By 2022, “that number has shrunk to 13%.” Meanwhile, 67% are employed gastroenterologists (not in private practice), 7% work in large group practices, and 13% are private equity (PE) backed.
That makes effective retention strategies crucial for private practices, Khapra said. She first addressed the common attractions of private practices, then the challenges, and finally the winning strategies to retain and keep a viable private practice gastroenterology workforce.
The Attractions of Private Practice
The reasons for choosing private practice are many, Khapra said, including:
- Autonomy,
- Flexibility,
- Competitive compensation,
- Ownership mindset,
- Partnership paths, and
- Work-life balance including involvement in community and culture.
On the other hand, private practices have unique challenges, including:
- Administrative burdens such as EHR documentation, paperwork, prior authorizations, and staffing issues,
- Financial pressures, including competition with the employment packages offered by hospitals, as reimbursements continue to drop and staffing costs increase,
- Burnout,
- Variety of buy-ins and partnership tracks,
- Limited career development, and
- The strains of aging and endoscopy. “We used to joke in our practice that at any given time, three staff members are in physical therapy due to injuries and disabilities.”
Employing the Iceberg Model
One strategy, Khapra said, is to follow Edward T. Hall’s Iceberg Model of Culture , which focuses on the importance of both visible and invisible elements.
“The key to retention in private practice is to develop a value system where everyone is treated well and respected and compensated fairly,” she said. “That doesn’t mean you split the pie [equally].”
“Visible” elements of the model include the physical environment, policies and practices, symbols and behaviors, she said. While under the surface (“invisible” elements) are shared values, perceptions and attitudes, leadership style, conflict resolution, decision making and unwritten rules.
The key, she said, is to provide physicians an actual voice in decision making and to avoid favouritism, thus avoiding comments such as “Why do the same two people always get the prime scoping blocks?”
Financial transparency is also important, Khapra said. And people want flexibility without it being called special treatment. She provided several practical suggestions to accomplish the invisible Iceberg goals.
For instance, she suggested paying for activities outside the practice that physicians do, such as serving on committees. If the practice can’t afford that, she suggested asking the affiliated hospitals to do so, noting that such an initiative can often build community support.
Paying more attention to early associates than is typical can also benefit the practice, Khapra said. “So much effort is made to recruit them, and then once there, we’re on to the next [recruits].” Instead, she suggested, “pay attention to their needs.”
Providing support to physicians who are injured is also crucial and can foster a community culture, she said. For example, one Gastro Health physician was out for 4 weeks due to complications from surgery. “Everyone jumped in” to help fill the injured physician’s shifts, she said, reassuring the physician that the money would be figured out later. “That’s the culture you want to instill.”
To prevent burnout, another key to retaining physicians, “you have to provide support staff.” And offering good benefits, including parental and maternal leave and disability benefits, is also crucial, Khapra said. Consider practices such as having social dinners, another way to build a sense of community.
Finally, bring in national and local gastroenterologist organizations for discussions, including advocating for fair reimbursement for private practice. Consider working with the Digestive Health Physicians Alliance, which describes itself as the voice of independent gastroenterology, she suggested.
More Perspectives
Jami Kinnucan, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist and associate professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville , Florida, spoke about optimizing recruitment of young gastroenterologists and provided perspective on Khapra’s talk.
“I think there’s a lot of overlap” with her topic and retaining private practice gastroenterologists, she said in an interview with GI & Hepatology News. Most important, she said, is having an efficient system in which the administrative flow is left to digital tools or other staff, not physicians. “That will also help to reduce burnout,” she said, and allow physicians to do what they most want to do, which is to focus on providing care to patients.
“People want to feel valued for their work,” she agreed. “People want opportunity for career development, opportunities for growth.”
As gastroenterologists age, flexibility is important, as it in in general for all physicians, Kinnucan said. She suggested schedule flexibility as one way. For instance, “if I tell 10 providers, ‘I need you to see 100 patients this week, but you can do it however you want,’ that promotes flexibility. They might want to see all of them on Monday and Tuesday, for instance. If you give people choice and autonomy, they are more likely to feel like they are part of the decision.”
How do you build a high-functioning team? “You do it by letting them operate autonomously,” and “you let people do the things they are really excited about.” And always, as Khapra said, focus on the invisible elements that are so crucial.
Khapra and Kinnucan had no relevant disclosures. Khapra received no funding for her presentation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DDW 2025
Building Your Referral Base

In this video, Lisa Mathew, MD, of South Denver Gastroenterology in Denver, Colorado, and Raja Taunk, MD, of Anne Arundel Gastroenterology Associates, in Annapolis, Maryland, share insights on private practice gastroenterology and offer tips on building your practice – specifically improving your referral base.

In this video, Lisa Mathew, MD, of South Denver Gastroenterology in Denver, Colorado, and Raja Taunk, MD, of Anne Arundel Gastroenterology Associates, in Annapolis, Maryland, share insights on private practice gastroenterology and offer tips on building your practice – specifically improving your referral base.

In this video, Lisa Mathew, MD, of South Denver Gastroenterology in Denver, Colorado, and Raja Taunk, MD, of Anne Arundel Gastroenterology Associates, in Annapolis, Maryland, share insights on private practice gastroenterology and offer tips on building your practice – specifically improving your referral base.
Five Reasons to Update Your Will
You have a will, so you can rest easy, right? Not necessarily. If your will is outdated, it can cause more harm than good.
Even though it can provide for some contingencies, an old will can’t cover every change that may have occurred since it was first drawn. Professionals advise that you review your will every few years and more often if situations such as the following five have occurred since you last updated your will.
1. Family Changes
If you’ve had any changes in your family situation, you will probably need to update your will. Events such as marriage, divorce, death, birth, adoption, or a falling out with a loved one may affect how your estate will be distributed, who should act as guardian for your dependents, and who should be named as executor of your estate.
2. Relocating to a New State
The laws among the states vary. Moving to a new state or purchasing property in another state can affect your estate plan and how property in that state will be taxed and distributed.
3. Tax Law Changes
Federal and state legislatures are continually tinkering with federal estate and state inheritance tax laws. An old will may fail to take advantage of strategies that will minimize estate taxes.
4. You Want to Support a Favorite Cause
If you have developed a connection to a cause, you may want to benefit a particular charity with a gift in your estate. Contact us for sample language you can share with your attorney to include a gift to us in your will.
5. Changes in Your Estate’s Value
When you made your will, your assets may have been relatively modest. Now the value may be larger and your will no longer reflects how you would like your estate divided.
You will help spark future discoveries in GI. Visit our website at https://gastro.planmylegacy.org or contact us at [email protected].
You have a will, so you can rest easy, right? Not necessarily. If your will is outdated, it can cause more harm than good.
Even though it can provide for some contingencies, an old will can’t cover every change that may have occurred since it was first drawn. Professionals advise that you review your will every few years and more often if situations such as the following five have occurred since you last updated your will.
1. Family Changes
If you’ve had any changes in your family situation, you will probably need to update your will. Events such as marriage, divorce, death, birth, adoption, or a falling out with a loved one may affect how your estate will be distributed, who should act as guardian for your dependents, and who should be named as executor of your estate.
2. Relocating to a New State
The laws among the states vary. Moving to a new state or purchasing property in another state can affect your estate plan and how property in that state will be taxed and distributed.
3. Tax Law Changes
Federal and state legislatures are continually tinkering with federal estate and state inheritance tax laws. An old will may fail to take advantage of strategies that will minimize estate taxes.
4. You Want to Support a Favorite Cause
If you have developed a connection to a cause, you may want to benefit a particular charity with a gift in your estate. Contact us for sample language you can share with your attorney to include a gift to us in your will.
5. Changes in Your Estate’s Value
When you made your will, your assets may have been relatively modest. Now the value may be larger and your will no longer reflects how you would like your estate divided.
You will help spark future discoveries in GI. Visit our website at https://gastro.planmylegacy.org or contact us at [email protected].
You have a will, so you can rest easy, right? Not necessarily. If your will is outdated, it can cause more harm than good.
Even though it can provide for some contingencies, an old will can’t cover every change that may have occurred since it was first drawn. Professionals advise that you review your will every few years and more often if situations such as the following five have occurred since you last updated your will.
1. Family Changes
If you’ve had any changes in your family situation, you will probably need to update your will. Events such as marriage, divorce, death, birth, adoption, or a falling out with a loved one may affect how your estate will be distributed, who should act as guardian for your dependents, and who should be named as executor of your estate.
2. Relocating to a New State
The laws among the states vary. Moving to a new state or purchasing property in another state can affect your estate plan and how property in that state will be taxed and distributed.
3. Tax Law Changes
Federal and state legislatures are continually tinkering with federal estate and state inheritance tax laws. An old will may fail to take advantage of strategies that will minimize estate taxes.
4. You Want to Support a Favorite Cause
If you have developed a connection to a cause, you may want to benefit a particular charity with a gift in your estate. Contact us for sample language you can share with your attorney to include a gift to us in your will.
5. Changes in Your Estate’s Value
When you made your will, your assets may have been relatively modest. Now the value may be larger and your will no longer reflects how you would like your estate divided.
You will help spark future discoveries in GI. Visit our website at https://gastro.planmylegacy.org or contact us at [email protected].
Clinical Research in Early Career Academic Medicine
Conducting clinical research as an early career gastroenterologist can take on many forms and has varying definitions of success. This article focuses on key factors to consider and should be supplemented with mentorship tailored to personal interests, goals, and institutional criteria for success. In this article, we will discuss selected high-yield topics that assist in early-career research. We will briefly discuss 1. Defining your niche, 2. Collaboration, 3. Visibility, 4. Time management, 5. Funding, 6. Receiving mentorship, and 7. Providing mentorship. We will conclude with discussing several authors’ experience in the research lab of the first author (FELD Lab – Fostering Equity in Liver and Digestive disease).
Defining Your Niche
Defining your niche is an essential component of an early career, as when academicians must transition from a trainee, who is supporting the research of an established mentor, to defining their own subspeciality area of investigation. Early-career academics should build on their prior work, but should also explore their own passions and skill set to define what will be unique about their research program and contributions to the field. Of course, positioning oneself at the intersection of two or more seemingly unrelated fields opens much opportunity for large impact but comes at a cost of identifying mentorship and justifying the niche to funders.
Collaboration
Fostering a collaborative environment is essential for early-career physician-researchers. One effective approach is to establish collaboration circles with other early career academics. Expanding research endeavors beyond a single institution to a multi-center framework enriches both scope and impact. This collaborative approach not only amplifies the depth of research but also facilitates peer mentorship and sponsorship. Participation in such networks can significantly enhance scholarly output and broaden professional reach during this critical phase of academic progression. Furthermore, prioritizing the promotion of colleagues within these networks is crucial. Proactive sponsorship opportunities, such as inviting peers to present at institutional seminars, strengthen both individual and collective academic visibility.
Collaboration is also essential to foster between trainees involved in early-career investigators’ work. An interconnected lab environment ensures that trainees remain informed about concurrent projects, thereby fostering a culture of shared knowledge and optimized productivity. Encouraging trainees to spearhead research aligned with their interests, under mentor guidance, nurtures independent inquiry and leadership. By establishing explicit roles, responsibilities, and authorship agreements at the outset of collaborative projects, early career mentors can avoid future conflicts and preserve a collaborative culture within the lab. This structured approach cultivates a supportive ecosystem, advancing both individual and collective research achievements.
Visibility
Establishing visibility and developing name recognition are crucial components of career advancement for early-career academic physicians. By clearly defining their areas of expertise, faculty can position themselves as leaders within their discipline. Active participation in professional societies, both at the local and national level, engagement with interest groups, and frequent contributions to educational events can be effective strategies for gaining recognition. Leveraging social media platforms can be helpful in enhancing visibility by facilitating connections and promoting research to a broader audience.
Moreover, research visibility plays a vital role in academic promotion. A strong publication record, reflected by an increasing h-index, demonstrates the impact and relevance of one’s research. Self-citation, when appropriate, can reinforce the continuity and progression of scholarly contributions. While publishing in high-impact journals is desirable, adaptability in resubmitting to other journals following rejections ensures that research remains visible and accessible. It also clearly establishes by whom the work was first done, before someone else investigates the line of inquiry. Through a combination of strategic engagement and publication efforts, early-career physicians can effectively build their professional reputation and advance their academic careers.
Time Management
Time management is essential for any research, and particularly in early career when efficiency in clinical care duties is still being gained. Securing protected time for research is essential to develop a niche, build connections (both institutionally and beyond their institutions), and demonstrate productivity that can be utilized to support future grant efforts.
Similarly, using protected time efficiently is required. Without organization and planning, research time can be spent with scattered meetings and responding to various tasks that do not directly support your research. It is helpful to be introspective about the time of the day you are most productive in your research efforts and blocking off that time to focus on research tasks and minimizing distractions. Blocking monthly time for larger scale thinking and planning is also important. Weekly lab and individual one-on-one meetings also support time management for trainees and lab members, to ensure efficiency and progress. Additionally, robust clinical support is essential to ensure that research time remains protected and patient care moves forward. When negotiating for positions, and in regular meetings thereafter, it is important to advocate for sufficient clinical staffing such that non-physician tasks can be appropriately delegated to another member of the care team.
Funding
Securing adequate funding poses a significant challenge for all early-career physician-scientists, particularly because of the discrepancy between National Institutes of Health salary caps and the higher average salaries in academic gastroenterology. This financial gap can deter physicians from pursuing research-intensive careers altogether and can derail early investigators who do not obtain funding rapidly. To overcome this, early-career investigators may need to adopt flexible strategies, such as accepting a lower salary that aligns with grant funding limits or funneling incentive or bonus pay to research accounts. Alternatively, they can advocate for institutional support to bridge the salary gap, ensuring their research efforts remain financially viable.
Institutions committed to fostering research excellence may offer supplemental funding or bridge programs to retain talented physician-scientists, thereby mitigating the financial strain and encouraging long-term engagement in research. Regular meetings to review salary and support sources, including philanthropy, foundation grants, and other streams, should be undertaken with leadership to align the researcher’s timeline and available funding. If career development funding appears untenable, consideration of multi–principal investigator R01s or equivalent with senior established investigators can be a promising path.
Receiving Mentorship
Effective mentorship for early-career physician-scientists should be approached through a team-based model that leverages both internal and external mentors. Internal mentors, familiar with the specific culture, expectations, and advancement pathways of the institution, can provide invaluable guidance on navigating institutional metrics for success, such as promotion criteria, grant acquisition, and clinical-research balance. External mentors, on the other hand, bring a broader perspective by offering innovative career development strategies and solutions derived from experiences at their home institutions. This multimodal mentorship model ensures a well-rounded approach to professional growth.
All national gastroenterology societies, including the American Gastroenterological Association, the American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, offer structured early-career mentorship programs designed to connect emerging researchers with experienced leaders in the field (see below). These programs typically require a formal application process and are highly regarded for their exceptional quality and impact. Participation in such initiatives can significantly enhance career development by expanding networks, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, and providing tailored guidance that complements institutional support. Integrating both internal and external mentorship opportunities ensures a robust and dynamic foundation for long-term success in academic medicine.
- AGA Career Compass (https://gastro.org/fellows-and-early-career/mentoring/)
- ACG Early Career Leadership Program (https://gi.org/acg-institute/early-career-leadership-program/)
- AGA-AASLD Academic Skills Workshop (https://gastro.org/news/applications-now-being-accepted-for-the-2024-aga-aasld-academic-skills-workshop/)
- AASLD Women’s Initiative Committee Leadership Program (https://www.aasld.org/promoting-leadership-potential-women-hepatology)
- Scrubs n Heels Mentorship Matrix (https://scrubsandheels.com/matrix/)
Providing Mentorship
The trainee authors on this manuscript describe in this section what has been helpful for them as mentees in the FELD research lab.
Student doctor Nguyen describes her experience as a lab member and things she finds most helpful as a medical student in the lab:
- Upon joining the team, a one-to-one meeting to discuss trainee’s personal and professional goals, and availability, was crucial to building the mentor-mentee relationship. Establishing this meaningful mentorship early on clarified expectations on both sides, built trust, and increased motivation. As a trainee, it is essential for me to see how my work aligns with a long-term goal and to receive ample guidance throughout the process.
- One of the most impactful experiences has been joining informal lunch sessions where trainees discussed data collection protocols and exchanged insights. In doing so, Dr. Feld has cultivated a lab culture that encourages curiosity, constructive feedback, and collaborative learning.
- To increase productivity, our team of trainees created a useful group message thread where we coordinated more sessions to collaborate. This coordination formed stronger relationships between team members and fostered a sense of shared purpose.
Dr. Cooper, a third year internal medicine resident, describes her experience as both a research mentee and a mentor to the junior trainees: “As a resident pursuing a career in academic gastroenterology and hepatology, I have found three key elements to be most helpful: intentional mentorship, structured meetings, and leadership development.”
- Intentional mentorship: Prior to joining the lab, I met with Dr. Feld to discuss my research experience and my goals. She took the time to understand these within the context of my training timeline and tailored project opportunities that aligned with my interests and were both feasible and impactful for my next steps. This intentional approach not only fostered a productive research experience but also established a mentor-mentee relationship built on genuine care for my growth and development.
- Regular meetings: Frequent lab meetings promote accountability, teamwork, and shared problem-solving skills. The open exchange of ideas fosters collaboration and joint problem solving to elevate the quality of our research. They are also an opportunity to observe key decision-making points during the research process and have been a great way to learn more about solid methodology.
- Supervised leadership: I have had ample time to lead discussions and coordinate projects among the junior trainees. These monitored leadership experiences promote project management skills, mentorship, and team dynamic awareness while maintaining the safety net of senior guidance. This model helped me transition from a trainee supporting others’ research to a more independent role, contributing to multi-disciplinary projects while mentoring junior members.
Conclusion
In conclusion, many exciting opportunities and notable barriers exist to establishing a clinical research laboratory in the early career. While excellence in each of the areas outlined may evolve, some aspects will come easier than others and with time, persistence, and a bit of luck, the research world will be a better place because of your contributions!
Dr. Feld is assistant professor of gastroenterology and hepatology and physician executive of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion and Belonging for the department of medicine at the University of Massachusetts (UMass) Chan Medical School, Worcester. Ms. Nguyen is a medical student at UMass Chan Medical School. Dr. Cooper is a resident physician at UMass Chan Medical School. Dr. Rabinowitz is an attending physician in the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Mass. Dr. Uchida is codirector of the Multidisciplinary Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disease Clinic at the University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City.
Conducting clinical research as an early career gastroenterologist can take on many forms and has varying definitions of success. This article focuses on key factors to consider and should be supplemented with mentorship tailored to personal interests, goals, and institutional criteria for success. In this article, we will discuss selected high-yield topics that assist in early-career research. We will briefly discuss 1. Defining your niche, 2. Collaboration, 3. Visibility, 4. Time management, 5. Funding, 6. Receiving mentorship, and 7. Providing mentorship. We will conclude with discussing several authors’ experience in the research lab of the first author (FELD Lab – Fostering Equity in Liver and Digestive disease).
Defining Your Niche
Defining your niche is an essential component of an early career, as when academicians must transition from a trainee, who is supporting the research of an established mentor, to defining their own subspeciality area of investigation. Early-career academics should build on their prior work, but should also explore their own passions and skill set to define what will be unique about their research program and contributions to the field. Of course, positioning oneself at the intersection of two or more seemingly unrelated fields opens much opportunity for large impact but comes at a cost of identifying mentorship and justifying the niche to funders.
Collaboration
Fostering a collaborative environment is essential for early-career physician-researchers. One effective approach is to establish collaboration circles with other early career academics. Expanding research endeavors beyond a single institution to a multi-center framework enriches both scope and impact. This collaborative approach not only amplifies the depth of research but also facilitates peer mentorship and sponsorship. Participation in such networks can significantly enhance scholarly output and broaden professional reach during this critical phase of academic progression. Furthermore, prioritizing the promotion of colleagues within these networks is crucial. Proactive sponsorship opportunities, such as inviting peers to present at institutional seminars, strengthen both individual and collective academic visibility.
Collaboration is also essential to foster between trainees involved in early-career investigators’ work. An interconnected lab environment ensures that trainees remain informed about concurrent projects, thereby fostering a culture of shared knowledge and optimized productivity. Encouraging trainees to spearhead research aligned with their interests, under mentor guidance, nurtures independent inquiry and leadership. By establishing explicit roles, responsibilities, and authorship agreements at the outset of collaborative projects, early career mentors can avoid future conflicts and preserve a collaborative culture within the lab. This structured approach cultivates a supportive ecosystem, advancing both individual and collective research achievements.
Visibility
Establishing visibility and developing name recognition are crucial components of career advancement for early-career academic physicians. By clearly defining their areas of expertise, faculty can position themselves as leaders within their discipline. Active participation in professional societies, both at the local and national level, engagement with interest groups, and frequent contributions to educational events can be effective strategies for gaining recognition. Leveraging social media platforms can be helpful in enhancing visibility by facilitating connections and promoting research to a broader audience.
Moreover, research visibility plays a vital role in academic promotion. A strong publication record, reflected by an increasing h-index, demonstrates the impact and relevance of one’s research. Self-citation, when appropriate, can reinforce the continuity and progression of scholarly contributions. While publishing in high-impact journals is desirable, adaptability in resubmitting to other journals following rejections ensures that research remains visible and accessible. It also clearly establishes by whom the work was first done, before someone else investigates the line of inquiry. Through a combination of strategic engagement and publication efforts, early-career physicians can effectively build their professional reputation and advance their academic careers.
Time Management
Time management is essential for any research, and particularly in early career when efficiency in clinical care duties is still being gained. Securing protected time for research is essential to develop a niche, build connections (both institutionally and beyond their institutions), and demonstrate productivity that can be utilized to support future grant efforts.
Similarly, using protected time efficiently is required. Without organization and planning, research time can be spent with scattered meetings and responding to various tasks that do not directly support your research. It is helpful to be introspective about the time of the day you are most productive in your research efforts and blocking off that time to focus on research tasks and minimizing distractions. Blocking monthly time for larger scale thinking and planning is also important. Weekly lab and individual one-on-one meetings also support time management for trainees and lab members, to ensure efficiency and progress. Additionally, robust clinical support is essential to ensure that research time remains protected and patient care moves forward. When negotiating for positions, and in regular meetings thereafter, it is important to advocate for sufficient clinical staffing such that non-physician tasks can be appropriately delegated to another member of the care team.
Funding
Securing adequate funding poses a significant challenge for all early-career physician-scientists, particularly because of the discrepancy between National Institutes of Health salary caps and the higher average salaries in academic gastroenterology. This financial gap can deter physicians from pursuing research-intensive careers altogether and can derail early investigators who do not obtain funding rapidly. To overcome this, early-career investigators may need to adopt flexible strategies, such as accepting a lower salary that aligns with grant funding limits or funneling incentive or bonus pay to research accounts. Alternatively, they can advocate for institutional support to bridge the salary gap, ensuring their research efforts remain financially viable.
Institutions committed to fostering research excellence may offer supplemental funding or bridge programs to retain talented physician-scientists, thereby mitigating the financial strain and encouraging long-term engagement in research. Regular meetings to review salary and support sources, including philanthropy, foundation grants, and other streams, should be undertaken with leadership to align the researcher’s timeline and available funding. If career development funding appears untenable, consideration of multi–principal investigator R01s or equivalent with senior established investigators can be a promising path.
Receiving Mentorship
Effective mentorship for early-career physician-scientists should be approached through a team-based model that leverages both internal and external mentors. Internal mentors, familiar with the specific culture, expectations, and advancement pathways of the institution, can provide invaluable guidance on navigating institutional metrics for success, such as promotion criteria, grant acquisition, and clinical-research balance. External mentors, on the other hand, bring a broader perspective by offering innovative career development strategies and solutions derived from experiences at their home institutions. This multimodal mentorship model ensures a well-rounded approach to professional growth.
All national gastroenterology societies, including the American Gastroenterological Association, the American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, offer structured early-career mentorship programs designed to connect emerging researchers with experienced leaders in the field (see below). These programs typically require a formal application process and are highly regarded for their exceptional quality and impact. Participation in such initiatives can significantly enhance career development by expanding networks, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, and providing tailored guidance that complements institutional support. Integrating both internal and external mentorship opportunities ensures a robust and dynamic foundation for long-term success in academic medicine.
- AGA Career Compass (https://gastro.org/fellows-and-early-career/mentoring/)
- ACG Early Career Leadership Program (https://gi.org/acg-institute/early-career-leadership-program/)
- AGA-AASLD Academic Skills Workshop (https://gastro.org/news/applications-now-being-accepted-for-the-2024-aga-aasld-academic-skills-workshop/)
- AASLD Women’s Initiative Committee Leadership Program (https://www.aasld.org/promoting-leadership-potential-women-hepatology)
- Scrubs n Heels Mentorship Matrix (https://scrubsandheels.com/matrix/)
Providing Mentorship
The trainee authors on this manuscript describe in this section what has been helpful for them as mentees in the FELD research lab.
Student doctor Nguyen describes her experience as a lab member and things she finds most helpful as a medical student in the lab:
- Upon joining the team, a one-to-one meeting to discuss trainee’s personal and professional goals, and availability, was crucial to building the mentor-mentee relationship. Establishing this meaningful mentorship early on clarified expectations on both sides, built trust, and increased motivation. As a trainee, it is essential for me to see how my work aligns with a long-term goal and to receive ample guidance throughout the process.
- One of the most impactful experiences has been joining informal lunch sessions where trainees discussed data collection protocols and exchanged insights. In doing so, Dr. Feld has cultivated a lab culture that encourages curiosity, constructive feedback, and collaborative learning.
- To increase productivity, our team of trainees created a useful group message thread where we coordinated more sessions to collaborate. This coordination formed stronger relationships between team members and fostered a sense of shared purpose.
Dr. Cooper, a third year internal medicine resident, describes her experience as both a research mentee and a mentor to the junior trainees: “As a resident pursuing a career in academic gastroenterology and hepatology, I have found three key elements to be most helpful: intentional mentorship, structured meetings, and leadership development.”
- Intentional mentorship: Prior to joining the lab, I met with Dr. Feld to discuss my research experience and my goals. She took the time to understand these within the context of my training timeline and tailored project opportunities that aligned with my interests and were both feasible and impactful for my next steps. This intentional approach not only fostered a productive research experience but also established a mentor-mentee relationship built on genuine care for my growth and development.
- Regular meetings: Frequent lab meetings promote accountability, teamwork, and shared problem-solving skills. The open exchange of ideas fosters collaboration and joint problem solving to elevate the quality of our research. They are also an opportunity to observe key decision-making points during the research process and have been a great way to learn more about solid methodology.
- Supervised leadership: I have had ample time to lead discussions and coordinate projects among the junior trainees. These monitored leadership experiences promote project management skills, mentorship, and team dynamic awareness while maintaining the safety net of senior guidance. This model helped me transition from a trainee supporting others’ research to a more independent role, contributing to multi-disciplinary projects while mentoring junior members.
Conclusion
In conclusion, many exciting opportunities and notable barriers exist to establishing a clinical research laboratory in the early career. While excellence in each of the areas outlined may evolve, some aspects will come easier than others and with time, persistence, and a bit of luck, the research world will be a better place because of your contributions!
Dr. Feld is assistant professor of gastroenterology and hepatology and physician executive of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion and Belonging for the department of medicine at the University of Massachusetts (UMass) Chan Medical School, Worcester. Ms. Nguyen is a medical student at UMass Chan Medical School. Dr. Cooper is a resident physician at UMass Chan Medical School. Dr. Rabinowitz is an attending physician in the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Mass. Dr. Uchida is codirector of the Multidisciplinary Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disease Clinic at the University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City.
Conducting clinical research as an early career gastroenterologist can take on many forms and has varying definitions of success. This article focuses on key factors to consider and should be supplemented with mentorship tailored to personal interests, goals, and institutional criteria for success. In this article, we will discuss selected high-yield topics that assist in early-career research. We will briefly discuss 1. Defining your niche, 2. Collaboration, 3. Visibility, 4. Time management, 5. Funding, 6. Receiving mentorship, and 7. Providing mentorship. We will conclude with discussing several authors’ experience in the research lab of the first author (FELD Lab – Fostering Equity in Liver and Digestive disease).
Defining Your Niche
Defining your niche is an essential component of an early career, as when academicians must transition from a trainee, who is supporting the research of an established mentor, to defining their own subspeciality area of investigation. Early-career academics should build on their prior work, but should also explore their own passions and skill set to define what will be unique about their research program and contributions to the field. Of course, positioning oneself at the intersection of two or more seemingly unrelated fields opens much opportunity for large impact but comes at a cost of identifying mentorship and justifying the niche to funders.
Collaboration
Fostering a collaborative environment is essential for early-career physician-researchers. One effective approach is to establish collaboration circles with other early career academics. Expanding research endeavors beyond a single institution to a multi-center framework enriches both scope and impact. This collaborative approach not only amplifies the depth of research but also facilitates peer mentorship and sponsorship. Participation in such networks can significantly enhance scholarly output and broaden professional reach during this critical phase of academic progression. Furthermore, prioritizing the promotion of colleagues within these networks is crucial. Proactive sponsorship opportunities, such as inviting peers to present at institutional seminars, strengthen both individual and collective academic visibility.
Collaboration is also essential to foster between trainees involved in early-career investigators’ work. An interconnected lab environment ensures that trainees remain informed about concurrent projects, thereby fostering a culture of shared knowledge and optimized productivity. Encouraging trainees to spearhead research aligned with their interests, under mentor guidance, nurtures independent inquiry and leadership. By establishing explicit roles, responsibilities, and authorship agreements at the outset of collaborative projects, early career mentors can avoid future conflicts and preserve a collaborative culture within the lab. This structured approach cultivates a supportive ecosystem, advancing both individual and collective research achievements.
Visibility
Establishing visibility and developing name recognition are crucial components of career advancement for early-career academic physicians. By clearly defining their areas of expertise, faculty can position themselves as leaders within their discipline. Active participation in professional societies, both at the local and national level, engagement with interest groups, and frequent contributions to educational events can be effective strategies for gaining recognition. Leveraging social media platforms can be helpful in enhancing visibility by facilitating connections and promoting research to a broader audience.
Moreover, research visibility plays a vital role in academic promotion. A strong publication record, reflected by an increasing h-index, demonstrates the impact and relevance of one’s research. Self-citation, when appropriate, can reinforce the continuity and progression of scholarly contributions. While publishing in high-impact journals is desirable, adaptability in resubmitting to other journals following rejections ensures that research remains visible and accessible. It also clearly establishes by whom the work was first done, before someone else investigates the line of inquiry. Through a combination of strategic engagement and publication efforts, early-career physicians can effectively build their professional reputation and advance their academic careers.
Time Management
Time management is essential for any research, and particularly in early career when efficiency in clinical care duties is still being gained. Securing protected time for research is essential to develop a niche, build connections (both institutionally and beyond their institutions), and demonstrate productivity that can be utilized to support future grant efforts.
Similarly, using protected time efficiently is required. Without organization and planning, research time can be spent with scattered meetings and responding to various tasks that do not directly support your research. It is helpful to be introspective about the time of the day you are most productive in your research efforts and blocking off that time to focus on research tasks and minimizing distractions. Blocking monthly time for larger scale thinking and planning is also important. Weekly lab and individual one-on-one meetings also support time management for trainees and lab members, to ensure efficiency and progress. Additionally, robust clinical support is essential to ensure that research time remains protected and patient care moves forward. When negotiating for positions, and in regular meetings thereafter, it is important to advocate for sufficient clinical staffing such that non-physician tasks can be appropriately delegated to another member of the care team.
Funding
Securing adequate funding poses a significant challenge for all early-career physician-scientists, particularly because of the discrepancy between National Institutes of Health salary caps and the higher average salaries in academic gastroenterology. This financial gap can deter physicians from pursuing research-intensive careers altogether and can derail early investigators who do not obtain funding rapidly. To overcome this, early-career investigators may need to adopt flexible strategies, such as accepting a lower salary that aligns with grant funding limits or funneling incentive or bonus pay to research accounts. Alternatively, they can advocate for institutional support to bridge the salary gap, ensuring their research efforts remain financially viable.
Institutions committed to fostering research excellence may offer supplemental funding or bridge programs to retain talented physician-scientists, thereby mitigating the financial strain and encouraging long-term engagement in research. Regular meetings to review salary and support sources, including philanthropy, foundation grants, and other streams, should be undertaken with leadership to align the researcher’s timeline and available funding. If career development funding appears untenable, consideration of multi–principal investigator R01s or equivalent with senior established investigators can be a promising path.
Receiving Mentorship
Effective mentorship for early-career physician-scientists should be approached through a team-based model that leverages both internal and external mentors. Internal mentors, familiar with the specific culture, expectations, and advancement pathways of the institution, can provide invaluable guidance on navigating institutional metrics for success, such as promotion criteria, grant acquisition, and clinical-research balance. External mentors, on the other hand, bring a broader perspective by offering innovative career development strategies and solutions derived from experiences at their home institutions. This multimodal mentorship model ensures a well-rounded approach to professional growth.
All national gastroenterology societies, including the American Gastroenterological Association, the American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, offer structured early-career mentorship programs designed to connect emerging researchers with experienced leaders in the field (see below). These programs typically require a formal application process and are highly regarded for their exceptional quality and impact. Participation in such initiatives can significantly enhance career development by expanding networks, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, and providing tailored guidance that complements institutional support. Integrating both internal and external mentorship opportunities ensures a robust and dynamic foundation for long-term success in academic medicine.
- AGA Career Compass (https://gastro.org/fellows-and-early-career/mentoring/)
- ACG Early Career Leadership Program (https://gi.org/acg-institute/early-career-leadership-program/)
- AGA-AASLD Academic Skills Workshop (https://gastro.org/news/applications-now-being-accepted-for-the-2024-aga-aasld-academic-skills-workshop/)
- AASLD Women’s Initiative Committee Leadership Program (https://www.aasld.org/promoting-leadership-potential-women-hepatology)
- Scrubs n Heels Mentorship Matrix (https://scrubsandheels.com/matrix/)
Providing Mentorship
The trainee authors on this manuscript describe in this section what has been helpful for them as mentees in the FELD research lab.
Student doctor Nguyen describes her experience as a lab member and things she finds most helpful as a medical student in the lab:
- Upon joining the team, a one-to-one meeting to discuss trainee’s personal and professional goals, and availability, was crucial to building the mentor-mentee relationship. Establishing this meaningful mentorship early on clarified expectations on both sides, built trust, and increased motivation. As a trainee, it is essential for me to see how my work aligns with a long-term goal and to receive ample guidance throughout the process.
- One of the most impactful experiences has been joining informal lunch sessions where trainees discussed data collection protocols and exchanged insights. In doing so, Dr. Feld has cultivated a lab culture that encourages curiosity, constructive feedback, and collaborative learning.
- To increase productivity, our team of trainees created a useful group message thread where we coordinated more sessions to collaborate. This coordination formed stronger relationships between team members and fostered a sense of shared purpose.
Dr. Cooper, a third year internal medicine resident, describes her experience as both a research mentee and a mentor to the junior trainees: “As a resident pursuing a career in academic gastroenterology and hepatology, I have found three key elements to be most helpful: intentional mentorship, structured meetings, and leadership development.”
- Intentional mentorship: Prior to joining the lab, I met with Dr. Feld to discuss my research experience and my goals. She took the time to understand these within the context of my training timeline and tailored project opportunities that aligned with my interests and were both feasible and impactful for my next steps. This intentional approach not only fostered a productive research experience but also established a mentor-mentee relationship built on genuine care for my growth and development.
- Regular meetings: Frequent lab meetings promote accountability, teamwork, and shared problem-solving skills. The open exchange of ideas fosters collaboration and joint problem solving to elevate the quality of our research. They are also an opportunity to observe key decision-making points during the research process and have been a great way to learn more about solid methodology.
- Supervised leadership: I have had ample time to lead discussions and coordinate projects among the junior trainees. These monitored leadership experiences promote project management skills, mentorship, and team dynamic awareness while maintaining the safety net of senior guidance. This model helped me transition from a trainee supporting others’ research to a more independent role, contributing to multi-disciplinary projects while mentoring junior members.
Conclusion
In conclusion, many exciting opportunities and notable barriers exist to establishing a clinical research laboratory in the early career. While excellence in each of the areas outlined may evolve, some aspects will come easier than others and with time, persistence, and a bit of luck, the research world will be a better place because of your contributions!
Dr. Feld is assistant professor of gastroenterology and hepatology and physician executive of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion and Belonging for the department of medicine at the University of Massachusetts (UMass) Chan Medical School, Worcester. Ms. Nguyen is a medical student at UMass Chan Medical School. Dr. Cooper is a resident physician at UMass Chan Medical School. Dr. Rabinowitz is an attending physician in the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Mass. Dr. Uchida is codirector of the Multidisciplinary Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disease Clinic at the University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City.