User login
Long COVID doubles risk of some serious outcomes in children, teens
Researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that
Heart inflammation; a blood clot in the lung; or a blood clot in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis were the most common bad outcomes in a new study. Even though the risk was higher for these and some other serious events, the overall numbers were small.
“Many of these conditions were rare or uncommon among children in this analysis, but even a small increase in these conditions is notable,” a CDC new release stated.
The investigators said their findings stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccination in Americans under the age of 18.
The study was published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Less is known about long COVID in children
Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, PhD, and colleagues noted that most research on long COVID to date has been done in adults, so little information is available about the risks to Americans ages 17 and younger.
To learn more, they compared post–COVID-19 symptoms and conditions between 781,419 children and teenagers with confirmed COVID-19 to another 2,344,257 without COVID-19. They looked at medical claims and laboratory data for these children and teenagers from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2022, to see who got any of 15 specific outcomes linked to long COVID-19.
Long COVID was defined as a condition where symptoms that last for or begin at least 4 weeks after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Compared to children with no history of a COVID-19 diagnosis, the long COVID-19 group was 101% more likely to have an acute pulmonary embolism, 99% more likely to have myocarditis or cardiomyopathy, 87% more likely to have a venous thromboembolic event, 32% more likely to have acute and unspecified renal failure, and 23% more likely to have type 1 diabetes.
“This report points to the fact that the risks of COVID infection itself, both in terms of the acute effects, MIS-C [multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children], as well as the long-term effects, are real, are concerning, and are potentially very serious,” said Stuart Berger, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery.
“The message that we should take away from this is that we should be very keen on all the methods of prevention for COVID, especially the vaccine,” said Dr. Berger, chief of cardiology in the department of pediatrics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
A ‘wake-up call’
The study findings are “sobering” and are “a reminder of the seriousness of COVID infection,” says Gregory Poland, MD, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“When you look in particular at the more serious complications from COVID in this young age group, those are life-altering complications that will have consequences and ramifications throughout their lives,” he said.
“I would take this as a serious wake-up call to parents [at a time when] the immunization rates in younger children are so pitifully low,” Dr. Poland said.
Still early days
The study is suggestive but not definitive, said Peter Katona, MD, professor of medicine and infectious diseases expert at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health.
It’s still too early to draw conclusions about long COVID, including in children, because many questions remain, he said: Should long COVID be defined as symptoms at 1 month or 3 months after infection? How do you define brain fog?
Dr. Katona and colleagues are studying long COVID intervention among students at UCLA to answer some of these questions, including the incidence and effect of early intervention.
The study had “at least seven limitations,” the researchers noted. Among them was the use of medical claims data that noted long COVID outcomes but not how severe they were; some people in the no COVID group might have had the illness but not been diagnosed; and the researchers did not adjust for vaccination status.
Dr. Poland noted that the study was done during surges in COVID variants including Delta and Omicron. In other words, any long COVID effects linked to more recent variants such as BA.5 or BA.2.75 are unknown.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that
Heart inflammation; a blood clot in the lung; or a blood clot in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis were the most common bad outcomes in a new study. Even though the risk was higher for these and some other serious events, the overall numbers were small.
“Many of these conditions were rare or uncommon among children in this analysis, but even a small increase in these conditions is notable,” a CDC new release stated.
The investigators said their findings stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccination in Americans under the age of 18.
The study was published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Less is known about long COVID in children
Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, PhD, and colleagues noted that most research on long COVID to date has been done in adults, so little information is available about the risks to Americans ages 17 and younger.
To learn more, they compared post–COVID-19 symptoms and conditions between 781,419 children and teenagers with confirmed COVID-19 to another 2,344,257 without COVID-19. They looked at medical claims and laboratory data for these children and teenagers from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2022, to see who got any of 15 specific outcomes linked to long COVID-19.
Long COVID was defined as a condition where symptoms that last for or begin at least 4 weeks after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Compared to children with no history of a COVID-19 diagnosis, the long COVID-19 group was 101% more likely to have an acute pulmonary embolism, 99% more likely to have myocarditis or cardiomyopathy, 87% more likely to have a venous thromboembolic event, 32% more likely to have acute and unspecified renal failure, and 23% more likely to have type 1 diabetes.
“This report points to the fact that the risks of COVID infection itself, both in terms of the acute effects, MIS-C [multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children], as well as the long-term effects, are real, are concerning, and are potentially very serious,” said Stuart Berger, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery.
“The message that we should take away from this is that we should be very keen on all the methods of prevention for COVID, especially the vaccine,” said Dr. Berger, chief of cardiology in the department of pediatrics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
A ‘wake-up call’
The study findings are “sobering” and are “a reminder of the seriousness of COVID infection,” says Gregory Poland, MD, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“When you look in particular at the more serious complications from COVID in this young age group, those are life-altering complications that will have consequences and ramifications throughout their lives,” he said.
“I would take this as a serious wake-up call to parents [at a time when] the immunization rates in younger children are so pitifully low,” Dr. Poland said.
Still early days
The study is suggestive but not definitive, said Peter Katona, MD, professor of medicine and infectious diseases expert at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health.
It’s still too early to draw conclusions about long COVID, including in children, because many questions remain, he said: Should long COVID be defined as symptoms at 1 month or 3 months after infection? How do you define brain fog?
Dr. Katona and colleagues are studying long COVID intervention among students at UCLA to answer some of these questions, including the incidence and effect of early intervention.
The study had “at least seven limitations,” the researchers noted. Among them was the use of medical claims data that noted long COVID outcomes but not how severe they were; some people in the no COVID group might have had the illness but not been diagnosed; and the researchers did not adjust for vaccination status.
Dr. Poland noted that the study was done during surges in COVID variants including Delta and Omicron. In other words, any long COVID effects linked to more recent variants such as BA.5 or BA.2.75 are unknown.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that
Heart inflammation; a blood clot in the lung; or a blood clot in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis were the most common bad outcomes in a new study. Even though the risk was higher for these and some other serious events, the overall numbers were small.
“Many of these conditions were rare or uncommon among children in this analysis, but even a small increase in these conditions is notable,” a CDC new release stated.
The investigators said their findings stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccination in Americans under the age of 18.
The study was published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Less is known about long COVID in children
Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, PhD, and colleagues noted that most research on long COVID to date has been done in adults, so little information is available about the risks to Americans ages 17 and younger.
To learn more, they compared post–COVID-19 symptoms and conditions between 781,419 children and teenagers with confirmed COVID-19 to another 2,344,257 without COVID-19. They looked at medical claims and laboratory data for these children and teenagers from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2022, to see who got any of 15 specific outcomes linked to long COVID-19.
Long COVID was defined as a condition where symptoms that last for or begin at least 4 weeks after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Compared to children with no history of a COVID-19 diagnosis, the long COVID-19 group was 101% more likely to have an acute pulmonary embolism, 99% more likely to have myocarditis or cardiomyopathy, 87% more likely to have a venous thromboembolic event, 32% more likely to have acute and unspecified renal failure, and 23% more likely to have type 1 diabetes.
“This report points to the fact that the risks of COVID infection itself, both in terms of the acute effects, MIS-C [multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children], as well as the long-term effects, are real, are concerning, and are potentially very serious,” said Stuart Berger, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery.
“The message that we should take away from this is that we should be very keen on all the methods of prevention for COVID, especially the vaccine,” said Dr. Berger, chief of cardiology in the department of pediatrics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
A ‘wake-up call’
The study findings are “sobering” and are “a reminder of the seriousness of COVID infection,” says Gregory Poland, MD, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“When you look in particular at the more serious complications from COVID in this young age group, those are life-altering complications that will have consequences and ramifications throughout their lives,” he said.
“I would take this as a serious wake-up call to parents [at a time when] the immunization rates in younger children are so pitifully low,” Dr. Poland said.
Still early days
The study is suggestive but not definitive, said Peter Katona, MD, professor of medicine and infectious diseases expert at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health.
It’s still too early to draw conclusions about long COVID, including in children, because many questions remain, he said: Should long COVID be defined as symptoms at 1 month or 3 months after infection? How do you define brain fog?
Dr. Katona and colleagues are studying long COVID intervention among students at UCLA to answer some of these questions, including the incidence and effect of early intervention.
The study had “at least seven limitations,” the researchers noted. Among them was the use of medical claims data that noted long COVID outcomes but not how severe they were; some people in the no COVID group might have had the illness but not been diagnosed; and the researchers did not adjust for vaccination status.
Dr. Poland noted that the study was done during surges in COVID variants including Delta and Omicron. In other words, any long COVID effects linked to more recent variants such as BA.5 or BA.2.75 are unknown.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE MMWR
‘Children are not little adults’ and need special protection during heat waves
After more than a week of record-breaking temperatures across much of the country, public health experts are cautioning that children are more susceptible to heat illness than adults are – even more so when they’re on the athletic field, living without air conditioning, or waiting in a parked car.
Cases of heat-related illness are rising with average air temperatures, and experts say almost half of those getting sick are children. The reason is twofold: Children’s bodies have more trouble regulating temperature than do those of adults, and they rely on adults to help protect them from overheating.
Parents, coaches, and other caretakers, who can experience the same heat very differently from the way children do, may struggle to identify a dangerous situation or catch the early symptoms of heat-related illness in children.
“Children are not little adults,” said Dr. Aaron Bernstein, a pediatric hospitalist at Boston Children’s Hospital.
Jan Null, a meteorologist in California, recalled being surprised at the effect of heat in a car. It was 86 degrees on a July afternoon more than 2 decades ago when an infant in San Jose was forgotten in a parked car and died of heatstroke.
Mr. Null said a reporter asked him after the death, “How hot could it have gotten in that car?”
Mr. Null’s research with two emergency doctors at Stanford University eventually produced a startling answer. Within an hour, the temperature in that car could have exceeded 120 degrees Fahrenheit. Their work revealed that a quick errand can be dangerous for a child left behind in the car – even for less than 15 minutes, even with the windows cracked, and even on a mild day.
As record heat becomes more frequent, posing serious risks even to healthy adults, the number of cases of heat-related illnesses has gone up, including among children. Those most at risk are young children in parked vehicles and adolescents returning to school and participating in sports during the hottest days of the year.
More than 9,000 high school athletes are treated for heat-related illnesses every year.
Heat-related illnesses occur when exposure to high temperatures and humidity, which can be intensified by physical exertion, overwhelms the body’s ability to cool itself. Cases range from mild, like benign heat rashes in infants, to more serious, when the body’s core temperature increases. That can lead to life-threatening instances of heatstroke, diagnosed once the body temperature rises above 104 degrees, potentially causing organ failure.
Prevention is key. Experts emphasize that drinking plenty of water, avoiding the outdoors during the hot midday and afternoon hours, and taking it slow when adjusting to exercise are the most effective ways to avoid getting sick.
Children’s bodies take longer to increase sweat production and otherwise acclimatize in a warm environment than adults’ do, research shows. Young children are more susceptible to dehydration because a larger percentage of their body weight is water.
Infants and younger children have more trouble regulating their body temperature, in part because they often don’t recognize when they should drink more water or remove clothing to cool down. A 1995 study showed that young children who spent 30 minutes in a 95-degree room saw their core temperatures rise significantly higher and faster than their mothers’ – even though they sweat more than adults do relative to their size.
Pediatricians advise caretakers to monitor how much water children consume and encourage them to drink before they ask for it. Thirst indicates the body is already dehydrated.
They should dress children in light-colored, lightweight clothes; limit outdoor time during the hottest hours; and look for ways to cool down, such as by visiting an air-conditioned place like a library, taking a cool bath, or going for a swim.
To address the risks to student athletes, the National Athletic Trainers’ Association recommends that high school athletes acclimatize by gradually building their activity over the course of 2 weeks when returning to their sport for a new season – including by slowly stepping up the amount of any protective equipment they wear.
“You’re gradually increasing that intensity over a week to 2 weeks so your body can get used to the heat,” said Kathy Dieringer, president of NATA.
Warning signs and solutions
Experts note a flushed face, fatigue, muscle cramps, headache, dizziness, vomiting, and a lot of sweating are among the symptoms of heat exhaustion, which can develop into heatstroke if untreated. A doctor should be notified if symptoms worsen, such as if the child seems disoriented or cannot drink.
Taking immediate steps to cool a child experiencing heat exhaustion or heatstroke is critical. The child should be taken to a shaded or cool area; be given cool fluids with salt, like sports drinks; and have any sweaty or heavy garments removed.
For adolescents, being submerged in an ice bath is the most effective way to cool the body, while younger children can be wrapped in cold, wet towels or misted with lukewarm water and placed in front of a fan.
Although children’s deaths in parked cars have been well documented, the tragic incidents continue to occur. According to federal statistics, 23 children died of vehicular heatstroke in 2021. Mr. Null, who collects his own data, said 13 children have died so far this year.
Caretakers should never leave children alone in a parked car, Mr. Null said. Take steps to prevent young children from entering the car themselves and becoming trapped, including locking the car while it’s parked at home.
More than half of cases of vehicular pediatric heatstroke occur because a caretaker accidentally left a child behind, he said. While in-car technology reminding adults to check their back seats has become more common, only a fraction of vehicles have it, requiring parents to come up with their own methods, like leaving a stuffed animal in the front seat.
The good news, Mr. Null said, is that simple behavioral changes can protect youngsters. “This is preventable in 100% of the cases,” he said.
A lopsided risk
People living in low-income areas fare worse when temperatures climb. Access to air conditioning, which includes the ability to afford the electricity bill, is a serious health concern.
A study of heat in urban areas released last year showed that low-income neighborhoods and communities of color experience much higher temperatures than those of wealthier, White residents. In more impoverished areas during the summer, temperatures can be as much as 7 degrees Fahrenheit warmer.
The study’s authors said their findings in the United States reflect that “the legacy of redlining looms large,” referring to a federal housing policy that refused to insure mortgages in or near predominantly Black neighborhoods.
“These areas have less tree canopy, more streets, and higher building densities, meaning that in addition to their other racist outcomes, redlining policies directly codified into law existing disparity in urban land use and reinforced urban design choices that magnify urban heating into the present,” they concluded.
Dr. Bernstein, who leads Harvard’s Center for Climate, Health, and the Global Environment, coauthored a commentary in JAMA arguing that advancing health equity is critical to action on climate change.
The center works with front-line health clinics to help their predominantly low-income patients respond to the health impacts of climate change. Federally backed clinics alone provide care to about 30 million Americans, including many children, he said.
Dr. Bernstein also recently led a nationwide study that found that from May through September, days with higher temperatures are associated with more visits to children’s hospital emergency rooms. Many visits were more directly linked to heat, although the study also pointed to how high temperatures can exacerbate existing health conditions such as neurological disorders.
“Children are more vulnerable to climate change through how these climate shocks reshape the world in which they grow up,” Dr. Bernstein said.
Helping people better understand the health risks of extreme heat and how to protect themselves and their families are among the public health system’s major challenges, experts said.
The National Weather Service’s heat alert system is mainly based on the heat index, a measure of how hot it feels when relative humidity is factored in with air temperature.
But the alerts are not related to effects on health, said Kathy Baughman McLeod, director of the Adrienne Arsht-Rockefeller Foundation Resilience Center. By the time temperatures rise to the level that a weather alert is issued, many vulnerable people – like children, pregnant women, and the elderly – may already be experiencing heat exhaustion or heatstroke.
The center developed a new heat alert system, which is being tested in Seville, Spain, historically one of the hottest cities in Europe.
The system marries metrics such as air temperature and humidity with public health data to categorize heat waves and, when they are serious enough, give them names – making it easier for people to understand heat as an environmental threat that requires prevention measures.
The categories are determined through a metric known as excess deaths, which compares how many people died on a day with the forecast temperature versus an average day. That may help health officials understand how severe a heat wave is expected to be and make informed recommendations to the public based on risk factors such as age or medical history.
The health-based alert system would also allow officials to target caretakers of children and seniors through school systems, preschools, and senior centers, Ms. Baughman McLeod said.
Giving people better ways to conceptualize heat is critical, she said.
“It’s not dramatic. It doesn’t rip the roof off of your house,” Ms. Baughman McLeod said. “It’s silent and invisible.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
After more than a week of record-breaking temperatures across much of the country, public health experts are cautioning that children are more susceptible to heat illness than adults are – even more so when they’re on the athletic field, living without air conditioning, or waiting in a parked car.
Cases of heat-related illness are rising with average air temperatures, and experts say almost half of those getting sick are children. The reason is twofold: Children’s bodies have more trouble regulating temperature than do those of adults, and they rely on adults to help protect them from overheating.
Parents, coaches, and other caretakers, who can experience the same heat very differently from the way children do, may struggle to identify a dangerous situation or catch the early symptoms of heat-related illness in children.
“Children are not little adults,” said Dr. Aaron Bernstein, a pediatric hospitalist at Boston Children’s Hospital.
Jan Null, a meteorologist in California, recalled being surprised at the effect of heat in a car. It was 86 degrees on a July afternoon more than 2 decades ago when an infant in San Jose was forgotten in a parked car and died of heatstroke.
Mr. Null said a reporter asked him after the death, “How hot could it have gotten in that car?”
Mr. Null’s research with two emergency doctors at Stanford University eventually produced a startling answer. Within an hour, the temperature in that car could have exceeded 120 degrees Fahrenheit. Their work revealed that a quick errand can be dangerous for a child left behind in the car – even for less than 15 minutes, even with the windows cracked, and even on a mild day.
As record heat becomes more frequent, posing serious risks even to healthy adults, the number of cases of heat-related illnesses has gone up, including among children. Those most at risk are young children in parked vehicles and adolescents returning to school and participating in sports during the hottest days of the year.
More than 9,000 high school athletes are treated for heat-related illnesses every year.
Heat-related illnesses occur when exposure to high temperatures and humidity, which can be intensified by physical exertion, overwhelms the body’s ability to cool itself. Cases range from mild, like benign heat rashes in infants, to more serious, when the body’s core temperature increases. That can lead to life-threatening instances of heatstroke, diagnosed once the body temperature rises above 104 degrees, potentially causing organ failure.
Prevention is key. Experts emphasize that drinking plenty of water, avoiding the outdoors during the hot midday and afternoon hours, and taking it slow when adjusting to exercise are the most effective ways to avoid getting sick.
Children’s bodies take longer to increase sweat production and otherwise acclimatize in a warm environment than adults’ do, research shows. Young children are more susceptible to dehydration because a larger percentage of their body weight is water.
Infants and younger children have more trouble regulating their body temperature, in part because they often don’t recognize when they should drink more water or remove clothing to cool down. A 1995 study showed that young children who spent 30 minutes in a 95-degree room saw their core temperatures rise significantly higher and faster than their mothers’ – even though they sweat more than adults do relative to their size.
Pediatricians advise caretakers to monitor how much water children consume and encourage them to drink before they ask for it. Thirst indicates the body is already dehydrated.
They should dress children in light-colored, lightweight clothes; limit outdoor time during the hottest hours; and look for ways to cool down, such as by visiting an air-conditioned place like a library, taking a cool bath, or going for a swim.
To address the risks to student athletes, the National Athletic Trainers’ Association recommends that high school athletes acclimatize by gradually building their activity over the course of 2 weeks when returning to their sport for a new season – including by slowly stepping up the amount of any protective equipment they wear.
“You’re gradually increasing that intensity over a week to 2 weeks so your body can get used to the heat,” said Kathy Dieringer, president of NATA.
Warning signs and solutions
Experts note a flushed face, fatigue, muscle cramps, headache, dizziness, vomiting, and a lot of sweating are among the symptoms of heat exhaustion, which can develop into heatstroke if untreated. A doctor should be notified if symptoms worsen, such as if the child seems disoriented or cannot drink.
Taking immediate steps to cool a child experiencing heat exhaustion or heatstroke is critical. The child should be taken to a shaded or cool area; be given cool fluids with salt, like sports drinks; and have any sweaty or heavy garments removed.
For adolescents, being submerged in an ice bath is the most effective way to cool the body, while younger children can be wrapped in cold, wet towels or misted with lukewarm water and placed in front of a fan.
Although children’s deaths in parked cars have been well documented, the tragic incidents continue to occur. According to federal statistics, 23 children died of vehicular heatstroke in 2021. Mr. Null, who collects his own data, said 13 children have died so far this year.
Caretakers should never leave children alone in a parked car, Mr. Null said. Take steps to prevent young children from entering the car themselves and becoming trapped, including locking the car while it’s parked at home.
More than half of cases of vehicular pediatric heatstroke occur because a caretaker accidentally left a child behind, he said. While in-car technology reminding adults to check their back seats has become more common, only a fraction of vehicles have it, requiring parents to come up with their own methods, like leaving a stuffed animal in the front seat.
The good news, Mr. Null said, is that simple behavioral changes can protect youngsters. “This is preventable in 100% of the cases,” he said.
A lopsided risk
People living in low-income areas fare worse when temperatures climb. Access to air conditioning, which includes the ability to afford the electricity bill, is a serious health concern.
A study of heat in urban areas released last year showed that low-income neighborhoods and communities of color experience much higher temperatures than those of wealthier, White residents. In more impoverished areas during the summer, temperatures can be as much as 7 degrees Fahrenheit warmer.
The study’s authors said their findings in the United States reflect that “the legacy of redlining looms large,” referring to a federal housing policy that refused to insure mortgages in or near predominantly Black neighborhoods.
“These areas have less tree canopy, more streets, and higher building densities, meaning that in addition to their other racist outcomes, redlining policies directly codified into law existing disparity in urban land use and reinforced urban design choices that magnify urban heating into the present,” they concluded.
Dr. Bernstein, who leads Harvard’s Center for Climate, Health, and the Global Environment, coauthored a commentary in JAMA arguing that advancing health equity is critical to action on climate change.
The center works with front-line health clinics to help their predominantly low-income patients respond to the health impacts of climate change. Federally backed clinics alone provide care to about 30 million Americans, including many children, he said.
Dr. Bernstein also recently led a nationwide study that found that from May through September, days with higher temperatures are associated with more visits to children’s hospital emergency rooms. Many visits were more directly linked to heat, although the study also pointed to how high temperatures can exacerbate existing health conditions such as neurological disorders.
“Children are more vulnerable to climate change through how these climate shocks reshape the world in which they grow up,” Dr. Bernstein said.
Helping people better understand the health risks of extreme heat and how to protect themselves and their families are among the public health system’s major challenges, experts said.
The National Weather Service’s heat alert system is mainly based on the heat index, a measure of how hot it feels when relative humidity is factored in with air temperature.
But the alerts are not related to effects on health, said Kathy Baughman McLeod, director of the Adrienne Arsht-Rockefeller Foundation Resilience Center. By the time temperatures rise to the level that a weather alert is issued, many vulnerable people – like children, pregnant women, and the elderly – may already be experiencing heat exhaustion or heatstroke.
The center developed a new heat alert system, which is being tested in Seville, Spain, historically one of the hottest cities in Europe.
The system marries metrics such as air temperature and humidity with public health data to categorize heat waves and, when they are serious enough, give them names – making it easier for people to understand heat as an environmental threat that requires prevention measures.
The categories are determined through a metric known as excess deaths, which compares how many people died on a day with the forecast temperature versus an average day. That may help health officials understand how severe a heat wave is expected to be and make informed recommendations to the public based on risk factors such as age or medical history.
The health-based alert system would also allow officials to target caretakers of children and seniors through school systems, preschools, and senior centers, Ms. Baughman McLeod said.
Giving people better ways to conceptualize heat is critical, she said.
“It’s not dramatic. It doesn’t rip the roof off of your house,” Ms. Baughman McLeod said. “It’s silent and invisible.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
After more than a week of record-breaking temperatures across much of the country, public health experts are cautioning that children are more susceptible to heat illness than adults are – even more so when they’re on the athletic field, living without air conditioning, or waiting in a parked car.
Cases of heat-related illness are rising with average air temperatures, and experts say almost half of those getting sick are children. The reason is twofold: Children’s bodies have more trouble regulating temperature than do those of adults, and they rely on adults to help protect them from overheating.
Parents, coaches, and other caretakers, who can experience the same heat very differently from the way children do, may struggle to identify a dangerous situation or catch the early symptoms of heat-related illness in children.
“Children are not little adults,” said Dr. Aaron Bernstein, a pediatric hospitalist at Boston Children’s Hospital.
Jan Null, a meteorologist in California, recalled being surprised at the effect of heat in a car. It was 86 degrees on a July afternoon more than 2 decades ago when an infant in San Jose was forgotten in a parked car and died of heatstroke.
Mr. Null said a reporter asked him after the death, “How hot could it have gotten in that car?”
Mr. Null’s research with two emergency doctors at Stanford University eventually produced a startling answer. Within an hour, the temperature in that car could have exceeded 120 degrees Fahrenheit. Their work revealed that a quick errand can be dangerous for a child left behind in the car – even for less than 15 minutes, even with the windows cracked, and even on a mild day.
As record heat becomes more frequent, posing serious risks even to healthy adults, the number of cases of heat-related illnesses has gone up, including among children. Those most at risk are young children in parked vehicles and adolescents returning to school and participating in sports during the hottest days of the year.
More than 9,000 high school athletes are treated for heat-related illnesses every year.
Heat-related illnesses occur when exposure to high temperatures and humidity, which can be intensified by physical exertion, overwhelms the body’s ability to cool itself. Cases range from mild, like benign heat rashes in infants, to more serious, when the body’s core temperature increases. That can lead to life-threatening instances of heatstroke, diagnosed once the body temperature rises above 104 degrees, potentially causing organ failure.
Prevention is key. Experts emphasize that drinking plenty of water, avoiding the outdoors during the hot midday and afternoon hours, and taking it slow when adjusting to exercise are the most effective ways to avoid getting sick.
Children’s bodies take longer to increase sweat production and otherwise acclimatize in a warm environment than adults’ do, research shows. Young children are more susceptible to dehydration because a larger percentage of their body weight is water.
Infants and younger children have more trouble regulating their body temperature, in part because they often don’t recognize when they should drink more water or remove clothing to cool down. A 1995 study showed that young children who spent 30 minutes in a 95-degree room saw their core temperatures rise significantly higher and faster than their mothers’ – even though they sweat more than adults do relative to their size.
Pediatricians advise caretakers to monitor how much water children consume and encourage them to drink before they ask for it. Thirst indicates the body is already dehydrated.
They should dress children in light-colored, lightweight clothes; limit outdoor time during the hottest hours; and look for ways to cool down, such as by visiting an air-conditioned place like a library, taking a cool bath, or going for a swim.
To address the risks to student athletes, the National Athletic Trainers’ Association recommends that high school athletes acclimatize by gradually building their activity over the course of 2 weeks when returning to their sport for a new season – including by slowly stepping up the amount of any protective equipment they wear.
“You’re gradually increasing that intensity over a week to 2 weeks so your body can get used to the heat,” said Kathy Dieringer, president of NATA.
Warning signs and solutions
Experts note a flushed face, fatigue, muscle cramps, headache, dizziness, vomiting, and a lot of sweating are among the symptoms of heat exhaustion, which can develop into heatstroke if untreated. A doctor should be notified if symptoms worsen, such as if the child seems disoriented or cannot drink.
Taking immediate steps to cool a child experiencing heat exhaustion or heatstroke is critical. The child should be taken to a shaded or cool area; be given cool fluids with salt, like sports drinks; and have any sweaty or heavy garments removed.
For adolescents, being submerged in an ice bath is the most effective way to cool the body, while younger children can be wrapped in cold, wet towels or misted with lukewarm water and placed in front of a fan.
Although children’s deaths in parked cars have been well documented, the tragic incidents continue to occur. According to federal statistics, 23 children died of vehicular heatstroke in 2021. Mr. Null, who collects his own data, said 13 children have died so far this year.
Caretakers should never leave children alone in a parked car, Mr. Null said. Take steps to prevent young children from entering the car themselves and becoming trapped, including locking the car while it’s parked at home.
More than half of cases of vehicular pediatric heatstroke occur because a caretaker accidentally left a child behind, he said. While in-car technology reminding adults to check their back seats has become more common, only a fraction of vehicles have it, requiring parents to come up with their own methods, like leaving a stuffed animal in the front seat.
The good news, Mr. Null said, is that simple behavioral changes can protect youngsters. “This is preventable in 100% of the cases,” he said.
A lopsided risk
People living in low-income areas fare worse when temperatures climb. Access to air conditioning, which includes the ability to afford the electricity bill, is a serious health concern.
A study of heat in urban areas released last year showed that low-income neighborhoods and communities of color experience much higher temperatures than those of wealthier, White residents. In more impoverished areas during the summer, temperatures can be as much as 7 degrees Fahrenheit warmer.
The study’s authors said their findings in the United States reflect that “the legacy of redlining looms large,” referring to a federal housing policy that refused to insure mortgages in or near predominantly Black neighborhoods.
“These areas have less tree canopy, more streets, and higher building densities, meaning that in addition to their other racist outcomes, redlining policies directly codified into law existing disparity in urban land use and reinforced urban design choices that magnify urban heating into the present,” they concluded.
Dr. Bernstein, who leads Harvard’s Center for Climate, Health, and the Global Environment, coauthored a commentary in JAMA arguing that advancing health equity is critical to action on climate change.
The center works with front-line health clinics to help their predominantly low-income patients respond to the health impacts of climate change. Federally backed clinics alone provide care to about 30 million Americans, including many children, he said.
Dr. Bernstein also recently led a nationwide study that found that from May through September, days with higher temperatures are associated with more visits to children’s hospital emergency rooms. Many visits were more directly linked to heat, although the study also pointed to how high temperatures can exacerbate existing health conditions such as neurological disorders.
“Children are more vulnerable to climate change through how these climate shocks reshape the world in which they grow up,” Dr. Bernstein said.
Helping people better understand the health risks of extreme heat and how to protect themselves and their families are among the public health system’s major challenges, experts said.
The National Weather Service’s heat alert system is mainly based on the heat index, a measure of how hot it feels when relative humidity is factored in with air temperature.
But the alerts are not related to effects on health, said Kathy Baughman McLeod, director of the Adrienne Arsht-Rockefeller Foundation Resilience Center. By the time temperatures rise to the level that a weather alert is issued, many vulnerable people – like children, pregnant women, and the elderly – may already be experiencing heat exhaustion or heatstroke.
The center developed a new heat alert system, which is being tested in Seville, Spain, historically one of the hottest cities in Europe.
The system marries metrics such as air temperature and humidity with public health data to categorize heat waves and, when they are serious enough, give them names – making it easier for people to understand heat as an environmental threat that requires prevention measures.
The categories are determined through a metric known as excess deaths, which compares how many people died on a day with the forecast temperature versus an average day. That may help health officials understand how severe a heat wave is expected to be and make informed recommendations to the public based on risk factors such as age or medical history.
The health-based alert system would also allow officials to target caretakers of children and seniors through school systems, preschools, and senior centers, Ms. Baughman McLeod said.
Giving people better ways to conceptualize heat is critical, she said.
“It’s not dramatic. It doesn’t rip the roof off of your house,” Ms. Baughman McLeod said. “It’s silent and invisible.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
‘Go Ask Alice’: A fake view of teen mental health
If you grew up in the 1970s and 1980s, chances are high you’re familiar with “Go Ask Alice.”
What was then said to be the real diary of a 15-year-old promising teen turned drug addict was released in 1971 as a cautionary tale and has since sold over 5 million copies. The diary was harrowing against the backdrop of the war on drugs and soon became both acclaimed and banned from classrooms across the country.
Schools citied “inappropriate” language that “borders on pornography” as grounds to prohibit teenagers from reading Alice’s story. But as much as the book’s vivid writing offended readers, it drew millions in with its profanity and graphic descriptions of sex, drugs, and mental health struggles.
At the time, The New York Times reviewed the book as “a strong, painfully honest, nakedly candid and true story ... a document of horrifying reality,” but the popular diary was later found to be a ploy – a fake story written by a 54-year-old Mormon youth counselor named Beatrice Sparks.
Now, Ms. Sparks, who died in 2012, has been further exposed in radio personality Rick Emerson’s new book, “Unmask Alice: LSD, Satanic Panic, and the Imposter Behind the World’s Most Notorious Diaries.” Mr. Emerson published the exposé in July, years after he had the idea to investigate Ms. Sparks’s work in 2015. The book details Ms. Sparks’s background, her journey in creating Alice, and her quest to be recognized for the teen diary she had published as “Anonymous.”
“After 30 years of trying, Beatrice Sparks had changed the world. And nobody knew it,” Mr. Emerson told the New York Post.In his work, Mr. Emerson also dives into the profound impact of the diary at a time when not as much research existed on teen mental health.
When the teenager whose diary inspired Ms. Sparks’s writing “died in March 1971, the very first true study of adolescent psychology had just barely come out,” Mr. Emerson said to Rolling Stone. “Mental health, especially for young people, was still very much on training wheels.”
According to Mr. Emerson, a lack of insight into mental health issues allowed Ms. Sparks’s description to go relatively unchallenged and for the book’s influence to spread despite its misinformation.
“It’s indisputable that large sections of ‘Go Ask Alice’ are just embellished and/or false,” he told the Post.
Then versus now
This landscape is in stark contrast to today, where thousands of studies on the topic have been done, compared with the mere dozens in the 1970s.
Anxiety and depression in minors have increased over time, a trend worsened by the COVID-19 pandemic, according to the CDC. Studies have shown that reported drug use in teens has decreased over time, proving significant during the pandemic, according to the National Institutes of Health.
While Alice from “Go Ask Alice” has not existed in either, comparing the two periods can offer insight into teen struggles in the 1970s versus today and sheds light on how literature – fiction or even faked nonfiction – can transform a nation.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
If you grew up in the 1970s and 1980s, chances are high you’re familiar with “Go Ask Alice.”
What was then said to be the real diary of a 15-year-old promising teen turned drug addict was released in 1971 as a cautionary tale and has since sold over 5 million copies. The diary was harrowing against the backdrop of the war on drugs and soon became both acclaimed and banned from classrooms across the country.
Schools citied “inappropriate” language that “borders on pornography” as grounds to prohibit teenagers from reading Alice’s story. But as much as the book’s vivid writing offended readers, it drew millions in with its profanity and graphic descriptions of sex, drugs, and mental health struggles.
At the time, The New York Times reviewed the book as “a strong, painfully honest, nakedly candid and true story ... a document of horrifying reality,” but the popular diary was later found to be a ploy – a fake story written by a 54-year-old Mormon youth counselor named Beatrice Sparks.
Now, Ms. Sparks, who died in 2012, has been further exposed in radio personality Rick Emerson’s new book, “Unmask Alice: LSD, Satanic Panic, and the Imposter Behind the World’s Most Notorious Diaries.” Mr. Emerson published the exposé in July, years after he had the idea to investigate Ms. Sparks’s work in 2015. The book details Ms. Sparks’s background, her journey in creating Alice, and her quest to be recognized for the teen diary she had published as “Anonymous.”
“After 30 years of trying, Beatrice Sparks had changed the world. And nobody knew it,” Mr. Emerson told the New York Post.In his work, Mr. Emerson also dives into the profound impact of the diary at a time when not as much research existed on teen mental health.
When the teenager whose diary inspired Ms. Sparks’s writing “died in March 1971, the very first true study of adolescent psychology had just barely come out,” Mr. Emerson said to Rolling Stone. “Mental health, especially for young people, was still very much on training wheels.”
According to Mr. Emerson, a lack of insight into mental health issues allowed Ms. Sparks’s description to go relatively unchallenged and for the book’s influence to spread despite its misinformation.
“It’s indisputable that large sections of ‘Go Ask Alice’ are just embellished and/or false,” he told the Post.
Then versus now
This landscape is in stark contrast to today, where thousands of studies on the topic have been done, compared with the mere dozens in the 1970s.
Anxiety and depression in minors have increased over time, a trend worsened by the COVID-19 pandemic, according to the CDC. Studies have shown that reported drug use in teens has decreased over time, proving significant during the pandemic, according to the National Institutes of Health.
While Alice from “Go Ask Alice” has not existed in either, comparing the two periods can offer insight into teen struggles in the 1970s versus today and sheds light on how literature – fiction or even faked nonfiction – can transform a nation.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
If you grew up in the 1970s and 1980s, chances are high you’re familiar with “Go Ask Alice.”
What was then said to be the real diary of a 15-year-old promising teen turned drug addict was released in 1971 as a cautionary tale and has since sold over 5 million copies. The diary was harrowing against the backdrop of the war on drugs and soon became both acclaimed and banned from classrooms across the country.
Schools citied “inappropriate” language that “borders on pornography” as grounds to prohibit teenagers from reading Alice’s story. But as much as the book’s vivid writing offended readers, it drew millions in with its profanity and graphic descriptions of sex, drugs, and mental health struggles.
At the time, The New York Times reviewed the book as “a strong, painfully honest, nakedly candid and true story ... a document of horrifying reality,” but the popular diary was later found to be a ploy – a fake story written by a 54-year-old Mormon youth counselor named Beatrice Sparks.
Now, Ms. Sparks, who died in 2012, has been further exposed in radio personality Rick Emerson’s new book, “Unmask Alice: LSD, Satanic Panic, and the Imposter Behind the World’s Most Notorious Diaries.” Mr. Emerson published the exposé in July, years after he had the idea to investigate Ms. Sparks’s work in 2015. The book details Ms. Sparks’s background, her journey in creating Alice, and her quest to be recognized for the teen diary she had published as “Anonymous.”
“After 30 years of trying, Beatrice Sparks had changed the world. And nobody knew it,” Mr. Emerson told the New York Post.In his work, Mr. Emerson also dives into the profound impact of the diary at a time when not as much research existed on teen mental health.
When the teenager whose diary inspired Ms. Sparks’s writing “died in March 1971, the very first true study of adolescent psychology had just barely come out,” Mr. Emerson said to Rolling Stone. “Mental health, especially for young people, was still very much on training wheels.”
According to Mr. Emerson, a lack of insight into mental health issues allowed Ms. Sparks’s description to go relatively unchallenged and for the book’s influence to spread despite its misinformation.
“It’s indisputable that large sections of ‘Go Ask Alice’ are just embellished and/or false,” he told the Post.
Then versus now
This landscape is in stark contrast to today, where thousands of studies on the topic have been done, compared with the mere dozens in the 1970s.
Anxiety and depression in minors have increased over time, a trend worsened by the COVID-19 pandemic, according to the CDC. Studies have shown that reported drug use in teens has decreased over time, proving significant during the pandemic, according to the National Institutes of Health.
While Alice from “Go Ask Alice” has not existed in either, comparing the two periods can offer insight into teen struggles in the 1970s versus today and sheds light on how literature – fiction or even faked nonfiction – can transform a nation.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
AAP updates hyperbilirubinemia guideline
Raising phototherapy thresholds and revising risk assessment are among the key changes in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ updated guidelines for managing hyperbilirubinemia in infants 35 weeks’ gestation and older.
“More than 80% of newborn infants will have some degree of jaundice,” Alex R. Kemper, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors wrote. Careful monitoring is needed manage high bilirubin concentrations and avoid acute bilirubin encephalopathy (ABE) and kernicterus, a disabling neurologic condition.
The current revision, published in Pediatrics, updates and replaces the 2004 AAP clinical practice guidelines for the management and prevention of hyperbilirubinemia in newborns of at least 35 weeks’ gestation.
The guideline committee reviewed evidence published since the previous guidelines were issued in 2004, and addressed similar issues of prevention, risk assessment, monitoring, and treatment.
A notable change from 2004 was the inclusion of a 2009 recommendation update for “universal predischarge bilirubin screening with measures of total serum bilirubin (TSB) or transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) linked to specific recommendations for follow-up,” the authors wrote.
In terms of prevention, recommendations include a direct antiglobulin test (DAT) for infants whose mother’s antibody screen was positive or unknown. In addition, exclusive breastfeeding is known to be associated with hyperbilirubinemia, but clinicians should support breastfeeding while monitoring for signs of hyperbilirubinemia because of suboptimal feeding, the authors noted. However, the guidelines recommend against oral supplementation with water or dextrose water to prevent hyperbilirubinemia.
For assessment and monitoring, the guidelines advise the use of total serum bilirubin (TSB) as the definitive test for hyperbilirubinemia to guide phototherapy and escalation of care, including exchange transfusion. “The presence of hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors lowers the threshold for treatment with phototherapy and the level at which care should be escalated,” the authors wrote. They also emphasized the need to consider glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, a genetic condition that decreases protection against oxidative stress and has been identified as a leading cause of hazardous hyperbilirubinemia worldwide.
The guidelines recommend assessing all infants for jaundice at least every 12 hours after delivery until discharge, with TSB or TcB measured as soon as possible for those with suspected jaundice. The complete guidelines include charts for TSB levels to guide escalation of care. “Blood for TSB can be obtained at the time it is collected for newborn screening tests to avoid an additional heel stick,” the authors noted.
The rate of increase in TSB or TcB, if more than one measure is available, may identify infants at higher risk of hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines, and a possible delay of hospital discharge may be needed for infants if appropriate follow-up is not feasible.
In terms of treatment, new evidence that bilirubin neurotoxicity does not occur until concentrations well above those given in the 2004 guidelines justified raising the treatment thresholds, although by a narrow range. “With the increased phototherapy thresholds, appropriately following the current guidelines including bilirubin screening during the birth hospitalization and timely postdischarge follow-up is important,” the authors wrote. The new thresholds, outlined in the complete guidelines, are based on gestational age, hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors, and the age of the infant in hours. However, infants may be treated at lower levels, based on individual circumstances, family preferences, and shared decision-making with clinicians. Home-based phototherapy may be used in some infants, but should not be used if there is a question about the device quality, delivery time, and ability of caregivers to use the device correctly.
“Discontinuing phototherapy is an option when the TSB has decreased by at least 2 mg/dL below the hour-specific threshold at the initiation of phototherapy,” and follow-up should be based on risk of rebound hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines.
“This clinical practice guideline provides indications and approaches for phototherapy and escalation of care and when treatment and monitoring can be safely discontinued,” However, clinicians should understand the rationale for the recommendations and combine them with their clinical judgment, including shared decision-making when appropriate, the authors concluded.
Updated evidence supports escalating care
The take-home message for pediatricians is that neonatal hyperbilirubinemia is a very common finding, and complications are rare, but the condition can result in devastating life-long results, Cathy Haut, DNP, CPNP-AC, CPNP-PC, a pediatric nurse practitioner in Rehoboth Beach, Del., said in an interview.
“Previous guidelines published in 2004 and updated in 2009 included evidence-based recommendations, but additional research was still needed to provide guidance for providers to prevent complications of hyperbilirubinemia,” said Dr. Haut, who was not involved in producing the guidelines.
“New data documenting additional risk factors, the importance of ongoing breastfeeding support, and addressing hyperbilirubinemia as an urgent problem” are additions to prevention methods in the latest published guidelines, she said.
“Acute encephalopathy and kernicterus can result from hyperbilirubinemia with severe and devastating neurologic effects, but are preventable by early identification and treatment,” said Dr. Haut. Therefore, “it is not surprising that the AAP utilized continuing and more recent evidence to support new recommendations. Both maternal and neonatal risk factors have long been considered in the development of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, but recent recommendations incorporate additional risk factor evaluation and urgency in time to appropriate care. Detailed thresholds for phototherapy and exchange transfusion will benefit the families of full-term infants without other risk factors and escalate care for those neonates with risk factors.”
However, potential barriers to following the guidelines persist, Dr. Haut noted.
“Frequent infant follow-up can be challenging for busy primary care offices with outpatient laboratory results often taking much longer to obtain than in a hospital setting,” she said.
Also, “taking a newborn to the emergency department or an inpatient laboratory can be frightening for families with the risk of illness exposure. Frequent monitoring of serum bilirubin levels is disturbing for parents and inconvenient immediately postpartum,” Dr. Haut explained. “Few practices utilize transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring which may be one method of added screening.”
In addition, “despite the importance of breastfeeding, ongoing support is not readily available for mothers after hospital discharge. A lactation specialist in the office setting can take the burden off providers and add opportunity for family education.”
As for additional research, “continued evaluation of the comparison of transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring and serum levels along with the use of transcutaneous monitoring in facilities outside the hospital setting may be warranted,” Dr. Haut said. “Data collection on incidence and accompanying risk factors of neonates who develop acute hyperbilirubinemia encephalopathy and kernicterus is a long-term study opportunity.”
The guidelines received no external funding. Lead author Dr. Kemper had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Haut had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Raising phototherapy thresholds and revising risk assessment are among the key changes in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ updated guidelines for managing hyperbilirubinemia in infants 35 weeks’ gestation and older.
“More than 80% of newborn infants will have some degree of jaundice,” Alex R. Kemper, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors wrote. Careful monitoring is needed manage high bilirubin concentrations and avoid acute bilirubin encephalopathy (ABE) and kernicterus, a disabling neurologic condition.
The current revision, published in Pediatrics, updates and replaces the 2004 AAP clinical practice guidelines for the management and prevention of hyperbilirubinemia in newborns of at least 35 weeks’ gestation.
The guideline committee reviewed evidence published since the previous guidelines were issued in 2004, and addressed similar issues of prevention, risk assessment, monitoring, and treatment.
A notable change from 2004 was the inclusion of a 2009 recommendation update for “universal predischarge bilirubin screening with measures of total serum bilirubin (TSB) or transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) linked to specific recommendations for follow-up,” the authors wrote.
In terms of prevention, recommendations include a direct antiglobulin test (DAT) for infants whose mother’s antibody screen was positive or unknown. In addition, exclusive breastfeeding is known to be associated with hyperbilirubinemia, but clinicians should support breastfeeding while monitoring for signs of hyperbilirubinemia because of suboptimal feeding, the authors noted. However, the guidelines recommend against oral supplementation with water or dextrose water to prevent hyperbilirubinemia.
For assessment and monitoring, the guidelines advise the use of total serum bilirubin (TSB) as the definitive test for hyperbilirubinemia to guide phototherapy and escalation of care, including exchange transfusion. “The presence of hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors lowers the threshold for treatment with phototherapy and the level at which care should be escalated,” the authors wrote. They also emphasized the need to consider glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, a genetic condition that decreases protection against oxidative stress and has been identified as a leading cause of hazardous hyperbilirubinemia worldwide.
The guidelines recommend assessing all infants for jaundice at least every 12 hours after delivery until discharge, with TSB or TcB measured as soon as possible for those with suspected jaundice. The complete guidelines include charts for TSB levels to guide escalation of care. “Blood for TSB can be obtained at the time it is collected for newborn screening tests to avoid an additional heel stick,” the authors noted.
The rate of increase in TSB or TcB, if more than one measure is available, may identify infants at higher risk of hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines, and a possible delay of hospital discharge may be needed for infants if appropriate follow-up is not feasible.
In terms of treatment, new evidence that bilirubin neurotoxicity does not occur until concentrations well above those given in the 2004 guidelines justified raising the treatment thresholds, although by a narrow range. “With the increased phototherapy thresholds, appropriately following the current guidelines including bilirubin screening during the birth hospitalization and timely postdischarge follow-up is important,” the authors wrote. The new thresholds, outlined in the complete guidelines, are based on gestational age, hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors, and the age of the infant in hours. However, infants may be treated at lower levels, based on individual circumstances, family preferences, and shared decision-making with clinicians. Home-based phototherapy may be used in some infants, but should not be used if there is a question about the device quality, delivery time, and ability of caregivers to use the device correctly.
“Discontinuing phototherapy is an option when the TSB has decreased by at least 2 mg/dL below the hour-specific threshold at the initiation of phototherapy,” and follow-up should be based on risk of rebound hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines.
“This clinical practice guideline provides indications and approaches for phototherapy and escalation of care and when treatment and monitoring can be safely discontinued,” However, clinicians should understand the rationale for the recommendations and combine them with their clinical judgment, including shared decision-making when appropriate, the authors concluded.
Updated evidence supports escalating care
The take-home message for pediatricians is that neonatal hyperbilirubinemia is a very common finding, and complications are rare, but the condition can result in devastating life-long results, Cathy Haut, DNP, CPNP-AC, CPNP-PC, a pediatric nurse practitioner in Rehoboth Beach, Del., said in an interview.
“Previous guidelines published in 2004 and updated in 2009 included evidence-based recommendations, but additional research was still needed to provide guidance for providers to prevent complications of hyperbilirubinemia,” said Dr. Haut, who was not involved in producing the guidelines.
“New data documenting additional risk factors, the importance of ongoing breastfeeding support, and addressing hyperbilirubinemia as an urgent problem” are additions to prevention methods in the latest published guidelines, she said.
“Acute encephalopathy and kernicterus can result from hyperbilirubinemia with severe and devastating neurologic effects, but are preventable by early identification and treatment,” said Dr. Haut. Therefore, “it is not surprising that the AAP utilized continuing and more recent evidence to support new recommendations. Both maternal and neonatal risk factors have long been considered in the development of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, but recent recommendations incorporate additional risk factor evaluation and urgency in time to appropriate care. Detailed thresholds for phototherapy and exchange transfusion will benefit the families of full-term infants without other risk factors and escalate care for those neonates with risk factors.”
However, potential barriers to following the guidelines persist, Dr. Haut noted.
“Frequent infant follow-up can be challenging for busy primary care offices with outpatient laboratory results often taking much longer to obtain than in a hospital setting,” she said.
Also, “taking a newborn to the emergency department or an inpatient laboratory can be frightening for families with the risk of illness exposure. Frequent monitoring of serum bilirubin levels is disturbing for parents and inconvenient immediately postpartum,” Dr. Haut explained. “Few practices utilize transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring which may be one method of added screening.”
In addition, “despite the importance of breastfeeding, ongoing support is not readily available for mothers after hospital discharge. A lactation specialist in the office setting can take the burden off providers and add opportunity for family education.”
As for additional research, “continued evaluation of the comparison of transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring and serum levels along with the use of transcutaneous monitoring in facilities outside the hospital setting may be warranted,” Dr. Haut said. “Data collection on incidence and accompanying risk factors of neonates who develop acute hyperbilirubinemia encephalopathy and kernicterus is a long-term study opportunity.”
The guidelines received no external funding. Lead author Dr. Kemper had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Haut had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Raising phototherapy thresholds and revising risk assessment are among the key changes in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ updated guidelines for managing hyperbilirubinemia in infants 35 weeks’ gestation and older.
“More than 80% of newborn infants will have some degree of jaundice,” Alex R. Kemper, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors wrote. Careful monitoring is needed manage high bilirubin concentrations and avoid acute bilirubin encephalopathy (ABE) and kernicterus, a disabling neurologic condition.
The current revision, published in Pediatrics, updates and replaces the 2004 AAP clinical practice guidelines for the management and prevention of hyperbilirubinemia in newborns of at least 35 weeks’ gestation.
The guideline committee reviewed evidence published since the previous guidelines were issued in 2004, and addressed similar issues of prevention, risk assessment, monitoring, and treatment.
A notable change from 2004 was the inclusion of a 2009 recommendation update for “universal predischarge bilirubin screening with measures of total serum bilirubin (TSB) or transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) linked to specific recommendations for follow-up,” the authors wrote.
In terms of prevention, recommendations include a direct antiglobulin test (DAT) for infants whose mother’s antibody screen was positive or unknown. In addition, exclusive breastfeeding is known to be associated with hyperbilirubinemia, but clinicians should support breastfeeding while monitoring for signs of hyperbilirubinemia because of suboptimal feeding, the authors noted. However, the guidelines recommend against oral supplementation with water or dextrose water to prevent hyperbilirubinemia.
For assessment and monitoring, the guidelines advise the use of total serum bilirubin (TSB) as the definitive test for hyperbilirubinemia to guide phototherapy and escalation of care, including exchange transfusion. “The presence of hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors lowers the threshold for treatment with phototherapy and the level at which care should be escalated,” the authors wrote. They also emphasized the need to consider glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, a genetic condition that decreases protection against oxidative stress and has been identified as a leading cause of hazardous hyperbilirubinemia worldwide.
The guidelines recommend assessing all infants for jaundice at least every 12 hours after delivery until discharge, with TSB or TcB measured as soon as possible for those with suspected jaundice. The complete guidelines include charts for TSB levels to guide escalation of care. “Blood for TSB can be obtained at the time it is collected for newborn screening tests to avoid an additional heel stick,” the authors noted.
The rate of increase in TSB or TcB, if more than one measure is available, may identify infants at higher risk of hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines, and a possible delay of hospital discharge may be needed for infants if appropriate follow-up is not feasible.
In terms of treatment, new evidence that bilirubin neurotoxicity does not occur until concentrations well above those given in the 2004 guidelines justified raising the treatment thresholds, although by a narrow range. “With the increased phototherapy thresholds, appropriately following the current guidelines including bilirubin screening during the birth hospitalization and timely postdischarge follow-up is important,” the authors wrote. The new thresholds, outlined in the complete guidelines, are based on gestational age, hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors, and the age of the infant in hours. However, infants may be treated at lower levels, based on individual circumstances, family preferences, and shared decision-making with clinicians. Home-based phototherapy may be used in some infants, but should not be used if there is a question about the device quality, delivery time, and ability of caregivers to use the device correctly.
“Discontinuing phototherapy is an option when the TSB has decreased by at least 2 mg/dL below the hour-specific threshold at the initiation of phototherapy,” and follow-up should be based on risk of rebound hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines.
“This clinical practice guideline provides indications and approaches for phototherapy and escalation of care and when treatment and monitoring can be safely discontinued,” However, clinicians should understand the rationale for the recommendations and combine them with their clinical judgment, including shared decision-making when appropriate, the authors concluded.
Updated evidence supports escalating care
The take-home message for pediatricians is that neonatal hyperbilirubinemia is a very common finding, and complications are rare, but the condition can result in devastating life-long results, Cathy Haut, DNP, CPNP-AC, CPNP-PC, a pediatric nurse practitioner in Rehoboth Beach, Del., said in an interview.
“Previous guidelines published in 2004 and updated in 2009 included evidence-based recommendations, but additional research was still needed to provide guidance for providers to prevent complications of hyperbilirubinemia,” said Dr. Haut, who was not involved in producing the guidelines.
“New data documenting additional risk factors, the importance of ongoing breastfeeding support, and addressing hyperbilirubinemia as an urgent problem” are additions to prevention methods in the latest published guidelines, she said.
“Acute encephalopathy and kernicterus can result from hyperbilirubinemia with severe and devastating neurologic effects, but are preventable by early identification and treatment,” said Dr. Haut. Therefore, “it is not surprising that the AAP utilized continuing and more recent evidence to support new recommendations. Both maternal and neonatal risk factors have long been considered in the development of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, but recent recommendations incorporate additional risk factor evaluation and urgency in time to appropriate care. Detailed thresholds for phototherapy and exchange transfusion will benefit the families of full-term infants without other risk factors and escalate care for those neonates with risk factors.”
However, potential barriers to following the guidelines persist, Dr. Haut noted.
“Frequent infant follow-up can be challenging for busy primary care offices with outpatient laboratory results often taking much longer to obtain than in a hospital setting,” she said.
Also, “taking a newborn to the emergency department or an inpatient laboratory can be frightening for families with the risk of illness exposure. Frequent monitoring of serum bilirubin levels is disturbing for parents and inconvenient immediately postpartum,” Dr. Haut explained. “Few practices utilize transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring which may be one method of added screening.”
In addition, “despite the importance of breastfeeding, ongoing support is not readily available for mothers after hospital discharge. A lactation specialist in the office setting can take the burden off providers and add opportunity for family education.”
As for additional research, “continued evaluation of the comparison of transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring and serum levels along with the use of transcutaneous monitoring in facilities outside the hospital setting may be warranted,” Dr. Haut said. “Data collection on incidence and accompanying risk factors of neonates who develop acute hyperbilirubinemia encephalopathy and kernicterus is a long-term study opportunity.”
The guidelines received no external funding. Lead author Dr. Kemper had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Haut had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Death risk doubles for Black infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) who were born to Black mothers were significantly more likely to die or to have a longer hospital stay than infants of other ethnicities, based on data from more than 800 infants.
The overall incidence of BPD is rising, in part because of improved survival for extremely preterm infants, wrote Tamorah R. Lewis, MD, of the University of Missouri, Kansas City, and colleagues.
Previous studies suggest that racial disparities may affect outcomes for preterm infants with a range of neonatal morbidities during neonatal ICU (NICU) hospitalization, including respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular hemorrhage, and necrotizing enterocolitis. However, the association of racial disparities with outcomes for preterm infants with BPD remains unclear, they said.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers, on behalf of the Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Collaborative, reviewed data from 834 preterm infants enrolled in the BPD Collaborative registry from Jan. 1, 2015, to July 19, 2021, at eight centers in the United States.
The study infants were born at less than 32 weeks’ gestation and were diagnosed with severe BPD according to the 2001 National Institutes of Health Consensus Criteria. The study population included 276 Black infants and 558 white infants. The median gestational age was 24 weeks, and 41% of the infants were female.
The primary outcomes were infant death and length of hospital stay.
Although death was infrequent (4% overall), Black maternal race was significantly associated with an increased risk of death from BPD (adjusted odds ratio, 2.1). Black maternal race also was significantly associated with a longer hospital stay for the infants, with an adjusted between-group difference of 10 days.
Infants of Black mothers also were more likely than those with White mothers to receive invasive respiratory support at the time of delivery. Black infants were more likely than White infants to have lower gestational age, lower birth weight and length, and smaller head circumference.
However, the proportions of cesarean deliveries, gender distribution, and infants small for gestational age were similar between Black and White infant groups. Medication exposure at 36 weeks postmenstrual age (PMA) also was similar for Black and White infants, and 50% of patients overall were treated with nasal continuous positive airway pressure at 36 weeks’ PMA. Awareness of the increased risk of death and longer hospital stay for Black infants is critical, “given the highly variable outcomes for patients with BPD and the uncertainty regarding demographic factors that contribute to late respiratory morbidity in severe BPD,” the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including variations among study centers in the identification and recording of maternal race, lack of data on paternal race, and the focus specifically on Black maternal race and not other ethnicities. Given the documented health disparities for Black individuals in the United States, “we restricted our cohort to only those patients born to Black or White mothers to estimate the association of Black maternal race and adverse in-hospital outcomes in infants with severe BPD,” the researchers wrote
Other limitations include the lack of data surrounding infant death and inability to adjust for all potential modifiers of BPD pathogenesis and progression, such as BPD comorbidities.
Prospective studies are needed to identify the sociodemographic mechanisms that may contribute to health outcome disparities for Black infants with severe BPD, the researchers emphasized.
In the meantime, the results highlight the need for more attention to variations in care for infants with BPD of different races, and approaches to family-centered care should consider “the precise needs of high-risk, structurally disadvantaged families while informing the design of prospective trials that improve outcomes for high-risk subgroups of children with severe BPD,” they concluded.
Data raise questions about the origin of disparities
The current study findings contribute to the knowledge and awareness of disparities in the high-risk NICU population, Nicolas A. Bamat, MD, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial. “Further, their findings oppose the central tendency in the literature: that infants of Black mothers have less severe lung disease of prematurity during the birth hospitalization.”
The editorial authors noted that the study’s inclusion of racial characteristics as confounding variables to assess the effect of race on health “can imply questionable assumptions about where in a causal pathway racism begins to exert an effect,” whether after a diagnosis of BPD, during pregnancy in response to inequitable obstetric care, or “centuries ago, propagating forward through the shared experience of communities oppressed by the legacy of racism and its ongoing contemporary manifestations.”
The editorial authors added that, “in lung disease of prematurity, few variables are reliable antecedents to race as an exposure. Complex adjustment is necessary to reduce bias in targeted research questions.” However, the current study findings highlight the need to move toward more equitable neonatal care, and to prioritize interventions to reduce racial health disparities at the level of the NICU as well as at the hospital and government policy levels.
Consider range of contributing factors and confounders
The current study is important because “it is imperative to measure racial outcomes in health care in order to highlight and address disparities and biases,” Tim Joos, MD, said in an interview. However, “it can be difficult to determine how much race is a factor in itself versus a proxy for other important characteristics, such as socioeconomic status and level of education, that can confound the results.”
In the current study, the twofold-increased death rate in the premature infants of Black mothers is concerning and deserves further attention, Dr. Joos said. “The 10-day longer length of stay for infants of Black mothers seems quite shocking at first glance, but because of the long hospital stays for these extremely premature infants in general, it is about 7% longer than the infants born to White mothers.”
The take-home message is that this difference is still significant, and can reflect many factors including disease severity and complications, need for feeding assistance, teaching, and setting up home supports, said Dr. Joos.
As for additional research, “it would be useful for hospitals to break down why the differences exist, although I worry a provider or institution will feel they need to discharge Black families sooner to avoid being biased. Family preference and comfort level should be given high priority,” he emphasized.
The study received no outside funding, but lead author Dr. Lewis was supported by the National Institute on Child Health and Development and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. Several coauthors were supported by other grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Barnat and one coauthor were supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) who were born to Black mothers were significantly more likely to die or to have a longer hospital stay than infants of other ethnicities, based on data from more than 800 infants.
The overall incidence of BPD is rising, in part because of improved survival for extremely preterm infants, wrote Tamorah R. Lewis, MD, of the University of Missouri, Kansas City, and colleagues.
Previous studies suggest that racial disparities may affect outcomes for preterm infants with a range of neonatal morbidities during neonatal ICU (NICU) hospitalization, including respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular hemorrhage, and necrotizing enterocolitis. However, the association of racial disparities with outcomes for preterm infants with BPD remains unclear, they said.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers, on behalf of the Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Collaborative, reviewed data from 834 preterm infants enrolled in the BPD Collaborative registry from Jan. 1, 2015, to July 19, 2021, at eight centers in the United States.
The study infants were born at less than 32 weeks’ gestation and were diagnosed with severe BPD according to the 2001 National Institutes of Health Consensus Criteria. The study population included 276 Black infants and 558 white infants. The median gestational age was 24 weeks, and 41% of the infants were female.
The primary outcomes were infant death and length of hospital stay.
Although death was infrequent (4% overall), Black maternal race was significantly associated with an increased risk of death from BPD (adjusted odds ratio, 2.1). Black maternal race also was significantly associated with a longer hospital stay for the infants, with an adjusted between-group difference of 10 days.
Infants of Black mothers also were more likely than those with White mothers to receive invasive respiratory support at the time of delivery. Black infants were more likely than White infants to have lower gestational age, lower birth weight and length, and smaller head circumference.
However, the proportions of cesarean deliveries, gender distribution, and infants small for gestational age were similar between Black and White infant groups. Medication exposure at 36 weeks postmenstrual age (PMA) also was similar for Black and White infants, and 50% of patients overall were treated with nasal continuous positive airway pressure at 36 weeks’ PMA. Awareness of the increased risk of death and longer hospital stay for Black infants is critical, “given the highly variable outcomes for patients with BPD and the uncertainty regarding demographic factors that contribute to late respiratory morbidity in severe BPD,” the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including variations among study centers in the identification and recording of maternal race, lack of data on paternal race, and the focus specifically on Black maternal race and not other ethnicities. Given the documented health disparities for Black individuals in the United States, “we restricted our cohort to only those patients born to Black or White mothers to estimate the association of Black maternal race and adverse in-hospital outcomes in infants with severe BPD,” the researchers wrote
Other limitations include the lack of data surrounding infant death and inability to adjust for all potential modifiers of BPD pathogenesis and progression, such as BPD comorbidities.
Prospective studies are needed to identify the sociodemographic mechanisms that may contribute to health outcome disparities for Black infants with severe BPD, the researchers emphasized.
In the meantime, the results highlight the need for more attention to variations in care for infants with BPD of different races, and approaches to family-centered care should consider “the precise needs of high-risk, structurally disadvantaged families while informing the design of prospective trials that improve outcomes for high-risk subgroups of children with severe BPD,” they concluded.
Data raise questions about the origin of disparities
The current study findings contribute to the knowledge and awareness of disparities in the high-risk NICU population, Nicolas A. Bamat, MD, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial. “Further, their findings oppose the central tendency in the literature: that infants of Black mothers have less severe lung disease of prematurity during the birth hospitalization.”
The editorial authors noted that the study’s inclusion of racial characteristics as confounding variables to assess the effect of race on health “can imply questionable assumptions about where in a causal pathway racism begins to exert an effect,” whether after a diagnosis of BPD, during pregnancy in response to inequitable obstetric care, or “centuries ago, propagating forward through the shared experience of communities oppressed by the legacy of racism and its ongoing contemporary manifestations.”
The editorial authors added that, “in lung disease of prematurity, few variables are reliable antecedents to race as an exposure. Complex adjustment is necessary to reduce bias in targeted research questions.” However, the current study findings highlight the need to move toward more equitable neonatal care, and to prioritize interventions to reduce racial health disparities at the level of the NICU as well as at the hospital and government policy levels.
Consider range of contributing factors and confounders
The current study is important because “it is imperative to measure racial outcomes in health care in order to highlight and address disparities and biases,” Tim Joos, MD, said in an interview. However, “it can be difficult to determine how much race is a factor in itself versus a proxy for other important characteristics, such as socioeconomic status and level of education, that can confound the results.”
In the current study, the twofold-increased death rate in the premature infants of Black mothers is concerning and deserves further attention, Dr. Joos said. “The 10-day longer length of stay for infants of Black mothers seems quite shocking at first glance, but because of the long hospital stays for these extremely premature infants in general, it is about 7% longer than the infants born to White mothers.”
The take-home message is that this difference is still significant, and can reflect many factors including disease severity and complications, need for feeding assistance, teaching, and setting up home supports, said Dr. Joos.
As for additional research, “it would be useful for hospitals to break down why the differences exist, although I worry a provider or institution will feel they need to discharge Black families sooner to avoid being biased. Family preference and comfort level should be given high priority,” he emphasized.
The study received no outside funding, but lead author Dr. Lewis was supported by the National Institute on Child Health and Development and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. Several coauthors were supported by other grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Barnat and one coauthor were supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) who were born to Black mothers were significantly more likely to die or to have a longer hospital stay than infants of other ethnicities, based on data from more than 800 infants.
The overall incidence of BPD is rising, in part because of improved survival for extremely preterm infants, wrote Tamorah R. Lewis, MD, of the University of Missouri, Kansas City, and colleagues.
Previous studies suggest that racial disparities may affect outcomes for preterm infants with a range of neonatal morbidities during neonatal ICU (NICU) hospitalization, including respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular hemorrhage, and necrotizing enterocolitis. However, the association of racial disparities with outcomes for preterm infants with BPD remains unclear, they said.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers, on behalf of the Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Collaborative, reviewed data from 834 preterm infants enrolled in the BPD Collaborative registry from Jan. 1, 2015, to July 19, 2021, at eight centers in the United States.
The study infants were born at less than 32 weeks’ gestation and were diagnosed with severe BPD according to the 2001 National Institutes of Health Consensus Criteria. The study population included 276 Black infants and 558 white infants. The median gestational age was 24 weeks, and 41% of the infants were female.
The primary outcomes were infant death and length of hospital stay.
Although death was infrequent (4% overall), Black maternal race was significantly associated with an increased risk of death from BPD (adjusted odds ratio, 2.1). Black maternal race also was significantly associated with a longer hospital stay for the infants, with an adjusted between-group difference of 10 days.
Infants of Black mothers also were more likely than those with White mothers to receive invasive respiratory support at the time of delivery. Black infants were more likely than White infants to have lower gestational age, lower birth weight and length, and smaller head circumference.
However, the proportions of cesarean deliveries, gender distribution, and infants small for gestational age were similar between Black and White infant groups. Medication exposure at 36 weeks postmenstrual age (PMA) also was similar for Black and White infants, and 50% of patients overall were treated with nasal continuous positive airway pressure at 36 weeks’ PMA. Awareness of the increased risk of death and longer hospital stay for Black infants is critical, “given the highly variable outcomes for patients with BPD and the uncertainty regarding demographic factors that contribute to late respiratory morbidity in severe BPD,” the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including variations among study centers in the identification and recording of maternal race, lack of data on paternal race, and the focus specifically on Black maternal race and not other ethnicities. Given the documented health disparities for Black individuals in the United States, “we restricted our cohort to only those patients born to Black or White mothers to estimate the association of Black maternal race and adverse in-hospital outcomes in infants with severe BPD,” the researchers wrote
Other limitations include the lack of data surrounding infant death and inability to adjust for all potential modifiers of BPD pathogenesis and progression, such as BPD comorbidities.
Prospective studies are needed to identify the sociodemographic mechanisms that may contribute to health outcome disparities for Black infants with severe BPD, the researchers emphasized.
In the meantime, the results highlight the need for more attention to variations in care for infants with BPD of different races, and approaches to family-centered care should consider “the precise needs of high-risk, structurally disadvantaged families while informing the design of prospective trials that improve outcomes for high-risk subgroups of children with severe BPD,” they concluded.
Data raise questions about the origin of disparities
The current study findings contribute to the knowledge and awareness of disparities in the high-risk NICU population, Nicolas A. Bamat, MD, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial. “Further, their findings oppose the central tendency in the literature: that infants of Black mothers have less severe lung disease of prematurity during the birth hospitalization.”
The editorial authors noted that the study’s inclusion of racial characteristics as confounding variables to assess the effect of race on health “can imply questionable assumptions about where in a causal pathway racism begins to exert an effect,” whether after a diagnosis of BPD, during pregnancy in response to inequitable obstetric care, or “centuries ago, propagating forward through the shared experience of communities oppressed by the legacy of racism and its ongoing contemporary manifestations.”
The editorial authors added that, “in lung disease of prematurity, few variables are reliable antecedents to race as an exposure. Complex adjustment is necessary to reduce bias in targeted research questions.” However, the current study findings highlight the need to move toward more equitable neonatal care, and to prioritize interventions to reduce racial health disparities at the level of the NICU as well as at the hospital and government policy levels.
Consider range of contributing factors and confounders
The current study is important because “it is imperative to measure racial outcomes in health care in order to highlight and address disparities and biases,” Tim Joos, MD, said in an interview. However, “it can be difficult to determine how much race is a factor in itself versus a proxy for other important characteristics, such as socioeconomic status and level of education, that can confound the results.”
In the current study, the twofold-increased death rate in the premature infants of Black mothers is concerning and deserves further attention, Dr. Joos said. “The 10-day longer length of stay for infants of Black mothers seems quite shocking at first glance, but because of the long hospital stays for these extremely premature infants in general, it is about 7% longer than the infants born to White mothers.”
The take-home message is that this difference is still significant, and can reflect many factors including disease severity and complications, need for feeding assistance, teaching, and setting up home supports, said Dr. Joos.
As for additional research, “it would be useful for hospitals to break down why the differences exist, although I worry a provider or institution will feel they need to discharge Black families sooner to avoid being biased. Family preference and comfort level should be given high priority,” he emphasized.
The study received no outside funding, but lead author Dr. Lewis was supported by the National Institute on Child Health and Development and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. Several coauthors were supported by other grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Barnat and one coauthor were supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Cultural humility required to optimize treatment of eczema patients with skin of color
INDIANAPOLIS – Treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in children and adolescents with skin of color requires an acumen that extends well beyond the skin, said Candrice R. Heath, MD, at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
This involves the practice of cultural humility, which Dr. Heath defined as a commitment to learn about all aspects of patients to truly understand them, including their race, access to health care, and socioeconomic status.
“We can continue to prioritize learning about all different types of skin tones and hair types, but we really have to commit to advocating for what our patients deserve in every way,” Dr. Heath, director of pediatric dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, said during her presentation at the meeting.
“That means advocating for kids to have access to better housing and for increasing health literacy programs in our hospitals, so that all our patients can understand what’s happening and how to navigate the health system,” she said. “It also means increasing diversity in our clinical trials by taking a few extra moments with the patient and family of color who might be eligible to participate in a clinical trial. We have work to do.”
To illustrate her points, she discussed the case of a 6-year-old Black patient, whose parents bring him into the clinic complaining about dark marks on the skin. The areas are itchy and the doctor figures, “this is a slam dunk; this is AD,” Dr. Heath said. “You talk about the diagnosis, and you give your treatment plan.
“But the issue is, in the parking lot when the patient’s family leaves, they feel like you didn’t help them at all,” she continued. “You didn’t understand what they came in for. They didn’t receive a treatment for what they came in for, because the initial complaint was dark marks on the skin, which is postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. We know that patients are distressed by this.”
As evidence, she cited a cross-sectional study that assessed the impact of hyperpigmentation and hyperchromia on quality of life in adults, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. People who reported the highest levels of distress were women, those with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, those with fewer formal years of education, and those who had higher out-of-pocket spending on skin-enhancing products.
“So, when you see hyperpigmentation in your AD patients of color, acknowledge it; say, ‘I see this pigmentation change,’ ” Dr. Heath advised. “Talk about how controlling the AD with a topical steroid or other treatment option can have a positive impact on that.”
However, she added that sometimes patients have steroid phobia, possibly because they believe the topical steroids are causing the pigmentation changes, “especially in cases of hypopigmentation, so I take the time to reassure patients so that they will not be fearful about using the medication.”
Parents of patients with skin of color who have AD may harbor other “invisible” concerns during office visits, she continued, including prior experiences with dermatologists that may not have been positive, difficulty accessing pediatric dermatologists, or a general mistrust of the health care system.
“All of that is going on in the room with your patients, particularly those with skin of color and those who feel marginalized,” said Dr. Heath, who is also a faculty scholar at Temple University medical school’s office of health equity, diversity and inclusion. “Of course, we can’t fix everything. But we can commit to approaching our visits with cultural humility.”
For patients with skin of color, she pointed out, other upstream effects impact AD care and outcomes, including well-documented socioeconomic factors.
“One of the equalizing factors is that we as pediatric dermatologists can think about increasing our education regarding skin of color,” Dr. Heath said.
For example, an analysis of data from the 2002 to 2012 National Inpatient Sample found that the main risk factors for inpatient hospitalization for AD were being non-White, having lowest-quartile household income, and having Medicaid or no insurance, researchers reported in 2018.
A separate multicenter study of 1,437 mother-child pairs with known AD found that non-Hispanic Black children and Hispanic children had greater odds of persistent AD than non-Hispanic White children, according to a 2019 study. Another large prospective cohort study published in 2019 found that AD prevalence and persistence is highest in U.S. urban children who are female or Black, and urban children with AD are more likely to have poor quality of life and asthma.
A few months after that study was published, researchers reported results from an analysis of data from the 2007-2008 National Survey of Children’s Health, which found that children who perceive the neighborhood they lived in as unsafe, unsupportive, or underdeveloped had a higher prevalence of AD and a higher severity of AD. The same year, a study of the social and economic risk factors for moderate to severe AD found that Black children were more likely to come from homes with a lower household income, lower parental education attainment, lack of home ownership, and live between two residences, and have exposure to smoke.
“Disease recognition is one thing, but we also want everyone to be aware of these other factors,” she said, “because some patients do need a little bit more care and help to be able to access the medications that they need and gain access to us.”
Follicular, nummular eczema
In her clinical experience, the most common clinical variants of AD in patients with skin of color is follicular eczema. “Examine the patient, apply your hand to the affected area, and you can feel the papules beneath your fingertips,” she advised.
“That’s what I teach my residents and medical students,” she said. “If you are looking for erythema to seal your diagnosis of AD, it may not happen. You may see more of a violaceous hue and sometimes you may not find it at all, depending on the patient’s skin tone. If I find an area of normal appearing skin and then look back at the area of active skin disease, I go back and forth until I’m able to train my eye to be able to see those violaceous and erythematous hues more easily.”
Nummular eczema can also be a challenge in AD patients with skin of color.
“I like to listen to buzz words,” Dr. Heath said. “If a parent says, ‘my child has been diagnosed with ringworm multiple times,’ I zoom in on that. We know that kids can get tinea corporis, but usually not multiple times. I ask about all the things that can be associated with AD, and often we do see these nummular plaques on the skin and do some education about that. I also talk to their pediatrician or send information to that person so that they can be aware that nummular eczema is a form of AD.”
She noted that AD of the scalp may be confused with tinea capitis, especially in young Black children with moderate to severe AD. In her experience, triamcinolone 0.1% ointment works well for AD of the scalp.
She concluded her presentation by noting that there is no easy solution to treating AD in young patients with skin of color. “It’s way more than just eczema. We can help people see AD in a different way. My goal is to see the value in challenging ourselves to understand the impact of what happens outside of the exam room on these patients.”
Dr. Heath disclosed that she has served as a consultant for several pharmaceutical companies, including Regeneron, Janssen, Arcutis, Johnson and Johnson, Cassiopea, and Lilly.
INDIANAPOLIS – Treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in children and adolescents with skin of color requires an acumen that extends well beyond the skin, said Candrice R. Heath, MD, at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
This involves the practice of cultural humility, which Dr. Heath defined as a commitment to learn about all aspects of patients to truly understand them, including their race, access to health care, and socioeconomic status.
“We can continue to prioritize learning about all different types of skin tones and hair types, but we really have to commit to advocating for what our patients deserve in every way,” Dr. Heath, director of pediatric dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, said during her presentation at the meeting.
“That means advocating for kids to have access to better housing and for increasing health literacy programs in our hospitals, so that all our patients can understand what’s happening and how to navigate the health system,” she said. “It also means increasing diversity in our clinical trials by taking a few extra moments with the patient and family of color who might be eligible to participate in a clinical trial. We have work to do.”
To illustrate her points, she discussed the case of a 6-year-old Black patient, whose parents bring him into the clinic complaining about dark marks on the skin. The areas are itchy and the doctor figures, “this is a slam dunk; this is AD,” Dr. Heath said. “You talk about the diagnosis, and you give your treatment plan.
“But the issue is, in the parking lot when the patient’s family leaves, they feel like you didn’t help them at all,” she continued. “You didn’t understand what they came in for. They didn’t receive a treatment for what they came in for, because the initial complaint was dark marks on the skin, which is postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. We know that patients are distressed by this.”
As evidence, she cited a cross-sectional study that assessed the impact of hyperpigmentation and hyperchromia on quality of life in adults, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. People who reported the highest levels of distress were women, those with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, those with fewer formal years of education, and those who had higher out-of-pocket spending on skin-enhancing products.
“So, when you see hyperpigmentation in your AD patients of color, acknowledge it; say, ‘I see this pigmentation change,’ ” Dr. Heath advised. “Talk about how controlling the AD with a topical steroid or other treatment option can have a positive impact on that.”
However, she added that sometimes patients have steroid phobia, possibly because they believe the topical steroids are causing the pigmentation changes, “especially in cases of hypopigmentation, so I take the time to reassure patients so that they will not be fearful about using the medication.”
Parents of patients with skin of color who have AD may harbor other “invisible” concerns during office visits, she continued, including prior experiences with dermatologists that may not have been positive, difficulty accessing pediatric dermatologists, or a general mistrust of the health care system.
“All of that is going on in the room with your patients, particularly those with skin of color and those who feel marginalized,” said Dr. Heath, who is also a faculty scholar at Temple University medical school’s office of health equity, diversity and inclusion. “Of course, we can’t fix everything. But we can commit to approaching our visits with cultural humility.”
For patients with skin of color, she pointed out, other upstream effects impact AD care and outcomes, including well-documented socioeconomic factors.
“One of the equalizing factors is that we as pediatric dermatologists can think about increasing our education regarding skin of color,” Dr. Heath said.
For example, an analysis of data from the 2002 to 2012 National Inpatient Sample found that the main risk factors for inpatient hospitalization for AD were being non-White, having lowest-quartile household income, and having Medicaid or no insurance, researchers reported in 2018.
A separate multicenter study of 1,437 mother-child pairs with known AD found that non-Hispanic Black children and Hispanic children had greater odds of persistent AD than non-Hispanic White children, according to a 2019 study. Another large prospective cohort study published in 2019 found that AD prevalence and persistence is highest in U.S. urban children who are female or Black, and urban children with AD are more likely to have poor quality of life and asthma.
A few months after that study was published, researchers reported results from an analysis of data from the 2007-2008 National Survey of Children’s Health, which found that children who perceive the neighborhood they lived in as unsafe, unsupportive, or underdeveloped had a higher prevalence of AD and a higher severity of AD. The same year, a study of the social and economic risk factors for moderate to severe AD found that Black children were more likely to come from homes with a lower household income, lower parental education attainment, lack of home ownership, and live between two residences, and have exposure to smoke.
“Disease recognition is one thing, but we also want everyone to be aware of these other factors,” she said, “because some patients do need a little bit more care and help to be able to access the medications that they need and gain access to us.”
Follicular, nummular eczema
In her clinical experience, the most common clinical variants of AD in patients with skin of color is follicular eczema. “Examine the patient, apply your hand to the affected area, and you can feel the papules beneath your fingertips,” she advised.
“That’s what I teach my residents and medical students,” she said. “If you are looking for erythema to seal your diagnosis of AD, it may not happen. You may see more of a violaceous hue and sometimes you may not find it at all, depending on the patient’s skin tone. If I find an area of normal appearing skin and then look back at the area of active skin disease, I go back and forth until I’m able to train my eye to be able to see those violaceous and erythematous hues more easily.”
Nummular eczema can also be a challenge in AD patients with skin of color.
“I like to listen to buzz words,” Dr. Heath said. “If a parent says, ‘my child has been diagnosed with ringworm multiple times,’ I zoom in on that. We know that kids can get tinea corporis, but usually not multiple times. I ask about all the things that can be associated with AD, and often we do see these nummular plaques on the skin and do some education about that. I also talk to their pediatrician or send information to that person so that they can be aware that nummular eczema is a form of AD.”
She noted that AD of the scalp may be confused with tinea capitis, especially in young Black children with moderate to severe AD. In her experience, triamcinolone 0.1% ointment works well for AD of the scalp.
She concluded her presentation by noting that there is no easy solution to treating AD in young patients with skin of color. “It’s way more than just eczema. We can help people see AD in a different way. My goal is to see the value in challenging ourselves to understand the impact of what happens outside of the exam room on these patients.”
Dr. Heath disclosed that she has served as a consultant for several pharmaceutical companies, including Regeneron, Janssen, Arcutis, Johnson and Johnson, Cassiopea, and Lilly.
INDIANAPOLIS – Treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in children and adolescents with skin of color requires an acumen that extends well beyond the skin, said Candrice R. Heath, MD, at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
This involves the practice of cultural humility, which Dr. Heath defined as a commitment to learn about all aspects of patients to truly understand them, including their race, access to health care, and socioeconomic status.
“We can continue to prioritize learning about all different types of skin tones and hair types, but we really have to commit to advocating for what our patients deserve in every way,” Dr. Heath, director of pediatric dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, said during her presentation at the meeting.
“That means advocating for kids to have access to better housing and for increasing health literacy programs in our hospitals, so that all our patients can understand what’s happening and how to navigate the health system,” she said. “It also means increasing diversity in our clinical trials by taking a few extra moments with the patient and family of color who might be eligible to participate in a clinical trial. We have work to do.”
To illustrate her points, she discussed the case of a 6-year-old Black patient, whose parents bring him into the clinic complaining about dark marks on the skin. The areas are itchy and the doctor figures, “this is a slam dunk; this is AD,” Dr. Heath said. “You talk about the diagnosis, and you give your treatment plan.
“But the issue is, in the parking lot when the patient’s family leaves, they feel like you didn’t help them at all,” she continued. “You didn’t understand what they came in for. They didn’t receive a treatment for what they came in for, because the initial complaint was dark marks on the skin, which is postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. We know that patients are distressed by this.”
As evidence, she cited a cross-sectional study that assessed the impact of hyperpigmentation and hyperchromia on quality of life in adults, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. People who reported the highest levels of distress were women, those with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, those with fewer formal years of education, and those who had higher out-of-pocket spending on skin-enhancing products.
“So, when you see hyperpigmentation in your AD patients of color, acknowledge it; say, ‘I see this pigmentation change,’ ” Dr. Heath advised. “Talk about how controlling the AD with a topical steroid or other treatment option can have a positive impact on that.”
However, she added that sometimes patients have steroid phobia, possibly because they believe the topical steroids are causing the pigmentation changes, “especially in cases of hypopigmentation, so I take the time to reassure patients so that they will not be fearful about using the medication.”
Parents of patients with skin of color who have AD may harbor other “invisible” concerns during office visits, she continued, including prior experiences with dermatologists that may not have been positive, difficulty accessing pediatric dermatologists, or a general mistrust of the health care system.
“All of that is going on in the room with your patients, particularly those with skin of color and those who feel marginalized,” said Dr. Heath, who is also a faculty scholar at Temple University medical school’s office of health equity, diversity and inclusion. “Of course, we can’t fix everything. But we can commit to approaching our visits with cultural humility.”
For patients with skin of color, she pointed out, other upstream effects impact AD care and outcomes, including well-documented socioeconomic factors.
“One of the equalizing factors is that we as pediatric dermatologists can think about increasing our education regarding skin of color,” Dr. Heath said.
For example, an analysis of data from the 2002 to 2012 National Inpatient Sample found that the main risk factors for inpatient hospitalization for AD were being non-White, having lowest-quartile household income, and having Medicaid or no insurance, researchers reported in 2018.
A separate multicenter study of 1,437 mother-child pairs with known AD found that non-Hispanic Black children and Hispanic children had greater odds of persistent AD than non-Hispanic White children, according to a 2019 study. Another large prospective cohort study published in 2019 found that AD prevalence and persistence is highest in U.S. urban children who are female or Black, and urban children with AD are more likely to have poor quality of life and asthma.
A few months after that study was published, researchers reported results from an analysis of data from the 2007-2008 National Survey of Children’s Health, which found that children who perceive the neighborhood they lived in as unsafe, unsupportive, or underdeveloped had a higher prevalence of AD and a higher severity of AD. The same year, a study of the social and economic risk factors for moderate to severe AD found that Black children were more likely to come from homes with a lower household income, lower parental education attainment, lack of home ownership, and live between two residences, and have exposure to smoke.
“Disease recognition is one thing, but we also want everyone to be aware of these other factors,” she said, “because some patients do need a little bit more care and help to be able to access the medications that they need and gain access to us.”
Follicular, nummular eczema
In her clinical experience, the most common clinical variants of AD in patients with skin of color is follicular eczema. “Examine the patient, apply your hand to the affected area, and you can feel the papules beneath your fingertips,” she advised.
“That’s what I teach my residents and medical students,” she said. “If you are looking for erythema to seal your diagnosis of AD, it may not happen. You may see more of a violaceous hue and sometimes you may not find it at all, depending on the patient’s skin tone. If I find an area of normal appearing skin and then look back at the area of active skin disease, I go back and forth until I’m able to train my eye to be able to see those violaceous and erythematous hues more easily.”
Nummular eczema can also be a challenge in AD patients with skin of color.
“I like to listen to buzz words,” Dr. Heath said. “If a parent says, ‘my child has been diagnosed with ringworm multiple times,’ I zoom in on that. We know that kids can get tinea corporis, but usually not multiple times. I ask about all the things that can be associated with AD, and often we do see these nummular plaques on the skin and do some education about that. I also talk to their pediatrician or send information to that person so that they can be aware that nummular eczema is a form of AD.”
She noted that AD of the scalp may be confused with tinea capitis, especially in young Black children with moderate to severe AD. In her experience, triamcinolone 0.1% ointment works well for AD of the scalp.
She concluded her presentation by noting that there is no easy solution to treating AD in young patients with skin of color. “It’s way more than just eczema. We can help people see AD in a different way. My goal is to see the value in challenging ourselves to understand the impact of what happens outside of the exam room on these patients.”
Dr. Heath disclosed that she has served as a consultant for several pharmaceutical companies, including Regeneron, Janssen, Arcutis, Johnson and Johnson, Cassiopea, and Lilly.
AT SPD 2022
Summer flu, RSV in July, ‘super colds?’
Richard Martinello, MD, a professor of medicine and pediatric infectious diseases at Yale University, New haven, Conn., doesn’t expect to see a child hospitalized with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in the middle of summer. The illness, which can strike infants and older adults especially hard, is known as a “winter virus.”
But not this year. Over the last several weeks, he says, admissions for children with RSV have increased at the Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital. While the numbers aren’t large, they are out of the ordinary, he says, “because usually, at this time of year, we see zero. For lack of a better term, it’s weird.”
Likewise, William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, says RSV is on the rise there. Tennessee is one of 10 states taking part in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention surveillance system that tracks influenza, RSV, and COVID-19.
He says RSV cases have risen by at least a third during the past week, including all age ranges. At this time of year, he says, “We aren’t supposed to have any RSV.”
RSV isn’t the only virus thriving out of season or otherwise acting strangely. Since the pandemic began, flu seasons have been out of whack – sometimes nearly nonexistent and other times extending well beyond “normal” seasons. Some experts say one influenza “B” strain may now be extinct, while others say it will be back.
Severe colds – what some call “super colds” – also seem to be on the rise in recent warm-weather months, although that evidence is mostly based on personal experience, not science.
Trying to explain these out-of-season variations has sparked much discussion among epidemiologists and virologists, Dr. Schaffner says, with debates ongoing about whether human behavior and habits or the seasons play a bigger role in the transmission of viral illness.
On top of that, scientists are also looking at the interactions between the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 and other viruses. When people get hit with COVID-19 and other viruses at the same time, does that make COVID-19 more severe, or less?
Research is conflicting.
Summer of 2022: A repeat of 2021?
RSV. Most children contract the virus by age 2, and while it’s generally mild, about 58,000 children under age 5 years are hospitalized each year. During the pandemic, RSV cases decreased from January to April 2020, the CDC reported, and then remained at “historically low levels”: less than 1% positive RSV results a week, for the next year.
But cases began rising in April 2021.
“Last year, we did have an unusual summer,” Dr. Schaffner says. After lockdown ended, to everyone’s surprise, RSV infections rose.
That increase triggered a CDC health advisory in June 2021, telling doctors and caregivers about the increase in “interseasonal” RSV cases across parts of the Southern United States, recommending broader testing for RSV in patients who had a respiratory illness but tested negative for COVID.
Because of the reduced circulation of RSV during the winter of 2020 to 2021, the CDC warned, older infants and toddlers might have a higher risk of RSV since they weren’t exposed to typical levels of RSV for the previous 15 months.
What about 2022? “At the moment,” Dr. Schaffner says, “it looks like we are having a repeat [of 2021].”
On Twitter, other pediatricians, including those from Maine and Texas, have reported an increase in RSV cases this summer.
Influenza. From October 2020 until May 2021, flu activity was lower than during any previous flu season since at least 1997, according to the CDC.
In late 2021, researchers suggested that one line of influenza known as B/Yamagata may have become extinct.
The 2021-2022 flu season has been mild, the CDC says, but it has come in two waves, with the second wave lingering longer than previous ones. While flu activity is decreasing, last week the CDC said doctors should be alert to flu infections throughout the summer.
Colds. In reports on colds that aren’t based on science, several doctors say they are seeing more colds than usual in the summer, and they’re more severe than usual. According to the CDC, common coronaviruses and respiratory adenoviruses have been increasing since early 2021, and rhinoviruses since June 2020.
Behavior vs. seasons
In explaining the spread of viral respiratory diseases, infectious disease doctors consider two things. “One is that temperature and humidity in the winter favors longer survival of some viruses, leading to longer periods of possible transmission,” says Dean Blumberg, MD, a professor of pediatrics and chief of pediatric infectious disease at University of California Davis Health.
“The other is differences in human behavior, with people spending more time outside in the summer, which results in more distancing and [less] virus concentration due to very large air volume,” he says, and vice versa in winter.
What about the “super colds?” COVID-19 lockdowns and social distancing greatly reduced people’s exposure to common viruses like those that cause colds, says Neil A. Mabbott, PhD, a professor of immunopathology at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland).
“Immunity to these common cold viruses gained through natural infection is considered to last around 8 or 9 months or so,” he says. “Each winter, when we are exposed to the new circulating variants of these viruses, our immunity receives a natural boost.”
That explains why most people get a cold that’s relatively mild. But with all the pandemic lockdowns and the use of hand sanitizers, most people had limited exposure to other viruses, including the common cold. When people emerged from lockdown, the common cold viruses were beginning to circulate again.
“Our immune systems were less able to clear the infection than previously,” Dr. Mabbott says. “As a consequence, some may have experienced increased symptoms, giving the impression of being infected with a ‘super cold.’ ”
“The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic,” says Ian Mackay, PhD, a virologist at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia. “But there might be more of them. So I doubt they are ‘super colds’ as much as they are ‘super-perfect circumstances.’ ”
The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic. But there might be more of them.
Those super-perfect circumstances, he says, include people gathering after lockdown; a lack of immunity in new babies; viruses that have remained, even if at low levels, but continue to mutate; and our waning immunity to the range of viruses we’d normally encounter.
While lack of exposure may partly explain why some viruses become rampant out of season, it’s likely not the only reason. For example, the reduced circulation of RSV in the population as a whole also may have reduced the transfer of immunity from mothers to infants, some researchers say, making those infants more vulnerable than usual.
Interactions of viruses
Another thing that may be driving the different behavior of viruses is that the SARS-CoV-2 virus could somehow be interacting with other respiratory viruses, Dr. Schaffner says. “And if so, what sort of interactions?”
Many researchers are looking into that, and how coinfections with other respiratory diseases, including the common cold and flu, may affect the course of COVID-19. Some studies have found that the T cells – a source of deeper, cellular immunity in people – generated after a common cold “may also provide cross-protection in some people against COVID-19.”
But another study found immunity against common cold–causing coronaviruses might make COVID-19 more severe.
When researchers in the United Kingdom studied nearly 7,000 patients infected with COVID-19, including 583 also infected with RSV, flu, or adenoviruses (causing flulike or coldlike illness), those with flu or adenovirus, compared with the others, were at higher risk of death.
To be continued …
Exactly how COVID-19 will be changing what we know of other viruses is yet to be determined, too.
Even before the pandemic, Dr. Martinello says, there were already some shifts in RSV. Florida, for instance, has an RSV season longer than the rest of the country, mimicking the pattern in the tropics.
Will the atypical patterns continue? “My guess is that this will settle out,” he says, with some sort of pattern developing. At this point, there are many unknowns. “We still can’t answer whether there will be some seasonality to COVID.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Richard Martinello, MD, a professor of medicine and pediatric infectious diseases at Yale University, New haven, Conn., doesn’t expect to see a child hospitalized with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in the middle of summer. The illness, which can strike infants and older adults especially hard, is known as a “winter virus.”
But not this year. Over the last several weeks, he says, admissions for children with RSV have increased at the Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital. While the numbers aren’t large, they are out of the ordinary, he says, “because usually, at this time of year, we see zero. For lack of a better term, it’s weird.”
Likewise, William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, says RSV is on the rise there. Tennessee is one of 10 states taking part in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention surveillance system that tracks influenza, RSV, and COVID-19.
He says RSV cases have risen by at least a third during the past week, including all age ranges. At this time of year, he says, “We aren’t supposed to have any RSV.”
RSV isn’t the only virus thriving out of season or otherwise acting strangely. Since the pandemic began, flu seasons have been out of whack – sometimes nearly nonexistent and other times extending well beyond “normal” seasons. Some experts say one influenza “B” strain may now be extinct, while others say it will be back.
Severe colds – what some call “super colds” – also seem to be on the rise in recent warm-weather months, although that evidence is mostly based on personal experience, not science.
Trying to explain these out-of-season variations has sparked much discussion among epidemiologists and virologists, Dr. Schaffner says, with debates ongoing about whether human behavior and habits or the seasons play a bigger role in the transmission of viral illness.
On top of that, scientists are also looking at the interactions between the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 and other viruses. When people get hit with COVID-19 and other viruses at the same time, does that make COVID-19 more severe, or less?
Research is conflicting.
Summer of 2022: A repeat of 2021?
RSV. Most children contract the virus by age 2, and while it’s generally mild, about 58,000 children under age 5 years are hospitalized each year. During the pandemic, RSV cases decreased from January to April 2020, the CDC reported, and then remained at “historically low levels”: less than 1% positive RSV results a week, for the next year.
But cases began rising in April 2021.
“Last year, we did have an unusual summer,” Dr. Schaffner says. After lockdown ended, to everyone’s surprise, RSV infections rose.
That increase triggered a CDC health advisory in June 2021, telling doctors and caregivers about the increase in “interseasonal” RSV cases across parts of the Southern United States, recommending broader testing for RSV in patients who had a respiratory illness but tested negative for COVID.
Because of the reduced circulation of RSV during the winter of 2020 to 2021, the CDC warned, older infants and toddlers might have a higher risk of RSV since they weren’t exposed to typical levels of RSV for the previous 15 months.
What about 2022? “At the moment,” Dr. Schaffner says, “it looks like we are having a repeat [of 2021].”
On Twitter, other pediatricians, including those from Maine and Texas, have reported an increase in RSV cases this summer.
Influenza. From October 2020 until May 2021, flu activity was lower than during any previous flu season since at least 1997, according to the CDC.
In late 2021, researchers suggested that one line of influenza known as B/Yamagata may have become extinct.
The 2021-2022 flu season has been mild, the CDC says, but it has come in two waves, with the second wave lingering longer than previous ones. While flu activity is decreasing, last week the CDC said doctors should be alert to flu infections throughout the summer.
Colds. In reports on colds that aren’t based on science, several doctors say they are seeing more colds than usual in the summer, and they’re more severe than usual. According to the CDC, common coronaviruses and respiratory adenoviruses have been increasing since early 2021, and rhinoviruses since June 2020.
Behavior vs. seasons
In explaining the spread of viral respiratory diseases, infectious disease doctors consider two things. “One is that temperature and humidity in the winter favors longer survival of some viruses, leading to longer periods of possible transmission,” says Dean Blumberg, MD, a professor of pediatrics and chief of pediatric infectious disease at University of California Davis Health.
“The other is differences in human behavior, with people spending more time outside in the summer, which results in more distancing and [less] virus concentration due to very large air volume,” he says, and vice versa in winter.
What about the “super colds?” COVID-19 lockdowns and social distancing greatly reduced people’s exposure to common viruses like those that cause colds, says Neil A. Mabbott, PhD, a professor of immunopathology at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland).
“Immunity to these common cold viruses gained through natural infection is considered to last around 8 or 9 months or so,” he says. “Each winter, when we are exposed to the new circulating variants of these viruses, our immunity receives a natural boost.”
That explains why most people get a cold that’s relatively mild. But with all the pandemic lockdowns and the use of hand sanitizers, most people had limited exposure to other viruses, including the common cold. When people emerged from lockdown, the common cold viruses were beginning to circulate again.
“Our immune systems were less able to clear the infection than previously,” Dr. Mabbott says. “As a consequence, some may have experienced increased symptoms, giving the impression of being infected with a ‘super cold.’ ”
“The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic,” says Ian Mackay, PhD, a virologist at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia. “But there might be more of them. So I doubt they are ‘super colds’ as much as they are ‘super-perfect circumstances.’ ”
The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic. But there might be more of them.
Those super-perfect circumstances, he says, include people gathering after lockdown; a lack of immunity in new babies; viruses that have remained, even if at low levels, but continue to mutate; and our waning immunity to the range of viruses we’d normally encounter.
While lack of exposure may partly explain why some viruses become rampant out of season, it’s likely not the only reason. For example, the reduced circulation of RSV in the population as a whole also may have reduced the transfer of immunity from mothers to infants, some researchers say, making those infants more vulnerable than usual.
Interactions of viruses
Another thing that may be driving the different behavior of viruses is that the SARS-CoV-2 virus could somehow be interacting with other respiratory viruses, Dr. Schaffner says. “And if so, what sort of interactions?”
Many researchers are looking into that, and how coinfections with other respiratory diseases, including the common cold and flu, may affect the course of COVID-19. Some studies have found that the T cells – a source of deeper, cellular immunity in people – generated after a common cold “may also provide cross-protection in some people against COVID-19.”
But another study found immunity against common cold–causing coronaviruses might make COVID-19 more severe.
When researchers in the United Kingdom studied nearly 7,000 patients infected with COVID-19, including 583 also infected with RSV, flu, or adenoviruses (causing flulike or coldlike illness), those with flu or adenovirus, compared with the others, were at higher risk of death.
To be continued …
Exactly how COVID-19 will be changing what we know of other viruses is yet to be determined, too.
Even before the pandemic, Dr. Martinello says, there were already some shifts in RSV. Florida, for instance, has an RSV season longer than the rest of the country, mimicking the pattern in the tropics.
Will the atypical patterns continue? “My guess is that this will settle out,” he says, with some sort of pattern developing. At this point, there are many unknowns. “We still can’t answer whether there will be some seasonality to COVID.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Richard Martinello, MD, a professor of medicine and pediatric infectious diseases at Yale University, New haven, Conn., doesn’t expect to see a child hospitalized with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in the middle of summer. The illness, which can strike infants and older adults especially hard, is known as a “winter virus.”
But not this year. Over the last several weeks, he says, admissions for children with RSV have increased at the Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital. While the numbers aren’t large, they are out of the ordinary, he says, “because usually, at this time of year, we see zero. For lack of a better term, it’s weird.”
Likewise, William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, says RSV is on the rise there. Tennessee is one of 10 states taking part in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention surveillance system that tracks influenza, RSV, and COVID-19.
He says RSV cases have risen by at least a third during the past week, including all age ranges. At this time of year, he says, “We aren’t supposed to have any RSV.”
RSV isn’t the only virus thriving out of season or otherwise acting strangely. Since the pandemic began, flu seasons have been out of whack – sometimes nearly nonexistent and other times extending well beyond “normal” seasons. Some experts say one influenza “B” strain may now be extinct, while others say it will be back.
Severe colds – what some call “super colds” – also seem to be on the rise in recent warm-weather months, although that evidence is mostly based on personal experience, not science.
Trying to explain these out-of-season variations has sparked much discussion among epidemiologists and virologists, Dr. Schaffner says, with debates ongoing about whether human behavior and habits or the seasons play a bigger role in the transmission of viral illness.
On top of that, scientists are also looking at the interactions between the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 and other viruses. When people get hit with COVID-19 and other viruses at the same time, does that make COVID-19 more severe, or less?
Research is conflicting.
Summer of 2022: A repeat of 2021?
RSV. Most children contract the virus by age 2, and while it’s generally mild, about 58,000 children under age 5 years are hospitalized each year. During the pandemic, RSV cases decreased from January to April 2020, the CDC reported, and then remained at “historically low levels”: less than 1% positive RSV results a week, for the next year.
But cases began rising in April 2021.
“Last year, we did have an unusual summer,” Dr. Schaffner says. After lockdown ended, to everyone’s surprise, RSV infections rose.
That increase triggered a CDC health advisory in June 2021, telling doctors and caregivers about the increase in “interseasonal” RSV cases across parts of the Southern United States, recommending broader testing for RSV in patients who had a respiratory illness but tested negative for COVID.
Because of the reduced circulation of RSV during the winter of 2020 to 2021, the CDC warned, older infants and toddlers might have a higher risk of RSV since they weren’t exposed to typical levels of RSV for the previous 15 months.
What about 2022? “At the moment,” Dr. Schaffner says, “it looks like we are having a repeat [of 2021].”
On Twitter, other pediatricians, including those from Maine and Texas, have reported an increase in RSV cases this summer.
Influenza. From October 2020 until May 2021, flu activity was lower than during any previous flu season since at least 1997, according to the CDC.
In late 2021, researchers suggested that one line of influenza known as B/Yamagata may have become extinct.
The 2021-2022 flu season has been mild, the CDC says, but it has come in two waves, with the second wave lingering longer than previous ones. While flu activity is decreasing, last week the CDC said doctors should be alert to flu infections throughout the summer.
Colds. In reports on colds that aren’t based on science, several doctors say they are seeing more colds than usual in the summer, and they’re more severe than usual. According to the CDC, common coronaviruses and respiratory adenoviruses have been increasing since early 2021, and rhinoviruses since June 2020.
Behavior vs. seasons
In explaining the spread of viral respiratory diseases, infectious disease doctors consider two things. “One is that temperature and humidity in the winter favors longer survival of some viruses, leading to longer periods of possible transmission,” says Dean Blumberg, MD, a professor of pediatrics and chief of pediatric infectious disease at University of California Davis Health.
“The other is differences in human behavior, with people spending more time outside in the summer, which results in more distancing and [less] virus concentration due to very large air volume,” he says, and vice versa in winter.
What about the “super colds?” COVID-19 lockdowns and social distancing greatly reduced people’s exposure to common viruses like those that cause colds, says Neil A. Mabbott, PhD, a professor of immunopathology at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland).
“Immunity to these common cold viruses gained through natural infection is considered to last around 8 or 9 months or so,” he says. “Each winter, when we are exposed to the new circulating variants of these viruses, our immunity receives a natural boost.”
That explains why most people get a cold that’s relatively mild. But with all the pandemic lockdowns and the use of hand sanitizers, most people had limited exposure to other viruses, including the common cold. When people emerged from lockdown, the common cold viruses were beginning to circulate again.
“Our immune systems were less able to clear the infection than previously,” Dr. Mabbott says. “As a consequence, some may have experienced increased symptoms, giving the impression of being infected with a ‘super cold.’ ”
“The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic,” says Ian Mackay, PhD, a virologist at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia. “But there might be more of them. So I doubt they are ‘super colds’ as much as they are ‘super-perfect circumstances.’ ”
The colds themselves are probably not different to those we got prepandemic. But there might be more of them.
Those super-perfect circumstances, he says, include people gathering after lockdown; a lack of immunity in new babies; viruses that have remained, even if at low levels, but continue to mutate; and our waning immunity to the range of viruses we’d normally encounter.
While lack of exposure may partly explain why some viruses become rampant out of season, it’s likely not the only reason. For example, the reduced circulation of RSV in the population as a whole also may have reduced the transfer of immunity from mothers to infants, some researchers say, making those infants more vulnerable than usual.
Interactions of viruses
Another thing that may be driving the different behavior of viruses is that the SARS-CoV-2 virus could somehow be interacting with other respiratory viruses, Dr. Schaffner says. “And if so, what sort of interactions?”
Many researchers are looking into that, and how coinfections with other respiratory diseases, including the common cold and flu, may affect the course of COVID-19. Some studies have found that the T cells – a source of deeper, cellular immunity in people – generated after a common cold “may also provide cross-protection in some people against COVID-19.”
But another study found immunity against common cold–causing coronaviruses might make COVID-19 more severe.
When researchers in the United Kingdom studied nearly 7,000 patients infected with COVID-19, including 583 also infected with RSV, flu, or adenoviruses (causing flulike or coldlike illness), those with flu or adenovirus, compared with the others, were at higher risk of death.
To be continued …
Exactly how COVID-19 will be changing what we know of other viruses is yet to be determined, too.
Even before the pandemic, Dr. Martinello says, there were already some shifts in RSV. Florida, for instance, has an RSV season longer than the rest of the country, mimicking the pattern in the tropics.
Will the atypical patterns continue? “My guess is that this will settle out,” he says, with some sort of pattern developing. At this point, there are many unknowns. “We still can’t answer whether there will be some seasonality to COVID.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Solitary Pink Plaque on the Neck
The Diagnosis: Plaque-type Syringoma
A biopsy demonstrated multiple basaloid islands of tumor cells in the reticular dermis with ductal differentiation, some with a commalike tail. The ducts were lined by 2 to 3 layers of small uniform cuboidal cells without atypia and contained inspissated secretions within the lumina of scattered ducts. There was an associated fibrotic collagenous stroma. There was no evidence of perineural invasion and no deep dermal or subcutaneous extension (Figure 1). Additional cytokeratin immunohistochemical staining highlighted the adnexal proliferation (Figure 2). A diagnosis of plaque-type syringoma (PTS) was made.
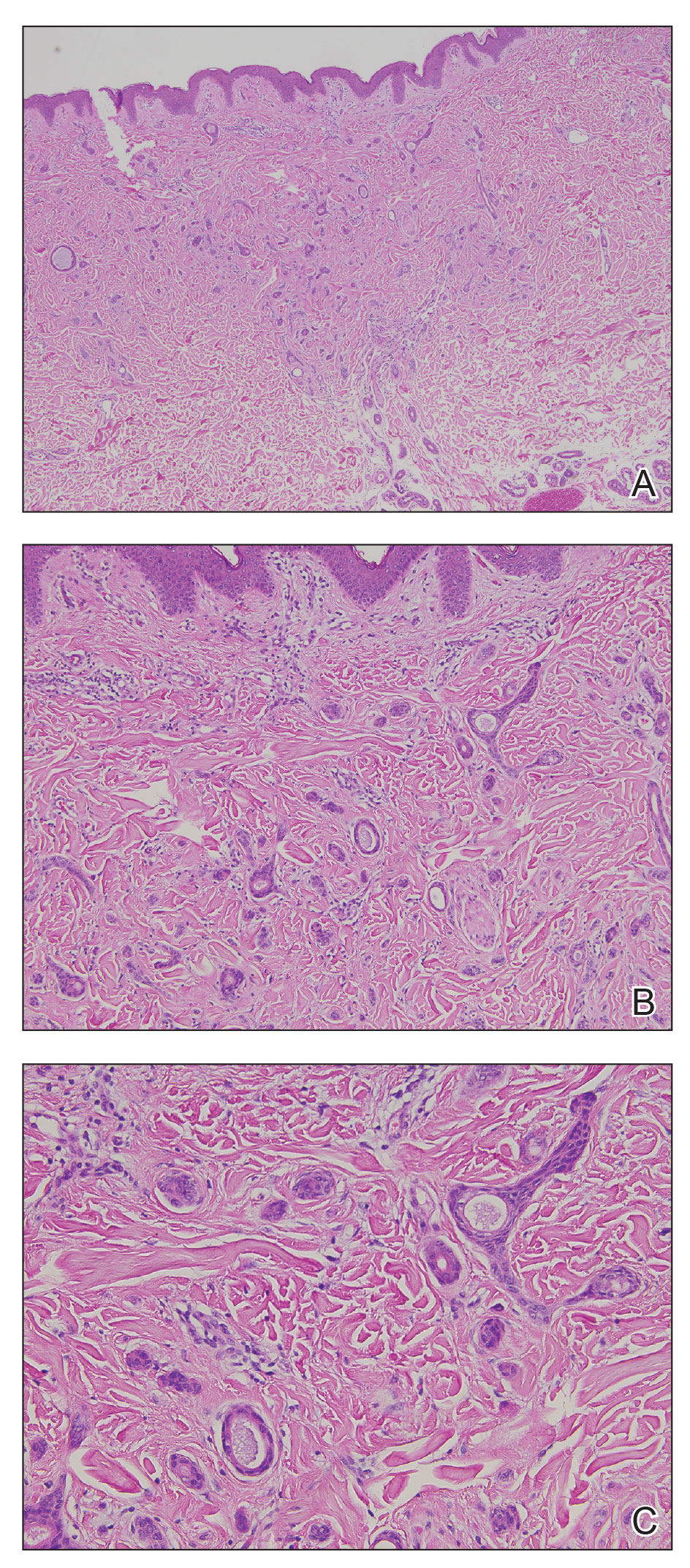
Syringomas are benign dermal sweat gland tumors that typically present as flesh-colored papules on the cheeks or periorbital area of young females. Plaque-type tumors as well as papulonodular, eruptive, disseminated, urticaria pigmentosa–like, lichen planus–like, or milialike syringomas also have been reported. Syringomas may be associated with certain medical conditions such as Down syndrome, Nicolau-Balus syndrome, and both scarring and nonscarring alopecias.1 The clear cell variant of syringoma often is associated with diabetes mellitus.2 Kikuchi et al3 first described PTS in 1979. Plaque-type syringomas rarely are reported in the literature, and sites of involvement include the head and neck region, upper lip, chest, upper extremities, vulva, penis, and scrotum.4-6
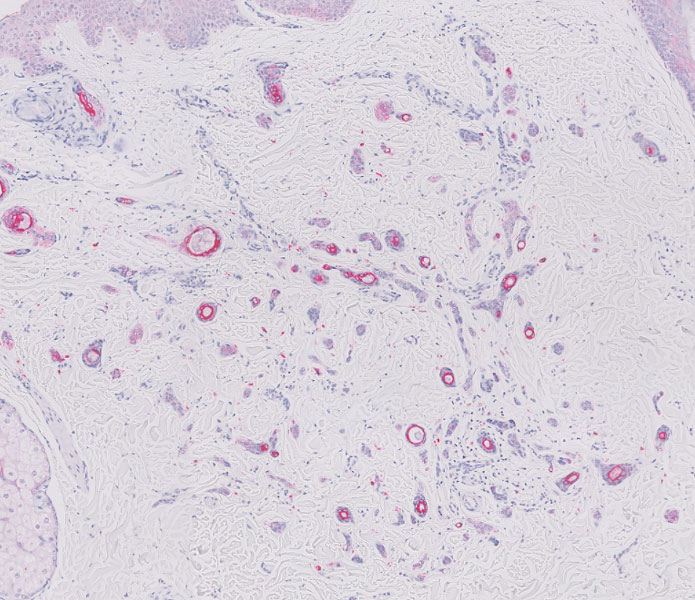
Histologically, syringomatous lesions are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 to 3 layers of cuboidal epithelium. The ducts may be arranged in nests or strands of basaloid cells surrounded by a dense fibrotic stroma. Occasionally, the ducts will form a comma- or teardropshaped tail; however, this also may be observed in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (DTE).7 Perineural invasion is absent in syringomas. Syringomas exhibit a lateral growth pattern that typically is limited to the upper half of the reticular dermis and spares the underlying subcutis, muscle, and bone. The growth pattern may be discontinuous with proliferations juxtaposed by normal-appearing skin.8 Syringomas usually express progesterone receptors and are known to proliferate at puberty, suggesting that these neoplasms are under hormonal control.9 Although syringomas are benign, various treatment options that may be pursued for cosmetic purposes include radiofrequency, staged excision, laser ablation, and oral isotretinoin.8,10 If only a superficial biopsy is obtained, syringomas may display features of other adnexal neoplasms, including microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC), DTE, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a locally aggressive neoplasm first described by Goldstein et al11 in 1982 an indurated, ill-defined plaque or nodule on the face with a predilection for the upper and lower lip. Prior radiation therapy and immunosuppression are risk factors for the development of MAC.12 Histologically, the superficial portion displays small cornifying cysts interspersed with islands of basaloid cells and may mimic a syringoma. However, the deeper portions demonstrate ducts lined by a single layer of cells with a background of hyalinized and sclerotic stroma. The tumor cells may occupy the deep dermis and underlying subcutis, muscle, or bone and demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern and perineural invasion. Treatment includes Mohs micrographic surgery.
Desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas most commonly present as solitary white to yellowish annular papules or plaques with a central dell located on sun-exposed areas of the face, cheeks, or chin. This benign neoplasm has a bimodal age distribution, primarily affecting females either in childhood or adulthood.13 Histologically, strands and nests of basaloid epithelial cells proliferate in a dense eosinophilic desmoplastic stroma. The basaloid islands are narrow and cordlike with growth parallel to the surface epidermis and do not dive deeply into the deep dermis or subcutis. Ductal differentiation with associated secretions typically is not seen in DTE.1 Calcifications and foreign body granulomatous infiltrates may be present. Merkel cells also are present in this tumor and may be highlighted by immunohistochemistry with cytokeratin 20.14 Rarely, desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas may transform into trichoblastic carcinomas. Treatment may consist of surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery.
Morpheaform BCC also is included in the clinical and histopathologic differential diagnosis of infiltrative basaloid neoplasms. It is one of the more aggressive variants of BCC. The use of immunohistochemical staining may aid in differentiating between these sclerosing adnexal neoplasms.15 For example, pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1 (PHLDA1) is a stem cell marker that is heavily expressed in DTE as a specific follicular bulge marker but is not present in a morpheaform BCC. This highlights the follicular nature of DTEs at the molecular level. BerEP4 is a monoclonal antibody that serves as an epithelial marker for 2 glycopolypeptides: 34 and 39 kDa. This antibody may demonstrate positivity in morpheaform BCC but does not stain cells of interest in MAC.
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus clinically presents with erythematous and warty papules in a linear distribution following the Blaschko lines. The papules often are reported to be intensely pruritic and usually are localized to one extremity.16 Although adultonset forms of ILVEN have been described,17 it most commonly is diagnosed in young children. Histologically, ILVEN consists of psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with alternating areas of parakeratosis and orthokeratosis with underlying agranulosis and hypergranulosis, respectively.18 The upper dermis contains a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Treatment with laser therapy and surgical excision has led to both symptomatic and clinical improvement of ILVEN.16
Plaque-type syringomas are a rare variant of syringomas that clinically may mimic other common inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. An adequate biopsy is imperative to differentiate between adnexal neoplasms, as a small superficial biopsy of a syringoma may demonstrate features observed in other malignant or locally aggressive neoplasms. In our patient, the small ducts lined by cuboidal epithelium with no cellular atypia and no deep dermal growth or perineural invasion allowed for the diagnosis of PTS. Therapeutic options were reviewed with our patient, including oral isotretinoin, laser therapy, and staged excision. Ultimately, our patient elected not to pursue treatment, and she is being monitored clinically for any changes in appearance or symptoms.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma [published online November 12, 2007]. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Furue M, Hori Y, Nakabayashi Y. Clear-cell syringoma. association with diabetes mellitus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:131-138.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Okuda H, Tei N, Shimizu K, et al. Chondroid syringoma of the scrotum. Int J Urol. 2008;15:944-945.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaquetype syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:442-445.
- Mainitz M, Schmidt JB, Gebhart W. Response of multiple syringomas to isotretinoin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66:51-55.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Pujol RM, LeBoit PE, Su WP. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma with extensive sebaceous differentiation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:358-362.
- Rahman J, Tahir M, Arekemase H, et al. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma: histopathologic and immunohistochemical criteria for differentiation of a rare benign hair follicle tumor from other cutaneous adnexal tumors. Cureus. 2020;12:E9703.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Sellheyer K, Nelson P, Kutzner H, et al. The immunohistochemical differential diagnosis of microcystic adnexal carcinoma, desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and morpheaform basal cell carcinoma using BerEP4 and stem cell markers. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:363-370.
- Gianfaldoni S, Tchernev G, Gianfaldoni R, et al. A case of “inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus” (ILVEN) treated with CO2 laser ablation. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:454-457.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus [published online October 27, 1999]. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA, Prenshaw KL, et al. The psoriasiform reaction pattern. In: Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2021:99-120.
The Diagnosis: Plaque-type Syringoma
A biopsy demonstrated multiple basaloid islands of tumor cells in the reticular dermis with ductal differentiation, some with a commalike tail. The ducts were lined by 2 to 3 layers of small uniform cuboidal cells without atypia and contained inspissated secretions within the lumina of scattered ducts. There was an associated fibrotic collagenous stroma. There was no evidence of perineural invasion and no deep dermal or subcutaneous extension (Figure 1). Additional cytokeratin immunohistochemical staining highlighted the adnexal proliferation (Figure 2). A diagnosis of plaque-type syringoma (PTS) was made.

Syringomas are benign dermal sweat gland tumors that typically present as flesh-colored papules on the cheeks or periorbital area of young females. Plaque-type tumors as well as papulonodular, eruptive, disseminated, urticaria pigmentosa–like, lichen planus–like, or milialike syringomas also have been reported. Syringomas may be associated with certain medical conditions such as Down syndrome, Nicolau-Balus syndrome, and both scarring and nonscarring alopecias.1 The clear cell variant of syringoma often is associated with diabetes mellitus.2 Kikuchi et al3 first described PTS in 1979. Plaque-type syringomas rarely are reported in the literature, and sites of involvement include the head and neck region, upper lip, chest, upper extremities, vulva, penis, and scrotum.4-6

Histologically, syringomatous lesions are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 to 3 layers of cuboidal epithelium. The ducts may be arranged in nests or strands of basaloid cells surrounded by a dense fibrotic stroma. Occasionally, the ducts will form a comma- or teardropshaped tail; however, this also may be observed in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (DTE).7 Perineural invasion is absent in syringomas. Syringomas exhibit a lateral growth pattern that typically is limited to the upper half of the reticular dermis and spares the underlying subcutis, muscle, and bone. The growth pattern may be discontinuous with proliferations juxtaposed by normal-appearing skin.8 Syringomas usually express progesterone receptors and are known to proliferate at puberty, suggesting that these neoplasms are under hormonal control.9 Although syringomas are benign, various treatment options that may be pursued for cosmetic purposes include radiofrequency, staged excision, laser ablation, and oral isotretinoin.8,10 If only a superficial biopsy is obtained, syringomas may display features of other adnexal neoplasms, including microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC), DTE, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a locally aggressive neoplasm first described by Goldstein et al11 in 1982 an indurated, ill-defined plaque or nodule on the face with a predilection for the upper and lower lip. Prior radiation therapy and immunosuppression are risk factors for the development of MAC.12 Histologically, the superficial portion displays small cornifying cysts interspersed with islands of basaloid cells and may mimic a syringoma. However, the deeper portions demonstrate ducts lined by a single layer of cells with a background of hyalinized and sclerotic stroma. The tumor cells may occupy the deep dermis and underlying subcutis, muscle, or bone and demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern and perineural invasion. Treatment includes Mohs micrographic surgery.
Desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas most commonly present as solitary white to yellowish annular papules or plaques with a central dell located on sun-exposed areas of the face, cheeks, or chin. This benign neoplasm has a bimodal age distribution, primarily affecting females either in childhood or adulthood.13 Histologically, strands and nests of basaloid epithelial cells proliferate in a dense eosinophilic desmoplastic stroma. The basaloid islands are narrow and cordlike with growth parallel to the surface epidermis and do not dive deeply into the deep dermis or subcutis. Ductal differentiation with associated secretions typically is not seen in DTE.1 Calcifications and foreign body granulomatous infiltrates may be present. Merkel cells also are present in this tumor and may be highlighted by immunohistochemistry with cytokeratin 20.14 Rarely, desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas may transform into trichoblastic carcinomas. Treatment may consist of surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery.
Morpheaform BCC also is included in the clinical and histopathologic differential diagnosis of infiltrative basaloid neoplasms. It is one of the more aggressive variants of BCC. The use of immunohistochemical staining may aid in differentiating between these sclerosing adnexal neoplasms.15 For example, pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1 (PHLDA1) is a stem cell marker that is heavily expressed in DTE as a specific follicular bulge marker but is not present in a morpheaform BCC. This highlights the follicular nature of DTEs at the molecular level. BerEP4 is a monoclonal antibody that serves as an epithelial marker for 2 glycopolypeptides: 34 and 39 kDa. This antibody may demonstrate positivity in morpheaform BCC but does not stain cells of interest in MAC.
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus clinically presents with erythematous and warty papules in a linear distribution following the Blaschko lines. The papules often are reported to be intensely pruritic and usually are localized to one extremity.16 Although adultonset forms of ILVEN have been described,17 it most commonly is diagnosed in young children. Histologically, ILVEN consists of psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with alternating areas of parakeratosis and orthokeratosis with underlying agranulosis and hypergranulosis, respectively.18 The upper dermis contains a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Treatment with laser therapy and surgical excision has led to both symptomatic and clinical improvement of ILVEN.16
Plaque-type syringomas are a rare variant of syringomas that clinically may mimic other common inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. An adequate biopsy is imperative to differentiate between adnexal neoplasms, as a small superficial biopsy of a syringoma may demonstrate features observed in other malignant or locally aggressive neoplasms. In our patient, the small ducts lined by cuboidal epithelium with no cellular atypia and no deep dermal growth or perineural invasion allowed for the diagnosis of PTS. Therapeutic options were reviewed with our patient, including oral isotretinoin, laser therapy, and staged excision. Ultimately, our patient elected not to pursue treatment, and she is being monitored clinically for any changes in appearance or symptoms.
The Diagnosis: Plaque-type Syringoma
A biopsy demonstrated multiple basaloid islands of tumor cells in the reticular dermis with ductal differentiation, some with a commalike tail. The ducts were lined by 2 to 3 layers of small uniform cuboidal cells without atypia and contained inspissated secretions within the lumina of scattered ducts. There was an associated fibrotic collagenous stroma. There was no evidence of perineural invasion and no deep dermal or subcutaneous extension (Figure 1). Additional cytokeratin immunohistochemical staining highlighted the adnexal proliferation (Figure 2). A diagnosis of plaque-type syringoma (PTS) was made.

Syringomas are benign dermal sweat gland tumors that typically present as flesh-colored papules on the cheeks or periorbital area of young females. Plaque-type tumors as well as papulonodular, eruptive, disseminated, urticaria pigmentosa–like, lichen planus–like, or milialike syringomas also have been reported. Syringomas may be associated with certain medical conditions such as Down syndrome, Nicolau-Balus syndrome, and both scarring and nonscarring alopecias.1 The clear cell variant of syringoma often is associated with diabetes mellitus.2 Kikuchi et al3 first described PTS in 1979. Plaque-type syringomas rarely are reported in the literature, and sites of involvement include the head and neck region, upper lip, chest, upper extremities, vulva, penis, and scrotum.4-6

Histologically, syringomatous lesions are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 to 3 layers of cuboidal epithelium. The ducts may be arranged in nests or strands of basaloid cells surrounded by a dense fibrotic stroma. Occasionally, the ducts will form a comma- or teardropshaped tail; however, this also may be observed in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (DTE).7 Perineural invasion is absent in syringomas. Syringomas exhibit a lateral growth pattern that typically is limited to the upper half of the reticular dermis and spares the underlying subcutis, muscle, and bone. The growth pattern may be discontinuous with proliferations juxtaposed by normal-appearing skin.8 Syringomas usually express progesterone receptors and are known to proliferate at puberty, suggesting that these neoplasms are under hormonal control.9 Although syringomas are benign, various treatment options that may be pursued for cosmetic purposes include radiofrequency, staged excision, laser ablation, and oral isotretinoin.8,10 If only a superficial biopsy is obtained, syringomas may display features of other adnexal neoplasms, including microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC), DTE, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a locally aggressive neoplasm first described by Goldstein et al11 in 1982 an indurated, ill-defined plaque or nodule on the face with a predilection for the upper and lower lip. Prior radiation therapy and immunosuppression are risk factors for the development of MAC.12 Histologically, the superficial portion displays small cornifying cysts interspersed with islands of basaloid cells and may mimic a syringoma. However, the deeper portions demonstrate ducts lined by a single layer of cells with a background of hyalinized and sclerotic stroma. The tumor cells may occupy the deep dermis and underlying subcutis, muscle, or bone and demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern and perineural invasion. Treatment includes Mohs micrographic surgery.
Desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas most commonly present as solitary white to yellowish annular papules or plaques with a central dell located on sun-exposed areas of the face, cheeks, or chin. This benign neoplasm has a bimodal age distribution, primarily affecting females either in childhood or adulthood.13 Histologically, strands and nests of basaloid epithelial cells proliferate in a dense eosinophilic desmoplastic stroma. The basaloid islands are narrow and cordlike with growth parallel to the surface epidermis and do not dive deeply into the deep dermis or subcutis. Ductal differentiation with associated secretions typically is not seen in DTE.1 Calcifications and foreign body granulomatous infiltrates may be present. Merkel cells also are present in this tumor and may be highlighted by immunohistochemistry with cytokeratin 20.14 Rarely, desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas may transform into trichoblastic carcinomas. Treatment may consist of surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery.
Morpheaform BCC also is included in the clinical and histopathologic differential diagnosis of infiltrative basaloid neoplasms. It is one of the more aggressive variants of BCC. The use of immunohistochemical staining may aid in differentiating between these sclerosing adnexal neoplasms.15 For example, pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1 (PHLDA1) is a stem cell marker that is heavily expressed in DTE as a specific follicular bulge marker but is not present in a morpheaform BCC. This highlights the follicular nature of DTEs at the molecular level. BerEP4 is a monoclonal antibody that serves as an epithelial marker for 2 glycopolypeptides: 34 and 39 kDa. This antibody may demonstrate positivity in morpheaform BCC but does not stain cells of interest in MAC.
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus clinically presents with erythematous and warty papules in a linear distribution following the Blaschko lines. The papules often are reported to be intensely pruritic and usually are localized to one extremity.16 Although adultonset forms of ILVEN have been described,17 it most commonly is diagnosed in young children. Histologically, ILVEN consists of psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with alternating areas of parakeratosis and orthokeratosis with underlying agranulosis and hypergranulosis, respectively.18 The upper dermis contains a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Treatment with laser therapy and surgical excision has led to both symptomatic and clinical improvement of ILVEN.16
Plaque-type syringomas are a rare variant of syringomas that clinically may mimic other common inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. An adequate biopsy is imperative to differentiate between adnexal neoplasms, as a small superficial biopsy of a syringoma may demonstrate features observed in other malignant or locally aggressive neoplasms. In our patient, the small ducts lined by cuboidal epithelium with no cellular atypia and no deep dermal growth or perineural invasion allowed for the diagnosis of PTS. Therapeutic options were reviewed with our patient, including oral isotretinoin, laser therapy, and staged excision. Ultimately, our patient elected not to pursue treatment, and she is being monitored clinically for any changes in appearance or symptoms.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma [published online November 12, 2007]. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Furue M, Hori Y, Nakabayashi Y. Clear-cell syringoma. association with diabetes mellitus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:131-138.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Okuda H, Tei N, Shimizu K, et al. Chondroid syringoma of the scrotum. Int J Urol. 2008;15:944-945.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaquetype syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:442-445.
- Mainitz M, Schmidt JB, Gebhart W. Response of multiple syringomas to isotretinoin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66:51-55.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Pujol RM, LeBoit PE, Su WP. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma with extensive sebaceous differentiation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:358-362.
- Rahman J, Tahir M, Arekemase H, et al. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma: histopathologic and immunohistochemical criteria for differentiation of a rare benign hair follicle tumor from other cutaneous adnexal tumors. Cureus. 2020;12:E9703.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Sellheyer K, Nelson P, Kutzner H, et al. The immunohistochemical differential diagnosis of microcystic adnexal carcinoma, desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and morpheaform basal cell carcinoma using BerEP4 and stem cell markers. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:363-370.
- Gianfaldoni S, Tchernev G, Gianfaldoni R, et al. A case of “inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus” (ILVEN) treated with CO2 laser ablation. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:454-457.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus [published online October 27, 1999]. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA, Prenshaw KL, et al. The psoriasiform reaction pattern. In: Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2021:99-120.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma [published online November 12, 2007]. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Furue M, Hori Y, Nakabayashi Y. Clear-cell syringoma. association with diabetes mellitus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:131-138.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Okuda H, Tei N, Shimizu K, et al. Chondroid syringoma of the scrotum. Int J Urol. 2008;15:944-945.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaquetype syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:442-445.
- Mainitz M, Schmidt JB, Gebhart W. Response of multiple syringomas to isotretinoin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66:51-55.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Pujol RM, LeBoit PE, Su WP. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma with extensive sebaceous differentiation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:358-362.
- Rahman J, Tahir M, Arekemase H, et al. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma: histopathologic and immunohistochemical criteria for differentiation of a rare benign hair follicle tumor from other cutaneous adnexal tumors. Cureus. 2020;12:E9703.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Sellheyer K, Nelson P, Kutzner H, et al. The immunohistochemical differential diagnosis of microcystic adnexal carcinoma, desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and morpheaform basal cell carcinoma using BerEP4 and stem cell markers. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:363-370.
- Gianfaldoni S, Tchernev G, Gianfaldoni R, et al. A case of “inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus” (ILVEN) treated with CO2 laser ablation. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:454-457.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus [published online October 27, 1999]. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA, Prenshaw KL, et al. The psoriasiform reaction pattern. In: Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2021:99-120.
A 17-year-old adolescent girl presented with a solitary, 8-cm, pink plaque on the anterior aspect of the neck of 5 years’ duration. No similar skin findings were present elsewhere on the body. The rash was not painful or pruritic, and she denied prior trauma to the site. The patient previously had tried a salicylic acid bodywash as well as mupirocin cream 2% and mometasone ointment with no improvement. Her medical history was unremarkable, and she had no known allergies. There was no family history of a similar rash. Physical examination revealed no palpable subcutaneous lumps or masses and no lymphadenopathy of the head or neck. An incisional biopsy was performed.
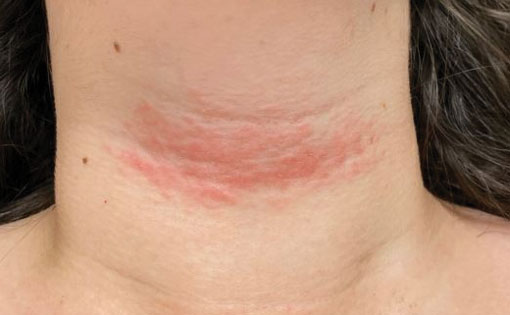
Ustekinumab becomes second biologic approved for PsA in kids
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Weekly cases top 95,000, admissions continue to rise
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.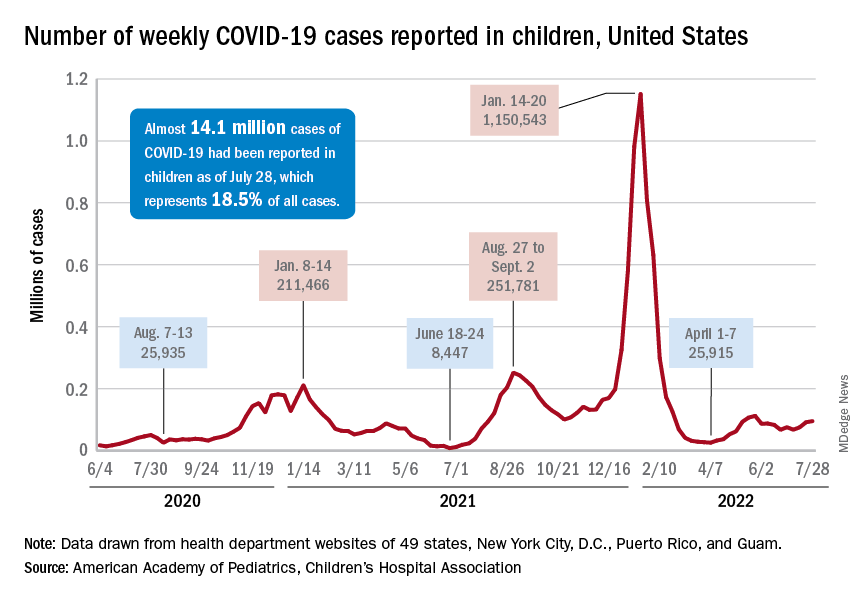
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.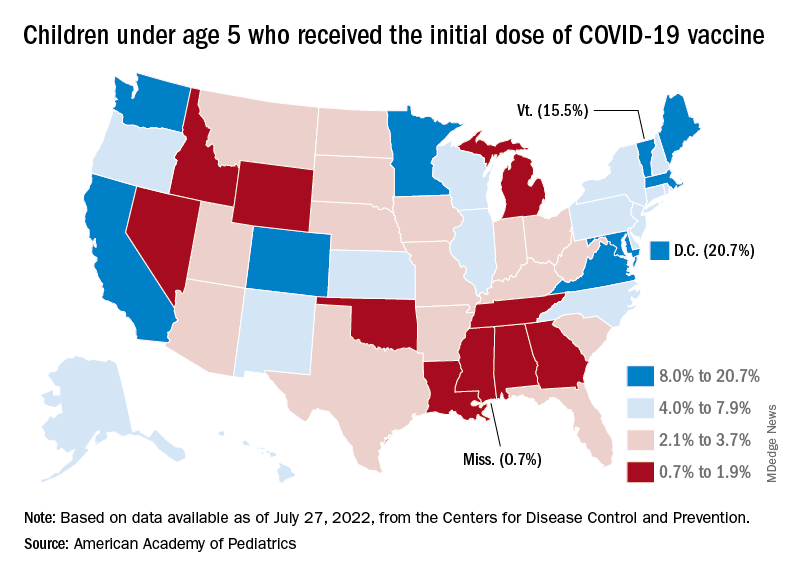
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.