User login
Poor diet causes 70% of type 2 diabetes, says new study
Poor diets account for most newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes cases worldwide, a new analysis has found.
More specifically, the modeling study showed that roughly 14 million cases of type 2 diabetes – or 70% of total type 2 diabetes diagnoses in 2018 – were linked with a poor diet, found Meghan O’Hearn, a doctoral student at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy, Tufts University, Boston, and colleagues. The study was published online in Nature Medicine.
The results also indicate that the greatest burdens of type 2 diabetes were accounted for by excess wheat intake and refined rice (24.6%), excess processed meat consumption (20.3%), and inadequate whole-grain consumption (26.1%). Factors such as drinking too much fruit juice and not eating enough nonstarchy vegetables, nuts, or seeds, had less of an impact on new cases of the disease, the researchers determined.
“These findings can help inform nutritional priorities for clinicians, policymakers, and private sector actors as they encourage healthier dietary choices that address this global epidemic,” Ms. O’Hearn said in a press release.
Prior research has suggested that poor diet contributes to about 40% of type 2 diabetes cases worldwide, the researchers note.
The team attributes their finding of a 70% contribution to the new information in their analysis, such as the first-ever inclusion of refined grains, which was one of the top contributors to diabetes burden, and updated data on dietary habits based on national individual-level dietary surveys rather than agricultural estimates.
“Our study suggests poor carbohydrate quality is a leading driver of diet-attributable type 2 diabetes globally and with important variation by nation and over time,” said senior author Dariush Mozaffarian, MD, DrPh, MPH, who is the Jean Mayer Professor of Nutrition at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy.
“These new findings reveal critical areas for national and global focus to improve nutrition and reduce devastating burdens of diabetes,” he noted.
“Left unchecked and with incidence only projected to rise, type 2 diabetes will continue to impact population health, economic productivity, [and] health care system capacity, [as well as] drive health inequities worldwide,” Ms. O’Hearn said.
It’s about reducing harmful dietary components
Ms. O’Hearn and colleagues set out to fill information gaps in knowledge about how the global burden of diet-associated type 2 diabetes is impacted by disparities and other factors known to influence risk, including dietary components.
They used information from the Global Dietary Database to study dietary intake in 184 nations from 1990 to 2018. They also studied demographics from multiple sources, estimates of type 2 diabetes incidence around the world, and data on food choices, including the effect of 11 dietary factors, from prior research.
They found that there were 8.6 million more cases of type 2 diabetes in 2018 than in 1990 because of poor diet.
Regionally, Central and Eastern Europe and Central Asia had the greatest number of type 2 diabetes cases linked to diet, particularly Poland and Russia, where diets tend to be rich in red meat, processed meat, and potatoes. Incidence was also high in Latin America and the Caribbean, especially in Colombia and Mexico, which was attributed to high consumption of sugary drinks and processed meat and low intake of whole grains.
Regions where diet had less of an impact on type 2 diabetes cases included South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, although the largest increases in type 2 diabetes due to poor diet between 1990 and 2018 were observed in sub-Saharan Africa.
Diet-attributable type 2 diabetes was generally larger among urban versus rural residents and higher versus lower educated individuals, except in high-income countries, Central and Eastern Europe, and Central Asia, where burdens were larger in rural residents and in lower educated individuals.
Notably, women had lower proportions of diet-related type 2 diabetes, compared with men, and these proportions were inversely related to age.
Excess intake of harmful dietary factors contributed a greater percentage of the burden of type 2 diabetes globally (60.8%) than did insufficient intake of protective dietary factors (39.2%).
“Future research should address whether more complex diet–type 2 diabetes dose–response relationships exist,” the authors conclude.
Ms. O’Hearn has reported receiving research funding from the Gates Foundation, as well as the National Institutes of Health and Vail Innovative Global Research and employment with Food Systems for the Future. Dr. Mozaffarian has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health, the Gates Foundation, the Rockefeller Foundation, Vail Innovative Global Research, and the Kaiser Permanente Fund at East Bay Community Foundation; personal fees from Acasti Pharma, Barilla, Danone, and Motif FoodWorks; is on the scientific advisory board for Beren Therapeutics, Brightseed, Calibrate, DiscernDx, Elysium Health, Filtricine, HumanCo, January, Perfect Day, Tiny Organics and (ended) Day Two and Season Health; has stock ownership in Calibrate and HumanCo; and receives chapter royalties from UpToDate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Poor diets account for most newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes cases worldwide, a new analysis has found.
More specifically, the modeling study showed that roughly 14 million cases of type 2 diabetes – or 70% of total type 2 diabetes diagnoses in 2018 – were linked with a poor diet, found Meghan O’Hearn, a doctoral student at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy, Tufts University, Boston, and colleagues. The study was published online in Nature Medicine.
The results also indicate that the greatest burdens of type 2 diabetes were accounted for by excess wheat intake and refined rice (24.6%), excess processed meat consumption (20.3%), and inadequate whole-grain consumption (26.1%). Factors such as drinking too much fruit juice and not eating enough nonstarchy vegetables, nuts, or seeds, had less of an impact on new cases of the disease, the researchers determined.
“These findings can help inform nutritional priorities for clinicians, policymakers, and private sector actors as they encourage healthier dietary choices that address this global epidemic,” Ms. O’Hearn said in a press release.
Prior research has suggested that poor diet contributes to about 40% of type 2 diabetes cases worldwide, the researchers note.
The team attributes their finding of a 70% contribution to the new information in their analysis, such as the first-ever inclusion of refined grains, which was one of the top contributors to diabetes burden, and updated data on dietary habits based on national individual-level dietary surveys rather than agricultural estimates.
“Our study suggests poor carbohydrate quality is a leading driver of diet-attributable type 2 diabetes globally and with important variation by nation and over time,” said senior author Dariush Mozaffarian, MD, DrPh, MPH, who is the Jean Mayer Professor of Nutrition at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy.
“These new findings reveal critical areas for national and global focus to improve nutrition and reduce devastating burdens of diabetes,” he noted.
“Left unchecked and with incidence only projected to rise, type 2 diabetes will continue to impact population health, economic productivity, [and] health care system capacity, [as well as] drive health inequities worldwide,” Ms. O’Hearn said.
It’s about reducing harmful dietary components
Ms. O’Hearn and colleagues set out to fill information gaps in knowledge about how the global burden of diet-associated type 2 diabetes is impacted by disparities and other factors known to influence risk, including dietary components.
They used information from the Global Dietary Database to study dietary intake in 184 nations from 1990 to 2018. They also studied demographics from multiple sources, estimates of type 2 diabetes incidence around the world, and data on food choices, including the effect of 11 dietary factors, from prior research.
They found that there were 8.6 million more cases of type 2 diabetes in 2018 than in 1990 because of poor diet.
Regionally, Central and Eastern Europe and Central Asia had the greatest number of type 2 diabetes cases linked to diet, particularly Poland and Russia, where diets tend to be rich in red meat, processed meat, and potatoes. Incidence was also high in Latin America and the Caribbean, especially in Colombia and Mexico, which was attributed to high consumption of sugary drinks and processed meat and low intake of whole grains.
Regions where diet had less of an impact on type 2 diabetes cases included South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, although the largest increases in type 2 diabetes due to poor diet between 1990 and 2018 were observed in sub-Saharan Africa.
Diet-attributable type 2 diabetes was generally larger among urban versus rural residents and higher versus lower educated individuals, except in high-income countries, Central and Eastern Europe, and Central Asia, where burdens were larger in rural residents and in lower educated individuals.
Notably, women had lower proportions of diet-related type 2 diabetes, compared with men, and these proportions were inversely related to age.
Excess intake of harmful dietary factors contributed a greater percentage of the burden of type 2 diabetes globally (60.8%) than did insufficient intake of protective dietary factors (39.2%).
“Future research should address whether more complex diet–type 2 diabetes dose–response relationships exist,” the authors conclude.
Ms. O’Hearn has reported receiving research funding from the Gates Foundation, as well as the National Institutes of Health and Vail Innovative Global Research and employment with Food Systems for the Future. Dr. Mozaffarian has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health, the Gates Foundation, the Rockefeller Foundation, Vail Innovative Global Research, and the Kaiser Permanente Fund at East Bay Community Foundation; personal fees from Acasti Pharma, Barilla, Danone, and Motif FoodWorks; is on the scientific advisory board for Beren Therapeutics, Brightseed, Calibrate, DiscernDx, Elysium Health, Filtricine, HumanCo, January, Perfect Day, Tiny Organics and (ended) Day Two and Season Health; has stock ownership in Calibrate and HumanCo; and receives chapter royalties from UpToDate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Poor diets account for most newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes cases worldwide, a new analysis has found.
More specifically, the modeling study showed that roughly 14 million cases of type 2 diabetes – or 70% of total type 2 diabetes diagnoses in 2018 – were linked with a poor diet, found Meghan O’Hearn, a doctoral student at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy, Tufts University, Boston, and colleagues. The study was published online in Nature Medicine.
The results also indicate that the greatest burdens of type 2 diabetes were accounted for by excess wheat intake and refined rice (24.6%), excess processed meat consumption (20.3%), and inadequate whole-grain consumption (26.1%). Factors such as drinking too much fruit juice and not eating enough nonstarchy vegetables, nuts, or seeds, had less of an impact on new cases of the disease, the researchers determined.
“These findings can help inform nutritional priorities for clinicians, policymakers, and private sector actors as they encourage healthier dietary choices that address this global epidemic,” Ms. O’Hearn said in a press release.
Prior research has suggested that poor diet contributes to about 40% of type 2 diabetes cases worldwide, the researchers note.
The team attributes their finding of a 70% contribution to the new information in their analysis, such as the first-ever inclusion of refined grains, which was one of the top contributors to diabetes burden, and updated data on dietary habits based on national individual-level dietary surveys rather than agricultural estimates.
“Our study suggests poor carbohydrate quality is a leading driver of diet-attributable type 2 diabetes globally and with important variation by nation and over time,” said senior author Dariush Mozaffarian, MD, DrPh, MPH, who is the Jean Mayer Professor of Nutrition at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy.
“These new findings reveal critical areas for national and global focus to improve nutrition and reduce devastating burdens of diabetes,” he noted.
“Left unchecked and with incidence only projected to rise, type 2 diabetes will continue to impact population health, economic productivity, [and] health care system capacity, [as well as] drive health inequities worldwide,” Ms. O’Hearn said.
It’s about reducing harmful dietary components
Ms. O’Hearn and colleagues set out to fill information gaps in knowledge about how the global burden of diet-associated type 2 diabetes is impacted by disparities and other factors known to influence risk, including dietary components.
They used information from the Global Dietary Database to study dietary intake in 184 nations from 1990 to 2018. They also studied demographics from multiple sources, estimates of type 2 diabetes incidence around the world, and data on food choices, including the effect of 11 dietary factors, from prior research.
They found that there were 8.6 million more cases of type 2 diabetes in 2018 than in 1990 because of poor diet.
Regionally, Central and Eastern Europe and Central Asia had the greatest number of type 2 diabetes cases linked to diet, particularly Poland and Russia, where diets tend to be rich in red meat, processed meat, and potatoes. Incidence was also high in Latin America and the Caribbean, especially in Colombia and Mexico, which was attributed to high consumption of sugary drinks and processed meat and low intake of whole grains.
Regions where diet had less of an impact on type 2 diabetes cases included South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, although the largest increases in type 2 diabetes due to poor diet between 1990 and 2018 were observed in sub-Saharan Africa.
Diet-attributable type 2 diabetes was generally larger among urban versus rural residents and higher versus lower educated individuals, except in high-income countries, Central and Eastern Europe, and Central Asia, where burdens were larger in rural residents and in lower educated individuals.
Notably, women had lower proportions of diet-related type 2 diabetes, compared with men, and these proportions were inversely related to age.
Excess intake of harmful dietary factors contributed a greater percentage of the burden of type 2 diabetes globally (60.8%) than did insufficient intake of protective dietary factors (39.2%).
“Future research should address whether more complex diet–type 2 diabetes dose–response relationships exist,” the authors conclude.
Ms. O’Hearn has reported receiving research funding from the Gates Foundation, as well as the National Institutes of Health and Vail Innovative Global Research and employment with Food Systems for the Future. Dr. Mozaffarian has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health, the Gates Foundation, the Rockefeller Foundation, Vail Innovative Global Research, and the Kaiser Permanente Fund at East Bay Community Foundation; personal fees from Acasti Pharma, Barilla, Danone, and Motif FoodWorks; is on the scientific advisory board for Beren Therapeutics, Brightseed, Calibrate, DiscernDx, Elysium Health, Filtricine, HumanCo, January, Perfect Day, Tiny Organics and (ended) Day Two and Season Health; has stock ownership in Calibrate and HumanCo; and receives chapter royalties from UpToDate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
AI predicts endometrial cancer recurrence
Endometrial cancer is the most frequently occurring uterine cancer. Early-stage patients have about a 95% 5-year survival, but distant recurrence is associated with very poor survival, according to Sarah Fremond, MSc, an author of the research (Abstract 5695), which she presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
“Most patients with endometrial cancer have a good prognosis and would not require any adjuvant treatment, but there is a proportion that will develop distant recurrence. For those you want to recommend adjuvant chemotherapy, because currently in the adjuvant setting, that’s the only treatment that is known to lower the risk of distant recurrence. But that also causes morbidity. Therefore, our clinical question was how to accurately identify patients at low and high risk of distant recurrence to reduce under- and overtreatment,” said Ms. Fremond, a PhD candidate at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center.
Pathologists can attempt such predictions, but Ms. Fremond noted that there are challenges. “There is a lot of variability between pathologists, and we don’t even use the entire visual information present in the H&E [hematoxylin and eosin] tumor slide. When it comes to molecular testing, it is hampered by cost, turnaround time, and sometimes interpretation. It’s quite complex to combine those data to specifically target risk of distant recurrence for patients with endometrial cancer.”
In her presentation, Ms. Fremond described how she and her colleagues used digitized histopathological slides in their research. She and her coauthors developed the AI model as part of a collaboration that included the AIRMEC Consortium, Leiden University Medical Center, the TransPORTEC Consortium, and the University of Zürich.
The researchers used long-term follow-up data from 1,408 patients drawn from three clinical cohorts and participants in the PORTEC-1, PORTEC-2, and PORTEC-3 studies, which tested radiotherapy and adjuvant therapy outcomes in endometrial cancer. Patients who had received prior adjuvant chemotherapy were excluded. In the model development phase, the system analyzed a single representative histopathological slide image from each patient and compared it with the known time to distant recurrence to identify patterns.
Once the system had been trained, the researchers applied it to a novel group of 353 patients. It ranked 89 patients as having a low risk of recurrence, 175 at intermediate risk, and 89 at high risk of recurrence. The system performed well: 3.37% of low-risk patients experienced a distant recurrence, as did 15.43% of the intermediate-risk group and 36% of the high-risk group.
The researchers also employed an external validation group with 152 patients and three slides per patient, with a 2.8-year follow-up. The model performed with a C index of 0.805 (±0.0136) when a random slide was selected for each patient, and the median predicted risk score per patient was associated with differences in distant recurrence-free survival between the three risk groups with a C index of 0.816 (P < .0001).
Questions about research and their answers
Session moderator Kristin Swanson, PhD, asked if the AI could be used with the pathology slide’s visible features to learn more about the underlying biology and pathophysiology of tumors.
“Overlying the HECTOR on to the tissue seems like a logical opportunity to go and then explore the biology and what’s attributed as a high-risk region,” said Dr. Swanson, who is director of the Mathematical NeuroOncology Lab and codirector of the Precision NeuroTherapeutics Innovation Program at Mayo Clinic Arizona, Phoenix.
Ms. Fremond agreed that the AI has the potential to be used that way.”
During the Q&A, an audience member asked how likely the model is to perform in populations that differ significantly from the populations used in her study.
Ms. Fremond responded that the populations used to develop and test the models were in or close to the Netherlands, and little information was available regarding patient ethnicity. “There is a possibility that perhaps we would have a different performance on a population that includes more minorities. That needs to be checked,” said Ms. Fremond.
The study is limited by its retrospective nature.
Ms. Fremond and Dr. Swanson have no relevant financial disclosures.
Endometrial cancer is the most frequently occurring uterine cancer. Early-stage patients have about a 95% 5-year survival, but distant recurrence is associated with very poor survival, according to Sarah Fremond, MSc, an author of the research (Abstract 5695), which she presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
“Most patients with endometrial cancer have a good prognosis and would not require any adjuvant treatment, but there is a proportion that will develop distant recurrence. For those you want to recommend adjuvant chemotherapy, because currently in the adjuvant setting, that’s the only treatment that is known to lower the risk of distant recurrence. But that also causes morbidity. Therefore, our clinical question was how to accurately identify patients at low and high risk of distant recurrence to reduce under- and overtreatment,” said Ms. Fremond, a PhD candidate at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center.
Pathologists can attempt such predictions, but Ms. Fremond noted that there are challenges. “There is a lot of variability between pathologists, and we don’t even use the entire visual information present in the H&E [hematoxylin and eosin] tumor slide. When it comes to molecular testing, it is hampered by cost, turnaround time, and sometimes interpretation. It’s quite complex to combine those data to specifically target risk of distant recurrence for patients with endometrial cancer.”
In her presentation, Ms. Fremond described how she and her colleagues used digitized histopathological slides in their research. She and her coauthors developed the AI model as part of a collaboration that included the AIRMEC Consortium, Leiden University Medical Center, the TransPORTEC Consortium, and the University of Zürich.
The researchers used long-term follow-up data from 1,408 patients drawn from three clinical cohorts and participants in the PORTEC-1, PORTEC-2, and PORTEC-3 studies, which tested radiotherapy and adjuvant therapy outcomes in endometrial cancer. Patients who had received prior adjuvant chemotherapy were excluded. In the model development phase, the system analyzed a single representative histopathological slide image from each patient and compared it with the known time to distant recurrence to identify patterns.
Once the system had been trained, the researchers applied it to a novel group of 353 patients. It ranked 89 patients as having a low risk of recurrence, 175 at intermediate risk, and 89 at high risk of recurrence. The system performed well: 3.37% of low-risk patients experienced a distant recurrence, as did 15.43% of the intermediate-risk group and 36% of the high-risk group.
The researchers also employed an external validation group with 152 patients and three slides per patient, with a 2.8-year follow-up. The model performed with a C index of 0.805 (±0.0136) when a random slide was selected for each patient, and the median predicted risk score per patient was associated with differences in distant recurrence-free survival between the three risk groups with a C index of 0.816 (P < .0001).
Questions about research and their answers
Session moderator Kristin Swanson, PhD, asked if the AI could be used with the pathology slide’s visible features to learn more about the underlying biology and pathophysiology of tumors.
“Overlying the HECTOR on to the tissue seems like a logical opportunity to go and then explore the biology and what’s attributed as a high-risk region,” said Dr. Swanson, who is director of the Mathematical NeuroOncology Lab and codirector of the Precision NeuroTherapeutics Innovation Program at Mayo Clinic Arizona, Phoenix.
Ms. Fremond agreed that the AI has the potential to be used that way.”
During the Q&A, an audience member asked how likely the model is to perform in populations that differ significantly from the populations used in her study.
Ms. Fremond responded that the populations used to develop and test the models were in or close to the Netherlands, and little information was available regarding patient ethnicity. “There is a possibility that perhaps we would have a different performance on a population that includes more minorities. That needs to be checked,” said Ms. Fremond.
The study is limited by its retrospective nature.
Ms. Fremond and Dr. Swanson have no relevant financial disclosures.
Endometrial cancer is the most frequently occurring uterine cancer. Early-stage patients have about a 95% 5-year survival, but distant recurrence is associated with very poor survival, according to Sarah Fremond, MSc, an author of the research (Abstract 5695), which she presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
“Most patients with endometrial cancer have a good prognosis and would not require any adjuvant treatment, but there is a proportion that will develop distant recurrence. For those you want to recommend adjuvant chemotherapy, because currently in the adjuvant setting, that’s the only treatment that is known to lower the risk of distant recurrence. But that also causes morbidity. Therefore, our clinical question was how to accurately identify patients at low and high risk of distant recurrence to reduce under- and overtreatment,” said Ms. Fremond, a PhD candidate at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center.
Pathologists can attempt such predictions, but Ms. Fremond noted that there are challenges. “There is a lot of variability between pathologists, and we don’t even use the entire visual information present in the H&E [hematoxylin and eosin] tumor slide. When it comes to molecular testing, it is hampered by cost, turnaround time, and sometimes interpretation. It’s quite complex to combine those data to specifically target risk of distant recurrence for patients with endometrial cancer.”
In her presentation, Ms. Fremond described how she and her colleagues used digitized histopathological slides in their research. She and her coauthors developed the AI model as part of a collaboration that included the AIRMEC Consortium, Leiden University Medical Center, the TransPORTEC Consortium, and the University of Zürich.
The researchers used long-term follow-up data from 1,408 patients drawn from three clinical cohorts and participants in the PORTEC-1, PORTEC-2, and PORTEC-3 studies, which tested radiotherapy and adjuvant therapy outcomes in endometrial cancer. Patients who had received prior adjuvant chemotherapy were excluded. In the model development phase, the system analyzed a single representative histopathological slide image from each patient and compared it with the known time to distant recurrence to identify patterns.
Once the system had been trained, the researchers applied it to a novel group of 353 patients. It ranked 89 patients as having a low risk of recurrence, 175 at intermediate risk, and 89 at high risk of recurrence. The system performed well: 3.37% of low-risk patients experienced a distant recurrence, as did 15.43% of the intermediate-risk group and 36% of the high-risk group.
The researchers also employed an external validation group with 152 patients and three slides per patient, with a 2.8-year follow-up. The model performed with a C index of 0.805 (±0.0136) when a random slide was selected for each patient, and the median predicted risk score per patient was associated with differences in distant recurrence-free survival between the three risk groups with a C index of 0.816 (P < .0001).
Questions about research and their answers
Session moderator Kristin Swanson, PhD, asked if the AI could be used with the pathology slide’s visible features to learn more about the underlying biology and pathophysiology of tumors.
“Overlying the HECTOR on to the tissue seems like a logical opportunity to go and then explore the biology and what’s attributed as a high-risk region,” said Dr. Swanson, who is director of the Mathematical NeuroOncology Lab and codirector of the Precision NeuroTherapeutics Innovation Program at Mayo Clinic Arizona, Phoenix.
Ms. Fremond agreed that the AI has the potential to be used that way.”
During the Q&A, an audience member asked how likely the model is to perform in populations that differ significantly from the populations used in her study.
Ms. Fremond responded that the populations used to develop and test the models were in or close to the Netherlands, and little information was available regarding patient ethnicity. “There is a possibility that perhaps we would have a different performance on a population that includes more minorities. That needs to be checked,” said Ms. Fremond.
The study is limited by its retrospective nature.
Ms. Fremond and Dr. Swanson have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM AACR 2023
CDC backs FDA’s call for second COVID booster for those at high risk
This backs the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization April 18 of the additional shot.
“Following FDA regulatory action, CDC has taken steps to simplify COVID-19 vaccine recommendations and allow more flexibility for people at higher risk who want the option of added protection from additional COVID-19 vaccine doses,” the CDC said in a statement.
The agency is following the recommendations made by its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). While there was no vote, the group reaffirmed its commitment to boosters overall, proposing that all Americans over age 6 who have not had a bivalent mRNA COVID-19 booster vaccine go ahead and get one.
But most others who’ve already had the bivalent shot – which targets the original COVID strain and the two Omicron variants BA.4 and BA.5 – should wait until the fall to get whatever updated vaccine is available.
The panel did carve out exceptions for people over age 65 and those who are immunocompromised because they are at higher risk for severe COVID-19 complications, Evelyn Twentyman, MD, MPH, the lead official in the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Policy Unit, said during the meeting.
People over 65 can now choose to get a second bivalent mRNA booster shot as long as it has been at least 4 months since the last one, she said, and people who are immunocompromised also should have the flexibility to receive one or more additional bivalent boosters at least 2 months after an initial dose.
Regardless of whether someone is unvaccinated, and regardless of how many single-strain COVID vaccines an individual has previously received, they should get a mRNA bivalent shot, Dr. Twentyman said.
If an individual has already received a bivalent mRNA booster – made by either Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna – “your vaccination is complete,” she said. “No doses indicated at this time, come back and see us in autumn of 2023.”
The CDC is trying to encourage more people to get the updated COVID shot, as just 17% of Americans of any age have received a bivalent booster and only 43% of those age 65 and over.
The CDC followed the FDA’s lead in its statement, phasing out the original single-strain COVID vaccine, saying it will no longer be recommended for use in the United States.
‘Unnecessary drama’ over children’s recs
The CDC panel mostly followed the FDA’s guidance on who should get a booster, but many ACIP members expressed consternation and confusion about what was being recommended for children.
For children aged 6 months to 4 years, the CDC will offer tables to help physicians determine how many bivalent doses to give, depending on the child’s vaccination history.
All children those ages should get at least two vaccine doses, one of which is bivalent, Dr. Twentyman said. For children in that age group who have already received a monovalent series and a bivalent dose, “their vaccination is complete,” she said.
For 5-year-olds, the recommendations will be similar if they received a Pfizer monovalent series, but the shot regimen will have to be customized if they had previously received a Moderna shot, because of differences in the dosages.
ACIP member Sarah S. Long, MD, professor of pediatrics, Drexel University, Philadelphia, said that it was unclear why a set age couldn’t be established for COVID-19 vaccination as it had been for other immunizations.
“We picked 60 months for most immunizations in children,” Dr. Long said. “Immunologically there is not a difference between a 4-, a 5- and a 6-year-old.
“There isn’t a reason to have all this unnecessary drama around those ages,” she said, adding that having the different ages would make it harder for pediatricians to appropriately stock vaccines.
Dr. Twentyman said that the CDC would be providing more detailed guidance on its COVID-19 website soon and would be holding a call with health care professionals to discuss the updated recommendations on May 11.
New vaccine by fall
CDC and ACIP members both said they hoped to have an even simpler vaccine schedule by the fall, when it is anticipated that the FDA may have authorized a new, updated bivalent vaccine that targets other COVID variants.
“We all recognize this is a work in progress,” said ACIP Chair Grace M. Lee, MD, MPH, acknowledging that there is continued confusion over COVID-19 vaccination.
“The goal really is to try to simplify things over time to be able to help communicate with our provider community, and our patients and families what vaccine is right for them, when do they need it, and how often should they get it,” said Dr. Lee, professor of pediatrics, Stanford (Calif.) University.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com .
This backs the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization April 18 of the additional shot.
“Following FDA regulatory action, CDC has taken steps to simplify COVID-19 vaccine recommendations and allow more flexibility for people at higher risk who want the option of added protection from additional COVID-19 vaccine doses,” the CDC said in a statement.
The agency is following the recommendations made by its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). While there was no vote, the group reaffirmed its commitment to boosters overall, proposing that all Americans over age 6 who have not had a bivalent mRNA COVID-19 booster vaccine go ahead and get one.
But most others who’ve already had the bivalent shot – which targets the original COVID strain and the two Omicron variants BA.4 and BA.5 – should wait until the fall to get whatever updated vaccine is available.
The panel did carve out exceptions for people over age 65 and those who are immunocompromised because they are at higher risk for severe COVID-19 complications, Evelyn Twentyman, MD, MPH, the lead official in the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Policy Unit, said during the meeting.
People over 65 can now choose to get a second bivalent mRNA booster shot as long as it has been at least 4 months since the last one, she said, and people who are immunocompromised also should have the flexibility to receive one or more additional bivalent boosters at least 2 months after an initial dose.
Regardless of whether someone is unvaccinated, and regardless of how many single-strain COVID vaccines an individual has previously received, they should get a mRNA bivalent shot, Dr. Twentyman said.
If an individual has already received a bivalent mRNA booster – made by either Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna – “your vaccination is complete,” she said. “No doses indicated at this time, come back and see us in autumn of 2023.”
The CDC is trying to encourage more people to get the updated COVID shot, as just 17% of Americans of any age have received a bivalent booster and only 43% of those age 65 and over.
The CDC followed the FDA’s lead in its statement, phasing out the original single-strain COVID vaccine, saying it will no longer be recommended for use in the United States.
‘Unnecessary drama’ over children’s recs
The CDC panel mostly followed the FDA’s guidance on who should get a booster, but many ACIP members expressed consternation and confusion about what was being recommended for children.
For children aged 6 months to 4 years, the CDC will offer tables to help physicians determine how many bivalent doses to give, depending on the child’s vaccination history.
All children those ages should get at least two vaccine doses, one of which is bivalent, Dr. Twentyman said. For children in that age group who have already received a monovalent series and a bivalent dose, “their vaccination is complete,” she said.
For 5-year-olds, the recommendations will be similar if they received a Pfizer monovalent series, but the shot regimen will have to be customized if they had previously received a Moderna shot, because of differences in the dosages.
ACIP member Sarah S. Long, MD, professor of pediatrics, Drexel University, Philadelphia, said that it was unclear why a set age couldn’t be established for COVID-19 vaccination as it had been for other immunizations.
“We picked 60 months for most immunizations in children,” Dr. Long said. “Immunologically there is not a difference between a 4-, a 5- and a 6-year-old.
“There isn’t a reason to have all this unnecessary drama around those ages,” she said, adding that having the different ages would make it harder for pediatricians to appropriately stock vaccines.
Dr. Twentyman said that the CDC would be providing more detailed guidance on its COVID-19 website soon and would be holding a call with health care professionals to discuss the updated recommendations on May 11.
New vaccine by fall
CDC and ACIP members both said they hoped to have an even simpler vaccine schedule by the fall, when it is anticipated that the FDA may have authorized a new, updated bivalent vaccine that targets other COVID variants.
“We all recognize this is a work in progress,” said ACIP Chair Grace M. Lee, MD, MPH, acknowledging that there is continued confusion over COVID-19 vaccination.
“The goal really is to try to simplify things over time to be able to help communicate with our provider community, and our patients and families what vaccine is right for them, when do they need it, and how often should they get it,” said Dr. Lee, professor of pediatrics, Stanford (Calif.) University.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com .
This backs the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization April 18 of the additional shot.
“Following FDA regulatory action, CDC has taken steps to simplify COVID-19 vaccine recommendations and allow more flexibility for people at higher risk who want the option of added protection from additional COVID-19 vaccine doses,” the CDC said in a statement.
The agency is following the recommendations made by its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). While there was no vote, the group reaffirmed its commitment to boosters overall, proposing that all Americans over age 6 who have not had a bivalent mRNA COVID-19 booster vaccine go ahead and get one.
But most others who’ve already had the bivalent shot – which targets the original COVID strain and the two Omicron variants BA.4 and BA.5 – should wait until the fall to get whatever updated vaccine is available.
The panel did carve out exceptions for people over age 65 and those who are immunocompromised because they are at higher risk for severe COVID-19 complications, Evelyn Twentyman, MD, MPH, the lead official in the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Policy Unit, said during the meeting.
People over 65 can now choose to get a second bivalent mRNA booster shot as long as it has been at least 4 months since the last one, she said, and people who are immunocompromised also should have the flexibility to receive one or more additional bivalent boosters at least 2 months after an initial dose.
Regardless of whether someone is unvaccinated, and regardless of how many single-strain COVID vaccines an individual has previously received, they should get a mRNA bivalent shot, Dr. Twentyman said.
If an individual has already received a bivalent mRNA booster – made by either Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna – “your vaccination is complete,” she said. “No doses indicated at this time, come back and see us in autumn of 2023.”
The CDC is trying to encourage more people to get the updated COVID shot, as just 17% of Americans of any age have received a bivalent booster and only 43% of those age 65 and over.
The CDC followed the FDA’s lead in its statement, phasing out the original single-strain COVID vaccine, saying it will no longer be recommended for use in the United States.
‘Unnecessary drama’ over children’s recs
The CDC panel mostly followed the FDA’s guidance on who should get a booster, but many ACIP members expressed consternation and confusion about what was being recommended for children.
For children aged 6 months to 4 years, the CDC will offer tables to help physicians determine how many bivalent doses to give, depending on the child’s vaccination history.
All children those ages should get at least two vaccine doses, one of which is bivalent, Dr. Twentyman said. For children in that age group who have already received a monovalent series and a bivalent dose, “their vaccination is complete,” she said.
For 5-year-olds, the recommendations will be similar if they received a Pfizer monovalent series, but the shot regimen will have to be customized if they had previously received a Moderna shot, because of differences in the dosages.
ACIP member Sarah S. Long, MD, professor of pediatrics, Drexel University, Philadelphia, said that it was unclear why a set age couldn’t be established for COVID-19 vaccination as it had been for other immunizations.
“We picked 60 months for most immunizations in children,” Dr. Long said. “Immunologically there is not a difference between a 4-, a 5- and a 6-year-old.
“There isn’t a reason to have all this unnecessary drama around those ages,” she said, adding that having the different ages would make it harder for pediatricians to appropriately stock vaccines.
Dr. Twentyman said that the CDC would be providing more detailed guidance on its COVID-19 website soon and would be holding a call with health care professionals to discuss the updated recommendations on May 11.
New vaccine by fall
CDC and ACIP members both said they hoped to have an even simpler vaccine schedule by the fall, when it is anticipated that the FDA may have authorized a new, updated bivalent vaccine that targets other COVID variants.
“We all recognize this is a work in progress,” said ACIP Chair Grace M. Lee, MD, MPH, acknowledging that there is continued confusion over COVID-19 vaccination.
“The goal really is to try to simplify things over time to be able to help communicate with our provider community, and our patients and families what vaccine is right for them, when do they need it, and how often should they get it,” said Dr. Lee, professor of pediatrics, Stanford (Calif.) University.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com .
What are the healthiest drinks for patients with type 2 diabetes?
The researchers examined data on almost 15,500 participants with type 2 diabetes from two major studies, finding that the highest level of consumption of SSBs was associated with a 20% increased risk of all-cause mortality and a 25% raised risk of cardiovascular disease, compared with consumption of the least amounts of these products.
The research, published in BMJ, also showed that drinking coffee, tea, plain water, and low-fat milk reduced the risk of all-cause death and that switching from SSBs to the other beverages was linked to lower mortality.
“Overall, these results provide additional evidence that emphasizes the importance of beverage choices in maintaining overall health among adults with diabetes,” say senior author Le Ma, PhD, department of nutrition, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, and colleagues.
“Collectively, these findings all point in the same direction. Lower consumption of SSBs and higher consumption of coffee, tea, plain water, or low-fat milk are optimal for better health outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes,” Nita G. Forouhi, MD, PhD, emphasizes in an accompanying editorial.
Choice of drink matters
Dr. Forouhi, from the University of Cambridge (England), warned, however, that the findings “cannot be considered cause and effect,” despite the large-scale analysis.
Moreover, “questions remain,” such as the impact of beverage consumption on coronary heart disease and stroke risk, and cancer mortality, with the current study providing “inconclusive” data on the latter.
There was also no data on the addition of sugar to tea or coffee, “so the comparative health effects of unsweetened and sweetened hot beverages remain unclear,” Dr. Forouhi points out. Also unknown is whether the type of tea consumed has a differential effect.
Despite these and other reservations, she says that overall, “Choice of beverage clearly matters.”
“The case for avoiding sugar-sweetened beverages is compelling, and it is supported by various fiscal measures in more than 45 countries. It is reasonable to shift the focus to drinks that are most likely to have positive health impacts: coffee, tea, plain water, and low-fat milk,” she notes.
Dr. Forouhi ends by underlining that the current findings tally with those seen in the general population, so “one important message is that having diabetes does not have to be especially restrictive.”
Expanding the evidence
It was estimated that 537 million adults worldwide had type 2 diabetes in 2021, a figure set to increase to 783 million by 2045, say the authors.
Individuals with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, among many other comorbidities, as well as premature death. Dietary interventions can play an important role in managing these risks.
Recommendations on the healthiest beverages to drink are largely based on evidence from the general population, and data are limited on the best options for adults with type 2 diabetes, who have altered metabolism, the researchers note.
To expand on this, they examined data from the Nurses’ Health Study, which enrolled female registered nurses aged 30-55 years and was initiated in 1976, and the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, which included male health professionals aged 40-75 years and was initiated in 1996.
For the current analysis, 11,399 women and 4,087 men with type 2 diabetes were included from the two studies, of whom 2,715 were diagnosed before study entry.
Participants’ average daily beverage intake was assessed using a validated food frequency questionnaire administered every 2-4 years. SSBs included caffeinated and caffeine-free colas, other carbonated SSBs, and noncarbonated SSBs, such as fruit punches, lemonades, or other fruit drinks.
During 285,967 person-years of follow-up, there were 7,638 (49.3%) deaths, and 3,447 (22.3%) cases of incident cardiovascular disease were documented during 248,447 person-years of follow-up.
Fully adjusted multivariate analysis comparing the lowest and highest beverage intake indicated that SSBs were associated with a significant increase in all-cause mortality, at a pooled hazard ratio of 1.20, or 1.08 for each additional serving per day (P = .01).
In contrast, the associations between all-cause mortality and consumption of artificially sweetened beverages, fruit juice, and full-fat milk were not significant, whereas coffee (HR, 0.74), tea (HR, 0.79), plain water (HR, 0.77), and low-fat milk (HR, 0.88) were linked to a reduced risk.
The team reported that there were similar associations between beverage intake and cardiovascular disease incidence, at an HR of 1.25 for SSBs, as well as for cardiovascular disease mortality, at an HR of 1.29.
Participants who increased their tea, coffee, and low-fat milk consumption during the course of the study had lower all-cause mortality than those who did not. Switching from SSBs to other beverages was also associated with lower mortality.
The researchers note, however, that there are “several potential limitations” to their study, including that “individual beverage consumption may be correlated with other dietary and lifestyle risk factors for cardiovascular disease incidence and mortality among adults with [type 2] diabetes.”
The study was sponsored by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ma has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article. Dr. Forouhi has declared receiving support from the U.K. Medical Research Council Epidemiology Unit and U.K. National Institute for Health and Care Research Biomedical Research Centre Cambridge.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The researchers examined data on almost 15,500 participants with type 2 diabetes from two major studies, finding that the highest level of consumption of SSBs was associated with a 20% increased risk of all-cause mortality and a 25% raised risk of cardiovascular disease, compared with consumption of the least amounts of these products.
The research, published in BMJ, also showed that drinking coffee, tea, plain water, and low-fat milk reduced the risk of all-cause death and that switching from SSBs to the other beverages was linked to lower mortality.
“Overall, these results provide additional evidence that emphasizes the importance of beverage choices in maintaining overall health among adults with diabetes,” say senior author Le Ma, PhD, department of nutrition, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, and colleagues.
“Collectively, these findings all point in the same direction. Lower consumption of SSBs and higher consumption of coffee, tea, plain water, or low-fat milk are optimal for better health outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes,” Nita G. Forouhi, MD, PhD, emphasizes in an accompanying editorial.
Choice of drink matters
Dr. Forouhi, from the University of Cambridge (England), warned, however, that the findings “cannot be considered cause and effect,” despite the large-scale analysis.
Moreover, “questions remain,” such as the impact of beverage consumption on coronary heart disease and stroke risk, and cancer mortality, with the current study providing “inconclusive” data on the latter.
There was also no data on the addition of sugar to tea or coffee, “so the comparative health effects of unsweetened and sweetened hot beverages remain unclear,” Dr. Forouhi points out. Also unknown is whether the type of tea consumed has a differential effect.
Despite these and other reservations, she says that overall, “Choice of beverage clearly matters.”
“The case for avoiding sugar-sweetened beverages is compelling, and it is supported by various fiscal measures in more than 45 countries. It is reasonable to shift the focus to drinks that are most likely to have positive health impacts: coffee, tea, plain water, and low-fat milk,” she notes.
Dr. Forouhi ends by underlining that the current findings tally with those seen in the general population, so “one important message is that having diabetes does not have to be especially restrictive.”
Expanding the evidence
It was estimated that 537 million adults worldwide had type 2 diabetes in 2021, a figure set to increase to 783 million by 2045, say the authors.
Individuals with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, among many other comorbidities, as well as premature death. Dietary interventions can play an important role in managing these risks.
Recommendations on the healthiest beverages to drink are largely based on evidence from the general population, and data are limited on the best options for adults with type 2 diabetes, who have altered metabolism, the researchers note.
To expand on this, they examined data from the Nurses’ Health Study, which enrolled female registered nurses aged 30-55 years and was initiated in 1976, and the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, which included male health professionals aged 40-75 years and was initiated in 1996.
For the current analysis, 11,399 women and 4,087 men with type 2 diabetes were included from the two studies, of whom 2,715 were diagnosed before study entry.
Participants’ average daily beverage intake was assessed using a validated food frequency questionnaire administered every 2-4 years. SSBs included caffeinated and caffeine-free colas, other carbonated SSBs, and noncarbonated SSBs, such as fruit punches, lemonades, or other fruit drinks.
During 285,967 person-years of follow-up, there were 7,638 (49.3%) deaths, and 3,447 (22.3%) cases of incident cardiovascular disease were documented during 248,447 person-years of follow-up.
Fully adjusted multivariate analysis comparing the lowest and highest beverage intake indicated that SSBs were associated with a significant increase in all-cause mortality, at a pooled hazard ratio of 1.20, or 1.08 for each additional serving per day (P = .01).
In contrast, the associations between all-cause mortality and consumption of artificially sweetened beverages, fruit juice, and full-fat milk were not significant, whereas coffee (HR, 0.74), tea (HR, 0.79), plain water (HR, 0.77), and low-fat milk (HR, 0.88) were linked to a reduced risk.
The team reported that there were similar associations between beverage intake and cardiovascular disease incidence, at an HR of 1.25 for SSBs, as well as for cardiovascular disease mortality, at an HR of 1.29.
Participants who increased their tea, coffee, and low-fat milk consumption during the course of the study had lower all-cause mortality than those who did not. Switching from SSBs to other beverages was also associated with lower mortality.
The researchers note, however, that there are “several potential limitations” to their study, including that “individual beverage consumption may be correlated with other dietary and lifestyle risk factors for cardiovascular disease incidence and mortality among adults with [type 2] diabetes.”
The study was sponsored by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ma has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article. Dr. Forouhi has declared receiving support from the U.K. Medical Research Council Epidemiology Unit and U.K. National Institute for Health and Care Research Biomedical Research Centre Cambridge.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The researchers examined data on almost 15,500 participants with type 2 diabetes from two major studies, finding that the highest level of consumption of SSBs was associated with a 20% increased risk of all-cause mortality and a 25% raised risk of cardiovascular disease, compared with consumption of the least amounts of these products.
The research, published in BMJ, also showed that drinking coffee, tea, plain water, and low-fat milk reduced the risk of all-cause death and that switching from SSBs to the other beverages was linked to lower mortality.
“Overall, these results provide additional evidence that emphasizes the importance of beverage choices in maintaining overall health among adults with diabetes,” say senior author Le Ma, PhD, department of nutrition, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, and colleagues.
“Collectively, these findings all point in the same direction. Lower consumption of SSBs and higher consumption of coffee, tea, plain water, or low-fat milk are optimal for better health outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes,” Nita G. Forouhi, MD, PhD, emphasizes in an accompanying editorial.
Choice of drink matters
Dr. Forouhi, from the University of Cambridge (England), warned, however, that the findings “cannot be considered cause and effect,” despite the large-scale analysis.
Moreover, “questions remain,” such as the impact of beverage consumption on coronary heart disease and stroke risk, and cancer mortality, with the current study providing “inconclusive” data on the latter.
There was also no data on the addition of sugar to tea or coffee, “so the comparative health effects of unsweetened and sweetened hot beverages remain unclear,” Dr. Forouhi points out. Also unknown is whether the type of tea consumed has a differential effect.
Despite these and other reservations, she says that overall, “Choice of beverage clearly matters.”
“The case for avoiding sugar-sweetened beverages is compelling, and it is supported by various fiscal measures in more than 45 countries. It is reasonable to shift the focus to drinks that are most likely to have positive health impacts: coffee, tea, plain water, and low-fat milk,” she notes.
Dr. Forouhi ends by underlining that the current findings tally with those seen in the general population, so “one important message is that having diabetes does not have to be especially restrictive.”
Expanding the evidence
It was estimated that 537 million adults worldwide had type 2 diabetes in 2021, a figure set to increase to 783 million by 2045, say the authors.
Individuals with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, among many other comorbidities, as well as premature death. Dietary interventions can play an important role in managing these risks.
Recommendations on the healthiest beverages to drink are largely based on evidence from the general population, and data are limited on the best options for adults with type 2 diabetes, who have altered metabolism, the researchers note.
To expand on this, they examined data from the Nurses’ Health Study, which enrolled female registered nurses aged 30-55 years and was initiated in 1976, and the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, which included male health professionals aged 40-75 years and was initiated in 1996.
For the current analysis, 11,399 women and 4,087 men with type 2 diabetes were included from the two studies, of whom 2,715 were diagnosed before study entry.
Participants’ average daily beverage intake was assessed using a validated food frequency questionnaire administered every 2-4 years. SSBs included caffeinated and caffeine-free colas, other carbonated SSBs, and noncarbonated SSBs, such as fruit punches, lemonades, or other fruit drinks.
During 285,967 person-years of follow-up, there were 7,638 (49.3%) deaths, and 3,447 (22.3%) cases of incident cardiovascular disease were documented during 248,447 person-years of follow-up.
Fully adjusted multivariate analysis comparing the lowest and highest beverage intake indicated that SSBs were associated with a significant increase in all-cause mortality, at a pooled hazard ratio of 1.20, or 1.08 for each additional serving per day (P = .01).
In contrast, the associations between all-cause mortality and consumption of artificially sweetened beverages, fruit juice, and full-fat milk were not significant, whereas coffee (HR, 0.74), tea (HR, 0.79), plain water (HR, 0.77), and low-fat milk (HR, 0.88) were linked to a reduced risk.
The team reported that there were similar associations between beverage intake and cardiovascular disease incidence, at an HR of 1.25 for SSBs, as well as for cardiovascular disease mortality, at an HR of 1.29.
Participants who increased their tea, coffee, and low-fat milk consumption during the course of the study had lower all-cause mortality than those who did not. Switching from SSBs to other beverages was also associated with lower mortality.
The researchers note, however, that there are “several potential limitations” to their study, including that “individual beverage consumption may be correlated with other dietary and lifestyle risk factors for cardiovascular disease incidence and mortality among adults with [type 2] diabetes.”
The study was sponsored by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ma has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article. Dr. Forouhi has declared receiving support from the U.K. Medical Research Council Epidemiology Unit and U.K. National Institute for Health and Care Research Biomedical Research Centre Cambridge.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE BMJ
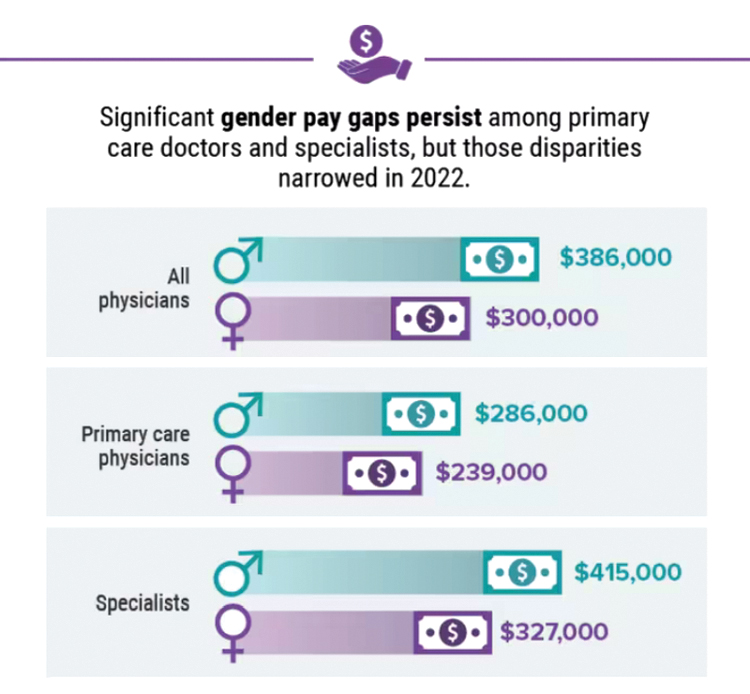
Infographic: Is your compensation rising as fast as your peers?
Did doctors’ salaries continue their zesty postpandemic rise in 2022? Are female physicians making pay gains versus their male counterparts that spark optimism for the future?
reveals which medical specialties pay better than others, and evaluates the current gender pay gap in medicine. If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out Your Income vs. Your Peers’: Physician Compensation Report 2023.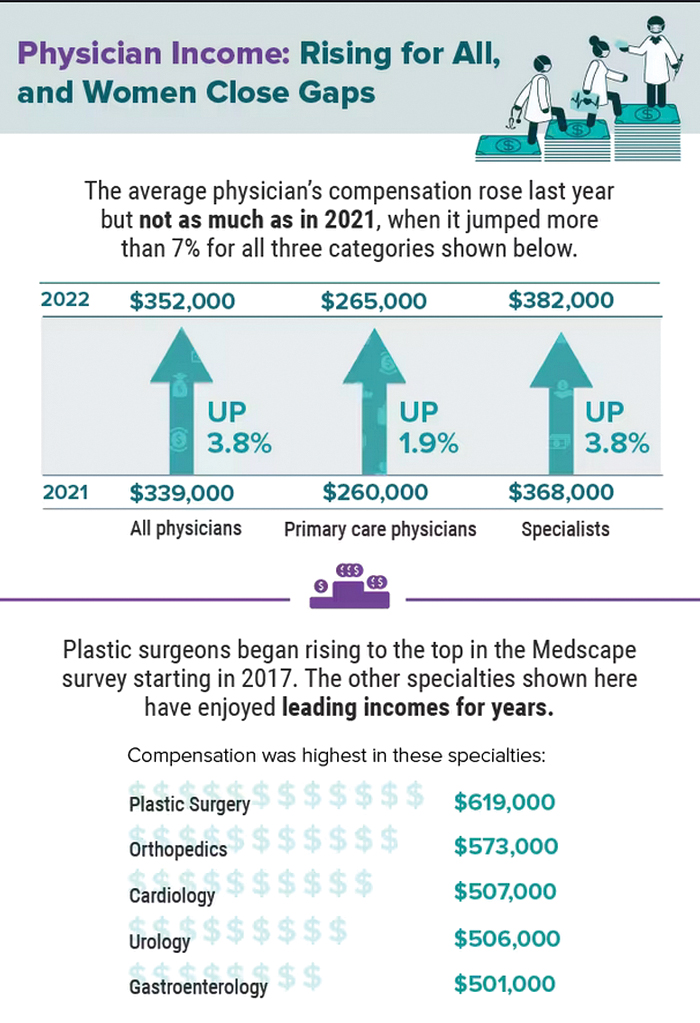
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Did doctors’ salaries continue their zesty postpandemic rise in 2022? Are female physicians making pay gains versus their male counterparts that spark optimism for the future?
reveals which medical specialties pay better than others, and evaluates the current gender pay gap in medicine. If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out Your Income vs. Your Peers’: Physician Compensation Report 2023.

A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Did doctors’ salaries continue their zesty postpandemic rise in 2022? Are female physicians making pay gains versus their male counterparts that spark optimism for the future?
reveals which medical specialties pay better than others, and evaluates the current gender pay gap in medicine. If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out Your Income vs. Your Peers’: Physician Compensation Report 2023.

A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A baby stops breathing at a grocery store – An ICU nurse steps in
My son needed a physical for his football team, and we couldn’t get an appointment. So, we went to the urgent care next to the H Mart in Cary, N.C. While I was waiting, I thought, let me go get a coffee or an iced tea at the H Mart. They have this French bakery in there.
I went in and ordered my drink, and I was waiting in line. I saw this woman pass me running with a baby. Another woman – I found out later it was her sister – was running after her, and she said: “Call 911!”
“I don’t have my phone,” I said. I left my phone with my son; he was using it.
I said: “Are you okay?” And she just handed me the baby. The baby was gray, and there was blood in her nose and mouth. The woman said: “She’s my baby. She’s 1 week old.”
I was trying to think very quickly. I didn’t see any bubbles in the blood around the baby’s nose or mouth to tell me if she was breathing. She was just limp. The mom was still screaming, but I couldn’t even hear her anymore. It was like I was having an out-of-body experience. All I could hear were my thoughts: “I need to put this baby down to start CPR. Someone was calling 911. I should go in the front of the store to save time, so EMS doesn’t have to look for me when they come.”
I started moving and trying to clean the blood from the baby’s face with her blanket. At the front of the store, I saw a display of rice bags. I put the baby on top of one of the bags. “Okay, where do I check for a pulse on a baby?” I took care of adults, never pediatric patients, never babies. She was so tiny. I put my hand on her chest and felt nothing. No heartbeat. She still wasn’t breathing.
People were around me, but I couldn’t see or hear anybody. All I was thinking was: “What can I do for this patient right now?” I started CPR with two fingers. Nothing was happening. It wasn’t that long, but it felt like forever for me. I couldn’t do mouth-to-mouth because there was so much blood on her face. I still don’t know what caused the bleeding.
It was COVID time, so I had my mask on. I was, like: “You know what? Screw this. She’s a 1-week-old baby. Her lungs are tiny. Maybe I don’t have to do mouth-to-mouth. I can just blow in her mouth.” I took off my mask and opened her mouth. I took a deep breath and blew a little bit of air in her mouth. I continued CPR for maybe 5 or 10 seconds.
And then she gasped! She opened her eyes, but they were rolled up. I was still doing CPR, and maybe 2 second after that, I could feel under my hand a very rapid heart rate. I took my hand away and lifted her up.
Just then the EMS got there. I gave them the baby and said: “I did CPR. I don’t know how long it lasted.” The EMS person looked at me, said: “Thank you for what you did. Now we need you to help us with mom.” I said, “okay.”
I turned around, and the mom was still screaming and crying. I asked one of the ladies that worked there, “Can you get me water?” She brought it, and I gave some to the mom, and she started talking to EMS.
People were asking me: “What happened? What happened?” It’s funny, I guess the nurse in me didn’t want to give out information. And I didn’t want to ask for information. I was thinking about privacy. I said, “I don’t know,” and walked away.
The mom’s sister came and hugged me and said thank you. I was still in this out-of-body zone, and I just wanted to get the hell out of there. So, I left. I went to my car and when I got in it, I started shaking and sweating and crying.
I had been so calm in the moment, not thinking about if the baby was going to survive or not. I didn’t know how long she was without oxygen, if she would have some anoxic brain injury or stroke. I’m a mom, too. I would have been just as terrified as that mom. I just hoped there was a chance that she could take her baby home.
I went back to the urgent care, and my son was, like, “are you okay?” I said: “You will not believe this. I just did CPR on a baby.” He said: “Oh. Okay.” I don’t think he even knew what that meant.
I’ve been an ICU nurse since 2008. I’ve been in very critical moments with patients, life or death situations. I help save people all the time at the hospital. Most of the time, you know what you’re getting. You can prepare. You have everything you need, and everyone knows what to do. You know what the worst will look like. You know the outcome.
But this was something else. You read about things like this. You hear about them. But you never think it’ll happen to you – until it happens.
I couldn’t stop thinking about the baby. So, 2 days later, I posted on Next Door to see if somebody would read it and say, “hey, the baby survived.” I was amazed at how many people responded, but no one knew the family.
The local news got hold of me and asked me to do a story. I told them, “the only way I can do a story is if the baby survived. I’m not going to do a story about a dead baby, and the mom has to live through it again.”
The reporter called me later on that day and said she had talked to the police. They said the family was visiting from out of state. The baby went to the hospital and was discharged home 2 days later. I said, “okay, then I can talk.”
When the news story came out, I started getting texts from people at work the same night. So many people were reaching out. Even people from out of state. But I never heard from the family. No one knew how to reach them.
Since I was very young, I wanted to work in a hospital, to help people. It really brings me joy, seeing somebody go home, knowing, yes, we did this. It’s a great feeling. I love this job. I wouldn’t trade it for anything.
I just wish I had asked the mom’s name. Because I always think about that baby. I always wonder, what did she become? I hope somebody reads this who might know that little girl. It would be so nice to meet her one day.
Ms. Diallo is an ICU nurse and now works as nurse care coordinator at the University of North Carolina’s Children’s Neurology Clinic in Chapel Hill.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
My son needed a physical for his football team, and we couldn’t get an appointment. So, we went to the urgent care next to the H Mart in Cary, N.C. While I was waiting, I thought, let me go get a coffee or an iced tea at the H Mart. They have this French bakery in there.
I went in and ordered my drink, and I was waiting in line. I saw this woman pass me running with a baby. Another woman – I found out later it was her sister – was running after her, and she said: “Call 911!”
“I don’t have my phone,” I said. I left my phone with my son; he was using it.
I said: “Are you okay?” And she just handed me the baby. The baby was gray, and there was blood in her nose and mouth. The woman said: “She’s my baby. She’s 1 week old.”
I was trying to think very quickly. I didn’t see any bubbles in the blood around the baby’s nose or mouth to tell me if she was breathing. She was just limp. The mom was still screaming, but I couldn’t even hear her anymore. It was like I was having an out-of-body experience. All I could hear were my thoughts: “I need to put this baby down to start CPR. Someone was calling 911. I should go in the front of the store to save time, so EMS doesn’t have to look for me when they come.”
I started moving and trying to clean the blood from the baby’s face with her blanket. At the front of the store, I saw a display of rice bags. I put the baby on top of one of the bags. “Okay, where do I check for a pulse on a baby?” I took care of adults, never pediatric patients, never babies. She was so tiny. I put my hand on her chest and felt nothing. No heartbeat. She still wasn’t breathing.
People were around me, but I couldn’t see or hear anybody. All I was thinking was: “What can I do for this patient right now?” I started CPR with two fingers. Nothing was happening. It wasn’t that long, but it felt like forever for me. I couldn’t do mouth-to-mouth because there was so much blood on her face. I still don’t know what caused the bleeding.
It was COVID time, so I had my mask on. I was, like: “You know what? Screw this. She’s a 1-week-old baby. Her lungs are tiny. Maybe I don’t have to do mouth-to-mouth. I can just blow in her mouth.” I took off my mask and opened her mouth. I took a deep breath and blew a little bit of air in her mouth. I continued CPR for maybe 5 or 10 seconds.
And then she gasped! She opened her eyes, but they were rolled up. I was still doing CPR, and maybe 2 second after that, I could feel under my hand a very rapid heart rate. I took my hand away and lifted her up.
Just then the EMS got there. I gave them the baby and said: “I did CPR. I don’t know how long it lasted.” The EMS person looked at me, said: “Thank you for what you did. Now we need you to help us with mom.” I said, “okay.”
I turned around, and the mom was still screaming and crying. I asked one of the ladies that worked there, “Can you get me water?” She brought it, and I gave some to the mom, and she started talking to EMS.
People were asking me: “What happened? What happened?” It’s funny, I guess the nurse in me didn’t want to give out information. And I didn’t want to ask for information. I was thinking about privacy. I said, “I don’t know,” and walked away.
The mom’s sister came and hugged me and said thank you. I was still in this out-of-body zone, and I just wanted to get the hell out of there. So, I left. I went to my car and when I got in it, I started shaking and sweating and crying.
I had been so calm in the moment, not thinking about if the baby was going to survive or not. I didn’t know how long she was without oxygen, if she would have some anoxic brain injury or stroke. I’m a mom, too. I would have been just as terrified as that mom. I just hoped there was a chance that she could take her baby home.
I went back to the urgent care, and my son was, like, “are you okay?” I said: “You will not believe this. I just did CPR on a baby.” He said: “Oh. Okay.” I don’t think he even knew what that meant.
I’ve been an ICU nurse since 2008. I’ve been in very critical moments with patients, life or death situations. I help save people all the time at the hospital. Most of the time, you know what you’re getting. You can prepare. You have everything you need, and everyone knows what to do. You know what the worst will look like. You know the outcome.
But this was something else. You read about things like this. You hear about them. But you never think it’ll happen to you – until it happens.
I couldn’t stop thinking about the baby. So, 2 days later, I posted on Next Door to see if somebody would read it and say, “hey, the baby survived.” I was amazed at how many people responded, but no one knew the family.
The local news got hold of me and asked me to do a story. I told them, “the only way I can do a story is if the baby survived. I’m not going to do a story about a dead baby, and the mom has to live through it again.”
The reporter called me later on that day and said she had talked to the police. They said the family was visiting from out of state. The baby went to the hospital and was discharged home 2 days later. I said, “okay, then I can talk.”
When the news story came out, I started getting texts from people at work the same night. So many people were reaching out. Even people from out of state. But I never heard from the family. No one knew how to reach them.
Since I was very young, I wanted to work in a hospital, to help people. It really brings me joy, seeing somebody go home, knowing, yes, we did this. It’s a great feeling. I love this job. I wouldn’t trade it for anything.
I just wish I had asked the mom’s name. Because I always think about that baby. I always wonder, what did she become? I hope somebody reads this who might know that little girl. It would be so nice to meet her one day.
Ms. Diallo is an ICU nurse and now works as nurse care coordinator at the University of North Carolina’s Children’s Neurology Clinic in Chapel Hill.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
My son needed a physical for his football team, and we couldn’t get an appointment. So, we went to the urgent care next to the H Mart in Cary, N.C. While I was waiting, I thought, let me go get a coffee or an iced tea at the H Mart. They have this French bakery in there.
I went in and ordered my drink, and I was waiting in line. I saw this woman pass me running with a baby. Another woman – I found out later it was her sister – was running after her, and she said: “Call 911!”
“I don’t have my phone,” I said. I left my phone with my son; he was using it.
I said: “Are you okay?” And she just handed me the baby. The baby was gray, and there was blood in her nose and mouth. The woman said: “She’s my baby. She’s 1 week old.”
I was trying to think very quickly. I didn’t see any bubbles in the blood around the baby’s nose or mouth to tell me if she was breathing. She was just limp. The mom was still screaming, but I couldn’t even hear her anymore. It was like I was having an out-of-body experience. All I could hear were my thoughts: “I need to put this baby down to start CPR. Someone was calling 911. I should go in the front of the store to save time, so EMS doesn’t have to look for me when they come.”
I started moving and trying to clean the blood from the baby’s face with her blanket. At the front of the store, I saw a display of rice bags. I put the baby on top of one of the bags. “Okay, where do I check for a pulse on a baby?” I took care of adults, never pediatric patients, never babies. She was so tiny. I put my hand on her chest and felt nothing. No heartbeat. She still wasn’t breathing.
People were around me, but I couldn’t see or hear anybody. All I was thinking was: “What can I do for this patient right now?” I started CPR with two fingers. Nothing was happening. It wasn’t that long, but it felt like forever for me. I couldn’t do mouth-to-mouth because there was so much blood on her face. I still don’t know what caused the bleeding.
It was COVID time, so I had my mask on. I was, like: “You know what? Screw this. She’s a 1-week-old baby. Her lungs are tiny. Maybe I don’t have to do mouth-to-mouth. I can just blow in her mouth.” I took off my mask and opened her mouth. I took a deep breath and blew a little bit of air in her mouth. I continued CPR for maybe 5 or 10 seconds.
And then she gasped! She opened her eyes, but they were rolled up. I was still doing CPR, and maybe 2 second after that, I could feel under my hand a very rapid heart rate. I took my hand away and lifted her up.
Just then the EMS got there. I gave them the baby and said: “I did CPR. I don’t know how long it lasted.” The EMS person looked at me, said: “Thank you for what you did. Now we need you to help us with mom.” I said, “okay.”
I turned around, and the mom was still screaming and crying. I asked one of the ladies that worked there, “Can you get me water?” She brought it, and I gave some to the mom, and she started talking to EMS.
People were asking me: “What happened? What happened?” It’s funny, I guess the nurse in me didn’t want to give out information. And I didn’t want to ask for information. I was thinking about privacy. I said, “I don’t know,” and walked away.
The mom’s sister came and hugged me and said thank you. I was still in this out-of-body zone, and I just wanted to get the hell out of there. So, I left. I went to my car and when I got in it, I started shaking and sweating and crying.
I had been so calm in the moment, not thinking about if the baby was going to survive or not. I didn’t know how long she was without oxygen, if she would have some anoxic brain injury or stroke. I’m a mom, too. I would have been just as terrified as that mom. I just hoped there was a chance that she could take her baby home.
I went back to the urgent care, and my son was, like, “are you okay?” I said: “You will not believe this. I just did CPR on a baby.” He said: “Oh. Okay.” I don’t think he even knew what that meant.
I’ve been an ICU nurse since 2008. I’ve been in very critical moments with patients, life or death situations. I help save people all the time at the hospital. Most of the time, you know what you’re getting. You can prepare. You have everything you need, and everyone knows what to do. You know what the worst will look like. You know the outcome.
But this was something else. You read about things like this. You hear about them. But you never think it’ll happen to you – until it happens.
I couldn’t stop thinking about the baby. So, 2 days later, I posted on Next Door to see if somebody would read it and say, “hey, the baby survived.” I was amazed at how many people responded, but no one knew the family.
The local news got hold of me and asked me to do a story. I told them, “the only way I can do a story is if the baby survived. I’m not going to do a story about a dead baby, and the mom has to live through it again.”
The reporter called me later on that day and said she had talked to the police. They said the family was visiting from out of state. The baby went to the hospital and was discharged home 2 days later. I said, “okay, then I can talk.”
When the news story came out, I started getting texts from people at work the same night. So many people were reaching out. Even people from out of state. But I never heard from the family. No one knew how to reach them.
Since I was very young, I wanted to work in a hospital, to help people. It really brings me joy, seeing somebody go home, knowing, yes, we did this. It’s a great feeling. I love this job. I wouldn’t trade it for anything.
I just wish I had asked the mom’s name. Because I always think about that baby. I always wonder, what did she become? I hope somebody reads this who might know that little girl. It would be so nice to meet her one day.
Ms. Diallo is an ICU nurse and now works as nurse care coordinator at the University of North Carolina’s Children’s Neurology Clinic in Chapel Hill.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
From Beirut to frontline hematology research
“If we start treatment earlier, in the smoldering phase, maybe there is a chance of actually curing the disease and completely getting rid of it,” said Dr. Mouhieddine, 31, a research fellow at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, in New York. “We haven’t proven that yet, and it’s going to take years before we’re able to prove it. I’m hoping to be one of those spearheading the initiative.”
As he develops clinical trials, the young physician scientist has another focus: A deeply personal connection to the very disease he’s trying to cure. Last year Dr. Mouhieddine diagnosed his aunt back in Lebanon with multiple myeloma. “I have always been close to her, and I’m like her son,” he said, and her situation is especially scary because she lives in a country where treatment options are limited.
Dr. Mouhieddine was born and raised in Beirut, the son of a sports journalist father and a mother who worked in a bank. Lebanon’s civil war ended in 1990, shortly before his birth, but political instability returned when he was a child.
“Everything was a disaster,” he recalled. “There was a period of time when there were bombs throughout the city because certain politicians were being targeted. I remember when groups of people would have gunfights in the street.”
Dr. Mouhieddine attended the American University of Beirut, then after college and medical school there, he headed to the United States.
“I wanted to make a difference in medicine. And I knew that if I stayed back home, I wouldn’t be able to,” he said. Fortunately, “everybody has made me feel that I really belong here, and I’ve never felt like I’m an outsider.”
Early on, as he went through fellowships and residency, he developed an interest in multiple myeloma.
Ajai Chari, MD, a colleague of Dr. Mouhieddine’s at Icahn School of Medicine, said in an interview, “I remember meeting him at a conference before he had even started an internal medicine residency, let alone a hematology oncology fellowship. He was already certain he wanted to work in multiple myeloma, due to his work at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.”
Myeloma was especially intriguing to Dr. Mouhieddine because of the rapid rate of progress in treating the disease. “Over the past 10 years, the myeloma field has advanced at such an extremely fast pace, more than any other cancer,” he said. “Maybe 15 years ago, you would tell someone with newly diagnosed myeloma that they had a chance for an average of another 2 years. Now, we tell patients they have 10 years to live on average, which means you could live 15 or 20 years. That alone was astounding to me and piqued my interest in myeloma.”
At the same time, smoldering myeloma – which can be discovered during routine blood work – remains little understood. As the National Cancer Institute explains, “smoldering myeloma is a precancerous condition that alters certain proteins in blood and/or increases plasma cells in bone marrow, but it does not cause symptoms of disease. About half of those diagnosed with the condition, however, will develop multiple myeloma within 5 years.”
“If we understand what drives smoldering myeloma, we may be able to prevent it from progressing to its active form,” said hematologist oncologist Samir Parekh, MD, who works with Dr. Mouhieddine at Icahn School of Medicine. “Or at the minimum, we could better predict who will progress so we can tailor therapy for high-risk patients and minimize toxicity by not overtreating patients who may not need therapy.”
Dr. Mouhieddine’s current work is focusing on developing clinical trials to test whether immunotherapy can snuff out myeloma when it’s at the smoldering stage, “before anything bad happens.
“If a myeloma patient comes in with renal failure, and we treat the myeloma at that stage, it doesn’t mean that the patient’s kidneys are gonna go back to normal. A lot of the damage can be permanent,” he said. “Even when you treat multiple myeloma, and it goes into remission, it ends up coming back. And you just have to go from one therapy to the other.”
In contrast, a successful treatment for smoldering myeloma would prevent progression to the full disease. In other words, it would be a cure – which is now elusive.
Specifically, Dr. Mouhieddine hopes to test whether bispecific antibodies, a type of immunotherapy that enlists the body’s T cells to kill myeloma cells, will be effective in the smoldering phase. Bispecific antibodies are now being explored as treatments for full multiple myeloma when the immune system is weaker, he said, and they may be even more effective earlier, when the body is better equipped to fight off the disease.
Dr. Mouhieddine hopes better treatments for multiple myeloma itself will help save his 64-year-old aunt Hassana, back in Beirut. He diagnosed her in 2022 after she told him that she felt tired all the time and underwent various tests. The woman he calls his “second mom” is doing well, despite struggles to buy medication due to the lack of access to bank funds in Lebanon.
“I’m always going to be afraid that the disease is going to progress or come back at some point,” he said. “Lebanon doesn’t have as many options as people in the U.S. do. Once you exhaust your first option, and maybe your second option, then you don’t have any other options. Here, we have outpatients who exhaust option number 15 and go to option number 16. That’s definitely not the case over there.”
For now, Dr. Mouhieddine is treating patients and working to launch clinical trials into smoldering myeloma. “His work ethic is incredible,” said his colleague, Dr. Chari. “He has seen multiple projects to publication, and he develops deep connections with his patients and follows up on their care whether or not he is in clinic on a particular day.”
Dr. Parekh, another colleague, said Dr. Mouhieddine can even be a role model. “Other trainees may benefit from thinking about their career early on and exploring both lab and clinical research projects, so that they can develop the necessary experience to be competitive in academia later on.”
His workload can a burden for Dr. Mouhieddine, who is Muslim. He expressed regret that his busy schedule does not always permit him to fast during Ramadan. On a nonmedical front, his recent efforts have paid off. In March 2023 Dr. Mouhieddine became a U.S. citizen.
“It’s surreal,” he said, “but also a dream come true. I feel very grateful, like it’s like an appreciation of who I am, what I’ve done, and what I can do for this country.”
“If we start treatment earlier, in the smoldering phase, maybe there is a chance of actually curing the disease and completely getting rid of it,” said Dr. Mouhieddine, 31, a research fellow at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, in New York. “We haven’t proven that yet, and it’s going to take years before we’re able to prove it. I’m hoping to be one of those spearheading the initiative.”
As he develops clinical trials, the young physician scientist has another focus: A deeply personal connection to the very disease he’s trying to cure. Last year Dr. Mouhieddine diagnosed his aunt back in Lebanon with multiple myeloma. “I have always been close to her, and I’m like her son,” he said, and her situation is especially scary because she lives in a country where treatment options are limited.
Dr. Mouhieddine was born and raised in Beirut, the son of a sports journalist father and a mother who worked in a bank. Lebanon’s civil war ended in 1990, shortly before his birth, but political instability returned when he was a child.
“Everything was a disaster,” he recalled. “There was a period of time when there were bombs throughout the city because certain politicians were being targeted. I remember when groups of people would have gunfights in the street.”
Dr. Mouhieddine attended the American University of Beirut, then after college and medical school there, he headed to the United States.
“I wanted to make a difference in medicine. And I knew that if I stayed back home, I wouldn’t be able to,” he said. Fortunately, “everybody has made me feel that I really belong here, and I’ve never felt like I’m an outsider.”
Early on, as he went through fellowships and residency, he developed an interest in multiple myeloma.
Ajai Chari, MD, a colleague of Dr. Mouhieddine’s at Icahn School of Medicine, said in an interview, “I remember meeting him at a conference before he had even started an internal medicine residency, let alone a hematology oncology fellowship. He was already certain he wanted to work in multiple myeloma, due to his work at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.”
Myeloma was especially intriguing to Dr. Mouhieddine because of the rapid rate of progress in treating the disease. “Over the past 10 years, the myeloma field has advanced at such an extremely fast pace, more than any other cancer,” he said. “Maybe 15 years ago, you would tell someone with newly diagnosed myeloma that they had a chance for an average of another 2 years. Now, we tell patients they have 10 years to live on average, which means you could live 15 or 20 years. That alone was astounding to me and piqued my interest in myeloma.”
At the same time, smoldering myeloma – which can be discovered during routine blood work – remains little understood. As the National Cancer Institute explains, “smoldering myeloma is a precancerous condition that alters certain proteins in blood and/or increases plasma cells in bone marrow, but it does not cause symptoms of disease. About half of those diagnosed with the condition, however, will develop multiple myeloma within 5 years.”
“If we understand what drives smoldering myeloma, we may be able to prevent it from progressing to its active form,” said hematologist oncologist Samir Parekh, MD, who works with Dr. Mouhieddine at Icahn School of Medicine. “Or at the minimum, we could better predict who will progress so we can tailor therapy for high-risk patients and minimize toxicity by not overtreating patients who may not need therapy.”
Dr. Mouhieddine’s current work is focusing on developing clinical trials to test whether immunotherapy can snuff out myeloma when it’s at the smoldering stage, “before anything bad happens.
“If a myeloma patient comes in with renal failure, and we treat the myeloma at that stage, it doesn’t mean that the patient’s kidneys are gonna go back to normal. A lot of the damage can be permanent,” he said. “Even when you treat multiple myeloma, and it goes into remission, it ends up coming back. And you just have to go from one therapy to the other.”
In contrast, a successful treatment for smoldering myeloma would prevent progression to the full disease. In other words, it would be a cure – which is now elusive.
Specifically, Dr. Mouhieddine hopes to test whether bispecific antibodies, a type of immunotherapy that enlists the body’s T cells to kill myeloma cells, will be effective in the smoldering phase. Bispecific antibodies are now being explored as treatments for full multiple myeloma when the immune system is weaker, he said, and they may be even more effective earlier, when the body is better equipped to fight off the disease.
Dr. Mouhieddine hopes better treatments for multiple myeloma itself will help save his 64-year-old aunt Hassana, back in Beirut. He diagnosed her in 2022 after she told him that she felt tired all the time and underwent various tests. The woman he calls his “second mom” is doing well, despite struggles to buy medication due to the lack of access to bank funds in Lebanon.
“I’m always going to be afraid that the disease is going to progress or come back at some point,” he said. “Lebanon doesn’t have as many options as people in the U.S. do. Once you exhaust your first option, and maybe your second option, then you don’t have any other options. Here, we have outpatients who exhaust option number 15 and go to option number 16. That’s definitely not the case over there.”
For now, Dr. Mouhieddine is treating patients and working to launch clinical trials into smoldering myeloma. “His work ethic is incredible,” said his colleague, Dr. Chari. “He has seen multiple projects to publication, and he develops deep connections with his patients and follows up on their care whether or not he is in clinic on a particular day.”
Dr. Parekh, another colleague, said Dr. Mouhieddine can even be a role model. “Other trainees may benefit from thinking about their career early on and exploring both lab and clinical research projects, so that they can develop the necessary experience to be competitive in academia later on.”
His workload can a burden for Dr. Mouhieddine, who is Muslim. He expressed regret that his busy schedule does not always permit him to fast during Ramadan. On a nonmedical front, his recent efforts have paid off. In March 2023 Dr. Mouhieddine became a U.S. citizen.
“It’s surreal,” he said, “but also a dream come true. I feel very grateful, like it’s like an appreciation of who I am, what I’ve done, and what I can do for this country.”
“If we start treatment earlier, in the smoldering phase, maybe there is a chance of actually curing the disease and completely getting rid of it,” said Dr. Mouhieddine, 31, a research fellow at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, in New York. “We haven’t proven that yet, and it’s going to take years before we’re able to prove it. I’m hoping to be one of those spearheading the initiative.”
As he develops clinical trials, the young physician scientist has another focus: A deeply personal connection to the very disease he’s trying to cure. Last year Dr. Mouhieddine diagnosed his aunt back in Lebanon with multiple myeloma. “I have always been close to her, and I’m like her son,” he said, and her situation is especially scary because she lives in a country where treatment options are limited.
Dr. Mouhieddine was born and raised in Beirut, the son of a sports journalist father and a mother who worked in a bank. Lebanon’s civil war ended in 1990, shortly before his birth, but political instability returned when he was a child.
“Everything was a disaster,” he recalled. “There was a period of time when there were bombs throughout the city because certain politicians were being targeted. I remember when groups of people would have gunfights in the street.”
Dr. Mouhieddine attended the American University of Beirut, then after college and medical school there, he headed to the United States.
“I wanted to make a difference in medicine. And I knew that if I stayed back home, I wouldn’t be able to,” he said. Fortunately, “everybody has made me feel that I really belong here, and I’ve never felt like I’m an outsider.”
Early on, as he went through fellowships and residency, he developed an interest in multiple myeloma.
Ajai Chari, MD, a colleague of Dr. Mouhieddine’s at Icahn School of Medicine, said in an interview, “I remember meeting him at a conference before he had even started an internal medicine residency, let alone a hematology oncology fellowship. He was already certain he wanted to work in multiple myeloma, due to his work at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.”
Myeloma was especially intriguing to Dr. Mouhieddine because of the rapid rate of progress in treating the disease. “Over the past 10 years, the myeloma field has advanced at such an extremely fast pace, more than any other cancer,” he said. “Maybe 15 years ago, you would tell someone with newly diagnosed myeloma that they had a chance for an average of another 2 years. Now, we tell patients they have 10 years to live on average, which means you could live 15 or 20 years. That alone was astounding to me and piqued my interest in myeloma.”
At the same time, smoldering myeloma – which can be discovered during routine blood work – remains little understood. As the National Cancer Institute explains, “smoldering myeloma is a precancerous condition that alters certain proteins in blood and/or increases plasma cells in bone marrow, but it does not cause symptoms of disease. About half of those diagnosed with the condition, however, will develop multiple myeloma within 5 years.”
“If we understand what drives smoldering myeloma, we may be able to prevent it from progressing to its active form,” said hematologist oncologist Samir Parekh, MD, who works with Dr. Mouhieddine at Icahn School of Medicine. “Or at the minimum, we could better predict who will progress so we can tailor therapy for high-risk patients and minimize toxicity by not overtreating patients who may not need therapy.”
Dr. Mouhieddine’s current work is focusing on developing clinical trials to test whether immunotherapy can snuff out myeloma when it’s at the smoldering stage, “before anything bad happens.
“If a myeloma patient comes in with renal failure, and we treat the myeloma at that stage, it doesn’t mean that the patient’s kidneys are gonna go back to normal. A lot of the damage can be permanent,” he said. “Even when you treat multiple myeloma, and it goes into remission, it ends up coming back. And you just have to go from one therapy to the other.”
In contrast, a successful treatment for smoldering myeloma would prevent progression to the full disease. In other words, it would be a cure – which is now elusive.
Specifically, Dr. Mouhieddine hopes to test whether bispecific antibodies, a type of immunotherapy that enlists the body’s T cells to kill myeloma cells, will be effective in the smoldering phase. Bispecific antibodies are now being explored as treatments for full multiple myeloma when the immune system is weaker, he said, and they may be even more effective earlier, when the body is better equipped to fight off the disease.
Dr. Mouhieddine hopes better treatments for multiple myeloma itself will help save his 64-year-old aunt Hassana, back in Beirut. He diagnosed her in 2022 after she told him that she felt tired all the time and underwent various tests. The woman he calls his “second mom” is doing well, despite struggles to buy medication due to the lack of access to bank funds in Lebanon.
“I’m always going to be afraid that the disease is going to progress or come back at some point,” he said. “Lebanon doesn’t have as many options as people in the U.S. do. Once you exhaust your first option, and maybe your second option, then you don’t have any other options. Here, we have outpatients who exhaust option number 15 and go to option number 16. That’s definitely not the case over there.”
For now, Dr. Mouhieddine is treating patients and working to launch clinical trials into smoldering myeloma. “His work ethic is incredible,” said his colleague, Dr. Chari. “He has seen multiple projects to publication, and he develops deep connections with his patients and follows up on their care whether or not he is in clinic on a particular day.”
Dr. Parekh, another colleague, said Dr. Mouhieddine can even be a role model. “Other trainees may benefit from thinking about their career early on and exploring both lab and clinical research projects, so that they can develop the necessary experience to be competitive in academia later on.”
His workload can a burden for Dr. Mouhieddine, who is Muslim. He expressed regret that his busy schedule does not always permit him to fast during Ramadan. On a nonmedical front, his recent efforts have paid off. In March 2023 Dr. Mouhieddine became a U.S. citizen.
“It’s surreal,” he said, “but also a dream come true. I feel very grateful, like it’s like an appreciation of who I am, what I’ve done, and what I can do for this country.”
PARP/ATR inhibitor combo shows hints of promise in children with tumors
The small phase 1 trial also identified some molecular signatures in responders that may inform future clinical trials.
The results, presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Cancer Research, came from a single arm of the European Proof-of-Concept Therapeutic Stratification Trial of Molecular Anomalies in Relapsed or Refractory Tumors (ESMART) trial. This trial matches pediatric, adolescent, and young adult cancer patients with treatment regimens based on the molecular profile of their tumors.
In over 220 children to date, the trial has investigated 15 different treatment regimens, most of which are combination therapies.
In adults, PARP) inhibitors have been shown to be effective in tumors with deficiencies in homologous repair, which is a DNA repair mechanism, with notable successes in patients carrying the BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. But BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations are rare in pediatric cancer, and there is a belief that there may be primary resistance to PARP inhibitors in pediatric tumors, according to Susanne Gatz, MD, PhD, who presented the research at the meeting.
Previous research identified alterations in pediatric tumors that are candidates for patient selection. “These tumors have alterations which could potentially cause this resistance effect [against PARP inhibitors] and [also cause] sensitivity to ataxia telangiectasia–mutated Rad3-related inhibitors. This is how this arm [of the ESMART trial] was born,” said Dr. Gatz.
The phase 1 portion of the study included 18 pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed or treatment-refractory tumors. There were eight sarcomas, five central nervous system tumors, four neuroblastomas, and one carcinoma. Each had mutations thought to lead to HR deficiency or replication stress. The study included three dose levels of twice-daily oral olaparib that was given continuously, and ceralasertib, which was given day 1-14 of each 28-day cycle.
Patients underwent a median of 3.5 cycles of treatment. There were dose-limiting adverse events of thrombocytopenia and neutropenia in five patients, two of which occurred at the dose that was recommended for phase 2.
There were some positive clinical signs, including one partial response in a pineoblastoma patient who received treatment for 11 cycles. A neuroblastoma patient had stable disease until cycle 9 of treatment, and then converted to a partial response and is currently in cycle 12. Two other patients remain in treatment at cycle 8 and one is in treatment at cycle 15. None of the patients who experienced clinical benefit had BRCA mutations.
An important goal of the study was to understand molecular signature that might predict response to the drug combination. Although no firm conclusions could be drawn, there were some interesting patterns. In particular, five of the six worst responders had TP53 mutations. “It is striking ... so we need to learn what TP53 in this setting means if it’s mutated, and if it could be a resistance factor,” said Dr. Gatz, an associate clinical professor in pediatric oncology at the Institute of Cancer and Genomic Sciences of the University of Birmingham, during her talk.
Although the study is too small and included too many tumor types to identify tumor-based patterns of response, it did provide some hints as to biomarkers that could inform future studies, according to Julia Glade Bender, MD, who served as a discussant following the presentation and is a pediatric oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“The pediatric frequency of the common DNA damage repair biomarkers that have been [identified in] the adult literature – that is to say, BRCA1 and 2 and [ataxia-telangiectasia mutation] – are exceedingly rare in pediatrics,” said Dr. Bender during the session while serving as a discussant. She highlighted the following findings: Loss of the 11q region on chromosome 11 is common among the patients and that region contains three genes involved in the DNA damage response, along with a gene involved in homologous recombination, telomere maintenance, and double strand break repair.
She added that 11q deletion is also found in up to 40% of neuroblastomas, and is associated with poor prognosis, and the patients have multiple segmental chromosomal abnormalities. “That begs the question [of] whether chromosomal instability is another biomarker for pediatric cancer,” said Dr. Bender.
“The research highlights the complexity of pediatric cancers, whose distinct biology could make them more vulnerable to ATR [kinase], [checkpoint kinase 1], and WEE1 pathway inhibition with a PARP inhibitor used to induce replication stress and be the sensitizer. The biomarker profiles are going to be complex, context-dependent, and likely to reflect a constellation of findings that would be signatures or algorithms, rather than single gene alterations. The post hoc iterative analysis of responders and nonresponders is going to be absolutely critical to understanding those biomarkers and the role of DNA damage response inhibitors in pediatrics. Given the rarity of these diagnoses, and then the molecular subclasses, I think collaboration across ages and geography is absolutely critical, and I really congratulate the ESMART consortium for doing just that in Europe,” said Dr. Bender.
The study is limited by its small sample size and the fact that it was not randomized.
The study received funding from French Institut National de Cancer, Imagine for Margo, Fondation ARC, AstraZeneca France, AstraZeneca Global R&D, AstraZeneca UK, Cancer Research UK, Fondation Gustave Roussy, and Little Princess Trust/Children’s Cancer and Leukaemia Group. Dr. Gatz has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Bender has done paid consulting for Jazz Pharmaceuticals and has done unpaid work for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Springworks Therapeutics, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer. She has received research support from Eli Lilly, Loxo-oncology, Eisai, Cellectar, Bayer, Amgen, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals.
From American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023: Abstract CT019. Presented Tuesday, April 18.
The small phase 1 trial also identified some molecular signatures in responders that may inform future clinical trials.
The results, presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Cancer Research, came from a single arm of the European Proof-of-Concept Therapeutic Stratification Trial of Molecular Anomalies in Relapsed or Refractory Tumors (ESMART) trial. This trial matches pediatric, adolescent, and young adult cancer patients with treatment regimens based on the molecular profile of their tumors.
In over 220 children to date, the trial has investigated 15 different treatment regimens, most of which are combination therapies.
In adults, PARP) inhibitors have been shown to be effective in tumors with deficiencies in homologous repair, which is a DNA repair mechanism, with notable successes in patients carrying the BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. But BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations are rare in pediatric cancer, and there is a belief that there may be primary resistance to PARP inhibitors in pediatric tumors, according to Susanne Gatz, MD, PhD, who presented the research at the meeting.
Previous research identified alterations in pediatric tumors that are candidates for patient selection. “These tumors have alterations which could potentially cause this resistance effect [against PARP inhibitors] and [also cause] sensitivity to ataxia telangiectasia–mutated Rad3-related inhibitors. This is how this arm [of the ESMART trial] was born,” said Dr. Gatz.
The phase 1 portion of the study included 18 pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed or treatment-refractory tumors. There were eight sarcomas, five central nervous system tumors, four neuroblastomas, and one carcinoma. Each had mutations thought to lead to HR deficiency or replication stress. The study included three dose levels of twice-daily oral olaparib that was given continuously, and ceralasertib, which was given day 1-14 of each 28-day cycle.
Patients underwent a median of 3.5 cycles of treatment. There were dose-limiting adverse events of thrombocytopenia and neutropenia in five patients, two of which occurred at the dose that was recommended for phase 2.
There were some positive clinical signs, including one partial response in a pineoblastoma patient who received treatment for 11 cycles. A neuroblastoma patient had stable disease until cycle 9 of treatment, and then converted to a partial response and is currently in cycle 12. Two other patients remain in treatment at cycle 8 and one is in treatment at cycle 15. None of the patients who experienced clinical benefit had BRCA mutations.
An important goal of the study was to understand molecular signature that might predict response to the drug combination. Although no firm conclusions could be drawn, there were some interesting patterns. In particular, five of the six worst responders had TP53 mutations. “It is striking ... so we need to learn what TP53 in this setting means if it’s mutated, and if it could be a resistance factor,” said Dr. Gatz, an associate clinical professor in pediatric oncology at the Institute of Cancer and Genomic Sciences of the University of Birmingham, during her talk.
Although the study is too small and included too many tumor types to identify tumor-based patterns of response, it did provide some hints as to biomarkers that could inform future studies, according to Julia Glade Bender, MD, who served as a discussant following the presentation and is a pediatric oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“The pediatric frequency of the common DNA damage repair biomarkers that have been [identified in] the adult literature – that is to say, BRCA1 and 2 and [ataxia-telangiectasia mutation] – are exceedingly rare in pediatrics,” said Dr. Bender during the session while serving as a discussant. She highlighted the following findings: Loss of the 11q region on chromosome 11 is common among the patients and that region contains three genes involved in the DNA damage response, along with a gene involved in homologous recombination, telomere maintenance, and double strand break repair.
She added that 11q deletion is also found in up to 40% of neuroblastomas, and is associated with poor prognosis, and the patients have multiple segmental chromosomal abnormalities. “That begs the question [of] whether chromosomal instability is another biomarker for pediatric cancer,” said Dr. Bender.
“The research highlights the complexity of pediatric cancers, whose distinct biology could make them more vulnerable to ATR [kinase], [checkpoint kinase 1], and WEE1 pathway inhibition with a PARP inhibitor used to induce replication stress and be the sensitizer. The biomarker profiles are going to be complex, context-dependent, and likely to reflect a constellation of findings that would be signatures or algorithms, rather than single gene alterations. The post hoc iterative analysis of responders and nonresponders is going to be absolutely critical to understanding those biomarkers and the role of DNA damage response inhibitors in pediatrics. Given the rarity of these diagnoses, and then the molecular subclasses, I think collaboration across ages and geography is absolutely critical, and I really congratulate the ESMART consortium for doing just that in Europe,” said Dr. Bender.
The study is limited by its small sample size and the fact that it was not randomized.
The study received funding from French Institut National de Cancer, Imagine for Margo, Fondation ARC, AstraZeneca France, AstraZeneca Global R&D, AstraZeneca UK, Cancer Research UK, Fondation Gustave Roussy, and Little Princess Trust/Children’s Cancer and Leukaemia Group. Dr. Gatz has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Bender has done paid consulting for Jazz Pharmaceuticals and has done unpaid work for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Springworks Therapeutics, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer. She has received research support from Eli Lilly, Loxo-oncology, Eisai, Cellectar, Bayer, Amgen, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals.
From American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023: Abstract CT019. Presented Tuesday, April 18.
The small phase 1 trial also identified some molecular signatures in responders that may inform future clinical trials.
The results, presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Cancer Research, came from a single arm of the European Proof-of-Concept Therapeutic Stratification Trial of Molecular Anomalies in Relapsed or Refractory Tumors (ESMART) trial. This trial matches pediatric, adolescent, and young adult cancer patients with treatment regimens based on the molecular profile of their tumors.
In over 220 children to date, the trial has investigated 15 different treatment regimens, most of which are combination therapies.
In adults, PARP) inhibitors have been shown to be effective in tumors with deficiencies in homologous repair, which is a DNA repair mechanism, with notable successes in patients carrying the BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. But BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations are rare in pediatric cancer, and there is a belief that there may be primary resistance to PARP inhibitors in pediatric tumors, according to Susanne Gatz, MD, PhD, who presented the research at the meeting.
Previous research identified alterations in pediatric tumors that are candidates for patient selection. “These tumors have alterations which could potentially cause this resistance effect [against PARP inhibitors] and [also cause] sensitivity to ataxia telangiectasia–mutated Rad3-related inhibitors. This is how this arm [of the ESMART trial] was born,” said Dr. Gatz.
The phase 1 portion of the study included 18 pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed or treatment-refractory tumors. There were eight sarcomas, five central nervous system tumors, four neuroblastomas, and one carcinoma. Each had mutations thought to lead to HR deficiency or replication stress. The study included three dose levels of twice-daily oral olaparib that was given continuously, and ceralasertib, which was given day 1-14 of each 28-day cycle.
Patients underwent a median of 3.5 cycles of treatment. There were dose-limiting adverse events of thrombocytopenia and neutropenia in five patients, two of which occurred at the dose that was recommended for phase 2.
There were some positive clinical signs, including one partial response in a pineoblastoma patient who received treatment for 11 cycles. A neuroblastoma patient had stable disease until cycle 9 of treatment, and then converted to a partial response and is currently in cycle 12. Two other patients remain in treatment at cycle 8 and one is in treatment at cycle 15. None of the patients who experienced clinical benefit had BRCA mutations.
An important goal of the study was to understand molecular signature that might predict response to the drug combination. Although no firm conclusions could be drawn, there were some interesting patterns. In particular, five of the six worst responders had TP53 mutations. “It is striking ... so we need to learn what TP53 in this setting means if it’s mutated, and if it could be a resistance factor,” said Dr. Gatz, an associate clinical professor in pediatric oncology at the Institute of Cancer and Genomic Sciences of the University of Birmingham, during her talk.
Although the study is too small and included too many tumor types to identify tumor-based patterns of response, it did provide some hints as to biomarkers that could inform future studies, according to Julia Glade Bender, MD, who served as a discussant following the presentation and is a pediatric oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“The pediatric frequency of the common DNA damage repair biomarkers that have been [identified in] the adult literature – that is to say, BRCA1 and 2 and [ataxia-telangiectasia mutation] – are exceedingly rare in pediatrics,” said Dr. Bender during the session while serving as a discussant. She highlighted the following findings: Loss of the 11q region on chromosome 11 is common among the patients and that region contains three genes involved in the DNA damage response, along with a gene involved in homologous recombination, telomere maintenance, and double strand break repair.
She added that 11q deletion is also found in up to 40% of neuroblastomas, and is associated with poor prognosis, and the patients have multiple segmental chromosomal abnormalities. “That begs the question [of] whether chromosomal instability is another biomarker for pediatric cancer,” said Dr. Bender.
“The research highlights the complexity of pediatric cancers, whose distinct biology could make them more vulnerable to ATR [kinase], [checkpoint kinase 1], and WEE1 pathway inhibition with a PARP inhibitor used to induce replication stress and be the sensitizer. The biomarker profiles are going to be complex, context-dependent, and likely to reflect a constellation of findings that would be signatures or algorithms, rather than single gene alterations. The post hoc iterative analysis of responders and nonresponders is going to be absolutely critical to understanding those biomarkers and the role of DNA damage response inhibitors in pediatrics. Given the rarity of these diagnoses, and then the molecular subclasses, I think collaboration across ages and geography is absolutely critical, and I really congratulate the ESMART consortium for doing just that in Europe,” said Dr. Bender.
The study is limited by its small sample size and the fact that it was not randomized.
The study received funding from French Institut National de Cancer, Imagine for Margo, Fondation ARC, AstraZeneca France, AstraZeneca Global R&D, AstraZeneca UK, Cancer Research UK, Fondation Gustave Roussy, and Little Princess Trust/Children’s Cancer and Leukaemia Group. Dr. Gatz has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Bender has done paid consulting for Jazz Pharmaceuticals and has done unpaid work for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Springworks Therapeutics, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer. She has received research support from Eli Lilly, Loxo-oncology, Eisai, Cellectar, Bayer, Amgen, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals.
From American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023: Abstract CT019. Presented Tuesday, April 18.
FROM AACR 2023
Circulating DNA has promise for cancer detection, but faces challenges
Cancer screening remains challenging. There are screens available for a handful of solid tumors, but uptake is low caused in part by health care access barriers as well as the potential for unnecessary follow-up procedures, according to Phillip Febbo, MD.
These issues could threaten efforts like that of President Joe Biden’s Cancer Moonshot initiative, which aims to reduce cancer mortality by 50%. Advances in circulating tumor (ct) DNA analysis could help address these problems, but a lack of diversity among study participants needs to be addressed to ensure it has broad utility, continued Dr. Febbo, during his presentation at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
The problem is particularly acute among African American, Hispanic, and other underserved populations who often face health care barriers that can exacerbate the issue, said Dr. Febbo, who is chief medical officer for Illumina. The lack of access is compounded by the fact that there are only currently screens for lung, breast, colorectal, cervical, and prostate cancer, leaving a vast unmet need.
“We still do not have screening tests for 70% of the deaths that are due to cancer,” he said.
ctDNA released from dying cancer cells has the potential to reveal a wide range of cancer types and reduce barriers to access, because it is based on a blood test. It can be analyzed for various factors, including mutations, chromosomal rearrangements, methylation patterns, and other characteristics that hint at the presence of cancer. However, it can’t be successful without sufficient inclusion in research studies, Dr. Febbo explained.
“We have to ensure we have the right representation [of] populations when we develop these tests, when we go through the clinical trials, and as we bring these into communities,” he said.
During his presentation, Dr. Febbo shared a slide showing that about 78% of participants in published gene-association studies were White.
ctDNA showed promise in at least on recent study. Dr. Febbo discussed the ECLIPSE trial, which used the Guardant Health SHIELD assay for colorectal cancer (CRC). About 13% of its approximately 20,000 participants were Black or African American, 15% were Hispanic, and 7% were Asian Americans. It also included both urban and rural individuals. In results announced in December 2022, the researchers found a sensitivity of 83%, which was lower than the 92.3% found in standard CRC screening, but above the 74% threshold set by the Food and Drug Administration. The specificity was 90%.
One approach that could dramatically change the landscape of cancer screening is a multicancer early detection (MCED) test, according to Dr. Febbo. The CancerSeek MCED test, developed by Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center researchers, uses a series of genetic and protein biomarkers to detect all cancers, with the exception of leukemia, skin cancer, and central nervous system tumors. Among 10,006 women aged between 65 and 75 years with no history of cancer, it had a sensitivity of 27.1% and a specificity of 98.9%, with a positive predictive value of 19.4%. The study’s population was 95% non-Hispanic White.
He also discussed the Pathfinder study, sponsored by the Illumina subsidiary Grail, which included 6,662 individuals age 50 and over from seven sites in the United States, and grouped them into normal and increased risk; 92% were non-Hispanic White. It used the Galleri MCED test, which performed with a sensitivity of 29%, specificity of 99.1%, and a positive predictive value of 38.0%. False positives produced to limited burden, with 93% undergoing imaging, 28% nonsurgical invasive procedures, and 2% undergoing fruitless invasive surgical procedures.
Dr. Febbo touted the potential for such tests to greatly reduce cancer mortality, but only if there is adequate uptake of screening procedures, particularly in underserved groups. He put up a slide of a model showing that MCED has the potential to reduce cancer mortality by 20%, but only if the screen is widely accepted among all groups. “I’ve had my team model this. If we accept the current use of screening tests, and we don’t address disparities, and we don’t ensure everybody feels included and participates actively – not only in the research, but also in the testing and adoption, you would cut that potential benefit in half. That would be hundreds of thousands of lives lost because we didn’t address disparities.”
Successful recruiting of African Americans for research
Following Dr. Febbo’s talk, Karriem Watson, MS, spoke about some potential solutions to the issue, including his own experiences and success stories in recruiting African Americans to play active roles in research. He is chief engagement officer for the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program, which aims to gather health data on at least 1 million residents of the United States. Mr. Watson has spent time reaching out to people living in communities in the Chicago area to encourage participation in breast cancer screening. An event at his church inspired his own sister to get a mammogram, and she was diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer.
“I’m a living witness that early engagement can lead to early detection,” said Mr. Watson during his talk.
He reported that the All of Us research program has succeeded in creating diversity within its data collection, as 46.7% of participants identify as racial and ethnic minorities.
Mr. Watson took issue with the common perception that underrepresented communities may be hard to reach.
“I want to challenge us to think outside the box and really ask ourselves: Are populations hard to reach, or are there opportunities for us to do better and more intentional engagement?” He went on to describe a program to recruit African American men as citizen scientists. He and his colleagues developed a network that included barbers, faith leaders, and fraternity and civic organization members to help recruit participants for a prostate cancer screening project. They exceeded their initial recruitment goal.
They went on to develop a network of barbers in the south and west sides of Chicago to recruit individuals to participate in studies of protein methylation and lung cancer screening, as well as a project that investigated associations between neighborhood of residence and lung cancer. The results of those efforts have also informed other projects, including a smoking cessation study. “We’ve not only included African American men in our research, but we’ve included them as part of our research team,” said Mr. Watson.
Dr. Febbo is also a stockholder of Illumina. Mr. Watson has no relevant financial disclosures.
From American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023: Improving cancer outcomes through equitable access to cfDNA tests. Presented Monday, April 17, 2023.
Cancer screening remains challenging. There are screens available for a handful of solid tumors, but uptake is low caused in part by health care access barriers as well as the potential for unnecessary follow-up procedures, according to Phillip Febbo, MD.
These issues could threaten efforts like that of President Joe Biden’s Cancer Moonshot initiative, which aims to reduce cancer mortality by 50%. Advances in circulating tumor (ct) DNA analysis could help address these problems, but a lack of diversity among study participants needs to be addressed to ensure it has broad utility, continued Dr. Febbo, during his presentation at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
The problem is particularly acute among African American, Hispanic, and other underserved populations who often face health care barriers that can exacerbate the issue, said Dr. Febbo, who is chief medical officer for Illumina. The lack of access is compounded by the fact that there are only currently screens for lung, breast, colorectal, cervical, and prostate cancer, leaving a vast unmet need.
“We still do not have screening tests for 70% of the deaths that are due to cancer,” he said.
ctDNA released from dying cancer cells has the potential to reveal a wide range of cancer types and reduce barriers to access, because it is based on a blood test. It can be analyzed for various factors, including mutations, chromosomal rearrangements, methylation patterns, and other characteristics that hint at the presence of cancer. However, it can’t be successful without sufficient inclusion in research studies, Dr. Febbo explained.
“We have to ensure we have the right representation [of] populations when we develop these tests, when we go through the clinical trials, and as we bring these into communities,” he said.
During his presentation, Dr. Febbo shared a slide showing that about 78% of participants in published gene-association studies were White.
ctDNA showed promise in at least on recent study. Dr. Febbo discussed the ECLIPSE trial, which used the Guardant Health SHIELD assay for colorectal cancer (CRC). About 13% of its approximately 20,000 participants were Black or African American, 15% were Hispanic, and 7% were Asian Americans. It also included both urban and rural individuals. In results announced in December 2022, the researchers found a sensitivity of 83%, which was lower than the 92.3% found in standard CRC screening, but above the 74% threshold set by the Food and Drug Administration. The specificity was 90%.
One approach that could dramatically change the landscape of cancer screening is a multicancer early detection (MCED) test, according to Dr. Febbo. The CancerSeek MCED test, developed by Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center researchers, uses a series of genetic and protein biomarkers to detect all cancers, with the exception of leukemia, skin cancer, and central nervous system tumors. Among 10,006 women aged between 65 and 75 years with no history of cancer, it had a sensitivity of 27.1% and a specificity of 98.9%, with a positive predictive value of 19.4%. The study’s population was 95% non-Hispanic White.
He also discussed the Pathfinder study, sponsored by the Illumina subsidiary Grail, which included 6,662 individuals age 50 and over from seven sites in the United States, and grouped them into normal and increased risk; 92% were non-Hispanic White. It used the Galleri MCED test, which performed with a sensitivity of 29%, specificity of 99.1%, and a positive predictive value of 38.0%. False positives produced to limited burden, with 93% undergoing imaging, 28% nonsurgical invasive procedures, and 2% undergoing fruitless invasive surgical procedures.
Dr. Febbo touted the potential for such tests to greatly reduce cancer mortality, but only if there is adequate uptake of screening procedures, particularly in underserved groups. He put up a slide of a model showing that MCED has the potential to reduce cancer mortality by 20%, but only if the screen is widely accepted among all groups. “I’ve had my team model this. If we accept the current use of screening tests, and we don’t address disparities, and we don’t ensure everybody feels included and participates actively – not only in the research, but also in the testing and adoption, you would cut that potential benefit in half. That would be hundreds of thousands of lives lost because we didn’t address disparities.”
Successful recruiting of African Americans for research
Following Dr. Febbo’s talk, Karriem Watson, MS, spoke about some potential solutions to the issue, including his own experiences and success stories in recruiting African Americans to play active roles in research. He is chief engagement officer for the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program, which aims to gather health data on at least 1 million residents of the United States. Mr. Watson has spent time reaching out to people living in communities in the Chicago area to encourage participation in breast cancer screening. An event at his church inspired his own sister to get a mammogram, and she was diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer.
“I’m a living witness that early engagement can lead to early detection,” said Mr. Watson during his talk.
He reported that the All of Us research program has succeeded in creating diversity within its data collection, as 46.7% of participants identify as racial and ethnic minorities.
Mr. Watson took issue with the common perception that underrepresented communities may be hard to reach.
“I want to challenge us to think outside the box and really ask ourselves: Are populations hard to reach, or are there opportunities for us to do better and more intentional engagement?” He went on to describe a program to recruit African American men as citizen scientists. He and his colleagues developed a network that included barbers, faith leaders, and fraternity and civic organization members to help recruit participants for a prostate cancer screening project. They exceeded their initial recruitment goal.
They went on to develop a network of barbers in the south and west sides of Chicago to recruit individuals to participate in studies of protein methylation and lung cancer screening, as well as a project that investigated associations between neighborhood of residence and lung cancer. The results of those efforts have also informed other projects, including a smoking cessation study. “We’ve not only included African American men in our research, but we’ve included them as part of our research team,” said Mr. Watson.
Dr. Febbo is also a stockholder of Illumina. Mr. Watson has no relevant financial disclosures.
From American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023: Improving cancer outcomes through equitable access to cfDNA tests. Presented Monday, April 17, 2023.
Cancer screening remains challenging. There are screens available for a handful of solid tumors, but uptake is low caused in part by health care access barriers as well as the potential for unnecessary follow-up procedures, according to Phillip Febbo, MD.
These issues could threaten efforts like that of President Joe Biden’s Cancer Moonshot initiative, which aims to reduce cancer mortality by 50%. Advances in circulating tumor (ct) DNA analysis could help address these problems, but a lack of diversity among study participants needs to be addressed to ensure it has broad utility, continued Dr. Febbo, during his presentation at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
The problem is particularly acute among African American, Hispanic, and other underserved populations who often face health care barriers that can exacerbate the issue, said Dr. Febbo, who is chief medical officer for Illumina. The lack of access is compounded by the fact that there are only currently screens for lung, breast, colorectal, cervical, and prostate cancer, leaving a vast unmet need.
“We still do not have screening tests for 70% of the deaths that are due to cancer,” he said.
ctDNA released from dying cancer cells has the potential to reveal a wide range of cancer types and reduce barriers to access, because it is based on a blood test. It can be analyzed for various factors, including mutations, chromosomal rearrangements, methylation patterns, and other characteristics that hint at the presence of cancer. However, it can’t be successful without sufficient inclusion in research studies, Dr. Febbo explained.
“We have to ensure we have the right representation [of] populations when we develop these tests, when we go through the clinical trials, and as we bring these into communities,” he said.
During his presentation, Dr. Febbo shared a slide showing that about 78% of participants in published gene-association studies were White.
ctDNA showed promise in at least on recent study. Dr. Febbo discussed the ECLIPSE trial, which used the Guardant Health SHIELD assay for colorectal cancer (CRC). About 13% of its approximately 20,000 participants were Black or African American, 15% were Hispanic, and 7% were Asian Americans. It also included both urban and rural individuals. In results announced in December 2022, the researchers found a sensitivity of 83%, which was lower than the 92.3% found in standard CRC screening, but above the 74% threshold set by the Food and Drug Administration. The specificity was 90%.
One approach that could dramatically change the landscape of cancer screening is a multicancer early detection (MCED) test, according to Dr. Febbo. The CancerSeek MCED test, developed by Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center researchers, uses a series of genetic and protein biomarkers to detect all cancers, with the exception of leukemia, skin cancer, and central nervous system tumors. Among 10,006 women aged between 65 and 75 years with no history of cancer, it had a sensitivity of 27.1% and a specificity of 98.9%, with a positive predictive value of 19.4%. The study’s population was 95% non-Hispanic White.
He also discussed the Pathfinder study, sponsored by the Illumina subsidiary Grail, which included 6,662 individuals age 50 and over from seven sites in the United States, and grouped them into normal and increased risk; 92% were non-Hispanic White. It used the Galleri MCED test, which performed with a sensitivity of 29%, specificity of 99.1%, and a positive predictive value of 38.0%. False positives produced to limited burden, with 93% undergoing imaging, 28% nonsurgical invasive procedures, and 2% undergoing fruitless invasive surgical procedures.
Dr. Febbo touted the potential for such tests to greatly reduce cancer mortality, but only if there is adequate uptake of screening procedures, particularly in underserved groups. He put up a slide of a model showing that MCED has the potential to reduce cancer mortality by 20%, but only if the screen is widely accepted among all groups. “I’ve had my team model this. If we accept the current use of screening tests, and we don’t address disparities, and we don’t ensure everybody feels included and participates actively – not only in the research, but also in the testing and adoption, you would cut that potential benefit in half. That would be hundreds of thousands of lives lost because we didn’t address disparities.”
Successful recruiting of African Americans for research
Following Dr. Febbo’s talk, Karriem Watson, MS, spoke about some potential solutions to the issue, including his own experiences and success stories in recruiting African Americans to play active roles in research. He is chief engagement officer for the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program, which aims to gather health data on at least 1 million residents of the United States. Mr. Watson has spent time reaching out to people living in communities in the Chicago area to encourage participation in breast cancer screening. An event at his church inspired his own sister to get a mammogram, and she was diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer.
“I’m a living witness that early engagement can lead to early detection,” said Mr. Watson during his talk.
He reported that the All of Us research program has succeeded in creating diversity within its data collection, as 46.7% of participants identify as racial and ethnic minorities.
Mr. Watson took issue with the common perception that underrepresented communities may be hard to reach.
“I want to challenge us to think outside the box and really ask ourselves: Are populations hard to reach, or are there opportunities for us to do better and more intentional engagement?” He went on to describe a program to recruit African American men as citizen scientists. He and his colleagues developed a network that included barbers, faith leaders, and fraternity and civic organization members to help recruit participants for a prostate cancer screening project. They exceeded their initial recruitment goal.
They went on to develop a network of barbers in the south and west sides of Chicago to recruit individuals to participate in studies of protein methylation and lung cancer screening, as well as a project that investigated associations between neighborhood of residence and lung cancer. The results of those efforts have also informed other projects, including a smoking cessation study. “We’ve not only included African American men in our research, but we’ve included them as part of our research team,” said Mr. Watson.
Dr. Febbo is also a stockholder of Illumina. Mr. Watson has no relevant financial disclosures.
From American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023: Improving cancer outcomes through equitable access to cfDNA tests. Presented Monday, April 17, 2023.
FROM AACR 2023
Green Mediterranean diet may relieve aortic stiffness
A green adaptation to the traditional Mediterranean diet improves proximal aortic stiffness (PAS), a distinct marker of vascular aging and increased cardiovascular risk, according to an exploratory post hoc analysis of the DIRECT-PLUS randomized clinical trial.
The green Mediterranean diet is distinct from the traditional Mediterranean diet because of its more abundant dietary polyphenols, from green tea and a Wolffia globosa (Mankai) plant green shake, and lower intake of red or processed meat.
Independent of weight loss, the modified green Mediterranean diet regressed PAS by 15%, the traditional Mediterranean diet by 7.3%, and the healthy dietary guideline–based diet by 4.8%, the study team observed.
“The DIRECT-PLUS trial research team was the first to introduce the concept of the green-Mediterranean/high polyphenols diet,” lead researcher Iris Shai, RD, PhD, with Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Be’er-Sheva, Israel, told this news organization.
This diet promoted “dramatic proximal aortic de-stiffening” as assessed by MRI over 18 months in roughly 300 participants with abdominal obesity/dyslipidemia. “To date, no dietary strategies have been shown to impact vascular aging physiology,” Dr. Shai said.
The analysis was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Not all healthy diets are equal
Of the 294 participants, 281 had valid PAS measurements at baseline. The baseline PAS (6.1 m/s) was similar across intervention groups (P = .20). Increased PAS was associated with aging, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and visceral adiposity (P < .05).
After 18 months’ intervention (retention rate 89.8%), all diet groups showed significant PAS reductions: –0.05 m/s with the standard healthy diet (4.8%), –0.08 m/s with the traditional Mediterranean diet (7.3%) and –0.15 the green Mediterranean diet (15%).
In the multivariable model, the green Mediterranean dieters had greater PAS reduction than did the healthy-diet and Mediterranean dieters (P = .003 and P = .032, respectively).
The researchers caution that DIRECT-PLUS had multiple endpoints and this exploratory post hoc analysis might be sensitive to type I statistical error and should be considered “hypothesis-generating.”
High-quality study, believable results
Reached for comment on the study, Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, director of Mount Sinai Heart in New York, said, “There is not a lot of high-quality research on diet, and I would call this high-quality research in as much as they used randomization which most dietary studies don’t do.
“The greener Mediterranean diet seemed to be the best one on the surrogate marker of MRI-defined aortic stiffness,” Dr. Bhatt, professor of cardiovascular medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, who wasn’t involved in the study, told this news organization.
“It makes sense that a diet that has more green in it, more polyphenols, would be healthier. This has been shown in some other studies, that these plant-based polyphenols might have various cardiovascular protective aspects to them,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Overall, he said the results are “quite believable, with the caveat that it would be nice to see the results reproduced in a more diverse and larger sample.”
“There is emerging evidence that diets that are higher in fresh fruits and vegetables and whole grains and lower in overall caloric intake, in general, seem to be good diets to reduce cardiovascular risk factors and maybe even reduce actual cardiovascular risk,” Dr. Bhatt added.
The study was funded by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation), the Rosetrees Trust, Israel Ministry of Health, Israel Ministry of Science and Technology, and the California Walnuts Commission. Dr. Shai and Dr. Bhatt have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A green adaptation to the traditional Mediterranean diet improves proximal aortic stiffness (PAS), a distinct marker of vascular aging and increased cardiovascular risk, according to an exploratory post hoc analysis of the DIRECT-PLUS randomized clinical trial.
The green Mediterranean diet is distinct from the traditional Mediterranean diet because of its more abundant dietary polyphenols, from green tea and a Wolffia globosa (Mankai) plant green shake, and lower intake of red or processed meat.
Independent of weight loss, the modified green Mediterranean diet regressed PAS by 15%, the traditional Mediterranean diet by 7.3%, and the healthy dietary guideline–based diet by 4.8%, the study team observed.
“The DIRECT-PLUS trial research team was the first to introduce the concept of the green-Mediterranean/high polyphenols diet,” lead researcher Iris Shai, RD, PhD, with Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Be’er-Sheva, Israel, told this news organization.
This diet promoted “dramatic proximal aortic de-stiffening” as assessed by MRI over 18 months in roughly 300 participants with abdominal obesity/dyslipidemia. “To date, no dietary strategies have been shown to impact vascular aging physiology,” Dr. Shai said.
The analysis was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Not all healthy diets are equal
Of the 294 participants, 281 had valid PAS measurements at baseline. The baseline PAS (6.1 m/s) was similar across intervention groups (P = .20). Increased PAS was associated with aging, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and visceral adiposity (P < .05).
After 18 months’ intervention (retention rate 89.8%), all diet groups showed significant PAS reductions: –0.05 m/s with the standard healthy diet (4.8%), –0.08 m/s with the traditional Mediterranean diet (7.3%) and –0.15 the green Mediterranean diet (15%).
In the multivariable model, the green Mediterranean dieters had greater PAS reduction than did the healthy-diet and Mediterranean dieters (P = .003 and P = .032, respectively).
The researchers caution that DIRECT-PLUS had multiple endpoints and this exploratory post hoc analysis might be sensitive to type I statistical error and should be considered “hypothesis-generating.”
High-quality study, believable results
Reached for comment on the study, Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, director of Mount Sinai Heart in New York, said, “There is not a lot of high-quality research on diet, and I would call this high-quality research in as much as they used randomization which most dietary studies don’t do.
“The greener Mediterranean diet seemed to be the best one on the surrogate marker of MRI-defined aortic stiffness,” Dr. Bhatt, professor of cardiovascular medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, who wasn’t involved in the study, told this news organization.
“It makes sense that a diet that has more green in it, more polyphenols, would be healthier. This has been shown in some other studies, that these plant-based polyphenols might have various cardiovascular protective aspects to them,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Overall, he said the results are “quite believable, with the caveat that it would be nice to see the results reproduced in a more diverse and larger sample.”
“There is emerging evidence that diets that are higher in fresh fruits and vegetables and whole grains and lower in overall caloric intake, in general, seem to be good diets to reduce cardiovascular risk factors and maybe even reduce actual cardiovascular risk,” Dr. Bhatt added.
The study was funded by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation), the Rosetrees Trust, Israel Ministry of Health, Israel Ministry of Science and Technology, and the California Walnuts Commission. Dr. Shai and Dr. Bhatt have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A green adaptation to the traditional Mediterranean diet improves proximal aortic stiffness (PAS), a distinct marker of vascular aging and increased cardiovascular risk, according to an exploratory post hoc analysis of the DIRECT-PLUS randomized clinical trial.
The green Mediterranean diet is distinct from the traditional Mediterranean diet because of its more abundant dietary polyphenols, from green tea and a Wolffia globosa (Mankai) plant green shake, and lower intake of red or processed meat.
Independent of weight loss, the modified green Mediterranean diet regressed PAS by 15%, the traditional Mediterranean diet by 7.3%, and the healthy dietary guideline–based diet by 4.8%, the study team observed.
“The DIRECT-PLUS trial research team was the first to introduce the concept of the green-Mediterranean/high polyphenols diet,” lead researcher Iris Shai, RD, PhD, with Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Be’er-Sheva, Israel, told this news organization.
This diet promoted “dramatic proximal aortic de-stiffening” as assessed by MRI over 18 months in roughly 300 participants with abdominal obesity/dyslipidemia. “To date, no dietary strategies have been shown to impact vascular aging physiology,” Dr. Shai said.
The analysis was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Not all healthy diets are equal
Of the 294 participants, 281 had valid PAS measurements at baseline. The baseline PAS (6.1 m/s) was similar across intervention groups (P = .20). Increased PAS was associated with aging, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and visceral adiposity (P < .05).
After 18 months’ intervention (retention rate 89.8%), all diet groups showed significant PAS reductions: –0.05 m/s with the standard healthy diet (4.8%), –0.08 m/s with the traditional Mediterranean diet (7.3%) and –0.15 the green Mediterranean diet (15%).
In the multivariable model, the green Mediterranean dieters had greater PAS reduction than did the healthy-diet and Mediterranean dieters (P = .003 and P = .032, respectively).
The researchers caution that DIRECT-PLUS had multiple endpoints and this exploratory post hoc analysis might be sensitive to type I statistical error and should be considered “hypothesis-generating.”
High-quality study, believable results
Reached for comment on the study, Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, director of Mount Sinai Heart in New York, said, “There is not a lot of high-quality research on diet, and I would call this high-quality research in as much as they used randomization which most dietary studies don’t do.
“The greener Mediterranean diet seemed to be the best one on the surrogate marker of MRI-defined aortic stiffness,” Dr. Bhatt, professor of cardiovascular medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, who wasn’t involved in the study, told this news organization.
“It makes sense that a diet that has more green in it, more polyphenols, would be healthier. This has been shown in some other studies, that these plant-based polyphenols might have various cardiovascular protective aspects to them,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Overall, he said the results are “quite believable, with the caveat that it would be nice to see the results reproduced in a more diverse and larger sample.”
“There is emerging evidence that diets that are higher in fresh fruits and vegetables and whole grains and lower in overall caloric intake, in general, seem to be good diets to reduce cardiovascular risk factors and maybe even reduce actual cardiovascular risk,” Dr. Bhatt added.
The study was funded by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation), the Rosetrees Trust, Israel Ministry of Health, Israel Ministry of Science and Technology, and the California Walnuts Commission. Dr. Shai and Dr. Bhatt have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.




