User login
Plasma biomarkers predict COVID’s neurological sequelae
SAN DIEGO – Even after recovery of an acute COVID-19 infection, some patients experience extended or even long-term symptoms that can range from mild to debilitating. Some of these symptoms are neurological: headaches, brain fog, cognitive impairment, loss of taste or smell, and even cerebrovascular complications such stroke. There are even hints that COVID-19 infection could lead to future neurodegeneration.
Those issues have prompted efforts to identify biomarkers that can help track and monitor neurological complications of COVID-19. “Throughout the course of the pandemic, it has become apparent that COVID-19 can cause various neurological symptoms. Because of this, ,” Jennifer Cooper said during a lecture at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference. She presented new research suggesting that neurofilament light (NfL) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) may prove useful.
Ms. Cooper is a master’s degree student at the University of British Columbia and Canada.
Looking for sensitivity and specificity in plasma biomarkers
The researchers turned to plasma-based markers because they can reflect underlying pathology in the central nervous system. They focused on NfL, which reflects axonal damage, and GFAP, which is a marker of astrocyte activation.
The researchers analyzed data from 209 patients with COVID-19 who were admitted to the Vancouver (B.C.) General Hospital intensive care unit. Sixty-four percent were male, and the median age was 61 years. Sixty percent were ventilated, and 17% died.
The researchers determined if an individual patient’s biomarker level at hospital admission fell within a normal biomarker reference interval. A total of 53% had NfL levels outside the normal range, and 42% had GFAP levels outside the normal range. In addition, 31% of patients had both GFAP and NfL levels outside of the normal range.
Among all patients, 12% experienced ischemia, 4% hemorrhage, 2% seizures, and 10% degeneration.
At admission, NfL predicted a neurological complication with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.702. GFAP had an AUC of 0.722. In combination, they had an AUC of 0.743. At 1 week, NfL had an AUC of 0.802, GFAP an AUC of 0.733, and the combination an AUC of 0.812.
Using age-specific cutoff values, the researchers found increased risks for neurological complications at admission (NfL odds ratio [OR], 2.9; GFAP OR, 1.6; combined OR, 2.1) and at 1 week (NfL OR, not significant; GFAP OR, 4.8; combined OR, 6.6). “We can see that both NFL and GFAP have utility in detecting neurological complications. And combining both of our markers improves detection at both time points. NfL is a marker that provides more sensitivity, where in this cohort GFAP is a marker that provides a little bit more specificity,” said Ms. Cooper.
Will additional biomarkers help?
The researchers are continuing to follow up patients at 6 months and 18 months post diagnosis, using neuropsychiatric tests and additional biomarker analysis, as well as PET and MRI scans. The patient sample is being expanded to those in the general hospital ward and some who were not hospitalized.
During the Q&A session, Ms. Cooper was asked if the group had collected reference data from patients who were admitted to the ICU with non-COVID disease. She responded that the group has some of that data, but as the pandemic went on they had difficulty finding patients who had never been infected with COVID to serve as reliable controls. To date, they have identified 33 controls who had a respiratory condition when admitted to the ICU. “What we see is the neurological biomarker levels in COVID are slightly lower than those with another respiratory condition in the ICU. But the data has a massive spread and the significance is very small between the two groups,” said Ms. Cooper.
Unanswered questions
The study is interesting, but leaves a lot of unanswered questions, according to Wiesje van der Flier, PhD, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “There are a lot of unknowns still: Will [the biomarkers] become normal again, once the COVID is over? Also, there was an increased risk, but it was not a one-to-one correspondence, so you can also have the increased markers but not have the neurological signs or symptoms. So I thought there were lots of questions as well,” said Dr. van der Flier, professor of neurology at Amsterdam University Medical Center.
She noted that researchers at her institution in Amsterdam have observed similar relationships, and that the associations between neurological complications and plasma biomarkers over time will be an important topic of study.
The work could provide more information on neurological manifestations of long COVID, such as long-haul fatigue. “You might also think that’s some response in their brain. It would be great if we could actually capture that [using biomarkers],” said Dr. van der Flier.
Ms. Cooper and Dr. van der Flier have no relevant financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – Even after recovery of an acute COVID-19 infection, some patients experience extended or even long-term symptoms that can range from mild to debilitating. Some of these symptoms are neurological: headaches, brain fog, cognitive impairment, loss of taste or smell, and even cerebrovascular complications such stroke. There are even hints that COVID-19 infection could lead to future neurodegeneration.
Those issues have prompted efforts to identify biomarkers that can help track and monitor neurological complications of COVID-19. “Throughout the course of the pandemic, it has become apparent that COVID-19 can cause various neurological symptoms. Because of this, ,” Jennifer Cooper said during a lecture at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference. She presented new research suggesting that neurofilament light (NfL) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) may prove useful.
Ms. Cooper is a master’s degree student at the University of British Columbia and Canada.
Looking for sensitivity and specificity in plasma biomarkers
The researchers turned to plasma-based markers because they can reflect underlying pathology in the central nervous system. They focused on NfL, which reflects axonal damage, and GFAP, which is a marker of astrocyte activation.
The researchers analyzed data from 209 patients with COVID-19 who were admitted to the Vancouver (B.C.) General Hospital intensive care unit. Sixty-four percent were male, and the median age was 61 years. Sixty percent were ventilated, and 17% died.
The researchers determined if an individual patient’s biomarker level at hospital admission fell within a normal biomarker reference interval. A total of 53% had NfL levels outside the normal range, and 42% had GFAP levels outside the normal range. In addition, 31% of patients had both GFAP and NfL levels outside of the normal range.
Among all patients, 12% experienced ischemia, 4% hemorrhage, 2% seizures, and 10% degeneration.
At admission, NfL predicted a neurological complication with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.702. GFAP had an AUC of 0.722. In combination, they had an AUC of 0.743. At 1 week, NfL had an AUC of 0.802, GFAP an AUC of 0.733, and the combination an AUC of 0.812.
Using age-specific cutoff values, the researchers found increased risks for neurological complications at admission (NfL odds ratio [OR], 2.9; GFAP OR, 1.6; combined OR, 2.1) and at 1 week (NfL OR, not significant; GFAP OR, 4.8; combined OR, 6.6). “We can see that both NFL and GFAP have utility in detecting neurological complications. And combining both of our markers improves detection at both time points. NfL is a marker that provides more sensitivity, where in this cohort GFAP is a marker that provides a little bit more specificity,” said Ms. Cooper.
Will additional biomarkers help?
The researchers are continuing to follow up patients at 6 months and 18 months post diagnosis, using neuropsychiatric tests and additional biomarker analysis, as well as PET and MRI scans. The patient sample is being expanded to those in the general hospital ward and some who were not hospitalized.
During the Q&A session, Ms. Cooper was asked if the group had collected reference data from patients who were admitted to the ICU with non-COVID disease. She responded that the group has some of that data, but as the pandemic went on they had difficulty finding patients who had never been infected with COVID to serve as reliable controls. To date, they have identified 33 controls who had a respiratory condition when admitted to the ICU. “What we see is the neurological biomarker levels in COVID are slightly lower than those with another respiratory condition in the ICU. But the data has a massive spread and the significance is very small between the two groups,” said Ms. Cooper.
Unanswered questions
The study is interesting, but leaves a lot of unanswered questions, according to Wiesje van der Flier, PhD, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “There are a lot of unknowns still: Will [the biomarkers] become normal again, once the COVID is over? Also, there was an increased risk, but it was not a one-to-one correspondence, so you can also have the increased markers but not have the neurological signs or symptoms. So I thought there were lots of questions as well,” said Dr. van der Flier, professor of neurology at Amsterdam University Medical Center.
She noted that researchers at her institution in Amsterdam have observed similar relationships, and that the associations between neurological complications and plasma biomarkers over time will be an important topic of study.
The work could provide more information on neurological manifestations of long COVID, such as long-haul fatigue. “You might also think that’s some response in their brain. It would be great if we could actually capture that [using biomarkers],” said Dr. van der Flier.
Ms. Cooper and Dr. van der Flier have no relevant financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – Even after recovery of an acute COVID-19 infection, some patients experience extended or even long-term symptoms that can range from mild to debilitating. Some of these symptoms are neurological: headaches, brain fog, cognitive impairment, loss of taste or smell, and even cerebrovascular complications such stroke. There are even hints that COVID-19 infection could lead to future neurodegeneration.
Those issues have prompted efforts to identify biomarkers that can help track and monitor neurological complications of COVID-19. “Throughout the course of the pandemic, it has become apparent that COVID-19 can cause various neurological symptoms. Because of this, ,” Jennifer Cooper said during a lecture at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference. She presented new research suggesting that neurofilament light (NfL) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) may prove useful.
Ms. Cooper is a master’s degree student at the University of British Columbia and Canada.
Looking for sensitivity and specificity in plasma biomarkers
The researchers turned to plasma-based markers because they can reflect underlying pathology in the central nervous system. They focused on NfL, which reflects axonal damage, and GFAP, which is a marker of astrocyte activation.
The researchers analyzed data from 209 patients with COVID-19 who were admitted to the Vancouver (B.C.) General Hospital intensive care unit. Sixty-four percent were male, and the median age was 61 years. Sixty percent were ventilated, and 17% died.
The researchers determined if an individual patient’s biomarker level at hospital admission fell within a normal biomarker reference interval. A total of 53% had NfL levels outside the normal range, and 42% had GFAP levels outside the normal range. In addition, 31% of patients had both GFAP and NfL levels outside of the normal range.
Among all patients, 12% experienced ischemia, 4% hemorrhage, 2% seizures, and 10% degeneration.
At admission, NfL predicted a neurological complication with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.702. GFAP had an AUC of 0.722. In combination, they had an AUC of 0.743. At 1 week, NfL had an AUC of 0.802, GFAP an AUC of 0.733, and the combination an AUC of 0.812.
Using age-specific cutoff values, the researchers found increased risks for neurological complications at admission (NfL odds ratio [OR], 2.9; GFAP OR, 1.6; combined OR, 2.1) and at 1 week (NfL OR, not significant; GFAP OR, 4.8; combined OR, 6.6). “We can see that both NFL and GFAP have utility in detecting neurological complications. And combining both of our markers improves detection at both time points. NfL is a marker that provides more sensitivity, where in this cohort GFAP is a marker that provides a little bit more specificity,” said Ms. Cooper.
Will additional biomarkers help?
The researchers are continuing to follow up patients at 6 months and 18 months post diagnosis, using neuropsychiatric tests and additional biomarker analysis, as well as PET and MRI scans. The patient sample is being expanded to those in the general hospital ward and some who were not hospitalized.
During the Q&A session, Ms. Cooper was asked if the group had collected reference data from patients who were admitted to the ICU with non-COVID disease. She responded that the group has some of that data, but as the pandemic went on they had difficulty finding patients who had never been infected with COVID to serve as reliable controls. To date, they have identified 33 controls who had a respiratory condition when admitted to the ICU. “What we see is the neurological biomarker levels in COVID are slightly lower than those with another respiratory condition in the ICU. But the data has a massive spread and the significance is very small between the two groups,” said Ms. Cooper.
Unanswered questions
The study is interesting, but leaves a lot of unanswered questions, according to Wiesje van der Flier, PhD, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “There are a lot of unknowns still: Will [the biomarkers] become normal again, once the COVID is over? Also, there was an increased risk, but it was not a one-to-one correspondence, so you can also have the increased markers but not have the neurological signs or symptoms. So I thought there were lots of questions as well,” said Dr. van der Flier, professor of neurology at Amsterdam University Medical Center.
She noted that researchers at her institution in Amsterdam have observed similar relationships, and that the associations between neurological complications and plasma biomarkers over time will be an important topic of study.
The work could provide more information on neurological manifestations of long COVID, such as long-haul fatigue. “You might also think that’s some response in their brain. It would be great if we could actually capture that [using biomarkers],” said Dr. van der Flier.
Ms. Cooper and Dr. van der Flier have no relevant financial disclosures.
AT AAIC 2022
Guidance From the National Psoriasis Foundation COVID-19 Task Force
When COVID-19 emerged in March 2020, physicians were forced to evaluate the potential impacts of the pandemic on our patients and the conditions that we treat. For dermatologists, psoriasis came into particular focus, as many patients were being treated with biologic therapies. The initial concern was that these biologics might render our patients more susceptible to both COVID-19 infection and/or a more severe disease course.
In early 2020, the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) presented its own recommendations for treating patients with psoriatic disease during the pandemic.1 Some highlights included the following1:
• At the time, it was stipulated that patients with COVID-19 infection should stop taking a biologic.
• Psoriasis patients in high-risk groups (eg, concomitant systemic disease) should discuss with their dermatologist if their therapeutic regimen should be continued or altered.
• Patients taking oral immunosuppressive therapy may be at greater risk for COVID-19 infection, though there is no strong COVID-19–related evidence to provide specific guidelines or risk level.
In May 2020, the NPF COVID-19 Task Force was formed. This group—chaired by dermatologist Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), and rheumatologist Christopher T. Ritchlin, MD, MPH (Rochester, New York)—was comprised of members from both the NPF Medical Board and Scientific Advisory Committee in dermatology, rheumatology, infectious disease, and critical care. The NPF COVID-19 Task Force has been critical in keeping the dermatology community apprised of the latest scientific thinking related to COVID-19 and publishing guidance statements that are updated and amended on a regular basis as new data becomes available.2 Key recommendations most relevant to the daily care of patients with psoriatic disease included the following2:
• Patients with psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis have similar rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 outcomes as the general population based on existing data, with some exceptions.
• Therapies for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis do not meaningfully alter the risk for acquiring SARS-CoV-2 infection or having worse COVID-19 outcomes.
• Patients should continue their biologic or oral therapies for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis in most cases, unless they become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
• Chronic systemic steroid use for psoriatic disease in the setting of acute infection with COVID-19 may be associated with worse outcomes; however, steroids may improve outcomes for COVID-19 when initiated in hospitalized patients who require oxygen therapy.
• When local restrictions or pandemic conditions limit the ability for in-person visits, offer telemedicine to manage patients.
• Patients with psoriatic disease who do not have contraindications to vaccination should receive a messenger RNA (mRNA)–based COVID-19 vaccine and boosters, based on federal, state, and local guidance. Systemic medications for psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis are not a contraindication to the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine.
• Patients who are to receive an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine should continue their biologic or oral therapies for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis in most cases.
• The use of hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, and ivermectin is not suggested for the prevention or treatment of COVID-19 disease.
These guidelines have been critical in addressing some of the most pressing issues in psoriasis patient care, particularly the susceptibility to COVID-19, the role of psoriasis therapies in initial infection and health outcomes, and issues related to the administration of vaccines in those on systemic therapies. Based on these recommendations, we have been given a solid foundation that our current standard of care can (for the most part) continue with the continued presence of COVID-19 in our society. I encourage all providers to familiarize themselves with the NPF COVID-19 Task Force guidelines and keep abreast of updates as they become available (https://www.psoriasis.org/covid-19-task-force-guidance-statements/).
- Gelfand JM, Armstrong AW, Bell S, et al. National Psoriasis Foundation COVID-19 Task Force guidance for management of psoriatic disease during the pandemic: version 1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1704-1716.
- COVID-19 Task Force guidance statements. National Psoriasis Foundation website. Updated April 28, 2022. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.psoriasis.org/covid-19-task-force-guidance-statements/
When COVID-19 emerged in March 2020, physicians were forced to evaluate the potential impacts of the pandemic on our patients and the conditions that we treat. For dermatologists, psoriasis came into particular focus, as many patients were being treated with biologic therapies. The initial concern was that these biologics might render our patients more susceptible to both COVID-19 infection and/or a more severe disease course.
In early 2020, the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) presented its own recommendations for treating patients with psoriatic disease during the pandemic.1 Some highlights included the following1:
• At the time, it was stipulated that patients with COVID-19 infection should stop taking a biologic.
• Psoriasis patients in high-risk groups (eg, concomitant systemic disease) should discuss with their dermatologist if their therapeutic regimen should be continued or altered.
• Patients taking oral immunosuppressive therapy may be at greater risk for COVID-19 infection, though there is no strong COVID-19–related evidence to provide specific guidelines or risk level.
In May 2020, the NPF COVID-19 Task Force was formed. This group—chaired by dermatologist Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), and rheumatologist Christopher T. Ritchlin, MD, MPH (Rochester, New York)—was comprised of members from both the NPF Medical Board and Scientific Advisory Committee in dermatology, rheumatology, infectious disease, and critical care. The NPF COVID-19 Task Force has been critical in keeping the dermatology community apprised of the latest scientific thinking related to COVID-19 and publishing guidance statements that are updated and amended on a regular basis as new data becomes available.2 Key recommendations most relevant to the daily care of patients with psoriatic disease included the following2:
• Patients with psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis have similar rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 outcomes as the general population based on existing data, with some exceptions.
• Therapies for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis do not meaningfully alter the risk for acquiring SARS-CoV-2 infection or having worse COVID-19 outcomes.
• Patients should continue their biologic or oral therapies for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis in most cases, unless they become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
• Chronic systemic steroid use for psoriatic disease in the setting of acute infection with COVID-19 may be associated with worse outcomes; however, steroids may improve outcomes for COVID-19 when initiated in hospitalized patients who require oxygen therapy.
• When local restrictions or pandemic conditions limit the ability for in-person visits, offer telemedicine to manage patients.
• Patients with psoriatic disease who do not have contraindications to vaccination should receive a messenger RNA (mRNA)–based COVID-19 vaccine and boosters, based on federal, state, and local guidance. Systemic medications for psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis are not a contraindication to the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine.
• Patients who are to receive an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine should continue their biologic or oral therapies for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis in most cases.
• The use of hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, and ivermectin is not suggested for the prevention or treatment of COVID-19 disease.
These guidelines have been critical in addressing some of the most pressing issues in psoriasis patient care, particularly the susceptibility to COVID-19, the role of psoriasis therapies in initial infection and health outcomes, and issues related to the administration of vaccines in those on systemic therapies. Based on these recommendations, we have been given a solid foundation that our current standard of care can (for the most part) continue with the continued presence of COVID-19 in our society. I encourage all providers to familiarize themselves with the NPF COVID-19 Task Force guidelines and keep abreast of updates as they become available (https://www.psoriasis.org/covid-19-task-force-guidance-statements/).
When COVID-19 emerged in March 2020, physicians were forced to evaluate the potential impacts of the pandemic on our patients and the conditions that we treat. For dermatologists, psoriasis came into particular focus, as many patients were being treated with biologic therapies. The initial concern was that these biologics might render our patients more susceptible to both COVID-19 infection and/or a more severe disease course.
In early 2020, the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) presented its own recommendations for treating patients with psoriatic disease during the pandemic.1 Some highlights included the following1:
• At the time, it was stipulated that patients with COVID-19 infection should stop taking a biologic.
• Psoriasis patients in high-risk groups (eg, concomitant systemic disease) should discuss with their dermatologist if their therapeutic regimen should be continued or altered.
• Patients taking oral immunosuppressive therapy may be at greater risk for COVID-19 infection, though there is no strong COVID-19–related evidence to provide specific guidelines or risk level.
In May 2020, the NPF COVID-19 Task Force was formed. This group—chaired by dermatologist Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), and rheumatologist Christopher T. Ritchlin, MD, MPH (Rochester, New York)—was comprised of members from both the NPF Medical Board and Scientific Advisory Committee in dermatology, rheumatology, infectious disease, and critical care. The NPF COVID-19 Task Force has been critical in keeping the dermatology community apprised of the latest scientific thinking related to COVID-19 and publishing guidance statements that are updated and amended on a regular basis as new data becomes available.2 Key recommendations most relevant to the daily care of patients with psoriatic disease included the following2:
• Patients with psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis have similar rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 outcomes as the general population based on existing data, with some exceptions.
• Therapies for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis do not meaningfully alter the risk for acquiring SARS-CoV-2 infection or having worse COVID-19 outcomes.
• Patients should continue their biologic or oral therapies for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis in most cases, unless they become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
• Chronic systemic steroid use for psoriatic disease in the setting of acute infection with COVID-19 may be associated with worse outcomes; however, steroids may improve outcomes for COVID-19 when initiated in hospitalized patients who require oxygen therapy.
• When local restrictions or pandemic conditions limit the ability for in-person visits, offer telemedicine to manage patients.
• Patients with psoriatic disease who do not have contraindications to vaccination should receive a messenger RNA (mRNA)–based COVID-19 vaccine and boosters, based on federal, state, and local guidance. Systemic medications for psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis are not a contraindication to the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine.
• Patients who are to receive an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine should continue their biologic or oral therapies for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis in most cases.
• The use of hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, and ivermectin is not suggested for the prevention or treatment of COVID-19 disease.
These guidelines have been critical in addressing some of the most pressing issues in psoriasis patient care, particularly the susceptibility to COVID-19, the role of psoriasis therapies in initial infection and health outcomes, and issues related to the administration of vaccines in those on systemic therapies. Based on these recommendations, we have been given a solid foundation that our current standard of care can (for the most part) continue with the continued presence of COVID-19 in our society. I encourage all providers to familiarize themselves with the NPF COVID-19 Task Force guidelines and keep abreast of updates as they become available (https://www.psoriasis.org/covid-19-task-force-guidance-statements/).
- Gelfand JM, Armstrong AW, Bell S, et al. National Psoriasis Foundation COVID-19 Task Force guidance for management of psoriatic disease during the pandemic: version 1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1704-1716.
- COVID-19 Task Force guidance statements. National Psoriasis Foundation website. Updated April 28, 2022. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.psoriasis.org/covid-19-task-force-guidance-statements/
- Gelfand JM, Armstrong AW, Bell S, et al. National Psoriasis Foundation COVID-19 Task Force guidance for management of psoriatic disease during the pandemic: version 1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1704-1716.
- COVID-19 Task Force guidance statements. National Psoriasis Foundation website. Updated April 28, 2022. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.psoriasis.org/covid-19-task-force-guidance-statements/
Children and COVID: Severe illness rising as vaccination effort stalls
, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
After new child cases jumped by 22% during the week of July 15-21, the two successive weeks have produced increases of 3.9% (July 22-29) and 1.2% (July 30-Aug. 4). The latest weekly count from all states and territories still reporting was 96,599, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report, noting that several states have stopped reporting child cases and that others are reporting every other week.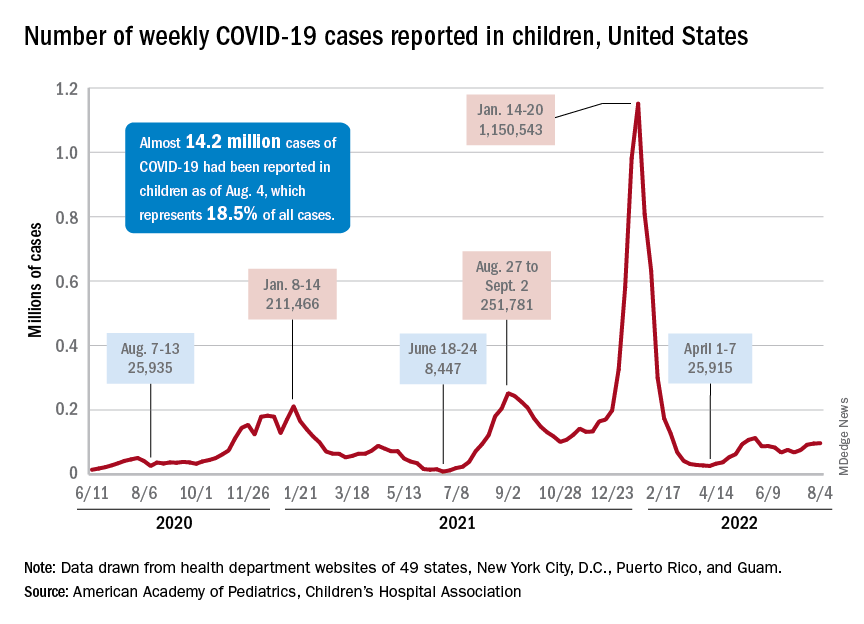
The deceleration in new cases, however, does not apply to emergency department visits and hospital admissions. The proportion of ED visits with diagnosed COVID rose steadily throughout June and July, as 7-day averages went from 2.6% on June 1 to 6.3% on July 31 for children aged 0-11 years, from 2.1% to 3.1% for children aged 12-15, and from 2.4% to 3.5% for 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The rate of new admissions with confirmed COVID, which reached 0.46 per 100,000 population for children aged 0-17 years on July 30, has more than tripled since early April, when it had fallen to 0.13 per 100,000 in the wake of the Omicron surge, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
A smaller but more detailed sample of children from the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Network (COVID-NET), which covers nearly 100 counties in 14 states, indicates that the increase in new admissions is occurring almost entirely among children aged 0-4 years, who had a rate of 5.6 per 100,000 for the week of July 17-23, compared with 0.8 per 100,000 for 5- to 11-year-olds and 1.5 per 100,000 for those aged 12-17, the CDC said.
Vaccine’s summer rollout gets lukewarm reception
As a group, children aged 0-4 years have not exactly flocked to the COVID-19 vaccine. As of Aug. 2 – about 6 weeks since the vaccine was authorized for children aged 6 months to 4 years – just 3.8% of those eligible had received at least one dose. Among children aged 5-11 the corresponding number on Aug. 2 was 37.4%, and for those aged 12-17 years it was 70.3%, the CDC data show.
That 3.8% of children aged less than 5 years represents almost 756,000 initial doses. That compares with over 6 million children aged 5-11 years who had received at least one dose through the first 6 weeks of their vaccination experience and over 5 million children aged 12-15, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
After new child cases jumped by 22% during the week of July 15-21, the two successive weeks have produced increases of 3.9% (July 22-29) and 1.2% (July 30-Aug. 4). The latest weekly count from all states and territories still reporting was 96,599, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report, noting that several states have stopped reporting child cases and that others are reporting every other week.
The deceleration in new cases, however, does not apply to emergency department visits and hospital admissions. The proportion of ED visits with diagnosed COVID rose steadily throughout June and July, as 7-day averages went from 2.6% on June 1 to 6.3% on July 31 for children aged 0-11 years, from 2.1% to 3.1% for children aged 12-15, and from 2.4% to 3.5% for 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The rate of new admissions with confirmed COVID, which reached 0.46 per 100,000 population for children aged 0-17 years on July 30, has more than tripled since early April, when it had fallen to 0.13 per 100,000 in the wake of the Omicron surge, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
A smaller but more detailed sample of children from the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Network (COVID-NET), which covers nearly 100 counties in 14 states, indicates that the increase in new admissions is occurring almost entirely among children aged 0-4 years, who had a rate of 5.6 per 100,000 for the week of July 17-23, compared with 0.8 per 100,000 for 5- to 11-year-olds and 1.5 per 100,000 for those aged 12-17, the CDC said.
Vaccine’s summer rollout gets lukewarm reception
As a group, children aged 0-4 years have not exactly flocked to the COVID-19 vaccine. As of Aug. 2 – about 6 weeks since the vaccine was authorized for children aged 6 months to 4 years – just 3.8% of those eligible had received at least one dose. Among children aged 5-11 the corresponding number on Aug. 2 was 37.4%, and for those aged 12-17 years it was 70.3%, the CDC data show.
That 3.8% of children aged less than 5 years represents almost 756,000 initial doses. That compares with over 6 million children aged 5-11 years who had received at least one dose through the first 6 weeks of their vaccination experience and over 5 million children aged 12-15, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
After new child cases jumped by 22% during the week of July 15-21, the two successive weeks have produced increases of 3.9% (July 22-29) and 1.2% (July 30-Aug. 4). The latest weekly count from all states and territories still reporting was 96,599, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report, noting that several states have stopped reporting child cases and that others are reporting every other week.
The deceleration in new cases, however, does not apply to emergency department visits and hospital admissions. The proportion of ED visits with diagnosed COVID rose steadily throughout June and July, as 7-day averages went from 2.6% on June 1 to 6.3% on July 31 for children aged 0-11 years, from 2.1% to 3.1% for children aged 12-15, and from 2.4% to 3.5% for 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The rate of new admissions with confirmed COVID, which reached 0.46 per 100,000 population for children aged 0-17 years on July 30, has more than tripled since early April, when it had fallen to 0.13 per 100,000 in the wake of the Omicron surge, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
A smaller but more detailed sample of children from the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Network (COVID-NET), which covers nearly 100 counties in 14 states, indicates that the increase in new admissions is occurring almost entirely among children aged 0-4 years, who had a rate of 5.6 per 100,000 for the week of July 17-23, compared with 0.8 per 100,000 for 5- to 11-year-olds and 1.5 per 100,000 for those aged 12-17, the CDC said.
Vaccine’s summer rollout gets lukewarm reception
As a group, children aged 0-4 years have not exactly flocked to the COVID-19 vaccine. As of Aug. 2 – about 6 weeks since the vaccine was authorized for children aged 6 months to 4 years – just 3.8% of those eligible had received at least one dose. Among children aged 5-11 the corresponding number on Aug. 2 was 37.4%, and for those aged 12-17 years it was 70.3%, the CDC data show.
That 3.8% of children aged less than 5 years represents almost 756,000 initial doses. That compares with over 6 million children aged 5-11 years who had received at least one dose through the first 6 weeks of their vaccination experience and over 5 million children aged 12-15, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
Updates on treatment/prevention of VTE in cancer patients
Updated clinical practice guidelines for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism for patients with cancer, including those with cancer and COVID-19, have been released by the International Initiative on Thrombosis and Cancer (ITAC), an academic working group of VTE experts.
“Because patients with cancer have a baseline increased risk of VTE, compared with patients without cancer, the combination of both COVID-19 and cancer – and its effect on VTE risk and treatment – is of concern,” said the authors, led by Dominique Farge, MD, PhD, Nord Universite de Paris.
they added.
The new guidelines were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
“Cancer-associated VTE remains an important clinical problem, associated with increased morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Farge and colleagues observed.
“The ITAC guidelines’ companion free web-based mobile application will assist the practicing clinician with decision making at various levels to provide optimal care of patients with cancer to treat and prevent VTE,” they emphasized. More information is available at itaccme.com.
Cancer patients with COVID
The new section of the guidelines notes that the treatment and prevention of VTE for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 remain the same as for patients without COVID.
Whether or not cancer patients with COVID-19 are hospitalized, have been discharged, or are ambulatory, they should be assessed for the risk of VTE, as should any other patient. For cancer patients with COVID-19 who are hospitalized, pharmacologic prophylaxis should be given at the same dose and anticoagulant type as for hospitalized cancer patients who do not have COVID-19.
Following discharge, VTE prophylaxis is not advised for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, and routine primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE for ambulatory patients with COVID-19 is also not recommended, the authors noted.
Initial treatment of established VTE
Initial treatment of established VTE for up to 10 days of anticoagulation should include low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) when creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“A regimen of LMWH, taken once per day, is recommended unless a twice-per-day regimen is required because of patients’ characteristics,” the authors noted. These characteristics include a high risk of bleeding, moderate renal failure, and the need for technical intervention, including surgery.
If a twice-a-day regimen is required, only enoxaparin at a dose of 1 mg/kg twice daily can be used, the authors cautioned.
For patients with a low risk of gastrointestinal or genitourinary bleeding, rivaroxaban (Xarelto) or apixaban (Eliquis) can be given in the first 10 days, as well as edoxaban (Lixiana). The latter should be started after at least 5 days of parenteral anticoagulation, provided creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“Unfractionated heparin as well as fondaparinux (GlaxoSmithKline) can be also used for the initial treatment of established VTE when LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants are contraindicated,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Thrombolysis can be considered on a case-by-case basis, although physicians must pay attention to specific contraindications, especially bleeding risk.
“In the initial treatment of VTE, inferior vena cava filters might be considered when anticoagulant treatment is contraindicated or, in the case of pulmonary embolism, when recurrence occurs under optimal anticoagulation,” the authors noted.
Maintenance VTE treatment
For maintenance therapy, which the authors define as early maintenance for up to 6 months and long-term maintenance beyond 6 months, they point out that LMWHs are preferred over vitamin K antagonists for the treatment of VTE when the creatinine clearance is again at least 30 mL/min.
Any of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOAs) – edoxaban, rivaroxaban, or apixaban – is also recommended for the same patients, provided there is no risk of inducing a strong drug-drug interaction or GI absorption is impaired.
However, the DOAs should be used with caution for patients with GI malignancies, especially upper GI cancers, because data show there is an increased risk of GI bleeding with both edoxaban and rivaroxaban.
“LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants should be used for a minimum of 6 months to treat established VTE in patients with cancer,” the authors wrote.
“After 6 months, termination or continuation of anticoagulation (LMWH, direct oral anticoagulants, or vitamin K antagonists) should be based on individual evaluation of the benefit-risk ratio,” they added.
Treatment of VTE recurrence
The guideline authors explain that three options can be considered in the event of VTE recurrence. These include an increase in the LMWH dose by 20%-25%, or a switch to a DOA, or, if patients are taking a DOA, a switch to an LMWH. If the patient is taking a vitamin K antagonist, it can be switched to either an LMWH or a DOA.
For treatment of catheter-related thrombosis, anticoagulant treatment is recommended for a minimum of 3 months and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. In this setting, the LMWHs are recommended.
The central venous catheter can be kept in place if it is functional, well positioned, and is not infected, provided there is good resolution of symptoms under close surveillance while anticoagulants are being administered.
In surgically treated patients, the LMWH, given once a day, to patients with a serum creatinine concentration of at least 30 mL/min can be used to prevent VTE. Alternatively, VTE can be prevented by the use low-dose unfractionated heparin, given three times a day.
“Pharmacological prophylaxis should be started 2-12 h preoperatively and continued for at least 7–10 days,” Dr. Farge and colleagues advised. In this setting, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of fondaparinux or a DOA as an alternative to an LMWH for the prophylaxis of postoperative VTE. “Use of the highest prophylactic dose of LMWH to prevent postoperative VTE in patients with cancer is recommended,” the authors advised.
Furthermore, extended prophylaxis of at least 4 weeks with LMWH is advised to prevent postoperative VTE after major abdominal or pelvic surgery. Mechanical methods are not recommended except when pharmacologic methods are contraindicated. Inferior vena cava filters are also not recommended for routine prophylaxis.
Patients with reduced mobility
For medically treated hospitalized patients with cancer whose mobility is reduced, the authors recommend prophylaxis with either an LMWH or fondaparinux, provided their creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min. These patients can also be treated with unfractionated heparin, they add.
In contrast, DOAs are not recommended – at least not routinely – in this setting, the authors cautioned. Primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE with either LMWH or DOAs – either rivaroxaban or apixaban – is indicated in ambulatory patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy, provided they are at low risk of bleeding.
However, primary pharmacologic prophylaxis with LMWH is not recommended outside of a clinical trial for patients with locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer who are undergoing systemic anticancer therapy, even for patients who are at low risk of bleeding.
For ambulatory patients who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy and who are at intermediate risk of VTE, primary prophylaxis with rivaroxaban or apixaban is recommended for those with myeloma who are receiving immunomodulatory therapy plus steroids or other systemic therapies.
In this setting, oral anticoagulants should consist of a vitamin K antagonist, given at low or therapeutic doses, or apixaban, given at prophylactic doses. Alternatively, LMWH, given at prophylactic doses, or low-dose aspirin, given at a dose of 100 mg/day, can be used.
Catheter-related thrombosis
Use of anticoagulation for routine prophylaxis of catheter-related thrombosis is not recommended. Catheters should be inserted on the right side in the jugular vein, and the distal extremity of the central catheter should be located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. “In patients requiring central venous catheters, we suggest the use of implanted ports over peripheral inserted central catheter lines,” the authors noted.
The authors described a number of unique situations regarding the treatment of VTE. These situations include patients with a brain tumor, for whom treatment of established VTE should favor either LMWH or a DOA. The authors also recommended the use of LMWH or unfractionated heparin, started postoperatively, for the prevention of VTE for patients undergoing neurosurgery.
In contrast, pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE in medically treated patients with a brain tumor who are not undergoing neurosurgery is not recommended. “In the presence of severe renal failure...we suggest using unfractionated heparin followed by early vitamin K antagonists (possibly from day 1) or LMWH adjusted to anti-Xa concentration of the treatment of established VTE,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Anticoagulant treatment is also recommended for a minimum of 3 months for children with symptomatic catheter-related thrombosis and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. For children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are undergoing induction chemotherapy, LMWH is also recommended as thromboprophylaxis.
For children who require a central venous catheter, the authors suggested that physicians use implanted ports over peripherally inserted central lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated clinical practice guidelines for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism for patients with cancer, including those with cancer and COVID-19, have been released by the International Initiative on Thrombosis and Cancer (ITAC), an academic working group of VTE experts.
“Because patients with cancer have a baseline increased risk of VTE, compared with patients without cancer, the combination of both COVID-19 and cancer – and its effect on VTE risk and treatment – is of concern,” said the authors, led by Dominique Farge, MD, PhD, Nord Universite de Paris.
they added.
The new guidelines were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
“Cancer-associated VTE remains an important clinical problem, associated with increased morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Farge and colleagues observed.
“The ITAC guidelines’ companion free web-based mobile application will assist the practicing clinician with decision making at various levels to provide optimal care of patients with cancer to treat and prevent VTE,” they emphasized. More information is available at itaccme.com.
Cancer patients with COVID
The new section of the guidelines notes that the treatment and prevention of VTE for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 remain the same as for patients without COVID.
Whether or not cancer patients with COVID-19 are hospitalized, have been discharged, or are ambulatory, they should be assessed for the risk of VTE, as should any other patient. For cancer patients with COVID-19 who are hospitalized, pharmacologic prophylaxis should be given at the same dose and anticoagulant type as for hospitalized cancer patients who do not have COVID-19.
Following discharge, VTE prophylaxis is not advised for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, and routine primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE for ambulatory patients with COVID-19 is also not recommended, the authors noted.
Initial treatment of established VTE
Initial treatment of established VTE for up to 10 days of anticoagulation should include low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) when creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“A regimen of LMWH, taken once per day, is recommended unless a twice-per-day regimen is required because of patients’ characteristics,” the authors noted. These characteristics include a high risk of bleeding, moderate renal failure, and the need for technical intervention, including surgery.
If a twice-a-day regimen is required, only enoxaparin at a dose of 1 mg/kg twice daily can be used, the authors cautioned.
For patients with a low risk of gastrointestinal or genitourinary bleeding, rivaroxaban (Xarelto) or apixaban (Eliquis) can be given in the first 10 days, as well as edoxaban (Lixiana). The latter should be started after at least 5 days of parenteral anticoagulation, provided creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“Unfractionated heparin as well as fondaparinux (GlaxoSmithKline) can be also used for the initial treatment of established VTE when LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants are contraindicated,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Thrombolysis can be considered on a case-by-case basis, although physicians must pay attention to specific contraindications, especially bleeding risk.
“In the initial treatment of VTE, inferior vena cava filters might be considered when anticoagulant treatment is contraindicated or, in the case of pulmonary embolism, when recurrence occurs under optimal anticoagulation,” the authors noted.
Maintenance VTE treatment
For maintenance therapy, which the authors define as early maintenance for up to 6 months and long-term maintenance beyond 6 months, they point out that LMWHs are preferred over vitamin K antagonists for the treatment of VTE when the creatinine clearance is again at least 30 mL/min.
Any of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOAs) – edoxaban, rivaroxaban, or apixaban – is also recommended for the same patients, provided there is no risk of inducing a strong drug-drug interaction or GI absorption is impaired.
However, the DOAs should be used with caution for patients with GI malignancies, especially upper GI cancers, because data show there is an increased risk of GI bleeding with both edoxaban and rivaroxaban.
“LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants should be used for a minimum of 6 months to treat established VTE in patients with cancer,” the authors wrote.
“After 6 months, termination or continuation of anticoagulation (LMWH, direct oral anticoagulants, or vitamin K antagonists) should be based on individual evaluation of the benefit-risk ratio,” they added.
Treatment of VTE recurrence
The guideline authors explain that three options can be considered in the event of VTE recurrence. These include an increase in the LMWH dose by 20%-25%, or a switch to a DOA, or, if patients are taking a DOA, a switch to an LMWH. If the patient is taking a vitamin K antagonist, it can be switched to either an LMWH or a DOA.
For treatment of catheter-related thrombosis, anticoagulant treatment is recommended for a minimum of 3 months and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. In this setting, the LMWHs are recommended.
The central venous catheter can be kept in place if it is functional, well positioned, and is not infected, provided there is good resolution of symptoms under close surveillance while anticoagulants are being administered.
In surgically treated patients, the LMWH, given once a day, to patients with a serum creatinine concentration of at least 30 mL/min can be used to prevent VTE. Alternatively, VTE can be prevented by the use low-dose unfractionated heparin, given three times a day.
“Pharmacological prophylaxis should be started 2-12 h preoperatively and continued for at least 7–10 days,” Dr. Farge and colleagues advised. In this setting, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of fondaparinux or a DOA as an alternative to an LMWH for the prophylaxis of postoperative VTE. “Use of the highest prophylactic dose of LMWH to prevent postoperative VTE in patients with cancer is recommended,” the authors advised.
Furthermore, extended prophylaxis of at least 4 weeks with LMWH is advised to prevent postoperative VTE after major abdominal or pelvic surgery. Mechanical methods are not recommended except when pharmacologic methods are contraindicated. Inferior vena cava filters are also not recommended for routine prophylaxis.
Patients with reduced mobility
For medically treated hospitalized patients with cancer whose mobility is reduced, the authors recommend prophylaxis with either an LMWH or fondaparinux, provided their creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min. These patients can also be treated with unfractionated heparin, they add.
In contrast, DOAs are not recommended – at least not routinely – in this setting, the authors cautioned. Primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE with either LMWH or DOAs – either rivaroxaban or apixaban – is indicated in ambulatory patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy, provided they are at low risk of bleeding.
However, primary pharmacologic prophylaxis with LMWH is not recommended outside of a clinical trial for patients with locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer who are undergoing systemic anticancer therapy, even for patients who are at low risk of bleeding.
For ambulatory patients who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy and who are at intermediate risk of VTE, primary prophylaxis with rivaroxaban or apixaban is recommended for those with myeloma who are receiving immunomodulatory therapy plus steroids or other systemic therapies.
In this setting, oral anticoagulants should consist of a vitamin K antagonist, given at low or therapeutic doses, or apixaban, given at prophylactic doses. Alternatively, LMWH, given at prophylactic doses, or low-dose aspirin, given at a dose of 100 mg/day, can be used.
Catheter-related thrombosis
Use of anticoagulation for routine prophylaxis of catheter-related thrombosis is not recommended. Catheters should be inserted on the right side in the jugular vein, and the distal extremity of the central catheter should be located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. “In patients requiring central venous catheters, we suggest the use of implanted ports over peripheral inserted central catheter lines,” the authors noted.
The authors described a number of unique situations regarding the treatment of VTE. These situations include patients with a brain tumor, for whom treatment of established VTE should favor either LMWH or a DOA. The authors also recommended the use of LMWH or unfractionated heparin, started postoperatively, for the prevention of VTE for patients undergoing neurosurgery.
In contrast, pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE in medically treated patients with a brain tumor who are not undergoing neurosurgery is not recommended. “In the presence of severe renal failure...we suggest using unfractionated heparin followed by early vitamin K antagonists (possibly from day 1) or LMWH adjusted to anti-Xa concentration of the treatment of established VTE,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Anticoagulant treatment is also recommended for a minimum of 3 months for children with symptomatic catheter-related thrombosis and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. For children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are undergoing induction chemotherapy, LMWH is also recommended as thromboprophylaxis.
For children who require a central venous catheter, the authors suggested that physicians use implanted ports over peripherally inserted central lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated clinical practice guidelines for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism for patients with cancer, including those with cancer and COVID-19, have been released by the International Initiative on Thrombosis and Cancer (ITAC), an academic working group of VTE experts.
“Because patients with cancer have a baseline increased risk of VTE, compared with patients without cancer, the combination of both COVID-19 and cancer – and its effect on VTE risk and treatment – is of concern,” said the authors, led by Dominique Farge, MD, PhD, Nord Universite de Paris.
they added.
The new guidelines were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
“Cancer-associated VTE remains an important clinical problem, associated with increased morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Farge and colleagues observed.
“The ITAC guidelines’ companion free web-based mobile application will assist the practicing clinician with decision making at various levels to provide optimal care of patients with cancer to treat and prevent VTE,” they emphasized. More information is available at itaccme.com.
Cancer patients with COVID
The new section of the guidelines notes that the treatment and prevention of VTE for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 remain the same as for patients without COVID.
Whether or not cancer patients with COVID-19 are hospitalized, have been discharged, or are ambulatory, they should be assessed for the risk of VTE, as should any other patient. For cancer patients with COVID-19 who are hospitalized, pharmacologic prophylaxis should be given at the same dose and anticoagulant type as for hospitalized cancer patients who do not have COVID-19.
Following discharge, VTE prophylaxis is not advised for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, and routine primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE for ambulatory patients with COVID-19 is also not recommended, the authors noted.
Initial treatment of established VTE
Initial treatment of established VTE for up to 10 days of anticoagulation should include low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) when creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“A regimen of LMWH, taken once per day, is recommended unless a twice-per-day regimen is required because of patients’ characteristics,” the authors noted. These characteristics include a high risk of bleeding, moderate renal failure, and the need for technical intervention, including surgery.
If a twice-a-day regimen is required, only enoxaparin at a dose of 1 mg/kg twice daily can be used, the authors cautioned.
For patients with a low risk of gastrointestinal or genitourinary bleeding, rivaroxaban (Xarelto) or apixaban (Eliquis) can be given in the first 10 days, as well as edoxaban (Lixiana). The latter should be started after at least 5 days of parenteral anticoagulation, provided creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“Unfractionated heparin as well as fondaparinux (GlaxoSmithKline) can be also used for the initial treatment of established VTE when LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants are contraindicated,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Thrombolysis can be considered on a case-by-case basis, although physicians must pay attention to specific contraindications, especially bleeding risk.
“In the initial treatment of VTE, inferior vena cava filters might be considered when anticoagulant treatment is contraindicated or, in the case of pulmonary embolism, when recurrence occurs under optimal anticoagulation,” the authors noted.
Maintenance VTE treatment
For maintenance therapy, which the authors define as early maintenance for up to 6 months and long-term maintenance beyond 6 months, they point out that LMWHs are preferred over vitamin K antagonists for the treatment of VTE when the creatinine clearance is again at least 30 mL/min.
Any of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOAs) – edoxaban, rivaroxaban, or apixaban – is also recommended for the same patients, provided there is no risk of inducing a strong drug-drug interaction or GI absorption is impaired.
However, the DOAs should be used with caution for patients with GI malignancies, especially upper GI cancers, because data show there is an increased risk of GI bleeding with both edoxaban and rivaroxaban.
“LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants should be used for a minimum of 6 months to treat established VTE in patients with cancer,” the authors wrote.
“After 6 months, termination or continuation of anticoagulation (LMWH, direct oral anticoagulants, or vitamin K antagonists) should be based on individual evaluation of the benefit-risk ratio,” they added.
Treatment of VTE recurrence
The guideline authors explain that three options can be considered in the event of VTE recurrence. These include an increase in the LMWH dose by 20%-25%, or a switch to a DOA, or, if patients are taking a DOA, a switch to an LMWH. If the patient is taking a vitamin K antagonist, it can be switched to either an LMWH or a DOA.
For treatment of catheter-related thrombosis, anticoagulant treatment is recommended for a minimum of 3 months and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. In this setting, the LMWHs are recommended.
The central venous catheter can be kept in place if it is functional, well positioned, and is not infected, provided there is good resolution of symptoms under close surveillance while anticoagulants are being administered.
In surgically treated patients, the LMWH, given once a day, to patients with a serum creatinine concentration of at least 30 mL/min can be used to prevent VTE. Alternatively, VTE can be prevented by the use low-dose unfractionated heparin, given three times a day.
“Pharmacological prophylaxis should be started 2-12 h preoperatively and continued for at least 7–10 days,” Dr. Farge and colleagues advised. In this setting, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of fondaparinux or a DOA as an alternative to an LMWH for the prophylaxis of postoperative VTE. “Use of the highest prophylactic dose of LMWH to prevent postoperative VTE in patients with cancer is recommended,” the authors advised.
Furthermore, extended prophylaxis of at least 4 weeks with LMWH is advised to prevent postoperative VTE after major abdominal or pelvic surgery. Mechanical methods are not recommended except when pharmacologic methods are contraindicated. Inferior vena cava filters are also not recommended for routine prophylaxis.
Patients with reduced mobility
For medically treated hospitalized patients with cancer whose mobility is reduced, the authors recommend prophylaxis with either an LMWH or fondaparinux, provided their creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min. These patients can also be treated with unfractionated heparin, they add.
In contrast, DOAs are not recommended – at least not routinely – in this setting, the authors cautioned. Primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE with either LMWH or DOAs – either rivaroxaban or apixaban – is indicated in ambulatory patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy, provided they are at low risk of bleeding.
However, primary pharmacologic prophylaxis with LMWH is not recommended outside of a clinical trial for patients with locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer who are undergoing systemic anticancer therapy, even for patients who are at low risk of bleeding.
For ambulatory patients who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy and who are at intermediate risk of VTE, primary prophylaxis with rivaroxaban or apixaban is recommended for those with myeloma who are receiving immunomodulatory therapy plus steroids or other systemic therapies.
In this setting, oral anticoagulants should consist of a vitamin K antagonist, given at low or therapeutic doses, or apixaban, given at prophylactic doses. Alternatively, LMWH, given at prophylactic doses, or low-dose aspirin, given at a dose of 100 mg/day, can be used.
Catheter-related thrombosis
Use of anticoagulation for routine prophylaxis of catheter-related thrombosis is not recommended. Catheters should be inserted on the right side in the jugular vein, and the distal extremity of the central catheter should be located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. “In patients requiring central venous catheters, we suggest the use of implanted ports over peripheral inserted central catheter lines,” the authors noted.
The authors described a number of unique situations regarding the treatment of VTE. These situations include patients with a brain tumor, for whom treatment of established VTE should favor either LMWH or a DOA. The authors also recommended the use of LMWH or unfractionated heparin, started postoperatively, for the prevention of VTE for patients undergoing neurosurgery.
In contrast, pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE in medically treated patients with a brain tumor who are not undergoing neurosurgery is not recommended. “In the presence of severe renal failure...we suggest using unfractionated heparin followed by early vitamin K antagonists (possibly from day 1) or LMWH adjusted to anti-Xa concentration of the treatment of established VTE,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Anticoagulant treatment is also recommended for a minimum of 3 months for children with symptomatic catheter-related thrombosis and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. For children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are undergoing induction chemotherapy, LMWH is also recommended as thromboprophylaxis.
For children who require a central venous catheter, the authors suggested that physicians use implanted ports over peripherally inserted central lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET ONCOLOGY
One in eight COVID patients likely to develop long COVID: Large study
a large study published in The Lancet indicates.
The researchers determined that percentage by comparing long-term symptoms in people infected by SARS-CoV-2 with similar symptoms in uninfected people over the same time period.
Among the group of infected study participants in the Netherlands, 21.4% had at least one new or severely increased symptom 3-5 months after infection compared with before infection. When that group of 21.4% was compared with 8.7% of uninfected people in the same study, the researchers were able to calculate a prevalence 12.7% with long COVID.
“This finding shows that post–COVID-19 condition is an urgent problem with a mounting human toll,” the study authors wrote.
The research design was novel, two editorialists said in an accompanying commentary.
Christopher Brightling, PhD, and Rachael Evans, MBChB, PhD, of the Institute for Lung Health, University of Leicester (England), noted: “This is a major advance on prior long COVID prevalence estimates as it includes a matched uninfected group and accounts for symptoms before COVID-19 infection.”
Symptoms that persist
The Lancet study found that 3-5 months after COVID (compared with before COVID) and compared with the non-COVID comparison group, the symptoms that persist were chest pain, breathing difficulties, pain when breathing, muscle pain, loss of taste and/or smell, tingling extremities, lump in throat, feeling hot and cold alternately, heavy limbs, and tiredness.
The authors noted that symptoms such as brain fog were found to be relevant to long COVID after the data collection period for this paper and were not included in this research.
Researcher Aranka V. Ballering, MSc, PhD candidate, said in an interview that the researchers found fever is a symptom that is clearly present during the acute phase of the disease and it peaks the day of the COVID-19 diagnosis, but also wears off.
Loss of taste and smell, however, rapidly increases in severity when COVID-19 is diagnosed, but also persists and is still present 3-5 months after COVID.
Ms. Ballering, with the department of psychiatry at the University of Groningen (the Netherlands), said she was surprised by the sex difference made evident in their research: “Women showed more severe persistent symptoms than men.”
Closer to a clearer definition
The authors said their findings also pinpoint symptoms that bring us closer to a better definition of long COVID, which has many different definitions globally.
“These symptoms have the highest discriminative ability to distinguish between post–COVID-19 condition and non–COVID-19–related symptoms,” they wrote.
Researchers collected data by asking participants in the northern Netherlands, who were part of the population-based Lifelines COVID-19 study, to regularly complete digital questionnaires on 23 symptoms commonly associated with long COVID. The questionnaire was sent out 24 times to the same people between March 2020 and August 2021. At that time, people had the Alpha or earlier variants.
Participants were considered COVID-19 positive if they had either a positive test or a doctor’s diagnosis of COVID-19.
Of 76,422 study participants, the 5.5% (4,231) who had COVID were matched to 8,462 controls. Researchers accounted for sex, age, and time of completing questionnaires.
Effect of hospitalization, vaccination unclear
Ms. Ballering said it’s unclear from this data whether vaccination or whether a person was hospitalized would change the prevalence of persistent symptoms.
Because of the period when the data were collected, “the vast majority of our study population was not fully vaccinated,” she said.
However, she pointed to recent research that shows that immunization against COVID is only partially effective against persistent somatic symptoms after COVID.
Also, only 5% of men and 2.5% of women in the study were hospitalized as a result of COVID-19, so the findings can’t easily be generalized to hospitalized patients.
The Lifelines study was an add-on study to the multidisciplinary, prospective, population-based, observational Dutch Lifelines cohort study examining 167,729 people in the Netherlands. Almost all were White, a limitation of the study, and 58% were female. Average age was 54.
The editorialists also noted additional limitations of the study were that this research “did not fully consider the impact on mental health” and was conducted in one region in the Netherlands.
Janko Nikolich-Žugich, MD, PhD, director of the Aegis Consortium for Pandemic-Free Future and head of the immunobiology department at University of Arizona, Tucson, said in an interview that he agreed with the editorialists that a primary benefit of this study is that it corrected for symptoms people had before COVID, something other studies have not been able to do.
However, he cautioned about generalizing the results for the United States and other countries because of the lack of diversity in the study population with regard to education level, socioeconomic factors, and race. He pointed out that access issues are also different in the Netherlands, which has universal health care.
He said brain fog as a symptom of long COVID is of high interest and will be important to include in future studies that are able to extend the study period.
The work was funded by ZonMw; the Dutch Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Sport; Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs; University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen; and the provinces of Drenthe, Friesland, and Groningen. The study authors and Dr. Nikolich-Žugich have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Brightling has received consultancy and or grants paid to his institution from GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Chiesi, Genentech, Roche, Sanofi, Regeneron, Mologic, and 4DPharma for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease research. Dr. Evans has received consultancy fees from AstraZeneca on the topic of long COVID and from GlaxoSmithKline on digital health, and speaker’s fees from Boehringer Ingelheim on long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a large study published in The Lancet indicates.
The researchers determined that percentage by comparing long-term symptoms in people infected by SARS-CoV-2 with similar symptoms in uninfected people over the same time period.
Among the group of infected study participants in the Netherlands, 21.4% had at least one new or severely increased symptom 3-5 months after infection compared with before infection. When that group of 21.4% was compared with 8.7% of uninfected people in the same study, the researchers were able to calculate a prevalence 12.7% with long COVID.
“This finding shows that post–COVID-19 condition is an urgent problem with a mounting human toll,” the study authors wrote.
The research design was novel, two editorialists said in an accompanying commentary.
Christopher Brightling, PhD, and Rachael Evans, MBChB, PhD, of the Institute for Lung Health, University of Leicester (England), noted: “This is a major advance on prior long COVID prevalence estimates as it includes a matched uninfected group and accounts for symptoms before COVID-19 infection.”
Symptoms that persist
The Lancet study found that 3-5 months after COVID (compared with before COVID) and compared with the non-COVID comparison group, the symptoms that persist were chest pain, breathing difficulties, pain when breathing, muscle pain, loss of taste and/or smell, tingling extremities, lump in throat, feeling hot and cold alternately, heavy limbs, and tiredness.
The authors noted that symptoms such as brain fog were found to be relevant to long COVID after the data collection period for this paper and were not included in this research.
Researcher Aranka V. Ballering, MSc, PhD candidate, said in an interview that the researchers found fever is a symptom that is clearly present during the acute phase of the disease and it peaks the day of the COVID-19 diagnosis, but also wears off.
Loss of taste and smell, however, rapidly increases in severity when COVID-19 is diagnosed, but also persists and is still present 3-5 months after COVID.
Ms. Ballering, with the department of psychiatry at the University of Groningen (the Netherlands), said she was surprised by the sex difference made evident in their research: “Women showed more severe persistent symptoms than men.”
Closer to a clearer definition
The authors said their findings also pinpoint symptoms that bring us closer to a better definition of long COVID, which has many different definitions globally.
“These symptoms have the highest discriminative ability to distinguish between post–COVID-19 condition and non–COVID-19–related symptoms,” they wrote.
Researchers collected data by asking participants in the northern Netherlands, who were part of the population-based Lifelines COVID-19 study, to regularly complete digital questionnaires on 23 symptoms commonly associated with long COVID. The questionnaire was sent out 24 times to the same people between March 2020 and August 2021. At that time, people had the Alpha or earlier variants.
Participants were considered COVID-19 positive if they had either a positive test or a doctor’s diagnosis of COVID-19.
Of 76,422 study participants, the 5.5% (4,231) who had COVID were matched to 8,462 controls. Researchers accounted for sex, age, and time of completing questionnaires.
Effect of hospitalization, vaccination unclear
Ms. Ballering said it’s unclear from this data whether vaccination or whether a person was hospitalized would change the prevalence of persistent symptoms.
Because of the period when the data were collected, “the vast majority of our study population was not fully vaccinated,” she said.
However, she pointed to recent research that shows that immunization against COVID is only partially effective against persistent somatic symptoms after COVID.
Also, only 5% of men and 2.5% of women in the study were hospitalized as a result of COVID-19, so the findings can’t easily be generalized to hospitalized patients.
The Lifelines study was an add-on study to the multidisciplinary, prospective, population-based, observational Dutch Lifelines cohort study examining 167,729 people in the Netherlands. Almost all were White, a limitation of the study, and 58% were female. Average age was 54.
The editorialists also noted additional limitations of the study were that this research “did not fully consider the impact on mental health” and was conducted in one region in the Netherlands.
Janko Nikolich-Žugich, MD, PhD, director of the Aegis Consortium for Pandemic-Free Future and head of the immunobiology department at University of Arizona, Tucson, said in an interview that he agreed with the editorialists that a primary benefit of this study is that it corrected for symptoms people had before COVID, something other studies have not been able to do.
However, he cautioned about generalizing the results for the United States and other countries because of the lack of diversity in the study population with regard to education level, socioeconomic factors, and race. He pointed out that access issues are also different in the Netherlands, which has universal health care.
He said brain fog as a symptom of long COVID is of high interest and will be important to include in future studies that are able to extend the study period.
The work was funded by ZonMw; the Dutch Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Sport; Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs; University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen; and the provinces of Drenthe, Friesland, and Groningen. The study authors and Dr. Nikolich-Žugich have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Brightling has received consultancy and or grants paid to his institution from GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Chiesi, Genentech, Roche, Sanofi, Regeneron, Mologic, and 4DPharma for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease research. Dr. Evans has received consultancy fees from AstraZeneca on the topic of long COVID and from GlaxoSmithKline on digital health, and speaker’s fees from Boehringer Ingelheim on long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a large study published in The Lancet indicates.
The researchers determined that percentage by comparing long-term symptoms in people infected by SARS-CoV-2 with similar symptoms in uninfected people over the same time period.
Among the group of infected study participants in the Netherlands, 21.4% had at least one new or severely increased symptom 3-5 months after infection compared with before infection. When that group of 21.4% was compared with 8.7% of uninfected people in the same study, the researchers were able to calculate a prevalence 12.7% with long COVID.
“This finding shows that post–COVID-19 condition is an urgent problem with a mounting human toll,” the study authors wrote.
The research design was novel, two editorialists said in an accompanying commentary.
Christopher Brightling, PhD, and Rachael Evans, MBChB, PhD, of the Institute for Lung Health, University of Leicester (England), noted: “This is a major advance on prior long COVID prevalence estimates as it includes a matched uninfected group and accounts for symptoms before COVID-19 infection.”
Symptoms that persist
The Lancet study found that 3-5 months after COVID (compared with before COVID) and compared with the non-COVID comparison group, the symptoms that persist were chest pain, breathing difficulties, pain when breathing, muscle pain, loss of taste and/or smell, tingling extremities, lump in throat, feeling hot and cold alternately, heavy limbs, and tiredness.
The authors noted that symptoms such as brain fog were found to be relevant to long COVID after the data collection period for this paper and were not included in this research.
Researcher Aranka V. Ballering, MSc, PhD candidate, said in an interview that the researchers found fever is a symptom that is clearly present during the acute phase of the disease and it peaks the day of the COVID-19 diagnosis, but also wears off.
Loss of taste and smell, however, rapidly increases in severity when COVID-19 is diagnosed, but also persists and is still present 3-5 months after COVID.
Ms. Ballering, with the department of psychiatry at the University of Groningen (the Netherlands), said she was surprised by the sex difference made evident in their research: “Women showed more severe persistent symptoms than men.”
Closer to a clearer definition
The authors said their findings also pinpoint symptoms that bring us closer to a better definition of long COVID, which has many different definitions globally.
“These symptoms have the highest discriminative ability to distinguish between post–COVID-19 condition and non–COVID-19–related symptoms,” they wrote.
Researchers collected data by asking participants in the northern Netherlands, who were part of the population-based Lifelines COVID-19 study, to regularly complete digital questionnaires on 23 symptoms commonly associated with long COVID. The questionnaire was sent out 24 times to the same people between March 2020 and August 2021. At that time, people had the Alpha or earlier variants.
Participants were considered COVID-19 positive if they had either a positive test or a doctor’s diagnosis of COVID-19.
Of 76,422 study participants, the 5.5% (4,231) who had COVID were matched to 8,462 controls. Researchers accounted for sex, age, and time of completing questionnaires.
Effect of hospitalization, vaccination unclear
Ms. Ballering said it’s unclear from this data whether vaccination or whether a person was hospitalized would change the prevalence of persistent symptoms.
Because of the period when the data were collected, “the vast majority of our study population was not fully vaccinated,” she said.
However, she pointed to recent research that shows that immunization against COVID is only partially effective against persistent somatic symptoms after COVID.
Also, only 5% of men and 2.5% of women in the study were hospitalized as a result of COVID-19, so the findings can’t easily be generalized to hospitalized patients.
The Lifelines study was an add-on study to the multidisciplinary, prospective, population-based, observational Dutch Lifelines cohort study examining 167,729 people in the Netherlands. Almost all were White, a limitation of the study, and 58% were female. Average age was 54.
The editorialists also noted additional limitations of the study were that this research “did not fully consider the impact on mental health” and was conducted in one region in the Netherlands.
Janko Nikolich-Žugich, MD, PhD, director of the Aegis Consortium for Pandemic-Free Future and head of the immunobiology department at University of Arizona, Tucson, said in an interview that he agreed with the editorialists that a primary benefit of this study is that it corrected for symptoms people had before COVID, something other studies have not been able to do.
However, he cautioned about generalizing the results for the United States and other countries because of the lack of diversity in the study population with regard to education level, socioeconomic factors, and race. He pointed out that access issues are also different in the Netherlands, which has universal health care.
He said brain fog as a symptom of long COVID is of high interest and will be important to include in future studies that are able to extend the study period.
The work was funded by ZonMw; the Dutch Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Sport; Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs; University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen; and the provinces of Drenthe, Friesland, and Groningen. The study authors and Dr. Nikolich-Žugich have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Brightling has received consultancy and or grants paid to his institution from GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Chiesi, Genentech, Roche, Sanofi, Regeneron, Mologic, and 4DPharma for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease research. Dr. Evans has received consultancy fees from AstraZeneca on the topic of long COVID and from GlaxoSmithKline on digital health, and speaker’s fees from Boehringer Ingelheim on long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET
Long COVID doubles risk of some serious outcomes in children, teens
Researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that
Heart inflammation; a blood clot in the lung; or a blood clot in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis were the most common bad outcomes in a new study. Even though the risk was higher for these and some other serious events, the overall numbers were small.
“Many of these conditions were rare or uncommon among children in this analysis, but even a small increase in these conditions is notable,” a CDC new release stated.
The investigators said their findings stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccination in Americans under the age of 18.
The study was published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Less is known about long COVID in children
Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, PhD, and colleagues noted that most research on long COVID to date has been done in adults, so little information is available about the risks to Americans ages 17 and younger.
To learn more, they compared post–COVID-19 symptoms and conditions between 781,419 children and teenagers with confirmed COVID-19 to another 2,344,257 without COVID-19. They looked at medical claims and laboratory data for these children and teenagers from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2022, to see who got any of 15 specific outcomes linked to long COVID-19.
Long COVID was defined as a condition where symptoms that last for or begin at least 4 weeks after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Compared to children with no history of a COVID-19 diagnosis, the long COVID-19 group was 101% more likely to have an acute pulmonary embolism, 99% more likely to have myocarditis or cardiomyopathy, 87% more likely to have a venous thromboembolic event, 32% more likely to have acute and unspecified renal failure, and 23% more likely to have type 1 diabetes.
“This report points to the fact that the risks of COVID infection itself, both in terms of the acute effects, MIS-C [multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children], as well as the long-term effects, are real, are concerning, and are potentially very serious,” said Stuart Berger, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery.
“The message that we should take away from this is that we should be very keen on all the methods of prevention for COVID, especially the vaccine,” said Dr. Berger, chief of cardiology in the department of pediatrics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
A ‘wake-up call’
The study findings are “sobering” and are “a reminder of the seriousness of COVID infection,” says Gregory Poland, MD, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“When you look in particular at the more serious complications from COVID in this young age group, those are life-altering complications that will have consequences and ramifications throughout their lives,” he said.
“I would take this as a serious wake-up call to parents [at a time when] the immunization rates in younger children are so pitifully low,” Dr. Poland said.
Still early days
The study is suggestive but not definitive, said Peter Katona, MD, professor of medicine and infectious diseases expert at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health.
It’s still too early to draw conclusions about long COVID, including in children, because many questions remain, he said: Should long COVID be defined as symptoms at 1 month or 3 months after infection? How do you define brain fog?
Dr. Katona and colleagues are studying long COVID intervention among students at UCLA to answer some of these questions, including the incidence and effect of early intervention.
The study had “at least seven limitations,” the researchers noted. Among them was the use of medical claims data that noted long COVID outcomes but not how severe they were; some people in the no COVID group might have had the illness but not been diagnosed; and the researchers did not adjust for vaccination status.
Dr. Poland noted that the study was done during surges in COVID variants including Delta and Omicron. In other words, any long COVID effects linked to more recent variants such as BA.5 or BA.2.75 are unknown.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that
Heart inflammation; a blood clot in the lung; or a blood clot in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis were the most common bad outcomes in a new study. Even though the risk was higher for these and some other serious events, the overall numbers were small.
“Many of these conditions were rare or uncommon among children in this analysis, but even a small increase in these conditions is notable,” a CDC new release stated.
The investigators said their findings stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccination in Americans under the age of 18.
The study was published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Less is known about long COVID in children
Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, PhD, and colleagues noted that most research on long COVID to date has been done in adults, so little information is available about the risks to Americans ages 17 and younger.
To learn more, they compared post–COVID-19 symptoms and conditions between 781,419 children and teenagers with confirmed COVID-19 to another 2,344,257 without COVID-19. They looked at medical claims and laboratory data for these children and teenagers from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2022, to see who got any of 15 specific outcomes linked to long COVID-19.
Long COVID was defined as a condition where symptoms that last for or begin at least 4 weeks after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Compared to children with no history of a COVID-19 diagnosis, the long COVID-19 group was 101% more likely to have an acute pulmonary embolism, 99% more likely to have myocarditis or cardiomyopathy, 87% more likely to have a venous thromboembolic event, 32% more likely to have acute and unspecified renal failure, and 23% more likely to have type 1 diabetes.
“This report points to the fact that the risks of COVID infection itself, both in terms of the acute effects, MIS-C [multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children], as well as the long-term effects, are real, are concerning, and are potentially very serious,” said Stuart Berger, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery.
“The message that we should take away from this is that we should be very keen on all the methods of prevention for COVID, especially the vaccine,” said Dr. Berger, chief of cardiology in the department of pediatrics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
A ‘wake-up call’
The study findings are “sobering” and are “a reminder of the seriousness of COVID infection,” says Gregory Poland, MD, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“When you look in particular at the more serious complications from COVID in this young age group, those are life-altering complications that will have consequences and ramifications throughout their lives,” he said.
“I would take this as a serious wake-up call to parents [at a time when] the immunization rates in younger children are so pitifully low,” Dr. Poland said.
Still early days
The study is suggestive but not definitive, said Peter Katona, MD, professor of medicine and infectious diseases expert at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health.
It’s still too early to draw conclusions about long COVID, including in children, because many questions remain, he said: Should long COVID be defined as symptoms at 1 month or 3 months after infection? How do you define brain fog?
Dr. Katona and colleagues are studying long COVID intervention among students at UCLA to answer some of these questions, including the incidence and effect of early intervention.
The study had “at least seven limitations,” the researchers noted. Among them was the use of medical claims data that noted long COVID outcomes but not how severe they were; some people in the no COVID group might have had the illness but not been diagnosed; and the researchers did not adjust for vaccination status.
Dr. Poland noted that the study was done during surges in COVID variants including Delta and Omicron. In other words, any long COVID effects linked to more recent variants such as BA.5 or BA.2.75 are unknown.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that
Heart inflammation; a blood clot in the lung; or a blood clot in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis were the most common bad outcomes in a new study. Even though the risk was higher for these and some other serious events, the overall numbers were small.
“Many of these conditions were rare or uncommon among children in this analysis, but even a small increase in these conditions is notable,” a CDC new release stated.
The investigators said their findings stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccination in Americans under the age of 18.
The study was published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Less is known about long COVID in children
Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, PhD, and colleagues noted that most research on long COVID to date has been done in adults, so little information is available about the risks to Americans ages 17 and younger.
To learn more, they compared post–COVID-19 symptoms and conditions between 781,419 children and teenagers with confirmed COVID-19 to another 2,344,257 without COVID-19. They looked at medical claims and laboratory data for these children and teenagers from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2022, to see who got any of 15 specific outcomes linked to long COVID-19.
Long COVID was defined as a condition where symptoms that last for or begin at least 4 weeks after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Compared to children with no history of a COVID-19 diagnosis, the long COVID-19 group was 101% more likely to have an acute pulmonary embolism, 99% more likely to have myocarditis or cardiomyopathy, 87% more likely to have a venous thromboembolic event, 32% more likely to have acute and unspecified renal failure, and 23% more likely to have type 1 diabetes.
“This report points to the fact that the risks of COVID infection itself, both in terms of the acute effects, MIS-C [multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children], as well as the long-term effects, are real, are concerning, and are potentially very serious,” said Stuart Berger, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery.
“The message that we should take away from this is that we should be very keen on all the methods of prevention for COVID, especially the vaccine,” said Dr. Berger, chief of cardiology in the department of pediatrics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
A ‘wake-up call’
The study findings are “sobering” and are “a reminder of the seriousness of COVID infection,” says Gregory Poland, MD, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“When you look in particular at the more serious complications from COVID in this young age group, those are life-altering complications that will have consequences and ramifications throughout their lives,” he said.
“I would take this as a serious wake-up call to parents [at a time when] the immunization rates in younger children are so pitifully low,” Dr. Poland said.
Still early days
The study is suggestive but not definitive, said Peter Katona, MD, professor of medicine and infectious diseases expert at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health.
It’s still too early to draw conclusions about long COVID, including in children, because many questions remain, he said: Should long COVID be defined as symptoms at 1 month or 3 months after infection? How do you define brain fog?
Dr. Katona and colleagues are studying long COVID intervention among students at UCLA to answer some of these questions, including the incidence and effect of early intervention.
The study had “at least seven limitations,” the researchers noted. Among them was the use of medical claims data that noted long COVID outcomes but not how severe they were; some people in the no COVID group might have had the illness but not been diagnosed; and the researchers did not adjust for vaccination status.
Dr. Poland noted that the study was done during surges in COVID variants including Delta and Omicron. In other words, any long COVID effects linked to more recent variants such as BA.5 or BA.2.75 are unknown.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE MMWR
New Omicron COVID boosters coming soon: What to know now
– a month ahead of schedule, the Biden administration announced this week.
Moderna has signed a $1.74 billion federal contract to supply 66 million initial doses of the “bivalent” booster, which includes the original “ancestral” virus strain and elements of the Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 variants. Pfizer also announced a $3.2 billion U.S. agreement for another 105 million shots. Both vaccine suppliers have signed options to provide millions more boosters in the months ahead.
About 83.5% of Americans have received at least one COVID-19 shot, with 71.5% fully vaccinated with the initial series, 48% receiving one booster shot, and 31% two boosters, according to the CDC. With about 130,000 new COVID cases per day, and about 440 deaths, officials say the updated boosters may help rein in those figures by targeting the highly transmissible and widely circulating Omicron strains.
Federal health officials are still hammering out details of guidelines and recommendations of who should get the boosters, which are expected to come from the CDC and FDA. For now, authorities have decided not to expand eligibility for second boosters of the existing vaccines – now recommended only for adults over 50 and those 12 and older with immune deficiencies. Children 5 through 11 are advised to receive a single booster, 5 months after their initial vaccine series.
For a preview of what to expect from the CDC and FDA, this news organization spoke with Keri Althoff, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Q: Based on what we know now, who should be getting one of these new bivalent boosters?A: Of course, there is a process here regarding the specific recommendations, but it appears there will likely be a recommendation for all individuals to get this bivalent booster, similar to the first booster. And there will likely be a recommended time frame as to time since the last booster.
Right now, we have a recommendation for adults over the age of 50 or adults who are at higher risk for severe COVID-related illness [to get] a second booster. For them, there will probably be a timeline that says you should get the booster if you’re X amount of months or more from your second booster; or X amount of months or more from your first booster, if you’ve only had one.
Q: What about pregnant women or those being treated for chronic health conditions?A: I would imagine that once this bivalent booster becomes available, it will be recommended for all adults.
Q: And for children?A: That’s a good question. It’s something I have been digging into, [and] I think parents are really interested in this. Most kids, 5 and above, are supposed to be boosted with one shot right now, if they’re X amount of days from their primary vaccine series. Of course those 6 months to 4.99 years are not yet eligible [for boosters].
As a parent, I would love to see my children become eligible for the bivalent booster. It would be great if these boosters are conveying some additional protection that the kids could get access to before we send them off to school this fall. But there are questions as to whether or not that is going to happen.
Q: If you never received a booster, but only the preliminary vaccine series, do you need to get those earlier boosters before having the new bivalent booster shot?A: I don’t think they will likely make that a requirement – to restrict the bivalent booster only to those who are already boosted or up to date on their vaccines at the time the bivalent booster becomes available. But that will be up to the [CDC] vaccine recommendation committee to decide.
Q: Are there any new risks associated with these boosters, since they were developed so rapidly?A: No. We continue to monitor this technology, and with all the mRNA vaccines that have been delivered, you have seen all that monitoring play out with the detection, for example, of different forms of inflammation of the heart tissue and who that may impact. So, those monitoring systems work, and they work really, really well, so we can detect those things. And we know these vaccines are definitely safe.
Q: Some health experts are concerned “vaccine fatigue” will have an impact on the booster campaign. What’s your take?A: We have seen this fatigue in the proportion of individuals who are boosted with a first booster and even boosted with a second. But having those earlier boosters along with this new bivalent booster is important, because essentially, what we’re doing is really priming the immune system.
We’re trying to expedite the process of getting people’s immune system up to speed so that when the virus comes our way – as we know it will, because [of] these Omicron strains that are highly infectious and really whipping through our communities – we’re able to get the highest level of population immunity, you don’t end up in the hospital.
Q: What other challenges do you see in persuading Americans to get another round of boosters?A: One of the things that I’ve been hearing a lot, which I get very nervous about, is people saying: “Oh, I got fully vaccinated, I did or did not get the booster, and I had COVID anyway and it was really nothing, it didn’t feel like much to me, and so I’m not going to be boosted anymore.” We are not in a place quite yet where those guidelines are being rolled back in any way, shape, or form. We still have highly vulnerable people to severe disease and death in our communities, and we’re seeing hundreds of deaths every day.
There are consequences, even if it isn’t in severity of disease, meaning hospitalization and death. And let’s not let the actual quality of the vaccine being so successful that it can keep you out of the hospital. Don’t mistake that for “I don’t need another one.”
Q: Unlike the flu shot, which is reformulated each year to match circulating strains, the new COVID boosters offer protection against older strains as well as the newer ones. Why?A: It’s all about creating a broader immune response in individuals so that as more strains emerge, which they likely will, we can create a broader population immune response [to all strains]. Our individual bodies are seeing differences in these strains through vaccination that helps everyone stay healthy.
Q: There haven’t been clinical trials of these new mRNA boosters. How strong is the evidence that they will be effective against the emerging Omicron variants?A: There have been some studies – some great studies – looking at things like neutralizing antibodies, which we use as a surrogate for clinical trials. But that is not the same as studying the outcome of interest, which would be hospitalizations. So, part of the challenge is to be able to say: “Okay, this is what we know about the safety and effectiveness of the prior vaccines ... and how can we relate that to outcomes with these new boosters at an earlier stage [before] clinical data is available?”
Q: How long will the new boosters’ protections last – do we know yet?A: That timing is still a question, but of course what plays a big role in that is what COVID strains are circulating. If we prep these boosters that are Omicron specific, and then we have something totally new emerge ... we have to be more nimble because the variants are outpacing what we’re able to do.
This turns out to be a bit of a game of probability – the more infection we have, the more replication of the virus; the more replication, the more opportunity for mutations and subsequent variants.
Q: What about a combined flu-COVID vaccine; is that on the horizon?A: My children, who like most children do not like vaccines, always tell me: “Mom, why can’t they just put the influenza vaccine and the COVID vaccine into the same shot?” And I’m like: “Oh, from your lips to some scientist’s ears.”
At a time like this, where mRNA technology has totally disrupted what we can do with vaccines, in such a good way, I think we should push for the limits, because that would be incredible.
Q: If you’ve received a non-mRNA COVID vaccine, like those produced by Johnson & Johnson and Novavax, should you also get an mRNA booster?A: Right now, the CDC guidelines do state that if your primary vaccine series was not with an mRNA vaccine then being boosted with an mRNA is a fine thing to do, and it’s actually encouraged. So that’s not going to change with the bivalent booster.
Q: Is it okay to get a flu shot and a COVID booster at the same time, as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended with past vaccines?A: I don’t anticipate there being recommendations against that. But I would also say watch for the recommendations that come out this fall on the bivalent boosters.
I do hope in the recommendations the CDC makes about the COVID boosters, they will say think about also getting your influenza vaccine, too. You could also get your COVID booster first, then by October get your influenza vaccine.
Q: Once you’re fully boosted, is it safe to stop wearing a mask, social distancing, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and taking other precautions to avoid COVID-19?A: The virus is going to do what it does, which is infect whomever it can, and make them sick. So, if you see a lot of community transmission – you know who is ill with COVID in your kids’ schools, you know in your workplace and when people go out – that still signals there’s some increases in the circulation of virus. So, look at that to understand what your risk is.
If you know someone or have a colleague who is currently pregnant or immune suppressed, think about how you can protect them with mask-wearing, even if it’s just when you’re in one-on-one closed-door meetings with that individual.
So, your masking question is an important one, and it’s important for people to continue to hang onto those masks and wear them the week before you go see Grandma, for instance, to further reduce your risk so you don’t bring anything to here.
The high-level community risk nationwide is high right now. COVID is here.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
– a month ahead of schedule, the Biden administration announced this week.
Moderna has signed a $1.74 billion federal contract to supply 66 million initial doses of the “bivalent” booster, which includes the original “ancestral” virus strain and elements of the Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 variants. Pfizer also announced a $3.2 billion U.S. agreement for another 105 million shots. Both vaccine suppliers have signed options to provide millions more boosters in the months ahead.
About 83.5% of Americans have received at least one COVID-19 shot, with 71.5% fully vaccinated with the initial series, 48% receiving one booster shot, and 31% two boosters, according to the CDC. With about 130,000 new COVID cases per day, and about 440 deaths, officials say the updated boosters may help rein in those figures by targeting the highly transmissible and widely circulating Omicron strains.
Federal health officials are still hammering out details of guidelines and recommendations of who should get the boosters, which are expected to come from the CDC and FDA. For now, authorities have decided not to expand eligibility for second boosters of the existing vaccines – now recommended only for adults over 50 and those 12 and older with immune deficiencies. Children 5 through 11 are advised to receive a single booster, 5 months after their initial vaccine series.
For a preview of what to expect from the CDC and FDA, this news organization spoke with Keri Althoff, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Q: Based on what we know now, who should be getting one of these new bivalent boosters?A: Of course, there is a process here regarding the specific recommendations, but it appears there will likely be a recommendation for all individuals to get this bivalent booster, similar to the first booster. And there will likely be a recommended time frame as to time since the last booster.
Right now, we have a recommendation for adults over the age of 50 or adults who are at higher risk for severe COVID-related illness [to get] a second booster. For them, there will probably be a timeline that says you should get the booster if you’re X amount of months or more from your second booster; or X amount of months or more from your first booster, if you’ve only had one.
Q: What about pregnant women or those being treated for chronic health conditions?A: I would imagine that once this bivalent booster becomes available, it will be recommended for all adults.
Q: And for children?A: That’s a good question. It’s something I have been digging into, [and] I think parents are really interested in this. Most kids, 5 and above, are supposed to be boosted with one shot right now, if they’re X amount of days from their primary vaccine series. Of course those 6 months to 4.99 years are not yet eligible [for boosters].
As a parent, I would love to see my children become eligible for the bivalent booster. It would be great if these boosters are conveying some additional protection that the kids could get access to before we send them off to school this fall. But there are questions as to whether or not that is going to happen.
Q: If you never received a booster, but only the preliminary vaccine series, do you need to get those earlier boosters before having the new bivalent booster shot?A: I don’t think they will likely make that a requirement – to restrict the bivalent booster only to those who are already boosted or up to date on their vaccines at the time the bivalent booster becomes available. But that will be up to the [CDC] vaccine recommendation committee to decide.
Q: Are there any new risks associated with these boosters, since they were developed so rapidly?A: No. We continue to monitor this technology, and with all the mRNA vaccines that have been delivered, you have seen all that monitoring play out with the detection, for example, of different forms of inflammation of the heart tissue and who that may impact. So, those monitoring systems work, and they work really, really well, so we can detect those things. And we know these vaccines are definitely safe.
Q: Some health experts are concerned “vaccine fatigue” will have an impact on the booster campaign. What’s your take?A: We have seen this fatigue in the proportion of individuals who are boosted with a first booster and even boosted with a second. But having those earlier boosters along with this new bivalent booster is important, because essentially, what we’re doing is really priming the immune system.
We’re trying to expedite the process of getting people’s immune system up to speed so that when the virus comes our way – as we know it will, because [of] these Omicron strains that are highly infectious and really whipping through our communities – we’re able to get the highest level of population immunity, you don’t end up in the hospital.
Q: What other challenges do you see in persuading Americans to get another round of boosters?A: One of the things that I’ve been hearing a lot, which I get very nervous about, is people saying: “Oh, I got fully vaccinated, I did or did not get the booster, and I had COVID anyway and it was really nothing, it didn’t feel like much to me, and so I’m not going to be boosted anymore.” We are not in a place quite yet where those guidelines are being rolled back in any way, shape, or form. We still have highly vulnerable people to severe disease and death in our communities, and we’re seeing hundreds of deaths every day.
There are consequences, even if it isn’t in severity of disease, meaning hospitalization and death. And let’s not let the actual quality of the vaccine being so successful that it can keep you out of the hospital. Don’t mistake that for “I don’t need another one.”
Q: Unlike the flu shot, which is reformulated each year to match circulating strains, the new COVID boosters offer protection against older strains as well as the newer ones. Why?A: It’s all about creating a broader immune response in individuals so that as more strains emerge, which they likely will, we can create a broader population immune response [to all strains]. Our individual bodies are seeing differences in these strains through vaccination that helps everyone stay healthy.
Q: There haven’t been clinical trials of these new mRNA boosters. How strong is the evidence that they will be effective against the emerging Omicron variants?A: There have been some studies – some great studies – looking at things like neutralizing antibodies, which we use as a surrogate for clinical trials. But that is not the same as studying the outcome of interest, which would be hospitalizations. So, part of the challenge is to be able to say: “Okay, this is what we know about the safety and effectiveness of the prior vaccines ... and how can we relate that to outcomes with these new boosters at an earlier stage [before] clinical data is available?”
Q: How long will the new boosters’ protections last – do we know yet?A: That timing is still a question, but of course what plays a big role in that is what COVID strains are circulating. If we prep these boosters that are Omicron specific, and then we have something totally new emerge ... we have to be more nimble because the variants are outpacing what we’re able to do.
This turns out to be a bit of a game of probability – the more infection we have, the more replication of the virus; the more replication, the more opportunity for mutations and subsequent variants.
Q: What about a combined flu-COVID vaccine; is that on the horizon?A: My children, who like most children do not like vaccines, always tell me: “Mom, why can’t they just put the influenza vaccine and the COVID vaccine into the same shot?” And I’m like: “Oh, from your lips to some scientist’s ears.”
At a time like this, where mRNA technology has totally disrupted what we can do with vaccines, in such a good way, I think we should push for the limits, because that would be incredible.
Q: If you’ve received a non-mRNA COVID vaccine, like those produced by Johnson & Johnson and Novavax, should you also get an mRNA booster?A: Right now, the CDC guidelines do state that if your primary vaccine series was not with an mRNA vaccine then being boosted with an mRNA is a fine thing to do, and it’s actually encouraged. So that’s not going to change with the bivalent booster.
Q: Is it okay to get a flu shot and a COVID booster at the same time, as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended with past vaccines?A: I don’t anticipate there being recommendations against that. But I would also say watch for the recommendations that come out this fall on the bivalent boosters.
I do hope in the recommendations the CDC makes about the COVID boosters, they will say think about also getting your influenza vaccine, too. You could also get your COVID booster first, then by October get your influenza vaccine.
Q: Once you’re fully boosted, is it safe to stop wearing a mask, social distancing, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and taking other precautions to avoid COVID-19?A: The virus is going to do what it does, which is infect whomever it can, and make them sick. So, if you see a lot of community transmission – you know who is ill with COVID in your kids’ schools, you know in your workplace and when people go out – that still signals there’s some increases in the circulation of virus. So, look at that to understand what your risk is.
If you know someone or have a colleague who is currently pregnant or immune suppressed, think about how you can protect them with mask-wearing, even if it’s just when you’re in one-on-one closed-door meetings with that individual.
So, your masking question is an important one, and it’s important for people to continue to hang onto those masks and wear them the week before you go see Grandma, for instance, to further reduce your risk so you don’t bring anything to here.
The high-level community risk nationwide is high right now. COVID is here.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
– a month ahead of schedule, the Biden administration announced this week.
Moderna has signed a $1.74 billion federal contract to supply 66 million initial doses of the “bivalent” booster, which includes the original “ancestral” virus strain and elements of the Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 variants. Pfizer also announced a $3.2 billion U.S. agreement for another 105 million shots. Both vaccine suppliers have signed options to provide millions more boosters in the months ahead.
About 83.5% of Americans have received at least one COVID-19 shot, with 71.5% fully vaccinated with the initial series, 48% receiving one booster shot, and 31% two boosters, according to the CDC. With about 130,000 new COVID cases per day, and about 440 deaths, officials say the updated boosters may help rein in those figures by targeting the highly transmissible and widely circulating Omicron strains.
Federal health officials are still hammering out details of guidelines and recommendations of who should get the boosters, which are expected to come from the CDC and FDA. For now, authorities have decided not to expand eligibility for second boosters of the existing vaccines – now recommended only for adults over 50 and those 12 and older with immune deficiencies. Children 5 through 11 are advised to receive a single booster, 5 months after their initial vaccine series.
For a preview of what to expect from the CDC and FDA, this news organization spoke with Keri Althoff, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Q: Based on what we know now, who should be getting one of these new bivalent boosters?A: Of course, there is a process here regarding the specific recommendations, but it appears there will likely be a recommendation for all individuals to get this bivalent booster, similar to the first booster. And there will likely be a recommended time frame as to time since the last booster.
Right now, we have a recommendation for adults over the age of 50 or adults who are at higher risk for severe COVID-related illness [to get] a second booster. For them, there will probably be a timeline that says you should get the booster if you’re X amount of months or more from your second booster; or X amount of months or more from your first booster, if you’ve only had one.
Q: What about pregnant women or those being treated for chronic health conditions?A: I would imagine that once this bivalent booster becomes available, it will be recommended for all adults.
Q: And for children?A: That’s a good question. It’s something I have been digging into, [and] I think parents are really interested in this. Most kids, 5 and above, are supposed to be boosted with one shot right now, if they’re X amount of days from their primary vaccine series. Of course those 6 months to 4.99 years are not yet eligible [for boosters].
As a parent, I would love to see my children become eligible for the bivalent booster. It would be great if these boosters are conveying some additional protection that the kids could get access to before we send them off to school this fall. But there are questions as to whether or not that is going to happen.
Q: If you never received a booster, but only the preliminary vaccine series, do you need to get those earlier boosters before having the new bivalent booster shot?A: I don’t think they will likely make that a requirement – to restrict the bivalent booster only to those who are already boosted or up to date on their vaccines at the time the bivalent booster becomes available. But that will be up to the [CDC] vaccine recommendation committee to decide.
Q: Are there any new risks associated with these boosters, since they were developed so rapidly?A: No. We continue to monitor this technology, and with all the mRNA vaccines that have been delivered, you have seen all that monitoring play out with the detection, for example, of different forms of inflammation of the heart tissue and who that may impact. So, those monitoring systems work, and they work really, really well, so we can detect those things. And we know these vaccines are definitely safe.
Q: Some health experts are concerned “vaccine fatigue” will have an impact on the booster campaign. What’s your take?A: We have seen this fatigue in the proportion of individuals who are boosted with a first booster and even boosted with a second. But having those earlier boosters along with this new bivalent booster is important, because essentially, what we’re doing is really priming the immune system.
We’re trying to expedite the process of getting people’s immune system up to speed so that when the virus comes our way – as we know it will, because [of] these Omicron strains that are highly infectious and really whipping through our communities – we’re able to get the highest level of population immunity, you don’t end up in the hospital.
Q: What other challenges do you see in persuading Americans to get another round of boosters?A: One of the things that I’ve been hearing a lot, which I get very nervous about, is people saying: “Oh, I got fully vaccinated, I did or did not get the booster, and I had COVID anyway and it was really nothing, it didn’t feel like much to me, and so I’m not going to be boosted anymore.” We are not in a place quite yet where those guidelines are being rolled back in any way, shape, or form. We still have highly vulnerable people to severe disease and death in our communities, and we’re seeing hundreds of deaths every day.
There are consequences, even if it isn’t in severity of disease, meaning hospitalization and death. And let’s not let the actual quality of the vaccine being so successful that it can keep you out of the hospital. Don’t mistake that for “I don’t need another one.”
Q: Unlike the flu shot, which is reformulated each year to match circulating strains, the new COVID boosters offer protection against older strains as well as the newer ones. Why?A: It’s all about creating a broader immune response in individuals so that as more strains emerge, which they likely will, we can create a broader population immune response [to all strains]. Our individual bodies are seeing differences in these strains through vaccination that helps everyone stay healthy.
Q: There haven’t been clinical trials of these new mRNA boosters. How strong is the evidence that they will be effective against the emerging Omicron variants?A: There have been some studies – some great studies – looking at things like neutralizing antibodies, which we use as a surrogate for clinical trials. But that is not the same as studying the outcome of interest, which would be hospitalizations. So, part of the challenge is to be able to say: “Okay, this is what we know about the safety and effectiveness of the prior vaccines ... and how can we relate that to outcomes with these new boosters at an earlier stage [before] clinical data is available?”
Q: How long will the new boosters’ protections last – do we know yet?A: That timing is still a question, but of course what plays a big role in that is what COVID strains are circulating. If we prep these boosters that are Omicron specific, and then we have something totally new emerge ... we have to be more nimble because the variants are outpacing what we’re able to do.
This turns out to be a bit of a game of probability – the more infection we have, the more replication of the virus; the more replication, the more opportunity for mutations and subsequent variants.
Q: What about a combined flu-COVID vaccine; is that on the horizon?A: My children, who like most children do not like vaccines, always tell me: “Mom, why can’t they just put the influenza vaccine and the COVID vaccine into the same shot?” And I’m like: “Oh, from your lips to some scientist’s ears.”
At a time like this, where mRNA technology has totally disrupted what we can do with vaccines, in such a good way, I think we should push for the limits, because that would be incredible.
Q: If you’ve received a non-mRNA COVID vaccine, like those produced by Johnson & Johnson and Novavax, should you also get an mRNA booster?A: Right now, the CDC guidelines do state that if your primary vaccine series was not with an mRNA vaccine then being boosted with an mRNA is a fine thing to do, and it’s actually encouraged. So that’s not going to change with the bivalent booster.
Q: Is it okay to get a flu shot and a COVID booster at the same time, as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended with past vaccines?A: I don’t anticipate there being recommendations against that. But I would also say watch for the recommendations that come out this fall on the bivalent boosters.
I do hope in the recommendations the CDC makes about the COVID boosters, they will say think about also getting your influenza vaccine, too. You could also get your COVID booster first, then by October get your influenza vaccine.
Q: Once you’re fully boosted, is it safe to stop wearing a mask, social distancing, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and taking other precautions to avoid COVID-19?A: The virus is going to do what it does, which is infect whomever it can, and make them sick. So, if you see a lot of community transmission – you know who is ill with COVID in your kids’ schools, you know in your workplace and when people go out – that still signals there’s some increases in the circulation of virus. So, look at that to understand what your risk is.
If you know someone or have a colleague who is currently pregnant or immune suppressed, think about how you can protect them with mask-wearing, even if it’s just when you’re in one-on-one closed-door meetings with that individual.
So, your masking question is an important one, and it’s important for people to continue to hang onto those masks and wear them the week before you go see Grandma, for instance, to further reduce your risk so you don’t bring anything to here.
The high-level community risk nationwide is high right now. COVID is here.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
Haven’t had COVID yet? Wanna bet?
We all have friends or relatives who, somehow, have managed to avoid catching COVID-19, which has infected more than 91.5 million Americans. You may even be one of the lucky ones yourself.
But health experts are saying: Not so fast. because they didn’t have symptoms or had mild cases they mistook for a cold or allergies.
The upshot: These silent COVID-19 cases reflect a hidden side of the pandemic that may be helping to drive new surges and viral variants.
Still, infectious disease experts say there is little doubt that some people have indeed managed to avoid COVID-19 infection altogether, and they are trying to understand why.
Several recent studies have suggested certain genetic and immune system traits may better protect this group of people against the coronavirus, making them less likely than others to be infected or seriously sickened. Researchers around the world are now studying these seemingly super-immune people for clues to what makes them so special, with an eye toward better vaccines, treatments, and prevention strategies.
Infectious disease specialists say both types of cases – those unknowingly infected by COVID-19 and people who’ve avoided the virus altogether – matter greatly to public health, more than 2 years into the pandemic.
“It’s definitely true that some people have had COVID and don’t realize it,” says Stephen Kissler, PhD, an infectious disease researcher with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “It is potentially good news if there’s more immunity in the population than we realize.”
But he says that being able to identify genetic and other factors that may offer some people protection against COVID-19 is an “exciting prospect” that could help find out who’s most at risk and improve efforts to get the pandemic under control.
Some studies have found a person’s genetic profile, past exposure to other COVID-like viruses, allergies, and even drugs they take for other conditions may all provide some defense – even for people who have not been vaccinated, don’t use masks, or don’t practice social distancing.
A person’s medical history and genetics may help decide their risk from new diseases, meaning “we may be able to help identify people who are at especially high risk from infection,” Dr. Kissler says. “That knowledge could help those people better shield themselves from infection and get quicker access to treatment and vaccines, if necessary. … We don’t yet know, but studies are ongoing for these things.”
Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease specialist with the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, agrees that emerging research on people who’ve avoided infection offers the chance of new public health strategies to combat COVID-19.
“I’m sure there is some subset of people who are [COVID] negative,” he says. “So what explains that phenomenon, especially if that person was out there getting significant exposures?”
Have you had COVID without knowing it?
In a media briefing late last month, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Ashish Jha, MD, said more than 70% of the U.S. population has had the virus, according to the latest CDC data. That’s up from 33.5% in December.
But the actual number of people in the U.S. who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, the scientific name for the virus that causes COVID-19, is likely to be much higher due to cases without symptoms that are unreported, experts say.
Since the early days of the pandemic, researchers have tried to put a number on these hidden cases, but that figure has been evolving and a clear consensus has not emerged.
In September 2020, a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine said “approximately 40% to 45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic.”
A follow-up analysis of 95 studies, published last December, reached similar findings, estimating that more than 40% of COVID-19 infections didn’t come with symptoms.
To get a better handle on the issue, CDC officials have been working with the American Red Cross and other blood banks to track COVID-19 antibodies – proteins your body makes after exposure to the virus to fight off an infection – in donors who said they have never had COVID-19.
While that joint effort is still ongoing, early findings say the number of donors with antibodies from COVID-19 infection increased in blood donors from 3.5% in July 2020 to at least 20.2% in May 2021. Since then, those percentages have soared, in part due to the introduction of vaccines, which also make the body produce COVID-19 antibodies.
The most current findings show that 83.3% of donors have combined COVID infection– and vaccine-induced antibodies in their blood. Those findings are based on 1.4 million blood donations.
Health experts say all of these studies are strong evidence that many COVID-19 cases continue to go undetected. In fact, the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation estimates that only 7% of positive COVID-19 cases in the U.S. are being detected. That means case rates are actually 14.5 times higher than the official count of 131,000 new COVID infections each day, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which reports the virus is still killing about 440 Americans daily.
So, why is all this important, in terms of public health?
Experts say people are more likely to be cautious if they know COVID-19 cases are high where they live, work, and play. On the other hand, if they believe case rates in their communities are lower than they actually are, they may be less likely to get vaccinated and boosted, wear masks indoors, avoid crowded indoor spaces, and take other precautions to fend off infection.
How do some avoid infection altogether?
In addition to tracking cases that go unreported and don’t have symptoms, infectious disease experts have also been trying to figure out why some people have managed to avoid getting the highly contagious virus.
Several leading lines of research have produced promising early results – suggesting that a person’s genetic makeup, past exposure to less-lethal coronaviruses, allergies, and even certain drugs they take for other conditions may all provide at least some protection against COVID.
“Our study showed that there are many human genes – hundreds of genes – that can impact SARS-CoV-2 infection,” says Neville Sanjana, PhD, a geneticist at New York University and the New York Genome Center who co-led the study. “With a better understanding of host genetic factors, we can find new kinds of therapies that target these host factors to block infection.”
In addition, he says several studies show some drugs that regulate genes, such as the breast cancer drug tamoxifen, also appear to knock down COVID-19 risk. He suggests such drugs, already approved by the Food and Drug Administration, might be “repurposed” to target the virus.
Studies in other countries show that patients taking tamoxifen before the pandemic were protected against severe COVID-19, Dr. Sanjana says. “That was a really cool thing, highlighting the power of harnessing host genetics. The virus critically depends on our genes to complete key parts of its life cycle.”
The NYU research findings echo other studies that have been published in recent months.
In July, a team of researchers led by the National Cancer Institute identified a genetic factor that appears to determine how severe an infection will be. In a study involving 3,000 people, they found that two gene changes, or mutations, that decrease the expression of a gene called OAS1 boosted the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19. OAS1 is part of the immune system’s response to viral infections.
As a result, developing a genetic therapy designed to increase the OAS1 gene’s expression might reduce the risk of severe disease.
“It’s very natural to get infected once you are exposed. There’s no magic bullet for that. But after you get infected, how you’re going to respond to this infection, that’s what is going to be affected by your genetic variants,” said Ludmila Prokunina-Olsson, PhD, the study’s lead researcher and chief of the National Cancer Institute’s Laboratory of Translational Genomics, Bethesda, Md., in an interview with NBC News.
Benjamin tenOever, PhD, a New York University virologist who co-authored the 2020 research, says the new genetic research is promising, but he believes it’s unlikely scientists will be able to identify a single gene responsible for actually preventing a COVID-19 infection.
“On the flip side, we have identified many genes that makes the disease worse,” he says.
T cells ‘remember’ past viral infections
As Dr. tenOever and Dr. Sanjana suggest, another intriguing line of research has found that prior viral infections may prime the body’s immune system to fight COVID-19.
Four other common coronaviruses – aside from SARS-CoV-2 – infect people worldwide, typically causing mild to moderate upper respiratory illnesses like the common cold, says Alessandro Sette, PhD, an infectious disease expert and vaccine researcher with the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology.
In a recent study published in Science, he and his team found past infection with these other coronaviruses may give some protection against SARS-CoV-2.
T cells – white blood cells that act like immunological ninjas to ferret out and fight infections – appear to maintain a kind of “biological memory” of coronaviruses they have seen before and can mount an attack on similar pathogens, such SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Sette says.
The new work builds on a prior research he helped lead that found 40%-60% of people never exposed to SARS-CoV-2 had T cells that reacted to the virus – with their immune systems recognizing fragments of a virus they had never seen before.
Dr. Sette says his research shows that people whose T cells have this “preexisting memory” of past coronavirus exposures also tend to respond better to vaccination for reasons not yet well understood.
“The question is, at which point will there be enough immunity from vaccination, repeated infections from other coronaviruses, but also some of the variants of the SARS-CoV-2 … where infections become less frequent? We’re not there yet,” he says.
In addition to these exciting genetic and T-cell findings, other research has suggested low-grade inflammation from allergies – a key part of the body’s immune response to foreign substances – may also give some people an extra leg up, in terms of avoiding COVID infection.
Last May, a study of 1,400 households published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that having a food allergy cut the risk of COVID-19 infection in half.
The researchers said it’s unclear why allergies may reduce the risk of infection, but they noted that people with food allergies express fewer ACE2 receptors on the surface of their airway cells, making it harder for the virus to enter cells.
The big picture: Prevention still your best bet
So, what’s the takeaway from all of this emerging research?
New York University’s Dr. tenOever says that while genes, T cells and allergies may offer some protection against COVID, tried-and-true precautions – vaccination, wearing masks, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and social distancing – are likely to provide a greater defense.
He believes these precautions are likely why he and his family have never contracted COVID-19.
“I was tested weekly, as were my kids at school,” he says. “We definitely never got COVID, despite the fact that we live in New York City and I worked in a hospital every single day of the pandemic.”
Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and director of clinical epidemiology at Washington University in St. Louis, agrees that the new research on COVID-19 is intriguing but won’t likely result in practical changes in the approach to fighting the virus in the near term.
“Getting a deeper understanding of potential genetic factors or other characteristics – that could really help us understand why the virus just comes and goes without any ill effects in some people, and in other people it produces really serious disease,” he says. “That will really help us eventually to design better vaccines to prevent it or reduce severity or even [treat] people who get severe disease.”
In the meantime, Dr. Al-Aly says, “it’s still best to do everything you can to avoid infection in the first place – even if you’re vaccinated or previously infected, you should really try to avoid reinfection.”
That means sit outside if you can when visiting a restaurant. Wear a mask on a plane, even though it’s not required. And get vaccinated and boosted.
“In the future, there may be more tools to address this pandemic, but that’s really the best advice for now,” Dr. Al-Aly says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
We all have friends or relatives who, somehow, have managed to avoid catching COVID-19, which has infected more than 91.5 million Americans. You may even be one of the lucky ones yourself.
But health experts are saying: Not so fast. because they didn’t have symptoms or had mild cases they mistook for a cold or allergies.
The upshot: These silent COVID-19 cases reflect a hidden side of the pandemic that may be helping to drive new surges and viral variants.
Still, infectious disease experts say there is little doubt that some people have indeed managed to avoid COVID-19 infection altogether, and they are trying to understand why.
Several recent studies have suggested certain genetic and immune system traits may better protect this group of people against the coronavirus, making them less likely than others to be infected or seriously sickened. Researchers around the world are now studying these seemingly super-immune people for clues to what makes them so special, with an eye toward better vaccines, treatments, and prevention strategies.
Infectious disease specialists say both types of cases – those unknowingly infected by COVID-19 and people who’ve avoided the virus altogether – matter greatly to public health, more than 2 years into the pandemic.
“It’s definitely true that some people have had COVID and don’t realize it,” says Stephen Kissler, PhD, an infectious disease researcher with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “It is potentially good news if there’s more immunity in the population than we realize.”
But he says that being able to identify genetic and other factors that may offer some people protection against COVID-19 is an “exciting prospect” that could help find out who’s most at risk and improve efforts to get the pandemic under control.
Some studies have found a person’s genetic profile, past exposure to other COVID-like viruses, allergies, and even drugs they take for other conditions may all provide some defense – even for people who have not been vaccinated, don’t use masks, or don’t practice social distancing.
A person’s medical history and genetics may help decide their risk from new diseases, meaning “we may be able to help identify people who are at especially high risk from infection,” Dr. Kissler says. “That knowledge could help those people better shield themselves from infection and get quicker access to treatment and vaccines, if necessary. … We don’t yet know, but studies are ongoing for these things.”
Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease specialist with the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, agrees that emerging research on people who’ve avoided infection offers the chance of new public health strategies to combat COVID-19.
“I’m sure there is some subset of people who are [COVID] negative,” he says. “So what explains that phenomenon, especially if that person was out there getting significant exposures?”
Have you had COVID without knowing it?
In a media briefing late last month, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Ashish Jha, MD, said more than 70% of the U.S. population has had the virus, according to the latest CDC data. That’s up from 33.5% in December.
But the actual number of people in the U.S. who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, the scientific name for the virus that causes COVID-19, is likely to be much higher due to cases without symptoms that are unreported, experts say.
Since the early days of the pandemic, researchers have tried to put a number on these hidden cases, but that figure has been evolving and a clear consensus has not emerged.
In September 2020, a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine said “approximately 40% to 45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic.”
A follow-up analysis of 95 studies, published last December, reached similar findings, estimating that more than 40% of COVID-19 infections didn’t come with symptoms.
To get a better handle on the issue, CDC officials have been working with the American Red Cross and other blood banks to track COVID-19 antibodies – proteins your body makes after exposure to the virus to fight off an infection – in donors who said they have never had COVID-19.
While that joint effort is still ongoing, early findings say the number of donors with antibodies from COVID-19 infection increased in blood donors from 3.5% in July 2020 to at least 20.2% in May 2021. Since then, those percentages have soared, in part due to the introduction of vaccines, which also make the body produce COVID-19 antibodies.
The most current findings show that 83.3% of donors have combined COVID infection– and vaccine-induced antibodies in their blood. Those findings are based on 1.4 million blood donations.
Health experts say all of these studies are strong evidence that many COVID-19 cases continue to go undetected. In fact, the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation estimates that only 7% of positive COVID-19 cases in the U.S. are being detected. That means case rates are actually 14.5 times higher than the official count of 131,000 new COVID infections each day, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which reports the virus is still killing about 440 Americans daily.
So, why is all this important, in terms of public health?
Experts say people are more likely to be cautious if they know COVID-19 cases are high where they live, work, and play. On the other hand, if they believe case rates in their communities are lower than they actually are, they may be less likely to get vaccinated and boosted, wear masks indoors, avoid crowded indoor spaces, and take other precautions to fend off infection.
How do some avoid infection altogether?
In addition to tracking cases that go unreported and don’t have symptoms, infectious disease experts have also been trying to figure out why some people have managed to avoid getting the highly contagious virus.
Several leading lines of research have produced promising early results – suggesting that a person’s genetic makeup, past exposure to less-lethal coronaviruses, allergies, and even certain drugs they take for other conditions may all provide at least some protection against COVID.
“Our study showed that there are many human genes – hundreds of genes – that can impact SARS-CoV-2 infection,” says Neville Sanjana, PhD, a geneticist at New York University and the New York Genome Center who co-led the study. “With a better understanding of host genetic factors, we can find new kinds of therapies that target these host factors to block infection.”
In addition, he says several studies show some drugs that regulate genes, such as the breast cancer drug tamoxifen, also appear to knock down COVID-19 risk. He suggests such drugs, already approved by the Food and Drug Administration, might be “repurposed” to target the virus.
Studies in other countries show that patients taking tamoxifen before the pandemic were protected against severe COVID-19, Dr. Sanjana says. “That was a really cool thing, highlighting the power of harnessing host genetics. The virus critically depends on our genes to complete key parts of its life cycle.”
The NYU research findings echo other studies that have been published in recent months.
In July, a team of researchers led by the National Cancer Institute identified a genetic factor that appears to determine how severe an infection will be. In a study involving 3,000 people, they found that two gene changes, or mutations, that decrease the expression of a gene called OAS1 boosted the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19. OAS1 is part of the immune system’s response to viral infections.
As a result, developing a genetic therapy designed to increase the OAS1 gene’s expression might reduce the risk of severe disease.
“It’s very natural to get infected once you are exposed. There’s no magic bullet for that. But after you get infected, how you’re going to respond to this infection, that’s what is going to be affected by your genetic variants,” said Ludmila Prokunina-Olsson, PhD, the study’s lead researcher and chief of the National Cancer Institute’s Laboratory of Translational Genomics, Bethesda, Md., in an interview with NBC News.
Benjamin tenOever, PhD, a New York University virologist who co-authored the 2020 research, says the new genetic research is promising, but he believes it’s unlikely scientists will be able to identify a single gene responsible for actually preventing a COVID-19 infection.
“On the flip side, we have identified many genes that makes the disease worse,” he says.
T cells ‘remember’ past viral infections
As Dr. tenOever and Dr. Sanjana suggest, another intriguing line of research has found that prior viral infections may prime the body’s immune system to fight COVID-19.
Four other common coronaviruses – aside from SARS-CoV-2 – infect people worldwide, typically causing mild to moderate upper respiratory illnesses like the common cold, says Alessandro Sette, PhD, an infectious disease expert and vaccine researcher with the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology.
In a recent study published in Science, he and his team found past infection with these other coronaviruses may give some protection against SARS-CoV-2.
T cells – white blood cells that act like immunological ninjas to ferret out and fight infections – appear to maintain a kind of “biological memory” of coronaviruses they have seen before and can mount an attack on similar pathogens, such SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Sette says.
The new work builds on a prior research he helped lead that found 40%-60% of people never exposed to SARS-CoV-2 had T cells that reacted to the virus – with their immune systems recognizing fragments of a virus they had never seen before.
Dr. Sette says his research shows that people whose T cells have this “preexisting memory” of past coronavirus exposures also tend to respond better to vaccination for reasons not yet well understood.
“The question is, at which point will there be enough immunity from vaccination, repeated infections from other coronaviruses, but also some of the variants of the SARS-CoV-2 … where infections become less frequent? We’re not there yet,” he says.
In addition to these exciting genetic and T-cell findings, other research has suggested low-grade inflammation from allergies – a key part of the body’s immune response to foreign substances – may also give some people an extra leg up, in terms of avoiding COVID infection.
Last May, a study of 1,400 households published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that having a food allergy cut the risk of COVID-19 infection in half.
The researchers said it’s unclear why allergies may reduce the risk of infection, but they noted that people with food allergies express fewer ACE2 receptors on the surface of their airway cells, making it harder for the virus to enter cells.
The big picture: Prevention still your best bet
So, what’s the takeaway from all of this emerging research?
New York University’s Dr. tenOever says that while genes, T cells and allergies may offer some protection against COVID, tried-and-true precautions – vaccination, wearing masks, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and social distancing – are likely to provide a greater defense.
He believes these precautions are likely why he and his family have never contracted COVID-19.
“I was tested weekly, as were my kids at school,” he says. “We definitely never got COVID, despite the fact that we live in New York City and I worked in a hospital every single day of the pandemic.”
Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and director of clinical epidemiology at Washington University in St. Louis, agrees that the new research on COVID-19 is intriguing but won’t likely result in practical changes in the approach to fighting the virus in the near term.
“Getting a deeper understanding of potential genetic factors or other characteristics – that could really help us understand why the virus just comes and goes without any ill effects in some people, and in other people it produces really serious disease,” he says. “That will really help us eventually to design better vaccines to prevent it or reduce severity or even [treat] people who get severe disease.”
In the meantime, Dr. Al-Aly says, “it’s still best to do everything you can to avoid infection in the first place – even if you’re vaccinated or previously infected, you should really try to avoid reinfection.”
That means sit outside if you can when visiting a restaurant. Wear a mask on a plane, even though it’s not required. And get vaccinated and boosted.
“In the future, there may be more tools to address this pandemic, but that’s really the best advice for now,” Dr. Al-Aly says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
We all have friends or relatives who, somehow, have managed to avoid catching COVID-19, which has infected more than 91.5 million Americans. You may even be one of the lucky ones yourself.
But health experts are saying: Not so fast. because they didn’t have symptoms or had mild cases they mistook for a cold or allergies.
The upshot: These silent COVID-19 cases reflect a hidden side of the pandemic that may be helping to drive new surges and viral variants.
Still, infectious disease experts say there is little doubt that some people have indeed managed to avoid COVID-19 infection altogether, and they are trying to understand why.
Several recent studies have suggested certain genetic and immune system traits may better protect this group of people against the coronavirus, making them less likely than others to be infected or seriously sickened. Researchers around the world are now studying these seemingly super-immune people for clues to what makes them so special, with an eye toward better vaccines, treatments, and prevention strategies.
Infectious disease specialists say both types of cases – those unknowingly infected by COVID-19 and people who’ve avoided the virus altogether – matter greatly to public health, more than 2 years into the pandemic.
“It’s definitely true that some people have had COVID and don’t realize it,” says Stephen Kissler, PhD, an infectious disease researcher with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “It is potentially good news if there’s more immunity in the population than we realize.”
But he says that being able to identify genetic and other factors that may offer some people protection against COVID-19 is an “exciting prospect” that could help find out who’s most at risk and improve efforts to get the pandemic under control.
Some studies have found a person’s genetic profile, past exposure to other COVID-like viruses, allergies, and even drugs they take for other conditions may all provide some defense – even for people who have not been vaccinated, don’t use masks, or don’t practice social distancing.
A person’s medical history and genetics may help decide their risk from new diseases, meaning “we may be able to help identify people who are at especially high risk from infection,” Dr. Kissler says. “That knowledge could help those people better shield themselves from infection and get quicker access to treatment and vaccines, if necessary. … We don’t yet know, but studies are ongoing for these things.”
Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease specialist with the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, agrees that emerging research on people who’ve avoided infection offers the chance of new public health strategies to combat COVID-19.
“I’m sure there is some subset of people who are [COVID] negative,” he says. “So what explains that phenomenon, especially if that person was out there getting significant exposures?”
Have you had COVID without knowing it?
In a media briefing late last month, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Ashish Jha, MD, said more than 70% of the U.S. population has had the virus, according to the latest CDC data. That’s up from 33.5% in December.
But the actual number of people in the U.S. who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, the scientific name for the virus that causes COVID-19, is likely to be much higher due to cases without symptoms that are unreported, experts say.
Since the early days of the pandemic, researchers have tried to put a number on these hidden cases, but that figure has been evolving and a clear consensus has not emerged.
In September 2020, a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine said “approximately 40% to 45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic.”
A follow-up analysis of 95 studies, published last December, reached similar findings, estimating that more than 40% of COVID-19 infections didn’t come with symptoms.
To get a better handle on the issue, CDC officials have been working with the American Red Cross and other blood banks to track COVID-19 antibodies – proteins your body makes after exposure to the virus to fight off an infection – in donors who said they have never had COVID-19.
While that joint effort is still ongoing, early findings say the number of donors with antibodies from COVID-19 infection increased in blood donors from 3.5% in July 2020 to at least 20.2% in May 2021. Since then, those percentages have soared, in part due to the introduction of vaccines, which also make the body produce COVID-19 antibodies.
The most current findings show that 83.3% of donors have combined COVID infection– and vaccine-induced antibodies in their blood. Those findings are based on 1.4 million blood donations.
Health experts say all of these studies are strong evidence that many COVID-19 cases continue to go undetected. In fact, the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation estimates that only 7% of positive COVID-19 cases in the U.S. are being detected. That means case rates are actually 14.5 times higher than the official count of 131,000 new COVID infections each day, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which reports the virus is still killing about 440 Americans daily.
So, why is all this important, in terms of public health?
Experts say people are more likely to be cautious if they know COVID-19 cases are high where they live, work, and play. On the other hand, if they believe case rates in their communities are lower than they actually are, they may be less likely to get vaccinated and boosted, wear masks indoors, avoid crowded indoor spaces, and take other precautions to fend off infection.
How do some avoid infection altogether?
In addition to tracking cases that go unreported and don’t have symptoms, infectious disease experts have also been trying to figure out why some people have managed to avoid getting the highly contagious virus.
Several leading lines of research have produced promising early results – suggesting that a person’s genetic makeup, past exposure to less-lethal coronaviruses, allergies, and even certain drugs they take for other conditions may all provide at least some protection against COVID.
“Our study showed that there are many human genes – hundreds of genes – that can impact SARS-CoV-2 infection,” says Neville Sanjana, PhD, a geneticist at New York University and the New York Genome Center who co-led the study. “With a better understanding of host genetic factors, we can find new kinds of therapies that target these host factors to block infection.”
In addition, he says several studies show some drugs that regulate genes, such as the breast cancer drug tamoxifen, also appear to knock down COVID-19 risk. He suggests such drugs, already approved by the Food and Drug Administration, might be “repurposed” to target the virus.
Studies in other countries show that patients taking tamoxifen before the pandemic were protected against severe COVID-19, Dr. Sanjana says. “That was a really cool thing, highlighting the power of harnessing host genetics. The virus critically depends on our genes to complete key parts of its life cycle.”
The NYU research findings echo other studies that have been published in recent months.
In July, a team of researchers led by the National Cancer Institute identified a genetic factor that appears to determine how severe an infection will be. In a study involving 3,000 people, they found that two gene changes, or mutations, that decrease the expression of a gene called OAS1 boosted the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19. OAS1 is part of the immune system’s response to viral infections.
As a result, developing a genetic therapy designed to increase the OAS1 gene’s expression might reduce the risk of severe disease.
“It’s very natural to get infected once you are exposed. There’s no magic bullet for that. But after you get infected, how you’re going to respond to this infection, that’s what is going to be affected by your genetic variants,” said Ludmila Prokunina-Olsson, PhD, the study’s lead researcher and chief of the National Cancer Institute’s Laboratory of Translational Genomics, Bethesda, Md., in an interview with NBC News.
Benjamin tenOever, PhD, a New York University virologist who co-authored the 2020 research, says the new genetic research is promising, but he believes it’s unlikely scientists will be able to identify a single gene responsible for actually preventing a COVID-19 infection.
“On the flip side, we have identified many genes that makes the disease worse,” he says.
T cells ‘remember’ past viral infections
As Dr. tenOever and Dr. Sanjana suggest, another intriguing line of research has found that prior viral infections may prime the body’s immune system to fight COVID-19.
Four other common coronaviruses – aside from SARS-CoV-2 – infect people worldwide, typically causing mild to moderate upper respiratory illnesses like the common cold, says Alessandro Sette, PhD, an infectious disease expert and vaccine researcher with the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology.
In a recent study published in Science, he and his team found past infection with these other coronaviruses may give some protection against SARS-CoV-2.
T cells – white blood cells that act like immunological ninjas to ferret out and fight infections – appear to maintain a kind of “biological memory” of coronaviruses they have seen before and can mount an attack on similar pathogens, such SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Sette says.
The new work builds on a prior research he helped lead that found 40%-60% of people never exposed to SARS-CoV-2 had T cells that reacted to the virus – with their immune systems recognizing fragments of a virus they had never seen before.
Dr. Sette says his research shows that people whose T cells have this “preexisting memory” of past coronavirus exposures also tend to respond better to vaccination for reasons not yet well understood.
“The question is, at which point will there be enough immunity from vaccination, repeated infections from other coronaviruses, but also some of the variants of the SARS-CoV-2 … where infections become less frequent? We’re not there yet,” he says.
In addition to these exciting genetic and T-cell findings, other research has suggested low-grade inflammation from allergies – a key part of the body’s immune response to foreign substances – may also give some people an extra leg up, in terms of avoiding COVID infection.
Last May, a study of 1,400 households published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that having a food allergy cut the risk of COVID-19 infection in half.
The researchers said it’s unclear why allergies may reduce the risk of infection, but they noted that people with food allergies express fewer ACE2 receptors on the surface of their airway cells, making it harder for the virus to enter cells.
The big picture: Prevention still your best bet
So, what’s the takeaway from all of this emerging research?
New York University’s Dr. tenOever says that while genes, T cells and allergies may offer some protection against COVID, tried-and-true precautions – vaccination, wearing masks, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and social distancing – are likely to provide a greater defense.
He believes these precautions are likely why he and his family have never contracted COVID-19.
“I was tested weekly, as were my kids at school,” he says. “We definitely never got COVID, despite the fact that we live in New York City and I worked in a hospital every single day of the pandemic.”
Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and director of clinical epidemiology at Washington University in St. Louis, agrees that the new research on COVID-19 is intriguing but won’t likely result in practical changes in the approach to fighting the virus in the near term.
“Getting a deeper understanding of potential genetic factors or other characteristics – that could really help us understand why the virus just comes and goes without any ill effects in some people, and in other people it produces really serious disease,” he says. “That will really help us eventually to design better vaccines to prevent it or reduce severity or even [treat] people who get severe disease.”
In the meantime, Dr. Al-Aly says, “it’s still best to do everything you can to avoid infection in the first place – even if you’re vaccinated or previously infected, you should really try to avoid reinfection.”
That means sit outside if you can when visiting a restaurant. Wear a mask on a plane, even though it’s not required. And get vaccinated and boosted.
“In the future, there may be more tools to address this pandemic, but that’s really the best advice for now,” Dr. Al-Aly says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID smell loss tops disease severity as a predictor of long-term cognitive impairment
preliminary results of new research suggest.
The findings provide important insight into the long-term cognitive impact of COVID-19, said study investigator Gabriela Gonzalez-Alemán, PhD, professor at Pontifical Catholic University of Argentina, Buenos Aires.
The more information that can be gathered on factors increasing risks for this cognitive impact, “the better we can track it and begin to develop methods to prevent it,” she said.
The findings were presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Memory, attention problems
COVID-19 has infected more than 570 million people worldwide. Related infections may result in long-term sequelae, including neuropsychiatric symptoms, said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán.
In older adults, COVID-19 sequelae may resemble early Alzheimer’s disease, and the two conditions may share risk factors and blood biomarkers.
The new study highlighted 1-year results from a large, prospective cohort study from Argentina. Researchers used measures to evaluate long-term consequences of COVID-19 in older adults recommended by the Alzheimer’s Association Consortium on Chronic Neuropsychiatric Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (CNS SC2).
Harmonizing definitions and methodologies for studying COVID-19’s impact on the brain allows consortium members to compare study results, said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán.
The investigators used the health registry in the province of Jujuy, situated in the extreme northwestern part of Argentina. The registry includes all SARS-CoV-2 testing data for the entire region.
The investigators randomly invited adults aged 60 years and older from the registry to participate in the study. The current analysis included 766 adults aged 55-95 years (mean age 66.9 years; 57% female) with an average of 10.4 years of education. The education system in Argentina includes 12 years of school before university.
Investigators stratified subjects by polymerase chain reaction testing status. Of the total, 88.4% were infected with COVID and 11.6% were controls (subjects without COVID).
The neurocognitive assessment of participants included four cognitive domains: memory, attention, language, and executive function, and an olfactory test that determined degree of olfactory dysfunction. Cognitive impairment was defined as z scores below –2.
Researchers divided participants into groups according to cognitive performance. These included normal cognition, memory-only impairment (single domain; 11.7%), impairment in attention and executive function without memory impairment (two domains; 8.3%), and multiple domain impairment (11.6%).
“Our participants showed a predominance of memory impairment as would be seen in Alzheimer’s disease,” noted Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán. “And a large group showed a combination of memory and attention problems.”
About 40% of the study sample – but no controls – had olfactory dysfunction.
“All the subjects that had a severe cognitive impairment also had anosmia [loss of smell],” said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán. “We established an association between olfactory dysfunction and cognitive performance and impairment.”
The analysis showed that severity of anosmia, but not clinical status, significantly predicted cognitive impairment. “So, anosmia could be a good predictor of cognitive impairment after COVID-19 infection,” said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán.
For individuals older than 60 years, cognitive impairment can be persistent, as can be olfactory dysfunction, she added.
Results of a 1-year phone survey showed about 71.8% of subjects had received three vaccine doses and 24.9% two doses. About 12.5% of those with three doses were reinfected and 23.3% of those with two doses were reinfected.
Longest follow-up to date
Commenting on the research, Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president, medical and scientific relations at the Alzheimer’s Association, noted the study is “the longest follow-up we’ve seen” looking at the connection between persistent loss of smell and cognitive changes after a COVID-19 infection.
The study included a “fairly large” sample size and was “unique” in that it was set up in a part of the country with centralized testing, said Dr. Snyder.
The Argentinian group is among the most advanced of those connected to the CNS SC2, said Dr. Snyder.
Members of this Alzheimer’s Association consortium, said Dr. Snyder, regularly share updates of ongoing studies, which are at different stages and looking at various neuropsychiatric impacts of COVID-19. It is important to bring these groups together to determine what those impacts are “because no one group will be able to do this on their own,” she said. “We saw pretty early on that some individuals had changes in the brain, or changes in cognition, and loss of sense of smell or taste, which indicates there’s a connection to the brain.”
However, she added, “there’s still a lot we don’t know” about this connection.
The study was funded by Alzheimer’s Association and FULTRA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
preliminary results of new research suggest.
The findings provide important insight into the long-term cognitive impact of COVID-19, said study investigator Gabriela Gonzalez-Alemán, PhD, professor at Pontifical Catholic University of Argentina, Buenos Aires.
The more information that can be gathered on factors increasing risks for this cognitive impact, “the better we can track it and begin to develop methods to prevent it,” she said.
The findings were presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Memory, attention problems
COVID-19 has infected more than 570 million people worldwide. Related infections may result in long-term sequelae, including neuropsychiatric symptoms, said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán.
In older adults, COVID-19 sequelae may resemble early Alzheimer’s disease, and the two conditions may share risk factors and blood biomarkers.
The new study highlighted 1-year results from a large, prospective cohort study from Argentina. Researchers used measures to evaluate long-term consequences of COVID-19 in older adults recommended by the Alzheimer’s Association Consortium on Chronic Neuropsychiatric Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (CNS SC2).
Harmonizing definitions and methodologies for studying COVID-19’s impact on the brain allows consortium members to compare study results, said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán.
The investigators used the health registry in the province of Jujuy, situated in the extreme northwestern part of Argentina. The registry includes all SARS-CoV-2 testing data for the entire region.
The investigators randomly invited adults aged 60 years and older from the registry to participate in the study. The current analysis included 766 adults aged 55-95 years (mean age 66.9 years; 57% female) with an average of 10.4 years of education. The education system in Argentina includes 12 years of school before university.
Investigators stratified subjects by polymerase chain reaction testing status. Of the total, 88.4% were infected with COVID and 11.6% were controls (subjects without COVID).
The neurocognitive assessment of participants included four cognitive domains: memory, attention, language, and executive function, and an olfactory test that determined degree of olfactory dysfunction. Cognitive impairment was defined as z scores below –2.
Researchers divided participants into groups according to cognitive performance. These included normal cognition, memory-only impairment (single domain; 11.7%), impairment in attention and executive function without memory impairment (two domains; 8.3%), and multiple domain impairment (11.6%).
“Our participants showed a predominance of memory impairment as would be seen in Alzheimer’s disease,” noted Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán. “And a large group showed a combination of memory and attention problems.”
About 40% of the study sample – but no controls – had olfactory dysfunction.
“All the subjects that had a severe cognitive impairment also had anosmia [loss of smell],” said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán. “We established an association between olfactory dysfunction and cognitive performance and impairment.”
The analysis showed that severity of anosmia, but not clinical status, significantly predicted cognitive impairment. “So, anosmia could be a good predictor of cognitive impairment after COVID-19 infection,” said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán.
For individuals older than 60 years, cognitive impairment can be persistent, as can be olfactory dysfunction, she added.
Results of a 1-year phone survey showed about 71.8% of subjects had received three vaccine doses and 24.9% two doses. About 12.5% of those with three doses were reinfected and 23.3% of those with two doses were reinfected.
Longest follow-up to date
Commenting on the research, Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president, medical and scientific relations at the Alzheimer’s Association, noted the study is “the longest follow-up we’ve seen” looking at the connection between persistent loss of smell and cognitive changes after a COVID-19 infection.
The study included a “fairly large” sample size and was “unique” in that it was set up in a part of the country with centralized testing, said Dr. Snyder.
The Argentinian group is among the most advanced of those connected to the CNS SC2, said Dr. Snyder.
Members of this Alzheimer’s Association consortium, said Dr. Snyder, regularly share updates of ongoing studies, which are at different stages and looking at various neuropsychiatric impacts of COVID-19. It is important to bring these groups together to determine what those impacts are “because no one group will be able to do this on their own,” she said. “We saw pretty early on that some individuals had changes in the brain, or changes in cognition, and loss of sense of smell or taste, which indicates there’s a connection to the brain.”
However, she added, “there’s still a lot we don’t know” about this connection.
The study was funded by Alzheimer’s Association and FULTRA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
preliminary results of new research suggest.
The findings provide important insight into the long-term cognitive impact of COVID-19, said study investigator Gabriela Gonzalez-Alemán, PhD, professor at Pontifical Catholic University of Argentina, Buenos Aires.
The more information that can be gathered on factors increasing risks for this cognitive impact, “the better we can track it and begin to develop methods to prevent it,” she said.
The findings were presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Memory, attention problems
COVID-19 has infected more than 570 million people worldwide. Related infections may result in long-term sequelae, including neuropsychiatric symptoms, said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán.
In older adults, COVID-19 sequelae may resemble early Alzheimer’s disease, and the two conditions may share risk factors and blood biomarkers.
The new study highlighted 1-year results from a large, prospective cohort study from Argentina. Researchers used measures to evaluate long-term consequences of COVID-19 in older adults recommended by the Alzheimer’s Association Consortium on Chronic Neuropsychiatric Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (CNS SC2).
Harmonizing definitions and methodologies for studying COVID-19’s impact on the brain allows consortium members to compare study results, said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán.
The investigators used the health registry in the province of Jujuy, situated in the extreme northwestern part of Argentina. The registry includes all SARS-CoV-2 testing data for the entire region.
The investigators randomly invited adults aged 60 years and older from the registry to participate in the study. The current analysis included 766 adults aged 55-95 years (mean age 66.9 years; 57% female) with an average of 10.4 years of education. The education system in Argentina includes 12 years of school before university.
Investigators stratified subjects by polymerase chain reaction testing status. Of the total, 88.4% were infected with COVID and 11.6% were controls (subjects without COVID).
The neurocognitive assessment of participants included four cognitive domains: memory, attention, language, and executive function, and an olfactory test that determined degree of olfactory dysfunction. Cognitive impairment was defined as z scores below –2.
Researchers divided participants into groups according to cognitive performance. These included normal cognition, memory-only impairment (single domain; 11.7%), impairment in attention and executive function without memory impairment (two domains; 8.3%), and multiple domain impairment (11.6%).
“Our participants showed a predominance of memory impairment as would be seen in Alzheimer’s disease,” noted Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán. “And a large group showed a combination of memory and attention problems.”
About 40% of the study sample – but no controls – had olfactory dysfunction.
“All the subjects that had a severe cognitive impairment also had anosmia [loss of smell],” said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán. “We established an association between olfactory dysfunction and cognitive performance and impairment.”
The analysis showed that severity of anosmia, but not clinical status, significantly predicted cognitive impairment. “So, anosmia could be a good predictor of cognitive impairment after COVID-19 infection,” said Dr. Gonzalez-Alemán.
For individuals older than 60 years, cognitive impairment can be persistent, as can be olfactory dysfunction, she added.
Results of a 1-year phone survey showed about 71.8% of subjects had received three vaccine doses and 24.9% two doses. About 12.5% of those with three doses were reinfected and 23.3% of those with two doses were reinfected.
Longest follow-up to date
Commenting on the research, Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president, medical and scientific relations at the Alzheimer’s Association, noted the study is “the longest follow-up we’ve seen” looking at the connection between persistent loss of smell and cognitive changes after a COVID-19 infection.
The study included a “fairly large” sample size and was “unique” in that it was set up in a part of the country with centralized testing, said Dr. Snyder.
The Argentinian group is among the most advanced of those connected to the CNS SC2, said Dr. Snyder.
Members of this Alzheimer’s Association consortium, said Dr. Snyder, regularly share updates of ongoing studies, which are at different stages and looking at various neuropsychiatric impacts of COVID-19. It is important to bring these groups together to determine what those impacts are “because no one group will be able to do this on their own,” she said. “We saw pretty early on that some individuals had changes in the brain, or changes in cognition, and loss of sense of smell or taste, which indicates there’s a connection to the brain.”
However, she added, “there’s still a lot we don’t know” about this connection.
The study was funded by Alzheimer’s Association and FULTRA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAIC 2022
One in four NSCLC patients respond poorly to COVID-19 vaccine
according to a new study.
The study was published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“Booster vaccination increased binding and neutralizing antibody titers to Omicron, but antibody titers declined after 3 months. These data highlight the concern for patients with cancer given the rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant,” wrote the authors, who were led by Rafi Ahmed, PhD, Emory University, Atlanta.
Researchers found that 18% had no detectable antibody at all and active treatment type had no association with vaccine response.
Researchers examined antibody titers among 82 NSCLC patients and 53 healthy volunteers. They collected blood samples longitudinally for analysis. While most patients had binding and neutralizing antibody titers that were comparable with healthy volunteers, 25% had poor responses, which led to six- to sevenfold lower titers than healthy controls. There was no association between worse vaccine responses and history of programmed death–1 monotherapy, chemotherapy, or both in combination. Receipt of a booster vaccine improved binding and neutralizing antibody titers to both the wild type and the Omicron variant, but 2-4 months after the booster there was a five- to sevenfold decrease in neutralizing titers to both the wild type and Omicron variant.
“This study indicates both the need to monitor our patients with lung cancer for response to COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, identify the nonresponders for follow-up and further attempts at immunization, and continue collecting and analyzing clinicodemographic information and biospecimens from our patients,” wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
Although the findings reveal potential concerns, the good news is that most patients NSCLC patients do respond normally to COVID-19 vaccination, said John D. Minna, MD, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, lead author of the editorial.
He offered some advice to physicians. “You can test your patients using currently available [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments]–approved lab tests to determine what their antibody titers are. This should be done after boosting since titers will go down after time. We know that if a patient has lung cancer and they do get infected with SARS-CoV-2 that potentially they could develop serious COVID-19 disease. Besides giving antiviral treatment, it is important that they be closely monitored for symptoms of progression so if they need to be hospitalized it can be done in a prudent manner,” said Dr. Minna, who is director of the Hamon Center for Therapeutic Oncology Research at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
No clinical details have emerged that might predict which patients have an insufficient response to vaccination. “When we started these studies, a lot of us thought that anyone who did not develop a good antibody response would be weak or sicker. For example, [patients with] late-stage disease, or having had a lot of therapy, or perhaps immune checkpoint blockade. However, none of these things are correlated. The main advice we are giving our lung cancer patients are to get vaccinated, get boosted (double boosted), and just do the smart thing to protect yourself from exposure,” he said.
For example, when traveling on a plane, patients should wear a mask. They should also avoid large indoor events. He also recommended that, following vaccination and boosters, patients seek out CLIA-certified tests to get their titer checked.
“Upon any COVID infection, even if their titer is at or above 80%, patients should see their physician to consider treatment with Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir), which has emergency use authorization. For patients with a lower titer, it’s important to seek out a physician and consider Paxlovid and possibly antibody therapy. But these are individual decisions to be made with your doctor,” Dr. Minna said.
The next important research question is what happens to T-cell immune response following vaccination. “We know that a good cellular immune response is also important in preventing infection and severe infection, but we don’t yet know which persons (with or without cancer) have good T-cell responses. This information will also likely impact what we tell our patients and will add to the antibody data,” he said.
Studies are ongoing to determine specific T-cell responses to mRNA vaccines, and how well those T-cell responses respond to SARS-CoV-2 infection in the laboratory.
according to a new study.
The study was published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“Booster vaccination increased binding and neutralizing antibody titers to Omicron, but antibody titers declined after 3 months. These data highlight the concern for patients with cancer given the rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant,” wrote the authors, who were led by Rafi Ahmed, PhD, Emory University, Atlanta.
Researchers found that 18% had no detectable antibody at all and active treatment type had no association with vaccine response.
Researchers examined antibody titers among 82 NSCLC patients and 53 healthy volunteers. They collected blood samples longitudinally for analysis. While most patients had binding and neutralizing antibody titers that were comparable with healthy volunteers, 25% had poor responses, which led to six- to sevenfold lower titers than healthy controls. There was no association between worse vaccine responses and history of programmed death–1 monotherapy, chemotherapy, or both in combination. Receipt of a booster vaccine improved binding and neutralizing antibody titers to both the wild type and the Omicron variant, but 2-4 months after the booster there was a five- to sevenfold decrease in neutralizing titers to both the wild type and Omicron variant.
“This study indicates both the need to monitor our patients with lung cancer for response to COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, identify the nonresponders for follow-up and further attempts at immunization, and continue collecting and analyzing clinicodemographic information and biospecimens from our patients,” wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
Although the findings reveal potential concerns, the good news is that most patients NSCLC patients do respond normally to COVID-19 vaccination, said John D. Minna, MD, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, lead author of the editorial.
He offered some advice to physicians. “You can test your patients using currently available [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments]–approved lab tests to determine what their antibody titers are. This should be done after boosting since titers will go down after time. We know that if a patient has lung cancer and they do get infected with SARS-CoV-2 that potentially they could develop serious COVID-19 disease. Besides giving antiviral treatment, it is important that they be closely monitored for symptoms of progression so if they need to be hospitalized it can be done in a prudent manner,” said Dr. Minna, who is director of the Hamon Center for Therapeutic Oncology Research at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
No clinical details have emerged that might predict which patients have an insufficient response to vaccination. “When we started these studies, a lot of us thought that anyone who did not develop a good antibody response would be weak or sicker. For example, [patients with] late-stage disease, or having had a lot of therapy, or perhaps immune checkpoint blockade. However, none of these things are correlated. The main advice we are giving our lung cancer patients are to get vaccinated, get boosted (double boosted), and just do the smart thing to protect yourself from exposure,” he said.
For example, when traveling on a plane, patients should wear a mask. They should also avoid large indoor events. He also recommended that, following vaccination and boosters, patients seek out CLIA-certified tests to get their titer checked.
“Upon any COVID infection, even if their titer is at or above 80%, patients should see their physician to consider treatment with Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir), which has emergency use authorization. For patients with a lower titer, it’s important to seek out a physician and consider Paxlovid and possibly antibody therapy. But these are individual decisions to be made with your doctor,” Dr. Minna said.
The next important research question is what happens to T-cell immune response following vaccination. “We know that a good cellular immune response is also important in preventing infection and severe infection, but we don’t yet know which persons (with or without cancer) have good T-cell responses. This information will also likely impact what we tell our patients and will add to the antibody data,” he said.
Studies are ongoing to determine specific T-cell responses to mRNA vaccines, and how well those T-cell responses respond to SARS-CoV-2 infection in the laboratory.
according to a new study.
The study was published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“Booster vaccination increased binding and neutralizing antibody titers to Omicron, but antibody titers declined after 3 months. These data highlight the concern for patients with cancer given the rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant,” wrote the authors, who were led by Rafi Ahmed, PhD, Emory University, Atlanta.
Researchers found that 18% had no detectable antibody at all and active treatment type had no association with vaccine response.
Researchers examined antibody titers among 82 NSCLC patients and 53 healthy volunteers. They collected blood samples longitudinally for analysis. While most patients had binding and neutralizing antibody titers that were comparable with healthy volunteers, 25% had poor responses, which led to six- to sevenfold lower titers than healthy controls. There was no association between worse vaccine responses and history of programmed death–1 monotherapy, chemotherapy, or both in combination. Receipt of a booster vaccine improved binding and neutralizing antibody titers to both the wild type and the Omicron variant, but 2-4 months after the booster there was a five- to sevenfold decrease in neutralizing titers to both the wild type and Omicron variant.
“This study indicates both the need to monitor our patients with lung cancer for response to COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, identify the nonresponders for follow-up and further attempts at immunization, and continue collecting and analyzing clinicodemographic information and biospecimens from our patients,” wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
Although the findings reveal potential concerns, the good news is that most patients NSCLC patients do respond normally to COVID-19 vaccination, said John D. Minna, MD, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, lead author of the editorial.
He offered some advice to physicians. “You can test your patients using currently available [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments]–approved lab tests to determine what their antibody titers are. This should be done after boosting since titers will go down after time. We know that if a patient has lung cancer and they do get infected with SARS-CoV-2 that potentially they could develop serious COVID-19 disease. Besides giving antiviral treatment, it is important that they be closely monitored for symptoms of progression so if they need to be hospitalized it can be done in a prudent manner,” said Dr. Minna, who is director of the Hamon Center for Therapeutic Oncology Research at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
No clinical details have emerged that might predict which patients have an insufficient response to vaccination. “When we started these studies, a lot of us thought that anyone who did not develop a good antibody response would be weak or sicker. For example, [patients with] late-stage disease, or having had a lot of therapy, or perhaps immune checkpoint blockade. However, none of these things are correlated. The main advice we are giving our lung cancer patients are to get vaccinated, get boosted (double boosted), and just do the smart thing to protect yourself from exposure,” he said.
For example, when traveling on a plane, patients should wear a mask. They should also avoid large indoor events. He also recommended that, following vaccination and boosters, patients seek out CLIA-certified tests to get their titer checked.
“Upon any COVID infection, even if their titer is at or above 80%, patients should see their physician to consider treatment with Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir), which has emergency use authorization. For patients with a lower titer, it’s important to seek out a physician and consider Paxlovid and possibly antibody therapy. But these are individual decisions to be made with your doctor,” Dr. Minna said.
The next important research question is what happens to T-cell immune response following vaccination. “We know that a good cellular immune response is also important in preventing infection and severe infection, but we don’t yet know which persons (with or without cancer) have good T-cell responses. This information will also likely impact what we tell our patients and will add to the antibody data,” he said.
Studies are ongoing to determine specific T-cell responses to mRNA vaccines, and how well those T-cell responses respond to SARS-CoV-2 infection in the laboratory.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY