User login
Pandemic pushed death rates to historic highs
Excess mortality is a way of quantifying the impact of a pandemic, based on overall mortality from nonpandemic periods. Mortality data over long periods of time are not available for many countries, but Switzerland, Sweden, and Spain have accumulated death count data for an uninterrupted period of more than 100 years.
In a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, Kaspar Staub, PhD, of the University of Zurich led a team of researchers in reviewing data on monthly excess deaths from all causes for Switzerland, Sweden, and Spain for 2020 to 2021. Dr. Staub and colleagues also compared these numbers to other pandemic and nonpandemic periods since the end of the 19th century. The starting years were 1877 for Switzerland, 1851 for Sweden, and 1908 for Spain.
The researchers collected data for monthly all-cause deaths from the statistical offices of each country and determined excess mortality by comparing these numbers to population size and age structure.
They found that 2020 showed the highest number of excess deaths since 1918, with relative excess of deaths of 12.5% in Switzerland, 8.5% in Sweden, and 17.3 % in Spain.
To put it another way, the number of excess deaths per 100,000 people was 100 for Switzerland, 75 for Sweden, and 155 for Spain.
“Our findings suggest that the pandemic led to the second-largest mortality disaster driven by a viral infection in more than 100 years in the three countries we studied, second only to the 1918 influenza pandemic,” the researchers wrote.
They explained that the excess mortality for the year 1918 was six to seven times higher than the 2020 numbers, but that the 2020 numbers might have been higher without the strong public health interventions taken worldwide to mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Early estimates suggest that vaccination prevented approximately 470,000 deaths in persons aged 60 years or older across 33 European countries between December 2019 and November 2021,” they wrote. However, because the COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing, “a more conclusive assessment will have to wait,” they added.
The 2020 numbers also were higher than most mortality rates since 1918, including peak years of previous influenza pandemics that occurred in 1957, 1968, 1977, and, most recently, the swine flu pandemic of 2009 which was caused by a novel strain of the H1N1 influenza virus.
The study findings had some limitations. For example, only three countries were included. Also, monthly death numbers according to sex, age, and cause of death were available only for the past 60 years, and data from years before the 20th century may not be reliable, the researchers said.
The new study does not account for the long-term effects of patients suffering from long COVID, they noted.
Study findings support strong public health response
“With the COVID-19 pandemic ongoing, this study reinforces the historic magnitude of the problem in terms of mortality and could add to the justification for ongoing public health measures such as vaccination drives and vaccine mandates to curb deaths,” said Suman Pal, MD, an internal medicine physician at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, in an interview.
“The results are surprising because when we view the rapid advancement in medical science over the last few decades, which have led to a decline in mortality from many previously fatal diseases, the scale of excess mortality from COVID-19 seems to have offset many such gains in the past 2 years.”
Prior studies of United States mortality data have estimated that excess deaths in the United States in 2020 exceeded the deaths attributed to COVID-19, said Dr. Pal. “The findings of this study could help clinicians in their discussion of the need for COVID-19 prevention measures with their patients” and inform discussions between doctors and patients about prevention strategies, he explained.
“Emphasizing that this pandemic is the second-largest cause of death due to a viral infection in a century could help patients understand the need for public health measures that may be viewed as unprecedented, such as government-imposed lockdowns, contact tracing, mask requirements, restrictions on travel, and vaccine mandates,” Dr. Pal noted. Better understanding of the evidence behind such measures may decrease the public’s resistance to following them, he added.As for additional research, “region-specific analysis of excess deaths may help estimate the impact of COVID-19 better, especially in regions where data reporting may be unreliable.”
Dr. F. Perry Wilson's take on study
“All-cause mortality is a key metric to assess the impact of the pandemic, because each death is treated equally,” said F. Perry Wilson, MD, of Yale University, in an interview. “With this type of analysis, there is no vague definition of a death from COVID or with COVID,” he explained. “A death is a death, and more deaths than expected is, of course, a bad thing. These analyses give a high-level view of the true human cost of the pandemic,” he said.
Dr. Wilson said he was not surprised by the findings. “There have been multiple studies, across multiple countries including the United States, which show similar findings—that observed deaths during this pandemic are substantially higher than expected,” he said. The current study findings are unique in that they compare the current pandemic to death rates in a nearly unbroken chain into the last century using data that only a few countries can provide, he noted.
The mortality data are “quite similar to what we see in the United States, with the exception that Spain was particularly hard-hit in the first COVID-19 wave in April 2020, said Dr. Wilson. By contrast, “the U.S. had substantially more excess deaths in the recent Delta wave, presumably due to lower vaccination uptake,” he added.
The current study is important for clinicians and their patients, said Dr. Wilson. “Data like these can help cut through some of the misinformation, such as the idea that only people who would have died anyway die of COVID, or that COVID is not severe,” he emphasized. “Overall death data are quite clear that far more people, millions more people, died over the last 22 months than could possibly be explained except by a global-level mortality event,” he said.
“One thing this study reminds us of is the value of high-quality data,” said Dr. Wilson. “Few countries have near complete vital statistics records on their entire populations and these can be so crucial to understand the true impact of pandemics and other disasters,” he explained. Of course, mortality data also serve as a reminder “that COVID is a serious disease: a once-in-a-century (we hope) pandemic,” he added.
The current study showed that excess death rates were similar, but not the same, from country to country, Dr. Wilson noted. “Moving forward, we need to learn what factors, from vaccination to social distancing strategies,” saved lives around the world,” he said.
The study was supported by the Foundation for Research in Science and the Humanities at the University of Zurich, the Swiss National Science Foundation, and the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. The researchers, Dr. Pal, and Dr. Wilson had no financial conflicts.
*This article was updated on 2/1/2022.
Excess mortality is a way of quantifying the impact of a pandemic, based on overall mortality from nonpandemic periods. Mortality data over long periods of time are not available for many countries, but Switzerland, Sweden, and Spain have accumulated death count data for an uninterrupted period of more than 100 years.
In a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, Kaspar Staub, PhD, of the University of Zurich led a team of researchers in reviewing data on monthly excess deaths from all causes for Switzerland, Sweden, and Spain for 2020 to 2021. Dr. Staub and colleagues also compared these numbers to other pandemic and nonpandemic periods since the end of the 19th century. The starting years were 1877 for Switzerland, 1851 for Sweden, and 1908 for Spain.
The researchers collected data for monthly all-cause deaths from the statistical offices of each country and determined excess mortality by comparing these numbers to population size and age structure.
They found that 2020 showed the highest number of excess deaths since 1918, with relative excess of deaths of 12.5% in Switzerland, 8.5% in Sweden, and 17.3 % in Spain.
To put it another way, the number of excess deaths per 100,000 people was 100 for Switzerland, 75 for Sweden, and 155 for Spain.
“Our findings suggest that the pandemic led to the second-largest mortality disaster driven by a viral infection in more than 100 years in the three countries we studied, second only to the 1918 influenza pandemic,” the researchers wrote.
They explained that the excess mortality for the year 1918 was six to seven times higher than the 2020 numbers, but that the 2020 numbers might have been higher without the strong public health interventions taken worldwide to mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Early estimates suggest that vaccination prevented approximately 470,000 deaths in persons aged 60 years or older across 33 European countries between December 2019 and November 2021,” they wrote. However, because the COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing, “a more conclusive assessment will have to wait,” they added.
The 2020 numbers also were higher than most mortality rates since 1918, including peak years of previous influenza pandemics that occurred in 1957, 1968, 1977, and, most recently, the swine flu pandemic of 2009 which was caused by a novel strain of the H1N1 influenza virus.
The study findings had some limitations. For example, only three countries were included. Also, monthly death numbers according to sex, age, and cause of death were available only for the past 60 years, and data from years before the 20th century may not be reliable, the researchers said.
The new study does not account for the long-term effects of patients suffering from long COVID, they noted.
Study findings support strong public health response
“With the COVID-19 pandemic ongoing, this study reinforces the historic magnitude of the problem in terms of mortality and could add to the justification for ongoing public health measures such as vaccination drives and vaccine mandates to curb deaths,” said Suman Pal, MD, an internal medicine physician at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, in an interview.
“The results are surprising because when we view the rapid advancement in medical science over the last few decades, which have led to a decline in mortality from many previously fatal diseases, the scale of excess mortality from COVID-19 seems to have offset many such gains in the past 2 years.”
Prior studies of United States mortality data have estimated that excess deaths in the United States in 2020 exceeded the deaths attributed to COVID-19, said Dr. Pal. “The findings of this study could help clinicians in their discussion of the need for COVID-19 prevention measures with their patients” and inform discussions between doctors and patients about prevention strategies, he explained.
“Emphasizing that this pandemic is the second-largest cause of death due to a viral infection in a century could help patients understand the need for public health measures that may be viewed as unprecedented, such as government-imposed lockdowns, contact tracing, mask requirements, restrictions on travel, and vaccine mandates,” Dr. Pal noted. Better understanding of the evidence behind such measures may decrease the public’s resistance to following them, he added.As for additional research, “region-specific analysis of excess deaths may help estimate the impact of COVID-19 better, especially in regions where data reporting may be unreliable.”
Dr. F. Perry Wilson's take on study
“All-cause mortality is a key metric to assess the impact of the pandemic, because each death is treated equally,” said F. Perry Wilson, MD, of Yale University, in an interview. “With this type of analysis, there is no vague definition of a death from COVID or with COVID,” he explained. “A death is a death, and more deaths than expected is, of course, a bad thing. These analyses give a high-level view of the true human cost of the pandemic,” he said.
Dr. Wilson said he was not surprised by the findings. “There have been multiple studies, across multiple countries including the United States, which show similar findings—that observed deaths during this pandemic are substantially higher than expected,” he said. The current study findings are unique in that they compare the current pandemic to death rates in a nearly unbroken chain into the last century using data that only a few countries can provide, he noted.
The mortality data are “quite similar to what we see in the United States, with the exception that Spain was particularly hard-hit in the first COVID-19 wave in April 2020, said Dr. Wilson. By contrast, “the U.S. had substantially more excess deaths in the recent Delta wave, presumably due to lower vaccination uptake,” he added.
The current study is important for clinicians and their patients, said Dr. Wilson. “Data like these can help cut through some of the misinformation, such as the idea that only people who would have died anyway die of COVID, or that COVID is not severe,” he emphasized. “Overall death data are quite clear that far more people, millions more people, died over the last 22 months than could possibly be explained except by a global-level mortality event,” he said.
“One thing this study reminds us of is the value of high-quality data,” said Dr. Wilson. “Few countries have near complete vital statistics records on their entire populations and these can be so crucial to understand the true impact of pandemics and other disasters,” he explained. Of course, mortality data also serve as a reminder “that COVID is a serious disease: a once-in-a-century (we hope) pandemic,” he added.
The current study showed that excess death rates were similar, but not the same, from country to country, Dr. Wilson noted. “Moving forward, we need to learn what factors, from vaccination to social distancing strategies,” saved lives around the world,” he said.
The study was supported by the Foundation for Research in Science and the Humanities at the University of Zurich, the Swiss National Science Foundation, and the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. The researchers, Dr. Pal, and Dr. Wilson had no financial conflicts.
*This article was updated on 2/1/2022.
Excess mortality is a way of quantifying the impact of a pandemic, based on overall mortality from nonpandemic periods. Mortality data over long periods of time are not available for many countries, but Switzerland, Sweden, and Spain have accumulated death count data for an uninterrupted period of more than 100 years.
In a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, Kaspar Staub, PhD, of the University of Zurich led a team of researchers in reviewing data on monthly excess deaths from all causes for Switzerland, Sweden, and Spain for 2020 to 2021. Dr. Staub and colleagues also compared these numbers to other pandemic and nonpandemic periods since the end of the 19th century. The starting years were 1877 for Switzerland, 1851 for Sweden, and 1908 for Spain.
The researchers collected data for monthly all-cause deaths from the statistical offices of each country and determined excess mortality by comparing these numbers to population size and age structure.
They found that 2020 showed the highest number of excess deaths since 1918, with relative excess of deaths of 12.5% in Switzerland, 8.5% in Sweden, and 17.3 % in Spain.
To put it another way, the number of excess deaths per 100,000 people was 100 for Switzerland, 75 for Sweden, and 155 for Spain.
“Our findings suggest that the pandemic led to the second-largest mortality disaster driven by a viral infection in more than 100 years in the three countries we studied, second only to the 1918 influenza pandemic,” the researchers wrote.
They explained that the excess mortality for the year 1918 was six to seven times higher than the 2020 numbers, but that the 2020 numbers might have been higher without the strong public health interventions taken worldwide to mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Early estimates suggest that vaccination prevented approximately 470,000 deaths in persons aged 60 years or older across 33 European countries between December 2019 and November 2021,” they wrote. However, because the COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing, “a more conclusive assessment will have to wait,” they added.
The 2020 numbers also were higher than most mortality rates since 1918, including peak years of previous influenza pandemics that occurred in 1957, 1968, 1977, and, most recently, the swine flu pandemic of 2009 which was caused by a novel strain of the H1N1 influenza virus.
The study findings had some limitations. For example, only three countries were included. Also, monthly death numbers according to sex, age, and cause of death were available only for the past 60 years, and data from years before the 20th century may not be reliable, the researchers said.
The new study does not account for the long-term effects of patients suffering from long COVID, they noted.
Study findings support strong public health response
“With the COVID-19 pandemic ongoing, this study reinforces the historic magnitude of the problem in terms of mortality and could add to the justification for ongoing public health measures such as vaccination drives and vaccine mandates to curb deaths,” said Suman Pal, MD, an internal medicine physician at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, in an interview.
“The results are surprising because when we view the rapid advancement in medical science over the last few decades, which have led to a decline in mortality from many previously fatal diseases, the scale of excess mortality from COVID-19 seems to have offset many such gains in the past 2 years.”
Prior studies of United States mortality data have estimated that excess deaths in the United States in 2020 exceeded the deaths attributed to COVID-19, said Dr. Pal. “The findings of this study could help clinicians in their discussion of the need for COVID-19 prevention measures with their patients” and inform discussions between doctors and patients about prevention strategies, he explained.
“Emphasizing that this pandemic is the second-largest cause of death due to a viral infection in a century could help patients understand the need for public health measures that may be viewed as unprecedented, such as government-imposed lockdowns, contact tracing, mask requirements, restrictions on travel, and vaccine mandates,” Dr. Pal noted. Better understanding of the evidence behind such measures may decrease the public’s resistance to following them, he added.As for additional research, “region-specific analysis of excess deaths may help estimate the impact of COVID-19 better, especially in regions where data reporting may be unreliable.”
Dr. F. Perry Wilson's take on study
“All-cause mortality is a key metric to assess the impact of the pandemic, because each death is treated equally,” said F. Perry Wilson, MD, of Yale University, in an interview. “With this type of analysis, there is no vague definition of a death from COVID or with COVID,” he explained. “A death is a death, and more deaths than expected is, of course, a bad thing. These analyses give a high-level view of the true human cost of the pandemic,” he said.
Dr. Wilson said he was not surprised by the findings. “There have been multiple studies, across multiple countries including the United States, which show similar findings—that observed deaths during this pandemic are substantially higher than expected,” he said. The current study findings are unique in that they compare the current pandemic to death rates in a nearly unbroken chain into the last century using data that only a few countries can provide, he noted.
The mortality data are “quite similar to what we see in the United States, with the exception that Spain was particularly hard-hit in the first COVID-19 wave in April 2020, said Dr. Wilson. By contrast, “the U.S. had substantially more excess deaths in the recent Delta wave, presumably due to lower vaccination uptake,” he added.
The current study is important for clinicians and their patients, said Dr. Wilson. “Data like these can help cut through some of the misinformation, such as the idea that only people who would have died anyway die of COVID, or that COVID is not severe,” he emphasized. “Overall death data are quite clear that far more people, millions more people, died over the last 22 months than could possibly be explained except by a global-level mortality event,” he said.
“One thing this study reminds us of is the value of high-quality data,” said Dr. Wilson. “Few countries have near complete vital statistics records on their entire populations and these can be so crucial to understand the true impact of pandemics and other disasters,” he explained. Of course, mortality data also serve as a reminder “that COVID is a serious disease: a once-in-a-century (we hope) pandemic,” he added.
The current study showed that excess death rates were similar, but not the same, from country to country, Dr. Wilson noted. “Moving forward, we need to learn what factors, from vaccination to social distancing strategies,” saved lives around the world,” he said.
The study was supported by the Foundation for Research in Science and the Humanities at the University of Zurich, the Swiss National Science Foundation, and the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. The researchers, Dr. Pal, and Dr. Wilson had no financial conflicts.
*This article was updated on 2/1/2022.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Kids’ mask use linked with fewer childcare closings
Mask-wearing in childcare programs is linked with fewer COVID-19–related program closures, new data released suggest.
Researchers included 6,654 childcare professionals in a prospective, 1-year, longitudinal electronic survey study of home- and center-based childcare programs in all 50 states.
Findings by Thomas S. Murray, MD, PhD, with the department of pediatrics, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and coauthors, were published in JAMA Network Open on Jan. 28, 2022.
They found that mask-wearing from the May 22, 2020, baseline to June 8, 2020, was associated with a 13% reduction in program closures within the following year (adjusted relative risk, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.99). Continued mask-wearing throughout the 1-year follow-up was associated with a 14% reduction in program closures (aRR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.74-1.00).
The authors said the evidence supports current masking recommendation in younger children provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
They wrote: “This finding has important public health policy implications for families that rely on childcare to sustain employment.”
The benefits of masking in preventing COVID-19 transmission within kindergarten through 12th-grade classes are well documented. Masks are particularly important in areas where vaccinations are not widespread.
Masks can be worn safely by young children without harming respiratory function, studies have shown.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that the American Academy of Pediatrics has said there are no noteworthy effects on breathing function for most children.
“There’s been so much discussion about the contribution of masks to reducing the risk of COVID that it’s nice to have the data,” he said, adding that this is a relationship that has been difficult to study, but this analysis was able to make the connection with hard numbers.
“It’s an important outcome,” he said in an interview.
The authors pointed out there is evidence that school-age children can identify most emotions in masked faces.
They added that “2-year-old children recognize spoken words better through an opaque mask, compared with a clear face shield, suggesting verbal communication to infants is not harmed by face masks.”
Studies have shown that childhood infection with other respiratory viruses also decreased and asthma symptoms were not reported when preschool children wore masks and used other preventative steps.
The authors wrote that a potential reason for that may be that those who wear masks have less face touching, known to increase the spread of COVID-19.
Paloma Beamer, PhD, an engineer and exposure scientist at University of Arizona, Tucson, who also has a 3-year-old son who wears masks at his daycare center, said in an interview that she works closely with his school on training kids how to wear their masks because getting young children to keep them on and finding ones that fit is challenging.
“We need layered controls and protections in place at schools as much as possible,” she said, adding that the authors didn’t mention ventilation, but that’s another important component as well.
“We’re fortunate in Arizona that we are in an old school and the windows are open as much as possible,” she said.
She said this study shows that “masks are a great form of additional control.” Her son is on his third quarantine this month after three kids tested positive, she added.
She said: “I think these newer variants perhaps make the findings of this study more compelling and it will be interesting to see if the researchers do a follow-up study.”
Strengths of the study include that it utilized prospective data from a large national cohort of childcare professionals. Additionally, the retention rate was high at 1 year. And the self-reported information likely gives better information than looking at policies that may or may not be well followed.
Limitations include potential reporting bias because the self-reports were not independently confirmed. Also, family behavior outside childcare, such as social gatherings where masking is not enforced, also influence COVID-19 cases when children gather and may affect the numbers of closures.
Having the option of childcare centers benefits kids with in-person early education and social interactions with staff, the authors noted. The centers also help parents return to work without interruptions at home.
“Our findings support current national recommendations endorsed by many local and state governments for masking children 2 years and older in childcare programs when community COVID-19 transmission levels are elevated,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Schaffner said the results have implications outside of childcare centers and should be included in discussions of masking in schools and in the general public.
All phases of this study were supported by and coauthors report grants from the Andrew & Julie Klingenstein Family Fund, Esther A. & Joseph Klingenstein Fund, Heising-Simons Foundation, W.K. Kellogg Foundation, Foundation for Child Development, Early Educator Investment Collaborative, and Scholastic. The study was partially funded by the Yale Institute for Global Health. Dr. Schaffner and Dr. Beamer reported no relevant financial relationships.
Mask-wearing in childcare programs is linked with fewer COVID-19–related program closures, new data released suggest.
Researchers included 6,654 childcare professionals in a prospective, 1-year, longitudinal electronic survey study of home- and center-based childcare programs in all 50 states.
Findings by Thomas S. Murray, MD, PhD, with the department of pediatrics, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and coauthors, were published in JAMA Network Open on Jan. 28, 2022.
They found that mask-wearing from the May 22, 2020, baseline to June 8, 2020, was associated with a 13% reduction in program closures within the following year (adjusted relative risk, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.99). Continued mask-wearing throughout the 1-year follow-up was associated with a 14% reduction in program closures (aRR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.74-1.00).
The authors said the evidence supports current masking recommendation in younger children provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
They wrote: “This finding has important public health policy implications for families that rely on childcare to sustain employment.”
The benefits of masking in preventing COVID-19 transmission within kindergarten through 12th-grade classes are well documented. Masks are particularly important in areas where vaccinations are not widespread.
Masks can be worn safely by young children without harming respiratory function, studies have shown.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that the American Academy of Pediatrics has said there are no noteworthy effects on breathing function for most children.
“There’s been so much discussion about the contribution of masks to reducing the risk of COVID that it’s nice to have the data,” he said, adding that this is a relationship that has been difficult to study, but this analysis was able to make the connection with hard numbers.
“It’s an important outcome,” he said in an interview.
The authors pointed out there is evidence that school-age children can identify most emotions in masked faces.
They added that “2-year-old children recognize spoken words better through an opaque mask, compared with a clear face shield, suggesting verbal communication to infants is not harmed by face masks.”
Studies have shown that childhood infection with other respiratory viruses also decreased and asthma symptoms were not reported when preschool children wore masks and used other preventative steps.
The authors wrote that a potential reason for that may be that those who wear masks have less face touching, known to increase the spread of COVID-19.
Paloma Beamer, PhD, an engineer and exposure scientist at University of Arizona, Tucson, who also has a 3-year-old son who wears masks at his daycare center, said in an interview that she works closely with his school on training kids how to wear their masks because getting young children to keep them on and finding ones that fit is challenging.
“We need layered controls and protections in place at schools as much as possible,” she said, adding that the authors didn’t mention ventilation, but that’s another important component as well.
“We’re fortunate in Arizona that we are in an old school and the windows are open as much as possible,” she said.
She said this study shows that “masks are a great form of additional control.” Her son is on his third quarantine this month after three kids tested positive, she added.
She said: “I think these newer variants perhaps make the findings of this study more compelling and it will be interesting to see if the researchers do a follow-up study.”
Strengths of the study include that it utilized prospective data from a large national cohort of childcare professionals. Additionally, the retention rate was high at 1 year. And the self-reported information likely gives better information than looking at policies that may or may not be well followed.
Limitations include potential reporting bias because the self-reports were not independently confirmed. Also, family behavior outside childcare, such as social gatherings where masking is not enforced, also influence COVID-19 cases when children gather and may affect the numbers of closures.
Having the option of childcare centers benefits kids with in-person early education and social interactions with staff, the authors noted. The centers also help parents return to work without interruptions at home.
“Our findings support current national recommendations endorsed by many local and state governments for masking children 2 years and older in childcare programs when community COVID-19 transmission levels are elevated,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Schaffner said the results have implications outside of childcare centers and should be included in discussions of masking in schools and in the general public.
All phases of this study were supported by and coauthors report grants from the Andrew & Julie Klingenstein Family Fund, Esther A. & Joseph Klingenstein Fund, Heising-Simons Foundation, W.K. Kellogg Foundation, Foundation for Child Development, Early Educator Investment Collaborative, and Scholastic. The study was partially funded by the Yale Institute for Global Health. Dr. Schaffner and Dr. Beamer reported no relevant financial relationships.
Mask-wearing in childcare programs is linked with fewer COVID-19–related program closures, new data released suggest.
Researchers included 6,654 childcare professionals in a prospective, 1-year, longitudinal electronic survey study of home- and center-based childcare programs in all 50 states.
Findings by Thomas S. Murray, MD, PhD, with the department of pediatrics, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and coauthors, were published in JAMA Network Open on Jan. 28, 2022.
They found that mask-wearing from the May 22, 2020, baseline to June 8, 2020, was associated with a 13% reduction in program closures within the following year (adjusted relative risk, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.99). Continued mask-wearing throughout the 1-year follow-up was associated with a 14% reduction in program closures (aRR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.74-1.00).
The authors said the evidence supports current masking recommendation in younger children provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
They wrote: “This finding has important public health policy implications for families that rely on childcare to sustain employment.”
The benefits of masking in preventing COVID-19 transmission within kindergarten through 12th-grade classes are well documented. Masks are particularly important in areas where vaccinations are not widespread.
Masks can be worn safely by young children without harming respiratory function, studies have shown.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that the American Academy of Pediatrics has said there are no noteworthy effects on breathing function for most children.
“There’s been so much discussion about the contribution of masks to reducing the risk of COVID that it’s nice to have the data,” he said, adding that this is a relationship that has been difficult to study, but this analysis was able to make the connection with hard numbers.
“It’s an important outcome,” he said in an interview.
The authors pointed out there is evidence that school-age children can identify most emotions in masked faces.
They added that “2-year-old children recognize spoken words better through an opaque mask, compared with a clear face shield, suggesting verbal communication to infants is not harmed by face masks.”
Studies have shown that childhood infection with other respiratory viruses also decreased and asthma symptoms were not reported when preschool children wore masks and used other preventative steps.
The authors wrote that a potential reason for that may be that those who wear masks have less face touching, known to increase the spread of COVID-19.
Paloma Beamer, PhD, an engineer and exposure scientist at University of Arizona, Tucson, who also has a 3-year-old son who wears masks at his daycare center, said in an interview that she works closely with his school on training kids how to wear their masks because getting young children to keep them on and finding ones that fit is challenging.
“We need layered controls and protections in place at schools as much as possible,” she said, adding that the authors didn’t mention ventilation, but that’s another important component as well.
“We’re fortunate in Arizona that we are in an old school and the windows are open as much as possible,” she said.
She said this study shows that “masks are a great form of additional control.” Her son is on his third quarantine this month after three kids tested positive, she added.
She said: “I think these newer variants perhaps make the findings of this study more compelling and it will be interesting to see if the researchers do a follow-up study.”
Strengths of the study include that it utilized prospective data from a large national cohort of childcare professionals. Additionally, the retention rate was high at 1 year. And the self-reported information likely gives better information than looking at policies that may or may not be well followed.
Limitations include potential reporting bias because the self-reports were not independently confirmed. Also, family behavior outside childcare, such as social gatherings where masking is not enforced, also influence COVID-19 cases when children gather and may affect the numbers of closures.
Having the option of childcare centers benefits kids with in-person early education and social interactions with staff, the authors noted. The centers also help parents return to work without interruptions at home.
“Our findings support current national recommendations endorsed by many local and state governments for masking children 2 years and older in childcare programs when community COVID-19 transmission levels are elevated,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Schaffner said the results have implications outside of childcare centers and should be included in discussions of masking in schools and in the general public.
All phases of this study were supported by and coauthors report grants from the Andrew & Julie Klingenstein Family Fund, Esther A. & Joseph Klingenstein Fund, Heising-Simons Foundation, W.K. Kellogg Foundation, Foundation for Child Development, Early Educator Investment Collaborative, and Scholastic. The study was partially funded by the Yale Institute for Global Health. Dr. Schaffner and Dr. Beamer reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Another winter for our discontent
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
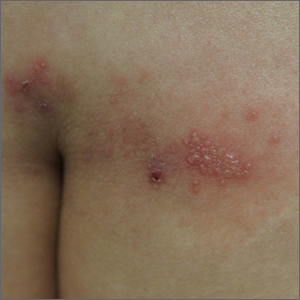
Sacral blisters
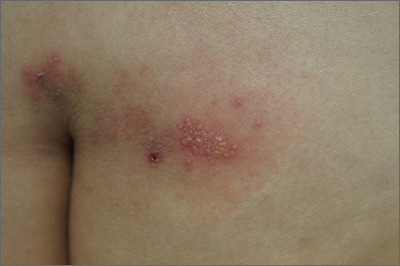
Grouped vesicles on an erythematous base should prompt concern for herpes viruses including varicella zoster (VZV) and herpes simplex (HSV). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for both VZV and HSV revealed this to be sacral HSV.
VZV classically presents in a dermatomal distribution, whereas HSV more commonly manifests along a single peripheral sensory nerve. Zosteriform presentations of HSV, however, have been reported.
Nongenital and nonoral HSV aren’t uncommon and can be associated with genital herpes, whether from self-inoculation or viremia.1 These outbreaks usually occur in the distribution of the pudendal nerve, which arises from the S2-S4 spinal nerves. There is an association of genital viral shedding even in the absence of lesions when sacral flaring manifests, and patients should be cautioned about sexual transmission or vertically transmitted perinatal infection in pregnant patients near term.
Treatment for an initial episode of genital infection with HSV is valacyclovir 1 g bid for 10 days. The regimen is ideally started within 48 to 72 hours of symptom onset.
This patient was empirically started on VZV dosing, then switched to HSV dosing when the PCR testing confirmed HSV. Knowledge of the exact pathogen is helpful in counseling the patient about the potential for spread and the risk of recurrence. With HSV, the patient may be prescribed a suppressive dose of valacyclovir 500 mg bid for 3 days, started at the onset of symptoms.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Vassantachart JM, Menter A. Recurrent lumbosacral herpes simplex virus infection. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2016;29:48-49. doi:10.1080/08998280.2016.11929356

Grouped vesicles on an erythematous base should prompt concern for herpes viruses including varicella zoster (VZV) and herpes simplex (HSV). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for both VZV and HSV revealed this to be sacral HSV.
VZV classically presents in a dermatomal distribution, whereas HSV more commonly manifests along a single peripheral sensory nerve. Zosteriform presentations of HSV, however, have been reported.
Nongenital and nonoral HSV aren’t uncommon and can be associated with genital herpes, whether from self-inoculation or viremia.1 These outbreaks usually occur in the distribution of the pudendal nerve, which arises from the S2-S4 spinal nerves. There is an association of genital viral shedding even in the absence of lesions when sacral flaring manifests, and patients should be cautioned about sexual transmission or vertically transmitted perinatal infection in pregnant patients near term.
Treatment for an initial episode of genital infection with HSV is valacyclovir 1 g bid for 10 days. The regimen is ideally started within 48 to 72 hours of symptom onset.
This patient was empirically started on VZV dosing, then switched to HSV dosing when the PCR testing confirmed HSV. Knowledge of the exact pathogen is helpful in counseling the patient about the potential for spread and the risk of recurrence. With HSV, the patient may be prescribed a suppressive dose of valacyclovir 500 mg bid for 3 days, started at the onset of symptoms.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

Grouped vesicles on an erythematous base should prompt concern for herpes viruses including varicella zoster (VZV) and herpes simplex (HSV). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for both VZV and HSV revealed this to be sacral HSV.
VZV classically presents in a dermatomal distribution, whereas HSV more commonly manifests along a single peripheral sensory nerve. Zosteriform presentations of HSV, however, have been reported.
Nongenital and nonoral HSV aren’t uncommon and can be associated with genital herpes, whether from self-inoculation or viremia.1 These outbreaks usually occur in the distribution of the pudendal nerve, which arises from the S2-S4 spinal nerves. There is an association of genital viral shedding even in the absence of lesions when sacral flaring manifests, and patients should be cautioned about sexual transmission or vertically transmitted perinatal infection in pregnant patients near term.
Treatment for an initial episode of genital infection with HSV is valacyclovir 1 g bid for 10 days. The regimen is ideally started within 48 to 72 hours of symptom onset.
This patient was empirically started on VZV dosing, then switched to HSV dosing when the PCR testing confirmed HSV. Knowledge of the exact pathogen is helpful in counseling the patient about the potential for spread and the risk of recurrence. With HSV, the patient may be prescribed a suppressive dose of valacyclovir 500 mg bid for 3 days, started at the onset of symptoms.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Vassantachart JM, Menter A. Recurrent lumbosacral herpes simplex virus infection. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2016;29:48-49. doi:10.1080/08998280.2016.11929356
1. Vassantachart JM, Menter A. Recurrent lumbosacral herpes simplex virus infection. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2016;29:48-49. doi:10.1080/08998280.2016.11929356
Omicron survives longer on plastic, skin than other COVID variants
, one possible explanation for why Omicron has spread so rapidly around the world.
In a lab experiment, samples of different variants were applied to pieces of plastic and human skin collected from autopsies, researchers from Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine wrote in bioRxiv. A variant “survived” until it could no longer be detected on the surface.
“This study showed that the Omicron variant also has the highest environmental stability among VOCs (variants of concern), which suggests that this high stability might also be one of the factors that have allowed the Omicron variant to replace the Delta variant and spread rapidly,” the researchers wrote.
On plastic, the Omicron variant samples survived an average of 193.5 hours, a little more than 8 days. By comparison, the other survival times on plastic were 56 hours for the original COVID strain, 191.3 hours for Alpha, 156.6 hours for Beta, 59.3 hours for Gamma, and 114 hours for Delta.
On skin samples, the Omicron samples survived an average of 21.1 hours. The other variants had these average survival times on skin: 8.6 hours for the original version, 19.6 hours for Alpha, 19.1 hours for Beta, 11 hours for Gamma, and 16.8 hours for Delta.
The study found that the variants had more resistance to ethanol than the original strain of COVID. That said, all COVID samples were inactivated after being exposed to alcohol-based hand sanitizers for 15 seconds.
“Therefore, it is highly recommended that current infection control (hand hygiene) practices use disinfectants ... as proposed by the World Health Organization,” the researchers said.
The study has not been peer-reviewed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, one possible explanation for why Omicron has spread so rapidly around the world.
In a lab experiment, samples of different variants were applied to pieces of plastic and human skin collected from autopsies, researchers from Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine wrote in bioRxiv. A variant “survived” until it could no longer be detected on the surface.
“This study showed that the Omicron variant also has the highest environmental stability among VOCs (variants of concern), which suggests that this high stability might also be one of the factors that have allowed the Omicron variant to replace the Delta variant and spread rapidly,” the researchers wrote.
On plastic, the Omicron variant samples survived an average of 193.5 hours, a little more than 8 days. By comparison, the other survival times on plastic were 56 hours for the original COVID strain, 191.3 hours for Alpha, 156.6 hours for Beta, 59.3 hours for Gamma, and 114 hours for Delta.
On skin samples, the Omicron samples survived an average of 21.1 hours. The other variants had these average survival times on skin: 8.6 hours for the original version, 19.6 hours for Alpha, 19.1 hours for Beta, 11 hours for Gamma, and 16.8 hours for Delta.
The study found that the variants had more resistance to ethanol than the original strain of COVID. That said, all COVID samples were inactivated after being exposed to alcohol-based hand sanitizers for 15 seconds.
“Therefore, it is highly recommended that current infection control (hand hygiene) practices use disinfectants ... as proposed by the World Health Organization,” the researchers said.
The study has not been peer-reviewed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, one possible explanation for why Omicron has spread so rapidly around the world.
In a lab experiment, samples of different variants were applied to pieces of plastic and human skin collected from autopsies, researchers from Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine wrote in bioRxiv. A variant “survived” until it could no longer be detected on the surface.
“This study showed that the Omicron variant also has the highest environmental stability among VOCs (variants of concern), which suggests that this high stability might also be one of the factors that have allowed the Omicron variant to replace the Delta variant and spread rapidly,” the researchers wrote.
On plastic, the Omicron variant samples survived an average of 193.5 hours, a little more than 8 days. By comparison, the other survival times on plastic were 56 hours for the original COVID strain, 191.3 hours for Alpha, 156.6 hours for Beta, 59.3 hours for Gamma, and 114 hours for Delta.
On skin samples, the Omicron samples survived an average of 21.1 hours. The other variants had these average survival times on skin: 8.6 hours for the original version, 19.6 hours for Alpha, 19.1 hours for Beta, 11 hours for Gamma, and 16.8 hours for Delta.
The study found that the variants had more resistance to ethanol than the original strain of COVID. That said, all COVID samples were inactivated after being exposed to alcohol-based hand sanitizers for 15 seconds.
“Therefore, it is highly recommended that current infection control (hand hygiene) practices use disinfectants ... as proposed by the World Health Organization,” the researchers said.
The study has not been peer-reviewed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Presence of autoantibodies most predictive of long COVID in study
Other significant early predictors of prolonged COVID symptoms – which the researchers called postacute sequelae – were having type 2 diabetes, SARS-CoV-2 RNAemia, and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) viremia, Yapeng Su, PhD, of the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) in Seattle, and colleagues wrote in Cell.
Having EBV viremia suggested that latent EBV has been reactivated, the authors noted.
“The most important postacute sequelae [that is conditions that are consequences of a disease] of COVID is the presence of autoantibodies,” James R. Heath, PhD, president of ISB and a bioengineering professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “It’s about two times more important than the others.”
Dr. Heath and coauthors said early detection of this and other variables could prompt earlier aggressive treatment in patients susceptible to long COVID and ward off lingering symptoms.
“These predictive measures of long COVID can also help to better inform patients of their possible disease course,” study coauthor Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB, said in an interview. “We were also able to partially resolve the immunological underpinnings of some postacute sequelae of COVID in a way that suggested potential therapies, and the timing of those therapies.”
For example, he continued, the use of antivirals very early in the infectious course may mitigate the later development of long COVID. “This will, of course, have to be explored in an appropriately designed clinical trial.
“We also identified biomarkers of certain types of long COVID, such as neurological sequelae. Those biomarkers can help define the condition, which is a first step towards developing treatments.”
Study findings
With COVID patients monitored for 2 or 3 months, the study findings of the international “multiomic profiling” analysis include:
- Subclinical patient autoantibodies that reduce anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies suggest there is immune dysregulation during COVID-19 infection.
- Reactivation of latent other viruses during initial infection may be contributing to long COVID.
- Gastrointestinal postacute sequelae of COVID presents with a unique postacute expansion of cytotoxic T cells.
- SARS-CoV-2–specific and cytomegalovirus-specific CD8+ T cells displayed unique dynamics during recovery from infection.
According to the authors, as many as 69% of COVID-19 patients suffer from long COVID – a range of new, recurrent, or ongoing problems 4 or more weeks following initial SARS-CoV-2 infection. These may include memory loss, gastrointestinal distress, fatigue, anosmia, and shortness of breath.
Long COVID has been associated with acute disease severity, and is suspected to be related to autoimmune factors and unresolved viral fragments, according to the paper.
Research methods
The international study did a deep and detailed dive into multiple molecular markers of long COVID. It enrolled 209 COVID-19 patients with varying degrees of disease severity and matched them to 457 healthy controls. The researchers’ goal was to identify discrete and quantifiable long COVID factors and guide possible preemptive treatment.
Patients were assessed at three time points: at initial diagnosis, during the acute disease phase about a week later, and again 2 to 3 months post onset of symptoms after recovery from the acute phase of COVID. At the third assessment, some patients had lingering symptoms such as fatigue (52% ), cough (25%), and loss of taste or sense of smell (18%).
Blood draws were analyzed for autoantibodies and SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies, global plasma proteomic and metabolomic profiles, and single-cell multiomic characterizations of peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Each blood draw was paired with nasal-swab and plasma measurements of SARS-CoV-2 viral load and the data sets were integrated with electronic health records and self-reported patient symptoms to guide the interpretation of the molecular signatures of long COVID.
Author conclusions
The authors found an association between T2 hyperinflammation and long COVID–anticipating autoantibodies. This association further implies that hyperinflammation-controlling therapies in the acute stage of COVID may influence whether a patient experiences long COVID. “However, the detailed timing and context of these therapies matter, and, thus, future well-controlled studies will be needed to test these and other therapeutic implications,” Dr. Su and colleagues wrote.
Moreover, the negative correlations between anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG and certain autoantibodies may suggest that patients with elevated autoantibody levels are more susceptible to breakthrough infections, the authors said.
“Many patients with high autoantibodies simultaneously have low protective antibodies that neutralize SARS-CoV-2, and that’s going to make them more susceptible to breakthrough infections,” Mr. Chen explained.*
“Detectability of most [long COVID-19 factors] at COVID diagnosis emphasizes the importance of early disease measurements for understanding emergent chronic conditions and suggests [long COVID] treatment strategies,” they wrote.
According to Mr. Chen, there are clear similarities in underlying immunobiology between patients with COVID autoantibodies and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
“These findings are also helping us frame our thinking around other chronic autoimmune conditions, such as postacute Lyme syndrome, for example,” said Dr. Heath.
The bottom line, said Mr. Chen, is that measuring early long COVID indicators may result in preventive treatments. “An example is the cortisol deficiency we see in certain long COVID patients. There are known treatments such as cortisol replacement therapy that should be explored for this group.”
Outside expert’s take on findings
Commenting on the study, Sherry Hsiang-Yi Chou, MD, who was not involved in the research, called the study a very important first step in understanding the path of this complex phenomenon and perhaps other conditions with long-term side effects.
“The researchers have done huge amount of innovative scientific work. They’ve shown the DNA signature of how our bodies respond to this disease,” said Dr. Chou, who is chief of the division of neurocritical care at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
“This type of research will help us scientifically understand and differentiate the various syndromes within long COVID. It will help identify who’s at risk for different aspects of this syndrome and lead to following them for longer periods in clinical trials,” she added.
The authors acknowledged that lengthier studies in larger cohorts were needed to see which patients will develop long-term chronic postacute sequelae of COVID.
This research was supported by the Wilke Family Foundation, the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, Merck, and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority. Other support came from the National Institutes of Health, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Saint John’s Cancer Center, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, and the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. Dr. Heath is a cofounder of Pact Pharma. He and several coauthors disclosed various ties to multiple private-sector companies. Mr. Chen and Dr. Chou had no competing interests.
*Correction, 1/28: An earlier version of this story misidentified Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB.
Other significant early predictors of prolonged COVID symptoms – which the researchers called postacute sequelae – were having type 2 diabetes, SARS-CoV-2 RNAemia, and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) viremia, Yapeng Su, PhD, of the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) in Seattle, and colleagues wrote in Cell.
Having EBV viremia suggested that latent EBV has been reactivated, the authors noted.
“The most important postacute sequelae [that is conditions that are consequences of a disease] of COVID is the presence of autoantibodies,” James R. Heath, PhD, president of ISB and a bioengineering professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “It’s about two times more important than the others.”
Dr. Heath and coauthors said early detection of this and other variables could prompt earlier aggressive treatment in patients susceptible to long COVID and ward off lingering symptoms.
“These predictive measures of long COVID can also help to better inform patients of their possible disease course,” study coauthor Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB, said in an interview. “We were also able to partially resolve the immunological underpinnings of some postacute sequelae of COVID in a way that suggested potential therapies, and the timing of those therapies.”
For example, he continued, the use of antivirals very early in the infectious course may mitigate the later development of long COVID. “This will, of course, have to be explored in an appropriately designed clinical trial.
“We also identified biomarkers of certain types of long COVID, such as neurological sequelae. Those biomarkers can help define the condition, which is a first step towards developing treatments.”
Study findings
With COVID patients monitored for 2 or 3 months, the study findings of the international “multiomic profiling” analysis include:
- Subclinical patient autoantibodies that reduce anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies suggest there is immune dysregulation during COVID-19 infection.
- Reactivation of latent other viruses during initial infection may be contributing to long COVID.
- Gastrointestinal postacute sequelae of COVID presents with a unique postacute expansion of cytotoxic T cells.
- SARS-CoV-2–specific and cytomegalovirus-specific CD8+ T cells displayed unique dynamics during recovery from infection.
According to the authors, as many as 69% of COVID-19 patients suffer from long COVID – a range of new, recurrent, or ongoing problems 4 or more weeks following initial SARS-CoV-2 infection. These may include memory loss, gastrointestinal distress, fatigue, anosmia, and shortness of breath.
Long COVID has been associated with acute disease severity, and is suspected to be related to autoimmune factors and unresolved viral fragments, according to the paper.
Research methods
The international study did a deep and detailed dive into multiple molecular markers of long COVID. It enrolled 209 COVID-19 patients with varying degrees of disease severity and matched them to 457 healthy controls. The researchers’ goal was to identify discrete and quantifiable long COVID factors and guide possible preemptive treatment.
Patients were assessed at three time points: at initial diagnosis, during the acute disease phase about a week later, and again 2 to 3 months post onset of symptoms after recovery from the acute phase of COVID. At the third assessment, some patients had lingering symptoms such as fatigue (52% ), cough (25%), and loss of taste or sense of smell (18%).
Blood draws were analyzed for autoantibodies and SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies, global plasma proteomic and metabolomic profiles, and single-cell multiomic characterizations of peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Each blood draw was paired with nasal-swab and plasma measurements of SARS-CoV-2 viral load and the data sets were integrated with electronic health records and self-reported patient symptoms to guide the interpretation of the molecular signatures of long COVID.
Author conclusions
The authors found an association between T2 hyperinflammation and long COVID–anticipating autoantibodies. This association further implies that hyperinflammation-controlling therapies in the acute stage of COVID may influence whether a patient experiences long COVID. “However, the detailed timing and context of these therapies matter, and, thus, future well-controlled studies will be needed to test these and other therapeutic implications,” Dr. Su and colleagues wrote.
Moreover, the negative correlations between anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG and certain autoantibodies may suggest that patients with elevated autoantibody levels are more susceptible to breakthrough infections, the authors said.
“Many patients with high autoantibodies simultaneously have low protective antibodies that neutralize SARS-CoV-2, and that’s going to make them more susceptible to breakthrough infections,” Mr. Chen explained.*
“Detectability of most [long COVID-19 factors] at COVID diagnosis emphasizes the importance of early disease measurements for understanding emergent chronic conditions and suggests [long COVID] treatment strategies,” they wrote.
According to Mr. Chen, there are clear similarities in underlying immunobiology between patients with COVID autoantibodies and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
“These findings are also helping us frame our thinking around other chronic autoimmune conditions, such as postacute Lyme syndrome, for example,” said Dr. Heath.
The bottom line, said Mr. Chen, is that measuring early long COVID indicators may result in preventive treatments. “An example is the cortisol deficiency we see in certain long COVID patients. There are known treatments such as cortisol replacement therapy that should be explored for this group.”
Outside expert’s take on findings
Commenting on the study, Sherry Hsiang-Yi Chou, MD, who was not involved in the research, called the study a very important first step in understanding the path of this complex phenomenon and perhaps other conditions with long-term side effects.
“The researchers have done huge amount of innovative scientific work. They’ve shown the DNA signature of how our bodies respond to this disease,” said Dr. Chou, who is chief of the division of neurocritical care at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
“This type of research will help us scientifically understand and differentiate the various syndromes within long COVID. It will help identify who’s at risk for different aspects of this syndrome and lead to following them for longer periods in clinical trials,” she added.
The authors acknowledged that lengthier studies in larger cohorts were needed to see which patients will develop long-term chronic postacute sequelae of COVID.
This research was supported by the Wilke Family Foundation, the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, Merck, and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority. Other support came from the National Institutes of Health, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Saint John’s Cancer Center, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, and the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. Dr. Heath is a cofounder of Pact Pharma. He and several coauthors disclosed various ties to multiple private-sector companies. Mr. Chen and Dr. Chou had no competing interests.
*Correction, 1/28: An earlier version of this story misidentified Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB.
Other significant early predictors of prolonged COVID symptoms – which the researchers called postacute sequelae – were having type 2 diabetes, SARS-CoV-2 RNAemia, and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) viremia, Yapeng Su, PhD, of the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) in Seattle, and colleagues wrote in Cell.
Having EBV viremia suggested that latent EBV has been reactivated, the authors noted.
“The most important postacute sequelae [that is conditions that are consequences of a disease] of COVID is the presence of autoantibodies,” James R. Heath, PhD, president of ISB and a bioengineering professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “It’s about two times more important than the others.”
Dr. Heath and coauthors said early detection of this and other variables could prompt earlier aggressive treatment in patients susceptible to long COVID and ward off lingering symptoms.
“These predictive measures of long COVID can also help to better inform patients of their possible disease course,” study coauthor Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB, said in an interview. “We were also able to partially resolve the immunological underpinnings of some postacute sequelae of COVID in a way that suggested potential therapies, and the timing of those therapies.”
For example, he continued, the use of antivirals very early in the infectious course may mitigate the later development of long COVID. “This will, of course, have to be explored in an appropriately designed clinical trial.
“We also identified biomarkers of certain types of long COVID, such as neurological sequelae. Those biomarkers can help define the condition, which is a first step towards developing treatments.”
Study findings
With COVID patients monitored for 2 or 3 months, the study findings of the international “multiomic profiling” analysis include:
- Subclinical patient autoantibodies that reduce anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies suggest there is immune dysregulation during COVID-19 infection.
- Reactivation of latent other viruses during initial infection may be contributing to long COVID.
- Gastrointestinal postacute sequelae of COVID presents with a unique postacute expansion of cytotoxic T cells.
- SARS-CoV-2–specific and cytomegalovirus-specific CD8+ T cells displayed unique dynamics during recovery from infection.
According to the authors, as many as 69% of COVID-19 patients suffer from long COVID – a range of new, recurrent, or ongoing problems 4 or more weeks following initial SARS-CoV-2 infection. These may include memory loss, gastrointestinal distress, fatigue, anosmia, and shortness of breath.
Long COVID has been associated with acute disease severity, and is suspected to be related to autoimmune factors and unresolved viral fragments, according to the paper.
Research methods
The international study did a deep and detailed dive into multiple molecular markers of long COVID. It enrolled 209 COVID-19 patients with varying degrees of disease severity and matched them to 457 healthy controls. The researchers’ goal was to identify discrete and quantifiable long COVID factors and guide possible preemptive treatment.
Patients were assessed at three time points: at initial diagnosis, during the acute disease phase about a week later, and again 2 to 3 months post onset of symptoms after recovery from the acute phase of COVID. At the third assessment, some patients had lingering symptoms such as fatigue (52% ), cough (25%), and loss of taste or sense of smell (18%).
Blood draws were analyzed for autoantibodies and SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies, global plasma proteomic and metabolomic profiles, and single-cell multiomic characterizations of peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Each blood draw was paired with nasal-swab and plasma measurements of SARS-CoV-2 viral load and the data sets were integrated with electronic health records and self-reported patient symptoms to guide the interpretation of the molecular signatures of long COVID.
Author conclusions
The authors found an association between T2 hyperinflammation and long COVID–anticipating autoantibodies. This association further implies that hyperinflammation-controlling therapies in the acute stage of COVID may influence whether a patient experiences long COVID. “However, the detailed timing and context of these therapies matter, and, thus, future well-controlled studies will be needed to test these and other therapeutic implications,” Dr. Su and colleagues wrote.
Moreover, the negative correlations between anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG and certain autoantibodies may suggest that patients with elevated autoantibody levels are more susceptible to breakthrough infections, the authors said.
“Many patients with high autoantibodies simultaneously have low protective antibodies that neutralize SARS-CoV-2, and that’s going to make them more susceptible to breakthrough infections,” Mr. Chen explained.*
“Detectability of most [long COVID-19 factors] at COVID diagnosis emphasizes the importance of early disease measurements for understanding emergent chronic conditions and suggests [long COVID] treatment strategies,” they wrote.
According to Mr. Chen, there are clear similarities in underlying immunobiology between patients with COVID autoantibodies and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
“These findings are also helping us frame our thinking around other chronic autoimmune conditions, such as postacute Lyme syndrome, for example,” said Dr. Heath.
The bottom line, said Mr. Chen, is that measuring early long COVID indicators may result in preventive treatments. “An example is the cortisol deficiency we see in certain long COVID patients. There are known treatments such as cortisol replacement therapy that should be explored for this group.”
Outside expert’s take on findings
Commenting on the study, Sherry Hsiang-Yi Chou, MD, who was not involved in the research, called the study a very important first step in understanding the path of this complex phenomenon and perhaps other conditions with long-term side effects.
“The researchers have done huge amount of innovative scientific work. They’ve shown the DNA signature of how our bodies respond to this disease,” said Dr. Chou, who is chief of the division of neurocritical care at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
“This type of research will help us scientifically understand and differentiate the various syndromes within long COVID. It will help identify who’s at risk for different aspects of this syndrome and lead to following them for longer periods in clinical trials,” she added.
The authors acknowledged that lengthier studies in larger cohorts were needed to see which patients will develop long-term chronic postacute sequelae of COVID.
This research was supported by the Wilke Family Foundation, the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, Merck, and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority. Other support came from the National Institutes of Health, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Saint John’s Cancer Center, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, and the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. Dr. Heath is a cofounder of Pact Pharma. He and several coauthors disclosed various ties to multiple private-sector companies. Mr. Chen and Dr. Chou had no competing interests.
*Correction, 1/28: An earlier version of this story misidentified Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB.
FROM CELL
Dapivirine vaginal ring for HIV prevention no longer under consideration by the FDA
Tosha Rogers, MD, is a one-woman HIV prevention evangelist. For nearly a decade now, the Atlanta-based ob/gyn has been on a mission to increase her gynecological colleagues’ awareness and prescribing of the oral HIV prevention pill. At the same time, she’s been tracking the development of a flexible vaginal ring loaded with a month’s worth of the HIV prevention medication dapivirine. That, she thought, would fit easily into women’s lives and into the toolbox of methods women already use to prevent pregnancy.
But now she’s not sure when – or if – the ring will find its way to her patients. In December, the ring’s maker, the International Partnership for Microbicides (IPM), pulled its application for FDA approval for the pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) ring. Now, one year after the World Health Organization recommended the ring for member nations, there appears to be no path forward in the United States for either the dapivirine-only ring or an approach Dr. Rogers said would change the game: a vaginal ring that supplies both contraception and HIV prevention.
“It would take things to a whole other level,” she said. “It sucks that this happened, and I do think it was not anything medical. I think it was everything political.”
That leaves cisgender women – especially the Black and Latinx women who make up the vast majority of women who acquire HIV every year – with two HIV prevention options. One is the daily pill, first approved in 2012. It’s now generic but previously sold as Truvada by Gilead Sciences. The other is monthly injectable cabotegravir long-acting (Apretude). Another HIV prevention pill, tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine (Descovy), is approved for gay men and transgender women but not cisgender women.
Vagina-specific protection from HIV
The WHO recommendation for the vaginal ring was followed last July by a positive opinion from the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for women in low- and middle-income countries outside the European Union.
The flexible silicone ring, similar to the hormonal NuvaRing contraceptive, works by slowly releasing the antiretroviral dapivirine directly into the vaginal canal, thereby protecting women who might be exposed to the virus through vaginal sex only. Because the medicine stays where it’s delivered and doesn’t circulate through the body, it has been found to be extremely safe with few adverse events.
However, in initial studies, the ring was found to be just 27% effective overall. Later studies, where scientists divided women by how much drug was missing from the ring – a proxy for use – found that higher use was associated with higher protection (as much as 54%). By comparison, Truvada has been found to be up to 99% effective when used daily, though it can take up to 21 days to be available in the vagina in high enough concentrations to protect women from vaginal exposure. And the HIV prevention shot was found to be 90% more effective than that in a recent trial of the two methods conducted by the HIV Prevention Trials Network.
This, and an orientation away from topical HIV prevention drugs and toward systemic options, led the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to discontinue funding for such projects under its Microbicide Trials Network.
“Clearly you want to counsel women to use the highest efficacy method, and that is part of our label,” Zeda Rosenberg, ScD, IPM’s founder and chief executive officer, told this news organization. “Women should not choose the ring if they can and will use oral PrEP, and I would argue it should be the same thing for [cabotegravir shots]. But if they can’t or don’t want to – and we know that especially many young women don’t want to use systemic methods – then the dapivirine ring is a great option.”
Still, Dr. Rosenberg said that the gap in efficacy, the relatively small number of women affected by HIV in the U.S. compared with gay and bisexual men, and the emergence of products like the HIV prevention shot cabotegravir, made it “very unlikely” that FDA regulators would approve the ring. And rather than be “distracted” by the FDA process, Dr. Rosenberg said IPM chose to concentrate on the countries where the ring has already been approved or where women make up the vast majority of people affected by HIV.
Zimbabwe publicly announced it has approved the ring, and three other countries may have approved it, according to Dr. Rosenberg. She declined to name them, saying they had requested silence while they formulate their new HIV prevention guidelines. Aside from Zimbabwe, the other countries where women participated in the ring clinical trials were South Africa, Malawi, and Uganda.
“The U.S. population ... has widespread access to oral PrEP, which is unlike countries in Africa, and which would have widespread access to injectable cabotegravir,” she said. “The U.S. FDA may not see choice in the same way that African women and African activists and advocates see the need for choice.”
But women’s rates of accessing HIV prevention medications in the U.S. continues to be frustratingly low. At the end of 2018, just 7% of women who could benefit from HIV prevention drugs were taking them, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data.
New CDC guidelines recommend clinicians talk to every sexually active adult and adolescent about HIV prevention medications at least once and prescribe it to anyone who asks for it, whether or not they understand their patients’ HIV risks. However, research continues to show that clinicians struggle with willingness to prescribe PrEP to Black women, and the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology’s committee opinion on managing women using HIV prevention drugs has not been updated to reflect the new guidelines. And while the HIV prevention shot is approved for women and its maker ViiV Healthcare is already initiating postmarket studies of the ring in key populations including women, there are lots of things that need to line up in order for clinicians to be willing to stock it and prescribe it to women.
From where Dázon Dixon Diallo, executive director of the nonprofit SisterLove, sits, the decision to withdraw the ring from FDA consideration and the FDA’s seeming argument that the epidemiology in the U.S. doesn’t warrant the ring’s approval is a slap in the face to the Black women who have led the movement to end HIV in the U.S. for decades.
“No matter how you slice it, we’re talking about Black women, and then we’re talking about brown women,” said Ms. Diallo. “The value [they place on us] from a government standpoint, from a political standpoint, from a public health standpoint is just woeful. It’s woeful and it’s disrespectful and it’s insulting and I’m sick of it.”
‘America sneezes and Africa catches a cold’
When she first heard the decision to pull the ring from FDA consideration, Yvette Raphael, the South Africa-based executive director of Advocates for the Prevention of HIV in Africa, started asking, “What can we do to help our sisters in America get this ring?” And then she started worrying about other women in her own country and those nearby.
“The FDA plays a big role,” she said. “You know, America sneezes and Africa catches a cold.”
She worries that IPM’s decision to withdraw the ring from FDA consideration will signal to regulators in other countries either (a) that they should not approve it or (b) in countries where it’s already been approved but guidelines have not been issued, that they won’t invest money in rolling it out to women in those countries – especially now with the U.S. approval of the prevention shot. In much of Africa, ministries of health prefer to provide injectable contraception, often giving women few or no other options. But women, she said, think about more than administration of the drug. They look at if it’s an easier option for them to manage.
“This is a long journey, an emotional one too, for women in South Africa, because the idea of a microbicide is one of the ideas that came directly from women in South Africa,” she said. “[The jab] can be seen as a solution to all. We can just give jabs to all the women. And after all, we know that women don’t adhere, so we can just grab them.”
Dr. Rosenberg pointed to the positive opinion from the EMA as another “rigorous review” process that she said ought to equally influence ministries of health in countries where women tested the ring. And she pointed to the WHO statement released last month, the same day as IPM’s announcement that it was withdrawing the ring from FDA considerations, recommitting the ring as a good option in sub-Saharan Africa: “The U.S. FDA decision is not based on any new or additional data on efficacy and safety,” it stated. “WHO will continue to support countries as they consider whether to include the [dapivirine vaginal ring]. WHO recognizes that country decisionmaking will vary based on their context and that women’s voices remain central to discussions about their prevention choices.”
Dual action ring on the horizon, but not in U.S.
What this means, though, is that the next step in the ring’s development – the combination dapivirine ring with contraceptive levonorgestrel (used in the Mirena intrauterine device) – may not come to the U.S., at least for a long while.
“It’s not out of the question,” Dr. Rosenberg said of conducting HIV/pregnancy prevention ring trials in the U.S. “But without the approval of the dapivirine-only ring by FDA, I imagine they would want to see new efficacy data on dapivirine. That is a very difficult hill to climb. There would have to be an active control group [using oral PrEP or injectable cabotegravir], and it would be very difficult for the dapivirine ring to be able to go head-to-head for either noninferiority and certainly for superiority.”
The study would need to be quite large to get enough results to prove anything, and IPM is a research organization, not a large pharmaceutical company with deep enough pockets to fund that, she said. Raising those funds “would be difficult.”
In addition to NIAID discontinuing its funding for the Microbicides Trials Network, a new 5-year, $85 million research collaboration through USAID hasn’t slated any money to fund trials of the combination HIV prevention and contraceptive ring, according to Dr. Rosenberg.
But that doesn’t mean avenues for its development are closed. NIH’s Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) is currently funding a phase 1/2 trial of the combination ring, and IPM continues to receive funding from research agencies in Germany, the Netherlands, Denmark, and Ireland. And this means, she said, that the E.U. – not the U.S. – is where they would seek approval for a combination ring first.
That leaves Ms. Rafael and Ms. Diallo debating how to work together to push the FDA – and maybe IPM – to reconsider the ring. For instance, Ms. Diallo suggested that instead of seeking an indication for all women, the FDA might consider the ring for women with very high risk of HIV, such as sex workers or women with HIV positive partners not on treatment. And she said that this has to be bigger than HIV prevention. It has to be about the ways in which women’s health issues in general lag at the FDA. For instance, she pointed to the movement to get contraceptive pills available over the counter, fights against FDA rulings on hormone replacement therapy, and fights for emergency contraception.
In the meantime, ob/gyn Dr. Rogers is expecting access to the ring to follow a similar path as the copper IUD, which migrated to the U.S. from Europe, where it has been among the most popular contraceptive methods for women.
“Contrary to what we may think, we are not innovators, especially for something like this,” she said. “Once we see it is working and doing a good job – that women in Europe love it – then someone here is going to pick it up and make it as if it’s the greatest thing. But for now, I think we’re going to have to take a back seat to Europe.”
Ms. Diallo reports receiving fees from Johnson & Johnson, ViiV Healthcare, and Gilead Sciences. Dr. Rosenberg and Dr. Rogers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tosha Rogers, MD, is a one-woman HIV prevention evangelist. For nearly a decade now, the Atlanta-based ob/gyn has been on a mission to increase her gynecological colleagues’ awareness and prescribing of the oral HIV prevention pill. At the same time, she’s been tracking the development of a flexible vaginal ring loaded with a month’s worth of the HIV prevention medication dapivirine. That, she thought, would fit easily into women’s lives and into the toolbox of methods women already use to prevent pregnancy.
But now she’s not sure when – or if – the ring will find its way to her patients. In December, the ring’s maker, the International Partnership for Microbicides (IPM), pulled its application for FDA approval for the pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) ring. Now, one year after the World Health Organization recommended the ring for member nations, there appears to be no path forward in the United States for either the dapivirine-only ring or an approach Dr. Rogers said would change the game: a vaginal ring that supplies both contraception and HIV prevention.
“It would take things to a whole other level,” she said. “It sucks that this happened, and I do think it was not anything medical. I think it was everything political.”
That leaves cisgender women – especially the Black and Latinx women who make up the vast majority of women who acquire HIV every year – with two HIV prevention options. One is the daily pill, first approved in 2012. It’s now generic but previously sold as Truvada by Gilead Sciences. The other is monthly injectable cabotegravir long-acting (Apretude). Another HIV prevention pill, tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine (Descovy), is approved for gay men and transgender women but not cisgender women.
Vagina-specific protection from HIV
The WHO recommendation for the vaginal ring was followed last July by a positive opinion from the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for women in low- and middle-income countries outside the European Union.
The flexible silicone ring, similar to the hormonal NuvaRing contraceptive, works by slowly releasing the antiretroviral dapivirine directly into the vaginal canal, thereby protecting women who might be exposed to the virus through vaginal sex only. Because the medicine stays where it’s delivered and doesn’t circulate through the body, it has been found to be extremely safe with few adverse events.
However, in initial studies, the ring was found to be just 27% effective overall. Later studies, where scientists divided women by how much drug was missing from the ring – a proxy for use – found that higher use was associated with higher protection (as much as 54%). By comparison, Truvada has been found to be up to 99% effective when used daily, though it can take up to 21 days to be available in the vagina in high enough concentrations to protect women from vaginal exposure. And the HIV prevention shot was found to be 90% more effective than that in a recent trial of the two methods conducted by the HIV Prevention Trials Network.
This, and an orientation away from topical HIV prevention drugs and toward systemic options, led the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to discontinue funding for such projects under its Microbicide Trials Network.
“Clearly you want to counsel women to use the highest efficacy method, and that is part of our label,” Zeda Rosenberg, ScD, IPM’s founder and chief executive officer, told this news organization. “Women should not choose the ring if they can and will use oral PrEP, and I would argue it should be the same thing for [cabotegravir shots]. But if they can’t or don’t want to – and we know that especially many young women don’t want to use systemic methods – then the dapivirine ring is a great option.”
Still, Dr. Rosenberg said that the gap in efficacy, the relatively small number of women affected by HIV in the U.S. compared with gay and bisexual men, and the emergence of products like the HIV prevention shot cabotegravir, made it “very unlikely” that FDA regulators would approve the ring. And rather than be “distracted” by the FDA process, Dr. Rosenberg said IPM chose to concentrate on the countries where the ring has already been approved or where women make up the vast majority of people affected by HIV.
Zimbabwe publicly announced it has approved the ring, and three other countries may have approved it, according to Dr. Rosenberg. She declined to name them, saying they had requested silence while they formulate their new HIV prevention guidelines. Aside from Zimbabwe, the other countries where women participated in the ring clinical trials were South Africa, Malawi, and Uganda.
“The U.S. population ... has widespread access to oral PrEP, which is unlike countries in Africa, and which would have widespread access to injectable cabotegravir,” she said. “The U.S. FDA may not see choice in the same way that African women and African activists and advocates see the need for choice.”
But women’s rates of accessing HIV prevention medications in the U.S. continues to be frustratingly low. At the end of 2018, just 7% of women who could benefit from HIV prevention drugs were taking them, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data.
New CDC guidelines recommend clinicians talk to every sexually active adult and adolescent about HIV prevention medications at least once and prescribe it to anyone who asks for it, whether or not they understand their patients’ HIV risks. However, research continues to show that clinicians struggle with willingness to prescribe PrEP to Black women, and the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology’s committee opinion on managing women using HIV prevention drugs has not been updated to reflect the new guidelines. And while the HIV prevention shot is approved for women and its maker ViiV Healthcare is already initiating postmarket studies of the ring in key populations including women, there are lots of things that need to line up in order for clinicians to be willing to stock it and prescribe it to women.
From where Dázon Dixon Diallo, executive director of the nonprofit SisterLove, sits, the decision to withdraw the ring from FDA consideration and the FDA’s seeming argument that the epidemiology in the U.S. doesn’t warrant the ring’s approval is a slap in the face to the Black women who have led the movement to end HIV in the U.S. for decades.
“No matter how you slice it, we’re talking about Black women, and then we’re talking about brown women,” said Ms. Diallo. “The value [they place on us] from a government standpoint, from a political standpoint, from a public health standpoint is just woeful. It’s woeful and it’s disrespectful and it’s insulting and I’m sick of it.”
‘America sneezes and Africa catches a cold’
When she first heard the decision to pull the ring from FDA consideration, Yvette Raphael, the South Africa-based executive director of Advocates for the Prevention of HIV in Africa, started asking, “What can we do to help our sisters in America get this ring?” And then she started worrying about other women in her own country and those nearby.
“The FDA plays a big role,” she said. “You know, America sneezes and Africa catches a cold.”
She worries that IPM’s decision to withdraw the ring from FDA consideration will signal to regulators in other countries either (a) that they should not approve it or (b) in countries where it’s already been approved but guidelines have not been issued, that they won’t invest money in rolling it out to women in those countries – especially now with the U.S. approval of the prevention shot. In much of Africa, ministries of health prefer to provide injectable contraception, often giving women few or no other options. But women, she said, think about more than administration of the drug. They look at if it’s an easier option for them to manage.
“This is a long journey, an emotional one too, for women in South Africa, because the idea of a microbicide is one of the ideas that came directly from women in South Africa,” she said. “[The jab] can be seen as a solution to all. We can just give jabs to all the women. And after all, we know that women don’t adhere, so we can just grab them.”
Dr. Rosenberg pointed to the positive opinion from the EMA as another “rigorous review” process that she said ought to equally influence ministries of health in countries where women tested the ring. And she pointed to the WHO statement released last month, the same day as IPM’s announcement that it was withdrawing the ring from FDA considerations, recommitting the ring as a good option in sub-Saharan Africa: “The U.S. FDA decision is not based on any new or additional data on efficacy and safety,” it stated. “WHO will continue to support countries as they consider whether to include the [dapivirine vaginal ring]. WHO recognizes that country decisionmaking will vary based on their context and that women’s voices remain central to discussions about their prevention choices.”
Dual action ring on the horizon, but not in U.S.
What this means, though, is that the next step in the ring’s development – the combination dapivirine ring with contraceptive levonorgestrel (used in the Mirena intrauterine device) – may not come to the U.S., at least for a long while.
“It’s not out of the question,” Dr. Rosenberg said of conducting HIV/pregnancy prevention ring trials in the U.S. “But without the approval of the dapivirine-only ring by FDA, I imagine they would want to see new efficacy data on dapivirine. That is a very difficult hill to climb. There would have to be an active control group [using oral PrEP or injectable cabotegravir], and it would be very difficult for the dapivirine ring to be able to go head-to-head for either noninferiority and certainly for superiority.”
The study would need to be quite large to get enough results to prove anything, and IPM is a research organization, not a large pharmaceutical company with deep enough pockets to fund that, she said. Raising those funds “would be difficult.”
In addition to NIAID discontinuing its funding for the Microbicides Trials Network, a new 5-year, $85 million research collaboration through USAID hasn’t slated any money to fund trials of the combination HIV prevention and contraceptive ring, according to Dr. Rosenberg.
But that doesn’t mean avenues for its development are closed. NIH’s Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) is currently funding a phase 1/2 trial of the combination ring, and IPM continues to receive funding from research agencies in Germany, the Netherlands, Denmark, and Ireland. And this means, she said, that the E.U. – not the U.S. – is where they would seek approval for a combination ring first.
That leaves Ms. Rafael and Ms. Diallo debating how to work together to push the FDA – and maybe IPM – to reconsider the ring. For instance, Ms. Diallo suggested that instead of seeking an indication for all women, the FDA might consider the ring for women with very high risk of HIV, such as sex workers or women with HIV positive partners not on treatment. And she said that this has to be bigger than HIV prevention. It has to be about the ways in which women’s health issues in general lag at the FDA. For instance, she pointed to the movement to get contraceptive pills available over the counter, fights against FDA rulings on hormone replacement therapy, and fights for emergency contraception.
In the meantime, ob/gyn Dr. Rogers is expecting access to the ring to follow a similar path as the copper IUD, which migrated to the U.S. from Europe, where it has been among the most popular contraceptive methods for women.
“Contrary to what we may think, we are not innovators, especially for something like this,” she said. “Once we see it is working and doing a good job – that women in Europe love it – then someone here is going to pick it up and make it as if it’s the greatest thing. But for now, I think we’re going to have to take a back seat to Europe.”
Ms. Diallo reports receiving fees from Johnson & Johnson, ViiV Healthcare, and Gilead Sciences. Dr. Rosenberg and Dr. Rogers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tosha Rogers, MD, is a one-woman HIV prevention evangelist. For nearly a decade now, the Atlanta-based ob/gyn has been on a mission to increase her gynecological colleagues’ awareness and prescribing of the oral HIV prevention pill. At the same time, she’s been tracking the development of a flexible vaginal ring loaded with a month’s worth of the HIV prevention medication dapivirine. That, she thought, would fit easily into women’s lives and into the toolbox of methods women already use to prevent pregnancy.
But now she’s not sure when – or if – the ring will find its way to her patients. In December, the ring’s maker, the International Partnership for Microbicides (IPM), pulled its application for FDA approval for the pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) ring. Now, one year after the World Health Organization recommended the ring for member nations, there appears to be no path forward in the United States for either the dapivirine-only ring or an approach Dr. Rogers said would change the game: a vaginal ring that supplies both contraception and HIV prevention.
“It would take things to a whole other level,” she said. “It sucks that this happened, and I do think it was not anything medical. I think it was everything political.”
That leaves cisgender women – especially the Black and Latinx women who make up the vast majority of women who acquire HIV every year – with two HIV prevention options. One is the daily pill, first approved in 2012. It’s now generic but previously sold as Truvada by Gilead Sciences. The other is monthly injectable cabotegravir long-acting (Apretude). Another HIV prevention pill, tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine (Descovy), is approved for gay men and transgender women but not cisgender women.
Vagina-specific protection from HIV
The WHO recommendation for the vaginal ring was followed last July by a positive opinion from the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for women in low- and middle-income countries outside the European Union.
The flexible silicone ring, similar to the hormonal NuvaRing contraceptive, works by slowly releasing the antiretroviral dapivirine directly into the vaginal canal, thereby protecting women who might be exposed to the virus through vaginal sex only. Because the medicine stays where it’s delivered and doesn’t circulate through the body, it has been found to be extremely safe with few adverse events.
However, in initial studies, the ring was found to be just 27% effective overall. Later studies, where scientists divided women by how much drug was missing from the ring – a proxy for use – found that higher use was associated with higher protection (as much as 54%). By comparison, Truvada has been found to be up to 99% effective when used daily, though it can take up to 21 days to be available in the vagina in high enough concentrations to protect women from vaginal exposure. And the HIV prevention shot was found to be 90% more effective than that in a recent trial of the two methods conducted by the HIV Prevention Trials Network.
This, and an orientation away from topical HIV prevention drugs and toward systemic options, led the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to discontinue funding for such projects under its Microbicide Trials Network.
“Clearly you want to counsel women to use the highest efficacy method, and that is part of our label,” Zeda Rosenberg, ScD, IPM’s founder and chief executive officer, told this news organization. “Women should not choose the ring if they can and will use oral PrEP, and I would argue it should be the same thing for [cabotegravir shots]. But if they can’t or don’t want to – and we know that especially many young women don’t want to use systemic methods – then the dapivirine ring is a great option.”
Still, Dr. Rosenberg said that the gap in efficacy, the relatively small number of women affected by HIV in the U.S. compared with gay and bisexual men, and the emergence of products like the HIV prevention shot cabotegravir, made it “very unlikely” that FDA regulators would approve the ring. And rather than be “distracted” by the FDA process, Dr. Rosenberg said IPM chose to concentrate on the countries where the ring has already been approved or where women make up the vast majority of people affected by HIV.
Zimbabwe publicly announced it has approved the ring, and three other countries may have approved it, according to Dr. Rosenberg. She declined to name them, saying they had requested silence while they formulate their new HIV prevention guidelines. Aside from Zimbabwe, the other countries where women participated in the ring clinical trials were South Africa, Malawi, and Uganda.
“The U.S. population ... has widespread access to oral PrEP, which is unlike countries in Africa, and which would have widespread access to injectable cabotegravir,” she said. “The U.S. FDA may not see choice in the same way that African women and African activists and advocates see the need for choice.”
But women’s rates of accessing HIV prevention medications in the U.S. continues to be frustratingly low. At the end of 2018, just 7% of women who could benefit from HIV prevention drugs were taking them, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data.
New CDC guidelines recommend clinicians talk to every sexually active adult and adolescent about HIV prevention medications at least once and prescribe it to anyone who asks for it, whether or not they understand their patients’ HIV risks. However, research continues to show that clinicians struggle with willingness to prescribe PrEP to Black women, and the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology’s committee opinion on managing women using HIV prevention drugs has not been updated to reflect the new guidelines. And while the HIV prevention shot is approved for women and its maker ViiV Healthcare is already initiating postmarket studies of the ring in key populations including women, there are lots of things that need to line up in order for clinicians to be willing to stock it and prescribe it to women.
From where Dázon Dixon Diallo, executive director of the nonprofit SisterLove, sits, the decision to withdraw the ring from FDA consideration and the FDA’s seeming argument that the epidemiology in the U.S. doesn’t warrant the ring’s approval is a slap in the face to the Black women who have led the movement to end HIV in the U.S. for decades.
“No matter how you slice it, we’re talking about Black women, and then we’re talking about brown women,” said Ms. Diallo. “The value [they place on us] from a government standpoint, from a political standpoint, from a public health standpoint is just woeful. It’s woeful and it’s disrespectful and it’s insulting and I’m sick of it.”
‘America sneezes and Africa catches a cold’
When she first heard the decision to pull the ring from FDA consideration, Yvette Raphael, the South Africa-based executive director of Advocates for the Prevention of HIV in Africa, started asking, “What can we do to help our sisters in America get this ring?” And then she started worrying about other women in her own country and those nearby.
“The FDA plays a big role,” she said. “You know, America sneezes and Africa catches a cold.”
She worries that IPM’s decision to withdraw the ring from FDA consideration will signal to regulators in other countries either (a) that they should not approve it or (b) in countries where it’s already been approved but guidelines have not been issued, that they won’t invest money in rolling it out to women in those countries – especially now with the U.S. approval of the prevention shot. In much of Africa, ministries of health prefer to provide injectable contraception, often giving women few or no other options. But women, she said, think about more than administration of the drug. They look at if it’s an easier option for them to manage.
“This is a long journey, an emotional one too, for women in South Africa, because the idea of a microbicide is one of the ideas that came directly from women in South Africa,” she said. “[The jab] can be seen as a solution to all. We can just give jabs to all the women. And after all, we know that women don’t adhere, so we can just grab them.”
Dr. Rosenberg pointed to the positive opinion from the EMA as another “rigorous review” process that she said ought to equally influence ministries of health in countries where women tested the ring. And she pointed to the WHO statement released last month, the same day as IPM’s announcement that it was withdrawing the ring from FDA considerations, recommitting the ring as a good option in sub-Saharan Africa: “The U.S. FDA decision is not based on any new or additional data on efficacy and safety,” it stated. “WHO will continue to support countries as they consider whether to include the [dapivirine vaginal ring]. WHO recognizes that country decisionmaking will vary based on their context and that women’s voices remain central to discussions about their prevention choices.”
Dual action ring on the horizon, but not in U.S.
What this means, though, is that the next step in the ring’s development – the combination dapivirine ring with contraceptive levonorgestrel (used in the Mirena intrauterine device) – may not come to the U.S., at least for a long while.
“It’s not out of the question,” Dr. Rosenberg said of conducting HIV/pregnancy prevention ring trials in the U.S. “But without the approval of the dapivirine-only ring by FDA, I imagine they would want to see new efficacy data on dapivirine. That is a very difficult hill to climb. There would have to be an active control group [using oral PrEP or injectable cabotegravir], and it would be very difficult for the dapivirine ring to be able to go head-to-head for either noninferiority and certainly for superiority.”
The study would need to be quite large to get enough results to prove anything, and IPM is a research organization, not a large pharmaceutical company with deep enough pockets to fund that, she said. Raising those funds “would be difficult.”
In addition to NIAID discontinuing its funding for the Microbicides Trials Network, a new 5-year, $85 million research collaboration through USAID hasn’t slated any money to fund trials of the combination HIV prevention and contraceptive ring, according to Dr. Rosenberg.
But that doesn’t mean avenues for its development are closed. NIH’s Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) is currently funding a phase 1/2 trial of the combination ring, and IPM continues to receive funding from research agencies in Germany, the Netherlands, Denmark, and Ireland. And this means, she said, that the E.U. – not the U.S. – is where they would seek approval for a combination ring first.
That leaves Ms. Rafael and Ms. Diallo debating how to work together to push the FDA – and maybe IPM – to reconsider the ring. For instance, Ms. Diallo suggested that instead of seeking an indication for all women, the FDA might consider the ring for women with very high risk of HIV, such as sex workers or women with HIV positive partners not on treatment. And she said that this has to be bigger than HIV prevention. It has to be about the ways in which women’s health issues in general lag at the FDA. For instance, she pointed to the movement to get contraceptive pills available over the counter, fights against FDA rulings on hormone replacement therapy, and fights for emergency contraception.
In the meantime, ob/gyn Dr. Rogers is expecting access to the ring to follow a similar path as the copper IUD, which migrated to the U.S. from Europe, where it has been among the most popular contraceptive methods for women.
“Contrary to what we may think, we are not innovators, especially for something like this,” she said. “Once we see it is working and doing a good job – that women in Europe love it – then someone here is going to pick it up and make it as if it’s the greatest thing. But for now, I think we’re going to have to take a back seat to Europe.”
Ms. Diallo reports receiving fees from Johnson & Johnson, ViiV Healthcare, and Gilead Sciences. Dr. Rosenberg and Dr. Rogers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: United States passes 10 million total cases
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children topped 1 million for the first time as the cumulative count surpassed 10 million since the start of the pandemic, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. Those 10.6 million child cases represent 18.4% of all cases, and the latest 1.15 million represented 25.5% of all cases for the week.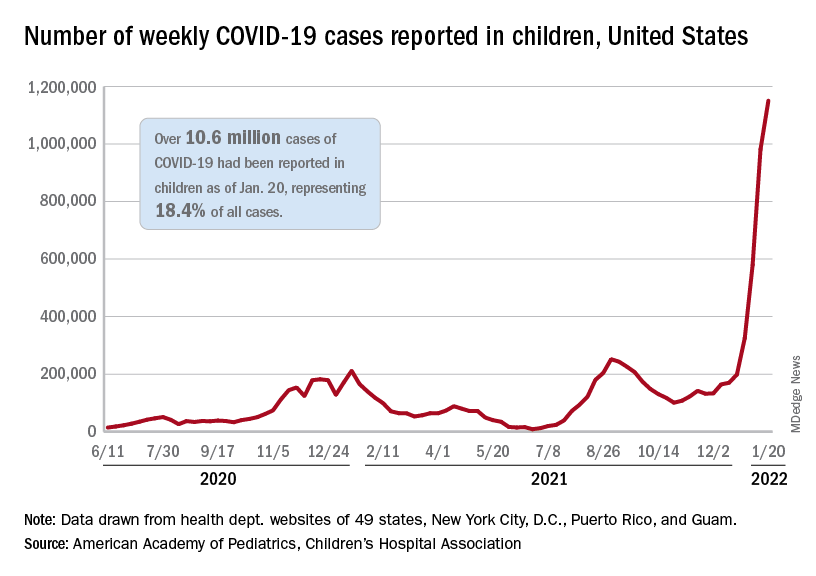
Regionally, the South had the most cases with over 380,000 for the week of Jan. 14-20, while the West was next with close to 350,000, followed by the Midwest and then the East. Among the states, the largest percent increases – on the order of 30% – came in New England (Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont), as well as Virginia and California, the AAP and CHA said.
Examining all those cases by vaccination status shows an obvious difference between the Omicron and Delta variants: The fully vaccinated have been hit much harder than before. For the week ending Dec. 25, 2021, the incidence of COVID-19 in children aged 12-17 years was 704 per 100,000 among those were unvaccinated and 384 per 100,000 in those who were fully vaccinated. During the Delta surge in the summer of 2021, the peak rates were 938 (unvaccinated) and 79 (vaccinated), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.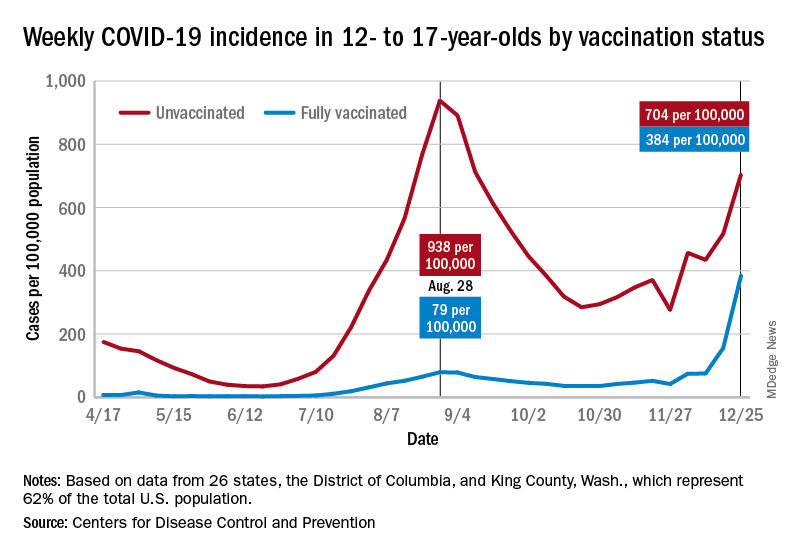
Hospitalizations are also at record levels, but two separate CDC databases seem to show a decline in child admissions over the last available week or so of data, which follows the trend among all ages. The peak among children aged 0-17 years came on Jan. 15, when the rate of new admissions reached 1.25 per 100,000, based on reporting to the CDC from 5,265 hospitals nationwide.
The second database, the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET), indicates that children aged 0-4 years had the highest admission rate, 14.5 per 100,000, for the week ending Jan. 8, compared with 5.5 per 100,000 for 12- to 17-year-olds and 2.3 per 100,000 for those aged 5-11 years. COVID-NET covers almost 100 counties in 10 states, along with 4 entire states, and represents about 10% of the U.S. population.
Vaccinations rose briefly in late December and into January to meet the Omicron surge, but the numbers for the latest week show a return to their earlier levels. In children aged 5-11 years, new vaccinations went from 381,000 for the week of Dec. 20-26 to 524,000 for Jan. 3-9, but fell to just 260,000 during Jan. 17-23. The response was a little later for those aged 12-17, with the big week coming Jan. 10-16, but there was still a 38% drop for Jan. 17-23, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
Currently, 29.3% of all 5- to 11-year-olds have received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, and an even 20.0% are fully vaccinated. For children aged 12-17, the corresponding figures are 65.8% and 55.1%, the CDC said.
Statewide vaccination rates vary from Vermont’s high of 61% for those aged 5-11 to 12% for Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, while Hawaii has the highest rate for 12- to 17-year-olds at 92% and Wyoming has the lowest at 39%, the AAP reported.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children topped 1 million for the first time as the cumulative count surpassed 10 million since the start of the pandemic, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. Those 10.6 million child cases represent 18.4% of all cases, and the latest 1.15 million represented 25.5% of all cases for the week.
Regionally, the South had the most cases with over 380,000 for the week of Jan. 14-20, while the West was next with close to 350,000, followed by the Midwest and then the East. Among the states, the largest percent increases – on the order of 30% – came in New England (Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont), as well as Virginia and California, the AAP and CHA said.
Examining all those cases by vaccination status shows an obvious difference between the Omicron and Delta variants: The fully vaccinated have been hit much harder than before. For the week ending Dec. 25, 2021, the incidence of COVID-19 in children aged 12-17 years was 704 per 100,000 among those were unvaccinated and 384 per 100,000 in those who were fully vaccinated. During the Delta surge in the summer of 2021, the peak rates were 938 (unvaccinated) and 79 (vaccinated), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
Hospitalizations are also at record levels, but two separate CDC databases seem to show a decline in child admissions over the last available week or so of data, which follows the trend among all ages. The peak among children aged 0-17 years came on Jan. 15, when the rate of new admissions reached 1.25 per 100,000, based on reporting to the CDC from 5,265 hospitals nationwide.
The second database, the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET), indicates that children aged 0-4 years had the highest admission rate, 14.5 per 100,000, for the week ending Jan. 8, compared with 5.5 per 100,000 for 12- to 17-year-olds and 2.3 per 100,000 for those aged 5-11 years. COVID-NET covers almost 100 counties in 10 states, along with 4 entire states, and represents about 10% of the U.S. population.
Vaccinations rose briefly in late December and into January to meet the Omicron surge, but the numbers for the latest week show a return to their earlier levels. In children aged 5-11 years, new vaccinations went from 381,000 for the week of Dec. 20-26 to 524,000 for Jan. 3-9, but fell to just 260,000 during Jan. 17-23. The response was a little later for those aged 12-17, with the big week coming Jan. 10-16, but there was still a 38% drop for Jan. 17-23, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
Currently, 29.3% of all 5- to 11-year-olds have received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, and an even 20.0% are fully vaccinated. For children aged 12-17, the corresponding figures are 65.8% and 55.1%, the CDC said.
Statewide vaccination rates vary from Vermont’s high of 61% for those aged 5-11 to 12% for Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, while Hawaii has the highest rate for 12- to 17-year-olds at 92% and Wyoming has the lowest at 39%, the AAP reported.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children topped 1 million for the first time as the cumulative count surpassed 10 million since the start of the pandemic, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. Those 10.6 million child cases represent 18.4% of all cases, and the latest 1.15 million represented 25.5% of all cases for the week.
Regionally, the South had the most cases with over 380,000 for the week of Jan. 14-20, while the West was next with close to 350,000, followed by the Midwest and then the East. Among the states, the largest percent increases – on the order of 30% – came in New England (Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont), as well as Virginia and California, the AAP and CHA said.
Examining all those cases by vaccination status shows an obvious difference between the Omicron and Delta variants: The fully vaccinated have been hit much harder than before. For the week ending Dec. 25, 2021, the incidence of COVID-19 in children aged 12-17 years was 704 per 100,000 among those were unvaccinated and 384 per 100,000 in those who were fully vaccinated. During the Delta surge in the summer of 2021, the peak rates were 938 (unvaccinated) and 79 (vaccinated), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
Hospitalizations are also at record levels, but two separate CDC databases seem to show a decline in child admissions over the last available week or so of data, which follows the trend among all ages. The peak among children aged 0-17 years came on Jan. 15, when the rate of new admissions reached 1.25 per 100,000, based on reporting to the CDC from 5,265 hospitals nationwide.
The second database, the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET), indicates that children aged 0-4 years had the highest admission rate, 14.5 per 100,000, for the week ending Jan. 8, compared with 5.5 per 100,000 for 12- to 17-year-olds and 2.3 per 100,000 for those aged 5-11 years. COVID-NET covers almost 100 counties in 10 states, along with 4 entire states, and represents about 10% of the U.S. population.
Vaccinations rose briefly in late December and into January to meet the Omicron surge, but the numbers for the latest week show a return to their earlier levels. In children aged 5-11 years, new vaccinations went from 381,000 for the week of Dec. 20-26 to 524,000 for Jan. 3-9, but fell to just 260,000 during Jan. 17-23. The response was a little later for those aged 12-17, with the big week coming Jan. 10-16, but there was still a 38% drop for Jan. 17-23, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
Currently, 29.3% of all 5- to 11-year-olds have received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, and an even 20.0% are fully vaccinated. For children aged 12-17, the corresponding figures are 65.8% and 55.1%, the CDC said.
Statewide vaccination rates vary from Vermont’s high of 61% for those aged 5-11 to 12% for Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, while Hawaii has the highest rate for 12- to 17-year-olds at 92% and Wyoming has the lowest at 39%, the AAP reported.
Ways to make sure 2022 doesn’t stink for docs
Depending on the data you’re looking at, 40%-60% of physicians are burned out.
Research studies and the eye test reveal the painfully obvious: Colleagues are tired, winded, spent, and at times way past burned out. People aren’t asking me if they’re burned out. They know they’re burned out; heck, they can even recite the Maslach burnout inventory, forward and backward, in a mask, or while completing a COVID quarantine. A fair share of people know the key steps to prevent burnout and promote recovery.
What I’m starting to see more of is, “Why should I even bother to recover from this? Why pick myself up again just to get another occupational stress injury (burnout, demoralization, moral injury, etc.)?” In other words, it’s not just simply about negating burnout; it’s about supporting and facilitating the motivation to work.
We’ve been through so much with COVID that it might be challenging to remember when you saw a truly engaged work environment. No doubt, we have outstanding professionals across medicine who answer the bell every day. However, if you’ve been looking closely, many teams/units have lost a bit of the zip and pep. The synergy and trust aren’t as smooth, and at noon, everyone counts the hours to the end of the shift.
You may be thinking, Well, of course, they are; we’re still amid a pandemic, and people have been through hell. Your observation would be correct, except I’ve personally seen some teams weather the pandemic storm and still remain engaged (some even more involved).
The No. 1 consult result for the GW Resiliency and Well-Being Center, where I work, has been on lectures for burnout. The R&WC has given so many of these lectures that my dreams take the form of a PowerPoint presentation. Overall the talks have gone very well. We’ve added skills sections on practices of whole-person care. We’ve blitzed the daylights out of restorative sleep, yet I know we are still searching for the correct narrative.
Motivated staff, faculty, and students will genuinely take in the information and follow the recommendations; however, they still struggle to find that drive and zest for work. Yes, moving from burnout to neutral is reasonable but likely won’t move the needle of your professional or personal life. We need to have the emotional energy and the clear desire to utilize that energy for a meaningful purpose.
Talking about burnout in specific ways is straightforward and, in my opinion, much easier than talking about engagement. Part of the challenge when trying to discuss engagement is that people can feel invalidated or that you’re telling them to be stoic. Or worse yet, that the problem of burnout primarily lies with them. It’s essential to recognize the role of an organizational factor in burnout (approximately 80%, depending on the study); still, even if you address burnout, people may not be miserable, but it doesn’t mean they will stay at their current job (please cue intro music for the Great Resignation).
Engagement models have existed for some time and certainly have gained much more attention in health care settings over the past 2 decades. Engagement can be described as having three components: dedication, vigor, and absorption. When a person is filling all three of these components over time, presto – you get the much-sought-after state of the supremely engaged professional.
These models definitely give us excellent starting points to approach engagement from a pre-COVID era. In COVID and beyond, I’m not sure how these models will stand up in a hybrid work environment, where autonomy and flexibility could be more valued than ever. Personally, COVID revealed some things I was missing in my work pre-COVID:
- Time to think and process. This was one of the great things about being a consultation-liaison psychiatrist; it was literally feast or famine.
- Doing what I’m talented at and really enjoy.
- Time is short, and I want to be more present in the life of my family.
The list above isn’t exhaustive, but I’ve found them to be my own personal recipe for being engaged. Over the next series of articles, I’m going to focus on engagement and factors related to key resilience. These articles will be informed by a front-line view from my colleagues, and hopefully start to separate the myth from reality on the subject of health professional engagement and resilience.
Everyone be safe and well!
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Depending on the data you’re looking at, 40%-60% of physicians are burned out.
Research studies and the eye test reveal the painfully obvious: Colleagues are tired, winded, spent, and at times way past burned out. People aren’t asking me if they’re burned out. They know they’re burned out; heck, they can even recite the Maslach burnout inventory, forward and backward, in a mask, or while completing a COVID quarantine. A fair share of people know the key steps to prevent burnout and promote recovery.
What I’m starting to see more of is, “Why should I even bother to recover from this? Why pick myself up again just to get another occupational stress injury (burnout, demoralization, moral injury, etc.)?” In other words, it’s not just simply about negating burnout; it’s about supporting and facilitating the motivation to work.
We’ve been through so much with COVID that it might be challenging to remember when you saw a truly engaged work environment. No doubt, we have outstanding professionals across medicine who answer the bell every day. However, if you’ve been looking closely, many teams/units have lost a bit of the zip and pep. The synergy and trust aren’t as smooth, and at noon, everyone counts the hours to the end of the shift.
You may be thinking, Well, of course, they are; we’re still amid a pandemic, and people have been through hell. Your observation would be correct, except I’ve personally seen some teams weather the pandemic storm and still remain engaged (some even more involved).
The No. 1 consult result for the GW Resiliency and Well-Being Center, where I work, has been on lectures for burnout. The R&WC has given so many of these lectures that my dreams take the form of a PowerPoint presentation. Overall the talks have gone very well. We’ve added skills sections on practices of whole-person care. We’ve blitzed the daylights out of restorative sleep, yet I know we are still searching for the correct narrative.
Motivated staff, faculty, and students will genuinely take in the information and follow the recommendations; however, they still struggle to find that drive and zest for work. Yes, moving from burnout to neutral is reasonable but likely won’t move the needle of your professional or personal life. We need to have the emotional energy and the clear desire to utilize that energy for a meaningful purpose.
Talking about burnout in specific ways is straightforward and, in my opinion, much easier than talking about engagement. Part of the challenge when trying to discuss engagement is that people can feel invalidated or that you’re telling them to be stoic. Or worse yet, that the problem of burnout primarily lies with them. It’s essential to recognize the role of an organizational factor in burnout (approximately 80%, depending on the study); still, even if you address burnout, people may not be miserable, but it doesn’t mean they will stay at their current job (please cue intro music for the Great Resignation).
Engagement models have existed for some time and certainly have gained much more attention in health care settings over the past 2 decades. Engagement can be described as having three components: dedication, vigor, and absorption. When a person is filling all three of these components over time, presto – you get the much-sought-after state of the supremely engaged professional.
These models definitely give us excellent starting points to approach engagement from a pre-COVID era. In COVID and beyond, I’m not sure how these models will stand up in a hybrid work environment, where autonomy and flexibility could be more valued than ever. Personally, COVID revealed some things I was missing in my work pre-COVID:
- Time to think and process. This was one of the great things about being a consultation-liaison psychiatrist; it was literally feast or famine.
- Doing what I’m talented at and really enjoy.
- Time is short, and I want to be more present in the life of my family.
The list above isn’t exhaustive, but I’ve found them to be my own personal recipe for being engaged. Over the next series of articles, I’m going to focus on engagement and factors related to key resilience. These articles will be informed by a front-line view from my colleagues, and hopefully start to separate the myth from reality on the subject of health professional engagement and resilience.
Everyone be safe and well!
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Depending on the data you’re looking at, 40%-60% of physicians are burned out.
Research studies and the eye test reveal the painfully obvious: Colleagues are tired, winded, spent, and at times way past burned out. People aren’t asking me if they’re burned out. They know they’re burned out; heck, they can even recite the Maslach burnout inventory, forward and backward, in a mask, or while completing a COVID quarantine. A fair share of people know the key steps to prevent burnout and promote recovery.
What I’m starting to see more of is, “Why should I even bother to recover from this? Why pick myself up again just to get another occupational stress injury (burnout, demoralization, moral injury, etc.)?” In other words, it’s not just simply about negating burnout; it’s about supporting and facilitating the motivation to work.
We’ve been through so much with COVID that it might be challenging to remember when you saw a truly engaged work environment. No doubt, we have outstanding professionals across medicine who answer the bell every day. However, if you’ve been looking closely, many teams/units have lost a bit of the zip and pep. The synergy and trust aren’t as smooth, and at noon, everyone counts the hours to the end of the shift.
You may be thinking, Well, of course, they are; we’re still amid a pandemic, and people have been through hell. Your observation would be correct, except I’ve personally seen some teams weather the pandemic storm and still remain engaged (some even more involved).
The No. 1 consult result for the GW Resiliency and Well-Being Center, where I work, has been on lectures for burnout. The R&WC has given so many of these lectures that my dreams take the form of a PowerPoint presentation. Overall the talks have gone very well. We’ve added skills sections on practices of whole-person care. We’ve blitzed the daylights out of restorative sleep, yet I know we are still searching for the correct narrative.
Motivated staff, faculty, and students will genuinely take in the information and follow the recommendations; however, they still struggle to find that drive and zest for work. Yes, moving from burnout to neutral is reasonable but likely won’t move the needle of your professional or personal life. We need to have the emotional energy and the clear desire to utilize that energy for a meaningful purpose.
Talking about burnout in specific ways is straightforward and, in my opinion, much easier than talking about engagement. Part of the challenge when trying to discuss engagement is that people can feel invalidated or that you’re telling them to be stoic. Or worse yet, that the problem of burnout primarily lies with them. It’s essential to recognize the role of an organizational factor in burnout (approximately 80%, depending on the study); still, even if you address burnout, people may not be miserable, but it doesn’t mean they will stay at their current job (please cue intro music for the Great Resignation).
Engagement models have existed for some time and certainly have gained much more attention in health care settings over the past 2 decades. Engagement can be described as having three components: dedication, vigor, and absorption. When a person is filling all three of these components over time, presto – you get the much-sought-after state of the supremely engaged professional.
These models definitely give us excellent starting points to approach engagement from a pre-COVID era. In COVID and beyond, I’m not sure how these models will stand up in a hybrid work environment, where autonomy and flexibility could be more valued than ever. Personally, COVID revealed some things I was missing in my work pre-COVID:
- Time to think and process. This was one of the great things about being a consultation-liaison psychiatrist; it was literally feast or famine.
- Doing what I’m talented at and really enjoy.
- Time is short, and I want to be more present in the life of my family.
The list above isn’t exhaustive, but I’ve found them to be my own personal recipe for being engaged. Over the next series of articles, I’m going to focus on engagement and factors related to key resilience. These articles will be informed by a front-line view from my colleagues, and hopefully start to separate the myth from reality on the subject of health professional engagement and resilience.
Everyone be safe and well!
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alternative birthing practices tied to neonatal infection risk
Increasingly popular alternative peripartum practices such as water immersion and nonseverance of the umbilical cord may increase the risk of infections in newborns, a new clinical report from the American Academy of Pediatrics found.
Another perinatal measure potentially raising infection risk was placentophagy, according to a review led by Dawn Nolt, MD, MPH, a professor of pediatric infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
“Awareness of emerging alternative peripartum and neonatal practices helps pediatricians provide counseling to families before birth and to appropriately evaluate and treat neonates who have been exposed to these practices,” Dr. Nolt and colleagues wrote online in Pediatrics.
Amid growing inquiries made from women seeking a positive and meaningful birth experience through alternative approaches as well as reports of possibly related illness in newborns, Dr. Nolt’s group reviewed observational studies, case series, and medical society guidance on the risks associated with seven alternative birthing practices.
Based on their summation, it was not possible to quantify the actual risk associated with any one practice. “But of the seven we reviewed, as an infectious disease pediatrician I would say the most discernible immediate risk is likely attached to nonseverance of the cord,” Dr. Nolt said in an interview. “Left attached, the tissue can potentially necrote and transfer bacteria directly to the child.”
The authors made the following recommendations:
- Water immersion for labor and delivery. While this can increase the comfort of the mother in the first stages of labor, the water can become contaminated and increase the infant’s exposure to water-borne pathogens such as Legionella and Pseudomonas. It is not recommended after the second stage of labor and if offered, requires rigorous prophylactic and infection-control measures. This practice has also been linked to aspiration, drowning, hyponatremia, cord rupture, and death.
- Vaginal seeding. The skin, noses, and mouths of infants born by cesarean section are inoculated with swabs of vaginal fluid in order to expose them to vaginal bacteria that positively influence the infant’s microbiome. Of no known benefit, this measure can expose newborns to microbes such as group B Streptococcus and herpes simplex virus. Infants born by C-section receiving vaginal seeding should be evaluated the same way as those delivered vaginally.
- Umbilical cord nonseverance. Colloquially known as lotus birth, this is another practice with no evidence of advantage but with the potential to raise the risk of neonatal sepsis owing to the presence of necrotic umbilical or placental tissue. Some parents may view the placenta as a spiritual entity and fail to recognize it may be contaminated with harmful pathogens. Any placenta and umbilical cord attached to a febrile or ill-seeming neonate should be immediately removed.
- Placentophagy. Proponents believe placental consumption has antidepressive, analgesic, galactogogic, and nutritional properties. But eating raw, cooked, or dehydrated afterbirth tissue – viewed by some as a spiritual event – can expose a neonate to flora from the mother’s genitourinary tract and other sources encountered during preparation. Placentophagy has been associated with a case of recurrent late-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a newborn. Strict food-handling practices at the level for raw meat should be maintained.
- HBV vaccine deferral. Viewed as “a critical safety net in preventing HBV infection,” the birth dose of the hepatitis B virus vaccine should not be postponed except for medical reasons. An estimated 1,000 new perinatally acquired HBV cases occurred annually in the United States from 2000 to 2009.
- Deferral of ocular prophylaxis. While ocular prophylaxis with topical erythromycin protects against gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum, particularly in infants of high-risk mothers, it is not effective against other common pathogens. Parents and health care providers have recently questioned the need for its routine application, with concerns including its limited range of effectiveness as well as antibiotic resistance and shortages. With adequate prenatal testing, the risk of this neonatal conjunctivitis is significantly reduced, and deferral of prophylaxis may be considered in low-risk situations although it may be mandated by state legislation.
- Delayed bathing. The practice of delaying the infant’s first bath until several hours after birth may have several benefits. These include the initiation and exclusivity of breastfeeding, decreased mother/child separation time and risk of hypothermia, and protection of the neonatal skin microbiome. It should be discouraged, however, in neonates exposed to active herpes simplex virus lesions or whose mothers have a known history of HIV infection.
When women inquire about alternative practices, physicians need to strike a diplomatic balance between respecting women’s wishes and the benefits they hope to gain and at the same time informing them of potential risks, Dr. Nolt said. “The conversation we want to have with them should show compassion and sympathy but also tell them what the medical literature shows.” Patient and doctor should engage in shared decision-making about the safety of various alternative approaches.
“Over the last decade information on a variety of birth practices have become more widely available through social media and other Internet forums, which certainly has increased the variety of questions to health professionals, Amy C. Hermesch, MD, PhD, director of obstetric services at OHSC, said in an interview.
“We counsel about rare but serious risk, as noted in Dr. Nolt’s article,” said Dr. Hermesch, who was not involved in the AAP report. Most important is a discussion about appropriate pregnancy risk stratification. “For example, persons considering water immersion birth, probably the most common one I get inquiries about, should have an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy with good mobility to get in and out of tub in the event of an emergency.”
While adverse events can happen during any birth, she sees these more often in mothers who underestimate the risk level of their situation or pregnancy when declining provider-recommended interventions. “I encourage pregnant persons to find a health care professional they trust who is knowledgeable about the benefits and the risk of all birth environments and interventions.”
Dr. Hermesch added that most alternative practices have little data to guide decisions, so she offers professional society recommendations, evidence review, and her own professional experiences. “The patient must weight the risk and benefits in the context of their value system and sometimes this means not following my advice or recommendations. My medical recommendation with the best of intentions does not remove patient autonomy.”
This report had no external funding. The authors had no potential conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Hermesch had no competing interests to declare.
Increasingly popular alternative peripartum practices such as water immersion and nonseverance of the umbilical cord may increase the risk of infections in newborns, a new clinical report from the American Academy of Pediatrics found.
Another perinatal measure potentially raising infection risk was placentophagy, according to a review led by Dawn Nolt, MD, MPH, a professor of pediatric infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
“Awareness of emerging alternative peripartum and neonatal practices helps pediatricians provide counseling to families before birth and to appropriately evaluate and treat neonates who have been exposed to these practices,” Dr. Nolt and colleagues wrote online in Pediatrics.
Amid growing inquiries made from women seeking a positive and meaningful birth experience through alternative approaches as well as reports of possibly related illness in newborns, Dr. Nolt’s group reviewed observational studies, case series, and medical society guidance on the risks associated with seven alternative birthing practices.
Based on their summation, it was not possible to quantify the actual risk associated with any one practice. “But of the seven we reviewed, as an infectious disease pediatrician I would say the most discernible immediate risk is likely attached to nonseverance of the cord,” Dr. Nolt said in an interview. “Left attached, the tissue can potentially necrote and transfer bacteria directly to the child.”
The authors made the following recommendations:
- Water immersion for labor and delivery. While this can increase the comfort of the mother in the first stages of labor, the water can become contaminated and increase the infant’s exposure to water-borne pathogens such as Legionella and Pseudomonas. It is not recommended after the second stage of labor and if offered, requires rigorous prophylactic and infection-control measures. This practice has also been linked to aspiration, drowning, hyponatremia, cord rupture, and death.
- Vaginal seeding. The skin, noses, and mouths of infants born by cesarean section are inoculated with swabs of vaginal fluid in order to expose them to vaginal bacteria that positively influence the infant’s microbiome. Of no known benefit, this measure can expose newborns to microbes such as group B Streptococcus and herpes simplex virus. Infants born by C-section receiving vaginal seeding should be evaluated the same way as those delivered vaginally.
- Umbilical cord nonseverance. Colloquially known as lotus birth, this is another practice with no evidence of advantage but with the potential to raise the risk of neonatal sepsis owing to the presence of necrotic umbilical or placental tissue. Some parents may view the placenta as a spiritual entity and fail to recognize it may be contaminated with harmful pathogens. Any placenta and umbilical cord attached to a febrile or ill-seeming neonate should be immediately removed.
- Placentophagy. Proponents believe placental consumption has antidepressive, analgesic, galactogogic, and nutritional properties. But eating raw, cooked, or dehydrated afterbirth tissue – viewed by some as a spiritual event – can expose a neonate to flora from the mother’s genitourinary tract and other sources encountered during preparation. Placentophagy has been associated with a case of recurrent late-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a newborn. Strict food-handling practices at the level for raw meat should be maintained.
- HBV vaccine deferral. Viewed as “a critical safety net in preventing HBV infection,” the birth dose of the hepatitis B virus vaccine should not be postponed except for medical reasons. An estimated 1,000 new perinatally acquired HBV cases occurred annually in the United States from 2000 to 2009.
- Deferral of ocular prophylaxis. While ocular prophylaxis with topical erythromycin protects against gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum, particularly in infants of high-risk mothers, it is not effective against other common pathogens. Parents and health care providers have recently questioned the need for its routine application, with concerns including its limited range of effectiveness as well as antibiotic resistance and shortages. With adequate prenatal testing, the risk of this neonatal conjunctivitis is significantly reduced, and deferral of prophylaxis may be considered in low-risk situations although it may be mandated by state legislation.
- Delayed bathing. The practice of delaying the infant’s first bath until several hours after birth may have several benefits. These include the initiation and exclusivity of breastfeeding, decreased mother/child separation time and risk of hypothermia, and protection of the neonatal skin microbiome. It should be discouraged, however, in neonates exposed to active herpes simplex virus lesions or whose mothers have a known history of HIV infection.
When women inquire about alternative practices, physicians need to strike a diplomatic balance between respecting women’s wishes and the benefits they hope to gain and at the same time informing them of potential risks, Dr. Nolt said. “The conversation we want to have with them should show compassion and sympathy but also tell them what the medical literature shows.” Patient and doctor should engage in shared decision-making about the safety of various alternative approaches.
“Over the last decade information on a variety of birth practices have become more widely available through social media and other Internet forums, which certainly has increased the variety of questions to health professionals, Amy C. Hermesch, MD, PhD, director of obstetric services at OHSC, said in an interview.
“We counsel about rare but serious risk, as noted in Dr. Nolt’s article,” said Dr. Hermesch, who was not involved in the AAP report. Most important is a discussion about appropriate pregnancy risk stratification. “For example, persons considering water immersion birth, probably the most common one I get inquiries about, should have an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy with good mobility to get in and out of tub in the event of an emergency.”
While adverse events can happen during any birth, she sees these more often in mothers who underestimate the risk level of their situation or pregnancy when declining provider-recommended interventions. “I encourage pregnant persons to find a health care professional they trust who is knowledgeable about the benefits and the risk of all birth environments and interventions.”
Dr. Hermesch added that most alternative practices have little data to guide decisions, so she offers professional society recommendations, evidence review, and her own professional experiences. “The patient must weight the risk and benefits in the context of their value system and sometimes this means not following my advice or recommendations. My medical recommendation with the best of intentions does not remove patient autonomy.”
This report had no external funding. The authors had no potential conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Hermesch had no competing interests to declare.
Increasingly popular alternative peripartum practices such as water immersion and nonseverance of the umbilical cord may increase the risk of infections in newborns, a new clinical report from the American Academy of Pediatrics found.
Another perinatal measure potentially raising infection risk was placentophagy, according to a review led by Dawn Nolt, MD, MPH, a professor of pediatric infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
“Awareness of emerging alternative peripartum and neonatal practices helps pediatricians provide counseling to families before birth and to appropriately evaluate and treat neonates who have been exposed to these practices,” Dr. Nolt and colleagues wrote online in Pediatrics.
Amid growing inquiries made from women seeking a positive and meaningful birth experience through alternative approaches as well as reports of possibly related illness in newborns, Dr. Nolt’s group reviewed observational studies, case series, and medical society guidance on the risks associated with seven alternative birthing practices.
Based on their summation, it was not possible to quantify the actual risk associated with any one practice. “But of the seven we reviewed, as an infectious disease pediatrician I would say the most discernible immediate risk is likely attached to nonseverance of the cord,” Dr. Nolt said in an interview. “Left attached, the tissue can potentially necrote and transfer bacteria directly to the child.”
The authors made the following recommendations:
- Water immersion for labor and delivery. While this can increase the comfort of the mother in the first stages of labor, the water can become contaminated and increase the infant’s exposure to water-borne pathogens such as Legionella and Pseudomonas. It is not recommended after the second stage of labor and if offered, requires rigorous prophylactic and infection-control measures. This practice has also been linked to aspiration, drowning, hyponatremia, cord rupture, and death.
- Vaginal seeding. The skin, noses, and mouths of infants born by cesarean section are inoculated with swabs of vaginal fluid in order to expose them to vaginal bacteria that positively influence the infant’s microbiome. Of no known benefit, this measure can expose newborns to microbes such as group B Streptococcus and herpes simplex virus. Infants born by C-section receiving vaginal seeding should be evaluated the same way as those delivered vaginally.
- Umbilical cord nonseverance. Colloquially known as lotus birth, this is another practice with no evidence of advantage but with the potential to raise the risk of neonatal sepsis owing to the presence of necrotic umbilical or placental tissue. Some parents may view the placenta as a spiritual entity and fail to recognize it may be contaminated with harmful pathogens. Any placenta and umbilical cord attached to a febrile or ill-seeming neonate should be immediately removed.
- Placentophagy. Proponents believe placental consumption has antidepressive, analgesic, galactogogic, and nutritional properties. But eating raw, cooked, or dehydrated afterbirth tissue – viewed by some as a spiritual event – can expose a neonate to flora from the mother’s genitourinary tract and other sources encountered during preparation. Placentophagy has been associated with a case of recurrent late-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a newborn. Strict food-handling practices at the level for raw meat should be maintained.
- HBV vaccine deferral. Viewed as “a critical safety net in preventing HBV infection,” the birth dose of the hepatitis B virus vaccine should not be postponed except for medical reasons. An estimated 1,000 new perinatally acquired HBV cases occurred annually in the United States from 2000 to 2009.
- Deferral of ocular prophylaxis. While ocular prophylaxis with topical erythromycin protects against gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum, particularly in infants of high-risk mothers, it is not effective against other common pathogens. Parents and health care providers have recently questioned the need for its routine application, with concerns including its limited range of effectiveness as well as antibiotic resistance and shortages. With adequate prenatal testing, the risk of this neonatal conjunctivitis is significantly reduced, and deferral of prophylaxis may be considered in low-risk situations although it may be mandated by state legislation.
- Delayed bathing. The practice of delaying the infant’s first bath until several hours after birth may have several benefits. These include the initiation and exclusivity of breastfeeding, decreased mother/child separation time and risk of hypothermia, and protection of the neonatal skin microbiome. It should be discouraged, however, in neonates exposed to active herpes simplex virus lesions or whose mothers have a known history of HIV infection.
When women inquire about alternative practices, physicians need to strike a diplomatic balance between respecting women’s wishes and the benefits they hope to gain and at the same time informing them of potential risks, Dr. Nolt said. “The conversation we want to have with them should show compassion and sympathy but also tell them what the medical literature shows.” Patient and doctor should engage in shared decision-making about the safety of various alternative approaches.
“Over the last decade information on a variety of birth practices have become more widely available through social media and other Internet forums, which certainly has increased the variety of questions to health professionals, Amy C. Hermesch, MD, PhD, director of obstetric services at OHSC, said in an interview.
“We counsel about rare but serious risk, as noted in Dr. Nolt’s article,” said Dr. Hermesch, who was not involved in the AAP report. Most important is a discussion about appropriate pregnancy risk stratification. “For example, persons considering water immersion birth, probably the most common one I get inquiries about, should have an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy with good mobility to get in and out of tub in the event of an emergency.”
While adverse events can happen during any birth, she sees these more often in mothers who underestimate the risk level of their situation or pregnancy when declining provider-recommended interventions. “I encourage pregnant persons to find a health care professional they trust who is knowledgeable about the benefits and the risk of all birth environments and interventions.”
Dr. Hermesch added that most alternative practices have little data to guide decisions, so she offers professional society recommendations, evidence review, and her own professional experiences. “The patient must weight the risk and benefits in the context of their value system and sometimes this means not following my advice or recommendations. My medical recommendation with the best of intentions does not remove patient autonomy.”
This report had no external funding. The authors had no potential conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Hermesch had no competing interests to declare.
FROM PEDIATRICS