User login
AAP issues clinical update to cerebral palsy guidelines
Updated clinical guidelines for the early diagnosis and management of cerebral palsy have been issued by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Coauthored with the American Academy for Cerebral Palsy and Developmental Medicine, the report builds on new evidence for improved care and outcomes since the 2006 consensus guidelines.
Cerebral palsy, the most common neuromotor disorder of childhood, is often accompanied by cognitive impairments, epilepsy, sensory impairments, behavioral problems, communication difficulties, breathing and sleep problems, gastrointestinal and nutritional problems, and bone and orthopedic problems.
In the United States, the estimated prevalence of cerebral palsy ranges from 1.5 to 4 per 1,000 live births.
“Early identification and initiation of evidence-based motor therapies can improve outcomes by taking advantage of the neuroplasticity in the infant brain,” said the guideline authors in an executive summary.
The guideline, published in Pediatrics, is directed to primary care physicians with pediatrics, family practice, or internal medicine training. “It’s a much more comprehensive overview of the important role that primary care providers play in the lifetime care of people with cerebral palsy,” explained Garey Noritz, MD, chair of the 2021-2022 Executive Committee of the Council on Children with Disabilities. Dr. Noritz, a professor of pediatrics at Ohio State University and division chief of the complex health care program at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, both in Columbus, said: “The combined efforts of the primary care physician and specialty providers are needed to achieve the best outcomes.”
The AAP recommends that primary care pediatricians, neonatologists, and other specialists caring for hospitalized newborns recognize those at high risk of cerebral palsy, diagnose them as early as possible, and promptly refer them for therapy. Primary care physicians are advised to identify motor delays early by formalizing standardized developmental surveillance and screening at 9, 18, and 30 months, and to implement family-centered care across multiple specialists.
“If a motor disorder is suspected, primary care physicians should simultaneously begin a medical evaluation, refer to a specialist for definitive diagnosis, and to therapists for treatment,” Dr. Noritz emphasized.
“The earlier any possible movement disorder is recognized and intervention begins, the better a child can develop a gait pattern and work toward living an independent life, said Manish N. Shah, MD, associate professor of pediatric neurosurgery at the University of Texas, Houston, who was not involved in developing the guidelines.
For children in whom physical therapy and medication have not reduced leg spasticity, a minimally invasive spinal procedure can help release contracted tendons and encourage independent walking. The optimal age for selective dorsal rhizotomy is about 4 years, said Dr. Shah, who is director of the Texas Comprehensive Spasticity Center at Children’s Memorial Hermann Hospital in Houston. “You can turn these children into walkers. As adults, they can get jobs, have their own families. It’s life-changing.”
Importantly, the guidelines address the health care disparities leading to a higher prevalence of cerebral palsy in Black children and in those from families with lower socioeconomic status. “Efforts to combat racism and eliminate barriers to culturally sensitive prenatal, perinatal, and later pediatric care may help to improve outcomes for all children with cerebral palsy,” the authors said.
“Every child with cerebral palsy needs an individual plan, but only 30% or 40% are getting interventions,” said Dr. Shah. The updated guidelines could help payers rethink the 15-20 visits a year that are often approved, compared with the 2-3 visits per week that are needed for speech, physical, and occupational therapy, he pointed out.
“Financial issues often compromise the interdisciplinary and coordinated care associated with favorable outcomes in children with cerebral palsy,” said Heidi Feldman, MD, PhD, a developmental and behavioral pediatric specialist at Stanford (Calif.) Medicine Children’s Health’s Johnson Center for Pregnancy and Newborn Services. “With a new guideline, there may be greater willingness to fund these essential services.”
In the meantime, the AAP recommends that pediatricians advise families about available medical, social, and educational services, such as early intervention services, the Title V Maternal and Child Health block grant program, and special education services through the public school system.
Children with cerebral palsy need the same standardized primary care as any child, including the full schedule of recommended vaccinations and vision and hearing testing. They also need to be monitored and treated for the many problems that commonly co-occur, including chronic pain.
When secondary complications arise, the frequency of visits should increase.
Pneumonia, the leading cause of death in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy, can be prevented or minimized through immunization against respiratory diseases and screening for signs and symptoms of aspiration and sleep-disordered breathing.
The AAP also recommends that symptoms or functional declines undergo full investigation into other potential causes.
Since the sedentary lifestyle associated with cerebral palsy is now known to be related to the higher rates of cardiovascular complications in this patient population, the AAP recommends more attention be paid to physical activity and a healthy diet early in life. Pediatricians are advised to help families locate suitable opportunities for adaptive sports and recreation.
Almost 50% of children and adolescents with cerebral palsy have intellectual disability, 60%-80% have difficulty speaking, and about 25% are nonverbal. To address this, pediatricians should maximize the use of augmentative and alternative communication devices and involve experts in speech and language pathology, according to the guidelines.
“Many individuals with cerebral palsy and severe motor limitations have active, creative minds, and may need assistive technology, such as electronic talking devices, to demonstrate that mental life,” said Dr. Feldman. “Primary care clinicians should advocate for assistive technology.”
For challenging behavior, especially in the patient with limited verbal skills, potential nonbehavioral culprits such as constipation, esophageal reflux disease, and musculoskeletal or dental pain must be ruled out.
In the lead-up to adolescence, youth with cerebral palsy must be prepared for puberty, menstruation, and healthy, safe sexual relationships, much like their nonaffected peers. Since a disproportionate number of children with cerebral palsy experience neglect and physical, sexual, and emotional abuse, however, family stressors should be identified and caregivers referred for support services.
For the transition from pediatric to adult health care, the AAP recommends that structured planning begin between 12 and 14 years of age. Before transfer, the pediatrician should prepare a comprehensive medical summary with the input of the patient, parent/guardian, and pediatric subspecialists.
Without a proper handoff, “there is an increased risk of morbidity, medical complications, unnecessary emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and procedures,” the authors warned.
Transitions are likely to run more smoothly when youth are given the opportunity to understand their medical condition and be involved in decisions about their health. With this in mind, the AAP recommends that pediatricians actively discourage overprotective parents from getting in the way of their child developing “maximal independence.”
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors, Dr. Shah, or Dr. Feldman.
*This story was updated on Nov. 28, 2022.
Updated clinical guidelines for the early diagnosis and management of cerebral palsy have been issued by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Coauthored with the American Academy for Cerebral Palsy and Developmental Medicine, the report builds on new evidence for improved care and outcomes since the 2006 consensus guidelines.
Cerebral palsy, the most common neuromotor disorder of childhood, is often accompanied by cognitive impairments, epilepsy, sensory impairments, behavioral problems, communication difficulties, breathing and sleep problems, gastrointestinal and nutritional problems, and bone and orthopedic problems.
In the United States, the estimated prevalence of cerebral palsy ranges from 1.5 to 4 per 1,000 live births.
“Early identification and initiation of evidence-based motor therapies can improve outcomes by taking advantage of the neuroplasticity in the infant brain,” said the guideline authors in an executive summary.
The guideline, published in Pediatrics, is directed to primary care physicians with pediatrics, family practice, or internal medicine training. “It’s a much more comprehensive overview of the important role that primary care providers play in the lifetime care of people with cerebral palsy,” explained Garey Noritz, MD, chair of the 2021-2022 Executive Committee of the Council on Children with Disabilities. Dr. Noritz, a professor of pediatrics at Ohio State University and division chief of the complex health care program at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, both in Columbus, said: “The combined efforts of the primary care physician and specialty providers are needed to achieve the best outcomes.”
The AAP recommends that primary care pediatricians, neonatologists, and other specialists caring for hospitalized newborns recognize those at high risk of cerebral palsy, diagnose them as early as possible, and promptly refer them for therapy. Primary care physicians are advised to identify motor delays early by formalizing standardized developmental surveillance and screening at 9, 18, and 30 months, and to implement family-centered care across multiple specialists.
“If a motor disorder is suspected, primary care physicians should simultaneously begin a medical evaluation, refer to a specialist for definitive diagnosis, and to therapists for treatment,” Dr. Noritz emphasized.
“The earlier any possible movement disorder is recognized and intervention begins, the better a child can develop a gait pattern and work toward living an independent life, said Manish N. Shah, MD, associate professor of pediatric neurosurgery at the University of Texas, Houston, who was not involved in developing the guidelines.
For children in whom physical therapy and medication have not reduced leg spasticity, a minimally invasive spinal procedure can help release contracted tendons and encourage independent walking. The optimal age for selective dorsal rhizotomy is about 4 years, said Dr. Shah, who is director of the Texas Comprehensive Spasticity Center at Children’s Memorial Hermann Hospital in Houston. “You can turn these children into walkers. As adults, they can get jobs, have their own families. It’s life-changing.”
Importantly, the guidelines address the health care disparities leading to a higher prevalence of cerebral palsy in Black children and in those from families with lower socioeconomic status. “Efforts to combat racism and eliminate barriers to culturally sensitive prenatal, perinatal, and later pediatric care may help to improve outcomes for all children with cerebral palsy,” the authors said.
“Every child with cerebral palsy needs an individual plan, but only 30% or 40% are getting interventions,” said Dr. Shah. The updated guidelines could help payers rethink the 15-20 visits a year that are often approved, compared with the 2-3 visits per week that are needed for speech, physical, and occupational therapy, he pointed out.
“Financial issues often compromise the interdisciplinary and coordinated care associated with favorable outcomes in children with cerebral palsy,” said Heidi Feldman, MD, PhD, a developmental and behavioral pediatric specialist at Stanford (Calif.) Medicine Children’s Health’s Johnson Center for Pregnancy and Newborn Services. “With a new guideline, there may be greater willingness to fund these essential services.”
In the meantime, the AAP recommends that pediatricians advise families about available medical, social, and educational services, such as early intervention services, the Title V Maternal and Child Health block grant program, and special education services through the public school system.
Children with cerebral palsy need the same standardized primary care as any child, including the full schedule of recommended vaccinations and vision and hearing testing. They also need to be monitored and treated for the many problems that commonly co-occur, including chronic pain.
When secondary complications arise, the frequency of visits should increase.
Pneumonia, the leading cause of death in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy, can be prevented or minimized through immunization against respiratory diseases and screening for signs and symptoms of aspiration and sleep-disordered breathing.
The AAP also recommends that symptoms or functional declines undergo full investigation into other potential causes.
Since the sedentary lifestyle associated with cerebral palsy is now known to be related to the higher rates of cardiovascular complications in this patient population, the AAP recommends more attention be paid to physical activity and a healthy diet early in life. Pediatricians are advised to help families locate suitable opportunities for adaptive sports and recreation.
Almost 50% of children and adolescents with cerebral palsy have intellectual disability, 60%-80% have difficulty speaking, and about 25% are nonverbal. To address this, pediatricians should maximize the use of augmentative and alternative communication devices and involve experts in speech and language pathology, according to the guidelines.
“Many individuals with cerebral palsy and severe motor limitations have active, creative minds, and may need assistive technology, such as electronic talking devices, to demonstrate that mental life,” said Dr. Feldman. “Primary care clinicians should advocate for assistive technology.”
For challenging behavior, especially in the patient with limited verbal skills, potential nonbehavioral culprits such as constipation, esophageal reflux disease, and musculoskeletal or dental pain must be ruled out.
In the lead-up to adolescence, youth with cerebral palsy must be prepared for puberty, menstruation, and healthy, safe sexual relationships, much like their nonaffected peers. Since a disproportionate number of children with cerebral palsy experience neglect and physical, sexual, and emotional abuse, however, family stressors should be identified and caregivers referred for support services.
For the transition from pediatric to adult health care, the AAP recommends that structured planning begin between 12 and 14 years of age. Before transfer, the pediatrician should prepare a comprehensive medical summary with the input of the patient, parent/guardian, and pediatric subspecialists.
Without a proper handoff, “there is an increased risk of morbidity, medical complications, unnecessary emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and procedures,” the authors warned.
Transitions are likely to run more smoothly when youth are given the opportunity to understand their medical condition and be involved in decisions about their health. With this in mind, the AAP recommends that pediatricians actively discourage overprotective parents from getting in the way of their child developing “maximal independence.”
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors, Dr. Shah, or Dr. Feldman.
*This story was updated on Nov. 28, 2022.
Updated clinical guidelines for the early diagnosis and management of cerebral palsy have been issued by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Coauthored with the American Academy for Cerebral Palsy and Developmental Medicine, the report builds on new evidence for improved care and outcomes since the 2006 consensus guidelines.
Cerebral palsy, the most common neuromotor disorder of childhood, is often accompanied by cognitive impairments, epilepsy, sensory impairments, behavioral problems, communication difficulties, breathing and sleep problems, gastrointestinal and nutritional problems, and bone and orthopedic problems.
In the United States, the estimated prevalence of cerebral palsy ranges from 1.5 to 4 per 1,000 live births.
“Early identification and initiation of evidence-based motor therapies can improve outcomes by taking advantage of the neuroplasticity in the infant brain,” said the guideline authors in an executive summary.
The guideline, published in Pediatrics, is directed to primary care physicians with pediatrics, family practice, or internal medicine training. “It’s a much more comprehensive overview of the important role that primary care providers play in the lifetime care of people with cerebral palsy,” explained Garey Noritz, MD, chair of the 2021-2022 Executive Committee of the Council on Children with Disabilities. Dr. Noritz, a professor of pediatrics at Ohio State University and division chief of the complex health care program at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, both in Columbus, said: “The combined efforts of the primary care physician and specialty providers are needed to achieve the best outcomes.”
The AAP recommends that primary care pediatricians, neonatologists, and other specialists caring for hospitalized newborns recognize those at high risk of cerebral palsy, diagnose them as early as possible, and promptly refer them for therapy. Primary care physicians are advised to identify motor delays early by formalizing standardized developmental surveillance and screening at 9, 18, and 30 months, and to implement family-centered care across multiple specialists.
“If a motor disorder is suspected, primary care physicians should simultaneously begin a medical evaluation, refer to a specialist for definitive diagnosis, and to therapists for treatment,” Dr. Noritz emphasized.
“The earlier any possible movement disorder is recognized and intervention begins, the better a child can develop a gait pattern and work toward living an independent life, said Manish N. Shah, MD, associate professor of pediatric neurosurgery at the University of Texas, Houston, who was not involved in developing the guidelines.
For children in whom physical therapy and medication have not reduced leg spasticity, a minimally invasive spinal procedure can help release contracted tendons and encourage independent walking. The optimal age for selective dorsal rhizotomy is about 4 years, said Dr. Shah, who is director of the Texas Comprehensive Spasticity Center at Children’s Memorial Hermann Hospital in Houston. “You can turn these children into walkers. As adults, they can get jobs, have their own families. It’s life-changing.”
Importantly, the guidelines address the health care disparities leading to a higher prevalence of cerebral palsy in Black children and in those from families with lower socioeconomic status. “Efforts to combat racism and eliminate barriers to culturally sensitive prenatal, perinatal, and later pediatric care may help to improve outcomes for all children with cerebral palsy,” the authors said.
“Every child with cerebral palsy needs an individual plan, but only 30% or 40% are getting interventions,” said Dr. Shah. The updated guidelines could help payers rethink the 15-20 visits a year that are often approved, compared with the 2-3 visits per week that are needed for speech, physical, and occupational therapy, he pointed out.
“Financial issues often compromise the interdisciplinary and coordinated care associated with favorable outcomes in children with cerebral palsy,” said Heidi Feldman, MD, PhD, a developmental and behavioral pediatric specialist at Stanford (Calif.) Medicine Children’s Health’s Johnson Center for Pregnancy and Newborn Services. “With a new guideline, there may be greater willingness to fund these essential services.”
In the meantime, the AAP recommends that pediatricians advise families about available medical, social, and educational services, such as early intervention services, the Title V Maternal and Child Health block grant program, and special education services through the public school system.
Children with cerebral palsy need the same standardized primary care as any child, including the full schedule of recommended vaccinations and vision and hearing testing. They also need to be monitored and treated for the many problems that commonly co-occur, including chronic pain.
When secondary complications arise, the frequency of visits should increase.
Pneumonia, the leading cause of death in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy, can be prevented or minimized through immunization against respiratory diseases and screening for signs and symptoms of aspiration and sleep-disordered breathing.
The AAP also recommends that symptoms or functional declines undergo full investigation into other potential causes.
Since the sedentary lifestyle associated with cerebral palsy is now known to be related to the higher rates of cardiovascular complications in this patient population, the AAP recommends more attention be paid to physical activity and a healthy diet early in life. Pediatricians are advised to help families locate suitable opportunities for adaptive sports and recreation.
Almost 50% of children and adolescents with cerebral palsy have intellectual disability, 60%-80% have difficulty speaking, and about 25% are nonverbal. To address this, pediatricians should maximize the use of augmentative and alternative communication devices and involve experts in speech and language pathology, according to the guidelines.
“Many individuals with cerebral palsy and severe motor limitations have active, creative minds, and may need assistive technology, such as electronic talking devices, to demonstrate that mental life,” said Dr. Feldman. “Primary care clinicians should advocate for assistive technology.”
For challenging behavior, especially in the patient with limited verbal skills, potential nonbehavioral culprits such as constipation, esophageal reflux disease, and musculoskeletal or dental pain must be ruled out.
In the lead-up to adolescence, youth with cerebral palsy must be prepared for puberty, menstruation, and healthy, safe sexual relationships, much like their nonaffected peers. Since a disproportionate number of children with cerebral palsy experience neglect and physical, sexual, and emotional abuse, however, family stressors should be identified and caregivers referred for support services.
For the transition from pediatric to adult health care, the AAP recommends that structured planning begin between 12 and 14 years of age. Before transfer, the pediatrician should prepare a comprehensive medical summary with the input of the patient, parent/guardian, and pediatric subspecialists.
Without a proper handoff, “there is an increased risk of morbidity, medical complications, unnecessary emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and procedures,” the authors warned.
Transitions are likely to run more smoothly when youth are given the opportunity to understand their medical condition and be involved in decisions about their health. With this in mind, the AAP recommends that pediatricians actively discourage overprotective parents from getting in the way of their child developing “maximal independence.”
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors, Dr. Shah, or Dr. Feldman.
*This story was updated on Nov. 28, 2022.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Children and COVID: Weekly cases maintain a low-level plateau
A less-than-1% decrease in weekly COVID-19 cases in children demonstrated continued stability in the pandemic situation as the nation heads into the holiday season.
the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in the latest edition of their joint COVID report.
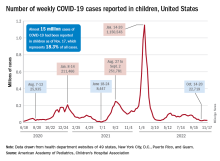
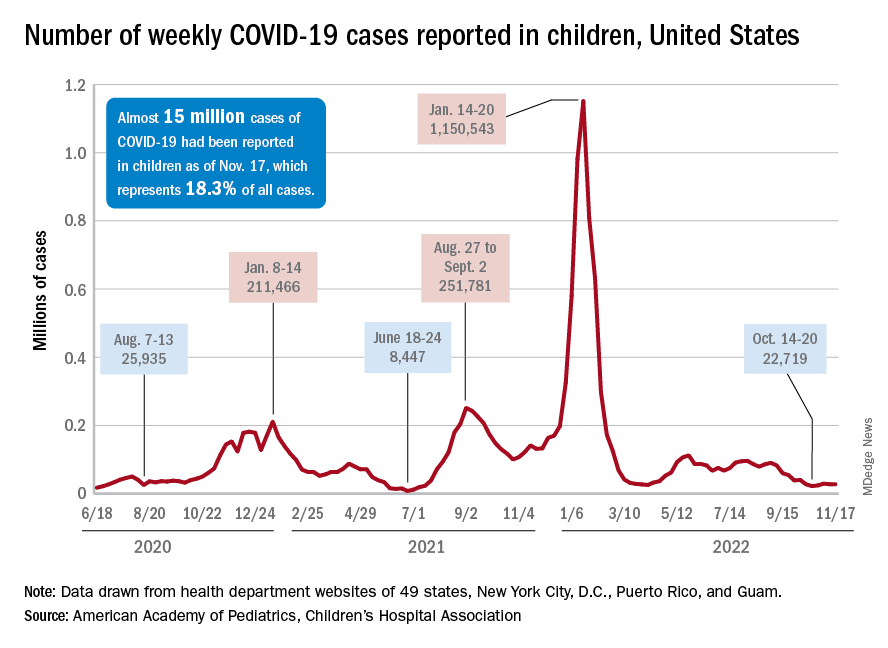
New cases for the week of Nov. 11-17 totaled 27,899, down by 0.9% from the previous week and just 4 weeks removed from the lowest total of the year: 22,719 for Oct. 14-20. There have been just under 15 million cases of COVID-19 in children since the pandemic began, and children represent 18.3% of cases in all ages, the AAP and CHA reported.
Conditions look favorable for that plateau to continue, despite the upcoming holidays, White House COVID-19 coordinator Ashish Jha said recently. “We are in a very different place and we will remain in a different place,” Dr. Jha said, according to STAT News. “We are now at a point where I believe if you’re up to date on your vaccines, you have access to treatments ... there really should be no restrictions on people’s activities.”
One possible spoiler, an apparent spike in COVID-related hospitalizations in children we reported last week, seems to have been a false alarm. The rate of new admissions for Nov. 11, which preliminary data suggested was 0.48 per 100,000 population, has now been revised with more solid data to 0.20 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We continue to monitor the recent increases in admissions among children. Some of these may be admissions with COVID-19, not because of COVID-19. Co-infections are being noted in our surveillance systems for hospitalizations among children; as much as 10% of admissions or higher have viruses codetected (RSV, influenza, enterovirus/rhinovirus, and other respiratory viruses),” a CDC spokesperson told this news organization.
For children aged 0-17 years, the current 7-day (Nov. 13-19) average number of new admissions with confirmed COVID is 129 per day, down from 147 for the previous 7-day average. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, are largely holding steady. The latest 7-day averages available (Nov. 18) – 1.0% for children aged 0-11 years, 0.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds, and 0.8% in 16- to 17-year-olds – are the same or within a tenth of a percent of the rates recorded on Oct. 18, CDC data show.
New vaccinations for the week of Nov. 10-16 were down just slightly for children under age 5 years and for those aged 5-11 years, with a larger drop seen among 12- to 17-year-olds, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. So far, 7.9% of all children under age 5 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have 39.1% of 5 to 11-year-olds and 71.5% of those aged 12-17years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
A less-than-1% decrease in weekly COVID-19 cases in children demonstrated continued stability in the pandemic situation as the nation heads into the holiday season.
the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in the latest edition of their joint COVID report.
New cases for the week of Nov. 11-17 totaled 27,899, down by 0.9% from the previous week and just 4 weeks removed from the lowest total of the year: 22,719 for Oct. 14-20. There have been just under 15 million cases of COVID-19 in children since the pandemic began, and children represent 18.3% of cases in all ages, the AAP and CHA reported.
Conditions look favorable for that plateau to continue, despite the upcoming holidays, White House COVID-19 coordinator Ashish Jha said recently. “We are in a very different place and we will remain in a different place,” Dr. Jha said, according to STAT News. “We are now at a point where I believe if you’re up to date on your vaccines, you have access to treatments ... there really should be no restrictions on people’s activities.”
One possible spoiler, an apparent spike in COVID-related hospitalizations in children we reported last week, seems to have been a false alarm. The rate of new admissions for Nov. 11, which preliminary data suggested was 0.48 per 100,000 population, has now been revised with more solid data to 0.20 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We continue to monitor the recent increases in admissions among children. Some of these may be admissions with COVID-19, not because of COVID-19. Co-infections are being noted in our surveillance systems for hospitalizations among children; as much as 10% of admissions or higher have viruses codetected (RSV, influenza, enterovirus/rhinovirus, and other respiratory viruses),” a CDC spokesperson told this news organization.
For children aged 0-17 years, the current 7-day (Nov. 13-19) average number of new admissions with confirmed COVID is 129 per day, down from 147 for the previous 7-day average. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, are largely holding steady. The latest 7-day averages available (Nov. 18) – 1.0% for children aged 0-11 years, 0.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds, and 0.8% in 16- to 17-year-olds – are the same or within a tenth of a percent of the rates recorded on Oct. 18, CDC data show.
New vaccinations for the week of Nov. 10-16 were down just slightly for children under age 5 years and for those aged 5-11 years, with a larger drop seen among 12- to 17-year-olds, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. So far, 7.9% of all children under age 5 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have 39.1% of 5 to 11-year-olds and 71.5% of those aged 12-17years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
A less-than-1% decrease in weekly COVID-19 cases in children demonstrated continued stability in the pandemic situation as the nation heads into the holiday season.
the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in the latest edition of their joint COVID report.
New cases for the week of Nov. 11-17 totaled 27,899, down by 0.9% from the previous week and just 4 weeks removed from the lowest total of the year: 22,719 for Oct. 14-20. There have been just under 15 million cases of COVID-19 in children since the pandemic began, and children represent 18.3% of cases in all ages, the AAP and CHA reported.
Conditions look favorable for that plateau to continue, despite the upcoming holidays, White House COVID-19 coordinator Ashish Jha said recently. “We are in a very different place and we will remain in a different place,” Dr. Jha said, according to STAT News. “We are now at a point where I believe if you’re up to date on your vaccines, you have access to treatments ... there really should be no restrictions on people’s activities.”
One possible spoiler, an apparent spike in COVID-related hospitalizations in children we reported last week, seems to have been a false alarm. The rate of new admissions for Nov. 11, which preliminary data suggested was 0.48 per 100,000 population, has now been revised with more solid data to 0.20 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We continue to monitor the recent increases in admissions among children. Some of these may be admissions with COVID-19, not because of COVID-19. Co-infections are being noted in our surveillance systems for hospitalizations among children; as much as 10% of admissions or higher have viruses codetected (RSV, influenza, enterovirus/rhinovirus, and other respiratory viruses),” a CDC spokesperson told this news organization.
For children aged 0-17 years, the current 7-day (Nov. 13-19) average number of new admissions with confirmed COVID is 129 per day, down from 147 for the previous 7-day average. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, are largely holding steady. The latest 7-day averages available (Nov. 18) – 1.0% for children aged 0-11 years, 0.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds, and 0.8% in 16- to 17-year-olds – are the same or within a tenth of a percent of the rates recorded on Oct. 18, CDC data show.
New vaccinations for the week of Nov. 10-16 were down just slightly for children under age 5 years and for those aged 5-11 years, with a larger drop seen among 12- to 17-year-olds, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. So far, 7.9% of all children under age 5 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have 39.1% of 5 to 11-year-olds and 71.5% of those aged 12-17years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Local-level youth suicides reflect mental health care shortages
Rates of youth suicides at the county level increased as mental health professional shortages increased, based on data from more than 5,000 youth suicides across all counties in the United States.
Suicide remains the second leading cause of death among adolescents in the United States, and shortages of pediatric mental health providers are well known, but the association between mental health workforce shortages and youth suicides at the local level has not been well studied, Jennifer A. Hoffmann, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues wrote.
Previous studies have shown few or no child psychiatrists or child-focused mental health professionals in most counties across the United States, and shortages are more likely in rural and high-poverty counties, the researchers noted.
In a cross-sectional study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed all youth suicide data from January 2015 to Dec. 31, 2016 using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Compressed Mortality File. They used a multivariate binomial regression model to examine the association between youth suicide rates and the presence or absence of mental health care. Mental health care shortages were based on data from the U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration’s assessment of the number of mental health professionals relative to the country population and the availability of nearby services. Areas identified as having shortages were designated as Health Professional Shortage Areas (HPSAs) and scored on a severity level of 0-25, with higher scores indicating greater shortages. Approximately two-thirds (67.6%) of the 3,133 counties included in the study met criteria for mental health workforce shortage areas.
The researchers identified 5,034 suicides in youth aged 5-19 years during the study period, for an annual rate of 3.99 per 100,000 individuals. Of these, 72.8% were male and 68.2% were non-Hispanic White.
Overall, a county designation of mental health care shortage was significantly associated with an increased rate of youth suicide (adjusted incidence rate ratio, 1.16) and also increased rate of youth firearm suicide (aIRR, 1.27) after controlling for county and socioeconomic characteristics including the presence of a children’s mental health hospital, the percentage of children without health insurance, median household income, and racial makeup of the county.
The adjusted youth suicide rate increased by 4% for every 1-point increase in the HPSA score in counties with designated mental health workforce shortages.
The adjusted youth suicide rates were higher in counties with a lower median household income, and youth suicides increased with increases in the percentages of uninsured children, the researchers wrote.
“Reducing poverty, addressing social determinants of health, and improving insurance coverage may be considered as components of a multipronged societal strategy to improve child health and reduce youth suicides,” they said. “Efforts are needed to enhance the mental health professional workforce to match current levels of need.” Possible strategies to increase the pediatric mental health workforce may include improving reimbursement and integrating mental health care into primary care and schools by expanding telehealth services.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential misclassification of demographics or cause of death, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the inability to assess actual use of mental health services or firearm ownership in a household, and the possible differences between county-level associations and those of a city, neighborhood, or individual.
However, the results indicate that mental health professional workforce shortages were associated with increased youth suicide rates, and the data may inform local-level suicide prevention efforts, they concluded.
Data support the need for early intervention
“It was very important to conduct this study at this time because mental health problems, to include suicidal ideation, continue to increase in adolescents,” Peter L. Loper Jr., MD, of the University of South Carolina, Columbia, said in an interview. “This study reinforces the immense import of sufficient mental health workforce to mitigate this increasing risk of suicide in adolescents.”
Dr. Loper said: “I believe that early intervention, or consistent access to mental health services, can go a very long way in preventing suicide in adolescents.
“I think the primary implications of this study are more relevant at the systems level, and reinforce the necessity of clinicians advocating for policies that address mental health workforce shortages in counties that are underserved,” he added.
However, “One primary barrier to increasing the number of mental health professionals at a local level, and specifically the number of child psychiatrists, is that demand is currently outpacing supply,” said Dr. Loper, a pediatrician and psychiatrist who was not involved in the study. “As the study authors cite, increasing telepsychiatry services and increasing mental health workforce specifically in the primary care setting may help offset these deficiencies,” he noted. Looking ahead, primary prevention of mental health problems by grassroots efforts is vital to stopping the trend in increased youth suicides and more mental health professionals are needed to mitigate the phenomenon of isolation and the degradation of community constructs.
As for additional research, Dr. Loper agreed with the study authors comments on the need for “more granular data” to better understand the correlation between mental health workforce and suicide in adolescents. “Data that captures city or neighborhood statistics related to mental health workforce and adolescent suicide could go a long way in our efforts to continue to better understand this very important correlation.”
The study was supported by an Academic Pediatric Association Young Investigator Award. Dr. Hoffmann disclosed research funding from the U.S. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality unrelated to the current study. Dr. Loper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Rates of youth suicides at the county level increased as mental health professional shortages increased, based on data from more than 5,000 youth suicides across all counties in the United States.
Suicide remains the second leading cause of death among adolescents in the United States, and shortages of pediatric mental health providers are well known, but the association between mental health workforce shortages and youth suicides at the local level has not been well studied, Jennifer A. Hoffmann, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues wrote.
Previous studies have shown few or no child psychiatrists or child-focused mental health professionals in most counties across the United States, and shortages are more likely in rural and high-poverty counties, the researchers noted.
In a cross-sectional study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed all youth suicide data from January 2015 to Dec. 31, 2016 using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Compressed Mortality File. They used a multivariate binomial regression model to examine the association between youth suicide rates and the presence or absence of mental health care. Mental health care shortages were based on data from the U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration’s assessment of the number of mental health professionals relative to the country population and the availability of nearby services. Areas identified as having shortages were designated as Health Professional Shortage Areas (HPSAs) and scored on a severity level of 0-25, with higher scores indicating greater shortages. Approximately two-thirds (67.6%) of the 3,133 counties included in the study met criteria for mental health workforce shortage areas.
The researchers identified 5,034 suicides in youth aged 5-19 years during the study period, for an annual rate of 3.99 per 100,000 individuals. Of these, 72.8% were male and 68.2% were non-Hispanic White.
Overall, a county designation of mental health care shortage was significantly associated with an increased rate of youth suicide (adjusted incidence rate ratio, 1.16) and also increased rate of youth firearm suicide (aIRR, 1.27) after controlling for county and socioeconomic characteristics including the presence of a children’s mental health hospital, the percentage of children without health insurance, median household income, and racial makeup of the county.
The adjusted youth suicide rate increased by 4% for every 1-point increase in the HPSA score in counties with designated mental health workforce shortages.
The adjusted youth suicide rates were higher in counties with a lower median household income, and youth suicides increased with increases in the percentages of uninsured children, the researchers wrote.
“Reducing poverty, addressing social determinants of health, and improving insurance coverage may be considered as components of a multipronged societal strategy to improve child health and reduce youth suicides,” they said. “Efforts are needed to enhance the mental health professional workforce to match current levels of need.” Possible strategies to increase the pediatric mental health workforce may include improving reimbursement and integrating mental health care into primary care and schools by expanding telehealth services.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential misclassification of demographics or cause of death, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the inability to assess actual use of mental health services or firearm ownership in a household, and the possible differences between county-level associations and those of a city, neighborhood, or individual.
However, the results indicate that mental health professional workforce shortages were associated with increased youth suicide rates, and the data may inform local-level suicide prevention efforts, they concluded.
Data support the need for early intervention
“It was very important to conduct this study at this time because mental health problems, to include suicidal ideation, continue to increase in adolescents,” Peter L. Loper Jr., MD, of the University of South Carolina, Columbia, said in an interview. “This study reinforces the immense import of sufficient mental health workforce to mitigate this increasing risk of suicide in adolescents.”
Dr. Loper said: “I believe that early intervention, or consistent access to mental health services, can go a very long way in preventing suicide in adolescents.
“I think the primary implications of this study are more relevant at the systems level, and reinforce the necessity of clinicians advocating for policies that address mental health workforce shortages in counties that are underserved,” he added.
However, “One primary barrier to increasing the number of mental health professionals at a local level, and specifically the number of child psychiatrists, is that demand is currently outpacing supply,” said Dr. Loper, a pediatrician and psychiatrist who was not involved in the study. “As the study authors cite, increasing telepsychiatry services and increasing mental health workforce specifically in the primary care setting may help offset these deficiencies,” he noted. Looking ahead, primary prevention of mental health problems by grassroots efforts is vital to stopping the trend in increased youth suicides and more mental health professionals are needed to mitigate the phenomenon of isolation and the degradation of community constructs.
As for additional research, Dr. Loper agreed with the study authors comments on the need for “more granular data” to better understand the correlation between mental health workforce and suicide in adolescents. “Data that captures city or neighborhood statistics related to mental health workforce and adolescent suicide could go a long way in our efforts to continue to better understand this very important correlation.”
The study was supported by an Academic Pediatric Association Young Investigator Award. Dr. Hoffmann disclosed research funding from the U.S. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality unrelated to the current study. Dr. Loper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Rates of youth suicides at the county level increased as mental health professional shortages increased, based on data from more than 5,000 youth suicides across all counties in the United States.
Suicide remains the second leading cause of death among adolescents in the United States, and shortages of pediatric mental health providers are well known, but the association between mental health workforce shortages and youth suicides at the local level has not been well studied, Jennifer A. Hoffmann, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues wrote.
Previous studies have shown few or no child psychiatrists or child-focused mental health professionals in most counties across the United States, and shortages are more likely in rural and high-poverty counties, the researchers noted.
In a cross-sectional study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed all youth suicide data from January 2015 to Dec. 31, 2016 using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Compressed Mortality File. They used a multivariate binomial regression model to examine the association between youth suicide rates and the presence or absence of mental health care. Mental health care shortages were based on data from the U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration’s assessment of the number of mental health professionals relative to the country population and the availability of nearby services. Areas identified as having shortages were designated as Health Professional Shortage Areas (HPSAs) and scored on a severity level of 0-25, with higher scores indicating greater shortages. Approximately two-thirds (67.6%) of the 3,133 counties included in the study met criteria for mental health workforce shortage areas.
The researchers identified 5,034 suicides in youth aged 5-19 years during the study period, for an annual rate of 3.99 per 100,000 individuals. Of these, 72.8% were male and 68.2% were non-Hispanic White.
Overall, a county designation of mental health care shortage was significantly associated with an increased rate of youth suicide (adjusted incidence rate ratio, 1.16) and also increased rate of youth firearm suicide (aIRR, 1.27) after controlling for county and socioeconomic characteristics including the presence of a children’s mental health hospital, the percentage of children without health insurance, median household income, and racial makeup of the county.
The adjusted youth suicide rate increased by 4% for every 1-point increase in the HPSA score in counties with designated mental health workforce shortages.
The adjusted youth suicide rates were higher in counties with a lower median household income, and youth suicides increased with increases in the percentages of uninsured children, the researchers wrote.
“Reducing poverty, addressing social determinants of health, and improving insurance coverage may be considered as components of a multipronged societal strategy to improve child health and reduce youth suicides,” they said. “Efforts are needed to enhance the mental health professional workforce to match current levels of need.” Possible strategies to increase the pediatric mental health workforce may include improving reimbursement and integrating mental health care into primary care and schools by expanding telehealth services.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential misclassification of demographics or cause of death, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the inability to assess actual use of mental health services or firearm ownership in a household, and the possible differences between county-level associations and those of a city, neighborhood, or individual.
However, the results indicate that mental health professional workforce shortages were associated with increased youth suicide rates, and the data may inform local-level suicide prevention efforts, they concluded.
Data support the need for early intervention
“It was very important to conduct this study at this time because mental health problems, to include suicidal ideation, continue to increase in adolescents,” Peter L. Loper Jr., MD, of the University of South Carolina, Columbia, said in an interview. “This study reinforces the immense import of sufficient mental health workforce to mitigate this increasing risk of suicide in adolescents.”
Dr. Loper said: “I believe that early intervention, or consistent access to mental health services, can go a very long way in preventing suicide in adolescents.
“I think the primary implications of this study are more relevant at the systems level, and reinforce the necessity of clinicians advocating for policies that address mental health workforce shortages in counties that are underserved,” he added.
However, “One primary barrier to increasing the number of mental health professionals at a local level, and specifically the number of child psychiatrists, is that demand is currently outpacing supply,” said Dr. Loper, a pediatrician and psychiatrist who was not involved in the study. “As the study authors cite, increasing telepsychiatry services and increasing mental health workforce specifically in the primary care setting may help offset these deficiencies,” he noted. Looking ahead, primary prevention of mental health problems by grassroots efforts is vital to stopping the trend in increased youth suicides and more mental health professionals are needed to mitigate the phenomenon of isolation and the degradation of community constructs.
As for additional research, Dr. Loper agreed with the study authors comments on the need for “more granular data” to better understand the correlation between mental health workforce and suicide in adolescents. “Data that captures city or neighborhood statistics related to mental health workforce and adolescent suicide could go a long way in our efforts to continue to better understand this very important correlation.”
The study was supported by an Academic Pediatric Association Young Investigator Award. Dr. Hoffmann disclosed research funding from the U.S. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality unrelated to the current study. Dr. Loper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
AAP issues guidelines to combat rise in respiratory illness
Updated guidance from the group outlines measures to optimize resources to manage a surge of patients filling hospital beds, emergency departments, and physicians’ practices.
A separate document from the AAP endorses giving extra doses of palivizumab, a monoclonal antibody used to prevent severe infection in infants at high risk of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), as long as the illness is prevalent in the community.
Upticks in rates of RSV and influenza, along with a crisis in children’s mental health, prompted the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association to petition the Biden administration on Nov. 14 to declare an emergency. Such a move would free up extra funding and waivers to allow physicians and hospitals to pool resources, the organizations said.
Despite those challenges, the AAP stressed in its new guidance that routine care, such as immunizations and chronic disease management, “cannot be neglected.”
Shifting resources
Officials at some children’s hospitals said that they have already implemented many of the AAP’s recommended measures for providing care during a surge, such as cross-training staff who usually treat adults, expanding telehealth and urgent care, and optimizing the use of ancillary care spaces.
“A lot of this is just reinforcing the things that I think children’s hospitals have been doing,” Lindsay Ragsdale, MD, chief medical officer for Kentucky Children’s Hospital, Lexington, said. “Can we shift adults around? Can we use an adult unit? Can we use an occupied space creatively? We’re really thinking outside the box.”
Andrew Pavia, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at University of Utah Health, Salt Lake City, said large children’s hospitals have been actively sharing practices for handling a surge through various channels, but the new guidance could be a useful “checklist” for small hospitals and physician practices that lack well-developed plans.
The AAP’s suggestions for pediatricians in outpatient settings include stocking up on personal protective equipment, using social media and office staff to increase communication with families, and keeping abreast of wait times at local emergency departments.
Addressing a subset of kids
In updated guidance for palivizumab, the AAP noted that earlier-than-usual circulation of RSV prompted pediatricians in some areas to begin administering the drug in the summer and early fall.
Palivizumab is typically given in five consecutive monthly intramuscular injections during RSV season, starting in November. Eligible infants and young children include those born prematurely or who have conditions such as chronic lung disease, hemodynamically significant congenital heart disease, or a suppressed immune system.
The AAP said it supports giving extra doses if RSV activity “persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter.” Published studies are sparse but contain “no evidence of increased frequency or severity of adverse events with later doses in a five-dose series nor with doses beyond five doses,” the group added.
The guidance may encourage payers to pick up the tab for extra doses, which are priced at more than $1,800 for cash customers, Dr. Pavia said. However, that recommendation addresses “a pretty small part of the problem overall because the injections are used for a very small subset of kids who are at the highest risk, and more than 80% of hospitalizations for RSV are among healthy kids,” he added.
Dr. Ragsdale and Dr. Pavia have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated guidance from the group outlines measures to optimize resources to manage a surge of patients filling hospital beds, emergency departments, and physicians’ practices.
A separate document from the AAP endorses giving extra doses of palivizumab, a monoclonal antibody used to prevent severe infection in infants at high risk of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), as long as the illness is prevalent in the community.
Upticks in rates of RSV and influenza, along with a crisis in children’s mental health, prompted the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association to petition the Biden administration on Nov. 14 to declare an emergency. Such a move would free up extra funding and waivers to allow physicians and hospitals to pool resources, the organizations said.
Despite those challenges, the AAP stressed in its new guidance that routine care, such as immunizations and chronic disease management, “cannot be neglected.”
Shifting resources
Officials at some children’s hospitals said that they have already implemented many of the AAP’s recommended measures for providing care during a surge, such as cross-training staff who usually treat adults, expanding telehealth and urgent care, and optimizing the use of ancillary care spaces.
“A lot of this is just reinforcing the things that I think children’s hospitals have been doing,” Lindsay Ragsdale, MD, chief medical officer for Kentucky Children’s Hospital, Lexington, said. “Can we shift adults around? Can we use an adult unit? Can we use an occupied space creatively? We’re really thinking outside the box.”
Andrew Pavia, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at University of Utah Health, Salt Lake City, said large children’s hospitals have been actively sharing practices for handling a surge through various channels, but the new guidance could be a useful “checklist” for small hospitals and physician practices that lack well-developed plans.
The AAP’s suggestions for pediatricians in outpatient settings include stocking up on personal protective equipment, using social media and office staff to increase communication with families, and keeping abreast of wait times at local emergency departments.
Addressing a subset of kids
In updated guidance for palivizumab, the AAP noted that earlier-than-usual circulation of RSV prompted pediatricians in some areas to begin administering the drug in the summer and early fall.
Palivizumab is typically given in five consecutive monthly intramuscular injections during RSV season, starting in November. Eligible infants and young children include those born prematurely or who have conditions such as chronic lung disease, hemodynamically significant congenital heart disease, or a suppressed immune system.
The AAP said it supports giving extra doses if RSV activity “persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter.” Published studies are sparse but contain “no evidence of increased frequency or severity of adverse events with later doses in a five-dose series nor with doses beyond five doses,” the group added.
The guidance may encourage payers to pick up the tab for extra doses, which are priced at more than $1,800 for cash customers, Dr. Pavia said. However, that recommendation addresses “a pretty small part of the problem overall because the injections are used for a very small subset of kids who are at the highest risk, and more than 80% of hospitalizations for RSV are among healthy kids,” he added.
Dr. Ragsdale and Dr. Pavia have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated guidance from the group outlines measures to optimize resources to manage a surge of patients filling hospital beds, emergency departments, and physicians’ practices.
A separate document from the AAP endorses giving extra doses of palivizumab, a monoclonal antibody used to prevent severe infection in infants at high risk of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), as long as the illness is prevalent in the community.
Upticks in rates of RSV and influenza, along with a crisis in children’s mental health, prompted the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association to petition the Biden administration on Nov. 14 to declare an emergency. Such a move would free up extra funding and waivers to allow physicians and hospitals to pool resources, the organizations said.
Despite those challenges, the AAP stressed in its new guidance that routine care, such as immunizations and chronic disease management, “cannot be neglected.”
Shifting resources
Officials at some children’s hospitals said that they have already implemented many of the AAP’s recommended measures for providing care during a surge, such as cross-training staff who usually treat adults, expanding telehealth and urgent care, and optimizing the use of ancillary care spaces.
“A lot of this is just reinforcing the things that I think children’s hospitals have been doing,” Lindsay Ragsdale, MD, chief medical officer for Kentucky Children’s Hospital, Lexington, said. “Can we shift adults around? Can we use an adult unit? Can we use an occupied space creatively? We’re really thinking outside the box.”
Andrew Pavia, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at University of Utah Health, Salt Lake City, said large children’s hospitals have been actively sharing practices for handling a surge through various channels, but the new guidance could be a useful “checklist” for small hospitals and physician practices that lack well-developed plans.
The AAP’s suggestions for pediatricians in outpatient settings include stocking up on personal protective equipment, using social media and office staff to increase communication with families, and keeping abreast of wait times at local emergency departments.
Addressing a subset of kids
In updated guidance for palivizumab, the AAP noted that earlier-than-usual circulation of RSV prompted pediatricians in some areas to begin administering the drug in the summer and early fall.
Palivizumab is typically given in five consecutive monthly intramuscular injections during RSV season, starting in November. Eligible infants and young children include those born prematurely or who have conditions such as chronic lung disease, hemodynamically significant congenital heart disease, or a suppressed immune system.
The AAP said it supports giving extra doses if RSV activity “persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter.” Published studies are sparse but contain “no evidence of increased frequency or severity of adverse events with later doses in a five-dose series nor with doses beyond five doses,” the group added.
The guidance may encourage payers to pick up the tab for extra doses, which are priced at more than $1,800 for cash customers, Dr. Pavia said. However, that recommendation addresses “a pretty small part of the problem overall because the injections are used for a very small subset of kids who are at the highest risk, and more than 80% of hospitalizations for RSV are among healthy kids,” he added.
Dr. Ragsdale and Dr. Pavia have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children with autism show distinct brain features related to motor impairment
Previous research suggests that individuals with ASD overlap in motor impairment with those with DCD. But these two conditions may differ significantly in some areas, as children with ASD tend to show weaker skills in social motor tasks such as imitation, wrote Emil Kilroy, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and colleagues.
The neurobiological basis of autism remains unknown, despite many research efforts, in part because of the heterogeneity of the disease, said corresponding author Lisa Aziz-Zadeh, PhD, also of the University of Southern California, in an interview.
Comorbidity with other disorders is a strong contributing factor to heterogeneity, and approximately 80% of autistic individuals have motor impairments and meet criteria for a diagnosis of DCD, said Dr. Aziz-Zadeh. “Controlling for other comorbidities, such as developmental coordination disorder, when trying to understand the neural basis of autism is important, so that we can understand which neural circuits are related to [core symptoms of autism] and which ones are related to motor impairments that are comorbid with autism, but not necessarily part of the core symptomology,” she explained. “We focused on white matter pathways here because many researchers now think the underlying basis of autism, besides genetics, is brain connectivity differences.”
In their study published in Scientific Reports, the researchers reviewed data from whole-brain correlational tractography for 22 individuals with autism spectrum disorder, 16 with developmental coordination disorder, and 21 normally developing individuals, who served as the control group. The mean age of the participants was approximately 11 years; the age range was 8-17 years.
Overall, patterns of brain diffusion (movement of fluid, mainly water molecules, in the brain) were significantly different in ASD children, compared with typically developing children.
The ASD group showed significantly reduced diffusivity in the bilateral fronto-parietal cingulum and the left parolfactory cingulum. This finding reflects previous studies suggesting an association between brain patterns in the cingulum area and ASD. But the current study is “the first to identify the fronto-parietal and the parolfactory portions of the cingulum as well as the anterior caudal u-fibers as specific to core ASD symptomatology and not related to motor-related comorbidity,” the researchers wrote.
Differences in brain diffusivity were associated with worse performance on motor skills and behavioral measures for children with ASD and children with DCD, compared with controls.
Motor development was assessed using the Total Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2 (MABC-2) and the Florida Apraxia Battery modified for children (FAB-M). The MABC-2 is among the most common tools for measuring motor skills and identifying clinically relevant motor deficits in children and teens aged 3-16 years. The test includes three subtest scores (manual dexterity, gross-motor aiming and catching, and balance) and a total score. Scores are based on a child’s best performance on each component, and higher scores indicate better functioning. In the new study, The MABC-2 total scores averaged 10.57 for controls, compared with 5.76 in the ASD group, and 4.31 in the DCD group.
Children with ASD differed from the other groups in social measures. Social skills were measured using several tools, including the Social Responsivity Scale (SRS Total), which is a parent-completed survey that includes a total score designed to reflect the severity of social deficits in ASD. It is divided into five subscales for parents to assess a child’s social skill impairment: social awareness, social cognition, social communication, social motivation, and mannerisms. Scores for the SRS are calculated in T-scores, in which a score of 50 represents the mean. T-scores of 59 and below are generally not associated with ASD, and patients with these scores are considered to have low to no symptomatology. Scores on the SRS Total in the new study were 45.95, 77.45, and 55.81 for the controls, ASD group, and DCD group, respectively.
Results should raise awareness
“The results were largely predicted in our hypotheses – that we would find specific white matter pathways in autism that would differ from [what we saw in typically developing patients and those with DCD], and that diffusivity in ASD would be related to socioemotional differences,” Dr. Aziz-Zadeh said, in an interview.
“What was surprising was that some pathways that had previously been thought to be different in autism were also compromised in DCD, indicating that they were common to motor deficits which both groups shared, not to core autism symptomology,” she noted.
A message for clinicians from the study is that a dual diagnosis of DCD is often missing in ASD practice, said Dr. Aziz-Zadeh. “Given that approximately 80% of children with ASD have DCD, testing for DCD and addressing potential motor issues should be more common practice,” she said.
Dr. Aziz-Zadeh and colleagues are now investigating relationships between the brain, behavior, and the gut microbiome. “We think that understanding autism from a full-body perspective, examining interactions between the brain and the body, will be an important step in this field,” she emphasized.
The study was limited by several factors, including the small sample size, the use of only right-handed participants, and the use of self-reports by children and parents, the researchers noted. Additionally, they noted that white matter develops at different rates in different age groups, and future studies might consider age as a factor, as well as further behavioral assessments, they said.
Small sample size limits conclusions
“Understanding the neuroanatomic differences that may contribute to the core symptoms of ASD is a very important goal for the field, particularly how they relate to other comorbid symptoms and neurodevelopmental disorders,” said Michael Gandal, MD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and a member of the Lifespan Brain Institute at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, in an interview.
“While this study provides some clues into how structural connectivity may relate to motor coordination in ASD, it will be important to replicate these findings in a much larger sample before we can really appreciate how robust these findings are and how well they generalize to the broader ASD population,” Dr. Gandal emphasized.
The study was supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gandal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Previous research suggests that individuals with ASD overlap in motor impairment with those with DCD. But these two conditions may differ significantly in some areas, as children with ASD tend to show weaker skills in social motor tasks such as imitation, wrote Emil Kilroy, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and colleagues.
The neurobiological basis of autism remains unknown, despite many research efforts, in part because of the heterogeneity of the disease, said corresponding author Lisa Aziz-Zadeh, PhD, also of the University of Southern California, in an interview.
Comorbidity with other disorders is a strong contributing factor to heterogeneity, and approximately 80% of autistic individuals have motor impairments and meet criteria for a diagnosis of DCD, said Dr. Aziz-Zadeh. “Controlling for other comorbidities, such as developmental coordination disorder, when trying to understand the neural basis of autism is important, so that we can understand which neural circuits are related to [core symptoms of autism] and which ones are related to motor impairments that are comorbid with autism, but not necessarily part of the core symptomology,” she explained. “We focused on white matter pathways here because many researchers now think the underlying basis of autism, besides genetics, is brain connectivity differences.”
In their study published in Scientific Reports, the researchers reviewed data from whole-brain correlational tractography for 22 individuals with autism spectrum disorder, 16 with developmental coordination disorder, and 21 normally developing individuals, who served as the control group. The mean age of the participants was approximately 11 years; the age range was 8-17 years.
Overall, patterns of brain diffusion (movement of fluid, mainly water molecules, in the brain) were significantly different in ASD children, compared with typically developing children.
The ASD group showed significantly reduced diffusivity in the bilateral fronto-parietal cingulum and the left parolfactory cingulum. This finding reflects previous studies suggesting an association between brain patterns in the cingulum area and ASD. But the current study is “the first to identify the fronto-parietal and the parolfactory portions of the cingulum as well as the anterior caudal u-fibers as specific to core ASD symptomatology and not related to motor-related comorbidity,” the researchers wrote.
Differences in brain diffusivity were associated with worse performance on motor skills and behavioral measures for children with ASD and children with DCD, compared with controls.
Motor development was assessed using the Total Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2 (MABC-2) and the Florida Apraxia Battery modified for children (FAB-M). The MABC-2 is among the most common tools for measuring motor skills and identifying clinically relevant motor deficits in children and teens aged 3-16 years. The test includes three subtest scores (manual dexterity, gross-motor aiming and catching, and balance) and a total score. Scores are based on a child’s best performance on each component, and higher scores indicate better functioning. In the new study, The MABC-2 total scores averaged 10.57 for controls, compared with 5.76 in the ASD group, and 4.31 in the DCD group.
Children with ASD differed from the other groups in social measures. Social skills were measured using several tools, including the Social Responsivity Scale (SRS Total), which is a parent-completed survey that includes a total score designed to reflect the severity of social deficits in ASD. It is divided into five subscales for parents to assess a child’s social skill impairment: social awareness, social cognition, social communication, social motivation, and mannerisms. Scores for the SRS are calculated in T-scores, in which a score of 50 represents the mean. T-scores of 59 and below are generally not associated with ASD, and patients with these scores are considered to have low to no symptomatology. Scores on the SRS Total in the new study were 45.95, 77.45, and 55.81 for the controls, ASD group, and DCD group, respectively.
Results should raise awareness
“The results were largely predicted in our hypotheses – that we would find specific white matter pathways in autism that would differ from [what we saw in typically developing patients and those with DCD], and that diffusivity in ASD would be related to socioemotional differences,” Dr. Aziz-Zadeh said, in an interview.
“What was surprising was that some pathways that had previously been thought to be different in autism were also compromised in DCD, indicating that they were common to motor deficits which both groups shared, not to core autism symptomology,” she noted.
A message for clinicians from the study is that a dual diagnosis of DCD is often missing in ASD practice, said Dr. Aziz-Zadeh. “Given that approximately 80% of children with ASD have DCD, testing for DCD and addressing potential motor issues should be more common practice,” she said.
Dr. Aziz-Zadeh and colleagues are now investigating relationships between the brain, behavior, and the gut microbiome. “We think that understanding autism from a full-body perspective, examining interactions between the brain and the body, will be an important step in this field,” she emphasized.
The study was limited by several factors, including the small sample size, the use of only right-handed participants, and the use of self-reports by children and parents, the researchers noted. Additionally, they noted that white matter develops at different rates in different age groups, and future studies might consider age as a factor, as well as further behavioral assessments, they said.
Small sample size limits conclusions
“Understanding the neuroanatomic differences that may contribute to the core symptoms of ASD is a very important goal for the field, particularly how they relate to other comorbid symptoms and neurodevelopmental disorders,” said Michael Gandal, MD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and a member of the Lifespan Brain Institute at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, in an interview.
“While this study provides some clues into how structural connectivity may relate to motor coordination in ASD, it will be important to replicate these findings in a much larger sample before we can really appreciate how robust these findings are and how well they generalize to the broader ASD population,” Dr. Gandal emphasized.
The study was supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gandal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Previous research suggests that individuals with ASD overlap in motor impairment with those with DCD. But these two conditions may differ significantly in some areas, as children with ASD tend to show weaker skills in social motor tasks such as imitation, wrote Emil Kilroy, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and colleagues.
The neurobiological basis of autism remains unknown, despite many research efforts, in part because of the heterogeneity of the disease, said corresponding author Lisa Aziz-Zadeh, PhD, also of the University of Southern California, in an interview.
Comorbidity with other disorders is a strong contributing factor to heterogeneity, and approximately 80% of autistic individuals have motor impairments and meet criteria for a diagnosis of DCD, said Dr. Aziz-Zadeh. “Controlling for other comorbidities, such as developmental coordination disorder, when trying to understand the neural basis of autism is important, so that we can understand which neural circuits are related to [core symptoms of autism] and which ones are related to motor impairments that are comorbid with autism, but not necessarily part of the core symptomology,” she explained. “We focused on white matter pathways here because many researchers now think the underlying basis of autism, besides genetics, is brain connectivity differences.”
In their study published in Scientific Reports, the researchers reviewed data from whole-brain correlational tractography for 22 individuals with autism spectrum disorder, 16 with developmental coordination disorder, and 21 normally developing individuals, who served as the control group. The mean age of the participants was approximately 11 years; the age range was 8-17 years.
Overall, patterns of brain diffusion (movement of fluid, mainly water molecules, in the brain) were significantly different in ASD children, compared with typically developing children.
The ASD group showed significantly reduced diffusivity in the bilateral fronto-parietal cingulum and the left parolfactory cingulum. This finding reflects previous studies suggesting an association between brain patterns in the cingulum area and ASD. But the current study is “the first to identify the fronto-parietal and the parolfactory portions of the cingulum as well as the anterior caudal u-fibers as specific to core ASD symptomatology and not related to motor-related comorbidity,” the researchers wrote.
Differences in brain diffusivity were associated with worse performance on motor skills and behavioral measures for children with ASD and children with DCD, compared with controls.
Motor development was assessed using the Total Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2 (MABC-2) and the Florida Apraxia Battery modified for children (FAB-M). The MABC-2 is among the most common tools for measuring motor skills and identifying clinically relevant motor deficits in children and teens aged 3-16 years. The test includes three subtest scores (manual dexterity, gross-motor aiming and catching, and balance) and a total score. Scores are based on a child’s best performance on each component, and higher scores indicate better functioning. In the new study, The MABC-2 total scores averaged 10.57 for controls, compared with 5.76 in the ASD group, and 4.31 in the DCD group.
Children with ASD differed from the other groups in social measures. Social skills were measured using several tools, including the Social Responsivity Scale (SRS Total), which is a parent-completed survey that includes a total score designed to reflect the severity of social deficits in ASD. It is divided into five subscales for parents to assess a child’s social skill impairment: social awareness, social cognition, social communication, social motivation, and mannerisms. Scores for the SRS are calculated in T-scores, in which a score of 50 represents the mean. T-scores of 59 and below are generally not associated with ASD, and patients with these scores are considered to have low to no symptomatology. Scores on the SRS Total in the new study were 45.95, 77.45, and 55.81 for the controls, ASD group, and DCD group, respectively.
Results should raise awareness
“The results were largely predicted in our hypotheses – that we would find specific white matter pathways in autism that would differ from [what we saw in typically developing patients and those with DCD], and that diffusivity in ASD would be related to socioemotional differences,” Dr. Aziz-Zadeh said, in an interview.
“What was surprising was that some pathways that had previously been thought to be different in autism were also compromised in DCD, indicating that they were common to motor deficits which both groups shared, not to core autism symptomology,” she noted.
A message for clinicians from the study is that a dual diagnosis of DCD is often missing in ASD practice, said Dr. Aziz-Zadeh. “Given that approximately 80% of children with ASD have DCD, testing for DCD and addressing potential motor issues should be more common practice,” she said.
Dr. Aziz-Zadeh and colleagues are now investigating relationships between the brain, behavior, and the gut microbiome. “We think that understanding autism from a full-body perspective, examining interactions between the brain and the body, will be an important step in this field,” she emphasized.
The study was limited by several factors, including the small sample size, the use of only right-handed participants, and the use of self-reports by children and parents, the researchers noted. Additionally, they noted that white matter develops at different rates in different age groups, and future studies might consider age as a factor, as well as further behavioral assessments, they said.
Small sample size limits conclusions
“Understanding the neuroanatomic differences that may contribute to the core symptoms of ASD is a very important goal for the field, particularly how they relate to other comorbid symptoms and neurodevelopmental disorders,” said Michael Gandal, MD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and a member of the Lifespan Brain Institute at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, in an interview.
“While this study provides some clues into how structural connectivity may relate to motor coordination in ASD, it will be important to replicate these findings in a much larger sample before we can really appreciate how robust these findings are and how well they generalize to the broader ASD population,” Dr. Gandal emphasized.
The study was supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gandal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM SCIENTIFIC REPORTS
Her child was stillborn at 39 weeks. She blames a system that doesn’t always listen to mothers
The day before doctors had scheduled Amanda Duffy to give birth, the baby jolted her awake with a kick.
A few hours later, on that bright Sunday in November 2014, she leaned back on a park bench to watch her 19-month-old son Rogen enjoy his final day of being an only child. In that moment of calm, she realized that the kick that morning was the last time she had felt the baby move.
She told herself not to worry. She had heard that babies can slow down toward the end of a pregnancy and remembered reading that sugary snacks and cold fluids can stimulate a baby’s movement. When she got back to the family’s home in suburban Minneapolis, she drank a large glass of ice water and grabbed a few Tootsie Rolls off the kitchen counter.
But something about seeing her husband, Chris, lace up his shoes to leave for a run prompted her to blurt out, “I haven’t felt the baby kick.”
Chris called Amanda’s doctor, and they headed to the hospital to be checked. Once there, a nurse maneuvered a fetal monitor around Amanda’s belly. When she had trouble locating a heartbeat, she remarked that the baby must be tucked in tight. The doctor walked into the room, turned the screen away from Amanda and Chris and began searching. She was sorry, Amanda remembers her telling them, but she could not find a heartbeat.
Amanda let out a guttural scream. She said the doctor quickly performed an internal exam, which detected faint heart activity, then rushed Amanda into an emergency cesarean section.
She woke up to the sound of doctors talking to Chris. She listened but couldn’t bring herself to face the news. Her doctor told her she needed to open her eyes.
Amanda, then 31, couldn’t fathom that her daughter had died. She said her doctors had never discussed stillbirth with her. It was not mentioned in any of the pregnancy materials she had read. She didn’t even know that stillbirth was a possibility.
But every year more than 20,000 pregnancies in the United States end in stillbirth, the death of an expected child at 20 weeks or more. That number has exceeded infant mortality every year for the last 10 years. It’s 15 times the number of babies who, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, died of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, or SIDS, in 2020.
The deaths are not inevitable. One study found that nearly one in four U.S. stillbirths may be preventable. For pregnancies that last 37 weeks or more, that research shows, the figure jumps to nearly half. Thousands more babies could potentially be delivered safely every year.
But federal agencies have not prioritized critical stillbirth-focused studies that could lead to fewer deaths. Nearly two decades ago, both the CDC and the National Institutes of Health launched key stillbirth tracking and research studies, but the agencies ended those projects within about a decade. The CDC never analyzed some of the data that was collected.
Unlike with SIDS, a leading cause of infant death, federal officials have failed to launch a national campaign to reduce the risk of stillbirth or adequately raise awareness about it. Placental exams and autopsies, which can sometimes explain why stillbirths happened, are underutilized, in part because parents are not counseled on their benefits.
Federal agencies, state health departments, hospitals and doctors have also done a poor job of educating expectant parents about stillbirth or diligently counseling on fetal movement, despite research showing that patients who have had a stillbirth are more likely to have experienced abnormal fetal movements, including decreased activity. Neither the CDC nor the NIH have consistently promoted guidance telling those who are pregnant to be aware of their babies’ movement in the womb as a way to possibly reduce their risk of stillbirth.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the nation’s leading obstetrics organization, has been slow to update its own guidance to doctors on managing a stillbirth. In 2009, ACOG issued a set of guidelines that included a single paragraph regarding fetal movement. Those guidelines weren’t significantly updated for another 11 years.
Perhaps it’s no surprise that federal goals for reducing stillbirths keep moving in the wrong direction. In 2005, the U.S. stillbirth rate was 6.2 per 1,000 live births. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, in an effort to eliminate health disparities and establish a target that was “better than the best racial or ethnic group rate,” set a goal of reducing it to 4.1 for 2010. When that wasn’t met, federal officials changed their approach and set what they called more “science-based” and “realistic” goals, raising the 2020 target to 5.6. The U.S. still fell short. The 2030 goal of 5.7 was so attainable that it was met before the decade started. The 2020 rate, the most current according to the CDC, is 5.74.
By comparison, other wealthy countries have implemented national action plans to prevent stillbirth through awareness, research and care. Among other approaches, those countries have focused on increasing education around stillbirth and the importance of a baby’s movements, reducing rates of smoking and identifying fetuses that grow too slowly in the womb.
The efforts have paid off. The Netherlands, for instance, has reduced its rate of stillbirths at 28 weeks or later by more than half, from 5.2 in 2000 to 2.3 in 2019, according to a study published last year in The Lancet.
Dr. Bob Silver, chair of the obstetrics/gynecology department at University of Utah Health and a leading stillbirth expert, coauthored the study that estimated nearly one in four stillbirths are potentially preventable, a figure he referred to as conservative. He called on federal agencies to declare stillbirth reduction a priority the same way they have done for premature birth and maternal mortality.
“I’d like to see us say we really want to reduce the rate of stillbirth and raise awareness and try to do all of the reasonable things that may contribute to reducing stillbirths that other countries have done,” Silver said.
The lack of comprehensive attention and action has contributed to a stillbirth crisis, shrouded in an acceptance that some babies just die. Compounding the tragedy is a stigma and guilt so crushing that the first words some mothers utter when their lifeless babies are placed in their arms are “I’m sorry.”
In the hospital room, Amanda Duffy finally opened her eyes. She named her daughter Reese Christine, the name she had picked out for her before they found out she had died. She was 8 pounds, 3 ounces and 20 1/2 inches long and was born with her umbilical cord wrapped tightly around her neck twice. The baby was still warm when the nurse placed her in Amanda’s arms. Amanda was struck by how lovely her daughter was. Rosy skin. Chris’ red hair. Rogen’s chubby cheeks.
As Amanda held Reese, Chris hunched over the toilet, vomiting. Later that night, as he lay next to Amanda on the hospital bed, he held his daughter. He hadn’t initially wanted to see her. He worried she would be disfigured or, worse, that she would be beautiful and he would fall apart when he couldn’t take her home.
The nurses taught Amanda and Chris how to grieve and love simultaneously. One nurse told Amanda how cute Reese was and asked if she could hold her. Another placed ice packs in Reese’s swaddle to preserve her body so Amanda could keep holding her. Amanda asked the nurses to tuck cotton balls soaked in an orange scent into Reese’s blanket so the smell would trigger the memory of her daughter. And just as if Reese had been born alive, the nurses took pictures and made prints of her hands and feet.
“I felt such a deep, abiding love for her,” Amanda said. “And I was so proud to be her mom.”
On the way home from the hospital, Amanda broke down at the sight of Reese’s empty car seat. The next few weeks passed in a sleep-filled fog punctuated by intense periods of crying. The smell of oranges wrecked her. Her breast milk coming in was agonizing, physically and emotionally. She wore sports bras stuffed with ice packs to ease the pain and dry up her milk supply. While Rogen was at day care, she sobbed in his bed.
In the months that followed, Amanda and Chris searched for answers and wondered whether their medical team had missed warning signs. Late at night, Amanda turned to Google to find information about stillbirths. She mailed her medical records to a doctor who studies stillbirths, who she said told her that Reese’s death could have been prevented. They briefly discussed legal action against her doctors, but she said a lawyer told her it would be difficult to sue.
Amanda and Chris pinpointed her last two months of pregnancy as the time things started to go wrong. She had been diagnosed with polyhydramnios, meaning there was excess amniotic fluid in the womb. Her doctor had scheduled additional weekly testing.
One of those ultrasounds revealed problems with the blood flow in the umbilical cord. Reese’s cord also appeared to be wrapped around her neck, Amanda said later, but was told that was less of a concern, since it occurs in about 20% of normal deliveries. At another appointment, Amanda’s medical records show, Reese failed the portion of a test that measures fetal breathing movements.
At 37 weeks, Amanda told one of the midwives the baby’s movements felt different, but, she said, the midwife told her that it was common for movements to feel weaker with polyhydramnios. At that point, Amanda felt her baby was safer outside than inside and, her medical records show, she asked to schedule a C-section.
Despite voicing concerns about a change in the baby’s movement and asking to deliver earlier, Amanda said she and her husband were told by her midwife she couldn’t deliver for another two weeks. The doctor “continues to advise 39wks,” her medical records show. Waiting until 39 weeks is usually based on a guideline that deliveries should not happen before then unless a medical condition specifically warrants it, because early delivery can lead to complications.
Amanda would have to wait until 39 weeks and one day because, she said, her doctors didn’t typically do elective deliveries on weekends. Amanda was disappointed but said she trusted her team of doctors and midwives.
“I’m not a pushy person,” she said. “My husband is not a pushy person. That was out of our comfort zone to be, like, ‘What are we waiting for?’ But really what we wanted them to say was ‘We should deliver you.’”
Amanda’s final appointment was a maximum 30-minute-long ultrasound that combined a number of assessments to check amniotic fluid, fetal muscle tone, breathing and body movement. After 29 minutes of inactivity, Amanda said, the baby moved a hand. In the parking lot, Amanda called her mother, crying in relief. Four more days, she told her.
Less than 24 hours before the scheduled C-section, Reese was stillborn.
Four months after her death, Amanda, then a career advisor at the University of Minnesota, and Chris, a public relations specialist, wrote a letter to the University of Minnesota Medical Center, where Amanda had given birth to her dead daughter. They said they had “no ill feelings” toward anyone, but “it pains us to know that her death could’ve been prevented if we would have been sent to labor and delivery following that ultrasound.”
They noted that though they were told that Reese had passed the final ultrasound where she took 29 minutes to move, they had since come to believe that she had failed because, according to national standards, at least three movements were required. They also blamed a strict adherence to the 39-week guideline. And they encouraged the hospital staff to read more on umbilical cord accidents and acute polyhydramnios, which they later learned carries an increased stillbirth risk.
The positive feelings they had from speaking up were replaced by dismay when the hospital responded with a three-paragraph letter, signed by seven doctors and eight nurses. They said they had reexamined each medical decision in her case and concluded they had made “the best decisions medically possible.” They expressed their sympathy and said it was “so very heartwarming that you are trying to turn your tragic loss into something that will benefit others.”
Amanda felt dismissed by the medical team all over again. She didn’t expect them to admit fault, but she said she hoped that they would at least learn from Reese’s death to do things differently in the future. She was angry, and hurt, and knew that she would need to find a new doctor.
A spokesperson for the University of Minnesota Medical School told ProPublica she could not comment on individual patient cases and did not respond to questions about general protocols. “We share the physicians’ condolences,” she wrote, adding that the doctors and the university “are dedicated to delivering high quality, accessible and inclusive health care.”
For many expectant parents, it’s hard to muster the courage to call a doctor about something they’re not even sure is a problem.
“Moms self-censor a lot. No one wants to be that mom that all the doctors are rolling their eyes at because she’s freaking out over nothing,” said Samantha Banerjee, executive director of PUSH for Empowered Pregnancy, a nonprofit based in New York state that works to prevent stillbirths. Banerjee’s daughter, Alana, was stillborn two days before her due date.
In addition to raising awareness that stillbirths can happen even in low-risk pregnancies, PUSH teaches pregnant people how to advocate for themselves. The volunteers advise them to put their requests in writing and not to spend time drinking juice or lying on their side if they are worried about their baby’s lack of movement. In the majority of cases, a call or visit to the hospital reassures them.
But, the group tells parents, if their baby is in distress, calling their doctor can save their life.
Debbie Haine Vijayvergiya is fighting another narrative: that stillbirths are a rare fluke that “just happen.” When her daughter Autumn Joy was born without a heartbeat in 2011, Haine Vijayvergiya said, her doctor told her having a stillborn baby was as rare as being struck by lightning.
She believed him, but then she looked up the odds of a lightning strike and found they are less than one in a million – and most people survive. In 2020, according to the CDC, there was one stillbirth for about every 175 births.
“I’ve spoken to more women than I can count that said, ‘I raised the red flag, and I was sent home. I was told to eat a piece of cake and have some orange juice and lay on my left side,’ only to wake up the next day and their baby is not alive,” said Haine Vijayvergiya, a New Jersey mother and maternal health advocate.
She has fought for more than a decade to pass stillbirth legislation as her daughter’s legacy. Her current undertaking is her most ambitious. The federal Stillbirth Health Improvement and Education (SHINE) for Autumn Act, named after her daughter, would authorize $9 million a year for five years in federal funding for research, better data collection and training for fetal autopsies. But it is currently sitting in the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions.
Not all stillbirths are preventable, and medical experts agree more research is needed to determine who is most at risk and which babies can potentially be saved. Complicating matters is the wide range of risk factors, including hypertension and diabetes, smoking, obesity, being pregnant with multiples, being 35 or older and having had a previous stillbirth.
ProPublica reported this summer on how the U.S. botched the rollout of COVID-19 vaccines for pregnant people, who faced an increased risk for stillbirth if they were unvaccinated and contracted the virus, especially during the Delta wave.
Doctors often work to balance the risk of stillbirth with other dangers, particularly an increased chance of being admitted to neonatal intensive care units or even death of the baby if it is born too early. ACOG and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine have issued guidance to try to slow a rise in elective deliveries before 39 weeks and the potential harm that can result. The Joint Commission, a national accrediting organization, began evaluating hospitals in 2010 based on that standard.
A 2019 study found that the risks of stillbirth slightly increased after the rule went into effect, but fewer infants died after birth. Other studies have not found an effect on stillbirths.
Last year, the obstetric groups updated their guidance to allow doctors to consider an early delivery if a woman has anxiety and a history of stillbirth, writing that a previous stillbirth “may” warrant an early delivery for patients who understand and accept the risks. For those who have previously had a stillbirth, one modeling analysis found that 38 weeks is the optimal timing of delivery, considering the increased risk of another stillbirth.
“A woman who has had a previous stillbirth at 37 weeks – one could argue that it’s cruel and unusual punishment to make her go to 39 weeks with her next pregnancy, although that is the current recommendation,” said Dr. Neil Mandsager, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist in Iowa and a medical advisor to a stillbirth prevention nonprofit.
At or after 40 weeks, the risk of stillbirth increases, especially for women 35 or older. Their risk, research shows, is doubled from 39 weeks to 40 and is more than six times as high at 42 weeks. In 2019 and 2020, a combined 1,200 stillbirths occurred between 40 and 42 weeks, according to the most recent CDC data.
Deciding when a patient should deliver entails weighing the risks to the mother and the infant against a possible stillbirth as the pregnancy continues, said Dr. Mark Turrentine, chair of ACOG’s Clinical Consensus Committee-Obstetrics, which helped create the guidance on managing a stillbirth. He said ACOG has addressed stillbirth in other documents and extensively in its 2021 guidance on fetal surveillance and testing, which is done to reduce the risk of stillbirth.
ACOG said it routinely reviewed its guidance on management of stillbirth but was unable to make significant updates “due to the lack of new, evidence-based research.” While prevention is a great concern to ACOG, Turrentine said it’s difficult to know how many stillbirths are preventable.
He said it’s standard practice for doctors to ask about fetal movement, and ACOG updated its guidance after new research became available. Doctors also need to include patients in decision-making and tailor care to them, he said, whether that›s using aspirin in patients at high risk of preeclampsia – a serious high blood pressure condition during pregnancy – or ordering additional tests.
After Reese’s death, Amanda and Chris Duffy wanted to get pregnant again. They sought out an obstetrician-gynecologist who would educate and listen to them. They set up several consultations until they found Dr. Emily Hawes-Van Pelt, who was recommended by another family who had had a stillbirth.
Hawes-Van Pelt cried with Amanda and Chris at their first meeting.
“I told her I was scared to be involved,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “It’s such a tricky subsequent pregnancy because there’s so much worry and anxiety about the horrible, awful thing happening again.”
Amanda’s fear of delivering another dead baby led to an all-consuming anxiety, but Hawes-Van Pelt supported her when she asked for additional monitoring, testing and an early delivery.
When Hawes-Van Pelt switched practices midway through Amanda’s pregnancy, Amanda followed her. But the new hospital pushed back on the early delivery.
“We intervene early for poorly controlled diabetes,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “We intervene early for all sorts of medical issues. Anxiety and prior stillbirth are two medical issues that we can intervene earlier for.”
Hawes-Van Pelt said she learned a lot from caring for Amanda, who made her reevaluate some of her own assumptions around stillbirths.
“I had a horrible fear of scaring women unnecessarily, and then realized that I was just not preparing women or educating them because of my own fears around it,” she said. “If you can carry a human being in your body and birth that human being and take care of it, you can hear those words.”
The hospital eventually agreed to let Hawes-Van Pelt schedule Amanda for a 37-week C-section. But after Amanda was again diagnosed with polyhydramnios, she went in for a C-section even earlier. She gave birth in 2015 to a healthy boy she and Chris named Rhett. Two years later, Amanda and Hawes-Van Pelt followed the same pregnancy plan, and she delivered a girl named Maeda Reese. Amanda chose the name because, when said quickly, it sounds like “made of Reese.”
Federal agencies, national organizations and state and city officials have mobilized in recent years to address maternal mortality, when mothers die during pregnancy, at delivery or soon after childbirth. They have focused on improving data collection, passing legislation and creating awareness campaigns that encourage medical professionals and others to listen when women say something doesn›t feel right.
In 2017, ProPublica and NPR documented the U.S. maternal mortality crisis, including alarming racial disparities.
According to CDC data, Black women face nearly three times the risk of maternal mortality. They also are more than twice – and in some states close to three times – as likely to have a stillbirth than white women, meaning not only are Black mothers dying at a disproportionate rate, so are their babies.
Janet Petersen, a state senator from Iowa, said it gives her hope to see how the country has turned its attention to maternal mortality and disparities in health care. She simply cannot understand why stillbirth isn’t being met with the same urgency.
In 2020, the CDC reported 861 mothers died either while pregnant or within six weeks of giving birth. That same year, 20,854 babies were stillborn.
Stillbirth, Petersen said, is a missing piece of the puzzle. Research shows the likelihood of severe maternal complications was more than four times higher for pregnancies that ended in stillbirths, and mothers who died within six weeks of delivery were more likely to have had a stillbirth.
“We see it over and over again that stillbirth is one of the maternal health care issues that continuously gets ignored,” said Petersen, a Democrat.
Petersen was a young legislator in 2003 when her daughter Grace was born still. Devastated, she thought of her grandmother, who lost a baby to stillbirth in 1920, just a few weeks before women got the right to vote.
“I was laying in my hospital bed thinking, ‘How could this still be happening in our country?’” Petersen recalled. “And it seemed, from the medical perspective, that, well, stillbirth happens. We can’t do anything to prevent them.”
Over the next few months, Petersen heard from other mothers who had lost their babies and wanted to spark change. As an elected official, Petersen was in a position to do that. In 2004, she introduced legislation that required the Iowa Department of Public Health to create a stillbirths work group, later securing funding through the CDC to create a stillbirth registry.
But the CDC didn’t renew the funding and never analyzed the data from the registry, though a CDC spokesperson said the Iowa Department of Public Health examined the data. Officials from the department did not respond to requests for comment.
Petersen and her fellow mothers pivoted. After hearing how researchers in Norway were able to increase awareness around fetal movement, they co-founded a nonprofit aimed at doing the same in the U.S.
The group, Healthy Birth Day, created colorful “Count the Kicks” pamphlets – and later an app – teaching pregnant people how to track a baby’s movements and establish what is normal for them. Monitoring a baby’s movements is the earliest and sometimes only indication that something may be wrong, said Emily Price, chief executive officer of Healthy Birth Day. One of the organization’s main messages is for pregnant people to speak up and clinicians to listen.
“Unfortunately, there are still doctors who brush women off or send them home when they come in with a complaint of a change in their baby’s movements,” Price said. “And babies are dying because of it.”
One Indiana county, which recorded 65 stillbirths from 2017 through 2019, reported that 74% had either some chance or a good chance of prevention, according to St. Joseph County Department of Health’s Fetal Infant Mortality Review program. For mothers who experienced decreased fetal movement in the few hours or days before the stillbirth, that estimate jumped to 90%.
Although there is not a scientific consensus that kick counting can prevent stillbirths, national groups, including ACOG, recommend that medical professionals encourage their patients to be aware of fetal movement patterns. ACOG also advises medical professionals to be attentive to a mother’s concerns about reduced movement and address them “in a systematic way.”
One complaint the CDC hears too often, an agency spokesperson said, is that pregnant people and those who gave birth recently find that their concerns are dismissed or ignored. “Listening and taking the concerns of pregnant and recently pregnant people seriously,” she said, “is a simple, yet powerful action to prevent serious health complications and even death.”
The CDC, she said, is “very interested” in expanding its research on stillbirth, which is “a crucial part of the development of any awareness or prevention campaigns.” In addition to working to improve its stillbirth data quality, the agency has funded some pilot programs at the city and state level to better track stillbirths, survey people who have had a stillbirth and research risk factors and causes. The Iowa registry, she said, led the CDC to fund different research projects in Arkansas and Massachusetts, which are ongoing.
In 2009, the CDC acknowledged that fetal mortality remained a “major, but often overlooked, public health problem.” Officials wrote that much of the public health concern had been focused on infant mortality “in part due to lesser awareness of the magnitude of fetal mortality, its causes, and prevention strategies.”
But little has changed over the past 13 years. Echoing its earlier message, the CDC this year declared that “much work remains” and that “stillbirth is not often viewed as a public health issue, so increased awareness is key.”
A spokesperson for the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, which is part of the NIH, said the agency has continually funded research on stillbirths, even after one of its key studies ended. The agency, she said, also supports research on conditions that increase the risk of stillbirth.
As a scientific research institute, it does not issue clinical guidelines or recommendations, she said, though it did launch the Safe to Sleep campaign in 1994, two decades after Congress put it in charge of SIDS federal research efforts. That campaign, which educates parents and caregivers on ways to reduce the risk of SIDS, highlights recommendations issued by the American Academy of Pediatrics. She said the agency will continue to collaborate with organizations that raise awareness about stillbirth and other pregnancy complications “to amplify their messages and efforts.”
“NICHD continues to support research on the prevention, causes, frequency, and risk factors of stillbirth,” the spokesperson said in an email. “Our commitment to enhancing understanding of stillbirth and improving outcomes focuses on building the scientific knowledge base.”
But getting laws on the books that could raise awareness around stillbirth – even when they don’t require additional funding – has been a struggle. Petersen and Price are pushing Congress to pass legislation that would add stillbirth research and prevention to the list of activities approved for federal maternal health dollars.
Though the bill doesn’t ask for any additional funding, it has not yet passed.
In addition, the SHINE for Autumn Act breezed through the House of Representatives in December 2021. After Haine Vijayvergiya, the New Jersey mother who has championed it, secured bipartisan support from U.S. Sens. Cory Booker, D-N.J., and Marco Rubio, R-Fla., she thought the most comprehensive stillbirth legislation in U.S. history would finally become law.
Neither bill has sparked controversy.
But months after press releases announced the SHINE legislation and referred to the U.S. stillbirth rate as “unacceptable,” lawmakers and the families they represent are running out of time as this session of Congress prepares to adjourn.
“From the day that the bill was introduced into the Senate,” Haine Vijayvergiya said, “approximately 13,000 babies have been born still.”
Last month, on a brilliant fall day much like the one when Reese was stillborn, Amanda Duffy bent down to kiss her son Rogen’s head before they walked on stage.
She wore a soft blue T-shirt tucked into her jeans that read “Be courageous.” The message was as much for her as it was for the crowd on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., many of them like her, mothers who didn’t know stillbirth happened until it happened to them. Since Reese’s death, she has coached doctors and nurses on improving care for patients who have suffered pregnancy loss. Among her many suggestions, she tells them their first words when a concerned patient reaches out should be “I’m so glad you called.”
A few hundred people had gathered for The Big PUSH to End Preventable Stillbirth, billed as the first-ever march on the issue. As part of an art installation, Amanda wrote a note to Reese: “You’re pretty magical & for that I’m grateful. You’re a change maker and you are so very loved. Love, Mama.” Before she slipped the folded paper into a sea of more than 20,000 baby hats, Rogen added his own message: “Hope you are having a good time – Rogen.”
Reese would have turned 8 this month.
Before Amanda spoke, she took a deep breath and silenced her nerves. She walked onto the stage and called on Congress to pass the stillbirth legislation before it. She didn’t ask. She demanded.
“It’s time to empower pregnant people and their care providers with information that leads to prevention,” she insisted.
With the afternoon sun bearing down, Amanda and Rogen disappeared into the crowd of families marching toward the Capitol. Many carried signs. Some pushed empty strollers. Amanda was still wearing the orange-scented oil she had rubbed on her wrists that morning.
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published
The day before doctors had scheduled Amanda Duffy to give birth, the baby jolted her awake with a kick.
A few hours later, on that bright Sunday in November 2014, she leaned back on a park bench to watch her 19-month-old son Rogen enjoy his final day of being an only child. In that moment of calm, she realized that the kick that morning was the last time she had felt the baby move.
She told herself not to worry. She had heard that babies can slow down toward the end of a pregnancy and remembered reading that sugary snacks and cold fluids can stimulate a baby’s movement. When she got back to the family’s home in suburban Minneapolis, she drank a large glass of ice water and grabbed a few Tootsie Rolls off the kitchen counter.
But something about seeing her husband, Chris, lace up his shoes to leave for a run prompted her to blurt out, “I haven’t felt the baby kick.”
Chris called Amanda’s doctor, and they headed to the hospital to be checked. Once there, a nurse maneuvered a fetal monitor around Amanda’s belly. When she had trouble locating a heartbeat, she remarked that the baby must be tucked in tight. The doctor walked into the room, turned the screen away from Amanda and Chris and began searching. She was sorry, Amanda remembers her telling them, but she could not find a heartbeat.
Amanda let out a guttural scream. She said the doctor quickly performed an internal exam, which detected faint heart activity, then rushed Amanda into an emergency cesarean section.
She woke up to the sound of doctors talking to Chris. She listened but couldn’t bring herself to face the news. Her doctor told her she needed to open her eyes.
Amanda, then 31, couldn’t fathom that her daughter had died. She said her doctors had never discussed stillbirth with her. It was not mentioned in any of the pregnancy materials she had read. She didn’t even know that stillbirth was a possibility.
But every year more than 20,000 pregnancies in the United States end in stillbirth, the death of an expected child at 20 weeks or more. That number has exceeded infant mortality every year for the last 10 years. It’s 15 times the number of babies who, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, died of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, or SIDS, in 2020.
The deaths are not inevitable. One study found that nearly one in four U.S. stillbirths may be preventable. For pregnancies that last 37 weeks or more, that research shows, the figure jumps to nearly half. Thousands more babies could potentially be delivered safely every year.
But federal agencies have not prioritized critical stillbirth-focused studies that could lead to fewer deaths. Nearly two decades ago, both the CDC and the National Institutes of Health launched key stillbirth tracking and research studies, but the agencies ended those projects within about a decade. The CDC never analyzed some of the data that was collected.
Unlike with SIDS, a leading cause of infant death, federal officials have failed to launch a national campaign to reduce the risk of stillbirth or adequately raise awareness about it. Placental exams and autopsies, which can sometimes explain why stillbirths happened, are underutilized, in part because parents are not counseled on their benefits.
Federal agencies, state health departments, hospitals and doctors have also done a poor job of educating expectant parents about stillbirth or diligently counseling on fetal movement, despite research showing that patients who have had a stillbirth are more likely to have experienced abnormal fetal movements, including decreased activity. Neither the CDC nor the NIH have consistently promoted guidance telling those who are pregnant to be aware of their babies’ movement in the womb as a way to possibly reduce their risk of stillbirth.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the nation’s leading obstetrics organization, has been slow to update its own guidance to doctors on managing a stillbirth. In 2009, ACOG issued a set of guidelines that included a single paragraph regarding fetal movement. Those guidelines weren’t significantly updated for another 11 years.
Perhaps it’s no surprise that federal goals for reducing stillbirths keep moving in the wrong direction. In 2005, the U.S. stillbirth rate was 6.2 per 1,000 live births. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, in an effort to eliminate health disparities and establish a target that was “better than the best racial or ethnic group rate,” set a goal of reducing it to 4.1 for 2010. When that wasn’t met, federal officials changed their approach and set what they called more “science-based” and “realistic” goals, raising the 2020 target to 5.6. The U.S. still fell short. The 2030 goal of 5.7 was so attainable that it was met before the decade started. The 2020 rate, the most current according to the CDC, is 5.74.
By comparison, other wealthy countries have implemented national action plans to prevent stillbirth through awareness, research and care. Among other approaches, those countries have focused on increasing education around stillbirth and the importance of a baby’s movements, reducing rates of smoking and identifying fetuses that grow too slowly in the womb.
The efforts have paid off. The Netherlands, for instance, has reduced its rate of stillbirths at 28 weeks or later by more than half, from 5.2 in 2000 to 2.3 in 2019, according to a study published last year in The Lancet.
Dr. Bob Silver, chair of the obstetrics/gynecology department at University of Utah Health and a leading stillbirth expert, coauthored the study that estimated nearly one in four stillbirths are potentially preventable, a figure he referred to as conservative. He called on federal agencies to declare stillbirth reduction a priority the same way they have done for premature birth and maternal mortality.
“I’d like to see us say we really want to reduce the rate of stillbirth and raise awareness and try to do all of the reasonable things that may contribute to reducing stillbirths that other countries have done,” Silver said.
The lack of comprehensive attention and action has contributed to a stillbirth crisis, shrouded in an acceptance that some babies just die. Compounding the tragedy is a stigma and guilt so crushing that the first words some mothers utter when their lifeless babies are placed in their arms are “I’m sorry.”
In the hospital room, Amanda Duffy finally opened her eyes. She named her daughter Reese Christine, the name she had picked out for her before they found out she had died. She was 8 pounds, 3 ounces and 20 1/2 inches long and was born with her umbilical cord wrapped tightly around her neck twice. The baby was still warm when the nurse placed her in Amanda’s arms. Amanda was struck by how lovely her daughter was. Rosy skin. Chris’ red hair. Rogen’s chubby cheeks.
As Amanda held Reese, Chris hunched over the toilet, vomiting. Later that night, as he lay next to Amanda on the hospital bed, he held his daughter. He hadn’t initially wanted to see her. He worried she would be disfigured or, worse, that she would be beautiful and he would fall apart when he couldn’t take her home.
The nurses taught Amanda and Chris how to grieve and love simultaneously. One nurse told Amanda how cute Reese was and asked if she could hold her. Another placed ice packs in Reese’s swaddle to preserve her body so Amanda could keep holding her. Amanda asked the nurses to tuck cotton balls soaked in an orange scent into Reese’s blanket so the smell would trigger the memory of her daughter. And just as if Reese had been born alive, the nurses took pictures and made prints of her hands and feet.
“I felt such a deep, abiding love for her,” Amanda said. “And I was so proud to be her mom.”
On the way home from the hospital, Amanda broke down at the sight of Reese’s empty car seat. The next few weeks passed in a sleep-filled fog punctuated by intense periods of crying. The smell of oranges wrecked her. Her breast milk coming in was agonizing, physically and emotionally. She wore sports bras stuffed with ice packs to ease the pain and dry up her milk supply. While Rogen was at day care, she sobbed in his bed.
In the months that followed, Amanda and Chris searched for answers and wondered whether their medical team had missed warning signs. Late at night, Amanda turned to Google to find information about stillbirths. She mailed her medical records to a doctor who studies stillbirths, who she said told her that Reese’s death could have been prevented. They briefly discussed legal action against her doctors, but she said a lawyer told her it would be difficult to sue.
Amanda and Chris pinpointed her last two months of pregnancy as the time things started to go wrong. She had been diagnosed with polyhydramnios, meaning there was excess amniotic fluid in the womb. Her doctor had scheduled additional weekly testing.
One of those ultrasounds revealed problems with the blood flow in the umbilical cord. Reese’s cord also appeared to be wrapped around her neck, Amanda said later, but was told that was less of a concern, since it occurs in about 20% of normal deliveries. At another appointment, Amanda’s medical records show, Reese failed the portion of a test that measures fetal breathing movements.
At 37 weeks, Amanda told one of the midwives the baby’s movements felt different, but, she said, the midwife told her that it was common for movements to feel weaker with polyhydramnios. At that point, Amanda felt her baby was safer outside than inside and, her medical records show, she asked to schedule a C-section.
Despite voicing concerns about a change in the baby’s movement and asking to deliver earlier, Amanda said she and her husband were told by her midwife she couldn’t deliver for another two weeks. The doctor “continues to advise 39wks,” her medical records show. Waiting until 39 weeks is usually based on a guideline that deliveries should not happen before then unless a medical condition specifically warrants it, because early delivery can lead to complications.
Amanda would have to wait until 39 weeks and one day because, she said, her doctors didn’t typically do elective deliveries on weekends. Amanda was disappointed but said she trusted her team of doctors and midwives.
“I’m not a pushy person,” she said. “My husband is not a pushy person. That was out of our comfort zone to be, like, ‘What are we waiting for?’ But really what we wanted them to say was ‘We should deliver you.’”
Amanda’s final appointment was a maximum 30-minute-long ultrasound that combined a number of assessments to check amniotic fluid, fetal muscle tone, breathing and body movement. After 29 minutes of inactivity, Amanda said, the baby moved a hand. In the parking lot, Amanda called her mother, crying in relief. Four more days, she told her.
Less than 24 hours before the scheduled C-section, Reese was stillborn.
Four months after her death, Amanda, then a career advisor at the University of Minnesota, and Chris, a public relations specialist, wrote a letter to the University of Minnesota Medical Center, where Amanda had given birth to her dead daughter. They said they had “no ill feelings” toward anyone, but “it pains us to know that her death could’ve been prevented if we would have been sent to labor and delivery following that ultrasound.”
They noted that though they were told that Reese had passed the final ultrasound where she took 29 minutes to move, they had since come to believe that she had failed because, according to national standards, at least three movements were required. They also blamed a strict adherence to the 39-week guideline. And they encouraged the hospital staff to read more on umbilical cord accidents and acute polyhydramnios, which they later learned carries an increased stillbirth risk.
The positive feelings they had from speaking up were replaced by dismay when the hospital responded with a three-paragraph letter, signed by seven doctors and eight nurses. They said they had reexamined each medical decision in her case and concluded they had made “the best decisions medically possible.” They expressed their sympathy and said it was “so very heartwarming that you are trying to turn your tragic loss into something that will benefit others.”
Amanda felt dismissed by the medical team all over again. She didn’t expect them to admit fault, but she said she hoped that they would at least learn from Reese’s death to do things differently in the future. She was angry, and hurt, and knew that she would need to find a new doctor.
A spokesperson for the University of Minnesota Medical School told ProPublica she could not comment on individual patient cases and did not respond to questions about general protocols. “We share the physicians’ condolences,” she wrote, adding that the doctors and the university “are dedicated to delivering high quality, accessible and inclusive health care.”
For many expectant parents, it’s hard to muster the courage to call a doctor about something they’re not even sure is a problem.
“Moms self-censor a lot. No one wants to be that mom that all the doctors are rolling their eyes at because she’s freaking out over nothing,” said Samantha Banerjee, executive director of PUSH for Empowered Pregnancy, a nonprofit based in New York state that works to prevent stillbirths. Banerjee’s daughter, Alana, was stillborn two days before her due date.
In addition to raising awareness that stillbirths can happen even in low-risk pregnancies, PUSH teaches pregnant people how to advocate for themselves. The volunteers advise them to put their requests in writing and not to spend time drinking juice or lying on their side if they are worried about their baby’s lack of movement. In the majority of cases, a call or visit to the hospital reassures them.
But, the group tells parents, if their baby is in distress, calling their doctor can save their life.
Debbie Haine Vijayvergiya is fighting another narrative: that stillbirths are a rare fluke that “just happen.” When her daughter Autumn Joy was born without a heartbeat in 2011, Haine Vijayvergiya said, her doctor told her having a stillborn baby was as rare as being struck by lightning.
She believed him, but then she looked up the odds of a lightning strike and found they are less than one in a million – and most people survive. In 2020, according to the CDC, there was one stillbirth for about every 175 births.
“I’ve spoken to more women than I can count that said, ‘I raised the red flag, and I was sent home. I was told to eat a piece of cake and have some orange juice and lay on my left side,’ only to wake up the next day and their baby is not alive,” said Haine Vijayvergiya, a New Jersey mother and maternal health advocate.
She has fought for more than a decade to pass stillbirth legislation as her daughter’s legacy. Her current undertaking is her most ambitious. The federal Stillbirth Health Improvement and Education (SHINE) for Autumn Act, named after her daughter, would authorize $9 million a year for five years in federal funding for research, better data collection and training for fetal autopsies. But it is currently sitting in the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions.
Not all stillbirths are preventable, and medical experts agree more research is needed to determine who is most at risk and which babies can potentially be saved. Complicating matters is the wide range of risk factors, including hypertension and diabetes, smoking, obesity, being pregnant with multiples, being 35 or older and having had a previous stillbirth.
ProPublica reported this summer on how the U.S. botched the rollout of COVID-19 vaccines for pregnant people, who faced an increased risk for stillbirth if they were unvaccinated and contracted the virus, especially during the Delta wave.
Doctors often work to balance the risk of stillbirth with other dangers, particularly an increased chance of being admitted to neonatal intensive care units or even death of the baby if it is born too early. ACOG and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine have issued guidance to try to slow a rise in elective deliveries before 39 weeks and the potential harm that can result. The Joint Commission, a national accrediting organization, began evaluating hospitals in 2010 based on that standard.
A 2019 study found that the risks of stillbirth slightly increased after the rule went into effect, but fewer infants died after birth. Other studies have not found an effect on stillbirths.
Last year, the obstetric groups updated their guidance to allow doctors to consider an early delivery if a woman has anxiety and a history of stillbirth, writing that a previous stillbirth “may” warrant an early delivery for patients who understand and accept the risks. For those who have previously had a stillbirth, one modeling analysis found that 38 weeks is the optimal timing of delivery, considering the increased risk of another stillbirth.
“A woman who has had a previous stillbirth at 37 weeks – one could argue that it’s cruel and unusual punishment to make her go to 39 weeks with her next pregnancy, although that is the current recommendation,” said Dr. Neil Mandsager, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist in Iowa and a medical advisor to a stillbirth prevention nonprofit.
At or after 40 weeks, the risk of stillbirth increases, especially for women 35 or older. Their risk, research shows, is doubled from 39 weeks to 40 and is more than six times as high at 42 weeks. In 2019 and 2020, a combined 1,200 stillbirths occurred between 40 and 42 weeks, according to the most recent CDC data.
Deciding when a patient should deliver entails weighing the risks to the mother and the infant against a possible stillbirth as the pregnancy continues, said Dr. Mark Turrentine, chair of ACOG’s Clinical Consensus Committee-Obstetrics, which helped create the guidance on managing a stillbirth. He said ACOG has addressed stillbirth in other documents and extensively in its 2021 guidance on fetal surveillance and testing, which is done to reduce the risk of stillbirth.
ACOG said it routinely reviewed its guidance on management of stillbirth but was unable to make significant updates “due to the lack of new, evidence-based research.” While prevention is a great concern to ACOG, Turrentine said it’s difficult to know how many stillbirths are preventable.
He said it’s standard practice for doctors to ask about fetal movement, and ACOG updated its guidance after new research became available. Doctors also need to include patients in decision-making and tailor care to them, he said, whether that›s using aspirin in patients at high risk of preeclampsia – a serious high blood pressure condition during pregnancy – or ordering additional tests.
After Reese’s death, Amanda and Chris Duffy wanted to get pregnant again. They sought out an obstetrician-gynecologist who would educate and listen to them. They set up several consultations until they found Dr. Emily Hawes-Van Pelt, who was recommended by another family who had had a stillbirth.
Hawes-Van Pelt cried with Amanda and Chris at their first meeting.
“I told her I was scared to be involved,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “It’s such a tricky subsequent pregnancy because there’s so much worry and anxiety about the horrible, awful thing happening again.”
Amanda’s fear of delivering another dead baby led to an all-consuming anxiety, but Hawes-Van Pelt supported her when she asked for additional monitoring, testing and an early delivery.
When Hawes-Van Pelt switched practices midway through Amanda’s pregnancy, Amanda followed her. But the new hospital pushed back on the early delivery.
“We intervene early for poorly controlled diabetes,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “We intervene early for all sorts of medical issues. Anxiety and prior stillbirth are two medical issues that we can intervene earlier for.”
Hawes-Van Pelt said she learned a lot from caring for Amanda, who made her reevaluate some of her own assumptions around stillbirths.
“I had a horrible fear of scaring women unnecessarily, and then realized that I was just not preparing women or educating them because of my own fears around it,” she said. “If you can carry a human being in your body and birth that human being and take care of it, you can hear those words.”
The hospital eventually agreed to let Hawes-Van Pelt schedule Amanda for a 37-week C-section. But after Amanda was again diagnosed with polyhydramnios, she went in for a C-section even earlier. She gave birth in 2015 to a healthy boy she and Chris named Rhett. Two years later, Amanda and Hawes-Van Pelt followed the same pregnancy plan, and she delivered a girl named Maeda Reese. Amanda chose the name because, when said quickly, it sounds like “made of Reese.”
Federal agencies, national organizations and state and city officials have mobilized in recent years to address maternal mortality, when mothers die during pregnancy, at delivery or soon after childbirth. They have focused on improving data collection, passing legislation and creating awareness campaigns that encourage medical professionals and others to listen when women say something doesn›t feel right.
In 2017, ProPublica and NPR documented the U.S. maternal mortality crisis, including alarming racial disparities.
According to CDC data, Black women face nearly three times the risk of maternal mortality. They also are more than twice – and in some states close to three times – as likely to have a stillbirth than white women, meaning not only are Black mothers dying at a disproportionate rate, so are their babies.
Janet Petersen, a state senator from Iowa, said it gives her hope to see how the country has turned its attention to maternal mortality and disparities in health care. She simply cannot understand why stillbirth isn’t being met with the same urgency.
In 2020, the CDC reported 861 mothers died either while pregnant or within six weeks of giving birth. That same year, 20,854 babies were stillborn.
Stillbirth, Petersen said, is a missing piece of the puzzle. Research shows the likelihood of severe maternal complications was more than four times higher for pregnancies that ended in stillbirths, and mothers who died within six weeks of delivery were more likely to have had a stillbirth.
“We see it over and over again that stillbirth is one of the maternal health care issues that continuously gets ignored,” said Petersen, a Democrat.
Petersen was a young legislator in 2003 when her daughter Grace was born still. Devastated, she thought of her grandmother, who lost a baby to stillbirth in 1920, just a few weeks before women got the right to vote.
“I was laying in my hospital bed thinking, ‘How could this still be happening in our country?’” Petersen recalled. “And it seemed, from the medical perspective, that, well, stillbirth happens. We can’t do anything to prevent them.”
Over the next few months, Petersen heard from other mothers who had lost their babies and wanted to spark change. As an elected official, Petersen was in a position to do that. In 2004, she introduced legislation that required the Iowa Department of Public Health to create a stillbirths work group, later securing funding through the CDC to create a stillbirth registry.
But the CDC didn’t renew the funding and never analyzed the data from the registry, though a CDC spokesperson said the Iowa Department of Public Health examined the data. Officials from the department did not respond to requests for comment.
Petersen and her fellow mothers pivoted. After hearing how researchers in Norway were able to increase awareness around fetal movement, they co-founded a nonprofit aimed at doing the same in the U.S.
The group, Healthy Birth Day, created colorful “Count the Kicks” pamphlets – and later an app – teaching pregnant people how to track a baby’s movements and establish what is normal for them. Monitoring a baby’s movements is the earliest and sometimes only indication that something may be wrong, said Emily Price, chief executive officer of Healthy Birth Day. One of the organization’s main messages is for pregnant people to speak up and clinicians to listen.
“Unfortunately, there are still doctors who brush women off or send them home when they come in with a complaint of a change in their baby’s movements,” Price said. “And babies are dying because of it.”
One Indiana county, which recorded 65 stillbirths from 2017 through 2019, reported that 74% had either some chance or a good chance of prevention, according to St. Joseph County Department of Health’s Fetal Infant Mortality Review program. For mothers who experienced decreased fetal movement in the few hours or days before the stillbirth, that estimate jumped to 90%.
Although there is not a scientific consensus that kick counting can prevent stillbirths, national groups, including ACOG, recommend that medical professionals encourage their patients to be aware of fetal movement patterns. ACOG also advises medical professionals to be attentive to a mother’s concerns about reduced movement and address them “in a systematic way.”
One complaint the CDC hears too often, an agency spokesperson said, is that pregnant people and those who gave birth recently find that their concerns are dismissed or ignored. “Listening and taking the concerns of pregnant and recently pregnant people seriously,” she said, “is a simple, yet powerful action to prevent serious health complications and even death.”
The CDC, she said, is “very interested” in expanding its research on stillbirth, which is “a crucial part of the development of any awareness or prevention campaigns.” In addition to working to improve its stillbirth data quality, the agency has funded some pilot programs at the city and state level to better track stillbirths, survey people who have had a stillbirth and research risk factors and causes. The Iowa registry, she said, led the CDC to fund different research projects in Arkansas and Massachusetts, which are ongoing.
In 2009, the CDC acknowledged that fetal mortality remained a “major, but often overlooked, public health problem.” Officials wrote that much of the public health concern had been focused on infant mortality “in part due to lesser awareness of the magnitude of fetal mortality, its causes, and prevention strategies.”
But little has changed over the past 13 years. Echoing its earlier message, the CDC this year declared that “much work remains” and that “stillbirth is not often viewed as a public health issue, so increased awareness is key.”
A spokesperson for the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, which is part of the NIH, said the agency has continually funded research on stillbirths, even after one of its key studies ended. The agency, she said, also supports research on conditions that increase the risk of stillbirth.
As a scientific research institute, it does not issue clinical guidelines or recommendations, she said, though it did launch the Safe to Sleep campaign in 1994, two decades after Congress put it in charge of SIDS federal research efforts. That campaign, which educates parents and caregivers on ways to reduce the risk of SIDS, highlights recommendations issued by the American Academy of Pediatrics. She said the agency will continue to collaborate with organizations that raise awareness about stillbirth and other pregnancy complications “to amplify their messages and efforts.”
“NICHD continues to support research on the prevention, causes, frequency, and risk factors of stillbirth,” the spokesperson said in an email. “Our commitment to enhancing understanding of stillbirth and improving outcomes focuses on building the scientific knowledge base.”
But getting laws on the books that could raise awareness around stillbirth – even when they don’t require additional funding – has been a struggle. Petersen and Price are pushing Congress to pass legislation that would add stillbirth research and prevention to the list of activities approved for federal maternal health dollars.
Though the bill doesn’t ask for any additional funding, it has not yet passed.
In addition, the SHINE for Autumn Act breezed through the House of Representatives in December 2021. After Haine Vijayvergiya, the New Jersey mother who has championed it, secured bipartisan support from U.S. Sens. Cory Booker, D-N.J., and Marco Rubio, R-Fla., she thought the most comprehensive stillbirth legislation in U.S. history would finally become law.
Neither bill has sparked controversy.
But months after press releases announced the SHINE legislation and referred to the U.S. stillbirth rate as “unacceptable,” lawmakers and the families they represent are running out of time as this session of Congress prepares to adjourn.
“From the day that the bill was introduced into the Senate,” Haine Vijayvergiya said, “approximately 13,000 babies have been born still.”
Last month, on a brilliant fall day much like the one when Reese was stillborn, Amanda Duffy bent down to kiss her son Rogen’s head before they walked on stage.
She wore a soft blue T-shirt tucked into her jeans that read “Be courageous.” The message was as much for her as it was for the crowd on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., many of them like her, mothers who didn’t know stillbirth happened until it happened to them. Since Reese’s death, she has coached doctors and nurses on improving care for patients who have suffered pregnancy loss. Among her many suggestions, she tells them their first words when a concerned patient reaches out should be “I’m so glad you called.”
A few hundred people had gathered for The Big PUSH to End Preventable Stillbirth, billed as the first-ever march on the issue. As part of an art installation, Amanda wrote a note to Reese: “You’re pretty magical & for that I’m grateful. You’re a change maker and you are so very loved. Love, Mama.” Before she slipped the folded paper into a sea of more than 20,000 baby hats, Rogen added his own message: “Hope you are having a good time – Rogen.”
Reese would have turned 8 this month.
Before Amanda spoke, she took a deep breath and silenced her nerves. She walked onto the stage and called on Congress to pass the stillbirth legislation before it. She didn’t ask. She demanded.
“It’s time to empower pregnant people and their care providers with information that leads to prevention,” she insisted.
With the afternoon sun bearing down, Amanda and Rogen disappeared into the crowd of families marching toward the Capitol. Many carried signs. Some pushed empty strollers. Amanda was still wearing the orange-scented oil she had rubbed on her wrists that morning.
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published
The day before doctors had scheduled Amanda Duffy to give birth, the baby jolted her awake with a kick.
A few hours later, on that bright Sunday in November 2014, she leaned back on a park bench to watch her 19-month-old son Rogen enjoy his final day of being an only child. In that moment of calm, she realized that the kick that morning was the last time she had felt the baby move.
She told herself not to worry. She had heard that babies can slow down toward the end of a pregnancy and remembered reading that sugary snacks and cold fluids can stimulate a baby’s movement. When she got back to the family’s home in suburban Minneapolis, she drank a large glass of ice water and grabbed a few Tootsie Rolls off the kitchen counter.
But something about seeing her husband, Chris, lace up his shoes to leave for a run prompted her to blurt out, “I haven’t felt the baby kick.”
Chris called Amanda’s doctor, and they headed to the hospital to be checked. Once there, a nurse maneuvered a fetal monitor around Amanda’s belly. When she had trouble locating a heartbeat, she remarked that the baby must be tucked in tight. The doctor walked into the room, turned the screen away from Amanda and Chris and began searching. She was sorry, Amanda remembers her telling them, but she could not find a heartbeat.
Amanda let out a guttural scream. She said the doctor quickly performed an internal exam, which detected faint heart activity, then rushed Amanda into an emergency cesarean section.
She woke up to the sound of doctors talking to Chris. She listened but couldn’t bring herself to face the news. Her doctor told her she needed to open her eyes.
Amanda, then 31, couldn’t fathom that her daughter had died. She said her doctors had never discussed stillbirth with her. It was not mentioned in any of the pregnancy materials she had read. She didn’t even know that stillbirth was a possibility.
But every year more than 20,000 pregnancies in the United States end in stillbirth, the death of an expected child at 20 weeks or more. That number has exceeded infant mortality every year for the last 10 years. It’s 15 times the number of babies who, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, died of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, or SIDS, in 2020.
The deaths are not inevitable. One study found that nearly one in four U.S. stillbirths may be preventable. For pregnancies that last 37 weeks or more, that research shows, the figure jumps to nearly half. Thousands more babies could potentially be delivered safely every year.
But federal agencies have not prioritized critical stillbirth-focused studies that could lead to fewer deaths. Nearly two decades ago, both the CDC and the National Institutes of Health launched key stillbirth tracking and research studies, but the agencies ended those projects within about a decade. The CDC never analyzed some of the data that was collected.
Unlike with SIDS, a leading cause of infant death, federal officials have failed to launch a national campaign to reduce the risk of stillbirth or adequately raise awareness about it. Placental exams and autopsies, which can sometimes explain why stillbirths happened, are underutilized, in part because parents are not counseled on their benefits.
Federal agencies, state health departments, hospitals and doctors have also done a poor job of educating expectant parents about stillbirth or diligently counseling on fetal movement, despite research showing that patients who have had a stillbirth are more likely to have experienced abnormal fetal movements, including decreased activity. Neither the CDC nor the NIH have consistently promoted guidance telling those who are pregnant to be aware of their babies’ movement in the womb as a way to possibly reduce their risk of stillbirth.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the nation’s leading obstetrics organization, has been slow to update its own guidance to doctors on managing a stillbirth. In 2009, ACOG issued a set of guidelines that included a single paragraph regarding fetal movement. Those guidelines weren’t significantly updated for another 11 years.
Perhaps it’s no surprise that federal goals for reducing stillbirths keep moving in the wrong direction. In 2005, the U.S. stillbirth rate was 6.2 per 1,000 live births. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, in an effort to eliminate health disparities and establish a target that was “better than the best racial or ethnic group rate,” set a goal of reducing it to 4.1 for 2010. When that wasn’t met, federal officials changed their approach and set what they called more “science-based” and “realistic” goals, raising the 2020 target to 5.6. The U.S. still fell short. The 2030 goal of 5.7 was so attainable that it was met before the decade started. The 2020 rate, the most current according to the CDC, is 5.74.
By comparison, other wealthy countries have implemented national action plans to prevent stillbirth through awareness, research and care. Among other approaches, those countries have focused on increasing education around stillbirth and the importance of a baby’s movements, reducing rates of smoking and identifying fetuses that grow too slowly in the womb.
The efforts have paid off. The Netherlands, for instance, has reduced its rate of stillbirths at 28 weeks or later by more than half, from 5.2 in 2000 to 2.3 in 2019, according to a study published last year in The Lancet.
Dr. Bob Silver, chair of the obstetrics/gynecology department at University of Utah Health and a leading stillbirth expert, coauthored the study that estimated nearly one in four stillbirths are potentially preventable, a figure he referred to as conservative. He called on federal agencies to declare stillbirth reduction a priority the same way they have done for premature birth and maternal mortality.
“I’d like to see us say we really want to reduce the rate of stillbirth and raise awareness and try to do all of the reasonable things that may contribute to reducing stillbirths that other countries have done,” Silver said.
The lack of comprehensive attention and action has contributed to a stillbirth crisis, shrouded in an acceptance that some babies just die. Compounding the tragedy is a stigma and guilt so crushing that the first words some mothers utter when their lifeless babies are placed in their arms are “I’m sorry.”
In the hospital room, Amanda Duffy finally opened her eyes. She named her daughter Reese Christine, the name she had picked out for her before they found out she had died. She was 8 pounds, 3 ounces and 20 1/2 inches long and was born with her umbilical cord wrapped tightly around her neck twice. The baby was still warm when the nurse placed her in Amanda’s arms. Amanda was struck by how lovely her daughter was. Rosy skin. Chris’ red hair. Rogen’s chubby cheeks.
As Amanda held Reese, Chris hunched over the toilet, vomiting. Later that night, as he lay next to Amanda on the hospital bed, he held his daughter. He hadn’t initially wanted to see her. He worried she would be disfigured or, worse, that she would be beautiful and he would fall apart when he couldn’t take her home.
The nurses taught Amanda and Chris how to grieve and love simultaneously. One nurse told Amanda how cute Reese was and asked if she could hold her. Another placed ice packs in Reese’s swaddle to preserve her body so Amanda could keep holding her. Amanda asked the nurses to tuck cotton balls soaked in an orange scent into Reese’s blanket so the smell would trigger the memory of her daughter. And just as if Reese had been born alive, the nurses took pictures and made prints of her hands and feet.
“I felt such a deep, abiding love for her,” Amanda said. “And I was so proud to be her mom.”
On the way home from the hospital, Amanda broke down at the sight of Reese’s empty car seat. The next few weeks passed in a sleep-filled fog punctuated by intense periods of crying. The smell of oranges wrecked her. Her breast milk coming in was agonizing, physically and emotionally. She wore sports bras stuffed with ice packs to ease the pain and dry up her milk supply. While Rogen was at day care, she sobbed in his bed.
In the months that followed, Amanda and Chris searched for answers and wondered whether their medical team had missed warning signs. Late at night, Amanda turned to Google to find information about stillbirths. She mailed her medical records to a doctor who studies stillbirths, who she said told her that Reese’s death could have been prevented. They briefly discussed legal action against her doctors, but she said a lawyer told her it would be difficult to sue.
Amanda and Chris pinpointed her last two months of pregnancy as the time things started to go wrong. She had been diagnosed with polyhydramnios, meaning there was excess amniotic fluid in the womb. Her doctor had scheduled additional weekly testing.
One of those ultrasounds revealed problems with the blood flow in the umbilical cord. Reese’s cord also appeared to be wrapped around her neck, Amanda said later, but was told that was less of a concern, since it occurs in about 20% of normal deliveries. At another appointment, Amanda’s medical records show, Reese failed the portion of a test that measures fetal breathing movements.
At 37 weeks, Amanda told one of the midwives the baby’s movements felt different, but, she said, the midwife told her that it was common for movements to feel weaker with polyhydramnios. At that point, Amanda felt her baby was safer outside than inside and, her medical records show, she asked to schedule a C-section.
Despite voicing concerns about a change in the baby’s movement and asking to deliver earlier, Amanda said she and her husband were told by her midwife she couldn’t deliver for another two weeks. The doctor “continues to advise 39wks,” her medical records show. Waiting until 39 weeks is usually based on a guideline that deliveries should not happen before then unless a medical condition specifically warrants it, because early delivery can lead to complications.
Amanda would have to wait until 39 weeks and one day because, she said, her doctors didn’t typically do elective deliveries on weekends. Amanda was disappointed but said she trusted her team of doctors and midwives.
“I’m not a pushy person,” she said. “My husband is not a pushy person. That was out of our comfort zone to be, like, ‘What are we waiting for?’ But really what we wanted them to say was ‘We should deliver you.’”
Amanda’s final appointment was a maximum 30-minute-long ultrasound that combined a number of assessments to check amniotic fluid, fetal muscle tone, breathing and body movement. After 29 minutes of inactivity, Amanda said, the baby moved a hand. In the parking lot, Amanda called her mother, crying in relief. Four more days, she told her.
Less than 24 hours before the scheduled C-section, Reese was stillborn.
Four months after her death, Amanda, then a career advisor at the University of Minnesota, and Chris, a public relations specialist, wrote a letter to the University of Minnesota Medical Center, where Amanda had given birth to her dead daughter. They said they had “no ill feelings” toward anyone, but “it pains us to know that her death could’ve been prevented if we would have been sent to labor and delivery following that ultrasound.”
They noted that though they were told that Reese had passed the final ultrasound where she took 29 minutes to move, they had since come to believe that she had failed because, according to national standards, at least three movements were required. They also blamed a strict adherence to the 39-week guideline. And they encouraged the hospital staff to read more on umbilical cord accidents and acute polyhydramnios, which they later learned carries an increased stillbirth risk.
The positive feelings they had from speaking up were replaced by dismay when the hospital responded with a three-paragraph letter, signed by seven doctors and eight nurses. They said they had reexamined each medical decision in her case and concluded they had made “the best decisions medically possible.” They expressed their sympathy and said it was “so very heartwarming that you are trying to turn your tragic loss into something that will benefit others.”
Amanda felt dismissed by the medical team all over again. She didn’t expect them to admit fault, but she said she hoped that they would at least learn from Reese’s death to do things differently in the future. She was angry, and hurt, and knew that she would need to find a new doctor.
A spokesperson for the University of Minnesota Medical School told ProPublica she could not comment on individual patient cases and did not respond to questions about general protocols. “We share the physicians’ condolences,” she wrote, adding that the doctors and the university “are dedicated to delivering high quality, accessible and inclusive health care.”
For many expectant parents, it’s hard to muster the courage to call a doctor about something they’re not even sure is a problem.
“Moms self-censor a lot. No one wants to be that mom that all the doctors are rolling their eyes at because she’s freaking out over nothing,” said Samantha Banerjee, executive director of PUSH for Empowered Pregnancy, a nonprofit based in New York state that works to prevent stillbirths. Banerjee’s daughter, Alana, was stillborn two days before her due date.
In addition to raising awareness that stillbirths can happen even in low-risk pregnancies, PUSH teaches pregnant people how to advocate for themselves. The volunteers advise them to put their requests in writing and not to spend time drinking juice or lying on their side if they are worried about their baby’s lack of movement. In the majority of cases, a call or visit to the hospital reassures them.
But, the group tells parents, if their baby is in distress, calling their doctor can save their life.
Debbie Haine Vijayvergiya is fighting another narrative: that stillbirths are a rare fluke that “just happen.” When her daughter Autumn Joy was born without a heartbeat in 2011, Haine Vijayvergiya said, her doctor told her having a stillborn baby was as rare as being struck by lightning.
She believed him, but then she looked up the odds of a lightning strike and found they are less than one in a million – and most people survive. In 2020, according to the CDC, there was one stillbirth for about every 175 births.
“I’ve spoken to more women than I can count that said, ‘I raised the red flag, and I was sent home. I was told to eat a piece of cake and have some orange juice and lay on my left side,’ only to wake up the next day and their baby is not alive,” said Haine Vijayvergiya, a New Jersey mother and maternal health advocate.
She has fought for more than a decade to pass stillbirth legislation as her daughter’s legacy. Her current undertaking is her most ambitious. The federal Stillbirth Health Improvement and Education (SHINE) for Autumn Act, named after her daughter, would authorize $9 million a year for five years in federal funding for research, better data collection and training for fetal autopsies. But it is currently sitting in the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions.
Not all stillbirths are preventable, and medical experts agree more research is needed to determine who is most at risk and which babies can potentially be saved. Complicating matters is the wide range of risk factors, including hypertension and diabetes, smoking, obesity, being pregnant with multiples, being 35 or older and having had a previous stillbirth.
ProPublica reported this summer on how the U.S. botched the rollout of COVID-19 vaccines for pregnant people, who faced an increased risk for stillbirth if they were unvaccinated and contracted the virus, especially during the Delta wave.
Doctors often work to balance the risk of stillbirth with other dangers, particularly an increased chance of being admitted to neonatal intensive care units or even death of the baby if it is born too early. ACOG and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine have issued guidance to try to slow a rise in elective deliveries before 39 weeks and the potential harm that can result. The Joint Commission, a national accrediting organization, began evaluating hospitals in 2010 based on that standard.
A 2019 study found that the risks of stillbirth slightly increased after the rule went into effect, but fewer infants died after birth. Other studies have not found an effect on stillbirths.
Last year, the obstetric groups updated their guidance to allow doctors to consider an early delivery if a woman has anxiety and a history of stillbirth, writing that a previous stillbirth “may” warrant an early delivery for patients who understand and accept the risks. For those who have previously had a stillbirth, one modeling analysis found that 38 weeks is the optimal timing of delivery, considering the increased risk of another stillbirth.
“A woman who has had a previous stillbirth at 37 weeks – one could argue that it’s cruel and unusual punishment to make her go to 39 weeks with her next pregnancy, although that is the current recommendation,” said Dr. Neil Mandsager, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist in Iowa and a medical advisor to a stillbirth prevention nonprofit.
At or after 40 weeks, the risk of stillbirth increases, especially for women 35 or older. Their risk, research shows, is doubled from 39 weeks to 40 and is more than six times as high at 42 weeks. In 2019 and 2020, a combined 1,200 stillbirths occurred between 40 and 42 weeks, according to the most recent CDC data.
Deciding when a patient should deliver entails weighing the risks to the mother and the infant against a possible stillbirth as the pregnancy continues, said Dr. Mark Turrentine, chair of ACOG’s Clinical Consensus Committee-Obstetrics, which helped create the guidance on managing a stillbirth. He said ACOG has addressed stillbirth in other documents and extensively in its 2021 guidance on fetal surveillance and testing, which is done to reduce the risk of stillbirth.
ACOG said it routinely reviewed its guidance on management of stillbirth but was unable to make significant updates “due to the lack of new, evidence-based research.” While prevention is a great concern to ACOG, Turrentine said it’s difficult to know how many stillbirths are preventable.
He said it’s standard practice for doctors to ask about fetal movement, and ACOG updated its guidance after new research became available. Doctors also need to include patients in decision-making and tailor care to them, he said, whether that›s using aspirin in patients at high risk of preeclampsia – a serious high blood pressure condition during pregnancy – or ordering additional tests.
After Reese’s death, Amanda and Chris Duffy wanted to get pregnant again. They sought out an obstetrician-gynecologist who would educate and listen to them. They set up several consultations until they found Dr. Emily Hawes-Van Pelt, who was recommended by another family who had had a stillbirth.
Hawes-Van Pelt cried with Amanda and Chris at their first meeting.
“I told her I was scared to be involved,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “It’s such a tricky subsequent pregnancy because there’s so much worry and anxiety about the horrible, awful thing happening again.”
Amanda’s fear of delivering another dead baby led to an all-consuming anxiety, but Hawes-Van Pelt supported her when she asked for additional monitoring, testing and an early delivery.
When Hawes-Van Pelt switched practices midway through Amanda’s pregnancy, Amanda followed her. But the new hospital pushed back on the early delivery.
“We intervene early for poorly controlled diabetes,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “We intervene early for all sorts of medical issues. Anxiety and prior stillbirth are two medical issues that we can intervene earlier for.”
Hawes-Van Pelt said she learned a lot from caring for Amanda, who made her reevaluate some of her own assumptions around stillbirths.
“I had a horrible fear of scaring women unnecessarily, and then realized that I was just not preparing women or educating them because of my own fears around it,” she said. “If you can carry a human being in your body and birth that human being and take care of it, you can hear those words.”
The hospital eventually agreed to let Hawes-Van Pelt schedule Amanda for a 37-week C-section. But after Amanda was again diagnosed with polyhydramnios, she went in for a C-section even earlier. She gave birth in 2015 to a healthy boy she and Chris named Rhett. Two years later, Amanda and Hawes-Van Pelt followed the same pregnancy plan, and she delivered a girl named Maeda Reese. Amanda chose the name because, when said quickly, it sounds like “made of Reese.”
Federal agencies, national organizations and state and city officials have mobilized in recent years to address maternal mortality, when mothers die during pregnancy, at delivery or soon after childbirth. They have focused on improving data collection, passing legislation and creating awareness campaigns that encourage medical professionals and others to listen when women say something doesn›t feel right.
In 2017, ProPublica and NPR documented the U.S. maternal mortality crisis, including alarming racial disparities.
According to CDC data, Black women face nearly three times the risk of maternal mortality. They also are more than twice – and in some states close to three times – as likely to have a stillbirth than white women, meaning not only are Black mothers dying at a disproportionate rate, so are their babies.
Janet Petersen, a state senator from Iowa, said it gives her hope to see how the country has turned its attention to maternal mortality and disparities in health care. She simply cannot understand why stillbirth isn’t being met with the same urgency.
In 2020, the CDC reported 861 mothers died either while pregnant or within six weeks of giving birth. That same year, 20,854 babies were stillborn.
Stillbirth, Petersen said, is a missing piece of the puzzle. Research shows the likelihood of severe maternal complications was more than four times higher for pregnancies that ended in stillbirths, and mothers who died within six weeks of delivery were more likely to have had a stillbirth.
“We see it over and over again that stillbirth is one of the maternal health care issues that continuously gets ignored,” said Petersen, a Democrat.
Petersen was a young legislator in 2003 when her daughter Grace was born still. Devastated, she thought of her grandmother, who lost a baby to stillbirth in 1920, just a few weeks before women got the right to vote.
“I was laying in my hospital bed thinking, ‘How could this still be happening in our country?’” Petersen recalled. “And it seemed, from the medical perspective, that, well, stillbirth happens. We can’t do anything to prevent them.”
Over the next few months, Petersen heard from other mothers who had lost their babies and wanted to spark change. As an elected official, Petersen was in a position to do that. In 2004, she introduced legislation that required the Iowa Department of Public Health to create a stillbirths work group, later securing funding through the CDC to create a stillbirth registry.
But the CDC didn’t renew the funding and never analyzed the data from the registry, though a CDC spokesperson said the Iowa Department of Public Health examined the data. Officials from the department did not respond to requests for comment.
Petersen and her fellow mothers pivoted. After hearing how researchers in Norway were able to increase awareness around fetal movement, they co-founded a nonprofit aimed at doing the same in the U.S.
The group, Healthy Birth Day, created colorful “Count the Kicks” pamphlets – and later an app – teaching pregnant people how to track a baby’s movements and establish what is normal for them. Monitoring a baby’s movements is the earliest and sometimes only indication that something may be wrong, said Emily Price, chief executive officer of Healthy Birth Day. One of the organization’s main messages is for pregnant people to speak up and clinicians to listen.
“Unfortunately, there are still doctors who brush women off or send them home when they come in with a complaint of a change in their baby’s movements,” Price said. “And babies are dying because of it.”
One Indiana county, which recorded 65 stillbirths from 2017 through 2019, reported that 74% had either some chance or a good chance of prevention, according to St. Joseph County Department of Health’s Fetal Infant Mortality Review program. For mothers who experienced decreased fetal movement in the few hours or days before the stillbirth, that estimate jumped to 90%.
Although there is not a scientific consensus that kick counting can prevent stillbirths, national groups, including ACOG, recommend that medical professionals encourage their patients to be aware of fetal movement patterns. ACOG also advises medical professionals to be attentive to a mother’s concerns about reduced movement and address them “in a systematic way.”
One complaint the CDC hears too often, an agency spokesperson said, is that pregnant people and those who gave birth recently find that their concerns are dismissed or ignored. “Listening and taking the concerns of pregnant and recently pregnant people seriously,” she said, “is a simple, yet powerful action to prevent serious health complications and even death.”
The CDC, she said, is “very interested” in expanding its research on stillbirth, which is “a crucial part of the development of any awareness or prevention campaigns.” In addition to working to improve its stillbirth data quality, the agency has funded some pilot programs at the city and state level to better track stillbirths, survey people who have had a stillbirth and research risk factors and causes. The Iowa registry, she said, led the CDC to fund different research projects in Arkansas and Massachusetts, which are ongoing.
In 2009, the CDC acknowledged that fetal mortality remained a “major, but often overlooked, public health problem.” Officials wrote that much of the public health concern had been focused on infant mortality “in part due to lesser awareness of the magnitude of fetal mortality, its causes, and prevention strategies.”
But little has changed over the past 13 years. Echoing its earlier message, the CDC this year declared that “much work remains” and that “stillbirth is not often viewed as a public health issue, so increased awareness is key.”
A spokesperson for the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, which is part of the NIH, said the agency has continually funded research on stillbirths, even after one of its key studies ended. The agency, she said, also supports research on conditions that increase the risk of stillbirth.
As a scientific research institute, it does not issue clinical guidelines or recommendations, she said, though it did launch the Safe to Sleep campaign in 1994, two decades after Congress put it in charge of SIDS federal research efforts. That campaign, which educates parents and caregivers on ways to reduce the risk of SIDS, highlights recommendations issued by the American Academy of Pediatrics. She said the agency will continue to collaborate with organizations that raise awareness about stillbirth and other pregnancy complications “to amplify their messages and efforts.”
“NICHD continues to support research on the prevention, causes, frequency, and risk factors of stillbirth,” the spokesperson said in an email. “Our commitment to enhancing understanding of stillbirth and improving outcomes focuses on building the scientific knowledge base.”
But getting laws on the books that could raise awareness around stillbirth – even when they don’t require additional funding – has been a struggle. Petersen and Price are pushing Congress to pass legislation that would add stillbirth research and prevention to the list of activities approved for federal maternal health dollars.
Though the bill doesn’t ask for any additional funding, it has not yet passed.
In addition, the SHINE for Autumn Act breezed through the House of Representatives in December 2021. After Haine Vijayvergiya, the New Jersey mother who has championed it, secured bipartisan support from U.S. Sens. Cory Booker, D-N.J., and Marco Rubio, R-Fla., she thought the most comprehensive stillbirth legislation in U.S. history would finally become law.
Neither bill has sparked controversy.
But months after press releases announced the SHINE legislation and referred to the U.S. stillbirth rate as “unacceptable,” lawmakers and the families they represent are running out of time as this session of Congress prepares to adjourn.
“From the day that the bill was introduced into the Senate,” Haine Vijayvergiya said, “approximately 13,000 babies have been born still.”
Last month, on a brilliant fall day much like the one when Reese was stillborn, Amanda Duffy bent down to kiss her son Rogen’s head before they walked on stage.
She wore a soft blue T-shirt tucked into her jeans that read “Be courageous.” The message was as much for her as it was for the crowd on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., many of them like her, mothers who didn’t know stillbirth happened until it happened to them. Since Reese’s death, she has coached doctors and nurses on improving care for patients who have suffered pregnancy loss. Among her many suggestions, she tells them their first words when a concerned patient reaches out should be “I’m so glad you called.”
A few hundred people had gathered for The Big PUSH to End Preventable Stillbirth, billed as the first-ever march on the issue. As part of an art installation, Amanda wrote a note to Reese: “You’re pretty magical & for that I’m grateful. You’re a change maker and you are so very loved. Love, Mama.” Before she slipped the folded paper into a sea of more than 20,000 baby hats, Rogen added his own message: “Hope you are having a good time – Rogen.”
Reese would have turned 8 this month.
Before Amanda spoke, she took a deep breath and silenced her nerves. She walked onto the stage and called on Congress to pass the stillbirth legislation before it. She didn’t ask. She demanded.
“It’s time to empower pregnant people and their care providers with information that leads to prevention,” she insisted.
With the afternoon sun bearing down, Amanda and Rogen disappeared into the crowd of families marching toward the Capitol. Many carried signs. Some pushed empty strollers. Amanda was still wearing the orange-scented oil she had rubbed on her wrists that morning.
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published
First classification criteria proposed for chronic osteomyelitis
PHILADELPHIA – An international group of researchers has proposed the first classification criteria for chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis (CNO) and a severe form of it, chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO).
CNO/CRMO most frequently affect children and adolescents and can significantly affect quality of life.
Yongdong (Dan) Zhao, MD, PhD, a pediatric rheumatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, Seattle, Washington, and Seza Ozen, MD, MSc, medical faculty head at Hacettepe University in Ankara, Turkey – members of the expert panel for criteria development – explained the proposed criteria, developed over 6 years, at the American College of Rheumatology 2022 Annual Meeting.
They gave examples of the point system that will help researchers correctly classify CNO/CRMO if the criteria are approved by ACR and the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR).
Melissa S. Oliver, MD, a pediatric rheumatologist at Riley Children’s Hospital and Indiana University, Indianapolis, told this news organization: “This proposal is important because CNO/CRMO has primarily been a diagnosis of exclusion. There are no specific tests or biomarkers for this disease. It can mimic malignancy and infectious osteomyelitis in its presentation, and these must be ruled out thoroughly first.”
However, she noted, this can be challenging and can delay diagnosis and treatment.
The classification criteria are novel, she said, because an international collaborative group used a consensus process involving physicians managing CNO and patients or caregivers of children with CNO.
Findings for and against CNO
Dr. Ozen summarized some examples of findings for and against a CNO/CRMO classification.
Statistically significant findings in favor of CNO/CRMO, she said, include intermittent bone pain; bone pain in upper torso; swelling of upper torso; presence of symmetric lesions; and presence of adaptive immune cell and/or fibrosis in biopsy.
Conversely, findings against CNO/CRMO include fever; signs of infection by labs; signs of cancer by biopsy; specific abnormal x-ray/CT scan; specific abnormal MRI; or pain resolved with antibiotics alone.
Dr. Zhao described a point system with a threshold of 55 points for classification of CNO/CRMO.
He gave actual examples from the registry to demonstrate high and low probability of CNO/CRMO.
Pro-CNO example
The first was a boy, aged 7 years 10 months, who had a year and a half of pain in his back and legs, but no fever. Pain was constant, waxing and waning. He had a personal and family history of psoriasis and was tender to palpation at multiple sites. Labs were normal and bone biopsy and vitamin C tests were not done; imaging findings showed multiple bones were affected. There was no antibiotic treatment.
That patient was scored 81, much higher than the threshold of 55, and would be classified as having CNO.
Non-CNO example
Conversely, the following example of a patient would score 47 – under the threshold – and would not be classified as having CNO.
That patient was an 11-year-old boy who had 2 months of pain in his right thigh with no fever. The pain was constantly waxing and waning. He was tender to palpation at only his right thigh without swelling. Labs were normal. He had no coexisting conditions. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were not measured, and no vitamin C test was performed. Imaging showed one right femur lesion on a PET-CT scan. There was no antibiotic treatment, and a bone biopsy culture showed malignancy but no inflammation or fibrosis.
Dr. Zhao said the mimickers most likely to be misclassified are vitamin C deficiency; hypophosphatasia; benign bone tumor, such as osteogenic osteoma; and a malignancy with normal labs and multifocal pattern of bone lesions.
The classification criteria will be “extremely helpful to diagnose patients with CNO/CRMO earlier,” said Dr. Oliver, who helped develop the criteria.
“The goal is that the proposed classification criteria will be used by all physicians to diagnose suspected CNO patients earlier and refer to a rheumatologist earlier so that appropriate therapies will not be delayed.”
The group will seek ACR and EULAR endorsement, and if granted, work toward widespread implementation. The criteria will allow researchers to have a more homogeneous study population for future clinical trials, Dr. Zhao said.
Dr. Zhao, Dr. Ozen, and Dr. Oliver declared no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Oliver helped develop the proposed guidelines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA – An international group of researchers has proposed the first classification criteria for chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis (CNO) and a severe form of it, chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO).
CNO/CRMO most frequently affect children and adolescents and can significantly affect quality of life.
Yongdong (Dan) Zhao, MD, PhD, a pediatric rheumatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, Seattle, Washington, and Seza Ozen, MD, MSc, medical faculty head at Hacettepe University in Ankara, Turkey – members of the expert panel for criteria development – explained the proposed criteria, developed over 6 years, at the American College of Rheumatology 2022 Annual Meeting.
They gave examples of the point system that will help researchers correctly classify CNO/CRMO if the criteria are approved by ACR and the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR).
Melissa S. Oliver, MD, a pediatric rheumatologist at Riley Children’s Hospital and Indiana University, Indianapolis, told this news organization: “This proposal is important because CNO/CRMO has primarily been a diagnosis of exclusion. There are no specific tests or biomarkers for this disease. It can mimic malignancy and infectious osteomyelitis in its presentation, and these must be ruled out thoroughly first.”
However, she noted, this can be challenging and can delay diagnosis and treatment.
The classification criteria are novel, she said, because an international collaborative group used a consensus process involving physicians managing CNO and patients or caregivers of children with CNO.
Findings for and against CNO
Dr. Ozen summarized some examples of findings for and against a CNO/CRMO classification.
Statistically significant findings in favor of CNO/CRMO, she said, include intermittent bone pain; bone pain in upper torso; swelling of upper torso; presence of symmetric lesions; and presence of adaptive immune cell and/or fibrosis in biopsy.
Conversely, findings against CNO/CRMO include fever; signs of infection by labs; signs of cancer by biopsy; specific abnormal x-ray/CT scan; specific abnormal MRI; or pain resolved with antibiotics alone.
Dr. Zhao described a point system with a threshold of 55 points for classification of CNO/CRMO.
He gave actual examples from the registry to demonstrate high and low probability of CNO/CRMO.
Pro-CNO example
The first was a boy, aged 7 years 10 months, who had a year and a half of pain in his back and legs, but no fever. Pain was constant, waxing and waning. He had a personal and family history of psoriasis and was tender to palpation at multiple sites. Labs were normal and bone biopsy and vitamin C tests were not done; imaging findings showed multiple bones were affected. There was no antibiotic treatment.
That patient was scored 81, much higher than the threshold of 55, and would be classified as having CNO.
Non-CNO example
Conversely, the following example of a patient would score 47 – under the threshold – and would not be classified as having CNO.
That patient was an 11-year-old boy who had 2 months of pain in his right thigh with no fever. The pain was constantly waxing and waning. He was tender to palpation at only his right thigh without swelling. Labs were normal. He had no coexisting conditions. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were not measured, and no vitamin C test was performed. Imaging showed one right femur lesion on a PET-CT scan. There was no antibiotic treatment, and a bone biopsy culture showed malignancy but no inflammation or fibrosis.
Dr. Zhao said the mimickers most likely to be misclassified are vitamin C deficiency; hypophosphatasia; benign bone tumor, such as osteogenic osteoma; and a malignancy with normal labs and multifocal pattern of bone lesions.
The classification criteria will be “extremely helpful to diagnose patients with CNO/CRMO earlier,” said Dr. Oliver, who helped develop the criteria.
“The goal is that the proposed classification criteria will be used by all physicians to diagnose suspected CNO patients earlier and refer to a rheumatologist earlier so that appropriate therapies will not be delayed.”
The group will seek ACR and EULAR endorsement, and if granted, work toward widespread implementation. The criteria will allow researchers to have a more homogeneous study population for future clinical trials, Dr. Zhao said.
Dr. Zhao, Dr. Ozen, and Dr. Oliver declared no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Oliver helped develop the proposed guidelines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA – An international group of researchers has proposed the first classification criteria for chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis (CNO) and a severe form of it, chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO).
CNO/CRMO most frequently affect children and adolescents and can significantly affect quality of life.
Yongdong (Dan) Zhao, MD, PhD, a pediatric rheumatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, Seattle, Washington, and Seza Ozen, MD, MSc, medical faculty head at Hacettepe University in Ankara, Turkey – members of the expert panel for criteria development – explained the proposed criteria, developed over 6 years, at the American College of Rheumatology 2022 Annual Meeting.
They gave examples of the point system that will help researchers correctly classify CNO/CRMO if the criteria are approved by ACR and the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR).
Melissa S. Oliver, MD, a pediatric rheumatologist at Riley Children’s Hospital and Indiana University, Indianapolis, told this news organization: “This proposal is important because CNO/CRMO has primarily been a diagnosis of exclusion. There are no specific tests or biomarkers for this disease. It can mimic malignancy and infectious osteomyelitis in its presentation, and these must be ruled out thoroughly first.”
However, she noted, this can be challenging and can delay diagnosis and treatment.
The classification criteria are novel, she said, because an international collaborative group used a consensus process involving physicians managing CNO and patients or caregivers of children with CNO.
Findings for and against CNO
Dr. Ozen summarized some examples of findings for and against a CNO/CRMO classification.
Statistically significant findings in favor of CNO/CRMO, she said, include intermittent bone pain; bone pain in upper torso; swelling of upper torso; presence of symmetric lesions; and presence of adaptive immune cell and/or fibrosis in biopsy.
Conversely, findings against CNO/CRMO include fever; signs of infection by labs; signs of cancer by biopsy; specific abnormal x-ray/CT scan; specific abnormal MRI; or pain resolved with antibiotics alone.
Dr. Zhao described a point system with a threshold of 55 points for classification of CNO/CRMO.
He gave actual examples from the registry to demonstrate high and low probability of CNO/CRMO.
Pro-CNO example
The first was a boy, aged 7 years 10 months, who had a year and a half of pain in his back and legs, but no fever. Pain was constant, waxing and waning. He had a personal and family history of psoriasis and was tender to palpation at multiple sites. Labs were normal and bone biopsy and vitamin C tests were not done; imaging findings showed multiple bones were affected. There was no antibiotic treatment.
That patient was scored 81, much higher than the threshold of 55, and would be classified as having CNO.
Non-CNO example
Conversely, the following example of a patient would score 47 – under the threshold – and would not be classified as having CNO.
That patient was an 11-year-old boy who had 2 months of pain in his right thigh with no fever. The pain was constantly waxing and waning. He was tender to palpation at only his right thigh without swelling. Labs were normal. He had no coexisting conditions. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were not measured, and no vitamin C test was performed. Imaging showed one right femur lesion on a PET-CT scan. There was no antibiotic treatment, and a bone biopsy culture showed malignancy but no inflammation or fibrosis.
Dr. Zhao said the mimickers most likely to be misclassified are vitamin C deficiency; hypophosphatasia; benign bone tumor, such as osteogenic osteoma; and a malignancy with normal labs and multifocal pattern of bone lesions.
The classification criteria will be “extremely helpful to diagnose patients with CNO/CRMO earlier,” said Dr. Oliver, who helped develop the criteria.
“The goal is that the proposed classification criteria will be used by all physicians to diagnose suspected CNO patients earlier and refer to a rheumatologist earlier so that appropriate therapies will not be delayed.”
The group will seek ACR and EULAR endorsement, and if granted, work toward widespread implementation. The criteria will allow researchers to have a more homogeneous study population for future clinical trials, Dr. Zhao said.
Dr. Zhao, Dr. Ozen, and Dr. Oliver declared no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Oliver helped develop the proposed guidelines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACR 2022
New ACR vaccination guideline: Take your best shot
PHILADELPHIA – The new American College of Rheumatology Guideline for Vaccinations in Patients with Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases (RMDs) emphasizes that both adult and pediatric patients should receive recommended vaccinations whenever possible.
But the guideline, currently in press, also offers recommendations about whether and when to withhold vaccines from patients with RMDs, such as avoiding the use of live attenuated virus vaccines in patients who are on immunosuppressive drug regimens, such as conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic DMARDs, or targeted synthetic DMARDs.
The new consensus guideline was formulated with the understanding that patients with RMDs are at increased risk for vaccine-preventable infections and more serious complications from infections, compared with the general population.
However, the guideline also acknowledges that the immunogenicity and safety of vaccines may differ among patients with RMDs, and that, depending on the patient age and disease state, individuals may benefit from modified vaccine indications, schedules, or modified medication schedules, said guideline panel member Anne Bass, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery and a professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who presented the guideline with other panel members in a session outlining the recommendations at the annual meeting of the ACR.
“In addition, vaccination recommendations – since much of it relates to medications – really applies across diseases, and so the ACR felt that, rather than having vaccine recommendations tacked onto the end of treatment guidelines for each individual disease, that the topic should be discussed or tackled as a whole,” she said.
The guideline does not cover vaccinations in patients taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs because this class of agents has minimal or no impact on antibody responses to vaccines. The guideline also does not address vaccinations against COVID-19 infections since the rapidly changing formulations would make the recommendations obsolete before they were even published, and because the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides up-to-date guidance on COVID-19 vaccinations in patients with compromised immunity, she said.
Guiding principles
The overarching principles of the guideline are to give indicated vaccines to patients with RMD whenever possible and that any decision to hold medications before or after vaccination consider the dosage used, RMD disease activity, and the patient’s risk for vaccine-preventable infection.
The guideline also states that “shared decision-making with patients is a key component of any vaccination strategy.”
Panel member Clifton O. Bingham III, MD, professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, outlined expanded indications for vaccinations against influenza, pneumococcal infections, varicella zoster virus (VZV) and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Influenza
The guideline conditionally recommends that patients with RMD aged 65 years and older and adults older than age 18 years who are on immunosuppressive medications should receive either high-dose or adjuvanted influenza vaccination rather than regular-dose vaccines.
“It’s recognized that the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccinations may be unavailable for patients when they’re seen in your practice,” Dr. Bingham said,” and we came out with two additional statements within the guidelines that said that any flu vaccine is recommended over no flu vaccinations, because we do know that responses are elicited, and a flu vaccination today is preferred over a flu vaccination delay.”
Pneumococcal vaccination
The panelists strongly recommended that patients with RMD younger than age 65 years who are on immunosuppressive medication receive pneumococcal vaccinations.
The ACR guideline is in sync with those issued by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, Dr. Bingham said. He urged audience members to visit a CDC-ACIP web page for more information on who should receive pneumococcal vaccination and when.
Recombinant varicella zoster
The recommendations strongly support that patients aged 18 years and over who are on immunosuppressive therapies should receive the recombinant VZV vaccine (Shingrix).
HPV
A less robust, conditional recommendation is for patients with RMDs who are between the ages of 26 and 45 years and on immunosuppressive medications to receive the HPV vaccine (if they have not already received the vaccine).
Non-live attenuated vaccines
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, summarized the recommendations for managing immunosuppressive therapies in patients scheduled to receive vaccinations using killed or nonactive antigens.
“In influenza season, don’t pass up the opportunity to vaccinate,” he said, adding, “if you can wait on rituximab dosing, do it, and if you can’t, go ahead and vaccinate.”
The guidelines also recommend a 2-week methotrexate hold at the time of influenza vaccination; other DMARD dosing changes are likely not necessary at the time of vaccination, “but this is an area of fervent study, and I think in a year or two we’ll have more experimental hold data with regard to other DMARDs,” Dr. Winthrop said.
For other nonlive attenuated vaccinations, recommendations are similar to those for influenza, except with more flexible timing because these vaccinations are not seasonal. When and how to hold methotrexate is still up in the air, he said.
Additionally, it’s recommended that vaccinations be delayed in patients on high-dose prednisone until the drug is tapered to below 20 mg per day, and ideally to less than 10 mg per day, he said.
Live-attenuated vaccines
The guideline conditionally recommends deferring live-attenuated vaccines in patients on immunosuppressive drugs. It also recommends holding these medications “for an appropriate period before” vaccination and for 4 weeks afterward.
“Although the evidence around conventional synthetic DMARDs and TNF inhibitors is reassuring in terms of their safety at the time of live attenuated vaccines, as you can see the number of studies is quite small, and so the voting panel conditionally recommend against administering live-attenuated virus vaccines to patients who are on conventional synthetics, biologic, or targeted DMARDs,” Dr. Bass said.
In utero exposures
Most women with RMD who have recently given birth will consult their general pediatricians rather than rheumatologists for infant vaccinations, but pediatricians may not be aware of the affect that in utero exposures to biologic DMARDs can have on vaccine safety and immunogenicity in infants, Dr, Bass said.
“It’s important that you, as a provider, give your recommendations regarding infant rotavirus vaccination after in utero exposure to the pregnant rheumatic disease patient prior to delivery, and let that patient know that this is something that they should share with their pediatrician to be,” she advised audience members.
Getting the message out
In an interview, session moderator and guidelines panelist Lisa F. Imundo, MD, director of the center for adolescent rheumatology at Columbia University in New York, noted that rheumatologists don’t usually have the full schedule of pediatric vaccinations in stock and often leave the decisions about what to give – and when – to general practitioners.
“Pediatric rheumatologists sometimes will give patients flu vaccinations because they’re a high-risk population of patients, and we want to make sure that they’re getting it in a timely manner,” she said.
In addition, because pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines are not indicated in the general pediatric population, children on biologic DMARDs who have completed their standard series of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV13 or PVC15) are recommended to get a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, Dr. Imundo said.
She also noted that communication between pediatric rheumatologists and general practitioners about vaccine recommendations can be challenging.
“It’s a huge issue, figuring out how we’re going to communicate all of this information to our pediatric colleagues,” she said. “With individual patients, we may sometimes remind doctors, especially with our younger patients who haven’t gotten their live vaccines, that they really shouldn’t get live vaccines until they’re off medication or until we arrange holding medication for some period of time.”
She said that ACR vaccine committee members are working with infectious disease specialists and guideline developers for the American Academy of Pediatrics to ensure guidelines include the most important vaccination recommendations for pediatric patients with RMDs.
The development process for the guidelines was supported by the ACR. Dr. Bass reported no relevant disclosures, Dr. Bingham disclosed consulting activities, grant/research support, and royalties from various corporate entities. Dr. Winthrop disclosed consulting activities for and research funding from various companies. Dr. Imundo reported no relevant financial relationships.
PHILADELPHIA – The new American College of Rheumatology Guideline for Vaccinations in Patients with Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases (RMDs) emphasizes that both adult and pediatric patients should receive recommended vaccinations whenever possible.
But the guideline, currently in press, also offers recommendations about whether and when to withhold vaccines from patients with RMDs, such as avoiding the use of live attenuated virus vaccines in patients who are on immunosuppressive drug regimens, such as conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic DMARDs, or targeted synthetic DMARDs.
The new consensus guideline was formulated with the understanding that patients with RMDs are at increased risk for vaccine-preventable infections and more serious complications from infections, compared with the general population.
However, the guideline also acknowledges that the immunogenicity and safety of vaccines may differ among patients with RMDs, and that, depending on the patient age and disease state, individuals may benefit from modified vaccine indications, schedules, or modified medication schedules, said guideline panel member Anne Bass, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery and a professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who presented the guideline with other panel members in a session outlining the recommendations at the annual meeting of the ACR.
“In addition, vaccination recommendations – since much of it relates to medications – really applies across diseases, and so the ACR felt that, rather than having vaccine recommendations tacked onto the end of treatment guidelines for each individual disease, that the topic should be discussed or tackled as a whole,” she said.
The guideline does not cover vaccinations in patients taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs because this class of agents has minimal or no impact on antibody responses to vaccines. The guideline also does not address vaccinations against COVID-19 infections since the rapidly changing formulations would make the recommendations obsolete before they were even published, and because the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides up-to-date guidance on COVID-19 vaccinations in patients with compromised immunity, she said.
Guiding principles
The overarching principles of the guideline are to give indicated vaccines to patients with RMD whenever possible and that any decision to hold medications before or after vaccination consider the dosage used, RMD disease activity, and the patient’s risk for vaccine-preventable infection.
The guideline also states that “shared decision-making with patients is a key component of any vaccination strategy.”
Panel member Clifton O. Bingham III, MD, professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, outlined expanded indications for vaccinations against influenza, pneumococcal infections, varicella zoster virus (VZV) and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Influenza
The guideline conditionally recommends that patients with RMD aged 65 years and older and adults older than age 18 years who are on immunosuppressive medications should receive either high-dose or adjuvanted influenza vaccination rather than regular-dose vaccines.
“It’s recognized that the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccinations may be unavailable for patients when they’re seen in your practice,” Dr. Bingham said,” and we came out with two additional statements within the guidelines that said that any flu vaccine is recommended over no flu vaccinations, because we do know that responses are elicited, and a flu vaccination today is preferred over a flu vaccination delay.”
Pneumococcal vaccination
The panelists strongly recommended that patients with RMD younger than age 65 years who are on immunosuppressive medication receive pneumococcal vaccinations.
The ACR guideline is in sync with those issued by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, Dr. Bingham said. He urged audience members to visit a CDC-ACIP web page for more information on who should receive pneumococcal vaccination and when.
Recombinant varicella zoster
The recommendations strongly support that patients aged 18 years and over who are on immunosuppressive therapies should receive the recombinant VZV vaccine (Shingrix).
HPV
A less robust, conditional recommendation is for patients with RMDs who are between the ages of 26 and 45 years and on immunosuppressive medications to receive the HPV vaccine (if they have not already received the vaccine).
Non-live attenuated vaccines
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, summarized the recommendations for managing immunosuppressive therapies in patients scheduled to receive vaccinations using killed or nonactive antigens.
“In influenza season, don’t pass up the opportunity to vaccinate,” he said, adding, “if you can wait on rituximab dosing, do it, and if you can’t, go ahead and vaccinate.”
The guidelines also recommend a 2-week methotrexate hold at the time of influenza vaccination; other DMARD dosing changes are likely not necessary at the time of vaccination, “but this is an area of fervent study, and I think in a year or two we’ll have more experimental hold data with regard to other DMARDs,” Dr. Winthrop said.
For other nonlive attenuated vaccinations, recommendations are similar to those for influenza, except with more flexible timing because these vaccinations are not seasonal. When and how to hold methotrexate is still up in the air, he said.
Additionally, it’s recommended that vaccinations be delayed in patients on high-dose prednisone until the drug is tapered to below 20 mg per day, and ideally to less than 10 mg per day, he said.
Live-attenuated vaccines
The guideline conditionally recommends deferring live-attenuated vaccines in patients on immunosuppressive drugs. It also recommends holding these medications “for an appropriate period before” vaccination and for 4 weeks afterward.
“Although the evidence around conventional synthetic DMARDs and TNF inhibitors is reassuring in terms of their safety at the time of live attenuated vaccines, as you can see the number of studies is quite small, and so the voting panel conditionally recommend against administering live-attenuated virus vaccines to patients who are on conventional synthetics, biologic, or targeted DMARDs,” Dr. Bass said.
In utero exposures
Most women with RMD who have recently given birth will consult their general pediatricians rather than rheumatologists for infant vaccinations, but pediatricians may not be aware of the affect that in utero exposures to biologic DMARDs can have on vaccine safety and immunogenicity in infants, Dr, Bass said.
“It’s important that you, as a provider, give your recommendations regarding infant rotavirus vaccination after in utero exposure to the pregnant rheumatic disease patient prior to delivery, and let that patient know that this is something that they should share with their pediatrician to be,” she advised audience members.
Getting the message out
In an interview, session moderator and guidelines panelist Lisa F. Imundo, MD, director of the center for adolescent rheumatology at Columbia University in New York, noted that rheumatologists don’t usually have the full schedule of pediatric vaccinations in stock and often leave the decisions about what to give – and when – to general practitioners.
“Pediatric rheumatologists sometimes will give patients flu vaccinations because they’re a high-risk population of patients, and we want to make sure that they’re getting it in a timely manner,” she said.
In addition, because pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines are not indicated in the general pediatric population, children on biologic DMARDs who have completed their standard series of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV13 or PVC15) are recommended to get a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, Dr. Imundo said.
She also noted that communication between pediatric rheumatologists and general practitioners about vaccine recommendations can be challenging.
“It’s a huge issue, figuring out how we’re going to communicate all of this information to our pediatric colleagues,” she said. “With individual patients, we may sometimes remind doctors, especially with our younger patients who haven’t gotten their live vaccines, that they really shouldn’t get live vaccines until they’re off medication or until we arrange holding medication for some period of time.”
She said that ACR vaccine committee members are working with infectious disease specialists and guideline developers for the American Academy of Pediatrics to ensure guidelines include the most important vaccination recommendations for pediatric patients with RMDs.
The development process for the guidelines was supported by the ACR. Dr. Bass reported no relevant disclosures, Dr. Bingham disclosed consulting activities, grant/research support, and royalties from various corporate entities. Dr. Winthrop disclosed consulting activities for and research funding from various companies. Dr. Imundo reported no relevant financial relationships.
PHILADELPHIA – The new American College of Rheumatology Guideline for Vaccinations in Patients with Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases (RMDs) emphasizes that both adult and pediatric patients should receive recommended vaccinations whenever possible.
But the guideline, currently in press, also offers recommendations about whether and when to withhold vaccines from patients with RMDs, such as avoiding the use of live attenuated virus vaccines in patients who are on immunosuppressive drug regimens, such as conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic DMARDs, or targeted synthetic DMARDs.
The new consensus guideline was formulated with the understanding that patients with RMDs are at increased risk for vaccine-preventable infections and more serious complications from infections, compared with the general population.
However, the guideline also acknowledges that the immunogenicity and safety of vaccines may differ among patients with RMDs, and that, depending on the patient age and disease state, individuals may benefit from modified vaccine indications, schedules, or modified medication schedules, said guideline panel member Anne Bass, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery and a professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who presented the guideline with other panel members in a session outlining the recommendations at the annual meeting of the ACR.
“In addition, vaccination recommendations – since much of it relates to medications – really applies across diseases, and so the ACR felt that, rather than having vaccine recommendations tacked onto the end of treatment guidelines for each individual disease, that the topic should be discussed or tackled as a whole,” she said.
The guideline does not cover vaccinations in patients taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs because this class of agents has minimal or no impact on antibody responses to vaccines. The guideline also does not address vaccinations against COVID-19 infections since the rapidly changing formulations would make the recommendations obsolete before they were even published, and because the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides up-to-date guidance on COVID-19 vaccinations in patients with compromised immunity, she said.
Guiding principles
The overarching principles of the guideline are to give indicated vaccines to patients with RMD whenever possible and that any decision to hold medications before or after vaccination consider the dosage used, RMD disease activity, and the patient’s risk for vaccine-preventable infection.
The guideline also states that “shared decision-making with patients is a key component of any vaccination strategy.”
Panel member Clifton O. Bingham III, MD, professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, outlined expanded indications for vaccinations against influenza, pneumococcal infections, varicella zoster virus (VZV) and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Influenza
The guideline conditionally recommends that patients with RMD aged 65 years and older and adults older than age 18 years who are on immunosuppressive medications should receive either high-dose or adjuvanted influenza vaccination rather than regular-dose vaccines.
“It’s recognized that the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccinations may be unavailable for patients when they’re seen in your practice,” Dr. Bingham said,” and we came out with two additional statements within the guidelines that said that any flu vaccine is recommended over no flu vaccinations, because we do know that responses are elicited, and a flu vaccination today is preferred over a flu vaccination delay.”
Pneumococcal vaccination
The panelists strongly recommended that patients with RMD younger than age 65 years who are on immunosuppressive medication receive pneumococcal vaccinations.
The ACR guideline is in sync with those issued by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, Dr. Bingham said. He urged audience members to visit a CDC-ACIP web page for more information on who should receive pneumococcal vaccination and when.
Recombinant varicella zoster
The recommendations strongly support that patients aged 18 years and over who are on immunosuppressive therapies should receive the recombinant VZV vaccine (Shingrix).
HPV
A less robust, conditional recommendation is for patients with RMDs who are between the ages of 26 and 45 years and on immunosuppressive medications to receive the HPV vaccine (if they have not already received the vaccine).
Non-live attenuated vaccines
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, summarized the recommendations for managing immunosuppressive therapies in patients scheduled to receive vaccinations using killed or nonactive antigens.
“In influenza season, don’t pass up the opportunity to vaccinate,” he said, adding, “if you can wait on rituximab dosing, do it, and if you can’t, go ahead and vaccinate.”
The guidelines also recommend a 2-week methotrexate hold at the time of influenza vaccination; other DMARD dosing changes are likely not necessary at the time of vaccination, “but this is an area of fervent study, and I think in a year or two we’ll have more experimental hold data with regard to other DMARDs,” Dr. Winthrop said.
For other nonlive attenuated vaccinations, recommendations are similar to those for influenza, except with more flexible timing because these vaccinations are not seasonal. When and how to hold methotrexate is still up in the air, he said.
Additionally, it’s recommended that vaccinations be delayed in patients on high-dose prednisone until the drug is tapered to below 20 mg per day, and ideally to less than 10 mg per day, he said.
Live-attenuated vaccines
The guideline conditionally recommends deferring live-attenuated vaccines in patients on immunosuppressive drugs. It also recommends holding these medications “for an appropriate period before” vaccination and for 4 weeks afterward.
“Although the evidence around conventional synthetic DMARDs and TNF inhibitors is reassuring in terms of their safety at the time of live attenuated vaccines, as you can see the number of studies is quite small, and so the voting panel conditionally recommend against administering live-attenuated virus vaccines to patients who are on conventional synthetics, biologic, or targeted DMARDs,” Dr. Bass said.
In utero exposures
Most women with RMD who have recently given birth will consult their general pediatricians rather than rheumatologists for infant vaccinations, but pediatricians may not be aware of the affect that in utero exposures to biologic DMARDs can have on vaccine safety and immunogenicity in infants, Dr, Bass said.
“It’s important that you, as a provider, give your recommendations regarding infant rotavirus vaccination after in utero exposure to the pregnant rheumatic disease patient prior to delivery, and let that patient know that this is something that they should share with their pediatrician to be,” she advised audience members.
Getting the message out
In an interview, session moderator and guidelines panelist Lisa F. Imundo, MD, director of the center for adolescent rheumatology at Columbia University in New York, noted that rheumatologists don’t usually have the full schedule of pediatric vaccinations in stock and often leave the decisions about what to give – and when – to general practitioners.
“Pediatric rheumatologists sometimes will give patients flu vaccinations because they’re a high-risk population of patients, and we want to make sure that they’re getting it in a timely manner,” she said.
In addition, because pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines are not indicated in the general pediatric population, children on biologic DMARDs who have completed their standard series of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV13 or PVC15) are recommended to get a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, Dr. Imundo said.
She also noted that communication between pediatric rheumatologists and general practitioners about vaccine recommendations can be challenging.
“It’s a huge issue, figuring out how we’re going to communicate all of this information to our pediatric colleagues,” she said. “With individual patients, we may sometimes remind doctors, especially with our younger patients who haven’t gotten their live vaccines, that they really shouldn’t get live vaccines until they’re off medication or until we arrange holding medication for some period of time.”
She said that ACR vaccine committee members are working with infectious disease specialists and guideline developers for the American Academy of Pediatrics to ensure guidelines include the most important vaccination recommendations for pediatric patients with RMDs.
The development process for the guidelines was supported by the ACR. Dr. Bass reported no relevant disclosures, Dr. Bingham disclosed consulting activities, grant/research support, and royalties from various corporate entities. Dr. Winthrop disclosed consulting activities for and research funding from various companies. Dr. Imundo reported no relevant financial relationships.
AT ACR 2022
Screen time may help concussion recovery
research shows.
Now a study suggests that getting back on TikTok and Snapchat may help, too.
After surveying 700 patients ages 8-16 following an injury, researchers for the Pediatric Emergency Research Canada A-CAP study team found that
A “moderate” amount was between 2 and 7 hours per day on various screens. “That includes their phones, computers, and televisions,” says lead author Molly Cairncross, PhD, of Simon Fraser University, Vancouver.
People in the study who reported either less or more screen time than that in the 7-10 days after injury also reported more symptoms, such as headaches and fatigue, during the first month. After that month, all the participants reported similar symptoms, regardless of their early screen use – suggesting that screen time makes little difference long term in pediatric concussion recovery.
The findings differ from a 2021 study by researchers at the University of Massachusetts, Boston, that found screen time slowed recovery. Why the clashing results? “I think what it comes down to are differences in study design,” says Dr. Cairncross. While the earlier study measured screen use in the first 48 hours, and recovery over 10 days, “we focused on screen time use over the first 7-10 days, and tracked recovery over 6 months,” she says.
“Taken together, the studies suggest a need to find balance – not too little and not too much time on screens for kids and teens following a concussion,” Dr. Cairncross says.
Ultimately, the findings support moderation rather than blanket restrictions on screen time as the best way to manage pediatric concussion, especially after the first 48 hours.
“It’s actually unsurprising,” says Sarah Brittain, MS, a speech-language pathologist and founder of Colorado Brain Recovery in Wheat Ridge, who was not involved in the study. “An early return to both cognitive and physical activity in a controlled fashion is really important. Sitting in a dark room and resting is not the answer and has been disproven in the literature.”
Old advice involved lying in a quiet, dark room for days, but recent evidence reveals that such “cocoon therapy” may actually prolong symptoms.
“With time, we have found this can negatively impact quality of life and depression scores, especially in teenagers,” says Katherine Labiner, MD, a child neurologist at Pediatrix Child Neurology Consultants of Austin, Tex., who was not involved in the study.
So, how might screens help? Dr. Labiner, Ms. Brittain, and Dr. Cairncross all point to the importance of connection – not the Internet kind, but the social kind. Children and teens use smartphones and computers to stay connected with peers, so banning screen time could have a negative impact on mental health by leading to loneliness, separation, and lack of social support.
“Depression can prolong the course of recovery,” says Ms. Brittain.
It’s worth noting that screen time could trigger visual symptoms in some patients, she says. “If someone feels worse within 2 minutes of being on a screen, that’s a good indicator that screens aren’t working for them,” Ms. Brittain says. “If being on a screen makes them dizzy or wiped out, or the words on the screen look like they’re moving when they’re not, that means it’s time to back off.”
She advises parents to watch for behavior changes like increased crankiness, impatience, and/or fatigue, which could mean that the child has returned to screen time – or any activity – too soon and should scale back until symptoms subside.
“The most important thing to stress with concussion is full recovery before complete return to activity,” Dr. Labiner says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
research shows.
Now a study suggests that getting back on TikTok and Snapchat may help, too.
After surveying 700 patients ages 8-16 following an injury, researchers for the Pediatric Emergency Research Canada A-CAP study team found that
A “moderate” amount was between 2 and 7 hours per day on various screens. “That includes their phones, computers, and televisions,” says lead author Molly Cairncross, PhD, of Simon Fraser University, Vancouver.
People in the study who reported either less or more screen time than that in the 7-10 days after injury also reported more symptoms, such as headaches and fatigue, during the first month. After that month, all the participants reported similar symptoms, regardless of their early screen use – suggesting that screen time makes little difference long term in pediatric concussion recovery.
The findings differ from a 2021 study by researchers at the University of Massachusetts, Boston, that found screen time slowed recovery. Why the clashing results? “I think what it comes down to are differences in study design,” says Dr. Cairncross. While the earlier study measured screen use in the first 48 hours, and recovery over 10 days, “we focused on screen time use over the first 7-10 days, and tracked recovery over 6 months,” she says.
“Taken together, the studies suggest a need to find balance – not too little and not too much time on screens for kids and teens following a concussion,” Dr. Cairncross says.
Ultimately, the findings support moderation rather than blanket restrictions on screen time as the best way to manage pediatric concussion, especially after the first 48 hours.
“It’s actually unsurprising,” says Sarah Brittain, MS, a speech-language pathologist and founder of Colorado Brain Recovery in Wheat Ridge, who was not involved in the study. “An early return to both cognitive and physical activity in a controlled fashion is really important. Sitting in a dark room and resting is not the answer and has been disproven in the literature.”
Old advice involved lying in a quiet, dark room for days, but recent evidence reveals that such “cocoon therapy” may actually prolong symptoms.
“With time, we have found this can negatively impact quality of life and depression scores, especially in teenagers,” says Katherine Labiner, MD, a child neurologist at Pediatrix Child Neurology Consultants of Austin, Tex., who was not involved in the study.
So, how might screens help? Dr. Labiner, Ms. Brittain, and Dr. Cairncross all point to the importance of connection – not the Internet kind, but the social kind. Children and teens use smartphones and computers to stay connected with peers, so banning screen time could have a negative impact on mental health by leading to loneliness, separation, and lack of social support.
“Depression can prolong the course of recovery,” says Ms. Brittain.
It’s worth noting that screen time could trigger visual symptoms in some patients, she says. “If someone feels worse within 2 minutes of being on a screen, that’s a good indicator that screens aren’t working for them,” Ms. Brittain says. “If being on a screen makes them dizzy or wiped out, or the words on the screen look like they’re moving when they’re not, that means it’s time to back off.”
She advises parents to watch for behavior changes like increased crankiness, impatience, and/or fatigue, which could mean that the child has returned to screen time – or any activity – too soon and should scale back until symptoms subside.
“The most important thing to stress with concussion is full recovery before complete return to activity,” Dr. Labiner says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
research shows.
Now a study suggests that getting back on TikTok and Snapchat may help, too.
After surveying 700 patients ages 8-16 following an injury, researchers for the Pediatric Emergency Research Canada A-CAP study team found that
A “moderate” amount was between 2 and 7 hours per day on various screens. “That includes their phones, computers, and televisions,” says lead author Molly Cairncross, PhD, of Simon Fraser University, Vancouver.
People in the study who reported either less or more screen time than that in the 7-10 days after injury also reported more symptoms, such as headaches and fatigue, during the first month. After that month, all the participants reported similar symptoms, regardless of their early screen use – suggesting that screen time makes little difference long term in pediatric concussion recovery.
The findings differ from a 2021 study by researchers at the University of Massachusetts, Boston, that found screen time slowed recovery. Why the clashing results? “I think what it comes down to are differences in study design,” says Dr. Cairncross. While the earlier study measured screen use in the first 48 hours, and recovery over 10 days, “we focused on screen time use over the first 7-10 days, and tracked recovery over 6 months,” she says.
“Taken together, the studies suggest a need to find balance – not too little and not too much time on screens for kids and teens following a concussion,” Dr. Cairncross says.
Ultimately, the findings support moderation rather than blanket restrictions on screen time as the best way to manage pediatric concussion, especially after the first 48 hours.
“It’s actually unsurprising,” says Sarah Brittain, MS, a speech-language pathologist and founder of Colorado Brain Recovery in Wheat Ridge, who was not involved in the study. “An early return to both cognitive and physical activity in a controlled fashion is really important. Sitting in a dark room and resting is not the answer and has been disproven in the literature.”
Old advice involved lying in a quiet, dark room for days, but recent evidence reveals that such “cocoon therapy” may actually prolong symptoms.
“With time, we have found this can negatively impact quality of life and depression scores, especially in teenagers,” says Katherine Labiner, MD, a child neurologist at Pediatrix Child Neurology Consultants of Austin, Tex., who was not involved in the study.
So, how might screens help? Dr. Labiner, Ms. Brittain, and Dr. Cairncross all point to the importance of connection – not the Internet kind, but the social kind. Children and teens use smartphones and computers to stay connected with peers, so banning screen time could have a negative impact on mental health by leading to loneliness, separation, and lack of social support.
“Depression can prolong the course of recovery,” says Ms. Brittain.
It’s worth noting that screen time could trigger visual symptoms in some patients, she says. “If someone feels worse within 2 minutes of being on a screen, that’s a good indicator that screens aren’t working for them,” Ms. Brittain says. “If being on a screen makes them dizzy or wiped out, or the words on the screen look like they’re moving when they’re not, that means it’s time to back off.”
She advises parents to watch for behavior changes like increased crankiness, impatience, and/or fatigue, which could mean that the child has returned to screen time – or any activity – too soon and should scale back until symptoms subside.
“The most important thing to stress with concussion is full recovery before complete return to activity,” Dr. Labiner says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PEDIATRICS
EHR reminders boost well-child visits, vax rates
Reminder messages sent through electronic health records (EHRs) to patient portals increased rates of scheduling and completion of well-child visits for those overdue for well care, as well as vaccination rates, according to data published today in JAMA Network Open.
Anne E. Berset, BA, with general and community pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, led a randomized clinical trial conducted at three academic primary care practices from July 30 to Oct. 4, 2021.
The practices serve a mostly non-Hispanic Black, low-income population and provide more than 60,000 visits a year to 30,000 patients.
The study population included 945 patients, 62.4% of them non-Hispanic Black and 807 (85.4%) covered by public insurance.
Standard message and tailored message compared
The study population was randomized to get either a standard reminder message, a tailored message, or no message (control group).
The standard messages referenced the patient’s first name and reminded parents their child was due for a well-child visit, and asked them to schedule it using the portal or by calling the number provided.
The tailored message added the date of the last well-child check-up “to address distortions of time perception experienced during the pandemic,” the authors write.
The primary outcome was whether the well-child visit was completed within 8 weeks. Other outcomes included whether a well-child visit was scheduled within 2 weeks of the first reminder message and whether the patient received a COVID-19 vaccine within 8 weeks of the reminder.
Reminders outperform control group
There was a significant increase in scheduling and completion of appointments after parents received the standard and tailored messages compared with controls.
The results with the COVID reminders were particularly striking. While only 3.7% of the eligible patients got a vaccine when they got no message, 17.3% got the vaccine in that time frame when they got the standard message. Interestingly, only 2.7% received the shot after the tailored message.
J. Howard Smart, MD, with Sharp HealthCare in San Diego, told this publication he was not surprised that a patient portal reminder would increase the rate of scheduling overdue well-child visits. “Parents may indeed have lost track of when their children need to have check-ups” during the pandemic, he said.
Reminders without tailored information more effective
He said he was surprised, just as the investigators were, that the reminders without the tailored information seemed to be more effective for some outcomes.
The authors explained that a focus group found “that families with patient portal accounts prefer straightforward, brief, and user-friendly messages.”
That may help explain why the standard message outperformed the tailored message, the authors write.
“Families may have been distracted by the additional information related to the child’s age and date of last WCC [well-child check-up] in the tailored message,” they write.
Dr. Smart said, “Their discussion of why this might be the case sounds reasonable. Simple, short messages may be better received.”
“Evidence like this should stimulate portal software vendors to make this kind of outgoing messaging easy to set up for providers,” he said.
Simple measure, large effect
Tim Joos, MD, a pediatrician in Seattle, told this publication he “was impressed by how such a simple measure increased rates of well-child care completion.”
Minority and low-income patients have traditionally had more access challenges to completing health care visits and vaccinations on schedule, he noted, so he was glad to see positive results from the intervention in this study population.
The authors note that research on portal messages have largely looked at use in non-Hispanic Whites and the privately insured.
Dr. Joos said the intervention also offers convenience in that once patients get into the portal, they can schedule an appointment there without having to wait on the phone or leave a message.
Funding/support was received from the Center for Clinical and Translational Science and Training at the University of Cincinnati, which is funded by the National Institutes of Health. William B. Brinkman, MD, MEd, MSc, one of the study authors, holds common stock in Pfizer, Merck, Abbott Laboratories, Viatris, and Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. No other author disclosures were reported. Dr. Smart and Dr. Joos declared no relevant financial relationships.
Reminder messages sent through electronic health records (EHRs) to patient portals increased rates of scheduling and completion of well-child visits for those overdue for well care, as well as vaccination rates, according to data published today in JAMA Network Open.
Anne E. Berset, BA, with general and community pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, led a randomized clinical trial conducted at three academic primary care practices from July 30 to Oct. 4, 2021.
The practices serve a mostly non-Hispanic Black, low-income population and provide more than 60,000 visits a year to 30,000 patients.
The study population included 945 patients, 62.4% of them non-Hispanic Black and 807 (85.4%) covered by public insurance.
Standard message and tailored message compared
The study population was randomized to get either a standard reminder message, a tailored message, or no message (control group).
The standard messages referenced the patient’s first name and reminded parents their child was due for a well-child visit, and asked them to schedule it using the portal or by calling the number provided.
The tailored message added the date of the last well-child check-up “to address distortions of time perception experienced during the pandemic,” the authors write.
The primary outcome was whether the well-child visit was completed within 8 weeks. Other outcomes included whether a well-child visit was scheduled within 2 weeks of the first reminder message and whether the patient received a COVID-19 vaccine within 8 weeks of the reminder.
Reminders outperform control group
There was a significant increase in scheduling and completion of appointments after parents received the standard and tailored messages compared with controls.
The results with the COVID reminders were particularly striking. While only 3.7% of the eligible patients got a vaccine when they got no message, 17.3% got the vaccine in that time frame when they got the standard message. Interestingly, only 2.7% received the shot after the tailored message.
J. Howard Smart, MD, with Sharp HealthCare in San Diego, told this publication he was not surprised that a patient portal reminder would increase the rate of scheduling overdue well-child visits. “Parents may indeed have lost track of when their children need to have check-ups” during the pandemic, he said.
Reminders without tailored information more effective
He said he was surprised, just as the investigators were, that the reminders without the tailored information seemed to be more effective for some outcomes.
The authors explained that a focus group found “that families with patient portal accounts prefer straightforward, brief, and user-friendly messages.”
That may help explain why the standard message outperformed the tailored message, the authors write.
“Families may have been distracted by the additional information related to the child’s age and date of last WCC [well-child check-up] in the tailored message,” they write.
Dr. Smart said, “Their discussion of why this might be the case sounds reasonable. Simple, short messages may be better received.”
“Evidence like this should stimulate portal software vendors to make this kind of outgoing messaging easy to set up for providers,” he said.
Simple measure, large effect
Tim Joos, MD, a pediatrician in Seattle, told this publication he “was impressed by how such a simple measure increased rates of well-child care completion.”
Minority and low-income patients have traditionally had more access challenges to completing health care visits and vaccinations on schedule, he noted, so he was glad to see positive results from the intervention in this study population.
The authors note that research on portal messages have largely looked at use in non-Hispanic Whites and the privately insured.
Dr. Joos said the intervention also offers convenience in that once patients get into the portal, they can schedule an appointment there without having to wait on the phone or leave a message.
Funding/support was received from the Center for Clinical and Translational Science and Training at the University of Cincinnati, which is funded by the National Institutes of Health. William B. Brinkman, MD, MEd, MSc, one of the study authors, holds common stock in Pfizer, Merck, Abbott Laboratories, Viatris, and Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. No other author disclosures were reported. Dr. Smart and Dr. Joos declared no relevant financial relationships.
Reminder messages sent through electronic health records (EHRs) to patient portals increased rates of scheduling and completion of well-child visits for those overdue for well care, as well as vaccination rates, according to data published today in JAMA Network Open.
Anne E. Berset, BA, with general and community pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, led a randomized clinical trial conducted at three academic primary care practices from July 30 to Oct. 4, 2021.
The practices serve a mostly non-Hispanic Black, low-income population and provide more than 60,000 visits a year to 30,000 patients.
The study population included 945 patients, 62.4% of them non-Hispanic Black and 807 (85.4%) covered by public insurance.
Standard message and tailored message compared
The study population was randomized to get either a standard reminder message, a tailored message, or no message (control group).
The standard messages referenced the patient’s first name and reminded parents their child was due for a well-child visit, and asked them to schedule it using the portal or by calling the number provided.
The tailored message added the date of the last well-child check-up “to address distortions of time perception experienced during the pandemic,” the authors write.
The primary outcome was whether the well-child visit was completed within 8 weeks. Other outcomes included whether a well-child visit was scheduled within 2 weeks of the first reminder message and whether the patient received a COVID-19 vaccine within 8 weeks of the reminder.
Reminders outperform control group
There was a significant increase in scheduling and completion of appointments after parents received the standard and tailored messages compared with controls.
The results with the COVID reminders were particularly striking. While only 3.7% of the eligible patients got a vaccine when they got no message, 17.3% got the vaccine in that time frame when they got the standard message. Interestingly, only 2.7% received the shot after the tailored message.
J. Howard Smart, MD, with Sharp HealthCare in San Diego, told this publication he was not surprised that a patient portal reminder would increase the rate of scheduling overdue well-child visits. “Parents may indeed have lost track of when their children need to have check-ups” during the pandemic, he said.
Reminders without tailored information more effective
He said he was surprised, just as the investigators were, that the reminders without the tailored information seemed to be more effective for some outcomes.
The authors explained that a focus group found “that families with patient portal accounts prefer straightforward, brief, and user-friendly messages.”
That may help explain why the standard message outperformed the tailored message, the authors write.
“Families may have been distracted by the additional information related to the child’s age and date of last WCC [well-child check-up] in the tailored message,” they write.
Dr. Smart said, “Their discussion of why this might be the case sounds reasonable. Simple, short messages may be better received.”
“Evidence like this should stimulate portal software vendors to make this kind of outgoing messaging easy to set up for providers,” he said.
Simple measure, large effect
Tim Joos, MD, a pediatrician in Seattle, told this publication he “was impressed by how such a simple measure increased rates of well-child care completion.”
Minority and low-income patients have traditionally had more access challenges to completing health care visits and vaccinations on schedule, he noted, so he was glad to see positive results from the intervention in this study population.
The authors note that research on portal messages have largely looked at use in non-Hispanic Whites and the privately insured.
Dr. Joos said the intervention also offers convenience in that once patients get into the portal, they can schedule an appointment there without having to wait on the phone or leave a message.
Funding/support was received from the Center for Clinical and Translational Science and Training at the University of Cincinnati, which is funded by the National Institutes of Health. William B. Brinkman, MD, MEd, MSc, one of the study authors, holds common stock in Pfizer, Merck, Abbott Laboratories, Viatris, and Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. No other author disclosures were reported. Dr. Smart and Dr. Joos declared no relevant financial relationships.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN