User login
Long-term antibiotic use may heighten stroke, CHD risk
, according to a study in the European Heart Journal.
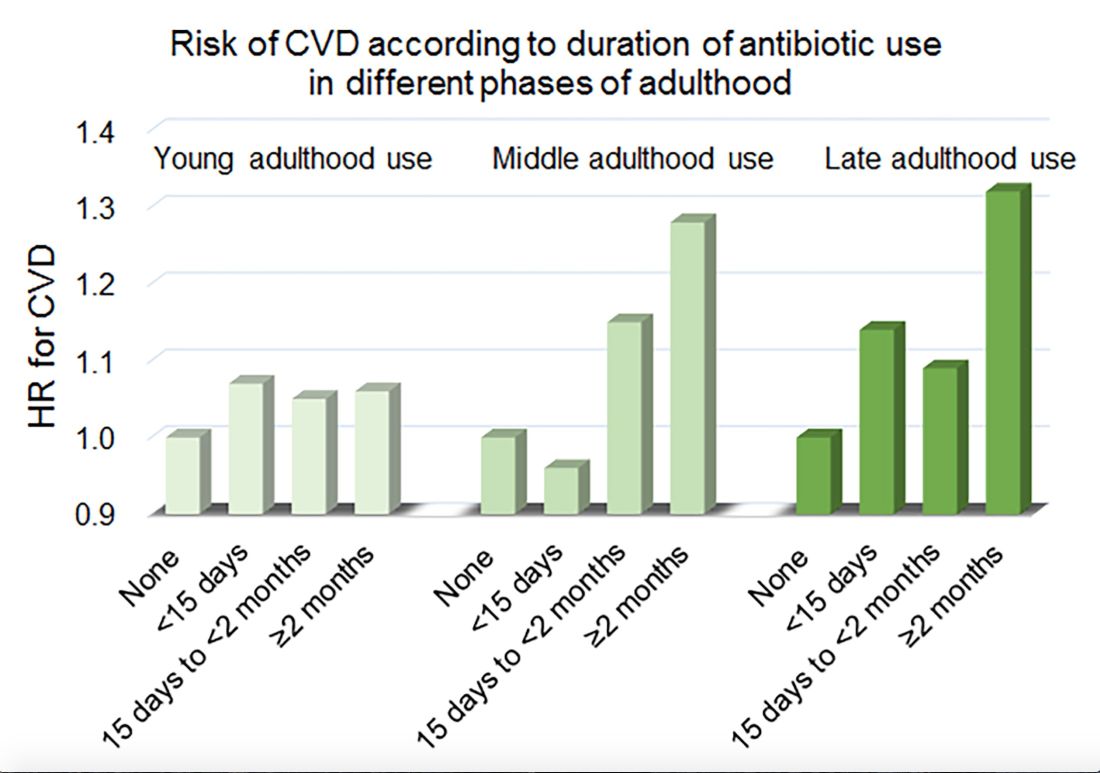
Women in the Nurses’ Health Study who used antibiotics for 2 or more months between ages 40 and 59 years or at age 60 years and older had a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease, compared with those who did not use antibiotics. Antibiotic use between 20 and 39 years old was not significantly related to cardiovascular disease.
Prior research has found that antibiotics may have long-lasting effects on gut microbiota and relate to cardiovascular disease risk.
“Antibiotic use is the most critical factor in altering the balance of microorganisms in the gut,” said lead investigator Lu Qi, MD, PhD, in a news release. “Previous studies have shown a link between alterations in the microbiotic environment of the gut and inflammation and narrowing of the blood vessels, stroke, and heart disease,” said Dr. Qi, who is the director of the Tulane University Obesity Research Center in New Orleans and an adjunct professor of nutrition at Harvard T.C. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
To evaluate associations between life stage, antibiotic exposure, and subsequent cardiovascular disease, researchers analyzed data from 36,429 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study. The women were at least 60 years old and had no history of cardiovascular disease or cancer when they completed a 2004 questionnaire about antibiotic usage during young, middle, and late adulthood. The questionnaire asked participants to indicate the total time using antibiotics with eight categories ranging from none to 5 or more years.
The researchers defined incident cardiovascular disease as a composite endpoint of coronary heart disease (nonfatal myocardial infarction or fatal coronary heart disease) and stroke (nonfatal or fatal). They calculated person-years of follow-up from the questionnaire return date until date of cardiovascular disease diagnosis, death, or end of follow-up in 2012.
Women with longer duration of antibiotic use were more likely to use other medications and have unfavorable cardiovascular risk profiles, including family history of myocardial infarction and higher body mass index. Antibiotics most often were used to treat respiratory infections. During an average follow-up of 7.6 years, 1,056 participants developed cardiovascular disease.
In a multivariable model that adjusted for demographics, diet, lifestyle, reason for antibiotic use, medications, overweight status, and other factors, long-term antibiotic use – 2 months or more – in late adulthood was associated with significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease (hazard ratio, 1.32), as was long-term antibiotic use in middle adulthood (HR, 1.28).
Although antibiotic use was self-reported, which could lead to misclassification, the participants were health professionals, which may mitigate this limitation, the authors noted. Whether these findings apply to men and other populations requires further study, they said.
Because of the study’s observational design, the results “cannot show that antibiotics cause heart disease and stroke, only that there is a link between them,” Dr. Qi said. “It’s possible that women who reported more antibiotic use might be sicker in other ways that we were unable to measure, or there may be other factors that could affect the results that we have not been able take account of.”
“Our study suggests that antibiotics should be used only when they are absolutely needed,” he concluded. “Considering the potentially cumulative adverse effects, the shorter time of antibiotic use the better.”
The study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants, the Boston Obesity Nutrition Research Center, and the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation. One author received support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The authors had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Heianza Y et al. Eur Heart J. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz231.
, according to a study in the European Heart Journal.

Women in the Nurses’ Health Study who used antibiotics for 2 or more months between ages 40 and 59 years or at age 60 years and older had a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease, compared with those who did not use antibiotics. Antibiotic use between 20 and 39 years old was not significantly related to cardiovascular disease.
Prior research has found that antibiotics may have long-lasting effects on gut microbiota and relate to cardiovascular disease risk.
“Antibiotic use is the most critical factor in altering the balance of microorganisms in the gut,” said lead investigator Lu Qi, MD, PhD, in a news release. “Previous studies have shown a link between alterations in the microbiotic environment of the gut and inflammation and narrowing of the blood vessels, stroke, and heart disease,” said Dr. Qi, who is the director of the Tulane University Obesity Research Center in New Orleans and an adjunct professor of nutrition at Harvard T.C. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
To evaluate associations between life stage, antibiotic exposure, and subsequent cardiovascular disease, researchers analyzed data from 36,429 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study. The women were at least 60 years old and had no history of cardiovascular disease or cancer when they completed a 2004 questionnaire about antibiotic usage during young, middle, and late adulthood. The questionnaire asked participants to indicate the total time using antibiotics with eight categories ranging from none to 5 or more years.
The researchers defined incident cardiovascular disease as a composite endpoint of coronary heart disease (nonfatal myocardial infarction or fatal coronary heart disease) and stroke (nonfatal or fatal). They calculated person-years of follow-up from the questionnaire return date until date of cardiovascular disease diagnosis, death, or end of follow-up in 2012.
Women with longer duration of antibiotic use were more likely to use other medications and have unfavorable cardiovascular risk profiles, including family history of myocardial infarction and higher body mass index. Antibiotics most often were used to treat respiratory infections. During an average follow-up of 7.6 years, 1,056 participants developed cardiovascular disease.
In a multivariable model that adjusted for demographics, diet, lifestyle, reason for antibiotic use, medications, overweight status, and other factors, long-term antibiotic use – 2 months or more – in late adulthood was associated with significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease (hazard ratio, 1.32), as was long-term antibiotic use in middle adulthood (HR, 1.28).
Although antibiotic use was self-reported, which could lead to misclassification, the participants were health professionals, which may mitigate this limitation, the authors noted. Whether these findings apply to men and other populations requires further study, they said.
Because of the study’s observational design, the results “cannot show that antibiotics cause heart disease and stroke, only that there is a link between them,” Dr. Qi said. “It’s possible that women who reported more antibiotic use might be sicker in other ways that we were unable to measure, or there may be other factors that could affect the results that we have not been able take account of.”
“Our study suggests that antibiotics should be used only when they are absolutely needed,” he concluded. “Considering the potentially cumulative adverse effects, the shorter time of antibiotic use the better.”
The study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants, the Boston Obesity Nutrition Research Center, and the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation. One author received support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The authors had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Heianza Y et al. Eur Heart J. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz231.
, according to a study in the European Heart Journal.

Women in the Nurses’ Health Study who used antibiotics for 2 or more months between ages 40 and 59 years or at age 60 years and older had a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease, compared with those who did not use antibiotics. Antibiotic use between 20 and 39 years old was not significantly related to cardiovascular disease.
Prior research has found that antibiotics may have long-lasting effects on gut microbiota and relate to cardiovascular disease risk.
“Antibiotic use is the most critical factor in altering the balance of microorganisms in the gut,” said lead investigator Lu Qi, MD, PhD, in a news release. “Previous studies have shown a link between alterations in the microbiotic environment of the gut and inflammation and narrowing of the blood vessels, stroke, and heart disease,” said Dr. Qi, who is the director of the Tulane University Obesity Research Center in New Orleans and an adjunct professor of nutrition at Harvard T.C. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
To evaluate associations between life stage, antibiotic exposure, and subsequent cardiovascular disease, researchers analyzed data from 36,429 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study. The women were at least 60 years old and had no history of cardiovascular disease or cancer when they completed a 2004 questionnaire about antibiotic usage during young, middle, and late adulthood. The questionnaire asked participants to indicate the total time using antibiotics with eight categories ranging from none to 5 or more years.
The researchers defined incident cardiovascular disease as a composite endpoint of coronary heart disease (nonfatal myocardial infarction or fatal coronary heart disease) and stroke (nonfatal or fatal). They calculated person-years of follow-up from the questionnaire return date until date of cardiovascular disease diagnosis, death, or end of follow-up in 2012.
Women with longer duration of antibiotic use were more likely to use other medications and have unfavorable cardiovascular risk profiles, including family history of myocardial infarction and higher body mass index. Antibiotics most often were used to treat respiratory infections. During an average follow-up of 7.6 years, 1,056 participants developed cardiovascular disease.
In a multivariable model that adjusted for demographics, diet, lifestyle, reason for antibiotic use, medications, overweight status, and other factors, long-term antibiotic use – 2 months or more – in late adulthood was associated with significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease (hazard ratio, 1.32), as was long-term antibiotic use in middle adulthood (HR, 1.28).
Although antibiotic use was self-reported, which could lead to misclassification, the participants were health professionals, which may mitigate this limitation, the authors noted. Whether these findings apply to men and other populations requires further study, they said.
Because of the study’s observational design, the results “cannot show that antibiotics cause heart disease and stroke, only that there is a link between them,” Dr. Qi said. “It’s possible that women who reported more antibiotic use might be sicker in other ways that we were unable to measure, or there may be other factors that could affect the results that we have not been able take account of.”
“Our study suggests that antibiotics should be used only when they are absolutely needed,” he concluded. “Considering the potentially cumulative adverse effects, the shorter time of antibiotic use the better.”
The study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants, the Boston Obesity Nutrition Research Center, and the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation. One author received support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The authors had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Heianza Y et al. Eur Heart J. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz231.
FROM THE EUROPEAN HEART JOURNAL
Key clinical point: Among middle-aged and older women, 2 or more months’ exposure to antibiotics is associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease or stroke.
Major finding: Long-term antibiotic use in late adulthood was associated with significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease (hazard ratio, 1.32), as was long-term antibiotic use in middle adulthood (HR, 1.28).
Study details: An analysis of data from nearly 36,500 women in the Nurses’ Health Study.
Disclosures: The study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants, the Boston Obesity Nutrition Research Center, and the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation. One author received support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The authors had no conflicts of interest.
Source: Heianza Y et al. Eur Heart J. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz231.
Tenofovir disoproxil treated HBV with fewer future HCCs
VIENNA – Treatment of individuals chronically infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) with the nucleotide analog tenofovir disoproxil fumarate significantly linked with a substantial cut in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with those who received the nucleoside analog entecavir, according to a review of more than 29,000 Hong Kong patients.
This is the second reported study to find that association. In January 2019, a study of more than 24,000 Korean residents chronically infected with HBV showed a similar, statistically significant link between treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Viread) and a lower incidence of HCC compared with patients treated with entecavir (Baraclude) (JAMA Oncol. 2019 Jan;5[1]:30-6), Grace L.H. Wong, MD, said at the meeting, sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL).
However, another report published just a few days before Dr. Wong spoke failed to find an association between tenofovir disoproxil treatment of HBV and the subsequent rate of HCC compared with patients treated with entecavir. That study comprised nearly 2,900 HBV patients treated at any of four Korean medical centers (J Hepatol. 2019 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.028).
Dr. Wong noted that although current guidelines from EASL cite both tenofovir disoproxil and entecavir (as well as tenofovir alafenamide [Vemlidy]) as first-line treatments for chronic HBV infection (J Hepatol. 2017 Aug;67[2]:370-98), some evidence suggests that tenofovir disoproxil might produce effects subtly different from those of entecavir.
At the meeting in Vienna, for example, a report on 176 Japanese patients with chronic HBV showed that those who were treated with a nucleotide analog such as tenofovir disoproxil produced higher serum levels of interferon-lamda3 compared with patients treated with entecavir, and increased levels of this interferon could improve clearance of HBV surface antigen (J Hepatol. 2019 April;70[1]:e477). The most recent EASL guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection also list tenofovir disoproxil, entecavir, and tenofovir alafenamide as preferred agents (Hepatology. 2018 April;67[4]:1560-99).
The data Dr. Wong and her associates analyzed came from health records kept for about 80% of Hong Kong’s population in the Clinical Data Analysis and Recording System of the Hospital Authority of Hong Kong. From January 2010 to June 2018, this database included 28,041 consecutive patients chronically infected with HBV and treated with entecavir, and 1,309 consecutive patients treated with tenofovir disoproxil. These numbers excluded patients treated for less than 6 months, patients coinfected with hepatitis C or D virus, patients with cancer diagnosed or a liver transplanted before or during their first 6 months on treatment, and patients previously treated with an interferon or nucleos(t)ide.
During an average follow-up of 2.8 years of tenofovir disoproxil treatment, 8 patients developed HCC, and during an average follow-up of 3.7 years of entecavir treatment, 1,386 patients developed HCC, reported Dr. Wong, a hepatologist and professor of medicine at the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
In a multivariate analysis that adjusted for demographic and clinical differences, treatment with tenofovir disoproxil linked with a statistically significant 68% reduced rate of HCC development compared with the entecavir-treated patients, she said. In a propensity score–weighted analysis, tenofovir disoproxil linked with a statistically significant 64% reduced rate of incident HCC, and in a propensity score–matched analysis tenofovir disoproxil linked with a 58% reduced rate of HCC, although in this analysis, which excluded many of the entecavir-treated patients and hence had less statistical power, the difference just missed statistical significance.
As an additional step to try to rule out the possible effect of unadjusted confounders, Dr. Wong and associates analyzed the links between tenofovir disoproxil and entecavir treatment and two negative-control outcomes, the incidence of lung cancer and the incidence of acute myocardial infarction. Neither of these outcomes showed a statistically significant link with one of the HBV treatments, suggesting that the link between treatment and HCC incidence did not appear because of an unadjusted confounding bias, Dr. Wong said. The Hong Kong database did not include enough patients treated with tenofovir alafenamide to allow assessment of this drug, she added.
Dr. Wong has been an adviser to Gilead and a speaker for Abbott, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, and Roche. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is marketed by Gilead, and entecavir is marketed by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Wong GL et al. J Hepatol. 2019 April;70[1]:e128.
VIENNA – Treatment of individuals chronically infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) with the nucleotide analog tenofovir disoproxil fumarate significantly linked with a substantial cut in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with those who received the nucleoside analog entecavir, according to a review of more than 29,000 Hong Kong patients.
This is the second reported study to find that association. In January 2019, a study of more than 24,000 Korean residents chronically infected with HBV showed a similar, statistically significant link between treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Viread) and a lower incidence of HCC compared with patients treated with entecavir (Baraclude) (JAMA Oncol. 2019 Jan;5[1]:30-6), Grace L.H. Wong, MD, said at the meeting, sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL).
However, another report published just a few days before Dr. Wong spoke failed to find an association between tenofovir disoproxil treatment of HBV and the subsequent rate of HCC compared with patients treated with entecavir. That study comprised nearly 2,900 HBV patients treated at any of four Korean medical centers (J Hepatol. 2019 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.028).
Dr. Wong noted that although current guidelines from EASL cite both tenofovir disoproxil and entecavir (as well as tenofovir alafenamide [Vemlidy]) as first-line treatments for chronic HBV infection (J Hepatol. 2017 Aug;67[2]:370-98), some evidence suggests that tenofovir disoproxil might produce effects subtly different from those of entecavir.
At the meeting in Vienna, for example, a report on 176 Japanese patients with chronic HBV showed that those who were treated with a nucleotide analog such as tenofovir disoproxil produced higher serum levels of interferon-lamda3 compared with patients treated with entecavir, and increased levels of this interferon could improve clearance of HBV surface antigen (J Hepatol. 2019 April;70[1]:e477). The most recent EASL guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection also list tenofovir disoproxil, entecavir, and tenofovir alafenamide as preferred agents (Hepatology. 2018 April;67[4]:1560-99).
The data Dr. Wong and her associates analyzed came from health records kept for about 80% of Hong Kong’s population in the Clinical Data Analysis and Recording System of the Hospital Authority of Hong Kong. From January 2010 to June 2018, this database included 28,041 consecutive patients chronically infected with HBV and treated with entecavir, and 1,309 consecutive patients treated with tenofovir disoproxil. These numbers excluded patients treated for less than 6 months, patients coinfected with hepatitis C or D virus, patients with cancer diagnosed or a liver transplanted before or during their first 6 months on treatment, and patients previously treated with an interferon or nucleos(t)ide.
During an average follow-up of 2.8 years of tenofovir disoproxil treatment, 8 patients developed HCC, and during an average follow-up of 3.7 years of entecavir treatment, 1,386 patients developed HCC, reported Dr. Wong, a hepatologist and professor of medicine at the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
In a multivariate analysis that adjusted for demographic and clinical differences, treatment with tenofovir disoproxil linked with a statistically significant 68% reduced rate of HCC development compared with the entecavir-treated patients, she said. In a propensity score–weighted analysis, tenofovir disoproxil linked with a statistically significant 64% reduced rate of incident HCC, and in a propensity score–matched analysis tenofovir disoproxil linked with a 58% reduced rate of HCC, although in this analysis, which excluded many of the entecavir-treated patients and hence had less statistical power, the difference just missed statistical significance.
As an additional step to try to rule out the possible effect of unadjusted confounders, Dr. Wong and associates analyzed the links between tenofovir disoproxil and entecavir treatment and two negative-control outcomes, the incidence of lung cancer and the incidence of acute myocardial infarction. Neither of these outcomes showed a statistically significant link with one of the HBV treatments, suggesting that the link between treatment and HCC incidence did not appear because of an unadjusted confounding bias, Dr. Wong said. The Hong Kong database did not include enough patients treated with tenofovir alafenamide to allow assessment of this drug, she added.
Dr. Wong has been an adviser to Gilead and a speaker for Abbott, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, and Roche. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is marketed by Gilead, and entecavir is marketed by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Wong GL et al. J Hepatol. 2019 April;70[1]:e128.
VIENNA – Treatment of individuals chronically infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) with the nucleotide analog tenofovir disoproxil fumarate significantly linked with a substantial cut in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with those who received the nucleoside analog entecavir, according to a review of more than 29,000 Hong Kong patients.
This is the second reported study to find that association. In January 2019, a study of more than 24,000 Korean residents chronically infected with HBV showed a similar, statistically significant link between treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Viread) and a lower incidence of HCC compared with patients treated with entecavir (Baraclude) (JAMA Oncol. 2019 Jan;5[1]:30-6), Grace L.H. Wong, MD, said at the meeting, sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL).
However, another report published just a few days before Dr. Wong spoke failed to find an association between tenofovir disoproxil treatment of HBV and the subsequent rate of HCC compared with patients treated with entecavir. That study comprised nearly 2,900 HBV patients treated at any of four Korean medical centers (J Hepatol. 2019 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.028).
Dr. Wong noted that although current guidelines from EASL cite both tenofovir disoproxil and entecavir (as well as tenofovir alafenamide [Vemlidy]) as first-line treatments for chronic HBV infection (J Hepatol. 2017 Aug;67[2]:370-98), some evidence suggests that tenofovir disoproxil might produce effects subtly different from those of entecavir.
At the meeting in Vienna, for example, a report on 176 Japanese patients with chronic HBV showed that those who were treated with a nucleotide analog such as tenofovir disoproxil produced higher serum levels of interferon-lamda3 compared with patients treated with entecavir, and increased levels of this interferon could improve clearance of HBV surface antigen (J Hepatol. 2019 April;70[1]:e477). The most recent EASL guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection also list tenofovir disoproxil, entecavir, and tenofovir alafenamide as preferred agents (Hepatology. 2018 April;67[4]:1560-99).
The data Dr. Wong and her associates analyzed came from health records kept for about 80% of Hong Kong’s population in the Clinical Data Analysis and Recording System of the Hospital Authority of Hong Kong. From January 2010 to June 2018, this database included 28,041 consecutive patients chronically infected with HBV and treated with entecavir, and 1,309 consecutive patients treated with tenofovir disoproxil. These numbers excluded patients treated for less than 6 months, patients coinfected with hepatitis C or D virus, patients with cancer diagnosed or a liver transplanted before or during their first 6 months on treatment, and patients previously treated with an interferon or nucleos(t)ide.
During an average follow-up of 2.8 years of tenofovir disoproxil treatment, 8 patients developed HCC, and during an average follow-up of 3.7 years of entecavir treatment, 1,386 patients developed HCC, reported Dr. Wong, a hepatologist and professor of medicine at the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
In a multivariate analysis that adjusted for demographic and clinical differences, treatment with tenofovir disoproxil linked with a statistically significant 68% reduced rate of HCC development compared with the entecavir-treated patients, she said. In a propensity score–weighted analysis, tenofovir disoproxil linked with a statistically significant 64% reduced rate of incident HCC, and in a propensity score–matched analysis tenofovir disoproxil linked with a 58% reduced rate of HCC, although in this analysis, which excluded many of the entecavir-treated patients and hence had less statistical power, the difference just missed statistical significance.
As an additional step to try to rule out the possible effect of unadjusted confounders, Dr. Wong and associates analyzed the links between tenofovir disoproxil and entecavir treatment and two negative-control outcomes, the incidence of lung cancer and the incidence of acute myocardial infarction. Neither of these outcomes showed a statistically significant link with one of the HBV treatments, suggesting that the link between treatment and HCC incidence did not appear because of an unadjusted confounding bias, Dr. Wong said. The Hong Kong database did not include enough patients treated with tenofovir alafenamide to allow assessment of this drug, she added.
Dr. Wong has been an adviser to Gilead and a speaker for Abbott, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, and Roche. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is marketed by Gilead, and entecavir is marketed by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Wong GL et al. J Hepatol. 2019 April;70[1]:e128.
REPORTING FROM ILC 2019
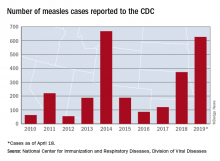
Measles cases for 2019 now at postelimination high
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
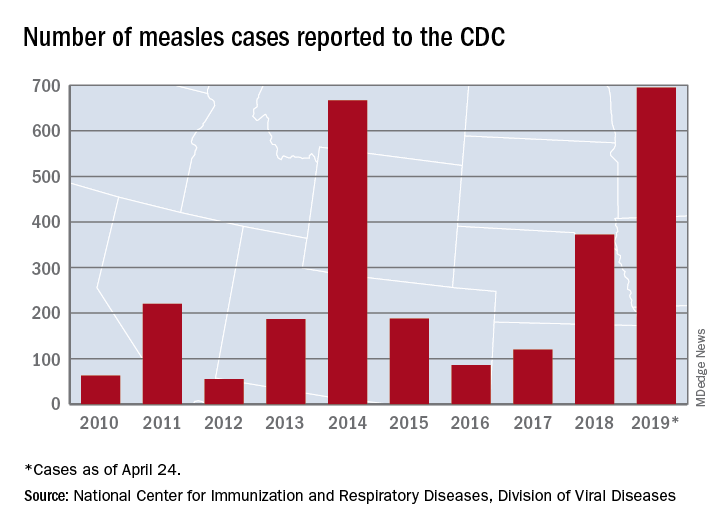
As of Wednesday, April 24, the case count for measles is 695, which eclipses the mark of 667 cases that had been the highest since the disease was declared to be eliminated from this country in 2000, the CDC reported.
“The high number of cases in 2019 is primarily the result of a few large outbreaks – one in Washington State and two large outbreaks in New York that started in late 2018. The outbreaks in New York City and New York State are among the largest and longest lasting since measles elimination in 2000. The longer these outbreaks continue, the greater the chance measles will again get a sustained foothold in the United States,” according to a written statement by the CDC.
Although these outbreaks began when the virus was brought into this country by unvaccinated travelers from other countries where there is widespread transmission, “a significant factor contributing to the outbreaks in New York is misinformation in the communities about the safety of the measles/mumps/rubella vaccine. Some organizations are deliberately targeting these communities with inaccurate and misleading information about vaccines,” according to the statement.
“Measles is not a harmless childhood illness, but a highly contagious, potentially life-threatening disease,” Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar said in a separate statement. “We have the ability to safely protect our children and our communities. Vaccines are a safe, highly effective public health solution that can prevent this disease. The measles vaccines are among the most extensively studied medical products we have, and their safety has been firmly established over many years in some of the largest vaccine studies ever undertaken. With a safe and effective vaccine that protects against measles, the suffering we are seeing is avoidable.”
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

As of Wednesday, April 24, the case count for measles is 695, which eclipses the mark of 667 cases that had been the highest since the disease was declared to be eliminated from this country in 2000, the CDC reported.
“The high number of cases in 2019 is primarily the result of a few large outbreaks – one in Washington State and two large outbreaks in New York that started in late 2018. The outbreaks in New York City and New York State are among the largest and longest lasting since measles elimination in 2000. The longer these outbreaks continue, the greater the chance measles will again get a sustained foothold in the United States,” according to a written statement by the CDC.
Although these outbreaks began when the virus was brought into this country by unvaccinated travelers from other countries where there is widespread transmission, “a significant factor contributing to the outbreaks in New York is misinformation in the communities about the safety of the measles/mumps/rubella vaccine. Some organizations are deliberately targeting these communities with inaccurate and misleading information about vaccines,” according to the statement.
“Measles is not a harmless childhood illness, but a highly contagious, potentially life-threatening disease,” Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar said in a separate statement. “We have the ability to safely protect our children and our communities. Vaccines are a safe, highly effective public health solution that can prevent this disease. The measles vaccines are among the most extensively studied medical products we have, and their safety has been firmly established over many years in some of the largest vaccine studies ever undertaken. With a safe and effective vaccine that protects against measles, the suffering we are seeing is avoidable.”
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

As of Wednesday, April 24, the case count for measles is 695, which eclipses the mark of 667 cases that had been the highest since the disease was declared to be eliminated from this country in 2000, the CDC reported.
“The high number of cases in 2019 is primarily the result of a few large outbreaks – one in Washington State and two large outbreaks in New York that started in late 2018. The outbreaks in New York City and New York State are among the largest and longest lasting since measles elimination in 2000. The longer these outbreaks continue, the greater the chance measles will again get a sustained foothold in the United States,” according to a written statement by the CDC.
Although these outbreaks began when the virus was brought into this country by unvaccinated travelers from other countries where there is widespread transmission, “a significant factor contributing to the outbreaks in New York is misinformation in the communities about the safety of the measles/mumps/rubella vaccine. Some organizations are deliberately targeting these communities with inaccurate and misleading information about vaccines,” according to the statement.
“Measles is not a harmless childhood illness, but a highly contagious, potentially life-threatening disease,” Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar said in a separate statement. “We have the ability to safely protect our children and our communities. Vaccines are a safe, highly effective public health solution that can prevent this disease. The measles vaccines are among the most extensively studied medical products we have, and their safety has been firmly established over many years in some of the largest vaccine studies ever undertaken. With a safe and effective vaccine that protects against measles, the suffering we are seeing is avoidable.”
Gaps exist in rotavirus vaccination coverage in young U.S. children
falling short of the Healthy People 2020 goal of 80% complete vaccination, according to Bethany K. Sederdahl, MPH, and her associates at Emory University, Atlanta.
In an analysis published in Pediatrics of data from 14,571 children included in the 2014 National Immunization Survey, 71% of children received full vaccination for rotavirus, 15% received partial vaccination, and 14% received no vaccination. Children whose mothers were not college graduates, lived in households with at least four children, or were uninsured at any point had an increased likelihood of being unvaccinated; African American children also faced an increased risk of being unvaccinated.
Among the unvaccinated, 72% had at least one missed opportunity according to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices schedule, and 83% had at least one missed opportunity according to the World Health Organization schedule. For the partially vaccinated, 54% at least one missed opportunity according to the ACIP schedule, and 96% had at least one missed opportunity according to the WHO schedule. While poorer socioeconomic conditions were associated with the risk of being unvaccinated, children who were partially vaccinated and who missed vaccination opportunities according to the ACIP-recommended schedule were more likely to have mothers with a college degree or an income of more than $75,000.
According to the investigators, if all missed opportunities for vaccination according to the ACIP schedule were addressed, coverage would improve from 71% to 81%; if all opportunities according to the WHO schedule were addressed, coverage would increase to 94%.
“Low rotavirus vaccine uptake may be attributable to both socioeconomic barriers and possibly vaccine hesitancy. Understanding the barriers to rotavirus vaccine uptake and developing effective public health measures to promote vaccine use will be essential to reducing rotavirus morbidity in the United States,” Ms. Sederdahl and her associates wrote.
The study received no external funding. One coauthor reported receiving personal fees from AbbVie, funds to conduct clinical research from Merck, and that his institution receives funds to conduct clinical research from MedImmune, Regeneron, PaxVax, Pfizer, Merck, Novavax, Sanofi Pasteur, and Micron Technology.
SOURCE: Sederdahl BK et al. Pediatrics. 2019 Apr 25. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2498.
falling short of the Healthy People 2020 goal of 80% complete vaccination, according to Bethany K. Sederdahl, MPH, and her associates at Emory University, Atlanta.
In an analysis published in Pediatrics of data from 14,571 children included in the 2014 National Immunization Survey, 71% of children received full vaccination for rotavirus, 15% received partial vaccination, and 14% received no vaccination. Children whose mothers were not college graduates, lived in households with at least four children, or were uninsured at any point had an increased likelihood of being unvaccinated; African American children also faced an increased risk of being unvaccinated.
Among the unvaccinated, 72% had at least one missed opportunity according to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices schedule, and 83% had at least one missed opportunity according to the World Health Organization schedule. For the partially vaccinated, 54% at least one missed opportunity according to the ACIP schedule, and 96% had at least one missed opportunity according to the WHO schedule. While poorer socioeconomic conditions were associated with the risk of being unvaccinated, children who were partially vaccinated and who missed vaccination opportunities according to the ACIP-recommended schedule were more likely to have mothers with a college degree or an income of more than $75,000.
According to the investigators, if all missed opportunities for vaccination according to the ACIP schedule were addressed, coverage would improve from 71% to 81%; if all opportunities according to the WHO schedule were addressed, coverage would increase to 94%.
“Low rotavirus vaccine uptake may be attributable to both socioeconomic barriers and possibly vaccine hesitancy. Understanding the barriers to rotavirus vaccine uptake and developing effective public health measures to promote vaccine use will be essential to reducing rotavirus morbidity in the United States,” Ms. Sederdahl and her associates wrote.
The study received no external funding. One coauthor reported receiving personal fees from AbbVie, funds to conduct clinical research from Merck, and that his institution receives funds to conduct clinical research from MedImmune, Regeneron, PaxVax, Pfizer, Merck, Novavax, Sanofi Pasteur, and Micron Technology.
SOURCE: Sederdahl BK et al. Pediatrics. 2019 Apr 25. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2498.
falling short of the Healthy People 2020 goal of 80% complete vaccination, according to Bethany K. Sederdahl, MPH, and her associates at Emory University, Atlanta.
In an analysis published in Pediatrics of data from 14,571 children included in the 2014 National Immunization Survey, 71% of children received full vaccination for rotavirus, 15% received partial vaccination, and 14% received no vaccination. Children whose mothers were not college graduates, lived in households with at least four children, or were uninsured at any point had an increased likelihood of being unvaccinated; African American children also faced an increased risk of being unvaccinated.
Among the unvaccinated, 72% had at least one missed opportunity according to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices schedule, and 83% had at least one missed opportunity according to the World Health Organization schedule. For the partially vaccinated, 54% at least one missed opportunity according to the ACIP schedule, and 96% had at least one missed opportunity according to the WHO schedule. While poorer socioeconomic conditions were associated with the risk of being unvaccinated, children who were partially vaccinated and who missed vaccination opportunities according to the ACIP-recommended schedule were more likely to have mothers with a college degree or an income of more than $75,000.
According to the investigators, if all missed opportunities for vaccination according to the ACIP schedule were addressed, coverage would improve from 71% to 81%; if all opportunities according to the WHO schedule were addressed, coverage would increase to 94%.
“Low rotavirus vaccine uptake may be attributable to both socioeconomic barriers and possibly vaccine hesitancy. Understanding the barriers to rotavirus vaccine uptake and developing effective public health measures to promote vaccine use will be essential to reducing rotavirus morbidity in the United States,” Ms. Sederdahl and her associates wrote.
The study received no external funding. One coauthor reported receiving personal fees from AbbVie, funds to conduct clinical research from Merck, and that his institution receives funds to conduct clinical research from MedImmune, Regeneron, PaxVax, Pfizer, Merck, Novavax, Sanofi Pasteur, and Micron Technology.
SOURCE: Sederdahl BK et al. Pediatrics. 2019 Apr 25. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2498.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Are you offering vaccines to adults for these 5 conditions?
References
1. Grohskopf LA, Sokolow LZ, Broder KR, et al. Prevention and control of seasonal influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, 2018-19 influenza season. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2018;67:1-20.
2. Liang JL, Tiwari T, Moro P, et al. Prevention of pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria with vaccines in the United States: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2018;67:1-44.
3. Dooling KL, Guo A, Patel M, et al. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for use of herpes zoster vaccines. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:103-108.
4. Kobayashi M, Bennett NM, Gierke R, et al. Intervals between PCV13 and PPSV23 vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64;944-947.
5. Meites E, Kempe A, Markowitz LE. Use of a 2-dose schedule for human papillomavirus vaccination—updated recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65:1405-1408.
6. Adult immunization schedule. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/imz/adult.html. Reviewed February 5, 2019. Accessed April 23, 2019.
References
1. Grohskopf LA, Sokolow LZ, Broder KR, et al. Prevention and control of seasonal influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, 2018-19 influenza season. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2018;67:1-20.
2. Liang JL, Tiwari T, Moro P, et al. Prevention of pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria with vaccines in the United States: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2018;67:1-44.
3. Dooling KL, Guo A, Patel M, et al. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for use of herpes zoster vaccines. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:103-108.
4. Kobayashi M, Bennett NM, Gierke R, et al. Intervals between PCV13 and PPSV23 vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64;944-947.
5. Meites E, Kempe A, Markowitz LE. Use of a 2-dose schedule for human papillomavirus vaccination—updated recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65:1405-1408.
6. Adult immunization schedule. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/imz/adult.html. Reviewed February 5, 2019. Accessed April 23, 2019.
References
1. Grohskopf LA, Sokolow LZ, Broder KR, et al. Prevention and control of seasonal influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, 2018-19 influenza season. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2018;67:1-20.
2. Liang JL, Tiwari T, Moro P, et al. Prevention of pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria with vaccines in the United States: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2018;67:1-44.
3. Dooling KL, Guo A, Patel M, et al. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for use of herpes zoster vaccines. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:103-108.
4. Kobayashi M, Bennett NM, Gierke R, et al. Intervals between PCV13 and PPSV23 vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64;944-947.
5. Meites E, Kempe A, Markowitz LE. Use of a 2-dose schedule for human papillomavirus vaccination—updated recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65:1405-1408.
6. Adult immunization schedule. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/imz/adult.html. Reviewed February 5, 2019. Accessed April 23, 2019.
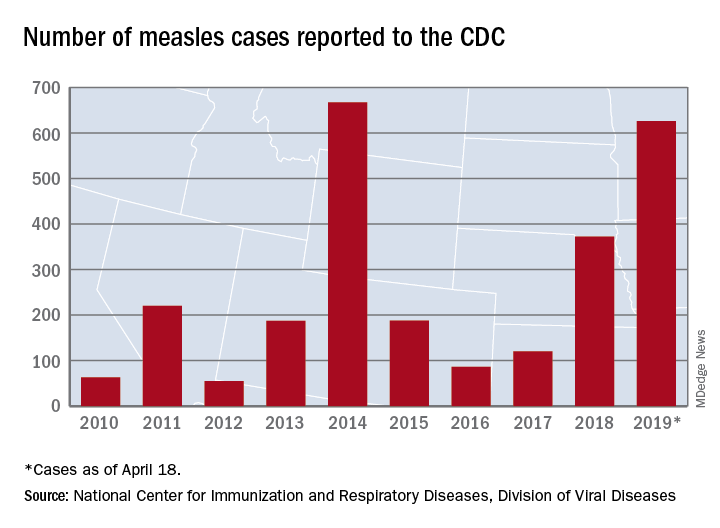
U.S. measles cases nearing postelimination-era high
The United States has topped 600 cases of measles for 2019 and is likely to pass the postelimination high set in 2014 “in the coming weeks,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The 71 new measles cases reported during the week ending April 18 bring the total for the year to 626 in 22 states, the CDC reported April 22. Two states, Iowa and Tennessee, reported their first cases last week.
Outbreaks continue in five states: one in California (Butte County), one in Michigan (Oakland County/Wayne County/Detroit), one in New Jersey (Ocean County/Monmouth County), two in New York (New York City and Rockland County), and one in Washington (Clark County/King County), the CDC said.
The most active outbreak since mid-February has been the one occurring in New York City, mainly in Brooklyn, and last week was no exception as 50 of the 71 new U.S. cases were reported in the borough.
On April 18, a judge in Brooklyn “ruled against a group of parents who challenged New York City’s recently imposed mandatory measles vaccination order,” Reuters reported. That same day, the city issued a summons, subject to a fine of $1,000 each, to three people in Brooklyn who were still unvaccinated, according to NYC Health, which also said that four additional schools would be closed for not complying with an order to exclude unvaccinated students.
On April 15, the Iowa Department of Public Health confirmed the state’s first case of measles since 2011. The individual from Northeastern Iowa had not been vaccinated and had recently returned from Israel. The state’s second case of the year, a household contact of the first individual, was confirmed on April 18.
Also on April 18, the Tennessee Department of Health confirmed its first case of the year in a resident of the eastern part of the state. Meanwhile, media are reporting that state health officials in Mississippi are investigating possible exposures on April 9 and 10 in the Hattiesburg area by the infected Tennessee man.
Outside the United States, “many countries are in the midst of sizeable measles outbreaks, with all regions of the world experiencing sustained rises in cases,” the World Health Organization said. Current outbreaks include the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Madagascar, Myanmar, Philippines, Sudan, Thailand, and Ukraine.
Preliminary data for the first 3 months of 2019 show that cases worldwide were up by 300% over the first 3 months of 2018: 112,163 cases vs. 28,124. The actual numbers for 2019 are expected to be considerably higher than those reported so far, and WHO estimates that, globally, less than 1 in 10 cases are actually reported.
The United States has topped 600 cases of measles for 2019 and is likely to pass the postelimination high set in 2014 “in the coming weeks,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The 71 new measles cases reported during the week ending April 18 bring the total for the year to 626 in 22 states, the CDC reported April 22. Two states, Iowa and Tennessee, reported their first cases last week.
Outbreaks continue in five states: one in California (Butte County), one in Michigan (Oakland County/Wayne County/Detroit), one in New Jersey (Ocean County/Monmouth County), two in New York (New York City and Rockland County), and one in Washington (Clark County/King County), the CDC said.
The most active outbreak since mid-February has been the one occurring in New York City, mainly in Brooklyn, and last week was no exception as 50 of the 71 new U.S. cases were reported in the borough.
On April 18, a judge in Brooklyn “ruled against a group of parents who challenged New York City’s recently imposed mandatory measles vaccination order,” Reuters reported. That same day, the city issued a summons, subject to a fine of $1,000 each, to three people in Brooklyn who were still unvaccinated, according to NYC Health, which also said that four additional schools would be closed for not complying with an order to exclude unvaccinated students.
On April 15, the Iowa Department of Public Health confirmed the state’s first case of measles since 2011. The individual from Northeastern Iowa had not been vaccinated and had recently returned from Israel. The state’s second case of the year, a household contact of the first individual, was confirmed on April 18.
Also on April 18, the Tennessee Department of Health confirmed its first case of the year in a resident of the eastern part of the state. Meanwhile, media are reporting that state health officials in Mississippi are investigating possible exposures on April 9 and 10 in the Hattiesburg area by the infected Tennessee man.
Outside the United States, “many countries are in the midst of sizeable measles outbreaks, with all regions of the world experiencing sustained rises in cases,” the World Health Organization said. Current outbreaks include the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Madagascar, Myanmar, Philippines, Sudan, Thailand, and Ukraine.
Preliminary data for the first 3 months of 2019 show that cases worldwide were up by 300% over the first 3 months of 2018: 112,163 cases vs. 28,124. The actual numbers for 2019 are expected to be considerably higher than those reported so far, and WHO estimates that, globally, less than 1 in 10 cases are actually reported.
The United States has topped 600 cases of measles for 2019 and is likely to pass the postelimination high set in 2014 “in the coming weeks,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The 71 new measles cases reported during the week ending April 18 bring the total for the year to 626 in 22 states, the CDC reported April 22. Two states, Iowa and Tennessee, reported their first cases last week.
Outbreaks continue in five states: one in California (Butte County), one in Michigan (Oakland County/Wayne County/Detroit), one in New Jersey (Ocean County/Monmouth County), two in New York (New York City and Rockland County), and one in Washington (Clark County/King County), the CDC said.
The most active outbreak since mid-February has been the one occurring in New York City, mainly in Brooklyn, and last week was no exception as 50 of the 71 new U.S. cases were reported in the borough.
On April 18, a judge in Brooklyn “ruled against a group of parents who challenged New York City’s recently imposed mandatory measles vaccination order,” Reuters reported. That same day, the city issued a summons, subject to a fine of $1,000 each, to three people in Brooklyn who were still unvaccinated, according to NYC Health, which also said that four additional schools would be closed for not complying with an order to exclude unvaccinated students.
On April 15, the Iowa Department of Public Health confirmed the state’s first case of measles since 2011. The individual from Northeastern Iowa had not been vaccinated and had recently returned from Israel. The state’s second case of the year, a household contact of the first individual, was confirmed on April 18.
Also on April 18, the Tennessee Department of Health confirmed its first case of the year in a resident of the eastern part of the state. Meanwhile, media are reporting that state health officials in Mississippi are investigating possible exposures on April 9 and 10 in the Hattiesburg area by the infected Tennessee man.
Outside the United States, “many countries are in the midst of sizeable measles outbreaks, with all regions of the world experiencing sustained rises in cases,” the World Health Organization said. Current outbreaks include the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Madagascar, Myanmar, Philippines, Sudan, Thailand, and Ukraine.
Preliminary data for the first 3 months of 2019 show that cases worldwide were up by 300% over the first 3 months of 2018: 112,163 cases vs. 28,124. The actual numbers for 2019 are expected to be considerably higher than those reported so far, and WHO estimates that, globally, less than 1 in 10 cases are actually reported.
Gut bacterium R. gnavus linked to lupus flares
SAN FRANCISCO –
Not only that, but those patients also had highly elevated antibodies to an endotoxin-like antigen released by one particular R. gnavus strain.
That antigen is “very proinflammatory, very immunogenic. We are wondering if this is actually [what drives] the immune activation that results in immune complexes in the glomeruli” of patients with lupus nephritis, said investigator Gregg Silverman, MD, a professor of medicine and pathology and head of the laboratory of B-cell immunobiology at New York University.
R. gnavus is an obligate anaerobe found in the guts of most people, but in lupus, it might be a problem.
“We are finding a very specific relationship with lupus patients and this bacteria – and this particular antibody,” Dr. Silverman explained in an interview at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus. “There’s an expansion of this particular bug, but also a contraction of others” as disease activity progresses.
“It speaks to an imbalance,” he added, and it suggests a role for probiotics or even fecal transplants to restore order.
“What if instead of killing the immune system” in lupus treatment, “we should be reducing or removing a single bacterium or a single molecule?” he asked.
Dr. Silverman is one of many researchers working to unravel the role of the human microbiome in both disease and health. His findings are preliminary, and, as he cautioned, correlation is not causation. But the implications are remarkable, Dr. Silverman noted.
SAN FRANCISCO –
Not only that, but those patients also had highly elevated antibodies to an endotoxin-like antigen released by one particular R. gnavus strain.
That antigen is “very proinflammatory, very immunogenic. We are wondering if this is actually [what drives] the immune activation that results in immune complexes in the glomeruli” of patients with lupus nephritis, said investigator Gregg Silverman, MD, a professor of medicine and pathology and head of the laboratory of B-cell immunobiology at New York University.
R. gnavus is an obligate anaerobe found in the guts of most people, but in lupus, it might be a problem.
“We are finding a very specific relationship with lupus patients and this bacteria – and this particular antibody,” Dr. Silverman explained in an interview at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus. “There’s an expansion of this particular bug, but also a contraction of others” as disease activity progresses.
“It speaks to an imbalance,” he added, and it suggests a role for probiotics or even fecal transplants to restore order.
“What if instead of killing the immune system” in lupus treatment, “we should be reducing or removing a single bacterium or a single molecule?” he asked.
Dr. Silverman is one of many researchers working to unravel the role of the human microbiome in both disease and health. His findings are preliminary, and, as he cautioned, correlation is not causation. But the implications are remarkable, Dr. Silverman noted.
SAN FRANCISCO –
Not only that, but those patients also had highly elevated antibodies to an endotoxin-like antigen released by one particular R. gnavus strain.
That antigen is “very proinflammatory, very immunogenic. We are wondering if this is actually [what drives] the immune activation that results in immune complexes in the glomeruli” of patients with lupus nephritis, said investigator Gregg Silverman, MD, a professor of medicine and pathology and head of the laboratory of B-cell immunobiology at New York University.
R. gnavus is an obligate anaerobe found in the guts of most people, but in lupus, it might be a problem.
“We are finding a very specific relationship with lupus patients and this bacteria – and this particular antibody,” Dr. Silverman explained in an interview at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus. “There’s an expansion of this particular bug, but also a contraction of others” as disease activity progresses.
“It speaks to an imbalance,” he added, and it suggests a role for probiotics or even fecal transplants to restore order.
“What if instead of killing the immune system” in lupus treatment, “we should be reducing or removing a single bacterium or a single molecule?” he asked.
Dr. Silverman is one of many researchers working to unravel the role of the human microbiome in both disease and health. His findings are preliminary, and, as he cautioned, correlation is not causation. But the implications are remarkable, Dr. Silverman noted.
REPORTING FROM LUPUS 2019
Decline in CIN2+ in younger women after HPV vaccine introduced
The introduction of human papillomavirus vaccination in the United States in 2006 was associated with a significant decrease in the rates of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grades 2 and above (CIN2+) in younger women.
The overall rate of CIN2+ declined from an estimated 216,000 cases in 2008 – 55% of which were in women aged 18-29 years – to 196,000 cases in 2016, of which 36% were in women aged 18-29 years, according to analysis of data from the Human Papillomavirus Vaccine Impact Monitoring Program (MMWR. 2019 Apr 19;68:337-43.
In 2008, the highest rates of CIN2+ were seen in women aged 20-24 years and decreased with age, but in 2016, the highest rates were in women aged 25-29 years. The rates of CIN2+ declined significantly in women aged 18-19 years from 2008-2016, but increased in women aged 40-64 years.
In 2008 and 2016, around three-quarters of all CIN2+ cases were attributable to HPV types that are targeted by the HPV vaccine. However the rates of vaccine-preventable CIN2+ declined among women aged 18-24 years, from 52% in 2008 to 30% in 2016.
“Both the estimated number and rates of U.S. CIN2+ cases in this report must be interpreted in the context of cervical cancer prevention strategies, including HPV vaccination and cervical cancer screening,” wrote Nancy M. McClung, PhD, of the Epidemic Intelligence Service at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and coauthors.
Notably, the screening interval for cervical cancer was increased from yearly in 2008 to once in 3 years with cytology alone or once in 5 years with cytology plus HPV testing for women aged 30 or above in 2016.
“Older age at screening initiation, longer screening intervals, and more conservative management in young women might be expected to reduce the number of CIN2+ cases detected in younger age groups in whom lesions are most likely to regress and shift detection of some CIN2+ to older age groups, resulting in a transient increase in rates,” Dr. McClung and colleagues wrote.
However they noted that the decrease in HPV 16/18–attributable CIN2+ rates among younger age groups was likely a reflection of the impact of the introduction of the quadrivalent vaccine immunization program.
One author declared personal fees from Merck during the course of the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: McClung N et al. MMWR. 2019 Apr 19;68:337-43.
The introduction of human papillomavirus vaccination in the United States in 2006 was associated with a significant decrease in the rates of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grades 2 and above (CIN2+) in younger women.
The overall rate of CIN2+ declined from an estimated 216,000 cases in 2008 – 55% of which were in women aged 18-29 years – to 196,000 cases in 2016, of which 36% were in women aged 18-29 years, according to analysis of data from the Human Papillomavirus Vaccine Impact Monitoring Program (MMWR. 2019 Apr 19;68:337-43.
In 2008, the highest rates of CIN2+ were seen in women aged 20-24 years and decreased with age, but in 2016, the highest rates were in women aged 25-29 years. The rates of CIN2+ declined significantly in women aged 18-19 years from 2008-2016, but increased in women aged 40-64 years.
In 2008 and 2016, around three-quarters of all CIN2+ cases were attributable to HPV types that are targeted by the HPV vaccine. However the rates of vaccine-preventable CIN2+ declined among women aged 18-24 years, from 52% in 2008 to 30% in 2016.
“Both the estimated number and rates of U.S. CIN2+ cases in this report must be interpreted in the context of cervical cancer prevention strategies, including HPV vaccination and cervical cancer screening,” wrote Nancy M. McClung, PhD, of the Epidemic Intelligence Service at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and coauthors.
Notably, the screening interval for cervical cancer was increased from yearly in 2008 to once in 3 years with cytology alone or once in 5 years with cytology plus HPV testing for women aged 30 or above in 2016.
“Older age at screening initiation, longer screening intervals, and more conservative management in young women might be expected to reduce the number of CIN2+ cases detected in younger age groups in whom lesions are most likely to regress and shift detection of some CIN2+ to older age groups, resulting in a transient increase in rates,” Dr. McClung and colleagues wrote.
However they noted that the decrease in HPV 16/18–attributable CIN2+ rates among younger age groups was likely a reflection of the impact of the introduction of the quadrivalent vaccine immunization program.
One author declared personal fees from Merck during the course of the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: McClung N et al. MMWR. 2019 Apr 19;68:337-43.
The introduction of human papillomavirus vaccination in the United States in 2006 was associated with a significant decrease in the rates of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grades 2 and above (CIN2+) in younger women.
The overall rate of CIN2+ declined from an estimated 216,000 cases in 2008 – 55% of which were in women aged 18-29 years – to 196,000 cases in 2016, of which 36% were in women aged 18-29 years, according to analysis of data from the Human Papillomavirus Vaccine Impact Monitoring Program (MMWR. 2019 Apr 19;68:337-43.
In 2008, the highest rates of CIN2+ were seen in women aged 20-24 years and decreased with age, but in 2016, the highest rates were in women aged 25-29 years. The rates of CIN2+ declined significantly in women aged 18-19 years from 2008-2016, but increased in women aged 40-64 years.
In 2008 and 2016, around three-quarters of all CIN2+ cases were attributable to HPV types that are targeted by the HPV vaccine. However the rates of vaccine-preventable CIN2+ declined among women aged 18-24 years, from 52% in 2008 to 30% in 2016.
“Both the estimated number and rates of U.S. CIN2+ cases in this report must be interpreted in the context of cervical cancer prevention strategies, including HPV vaccination and cervical cancer screening,” wrote Nancy M. McClung, PhD, of the Epidemic Intelligence Service at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and coauthors.
Notably, the screening interval for cervical cancer was increased from yearly in 2008 to once in 3 years with cytology alone or once in 5 years with cytology plus HPV testing for women aged 30 or above in 2016.
“Older age at screening initiation, longer screening intervals, and more conservative management in young women might be expected to reduce the number of CIN2+ cases detected in younger age groups in whom lesions are most likely to regress and shift detection of some CIN2+ to older age groups, resulting in a transient increase in rates,” Dr. McClung and colleagues wrote.
However they noted that the decrease in HPV 16/18–attributable CIN2+ rates among younger age groups was likely a reflection of the impact of the introduction of the quadrivalent vaccine immunization program.
One author declared personal fees from Merck during the course of the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: McClung N et al. MMWR. 2019 Apr 19;68:337-43.
FROM MMWR
Ibrexafungerp effective against C. auris in two early case reports
A novel antifungal successfully eradicated Candida auris in two critically ill patients with fungemia, according to data presented in a poster session at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
The case reports, drawn from the phase 3 CARES study of the oral formulation of ibrexafungerp, demonstrated complete response to the glucan synthase inhibitor, according to Deven Juneja, MD, and his coauthors of the Max Super Specialty Hospital, New Delhi.
The first patient was an Asian male, aged 58 years, who had a previous history of diabetes and experienced a protracted ICU stay after acute ischemic stroke. He developed septic shock after aspiration pneumonia, and also experienced a popliteal thrombosis and liver, spleen, and kidney infarcts.
The patient had received empiric antibiotics with the addition of fluconazole; the antifungal was later switched to micafungin after C. auris was identified from blood cultures. Despite clinical improvement on micafungin, blood cultures remained positive for C. auris, so ibrexafungerp was started and continued for 17 days. Blood cultures became negative by day 3 of ibrexafungerp and remained negative for the follow-up period. The patient later developed Klebsiella pneumonia and died.
The second patient, an Asian female, aged 64 years, presented with a lower respiratory tract infection accompanied by fever and hypotension. She had a previous history of diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease with maintenance hemodialysis. Her fever also persisted despite antibiotics, and C. auris was isolated from her blood cultures with the subsequent initiation of ibrexafungerp. Her blood cultures were still positive at day 3 of ibrexafungerp, but negative at day 9 and 21. She completed 22 days of ibrexafungerp therapy and was asymptomatic with no evidence of C. auris recurrence at a 6-week follow-up visit.
The male patient experienced 2 days of loose stools soon after initiating ibrexafungerp; the female patient had no adverse events.
“These cases provide initial evidence of efficacy and safety of ibrexafungerp in the treatment of candidemia caused by C. auris, including in patients who failed previous therapies,” wrote Dr. Juneja and his coauthors in the late-breaking poster.
Ibrexafungerp belongs to a novel class of glucan synthase inhibitors called triterpenoids. Scynexis funded the CARES study and also is evaluating it alone or in combination with other antifungals for treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis, invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, and refractory invasive and/or severe fungal disease.
SOURCE: Juneja D et al. ECCMID 2019, Poster L0028.
A novel antifungal successfully eradicated Candida auris in two critically ill patients with fungemia, according to data presented in a poster session at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
The case reports, drawn from the phase 3 CARES study of the oral formulation of ibrexafungerp, demonstrated complete response to the glucan synthase inhibitor, according to Deven Juneja, MD, and his coauthors of the Max Super Specialty Hospital, New Delhi.
The first patient was an Asian male, aged 58 years, who had a previous history of diabetes and experienced a protracted ICU stay after acute ischemic stroke. He developed septic shock after aspiration pneumonia, and also experienced a popliteal thrombosis and liver, spleen, and kidney infarcts.
The patient had received empiric antibiotics with the addition of fluconazole; the antifungal was later switched to micafungin after C. auris was identified from blood cultures. Despite clinical improvement on micafungin, blood cultures remained positive for C. auris, so ibrexafungerp was started and continued for 17 days. Blood cultures became negative by day 3 of ibrexafungerp and remained negative for the follow-up period. The patient later developed Klebsiella pneumonia and died.
The second patient, an Asian female, aged 64 years, presented with a lower respiratory tract infection accompanied by fever and hypotension. She had a previous history of diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease with maintenance hemodialysis. Her fever also persisted despite antibiotics, and C. auris was isolated from her blood cultures with the subsequent initiation of ibrexafungerp. Her blood cultures were still positive at day 3 of ibrexafungerp, but negative at day 9 and 21. She completed 22 days of ibrexafungerp therapy and was asymptomatic with no evidence of C. auris recurrence at a 6-week follow-up visit.
The male patient experienced 2 days of loose stools soon after initiating ibrexafungerp; the female patient had no adverse events.
“These cases provide initial evidence of efficacy and safety of ibrexafungerp in the treatment of candidemia caused by C. auris, including in patients who failed previous therapies,” wrote Dr. Juneja and his coauthors in the late-breaking poster.
Ibrexafungerp belongs to a novel class of glucan synthase inhibitors called triterpenoids. Scynexis funded the CARES study and also is evaluating it alone or in combination with other antifungals for treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis, invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, and refractory invasive and/or severe fungal disease.
SOURCE: Juneja D et al. ECCMID 2019, Poster L0028.
A novel antifungal successfully eradicated Candida auris in two critically ill patients with fungemia, according to data presented in a poster session at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
The case reports, drawn from the phase 3 CARES study of the oral formulation of ibrexafungerp, demonstrated complete response to the glucan synthase inhibitor, according to Deven Juneja, MD, and his coauthors of the Max Super Specialty Hospital, New Delhi.
The first patient was an Asian male, aged 58 years, who had a previous history of diabetes and experienced a protracted ICU stay after acute ischemic stroke. He developed septic shock after aspiration pneumonia, and also experienced a popliteal thrombosis and liver, spleen, and kidney infarcts.
The patient had received empiric antibiotics with the addition of fluconazole; the antifungal was later switched to micafungin after C. auris was identified from blood cultures. Despite clinical improvement on micafungin, blood cultures remained positive for C. auris, so ibrexafungerp was started and continued for 17 days. Blood cultures became negative by day 3 of ibrexafungerp and remained negative for the follow-up period. The patient later developed Klebsiella pneumonia and died.
The second patient, an Asian female, aged 64 years, presented with a lower respiratory tract infection accompanied by fever and hypotension. She had a previous history of diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease with maintenance hemodialysis. Her fever also persisted despite antibiotics, and C. auris was isolated from her blood cultures with the subsequent initiation of ibrexafungerp. Her blood cultures were still positive at day 3 of ibrexafungerp, but negative at day 9 and 21. She completed 22 days of ibrexafungerp therapy and was asymptomatic with no evidence of C. auris recurrence at a 6-week follow-up visit.
The male patient experienced 2 days of loose stools soon after initiating ibrexafungerp; the female patient had no adverse events.
“These cases provide initial evidence of efficacy and safety of ibrexafungerp in the treatment of candidemia caused by C. auris, including in patients who failed previous therapies,” wrote Dr. Juneja and his coauthors in the late-breaking poster.
Ibrexafungerp belongs to a novel class of glucan synthase inhibitors called triterpenoids. Scynexis funded the CARES study and also is evaluating it alone or in combination with other antifungals for treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis, invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, and refractory invasive and/or severe fungal disease.
SOURCE: Juneja D et al. ECCMID 2019, Poster L0028.
FROM ECCMID 2019
Candida auris: Dangerous and here to stay
Critical care units and long-term care facilities are on alert for cases of Candida auris, a novel fungal infection that is both dangerous to vulnerable patients and difficult to eradicate. The increased profile of C. auris is not a welcome development but is no surprise to critical care physicians.
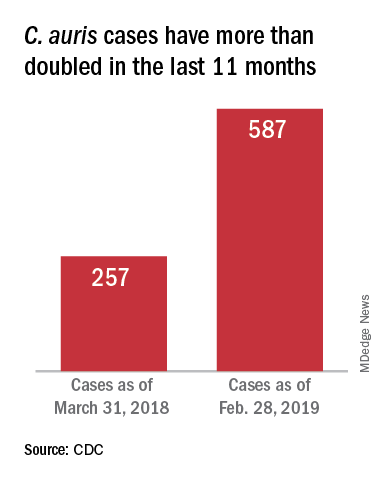
This pathogen was first identified in 2009 and has since been found in increasing numbers of patients all over the world. As expected, cases of C. auris are on the rise in the United States.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention stated “Candida auris is an emerging fungus that presents a serious global health threat.” This is an opportunistic pathogen that hits critically ill patients and those with compromised immunity.
On March 29, 2019, CDC reported that confirmed clinical cases of C. auris in the United States have more than doubled over the past year, from 257 cases in 2018 to 587 cases with an additional 1,056 colonized patients identified as of February 2019. “Most C. auris cases in the United States have been detected in the New York City area, New Jersey, and the Chicago area. Strains of C. auris in the United States have been linked to other parts of the world. U.S. C. auris cases are a result of inadvertent introduction into the United States from a patient who recently received health care in a country where C. auris has been reported or a result of local spread after such an introduction.”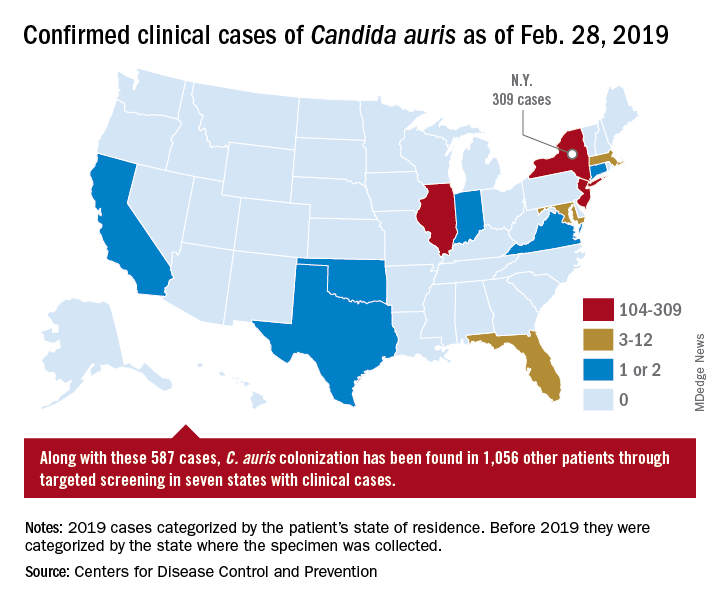
Case reports have found a mortality rate of up to 50% in patients with C. auris candidemia. The total number of cases is still small, but the trajectory is clear. The hunt is on in labs all over the world for optimal treatments and processes to handle outbreaks.
Jeniel Nett, MD, an infectious disease specialist, and a team of investigators at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, have focused their research on the characteristics of C. auris and its progression in patients and in medical facilities.
According to Dr. Nett, it’s not clear why this emerging threat has cropped up in multiple locations globally. “Candida auris was first recognized in 2009, in Japan, and relatively quickly we saw emergence of this species in relatively distant locations,” she said, adding that independent clades in these locations ruled out transmission as the source of the multiple outbreaks. Antifungal resistance is an epidemiologic area of concern and increased antifungal use may be a contributor, she said.

Once established, the organism is persistent: “It is found on mattresses, on bedsheets, IV poles, and a lot of reusable equipment,” said Dr. Nett in an interview. “It appears to persist in the environment for weeks – maybe longer.” In addition, “it seems to behave differently than a lot of the Candida species that we see; it readily colonizes the skin” to a much greater extent than does other Candida species, she said. “This allows it to be transmitted readily person to person, particularly in the hospitalized setting.” However, it can also colonize both the urinary and respiratory tracts, she said.
Which patients are susceptible to C. auris candidemia? “Many of these patients have undergone multiple procedures; they may have undergone mechanical ventilation as well as different surgical procedures,” said Dr. Nett. Affected patients often have received many rounds of antibiotic and antifungal treatment as well, she said, and may have an underlying illness like diabetes or malignancy.
Studies of C. auris outbreaks have begun to appear in the literature and give clinicians some perspective on the progression of an outbreak and potential strategies for containment. A prospective cohort study of a large outbreak of C. auris was conducted by Alba Ruiz-Gaitán, MD, and her colleagues at La Fe University and Polytechnic Hospital, Valencia, Spain (Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2019 Apr;17[4]:295-305). The researchers followed 114 patients who were colonized with C. auris or had C. auris candidemia. The patients were compared with 114 case-matched controls within the hospital’s adult surgical and medical intensive care units over an 11-month period during the hospital’s protracted outbreak.
The investigators found a crude mortality rate of 58.5% at 30 days for patients with C. auris candidemia. All isolates in the study were completely resistant to fluconazole and had reduced susceptibility to voriconazole.
In critical care units at Hospital La Fe, investigators found C. auris on 25% of blood pressure cuffs, 10% of patient tables and keyboards, and 8% of infusion pumps.
Among the patients at Hospital La Fe, multivariable analysis revealed that those most likely to develop C. auris colonization or candidemia were individuals with polytrauma, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
Patients receiving parenteral nutrition (odds ratio, 3.49), mechanical ventilation (OR, 2.43), and especially those having indwelling central venous catheters (OR, 13.48) were more likely to be colonized or have candidemia as well, according to Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her coauthors.
Once identified, how should C. auris be treated? “The majority of strains – upward of 90% – are resistant to fluconazole,” said Dr. Nett. “Moreover, 30%-50% of them are resistant to another antifungal, often amphotericin B. The isolates that we see in the United States are most often susceptible to an echinocandin, and echinocandins remain the choice for treatment of Candida auris pending susceptibility tests.”
However, in Valencia, “The susceptibility to echinocandins presented interesting features. These antifungals were not fungicidal against C. auris,” wrote Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her colleagues. They found that for caspofungin, “most isolates presented a clear paradoxical growth after 24 hours of incubation.” Additionally, fungal growth was inhibited at lower caspofungin concentrations, but rebounded at higher levels. Similar patterns were seen for anidulafungin and micafungin, they said.
These findings meant that Hospital La Fe patients received initial treatment with echinocandins, with the addition of liposomal amphotericin B or isavuconazole if candidemia persisted or clinical response was not seen, wrote the investigators.
Patient presentation is similar to other forms of candidiasis, said Dr. Nett. “Patients often have fever, chills, leukocytosis, and this persists despite antibacterial therapy… If Candida auris is suspected, the first course of action would be to place the patient in isolation, and laboratory staff should be alerted regarding the diagnosis.”
Most large clinical laboratories, she said, can now detect C. auris. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization–time of flight is the identification technique of choice, provided that the databases are updated.
Smaller laboratories that use phenotypic tests may misidentify C. auris as another Candida species, or even as Saccharomyces cerevisiae – common beer yeast. Facilities without matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization can find guidance for interpretation of phenotypic testing on the CDC website as well, said Dr. Nett.
After experiencing what they believe to be the largest C. auris outbreak at a single European hospital, Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her colleagues offered best-practice tips for treatment of patients with C. auris candidemia. These include removing mechanical devices as early as is safely practical; performing ophthalmologic examinations for endophthalmitis, a known C. auris complication; obtaining blood cultures every other day to track antimicrobial therapy to the point of sterilization; and searching for metastatic foci if blood cultures remain positive.
All instances of C. auris laboratory identification should be reported to the CDC at [email protected], and to local and state health agencies. The CDC recommends strict isolation and cleaning protocols, similar to those used for the spore-forming Clostridium difficile.
Dr. Nett reported funding support from the National Institutes of Health, the Burroughs Wellcome Fund, and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation. She reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her collaborators reported funding from Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain, and the Spanish Ministry of Science and University. They reported no conflicts of interest.
Critical care units and long-term care facilities are on alert for cases of Candida auris, a novel fungal infection that is both dangerous to vulnerable patients and difficult to eradicate. The increased profile of C. auris is not a welcome development but is no surprise to critical care physicians.

This pathogen was first identified in 2009 and has since been found in increasing numbers of patients all over the world. As expected, cases of C. auris are on the rise in the United States.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention stated “Candida auris is an emerging fungus that presents a serious global health threat.” This is an opportunistic pathogen that hits critically ill patients and those with compromised immunity.
On March 29, 2019, CDC reported that confirmed clinical cases of C. auris in the United States have more than doubled over the past year, from 257 cases in 2018 to 587 cases with an additional 1,056 colonized patients identified as of February 2019. “Most C. auris cases in the United States have been detected in the New York City area, New Jersey, and the Chicago area. Strains of C. auris in the United States have been linked to other parts of the world. U.S. C. auris cases are a result of inadvertent introduction into the United States from a patient who recently received health care in a country where C. auris has been reported or a result of local spread after such an introduction.”
Case reports have found a mortality rate of up to 50% in patients with C. auris candidemia. The total number of cases is still small, but the trajectory is clear. The hunt is on in labs all over the world for optimal treatments and processes to handle outbreaks.
Jeniel Nett, MD, an infectious disease specialist, and a team of investigators at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, have focused their research on the characteristics of C. auris and its progression in patients and in medical facilities.
According to Dr. Nett, it’s not clear why this emerging threat has cropped up in multiple locations globally. “Candida auris was first recognized in 2009, in Japan, and relatively quickly we saw emergence of this species in relatively distant locations,” she said, adding that independent clades in these locations ruled out transmission as the source of the multiple outbreaks. Antifungal resistance is an epidemiologic area of concern and increased antifungal use may be a contributor, she said.

Once established, the organism is persistent: “It is found on mattresses, on bedsheets, IV poles, and a lot of reusable equipment,” said Dr. Nett in an interview. “It appears to persist in the environment for weeks – maybe longer.” In addition, “it seems to behave differently than a lot of the Candida species that we see; it readily colonizes the skin” to a much greater extent than does other Candida species, she said. “This allows it to be transmitted readily person to person, particularly in the hospitalized setting.” However, it can also colonize both the urinary and respiratory tracts, she said.
Which patients are susceptible to C. auris candidemia? “Many of these patients have undergone multiple procedures; they may have undergone mechanical ventilation as well as different surgical procedures,” said Dr. Nett. Affected patients often have received many rounds of antibiotic and antifungal treatment as well, she said, and may have an underlying illness like diabetes or malignancy.
Studies of C. auris outbreaks have begun to appear in the literature and give clinicians some perspective on the progression of an outbreak and potential strategies for containment. A prospective cohort study of a large outbreak of C. auris was conducted by Alba Ruiz-Gaitán, MD, and her colleagues at La Fe University and Polytechnic Hospital, Valencia, Spain (Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2019 Apr;17[4]:295-305). The researchers followed 114 patients who were colonized with C. auris or had C. auris candidemia. The patients were compared with 114 case-matched controls within the hospital’s adult surgical and medical intensive care units over an 11-month period during the hospital’s protracted outbreak.
The investigators found a crude mortality rate of 58.5% at 30 days for patients with C. auris candidemia. All isolates in the study were completely resistant to fluconazole and had reduced susceptibility to voriconazole.
In critical care units at Hospital La Fe, investigators found C. auris on 25% of blood pressure cuffs, 10% of patient tables and keyboards, and 8% of infusion pumps.
Among the patients at Hospital La Fe, multivariable analysis revealed that those most likely to develop C. auris colonization or candidemia were individuals with polytrauma, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
Patients receiving parenteral nutrition (odds ratio, 3.49), mechanical ventilation (OR, 2.43), and especially those having indwelling central venous catheters (OR, 13.48) were more likely to be colonized or have candidemia as well, according to Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her coauthors.
Once identified, how should C. auris be treated? “The majority of strains – upward of 90% – are resistant to fluconazole,” said Dr. Nett. “Moreover, 30%-50% of them are resistant to another antifungal, often amphotericin B. The isolates that we see in the United States are most often susceptible to an echinocandin, and echinocandins remain the choice for treatment of Candida auris pending susceptibility tests.”
However, in Valencia, “The susceptibility to echinocandins presented interesting features. These antifungals were not fungicidal against C. auris,” wrote Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her colleagues. They found that for caspofungin, “most isolates presented a clear paradoxical growth after 24 hours of incubation.” Additionally, fungal growth was inhibited at lower caspofungin concentrations, but rebounded at higher levels. Similar patterns were seen for anidulafungin and micafungin, they said.
These findings meant that Hospital La Fe patients received initial treatment with echinocandins, with the addition of liposomal amphotericin B or isavuconazole if candidemia persisted or clinical response was not seen, wrote the investigators.
Patient presentation is similar to other forms of candidiasis, said Dr. Nett. “Patients often have fever, chills, leukocytosis, and this persists despite antibacterial therapy… If Candida auris is suspected, the first course of action would be to place the patient in isolation, and laboratory staff should be alerted regarding the diagnosis.”
Most large clinical laboratories, she said, can now detect C. auris. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization–time of flight is the identification technique of choice, provided that the databases are updated.
Smaller laboratories that use phenotypic tests may misidentify C. auris as another Candida species, or even as Saccharomyces cerevisiae – common beer yeast. Facilities without matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization can find guidance for interpretation of phenotypic testing on the CDC website as well, said Dr. Nett.
After experiencing what they believe to be the largest C. auris outbreak at a single European hospital, Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her colleagues offered best-practice tips for treatment of patients with C. auris candidemia. These include removing mechanical devices as early as is safely practical; performing ophthalmologic examinations for endophthalmitis, a known C. auris complication; obtaining blood cultures every other day to track antimicrobial therapy to the point of sterilization; and searching for metastatic foci if blood cultures remain positive.
All instances of C. auris laboratory identification should be reported to the CDC at [email protected], and to local and state health agencies. The CDC recommends strict isolation and cleaning protocols, similar to those used for the spore-forming Clostridium difficile.
Dr. Nett reported funding support from the National Institutes of Health, the Burroughs Wellcome Fund, and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation. She reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her collaborators reported funding from Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain, and the Spanish Ministry of Science and University. They reported no conflicts of interest.
Critical care units and long-term care facilities are on alert for cases of Candida auris, a novel fungal infection that is both dangerous to vulnerable patients and difficult to eradicate. The increased profile of C. auris is not a welcome development but is no surprise to critical care physicians.

This pathogen was first identified in 2009 and has since been found in increasing numbers of patients all over the world. As expected, cases of C. auris are on the rise in the United States.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention stated “Candida auris is an emerging fungus that presents a serious global health threat.” This is an opportunistic pathogen that hits critically ill patients and those with compromised immunity.
On March 29, 2019, CDC reported that confirmed clinical cases of C. auris in the United States have more than doubled over the past year, from 257 cases in 2018 to 587 cases with an additional 1,056 colonized patients identified as of February 2019. “Most C. auris cases in the United States have been detected in the New York City area, New Jersey, and the Chicago area. Strains of C. auris in the United States have been linked to other parts of the world. U.S. C. auris cases are a result of inadvertent introduction into the United States from a patient who recently received health care in a country where C. auris has been reported or a result of local spread after such an introduction.”
Case reports have found a mortality rate of up to 50% in patients with C. auris candidemia. The total number of cases is still small, but the trajectory is clear. The hunt is on in labs all over the world for optimal treatments and processes to handle outbreaks.
Jeniel Nett, MD, an infectious disease specialist, and a team of investigators at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, have focused their research on the characteristics of C. auris and its progression in patients and in medical facilities.
According to Dr. Nett, it’s not clear why this emerging threat has cropped up in multiple locations globally. “Candida auris was first recognized in 2009, in Japan, and relatively quickly we saw emergence of this species in relatively distant locations,” she said, adding that independent clades in these locations ruled out transmission as the source of the multiple outbreaks. Antifungal resistance is an epidemiologic area of concern and increased antifungal use may be a contributor, she said.

Once established, the organism is persistent: “It is found on mattresses, on bedsheets, IV poles, and a lot of reusable equipment,” said Dr. Nett in an interview. “It appears to persist in the environment for weeks – maybe longer.” In addition, “it seems to behave differently than a lot of the Candida species that we see; it readily colonizes the skin” to a much greater extent than does other Candida species, she said. “This allows it to be transmitted readily person to person, particularly in the hospitalized setting.” However, it can also colonize both the urinary and respiratory tracts, she said.
Which patients are susceptible to C. auris candidemia? “Many of these patients have undergone multiple procedures; they may have undergone mechanical ventilation as well as different surgical procedures,” said Dr. Nett. Affected patients often have received many rounds of antibiotic and antifungal treatment as well, she said, and may have an underlying illness like diabetes or malignancy.
Studies of C. auris outbreaks have begun to appear in the literature and give clinicians some perspective on the progression of an outbreak and potential strategies for containment. A prospective cohort study of a large outbreak of C. auris was conducted by Alba Ruiz-Gaitán, MD, and her colleagues at La Fe University and Polytechnic Hospital, Valencia, Spain (Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2019 Apr;17[4]:295-305). The researchers followed 114 patients who were colonized with C. auris or had C. auris candidemia. The patients were compared with 114 case-matched controls within the hospital’s adult surgical and medical intensive care units over an 11-month period during the hospital’s protracted outbreak.
The investigators found a crude mortality rate of 58.5% at 30 days for patients with C. auris candidemia. All isolates in the study were completely resistant to fluconazole and had reduced susceptibility to voriconazole.
In critical care units at Hospital La Fe, investigators found C. auris on 25% of blood pressure cuffs, 10% of patient tables and keyboards, and 8% of infusion pumps.
Among the patients at Hospital La Fe, multivariable analysis revealed that those most likely to develop C. auris colonization or candidemia were individuals with polytrauma, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
Patients receiving parenteral nutrition (odds ratio, 3.49), mechanical ventilation (OR, 2.43), and especially those having indwelling central venous catheters (OR, 13.48) were more likely to be colonized or have candidemia as well, according to Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her coauthors.
Once identified, how should C. auris be treated? “The majority of strains – upward of 90% – are resistant to fluconazole,” said Dr. Nett. “Moreover, 30%-50% of them are resistant to another antifungal, often amphotericin B. The isolates that we see in the United States are most often susceptible to an echinocandin, and echinocandins remain the choice for treatment of Candida auris pending susceptibility tests.”
However, in Valencia, “The susceptibility to echinocandins presented interesting features. These antifungals were not fungicidal against C. auris,” wrote Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her colleagues. They found that for caspofungin, “most isolates presented a clear paradoxical growth after 24 hours of incubation.” Additionally, fungal growth was inhibited at lower caspofungin concentrations, but rebounded at higher levels. Similar patterns were seen for anidulafungin and micafungin, they said.
These findings meant that Hospital La Fe patients received initial treatment with echinocandins, with the addition of liposomal amphotericin B or isavuconazole if candidemia persisted or clinical response was not seen, wrote the investigators.
Patient presentation is similar to other forms of candidiasis, said Dr. Nett. “Patients often have fever, chills, leukocytosis, and this persists despite antibacterial therapy… If Candida auris is suspected, the first course of action would be to place the patient in isolation, and laboratory staff should be alerted regarding the diagnosis.”
Most large clinical laboratories, she said, can now detect C. auris. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization–time of flight is the identification technique of choice, provided that the databases are updated.
Smaller laboratories that use phenotypic tests may misidentify C. auris as another Candida species, or even as Saccharomyces cerevisiae – common beer yeast. Facilities without matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization can find guidance for interpretation of phenotypic testing on the CDC website as well, said Dr. Nett.
After experiencing what they believe to be the largest C. auris outbreak at a single European hospital, Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her colleagues offered best-practice tips for treatment of patients with C. auris candidemia. These include removing mechanical devices as early as is safely practical; performing ophthalmologic examinations for endophthalmitis, a known C. auris complication; obtaining blood cultures every other day to track antimicrobial therapy to the point of sterilization; and searching for metastatic foci if blood cultures remain positive.
All instances of C. auris laboratory identification should be reported to the CDC at [email protected], and to local and state health agencies. The CDC recommends strict isolation and cleaning protocols, similar to those used for the spore-forming Clostridium difficile.
Dr. Nett reported funding support from the National Institutes of Health, the Burroughs Wellcome Fund, and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation. She reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Ruiz-Gaitán and her collaborators reported funding from Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain, and the Spanish Ministry of Science and University. They reported no conflicts of interest.