User login
Could the Omicron surge hasten the transition from pandemic to endemic?
The record-setting surge in COVID-19 cases nationwide – including more than one million new infections reported on Jan. 3 – raises questions about whether the higher Omicron variant transmissibility will accelerate a transition from pandemic to endemic disease.
Furthermore,
Infectious disease experts weigh in on these possibilities.
An endemic eventuality?
Whether the current surge will mean the predicted switch to endemic COVID-19 will come sooner “is very hard to predict,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“It’s an open question,” he said, “if another highly transmissible variant will emerge.”
On a positive note, “at this point many more people have received their vaccinations or been infected. And over time, repeated infections have led to milder symptoms,” added Dr. Lin, hospital epidemiologist at Rush Medical College, Chicago.
“It could end up being a seasonal variant,” he said.
COVID-19 going endemic is “a real possibility, but unfortunately ... it doesn’t seem necessarily that we’re going to have the same predictable pattern we have with the flu,” said Eleftherios Mylonakis, MD, PhD, chief of infectious diseases for Lifespan and its affiliates at Rhode Island Hospital and Miriam Hospital in Providence.
“We have a number of other viruses that don’t follow the same annual pattern,” he said.
Unknowns include how long individuals’ immune responses, including T-cell defenses, will last going forward.
A transition from pandemic to endemic is “not a light switch, and there are no metrics associated with what endemic means for COVID-19,” said Syra Madad, DHSc., MSc, MCP, an infectious disease epidemiologist at Harvard’s Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, Boston.
“Instead, we should continue to focus on decreasing transmission rates and preventing our hospitals from getting overwhelmed,” she said.
A hastening to herd immunity?
“The short answer is yes,” Dr. Lin said when asked if the increased transmissibility and increased cases linked to the Omicron surge could get the U.S. closer to herd immunity.
“The twist in this whole story,” he said, “is the virus mutated enough to escape first-line immune defenses, specifically antibodies. That is why we are seeing breakthrough infections, even in highly vaccinated populations.”
Dr. Mylonakis was more skeptical regarding herd immunity.
“The concept of herd immunity with a rapidly evolving virus is very difficult” to address, he said.
One reason is the number of unknown factors, Dr. Mylonakis said. He predicted a clearer picture will emerge after the Omicrons surge subsides. Also, with so many people infected by the Omicron variant, immune protection should peak.
“People will have boosted immunity. Not everybody, unfortunately, because there are people who cannot really mount [a full immune response] because of age, because of immunosuppression, etc.,” said Dr. Mylonakis, who is also professor of infectious diseases at Brown University.
“But the majority of the population will be exposed and will mount some degree of immunity.”
Dr. Madad agreed. “The omicron variant will add much more immunity into our population by both the preferred pathway – which is through vaccination – as well as through those that are unvaccinated and get infected with omicron,” she said.
“The pathway to gain immunity from vaccination is the safest option, and already over 1 million doses of the COVID-19 vaccine are going into arms per day – this includes first, second, and additional doses like boosters,” added Dr. Madad, who is also senior director of the System-wide Special Pathogens Program at New York City Health and Hospitals.
A shorter, more intense surge?
The United Kingdom’s experience with COVID-19 has often served as a bellwether of what is likely to happen in the U.S. If that is the case with the Omicron surge, the peak should last about 4 weeks, Dr. Mylonakis said.
In other words, the accelerated spread of Omicron could mean this surge passes more quickly than Delta.
Furthermore, some evidence suggests neutralizing antibodies produced by Omicron infection remain effective against the Delta variant – thereby reducing the risk of Delta reinfections over time.
The ability to neutralize the Delta variant increased more than fourfold after a median 14 days, according to data from a preprint study posted Dec. 27 on MedRxiv.
At the same time, neutralization of the Omicron variant increased 14-fold as participants mounted an antibody response. The study was conducted in vaccinated and unvaccinated people infected by Omicron in South Africa shortly after symptoms started. It has yet to be peer reviewed.
Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, described the results as “especially good news” in a tweet.
The current surge could also mean enhanced protection in the future.
“As we look at getting to the other side of this Omicron wave, we will end up with more immunity,” Dr. Madad said. “And with more immunity means we’ll be better guarded against the next emerging variant.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The record-setting surge in COVID-19 cases nationwide – including more than one million new infections reported on Jan. 3 – raises questions about whether the higher Omicron variant transmissibility will accelerate a transition from pandemic to endemic disease.
Furthermore,
Infectious disease experts weigh in on these possibilities.
An endemic eventuality?
Whether the current surge will mean the predicted switch to endemic COVID-19 will come sooner “is very hard to predict,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“It’s an open question,” he said, “if another highly transmissible variant will emerge.”
On a positive note, “at this point many more people have received their vaccinations or been infected. And over time, repeated infections have led to milder symptoms,” added Dr. Lin, hospital epidemiologist at Rush Medical College, Chicago.
“It could end up being a seasonal variant,” he said.
COVID-19 going endemic is “a real possibility, but unfortunately ... it doesn’t seem necessarily that we’re going to have the same predictable pattern we have with the flu,” said Eleftherios Mylonakis, MD, PhD, chief of infectious diseases for Lifespan and its affiliates at Rhode Island Hospital and Miriam Hospital in Providence.
“We have a number of other viruses that don’t follow the same annual pattern,” he said.
Unknowns include how long individuals’ immune responses, including T-cell defenses, will last going forward.
A transition from pandemic to endemic is “not a light switch, and there are no metrics associated with what endemic means for COVID-19,” said Syra Madad, DHSc., MSc, MCP, an infectious disease epidemiologist at Harvard’s Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, Boston.
“Instead, we should continue to focus on decreasing transmission rates and preventing our hospitals from getting overwhelmed,” she said.
A hastening to herd immunity?
“The short answer is yes,” Dr. Lin said when asked if the increased transmissibility and increased cases linked to the Omicron surge could get the U.S. closer to herd immunity.
“The twist in this whole story,” he said, “is the virus mutated enough to escape first-line immune defenses, specifically antibodies. That is why we are seeing breakthrough infections, even in highly vaccinated populations.”
Dr. Mylonakis was more skeptical regarding herd immunity.
“The concept of herd immunity with a rapidly evolving virus is very difficult” to address, he said.
One reason is the number of unknown factors, Dr. Mylonakis said. He predicted a clearer picture will emerge after the Omicrons surge subsides. Also, with so many people infected by the Omicron variant, immune protection should peak.
“People will have boosted immunity. Not everybody, unfortunately, because there are people who cannot really mount [a full immune response] because of age, because of immunosuppression, etc.,” said Dr. Mylonakis, who is also professor of infectious diseases at Brown University.
“But the majority of the population will be exposed and will mount some degree of immunity.”
Dr. Madad agreed. “The omicron variant will add much more immunity into our population by both the preferred pathway – which is through vaccination – as well as through those that are unvaccinated and get infected with omicron,” she said.
“The pathway to gain immunity from vaccination is the safest option, and already over 1 million doses of the COVID-19 vaccine are going into arms per day – this includes first, second, and additional doses like boosters,” added Dr. Madad, who is also senior director of the System-wide Special Pathogens Program at New York City Health and Hospitals.
A shorter, more intense surge?
The United Kingdom’s experience with COVID-19 has often served as a bellwether of what is likely to happen in the U.S. If that is the case with the Omicron surge, the peak should last about 4 weeks, Dr. Mylonakis said.
In other words, the accelerated spread of Omicron could mean this surge passes more quickly than Delta.
Furthermore, some evidence suggests neutralizing antibodies produced by Omicron infection remain effective against the Delta variant – thereby reducing the risk of Delta reinfections over time.
The ability to neutralize the Delta variant increased more than fourfold after a median 14 days, according to data from a preprint study posted Dec. 27 on MedRxiv.
At the same time, neutralization of the Omicron variant increased 14-fold as participants mounted an antibody response. The study was conducted in vaccinated and unvaccinated people infected by Omicron in South Africa shortly after symptoms started. It has yet to be peer reviewed.
Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, described the results as “especially good news” in a tweet.
The current surge could also mean enhanced protection in the future.
“As we look at getting to the other side of this Omicron wave, we will end up with more immunity,” Dr. Madad said. “And with more immunity means we’ll be better guarded against the next emerging variant.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The record-setting surge in COVID-19 cases nationwide – including more than one million new infections reported on Jan. 3 – raises questions about whether the higher Omicron variant transmissibility will accelerate a transition from pandemic to endemic disease.
Furthermore,
Infectious disease experts weigh in on these possibilities.
An endemic eventuality?
Whether the current surge will mean the predicted switch to endemic COVID-19 will come sooner “is very hard to predict,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“It’s an open question,” he said, “if another highly transmissible variant will emerge.”
On a positive note, “at this point many more people have received their vaccinations or been infected. And over time, repeated infections have led to milder symptoms,” added Dr. Lin, hospital epidemiologist at Rush Medical College, Chicago.
“It could end up being a seasonal variant,” he said.
COVID-19 going endemic is “a real possibility, but unfortunately ... it doesn’t seem necessarily that we’re going to have the same predictable pattern we have with the flu,” said Eleftherios Mylonakis, MD, PhD, chief of infectious diseases for Lifespan and its affiliates at Rhode Island Hospital and Miriam Hospital in Providence.
“We have a number of other viruses that don’t follow the same annual pattern,” he said.
Unknowns include how long individuals’ immune responses, including T-cell defenses, will last going forward.
A transition from pandemic to endemic is “not a light switch, and there are no metrics associated with what endemic means for COVID-19,” said Syra Madad, DHSc., MSc, MCP, an infectious disease epidemiologist at Harvard’s Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, Boston.
“Instead, we should continue to focus on decreasing transmission rates and preventing our hospitals from getting overwhelmed,” she said.
A hastening to herd immunity?
“The short answer is yes,” Dr. Lin said when asked if the increased transmissibility and increased cases linked to the Omicron surge could get the U.S. closer to herd immunity.
“The twist in this whole story,” he said, “is the virus mutated enough to escape first-line immune defenses, specifically antibodies. That is why we are seeing breakthrough infections, even in highly vaccinated populations.”
Dr. Mylonakis was more skeptical regarding herd immunity.
“The concept of herd immunity with a rapidly evolving virus is very difficult” to address, he said.
One reason is the number of unknown factors, Dr. Mylonakis said. He predicted a clearer picture will emerge after the Omicrons surge subsides. Also, with so many people infected by the Omicron variant, immune protection should peak.
“People will have boosted immunity. Not everybody, unfortunately, because there are people who cannot really mount [a full immune response] because of age, because of immunosuppression, etc.,” said Dr. Mylonakis, who is also professor of infectious diseases at Brown University.
“But the majority of the population will be exposed and will mount some degree of immunity.”
Dr. Madad agreed. “The omicron variant will add much more immunity into our population by both the preferred pathway – which is through vaccination – as well as through those that are unvaccinated and get infected with omicron,” she said.
“The pathway to gain immunity from vaccination is the safest option, and already over 1 million doses of the COVID-19 vaccine are going into arms per day – this includes first, second, and additional doses like boosters,” added Dr. Madad, who is also senior director of the System-wide Special Pathogens Program at New York City Health and Hospitals.
A shorter, more intense surge?
The United Kingdom’s experience with COVID-19 has often served as a bellwether of what is likely to happen in the U.S. If that is the case with the Omicron surge, the peak should last about 4 weeks, Dr. Mylonakis said.
In other words, the accelerated spread of Omicron could mean this surge passes more quickly than Delta.
Furthermore, some evidence suggests neutralizing antibodies produced by Omicron infection remain effective against the Delta variant – thereby reducing the risk of Delta reinfections over time.
The ability to neutralize the Delta variant increased more than fourfold after a median 14 days, according to data from a preprint study posted Dec. 27 on MedRxiv.
At the same time, neutralization of the Omicron variant increased 14-fold as participants mounted an antibody response. The study was conducted in vaccinated and unvaccinated people infected by Omicron in South Africa shortly after symptoms started. It has yet to be peer reviewed.
Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, described the results as “especially good news” in a tweet.
The current surge could also mean enhanced protection in the future.
“As we look at getting to the other side of this Omicron wave, we will end up with more immunity,” Dr. Madad said. “And with more immunity means we’ll be better guarded against the next emerging variant.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As Omicron surges, hospital beds fill, but ICUs less affected
So far, hospitalizations caused by the Omicron variant appear to be milder than in previous waves.
“We are seeing an increase in the number of hospitalizations,” Rahul Sharma, MD, emergency physician-in-chief for New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medicine, told the New York Times.
“We’re not sending as many patients to the ICU, we’re not intubating as many patients, and actually, most of our patients that are coming to the emergency department that do test positive are actually being discharged,” he said.
Most Omicron patients in ICUs are unvaccinated or have severely compromised immune systems, doctors told the newspaper.
Currently, about 113,000 COVID-19 patients are hospitalized across the country, according to the latest data from the Department of Health & Human Services. About 76% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, with about 16% of inpatient beds in use for COVID-19.
Early data suggests that the Omicron variant may cause less severe disease. But it’s easier to catch the variant, so more people are getting the virus, including people who have some immunity through prior infection or vaccination, which is driving up hospitalization numbers.
In New York, for instance, COVID-19 hospitalizations have surpassed the peak of last winter’s surge, the newspaper reported. In addition, Maryland Gov. Larry Hogan declared a state of emergency on Jan. 4, noting that the state had more hospitalized COVID-19 patients than at any other time during the pandemic.
“We’re in truly crushed mode,” Gabe Kelen, MD, chair of the department of emergency medicine for the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, told the Times.
Earlier in the pandemic, hospitals faced challenges with stockpiling ventilators and personal protective equipment, doctors told the newspaper. Now they’re dealing with limits on hospital beds and staffing as health care workers test positive. The increase in COVID-19 cases has also come along with a rise in hospitalizations for other conditions such as heart attacks and strokes.
In response, some hospitals are considering cutting elective surgeries because of staff shortages and limited bed capacity, the newspaper reported. In the meantime, hospital staff and administrators are watching case numbers to see how high hospitalizations may soar because of the Omicron variant.
“How high will it go? Can’t tell you. Don’t know,” James Musser, MD, chair of pathology and genomic medicine at Houston Methodist, told the Times. “We’re all watching it, obviously, very, very closely.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
So far, hospitalizations caused by the Omicron variant appear to be milder than in previous waves.
“We are seeing an increase in the number of hospitalizations,” Rahul Sharma, MD, emergency physician-in-chief for New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medicine, told the New York Times.
“We’re not sending as many patients to the ICU, we’re not intubating as many patients, and actually, most of our patients that are coming to the emergency department that do test positive are actually being discharged,” he said.
Most Omicron patients in ICUs are unvaccinated or have severely compromised immune systems, doctors told the newspaper.
Currently, about 113,000 COVID-19 patients are hospitalized across the country, according to the latest data from the Department of Health & Human Services. About 76% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, with about 16% of inpatient beds in use for COVID-19.
Early data suggests that the Omicron variant may cause less severe disease. But it’s easier to catch the variant, so more people are getting the virus, including people who have some immunity through prior infection or vaccination, which is driving up hospitalization numbers.
In New York, for instance, COVID-19 hospitalizations have surpassed the peak of last winter’s surge, the newspaper reported. In addition, Maryland Gov. Larry Hogan declared a state of emergency on Jan. 4, noting that the state had more hospitalized COVID-19 patients than at any other time during the pandemic.
“We’re in truly crushed mode,” Gabe Kelen, MD, chair of the department of emergency medicine for the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, told the Times.
Earlier in the pandemic, hospitals faced challenges with stockpiling ventilators and personal protective equipment, doctors told the newspaper. Now they’re dealing with limits on hospital beds and staffing as health care workers test positive. The increase in COVID-19 cases has also come along with a rise in hospitalizations for other conditions such as heart attacks and strokes.
In response, some hospitals are considering cutting elective surgeries because of staff shortages and limited bed capacity, the newspaper reported. In the meantime, hospital staff and administrators are watching case numbers to see how high hospitalizations may soar because of the Omicron variant.
“How high will it go? Can’t tell you. Don’t know,” James Musser, MD, chair of pathology and genomic medicine at Houston Methodist, told the Times. “We’re all watching it, obviously, very, very closely.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
So far, hospitalizations caused by the Omicron variant appear to be milder than in previous waves.
“We are seeing an increase in the number of hospitalizations,” Rahul Sharma, MD, emergency physician-in-chief for New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medicine, told the New York Times.
“We’re not sending as many patients to the ICU, we’re not intubating as many patients, and actually, most of our patients that are coming to the emergency department that do test positive are actually being discharged,” he said.
Most Omicron patients in ICUs are unvaccinated or have severely compromised immune systems, doctors told the newspaper.
Currently, about 113,000 COVID-19 patients are hospitalized across the country, according to the latest data from the Department of Health & Human Services. About 76% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, with about 16% of inpatient beds in use for COVID-19.
Early data suggests that the Omicron variant may cause less severe disease. But it’s easier to catch the variant, so more people are getting the virus, including people who have some immunity through prior infection or vaccination, which is driving up hospitalization numbers.
In New York, for instance, COVID-19 hospitalizations have surpassed the peak of last winter’s surge, the newspaper reported. In addition, Maryland Gov. Larry Hogan declared a state of emergency on Jan. 4, noting that the state had more hospitalized COVID-19 patients than at any other time during the pandemic.
“We’re in truly crushed mode,” Gabe Kelen, MD, chair of the department of emergency medicine for the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, told the Times.
Earlier in the pandemic, hospitals faced challenges with stockpiling ventilators and personal protective equipment, doctors told the newspaper. Now they’re dealing with limits on hospital beds and staffing as health care workers test positive. The increase in COVID-19 cases has also come along with a rise in hospitalizations for other conditions such as heart attacks and strokes.
In response, some hospitals are considering cutting elective surgeries because of staff shortages and limited bed capacity, the newspaper reported. In the meantime, hospital staff and administrators are watching case numbers to see how high hospitalizations may soar because of the Omicron variant.
“How high will it go? Can’t tell you. Don’t know,” James Musser, MD, chair of pathology and genomic medicine at Houston Methodist, told the Times. “We’re all watching it, obviously, very, very closely.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
CDC panel recommends Pfizer COVID-19 boosters for ages 12-15
The CDC had already said 16- and 17-year-olds “may” receive a Pfizer booster but the new recommendation adds the 12- to 15-year-old group and strengthens the “may” to “should” for 16- and 17-year-olds.
The committee voted 13-1 to recommend the booster for ages 12-17. CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, must still approve the recommendation for it to take effect.
The vote comes after the FDA on Jan. 3 authorized the Pfizer vaccine booster dose for 12- to 15-year-olds.
The FDA action updated the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, and the agency also shortened the recommended time between a second dose and the booster to 5 months or more (from 6 months). A third primary series dose is also now authorized for certain immunocompromised children between 5 and 11 years old. Full details are available in an FDA news release.
The CDC on Jan. 4 also backed the shortened time frame and a third primary series dose for some immunocompromised children 5-11 years old. But the CDC delayed a decision on a booster for 12- to 15-year-olds until it heard from its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on Jan. 5.
The decision came as school districts nationwide are wrestling with decisions of whether to keep schools open or revert to a virtual format as cases surge, and as pediatric COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations reach new highs.
The only dissenting vote came from Helen Keipp Talbot, MD, associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn.
She said after the vote, “I am just fine with kids getting a booster. This is not me against all boosters. I just really want the U.S. to move forward with all kids.”
Dr. Talbot said earlier in the comment period, “If we divert our public health from the unvaccinated to the vaccinated, we are not going to make a big impact. Boosters are incredibly important but they won’t solve this problem of the crowded hospitals.”
She said vaccinating the unvaccinated must be the priority.
“If you are a parent out there who has not yet vaccinated your child because you have questions, please, please talk to a health care provider,” she said.
Among the 13 supporters of the recommendation was Oliver Brooks, MD, chief medical officer of Watts HealthCare Corporation in Los Angeles.
Dr. Brooks said extending the population for boosters is another tool in the toolbox.
“If it’s a hammer, we should hit that nail hard,” he said.
Sara Oliver, MD, ACIP’s lead for the COVID-19 work group, presented the case behind the recommendation.
She noted the soaring Omicron cases.
“As of Jan. 3, the 7-day average had reached an all-time high of nearly 500,000 cases,” Dr. Oliver noted.
Since this summer, she said, adolescents have had a higher rate of incidence than that of adults.
“The majority of COVID cases continue to occur among the unvaccinated,” she said, “with unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds having a 7-times-higher risk of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 compared to vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds. Unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds have around 11 times higher risk of hospitalization than vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds.
“Vaccine effectiveness in adolescents 12-15 years old remains high,” Dr. Oliver said, but evidence shows there may be “some waning over time.”
Discussion of risk centered on myocarditis.
Dr. Oliver said myocarditis rates reported after the Pfizer vaccine in Israel across all populations as of Dec. 15 show that “the rates of myocarditis after a third dose are lower than what is seen after the second dose.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The CDC had already said 16- and 17-year-olds “may” receive a Pfizer booster but the new recommendation adds the 12- to 15-year-old group and strengthens the “may” to “should” for 16- and 17-year-olds.
The committee voted 13-1 to recommend the booster for ages 12-17. CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, must still approve the recommendation for it to take effect.
The vote comes after the FDA on Jan. 3 authorized the Pfizer vaccine booster dose for 12- to 15-year-olds.
The FDA action updated the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, and the agency also shortened the recommended time between a second dose and the booster to 5 months or more (from 6 months). A third primary series dose is also now authorized for certain immunocompromised children between 5 and 11 years old. Full details are available in an FDA news release.
The CDC on Jan. 4 also backed the shortened time frame and a third primary series dose for some immunocompromised children 5-11 years old. But the CDC delayed a decision on a booster for 12- to 15-year-olds until it heard from its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on Jan. 5.
The decision came as school districts nationwide are wrestling with decisions of whether to keep schools open or revert to a virtual format as cases surge, and as pediatric COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations reach new highs.
The only dissenting vote came from Helen Keipp Talbot, MD, associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn.
She said after the vote, “I am just fine with kids getting a booster. This is not me against all boosters. I just really want the U.S. to move forward with all kids.”
Dr. Talbot said earlier in the comment period, “If we divert our public health from the unvaccinated to the vaccinated, we are not going to make a big impact. Boosters are incredibly important but they won’t solve this problem of the crowded hospitals.”
She said vaccinating the unvaccinated must be the priority.
“If you are a parent out there who has not yet vaccinated your child because you have questions, please, please talk to a health care provider,” she said.
Among the 13 supporters of the recommendation was Oliver Brooks, MD, chief medical officer of Watts HealthCare Corporation in Los Angeles.
Dr. Brooks said extending the population for boosters is another tool in the toolbox.
“If it’s a hammer, we should hit that nail hard,” he said.
Sara Oliver, MD, ACIP’s lead for the COVID-19 work group, presented the case behind the recommendation.
She noted the soaring Omicron cases.
“As of Jan. 3, the 7-day average had reached an all-time high of nearly 500,000 cases,” Dr. Oliver noted.
Since this summer, she said, adolescents have had a higher rate of incidence than that of adults.
“The majority of COVID cases continue to occur among the unvaccinated,” she said, “with unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds having a 7-times-higher risk of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 compared to vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds. Unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds have around 11 times higher risk of hospitalization than vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds.
“Vaccine effectiveness in adolescents 12-15 years old remains high,” Dr. Oliver said, but evidence shows there may be “some waning over time.”
Discussion of risk centered on myocarditis.
Dr. Oliver said myocarditis rates reported after the Pfizer vaccine in Israel across all populations as of Dec. 15 show that “the rates of myocarditis after a third dose are lower than what is seen after the second dose.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The CDC had already said 16- and 17-year-olds “may” receive a Pfizer booster but the new recommendation adds the 12- to 15-year-old group and strengthens the “may” to “should” for 16- and 17-year-olds.
The committee voted 13-1 to recommend the booster for ages 12-17. CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, must still approve the recommendation for it to take effect.
The vote comes after the FDA on Jan. 3 authorized the Pfizer vaccine booster dose for 12- to 15-year-olds.
The FDA action updated the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, and the agency also shortened the recommended time between a second dose and the booster to 5 months or more (from 6 months). A third primary series dose is also now authorized for certain immunocompromised children between 5 and 11 years old. Full details are available in an FDA news release.
The CDC on Jan. 4 also backed the shortened time frame and a third primary series dose for some immunocompromised children 5-11 years old. But the CDC delayed a decision on a booster for 12- to 15-year-olds until it heard from its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on Jan. 5.
The decision came as school districts nationwide are wrestling with decisions of whether to keep schools open or revert to a virtual format as cases surge, and as pediatric COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations reach new highs.
The only dissenting vote came from Helen Keipp Talbot, MD, associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn.
She said after the vote, “I am just fine with kids getting a booster. This is not me against all boosters. I just really want the U.S. to move forward with all kids.”
Dr. Talbot said earlier in the comment period, “If we divert our public health from the unvaccinated to the vaccinated, we are not going to make a big impact. Boosters are incredibly important but they won’t solve this problem of the crowded hospitals.”
She said vaccinating the unvaccinated must be the priority.
“If you are a parent out there who has not yet vaccinated your child because you have questions, please, please talk to a health care provider,” she said.
Among the 13 supporters of the recommendation was Oliver Brooks, MD, chief medical officer of Watts HealthCare Corporation in Los Angeles.
Dr. Brooks said extending the population for boosters is another tool in the toolbox.
“If it’s a hammer, we should hit that nail hard,” he said.
Sara Oliver, MD, ACIP’s lead for the COVID-19 work group, presented the case behind the recommendation.
She noted the soaring Omicron cases.
“As of Jan. 3, the 7-day average had reached an all-time high of nearly 500,000 cases,” Dr. Oliver noted.
Since this summer, she said, adolescents have had a higher rate of incidence than that of adults.
“The majority of COVID cases continue to occur among the unvaccinated,” she said, “with unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds having a 7-times-higher risk of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 compared to vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds. Unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds have around 11 times higher risk of hospitalization than vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds.
“Vaccine effectiveness in adolescents 12-15 years old remains high,” Dr. Oliver said, but evidence shows there may be “some waning over time.”
Discussion of risk centered on myocarditis.
Dr. Oliver said myocarditis rates reported after the Pfizer vaccine in Israel across all populations as of Dec. 15 show that “the rates of myocarditis after a third dose are lower than what is seen after the second dose.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Who needs self-driving cars when we’ve got goldfish?
If a fish can drive …
Have you ever seen a sparrow swim? Have you ever seen an elephant fly? How about a goldfish driving a car? Well, one of these is not just something out of a children’s book.
In a recent study, investigators from Ben-Gurion University did the impossible and got a fish to drive a robotic car on land. How?
No, there wasn’t a tiny steering wheel inside the tank. The researchers created a tank with video recognition ability to sync with the fish. This video shows that the car, on which the tank sat, would navigate in the direction that the fish swam. The goal was to get the fish to “drive” toward a visual target, and with a little training the fish was successful regardless of start point, the researchers explained.
So what does that tell us about the brain and behavior? Shachar Givon, who was part of the research team, said the “study hints that navigational ability is universal rather than specific to the environment.”
The study’s domain transfer methodology (putting one species in the environment of another and have them cope with an unfamiliar task) shows that other animals also have the cognitive ability to transfer skills from one terrestrial environment to another.
That leads us to lesson two. Goldfish are much smarter than we think. So please don’t tap on the glass.
We prefer ‘It’s not writing a funny LOTME article’!
So many medical journals spend all their time grappling with such silly dilemmas as curing cancer or beating COVID-19. Boring! Fortunately, the BMJ dares to stand above the rest by dedicating its Christmas issue to answering the real issues in medicine. And what was the biggest question? Which is the more accurate idiom: “It’s not rocket science,” or “It’s not brain surgery”?
English researchers collected data from 329 aerospace engineers and 72 neurosurgeons who took the Great British Intelligence Test and compared the results against 18,000 people in the general public.
The engineers and neurosurgeons were basically identical in four of the six domains, but neurosurgeons had the advantage when it came to semantic problem solving and engineers had an edge at mental manipulation and attention. The aerospace engineers were identical to the public in all domains, but neurosurgeons held an advantage in problem-solving speed and a disadvantage in memory recall speed.
The researchers noted that exposure to Latin and Greek etymologies during their education gave neurosurgeons the advantage in semantic problem solving, while the aerospace engineers’ advantage in mental manipulation stems from skills taught during engineering training.
But is there a definitive answer to the question? If you’ve got an easy task in front of you, which is more accurate to say: “It’s not rocket science” or “It’s not brain surgery”? Can we get a drum roll?
It’s not brain surgery! At least, as long as the task doesn’t involve rapid problem solving. The investigators hedged further by saying that “It’s a walk in the park” is probably more accurate. Plus, “other specialties might deserve to be on that pedestal, and future work should aim to determine the most deserving profession,” they wrote. Well, at least we’ve got something to look forward to in BMJ’s next Christmas issue.
For COVID-19, a syringe is the sheep of things to come
The logical approach to fighting COVID-19 hasn’t really worked with a lot of people, so how about something more emotional?
People love animals, so they might be a good way to promote the use of vaccines and masks. Puppies are awfully cute, and so are koalas and pandas. And who can say no to a sea otter?
Well, forget it. Instead, we’ve got elephants … and sheep … and goats. Oh my.
First, elephant Santas. The Jirasartwitthaya school in Ayutthaya, Thailand, was recently visited by five elephants in Santa Claus costumes who handed out hand sanitizer and face masks to the students, Reuters said.
“I’m so glad that I got a balloon from the elephant. My heart is pounding very fast,” student Biuon Greham said. And balloons. The elephants handed out sanitizer and masks and balloons. There’s a sentence we never thought we’d write.
And those sheep and goats we mentioned? That was a different party.
Hanspeter Etzold, who “works with shepherds, companies, and animals to run team-building events in the northern German town of Schneverdingen,” according to Reuters, had an idea to promote the use of the COVID-19 vaccine. And yes, it involved sheep and goats.
Mr. Etzold worked with shepherd Wiebke Schmidt-Kochan, who arranged her 700 goats and sheep into the shape of a 100-meter-long syringe using bits of bread laying on the ground. “Sheep are such likable animals – maybe they can get the message over better,” Mr. Etzold told AP.
If those are the carrots in an animals-as-carrots-and-sticks approach, then maybe this golf-club-chomping crab could be the stick. We’re certainly not going to argue with it.
To be or not to be … seen
Increased Zoom meetings have been another side effect of the COVID-19 pandemic as more and more people have been working and learning from home.
A recent study from Washington State University looked at two groups of people who Zoomed on a regular basis: employees and students. Individuals who made the change to remote work/learning were surveyed in the summer and fall of 2020. They completed assessments with questions on their work/classes and their level of self-consciousness.
Those with low self-esteem did not enjoy having to see themselves on camera, and those with higher self-esteem actually enjoyed it more. “Most people believe that seeing yourself during virtual meetings contributes to making the overall experience worse, but that’s not what showed up in my data,” said Kristine Kuhn, PhD, the study’s author.
Dr. Kuhn found that having the choice of whether to have the camera on made a big difference in how the participants felt. Having that control made it a more positive experience. Most professors/bosses would probably like to see the faces of those in the Zoom meetings, but it might be better to let people choose for themselves. The unbrushed-hair club would certainly agree.
If a fish can drive …
Have you ever seen a sparrow swim? Have you ever seen an elephant fly? How about a goldfish driving a car? Well, one of these is not just something out of a children’s book.
In a recent study, investigators from Ben-Gurion University did the impossible and got a fish to drive a robotic car on land. How?
No, there wasn’t a tiny steering wheel inside the tank. The researchers created a tank with video recognition ability to sync with the fish. This video shows that the car, on which the tank sat, would navigate in the direction that the fish swam. The goal was to get the fish to “drive” toward a visual target, and with a little training the fish was successful regardless of start point, the researchers explained.
So what does that tell us about the brain and behavior? Shachar Givon, who was part of the research team, said the “study hints that navigational ability is universal rather than specific to the environment.”
The study’s domain transfer methodology (putting one species in the environment of another and have them cope with an unfamiliar task) shows that other animals also have the cognitive ability to transfer skills from one terrestrial environment to another.
That leads us to lesson two. Goldfish are much smarter than we think. So please don’t tap on the glass.
We prefer ‘It’s not writing a funny LOTME article’!
So many medical journals spend all their time grappling with such silly dilemmas as curing cancer or beating COVID-19. Boring! Fortunately, the BMJ dares to stand above the rest by dedicating its Christmas issue to answering the real issues in medicine. And what was the biggest question? Which is the more accurate idiom: “It’s not rocket science,” or “It’s not brain surgery”?
English researchers collected data from 329 aerospace engineers and 72 neurosurgeons who took the Great British Intelligence Test and compared the results against 18,000 people in the general public.
The engineers and neurosurgeons were basically identical in four of the six domains, but neurosurgeons had the advantage when it came to semantic problem solving and engineers had an edge at mental manipulation and attention. The aerospace engineers were identical to the public in all domains, but neurosurgeons held an advantage in problem-solving speed and a disadvantage in memory recall speed.
The researchers noted that exposure to Latin and Greek etymologies during their education gave neurosurgeons the advantage in semantic problem solving, while the aerospace engineers’ advantage in mental manipulation stems from skills taught during engineering training.
But is there a definitive answer to the question? If you’ve got an easy task in front of you, which is more accurate to say: “It’s not rocket science” or “It’s not brain surgery”? Can we get a drum roll?
It’s not brain surgery! At least, as long as the task doesn’t involve rapid problem solving. The investigators hedged further by saying that “It’s a walk in the park” is probably more accurate. Plus, “other specialties might deserve to be on that pedestal, and future work should aim to determine the most deserving profession,” they wrote. Well, at least we’ve got something to look forward to in BMJ’s next Christmas issue.
For COVID-19, a syringe is the sheep of things to come
The logical approach to fighting COVID-19 hasn’t really worked with a lot of people, so how about something more emotional?
People love animals, so they might be a good way to promote the use of vaccines and masks. Puppies are awfully cute, and so are koalas and pandas. And who can say no to a sea otter?
Well, forget it. Instead, we’ve got elephants … and sheep … and goats. Oh my.
First, elephant Santas. The Jirasartwitthaya school in Ayutthaya, Thailand, was recently visited by five elephants in Santa Claus costumes who handed out hand sanitizer and face masks to the students, Reuters said.
“I’m so glad that I got a balloon from the elephant. My heart is pounding very fast,” student Biuon Greham said. And balloons. The elephants handed out sanitizer and masks and balloons. There’s a sentence we never thought we’d write.
And those sheep and goats we mentioned? That was a different party.
Hanspeter Etzold, who “works with shepherds, companies, and animals to run team-building events in the northern German town of Schneverdingen,” according to Reuters, had an idea to promote the use of the COVID-19 vaccine. And yes, it involved sheep and goats.
Mr. Etzold worked with shepherd Wiebke Schmidt-Kochan, who arranged her 700 goats and sheep into the shape of a 100-meter-long syringe using bits of bread laying on the ground. “Sheep are such likable animals – maybe they can get the message over better,” Mr. Etzold told AP.
If those are the carrots in an animals-as-carrots-and-sticks approach, then maybe this golf-club-chomping crab could be the stick. We’re certainly not going to argue with it.
To be or not to be … seen
Increased Zoom meetings have been another side effect of the COVID-19 pandemic as more and more people have been working and learning from home.
A recent study from Washington State University looked at two groups of people who Zoomed on a regular basis: employees and students. Individuals who made the change to remote work/learning were surveyed in the summer and fall of 2020. They completed assessments with questions on their work/classes and their level of self-consciousness.
Those with low self-esteem did not enjoy having to see themselves on camera, and those with higher self-esteem actually enjoyed it more. “Most people believe that seeing yourself during virtual meetings contributes to making the overall experience worse, but that’s not what showed up in my data,” said Kristine Kuhn, PhD, the study’s author.
Dr. Kuhn found that having the choice of whether to have the camera on made a big difference in how the participants felt. Having that control made it a more positive experience. Most professors/bosses would probably like to see the faces of those in the Zoom meetings, but it might be better to let people choose for themselves. The unbrushed-hair club would certainly agree.
If a fish can drive …
Have you ever seen a sparrow swim? Have you ever seen an elephant fly? How about a goldfish driving a car? Well, one of these is not just something out of a children’s book.
In a recent study, investigators from Ben-Gurion University did the impossible and got a fish to drive a robotic car on land. How?
No, there wasn’t a tiny steering wheel inside the tank. The researchers created a tank with video recognition ability to sync with the fish. This video shows that the car, on which the tank sat, would navigate in the direction that the fish swam. The goal was to get the fish to “drive” toward a visual target, and with a little training the fish was successful regardless of start point, the researchers explained.
So what does that tell us about the brain and behavior? Shachar Givon, who was part of the research team, said the “study hints that navigational ability is universal rather than specific to the environment.”
The study’s domain transfer methodology (putting one species in the environment of another and have them cope with an unfamiliar task) shows that other animals also have the cognitive ability to transfer skills from one terrestrial environment to another.
That leads us to lesson two. Goldfish are much smarter than we think. So please don’t tap on the glass.
We prefer ‘It’s not writing a funny LOTME article’!
So many medical journals spend all their time grappling with such silly dilemmas as curing cancer or beating COVID-19. Boring! Fortunately, the BMJ dares to stand above the rest by dedicating its Christmas issue to answering the real issues in medicine. And what was the biggest question? Which is the more accurate idiom: “It’s not rocket science,” or “It’s not brain surgery”?
English researchers collected data from 329 aerospace engineers and 72 neurosurgeons who took the Great British Intelligence Test and compared the results against 18,000 people in the general public.
The engineers and neurosurgeons were basically identical in four of the six domains, but neurosurgeons had the advantage when it came to semantic problem solving and engineers had an edge at mental manipulation and attention. The aerospace engineers were identical to the public in all domains, but neurosurgeons held an advantage in problem-solving speed and a disadvantage in memory recall speed.
The researchers noted that exposure to Latin and Greek etymologies during their education gave neurosurgeons the advantage in semantic problem solving, while the aerospace engineers’ advantage in mental manipulation stems from skills taught during engineering training.
But is there a definitive answer to the question? If you’ve got an easy task in front of you, which is more accurate to say: “It’s not rocket science” or “It’s not brain surgery”? Can we get a drum roll?
It’s not brain surgery! At least, as long as the task doesn’t involve rapid problem solving. The investigators hedged further by saying that “It’s a walk in the park” is probably more accurate. Plus, “other specialties might deserve to be on that pedestal, and future work should aim to determine the most deserving profession,” they wrote. Well, at least we’ve got something to look forward to in BMJ’s next Christmas issue.
For COVID-19, a syringe is the sheep of things to come
The logical approach to fighting COVID-19 hasn’t really worked with a lot of people, so how about something more emotional?
People love animals, so they might be a good way to promote the use of vaccines and masks. Puppies are awfully cute, and so are koalas and pandas. And who can say no to a sea otter?
Well, forget it. Instead, we’ve got elephants … and sheep … and goats. Oh my.
First, elephant Santas. The Jirasartwitthaya school in Ayutthaya, Thailand, was recently visited by five elephants in Santa Claus costumes who handed out hand sanitizer and face masks to the students, Reuters said.
“I’m so glad that I got a balloon from the elephant. My heart is pounding very fast,” student Biuon Greham said. And balloons. The elephants handed out sanitizer and masks and balloons. There’s a sentence we never thought we’d write.
And those sheep and goats we mentioned? That was a different party.
Hanspeter Etzold, who “works with shepherds, companies, and animals to run team-building events in the northern German town of Schneverdingen,” according to Reuters, had an idea to promote the use of the COVID-19 vaccine. And yes, it involved sheep and goats.
Mr. Etzold worked with shepherd Wiebke Schmidt-Kochan, who arranged her 700 goats and sheep into the shape of a 100-meter-long syringe using bits of bread laying on the ground. “Sheep are such likable animals – maybe they can get the message over better,” Mr. Etzold told AP.
If those are the carrots in an animals-as-carrots-and-sticks approach, then maybe this golf-club-chomping crab could be the stick. We’re certainly not going to argue with it.
To be or not to be … seen
Increased Zoom meetings have been another side effect of the COVID-19 pandemic as more and more people have been working and learning from home.
A recent study from Washington State University looked at two groups of people who Zoomed on a regular basis: employees and students. Individuals who made the change to remote work/learning were surveyed in the summer and fall of 2020. They completed assessments with questions on their work/classes and their level of self-consciousness.
Those with low self-esteem did not enjoy having to see themselves on camera, and those with higher self-esteem actually enjoyed it more. “Most people believe that seeing yourself during virtual meetings contributes to making the overall experience worse, but that’s not what showed up in my data,” said Kristine Kuhn, PhD, the study’s author.
Dr. Kuhn found that having the choice of whether to have the camera on made a big difference in how the participants felt. Having that control made it a more positive experience. Most professors/bosses would probably like to see the faces of those in the Zoom meetings, but it might be better to let people choose for themselves. The unbrushed-hair club would certainly agree.
CDC defends new COVID guidance as doctors raise concerns
, Director Rochelle Walenksy, MD, said during a White House briefing Jan. 5.
Health officials recently shortened the recommended COVID-19 isolation and quarantine period from 10 days to 5, creating confusion amid an outbreak of the highly transmissible Omicron variant, which now accounts for 95% of cases in the United States.
Then, in slightly updated guidance, the CDC recommended using an at-home antigen test after 5 days of isolation if possible, even though these tests having aren’t as sensitive to the Omicron variant, according to the FDA.
“After we released our recs early last week, it became very clear people were interested in using the rapid test, though not authorized for this purpose after the end of their isolation period,” Dr. Walensky said. “We then provided guidance on how they should be used.”
“If that test is negative, people really do need to understand they must continue to wear their mask for those 5 days,” Dr. Walensky said.
But for many, the CDC guidelines are murky and seem to always change.
“Nearly 2 years into this pandemic, with Omicron cases surging across the country, the American people should be able to count on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for timely, accurate, clear guidance to protect themselves, their loved ones, and their communities,” American Medical Association president Gerald Harmon, MD, said in a statement. “Instead, the new recommendations on quarantine and isolation are not only confusing, but are risking further spread of the virus.”
About 31% of people remain infectious 5 days after a positive COVID-19 test, Dr. Harmon said, quoting the CDC’s own rationale for changing its guidance.
“With hundreds of thousands of new cases daily and more than a million positive reported cases on January 3, tens of thousands – potentially hundreds of thousands of people – could return to work and school infectious if they follow the CDC’s new guidance on ending isolation after 5 days without a negative test,” he said. “Physicians are concerned that these recommendations put our patients at risk and could further overwhelm our health care system.”
Instead, Dr. Harmon said a negative test should be required for ending isolation.
“Reemerging without knowing one’s status unnecessarily risks further transmission of the virus,” he said.
Meanwhile, also during the White House briefing, officials said that early data continue to show that Omicron infections are less severe than those from other variants, but skyrocketing cases will still put a strain on the health care system.
“The big caveat is we should not be complacent,” presidential Chief Medical Adviser Anthony Fauci, MD, said a White House briefing Jan. 5.
He added that Omicron “could still stress our hospital system because a certain proportion of a large volume of cases, no matter what, are going to be severe.”
Cases continue to increase greatly. This week’s 7-day daily average of infections is 491,700 -- an increase of 98% over last week, Dr. Walensky said. Hospitalizations, while lagging behind case numbers, are still rising significantly: The daily average is 14,800 admissions, up 63% from last week. Daily deaths this week are 1,200, an increase of only 5%.
Dr. Walensky continues to encourage vaccinations, boosters, and other precautions.
“Vaccines and boosters are protecting people from the severe and tragic outcomes that can occur from COVID-19 infection,” she said. “Get vaccinated and get boosted if eligible, wear a mask, stay home when you’re sick, and take a test if you have symptoms or are looking for greater reassurance before you gather with others.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, Director Rochelle Walenksy, MD, said during a White House briefing Jan. 5.
Health officials recently shortened the recommended COVID-19 isolation and quarantine period from 10 days to 5, creating confusion amid an outbreak of the highly transmissible Omicron variant, which now accounts for 95% of cases in the United States.
Then, in slightly updated guidance, the CDC recommended using an at-home antigen test after 5 days of isolation if possible, even though these tests having aren’t as sensitive to the Omicron variant, according to the FDA.
“After we released our recs early last week, it became very clear people were interested in using the rapid test, though not authorized for this purpose after the end of their isolation period,” Dr. Walensky said. “We then provided guidance on how they should be used.”
“If that test is negative, people really do need to understand they must continue to wear their mask for those 5 days,” Dr. Walensky said.
But for many, the CDC guidelines are murky and seem to always change.
“Nearly 2 years into this pandemic, with Omicron cases surging across the country, the American people should be able to count on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for timely, accurate, clear guidance to protect themselves, their loved ones, and their communities,” American Medical Association president Gerald Harmon, MD, said in a statement. “Instead, the new recommendations on quarantine and isolation are not only confusing, but are risking further spread of the virus.”
About 31% of people remain infectious 5 days after a positive COVID-19 test, Dr. Harmon said, quoting the CDC’s own rationale for changing its guidance.
“With hundreds of thousands of new cases daily and more than a million positive reported cases on January 3, tens of thousands – potentially hundreds of thousands of people – could return to work and school infectious if they follow the CDC’s new guidance on ending isolation after 5 days without a negative test,” he said. “Physicians are concerned that these recommendations put our patients at risk and could further overwhelm our health care system.”
Instead, Dr. Harmon said a negative test should be required for ending isolation.
“Reemerging without knowing one’s status unnecessarily risks further transmission of the virus,” he said.
Meanwhile, also during the White House briefing, officials said that early data continue to show that Omicron infections are less severe than those from other variants, but skyrocketing cases will still put a strain on the health care system.
“The big caveat is we should not be complacent,” presidential Chief Medical Adviser Anthony Fauci, MD, said a White House briefing Jan. 5.
He added that Omicron “could still stress our hospital system because a certain proportion of a large volume of cases, no matter what, are going to be severe.”
Cases continue to increase greatly. This week’s 7-day daily average of infections is 491,700 -- an increase of 98% over last week, Dr. Walensky said. Hospitalizations, while lagging behind case numbers, are still rising significantly: The daily average is 14,800 admissions, up 63% from last week. Daily deaths this week are 1,200, an increase of only 5%.
Dr. Walensky continues to encourage vaccinations, boosters, and other precautions.
“Vaccines and boosters are protecting people from the severe and tragic outcomes that can occur from COVID-19 infection,” she said. “Get vaccinated and get boosted if eligible, wear a mask, stay home when you’re sick, and take a test if you have symptoms or are looking for greater reassurance before you gather with others.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, Director Rochelle Walenksy, MD, said during a White House briefing Jan. 5.
Health officials recently shortened the recommended COVID-19 isolation and quarantine period from 10 days to 5, creating confusion amid an outbreak of the highly transmissible Omicron variant, which now accounts for 95% of cases in the United States.
Then, in slightly updated guidance, the CDC recommended using an at-home antigen test after 5 days of isolation if possible, even though these tests having aren’t as sensitive to the Omicron variant, according to the FDA.
“After we released our recs early last week, it became very clear people were interested in using the rapid test, though not authorized for this purpose after the end of their isolation period,” Dr. Walensky said. “We then provided guidance on how they should be used.”
“If that test is negative, people really do need to understand they must continue to wear their mask for those 5 days,” Dr. Walensky said.
But for many, the CDC guidelines are murky and seem to always change.
“Nearly 2 years into this pandemic, with Omicron cases surging across the country, the American people should be able to count on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for timely, accurate, clear guidance to protect themselves, their loved ones, and their communities,” American Medical Association president Gerald Harmon, MD, said in a statement. “Instead, the new recommendations on quarantine and isolation are not only confusing, but are risking further spread of the virus.”
About 31% of people remain infectious 5 days after a positive COVID-19 test, Dr. Harmon said, quoting the CDC’s own rationale for changing its guidance.
“With hundreds of thousands of new cases daily and more than a million positive reported cases on January 3, tens of thousands – potentially hundreds of thousands of people – could return to work and school infectious if they follow the CDC’s new guidance on ending isolation after 5 days without a negative test,” he said. “Physicians are concerned that these recommendations put our patients at risk and could further overwhelm our health care system.”
Instead, Dr. Harmon said a negative test should be required for ending isolation.
“Reemerging without knowing one’s status unnecessarily risks further transmission of the virus,” he said.
Meanwhile, also during the White House briefing, officials said that early data continue to show that Omicron infections are less severe than those from other variants, but skyrocketing cases will still put a strain on the health care system.
“The big caveat is we should not be complacent,” presidential Chief Medical Adviser Anthony Fauci, MD, said a White House briefing Jan. 5.
He added that Omicron “could still stress our hospital system because a certain proportion of a large volume of cases, no matter what, are going to be severe.”
Cases continue to increase greatly. This week’s 7-day daily average of infections is 491,700 -- an increase of 98% over last week, Dr. Walensky said. Hospitalizations, while lagging behind case numbers, are still rising significantly: The daily average is 14,800 admissions, up 63% from last week. Daily deaths this week are 1,200, an increase of only 5%.
Dr. Walensky continues to encourage vaccinations, boosters, and other precautions.
“Vaccines and boosters are protecting people from the severe and tragic outcomes that can occur from COVID-19 infection,” she said. “Get vaccinated and get boosted if eligible, wear a mask, stay home when you’re sick, and take a test if you have symptoms or are looking for greater reassurance before you gather with others.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID affects executive functioning in young to middle-age adults: Study
than people in the general population with no such infection, according to new data published on the preprint server medRxiv.
Researchers, led by Peter A. Hall, PhD, with the University of Waterloo (Ont.), found that COVID infection is associated with executive dysfunction among young and middle-aged adults, including for those not exposed to intubation or hospitalization.
The findings have not been peer reviewed.
The study included a representative cohort of 1,958 community-dwelling young and middle-aged adults. It used a balanced proportion of infected and uninfected people to estimate the link between SARS-CoV-2 infection and cognitive/executive dysfunction.
The authors noted that the survey was conducted from Sept. 28 to Oct. 21, 2021, when the primary variant in Canada was Delta.
The research was a cross-sectional observational study with data from the ongoing Canadian COVID-19 Experiences Survey. It included equal representation of vaccinated and vaccine-hesitant adults aged 18-54 years. COVID-19 symptoms ranged from negligible to life-threatening cases requiring hospitalization.
Half in the cohort (50.2%) received two vaccine shots; 43.3% had received no shots; and 5.5% received one shot, but were not intending to receive a second shot.
Dose-response relationship
According to the paper, those with prior COVID-19 infection, regardless of symptom severity, reported a significantly higher number of symptoms of executive dysfunction than their noninfected counterparts (mechanical adjustment, 1.63, standard error, 0.08; 95% confidence interval, 1.47-1.80; P = .001).
The researchers also found a dose-response relationship between COVID-19 symptom severity and cognitive dysfunction. Those with moderate and very/extremely severe COVID-19 symptoms were linked with significantly greater dysfunction.
“This reinforces what we’re hearing about – that COVID is not ‘one and done.’ It can have lasting and quite subtle and damaging effects on the human body,” William Schaffner, MD, infectious disease specialist with Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
Measuring executive functioning – including the ability to make sound decisions – is something other studies haven’t typically addressed, he said.
Men were likely to report more cognitive dysfunction symptoms than women (beta, 0.15; P < .001). Younger adults (25-39 years) were more likely to experience cognitive dysfunction than those age 40-54 (beta, 0.30; P < .001).
Dr. Schaffner said it was troubling that young people are more likely to experience the dysfunction.
“When we think of ‘brain fog’ we think of older persons who are already predisposed to have more memory lapses as they get older,” he said.
The link between cognitive dysfunction and COVID-19 infection has been shown in other studies, but many have not used representative samples and have not compared results with noninfected controls in the general population, the authors wrote.
Executive dysfunction was measured using four questions from the Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale. Respondents were asked how often they have experienced these scenarios in the past 6 months:
- “I am unable to inhibit my reactions or responses to events or to other people.”
- “I make impulsive comments to others.”
- “I am likely to do things without considering the consequences for doing them.”
- “I act without thinking.”
“This makes it even more important that we talk about vaccination,” Dr. Schaffner said, “because clearly the more seriously ill you are, the more likely this sort of thing is likely to happen and vaccines have been shown time and again to avert hospitalizations and more serious illness. It also makes more important the monoclonal antibody treatments we have and the antivirals, which will prevent the evolution of mild disease into something more serious.”
This research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Institute for Population and Public Health. The study authors and Dr. Schaffner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
than people in the general population with no such infection, according to new data published on the preprint server medRxiv.
Researchers, led by Peter A. Hall, PhD, with the University of Waterloo (Ont.), found that COVID infection is associated with executive dysfunction among young and middle-aged adults, including for those not exposed to intubation or hospitalization.
The findings have not been peer reviewed.
The study included a representative cohort of 1,958 community-dwelling young and middle-aged adults. It used a balanced proportion of infected and uninfected people to estimate the link between SARS-CoV-2 infection and cognitive/executive dysfunction.
The authors noted that the survey was conducted from Sept. 28 to Oct. 21, 2021, when the primary variant in Canada was Delta.
The research was a cross-sectional observational study with data from the ongoing Canadian COVID-19 Experiences Survey. It included equal representation of vaccinated and vaccine-hesitant adults aged 18-54 years. COVID-19 symptoms ranged from negligible to life-threatening cases requiring hospitalization.
Half in the cohort (50.2%) received two vaccine shots; 43.3% had received no shots; and 5.5% received one shot, but were not intending to receive a second shot.
Dose-response relationship
According to the paper, those with prior COVID-19 infection, regardless of symptom severity, reported a significantly higher number of symptoms of executive dysfunction than their noninfected counterparts (mechanical adjustment, 1.63, standard error, 0.08; 95% confidence interval, 1.47-1.80; P = .001).
The researchers also found a dose-response relationship between COVID-19 symptom severity and cognitive dysfunction. Those with moderate and very/extremely severe COVID-19 symptoms were linked with significantly greater dysfunction.
“This reinforces what we’re hearing about – that COVID is not ‘one and done.’ It can have lasting and quite subtle and damaging effects on the human body,” William Schaffner, MD, infectious disease specialist with Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
Measuring executive functioning – including the ability to make sound decisions – is something other studies haven’t typically addressed, he said.
Men were likely to report more cognitive dysfunction symptoms than women (beta, 0.15; P < .001). Younger adults (25-39 years) were more likely to experience cognitive dysfunction than those age 40-54 (beta, 0.30; P < .001).
Dr. Schaffner said it was troubling that young people are more likely to experience the dysfunction.
“When we think of ‘brain fog’ we think of older persons who are already predisposed to have more memory lapses as they get older,” he said.
The link between cognitive dysfunction and COVID-19 infection has been shown in other studies, but many have not used representative samples and have not compared results with noninfected controls in the general population, the authors wrote.
Executive dysfunction was measured using four questions from the Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale. Respondents were asked how often they have experienced these scenarios in the past 6 months:
- “I am unable to inhibit my reactions or responses to events or to other people.”
- “I make impulsive comments to others.”
- “I am likely to do things without considering the consequences for doing them.”
- “I act without thinking.”
“This makes it even more important that we talk about vaccination,” Dr. Schaffner said, “because clearly the more seriously ill you are, the more likely this sort of thing is likely to happen and vaccines have been shown time and again to avert hospitalizations and more serious illness. It also makes more important the monoclonal antibody treatments we have and the antivirals, which will prevent the evolution of mild disease into something more serious.”
This research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Institute for Population and Public Health. The study authors and Dr. Schaffner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
than people in the general population with no such infection, according to new data published on the preprint server medRxiv.
Researchers, led by Peter A. Hall, PhD, with the University of Waterloo (Ont.), found that COVID infection is associated with executive dysfunction among young and middle-aged adults, including for those not exposed to intubation or hospitalization.
The findings have not been peer reviewed.
The study included a representative cohort of 1,958 community-dwelling young and middle-aged adults. It used a balanced proportion of infected and uninfected people to estimate the link between SARS-CoV-2 infection and cognitive/executive dysfunction.
The authors noted that the survey was conducted from Sept. 28 to Oct. 21, 2021, when the primary variant in Canada was Delta.
The research was a cross-sectional observational study with data from the ongoing Canadian COVID-19 Experiences Survey. It included equal representation of vaccinated and vaccine-hesitant adults aged 18-54 years. COVID-19 symptoms ranged from negligible to life-threatening cases requiring hospitalization.
Half in the cohort (50.2%) received two vaccine shots; 43.3% had received no shots; and 5.5% received one shot, but were not intending to receive a second shot.
Dose-response relationship
According to the paper, those with prior COVID-19 infection, regardless of symptom severity, reported a significantly higher number of symptoms of executive dysfunction than their noninfected counterparts (mechanical adjustment, 1.63, standard error, 0.08; 95% confidence interval, 1.47-1.80; P = .001).
The researchers also found a dose-response relationship between COVID-19 symptom severity and cognitive dysfunction. Those with moderate and very/extremely severe COVID-19 symptoms were linked with significantly greater dysfunction.
“This reinforces what we’re hearing about – that COVID is not ‘one and done.’ It can have lasting and quite subtle and damaging effects on the human body,” William Schaffner, MD, infectious disease specialist with Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
Measuring executive functioning – including the ability to make sound decisions – is something other studies haven’t typically addressed, he said.
Men were likely to report more cognitive dysfunction symptoms than women (beta, 0.15; P < .001). Younger adults (25-39 years) were more likely to experience cognitive dysfunction than those age 40-54 (beta, 0.30; P < .001).
Dr. Schaffner said it was troubling that young people are more likely to experience the dysfunction.
“When we think of ‘brain fog’ we think of older persons who are already predisposed to have more memory lapses as they get older,” he said.
The link between cognitive dysfunction and COVID-19 infection has been shown in other studies, but many have not used representative samples and have not compared results with noninfected controls in the general population, the authors wrote.
Executive dysfunction was measured using four questions from the Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale. Respondents were asked how often they have experienced these scenarios in the past 6 months:
- “I am unable to inhibit my reactions or responses to events or to other people.”
- “I make impulsive comments to others.”
- “I am likely to do things without considering the consequences for doing them.”
- “I act without thinking.”
“This makes it even more important that we talk about vaccination,” Dr. Schaffner said, “because clearly the more seriously ill you are, the more likely this sort of thing is likely to happen and vaccines have been shown time and again to avert hospitalizations and more serious illness. It also makes more important the monoclonal antibody treatments we have and the antivirals, which will prevent the evolution of mild disease into something more serious.”
This research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Institute for Population and Public Health. The study authors and Dr. Schaffner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MEDRXIV
10 reasons why Omicron could cause big destruction
As a physician first and a mental health clinician second, I hope to provide factual medical information on the Omicron variant to my patients, family members, and friends. I also try to remain curious instead of angry about why some choose not to vaccinate.
The most effective way to encourage people to obtain a vaccination is to use communication free of judgment and criticism, which allows a safe space for the unvaccinated to express their motivations and fears behind their current choice of not vaccinating and explore possible barriers to an alternative option that could lead to vaccination.
As an adult psychiatrist, ADHD specialist, and amateur COVID-19 expert, I’d like to offer 10 reasons why Omicron – which ironically means “small” in Latin, can still cause big destruction. Please share these 10 reasons with your patients.
- If you are not vaccinated, this virus will find you within the next few weeks and likely lead to severe symptoms.
- Long-haul symptoms from COVID-19 infection are still possible even for people who contract a milder case of the Omicron variant.
- The monoclonal antibody and antiviral treatments recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for pre-exposure prevention of COVID-19 are limited. For many reasons, now is not the best time to play Russian roulette and intentionally get infected with a “mild” variant.
- There are not enough testing sites or over-the-counter rapid COVID tests available to keep up with the demand, and the latter are cost prohibitive for many people.
- Emergency care during the next few weeks for unforeseen non–COVID-related illnesses, such as a sudden heart attack or stroke, may be affected by the shortage of medical providers because of illness, quarantine, and burnout.
- There will be fewer first responders, including EMTs, police officers, and firefighters, because of COVID quarantines from illness and exposure.
- Although most Americans oppose temporary shutdowns, de facto shutdowns might be necessary because of the absence of healthy, COVID-negative individuals to maintain a functional society.
- Omicron math is deceiving, since the risk of hospitalization with Omicron appears to be far lower than with the Delta variant. However, the higher volume of infections with Omicron will offset the lower severity leading to comparable numbers of hospitalizations.
- Omicron has made it difficult for some schools to reopen after the holiday break, and reopening might become even more difficult as the surge progresses. Many schools already were in desperate need of substitute teachers, bus drivers, and additional staff necessary for COVID safety precautions before the emergence of the Omicron variant.
- And, for a less altruistic reason, as if the nine reasons above weren’t enough – if infections continue, especially among the unvaccinated – where the virus mutates the most – this can lead to a trifecta variant that not only evades the immune system and is highly infectious but causes severe disease in both the unvaccinated as well as the vaccinated.
Because of its extremely high transmissibility, the Omicron variant – layered atop Delta – presents great risk to us as a society. We must do all we can as clinicians to educate our patients so that they can protect themselves and their families.
Dr. Abraham is a psychiatrist in private practice in Philadelphia. She has no disclosures.
As a physician first and a mental health clinician second, I hope to provide factual medical information on the Omicron variant to my patients, family members, and friends. I also try to remain curious instead of angry about why some choose not to vaccinate.
The most effective way to encourage people to obtain a vaccination is to use communication free of judgment and criticism, which allows a safe space for the unvaccinated to express their motivations and fears behind their current choice of not vaccinating and explore possible barriers to an alternative option that could lead to vaccination.
As an adult psychiatrist, ADHD specialist, and amateur COVID-19 expert, I’d like to offer 10 reasons why Omicron – which ironically means “small” in Latin, can still cause big destruction. Please share these 10 reasons with your patients.
- If you are not vaccinated, this virus will find you within the next few weeks and likely lead to severe symptoms.
- Long-haul symptoms from COVID-19 infection are still possible even for people who contract a milder case of the Omicron variant.
- The monoclonal antibody and antiviral treatments recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for pre-exposure prevention of COVID-19 are limited. For many reasons, now is not the best time to play Russian roulette and intentionally get infected with a “mild” variant.
- There are not enough testing sites or over-the-counter rapid COVID tests available to keep up with the demand, and the latter are cost prohibitive for many people.
- Emergency care during the next few weeks for unforeseen non–COVID-related illnesses, such as a sudden heart attack or stroke, may be affected by the shortage of medical providers because of illness, quarantine, and burnout.
- There will be fewer first responders, including EMTs, police officers, and firefighters, because of COVID quarantines from illness and exposure.
- Although most Americans oppose temporary shutdowns, de facto shutdowns might be necessary because of the absence of healthy, COVID-negative individuals to maintain a functional society.
- Omicron math is deceiving, since the risk of hospitalization with Omicron appears to be far lower than with the Delta variant. However, the higher volume of infections with Omicron will offset the lower severity leading to comparable numbers of hospitalizations.
- Omicron has made it difficult for some schools to reopen after the holiday break, and reopening might become even more difficult as the surge progresses. Many schools already were in desperate need of substitute teachers, bus drivers, and additional staff necessary for COVID safety precautions before the emergence of the Omicron variant.
- And, for a less altruistic reason, as if the nine reasons above weren’t enough – if infections continue, especially among the unvaccinated – where the virus mutates the most – this can lead to a trifecta variant that not only evades the immune system and is highly infectious but causes severe disease in both the unvaccinated as well as the vaccinated.
Because of its extremely high transmissibility, the Omicron variant – layered atop Delta – presents great risk to us as a society. We must do all we can as clinicians to educate our patients so that they can protect themselves and their families.
Dr. Abraham is a psychiatrist in private practice in Philadelphia. She has no disclosures.
As a physician first and a mental health clinician second, I hope to provide factual medical information on the Omicron variant to my patients, family members, and friends. I also try to remain curious instead of angry about why some choose not to vaccinate.
The most effective way to encourage people to obtain a vaccination is to use communication free of judgment and criticism, which allows a safe space for the unvaccinated to express their motivations and fears behind their current choice of not vaccinating and explore possible barriers to an alternative option that could lead to vaccination.
As an adult psychiatrist, ADHD specialist, and amateur COVID-19 expert, I’d like to offer 10 reasons why Omicron – which ironically means “small” in Latin, can still cause big destruction. Please share these 10 reasons with your patients.
- If you are not vaccinated, this virus will find you within the next few weeks and likely lead to severe symptoms.
- Long-haul symptoms from COVID-19 infection are still possible even for people who contract a milder case of the Omicron variant.
- The monoclonal antibody and antiviral treatments recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for pre-exposure prevention of COVID-19 are limited. For many reasons, now is not the best time to play Russian roulette and intentionally get infected with a “mild” variant.
- There are not enough testing sites or over-the-counter rapid COVID tests available to keep up with the demand, and the latter are cost prohibitive for many people.
- Emergency care during the next few weeks for unforeseen non–COVID-related illnesses, such as a sudden heart attack or stroke, may be affected by the shortage of medical providers because of illness, quarantine, and burnout.
- There will be fewer first responders, including EMTs, police officers, and firefighters, because of COVID quarantines from illness and exposure.
- Although most Americans oppose temporary shutdowns, de facto shutdowns might be necessary because of the absence of healthy, COVID-negative individuals to maintain a functional society.
- Omicron math is deceiving, since the risk of hospitalization with Omicron appears to be far lower than with the Delta variant. However, the higher volume of infections with Omicron will offset the lower severity leading to comparable numbers of hospitalizations.
- Omicron has made it difficult for some schools to reopen after the holiday break, and reopening might become even more difficult as the surge progresses. Many schools already were in desperate need of substitute teachers, bus drivers, and additional staff necessary for COVID safety precautions before the emergence of the Omicron variant.
- And, for a less altruistic reason, as if the nine reasons above weren’t enough – if infections continue, especially among the unvaccinated – where the virus mutates the most – this can lead to a trifecta variant that not only evades the immune system and is highly infectious but causes severe disease in both the unvaccinated as well as the vaccinated.
Because of its extremely high transmissibility, the Omicron variant – layered atop Delta – presents great risk to us as a society. We must do all we can as clinicians to educate our patients so that they can protect themselves and their families.
Dr. Abraham is a psychiatrist in private practice in Philadelphia. She has no disclosures.
Children and COVID: New cases, admissions are higher than ever
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children passed 300,000 for the first time since the pandemic started, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The rate of new COVID-related hospital admissions also reached a new high of 0.74 per 100,000 children as of Dec. 31. The highest rate seen before the current Omicron-fueled surge was 0.47 per 100,000 in early September, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.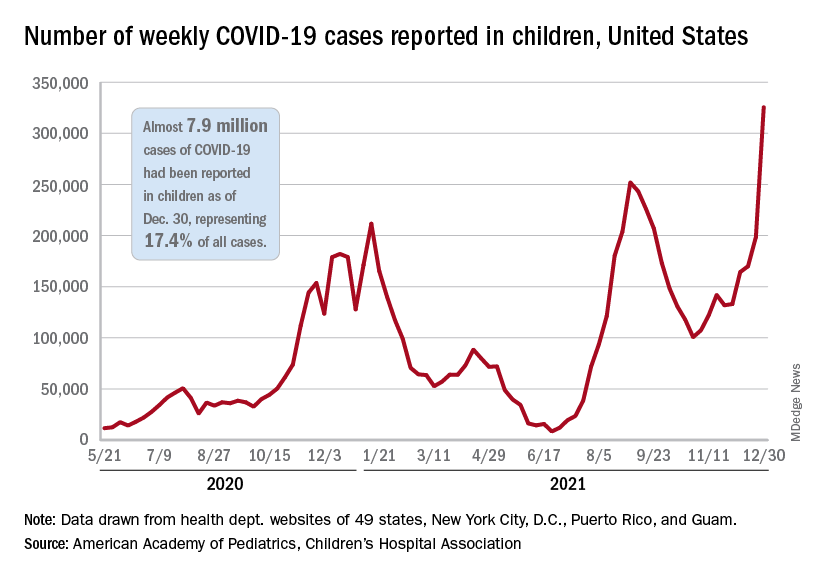
and exceeding the previous week’s count by almost 64%, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
New cases were up in all four regions of the United States, with the Northeast adding the most newly infected children while setting a new high for the fifth consecutive week. The South was just behind for the week but still well off the record it reached in September, the Midwest was third but recorded its busiest week ever, and the West was fourth and nowhere near its previous high, the AAP/CHA report indicated.
The total number of child cases since the pandemic began is almost 7.9 million, they said based on data collected from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. That figure represents 17.4% of all cases reported in the United States, and the cumulative rate of COVID infection is up to almost 10,500 per 100,000 children, meaning that 1 in 10 children have been infected.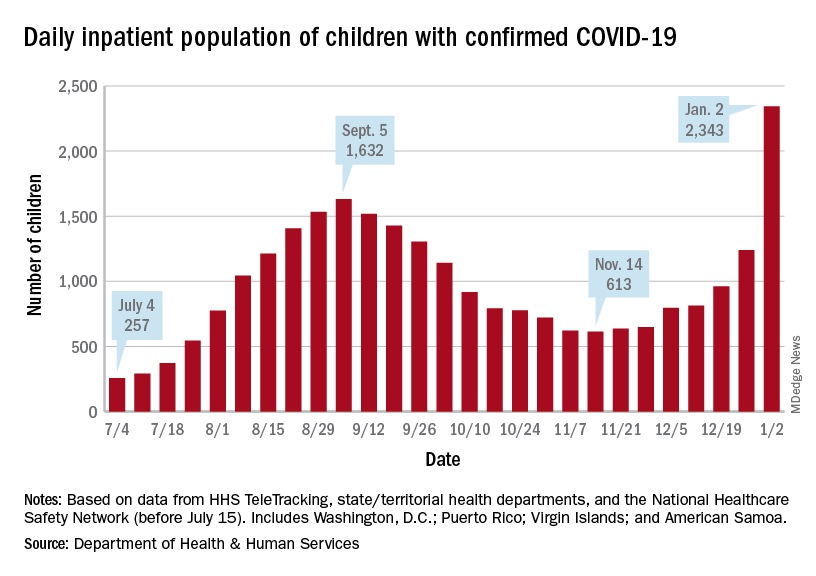
Children are still less likely to be hospitalized than adults, but the gap appears to be closing. On Jan. 2 there were 2,343 children and 87,690 adults in the hospital with confirmed COVID, a ratio of 37 adults for each child, but on Sept. 5, at the height of the previous surge, the ratio of hospitalized adults (93,647) to children (1,632) was 57:1, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
New admissions show a similar pattern: The 0.74 admissions per 100,000 children recorded on Dec. 31 was lower than, for example, adults aged 30-39 years (2.7 per 100,000) or 50-59 years (4.25 per 100,000), but on Sept. 5 the corresponding figures were 0.46 (children), 2.74 (ages 30-39), and 5.03 (aged 50-59), based on the HHS data.
A look at vaccinations
The vaccination response to Omicron, however, has been more subdued and somewhat inconsistent. Vaccine initiation, not surprisingly, was down among eligible children for the week of Dec. 23-29. Before that, both the 5- to 11-year-olds and 12- to 15-year-olds were down for the second week of December and then up a bit (5.6% and 14.3%, respectively) during the third week, while the 16- to 17-year-olds, increased initiation by 63.2%, CDC’s COVID Data Tracker shows.
Less than a quarter (23.5%) of children aged 5-11 received at least one dose of the vaccine in the first 2 months of their eligibility, and only 14.7% are fully vaccinated. Among the older children, coverage looks like this: at least one dose for 61.2% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 67.4% of 16- to 17-year-olds and full vaccination for 51.3% and 57.6%, respectively, the CDC said.
At the state level, Massachusetts and Hawaii have the highest rates for children aged 12-17 years, with 86% having received a least one dose, and Vermont is highest for children aged 5-11 at 56%. The lowest rates can be found in Wyoming (38%) for 12- to 17-year-olds and in Mississippi (6%) for 5- to 11-year-olds, the AAP said in a separate report.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children passed 300,000 for the first time since the pandemic started, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The rate of new COVID-related hospital admissions also reached a new high of 0.74 per 100,000 children as of Dec. 31. The highest rate seen before the current Omicron-fueled surge was 0.47 per 100,000 in early September, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.
and exceeding the previous week’s count by almost 64%, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
New cases were up in all four regions of the United States, with the Northeast adding the most newly infected children while setting a new high for the fifth consecutive week. The South was just behind for the week but still well off the record it reached in September, the Midwest was third but recorded its busiest week ever, and the West was fourth and nowhere near its previous high, the AAP/CHA report indicated.
The total number of child cases since the pandemic began is almost 7.9 million, they said based on data collected from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. That figure represents 17.4% of all cases reported in the United States, and the cumulative rate of COVID infection is up to almost 10,500 per 100,000 children, meaning that 1 in 10 children have been infected.
Children are still less likely to be hospitalized than adults, but the gap appears to be closing. On Jan. 2 there were 2,343 children and 87,690 adults in the hospital with confirmed COVID, a ratio of 37 adults for each child, but on Sept. 5, at the height of the previous surge, the ratio of hospitalized adults (93,647) to children (1,632) was 57:1, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
New admissions show a similar pattern: The 0.74 admissions per 100,000 children recorded on Dec. 31 was lower than, for example, adults aged 30-39 years (2.7 per 100,000) or 50-59 years (4.25 per 100,000), but on Sept. 5 the corresponding figures were 0.46 (children), 2.74 (ages 30-39), and 5.03 (aged 50-59), based on the HHS data.
A look at vaccinations
The vaccination response to Omicron, however, has been more subdued and somewhat inconsistent. Vaccine initiation, not surprisingly, was down among eligible children for the week of Dec. 23-29. Before that, both the 5- to 11-year-olds and 12- to 15-year-olds were down for the second week of December and then up a bit (5.6% and 14.3%, respectively) during the third week, while the 16- to 17-year-olds, increased initiation by 63.2%, CDC’s COVID Data Tracker shows.
Less than a quarter (23.5%) of children aged 5-11 received at least one dose of the vaccine in the first 2 months of their eligibility, and only 14.7% are fully vaccinated. Among the older children, coverage looks like this: at least one dose for 61.2% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 67.4% of 16- to 17-year-olds and full vaccination for 51.3% and 57.6%, respectively, the CDC said.
At the state level, Massachusetts and Hawaii have the highest rates for children aged 12-17 years, with 86% having received a least one dose, and Vermont is highest for children aged 5-11 at 56%. The lowest rates can be found in Wyoming (38%) for 12- to 17-year-olds and in Mississippi (6%) for 5- to 11-year-olds, the AAP said in a separate report.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children passed 300,000 for the first time since the pandemic started, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The rate of new COVID-related hospital admissions also reached a new high of 0.74 per 100,000 children as of Dec. 31. The highest rate seen before the current Omicron-fueled surge was 0.47 per 100,000 in early September, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.
and exceeding the previous week’s count by almost 64%, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
New cases were up in all four regions of the United States, with the Northeast adding the most newly infected children while setting a new high for the fifth consecutive week. The South was just behind for the week but still well off the record it reached in September, the Midwest was third but recorded its busiest week ever, and the West was fourth and nowhere near its previous high, the AAP/CHA report indicated.
The total number of child cases since the pandemic began is almost 7.9 million, they said based on data collected from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. That figure represents 17.4% of all cases reported in the United States, and the cumulative rate of COVID infection is up to almost 10,500 per 100,000 children, meaning that 1 in 10 children have been infected.
Children are still less likely to be hospitalized than adults, but the gap appears to be closing. On Jan. 2 there were 2,343 children and 87,690 adults in the hospital with confirmed COVID, a ratio of 37 adults for each child, but on Sept. 5, at the height of the previous surge, the ratio of hospitalized adults (93,647) to children (1,632) was 57:1, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
New admissions show a similar pattern: The 0.74 admissions per 100,000 children recorded on Dec. 31 was lower than, for example, adults aged 30-39 years (2.7 per 100,000) or 50-59 years (4.25 per 100,000), but on Sept. 5 the corresponding figures were 0.46 (children), 2.74 (ages 30-39), and 5.03 (aged 50-59), based on the HHS data.
A look at vaccinations
The vaccination response to Omicron, however, has been more subdued and somewhat inconsistent. Vaccine initiation, not surprisingly, was down among eligible children for the week of Dec. 23-29. Before that, both the 5- to 11-year-olds and 12- to 15-year-olds were down for the second week of December and then up a bit (5.6% and 14.3%, respectively) during the third week, while the 16- to 17-year-olds, increased initiation by 63.2%, CDC’s COVID Data Tracker shows.
Less than a quarter (23.5%) of children aged 5-11 received at least one dose of the vaccine in the first 2 months of their eligibility, and only 14.7% are fully vaccinated. Among the older children, coverage looks like this: at least one dose for 61.2% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 67.4% of 16- to 17-year-olds and full vaccination for 51.3% and 57.6%, respectively, the CDC said.
At the state level, Massachusetts and Hawaii have the highest rates for children aged 12-17 years, with 86% having received a least one dose, and Vermont is highest for children aged 5-11 at 56%. The lowest rates can be found in Wyoming (38%) for 12- to 17-year-olds and in Mississippi (6%) for 5- to 11-year-olds, the AAP said in a separate report.
New CDC COVID-19 isolation guidelines still up for debate among experts
It’s a true Goldilocks debate: , with some calling them suitable, some saying they’re “reckless,” and at least one expert saying they’re “right in the middle.”
The controversy may lead to more updates. On Jan. 2, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, President Joe Biden’s chief medical adviser, said on CNN’s State of the Union that he anticipates further clarification of the guidelines soon.
Sparking the most debate: Infected people are not told to test before leaving isolation, the vaccinated and unvaccinated who are exposed are given some of the same advice, and the mask advice is not specific enough.
As issued on Dec. 27, the guidelines for the general public recommend:
- Anyone who tests positive should stay home and isolate for 5 days (instead of 10) and if the person has no symptoms or the symptoms resolve after 5 days, leaving the house is okay. A mask should be worn around others for 5 more days. In the event of a fever, the person must stay home until it resolves.
- If people are exposed to someone infected with COVID-19 and they have been boosted, finished the primary series of either the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine within the past 6 months, or finished the primary series of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine within the past 2 months, they should wear a mask around others for 10 days and, if possible, test on day 5. However, if symptoms develop, they should get a test and stay home.
- If people are exposed to someone infected with COVID-19 and they are unvaccinated or are more than 6 months out from their second dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine (or more than 2 months after the J&J vaccine) and not boosted, they should quarantine for 5 days and then wear a mask for 5 more days. If quarantine is impossible, a mask should be worn for 10 days. A test on day 5 is suggested if possible. If symptoms occur, they should quarantine and test.
On social media and in interviews with this news organization, public health experts expressed an array of opinions.
A tweet from Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, posted the day after the new guidelines came out, had an empty box and this: “The data that support the new @CDCgov 5 day isolation period without a negative test.”
In a tweet on Jan. 2, Ashish K. Jha, MD, MPH, dean of the Brown University School of Public Health, said: “Hearing that CDC considering adding testing to isolation guidelines. That would be great. I’ve been arguing for a while that serial negative antigen tests provide a lot of confidence that someone is not contagious.”
Michael Mina, MD, PhD, chief science officer of eMed, a digital point-of-care platform enabling at-home diagnostic testing, tweeted: “CDC’s new guidance to drop isolation of positives to 5 days without a negative test is reckless. Some [people] stay infectious 3 days, some 12. I absolutely don’t want to sit next to someone who turned [positive] 5 days ago and hasn’t tested Neg. Test Neg to leave isolation early is just smart.”
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and an infectious disease specialist, disagrees. Typically, he said, an infected person sheds virus for 7 days.
“If you are asymptomatic, the chances that you are shedding a significant amount of virus is very, very small,” he said in an interview.
Under debate
Testing: While many public health experts say a recommendation to test before leaving isolation is needed, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, explained testing was not recommended before leaving isolation because PCR testing can stay positive up to 12 weeks after a person is first infected with COVID-19.
Asked why there was not a recommendation for a rapid antigen test before leaving isolation, Dr. Walensky told CNN that it is not known how these tests perform at the end of infection and that the tests are not Food and Drug Administration–authorized for that purpose.
And while the guidelines suggest that those exposed – whether they are boosted, vaccinated, or not – should test on day 5 if possible, that recommendation should be stronger, some said. “At the very least recommend a test in those who can get it done,” said Dr. Topol.
However, making that recommendation is difficult when experts know how difficult it is for people to obtain tests now, William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“I am sure this was intensely debated,” Dr. Schaffner said of the recommendation on testing.
Vaccination status categories: Amesh Adalja, MD, senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, questioned the scientific basis behind treating the fully vaccinated (with two mRNA or one J&J vaccine) who are exposed ‘’as the equivalent of the unvaccinated when it comes to the quarantine requirement since the fully vaccinated are protected against what matters.”
Dr. Topol agreed: Guidelines “should be different for vaccinated versus unvaccinated.”
The recommendations for the exposed should definitely be simpler, Dr. Offit said. “I think it would be much simpler to just say, ‘If you are exposed, mask for 10 days,’ “ regardless of vaccination status.
Masks: The guidelines should also be more specific about the type of masks, Dr. Topol said. They should spell out that the masks need to be N95 or KN95, he said.
Science-driven or economy-driven? Was the guidance changed due more to concerns about the economy than to scientific information about infection and transmission? “It was,” Dr. Topol said.
Dr. Adalja sees it differently. “While it is true that this updated guidance will help the economy, it is based on a scientific foundation and should have been issued much earlier than it was.”
Tough decisions
The agency is walking a tightrope, Dr. Schaffner said, adding that he is in general agreement with what the CDC is trying to do. “The tightrope is between the public health ideal and trying to determine what will be acceptable,’’ he said.
The revised guidelines are more practical than before, others said. “The goal is harm reduction and many people just don’t do any isolation if they are faced with a 10-day period,” Dr. Adalja said.
Before issuing the new guidance, the CDC looked at the accumulating science and also took into account stresses on the health care system and other factors, Dr. Schaffner said. “Is it perfect?” Dr. Schaffner said of the new guideline. “No. Is it carefree? No. It’s right in the middle.”
Dr. Schaffner does think the messages about the new recommendations and how they were decided upon could have been communicated better, and in a more understandable manner. Some experts, for instance, led with the economy and the need for people to return to work and school when explaining the guidelines and then brought up the science behind the revisions.
That order should have been reversed, Dr. Schaffner said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s a true Goldilocks debate: , with some calling them suitable, some saying they’re “reckless,” and at least one expert saying they’re “right in the middle.”
The controversy may lead to more updates. On Jan. 2, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, President Joe Biden’s chief medical adviser, said on CNN’s State of the Union that he anticipates further clarification of the guidelines soon.
Sparking the most debate: Infected people are not told to test before leaving isolation, the vaccinated and unvaccinated who are exposed are given some of the same advice, and the mask advice is not specific enough.
As issued on Dec. 27, the guidelines for the general public recommend:
- Anyone who tests positive should stay home and isolate for 5 days (instead of 10) and if the person has no symptoms or the symptoms resolve after 5 days, leaving the house is okay. A mask should be worn around others for 5 more days. In the event of a fever, the person must stay home until it resolves.
- If people are exposed to someone infected with COVID-19 and they have been boosted, finished the primary series of either the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine within the past 6 months, or finished the primary series of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine within the past 2 months, they should wear a mask around others for 10 days and, if possible, test on day 5. However, if symptoms develop, they should get a test and stay home.
- If people are exposed to someone infected with COVID-19 and they are unvaccinated or are more than 6 months out from their second dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine (or more than 2 months after the J&J vaccine) and not boosted, they should quarantine for 5 days and then wear a mask for 5 more days. If quarantine is impossible, a mask should be worn for 10 days. A test on day 5 is suggested if possible. If symptoms occur, they should quarantine and test.
On social media and in interviews with this news organization, public health experts expressed an array of opinions.
A tweet from Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, posted the day after the new guidelines came out, had an empty box and this: “The data that support the new @CDCgov 5 day isolation period without a negative test.”
In a tweet on Jan. 2, Ashish K. Jha, MD, MPH, dean of the Brown University School of Public Health, said: “Hearing that CDC considering adding testing to isolation guidelines. That would be great. I’ve been arguing for a while that serial negative antigen tests provide a lot of confidence that someone is not contagious.”
Michael Mina, MD, PhD, chief science officer of eMed, a digital point-of-care platform enabling at-home diagnostic testing, tweeted: “CDC’s new guidance to drop isolation of positives to 5 days without a negative test is reckless. Some [people] stay infectious 3 days, some 12. I absolutely don’t want to sit next to someone who turned [positive] 5 days ago and hasn’t tested Neg. Test Neg to leave isolation early is just smart.”
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and an infectious disease specialist, disagrees. Typically, he said, an infected person sheds virus for 7 days.
“If you are asymptomatic, the chances that you are shedding a significant amount of virus is very, very small,” he said in an interview.
Under debate
Testing: While many public health experts say a recommendation to test before leaving isolation is needed, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, explained testing was not recommended before leaving isolation because PCR testing can stay positive up to 12 weeks after a person is first infected with COVID-19.
Asked why there was not a recommendation for a rapid antigen test before leaving isolation, Dr. Walensky told CNN that it is not known how these tests perform at the end of infection and that the tests are not Food and Drug Administration–authorized for that purpose.
And while the guidelines suggest that those exposed – whether they are boosted, vaccinated, or not – should test on day 5 if possible, that recommendation should be stronger, some said. “At the very least recommend a test in those who can get it done,” said Dr. Topol.
However, making that recommendation is difficult when experts know how difficult it is for people to obtain tests now, William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“I am sure this was intensely debated,” Dr. Schaffner said of the recommendation on testing.
Vaccination status categories: Amesh Adalja, MD, senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, questioned the scientific basis behind treating the fully vaccinated (with two mRNA or one J&J vaccine) who are exposed ‘’as the equivalent of the unvaccinated when it comes to the quarantine requirement since the fully vaccinated are protected against what matters.”
Dr. Topol agreed: Guidelines “should be different for vaccinated versus unvaccinated.”
The recommendations for the exposed should definitely be simpler, Dr. Offit said. “I think it would be much simpler to just say, ‘If you are exposed, mask for 10 days,’ “ regardless of vaccination status.
Masks: The guidelines should also be more specific about the type of masks, Dr. Topol said. They should spell out that the masks need to be N95 or KN95, he said.
Science-driven or economy-driven? Was the guidance changed due more to concerns about the economy than to scientific information about infection and transmission? “It was,” Dr. Topol said.
Dr. Adalja sees it differently. “While it is true that this updated guidance will help the economy, it is based on a scientific foundation and should have been issued much earlier than it was.”
Tough decisions
The agency is walking a tightrope, Dr. Schaffner said, adding that he is in general agreement with what the CDC is trying to do. “The tightrope is between the public health ideal and trying to determine what will be acceptable,’’ he said.
The revised guidelines are more practical than before, others said. “The goal is harm reduction and many people just don’t do any isolation if they are faced with a 10-day period,” Dr. Adalja said.
Before issuing the new guidance, the CDC looked at the accumulating science and also took into account stresses on the health care system and other factors, Dr. Schaffner said. “Is it perfect?” Dr. Schaffner said of the new guideline. “No. Is it carefree? No. It’s right in the middle.”
Dr. Schaffner does think the messages about the new recommendations and how they were decided upon could have been communicated better, and in a more understandable manner. Some experts, for instance, led with the economy and the need for people to return to work and school when explaining the guidelines and then brought up the science behind the revisions.
That order should have been reversed, Dr. Schaffner said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s a true Goldilocks debate: , with some calling them suitable, some saying they’re “reckless,” and at least one expert saying they’re “right in the middle.”
The controversy may lead to more updates. On Jan. 2, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, President Joe Biden’s chief medical adviser, said on CNN’s State of the Union that he anticipates further clarification of the guidelines soon.
Sparking the most debate: Infected people are not told to test before leaving isolation, the vaccinated and unvaccinated who are exposed are given some of the same advice, and the mask advice is not specific enough.
As issued on Dec. 27, the guidelines for the general public recommend:
- Anyone who tests positive should stay home and isolate for 5 days (instead of 10) and if the person has no symptoms or the symptoms resolve after 5 days, leaving the house is okay. A mask should be worn around others for 5 more days. In the event of a fever, the person must stay home until it resolves.
- If people are exposed to someone infected with COVID-19 and they have been boosted, finished the primary series of either the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine within the past 6 months, or finished the primary series of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine within the past 2 months, they should wear a mask around others for 10 days and, if possible, test on day 5. However, if symptoms develop, they should get a test and stay home.
- If people are exposed to someone infected with COVID-19 and they are unvaccinated or are more than 6 months out from their second dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine (or more than 2 months after the J&J vaccine) and not boosted, they should quarantine for 5 days and then wear a mask for 5 more days. If quarantine is impossible, a mask should be worn for 10 days. A test on day 5 is suggested if possible. If symptoms occur, they should quarantine and test.
On social media and in interviews with this news organization, public health experts expressed an array of opinions.
A tweet from Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, posted the day after the new guidelines came out, had an empty box and this: “The data that support the new @CDCgov 5 day isolation period without a negative test.”
In a tweet on Jan. 2, Ashish K. Jha, MD, MPH, dean of the Brown University School of Public Health, said: “Hearing that CDC considering adding testing to isolation guidelines. That would be great. I’ve been arguing for a while that serial negative antigen tests provide a lot of confidence that someone is not contagious.”
Michael Mina, MD, PhD, chief science officer of eMed, a digital point-of-care platform enabling at-home diagnostic testing, tweeted: “CDC’s new guidance to drop isolation of positives to 5 days without a negative test is reckless. Some [people] stay infectious 3 days, some 12. I absolutely don’t want to sit next to someone who turned [positive] 5 days ago and hasn’t tested Neg. Test Neg to leave isolation early is just smart.”
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and an infectious disease specialist, disagrees. Typically, he said, an infected person sheds virus for 7 days.
“If you are asymptomatic, the chances that you are shedding a significant amount of virus is very, very small,” he said in an interview.
Under debate
Testing: While many public health experts say a recommendation to test before leaving isolation is needed, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, explained testing was not recommended before leaving isolation because PCR testing can stay positive up to 12 weeks after a person is first infected with COVID-19.
Asked why there was not a recommendation for a rapid antigen test before leaving isolation, Dr. Walensky told CNN that it is not known how these tests perform at the end of infection and that the tests are not Food and Drug Administration–authorized for that purpose.
And while the guidelines suggest that those exposed – whether they are boosted, vaccinated, or not – should test on day 5 if possible, that recommendation should be stronger, some said. “At the very least recommend a test in those who can get it done,” said Dr. Topol.
However, making that recommendation is difficult when experts know how difficult it is for people to obtain tests now, William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“I am sure this was intensely debated,” Dr. Schaffner said of the recommendation on testing.
Vaccination status categories: Amesh Adalja, MD, senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, questioned the scientific basis behind treating the fully vaccinated (with two mRNA or one J&J vaccine) who are exposed ‘’as the equivalent of the unvaccinated when it comes to the quarantine requirement since the fully vaccinated are protected against what matters.”
Dr. Topol agreed: Guidelines “should be different for vaccinated versus unvaccinated.”
The recommendations for the exposed should definitely be simpler, Dr. Offit said. “I think it would be much simpler to just say, ‘If you are exposed, mask for 10 days,’ “ regardless of vaccination status.
Masks: The guidelines should also be more specific about the type of masks, Dr. Topol said. They should spell out that the masks need to be N95 or KN95, he said.
Science-driven or economy-driven? Was the guidance changed due more to concerns about the economy than to scientific information about infection and transmission? “It was,” Dr. Topol said.
Dr. Adalja sees it differently. “While it is true that this updated guidance will help the economy, it is based on a scientific foundation and should have been issued much earlier than it was.”
Tough decisions
The agency is walking a tightrope, Dr. Schaffner said, adding that he is in general agreement with what the CDC is trying to do. “The tightrope is between the public health ideal and trying to determine what will be acceptable,’’ he said.
The revised guidelines are more practical than before, others said. “The goal is harm reduction and many people just don’t do any isolation if they are faced with a 10-day period,” Dr. Adalja said.
Before issuing the new guidance, the CDC looked at the accumulating science and also took into account stresses on the health care system and other factors, Dr. Schaffner said. “Is it perfect?” Dr. Schaffner said of the new guideline. “No. Is it carefree? No. It’s right in the middle.”
Dr. Schaffner does think the messages about the new recommendations and how they were decided upon could have been communicated better, and in a more understandable manner. Some experts, for instance, led with the economy and the need for people to return to work and school when explaining the guidelines and then brought up the science behind the revisions.
That order should have been reversed, Dr. Schaffner said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 outbreak hits research station in Antarctica
Two-thirds of the 25 workers have tested positive at the station, despite all of them being fully vaccinated and going through several testing stages before being allowed entrance, the Belgium publication Le Soir reported.
So far, all the cases are mild at the station, which is owned by Belgium and operated by a private group: the International Polar Foundation.
The first case was discovered Dec. 14 among a group that arrived a week earlier in Antarctica, Le Soir reported. The first three people to test positive evacuated Dec. 23, Le Soir said, but the virus continued to spread among the remaining workers at the base.
Le Soir, citing a virologist, said the Omicron variant probably caused the outbreak, because the crew made its last stop in South Africa before arriving in Antarctica.
New arrivals to the station have been put on hold until the outbreak is brought under control, and one of the missions planned for the base has been postponed, Le Soir said.
“The situation isn’t dramatic,” Joseph Cheek, a project manager for the International Polar Foundation, told the BBC. “While it has been an inconvenience to have to quarantine certain members of the staff who caught the virus, it hasn’t significantly affected our work at the station overall.”
The BBC said there was another COVID outbreak in Antarctica about a year ago at the Bernardo O’Higgins research station operated by Chile.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Two-thirds of the 25 workers have tested positive at the station, despite all of them being fully vaccinated and going through several testing stages before being allowed entrance, the Belgium publication Le Soir reported.
So far, all the cases are mild at the station, which is owned by Belgium and operated by a private group: the International Polar Foundation.
The first case was discovered Dec. 14 among a group that arrived a week earlier in Antarctica, Le Soir reported. The first three people to test positive evacuated Dec. 23, Le Soir said, but the virus continued to spread among the remaining workers at the base.
Le Soir, citing a virologist, said the Omicron variant probably caused the outbreak, because the crew made its last stop in South Africa before arriving in Antarctica.
New arrivals to the station have been put on hold until the outbreak is brought under control, and one of the missions planned for the base has been postponed, Le Soir said.
“The situation isn’t dramatic,” Joseph Cheek, a project manager for the International Polar Foundation, told the BBC. “While it has been an inconvenience to have to quarantine certain members of the staff who caught the virus, it hasn’t significantly affected our work at the station overall.”
The BBC said there was another COVID outbreak in Antarctica about a year ago at the Bernardo O’Higgins research station operated by Chile.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Two-thirds of the 25 workers have tested positive at the station, despite all of them being fully vaccinated and going through several testing stages before being allowed entrance, the Belgium publication Le Soir reported.
So far, all the cases are mild at the station, which is owned by Belgium and operated by a private group: the International Polar Foundation.
The first case was discovered Dec. 14 among a group that arrived a week earlier in Antarctica, Le Soir reported. The first three people to test positive evacuated Dec. 23, Le Soir said, but the virus continued to spread among the remaining workers at the base.
Le Soir, citing a virologist, said the Omicron variant probably caused the outbreak, because the crew made its last stop in South Africa before arriving in Antarctica.
New arrivals to the station have been put on hold until the outbreak is brought under control, and one of the missions planned for the base has been postponed, Le Soir said.
“The situation isn’t dramatic,” Joseph Cheek, a project manager for the International Polar Foundation, told the BBC. “While it has been an inconvenience to have to quarantine certain members of the staff who caught the virus, it hasn’t significantly affected our work at the station overall.”
The BBC said there was another COVID outbreak in Antarctica about a year ago at the Bernardo O’Higgins research station operated by Chile.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.






