User login
Antioxidant-rich diet may reduce Helicobacter pylori risk
People who eat a balanced diet with sufficient antioxidants from fruits and vegetables may face reduced risks for Heliobacter pylori infections, according to a new report.
In particular, patients with an H. pylori infection were more likely to score lower on the Dietary Antioxidant Index (DAI), which was created to consider a diet’s entire antioxidant profile.
“Available evidence indicates that diet has an important role in developing H. pylori infection. Therefore, protective dietary factors are important from a public health point of view,” Farzad Shidfar, a professor of nutrition at the Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, and member of the university’s colorectal research center, and colleagues write.
“While some nutritional research has widely focused on single nutrients or foods in diet-disease relations, the overall diet could be more informative because humans typically consume a combination of nutrients and foods,” they write. “Dietary indices such as DAI are one of the approaches for this purpose.”
The study was published online in BMC Gastroenterology.
Measuring antioxidant intake
Previous research has indicated an inverse association between the DAI and inflammatory diseases, the study authors write, including gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and obesity. Studies have also indicated that H. pylori infection is related to deficiencies in vitamins A, C, and E, which have antioxidant properties.
In a case-control study, the research team compared the dietary intake of 148 patients with H. pylori to 302 healthy controls without infection. The patients in the H. pylori–positive group were recruited between June 2021 and November 2021 from the gastroenterology clinic at Rasoul-e-Akram Hospital in Tehran, where they were newly diagnosed with active infection and not yet under treatment.
The researchers calculated the DAI based on dietary intake information from a validated, 168-item food frequency questionnaire used in Iran. The participants were asked about their dietary intake based on the average day, week, month, and year. They also discussed serving sizes of food items, and to increase the accuracy of estimates, interviewers showed household measurements or serving sizes to confirm the measurements with participants.
The average age of the study participants was 39 years, and about 60% were women. Compared with the healthy controls, those with H. pylori were significantly older, had higher body mass index, and smoked more.
Overall, patients with H. pylori had a significantly lower intake of vitamin A, vitamin E, manganese, and selenium. Other differences in dietary intake – for vitamin C and zinc – were not significant.
The average total DAI was significantly higher in the healthy controls, at 7.67, as compared with 3.57 in the patients with H. pylori. The risk for infection decreased as continuous DAI increased.
After adjusting for several variables, the researchers found that participants with less than the median DAI values had an increased risk of developing an H. pylori infection.
“A balanced diet, especially high consumption of fruits and vegetables, might protect people against the consequences of H. pylori infection,” the study authors write. “On the contrary, a diet full of carbohydrates and sweets is related to a higher H. pylori infection prevalence.”
Why a good diet may help combat infection
The findings are consistent with other studies that have noted a higher intake of fruits and vegetables among healthy people compared with those who have H. pylori infections, the study authors write. Animal studies have also indicated that taking vitamins A, C, and E and selenium can lead to a reduction in H. pylori growth.
“Several biologically plausible reasons may explain why dietary antioxidants might be, either directly or indirectly, a protective factor against H. pylori infection,” the researchers write. “It is well-known that antioxidants, with their free radical scavenging activities, can inhibit the growth of H. pylori.”
H. pylori is urease-positive and can synthesize a large amount of urease for ammonia production to neutralize gastric acid, which allows it to colonize in the stomach epithelium, the study authors write. Vitamin C inhibits urease activity and improves the stimulation of granulocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, and immunoglobulin production. Other nutrients, such as zinc, may inhibit the urease enzyme and prevent H. pylori adhesion to gastric tissues, they write.
“Dietary elements have previously been shown to dramatically alter pathogenic responses to H. pylori infections,” Richard Peek Jr., MD, professor of medicine and director of gastroenterology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told this news organization.
Dr. Peek, who wasn’t involved with this study, and colleagues found that iron deficiency is linked with altered bile metabolism, which can promote H. pylori–induced gastric carcinogenesis.
“The current study is important, as it suggests that shifting to a diet rich in antioxidants may be beneficial in terms of H. pylori infection,” he said.
At the same time, Dr. Peek expressed caution about generalizing the results across populations.
“Most of the persons enrolled in this study were likely infected with H. pylori as children,” he noted. “Therefore, the inverse role of antioxidant-rich diets and H. pylori infection must be interpreted with caution.”
Future studies should confirm the findings in other groups and determine whether antioxidant-rich diets limit the diseases caused by H. pylori infection, Dr. Peek added.
The study was not funded by any research center, and the authors declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Peek reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who eat a balanced diet with sufficient antioxidants from fruits and vegetables may face reduced risks for Heliobacter pylori infections, according to a new report.
In particular, patients with an H. pylori infection were more likely to score lower on the Dietary Antioxidant Index (DAI), which was created to consider a diet’s entire antioxidant profile.
“Available evidence indicates that diet has an important role in developing H. pylori infection. Therefore, protective dietary factors are important from a public health point of view,” Farzad Shidfar, a professor of nutrition at the Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, and member of the university’s colorectal research center, and colleagues write.
“While some nutritional research has widely focused on single nutrients or foods in diet-disease relations, the overall diet could be more informative because humans typically consume a combination of nutrients and foods,” they write. “Dietary indices such as DAI are one of the approaches for this purpose.”
The study was published online in BMC Gastroenterology.
Measuring antioxidant intake
Previous research has indicated an inverse association between the DAI and inflammatory diseases, the study authors write, including gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and obesity. Studies have also indicated that H. pylori infection is related to deficiencies in vitamins A, C, and E, which have antioxidant properties.
In a case-control study, the research team compared the dietary intake of 148 patients with H. pylori to 302 healthy controls without infection. The patients in the H. pylori–positive group were recruited between June 2021 and November 2021 from the gastroenterology clinic at Rasoul-e-Akram Hospital in Tehran, where they were newly diagnosed with active infection and not yet under treatment.
The researchers calculated the DAI based on dietary intake information from a validated, 168-item food frequency questionnaire used in Iran. The participants were asked about their dietary intake based on the average day, week, month, and year. They also discussed serving sizes of food items, and to increase the accuracy of estimates, interviewers showed household measurements or serving sizes to confirm the measurements with participants.
The average age of the study participants was 39 years, and about 60% were women. Compared with the healthy controls, those with H. pylori were significantly older, had higher body mass index, and smoked more.
Overall, patients with H. pylori had a significantly lower intake of vitamin A, vitamin E, manganese, and selenium. Other differences in dietary intake – for vitamin C and zinc – were not significant.
The average total DAI was significantly higher in the healthy controls, at 7.67, as compared with 3.57 in the patients with H. pylori. The risk for infection decreased as continuous DAI increased.
After adjusting for several variables, the researchers found that participants with less than the median DAI values had an increased risk of developing an H. pylori infection.
“A balanced diet, especially high consumption of fruits and vegetables, might protect people against the consequences of H. pylori infection,” the study authors write. “On the contrary, a diet full of carbohydrates and sweets is related to a higher H. pylori infection prevalence.”
Why a good diet may help combat infection
The findings are consistent with other studies that have noted a higher intake of fruits and vegetables among healthy people compared with those who have H. pylori infections, the study authors write. Animal studies have also indicated that taking vitamins A, C, and E and selenium can lead to a reduction in H. pylori growth.
“Several biologically plausible reasons may explain why dietary antioxidants might be, either directly or indirectly, a protective factor against H. pylori infection,” the researchers write. “It is well-known that antioxidants, with their free radical scavenging activities, can inhibit the growth of H. pylori.”
H. pylori is urease-positive and can synthesize a large amount of urease for ammonia production to neutralize gastric acid, which allows it to colonize in the stomach epithelium, the study authors write. Vitamin C inhibits urease activity and improves the stimulation of granulocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, and immunoglobulin production. Other nutrients, such as zinc, may inhibit the urease enzyme and prevent H. pylori adhesion to gastric tissues, they write.
“Dietary elements have previously been shown to dramatically alter pathogenic responses to H. pylori infections,” Richard Peek Jr., MD, professor of medicine and director of gastroenterology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told this news organization.
Dr. Peek, who wasn’t involved with this study, and colleagues found that iron deficiency is linked with altered bile metabolism, which can promote H. pylori–induced gastric carcinogenesis.
“The current study is important, as it suggests that shifting to a diet rich in antioxidants may be beneficial in terms of H. pylori infection,” he said.
At the same time, Dr. Peek expressed caution about generalizing the results across populations.
“Most of the persons enrolled in this study were likely infected with H. pylori as children,” he noted. “Therefore, the inverse role of antioxidant-rich diets and H. pylori infection must be interpreted with caution.”
Future studies should confirm the findings in other groups and determine whether antioxidant-rich diets limit the diseases caused by H. pylori infection, Dr. Peek added.
The study was not funded by any research center, and the authors declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Peek reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who eat a balanced diet with sufficient antioxidants from fruits and vegetables may face reduced risks for Heliobacter pylori infections, according to a new report.
In particular, patients with an H. pylori infection were more likely to score lower on the Dietary Antioxidant Index (DAI), which was created to consider a diet’s entire antioxidant profile.
“Available evidence indicates that diet has an important role in developing H. pylori infection. Therefore, protective dietary factors are important from a public health point of view,” Farzad Shidfar, a professor of nutrition at the Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, and member of the university’s colorectal research center, and colleagues write.
“While some nutritional research has widely focused on single nutrients or foods in diet-disease relations, the overall diet could be more informative because humans typically consume a combination of nutrients and foods,” they write. “Dietary indices such as DAI are one of the approaches for this purpose.”
The study was published online in BMC Gastroenterology.
Measuring antioxidant intake
Previous research has indicated an inverse association between the DAI and inflammatory diseases, the study authors write, including gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and obesity. Studies have also indicated that H. pylori infection is related to deficiencies in vitamins A, C, and E, which have antioxidant properties.
In a case-control study, the research team compared the dietary intake of 148 patients with H. pylori to 302 healthy controls without infection. The patients in the H. pylori–positive group were recruited between June 2021 and November 2021 from the gastroenterology clinic at Rasoul-e-Akram Hospital in Tehran, where they were newly diagnosed with active infection and not yet under treatment.
The researchers calculated the DAI based on dietary intake information from a validated, 168-item food frequency questionnaire used in Iran. The participants were asked about their dietary intake based on the average day, week, month, and year. They also discussed serving sizes of food items, and to increase the accuracy of estimates, interviewers showed household measurements or serving sizes to confirm the measurements with participants.
The average age of the study participants was 39 years, and about 60% were women. Compared with the healthy controls, those with H. pylori were significantly older, had higher body mass index, and smoked more.
Overall, patients with H. pylori had a significantly lower intake of vitamin A, vitamin E, manganese, and selenium. Other differences in dietary intake – for vitamin C and zinc – were not significant.
The average total DAI was significantly higher in the healthy controls, at 7.67, as compared with 3.57 in the patients with H. pylori. The risk for infection decreased as continuous DAI increased.
After adjusting for several variables, the researchers found that participants with less than the median DAI values had an increased risk of developing an H. pylori infection.
“A balanced diet, especially high consumption of fruits and vegetables, might protect people against the consequences of H. pylori infection,” the study authors write. “On the contrary, a diet full of carbohydrates and sweets is related to a higher H. pylori infection prevalence.”
Why a good diet may help combat infection
The findings are consistent with other studies that have noted a higher intake of fruits and vegetables among healthy people compared with those who have H. pylori infections, the study authors write. Animal studies have also indicated that taking vitamins A, C, and E and selenium can lead to a reduction in H. pylori growth.
“Several biologically plausible reasons may explain why dietary antioxidants might be, either directly or indirectly, a protective factor against H. pylori infection,” the researchers write. “It is well-known that antioxidants, with their free radical scavenging activities, can inhibit the growth of H. pylori.”
H. pylori is urease-positive and can synthesize a large amount of urease for ammonia production to neutralize gastric acid, which allows it to colonize in the stomach epithelium, the study authors write. Vitamin C inhibits urease activity and improves the stimulation of granulocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, and immunoglobulin production. Other nutrients, such as zinc, may inhibit the urease enzyme and prevent H. pylori adhesion to gastric tissues, they write.
“Dietary elements have previously been shown to dramatically alter pathogenic responses to H. pylori infections,” Richard Peek Jr., MD, professor of medicine and director of gastroenterology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told this news organization.
Dr. Peek, who wasn’t involved with this study, and colleagues found that iron deficiency is linked with altered bile metabolism, which can promote H. pylori–induced gastric carcinogenesis.
“The current study is important, as it suggests that shifting to a diet rich in antioxidants may be beneficial in terms of H. pylori infection,” he said.
At the same time, Dr. Peek expressed caution about generalizing the results across populations.
“Most of the persons enrolled in this study were likely infected with H. pylori as children,” he noted. “Therefore, the inverse role of antioxidant-rich diets and H. pylori infection must be interpreted with caution.”
Future studies should confirm the findings in other groups and determine whether antioxidant-rich diets limit the diseases caused by H. pylori infection, Dr. Peek added.
The study was not funded by any research center, and the authors declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Peek reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BMC GASTROENTEROLOGY
Emerging invasive fungal infections call for multidisciplinary cooperation
BUENOS AIRES – Emerging invasive fungal infections represent a new diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. To address their growing clinical impact on immunocompromised patients requires better local epidemiologic records, said a specialist at the XXII Congress of the Argentine Society of Infectology.
“To know that these fungal infections exist, I believe that in this respect we are falling short,” said Javier Afeltra, PhD, a mycologist at the Ramos Mejía Hospital in Buenos Aires, professor of microbiology at the School of Medicine of the University of Buenos Aires, and coordinator of the commission of immunocompromised patients of the Argentine Society of Infectious Diseases.
“There is some change in mentality that encourages professionals to report the cases they detect – for example, in scientific meetings,” Dr. Afeltra told this news orgnization. “But the problem is that there is no unified registry.
“That’s what we lack: a place to record all those isolated cases. Records where clinical and microbiological data are together within a click. Perhaps the microbiologists report their findings to the Malbrán Institute, an Argentine reference center for infectious disease research, but we do not know what the patients had. And we doctors may get together to make records of what happens clinically with the patient, but the germ data are elsewhere. We need a common registry,” he stressed.
“The main importance of a registry of this type is that it would allow a diagnostic and therapeutic decision to be made that is appropriate to the epidemiological profile of the country and the region, not looking at what they do in the North. Most likely, the best antifungal treatment for our country differs from what is indicated in the guidelines written elsewhere,” said Dr. Afeltra.
Dr. Afeltra pointed out that in the United States, when an oncohematology patient does not respond to antimicrobial treatment, the first thing that doctors think is that the patient has aspergillosis or mucormycosis, in which the fungal infection is caused by filamentous fungi.
But an analysis of data from the REMINI registry – the only prospective, observational, multicenter surveillance registry for invasive mycoses in immunocompromised patients (excluding HIV infection) in Argentina, which has been in existence since 2010 – tells a different story. The most prevalent fungal infections turned out to be those caused by Aspergillus species, followed by Fusarium species. Together, they account for more than half of cases. Mucoral infections (mucormycosis) account for less than 6%. And the initial treatments for these diseases could be different.
Changes in the local epidemiology can occur because the behavior of phytopathogenic fungi found in the environment can be modified. For example, cases of chronic mucormycosis can be detected in China but are virtually nonexistent on this side of the Greenwich meridian, Dr. Afeltra said.
“Nature is not the same in geographical areas, and the fungi … we breathe are completely different, so patients have different infections and require different diagnostic and treatment approaches,” he stressed.
Dr. Afeltra mentioned different fungi that are emerging locally and globally, including yeasts, septate, dimorphic, and pigmented hyaline fungi, that have a variable response to antifungal drugs and are associated with high mortality, “which has a lot to do with a later diagnosis,” he said, noting that reports have increased worldwide. A barrier to sharing this information more widely with the professional community, in addition to the lack of records, is the difficulty in publishing cases or series of cases in indexed journals.
Another challenge in characterizing the phenomenon is in regard to taxonomic reclassifications of fungi. Such reclassifications can mean that “perhaps we are speaking of the same pathogen in similar situations, believing that we are referring to different pathogens,” said Dr. Afeltra.
Clinical pearls related to emerging fungal pathogens
Candida auris. This organism has emerged simultaneously on several continents. It has pathogenicity factors typical of the genus, such as biofilm formation and production of phospholipases and proteinases, although it has greater thermal tolerance. In hospitals, it colonizes for weeks and months. In Argentina, it is resistant to multiple antifungal agents. Sensitivity is variable in different geographical regions. Most strains are resistant to fluconazole, and there is variable resistance to the other triazoles [which are not normally used to treat candidemia]. In the United States, in vitro resistance to amphotericin B is up to 30%, and resistance to echinocandins is up to 5%. New drugs such as rezafungin and ibrexafungerp are being studied. Infection control is similar to that used to control Clostridium difficile.
Fusarium. This genus affects immunocompromised patients, including transplant recipients of solid organs and hematopoietic progenitor cells and patients with neutropenia. The genus has various species, included within complexes, such as F. solani SC, F. oxysporum SC, and F. fujikuroi SC, with clinical manifestations similar to those of aspergillosis. In addition to the pulmonary and disseminated forms, there may be skin involvement attributable to dissemination from a respiratory focus or by contiguity from a focus of onychomycosis. In general, mortality is high, and responses to antifungal agents are variable. Some species are more sensitive to voriconazole or posaconazole, and others less so. All show in vitro resistance to itraconazole. In Argentina, voriconazole is usually used as initial treatment, and in special cases, liposomal amphotericin B or combinations. Fosmanogepix is being evaluated for the future.
Azole-resistant aspergillosis. This infection has shown resistance to itraconazole and third-generation azole drugs. In immunocompromised patients, mortlaity is high. Early detection is key. It is sensitive to amphotericin B and echinocandins. It is generally treated with liposomal amphotericin B. Olorofim and fosmanogepix are being studied.
Pulmonary aspergillosis associated with COVID-19. This infection is associated with high mortality among intubated patients. Signs and symptoms include fever, pleural effusion, hemoptysis, and chest pain, with infiltrates or cavitations on imaging. Determining the diagnosis is difficult. “We couldn’t perform lung biopsies, and it was difficult for us to get patients out of intensive care units for CT scans. We treated the proven cases. We treated the probable cases, and those that had a very low certainty of disease were also treated. We came across this emergency and tried to do the best we could,” said Dr. Afeltra. A digital readout lateral flow trial (Sona Aspergillus Galactomannan LFA) for the quantification of galactomannan, a cell wall component of the Aspergillus genus, proved to be a useful tool for screening and diagnosing patients with probable pulmonary aspergillosis associated with COVID-19. The incidence of invasive mycosis was around 10% among 185 seriously ill COVID-19 patients, according to an Argentine multicenter prospective study in which Dr. Afeltra participated.
Scedosporium and Lomentospora. These genera are rarer septate hyaline fungi. Scedosporium is a complex of species. One species, S. apiospermum, can colonize pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis. Lomentospora prolificans is a multiresistant fungus. It produces pulmonary compromise or disseminated infection. The response to antifungal agents is variable, with a high minimum inhibitory concentration for amphotericin B and isavuconazole. Patients are usually treated with voriconazole alone or in combination with terbinafine or micafungin. Olorofim is emerging as a promising treatment.
Dr. Afeltra has received fees from Biotoscana, Gador, Pfizer, Merck, and Sandoz.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition, a version appeared on Medscape.com.
BUENOS AIRES – Emerging invasive fungal infections represent a new diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. To address their growing clinical impact on immunocompromised patients requires better local epidemiologic records, said a specialist at the XXII Congress of the Argentine Society of Infectology.
“To know that these fungal infections exist, I believe that in this respect we are falling short,” said Javier Afeltra, PhD, a mycologist at the Ramos Mejía Hospital in Buenos Aires, professor of microbiology at the School of Medicine of the University of Buenos Aires, and coordinator of the commission of immunocompromised patients of the Argentine Society of Infectious Diseases.
“There is some change in mentality that encourages professionals to report the cases they detect – for example, in scientific meetings,” Dr. Afeltra told this news orgnization. “But the problem is that there is no unified registry.
“That’s what we lack: a place to record all those isolated cases. Records where clinical and microbiological data are together within a click. Perhaps the microbiologists report their findings to the Malbrán Institute, an Argentine reference center for infectious disease research, but we do not know what the patients had. And we doctors may get together to make records of what happens clinically with the patient, but the germ data are elsewhere. We need a common registry,” he stressed.
“The main importance of a registry of this type is that it would allow a diagnostic and therapeutic decision to be made that is appropriate to the epidemiological profile of the country and the region, not looking at what they do in the North. Most likely, the best antifungal treatment for our country differs from what is indicated in the guidelines written elsewhere,” said Dr. Afeltra.
Dr. Afeltra pointed out that in the United States, when an oncohematology patient does not respond to antimicrobial treatment, the first thing that doctors think is that the patient has aspergillosis or mucormycosis, in which the fungal infection is caused by filamentous fungi.
But an analysis of data from the REMINI registry – the only prospective, observational, multicenter surveillance registry for invasive mycoses in immunocompromised patients (excluding HIV infection) in Argentina, which has been in existence since 2010 – tells a different story. The most prevalent fungal infections turned out to be those caused by Aspergillus species, followed by Fusarium species. Together, they account for more than half of cases. Mucoral infections (mucormycosis) account for less than 6%. And the initial treatments for these diseases could be different.
Changes in the local epidemiology can occur because the behavior of phytopathogenic fungi found in the environment can be modified. For example, cases of chronic mucormycosis can be detected in China but are virtually nonexistent on this side of the Greenwich meridian, Dr. Afeltra said.
“Nature is not the same in geographical areas, and the fungi … we breathe are completely different, so patients have different infections and require different diagnostic and treatment approaches,” he stressed.
Dr. Afeltra mentioned different fungi that are emerging locally and globally, including yeasts, septate, dimorphic, and pigmented hyaline fungi, that have a variable response to antifungal drugs and are associated with high mortality, “which has a lot to do with a later diagnosis,” he said, noting that reports have increased worldwide. A barrier to sharing this information more widely with the professional community, in addition to the lack of records, is the difficulty in publishing cases or series of cases in indexed journals.
Another challenge in characterizing the phenomenon is in regard to taxonomic reclassifications of fungi. Such reclassifications can mean that “perhaps we are speaking of the same pathogen in similar situations, believing that we are referring to different pathogens,” said Dr. Afeltra.
Clinical pearls related to emerging fungal pathogens
Candida auris. This organism has emerged simultaneously on several continents. It has pathogenicity factors typical of the genus, such as biofilm formation and production of phospholipases and proteinases, although it has greater thermal tolerance. In hospitals, it colonizes for weeks and months. In Argentina, it is resistant to multiple antifungal agents. Sensitivity is variable in different geographical regions. Most strains are resistant to fluconazole, and there is variable resistance to the other triazoles [which are not normally used to treat candidemia]. In the United States, in vitro resistance to amphotericin B is up to 30%, and resistance to echinocandins is up to 5%. New drugs such as rezafungin and ibrexafungerp are being studied. Infection control is similar to that used to control Clostridium difficile.
Fusarium. This genus affects immunocompromised patients, including transplant recipients of solid organs and hematopoietic progenitor cells and patients with neutropenia. The genus has various species, included within complexes, such as F. solani SC, F. oxysporum SC, and F. fujikuroi SC, with clinical manifestations similar to those of aspergillosis. In addition to the pulmonary and disseminated forms, there may be skin involvement attributable to dissemination from a respiratory focus or by contiguity from a focus of onychomycosis. In general, mortality is high, and responses to antifungal agents are variable. Some species are more sensitive to voriconazole or posaconazole, and others less so. All show in vitro resistance to itraconazole. In Argentina, voriconazole is usually used as initial treatment, and in special cases, liposomal amphotericin B or combinations. Fosmanogepix is being evaluated for the future.
Azole-resistant aspergillosis. This infection has shown resistance to itraconazole and third-generation azole drugs. In immunocompromised patients, mortlaity is high. Early detection is key. It is sensitive to amphotericin B and echinocandins. It is generally treated with liposomal amphotericin B. Olorofim and fosmanogepix are being studied.
Pulmonary aspergillosis associated with COVID-19. This infection is associated with high mortality among intubated patients. Signs and symptoms include fever, pleural effusion, hemoptysis, and chest pain, with infiltrates or cavitations on imaging. Determining the diagnosis is difficult. “We couldn’t perform lung biopsies, and it was difficult for us to get patients out of intensive care units for CT scans. We treated the proven cases. We treated the probable cases, and those that had a very low certainty of disease were also treated. We came across this emergency and tried to do the best we could,” said Dr. Afeltra. A digital readout lateral flow trial (Sona Aspergillus Galactomannan LFA) for the quantification of galactomannan, a cell wall component of the Aspergillus genus, proved to be a useful tool for screening and diagnosing patients with probable pulmonary aspergillosis associated with COVID-19. The incidence of invasive mycosis was around 10% among 185 seriously ill COVID-19 patients, according to an Argentine multicenter prospective study in which Dr. Afeltra participated.
Scedosporium and Lomentospora. These genera are rarer septate hyaline fungi. Scedosporium is a complex of species. One species, S. apiospermum, can colonize pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis. Lomentospora prolificans is a multiresistant fungus. It produces pulmonary compromise or disseminated infection. The response to antifungal agents is variable, with a high minimum inhibitory concentration for amphotericin B and isavuconazole. Patients are usually treated with voriconazole alone or in combination with terbinafine or micafungin. Olorofim is emerging as a promising treatment.
Dr. Afeltra has received fees from Biotoscana, Gador, Pfizer, Merck, and Sandoz.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition, a version appeared on Medscape.com.
BUENOS AIRES – Emerging invasive fungal infections represent a new diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. To address their growing clinical impact on immunocompromised patients requires better local epidemiologic records, said a specialist at the XXII Congress of the Argentine Society of Infectology.
“To know that these fungal infections exist, I believe that in this respect we are falling short,” said Javier Afeltra, PhD, a mycologist at the Ramos Mejía Hospital in Buenos Aires, professor of microbiology at the School of Medicine of the University of Buenos Aires, and coordinator of the commission of immunocompromised patients of the Argentine Society of Infectious Diseases.
“There is some change in mentality that encourages professionals to report the cases they detect – for example, in scientific meetings,” Dr. Afeltra told this news orgnization. “But the problem is that there is no unified registry.
“That’s what we lack: a place to record all those isolated cases. Records where clinical and microbiological data are together within a click. Perhaps the microbiologists report their findings to the Malbrán Institute, an Argentine reference center for infectious disease research, but we do not know what the patients had. And we doctors may get together to make records of what happens clinically with the patient, but the germ data are elsewhere. We need a common registry,” he stressed.
“The main importance of a registry of this type is that it would allow a diagnostic and therapeutic decision to be made that is appropriate to the epidemiological profile of the country and the region, not looking at what they do in the North. Most likely, the best antifungal treatment for our country differs from what is indicated in the guidelines written elsewhere,” said Dr. Afeltra.
Dr. Afeltra pointed out that in the United States, when an oncohematology patient does not respond to antimicrobial treatment, the first thing that doctors think is that the patient has aspergillosis or mucormycosis, in which the fungal infection is caused by filamentous fungi.
But an analysis of data from the REMINI registry – the only prospective, observational, multicenter surveillance registry for invasive mycoses in immunocompromised patients (excluding HIV infection) in Argentina, which has been in existence since 2010 – tells a different story. The most prevalent fungal infections turned out to be those caused by Aspergillus species, followed by Fusarium species. Together, they account for more than half of cases. Mucoral infections (mucormycosis) account for less than 6%. And the initial treatments for these diseases could be different.
Changes in the local epidemiology can occur because the behavior of phytopathogenic fungi found in the environment can be modified. For example, cases of chronic mucormycosis can be detected in China but are virtually nonexistent on this side of the Greenwich meridian, Dr. Afeltra said.
“Nature is not the same in geographical areas, and the fungi … we breathe are completely different, so patients have different infections and require different diagnostic and treatment approaches,” he stressed.
Dr. Afeltra mentioned different fungi that are emerging locally and globally, including yeasts, septate, dimorphic, and pigmented hyaline fungi, that have a variable response to antifungal drugs and are associated with high mortality, “which has a lot to do with a later diagnosis,” he said, noting that reports have increased worldwide. A barrier to sharing this information more widely with the professional community, in addition to the lack of records, is the difficulty in publishing cases or series of cases in indexed journals.
Another challenge in characterizing the phenomenon is in regard to taxonomic reclassifications of fungi. Such reclassifications can mean that “perhaps we are speaking of the same pathogen in similar situations, believing that we are referring to different pathogens,” said Dr. Afeltra.
Clinical pearls related to emerging fungal pathogens
Candida auris. This organism has emerged simultaneously on several continents. It has pathogenicity factors typical of the genus, such as biofilm formation and production of phospholipases and proteinases, although it has greater thermal tolerance. In hospitals, it colonizes for weeks and months. In Argentina, it is resistant to multiple antifungal agents. Sensitivity is variable in different geographical regions. Most strains are resistant to fluconazole, and there is variable resistance to the other triazoles [which are not normally used to treat candidemia]. In the United States, in vitro resistance to amphotericin B is up to 30%, and resistance to echinocandins is up to 5%. New drugs such as rezafungin and ibrexafungerp are being studied. Infection control is similar to that used to control Clostridium difficile.
Fusarium. This genus affects immunocompromised patients, including transplant recipients of solid organs and hematopoietic progenitor cells and patients with neutropenia. The genus has various species, included within complexes, such as F. solani SC, F. oxysporum SC, and F. fujikuroi SC, with clinical manifestations similar to those of aspergillosis. In addition to the pulmonary and disseminated forms, there may be skin involvement attributable to dissemination from a respiratory focus or by contiguity from a focus of onychomycosis. In general, mortality is high, and responses to antifungal agents are variable. Some species are more sensitive to voriconazole or posaconazole, and others less so. All show in vitro resistance to itraconazole. In Argentina, voriconazole is usually used as initial treatment, and in special cases, liposomal amphotericin B or combinations. Fosmanogepix is being evaluated for the future.
Azole-resistant aspergillosis. This infection has shown resistance to itraconazole and third-generation azole drugs. In immunocompromised patients, mortlaity is high. Early detection is key. It is sensitive to amphotericin B and echinocandins. It is generally treated with liposomal amphotericin B. Olorofim and fosmanogepix are being studied.
Pulmonary aspergillosis associated with COVID-19. This infection is associated with high mortality among intubated patients. Signs and symptoms include fever, pleural effusion, hemoptysis, and chest pain, with infiltrates or cavitations on imaging. Determining the diagnosis is difficult. “We couldn’t perform lung biopsies, and it was difficult for us to get patients out of intensive care units for CT scans. We treated the proven cases. We treated the probable cases, and those that had a very low certainty of disease were also treated. We came across this emergency and tried to do the best we could,” said Dr. Afeltra. A digital readout lateral flow trial (Sona Aspergillus Galactomannan LFA) for the quantification of galactomannan, a cell wall component of the Aspergillus genus, proved to be a useful tool for screening and diagnosing patients with probable pulmonary aspergillosis associated with COVID-19. The incidence of invasive mycosis was around 10% among 185 seriously ill COVID-19 patients, according to an Argentine multicenter prospective study in which Dr. Afeltra participated.
Scedosporium and Lomentospora. These genera are rarer septate hyaline fungi. Scedosporium is a complex of species. One species, S. apiospermum, can colonize pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis. Lomentospora prolificans is a multiresistant fungus. It produces pulmonary compromise or disseminated infection. The response to antifungal agents is variable, with a high minimum inhibitory concentration for amphotericin B and isavuconazole. Patients are usually treated with voriconazole alone or in combination with terbinafine or micafungin. Olorofim is emerging as a promising treatment.
Dr. Afeltra has received fees from Biotoscana, Gador, Pfizer, Merck, and Sandoz.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition, a version appeared on Medscape.com.
AT SADI 2022
New technology a sepsis breakthrough?
Sepsis is among the most feared conditions for health care providers. These blood infections strike with such rapid intensity that treating them demands a mix of both clinical skill and luck – recognizing symptoms early enough while choosing the right drug to tame the bacterial culprit before the germs have overwhelmed the body’s immune system.
All too often, sepsis wins the race. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at least 1.7 million people in this country develop sepsis annually. About 350,000 die during hospitalization or are discharged to hospice.
But new research, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, offers hope that clinicians may one day be able to detect and treat sepsis more quickly.
The researchers broke down whole blood and dried it by heating, resulting in a solid porous structure with the bacterial DNA trapped inside. They then used chemicals – primers and enzymes – to reach inside the porous structure and amplify the target DNA.
The team was able to detect four causes of bloodstream infections – the bacteria methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), gram-negative Escherichia coli, and the fungal species Candida albicans. They validated their method against clinical laboratory results that used blood cultures and DNA analyses to detect sepsis.
The technique took just 2.5 hours and required roughly 1 mL of blood, according to the researchers.
“This technique can have broad applications in detection of bacterial infection and presence of bacteria in large values of blood,” Rashid Bashir, PhD, dean of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign’s Grainger College of Engineering, and a co-author of the study, told this news organization.
While infection control experts and sepsis prevention advocates said the new study offers no clues about how to treat sepsis once detected, they hope the innovation eventually could save lives.
A rapid killer
Sepsis occurs when the body overreacts to an infection. The severe response can lead to tissue damage, organ failure, and death.
Thomas Heymann, MBA, president and CEO of Sepsis Alliance, an advocacy group, said mortality can rise 8% for each hour treatment is delayed.
Infants born prematurely are particularly vulnerable. Dr. Bashir and his colleagues noted that 25% of all infants admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit are diagnosed with sepsis. Of those, as many as 35% may die from infection. Sepsis is the most expensive condition treated in U.S. hospitals, accounting for $23.7 billion in costs annually, they added.
Despite high mortality rates and hospital costs, according to a Sepsis Alliance survey, only 66% of Americans are aware of the term sepsis. Only 19% can name the four primary signs of the condition: Altered body Temperature, an Infection, Mental decline, and feeling Extremely ill, or “TIME.”
Getting the appropriate antibiotics to sepsis patients quickly can greatly improve chances of survival, but Dr. Bashir said the current method of confirming the diagnosis is too slow.
Blood cultures too slow
Traditional blood cultures are among the most common methods of determining if a patient has a bloodstream infection. But the process takes about 24 hours for a culture to detect the category of bacteria and an additional day to determine exactly which bacteria is present, according to Cindy Hou, DO, infection control officer and medical director of research at Jefferson Health, Voorhees Township, New Jersey. At 72 hours, Dr. Hou said, a blood culture will finally be able to produce a “sensitivity” result, which tells doctors which antibiotics will be most effective against the pathogen.
By then, patients often are already past the point of saving. The bottom line, according to Dr. Bashir and his colleagues: Blood cultures are “too slow and cumbersome to allow for initial management of patients and thus contribute to high mortality.”
Dr. Hou called the ability to identify the type of infection in just 2.5 hours an “amazing” feat.
,” she said. “These researchers are pushing the bar for what rapid means.”
The new detection method is not yet available commercially. Dr. Bashir said he and his colleagues plan to scale their study and hope to find a way to bypass the long culture steps to identify target pathogens directly from a large volume of blood.
Dr. Hou said she believes a blood culture would still be necessary since clinicians would need sensitivity results to guide targeted treatment of infections.
“There is a lot more we need, but this paper is a call to arms for the field of rapid diagnostics to make rapid as fast as it really needs to be, but we still need to find solutions which are affordable,” Dr. Hou said.
Even without a blood culture, Dr. Bashir’s technology could improve care. Mr. Heymann said the technology could help convince clinicians worried about antibiotic resistance to prescribe treatment faster.
“We know we’re overusing antibiotics, and that’s creating a new big problem” when it comes to sepsis treatment, he said. “Getting a diagnostic read earlier is a game changer.”
Combined with a blood culture that can later confirm or help adjust the course of treatment, Dr. Hou said this new method of sepsis detection could improve care, especially in places where rapid diagnostics are not available and particularly if combined with physician education so they understand what treatment is best for various types of infection.
Mr. Heymann agreed. Sepsis Alliance also operates the Sepsis Innovation Collaborative, a group that supports public-private innovation on sepsis care.
“We’re losing someone every 90 seconds in the United States to sepsis,” Mr. Heymann said. “There is a huge opportunity to do better, and it’s this kind of innovation that is really inspiring.”
Dr. Hou is chief medical officer for Sepsis Alliance, a medical advisor for the Sepsis Innovation Collaborative, an advisor for Janssen, and a key opinion leader for T2 Biosystems. Dr. Bashir and Mr. Heymann report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sepsis is among the most feared conditions for health care providers. These blood infections strike with such rapid intensity that treating them demands a mix of both clinical skill and luck – recognizing symptoms early enough while choosing the right drug to tame the bacterial culprit before the germs have overwhelmed the body’s immune system.
All too often, sepsis wins the race. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at least 1.7 million people in this country develop sepsis annually. About 350,000 die during hospitalization or are discharged to hospice.
But new research, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, offers hope that clinicians may one day be able to detect and treat sepsis more quickly.
The researchers broke down whole blood and dried it by heating, resulting in a solid porous structure with the bacterial DNA trapped inside. They then used chemicals – primers and enzymes – to reach inside the porous structure and amplify the target DNA.
The team was able to detect four causes of bloodstream infections – the bacteria methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), gram-negative Escherichia coli, and the fungal species Candida albicans. They validated their method against clinical laboratory results that used blood cultures and DNA analyses to detect sepsis.
The technique took just 2.5 hours and required roughly 1 mL of blood, according to the researchers.
“This technique can have broad applications in detection of bacterial infection and presence of bacteria in large values of blood,” Rashid Bashir, PhD, dean of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign’s Grainger College of Engineering, and a co-author of the study, told this news organization.
While infection control experts and sepsis prevention advocates said the new study offers no clues about how to treat sepsis once detected, they hope the innovation eventually could save lives.
A rapid killer
Sepsis occurs when the body overreacts to an infection. The severe response can lead to tissue damage, organ failure, and death.
Thomas Heymann, MBA, president and CEO of Sepsis Alliance, an advocacy group, said mortality can rise 8% for each hour treatment is delayed.
Infants born prematurely are particularly vulnerable. Dr. Bashir and his colleagues noted that 25% of all infants admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit are diagnosed with sepsis. Of those, as many as 35% may die from infection. Sepsis is the most expensive condition treated in U.S. hospitals, accounting for $23.7 billion in costs annually, they added.
Despite high mortality rates and hospital costs, according to a Sepsis Alliance survey, only 66% of Americans are aware of the term sepsis. Only 19% can name the four primary signs of the condition: Altered body Temperature, an Infection, Mental decline, and feeling Extremely ill, or “TIME.”
Getting the appropriate antibiotics to sepsis patients quickly can greatly improve chances of survival, but Dr. Bashir said the current method of confirming the diagnosis is too slow.
Blood cultures too slow
Traditional blood cultures are among the most common methods of determining if a patient has a bloodstream infection. But the process takes about 24 hours for a culture to detect the category of bacteria and an additional day to determine exactly which bacteria is present, according to Cindy Hou, DO, infection control officer and medical director of research at Jefferson Health, Voorhees Township, New Jersey. At 72 hours, Dr. Hou said, a blood culture will finally be able to produce a “sensitivity” result, which tells doctors which antibiotics will be most effective against the pathogen.
By then, patients often are already past the point of saving. The bottom line, according to Dr. Bashir and his colleagues: Blood cultures are “too slow and cumbersome to allow for initial management of patients and thus contribute to high mortality.”
Dr. Hou called the ability to identify the type of infection in just 2.5 hours an “amazing” feat.
,” she said. “These researchers are pushing the bar for what rapid means.”
The new detection method is not yet available commercially. Dr. Bashir said he and his colleagues plan to scale their study and hope to find a way to bypass the long culture steps to identify target pathogens directly from a large volume of blood.
Dr. Hou said she believes a blood culture would still be necessary since clinicians would need sensitivity results to guide targeted treatment of infections.
“There is a lot more we need, but this paper is a call to arms for the field of rapid diagnostics to make rapid as fast as it really needs to be, but we still need to find solutions which are affordable,” Dr. Hou said.
Even without a blood culture, Dr. Bashir’s technology could improve care. Mr. Heymann said the technology could help convince clinicians worried about antibiotic resistance to prescribe treatment faster.
“We know we’re overusing antibiotics, and that’s creating a new big problem” when it comes to sepsis treatment, he said. “Getting a diagnostic read earlier is a game changer.”
Combined with a blood culture that can later confirm or help adjust the course of treatment, Dr. Hou said this new method of sepsis detection could improve care, especially in places where rapid diagnostics are not available and particularly if combined with physician education so they understand what treatment is best for various types of infection.
Mr. Heymann agreed. Sepsis Alliance also operates the Sepsis Innovation Collaborative, a group that supports public-private innovation on sepsis care.
“We’re losing someone every 90 seconds in the United States to sepsis,” Mr. Heymann said. “There is a huge opportunity to do better, and it’s this kind of innovation that is really inspiring.”
Dr. Hou is chief medical officer for Sepsis Alliance, a medical advisor for the Sepsis Innovation Collaborative, an advisor for Janssen, and a key opinion leader for T2 Biosystems. Dr. Bashir and Mr. Heymann report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sepsis is among the most feared conditions for health care providers. These blood infections strike with such rapid intensity that treating them demands a mix of both clinical skill and luck – recognizing symptoms early enough while choosing the right drug to tame the bacterial culprit before the germs have overwhelmed the body’s immune system.
All too often, sepsis wins the race. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at least 1.7 million people in this country develop sepsis annually. About 350,000 die during hospitalization or are discharged to hospice.
But new research, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, offers hope that clinicians may one day be able to detect and treat sepsis more quickly.
The researchers broke down whole blood and dried it by heating, resulting in a solid porous structure with the bacterial DNA trapped inside. They then used chemicals – primers and enzymes – to reach inside the porous structure and amplify the target DNA.
The team was able to detect four causes of bloodstream infections – the bacteria methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), gram-negative Escherichia coli, and the fungal species Candida albicans. They validated their method against clinical laboratory results that used blood cultures and DNA analyses to detect sepsis.
The technique took just 2.5 hours and required roughly 1 mL of blood, according to the researchers.
“This technique can have broad applications in detection of bacterial infection and presence of bacteria in large values of blood,” Rashid Bashir, PhD, dean of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign’s Grainger College of Engineering, and a co-author of the study, told this news organization.
While infection control experts and sepsis prevention advocates said the new study offers no clues about how to treat sepsis once detected, they hope the innovation eventually could save lives.
A rapid killer
Sepsis occurs when the body overreacts to an infection. The severe response can lead to tissue damage, organ failure, and death.
Thomas Heymann, MBA, president and CEO of Sepsis Alliance, an advocacy group, said mortality can rise 8% for each hour treatment is delayed.
Infants born prematurely are particularly vulnerable. Dr. Bashir and his colleagues noted that 25% of all infants admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit are diagnosed with sepsis. Of those, as many as 35% may die from infection. Sepsis is the most expensive condition treated in U.S. hospitals, accounting for $23.7 billion in costs annually, they added.
Despite high mortality rates and hospital costs, according to a Sepsis Alliance survey, only 66% of Americans are aware of the term sepsis. Only 19% can name the four primary signs of the condition: Altered body Temperature, an Infection, Mental decline, and feeling Extremely ill, or “TIME.”
Getting the appropriate antibiotics to sepsis patients quickly can greatly improve chances of survival, but Dr. Bashir said the current method of confirming the diagnosis is too slow.
Blood cultures too slow
Traditional blood cultures are among the most common methods of determining if a patient has a bloodstream infection. But the process takes about 24 hours for a culture to detect the category of bacteria and an additional day to determine exactly which bacteria is present, according to Cindy Hou, DO, infection control officer and medical director of research at Jefferson Health, Voorhees Township, New Jersey. At 72 hours, Dr. Hou said, a blood culture will finally be able to produce a “sensitivity” result, which tells doctors which antibiotics will be most effective against the pathogen.
By then, patients often are already past the point of saving. The bottom line, according to Dr. Bashir and his colleagues: Blood cultures are “too slow and cumbersome to allow for initial management of patients and thus contribute to high mortality.”
Dr. Hou called the ability to identify the type of infection in just 2.5 hours an “amazing” feat.
,” she said. “These researchers are pushing the bar for what rapid means.”
The new detection method is not yet available commercially. Dr. Bashir said he and his colleagues plan to scale their study and hope to find a way to bypass the long culture steps to identify target pathogens directly from a large volume of blood.
Dr. Hou said she believes a blood culture would still be necessary since clinicians would need sensitivity results to guide targeted treatment of infections.
“There is a lot more we need, but this paper is a call to arms for the field of rapid diagnostics to make rapid as fast as it really needs to be, but we still need to find solutions which are affordable,” Dr. Hou said.
Even without a blood culture, Dr. Bashir’s technology could improve care. Mr. Heymann said the technology could help convince clinicians worried about antibiotic resistance to prescribe treatment faster.
“We know we’re overusing antibiotics, and that’s creating a new big problem” when it comes to sepsis treatment, he said. “Getting a diagnostic read earlier is a game changer.”
Combined with a blood culture that can later confirm or help adjust the course of treatment, Dr. Hou said this new method of sepsis detection could improve care, especially in places where rapid diagnostics are not available and particularly if combined with physician education so they understand what treatment is best for various types of infection.
Mr. Heymann agreed. Sepsis Alliance also operates the Sepsis Innovation Collaborative, a group that supports public-private innovation on sepsis care.
“We’re losing someone every 90 seconds in the United States to sepsis,” Mr. Heymann said. “There is a huge opportunity to do better, and it’s this kind of innovation that is really inspiring.”
Dr. Hou is chief medical officer for Sepsis Alliance, a medical advisor for the Sepsis Innovation Collaborative, an advisor for Janssen, and a key opinion leader for T2 Biosystems. Dr. Bashir and Mr. Heymann report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Evusheld PrEP may protect immunocompromised patients from severe COVID-19
Tixagevimab copackaged with cilgavimab (Evusheld) is a safe and effective preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in patients undergoing B-cell-depleting therapies who have poor immune response to COVID-19 vaccination and are at high risk for serious COVID-19 illness, a small, single-site study suggests.
Evusheld, the only COVID-19 PrEP option available, has Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of immunocompromised patients who may not respond sufficiently to COVID-19 vaccination and patients who’ve had a severe adverse reaction to COVID-19 vaccination.
“We report the largest real-world experience of Evusheld in this population, and our findings are encouraging,” lead study author Cassandra Calabrese, DO, rheumatologist and infectious disease specialist at Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“Of 412 patients who received Evusheld, 12 [2.9%] developed breakthrough COVID-19, with 11 having mild courses and 1 who required hospitalization but recovered,” she added.
“Our data suggest that Evusheld PrEP, in combination with aggressive outpatient treatment of COVID-19, is likely effective in lowering risk of severe COVID in this vulnerable group.
“Practitioners who care for patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases should triage high-risk patients for Evusheld as well as rapid diagnosis and aggressive outpatient therapy if infected,” Dr. Calabrese advised.
For the study, Dr. Calabrese and colleagues at Cleveland Clinic searched the health care system pharmacy records for patients with immune‐mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) or inborn errors of humoral immunity (IEI) who met the criteria to receive Evusheld. The researchers included patients on B-cell-depleting therapies or with humoral IEI who had received at least one dose of Evusheld and were later diagnosed with COVID-19, and they excluded those treated with B-cell-depleting therapies for cancer.
EVUSHELD was well tolerated
After extracting data on COVID-19 infection, vaccination status, and outcomes, they found that, between Jan. 18 and May 28, 2022, 412 patients with IMIDs or humoral IEI received Evusheld. No deaths occurred among these patients and, overall, they tolerated the medication well.
All 12 patients who experienced breakthrough COVID-19 infection were treated with B-cell-depleting therapies. Among the 12 patients:
- Six patients developed infection 13-84 (median 19) days after receiving 150 mg/150 mg tixagevimab/cilgavimab.
- Six patients developed infection 19-72 (median of 38.5) days after either a single dose of 300 mg/300 mg or a second dose of 150 mg/150 mg.
- Eleven patients had mild illness and recovered at home; one patient was hospitalized and treated with high-flow oxygen. All cases had been vaccinated against COVID-19 (five received two vaccinations, six received three, and one received four).
- One possible serious adverse event involved a patient with COVID-19 and immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (ITP) who was hospitalized soon after receiving Evusheld with ITP flare that resolved with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Dr. Calabrese acknowledged limitations to the study, including few patients, lack of a comparator group, and the study period falling during the Omicron wave.
“Also, nine of the breakthrough cases received additional COVID-19 therapy (oral antiviral or monoclonal antibody), which falls within standard of care for this high-risk group but prevents ascribing effectiveness to individual components of the regimen,” she added.
“Evusheld is authorized for PrEP against COVID-19 in patients at high risk for severe COVID due to suboptimal vaccine responses. This includes patients receiving B-cell-depleting drugs like rituximab, and patients with inborn errors of humoral immunity,” Dr. Calabrese explained.
“It is well known that this group of patients is at very high risk for severe COVID and death, even when fully vaccinated, and it has become clear that more strategies are needed to protect this vulnerable group, including use of Evusheld as well as aggressive treatment if infected,” she added.
Evusheld not always easy to obtain
Although the medication has been available in the United States since January 2022, Dr. Calabrese said, patients may not receive it because of barriers including lack of both awareness and access.
Davey Smith, MD, professor of medicine and head of infectious diseases and global public health at the University of California San Diego, in La Jolla, said in an interview that he was not surprised by the results, but added that the study was conducted in too few patients to draw any strong conclusions or affect patient care.
“This small study that showed that breakthrough infections occurred but were generally mild, provides a small glimpse of real-world use of tixagevimab/cilgavimab as PrEP for immunocompromised persons,” said Dr. Smith, who was not involved in the study.
“In the setting of Omicron and vaccination, I would expect the same outcomes reported even without the treatment,” he added.
Dr. Smith recommends larger related randomized, controlled trials to provide clinicians with sufficient data to guide them in their patient care.
Graham Snyder, MD, associate professor in the division of infectious diseases at the University of Pittsburgh and medical director of infection prevention and hospital epidemiology at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, noted that the study “adds to a quickly growing literature on the real-world benefits of tixagevimab/cilgavimab to protect vulnerable individuals with weakened immune systems from the complications of COVID-19.
“This study provides a modest addition to our understanding of the role and benefit of Evusheld,” Dr. Snyder said in an interview. “By characterizing only patients who have received Evusheld without an untreated comparison group, we can’t draw any inference about the extent of benefit the agent provided to these patients.
“Substantial data already show that this agent is effective in preventing complications of COVID-19 infection in immunocompromised individuals,” added Dr. Snyder, who was not involved in the study.
“ ‘Immunocompromised’ represents a very diverse set of clinical conditions,” he said. “The research agenda should therefore focus on a more refined description of the effect in specific populations and a continued understanding of the effect of Evusheld in the context of updated vaccination strategies and changing virus ecology.”
Dr. Calabrese and her colleagues wrote that larger, controlled trials are underway.
FDA: Evusheld may not neutralize certain SARS-CoV-2 variants
“The biggest unanswered question is how Evusheld will hold up against new variants,” Dr. Calabrese said.
In an Oct. 3, 2022, update, the Food and Drug Administration released a statement about the risk of developing COVID-19 from SARS-CoV-2 variants that are not neutralized by Evusheld. The statement mentions an updated fact sheet that describes reduced protection from Evusheld against the Omicron subvariant BA.4.6, which accounted for nearly 13% of all new COVID-19 cases in the United States in the week ending Oct. 1.
There was no outside funding for the study. Dr. Smith reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Snyder said he is an unpaid adviser to an AstraZeneca observational study that’s assessing the real-world effectiveness of Evusheld.
Tixagevimab copackaged with cilgavimab (Evusheld) is a safe and effective preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in patients undergoing B-cell-depleting therapies who have poor immune response to COVID-19 vaccination and are at high risk for serious COVID-19 illness, a small, single-site study suggests.
Evusheld, the only COVID-19 PrEP option available, has Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of immunocompromised patients who may not respond sufficiently to COVID-19 vaccination and patients who’ve had a severe adverse reaction to COVID-19 vaccination.
“We report the largest real-world experience of Evusheld in this population, and our findings are encouraging,” lead study author Cassandra Calabrese, DO, rheumatologist and infectious disease specialist at Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“Of 412 patients who received Evusheld, 12 [2.9%] developed breakthrough COVID-19, with 11 having mild courses and 1 who required hospitalization but recovered,” she added.
“Our data suggest that Evusheld PrEP, in combination with aggressive outpatient treatment of COVID-19, is likely effective in lowering risk of severe COVID in this vulnerable group.
“Practitioners who care for patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases should triage high-risk patients for Evusheld as well as rapid diagnosis and aggressive outpatient therapy if infected,” Dr. Calabrese advised.
For the study, Dr. Calabrese and colleagues at Cleveland Clinic searched the health care system pharmacy records for patients with immune‐mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) or inborn errors of humoral immunity (IEI) who met the criteria to receive Evusheld. The researchers included patients on B-cell-depleting therapies or with humoral IEI who had received at least one dose of Evusheld and were later diagnosed with COVID-19, and they excluded those treated with B-cell-depleting therapies for cancer.
EVUSHELD was well tolerated
After extracting data on COVID-19 infection, vaccination status, and outcomes, they found that, between Jan. 18 and May 28, 2022, 412 patients with IMIDs or humoral IEI received Evusheld. No deaths occurred among these patients and, overall, they tolerated the medication well.
All 12 patients who experienced breakthrough COVID-19 infection were treated with B-cell-depleting therapies. Among the 12 patients:
- Six patients developed infection 13-84 (median 19) days after receiving 150 mg/150 mg tixagevimab/cilgavimab.
- Six patients developed infection 19-72 (median of 38.5) days after either a single dose of 300 mg/300 mg or a second dose of 150 mg/150 mg.
- Eleven patients had mild illness and recovered at home; one patient was hospitalized and treated with high-flow oxygen. All cases had been vaccinated against COVID-19 (five received two vaccinations, six received three, and one received four).
- One possible serious adverse event involved a patient with COVID-19 and immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (ITP) who was hospitalized soon after receiving Evusheld with ITP flare that resolved with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Dr. Calabrese acknowledged limitations to the study, including few patients, lack of a comparator group, and the study period falling during the Omicron wave.
“Also, nine of the breakthrough cases received additional COVID-19 therapy (oral antiviral or monoclonal antibody), which falls within standard of care for this high-risk group but prevents ascribing effectiveness to individual components of the regimen,” she added.
“Evusheld is authorized for PrEP against COVID-19 in patients at high risk for severe COVID due to suboptimal vaccine responses. This includes patients receiving B-cell-depleting drugs like rituximab, and patients with inborn errors of humoral immunity,” Dr. Calabrese explained.
“It is well known that this group of patients is at very high risk for severe COVID and death, even when fully vaccinated, and it has become clear that more strategies are needed to protect this vulnerable group, including use of Evusheld as well as aggressive treatment if infected,” she added.
Evusheld not always easy to obtain
Although the medication has been available in the United States since January 2022, Dr. Calabrese said, patients may not receive it because of barriers including lack of both awareness and access.
Davey Smith, MD, professor of medicine and head of infectious diseases and global public health at the University of California San Diego, in La Jolla, said in an interview that he was not surprised by the results, but added that the study was conducted in too few patients to draw any strong conclusions or affect patient care.
“This small study that showed that breakthrough infections occurred but were generally mild, provides a small glimpse of real-world use of tixagevimab/cilgavimab as PrEP for immunocompromised persons,” said Dr. Smith, who was not involved in the study.
“In the setting of Omicron and vaccination, I would expect the same outcomes reported even without the treatment,” he added.
Dr. Smith recommends larger related randomized, controlled trials to provide clinicians with sufficient data to guide them in their patient care.
Graham Snyder, MD, associate professor in the division of infectious diseases at the University of Pittsburgh and medical director of infection prevention and hospital epidemiology at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, noted that the study “adds to a quickly growing literature on the real-world benefits of tixagevimab/cilgavimab to protect vulnerable individuals with weakened immune systems from the complications of COVID-19.
“This study provides a modest addition to our understanding of the role and benefit of Evusheld,” Dr. Snyder said in an interview. “By characterizing only patients who have received Evusheld without an untreated comparison group, we can’t draw any inference about the extent of benefit the agent provided to these patients.
“Substantial data already show that this agent is effective in preventing complications of COVID-19 infection in immunocompromised individuals,” added Dr. Snyder, who was not involved in the study.
“ ‘Immunocompromised’ represents a very diverse set of clinical conditions,” he said. “The research agenda should therefore focus on a more refined description of the effect in specific populations and a continued understanding of the effect of Evusheld in the context of updated vaccination strategies and changing virus ecology.”
Dr. Calabrese and her colleagues wrote that larger, controlled trials are underway.
FDA: Evusheld may not neutralize certain SARS-CoV-2 variants
“The biggest unanswered question is how Evusheld will hold up against new variants,” Dr. Calabrese said.
In an Oct. 3, 2022, update, the Food and Drug Administration released a statement about the risk of developing COVID-19 from SARS-CoV-2 variants that are not neutralized by Evusheld. The statement mentions an updated fact sheet that describes reduced protection from Evusheld against the Omicron subvariant BA.4.6, which accounted for nearly 13% of all new COVID-19 cases in the United States in the week ending Oct. 1.
There was no outside funding for the study. Dr. Smith reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Snyder said he is an unpaid adviser to an AstraZeneca observational study that’s assessing the real-world effectiveness of Evusheld.
Tixagevimab copackaged with cilgavimab (Evusheld) is a safe and effective preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in patients undergoing B-cell-depleting therapies who have poor immune response to COVID-19 vaccination and are at high risk for serious COVID-19 illness, a small, single-site study suggests.
Evusheld, the only COVID-19 PrEP option available, has Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of immunocompromised patients who may not respond sufficiently to COVID-19 vaccination and patients who’ve had a severe adverse reaction to COVID-19 vaccination.
“We report the largest real-world experience of Evusheld in this population, and our findings are encouraging,” lead study author Cassandra Calabrese, DO, rheumatologist and infectious disease specialist at Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“Of 412 patients who received Evusheld, 12 [2.9%] developed breakthrough COVID-19, with 11 having mild courses and 1 who required hospitalization but recovered,” she added.
“Our data suggest that Evusheld PrEP, in combination with aggressive outpatient treatment of COVID-19, is likely effective in lowering risk of severe COVID in this vulnerable group.
“Practitioners who care for patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases should triage high-risk patients for Evusheld as well as rapid diagnosis and aggressive outpatient therapy if infected,” Dr. Calabrese advised.
For the study, Dr. Calabrese and colleagues at Cleveland Clinic searched the health care system pharmacy records for patients with immune‐mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) or inborn errors of humoral immunity (IEI) who met the criteria to receive Evusheld. The researchers included patients on B-cell-depleting therapies or with humoral IEI who had received at least one dose of Evusheld and were later diagnosed with COVID-19, and they excluded those treated with B-cell-depleting therapies for cancer.
EVUSHELD was well tolerated
After extracting data on COVID-19 infection, vaccination status, and outcomes, they found that, between Jan. 18 and May 28, 2022, 412 patients with IMIDs or humoral IEI received Evusheld. No deaths occurred among these patients and, overall, they tolerated the medication well.
All 12 patients who experienced breakthrough COVID-19 infection were treated with B-cell-depleting therapies. Among the 12 patients:
- Six patients developed infection 13-84 (median 19) days after receiving 150 mg/150 mg tixagevimab/cilgavimab.
- Six patients developed infection 19-72 (median of 38.5) days after either a single dose of 300 mg/300 mg or a second dose of 150 mg/150 mg.
- Eleven patients had mild illness and recovered at home; one patient was hospitalized and treated with high-flow oxygen. All cases had been vaccinated against COVID-19 (five received two vaccinations, six received three, and one received four).
- One possible serious adverse event involved a patient with COVID-19 and immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (ITP) who was hospitalized soon after receiving Evusheld with ITP flare that resolved with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Dr. Calabrese acknowledged limitations to the study, including few patients, lack of a comparator group, and the study period falling during the Omicron wave.
“Also, nine of the breakthrough cases received additional COVID-19 therapy (oral antiviral or monoclonal antibody), which falls within standard of care for this high-risk group but prevents ascribing effectiveness to individual components of the regimen,” she added.
“Evusheld is authorized for PrEP against COVID-19 in patients at high risk for severe COVID due to suboptimal vaccine responses. This includes patients receiving B-cell-depleting drugs like rituximab, and patients with inborn errors of humoral immunity,” Dr. Calabrese explained.
“It is well known that this group of patients is at very high risk for severe COVID and death, even when fully vaccinated, and it has become clear that more strategies are needed to protect this vulnerable group, including use of Evusheld as well as aggressive treatment if infected,” she added.
Evusheld not always easy to obtain
Although the medication has been available in the United States since January 2022, Dr. Calabrese said, patients may not receive it because of barriers including lack of both awareness and access.
Davey Smith, MD, professor of medicine and head of infectious diseases and global public health at the University of California San Diego, in La Jolla, said in an interview that he was not surprised by the results, but added that the study was conducted in too few patients to draw any strong conclusions or affect patient care.
“This small study that showed that breakthrough infections occurred but were generally mild, provides a small glimpse of real-world use of tixagevimab/cilgavimab as PrEP for immunocompromised persons,” said Dr. Smith, who was not involved in the study.
“In the setting of Omicron and vaccination, I would expect the same outcomes reported even without the treatment,” he added.
Dr. Smith recommends larger related randomized, controlled trials to provide clinicians with sufficient data to guide them in their patient care.
Graham Snyder, MD, associate professor in the division of infectious diseases at the University of Pittsburgh and medical director of infection prevention and hospital epidemiology at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, noted that the study “adds to a quickly growing literature on the real-world benefits of tixagevimab/cilgavimab to protect vulnerable individuals with weakened immune systems from the complications of COVID-19.
“This study provides a modest addition to our understanding of the role and benefit of Evusheld,” Dr. Snyder said in an interview. “By characterizing only patients who have received Evusheld without an untreated comparison group, we can’t draw any inference about the extent of benefit the agent provided to these patients.
“Substantial data already show that this agent is effective in preventing complications of COVID-19 infection in immunocompromised individuals,” added Dr. Snyder, who was not involved in the study.
“ ‘Immunocompromised’ represents a very diverse set of clinical conditions,” he said. “The research agenda should therefore focus on a more refined description of the effect in specific populations and a continued understanding of the effect of Evusheld in the context of updated vaccination strategies and changing virus ecology.”
Dr. Calabrese and her colleagues wrote that larger, controlled trials are underway.
FDA: Evusheld may not neutralize certain SARS-CoV-2 variants
“The biggest unanswered question is how Evusheld will hold up against new variants,” Dr. Calabrese said.
In an Oct. 3, 2022, update, the Food and Drug Administration released a statement about the risk of developing COVID-19 from SARS-CoV-2 variants that are not neutralized by Evusheld. The statement mentions an updated fact sheet that describes reduced protection from Evusheld against the Omicron subvariant BA.4.6, which accounted for nearly 13% of all new COVID-19 cases in the United States in the week ending Oct. 1.
There was no outside funding for the study. Dr. Smith reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Snyder said he is an unpaid adviser to an AstraZeneca observational study that’s assessing the real-world effectiveness of Evusheld.
FROM RMD OPEN
Increased HIV infection linked to pandemic-related access to PrEP
Changes to HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) access during the COVID-19 pandemic were linked to higher rates of HIV infection among young sexual minority men and gender-diverse individuals who identified as Black and/or Hispanic/Latino, according to a national survey.
“The public health crisis surrounding COVID-19 had clear impact on PrEP access and risk of HIV acquisition overall,” said lead investigator Ethan Morgan, PhD, College of Nursing and the Infectious Disease Institute at Ohio State University, Columbus.
he said in an interview.
The online survey was administered in four waves during the first year and a half of the pandemic, starting in March 2020. Participants were recruited through mailing lists, national networks, community partners, and social media.
Among 796 baseline respondents, 300 agreed to three follow-up surveys administered between February and March 2021, between July and August 2021, and between October and November 2021.
Inclusion required participants to identify as Black and/or Hispanic/Latino, be between ages 18-29 years, be assigned male at birth, reside in the United States, and have reported anal intercourse with a man in the past 12 months. The researchers noted that given the limited uptake of and adherence to PrEP in the targeted population, they prioritized baseline respondents who reported either current PrEP use or use at least once in their lifetime.
The researchers used separate multivariable logistic regression models to assess the association between odds of testing positive for HIV and other STIs across the four online study visits and pandemic-related changes to PrEP access, and pandemic-related changes to sexual activity.
Changes in PrEP access were reported by a total of 109 (13.8%) of baseline respondents, and HIV seroconversion was reported in 25 of 292 respondents (8.6%) who reported their HIV and other STI status at follow-up. STI positivity was reported 25.6% of the baseline cohort (n = 204).
Compared with respondents who reported no changes to PrEP access, those who did report change to access were significantly more likely to report HIV seroconversion (adjusted odds ratio, 2.80; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-7.68). However, Dr. Morgan emphasized that the study question did not ask how PrEP had changed, only if it had.
“While we presume this survey question corresponds to a diminished access to PrEP medication during the COVID-19 pandemic, the question was: ‘Has your access to PrEP been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic?’ So, it is unfortunately unclear whether access was diminished or improved,” he explained. STI positivity was not associated with PrEP access.
The survey also asked respondents how much the pandemic had impacted their sexual activity (measured on a Likert scale of not at all, a little, moderately, quite a bit, and extremely). Respondents reporting greater impact on their sexual activity were more likely to report an STI (aOR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.10-1.40) during the study period.
In addition, though participants reported a mean of 2.8 sexual partners in the past 3 months, those reporting a greater number were more likely to report an STI (aOR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.21-1.38).
The researchers suggested that expansion of telehealth and mail-order prescriptions as well as structural-level interventions addressing pandemic-related unemployment and loss of health insurance could have helped preserve access to PrEP.
Commenting on the study, Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, who was not involved in the research, noted that self-reported data can be subject to bias. “However, reduction in services for other medical care has been reported frequently throughout COVID and so this finding of reduced PrEP access, and subsequent HIV infection, is completely in line with the other studies,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Gandhi, who is director of the University of California, San Francisco Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV/AIDS Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital, added: “We knew early on in the COVID-19 pandemic that access to and uptake of PrEP was decreased based on data from Boston’s Fenway Institute.”
The Boston data, reported July 2020 at the virtual International AIDS Conference, prompted “a real attempt” by clinicians to increase PrEP access and uptake – raising community awareness, dispensing PrEP through mobile units, and changing prescribing patterns, Dr. Gandhi said. “We usually see patients every 3 months for PrEP but with HIV self-testing, we can extend that interval to every 6 months, and we did so in many centers during COVID.”
The study was funded by National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Morgan and Dr. Gandhi reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Changes to HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) access during the COVID-19 pandemic were linked to higher rates of HIV infection among young sexual minority men and gender-diverse individuals who identified as Black and/or Hispanic/Latino, according to a national survey.
“The public health crisis surrounding COVID-19 had clear impact on PrEP access and risk of HIV acquisition overall,” said lead investigator Ethan Morgan, PhD, College of Nursing and the Infectious Disease Institute at Ohio State University, Columbus.
he said in an interview.
The online survey was administered in four waves during the first year and a half of the pandemic, starting in March 2020. Participants were recruited through mailing lists, national networks, community partners, and social media.
Among 796 baseline respondents, 300 agreed to three follow-up surveys administered between February and March 2021, between July and August 2021, and between October and November 2021.
Inclusion required participants to identify as Black and/or Hispanic/Latino, be between ages 18-29 years, be assigned male at birth, reside in the United States, and have reported anal intercourse with a man in the past 12 months. The researchers noted that given the limited uptake of and adherence to PrEP in the targeted population, they prioritized baseline respondents who reported either current PrEP use or use at least once in their lifetime.
The researchers used separate multivariable logistic regression models to assess the association between odds of testing positive for HIV and other STIs across the four online study visits and pandemic-related changes to PrEP access, and pandemic-related changes to sexual activity.
Changes in PrEP access were reported by a total of 109 (13.8%) of baseline respondents, and HIV seroconversion was reported in 25 of 292 respondents (8.6%) who reported their HIV and other STI status at follow-up. STI positivity was reported 25.6% of the baseline cohort (n = 204).
Compared with respondents who reported no changes to PrEP access, those who did report change to access were significantly more likely to report HIV seroconversion (adjusted odds ratio, 2.80; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-7.68). However, Dr. Morgan emphasized that the study question did not ask how PrEP had changed, only if it had.
“While we presume this survey question corresponds to a diminished access to PrEP medication during the COVID-19 pandemic, the question was: ‘Has your access to PrEP been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic?’ So, it is unfortunately unclear whether access was diminished or improved,” he explained. STI positivity was not associated with PrEP access.
The survey also asked respondents how much the pandemic had impacted their sexual activity (measured on a Likert scale of not at all, a little, moderately, quite a bit, and extremely). Respondents reporting greater impact on their sexual activity were more likely to report an STI (aOR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.10-1.40) during the study period.
In addition, though participants reported a mean of 2.8 sexual partners in the past 3 months, those reporting a greater number were more likely to report an STI (aOR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.21-1.38).
The researchers suggested that expansion of telehealth and mail-order prescriptions as well as structural-level interventions addressing pandemic-related unemployment and loss of health insurance could have helped preserve access to PrEP.
Commenting on the study, Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, who was not involved in the research, noted that self-reported data can be subject to bias. “However, reduction in services for other medical care has been reported frequently throughout COVID and so this finding of reduced PrEP access, and subsequent HIV infection, is completely in line with the other studies,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Gandhi, who is director of the University of California, San Francisco Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV/AIDS Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital, added: “We knew early on in the COVID-19 pandemic that access to and uptake of PrEP was decreased based on data from Boston’s Fenway Institute.”
The Boston data, reported July 2020 at the virtual International AIDS Conference, prompted “a real attempt” by clinicians to increase PrEP access and uptake – raising community awareness, dispensing PrEP through mobile units, and changing prescribing patterns, Dr. Gandhi said. “We usually see patients every 3 months for PrEP but with HIV self-testing, we can extend that interval to every 6 months, and we did so in many centers during COVID.”
The study was funded by National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Morgan and Dr. Gandhi reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Changes to HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) access during the COVID-19 pandemic were linked to higher rates of HIV infection among young sexual minority men and gender-diverse individuals who identified as Black and/or Hispanic/Latino, according to a national survey.
“The public health crisis surrounding COVID-19 had clear impact on PrEP access and risk of HIV acquisition overall,” said lead investigator Ethan Morgan, PhD, College of Nursing and the Infectious Disease Institute at Ohio State University, Columbus.
he said in an interview.
The online survey was administered in four waves during the first year and a half of the pandemic, starting in March 2020. Participants were recruited through mailing lists, national networks, community partners, and social media.
Among 796 baseline respondents, 300 agreed to three follow-up surveys administered between February and March 2021, between July and August 2021, and between October and November 2021.
Inclusion required participants to identify as Black and/or Hispanic/Latino, be between ages 18-29 years, be assigned male at birth, reside in the United States, and have reported anal intercourse with a man in the past 12 months. The researchers noted that given the limited uptake of and adherence to PrEP in the targeted population, they prioritized baseline respondents who reported either current PrEP use or use at least once in their lifetime.
The researchers used separate multivariable logistic regression models to assess the association between odds of testing positive for HIV and other STIs across the four online study visits and pandemic-related changes to PrEP access, and pandemic-related changes to sexual activity.
Changes in PrEP access were reported by a total of 109 (13.8%) of baseline respondents, and HIV seroconversion was reported in 25 of 292 respondents (8.6%) who reported their HIV and other STI status at follow-up. STI positivity was reported 25.6% of the baseline cohort (n = 204).
Compared with respondents who reported no changes to PrEP access, those who did report change to access were significantly more likely to report HIV seroconversion (adjusted odds ratio, 2.80; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-7.68). However, Dr. Morgan emphasized that the study question did not ask how PrEP had changed, only if it had.
“While we presume this survey question corresponds to a diminished access to PrEP medication during the COVID-19 pandemic, the question was: ‘Has your access to PrEP been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic?’ So, it is unfortunately unclear whether access was diminished or improved,” he explained. STI positivity was not associated with PrEP access.
The survey also asked respondents how much the pandemic had impacted their sexual activity (measured on a Likert scale of not at all, a little, moderately, quite a bit, and extremely). Respondents reporting greater impact on their sexual activity were more likely to report an STI (aOR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.10-1.40) during the study period.
In addition, though participants reported a mean of 2.8 sexual partners in the past 3 months, those reporting a greater number were more likely to report an STI (aOR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.21-1.38).
The researchers suggested that expansion of telehealth and mail-order prescriptions as well as structural-level interventions addressing pandemic-related unemployment and loss of health insurance could have helped preserve access to PrEP.
Commenting on the study, Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, who was not involved in the research, noted that self-reported data can be subject to bias. “However, reduction in services for other medical care has been reported frequently throughout COVID and so this finding of reduced PrEP access, and subsequent HIV infection, is completely in line with the other studies,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Gandhi, who is director of the University of California, San Francisco Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV/AIDS Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital, added: “We knew early on in the COVID-19 pandemic that access to and uptake of PrEP was decreased based on data from Boston’s Fenway Institute.”
The Boston data, reported July 2020 at the virtual International AIDS Conference, prompted “a real attempt” by clinicians to increase PrEP access and uptake – raising community awareness, dispensing PrEP through mobile units, and changing prescribing patterns, Dr. Gandhi said. “We usually see patients every 3 months for PrEP but with HIV self-testing, we can extend that interval to every 6 months, and we did so in many centers during COVID.”
The study was funded by National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Morgan and Dr. Gandhi reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ACQUIRED IMMUNE DEFICIENCY SYNDROME
HPV infection in pregnancy higher among women living with HIV
Pregnant women living with HIV were more likely to be infected with human papillomavirus (HPV) than were pregnant women without HIV, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis reports.
“High prevalence of HPV was documented in pregnant WLWH [women living with HIV], exceeding the prevalence among pregnant women without HIV,” Elisabeth McClymont, PhD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues wrote in the Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Their results contribute to two major global public health goals: eliminating cervical cancer and improving the health outcomes of newborn babies.
“Our findings of a high prevalence of HPV infection during pregnancy in WLWH, particularly of highly oncogenic HPV types, emphasize the need for HPV screening and vaccination in WLWH,” they added. “WLWH are a key population for both HPV and adverse pregnancy outcome prevention.”
Emerging evidence suggests that being infected with HPV during pregnancy may be linked with adverse pregnancy outcomes. Although women living with HIV have higher rates of HPV infection and adverse pregnancy outcomes, no prior reviews have reported on HPV infection during pregnancy in women living with HIV, the authors explained.
A study of studies
Dr. McClymont and colleagues searched the standard medical research databases through Jan. 18, 2022, for pooled and type-specific HPV prevalence and associated pregnancy outcomes among pregnant women living with HIV, including available within-study comparators of women without HIV.
They performed subgroup analyses according to polymerase chain reaction primers used to detect HPV type and according to region (Africa, Asia and Europe, the Americas).
Their analysis of 10 studies describing HPV prevalence in 1,594 pregnant women living with HIV found:
- The pooled HPV prevalence in pregnant women living with HIV was 75.5% (95% confidence interval, 50.2%-90.4%) but ranged from 23% to 98% between individual studies.
- Among the five studies that also analyzed HPV prevalence in pregnant women without HIV, the pooled prevalence was 48.1% (95% CI, 27.1%-69.8%).
- Pregnant women living with HIV had 54% higher odds of being HPV positive than did pregnant women without HIV.
- HPV-16 was the most common HPV type detected in pregnant women living with HIV, followed by HPV-52; other common types included HPV-18 and HPV-58.
- One study provided data on pregnancy outcomes in women living with HIV but did not correlate pregnancy outcomes with HPV status.
Experts urge HPV, cervical cancer screening for women living with HIV
“HPV is a common virus that can lead to cervical dysplasia and cervical cancer,” cautioned Clara Paik, MD, professor and clinic medical director of obstetrics and gynecology at UC Davis Health, Sacramento.
“HPV can also be associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, including preterm birth and premature membrane rupture,” she said in an interview. “It is important to know the prevalence of HPV infection in pregnant women living with HIV in order to assess if this specific population is at higher risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes.”
Dr. Paik, who was not involved in the study, would like these results to lead to better HPV screening in pregnant women living with HIV.
“The study’s strengths include the large number of women studied when all the research studies were pooled,” she said. “A weakness is that, if individual studies had limitations, a systematic review based on weaker studies may not necessarily yield results that are conclusive.”
Linda Eckert, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle, said that the study highlights the importance of including cervical cancer screening in antepartum care, especially in areas of high HIV prevalence.
“Women living with HIV have a sixfold increased rate of developing cervical cancer compared to women without HIV,” she added, citing a 2020 analysis in The Lancet Global Health that estimated global cervical cancer risk among women living with HIV.
“This [new] study allows us to definitively say that pregnant women living with HIV have higher rates of HPV than do pregnant women without HIV,” noted Dr. Eckert, who was not involved in either study. “And HPV type 16 – the HPV type most associated with developing cervical cancer – was the most common high-risk HPV type found in these patients.”
HPV vaccination recommended
The World Health Organization’s call to eliminate cervical cancer has generated interest and funding for cervical cancer screening of women with HIV, Dr. Eckert said. “WHO recommends that women living with HIV who are 25 years of age and above be screened for cervical cancer annually.”
The authors urged that women living with HIV not only be screened for HPV but that they also be vaccinated against HPV.
“We know that HPV vaccination is unprecedented in its ability to prevent HPV infections when it is received prior to acquiring HPV infection,” Dr. Eckert said, “but currently data showing that HPV vaccination would treat HPV16 in pregnant women already infected with HPV16 are lacking.
“This study points to the need for a trial to investigate HPV vaccination in pregnant women living with HIV who have the high-risk HPV types,” she suggested.
Dr. Eckert contributed to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ 2020 Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Committee Opinion. One study coauthor reported financial relationships with Merck. Dr. McClymont, the other coauthors, as well as Dr. Paik and Dr. Eckert reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant women living with HIV were more likely to be infected with human papillomavirus (HPV) than were pregnant women without HIV, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis reports.
“High prevalence of HPV was documented in pregnant WLWH [women living with HIV], exceeding the prevalence among pregnant women without HIV,” Elisabeth McClymont, PhD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues wrote in the Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Their results contribute to two major global public health goals: eliminating cervical cancer and improving the health outcomes of newborn babies.
“Our findings of a high prevalence of HPV infection during pregnancy in WLWH, particularly of highly oncogenic HPV types, emphasize the need for HPV screening and vaccination in WLWH,” they added. “WLWH are a key population for both HPV and adverse pregnancy outcome prevention.”
Emerging evidence suggests that being infected with HPV during pregnancy may be linked with adverse pregnancy outcomes. Although women living with HIV have higher rates of HPV infection and adverse pregnancy outcomes, no prior reviews have reported on HPV infection during pregnancy in women living with HIV, the authors explained.
A study of studies
Dr. McClymont and colleagues searched the standard medical research databases through Jan. 18, 2022, for pooled and type-specific HPV prevalence and associated pregnancy outcomes among pregnant women living with HIV, including available within-study comparators of women without HIV.
They performed subgroup analyses according to polymerase chain reaction primers used to detect HPV type and according to region (Africa, Asia and Europe, the Americas).
Their analysis of 10 studies describing HPV prevalence in 1,594 pregnant women living with HIV found:
- The pooled HPV prevalence in pregnant women living with HIV was 75.5% (95% confidence interval, 50.2%-90.4%) but ranged from 23% to 98% between individual studies.
- Among the five studies that also analyzed HPV prevalence in pregnant women without HIV, the pooled prevalence was 48.1% (95% CI, 27.1%-69.8%).
- Pregnant women living with HIV had 54% higher odds of being HPV positive than did pregnant women without HIV.
- HPV-16 was the most common HPV type detected in pregnant women living with HIV, followed by HPV-52; other common types included HPV-18 and HPV-58.
- One study provided data on pregnancy outcomes in women living with HIV but did not correlate pregnancy outcomes with HPV status.
Experts urge HPV, cervical cancer screening for women living with HIV
“HPV is a common virus that can lead to cervical dysplasia and cervical cancer,” cautioned Clara Paik, MD, professor and clinic medical director of obstetrics and gynecology at UC Davis Health, Sacramento.
“HPV can also be associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, including preterm birth and premature membrane rupture,” she said in an interview. “It is important to know the prevalence of HPV infection in pregnant women living with HIV in order to assess if this specific population is at higher risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes.”
Dr. Paik, who was not involved in the study, would like these results to lead to better HPV screening in pregnant women living with HIV.
“The study’s strengths include the large number of women studied when all the research studies were pooled,” she said. “A weakness is that, if individual studies had limitations, a systematic review based on weaker studies may not necessarily yield results that are conclusive.”
Linda Eckert, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle, said that the study highlights the importance of including cervical cancer screening in antepartum care, especially in areas of high HIV prevalence.
“Women living with HIV have a sixfold increased rate of developing cervical cancer compared to women without HIV,” she added, citing a 2020 analysis in The Lancet Global Health that estimated global cervical cancer risk among women living with HIV.
“This [new] study allows us to definitively say that pregnant women living with HIV have higher rates of HPV than do pregnant women without HIV,” noted Dr. Eckert, who was not involved in either study. “And HPV type 16 – the HPV type most associated with developing cervical cancer – was the most common high-risk HPV type found in these patients.”
HPV vaccination recommended
The World Health Organization’s call to eliminate cervical cancer has generated interest and funding for cervical cancer screening of women with HIV, Dr. Eckert said. “WHO recommends that women living with HIV who are 25 years of age and above be screened for cervical cancer annually.”
The authors urged that women living with HIV not only be screened for HPV but that they also be vaccinated against HPV.
“We know that HPV vaccination is unprecedented in its ability to prevent HPV infections when it is received prior to acquiring HPV infection,” Dr. Eckert said, “but currently data showing that HPV vaccination would treat HPV16 in pregnant women already infected with HPV16 are lacking.
“This study points to the need for a trial to investigate HPV vaccination in pregnant women living with HIV who have the high-risk HPV types,” she suggested.
Dr. Eckert contributed to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ 2020 Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Committee Opinion. One study coauthor reported financial relationships with Merck. Dr. McClymont, the other coauthors, as well as Dr. Paik and Dr. Eckert reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant women living with HIV were more likely to be infected with human papillomavirus (HPV) than were pregnant women without HIV, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis reports.
“High prevalence of HPV was documented in pregnant WLWH [women living with HIV], exceeding the prevalence among pregnant women without HIV,” Elisabeth McClymont, PhD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues wrote in the Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Their results contribute to two major global public health goals: eliminating cervical cancer and improving the health outcomes of newborn babies.
“Our findings of a high prevalence of HPV infection during pregnancy in WLWH, particularly of highly oncogenic HPV types, emphasize the need for HPV screening and vaccination in WLWH,” they added. “WLWH are a key population for both HPV and adverse pregnancy outcome prevention.”
Emerging evidence suggests that being infected with HPV during pregnancy may be linked with adverse pregnancy outcomes. Although women living with HIV have higher rates of HPV infection and adverse pregnancy outcomes, no prior reviews have reported on HPV infection during pregnancy in women living with HIV, the authors explained.
A study of studies
Dr. McClymont and colleagues searched the standard medical research databases through Jan. 18, 2022, for pooled and type-specific HPV prevalence and associated pregnancy outcomes among pregnant women living with HIV, including available within-study comparators of women without HIV.
They performed subgroup analyses according to polymerase chain reaction primers used to detect HPV type and according to region (Africa, Asia and Europe, the Americas).
Their analysis of 10 studies describing HPV prevalence in 1,594 pregnant women living with HIV found:
- The pooled HPV prevalence in pregnant women living with HIV was 75.5% (95% confidence interval, 50.2%-90.4%) but ranged from 23% to 98% between individual studies.
- Among the five studies that also analyzed HPV prevalence in pregnant women without HIV, the pooled prevalence was 48.1% (95% CI, 27.1%-69.8%).
- Pregnant women living with HIV had 54% higher odds of being HPV positive than did pregnant women without HIV.
- HPV-16 was the most common HPV type detected in pregnant women living with HIV, followed by HPV-52; other common types included HPV-18 and HPV-58.
- One study provided data on pregnancy outcomes in women living with HIV but did not correlate pregnancy outcomes with HPV status.
Experts urge HPV, cervical cancer screening for women living with HIV
“HPV is a common virus that can lead to cervical dysplasia and cervical cancer,” cautioned Clara Paik, MD, professor and clinic medical director of obstetrics and gynecology at UC Davis Health, Sacramento.
“HPV can also be associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, including preterm birth and premature membrane rupture,” she said in an interview. “It is important to know the prevalence of HPV infection in pregnant women living with HIV in order to assess if this specific population is at higher risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes.”
Dr. Paik, who was not involved in the study, would like these results to lead to better HPV screening in pregnant women living with HIV.
“The study’s strengths include the large number of women studied when all the research studies were pooled,” she said. “A weakness is that, if individual studies had limitations, a systematic review based on weaker studies may not necessarily yield results that are conclusive.”
Linda Eckert, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle, said that the study highlights the importance of including cervical cancer screening in antepartum care, especially in areas of high HIV prevalence.
“Women living with HIV have a sixfold increased rate of developing cervical cancer compared to women without HIV,” she added, citing a 2020 analysis in The Lancet Global Health that estimated global cervical cancer risk among women living with HIV.
“This [new] study allows us to definitively say that pregnant women living with HIV have higher rates of HPV than do pregnant women without HIV,” noted Dr. Eckert, who was not involved in either study. “And HPV type 16 – the HPV type most associated with developing cervical cancer – was the most common high-risk HPV type found in these patients.”
HPV vaccination recommended
The World Health Organization’s call to eliminate cervical cancer has generated interest and funding for cervical cancer screening of women with HIV, Dr. Eckert said. “WHO recommends that women living with HIV who are 25 years of age and above be screened for cervical cancer annually.”
The authors urged that women living with HIV not only be screened for HPV but that they also be vaccinated against HPV.
“We know that HPV vaccination is unprecedented in its ability to prevent HPV infections when it is received prior to acquiring HPV infection,” Dr. Eckert said, “but currently data showing that HPV vaccination would treat HPV16 in pregnant women already infected with HPV16 are lacking.
“This study points to the need for a trial to investigate HPV vaccination in pregnant women living with HIV who have the high-risk HPV types,” she suggested.
Dr. Eckert contributed to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ 2020 Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Committee Opinion. One study coauthor reported financial relationships with Merck. Dr. McClymont, the other coauthors, as well as Dr. Paik and Dr. Eckert reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ACQUIRED IMMUNE DEFICIENCY SYNDROME.
Is another COVID-19 booster really needed?
Many countries around the globe are starting to roll out another booster of the COVID-19 vaccine but, with public interest waning and a sense of normalcy firmly installed in our minds, this may prove an ill-fated effort, unless authorities can provide a coherent answer to the question “Is another jab really needed?” (The short answer is a firm “yes,” of course.)
In what we could call the “chronic” phase of the pandemic, most countries have now settled for a certain number of daily cases and a (relatively low) number of complications and deaths. It’s the vaccines that have afforded us this peace of mind, lest we forget. But they are different to other vaccines that we are more familiar with, such as the MMR that we get as kids and then forget about for the rest of our lives. As good as the different COVID-19 vaccines are, they never came with the promise of generating lifelong antibodies. We knew early on that the immunity they provide slowly wanes with time. That doesn’t mean that those who have their vaccination records up to date (which included a booster probably earlier in 2022) are suddenly exposed. Data suggest that although people several months past their last booster would now be more prone to getting reinfected, the protection against severe disease still hangs around 85%. In other words, their chances of ending up in the hospital are low.
Why worry, then, about further boosting the immune system? The same studies show that an additional jab would increase this percentage up to 99%. Is this roughly 10% improvement really worth another worldwide vaccination campaign? Well, this is a numbers game, after all. The current form of the virus is extremely infectious, and the Northern Hemisphere is heading toward the cold months of the year, which we have seen in past years increases COVID-19 contagions, as you would expect from any airborne virus. Thus, it’s easy to expect a new peak in the number of cases, especially considering that we are not going to apply any of the usual restrictions to prevent this. In these conditions, extending the safety net to a further 10% of the population would substantially reduce the total number of victims. It seems like a good investment of resources.
We can be more surgical about it and direct this new vaccination campaign to the population most likely to end up in the hospital. People with concomitant pathologies are at the top of the list, but it’s also an age issue. On the basis of different studies of the most common ages of admission, the cutoff point for the booster varies from country to country, with the lowest being 50 and in other cases hovering around 65 years of age. Given the safety of these vaccines, if we can afford it, the wider we cast the net, the better, but at least we should make every effort to fully vaccinate the higher age brackets.
The final question is which vaccine to give. There are confounding studies about the importance of switching to Omicron-specific jabs, which are finally available. Although this seems like a good idea, since Omicron infections elicit a more effective range of antibodies and new variants seem to better escape our defenses, recent studies suggest that there actually may not be so much difference with the old formula.
The conclusion? This regimen of yearly boosters for some may be the scenario for the upcoming years, similar to what we already do for the flu, so we should get used to it.
Dr. Macip is associate professor, department of molecular and cellular biology, University of Leicester (England). He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many countries around the globe are starting to roll out another booster of the COVID-19 vaccine but, with public interest waning and a sense of normalcy firmly installed in our minds, this may prove an ill-fated effort, unless authorities can provide a coherent answer to the question “Is another jab really needed?” (The short answer is a firm “yes,” of course.)
In what we could call the “chronic” phase of the pandemic, most countries have now settled for a certain number of daily cases and a (relatively low) number of complications and deaths. It’s the vaccines that have afforded us this peace of mind, lest we forget. But they are different to other vaccines that we are more familiar with, such as the MMR that we get as kids and then forget about for the rest of our lives. As good as the different COVID-19 vaccines are, they never came with the promise of generating lifelong antibodies. We knew early on that the immunity they provide slowly wanes with time. That doesn’t mean that those who have their vaccination records up to date (which included a booster probably earlier in 2022) are suddenly exposed. Data suggest that although people several months past their last booster would now be more prone to getting reinfected, the protection against severe disease still hangs around 85%. In other words, their chances of ending up in the hospital are low.
Why worry, then, about further boosting the immune system? The same studies show that an additional jab would increase this percentage up to 99%. Is this roughly 10% improvement really worth another worldwide vaccination campaign? Well, this is a numbers game, after all. The current form of the virus is extremely infectious, and the Northern Hemisphere is heading toward the cold months of the year, which we have seen in past years increases COVID-19 contagions, as you would expect from any airborne virus. Thus, it’s easy to expect a new peak in the number of cases, especially considering that we are not going to apply any of the usual restrictions to prevent this. In these conditions, extending the safety net to a further 10% of the population would substantially reduce the total number of victims. It seems like a good investment of resources.
We can be more surgical about it and direct this new vaccination campaign to the population most likely to end up in the hospital. People with concomitant pathologies are at the top of the list, but it’s also an age issue. On the basis of different studies of the most common ages of admission, the cutoff point for the booster varies from country to country, with the lowest being 50 and in other cases hovering around 65 years of age. Given the safety of these vaccines, if we can afford it, the wider we cast the net, the better, but at least we should make every effort to fully vaccinate the higher age brackets.
The final question is which vaccine to give. There are confounding studies about the importance of switching to Omicron-specific jabs, which are finally available. Although this seems like a good idea, since Omicron infections elicit a more effective range of antibodies and new variants seem to better escape our defenses, recent studies suggest that there actually may not be so much difference with the old formula.
The conclusion? This regimen of yearly boosters for some may be the scenario for the upcoming years, similar to what we already do for the flu, so we should get used to it.
Dr. Macip is associate professor, department of molecular and cellular biology, University of Leicester (England). He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many countries around the globe are starting to roll out another booster of the COVID-19 vaccine but, with public interest waning and a sense of normalcy firmly installed in our minds, this may prove an ill-fated effort, unless authorities can provide a coherent answer to the question “Is another jab really needed?” (The short answer is a firm “yes,” of course.)
In what we could call the “chronic” phase of the pandemic, most countries have now settled for a certain number of daily cases and a (relatively low) number of complications and deaths. It’s the vaccines that have afforded us this peace of mind, lest we forget. But they are different to other vaccines that we are more familiar with, such as the MMR that we get as kids and then forget about for the rest of our lives. As good as the different COVID-19 vaccines are, they never came with the promise of generating lifelong antibodies. We knew early on that the immunity they provide slowly wanes with time. That doesn’t mean that those who have their vaccination records up to date (which included a booster probably earlier in 2022) are suddenly exposed. Data suggest that although people several months past their last booster would now be more prone to getting reinfected, the protection against severe disease still hangs around 85%. In other words, their chances of ending up in the hospital are low.
Why worry, then, about further boosting the immune system? The same studies show that an additional jab would increase this percentage up to 99%. Is this roughly 10% improvement really worth another worldwide vaccination campaign? Well, this is a numbers game, after all. The current form of the virus is extremely infectious, and the Northern Hemisphere is heading toward the cold months of the year, which we have seen in past years increases COVID-19 contagions, as you would expect from any airborne virus. Thus, it’s easy to expect a new peak in the number of cases, especially considering that we are not going to apply any of the usual restrictions to prevent this. In these conditions, extending the safety net to a further 10% of the population would substantially reduce the total number of victims. It seems like a good investment of resources.
We can be more surgical about it and direct this new vaccination campaign to the population most likely to end up in the hospital. People with concomitant pathologies are at the top of the list, but it’s also an age issue. On the basis of different studies of the most common ages of admission, the cutoff point for the booster varies from country to country, with the lowest being 50 and in other cases hovering around 65 years of age. Given the safety of these vaccines, if we can afford it, the wider we cast the net, the better, but at least we should make every effort to fully vaccinate the higher age brackets.
The final question is which vaccine to give. There are confounding studies about the importance of switching to Omicron-specific jabs, which are finally available. Although this seems like a good idea, since Omicron infections elicit a more effective range of antibodies and new variants seem to better escape our defenses, recent studies suggest that there actually may not be so much difference with the old formula.
The conclusion? This regimen of yearly boosters for some may be the scenario for the upcoming years, similar to what we already do for the flu, so we should get used to it.
Dr. Macip is associate professor, department of molecular and cellular biology, University of Leicester (England). He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Death of son reinforces flu vaccination message
“It was what the CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] would call classic influenza-like illness,” Dr. Teichman said. “It was too late to start antivirals, so I gave him advice on symptomatic treatment. We texted the next day, and I was glad to hear that his fever was trending down and that he was feeling a little bit better.”
Two days later, his son called again.
“He said he was having trouble breathing, and over the phone I could hear him hyperventilating.” The retired pediatrician and health care executive told his son to seek medical care.
“Then I got the call that no parent wants to get.”
Brent’s cousin Jake called saying he couldn’t wake Brent up.
“I called Jake back a few minutes later and asked him to hold up the phone,” Dr. Teichman said. “I listened to EMS working on my son, calling for round after round of many medications. He was in arrest and they couldn’t revive him.”
“To this day when I close my eyes at night, I still hear the beeping of those monitors.”
Brent had no health conditions to put him at higher risk for complications of the flu. “Brent was a wonderful son, brother, uncle, and friend. He had a passion for everything he did, and that included his chosen calling of the culinary arts but also included University of Kentucky sports,” Dr. Teichman said.
Brent planned to get a flu vaccine but had not done it yet. “In his obituary, we requested that, in lieu of flowers or donations, people go get their flu shot,” Dr. Teichman said.
“I’m here today to put a face on influenza,” Dr. Teichman said at a news briefing Oct. 4 on preventing the flu and pneumococcal disease, sponsored by the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases.
New survey numbers ‘alarming’
The NFID commissioned a national survey of more than 1,000 U.S. adults to better understand their knowledge and attitudes about the flu, pneumococcal disease, vaccines, and the impact of COVID-19.
“We were alarmed to learn that only 49% of U.S. adults plan to get their flu vaccine this season,” said Patricia A. “Patsy” Stinchfield, a registered nurse, NFID president, and moderator of the news briefing. “That is not good enough.”
In addition, 22% of people at higher risk for flu-related complications do not plan to get vaccinated this season. “That’s a dangerous risk to take,” Ms. Stinchfield said.
An encouraging finding, she said, is that 69% of adults surveyed recognize that an annual flu vaccination is the best way to prevent flu-related hospitalizations and death.
“So, most people know what to do. We just need to do it,” she said.
The top reason for not getting a flu shot in 2022 mentioned by 41% of people surveyed, is they do not think vaccines work very well. Another 39% are concerned about vaccine side effects, and 28% skip the vaccine because they “never get the flu.”
The experts on the panel emphasized the recommendation that all Americans 6 months or older get the flu vaccine, preferably by the end of October. Vaccination is especially important for those at higher risk of complications from the flu, including children under 5, pregnant women, people with one or more health conditions, the immunocompromised, and Americans 65 years and older.
Ms. Stinchfield acknowledged that the effectiveness of the flu vaccine varies season to season, but even if the vaccine does not completely match the circulating viruses, it can help prevent serious outcomes like hospitalization and death. One of the serious potential complications is pneumonia or “pneumococcal disease.”
“Our survey shows that only 29% of those at risk have been advised to receive a pneumococcal vaccine,” Ms. Stinchfield said. “The good news is that, among those who were advised to get the vaccine, 74% did receive their pneumococcal vaccine,” she said. “This underscores a key point to you, my fellow clinicians: As health professionals, our recommendations matter.”
Higher doses for 65+ Americans
The CDC updated recommendations this flu season for adults 65 and older to receive one of three preferentially recommended flu vaccines, said CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD. The CDC is recommending higher-dose, stronger vaccines for older Americans “based on a review of the available studies, which suggested that in this age group, these vaccines are potentially more effective than standard-dose ... vaccines.”
During most seasons, people 65 and older bear the greatest burden of severe flu disease, accounting for most flu-related hospitalizations and deaths.
“They are the largest vulnerable segment of our society,” Dr. Walensky said.
What will this flu season be like?
Health officials in the flu vaccine business also tend to be in the flu season prediction business. That includes Dr. Walensky.
“While we will never exactly know what each flu season will hold, we do know that every year, the best way you can protect yourself and those around you is to get your annual flu vaccine,” she said while taking part remotely in the briefing.
How severe will the flu season be in 2022-23? William Schaffner, MD, said he gets that question a lot. “Don’t think about that. Just focus on the fact that flu will be with us each year.
“We were a little bit spoiled. We’ve had two mild influenza seasons,” said Dr. Schaffner, medical director of NFID and a professor of infectious diseases and preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “I think with all the interest in COVID, people have rather forgotten about influenza. I’ve had to remind them that this is yet another serious winter respiratory virus.
“As I like to say, flu is fickle. It’s difficult to predict how serious this next outbreak of influenza this season is going to be. We could look at what happened in the Southern Hemisphere,” he said.
For example, Australia had the worst influenza season in the past 5 years, Schaffner said. “If you want a hint of what might happen here and you want yet another reason to be vaccinated, there it is.”
What we do know, Dr. Walensky said, is that the timing and severity of the past two flu seasons in the U.S. have been different than typical flu seasons. “And this is likely due to the COVID mitigation measures and other changes in circulating respiratory viruses.” Also, although last flu season was “relatively mild,” there was more flu activity than in the prior, 2020-21 season.
Also, Dr. Walensky said, last season’s flu cases began to increase in November and remained elevated until mid-June, “making it the latest season on record.”
The official cause of Brent Teichman’s death was multilobar pneumonia, cause undetermined. “But after 30-plus years as a pediatrician ... I know influenza when I see it,” Dr. Teichman said.
“There’s a hole in our hearts that will never heal. Loss of a child is devastating,” he said. The flu “can take the life of a healthy young person, as it did to my son.
“And for all those listening to my story who are vaccine hesitant, do it for those who love you. So that they won’t walk the path that we and many other families in this country have walked.”
To prove their point, Dr. Teichman and Ms. Stinchfield raised their sleeves and received flu shots during the news briefing.
“This one is for Brent,” Dr. Teichman said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“It was what the CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] would call classic influenza-like illness,” Dr. Teichman said. “It was too late to start antivirals, so I gave him advice on symptomatic treatment. We texted the next day, and I was glad to hear that his fever was trending down and that he was feeling a little bit better.”
Two days later, his son called again.
“He said he was having trouble breathing, and over the phone I could hear him hyperventilating.” The retired pediatrician and health care executive told his son to seek medical care.
“Then I got the call that no parent wants to get.”
Brent’s cousin Jake called saying he couldn’t wake Brent up.
“I called Jake back a few minutes later and asked him to hold up the phone,” Dr. Teichman said. “I listened to EMS working on my son, calling for round after round of many medications. He was in arrest and they couldn’t revive him.”
“To this day when I close my eyes at night, I still hear the beeping of those monitors.”
Brent had no health conditions to put him at higher risk for complications of the flu. “Brent was a wonderful son, brother, uncle, and friend. He had a passion for everything he did, and that included his chosen calling of the culinary arts but also included University of Kentucky sports,” Dr. Teichman said.
Brent planned to get a flu vaccine but had not done it yet. “In his obituary, we requested that, in lieu of flowers or donations, people go get their flu shot,” Dr. Teichman said.
“I’m here today to put a face on influenza,” Dr. Teichman said at a news briefing Oct. 4 on preventing the flu and pneumococcal disease, sponsored by the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases.
New survey numbers ‘alarming’
The NFID commissioned a national survey of more than 1,000 U.S. adults to better understand their knowledge and attitudes about the flu, pneumococcal disease, vaccines, and the impact of COVID-19.
“We were alarmed to learn that only 49% of U.S. adults plan to get their flu vaccine this season,” said Patricia A. “Patsy” Stinchfield, a registered nurse, NFID president, and moderator of the news briefing. “That is not good enough.”
In addition, 22% of people at higher risk for flu-related complications do not plan to get vaccinated this season. “That’s a dangerous risk to take,” Ms. Stinchfield said.
An encouraging finding, she said, is that 69% of adults surveyed recognize that an annual flu vaccination is the best way to prevent flu-related hospitalizations and death.
“So, most people know what to do. We just need to do it,” she said.
The top reason for not getting a flu shot in 2022 mentioned by 41% of people surveyed, is they do not think vaccines work very well. Another 39% are concerned about vaccine side effects, and 28% skip the vaccine because they “never get the flu.”
The experts on the panel emphasized the recommendation that all Americans 6 months or older get the flu vaccine, preferably by the end of October. Vaccination is especially important for those at higher risk of complications from the flu, including children under 5, pregnant women, people with one or more health conditions, the immunocompromised, and Americans 65 years and older.
Ms. Stinchfield acknowledged that the effectiveness of the flu vaccine varies season to season, but even if the vaccine does not completely match the circulating viruses, it can help prevent serious outcomes like hospitalization and death. One of the serious potential complications is pneumonia or “pneumococcal disease.”
“Our survey shows that only 29% of those at risk have been advised to receive a pneumococcal vaccine,” Ms. Stinchfield said. “The good news is that, among those who were advised to get the vaccine, 74% did receive their pneumococcal vaccine,” she said. “This underscores a key point to you, my fellow clinicians: As health professionals, our recommendations matter.”
Higher doses for 65+ Americans
The CDC updated recommendations this flu season for adults 65 and older to receive one of three preferentially recommended flu vaccines, said CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD. The CDC is recommending higher-dose, stronger vaccines for older Americans “based on a review of the available studies, which suggested that in this age group, these vaccines are potentially more effective than standard-dose ... vaccines.”
During most seasons, people 65 and older bear the greatest burden of severe flu disease, accounting for most flu-related hospitalizations and deaths.
“They are the largest vulnerable segment of our society,” Dr. Walensky said.
What will this flu season be like?
Health officials in the flu vaccine business also tend to be in the flu season prediction business. That includes Dr. Walensky.
“While we will never exactly know what each flu season will hold, we do know that every year, the best way you can protect yourself and those around you is to get your annual flu vaccine,” she said while taking part remotely in the briefing.
How severe will the flu season be in 2022-23? William Schaffner, MD, said he gets that question a lot. “Don’t think about that. Just focus on the fact that flu will be with us each year.
“We were a little bit spoiled. We’ve had two mild influenza seasons,” said Dr. Schaffner, medical director of NFID and a professor of infectious diseases and preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “I think with all the interest in COVID, people have rather forgotten about influenza. I’ve had to remind them that this is yet another serious winter respiratory virus.
“As I like to say, flu is fickle. It’s difficult to predict how serious this next outbreak of influenza this season is going to be. We could look at what happened in the Southern Hemisphere,” he said.
For example, Australia had the worst influenza season in the past 5 years, Schaffner said. “If you want a hint of what might happen here and you want yet another reason to be vaccinated, there it is.”
What we do know, Dr. Walensky said, is that the timing and severity of the past two flu seasons in the U.S. have been different than typical flu seasons. “And this is likely due to the COVID mitigation measures and other changes in circulating respiratory viruses.” Also, although last flu season was “relatively mild,” there was more flu activity than in the prior, 2020-21 season.
Also, Dr. Walensky said, last season’s flu cases began to increase in November and remained elevated until mid-June, “making it the latest season on record.”
The official cause of Brent Teichman’s death was multilobar pneumonia, cause undetermined. “But after 30-plus years as a pediatrician ... I know influenza when I see it,” Dr. Teichman said.
“There’s a hole in our hearts that will never heal. Loss of a child is devastating,” he said. The flu “can take the life of a healthy young person, as it did to my son.
“And for all those listening to my story who are vaccine hesitant, do it for those who love you. So that they won’t walk the path that we and many other families in this country have walked.”
To prove their point, Dr. Teichman and Ms. Stinchfield raised their sleeves and received flu shots during the news briefing.
“This one is for Brent,” Dr. Teichman said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“It was what the CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] would call classic influenza-like illness,” Dr. Teichman said. “It was too late to start antivirals, so I gave him advice on symptomatic treatment. We texted the next day, and I was glad to hear that his fever was trending down and that he was feeling a little bit better.”
Two days later, his son called again.
“He said he was having trouble breathing, and over the phone I could hear him hyperventilating.” The retired pediatrician and health care executive told his son to seek medical care.
“Then I got the call that no parent wants to get.”
Brent’s cousin Jake called saying he couldn’t wake Brent up.
“I called Jake back a few minutes later and asked him to hold up the phone,” Dr. Teichman said. “I listened to EMS working on my son, calling for round after round of many medications. He was in arrest and they couldn’t revive him.”
“To this day when I close my eyes at night, I still hear the beeping of those monitors.”
Brent had no health conditions to put him at higher risk for complications of the flu. “Brent was a wonderful son, brother, uncle, and friend. He had a passion for everything he did, and that included his chosen calling of the culinary arts but also included University of Kentucky sports,” Dr. Teichman said.
Brent planned to get a flu vaccine but had not done it yet. “In his obituary, we requested that, in lieu of flowers or donations, people go get their flu shot,” Dr. Teichman said.
“I’m here today to put a face on influenza,” Dr. Teichman said at a news briefing Oct. 4 on preventing the flu and pneumococcal disease, sponsored by the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases.
New survey numbers ‘alarming’
The NFID commissioned a national survey of more than 1,000 U.S. adults to better understand their knowledge and attitudes about the flu, pneumococcal disease, vaccines, and the impact of COVID-19.
“We were alarmed to learn that only 49% of U.S. adults plan to get their flu vaccine this season,” said Patricia A. “Patsy” Stinchfield, a registered nurse, NFID president, and moderator of the news briefing. “That is not good enough.”
In addition, 22% of people at higher risk for flu-related complications do not plan to get vaccinated this season. “That’s a dangerous risk to take,” Ms. Stinchfield said.
An encouraging finding, she said, is that 69% of adults surveyed recognize that an annual flu vaccination is the best way to prevent flu-related hospitalizations and death.
“So, most people know what to do. We just need to do it,” she said.
The top reason for not getting a flu shot in 2022 mentioned by 41% of people surveyed, is they do not think vaccines work very well. Another 39% are concerned about vaccine side effects, and 28% skip the vaccine because they “never get the flu.”
The experts on the panel emphasized the recommendation that all Americans 6 months or older get the flu vaccine, preferably by the end of October. Vaccination is especially important for those at higher risk of complications from the flu, including children under 5, pregnant women, people with one or more health conditions, the immunocompromised, and Americans 65 years and older.
Ms. Stinchfield acknowledged that the effectiveness of the flu vaccine varies season to season, but even if the vaccine does not completely match the circulating viruses, it can help prevent serious outcomes like hospitalization and death. One of the serious potential complications is pneumonia or “pneumococcal disease.”
“Our survey shows that only 29% of those at risk have been advised to receive a pneumococcal vaccine,” Ms. Stinchfield said. “The good news is that, among those who were advised to get the vaccine, 74% did receive their pneumococcal vaccine,” she said. “This underscores a key point to you, my fellow clinicians: As health professionals, our recommendations matter.”
Higher doses for 65+ Americans
The CDC updated recommendations this flu season for adults 65 and older to receive one of three preferentially recommended flu vaccines, said CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD. The CDC is recommending higher-dose, stronger vaccines for older Americans “based on a review of the available studies, which suggested that in this age group, these vaccines are potentially more effective than standard-dose ... vaccines.”
During most seasons, people 65 and older bear the greatest burden of severe flu disease, accounting for most flu-related hospitalizations and deaths.
“They are the largest vulnerable segment of our society,” Dr. Walensky said.
What will this flu season be like?
Health officials in the flu vaccine business also tend to be in the flu season prediction business. That includes Dr. Walensky.
“While we will never exactly know what each flu season will hold, we do know that every year, the best way you can protect yourself and those around you is to get your annual flu vaccine,” she said while taking part remotely in the briefing.
How severe will the flu season be in 2022-23? William Schaffner, MD, said he gets that question a lot. “Don’t think about that. Just focus on the fact that flu will be with us each year.
“We were a little bit spoiled. We’ve had two mild influenza seasons,” said Dr. Schaffner, medical director of NFID and a professor of infectious diseases and preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “I think with all the interest in COVID, people have rather forgotten about influenza. I’ve had to remind them that this is yet another serious winter respiratory virus.
“As I like to say, flu is fickle. It’s difficult to predict how serious this next outbreak of influenza this season is going to be. We could look at what happened in the Southern Hemisphere,” he said.
For example, Australia had the worst influenza season in the past 5 years, Schaffner said. “If you want a hint of what might happen here and you want yet another reason to be vaccinated, there it is.”
What we do know, Dr. Walensky said, is that the timing and severity of the past two flu seasons in the U.S. have been different than typical flu seasons. “And this is likely due to the COVID mitigation measures and other changes in circulating respiratory viruses.” Also, although last flu season was “relatively mild,” there was more flu activity than in the prior, 2020-21 season.
Also, Dr. Walensky said, last season’s flu cases began to increase in November and remained elevated until mid-June, “making it the latest season on record.”
The official cause of Brent Teichman’s death was multilobar pneumonia, cause undetermined. “But after 30-plus years as a pediatrician ... I know influenza when I see it,” Dr. Teichman said.
“There’s a hole in our hearts that will never heal. Loss of a child is devastating,” he said. The flu “can take the life of a healthy young person, as it did to my son.
“And for all those listening to my story who are vaccine hesitant, do it for those who love you. So that they won’t walk the path that we and many other families in this country have walked.”
To prove their point, Dr. Teichman and Ms. Stinchfield raised their sleeves and received flu shots during the news briefing.
“This one is for Brent,” Dr. Teichman said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Malaria vaccine gets special delivery by tiny health personnel
Don’t like needles? Have we got a vaccine for you
Here’s a quick question: How do you turn the most annoying thing ever into something positive?
No, we’re not talking about politicians this time. No, not Elon Musk, either. Infomercials? Guess again. Humidity? Nope, even more annoying than that.
Give up? The most annoying thing ever is mosquitoes. This time, however, NPR reports that mosquitoes have been used to deliver a vaccine for the very disease they’ve been transmitting to their human food sources all these years.
In a recent proof-of-concept trial, investigators used CRISPR technology to genetically modify malaria-causing Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites, which just happen to live in the salivary glands of Anopheles mosquitoes. And since the Plasmodium parasites are already in the mosquitoes, it made sense to use the buzzy little critters as the delivery device for the vaccine.
More sense than a syringe, you ask? Have you ever tried to poke a syringe into the salivary gland of a mosquito? No, we thought not. Well, we can tell you from experience that it’s really, really hard. Never mind how we know. We just do.
The 14 study volunteers – who were paid $4,100 for their participation – were first exposed to hundreds of mosquitoes carrying the altered Plasmodium parasites. Then, to test the vaccine, they were exposed to mosquitoes that had actual, malaria-carrying Plasmodium. Half of the subjects got malaria, so the vaccine was only 50% effective, meaning there’s still work to do.
Meanwhile, the scientists here at LOTMEco are all over this mosquito-delivery business, working on a vaccine to prevent Elon Musk. Plan B involves some sort of really big swatter.
Climate change: Sleeping your life away
It’s no secret that climate change is raising the temperature on everything. You may think you’re getting relief when the sun goes down, but in some places it’s still hot. A new survey conducted in central Japan shows how bad it can be and how higher nighttime temperatures can have a serious impact on people’s health.
That online survey, the Sleep Quality Index for Daily Sleep, enabled the investigators to correlate sleep quality with daily temperature for 1,284 adults in 2011 and 2012 who completed the survey over 10 days.
Not only was there a significant difference in sleep disturbance among younger men (higher) versus older men, but the prevalence of sleep disturbance went up when the daytime temperature was above 24.8° C. They also found that disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), which measure time lost through premature death and time lived in certain conditions that put one’s health at risk, were 81.8 years for the city of Nagoya (population, 2.2 million) in 2012.
The damage to health from sleep disorders caused by daily temperatures higher than 25° C “is comparable to that of heatstroke and must be addressed,” lead author Tomohiko Ihara of the University of Tokyo said in a written statement.
The researchers hope that this information will help sway legislators to consider the impact of higher nighttime temperatures and that it can be used to provide guidance for better sleep. The solution for now? Sleep with the air conditioner on. Your energy bill might increase, but just think about those DALYs. If using the AC lowers DALYs and increases time lived, then we say it’s worth it.
Maybe it would have been a dragon WITH cancer
If you ask a random person on the street to tell you all they know about the country of Wales, they’ll probably mention two things: One, the contorted collection of jumbled-up letters that is the Welsh language (looking at you, Llanfairpwllgwyngyllgogerychwyrndrobwllllantysiliogogogoch) and, two, the association with dragons. The Welsh flag even has a dragon on it.
With that in mind, take a guess as to what sort of statue art dealer Simon Wingett wanted to build in the Welsh town of Wrexham. No, not a monument to the second-longest place name in the world. Try again. His dragon would not be some piddly little thing either; he wanted a virtual kaiju overlooking the town, with the whole statue to stand about 60 meters high. That’s taller than the original 1954 Godzilla.
Artistic masterpieces may sell for frankly insane prices, but art dealers themselves are not the wealthiest of individuals, so Mr. Wingett needed money to fund his dragon-based dream. Lucky for him, he also happened to be the manager of a cancer charity – initially set up by Mr. Wingett’s father, who had throat cancer – which nominally aimed to provide equipment and resources to cancer patients in the Wrexham area.
Yes, this is going precisely where you think it’s going. From 2011 to 2018, when the charity closed, Mr. Wingett used the charity’s donations to fund his dragon statue – which never actually got built, by the way – to the tune of over 400,000 pounds. Of course, Mr. Wingett came under scrutiny when people started to notice that his cancer charity hadn’t actually done anything charitable since 2011, and he was recently banned by the Welsh High Court from serving as trustee of any charity for 10 years. Oh no, tragedy and horror! Truly a punishment worse than death itself.
Okay fine, he also has to pay back 117,000 pounds to actual legitimate cancer charities. The astute mathematicians out there may notice that 117,000 is a lot less than 400,000. But it’s just as the old saying goes: One-quarter of crime doesn’t pay. You can keep three-quarters of it, though, that’s completely fine.
Don’t like needles? Have we got a vaccine for you
Here’s a quick question: How do you turn the most annoying thing ever into something positive?
No, we’re not talking about politicians this time. No, not Elon Musk, either. Infomercials? Guess again. Humidity? Nope, even more annoying than that.
Give up? The most annoying thing ever is mosquitoes. This time, however, NPR reports that mosquitoes have been used to deliver a vaccine for the very disease they’ve been transmitting to their human food sources all these years.
In a recent proof-of-concept trial, investigators used CRISPR technology to genetically modify malaria-causing Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites, which just happen to live in the salivary glands of Anopheles mosquitoes. And since the Plasmodium parasites are already in the mosquitoes, it made sense to use the buzzy little critters as the delivery device for the vaccine.
More sense than a syringe, you ask? Have you ever tried to poke a syringe into the salivary gland of a mosquito? No, we thought not. Well, we can tell you from experience that it’s really, really hard. Never mind how we know. We just do.
The 14 study volunteers – who were paid $4,100 for their participation – were first exposed to hundreds of mosquitoes carrying the altered Plasmodium parasites. Then, to test the vaccine, they were exposed to mosquitoes that had actual, malaria-carrying Plasmodium. Half of the subjects got malaria, so the vaccine was only 50% effective, meaning there’s still work to do.
Meanwhile, the scientists here at LOTMEco are all over this mosquito-delivery business, working on a vaccine to prevent Elon Musk. Plan B involves some sort of really big swatter.
Climate change: Sleeping your life away
It’s no secret that climate change is raising the temperature on everything. You may think you’re getting relief when the sun goes down, but in some places it’s still hot. A new survey conducted in central Japan shows how bad it can be and how higher nighttime temperatures can have a serious impact on people’s health.
That online survey, the Sleep Quality Index for Daily Sleep, enabled the investigators to correlate sleep quality with daily temperature for 1,284 adults in 2011 and 2012 who completed the survey over 10 days.
Not only was there a significant difference in sleep disturbance among younger men (higher) versus older men, but the prevalence of sleep disturbance went up when the daytime temperature was above 24.8° C. They also found that disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), which measure time lost through premature death and time lived in certain conditions that put one’s health at risk, were 81.8 years for the city of Nagoya (population, 2.2 million) in 2012.
The damage to health from sleep disorders caused by daily temperatures higher than 25° C “is comparable to that of heatstroke and must be addressed,” lead author Tomohiko Ihara of the University of Tokyo said in a written statement.
The researchers hope that this information will help sway legislators to consider the impact of higher nighttime temperatures and that it can be used to provide guidance for better sleep. The solution for now? Sleep with the air conditioner on. Your energy bill might increase, but just think about those DALYs. If using the AC lowers DALYs and increases time lived, then we say it’s worth it.
Maybe it would have been a dragon WITH cancer
If you ask a random person on the street to tell you all they know about the country of Wales, they’ll probably mention two things: One, the contorted collection of jumbled-up letters that is the Welsh language (looking at you, Llanfairpwllgwyngyllgogerychwyrndrobwllllantysiliogogogoch) and, two, the association with dragons. The Welsh flag even has a dragon on it.
With that in mind, take a guess as to what sort of statue art dealer Simon Wingett wanted to build in the Welsh town of Wrexham. No, not a monument to the second-longest place name in the world. Try again. His dragon would not be some piddly little thing either; he wanted a virtual kaiju overlooking the town, with the whole statue to stand about 60 meters high. That’s taller than the original 1954 Godzilla.
Artistic masterpieces may sell for frankly insane prices, but art dealers themselves are not the wealthiest of individuals, so Mr. Wingett needed money to fund his dragon-based dream. Lucky for him, he also happened to be the manager of a cancer charity – initially set up by Mr. Wingett’s father, who had throat cancer – which nominally aimed to provide equipment and resources to cancer patients in the Wrexham area.
Yes, this is going precisely where you think it’s going. From 2011 to 2018, when the charity closed, Mr. Wingett used the charity’s donations to fund his dragon statue – which never actually got built, by the way – to the tune of over 400,000 pounds. Of course, Mr. Wingett came under scrutiny when people started to notice that his cancer charity hadn’t actually done anything charitable since 2011, and he was recently banned by the Welsh High Court from serving as trustee of any charity for 10 years. Oh no, tragedy and horror! Truly a punishment worse than death itself.
Okay fine, he also has to pay back 117,000 pounds to actual legitimate cancer charities. The astute mathematicians out there may notice that 117,000 is a lot less than 400,000. But it’s just as the old saying goes: One-quarter of crime doesn’t pay. You can keep three-quarters of it, though, that’s completely fine.
Don’t like needles? Have we got a vaccine for you
Here’s a quick question: How do you turn the most annoying thing ever into something positive?
No, we’re not talking about politicians this time. No, not Elon Musk, either. Infomercials? Guess again. Humidity? Nope, even more annoying than that.
Give up? The most annoying thing ever is mosquitoes. This time, however, NPR reports that mosquitoes have been used to deliver a vaccine for the very disease they’ve been transmitting to their human food sources all these years.
In a recent proof-of-concept trial, investigators used CRISPR technology to genetically modify malaria-causing Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites, which just happen to live in the salivary glands of Anopheles mosquitoes. And since the Plasmodium parasites are already in the mosquitoes, it made sense to use the buzzy little critters as the delivery device for the vaccine.
More sense than a syringe, you ask? Have you ever tried to poke a syringe into the salivary gland of a mosquito? No, we thought not. Well, we can tell you from experience that it’s really, really hard. Never mind how we know. We just do.
The 14 study volunteers – who were paid $4,100 for their participation – were first exposed to hundreds of mosquitoes carrying the altered Plasmodium parasites. Then, to test the vaccine, they were exposed to mosquitoes that had actual, malaria-carrying Plasmodium. Half of the subjects got malaria, so the vaccine was only 50% effective, meaning there’s still work to do.
Meanwhile, the scientists here at LOTMEco are all over this mosquito-delivery business, working on a vaccine to prevent Elon Musk. Plan B involves some sort of really big swatter.
Climate change: Sleeping your life away
It’s no secret that climate change is raising the temperature on everything. You may think you’re getting relief when the sun goes down, but in some places it’s still hot. A new survey conducted in central Japan shows how bad it can be and how higher nighttime temperatures can have a serious impact on people’s health.
That online survey, the Sleep Quality Index for Daily Sleep, enabled the investigators to correlate sleep quality with daily temperature for 1,284 adults in 2011 and 2012 who completed the survey over 10 days.
Not only was there a significant difference in sleep disturbance among younger men (higher) versus older men, but the prevalence of sleep disturbance went up when the daytime temperature was above 24.8° C. They also found that disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), which measure time lost through premature death and time lived in certain conditions that put one’s health at risk, were 81.8 years for the city of Nagoya (population, 2.2 million) in 2012.
The damage to health from sleep disorders caused by daily temperatures higher than 25° C “is comparable to that of heatstroke and must be addressed,” lead author Tomohiko Ihara of the University of Tokyo said in a written statement.
The researchers hope that this information will help sway legislators to consider the impact of higher nighttime temperatures and that it can be used to provide guidance for better sleep. The solution for now? Sleep with the air conditioner on. Your energy bill might increase, but just think about those DALYs. If using the AC lowers DALYs and increases time lived, then we say it’s worth it.
Maybe it would have been a dragon WITH cancer
If you ask a random person on the street to tell you all they know about the country of Wales, they’ll probably mention two things: One, the contorted collection of jumbled-up letters that is the Welsh language (looking at you, Llanfairpwllgwyngyllgogerychwyrndrobwllllantysiliogogogoch) and, two, the association with dragons. The Welsh flag even has a dragon on it.
With that in mind, take a guess as to what sort of statue art dealer Simon Wingett wanted to build in the Welsh town of Wrexham. No, not a monument to the second-longest place name in the world. Try again. His dragon would not be some piddly little thing either; he wanted a virtual kaiju overlooking the town, with the whole statue to stand about 60 meters high. That’s taller than the original 1954 Godzilla.
Artistic masterpieces may sell for frankly insane prices, but art dealers themselves are not the wealthiest of individuals, so Mr. Wingett needed money to fund his dragon-based dream. Lucky for him, he also happened to be the manager of a cancer charity – initially set up by Mr. Wingett’s father, who had throat cancer – which nominally aimed to provide equipment and resources to cancer patients in the Wrexham area.
Yes, this is going precisely where you think it’s going. From 2011 to 2018, when the charity closed, Mr. Wingett used the charity’s donations to fund his dragon statue – which never actually got built, by the way – to the tune of over 400,000 pounds. Of course, Mr. Wingett came under scrutiny when people started to notice that his cancer charity hadn’t actually done anything charitable since 2011, and he was recently banned by the Welsh High Court from serving as trustee of any charity for 10 years. Oh no, tragedy and horror! Truly a punishment worse than death itself.
Okay fine, he also has to pay back 117,000 pounds to actual legitimate cancer charities. The astute mathematicians out there may notice that 117,000 is a lot less than 400,000. But it’s just as the old saying goes: One-quarter of crime doesn’t pay. You can keep three-quarters of it, though, that’s completely fine.
Children and COVID: Weekly cases dropped by 57% in September
The last full week of September brought a 4th straight week of declines in the number of new COVID-19 cases reported among children, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, with the month of September bringing a decline of about 57% in reported cases for the 45 states and territories that are still releasing pediatric COVID data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said in their joint weekly report.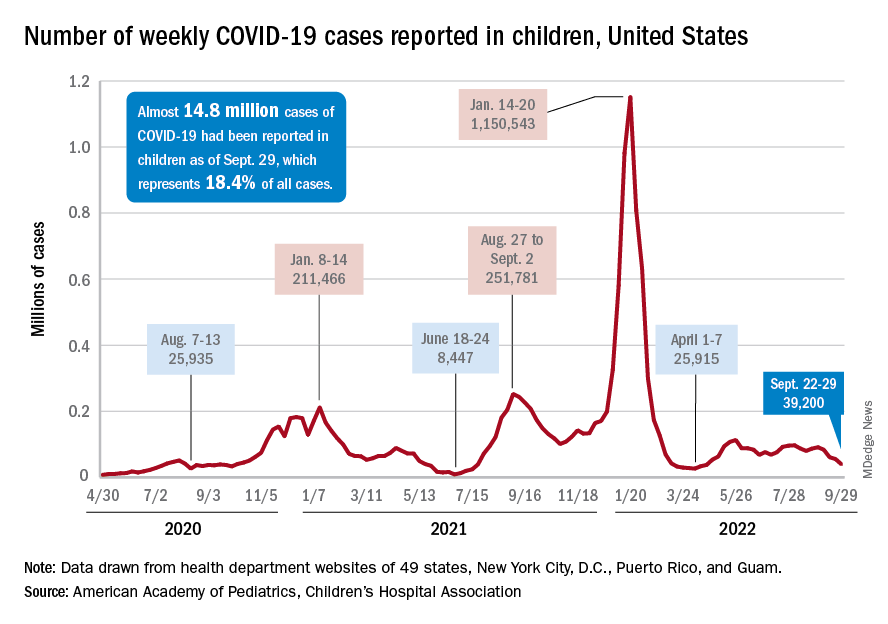
New cases dropped in all four regions after the Northeast and West had seen increases the previous week, and the distribution of cases for the latest week was fairly even, with the Midwest and Northeast right around 10,000, the South slightly over 10,000, and the West under 10,000 by about the same amount. At the state level, the largest increases – around 1.5% – over the last 2 weeks occurred in Kentucky and Nevada, the AAP/CHA data show.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children was almost 14.8 million as of Sept. 29, with children representing 18.4% of all cases since the pandemic began, the AAP and CHA said. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is able to use a uniform age range of 0-17 years, puts total cases at 15.2 million and the proportion of child cases at 17.4%. Total deaths in children from COVID as of Oct. 3 were 1,745, the CDC reported.
New vaccinations, in the meantime, are being added in numbers only slightly higher than new cases. Initial COVID vaccinations for the week of Sept. 22-28 were about 44,000 for children under 5 years of age (down from 51,000 the week before), 24,000 for children aged 5-11 years (down from 28,000), and 17,000 for those aged 12-17 (down from 18,000), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
To look at it another way, the total proportion of children under 5 years of age who had received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Sept. 28 was 6.5%, compared with 6.4% on Sept. 21, while the corresponding rates for children aged 5-11 and 12-17 were unchanged at 38.5% and 70.9%. The 12- to 17-year-olds, in fact, have been stuck at 70.9% since Sept. 13, according to data from the CDC.
In a recent study published in Vaccine, investigators attributed the discrepancies between age groups at least partly to the acceptance of misinformation about vaccine safety in general and the COVID-19 vaccines in particular.
“All of the misconceptions we studied focused in one way or another on the safety of vaccination, and that explains why people’s misbeliefs about vaccinating kids are so highly related to their concerns about vaccines in general. Unfortunately, those concerns weigh even more heavily when adults consider vaccinating children,” lead author Dan Romer, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a written statement.
The last full week of September brought a 4th straight week of declines in the number of new COVID-19 cases reported among children, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, with the month of September bringing a decline of about 57% in reported cases for the 45 states and territories that are still releasing pediatric COVID data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said in their joint weekly report.
New cases dropped in all four regions after the Northeast and West had seen increases the previous week, and the distribution of cases for the latest week was fairly even, with the Midwest and Northeast right around 10,000, the South slightly over 10,000, and the West under 10,000 by about the same amount. At the state level, the largest increases – around 1.5% – over the last 2 weeks occurred in Kentucky and Nevada, the AAP/CHA data show.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children was almost 14.8 million as of Sept. 29, with children representing 18.4% of all cases since the pandemic began, the AAP and CHA said. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is able to use a uniform age range of 0-17 years, puts total cases at 15.2 million and the proportion of child cases at 17.4%. Total deaths in children from COVID as of Oct. 3 were 1,745, the CDC reported.
New vaccinations, in the meantime, are being added in numbers only slightly higher than new cases. Initial COVID vaccinations for the week of Sept. 22-28 were about 44,000 for children under 5 years of age (down from 51,000 the week before), 24,000 for children aged 5-11 years (down from 28,000), and 17,000 for those aged 12-17 (down from 18,000), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
To look at it another way, the total proportion of children under 5 years of age who had received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Sept. 28 was 6.5%, compared with 6.4% on Sept. 21, while the corresponding rates for children aged 5-11 and 12-17 were unchanged at 38.5% and 70.9%. The 12- to 17-year-olds, in fact, have been stuck at 70.9% since Sept. 13, according to data from the CDC.
In a recent study published in Vaccine, investigators attributed the discrepancies between age groups at least partly to the acceptance of misinformation about vaccine safety in general and the COVID-19 vaccines in particular.
“All of the misconceptions we studied focused in one way or another on the safety of vaccination, and that explains why people’s misbeliefs about vaccinating kids are so highly related to their concerns about vaccines in general. Unfortunately, those concerns weigh even more heavily when adults consider vaccinating children,” lead author Dan Romer, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a written statement.
The last full week of September brought a 4th straight week of declines in the number of new COVID-19 cases reported among children, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, with the month of September bringing a decline of about 57% in reported cases for the 45 states and territories that are still releasing pediatric COVID data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said in their joint weekly report.
New cases dropped in all four regions after the Northeast and West had seen increases the previous week, and the distribution of cases for the latest week was fairly even, with the Midwest and Northeast right around 10,000, the South slightly over 10,000, and the West under 10,000 by about the same amount. At the state level, the largest increases – around 1.5% – over the last 2 weeks occurred in Kentucky and Nevada, the AAP/CHA data show.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children was almost 14.8 million as of Sept. 29, with children representing 18.4% of all cases since the pandemic began, the AAP and CHA said. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is able to use a uniform age range of 0-17 years, puts total cases at 15.2 million and the proportion of child cases at 17.4%. Total deaths in children from COVID as of Oct. 3 were 1,745, the CDC reported.
New vaccinations, in the meantime, are being added in numbers only slightly higher than new cases. Initial COVID vaccinations for the week of Sept. 22-28 were about 44,000 for children under 5 years of age (down from 51,000 the week before), 24,000 for children aged 5-11 years (down from 28,000), and 17,000 for those aged 12-17 (down from 18,000), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
To look at it another way, the total proportion of children under 5 years of age who had received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Sept. 28 was 6.5%, compared with 6.4% on Sept. 21, while the corresponding rates for children aged 5-11 and 12-17 were unchanged at 38.5% and 70.9%. The 12- to 17-year-olds, in fact, have been stuck at 70.9% since Sept. 13, according to data from the CDC.
In a recent study published in Vaccine, investigators attributed the discrepancies between age groups at least partly to the acceptance of misinformation about vaccine safety in general and the COVID-19 vaccines in particular.
“All of the misconceptions we studied focused in one way or another on the safety of vaccination, and that explains why people’s misbeliefs about vaccinating kids are so highly related to their concerns about vaccines in general. Unfortunately, those concerns weigh even more heavily when adults consider vaccinating children,” lead author Dan Romer, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a written statement.