User login
‘Empathy fatigue’ in clinicians rises with latest COVID-19 surge
Heidi Erickson, MD, is tired. As a pulmonary and critical care physician at Hennepin Healthcare in Minneapolis, she has been providing care for patients with COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic.
It was exhausting from the beginning, as she and her colleagues scrambled to understand how to deal with this new disease. But lately, she has noticed a different kind of exhaustion arising from the knowledge that with vaccines widely available, the latest surge was preventable.
Her intensive care unit is currently as full as it has ever been with COVID-19 patients, many of them young adults and most of them unvaccinated. After the recent death of one patient, an unvaccinated man with teenage children, she had to face his family’s questions about why ivermectin, an antiparasitic medication that was falsely promoted as a COVID-19 treatment, was not administered.
“I’m fatigued because I’m working more than ever, but more people don’t have to die,” Dr. Erickson said in an interview . “It’s been very hard physically, mentally, emotionally.”
Amid yet another surge in COVID-19 cases around the United States, clinicians are speaking out about their growing frustration with this preventable crisis.
Some are using the terms “empathy fatigue” and “compassion fatigue” – a sense that they are losing empathy for unvaccinated individuals who are fueling the pandemic.
Dr. Erickson says she is frustrated not by individual patients but by a system that has allowed disinformation to proliferate. Experts say these types of feelings fit into a widespread pattern of physician burnout that has taken a new turn at this stage of the pandemic.
Paradoxical choices
Empathy is a cornerstone of what clinicians do, and the ability to understand and share a patient’s feelings is an essential skill for providing effective care, says Kaz Nelson, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Practitioners face paradoxical situations all the time, she notes. These include individuals who break bones and go skydiving again, people who have high cholesterol but continue to eat fried foods, and those with advanced lung cancer who continue to smoke.
To treat patients with compassion, practitioners learn to set aside judgment by acknowledging the complexity of human behavior. They may lament the addictive nature of nicotine and advertising that targets children, for example, while still listening and caring.
Empathy requires high-level brain function, but as stress levels rise, brain function that drives empathy tends to shut down. It’s a survival mechanism, Dr. Nelson says.
When health care workers feel overwhelmed, trapped, or threatened by patients demanding unproven treatments or by ICUs with more patients than ventilators, they may experience a fight-or-flight response that makes them defensive, frustrated, angry, or uncaring, notes Mona Masood, DO, a Philadelphia-area psychiatrist and founder of Physician Support Line, a free mental health hotline for doctors.
Some clinicians have taken to Twitter and other social media platforms to post about these types of experiences.
These feelings, which have been brewing for months, have been exacerbated by the complexity of the current situation. Clinicians see a disconnect between what is and what could be, Dr. Nelson notes.
“Prior to vaccines, there weren’t other options, and so we had toxic stress and we had fatigue, but we could still maintain little bits of empathy by saying, ‘You know, people didn’t choose to get infected, and we are in a pandemic.’ We could kind of hate the virus. Now with access to vaccines, that last connection to empathy is removed for many people,” she says.
Self-preservation vs. empathy
Compassion fatigue or empathy fatigue is just one reaction to feeling completely maxed out and overstressed, Dr. Nelson says. Anger at society, such as what Dr. Erickson experienced, is another response.
Practitioners may also feel as if they are just going through the motions of their job, or they might disassociate, ceasing to feel that their patients are human. Plenty of doctors and nurses have cried in their cars after shifts and have posted tearful videos on social media.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Masood says, physicians who called the support hotline expressed sadness and grief. Now, she had her colleagues hear frustration and anger, along with guilt and shame for having feelings they believe they shouldn’t be having, especially toward patients. They may feel unprofessional or worse – unworthy of being physicians, she says.
One recent caller to the hotline was a long-time ICU physician who had been told so many times by patients that ivermectin was the only medicine that would cure them that he began to doubt himself, says Dr. Masood. This caller needed to be reassured by another physician that he was doing the right thing.
Another emergency department physician told Dr. Masood about a young child who had arrived at the hospital with COVID-19 symptoms. When asked whether the family had been exposed to anyone with COVID-19, the child’s parent lied so that they could be triaged faster.
The physician, who needed to step away from the situation, reached out to Dr. Masood to express her frustration so that she wouldn’t “let it out” on the patient.
“It’s hard to have empathy for people who, for all intents and purposes, are very self-centered,” Dr. Masood says. “We’re at a place where we’re having to choose between self-preservation and empathy.”
How to cope
To help practitioners cope, Dr. Masood offers words that describe what they’re experiencing. She often hears clinicians say things such as, “This is a type of burnout that I feel to my bones,” or “This makes me want to quit,” or “I feel like I’m at the end of my rope.”
She encourages them to consider the terms “empathy fatigue,” and “moral injury” in order to reconcile how their sense of responsibility to take care of people is compromised by factors outside of their control.
It is not shameful to acknowledge that they experience emotions, including difficult ones such as frustration, anger, sadness, and anxiety, Dr. Masood adds.
Being frustrated with a patient doesn’t make someone a bad doctor, and admitting those emotions is the first step toward dealing with them, she says.
before they cause a sense of callousness or other consequences that become harder to heal from as time goes on.
“We’re trained to just go, go, go and sometimes not pause and check in,” she says. Clinicians who open up are likely to find they are not the only ones feeling tired or frustrated right now, she adds.
“Connect with peers and colleagues, because chances are, they can relate,” Dr. Nelson says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heidi Erickson, MD, is tired. As a pulmonary and critical care physician at Hennepin Healthcare in Minneapolis, she has been providing care for patients with COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic.
It was exhausting from the beginning, as she and her colleagues scrambled to understand how to deal with this new disease. But lately, she has noticed a different kind of exhaustion arising from the knowledge that with vaccines widely available, the latest surge was preventable.
Her intensive care unit is currently as full as it has ever been with COVID-19 patients, many of them young adults and most of them unvaccinated. After the recent death of one patient, an unvaccinated man with teenage children, she had to face his family’s questions about why ivermectin, an antiparasitic medication that was falsely promoted as a COVID-19 treatment, was not administered.
“I’m fatigued because I’m working more than ever, but more people don’t have to die,” Dr. Erickson said in an interview . “It’s been very hard physically, mentally, emotionally.”
Amid yet another surge in COVID-19 cases around the United States, clinicians are speaking out about their growing frustration with this preventable crisis.
Some are using the terms “empathy fatigue” and “compassion fatigue” – a sense that they are losing empathy for unvaccinated individuals who are fueling the pandemic.
Dr. Erickson says she is frustrated not by individual patients but by a system that has allowed disinformation to proliferate. Experts say these types of feelings fit into a widespread pattern of physician burnout that has taken a new turn at this stage of the pandemic.
Paradoxical choices
Empathy is a cornerstone of what clinicians do, and the ability to understand and share a patient’s feelings is an essential skill for providing effective care, says Kaz Nelson, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Practitioners face paradoxical situations all the time, she notes. These include individuals who break bones and go skydiving again, people who have high cholesterol but continue to eat fried foods, and those with advanced lung cancer who continue to smoke.
To treat patients with compassion, practitioners learn to set aside judgment by acknowledging the complexity of human behavior. They may lament the addictive nature of nicotine and advertising that targets children, for example, while still listening and caring.
Empathy requires high-level brain function, but as stress levels rise, brain function that drives empathy tends to shut down. It’s a survival mechanism, Dr. Nelson says.
When health care workers feel overwhelmed, trapped, or threatened by patients demanding unproven treatments or by ICUs with more patients than ventilators, they may experience a fight-or-flight response that makes them defensive, frustrated, angry, or uncaring, notes Mona Masood, DO, a Philadelphia-area psychiatrist and founder of Physician Support Line, a free mental health hotline for doctors.
Some clinicians have taken to Twitter and other social media platforms to post about these types of experiences.
These feelings, which have been brewing for months, have been exacerbated by the complexity of the current situation. Clinicians see a disconnect between what is and what could be, Dr. Nelson notes.
“Prior to vaccines, there weren’t other options, and so we had toxic stress and we had fatigue, but we could still maintain little bits of empathy by saying, ‘You know, people didn’t choose to get infected, and we are in a pandemic.’ We could kind of hate the virus. Now with access to vaccines, that last connection to empathy is removed for many people,” she says.
Self-preservation vs. empathy
Compassion fatigue or empathy fatigue is just one reaction to feeling completely maxed out and overstressed, Dr. Nelson says. Anger at society, such as what Dr. Erickson experienced, is another response.
Practitioners may also feel as if they are just going through the motions of their job, or they might disassociate, ceasing to feel that their patients are human. Plenty of doctors and nurses have cried in their cars after shifts and have posted tearful videos on social media.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Masood says, physicians who called the support hotline expressed sadness and grief. Now, she had her colleagues hear frustration and anger, along with guilt and shame for having feelings they believe they shouldn’t be having, especially toward patients. They may feel unprofessional or worse – unworthy of being physicians, she says.
One recent caller to the hotline was a long-time ICU physician who had been told so many times by patients that ivermectin was the only medicine that would cure them that he began to doubt himself, says Dr. Masood. This caller needed to be reassured by another physician that he was doing the right thing.
Another emergency department physician told Dr. Masood about a young child who had arrived at the hospital with COVID-19 symptoms. When asked whether the family had been exposed to anyone with COVID-19, the child’s parent lied so that they could be triaged faster.
The physician, who needed to step away from the situation, reached out to Dr. Masood to express her frustration so that she wouldn’t “let it out” on the patient.
“It’s hard to have empathy for people who, for all intents and purposes, are very self-centered,” Dr. Masood says. “We’re at a place where we’re having to choose between self-preservation and empathy.”
How to cope
To help practitioners cope, Dr. Masood offers words that describe what they’re experiencing. She often hears clinicians say things such as, “This is a type of burnout that I feel to my bones,” or “This makes me want to quit,” or “I feel like I’m at the end of my rope.”
She encourages them to consider the terms “empathy fatigue,” and “moral injury” in order to reconcile how their sense of responsibility to take care of people is compromised by factors outside of their control.
It is not shameful to acknowledge that they experience emotions, including difficult ones such as frustration, anger, sadness, and anxiety, Dr. Masood adds.
Being frustrated with a patient doesn’t make someone a bad doctor, and admitting those emotions is the first step toward dealing with them, she says.
before they cause a sense of callousness or other consequences that become harder to heal from as time goes on.
“We’re trained to just go, go, go and sometimes not pause and check in,” she says. Clinicians who open up are likely to find they are not the only ones feeling tired or frustrated right now, she adds.
“Connect with peers and colleagues, because chances are, they can relate,” Dr. Nelson says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heidi Erickson, MD, is tired. As a pulmonary and critical care physician at Hennepin Healthcare in Minneapolis, she has been providing care for patients with COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic.
It was exhausting from the beginning, as she and her colleagues scrambled to understand how to deal with this new disease. But lately, she has noticed a different kind of exhaustion arising from the knowledge that with vaccines widely available, the latest surge was preventable.
Her intensive care unit is currently as full as it has ever been with COVID-19 patients, many of them young adults and most of them unvaccinated. After the recent death of one patient, an unvaccinated man with teenage children, she had to face his family’s questions about why ivermectin, an antiparasitic medication that was falsely promoted as a COVID-19 treatment, was not administered.
“I’m fatigued because I’m working more than ever, but more people don’t have to die,” Dr. Erickson said in an interview . “It’s been very hard physically, mentally, emotionally.”
Amid yet another surge in COVID-19 cases around the United States, clinicians are speaking out about their growing frustration with this preventable crisis.
Some are using the terms “empathy fatigue” and “compassion fatigue” – a sense that they are losing empathy for unvaccinated individuals who are fueling the pandemic.
Dr. Erickson says she is frustrated not by individual patients but by a system that has allowed disinformation to proliferate. Experts say these types of feelings fit into a widespread pattern of physician burnout that has taken a new turn at this stage of the pandemic.
Paradoxical choices
Empathy is a cornerstone of what clinicians do, and the ability to understand and share a patient’s feelings is an essential skill for providing effective care, says Kaz Nelson, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Practitioners face paradoxical situations all the time, she notes. These include individuals who break bones and go skydiving again, people who have high cholesterol but continue to eat fried foods, and those with advanced lung cancer who continue to smoke.
To treat patients with compassion, practitioners learn to set aside judgment by acknowledging the complexity of human behavior. They may lament the addictive nature of nicotine and advertising that targets children, for example, while still listening and caring.
Empathy requires high-level brain function, but as stress levels rise, brain function that drives empathy tends to shut down. It’s a survival mechanism, Dr. Nelson says.
When health care workers feel overwhelmed, trapped, or threatened by patients demanding unproven treatments or by ICUs with more patients than ventilators, they may experience a fight-or-flight response that makes them defensive, frustrated, angry, or uncaring, notes Mona Masood, DO, a Philadelphia-area psychiatrist and founder of Physician Support Line, a free mental health hotline for doctors.
Some clinicians have taken to Twitter and other social media platforms to post about these types of experiences.
These feelings, which have been brewing for months, have been exacerbated by the complexity of the current situation. Clinicians see a disconnect between what is and what could be, Dr. Nelson notes.
“Prior to vaccines, there weren’t other options, and so we had toxic stress and we had fatigue, but we could still maintain little bits of empathy by saying, ‘You know, people didn’t choose to get infected, and we are in a pandemic.’ We could kind of hate the virus. Now with access to vaccines, that last connection to empathy is removed for many people,” she says.
Self-preservation vs. empathy
Compassion fatigue or empathy fatigue is just one reaction to feeling completely maxed out and overstressed, Dr. Nelson says. Anger at society, such as what Dr. Erickson experienced, is another response.
Practitioners may also feel as if they are just going through the motions of their job, or they might disassociate, ceasing to feel that their patients are human. Plenty of doctors and nurses have cried in their cars after shifts and have posted tearful videos on social media.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Masood says, physicians who called the support hotline expressed sadness and grief. Now, she had her colleagues hear frustration and anger, along with guilt and shame for having feelings they believe they shouldn’t be having, especially toward patients. They may feel unprofessional or worse – unworthy of being physicians, she says.
One recent caller to the hotline was a long-time ICU physician who had been told so many times by patients that ivermectin was the only medicine that would cure them that he began to doubt himself, says Dr. Masood. This caller needed to be reassured by another physician that he was doing the right thing.
Another emergency department physician told Dr. Masood about a young child who had arrived at the hospital with COVID-19 symptoms. When asked whether the family had been exposed to anyone with COVID-19, the child’s parent lied so that they could be triaged faster.
The physician, who needed to step away from the situation, reached out to Dr. Masood to express her frustration so that she wouldn’t “let it out” on the patient.
“It’s hard to have empathy for people who, for all intents and purposes, are very self-centered,” Dr. Masood says. “We’re at a place where we’re having to choose between self-preservation and empathy.”
How to cope
To help practitioners cope, Dr. Masood offers words that describe what they’re experiencing. She often hears clinicians say things such as, “This is a type of burnout that I feel to my bones,” or “This makes me want to quit,” or “I feel like I’m at the end of my rope.”
She encourages them to consider the terms “empathy fatigue,” and “moral injury” in order to reconcile how their sense of responsibility to take care of people is compromised by factors outside of their control.
It is not shameful to acknowledge that they experience emotions, including difficult ones such as frustration, anger, sadness, and anxiety, Dr. Masood adds.
Being frustrated with a patient doesn’t make someone a bad doctor, and admitting those emotions is the first step toward dealing with them, she says.
before they cause a sense of callousness or other consequences that become harder to heal from as time goes on.
“We’re trained to just go, go, go and sometimes not pause and check in,” she says. Clinicians who open up are likely to find they are not the only ones feeling tired or frustrated right now, she adds.
“Connect with peers and colleagues, because chances are, they can relate,” Dr. Nelson says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New Moderna vaccine data ‘support’ booster shot after 8 months
Moderna has released new data that it said support the argument for COVID-19 booster shots – specifically showing that people who received a first shot of their mRNA vaccine a median of 13 months ago are more likely to experience a breakthrough infection compared to individuals who received a first shot a median of 8 months ago.
The findings come from the ongoing phase 3 COVE clinical trial, the results of which the Food and Drug Administration considered in granting emergency use authorization for the vaccine. In the initial stage of the trial, people were randomly assigned to receive the company’s mRNA vaccine or placebo.
according to the analysis of the open-label extension of the study during which placebo participants could cross over and get immunized as well.
The updated COVE trial data show that 88 breakthrough cases of COVID-19 occurred among 11,431 participants vaccinated between December 2020 and March 2021 (49.0 cases per 1,000 person-years).
In contrast, there were 162 breakthrough cases among 14,746 people vaccinated between July and October 2020 (77.1 cases per 1,000 person-years).
The breakthrough infections include 19 severe cases. Although not statically different, there was a trend toward fewer severe cases among the more recently vaccinated, at a rate of 3.3 per 1,000 person-years, compared with 6.2 per 1,000 person-years in the group vaccinated in 2020
The findings were posted as a preprint to the medRxiv server and have not yet been peer reviewed.
“The increased risk of breakthrough infections in COVE study participants who were vaccinated last year compared to more recently illustrates the impact of waning immunity and supports the need for a booster to maintain high levels of protection,” Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel said in a company statement.
An FDA advisory committee is meeting Sept. 17 to look at the available evidence on boosters to help the agency decide whether the additional shots are warranted.
There is still a lot of debate in the medical community about the need for boosters. U.S. physicians and nurses are divided about the need for them and about how the country should prioritize its vaccine supplies, according to a Medscape poll of more than 1,700 clinicians that collected responses from Aug. 25 to Sept. 6, 2020.
The research was funded by Moderna, and also supported by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderna has released new data that it said support the argument for COVID-19 booster shots – specifically showing that people who received a first shot of their mRNA vaccine a median of 13 months ago are more likely to experience a breakthrough infection compared to individuals who received a first shot a median of 8 months ago.
The findings come from the ongoing phase 3 COVE clinical trial, the results of which the Food and Drug Administration considered in granting emergency use authorization for the vaccine. In the initial stage of the trial, people were randomly assigned to receive the company’s mRNA vaccine or placebo.
according to the analysis of the open-label extension of the study during which placebo participants could cross over and get immunized as well.
The updated COVE trial data show that 88 breakthrough cases of COVID-19 occurred among 11,431 participants vaccinated between December 2020 and March 2021 (49.0 cases per 1,000 person-years).
In contrast, there were 162 breakthrough cases among 14,746 people vaccinated between July and October 2020 (77.1 cases per 1,000 person-years).
The breakthrough infections include 19 severe cases. Although not statically different, there was a trend toward fewer severe cases among the more recently vaccinated, at a rate of 3.3 per 1,000 person-years, compared with 6.2 per 1,000 person-years in the group vaccinated in 2020
The findings were posted as a preprint to the medRxiv server and have not yet been peer reviewed.
“The increased risk of breakthrough infections in COVE study participants who were vaccinated last year compared to more recently illustrates the impact of waning immunity and supports the need for a booster to maintain high levels of protection,” Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel said in a company statement.
An FDA advisory committee is meeting Sept. 17 to look at the available evidence on boosters to help the agency decide whether the additional shots are warranted.
There is still a lot of debate in the medical community about the need for boosters. U.S. physicians and nurses are divided about the need for them and about how the country should prioritize its vaccine supplies, according to a Medscape poll of more than 1,700 clinicians that collected responses from Aug. 25 to Sept. 6, 2020.
The research was funded by Moderna, and also supported by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderna has released new data that it said support the argument for COVID-19 booster shots – specifically showing that people who received a first shot of their mRNA vaccine a median of 13 months ago are more likely to experience a breakthrough infection compared to individuals who received a first shot a median of 8 months ago.
The findings come from the ongoing phase 3 COVE clinical trial, the results of which the Food and Drug Administration considered in granting emergency use authorization for the vaccine. In the initial stage of the trial, people were randomly assigned to receive the company’s mRNA vaccine or placebo.
according to the analysis of the open-label extension of the study during which placebo participants could cross over and get immunized as well.
The updated COVE trial data show that 88 breakthrough cases of COVID-19 occurred among 11,431 participants vaccinated between December 2020 and March 2021 (49.0 cases per 1,000 person-years).
In contrast, there were 162 breakthrough cases among 14,746 people vaccinated between July and October 2020 (77.1 cases per 1,000 person-years).
The breakthrough infections include 19 severe cases. Although not statically different, there was a trend toward fewer severe cases among the more recently vaccinated, at a rate of 3.3 per 1,000 person-years, compared with 6.2 per 1,000 person-years in the group vaccinated in 2020
The findings were posted as a preprint to the medRxiv server and have not yet been peer reviewed.
“The increased risk of breakthrough infections in COVE study participants who were vaccinated last year compared to more recently illustrates the impact of waning immunity and supports the need for a booster to maintain high levels of protection,” Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel said in a company statement.
An FDA advisory committee is meeting Sept. 17 to look at the available evidence on boosters to help the agency decide whether the additional shots are warranted.
There is still a lot of debate in the medical community about the need for boosters. U.S. physicians and nurses are divided about the need for them and about how the country should prioritize its vaccine supplies, according to a Medscape poll of more than 1,700 clinicians that collected responses from Aug. 25 to Sept. 6, 2020.
The research was funded by Moderna, and also supported by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID vaccine preprint study prompts Twitter outrage
A preprint study finding that the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID vaccine is associated with an increased risk for cardiac adverse events in teenage boys has elicited a firestorm on Twitter. Although some people issued thoughtful critiques, others lobbed insults against the authors, and still others accused them of either being antivaccine or stoking the fires of the vaccine skeptic movement.
The controversy began soon after the study was posted online September 8 on medRxiv. The authors conclude that for boys, the risk for a cardiac adverse event or hospitalization after the second dose of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine was “considerably higher” than the 120-day risk for hospitalization for COVID-19, “even at times of peak disease prevalence.” This was especially true for those aged 12 to 15 years and even those with no underlying health conditions.
The conclusion – as well as the paper’s source, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), and its methodology, modeled after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention assessment of the database – did not sit well with many.
“Your methodology hugely overestimates risk, which many commentators who are specialists in the field have highlighted,” tweeted Deepti Gurdasani, senior lecturer in epidemiology at Queen Mary University of London. “Why make this claim when you must know it’s wrong?”
“The authors don’t know what they are doing and they are following their own ideology,” tweeted Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the cardiology division. Dr. Ziaeian also tweeted, “I believe the CDC is doing honest work and not dredging slop like you are.”
“Holy shit. Truly terrible methods in that paper,” tweeted Michael Mina, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and immunologist at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, more bluntly.
Some pointed out that VAERS is often used by vaccine skeptics to spread misinformation. “‘Dumpster diving’ describes studies using #VAERS by authors (almost always antivaxxers) who don’t understand its limitations,” tweeted David Gorski, MD, PhD, the editor of Science-Based Medicine, who says in his Twitter bio that he “exposes quackery.”
Added Dr. Gorski: “Doctors fell into this trap with their study suggesting #CovidVaccine is more dangerous to children than #COVID19.”
Dr. Gorski said he did not think that the authors were antivaccine. But, he tweeted, “I’d argue that at least one of the authors (Stevenson) is grossly unqualified to analyze the data. Mandrola? Marginal. The other two *might* be qualified in public health/epi, but they clearly either had no clue about #VAERS limitations or didn’t take them seriously enough.”
Two of the authors, John Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist who is also a columnist for Medscape, and Tracy Beth Hoeg, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and sports medicine specialist, told this news organization that their estimates are not definitive, owing to the nature of the VAERS database.
“I want to emphasize that our signal is hypothesis-generating,” said Dr. Mandrola. “There’s obviously more research that needs to be done.”
“I don’t think it should be used to establish a for-certain rate,” said Dr. Hoeg, about the study. “It’s not a perfect way of establishing what the rate of cardiac adverse events was, but it gives you an estimate, and generally with VAERS, it’s a significant underestimate.”
Both Dr. Hoeg and Dr. Mandrola said their analysis showed enough of a signal that it warranted a rush to publish. “We felt that it was super time-sensitive,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Vaccine risks versus COVID harm
The authors searched the VAERS system for children aged 12 to 17 years who had received one or two doses of an mRNA vaccine and had symptoms of myocarditis, pericarditis, myopericarditis, or chest pain, and also troponin levels available in the lab data.
Of the 257 patients they examined, 211 had peak troponin values available for analysis. All but one received the Pfizer vaccine. Results were stratified by age and sex.
The authors found that the rates of cardiac adverse events (CAEs) after dose 1 were 12.0 per million for 12- to 15-year-old boys and 8.2 per million for 16- and 17-year-old boys, compared with 0.0 per million and 2.0 per million for girls the same ages.
The estimates for the 12- to 15-year-old boys were 22% to 150% higher than what the CDC had previously reported.
After the second dose, the rate of CAEs for boys 12 to 15 years was 162.2 per million (143% to 280% higher than the CDC estimate) and for boys 16 and 17 years, it was 94.0 per million, or 30% to 40% higher than CDC estimate.
Dr. Mandrola said he and his colleagues found potentially more cases by using slightly broader search terms than those employed by the CDC but agreed with some critics that a limitation was that they did not call the reporting physicians, as is typical with CDC follow-up on VAERS reports.
The authors point to troponin levels as valid indicators of myocardial damage. Peak troponin levels exceeded 2 ng/mL in 71% of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 82% of 16- and 17-year-olds.
The study shows that for boys 12 to 15 years with no comorbidities, the risk for a CAE after the second dose would be 22.8 times higher than the risk for hospitalization for COVID-19 during periods of low disease burden, 6.0 times higher during periods of moderate transmission, and 4.3 times higher during periods of high transmission.
The authors acknowledge in the paper that their analysis “does not take into account any benefits the vaccine provides against transmission to others, long-term COVID-19 disease risk, or protection from nonsevere COVID-19 symptoms.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg told this news organization that they are currently recalculating their estimates because of the rising numbers of pediatric hospitalizations from the Delta variant surge.
Paper rejected by journals
Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that the paper went through peer-review at three journals but was rejected by all three, for reasons that were not made clear.
She and the other authors incorporated the reviewers’ feedback at each turn and included all of their suggestions in the paper that was ultimately uploaded to medRxiv, said Dr. Hoeg.
They decided to put it out as a preprint after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued its data and then a warning on June 25 about myocarditis with use of the Pfizer vaccine in children 12 to 15 years of age.
The preprint study was picked up by some media outlets, including The Telegraph and The Guardian newspapers, and tweeted out by vaccine skeptics like Robert W. Malone, MD.
Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia), an outspoken vaccine skeptic, tweeted out the Guardian story saying that the findings mean “there is every reason to stop the covid vaccine mandates.”
Dr. Gorski noted in tweets and in a blog post that one of the paper’s coauthors, Josh Stevenson, is part of Rational Ground, a group that supports the Great Barrington Declaration and is against lockdowns and mask mandates.
Mr. Stevenson did not disclose his affiliation in the paper, and Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that she was unaware of the group and Mr. Stevenson’s association with it and that she did not have the impression that he was altering the data to show any bias.
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they are provaccine and that they were dismayed to find their work being used to support any agenda. “It’s very frustrating,” said Dr. Hoeg, adding that she understands that “when you publish research on a controversial topic, people are going to take it and use it for their agendas.”
Some on Twitter blamed the open and free-wheeling nature of preprints.
Harlan Krumholz, MD, SM, the Harold H. Hines, junior professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., which oversees medRxiv, tweeted, “Do you get that the discussion about the preprint is exactly the purpose of #preprints. So that way when someone claims something, you can look at the source and experts can comment.”
But Dr. Ziaeian tweeted back, “Preprints like this one can be weaponized to stir anti-vaccine lies and damage public health.”
In turn, the Yale physician replied, “Unfortunately these days, almost anything can be weaponized, distorted, misunderstood.” Dr. Krumholz added: “There is no question that this preprint is worthy of deep vetting and discussion. But there is a #preprint artifact to examine.”
Measured support
Some clinicians signaled their support for open debate and the preprint’s findings.
“I’ve been very critical of preprints that are too quickly disseminated in the media, and this one is no exception,” tweeted Walid Gellad, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. “On the other hand, I think the vitriol directed at these authors is wrong,” he added.
“Like it or not, the issue of myocarditis in kids is an issue. Other countries have made vaccination decisions because of this issue, not because they’re driven by some ideology,” he tweeted.
Dr. Gellad also notes that the FDA has estimated the risk could be as high as one in 5,000 and that the preprint numbers could actually be underestimates.
In a long thread, Frank Han, MD, an adult congenital and pediatric cardiologist at the University of Illinois, tweets that relying on the VAERS reports might be faulty and that advanced cardiac imaging – guided by strict criteria – is the best way to determine myocarditis. And, he tweeted, “Physician review of VAERS reports really matters.”
Dr. Han concluded that vaccination “trades in a significant risk with a much smaller risk. That’s what counts in the end.”
In a response, Dr. Mandrola called Han’s tweets “reasoned criticism of our analysis.” He adds that his and Dr. Hoeg’s study have limits, but “our point is not to avoid protecting kids, but how to do so most safely.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they welcomed critiques, but they felt blindsided by the vehemence of some of the Twitter debate.
“Some of the vitriol was surprising,” Dr. Mandrola said. “I kind of have this naive notion that people would assume that we’re not bad people,” he added.
However, Dr. Mandrola is known on Twitter for sometimes being highly critical of other researchers’ work, referring to some studies as “howlers,” and has in the past called out others for citing those papers.
Dr. Hoeg said she found critiques about weaknesses in the methods to be helpful. But she said many tweets were “attacking us as people, or not really attacking anything about our study, but just attacking the finding,” which does not help anyone “figure out what we should do about the safety signal or how we can research it further.”
Said Dr. Mandrola: “Why would we just ignore that and go forward with two-shot vaccination as a mandate when other countries are looking at other strategies?”
He noted that the United Kingdom has announced that children 12 to 15 years of age should receive just one shot of the mRNA vaccines instead of two because of the risk for myocarditis. Sixteen- to 18-year-olds have already been advised to get only one dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A preprint study finding that the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID vaccine is associated with an increased risk for cardiac adverse events in teenage boys has elicited a firestorm on Twitter. Although some people issued thoughtful critiques, others lobbed insults against the authors, and still others accused them of either being antivaccine or stoking the fires of the vaccine skeptic movement.
The controversy began soon after the study was posted online September 8 on medRxiv. The authors conclude that for boys, the risk for a cardiac adverse event or hospitalization after the second dose of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine was “considerably higher” than the 120-day risk for hospitalization for COVID-19, “even at times of peak disease prevalence.” This was especially true for those aged 12 to 15 years and even those with no underlying health conditions.
The conclusion – as well as the paper’s source, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), and its methodology, modeled after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention assessment of the database – did not sit well with many.
“Your methodology hugely overestimates risk, which many commentators who are specialists in the field have highlighted,” tweeted Deepti Gurdasani, senior lecturer in epidemiology at Queen Mary University of London. “Why make this claim when you must know it’s wrong?”
“The authors don’t know what they are doing and they are following their own ideology,” tweeted Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the cardiology division. Dr. Ziaeian also tweeted, “I believe the CDC is doing honest work and not dredging slop like you are.”
“Holy shit. Truly terrible methods in that paper,” tweeted Michael Mina, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and immunologist at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, more bluntly.
Some pointed out that VAERS is often used by vaccine skeptics to spread misinformation. “‘Dumpster diving’ describes studies using #VAERS by authors (almost always antivaxxers) who don’t understand its limitations,” tweeted David Gorski, MD, PhD, the editor of Science-Based Medicine, who says in his Twitter bio that he “exposes quackery.”
Added Dr. Gorski: “Doctors fell into this trap with their study suggesting #CovidVaccine is more dangerous to children than #COVID19.”
Dr. Gorski said he did not think that the authors were antivaccine. But, he tweeted, “I’d argue that at least one of the authors (Stevenson) is grossly unqualified to analyze the data. Mandrola? Marginal. The other two *might* be qualified in public health/epi, but they clearly either had no clue about #VAERS limitations or didn’t take them seriously enough.”
Two of the authors, John Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist who is also a columnist for Medscape, and Tracy Beth Hoeg, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and sports medicine specialist, told this news organization that their estimates are not definitive, owing to the nature of the VAERS database.
“I want to emphasize that our signal is hypothesis-generating,” said Dr. Mandrola. “There’s obviously more research that needs to be done.”
“I don’t think it should be used to establish a for-certain rate,” said Dr. Hoeg, about the study. “It’s not a perfect way of establishing what the rate of cardiac adverse events was, but it gives you an estimate, and generally with VAERS, it’s a significant underestimate.”
Both Dr. Hoeg and Dr. Mandrola said their analysis showed enough of a signal that it warranted a rush to publish. “We felt that it was super time-sensitive,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Vaccine risks versus COVID harm
The authors searched the VAERS system for children aged 12 to 17 years who had received one or two doses of an mRNA vaccine and had symptoms of myocarditis, pericarditis, myopericarditis, or chest pain, and also troponin levels available in the lab data.
Of the 257 patients they examined, 211 had peak troponin values available for analysis. All but one received the Pfizer vaccine. Results were stratified by age and sex.
The authors found that the rates of cardiac adverse events (CAEs) after dose 1 were 12.0 per million for 12- to 15-year-old boys and 8.2 per million for 16- and 17-year-old boys, compared with 0.0 per million and 2.0 per million for girls the same ages.
The estimates for the 12- to 15-year-old boys were 22% to 150% higher than what the CDC had previously reported.
After the second dose, the rate of CAEs for boys 12 to 15 years was 162.2 per million (143% to 280% higher than the CDC estimate) and for boys 16 and 17 years, it was 94.0 per million, or 30% to 40% higher than CDC estimate.
Dr. Mandrola said he and his colleagues found potentially more cases by using slightly broader search terms than those employed by the CDC but agreed with some critics that a limitation was that they did not call the reporting physicians, as is typical with CDC follow-up on VAERS reports.
The authors point to troponin levels as valid indicators of myocardial damage. Peak troponin levels exceeded 2 ng/mL in 71% of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 82% of 16- and 17-year-olds.
The study shows that for boys 12 to 15 years with no comorbidities, the risk for a CAE after the second dose would be 22.8 times higher than the risk for hospitalization for COVID-19 during periods of low disease burden, 6.0 times higher during periods of moderate transmission, and 4.3 times higher during periods of high transmission.
The authors acknowledge in the paper that their analysis “does not take into account any benefits the vaccine provides against transmission to others, long-term COVID-19 disease risk, or protection from nonsevere COVID-19 symptoms.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg told this news organization that they are currently recalculating their estimates because of the rising numbers of pediatric hospitalizations from the Delta variant surge.
Paper rejected by journals
Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that the paper went through peer-review at three journals but was rejected by all three, for reasons that were not made clear.
She and the other authors incorporated the reviewers’ feedback at each turn and included all of their suggestions in the paper that was ultimately uploaded to medRxiv, said Dr. Hoeg.
They decided to put it out as a preprint after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued its data and then a warning on June 25 about myocarditis with use of the Pfizer vaccine in children 12 to 15 years of age.
The preprint study was picked up by some media outlets, including The Telegraph and The Guardian newspapers, and tweeted out by vaccine skeptics like Robert W. Malone, MD.
Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia), an outspoken vaccine skeptic, tweeted out the Guardian story saying that the findings mean “there is every reason to stop the covid vaccine mandates.”
Dr. Gorski noted in tweets and in a blog post that one of the paper’s coauthors, Josh Stevenson, is part of Rational Ground, a group that supports the Great Barrington Declaration and is against lockdowns and mask mandates.
Mr. Stevenson did not disclose his affiliation in the paper, and Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that she was unaware of the group and Mr. Stevenson’s association with it and that she did not have the impression that he was altering the data to show any bias.
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they are provaccine and that they were dismayed to find their work being used to support any agenda. “It’s very frustrating,” said Dr. Hoeg, adding that she understands that “when you publish research on a controversial topic, people are going to take it and use it for their agendas.”
Some on Twitter blamed the open and free-wheeling nature of preprints.
Harlan Krumholz, MD, SM, the Harold H. Hines, junior professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., which oversees medRxiv, tweeted, “Do you get that the discussion about the preprint is exactly the purpose of #preprints. So that way when someone claims something, you can look at the source and experts can comment.”
But Dr. Ziaeian tweeted back, “Preprints like this one can be weaponized to stir anti-vaccine lies and damage public health.”
In turn, the Yale physician replied, “Unfortunately these days, almost anything can be weaponized, distorted, misunderstood.” Dr. Krumholz added: “There is no question that this preprint is worthy of deep vetting and discussion. But there is a #preprint artifact to examine.”
Measured support
Some clinicians signaled their support for open debate and the preprint’s findings.
“I’ve been very critical of preprints that are too quickly disseminated in the media, and this one is no exception,” tweeted Walid Gellad, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. “On the other hand, I think the vitriol directed at these authors is wrong,” he added.
“Like it or not, the issue of myocarditis in kids is an issue. Other countries have made vaccination decisions because of this issue, not because they’re driven by some ideology,” he tweeted.
Dr. Gellad also notes that the FDA has estimated the risk could be as high as one in 5,000 and that the preprint numbers could actually be underestimates.
In a long thread, Frank Han, MD, an adult congenital and pediatric cardiologist at the University of Illinois, tweets that relying on the VAERS reports might be faulty and that advanced cardiac imaging – guided by strict criteria – is the best way to determine myocarditis. And, he tweeted, “Physician review of VAERS reports really matters.”
Dr. Han concluded that vaccination “trades in a significant risk with a much smaller risk. That’s what counts in the end.”
In a response, Dr. Mandrola called Han’s tweets “reasoned criticism of our analysis.” He adds that his and Dr. Hoeg’s study have limits, but “our point is not to avoid protecting kids, but how to do so most safely.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they welcomed critiques, but they felt blindsided by the vehemence of some of the Twitter debate.
“Some of the vitriol was surprising,” Dr. Mandrola said. “I kind of have this naive notion that people would assume that we’re not bad people,” he added.
However, Dr. Mandrola is known on Twitter for sometimes being highly critical of other researchers’ work, referring to some studies as “howlers,” and has in the past called out others for citing those papers.
Dr. Hoeg said she found critiques about weaknesses in the methods to be helpful. But she said many tweets were “attacking us as people, or not really attacking anything about our study, but just attacking the finding,” which does not help anyone “figure out what we should do about the safety signal or how we can research it further.”
Said Dr. Mandrola: “Why would we just ignore that and go forward with two-shot vaccination as a mandate when other countries are looking at other strategies?”
He noted that the United Kingdom has announced that children 12 to 15 years of age should receive just one shot of the mRNA vaccines instead of two because of the risk for myocarditis. Sixteen- to 18-year-olds have already been advised to get only one dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A preprint study finding that the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID vaccine is associated with an increased risk for cardiac adverse events in teenage boys has elicited a firestorm on Twitter. Although some people issued thoughtful critiques, others lobbed insults against the authors, and still others accused them of either being antivaccine or stoking the fires of the vaccine skeptic movement.
The controversy began soon after the study was posted online September 8 on medRxiv. The authors conclude that for boys, the risk for a cardiac adverse event or hospitalization after the second dose of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine was “considerably higher” than the 120-day risk for hospitalization for COVID-19, “even at times of peak disease prevalence.” This was especially true for those aged 12 to 15 years and even those with no underlying health conditions.
The conclusion – as well as the paper’s source, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), and its methodology, modeled after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention assessment of the database – did not sit well with many.
“Your methodology hugely overestimates risk, which many commentators who are specialists in the field have highlighted,” tweeted Deepti Gurdasani, senior lecturer in epidemiology at Queen Mary University of London. “Why make this claim when you must know it’s wrong?”
“The authors don’t know what they are doing and they are following their own ideology,” tweeted Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the cardiology division. Dr. Ziaeian also tweeted, “I believe the CDC is doing honest work and not dredging slop like you are.”
“Holy shit. Truly terrible methods in that paper,” tweeted Michael Mina, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and immunologist at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, more bluntly.
Some pointed out that VAERS is often used by vaccine skeptics to spread misinformation. “‘Dumpster diving’ describes studies using #VAERS by authors (almost always antivaxxers) who don’t understand its limitations,” tweeted David Gorski, MD, PhD, the editor of Science-Based Medicine, who says in his Twitter bio that he “exposes quackery.”
Added Dr. Gorski: “Doctors fell into this trap with their study suggesting #CovidVaccine is more dangerous to children than #COVID19.”
Dr. Gorski said he did not think that the authors were antivaccine. But, he tweeted, “I’d argue that at least one of the authors (Stevenson) is grossly unqualified to analyze the data. Mandrola? Marginal. The other two *might* be qualified in public health/epi, but they clearly either had no clue about #VAERS limitations or didn’t take them seriously enough.”
Two of the authors, John Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist who is also a columnist for Medscape, and Tracy Beth Hoeg, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and sports medicine specialist, told this news organization that their estimates are not definitive, owing to the nature of the VAERS database.
“I want to emphasize that our signal is hypothesis-generating,” said Dr. Mandrola. “There’s obviously more research that needs to be done.”
“I don’t think it should be used to establish a for-certain rate,” said Dr. Hoeg, about the study. “It’s not a perfect way of establishing what the rate of cardiac adverse events was, but it gives you an estimate, and generally with VAERS, it’s a significant underestimate.”
Both Dr. Hoeg and Dr. Mandrola said their analysis showed enough of a signal that it warranted a rush to publish. “We felt that it was super time-sensitive,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Vaccine risks versus COVID harm
The authors searched the VAERS system for children aged 12 to 17 years who had received one or two doses of an mRNA vaccine and had symptoms of myocarditis, pericarditis, myopericarditis, or chest pain, and also troponin levels available in the lab data.
Of the 257 patients they examined, 211 had peak troponin values available for analysis. All but one received the Pfizer vaccine. Results were stratified by age and sex.
The authors found that the rates of cardiac adverse events (CAEs) after dose 1 were 12.0 per million for 12- to 15-year-old boys and 8.2 per million for 16- and 17-year-old boys, compared with 0.0 per million and 2.0 per million for girls the same ages.
The estimates for the 12- to 15-year-old boys were 22% to 150% higher than what the CDC had previously reported.
After the second dose, the rate of CAEs for boys 12 to 15 years was 162.2 per million (143% to 280% higher than the CDC estimate) and for boys 16 and 17 years, it was 94.0 per million, or 30% to 40% higher than CDC estimate.
Dr. Mandrola said he and his colleagues found potentially more cases by using slightly broader search terms than those employed by the CDC but agreed with some critics that a limitation was that they did not call the reporting physicians, as is typical with CDC follow-up on VAERS reports.
The authors point to troponin levels as valid indicators of myocardial damage. Peak troponin levels exceeded 2 ng/mL in 71% of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 82% of 16- and 17-year-olds.
The study shows that for boys 12 to 15 years with no comorbidities, the risk for a CAE after the second dose would be 22.8 times higher than the risk for hospitalization for COVID-19 during periods of low disease burden, 6.0 times higher during periods of moderate transmission, and 4.3 times higher during periods of high transmission.
The authors acknowledge in the paper that their analysis “does not take into account any benefits the vaccine provides against transmission to others, long-term COVID-19 disease risk, or protection from nonsevere COVID-19 symptoms.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg told this news organization that they are currently recalculating their estimates because of the rising numbers of pediatric hospitalizations from the Delta variant surge.
Paper rejected by journals
Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that the paper went through peer-review at three journals but was rejected by all three, for reasons that were not made clear.
She and the other authors incorporated the reviewers’ feedback at each turn and included all of their suggestions in the paper that was ultimately uploaded to medRxiv, said Dr. Hoeg.
They decided to put it out as a preprint after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued its data and then a warning on June 25 about myocarditis with use of the Pfizer vaccine in children 12 to 15 years of age.
The preprint study was picked up by some media outlets, including The Telegraph and The Guardian newspapers, and tweeted out by vaccine skeptics like Robert W. Malone, MD.
Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia), an outspoken vaccine skeptic, tweeted out the Guardian story saying that the findings mean “there is every reason to stop the covid vaccine mandates.”
Dr. Gorski noted in tweets and in a blog post that one of the paper’s coauthors, Josh Stevenson, is part of Rational Ground, a group that supports the Great Barrington Declaration and is against lockdowns and mask mandates.
Mr. Stevenson did not disclose his affiliation in the paper, and Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that she was unaware of the group and Mr. Stevenson’s association with it and that she did not have the impression that he was altering the data to show any bias.
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they are provaccine and that they were dismayed to find their work being used to support any agenda. “It’s very frustrating,” said Dr. Hoeg, adding that she understands that “when you publish research on a controversial topic, people are going to take it and use it for their agendas.”
Some on Twitter blamed the open and free-wheeling nature of preprints.
Harlan Krumholz, MD, SM, the Harold H. Hines, junior professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., which oversees medRxiv, tweeted, “Do you get that the discussion about the preprint is exactly the purpose of #preprints. So that way when someone claims something, you can look at the source and experts can comment.”
But Dr. Ziaeian tweeted back, “Preprints like this one can be weaponized to stir anti-vaccine lies and damage public health.”
In turn, the Yale physician replied, “Unfortunately these days, almost anything can be weaponized, distorted, misunderstood.” Dr. Krumholz added: “There is no question that this preprint is worthy of deep vetting and discussion. But there is a #preprint artifact to examine.”
Measured support
Some clinicians signaled their support for open debate and the preprint’s findings.
“I’ve been very critical of preprints that are too quickly disseminated in the media, and this one is no exception,” tweeted Walid Gellad, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. “On the other hand, I think the vitriol directed at these authors is wrong,” he added.
“Like it or not, the issue of myocarditis in kids is an issue. Other countries have made vaccination decisions because of this issue, not because they’re driven by some ideology,” he tweeted.
Dr. Gellad also notes that the FDA has estimated the risk could be as high as one in 5,000 and that the preprint numbers could actually be underestimates.
In a long thread, Frank Han, MD, an adult congenital and pediatric cardiologist at the University of Illinois, tweets that relying on the VAERS reports might be faulty and that advanced cardiac imaging – guided by strict criteria – is the best way to determine myocarditis. And, he tweeted, “Physician review of VAERS reports really matters.”
Dr. Han concluded that vaccination “trades in a significant risk with a much smaller risk. That’s what counts in the end.”
In a response, Dr. Mandrola called Han’s tweets “reasoned criticism of our analysis.” He adds that his and Dr. Hoeg’s study have limits, but “our point is not to avoid protecting kids, but how to do so most safely.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they welcomed critiques, but they felt blindsided by the vehemence of some of the Twitter debate.
“Some of the vitriol was surprising,” Dr. Mandrola said. “I kind of have this naive notion that people would assume that we’re not bad people,” he added.
However, Dr. Mandrola is known on Twitter for sometimes being highly critical of other researchers’ work, referring to some studies as “howlers,” and has in the past called out others for citing those papers.
Dr. Hoeg said she found critiques about weaknesses in the methods to be helpful. But she said many tweets were “attacking us as people, or not really attacking anything about our study, but just attacking the finding,” which does not help anyone “figure out what we should do about the safety signal or how we can research it further.”
Said Dr. Mandrola: “Why would we just ignore that and go forward with two-shot vaccination as a mandate when other countries are looking at other strategies?”
He noted that the United Kingdom has announced that children 12 to 15 years of age should receive just one shot of the mRNA vaccines instead of two because of the risk for myocarditis. Sixteen- to 18-year-olds have already been advised to get only one dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A boy went to a COVID-swamped ER. He waited for hours. Then his appendix burst.
Seth was finally diagnosed with appendicitis more than six hours after arriving at Cleveland Clinic Martin Health North Hospital in late July. Around midnight, he was taken by ambulance to a sister hospital about a half-hour away that was better equipped to perform pediatric emergency surgery, his father said.
But by the time the doctor operated in the early morning hours, Seth’s appendix had burst – a potentially fatal complication.
They, too, need emergency care, but the sheer number of COVID-19 cases is crowding them out. Treatment has often been delayed as ERs scramble to find a bed that may be hundreds of miles away.
Some health officials now worry about looming ethical decisions. Last week, Idaho activated a “crisis standard of care,” which one official described as a “last resort.” It allows overwhelmed hospitals to ration care, including “in rare cases, ventilator (breathing machines) or intensive care unit (ICU) beds may need to be used for those who are most likely to survive, while patients who are not likely to survive may not be able to receive one,” the state’s website said.
The federal government’s latest data shows Alabama is at 100% of its intensive care unit capacity, with Texas, Georgia, Mississippi and Arkansas at more than 90% ICU capacity. Florida is just under 90%.
It’s the COVID-19 cases that are dominating. In Georgia, 62% of the ICU beds are now filled with just COVID-19 patients. In Texas, the percentage is nearly half.
To have so many ICU beds pressed into service for a single diagnosis is “unheard of,” said Dr. Hasan Kakli, an emergency room physician at Bellville Medical Center in Bellville, Texas, about an hour from Houston. “It’s approaching apocalyptic.”
In Texas, state data released Monday showed there were only 319 adult and 104 pediatric staffed ICU beds available across a state of 29 million people.
Hospitals need to hold some ICU beds for other patients, such as those recovering from major surgery or other critical conditions such as stroke, trauma or heart failure.
“This is not just a COVID issue,” said Dr. Normaliz Rodriguez, pediatric emergency physician at Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital in St. Petersburg, Florida. “This is an everyone issue.”
While the latest hospital crisis echoes previous pandemic spikes, there are troubling differences this time around.
Before, localized COVID-19 hot spots led to bed shortages, but there were usually hospitals in the region not as affected that could accept a transfer.
Now, as the highly contagious delta variant envelops swaths of low-vaccination states all at once, it becomes harder to find nearby hospitals that are not slammed.
“Wait times can now be measured in days,” said Darrell Pile, CEO of the SouthEast Texas Regional Advisory Council, which helps coordinate patient transfers across a 25-county region.
Recently, Dr. Cedric Dark, a Houston emergency physician and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, said he saw a critically ill COVID-19 patient waiting in the emergency room for an ICU bed to open. The doctor worked eight hours, went home and came in the next day. The patient was still waiting.
Holding a seriously ill patient in an emergency room while waiting for an in-patient bed to open is known as boarding. The longer the wait, the more dangerous it can be for the patient, studies have found.
Not only do patients ultimately end up staying in the hospital or the ICU longer, some research suggests that long waits for a bed will worsen their condition and may increase the risk of in-hospital death.
That’s what happened last month in Texas.
On Aug. 21, around 11:30 a.m., Michelle Puget took her adult son, Daniel Wilkinson, to the Bellville Medical Center’s emergency room as a pain in his abdomen became unbearable. “Mama,” he said, “take me to the hospital.”
Wilkinson, a 46-year-old decorated Army veteran who did two tours of duty in Afghanistan, was ushered into an exam room about half an hour later. Kakli, the emergency room physician there, diagnosed gallstone pancreatitis, a serious but treatable condition that required a specialist to perform a surgical procedure and an ICU bed.
In other times, the transfer to a larger facility would be easy. But soon Kakli found himself on a frantic, six-hour quest to find a bed for his patient. Not only did he call hospitals across Texas, but he also tried Kansas, Missouri, Oklahoma and Colorado. It was like throwing darts at a map and hoping to get lucky, he told ProPublica. But no one could or would take the transfer.
By 2:30 p.m., Wilkinson’s condition was deteriorating. Kakli told Puget to come back to the hospital. “I have to tell you,” she said he told her, “Your son is a very, very sick man. If he doesn’t get this procedure he will die.” She began to weep.
Two hours later, Wilkinson’s blood pressure was dropping, signaling his organs were failing, she said.
Kakli went on Facebook and posted an all-caps plea to physician groups around the nation: “GETTING REJECTED BY ALL HOSPITALS IN TEXAS DUE TO NO ICU BEDS. PLEASE HELP. MESSAGE ME IF YOU HAVE A BED. PATIENT IS IN ER NOW. I AM THE ER DOC. WILL FLY ANYWHERE.”
The doctor tried Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center in Houston for a second time. This time he found a bed.
Around 7 p.m., Wilkinson, still conscious but in grave condition, was flown by helicopter to the hospital. He was put in a medically induced coma. Through the night and into the next morning, medical teams worked to stabilize him enough to perform the procedure. They could not.
Doctors told his family the internal damage was catastrophic. “We made the decision we had to let him go,” Puget said.
Time of death: 1:37 p.m. Aug. 22 – 26 hours after he first arrived in the emergency room.
The story was first reported by CBS News. Kakli told ProPublica last week he still sometimes does the math in his head: It should have been 40 minutes from diagnosis in Bellville to transfer to the ICU in Houston. “If he had 40 minutes to wait instead of six hours, I strongly believe he would have had a different outcome.”
Another difference with the latest surge is how it’s affecting children.
Last year, schools were closed, and children were more protected because they were mostly isolated at home. In fact, children’s hospitals were often so empty during previous spikes they opened beds to adult patients.
Now, families are out more. Schools have reopened, some with mask mandates, some without. Vaccines are not yet available to those under 12. Suddenly the numbers of hospitalized children are on the rise, setting up the same type of competition for resources between young COVID-19 patients and those with other illnesses such as new onset diabetes, trauma, pneumonia or appendicitis.
Dr. Rafael Santiago, a pediatric emergency physician in Central Florida, said at Lakeland Regional Health Medical Center, the average number of children coming into the emergency room is around 130 per day. During the lockdown last spring, that number dropped to 33. Last month – “the busiest month ever” – the average daily number of children in the emergency room was 160.
Pediatric transfers are not yet as fraught as adult ones, Santiago said, but it does take more calls than it once did to secure a bed.
Seth Osborn, the 12-year-old whose appendix burst after a long wait, spent five days and four nights in the hospital as doctors pumped his body full of antibiotics to stave off infection from the rupture. The typical hospitalization for a routine appendectomy is about 24 hours.
The initial hospital bill for the stay came to more than $48,000, Nathaniel Osborn said. Although insurance paid for most of it, he said the family still borrowed against its house to cover the more than $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs so far.
While the hospital system where Seth was treated declined to comment about his case because of patient privacy laws, it did email a statement about the strain the pandemic is creating.
“Since July 2021, we have seen a tremendous spike in COVID-19 patients needing care and hospitalization. In mid-August, we saw the highest number of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 across the Cleveland Clinic Florida region, a total of 395 COVID-19 patients in four hospitals. Those hospitals have approximately 1,000 total beds,” the email to ProPublica said. “We strongly encourage vaccination. Approximately 90% of our patients hospitalized due to COVID-19 are unvaccinated.”
On Sunday, The Washington Post reported that a hospital in Alabama called 43 others across three states before finding a bed for Ray DeMonia, a critically ill heart patient who later died. In his obituary his family wrote: “In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies. ... He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Today, Seth is mostly recovered. “Twelve-year-old boys bounce back,” his father said. Still, the experience has left Nathaniel Osborn shaken.
The high school history teacher said he likes to stay upbeat and apolitical in his social media musings, posting about Florida wildlife preservation and favorite books. But on Sept. 7, he tweeted: “My 12-year-old had appendicitis. The ER was overwhelmed with unvaccinated Covid patients and we had to wait 6+ hours. While waiting, his appendix ruptured and had to spend 5 days in hospital. ... So yeah, your decision to not vaccinate does affect others.”
It was retweeted 34,700 times, with 143,000 likes. Most comments were sympathetic and wished his child a speedy recovery. Some, though, went straight to hate, apparently triggered by his last line. He was attacked personally and accused of making up the story: “Good try with the guilt, jerk.”
Osborn, who is vaccinated, as are his wife and son, told ProPublica he only shared Seth’s story on Twitter to encourage vaccinations.
“I have no ill will towards the hospitals or the care received at either hospital,” he said this week, “but had these hospitals not been so crowded with COVID patients, we wouldn’t have had to wait so long and perhaps my son’s appendix would not have burst.”
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
Seth was finally diagnosed with appendicitis more than six hours after arriving at Cleveland Clinic Martin Health North Hospital in late July. Around midnight, he was taken by ambulance to a sister hospital about a half-hour away that was better equipped to perform pediatric emergency surgery, his father said.
But by the time the doctor operated in the early morning hours, Seth’s appendix had burst – a potentially fatal complication.
They, too, need emergency care, but the sheer number of COVID-19 cases is crowding them out. Treatment has often been delayed as ERs scramble to find a bed that may be hundreds of miles away.
Some health officials now worry about looming ethical decisions. Last week, Idaho activated a “crisis standard of care,” which one official described as a “last resort.” It allows overwhelmed hospitals to ration care, including “in rare cases, ventilator (breathing machines) or intensive care unit (ICU) beds may need to be used for those who are most likely to survive, while patients who are not likely to survive may not be able to receive one,” the state’s website said.
The federal government’s latest data shows Alabama is at 100% of its intensive care unit capacity, with Texas, Georgia, Mississippi and Arkansas at more than 90% ICU capacity. Florida is just under 90%.
It’s the COVID-19 cases that are dominating. In Georgia, 62% of the ICU beds are now filled with just COVID-19 patients. In Texas, the percentage is nearly half.
To have so many ICU beds pressed into service for a single diagnosis is “unheard of,” said Dr. Hasan Kakli, an emergency room physician at Bellville Medical Center in Bellville, Texas, about an hour from Houston. “It’s approaching apocalyptic.”
In Texas, state data released Monday showed there were only 319 adult and 104 pediatric staffed ICU beds available across a state of 29 million people.
Hospitals need to hold some ICU beds for other patients, such as those recovering from major surgery or other critical conditions such as stroke, trauma or heart failure.
“This is not just a COVID issue,” said Dr. Normaliz Rodriguez, pediatric emergency physician at Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital in St. Petersburg, Florida. “This is an everyone issue.”
While the latest hospital crisis echoes previous pandemic spikes, there are troubling differences this time around.
Before, localized COVID-19 hot spots led to bed shortages, but there were usually hospitals in the region not as affected that could accept a transfer.
Now, as the highly contagious delta variant envelops swaths of low-vaccination states all at once, it becomes harder to find nearby hospitals that are not slammed.
“Wait times can now be measured in days,” said Darrell Pile, CEO of the SouthEast Texas Regional Advisory Council, which helps coordinate patient transfers across a 25-county region.
Recently, Dr. Cedric Dark, a Houston emergency physician and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, said he saw a critically ill COVID-19 patient waiting in the emergency room for an ICU bed to open. The doctor worked eight hours, went home and came in the next day. The patient was still waiting.
Holding a seriously ill patient in an emergency room while waiting for an in-patient bed to open is known as boarding. The longer the wait, the more dangerous it can be for the patient, studies have found.
Not only do patients ultimately end up staying in the hospital or the ICU longer, some research suggests that long waits for a bed will worsen their condition and may increase the risk of in-hospital death.
That’s what happened last month in Texas.
On Aug. 21, around 11:30 a.m., Michelle Puget took her adult son, Daniel Wilkinson, to the Bellville Medical Center’s emergency room as a pain in his abdomen became unbearable. “Mama,” he said, “take me to the hospital.”
Wilkinson, a 46-year-old decorated Army veteran who did two tours of duty in Afghanistan, was ushered into an exam room about half an hour later. Kakli, the emergency room physician there, diagnosed gallstone pancreatitis, a serious but treatable condition that required a specialist to perform a surgical procedure and an ICU bed.
In other times, the transfer to a larger facility would be easy. But soon Kakli found himself on a frantic, six-hour quest to find a bed for his patient. Not only did he call hospitals across Texas, but he also tried Kansas, Missouri, Oklahoma and Colorado. It was like throwing darts at a map and hoping to get lucky, he told ProPublica. But no one could or would take the transfer.
By 2:30 p.m., Wilkinson’s condition was deteriorating. Kakli told Puget to come back to the hospital. “I have to tell you,” she said he told her, “Your son is a very, very sick man. If he doesn’t get this procedure he will die.” She began to weep.
Two hours later, Wilkinson’s blood pressure was dropping, signaling his organs were failing, she said.
Kakli went on Facebook and posted an all-caps plea to physician groups around the nation: “GETTING REJECTED BY ALL HOSPITALS IN TEXAS DUE TO NO ICU BEDS. PLEASE HELP. MESSAGE ME IF YOU HAVE A BED. PATIENT IS IN ER NOW. I AM THE ER DOC. WILL FLY ANYWHERE.”
The doctor tried Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center in Houston for a second time. This time he found a bed.
Around 7 p.m., Wilkinson, still conscious but in grave condition, was flown by helicopter to the hospital. He was put in a medically induced coma. Through the night and into the next morning, medical teams worked to stabilize him enough to perform the procedure. They could not.
Doctors told his family the internal damage was catastrophic. “We made the decision we had to let him go,” Puget said.
Time of death: 1:37 p.m. Aug. 22 – 26 hours after he first arrived in the emergency room.
The story was first reported by CBS News. Kakli told ProPublica last week he still sometimes does the math in his head: It should have been 40 minutes from diagnosis in Bellville to transfer to the ICU in Houston. “If he had 40 minutes to wait instead of six hours, I strongly believe he would have had a different outcome.”
Another difference with the latest surge is how it’s affecting children.
Last year, schools were closed, and children were more protected because they were mostly isolated at home. In fact, children’s hospitals were often so empty during previous spikes they opened beds to adult patients.
Now, families are out more. Schools have reopened, some with mask mandates, some without. Vaccines are not yet available to those under 12. Suddenly the numbers of hospitalized children are on the rise, setting up the same type of competition for resources between young COVID-19 patients and those with other illnesses such as new onset diabetes, trauma, pneumonia or appendicitis.
Dr. Rafael Santiago, a pediatric emergency physician in Central Florida, said at Lakeland Regional Health Medical Center, the average number of children coming into the emergency room is around 130 per day. During the lockdown last spring, that number dropped to 33. Last month – “the busiest month ever” – the average daily number of children in the emergency room was 160.
Pediatric transfers are not yet as fraught as adult ones, Santiago said, but it does take more calls than it once did to secure a bed.
Seth Osborn, the 12-year-old whose appendix burst after a long wait, spent five days and four nights in the hospital as doctors pumped his body full of antibiotics to stave off infection from the rupture. The typical hospitalization for a routine appendectomy is about 24 hours.
The initial hospital bill for the stay came to more than $48,000, Nathaniel Osborn said. Although insurance paid for most of it, he said the family still borrowed against its house to cover the more than $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs so far.
While the hospital system where Seth was treated declined to comment about his case because of patient privacy laws, it did email a statement about the strain the pandemic is creating.
“Since July 2021, we have seen a tremendous spike in COVID-19 patients needing care and hospitalization. In mid-August, we saw the highest number of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 across the Cleveland Clinic Florida region, a total of 395 COVID-19 patients in four hospitals. Those hospitals have approximately 1,000 total beds,” the email to ProPublica said. “We strongly encourage vaccination. Approximately 90% of our patients hospitalized due to COVID-19 are unvaccinated.”
On Sunday, The Washington Post reported that a hospital in Alabama called 43 others across three states before finding a bed for Ray DeMonia, a critically ill heart patient who later died. In his obituary his family wrote: “In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies. ... He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Today, Seth is mostly recovered. “Twelve-year-old boys bounce back,” his father said. Still, the experience has left Nathaniel Osborn shaken.
The high school history teacher said he likes to stay upbeat and apolitical in his social media musings, posting about Florida wildlife preservation and favorite books. But on Sept. 7, he tweeted: “My 12-year-old had appendicitis. The ER was overwhelmed with unvaccinated Covid patients and we had to wait 6+ hours. While waiting, his appendix ruptured and had to spend 5 days in hospital. ... So yeah, your decision to not vaccinate does affect others.”
It was retweeted 34,700 times, with 143,000 likes. Most comments were sympathetic and wished his child a speedy recovery. Some, though, went straight to hate, apparently triggered by his last line. He was attacked personally and accused of making up the story: “Good try with the guilt, jerk.”
Osborn, who is vaccinated, as are his wife and son, told ProPublica he only shared Seth’s story on Twitter to encourage vaccinations.
“I have no ill will towards the hospitals or the care received at either hospital,” he said this week, “but had these hospitals not been so crowded with COVID patients, we wouldn’t have had to wait so long and perhaps my son’s appendix would not have burst.”
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
Seth was finally diagnosed with appendicitis more than six hours after arriving at Cleveland Clinic Martin Health North Hospital in late July. Around midnight, he was taken by ambulance to a sister hospital about a half-hour away that was better equipped to perform pediatric emergency surgery, his father said.
But by the time the doctor operated in the early morning hours, Seth’s appendix had burst – a potentially fatal complication.
They, too, need emergency care, but the sheer number of COVID-19 cases is crowding them out. Treatment has often been delayed as ERs scramble to find a bed that may be hundreds of miles away.
Some health officials now worry about looming ethical decisions. Last week, Idaho activated a “crisis standard of care,” which one official described as a “last resort.” It allows overwhelmed hospitals to ration care, including “in rare cases, ventilator (breathing machines) or intensive care unit (ICU) beds may need to be used for those who are most likely to survive, while patients who are not likely to survive may not be able to receive one,” the state’s website said.
The federal government’s latest data shows Alabama is at 100% of its intensive care unit capacity, with Texas, Georgia, Mississippi and Arkansas at more than 90% ICU capacity. Florida is just under 90%.
It’s the COVID-19 cases that are dominating. In Georgia, 62% of the ICU beds are now filled with just COVID-19 patients. In Texas, the percentage is nearly half.
To have so many ICU beds pressed into service for a single diagnosis is “unheard of,” said Dr. Hasan Kakli, an emergency room physician at Bellville Medical Center in Bellville, Texas, about an hour from Houston. “It’s approaching apocalyptic.”
In Texas, state data released Monday showed there were only 319 adult and 104 pediatric staffed ICU beds available across a state of 29 million people.
Hospitals need to hold some ICU beds for other patients, such as those recovering from major surgery or other critical conditions such as stroke, trauma or heart failure.
“This is not just a COVID issue,” said Dr. Normaliz Rodriguez, pediatric emergency physician at Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital in St. Petersburg, Florida. “This is an everyone issue.”
While the latest hospital crisis echoes previous pandemic spikes, there are troubling differences this time around.
Before, localized COVID-19 hot spots led to bed shortages, but there were usually hospitals in the region not as affected that could accept a transfer.
Now, as the highly contagious delta variant envelops swaths of low-vaccination states all at once, it becomes harder to find nearby hospitals that are not slammed.
“Wait times can now be measured in days,” said Darrell Pile, CEO of the SouthEast Texas Regional Advisory Council, which helps coordinate patient transfers across a 25-county region.
Recently, Dr. Cedric Dark, a Houston emergency physician and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, said he saw a critically ill COVID-19 patient waiting in the emergency room for an ICU bed to open. The doctor worked eight hours, went home and came in the next day. The patient was still waiting.
Holding a seriously ill patient in an emergency room while waiting for an in-patient bed to open is known as boarding. The longer the wait, the more dangerous it can be for the patient, studies have found.
Not only do patients ultimately end up staying in the hospital or the ICU longer, some research suggests that long waits for a bed will worsen their condition and may increase the risk of in-hospital death.
That’s what happened last month in Texas.
On Aug. 21, around 11:30 a.m., Michelle Puget took her adult son, Daniel Wilkinson, to the Bellville Medical Center’s emergency room as a pain in his abdomen became unbearable. “Mama,” he said, “take me to the hospital.”
Wilkinson, a 46-year-old decorated Army veteran who did two tours of duty in Afghanistan, was ushered into an exam room about half an hour later. Kakli, the emergency room physician there, diagnosed gallstone pancreatitis, a serious but treatable condition that required a specialist to perform a surgical procedure and an ICU bed.
In other times, the transfer to a larger facility would be easy. But soon Kakli found himself on a frantic, six-hour quest to find a bed for his patient. Not only did he call hospitals across Texas, but he also tried Kansas, Missouri, Oklahoma and Colorado. It was like throwing darts at a map and hoping to get lucky, he told ProPublica. But no one could or would take the transfer.
By 2:30 p.m., Wilkinson’s condition was deteriorating. Kakli told Puget to come back to the hospital. “I have to tell you,” she said he told her, “Your son is a very, very sick man. If he doesn’t get this procedure he will die.” She began to weep.
Two hours later, Wilkinson’s blood pressure was dropping, signaling his organs were failing, she said.
Kakli went on Facebook and posted an all-caps plea to physician groups around the nation: “GETTING REJECTED BY ALL HOSPITALS IN TEXAS DUE TO NO ICU BEDS. PLEASE HELP. MESSAGE ME IF YOU HAVE A BED. PATIENT IS IN ER NOW. I AM THE ER DOC. WILL FLY ANYWHERE.”
The doctor tried Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center in Houston for a second time. This time he found a bed.
Around 7 p.m., Wilkinson, still conscious but in grave condition, was flown by helicopter to the hospital. He was put in a medically induced coma. Through the night and into the next morning, medical teams worked to stabilize him enough to perform the procedure. They could not.
Doctors told his family the internal damage was catastrophic. “We made the decision we had to let him go,” Puget said.
Time of death: 1:37 p.m. Aug. 22 – 26 hours after he first arrived in the emergency room.
The story was first reported by CBS News. Kakli told ProPublica last week he still sometimes does the math in his head: It should have been 40 minutes from diagnosis in Bellville to transfer to the ICU in Houston. “If he had 40 minutes to wait instead of six hours, I strongly believe he would have had a different outcome.”
Another difference with the latest surge is how it’s affecting children.
Last year, schools were closed, and children were more protected because they were mostly isolated at home. In fact, children’s hospitals were often so empty during previous spikes they opened beds to adult patients.
Now, families are out more. Schools have reopened, some with mask mandates, some without. Vaccines are not yet available to those under 12. Suddenly the numbers of hospitalized children are on the rise, setting up the same type of competition for resources between young COVID-19 patients and those with other illnesses such as new onset diabetes, trauma, pneumonia or appendicitis.
Dr. Rafael Santiago, a pediatric emergency physician in Central Florida, said at Lakeland Regional Health Medical Center, the average number of children coming into the emergency room is around 130 per day. During the lockdown last spring, that number dropped to 33. Last month – “the busiest month ever” – the average daily number of children in the emergency room was 160.
Pediatric transfers are not yet as fraught as adult ones, Santiago said, but it does take more calls than it once did to secure a bed.
Seth Osborn, the 12-year-old whose appendix burst after a long wait, spent five days and four nights in the hospital as doctors pumped his body full of antibiotics to stave off infection from the rupture. The typical hospitalization for a routine appendectomy is about 24 hours.
The initial hospital bill for the stay came to more than $48,000, Nathaniel Osborn said. Although insurance paid for most of it, he said the family still borrowed against its house to cover the more than $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs so far.
While the hospital system where Seth was treated declined to comment about his case because of patient privacy laws, it did email a statement about the strain the pandemic is creating.
“Since July 2021, we have seen a tremendous spike in COVID-19 patients needing care and hospitalization. In mid-August, we saw the highest number of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 across the Cleveland Clinic Florida region, a total of 395 COVID-19 patients in four hospitals. Those hospitals have approximately 1,000 total beds,” the email to ProPublica said. “We strongly encourage vaccination. Approximately 90% of our patients hospitalized due to COVID-19 are unvaccinated.”
On Sunday, The Washington Post reported that a hospital in Alabama called 43 others across three states before finding a bed for Ray DeMonia, a critically ill heart patient who later died. In his obituary his family wrote: “In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies. ... He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Today, Seth is mostly recovered. “Twelve-year-old boys bounce back,” his father said. Still, the experience has left Nathaniel Osborn shaken.
The high school history teacher said he likes to stay upbeat and apolitical in his social media musings, posting about Florida wildlife preservation and favorite books. But on Sept. 7, he tweeted: “My 12-year-old had appendicitis. The ER was overwhelmed with unvaccinated Covid patients and we had to wait 6+ hours. While waiting, his appendix ruptured and had to spend 5 days in hospital. ... So yeah, your decision to not vaccinate does affect others.”
It was retweeted 34,700 times, with 143,000 likes. Most comments were sympathetic and wished his child a speedy recovery. Some, though, went straight to hate, apparently triggered by his last line. He was attacked personally and accused of making up the story: “Good try with the guilt, jerk.”
Osborn, who is vaccinated, as are his wife and son, told ProPublica he only shared Seth’s story on Twitter to encourage vaccinations.
“I have no ill will towards the hospitals or the care received at either hospital,” he said this week, “but had these hospitals not been so crowded with COVID patients, we wouldn’t have had to wait so long and perhaps my son’s appendix would not have burst.”
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
Want to see what COVID strain you have? The government says no
Every day, more than 140,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with COVID-19. But no matter how curious they are about which variant they are fighting, none of them will find out.
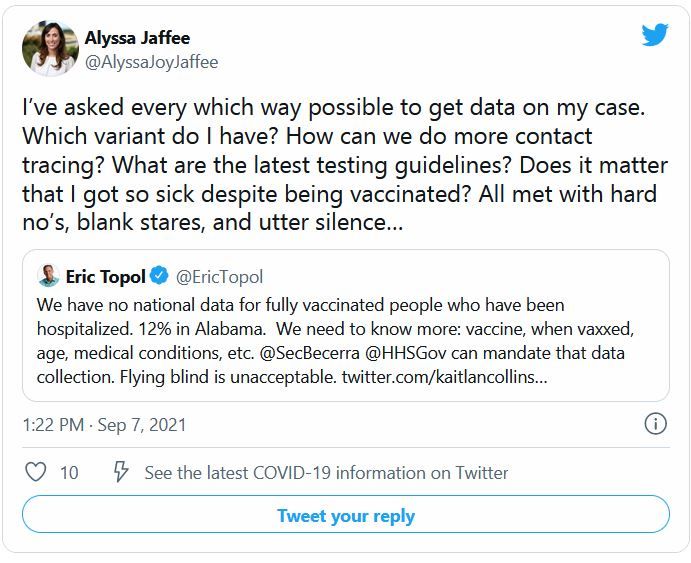
The country is dotted with labs that sequence the genomes of COVID-19 cases, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention tracks those results. But federal rules say those results are not allowed to make their way back to patients or doctors.
According to public health and infectious disease experts, this is unlikely to change any time soon.
“I know people want to know – I’ve had a lot of friends or family who’ve asked me how they can find out,” says Aubree Gordon, PhD, an epidemiology specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “I think it’s an interesting thing to find out, for sure. And it would certainly be nice to know. But because it probably isn’t necessary, there is little motivation to change the rules.”
Because the tests that are used have not been approved as diagnostic tools under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments program, which is overseen by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, they can only be used for research purposes.
In fact, the scientists doing the sequencing rarely have any patient information, Dr. Gordon says. For example, the Lauring Lab at University of Michigan – run by Adam Lauring, MD – focuses on viral evolution and currently tests for variants. But this is not done for the sake of the patient or the doctors treating the patient.
“The samples come in ... and they’ve been de-identified,”Dr. Gordon says. “This is just for research purposes. Not much patient information is shared with the researchers.”
But as of now, aside from sheer curiosity, there is not a reason to change this, says Timothy Brewer, MD, a professor of medicine and epidemiology at University of California, Los Angeles.
Although there are emerging variants – including the new Mu variant, also known as B.1.621 and recently classified as a “variant of interest” – the Delta variant accounts for about 99% of U.S. cases.
In addition, Dr. Brewer says, treatments are the same for all COVID-19 patients, regardless of the variant.
“There would have to be some clinical significance for there to be a good reason to give this information,” he says. “That would mean we would be doing something different treatment-wise depending on the variant. As of now, that is not the case.”
There is a loophole that allows labs to release variant information: They can develop their own tests. But they then must go through a lengthy validation process that proves their tests are as effective as the gold standard, says Mark Pandori, PhD, director of the Nevada State Public Health Laboratory.
But even with validation, it is too time-consuming and costly to sequence large numbers of cases, he says.
“The reason we’re not doing it routinely is there’s no way to do the genomic analysis on all the positives,” Dr. Pandori says. “It is about $110 dollars to do a sequence. It’s not like a standard PCR test.”
There is a hypothetical situation that may warrant the release of these results, Dr. Brewer says: If a variant emerges that evades vaccines.
“That would be a real public health issue,” he says. “You want to make sure there aren’t variants emerging somewhere that are escaping immunity.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Every day, more than 140,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with COVID-19. But no matter how curious they are about which variant they are fighting, none of them will find out.

The country is dotted with labs that sequence the genomes of COVID-19 cases, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention tracks those results. But federal rules say those results are not allowed to make their way back to patients or doctors.
According to public health and infectious disease experts, this is unlikely to change any time soon.
“I know people want to know – I’ve had a lot of friends or family who’ve asked me how they can find out,” says Aubree Gordon, PhD, an epidemiology specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “I think it’s an interesting thing to find out, for sure. And it would certainly be nice to know. But because it probably isn’t necessary, there is little motivation to change the rules.”
Because the tests that are used have not been approved as diagnostic tools under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments program, which is overseen by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, they can only be used for research purposes.
In fact, the scientists doing the sequencing rarely have any patient information, Dr. Gordon says. For example, the Lauring Lab at University of Michigan – run by Adam Lauring, MD – focuses on viral evolution and currently tests for variants. But this is not done for the sake of the patient or the doctors treating the patient.
“The samples come in ... and they’ve been de-identified,”Dr. Gordon says. “This is just for research purposes. Not much patient information is shared with the researchers.”
But as of now, aside from sheer curiosity, there is not a reason to change this, says Timothy Brewer, MD, a professor of medicine and epidemiology at University of California, Los Angeles.
Although there are emerging variants – including the new Mu variant, also known as B.1.621 and recently classified as a “variant of interest” – the Delta variant accounts for about 99% of U.S. cases.
In addition, Dr. Brewer says, treatments are the same for all COVID-19 patients, regardless of the variant.
“There would have to be some clinical significance for there to be a good reason to give this information,” he says. “That would mean we would be doing something different treatment-wise depending on the variant. As of now, that is not the case.”
There is a loophole that allows labs to release variant information: They can develop their own tests. But they then must go through a lengthy validation process that proves their tests are as effective as the gold standard, says Mark Pandori, PhD, director of the Nevada State Public Health Laboratory.
But even with validation, it is too time-consuming and costly to sequence large numbers of cases, he says.
“The reason we’re not doing it routinely is there’s no way to do the genomic analysis on all the positives,” Dr. Pandori says. “It is about $110 dollars to do a sequence. It’s not like a standard PCR test.”
There is a hypothetical situation that may warrant the release of these results, Dr. Brewer says: If a variant emerges that evades vaccines.
“That would be a real public health issue,” he says. “You want to make sure there aren’t variants emerging somewhere that are escaping immunity.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Every day, more than 140,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with COVID-19. But no matter how curious they are about which variant they are fighting, none of them will find out.

The country is dotted with labs that sequence the genomes of COVID-19 cases, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention tracks those results. But federal rules say those results are not allowed to make their way back to patients or doctors.
According to public health and infectious disease experts, this is unlikely to change any time soon.
“I know people want to know – I’ve had a lot of friends or family who’ve asked me how they can find out,” says Aubree Gordon, PhD, an epidemiology specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “I think it’s an interesting thing to find out, for sure. And it would certainly be nice to know. But because it probably isn’t necessary, there is little motivation to change the rules.”
Because the tests that are used have not been approved as diagnostic tools under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments program, which is overseen by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, they can only be used for research purposes.
In fact, the scientists doing the sequencing rarely have any patient information, Dr. Gordon says. For example, the Lauring Lab at University of Michigan – run by Adam Lauring, MD – focuses on viral evolution and currently tests for variants. But this is not done for the sake of the patient or the doctors treating the patient.
“The samples come in ... and they’ve been de-identified,”Dr. Gordon says. “This is just for research purposes. Not much patient information is shared with the researchers.”
But as of now, aside from sheer curiosity, there is not a reason to change this, says Timothy Brewer, MD, a professor of medicine and epidemiology at University of California, Los Angeles.
Although there are emerging variants – including the new Mu variant, also known as B.1.621 and recently classified as a “variant of interest” – the Delta variant accounts for about 99% of U.S. cases.
In addition, Dr. Brewer says, treatments are the same for all COVID-19 patients, regardless of the variant.
“There would have to be some clinical significance for there to be a good reason to give this information,” he says. “That would mean we would be doing something different treatment-wise depending on the variant. As of now, that is not the case.”
There is a loophole that allows labs to release variant information: They can develop their own tests. But they then must go through a lengthy validation process that proves their tests are as effective as the gold standard, says Mark Pandori, PhD, director of the Nevada State Public Health Laboratory.
But even with validation, it is too time-consuming and costly to sequence large numbers of cases, he says.
“The reason we’re not doing it routinely is there’s no way to do the genomic analysis on all the positives,” Dr. Pandori says. “It is about $110 dollars to do a sequence. It’s not like a standard PCR test.”
There is a hypothetical situation that may warrant the release of these results, Dr. Brewer says: If a variant emerges that evades vaccines.
“That would be a real public health issue,” he says. “You want to make sure there aren’t variants emerging somewhere that are escaping immunity.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: New cases down slightly from record high
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.
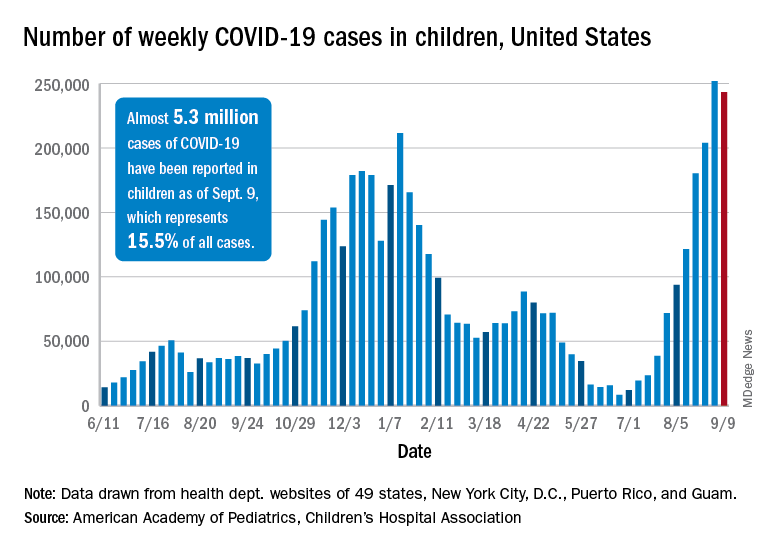
Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).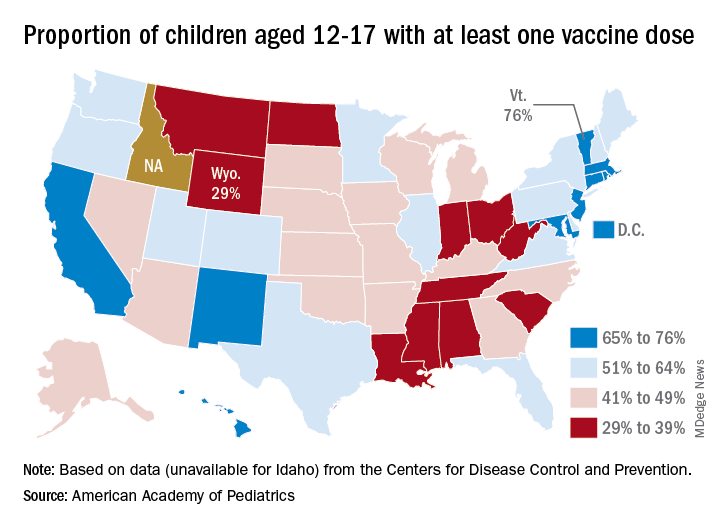
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.

Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.

Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
Man dies after 43 full ICUs turn him away
Ray Martin DeMonia, 73, of Cullman, Alabama, ran an antiques business for 40 years and served as an auctioneer at charity events, the obituary said.
He had a stroke in 2020 during the first months of the COVID pandemic and made sure to get vaccinated, his daughter, Raven DeMonia, told The Washington Post.
“He knew what the vaccine meant for his health and what it meant to staying alive,” she said. “He said, ‘I just want to get back to shaking hands with people, selling stuff, and talking antiques.’”
His daughter told the Post that her father went to Cullman Regional Medical Center on Aug. 23 with heart problems.
About 12 hours after he was admitted, her mother got a call from the hospital saying they’d called 43 hospitals and were unable to find a “specialized cardiac ICU bed” for him, Ms. DeMonia told the Post.
He was finally airlifted to Rush Foundation Hospital in Meridian, Mississippi, almost 200 miles from his home, but died there Sept. 1. His family decided to make a plea for increased vaccinations in his obituary.
“In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies,” the obit said. “Due to COVID 19, CRMC emergency staff contacted 43 hospitals in 3 states in search of a Cardiac ICU bed and finally located one in Meridian, MS. He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Mr. DeMonia is survived by his wife, daughter, grandson, and other family members.
The Alabama Hospital Association says state hospitals are still short of ICU beds. On Sept. 12, the AHA website said the state had 1,530 staffed ICU beds to accommodate 1,541 ICU patients.
The AHA said 83% of COVID patients in ICU had not been vaccinated against COVID, 4% were partially vaccinated, and 13% were fully vaccinated. Alabama trails other states in vaccination rates. Newsweek, citing CDC data, said 53.7% of people in Alabama were fully vaccinated. In comparison, 53.8% of all Americans nationally are fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Ray Martin DeMonia, 73, of Cullman, Alabama, ran an antiques business for 40 years and served as an auctioneer at charity events, the obituary said.
He had a stroke in 2020 during the first months of the COVID pandemic and made sure to get vaccinated, his daughter, Raven DeMonia, told The Washington Post.
“He knew what the vaccine meant for his health and what it meant to staying alive,” she said. “He said, ‘I just want to get back to shaking hands with people, selling stuff, and talking antiques.’”
His daughter told the Post that her father went to Cullman Regional Medical Center on Aug. 23 with heart problems.
About 12 hours after he was admitted, her mother got a call from the hospital saying they’d called 43 hospitals and were unable to find a “specialized cardiac ICU bed” for him, Ms. DeMonia told the Post.
He was finally airlifted to Rush Foundation Hospital in Meridian, Mississippi, almost 200 miles from his home, but died there Sept. 1. His family decided to make a plea for increased vaccinations in his obituary.
“In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies,” the obit said. “Due to COVID 19, CRMC emergency staff contacted 43 hospitals in 3 states in search of a Cardiac ICU bed and finally located one in Meridian, MS. He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Mr. DeMonia is survived by his wife, daughter, grandson, and other family members.
The Alabama Hospital Association says state hospitals are still short of ICU beds. On Sept. 12, the AHA website said the state had 1,530 staffed ICU beds to accommodate 1,541 ICU patients.
The AHA said 83% of COVID patients in ICU had not been vaccinated against COVID, 4% were partially vaccinated, and 13% were fully vaccinated. Alabama trails other states in vaccination rates. Newsweek, citing CDC data, said 53.7% of people in Alabama were fully vaccinated. In comparison, 53.8% of all Americans nationally are fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Ray Martin DeMonia, 73, of Cullman, Alabama, ran an antiques business for 40 years and served as an auctioneer at charity events, the obituary said.
He had a stroke in 2020 during the first months of the COVID pandemic and made sure to get vaccinated, his daughter, Raven DeMonia, told The Washington Post.
“He knew what the vaccine meant for his health and what it meant to staying alive,” she said. “He said, ‘I just want to get back to shaking hands with people, selling stuff, and talking antiques.’”
His daughter told the Post that her father went to Cullman Regional Medical Center on Aug. 23 with heart problems.
About 12 hours after he was admitted, her mother got a call from the hospital saying they’d called 43 hospitals and were unable to find a “specialized cardiac ICU bed” for him, Ms. DeMonia told the Post.
He was finally airlifted to Rush Foundation Hospital in Meridian, Mississippi, almost 200 miles from his home, but died there Sept. 1. His family decided to make a plea for increased vaccinations in his obituary.
“In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies,” the obit said. “Due to COVID 19, CRMC emergency staff contacted 43 hospitals in 3 states in search of a Cardiac ICU bed and finally located one in Meridian, MS. He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Mr. DeMonia is survived by his wife, daughter, grandson, and other family members.
The Alabama Hospital Association says state hospitals are still short of ICU beds. On Sept. 12, the AHA website said the state had 1,530 staffed ICU beds to accommodate 1,541 ICU patients.
The AHA said 83% of COVID patients in ICU had not been vaccinated against COVID, 4% were partially vaccinated, and 13% were fully vaccinated. Alabama trails other states in vaccination rates. Newsweek, citing CDC data, said 53.7% of people in Alabama were fully vaccinated. In comparison, 53.8% of all Americans nationally are fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
At 18 months, much still unknown about diabetes and COVID-19
At 18 months into the COVID-19 pandemic, many of the direct and indirect effects of SARS-CoV-2 on people with diabetes have become clearer, but knowledge gaps remain, say epidemiologists.
“COVID-19 has had a devastating effect on the population with diabetes, and conversely, the high prevalence of diabetes and uncontrolled diabetes has exacerbated the problem,” Edward W. Gregg, PhD, Imperial College London, lead author of a new literature review, told this news organization.
“As it becomes clear that the COVID-19 pandemic will be with us in different forms for the foreseeable future, the emphasis for people with diabetes needs to be continued primary care, glycemic management, and vaccination to reduce the long-term impact of COVID-19 in this population,” he added.
In data, mostly from case series, the review shows that more than one-third of people hospitalized with COVID-19 have diabetes. It is published in the September issue of Diabetes Care.
People with diabetes are more than three times as likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than those without diabetes, even after adjustment for age, sex, and other underlying conditions. Diabetes also accounts for 30%-40% of severe COVID-19 cases and deaths. Among those with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19, 21%-43% require intensive care, and the case fatality rate is about 25%.
In one of the few multivariate analyses that examined type 1 and type 2 diabetes separately, conducted in the U.K., the odds of in-hospital COVID-19–related deaths, compared with people without diabetes, were almost three times higher (odds ratio, 2.9) for individuals with type 1 diabetes and almost twice as high (OR, 1.8) for those with type 2, after adjustment for comorbidities.
The causes of death appear to be a combination of factors specific to the SARS-CoV-2 infection and to diabetes-related factors, Dr. Gregg said in an interview.
“Much of the increased risk is due to the fact that people with diabetes have more comorbid factors, but there are many other mechanisms that appear to further increase risk, including the inflammatory and immune responses of people with diabetes, and hyperglycemia appears to have an exacerbating effect by itself.”
Elevated glucose is clear risk factor for COVID-19 severity
Elevated A1c was identified among several other overall predictors of poor COVID-19 outcomes, including obesity as well as comorbid kidney and cardiovascular disease.
High blood glucose levels at the time of admission in people with previously diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes emerged as a clear predictor of worse outcomes. For example, among 605 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in China, those with fasting plasma glucose 6.1-6.9 mmol/L (110-125 mg/dL) and ≥7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) had odds ratios of poor outcomes within 28 days of 2.6 and 4.0 compared with FPG <6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL).
Population-based studies in the U.K. found that A1c levels measured months before COVID-19 hospitalization were associated with risk for intensive care unit admission and/or death, particularly among those with type 1 diabetes. Overall, the death rate was 36% higher for those with A1c of 9%-9.9% versus 6.5%-7%.
Despite the link between high A1c and death, there is as yet no clear evidence that normalizing blood glucose levels minimizes COVID-19 severity, Dr. Gregg said.
“There are data that suggest poor glycemic control is associated with higher risk of poor outcomes. This is indirect evidence that managing blood sugar will help, but more direct evidence is needed.”
Evidence gaps identified
Dr. Gregg and co-authors Marisa Sophiea, PhD, MSc, and Misghina Weldegiorgis, PhD, BSc, also from Imperial College London, identify three areas in which more data are needed.
First, more information is needed to determine whether exposure, infection, and hospitalization risks differ by diabetes status and how those factors affect outcomes. The same studies would also be important to identify how factors such as behavior, masking, and lockdown policies, risk factor control, and household/community environments affect risk in people with diabetes.
Second, studies are needed to better understand indirect effects of the pandemic, such as care and management factors. Some of these, such as the advent of telehealth, may turn out to be beneficial in the long run, they note.
Finally, the pandemic has “brought a wealth of natural experiments,” such as how vaccination programs and other interventions are affecting people with diabetes specifically. Finally, population studies are needed in many parts of the world beyond the U.S. and the U.K., where most of that work has been done thus far.
“Many of the most important unanswered questions lie in the potential indirect and long-term impact of the pandemic that require population-based studies,” Dr. Gregg said. “Most of our knowledge so far is from case series, which only assess patients from the time of hospitalization.”
Indeed, very little data are available for people with diabetes who get COVID-19 but are not hospitalized, so it’s not known whether they have a longer duration of illness or are at greater risk for “long COVID” than those without diabetes who experience COVID-19 at home.
“I have not seen published data on this yet, and it’s an important unanswered question,” Dr. Gregg said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At 18 months into the COVID-19 pandemic, many of the direct and indirect effects of SARS-CoV-2 on people with diabetes have become clearer, but knowledge gaps remain, say epidemiologists.
“COVID-19 has had a devastating effect on the population with diabetes, and conversely, the high prevalence of diabetes and uncontrolled diabetes has exacerbated the problem,” Edward W. Gregg, PhD, Imperial College London, lead author of a new literature review, told this news organization.
“As it becomes clear that the COVID-19 pandemic will be with us in different forms for the foreseeable future, the emphasis for people with diabetes needs to be continued primary care, glycemic management, and vaccination to reduce the long-term impact of COVID-19 in this population,” he added.
In data, mostly from case series, the review shows that more than one-third of people hospitalized with COVID-19 have diabetes. It is published in the September issue of Diabetes Care.
People with diabetes are more than three times as likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than those without diabetes, even after adjustment for age, sex, and other underlying conditions. Diabetes also accounts for 30%-40% of severe COVID-19 cases and deaths. Among those with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19, 21%-43% require intensive care, and the case fatality rate is about 25%.
In one of the few multivariate analyses that examined type 1 and type 2 diabetes separately, conducted in the U.K., the odds of in-hospital COVID-19–related deaths, compared with people without diabetes, were almost three times higher (odds ratio, 2.9) for individuals with type 1 diabetes and almost twice as high (OR, 1.8) for those with type 2, after adjustment for comorbidities.
The causes of death appear to be a combination of factors specific to the SARS-CoV-2 infection and to diabetes-related factors, Dr. Gregg said in an interview.
“Much of the increased risk is due to the fact that people with diabetes have more comorbid factors, but there are many other mechanisms that appear to further increase risk, including the inflammatory and immune responses of people with diabetes, and hyperglycemia appears to have an exacerbating effect by itself.”
Elevated glucose is clear risk factor for COVID-19 severity
Elevated A1c was identified among several other overall predictors of poor COVID-19 outcomes, including obesity as well as comorbid kidney and cardiovascular disease.
High blood glucose levels at the time of admission in people with previously diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes emerged as a clear predictor of worse outcomes. For example, among 605 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in China, those with fasting plasma glucose 6.1-6.9 mmol/L (110-125 mg/dL) and ≥7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) had odds ratios of poor outcomes within 28 days of 2.6 and 4.0 compared with FPG <6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL).
Population-based studies in the U.K. found that A1c levels measured months before COVID-19 hospitalization were associated with risk for intensive care unit admission and/or death, particularly among those with type 1 diabetes. Overall, the death rate was 36% higher for those with A1c of 9%-9.9% versus 6.5%-7%.
Despite the link between high A1c and death, there is as yet no clear evidence that normalizing blood glucose levels minimizes COVID-19 severity, Dr. Gregg said.
“There are data that suggest poor glycemic control is associated with higher risk of poor outcomes. This is indirect evidence that managing blood sugar will help, but more direct evidence is needed.”
Evidence gaps identified
Dr. Gregg and co-authors Marisa Sophiea, PhD, MSc, and Misghina Weldegiorgis, PhD, BSc, also from Imperial College London, identify three areas in which more data are needed.
First, more information is needed to determine whether exposure, infection, and hospitalization risks differ by diabetes status and how those factors affect outcomes. The same studies would also be important to identify how factors such as behavior, masking, and lockdown policies, risk factor control, and household/community environments affect risk in people with diabetes.
Second, studies are needed to better understand indirect effects of the pandemic, such as care and management factors. Some of these, such as the advent of telehealth, may turn out to be beneficial in the long run, they note.
Finally, the pandemic has “brought a wealth of natural experiments,” such as how vaccination programs and other interventions are affecting people with diabetes specifically. Finally, population studies are needed in many parts of the world beyond the U.S. and the U.K., where most of that work has been done thus far.
“Many of the most important unanswered questions lie in the potential indirect and long-term impact of the pandemic that require population-based studies,” Dr. Gregg said. “Most of our knowledge so far is from case series, which only assess patients from the time of hospitalization.”
Indeed, very little data are available for people with diabetes who get COVID-19 but are not hospitalized, so it’s not known whether they have a longer duration of illness or are at greater risk for “long COVID” than those without diabetes who experience COVID-19 at home.
“I have not seen published data on this yet, and it’s an important unanswered question,” Dr. Gregg said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At 18 months into the COVID-19 pandemic, many of the direct and indirect effects of SARS-CoV-2 on people with diabetes have become clearer, but knowledge gaps remain, say epidemiologists.
“COVID-19 has had a devastating effect on the population with diabetes, and conversely, the high prevalence of diabetes and uncontrolled diabetes has exacerbated the problem,” Edward W. Gregg, PhD, Imperial College London, lead author of a new literature review, told this news organization.
“As it becomes clear that the COVID-19 pandemic will be with us in different forms for the foreseeable future, the emphasis for people with diabetes needs to be continued primary care, glycemic management, and vaccination to reduce the long-term impact of COVID-19 in this population,” he added.
In data, mostly from case series, the review shows that more than one-third of people hospitalized with COVID-19 have diabetes. It is published in the September issue of Diabetes Care.
People with diabetes are more than three times as likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than those without diabetes, even after adjustment for age, sex, and other underlying conditions. Diabetes also accounts for 30%-40% of severe COVID-19 cases and deaths. Among those with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19, 21%-43% require intensive care, and the case fatality rate is about 25%.
In one of the few multivariate analyses that examined type 1 and type 2 diabetes separately, conducted in the U.K., the odds of in-hospital COVID-19–related deaths, compared with people without diabetes, were almost three times higher (odds ratio, 2.9) for individuals with type 1 diabetes and almost twice as high (OR, 1.8) for those with type 2, after adjustment for comorbidities.
The causes of death appear to be a combination of factors specific to the SARS-CoV-2 infection and to diabetes-related factors, Dr. Gregg said in an interview.
“Much of the increased risk is due to the fact that people with diabetes have more comorbid factors, but there are many other mechanisms that appear to further increase risk, including the inflammatory and immune responses of people with diabetes, and hyperglycemia appears to have an exacerbating effect by itself.”
Elevated glucose is clear risk factor for COVID-19 severity
Elevated A1c was identified among several other overall predictors of poor COVID-19 outcomes, including obesity as well as comorbid kidney and cardiovascular disease.
High blood glucose levels at the time of admission in people with previously diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes emerged as a clear predictor of worse outcomes. For example, among 605 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in China, those with fasting plasma glucose 6.1-6.9 mmol/L (110-125 mg/dL) and ≥7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) had odds ratios of poor outcomes within 28 days of 2.6 and 4.0 compared with FPG <6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL).
Population-based studies in the U.K. found that A1c levels measured months before COVID-19 hospitalization were associated with risk for intensive care unit admission and/or death, particularly among those with type 1 diabetes. Overall, the death rate was 36% higher for those with A1c of 9%-9.9% versus 6.5%-7%.
Despite the link between high A1c and death, there is as yet no clear evidence that normalizing blood glucose levels minimizes COVID-19 severity, Dr. Gregg said.
“There are data that suggest poor glycemic control is associated with higher risk of poor outcomes. This is indirect evidence that managing blood sugar will help, but more direct evidence is needed.”
Evidence gaps identified
Dr. Gregg and co-authors Marisa Sophiea, PhD, MSc, and Misghina Weldegiorgis, PhD, BSc, also from Imperial College London, identify three areas in which more data are needed.
First, more information is needed to determine whether exposure, infection, and hospitalization risks differ by diabetes status and how those factors affect outcomes. The same studies would also be important to identify how factors such as behavior, masking, and lockdown policies, risk factor control, and household/community environments affect risk in people with diabetes.
Second, studies are needed to better understand indirect effects of the pandemic, such as care and management factors. Some of these, such as the advent of telehealth, may turn out to be beneficial in the long run, they note.
Finally, the pandemic has “brought a wealth of natural experiments,” such as how vaccination programs and other interventions are affecting people with diabetes specifically. Finally, population studies are needed in many parts of the world beyond the U.S. and the U.K., where most of that work has been done thus far.
“Many of the most important unanswered questions lie in the potential indirect and long-term impact of the pandemic that require population-based studies,” Dr. Gregg said. “Most of our knowledge so far is from case series, which only assess patients from the time of hospitalization.”
Indeed, very little data are available for people with diabetes who get COVID-19 but are not hospitalized, so it’s not known whether they have a longer duration of illness or are at greater risk for “long COVID” than those without diabetes who experience COVID-19 at home.
“I have not seen published data on this yet, and it’s an important unanswered question,” Dr. Gregg said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA could authorize COVID-19 vaccine for ages 5-11 in October
The timeline is based on the expectation that Pfizer will have enough data from clinical trials to request Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization for the age group near the end of September. Then the FDA would likely make a decision about the vaccine’s safety and effectiveness in children within about 3 weeks, two sources told Reuters.
Anthony Fauci, MD, chief medical adviser to President Joe Biden and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, spoke about the timeline during an online town hall meeting Friday, Reuters reported. The meeting was attended by thousands of staff members at the National Institutes of Health.
If Pfizer submits paperwork to the FDA by the end of September, the vaccine could be available for kids around mid-October, Dr. Fauci said, and approval for the Moderna vaccine could come in November. Moderna will take about 3 weeks longer to collect and analyze data for ages 5-11.
Pfizer has said it would have enough data for ages 5-11 in September and would submit its documentation for FDA authorization soon after. Moderna told investors on Sept. 9 that data for ages 6-11 would be available by the end of the year.
On Sept. 10, the FDA said it would work to approve COVID-19 vaccines for children quickly once companies submit their data, according to Reuters. The agency said it would consider applications for emergency use, which would allow for faster approval.
Pfizer’s vaccine is the only one to receive full FDA approval, but only for people ages 16 and older. Adolescents ages 12-15 can receive the Pfizer vaccine under the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
For emergency use authorization, companies must submit 2 months of safety data versus 6 months for full approval. The FDA said on Sept. 10 that children in clinical trials should be monitored for at least 2 months to observe side effects.
BioNTech, Pfizer’s vaccine manufacturing partner, told a news outlet in Germany that it plans to request authorization globally for ages 5-11 in coming weeks, according to Reuters.
“Already over the next few weeks, we will file the results of our trial in 5- to 11-year-olds with regulators across the world and will request approval of the vaccine in this age group, also here in Europe,” Oezlem Tuereci, MD, the chief medical officer for BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
The company is completing the final production steps to make the vaccine at lower doses for the younger age group, she said. Pfizer and BioNTech will also seek vaccine approval for ages 6 months to 2 years later this year.
“Things are looking good, everything is going according to plan,” Ugur Sahin, MD, the CEO of BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The timeline is based on the expectation that Pfizer will have enough data from clinical trials to request Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization for the age group near the end of September. Then the FDA would likely make a decision about the vaccine’s safety and effectiveness in children within about 3 weeks, two sources told Reuters.
Anthony Fauci, MD, chief medical adviser to President Joe Biden and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, spoke about the timeline during an online town hall meeting Friday, Reuters reported. The meeting was attended by thousands of staff members at the National Institutes of Health.
If Pfizer submits paperwork to the FDA by the end of September, the vaccine could be available for kids around mid-October, Dr. Fauci said, and approval for the Moderna vaccine could come in November. Moderna will take about 3 weeks longer to collect and analyze data for ages 5-11.
Pfizer has said it would have enough data for ages 5-11 in September and would submit its documentation for FDA authorization soon after. Moderna told investors on Sept. 9 that data for ages 6-11 would be available by the end of the year.
On Sept. 10, the FDA said it would work to approve COVID-19 vaccines for children quickly once companies submit their data, according to Reuters. The agency said it would consider applications for emergency use, which would allow for faster approval.
Pfizer’s vaccine is the only one to receive full FDA approval, but only for people ages 16 and older. Adolescents ages 12-15 can receive the Pfizer vaccine under the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
For emergency use authorization, companies must submit 2 months of safety data versus 6 months for full approval. The FDA said on Sept. 10 that children in clinical trials should be monitored for at least 2 months to observe side effects.
BioNTech, Pfizer’s vaccine manufacturing partner, told a news outlet in Germany that it plans to request authorization globally for ages 5-11 in coming weeks, according to Reuters.
“Already over the next few weeks, we will file the results of our trial in 5- to 11-year-olds with regulators across the world and will request approval of the vaccine in this age group, also here in Europe,” Oezlem Tuereci, MD, the chief medical officer for BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
The company is completing the final production steps to make the vaccine at lower doses for the younger age group, she said. Pfizer and BioNTech will also seek vaccine approval for ages 6 months to 2 years later this year.
“Things are looking good, everything is going according to plan,” Ugur Sahin, MD, the CEO of BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The timeline is based on the expectation that Pfizer will have enough data from clinical trials to request Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization for the age group near the end of September. Then the FDA would likely make a decision about the vaccine’s safety and effectiveness in children within about 3 weeks, two sources told Reuters.
Anthony Fauci, MD, chief medical adviser to President Joe Biden and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, spoke about the timeline during an online town hall meeting Friday, Reuters reported. The meeting was attended by thousands of staff members at the National Institutes of Health.
If Pfizer submits paperwork to the FDA by the end of September, the vaccine could be available for kids around mid-October, Dr. Fauci said, and approval for the Moderna vaccine could come in November. Moderna will take about 3 weeks longer to collect and analyze data for ages 5-11.
Pfizer has said it would have enough data for ages 5-11 in September and would submit its documentation for FDA authorization soon after. Moderna told investors on Sept. 9 that data for ages 6-11 would be available by the end of the year.
On Sept. 10, the FDA said it would work to approve COVID-19 vaccines for children quickly once companies submit their data, according to Reuters. The agency said it would consider applications for emergency use, which would allow for faster approval.
Pfizer’s vaccine is the only one to receive full FDA approval, but only for people ages 16 and older. Adolescents ages 12-15 can receive the Pfizer vaccine under the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
For emergency use authorization, companies must submit 2 months of safety data versus 6 months for full approval. The FDA said on Sept. 10 that children in clinical trials should be monitored for at least 2 months to observe side effects.
BioNTech, Pfizer’s vaccine manufacturing partner, told a news outlet in Germany that it plans to request authorization globally for ages 5-11 in coming weeks, according to Reuters.
“Already over the next few weeks, we will file the results of our trial in 5- to 11-year-olds with regulators across the world and will request approval of the vaccine in this age group, also here in Europe,” Oezlem Tuereci, MD, the chief medical officer for BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
The company is completing the final production steps to make the vaccine at lower doses for the younger age group, she said. Pfizer and BioNTech will also seek vaccine approval for ages 6 months to 2 years later this year.
“Things are looking good, everything is going according to plan,” Ugur Sahin, MD, the CEO of BioNTech, told Der Spiegel.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Biden vaccine mandate rule could be ready within weeks
The emergency rule ordering large employers to require COVID-19 vaccines or weekly tests for their workers could be ready “within weeks,” officials said in a news briefing Sept. 10.
Labor Secretary Martin Walsh will oversee the Occupational Safety and Health Administration as the agency drafts what’s known as an emergency temporary standard, similar to the one that was issued a few months ago to protect health care workers during the pandemic.
The rule should be ready within weeks, said Jeff Zients, coordinator of the White House COVID-19 response team.
He said the ultimate goal of the president’s plan is to increase vaccinations as quickly as possible to keep schools open, the economy recovering, and to decrease hospitalizations and deaths from COVID.
Mr. Zients declined to set hard numbers around those goals, but other experts did.
“What we need to get to is 85% to 90% population immunity, and that’s going to be immunity both from vaccines and infections, before that really begins to have a substantial dampening effect on viral spread,” Ashish Jha, MD, dean of the Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, R.I., said on a call with reporters Sept. 9.
He said immunity needs to be that high because the Delta variant is so contagious.
Mandates are seen as the most effective way to increase immunity and do it quickly.
David Michaels, PhD, an epidemiologist and professor at George Washington University, Washington, says OSHA will have to work through a number of steps to develop the rule.
“OSHA will have to write a preamble explaining the standard, its justifications, its costs, and how it will be enforced,” says Dr. Michaels, who led OSHA for the Obama administration. After that, the rule will be reviewed by the White House. Then employers will have some time – typically 30 days – to comply.
In addition to drafting the standard, OSHA will oversee its enforcement.
Companies that refuse to follow the standard could be fined $13,600 per violation, Mr. Zients said.
Dr. Michaels said he doesn’t expect enforcement to be a big issue, and he said we’re likely to see the rule well before it is final.
“Most employers are law-abiding. When OSHA issues a standard, they try to meet whatever those requirements are, and generally that starts to happen when the rule is announced, even before it goes into effect,” he said.
The rule may face legal challenges as well. Several governors and state attorneys general, as well as the Republican National Committee, have promised lawsuits to stop the vaccine mandates.
Critics of the new mandates say they impinge on personal freedom and impose burdens on businesses.
But the president hit back at that notion Sept. 10.
“Look, I am so disappointed that, particularly some of the Republican governors, have been so cavalier with the health of these kids, so cavalier of the health of their communities,” President Biden told reporters.
“I don’t know of any scientist out there in this field who doesn’t think it makes considerable sense to do the six things I’ve suggested.”
Yet, others feel the new requirements didn’t go far enough.
“These are good steps in the right direction, but they’re not enough to get the job done,” said Leana Wen, MD, in an op-ed for The Washington Post.
Dr. Wen, an expert in public health, wondered why President Biden didn’t mandate vaccinations for plane and train travel. She was disappointed that children 12 and older weren’t required to be vaccinated, too.
“There are mandates for childhood immunizations in every state. The coronavirus vaccine should be no different,” she wrote.
Vaccines remain the cornerstone of U.S. plans to control the pandemic.
On Sept. 10, there was new research from the CDC and state health departments showing that the COVID-19 vaccines continue to be highly effective at preventing severe illness and death.
But the study also found that the vaccines became less effective in the United States after Delta became the dominant cause of infections here.
The study, which included more than 600,000 COVID-19 cases, analyzed breakthrough infections – cases where people got sick despite being fully vaccinated – in 13 jurisdictions in the United States between April 4 and July 17, 2021.
Epidemiologists compared breakthrough infections between two distinct points in time: Before and after the period when the Delta variant began causing most infections.
From April 4 to June 19, fully vaccinated people made up just 5% of cases, 7% of hospitalizations, and 8% of deaths. From June 20 to July 17, 18% of cases, 14% of hospitalizations, and 16% of deaths occurred in fully vaccinated people.
“After the week of June 20, 2021, when the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant became predominant, the percentage of fully vaccinated persons among cases increased more than expected,” the study authors wrote.
Even after Delta swept the United States, fully vaccinated people were 5 times less likely to get a COVID-19 infection and more than 10 times less likely to be hospitalized or die from one.
“As we have shown in study after study, vaccination works,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said during the White House news briefing.
“We have the scientific tools we need to turn the corner on this pandemic. Vaccination works and will protect us from the severe complications of COVID-19,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The emergency rule ordering large employers to require COVID-19 vaccines or weekly tests for their workers could be ready “within weeks,” officials said in a news briefing Sept. 10.
Labor Secretary Martin Walsh will oversee the Occupational Safety and Health Administration as the agency drafts what’s known as an emergency temporary standard, similar to the one that was issued a few months ago to protect health care workers during the pandemic.
The rule should be ready within weeks, said Jeff Zients, coordinator of the White House COVID-19 response team.
He said the ultimate goal of the president’s plan is to increase vaccinations as quickly as possible to keep schools open, the economy recovering, and to decrease hospitalizations and deaths from COVID.
Mr. Zients declined to set hard numbers around those goals, but other experts did.
“What we need to get to is 85% to 90% population immunity, and that’s going to be immunity both from vaccines and infections, before that really begins to have a substantial dampening effect on viral spread,” Ashish Jha, MD, dean of the Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, R.I., said on a call with reporters Sept. 9.
He said immunity needs to be that high because the Delta variant is so contagious.
Mandates are seen as the most effective way to increase immunity and do it quickly.
David Michaels, PhD, an epidemiologist and professor at George Washington University, Washington, says OSHA will have to work through a number of steps to develop the rule.
“OSHA will have to write a preamble explaining the standard, its justifications, its costs, and how it will be enforced,” says Dr. Michaels, who led OSHA for the Obama administration. After that, the rule will be reviewed by the White House. Then employers will have some time – typically 30 days – to comply.
In addition to drafting the standard, OSHA will oversee its enforcement.
Companies that refuse to follow the standard could be fined $13,600 per violation, Mr. Zients said.
Dr. Michaels said he doesn’t expect enforcement to be a big issue, and he said we’re likely to see the rule well before it is final.
“Most employers are law-abiding. When OSHA issues a standard, they try to meet whatever those requirements are, and generally that starts to happen when the rule is announced, even before it goes into effect,” he said.
The rule may face legal challenges as well. Several governors and state attorneys general, as well as the Republican National Committee, have promised lawsuits to stop the vaccine mandates.
Critics of the new mandates say they impinge on personal freedom and impose burdens on businesses.
But the president hit back at that notion Sept. 10.
“Look, I am so disappointed that, particularly some of the Republican governors, have been so cavalier with the health of these kids, so cavalier of the health of their communities,” President Biden told reporters.
“I don’t know of any scientist out there in this field who doesn’t think it makes considerable sense to do the six things I’ve suggested.”
Yet, others feel the new requirements didn’t go far enough.
“These are good steps in the right direction, but they’re not enough to get the job done,” said Leana Wen, MD, in an op-ed for The Washington Post.
Dr. Wen, an expert in public health, wondered why President Biden didn’t mandate vaccinations for plane and train travel. She was disappointed that children 12 and older weren’t required to be vaccinated, too.
“There are mandates for childhood immunizations in every state. The coronavirus vaccine should be no different,” she wrote.
Vaccines remain the cornerstone of U.S. plans to control the pandemic.
On Sept. 10, there was new research from the CDC and state health departments showing that the COVID-19 vaccines continue to be highly effective at preventing severe illness and death.
But the study also found that the vaccines became less effective in the United States after Delta became the dominant cause of infections here.
The study, which included more than 600,000 COVID-19 cases, analyzed breakthrough infections – cases where people got sick despite being fully vaccinated – in 13 jurisdictions in the United States between April 4 and July 17, 2021.
Epidemiologists compared breakthrough infections between two distinct points in time: Before and after the period when the Delta variant began causing most infections.
From April 4 to June 19, fully vaccinated people made up just 5% of cases, 7% of hospitalizations, and 8% of deaths. From June 20 to July 17, 18% of cases, 14% of hospitalizations, and 16% of deaths occurred in fully vaccinated people.
“After the week of June 20, 2021, when the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant became predominant, the percentage of fully vaccinated persons among cases increased more than expected,” the study authors wrote.
Even after Delta swept the United States, fully vaccinated people were 5 times less likely to get a COVID-19 infection and more than 10 times less likely to be hospitalized or die from one.
“As we have shown in study after study, vaccination works,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said during the White House news briefing.
“We have the scientific tools we need to turn the corner on this pandemic. Vaccination works and will protect us from the severe complications of COVID-19,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The emergency rule ordering large employers to require COVID-19 vaccines or weekly tests for their workers could be ready “within weeks,” officials said in a news briefing Sept. 10.
Labor Secretary Martin Walsh will oversee the Occupational Safety and Health Administration as the agency drafts what’s known as an emergency temporary standard, similar to the one that was issued a few months ago to protect health care workers during the pandemic.
The rule should be ready within weeks, said Jeff Zients, coordinator of the White House COVID-19 response team.
He said the ultimate goal of the president’s plan is to increase vaccinations as quickly as possible to keep schools open, the economy recovering, and to decrease hospitalizations and deaths from COVID.
Mr. Zients declined to set hard numbers around those goals, but other experts did.
“What we need to get to is 85% to 90% population immunity, and that’s going to be immunity both from vaccines and infections, before that really begins to have a substantial dampening effect on viral spread,” Ashish Jha, MD, dean of the Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, R.I., said on a call with reporters Sept. 9.
He said immunity needs to be that high because the Delta variant is so contagious.
Mandates are seen as the most effective way to increase immunity and do it quickly.
David Michaels, PhD, an epidemiologist and professor at George Washington University, Washington, says OSHA will have to work through a number of steps to develop the rule.
“OSHA will have to write a preamble explaining the standard, its justifications, its costs, and how it will be enforced,” says Dr. Michaels, who led OSHA for the Obama administration. After that, the rule will be reviewed by the White House. Then employers will have some time – typically 30 days – to comply.
In addition to drafting the standard, OSHA will oversee its enforcement.
Companies that refuse to follow the standard could be fined $13,600 per violation, Mr. Zients said.
Dr. Michaels said he doesn’t expect enforcement to be a big issue, and he said we’re likely to see the rule well before it is final.
“Most employers are law-abiding. When OSHA issues a standard, they try to meet whatever those requirements are, and generally that starts to happen when the rule is announced, even before it goes into effect,” he said.
The rule may face legal challenges as well. Several governors and state attorneys general, as well as the Republican National Committee, have promised lawsuits to stop the vaccine mandates.
Critics of the new mandates say they impinge on personal freedom and impose burdens on businesses.
But the president hit back at that notion Sept. 10.
“Look, I am so disappointed that, particularly some of the Republican governors, have been so cavalier with the health of these kids, so cavalier of the health of their communities,” President Biden told reporters.
“I don’t know of any scientist out there in this field who doesn’t think it makes considerable sense to do the six things I’ve suggested.”
Yet, others feel the new requirements didn’t go far enough.
“These are good steps in the right direction, but they’re not enough to get the job done,” said Leana Wen, MD, in an op-ed for The Washington Post.
Dr. Wen, an expert in public health, wondered why President Biden didn’t mandate vaccinations for plane and train travel. She was disappointed that children 12 and older weren’t required to be vaccinated, too.
“There are mandates for childhood immunizations in every state. The coronavirus vaccine should be no different,” she wrote.
Vaccines remain the cornerstone of U.S. plans to control the pandemic.
On Sept. 10, there was new research from the CDC and state health departments showing that the COVID-19 vaccines continue to be highly effective at preventing severe illness and death.
But the study also found that the vaccines became less effective in the United States after Delta became the dominant cause of infections here.
The study, which included more than 600,000 COVID-19 cases, analyzed breakthrough infections – cases where people got sick despite being fully vaccinated – in 13 jurisdictions in the United States between April 4 and July 17, 2021.
Epidemiologists compared breakthrough infections between two distinct points in time: Before and after the period when the Delta variant began causing most infections.
From April 4 to June 19, fully vaccinated people made up just 5% of cases, 7% of hospitalizations, and 8% of deaths. From June 20 to July 17, 18% of cases, 14% of hospitalizations, and 16% of deaths occurred in fully vaccinated people.
“After the week of June 20, 2021, when the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant became predominant, the percentage of fully vaccinated persons among cases increased more than expected,” the study authors wrote.
Even after Delta swept the United States, fully vaccinated people were 5 times less likely to get a COVID-19 infection and more than 10 times less likely to be hospitalized or die from one.
“As we have shown in study after study, vaccination works,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said during the White House news briefing.
“We have the scientific tools we need to turn the corner on this pandemic. Vaccination works and will protect us from the severe complications of COVID-19,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.