User login
Possible bivalent vaccine link to strokes in people over 65
who got the shot, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration said in a joint news release.
The release did not recommend people change their vaccine practices, saying the database finding probably did not represent a “true clinical risk.” The CDC said everybody, including people over 65, should stay up to date on their COVID vaccines, including the bivalent booster.
The news release said the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD), “a near real-time surveillance system,” raised a safety concern about the Pfizer/BioNTech booster.
“Rapid-response investigation of the signal in the VSD raised a question of whether people 65 and older who have received the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, Bivalent were more likely to have an ischemic stroke in the 21 days following vaccination compared with days 22-44 following vaccination,” the news release said.
Ischemic strokes are blockages of blood to the brain, often caused by blood clots.
“Although the totality of the data currently suggests that it is very unlikely that the signal in VSD (Vaccine Safety Datalink) represents a true clinical risk, we believe it is important to share this information with the public, as we have in the past, when one of our safety monitoring systems detects a signal,” the release said.
No higher likelihood of strokes linked to the Pfizer bivalent vaccine had been found by Pfizer/BioNTech, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System maintained by the CDC and the FDA, or other agencies that monitor reactions of vaccines, the news release said. No safety issues about strokes have been identified with the Moderna bivalent vaccine.
CNN, citing a CDC official, reported that about 550,000 seniors who got Pfizer bivalent boosters were tracked by the VSD, and 130 of them had strokes within 3 weeks of getting the shot. None of those 130 people died, CNN said. The official spoke on the condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to share the data.
The issue will be discussed at the January meeting of the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee.
In a joint statement, Pfizer and BioNTech said: “Neither Pfizer and BioNTech nor the CDC or FDA have observed similar findings across numerous other monitoring systems in the U.S. and globally and there is no evidence to conclude that ischemic stroke is associated with the use of the companies’ COVID-19 vaccines.”
Bivalent boosters contain two strains of vaccine – one to protect against the original COVID-19 virus and another targeting Omicron subvariants.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
who got the shot, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration said in a joint news release.
The release did not recommend people change their vaccine practices, saying the database finding probably did not represent a “true clinical risk.” The CDC said everybody, including people over 65, should stay up to date on their COVID vaccines, including the bivalent booster.
The news release said the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD), “a near real-time surveillance system,” raised a safety concern about the Pfizer/BioNTech booster.
“Rapid-response investigation of the signal in the VSD raised a question of whether people 65 and older who have received the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, Bivalent were more likely to have an ischemic stroke in the 21 days following vaccination compared with days 22-44 following vaccination,” the news release said.
Ischemic strokes are blockages of blood to the brain, often caused by blood clots.
“Although the totality of the data currently suggests that it is very unlikely that the signal in VSD (Vaccine Safety Datalink) represents a true clinical risk, we believe it is important to share this information with the public, as we have in the past, when one of our safety monitoring systems detects a signal,” the release said.
No higher likelihood of strokes linked to the Pfizer bivalent vaccine had been found by Pfizer/BioNTech, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System maintained by the CDC and the FDA, or other agencies that monitor reactions of vaccines, the news release said. No safety issues about strokes have been identified with the Moderna bivalent vaccine.
CNN, citing a CDC official, reported that about 550,000 seniors who got Pfizer bivalent boosters were tracked by the VSD, and 130 of them had strokes within 3 weeks of getting the shot. None of those 130 people died, CNN said. The official spoke on the condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to share the data.
The issue will be discussed at the January meeting of the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee.
In a joint statement, Pfizer and BioNTech said: “Neither Pfizer and BioNTech nor the CDC or FDA have observed similar findings across numerous other monitoring systems in the U.S. and globally and there is no evidence to conclude that ischemic stroke is associated with the use of the companies’ COVID-19 vaccines.”
Bivalent boosters contain two strains of vaccine – one to protect against the original COVID-19 virus and another targeting Omicron subvariants.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
who got the shot, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration said in a joint news release.
The release did not recommend people change their vaccine practices, saying the database finding probably did not represent a “true clinical risk.” The CDC said everybody, including people over 65, should stay up to date on their COVID vaccines, including the bivalent booster.
The news release said the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD), “a near real-time surveillance system,” raised a safety concern about the Pfizer/BioNTech booster.
“Rapid-response investigation of the signal in the VSD raised a question of whether people 65 and older who have received the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, Bivalent were more likely to have an ischemic stroke in the 21 days following vaccination compared with days 22-44 following vaccination,” the news release said.
Ischemic strokes are blockages of blood to the brain, often caused by blood clots.
“Although the totality of the data currently suggests that it is very unlikely that the signal in VSD (Vaccine Safety Datalink) represents a true clinical risk, we believe it is important to share this information with the public, as we have in the past, when one of our safety monitoring systems detects a signal,” the release said.
No higher likelihood of strokes linked to the Pfizer bivalent vaccine had been found by Pfizer/BioNTech, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System maintained by the CDC and the FDA, or other agencies that monitor reactions of vaccines, the news release said. No safety issues about strokes have been identified with the Moderna bivalent vaccine.
CNN, citing a CDC official, reported that about 550,000 seniors who got Pfizer bivalent boosters were tracked by the VSD, and 130 of them had strokes within 3 weeks of getting the shot. None of those 130 people died, CNN said. The official spoke on the condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to share the data.
The issue will be discussed at the January meeting of the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee.
In a joint statement, Pfizer and BioNTech said: “Neither Pfizer and BioNTech nor the CDC or FDA have observed similar findings across numerous other monitoring systems in the U.S. and globally and there is no evidence to conclude that ischemic stroke is associated with the use of the companies’ COVID-19 vaccines.”
Bivalent boosters contain two strains of vaccine – one to protect against the original COVID-19 virus and another targeting Omicron subvariants.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Add this to the list of long COVID symptoms: Stigma
Most people with long COVID find they’re facing stigma due to their condition, according to a new report from researchers in the United Kingdom. In short: Relatives and friends may not believe they’re truly sick.
The U.K. team found that more than three-quarters of people studied had experienced stigma often or always.
In fact, 95% of people with long COVID faced at least one type of stigma at least sometimes, according to the study, published in November in the journal PLOS One.
Those conclusions had surprised the study’s lead researcher, Marija Pantelic, PhD, a public health lecturer at Brighton and Sussex Medical School, England.
“After years of working on HIV-related stigma, I was shocked to see how many people were turning a blind eye to and dismissing the difficulties experienced by people with long COVID,” Dr. Pantelic says. “It has also been clear to me from the start that this stigma is detrimental not just for people’s dignity, but also public health.”
Even some doctors argue that the growing attention paid to long COVID is excessive.
“It’s often normal to experience mild fatigue or weaknesses for weeks after being sick and inactive and not eating well. Calling these cases long COVID is the medicalization of modern life,” Marty Makary, MD, a surgeon and public policy researcher at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in a commentary in the Wall Street Journal.
Other doctors strongly disagree, including Alba Azola, MD, codirector of the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team and an expert in the stigma surrounding long COVID.
“Putting that spin on things, it’s just hurting people,” she says.
One example is people who cannot return to work.
“A lot of their family members tell me that they’re being lazy,” Dr. Azola says. “That’s part of the public stigma, that these are people just trying to get out of work.”
Some experts say the U.K. study represents a landmark.
“When you have data like this on long COVID stigma, it becomes more difficult to deny its existence or address it,” says Naomi Torres-Mackie, PhD, a clinical psychologist at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York. She also is head of research at the New York–based Mental Health Coalition, a group of experts working to end the stigma surrounding mental health.
She recalls her first patient with long COVID.
“She experienced the discomfort and pain itself, and then she had this crushing feeling that it wasn’t valid, or real. She felt very alone in it,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Another one of her patients is working at her job from home but facing doubt about her condition from her employers.
“Every month, her medical doctor has to produce a letter confirming her medical condition,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Taking part in the British stigma survey were 1,166 people, including 966 residents of the United Kingdom, with the average age of 48. Nearly 85% were female, and more than three-quarters were educated at the university level or higher.
Half of them said they had a clinical diagnosis of long COVID.
More than 60% of them said that at least some of the time, they were cautious about who they talked to about their condition. And fully 34% of those who did disclose their diagnosis said that they regretted having done so.
That’s a difficult experience for those with long COVID, says Leonard Jason, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University in Chicago.
“It’s like they’re traumatized by the initial experience of being sick, and retraumatized by the response of others to them,” he says.
Unexplained illnesses are not well-regarded by the general public, Dr. Jason says.
He gave the example of multiple sclerosis. Before the 1980s, those with MS were considered to have a psychological illness, he says. “Then, in the 1980s, there were biomarkers that said, ‘Here’s the evidence.’ ”
The British study described three types of stigma stemming from the long COVID diagnosis of those questioned:
- Enacted stigma: People were directly treated unfairly because of their condition.
- Internalized stigma: People felt embarrassed by that condition.
- Anticipated stigma: People expected they would be treated poorly because of their diagnosis.
Dr. Azola calls the medical community a major problem when it comes to dealing with long COVID.
“What I see with my patients is medical trauma,” she says. They may have symptoms that send them to the emergency room, and then the tests come back negative. “Instead of tracking the patients’ symptoms, patients get told, ‘Everything looks good, you can go home, this is a panic attack,’ ” she says.
Some people go online to search for treatments, sometimes launching GoFundMe campaigns to raise money for unreliable treatments.
Long COVID patients may have gone through 5 to 10 doctors before they arrive for treatment with the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team. The clinic began in April 2020 remotely and in August of that year in person.
Today, the clinic staff spends an hour with a first-time long COVID patient, hearing their stories and helping relieve anxiety, Dr. Azola says.
The phenomenon of long COVID is similar to what patients have had with chronic fatigue syndrome, lupus, or fibromyalgia, where people have symptoms that are hard to explain, says Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, deputy public health officer for Riverside County, Calif.
“Stigma within medicine or health care is nothing new,” she says.
In Chicago, Dr. Jason notes that the federal government’s decision to invest hundreds of millions of dollars in long COVID research “shows the government is helping destigmatize it.”
Dr. Pantelic says she and her colleagues are continuing their research.
“We are interested in understanding the impacts of this stigma, and how to mitigate any adverse outcomes for patients and services,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Most people with long COVID find they’re facing stigma due to their condition, according to a new report from researchers in the United Kingdom. In short: Relatives and friends may not believe they’re truly sick.
The U.K. team found that more than three-quarters of people studied had experienced stigma often or always.
In fact, 95% of people with long COVID faced at least one type of stigma at least sometimes, according to the study, published in November in the journal PLOS One.
Those conclusions had surprised the study’s lead researcher, Marija Pantelic, PhD, a public health lecturer at Brighton and Sussex Medical School, England.
“After years of working on HIV-related stigma, I was shocked to see how many people were turning a blind eye to and dismissing the difficulties experienced by people with long COVID,” Dr. Pantelic says. “It has also been clear to me from the start that this stigma is detrimental not just for people’s dignity, but also public health.”
Even some doctors argue that the growing attention paid to long COVID is excessive.
“It’s often normal to experience mild fatigue or weaknesses for weeks after being sick and inactive and not eating well. Calling these cases long COVID is the medicalization of modern life,” Marty Makary, MD, a surgeon and public policy researcher at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in a commentary in the Wall Street Journal.
Other doctors strongly disagree, including Alba Azola, MD, codirector of the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team and an expert in the stigma surrounding long COVID.
“Putting that spin on things, it’s just hurting people,” she says.
One example is people who cannot return to work.
“A lot of their family members tell me that they’re being lazy,” Dr. Azola says. “That’s part of the public stigma, that these are people just trying to get out of work.”
Some experts say the U.K. study represents a landmark.
“When you have data like this on long COVID stigma, it becomes more difficult to deny its existence or address it,” says Naomi Torres-Mackie, PhD, a clinical psychologist at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York. She also is head of research at the New York–based Mental Health Coalition, a group of experts working to end the stigma surrounding mental health.
She recalls her first patient with long COVID.
“She experienced the discomfort and pain itself, and then she had this crushing feeling that it wasn’t valid, or real. She felt very alone in it,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Another one of her patients is working at her job from home but facing doubt about her condition from her employers.
“Every month, her medical doctor has to produce a letter confirming her medical condition,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Taking part in the British stigma survey were 1,166 people, including 966 residents of the United Kingdom, with the average age of 48. Nearly 85% were female, and more than three-quarters were educated at the university level or higher.
Half of them said they had a clinical diagnosis of long COVID.
More than 60% of them said that at least some of the time, they were cautious about who they talked to about their condition. And fully 34% of those who did disclose their diagnosis said that they regretted having done so.
That’s a difficult experience for those with long COVID, says Leonard Jason, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University in Chicago.
“It’s like they’re traumatized by the initial experience of being sick, and retraumatized by the response of others to them,” he says.
Unexplained illnesses are not well-regarded by the general public, Dr. Jason says.
He gave the example of multiple sclerosis. Before the 1980s, those with MS were considered to have a psychological illness, he says. “Then, in the 1980s, there were biomarkers that said, ‘Here’s the evidence.’ ”
The British study described three types of stigma stemming from the long COVID diagnosis of those questioned:
- Enacted stigma: People were directly treated unfairly because of their condition.
- Internalized stigma: People felt embarrassed by that condition.
- Anticipated stigma: People expected they would be treated poorly because of their diagnosis.
Dr. Azola calls the medical community a major problem when it comes to dealing with long COVID.
“What I see with my patients is medical trauma,” she says. They may have symptoms that send them to the emergency room, and then the tests come back negative. “Instead of tracking the patients’ symptoms, patients get told, ‘Everything looks good, you can go home, this is a panic attack,’ ” she says.
Some people go online to search for treatments, sometimes launching GoFundMe campaigns to raise money for unreliable treatments.
Long COVID patients may have gone through 5 to 10 doctors before they arrive for treatment with the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team. The clinic began in April 2020 remotely and in August of that year in person.
Today, the clinic staff spends an hour with a first-time long COVID patient, hearing their stories and helping relieve anxiety, Dr. Azola says.
The phenomenon of long COVID is similar to what patients have had with chronic fatigue syndrome, lupus, or fibromyalgia, where people have symptoms that are hard to explain, says Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, deputy public health officer for Riverside County, Calif.
“Stigma within medicine or health care is nothing new,” she says.
In Chicago, Dr. Jason notes that the federal government’s decision to invest hundreds of millions of dollars in long COVID research “shows the government is helping destigmatize it.”
Dr. Pantelic says she and her colleagues are continuing their research.
“We are interested in understanding the impacts of this stigma, and how to mitigate any adverse outcomes for patients and services,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Most people with long COVID find they’re facing stigma due to their condition, according to a new report from researchers in the United Kingdom. In short: Relatives and friends may not believe they’re truly sick.
The U.K. team found that more than three-quarters of people studied had experienced stigma often or always.
In fact, 95% of people with long COVID faced at least one type of stigma at least sometimes, according to the study, published in November in the journal PLOS One.
Those conclusions had surprised the study’s lead researcher, Marija Pantelic, PhD, a public health lecturer at Brighton and Sussex Medical School, England.
“After years of working on HIV-related stigma, I was shocked to see how many people were turning a blind eye to and dismissing the difficulties experienced by people with long COVID,” Dr. Pantelic says. “It has also been clear to me from the start that this stigma is detrimental not just for people’s dignity, but also public health.”
Even some doctors argue that the growing attention paid to long COVID is excessive.
“It’s often normal to experience mild fatigue or weaknesses for weeks after being sick and inactive and not eating well. Calling these cases long COVID is the medicalization of modern life,” Marty Makary, MD, a surgeon and public policy researcher at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in a commentary in the Wall Street Journal.
Other doctors strongly disagree, including Alba Azola, MD, codirector of the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team and an expert in the stigma surrounding long COVID.
“Putting that spin on things, it’s just hurting people,” she says.
One example is people who cannot return to work.
“A lot of their family members tell me that they’re being lazy,” Dr. Azola says. “That’s part of the public stigma, that these are people just trying to get out of work.”
Some experts say the U.K. study represents a landmark.
“When you have data like this on long COVID stigma, it becomes more difficult to deny its existence or address it,” says Naomi Torres-Mackie, PhD, a clinical psychologist at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York. She also is head of research at the New York–based Mental Health Coalition, a group of experts working to end the stigma surrounding mental health.
She recalls her first patient with long COVID.
“She experienced the discomfort and pain itself, and then she had this crushing feeling that it wasn’t valid, or real. She felt very alone in it,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Another one of her patients is working at her job from home but facing doubt about her condition from her employers.
“Every month, her medical doctor has to produce a letter confirming her medical condition,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Taking part in the British stigma survey were 1,166 people, including 966 residents of the United Kingdom, with the average age of 48. Nearly 85% were female, and more than three-quarters were educated at the university level or higher.
Half of them said they had a clinical diagnosis of long COVID.
More than 60% of them said that at least some of the time, they were cautious about who they talked to about their condition. And fully 34% of those who did disclose their diagnosis said that they regretted having done so.
That’s a difficult experience for those with long COVID, says Leonard Jason, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University in Chicago.
“It’s like they’re traumatized by the initial experience of being sick, and retraumatized by the response of others to them,” he says.
Unexplained illnesses are not well-regarded by the general public, Dr. Jason says.
He gave the example of multiple sclerosis. Before the 1980s, those with MS were considered to have a psychological illness, he says. “Then, in the 1980s, there were biomarkers that said, ‘Here’s the evidence.’ ”
The British study described three types of stigma stemming from the long COVID diagnosis of those questioned:
- Enacted stigma: People were directly treated unfairly because of their condition.
- Internalized stigma: People felt embarrassed by that condition.
- Anticipated stigma: People expected they would be treated poorly because of their diagnosis.
Dr. Azola calls the medical community a major problem when it comes to dealing with long COVID.
“What I see with my patients is medical trauma,” she says. They may have symptoms that send them to the emergency room, and then the tests come back negative. “Instead of tracking the patients’ symptoms, patients get told, ‘Everything looks good, you can go home, this is a panic attack,’ ” she says.
Some people go online to search for treatments, sometimes launching GoFundMe campaigns to raise money for unreliable treatments.
Long COVID patients may have gone through 5 to 10 doctors before they arrive for treatment with the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team. The clinic began in April 2020 remotely and in August of that year in person.
Today, the clinic staff spends an hour with a first-time long COVID patient, hearing their stories and helping relieve anxiety, Dr. Azola says.
The phenomenon of long COVID is similar to what patients have had with chronic fatigue syndrome, lupus, or fibromyalgia, where people have symptoms that are hard to explain, says Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, deputy public health officer for Riverside County, Calif.
“Stigma within medicine or health care is nothing new,” she says.
In Chicago, Dr. Jason notes that the federal government’s decision to invest hundreds of millions of dollars in long COVID research “shows the government is helping destigmatize it.”
Dr. Pantelic says she and her colleagues are continuing their research.
“We are interested in understanding the impacts of this stigma, and how to mitigate any adverse outcomes for patients and services,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
PLOS ONE
Can siRNA improve compliance in patients with hypertension?
Many approaches have been explored in recent years to make life easier for patients living with chronic conditions that require them to take daily medication: subcutaneous implantable devices, nanogels, and, more specifically in the case of hypertension, renal denervation or small interfering RNA (siRNA) with a long half-life.
It’s siRNA that Michel Azizi, MD, PhD, head of the blood pressure clinic at Georges Pompidou European Hospital (HEGP) in Paris, discussed at the International Meeting of the French Society of Hypertension.
These small molecules have already shown their worth in treating rare diseases such as transthyretin amyloidosis. More recently, treating hypercholesterolemia with the PCSK9 inhibitor inclisiran has proven effective. “One subcutaneous injection of inclisiran reduces LDL cholesterol by 50% for a period of 210 days,” said Dr. Azizi.
The benefit of a new therapeutic siRNA – zilebesiran, administered subcutaneously – in treating hypertension is currently the subject of a phase II clinical trial.
This is a double-stranded RNA. One of the strands is linked to a sugar, N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), which protects these highly fragile siRNA and binds with a very strong affinity in the liver. The second strand binds to a specific area of the RNA to prevent synthesis of the precursor peptide of angiotensin, angiotensinogen. The resulting effect is suppression of the production of angiotensin I and II, which leads to a long-lasting lowering of blood pressure.
Lasting efficacy
Phase I studies with zilebesiran have demonstrated a long-term effect, with a reduction of greater than 90% in circulating angiotensinogen over 6 months after a single subcutaneous dose (800 mg). The peak in reduction of circulating angiotensinogen occurs after approximately 3 weeks.
“It’s extremely powerful,” said Dr. Azizi.
Lasting reductions in blood pressure have also been observed, with 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring showing a reduction in systolic BP of greater than 15 mm Hg 8 weeks after administration of a single dose of zilebesiran (800 mg).
Zilebesiran was also well tolerated, with only mild to moderate reactions at the site of the injection (n = 5/56) and no serious treatment-related adverse events, hypotension, or significant changes in kidney or liver function.
“In terms of benefits, the effect is ongoing. Zilebesiran leads to reduced medication use and causes less variability in blood pressure response. Nevertheless, interfering RNA acts slowly, meaning that zilebesiran would not be suitable for people presenting with a hypertensive crisis. The fact that it blocks the renin-angiotensin system [RAS] for a very long period of time also poses the question of how to reverse its hypotensive effects,” said Dr. Azizi.
Unanswered questions
The lasting RAS antagonist and blood pressure–lowering effects pose a potential safety problem in circumstances involving patients in a state of hypovolemia and hypotension who require rapid blood pressure–raising interventions to prevent morbidity and mortality.
In recent studies, Estrellita Uijl et al. have thus examined strategies to counteract the blood pressure–lowering effect of siRNA in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Fludrocortisone and a high-salt diet were both successful in gradually increasing blood pressure, which returned to its baseline levels on days 5 and 7, respectively. Yet this rate of response would be wholly inadequate in an urgent clinical situation.
However, midodrine could not reduce blood pressure to normal levels, whether administered subcutaneously or orally.
A rapid and short-lasting increase in blood pressure was observed with bolus doses of vasopressors, but clinically, these would need to be administered intravenously to achieve a lasting effect. Such administration would require hospitalization, close monitoring, and the use of human resources and additional health care provisions.
Encouragingly, the laboratory that created this molecule, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, has come up with an antidote: Reversir. It is a GalNAc-conjugated, single-stranded, high-affinity oligonucleotide complementary to the zilebesiran strand that achieves effective reversal of siRNA activity in 24 hours.
In the future, after the phase 2 trials have been completed, whether or not zilebesiran reduces the incidence of cardiovascular events and mortality remains to be seen. But as for Dr. Azizi, the director of HEGP’s blood pressure clinic in Paris, he has no doubt that “this approach is about to shake up how we treat patients in the cardiovascular field.”
On the horizon
Zilebesiran is being studied in phase 2 trials in patients with mild to moderate hypertension not taking antihypertensive drugs (KARDIA-1: 375 patients; double-blind, placebo-controlled, five-arm trial; zilebesiran at 150, 300, and 600 mg twice per year and 300 mg once every 3 months) and in patients whose blood pressure is not controlled (KARDIA-2: 800 patients; initial open-label start-up period of 4 weeks with indapamide/amlodipine/olmesartan, followed by a double-blind, placebo-controlled study over 6 months, then an open-label extension study for up to 12 additional months; zilebesiran at 600 mg on the first day of the initial double-blind period, then every 6 months during the open-label extension period).
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition and a version appeared on Medscape.com.
Many approaches have been explored in recent years to make life easier for patients living with chronic conditions that require them to take daily medication: subcutaneous implantable devices, nanogels, and, more specifically in the case of hypertension, renal denervation or small interfering RNA (siRNA) with a long half-life.
It’s siRNA that Michel Azizi, MD, PhD, head of the blood pressure clinic at Georges Pompidou European Hospital (HEGP) in Paris, discussed at the International Meeting of the French Society of Hypertension.
These small molecules have already shown their worth in treating rare diseases such as transthyretin amyloidosis. More recently, treating hypercholesterolemia with the PCSK9 inhibitor inclisiran has proven effective. “One subcutaneous injection of inclisiran reduces LDL cholesterol by 50% for a period of 210 days,” said Dr. Azizi.
The benefit of a new therapeutic siRNA – zilebesiran, administered subcutaneously – in treating hypertension is currently the subject of a phase II clinical trial.
This is a double-stranded RNA. One of the strands is linked to a sugar, N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), which protects these highly fragile siRNA and binds with a very strong affinity in the liver. The second strand binds to a specific area of the RNA to prevent synthesis of the precursor peptide of angiotensin, angiotensinogen. The resulting effect is suppression of the production of angiotensin I and II, which leads to a long-lasting lowering of blood pressure.
Lasting efficacy
Phase I studies with zilebesiran have demonstrated a long-term effect, with a reduction of greater than 90% in circulating angiotensinogen over 6 months after a single subcutaneous dose (800 mg). The peak in reduction of circulating angiotensinogen occurs after approximately 3 weeks.
“It’s extremely powerful,” said Dr. Azizi.
Lasting reductions in blood pressure have also been observed, with 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring showing a reduction in systolic BP of greater than 15 mm Hg 8 weeks after administration of a single dose of zilebesiran (800 mg).
Zilebesiran was also well tolerated, with only mild to moderate reactions at the site of the injection (n = 5/56) and no serious treatment-related adverse events, hypotension, or significant changes in kidney or liver function.
“In terms of benefits, the effect is ongoing. Zilebesiran leads to reduced medication use and causes less variability in blood pressure response. Nevertheless, interfering RNA acts slowly, meaning that zilebesiran would not be suitable for people presenting with a hypertensive crisis. The fact that it blocks the renin-angiotensin system [RAS] for a very long period of time also poses the question of how to reverse its hypotensive effects,” said Dr. Azizi.
Unanswered questions
The lasting RAS antagonist and blood pressure–lowering effects pose a potential safety problem in circumstances involving patients in a state of hypovolemia and hypotension who require rapid blood pressure–raising interventions to prevent morbidity and mortality.
In recent studies, Estrellita Uijl et al. have thus examined strategies to counteract the blood pressure–lowering effect of siRNA in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Fludrocortisone and a high-salt diet were both successful in gradually increasing blood pressure, which returned to its baseline levels on days 5 and 7, respectively. Yet this rate of response would be wholly inadequate in an urgent clinical situation.
However, midodrine could not reduce blood pressure to normal levels, whether administered subcutaneously or orally.
A rapid and short-lasting increase in blood pressure was observed with bolus doses of vasopressors, but clinically, these would need to be administered intravenously to achieve a lasting effect. Such administration would require hospitalization, close monitoring, and the use of human resources and additional health care provisions.
Encouragingly, the laboratory that created this molecule, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, has come up with an antidote: Reversir. It is a GalNAc-conjugated, single-stranded, high-affinity oligonucleotide complementary to the zilebesiran strand that achieves effective reversal of siRNA activity in 24 hours.
In the future, after the phase 2 trials have been completed, whether or not zilebesiran reduces the incidence of cardiovascular events and mortality remains to be seen. But as for Dr. Azizi, the director of HEGP’s blood pressure clinic in Paris, he has no doubt that “this approach is about to shake up how we treat patients in the cardiovascular field.”
On the horizon
Zilebesiran is being studied in phase 2 trials in patients with mild to moderate hypertension not taking antihypertensive drugs (KARDIA-1: 375 patients; double-blind, placebo-controlled, five-arm trial; zilebesiran at 150, 300, and 600 mg twice per year and 300 mg once every 3 months) and in patients whose blood pressure is not controlled (KARDIA-2: 800 patients; initial open-label start-up period of 4 weeks with indapamide/amlodipine/olmesartan, followed by a double-blind, placebo-controlled study over 6 months, then an open-label extension study for up to 12 additional months; zilebesiran at 600 mg on the first day of the initial double-blind period, then every 6 months during the open-label extension period).
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition and a version appeared on Medscape.com.
Many approaches have been explored in recent years to make life easier for patients living with chronic conditions that require them to take daily medication: subcutaneous implantable devices, nanogels, and, more specifically in the case of hypertension, renal denervation or small interfering RNA (siRNA) with a long half-life.
It’s siRNA that Michel Azizi, MD, PhD, head of the blood pressure clinic at Georges Pompidou European Hospital (HEGP) in Paris, discussed at the International Meeting of the French Society of Hypertension.
These small molecules have already shown their worth in treating rare diseases such as transthyretin amyloidosis. More recently, treating hypercholesterolemia with the PCSK9 inhibitor inclisiran has proven effective. “One subcutaneous injection of inclisiran reduces LDL cholesterol by 50% for a period of 210 days,” said Dr. Azizi.
The benefit of a new therapeutic siRNA – zilebesiran, administered subcutaneously – in treating hypertension is currently the subject of a phase II clinical trial.
This is a double-stranded RNA. One of the strands is linked to a sugar, N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), which protects these highly fragile siRNA and binds with a very strong affinity in the liver. The second strand binds to a specific area of the RNA to prevent synthesis of the precursor peptide of angiotensin, angiotensinogen. The resulting effect is suppression of the production of angiotensin I and II, which leads to a long-lasting lowering of blood pressure.
Lasting efficacy
Phase I studies with zilebesiran have demonstrated a long-term effect, with a reduction of greater than 90% in circulating angiotensinogen over 6 months after a single subcutaneous dose (800 mg). The peak in reduction of circulating angiotensinogen occurs after approximately 3 weeks.
“It’s extremely powerful,” said Dr. Azizi.
Lasting reductions in blood pressure have also been observed, with 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring showing a reduction in systolic BP of greater than 15 mm Hg 8 weeks after administration of a single dose of zilebesiran (800 mg).
Zilebesiran was also well tolerated, with only mild to moderate reactions at the site of the injection (n = 5/56) and no serious treatment-related adverse events, hypotension, or significant changes in kidney or liver function.
“In terms of benefits, the effect is ongoing. Zilebesiran leads to reduced medication use and causes less variability in blood pressure response. Nevertheless, interfering RNA acts slowly, meaning that zilebesiran would not be suitable for people presenting with a hypertensive crisis. The fact that it blocks the renin-angiotensin system [RAS] for a very long period of time also poses the question of how to reverse its hypotensive effects,” said Dr. Azizi.
Unanswered questions
The lasting RAS antagonist and blood pressure–lowering effects pose a potential safety problem in circumstances involving patients in a state of hypovolemia and hypotension who require rapid blood pressure–raising interventions to prevent morbidity and mortality.
In recent studies, Estrellita Uijl et al. have thus examined strategies to counteract the blood pressure–lowering effect of siRNA in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Fludrocortisone and a high-salt diet were both successful in gradually increasing blood pressure, which returned to its baseline levels on days 5 and 7, respectively. Yet this rate of response would be wholly inadequate in an urgent clinical situation.
However, midodrine could not reduce blood pressure to normal levels, whether administered subcutaneously or orally.
A rapid and short-lasting increase in blood pressure was observed with bolus doses of vasopressors, but clinically, these would need to be administered intravenously to achieve a lasting effect. Such administration would require hospitalization, close monitoring, and the use of human resources and additional health care provisions.
Encouragingly, the laboratory that created this molecule, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, has come up with an antidote: Reversir. It is a GalNAc-conjugated, single-stranded, high-affinity oligonucleotide complementary to the zilebesiran strand that achieves effective reversal of siRNA activity in 24 hours.
In the future, after the phase 2 trials have been completed, whether or not zilebesiran reduces the incidence of cardiovascular events and mortality remains to be seen. But as for Dr. Azizi, the director of HEGP’s blood pressure clinic in Paris, he has no doubt that “this approach is about to shake up how we treat patients in the cardiovascular field.”
On the horizon
Zilebesiran is being studied in phase 2 trials in patients with mild to moderate hypertension not taking antihypertensive drugs (KARDIA-1: 375 patients; double-blind, placebo-controlled, five-arm trial; zilebesiran at 150, 300, and 600 mg twice per year and 300 mg once every 3 months) and in patients whose blood pressure is not controlled (KARDIA-2: 800 patients; initial open-label start-up period of 4 weeks with indapamide/amlodipine/olmesartan, followed by a double-blind, placebo-controlled study over 6 months, then an open-label extension study for up to 12 additional months; zilebesiran at 600 mg on the first day of the initial double-blind period, then every 6 months during the open-label extension period).
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition and a version appeared on Medscape.com.
AT INTERNATIONAL MEETING OF THE FRENCH SOCIETY OF HYPERTENSION
What the FTC’s proposed ban on noncompete agreements could mean for physicians, other clinicians
The proposed rule seeks to ban companies from enforcing noncompete clauses in employment contracts, a practice that represents an “unfair method of competition” with “exploitative and widespread” impacts, including suppression of wages, innovation, and entrepreneurial spirit, the FTC said. The public has 60 days to submit comments on the proposal before the FTC issues the final rule.
Employers often include noncompete clauses in physician contracts because they want to avoid having patients leave their health care system and follow a doctor to a competitor. A 2018 survey of primary care physicians found that about half of office-based physicians and 37% of physicians employed at hospitals or freestanding care centers were bound by restrictive covenants.
“A federal ban on noncompete agreements will ensure that physicians nationwide can finally change jobs without fear of being sued,” Erik B. Smith, MD, JD, clinical assistant professor of anesthesiology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Many doctors would like to see noncompete agreements vanish, but some physicians still favor them.
“As a small-practice owner, I am personally against this. The noncompete helps me take a risk and hire a physician. It typically takes 2-3 years for me to break even. I think this will further consolidate employment with large hospital systems unfortunately,” Texas cardiologist Rishin Shah, MD, recently tweeted in response to the FTC announcement.
Dr. Smith, who has advocated for noncompete reform, said about half of states currently allow the controversial clauses.
However, several states have recently passed laws restricting their use. California, North Dakota, and Oklahoma ban noncompetes, although some narrowly defined exceptions, such as the sale of a business, remain.
Other states, like Colorado, Illinois, and Oregon, broadly ban noncompete clauses, except for workers earning above a certain threshold. For example, in Colorado, noncompete agreements are permitted for highly compensated employees earning more than $101,250.
Despite additional restrictions on noncompete agreements for workers in the District of Columbia, the new legislation does not apply to physicians earning total compensation of $250,000 or more. However, their employers must define the geographic parameters of the noncompete and limit postemployment restrictions to 2 years.
Restrictive covenants are “uniquely challenging to family medicine’s emphasis on longitudinal care and the patient-physician relationship,” said Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians. The limitations imposed by noncompete agreements “potentially reduce patient choice, lower the quality of care for patients, and ultimately harm the foundation of family medicine – our relationships with our patients.”
Although the proposed rule aligns with President Biden’s executive order promoting economic competition, Dr. Smith said a national ban on noncompete agreements may push the limits of FTC authority.
“This new rule will certainly result in a ‘major questions doctrine’ Supreme Court challenge,” said Dr. Smith, and possibly be struck down if the court determines an administrative overstep into areas of “vast economic or political significance.”
A controversial policy
The American Medical Association’s code of ethics discourages covenants that “unreasonably restrict” the ability of physicians to practice following contract termination. And in 2022, the AMA cited “overly broad” noncompete language as a red flag young physicians should watch out for during contract negotiations.
But in 2020, the AMA asked the FTC not to use its rulemaking authority to regulate noncompete clauses in physician employment contracts, and instead, relegate enforcement of such agreements to each state. The American Hospital Association expressed similar views.
Still, the FTC said that eliminating noncompete clauses will increase annual wages by $300 billion, allow 30 million Americans to pursue better job opportunities, and encourage hiring competition among employers. It will also save consumers up to $148 billion in health care costs annually.
“Noncompetes block workers from freely switching jobs, depriving them of higher wages and better working conditions, and depriving businesses of a talent pool that they need to build and expand,” Lina M. Khan, FTC chair, said in a press release about the proposal.
A national ban on noncompetes would keep more physicians in the industry and practicing in their communities, a win for patients and providers, said Dr. Smith. It could also compel employers to offer more competitive employment packages, including fair wages, better work conditions, and a culture of well-being and patient safety.
“Whatever the final rule is, I’m certain it will be legally challenged,” said Dr. Smith, adding that the nation’s most prominent business lobbying group, the Chamber of Commerce, has already issued a statement calling the rule “blatantly unlawful."
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The proposed rule seeks to ban companies from enforcing noncompete clauses in employment contracts, a practice that represents an “unfair method of competition” with “exploitative and widespread” impacts, including suppression of wages, innovation, and entrepreneurial spirit, the FTC said. The public has 60 days to submit comments on the proposal before the FTC issues the final rule.
Employers often include noncompete clauses in physician contracts because they want to avoid having patients leave their health care system and follow a doctor to a competitor. A 2018 survey of primary care physicians found that about half of office-based physicians and 37% of physicians employed at hospitals or freestanding care centers were bound by restrictive covenants.
“A federal ban on noncompete agreements will ensure that physicians nationwide can finally change jobs without fear of being sued,” Erik B. Smith, MD, JD, clinical assistant professor of anesthesiology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Many doctors would like to see noncompete agreements vanish, but some physicians still favor them.
“As a small-practice owner, I am personally against this. The noncompete helps me take a risk and hire a physician. It typically takes 2-3 years for me to break even. I think this will further consolidate employment with large hospital systems unfortunately,” Texas cardiologist Rishin Shah, MD, recently tweeted in response to the FTC announcement.
Dr. Smith, who has advocated for noncompete reform, said about half of states currently allow the controversial clauses.
However, several states have recently passed laws restricting their use. California, North Dakota, and Oklahoma ban noncompetes, although some narrowly defined exceptions, such as the sale of a business, remain.
Other states, like Colorado, Illinois, and Oregon, broadly ban noncompete clauses, except for workers earning above a certain threshold. For example, in Colorado, noncompete agreements are permitted for highly compensated employees earning more than $101,250.
Despite additional restrictions on noncompete agreements for workers in the District of Columbia, the new legislation does not apply to physicians earning total compensation of $250,000 or more. However, their employers must define the geographic parameters of the noncompete and limit postemployment restrictions to 2 years.
Restrictive covenants are “uniquely challenging to family medicine’s emphasis on longitudinal care and the patient-physician relationship,” said Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians. The limitations imposed by noncompete agreements “potentially reduce patient choice, lower the quality of care for patients, and ultimately harm the foundation of family medicine – our relationships with our patients.”
Although the proposed rule aligns with President Biden’s executive order promoting economic competition, Dr. Smith said a national ban on noncompete agreements may push the limits of FTC authority.
“This new rule will certainly result in a ‘major questions doctrine’ Supreme Court challenge,” said Dr. Smith, and possibly be struck down if the court determines an administrative overstep into areas of “vast economic or political significance.”
A controversial policy
The American Medical Association’s code of ethics discourages covenants that “unreasonably restrict” the ability of physicians to practice following contract termination. And in 2022, the AMA cited “overly broad” noncompete language as a red flag young physicians should watch out for during contract negotiations.
But in 2020, the AMA asked the FTC not to use its rulemaking authority to regulate noncompete clauses in physician employment contracts, and instead, relegate enforcement of such agreements to each state. The American Hospital Association expressed similar views.
Still, the FTC said that eliminating noncompete clauses will increase annual wages by $300 billion, allow 30 million Americans to pursue better job opportunities, and encourage hiring competition among employers. It will also save consumers up to $148 billion in health care costs annually.
“Noncompetes block workers from freely switching jobs, depriving them of higher wages and better working conditions, and depriving businesses of a talent pool that they need to build and expand,” Lina M. Khan, FTC chair, said in a press release about the proposal.
A national ban on noncompetes would keep more physicians in the industry and practicing in their communities, a win for patients and providers, said Dr. Smith. It could also compel employers to offer more competitive employment packages, including fair wages, better work conditions, and a culture of well-being and patient safety.
“Whatever the final rule is, I’m certain it will be legally challenged,” said Dr. Smith, adding that the nation’s most prominent business lobbying group, the Chamber of Commerce, has already issued a statement calling the rule “blatantly unlawful."
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The proposed rule seeks to ban companies from enforcing noncompete clauses in employment contracts, a practice that represents an “unfair method of competition” with “exploitative and widespread” impacts, including suppression of wages, innovation, and entrepreneurial spirit, the FTC said. The public has 60 days to submit comments on the proposal before the FTC issues the final rule.
Employers often include noncompete clauses in physician contracts because they want to avoid having patients leave their health care system and follow a doctor to a competitor. A 2018 survey of primary care physicians found that about half of office-based physicians and 37% of physicians employed at hospitals or freestanding care centers were bound by restrictive covenants.
“A federal ban on noncompete agreements will ensure that physicians nationwide can finally change jobs without fear of being sued,” Erik B. Smith, MD, JD, clinical assistant professor of anesthesiology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Many doctors would like to see noncompete agreements vanish, but some physicians still favor them.
“As a small-practice owner, I am personally against this. The noncompete helps me take a risk and hire a physician. It typically takes 2-3 years for me to break even. I think this will further consolidate employment with large hospital systems unfortunately,” Texas cardiologist Rishin Shah, MD, recently tweeted in response to the FTC announcement.
Dr. Smith, who has advocated for noncompete reform, said about half of states currently allow the controversial clauses.
However, several states have recently passed laws restricting their use. California, North Dakota, and Oklahoma ban noncompetes, although some narrowly defined exceptions, such as the sale of a business, remain.
Other states, like Colorado, Illinois, and Oregon, broadly ban noncompete clauses, except for workers earning above a certain threshold. For example, in Colorado, noncompete agreements are permitted for highly compensated employees earning more than $101,250.
Despite additional restrictions on noncompete agreements for workers in the District of Columbia, the new legislation does not apply to physicians earning total compensation of $250,000 or more. However, their employers must define the geographic parameters of the noncompete and limit postemployment restrictions to 2 years.
Restrictive covenants are “uniquely challenging to family medicine’s emphasis on longitudinal care and the patient-physician relationship,” said Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians. The limitations imposed by noncompete agreements “potentially reduce patient choice, lower the quality of care for patients, and ultimately harm the foundation of family medicine – our relationships with our patients.”
Although the proposed rule aligns with President Biden’s executive order promoting economic competition, Dr. Smith said a national ban on noncompete agreements may push the limits of FTC authority.
“This new rule will certainly result in a ‘major questions doctrine’ Supreme Court challenge,” said Dr. Smith, and possibly be struck down if the court determines an administrative overstep into areas of “vast economic or political significance.”
A controversial policy
The American Medical Association’s code of ethics discourages covenants that “unreasonably restrict” the ability of physicians to practice following contract termination. And in 2022, the AMA cited “overly broad” noncompete language as a red flag young physicians should watch out for during contract negotiations.
But in 2020, the AMA asked the FTC not to use its rulemaking authority to regulate noncompete clauses in physician employment contracts, and instead, relegate enforcement of such agreements to each state. The American Hospital Association expressed similar views.
Still, the FTC said that eliminating noncompete clauses will increase annual wages by $300 billion, allow 30 million Americans to pursue better job opportunities, and encourage hiring competition among employers. It will also save consumers up to $148 billion in health care costs annually.
“Noncompetes block workers from freely switching jobs, depriving them of higher wages and better working conditions, and depriving businesses of a talent pool that they need to build and expand,” Lina M. Khan, FTC chair, said in a press release about the proposal.
A national ban on noncompetes would keep more physicians in the industry and practicing in their communities, a win for patients and providers, said Dr. Smith. It could also compel employers to offer more competitive employment packages, including fair wages, better work conditions, and a culture of well-being and patient safety.
“Whatever the final rule is, I’m certain it will be legally challenged,” said Dr. Smith, adding that the nation’s most prominent business lobbying group, the Chamber of Commerce, has already issued a statement calling the rule “blatantly unlawful."
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Components of coffee other than caffeine linked to reduced NAFLD severity
Increased intake of both regular and decaffeinated coffee was significantly associated with a reduced severity of NAFLD in the study, published in Nutrients. The study participants included 156 overweight adults, most of whom had type 2 diabetes.
A confluence of factors including diet and lifestyle changes and increased obesity have contributed to a rise in type 2 diabetes and of NAFLD, Margarida Coelho, of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra (Portugal), and colleagues wrote.
Previous studies support an association between coffee and protection against NAFLD, but the roles of the caffeine and noncaffeine components of coffee have not been examined, corresponding author John Griffith Jones, PhD, also of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra, said in an interview.
“There have been previous studies indicating a link between coffee intake and NAFLD amelioration, but these were entirely based on self-reporting questionnaire data, but the main limitation of this approach is that it does not provide any information on which components of coffee confer the beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “The development of new analytical techniques allowing reliable profiling of coffee metabolites in urine allowed this limitation to be addressed.”
Dr. Jones and associates examined the relationship between consumption of regular and decaffeinated coffee on the fatty liver index (FLI), a validated predictor of NAFLD. They measured coffee intake of 156 overweight adults, 135 of whom had type 2 diabetes. The study population included 76 women and 80 men with a mean age of 59 years and a mean body mass index of 29 kg/m2.
The participants reported coffee intake via questionnaires, and 98 participants (all with type 2 diabetes) also provided urine samples for measurement of caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites (the products of the body breaking down coffee). NAFLD was assessed using the FLI and a scanning measure of fibrosis.
Overall, no associations appeared between self-reported coffee intake and NAFLD measures. However, urine caffeine metabolite levels were significantly higher among individuals with no liver fibrosis, compared with those with fibrosis, and noncaffeine metabolites showed a significant negative association with FLI measures.
In a multiple regression analysis of 89 individuals with type 2 diabetes, both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites were negatively associated with FLI, which suggests less severe NAFLD, the researchers noted.
Although the mechanism of action remains unclear, the findings suggest that other noncaffeine coffee components such as polyphenols may reduce the risk of fibrosis by reducing oxidative stress on the liver, they said.
Benefits beyond caffeine
“The main surprise of the study was that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites had beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “We had anticipated caffeine, based on its well-known effects on inhibiting liver fibrosis, but the effects of other components were less well described.”
Clinicians can encourage their patients with type 2 diabetes who drink coffee to continue to do so within a normal range (up to three to four cups per day) including decaffeinated coffee; however, “they should be strongly encouraged to drink coffee without added fats and sugars, otherwise the protective benefits [against more severe NAFLD] will not be realized,” Dr. Jones said.
Additional research is needed to extend the analysis to include more coffee compounds, especially those truly unique to coffee, since caffeine can be found in many other foods and beverages, Dr. Jones added.
Limitations include 24-hour time frame
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use of 24-hour urine sample, which may not represent an individual’s habitual coffee consumption, the researchers noted. The urine metabolites measured also may be derived from foods and beverages other than coffee. In addition, the assessment of NAFLD was based on serum markers and ultrasound/elastography, which are less precise than liver biopsy and magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
However, the study is the first known to use urine data to examine coffee’s protective effect against NAFLD and suggests that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites are associated with less severe disease, they concluded.
Findings intriguing but not ready for prime time
“The bottom line is that we have a major epidemic of NAFLD in the United States,” Victor L. Roberts, MD, professor of internal medicine at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, said in an interview. NAFLD has become the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide, and will become one of the leading causes of cirrhosis – surpassing infections as the main driver of end-stage liver disease.
“In this country, the epidemic of obesity compounds the problem, and risks for NAFLD include obesity and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Roberts.
The concept of coffee as beneficial is not new, but data suggest that the effects vary with insulin resistance, he said. If liver disease is advanced, coffee and its components may not have much benefit, but early on, it might have a role.
The likely mechanism of action for the benefits of coffee on the reduction in liver fibrosis is through a complex set of metabolic steps that interrupt the promotion of collagen production and reduce liver stiffness, said Dr. Roberts.
The current study authors were up front about the limitations, mainly the use of self-reports, although including the urine collection provided more scientific data, he said. More studies are needed in other populations, but the findings are interesting enough to merit additional research.
The take-home message for primary care, however, is that drinking coffee – regular or decaf – does not replace standard of care, Dr. Roberts emphasized.
“If a patient is a coffee drinker and they have NAFLD or are at risk, they could be encouraged to continue drinking coffee,” in reasonable amounts, said Dr. Roberts. “Anywhere from 1-3 cups a day is unlikely to be a problem, and there is some hope and interest in this area,” but the findings of the current study “should not be taken as gospel or advocacy as a solution for people with NAFLD.”
Instead, clinicians should focus on the standard of care for management of patients at risk for NAFLD, promoting lifestyle changes such as weight loss, diet, and exercise (challenging as that may be), and prescribing appropriate medications, he said.
The study was supported by the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee, and the researchers received funding from the ISIC to conduct the study. Dr. Roberts had no financial conflicts to disclose, but he serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Increased intake of both regular and decaffeinated coffee was significantly associated with a reduced severity of NAFLD in the study, published in Nutrients. The study participants included 156 overweight adults, most of whom had type 2 diabetes.
A confluence of factors including diet and lifestyle changes and increased obesity have contributed to a rise in type 2 diabetes and of NAFLD, Margarida Coelho, of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra (Portugal), and colleagues wrote.
Previous studies support an association between coffee and protection against NAFLD, but the roles of the caffeine and noncaffeine components of coffee have not been examined, corresponding author John Griffith Jones, PhD, also of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra, said in an interview.
“There have been previous studies indicating a link between coffee intake and NAFLD amelioration, but these were entirely based on self-reporting questionnaire data, but the main limitation of this approach is that it does not provide any information on which components of coffee confer the beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “The development of new analytical techniques allowing reliable profiling of coffee metabolites in urine allowed this limitation to be addressed.”
Dr. Jones and associates examined the relationship between consumption of regular and decaffeinated coffee on the fatty liver index (FLI), a validated predictor of NAFLD. They measured coffee intake of 156 overweight adults, 135 of whom had type 2 diabetes. The study population included 76 women and 80 men with a mean age of 59 years and a mean body mass index of 29 kg/m2.
The participants reported coffee intake via questionnaires, and 98 participants (all with type 2 diabetes) also provided urine samples for measurement of caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites (the products of the body breaking down coffee). NAFLD was assessed using the FLI and a scanning measure of fibrosis.
Overall, no associations appeared between self-reported coffee intake and NAFLD measures. However, urine caffeine metabolite levels were significantly higher among individuals with no liver fibrosis, compared with those with fibrosis, and noncaffeine metabolites showed a significant negative association with FLI measures.
In a multiple regression analysis of 89 individuals with type 2 diabetes, both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites were negatively associated with FLI, which suggests less severe NAFLD, the researchers noted.
Although the mechanism of action remains unclear, the findings suggest that other noncaffeine coffee components such as polyphenols may reduce the risk of fibrosis by reducing oxidative stress on the liver, they said.
Benefits beyond caffeine
“The main surprise of the study was that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites had beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “We had anticipated caffeine, based on its well-known effects on inhibiting liver fibrosis, but the effects of other components were less well described.”
Clinicians can encourage their patients with type 2 diabetes who drink coffee to continue to do so within a normal range (up to three to four cups per day) including decaffeinated coffee; however, “they should be strongly encouraged to drink coffee without added fats and sugars, otherwise the protective benefits [against more severe NAFLD] will not be realized,” Dr. Jones said.
Additional research is needed to extend the analysis to include more coffee compounds, especially those truly unique to coffee, since caffeine can be found in many other foods and beverages, Dr. Jones added.
Limitations include 24-hour time frame
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use of 24-hour urine sample, which may not represent an individual’s habitual coffee consumption, the researchers noted. The urine metabolites measured also may be derived from foods and beverages other than coffee. In addition, the assessment of NAFLD was based on serum markers and ultrasound/elastography, which are less precise than liver biopsy and magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
However, the study is the first known to use urine data to examine coffee’s protective effect against NAFLD and suggests that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites are associated with less severe disease, they concluded.
Findings intriguing but not ready for prime time
“The bottom line is that we have a major epidemic of NAFLD in the United States,” Victor L. Roberts, MD, professor of internal medicine at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, said in an interview. NAFLD has become the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide, and will become one of the leading causes of cirrhosis – surpassing infections as the main driver of end-stage liver disease.
“In this country, the epidemic of obesity compounds the problem, and risks for NAFLD include obesity and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Roberts.
The concept of coffee as beneficial is not new, but data suggest that the effects vary with insulin resistance, he said. If liver disease is advanced, coffee and its components may not have much benefit, but early on, it might have a role.
The likely mechanism of action for the benefits of coffee on the reduction in liver fibrosis is through a complex set of metabolic steps that interrupt the promotion of collagen production and reduce liver stiffness, said Dr. Roberts.
The current study authors were up front about the limitations, mainly the use of self-reports, although including the urine collection provided more scientific data, he said. More studies are needed in other populations, but the findings are interesting enough to merit additional research.
The take-home message for primary care, however, is that drinking coffee – regular or decaf – does not replace standard of care, Dr. Roberts emphasized.
“If a patient is a coffee drinker and they have NAFLD or are at risk, they could be encouraged to continue drinking coffee,” in reasonable amounts, said Dr. Roberts. “Anywhere from 1-3 cups a day is unlikely to be a problem, and there is some hope and interest in this area,” but the findings of the current study “should not be taken as gospel or advocacy as a solution for people with NAFLD.”
Instead, clinicians should focus on the standard of care for management of patients at risk for NAFLD, promoting lifestyle changes such as weight loss, diet, and exercise (challenging as that may be), and prescribing appropriate medications, he said.
The study was supported by the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee, and the researchers received funding from the ISIC to conduct the study. Dr. Roberts had no financial conflicts to disclose, but he serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Increased intake of both regular and decaffeinated coffee was significantly associated with a reduced severity of NAFLD in the study, published in Nutrients. The study participants included 156 overweight adults, most of whom had type 2 diabetes.
A confluence of factors including diet and lifestyle changes and increased obesity have contributed to a rise in type 2 diabetes and of NAFLD, Margarida Coelho, of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra (Portugal), and colleagues wrote.
Previous studies support an association between coffee and protection against NAFLD, but the roles of the caffeine and noncaffeine components of coffee have not been examined, corresponding author John Griffith Jones, PhD, also of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra, said in an interview.
“There have been previous studies indicating a link between coffee intake and NAFLD amelioration, but these were entirely based on self-reporting questionnaire data, but the main limitation of this approach is that it does not provide any information on which components of coffee confer the beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “The development of new analytical techniques allowing reliable profiling of coffee metabolites in urine allowed this limitation to be addressed.”
Dr. Jones and associates examined the relationship between consumption of regular and decaffeinated coffee on the fatty liver index (FLI), a validated predictor of NAFLD. They measured coffee intake of 156 overweight adults, 135 of whom had type 2 diabetes. The study population included 76 women and 80 men with a mean age of 59 years and a mean body mass index of 29 kg/m2.
The participants reported coffee intake via questionnaires, and 98 participants (all with type 2 diabetes) also provided urine samples for measurement of caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites (the products of the body breaking down coffee). NAFLD was assessed using the FLI and a scanning measure of fibrosis.
Overall, no associations appeared between self-reported coffee intake and NAFLD measures. However, urine caffeine metabolite levels were significantly higher among individuals with no liver fibrosis, compared with those with fibrosis, and noncaffeine metabolites showed a significant negative association with FLI measures.
In a multiple regression analysis of 89 individuals with type 2 diabetes, both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites were negatively associated with FLI, which suggests less severe NAFLD, the researchers noted.
Although the mechanism of action remains unclear, the findings suggest that other noncaffeine coffee components such as polyphenols may reduce the risk of fibrosis by reducing oxidative stress on the liver, they said.
Benefits beyond caffeine
“The main surprise of the study was that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites had beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “We had anticipated caffeine, based on its well-known effects on inhibiting liver fibrosis, but the effects of other components were less well described.”
Clinicians can encourage their patients with type 2 diabetes who drink coffee to continue to do so within a normal range (up to three to four cups per day) including decaffeinated coffee; however, “they should be strongly encouraged to drink coffee without added fats and sugars, otherwise the protective benefits [against more severe NAFLD] will not be realized,” Dr. Jones said.
Additional research is needed to extend the analysis to include more coffee compounds, especially those truly unique to coffee, since caffeine can be found in many other foods and beverages, Dr. Jones added.
Limitations include 24-hour time frame
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use of 24-hour urine sample, which may not represent an individual’s habitual coffee consumption, the researchers noted. The urine metabolites measured also may be derived from foods and beverages other than coffee. In addition, the assessment of NAFLD was based on serum markers and ultrasound/elastography, which are less precise than liver biopsy and magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
However, the study is the first known to use urine data to examine coffee’s protective effect against NAFLD and suggests that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites are associated with less severe disease, they concluded.
Findings intriguing but not ready for prime time
“The bottom line is that we have a major epidemic of NAFLD in the United States,” Victor L. Roberts, MD, professor of internal medicine at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, said in an interview. NAFLD has become the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide, and will become one of the leading causes of cirrhosis – surpassing infections as the main driver of end-stage liver disease.
“In this country, the epidemic of obesity compounds the problem, and risks for NAFLD include obesity and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Roberts.
The concept of coffee as beneficial is not new, but data suggest that the effects vary with insulin resistance, he said. If liver disease is advanced, coffee and its components may not have much benefit, but early on, it might have a role.
The likely mechanism of action for the benefits of coffee on the reduction in liver fibrosis is through a complex set of metabolic steps that interrupt the promotion of collagen production and reduce liver stiffness, said Dr. Roberts.
The current study authors were up front about the limitations, mainly the use of self-reports, although including the urine collection provided more scientific data, he said. More studies are needed in other populations, but the findings are interesting enough to merit additional research.
The take-home message for primary care, however, is that drinking coffee – regular or decaf – does not replace standard of care, Dr. Roberts emphasized.
“If a patient is a coffee drinker and they have NAFLD or are at risk, they could be encouraged to continue drinking coffee,” in reasonable amounts, said Dr. Roberts. “Anywhere from 1-3 cups a day is unlikely to be a problem, and there is some hope and interest in this area,” but the findings of the current study “should not be taken as gospel or advocacy as a solution for people with NAFLD.”
Instead, clinicians should focus on the standard of care for management of patients at risk for NAFLD, promoting lifestyle changes such as weight loss, diet, and exercise (challenging as that may be), and prescribing appropriate medications, he said.
The study was supported by the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee, and the researchers received funding from the ISIC to conduct the study. Dr. Roberts had no financial conflicts to disclose, but he serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
FROM NUTRIENTS
By the numbers: Cardiology slow to add women, IMGs join more quickly
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.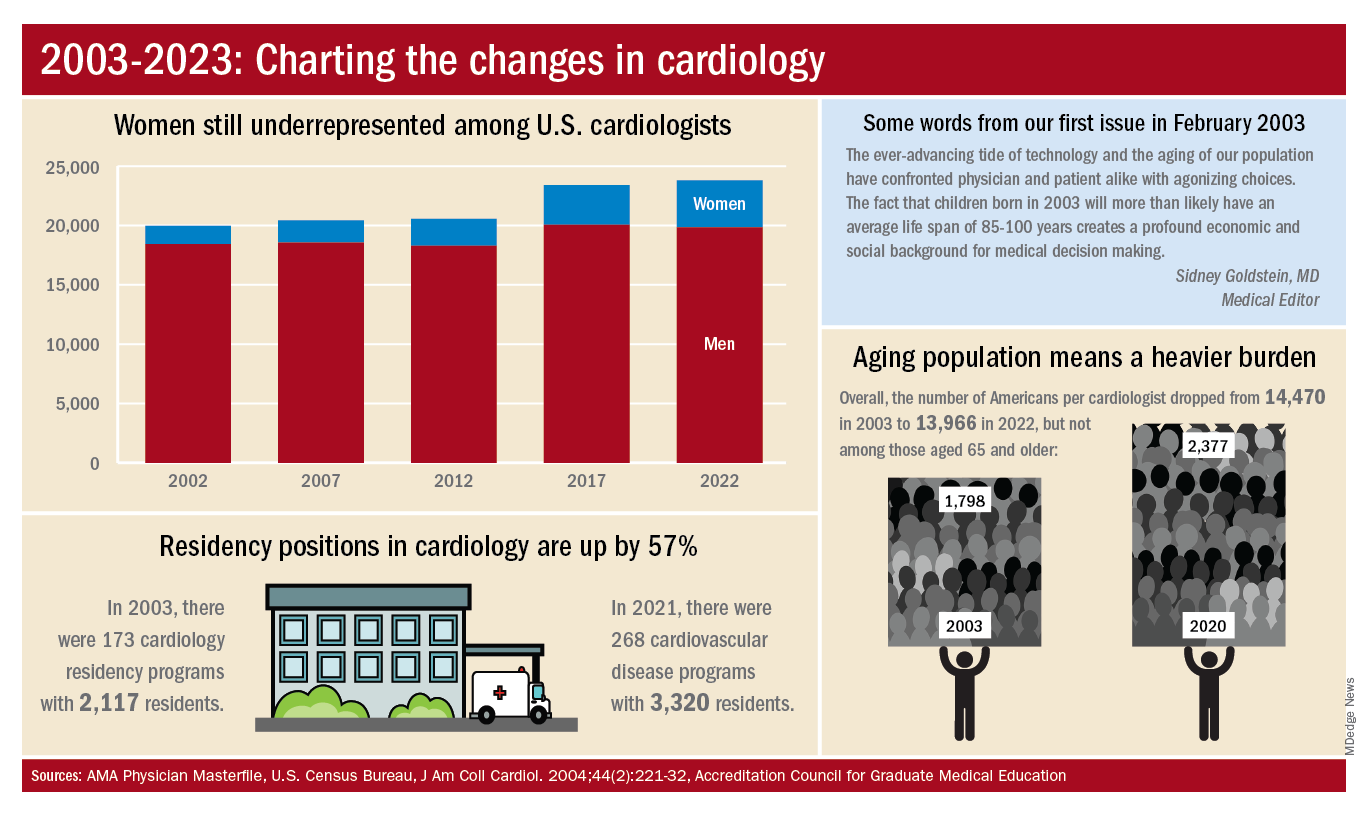
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.
Can 6 minutes of intense cycling put the brakes on Alzheimer’s?
new research suggests.
In a small study of healthy adults, 6 minutes of high-intensity cycling increased circulating levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) to a significantly greater extent than prolonged light cycling or fasting.
However, the data do not suggest that 6 minutes of high-intensity exercise “wards off dementia,” cautioned lead investigator Travis Gibbons, MSc, PhD candidate in environmental physiology at the University of Otago (New Zealand), Dunedin, and now postdoctoral fellow at the University of British Columbia – Okanagan, Kelowna.
“Like all science, this is just a small piece that supports a potential mechanistic role for how exercise might improve brain health,” Dr. Gibbons told this news organization.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Physiology.
Targeting BDNF
Both intermittent fasting and exercise have previously been shown to have potent neuroprotective effects; and an acute upregulation of BDNF appears to be a common mechanistic link.
To tease apart the influence of fasting and exercise on BDNF production, Dr. Gibbons and colleagues studied 12 aerobically fit, healthy men (n = 6) and women (n = 6) aged 20-40 years.
In a study that employed a repeated-measures crossover design, they assessed circulating BDNF levels after a 20-hour fast, prolonged (90-min) light cycling, short (6-min) high-intensity cycling, and combined fasting and exercise.
Six minutes of high-intensity exercise appeared to be the most efficient way to increase BDNF.
Fasting for 20 hours led to a ninefold increase in ketone body delivery to the brain but had no effect on any metric of BDNF in peripheral circulation at rest or during exercise.
Six minutes of high-intensity exercise increased every metric of circulating BDNF four to five times more than prolonged low-intensity exercise.
In addition, the increase in plasma-derived BDNF correlated with a sixfold increase in circulating lactate irrespective of feeding or fasting state.
Lactate delivery?
“My leading theory is that, during and following intense exercise, lactate produced by muscles is delivered and consumed by the brain,” Dr. Gibbons noted.
“It takes high-intensity exercise to provoke this ‘cerebral substrate switch’ from glucose to lactate. Critically, this cerebral substrate switch has been shown to contribute to the early processes that upregulate BDNF production in the brain,” he said.
However, “Whether this translates to ‘warding off dementia’ is not clear,” Dr. Gibbons added.
The study also suggests that increases in plasma volume and platelet concentration appear to play a role in concentrating BDNF in the circulation during exercise.
The investigators note that BDNF and other neurotrophic-based pharmaceutical therapies have shown “great promise” in slowing and even arresting neurodegenerative processes in animals, but attempts to harness the protective power of BDNF in human neurodegeneration have thus far failed.
“Whether episodically upregulating BDNF production with intense exercise is an effective strategy to curb age-related cognitive decline in humans is unknown, but animal models indicate that it is and that BDNF plays a primary role,” the researchers write.
Funding for the study was provided by the Healthcare Otago Charitable Trust. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
In a small study of healthy adults, 6 minutes of high-intensity cycling increased circulating levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) to a significantly greater extent than prolonged light cycling or fasting.
However, the data do not suggest that 6 minutes of high-intensity exercise “wards off dementia,” cautioned lead investigator Travis Gibbons, MSc, PhD candidate in environmental physiology at the University of Otago (New Zealand), Dunedin, and now postdoctoral fellow at the University of British Columbia – Okanagan, Kelowna.
“Like all science, this is just a small piece that supports a potential mechanistic role for how exercise might improve brain health,” Dr. Gibbons told this news organization.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Physiology.
Targeting BDNF
Both intermittent fasting and exercise have previously been shown to have potent neuroprotective effects; and an acute upregulation of BDNF appears to be a common mechanistic link.
To tease apart the influence of fasting and exercise on BDNF production, Dr. Gibbons and colleagues studied 12 aerobically fit, healthy men (n = 6) and women (n = 6) aged 20-40 years.
In a study that employed a repeated-measures crossover design, they assessed circulating BDNF levels after a 20-hour fast, prolonged (90-min) light cycling, short (6-min) high-intensity cycling, and combined fasting and exercise.
Six minutes of high-intensity exercise appeared to be the most efficient way to increase BDNF.
Fasting for 20 hours led to a ninefold increase in ketone body delivery to the brain but had no effect on any metric of BDNF in peripheral circulation at rest or during exercise.
Six minutes of high-intensity exercise increased every metric of circulating BDNF four to five times more than prolonged low-intensity exercise.
In addition, the increase in plasma-derived BDNF correlated with a sixfold increase in circulating lactate irrespective of feeding or fasting state.
Lactate delivery?
“My leading theory is that, during and following intense exercise, lactate produced by muscles is delivered and consumed by the brain,” Dr. Gibbons noted.
“It takes high-intensity exercise to provoke this ‘cerebral substrate switch’ from glucose to lactate. Critically, this cerebral substrate switch has been shown to contribute to the early processes that upregulate BDNF production in the brain,” he said.
However, “Whether this translates to ‘warding off dementia’ is not clear,” Dr. Gibbons added.
The study also suggests that increases in plasma volume and platelet concentration appear to play a role in concentrating BDNF in the circulation during exercise.
The investigators note that BDNF and other neurotrophic-based pharmaceutical therapies have shown “great promise” in slowing and even arresting neurodegenerative processes in animals, but attempts to harness the protective power of BDNF in human neurodegeneration have thus far failed.
“Whether episodically upregulating BDNF production with intense exercise is an effective strategy to curb age-related cognitive decline in humans is unknown, but animal models indicate that it is and that BDNF plays a primary role,” the researchers write.
Funding for the study was provided by the Healthcare Otago Charitable Trust. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
In a small study of healthy adults, 6 minutes of high-intensity cycling increased circulating levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) to a significantly greater extent than prolonged light cycling or fasting.
However, the data do not suggest that 6 minutes of high-intensity exercise “wards off dementia,” cautioned lead investigator Travis Gibbons, MSc, PhD candidate in environmental physiology at the University of Otago (New Zealand), Dunedin, and now postdoctoral fellow at the University of British Columbia – Okanagan, Kelowna.
“Like all science, this is just a small piece that supports a potential mechanistic role for how exercise might improve brain health,” Dr. Gibbons told this news organization.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Physiology.
Targeting BDNF
Both intermittent fasting and exercise have previously been shown to have potent neuroprotective effects; and an acute upregulation of BDNF appears to be a common mechanistic link.
To tease apart the influence of fasting and exercise on BDNF production, Dr. Gibbons and colleagues studied 12 aerobically fit, healthy men (n = 6) and women (n = 6) aged 20-40 years.
In a study that employed a repeated-measures crossover design, they assessed circulating BDNF levels after a 20-hour fast, prolonged (90-min) light cycling, short (6-min) high-intensity cycling, and combined fasting and exercise.
Six minutes of high-intensity exercise appeared to be the most efficient way to increase BDNF.
Fasting for 20 hours led to a ninefold increase in ketone body delivery to the brain but had no effect on any metric of BDNF in peripheral circulation at rest or during exercise.
Six minutes of high-intensity exercise increased every metric of circulating BDNF four to five times more than prolonged low-intensity exercise.
In addition, the increase in plasma-derived BDNF correlated with a sixfold increase in circulating lactate irrespective of feeding or fasting state.
Lactate delivery?
“My leading theory is that, during and following intense exercise, lactate produced by muscles is delivered and consumed by the brain,” Dr. Gibbons noted.
“It takes high-intensity exercise to provoke this ‘cerebral substrate switch’ from glucose to lactate. Critically, this cerebral substrate switch has been shown to contribute to the early processes that upregulate BDNF production in the brain,” he said.
However, “Whether this translates to ‘warding off dementia’ is not clear,” Dr. Gibbons added.
The study also suggests that increases in plasma volume and platelet concentration appear to play a role in concentrating BDNF in the circulation during exercise.
The investigators note that BDNF and other neurotrophic-based pharmaceutical therapies have shown “great promise” in slowing and even arresting neurodegenerative processes in animals, but attempts to harness the protective power of BDNF in human neurodegeneration have thus far failed.
“Whether episodically upregulating BDNF production with intense exercise is an effective strategy to curb age-related cognitive decline in humans is unknown, but animal models indicate that it is and that BDNF plays a primary role,” the researchers write.
Funding for the study was provided by the Healthcare Otago Charitable Trust. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY
Singer is paralyzed after delay in care; hospital must pay
Delay in treatment will cost hospital millions
according to a report on WFAA.com, among other news sites.
On March 21, 2019, Judy “Jessie” Adams, then part of a singing-songwriting duo with her husband, Richard, went to Premier Interventional Pain Management, in Flower Mound, Tex., prior to the couple’s drive to Ohio for a funeral. At Premier, Jesse received an epidural steroid injection (ESI) that she hoped would ease her back pain during the long drive.
Instead, the injection ended up increasing her pain.
“He [the pain physician] gave me the shot, but I couldn’t feel my legs. They were tingling, but I couldn’t feel them,” Mrs. Adams explained. “The pain was so bad in my back.” In their suit, Adams and her husband alleged that the doctor had probably “nicked a blood vessel during the ESI procedure, causing Jessie to hemorrhage.” (The couple’s suit against the doctor was settled prior to trial.)
Mrs. Adams remained under observation at the pain facility for about 1½ hours, at which point she was taken by ambulance to nearby Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital. There, in the emergency department, staff ordered a “STAT MRI” in preparation for an emergency laminectomy.
For reasons that remain murky, the MRI wasn’t performed for 1 hour and 37 minutes. The emergency laminectomy itself wasn’t started until more than 5 hours after Adams had been admitted to the ED. This was a direct violation of hospital protocol, which required that emergency surgeries be performed within 1 hour of admittance in the first available surgical suite. (At trial, Mrs. Adams’s attorneys from Lyons & Simmons offered evidence that a suite became available 49 minutes after Adams had arrived at the ED.)
During the wait, Mrs. Adams continued to experience excruciating pain. “I kept screaming: ‘Help me,’ ” she recalled. At trial, her attorneys argued that the hospital’s delay in addressing her spinal emergency led directly to her current paralysis, which keeps her confined to a wheelchair and renders her incontinent.
The hospital disagreed. In court, it maintained that Mrs. Adams was already paralyzed when she arrived at the ED and that there was no delay in care.
The jury saw things differently, however. Siding with the plaintiffs, it awarded Mrs. Adams and her husband $10.1 million, including $500,000 for Mr. Adams’s loss of future earnings and $1 million for his “loss of consortium” with his wife.
Their music career now effectively over, Mr. Adams spends most of his time taking care of Mrs. Adams.
“Music was our lifeblood for so many years, and he can’t do it anymore,” Mrs. Adams said. “He goes upstairs to play his guitar and write, and suddenly I need him to come and cath me. I just feel like I’m going to wake up from this bad dream, but it’s the same routine.”
Two doctors are absolved in woman’s sudden death
In a 3-2 decision in December 2022, the Pennsylvania Supreme Court ruled that the state’s 2-year statute of limitations in wrongful-death cases applies even in cases in which plaintiffs fail to identify the cause of death in a timely manner, as a report in the Claims Journal indicates.
The decision stems from a lawsuit filed by Linda Reibenstein on behalf of her mother, Mary Ann Whitman, who died in late April 2010 from a ruptured aortic aneurysm.
On April 12, 2010, Ms. Whitman visited Patrick D. Conaboy, MD, a Scranton family physician, complaining of a persistent cough, fever, and lower-back pain. Following an initial examination, Dr. Conaboy ordered an aortic duplex ultrasound scan and a CT scan of the patient’s abdomen.
The ultrasound was performed by radiologist Charles Barax, MD, who reviewed both scans. He identified a “poorly visualized aortic aneurysm.” At this point, Dr. Conaboy referred Ms. Whitman to a vascular surgeon. But before this visit could take place, Whitman’s aneurysm ruptured, killing her. This was listed as the medical cause of death on the patient’s death certificate.
In April 2011, Ms. Reibenstein filed a claim against Dr. Barax, alleging that he had failed to gauge the severity of her mother’s condition. Ms. Reibenstein’s attorney wasn’t able to question Dr. Barax on the record until well after the state’s 2-year statute of limitations had elapsed. When he did testify, Dr. Barax explained that the scans’ image quality prevented him from determining whether Whitman’s aneurysm was rupturing or simply bleeding. Despite this, he insisted that he had warned Dr. Conaboy of the potential for Ms. Whitman’s aneurysm to rupture.
In March 2016, nearly 6 years after her mother’s death, Ms. Reibenstein filed a new lawsuit, this one against Dr. Conaboy, whom she alleged had failed to properly treat her mother’s condition. Dr. Conaboy, in turn, asked the court for summary judgment – that is, a judgment in his favor without a full trial – arguing that the state’s window for filing a wrongful-death claim had long since closed. For their part, Ms. Reibenstein and her attorney argued that the state’s 2-year statute of limitations didn’t start until the plaintiff had discovered the cause of her mother’s death.
Initially refusing to dismiss the case, a lower court reconsidered Dr. Conaboy’s motion for summary judgment and ruled that Ms. Reibenstein had failed to present any evidence of “affirmative misrepresentation or fraudulent concealment.” In other words, in the absence of any willful attempt on the part of the defendant to hide the legal cause of death, which includes “acts, omissions, or events having some causative connection with the death,” the statute of limitations remained in effect, and the defendant’s motion was thereby granted.
Continuing the legal seesaw, a state appeals court reversed the lower-court ruling. Noting that the Pennsylvania malpractice statute was ambiguous, the court argued that it should be interpreted in a way that protects plaintiffs who seek “fair compensation” but encounter willfully erected obstacles in pursuit of their claim.
Dr. Conaboy then took his case to the state’s highest court. In its majority decision, the Pennsylvania Supreme Court staked out a narrow definition of cause of death – one based on the death certificate – and ruled that only willful fraud in that document would constitute the necessary condition for halting the claim’s clock. Furthermore, the high court said, when lawmakers adopted the Medical Care Availability and Reduction of Error Act in 2002, they did so with no guarantee “that all of the information necessary to sustain a claim will be gathered in the limitations period.”
Similarly, the court ruled, “at some point the clock must run out, lest health care providers remain subject to liability exposure indefinitely, with the prospect of a trial marred by the death or diminished memory of material witnesses or the loss of critical evidence.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Delay in treatment will cost hospital millions
according to a report on WFAA.com, among other news sites.
On March 21, 2019, Judy “Jessie” Adams, then part of a singing-songwriting duo with her husband, Richard, went to Premier Interventional Pain Management, in Flower Mound, Tex., prior to the couple’s drive to Ohio for a funeral. At Premier, Jesse received an epidural steroid injection (ESI) that she hoped would ease her back pain during the long drive.
Instead, the injection ended up increasing her pain.
“He [the pain physician] gave me the shot, but I couldn’t feel my legs. They were tingling, but I couldn’t feel them,” Mrs. Adams explained. “The pain was so bad in my back.” In their suit, Adams and her husband alleged that the doctor had probably “nicked a blood vessel during the ESI procedure, causing Jessie to hemorrhage.” (The couple’s suit against the doctor was settled prior to trial.)
Mrs. Adams remained under observation at the pain facility for about 1½ hours, at which point she was taken by ambulance to nearby Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital. There, in the emergency department, staff ordered a “STAT MRI” in preparation for an emergency laminectomy.
For reasons that remain murky, the MRI wasn’t performed for 1 hour and 37 minutes. The emergency laminectomy itself wasn’t started until more than 5 hours after Adams had been admitted to the ED. This was a direct violation of hospital protocol, which required that emergency surgeries be performed within 1 hour of admittance in the first available surgical suite. (At trial, Mrs. Adams’s attorneys from Lyons & Simmons offered evidence that a suite became available 49 minutes after Adams had arrived at the ED.)
During the wait, Mrs. Adams continued to experience excruciating pain. “I kept screaming: ‘Help me,’ ” she recalled. At trial, her attorneys argued that the hospital’s delay in addressing her spinal emergency led directly to her current paralysis, which keeps her confined to a wheelchair and renders her incontinent.
The hospital disagreed. In court, it maintained that Mrs. Adams was already paralyzed when she arrived at the ED and that there was no delay in care.
The jury saw things differently, however. Siding with the plaintiffs, it awarded Mrs. Adams and her husband $10.1 million, including $500,000 for Mr. Adams’s loss of future earnings and $1 million for his “loss of consortium” with his wife.
Their music career now effectively over, Mr. Adams spends most of his time taking care of Mrs. Adams.
“Music was our lifeblood for so many years, and he can’t do it anymore,” Mrs. Adams said. “He goes upstairs to play his guitar and write, and suddenly I need him to come and cath me. I just feel like I’m going to wake up from this bad dream, but it’s the same routine.”
Two doctors are absolved in woman’s sudden death
In a 3-2 decision in December 2022, the Pennsylvania Supreme Court ruled that the state’s 2-year statute of limitations in wrongful-death cases applies even in cases in which plaintiffs fail to identify the cause of death in a timely manner, as a report in the Claims Journal indicates.
The decision stems from a lawsuit filed by Linda Reibenstein on behalf of her mother, Mary Ann Whitman, who died in late April 2010 from a ruptured aortic aneurysm.
On April 12, 2010, Ms. Whitman visited Patrick D. Conaboy, MD, a Scranton family physician, complaining of a persistent cough, fever, and lower-back pain. Following an initial examination, Dr. Conaboy ordered an aortic duplex ultrasound scan and a CT scan of the patient’s abdomen.
The ultrasound was performed by radiologist Charles Barax, MD, who reviewed both scans. He identified a “poorly visualized aortic aneurysm.” At this point, Dr. Conaboy referred Ms. Whitman to a vascular surgeon. But before this visit could take place, Whitman’s aneurysm ruptured, killing her. This was listed as the medical cause of death on the patient’s death certificate.
In April 2011, Ms. Reibenstein filed a claim against Dr. Barax, alleging that he had failed to gauge the severity of her mother’s condition. Ms. Reibenstein’s attorney wasn’t able to question Dr. Barax on the record until well after the state’s 2-year statute of limitations had elapsed. When he did testify, Dr. Barax explained that the scans’ image quality prevented him from determining whether Whitman’s aneurysm was rupturing or simply bleeding. Despite this, he insisted that he had warned Dr. Conaboy of the potential for Ms. Whitman’s aneurysm to rupture.
In March 2016, nearly 6 years after her mother’s death, Ms. Reibenstein filed a new lawsuit, this one against Dr. Conaboy, whom she alleged had failed to properly treat her mother’s condition. Dr. Conaboy, in turn, asked the court for summary judgment – that is, a judgment in his favor without a full trial – arguing that the state’s window for filing a wrongful-death claim had long since closed. For their part, Ms. Reibenstein and her attorney argued that the state’s 2-year statute of limitations didn’t start until the plaintiff had discovered the cause of her mother’s death.
Initially refusing to dismiss the case, a lower court reconsidered Dr. Conaboy’s motion for summary judgment and ruled that Ms. Reibenstein had failed to present any evidence of “affirmative misrepresentation or fraudulent concealment.” In other words, in the absence of any willful attempt on the part of the defendant to hide the legal cause of death, which includes “acts, omissions, or events having some causative connection with the death,” the statute of limitations remained in effect, and the defendant’s motion was thereby granted.
Continuing the legal seesaw, a state appeals court reversed the lower-court ruling. Noting that the Pennsylvania malpractice statute was ambiguous, the court argued that it should be interpreted in a way that protects plaintiffs who seek “fair compensation” but encounter willfully erected obstacles in pursuit of their claim.
Dr. Conaboy then took his case to the state’s highest court. In its majority decision, the Pennsylvania Supreme Court staked out a narrow definition of cause of death – one based on the death certificate – and ruled that only willful fraud in that document would constitute the necessary condition for halting the claim’s clock. Furthermore, the high court said, when lawmakers adopted the Medical Care Availability and Reduction of Error Act in 2002, they did so with no guarantee “that all of the information necessary to sustain a claim will be gathered in the limitations period.”
Similarly, the court ruled, “at some point the clock must run out, lest health care providers remain subject to liability exposure indefinitely, with the prospect of a trial marred by the death or diminished memory of material witnesses or the loss of critical evidence.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Delay in treatment will cost hospital millions
according to a report on WFAA.com, among other news sites.
On March 21, 2019, Judy “Jessie” Adams, then part of a singing-songwriting duo with her husband, Richard, went to Premier Interventional Pain Management, in Flower Mound, Tex., prior to the couple’s drive to Ohio for a funeral. At Premier, Jesse received an epidural steroid injection (ESI) that she hoped would ease her back pain during the long drive.
Instead, the injection ended up increasing her pain.
“He [the pain physician] gave me the shot, but I couldn’t feel my legs. They were tingling, but I couldn’t feel them,” Mrs. Adams explained. “The pain was so bad in my back.” In their suit, Adams and her husband alleged that the doctor had probably “nicked a blood vessel during the ESI procedure, causing Jessie to hemorrhage.” (The couple’s suit against the doctor was settled prior to trial.)
Mrs. Adams remained under observation at the pain facility for about 1½ hours, at which point she was taken by ambulance to nearby Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital. There, in the emergency department, staff ordered a “STAT MRI” in preparation for an emergency laminectomy.
For reasons that remain murky, the MRI wasn’t performed for 1 hour and 37 minutes. The emergency laminectomy itself wasn’t started until more than 5 hours after Adams had been admitted to the ED. This was a direct violation of hospital protocol, which required that emergency surgeries be performed within 1 hour of admittance in the first available surgical suite. (At trial, Mrs. Adams’s attorneys from Lyons & Simmons offered evidence that a suite became available 49 minutes after Adams had arrived at the ED.)
During the wait, Mrs. Adams continued to experience excruciating pain. “I kept screaming: ‘Help me,’ ” she recalled. At trial, her attorneys argued that the hospital’s delay in addressing her spinal emergency led directly to her current paralysis, which keeps her confined to a wheelchair and renders her incontinent.
The hospital disagreed. In court, it maintained that Mrs. Adams was already paralyzed when she arrived at the ED and that there was no delay in care.
The jury saw things differently, however. Siding with the plaintiffs, it awarded Mrs. Adams and her husband $10.1 million, including $500,000 for Mr. Adams’s loss of future earnings and $1 million for his “loss of consortium” with his wife.
Their music career now effectively over, Mr. Adams spends most of his time taking care of Mrs. Adams.
“Music was our lifeblood for so many years, and he can’t do it anymore,” Mrs. Adams said. “He goes upstairs to play his guitar and write, and suddenly I need him to come and cath me. I just feel like I’m going to wake up from this bad dream, but it’s the same routine.”
Two doctors are absolved in woman’s sudden death
In a 3-2 decision in December 2022, the Pennsylvania Supreme Court ruled that the state’s 2-year statute of limitations in wrongful-death cases applies even in cases in which plaintiffs fail to identify the cause of death in a timely manner, as a report in the Claims Journal indicates.
The decision stems from a lawsuit filed by Linda Reibenstein on behalf of her mother, Mary Ann Whitman, who died in late April 2010 from a ruptured aortic aneurysm.
On April 12, 2010, Ms. Whitman visited Patrick D. Conaboy, MD, a Scranton family physician, complaining of a persistent cough, fever, and lower-back pain. Following an initial examination, Dr. Conaboy ordered an aortic duplex ultrasound scan and a CT scan of the patient’s abdomen.
The ultrasound was performed by radiologist Charles Barax, MD, who reviewed both scans. He identified a “poorly visualized aortic aneurysm.” At this point, Dr. Conaboy referred Ms. Whitman to a vascular surgeon. But before this visit could take place, Whitman’s aneurysm ruptured, killing her. This was listed as the medical cause of death on the patient’s death certificate.
In April 2011, Ms. Reibenstein filed a claim against Dr. Barax, alleging that he had failed to gauge the severity of her mother’s condition. Ms. Reibenstein’s attorney wasn’t able to question Dr. Barax on the record until well after the state’s 2-year statute of limitations had elapsed. When he did testify, Dr. Barax explained that the scans’ image quality prevented him from determining whether Whitman’s aneurysm was rupturing or simply bleeding. Despite this, he insisted that he had warned Dr. Conaboy of the potential for Ms. Whitman’s aneurysm to rupture.
In March 2016, nearly 6 years after her mother’s death, Ms. Reibenstein filed a new lawsuit, this one against Dr. Conaboy, whom she alleged had failed to properly treat her mother’s condition. Dr. Conaboy, in turn, asked the court for summary judgment – that is, a judgment in his favor without a full trial – arguing that the state’s window for filing a wrongful-death claim had long since closed. For their part, Ms. Reibenstein and her attorney argued that the state’s 2-year statute of limitations didn’t start until the plaintiff had discovered the cause of her mother’s death.
Initially refusing to dismiss the case, a lower court reconsidered Dr. Conaboy’s motion for summary judgment and ruled that Ms. Reibenstein had failed to present any evidence of “affirmative misrepresentation or fraudulent concealment.” In other words, in the absence of any willful attempt on the part of the defendant to hide the legal cause of death, which includes “acts, omissions, or events having some causative connection with the death,” the statute of limitations remained in effect, and the defendant’s motion was thereby granted.
Continuing the legal seesaw, a state appeals court reversed the lower-court ruling. Noting that the Pennsylvania malpractice statute was ambiguous, the court argued that it should be interpreted in a way that protects plaintiffs who seek “fair compensation” but encounter willfully erected obstacles in pursuit of their claim.
Dr. Conaboy then took his case to the state’s highest court. In its majority decision, the Pennsylvania Supreme Court staked out a narrow definition of cause of death – one based on the death certificate – and ruled that only willful fraud in that document would constitute the necessary condition for halting the claim’s clock. Furthermore, the high court said, when lawmakers adopted the Medical Care Availability and Reduction of Error Act in 2002, they did so with no guarantee “that all of the information necessary to sustain a claim will be gathered in the limitations period.”
Similarly, the court ruled, “at some point the clock must run out, lest health care providers remain subject to liability exposure indefinitely, with the prospect of a trial marred by the death or diminished memory of material witnesses or the loss of critical evidence.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID leading cause of death among law enforcement for third year
A new report says 70 officers died of COVID-related causes after getting the virus while on the job. The number is down dramatically from 2021, when 405 officer deaths were attributed to COVID.
The annual count was published Wednesday by the National Law Enforcement Officers Memorial Fund.
In total, 226 officers died in the line of duty in 2022, which is a decrease of 61% from 2021.
The decrease “is almost entirely related to the significant reduction in COVID-19 deaths,” the report stated. The authors said the decline was likely due to “reduced infection rates and the broad availability and use of vaccinations.”
Reported deaths included federal, state, tribal, and local law enforcement officers.
Firearms-related fatalities were the second-leading cause of death among officers, with 64 in 2022. That count sustains a 21% increase seen in 2021, up from the decade-long average of 53 firearms-related deaths annually from 2010 to 2020.
Traffic-related causes ranked third for cause of death in 2022, accounting for 56 deaths.
“While overall line-of-duty deaths are trending down, the continuing trend of greater-than-average firearms-related deaths continues to be a serious concern,” Marcia Ferranto, the organization’s chief executive officer, said in a news release. “Using and reporting on this data allows us to highlight the continuing cost of maintaining our democracy, regrettably measured in the lives of the many law enforcement professionals who sacrifice everything fulfilling their promise to serve and protect.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A new report says 70 officers died of COVID-related causes after getting the virus while on the job. The number is down dramatically from 2021, when 405 officer deaths were attributed to COVID.
The annual count was published Wednesday by the National Law Enforcement Officers Memorial Fund.
In total, 226 officers died in the line of duty in 2022, which is a decrease of 61% from 2021.
The decrease “is almost entirely related to the significant reduction in COVID-19 deaths,” the report stated. The authors said the decline was likely due to “reduced infection rates and the broad availability and use of vaccinations.”
Reported deaths included federal, state, tribal, and local law enforcement officers.
Firearms-related fatalities were the second-leading cause of death among officers, with 64 in 2022. That count sustains a 21% increase seen in 2021, up from the decade-long average of 53 firearms-related deaths annually from 2010 to 2020.
Traffic-related causes ranked third for cause of death in 2022, accounting for 56 deaths.
“While overall line-of-duty deaths are trending down, the continuing trend of greater-than-average firearms-related deaths continues to be a serious concern,” Marcia Ferranto, the organization’s chief executive officer, said in a news release. “Using and reporting on this data allows us to highlight the continuing cost of maintaining our democracy, regrettably measured in the lives of the many law enforcement professionals who sacrifice everything fulfilling their promise to serve and protect.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A new report says 70 officers died of COVID-related causes after getting the virus while on the job. The number is down dramatically from 2021, when 405 officer deaths were attributed to COVID.
The annual count was published Wednesday by the National Law Enforcement Officers Memorial Fund.
In total, 226 officers died in the line of duty in 2022, which is a decrease of 61% from 2021.
The decrease “is almost entirely related to the significant reduction in COVID-19 deaths,” the report stated. The authors said the decline was likely due to “reduced infection rates and the broad availability and use of vaccinations.”
Reported deaths included federal, state, tribal, and local law enforcement officers.
Firearms-related fatalities were the second-leading cause of death among officers, with 64 in 2022. That count sustains a 21% increase seen in 2021, up from the decade-long average of 53 firearms-related deaths annually from 2010 to 2020.
Traffic-related causes ranked third for cause of death in 2022, accounting for 56 deaths.
“While overall line-of-duty deaths are trending down, the continuing trend of greater-than-average firearms-related deaths continues to be a serious concern,” Marcia Ferranto, the organization’s chief executive officer, said in a news release. “Using and reporting on this data allows us to highlight the continuing cost of maintaining our democracy, regrettably measured in the lives of the many law enforcement professionals who sacrifice everything fulfilling their promise to serve and protect.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Oramed oral insulin fails to meet goal in type 2 diabetes
Oramed Pharmaceuticals’ investigational oral insulin failed to achieve its primary endpoint in a phase 3 trial, according to top-line results announced by the company.
“Therefore, Oramed expects to discontinue its oral insulin clinical activities for [type 2 diabetes],” according to a company statement.
, ORA-D-013-1, comparing the efficacy of the insulin product ORMD-0801 to placebo in 710 people with type 2 diabetes with inadequate glycemic control on two or three oral glucose-lowering agents.
The participants were randomized 2:2:1:1 into ORMD-0801 dosed at 8 mg once or twice daily, or placebo dosed once or twice daily. They completed a 21-day screening period, followed by a 26-week double-blind treatment period.
The product didn’t achieve the primary endpoint comparing reduction in hemoglobin A1c from baseline to 26 weeks, or the secondary endpoint of mean change in fasting plasma glucose at 26 weeks. There were no serious adverse events.
Oramed Pharmaceuticals specializes in developing oral delivery formulations of drugs currently delivered via injection. The company has offices in the United States and Israel.
Oramed CEO Nadav Kidron commented in the statement, “Today’s outcome is very disappointing, given the positive results from prior trials. Once full data from the studies are available, we expect to share relevant learnings and future plans. We thank all the patients, families, and health care professionals who participated in the trial.”
Insulin manufacturer Novo Nordisk had also been developing an oral insulin product. Successful phase 2a results were presented at the American Diabetes Association’s 2017 Scientific Sessions and full phase 2 feasibility results were published in Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology in 2019.
However, Novo Nordisk, which manufactures the oral glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist semaglutide (Rybelsus), subsequently discontinued development of their oral insulin product. According to a statement, “Initial results raised questions about truly addressing patients’ unmet needs with insulin therapy. Therefore, we discontinued this work to focus on projects that could in fact improve cardiometabolic outcomes for people living with diabetes.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oramed Pharmaceuticals’ investigational oral insulin failed to achieve its primary endpoint in a phase 3 trial, according to top-line results announced by the company.
“Therefore, Oramed expects to discontinue its oral insulin clinical activities for [type 2 diabetes],” according to a company statement.
, ORA-D-013-1, comparing the efficacy of the insulin product ORMD-0801 to placebo in 710 people with type 2 diabetes with inadequate glycemic control on two or three oral glucose-lowering agents.
The participants were randomized 2:2:1:1 into ORMD-0801 dosed at 8 mg once or twice daily, or placebo dosed once or twice daily. They completed a 21-day screening period, followed by a 26-week double-blind treatment period.
The product didn’t achieve the primary endpoint comparing reduction in hemoglobin A1c from baseline to 26 weeks, or the secondary endpoint of mean change in fasting plasma glucose at 26 weeks. There were no serious adverse events.
Oramed Pharmaceuticals specializes in developing oral delivery formulations of drugs currently delivered via injection. The company has offices in the United States and Israel.
Oramed CEO Nadav Kidron commented in the statement, “Today’s outcome is very disappointing, given the positive results from prior trials. Once full data from the studies are available, we expect to share relevant learnings and future plans. We thank all the patients, families, and health care professionals who participated in the trial.”
Insulin manufacturer Novo Nordisk had also been developing an oral insulin product. Successful phase 2a results were presented at the American Diabetes Association’s 2017 Scientific Sessions and full phase 2 feasibility results were published in Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology in 2019.
However, Novo Nordisk, which manufactures the oral glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist semaglutide (Rybelsus), subsequently discontinued development of their oral insulin product. According to a statement, “Initial results raised questions about truly addressing patients’ unmet needs with insulin therapy. Therefore, we discontinued this work to focus on projects that could in fact improve cardiometabolic outcomes for people living with diabetes.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oramed Pharmaceuticals’ investigational oral insulin failed to achieve its primary endpoint in a phase 3 trial, according to top-line results announced by the company.
“Therefore, Oramed expects to discontinue its oral insulin clinical activities for [type 2 diabetes],” according to a company statement.
, ORA-D-013-1, comparing the efficacy of the insulin product ORMD-0801 to placebo in 710 people with type 2 diabetes with inadequate glycemic control on two or three oral glucose-lowering agents.
The participants were randomized 2:2:1:1 into ORMD-0801 dosed at 8 mg once or twice daily, or placebo dosed once or twice daily. They completed a 21-day screening period, followed by a 26-week double-blind treatment period.
The product didn’t achieve the primary endpoint comparing reduction in hemoglobin A1c from baseline to 26 weeks, or the secondary endpoint of mean change in fasting plasma glucose at 26 weeks. There were no serious adverse events.
Oramed Pharmaceuticals specializes in developing oral delivery formulations of drugs currently delivered via injection. The company has offices in the United States and Israel.
Oramed CEO Nadav Kidron commented in the statement, “Today’s outcome is very disappointing, given the positive results from prior trials. Once full data from the studies are available, we expect to share relevant learnings and future plans. We thank all the patients, families, and health care professionals who participated in the trial.”
Insulin manufacturer Novo Nordisk had also been developing an oral insulin product. Successful phase 2a results were presented at the American Diabetes Association’s 2017 Scientific Sessions and full phase 2 feasibility results were published in Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology in 2019.
However, Novo Nordisk, which manufactures the oral glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist semaglutide (Rybelsus), subsequently discontinued development of their oral insulin product. According to a statement, “Initial results raised questions about truly addressing patients’ unmet needs with insulin therapy. Therefore, we discontinued this work to focus on projects that could in fact improve cardiometabolic outcomes for people living with diabetes.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.