User login
Tips for self-care during the COVID-19 crisis
I think it’s fair to say, none of us have seen anything like this before. Yet here we are, and we must lead. We are many weeks into the COVID-19 crisis. We moved our offices home and tried not to miss a beat. Our patients need us more than ever – and in different ways.
Lest we become like the shoemaker’s daughter who has no shoes, let’s make sure we take care of ourselves. The shock waves from this pandemic are going to be massive and long lasting. I am already witnessing massive psychological growth on the part of my patients, and I hope, myself and my family. We must be strong as individuals and as a group of professionals.
Now more than ever, we need to set boundaries. So many are suffering. We must take stock of our own lives. Many of us are extremely fortunate. We have homes, families, and plenty of food. We are doctors performing essential services, and we can do so without risking our lives.
The priority is to make sure you are safe, and keeping your family and loved ones safe. As physicians, we have learned to distance ourselves from illness, but the coronavirus has affected us in disproportionate numbers.
To be physically and mentally strong, we must get enough sleep. This is exhausting for some and energizing for others. It is definitely a marathon not a sprint, so pace yourself. Eat well. This is no time for empty calories, and that goes for alcohol as well.
Create new routines. Exercise at the same time each day or perhaps twice a day. Try to be productive during certain hours, and relax at other times. Eat at similar times each day. We must strive to quickly create a “new normal” as we spend our days at home.
Find safe alternatives to your usual workout routine. Use YouTube and Instagram to help you find ways to stay fit in your own home. Ask friends for tips and consider sharing workout time with them via Zoom or FaceTime. New options are coming on line daily.
Make sure you are getting enough information to stay safe, and follow the advice of experts. Then turn off the news. I offer the same advice for financial worries. Try not to stress too much about finances right now. Most of us are feeling the pain of lost income and lost savings. Many of us have spouses or partners who suddenly found themselves out of work. Most likely, we will have ample ability to recover financially as we move forward and find ourselves with more work than ever.
Meditate. This may be advice you have been telling your patients for years but never found the time to try yourself. You can begin very simply with an app called Headspace or Calm. Google “5-minute meditation” on YouTube or find a meditation of any length you desire. If not now, when?
Reach out to one another. We can all use a caring word, or some humor or advice about how to move our practices online.
You may find your concentration is decreased, so be realistic in your expectations of yourself. I am finding shorter sessions more often are providing more comfort to some patients. Other patients are digging deeper than ever emotionally, and the work is becoming more rewarding.
Make sure you take a break to engage in positive activities. Read a book. Listen to soft music. Dim the lights. Watch the sunset, or be in nature if you can do so safely. Watch a TedTalk. Brush up on a foreign language. Take a deep breath. Journal. Puzzles, games, cooking, magazines, and humor all provide much needed respite from the stress. If you are lucky enough to be with family, try to take advantage of this unique time.
Try to avoid or minimize conflict with others. We need one another now more than ever. If you lose your cool, forgive yourself and make amends.
Even in these most challenging times, we must focus on what we are grateful for. Express gratitude to those around you as it will lift their mood as well. I know I am extremely grateful to be able to continue meaningful work when so many are unable to do so.
The next waves of this virus will be hitting our specialty directly so be strong and be prepared. It is an honor to serve, and we must rise to the occasion.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018), and is the founder of the Bekindr Global Initiative, a movement aimed at cultivating kindness in the world. Dr. Ritvo also is the cofounder of the Bold Beauty Project, a nonprofit group that pairs women with disabilities with photographers who create art exhibitions to raise awareness.
I think it’s fair to say, none of us have seen anything like this before. Yet here we are, and we must lead. We are many weeks into the COVID-19 crisis. We moved our offices home and tried not to miss a beat. Our patients need us more than ever – and in different ways.
Lest we become like the shoemaker’s daughter who has no shoes, let’s make sure we take care of ourselves. The shock waves from this pandemic are going to be massive and long lasting. I am already witnessing massive psychological growth on the part of my patients, and I hope, myself and my family. We must be strong as individuals and as a group of professionals.
Now more than ever, we need to set boundaries. So many are suffering. We must take stock of our own lives. Many of us are extremely fortunate. We have homes, families, and plenty of food. We are doctors performing essential services, and we can do so without risking our lives.
The priority is to make sure you are safe, and keeping your family and loved ones safe. As physicians, we have learned to distance ourselves from illness, but the coronavirus has affected us in disproportionate numbers.
To be physically and mentally strong, we must get enough sleep. This is exhausting for some and energizing for others. It is definitely a marathon not a sprint, so pace yourself. Eat well. This is no time for empty calories, and that goes for alcohol as well.
Create new routines. Exercise at the same time each day or perhaps twice a day. Try to be productive during certain hours, and relax at other times. Eat at similar times each day. We must strive to quickly create a “new normal” as we spend our days at home.
Find safe alternatives to your usual workout routine. Use YouTube and Instagram to help you find ways to stay fit in your own home. Ask friends for tips and consider sharing workout time with them via Zoom or FaceTime. New options are coming on line daily.
Make sure you are getting enough information to stay safe, and follow the advice of experts. Then turn off the news. I offer the same advice for financial worries. Try not to stress too much about finances right now. Most of us are feeling the pain of lost income and lost savings. Many of us have spouses or partners who suddenly found themselves out of work. Most likely, we will have ample ability to recover financially as we move forward and find ourselves with more work than ever.
Meditate. This may be advice you have been telling your patients for years but never found the time to try yourself. You can begin very simply with an app called Headspace or Calm. Google “5-minute meditation” on YouTube or find a meditation of any length you desire. If not now, when?
Reach out to one another. We can all use a caring word, or some humor or advice about how to move our practices online.
You may find your concentration is decreased, so be realistic in your expectations of yourself. I am finding shorter sessions more often are providing more comfort to some patients. Other patients are digging deeper than ever emotionally, and the work is becoming more rewarding.
Make sure you take a break to engage in positive activities. Read a book. Listen to soft music. Dim the lights. Watch the sunset, or be in nature if you can do so safely. Watch a TedTalk. Brush up on a foreign language. Take a deep breath. Journal. Puzzles, games, cooking, magazines, and humor all provide much needed respite from the stress. If you are lucky enough to be with family, try to take advantage of this unique time.
Try to avoid or minimize conflict with others. We need one another now more than ever. If you lose your cool, forgive yourself and make amends.
Even in these most challenging times, we must focus on what we are grateful for. Express gratitude to those around you as it will lift their mood as well. I know I am extremely grateful to be able to continue meaningful work when so many are unable to do so.
The next waves of this virus will be hitting our specialty directly so be strong and be prepared. It is an honor to serve, and we must rise to the occasion.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018), and is the founder of the Bekindr Global Initiative, a movement aimed at cultivating kindness in the world. Dr. Ritvo also is the cofounder of the Bold Beauty Project, a nonprofit group that pairs women with disabilities with photographers who create art exhibitions to raise awareness.
I think it’s fair to say, none of us have seen anything like this before. Yet here we are, and we must lead. We are many weeks into the COVID-19 crisis. We moved our offices home and tried not to miss a beat. Our patients need us more than ever – and in different ways.
Lest we become like the shoemaker’s daughter who has no shoes, let’s make sure we take care of ourselves. The shock waves from this pandemic are going to be massive and long lasting. I am already witnessing massive psychological growth on the part of my patients, and I hope, myself and my family. We must be strong as individuals and as a group of professionals.
Now more than ever, we need to set boundaries. So many are suffering. We must take stock of our own lives. Many of us are extremely fortunate. We have homes, families, and plenty of food. We are doctors performing essential services, and we can do so without risking our lives.
The priority is to make sure you are safe, and keeping your family and loved ones safe. As physicians, we have learned to distance ourselves from illness, but the coronavirus has affected us in disproportionate numbers.
To be physically and mentally strong, we must get enough sleep. This is exhausting for some and energizing for others. It is definitely a marathon not a sprint, so pace yourself. Eat well. This is no time for empty calories, and that goes for alcohol as well.
Create new routines. Exercise at the same time each day or perhaps twice a day. Try to be productive during certain hours, and relax at other times. Eat at similar times each day. We must strive to quickly create a “new normal” as we spend our days at home.
Find safe alternatives to your usual workout routine. Use YouTube and Instagram to help you find ways to stay fit in your own home. Ask friends for tips and consider sharing workout time with them via Zoom or FaceTime. New options are coming on line daily.
Make sure you are getting enough information to stay safe, and follow the advice of experts. Then turn off the news. I offer the same advice for financial worries. Try not to stress too much about finances right now. Most of us are feeling the pain of lost income and lost savings. Many of us have spouses or partners who suddenly found themselves out of work. Most likely, we will have ample ability to recover financially as we move forward and find ourselves with more work than ever.
Meditate. This may be advice you have been telling your patients for years but never found the time to try yourself. You can begin very simply with an app called Headspace or Calm. Google “5-minute meditation” on YouTube or find a meditation of any length you desire. If not now, when?
Reach out to one another. We can all use a caring word, or some humor or advice about how to move our practices online.
You may find your concentration is decreased, so be realistic in your expectations of yourself. I am finding shorter sessions more often are providing more comfort to some patients. Other patients are digging deeper than ever emotionally, and the work is becoming more rewarding.
Make sure you take a break to engage in positive activities. Read a book. Listen to soft music. Dim the lights. Watch the sunset, or be in nature if you can do so safely. Watch a TedTalk. Brush up on a foreign language. Take a deep breath. Journal. Puzzles, games, cooking, magazines, and humor all provide much needed respite from the stress. If you are lucky enough to be with family, try to take advantage of this unique time.
Try to avoid or minimize conflict with others. We need one another now more than ever. If you lose your cool, forgive yourself and make amends.
Even in these most challenging times, we must focus on what we are grateful for. Express gratitude to those around you as it will lift their mood as well. I know I am extremely grateful to be able to continue meaningful work when so many are unable to do so.
The next waves of this virus will be hitting our specialty directly so be strong and be prepared. It is an honor to serve, and we must rise to the occasion.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018), and is the founder of the Bekindr Global Initiative, a movement aimed at cultivating kindness in the world. Dr. Ritvo also is the cofounder of the Bold Beauty Project, a nonprofit group that pairs women with disabilities with photographers who create art exhibitions to raise awareness.
JAK inhibitors may increase risk of herpes zoster
For patients with inflammatory bowel disease or other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors appear generally safe, though they may increase the risk of herpes zoster infection, according to a large-scale systematic review and meta-analysis.
Data from more than 66,000 patients revealed no significant links between JAK inhibitors and risks of serious infections, malignancy, or major adverse cardiovascular events, reported lead author Pablo Olivera, MD, of Centro de Educación Médica e Investigación Clínica (CEMIC) in Buenos Aires and colleagues.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic review evaluating the risk profile of JAK inhibitors in a wide spectrum of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases,” they wrote in Gastroenterology.
The investigators drew studies from the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, MEDLINE, and EMBASE from 1990 to 2019 and from conference databases from 2012 to 2018. Out of 973 studies identified, 82 were included in the final analysis, of which two-thirds were randomized clinical trials. In total, 101,925 subjects were included, of whom a majority had rheumatoid arthritis (n = 86,308), followed by psoriasis (n = 9,311), inflammatory bowel disease (n = 5,987), and ankylosing spondylitis (n = 319).
Meta-analysis of JAK inhibitor usage involved 66,159 patients. Four JAK inhibitors were included: tofacitinib, filgotinib, baricitinib, and upadacitinib. The primary outcomes were the incidence rates of adverse events and serious adverse events. The investigators also estimated incidence rates of herpes zoster infection, serious infections, mortality, malignancy, and major adverse cardiovascular events. These rates were compared with those of patients who received placebo or an active comparator in clinical trials.
Analysis showed that almost 9 out of 10 patients (87.16%) who were exposed to a JAK inhibitor received tofacitinib. The investigators described high variability in treatment duration and baseline characteristics of participants. Rates of adverse events and serious adverse events also fell across a broad spectrum, from 10% to 82% and from 0% to 29%, respectively.
“Most [adverse events] were mild, and included worsening of the underlying condition, probably showing lack of efficacy,” the investigators wrote.
Rates of mortality and most adverse events were not significantly associated with JAK inhibitor exposure. In contrast, relative risk of herpes zoster infection was 57% higher in patients who received a JAK inhibitor than in those who received a placebo or comparator (RR, 1.57; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.37).
“Regarding the risk of herpes zoster with JAK inhibitors, the largest evidence comes from the use of tofacitinib, but it appears to be a class effect, with a clear dose-dependent effect,” the investigators wrote.
Although risks of herpes zoster may be carried across the drug class, they may not be evenly distributed given that a subgroup analysis revealed that some JAK inhibitors may bring higher risks than others; specifically, tofacitinib and baricitinib were associated with higher relative risks of herpes zoster than were upadacitinib and filgotinib.
“Although this is merely a qualitative comparison, this difference could be related to the fact that both filgotinib and upadacitinib are selective JAK1 inhibitors, whereas tofacitinib is a JAK1/JAK3 inhibitor and baricitinib a JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor,” the investigators wrote. “Further studies are needed to determine if JAK isoform selectivity affects the risk of herpes zoster.”
The investigators emphasized this need for more research. While the present findings help illuminate the safety profile of JAK inhibitors, they are clouded by various other factors, such as disease-specific considerations, a lack of real-world data, and studies that are likely too short to accurately determine risk of malignancy, the investigators wrote.
“More studies with long follow-up and in the real world setting, in different conditions, will be needed to fully elucidate the safety profile of the different JAK inhibitors,” the investigators concluded.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, and others.
SOURCE: Olivera P et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jan 8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.01.001.
The multiple different cytokines contributing to intestinal inflammation in IBD patients have been a major challenge in the design of therapies. Because the JAK signaling pathway (comprised of JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2) is required for responses to a broad range of cytokines, therapies that inhibit JAK signaling have been an active area of interest. A simultaneous and important concern, however, has been the potential for adverse consequences when inhibiting the breadth of immune and hematopoietic molecules that depend on JAK family members for their functions. This meta-analysis by Olivera et al. examined adverse outcomes of four different JAK inhibitors in clinical trials across four immune-mediated diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, IBD, psoriasis, and ankylosing spondylitis), finding that herpes zoster infection was significantly increased (relative risk, 1.57). In contrast, patients treated with JAK inhibitors were not at a significantly increased risk for various other adverse events.
Reduced dosing of JAK inhibitors has been implemented as a means of improving safety profiles in select immune-mediated diseases. Another approach is more selective JAK inhibition, although it is unclear whether this will eliminate the risk of herpes zoster infection. In the current meta-analysis, about 87% of the studies had evaluated tofacitinib treatment, which inhibits both JAK1 and JAK3; more selective JAK inhibitors could not be evaluated in an equivalent manner. Of note, JAK1 is required for signaling by various cytokines that participate in the response to viruses, including type I IFNs and gamma c family members (such as IL-2 and IL-15); therefore, even the more selective JAK1 inhibitors do not leave this immune function fully intact. However, simply reducing the number of JAK family members inhibited simultaneously may be sufficient to reduce risk.
JAK inhibitors warrant further evaluation as additional infectious challenges arise, particularly with respect to viruses. In addition, more selective targeting of JAK inhibition of intestinal tissues may ultimately reduce systemic effects, including the risk of herpes zoster.
Clara Abraham, MD, professor of medicine, section of digestive diseases, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The multiple different cytokines contributing to intestinal inflammation in IBD patients have been a major challenge in the design of therapies. Because the JAK signaling pathway (comprised of JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2) is required for responses to a broad range of cytokines, therapies that inhibit JAK signaling have been an active area of interest. A simultaneous and important concern, however, has been the potential for adverse consequences when inhibiting the breadth of immune and hematopoietic molecules that depend on JAK family members for their functions. This meta-analysis by Olivera et al. examined adverse outcomes of four different JAK inhibitors in clinical trials across four immune-mediated diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, IBD, psoriasis, and ankylosing spondylitis), finding that herpes zoster infection was significantly increased (relative risk, 1.57). In contrast, patients treated with JAK inhibitors were not at a significantly increased risk for various other adverse events.
Reduced dosing of JAK inhibitors has been implemented as a means of improving safety profiles in select immune-mediated diseases. Another approach is more selective JAK inhibition, although it is unclear whether this will eliminate the risk of herpes zoster infection. In the current meta-analysis, about 87% of the studies had evaluated tofacitinib treatment, which inhibits both JAK1 and JAK3; more selective JAK inhibitors could not be evaluated in an equivalent manner. Of note, JAK1 is required for signaling by various cytokines that participate in the response to viruses, including type I IFNs and gamma c family members (such as IL-2 and IL-15); therefore, even the more selective JAK1 inhibitors do not leave this immune function fully intact. However, simply reducing the number of JAK family members inhibited simultaneously may be sufficient to reduce risk.
JAK inhibitors warrant further evaluation as additional infectious challenges arise, particularly with respect to viruses. In addition, more selective targeting of JAK inhibition of intestinal tissues may ultimately reduce systemic effects, including the risk of herpes zoster.
Clara Abraham, MD, professor of medicine, section of digestive diseases, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The multiple different cytokines contributing to intestinal inflammation in IBD patients have been a major challenge in the design of therapies. Because the JAK signaling pathway (comprised of JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2) is required for responses to a broad range of cytokines, therapies that inhibit JAK signaling have been an active area of interest. A simultaneous and important concern, however, has been the potential for adverse consequences when inhibiting the breadth of immune and hematopoietic molecules that depend on JAK family members for their functions. This meta-analysis by Olivera et al. examined adverse outcomes of four different JAK inhibitors in clinical trials across four immune-mediated diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, IBD, psoriasis, and ankylosing spondylitis), finding that herpes zoster infection was significantly increased (relative risk, 1.57). In contrast, patients treated with JAK inhibitors were not at a significantly increased risk for various other adverse events.
Reduced dosing of JAK inhibitors has been implemented as a means of improving safety profiles in select immune-mediated diseases. Another approach is more selective JAK inhibition, although it is unclear whether this will eliminate the risk of herpes zoster infection. In the current meta-analysis, about 87% of the studies had evaluated tofacitinib treatment, which inhibits both JAK1 and JAK3; more selective JAK inhibitors could not be evaluated in an equivalent manner. Of note, JAK1 is required for signaling by various cytokines that participate in the response to viruses, including type I IFNs and gamma c family members (such as IL-2 and IL-15); therefore, even the more selective JAK1 inhibitors do not leave this immune function fully intact. However, simply reducing the number of JAK family members inhibited simultaneously may be sufficient to reduce risk.
JAK inhibitors warrant further evaluation as additional infectious challenges arise, particularly with respect to viruses. In addition, more selective targeting of JAK inhibition of intestinal tissues may ultimately reduce systemic effects, including the risk of herpes zoster.
Clara Abraham, MD, professor of medicine, section of digestive diseases, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
For patients with inflammatory bowel disease or other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors appear generally safe, though they may increase the risk of herpes zoster infection, according to a large-scale systematic review and meta-analysis.
Data from more than 66,000 patients revealed no significant links between JAK inhibitors and risks of serious infections, malignancy, or major adverse cardiovascular events, reported lead author Pablo Olivera, MD, of Centro de Educación Médica e Investigación Clínica (CEMIC) in Buenos Aires and colleagues.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic review evaluating the risk profile of JAK inhibitors in a wide spectrum of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases,” they wrote in Gastroenterology.
The investigators drew studies from the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, MEDLINE, and EMBASE from 1990 to 2019 and from conference databases from 2012 to 2018. Out of 973 studies identified, 82 were included in the final analysis, of which two-thirds were randomized clinical trials. In total, 101,925 subjects were included, of whom a majority had rheumatoid arthritis (n = 86,308), followed by psoriasis (n = 9,311), inflammatory bowel disease (n = 5,987), and ankylosing spondylitis (n = 319).
Meta-analysis of JAK inhibitor usage involved 66,159 patients. Four JAK inhibitors were included: tofacitinib, filgotinib, baricitinib, and upadacitinib. The primary outcomes were the incidence rates of adverse events and serious adverse events. The investigators also estimated incidence rates of herpes zoster infection, serious infections, mortality, malignancy, and major adverse cardiovascular events. These rates were compared with those of patients who received placebo or an active comparator in clinical trials.
Analysis showed that almost 9 out of 10 patients (87.16%) who were exposed to a JAK inhibitor received tofacitinib. The investigators described high variability in treatment duration and baseline characteristics of participants. Rates of adverse events and serious adverse events also fell across a broad spectrum, from 10% to 82% and from 0% to 29%, respectively.
“Most [adverse events] were mild, and included worsening of the underlying condition, probably showing lack of efficacy,” the investigators wrote.
Rates of mortality and most adverse events were not significantly associated with JAK inhibitor exposure. In contrast, relative risk of herpes zoster infection was 57% higher in patients who received a JAK inhibitor than in those who received a placebo or comparator (RR, 1.57; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.37).
“Regarding the risk of herpes zoster with JAK inhibitors, the largest evidence comes from the use of tofacitinib, but it appears to be a class effect, with a clear dose-dependent effect,” the investigators wrote.
Although risks of herpes zoster may be carried across the drug class, they may not be evenly distributed given that a subgroup analysis revealed that some JAK inhibitors may bring higher risks than others; specifically, tofacitinib and baricitinib were associated with higher relative risks of herpes zoster than were upadacitinib and filgotinib.
“Although this is merely a qualitative comparison, this difference could be related to the fact that both filgotinib and upadacitinib are selective JAK1 inhibitors, whereas tofacitinib is a JAK1/JAK3 inhibitor and baricitinib a JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor,” the investigators wrote. “Further studies are needed to determine if JAK isoform selectivity affects the risk of herpes zoster.”
The investigators emphasized this need for more research. While the present findings help illuminate the safety profile of JAK inhibitors, they are clouded by various other factors, such as disease-specific considerations, a lack of real-world data, and studies that are likely too short to accurately determine risk of malignancy, the investigators wrote.
“More studies with long follow-up and in the real world setting, in different conditions, will be needed to fully elucidate the safety profile of the different JAK inhibitors,” the investigators concluded.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, and others.
SOURCE: Olivera P et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jan 8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.01.001.
For patients with inflammatory bowel disease or other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors appear generally safe, though they may increase the risk of herpes zoster infection, according to a large-scale systematic review and meta-analysis.
Data from more than 66,000 patients revealed no significant links between JAK inhibitors and risks of serious infections, malignancy, or major adverse cardiovascular events, reported lead author Pablo Olivera, MD, of Centro de Educación Médica e Investigación Clínica (CEMIC) in Buenos Aires and colleagues.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic review evaluating the risk profile of JAK inhibitors in a wide spectrum of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases,” they wrote in Gastroenterology.
The investigators drew studies from the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, MEDLINE, and EMBASE from 1990 to 2019 and from conference databases from 2012 to 2018. Out of 973 studies identified, 82 were included in the final analysis, of which two-thirds were randomized clinical trials. In total, 101,925 subjects were included, of whom a majority had rheumatoid arthritis (n = 86,308), followed by psoriasis (n = 9,311), inflammatory bowel disease (n = 5,987), and ankylosing spondylitis (n = 319).
Meta-analysis of JAK inhibitor usage involved 66,159 patients. Four JAK inhibitors were included: tofacitinib, filgotinib, baricitinib, and upadacitinib. The primary outcomes were the incidence rates of adverse events and serious adverse events. The investigators also estimated incidence rates of herpes zoster infection, serious infections, mortality, malignancy, and major adverse cardiovascular events. These rates were compared with those of patients who received placebo or an active comparator in clinical trials.
Analysis showed that almost 9 out of 10 patients (87.16%) who were exposed to a JAK inhibitor received tofacitinib. The investigators described high variability in treatment duration and baseline characteristics of participants. Rates of adverse events and serious adverse events also fell across a broad spectrum, from 10% to 82% and from 0% to 29%, respectively.
“Most [adverse events] were mild, and included worsening of the underlying condition, probably showing lack of efficacy,” the investigators wrote.
Rates of mortality and most adverse events were not significantly associated with JAK inhibitor exposure. In contrast, relative risk of herpes zoster infection was 57% higher in patients who received a JAK inhibitor than in those who received a placebo or comparator (RR, 1.57; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.37).
“Regarding the risk of herpes zoster with JAK inhibitors, the largest evidence comes from the use of tofacitinib, but it appears to be a class effect, with a clear dose-dependent effect,” the investigators wrote.
Although risks of herpes zoster may be carried across the drug class, they may not be evenly distributed given that a subgroup analysis revealed that some JAK inhibitors may bring higher risks than others; specifically, tofacitinib and baricitinib were associated with higher relative risks of herpes zoster than were upadacitinib and filgotinib.
“Although this is merely a qualitative comparison, this difference could be related to the fact that both filgotinib and upadacitinib are selective JAK1 inhibitors, whereas tofacitinib is a JAK1/JAK3 inhibitor and baricitinib a JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor,” the investigators wrote. “Further studies are needed to determine if JAK isoform selectivity affects the risk of herpes zoster.”
The investigators emphasized this need for more research. While the present findings help illuminate the safety profile of JAK inhibitors, they are clouded by various other factors, such as disease-specific considerations, a lack of real-world data, and studies that are likely too short to accurately determine risk of malignancy, the investigators wrote.
“More studies with long follow-up and in the real world setting, in different conditions, will be needed to fully elucidate the safety profile of the different JAK inhibitors,” the investigators concluded.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, and others.
SOURCE: Olivera P et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jan 8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.01.001.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Nearly 24 tests for the novel coronavirus are available
according to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
“Based on what we know about influenza, it’s unlikely that all of these tests are going to perform exactly the same way,” said Angela M. Caliendo, MD, executive vice chair of the department of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I., at a press briefing. Although these tests are good, no test is perfect, she added.
The development and availability of testing has improved over time, but clinical laboratories still face challenges, said Kimberly E. Hanson, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at University of Utah, Salt Lake City. These challenges include shortages of devices for specimen collection, media, test tubes, and reagents. Although the goal is to test all symptomatic patients, these shortages require laboratories to prioritize health care workers and the sickest patients.
Tests are being approved through an abbreviated process
Two types of test, rapid tests and serology tests, are in use. Rapid tests use polymerase chain reactions to detect the virus in a clinical specimen. This type of testing is used to diagnose infection. Serology tests measure antibodies to the virus and are more appropriate for indicating whether a patient has been exposed to the virus.
The declaration of a national emergency enabled the FDA to activate its EUA policy, which allows for quicker approval of tests. Normally, a test must be assessed in the laboratory (such as with a mock specimen or an inactivated virus) and in a clinical study of patients. Under the EUA, clinical assessment is not required for the approval of a test. Consequently, the clinical performance of a test approved under EUA is unknown.
Collecting a specimen of good quality is critical to the quality of the test result, said Dr. Caliendo, the secretary of IDSA’s board of directors. Clinicians and investigators have used nasopharyngeal swabs, sputum, and specimens collected from deep within the lung. “We’re still collecting data to determine which is the best specimen type.” As coronavirus testing expands, particularly to drive-through testing sites, “we may be using people who are not as experienced, and so you might not get as high a quality specimen in that situation,” Dr. Caliendo added.
The timing of the test influences the quality of the result, as well, because the amount of virus is lower at the onset of symptoms than it is later. Another factor that affects the quality of the results is the test’s sensitivity.
The time to obtain results varies
The value of having several tests available is that it enables many patients to be tested simultaneously, said Dr. Hanson, a member of IDSA’s board of directors. It also helps to reduce potential problems with the supply of test kits. A test manufacturer, however, may supply parts of the test kit but not the whole kit. This requires the hospital or laboratory to obtain the remaining parts from other suppliers. Furthermore, test manufacturers may need to prioritize areas with high rates of infection or transmission when they ship their tests, which limits testing in other areas.
One reason for the lack of a national plan for testing is that the virus has affected different regions at different times, said Dr. Caliendo. Some tests are more difficult to perform than others, and not all laboratories are equally sophisticated, which can limit testing. It is necessary to test not only symptomatic patients who have been hospitalized, but also symptomatic patients in the community, said Dr. Caliendo. “Ideally, we’re going to need to couple acute diagnostics [testing while people are sick] with serologic testing. Serologic testing is going to be important for us to see who has been infected. That will give us an idea of who is left in our community who is at risk for developing infection.”
How quickly test results are available depends on the type of test and where it is administered. Recently established drive-through clinics can provide results in about 30 minutes. Tests performed in hospitals may take between 1 and 6 hours to yield results. “The issue is, do we have reagents that day?” said Dr. Caliendo. “We have to be careful whom we choose to test, and we screen that in the hospital so that we have enough tests to run as we need them.” But many locations have backlogs. “When you have a backlog of testing, you’re going to wait days, unfortunately, to get a result,” said Dr. Caliendo.
Dr. Caliendo and Dr. Hanson did not report disclosures for this briefing.
according to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
“Based on what we know about influenza, it’s unlikely that all of these tests are going to perform exactly the same way,” said Angela M. Caliendo, MD, executive vice chair of the department of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I., at a press briefing. Although these tests are good, no test is perfect, she added.
The development and availability of testing has improved over time, but clinical laboratories still face challenges, said Kimberly E. Hanson, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at University of Utah, Salt Lake City. These challenges include shortages of devices for specimen collection, media, test tubes, and reagents. Although the goal is to test all symptomatic patients, these shortages require laboratories to prioritize health care workers and the sickest patients.
Tests are being approved through an abbreviated process
Two types of test, rapid tests and serology tests, are in use. Rapid tests use polymerase chain reactions to detect the virus in a clinical specimen. This type of testing is used to diagnose infection. Serology tests measure antibodies to the virus and are more appropriate for indicating whether a patient has been exposed to the virus.
The declaration of a national emergency enabled the FDA to activate its EUA policy, which allows for quicker approval of tests. Normally, a test must be assessed in the laboratory (such as with a mock specimen or an inactivated virus) and in a clinical study of patients. Under the EUA, clinical assessment is not required for the approval of a test. Consequently, the clinical performance of a test approved under EUA is unknown.
Collecting a specimen of good quality is critical to the quality of the test result, said Dr. Caliendo, the secretary of IDSA’s board of directors. Clinicians and investigators have used nasopharyngeal swabs, sputum, and specimens collected from deep within the lung. “We’re still collecting data to determine which is the best specimen type.” As coronavirus testing expands, particularly to drive-through testing sites, “we may be using people who are not as experienced, and so you might not get as high a quality specimen in that situation,” Dr. Caliendo added.
The timing of the test influences the quality of the result, as well, because the amount of virus is lower at the onset of symptoms than it is later. Another factor that affects the quality of the results is the test’s sensitivity.
The time to obtain results varies
The value of having several tests available is that it enables many patients to be tested simultaneously, said Dr. Hanson, a member of IDSA’s board of directors. It also helps to reduce potential problems with the supply of test kits. A test manufacturer, however, may supply parts of the test kit but not the whole kit. This requires the hospital or laboratory to obtain the remaining parts from other suppliers. Furthermore, test manufacturers may need to prioritize areas with high rates of infection or transmission when they ship their tests, which limits testing in other areas.
One reason for the lack of a national plan for testing is that the virus has affected different regions at different times, said Dr. Caliendo. Some tests are more difficult to perform than others, and not all laboratories are equally sophisticated, which can limit testing. It is necessary to test not only symptomatic patients who have been hospitalized, but also symptomatic patients in the community, said Dr. Caliendo. “Ideally, we’re going to need to couple acute diagnostics [testing while people are sick] with serologic testing. Serologic testing is going to be important for us to see who has been infected. That will give us an idea of who is left in our community who is at risk for developing infection.”
How quickly test results are available depends on the type of test and where it is administered. Recently established drive-through clinics can provide results in about 30 minutes. Tests performed in hospitals may take between 1 and 6 hours to yield results. “The issue is, do we have reagents that day?” said Dr. Caliendo. “We have to be careful whom we choose to test, and we screen that in the hospital so that we have enough tests to run as we need them.” But many locations have backlogs. “When you have a backlog of testing, you’re going to wait days, unfortunately, to get a result,” said Dr. Caliendo.
Dr. Caliendo and Dr. Hanson did not report disclosures for this briefing.
according to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
“Based on what we know about influenza, it’s unlikely that all of these tests are going to perform exactly the same way,” said Angela M. Caliendo, MD, executive vice chair of the department of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I., at a press briefing. Although these tests are good, no test is perfect, she added.
The development and availability of testing has improved over time, but clinical laboratories still face challenges, said Kimberly E. Hanson, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at University of Utah, Salt Lake City. These challenges include shortages of devices for specimen collection, media, test tubes, and reagents. Although the goal is to test all symptomatic patients, these shortages require laboratories to prioritize health care workers and the sickest patients.
Tests are being approved through an abbreviated process
Two types of test, rapid tests and serology tests, are in use. Rapid tests use polymerase chain reactions to detect the virus in a clinical specimen. This type of testing is used to diagnose infection. Serology tests measure antibodies to the virus and are more appropriate for indicating whether a patient has been exposed to the virus.
The declaration of a national emergency enabled the FDA to activate its EUA policy, which allows for quicker approval of tests. Normally, a test must be assessed in the laboratory (such as with a mock specimen or an inactivated virus) and in a clinical study of patients. Under the EUA, clinical assessment is not required for the approval of a test. Consequently, the clinical performance of a test approved under EUA is unknown.
Collecting a specimen of good quality is critical to the quality of the test result, said Dr. Caliendo, the secretary of IDSA’s board of directors. Clinicians and investigators have used nasopharyngeal swabs, sputum, and specimens collected from deep within the lung. “We’re still collecting data to determine which is the best specimen type.” As coronavirus testing expands, particularly to drive-through testing sites, “we may be using people who are not as experienced, and so you might not get as high a quality specimen in that situation,” Dr. Caliendo added.
The timing of the test influences the quality of the result, as well, because the amount of virus is lower at the onset of symptoms than it is later. Another factor that affects the quality of the results is the test’s sensitivity.
The time to obtain results varies
The value of having several tests available is that it enables many patients to be tested simultaneously, said Dr. Hanson, a member of IDSA’s board of directors. It also helps to reduce potential problems with the supply of test kits. A test manufacturer, however, may supply parts of the test kit but not the whole kit. This requires the hospital or laboratory to obtain the remaining parts from other suppliers. Furthermore, test manufacturers may need to prioritize areas with high rates of infection or transmission when they ship their tests, which limits testing in other areas.
One reason for the lack of a national plan for testing is that the virus has affected different regions at different times, said Dr. Caliendo. Some tests are more difficult to perform than others, and not all laboratories are equally sophisticated, which can limit testing. It is necessary to test not only symptomatic patients who have been hospitalized, but also symptomatic patients in the community, said Dr. Caliendo. “Ideally, we’re going to need to couple acute diagnostics [testing while people are sick] with serologic testing. Serologic testing is going to be important for us to see who has been infected. That will give us an idea of who is left in our community who is at risk for developing infection.”
How quickly test results are available depends on the type of test and where it is administered. Recently established drive-through clinics can provide results in about 30 minutes. Tests performed in hospitals may take between 1 and 6 hours to yield results. “The issue is, do we have reagents that day?” said Dr. Caliendo. “We have to be careful whom we choose to test, and we screen that in the hospital so that we have enough tests to run as we need them.” But many locations have backlogs. “When you have a backlog of testing, you’re going to wait days, unfortunately, to get a result,” said Dr. Caliendo.
Dr. Caliendo and Dr. Hanson did not report disclosures for this briefing.
Aerosolization of COVID-19 and Contamination Risks During Respiratory Treatments
Beyond asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), inhalation therapy is a mainstay in the management of bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis, and pulmonary artery hypertension. Several US Food and Drug Administration off-label indications for inhalational medications include hypoxia secondary to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and intraoperative and postoperative pulmonary hypertension during and following cardiac surgery, respectively.1-11 Therapeutic delivery of aerosols to the lung may be provided via nebulization, pressurized metered-dose inhalers (pMDI), and other devices (eg, dry powder inhalers, soft-mist inhalers, and smart inhalers).12 The most common aerosolized medications given in the clinical setting are bronchodilators.12
Product selection is often guided by practice guidelines (Table 1), consideration of the formulation’s advantages and disadvantages (Table 2), and/or formulary considerations. For example, current guidelines for COPD state that there is no evidence for superiority of nebulized bronchodilator therapy over handheld devices in patients who can use them properly.2 Due to equivalence, nebulized formulations are commonly used in hospitals, emergency departments (EDs) and ambulatory clinics based on the drug’s unit cost. In contrast, a pMDI is often more cost-effective for use in ambulatory patients who are administering multiple doses from the same canister.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend droplet and contact precautions for all patients suspected or diagnosed with novel coronavirus-19 (COVID-19).13,14 Airborne precautions must be applied when performing aerosol-generating medical procedures (AGMPs), including but not limited to, open suctioning of the respiratory tract, intubation, bronchoscopy, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Data from the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV) epidemic suggest that nebulization of medication is also an AGMP.15-17
Institutions must ensure that their health care workers (HCWs) are wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves, long-sleeved gowns, eye protection, and fit-tested particulate respirators (N95 mask) for airborne procedures and are carefully discarding PPE after use.13,14 Due to severe shortages in available respirators in the US supply chain, the CDC has temporarily modified WHO recommendations. Face masks are now an acceptable alternative to protect HCWs from splashes and sprays from procedures not likely to generate aerosols and for cleaning of rooms, although there is no evidence to support this decision.
Internationally, HCWs are falling ill with COVID-19. Data from Italy and Spain show that about 9% to 13% of these countries’ cases are HCWs.18,19 Within the US, the Ohio health department reports approximately 16% of cases are HCWs.20 It is possible that 20% of frontline HCWs will become infected.21 Evolving laboratory research shows that COVID-19 remains viable in aerosols for up to 3 hours postaerosolization, thus making aerosol transmission plausible.22 Nebulizers convert liquids into aerosols and during dispersal may potentially cause secondary inhalation of fugitive emissions.23 Since interim CDC infection control guidance is to allow only essential personnel to enter the room of patients with COVID-19, many facilities will rely on their frontline nursing staff to clean and disinfect high-touch surfaces following routine care activities.24
Achieving adequate fomite disinfection following viral aerosolization may pose a significant problem for any patient receiving scheduled doses of nebulized medications. Additionally, for personnel who clean rooms following intermittent drug nebulization while wearing PPE that includes a face mask, protection from aerosolized virus may be inadequate. Subsequently, fugitive emissions from nebulized medications may potentially contribute to both nosocomial COVID-19 transmission and viral infections in the medical staff until proven otherwise by studies conducted outside of the laboratory. Prevention of infection in the medical staff is imperative since federal health care systems cannot sustain a significant loss of its workforce.
Recommendations
We recommend that health care systems stop business as usual and adopt public health recommendations issued by Canadian and Hong Kong health care authorities for the management of suspected or confirmed COVID-19 disease.25-28 We have further clarified and expanded on these interventions. During viral pandemics, prescribers and health care systems should:
- Deprescribe nebulized therapies on medical wards and intensive care units as an infection control measure. Also avoid use in any outpatient health care setting (eg, community-based clinics, EDs, triage).
- Avoid initiation of nebulized unproven therapies (eg, n-acetylcysteine, hypertonic saline).1
- Use alternative bronchodilator formulations as appropriate (eg, oral β-2 agonist, recognizing its slower onset) before prescribing nebulized agents to patients who are uncooperative or unable to follow directions needed to use a pMDI with a spacer or have experienced a prior poor response to a pMDI with spacer (eg, OptiChamber Diamond, Philips).25,27
- Limit nebulized drug utilization (eg, bronchodilators, epoprostenol) to patients who are on mechanical ventilation and will receive nebulized therapies via a closed system or to patients housed in negative pressure hospital rooms.22 Use a viral filter (eg, Salter Labs system) to decrease the spread of infection for those receiving epoprostenol via face mask.25
- Adjust procurement practices (eg, pharmacy, logistics) to address the transition from nebulized drugs to alternatives.
- Add a safety net to the drug-ordering process by restricting new orders for nebulized therapies to the prior authorization process.27 Apply the exclusion criterion of suspected or definite COVID-19.
- Add a safety net to environmental service practices. Nursing staff should track patients who received ≥ 1 nebulizations via open (before diagnosis) or closed systems so that staff wear suitable PPE to include a N-95 mask while cleaning the room.
Conclusions
To implement the aggressive infection control guidance promulgated here, we recommend collaboration with infection control, pharmacy service (eg, prior authorization team, clinical pharmacy team, and procurement team), respiratory therapy, pulmonary and other critical care physicians, EDs, CPR committee, and other stakeholders. When making significant transitions in clinical care during a viral pandemic, guidelines must be timely, use imperative wording, and consist of easily identifiable education and/or instructions for the affected frontline staff in order to change attitudes.29 Additionally, when transitioning from nebulized bronchodilators to pMDI, educational in-services should be provided to frontline staff to avoid misconceptions regarding pMDI treatment efficacy and patients’ ability to use their pMDI with spacer.30
Acknowledgments
This material is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System in Nashville.
1. Strickland SL, Rubin BK, Haas CF, Volsko TA, Drescher GS, O’Malley CA. AARC Clinical Practice Guideline: effectiveness of pharmacologic airway clearance therapies in hospitalized patients. Respir Care. 2015;60(7):1071-1077.
2. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2020 GOLD Report. https://goldcopd.org/gold-reports/. Accessed March 26, 2020.
3. Van Geffen WH, Douma WR, Slebos DJ, Kerstjens HAM. Bronchodilators delivered by nebulizer versus pMDI with spacer or DPI for exacerbations of COPD (Review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;8:CD011826.
4. Global Initiative for Asthma. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GINA-2019-main-report-June-2019-wms.pdf. Accessed March 26, 2020.
5. Global Initiative for Asthma. Difficult-to-treat and severe asthma in adolescent and adult patients: diagnosis and management. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/GINA-Severe-asthma-Pocket-Guide-v2.0-wms-1.pdf. Accessed March 26, 2020.
6. Cates CJ, Welsh EJ, Rowe BH. Holding chambers (spacers) versus nebulizers for beta-agonist treatment of acute asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;9:CD000052.
7. Welsh EJ, Evans DJ, Fowler SJ, Spencer S. Interventions for bronchiectasis: an overview of Cochrane systematic reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;7:CD010337.
8. Taichman DB, Ornelas J, Chung L, et al. Pharmacologic therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension in adults: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. CHEST. 2014;146(2):449-475.
9. Griffiths MJD, McAuley DF, Perkins GD, et al. Guidelines on the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. BMJ Open Resp Res. 2019;6(1):e000420.
10. McGinn K, Reichert M. A comparison of inhaled nitric oxide versus inhaled epoprostenol for acute pulmonary hypertension following cardiac surgery. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50(1):22-26.
11. Dzierba AL, Abel EE, Buckley MS, Lat I. A review of inhaled nitric oxide and aerosolized epoprostenol in acute lung injury or acute respiratory distress syndrome. Pharmacotherapy. 2014;34(3):279-290.
12. Pleasants RA, Hess DR. Aerosol delivery devices for obstructive lung diseases. Respir Care. 2018;63(6):708-733.
13. World Health Organization. Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected. https://www.who.int/publications-detail/clinical-management-of-severe-acute-respiratory-infection-when-novel-coronavirus-(ncov)-infection-is-suspected Accessed March 26, 2020.
14. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim clinical guidance for management of patients with confirmed coronavirus disease (COVID-19). https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-guidance-management-patients.html. Revised March 7, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
15. Wong RSM, Hui DS. Index patient and SARS outbreak in Hong Kong. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10(2):339-341.
16. Wong T-W, Lee C-K, Tam W, et al; Outbreak Study Group. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10(2):269-276.
17. Seto WH, Tsang D, Yung RWH, et al; Advisors of Expert SARS group of Hospital Authority. Effectiveness of precautions against droplets and contact in prevention of nosocomial transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Lancet. 2003;361(9368):1519-1520.
18. Livingston E, Bucher K. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Italy. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2763401?resultClick=1. Published March 17, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
19. Jones S. Spain: doctors struggle to cope as 514 die from coronavirus in a day. The Guardian. March 24, 2020. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/24/spain-doctors-lack-protection-coronavirus-covid-19. Accessed March 27, 2020.
20. 16% of Ohio’s diagnosed COVID-19 cases are healthcare workers. https://www.wlwt.com/article/16-of-ohio-s-diagnosed-covid-19-cases-are-healthcare-workers/31930566#. Updated March 25, 2020. Accessed March 27, 2020.
21. Remuzzi A, Remuzzi G. COVID-19 and Italy: what next? Lancet. http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)30627-9/fulltext. Accessed March 27, 2020.
22. van Doremalen N, Bushmaker T, Morris DH, et al. Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as Compared with SARS-CoV-1 [published online ahead of print, 2020 Mar 17]. N Engl J Med. 2020;10.1056/NEJMc2004973.
23. McGrath JA, O’Sullivan A, Bennett G, et al. Investigation of the quantity of exhaled aerosol released into the environment during nebulization. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(2):75.
24. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Healthcare Infection prevention and control FAQs for COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/infection-control/infection-prevention-control-faq.html. Revised March 24, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
25. Practice standards of respiratory procedures: post SARS era. Use of aerosolized medications. December 2003. http://www.hkresp.com/hkts.php?page=page/hkts/detail&meid=93742. Accessed March 26, 2020.
26. Wax RS, Christian MD. Practical recommendations for critical care and anesthesiology teams caring for novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) patients. Can J Anesth. 2020. [ePub ahead of print.]
27. Newhouse MT. RE: transmission of coronavirus by nebulizer- as serious, underappreciated risk! https://www.cmaj.ca/content/re-transmission-corona-virus-nebulizer-serious-underappreciated-risk. Accessed March 26, 2020. [ePub ahead of print.]
28. Moira C-Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and healthcare workers. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2004;10(4):421-427.
29. Timen A, Hulscher MEJL, Rust L, et al. Barriers to implementing infection prevention and control guidelines during crises: experiences of health care professionals. Am J Infect Control. 2010;38(9):726-733.
30. Khoo SM, Tan LK, Said N, Lim TK. Metered-dose inhaler with spacer instead of nebulizer during the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Singapore. Respir Care. 2009;54(7):855-860.
Beyond asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), inhalation therapy is a mainstay in the management of bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis, and pulmonary artery hypertension. Several US Food and Drug Administration off-label indications for inhalational medications include hypoxia secondary to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and intraoperative and postoperative pulmonary hypertension during and following cardiac surgery, respectively.1-11 Therapeutic delivery of aerosols to the lung may be provided via nebulization, pressurized metered-dose inhalers (pMDI), and other devices (eg, dry powder inhalers, soft-mist inhalers, and smart inhalers).12 The most common aerosolized medications given in the clinical setting are bronchodilators.12
Product selection is often guided by practice guidelines (Table 1), consideration of the formulation’s advantages and disadvantages (Table 2), and/or formulary considerations. For example, current guidelines for COPD state that there is no evidence for superiority of nebulized bronchodilator therapy over handheld devices in patients who can use them properly.2 Due to equivalence, nebulized formulations are commonly used in hospitals, emergency departments (EDs) and ambulatory clinics based on the drug’s unit cost. In contrast, a pMDI is often more cost-effective for use in ambulatory patients who are administering multiple doses from the same canister.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend droplet and contact precautions for all patients suspected or diagnosed with novel coronavirus-19 (COVID-19).13,14 Airborne precautions must be applied when performing aerosol-generating medical procedures (AGMPs), including but not limited to, open suctioning of the respiratory tract, intubation, bronchoscopy, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Data from the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV) epidemic suggest that nebulization of medication is also an AGMP.15-17
Institutions must ensure that their health care workers (HCWs) are wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves, long-sleeved gowns, eye protection, and fit-tested particulate respirators (N95 mask) for airborne procedures and are carefully discarding PPE after use.13,14 Due to severe shortages in available respirators in the US supply chain, the CDC has temporarily modified WHO recommendations. Face masks are now an acceptable alternative to protect HCWs from splashes and sprays from procedures not likely to generate aerosols and for cleaning of rooms, although there is no evidence to support this decision.
Internationally, HCWs are falling ill with COVID-19. Data from Italy and Spain show that about 9% to 13% of these countries’ cases are HCWs.18,19 Within the US, the Ohio health department reports approximately 16% of cases are HCWs.20 It is possible that 20% of frontline HCWs will become infected.21 Evolving laboratory research shows that COVID-19 remains viable in aerosols for up to 3 hours postaerosolization, thus making aerosol transmission plausible.22 Nebulizers convert liquids into aerosols and during dispersal may potentially cause secondary inhalation of fugitive emissions.23 Since interim CDC infection control guidance is to allow only essential personnel to enter the room of patients with COVID-19, many facilities will rely on their frontline nursing staff to clean and disinfect high-touch surfaces following routine care activities.24
Achieving adequate fomite disinfection following viral aerosolization may pose a significant problem for any patient receiving scheduled doses of nebulized medications. Additionally, for personnel who clean rooms following intermittent drug nebulization while wearing PPE that includes a face mask, protection from aerosolized virus may be inadequate. Subsequently, fugitive emissions from nebulized medications may potentially contribute to both nosocomial COVID-19 transmission and viral infections in the medical staff until proven otherwise by studies conducted outside of the laboratory. Prevention of infection in the medical staff is imperative since federal health care systems cannot sustain a significant loss of its workforce.
Recommendations
We recommend that health care systems stop business as usual and adopt public health recommendations issued by Canadian and Hong Kong health care authorities for the management of suspected or confirmed COVID-19 disease.25-28 We have further clarified and expanded on these interventions. During viral pandemics, prescribers and health care systems should:
- Deprescribe nebulized therapies on medical wards and intensive care units as an infection control measure. Also avoid use in any outpatient health care setting (eg, community-based clinics, EDs, triage).
- Avoid initiation of nebulized unproven therapies (eg, n-acetylcysteine, hypertonic saline).1
- Use alternative bronchodilator formulations as appropriate (eg, oral β-2 agonist, recognizing its slower onset) before prescribing nebulized agents to patients who are uncooperative or unable to follow directions needed to use a pMDI with a spacer or have experienced a prior poor response to a pMDI with spacer (eg, OptiChamber Diamond, Philips).25,27
- Limit nebulized drug utilization (eg, bronchodilators, epoprostenol) to patients who are on mechanical ventilation and will receive nebulized therapies via a closed system or to patients housed in negative pressure hospital rooms.22 Use a viral filter (eg, Salter Labs system) to decrease the spread of infection for those receiving epoprostenol via face mask.25
- Adjust procurement practices (eg, pharmacy, logistics) to address the transition from nebulized drugs to alternatives.
- Add a safety net to the drug-ordering process by restricting new orders for nebulized therapies to the prior authorization process.27 Apply the exclusion criterion of suspected or definite COVID-19.
- Add a safety net to environmental service practices. Nursing staff should track patients who received ≥ 1 nebulizations via open (before diagnosis) or closed systems so that staff wear suitable PPE to include a N-95 mask while cleaning the room.
Conclusions
To implement the aggressive infection control guidance promulgated here, we recommend collaboration with infection control, pharmacy service (eg, prior authorization team, clinical pharmacy team, and procurement team), respiratory therapy, pulmonary and other critical care physicians, EDs, CPR committee, and other stakeholders. When making significant transitions in clinical care during a viral pandemic, guidelines must be timely, use imperative wording, and consist of easily identifiable education and/or instructions for the affected frontline staff in order to change attitudes.29 Additionally, when transitioning from nebulized bronchodilators to pMDI, educational in-services should be provided to frontline staff to avoid misconceptions regarding pMDI treatment efficacy and patients’ ability to use their pMDI with spacer.30
Acknowledgments
This material is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System in Nashville.
Beyond asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), inhalation therapy is a mainstay in the management of bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis, and pulmonary artery hypertension. Several US Food and Drug Administration off-label indications for inhalational medications include hypoxia secondary to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and intraoperative and postoperative pulmonary hypertension during and following cardiac surgery, respectively.1-11 Therapeutic delivery of aerosols to the lung may be provided via nebulization, pressurized metered-dose inhalers (pMDI), and other devices (eg, dry powder inhalers, soft-mist inhalers, and smart inhalers).12 The most common aerosolized medications given in the clinical setting are bronchodilators.12
Product selection is often guided by practice guidelines (Table 1), consideration of the formulation’s advantages and disadvantages (Table 2), and/or formulary considerations. For example, current guidelines for COPD state that there is no evidence for superiority of nebulized bronchodilator therapy over handheld devices in patients who can use them properly.2 Due to equivalence, nebulized formulations are commonly used in hospitals, emergency departments (EDs) and ambulatory clinics based on the drug’s unit cost. In contrast, a pMDI is often more cost-effective for use in ambulatory patients who are administering multiple doses from the same canister.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend droplet and contact precautions for all patients suspected or diagnosed with novel coronavirus-19 (COVID-19).13,14 Airborne precautions must be applied when performing aerosol-generating medical procedures (AGMPs), including but not limited to, open suctioning of the respiratory tract, intubation, bronchoscopy, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Data from the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV) epidemic suggest that nebulization of medication is also an AGMP.15-17
Institutions must ensure that their health care workers (HCWs) are wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves, long-sleeved gowns, eye protection, and fit-tested particulate respirators (N95 mask) for airborne procedures and are carefully discarding PPE after use.13,14 Due to severe shortages in available respirators in the US supply chain, the CDC has temporarily modified WHO recommendations. Face masks are now an acceptable alternative to protect HCWs from splashes and sprays from procedures not likely to generate aerosols and for cleaning of rooms, although there is no evidence to support this decision.
Internationally, HCWs are falling ill with COVID-19. Data from Italy and Spain show that about 9% to 13% of these countries’ cases are HCWs.18,19 Within the US, the Ohio health department reports approximately 16% of cases are HCWs.20 It is possible that 20% of frontline HCWs will become infected.21 Evolving laboratory research shows that COVID-19 remains viable in aerosols for up to 3 hours postaerosolization, thus making aerosol transmission plausible.22 Nebulizers convert liquids into aerosols and during dispersal may potentially cause secondary inhalation of fugitive emissions.23 Since interim CDC infection control guidance is to allow only essential personnel to enter the room of patients with COVID-19, many facilities will rely on their frontline nursing staff to clean and disinfect high-touch surfaces following routine care activities.24
Achieving adequate fomite disinfection following viral aerosolization may pose a significant problem for any patient receiving scheduled doses of nebulized medications. Additionally, for personnel who clean rooms following intermittent drug nebulization while wearing PPE that includes a face mask, protection from aerosolized virus may be inadequate. Subsequently, fugitive emissions from nebulized medications may potentially contribute to both nosocomial COVID-19 transmission and viral infections in the medical staff until proven otherwise by studies conducted outside of the laboratory. Prevention of infection in the medical staff is imperative since federal health care systems cannot sustain a significant loss of its workforce.
Recommendations
We recommend that health care systems stop business as usual and adopt public health recommendations issued by Canadian and Hong Kong health care authorities for the management of suspected or confirmed COVID-19 disease.25-28 We have further clarified and expanded on these interventions. During viral pandemics, prescribers and health care systems should:
- Deprescribe nebulized therapies on medical wards and intensive care units as an infection control measure. Also avoid use in any outpatient health care setting (eg, community-based clinics, EDs, triage).
- Avoid initiation of nebulized unproven therapies (eg, n-acetylcysteine, hypertonic saline).1
- Use alternative bronchodilator formulations as appropriate (eg, oral β-2 agonist, recognizing its slower onset) before prescribing nebulized agents to patients who are uncooperative or unable to follow directions needed to use a pMDI with a spacer or have experienced a prior poor response to a pMDI with spacer (eg, OptiChamber Diamond, Philips).25,27
- Limit nebulized drug utilization (eg, bronchodilators, epoprostenol) to patients who are on mechanical ventilation and will receive nebulized therapies via a closed system or to patients housed in negative pressure hospital rooms.22 Use a viral filter (eg, Salter Labs system) to decrease the spread of infection for those receiving epoprostenol via face mask.25
- Adjust procurement practices (eg, pharmacy, logistics) to address the transition from nebulized drugs to alternatives.
- Add a safety net to the drug-ordering process by restricting new orders for nebulized therapies to the prior authorization process.27 Apply the exclusion criterion of suspected or definite COVID-19.
- Add a safety net to environmental service practices. Nursing staff should track patients who received ≥ 1 nebulizations via open (before diagnosis) or closed systems so that staff wear suitable PPE to include a N-95 mask while cleaning the room.
Conclusions
To implement the aggressive infection control guidance promulgated here, we recommend collaboration with infection control, pharmacy service (eg, prior authorization team, clinical pharmacy team, and procurement team), respiratory therapy, pulmonary and other critical care physicians, EDs, CPR committee, and other stakeholders. When making significant transitions in clinical care during a viral pandemic, guidelines must be timely, use imperative wording, and consist of easily identifiable education and/or instructions for the affected frontline staff in order to change attitudes.29 Additionally, when transitioning from nebulized bronchodilators to pMDI, educational in-services should be provided to frontline staff to avoid misconceptions regarding pMDI treatment efficacy and patients’ ability to use their pMDI with spacer.30
Acknowledgments
This material is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System in Nashville.
1. Strickland SL, Rubin BK, Haas CF, Volsko TA, Drescher GS, O’Malley CA. AARC Clinical Practice Guideline: effectiveness of pharmacologic airway clearance therapies in hospitalized patients. Respir Care. 2015;60(7):1071-1077.
2. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2020 GOLD Report. https://goldcopd.org/gold-reports/. Accessed March 26, 2020.
3. Van Geffen WH, Douma WR, Slebos DJ, Kerstjens HAM. Bronchodilators delivered by nebulizer versus pMDI with spacer or DPI for exacerbations of COPD (Review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;8:CD011826.
4. Global Initiative for Asthma. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GINA-2019-main-report-June-2019-wms.pdf. Accessed March 26, 2020.
5. Global Initiative for Asthma. Difficult-to-treat and severe asthma in adolescent and adult patients: diagnosis and management. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/GINA-Severe-asthma-Pocket-Guide-v2.0-wms-1.pdf. Accessed March 26, 2020.
6. Cates CJ, Welsh EJ, Rowe BH. Holding chambers (spacers) versus nebulizers for beta-agonist treatment of acute asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;9:CD000052.
7. Welsh EJ, Evans DJ, Fowler SJ, Spencer S. Interventions for bronchiectasis: an overview of Cochrane systematic reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;7:CD010337.
8. Taichman DB, Ornelas J, Chung L, et al. Pharmacologic therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension in adults: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. CHEST. 2014;146(2):449-475.
9. Griffiths MJD, McAuley DF, Perkins GD, et al. Guidelines on the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. BMJ Open Resp Res. 2019;6(1):e000420.
10. McGinn K, Reichert M. A comparison of inhaled nitric oxide versus inhaled epoprostenol for acute pulmonary hypertension following cardiac surgery. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50(1):22-26.
11. Dzierba AL, Abel EE, Buckley MS, Lat I. A review of inhaled nitric oxide and aerosolized epoprostenol in acute lung injury or acute respiratory distress syndrome. Pharmacotherapy. 2014;34(3):279-290.
12. Pleasants RA, Hess DR. Aerosol delivery devices for obstructive lung diseases. Respir Care. 2018;63(6):708-733.
13. World Health Organization. Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected. https://www.who.int/publications-detail/clinical-management-of-severe-acute-respiratory-infection-when-novel-coronavirus-(ncov)-infection-is-suspected Accessed March 26, 2020.
14. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim clinical guidance for management of patients with confirmed coronavirus disease (COVID-19). https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-guidance-management-patients.html. Revised March 7, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
15. Wong RSM, Hui DS. Index patient and SARS outbreak in Hong Kong. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10(2):339-341.
16. Wong T-W, Lee C-K, Tam W, et al; Outbreak Study Group. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10(2):269-276.
17. Seto WH, Tsang D, Yung RWH, et al; Advisors of Expert SARS group of Hospital Authority. Effectiveness of precautions against droplets and contact in prevention of nosocomial transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Lancet. 2003;361(9368):1519-1520.
18. Livingston E, Bucher K. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Italy. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2763401?resultClick=1. Published March 17, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
19. Jones S. Spain: doctors struggle to cope as 514 die from coronavirus in a day. The Guardian. March 24, 2020. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/24/spain-doctors-lack-protection-coronavirus-covid-19. Accessed March 27, 2020.
20. 16% of Ohio’s diagnosed COVID-19 cases are healthcare workers. https://www.wlwt.com/article/16-of-ohio-s-diagnosed-covid-19-cases-are-healthcare-workers/31930566#. Updated March 25, 2020. Accessed March 27, 2020.
21. Remuzzi A, Remuzzi G. COVID-19 and Italy: what next? Lancet. http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)30627-9/fulltext. Accessed March 27, 2020.
22. van Doremalen N, Bushmaker T, Morris DH, et al. Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as Compared with SARS-CoV-1 [published online ahead of print, 2020 Mar 17]. N Engl J Med. 2020;10.1056/NEJMc2004973.
23. McGrath JA, O’Sullivan A, Bennett G, et al. Investigation of the quantity of exhaled aerosol released into the environment during nebulization. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(2):75.
24. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Healthcare Infection prevention and control FAQs for COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/infection-control/infection-prevention-control-faq.html. Revised March 24, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
25. Practice standards of respiratory procedures: post SARS era. Use of aerosolized medications. December 2003. http://www.hkresp.com/hkts.php?page=page/hkts/detail&meid=93742. Accessed March 26, 2020.
26. Wax RS, Christian MD. Practical recommendations for critical care and anesthesiology teams caring for novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) patients. Can J Anesth. 2020. [ePub ahead of print.]
27. Newhouse MT. RE: transmission of coronavirus by nebulizer- as serious, underappreciated risk! https://www.cmaj.ca/content/re-transmission-corona-virus-nebulizer-serious-underappreciated-risk. Accessed March 26, 2020. [ePub ahead of print.]
28. Moira C-Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and healthcare workers. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2004;10(4):421-427.
29. Timen A, Hulscher MEJL, Rust L, et al. Barriers to implementing infection prevention and control guidelines during crises: experiences of health care professionals. Am J Infect Control. 2010;38(9):726-733.
30. Khoo SM, Tan LK, Said N, Lim TK. Metered-dose inhaler with spacer instead of nebulizer during the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Singapore. Respir Care. 2009;54(7):855-860.
1. Strickland SL, Rubin BK, Haas CF, Volsko TA, Drescher GS, O’Malley CA. AARC Clinical Practice Guideline: effectiveness of pharmacologic airway clearance therapies in hospitalized patients. Respir Care. 2015;60(7):1071-1077.
2. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2020 GOLD Report. https://goldcopd.org/gold-reports/. Accessed March 26, 2020.
3. Van Geffen WH, Douma WR, Slebos DJ, Kerstjens HAM. Bronchodilators delivered by nebulizer versus pMDI with spacer or DPI for exacerbations of COPD (Review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;8:CD011826.
4. Global Initiative for Asthma. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GINA-2019-main-report-June-2019-wms.pdf. Accessed March 26, 2020.
5. Global Initiative for Asthma. Difficult-to-treat and severe asthma in adolescent and adult patients: diagnosis and management. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/GINA-Severe-asthma-Pocket-Guide-v2.0-wms-1.pdf. Accessed March 26, 2020.
6. Cates CJ, Welsh EJ, Rowe BH. Holding chambers (spacers) versus nebulizers for beta-agonist treatment of acute asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;9:CD000052.
7. Welsh EJ, Evans DJ, Fowler SJ, Spencer S. Interventions for bronchiectasis: an overview of Cochrane systematic reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;7:CD010337.
8. Taichman DB, Ornelas J, Chung L, et al. Pharmacologic therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension in adults: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. CHEST. 2014;146(2):449-475.
9. Griffiths MJD, McAuley DF, Perkins GD, et al. Guidelines on the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. BMJ Open Resp Res. 2019;6(1):e000420.
10. McGinn K, Reichert M. A comparison of inhaled nitric oxide versus inhaled epoprostenol for acute pulmonary hypertension following cardiac surgery. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50(1):22-26.
11. Dzierba AL, Abel EE, Buckley MS, Lat I. A review of inhaled nitric oxide and aerosolized epoprostenol in acute lung injury or acute respiratory distress syndrome. Pharmacotherapy. 2014;34(3):279-290.
12. Pleasants RA, Hess DR. Aerosol delivery devices for obstructive lung diseases. Respir Care. 2018;63(6):708-733.
13. World Health Organization. Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected. https://www.who.int/publications-detail/clinical-management-of-severe-acute-respiratory-infection-when-novel-coronavirus-(ncov)-infection-is-suspected Accessed March 26, 2020.
14. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim clinical guidance for management of patients with confirmed coronavirus disease (COVID-19). https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-guidance-management-patients.html. Revised March 7, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
15. Wong RSM, Hui DS. Index patient and SARS outbreak in Hong Kong. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10(2):339-341.
16. Wong T-W, Lee C-K, Tam W, et al; Outbreak Study Group. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10(2):269-276.
17. Seto WH, Tsang D, Yung RWH, et al; Advisors of Expert SARS group of Hospital Authority. Effectiveness of precautions against droplets and contact in prevention of nosocomial transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Lancet. 2003;361(9368):1519-1520.
18. Livingston E, Bucher K. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Italy. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2763401?resultClick=1. Published March 17, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
19. Jones S. Spain: doctors struggle to cope as 514 die from coronavirus in a day. The Guardian. March 24, 2020. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/24/spain-doctors-lack-protection-coronavirus-covid-19. Accessed March 27, 2020.
20. 16% of Ohio’s diagnosed COVID-19 cases are healthcare workers. https://www.wlwt.com/article/16-of-ohio-s-diagnosed-covid-19-cases-are-healthcare-workers/31930566#. Updated March 25, 2020. Accessed March 27, 2020.
21. Remuzzi A, Remuzzi G. COVID-19 and Italy: what next? Lancet. http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)30627-9/fulltext. Accessed March 27, 2020.
22. van Doremalen N, Bushmaker T, Morris DH, et al. Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as Compared with SARS-CoV-1 [published online ahead of print, 2020 Mar 17]. N Engl J Med. 2020;10.1056/NEJMc2004973.
23. McGrath JA, O’Sullivan A, Bennett G, et al. Investigation of the quantity of exhaled aerosol released into the environment during nebulization. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(2):75.
24. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Healthcare Infection prevention and control FAQs for COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/infection-control/infection-prevention-control-faq.html. Revised March 24, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
25. Practice standards of respiratory procedures: post SARS era. Use of aerosolized medications. December 2003. http://www.hkresp.com/hkts.php?page=page/hkts/detail&meid=93742. Accessed March 26, 2020.
26. Wax RS, Christian MD. Practical recommendations for critical care and anesthesiology teams caring for novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) patients. Can J Anesth. 2020. [ePub ahead of print.]
27. Newhouse MT. RE: transmission of coronavirus by nebulizer- as serious, underappreciated risk! https://www.cmaj.ca/content/re-transmission-corona-virus-nebulizer-serious-underappreciated-risk. Accessed March 26, 2020. [ePub ahead of print.]
28. Moira C-Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and healthcare workers. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2004;10(4):421-427.
29. Timen A, Hulscher MEJL, Rust L, et al. Barriers to implementing infection prevention and control guidelines during crises: experiences of health care professionals. Am J Infect Control. 2010;38(9):726-733.
30. Khoo SM, Tan LK, Said N, Lim TK. Metered-dose inhaler with spacer instead of nebulizer during the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Singapore. Respir Care. 2009;54(7):855-860.
Many children with COVID-19 don’t have cough or fever
according to the Centers for Disease and Prevention Control.
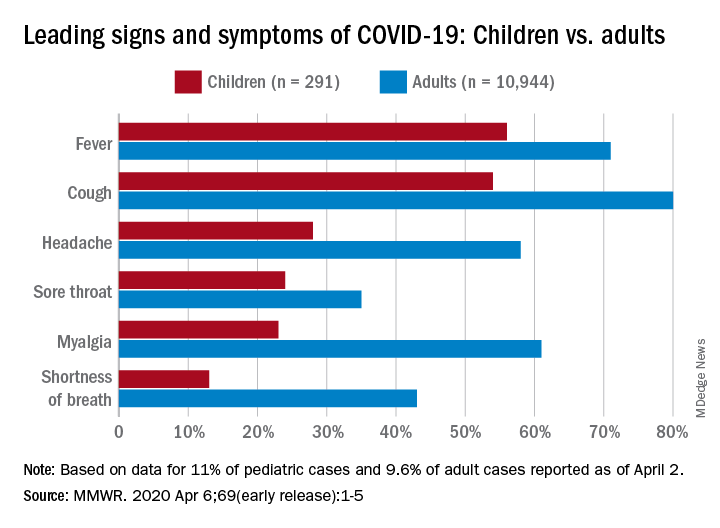
Among pediatric patients younger than 18 years in the United States, 73% had at least one of the trio of symptoms, compared with 93% of adults aged 18-64, noted Lucy A. McNamara, PhD, and the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, based on a preliminary analysis of the 149,082 cases reported as of April 2.
By a small margin, fever – present in 58% of pediatric patients – was the most common sign or symptom of COVID-19, compared with cough at 54% and shortness of breath in 13%. In adults, cough (81%) was seen most often, followed by fever (71%) and shortness of breath (43%), the investigators reported in the MMWR.
In both children and adults, headache and myalgia were more common than shortness of breath, as was sore throat in children, the team added.
“These findings are largely consistent with a report on pediatric COVID-19 patients aged <16 years in China, which found that only 41.5% of pediatric patients had fever [and] 48.5% had cough,” they wrote.
The CDC analysis of pediatric patients was limited by its small sample size, with data on signs and symptoms available for only 11% (291) of the 2,572 children known to have COVID-19 as of April 2. The adult population included 10,944 individuals, who represented 9.6% of the 113,985 U.S. patients aged 18-65, the response team said.
“As the number of COVID-19 cases continues to increase in many parts of the United States, it will be important to adapt COVID-19 surveillance strategies to maintain collection of critical case information without overburdening jurisdiction health departments,” they said.
SOURCE: McNamara LA et al. MMWR 2020 Apr 6;69(early release):1-5.
according to the Centers for Disease and Prevention Control.

Among pediatric patients younger than 18 years in the United States, 73% had at least one of the trio of symptoms, compared with 93% of adults aged 18-64, noted Lucy A. McNamara, PhD, and the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, based on a preliminary analysis of the 149,082 cases reported as of April 2.
By a small margin, fever – present in 58% of pediatric patients – was the most common sign or symptom of COVID-19, compared with cough at 54% and shortness of breath in 13%. In adults, cough (81%) was seen most often, followed by fever (71%) and shortness of breath (43%), the investigators reported in the MMWR.
In both children and adults, headache and myalgia were more common than shortness of breath, as was sore throat in children, the team added.
“These findings are largely consistent with a report on pediatric COVID-19 patients aged <16 years in China, which found that only 41.5% of pediatric patients had fever [and] 48.5% had cough,” they wrote.
The CDC analysis of pediatric patients was limited by its small sample size, with data on signs and symptoms available for only 11% (291) of the 2,572 children known to have COVID-19 as of April 2. The adult population included 10,944 individuals, who represented 9.6% of the 113,985 U.S. patients aged 18-65, the response team said.
“As the number of COVID-19 cases continues to increase in many parts of the United States, it will be important to adapt COVID-19 surveillance strategies to maintain collection of critical case information without overburdening jurisdiction health departments,” they said.
SOURCE: McNamara LA et al. MMWR 2020 Apr 6;69(early release):1-5.
according to the Centers for Disease and Prevention Control.

Among pediatric patients younger than 18 years in the United States, 73% had at least one of the trio of symptoms, compared with 93% of adults aged 18-64, noted Lucy A. McNamara, PhD, and the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, based on a preliminary analysis of the 149,082 cases reported as of April 2.
By a small margin, fever – present in 58% of pediatric patients – was the most common sign or symptom of COVID-19, compared with cough at 54% and shortness of breath in 13%. In adults, cough (81%) was seen most often, followed by fever (71%) and shortness of breath (43%), the investigators reported in the MMWR.
In both children and adults, headache and myalgia were more common than shortness of breath, as was sore throat in children, the team added.
“These findings are largely consistent with a report on pediatric COVID-19 patients aged <16 years in China, which found that only 41.5% of pediatric patients had fever [and] 48.5% had cough,” they wrote.
The CDC analysis of pediatric patients was limited by its small sample size, with data on signs and symptoms available for only 11% (291) of the 2,572 children known to have COVID-19 as of April 2. The adult population included 10,944 individuals, who represented 9.6% of the 113,985 U.S. patients aged 18-65, the response team said.
“As the number of COVID-19 cases continues to increase in many parts of the United States, it will be important to adapt COVID-19 surveillance strategies to maintain collection of critical case information without overburdening jurisdiction health departments,” they said.
SOURCE: McNamara LA et al. MMWR 2020 Apr 6;69(early release):1-5.
FROM MMWR
Climate Change and Expansion of Tick Geography
The expanding range of tick-borne diseases is a growing problem worldwide. Climate change plays a preeminent role in the expansion of tick species, especially for southern ticks in the United States such as Amblyomma species, which have introduced new pathogens to northern states.1-5 In addition to well-known tick-borne diseases, Amblyomma ticks have been implicated in the spread of emerging severe and potentially fatal viral illnesses, including Bourbon virus and Heartland virus.6 The increasing range of Amblyomma ticks also exposes new populations to tick-induced meat allergy (alpha-gal) syndrome, whereby development of specific IgE antibodies to the oligosaccharide galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal) following tick bites results in severe allergic responses to consumption of
Amblyomma ticks have now been identified close to the Canadian border in Michigan and New York, and predictions of continued climate change raise the possibility of northward range expansion into all provinces of Canada from Alberta to Newfoundland and Labrador during the coming decades.8,9 Additional factors that contribute to the expanding range of many tick species include international travel, migratory patterns of birds, competition, and natural predators such as fire ants that feed on tick eggs and influence the feeding behavior of adults.10
Traditional methods of tick identification rely on gross morphology, including the presence of festoons, shape of the coxae where the legs attach, and markings on the hard overlying scutum. More recently, molecular identification has improved tick identification, leading to more accurate assessment of tick prevalence. These modern identification studies include analysis of 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA), 12S rDNA, and ITS1 rDNA, and ITS2 rDNA genes.11
The spread of tick vectors has huge public health implications, and better methods to control tick populations are needed.12 New acaricides and growth regulators are being developed,13 and early spring applications of acaricides such as bifenthrin can suppress nymphs prior to the initiation of host-seeking activity.14 Controlled burns within tick habitats have proved helpful in reducing the risk for vector-borne disease.15,16 Personal protection is best accomplished with the use of a repellent together with clothing impregnated with an acaricide such as permethrin.17 Efforts to slow climate change and continued surveillance for the spread of tick vectors is urgently needed.
- Sanchez-Vicente S, Tagliafierro T, Coleman JL, et al. Polymicrobial nature of tick-borne diseases [published online September 10, 2019]. MBio. doi:10.1128/mBio.02055-19.
- Raghavan RK, Peterson AT, Cobos ME, et al. Current and future distribution of the Lone Star tick, Amblyomma americanum (L.) (Acari: Ixodidae) in North America. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0209082.
- Stafford KC 3rd, Molaei G, Little EAH, et al. Distribution and establishment of the Lone Star tick in Connecticut and implications for range expansion and public health. J Med Entomol. 2018;25:1561-1568.
- Gilliam ME, Rechkemmer WT, McCravy KW, et al. The influence of prescribed fire, habitat, and weather on Amblyomma americanum (Ixodida: Ixodidae) in West-Central Illinois, USA [published online March 22, 2018]. Insects. doi:10.3390/insects9020036.
- Sonenshine DE. Range expansion of tick disease vectors in North America: implications for spread of tick-borne disease [published online March 9, 2018]. Int J Environ Res Public Health. doi:10.3390/ijerph15030478.
- Savage HM, Godsey MS Jr, Panella NA, et al. Surveillance for tick-borne viruses near the location of a fatal human case of Bourbon virus (family Orthomyxoviridae: genus Thogotovirus) in eastern Kansas, 2015. J Med Entomol. 2018;55:701-705.
- Crispell G, Commins SP, Archer-Hartman SA, et al. Discovery of alpha-gal-containing antigens in North American tick species believed to induce red meat allergy. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1056.
- Gasmi S, Bouchard C, Ogden NH, et al. Evidence for increasing densities and geographic ranges of tick species of public health significance other than Ixodes scapularis in Québec, Canada. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0201924.
- Sagurova I, Ludwig A, Ogden NH, et al. Predicted northward expansion of the geographic range of the tick vector Amblyomma americanum in North America under future climate conditions. Environ Health Perspect. 2019;127:107014.
- Kjeldgaard MK, Takano OM, Bockoven AA, et al. Red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta) aggression influences the behavior of three hard tick species. Exp Appl Acarol. 2019;79:87-97.
- Abouelhassan EM, El-Gawady HM, Abdel-Aal AA, et al. Comparison of some molecular markers for tick species identification. J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2019;13:153-164.
- Jordan RA, Egizi A. The growing importance of lone star ticks in a Lyme disease endemic county: passive tick surveillance in Monmouth County, NJ, 2006–2016. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0211778.
- Showler AT, Donahue WA, Harlien JL, et al. Efficacy of novaluron + pyriproxyfen (Tekko Pro) insect growth regulators against Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae), Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, and Rhipicephalus sanguineus. J Med Entomol. 2019;56:1338-1345.
- Schulze TL, Jordan RA. Early season applications of bifenthrin suppress host-seeking Ixodes scapularis and Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) nymphs [published online November 26, 2019]. J Med Entomol. doi:10.1093/jme/tjz202.
- Hodo CL, Forgacs D, Auckland LD, et al. Presence of diverse Rickettsia spp. and absence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in ticks in an East Texas forest with reduced tick density associated with controlled burns. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020;11:101310.
- Gleim ER, Zemtsova GE, Berghaus RD, et al. Frequent prescribed fires can reduce risk of tick-borne diseases. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9974.
- Prose R, Breuner NE, Johnson TL, et al. Contact irritancy and toxicity of permethrin-treated clothing for Ixodes scapularis, Amblyomma americanum, and Dermacentor variabilis ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 2018;55:1217-1224.
The expanding range of tick-borne diseases is a growing problem worldwide. Climate change plays a preeminent role in the expansion of tick species, especially for southern ticks in the United States such as Amblyomma species, which have introduced new pathogens to northern states.1-5 In addition to well-known tick-borne diseases, Amblyomma ticks have been implicated in the spread of emerging severe and potentially fatal viral illnesses, including Bourbon virus and Heartland virus.6 The increasing range of Amblyomma ticks also exposes new populations to tick-induced meat allergy (alpha-gal) syndrome, whereby development of specific IgE antibodies to the oligosaccharide galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal) following tick bites results in severe allergic responses to consumption of
Amblyomma ticks have now been identified close to the Canadian border in Michigan and New York, and predictions of continued climate change raise the possibility of northward range expansion into all provinces of Canada from Alberta to Newfoundland and Labrador during the coming decades.8,9 Additional factors that contribute to the expanding range of many tick species include international travel, migratory patterns of birds, competition, and natural predators such as fire ants that feed on tick eggs and influence the feeding behavior of adults.10
Traditional methods of tick identification rely on gross morphology, including the presence of festoons, shape of the coxae where the legs attach, and markings on the hard overlying scutum. More recently, molecular identification has improved tick identification, leading to more accurate assessment of tick prevalence. These modern identification studies include analysis of 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA), 12S rDNA, and ITS1 rDNA, and ITS2 rDNA genes.11
The spread of tick vectors has huge public health implications, and better methods to control tick populations are needed.12 New acaricides and growth regulators are being developed,13 and early spring applications of acaricides such as bifenthrin can suppress nymphs prior to the initiation of host-seeking activity.14 Controlled burns within tick habitats have proved helpful in reducing the risk for vector-borne disease.15,16 Personal protection is best accomplished with the use of a repellent together with clothing impregnated with an acaricide such as permethrin.17 Efforts to slow climate change and continued surveillance for the spread of tick vectors is urgently needed.
The expanding range of tick-borne diseases is a growing problem worldwide. Climate change plays a preeminent role in the expansion of tick species, especially for southern ticks in the United States such as Amblyomma species, which have introduced new pathogens to northern states.1-5 In addition to well-known tick-borne diseases, Amblyomma ticks have been implicated in the spread of emerging severe and potentially fatal viral illnesses, including Bourbon virus and Heartland virus.6 The increasing range of Amblyomma ticks also exposes new populations to tick-induced meat allergy (alpha-gal) syndrome, whereby development of specific IgE antibodies to the oligosaccharide galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal) following tick bites results in severe allergic responses to consumption of
Amblyomma ticks have now been identified close to the Canadian border in Michigan and New York, and predictions of continued climate change raise the possibility of northward range expansion into all provinces of Canada from Alberta to Newfoundland and Labrador during the coming decades.8,9 Additional factors that contribute to the expanding range of many tick species include international travel, migratory patterns of birds, competition, and natural predators such as fire ants that feed on tick eggs and influence the feeding behavior of adults.10
Traditional methods of tick identification rely on gross morphology, including the presence of festoons, shape of the coxae where the legs attach, and markings on the hard overlying scutum. More recently, molecular identification has improved tick identification, leading to more accurate assessment of tick prevalence. These modern identification studies include analysis of 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA), 12S rDNA, and ITS1 rDNA, and ITS2 rDNA genes.11
The spread of tick vectors has huge public health implications, and better methods to control tick populations are needed.12 New acaricides and growth regulators are being developed,13 and early spring applications of acaricides such as bifenthrin can suppress nymphs prior to the initiation of host-seeking activity.14 Controlled burns within tick habitats have proved helpful in reducing the risk for vector-borne disease.15,16 Personal protection is best accomplished with the use of a repellent together with clothing impregnated with an acaricide such as permethrin.17 Efforts to slow climate change and continued surveillance for the spread of tick vectors is urgently needed.
- Sanchez-Vicente S, Tagliafierro T, Coleman JL, et al. Polymicrobial nature of tick-borne diseases [published online September 10, 2019]. MBio. doi:10.1128/mBio.02055-19.
- Raghavan RK, Peterson AT, Cobos ME, et al. Current and future distribution of the Lone Star tick, Amblyomma americanum (L.) (Acari: Ixodidae) in North America. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0209082.
- Stafford KC 3rd, Molaei G, Little EAH, et al. Distribution and establishment of the Lone Star tick in Connecticut and implications for range expansion and public health. J Med Entomol. 2018;25:1561-1568.
- Gilliam ME, Rechkemmer WT, McCravy KW, et al. The influence of prescribed fire, habitat, and weather on Amblyomma americanum (Ixodida: Ixodidae) in West-Central Illinois, USA [published online March 22, 2018]. Insects. doi:10.3390/insects9020036.
- Sonenshine DE. Range expansion of tick disease vectors in North America: implications for spread of tick-borne disease [published online March 9, 2018]. Int J Environ Res Public Health. doi:10.3390/ijerph15030478.
- Savage HM, Godsey MS Jr, Panella NA, et al. Surveillance for tick-borne viruses near the location of a fatal human case of Bourbon virus (family Orthomyxoviridae: genus Thogotovirus) in eastern Kansas, 2015. J Med Entomol. 2018;55:701-705.
- Crispell G, Commins SP, Archer-Hartman SA, et al. Discovery of alpha-gal-containing antigens in North American tick species believed to induce red meat allergy. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1056.
- Gasmi S, Bouchard C, Ogden NH, et al. Evidence for increasing densities and geographic ranges of tick species of public health significance other than Ixodes scapularis in Québec, Canada. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0201924.
- Sagurova I, Ludwig A, Ogden NH, et al. Predicted northward expansion of the geographic range of the tick vector Amblyomma americanum in North America under future climate conditions. Environ Health Perspect. 2019;127:107014.
- Kjeldgaard MK, Takano OM, Bockoven AA, et al. Red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta) aggression influences the behavior of three hard tick species. Exp Appl Acarol. 2019;79:87-97.
- Abouelhassan EM, El-Gawady HM, Abdel-Aal AA, et al. Comparison of some molecular markers for tick species identification. J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2019;13:153-164.
- Jordan RA, Egizi A. The growing importance of lone star ticks in a Lyme disease endemic county: passive tick surveillance in Monmouth County, NJ, 2006–2016. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0211778.
- Showler AT, Donahue WA, Harlien JL, et al. Efficacy of novaluron + pyriproxyfen (Tekko Pro) insect growth regulators against Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae), Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, and Rhipicephalus sanguineus. J Med Entomol. 2019;56:1338-1345.
- Schulze TL, Jordan RA. Early season applications of bifenthrin suppress host-seeking Ixodes scapularis and Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) nymphs [published online November 26, 2019]. J Med Entomol. doi:10.1093/jme/tjz202.
- Hodo CL, Forgacs D, Auckland LD, et al. Presence of diverse Rickettsia spp. and absence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in ticks in an East Texas forest with reduced tick density associated with controlled burns. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020;11:101310.
- Gleim ER, Zemtsova GE, Berghaus RD, et al. Frequent prescribed fires can reduce risk of tick-borne diseases. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9974.
- Prose R, Breuner NE, Johnson TL, et al. Contact irritancy and toxicity of permethrin-treated clothing for Ixodes scapularis, Amblyomma americanum, and Dermacentor variabilis ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 2018;55:1217-1224.
- Sanchez-Vicente S, Tagliafierro T, Coleman JL, et al. Polymicrobial nature of tick-borne diseases [published online September 10, 2019]. MBio. doi:10.1128/mBio.02055-19.
- Raghavan RK, Peterson AT, Cobos ME, et al. Current and future distribution of the Lone Star tick, Amblyomma americanum (L.) (Acari: Ixodidae) in North America. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0209082.
- Stafford KC 3rd, Molaei G, Little EAH, et al. Distribution and establishment of the Lone Star tick in Connecticut and implications for range expansion and public health. J Med Entomol. 2018;25:1561-1568.
- Gilliam ME, Rechkemmer WT, McCravy KW, et al. The influence of prescribed fire, habitat, and weather on Amblyomma americanum (Ixodida: Ixodidae) in West-Central Illinois, USA [published online March 22, 2018]. Insects. doi:10.3390/insects9020036.
- Sonenshine DE. Range expansion of tick disease vectors in North America: implications for spread of tick-borne disease [published online March 9, 2018]. Int J Environ Res Public Health. doi:10.3390/ijerph15030478.
- Savage HM, Godsey MS Jr, Panella NA, et al. Surveillance for tick-borne viruses near the location of a fatal human case of Bourbon virus (family Orthomyxoviridae: genus Thogotovirus) in eastern Kansas, 2015. J Med Entomol. 2018;55:701-705.
- Crispell G, Commins SP, Archer-Hartman SA, et al. Discovery of alpha-gal-containing antigens in North American tick species believed to induce red meat allergy. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1056.
- Gasmi S, Bouchard C, Ogden NH, et al. Evidence for increasing densities and geographic ranges of tick species of public health significance other than Ixodes scapularis in Québec, Canada. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0201924.
- Sagurova I, Ludwig A, Ogden NH, et al. Predicted northward expansion of the geographic range of the tick vector Amblyomma americanum in North America under future climate conditions. Environ Health Perspect. 2019;127:107014.
- Kjeldgaard MK, Takano OM, Bockoven AA, et al. Red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta) aggression influences the behavior of three hard tick species. Exp Appl Acarol. 2019;79:87-97.
- Abouelhassan EM, El-Gawady HM, Abdel-Aal AA, et al. Comparison of some molecular markers for tick species identification. J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2019;13:153-164.
- Jordan RA, Egizi A. The growing importance of lone star ticks in a Lyme disease endemic county: passive tick surveillance in Monmouth County, NJ, 2006–2016. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0211778.
- Showler AT, Donahue WA, Harlien JL, et al. Efficacy of novaluron + pyriproxyfen (Tekko Pro) insect growth regulators against Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae), Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, and Rhipicephalus sanguineus. J Med Entomol. 2019;56:1338-1345.
- Schulze TL, Jordan RA. Early season applications of bifenthrin suppress host-seeking Ixodes scapularis and Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) nymphs [published online November 26, 2019]. J Med Entomol. doi:10.1093/jme/tjz202.
- Hodo CL, Forgacs D, Auckland LD, et al. Presence of diverse Rickettsia spp. and absence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in ticks in an East Texas forest with reduced tick density associated with controlled burns. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020;11:101310.
- Gleim ER, Zemtsova GE, Berghaus RD, et al. Frequent prescribed fires can reduce risk of tick-borne diseases. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9974.
- Prose R, Breuner NE, Johnson TL, et al. Contact irritancy and toxicity of permethrin-treated clothing for Ixodes scapularis, Amblyomma americanum, and Dermacentor variabilis ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 2018;55:1217-1224.
AAP issues guidance on managing infants born to mothers with COVID-19
“Pediatric cases of COVID-19 are so far reported as less severe than disease occurring among older individuals,” Karen M. Puopolo, MD, PhD, a neonatologist and chief of the section on newborn pediatrics at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, and coauthors wrote in the 18-page document, which was released on April 2, 2020, along with an abbreviated “Frequently Asked Questions” summary. However, one study of children with COVID-19 in China found that 12% of confirmed cases occurred among 731 infants aged less than 1 year; 24% of those 86 infants “suffered severe or critical illness” (Pediatrics. 2020 March. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-0702). There were no deaths reported among these infants. Other case reports have documented COVID-19 in children aged as young as 2 days.
The document, which was assembled by members of the AAP Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Section on Neonatal Perinatal Medicine, and Committee on Infectious Diseases, pointed out that “considerable uncertainty” exists about the possibility for vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from infected pregnant women to their newborns. “Evidence-based guidelines for managing antenatal, intrapartum, and neonatal care around COVID-19 would require an understanding of whether the virus can be transmitted transplacentally; a determination of which maternal body fluids may be infectious; and data of adequate statistical power that describe which maternal, intrapartum, and neonatal factors influence perinatal transmission,” according to the document. “In the midst of the pandemic these data do not exist, with only limited information currently available to address these issues.”
Based on the best available evidence, the guidance authors recommend that clinicians temporarily separate newborns from affected mothers to minimize the risk of postnatal infant infection from maternal respiratory secretions. “Newborns should be bathed as soon as reasonably possible after birth to remove virus potentially present on skin surfaces,” they wrote. “Clinical staff should use airborne, droplet, and contact precautions until newborn virologic status is known to be negative by SARS-CoV-2 [polymerase chain reaction] testing.”
While SARS-CoV-2 has not been detected in breast milk to date, the authors noted that mothers with COVID-19 can express breast milk to be fed to their infants by uninfected caregivers until specific maternal criteria are met. In addition, infants born to mothers with COVID-19 should be tested for SARS-CoV-2 at 24 hours and, if still in the birth facility, at 48 hours after birth. Centers with limited resources for testing may make individual risk/benefit decisions regarding testing.
For infants infected with SARS-CoV-2 but have no symptoms of the disease, they “may be discharged home on a case-by-case basis with appropriate precautions and plans for frequent outpatient follow-up contacts (either by phone, telemedicine, or in office) through 14 days after birth,” according to the document.
If both infant and mother are discharged from the hospital and the mother still has COVID-19 symptoms, she should maintain at least 6 feet of distance from the baby; if she is in closer proximity she should use a mask and hand hygiene. The mother can stop such precautions until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, and it is at least 7 days since her symptoms first occurred.
In cases where infants require ongoing neonatal intensive care, mothers infected with COVID-19 should not visit their newborn until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, her respiratory symptoms are improved, and she has negative results of a molecular assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 from at least two consecutive nasopharyngeal swab specimens collected at least 24 hours apart.
“Pediatric cases of COVID-19 are so far reported as less severe than disease occurring among older individuals,” Karen M. Puopolo, MD, PhD, a neonatologist and chief of the section on newborn pediatrics at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, and coauthors wrote in the 18-page document, which was released on April 2, 2020, along with an abbreviated “Frequently Asked Questions” summary. However, one study of children with COVID-19 in China found that 12% of confirmed cases occurred among 731 infants aged less than 1 year; 24% of those 86 infants “suffered severe or critical illness” (Pediatrics. 2020 March. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-0702). There were no deaths reported among these infants. Other case reports have documented COVID-19 in children aged as young as 2 days.
The document, which was assembled by members of the AAP Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Section on Neonatal Perinatal Medicine, and Committee on Infectious Diseases, pointed out that “considerable uncertainty” exists about the possibility for vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from infected pregnant women to their newborns. “Evidence-based guidelines for managing antenatal, intrapartum, and neonatal care around COVID-19 would require an understanding of whether the virus can be transmitted transplacentally; a determination of which maternal body fluids may be infectious; and data of adequate statistical power that describe which maternal, intrapartum, and neonatal factors influence perinatal transmission,” according to the document. “In the midst of the pandemic these data do not exist, with only limited information currently available to address these issues.”
Based on the best available evidence, the guidance authors recommend that clinicians temporarily separate newborns from affected mothers to minimize the risk of postnatal infant infection from maternal respiratory secretions. “Newborns should be bathed as soon as reasonably possible after birth to remove virus potentially present on skin surfaces,” they wrote. “Clinical staff should use airborne, droplet, and contact precautions until newborn virologic status is known to be negative by SARS-CoV-2 [polymerase chain reaction] testing.”
While SARS-CoV-2 has not been detected in breast milk to date, the authors noted that mothers with COVID-19 can express breast milk to be fed to their infants by uninfected caregivers until specific maternal criteria are met. In addition, infants born to mothers with COVID-19 should be tested for SARS-CoV-2 at 24 hours and, if still in the birth facility, at 48 hours after birth. Centers with limited resources for testing may make individual risk/benefit decisions regarding testing.
For infants infected with SARS-CoV-2 but have no symptoms of the disease, they “may be discharged home on a case-by-case basis with appropriate precautions and plans for frequent outpatient follow-up contacts (either by phone, telemedicine, or in office) through 14 days after birth,” according to the document.
If both infant and mother are discharged from the hospital and the mother still has COVID-19 symptoms, she should maintain at least 6 feet of distance from the baby; if she is in closer proximity she should use a mask and hand hygiene. The mother can stop such precautions until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, and it is at least 7 days since her symptoms first occurred.
In cases where infants require ongoing neonatal intensive care, mothers infected with COVID-19 should not visit their newborn until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, her respiratory symptoms are improved, and she has negative results of a molecular assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 from at least two consecutive nasopharyngeal swab specimens collected at least 24 hours apart.
“Pediatric cases of COVID-19 are so far reported as less severe than disease occurring among older individuals,” Karen M. Puopolo, MD, PhD, a neonatologist and chief of the section on newborn pediatrics at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, and coauthors wrote in the 18-page document, which was released on April 2, 2020, along with an abbreviated “Frequently Asked Questions” summary. However, one study of children with COVID-19 in China found that 12% of confirmed cases occurred among 731 infants aged less than 1 year; 24% of those 86 infants “suffered severe or critical illness” (Pediatrics. 2020 March. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-0702). There were no deaths reported among these infants. Other case reports have documented COVID-19 in children aged as young as 2 days.
The document, which was assembled by members of the AAP Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Section on Neonatal Perinatal Medicine, and Committee on Infectious Diseases, pointed out that “considerable uncertainty” exists about the possibility for vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from infected pregnant women to their newborns. “Evidence-based guidelines for managing antenatal, intrapartum, and neonatal care around COVID-19 would require an understanding of whether the virus can be transmitted transplacentally; a determination of which maternal body fluids may be infectious; and data of adequate statistical power that describe which maternal, intrapartum, and neonatal factors influence perinatal transmission,” according to the document. “In the midst of the pandemic these data do not exist, with only limited information currently available to address these issues.”
Based on the best available evidence, the guidance authors recommend that clinicians temporarily separate newborns from affected mothers to minimize the risk of postnatal infant infection from maternal respiratory secretions. “Newborns should be bathed as soon as reasonably possible after birth to remove virus potentially present on skin surfaces,” they wrote. “Clinical staff should use airborne, droplet, and contact precautions until newborn virologic status is known to be negative by SARS-CoV-2 [polymerase chain reaction] testing.”
While SARS-CoV-2 has not been detected in breast milk to date, the authors noted that mothers with COVID-19 can express breast milk to be fed to their infants by uninfected caregivers until specific maternal criteria are met. In addition, infants born to mothers with COVID-19 should be tested for SARS-CoV-2 at 24 hours and, if still in the birth facility, at 48 hours after birth. Centers with limited resources for testing may make individual risk/benefit decisions regarding testing.
For infants infected with SARS-CoV-2 but have no symptoms of the disease, they “may be discharged home on a case-by-case basis with appropriate precautions and plans for frequent outpatient follow-up contacts (either by phone, telemedicine, or in office) through 14 days after birth,” according to the document.
If both infant and mother are discharged from the hospital and the mother still has COVID-19 symptoms, she should maintain at least 6 feet of distance from the baby; if she is in closer proximity she should use a mask and hand hygiene. The mother can stop such precautions until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, and it is at least 7 days since her symptoms first occurred.
In cases where infants require ongoing neonatal intensive care, mothers infected with COVID-19 should not visit their newborn until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, her respiratory symptoms are improved, and she has negative results of a molecular assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 from at least two consecutive nasopharyngeal swab specimens collected at least 24 hours apart.
Practicing solo and feeling grateful – despite COVID-19
I know that the world has gone upside down. It’s a nightmare, and people are filled with fear, and death is everywhere. In my little bubble of a world, however, I’ve been doing well.
I can’t lose my job, because I am my job. I’m a solo practitioner and have been for more than a decade. The restrictions to stay at home have not affected me, because I have a home office. Besides, I’m an introvert and see myself as a bit of a recluse, so the social distancing hasn’t been stressful. Conducting appointments by phone rather than face to face hasn’t undermined my work, since I can do everything that I do in my office over the phone. But I do it now in sweats and at my desk in my bedroom more often than not. I am prepared for a decrease in income as people lose their jobs, but that hasn’t happened yet. There are still people out there who are very motivated to come off their medications holistically. No rest for the wicked, as the saying goes.
On an emotional level, I feel calm because I’m not attached to material things, though I like them when they’re here. My children and friends have remained healthy, so I am grateful for that. I feel grounded in my belief that life goes on one way or another, and I trust in God to direct me wherever I need to go. Socially, I’ve been forced to be less lazy and cook more at home. As a result: less salt, MSG, and greasy food. I’ve spent a lot less on restaurants this past month and am eating less since I have to eat whatever I cook.
Can a person be more pandemic proof? I was joking with a friend about how pandemic-friendly my lifestyle is: spiritually, mentally, emotionally, physically, and socially. Oh, did I forget to mention the year supply of supplements in my office closet? They were for my patients, but those whole food green and red powders may come in handy, just in case.
So, that is how things are going for me. Please don’t hate me for not freaking out. When I read the news, I feel very sad for people who are suffering. I get angry at the politicians who can’t get their egos out of the way. But, I look at the sunshine outside my window, and I feel grateful that, at least in my case, I am not adding to the burden of suffering in the world. Not yet, anyway. I will keep trying to do the little bit that I do to help others for as long as I can.
Dr. Lee specializes in integrative and holistic psychiatry and has a private practice in Gaithersburg, Md. She has no disclosures.
I know that the world has gone upside down. It’s a nightmare, and people are filled with fear, and death is everywhere. In my little bubble of a world, however, I’ve been doing well.
I can’t lose my job, because I am my job. I’m a solo practitioner and have been for more than a decade. The restrictions to stay at home have not affected me, because I have a home office. Besides, I’m an introvert and see myself as a bit of a recluse, so the social distancing hasn’t been stressful. Conducting appointments by phone rather than face to face hasn’t undermined my work, since I can do everything that I do in my office over the phone. But I do it now in sweats and at my desk in my bedroom more often than not. I am prepared for a decrease in income as people lose their jobs, but that hasn’t happened yet. There are still people out there who are very motivated to come off their medications holistically. No rest for the wicked, as the saying goes.
On an emotional level, I feel calm because I’m not attached to material things, though I like them when they’re here. My children and friends have remained healthy, so I am grateful for that. I feel grounded in my belief that life goes on one way or another, and I trust in God to direct me wherever I need to go. Socially, I’ve been forced to be less lazy and cook more at home. As a result: less salt, MSG, and greasy food. I’ve spent a lot less on restaurants this past month and am eating less since I have to eat whatever I cook.
Can a person be more pandemic proof? I was joking with a friend about how pandemic-friendly my lifestyle is: spiritually, mentally, emotionally, physically, and socially. Oh, did I forget to mention the year supply of supplements in my office closet? They were for my patients, but those whole food green and red powders may come in handy, just in case.
So, that is how things are going for me. Please don’t hate me for not freaking out. When I read the news, I feel very sad for people who are suffering. I get angry at the politicians who can’t get their egos out of the way. But, I look at the sunshine outside my window, and I feel grateful that, at least in my case, I am not adding to the burden of suffering in the world. Not yet, anyway. I will keep trying to do the little bit that I do to help others for as long as I can.
Dr. Lee specializes in integrative and holistic psychiatry and has a private practice in Gaithersburg, Md. She has no disclosures.
I know that the world has gone upside down. It’s a nightmare, and people are filled with fear, and death is everywhere. In my little bubble of a world, however, I’ve been doing well.
I can’t lose my job, because I am my job. I’m a solo practitioner and have been for more than a decade. The restrictions to stay at home have not affected me, because I have a home office. Besides, I’m an introvert and see myself as a bit of a recluse, so the social distancing hasn’t been stressful. Conducting appointments by phone rather than face to face hasn’t undermined my work, since I can do everything that I do in my office over the phone. But I do it now in sweats and at my desk in my bedroom more often than not. I am prepared for a decrease in income as people lose their jobs, but that hasn’t happened yet. There are still people out there who are very motivated to come off their medications holistically. No rest for the wicked, as the saying goes.
On an emotional level, I feel calm because I’m not attached to material things, though I like them when they’re here. My children and friends have remained healthy, so I am grateful for that. I feel grounded in my belief that life goes on one way or another, and I trust in God to direct me wherever I need to go. Socially, I’ve been forced to be less lazy and cook more at home. As a result: less salt, MSG, and greasy food. I’ve spent a lot less on restaurants this past month and am eating less since I have to eat whatever I cook.
Can a person be more pandemic proof? I was joking with a friend about how pandemic-friendly my lifestyle is: spiritually, mentally, emotionally, physically, and socially. Oh, did I forget to mention the year supply of supplements in my office closet? They were for my patients, but those whole food green and red powders may come in handy, just in case.
So, that is how things are going for me. Please don’t hate me for not freaking out. When I read the news, I feel very sad for people who are suffering. I get angry at the politicians who can’t get their egos out of the way. But, I look at the sunshine outside my window, and I feel grateful that, at least in my case, I am not adding to the burden of suffering in the world. Not yet, anyway. I will keep trying to do the little bit that I do to help others for as long as I can.
Dr. Lee specializes in integrative and holistic psychiatry and has a private practice in Gaithersburg, Md. She has no disclosures.
COVID-19 CRISIS: We must care for ourselves as we care for others
“I do not shrink from this responsibility, I welcome it.” —John F. Kennedy, inaugural address
COVID-19 has changed our world. Social distancing is now the norm and flattening the curve is our motto. Family physicians’ place on the front line of medicine is more important now than it has ever been.
In the Pennsylvania community in which we work, the first person to don protective gear and sample patients for viral testing in a rapidly organized COVID-19 testing site was John Russell, MD, a family physician. When I asked him about his experience, Dr. Russell said, “No one became a fireman to get cats out of trees ... it was to fight fires. As doctors, this is the same idea ... this is a chance to help fight the fires in our community.”
And, of course, it is primary care providers—family physicians, internists, pediatricians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and nurses—who day in and day out are putting aside their own fears, while dealing with those of their family, to come to work with a sense of purpose and courage.
The military uses the term “operational tempo” to describe the speed and intensity of actions relative to the speed and intensity of unfolding events in the operational environment. Family physicians are being asked to work at an increased speed in unfamiliar terrain as our environments change by the hour. The challenge is to answer the call—and take care of ourselves—in unprecedented ways. We often use anticipatory guidance with our patients to help prepare them for the challenges they will face. So, too, must we anticipate the things we will need to be attentive to in the coming months in order to sustain the effort that will be required of us.
With this in mind, we would be wise to consider developing plans in 3 domains: physical, mental, and social.
Physical. With gyms closed and restaurants limiting their offerings to take-out, this is an opportune time to create an exercise regimen at home and experiment with healthy meal options. YouTube videos abound for workouts of every length. And of course, you can simply take a daily walk, go for a run, or take a bike ride. Similarly, good choices can be made with take-out and the foods we prepare at home.
Continue to: Mentally...
Mentally we need the discipline to take breaks, delegate when necessary, and use downtime to clear our minds. Need another option? Consider meditation. Google “best meditation apps” and take your pick.
Social distancing doesn’t have to mean emotional isolation; technology allows us to connect with others through messaging and face-to-face video. We need to remember to regularly check in with those we care about; few things in life are as affirming as the connections with those who are close to us: family, co-workers, and patients.
Out of crisis comes opportunity. Should we be quarantined, we can remind ourselves that Sir Isaac Newton, while in quarantine during the bubonic plague, laid the foundation for classical physics, composed theories on light and optics, and penned his first draft of the law of gravity.1
Life carries on, amidst the pandemic. Even though the current focus is on the COVID-19 crisis, our many needs, joys, and challenges as human beings remain. Today, someone will find out she is pregnant; someone else will be diagnosed with cancer, or plan a wedding, or attend the funeral of a loved one. We, as family physicians, have the training to lead with courage and empathy. We have the expertise gained through years of helping patients though diverse physical and emotional challenges.
We will continue to listen to our patients’ stories, diagnose and treat their diseases, and take steps to bring a sense of calm to the chaos around us. We need to be mindful of our own mindset, because we have a choice. As the psychologist Victor Frankl said in 1946, after being liberated from the concentration camps, “Everything can be taken from a man but one thing: the last of the human freedoms—to choose one’s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one’s own way.”2
1. Brockell G. During a pandemic, Isaac Newton had to work from home, too. He used the time wisely. The Washington Post. March 12, 2020. 2. Frankl VE. Man’s Search for Meaning. Boston, MA: Beacon Press; 2006.
“I do not shrink from this responsibility, I welcome it.” —John F. Kennedy, inaugural address
COVID-19 has changed our world. Social distancing is now the norm and flattening the curve is our motto. Family physicians’ place on the front line of medicine is more important now than it has ever been.
In the Pennsylvania community in which we work, the first person to don protective gear and sample patients for viral testing in a rapidly organized COVID-19 testing site was John Russell, MD, a family physician. When I asked him about his experience, Dr. Russell said, “No one became a fireman to get cats out of trees ... it was to fight fires. As doctors, this is the same idea ... this is a chance to help fight the fires in our community.”
And, of course, it is primary care providers—family physicians, internists, pediatricians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and nurses—who day in and day out are putting aside their own fears, while dealing with those of their family, to come to work with a sense of purpose and courage.
The military uses the term “operational tempo” to describe the speed and intensity of actions relative to the speed and intensity of unfolding events in the operational environment. Family physicians are being asked to work at an increased speed in unfamiliar terrain as our environments change by the hour. The challenge is to answer the call—and take care of ourselves—in unprecedented ways. We often use anticipatory guidance with our patients to help prepare them for the challenges they will face. So, too, must we anticipate the things we will need to be attentive to in the coming months in order to sustain the effort that will be required of us.
With this in mind, we would be wise to consider developing plans in 3 domains: physical, mental, and social.
Physical. With gyms closed and restaurants limiting their offerings to take-out, this is an opportune time to create an exercise regimen at home and experiment with healthy meal options. YouTube videos abound for workouts of every length. And of course, you can simply take a daily walk, go for a run, or take a bike ride. Similarly, good choices can be made with take-out and the foods we prepare at home.
Continue to: Mentally...
Mentally we need the discipline to take breaks, delegate when necessary, and use downtime to clear our minds. Need another option? Consider meditation. Google “best meditation apps” and take your pick.
Social distancing doesn’t have to mean emotional isolation; technology allows us to connect with others through messaging and face-to-face video. We need to remember to regularly check in with those we care about; few things in life are as affirming as the connections with those who are close to us: family, co-workers, and patients.
Out of crisis comes opportunity. Should we be quarantined, we can remind ourselves that Sir Isaac Newton, while in quarantine during the bubonic plague, laid the foundation for classical physics, composed theories on light and optics, and penned his first draft of the law of gravity.1
Life carries on, amidst the pandemic. Even though the current focus is on the COVID-19 crisis, our many needs, joys, and challenges as human beings remain. Today, someone will find out she is pregnant; someone else will be diagnosed with cancer, or plan a wedding, or attend the funeral of a loved one. We, as family physicians, have the training to lead with courage and empathy. We have the expertise gained through years of helping patients though diverse physical and emotional challenges.
We will continue to listen to our patients’ stories, diagnose and treat their diseases, and take steps to bring a sense of calm to the chaos around us. We need to be mindful of our own mindset, because we have a choice. As the psychologist Victor Frankl said in 1946, after being liberated from the concentration camps, “Everything can be taken from a man but one thing: the last of the human freedoms—to choose one’s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one’s own way.”2
“I do not shrink from this responsibility, I welcome it.” —John F. Kennedy, inaugural address
COVID-19 has changed our world. Social distancing is now the norm and flattening the curve is our motto. Family physicians’ place on the front line of medicine is more important now than it has ever been.
In the Pennsylvania community in which we work, the first person to don protective gear and sample patients for viral testing in a rapidly organized COVID-19 testing site was John Russell, MD, a family physician. When I asked him about his experience, Dr. Russell said, “No one became a fireman to get cats out of trees ... it was to fight fires. As doctors, this is the same idea ... this is a chance to help fight the fires in our community.”
And, of course, it is primary care providers—family physicians, internists, pediatricians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and nurses—who day in and day out are putting aside their own fears, while dealing with those of their family, to come to work with a sense of purpose and courage.
The military uses the term “operational tempo” to describe the speed and intensity of actions relative to the speed and intensity of unfolding events in the operational environment. Family physicians are being asked to work at an increased speed in unfamiliar terrain as our environments change by the hour. The challenge is to answer the call—and take care of ourselves—in unprecedented ways. We often use anticipatory guidance with our patients to help prepare them for the challenges they will face. So, too, must we anticipate the things we will need to be attentive to in the coming months in order to sustain the effort that will be required of us.
With this in mind, we would be wise to consider developing plans in 3 domains: physical, mental, and social.
Physical. With gyms closed and restaurants limiting their offerings to take-out, this is an opportune time to create an exercise regimen at home and experiment with healthy meal options. YouTube videos abound for workouts of every length. And of course, you can simply take a daily walk, go for a run, or take a bike ride. Similarly, good choices can be made with take-out and the foods we prepare at home.
Continue to: Mentally...
Mentally we need the discipline to take breaks, delegate when necessary, and use downtime to clear our minds. Need another option? Consider meditation. Google “best meditation apps” and take your pick.
Social distancing doesn’t have to mean emotional isolation; technology allows us to connect with others through messaging and face-to-face video. We need to remember to regularly check in with those we care about; few things in life are as affirming as the connections with those who are close to us: family, co-workers, and patients.
Out of crisis comes opportunity. Should we be quarantined, we can remind ourselves that Sir Isaac Newton, while in quarantine during the bubonic plague, laid the foundation for classical physics, composed theories on light and optics, and penned his first draft of the law of gravity.1
Life carries on, amidst the pandemic. Even though the current focus is on the COVID-19 crisis, our many needs, joys, and challenges as human beings remain. Today, someone will find out she is pregnant; someone else will be diagnosed with cancer, or plan a wedding, or attend the funeral of a loved one. We, as family physicians, have the training to lead with courage and empathy. We have the expertise gained through years of helping patients though diverse physical and emotional challenges.
We will continue to listen to our patients’ stories, diagnose and treat their diseases, and take steps to bring a sense of calm to the chaos around us. We need to be mindful of our own mindset, because we have a choice. As the psychologist Victor Frankl said in 1946, after being liberated from the concentration camps, “Everything can be taken from a man but one thing: the last of the human freedoms—to choose one’s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one’s own way.”2
1. Brockell G. During a pandemic, Isaac Newton had to work from home, too. He used the time wisely. The Washington Post. March 12, 2020. 2. Frankl VE. Man’s Search for Meaning. Boston, MA: Beacon Press; 2006.
1. Brockell G. During a pandemic, Isaac Newton had to work from home, too. He used the time wisely. The Washington Post. March 12, 2020. 2. Frankl VE. Man’s Search for Meaning. Boston, MA: Beacon Press; 2006.
Is protocol-driven COVID-19 respiratory therapy doing more harm than good?
Physicians in the COVID-19 trenches are beginning to question whether standard respiratory therapy protocols for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are the best approach for treating patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
At issue is the standard use of ventilators for a virus whose presentation has not followed the standard for ARDS, but is looking more like high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) in some patients.
In a letter to the editor published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine on March 30, and in an editorial accepted for publication in Intensive Care Medicine, Luciano Gattinoni, MD, of the Medical University of Göttingen in Germany and colleagues make the case that protocol-driven ventilator use for patients with COVID-19 could be doing more harm than good.
Dr. Gattinoni noted that COVID-19 patients in ICUs in northern Italy had an atypical ARDS presentation with severe hypoxemia and well-preserved lung gas volume. He and colleagues suggested that instead of high positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), physicians should consider the lowest possible PEEP and gentle ventilation–practicing patience to “buy time with minimum additional damage.”
Similar observations were made by Cameron Kyle-Sidell, MD, a critical care physician working in New York City, who has been speaking out about this issue on Twitter and who shared his own experiences in this video interview with WebMD chief medical officer John Whyte, MD.
The bottom line, as Dr. Kyle-Sidell and Dr. Gattinoni agree, is that protocol-driven ventilator use may be causing lung injury in COVID-19 patients.
Consider disease phenotype
In the editorial, Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues explained further that ventilator settings should be based on physiological findings – with different respiratory treatment based on disease phenotype rather than using standard protocols.
‘“This, of course, is a conceptual model, but based on the observations we have this far, I don’t know of any model which is better,” he said in an interview.
Anecdotal evidence has increasingly demonstrated that this proposed physiological approach is associated with much lower mortality rates among COVID-19 patients, he said.
While not willing to name the hospitals at this time, he said that one center in Europe has had a 0% mortality rate among COVID-19 patients in the ICU when using this approach, compared with a 60% mortality rate at a nearby hospital using a protocol-driven approach.
In his editorial, Dr. Gattinoni disputed the recently published recommendation from the Surviving Sepsis Campaign that “mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 should be managed similarly to other patients with acute respiratory failure in the ICU.”
“Yet, COVID-19 pneumonia, despite falling in most of the circumstances under the Berlin definition of ARDS, is a specific disease, whose distinctive features are severe hypoxemia often associated with near normal respiratory system compliance,” Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues wrote, noting that this was true for more than half of the 150 patients he and his colleagues had assessed, and that several other colleagues in northern Italy reported similar findings. “This remarkable combination is almost never seen in severe ARDS.”
Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues hypothesized that COVID-19 patterns at patient presentation depend on interaction between three sets of factors: 1) disease severity, host response, physiological reserve and comorbidities; 2) ventilatory responsiveness of the patient to hypoxemia; and 3) time elapsed between disease onset and hospitalization.
They identified two primary phenotypes based on the interaction of these factors: Type L, characterized by low elastance, low ventilator perfusion ratio, low lung weight, and low recruitability; and Type H, characterized by high elastance, high right-to-left shunt, high lung weight, and high recruitability.
“Given this conceptual model, it follows that the respiratory treatment offered to Type L and Type H patients must be different,” Dr. Gattinoni said.
Patients may transition between phenotypes as their disease evolves. “If you start with the wrong protocol, at the end they become similar,” he said.
Rather, it is important to identify the phenotype at presentation to understand the pathophysiology and treat accordingly, he advised.
The phenotypes are best identified by CT scan, but signs implicit in each of the phenotypes, including respiratory system elastance and recruitability, can be used as surrogates if CT is unavailable, he noted.
“This is a kind of disease in which you don’t have to follow the protocol – you have to follow the physiology,” he said. “Unfortunately, many, many doctors around the world cannot think outside the protocol.”
In his interview with Dr. Whyte, Dr. Kyle-Sidell stressed that doctors must begin to consider other approaches. “We are desperate now, in the sense that everything we are doing does not seem to be working,” Dr. Kyle-Sidell said, noting that the first step toward improving outcomes is admitting that “this is something new.”
“I think it all starts from there, and I think we have the kind of scientific technology and the human capital in this country to solve this or at least have a very good shot at it,” he said.
Proposed treatment model
Dr. Gattinoni and his colleagues offered a proposed treatment model based on their conceptualization:
- Reverse hypoxemia through an increase in FiO2 to a level at which the Type L patient responds well, particularly for Type L patients who are not experiencing dyspnea.
- In Type L patients with dyspnea, try noninvasive options such as high-flow nasal cannula, continuous positive airway pressure, or noninvasive ventilation, and be sure to measure inspiratory esophageal pressure using esophageal manometry or surrogate measures. In intubated patients, determine P0.1 and P occlusion. High PEEP may decrease pleural pressure swings “and stop the vicious cycle that exacerbates lung injury,” but may be associated with high failure rates and delayed intubation.
- Intubate as soon as possible for esophageal pressure swings that increase from 5-10 cm H2O to above 15 cm H2O, which marks a transition from Type L to Type H phenotype and represents the level at which lung injury risk increases.
- For intubated and deeply sedated Type L patients who are hypercapnic, ventilate with volumes greater than 6 mL/kg up to 8-9 mL/kg as this high compliance results in tolerable strain without risk of ventilator-associated lung injury. Prone positioning should be used only as a rescue maneuver. Reduce PEEP to 8-10 cm H2O, given that the recruitability is low and the risk of hemodynamic failure increases at higher levels. Early intubation may avert the transition to Type H phenotype.
- Treat Type H phenotype like severe ARDS, including with higher PEEP if compatible with hemodynamics, and with prone positioning and extracorporeal support.
Dr. Gattinoni reported having no financial disclosures.
[email protected]
Physicians in the COVID-19 trenches are beginning to question whether standard respiratory therapy protocols for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are the best approach for treating patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
At issue is the standard use of ventilators for a virus whose presentation has not followed the standard for ARDS, but is looking more like high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) in some patients.
In a letter to the editor published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine on March 30, and in an editorial accepted for publication in Intensive Care Medicine, Luciano Gattinoni, MD, of the Medical University of Göttingen in Germany and colleagues make the case that protocol-driven ventilator use for patients with COVID-19 could be doing more harm than good.
Dr. Gattinoni noted that COVID-19 patients in ICUs in northern Italy had an atypical ARDS presentation with severe hypoxemia and well-preserved lung gas volume. He and colleagues suggested that instead of high positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), physicians should consider the lowest possible PEEP and gentle ventilation–practicing patience to “buy time with minimum additional damage.”
Similar observations were made by Cameron Kyle-Sidell, MD, a critical care physician working in New York City, who has been speaking out about this issue on Twitter and who shared his own experiences in this video interview with WebMD chief medical officer John Whyte, MD.
The bottom line, as Dr. Kyle-Sidell and Dr. Gattinoni agree, is that protocol-driven ventilator use may be causing lung injury in COVID-19 patients.
Consider disease phenotype
In the editorial, Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues explained further that ventilator settings should be based on physiological findings – with different respiratory treatment based on disease phenotype rather than using standard protocols.
‘“This, of course, is a conceptual model, but based on the observations we have this far, I don’t know of any model which is better,” he said in an interview.
Anecdotal evidence has increasingly demonstrated that this proposed physiological approach is associated with much lower mortality rates among COVID-19 patients, he said.
While not willing to name the hospitals at this time, he said that one center in Europe has had a 0% mortality rate among COVID-19 patients in the ICU when using this approach, compared with a 60% mortality rate at a nearby hospital using a protocol-driven approach.
In his editorial, Dr. Gattinoni disputed the recently published recommendation from the Surviving Sepsis Campaign that “mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 should be managed similarly to other patients with acute respiratory failure in the ICU.”
“Yet, COVID-19 pneumonia, despite falling in most of the circumstances under the Berlin definition of ARDS, is a specific disease, whose distinctive features are severe hypoxemia often associated with near normal respiratory system compliance,” Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues wrote, noting that this was true for more than half of the 150 patients he and his colleagues had assessed, and that several other colleagues in northern Italy reported similar findings. “This remarkable combination is almost never seen in severe ARDS.”
Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues hypothesized that COVID-19 patterns at patient presentation depend on interaction between three sets of factors: 1) disease severity, host response, physiological reserve and comorbidities; 2) ventilatory responsiveness of the patient to hypoxemia; and 3) time elapsed between disease onset and hospitalization.
They identified two primary phenotypes based on the interaction of these factors: Type L, characterized by low elastance, low ventilator perfusion ratio, low lung weight, and low recruitability; and Type H, characterized by high elastance, high right-to-left shunt, high lung weight, and high recruitability.
“Given this conceptual model, it follows that the respiratory treatment offered to Type L and Type H patients must be different,” Dr. Gattinoni said.
Patients may transition between phenotypes as their disease evolves. “If you start with the wrong protocol, at the end they become similar,” he said.
Rather, it is important to identify the phenotype at presentation to understand the pathophysiology and treat accordingly, he advised.
The phenotypes are best identified by CT scan, but signs implicit in each of the phenotypes, including respiratory system elastance and recruitability, can be used as surrogates if CT is unavailable, he noted.
“This is a kind of disease in which you don’t have to follow the protocol – you have to follow the physiology,” he said. “Unfortunately, many, many doctors around the world cannot think outside the protocol.”
In his interview with Dr. Whyte, Dr. Kyle-Sidell stressed that doctors must begin to consider other approaches. “We are desperate now, in the sense that everything we are doing does not seem to be working,” Dr. Kyle-Sidell said, noting that the first step toward improving outcomes is admitting that “this is something new.”
“I think it all starts from there, and I think we have the kind of scientific technology and the human capital in this country to solve this or at least have a very good shot at it,” he said.
Proposed treatment model
Dr. Gattinoni and his colleagues offered a proposed treatment model based on their conceptualization:
- Reverse hypoxemia through an increase in FiO2 to a level at which the Type L patient responds well, particularly for Type L patients who are not experiencing dyspnea.
- In Type L patients with dyspnea, try noninvasive options such as high-flow nasal cannula, continuous positive airway pressure, or noninvasive ventilation, and be sure to measure inspiratory esophageal pressure using esophageal manometry or surrogate measures. In intubated patients, determine P0.1 and P occlusion. High PEEP may decrease pleural pressure swings “and stop the vicious cycle that exacerbates lung injury,” but may be associated with high failure rates and delayed intubation.
- Intubate as soon as possible for esophageal pressure swings that increase from 5-10 cm H2O to above 15 cm H2O, which marks a transition from Type L to Type H phenotype and represents the level at which lung injury risk increases.
- For intubated and deeply sedated Type L patients who are hypercapnic, ventilate with volumes greater than 6 mL/kg up to 8-9 mL/kg as this high compliance results in tolerable strain without risk of ventilator-associated lung injury. Prone positioning should be used only as a rescue maneuver. Reduce PEEP to 8-10 cm H2O, given that the recruitability is low and the risk of hemodynamic failure increases at higher levels. Early intubation may avert the transition to Type H phenotype.
- Treat Type H phenotype like severe ARDS, including with higher PEEP if compatible with hemodynamics, and with prone positioning and extracorporeal support.
Dr. Gattinoni reported having no financial disclosures.
[email protected]
Physicians in the COVID-19 trenches are beginning to question whether standard respiratory therapy protocols for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are the best approach for treating patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
At issue is the standard use of ventilators for a virus whose presentation has not followed the standard for ARDS, but is looking more like high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) in some patients.
In a letter to the editor published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine on March 30, and in an editorial accepted for publication in Intensive Care Medicine, Luciano Gattinoni, MD, of the Medical University of Göttingen in Germany and colleagues make the case that protocol-driven ventilator use for patients with COVID-19 could be doing more harm than good.
Dr. Gattinoni noted that COVID-19 patients in ICUs in northern Italy had an atypical ARDS presentation with severe hypoxemia and well-preserved lung gas volume. He and colleagues suggested that instead of high positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), physicians should consider the lowest possible PEEP and gentle ventilation–practicing patience to “buy time with minimum additional damage.”
Similar observations were made by Cameron Kyle-Sidell, MD, a critical care physician working in New York City, who has been speaking out about this issue on Twitter and who shared his own experiences in this video interview with WebMD chief medical officer John Whyte, MD.
The bottom line, as Dr. Kyle-Sidell and Dr. Gattinoni agree, is that protocol-driven ventilator use may be causing lung injury in COVID-19 patients.
Consider disease phenotype
In the editorial, Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues explained further that ventilator settings should be based on physiological findings – with different respiratory treatment based on disease phenotype rather than using standard protocols.
‘“This, of course, is a conceptual model, but based on the observations we have this far, I don’t know of any model which is better,” he said in an interview.
Anecdotal evidence has increasingly demonstrated that this proposed physiological approach is associated with much lower mortality rates among COVID-19 patients, he said.
While not willing to name the hospitals at this time, he said that one center in Europe has had a 0% mortality rate among COVID-19 patients in the ICU when using this approach, compared with a 60% mortality rate at a nearby hospital using a protocol-driven approach.
In his editorial, Dr. Gattinoni disputed the recently published recommendation from the Surviving Sepsis Campaign that “mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 should be managed similarly to other patients with acute respiratory failure in the ICU.”
“Yet, COVID-19 pneumonia, despite falling in most of the circumstances under the Berlin definition of ARDS, is a specific disease, whose distinctive features are severe hypoxemia often associated with near normal respiratory system compliance,” Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues wrote, noting that this was true for more than half of the 150 patients he and his colleagues had assessed, and that several other colleagues in northern Italy reported similar findings. “This remarkable combination is almost never seen in severe ARDS.”
Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues hypothesized that COVID-19 patterns at patient presentation depend on interaction between three sets of factors: 1) disease severity, host response, physiological reserve and comorbidities; 2) ventilatory responsiveness of the patient to hypoxemia; and 3) time elapsed between disease onset and hospitalization.
They identified two primary phenotypes based on the interaction of these factors: Type L, characterized by low elastance, low ventilator perfusion ratio, low lung weight, and low recruitability; and Type H, characterized by high elastance, high right-to-left shunt, high lung weight, and high recruitability.
“Given this conceptual model, it follows that the respiratory treatment offered to Type L and Type H patients must be different,” Dr. Gattinoni said.
Patients may transition between phenotypes as their disease evolves. “If you start with the wrong protocol, at the end they become similar,” he said.
Rather, it is important to identify the phenotype at presentation to understand the pathophysiology and treat accordingly, he advised.
The phenotypes are best identified by CT scan, but signs implicit in each of the phenotypes, including respiratory system elastance and recruitability, can be used as surrogates if CT is unavailable, he noted.
“This is a kind of disease in which you don’t have to follow the protocol – you have to follow the physiology,” he said. “Unfortunately, many, many doctors around the world cannot think outside the protocol.”
In his interview with Dr. Whyte, Dr. Kyle-Sidell stressed that doctors must begin to consider other approaches. “We are desperate now, in the sense that everything we are doing does not seem to be working,” Dr. Kyle-Sidell said, noting that the first step toward improving outcomes is admitting that “this is something new.”
“I think it all starts from there, and I think we have the kind of scientific technology and the human capital in this country to solve this or at least have a very good shot at it,” he said.
Proposed treatment model
Dr. Gattinoni and his colleagues offered a proposed treatment model based on their conceptualization:
- Reverse hypoxemia through an increase in FiO2 to a level at which the Type L patient responds well, particularly for Type L patients who are not experiencing dyspnea.
- In Type L patients with dyspnea, try noninvasive options such as high-flow nasal cannula, continuous positive airway pressure, or noninvasive ventilation, and be sure to measure inspiratory esophageal pressure using esophageal manometry or surrogate measures. In intubated patients, determine P0.1 and P occlusion. High PEEP may decrease pleural pressure swings “and stop the vicious cycle that exacerbates lung injury,” but may be associated with high failure rates and delayed intubation.
- Intubate as soon as possible for esophageal pressure swings that increase from 5-10 cm H2O to above 15 cm H2O, which marks a transition from Type L to Type H phenotype and represents the level at which lung injury risk increases.
- For intubated and deeply sedated Type L patients who are hypercapnic, ventilate with volumes greater than 6 mL/kg up to 8-9 mL/kg as this high compliance results in tolerable strain without risk of ventilator-associated lung injury. Prone positioning should be used only as a rescue maneuver. Reduce PEEP to 8-10 cm H2O, given that the recruitability is low and the risk of hemodynamic failure increases at higher levels. Early intubation may avert the transition to Type H phenotype.
- Treat Type H phenotype like severe ARDS, including with higher PEEP if compatible with hemodynamics, and with prone positioning and extracorporeal support.
Dr. Gattinoni reported having no financial disclosures.
[email protected]