User login
More Children Under Age 4 Have Severe Obesity: Study
Severe obesity among preschool-age children from low-income families is on the rise in the United States, according to a new analysis of federal data.
An estimated 2% of children ages 2 to 4 years old had severe obesity in 2020, up from 1.8% in 2016, according to the report that appeared Dec. 18 in Pediatrics, a journal published by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
The increase is “small but significant,” a group of experts not involved in the research wrote in a companion commentary published alongside the research.
The new data put an end to hopes that childhood obesity was on the retreat following a small decrease in rates from 2010 to 2016. Instead, the researchers noted that the new childhood obesity figures reflect those of the general population. In the United States, about 20% of children and teens are obese, and about 42% of adults are obese, according to the CDC.
This latest study looked for severe obesity, which was defined as being well above the 95th percentile for the combined height-weight measure known as body mass index. The figures are important because rates of severe obesity among young children can foreshadow health problems that may occur on a scale to warrant concerns among public health officials, policymakers, and health care professionals.
Compared with children who have moderate obesity, children with severe obesity “are at a greater risk of various health complications, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease, and premature death,” the study authors wrote.
The largest increases from 2016 to 2020 in severe obesity were observed among 4-year-olds and among Hispanic children. When looking at state-level data, Alaska was the only state to report a decline in severe obesity among young children from 2016 to 2020.
The new estimates were drawn from data on children enrolled in the federal Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC).
“WIC is a federal assistance program that provides healthy foods, nutrition education, health care referrals, and other services to millions of low-income pregnant and postpartum women, as well as infants and children up to age 5, who are at nutritional risk,” the researchers noted.
The new figures indicate 16.6 million children ages 2 to 4 years old have severe obesity. Having severe obesity at these early ages is “nearly irreversible,” the authors of the commentary article noted, adding that little research exists that indicates how to effectively treat obesity before age 6.
“The study underscores the need for ongoing monitoring ... post pandemic of children’s health status,” a news release from the American Academy of Pediatrics stated. “It also further supports the need for children and families from households with lower incomes across the nation to have access to early clinical detection, such as health care screenings and referrals to effective family-based interventions to support healthy growth.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Severe obesity among preschool-age children from low-income families is on the rise in the United States, according to a new analysis of federal data.
An estimated 2% of children ages 2 to 4 years old had severe obesity in 2020, up from 1.8% in 2016, according to the report that appeared Dec. 18 in Pediatrics, a journal published by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
The increase is “small but significant,” a group of experts not involved in the research wrote in a companion commentary published alongside the research.
The new data put an end to hopes that childhood obesity was on the retreat following a small decrease in rates from 2010 to 2016. Instead, the researchers noted that the new childhood obesity figures reflect those of the general population. In the United States, about 20% of children and teens are obese, and about 42% of adults are obese, according to the CDC.
This latest study looked for severe obesity, which was defined as being well above the 95th percentile for the combined height-weight measure known as body mass index. The figures are important because rates of severe obesity among young children can foreshadow health problems that may occur on a scale to warrant concerns among public health officials, policymakers, and health care professionals.
Compared with children who have moderate obesity, children with severe obesity “are at a greater risk of various health complications, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease, and premature death,” the study authors wrote.
The largest increases from 2016 to 2020 in severe obesity were observed among 4-year-olds and among Hispanic children. When looking at state-level data, Alaska was the only state to report a decline in severe obesity among young children from 2016 to 2020.
The new estimates were drawn from data on children enrolled in the federal Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC).
“WIC is a federal assistance program that provides healthy foods, nutrition education, health care referrals, and other services to millions of low-income pregnant and postpartum women, as well as infants and children up to age 5, who are at nutritional risk,” the researchers noted.
The new figures indicate 16.6 million children ages 2 to 4 years old have severe obesity. Having severe obesity at these early ages is “nearly irreversible,” the authors of the commentary article noted, adding that little research exists that indicates how to effectively treat obesity before age 6.
“The study underscores the need for ongoing monitoring ... post pandemic of children’s health status,” a news release from the American Academy of Pediatrics stated. “It also further supports the need for children and families from households with lower incomes across the nation to have access to early clinical detection, such as health care screenings and referrals to effective family-based interventions to support healthy growth.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Severe obesity among preschool-age children from low-income families is on the rise in the United States, according to a new analysis of federal data.
An estimated 2% of children ages 2 to 4 years old had severe obesity in 2020, up from 1.8% in 2016, according to the report that appeared Dec. 18 in Pediatrics, a journal published by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
The increase is “small but significant,” a group of experts not involved in the research wrote in a companion commentary published alongside the research.
The new data put an end to hopes that childhood obesity was on the retreat following a small decrease in rates from 2010 to 2016. Instead, the researchers noted that the new childhood obesity figures reflect those of the general population. In the United States, about 20% of children and teens are obese, and about 42% of adults are obese, according to the CDC.
This latest study looked for severe obesity, which was defined as being well above the 95th percentile for the combined height-weight measure known as body mass index. The figures are important because rates of severe obesity among young children can foreshadow health problems that may occur on a scale to warrant concerns among public health officials, policymakers, and health care professionals.
Compared with children who have moderate obesity, children with severe obesity “are at a greater risk of various health complications, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease, and premature death,” the study authors wrote.
The largest increases from 2016 to 2020 in severe obesity were observed among 4-year-olds and among Hispanic children. When looking at state-level data, Alaska was the only state to report a decline in severe obesity among young children from 2016 to 2020.
The new estimates were drawn from data on children enrolled in the federal Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC).
“WIC is a federal assistance program that provides healthy foods, nutrition education, health care referrals, and other services to millions of low-income pregnant and postpartum women, as well as infants and children up to age 5, who are at nutritional risk,” the researchers noted.
The new figures indicate 16.6 million children ages 2 to 4 years old have severe obesity. Having severe obesity at these early ages is “nearly irreversible,” the authors of the commentary article noted, adding that little research exists that indicates how to effectively treat obesity before age 6.
“The study underscores the need for ongoing monitoring ... post pandemic of children’s health status,” a news release from the American Academy of Pediatrics stated. “It also further supports the need for children and families from households with lower incomes across the nation to have access to early clinical detection, such as health care screenings and referrals to effective family-based interventions to support healthy growth.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Novel Solutions Needed to Attract Residents to Pediatric Rheumatology
Pediatric rheumatologists are calling a “Code (p)RED” — a pediatric rheumatology educational deficit.
There are too few pediatric rheumatologists to meet patient demand in the United States, and projections suggest that gap will continue to widen. Disappointing match trends also reflect issues with recruitment: Since 2019, only 50%-75% of pediatric rheumatology fellowship positions have been filled each year. For 2024, the subspecialty filled 32 of 52 positions.
Lack of exposure during medical school and residency, financial concerns, and a lengthy, research-focused fellowship are seen as major contributors to the workforce shortage, and novel solutions are needed to close the gap, experts argued in a recent presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“It’s so important now to get ahead of this because what I’m afraid of is in 10-20 years, we’re not going to have a field,” Colleen Correll, MD, MPH, an associate professor in the division of pediatric rheumatology at the University of Minnesota Medical School in Minneapolis, told this news organization.
Growing Demand, Falling Supply
Because the subspecialty was officially recognized by the American Board of Pediatrics in 1991, “it’s always been a small group of providers,” Dr. Correll said. “It’s honestly always been a recognized issue in our field.”
But a 2022 report by the ACR on the pediatric workforce has brought more attention to the issue. Dr. Correll led the study and is the chair of ACR›s Pediatric Rheumatology Committee. According to the report, an estimated 287 pediatric rheumatologists were working as full-time clinicians in 2015, while the estimated demand was 382 providers. By 2030, this projected supply of pediatric rheumatologists fell to 261, while demand rose to 461 full-time providers.
The distribution of pediatric rheumatologists is also an issue. It’s generally thought that there should be at least one pediatric rheumatologist per 100,000 children, Dr. Correll explained. According to ACR estimates, the northeast region had approximately 0.83 pediatric rheumatologists per 100,000 in 2015, while the south central and southwest regions had 0.17 and 0.20 providers per 100,000 children, respectively. Projected estimates for 2030 dipped to 0.04 or lower for the south central, southwest, and southeast regions.
A separate study from the American Board of Pediatrics, also led by Dr. Correll, that is still under review offered more optimistic projections, suggesting that there would be a 75% increase in pediatric rheumatologists from 0.27 per 100,000 children in 2020 to 0.47 per 100,000 children in 2040.
“This does look better than the ACR study, though 0.47 is still a really small number and an inadequate number to treat our children in need,” she said during her presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Lack of Exposure During Medical Education
Few medical schools have pediatric rheumatology built into their curriculum, whether that is a whole course or a single lecture, said Jay Mehta, MD, who directs the pediatric rheumatology fellowship at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. Dr. Mehta, for example, did not know that pediatric rheumatology was a field before entering residency, he said. But residencies can also lack exposure: An estimated one third of residencies do not have a single pediatric rheumatologist on staff, he said.
“Those are places where people aren’t necessarily getting exposure to pediatric rheumatology,” he told this news organization, “and we know that if you’re not exposed to a field, it’s very, very unlikely that you will go into that field.”
The ACR’s Pediatric Rheumatology Residency Program is one way that the organization is working to address this issue. The program sends pediatric residents with an interest in rheumatology to the ACR annual meeting. The Rheumatology Research Foundation also runs a visiting professorship program, where a pediatric rheumatologist conducts a rheumatology education forum at an institution with no pediatric rheumatology program.
“I’ve done it a couple of times,” Dr. Mehta said during his presentation at the annual meeting. “It’s one of the most rewarding things I’ve done.”
Financial Concerns
Additionally, although pediatric rheumatology requires more training, these subspecialists will likely make less than their general pediatric colleagues over their career. According to one study in Pediatrics, a pediatric resident pursuing rheumatology is projected to make $1.2 million dollars less over the course of their career compared with someone who started their career in general pediatrics immediately after residency. (Negative financial returns were also found for all pediatric subspecialities except for cardiology, critical care, and neonatology.)
This lower earning potential is likely a deterrent, especially for those with educational debt. In one analysis published in October, medical students with at least $200,000 in education debt were 43% more likely to go into higher-paying pediatric subspecialities than those with no debt. Nearly three out of four medical graduates have education debt, according to the American Association of Medical Colleges, with a median debt of $200,000.
While the Pediatric Specialty Loan Repayment Program was specifically designed to aid pediatric subspecialists with their educational debt, qualifying for the program is difficult for pediatric rheumatologists, explained Kristen N. Hayward, MD, of Seattle Children’s in Washington. The program provides up to $100,000 in loan forgiveness in exchange for 3 years of practicing in an underserved area; however, the program stipulates that providers must provide full-time (40 hours per week) clinical care. At academic institutions, where most pediatric rheumatologists practice, there is usually a research component to their position, and even if a provider works the equivalent of 40 hours per week in a clinic in addition to their research, they don’t qualify for the program, Dr. Hayward said.
“It’s very difficult to find someone who’s actually only doing clinical work,” she said.
The ACR has worked to combat some of these economic constraints by demonstrating the direct and downstream value of rheumatologic care, Dr. Hayward said. In a recent white paper, it was estimated that including office visits, consultations, lab testing, and radiology services, one full-time equivalent rheumatologist generates $3.5 million in revenue every year and saves health systems more than $2700 per patient per year.
In addition to placing greater value on rheumatologic care, the healthcare system also needs to recognize the current nonbillable hours that pediatric rheumatologists spend taking care of patients, Dr. Hayward noted.
Especially with electronic medical records (EMRs) and online communication with patients, “there is increasingly a lot of patient care that happens outside of clinic and that takes a lot of time,” Dr. Hayward said. For example, she spends between 1 and 2 hours every day in the EMR refilling medications and responding to patient concerns, and “that all is done in my spare time,” she said. “That’s not billed to the patient in anyway.”
Length of Fellowship
The pediatric rheumatology fellowship is a 3-year program — like other pediatric subspecialities — with a research requirement. By comparison, adult rheumatology fellowships are 2 years, and fellows can pursue additional research training if they have a strong interest.
“It sounds like just 1 more year, but I think it’s coming at a really pivotal point in people’s lives, and that 1 year can make a huge difference,” Dr. Hayward explained.
The 2 years of research might also be a deterrent for individuals who know they are only interested in clinical work, she added. About half of pediatric subspecialists only pursue clinical work after graduation, according to a recent report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) focused on the future pediatric physician workforce.
Additionally, only 17% of pediatric rheumatologists spend more than half of their time in research, said Fred Rivara, MD, MPH, chair of the NASEM report, in a statement included in Dr. Hayward’s ACR presentation. The report, which recommended strategies to bolster the pediatric workforce, argued that the American Board of Pediatrics should develop alternative training pathways, including 2-year, clinically heavy fellowships.
The ACR workforce team is also exploring alternative training models like competency-based education, Dr. Hayward said. The Education in Pediatrics Across the Continuum project is already using this approach from medical school to pediatric residency. While this type of outcome-based program has not been tried at the fellowship level, «this has been done, it could be done, and I think we could learn from our colleagues about how they have done this successfully,» she noted.
Ultimately, Dr. Hayward emphasized that there needs to be a “sea change” to close the workforce gap — with multiple interventions addressing these individual challenges.
“Unless we all pitch in and find one way that we can all move this issue forward, we are going to be drowning in a sea of Epic inbox messages,” she said, “and never get to see the patients we want to see.”
Dr. Hayward previously owned stock/stock options for AbbVie/Abbott, Cigna/Express Scripts, Merck, and Teva and has received an educational grant from Pfizer. Dr. Correll and Dr. Mehta had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatric rheumatologists are calling a “Code (p)RED” — a pediatric rheumatology educational deficit.
There are too few pediatric rheumatologists to meet patient demand in the United States, and projections suggest that gap will continue to widen. Disappointing match trends also reflect issues with recruitment: Since 2019, only 50%-75% of pediatric rheumatology fellowship positions have been filled each year. For 2024, the subspecialty filled 32 of 52 positions.
Lack of exposure during medical school and residency, financial concerns, and a lengthy, research-focused fellowship are seen as major contributors to the workforce shortage, and novel solutions are needed to close the gap, experts argued in a recent presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“It’s so important now to get ahead of this because what I’m afraid of is in 10-20 years, we’re not going to have a field,” Colleen Correll, MD, MPH, an associate professor in the division of pediatric rheumatology at the University of Minnesota Medical School in Minneapolis, told this news organization.
Growing Demand, Falling Supply
Because the subspecialty was officially recognized by the American Board of Pediatrics in 1991, “it’s always been a small group of providers,” Dr. Correll said. “It’s honestly always been a recognized issue in our field.”
But a 2022 report by the ACR on the pediatric workforce has brought more attention to the issue. Dr. Correll led the study and is the chair of ACR›s Pediatric Rheumatology Committee. According to the report, an estimated 287 pediatric rheumatologists were working as full-time clinicians in 2015, while the estimated demand was 382 providers. By 2030, this projected supply of pediatric rheumatologists fell to 261, while demand rose to 461 full-time providers.
The distribution of pediatric rheumatologists is also an issue. It’s generally thought that there should be at least one pediatric rheumatologist per 100,000 children, Dr. Correll explained. According to ACR estimates, the northeast region had approximately 0.83 pediatric rheumatologists per 100,000 in 2015, while the south central and southwest regions had 0.17 and 0.20 providers per 100,000 children, respectively. Projected estimates for 2030 dipped to 0.04 or lower for the south central, southwest, and southeast regions.
A separate study from the American Board of Pediatrics, also led by Dr. Correll, that is still under review offered more optimistic projections, suggesting that there would be a 75% increase in pediatric rheumatologists from 0.27 per 100,000 children in 2020 to 0.47 per 100,000 children in 2040.
“This does look better than the ACR study, though 0.47 is still a really small number and an inadequate number to treat our children in need,” she said during her presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Lack of Exposure During Medical Education
Few medical schools have pediatric rheumatology built into their curriculum, whether that is a whole course or a single lecture, said Jay Mehta, MD, who directs the pediatric rheumatology fellowship at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. Dr. Mehta, for example, did not know that pediatric rheumatology was a field before entering residency, he said. But residencies can also lack exposure: An estimated one third of residencies do not have a single pediatric rheumatologist on staff, he said.
“Those are places where people aren’t necessarily getting exposure to pediatric rheumatology,” he told this news organization, “and we know that if you’re not exposed to a field, it’s very, very unlikely that you will go into that field.”
The ACR’s Pediatric Rheumatology Residency Program is one way that the organization is working to address this issue. The program sends pediatric residents with an interest in rheumatology to the ACR annual meeting. The Rheumatology Research Foundation also runs a visiting professorship program, where a pediatric rheumatologist conducts a rheumatology education forum at an institution with no pediatric rheumatology program.
“I’ve done it a couple of times,” Dr. Mehta said during his presentation at the annual meeting. “It’s one of the most rewarding things I’ve done.”
Financial Concerns
Additionally, although pediatric rheumatology requires more training, these subspecialists will likely make less than their general pediatric colleagues over their career. According to one study in Pediatrics, a pediatric resident pursuing rheumatology is projected to make $1.2 million dollars less over the course of their career compared with someone who started their career in general pediatrics immediately after residency. (Negative financial returns were also found for all pediatric subspecialities except for cardiology, critical care, and neonatology.)
This lower earning potential is likely a deterrent, especially for those with educational debt. In one analysis published in October, medical students with at least $200,000 in education debt were 43% more likely to go into higher-paying pediatric subspecialities than those with no debt. Nearly three out of four medical graduates have education debt, according to the American Association of Medical Colleges, with a median debt of $200,000.
While the Pediatric Specialty Loan Repayment Program was specifically designed to aid pediatric subspecialists with their educational debt, qualifying for the program is difficult for pediatric rheumatologists, explained Kristen N. Hayward, MD, of Seattle Children’s in Washington. The program provides up to $100,000 in loan forgiveness in exchange for 3 years of practicing in an underserved area; however, the program stipulates that providers must provide full-time (40 hours per week) clinical care. At academic institutions, where most pediatric rheumatologists practice, there is usually a research component to their position, and even if a provider works the equivalent of 40 hours per week in a clinic in addition to their research, they don’t qualify for the program, Dr. Hayward said.
“It’s very difficult to find someone who’s actually only doing clinical work,” she said.
The ACR has worked to combat some of these economic constraints by demonstrating the direct and downstream value of rheumatologic care, Dr. Hayward said. In a recent white paper, it was estimated that including office visits, consultations, lab testing, and radiology services, one full-time equivalent rheumatologist generates $3.5 million in revenue every year and saves health systems more than $2700 per patient per year.
In addition to placing greater value on rheumatologic care, the healthcare system also needs to recognize the current nonbillable hours that pediatric rheumatologists spend taking care of patients, Dr. Hayward noted.
Especially with electronic medical records (EMRs) and online communication with patients, “there is increasingly a lot of patient care that happens outside of clinic and that takes a lot of time,” Dr. Hayward said. For example, she spends between 1 and 2 hours every day in the EMR refilling medications and responding to patient concerns, and “that all is done in my spare time,” she said. “That’s not billed to the patient in anyway.”
Length of Fellowship
The pediatric rheumatology fellowship is a 3-year program — like other pediatric subspecialities — with a research requirement. By comparison, adult rheumatology fellowships are 2 years, and fellows can pursue additional research training if they have a strong interest.
“It sounds like just 1 more year, but I think it’s coming at a really pivotal point in people’s lives, and that 1 year can make a huge difference,” Dr. Hayward explained.
The 2 years of research might also be a deterrent for individuals who know they are only interested in clinical work, she added. About half of pediatric subspecialists only pursue clinical work after graduation, according to a recent report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) focused on the future pediatric physician workforce.
Additionally, only 17% of pediatric rheumatologists spend more than half of their time in research, said Fred Rivara, MD, MPH, chair of the NASEM report, in a statement included in Dr. Hayward’s ACR presentation. The report, which recommended strategies to bolster the pediatric workforce, argued that the American Board of Pediatrics should develop alternative training pathways, including 2-year, clinically heavy fellowships.
The ACR workforce team is also exploring alternative training models like competency-based education, Dr. Hayward said. The Education in Pediatrics Across the Continuum project is already using this approach from medical school to pediatric residency. While this type of outcome-based program has not been tried at the fellowship level, «this has been done, it could be done, and I think we could learn from our colleagues about how they have done this successfully,» she noted.
Ultimately, Dr. Hayward emphasized that there needs to be a “sea change” to close the workforce gap — with multiple interventions addressing these individual challenges.
“Unless we all pitch in and find one way that we can all move this issue forward, we are going to be drowning in a sea of Epic inbox messages,” she said, “and never get to see the patients we want to see.”
Dr. Hayward previously owned stock/stock options for AbbVie/Abbott, Cigna/Express Scripts, Merck, and Teva and has received an educational grant from Pfizer. Dr. Correll and Dr. Mehta had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatric rheumatologists are calling a “Code (p)RED” — a pediatric rheumatology educational deficit.
There are too few pediatric rheumatologists to meet patient demand in the United States, and projections suggest that gap will continue to widen. Disappointing match trends also reflect issues with recruitment: Since 2019, only 50%-75% of pediatric rheumatology fellowship positions have been filled each year. For 2024, the subspecialty filled 32 of 52 positions.
Lack of exposure during medical school and residency, financial concerns, and a lengthy, research-focused fellowship are seen as major contributors to the workforce shortage, and novel solutions are needed to close the gap, experts argued in a recent presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“It’s so important now to get ahead of this because what I’m afraid of is in 10-20 years, we’re not going to have a field,” Colleen Correll, MD, MPH, an associate professor in the division of pediatric rheumatology at the University of Minnesota Medical School in Minneapolis, told this news organization.
Growing Demand, Falling Supply
Because the subspecialty was officially recognized by the American Board of Pediatrics in 1991, “it’s always been a small group of providers,” Dr. Correll said. “It’s honestly always been a recognized issue in our field.”
But a 2022 report by the ACR on the pediatric workforce has brought more attention to the issue. Dr. Correll led the study and is the chair of ACR›s Pediatric Rheumatology Committee. According to the report, an estimated 287 pediatric rheumatologists were working as full-time clinicians in 2015, while the estimated demand was 382 providers. By 2030, this projected supply of pediatric rheumatologists fell to 261, while demand rose to 461 full-time providers.
The distribution of pediatric rheumatologists is also an issue. It’s generally thought that there should be at least one pediatric rheumatologist per 100,000 children, Dr. Correll explained. According to ACR estimates, the northeast region had approximately 0.83 pediatric rheumatologists per 100,000 in 2015, while the south central and southwest regions had 0.17 and 0.20 providers per 100,000 children, respectively. Projected estimates for 2030 dipped to 0.04 or lower for the south central, southwest, and southeast regions.
A separate study from the American Board of Pediatrics, also led by Dr. Correll, that is still under review offered more optimistic projections, suggesting that there would be a 75% increase in pediatric rheumatologists from 0.27 per 100,000 children in 2020 to 0.47 per 100,000 children in 2040.
“This does look better than the ACR study, though 0.47 is still a really small number and an inadequate number to treat our children in need,” she said during her presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Lack of Exposure During Medical Education
Few medical schools have pediatric rheumatology built into their curriculum, whether that is a whole course or a single lecture, said Jay Mehta, MD, who directs the pediatric rheumatology fellowship at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. Dr. Mehta, for example, did not know that pediatric rheumatology was a field before entering residency, he said. But residencies can also lack exposure: An estimated one third of residencies do not have a single pediatric rheumatologist on staff, he said.
“Those are places where people aren’t necessarily getting exposure to pediatric rheumatology,” he told this news organization, “and we know that if you’re not exposed to a field, it’s very, very unlikely that you will go into that field.”
The ACR’s Pediatric Rheumatology Residency Program is one way that the organization is working to address this issue. The program sends pediatric residents with an interest in rheumatology to the ACR annual meeting. The Rheumatology Research Foundation also runs a visiting professorship program, where a pediatric rheumatologist conducts a rheumatology education forum at an institution with no pediatric rheumatology program.
“I’ve done it a couple of times,” Dr. Mehta said during his presentation at the annual meeting. “It’s one of the most rewarding things I’ve done.”
Financial Concerns
Additionally, although pediatric rheumatology requires more training, these subspecialists will likely make less than their general pediatric colleagues over their career. According to one study in Pediatrics, a pediatric resident pursuing rheumatology is projected to make $1.2 million dollars less over the course of their career compared with someone who started their career in general pediatrics immediately after residency. (Negative financial returns were also found for all pediatric subspecialities except for cardiology, critical care, and neonatology.)
This lower earning potential is likely a deterrent, especially for those with educational debt. In one analysis published in October, medical students with at least $200,000 in education debt were 43% more likely to go into higher-paying pediatric subspecialities than those with no debt. Nearly three out of four medical graduates have education debt, according to the American Association of Medical Colleges, with a median debt of $200,000.
While the Pediatric Specialty Loan Repayment Program was specifically designed to aid pediatric subspecialists with their educational debt, qualifying for the program is difficult for pediatric rheumatologists, explained Kristen N. Hayward, MD, of Seattle Children’s in Washington. The program provides up to $100,000 in loan forgiveness in exchange for 3 years of practicing in an underserved area; however, the program stipulates that providers must provide full-time (40 hours per week) clinical care. At academic institutions, where most pediatric rheumatologists practice, there is usually a research component to their position, and even if a provider works the equivalent of 40 hours per week in a clinic in addition to their research, they don’t qualify for the program, Dr. Hayward said.
“It’s very difficult to find someone who’s actually only doing clinical work,” she said.
The ACR has worked to combat some of these economic constraints by demonstrating the direct and downstream value of rheumatologic care, Dr. Hayward said. In a recent white paper, it was estimated that including office visits, consultations, lab testing, and radiology services, one full-time equivalent rheumatologist generates $3.5 million in revenue every year and saves health systems more than $2700 per patient per year.
In addition to placing greater value on rheumatologic care, the healthcare system also needs to recognize the current nonbillable hours that pediatric rheumatologists spend taking care of patients, Dr. Hayward noted.
Especially with electronic medical records (EMRs) and online communication with patients, “there is increasingly a lot of patient care that happens outside of clinic and that takes a lot of time,” Dr. Hayward said. For example, she spends between 1 and 2 hours every day in the EMR refilling medications and responding to patient concerns, and “that all is done in my spare time,” she said. “That’s not billed to the patient in anyway.”
Length of Fellowship
The pediatric rheumatology fellowship is a 3-year program — like other pediatric subspecialities — with a research requirement. By comparison, adult rheumatology fellowships are 2 years, and fellows can pursue additional research training if they have a strong interest.
“It sounds like just 1 more year, but I think it’s coming at a really pivotal point in people’s lives, and that 1 year can make a huge difference,” Dr. Hayward explained.
The 2 years of research might also be a deterrent for individuals who know they are only interested in clinical work, she added. About half of pediatric subspecialists only pursue clinical work after graduation, according to a recent report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) focused on the future pediatric physician workforce.
Additionally, only 17% of pediatric rheumatologists spend more than half of their time in research, said Fred Rivara, MD, MPH, chair of the NASEM report, in a statement included in Dr. Hayward’s ACR presentation. The report, which recommended strategies to bolster the pediatric workforce, argued that the American Board of Pediatrics should develop alternative training pathways, including 2-year, clinically heavy fellowships.
The ACR workforce team is also exploring alternative training models like competency-based education, Dr. Hayward said. The Education in Pediatrics Across the Continuum project is already using this approach from medical school to pediatric residency. While this type of outcome-based program has not been tried at the fellowship level, «this has been done, it could be done, and I think we could learn from our colleagues about how they have done this successfully,» she noted.
Ultimately, Dr. Hayward emphasized that there needs to be a “sea change” to close the workforce gap — with multiple interventions addressing these individual challenges.
“Unless we all pitch in and find one way that we can all move this issue forward, we are going to be drowning in a sea of Epic inbox messages,” she said, “and never get to see the patients we want to see.”
Dr. Hayward previously owned stock/stock options for AbbVie/Abbott, Cigna/Express Scripts, Merck, and Teva and has received an educational grant from Pfizer. Dr. Correll and Dr. Mehta had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2023
Roflumilast foam gets nod as new option for seborrheic dermatitis
The in a press release.
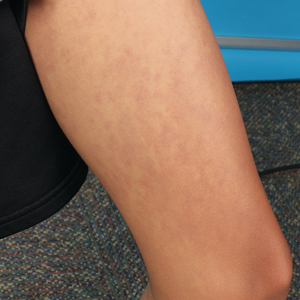
The 0.3% foam, marketed as Zoryve, applied once-daily, is indicated for patients aged 9 years and older with seborrheic dermatitis, and can be used anywhere on the body, including areas with hair, with no limits on duration of use, according to the company, Arcutis. A 0.3% cream formulation of roflumilast was previously approved by the FDA for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis in patients aged 6 years and older.
Approval was based on data from the phase 3 STRATUM trial and an accompanying phase 2 study known as Trial 203. These studies included a total of 683 adults and youth aged 9 years and older with seborrheic dermatitis. Participants were randomized to roflumilast or a placebo.
At 8 weeks, 79.5 % of patients on roflumilast met the primary efficacy endpoint of Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) scores of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) compared with 58.0% of patients on placebo (P < .001); the results were similar in the phase 2 Trial 203 (73.1% vs. 40.8%, respectively; P < .001). Overall, more than 50% of the patients on roflumilast achieved a clear score.
Patients in the roflumilast group also showed significant improvement in all secondary endpoints, including itching, scaling, and erythema, according to the company.
In the STRATUM study, 62.8% of roflumilast-treated patients and 40.6% of placebo patients achieved a 4-point or more reduction in itch based on the Worst Itch Numerical Rating Score (P =.0001), and 28% of roflumilast-treated patients reported significant itch improvement within the first 48 hours of use, compared with 13% of placebo patients (P = .0024).
Over a treatment period of up to 1 year, no treatment-related severe adverse events were reported in the phase 2 and 3 studies. The incidence of treatment emergent adverse events was similar between the treatment and placebo groups, and the most common adverse events (occurring in 1% of more of patients) across both studies were nasopharyngitis (1.5%), nausea (1.3%), and headache (1.1%).
Roflumilast foam is scheduled to be available by the end of January 2024, according to the company. The product is for topical use only, and contraindicated for individuals with severe liver impairment.
The in a press release.
The 0.3% foam, marketed as Zoryve, applied once-daily, is indicated for patients aged 9 years and older with seborrheic dermatitis, and can be used anywhere on the body, including areas with hair, with no limits on duration of use, according to the company, Arcutis. A 0.3% cream formulation of roflumilast was previously approved by the FDA for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis in patients aged 6 years and older.
Approval was based on data from the phase 3 STRATUM trial and an accompanying phase 2 study known as Trial 203. These studies included a total of 683 adults and youth aged 9 years and older with seborrheic dermatitis. Participants were randomized to roflumilast or a placebo.
At 8 weeks, 79.5 % of patients on roflumilast met the primary efficacy endpoint of Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) scores of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) compared with 58.0% of patients on placebo (P < .001); the results were similar in the phase 2 Trial 203 (73.1% vs. 40.8%, respectively; P < .001). Overall, more than 50% of the patients on roflumilast achieved a clear score.
Patients in the roflumilast group also showed significant improvement in all secondary endpoints, including itching, scaling, and erythema, according to the company.
In the STRATUM study, 62.8% of roflumilast-treated patients and 40.6% of placebo patients achieved a 4-point or more reduction in itch based on the Worst Itch Numerical Rating Score (P =.0001), and 28% of roflumilast-treated patients reported significant itch improvement within the first 48 hours of use, compared with 13% of placebo patients (P = .0024).
Over a treatment period of up to 1 year, no treatment-related severe adverse events were reported in the phase 2 and 3 studies. The incidence of treatment emergent adverse events was similar between the treatment and placebo groups, and the most common adverse events (occurring in 1% of more of patients) across both studies were nasopharyngitis (1.5%), nausea (1.3%), and headache (1.1%).
Roflumilast foam is scheduled to be available by the end of January 2024, according to the company. The product is for topical use only, and contraindicated for individuals with severe liver impairment.
The in a press release.
The 0.3% foam, marketed as Zoryve, applied once-daily, is indicated for patients aged 9 years and older with seborrheic dermatitis, and can be used anywhere on the body, including areas with hair, with no limits on duration of use, according to the company, Arcutis. A 0.3% cream formulation of roflumilast was previously approved by the FDA for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis in patients aged 6 years and older.
Approval was based on data from the phase 3 STRATUM trial and an accompanying phase 2 study known as Trial 203. These studies included a total of 683 adults and youth aged 9 years and older with seborrheic dermatitis. Participants were randomized to roflumilast or a placebo.
At 8 weeks, 79.5 % of patients on roflumilast met the primary efficacy endpoint of Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) scores of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) compared with 58.0% of patients on placebo (P < .001); the results were similar in the phase 2 Trial 203 (73.1% vs. 40.8%, respectively; P < .001). Overall, more than 50% of the patients on roflumilast achieved a clear score.
Patients in the roflumilast group also showed significant improvement in all secondary endpoints, including itching, scaling, and erythema, according to the company.
In the STRATUM study, 62.8% of roflumilast-treated patients and 40.6% of placebo patients achieved a 4-point or more reduction in itch based on the Worst Itch Numerical Rating Score (P =.0001), and 28% of roflumilast-treated patients reported significant itch improvement within the first 48 hours of use, compared with 13% of placebo patients (P = .0024).
Over a treatment period of up to 1 year, no treatment-related severe adverse events were reported in the phase 2 and 3 studies. The incidence of treatment emergent adverse events was similar between the treatment and placebo groups, and the most common adverse events (occurring in 1% of more of patients) across both studies were nasopharyngitis (1.5%), nausea (1.3%), and headache (1.1%).
Roflumilast foam is scheduled to be available by the end of January 2024, according to the company. The product is for topical use only, and contraindicated for individuals with severe liver impairment.
Sometimes well-intended mental health treatment hurts
We love psychiatry. We love the idea that someone can come to receive care from a physician to alleviate psychological suffering.
Some people experience such severe anguish that they are unable to relate to others. Some are so despondent that they are unable to make decisions. Some are so distressed that their thoughts become inconsistent with reality. We want all those people, and many more, to have access to effective psychiatric care. However, there are reasonable expectations that one should be able to have that a treatment will help, and that appropriate informed consent is given.
One recent article reminded us of this in a particularly poignant way.
The study in question is a recent publication looking at the universal use of psychotherapy for teenagers.1 At face value, we would have certainly considered this to be a benevolent and well-meaning intervention. Anyone who has been a teenager or has talked to one, is aware of the emotional instability punctuated by episodes of intense anxiety or irritability. It is age appropriate for a teenager to question and explore their identity. Teenagers are notoriously impulsive with a deep desire for validating interpersonal relationships. One could continue to list the symptoms of borderline personality disorder (BPD) and find a lot of similarity with the condition of transitioning from a child to an adult.
It is thus common sense to consider applying the most established therapy for BPD, dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT), to teenagers. The basics of DBT would seem to be helpful to anyone but appear particularly appropriate to this population. Mindfulness, the practice of paying attention to your present experience, allows one to realize that they are trapped in past or hypothetical future moments. Emotional regulation provides the tools that offer a frame for our feelings and involves recognizing feelings and understanding what they mean. Interpersonal work allows one to recognize and adapt to the feelings of others, while learning how to have a healthy voice with others. Distress tolerance is the exercise of learning to experience and contain our feelings.
The study looked at about 1,000 young adolescents, around 13 years old across high schools in Sydney, Australia: 598 adolescents were allocated to the intervention, and 566 to the control. The intervention consisted of eight weekly sessions of DBT lasting about 50 minutes. The results were “contrary to predictions.” Participants who received DBT “reported significantly increased total difficulties,” and “significant increases in depression and anxiety.” The effects were worse in males yet significant in both genders. The study concludes with “a reminder that present enthusiasm for universal dissemination of short-term DBT-based group skills training within schools, specifically in early adolescence, is ahead of the research evidence.”
We can’t help but wonder why the outcomes of the study were this way; here are some ideas:
• Society has natural ways of developing interpersonal skills, emotional regulation, and the ability to appreciate the present. Interpersonal skills are consistently fostered and tested in schools. Navigating high school parties, the process of organizing them, and getting invited to them requires significant social dexterity. Rejection from romantic interest, alienation from peers, rewards for accomplishment, and acceptance by other peers are some of the daily emotional obstacles that teenagers face. Being constantly taught by older individuals and scolded by parents is its own course in mindfulness. Those are few of the many natural processes of interpersonal growth that formalized therapy may impede.
• The universal discussion of psychological terms and psychiatric symptoms may not only destigmatize mental illness, but also normalize and possibly even promote it. While punishing or stigmatizing a child for having mental illness is obviously unacceptable and cruel, we do wonder if the compulsory psychotherapy may provide negative effects. Psychotherapies, especially manualized ones, were developed to alleviate mental suffering. It seems possible that this format normalizes pathology.
In 1961, Erving Goffman described the concept of sane people appearing insane in an asylum as “mortification.” In 2023, we have much improved, but have we done something to internalize patterns of suffering and alienation rather than dispel them? They are given forms that explain what the feeling of depression is when they may have never considered it. They are given tools to handle distress, when distress may not be present.
• Many human beings live on a fairly tight rope of suppression and the less adaptive repression. Suppression is the defense mechanism by which individuals make an effort to put distressing thoughts out of conscious awareness. After a difficult breakup a teenager may ask some friends to go out and watch a movie, making efforts to put negative feelings out of conscious awareness until there is an opportunity to cope adaptively with those stressors.
Repression is the defense mechanism by which individuals make an effort to prevent distressing thoughts from entering conscious awareness in the first place. After a difficult breakup a teenager acts like nothing happened. While not particularly adaptive, many people live with significant repression and without particular anguish. It is possible that uncovering all of those repressed and suppressed feelings through the exploratory work of therapy may destabilize individuals from their tight rope.
• A less problematic explanation could also be what was previously referred to as therapeutic regression. In psychoanalytic theory, patients are generally thought to have a compromise formation, a psychological strategy used to reconcile conflicting drives. The compromise formation is the way a patient balances their desires against moral expectations and the realities of the external world. In therapy, that compromise formation can be challenged, leading to therapeutic regression.
By uncovering and confronting deeply rooted feelings, a patient may find that their symptoms temporarily intensify. This may not be a problem, but a necessary step to growth in some patients. It is possible that a program longer than 8 weeks would have overcome a temporary worsening in outcome measures.
While it’s easy to highlight the darker moments in psychiatric history, psychiatry has grown into a field which offers well-accepted and uncontroversially promoted forms of treatment. This is evolution, exemplified by the mere consideration of the universal use of psychotherapy for teenagers. But this raises important questions about the potential unintended consequences of normalizing and formalizing therapy. It prompted us to reflect on whether psychiatric treatment is always the best solution and if it might, at times, impede natural processes of growth and coping.
In this context, the study on universal DBT-based group skills training for teenagers challenged our assumptions. The unexpected outcomes suggest that societal and educational systems may naturally foster many of the skills that formalized therapy seeks to provide, and may do so with greater efficacy than that which prescriptive psychiatric treatments have to offer. Moreover, the universal discussion of psychiatric symptoms may not only destigmatize mental illness but also normalize it, potentially leading to unnecessary pathology.
Finally, the study prompted us to consider the fine balance that people find themselves in, questioning whether we should be so certain that our interventions can always provide a better outcome than an individual’s current coping mechanisms. These findings serve as a valuable reminder that our enthusiasm for widespread psychiatric interventions should be tempered by rigorous research and a nuanced understanding of human psychology and development.
This study could be an example of the grandiose stance psychiatry has at times taken of late, suggesting the field has an intervention for all that ails you and can serve as a corrective to society’s maladaptive deviations. Rising rates of mental illness in the community are not interpreted as a failing of the field of psychiatry, but as evidence that we need more psychiatrists. Acts of gun violence, ever increasing rates suicides, and even political disagreements are met with the idea that if only we had more mental health capacity, this could be avoided.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. ZoBell is a fourth-year senior resident at UCSD Psychiatry Residency Program. She is currently serving as the program’s Chief Resident at the VA San Diego on the inpatient psychiatric unit. Dr. ZoBell is interested in outpatient and emergency psychiatry as well as psychotherapy. Dr. Lehman is a professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego. He is codirector of all acute and intensive psychiatric treatment at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Diego, where he practices clinical psychiatry. He has no conflicts of interest.
Reference
1. Harvey, LJ, et al. Investigating the efficacy of a Dialectical behaviour therapy-based universal intervention on adolescent social and emotional well-being outcomes. Behav Res Ther. 2023 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2023.104408.
We love psychiatry. We love the idea that someone can come to receive care from a physician to alleviate psychological suffering.
Some people experience such severe anguish that they are unable to relate to others. Some are so despondent that they are unable to make decisions. Some are so distressed that their thoughts become inconsistent with reality. We want all those people, and many more, to have access to effective psychiatric care. However, there are reasonable expectations that one should be able to have that a treatment will help, and that appropriate informed consent is given.
One recent article reminded us of this in a particularly poignant way.
The study in question is a recent publication looking at the universal use of psychotherapy for teenagers.1 At face value, we would have certainly considered this to be a benevolent and well-meaning intervention. Anyone who has been a teenager or has talked to one, is aware of the emotional instability punctuated by episodes of intense anxiety or irritability. It is age appropriate for a teenager to question and explore their identity. Teenagers are notoriously impulsive with a deep desire for validating interpersonal relationships. One could continue to list the symptoms of borderline personality disorder (BPD) and find a lot of similarity with the condition of transitioning from a child to an adult.
It is thus common sense to consider applying the most established therapy for BPD, dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT), to teenagers. The basics of DBT would seem to be helpful to anyone but appear particularly appropriate to this population. Mindfulness, the practice of paying attention to your present experience, allows one to realize that they are trapped in past or hypothetical future moments. Emotional regulation provides the tools that offer a frame for our feelings and involves recognizing feelings and understanding what they mean. Interpersonal work allows one to recognize and adapt to the feelings of others, while learning how to have a healthy voice with others. Distress tolerance is the exercise of learning to experience and contain our feelings.
The study looked at about 1,000 young adolescents, around 13 years old across high schools in Sydney, Australia: 598 adolescents were allocated to the intervention, and 566 to the control. The intervention consisted of eight weekly sessions of DBT lasting about 50 minutes. The results were “contrary to predictions.” Participants who received DBT “reported significantly increased total difficulties,” and “significant increases in depression and anxiety.” The effects were worse in males yet significant in both genders. The study concludes with “a reminder that present enthusiasm for universal dissemination of short-term DBT-based group skills training within schools, specifically in early adolescence, is ahead of the research evidence.”
We can’t help but wonder why the outcomes of the study were this way; here are some ideas:
• Society has natural ways of developing interpersonal skills, emotional regulation, and the ability to appreciate the present. Interpersonal skills are consistently fostered and tested in schools. Navigating high school parties, the process of organizing them, and getting invited to them requires significant social dexterity. Rejection from romantic interest, alienation from peers, rewards for accomplishment, and acceptance by other peers are some of the daily emotional obstacles that teenagers face. Being constantly taught by older individuals and scolded by parents is its own course in mindfulness. Those are few of the many natural processes of interpersonal growth that formalized therapy may impede.
• The universal discussion of psychological terms and psychiatric symptoms may not only destigmatize mental illness, but also normalize and possibly even promote it. While punishing or stigmatizing a child for having mental illness is obviously unacceptable and cruel, we do wonder if the compulsory psychotherapy may provide negative effects. Psychotherapies, especially manualized ones, were developed to alleviate mental suffering. It seems possible that this format normalizes pathology.
In 1961, Erving Goffman described the concept of sane people appearing insane in an asylum as “mortification.” In 2023, we have much improved, but have we done something to internalize patterns of suffering and alienation rather than dispel them? They are given forms that explain what the feeling of depression is when they may have never considered it. They are given tools to handle distress, when distress may not be present.
• Many human beings live on a fairly tight rope of suppression and the less adaptive repression. Suppression is the defense mechanism by which individuals make an effort to put distressing thoughts out of conscious awareness. After a difficult breakup a teenager may ask some friends to go out and watch a movie, making efforts to put negative feelings out of conscious awareness until there is an opportunity to cope adaptively with those stressors.
Repression is the defense mechanism by which individuals make an effort to prevent distressing thoughts from entering conscious awareness in the first place. After a difficult breakup a teenager acts like nothing happened. While not particularly adaptive, many people live with significant repression and without particular anguish. It is possible that uncovering all of those repressed and suppressed feelings through the exploratory work of therapy may destabilize individuals from their tight rope.
• A less problematic explanation could also be what was previously referred to as therapeutic regression. In psychoanalytic theory, patients are generally thought to have a compromise formation, a psychological strategy used to reconcile conflicting drives. The compromise formation is the way a patient balances their desires against moral expectations and the realities of the external world. In therapy, that compromise formation can be challenged, leading to therapeutic regression.
By uncovering and confronting deeply rooted feelings, a patient may find that their symptoms temporarily intensify. This may not be a problem, but a necessary step to growth in some patients. It is possible that a program longer than 8 weeks would have overcome a temporary worsening in outcome measures.
While it’s easy to highlight the darker moments in psychiatric history, psychiatry has grown into a field which offers well-accepted and uncontroversially promoted forms of treatment. This is evolution, exemplified by the mere consideration of the universal use of psychotherapy for teenagers. But this raises important questions about the potential unintended consequences of normalizing and formalizing therapy. It prompted us to reflect on whether psychiatric treatment is always the best solution and if it might, at times, impede natural processes of growth and coping.
In this context, the study on universal DBT-based group skills training for teenagers challenged our assumptions. The unexpected outcomes suggest that societal and educational systems may naturally foster many of the skills that formalized therapy seeks to provide, and may do so with greater efficacy than that which prescriptive psychiatric treatments have to offer. Moreover, the universal discussion of psychiatric symptoms may not only destigmatize mental illness but also normalize it, potentially leading to unnecessary pathology.
Finally, the study prompted us to consider the fine balance that people find themselves in, questioning whether we should be so certain that our interventions can always provide a better outcome than an individual’s current coping mechanisms. These findings serve as a valuable reminder that our enthusiasm for widespread psychiatric interventions should be tempered by rigorous research and a nuanced understanding of human psychology and development.
This study could be an example of the grandiose stance psychiatry has at times taken of late, suggesting the field has an intervention for all that ails you and can serve as a corrective to society’s maladaptive deviations. Rising rates of mental illness in the community are not interpreted as a failing of the field of psychiatry, but as evidence that we need more psychiatrists. Acts of gun violence, ever increasing rates suicides, and even political disagreements are met with the idea that if only we had more mental health capacity, this could be avoided.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. ZoBell is a fourth-year senior resident at UCSD Psychiatry Residency Program. She is currently serving as the program’s Chief Resident at the VA San Diego on the inpatient psychiatric unit. Dr. ZoBell is interested in outpatient and emergency psychiatry as well as psychotherapy. Dr. Lehman is a professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego. He is codirector of all acute and intensive psychiatric treatment at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Diego, where he practices clinical psychiatry. He has no conflicts of interest.
Reference
1. Harvey, LJ, et al. Investigating the efficacy of a Dialectical behaviour therapy-based universal intervention on adolescent social and emotional well-being outcomes. Behav Res Ther. 2023 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2023.104408.
We love psychiatry. We love the idea that someone can come to receive care from a physician to alleviate psychological suffering.
Some people experience such severe anguish that they are unable to relate to others. Some are so despondent that they are unable to make decisions. Some are so distressed that their thoughts become inconsistent with reality. We want all those people, and many more, to have access to effective psychiatric care. However, there are reasonable expectations that one should be able to have that a treatment will help, and that appropriate informed consent is given.
One recent article reminded us of this in a particularly poignant way.
The study in question is a recent publication looking at the universal use of psychotherapy for teenagers.1 At face value, we would have certainly considered this to be a benevolent and well-meaning intervention. Anyone who has been a teenager or has talked to one, is aware of the emotional instability punctuated by episodes of intense anxiety or irritability. It is age appropriate for a teenager to question and explore their identity. Teenagers are notoriously impulsive with a deep desire for validating interpersonal relationships. One could continue to list the symptoms of borderline personality disorder (BPD) and find a lot of similarity with the condition of transitioning from a child to an adult.
It is thus common sense to consider applying the most established therapy for BPD, dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT), to teenagers. The basics of DBT would seem to be helpful to anyone but appear particularly appropriate to this population. Mindfulness, the practice of paying attention to your present experience, allows one to realize that they are trapped in past or hypothetical future moments. Emotional regulation provides the tools that offer a frame for our feelings and involves recognizing feelings and understanding what they mean. Interpersonal work allows one to recognize and adapt to the feelings of others, while learning how to have a healthy voice with others. Distress tolerance is the exercise of learning to experience and contain our feelings.
The study looked at about 1,000 young adolescents, around 13 years old across high schools in Sydney, Australia: 598 adolescents were allocated to the intervention, and 566 to the control. The intervention consisted of eight weekly sessions of DBT lasting about 50 minutes. The results were “contrary to predictions.” Participants who received DBT “reported significantly increased total difficulties,” and “significant increases in depression and anxiety.” The effects were worse in males yet significant in both genders. The study concludes with “a reminder that present enthusiasm for universal dissemination of short-term DBT-based group skills training within schools, specifically in early adolescence, is ahead of the research evidence.”
We can’t help but wonder why the outcomes of the study were this way; here are some ideas:
• Society has natural ways of developing interpersonal skills, emotional regulation, and the ability to appreciate the present. Interpersonal skills are consistently fostered and tested in schools. Navigating high school parties, the process of organizing them, and getting invited to them requires significant social dexterity. Rejection from romantic interest, alienation from peers, rewards for accomplishment, and acceptance by other peers are some of the daily emotional obstacles that teenagers face. Being constantly taught by older individuals and scolded by parents is its own course in mindfulness. Those are few of the many natural processes of interpersonal growth that formalized therapy may impede.
• The universal discussion of psychological terms and psychiatric symptoms may not only destigmatize mental illness, but also normalize and possibly even promote it. While punishing or stigmatizing a child for having mental illness is obviously unacceptable and cruel, we do wonder if the compulsory psychotherapy may provide negative effects. Psychotherapies, especially manualized ones, were developed to alleviate mental suffering. It seems possible that this format normalizes pathology.
In 1961, Erving Goffman described the concept of sane people appearing insane in an asylum as “mortification.” In 2023, we have much improved, but have we done something to internalize patterns of suffering and alienation rather than dispel them? They are given forms that explain what the feeling of depression is when they may have never considered it. They are given tools to handle distress, when distress may not be present.
• Many human beings live on a fairly tight rope of suppression and the less adaptive repression. Suppression is the defense mechanism by which individuals make an effort to put distressing thoughts out of conscious awareness. After a difficult breakup a teenager may ask some friends to go out and watch a movie, making efforts to put negative feelings out of conscious awareness until there is an opportunity to cope adaptively with those stressors.
Repression is the defense mechanism by which individuals make an effort to prevent distressing thoughts from entering conscious awareness in the first place. After a difficult breakup a teenager acts like nothing happened. While not particularly adaptive, many people live with significant repression and without particular anguish. It is possible that uncovering all of those repressed and suppressed feelings through the exploratory work of therapy may destabilize individuals from their tight rope.
• A less problematic explanation could also be what was previously referred to as therapeutic regression. In psychoanalytic theory, patients are generally thought to have a compromise formation, a psychological strategy used to reconcile conflicting drives. The compromise formation is the way a patient balances their desires against moral expectations and the realities of the external world. In therapy, that compromise formation can be challenged, leading to therapeutic regression.
By uncovering and confronting deeply rooted feelings, a patient may find that their symptoms temporarily intensify. This may not be a problem, but a necessary step to growth in some patients. It is possible that a program longer than 8 weeks would have overcome a temporary worsening in outcome measures.
While it’s easy to highlight the darker moments in psychiatric history, psychiatry has grown into a field which offers well-accepted and uncontroversially promoted forms of treatment. This is evolution, exemplified by the mere consideration of the universal use of psychotherapy for teenagers. But this raises important questions about the potential unintended consequences of normalizing and formalizing therapy. It prompted us to reflect on whether psychiatric treatment is always the best solution and if it might, at times, impede natural processes of growth and coping.
In this context, the study on universal DBT-based group skills training for teenagers challenged our assumptions. The unexpected outcomes suggest that societal and educational systems may naturally foster many of the skills that formalized therapy seeks to provide, and may do so with greater efficacy than that which prescriptive psychiatric treatments have to offer. Moreover, the universal discussion of psychiatric symptoms may not only destigmatize mental illness but also normalize it, potentially leading to unnecessary pathology.
Finally, the study prompted us to consider the fine balance that people find themselves in, questioning whether we should be so certain that our interventions can always provide a better outcome than an individual’s current coping mechanisms. These findings serve as a valuable reminder that our enthusiasm for widespread psychiatric interventions should be tempered by rigorous research and a nuanced understanding of human psychology and development.
This study could be an example of the grandiose stance psychiatry has at times taken of late, suggesting the field has an intervention for all that ails you and can serve as a corrective to society’s maladaptive deviations. Rising rates of mental illness in the community are not interpreted as a failing of the field of psychiatry, but as evidence that we need more psychiatrists. Acts of gun violence, ever increasing rates suicides, and even political disagreements are met with the idea that if only we had more mental health capacity, this could be avoided.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. ZoBell is a fourth-year senior resident at UCSD Psychiatry Residency Program. She is currently serving as the program’s Chief Resident at the VA San Diego on the inpatient psychiatric unit. Dr. ZoBell is interested in outpatient and emergency psychiatry as well as psychotherapy. Dr. Lehman is a professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego. He is codirector of all acute and intensive psychiatric treatment at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Diego, where he practices clinical psychiatry. He has no conflicts of interest.
Reference
1. Harvey, LJ, et al. Investigating the efficacy of a Dialectical behaviour therapy-based universal intervention on adolescent social and emotional well-being outcomes. Behav Res Ther. 2023 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2023.104408.
How does lebrikizumab perform across different racial and ethnic subgroups?
.
The finding comes from an analysis of the 16-week induction periods of the phase 3 ADvocate1 and ADvocate2 trials, which Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, presented during a late-breaking abstract session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Virtual Conference. The efficacy of lebrikizumab monotherapy to treat moderate-to-severe AD has been established in phase 3 studies, “but disease characteristic and efficacy outcomes may vary among racial and ethnic subgroups,” said Dr. Chovatiya, assistant professor in the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “The goal of the current study is to report the week 16 efficacy of lebrikizumab-treated patients in racial and ethnic subgroups from ADvocate1 and ADvocate2.”
Key eligibility criteria for both trials included adults or adolescents with a diagnosis of AD as defined by the American Academy of Dermatology Consensus Criteria, for at least 1 year prior to screening. They had moderate-to-severe AD, were candidates for systemic therapy, and were dupilumab- and tralokinumab-naive. Outcomes of interest were the Investigator’s Global Assessment 0 or 1, with at least a 2-point improvement; and the proportions of patients who achieved Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI75) and EASI90 responses, and an improvement of 4 points or more on the Pruritus Numeric Rating Scale (NRS).
For statistical analysis, the researchers pooled data from Advocate1 and Advocate2 and applied imputation methodology to the 16-week induction period. Subsequent data from patients who received topical or systemic rescue medication or discontinued treatment due to lack of efficacy were imputed as nonresponders. Subsequent data from patients who discontinued treatment for other reasons were set to missing, and the researchers handled missing data with multiple imputation. They used logistic regression to test the interaction between the treatment and subgroup and the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel method to evaluate the treatment effect within each subgroup after adjusting for stratification factors.
Dr. Chovatiya reported findings from the 851 study participants in the combined studies. Of these, 542 were White, 192 were Asian, 84 were Black, and 33 were from other racial subgroups. By ethnic subgroup, 748 were not Hispanic or Latino, 91 were Hispanic or Latino, and ethnicity was unknown or not reported for 12 subjects. At baseline, the mean body mass index was slightly higher among Blacks (30.4 kg/m2) and Hispanics (29.4 kg/m2) compared with other racial and ethnic groups, “which reflects general epidemiologic data among these groups in the United States,” Dr. Chovatiya said. “You can also see a difference in the balance of IGA scores — they were a little bit more severe in the Black or African American and Hispanic groups as well.” The researchers also observed differences in the baseline EASI score across some of these groups, particularly in the Asian individuals, who had higher EASI scores. Prior use of systemic therapy was lower in the Black and “other” subgroups, compared with other racial subgroups.
At week 16, key efficacy endpoints were generally similar between the different racial subgroups. Specifically, 25.1% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an IGA of 0/1, compared with 4.1% of those in the placebo group (P < .001), while 33.2% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an IGA of 0/1, compared with 13.2% of those in the placebo group (no P value was established because this subgroup represented less than 10% of the entire study population). In addition, 43.3% of Whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an IGA of 0/1, compared with 14.1% of those in the placebo group (P < .001).
In other findings, 45.5% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI75, compared with 8.5% of those in the placebo group (P < .001), while 51.7% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI75, compared with 18.8% of those in the placebo group. Among whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group, 59.7% of achieved an EASI75, compared with 20.4% of those in the placebo group (P < .001).
Dr. Chovatiya said that 26.5% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI90, compared with 4.3% of those in the placebo group (P < .001), while 26.9% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI90, compared with 13.2% of those in the placebo group. In addition, 38.3% of Whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI90, compared with 10.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .001).
Finally, 36.4% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement on the NRS, compared with 5.7% of those in the placebo group (P <. 001), while 41.7% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement on the NRS, compared with 17.4% of those in the placebo group. In addition, 45.9% of Whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement on the NRS, compared with 14.8% of those in the placebo group (P < .001). Statistical analyses of efficacy endpoints conducted by ethnic group yielded similar results.
Dr. Chovatiya acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that differences in baseline demographics and disease characteristics limit direct comparison across racial and ethnic subgroups. “Due to the relatively small sample size of some racial and ethnic subgroups and the post hoc nature of this analysis, additional studies are needed to verify these results,” he concluded. But for now, he said, the data available indicate that “lebrikizumab is effective across racial and ethnic subgroups for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD after 16 weeks of monotherapy treatment.”
The study was funded by Dermira, a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly and Company. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is speaker for and/or a consult and advisory board member to many pharmaceutical companies, including Eli Lilly.
.
The finding comes from an analysis of the 16-week induction periods of the phase 3 ADvocate1 and ADvocate2 trials, which Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, presented during a late-breaking abstract session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Virtual Conference. The efficacy of lebrikizumab monotherapy to treat moderate-to-severe AD has been established in phase 3 studies, “but disease characteristic and efficacy outcomes may vary among racial and ethnic subgroups,” said Dr. Chovatiya, assistant professor in the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “The goal of the current study is to report the week 16 efficacy of lebrikizumab-treated patients in racial and ethnic subgroups from ADvocate1 and ADvocate2.”
Key eligibility criteria for both trials included adults or adolescents with a diagnosis of AD as defined by the American Academy of Dermatology Consensus Criteria, for at least 1 year prior to screening. They had moderate-to-severe AD, were candidates for systemic therapy, and were dupilumab- and tralokinumab-naive. Outcomes of interest were the Investigator’s Global Assessment 0 or 1, with at least a 2-point improvement; and the proportions of patients who achieved Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI75) and EASI90 responses, and an improvement of 4 points or more on the Pruritus Numeric Rating Scale (NRS).
For statistical analysis, the researchers pooled data from Advocate1 and Advocate2 and applied imputation methodology to the 16-week induction period. Subsequent data from patients who received topical or systemic rescue medication or discontinued treatment due to lack of efficacy were imputed as nonresponders. Subsequent data from patients who discontinued treatment for other reasons were set to missing, and the researchers handled missing data with multiple imputation. They used logistic regression to test the interaction between the treatment and subgroup and the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel method to evaluate the treatment effect within each subgroup after adjusting for stratification factors.
Dr. Chovatiya reported findings from the 851 study participants in the combined studies. Of these, 542 were White, 192 were Asian, 84 were Black, and 33 were from other racial subgroups. By ethnic subgroup, 748 were not Hispanic or Latino, 91 were Hispanic or Latino, and ethnicity was unknown or not reported for 12 subjects. At baseline, the mean body mass index was slightly higher among Blacks (30.4 kg/m2) and Hispanics (29.4 kg/m2) compared with other racial and ethnic groups, “which reflects general epidemiologic data among these groups in the United States,” Dr. Chovatiya said. “You can also see a difference in the balance of IGA scores — they were a little bit more severe in the Black or African American and Hispanic groups as well.” The researchers also observed differences in the baseline EASI score across some of these groups, particularly in the Asian individuals, who had higher EASI scores. Prior use of systemic therapy was lower in the Black and “other” subgroups, compared with other racial subgroups.
At week 16, key efficacy endpoints were generally similar between the different racial subgroups. Specifically, 25.1% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an IGA of 0/1, compared with 4.1% of those in the placebo group (P < .001), while 33.2% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an IGA of 0/1, compared with 13.2% of those in the placebo group (no P value was established because this subgroup represented less than 10% of the entire study population). In addition, 43.3% of Whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an IGA of 0/1, compared with 14.1% of those in the placebo group (P < .001).
In other findings, 45.5% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI75, compared with 8.5% of those in the placebo group (P < .001), while 51.7% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI75, compared with 18.8% of those in the placebo group. Among whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group, 59.7% of achieved an EASI75, compared with 20.4% of those in the placebo group (P < .001).
Dr. Chovatiya said that 26.5% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI90, compared with 4.3% of those in the placebo group (P < .001), while 26.9% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI90, compared with 13.2% of those in the placebo group. In addition, 38.3% of Whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI90, compared with 10.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .001).
Finally, 36.4% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement on the NRS, compared with 5.7% of those in the placebo group (P <. 001), while 41.7% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement on the NRS, compared with 17.4% of those in the placebo group. In addition, 45.9% of Whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement on the NRS, compared with 14.8% of those in the placebo group (P < .001). Statistical analyses of efficacy endpoints conducted by ethnic group yielded similar results.
Dr. Chovatiya acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that differences in baseline demographics and disease characteristics limit direct comparison across racial and ethnic subgroups. “Due to the relatively small sample size of some racial and ethnic subgroups and the post hoc nature of this analysis, additional studies are needed to verify these results,” he concluded. But for now, he said, the data available indicate that “lebrikizumab is effective across racial and ethnic subgroups for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD after 16 weeks of monotherapy treatment.”
The study was funded by Dermira, a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly and Company. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is speaker for and/or a consult and advisory board member to many pharmaceutical companies, including Eli Lilly.
.
The finding comes from an analysis of the 16-week induction periods of the phase 3 ADvocate1 and ADvocate2 trials, which Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, presented during a late-breaking abstract session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Virtual Conference. The efficacy of lebrikizumab monotherapy to treat moderate-to-severe AD has been established in phase 3 studies, “but disease characteristic and efficacy outcomes may vary among racial and ethnic subgroups,” said Dr. Chovatiya, assistant professor in the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “The goal of the current study is to report the week 16 efficacy of lebrikizumab-treated patients in racial and ethnic subgroups from ADvocate1 and ADvocate2.”
Key eligibility criteria for both trials included adults or adolescents with a diagnosis of AD as defined by the American Academy of Dermatology Consensus Criteria, for at least 1 year prior to screening. They had moderate-to-severe AD, were candidates for systemic therapy, and were dupilumab- and tralokinumab-naive. Outcomes of interest were the Investigator’s Global Assessment 0 or 1, with at least a 2-point improvement; and the proportions of patients who achieved Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI75) and EASI90 responses, and an improvement of 4 points or more on the Pruritus Numeric Rating Scale (NRS).
For statistical analysis, the researchers pooled data from Advocate1 and Advocate2 and applied imputation methodology to the 16-week induction period. Subsequent data from patients who received topical or systemic rescue medication or discontinued treatment due to lack of efficacy were imputed as nonresponders. Subsequent data from patients who discontinued treatment for other reasons were set to missing, and the researchers handled missing data with multiple imputation. They used logistic regression to test the interaction between the treatment and subgroup and the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel method to evaluate the treatment effect within each subgroup after adjusting for stratification factors.
Dr. Chovatiya reported findings from the 851 study participants in the combined studies. Of these, 542 were White, 192 were Asian, 84 were Black, and 33 were from other racial subgroups. By ethnic subgroup, 748 were not Hispanic or Latino, 91 were Hispanic or Latino, and ethnicity was unknown or not reported for 12 subjects. At baseline, the mean body mass index was slightly higher among Blacks (30.4 kg/m2) and Hispanics (29.4 kg/m2) compared with other racial and ethnic groups, “which reflects general epidemiologic data among these groups in the United States,” Dr. Chovatiya said. “You can also see a difference in the balance of IGA scores — they were a little bit more severe in the Black or African American and Hispanic groups as well.” The researchers also observed differences in the baseline EASI score across some of these groups, particularly in the Asian individuals, who had higher EASI scores. Prior use of systemic therapy was lower in the Black and “other” subgroups, compared with other racial subgroups.
At week 16, key efficacy endpoints were generally similar between the different racial subgroups. Specifically, 25.1% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an IGA of 0/1, compared with 4.1% of those in the placebo group (P < .001), while 33.2% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an IGA of 0/1, compared with 13.2% of those in the placebo group (no P value was established because this subgroup represented less than 10% of the entire study population). In addition, 43.3% of Whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an IGA of 0/1, compared with 14.1% of those in the placebo group (P < .001).
In other findings, 45.5% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI75, compared with 8.5% of those in the placebo group (P < .001), while 51.7% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI75, compared with 18.8% of those in the placebo group. Among whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group, 59.7% of achieved an EASI75, compared with 20.4% of those in the placebo group (P < .001).
Dr. Chovatiya said that 26.5% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI90, compared with 4.3% of those in the placebo group (P < .001), while 26.9% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI90, compared with 13.2% of those in the placebo group. In addition, 38.3% of Whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved an EASI90, compared with 10.9% of those in the placebo group (P < .001).
Finally, 36.4% of Asians in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement on the NRS, compared with 5.7% of those in the placebo group (P <. 001), while 41.7% of Blacks in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement on the NRS, compared with 17.4% of those in the placebo group. In addition, 45.9% of Whites in the lebrikizumab treatment group achieved a 4-point or greater improvement on the NRS, compared with 14.8% of those in the placebo group (P < .001). Statistical analyses of efficacy endpoints conducted by ethnic group yielded similar results.
Dr. Chovatiya acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that differences in baseline demographics and disease characteristics limit direct comparison across racial and ethnic subgroups. “Due to the relatively small sample size of some racial and ethnic subgroups and the post hoc nature of this analysis, additional studies are needed to verify these results,” he concluded. But for now, he said, the data available indicate that “lebrikizumab is effective across racial and ethnic subgroups for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD after 16 weeks of monotherapy treatment.”
The study was funded by Dermira, a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly and Company. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is speaker for and/or a consult and advisory board member to many pharmaceutical companies, including Eli Lilly.
FROM RAD 2023
Neighborhood Disadvantage Tied to Higher Risk for ASD
TOPLINE
, a population-based prospective cohort study shows.
METHODOLOGY
- Investigators analyzed data from a large cohort of singleton children with insurance born in Kaiser Permanente Southern California hospitals between 2001 and 2014.
- They ascertained ASD diagnosis, maternal race and ethnicity, and maternal address at time of birth.
- Neighborhood disadvantage was determined by the percentage of families in the mother’s neighborhood considered to be living in poverty, unemployed, have female-headed households with children, using public assistance, less than a high school education, among other variables.
TAKEAWAY
- Among 318,300 mothers who delivered babies during the study period, 6350 children were diagnosed with ASD during follow-up, and median age at diagnosis was 3.5 years.
- Greater neighborhood disadvantage at birth was associated with a higher likelihood of ASD diagnosis (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.07; 95% CI, 1.02-1.11)
- ASD diagnoses were more likely among children of mothers who were Black (aHR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.02-1.25), Asian/Pacific Islander (aHR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.02-1.20), or Hispanic (aHR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.00-1.15), even after the researchers controlled for neighborhood.
- While odds of an ASD diagnosis were higher among children from minority racial and ethnic groups, neighborhood disadvantage was significantly associated with ASD diagnosis only for children of White mothers (aHR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.09-1.26).
IN PRACTICE
Investigators noted that they could only speculate about the factors driving the association between neighborhood disadvantage and a stronger risk for ASD diagnosis in children of White mothers. “They may be due to systemic racism, discrimination, and their impact on maternal health during pregnancy,” they wrote.
SOURCE
Xin Yu, MS, and Daniel Hackman, PhD, of the University of Southern California Los Angeles, led the study, which was published online November 15 in JAMA Psychiatry.
LIMITATIONS
The research was limited by a lack of information on fathers and variables such as incomes, which may have confounded the findings. The authors also acknowledged that the study should be replicated in other health service settings.
DISCLOSURES
The study was funded by the National Institutes on Environmental Health Sciences, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and the Environmental Protection Agency. Dr. Hackman reported receiving grant funding from NIH during the conduct of the study. Other disclosures are available in the original study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
, a population-based prospective cohort study shows.
METHODOLOGY
- Investigators analyzed data from a large cohort of singleton children with insurance born in Kaiser Permanente Southern California hospitals between 2001 and 2014.
- They ascertained ASD diagnosis, maternal race and ethnicity, and maternal address at time of birth.
- Neighborhood disadvantage was determined by the percentage of families in the mother’s neighborhood considered to be living in poverty, unemployed, have female-headed households with children, using public assistance, less than a high school education, among other variables.
TAKEAWAY
- Among 318,300 mothers who delivered babies during the study period, 6350 children were diagnosed with ASD during follow-up, and median age at diagnosis was 3.5 years.
- Greater neighborhood disadvantage at birth was associated with a higher likelihood of ASD diagnosis (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.07; 95% CI, 1.02-1.11)
- ASD diagnoses were more likely among children of mothers who were Black (aHR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.02-1.25), Asian/Pacific Islander (aHR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.02-1.20), or Hispanic (aHR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.00-1.15), even after the researchers controlled for neighborhood.
- While odds of an ASD diagnosis were higher among children from minority racial and ethnic groups, neighborhood disadvantage was significantly associated with ASD diagnosis only for children of White mothers (aHR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.09-1.26).
IN PRACTICE
Investigators noted that they could only speculate about the factors driving the association between neighborhood disadvantage and a stronger risk for ASD diagnosis in children of White mothers. “They may be due to systemic racism, discrimination, and their impact on maternal health during pregnancy,” they wrote.
SOURCE
Xin Yu, MS, and Daniel Hackman, PhD, of the University of Southern California Los Angeles, led the study, which was published online November 15 in JAMA Psychiatry.
LIMITATIONS
The research was limited by a lack of information on fathers and variables such as incomes, which may have confounded the findings. The authors also acknowledged that the study should be replicated in other health service settings.
DISCLOSURES
The study was funded by the National Institutes on Environmental Health Sciences, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and the Environmental Protection Agency. Dr. Hackman reported receiving grant funding from NIH during the conduct of the study. Other disclosures are available in the original study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
, a population-based prospective cohort study shows.
METHODOLOGY
- Investigators analyzed data from a large cohort of singleton children with insurance born in Kaiser Permanente Southern California hospitals between 2001 and 2014.
- They ascertained ASD diagnosis, maternal race and ethnicity, and maternal address at time of birth.
- Neighborhood disadvantage was determined by the percentage of families in the mother’s neighborhood considered to be living in poverty, unemployed, have female-headed households with children, using public assistance, less than a high school education, among other variables.
TAKEAWAY
- Among 318,300 mothers who delivered babies during the study period, 6350 children were diagnosed with ASD during follow-up, and median age at diagnosis was 3.5 years.
- Greater neighborhood disadvantage at birth was associated with a higher likelihood of ASD diagnosis (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.07; 95% CI, 1.02-1.11)
- ASD diagnoses were more likely among children of mothers who were Black (aHR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.02-1.25), Asian/Pacific Islander (aHR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.02-1.20), or Hispanic (aHR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.00-1.15), even after the researchers controlled for neighborhood.
- While odds of an ASD diagnosis were higher among children from minority racial and ethnic groups, neighborhood disadvantage was significantly associated with ASD diagnosis only for children of White mothers (aHR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.09-1.26).
IN PRACTICE
Investigators noted that they could only speculate about the factors driving the association between neighborhood disadvantage and a stronger risk for ASD diagnosis in children of White mothers. “They may be due to systemic racism, discrimination, and their impact on maternal health during pregnancy,” they wrote.
SOURCE
Xin Yu, MS, and Daniel Hackman, PhD, of the University of Southern California Los Angeles, led the study, which was published online November 15 in JAMA Psychiatry.
LIMITATIONS
The research was limited by a lack of information on fathers and variables such as incomes, which may have confounded the findings. The authors also acknowledged that the study should be replicated in other health service settings.
DISCLOSURES
The study was funded by the National Institutes on Environmental Health Sciences, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and the Environmental Protection Agency. Dr. Hackman reported receiving grant funding from NIH during the conduct of the study. Other disclosures are available in the original study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. Task Force Takes on Rising BMIs Among Children
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force — a team of independent, volunteer experts in disease prevention who guide doctors’ decisions and influence insurance coverage — issued a draft recommendation statement outlining the interventions that should be taken when a child or teen has a high body mass index.
Nearly 20% of children between 2 and 19 years old have what are considered high BMIs, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data. While adults who have a BMI of 30 or higher are considered to have obesity, childhood obesity is determined if a child is at or above the 95th percentile of others their age and gender.
Given the prevalence of the issue, the task force recommends behavioral interventions that include at least 26 hours of supervised physical activity sessions for up to a year. This differs from the task force’s previous recommendations on the topic, which emphasized the importance of screening for high BMIs rather than describing the right ways to intervene.
Some of the most effective interventions are targeted at both parents and their children, whether that be together, separately, or a combination of the two. Additionally, the task force recommends that children attend group sessions about healthy eating habits, how to read food labels, and exercise techniques. Ideally, these would be led and guided by people of various professional backgrounds like pediatricians, physical therapists, dietitians, psychologists, and social workers. Other medical organizations, namely the American Academy of Pediatrics, have recommended medication for some children with obesity; the task force, however, takes a more conservative approach. They noted that although the body of evidence shows weight loss medications and surgery are effective for many, there isn’t enough research to lean on regarding the use of these interventions in children, especially in the long term.
“There are proven ways that clinicians can help the many children and teens who have a high BMI to manage their weight and stay healthy,” said Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, a member of the task force and professor of family medicine at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “Intensive behavioral interventions are effective in helping children achieve a healthy weight while improving quality of life.”
The guidelines are still in the draft stage and are available for public comment until Jan. 16, 2024.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force — a team of independent, volunteer experts in disease prevention who guide doctors’ decisions and influence insurance coverage — issued a draft recommendation statement outlining the interventions that should be taken when a child or teen has a high body mass index.
Nearly 20% of children between 2 and 19 years old have what are considered high BMIs, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data. While adults who have a BMI of 30 or higher are considered to have obesity, childhood obesity is determined if a child is at or above the 95th percentile of others their age and gender.
Given the prevalence of the issue, the task force recommends behavioral interventions that include at least 26 hours of supervised physical activity sessions for up to a year. This differs from the task force’s previous recommendations on the topic, which emphasized the importance of screening for high BMIs rather than describing the right ways to intervene.
Some of the most effective interventions are targeted at both parents and their children, whether that be together, separately, or a combination of the two. Additionally, the task force recommends that children attend group sessions about healthy eating habits, how to read food labels, and exercise techniques. Ideally, these would be led and guided by people of various professional backgrounds like pediatricians, physical therapists, dietitians, psychologists, and social workers. Other medical organizations, namely the American Academy of Pediatrics, have recommended medication for some children with obesity; the task force, however, takes a more conservative approach. They noted that although the body of evidence shows weight loss medications and surgery are effective for many, there isn’t enough research to lean on regarding the use of these interventions in children, especially in the long term.
“There are proven ways that clinicians can help the many children and teens who have a high BMI to manage their weight and stay healthy,” said Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, a member of the task force and professor of family medicine at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “Intensive behavioral interventions are effective in helping children achieve a healthy weight while improving quality of life.”
The guidelines are still in the draft stage and are available for public comment until Jan. 16, 2024.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force — a team of independent, volunteer experts in disease prevention who guide doctors’ decisions and influence insurance coverage — issued a draft recommendation statement outlining the interventions that should be taken when a child or teen has a high body mass index.
Nearly 20% of children between 2 and 19 years old have what are considered high BMIs, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data. While adults who have a BMI of 30 or higher are considered to have obesity, childhood obesity is determined if a child is at or above the 95th percentile of others their age and gender.
Given the prevalence of the issue, the task force recommends behavioral interventions that include at least 26 hours of supervised physical activity sessions for up to a year. This differs from the task force’s previous recommendations on the topic, which emphasized the importance of screening for high BMIs rather than describing the right ways to intervene.
Some of the most effective interventions are targeted at both parents and their children, whether that be together, separately, or a combination of the two. Additionally, the task force recommends that children attend group sessions about healthy eating habits, how to read food labels, and exercise techniques. Ideally, these would be led and guided by people of various professional backgrounds like pediatricians, physical therapists, dietitians, psychologists, and social workers. Other medical organizations, namely the American Academy of Pediatrics, have recommended medication for some children with obesity; the task force, however, takes a more conservative approach. They noted that although the body of evidence shows weight loss medications and surgery are effective for many, there isn’t enough research to lean on regarding the use of these interventions in children, especially in the long term.
“There are proven ways that clinicians can help the many children and teens who have a high BMI to manage their weight and stay healthy,” said Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, a member of the task force and professor of family medicine at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “Intensive behavioral interventions are effective in helping children achieve a healthy weight while improving quality of life.”
The guidelines are still in the draft stage and are available for public comment until Jan. 16, 2024.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Teen and young adult rheumatology patients report gaps in sexual health counseling
SAN DIEGO — Only half of teens and young adults on teratogenic medication report being asked about sexual activity by their rheumatologist, and 38% did not know that their medication would be harmful to a fetus, according to a new survey.
While pediatric rheumatology providers may think that health screenings and contraceptive counseling are happening elsewhere, “this study suggests that a lot of patients are being missed, including those on teratogens,” noted Brittany M. Huynh, MD, MPH, a pediatric rheumatology fellow at the Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis. She led the study and presented the findings at the American College of Rheumatology annual meeting.
For the study, Dr. Huynh and colleagues recruited patients aged 14-23 years who were assigned female at birth and were followed at pediatric rheumatology clinics affiliated with Indiana University. Participants completed a one-time survey between October 2020 and July 2022 and were asked about their sexual reproductive health experience and knowledge. Notably, all but four surveys were completed prior to the US Supreme Court Dobbs decision overturning Roe v. Wade.
Of responses from 108 participants, the most common diagnoses were juvenile idiopathic arthritis (52%) and systemic lupus erythematosus (16%). About one third (36%) of patients were on teratogenic medication, with the most common being methotrexate. About three fourths (76%) were White, and the average age of respondents was 16.7.
Most participants (82%) said they had been asked about sexual activity by a health care provider, but only 38% said their pediatric rheumatologist discussed this topic with them. Of the 39 patients on teratogenic medication, 54% said they had been asked about sexual activity by their pediatric rheumatologist, and only 51% said they had received teratogenicity counseling.
A larger percentage (85%) of this group reported receiving sexual activity screenings by any provider, but there was little difference in counseling about teratogenic medication.
This suggests that this type of risk counseling “is almost exclusively done by (pediatric rheumatologists), if at all,” Dr. Huynh noted during her presentation.
In total, 56% of all patients said a provider had talked to them about how to prevent pregnancy, and 20% said they had been counseled about how to get and use emergency contraception. Only 6% of patients said their pediatric rheumatologist had discussed emergency contraception during appointments.
Although sexual activity screenings were associated with current teratogen use, pregnancy prevention counseling and emergency contraceptive counseling were not associated with teratogen use or reported sexual activity.
The survey also revealed that there were gaps in knowledge about the health effects of rheumatic medication. Of the patients on teratogens, 38% did not know that their medication could harm a fetus if they became pregnant. Only 9% of patients not on teratogens correctly answered that their medication would not harm a fetus.
Previous studies have also shown that rheumatology patients do not know that their medications can be teratogenic, noted Cuoghi Edens, MD, a rheumatologist at the University of Chicago, who sees both adult and pediatric patients. She was not involved with the study. The larger challenge is how to best educate patients, she said.
While hopefully a patient’s primary care provider is discussing these issues with them, these patients often see their rheumatologist more frequently and more consistently than other providers, Dr. Edens said.
“We are sometimes the continuity of care for the patient versus their primary care, even though it should be a group effort of trying to some of these questions,” she said.
Conducting reproductive health screenings in pediatric rheumatology clinics can be difficult though, Dr. Edens noted, not only because of time constraints but also because parents often attend appointments with their child and likely have been for years. These screenings are most accurate when done one-on-one, so pivoting and removing the parents from the room can be awkward for providers, Dr. Edens said.
She advised that starting these conversations early on can be one way to ease into talking about reproductive health. In her own practice, Dr. Huynh sets aside time during appointments to speak with adolescent patients privately.
“We always discuss teratogenic medication. I always talk to them about the fact that I’m going to be doing pregnancy testing with their other screening labs because of the risks associated,” she said. “I also specifically set time aside for patients on teratogens to talk about emergency contraception and offer a prescription, if they’re interested.”
Dr. Huynh emphasized that providing easy access to emergency contraception is key. The ACR reproductive health guidelines — although geared toward adults — recommend discussing emergency contraception with patients, and Dr. Huynh advocates writing prescriptions for interested patients.
“They can fill it and have it easily accessible, so that there are no additional barriers, particularly for people who have these higher risks,” she said.
While emergency contraceptives are also available over the counter, it can be awkward for young people to ask for them, she said, and they can be expensive if not covered under insurance. Providing a prescription is one way to avoid those issues, Dr. Huynh said.
“Certainly, you have to have some parent buy-in, because if there is going to be a script, it’s probably going to be under insurance,” she said. “But in my experience, parents are happy to have it around as long as you’re talking it through with them as well as the young person.”
Dr. Huynh and Dr. Edens had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — Only half of teens and young adults on teratogenic medication report being asked about sexual activity by their rheumatologist, and 38% did not know that their medication would be harmful to a fetus, according to a new survey.
While pediatric rheumatology providers may think that health screenings and contraceptive counseling are happening elsewhere, “this study suggests that a lot of patients are being missed, including those on teratogens,” noted Brittany M. Huynh, MD, MPH, a pediatric rheumatology fellow at the Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis. She led the study and presented the findings at the American College of Rheumatology annual meeting.
For the study, Dr. Huynh and colleagues recruited patients aged 14-23 years who were assigned female at birth and were followed at pediatric rheumatology clinics affiliated with Indiana University. Participants completed a one-time survey between October 2020 and July 2022 and were asked about their sexual reproductive health experience and knowledge. Notably, all but four surveys were completed prior to the US Supreme Court Dobbs decision overturning Roe v. Wade.
Of responses from 108 participants, the most common diagnoses were juvenile idiopathic arthritis (52%) and systemic lupus erythematosus (16%). About one third (36%) of patients were on teratogenic medication, with the most common being methotrexate. About three fourths (76%) were White, and the average age of respondents was 16.7.
Most participants (82%) said they had been asked about sexual activity by a health care provider, but only 38% said their pediatric rheumatologist discussed this topic with them. Of the 39 patients on teratogenic medication, 54% said they had been asked about sexual activity by their pediatric rheumatologist, and only 51% said they had received teratogenicity counseling.
A larger percentage (85%) of this group reported receiving sexual activity screenings by any provider, but there was little difference in counseling about teratogenic medication.
This suggests that this type of risk counseling “is almost exclusively done by (pediatric rheumatologists), if at all,” Dr. Huynh noted during her presentation.
In total, 56% of all patients said a provider had talked to them about how to prevent pregnancy, and 20% said they had been counseled about how to get and use emergency contraception. Only 6% of patients said their pediatric rheumatologist had discussed emergency contraception during appointments.
Although sexual activity screenings were associated with current teratogen use, pregnancy prevention counseling and emergency contraceptive counseling were not associated with teratogen use or reported sexual activity.
The survey also revealed that there were gaps in knowledge about the health effects of rheumatic medication. Of the patients on teratogens, 38% did not know that their medication could harm a fetus if they became pregnant. Only 9% of patients not on teratogens correctly answered that their medication would not harm a fetus.
Previous studies have also shown that rheumatology patients do not know that their medications can be teratogenic, noted Cuoghi Edens, MD, a rheumatologist at the University of Chicago, who sees both adult and pediatric patients. She was not involved with the study. The larger challenge is how to best educate patients, she said.
While hopefully a patient’s primary care provider is discussing these issues with them, these patients often see their rheumatologist more frequently and more consistently than other providers, Dr. Edens said.
“We are sometimes the continuity of care for the patient versus their primary care, even though it should be a group effort of trying to some of these questions,” she said.
Conducting reproductive health screenings in pediatric rheumatology clinics can be difficult though, Dr. Edens noted, not only because of time constraints but also because parents often attend appointments with their child and likely have been for years. These screenings are most accurate when done one-on-one, so pivoting and removing the parents from the room can be awkward for providers, Dr. Edens said.
She advised that starting these conversations early on can be one way to ease into talking about reproductive health. In her own practice, Dr. Huynh sets aside time during appointments to speak with adolescent patients privately.
“We always discuss teratogenic medication. I always talk to them about the fact that I’m going to be doing pregnancy testing with their other screening labs because of the risks associated,” she said. “I also specifically set time aside for patients on teratogens to talk about emergency contraception and offer a prescription, if they’re interested.”
Dr. Huynh emphasized that providing easy access to emergency contraception is key. The ACR reproductive health guidelines — although geared toward adults — recommend discussing emergency contraception with patients, and Dr. Huynh advocates writing prescriptions for interested patients.
“They can fill it and have it easily accessible, so that there are no additional barriers, particularly for people who have these higher risks,” she said.
While emergency contraceptives are also available over the counter, it can be awkward for young people to ask for them, she said, and they can be expensive if not covered under insurance. Providing a prescription is one way to avoid those issues, Dr. Huynh said.
“Certainly, you have to have some parent buy-in, because if there is going to be a script, it’s probably going to be under insurance,” she said. “But in my experience, parents are happy to have it around as long as you’re talking it through with them as well as the young person.”
Dr. Huynh and Dr. Edens had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — Only half of teens and young adults on teratogenic medication report being asked about sexual activity by their rheumatologist, and 38% did not know that their medication would be harmful to a fetus, according to a new survey.
While pediatric rheumatology providers may think that health screenings and contraceptive counseling are happening elsewhere, “this study suggests that a lot of patients are being missed, including those on teratogens,” noted Brittany M. Huynh, MD, MPH, a pediatric rheumatology fellow at the Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis. She led the study and presented the findings at the American College of Rheumatology annual meeting.
For the study, Dr. Huynh and colleagues recruited patients aged 14-23 years who were assigned female at birth and were followed at pediatric rheumatology clinics affiliated with Indiana University. Participants completed a one-time survey between October 2020 and July 2022 and were asked about their sexual reproductive health experience and knowledge. Notably, all but four surveys were completed prior to the US Supreme Court Dobbs decision overturning Roe v. Wade.
Of responses from 108 participants, the most common diagnoses were juvenile idiopathic arthritis (52%) and systemic lupus erythematosus (16%). About one third (36%) of patients were on teratogenic medication, with the most common being methotrexate. About three fourths (76%) were White, and the average age of respondents was 16.7.
Most participants (82%) said they had been asked about sexual activity by a health care provider, but only 38% said their pediatric rheumatologist discussed this topic with them. Of the 39 patients on teratogenic medication, 54% said they had been asked about sexual activity by their pediatric rheumatologist, and only 51% said they had received teratogenicity counseling.
A larger percentage (85%) of this group reported receiving sexual activity screenings by any provider, but there was little difference in counseling about teratogenic medication.
This suggests that this type of risk counseling “is almost exclusively done by (pediatric rheumatologists), if at all,” Dr. Huynh noted during her presentation.
In total, 56% of all patients said a provider had talked to them about how to prevent pregnancy, and 20% said they had been counseled about how to get and use emergency contraception. Only 6% of patients said their pediatric rheumatologist had discussed emergency contraception during appointments.
Although sexual activity screenings were associated with current teratogen use, pregnancy prevention counseling and emergency contraceptive counseling were not associated with teratogen use or reported sexual activity.
The survey also revealed that there were gaps in knowledge about the health effects of rheumatic medication. Of the patients on teratogens, 38% did not know that their medication could harm a fetus if they became pregnant. Only 9% of patients not on teratogens correctly answered that their medication would not harm a fetus.
Previous studies have also shown that rheumatology patients do not know that their medications can be teratogenic, noted Cuoghi Edens, MD, a rheumatologist at the University of Chicago, who sees both adult and pediatric patients. She was not involved with the study. The larger challenge is how to best educate patients, she said.
While hopefully a patient’s primary care provider is discussing these issues with them, these patients often see their rheumatologist more frequently and more consistently than other providers, Dr. Edens said.
“We are sometimes the continuity of care for the patient versus their primary care, even though it should be a group effort of trying to some of these questions,” she said.
Conducting reproductive health screenings in pediatric rheumatology clinics can be difficult though, Dr. Edens noted, not only because of time constraints but also because parents often attend appointments with their child and likely have been for years. These screenings are most accurate when done one-on-one, so pivoting and removing the parents from the room can be awkward for providers, Dr. Edens said.
She advised that starting these conversations early on can be one way to ease into talking about reproductive health. In her own practice, Dr. Huynh sets aside time during appointments to speak with adolescent patients privately.
“We always discuss teratogenic medication. I always talk to them about the fact that I’m going to be doing pregnancy testing with their other screening labs because of the risks associated,” she said. “I also specifically set time aside for patients on teratogens to talk about emergency contraception and offer a prescription, if they’re interested.”
Dr. Huynh emphasized that providing easy access to emergency contraception is key. The ACR reproductive health guidelines — although geared toward adults — recommend discussing emergency contraception with patients, and Dr. Huynh advocates writing prescriptions for interested patients.
“They can fill it and have it easily accessible, so that there are no additional barriers, particularly for people who have these higher risks,” she said.
While emergency contraceptives are also available over the counter, it can be awkward for young people to ask for them, she said, and they can be expensive if not covered under insurance. Providing a prescription is one way to avoid those issues, Dr. Huynh said.
“Certainly, you have to have some parent buy-in, because if there is going to be a script, it’s probably going to be under insurance,” she said. “But in my experience, parents are happy to have it around as long as you’re talking it through with them as well as the young person.”
Dr. Huynh and Dr. Edens had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2023
Diffuse Capillary Malformation With Undergrowth of a Limb in a Boy
To the Editor:
Capillary malformations (CMs), the most common vascular malformations that can affect the skin,1 present clinically as macules and patches of various colors, shapes, and sizes. Congenital structural abnormalities are associated with conditions such as Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome (KTS), cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita (CMTC), and megalencephaly–capillary malformation syndrome.2 Diffuse CM with overgrowth (DCMO) of the soft tissue and bones is an established association of CMs; however, diffuse capillary malformation with undergrowth (DCMU) is a more recent term that describes the lesser-recognized counterpart to DCMO.3 Herein, we describe a case of CM with left-sided undergrowth.
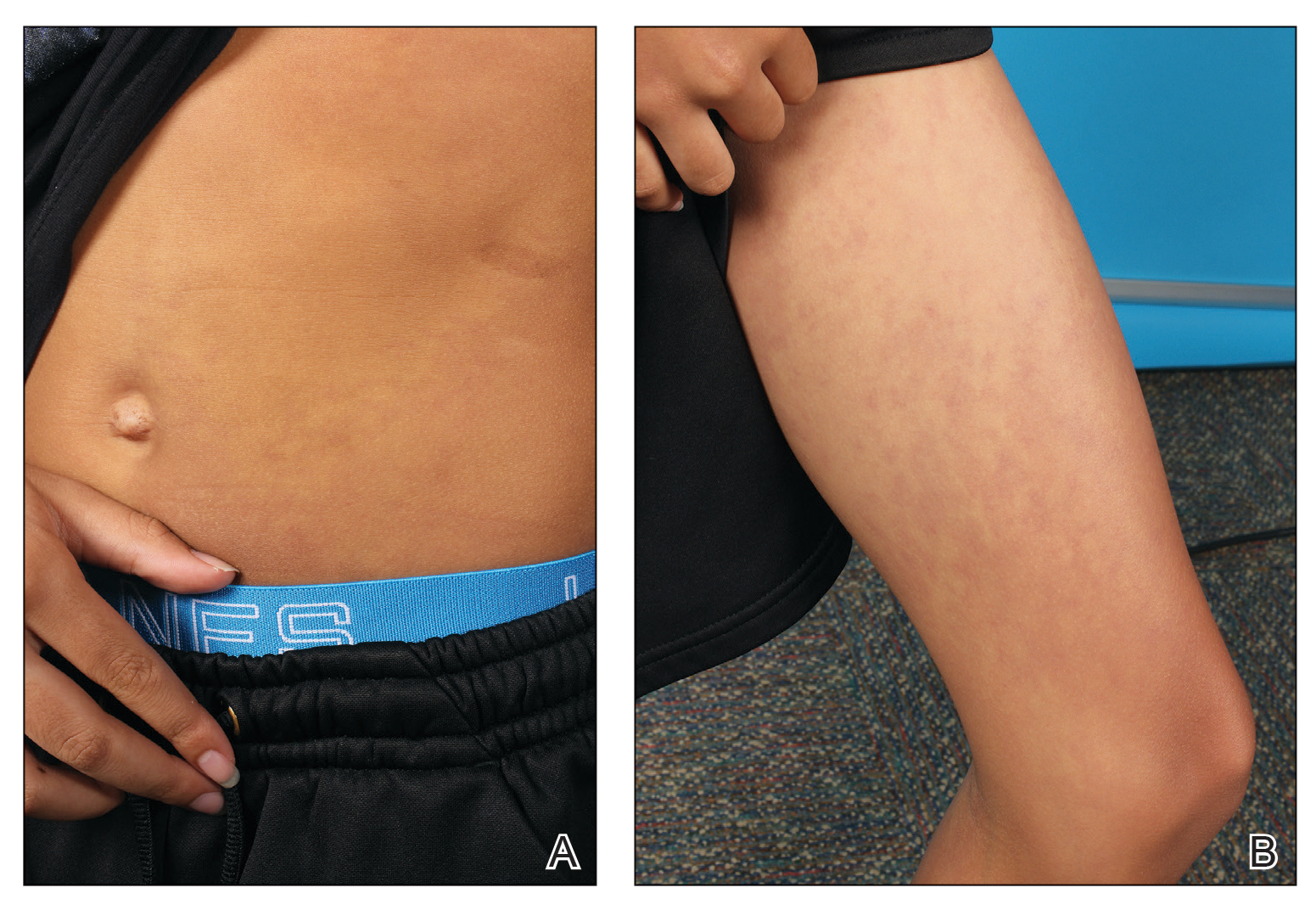
An 11-year-old boy presented to our clinic with asymptomatic vascular patterning on the left side of the body that had been present since birth. He previously was diagnosed with congenital right hemihypertrophy. He reported that the areas gradually lightened over time, and he denied any history of ulceration or venous or lymphatic malformations. Additionally, he explained how the left arm and leg have been noticeably smaller than the right extremities throughout his life. Physical examination revealed superficial, violaceous, reticulated patches along the left upper back tracking down the arm, abdomen (Figure 1A), and anterior thigh (Figure 1B) without crossing the midline. A few dilated veins were noted in the same region as the patches. There was no evidence of scarring or depression found in the skin. The right arms and legs were visibly larger compared to the left side (Figure 2A), and there also was macrodactyly of the third digit of the left hand (Figure 2B). Radiography confirmed the limb length discrepancy and showed the right and left legs to measure 73.2 cm and 71.3 cm, respectively. Given the patient’s multifocal reticulated CMs and ipsilateral undergrowth, a diagnosis of DCMU was rendered. The superficial vascular pattern is likely to fade over time, which will partially be hidden by his darker complexion. He also was advised to continue to see an orthopedist to monitor the limb length incongruity. Surgical intervention was not recommended.
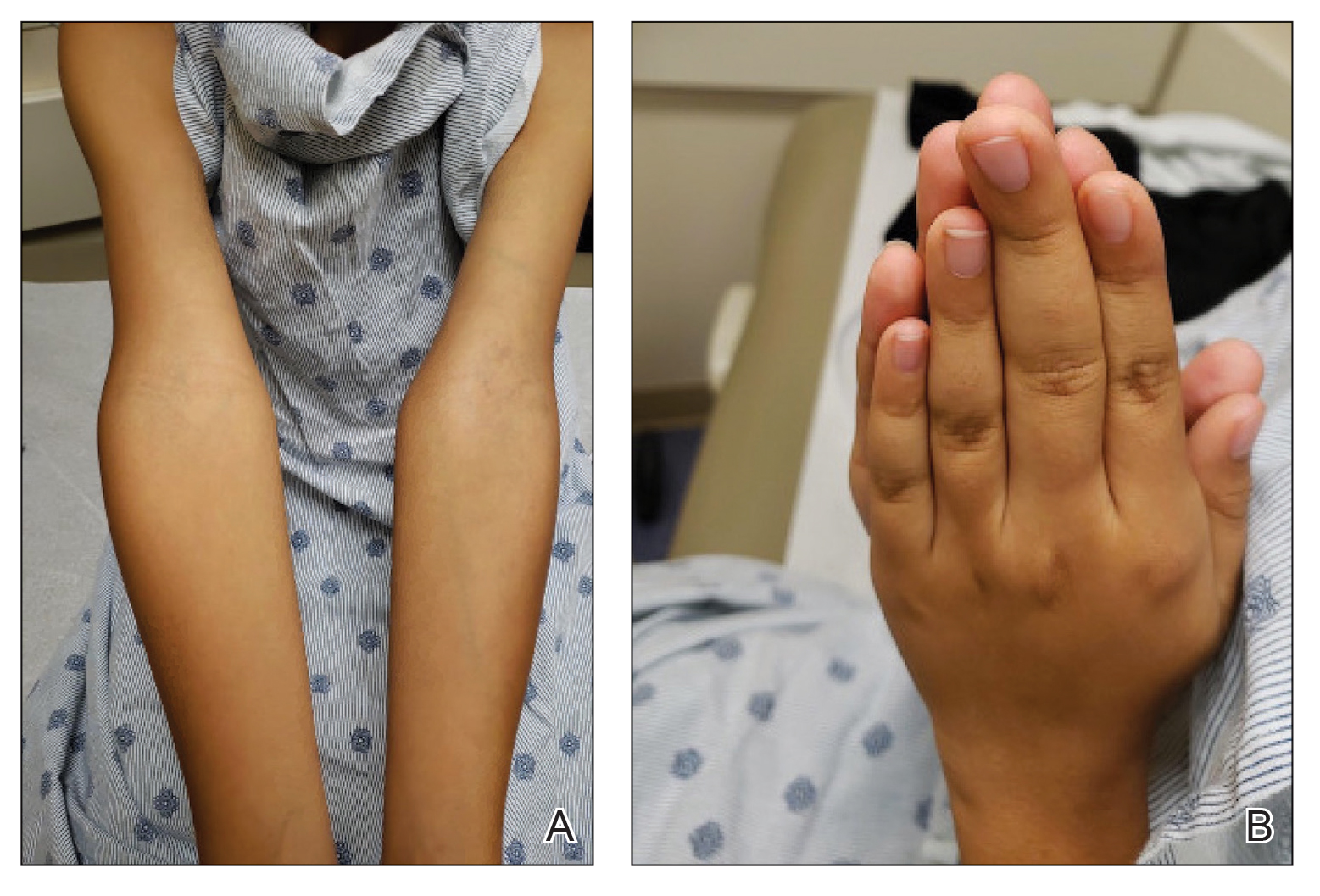
It ordinarily is thought that vascular anomalies of a limb may result in hypertrophy due to increased blood flow such as in KTS, but there are occasions where the affected limb(s) are inexplicably smaller.2,4 Cubiró et al3 observed that in 6 patients with unilateral CMs, all had ipsilateral limb undergrowth. They proposed the term diffuse capillary malformation with undergrowth as a distinct counterpart to DCMO. Diffuse capillary malformation with undergrowth is most similar to CMTC, as both can present with patchy or reticulated capillary staining with ipsilateral limb hypotrophy, but girth more often is affected than length; CMTC also may be associated with dermal atrophy and ulceration.2 The lesions of CMTC typically diminish within the first few years of life whereas those in DCMU tend to persist. Patients with KTS also can exhibit soft-tissue and bony undergrowth, which is termed inverse Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome3; however, the lack of the triad of capillary-lymphatic-venous malformation in our patient made this condition less likely. Additionally, it appears that our patient had left-sided undergrowth rather than the previously diagnosed right hemihypertrophy. The ipsilateral macrodactyly of the third digit of the left hand was an interesting observation and contrasted the undergrowth apparent in the rest of the left limb, which could be caused by increased blood flow specifically to the third digit resembling DCMO.4
Of note, genetic mutations have been implicated as a cause of vascular malformations and growth abnormalities. Specifically, mutations in the phosphoinositide-3-kinase–AKT pathway have been reported in these cases likely due its role in cell growth, proliferation, and angiogenesis.3,4 Future studies should investigate genetic associations in patients with DCMU to determine if there is a robust genotypic-phenotypic link.
Although CMs are a common occurrence in pediatric dermatology, CMs with concurrent limb undergrowth are rare. Our patient’s unique features included involvement of both an arm and leg as well as the presence of macrodactyly. We agree with the terminology for DCMU to describe multifocal reticulated vascular patterning with ipsilateral undergrowth.3
- Huang JT, Liang MG. Vascular malformations. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2010;57:1091-1110. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2010.08.003
- Lee MS, Liang MG, Mulliken JB. Diffuse capillary malformation with overgrowth: a clinical subtype of vascular anomalies with hypertrophy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:589-594. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.05.030
- Cubiró X, Rozas‐Muñoz E, Castel P, et al. Clinical and genetic evaluation of six children with diffuse capillary malformation and undergrowth. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:833-838. doi:10.1111/pde.14252
- Uihlein LC, Liang MG, Fishman SJ, et al. Capillary-venous malformation in the lower limb. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:541-548. doi:10.1111/pde.12186
To the Editor:
Capillary malformations (CMs), the most common vascular malformations that can affect the skin,1 present clinically as macules and patches of various colors, shapes, and sizes. Congenital structural abnormalities are associated with conditions such as Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome (KTS), cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita (CMTC), and megalencephaly–capillary malformation syndrome.2 Diffuse CM with overgrowth (DCMO) of the soft tissue and bones is an established association of CMs; however, diffuse capillary malformation with undergrowth (DCMU) is a more recent term that describes the lesser-recognized counterpart to DCMO.3 Herein, we describe a case of CM with left-sided undergrowth.

An 11-year-old boy presented to our clinic with asymptomatic vascular patterning on the left side of the body that had been present since birth. He previously was diagnosed with congenital right hemihypertrophy. He reported that the areas gradually lightened over time, and he denied any history of ulceration or venous or lymphatic malformations. Additionally, he explained how the left arm and leg have been noticeably smaller than the right extremities throughout his life. Physical examination revealed superficial, violaceous, reticulated patches along the left upper back tracking down the arm, abdomen (Figure 1A), and anterior thigh (Figure 1B) without crossing the midline. A few dilated veins were noted in the same region as the patches. There was no evidence of scarring or depression found in the skin. The right arms and legs were visibly larger compared to the left side (Figure 2A), and there also was macrodactyly of the third digit of the left hand (Figure 2B). Radiography confirmed the limb length discrepancy and showed the right and left legs to measure 73.2 cm and 71.3 cm, respectively. Given the patient’s multifocal reticulated CMs and ipsilateral undergrowth, a diagnosis of DCMU was rendered. The superficial vascular pattern is likely to fade over time, which will partially be hidden by his darker complexion. He also was advised to continue to see an orthopedist to monitor the limb length incongruity. Surgical intervention was not recommended.

It ordinarily is thought that vascular anomalies of a limb may result in hypertrophy due to increased blood flow such as in KTS, but there are occasions where the affected limb(s) are inexplicably smaller.2,4 Cubiró et al3 observed that in 6 patients with unilateral CMs, all had ipsilateral limb undergrowth. They proposed the term diffuse capillary malformation with undergrowth as a distinct counterpart to DCMO. Diffuse capillary malformation with undergrowth is most similar to CMTC, as both can present with patchy or reticulated capillary staining with ipsilateral limb hypotrophy, but girth more often is affected than length; CMTC also may be associated with dermal atrophy and ulceration.2 The lesions of CMTC typically diminish within the first few years of life whereas those in DCMU tend to persist. Patients with KTS also can exhibit soft-tissue and bony undergrowth, which is termed inverse Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome3; however, the lack of the triad of capillary-lymphatic-venous malformation in our patient made this condition less likely. Additionally, it appears that our patient had left-sided undergrowth rather than the previously diagnosed right hemihypertrophy. The ipsilateral macrodactyly of the third digit of the left hand was an interesting observation and contrasted the undergrowth apparent in the rest of the left limb, which could be caused by increased blood flow specifically to the third digit resembling DCMO.4
Of note, genetic mutations have been implicated as a cause of vascular malformations and growth abnormalities. Specifically, mutations in the phosphoinositide-3-kinase–AKT pathway have been reported in these cases likely due its role in cell growth, proliferation, and angiogenesis.3,4 Future studies should investigate genetic associations in patients with DCMU to determine if there is a robust genotypic-phenotypic link.
Although CMs are a common occurrence in pediatric dermatology, CMs with concurrent limb undergrowth are rare. Our patient’s unique features included involvement of both an arm and leg as well as the presence of macrodactyly. We agree with the terminology for DCMU to describe multifocal reticulated vascular patterning with ipsilateral undergrowth.3
To the Editor:
Capillary malformations (CMs), the most common vascular malformations that can affect the skin,1 present clinically as macules and patches of various colors, shapes, and sizes. Congenital structural abnormalities are associated with conditions such as Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome (KTS), cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita (CMTC), and megalencephaly–capillary malformation syndrome.2 Diffuse CM with overgrowth (DCMO) of the soft tissue and bones is an established association of CMs; however, diffuse capillary malformation with undergrowth (DCMU) is a more recent term that describes the lesser-recognized counterpart to DCMO.3 Herein, we describe a case of CM with left-sided undergrowth.

An 11-year-old boy presented to our clinic with asymptomatic vascular patterning on the left side of the body that had been present since birth. He previously was diagnosed with congenital right hemihypertrophy. He reported that the areas gradually lightened over time, and he denied any history of ulceration or venous or lymphatic malformations. Additionally, he explained how the left arm and leg have been noticeably smaller than the right extremities throughout his life. Physical examination revealed superficial, violaceous, reticulated patches along the left upper back tracking down the arm, abdomen (Figure 1A), and anterior thigh (Figure 1B) without crossing the midline. A few dilated veins were noted in the same region as the patches. There was no evidence of scarring or depression found in the skin. The right arms and legs were visibly larger compared to the left side (Figure 2A), and there also was macrodactyly of the third digit of the left hand (Figure 2B). Radiography confirmed the limb length discrepancy and showed the right and left legs to measure 73.2 cm and 71.3 cm, respectively. Given the patient’s multifocal reticulated CMs and ipsilateral undergrowth, a diagnosis of DCMU was rendered. The superficial vascular pattern is likely to fade over time, which will partially be hidden by his darker complexion. He also was advised to continue to see an orthopedist to monitor the limb length incongruity. Surgical intervention was not recommended.

It ordinarily is thought that vascular anomalies of a limb may result in hypertrophy due to increased blood flow such as in KTS, but there are occasions where the affected limb(s) are inexplicably smaller.2,4 Cubiró et al3 observed that in 6 patients with unilateral CMs, all had ipsilateral limb undergrowth. They proposed the term diffuse capillary malformation with undergrowth as a distinct counterpart to DCMO. Diffuse capillary malformation with undergrowth is most similar to CMTC, as both can present with patchy or reticulated capillary staining with ipsilateral limb hypotrophy, but girth more often is affected than length; CMTC also may be associated with dermal atrophy and ulceration.2 The lesions of CMTC typically diminish within the first few years of life whereas those in DCMU tend to persist. Patients with KTS also can exhibit soft-tissue and bony undergrowth, which is termed inverse Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome3; however, the lack of the triad of capillary-lymphatic-venous malformation in our patient made this condition less likely. Additionally, it appears that our patient had left-sided undergrowth rather than the previously diagnosed right hemihypertrophy. The ipsilateral macrodactyly of the third digit of the left hand was an interesting observation and contrasted the undergrowth apparent in the rest of the left limb, which could be caused by increased blood flow specifically to the third digit resembling DCMO.4
Of note, genetic mutations have been implicated as a cause of vascular malformations and growth abnormalities. Specifically, mutations in the phosphoinositide-3-kinase–AKT pathway have been reported in these cases likely due its role in cell growth, proliferation, and angiogenesis.3,4 Future studies should investigate genetic associations in patients with DCMU to determine if there is a robust genotypic-phenotypic link.
Although CMs are a common occurrence in pediatric dermatology, CMs with concurrent limb undergrowth are rare. Our patient’s unique features included involvement of both an arm and leg as well as the presence of macrodactyly. We agree with the terminology for DCMU to describe multifocal reticulated vascular patterning with ipsilateral undergrowth.3
- Huang JT, Liang MG. Vascular malformations. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2010;57:1091-1110. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2010.08.003
- Lee MS, Liang MG, Mulliken JB. Diffuse capillary malformation with overgrowth: a clinical subtype of vascular anomalies with hypertrophy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:589-594. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.05.030
- Cubiró X, Rozas‐Muñoz E, Castel P, et al. Clinical and genetic evaluation of six children with diffuse capillary malformation and undergrowth. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:833-838. doi:10.1111/pde.14252
- Uihlein LC, Liang MG, Fishman SJ, et al. Capillary-venous malformation in the lower limb. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:541-548. doi:10.1111/pde.12186
- Huang JT, Liang MG. Vascular malformations. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2010;57:1091-1110. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2010.08.003
- Lee MS, Liang MG, Mulliken JB. Diffuse capillary malformation with overgrowth: a clinical subtype of vascular anomalies with hypertrophy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:589-594. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.05.030
- Cubiró X, Rozas‐Muñoz E, Castel P, et al. Clinical and genetic evaluation of six children with diffuse capillary malformation and undergrowth. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:833-838. doi:10.1111/pde.14252
- Uihlein LC, Liang MG, Fishman SJ, et al. Capillary-venous malformation in the lower limb. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:541-548. doi:10.1111/pde.12186
Practice Points
- The term diffuse capillary malformation with undergrowth (DCMU) describes a distinct counterpart to diffuse capillary malformation with overgrowth. It can be challenging to distinguish from other vascular malformations associated with congenital structural abnormalities.
- The vascular patterning of DCMU may fade over time, but patients should continue to be monitored for their structural incongruity.
Children who are overweight at risk for chronic kidney disease
TOPLINE
, with the association, though weaker, still significant among those who do not develop type 2 diabetes or hypertension, in a large cohort study.
METHODOLOGY
- The study included data on 593,660 adolescents aged 16-20, born after January 1, 1975, who had medical assessments as part of mandatory military service in Israel.
- The mean age at study entry was 17.2 and 54.5% were male.
- Early CKD was defined as stage 1 to 2 CKD with moderately or severely increased albuminuria, with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or higher.
- The study excluded those with kidney pathology, albuminuria, hypertension, dysglycemia, or missing blood pressure or BMI data.
- Participants were followed up until early CKD onset, death, the last day insured, or August 23, 2020.
TAKEAWAY
- With a mean follow-up of 13.4 years, 1963 adolescents (0.3%) overall developed early chronic kidney disease. Among males, an increased risk of developing CKD was observed with a high-normal BMI in adolescence (hazard ratio [HR], 1.8); with overweight BMI (HR, 4.0); with mild obesity (HR, 6.7); and severe obesity (HR, 9.4).
- Among females, the increased risk was also observed with high-normal BMI (HR 1.4); overweight (HR, 2.3); mild obesity (HR, 2.7); and severe obesity (HR, 4.3).
- In excluding those who developed diabetes or hypertension, the overall rate of early CKD in the cohort was 0.2%.
- For males without diabetes or hypertension, the adjusted HR for early CKD with high-normal weight was 1.2; for overweight, HR 1.6; for mild obesity, HR 2.2; and for severe obesity, HR 2.7.
- For females without diabetes or hypertension, the corresponding increased risk for early CKD was HR 1.2 for high-normal BMI; HR 1.8 for overweight; 1.5 for mild obesity and 2.3 for severe obesity.
IN PRACTICE
“These findings suggest that adolescent obesity is a major risk factor for early CKD in young adulthood; this underscores the importance of mitigating adolescent obesity rates and managing risk factors for kidney disease in adolescents with high BMI,” the authors report.
“The association was evident even in persons with high-normal BMI in adolescence, was more pronounced in men, and appeared before the age of 30 years,” they say.
“Given the increasing obesity rates among adolescents, our findings are a harbinger of the potentially preventable increasing burden of CKD and subsequent cardiovascular disease.”
SOURCE
The study was conducted by first author Avishai M. Tsur, MD, of the Israel Defense Forces, Medical Corps, Tel Hashomer, Ramat Gan, Israel and Department of Military Medicine, Hebrew University of Jerusalem Faculty of Medicine, Jerusalem, Israel, and colleagues. The study was published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
LIMITATIONS
The study lacked longitudinal data on clinical and lifestyle factors, including stress, diet and physical activity. While adolescents were screened using urine dipstick, a lack of serum creatinine measurements could have missed some adolescents with reduced eGFR at the study entry. The generalizability of the results is limited by the lack of people from West Africa and East Asia in the study population.
DISCLOSURES
Coauthor Josef Coresh, MD, reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
, with the association, though weaker, still significant among those who do not develop type 2 diabetes or hypertension, in a large cohort study.
METHODOLOGY
- The study included data on 593,660 adolescents aged 16-20, born after January 1, 1975, who had medical assessments as part of mandatory military service in Israel.
- The mean age at study entry was 17.2 and 54.5% were male.
- Early CKD was defined as stage 1 to 2 CKD with moderately or severely increased albuminuria, with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or higher.
- The study excluded those with kidney pathology, albuminuria, hypertension, dysglycemia, or missing blood pressure or BMI data.
- Participants were followed up until early CKD onset, death, the last day insured, or August 23, 2020.
TAKEAWAY
- With a mean follow-up of 13.4 years, 1963 adolescents (0.3%) overall developed early chronic kidney disease. Among males, an increased risk of developing CKD was observed with a high-normal BMI in adolescence (hazard ratio [HR], 1.8); with overweight BMI (HR, 4.0); with mild obesity (HR, 6.7); and severe obesity (HR, 9.4).
- Among females, the increased risk was also observed with high-normal BMI (HR 1.4); overweight (HR, 2.3); mild obesity (HR, 2.7); and severe obesity (HR, 4.3).
- In excluding those who developed diabetes or hypertension, the overall rate of early CKD in the cohort was 0.2%.
- For males without diabetes or hypertension, the adjusted HR for early CKD with high-normal weight was 1.2; for overweight, HR 1.6; for mild obesity, HR 2.2; and for severe obesity, HR 2.7.
- For females without diabetes or hypertension, the corresponding increased risk for early CKD was HR 1.2 for high-normal BMI; HR 1.8 for overweight; 1.5 for mild obesity and 2.3 for severe obesity.
IN PRACTICE
“These findings suggest that adolescent obesity is a major risk factor for early CKD in young adulthood; this underscores the importance of mitigating adolescent obesity rates and managing risk factors for kidney disease in adolescents with high BMI,” the authors report.
“The association was evident even in persons with high-normal BMI in adolescence, was more pronounced in men, and appeared before the age of 30 years,” they say.
“Given the increasing obesity rates among adolescents, our findings are a harbinger of the potentially preventable increasing burden of CKD and subsequent cardiovascular disease.”
SOURCE
The study was conducted by first author Avishai M. Tsur, MD, of the Israel Defense Forces, Medical Corps, Tel Hashomer, Ramat Gan, Israel and Department of Military Medicine, Hebrew University of Jerusalem Faculty of Medicine, Jerusalem, Israel, and colleagues. The study was published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
LIMITATIONS
The study lacked longitudinal data on clinical and lifestyle factors, including stress, diet and physical activity. While adolescents were screened using urine dipstick, a lack of serum creatinine measurements could have missed some adolescents with reduced eGFR at the study entry. The generalizability of the results is limited by the lack of people from West Africa and East Asia in the study population.
DISCLOSURES
Coauthor Josef Coresh, MD, reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
, with the association, though weaker, still significant among those who do not develop type 2 diabetes or hypertension, in a large cohort study.
METHODOLOGY
- The study included data on 593,660 adolescents aged 16-20, born after January 1, 1975, who had medical assessments as part of mandatory military service in Israel.
- The mean age at study entry was 17.2 and 54.5% were male.
- Early CKD was defined as stage 1 to 2 CKD with moderately or severely increased albuminuria, with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or higher.
- The study excluded those with kidney pathology, albuminuria, hypertension, dysglycemia, or missing blood pressure or BMI data.
- Participants were followed up until early CKD onset, death, the last day insured, or August 23, 2020.
TAKEAWAY
- With a mean follow-up of 13.4 years, 1963 adolescents (0.3%) overall developed early chronic kidney disease. Among males, an increased risk of developing CKD was observed with a high-normal BMI in adolescence (hazard ratio [HR], 1.8); with overweight BMI (HR, 4.0); with mild obesity (HR, 6.7); and severe obesity (HR, 9.4).
- Among females, the increased risk was also observed with high-normal BMI (HR 1.4); overweight (HR, 2.3); mild obesity (HR, 2.7); and severe obesity (HR, 4.3).
- In excluding those who developed diabetes or hypertension, the overall rate of early CKD in the cohort was 0.2%.
- For males without diabetes or hypertension, the adjusted HR for early CKD with high-normal weight was 1.2; for overweight, HR 1.6; for mild obesity, HR 2.2; and for severe obesity, HR 2.7.
- For females without diabetes or hypertension, the corresponding increased risk for early CKD was HR 1.2 for high-normal BMI; HR 1.8 for overweight; 1.5 for mild obesity and 2.3 for severe obesity.
IN PRACTICE
“These findings suggest that adolescent obesity is a major risk factor for early CKD in young adulthood; this underscores the importance of mitigating adolescent obesity rates and managing risk factors for kidney disease in adolescents with high BMI,” the authors report.
“The association was evident even in persons with high-normal BMI in adolescence, was more pronounced in men, and appeared before the age of 30 years,” they say.
“Given the increasing obesity rates among adolescents, our findings are a harbinger of the potentially preventable increasing burden of CKD and subsequent cardiovascular disease.”
SOURCE
The study was conducted by first author Avishai M. Tsur, MD, of the Israel Defense Forces, Medical Corps, Tel Hashomer, Ramat Gan, Israel and Department of Military Medicine, Hebrew University of Jerusalem Faculty of Medicine, Jerusalem, Israel, and colleagues. The study was published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
LIMITATIONS
The study lacked longitudinal data on clinical and lifestyle factors, including stress, diet and physical activity. While adolescents were screened using urine dipstick, a lack of serum creatinine measurements could have missed some adolescents with reduced eGFR at the study entry. The generalizability of the results is limited by the lack of people from West Africa and East Asia in the study population.
DISCLOSURES
Coauthor Josef Coresh, MD, reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.