User login
FDA considers regulating CBD products
The products can have drug-like effects on the body and contain CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). Both CBD and THC can be derived from hemp, which was legalized by Congress in 2018.
“Given what we know about the safety of CBD so far, it raises concerns for FDA about whether these existing regulatory pathways for food and dietary supplements are appropriate for this substance,” FDA Principal Deputy Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, told The Wall Street Journal.
A 2021 FDA report valued the CBD market at $4.6 billion and projected it to quadruple by 2026. The only FDA-approved CBD product is an oil called Epidiolex, which can be prescribed for the seizure-associated disease epilepsy. Research on CBD to treat other diseases is ongoing.
Food, beverage, and beauty products containing CBD are sold in stores and online in many forms, including oils, vaporized liquids, and oil-based capsules, but “research supporting the drug’s benefits is still limited,” the Mayo Clinic said.
Recently, investigations have found that many CBD products also contain THC, which can be derived from legal hemp in a form that is referred to as Delta 8 and produces a psychoactive high. The CDC warned in 2022 that people “mistook” THC products for CBD products, which are often sold at the same stores, and experienced “adverse events.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and FDA warn that much is unknown about CBD and delta-8 products. The CDC says known CBD risks include liver damage; interference with other drugs you are taking, which may lead to injury or serious side effects; drowsiness or sleepiness; diarrhea or changes in appetite; changes in mood, such as crankiness; potential negative effects on fetuses during pregnancy or on babies during breastfeeding; or unintentional poisoning of children when mistaking THC products for CBD products or due to containing other ingredients such as THC or pesticides.
“I don’t think that we can have the perfect be the enemy of the good when we’re looking at such a vast market that is so available and utilized,” Norman Birenbaum, a senior FDA adviser who is working on the regulatory issue, told the Journal. “You’ve got a widely unregulated market.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The products can have drug-like effects on the body and contain CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). Both CBD and THC can be derived from hemp, which was legalized by Congress in 2018.
“Given what we know about the safety of CBD so far, it raises concerns for FDA about whether these existing regulatory pathways for food and dietary supplements are appropriate for this substance,” FDA Principal Deputy Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, told The Wall Street Journal.
A 2021 FDA report valued the CBD market at $4.6 billion and projected it to quadruple by 2026. The only FDA-approved CBD product is an oil called Epidiolex, which can be prescribed for the seizure-associated disease epilepsy. Research on CBD to treat other diseases is ongoing.
Food, beverage, and beauty products containing CBD are sold in stores and online in many forms, including oils, vaporized liquids, and oil-based capsules, but “research supporting the drug’s benefits is still limited,” the Mayo Clinic said.
Recently, investigations have found that many CBD products also contain THC, which can be derived from legal hemp in a form that is referred to as Delta 8 and produces a psychoactive high. The CDC warned in 2022 that people “mistook” THC products for CBD products, which are often sold at the same stores, and experienced “adverse events.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and FDA warn that much is unknown about CBD and delta-8 products. The CDC says known CBD risks include liver damage; interference with other drugs you are taking, which may lead to injury or serious side effects; drowsiness or sleepiness; diarrhea or changes in appetite; changes in mood, such as crankiness; potential negative effects on fetuses during pregnancy or on babies during breastfeeding; or unintentional poisoning of children when mistaking THC products for CBD products or due to containing other ingredients such as THC or pesticides.
“I don’t think that we can have the perfect be the enemy of the good when we’re looking at such a vast market that is so available and utilized,” Norman Birenbaum, a senior FDA adviser who is working on the regulatory issue, told the Journal. “You’ve got a widely unregulated market.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The products can have drug-like effects on the body and contain CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). Both CBD and THC can be derived from hemp, which was legalized by Congress in 2018.
“Given what we know about the safety of CBD so far, it raises concerns for FDA about whether these existing regulatory pathways for food and dietary supplements are appropriate for this substance,” FDA Principal Deputy Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, told The Wall Street Journal.
A 2021 FDA report valued the CBD market at $4.6 billion and projected it to quadruple by 2026. The only FDA-approved CBD product is an oil called Epidiolex, which can be prescribed for the seizure-associated disease epilepsy. Research on CBD to treat other diseases is ongoing.
Food, beverage, and beauty products containing CBD are sold in stores and online in many forms, including oils, vaporized liquids, and oil-based capsules, but “research supporting the drug’s benefits is still limited,” the Mayo Clinic said.
Recently, investigations have found that many CBD products also contain THC, which can be derived from legal hemp in a form that is referred to as Delta 8 and produces a psychoactive high. The CDC warned in 2022 that people “mistook” THC products for CBD products, which are often sold at the same stores, and experienced “adverse events.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and FDA warn that much is unknown about CBD and delta-8 products. The CDC says known CBD risks include liver damage; interference with other drugs you are taking, which may lead to injury or serious side effects; drowsiness or sleepiness; diarrhea or changes in appetite; changes in mood, such as crankiness; potential negative effects on fetuses during pregnancy or on babies during breastfeeding; or unintentional poisoning of children when mistaking THC products for CBD products or due to containing other ingredients such as THC or pesticides.
“I don’t think that we can have the perfect be the enemy of the good when we’re looking at such a vast market that is so available and utilized,” Norman Birenbaum, a senior FDA adviser who is working on the regulatory issue, told the Journal. “You’ve got a widely unregulated market.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Patient With Severe Headache After IV Immunoglobulin
A 35-year-old woman with a history of hypothyroidism and idiopathic small fiber autonomic and sensory neuropathy presented to the emergency department (ED) 48 hours after IV immunoglobulin (IG) infusion with a severe headache, nausea, neck stiffness, photophobia, and episodes of intense positional eye pressure. The patient reported previous episodes of headaches post-IVIG infusion but not nearly as severe. On ED arrival, the patient was afebrile with vital signs within normal limits. Initial laboratory results were notable for levels within reference range parameters: 5.9 × 109/L white blood cell (WBC) count, 13.3 g/dL hemoglobin, 38.7% hematocrit, and 279 × 109/L platelet count; there were no abnormal urinalysis findings, and she was negative for human chorionic gonadotropin.
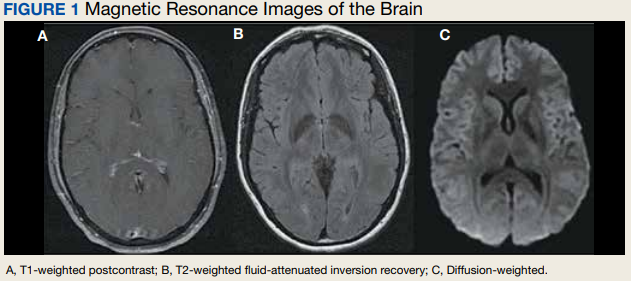
Due to the patient’s symptoms concerning for an acute intracranial process, a brain computed tomography (CT) without contrast was ordered. The CT demonstrated no intracranial abnormalities, but the patient’s symptoms continued to worsen. The patient was started on IV fluids and 1 g IV acetaminophen and underwent a lumbar puncture (LP). Her opening pressure was elevated at 29 cm H2O (reference range, 6-20 cm), and the fluid was notably clear. During the LP, 25 mL of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was collected for laboratory analysis to include a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) panel and cultures, and a closing pressure of 12 cm H2O was recorded at the end of the procedure with the patient reporting some relief of pressure. The patient was admitted to the medicine ward for further workup and observations.The patient’s meningitis/encephalitis PCR panel detected no pathogens in the CSF, but her WBC count was 84 × 109/L (reference range, 4-11) with 30 segmented neutrophils (reference range, 0-6) and red blood cell count of 24 (reference range, 0-1); her normal glucose at 60 mg/dL (reference range, 40-70) and protein of 33 mg/dL (reference range, 15-45) were within normal parameters. Brain magnetic resonance images with and without contrast was inconsistent with any acute intracranial pathology to include subarachnoid hemorrhage or central nervous system neoplasm (Figure 1). Bacterial and fungal cultures were negative.
- What is your diagnosis?
- How would you treat this patient?
Discussion
Aseptic meningitis presents with a typical clinical picture of meningitis to include headache, stiffened neck, and photophobia. In the event of negative CSF bacterial and fungal cultures and negative viral PCR, a diagnosis of aseptic meningitis is considered.1 Though the differential for aseptic meningitis is broad, in the immunocompetent patient, the most common etiology of aseptic meningitis in the United States is by far viral, and specifically, enterovirus (50.9%). It is less commonly caused by herpes simplex virus (8.3%), varicella zoster virus, and finally, the mosquito-borne St. Louis encephalitis and West Nile viruses typically acquired in the summer or early fall months. Other infectious agents that can present with aseptic meningitis are spirochetes (Lyme disease and syphilis), tuberculous meningitis, fungal infections (cryptococcal meningitis), and other bacterial infections that have a negative culture.
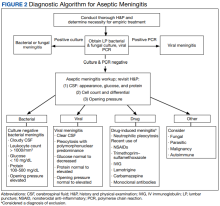
The patient’s history, physical examination, vital signs, imaging, and lumbar puncture findings were most concerning for drug-induced aseptic meningitis (DIAM) secondary to her recent IVIG infusion. An algorithm can be used to work through the diagnostic approach (Figure 2).3,4
Immediate and delayed adverse reactions to IVIG are known risks for IVIG therapy. About 1% to 15% of patients who receive IVIG will experience mild immediate reactions to the infusion.6 These immediate reactions include fever (78.6%), acrocyanosis (71.4%), rash (64.3%), headache (57.1%), shortness of breath (42.8%), hypotension (35.7%), and chest pain (21.4%).
IVIG is an increasingly used biologic pharmacologic agent used for a variety of medical conditions. This can be attributed to its multifaceted properties and ability to fight infection when given as replacement therapy and provide immunomodulation in conjunction with its more well-known anti-inflammatory properties.8 The number of conditions that can potentially benefit from IVIG is so vast that the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology had to divide the indication for IVIG therapy into definitely beneficial, probably beneficial, may provide benefit, and unlikely to provide benefit categories.8
Conclusions
We encourage heightened clinical suspicion of DIAM in patients who have recently undergone IVIG infusion and present with meningeal signs (stiff neck, headache, photophobia, and ear/eye pressure) without any evidence of infection on physical examination or laboratory results. With such, we hope to improve clinician suspicion, detection, as well as patient education and outcomes in cases of DIAM.
1. Kareva L, Mironska K, Stavric K, Hasani A. Adverse reactions to intravenous immunoglobulins—our experience. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018;6(12):2359-2362. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2018.513
2. Mount HR, Boyle SD. Aseptic and bacterial meningitis: evaluation, treatment, and prevention. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96(5):314-322.
3. Seehusen DA, Reeves MM, Fomin DA. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68(6):1103-1108.
4. Connolly KJ, Hammer SM. The acute aseptic meningitis syndrome. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1990;4(4):599-622.
5. Jolles S, Sewell WA, Leighton C. Drug-induced aseptic meningitis: diagnosis and management. Drug Saf. 2000;22(3):215-226. doi:10.2165/00002018-200022030-00005
6. Yelehe-Okouma M, Czmil-Garon J, Pape E, Petitpain N, Gillet P. Drug-induced aseptic meningitis: a mini-review. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2018;32(3):252-260. doi:10.1111/fcp.12349
7. Kepa L, Oczko-Grzesik B, Stolarz W, Sobala-Szczygiel B. Drug-induced aseptic meningitis in suspected central nervous system infections. J Clin Neurosci. 2005;12(5):562-564. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2004.08.024
8. Perez EE, Orange JS, Bonilla F, et al. Update on the use of immunoglobulin in human disease: a review of evidence. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(3S):S1-S46. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2016.09.023
9. Kaarthigeyan K, Burli VV. Aseptic meningitis following intravenous immunoglobulin therapy of common variable immunodeficiency. J Pediatr Neurosci. 2011;6(2):160-161. doi:10.4103/1817-1745.92858
A 35-year-old woman with a history of hypothyroidism and idiopathic small fiber autonomic and sensory neuropathy presented to the emergency department (ED) 48 hours after IV immunoglobulin (IG) infusion with a severe headache, nausea, neck stiffness, photophobia, and episodes of intense positional eye pressure. The patient reported previous episodes of headaches post-IVIG infusion but not nearly as severe. On ED arrival, the patient was afebrile with vital signs within normal limits. Initial laboratory results were notable for levels within reference range parameters: 5.9 × 109/L white blood cell (WBC) count, 13.3 g/dL hemoglobin, 38.7% hematocrit, and 279 × 109/L platelet count; there were no abnormal urinalysis findings, and she was negative for human chorionic gonadotropin.
Due to the patient’s symptoms concerning for an acute intracranial process, a brain computed tomography (CT) without contrast was ordered. The CT demonstrated no intracranial abnormalities, but the patient’s symptoms continued to worsen. The patient was started on IV fluids and 1 g IV acetaminophen and underwent a lumbar puncture (LP). Her opening pressure was elevated at 29 cm H2O (reference range, 6-20 cm), and the fluid was notably clear. During the LP, 25 mL of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was collected for laboratory analysis to include a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) panel and cultures, and a closing pressure of 12 cm H2O was recorded at the end of the procedure with the patient reporting some relief of pressure. The patient was admitted to the medicine ward for further workup and observations.The patient’s meningitis/encephalitis PCR panel detected no pathogens in the CSF, but her WBC count was 84 × 109/L (reference range, 4-11) with 30 segmented neutrophils (reference range, 0-6) and red blood cell count of 24 (reference range, 0-1); her normal glucose at 60 mg/dL (reference range, 40-70) and protein of 33 mg/dL (reference range, 15-45) were within normal parameters. Brain magnetic resonance images with and without contrast was inconsistent with any acute intracranial pathology to include subarachnoid hemorrhage or central nervous system neoplasm (Figure 1). Bacterial and fungal cultures were negative.
- What is your diagnosis?
- How would you treat this patient?

Discussion
Aseptic meningitis presents with a typical clinical picture of meningitis to include headache, stiffened neck, and photophobia. In the event of negative CSF bacterial and fungal cultures and negative viral PCR, a diagnosis of aseptic meningitis is considered.1 Though the differential for aseptic meningitis is broad, in the immunocompetent patient, the most common etiology of aseptic meningitis in the United States is by far viral, and specifically, enterovirus (50.9%). It is less commonly caused by herpes simplex virus (8.3%), varicella zoster virus, and finally, the mosquito-borne St. Louis encephalitis and West Nile viruses typically acquired in the summer or early fall months. Other infectious agents that can present with aseptic meningitis are spirochetes (Lyme disease and syphilis), tuberculous meningitis, fungal infections (cryptococcal meningitis), and other bacterial infections that have a negative culture.
The patient’s history, physical examination, vital signs, imaging, and lumbar puncture findings were most concerning for drug-induced aseptic meningitis (DIAM) secondary to her recent IVIG infusion. An algorithm can be used to work through the diagnostic approach (Figure 2).3,4
Immediate and delayed adverse reactions to IVIG are known risks for IVIG therapy. About 1% to 15% of patients who receive IVIG will experience mild immediate reactions to the infusion.6 These immediate reactions include fever (78.6%), acrocyanosis (71.4%), rash (64.3%), headache (57.1%), shortness of breath (42.8%), hypotension (35.7%), and chest pain (21.4%).
IVIG is an increasingly used biologic pharmacologic agent used for a variety of medical conditions. This can be attributed to its multifaceted properties and ability to fight infection when given as replacement therapy and provide immunomodulation in conjunction with its more well-known anti-inflammatory properties.8 The number of conditions that can potentially benefit from IVIG is so vast that the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology had to divide the indication for IVIG therapy into definitely beneficial, probably beneficial, may provide benefit, and unlikely to provide benefit categories.8
Conclusions
We encourage heightened clinical suspicion of DIAM in patients who have recently undergone IVIG infusion and present with meningeal signs (stiff neck, headache, photophobia, and ear/eye pressure) without any evidence of infection on physical examination or laboratory results. With such, we hope to improve clinician suspicion, detection, as well as patient education and outcomes in cases of DIAM.
A 35-year-old woman with a history of hypothyroidism and idiopathic small fiber autonomic and sensory neuropathy presented to the emergency department (ED) 48 hours after IV immunoglobulin (IG) infusion with a severe headache, nausea, neck stiffness, photophobia, and episodes of intense positional eye pressure. The patient reported previous episodes of headaches post-IVIG infusion but not nearly as severe. On ED arrival, the patient was afebrile with vital signs within normal limits. Initial laboratory results were notable for levels within reference range parameters: 5.9 × 109/L white blood cell (WBC) count, 13.3 g/dL hemoglobin, 38.7% hematocrit, and 279 × 109/L platelet count; there were no abnormal urinalysis findings, and she was negative for human chorionic gonadotropin.
Due to the patient’s symptoms concerning for an acute intracranial process, a brain computed tomography (CT) without contrast was ordered. The CT demonstrated no intracranial abnormalities, but the patient’s symptoms continued to worsen. The patient was started on IV fluids and 1 g IV acetaminophen and underwent a lumbar puncture (LP). Her opening pressure was elevated at 29 cm H2O (reference range, 6-20 cm), and the fluid was notably clear. During the LP, 25 mL of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was collected for laboratory analysis to include a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) panel and cultures, and a closing pressure of 12 cm H2O was recorded at the end of the procedure with the patient reporting some relief of pressure. The patient was admitted to the medicine ward for further workup and observations.The patient’s meningitis/encephalitis PCR panel detected no pathogens in the CSF, but her WBC count was 84 × 109/L (reference range, 4-11) with 30 segmented neutrophils (reference range, 0-6) and red blood cell count of 24 (reference range, 0-1); her normal glucose at 60 mg/dL (reference range, 40-70) and protein of 33 mg/dL (reference range, 15-45) were within normal parameters. Brain magnetic resonance images with and without contrast was inconsistent with any acute intracranial pathology to include subarachnoid hemorrhage or central nervous system neoplasm (Figure 1). Bacterial and fungal cultures were negative.
- What is your diagnosis?
- How would you treat this patient?

Discussion
Aseptic meningitis presents with a typical clinical picture of meningitis to include headache, stiffened neck, and photophobia. In the event of negative CSF bacterial and fungal cultures and negative viral PCR, a diagnosis of aseptic meningitis is considered.1 Though the differential for aseptic meningitis is broad, in the immunocompetent patient, the most common etiology of aseptic meningitis in the United States is by far viral, and specifically, enterovirus (50.9%). It is less commonly caused by herpes simplex virus (8.3%), varicella zoster virus, and finally, the mosquito-borne St. Louis encephalitis and West Nile viruses typically acquired in the summer or early fall months. Other infectious agents that can present with aseptic meningitis are spirochetes (Lyme disease and syphilis), tuberculous meningitis, fungal infections (cryptococcal meningitis), and other bacterial infections that have a negative culture.
The patient’s history, physical examination, vital signs, imaging, and lumbar puncture findings were most concerning for drug-induced aseptic meningitis (DIAM) secondary to her recent IVIG infusion. An algorithm can be used to work through the diagnostic approach (Figure 2).3,4
Immediate and delayed adverse reactions to IVIG are known risks for IVIG therapy. About 1% to 15% of patients who receive IVIG will experience mild immediate reactions to the infusion.6 These immediate reactions include fever (78.6%), acrocyanosis (71.4%), rash (64.3%), headache (57.1%), shortness of breath (42.8%), hypotension (35.7%), and chest pain (21.4%).
IVIG is an increasingly used biologic pharmacologic agent used for a variety of medical conditions. This can be attributed to its multifaceted properties and ability to fight infection when given as replacement therapy and provide immunomodulation in conjunction with its more well-known anti-inflammatory properties.8 The number of conditions that can potentially benefit from IVIG is so vast that the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology had to divide the indication for IVIG therapy into definitely beneficial, probably beneficial, may provide benefit, and unlikely to provide benefit categories.8
Conclusions
We encourage heightened clinical suspicion of DIAM in patients who have recently undergone IVIG infusion and present with meningeal signs (stiff neck, headache, photophobia, and ear/eye pressure) without any evidence of infection on physical examination or laboratory results. With such, we hope to improve clinician suspicion, detection, as well as patient education and outcomes in cases of DIAM.
1. Kareva L, Mironska K, Stavric K, Hasani A. Adverse reactions to intravenous immunoglobulins—our experience. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018;6(12):2359-2362. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2018.513
2. Mount HR, Boyle SD. Aseptic and bacterial meningitis: evaluation, treatment, and prevention. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96(5):314-322.
3. Seehusen DA, Reeves MM, Fomin DA. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68(6):1103-1108.
4. Connolly KJ, Hammer SM. The acute aseptic meningitis syndrome. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1990;4(4):599-622.
5. Jolles S, Sewell WA, Leighton C. Drug-induced aseptic meningitis: diagnosis and management. Drug Saf. 2000;22(3):215-226. doi:10.2165/00002018-200022030-00005
6. Yelehe-Okouma M, Czmil-Garon J, Pape E, Petitpain N, Gillet P. Drug-induced aseptic meningitis: a mini-review. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2018;32(3):252-260. doi:10.1111/fcp.12349
7. Kepa L, Oczko-Grzesik B, Stolarz W, Sobala-Szczygiel B. Drug-induced aseptic meningitis in suspected central nervous system infections. J Clin Neurosci. 2005;12(5):562-564. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2004.08.024
8. Perez EE, Orange JS, Bonilla F, et al. Update on the use of immunoglobulin in human disease: a review of evidence. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(3S):S1-S46. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2016.09.023
9. Kaarthigeyan K, Burli VV. Aseptic meningitis following intravenous immunoglobulin therapy of common variable immunodeficiency. J Pediatr Neurosci. 2011;6(2):160-161. doi:10.4103/1817-1745.92858
1. Kareva L, Mironska K, Stavric K, Hasani A. Adverse reactions to intravenous immunoglobulins—our experience. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018;6(12):2359-2362. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2018.513
2. Mount HR, Boyle SD. Aseptic and bacterial meningitis: evaluation, treatment, and prevention. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96(5):314-322.
3. Seehusen DA, Reeves MM, Fomin DA. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68(6):1103-1108.
4. Connolly KJ, Hammer SM. The acute aseptic meningitis syndrome. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1990;4(4):599-622.
5. Jolles S, Sewell WA, Leighton C. Drug-induced aseptic meningitis: diagnosis and management. Drug Saf. 2000;22(3):215-226. doi:10.2165/00002018-200022030-00005
6. Yelehe-Okouma M, Czmil-Garon J, Pape E, Petitpain N, Gillet P. Drug-induced aseptic meningitis: a mini-review. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2018;32(3):252-260. doi:10.1111/fcp.12349
7. Kepa L, Oczko-Grzesik B, Stolarz W, Sobala-Szczygiel B. Drug-induced aseptic meningitis in suspected central nervous system infections. J Clin Neurosci. 2005;12(5):562-564. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2004.08.024
8. Perez EE, Orange JS, Bonilla F, et al. Update on the use of immunoglobulin in human disease: a review of evidence. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(3S):S1-S46. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2016.09.023
9. Kaarthigeyan K, Burli VV. Aseptic meningitis following intravenous immunoglobulin therapy of common variable immunodeficiency. J Pediatr Neurosci. 2011;6(2):160-161. doi:10.4103/1817-1745.92858
HIV vaccine trial makes pivotal leap toward making ‘super antibodies’
The announcement comes from the journal Science, which published phase 1 results of a small clinical trial for a vaccine technology that aims to cause the body to create a rare kind of cell.
“At the most general level, the trial results show that one can design vaccines that induce antibodies with prespecified genetic features, and this may herald a new era of precision vaccines,” William Schief, PhD, a researcher at the Scripps Research Institute and study coauthor, told the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
The study was the first to test the approach in humans and was effective in 97% – or 35 of 36 – participants. The vaccine technology is called “germline targeting.” Trial results show that “one can design a vaccine that elicits made-to-order antibodies in humans,” Dr. Schief said in a news release.
In addition to possibly being a breakthrough for the treatment of HIV, the vaccine technology could also impact the development of treatments for flu, hepatitis C, and coronaviruses, study authors wrote.
There is no cure for HIV, but there are treatments to manage how the disease progresses. HIV attacks the body’s immune system, destroys white blood cells, and increases susceptibility to other infections, AAAS summarized. More than 1 million people in the United States and 38 million people worldwide have HIV.
Previous HIV vaccine attempts were not able to cause the production of specialized cells known as “broadly neutralizing antibodies,” CNN reported.
“Call them super antibodies, if you want,” University of Minnesota HIV researcher Timothy Schacker, MD, who was not involved in the research, told CNN. “The hope is that if you can induce this kind of immunity in people, you can protect them from some of these viruses that we’ve had a very hard time designing vaccines for that are effective. So this is an important step forward.”
Study authors said this is just the first step in the multiphase vaccine design, which so far is a theory. Further study is needed to see if the next steps also work in humans, and then if all the steps can be linked together and can be effective against HIV.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The announcement comes from the journal Science, which published phase 1 results of a small clinical trial for a vaccine technology that aims to cause the body to create a rare kind of cell.
“At the most general level, the trial results show that one can design vaccines that induce antibodies with prespecified genetic features, and this may herald a new era of precision vaccines,” William Schief, PhD, a researcher at the Scripps Research Institute and study coauthor, told the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
The study was the first to test the approach in humans and was effective in 97% – or 35 of 36 – participants. The vaccine technology is called “germline targeting.” Trial results show that “one can design a vaccine that elicits made-to-order antibodies in humans,” Dr. Schief said in a news release.
In addition to possibly being a breakthrough for the treatment of HIV, the vaccine technology could also impact the development of treatments for flu, hepatitis C, and coronaviruses, study authors wrote.
There is no cure for HIV, but there are treatments to manage how the disease progresses. HIV attacks the body’s immune system, destroys white blood cells, and increases susceptibility to other infections, AAAS summarized. More than 1 million people in the United States and 38 million people worldwide have HIV.
Previous HIV vaccine attempts were not able to cause the production of specialized cells known as “broadly neutralizing antibodies,” CNN reported.
“Call them super antibodies, if you want,” University of Minnesota HIV researcher Timothy Schacker, MD, who was not involved in the research, told CNN. “The hope is that if you can induce this kind of immunity in people, you can protect them from some of these viruses that we’ve had a very hard time designing vaccines for that are effective. So this is an important step forward.”
Study authors said this is just the first step in the multiphase vaccine design, which so far is a theory. Further study is needed to see if the next steps also work in humans, and then if all the steps can be linked together and can be effective against HIV.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The announcement comes from the journal Science, which published phase 1 results of a small clinical trial for a vaccine technology that aims to cause the body to create a rare kind of cell.
“At the most general level, the trial results show that one can design vaccines that induce antibodies with prespecified genetic features, and this may herald a new era of precision vaccines,” William Schief, PhD, a researcher at the Scripps Research Institute and study coauthor, told the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
The study was the first to test the approach in humans and was effective in 97% – or 35 of 36 – participants. The vaccine technology is called “germline targeting.” Trial results show that “one can design a vaccine that elicits made-to-order antibodies in humans,” Dr. Schief said in a news release.
In addition to possibly being a breakthrough for the treatment of HIV, the vaccine technology could also impact the development of treatments for flu, hepatitis C, and coronaviruses, study authors wrote.
There is no cure for HIV, but there are treatments to manage how the disease progresses. HIV attacks the body’s immune system, destroys white blood cells, and increases susceptibility to other infections, AAAS summarized. More than 1 million people in the United States and 38 million people worldwide have HIV.
Previous HIV vaccine attempts were not able to cause the production of specialized cells known as “broadly neutralizing antibodies,” CNN reported.
“Call them super antibodies, if you want,” University of Minnesota HIV researcher Timothy Schacker, MD, who was not involved in the research, told CNN. “The hope is that if you can induce this kind of immunity in people, you can protect them from some of these viruses that we’ve had a very hard time designing vaccines for that are effective. So this is an important step forward.”
Study authors said this is just the first step in the multiphase vaccine design, which so far is a theory. Further study is needed to see if the next steps also work in humans, and then if all the steps can be linked together and can be effective against HIV.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM SCIENCE
The new obesity breakthrough drugs
This article was originally published December 10 on Medscape editor-in-chief Eric Topol’s Substack ”Ground Truths.”
– achieving a substantial amount of weight loss without serious side effects. Many attempts to get there now fill a graveyard of failed drugs, such as fen-phen in the 1990s when a single small study of this drug combination in 121 people unleashed millions of prescriptions, some leading to serious heart valve lesions that resulted in withdrawal of the drug in 1995. The drug rimonabant, an endocannabinoid receptor blocker (think of blocking the munchies after marijuana) looked encouraging in randomized trials. However, subsequently, in a trial that I led of nearly 19,000 participants in 42 countries around the world, there was a significant excess of depression, neuropsychiatric side-effects and suicidal ideation which spelled the end of that drug’s life.
In the United States, where there had not been an antiobesity drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration since 2014, Wegovy (semaglutide), a once-weekly injection was approved in June 2021. The same drug, at a lower dose, is known as Ozempic (as in O-O-O, Ozempic, the ubiquitous commercial that you undoubtedly hear and see on TV) and had already been approved in January 2020 for improving glucose regulation in diabetes. The next drug on fast track at FDA to be imminently approved is tirzepatide (Mounjaro) following its approval for diabetes in May 2022. It is noteworthy that the discovery of these drugs for weight loss was serendipitous: they were being developed for improving glucose regulation and unexpectedly were found to achieve significant weight reduction.
Both semaglutide and tirzepatide underwent randomized, placebo-controlled trials for obesity, with marked reduction of weight as shown below. Tirzepatide at dose of 10-15 mg per week achieved greater than 20% body weight reduction. Semaglutide at a dose of 2.4 mg achieved about 17% reduction. These per cent changes in body weight are 7-9 fold more than seen with placebo (2%-3% reduction). Note: these levels of percent body-weight reduction resemble what is typically achieved with the different types of bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass.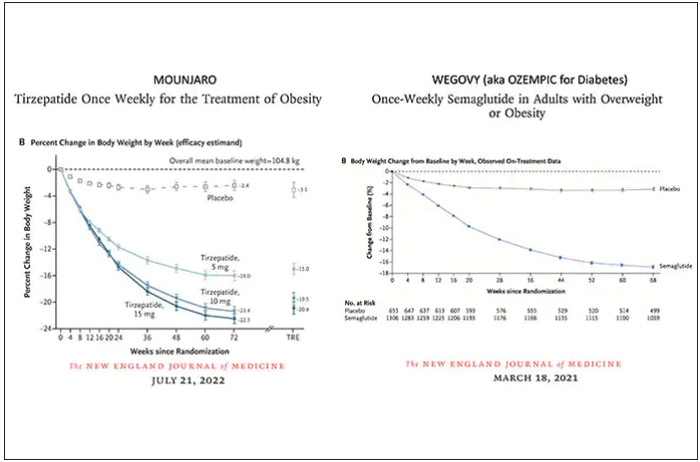
Another way to present the data for the two trials is shown here, with an edge for tirzepatide at high (10-15 mg) doses, extending to greater than 25% body-weight reduction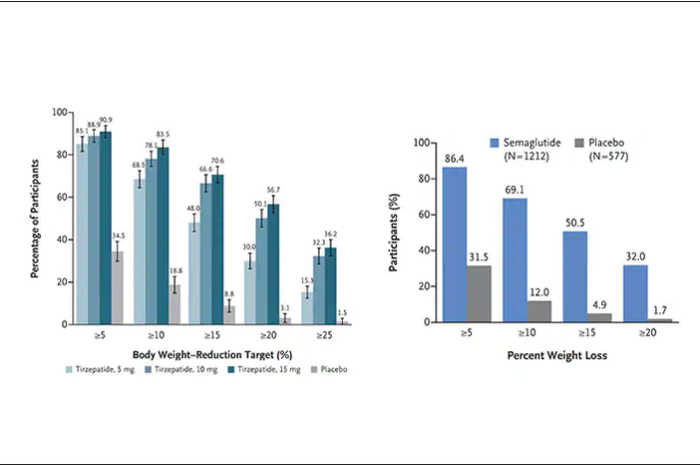
The results with semaglutide were extended to teens in a randomized trial (as shown below), and a similar trial with tirzepatide is in progress.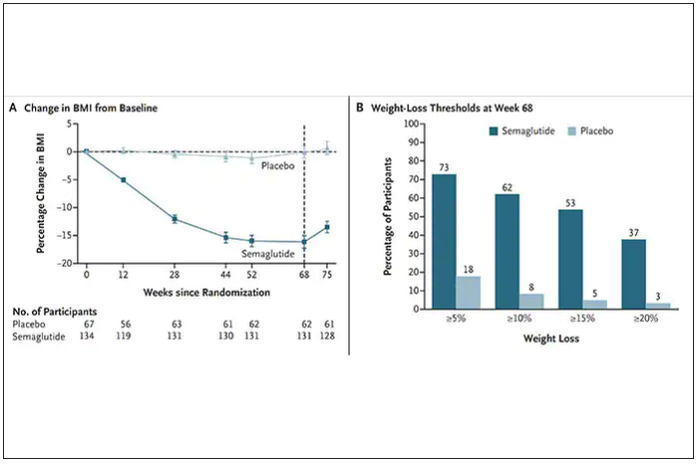
How do these drugs work?
These are peptides in the class of incretins, mimicking gut hormones that are secreted after food intake which stimulate insulin secretion.
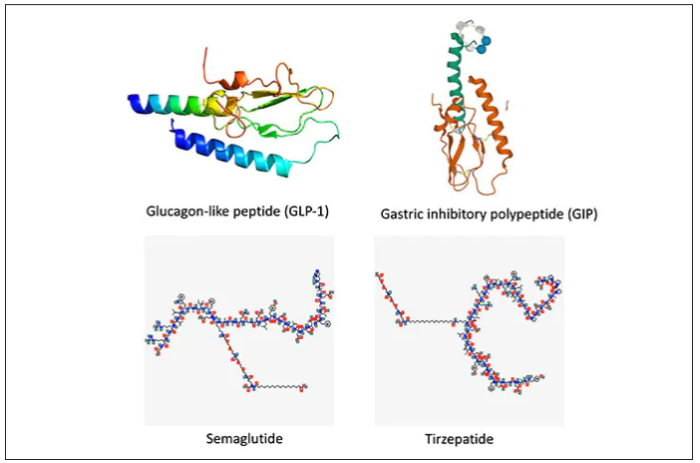
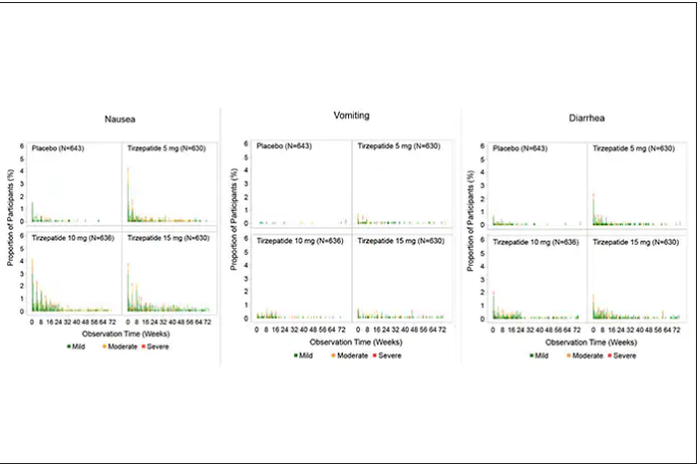
These two drugs have in common long half-lives (about 5 days), which affords once-weekly dosing, but have different mechanisms of action. Semaglutide activates (an agonist) the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor, while tirzepatide is in a new class of dual agonists: It activates (mimics) both the GLP-1 receptor and GIP receptors (Gastric inhibit polypeptide is also known as glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.) The potency of activation for tirzepatide is fivefold more for GIPR than GLP1. As seen below, there are body wide effects that include the brain, liver, pancreas, stomach, intestine, skeletal muscle and fat tissue. While their mode of action is somewhat different, their clinical effects are overlapping, which include enhancing satiety, delaying gastric emptying, increasing insulin and its sensitivity, decreasing glucagon, and, of course, reducing high glucose levels. The overlap extends to side effects of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea. Yet only 4%-6% of participants discontinued the drug in these trials, mostly owing to these GI side effects (and 1%-2% in the placebo group discontinued the study drug for the same reasons).
In randomized trials among people with type 2 diabetes, the drugs achieved hemoglobin A1c reduction of at least an absolute 2 percentage points which led to their FDA approvals (For semaglutide in January 2020, and for tirzepatide in May 2022). The edge that tirzepatide has exhibited for weight-loss reduction may be related to its dual agonist role, but the enhancement via GIP receptor activation is not fully resolved (as seen below with GIP? designation). The Amgen drug in development (AMG-133) has a marked weight loss effect but inhibits GIP rather than mimics it, clouding our precise understanding of the mechanism.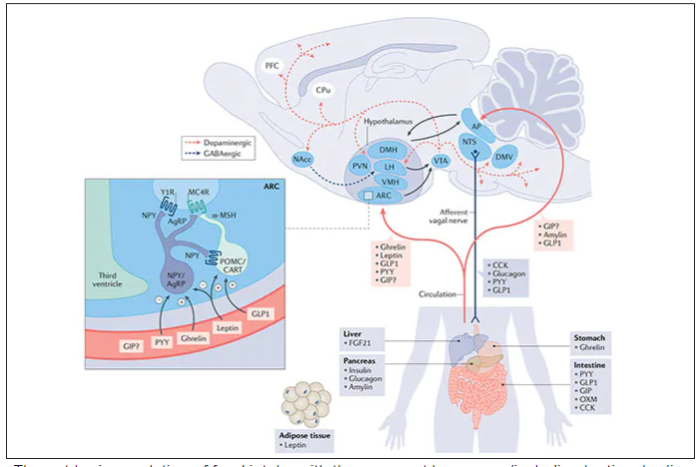
Nevertheless, when the two drugs were directly compared in a randomized trial for improving glucose regulation, tirzepatide was superior to semaglutide, as shown below. Of note, both drugs achieved very favorable effects on lipids, reducing triglycerides and LDL cholesterol and raising HDL cholesterol, along with reduction of blood pressure, an outgrowth of the indirect effect of weight reduction and direct metabolic effects of the drugs.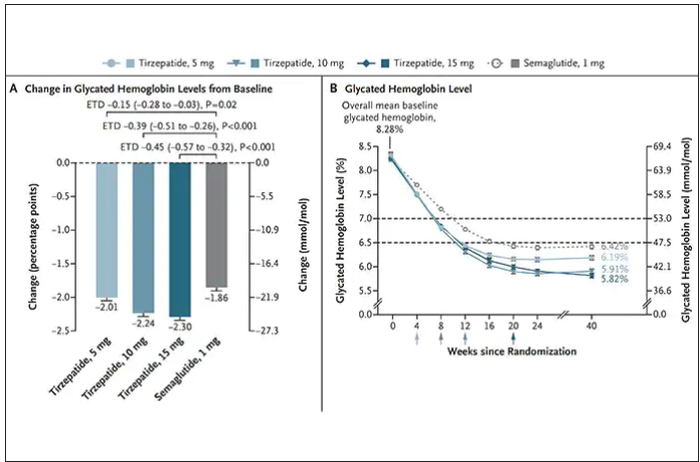
While there has been a concern about other side effects besides the GI ones noted above, review of all the trials to date in these classes of medication do not reinforce a risk of acute pancreatitis. Other rare side effects that have been noted with these drugs include allergic reactions, gallstones (which can occur with a large amount of weight loss), and potential of medullary thyroid cancer (so far only documented in rats, not people), which is why they are contraindicated in people with Type 2 multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome.
How they are given and practical considerations
For semaglutide, which has FDA approval, the indication is a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater than 27 and a weight-related medical condition (such as hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, or diabetes). To reduce the GI side effects, which mainly occur in the early dose escalation period, semaglutide is given in increasing doses by a prefilled pen by self-injection under the skin (abdomen, thigh, or arm) starting at 0.25 mg for a month and gradual increases each month reaching the maximum dose of 2.4 mg at month 5. The FDA label for dosing of tirzepatide has not been provided yet but in the weight loss trial there was a similar dose escalation from 2.5 mg up to 15 mg by month 5. The escalation is essential to reduce the frequent GI side effects, such as seen below in the tirzepatide trial.
Semaglutide is very expensive, about $1,500 per month, and not covered by Medicare. There are manufacturer starter coupons from Novo Nordisk, but that is just for the first month. These drugs have to be taken for a year to 18 months to have their full effect and without changes in lifestyle that are durable, it is likely that weight will be regained after stopping them.
What does this mean?
More than 650 million adults and 340 million children aged 5-18 are obese. The global obesity epidemic has been relentless, worsening each year, and a driver of “diabesity,” the combined dual epidemic. We now have a breakthrough class of drugs that can achieve profound weight loss equivalent to bariatric surgery, along with the side benefits of reducing cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension and hyperlipidemia), improving glucose regulation, reversing fatty liver, and the many detrimental long-term effects of obesity such as osteoarthritis and various cancers. That, in itself, is remarkable. Revolutionary.
But the downsides are also obvious. Self-injections, even though they are once a week, are not palatable for many. We have seen far more of these injectables in recent years such as the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors for hypercholesterolemia or the tumor necrosis factor blockers for autoimmune conditions. That still will not make them a popular item for such an enormous population of potential users.
That brings me to Rybelsus, the oral form of semaglutide, which is approved for glucose regulation improvement but not obesity. It effects for weight loss have been modest, compared with Wegovy (5 to 8 pounds for the 7- and 14-mg dose, respectively). But the potential for the very high efficacy of an injectable to be achievable via a pill represents an important path going forward—it could help markedly reduce the cost and uptake.
The problem of discontinuation of the drugs is big, since there are limited data and the likelihood is that the weight will be regained unless there are substantial changes in lifestyle. We know how hard it is to durably achieve such changes, along with the undesirability (and uncertainty with respect to unknown side effects) of having to take injectable drugs for many years, no less the cost of doing that.
The cost of these drugs will clearly and profoundly exacerbate inequities, since they are eminently affordable by the rich, but the need is extreme among the indigent. We’ve already seen celebrities take Wegovy for weight loss who are not obese, a window into how these drugs can and will be used without supportive data. As one physician recently observed, “Other than Viagra and Botox, I’ve seen no other medication so quickly become part of modern culture’s social vernacular.” Already there are concerns that such use is preventing access to the drugs for those who qualify and need them.
There are multiple agents in the class under development which should help increase competition and reduce cost, but they will remain expensive. There is private insurance reimbursement, often with a significant copay, for people who tightly fit the inclusion criteria. Eventual coverage by Medicare will markedly expand their use, and we can expect cost-effectiveness studies to be published showing how much saving there is for the drugs compared with bariatric surgery or not achieving the weight loss. But that doesn’t change the cost at the societal level. Even as we’ve seen with generics, which will ultimately be available, the alleviation of the cost problem isn’t what we’d hoped.
This is not unlike the recent triumphs of gene therapy, as in $3.5 million for a cure of hemophilia that just got FDA approval, but instead of a rare disease we are talking about the most common medical condition in the world. We finally get across the long sought after (what many would qualify as miraculous) goal line, but the economics collide with the uptake and real benefit.
These concerns can’t be put aside in the health inequity-laden world we live in, that will unquestionably be exacerbated. However, we cannot miss that this represents one of the most important, biggest medical breakthroughs in history. This may signify the end or marked reduction in the need for bariatric surgery. These drugs will likely become some of the most prescribed of all medications in the upcoming years. While there are many drawbacks, we shouldn’t miss such an extraordinary advance in medicine – the first real, potent and safe treatment of obesity.
Thanks for reading Ground Truths. I hope you will share these posts and subscribe, to be sure you don’t miss them.
Dr. Topol is director, Scripps Translational Science Institute; executive vice president and professor of molecular medicine at The Scripps Research Institute and senior consultant, division of cardiovascular diseases, at the Scripps Clinic, both in La Jolla, Calif. He disclosed relevant financial relationships with Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Walgreens, Quest Diagnostics, MyoKardia, and National Institutes of Health. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published December 10 on Medscape editor-in-chief Eric Topol’s Substack ”Ground Truths.”
– achieving a substantial amount of weight loss without serious side effects. Many attempts to get there now fill a graveyard of failed drugs, such as fen-phen in the 1990s when a single small study of this drug combination in 121 people unleashed millions of prescriptions, some leading to serious heart valve lesions that resulted in withdrawal of the drug in 1995. The drug rimonabant, an endocannabinoid receptor blocker (think of blocking the munchies after marijuana) looked encouraging in randomized trials. However, subsequently, in a trial that I led of nearly 19,000 participants in 42 countries around the world, there was a significant excess of depression, neuropsychiatric side-effects and suicidal ideation which spelled the end of that drug’s life.
In the United States, where there had not been an antiobesity drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration since 2014, Wegovy (semaglutide), a once-weekly injection was approved in June 2021. The same drug, at a lower dose, is known as Ozempic (as in O-O-O, Ozempic, the ubiquitous commercial that you undoubtedly hear and see on TV) and had already been approved in January 2020 for improving glucose regulation in diabetes. The next drug on fast track at FDA to be imminently approved is tirzepatide (Mounjaro) following its approval for diabetes in May 2022. It is noteworthy that the discovery of these drugs for weight loss was serendipitous: they were being developed for improving glucose regulation and unexpectedly were found to achieve significant weight reduction.
Both semaglutide and tirzepatide underwent randomized, placebo-controlled trials for obesity, with marked reduction of weight as shown below. Tirzepatide at dose of 10-15 mg per week achieved greater than 20% body weight reduction. Semaglutide at a dose of 2.4 mg achieved about 17% reduction. These per cent changes in body weight are 7-9 fold more than seen with placebo (2%-3% reduction). Note: these levels of percent body-weight reduction resemble what is typically achieved with the different types of bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass.
Another way to present the data for the two trials is shown here, with an edge for tirzepatide at high (10-15 mg) doses, extending to greater than 25% body-weight reduction
The results with semaglutide were extended to teens in a randomized trial (as shown below), and a similar trial with tirzepatide is in progress.
How do these drugs work?
These are peptides in the class of incretins, mimicking gut hormones that are secreted after food intake which stimulate insulin secretion.

These two drugs have in common long half-lives (about 5 days), which affords once-weekly dosing, but have different mechanisms of action. Semaglutide activates (an agonist) the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor, while tirzepatide is in a new class of dual agonists: It activates (mimics) both the GLP-1 receptor and GIP receptors (Gastric inhibit polypeptide is also known as glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.) The potency of activation for tirzepatide is fivefold more for GIPR than GLP1. As seen below, there are body wide effects that include the brain, liver, pancreas, stomach, intestine, skeletal muscle and fat tissue. While their mode of action is somewhat different, their clinical effects are overlapping, which include enhancing satiety, delaying gastric emptying, increasing insulin and its sensitivity, decreasing glucagon, and, of course, reducing high glucose levels. The overlap extends to side effects of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea. Yet only 4%-6% of participants discontinued the drug in these trials, mostly owing to these GI side effects (and 1%-2% in the placebo group discontinued the study drug for the same reasons).
In randomized trials among people with type 2 diabetes, the drugs achieved hemoglobin A1c reduction of at least an absolute 2 percentage points which led to their FDA approvals (For semaglutide in January 2020, and for tirzepatide in May 2022). The edge that tirzepatide has exhibited for weight-loss reduction may be related to its dual agonist role, but the enhancement via GIP receptor activation is not fully resolved (as seen below with GIP? designation). The Amgen drug in development (AMG-133) has a marked weight loss effect but inhibits GIP rather than mimics it, clouding our precise understanding of the mechanism.
Nevertheless, when the two drugs were directly compared in a randomized trial for improving glucose regulation, tirzepatide was superior to semaglutide, as shown below. Of note, both drugs achieved very favorable effects on lipids, reducing triglycerides and LDL cholesterol and raising HDL cholesterol, along with reduction of blood pressure, an outgrowth of the indirect effect of weight reduction and direct metabolic effects of the drugs.
While there has been a concern about other side effects besides the GI ones noted above, review of all the trials to date in these classes of medication do not reinforce a risk of acute pancreatitis. Other rare side effects that have been noted with these drugs include allergic reactions, gallstones (which can occur with a large amount of weight loss), and potential of medullary thyroid cancer (so far only documented in rats, not people), which is why they are contraindicated in people with Type 2 multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome.
How they are given and practical considerations
For semaglutide, which has FDA approval, the indication is a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater than 27 and a weight-related medical condition (such as hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, or diabetes). To reduce the GI side effects, which mainly occur in the early dose escalation period, semaglutide is given in increasing doses by a prefilled pen by self-injection under the skin (abdomen, thigh, or arm) starting at 0.25 mg for a month and gradual increases each month reaching the maximum dose of 2.4 mg at month 5. The FDA label for dosing of tirzepatide has not been provided yet but in the weight loss trial there was a similar dose escalation from 2.5 mg up to 15 mg by month 5. The escalation is essential to reduce the frequent GI side effects, such as seen below in the tirzepatide trial.

Semaglutide is very expensive, about $1,500 per month, and not covered by Medicare. There are manufacturer starter coupons from Novo Nordisk, but that is just for the first month. These drugs have to be taken for a year to 18 months to have their full effect and without changes in lifestyle that are durable, it is likely that weight will be regained after stopping them.
What does this mean?
More than 650 million adults and 340 million children aged 5-18 are obese. The global obesity epidemic has been relentless, worsening each year, and a driver of “diabesity,” the combined dual epidemic. We now have a breakthrough class of drugs that can achieve profound weight loss equivalent to bariatric surgery, along with the side benefits of reducing cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension and hyperlipidemia), improving glucose regulation, reversing fatty liver, and the many detrimental long-term effects of obesity such as osteoarthritis and various cancers. That, in itself, is remarkable. Revolutionary.
But the downsides are also obvious. Self-injections, even though they are once a week, are not palatable for many. We have seen far more of these injectables in recent years such as the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors for hypercholesterolemia or the tumor necrosis factor blockers for autoimmune conditions. That still will not make them a popular item for such an enormous population of potential users.
That brings me to Rybelsus, the oral form of semaglutide, which is approved for glucose regulation improvement but not obesity. It effects for weight loss have been modest, compared with Wegovy (5 to 8 pounds for the 7- and 14-mg dose, respectively). But the potential for the very high efficacy of an injectable to be achievable via a pill represents an important path going forward—it could help markedly reduce the cost and uptake.
The problem of discontinuation of the drugs is big, since there are limited data and the likelihood is that the weight will be regained unless there are substantial changes in lifestyle. We know how hard it is to durably achieve such changes, along with the undesirability (and uncertainty with respect to unknown side effects) of having to take injectable drugs for many years, no less the cost of doing that.
The cost of these drugs will clearly and profoundly exacerbate inequities, since they are eminently affordable by the rich, but the need is extreme among the indigent. We’ve already seen celebrities take Wegovy for weight loss who are not obese, a window into how these drugs can and will be used without supportive data. As one physician recently observed, “Other than Viagra and Botox, I’ve seen no other medication so quickly become part of modern culture’s social vernacular.” Already there are concerns that such use is preventing access to the drugs for those who qualify and need them.
There are multiple agents in the class under development which should help increase competition and reduce cost, but they will remain expensive. There is private insurance reimbursement, often with a significant copay, for people who tightly fit the inclusion criteria. Eventual coverage by Medicare will markedly expand their use, and we can expect cost-effectiveness studies to be published showing how much saving there is for the drugs compared with bariatric surgery or not achieving the weight loss. But that doesn’t change the cost at the societal level. Even as we’ve seen with generics, which will ultimately be available, the alleviation of the cost problem isn’t what we’d hoped.
This is not unlike the recent triumphs of gene therapy, as in $3.5 million for a cure of hemophilia that just got FDA approval, but instead of a rare disease we are talking about the most common medical condition in the world. We finally get across the long sought after (what many would qualify as miraculous) goal line, but the economics collide with the uptake and real benefit.
These concerns can’t be put aside in the health inequity-laden world we live in, that will unquestionably be exacerbated. However, we cannot miss that this represents one of the most important, biggest medical breakthroughs in history. This may signify the end or marked reduction in the need for bariatric surgery. These drugs will likely become some of the most prescribed of all medications in the upcoming years. While there are many drawbacks, we shouldn’t miss such an extraordinary advance in medicine – the first real, potent and safe treatment of obesity.
Thanks for reading Ground Truths. I hope you will share these posts and subscribe, to be sure you don’t miss them.
Dr. Topol is director, Scripps Translational Science Institute; executive vice president and professor of molecular medicine at The Scripps Research Institute and senior consultant, division of cardiovascular diseases, at the Scripps Clinic, both in La Jolla, Calif. He disclosed relevant financial relationships with Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Walgreens, Quest Diagnostics, MyoKardia, and National Institutes of Health. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published December 10 on Medscape editor-in-chief Eric Topol’s Substack ”Ground Truths.”
– achieving a substantial amount of weight loss without serious side effects. Many attempts to get there now fill a graveyard of failed drugs, such as fen-phen in the 1990s when a single small study of this drug combination in 121 people unleashed millions of prescriptions, some leading to serious heart valve lesions that resulted in withdrawal of the drug in 1995. The drug rimonabant, an endocannabinoid receptor blocker (think of blocking the munchies after marijuana) looked encouraging in randomized trials. However, subsequently, in a trial that I led of nearly 19,000 participants in 42 countries around the world, there was a significant excess of depression, neuropsychiatric side-effects and suicidal ideation which spelled the end of that drug’s life.
In the United States, where there had not been an antiobesity drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration since 2014, Wegovy (semaglutide), a once-weekly injection was approved in June 2021. The same drug, at a lower dose, is known as Ozempic (as in O-O-O, Ozempic, the ubiquitous commercial that you undoubtedly hear and see on TV) and had already been approved in January 2020 for improving glucose regulation in diabetes. The next drug on fast track at FDA to be imminently approved is tirzepatide (Mounjaro) following its approval for diabetes in May 2022. It is noteworthy that the discovery of these drugs for weight loss was serendipitous: they were being developed for improving glucose regulation and unexpectedly were found to achieve significant weight reduction.
Both semaglutide and tirzepatide underwent randomized, placebo-controlled trials for obesity, with marked reduction of weight as shown below. Tirzepatide at dose of 10-15 mg per week achieved greater than 20% body weight reduction. Semaglutide at a dose of 2.4 mg achieved about 17% reduction. These per cent changes in body weight are 7-9 fold more than seen with placebo (2%-3% reduction). Note: these levels of percent body-weight reduction resemble what is typically achieved with the different types of bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass.
Another way to present the data for the two trials is shown here, with an edge for tirzepatide at high (10-15 mg) doses, extending to greater than 25% body-weight reduction
The results with semaglutide were extended to teens in a randomized trial (as shown below), and a similar trial with tirzepatide is in progress.
How do these drugs work?
These are peptides in the class of incretins, mimicking gut hormones that are secreted after food intake which stimulate insulin secretion.

These two drugs have in common long half-lives (about 5 days), which affords once-weekly dosing, but have different mechanisms of action. Semaglutide activates (an agonist) the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor, while tirzepatide is in a new class of dual agonists: It activates (mimics) both the GLP-1 receptor and GIP receptors (Gastric inhibit polypeptide is also known as glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.) The potency of activation for tirzepatide is fivefold more for GIPR than GLP1. As seen below, there are body wide effects that include the brain, liver, pancreas, stomach, intestine, skeletal muscle and fat tissue. While their mode of action is somewhat different, their clinical effects are overlapping, which include enhancing satiety, delaying gastric emptying, increasing insulin and its sensitivity, decreasing glucagon, and, of course, reducing high glucose levels. The overlap extends to side effects of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea. Yet only 4%-6% of participants discontinued the drug in these trials, mostly owing to these GI side effects (and 1%-2% in the placebo group discontinued the study drug for the same reasons).
In randomized trials among people with type 2 diabetes, the drugs achieved hemoglobin A1c reduction of at least an absolute 2 percentage points which led to their FDA approvals (For semaglutide in January 2020, and for tirzepatide in May 2022). The edge that tirzepatide has exhibited for weight-loss reduction may be related to its dual agonist role, but the enhancement via GIP receptor activation is not fully resolved (as seen below with GIP? designation). The Amgen drug in development (AMG-133) has a marked weight loss effect but inhibits GIP rather than mimics it, clouding our precise understanding of the mechanism.
Nevertheless, when the two drugs were directly compared in a randomized trial for improving glucose regulation, tirzepatide was superior to semaglutide, as shown below. Of note, both drugs achieved very favorable effects on lipids, reducing triglycerides and LDL cholesterol and raising HDL cholesterol, along with reduction of blood pressure, an outgrowth of the indirect effect of weight reduction and direct metabolic effects of the drugs.
While there has been a concern about other side effects besides the GI ones noted above, review of all the trials to date in these classes of medication do not reinforce a risk of acute pancreatitis. Other rare side effects that have been noted with these drugs include allergic reactions, gallstones (which can occur with a large amount of weight loss), and potential of medullary thyroid cancer (so far only documented in rats, not people), which is why they are contraindicated in people with Type 2 multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome.
How they are given and practical considerations
For semaglutide, which has FDA approval, the indication is a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater than 27 and a weight-related medical condition (such as hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, or diabetes). To reduce the GI side effects, which mainly occur in the early dose escalation period, semaglutide is given in increasing doses by a prefilled pen by self-injection under the skin (abdomen, thigh, or arm) starting at 0.25 mg for a month and gradual increases each month reaching the maximum dose of 2.4 mg at month 5. The FDA label for dosing of tirzepatide has not been provided yet but in the weight loss trial there was a similar dose escalation from 2.5 mg up to 15 mg by month 5. The escalation is essential to reduce the frequent GI side effects, such as seen below in the tirzepatide trial.

Semaglutide is very expensive, about $1,500 per month, and not covered by Medicare. There are manufacturer starter coupons from Novo Nordisk, but that is just for the first month. These drugs have to be taken for a year to 18 months to have their full effect and without changes in lifestyle that are durable, it is likely that weight will be regained after stopping them.
What does this mean?
More than 650 million adults and 340 million children aged 5-18 are obese. The global obesity epidemic has been relentless, worsening each year, and a driver of “diabesity,” the combined dual epidemic. We now have a breakthrough class of drugs that can achieve profound weight loss equivalent to bariatric surgery, along with the side benefits of reducing cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension and hyperlipidemia), improving glucose regulation, reversing fatty liver, and the many detrimental long-term effects of obesity such as osteoarthritis and various cancers. That, in itself, is remarkable. Revolutionary.
But the downsides are also obvious. Self-injections, even though they are once a week, are not palatable for many. We have seen far more of these injectables in recent years such as the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors for hypercholesterolemia or the tumor necrosis factor blockers for autoimmune conditions. That still will not make them a popular item for such an enormous population of potential users.
That brings me to Rybelsus, the oral form of semaglutide, which is approved for glucose regulation improvement but not obesity. It effects for weight loss have been modest, compared with Wegovy (5 to 8 pounds for the 7- and 14-mg dose, respectively). But the potential for the very high efficacy of an injectable to be achievable via a pill represents an important path going forward—it could help markedly reduce the cost and uptake.
The problem of discontinuation of the drugs is big, since there are limited data and the likelihood is that the weight will be regained unless there are substantial changes in lifestyle. We know how hard it is to durably achieve such changes, along with the undesirability (and uncertainty with respect to unknown side effects) of having to take injectable drugs for many years, no less the cost of doing that.
The cost of these drugs will clearly and profoundly exacerbate inequities, since they are eminently affordable by the rich, but the need is extreme among the indigent. We’ve already seen celebrities take Wegovy for weight loss who are not obese, a window into how these drugs can and will be used without supportive data. As one physician recently observed, “Other than Viagra and Botox, I’ve seen no other medication so quickly become part of modern culture’s social vernacular.” Already there are concerns that such use is preventing access to the drugs for those who qualify and need them.
There are multiple agents in the class under development which should help increase competition and reduce cost, but they will remain expensive. There is private insurance reimbursement, often with a significant copay, for people who tightly fit the inclusion criteria. Eventual coverage by Medicare will markedly expand their use, and we can expect cost-effectiveness studies to be published showing how much saving there is for the drugs compared with bariatric surgery or not achieving the weight loss. But that doesn’t change the cost at the societal level. Even as we’ve seen with generics, which will ultimately be available, the alleviation of the cost problem isn’t what we’d hoped.
This is not unlike the recent triumphs of gene therapy, as in $3.5 million for a cure of hemophilia that just got FDA approval, but instead of a rare disease we are talking about the most common medical condition in the world. We finally get across the long sought after (what many would qualify as miraculous) goal line, but the economics collide with the uptake and real benefit.
These concerns can’t be put aside in the health inequity-laden world we live in, that will unquestionably be exacerbated. However, we cannot miss that this represents one of the most important, biggest medical breakthroughs in history. This may signify the end or marked reduction in the need for bariatric surgery. These drugs will likely become some of the most prescribed of all medications in the upcoming years. While there are many drawbacks, we shouldn’t miss such an extraordinary advance in medicine – the first real, potent and safe treatment of obesity.
Thanks for reading Ground Truths. I hope you will share these posts and subscribe, to be sure you don’t miss them.
Dr. Topol is director, Scripps Translational Science Institute; executive vice president and professor of molecular medicine at The Scripps Research Institute and senior consultant, division of cardiovascular diseases, at the Scripps Clinic, both in La Jolla, Calif. He disclosed relevant financial relationships with Dexcom, Illumina, Molecular Stethoscope, Walgreens, Quest Diagnostics, MyoKardia, and National Institutes of Health. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Terminally ill cancer patients struggle to access psilocybin
In March 2020, when the world was struck by the news of the COVID-19 pandemic, Erinn Baldeschwiler received her own gut punch. She was diagnosed with stage IV metastatic breast cancer and was given about 2 years to live.
Then 48, the mother of two teenagers had just started a new chapter in her life. She’d gotten divorced, moved to a new home, and left a small business she had spent 18 years cultivating. The prospect that her life story might soon be ending, that she wouldn’t see her children grow up, was a twist of fate almost too devastating to bear.
“Are you kidding me that this is happening?” she thought.
But she also wanted to keep learning and growing in her remaining years, to devote them to creating meaningful memories, contemplating her mortality, and trying to find inner peace.
“The last 2 years have kind of been this dance with Lady Death,” she said.
They have also been a dance with Lady Justice.
In March 2021, Ms. Baldeschwiler, along with Michal Bloom, who also has terminal cancer, and their palliative care physician, Sunil Aggarwal, MD, PhD, decided to sue the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) for the right to access psilocybin, the psychoactive ingredient in “magic” mushrooms.
Psilocybin-assisted therapy has been shown to help terminally ill people overcome their fear, anxiety, and despair about death and to experience the kind of peace Ms. Baldeschwiler is seeking.
Psilocybin is illegal in the United States, but the plaintiffs argue they should be able to take the substance through the Right to Try Act. The 2018 federal law says that people with life-threatening conditions who have exhausted all approved treatment options can access drugs that have not yet been approved by the Food and Drug Administration but have passed phase 1 clinical trials.
This case marks the first time patients have fought to use a Schedule I drug under the Right to Try Act.
The push to expand access to psilocybin is picking up steam in the United States. In 2023, facilitated use of psilocybin will become legal in Oregon and Colorado. Recent proposals from the Biden administration and members of Congress could make psilocybin more widely accessible in the next few years.
It is also gaining momentum outside the United States. In Canada, patients are suing the government to help patients obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy for medical purposes.
“I think what we have here is a confluence of events that are driving toward the mandatory opening of a path to access psilocybin for therapeutic use sooner rather than later,” said Kathryn Tucker, lead counsel in the case against the DEA.
Reverberations of Right to Try
The story of Right to Try began with Abigail Burroughs, who was diagnosed with head and neck cancer at age 19.
After conventional therapies failed, Ms. Burroughs’ oncologist recommended cetuximab, a drug targeting EGFR that was experimental at the time. Because the drug was available only through colon cancer trials, she was denied access.
She died in 2001 at age 21.
Ms. Burroughs’ father, Frank Burroughs, formed an organization that in 2003 sued the FDA to provide terminally ill patients access to unapproved drugs. In 2005, they lost, and subsequent attempts to appeal the decision failed.
Still, the case sparked a Right to Try movement.
“Right to Try laws swept the U.S. in a firestorm,” Ms. Tucker said.
Along with the federal law, which passed in 2018, 41 states have enacted Right to Try laws.
The movement intrigued Dr. Aggarwal, codirector of the Advanced Integrative Medical Science (AIMS) Institute in Seattle. Dr. Aggarwal had been treating patients with cannabis, and after taking psilocybin himself and finding it therapeutic, he thought Ms. Baldeschwiler could benefit.
“I always knew that the powerful medicines within Schedule I had a significant role to play in healing,” he said. “That was baked into my decision to become a doctor, to research, and to innovate.”
He applied for the right to cultivate psilocybin mushrooms, but the fungus doesn’t meet Right to Try requirements. He then found a manufacturer willing to supply synthesized psilocybin, but because it’s a Schedule I drug, the manufacturer needed an okay from the DEA.
Dr. Aggarwal joined forces with Ms. Tucker, who has spent 35 years protecting the rights of terminally ill patients. In January 2021, Ms. Tucker contacted the DEA about allowing dying patients, including Ms. Baldeschwiler and Mr. Bloom, to access psilocybin-assisted therapy.
The response, she said, was predictable.
“The DEA’s knee always jerks in the direction of no access,” Ms. Tucker said. “So it said ‘no access.’ “
The reason: In a letter dated February 2021, the DEA said it “has no authority to waive” any requirements of the Controlled Substances Act under Right to Try laws.
Suing the DEA
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker did not accept the DEA’s “no access” answer.
They decided to sue.
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker took the matter to the Ninth Circuit Court in March 2021. In January 2022, the court dismissed the case after the DEA claimed its initial denial was not final.
The following month, the plaintiffs petitioned the DEA to deliver a concrete answer.
In May, while waiting for a response, demonstrators gathered at the DEA’s headquarters to call for legal access to psilocybin. One of the protesters was Ms. Baldeschwiler, who choked back tears as she told the crowd she was likely missing her last Mother’s Day with her children to attend the event. She was arrested, along with 16 other people.
In late June, the DEA provided its final answer: No access.
In a letter addressed to Ms. Tucker, Thomas W. Prevoznik, the DEA’s deputy assistant administrator, said it “finds no basis” to reconsider its initial denial in February 2021 “because the legal and factual considerations remain unchanged.”
In an appeal, Ms. Tucker wrote: “In denying Petitioners’ requested accommodation in the Final Agency Action, DEA hides behind a smokescreen, neglecting its duty to implement the federal [Right to Try Act] and violating the state [Right to Try law].”
The government’s response is due in January 2023.
Ms. Tucker and her legal team also petitioned the DEA on behalf of Dr. Aggarwal to reschedule psilocybin from Schedule I to Schedule II.
The DEA defines Schedule I substances as “drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse.” But the FDA has designated psilocybin as a breakthrough therapy for depression, which, Ms. Tucker noted, “reflects that there is a currently accepted medical use.”
Nevertheless, in September, the DEA denied Ms. Tucker’s petition to reschedule psilocybin, and her team is now petitioning the Ninth Circuit Court for a review of that decision.
Despite the setbacks, actions from the Biden administration and members of Congress could help improve access.
In July, Senators Cory Booker and Rand Paul introduced the Right to Try Clarification Act to clarify that the federal law includes Schedule I substances. If passed, Ms. Tucker said, it would negate the DEA’s “no access” argument.
And earlier this year, the Biden administration announced plans to establish a federal task force to address the “myriad of complex issues” associated with the anticipated FDA approval of psilocybin to treat depression. The task force will explore “the potential of psychedelic-assisted therapies” to tackle the mental health crisis as well as any “risks to public health” that “may require harm reduction, risk mitigation, and safety monitoring.”
The fight north of the border
In 2016, Canadian resident Thomas Hartle, then 48, awoke from surgery for a bowel obstruction to learn he had stage IV colon cancer.
After another surgery, his doctors believed the tumors were gone. But in 2019, the cancer came back, along with extreme anxiety and distress over his impending death and how his two special-needs children would cope.
Mr. Hartle wanted to try magic mushroom–assisted psychotherapy. The Saskatoon resident sought help from TheraPsil, a Canadian nonprofit organization that advocates for therapeutic psilocybin. They applied for access under Section 56, which allows health officials to exempt patients from certain provisions of drug law.
In 2020, Hartle became the first Canadian to legally obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy.
“It has been nothing short of life changing for me,” Mr. Hartle said at a palliative care conference in Saskatoon this past June. “I am now no longer actively dying. I feel like I am genuinely actively living.”
TheraPsil has obtained Section 56 exemptions for around 60 patients to access psilocybin-assisted therapy as well as 19 health care professionals who are training to become psilocybin-assisted therapists.
But then an election ushered in new health ministers, and in early 2022, the exemptions evaporated. Thousands of patients and health care practitioners on TheraPsil’s waiting list were left in limbo.
Health Canada told CBC News that the rule change came about because “while psilocybin has shown promise in clinical trials for the treatment of some indications, further research is still needed to determine its safety and efficacy.”
As an alternative, TheraPsil began applying for access under Canada’s Special Access Program, which is similar to Right to Try laws in the United States. But Canada’s program doesn’t apply to therapists in training, and the petition process is so slow that many patients die before requests can be approved.
“People like to pretend that the Special Access Program is not political, but it is very political,” said TheraPsil’s CEO, Spencer Hawkswell. “It means a patient and a doctor are asking a politician for access to their medicine, which is absolutely unacceptable.”
Now, TheraPsil is helping patients take the Canadian government to court. In July, Mr. Hartle and seven others with conditions ranging from cancer to chronic pain filed a lawsuit against Canada’s health ministry that challenges the limited legal pathways to the use of psilocybin. The lawsuit argues that patients have a “constitutional right to access psilocybin for medicinal purposes,” and it advocates for access to regulated psilocybin products from licensed dealers, much like Canada’s medical marijuana program already does.
In the filing, TheraPsil said that as of February 2022, it has a wait-list of more than 800 patients who are requesting help in obtaining psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy.
An uncertain future
Despite the groundswell of support, many unknowns remain about the safety of expanding access to psilocybin-assisted therapy.
When Oregon and Colorado launch their psilocybin programs in 2023, the licensed centers will provide testing grounds for the safety and efficacy of broader access to psilocybin for people with depression or terminal cancer as well as those looking to grow spiritually.
Although in clinical trials psilocybin has been found to ease symptoms of depression and end-of-life demoralization for people with life-threatening conditions, it has not been adequately tested in people with a range of mental health problems, traumas, and racial backgrounds.
That uncertainty has given some people pause. In recent months, some researchers and journalists have pushed back against the frenzy over the promise of psychedelics.
In September, David Yaden, PhD, a psychedelics researcher at Johns Hopkins, spoke at the Interdisciplinary Conference on Psychedelic Research in the Netherlands. He encouraged people to pay more attention to potential adverse effects of psychedelics, which could include anything from headaches to lingering dysphoria.
“Oftentimes, we hear only the positive anecdotes,” Dr. Yaden said. “We don’t hear ... neutral or negative ones. So, I think all of those anecdotes need to be part of the picture.”
A recent piece in Wired noted that mentioning the potential harms of psychedelics amid its renaissance has been “taboo,” but the authors cautioned that as clinical trials involving psychedelics grow larger and the drugs become commercialized, “more negative outcomes are likely to transpire.”
But Ms. Baldeschwiler remains steadfast in her pursuit. While it’s important to approach broader access to psychedelics with caution, “end-of-life patients don’t have time to wait,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In March 2020, when the world was struck by the news of the COVID-19 pandemic, Erinn Baldeschwiler received her own gut punch. She was diagnosed with stage IV metastatic breast cancer and was given about 2 years to live.
Then 48, the mother of two teenagers had just started a new chapter in her life. She’d gotten divorced, moved to a new home, and left a small business she had spent 18 years cultivating. The prospect that her life story might soon be ending, that she wouldn’t see her children grow up, was a twist of fate almost too devastating to bear.
“Are you kidding me that this is happening?” she thought.
But she also wanted to keep learning and growing in her remaining years, to devote them to creating meaningful memories, contemplating her mortality, and trying to find inner peace.
“The last 2 years have kind of been this dance with Lady Death,” she said.
They have also been a dance with Lady Justice.
In March 2021, Ms. Baldeschwiler, along with Michal Bloom, who also has terminal cancer, and their palliative care physician, Sunil Aggarwal, MD, PhD, decided to sue the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) for the right to access psilocybin, the psychoactive ingredient in “magic” mushrooms.
Psilocybin-assisted therapy has been shown to help terminally ill people overcome their fear, anxiety, and despair about death and to experience the kind of peace Ms. Baldeschwiler is seeking.
Psilocybin is illegal in the United States, but the plaintiffs argue they should be able to take the substance through the Right to Try Act. The 2018 federal law says that people with life-threatening conditions who have exhausted all approved treatment options can access drugs that have not yet been approved by the Food and Drug Administration but have passed phase 1 clinical trials.
This case marks the first time patients have fought to use a Schedule I drug under the Right to Try Act.
The push to expand access to psilocybin is picking up steam in the United States. In 2023, facilitated use of psilocybin will become legal in Oregon and Colorado. Recent proposals from the Biden administration and members of Congress could make psilocybin more widely accessible in the next few years.
It is also gaining momentum outside the United States. In Canada, patients are suing the government to help patients obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy for medical purposes.
“I think what we have here is a confluence of events that are driving toward the mandatory opening of a path to access psilocybin for therapeutic use sooner rather than later,” said Kathryn Tucker, lead counsel in the case against the DEA.
Reverberations of Right to Try
The story of Right to Try began with Abigail Burroughs, who was diagnosed with head and neck cancer at age 19.
After conventional therapies failed, Ms. Burroughs’ oncologist recommended cetuximab, a drug targeting EGFR that was experimental at the time. Because the drug was available only through colon cancer trials, she was denied access.
She died in 2001 at age 21.
Ms. Burroughs’ father, Frank Burroughs, formed an organization that in 2003 sued the FDA to provide terminally ill patients access to unapproved drugs. In 2005, they lost, and subsequent attempts to appeal the decision failed.
Still, the case sparked a Right to Try movement.
“Right to Try laws swept the U.S. in a firestorm,” Ms. Tucker said.
Along with the federal law, which passed in 2018, 41 states have enacted Right to Try laws.
The movement intrigued Dr. Aggarwal, codirector of the Advanced Integrative Medical Science (AIMS) Institute in Seattle. Dr. Aggarwal had been treating patients with cannabis, and after taking psilocybin himself and finding it therapeutic, he thought Ms. Baldeschwiler could benefit.
“I always knew that the powerful medicines within Schedule I had a significant role to play in healing,” he said. “That was baked into my decision to become a doctor, to research, and to innovate.”
He applied for the right to cultivate psilocybin mushrooms, but the fungus doesn’t meet Right to Try requirements. He then found a manufacturer willing to supply synthesized psilocybin, but because it’s a Schedule I drug, the manufacturer needed an okay from the DEA.
Dr. Aggarwal joined forces with Ms. Tucker, who has spent 35 years protecting the rights of terminally ill patients. In January 2021, Ms. Tucker contacted the DEA about allowing dying patients, including Ms. Baldeschwiler and Mr. Bloom, to access psilocybin-assisted therapy.
The response, she said, was predictable.
“The DEA’s knee always jerks in the direction of no access,” Ms. Tucker said. “So it said ‘no access.’ “
The reason: In a letter dated February 2021, the DEA said it “has no authority to waive” any requirements of the Controlled Substances Act under Right to Try laws.
Suing the DEA
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker did not accept the DEA’s “no access” answer.
They decided to sue.
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker took the matter to the Ninth Circuit Court in March 2021. In January 2022, the court dismissed the case after the DEA claimed its initial denial was not final.
The following month, the plaintiffs petitioned the DEA to deliver a concrete answer.
In May, while waiting for a response, demonstrators gathered at the DEA’s headquarters to call for legal access to psilocybin. One of the protesters was Ms. Baldeschwiler, who choked back tears as she told the crowd she was likely missing her last Mother’s Day with her children to attend the event. She was arrested, along with 16 other people.
In late June, the DEA provided its final answer: No access.
In a letter addressed to Ms. Tucker, Thomas W. Prevoznik, the DEA’s deputy assistant administrator, said it “finds no basis” to reconsider its initial denial in February 2021 “because the legal and factual considerations remain unchanged.”
In an appeal, Ms. Tucker wrote: “In denying Petitioners’ requested accommodation in the Final Agency Action, DEA hides behind a smokescreen, neglecting its duty to implement the federal [Right to Try Act] and violating the state [Right to Try law].”
The government’s response is due in January 2023.
Ms. Tucker and her legal team also petitioned the DEA on behalf of Dr. Aggarwal to reschedule psilocybin from Schedule I to Schedule II.
The DEA defines Schedule I substances as “drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse.” But the FDA has designated psilocybin as a breakthrough therapy for depression, which, Ms. Tucker noted, “reflects that there is a currently accepted medical use.”
Nevertheless, in September, the DEA denied Ms. Tucker’s petition to reschedule psilocybin, and her team is now petitioning the Ninth Circuit Court for a review of that decision.
Despite the setbacks, actions from the Biden administration and members of Congress could help improve access.
In July, Senators Cory Booker and Rand Paul introduced the Right to Try Clarification Act to clarify that the federal law includes Schedule I substances. If passed, Ms. Tucker said, it would negate the DEA’s “no access” argument.
And earlier this year, the Biden administration announced plans to establish a federal task force to address the “myriad of complex issues” associated with the anticipated FDA approval of psilocybin to treat depression. The task force will explore “the potential of psychedelic-assisted therapies” to tackle the mental health crisis as well as any “risks to public health” that “may require harm reduction, risk mitigation, and safety monitoring.”
The fight north of the border
In 2016, Canadian resident Thomas Hartle, then 48, awoke from surgery for a bowel obstruction to learn he had stage IV colon cancer.
After another surgery, his doctors believed the tumors were gone. But in 2019, the cancer came back, along with extreme anxiety and distress over his impending death and how his two special-needs children would cope.
Mr. Hartle wanted to try magic mushroom–assisted psychotherapy. The Saskatoon resident sought help from TheraPsil, a Canadian nonprofit organization that advocates for therapeutic psilocybin. They applied for access under Section 56, which allows health officials to exempt patients from certain provisions of drug law.
In 2020, Hartle became the first Canadian to legally obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy.
“It has been nothing short of life changing for me,” Mr. Hartle said at a palliative care conference in Saskatoon this past June. “I am now no longer actively dying. I feel like I am genuinely actively living.”
TheraPsil has obtained Section 56 exemptions for around 60 patients to access psilocybin-assisted therapy as well as 19 health care professionals who are training to become psilocybin-assisted therapists.
But then an election ushered in new health ministers, and in early 2022, the exemptions evaporated. Thousands of patients and health care practitioners on TheraPsil’s waiting list were left in limbo.
Health Canada told CBC News that the rule change came about because “while psilocybin has shown promise in clinical trials for the treatment of some indications, further research is still needed to determine its safety and efficacy.”
As an alternative, TheraPsil began applying for access under Canada’s Special Access Program, which is similar to Right to Try laws in the United States. But Canada’s program doesn’t apply to therapists in training, and the petition process is so slow that many patients die before requests can be approved.
“People like to pretend that the Special Access Program is not political, but it is very political,” said TheraPsil’s CEO, Spencer Hawkswell. “It means a patient and a doctor are asking a politician for access to their medicine, which is absolutely unacceptable.”
Now, TheraPsil is helping patients take the Canadian government to court. In July, Mr. Hartle and seven others with conditions ranging from cancer to chronic pain filed a lawsuit against Canada’s health ministry that challenges the limited legal pathways to the use of psilocybin. The lawsuit argues that patients have a “constitutional right to access psilocybin for medicinal purposes,” and it advocates for access to regulated psilocybin products from licensed dealers, much like Canada’s medical marijuana program already does.
In the filing, TheraPsil said that as of February 2022, it has a wait-list of more than 800 patients who are requesting help in obtaining psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy.
An uncertain future
Despite the groundswell of support, many unknowns remain about the safety of expanding access to psilocybin-assisted therapy.
When Oregon and Colorado launch their psilocybin programs in 2023, the licensed centers will provide testing grounds for the safety and efficacy of broader access to psilocybin for people with depression or terminal cancer as well as those looking to grow spiritually.
Although in clinical trials psilocybin has been found to ease symptoms of depression and end-of-life demoralization for people with life-threatening conditions, it has not been adequately tested in people with a range of mental health problems, traumas, and racial backgrounds.
That uncertainty has given some people pause. In recent months, some researchers and journalists have pushed back against the frenzy over the promise of psychedelics.
In September, David Yaden, PhD, a psychedelics researcher at Johns Hopkins, spoke at the Interdisciplinary Conference on Psychedelic Research in the Netherlands. He encouraged people to pay more attention to potential adverse effects of psychedelics, which could include anything from headaches to lingering dysphoria.
“Oftentimes, we hear only the positive anecdotes,” Dr. Yaden said. “We don’t hear ... neutral or negative ones. So, I think all of those anecdotes need to be part of the picture.”
A recent piece in Wired noted that mentioning the potential harms of psychedelics amid its renaissance has been “taboo,” but the authors cautioned that as clinical trials involving psychedelics grow larger and the drugs become commercialized, “more negative outcomes are likely to transpire.”
But Ms. Baldeschwiler remains steadfast in her pursuit. While it’s important to approach broader access to psychedelics with caution, “end-of-life patients don’t have time to wait,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In March 2020, when the world was struck by the news of the COVID-19 pandemic, Erinn Baldeschwiler received her own gut punch. She was diagnosed with stage IV metastatic breast cancer and was given about 2 years to live.
Then 48, the mother of two teenagers had just started a new chapter in her life. She’d gotten divorced, moved to a new home, and left a small business she had spent 18 years cultivating. The prospect that her life story might soon be ending, that she wouldn’t see her children grow up, was a twist of fate almost too devastating to bear.
“Are you kidding me that this is happening?” she thought.
But she also wanted to keep learning and growing in her remaining years, to devote them to creating meaningful memories, contemplating her mortality, and trying to find inner peace.
“The last 2 years have kind of been this dance with Lady Death,” she said.
They have also been a dance with Lady Justice.
In March 2021, Ms. Baldeschwiler, along with Michal Bloom, who also has terminal cancer, and their palliative care physician, Sunil Aggarwal, MD, PhD, decided to sue the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) for the right to access psilocybin, the psychoactive ingredient in “magic” mushrooms.
Psilocybin-assisted therapy has been shown to help terminally ill people overcome their fear, anxiety, and despair about death and to experience the kind of peace Ms. Baldeschwiler is seeking.
Psilocybin is illegal in the United States, but the plaintiffs argue they should be able to take the substance through the Right to Try Act. The 2018 federal law says that people with life-threatening conditions who have exhausted all approved treatment options can access drugs that have not yet been approved by the Food and Drug Administration but have passed phase 1 clinical trials.
This case marks the first time patients have fought to use a Schedule I drug under the Right to Try Act.
The push to expand access to psilocybin is picking up steam in the United States. In 2023, facilitated use of psilocybin will become legal in Oregon and Colorado. Recent proposals from the Biden administration and members of Congress could make psilocybin more widely accessible in the next few years.
It is also gaining momentum outside the United States. In Canada, patients are suing the government to help patients obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy for medical purposes.
“I think what we have here is a confluence of events that are driving toward the mandatory opening of a path to access psilocybin for therapeutic use sooner rather than later,” said Kathryn Tucker, lead counsel in the case against the DEA.
Reverberations of Right to Try
The story of Right to Try began with Abigail Burroughs, who was diagnosed with head and neck cancer at age 19.
After conventional therapies failed, Ms. Burroughs’ oncologist recommended cetuximab, a drug targeting EGFR that was experimental at the time. Because the drug was available only through colon cancer trials, she was denied access.
She died in 2001 at age 21.
Ms. Burroughs’ father, Frank Burroughs, formed an organization that in 2003 sued the FDA to provide terminally ill patients access to unapproved drugs. In 2005, they lost, and subsequent attempts to appeal the decision failed.
Still, the case sparked a Right to Try movement.
“Right to Try laws swept the U.S. in a firestorm,” Ms. Tucker said.
Along with the federal law, which passed in 2018, 41 states have enacted Right to Try laws.
The movement intrigued Dr. Aggarwal, codirector of the Advanced Integrative Medical Science (AIMS) Institute in Seattle. Dr. Aggarwal had been treating patients with cannabis, and after taking psilocybin himself and finding it therapeutic, he thought Ms. Baldeschwiler could benefit.
“I always knew that the powerful medicines within Schedule I had a significant role to play in healing,” he said. “That was baked into my decision to become a doctor, to research, and to innovate.”
He applied for the right to cultivate psilocybin mushrooms, but the fungus doesn’t meet Right to Try requirements. He then found a manufacturer willing to supply synthesized psilocybin, but because it’s a Schedule I drug, the manufacturer needed an okay from the DEA.
Dr. Aggarwal joined forces with Ms. Tucker, who has spent 35 years protecting the rights of terminally ill patients. In January 2021, Ms. Tucker contacted the DEA about allowing dying patients, including Ms. Baldeschwiler and Mr. Bloom, to access psilocybin-assisted therapy.
The response, she said, was predictable.
“The DEA’s knee always jerks in the direction of no access,” Ms. Tucker said. “So it said ‘no access.’ “
The reason: In a letter dated February 2021, the DEA said it “has no authority to waive” any requirements of the Controlled Substances Act under Right to Try laws.
Suing the DEA
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker did not accept the DEA’s “no access” answer.
They decided to sue.
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker took the matter to the Ninth Circuit Court in March 2021. In January 2022, the court dismissed the case after the DEA claimed its initial denial was not final.
The following month, the plaintiffs petitioned the DEA to deliver a concrete answer.
In May, while waiting for a response, demonstrators gathered at the DEA’s headquarters to call for legal access to psilocybin. One of the protesters was Ms. Baldeschwiler, who choked back tears as she told the crowd she was likely missing her last Mother’s Day with her children to attend the event. She was arrested, along with 16 other people.
In late June, the DEA provided its final answer: No access.
In a letter addressed to Ms. Tucker, Thomas W. Prevoznik, the DEA’s deputy assistant administrator, said it “finds no basis” to reconsider its initial denial in February 2021 “because the legal and factual considerations remain unchanged.”
In an appeal, Ms. Tucker wrote: “In denying Petitioners’ requested accommodation in the Final Agency Action, DEA hides behind a smokescreen, neglecting its duty to implement the federal [Right to Try Act] and violating the state [Right to Try law].”
The government’s response is due in January 2023.
Ms. Tucker and her legal team also petitioned the DEA on behalf of Dr. Aggarwal to reschedule psilocybin from Schedule I to Schedule II.
The DEA defines Schedule I substances as “drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse.” But the FDA has designated psilocybin as a breakthrough therapy for depression, which, Ms. Tucker noted, “reflects that there is a currently accepted medical use.”
Nevertheless, in September, the DEA denied Ms. Tucker’s petition to reschedule psilocybin, and her team is now petitioning the Ninth Circuit Court for a review of that decision.
Despite the setbacks, actions from the Biden administration and members of Congress could help improve access.
In July, Senators Cory Booker and Rand Paul introduced the Right to Try Clarification Act to clarify that the federal law includes Schedule I substances. If passed, Ms. Tucker said, it would negate the DEA’s “no access” argument.
And earlier this year, the Biden administration announced plans to establish a federal task force to address the “myriad of complex issues” associated with the anticipated FDA approval of psilocybin to treat depression. The task force will explore “the potential of psychedelic-assisted therapies” to tackle the mental health crisis as well as any “risks to public health” that “may require harm reduction, risk mitigation, and safety monitoring.”
The fight north of the border
In 2016, Canadian resident Thomas Hartle, then 48, awoke from surgery for a bowel obstruction to learn he had stage IV colon cancer.
After another surgery, his doctors believed the tumors were gone. But in 2019, the cancer came back, along with extreme anxiety and distress over his impending death and how his two special-needs children would cope.
Mr. Hartle wanted to try magic mushroom–assisted psychotherapy. The Saskatoon resident sought help from TheraPsil, a Canadian nonprofit organization that advocates for therapeutic psilocybin. They applied for access under Section 56, which allows health officials to exempt patients from certain provisions of drug law.
In 2020, Hartle became the first Canadian to legally obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy.
“It has been nothing short of life changing for me,” Mr. Hartle said at a palliative care conference in Saskatoon this past June. “I am now no longer actively dying. I feel like I am genuinely actively living.”
TheraPsil has obtained Section 56 exemptions for around 60 patients to access psilocybin-assisted therapy as well as 19 health care professionals who are training to become psilocybin-assisted therapists.
But then an election ushered in new health ministers, and in early 2022, the exemptions evaporated. Thousands of patients and health care practitioners on TheraPsil’s waiting list were left in limbo.
Health Canada told CBC News that the rule change came about because “while psilocybin has shown promise in clinical trials for the treatment of some indications, further research is still needed to determine its safety and efficacy.”
As an alternative, TheraPsil began applying for access under Canada’s Special Access Program, which is similar to Right to Try laws in the United States. But Canada’s program doesn’t apply to therapists in training, and the petition process is so slow that many patients die before requests can be approved.
“People like to pretend that the Special Access Program is not political, but it is very political,” said TheraPsil’s CEO, Spencer Hawkswell. “It means a patient and a doctor are asking a politician for access to their medicine, which is absolutely unacceptable.”
Now, TheraPsil is helping patients take the Canadian government to court. In July, Mr. Hartle and seven others with conditions ranging from cancer to chronic pain filed a lawsuit against Canada’s health ministry that challenges the limited legal pathways to the use of psilocybin. The lawsuit argues that patients have a “constitutional right to access psilocybin for medicinal purposes,” and it advocates for access to regulated psilocybin products from licensed dealers, much like Canada’s medical marijuana program already does.
In the filing, TheraPsil said that as of February 2022, it has a wait-list of more than 800 patients who are requesting help in obtaining psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy.
An uncertain future
Despite the groundswell of support, many unknowns remain about the safety of expanding access to psilocybin-assisted therapy.
When Oregon and Colorado launch their psilocybin programs in 2023, the licensed centers will provide testing grounds for the safety and efficacy of broader access to psilocybin for people with depression or terminal cancer as well as those looking to grow spiritually.
Although in clinical trials psilocybin has been found to ease symptoms of depression and end-of-life demoralization for people with life-threatening conditions, it has not been adequately tested in people with a range of mental health problems, traumas, and racial backgrounds.
That uncertainty has given some people pause. In recent months, some researchers and journalists have pushed back against the frenzy over the promise of psychedelics.
In September, David Yaden, PhD, a psychedelics researcher at Johns Hopkins, spoke at the Interdisciplinary Conference on Psychedelic Research in the Netherlands. He encouraged people to pay more attention to potential adverse effects of psychedelics, which could include anything from headaches to lingering dysphoria.
“Oftentimes, we hear only the positive anecdotes,” Dr. Yaden said. “We don’t hear ... neutral or negative ones. So, I think all of those anecdotes need to be part of the picture.”
A recent piece in Wired noted that mentioning the potential harms of psychedelics amid its renaissance has been “taboo,” but the authors cautioned that as clinical trials involving psychedelics grow larger and the drugs become commercialized, “more negative outcomes are likely to transpire.”
But Ms. Baldeschwiler remains steadfast in her pursuit. While it’s important to approach broader access to psychedelics with caution, “end-of-life patients don’t have time to wait,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Direct-acting antivirals tied to better outcomes in chronic Hep C
Eiichi Ogawa, MD, PhD, with the department of general internal medicine, Kyushu University Hospital in Fukuoka, Japan, led the retrospective study of 245,596 adults with CHC. In the new research, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the authors analyzed data from the Optum Clinformatics Data Mart (CDM) database, 2010-2021.
It was important to do the study because of limited and conflicting information – mostly from case reports – on safety of the DAAs when they were approved for CHC in 2014, said coauthor Mindie H. Nguyen, MD, in an interview.
‘DAA treatment is safe’
“The main message is that DAA treatment is safe,” said Dr. Nguyen, of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center in Palo Alto. In the early days of treatment, physicians were treating the sickest patients with the DAAs, which may have introduced patient selection bias and caused lasting misperceptions about poor safety, she noted.
“I really hope to dispel this myth,” she said, adding that this study also shows improved liver and nonliver outcomes.
Of the total cohort in this study, 40,654 patients had one or more prescriptions for a DAA (without interferon) and 204,942 patients had not been treated.
All-cause mortality reduced by 57%
DAA treatment, vs. no treatment, was linked with a large and significant reduction (57%) in all-cause mortality. That finding was particularly notable, because it was seen regardless of age, sex, race and ethnicity, comorbidities, alcohol use, and presence of hepatocellular carcinoma or cirrhosis.
The authors noted that patients without cirrhosis are a population previously considered to receive less benefit from an HCV cure than patients with cirrhosis.
DAAs were associated with lower risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensation as well as risk of nonliver outcomes, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Lower risk of poor nonliver outcomes
The researchers found that when they compared DAA-treated patients with untreated patients, the incidences per 1,000 person-years of having diabetes were 30.2 vs. 37.2 (P less than .001), and of having kidney disease was 31.1 vs. 34.1 (P less than .001), respectively.
“This retrospective cohort study provides valuable information to physicians,” Noel Deep, MD, chief medical officer at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo, Wis., said, in an interview.
The study’s size helps confirm DAAs’ safety and benefit, and previously unknown added benefits, in treating CHC, he continued.
Large study confirms, introduces DAA benefits
Dr. Deep, who was not part of the study, noted that DAAs now show much promise in efficacy and tolerability in most people with chronic hepatitis C, including those with concomitant conditions such as CKD.
“Previous studies did not have such large-scale nationwide data. [The findings of the new study] greatly enhance our knowledge of DAA treatment for chronic hepatitis C patients across the spectrum from noncirrhotic to compensated cirrhotic to decompensated cirrhotic,” Dr. Deep said. “The added benefit of improved outcomes for diabetes, CVD, CKD, and nonliver cancers truly surprised me.”
Dr. Deep pointed out some limitations of the study, including that, as the authors acknowledge, only privately insured patients were included so results may not be generalizable to the underinsured/uninsured “who might have other risk factors, poorer health, and fewer resources.”
He added: “The data also may not be reflective of the outcomes in Asians who were, in my opinion, also underrepresented in this study.”
The authors cited the insurance claims database they used as a strength of the study, due to it containing information on 61 million people from across all regions of the United States.
Dr. Ogawa reports grants from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Nguyen reports institutional grants and advisory board fees from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Another coauthor reports speaking/consulting fees from Gilead and Merck Sharp & Dohme outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
The Stanford Center for Population Health Sciences (PHS) supported this study by providing access to the PHS Data Core.
Dr. Deep reports no relevant financial relationships. He serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Eiichi Ogawa, MD, PhD, with the department of general internal medicine, Kyushu University Hospital in Fukuoka, Japan, led the retrospective study of 245,596 adults with CHC. In the new research, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the authors analyzed data from the Optum Clinformatics Data Mart (CDM) database, 2010-2021.
It was important to do the study because of limited and conflicting information – mostly from case reports – on safety of the DAAs when they were approved for CHC in 2014, said coauthor Mindie H. Nguyen, MD, in an interview.
‘DAA treatment is safe’
“The main message is that DAA treatment is safe,” said Dr. Nguyen, of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center in Palo Alto. In the early days of treatment, physicians were treating the sickest patients with the DAAs, which may have introduced patient selection bias and caused lasting misperceptions about poor safety, she noted.
“I really hope to dispel this myth,” she said, adding that this study also shows improved liver and nonliver outcomes.
Of the total cohort in this study, 40,654 patients had one or more prescriptions for a DAA (without interferon) and 204,942 patients had not been treated.
All-cause mortality reduced by 57%
DAA treatment, vs. no treatment, was linked with a large and significant reduction (57%) in all-cause mortality. That finding was particularly notable, because it was seen regardless of age, sex, race and ethnicity, comorbidities, alcohol use, and presence of hepatocellular carcinoma or cirrhosis.
The authors noted that patients without cirrhosis are a population previously considered to receive less benefit from an HCV cure than patients with cirrhosis.
DAAs were associated with lower risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensation as well as risk of nonliver outcomes, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Lower risk of poor nonliver outcomes
The researchers found that when they compared DAA-treated patients with untreated patients, the incidences per 1,000 person-years of having diabetes were 30.2 vs. 37.2 (P less than .001), and of having kidney disease was 31.1 vs. 34.1 (P less than .001), respectively.
“This retrospective cohort study provides valuable information to physicians,” Noel Deep, MD, chief medical officer at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo, Wis., said, in an interview.
The study’s size helps confirm DAAs’ safety and benefit, and previously unknown added benefits, in treating CHC, he continued.
Large study confirms, introduces DAA benefits
Dr. Deep, who was not part of the study, noted that DAAs now show much promise in efficacy and tolerability in most people with chronic hepatitis C, including those with concomitant conditions such as CKD.
“Previous studies did not have such large-scale nationwide data. [The findings of the new study] greatly enhance our knowledge of DAA treatment for chronic hepatitis C patients across the spectrum from noncirrhotic to compensated cirrhotic to decompensated cirrhotic,” Dr. Deep said. “The added benefit of improved outcomes for diabetes, CVD, CKD, and nonliver cancers truly surprised me.”
Dr. Deep pointed out some limitations of the study, including that, as the authors acknowledge, only privately insured patients were included so results may not be generalizable to the underinsured/uninsured “who might have other risk factors, poorer health, and fewer resources.”
He added: “The data also may not be reflective of the outcomes in Asians who were, in my opinion, also underrepresented in this study.”
The authors cited the insurance claims database they used as a strength of the study, due to it containing information on 61 million people from across all regions of the United States.
Dr. Ogawa reports grants from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Nguyen reports institutional grants and advisory board fees from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Another coauthor reports speaking/consulting fees from Gilead and Merck Sharp & Dohme outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
The Stanford Center for Population Health Sciences (PHS) supported this study by providing access to the PHS Data Core.
Dr. Deep reports no relevant financial relationships. He serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Eiichi Ogawa, MD, PhD, with the department of general internal medicine, Kyushu University Hospital in Fukuoka, Japan, led the retrospective study of 245,596 adults with CHC. In the new research, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the authors analyzed data from the Optum Clinformatics Data Mart (CDM) database, 2010-2021.
It was important to do the study because of limited and conflicting information – mostly from case reports – on safety of the DAAs when they were approved for CHC in 2014, said coauthor Mindie H. Nguyen, MD, in an interview.
‘DAA treatment is safe’
“The main message is that DAA treatment is safe,” said Dr. Nguyen, of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center in Palo Alto. In the early days of treatment, physicians were treating the sickest patients with the DAAs, which may have introduced patient selection bias and caused lasting misperceptions about poor safety, she noted.
“I really hope to dispel this myth,” she said, adding that this study also shows improved liver and nonliver outcomes.
Of the total cohort in this study, 40,654 patients had one or more prescriptions for a DAA (without interferon) and 204,942 patients had not been treated.
All-cause mortality reduced by 57%
DAA treatment, vs. no treatment, was linked with a large and significant reduction (57%) in all-cause mortality. That finding was particularly notable, because it was seen regardless of age, sex, race and ethnicity, comorbidities, alcohol use, and presence of hepatocellular carcinoma or cirrhosis.
The authors noted that patients without cirrhosis are a population previously considered to receive less benefit from an HCV cure than patients with cirrhosis.
DAAs were associated with lower risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensation as well as risk of nonliver outcomes, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Lower risk of poor nonliver outcomes
The researchers found that when they compared DAA-treated patients with untreated patients, the incidences per 1,000 person-years of having diabetes were 30.2 vs. 37.2 (P less than .001), and of having kidney disease was 31.1 vs. 34.1 (P less than .001), respectively.
“This retrospective cohort study provides valuable information to physicians,” Noel Deep, MD, chief medical officer at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo, Wis., said, in an interview.
The study’s size helps confirm DAAs’ safety and benefit, and previously unknown added benefits, in treating CHC, he continued.
Large study confirms, introduces DAA benefits
Dr. Deep, who was not part of the study, noted that DAAs now show much promise in efficacy and tolerability in most people with chronic hepatitis C, including those with concomitant conditions such as CKD.
“Previous studies did not have such large-scale nationwide data. [The findings of the new study] greatly enhance our knowledge of DAA treatment for chronic hepatitis C patients across the spectrum from noncirrhotic to compensated cirrhotic to decompensated cirrhotic,” Dr. Deep said. “The added benefit of improved outcomes for diabetes, CVD, CKD, and nonliver cancers truly surprised me.”
Dr. Deep pointed out some limitations of the study, including that, as the authors acknowledge, only privately insured patients were included so results may not be generalizable to the underinsured/uninsured “who might have other risk factors, poorer health, and fewer resources.”
He added: “The data also may not be reflective of the outcomes in Asians who were, in my opinion, also underrepresented in this study.”
The authors cited the insurance claims database they used as a strength of the study, due to it containing information on 61 million people from across all regions of the United States.
Dr. Ogawa reports grants from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Nguyen reports institutional grants and advisory board fees from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Another coauthor reports speaking/consulting fees from Gilead and Merck Sharp & Dohme outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
The Stanford Center for Population Health Sciences (PHS) supported this study by providing access to the PHS Data Core.
Dr. Deep reports no relevant financial relationships. He serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
SSRI tied to improved cognition in comorbid depression, dementia
The results of the 12-week open-label, single-group study are positive, study investigator Michael Cronquist Christensen, MPA, DrPH, a director with the Lundbeck pharmaceutical company, told this news organization before presenting the results in a poster at the 15th Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease conference.
“The study confirms earlier findings of improvement in both depressive symptoms and cognitive performance with vortioxetine in patients with depression and dementia and adds to this research that these clinical effects also extend to improvement in health-related quality of life and patients’ daily functioning,” Dr. Christensen said.
“It also demonstrates that patients with depression and comorbid dementia can be safely treated with 20 mg vortioxetine – starting dose of 5 mg for the first week and up-titration to 10 mg at day 8,” he added.
However, he reported that Lundbeck doesn’t plan to seek approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for a new indication. Vortioxetine received FDA approval in 2013 to treat MDD, but 3 years later the agency rejected an expansion of its indication to include cognitive dysfunction.
“Vortioxetine is approved for MDD, but the product can be used in patients with MDD who have other diseases, including other mental illnesses,” Dr. Christensen said.
Potential neurotransmission modulator
Vortioxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and serotonin receptor modulator. According to Dr. Christensen, evidence suggests the drug’s receptor targets “have the potential to modulate neurotransmitter systems that are essential for regulation of cognitive function.”
The researchers recruited 83 individuals aged 55-85 with recurrent MDD that had started before the age of 55. All had MDD episodes within the previous 6 months and comorbid dementia for at least 6 months.
Of the participants, 65.9% were female. In addition, 42.7% had Alzheimer’s disease, 26.8% had mixed-type dementia, and the rest had other types of dementia.
The daily oral dose of vortioxetine started at 5 mg for up to week 1 and then was increased to 10 mg. It was then increased to 20 mg or decreased to 5 mg “based on investigator judgment and patient response.” The average daily dose was 12.3 mg.
In regard to the primary outcome, at week 12 (n = 70), scores on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) fell by a mean of –12.4 (.78, P < .0001), which researchers deemed to be a significant reduction in severe symptoms.
“A significant and clinically meaningful effect was observed from week 1,” the researchers reported.
“As a basis for comparison, we typically see an improvement around 13-14 points during 8 weeks of antidepressant treatment in adults with MDD who do not have dementia,” Dr. Christensen added.
More than a third of patients (35.7%) saw a reduction in MADRS score by more than 50% at week 12, and 17.2% were considered to have reached MDD depression remission, defined as a MADRS score at or under 10.
For secondary outcomes, the total Digit Symbol Substitution test score grew by 0.65 (standardized effect size) by week 12, showing significant improvement (P < .0001). In addition, participants improved on some other cognitive measures, and Dr. Christensen noted that “significant improvement was also observed in the patients’ health-related quality of life and daily functioning.”
A third of patients had drug-related treatment-emergent adverse events.
Vortioxetine is one of the most expensive antidepressants: It has a list price of $444 a month, and no generic version is currently available.
Small trial, open-label design
In a comment, Claire Sexton, DPhil, senior director of scientific programs and outreach at the Alzheimer’s Association, said the study “reflects a valuable aspect of treatment research because of the close connection between depression and dementia. Depression is a known risk factor for dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, and those who have dementia may experience depression.”
She cautioned, however, that the trial was small and had an open-label design instead of the “gold standard” of a double-blinded trial with a control group.
The study was funded by Lundbeck, where Dr. Christensen is an employee. Another author is a Lundbeck employee, and a third author reported various disclosures. Dr. Sexton reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The results of the 12-week open-label, single-group study are positive, study investigator Michael Cronquist Christensen, MPA, DrPH, a director with the Lundbeck pharmaceutical company, told this news organization before presenting the results in a poster at the 15th Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease conference.
“The study confirms earlier findings of improvement in both depressive symptoms and cognitive performance with vortioxetine in patients with depression and dementia and adds to this research that these clinical effects also extend to improvement in health-related quality of life and patients’ daily functioning,” Dr. Christensen said.
“It also demonstrates that patients with depression and comorbid dementia can be safely treated with 20 mg vortioxetine – starting dose of 5 mg for the first week and up-titration to 10 mg at day 8,” he added.
However, he reported that Lundbeck doesn’t plan to seek approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for a new indication. Vortioxetine received FDA approval in 2013 to treat MDD, but 3 years later the agency rejected an expansion of its indication to include cognitive dysfunction.
“Vortioxetine is approved for MDD, but the product can be used in patients with MDD who have other diseases, including other mental illnesses,” Dr. Christensen said.
Potential neurotransmission modulator
Vortioxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and serotonin receptor modulator. According to Dr. Christensen, evidence suggests the drug’s receptor targets “have the potential to modulate neurotransmitter systems that are essential for regulation of cognitive function.”
The researchers recruited 83 individuals aged 55-85 with recurrent MDD that had started before the age of 55. All had MDD episodes within the previous 6 months and comorbid dementia for at least 6 months.
Of the participants, 65.9% were female. In addition, 42.7% had Alzheimer’s disease, 26.8% had mixed-type dementia, and the rest had other types of dementia.
The daily oral dose of vortioxetine started at 5 mg for up to week 1 and then was increased to 10 mg. It was then increased to 20 mg or decreased to 5 mg “based on investigator judgment and patient response.” The average daily dose was 12.3 mg.
In regard to the primary outcome, at week 12 (n = 70), scores on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) fell by a mean of –12.4 (.78, P < .0001), which researchers deemed to be a significant reduction in severe symptoms.
“A significant and clinically meaningful effect was observed from week 1,” the researchers reported.
“As a basis for comparison, we typically see an improvement around 13-14 points during 8 weeks of antidepressant treatment in adults with MDD who do not have dementia,” Dr. Christensen added.
More than a third of patients (35.7%) saw a reduction in MADRS score by more than 50% at week 12, and 17.2% were considered to have reached MDD depression remission, defined as a MADRS score at or under 10.
For secondary outcomes, the total Digit Symbol Substitution test score grew by 0.65 (standardized effect size) by week 12, showing significant improvement (P < .0001). In addition, participants improved on some other cognitive measures, and Dr. Christensen noted that “significant improvement was also observed in the patients’ health-related quality of life and daily functioning.”
A third of patients had drug-related treatment-emergent adverse events.
Vortioxetine is one of the most expensive antidepressants: It has a list price of $444 a month, and no generic version is currently available.
Small trial, open-label design
In a comment, Claire Sexton, DPhil, senior director of scientific programs and outreach at the Alzheimer’s Association, said the study “reflects a valuable aspect of treatment research because of the close connection between depression and dementia. Depression is a known risk factor for dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, and those who have dementia may experience depression.”
She cautioned, however, that the trial was small and had an open-label design instead of the “gold standard” of a double-blinded trial with a control group.
The study was funded by Lundbeck, where Dr. Christensen is an employee. Another author is a Lundbeck employee, and a third author reported various disclosures. Dr. Sexton reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The results of the 12-week open-label, single-group study are positive, study investigator Michael Cronquist Christensen, MPA, DrPH, a director with the Lundbeck pharmaceutical company, told this news organization before presenting the results in a poster at the 15th Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease conference.
“The study confirms earlier findings of improvement in both depressive symptoms and cognitive performance with vortioxetine in patients with depression and dementia and adds to this research that these clinical effects also extend to improvement in health-related quality of life and patients’ daily functioning,” Dr. Christensen said.
“It also demonstrates that patients with depression and comorbid dementia can be safely treated with 20 mg vortioxetine – starting dose of 5 mg for the first week and up-titration to 10 mg at day 8,” he added.
However, he reported that Lundbeck doesn’t plan to seek approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for a new indication. Vortioxetine received FDA approval in 2013 to treat MDD, but 3 years later the agency rejected an expansion of its indication to include cognitive dysfunction.
“Vortioxetine is approved for MDD, but the product can be used in patients with MDD who have other diseases, including other mental illnesses,” Dr. Christensen said.
Potential neurotransmission modulator
Vortioxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and serotonin receptor modulator. According to Dr. Christensen, evidence suggests the drug’s receptor targets “have the potential to modulate neurotransmitter systems that are essential for regulation of cognitive function.”
The researchers recruited 83 individuals aged 55-85 with recurrent MDD that had started before the age of 55. All had MDD episodes within the previous 6 months and comorbid dementia for at least 6 months.
Of the participants, 65.9% were female. In addition, 42.7% had Alzheimer’s disease, 26.8% had mixed-type dementia, and the rest had other types of dementia.
The daily oral dose of vortioxetine started at 5 mg for up to week 1 and then was increased to 10 mg. It was then increased to 20 mg or decreased to 5 mg “based on investigator judgment and patient response.” The average daily dose was 12.3 mg.
In regard to the primary outcome, at week 12 (n = 70), scores on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) fell by a mean of –12.4 (.78, P < .0001), which researchers deemed to be a significant reduction in severe symptoms.
“A significant and clinically meaningful effect was observed from week 1,” the researchers reported.
“As a basis for comparison, we typically see an improvement around 13-14 points during 8 weeks of antidepressant treatment in adults with MDD who do not have dementia,” Dr. Christensen added.
More than a third of patients (35.7%) saw a reduction in MADRS score by more than 50% at week 12, and 17.2% were considered to have reached MDD depression remission, defined as a MADRS score at or under 10.
For secondary outcomes, the total Digit Symbol Substitution test score grew by 0.65 (standardized effect size) by week 12, showing significant improvement (P < .0001). In addition, participants improved on some other cognitive measures, and Dr. Christensen noted that “significant improvement was also observed in the patients’ health-related quality of life and daily functioning.”
A third of patients had drug-related treatment-emergent adverse events.
Vortioxetine is one of the most expensive antidepressants: It has a list price of $444 a month, and no generic version is currently available.
Small trial, open-label design
In a comment, Claire Sexton, DPhil, senior director of scientific programs and outreach at the Alzheimer’s Association, said the study “reflects a valuable aspect of treatment research because of the close connection between depression and dementia. Depression is a known risk factor for dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, and those who have dementia may experience depression.”
She cautioned, however, that the trial was small and had an open-label design instead of the “gold standard” of a double-blinded trial with a control group.
The study was funded by Lundbeck, where Dr. Christensen is an employee. Another author is a Lundbeck employee, and a third author reported various disclosures. Dr. Sexton reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CTAD 2022
New AHA statement on complementary medicine in heart failure
There are some benefits and potentially serious risks associated with complementary and alternative medicines (CAM) patients with heart failure (HF) may use to manage symptoms, the American Heart Association noted in a new scientific statement on the topic.
For example, yoga and tai chi can be helpful for people with HF, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids may also have benefits. However, there are safety concerns with other commonly used over-the-counter CAM therapies, including vitamin D, blue cohosh, and Lily of the Valley, the writing group said.
It’s estimated that roughly one in three patients with HF use CAM. But often patients don’t report their CAM use to their clinicians and clinicians may not routinely ask about CAM use or have the resources to evaluate CAM therapies, writing group chair Sheryl L. Chow, PharmD, told this news organization.
“This represents a major public health problem given that consumers are frequently purchasing these potentially dangerous and minimally regulated products without the knowledge or advice from a health care professional,” said Dr. Chow, of Western University of Health Sciences, Pomona, Calif., and University of California, Irvine.
The 27-page statement was published online in Circulation.
CAM use common in HF
The statement defines CAM as medical practices, supplements, and approaches that do not conform to the standards of conventional, evidence-based practice guidelines. CAM products are available without prescriptions or medical guidance at pharmacies, health food stores, and online retailers.
“These agents are largely unregulated by the [Food and Drug Administration] and manufacturers do not need to demonstrate efficacy or safety. It is important that both health care professionals and consumers improve communication with respect to OTC therapies and are educated about potential efficacy and risk of harm so that shared and informed decision-making can occur,” Dr. Chow said.
The writing group reviewed research published before November 2021 on CAM among people with HF.
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as fish oil, have the strongest evidence among CAM agents for clinical benefit in HF and may be used safely by patients in moderation and in consultation with their health care team, the writing group said.
Research has shown that omega-3 PUFAs are associated with a lower risk of developing HF as well as improvements in left ventricular systolic function in those with existing HF, they pointed out.
However, two clinical trials found a higher incidence of atrial fibrillation with high-dose omega-3 PUFA administration. “This risk appears to be dose-related and increased when exceeding 2 g/d of fish oil,” the writing group said.
Research suggests that yoga and tai chi, when added to standard HF treatment, may help improve exercise tolerance and quality of life and decrease blood pressure.
Inconclusive or potentially harmful CAM therapies
Other CAM therapies for HF have been shown as ineffective based on current data, have mixed findings, or appear to be harmful. The writers highlighted the following examples:
- Overall evidence regarding the value of vitamin D supplementation in patients with HF remains “inconclusive” and may be harmful when taken with HF medications such as digoxin, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics.
- Routine thiamine supplementation in patients with HF and without clinically significant thiamine deficiency may not be efficacious and should be avoided.
- Research on alcohol varies, with some data showing that drinking low-to-moderate amounts (one to two drinks per day) may help prevent HF, while habitual drinking or consuming higher amounts is known to contribute to HF.
- The literature is mixed on vitamin E. It may have some benefit in reducing the risk of HF with preserved ejection fraction but has also been associated with an increased risk of HF hospitalization.
- Coenzyme Q10 (Co-Q10), commonly taken as a dietary supplement, may help improve HF class, symptoms, and quality of life, but it also may interact with antihypertensive and anticoagulant medication. Co-Q10 remains of “uncertain” value in HF at this time. Large-scale randomized controlled trials are needed before any definitive conclusion can be reached.
- Hawthorn, a flowering shrub, has been shown in some studies to increase exercise tolerance and improve HF symptoms such as fatigue. Yet it also has the potential to worsen HF, and there is conflicting research about whether it interacts with digoxin.
- The herbal supplement blue cohosh, from the root of a flowering plant found in hardwood forests, could cause tachycardia, high blood pressure, chest pain, and increased blood glucose. It may also decrease the effect of medications taken to treat high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes, they noted.
- Lily of the Valley, the root, stems, and flower of which are used in supplements, has long been used in mild HF because it contains active chemicals similar to digoxin. But when taken with digoxin, it could lead to hypokalemia.
In an AHA news release, Dr. Chow said, “Overall, more quality research and well-powered randomized controlled trials are needed to better understand the risks and benefits” of CAM therapies for HF.
“This scientific statement provides critical information to health care professionals who treat people with heart failure and may be used as a resource for consumers about the potential benefit and harm associated with complementary and alternative medicine products,” Dr. Chow added.
The writing group encourages health care professionals to routinely ask their HF patients about their use of CAM therapies. They also say pharmacists should be included in the multidisciplinary health care team to provide consultations about the use of CAM therapies for HF patients.
The scientific statement does not include cannabis or traditional Chinese medicine, which have also been used in HF.
In 2020, the AHA published a separate scientific statement on the use of medical marijuana and recreational cannabis on cardiovascular health, as reported previously by this news organization.
The scientific statement on CAM for HF was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Clinical Pharmacology Committee and Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology; the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; and the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There are some benefits and potentially serious risks associated with complementary and alternative medicines (CAM) patients with heart failure (HF) may use to manage symptoms, the American Heart Association noted in a new scientific statement on the topic.
For example, yoga and tai chi can be helpful for people with HF, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids may also have benefits. However, there are safety concerns with other commonly used over-the-counter CAM therapies, including vitamin D, blue cohosh, and Lily of the Valley, the writing group said.
It’s estimated that roughly one in three patients with HF use CAM. But often patients don’t report their CAM use to their clinicians and clinicians may not routinely ask about CAM use or have the resources to evaluate CAM therapies, writing group chair Sheryl L. Chow, PharmD, told this news organization.
“This represents a major public health problem given that consumers are frequently purchasing these potentially dangerous and minimally regulated products without the knowledge or advice from a health care professional,” said Dr. Chow, of Western University of Health Sciences, Pomona, Calif., and University of California, Irvine.
The 27-page statement was published online in Circulation.
CAM use common in HF
The statement defines CAM as medical practices, supplements, and approaches that do not conform to the standards of conventional, evidence-based practice guidelines. CAM products are available without prescriptions or medical guidance at pharmacies, health food stores, and online retailers.
“These agents are largely unregulated by the [Food and Drug Administration] and manufacturers do not need to demonstrate efficacy or safety. It is important that both health care professionals and consumers improve communication with respect to OTC therapies and are educated about potential efficacy and risk of harm so that shared and informed decision-making can occur,” Dr. Chow said.
The writing group reviewed research published before November 2021 on CAM among people with HF.
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as fish oil, have the strongest evidence among CAM agents for clinical benefit in HF and may be used safely by patients in moderation and in consultation with their health care team, the writing group said.
Research has shown that omega-3 PUFAs are associated with a lower risk of developing HF as well as improvements in left ventricular systolic function in those with existing HF, they pointed out.
However, two clinical trials found a higher incidence of atrial fibrillation with high-dose omega-3 PUFA administration. “This risk appears to be dose-related and increased when exceeding 2 g/d of fish oil,” the writing group said.
Research suggests that yoga and tai chi, when added to standard HF treatment, may help improve exercise tolerance and quality of life and decrease blood pressure.
Inconclusive or potentially harmful CAM therapies
Other CAM therapies for HF have been shown as ineffective based on current data, have mixed findings, or appear to be harmful. The writers highlighted the following examples:
- Overall evidence regarding the value of vitamin D supplementation in patients with HF remains “inconclusive” and may be harmful when taken with HF medications such as digoxin, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics.
- Routine thiamine supplementation in patients with HF and without clinically significant thiamine deficiency may not be efficacious and should be avoided.
- Research on alcohol varies, with some data showing that drinking low-to-moderate amounts (one to two drinks per day) may help prevent HF, while habitual drinking or consuming higher amounts is known to contribute to HF.
- The literature is mixed on vitamin E. It may have some benefit in reducing the risk of HF with preserved ejection fraction but has also been associated with an increased risk of HF hospitalization.
- Coenzyme Q10 (Co-Q10), commonly taken as a dietary supplement, may help improve HF class, symptoms, and quality of life, but it also may interact with antihypertensive and anticoagulant medication. Co-Q10 remains of “uncertain” value in HF at this time. Large-scale randomized controlled trials are needed before any definitive conclusion can be reached.
- Hawthorn, a flowering shrub, has been shown in some studies to increase exercise tolerance and improve HF symptoms such as fatigue. Yet it also has the potential to worsen HF, and there is conflicting research about whether it interacts with digoxin.
- The herbal supplement blue cohosh, from the root of a flowering plant found in hardwood forests, could cause tachycardia, high blood pressure, chest pain, and increased blood glucose. It may also decrease the effect of medications taken to treat high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes, they noted.
- Lily of the Valley, the root, stems, and flower of which are used in supplements, has long been used in mild HF because it contains active chemicals similar to digoxin. But when taken with digoxin, it could lead to hypokalemia.
In an AHA news release, Dr. Chow said, “Overall, more quality research and well-powered randomized controlled trials are needed to better understand the risks and benefits” of CAM therapies for HF.
“This scientific statement provides critical information to health care professionals who treat people with heart failure and may be used as a resource for consumers about the potential benefit and harm associated with complementary and alternative medicine products,” Dr. Chow added.
The writing group encourages health care professionals to routinely ask their HF patients about their use of CAM therapies. They also say pharmacists should be included in the multidisciplinary health care team to provide consultations about the use of CAM therapies for HF patients.
The scientific statement does not include cannabis or traditional Chinese medicine, which have also been used in HF.
In 2020, the AHA published a separate scientific statement on the use of medical marijuana and recreational cannabis on cardiovascular health, as reported previously by this news organization.
The scientific statement on CAM for HF was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Clinical Pharmacology Committee and Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology; the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; and the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There are some benefits and potentially serious risks associated with complementary and alternative medicines (CAM) patients with heart failure (HF) may use to manage symptoms, the American Heart Association noted in a new scientific statement on the topic.
For example, yoga and tai chi can be helpful for people with HF, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids may also have benefits. However, there are safety concerns with other commonly used over-the-counter CAM therapies, including vitamin D, blue cohosh, and Lily of the Valley, the writing group said.
It’s estimated that roughly one in three patients with HF use CAM. But often patients don’t report their CAM use to their clinicians and clinicians may not routinely ask about CAM use or have the resources to evaluate CAM therapies, writing group chair Sheryl L. Chow, PharmD, told this news organization.
“This represents a major public health problem given that consumers are frequently purchasing these potentially dangerous and minimally regulated products without the knowledge or advice from a health care professional,” said Dr. Chow, of Western University of Health Sciences, Pomona, Calif., and University of California, Irvine.
The 27-page statement was published online in Circulation.
CAM use common in HF
The statement defines CAM as medical practices, supplements, and approaches that do not conform to the standards of conventional, evidence-based practice guidelines. CAM products are available without prescriptions or medical guidance at pharmacies, health food stores, and online retailers.
“These agents are largely unregulated by the [Food and Drug Administration] and manufacturers do not need to demonstrate efficacy or safety. It is important that both health care professionals and consumers improve communication with respect to OTC therapies and are educated about potential efficacy and risk of harm so that shared and informed decision-making can occur,” Dr. Chow said.
The writing group reviewed research published before November 2021 on CAM among people with HF.
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as fish oil, have the strongest evidence among CAM agents for clinical benefit in HF and may be used safely by patients in moderation and in consultation with their health care team, the writing group said.
Research has shown that omega-3 PUFAs are associated with a lower risk of developing HF as well as improvements in left ventricular systolic function in those with existing HF, they pointed out.
However, two clinical trials found a higher incidence of atrial fibrillation with high-dose omega-3 PUFA administration. “This risk appears to be dose-related and increased when exceeding 2 g/d of fish oil,” the writing group said.
Research suggests that yoga and tai chi, when added to standard HF treatment, may help improve exercise tolerance and quality of life and decrease blood pressure.
Inconclusive or potentially harmful CAM therapies
Other CAM therapies for HF have been shown as ineffective based on current data, have mixed findings, or appear to be harmful. The writers highlighted the following examples:
- Overall evidence regarding the value of vitamin D supplementation in patients with HF remains “inconclusive” and may be harmful when taken with HF medications such as digoxin, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics.
- Routine thiamine supplementation in patients with HF and without clinically significant thiamine deficiency may not be efficacious and should be avoided.
- Research on alcohol varies, with some data showing that drinking low-to-moderate amounts (one to two drinks per day) may help prevent HF, while habitual drinking or consuming higher amounts is known to contribute to HF.
- The literature is mixed on vitamin E. It may have some benefit in reducing the risk of HF with preserved ejection fraction but has also been associated with an increased risk of HF hospitalization.
- Coenzyme Q10 (Co-Q10), commonly taken as a dietary supplement, may help improve HF class, symptoms, and quality of life, but it also may interact with antihypertensive and anticoagulant medication. Co-Q10 remains of “uncertain” value in HF at this time. Large-scale randomized controlled trials are needed before any definitive conclusion can be reached.
- Hawthorn, a flowering shrub, has been shown in some studies to increase exercise tolerance and improve HF symptoms such as fatigue. Yet it also has the potential to worsen HF, and there is conflicting research about whether it interacts with digoxin.
- The herbal supplement blue cohosh, from the root of a flowering plant found in hardwood forests, could cause tachycardia, high blood pressure, chest pain, and increased blood glucose. It may also decrease the effect of medications taken to treat high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes, they noted.
- Lily of the Valley, the root, stems, and flower of which are used in supplements, has long been used in mild HF because it contains active chemicals similar to digoxin. But when taken with digoxin, it could lead to hypokalemia.
In an AHA news release, Dr. Chow said, “Overall, more quality research and well-powered randomized controlled trials are needed to better understand the risks and benefits” of CAM therapies for HF.
“This scientific statement provides critical information to health care professionals who treat people with heart failure and may be used as a resource for consumers about the potential benefit and harm associated with complementary and alternative medicine products,” Dr. Chow added.
The writing group encourages health care professionals to routinely ask their HF patients about their use of CAM therapies. They also say pharmacists should be included in the multidisciplinary health care team to provide consultations about the use of CAM therapies for HF patients.
The scientific statement does not include cannabis or traditional Chinese medicine, which have also been used in HF.
In 2020, the AHA published a separate scientific statement on the use of medical marijuana and recreational cannabis on cardiovascular health, as reported previously by this news organization.
The scientific statement on CAM for HF was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Clinical Pharmacology Committee and Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology; the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; and the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
Analysis suggests CV benefits for some antioxidant supplements
Other antioxidant supplements that showed some evidence of reducing cardiovascular risk were omega-6 fatty acids, L-arginine, L-citrulline, magnesium, zinc, alpha-lipoic acid, melatonin, catechin, curcumin, flavanol, genistein, and quercetin.
No effect was seen with vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E, or selenium, and beta-carotene supplementation was linked to an increase in all-cause mortality in the analysis.
The study is published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and was also published online.
“Our systematic assessment and quantification of multiple differential effects of a wide variety of micronutrients and phytochemicals on cardiometabolic health indicate that an optimal nutritional strategy to promote cardiometabolic health will likely involve personalized combinations of these nutrients,” the authors, led by Peng An, PhD, China Agricultural University, Beijing, conclude.
“Identifying the optimal mixture of micronutrients is important, as not all are beneficial, and some may even have harmful effects,” senior author Simin Liu, MD, professor of epidemiology and medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I., said in an American College of Cardiology press release.
“The micronutrients identified require further validation in large, high-quality interventional trials to establish clinical efficacy to determine their long-term balance of risks and benefits,” the authors add.
Experts cautious
Experts in the field of cardiovascular risk and preventative medicine have urged caution in interpreting these results.
JoAnn Manson, MD, chief of the division of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, told this news organization that she has concerns that some of the results in the meta-analysis may be inflated by publication bias and some are chance findings that haven’t been well replicated.
“Although this meta-analysis of micronutrients and cardiometabolic health was based on randomized clinical trials, the quality of randomized trials on this subject varies widely,” she noted.
“The study is informative, but the conclusions are only as good as the quality of the evidence. Some of the trials are limited by short duration, and included trials have a wide range of quality, dosing, inclusion criteria, imperfect blinding, and few of them focus on hard clinical events,” Dr. Manson said. “Also, with trials of this nature, the potential for publication bias warrants consideration, because many of the smaller trials with unfavorable or neutral results may remain unpublished or not even be submitted for publication.”
However, she added, “despite these limitations, this is an important contribution to the literature on micronutrients and health – and goes a long way in separating the wheat from the chaff.”
Steve Nissen, MD, chief academic officer of the Heart Vascular and Thoracic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic, was more critical of the meta-analysis.
“This study does not make sense. Some of the ‘micronutrients’ in this meta-analysis have undergone thorough testing in large randomized clinical trials that showed different results. I am skeptical whether any of the purported benefits of these supplements would be confirmed in a high-quality randomized controlled trial,” he said.
Dr. Nissen added that many of the included studies are low in quality. “I must quote [renowned cardiologist, Dr.] Franz Messerli: ‘A meta-analysis is like making bouillabaisse. ... One rotten fish can spoil the broth.’ This type of analysis does not override high-quality large, randomized trials.”
In the JACC paper, the study investigators note that the American Heart Association now recommends dietary patterns, including the Mediterranean diet and DASH (the Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension), as preventive or treatment approaches for cardiovascular disease. A common feature of these dietary patterns is that they are low in saturated fat and sodium and rich in micronutrients such as phytochemicals, unsaturated fatty acids, antioxidant vitamins, and minerals.
“To personalize cardiometabolic preventive and therapeutic dietary practices, it is of critical importance to have a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the balance of benefits and risks associated with constituent micronutrients in diverse dietary patterns,” they note.
They therefore conducted the current systematic review and meta-analyses of all available randomized controlled trials investigating the effect of micronutrients with antioxidant properties on cardiovascular risk factors and events in diverse populations.
The meta-analysis included a total of 884 randomized trials evaluating 27 types of micronutrients among 883,627 participants.
Results showed that supplementation with n-3 fatty acids, n-6 fatty acids, L-arginine, L-citrulline, folic acid, magnesium, zinc, alpha-lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10, melatonin, catechin, curcumin, flavanol, genistein, and quercetin had “moderate-to high-quality evidence” for reducing cardiovascular risk factors.
Specifically, n-3 fatty acid supplementation was linked to reduced rates of cardiovascular mortality (relative risk, 0.93), myocardial infarction (RR, 0.85), and coronary heart disease events (RR, 0.86). Folic acid supplementation was linked to a decreased stroke risk (RR, 0.84) and coenzyme Q10 was associated with a lower rate of all-cause mortality (RR, 0.68).
“The current study represents the first attempt in providing a comprehensive and most up-to-date evidence map that systematically assessed the quality and quantity of all randomized trials linking the effects of a wide variety of micronutrients on cardiovascular risk factors,” the authors say.
“The comprehensive evidence map presented here highlights the importance of micronutrient diversity and the balance of benefits and risks in the design of whole food–based dietary patterns to promote cardiometabolic health, which may require cultural adaptations to apply globally,” they conclude.
Commenting on some of the specific beneficial findings, Dr. Manson said: “I do believe that the marine omega-3s confer heart benefits, but results are not consistent and vary by dose and formulation.”
However, she pointed out that, regarding folic acid, a previous meta-analysis including eight large randomized trials in more than 37,000 participants found no reduction in coronary events, stroke, or major cardiovascular events with folic acid supplementation, compared with placebo, “so the reported stroke benefit would need further confirmation.”
In an accompanying editorial, Juan Gormaz, PhD, University of Chile, and Rodrigo Carrasco, MD, Chilean Society of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery, both in Santiago, state: “Given that the compounds with more pleiotropic properties produced the better outcomes, the antioxidant paradigm on cardiovascular prevention can be challenged. For example, inasmuch as n-3 fatty acids have antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory properties, they are too complex to enable attribution of the observed benefits solely to their antioxidant capacity.”
The editorialists note that from a research point of view, “although the current information opens interesting perspectives for future consolidation of some antioxidants in preventive cardiology, there is still a long way to go in terms of generating evidence.”
They add that the challenge now for some compounds is to begin establishing consensus in definitions of dose and combinations, as well as continue strengthening the evidence of effectiveness.
“Regarding routine clinical practice, these results begin to open spaces for the integration of new tools into the therapeutic arsenal aimed at cardiovascular prevention in selected populations, which could be easily accessible and, with specific exceptions, would present a low frequency of adverse effects,” they conclude.
This work was partly supported by the United States’ Fulbright Program and by the Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Food Nutrition and Human Health, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund, and the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation.
Dr. Liu has received honoraria for scientific presentations or reviews at Johns Hopkins University, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Harvard University, University of Buffalo, Guangdong General Hospital, Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and the National Institutes of Health; he is a member of the Data Safety and Monitoring Board for several trials, including the SELECT (Semaglutide Effects on Cardiovascular Outcomes in People with Overweight or Obesity) trial sponsored by Novo Nordisk and a trial of pulmonary hypertension in diabetes patients sponsored by Massachusetts General Hospital; he has received royalties from UpToDate and has received an honorarium from the American Society for Nutrition for his duties as Associate Editor. Co-author Jeffrey Mechanick, MD, has received honoraria from Abbott Nutrition for lectures and serves on the advisory boards of Aveta.Life, L-Nutra, and Twin Health. The other authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Other antioxidant supplements that showed some evidence of reducing cardiovascular risk were omega-6 fatty acids, L-arginine, L-citrulline, magnesium, zinc, alpha-lipoic acid, melatonin, catechin, curcumin, flavanol, genistein, and quercetin.
No effect was seen with vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E, or selenium, and beta-carotene supplementation was linked to an increase in all-cause mortality in the analysis.
The study is published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and was also published online.
“Our systematic assessment and quantification of multiple differential effects of a wide variety of micronutrients and phytochemicals on cardiometabolic health indicate that an optimal nutritional strategy to promote cardiometabolic health will likely involve personalized combinations of these nutrients,” the authors, led by Peng An, PhD, China Agricultural University, Beijing, conclude.
“Identifying the optimal mixture of micronutrients is important, as not all are beneficial, and some may even have harmful effects,” senior author Simin Liu, MD, professor of epidemiology and medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I., said in an American College of Cardiology press release.
“The micronutrients identified require further validation in large, high-quality interventional trials to establish clinical efficacy to determine their long-term balance of risks and benefits,” the authors add.
Experts cautious
Experts in the field of cardiovascular risk and preventative medicine have urged caution in interpreting these results.
JoAnn Manson, MD, chief of the division of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, told this news organization that she has concerns that some of the results in the meta-analysis may be inflated by publication bias and some are chance findings that haven’t been well replicated.
“Although this meta-analysis of micronutrients and cardiometabolic health was based on randomized clinical trials, the quality of randomized trials on this subject varies widely,” she noted.
“The study is informative, but the conclusions are only as good as the quality of the evidence. Some of the trials are limited by short duration, and included trials have a wide range of quality, dosing, inclusion criteria, imperfect blinding, and few of them focus on hard clinical events,” Dr. Manson said. “Also, with trials of this nature, the potential for publication bias warrants consideration, because many of the smaller trials with unfavorable or neutral results may remain unpublished or not even be submitted for publication.”
However, she added, “despite these limitations, this is an important contribution to the literature on micronutrients and health – and goes a long way in separating the wheat from the chaff.”
Steve Nissen, MD, chief academic officer of the Heart Vascular and Thoracic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic, was more critical of the meta-analysis.
“This study does not make sense. Some of the ‘micronutrients’ in this meta-analysis have undergone thorough testing in large randomized clinical trials that showed different results. I am skeptical whether any of the purported benefits of these supplements would be confirmed in a high-quality randomized controlled trial,” he said.
Dr. Nissen added that many of the included studies are low in quality. “I must quote [renowned cardiologist, Dr.] Franz Messerli: ‘A meta-analysis is like making bouillabaisse. ... One rotten fish can spoil the broth.’ This type of analysis does not override high-quality large, randomized trials.”
In the JACC paper, the study investigators note that the American Heart Association now recommends dietary patterns, including the Mediterranean diet and DASH (the Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension), as preventive or treatment approaches for cardiovascular disease. A common feature of these dietary patterns is that they are low in saturated fat and sodium and rich in micronutrients such as phytochemicals, unsaturated fatty acids, antioxidant vitamins, and minerals.
“To personalize cardiometabolic preventive and therapeutic dietary practices, it is of critical importance to have a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the balance of benefits and risks associated with constituent micronutrients in diverse dietary patterns,” they note.
They therefore conducted the current systematic review and meta-analyses of all available randomized controlled trials investigating the effect of micronutrients with antioxidant properties on cardiovascular risk factors and events in diverse populations.
The meta-analysis included a total of 884 randomized trials evaluating 27 types of micronutrients among 883,627 participants.
Results showed that supplementation with n-3 fatty acids, n-6 fatty acids, L-arginine, L-citrulline, folic acid, magnesium, zinc, alpha-lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10, melatonin, catechin, curcumin, flavanol, genistein, and quercetin had “moderate-to high-quality evidence” for reducing cardiovascular risk factors.
Specifically, n-3 fatty acid supplementation was linked to reduced rates of cardiovascular mortality (relative risk, 0.93), myocardial infarction (RR, 0.85), and coronary heart disease events (RR, 0.86). Folic acid supplementation was linked to a decreased stroke risk (RR, 0.84) and coenzyme Q10 was associated with a lower rate of all-cause mortality (RR, 0.68).
“The current study represents the first attempt in providing a comprehensive and most up-to-date evidence map that systematically assessed the quality and quantity of all randomized trials linking the effects of a wide variety of micronutrients on cardiovascular risk factors,” the authors say.
“The comprehensive evidence map presented here highlights the importance of micronutrient diversity and the balance of benefits and risks in the design of whole food–based dietary patterns to promote cardiometabolic health, which may require cultural adaptations to apply globally,” they conclude.
Commenting on some of the specific beneficial findings, Dr. Manson said: “I do believe that the marine omega-3s confer heart benefits, but results are not consistent and vary by dose and formulation.”
However, she pointed out that, regarding folic acid, a previous meta-analysis including eight large randomized trials in more than 37,000 participants found no reduction in coronary events, stroke, or major cardiovascular events with folic acid supplementation, compared with placebo, “so the reported stroke benefit would need further confirmation.”
In an accompanying editorial, Juan Gormaz, PhD, University of Chile, and Rodrigo Carrasco, MD, Chilean Society of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery, both in Santiago, state: “Given that the compounds with more pleiotropic properties produced the better outcomes, the antioxidant paradigm on cardiovascular prevention can be challenged. For example, inasmuch as n-3 fatty acids have antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory properties, they are too complex to enable attribution of the observed benefits solely to their antioxidant capacity.”
The editorialists note that from a research point of view, “although the current information opens interesting perspectives for future consolidation of some antioxidants in preventive cardiology, there is still a long way to go in terms of generating evidence.”
They add that the challenge now for some compounds is to begin establishing consensus in definitions of dose and combinations, as well as continue strengthening the evidence of effectiveness.
“Regarding routine clinical practice, these results begin to open spaces for the integration of new tools into the therapeutic arsenal aimed at cardiovascular prevention in selected populations, which could be easily accessible and, with specific exceptions, would present a low frequency of adverse effects,” they conclude.
This work was partly supported by the United States’ Fulbright Program and by the Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Food Nutrition and Human Health, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund, and the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation.
Dr. Liu has received honoraria for scientific presentations or reviews at Johns Hopkins University, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Harvard University, University of Buffalo, Guangdong General Hospital, Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and the National Institutes of Health; he is a member of the Data Safety and Monitoring Board for several trials, including the SELECT (Semaglutide Effects on Cardiovascular Outcomes in People with Overweight or Obesity) trial sponsored by Novo Nordisk and a trial of pulmonary hypertension in diabetes patients sponsored by Massachusetts General Hospital; he has received royalties from UpToDate and has received an honorarium from the American Society for Nutrition for his duties as Associate Editor. Co-author Jeffrey Mechanick, MD, has received honoraria from Abbott Nutrition for lectures and serves on the advisory boards of Aveta.Life, L-Nutra, and Twin Health. The other authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Other antioxidant supplements that showed some evidence of reducing cardiovascular risk were omega-6 fatty acids, L-arginine, L-citrulline, magnesium, zinc, alpha-lipoic acid, melatonin, catechin, curcumin, flavanol, genistein, and quercetin.
No effect was seen with vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E, or selenium, and beta-carotene supplementation was linked to an increase in all-cause mortality in the analysis.
The study is published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and was also published online.
“Our systematic assessment and quantification of multiple differential effects of a wide variety of micronutrients and phytochemicals on cardiometabolic health indicate that an optimal nutritional strategy to promote cardiometabolic health will likely involve personalized combinations of these nutrients,” the authors, led by Peng An, PhD, China Agricultural University, Beijing, conclude.
“Identifying the optimal mixture of micronutrients is important, as not all are beneficial, and some may even have harmful effects,” senior author Simin Liu, MD, professor of epidemiology and medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I., said in an American College of Cardiology press release.
“The micronutrients identified require further validation in large, high-quality interventional trials to establish clinical efficacy to determine their long-term balance of risks and benefits,” the authors add.
Experts cautious
Experts in the field of cardiovascular risk and preventative medicine have urged caution in interpreting these results.
JoAnn Manson, MD, chief of the division of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, told this news organization that she has concerns that some of the results in the meta-analysis may be inflated by publication bias and some are chance findings that haven’t been well replicated.
“Although this meta-analysis of micronutrients and cardiometabolic health was based on randomized clinical trials, the quality of randomized trials on this subject varies widely,” she noted.
“The study is informative, but the conclusions are only as good as the quality of the evidence. Some of the trials are limited by short duration, and included trials have a wide range of quality, dosing, inclusion criteria, imperfect blinding, and few of them focus on hard clinical events,” Dr. Manson said. “Also, with trials of this nature, the potential for publication bias warrants consideration, because many of the smaller trials with unfavorable or neutral results may remain unpublished or not even be submitted for publication.”
However, she added, “despite these limitations, this is an important contribution to the literature on micronutrients and health – and goes a long way in separating the wheat from the chaff.”
Steve Nissen, MD, chief academic officer of the Heart Vascular and Thoracic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic, was more critical of the meta-analysis.
“This study does not make sense. Some of the ‘micronutrients’ in this meta-analysis have undergone thorough testing in large randomized clinical trials that showed different results. I am skeptical whether any of the purported benefits of these supplements would be confirmed in a high-quality randomized controlled trial,” he said.
Dr. Nissen added that many of the included studies are low in quality. “I must quote [renowned cardiologist, Dr.] Franz Messerli: ‘A meta-analysis is like making bouillabaisse. ... One rotten fish can spoil the broth.’ This type of analysis does not override high-quality large, randomized trials.”
In the JACC paper, the study investigators note that the American Heart Association now recommends dietary patterns, including the Mediterranean diet and DASH (the Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension), as preventive or treatment approaches for cardiovascular disease. A common feature of these dietary patterns is that they are low in saturated fat and sodium and rich in micronutrients such as phytochemicals, unsaturated fatty acids, antioxidant vitamins, and minerals.
“To personalize cardiometabolic preventive and therapeutic dietary practices, it is of critical importance to have a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the balance of benefits and risks associated with constituent micronutrients in diverse dietary patterns,” they note.
They therefore conducted the current systematic review and meta-analyses of all available randomized controlled trials investigating the effect of micronutrients with antioxidant properties on cardiovascular risk factors and events in diverse populations.
The meta-analysis included a total of 884 randomized trials evaluating 27 types of micronutrients among 883,627 participants.
Results showed that supplementation with n-3 fatty acids, n-6 fatty acids, L-arginine, L-citrulline, folic acid, magnesium, zinc, alpha-lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10, melatonin, catechin, curcumin, flavanol, genistein, and quercetin had “moderate-to high-quality evidence” for reducing cardiovascular risk factors.
Specifically, n-3 fatty acid supplementation was linked to reduced rates of cardiovascular mortality (relative risk, 0.93), myocardial infarction (RR, 0.85), and coronary heart disease events (RR, 0.86). Folic acid supplementation was linked to a decreased stroke risk (RR, 0.84) and coenzyme Q10 was associated with a lower rate of all-cause mortality (RR, 0.68).
“The current study represents the first attempt in providing a comprehensive and most up-to-date evidence map that systematically assessed the quality and quantity of all randomized trials linking the effects of a wide variety of micronutrients on cardiovascular risk factors,” the authors say.
“The comprehensive evidence map presented here highlights the importance of micronutrient diversity and the balance of benefits and risks in the design of whole food–based dietary patterns to promote cardiometabolic health, which may require cultural adaptations to apply globally,” they conclude.
Commenting on some of the specific beneficial findings, Dr. Manson said: “I do believe that the marine omega-3s confer heart benefits, but results are not consistent and vary by dose and formulation.”
However, she pointed out that, regarding folic acid, a previous meta-analysis including eight large randomized trials in more than 37,000 participants found no reduction in coronary events, stroke, or major cardiovascular events with folic acid supplementation, compared with placebo, “so the reported stroke benefit would need further confirmation.”
In an accompanying editorial, Juan Gormaz, PhD, University of Chile, and Rodrigo Carrasco, MD, Chilean Society of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery, both in Santiago, state: “Given that the compounds with more pleiotropic properties produced the better outcomes, the antioxidant paradigm on cardiovascular prevention can be challenged. For example, inasmuch as n-3 fatty acids have antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory properties, they are too complex to enable attribution of the observed benefits solely to their antioxidant capacity.”
The editorialists note that from a research point of view, “although the current information opens interesting perspectives for future consolidation of some antioxidants in preventive cardiology, there is still a long way to go in terms of generating evidence.”
They add that the challenge now for some compounds is to begin establishing consensus in definitions of dose and combinations, as well as continue strengthening the evidence of effectiveness.
“Regarding routine clinical practice, these results begin to open spaces for the integration of new tools into the therapeutic arsenal aimed at cardiovascular prevention in selected populations, which could be easily accessible and, with specific exceptions, would present a low frequency of adverse effects,” they conclude.
This work was partly supported by the United States’ Fulbright Program and by the Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Food Nutrition and Human Health, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund, and the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation.
Dr. Liu has received honoraria for scientific presentations or reviews at Johns Hopkins University, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Harvard University, University of Buffalo, Guangdong General Hospital, Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and the National Institutes of Health; he is a member of the Data Safety and Monitoring Board for several trials, including the SELECT (Semaglutide Effects on Cardiovascular Outcomes in People with Overweight or Obesity) trial sponsored by Novo Nordisk and a trial of pulmonary hypertension in diabetes patients sponsored by Massachusetts General Hospital; he has received royalties from UpToDate and has received an honorarium from the American Society for Nutrition for his duties as Associate Editor. Co-author Jeffrey Mechanick, MD, has received honoraria from Abbott Nutrition for lectures and serves on the advisory boards of Aveta.Life, L-Nutra, and Twin Health. The other authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JACC
Dapagliflozin reduces hospitalizations in patients with CKD
These findings add to a growing body of evidence supporting a range of positive benefits from dapagliflozin, including reduced risks of mortality, cardiovascular events, and kidney events, lead author Meir Schechter, MD, PhD, of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and colleagues wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine.“Although cardiovascular and kidney outcomes with SGLT2 inhibitors have been studied extensively, there is a paucity of data evaluating the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on hospitalizations for any cause.”
The findings are based on a post hoc analysis of the DAPA-CKD trial, which involved 4,304 patients with CKD in 21 countries. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive dapagliflozin 10 mg orally once a day or matching placebo. The present analysis quantified first hospitalizations for any cause, all hospitalizations, cause-specific hospitalizations, and several related outcomes.
After a median follow-up of 2.4 years, 28% of the population had been hospitalized a total of 2,072 times.
Compared with placebo, dapagliflozin significantly reduced risk of first hospitalization by 16% (hazard ratio, 0.84; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-0.94) and rate of all hospitalizations by 21% (rate ratio, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.70-0.89). These findings remained significant regardless of type 2 diabetes status, with significant benefits seen across reasons for admission, including renal/urinary disorders, cardiac disorders, neoplasms, and metabolism/nutrition disorders. In addition, dapagliflozin was associated with shorter mean time in hospital (2.3 vs. 2.8 days; P = .027) and longer time alive and out of hospital (354.9 vs. 351.7; P = .023).
“These findings highlight additional benefits of dapagliflozin beyond those seen for cardiovascular and kidney events, all-cause and cause-specific mortality, eGFR [estimated glomerular filtration rate] slope, and albuminuria and should be considered when evaluating the totality of evidence favoring provision of dapagliflozin to patients with CKD,” the investigators concluded.
Positive data, positive experiences
Shree Mulay, MD, a nephrologist in private practice in western Tennessee, said this study is “one of several other articles that already exist” demonstrating the broad benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors.
“The evidence is pretty substantial,” Dr. Mulay said in an interview. “I think SGLT2 inhibitors are the new statin of this era. ... I won’t be surprised if in the next year or 2 or 3 they truly become the standard of care.”
Dr. Mulay also speaks from experience working in both the chronic and acute setting, where he’s observed “some magical stuff happening” in patients started on SGLT2 inhibitors, especially those in heart failure who are fluid overloaded.
“It’s phenomenal stuff,” Dr. Mulay said. “You can really stabilize patients’ hemodynamics.”
In the private health care setting, he described widespread enthusiasm among nephrologists, although others still appear skeptical.
“It’s really our cardiology colleagues that I feel are underprescribing it,” Dr. Mulay said. “So, I’m kind of taking it on myself, when I see a heart failure patient, to go ahead and put them on this.”
It’s unclear why some cardiologists seem apprehensive, Dr. Mulay continued, although he suggested that unclear guidelines and a lack of first-hand experience may be to blame.
Nephrologists and cardiologists sometimes agree
In the academic arena, Leslie Gewin, MD, associate professor at Washington University in St. Louis and the John Cochran VA Hospital, also in St. Louis, has seen similar support for SGLT2 inhibitors among both nephrologists and cardiologists.
“We had a joint nephrology-cardiology medicine grand rounds at Wash U in St. Louis maybe 2 weeks ago,” Dr. Gewin said in an interview. “The cardiologists and nephrologists tag-teamed to present data about SGLT2 inhibitors, and we kind of joked that this was the one thing we both could get behind and support.”
Still, she has seen some reluctance among non-nephrology clinicians lacking SGLT2 experience, specifically when managing patients who have poor kidney function.
“There can be some hesitancy among physicians if the GFR is low,” Dr. Gewin said. “That’s where I’ve had to sort of push the envelope with non-nephrologists, saying: ‘Look, we feel pretty comfortable starting down to a GFR of about 20.’ ”
Early rises in creatinine may also spook providers, she noted.
“Sometimes, when we start SGLT2 inhibitors, the creatinine increases slightly, and the [primary care provider] gets concerned,” Dr. Gewin said. “We say: ‘No, this is expected. Don’t worry, hold the course, this is a good drug.’ ”
Like Dr. Mulay, Dr. Gewin said the present study offers further encouragement for the efficacy of this drug class. She also said sufficient data have been published to allay earlier concerns about potential safety signals, such as bone fractures and amputations.
“SGLT2 inhibitors seem to be a lot safer than what we initially had thought,” Dr. Gewin said. “That’s very encouraging.”
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Bayer, Janssen, Gilead, and others. Dr. Gewin and Dr. Mulay disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
These findings add to a growing body of evidence supporting a range of positive benefits from dapagliflozin, including reduced risks of mortality, cardiovascular events, and kidney events, lead author Meir Schechter, MD, PhD, of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and colleagues wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine.“Although cardiovascular and kidney outcomes with SGLT2 inhibitors have been studied extensively, there is a paucity of data evaluating the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on hospitalizations for any cause.”
The findings are based on a post hoc analysis of the DAPA-CKD trial, which involved 4,304 patients with CKD in 21 countries. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive dapagliflozin 10 mg orally once a day or matching placebo. The present analysis quantified first hospitalizations for any cause, all hospitalizations, cause-specific hospitalizations, and several related outcomes.
After a median follow-up of 2.4 years, 28% of the population had been hospitalized a total of 2,072 times.
Compared with placebo, dapagliflozin significantly reduced risk of first hospitalization by 16% (hazard ratio, 0.84; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-0.94) and rate of all hospitalizations by 21% (rate ratio, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.70-0.89). These findings remained significant regardless of type 2 diabetes status, with significant benefits seen across reasons for admission, including renal/urinary disorders, cardiac disorders, neoplasms, and metabolism/nutrition disorders. In addition, dapagliflozin was associated with shorter mean time in hospital (2.3 vs. 2.8 days; P = .027) and longer time alive and out of hospital (354.9 vs. 351.7; P = .023).
“These findings highlight additional benefits of dapagliflozin beyond those seen for cardiovascular and kidney events, all-cause and cause-specific mortality, eGFR [estimated glomerular filtration rate] slope, and albuminuria and should be considered when evaluating the totality of evidence favoring provision of dapagliflozin to patients with CKD,” the investigators concluded.
Positive data, positive experiences
Shree Mulay, MD, a nephrologist in private practice in western Tennessee, said this study is “one of several other articles that already exist” demonstrating the broad benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors.
“The evidence is pretty substantial,” Dr. Mulay said in an interview. “I think SGLT2 inhibitors are the new statin of this era. ... I won’t be surprised if in the next year or 2 or 3 they truly become the standard of care.”
Dr. Mulay also speaks from experience working in both the chronic and acute setting, where he’s observed “some magical stuff happening” in patients started on SGLT2 inhibitors, especially those in heart failure who are fluid overloaded.
“It’s phenomenal stuff,” Dr. Mulay said. “You can really stabilize patients’ hemodynamics.”
In the private health care setting, he described widespread enthusiasm among nephrologists, although others still appear skeptical.
“It’s really our cardiology colleagues that I feel are underprescribing it,” Dr. Mulay said. “So, I’m kind of taking it on myself, when I see a heart failure patient, to go ahead and put them on this.”
It’s unclear why some cardiologists seem apprehensive, Dr. Mulay continued, although he suggested that unclear guidelines and a lack of first-hand experience may be to blame.
Nephrologists and cardiologists sometimes agree
In the academic arena, Leslie Gewin, MD, associate professor at Washington University in St. Louis and the John Cochran VA Hospital, also in St. Louis, has seen similar support for SGLT2 inhibitors among both nephrologists and cardiologists.
“We had a joint nephrology-cardiology medicine grand rounds at Wash U in St. Louis maybe 2 weeks ago,” Dr. Gewin said in an interview. “The cardiologists and nephrologists tag-teamed to present data about SGLT2 inhibitors, and we kind of joked that this was the one thing we both could get behind and support.”
Still, she has seen some reluctance among non-nephrology clinicians lacking SGLT2 experience, specifically when managing patients who have poor kidney function.
“There can be some hesitancy among physicians if the GFR is low,” Dr. Gewin said. “That’s where I’ve had to sort of push the envelope with non-nephrologists, saying: ‘Look, we feel pretty comfortable starting down to a GFR of about 20.’ ”
Early rises in creatinine may also spook providers, she noted.
“Sometimes, when we start SGLT2 inhibitors, the creatinine increases slightly, and the [primary care provider] gets concerned,” Dr. Gewin said. “We say: ‘No, this is expected. Don’t worry, hold the course, this is a good drug.’ ”
Like Dr. Mulay, Dr. Gewin said the present study offers further encouragement for the efficacy of this drug class. She also said sufficient data have been published to allay earlier concerns about potential safety signals, such as bone fractures and amputations.
“SGLT2 inhibitors seem to be a lot safer than what we initially had thought,” Dr. Gewin said. “That’s very encouraging.”
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Bayer, Janssen, Gilead, and others. Dr. Gewin and Dr. Mulay disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
These findings add to a growing body of evidence supporting a range of positive benefits from dapagliflozin, including reduced risks of mortality, cardiovascular events, and kidney events, lead author Meir Schechter, MD, PhD, of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and colleagues wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine.“Although cardiovascular and kidney outcomes with SGLT2 inhibitors have been studied extensively, there is a paucity of data evaluating the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on hospitalizations for any cause.”
The findings are based on a post hoc analysis of the DAPA-CKD trial, which involved 4,304 patients with CKD in 21 countries. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive dapagliflozin 10 mg orally once a day or matching placebo. The present analysis quantified first hospitalizations for any cause, all hospitalizations, cause-specific hospitalizations, and several related outcomes.
After a median follow-up of 2.4 years, 28% of the population had been hospitalized a total of 2,072 times.
Compared with placebo, dapagliflozin significantly reduced risk of first hospitalization by 16% (hazard ratio, 0.84; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-0.94) and rate of all hospitalizations by 21% (rate ratio, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.70-0.89). These findings remained significant regardless of type 2 diabetes status, with significant benefits seen across reasons for admission, including renal/urinary disorders, cardiac disorders, neoplasms, and metabolism/nutrition disorders. In addition, dapagliflozin was associated with shorter mean time in hospital (2.3 vs. 2.8 days; P = .027) and longer time alive and out of hospital (354.9 vs. 351.7; P = .023).
“These findings highlight additional benefits of dapagliflozin beyond those seen for cardiovascular and kidney events, all-cause and cause-specific mortality, eGFR [estimated glomerular filtration rate] slope, and albuminuria and should be considered when evaluating the totality of evidence favoring provision of dapagliflozin to patients with CKD,” the investigators concluded.
Positive data, positive experiences
Shree Mulay, MD, a nephrologist in private practice in western Tennessee, said this study is “one of several other articles that already exist” demonstrating the broad benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors.
“The evidence is pretty substantial,” Dr. Mulay said in an interview. “I think SGLT2 inhibitors are the new statin of this era. ... I won’t be surprised if in the next year or 2 or 3 they truly become the standard of care.”
Dr. Mulay also speaks from experience working in both the chronic and acute setting, where he’s observed “some magical stuff happening” in patients started on SGLT2 inhibitors, especially those in heart failure who are fluid overloaded.
“It’s phenomenal stuff,” Dr. Mulay said. “You can really stabilize patients’ hemodynamics.”
In the private health care setting, he described widespread enthusiasm among nephrologists, although others still appear skeptical.
“It’s really our cardiology colleagues that I feel are underprescribing it,” Dr. Mulay said. “So, I’m kind of taking it on myself, when I see a heart failure patient, to go ahead and put them on this.”
It’s unclear why some cardiologists seem apprehensive, Dr. Mulay continued, although he suggested that unclear guidelines and a lack of first-hand experience may be to blame.
Nephrologists and cardiologists sometimes agree
In the academic arena, Leslie Gewin, MD, associate professor at Washington University in St. Louis and the John Cochran VA Hospital, also in St. Louis, has seen similar support for SGLT2 inhibitors among both nephrologists and cardiologists.
“We had a joint nephrology-cardiology medicine grand rounds at Wash U in St. Louis maybe 2 weeks ago,” Dr. Gewin said in an interview. “The cardiologists and nephrologists tag-teamed to present data about SGLT2 inhibitors, and we kind of joked that this was the one thing we both could get behind and support.”
Still, she has seen some reluctance among non-nephrology clinicians lacking SGLT2 experience, specifically when managing patients who have poor kidney function.
“There can be some hesitancy among physicians if the GFR is low,” Dr. Gewin said. “That’s where I’ve had to sort of push the envelope with non-nephrologists, saying: ‘Look, we feel pretty comfortable starting down to a GFR of about 20.’ ”
Early rises in creatinine may also spook providers, she noted.
“Sometimes, when we start SGLT2 inhibitors, the creatinine increases slightly, and the [primary care provider] gets concerned,” Dr. Gewin said. “We say: ‘No, this is expected. Don’t worry, hold the course, this is a good drug.’ ”
Like Dr. Mulay, Dr. Gewin said the present study offers further encouragement for the efficacy of this drug class. She also said sufficient data have been published to allay earlier concerns about potential safety signals, such as bone fractures and amputations.
“SGLT2 inhibitors seem to be a lot safer than what we initially had thought,” Dr. Gewin said. “That’s very encouraging.”
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Bayer, Janssen, Gilead, and others. Dr. Gewin and Dr. Mulay disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE