User login
‘Uptake is only the first step’ for effective HIV PrEP protection
To Amanda Allmacher, DNP, RN, nurse practitioner at the Detroit Public Health STD Clinic, that means that same-day PrEP prescribing works and is acceptable. But there’s more work to do on the clinic and pharmacy side to make HIV protection a reality for most of her patients. Allmacher presented her data at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care 2020 virtual annual meeting.
Dawn K. Smith, MD, epidemiologist and medical officer in the Division of HIV/AIDS Prevention at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention, said this adds to other data to show that we’re now entering the next phase of PrEP implementation.
“Our original focus was on uptake — informing folks what PrEP is, why they might benefit from its use, and then prescribing it if accepted,” Smith told Medscape Medical News via email. “Whether standard or same-day [PrEP prescribing], it is clear that uptake is only the first step.”
Nurses help navigate
Patients who attended the Detroit Public Health STD Clinic are more likely to be younger, have no insurance, and otherwise “have little to no contact with the healthcare system,” Allmacher said in her presentation. They also tend to come from communities that bear the greatest burden of HIV in the US — in other words, they are often the people most missed in PrEP rollouts thus far.
In response, the clinic implemented a same-day PrEP protocol, in which registered nurses trained in HIV risk assessment identify clients who might most benefit from PrEP. Criteria often include the presence of other STIs. Once the nurse explains what PrEP is and how it works, if the patient is interested, clients meet with a nurse practitioner right then to get the prescription for PrEP. The clinic also does labs to rule out current HIV infection, hepatitis B, metabolic issues, and other STI screening.
But it doesn’t stop there. The clinic used grant funding to offer PrEP navigation and financial counseling services, which help clients navigate the sometimes-thorny process of paying for PrEP. Payment comes either through Medicaid, which in Michigan charges $3 a month for a PrEP prescription, through patient assistance programs, or through private insurance. With clients under age 18 who are interested in PrEP, the clinic works to find a way to access PrEP without having to inform their parents. These same navigators schedule follow-up appointments, offer appointment reminders, and contact clients when they miss an appointment.
“Our navigators and financial counselors are a huge support for our same-day PrEP starts, helping with financial assistance, prior authorization, navigating different plans, and helping patients apply for Medicaid when appropriate,” she said.
The clinic also offers community outreach and incentives, which can include gift cards, bus passes, and pill containers, among other things.
This was a key lesson in setting up the program, Allmacher told Medscape Medical News.
“Starting PrEP at that initial visit allows for clinicians to meet patients where they are and administer care in a more equitable manner,” Allmacher said via email. “Use all available resources and funding sources. We have a versatile team working together to increase access for patients and promote HIV prevention and risk reduction.”
Script vs. follow-up
This approach is common, used in places like New York City and San Francisco. So once it was set up Allmacher sat back and waited to see how the program helped clients protect themselves from HIV.
Of the 451 clients eligible for PrEP in 2019, 336 were gay and bisexual men, 6 were transgender women, 61 were heterosexual, cisgender men, and 48 were cisgender women. One transgender man also screened as eligible. Allmacher did not break down data by race.
Uptake was high: 70% of all eligible clients did receive a prescription for PrEP, either generic tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (Truvada) or tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine (Descovy). And uptake was high among people most at risk: 80% of gay and bisexual men who were eligible got a prescription, 60% of eligible cisgender women, 50% of the small number of transgender women, and 32.7% of heterosexual cisgender men did as well. The 1 transgender man also received a prescription.
This is a higher rate than found in a recent PrEP demonstration project, which found that despite gay and bisexual men, transgender adults, and Black people having the highest risk for HIV in the US, state health departments were more likely to refer heterosexual adults for PrEP.
That high uptake rate is encouraging, but follow-up? Not so much. After initial intake, clients are meant to return in a month to double-check their labs, ask about side effects, and start their 90-day supply of the medication. But just 40% showed up for their 30-day appointment, Allmacher said. And only one third of those showed up for the follow-up in 90 days.
By the end of 2019, just 73 of the original 451 clients screened were still taking PrEP.
“It was surprising to see just how significant the follow-up dropped off after that first visit, when the patient initially accepted the prescription,” Allmacher said.
And while it’s possible that some clients get their follow-up care from their primary care providers, “our clinic serves individuals regardless of insurance status and many do not identify having access to primary care for any type of service, PrEP or otherwise,” she said.
5 HIV acquisitions
In addition, the program review identified five clients who had been offered PrEP or had taken PrEP briefly who later acquired HIV. Those clients were offered same-day antiretroviral treatment, Allmacher said.
“So we’re finding people who are at high risk for HIV and we can prevent them, but we’re still not quite doing enough,” Allmacher said of those acquisitions. “Clearly we have a lot of work to do to focus on HIV prevention, and we are looking to create a more formal follow-up process” from the clinic’s side.
For instance, clinic staff call clients 1 week after their initial visit to share lab results. “This was identified as a missed opportunity for us to ask about their status, whether they filled their prescription, or if they need further assistance,” she said. “This is an area where our registered nurses are going to be taking on a greater role moving forward.”
Allmacher and team also discovered that, despite PrEP navigators arranging insurance coverage for clients on the day they receive their prescription, sometimes there were still barriers when the client showed up at the pharmacy to pick up their meds. The clinic does not have an in-house pharmacy and does not currently have the funding that would allow them to hand patients a bottle of the appropriate medication when they leave the clinic.
“Navigating the copays and the insurance coverage and using financial assistance through the drug manufacturer — even though we have the support in the clinic, it seems like there’s a disconnect between our clinic and getting to the pharmacy. Not every pharmacy is super familiar with navigating those,” she said. “So we have started to identify some area pharmacies near our clinic that are great at navigating these, and we really try to get our patients to go to places we know can give them assistance.”
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
To Amanda Allmacher, DNP, RN, nurse practitioner at the Detroit Public Health STD Clinic, that means that same-day PrEP prescribing works and is acceptable. But there’s more work to do on the clinic and pharmacy side to make HIV protection a reality for most of her patients. Allmacher presented her data at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care 2020 virtual annual meeting.
Dawn K. Smith, MD, epidemiologist and medical officer in the Division of HIV/AIDS Prevention at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention, said this adds to other data to show that we’re now entering the next phase of PrEP implementation.
“Our original focus was on uptake — informing folks what PrEP is, why they might benefit from its use, and then prescribing it if accepted,” Smith told Medscape Medical News via email. “Whether standard or same-day [PrEP prescribing], it is clear that uptake is only the first step.”
Nurses help navigate
Patients who attended the Detroit Public Health STD Clinic are more likely to be younger, have no insurance, and otherwise “have little to no contact with the healthcare system,” Allmacher said in her presentation. They also tend to come from communities that bear the greatest burden of HIV in the US — in other words, they are often the people most missed in PrEP rollouts thus far.
In response, the clinic implemented a same-day PrEP protocol, in which registered nurses trained in HIV risk assessment identify clients who might most benefit from PrEP. Criteria often include the presence of other STIs. Once the nurse explains what PrEP is and how it works, if the patient is interested, clients meet with a nurse practitioner right then to get the prescription for PrEP. The clinic also does labs to rule out current HIV infection, hepatitis B, metabolic issues, and other STI screening.
But it doesn’t stop there. The clinic used grant funding to offer PrEP navigation and financial counseling services, which help clients navigate the sometimes-thorny process of paying for PrEP. Payment comes either through Medicaid, which in Michigan charges $3 a month for a PrEP prescription, through patient assistance programs, or through private insurance. With clients under age 18 who are interested in PrEP, the clinic works to find a way to access PrEP without having to inform their parents. These same navigators schedule follow-up appointments, offer appointment reminders, and contact clients when they miss an appointment.
“Our navigators and financial counselors are a huge support for our same-day PrEP starts, helping with financial assistance, prior authorization, navigating different plans, and helping patients apply for Medicaid when appropriate,” she said.
The clinic also offers community outreach and incentives, which can include gift cards, bus passes, and pill containers, among other things.
This was a key lesson in setting up the program, Allmacher told Medscape Medical News.
“Starting PrEP at that initial visit allows for clinicians to meet patients where they are and administer care in a more equitable manner,” Allmacher said via email. “Use all available resources and funding sources. We have a versatile team working together to increase access for patients and promote HIV prevention and risk reduction.”
Script vs. follow-up
This approach is common, used in places like New York City and San Francisco. So once it was set up Allmacher sat back and waited to see how the program helped clients protect themselves from HIV.
Of the 451 clients eligible for PrEP in 2019, 336 were gay and bisexual men, 6 were transgender women, 61 were heterosexual, cisgender men, and 48 were cisgender women. One transgender man also screened as eligible. Allmacher did not break down data by race.
Uptake was high: 70% of all eligible clients did receive a prescription for PrEP, either generic tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (Truvada) or tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine (Descovy). And uptake was high among people most at risk: 80% of gay and bisexual men who were eligible got a prescription, 60% of eligible cisgender women, 50% of the small number of transgender women, and 32.7% of heterosexual cisgender men did as well. The 1 transgender man also received a prescription.
This is a higher rate than found in a recent PrEP demonstration project, which found that despite gay and bisexual men, transgender adults, and Black people having the highest risk for HIV in the US, state health departments were more likely to refer heterosexual adults for PrEP.
That high uptake rate is encouraging, but follow-up? Not so much. After initial intake, clients are meant to return in a month to double-check their labs, ask about side effects, and start their 90-day supply of the medication. But just 40% showed up for their 30-day appointment, Allmacher said. And only one third of those showed up for the follow-up in 90 days.
By the end of 2019, just 73 of the original 451 clients screened were still taking PrEP.
“It was surprising to see just how significant the follow-up dropped off after that first visit, when the patient initially accepted the prescription,” Allmacher said.
And while it’s possible that some clients get their follow-up care from their primary care providers, “our clinic serves individuals regardless of insurance status and many do not identify having access to primary care for any type of service, PrEP or otherwise,” she said.
5 HIV acquisitions
In addition, the program review identified five clients who had been offered PrEP or had taken PrEP briefly who later acquired HIV. Those clients were offered same-day antiretroviral treatment, Allmacher said.
“So we’re finding people who are at high risk for HIV and we can prevent them, but we’re still not quite doing enough,” Allmacher said of those acquisitions. “Clearly we have a lot of work to do to focus on HIV prevention, and we are looking to create a more formal follow-up process” from the clinic’s side.
For instance, clinic staff call clients 1 week after their initial visit to share lab results. “This was identified as a missed opportunity for us to ask about their status, whether they filled their prescription, or if they need further assistance,” she said. “This is an area where our registered nurses are going to be taking on a greater role moving forward.”
Allmacher and team also discovered that, despite PrEP navigators arranging insurance coverage for clients on the day they receive their prescription, sometimes there were still barriers when the client showed up at the pharmacy to pick up their meds. The clinic does not have an in-house pharmacy and does not currently have the funding that would allow them to hand patients a bottle of the appropriate medication when they leave the clinic.
“Navigating the copays and the insurance coverage and using financial assistance through the drug manufacturer — even though we have the support in the clinic, it seems like there’s a disconnect between our clinic and getting to the pharmacy. Not every pharmacy is super familiar with navigating those,” she said. “So we have started to identify some area pharmacies near our clinic that are great at navigating these, and we really try to get our patients to go to places we know can give them assistance.”
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
To Amanda Allmacher, DNP, RN, nurse practitioner at the Detroit Public Health STD Clinic, that means that same-day PrEP prescribing works and is acceptable. But there’s more work to do on the clinic and pharmacy side to make HIV protection a reality for most of her patients. Allmacher presented her data at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care 2020 virtual annual meeting.
Dawn K. Smith, MD, epidemiologist and medical officer in the Division of HIV/AIDS Prevention at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention, said this adds to other data to show that we’re now entering the next phase of PrEP implementation.
“Our original focus was on uptake — informing folks what PrEP is, why they might benefit from its use, and then prescribing it if accepted,” Smith told Medscape Medical News via email. “Whether standard or same-day [PrEP prescribing], it is clear that uptake is only the first step.”
Nurses help navigate
Patients who attended the Detroit Public Health STD Clinic are more likely to be younger, have no insurance, and otherwise “have little to no contact with the healthcare system,” Allmacher said in her presentation. They also tend to come from communities that bear the greatest burden of HIV in the US — in other words, they are often the people most missed in PrEP rollouts thus far.
In response, the clinic implemented a same-day PrEP protocol, in which registered nurses trained in HIV risk assessment identify clients who might most benefit from PrEP. Criteria often include the presence of other STIs. Once the nurse explains what PrEP is and how it works, if the patient is interested, clients meet with a nurse practitioner right then to get the prescription for PrEP. The clinic also does labs to rule out current HIV infection, hepatitis B, metabolic issues, and other STI screening.
But it doesn’t stop there. The clinic used grant funding to offer PrEP navigation and financial counseling services, which help clients navigate the sometimes-thorny process of paying for PrEP. Payment comes either through Medicaid, which in Michigan charges $3 a month for a PrEP prescription, through patient assistance programs, or through private insurance. With clients under age 18 who are interested in PrEP, the clinic works to find a way to access PrEP without having to inform their parents. These same navigators schedule follow-up appointments, offer appointment reminders, and contact clients when they miss an appointment.
“Our navigators and financial counselors are a huge support for our same-day PrEP starts, helping with financial assistance, prior authorization, navigating different plans, and helping patients apply for Medicaid when appropriate,” she said.
The clinic also offers community outreach and incentives, which can include gift cards, bus passes, and pill containers, among other things.
This was a key lesson in setting up the program, Allmacher told Medscape Medical News.
“Starting PrEP at that initial visit allows for clinicians to meet patients where they are and administer care in a more equitable manner,” Allmacher said via email. “Use all available resources and funding sources. We have a versatile team working together to increase access for patients and promote HIV prevention and risk reduction.”
Script vs. follow-up
This approach is common, used in places like New York City and San Francisco. So once it was set up Allmacher sat back and waited to see how the program helped clients protect themselves from HIV.
Of the 451 clients eligible for PrEP in 2019, 336 were gay and bisexual men, 6 were transgender women, 61 were heterosexual, cisgender men, and 48 were cisgender women. One transgender man also screened as eligible. Allmacher did not break down data by race.
Uptake was high: 70% of all eligible clients did receive a prescription for PrEP, either generic tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (Truvada) or tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine (Descovy). And uptake was high among people most at risk: 80% of gay and bisexual men who were eligible got a prescription, 60% of eligible cisgender women, 50% of the small number of transgender women, and 32.7% of heterosexual cisgender men did as well. The 1 transgender man also received a prescription.
This is a higher rate than found in a recent PrEP demonstration project, which found that despite gay and bisexual men, transgender adults, and Black people having the highest risk for HIV in the US, state health departments were more likely to refer heterosexual adults for PrEP.
That high uptake rate is encouraging, but follow-up? Not so much. After initial intake, clients are meant to return in a month to double-check their labs, ask about side effects, and start their 90-day supply of the medication. But just 40% showed up for their 30-day appointment, Allmacher said. And only one third of those showed up for the follow-up in 90 days.
By the end of 2019, just 73 of the original 451 clients screened were still taking PrEP.
“It was surprising to see just how significant the follow-up dropped off after that first visit, when the patient initially accepted the prescription,” Allmacher said.
And while it’s possible that some clients get their follow-up care from their primary care providers, “our clinic serves individuals regardless of insurance status and many do not identify having access to primary care for any type of service, PrEP or otherwise,” she said.
5 HIV acquisitions
In addition, the program review identified five clients who had been offered PrEP or had taken PrEP briefly who later acquired HIV. Those clients were offered same-day antiretroviral treatment, Allmacher said.
“So we’re finding people who are at high risk for HIV and we can prevent them, but we’re still not quite doing enough,” Allmacher said of those acquisitions. “Clearly we have a lot of work to do to focus on HIV prevention, and we are looking to create a more formal follow-up process” from the clinic’s side.
For instance, clinic staff call clients 1 week after their initial visit to share lab results. “This was identified as a missed opportunity for us to ask about their status, whether they filled their prescription, or if they need further assistance,” she said. “This is an area where our registered nurses are going to be taking on a greater role moving forward.”
Allmacher and team also discovered that, despite PrEP navigators arranging insurance coverage for clients on the day they receive their prescription, sometimes there were still barriers when the client showed up at the pharmacy to pick up their meds. The clinic does not have an in-house pharmacy and does not currently have the funding that would allow them to hand patients a bottle of the appropriate medication when they leave the clinic.
“Navigating the copays and the insurance coverage and using financial assistance through the drug manufacturer — even though we have the support in the clinic, it seems like there’s a disconnect between our clinic and getting to the pharmacy. Not every pharmacy is super familiar with navigating those,” she said. “So we have started to identify some area pharmacies near our clinic that are great at navigating these, and we really try to get our patients to go to places we know can give them assistance.”
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Hospital at home’ increases COVID capacity in large study
A “hospital at home” (HaH) program at Atrium Health, a large integrated delivery system in the Southeast, expanded its hospital capacity during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic by providing hospital-level acute care to COVID-19 patients at home, according to a new study in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Virtual hospital programs have the potential to provide health systems with additional inpatient capacity during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond,” wrote Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, from the Atrium Health Hospitalist Group, Monroe, N.C., and colleagues.
Whereas most previous HaH programs have relied on visiting nurses and physicians, the new study uses telemedicine to connect with patients. Advocate Health Care researchers published the only other study using the telemedicine-powered model in 2015.
The new Atrium Health study evaluated 1,477 patients who received care in the HaH program between March 23 and May 7 of this year after having been diagnosed with COVID-19. The program provided home monitoring and hospital-level care in a home-based virtual observation unit (VOU) and a virtual acute care unit (VACU).
Patients were tested for the virus in Atrium emergency departments, primary care clinics, urgent care centers, and external testing sites. Those who tested positive were invited to be cared for either in the VOU, if they had mild to moderate symptoms, or in the VACU, if they were sick enough to be admitted to the hospital.
Patients hop onboard
Nearly all COVID-positive patients tested in these sites agreed to be admitted to the hospital at home, coauthor Stephanie Murphy, DO, medical director of the Atrium Health HaH program, said in an interview.
Patients with moderate symptoms were glad to be monitored at home, she said. When they got to the point where the nurse supervising their care felt they needed escalation to acute care, they were asked whether they wanted to continue to be cared for at home. Most opted to stay home rather than be admitted to the hospital, where their loved ones couldn’t visit them.
Low-acuity patients in the VOU received daily telemonitoring by a nurse to identify disease progression and escalate care as needed. For those who required more care and were admitted to the VACU, a team of paramedics and registered nurses (RNs; mobile clinicians) visited the patient’s home within 24 hours, setting up a hospital bed, other necessary medical equipment, videoconferencing gear, and a remote-monitoring kit that included a blood pressure cuff, a pulse oximeter, and a thermometer.
Dedicated hospitalists and nurses managed patients with 24/7 coverage and monitoring, bringing in other specialties as needed for virtual consults. Mobile clinician and virtual provider visits continued daily until a patient’s condition improved to the point where they could be deescalated back to the VOU. After that, patients received mobile app-driven symptom monitoring and telephone follow-up with a nurse until they got better.
Few patients go to hospital
Overall, patients had a median length of stay of 11 days in the VOU or the VACU or both. The vast majority, 1,293 patients (88%), received care in the VOU only. In that cohort, just 40 patients (3%) required hospitalization in an Atrium facility. Sixteen of those patients spent time in an ICU, seven required ventilator support, and two died in the hospital.
A total of 184 patients (12%) were admitted to the VACU. Twenty-one (11%) required intravenous fluids, 16 (9%) received antibiotics, 40 (22%) required inhaler or nebulizer treatments, 41 (22%) used supplemental oxygen, and 24 (13%) were admitted to a conventional hospital. Of the latter patients, 10 were admitted to an ICU, one required a ventilator, and none died in the hospital.
Dr. Sitammagari, a hospitalist and comedical director for quality at Atrium Health, told this news organization that, overall, the outcomes for patients in the system’s HaH were comparable to those seen in the literature among other COVID-19 cohorts.
Augmenting hospital capacity
The authors note that treating the 160 VACU patients within the HaH saved hospital beds for other patients. The HaH maintained a consistent census of between 20 and 30 patients for the first 6 weeks as COVID-19 cases spread.
Since last spring, Dr. Murphy said, the Atrium HaH’s daily census has grown to between 30 and 45 patients. “We could absorb 50 patients if our hospitals required it.”
How much capacity does that add to Atrium Health? While there are 50 hospitals in the health system, the HaH was set up mainly to care for COVID-19 patients who would otherwise have been admitted to the 10 acute-care hospitals in the Charlotte, N.C., area. In the 4 weeks ending Nov. 16, these facilities carried an average daily census of around 160 COVID-19 patients, Dr. Murphy noted. “During that time, the Atrium Health HaH has carried, on average, about 20%-25% of that census.”
If the pandemic were to overwhelm area hospitals, she added, “the structure would support flexing up our staffing and supplies to expand to crisis capacity,” which could be up to 200 patients a day.
For the nurses who make most of the phone calls to patients, patients average about 12 to 15 per RN, Dr. Murphy said, and there’s one mobile clinician for every six to nine patients. That’s pretty consistent with the staffing on med-surg floors in hospitals, she said.
The physicians in the program include hospitalists dedicated to telemedicine and some doctors who can’t work in the regular hospital because they’re immunocompromised. The physicians round virtually, covering 12-17 HaH patients per day, according to Dr. Murphy.
Prior planning paid off
Unlike some other health care systems that have launched HaH programs with the aid of outside vendors, Atrium Health developed its own HaH and brought it online just 2 weeks after deciding to launch the program. Atrium was able to do this, Dr. Sitammagari explained, because before the pandemic its hospitalist program was already developing an HaH model to improve the care of high-risk patients after hospital discharge to prevent readmission.
While Atrium’s electronic health record system wasn’t designed for hospital at home, its health information technology department and clinicians collaborated in rewriting some of the workflows and order sets in the EHR. For example, they set up a nursing questionnaire to administer after VACU admission, and they created another form for automatic admission to the HaH after a patient tested positive for COVID-19. Atrium staff also modified a patient-doctor communications app to help clinicians monitor HaH patients, Dr. Murphy noted.
Other hospital systems have gotten up to speed on HaH pretty quickly by using platforms supplied by outside vendors. Adventist Health in Los Angeles, for example, started admitting patients to its hospital at home just a month after approaching a vendor called Medically Home.
COVID vs. non-COVID patients
Atrium’s decision to focus its HaH effort on COVID-19 patients is unusual among the small but growing number of health systems that have adopted the HaH model to increase their capacity. (Atrium is now transferring some hospitalized patients with other conditions to its HaH, but is still focusing mainly on COVID-19 in its HaH program.)
Bruce Leff, MD, a professor of health policy and management at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, a leading expert on the HaH model, agrees that it can increase hospital capacity significantly.
Dr. Leff praised the Atrium Health study. “It proves that within an integrated delivery system you can quickly deploy and implement a virtual hospital in the specific-use case of COVID, and help patients and help the system at scale,” he said. “They took a bunch of people into the virtual observation unit and thereby kept people from overwhelming their [emergency department] and treated those people safely at home.”
Dr. Leff had no problem with Atrium’s focus on patients with COVID-19 rather than other conditions. “My guess is that they have the ability to take what they developed and apply it to other conditions. Once you have the ability to do acute care at home, you can do a lot at home.”
The biggest barrier to the spread of hospital at home remains the lack of insurer coverage. Dr. Murphy said that health plans are covering virtual physician consultations with patients in the HaH, as well as some other bits and pieces, but not the entire episode of acute care.
Dr. Leff believes that this will start changing soon. COVID-19 has altered the attitudes of physicians and hospitals toward telehealth, he noted, “and it has moved policy makers and payers to start thinking about the new models – home-based care in general and hospital at home in particular. For the first time in 25 years, payers are starting to get interested.”
Most of the authors are employees of Atrium Health. In addition, one coauthor reports being the cofounder of a digital health company, iEnroll, and receiving grants from The Heineman Foundation. Dr. Leff is an advisor to Medically Home, which provides support to hospital at home programs.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A “hospital at home” (HaH) program at Atrium Health, a large integrated delivery system in the Southeast, expanded its hospital capacity during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic by providing hospital-level acute care to COVID-19 patients at home, according to a new study in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Virtual hospital programs have the potential to provide health systems with additional inpatient capacity during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond,” wrote Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, from the Atrium Health Hospitalist Group, Monroe, N.C., and colleagues.
Whereas most previous HaH programs have relied on visiting nurses and physicians, the new study uses telemedicine to connect with patients. Advocate Health Care researchers published the only other study using the telemedicine-powered model in 2015.
The new Atrium Health study evaluated 1,477 patients who received care in the HaH program between March 23 and May 7 of this year after having been diagnosed with COVID-19. The program provided home monitoring and hospital-level care in a home-based virtual observation unit (VOU) and a virtual acute care unit (VACU).
Patients were tested for the virus in Atrium emergency departments, primary care clinics, urgent care centers, and external testing sites. Those who tested positive were invited to be cared for either in the VOU, if they had mild to moderate symptoms, or in the VACU, if they were sick enough to be admitted to the hospital.
Patients hop onboard
Nearly all COVID-positive patients tested in these sites agreed to be admitted to the hospital at home, coauthor Stephanie Murphy, DO, medical director of the Atrium Health HaH program, said in an interview.
Patients with moderate symptoms were glad to be monitored at home, she said. When they got to the point where the nurse supervising their care felt they needed escalation to acute care, they were asked whether they wanted to continue to be cared for at home. Most opted to stay home rather than be admitted to the hospital, where their loved ones couldn’t visit them.
Low-acuity patients in the VOU received daily telemonitoring by a nurse to identify disease progression and escalate care as needed. For those who required more care and were admitted to the VACU, a team of paramedics and registered nurses (RNs; mobile clinicians) visited the patient’s home within 24 hours, setting up a hospital bed, other necessary medical equipment, videoconferencing gear, and a remote-monitoring kit that included a blood pressure cuff, a pulse oximeter, and a thermometer.
Dedicated hospitalists and nurses managed patients with 24/7 coverage and monitoring, bringing in other specialties as needed for virtual consults. Mobile clinician and virtual provider visits continued daily until a patient’s condition improved to the point where they could be deescalated back to the VOU. After that, patients received mobile app-driven symptom monitoring and telephone follow-up with a nurse until they got better.
Few patients go to hospital
Overall, patients had a median length of stay of 11 days in the VOU or the VACU or both. The vast majority, 1,293 patients (88%), received care in the VOU only. In that cohort, just 40 patients (3%) required hospitalization in an Atrium facility. Sixteen of those patients spent time in an ICU, seven required ventilator support, and two died in the hospital.
A total of 184 patients (12%) were admitted to the VACU. Twenty-one (11%) required intravenous fluids, 16 (9%) received antibiotics, 40 (22%) required inhaler or nebulizer treatments, 41 (22%) used supplemental oxygen, and 24 (13%) were admitted to a conventional hospital. Of the latter patients, 10 were admitted to an ICU, one required a ventilator, and none died in the hospital.
Dr. Sitammagari, a hospitalist and comedical director for quality at Atrium Health, told this news organization that, overall, the outcomes for patients in the system’s HaH were comparable to those seen in the literature among other COVID-19 cohorts.
Augmenting hospital capacity
The authors note that treating the 160 VACU patients within the HaH saved hospital beds for other patients. The HaH maintained a consistent census of between 20 and 30 patients for the first 6 weeks as COVID-19 cases spread.
Since last spring, Dr. Murphy said, the Atrium HaH’s daily census has grown to between 30 and 45 patients. “We could absorb 50 patients if our hospitals required it.”
How much capacity does that add to Atrium Health? While there are 50 hospitals in the health system, the HaH was set up mainly to care for COVID-19 patients who would otherwise have been admitted to the 10 acute-care hospitals in the Charlotte, N.C., area. In the 4 weeks ending Nov. 16, these facilities carried an average daily census of around 160 COVID-19 patients, Dr. Murphy noted. “During that time, the Atrium Health HaH has carried, on average, about 20%-25% of that census.”
If the pandemic were to overwhelm area hospitals, she added, “the structure would support flexing up our staffing and supplies to expand to crisis capacity,” which could be up to 200 patients a day.
For the nurses who make most of the phone calls to patients, patients average about 12 to 15 per RN, Dr. Murphy said, and there’s one mobile clinician for every six to nine patients. That’s pretty consistent with the staffing on med-surg floors in hospitals, she said.
The physicians in the program include hospitalists dedicated to telemedicine and some doctors who can’t work in the regular hospital because they’re immunocompromised. The physicians round virtually, covering 12-17 HaH patients per day, according to Dr. Murphy.
Prior planning paid off
Unlike some other health care systems that have launched HaH programs with the aid of outside vendors, Atrium Health developed its own HaH and brought it online just 2 weeks after deciding to launch the program. Atrium was able to do this, Dr. Sitammagari explained, because before the pandemic its hospitalist program was already developing an HaH model to improve the care of high-risk patients after hospital discharge to prevent readmission.
While Atrium’s electronic health record system wasn’t designed for hospital at home, its health information technology department and clinicians collaborated in rewriting some of the workflows and order sets in the EHR. For example, they set up a nursing questionnaire to administer after VACU admission, and they created another form for automatic admission to the HaH after a patient tested positive for COVID-19. Atrium staff also modified a patient-doctor communications app to help clinicians monitor HaH patients, Dr. Murphy noted.
Other hospital systems have gotten up to speed on HaH pretty quickly by using platforms supplied by outside vendors. Adventist Health in Los Angeles, for example, started admitting patients to its hospital at home just a month after approaching a vendor called Medically Home.
COVID vs. non-COVID patients
Atrium’s decision to focus its HaH effort on COVID-19 patients is unusual among the small but growing number of health systems that have adopted the HaH model to increase their capacity. (Atrium is now transferring some hospitalized patients with other conditions to its HaH, but is still focusing mainly on COVID-19 in its HaH program.)
Bruce Leff, MD, a professor of health policy and management at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, a leading expert on the HaH model, agrees that it can increase hospital capacity significantly.
Dr. Leff praised the Atrium Health study. “It proves that within an integrated delivery system you can quickly deploy and implement a virtual hospital in the specific-use case of COVID, and help patients and help the system at scale,” he said. “They took a bunch of people into the virtual observation unit and thereby kept people from overwhelming their [emergency department] and treated those people safely at home.”
Dr. Leff had no problem with Atrium’s focus on patients with COVID-19 rather than other conditions. “My guess is that they have the ability to take what they developed and apply it to other conditions. Once you have the ability to do acute care at home, you can do a lot at home.”
The biggest barrier to the spread of hospital at home remains the lack of insurer coverage. Dr. Murphy said that health plans are covering virtual physician consultations with patients in the HaH, as well as some other bits and pieces, but not the entire episode of acute care.
Dr. Leff believes that this will start changing soon. COVID-19 has altered the attitudes of physicians and hospitals toward telehealth, he noted, “and it has moved policy makers and payers to start thinking about the new models – home-based care in general and hospital at home in particular. For the first time in 25 years, payers are starting to get interested.”
Most of the authors are employees of Atrium Health. In addition, one coauthor reports being the cofounder of a digital health company, iEnroll, and receiving grants from The Heineman Foundation. Dr. Leff is an advisor to Medically Home, which provides support to hospital at home programs.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A “hospital at home” (HaH) program at Atrium Health, a large integrated delivery system in the Southeast, expanded its hospital capacity during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic by providing hospital-level acute care to COVID-19 patients at home, according to a new study in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Virtual hospital programs have the potential to provide health systems with additional inpatient capacity during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond,” wrote Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, from the Atrium Health Hospitalist Group, Monroe, N.C., and colleagues.
Whereas most previous HaH programs have relied on visiting nurses and physicians, the new study uses telemedicine to connect with patients. Advocate Health Care researchers published the only other study using the telemedicine-powered model in 2015.
The new Atrium Health study evaluated 1,477 patients who received care in the HaH program between March 23 and May 7 of this year after having been diagnosed with COVID-19. The program provided home monitoring and hospital-level care in a home-based virtual observation unit (VOU) and a virtual acute care unit (VACU).
Patients were tested for the virus in Atrium emergency departments, primary care clinics, urgent care centers, and external testing sites. Those who tested positive were invited to be cared for either in the VOU, if they had mild to moderate symptoms, or in the VACU, if they were sick enough to be admitted to the hospital.
Patients hop onboard
Nearly all COVID-positive patients tested in these sites agreed to be admitted to the hospital at home, coauthor Stephanie Murphy, DO, medical director of the Atrium Health HaH program, said in an interview.
Patients with moderate symptoms were glad to be monitored at home, she said. When they got to the point where the nurse supervising their care felt they needed escalation to acute care, they were asked whether they wanted to continue to be cared for at home. Most opted to stay home rather than be admitted to the hospital, where their loved ones couldn’t visit them.
Low-acuity patients in the VOU received daily telemonitoring by a nurse to identify disease progression and escalate care as needed. For those who required more care and were admitted to the VACU, a team of paramedics and registered nurses (RNs; mobile clinicians) visited the patient’s home within 24 hours, setting up a hospital bed, other necessary medical equipment, videoconferencing gear, and a remote-monitoring kit that included a blood pressure cuff, a pulse oximeter, and a thermometer.
Dedicated hospitalists and nurses managed patients with 24/7 coverage and monitoring, bringing in other specialties as needed for virtual consults. Mobile clinician and virtual provider visits continued daily until a patient’s condition improved to the point where they could be deescalated back to the VOU. After that, patients received mobile app-driven symptom monitoring and telephone follow-up with a nurse until they got better.
Few patients go to hospital
Overall, patients had a median length of stay of 11 days in the VOU or the VACU or both. The vast majority, 1,293 patients (88%), received care in the VOU only. In that cohort, just 40 patients (3%) required hospitalization in an Atrium facility. Sixteen of those patients spent time in an ICU, seven required ventilator support, and two died in the hospital.
A total of 184 patients (12%) were admitted to the VACU. Twenty-one (11%) required intravenous fluids, 16 (9%) received antibiotics, 40 (22%) required inhaler or nebulizer treatments, 41 (22%) used supplemental oxygen, and 24 (13%) were admitted to a conventional hospital. Of the latter patients, 10 were admitted to an ICU, one required a ventilator, and none died in the hospital.
Dr. Sitammagari, a hospitalist and comedical director for quality at Atrium Health, told this news organization that, overall, the outcomes for patients in the system’s HaH were comparable to those seen in the literature among other COVID-19 cohorts.
Augmenting hospital capacity
The authors note that treating the 160 VACU patients within the HaH saved hospital beds for other patients. The HaH maintained a consistent census of between 20 and 30 patients for the first 6 weeks as COVID-19 cases spread.
Since last spring, Dr. Murphy said, the Atrium HaH’s daily census has grown to between 30 and 45 patients. “We could absorb 50 patients if our hospitals required it.”
How much capacity does that add to Atrium Health? While there are 50 hospitals in the health system, the HaH was set up mainly to care for COVID-19 patients who would otherwise have been admitted to the 10 acute-care hospitals in the Charlotte, N.C., area. In the 4 weeks ending Nov. 16, these facilities carried an average daily census of around 160 COVID-19 patients, Dr. Murphy noted. “During that time, the Atrium Health HaH has carried, on average, about 20%-25% of that census.”
If the pandemic were to overwhelm area hospitals, she added, “the structure would support flexing up our staffing and supplies to expand to crisis capacity,” which could be up to 200 patients a day.
For the nurses who make most of the phone calls to patients, patients average about 12 to 15 per RN, Dr. Murphy said, and there’s one mobile clinician for every six to nine patients. That’s pretty consistent with the staffing on med-surg floors in hospitals, she said.
The physicians in the program include hospitalists dedicated to telemedicine and some doctors who can’t work in the regular hospital because they’re immunocompromised. The physicians round virtually, covering 12-17 HaH patients per day, according to Dr. Murphy.
Prior planning paid off
Unlike some other health care systems that have launched HaH programs with the aid of outside vendors, Atrium Health developed its own HaH and brought it online just 2 weeks after deciding to launch the program. Atrium was able to do this, Dr. Sitammagari explained, because before the pandemic its hospitalist program was already developing an HaH model to improve the care of high-risk patients after hospital discharge to prevent readmission.
While Atrium’s electronic health record system wasn’t designed for hospital at home, its health information technology department and clinicians collaborated in rewriting some of the workflows and order sets in the EHR. For example, they set up a nursing questionnaire to administer after VACU admission, and they created another form for automatic admission to the HaH after a patient tested positive for COVID-19. Atrium staff also modified a patient-doctor communications app to help clinicians monitor HaH patients, Dr. Murphy noted.
Other hospital systems have gotten up to speed on HaH pretty quickly by using platforms supplied by outside vendors. Adventist Health in Los Angeles, for example, started admitting patients to its hospital at home just a month after approaching a vendor called Medically Home.
COVID vs. non-COVID patients
Atrium’s decision to focus its HaH effort on COVID-19 patients is unusual among the small but growing number of health systems that have adopted the HaH model to increase their capacity. (Atrium is now transferring some hospitalized patients with other conditions to its HaH, but is still focusing mainly on COVID-19 in its HaH program.)
Bruce Leff, MD, a professor of health policy and management at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, a leading expert on the HaH model, agrees that it can increase hospital capacity significantly.
Dr. Leff praised the Atrium Health study. “It proves that within an integrated delivery system you can quickly deploy and implement a virtual hospital in the specific-use case of COVID, and help patients and help the system at scale,” he said. “They took a bunch of people into the virtual observation unit and thereby kept people from overwhelming their [emergency department] and treated those people safely at home.”
Dr. Leff had no problem with Atrium’s focus on patients with COVID-19 rather than other conditions. “My guess is that they have the ability to take what they developed and apply it to other conditions. Once you have the ability to do acute care at home, you can do a lot at home.”
The biggest barrier to the spread of hospital at home remains the lack of insurer coverage. Dr. Murphy said that health plans are covering virtual physician consultations with patients in the HaH, as well as some other bits and pieces, but not the entire episode of acute care.
Dr. Leff believes that this will start changing soon. COVID-19 has altered the attitudes of physicians and hospitals toward telehealth, he noted, “and it has moved policy makers and payers to start thinking about the new models – home-based care in general and hospital at home in particular. For the first time in 25 years, payers are starting to get interested.”
Most of the authors are employees of Atrium Health. In addition, one coauthor reports being the cofounder of a digital health company, iEnroll, and receiving grants from The Heineman Foundation. Dr. Leff is an advisor to Medically Home, which provides support to hospital at home programs.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Metapneumovirus infections clinically indistinguishable from flu, RSV
The all-consuming news about SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 has overshadowed other viral pathogens that are the cause of severe or fatal lower respiratory infections (LRI) including human metapneumovirus (HMPV).
“MPV is really a leading cause of LRI not just in children but in adults, with high mortality rates in the frail elderly, long-term care facilities, and cancer patients with pneumonia, “ said John Williams, MD, from the department of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center.
“Right now we have no effective antivirals. There are monoclonal antibodies in development that my group and others have discovered. In fact, some of these treat MPV and RSV [respiratory syncytial virus], so we may have good options,” he said in an online presentation during an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The virus preys, wolf-like, on the most vulnerable patients, including children and frail elderly adults, as well as other adults with predisposing conditions, he said.
HMPV causes acute respiratory illnesses in approximately 2%-11% of hospitalized adults, 3%-25% of organ transplant recipients or cancer patients, 4%-12% of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations, 5%-20% of asthma exacerbations, and it has been identified in multiple outbreaks at long-term care facilities.
Relative newcomer
Metapneumovirus was isolated and discovered from children with respiratory tract disease in the early 2000s. Once included in the family of paramyxoviruses (including measles, mumps, Nipah virus, and parainfluenza virus 1-4), HMPV and RSV are now classified as pneumoviruses, based on gene order and other characteristics, Dr. Williams explained.
Various studies have consistently placed the prevalence of HMPV ranging from 5%-14% in young children with LRI, children hospitalized for wheezing, adults with cancer and LRI, adults with asthma admissions, children with upper respiratory infections, and children hospitalized in the United States and Jordan for LRI, as well as children hospitalized in the United States and Peru with acute respiratory infections.
A study tracking respiratory infections in a Rochester, N.Y., cohort from 1999 through 2003 showed that healthy elderly patients had and annual incidence of HMPV infections of 5.9%, compared with 9.1% for high-risk patients, 13.1% for young patients, and 8.5% among hospitalized adult patients.
“These percentages are virtually identical to what has been seen in the same cohort for respiratory syncytial virus, so in this multiyear prospective cohort, metapneumovirus was as common as RSV,” Dr. Williams said.
Although the incidences of both HMPV and RSV were lower among hospitalized adults “clinically, we can’t tell these respiratory viruses apart. If we know it’s circulating we can make a guess, but we really can’t discriminate them,” he added.
In the Rochester cohort the frequency of clinical symptoms – including congestion, sore throat, cough, sputum production, dyspnea, and fever – were similar among patients infected with HMPV, RSV, or influenza A, with the exception of a slightly higher incidence of wheezing (80%) with HMPV, compared with influenza.
“I can tell you as a pediatrician, this is absolutely true in children, that metapneumovirus is indistinguishable from other respiratory viruses in kids,” he said.
Fatalities among older adults
As noted before, HMPV can cause severe and fatal illness in adults. For example, during an outbreak in North Dakota in 2016, 3 of 27 hospitalized adults with HMPV (median age, 69 years) died, and 10 required mechanical or noninvasive ventilation.
In a study from Korea comparing outcomes of severe HMPV-associated community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) with those of severe influenza-associated CAP, the investigators found that 30- and 60-day mortality rates were similar between the groups, at 24% of patients with HMPV-associated CAP and 32.1% for influenza-associated CAP, and 32% versus 38.5%, respectively.
Patients at high risk for severe disease or death from HMPV infection include those over 65 years, especially frail elderly, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, immunocompromised patients, and those with cardiopulmonary diseases such as congestive heart failure.
Supportive care only
“Do we have anything for treatment? The short answer is, No,” Dr. Williams.
Supportive care is currently the only effective approach for patients with severe HMPV infection.
Ribavirin, used to treat patients with acute RSV infection, has poor in vitro activity against HMPV and poor oral bioavailability and hemolysis, and there are no randomized controlled trials to support its use in this situation.
“It really can’t be recommended, and I don’t recommend it,” he said.
Virology may still help
Mark J. Siedner, MD, an infectious diseases physician at Mass General and associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, who was not involved in the study, said that, despite the inability to clinically distinguish HMPV from RSV or influenza A, there is still clinical value to identifying HMPV infections.
“We spend millions of dollar each year treating people for upper respiratory tract infections, often with antibacterials, sometimes with antivirals, but those have costs to the health care system, and they also have costs in terms of drug resistance,” he said in an interview seeking objective commentary.
“Diagnostic tests that determine the actual source or the cause of these upper respiratory tract infections and encourage both patients and physicians not to be using antibiotics have value,” he said.
Identifying the pathogen can also help clinicians take appropriate infection-control precautions to prevent patient-to-clinician or patient-to-patient transmission of viral infections, he added.
Dr. Williams’ research is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Henry L. Hillman Foundation, and Asher Krop Memorial Fund of Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh. Dr. Williams and Dr. Siedner reported no relevant conflict of interest disclosures.
The all-consuming news about SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 has overshadowed other viral pathogens that are the cause of severe or fatal lower respiratory infections (LRI) including human metapneumovirus (HMPV).
“MPV is really a leading cause of LRI not just in children but in adults, with high mortality rates in the frail elderly, long-term care facilities, and cancer patients with pneumonia, “ said John Williams, MD, from the department of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center.
“Right now we have no effective antivirals. There are monoclonal antibodies in development that my group and others have discovered. In fact, some of these treat MPV and RSV [respiratory syncytial virus], so we may have good options,” he said in an online presentation during an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The virus preys, wolf-like, on the most vulnerable patients, including children and frail elderly adults, as well as other adults with predisposing conditions, he said.
HMPV causes acute respiratory illnesses in approximately 2%-11% of hospitalized adults, 3%-25% of organ transplant recipients or cancer patients, 4%-12% of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations, 5%-20% of asthma exacerbations, and it has been identified in multiple outbreaks at long-term care facilities.
Relative newcomer
Metapneumovirus was isolated and discovered from children with respiratory tract disease in the early 2000s. Once included in the family of paramyxoviruses (including measles, mumps, Nipah virus, and parainfluenza virus 1-4), HMPV and RSV are now classified as pneumoviruses, based on gene order and other characteristics, Dr. Williams explained.
Various studies have consistently placed the prevalence of HMPV ranging from 5%-14% in young children with LRI, children hospitalized for wheezing, adults with cancer and LRI, adults with asthma admissions, children with upper respiratory infections, and children hospitalized in the United States and Jordan for LRI, as well as children hospitalized in the United States and Peru with acute respiratory infections.
A study tracking respiratory infections in a Rochester, N.Y., cohort from 1999 through 2003 showed that healthy elderly patients had and annual incidence of HMPV infections of 5.9%, compared with 9.1% for high-risk patients, 13.1% for young patients, and 8.5% among hospitalized adult patients.
“These percentages are virtually identical to what has been seen in the same cohort for respiratory syncytial virus, so in this multiyear prospective cohort, metapneumovirus was as common as RSV,” Dr. Williams said.
Although the incidences of both HMPV and RSV were lower among hospitalized adults “clinically, we can’t tell these respiratory viruses apart. If we know it’s circulating we can make a guess, but we really can’t discriminate them,” he added.
In the Rochester cohort the frequency of clinical symptoms – including congestion, sore throat, cough, sputum production, dyspnea, and fever – were similar among patients infected with HMPV, RSV, or influenza A, with the exception of a slightly higher incidence of wheezing (80%) with HMPV, compared with influenza.
“I can tell you as a pediatrician, this is absolutely true in children, that metapneumovirus is indistinguishable from other respiratory viruses in kids,” he said.
Fatalities among older adults
As noted before, HMPV can cause severe and fatal illness in adults. For example, during an outbreak in North Dakota in 2016, 3 of 27 hospitalized adults with HMPV (median age, 69 years) died, and 10 required mechanical or noninvasive ventilation.
In a study from Korea comparing outcomes of severe HMPV-associated community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) with those of severe influenza-associated CAP, the investigators found that 30- and 60-day mortality rates were similar between the groups, at 24% of patients with HMPV-associated CAP and 32.1% for influenza-associated CAP, and 32% versus 38.5%, respectively.
Patients at high risk for severe disease or death from HMPV infection include those over 65 years, especially frail elderly, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, immunocompromised patients, and those with cardiopulmonary diseases such as congestive heart failure.
Supportive care only
“Do we have anything for treatment? The short answer is, No,” Dr. Williams.
Supportive care is currently the only effective approach for patients with severe HMPV infection.
Ribavirin, used to treat patients with acute RSV infection, has poor in vitro activity against HMPV and poor oral bioavailability and hemolysis, and there are no randomized controlled trials to support its use in this situation.
“It really can’t be recommended, and I don’t recommend it,” he said.
Virology may still help
Mark J. Siedner, MD, an infectious diseases physician at Mass General and associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, who was not involved in the study, said that, despite the inability to clinically distinguish HMPV from RSV or influenza A, there is still clinical value to identifying HMPV infections.
“We spend millions of dollar each year treating people for upper respiratory tract infections, often with antibacterials, sometimes with antivirals, but those have costs to the health care system, and they also have costs in terms of drug resistance,” he said in an interview seeking objective commentary.
“Diagnostic tests that determine the actual source or the cause of these upper respiratory tract infections and encourage both patients and physicians not to be using antibiotics have value,” he said.
Identifying the pathogen can also help clinicians take appropriate infection-control precautions to prevent patient-to-clinician or patient-to-patient transmission of viral infections, he added.
Dr. Williams’ research is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Henry L. Hillman Foundation, and Asher Krop Memorial Fund of Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh. Dr. Williams and Dr. Siedner reported no relevant conflict of interest disclosures.
The all-consuming news about SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 has overshadowed other viral pathogens that are the cause of severe or fatal lower respiratory infections (LRI) including human metapneumovirus (HMPV).
“MPV is really a leading cause of LRI not just in children but in adults, with high mortality rates in the frail elderly, long-term care facilities, and cancer patients with pneumonia, “ said John Williams, MD, from the department of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center.
“Right now we have no effective antivirals. There are monoclonal antibodies in development that my group and others have discovered. In fact, some of these treat MPV and RSV [respiratory syncytial virus], so we may have good options,” he said in an online presentation during an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The virus preys, wolf-like, on the most vulnerable patients, including children and frail elderly adults, as well as other adults with predisposing conditions, he said.
HMPV causes acute respiratory illnesses in approximately 2%-11% of hospitalized adults, 3%-25% of organ transplant recipients or cancer patients, 4%-12% of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations, 5%-20% of asthma exacerbations, and it has been identified in multiple outbreaks at long-term care facilities.
Relative newcomer
Metapneumovirus was isolated and discovered from children with respiratory tract disease in the early 2000s. Once included in the family of paramyxoviruses (including measles, mumps, Nipah virus, and parainfluenza virus 1-4), HMPV and RSV are now classified as pneumoviruses, based on gene order and other characteristics, Dr. Williams explained.
Various studies have consistently placed the prevalence of HMPV ranging from 5%-14% in young children with LRI, children hospitalized for wheezing, adults with cancer and LRI, adults with asthma admissions, children with upper respiratory infections, and children hospitalized in the United States and Jordan for LRI, as well as children hospitalized in the United States and Peru with acute respiratory infections.
A study tracking respiratory infections in a Rochester, N.Y., cohort from 1999 through 2003 showed that healthy elderly patients had and annual incidence of HMPV infections of 5.9%, compared with 9.1% for high-risk patients, 13.1% for young patients, and 8.5% among hospitalized adult patients.
“These percentages are virtually identical to what has been seen in the same cohort for respiratory syncytial virus, so in this multiyear prospective cohort, metapneumovirus was as common as RSV,” Dr. Williams said.
Although the incidences of both HMPV and RSV were lower among hospitalized adults “clinically, we can’t tell these respiratory viruses apart. If we know it’s circulating we can make a guess, but we really can’t discriminate them,” he added.
In the Rochester cohort the frequency of clinical symptoms – including congestion, sore throat, cough, sputum production, dyspnea, and fever – were similar among patients infected with HMPV, RSV, or influenza A, with the exception of a slightly higher incidence of wheezing (80%) with HMPV, compared with influenza.
“I can tell you as a pediatrician, this is absolutely true in children, that metapneumovirus is indistinguishable from other respiratory viruses in kids,” he said.
Fatalities among older adults
As noted before, HMPV can cause severe and fatal illness in adults. For example, during an outbreak in North Dakota in 2016, 3 of 27 hospitalized adults with HMPV (median age, 69 years) died, and 10 required mechanical or noninvasive ventilation.
In a study from Korea comparing outcomes of severe HMPV-associated community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) with those of severe influenza-associated CAP, the investigators found that 30- and 60-day mortality rates were similar between the groups, at 24% of patients with HMPV-associated CAP and 32.1% for influenza-associated CAP, and 32% versus 38.5%, respectively.
Patients at high risk for severe disease or death from HMPV infection include those over 65 years, especially frail elderly, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, immunocompromised patients, and those with cardiopulmonary diseases such as congestive heart failure.
Supportive care only
“Do we have anything for treatment? The short answer is, No,” Dr. Williams.
Supportive care is currently the only effective approach for patients with severe HMPV infection.
Ribavirin, used to treat patients with acute RSV infection, has poor in vitro activity against HMPV and poor oral bioavailability and hemolysis, and there are no randomized controlled trials to support its use in this situation.
“It really can’t be recommended, and I don’t recommend it,” he said.
Virology may still help
Mark J. Siedner, MD, an infectious diseases physician at Mass General and associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, who was not involved in the study, said that, despite the inability to clinically distinguish HMPV from RSV or influenza A, there is still clinical value to identifying HMPV infections.
“We spend millions of dollar each year treating people for upper respiratory tract infections, often with antibacterials, sometimes with antivirals, but those have costs to the health care system, and they also have costs in terms of drug resistance,” he said in an interview seeking objective commentary.
“Diagnostic tests that determine the actual source or the cause of these upper respiratory tract infections and encourage both patients and physicians not to be using antibiotics have value,” he said.
Identifying the pathogen can also help clinicians take appropriate infection-control precautions to prevent patient-to-clinician or patient-to-patient transmission of viral infections, he added.
Dr. Williams’ research is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Henry L. Hillman Foundation, and Asher Krop Memorial Fund of Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh. Dr. Williams and Dr. Siedner reported no relevant conflict of interest disclosures.
FROM IDWEEK 2020
'Tragic' milestone: 1 million children with COVID-19
The number of new cases soared in the past week as the United States exceeded 1 million children infected with the coronavirus, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

For the first time, the number of cases in children for the week ending Nov. 12 passed 100,000, and it didn’t stop until it reached 111,946, bringing the total for the pandemic to 1,039,464 reported cases in 49 states (New York is not reporting ages), the District of Columbia, New York City, and Guam, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 update.
“As a pediatrician who has practiced medicine for over 3 decades, I find this number staggering and tragic. We haven’t seen a virus flash through our communities in this way since before we had vaccines for measles and polio,” AAP President Sally Goza, MD, said in a written statement.
The previous 1-week high of almost 74,000 cases came just last week, and that number had surpassed the previous week’s new high of 61,000. The number of cumulative child cases, meanwhile, has doubled since Sept. 3, when it was just over 513,000. Children now represent 11.5% of all COVID-19 cases since the start of the pandemic in the jurisdictions reporting age distribution, the AAP and CHA said.
For the week ending Nov. 12, COVID-19 cases children made up 14% of cases nationally, rising from 13% the week before and reversing a decline that started in mid-October, the AAP/CHA data show.
The two groups continue to note the rarity of severe illness in children, but the number of deaths nationally had its biggest 1-week increase since late July, as the total rose from 123 to 133 in the 42 states reporting such data by age, as well as New York City. The cumulative hospitalization rate for children decreased slightly in the past week and is now down to 1.6% in the 23 states (and NYC) with available data, the AAP and CHA said.
The AAP called on elected leaders to enact a national strategy to combat the spread of the virus and urged health authorities to do more to collect data on longer-term impacts on children.
We’re very concerned about how this will impact all children, including toddlers who are missing key educational opportunities, as well as adolescents who may be at higher risk for anxiety and depression,” Dr. Goza said.
The number of new cases soared in the past week as the United States exceeded 1 million children infected with the coronavirus, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

For the first time, the number of cases in children for the week ending Nov. 12 passed 100,000, and it didn’t stop until it reached 111,946, bringing the total for the pandemic to 1,039,464 reported cases in 49 states (New York is not reporting ages), the District of Columbia, New York City, and Guam, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 update.
“As a pediatrician who has practiced medicine for over 3 decades, I find this number staggering and tragic. We haven’t seen a virus flash through our communities in this way since before we had vaccines for measles and polio,” AAP President Sally Goza, MD, said in a written statement.
The previous 1-week high of almost 74,000 cases came just last week, and that number had surpassed the previous week’s new high of 61,000. The number of cumulative child cases, meanwhile, has doubled since Sept. 3, when it was just over 513,000. Children now represent 11.5% of all COVID-19 cases since the start of the pandemic in the jurisdictions reporting age distribution, the AAP and CHA said.
For the week ending Nov. 12, COVID-19 cases children made up 14% of cases nationally, rising from 13% the week before and reversing a decline that started in mid-October, the AAP/CHA data show.
The two groups continue to note the rarity of severe illness in children, but the number of deaths nationally had its biggest 1-week increase since late July, as the total rose from 123 to 133 in the 42 states reporting such data by age, as well as New York City. The cumulative hospitalization rate for children decreased slightly in the past week and is now down to 1.6% in the 23 states (and NYC) with available data, the AAP and CHA said.
The AAP called on elected leaders to enact a national strategy to combat the spread of the virus and urged health authorities to do more to collect data on longer-term impacts on children.
We’re very concerned about how this will impact all children, including toddlers who are missing key educational opportunities, as well as adolescents who may be at higher risk for anxiety and depression,” Dr. Goza said.
The number of new cases soared in the past week as the United States exceeded 1 million children infected with the coronavirus, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

For the first time, the number of cases in children for the week ending Nov. 12 passed 100,000, and it didn’t stop until it reached 111,946, bringing the total for the pandemic to 1,039,464 reported cases in 49 states (New York is not reporting ages), the District of Columbia, New York City, and Guam, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 update.
“As a pediatrician who has practiced medicine for over 3 decades, I find this number staggering and tragic. We haven’t seen a virus flash through our communities in this way since before we had vaccines for measles and polio,” AAP President Sally Goza, MD, said in a written statement.
The previous 1-week high of almost 74,000 cases came just last week, and that number had surpassed the previous week’s new high of 61,000. The number of cumulative child cases, meanwhile, has doubled since Sept. 3, when it was just over 513,000. Children now represent 11.5% of all COVID-19 cases since the start of the pandemic in the jurisdictions reporting age distribution, the AAP and CHA said.
For the week ending Nov. 12, COVID-19 cases children made up 14% of cases nationally, rising from 13% the week before and reversing a decline that started in mid-October, the AAP/CHA data show.
The two groups continue to note the rarity of severe illness in children, but the number of deaths nationally had its biggest 1-week increase since late July, as the total rose from 123 to 133 in the 42 states reporting such data by age, as well as New York City. The cumulative hospitalization rate for children decreased slightly in the past week and is now down to 1.6% in the 23 states (and NYC) with available data, the AAP and CHA said.
The AAP called on elected leaders to enact a national strategy to combat the spread of the virus and urged health authorities to do more to collect data on longer-term impacts on children.
We’re very concerned about how this will impact all children, including toddlers who are missing key educational opportunities, as well as adolescents who may be at higher risk for anxiety and depression,” Dr. Goza said.
Opt-out policy at a syringe service program increased HIV/HCV testing
Bundled opt-out HIV/hepatitis C virus (HCV) testing increased the percentage of syringe service program (SSP) clients who received HIV and HCV rapid tests at enrollment into the program. Researchers conducted a retrospective comparative analysis of patient testing patterns before and after opt-out policy implementation in a single SSP program, according to a report published online in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
Because HCV is the most common infectious disease among people who inject drugs (PWID), engaging PWID in harm reduction services, such as SSPs, is critical to reduce HCV and HIV transmission, according to Tyler S. Bartholomew of the University of Miami, and colleagues. They added that testing for HIV and HCV among PWID is important for improvement of diagnosis and linkage to care.
Their study, conducted in the 37 months between December 2016 and January 2020 assessed 512 SSP participants 15 months prior to and 547 SSP participants 22 months after implementation of bundled HIV/HCV opt-out testing.
Opt-out optimal
There was a significant increase in uptake of HIV/HCV testing by 42.4% (95% confidence interval, 26.2%-58.5%; P < 0.001) immediately after the policy changed to opt-out testing, according to the researchers. In addition, they found that the significant predictors of accepting both HIV/HCV tests were cocaine injection (adjusted odds ratio, 2.36), self-reported HIV-positive status (aOR, 0.39), and self-reported HCV-positive status (aOR, 0.27).
The authors explained that participants who injected cocaine in the previous 30 days, compared with other drugs, might have had higher odds of accepting HIV/HCV testing because of their known added risk factors. Previous studies have shown that people who use stimulants describe higher rates of condomless sex, sex work, and sex in exchange for money or drugs, compared with people who use nonstimulant drugs.
“Our paper is the first of which we are aware to suggest that implementation of routine opt-out HIV/HCV testing among PWID at SSPs could enhance HIV/HCV testing among this high incidence population,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported funding from the National Cancer Institute and the Frontlines of Communities in the United States, a program of Gilead Sciences. They provided no other disclosures.
SOURCE: Bartholomew TS et al. Int J Drug Policy. 2020; doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2020.102875.
Bundled opt-out HIV/hepatitis C virus (HCV) testing increased the percentage of syringe service program (SSP) clients who received HIV and HCV rapid tests at enrollment into the program. Researchers conducted a retrospective comparative analysis of patient testing patterns before and after opt-out policy implementation in a single SSP program, according to a report published online in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
Because HCV is the most common infectious disease among people who inject drugs (PWID), engaging PWID in harm reduction services, such as SSPs, is critical to reduce HCV and HIV transmission, according to Tyler S. Bartholomew of the University of Miami, and colleagues. They added that testing for HIV and HCV among PWID is important for improvement of diagnosis and linkage to care.
Their study, conducted in the 37 months between December 2016 and January 2020 assessed 512 SSP participants 15 months prior to and 547 SSP participants 22 months after implementation of bundled HIV/HCV opt-out testing.
Opt-out optimal
There was a significant increase in uptake of HIV/HCV testing by 42.4% (95% confidence interval, 26.2%-58.5%; P < 0.001) immediately after the policy changed to opt-out testing, according to the researchers. In addition, they found that the significant predictors of accepting both HIV/HCV tests were cocaine injection (adjusted odds ratio, 2.36), self-reported HIV-positive status (aOR, 0.39), and self-reported HCV-positive status (aOR, 0.27).
The authors explained that participants who injected cocaine in the previous 30 days, compared with other drugs, might have had higher odds of accepting HIV/HCV testing because of their known added risk factors. Previous studies have shown that people who use stimulants describe higher rates of condomless sex, sex work, and sex in exchange for money or drugs, compared with people who use nonstimulant drugs.
“Our paper is the first of which we are aware to suggest that implementation of routine opt-out HIV/HCV testing among PWID at SSPs could enhance HIV/HCV testing among this high incidence population,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported funding from the National Cancer Institute and the Frontlines of Communities in the United States, a program of Gilead Sciences. They provided no other disclosures.
SOURCE: Bartholomew TS et al. Int J Drug Policy. 2020; doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2020.102875.
Bundled opt-out HIV/hepatitis C virus (HCV) testing increased the percentage of syringe service program (SSP) clients who received HIV and HCV rapid tests at enrollment into the program. Researchers conducted a retrospective comparative analysis of patient testing patterns before and after opt-out policy implementation in a single SSP program, according to a report published online in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
Because HCV is the most common infectious disease among people who inject drugs (PWID), engaging PWID in harm reduction services, such as SSPs, is critical to reduce HCV and HIV transmission, according to Tyler S. Bartholomew of the University of Miami, and colleagues. They added that testing for HIV and HCV among PWID is important for improvement of diagnosis and linkage to care.
Their study, conducted in the 37 months between December 2016 and January 2020 assessed 512 SSP participants 15 months prior to and 547 SSP participants 22 months after implementation of bundled HIV/HCV opt-out testing.
Opt-out optimal
There was a significant increase in uptake of HIV/HCV testing by 42.4% (95% confidence interval, 26.2%-58.5%; P < 0.001) immediately after the policy changed to opt-out testing, according to the researchers. In addition, they found that the significant predictors of accepting both HIV/HCV tests were cocaine injection (adjusted odds ratio, 2.36), self-reported HIV-positive status (aOR, 0.39), and self-reported HCV-positive status (aOR, 0.27).
The authors explained that participants who injected cocaine in the previous 30 days, compared with other drugs, might have had higher odds of accepting HIV/HCV testing because of their known added risk factors. Previous studies have shown that people who use stimulants describe higher rates of condomless sex, sex work, and sex in exchange for money or drugs, compared with people who use nonstimulant drugs.
“Our paper is the first of which we are aware to suggest that implementation of routine opt-out HIV/HCV testing among PWID at SSPs could enhance HIV/HCV testing among this high incidence population,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported funding from the National Cancer Institute and the Frontlines of Communities in the United States, a program of Gilead Sciences. They provided no other disclosures.
SOURCE: Bartholomew TS et al. Int J Drug Policy. 2020; doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2020.102875.
FROM INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DRUG POLICY
Monthly needlestick rates suggest a steep learning curve
The rate of injuries with needles and other sharp instruments among hospital staff jumped sharply in July, which suggests the need for safety instruction early in the academic year, researchers say.
“The reason this is important is it gives us an idea of when the best time to intervene might be,” said Jonathan Zampella, MD, an assistant professor of dermatology at New York University.
The findings were published online Nov. 4 in a research letter in JAMA Surgery.
Hundreds of thousands of health care workers incur injuries with needles and other sharp instruments every year, which places them at risk for blood-borne infections.
“Especially amongst dermatologists, it’s not a question of if you get stuck, it’s a question of when,” Dr. Zampella said in an interview. “Most have been stuck at some point in their lives.”
Until now, studies of these injuries have mostly depended on surveys, he said. By contrast, for the current study, Dr. Zampella and colleagues used a dataset of injuries reported to NYU Langone Health’s Occupational Health Services.
They identified 5,395 such injuries that occurred between January 2000 and February 2020. The total number was similar among surgical and nonsurgical specialists, but the mean incident rate was 4.7 for every 10 people among the nonsurgical staff versus 9.4 for every 10 people in the surgical staff.
Dr. Zampella and colleagues further found that the highest rate of injury, at 16.0 incidents for every 10 people, occurred among urology house staff, followed by orthopedic surgery staff, with 14.1, and general surgery staff, with 14.0. The lowest staff rates were among psychiatrists (0.3), radiation oncologists (1.1), and neurologists (2.4).
But even some nonsurgical specialties had high rates. For example, the rate was 11.5 for pathology house staff and 11.3 for dermatology house staff.
Dr. Zampella said his first reaction to the data was, “What the heck? What are pathologists doing that they are getting needlestick injuries?
“But it makes sense,” he said. “Sometimes they do biopsies, and they do fine-needle aspirations – these kinds of things that we might not be paying as much attention to as we should.”
The finding suggests that nonsurgical specialists should receive more training in injury prevention, he said.
The training should be in person, and it should not just be for first-year residents. “Everybody needs to have refreshers on preventing needlesticks,” he said. “And we have to make sure everyone in the hospital is playing for the same team. Residents are learning, and if they see poor technique by one of their attendings, that’s something they may imitate.”
The study’s primary conclusion regards the importance of seasonality in needlestick and other injuries from sharp instruments.
Among house staff, 9.4% of the injuries occurred in July. The proportion then gradually rose to 10.5% in October before gradually going back down to a low of 6.2% in June.
The difference from one quarter to the next was statistically significant (P = .02).
July is when internships and residencies start, Dr. Zampella pointed out. Among the nonhouse staff, the rate was consistent throughout the year.
This suggests that the beginning of the academic year for trainees was the key factor driving the uptick in injuries, he said.
He said that residents are receiving instruction in injury prevention, but perhaps not at the right time of year. For example, dermatology residents at NYU are given a lecture in needlestick injury prevention in February.
Dr. Zampella has received personal fees from X4 pharmaceuticals. The other authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The rate of injuries with needles and other sharp instruments among hospital staff jumped sharply in July, which suggests the need for safety instruction early in the academic year, researchers say.
“The reason this is important is it gives us an idea of when the best time to intervene might be,” said Jonathan Zampella, MD, an assistant professor of dermatology at New York University.
The findings were published online Nov. 4 in a research letter in JAMA Surgery.
Hundreds of thousands of health care workers incur injuries with needles and other sharp instruments every year, which places them at risk for blood-borne infections.
“Especially amongst dermatologists, it’s not a question of if you get stuck, it’s a question of when,” Dr. Zampella said in an interview. “Most have been stuck at some point in their lives.”
Until now, studies of these injuries have mostly depended on surveys, he said. By contrast, for the current study, Dr. Zampella and colleagues used a dataset of injuries reported to NYU Langone Health’s Occupational Health Services.
They identified 5,395 such injuries that occurred between January 2000 and February 2020. The total number was similar among surgical and nonsurgical specialists, but the mean incident rate was 4.7 for every 10 people among the nonsurgical staff versus 9.4 for every 10 people in the surgical staff.
Dr. Zampella and colleagues further found that the highest rate of injury, at 16.0 incidents for every 10 people, occurred among urology house staff, followed by orthopedic surgery staff, with 14.1, and general surgery staff, with 14.0. The lowest staff rates were among psychiatrists (0.3), radiation oncologists (1.1), and neurologists (2.4).
But even some nonsurgical specialties had high rates. For example, the rate was 11.5 for pathology house staff and 11.3 for dermatology house staff.
Dr. Zampella said his first reaction to the data was, “What the heck? What are pathologists doing that they are getting needlestick injuries?
“But it makes sense,” he said. “Sometimes they do biopsies, and they do fine-needle aspirations – these kinds of things that we might not be paying as much attention to as we should.”
The finding suggests that nonsurgical specialists should receive more training in injury prevention, he said.
The training should be in person, and it should not just be for first-year residents. “Everybody needs to have refreshers on preventing needlesticks,” he said. “And we have to make sure everyone in the hospital is playing for the same team. Residents are learning, and if they see poor technique by one of their attendings, that’s something they may imitate.”
The study’s primary conclusion regards the importance of seasonality in needlestick and other injuries from sharp instruments.
Among house staff, 9.4% of the injuries occurred in July. The proportion then gradually rose to 10.5% in October before gradually going back down to a low of 6.2% in June.
The difference from one quarter to the next was statistically significant (P = .02).
July is when internships and residencies start, Dr. Zampella pointed out. Among the nonhouse staff, the rate was consistent throughout the year.
This suggests that the beginning of the academic year for trainees was the key factor driving the uptick in injuries, he said.
He said that residents are receiving instruction in injury prevention, but perhaps not at the right time of year. For example, dermatology residents at NYU are given a lecture in needlestick injury prevention in February.
Dr. Zampella has received personal fees from X4 pharmaceuticals. The other authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The rate of injuries with needles and other sharp instruments among hospital staff jumped sharply in July, which suggests the need for safety instruction early in the academic year, researchers say.
“The reason this is important is it gives us an idea of when the best time to intervene might be,” said Jonathan Zampella, MD, an assistant professor of dermatology at New York University.
The findings were published online Nov. 4 in a research letter in JAMA Surgery.
Hundreds of thousands of health care workers incur injuries with needles and other sharp instruments every year, which places them at risk for blood-borne infections.
“Especially amongst dermatologists, it’s not a question of if you get stuck, it’s a question of when,” Dr. Zampella said in an interview. “Most have been stuck at some point in their lives.”
Until now, studies of these injuries have mostly depended on surveys, he said. By contrast, for the current study, Dr. Zampella and colleagues used a dataset of injuries reported to NYU Langone Health’s Occupational Health Services.
They identified 5,395 such injuries that occurred between January 2000 and February 2020. The total number was similar among surgical and nonsurgical specialists, but the mean incident rate was 4.7 for every 10 people among the nonsurgical staff versus 9.4 for every 10 people in the surgical staff.
Dr. Zampella and colleagues further found that the highest rate of injury, at 16.0 incidents for every 10 people, occurred among urology house staff, followed by orthopedic surgery staff, with 14.1, and general surgery staff, with 14.0. The lowest staff rates were among psychiatrists (0.3), radiation oncologists (1.1), and neurologists (2.4).
But even some nonsurgical specialties had high rates. For example, the rate was 11.5 for pathology house staff and 11.3 for dermatology house staff.
Dr. Zampella said his first reaction to the data was, “What the heck? What are pathologists doing that they are getting needlestick injuries?
“But it makes sense,” he said. “Sometimes they do biopsies, and they do fine-needle aspirations – these kinds of things that we might not be paying as much attention to as we should.”
The finding suggests that nonsurgical specialists should receive more training in injury prevention, he said.
The training should be in person, and it should not just be for first-year residents. “Everybody needs to have refreshers on preventing needlesticks,” he said. “And we have to make sure everyone in the hospital is playing for the same team. Residents are learning, and if they see poor technique by one of their attendings, that’s something they may imitate.”
The study’s primary conclusion regards the importance of seasonality in needlestick and other injuries from sharp instruments.
Among house staff, 9.4% of the injuries occurred in July. The proportion then gradually rose to 10.5% in October before gradually going back down to a low of 6.2% in June.
The difference from one quarter to the next was statistically significant (P = .02).
July is when internships and residencies start, Dr. Zampella pointed out. Among the nonhouse staff, the rate was consistent throughout the year.
This suggests that the beginning of the academic year for trainees was the key factor driving the uptick in injuries, he said.
He said that residents are receiving instruction in injury prevention, but perhaps not at the right time of year. For example, dermatology residents at NYU are given a lecture in needlestick injury prevention in February.
Dr. Zampella has received personal fees from X4 pharmaceuticals. The other authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Should our patients really go home for the holidays?
As an East Coast transplant residing in Texas, I look forward to the annual sojourn home to celebrate the holidays with family and friends – as do many of our patients and their families. But this is 2020. SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, is still circulating. To make matters worse, cases are rising in 45 states and internationally. The day of this writing 102,831 new cases were reported in the United States. 
Social distancing, wearing masks, and hand washing have been strategies recommended to help mitigate the spread of the virus. We know adherence is not always 100%. The reality is that several families will consider traveling and gathering with others over the holidays. Their actions may lead to increased infections, hospitalizations, and even deaths. It behooves us to at least remind them of the potential consequences of the activity, and if travel and/or holiday gatherings are inevitable, to provide some guidance to help them look at both the risks and benefits and offer strategies to minimize infection and spread.
What should be considered prior to travel?
Here is a list of points to ponder:
- Is your patient is in a high-risk group for developing severe disease or visiting someone who is in a high-risk group?
- What is their mode of transportation?
- What is their destination?
- How prevalent is the disease at their destination, compared with their community?
- What will be their accommodations?
- How will attendees prepare for the gathering, if at all?
- Will multiple families congregate after quarantining for 2 weeks or simply arrive?
- At the destination, will people wear masks and socially distance?
- Is an outdoor venue an option?
All of these questions should be considered by patients.
Review high-risk groups
In terms of high-risk groups, we usually focus on underlying medical conditions or extremes of age, but Black and LatinX children and their families have been diagnosed with COVID-19 and hospitalized more frequently than other racial/ ethnic groups in the United States. Of 277,285 school-aged children infected between March 1 and Sept. 19, 2020, 42% were LatinX, 32% White, and 17% Black, yet they comprise 18%, 60%, and 11% of the U.S. population, respectively. Of those hospitalized, 45% were LatinX, 22% White, and 24% Black. LatinX and Black children also have disproportionately higher mortality rates.
Think about transmission and how to mitigate it
Many patients erroneously think combining multiple households for small group gatherings is inconsequential. These types of gatherings serve as a continued source of SARS-CoV-2 spread. For example, a person in Illinois with mild upper respiratory infection symptoms attended a funeral; he reported embracing the family members after the funeral. He dined with two people the evening prior to the funeral, sharing the meal using common serving dishes. Four days later, he attended a birthday party with nine family members. Some of the family members with symptoms subsequently attended church, infecting another church attendee. A cluster of 16 cases of COVID-19 was subsequently identified, including three deaths likely resulting from this one introduction of COVID-19 at these two family gatherings.
In Tennessee and Wisconsin, household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 was studied prospectively. A total of 101 index cases and 191 asymptomatic household contacts were enrolled between April and Sept. 2020; 102 of 191 (53%) had SARS-CoV-2 detected during the 14-day follow-up. Most infections (75%) were identified within 5 days and occurred whether the index case was an adult or child.
Lastly, one adolescent was identified as the source for an outbreak at a family gathering where 15 persons from five households and four states shared a house between 8 and 25 days in July 2020. Six additional members visited the house. The index case had an exposure to COVID-19 and had a negative antigen test 4 days after exposure. She was asymptomatic when tested. She developed nasal congestion 2 days later, the same day she and her family departed for the gathering. A total of 11 household contacts developed confirmed, suspected, or probable COVID-19, and the teen developed symptoms. This report illustrates how easily SARS-CoV-2 is transmitted, and how when implemented, mitigation strategies work because none of the six who only visited the house was infected. It also serves as a reminder that antigen testing is indicated only for use within the first 5-12 days of onset of symptoms. In this case, the adolescent was asymptomatic when tested and had a false-negative test result.
Ponder modes of transportation
How will your patient arrive to their holiday destination? Nonstop travel by car with household members is probably the safest way. However, for many families, buses and trains are the only options, and social distancing may be challenging. Air travel is a must for others. Acquisition of COVID-19 during air travel appears to be low, but not absent based on how air enters and leaves the cabin. The challenge is socially distancing throughout the check in and boarding processes, as well as minimizing contact with common surfaces. There also is loss of social distancing once on board. Ideally, masks should be worn during the flight. Additionally, for those with international destinations, most countries now require a negative polymerase chain reaction COVID-19 test within a specified time frame for entry.
Essentially the safest place for your patients during the holidays is celebrating at home with their household contacts. The risk for disease acquisition increases with travel. You will not have the opportunity to discuss holiday plans with most parents. However, you can encourage them to consider the pros and cons of travel with reminders via telephone, e-mail, and /or social messaging directly from your practices similar to those sent for other medically necessary interventions. As for me, I will be celebrating virtually this year. There is a first time for everything.
For additional information that also is patient friendly, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offers information about travel within the United States and international travel.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
As an East Coast transplant residing in Texas, I look forward to the annual sojourn home to celebrate the holidays with family and friends – as do many of our patients and their families. But this is 2020. SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, is still circulating. To make matters worse, cases are rising in 45 states and internationally. The day of this writing 102,831 new cases were reported in the United States. 
Social distancing, wearing masks, and hand washing have been strategies recommended to help mitigate the spread of the virus. We know adherence is not always 100%. The reality is that several families will consider traveling and gathering with others over the holidays. Their actions may lead to increased infections, hospitalizations, and even deaths. It behooves us to at least remind them of the potential consequences of the activity, and if travel and/or holiday gatherings are inevitable, to provide some guidance to help them look at both the risks and benefits and offer strategies to minimize infection and spread.
What should be considered prior to travel?
Here is a list of points to ponder:
- Is your patient is in a high-risk group for developing severe disease or visiting someone who is in a high-risk group?
- What is their mode of transportation?
- What is their destination?
- How prevalent is the disease at their destination, compared with their community?
- What will be their accommodations?
- How will attendees prepare for the gathering, if at all?
- Will multiple families congregate after quarantining for 2 weeks or simply arrive?
- At the destination, will people wear masks and socially distance?
- Is an outdoor venue an option?
All of these questions should be considered by patients.
Review high-risk groups
In terms of high-risk groups, we usually focus on underlying medical conditions or extremes of age, but Black and LatinX children and their families have been diagnosed with COVID-19 and hospitalized more frequently than other racial/ ethnic groups in the United States. Of 277,285 school-aged children infected between March 1 and Sept. 19, 2020, 42% were LatinX, 32% White, and 17% Black, yet they comprise 18%, 60%, and 11% of the U.S. population, respectively. Of those hospitalized, 45% were LatinX, 22% White, and 24% Black. LatinX and Black children also have disproportionately higher mortality rates.
Think about transmission and how to mitigate it
Many patients erroneously think combining multiple households for small group gatherings is inconsequential. These types of gatherings serve as a continued source of SARS-CoV-2 spread. For example, a person in Illinois with mild upper respiratory infection symptoms attended a funeral; he reported embracing the family members after the funeral. He dined with two people the evening prior to the funeral, sharing the meal using common serving dishes. Four days later, he attended a birthday party with nine family members. Some of the family members with symptoms subsequently attended church, infecting another church attendee. A cluster of 16 cases of COVID-19 was subsequently identified, including three deaths likely resulting from this one introduction of COVID-19 at these two family gatherings.
In Tennessee and Wisconsin, household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 was studied prospectively. A total of 101 index cases and 191 asymptomatic household contacts were enrolled between April and Sept. 2020; 102 of 191 (53%) had SARS-CoV-2 detected during the 14-day follow-up. Most infections (75%) were identified within 5 days and occurred whether the index case was an adult or child.
Lastly, one adolescent was identified as the source for an outbreak at a family gathering where 15 persons from five households and four states shared a house between 8 and 25 days in July 2020. Six additional members visited the house. The index case had an exposure to COVID-19 and had a negative antigen test 4 days after exposure. She was asymptomatic when tested. She developed nasal congestion 2 days later, the same day she and her family departed for the gathering. A total of 11 household contacts developed confirmed, suspected, or probable COVID-19, and the teen developed symptoms. This report illustrates how easily SARS-CoV-2 is transmitted, and how when implemented, mitigation strategies work because none of the six who only visited the house was infected. It also serves as a reminder that antigen testing is indicated only for use within the first 5-12 days of onset of symptoms. In this case, the adolescent was asymptomatic when tested and had a false-negative test result.
Ponder modes of transportation
How will your patient arrive to their holiday destination? Nonstop travel by car with household members is probably the safest way. However, for many families, buses and trains are the only options, and social distancing may be challenging. Air travel is a must for others. Acquisition of COVID-19 during air travel appears to be low, but not absent based on how air enters and leaves the cabin. The challenge is socially distancing throughout the check in and boarding processes, as well as minimizing contact with common surfaces. There also is loss of social distancing once on board. Ideally, masks should be worn during the flight. Additionally, for those with international destinations, most countries now require a negative polymerase chain reaction COVID-19 test within a specified time frame for entry.
Essentially the safest place for your patients during the holidays is celebrating at home with their household contacts. The risk for disease acquisition increases with travel. You will not have the opportunity to discuss holiday plans with most parents. However, you can encourage them to consider the pros and cons of travel with reminders via telephone, e-mail, and /or social messaging directly from your practices similar to those sent for other medically necessary interventions. As for me, I will be celebrating virtually this year. There is a first time for everything.
For additional information that also is patient friendly, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offers information about travel within the United States and international travel.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
As an East Coast transplant residing in Texas, I look forward to the annual sojourn home to celebrate the holidays with family and friends – as do many of our patients and their families. But this is 2020. SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, is still circulating. To make matters worse, cases are rising in 45 states and internationally. The day of this writing 102,831 new cases were reported in the United States. 
Social distancing, wearing masks, and hand washing have been strategies recommended to help mitigate the spread of the virus. We know adherence is not always 100%. The reality is that several families will consider traveling and gathering with others over the holidays. Their actions may lead to increased infections, hospitalizations, and even deaths. It behooves us to at least remind them of the potential consequences of the activity, and if travel and/or holiday gatherings are inevitable, to provide some guidance to help them look at both the risks and benefits and offer strategies to minimize infection and spread.
What should be considered prior to travel?
Here is a list of points to ponder:
- Is your patient is in a high-risk group for developing severe disease or visiting someone who is in a high-risk group?
- What is their mode of transportation?
- What is their destination?
- How prevalent is the disease at their destination, compared with their community?
- What will be their accommodations?
- How will attendees prepare for the gathering, if at all?
- Will multiple families congregate after quarantining for 2 weeks or simply arrive?
- At the destination, will people wear masks and socially distance?
- Is an outdoor venue an option?
All of these questions should be considered by patients.
Review high-risk groups
In terms of high-risk groups, we usually focus on underlying medical conditions or extremes of age, but Black and LatinX children and their families have been diagnosed with COVID-19 and hospitalized more frequently than other racial/ ethnic groups in the United States. Of 277,285 school-aged children infected between March 1 and Sept. 19, 2020, 42% were LatinX, 32% White, and 17% Black, yet they comprise 18%, 60%, and 11% of the U.S. population, respectively. Of those hospitalized, 45% were LatinX, 22% White, and 24% Black. LatinX and Black children also have disproportionately higher mortality rates.
Think about transmission and how to mitigate it
Many patients erroneously think combining multiple households for small group gatherings is inconsequential. These types of gatherings serve as a continued source of SARS-CoV-2 spread. For example, a person in Illinois with mild upper respiratory infection symptoms attended a funeral; he reported embracing the family members after the funeral. He dined with two people the evening prior to the funeral, sharing the meal using common serving dishes. Four days later, he attended a birthday party with nine family members. Some of the family members with symptoms subsequently attended church, infecting another church attendee. A cluster of 16 cases of COVID-19 was subsequently identified, including three deaths likely resulting from this one introduction of COVID-19 at these two family gatherings.
In Tennessee and Wisconsin, household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 was studied prospectively. A total of 101 index cases and 191 asymptomatic household contacts were enrolled between April and Sept. 2020; 102 of 191 (53%) had SARS-CoV-2 detected during the 14-day follow-up. Most infections (75%) were identified within 5 days and occurred whether the index case was an adult or child.
Lastly, one adolescent was identified as the source for an outbreak at a family gathering where 15 persons from five households and four states shared a house between 8 and 25 days in July 2020. Six additional members visited the house. The index case had an exposure to COVID-19 and had a negative antigen test 4 days after exposure. She was asymptomatic when tested. She developed nasal congestion 2 days later, the same day she and her family departed for the gathering. A total of 11 household contacts developed confirmed, suspected, or probable COVID-19, and the teen developed symptoms. This report illustrates how easily SARS-CoV-2 is transmitted, and how when implemented, mitigation strategies work because none of the six who only visited the house was infected. It also serves as a reminder that antigen testing is indicated only for use within the first 5-12 days of onset of symptoms. In this case, the adolescent was asymptomatic when tested and had a false-negative test result.
Ponder modes of transportation
How will your patient arrive to their holiday destination? Nonstop travel by car with household members is probably the safest way. However, for many families, buses and trains are the only options, and social distancing may be challenging. Air travel is a must for others. Acquisition of COVID-19 during air travel appears to be low, but not absent based on how air enters and leaves the cabin. The challenge is socially distancing throughout the check in and boarding processes, as well as minimizing contact with common surfaces. There also is loss of social distancing once on board. Ideally, masks should be worn during the flight. Additionally, for those with international destinations, most countries now require a negative polymerase chain reaction COVID-19 test within a specified time frame for entry.
Essentially the safest place for your patients during the holidays is celebrating at home with their household contacts. The risk for disease acquisition increases with travel. You will not have the opportunity to discuss holiday plans with most parents. However, you can encourage them to consider the pros and cons of travel with reminders via telephone, e-mail, and /or social messaging directly from your practices similar to those sent for other medically necessary interventions. As for me, I will be celebrating virtually this year. There is a first time for everything.
For additional information that also is patient friendly, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offers information about travel within the United States and international travel.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Treatments for COVID-19: Update for hospitalists
Most patients with COVID-19 will have a mild presentation and not require hospitalization or any treatment. Inpatient management revolves around the supportive management of the most common complications of severe COVID-19, which includes pneumonia, hypoxemic respiratory failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and septic shock.
Currently, there is no clinically proven specific antiviral treatment for COVID-19. A few antivirals and treatment modalities have been studied and used, with the hope of decreasing mortality and improving recovery time for those with moderate to severe cases of COVID-19.
Remdesivir
The antiviral remdesivir was the second drug to receive emergency use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of suspected or laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 in adults and children hospitalized with severe disease. Severe disease is defined as patients with an oxygen saturation less than 94% on room air or requiring supplemental oxygen or requiring mechanical ventilation or requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Remdesivir is a nucleotide analogue that has shown in vitro antiviral activity against a range of RNA viruses. It acts by causing premature termination of viral RNA transcription. Remdesivir is administered intravenously and the recommended dose is 200 mg on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for various time courses.
A few clinical studies have reported benefits of remdesivir rather than no remdesivir for treatment of severe COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) recommends 5 days of remdesivir in patients with severe COVID-19 on noninvasive supplemental oxygen and 10 days treatment for those on mechanical ventilation and ECMO. In a randomized, uncontrolled, phase 3 trial, investigators compared 5-day (n = 200) versus 10-day (n = 197) courses of remdesivir in patients with severe COVID-19. Clinical data revealed no differences in outcomes in the two groups.
Common reported adverse effects of the drug include elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and/or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and gastrointestinal symptoms including nausea, vomiting, and hematochezia. There is insufficient data on using remdesivir in patients requiring dialysis.
Corticosteroids
Is dexamethasone effective for treating COVID-19? In the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, corticosteroids were not recommended with the fear that, if started too soon, you could blunt the body’s natural defense system and that could allow the virus to thrive. Recent clinical data has shown clinical benefits and decreased mortality with the use of dexamethasone in patients with severe COVID-19 infection because glucocorticoids may modulate inflammation-mediated lung injury and reduce progression to respiratory failure and death.
The Recovery Trial was an open label study which used 6-mg once-daily doses of dexamethasone for up to 10 days or until hospital discharge if sooner. The study concluded that the use of dexamethasone for up to 10 days in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 resulted in lower 28-day mortality than usual care.
Dexamethasone is recommended in COVID-19 patients who require supplemental oxygen. If dexamethasone is not available, alternative forms of steroids – prednisone, methylprednisolone, or hydrocortisone – can be used. However, there is no clear evidence that the use of other steroids provides the same benefit as dexamethasone.
Both the IDSA and National Institutes of Health guidelines have recommended the use of steroids. However, clinicians should closely monitor the adverse effects like hyperglycemia, secondary infections, psychiatric effects, and avascular necrosis.
Convalescent plasma
Convalescent plasma is a blood product believed to provide passive antibody therapy through the transmission of neutralizing viral antibodies. Convalescent plasma has been used for decades for different viral infections including the treatment of H1N1 influenza virus, polio, chicken pox, measles, SARS-CoV-1, and MERS-CoV.
On Aug. 23, 2020, the FDA issued an emergency use authorization for investigational convalescent plasma for the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. The FDA recommends neutralizing antibodies of at least 1:160. However, such assays have not been widely available and titers in plasma have often not been assessed prior to infusion.
There is no current standard recommended dosing. Most study protocols infuse 1-2 units of convalescent plasma for persons with COVID-19.
There is insufficient data to recommend either for or against the use of convalescent plasma for the treatment of COVID-19. Existing data suggest that, if a benefit exists, convalescent plasma is most useful when given early and with a high titer of neutralizing antibodies.
The adverse effects of convalescent plasma is very similar to the receipt of other blood products, including allergic reactions to the plasma, transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO), transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI), and acquisition of infections, though the latter is rare because of the rigorous screening process.
Tocilizumab
Tocilizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to interleukin (IL)-6 receptors. Tocilizumab is currently FDA approved for the treatment of severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome that is associated with chimeric antigen–receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy and for the treatment of rheumatologic disorders.
The interest in using tocilizumab to treat persons with COVID-19 is based on the observations that a subset of patients with COVID-19 develop a severe inflammatory response that can result in cytokine storm resulting in ARDS, multiorgan failure, and potentially death. Very high levels of IL-6 have been observed in these individuals, thereby suggesting IL-6 may play a central role in the acute clinical decompensation seen with severe COVID-19.
The optimal dosing of tocilizumab in patients with COVID-19 is not known. The FDA recommends dosing of tocilizumab for cytokine release syndrome should not exceed 800 mg. There is limited data about the potential benefit of tocilizumab in patients with COVID-19. The COVACTA trial showed no difference between tocilizumab and placebo in regard to mortality. The time to hospital discharge was shorter in patients treated with tocilizumab; however, the difference was not statistically significant.
Reported adverse effects of tocilizumab include increase in ALT and AST, increased risk of serious infections (especially tuberculosis and invasive fungal infections), reactivation of hepatitis B virus, and rare reports of gastrointestinal perforation.
Hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxycholoroquine (HCQ) and its sister drug chloroquine, have been used for many decades as treatment for malaria and autoimmune diseases. HCQ gained widespread popularity in the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic when clinical studies showed that it had significant in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2, which provided the rationale for its use in the treatment and prevention of COVID-19 infection.
It was the first drug that was authorized for emergency use by the FDA during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, On June 15, 2020, because of accumulating harmful data, the FDA revoked the emergency authorization use of HCQ as a COVID-19 treatment.
Randomized controlled trials showed that patients treated with HCQ experienced a longer hospital stay with increase in mortality rates and increased likelihood of being placed on mechanical ventilation. In addition, studies revealed an increase in QT prolongation in patients treated with HCQ, especially when coadministered with azithromycin, which can lead to torsades de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, and sudden cardiac death.
The IDSA and National Institutes of Health, both recommend against the use of hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin to treat COVID-19 because the harms outweigh the benefits, even if high quality RCTs were to become available in the future.
Other drugs
There have been experimental studies on other medications for the treatment of COVID-19, including losartan, amlodipine, ivermectin, famotidine, Anakinra, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as ibrutinib, and Janus kinase inhibitors, such as tofacitinib. Additionally, a few supplements such as vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc have been used in both inpatient and outpatient settings for COVID-19 treatment. Polyclonal antibodies are being investigated in phase 3 trials. However, the data is insufficient, and the effectiveness of these drugs is unknown. The COVID-19 treatment guidelines panel recommends against the use of these treatment modalities.
Dr Tiyouh is an infectious diseases physician at Keystone Health in Chambersburg, Pa. Dr. Tenneti completed medical school at Vydehi Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre in Karnataka, India, and is interested in pursuing internal medicine residency. Dr. Tirupathi is the medical director of Keystone Infectious Diseases/HIV in Chambersburg, Pa., and currently chair of infection prevention at Wellspan Chambersburg Hospital and Waynesboro (Pa.) Hospitals. Dr. Palabindala is hospital medicine division chief at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, and a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Sources
Goldman JD et al. Remdesivir for 5 or 10 Days in Patients with Severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2015301.
Beigel JH et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 - Final Report. N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct 8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Wang Y et al. Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet. 2020 May 16;395(10236):1569-78.
National Institutes of Health. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines.
Infectious Diseases Society of America. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19.
Joyner et al. Early safety indicators of COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 5000 patients. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(9):4791-7.
Luo P et al. Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: A single center experience. J Med Virol. 2020 Jul;92(7):814-8.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Healthcare Workers: Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19).
University of Washington. COVID-19 Treatments: Prescribing Information, Clinical Studies, and Slide Decks.
Most patients with COVID-19 will have a mild presentation and not require hospitalization or any treatment. Inpatient management revolves around the supportive management of the most common complications of severe COVID-19, which includes pneumonia, hypoxemic respiratory failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and septic shock.
Currently, there is no clinically proven specific antiviral treatment for COVID-19. A few antivirals and treatment modalities have been studied and used, with the hope of decreasing mortality and improving recovery time for those with moderate to severe cases of COVID-19.
Remdesivir
The antiviral remdesivir was the second drug to receive emergency use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of suspected or laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 in adults and children hospitalized with severe disease. Severe disease is defined as patients with an oxygen saturation less than 94% on room air or requiring supplemental oxygen or requiring mechanical ventilation or requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Remdesivir is a nucleotide analogue that has shown in vitro antiviral activity against a range of RNA viruses. It acts by causing premature termination of viral RNA transcription. Remdesivir is administered intravenously and the recommended dose is 200 mg on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for various time courses.
A few clinical studies have reported benefits of remdesivir rather than no remdesivir for treatment of severe COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) recommends 5 days of remdesivir in patients with severe COVID-19 on noninvasive supplemental oxygen and 10 days treatment for those on mechanical ventilation and ECMO. In a randomized, uncontrolled, phase 3 trial, investigators compared 5-day (n = 200) versus 10-day (n = 197) courses of remdesivir in patients with severe COVID-19. Clinical data revealed no differences in outcomes in the two groups.
Common reported adverse effects of the drug include elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and/or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and gastrointestinal symptoms including nausea, vomiting, and hematochezia. There is insufficient data on using remdesivir in patients requiring dialysis.
Corticosteroids
Is dexamethasone effective for treating COVID-19? In the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, corticosteroids were not recommended with the fear that, if started too soon, you could blunt the body’s natural defense system and that could allow the virus to thrive. Recent clinical data has shown clinical benefits and decreased mortality with the use of dexamethasone in patients with severe COVID-19 infection because glucocorticoids may modulate inflammation-mediated lung injury and reduce progression to respiratory failure and death.
The Recovery Trial was an open label study which used 6-mg once-daily doses of dexamethasone for up to 10 days or until hospital discharge if sooner. The study concluded that the use of dexamethasone for up to 10 days in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 resulted in lower 28-day mortality than usual care.
Dexamethasone is recommended in COVID-19 patients who require supplemental oxygen. If dexamethasone is not available, alternative forms of steroids – prednisone, methylprednisolone, or hydrocortisone – can be used. However, there is no clear evidence that the use of other steroids provides the same benefit as dexamethasone.
Both the IDSA and National Institutes of Health guidelines have recommended the use of steroids. However, clinicians should closely monitor the adverse effects like hyperglycemia, secondary infections, psychiatric effects, and avascular necrosis.
Convalescent plasma
Convalescent plasma is a blood product believed to provide passive antibody therapy through the transmission of neutralizing viral antibodies. Convalescent plasma has been used for decades for different viral infections including the treatment of H1N1 influenza virus, polio, chicken pox, measles, SARS-CoV-1, and MERS-CoV.
On Aug. 23, 2020, the FDA issued an emergency use authorization for investigational convalescent plasma for the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. The FDA recommends neutralizing antibodies of at least 1:160. However, such assays have not been widely available and titers in plasma have often not been assessed prior to infusion.
There is no current standard recommended dosing. Most study protocols infuse 1-2 units of convalescent plasma for persons with COVID-19.
There is insufficient data to recommend either for or against the use of convalescent plasma for the treatment of COVID-19. Existing data suggest that, if a benefit exists, convalescent plasma is most useful when given early and with a high titer of neutralizing antibodies.
The adverse effects of convalescent plasma is very similar to the receipt of other blood products, including allergic reactions to the plasma, transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO), transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI), and acquisition of infections, though the latter is rare because of the rigorous screening process.
Tocilizumab
Tocilizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to interleukin (IL)-6 receptors. Tocilizumab is currently FDA approved for the treatment of severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome that is associated with chimeric antigen–receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy and for the treatment of rheumatologic disorders.
The interest in using tocilizumab to treat persons with COVID-19 is based on the observations that a subset of patients with COVID-19 develop a severe inflammatory response that can result in cytokine storm resulting in ARDS, multiorgan failure, and potentially death. Very high levels of IL-6 have been observed in these individuals, thereby suggesting IL-6 may play a central role in the acute clinical decompensation seen with severe COVID-19.
The optimal dosing of tocilizumab in patients with COVID-19 is not known. The FDA recommends dosing of tocilizumab for cytokine release syndrome should not exceed 800 mg. There is limited data about the potential benefit of tocilizumab in patients with COVID-19. The COVACTA trial showed no difference between tocilizumab and placebo in regard to mortality. The time to hospital discharge was shorter in patients treated with tocilizumab; however, the difference was not statistically significant.
Reported adverse effects of tocilizumab include increase in ALT and AST, increased risk of serious infections (especially tuberculosis and invasive fungal infections), reactivation of hepatitis B virus, and rare reports of gastrointestinal perforation.
Hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxycholoroquine (HCQ) and its sister drug chloroquine, have been used for many decades as treatment for malaria and autoimmune diseases. HCQ gained widespread popularity in the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic when clinical studies showed that it had significant in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2, which provided the rationale for its use in the treatment and prevention of COVID-19 infection.
It was the first drug that was authorized for emergency use by the FDA during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, On June 15, 2020, because of accumulating harmful data, the FDA revoked the emergency authorization use of HCQ as a COVID-19 treatment.
Randomized controlled trials showed that patients treated with HCQ experienced a longer hospital stay with increase in mortality rates and increased likelihood of being placed on mechanical ventilation. In addition, studies revealed an increase in QT prolongation in patients treated with HCQ, especially when coadministered with azithromycin, which can lead to torsades de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, and sudden cardiac death.
The IDSA and National Institutes of Health, both recommend against the use of hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin to treat COVID-19 because the harms outweigh the benefits, even if high quality RCTs were to become available in the future.
Other drugs
There have been experimental studies on other medications for the treatment of COVID-19, including losartan, amlodipine, ivermectin, famotidine, Anakinra, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as ibrutinib, and Janus kinase inhibitors, such as tofacitinib. Additionally, a few supplements such as vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc have been used in both inpatient and outpatient settings for COVID-19 treatment. Polyclonal antibodies are being investigated in phase 3 trials. However, the data is insufficient, and the effectiveness of these drugs is unknown. The COVID-19 treatment guidelines panel recommends against the use of these treatment modalities.
Dr Tiyouh is an infectious diseases physician at Keystone Health in Chambersburg, Pa. Dr. Tenneti completed medical school at Vydehi Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre in Karnataka, India, and is interested in pursuing internal medicine residency. Dr. Tirupathi is the medical director of Keystone Infectious Diseases/HIV in Chambersburg, Pa., and currently chair of infection prevention at Wellspan Chambersburg Hospital and Waynesboro (Pa.) Hospitals. Dr. Palabindala is hospital medicine division chief at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, and a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Sources
Goldman JD et al. Remdesivir for 5 or 10 Days in Patients with Severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2015301.
Beigel JH et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 - Final Report. N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct 8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Wang Y et al. Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet. 2020 May 16;395(10236):1569-78.
National Institutes of Health. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines.
Infectious Diseases Society of America. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19.
Joyner et al. Early safety indicators of COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 5000 patients. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(9):4791-7.
Luo P et al. Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: A single center experience. J Med Virol. 2020 Jul;92(7):814-8.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Healthcare Workers: Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19).
University of Washington. COVID-19 Treatments: Prescribing Information, Clinical Studies, and Slide Decks.
Most patients with COVID-19 will have a mild presentation and not require hospitalization or any treatment. Inpatient management revolves around the supportive management of the most common complications of severe COVID-19, which includes pneumonia, hypoxemic respiratory failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and septic shock.
Currently, there is no clinically proven specific antiviral treatment for COVID-19. A few antivirals and treatment modalities have been studied and used, with the hope of decreasing mortality and improving recovery time for those with moderate to severe cases of COVID-19.
Remdesivir
The antiviral remdesivir was the second drug to receive emergency use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of suspected or laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 in adults and children hospitalized with severe disease. Severe disease is defined as patients with an oxygen saturation less than 94% on room air or requiring supplemental oxygen or requiring mechanical ventilation or requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Remdesivir is a nucleotide analogue that has shown in vitro antiviral activity against a range of RNA viruses. It acts by causing premature termination of viral RNA transcription. Remdesivir is administered intravenously and the recommended dose is 200 mg on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for various time courses.
A few clinical studies have reported benefits of remdesivir rather than no remdesivir for treatment of severe COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) recommends 5 days of remdesivir in patients with severe COVID-19 on noninvasive supplemental oxygen and 10 days treatment for those on mechanical ventilation and ECMO. In a randomized, uncontrolled, phase 3 trial, investigators compared 5-day (n = 200) versus 10-day (n = 197) courses of remdesivir in patients with severe COVID-19. Clinical data revealed no differences in outcomes in the two groups.
Common reported adverse effects of the drug include elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and/or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and gastrointestinal symptoms including nausea, vomiting, and hematochezia. There is insufficient data on using remdesivir in patients requiring dialysis.
Corticosteroids
Is dexamethasone effective for treating COVID-19? In the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, corticosteroids were not recommended with the fear that, if started too soon, you could blunt the body’s natural defense system and that could allow the virus to thrive. Recent clinical data has shown clinical benefits and decreased mortality with the use of dexamethasone in patients with severe COVID-19 infection because glucocorticoids may modulate inflammation-mediated lung injury and reduce progression to respiratory failure and death.
The Recovery Trial was an open label study which used 6-mg once-daily doses of dexamethasone for up to 10 days or until hospital discharge if sooner. The study concluded that the use of dexamethasone for up to 10 days in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 resulted in lower 28-day mortality than usual care.
Dexamethasone is recommended in COVID-19 patients who require supplemental oxygen. If dexamethasone is not available, alternative forms of steroids – prednisone, methylprednisolone, or hydrocortisone – can be used. However, there is no clear evidence that the use of other steroids provides the same benefit as dexamethasone.
Both the IDSA and National Institutes of Health guidelines have recommended the use of steroids. However, clinicians should closely monitor the adverse effects like hyperglycemia, secondary infections, psychiatric effects, and avascular necrosis.
Convalescent plasma
Convalescent plasma is a blood product believed to provide passive antibody therapy through the transmission of neutralizing viral antibodies. Convalescent plasma has been used for decades for different viral infections including the treatment of H1N1 influenza virus, polio, chicken pox, measles, SARS-CoV-1, and MERS-CoV.
On Aug. 23, 2020, the FDA issued an emergency use authorization for investigational convalescent plasma for the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. The FDA recommends neutralizing antibodies of at least 1:160. However, such assays have not been widely available and titers in plasma have often not been assessed prior to infusion.
There is no current standard recommended dosing. Most study protocols infuse 1-2 units of convalescent plasma for persons with COVID-19.
There is insufficient data to recommend either for or against the use of convalescent plasma for the treatment of COVID-19. Existing data suggest that, if a benefit exists, convalescent plasma is most useful when given early and with a high titer of neutralizing antibodies.
The adverse effects of convalescent plasma is very similar to the receipt of other blood products, including allergic reactions to the plasma, transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO), transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI), and acquisition of infections, though the latter is rare because of the rigorous screening process.
Tocilizumab
Tocilizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to interleukin (IL)-6 receptors. Tocilizumab is currently FDA approved for the treatment of severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome that is associated with chimeric antigen–receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy and for the treatment of rheumatologic disorders.
The interest in using tocilizumab to treat persons with COVID-19 is based on the observations that a subset of patients with COVID-19 develop a severe inflammatory response that can result in cytokine storm resulting in ARDS, multiorgan failure, and potentially death. Very high levels of IL-6 have been observed in these individuals, thereby suggesting IL-6 may play a central role in the acute clinical decompensation seen with severe COVID-19.
The optimal dosing of tocilizumab in patients with COVID-19 is not known. The FDA recommends dosing of tocilizumab for cytokine release syndrome should not exceed 800 mg. There is limited data about the potential benefit of tocilizumab in patients with COVID-19. The COVACTA trial showed no difference between tocilizumab and placebo in regard to mortality. The time to hospital discharge was shorter in patients treated with tocilizumab; however, the difference was not statistically significant.
Reported adverse effects of tocilizumab include increase in ALT and AST, increased risk of serious infections (especially tuberculosis and invasive fungal infections), reactivation of hepatitis B virus, and rare reports of gastrointestinal perforation.
Hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxycholoroquine (HCQ) and its sister drug chloroquine, have been used for many decades as treatment for malaria and autoimmune diseases. HCQ gained widespread popularity in the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic when clinical studies showed that it had significant in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2, which provided the rationale for its use in the treatment and prevention of COVID-19 infection.
It was the first drug that was authorized for emergency use by the FDA during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, On June 15, 2020, because of accumulating harmful data, the FDA revoked the emergency authorization use of HCQ as a COVID-19 treatment.
Randomized controlled trials showed that patients treated with HCQ experienced a longer hospital stay with increase in mortality rates and increased likelihood of being placed on mechanical ventilation. In addition, studies revealed an increase in QT prolongation in patients treated with HCQ, especially when coadministered with azithromycin, which can lead to torsades de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, and sudden cardiac death.
The IDSA and National Institutes of Health, both recommend against the use of hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin to treat COVID-19 because the harms outweigh the benefits, even if high quality RCTs were to become available in the future.
Other drugs
There have been experimental studies on other medications for the treatment of COVID-19, including losartan, amlodipine, ivermectin, famotidine, Anakinra, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as ibrutinib, and Janus kinase inhibitors, such as tofacitinib. Additionally, a few supplements such as vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc have been used in both inpatient and outpatient settings for COVID-19 treatment. Polyclonal antibodies are being investigated in phase 3 trials. However, the data is insufficient, and the effectiveness of these drugs is unknown. The COVID-19 treatment guidelines panel recommends against the use of these treatment modalities.
Dr Tiyouh is an infectious diseases physician at Keystone Health in Chambersburg, Pa. Dr. Tenneti completed medical school at Vydehi Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre in Karnataka, India, and is interested in pursuing internal medicine residency. Dr. Tirupathi is the medical director of Keystone Infectious Diseases/HIV in Chambersburg, Pa., and currently chair of infection prevention at Wellspan Chambersburg Hospital and Waynesboro (Pa.) Hospitals. Dr. Palabindala is hospital medicine division chief at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, and a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Sources
Goldman JD et al. Remdesivir for 5 or 10 Days in Patients with Severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2015301.
Beigel JH et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 - Final Report. N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct 8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Wang Y et al. Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet. 2020 May 16;395(10236):1569-78.
National Institutes of Health. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines.
Infectious Diseases Society of America. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19.
Joyner et al. Early safety indicators of COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 5000 patients. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(9):4791-7.
Luo P et al. Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: A single center experience. J Med Virol. 2020 Jul;92(7):814-8.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Healthcare Workers: Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19).
University of Washington. COVID-19 Treatments: Prescribing Information, Clinical Studies, and Slide Decks.
United States adds nearly 74,000 more children with COVID-19
The new weekly high for COVID-19 cases in children announced last week has been surpassed already, as the United States experienced almost 74,000 new pediatric cases for the week ending Nov. 5, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
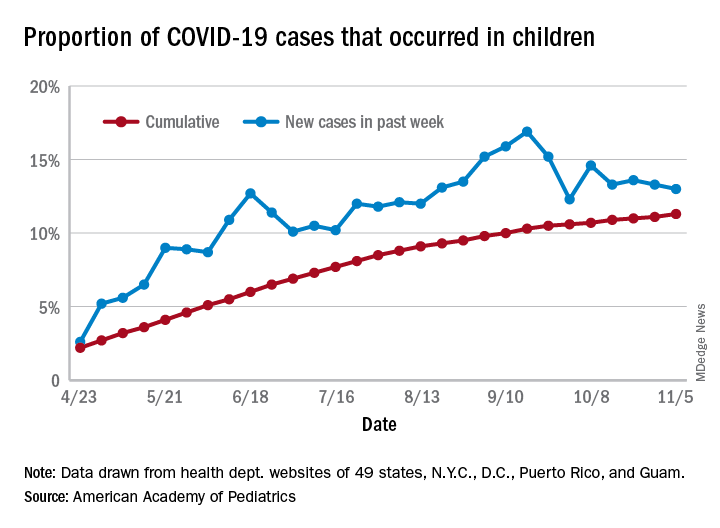
The total number of COVID-19 cases in children is now 927,518 in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report.
Cumulatively, children represent 11.3% of all COVID-19 cases in those jurisdictions, up from 11.1% a week ago. For just the past week, those 73,883 children represent 13.0% of the 567,672 new cases reported among all ages. That proportion peaked at 16.9% in mid-September, the AAP/CHA data show.
Dropping down to the state level, cumulative proportions as of Nov. 5 range from 5.2% in New Jersey to 23.3% in Wyoming, with 11 other states over 15%. California has had more cases, 100,856, than any other state, and Vermont the fewest at 329, the AAP and CHA said.
The national rate per 100,000 children is now 1,232, up from 1,134 the previous week and more than doubled since mid-August (582.2 per 100,000 on Aug. 20). North Dakota’s rate of 3,990 per 100,000 children is the highest of any state (South Dakota is next at 2,779), while Vermont is again the lowest at 245 per 100,000, based on data collected from state health department websites.
Two COVID-19–related deaths in children were reported during the week ending Nov. 5, bringing the total to 123 but leaving the overall proportion of deaths in children unchanged at 0.06% of all deaths. Texas has reported the most COVID-19 deaths in children with 29, while 15 states have recorded no deaths so far (mortality data in children reported by 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA said.
The new weekly high for COVID-19 cases in children announced last week has been surpassed already, as the United States experienced almost 74,000 new pediatric cases for the week ending Nov. 5, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of COVID-19 cases in children is now 927,518 in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report.
Cumulatively, children represent 11.3% of all COVID-19 cases in those jurisdictions, up from 11.1% a week ago. For just the past week, those 73,883 children represent 13.0% of the 567,672 new cases reported among all ages. That proportion peaked at 16.9% in mid-September, the AAP/CHA data show.
Dropping down to the state level, cumulative proportions as of Nov. 5 range from 5.2% in New Jersey to 23.3% in Wyoming, with 11 other states over 15%. California has had more cases, 100,856, than any other state, and Vermont the fewest at 329, the AAP and CHA said.
The national rate per 100,000 children is now 1,232, up from 1,134 the previous week and more than doubled since mid-August (582.2 per 100,000 on Aug. 20). North Dakota’s rate of 3,990 per 100,000 children is the highest of any state (South Dakota is next at 2,779), while Vermont is again the lowest at 245 per 100,000, based on data collected from state health department websites.
Two COVID-19–related deaths in children were reported during the week ending Nov. 5, bringing the total to 123 but leaving the overall proportion of deaths in children unchanged at 0.06% of all deaths. Texas has reported the most COVID-19 deaths in children with 29, while 15 states have recorded no deaths so far (mortality data in children reported by 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA said.
The new weekly high for COVID-19 cases in children announced last week has been surpassed already, as the United States experienced almost 74,000 new pediatric cases for the week ending Nov. 5, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of COVID-19 cases in children is now 927,518 in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report.
Cumulatively, children represent 11.3% of all COVID-19 cases in those jurisdictions, up from 11.1% a week ago. For just the past week, those 73,883 children represent 13.0% of the 567,672 new cases reported among all ages. That proportion peaked at 16.9% in mid-September, the AAP/CHA data show.
Dropping down to the state level, cumulative proportions as of Nov. 5 range from 5.2% in New Jersey to 23.3% in Wyoming, with 11 other states over 15%. California has had more cases, 100,856, than any other state, and Vermont the fewest at 329, the AAP and CHA said.
The national rate per 100,000 children is now 1,232, up from 1,134 the previous week and more than doubled since mid-August (582.2 per 100,000 on Aug. 20). North Dakota’s rate of 3,990 per 100,000 children is the highest of any state (South Dakota is next at 2,779), while Vermont is again the lowest at 245 per 100,000, based on data collected from state health department websites.
Two COVID-19–related deaths in children were reported during the week ending Nov. 5, bringing the total to 123 but leaving the overall proportion of deaths in children unchanged at 0.06% of all deaths. Texas has reported the most COVID-19 deaths in children with 29, while 15 states have recorded no deaths so far (mortality data in children reported by 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA said.
Infectious disease is an increasing threat from climate change
“I would argue that the most important reason to care about climate change is because of our children,” Saul Hymes, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year.
“Being able to point out to people how climate change harms the health of their children and affects their children’s risk of infections is a particularly effective argument to make,” said Dr. Hymes, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
Rachel Boykan, MD, a pediatrician at the university, found Dr. Hymes’ presentation excellent and highly relevant to issues all health care workers treating children face, even beyond infectious disease.
“It was data focused but also understandable for a broad audience,” Dr. Boykan, who was not involved in the presentation, said in an interview. “He explained the science of climate change in a way that all physicians, but especially pediatricians, would find relevant. I suspect if people who were listening didn’t already prioritize the issues of climate change, they certainly did after hearing the talk.”
She also appreciated that Dr. Hymes addressed how climate change affects everyone in both their professional and personal lives.
“We need to be prepared to address the clinical issues that ensue after a natural disaster, and we need to be advocates for change so that we can slow down the climate changes we are all dealing with,” said Dr. Boykan, adding that the presentation was also inspiring. “He presented many different viewpoints and many ways to be involved and to be an advocate. I would think that a good number of people who were there would be energized to do something differently to combat climate change.”
The multitudinous impacts of climate change
The impact of climate change on human health is broad and far-reaching, Dr. Hymes said. It doesn’t require much imagination to recognize that rising global temperatures can lead to prolonged extreme heat waves that can cause heat-related deaths and illnesses. But other effects can be more gradual or subtle. Changes in outdoor air quality can affect weather patterns, pollen counts, and air pollution that can increase risk of asthma, allergies, as well as acute and chronic respiratory and cardiovascular disease.
Sea level rise, more frequent and severe hurricanes, storm surges, and extreme precipitation all can lead to contaminated water and destruction of essential infrastructure. In addition to drowning and injuries from the storms themselves, these changes have mental health consequences, and can lead to gastrointestinal and other illnesses, including water-borne infectious disease. The distribution and prevalence of vector-borne diseases also will shift with changes in temperature, precipitation, and other weather patterns.
Distribution, prevalence of vector-borne diseases shift with climate change
One of the most common bacteria transmitted by vectors in the United States is Borrelia burgdorferi, the cause of Lyme disease. Transmitted by deer ticks, Lyme disease is listed by the Environmental Protection Agency as an indicator of climate change’s impact on human health and is becoming more common every year. Cases doubled from 1990 to 2014, from 4 to 8 cases per 100,000 people.
Increases were most dramatic in the Northeast, where Lyme disease is endemic. States such as Maine, Vermont, and New Hampshire all saw increases of 80-100 more cases per 100,000 people. Evidence now shows that Lyme disease is moving north as the climate warms. Toronto, for example, has seen more than a 400% increase in cases in less than a decade, from 128 cases per 100,000 people in 2009 to 700 cases per 100,000 in 2015.
“It’s a known phenomenon that climate change affects more northerly latitudes disproportionately to more than southerly latitudes,” Dr. Hymes said. He shared a 2013 study providing evidence that climate change is expanding the range of Lyme disease. Even when controlling for other confounding factors, the research found that areas being warmed proportionately more by climate change also are experiencing greater Lyme incidence. While Lyme cases declined in several Western and Deep South states, it significantly increased in nearly every Northeast state as well as Idaho, Arizona, and states in the northern Midwest near the Great Lakes.
“We find that this impact of climate change on the movement of vectors like ticks affects more than just Lyme disease,” Dr. Hymes said. Amblyomma americanum, the Lone Star tick, has historically been restricted to the southern United States but is now found further north, even up to New England. It carries bacteria that can cause multiple illnesses, including ehrlichiosis, heartland virus, and tularemia.
An alpha-gal meat allergy associated with this tick can lead to anaphylaxis about 6 hours after a person eats red meat or pork. Prevalence of this allergy, first reported in Georgia in 1989-1991, has been increasing and moving further north, and the Lone Star tick is a particularly heat-tolerant and heat-loving tick.
Climate change also affects how long during the year people are at risk. Lyme disease, for example, typically lasted from April/May to October, when ticks then hibernated during the cold weather. But the warming climate has expanded Lyme season: Local Lyme cases have begun occurring into November through January on Long Island over the past 5 years.
The impact of seasonal changes on infectious diseases overall is difficult to predict. The seasons for cold weather diseases such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, for example, may become shorter or milder while viruses more common in the summer, such as enteroviruses, may become a risk year-round.
Natural disasters pose multiple risks
Natural disasters can pose immediate dangers to families and have a significant impact on mental health, but that’s not their only potential impact.
“Severe weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes are well established in the climate change literature as an effect of increased temperatures and more volatile weather systems, but they also have a significant effect on infectious diseases and on children in particular,” Dr. Hymes said. “Hurricanes and flash floods can cause increases in infectious disease outbreaks through a variety of different ways.”
They can bring saltwater, freshwater, and sometimes soil organisms into the food and water supplies, and lead to sewage contamination from overloaded sewers, overflowing storm drains, and loss of power or pumps. Displaced animal vectors, such as rats, can lead to spread of other diseases, such as plague, hantavirus, typhus, and rabies.
Examples of saltwater organisms include Vibrio, Aeromonas, and Mycobacterium marinum, all of which can cause infections in wounds and/or diarrheal illness or bacteremia. Similarly, organisms from freshwater and soil that can cause serious illness or death include Aeromonas, Pseudomonas, Amebiasis, Giardia, and Legionella. Without access to clean water, or with contamination from overflowing sewage, cryptosporidium, Escherichia coli, salmonella, typhoid, norovirus, hepatitis A and E, and even cholera can also become problems as well.
In Houston following Hurricane Harvey, for example, cellulitis cases doubled and included infections from organisms different from the usual suspects. Scrapes and cuts that occurred during the storm also festered sooner.
Cases of disease linked to Hurricane Katrina in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report included 6 cases of cholera, 17 cases of other vibrio – including five that resulted in death – and reported cases of norovirus, Escherichia coli, salmonella, and influenza and pneumonia from overcrowding of evacuees.
You can help in a variety of ways
You can play several key roles as the world’s climate changes, starting with preparing for the changes. You should familiarize themselves with new and emerging infections, or those that have been around a while but not seen in your areas, such as Lyme, Zika, and Dengue.
“If you haven’t seen them already, you likely will due to movements of vector-borne infections that can occur due to climate change,” Dr. Hymes said. “You also want to expect the usual common diseases, but maybe at unsuspected times,” he added. “If you have a pediatric patient who looks like they have Coxsackie virus but it’s February, if it’s been a warm February, it may very well be Coxsackie virus.”
Following natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes and tornadoes, consider who your patients are. If they’re evacuees, are they living in overcrowded conditions? Do they have access to clean water? If not, explain the need to boil water if they can, or to use iodine tablets or a portable pump filter. Consider that some infections may involve unexpected or odd organisms, such as legionella pneumonia or vibrio cellulitis, and contact your local infectious disease doctor as needed.
You also can make personal lifestyle changes that, while small, can add up in the aggregate in reducing carbon footprints, such as purchasing an electric or hybrid car and converting their homes to solar power.
“For very little money, you can purchase carbon offsets,” Dr. Hymes said, such as $10-$15 a month for wind power offsets with home electricity or $5-$10 a month for car or plane travel.
“But really, the most important thing we can do as pediatricians is educate,” Dr. Hymes said. “Taking opportunities every day in your office to educate your patients and educate your colleagues about the importance of climate change in our patients’ health and our own children’s health is super, super important.”
Dr. Hymes and Dr. Boykan had no relevant financial disclosures.
“I would argue that the most important reason to care about climate change is because of our children,” Saul Hymes, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year.
“Being able to point out to people how climate change harms the health of their children and affects their children’s risk of infections is a particularly effective argument to make,” said Dr. Hymes, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
Rachel Boykan, MD, a pediatrician at the university, found Dr. Hymes’ presentation excellent and highly relevant to issues all health care workers treating children face, even beyond infectious disease.
“It was data focused but also understandable for a broad audience,” Dr. Boykan, who was not involved in the presentation, said in an interview. “He explained the science of climate change in a way that all physicians, but especially pediatricians, would find relevant. I suspect if people who were listening didn’t already prioritize the issues of climate change, they certainly did after hearing the talk.”
She also appreciated that Dr. Hymes addressed how climate change affects everyone in both their professional and personal lives.
“We need to be prepared to address the clinical issues that ensue after a natural disaster, and we need to be advocates for change so that we can slow down the climate changes we are all dealing with,” said Dr. Boykan, adding that the presentation was also inspiring. “He presented many different viewpoints and many ways to be involved and to be an advocate. I would think that a good number of people who were there would be energized to do something differently to combat climate change.”
The multitudinous impacts of climate change
The impact of climate change on human health is broad and far-reaching, Dr. Hymes said. It doesn’t require much imagination to recognize that rising global temperatures can lead to prolonged extreme heat waves that can cause heat-related deaths and illnesses. But other effects can be more gradual or subtle. Changes in outdoor air quality can affect weather patterns, pollen counts, and air pollution that can increase risk of asthma, allergies, as well as acute and chronic respiratory and cardiovascular disease.
Sea level rise, more frequent and severe hurricanes, storm surges, and extreme precipitation all can lead to contaminated water and destruction of essential infrastructure. In addition to drowning and injuries from the storms themselves, these changes have mental health consequences, and can lead to gastrointestinal and other illnesses, including water-borne infectious disease. The distribution and prevalence of vector-borne diseases also will shift with changes in temperature, precipitation, and other weather patterns.
Distribution, prevalence of vector-borne diseases shift with climate change
One of the most common bacteria transmitted by vectors in the United States is Borrelia burgdorferi, the cause of Lyme disease. Transmitted by deer ticks, Lyme disease is listed by the Environmental Protection Agency as an indicator of climate change’s impact on human health and is becoming more common every year. Cases doubled from 1990 to 2014, from 4 to 8 cases per 100,000 people.
Increases were most dramatic in the Northeast, where Lyme disease is endemic. States such as Maine, Vermont, and New Hampshire all saw increases of 80-100 more cases per 100,000 people. Evidence now shows that Lyme disease is moving north as the climate warms. Toronto, for example, has seen more than a 400% increase in cases in less than a decade, from 128 cases per 100,000 people in 2009 to 700 cases per 100,000 in 2015.
“It’s a known phenomenon that climate change affects more northerly latitudes disproportionately to more than southerly latitudes,” Dr. Hymes said. He shared a 2013 study providing evidence that climate change is expanding the range of Lyme disease. Even when controlling for other confounding factors, the research found that areas being warmed proportionately more by climate change also are experiencing greater Lyme incidence. While Lyme cases declined in several Western and Deep South states, it significantly increased in nearly every Northeast state as well as Idaho, Arizona, and states in the northern Midwest near the Great Lakes.
“We find that this impact of climate change on the movement of vectors like ticks affects more than just Lyme disease,” Dr. Hymes said. Amblyomma americanum, the Lone Star tick, has historically been restricted to the southern United States but is now found further north, even up to New England. It carries bacteria that can cause multiple illnesses, including ehrlichiosis, heartland virus, and tularemia.
An alpha-gal meat allergy associated with this tick can lead to anaphylaxis about 6 hours after a person eats red meat or pork. Prevalence of this allergy, first reported in Georgia in 1989-1991, has been increasing and moving further north, and the Lone Star tick is a particularly heat-tolerant and heat-loving tick.
Climate change also affects how long during the year people are at risk. Lyme disease, for example, typically lasted from April/May to October, when ticks then hibernated during the cold weather. But the warming climate has expanded Lyme season: Local Lyme cases have begun occurring into November through January on Long Island over the past 5 years.
The impact of seasonal changes on infectious diseases overall is difficult to predict. The seasons for cold weather diseases such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, for example, may become shorter or milder while viruses more common in the summer, such as enteroviruses, may become a risk year-round.
Natural disasters pose multiple risks
Natural disasters can pose immediate dangers to families and have a significant impact on mental health, but that’s not their only potential impact.
“Severe weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes are well established in the climate change literature as an effect of increased temperatures and more volatile weather systems, but they also have a significant effect on infectious diseases and on children in particular,” Dr. Hymes said. “Hurricanes and flash floods can cause increases in infectious disease outbreaks through a variety of different ways.”
They can bring saltwater, freshwater, and sometimes soil organisms into the food and water supplies, and lead to sewage contamination from overloaded sewers, overflowing storm drains, and loss of power or pumps. Displaced animal vectors, such as rats, can lead to spread of other diseases, such as plague, hantavirus, typhus, and rabies.
Examples of saltwater organisms include Vibrio, Aeromonas, and Mycobacterium marinum, all of which can cause infections in wounds and/or diarrheal illness or bacteremia. Similarly, organisms from freshwater and soil that can cause serious illness or death include Aeromonas, Pseudomonas, Amebiasis, Giardia, and Legionella. Without access to clean water, or with contamination from overflowing sewage, cryptosporidium, Escherichia coli, salmonella, typhoid, norovirus, hepatitis A and E, and even cholera can also become problems as well.
In Houston following Hurricane Harvey, for example, cellulitis cases doubled and included infections from organisms different from the usual suspects. Scrapes and cuts that occurred during the storm also festered sooner.
Cases of disease linked to Hurricane Katrina in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report included 6 cases of cholera, 17 cases of other vibrio – including five that resulted in death – and reported cases of norovirus, Escherichia coli, salmonella, and influenza and pneumonia from overcrowding of evacuees.
You can help in a variety of ways
You can play several key roles as the world’s climate changes, starting with preparing for the changes. You should familiarize themselves with new and emerging infections, or those that have been around a while but not seen in your areas, such as Lyme, Zika, and Dengue.
“If you haven’t seen them already, you likely will due to movements of vector-borne infections that can occur due to climate change,” Dr. Hymes said. “You also want to expect the usual common diseases, but maybe at unsuspected times,” he added. “If you have a pediatric patient who looks like they have Coxsackie virus but it’s February, if it’s been a warm February, it may very well be Coxsackie virus.”
Following natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes and tornadoes, consider who your patients are. If they’re evacuees, are they living in overcrowded conditions? Do they have access to clean water? If not, explain the need to boil water if they can, or to use iodine tablets or a portable pump filter. Consider that some infections may involve unexpected or odd organisms, such as legionella pneumonia or vibrio cellulitis, and contact your local infectious disease doctor as needed.
You also can make personal lifestyle changes that, while small, can add up in the aggregate in reducing carbon footprints, such as purchasing an electric or hybrid car and converting their homes to solar power.
“For very little money, you can purchase carbon offsets,” Dr. Hymes said, such as $10-$15 a month for wind power offsets with home electricity or $5-$10 a month for car or plane travel.
“But really, the most important thing we can do as pediatricians is educate,” Dr. Hymes said. “Taking opportunities every day in your office to educate your patients and educate your colleagues about the importance of climate change in our patients’ health and our own children’s health is super, super important.”
Dr. Hymes and Dr. Boykan had no relevant financial disclosures.
“I would argue that the most important reason to care about climate change is because of our children,” Saul Hymes, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year.
“Being able to point out to people how climate change harms the health of their children and affects their children’s risk of infections is a particularly effective argument to make,” said Dr. Hymes, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
Rachel Boykan, MD, a pediatrician at the university, found Dr. Hymes’ presentation excellent and highly relevant to issues all health care workers treating children face, even beyond infectious disease.
“It was data focused but also understandable for a broad audience,” Dr. Boykan, who was not involved in the presentation, said in an interview. “He explained the science of climate change in a way that all physicians, but especially pediatricians, would find relevant. I suspect if people who were listening didn’t already prioritize the issues of climate change, they certainly did after hearing the talk.”
She also appreciated that Dr. Hymes addressed how climate change affects everyone in both their professional and personal lives.
“We need to be prepared to address the clinical issues that ensue after a natural disaster, and we need to be advocates for change so that we can slow down the climate changes we are all dealing with,” said Dr. Boykan, adding that the presentation was also inspiring. “He presented many different viewpoints and many ways to be involved and to be an advocate. I would think that a good number of people who were there would be energized to do something differently to combat climate change.”
The multitudinous impacts of climate change
The impact of climate change on human health is broad and far-reaching, Dr. Hymes said. It doesn’t require much imagination to recognize that rising global temperatures can lead to prolonged extreme heat waves that can cause heat-related deaths and illnesses. But other effects can be more gradual or subtle. Changes in outdoor air quality can affect weather patterns, pollen counts, and air pollution that can increase risk of asthma, allergies, as well as acute and chronic respiratory and cardiovascular disease.
Sea level rise, more frequent and severe hurricanes, storm surges, and extreme precipitation all can lead to contaminated water and destruction of essential infrastructure. In addition to drowning and injuries from the storms themselves, these changes have mental health consequences, and can lead to gastrointestinal and other illnesses, including water-borne infectious disease. The distribution and prevalence of vector-borne diseases also will shift with changes in temperature, precipitation, and other weather patterns.
Distribution, prevalence of vector-borne diseases shift with climate change
One of the most common bacteria transmitted by vectors in the United States is Borrelia burgdorferi, the cause of Lyme disease. Transmitted by deer ticks, Lyme disease is listed by the Environmental Protection Agency as an indicator of climate change’s impact on human health and is becoming more common every year. Cases doubled from 1990 to 2014, from 4 to 8 cases per 100,000 people.
Increases were most dramatic in the Northeast, where Lyme disease is endemic. States such as Maine, Vermont, and New Hampshire all saw increases of 80-100 more cases per 100,000 people. Evidence now shows that Lyme disease is moving north as the climate warms. Toronto, for example, has seen more than a 400% increase in cases in less than a decade, from 128 cases per 100,000 people in 2009 to 700 cases per 100,000 in 2015.
“It’s a known phenomenon that climate change affects more northerly latitudes disproportionately to more than southerly latitudes,” Dr. Hymes said. He shared a 2013 study providing evidence that climate change is expanding the range of Lyme disease. Even when controlling for other confounding factors, the research found that areas being warmed proportionately more by climate change also are experiencing greater Lyme incidence. While Lyme cases declined in several Western and Deep South states, it significantly increased in nearly every Northeast state as well as Idaho, Arizona, and states in the northern Midwest near the Great Lakes.
“We find that this impact of climate change on the movement of vectors like ticks affects more than just Lyme disease,” Dr. Hymes said. Amblyomma americanum, the Lone Star tick, has historically been restricted to the southern United States but is now found further north, even up to New England. It carries bacteria that can cause multiple illnesses, including ehrlichiosis, heartland virus, and tularemia.
An alpha-gal meat allergy associated with this tick can lead to anaphylaxis about 6 hours after a person eats red meat or pork. Prevalence of this allergy, first reported in Georgia in 1989-1991, has been increasing and moving further north, and the Lone Star tick is a particularly heat-tolerant and heat-loving tick.
Climate change also affects how long during the year people are at risk. Lyme disease, for example, typically lasted from April/May to October, when ticks then hibernated during the cold weather. But the warming climate has expanded Lyme season: Local Lyme cases have begun occurring into November through January on Long Island over the past 5 years.
The impact of seasonal changes on infectious diseases overall is difficult to predict. The seasons for cold weather diseases such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, for example, may become shorter or milder while viruses more common in the summer, such as enteroviruses, may become a risk year-round.
Natural disasters pose multiple risks
Natural disasters can pose immediate dangers to families and have a significant impact on mental health, but that’s not their only potential impact.
“Severe weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes are well established in the climate change literature as an effect of increased temperatures and more volatile weather systems, but they also have a significant effect on infectious diseases and on children in particular,” Dr. Hymes said. “Hurricanes and flash floods can cause increases in infectious disease outbreaks through a variety of different ways.”
They can bring saltwater, freshwater, and sometimes soil organisms into the food and water supplies, and lead to sewage contamination from overloaded sewers, overflowing storm drains, and loss of power or pumps. Displaced animal vectors, such as rats, can lead to spread of other diseases, such as plague, hantavirus, typhus, and rabies.
Examples of saltwater organisms include Vibrio, Aeromonas, and Mycobacterium marinum, all of which can cause infections in wounds and/or diarrheal illness or bacteremia. Similarly, organisms from freshwater and soil that can cause serious illness or death include Aeromonas, Pseudomonas, Amebiasis, Giardia, and Legionella. Without access to clean water, or with contamination from overflowing sewage, cryptosporidium, Escherichia coli, salmonella, typhoid, norovirus, hepatitis A and E, and even cholera can also become problems as well.
In Houston following Hurricane Harvey, for example, cellulitis cases doubled and included infections from organisms different from the usual suspects. Scrapes and cuts that occurred during the storm also festered sooner.
Cases of disease linked to Hurricane Katrina in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report included 6 cases of cholera, 17 cases of other vibrio – including five that resulted in death – and reported cases of norovirus, Escherichia coli, salmonella, and influenza and pneumonia from overcrowding of evacuees.
You can help in a variety of ways
You can play several key roles as the world’s climate changes, starting with preparing for the changes. You should familiarize themselves with new and emerging infections, or those that have been around a while but not seen in your areas, such as Lyme, Zika, and Dengue.
“If you haven’t seen them already, you likely will due to movements of vector-borne infections that can occur due to climate change,” Dr. Hymes said. “You also want to expect the usual common diseases, but maybe at unsuspected times,” he added. “If you have a pediatric patient who looks like they have Coxsackie virus but it’s February, if it’s been a warm February, it may very well be Coxsackie virus.”
Following natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes and tornadoes, consider who your patients are. If they’re evacuees, are they living in overcrowded conditions? Do they have access to clean water? If not, explain the need to boil water if they can, or to use iodine tablets or a portable pump filter. Consider that some infections may involve unexpected or odd organisms, such as legionella pneumonia or vibrio cellulitis, and contact your local infectious disease doctor as needed.
You also can make personal lifestyle changes that, while small, can add up in the aggregate in reducing carbon footprints, such as purchasing an electric or hybrid car and converting their homes to solar power.
“For very little money, you can purchase carbon offsets,” Dr. Hymes said, such as $10-$15 a month for wind power offsets with home electricity or $5-$10 a month for car or plane travel.
“But really, the most important thing we can do as pediatricians is educate,” Dr. Hymes said. “Taking opportunities every day in your office to educate your patients and educate your colleagues about the importance of climate change in our patients’ health and our own children’s health is super, super important.”
Dr. Hymes and Dr. Boykan had no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM AAP 2020